Astaxanthin producing strain and application thereof
A technology of astaxanthin and strains, applied in the directions of bacteria, microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of the production process not meeting the requirements of industrial production, the difficulty of extraction and separation, and the complex culture conditions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
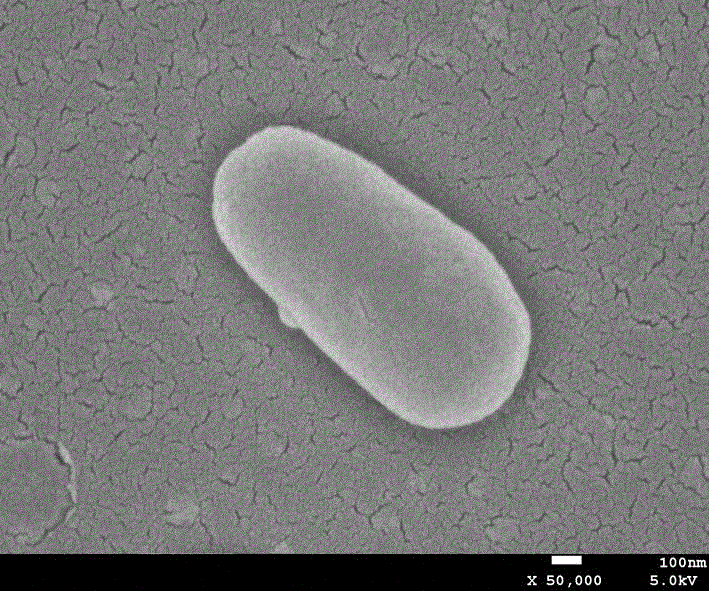
[0019] Embodiment one: Paracoccus Paracoccus Screening and isolation of sp. SCU-M53
[0020] The locust samples used in the experiment are adults of acrida cinerea, which are mostly distributed in farmland and vegetable gardens. They were captured in batches in May 2014 from the vegetable garden of Anren Town, Dayi County, Chengdu City, Sichuan Province (30°52' north latitude, 103°62' east longitude, 495 meters above sea level). After the microorganisms were eluted from the locust body surface with sterile water, they were spread on TSB, LB, Gaoshi No. 1, PDA, beef extract peptone and ISP-3 medium by dilution plate method for culture, 37 o C culture until visible colonies appear, and then identify the bacteria after purification.
[0021] Description of strains:
[0022] Aerobic bacteria, Gram-negative, the colonies are orange-red. Oxidase and catalase positive. The optimum pH growth range is 5 to 9, and the optimum growth salt concentration is 0 to 1%. The bacteria has...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Embodiment two: Paracoccus Paracoccus Multiphasic taxonomic identification of sp. SCU-M53
[0024] the strain Paracoccus The carbon source utilization of sp. SCU-M53 was identified by the Biolog automatic bacterial identification system, the fatty acid composition was determined by GC-MS analysis, and the enzymatic characteristics were identified by API ZYM reagent strips. The reference strain was Paracoccus niistensis KCTC 22789 T with Paracoccus chinensis NBRC 104937 T . The result is as follows:
[0025] Available carbon sources: dextrin, α-D-glucose, Tween 40, Tween 80, D-fructose, maltose, L-arabinose, β-hydroxybutyrate, α-ketoglutarate, D,L- Lactic Acid, Malonic Acid, Propionic Acid, Succinic Acid, Bromosuccinic Acid, Succinamic Acid, D-Alanine, L-Asparagine, L-Aspartic Acid, L-Glutamic Acid, Glycerin.
[0026] Enzyme activity: alkaline phosphatase, esterase (C4), lipase (C8), leucine arylase, chymotrypsin and naphthol-AS-BI-phosphohydrolase.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: 16S rRNA gene sequencing and evolutionary tree construction
[0028] The total bacterial DNA was extracted by SDS method, the 16S rRNA gene sequence of the strain was amplified by PCR method, and the DNA sequencing was completed by Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd. Go to the GenBank (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ) database and submit the partial sequence of the 16S rRNA gene measured by each strain for registration to obtain the sequence number. Then perform BLAST comparison on NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) to find the strain with the closest relationship. The sequences of the corresponding strains with the closest relatives were compared by BioEdit, and then the phylogenetic tree was constructed using the Neighbor-Joinin (N-J) method on the software MEGA 5.2. The corresponding primers, reaction system and conditions for PCR are as follows: Primer 27F: 5’-GAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3’ and 1492R: 5’-ACGGCTACCTTGTTACGAC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com