Method for remedying soil contaminated by DDT as pesticide residue through earthworm-based bioaugmentation and biodegradation
A bioaugmentation and pesticide residue technology, applied in the field of environmental biochemistry, can solve problems such as earthworm soil pollution, and achieve simple and effective restoration, accelerated decomposition, accelerated elimination and detoxification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
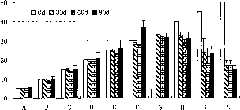
[0036] Embodiment 1. Effect test of different earthworm stocking densities
[0037] The soil for testing was collected from vegetable garden soil. The soil samples were fully air-dried at room temperature, then mixed and pulverized, and passed through a 2mm sieve. The earthworm species are selected from Eisenia chinensis (surface species) and Esperus magnifolia (inner species).
[0038] Experimental design Add 5 (A), 10 (B), 15 (C), 20 (D), 25 (E), 30 (F) and 35 (G) earthworms of two species , 40 (H), 45 (I), 50 (L) totally 20 processing samples. Each treated soil sample weighs 1kg, and 500g of fermented cow dung is added to each treatment. After the cow dung is ground, it is fully mixed with the soil. Every three months, 500g of the fermented cow dung that has been ground and fermented is put in again, and fully mixed with the soil. The water content of the soil was kept at 55-65% during the restoration process, and each treatment was repeated three times. The experimental...
Embodiment 2
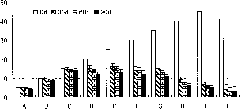
[0040] Example 2. The earthworm feeding effect test when the quality of fermented chicken manure and / or cow manure accounts for different percentages of the total mass
[0041]The soil to be tested was paddy soil, and the soil samples were fully air-dried at room temperature, then mixed and pulverized, and passed through a 2mm sieve. The earthworm species are selected from Eisenia chinensis (surface species) and Esperus magnifolia (inner species).
[0042] Experimental Design Two kinds of earthworms respectively add the quality of fermented chicken manure and / or cow manure to account for 5% (A), 10% (B), 15% (C), 20% (D), 25% ( E), 30% (F), 40% (G), 60% (H), 80% (I), 100% (L) a total of 20 treatments. The weight of each treatment sample is 1kg. The worms used in the experiment are 30 worms for the treatment of Eisenia chinensis, and 15 worms for the treatment of P. , and fully mixed with the soil, the soil moisture content was kept at 55-65% during the restoration process, a...
Embodiment 3
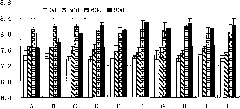
[0044] Embodiment 3. Different earthworm species, density are tested to DDT biodegradation effect
[0045] The experimental design weighs 2kg for each soil sample. The soil for testing is collected from the surface soil (0-20cm) near the green banyan circle (23°09.190N, 113°21.244E) of South China Agricultural University. For red soil, the content of pesticides in the soil is negligible. The soil samples were fully air-dried at room temperature, then mixed and pulverized, and passed through a 2mm sieve. As earthworm species, Eisenia chinensis (surface species, serial number: E) and Cyclochaetos grandiosa (inner species, serial number: A) were selected. The concentration of DDT in the soil is 2mg / kg (code: C1) and 4mg / kg (code: C2). Since it is difficult to ensure the uniformity of the sample directly by adding DDT to the soil, this experiment first dissolves DDT in ethanol (2mg / kg kg treatment shared DDT0.08g, ethanol 10mL; 4mg / kg treatment shared DDT0.16g, ethanol 20mL), the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com