Patents
Literature
41 results about "Paracoccus sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low-temperature-resistant petroleum degradation strains as well as culture method, culture medium and application thereof
InactiveCN102021128AImprove adaptabilityHigh activityWaste water treatment from quariesBacteriaBioremediationBiology
The invention relates to low-temperature-resistant petroleum degradation strains as well as a culture method, a culture medium and application thereof, wherein the low-temperature-resistant petroleum degradation strains are Paracoccus sp. D17 and Paracoccus sp. D24;a liquid culture medium for the two strains is screened, and per 1000ml of the liquid culture medium comprises 0.5g of NaCl, 0.1g of K2HPO4, 0.1g of NH4H2PO4, 0.1g of (NH4)2SO4, 0.02g of MgSO4.7H2O, 0.3g of KNO3, 700-900ml of oilfield wastewater and the balance of ultrapure water; a solid culture medium for the two strains is screened and is formed by additionally adding 15-20g of agar into each 1000ml of the liquid culture medium and further uniformly coating 20-30 mu l of sterile crude oil on the surface of the culture medium; and the two strains can be applied in degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon and bioremediation of petroleum pollution in soil or a water body. The two low-temperature strains can be applied in a low-temperature environment and have great value for controlling the petroleum pollution in the soil in the low-temperature environment.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Paracoccus and application thereof in nitrogenous heterocyclic compound degradation
InactiveCN101186898AStrong degradative activityThe cultivation method is simpleBacteriaWater contaminantsSynechococcusNitrogenous heterocyclic compound
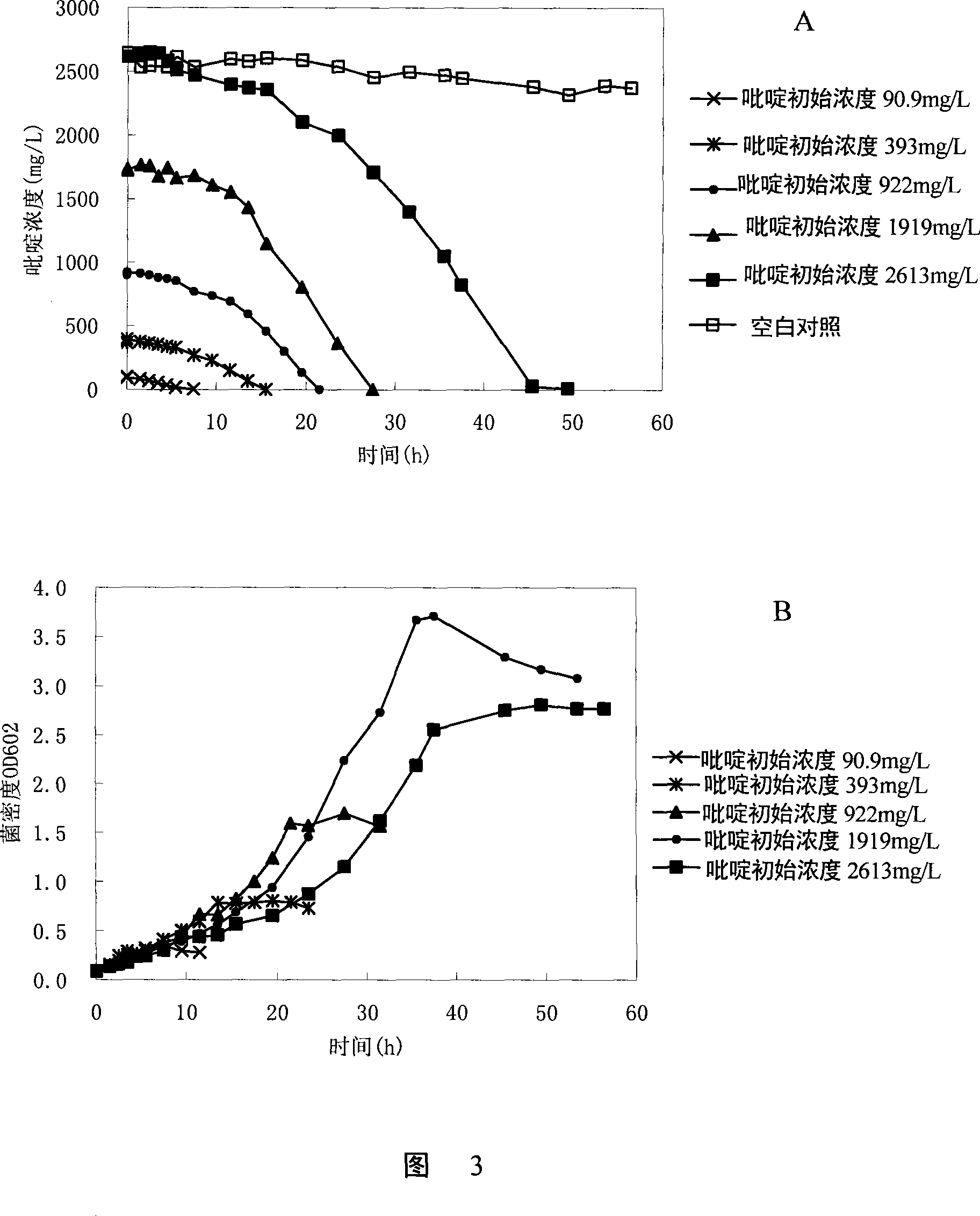
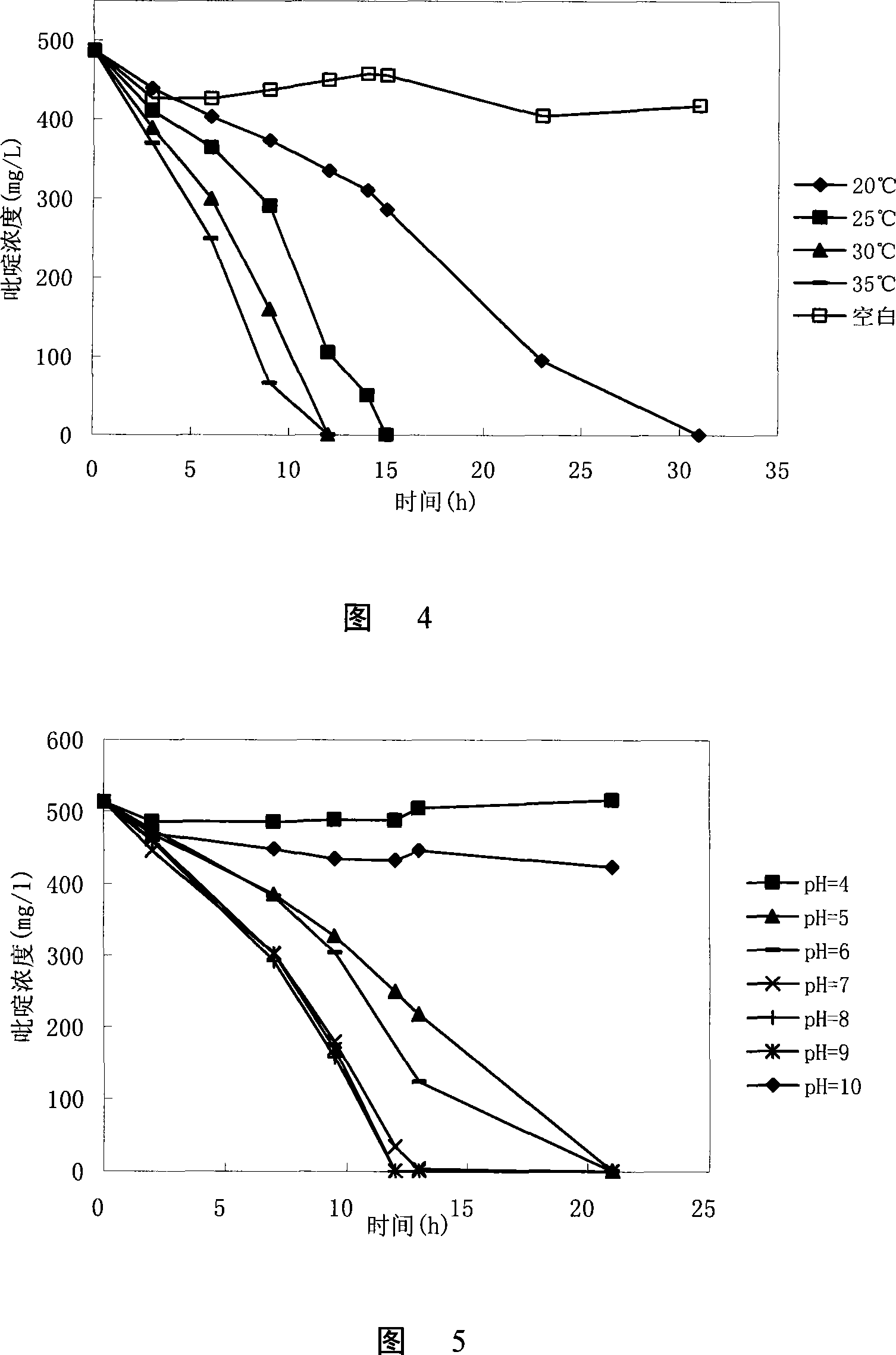
The invention discloses paracoccus and the application for degrading azotic heterocyclic compound. The paracoccus is paracoccus sp. BW001 CGMCC No. 2225. The paracoccus sp. BW001 CGMCC No. 2225 of the invention, on one hand, can grow into pyridine as the only carbon source and nitrogen source, which has a strong degradation activity (the degradation rate is 100%) for pyridine, is extremely suitable for biologic control of organic wastewater (such as coking wastewater) which contains pollutant of pyridine category, and can be used as biological hardening agent in the biological control technology of organic persistent wastewater, and corresponding environmental biological agent is exploited, thereby having relatively high value of study, application and marketing.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Salt-tolerant COD removal denitrifying microbial agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106635861ASimple compositionRapid cultivationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynechococcusMicrobial agent
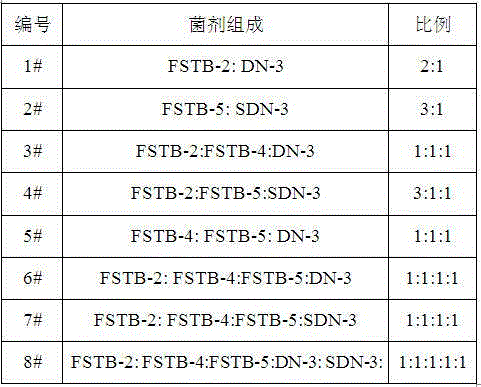
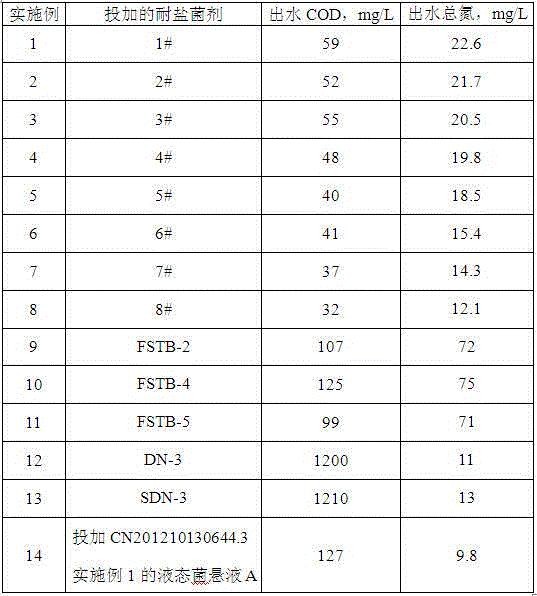
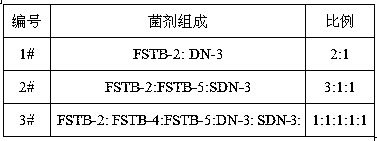
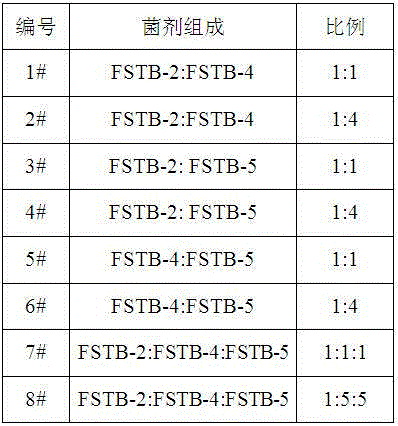
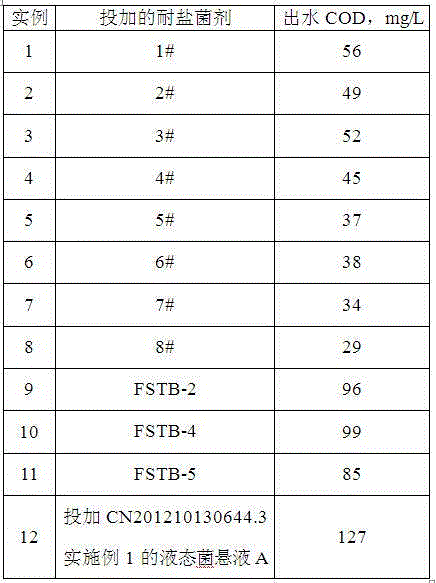
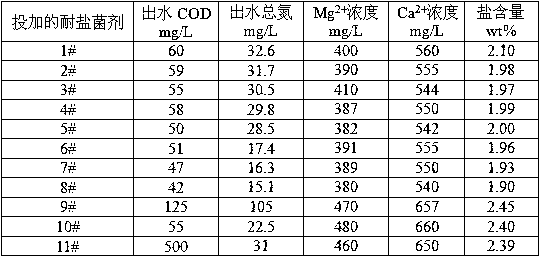
The invention relates to a salt-tolerant COD removal denitrifying microbial agent. The microbial agent consists of at least one of paracoccus sp FSTB-2, microbacterium kitamiense FSTB-4 and pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, and further consists of at least one of paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3, wherein the paracoccus sp FSTB-2, the microbacterium kitamiense FSTB-4 and the pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5 are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 1, 2015, with preservation numbers of CGMCC No.10938, CGMCC No.10939 and CGMCC No.10940; and the paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and the methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3 are disclosed in CN102465104A and CN102465103, and the preservation numbers of the paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and the methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3 are CGMCC No.3658 and CGMCC No.3660. The microbial agent can be used for directly processing total nitrogen and COD in high-salinity wastewater, and the microbial agent can be also added to various biochemical reaction constructions so as to improve microbiological composition, optimize the salt tolerance of a microbial system in wastewater treatment and improve total nitrogen and COD removal rate of the entire process.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Lincomycin production wastewater treatment method
ActiveCN106746155AEfficient and stable removalImprove processing efficiencyTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentWastewaterPseudomonas stutzeri
The invention relates to a lincomycin production wastewater treatment method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out pretreatment on lincomycin production wastewater by an advanced oxidation technology; (2) carrying out coagulating sedimentation on an oxidation effluent, filtering to remove generated precipitates; (3) carrying out anaerobic biochemical treatment on the filtered effluent; and (4) carrying out biological contact oxidation process on an anaerobic effluent while pouring salt-tolerant COD-removal strain. The salt-tolerant COD-removal strain is Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2 and / or Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, and was collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 1, 2015. The collection number is CGMCC No. 10938 and CGMCC No. 10940. By the technology of advanced oxidation-coagulating sedimentation-anaeronic biochemical treatment and by pouring specific salt-tolerant COD-removal strain into a contact oxidation unit, antibiotic in wastewater can be resisted, and efficient stable removal of COD in wastewater is realized. The method of the invention has characteristics of simple process, high treatment efficiency, low treatment cost and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Buprofezin pesticide residual degrading bacteria and produced microbial inoculum thereof
InactiveCN101560482AWill not affect the use effectEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGram stain negativeBiological property
The invention provides a degrading residual microbial inoculum of buprofezin pesticide, belonging to the field of biological high technology. The used bacterial strain is gram staining negative bacteria BF3, and is identified as Paracoccus (Paracoccus sp.). The main biological characteristic is gram-negative and cell is clubbed. Bacterial colony is milky yellowish, round, swollen and opaque, with neat margin and smooth surface. The bacterial strain is facultative anaerobic and chemoheterotropic. The culture solution obtained by fermenting BF3 strain is the microbial inoculum. The application of degrading bacteria product can ensure that buprofezin pesticide residue quantity in soil is reduced by more than 90%, and can solve the overproof problem of buprofezin pesticide residue in agricultural production.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Salt-tolerant pyrene degrading bactericide applied to oil-containing silt
InactiveCN104962545AFast degradationSuitable for a wide range of salinitySludge treatmentOn/in organic carrierPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonSynechococcus
The invention discloses a salt-tolerant pyrene degrading bactericide applied to oil-containing silt. The salt-tolerant pyrene degrading bactericide is characterized by comprising Paracoccus sp. PH205 and a carrier; the Paracoccus sp. PH205 is preserved in the common microorganism center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on May 16th, 2014, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 9174. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pyrene in the salt-containing and oil-containing silt can be degraded quickly by the aid of the salt-tolerant pyrene degrading bactericide; As proved by experiments, the salt-tolerant pyrene degrading bactericide has the advantages that the salt-tolerant pyrene degrading bactericide is high in pyrene degrading speed and wide in salinity application range, and can be used for the oil-containing silt with the salinity of 5% at most, and the content of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pyrene in the oil-containing silt can be reduced effectively.
Owner:中海石油环保服务(天津)有限公司
Treating method for wastewater produced in production of rifamycin
ActiveCN106746161AEfficient removalImprove processing efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntibiotic YOxidative treatment
The invention relates to a treating method for wastewater produced in production of rifamycin. The treating method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating wastewater produced in production of rifamycin by using advanced oxidation technology; (2) subjecting oxidation effluent to coagulating sedimentation and carrying out filtering to remove sediments; (3) carrying out anaerobic biochemical treatment on effluent of filtering; and (4) subjecting anaerobic effluent to treatment via a biological contact oxidation process and adding salt-resistant COD-removing bacteria, wherein the salt-resistant COD-removing bacteria are Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2 and / or Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, and Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2 and Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5 are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 1, 2015, with accession numbers of CGMCC NO. 10938 and CGMCC NO. 10940, respectively. According to the invention, the process of advanced oxidation, coagulating sedimentation, anaerobic biochemical treatment and biological contact oxidation is employed, and the specific salt-resistant COD-removing bacteria are added into a contact oxidation unit and can tolerate antibiotics in the wastewater, so high-efficiency stable removal of CODs in the wastewater is realized; and the treating method has the characteristics of simple process, high treating efficiency, low treating cost, etc.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Construction and application of broad spectrum organic phosphorus pesticide degradation genetic engineering strain
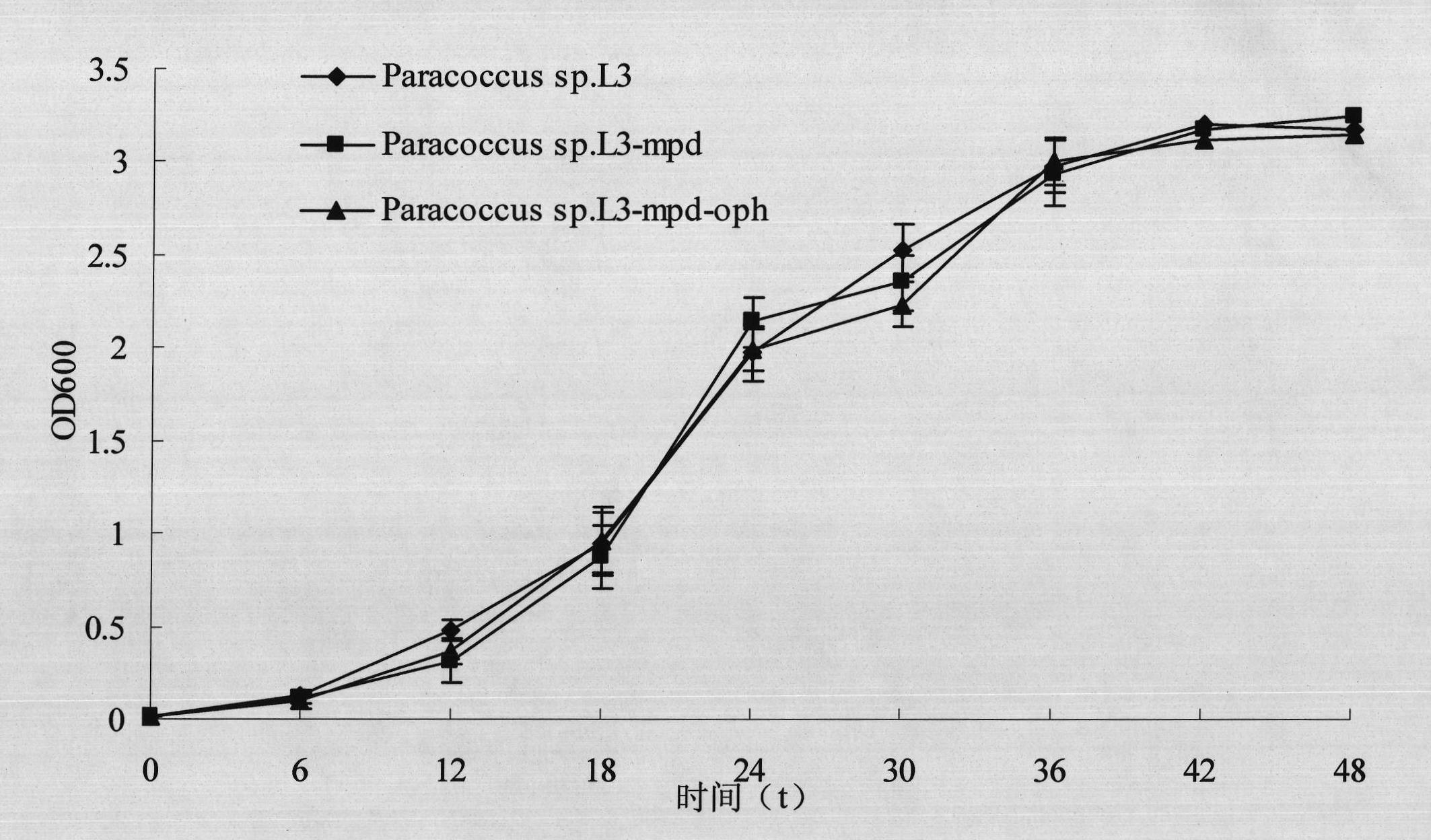
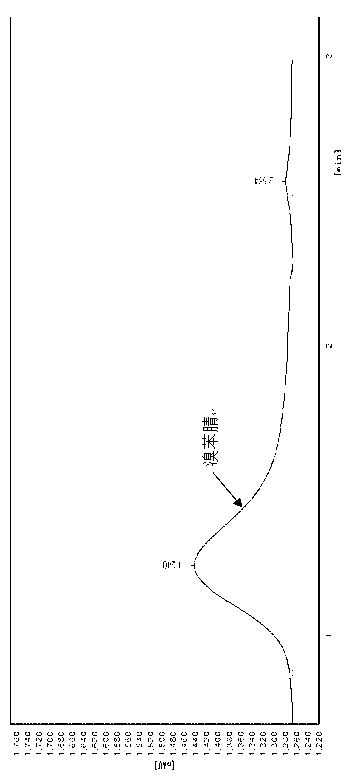
The invention discloses construction and application of a broad spectrum organic phosphorus pesticide degradation genetic engineering strain, and belongs to the field of biological engineering technology. The engineering strain 1gmp is the engineering strain paracoccus sp. 1gmp for degrading the organic phosphorus pesticide in a broad spectrum, which is constructed by sequentially inserting two organic phosphorus hydrolase genes mpd and oph with different substrate degradation spectrums into the chromosome of dimethoate high-efficiency degradation strain paracoccus sp. L3 by using random integration of a serious of vectors pUTTns and deleting a resistant gene by counter-selection marking; and degradation spectrum measurement shows that the engineering strain can efficiently degrade 17 organic phosphorus pesticides generally used in China at present. The engineering strain has the advantages of genetic stability, biological safety and great potential application prospect.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Paracoccus MXX-04 for bromoxynil degradation and application thereof
ActiveCN103243056AReduce manufacturing costEasy to useBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationSynechococcusMotility
The invention provides a degradation strain for eliminating residual bromoxynil, belonging to the field of biological high technology. The adopted bacterial strain is a gram staining reaction negative strain MXX-04 which is identified to be paracoccussp. The main biological properties are G-, short rod shape, no spores, no motility and positive oxidase and catalase. The strain provided by the invention can grow by taking bromoxynil as a unique nitrogen source and mineralize the bromoxynil. Under the condition of a shake flask in a laboratory, the strain can degrade 95.3% of 100mg / L bromoxynil within 24 hours, thus the problem that bromoxynil is hard to degrade biologically in the environment is solved.
Owner:JIANGSU NANZI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SCI & TECH
Treating method for reverse osmosis (RO) concentrated water
ActiveCN108117221ASolve removal puzzlesReduce concentrationMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentMicrobial agentReverse osmosis
The invention relates to a treating method for RO concentrated water. The treating method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) treatment with an advanced oxidation unit: subjecting RO concentrated water to advanced oxidation to improve the biodegradability of the RO concentrated water; and (2) biologically strengthened treatment: allowing the RO concentrated water having undergone advanced oxidation to enter a biologically strengthened treatment unit, and adding a salt-tolerant COD-removing denitrifying microbial agent into a treatment system, wherein the microbial agent comprises at least one selected from a group consisting of Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2, Microbacterium kitamiense FSTB-4 and Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, and further comprises at least one selected from a group consisting of Paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and Methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3. The treating method of the invention adopts a combination of an advanced oxidation treatment process and a biologically strengthened treatment process, and the salt-tolerant microbial agent is added into the biologically strengthened treatment unit, so COD and total nitrogen in the RO concentrated water are both removed efficiently, and effluent meets emission requirements.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Piperazine degraded paracoccus PQ-01 and application thereof
ActiveCN103114065AReduce manufacturing costEasy to useBacteriaWater contaminantsSynechococcusWater treatment
The invention provides a degradation microbial inoculum for eliminating piperazine residue, and belongs to the high technical field of biology. The strain is gram staining reaction negative strain PQ-01, and is identified to be paracoccus sp., wherein the main biological characteristics are gram negative, spherical or club shape, asporous and non-motile. The strain can grow by taking piperazine as the unique carbon source and nitrogen source, and can be completely mineralized. 100mg / L of piperazine can be degraded to a level which cannot be detected in 24 hours by the strain under a shaking condition in the lab, so that the problem that the piperazine is difficult to biodegrade in waste water treatment can be solved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
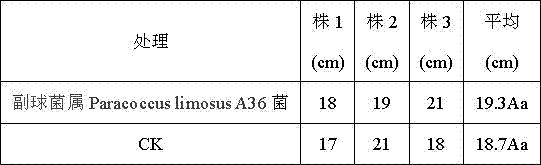
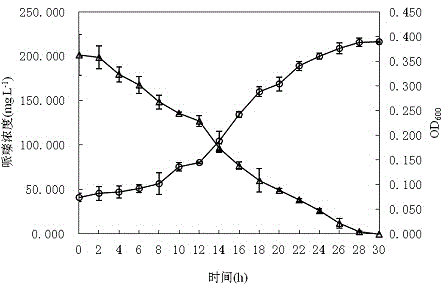
Paracoccus limosus, bacterium thereof, method for preparing bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN104877916AReduce applicationsIncrease contentFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyRhodobacterales
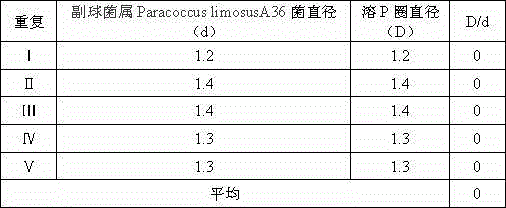
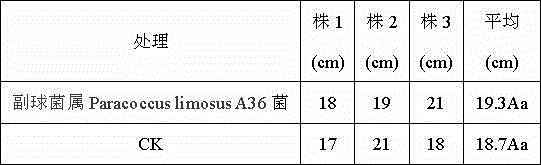
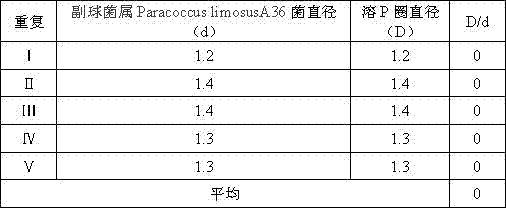
The invention discloses paracoccus limosus, a bacterium thereof, a method for preparing the bacterium and application thereof. The paracoccus limosus is paracoccus limosus A36, is preserved in preservation authority which is the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on November 21st, 2014, and the preservation number of the paracoccus limosus is CGMCC No.10032; the paracoccus limosus belongs to paracoccus versutus of rhodobacteraceae of rhodobacterales of alpha-proteobacteria of proteobacteria of bacteria. The radial paracoccus limosus is cultivated on a plate, and seeds are cultivated and fermented to obtain the bacterium with the paracoccus limosus which is an active ingredient. The method for preparing the bacterium with bacillus which is an active ingredient includes steps of cultivating the paracoccus limosus on the plate; cultivating the seeds; fermenting the seeds; preparing the bacterium. The bacterium can be applied to preparing basic fertilizers with functions of dissolving phosphorus and potassium and increasing quick-acting nitrogen in soil.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI +1
Astaxanthin producing strain and application thereof
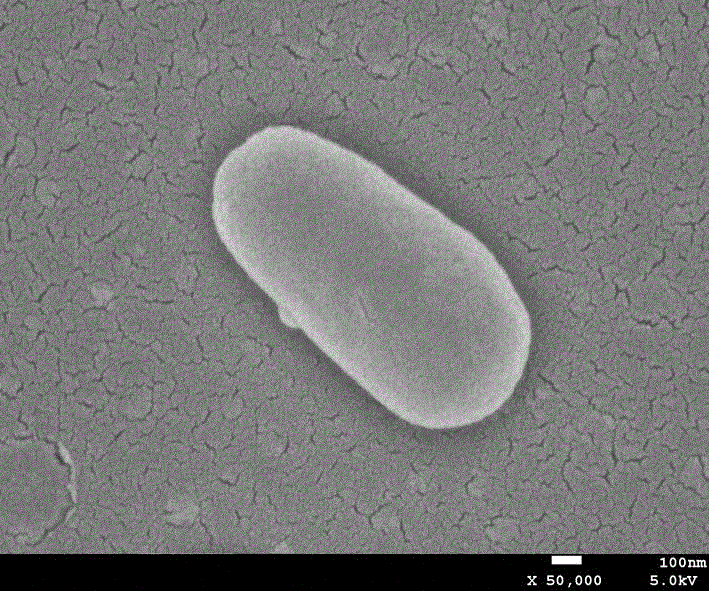
The invention discloses paracoccus sp. SCU-M53, wherein the preservation number of the paracoccus sp. SCU-M53 is KCTC 42932. By conducting such operations as isolating from an acrida cinerea body surface, screening, physiological-biochemical identification and the like, the strain is determined to be a bacilliform strain (as shown in Drawing 1), the strain belongs to gram-negative bacteria, the strain is aerobiotic and the colony of the strain is represented in orange. The paracoccus sp. SCU-M53 provided by the invention has the following features: oxidase positive and catalase positive, urease negative, and the strain has an indole producing capacity; meanwhile, the strain can produce astaxanthin and has the activities of such enzymes as alkaline phosphatase, esterase (C4), lipase (C8), leucine-arylamidase, chymotrypsin, naphthol-AS-BI-phosphoric acid hydrolase and the like; and the strain can be widely applied to the field of production of various bioengineering enzymatic preparations. The morphology of the strain SCU-M53 observed under a 50000-time scanning electron microscope, is as shown in Attached Drawing.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Salt-tolerant microbial agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106635860AEfficient removalGood removal effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismSynechococcus
The invention relates to a microbial agent with tolerance to high-salt wastewater and capability of efficiently removing COD as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The microbial agent contains two or three of (Paracoccus sp.) FSTB-2, (Microbacterium kitamiense) FSTB-4 and (Pseudomonas stutzeri) FSTB-5. The three strains are preserved in China General Microbiological Center of Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on June 1, 2015; the preservation numbers are CGMCC No.10938, CGMCC No.10939 and CGMCC No.10940. The microbial agent can be directly used for treating COD in high-salt wastewater and can also be added into various biochemical reaction structures for improving microbiological compositions, optimizing salt tolerance of the microbial system in the wastewater treatment and increasing the overall COD removal rate of the process.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Microbial agent with high salt resistance, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108118008AEfficient removalImprove removal rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh resistanceStaphylococcus cohnii
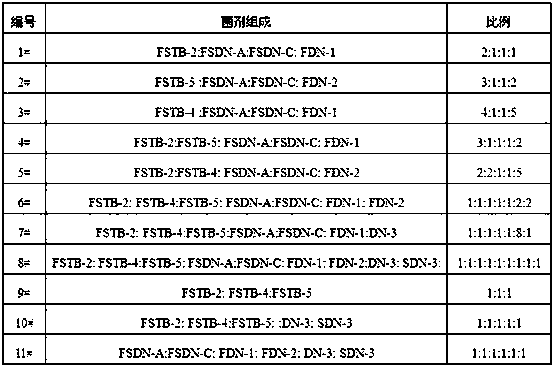
The invention relates to a microbial agent with high salt resistance. The microbial agent comprises at least one of selected from a group consisting of Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2, Microbacterium kitamienseFSTB-4 and Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, also comprises Kocuria palustris FSDN-A and Staphylococcus cohnii FSDN-C, and further comprises at least one of selected from a group consisting of Arthrobacter creatinolyticus FDN-1 and Flavobacterium mizutaii FDN-2. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the above microbial agent. The microbial agent can be directly used fortreating total nitrogen and COD in high-salt wastewater, and can also be added to various biochemical reaction structures to improve microbial composition, optimize the salt tolerance of a microbial system in wastewater treatment and enhance the capability of the system in removing total nitrogen and COD.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Paracoccus with denitrification and phosphorus removal functions and application thereof
ActiveCN114292789AEfficient removalStable survivalBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTotal nitrogen
The invention relates to a Paracoccus sp. With denitrification and phosphorus removal functions, which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) and has the preservation number of CGMCC No.19475. The screened Paracoccus sp. Has anaerobic denitrification and aerobic denitrification effects, and can be used for preparing a phosphorus removal agent. According to the present invention, the strain can efficiently remove the total nitrogen in the water body under the aerobic condition, can reduce the total phosphorus content in the wastewater, and can achieve the total phosphorus removal rate of 63.4% within 72 h when the bacterial liquid inoculation amount is 0.2 vol% and the initial phosphorus content is 13.4 mg / L.
Owner:青岛蔚蓝赛德生物科技有限公司
Bacterium-algae symbiotic system for enhancing pyridine biodegradation under microaerobic condition
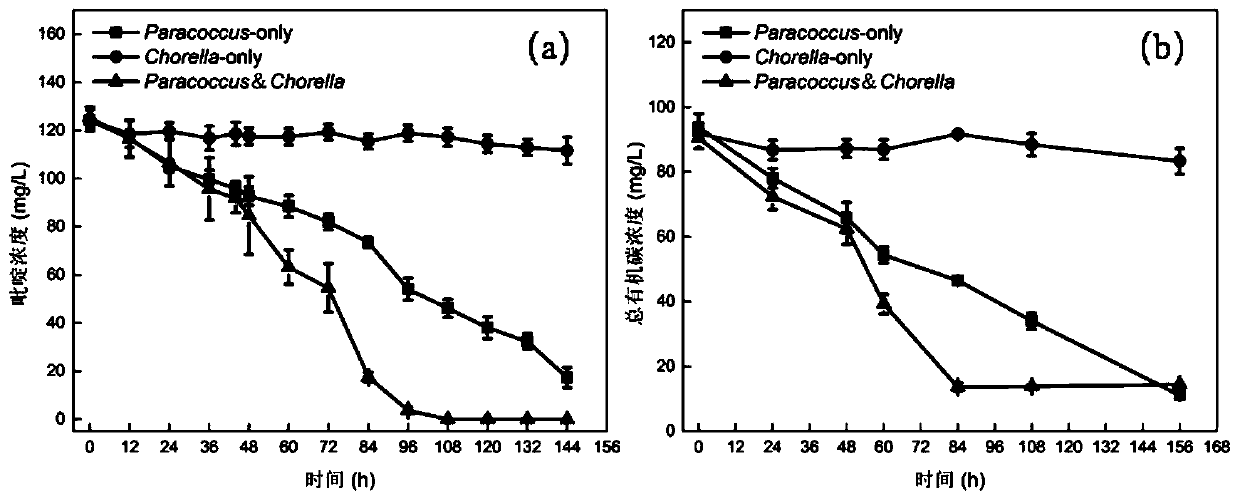
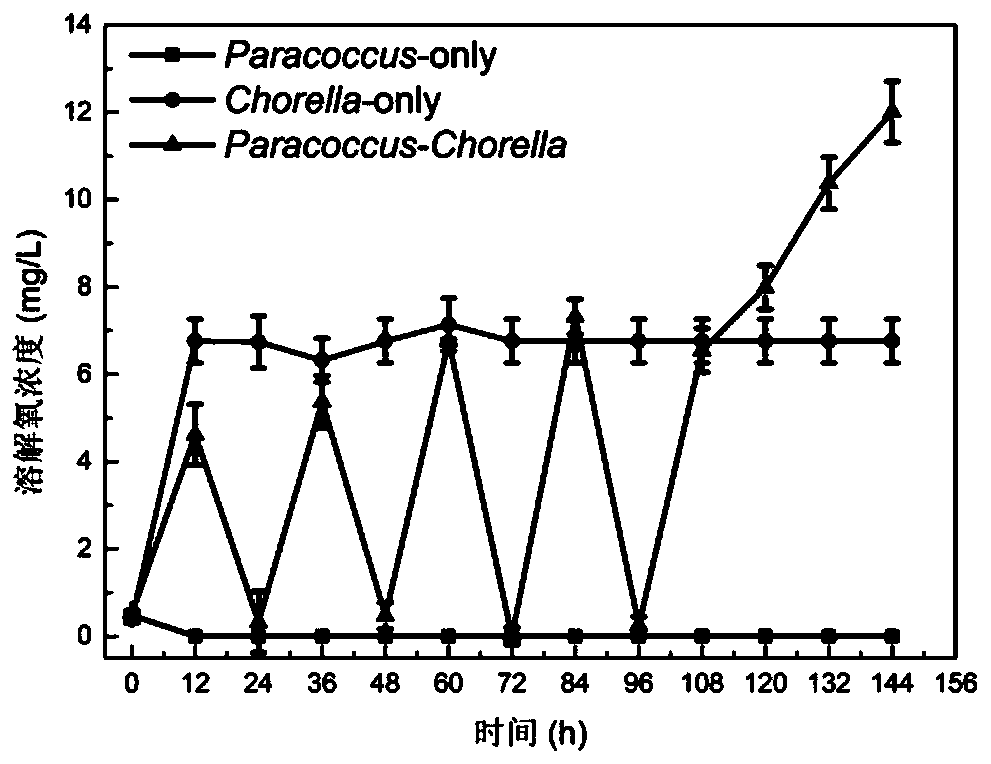
ActiveCN111040965APromote biodegradationPromote degradationBacteriaUnicellular algaeParacoccus sp.Chlorella sp.
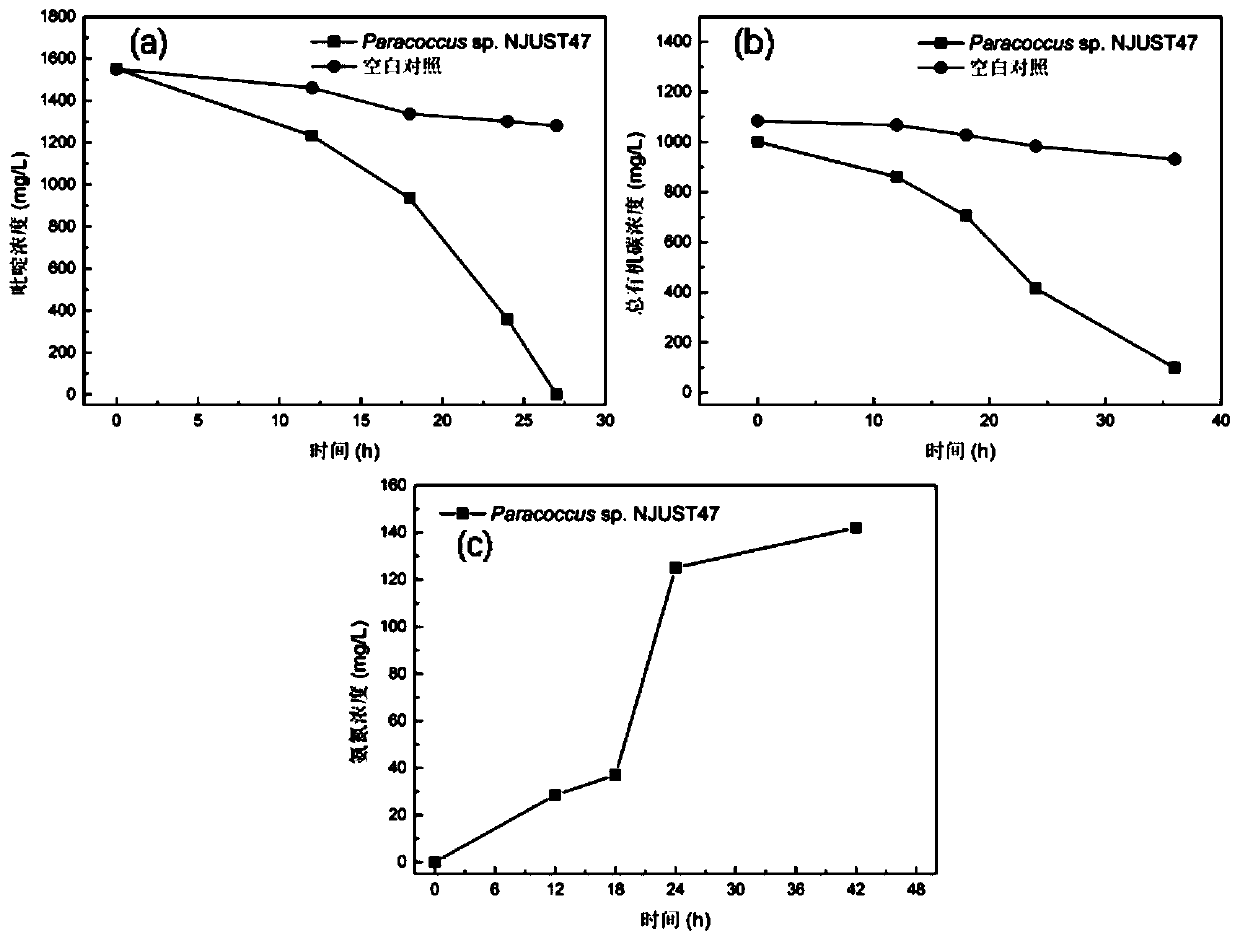
The invention discloses a bacterium-algae symbiotic system for enhancing pyridine biodegradation under a microaerobic condition. The bacterium-alga symbiotic system is formed by carrying out mixed culture on strain Paracoccus sp. NJUST47 with a pyridine degradation function and chlorella sorokiniana FACHB-275 which are used as inoculants. According to the bacterium-algae symbiotic system, paracoccus grows with pyridine as the sole carbon source and nitrogen source, and chlorella grows with ammonia nitrogen generated by pyridine degradation as the nitrogen source. Microalgae in the bacterium-algae symbiotic system generate dissolved oxygen through photosynthesis, the paracoccus realizes efficient degradation of the pyridine under a microaerobic condition by utilizing the dissolved oxygen generated by the photosynthesis of the microalgae, and the maximum degradation rate can reach 45.16 + / -2.4 mg / L / day; the pyridine at a concentration of 100 mg / L can be completely degraded within 60 hours. Meanwhile, in the bacterium-algae symbiotic system, the population growth and sedimentation performance of the microalgae can be obviously improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Paracoccus and application thereof for degrading resorcinol
ActiveCN106754574AIncreased degradation rateIncrease concentrationBacteriaWater contaminantsMicroorganismSynechococcus
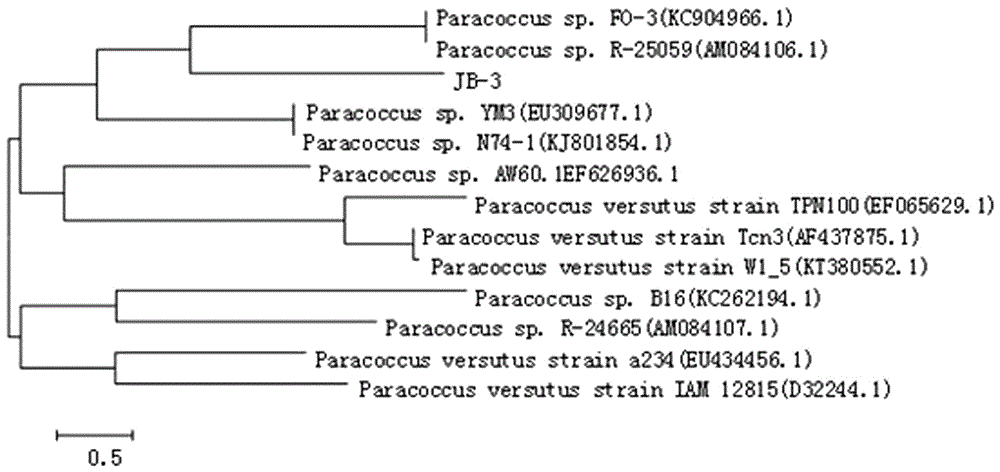
The invention discloses Paracoccus sp.. The paracoccus is Paracoccus sp. JB-3, and is conserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 13th, Jan, 2017, and the conservation number is CGMCC No. 13607. The invention further discloses application of the Paracoccus sp. JB-3 for degrading resorcinol. The Paracoccus sp. JB-3 disclosed by the invention is used for degrading resorcinol in industrial wastewater or natural water body containing the resorcinol; the Paracoccus sp. JB-3 not only has high degradation rate and tolerance concentration, but also is free from secondary pollution, convenient for use, and has a extensive application prospect.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
Treatment method of epichlorohydrin wastewater
ActiveCN106630172AEfficient removalImprove processing efficiencyTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesNature of treatment waterWastewaterHigh calcium
The invention relates to a treatment method of epichlorohydrin wastewater. The treatment method is characterized in that a biochemical method is used to treat the epichlorohydrin wastewater, a manner gradually increasing the concentration of COD and calcium ions in inlet water is adopted during treatment, a halotolerant bacterium is added at the same time, the halotolerant bacterium is (Paracoccus sp.) FSTB-2 which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 1st, 2015, and the preservation number of the (Paracoccus sp.) FSTB-2 is CGMCC No. 10938. The treatment method has the advantages that the specific halotolerant bacterium is added during the treatment of the epichlorohydrin wastewater, a treatment system can tolerate high-salt and high-calcium environments, COD in the wastewater can be removed efficiently, and the method is simple in process, high in treatment efficiency, low in treatment cost and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Opening type culture method and applications of Paracoccus FSTB-2
ActiveCN106635859AEasy to handleReduce pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynechococcusNalidixic acid
The present invention relates to an opening type culture method of Paracoccus FSTB-2, wherein a bactericide is poured during the opening type culture process of Paracoccus FSTB-2, the Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 1, 2015 and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.10938, and the bactericide is one or a plurality of materials selected from lincomycin, rifamycin SV, nalidixic acid, guanidine hydrochloride, and the like. According to the present invention, according to the bacterium characteristic of Paracoccus FSTB-2, the specific bactericide is poured during the opening type culture process of Paracoccus FSTB-2 by using the salt-containing and COD-containing wastewater, such that the bacterial contamination can be significantly reduced, and the Paracoccus FSTB-2 growth and reproduction and the wastewater treatment effect cannot be affected.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Paracoccus GN-9 and application thereof
ActiveCN114410545AShorten the growth cyclePromote growthAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaBiotechnologyMicroorganism resource
The invention belongs to the field of microbial resource development and utilization. The invention discloses a paracoccus sp. GN-9, and the preservation number of the paracoccus sp. GN-9 is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.23114. The paracoccus sp. The strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC for short) on August 5, 2021. The Paracoccus sp. GN-9 is short in culture period, free of ecological toxicity, rich in available carbon source variety, resistant to salt and alkali, capable of fixing nitrogen in a self-living mode, capable of decomposing insoluble phosphorus in soil and secreting indoleacetic acid and siderophores at the same time, capable of remarkably promoting growth of corn and rice and quite wide in application prospect in microbial fertilizer production.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compound microbial agent for treating black and odorous bottom mud and its application
ActiveCN111647530BPromote oxidative decompositionImprove degradation efficiencyBacteriaSludge treatment by oxidationBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
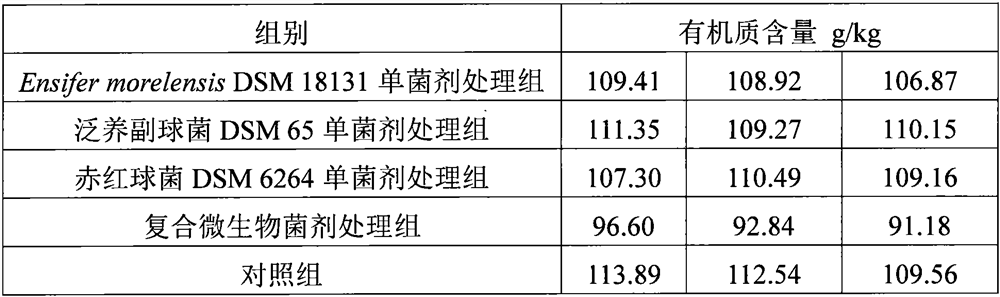
The invention discloses a composite microbial agent for treating black and odorous bottom mud and application thereof. The active ingredients of the composite microbial agent for treating the black and odorous bottom mud provided by the invention consist of Ensifer morelensis, Paracoccus pantotrophus and Rhodococcus ruber. The active ingredients of the microbial agent for treating the black and odorous bottom mud provided by the invention are cultures obtained by culturing the composite microbial agent for treating the black and odorous bottom mud by using a culture medium. The invention alsoprovides a biological oxidation reactor containing the composite microbial agent for treating the black and odorous bottom mud and / or the microbial agent. The composite microbial agent for treating the black and odorous bottom mud, the microbial agent or the biological oxidation reactor has obvious oxidation effect on the black and odorous bottom mud, has organic matter removal rate obviously higher than that of single-bacterium treatment, can be used for treating and repairing the black and odorous bottom mud, and has good application prospect.
Owner:微米环创生物科技(北京)有限公司
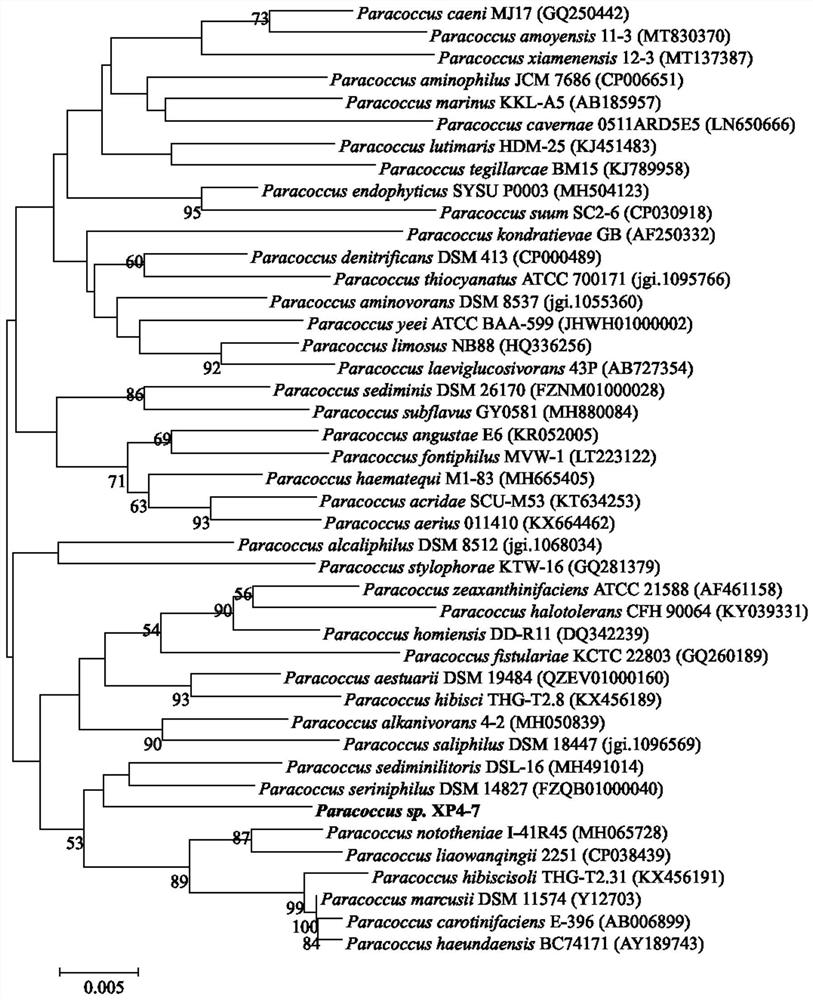
Alkane degrading functional bacterium XP4-7 and application thereof
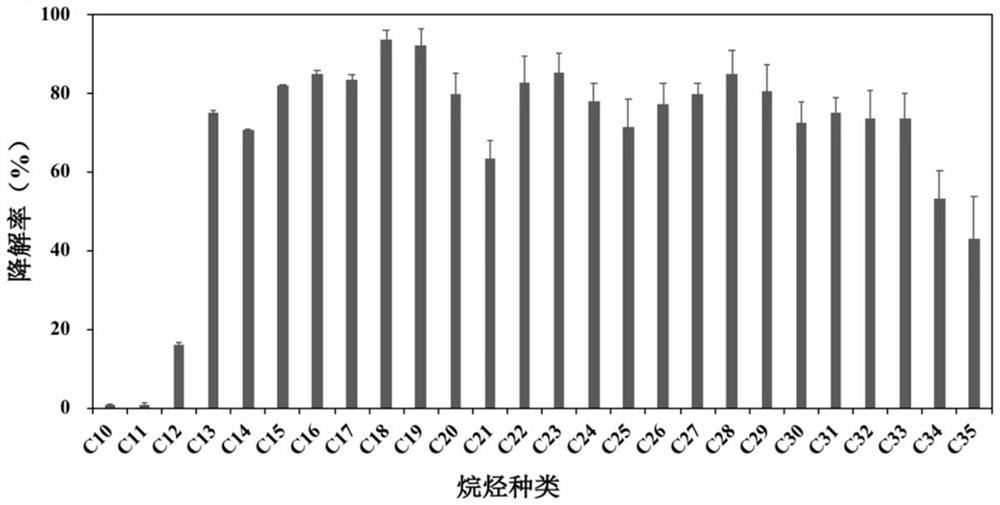
The invention discloses an alkane degrading functional bacterium XP4-7 and an application thereof. The strain is Paracoccus sp. XP4-7, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the preservation number is CGMCC No.22994, and the preservation date is July 30, 2021. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the paracoccus sp. Experiments prove that the strain XP4-7 has an excellent capability of degrading alkanes, the degradation rates of total alkanes in petroleum and diesel oil are 48% and 62% respectively, and the strain XP4-7 can be widely applied to alkane degradation and petroleum pollution remediation, such as petroleum pollution ocean water remediation and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of paracoccus and its culture application
ActiveCN106635858BRapid degradation and removalReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
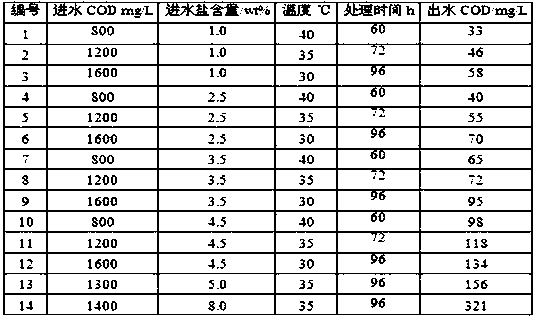
The invention relates to paracoccus sp. and a culture application thereof. The strain is paracoccus sp. FSTB-2, collected at 'China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center' on June 1, 2015, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 10938. The strain can be applied to efficiently removing COD (chemical oxygen demand) in salty wastewater with salt content of 1.0wt%-8.0wt%, and can grow at the high temperature of 40 DEG C. The invention further provides COD removing salt-tolerant bacteria which comprise the paracoccus sp. FSTB-2. The COD in the high-salt wastewater can be rapidly degraded by the paracoccus sp., the paracoccus sp. is high in salt resistance and good in treatment effect, combining strains are omitted, and the production cost of the salt-tolerant bacteria is greatly reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Enhanced CFBR process applied to treatment of wig wastewater containing high ammonia nitrogen
ActiveCN113292159AHigh removal rateNo secondary pollutionWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAmmoniacal nitrogenThauera
The invention discloses an enhanced CFBR process applied to treatment of wig wastewater containing high ammonia nitrogen. The method comprises the steps: performing amplification culture on Thauera sp. FDN-01 and Paracoccus sp. FDN-02 strains to prepare a high-efficiency denitrification engineering bacterial agent, respectively adding the high-efficiency denitrification engineering bacterial agent into an anoxic tank and a hypoxic tank of a CFBR treatment device, and intensively removing high-concentration ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen in the wig wastewater under the action of various denitrification functional enzymes. The process disclosed by the invention is applied to treatment of high-concentration ammonia nitrogen in the actual wig wastewater, the effluent quality stably reaches and is far lower than the A-level limit value of 'Water quality standard for sewage discharged into urban sewers' (GB / T 31962-2015) under the condition of normal temperature, and the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen in the wig wastewater is high. The method is free of secondary pollution to the environment and low in treatment cost and energy consumption.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
A kind of treatment method of rifamycin production wastewater
ActiveCN106746161BEfficient removalImprove processing efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention relates to a treating method for wastewater produced in production of rifamycin. The treating method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreating wastewater produced in production of rifamycin by using advanced oxidation technology; (2) subjecting oxidation effluent to coagulating sedimentation and carrying out filtering to remove sediments; (3) carrying out anaerobic biochemical treatment on effluent of filtering; and (4) subjecting anaerobic effluent to treatment via a biological contact oxidation process and adding salt-resistant COD-removing bacteria, wherein the salt-resistant COD-removing bacteria are Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2 and / or Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, and Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2 and Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5 are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 1, 2015, with accession numbers of CGMCC NO. 10938 and CGMCC NO. 10940, respectively. According to the invention, the process of advanced oxidation, coagulating sedimentation, anaerobic biochemical treatment and biological contact oxidation is employed, and the specific salt-resistant COD-removing bacteria are added into a contact oxidation unit and can tolerate antibiotics in the wastewater, so high-efficiency stable removal of CODs in the wastewater is realized; and the treating method has the characteristics of simple process, high treating efficiency, low treating cost, etc.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Paracoccus and its bacterial agent, preparation method and application
ActiveCN104877916BIncrease contentPromotes immediate releaseFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFamily Rhodobacteraceae
The invention discloses a paracoccus and its preparation, preparation method and application. The paracoccus is Paracoccus limosus (Paracoccus limosus) A36. Date: November 21, 2014, deposit number: CGMCC No. 10032; the Paracoccus belongs to the kingdom Bacteria, the phylum Proteobacteria, the class α-Proteobacteria, the order Rhodobacteria, the family Rhodobacteraceae, and the genus Paracoccus. The bacterial agent in which the paracoccus is the active ingredient is a bacterial agent made from the paracoccus actinomycetes through plate culture, seed culture, and fermentation; the preparation method of the bacterial agent in which the bacillus is the active ingredient includes a flat plate Cultivation, seed cultivation, fermentation, and bacterial agent preparation steps; the application of the bacterial agent in preparing phosphorus-dissolving, potassium-relieving, and improving soil quick-acting nitrogen-based fertilizers.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI +1
A kind of processing method of epichlorohydrin waste water
ActiveCN106630172BEfficient removalImprove processing efficiencyTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesNature of treatment waterWastewaterHigh calcium
The invention relates to a treatment method of epichlorohydrin wastewater. The treatment method is characterized in that a biochemical method is used to treat the epichlorohydrin wastewater, a manner gradually increasing the concentration of COD and calcium ions in inlet water is adopted during treatment, a halotolerant bacterium is added at the same time, the halotolerant bacterium is (Paracoccus sp.) FSTB-2 which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 1st, 2015, and the preservation number of the (Paracoccus sp.) FSTB-2 is CGMCC No. 10938. The treatment method has the advantages that the specific halotolerant bacterium is added during the treatment of the epichlorohydrin wastewater, a treatment system can tolerate high-salt and high-calcium environments, COD in the wastewater can be removed efficiently, and the method is simple in process, high in treatment efficiency, low in treatment cost and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Piperazine degraded paracoccus PQ-01 and application thereof
ActiveCN103114065BReduce manufacturing costEasy to useBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyStaining
The invention provides a degradation microbial inoculum for eliminating piperazine residue, and belongs to the high technical field of biology. The strain is gram staining reaction negative strain PQ-01, and is identified to be paracoccus sp., wherein the main biological characteristics are gram negative, spherical or club shape, asporous and non-motile. The strain can grow by taking piperazine as the unique carbon source and nitrogen source, and can be completely mineralized. 100mg / L of piperazine can be degraded to a level which cannot be detected in 24 hours by the strain under a shaking condition in the lab, so that the problem that the piperazine is difficult to biodegrade in waste water treatment can be solved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Buprofezin pesticide residual degrading bacteria and produced microbial inoculum thereof
InactiveCN101560482BEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGram stain negativeBiological property
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com