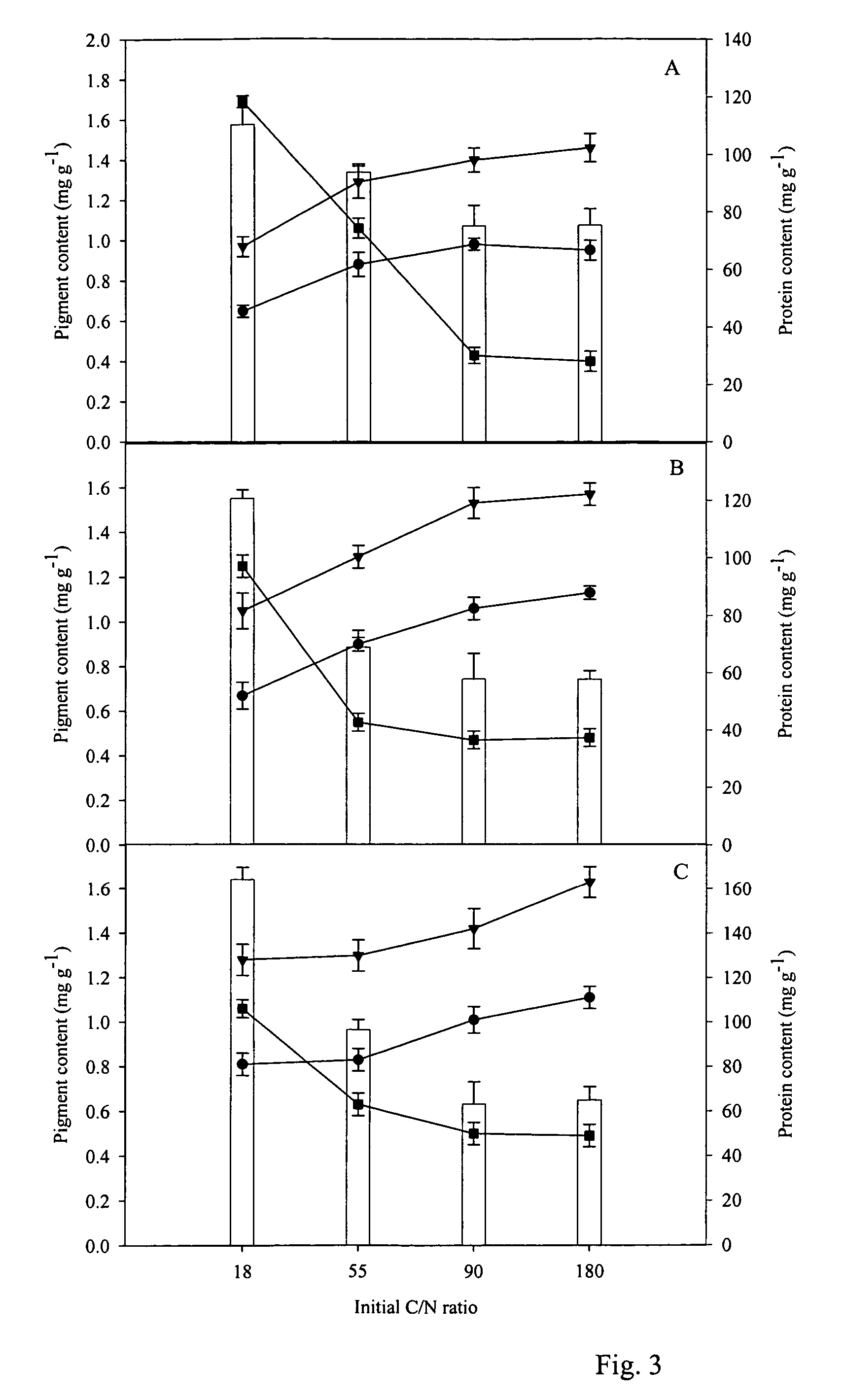
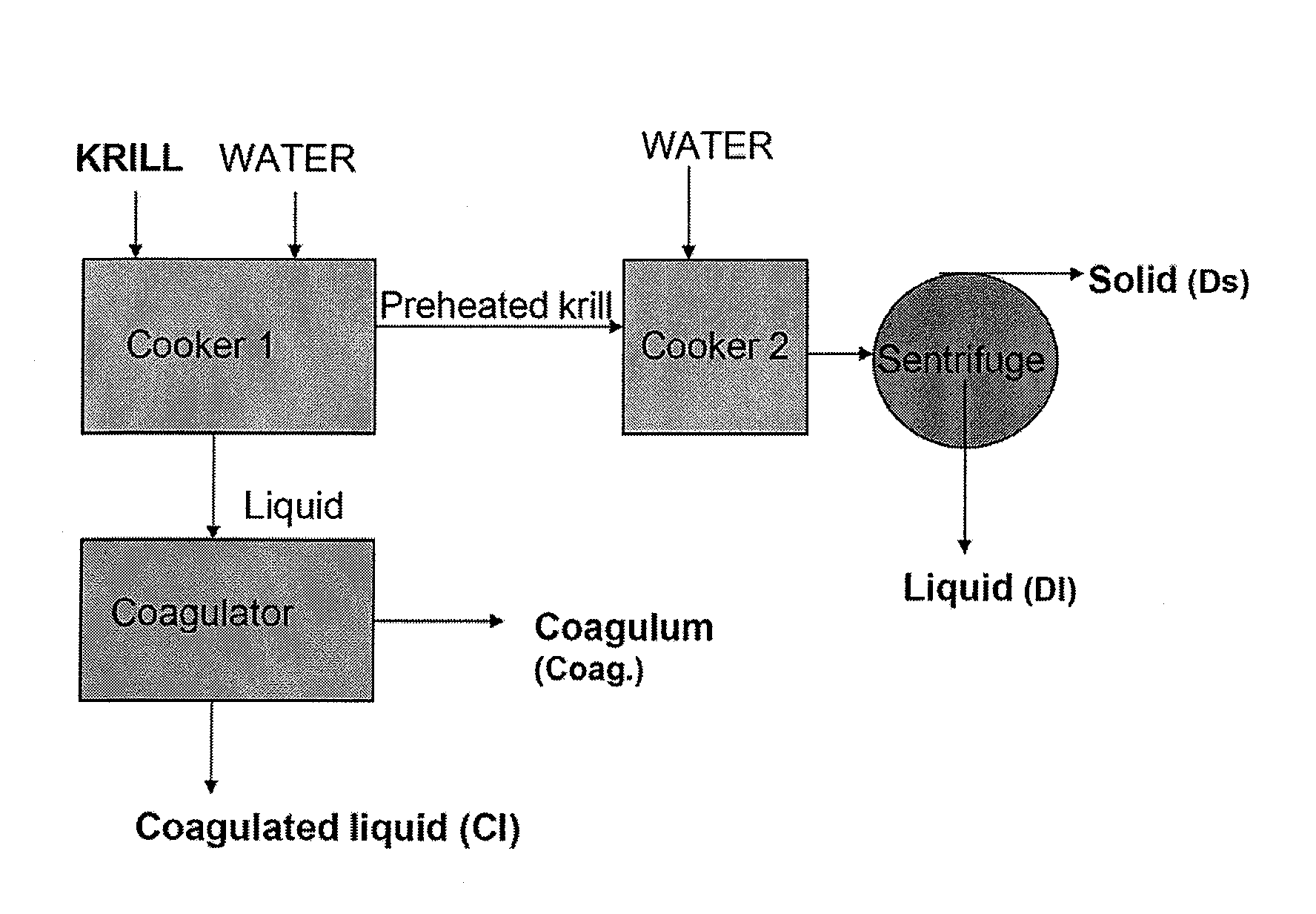
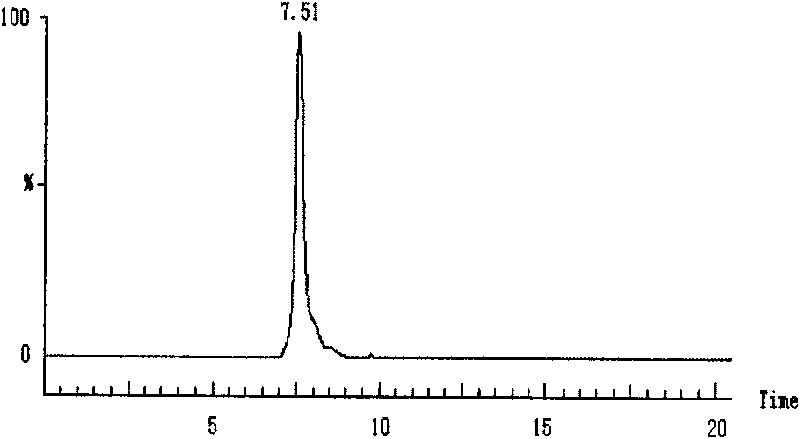
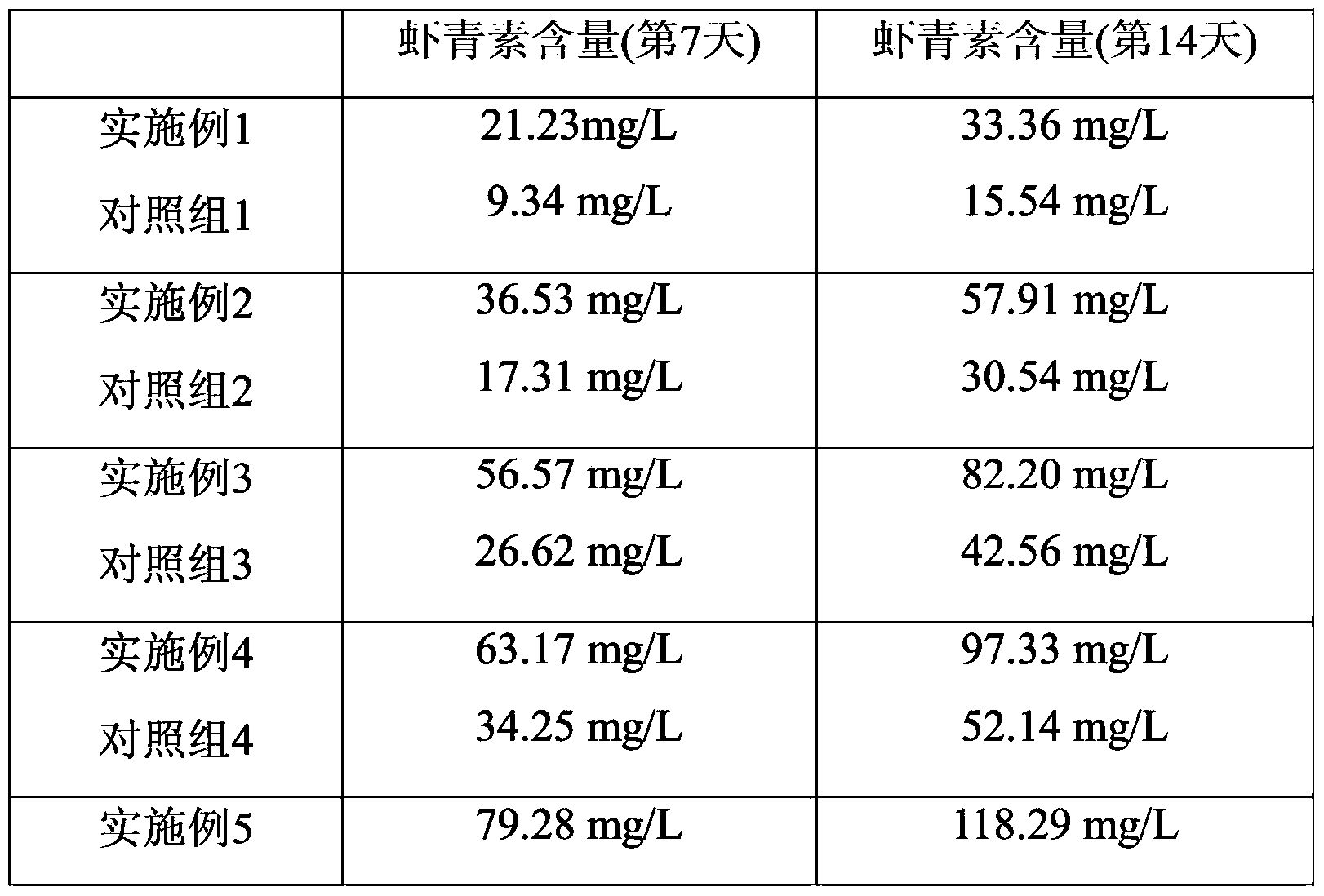
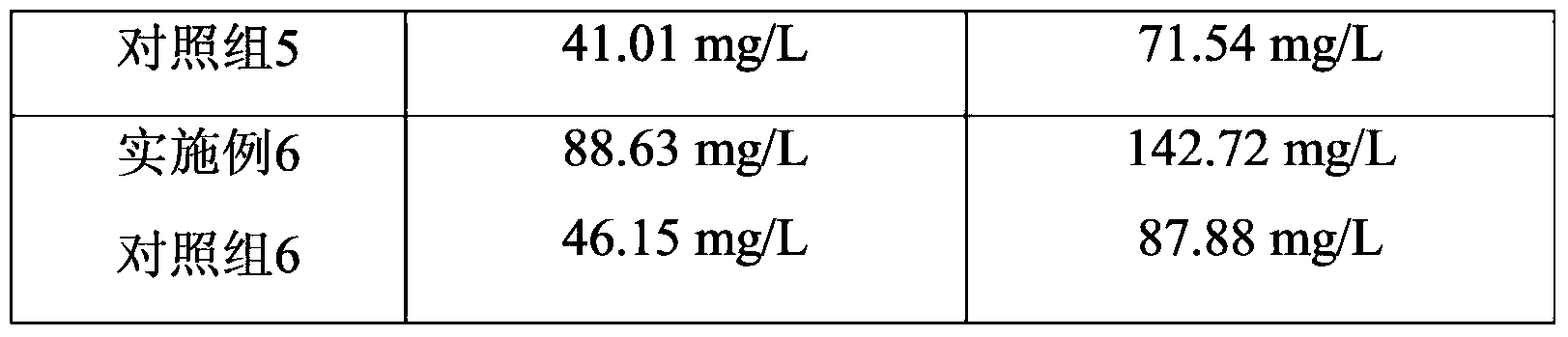
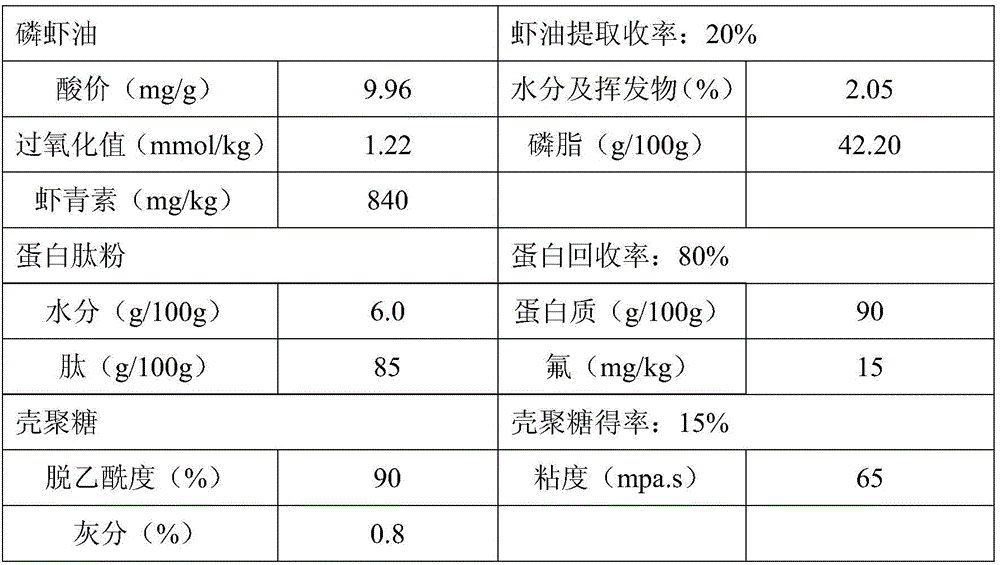
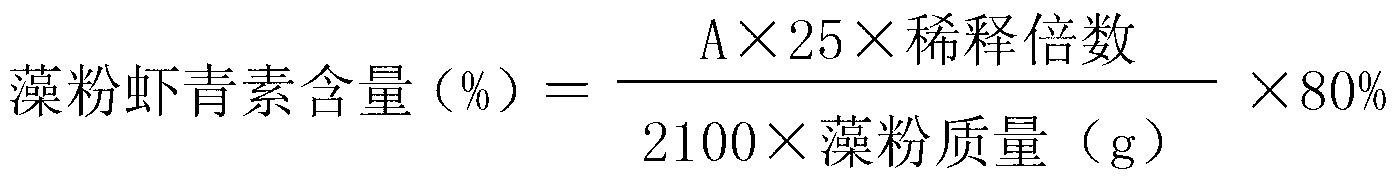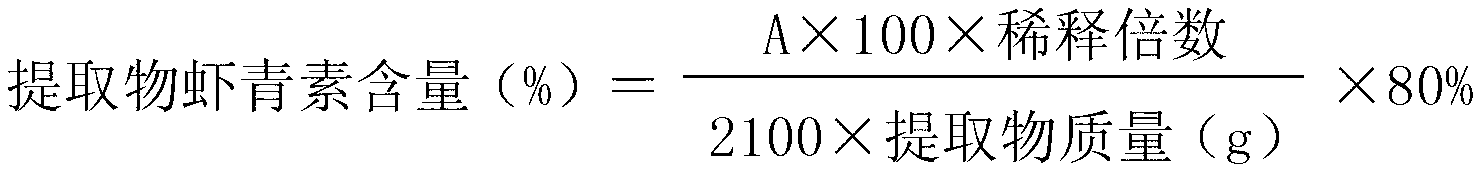Patents
Literature
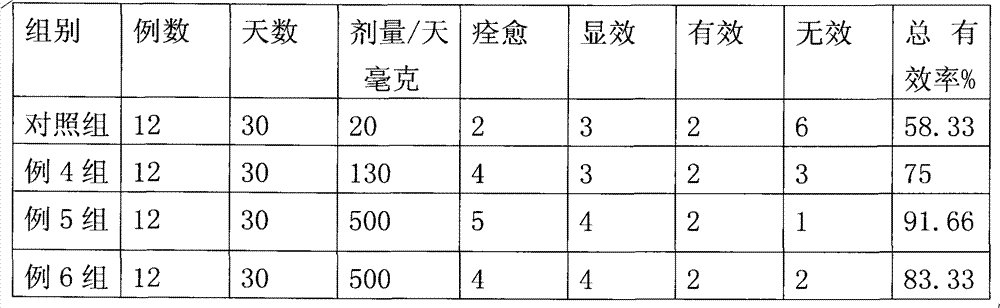
567 results about "Betaxanthins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
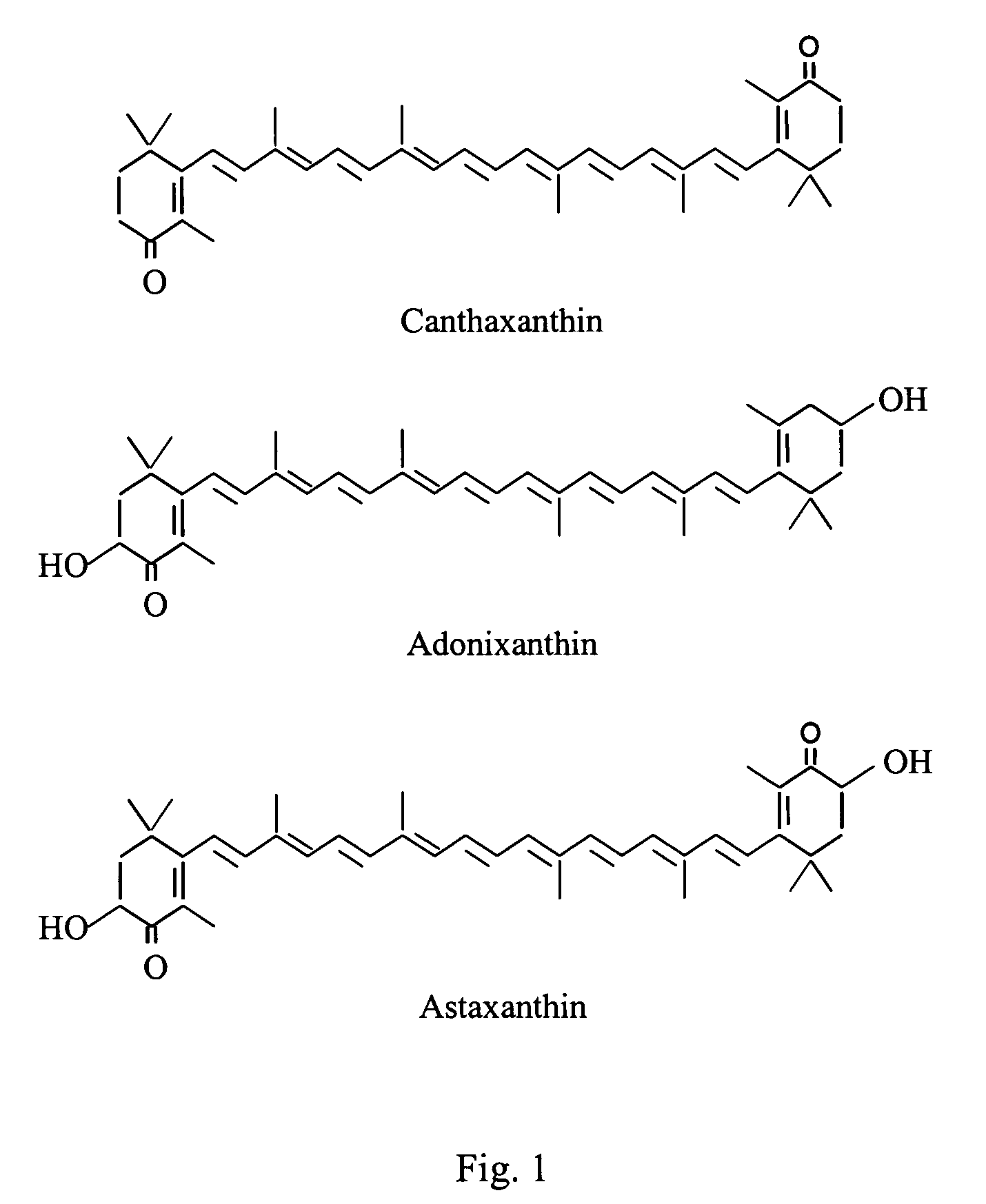
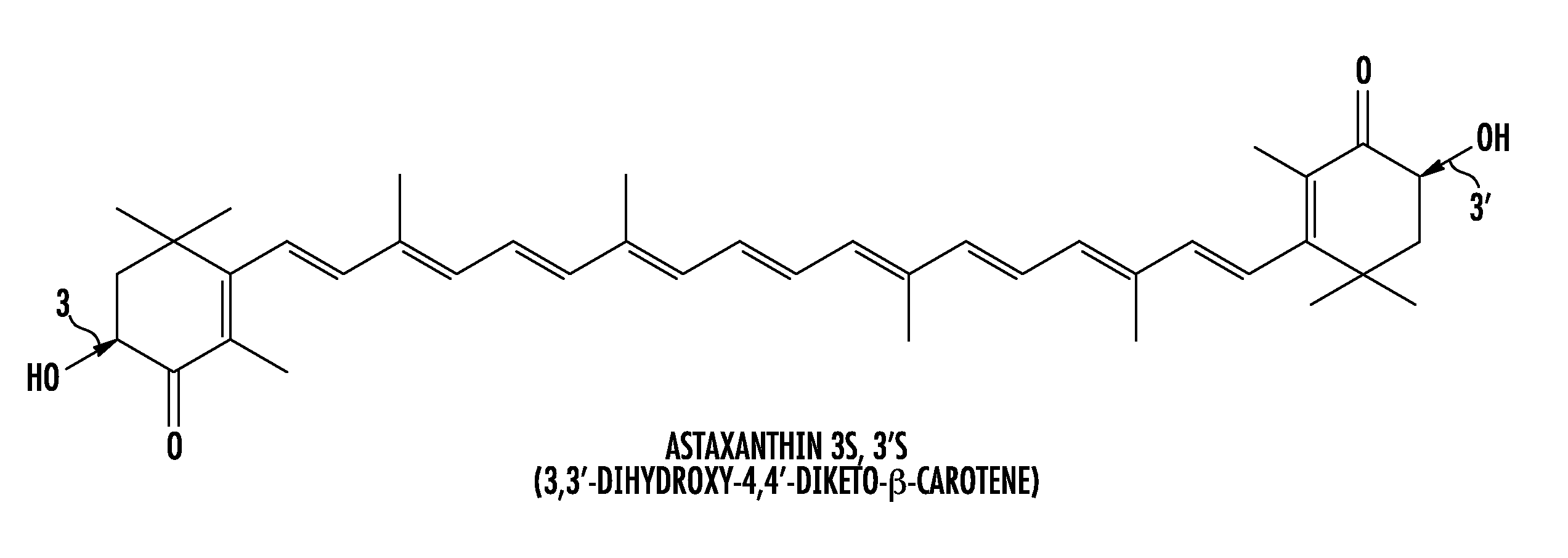
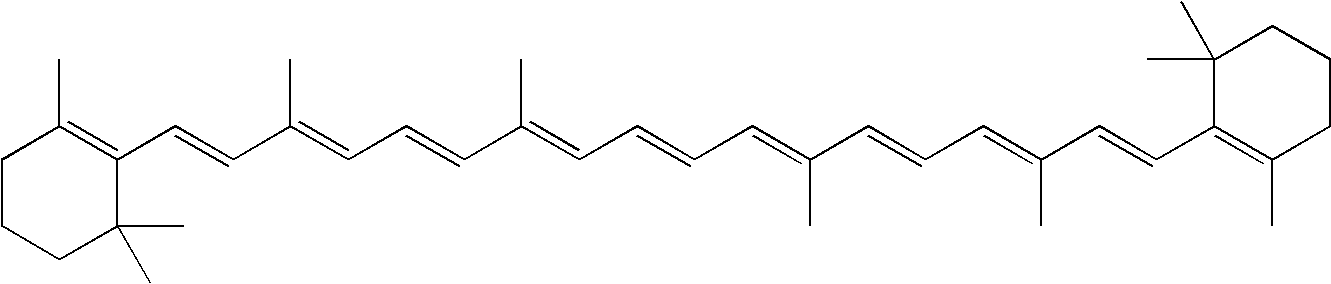
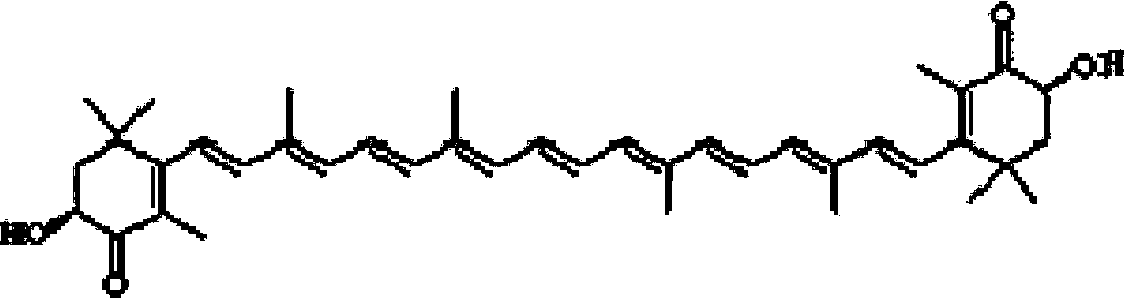
Conjugates of betalamic acid with AMINO ACIDS. Some of them are yellow COLORING AGENTS in the Caryophyllales order of PLANTS. This should not be confused with xanthin which is a term used for CAROTENES nor with XANTHINES.
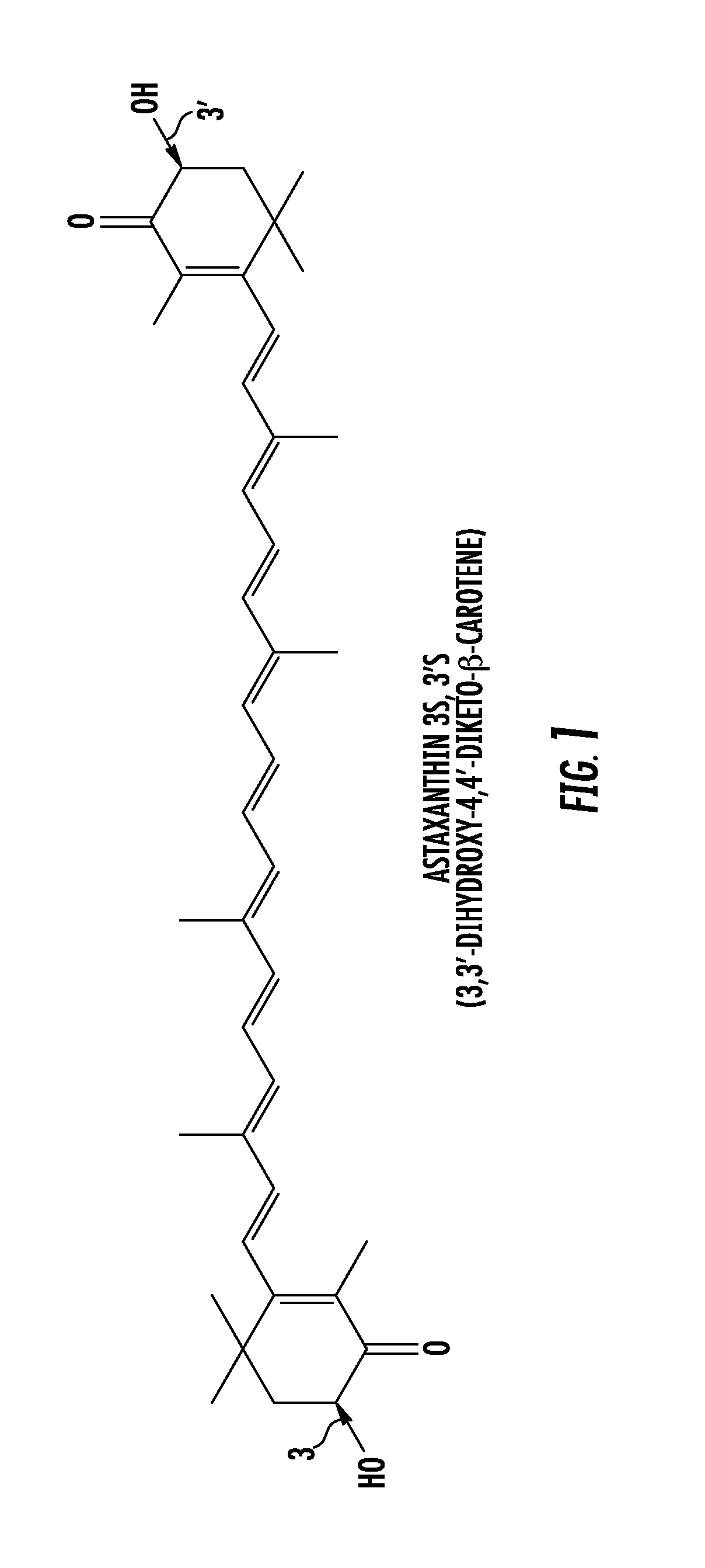
Green Algal Extract Containing Astaxanthin Having High Storage Stability
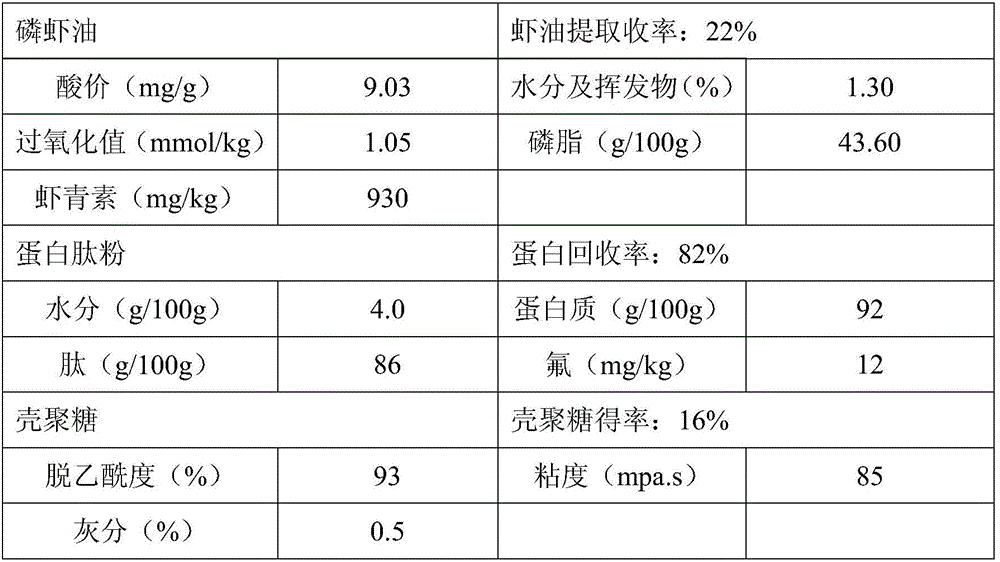
InactiveUS20070196383A1Good storage stabilityEasy to operateBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBetaxanthinsAstaxanthin
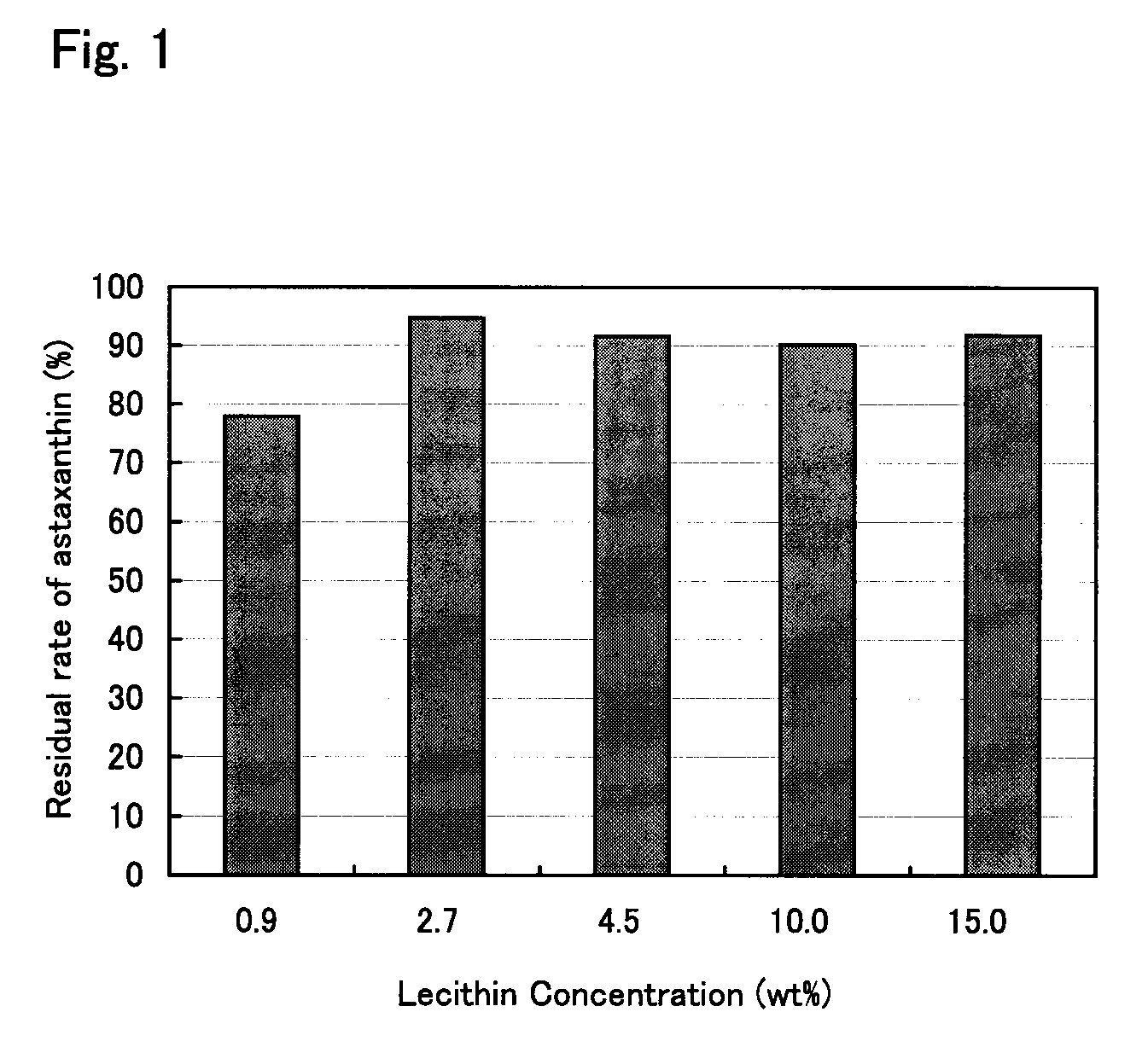
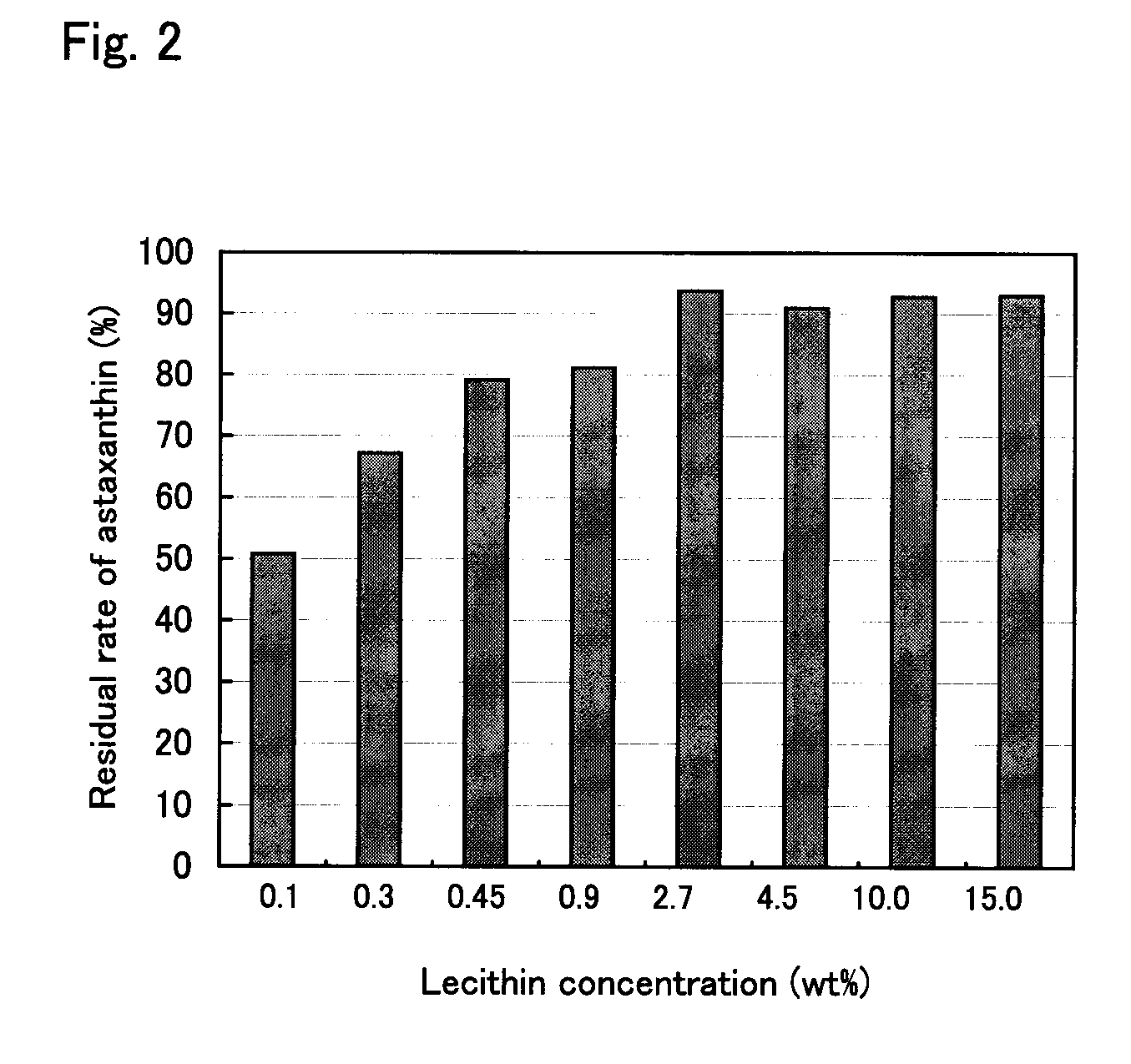
The present invention provides means for increasing the storage stability of astaxanthin in a green algal extract, and a green algal extract containing astaxanthin having high storage stability. The present invention provides a green algal extract comprising astaxanthin at a concentration of 0.5 to 20 wt % expressed in terms of free astaxanthin, and at least one phospholipid at a phospholipid concentration of 0.1 to 15 wt %. This green algal extract has an excellent ability to store stably astaxanthin, and even after storage for one week at 60° C. it is possible to retain approximately 80% or more of the astaxanthin.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Methods for production of astaxanthin from the green microalgae Chlorella in dark-heterotrophic cultures
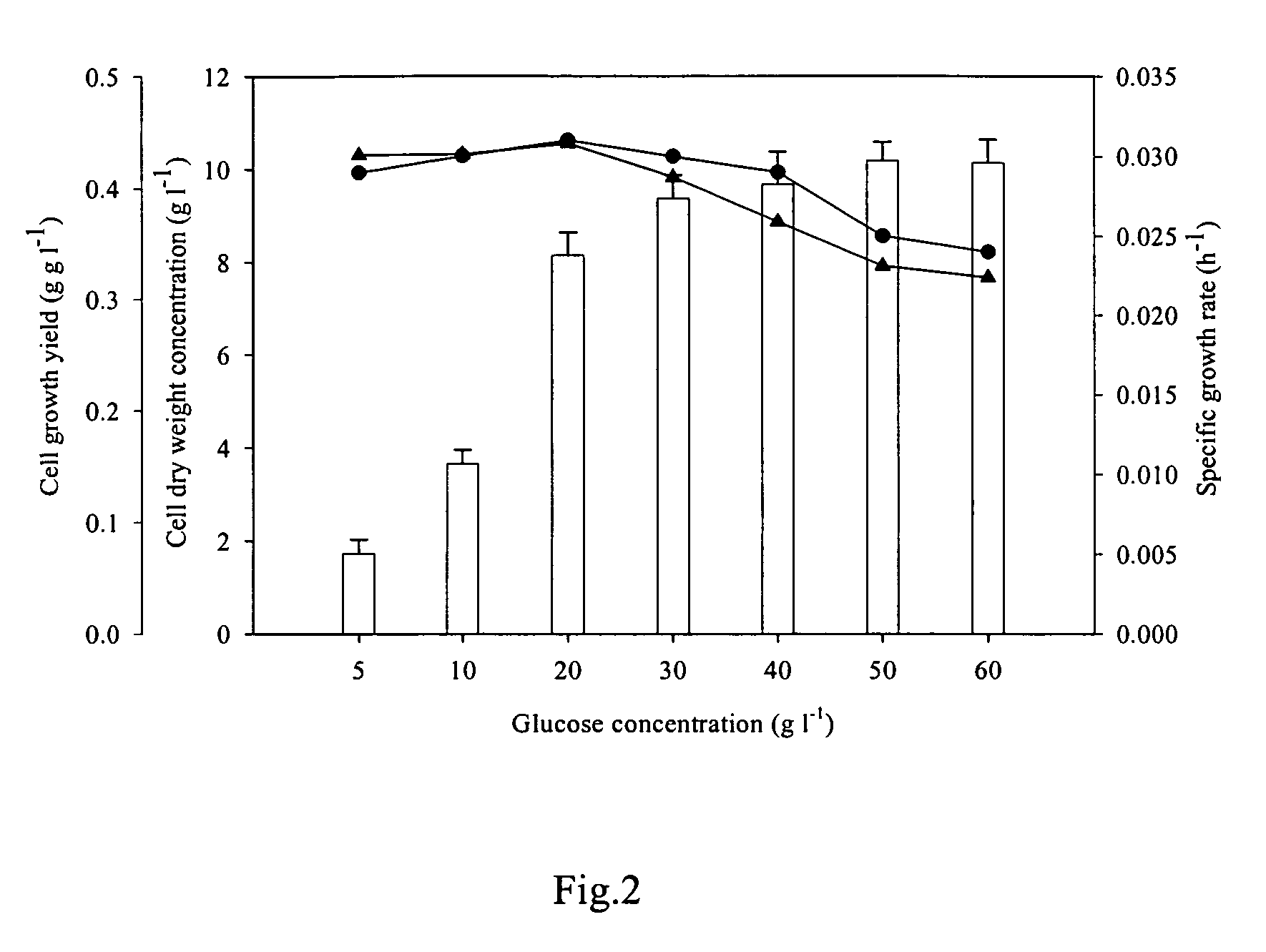
A method for producing the high-value ketocarotenoid astaxanthin by the green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis in dark-heterotrophic cultures shows excellent growth and high-yield astaxanthin production on glucose-supplemented media in the dark. The specific growth rate and astaxanthin yield can be as high as 0.031 h−1, and 10.3 mg l−1, respectively, which are the highest so far reported in heterotrophic algal cultures. The light-independent astaxanthin-producing ability of Chlorella zofingiensis can be employed for commercial production of astaxanthin using industrial fermenters.
Owner:HONG KONG UNIV OF
Method for producing astaxanthin by cultivating haematococcus pulvialis
InactiveCN1392244AEmission reductionSimple processUnicellular algaeChemical recyclingCulture fluidProper treatment
Owner:中国科学院武汉植物研究所
Novel high-efficiency extraction process for astaxanthin in Haematococcus pluvialis
ActiveCN103232375AMeet raw material requirementsSimple extraction methodOrganic chemistryOrganic solventBetaxanthins
The invention discloses a process for extraction of astaxanthin in Haematococcus pluvialis. According to the process, wall-broken Haematococcus pluvialis is obtained by using an acid method, and then an astaxanthin extract is obtained through ethanol dehydration and organic solvent extraction. The wall breaking and extraction process provided by the invention has the advantages of easiness, high efficiency, convenient operation, low energy consumption and controllable quality, and the wall breaking rate and the extraction ratio of Haematococcus pluvialis can reach more than 95%. The astaxanthin extract prepared by using the process is a dark red oily viscous substance and can meet requirements for raw materials needed in production of health food, cosmetics and medicines.
Owner:INNOBIO CORP LTD
Method for retarding and ameliorating fever blisters and canker sores
Astaxanthin is a potent antioxidant, over 500 times more powerful than Vitamin E and 10 times stronger than other carotenoids such as zeaxanthin, lutein, canthaxanthin and beta-carotene. Astaxanthin has also been shown to enhance and modulate the immune system and diminish the damaging effects of UVA sunlight. Disclosed is a method for retarding and ameliorating fever blisters (cold sores) and canker sores. The method comprises administering a source of astaxanthin in a therapeutically effective amount to prevent, retard and ameliorate fever blisters and canker sores. The astaxanthin may be administered orally, topically, or in a combination of oral and topical dosage.
Owner:CYANOTECH CORP
Low viscosity phospholipid compositions
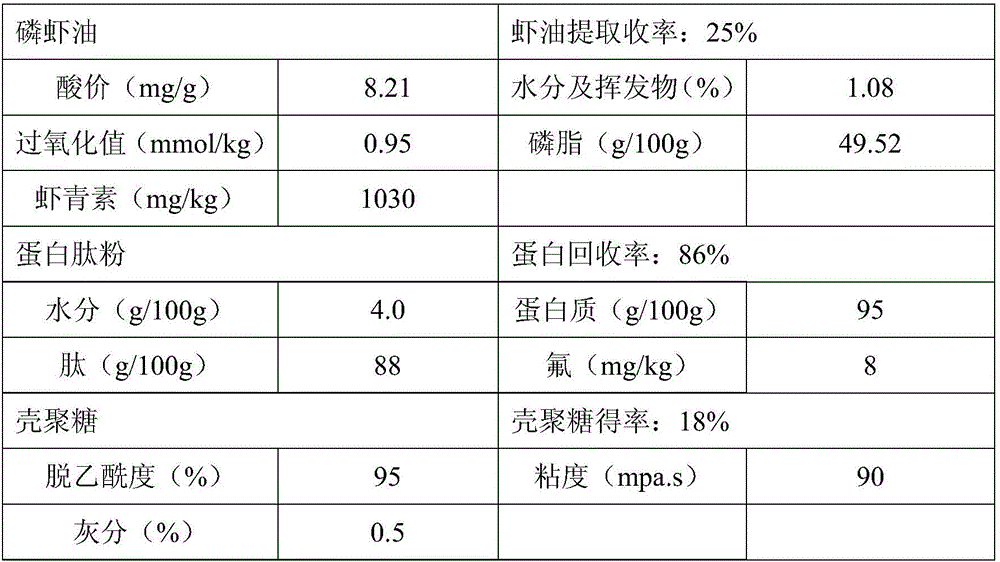
InactiveUS20100226977A1Low viscosityImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAstaxanthinBetaxanthins
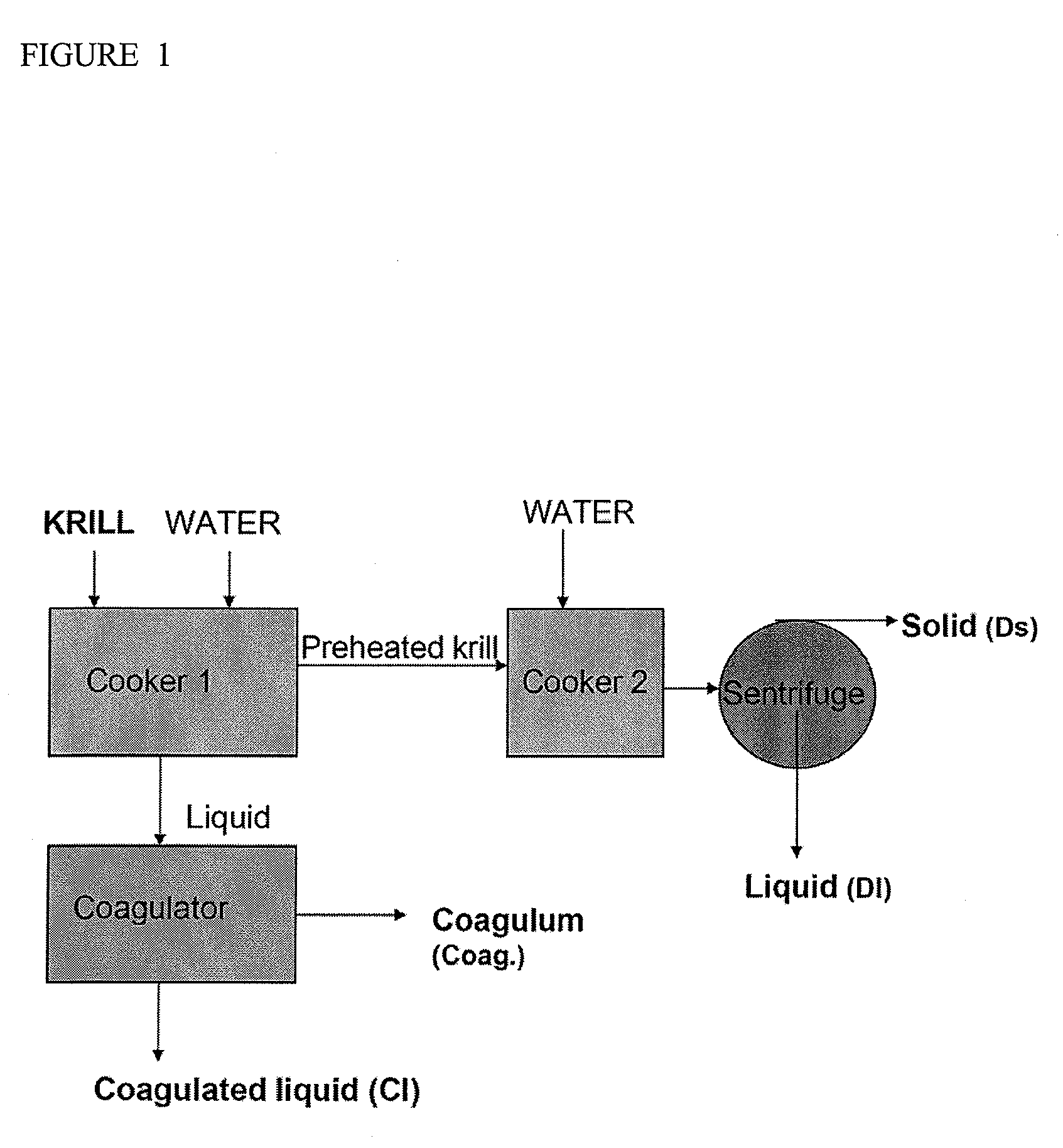
The invention relates to processing crustaceans such as krill to oils comprising phospholipids that are Newtonian fluids and / or and have low viscosity, and in particular to the production of oils containing astaxanthin and phospholipids that show Newtonian fluidity and have a low viscosity.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ANTARCTIC
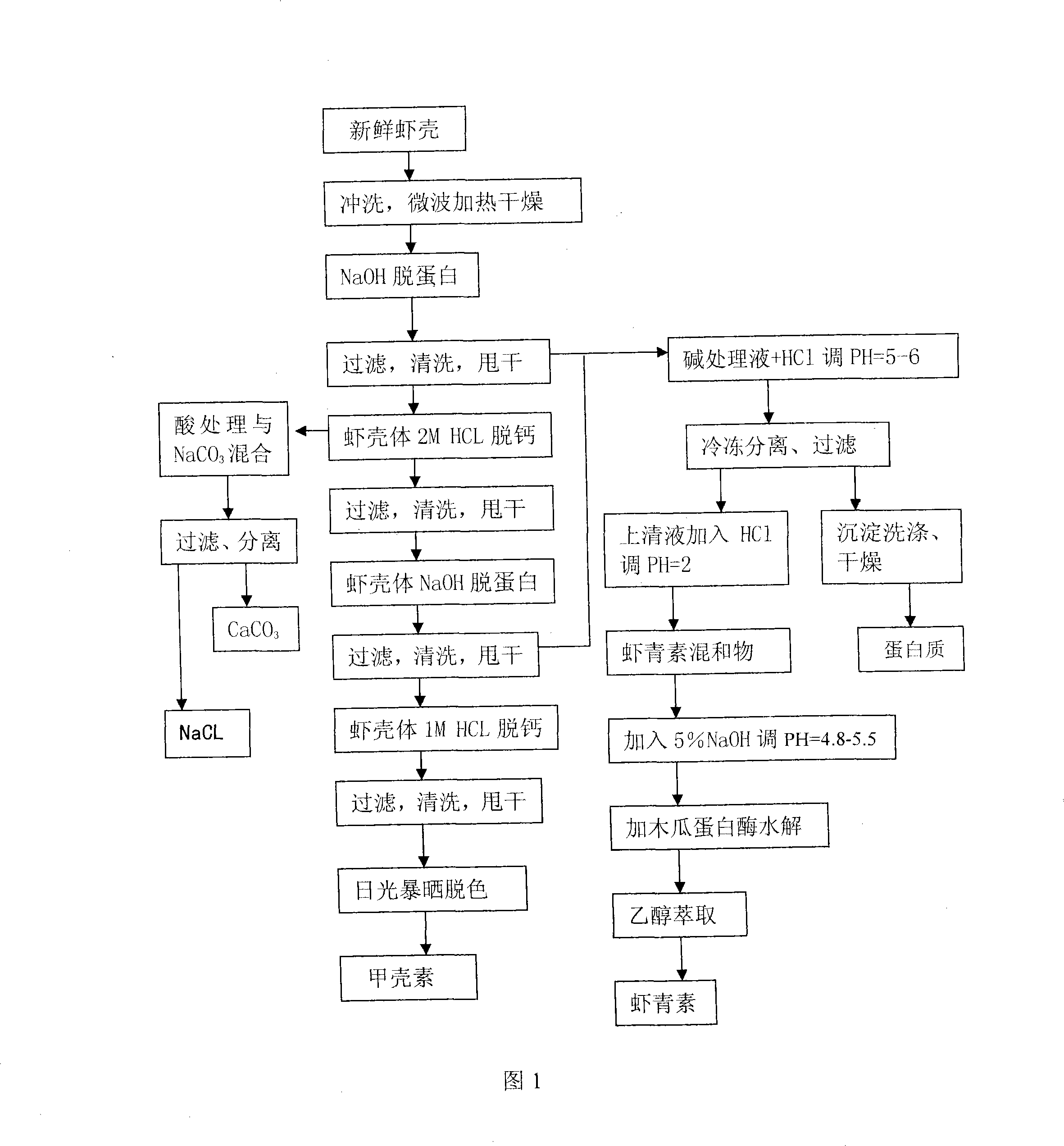
Method for producing chitin, astaxanthin, protein, calcium powder and biological fertilizer from shrimp shell
ActiveCN1715255AReduce pollutionGood effectAnimal corpse fertilisersClimate change adaptationBetaxanthinsPhytic acid
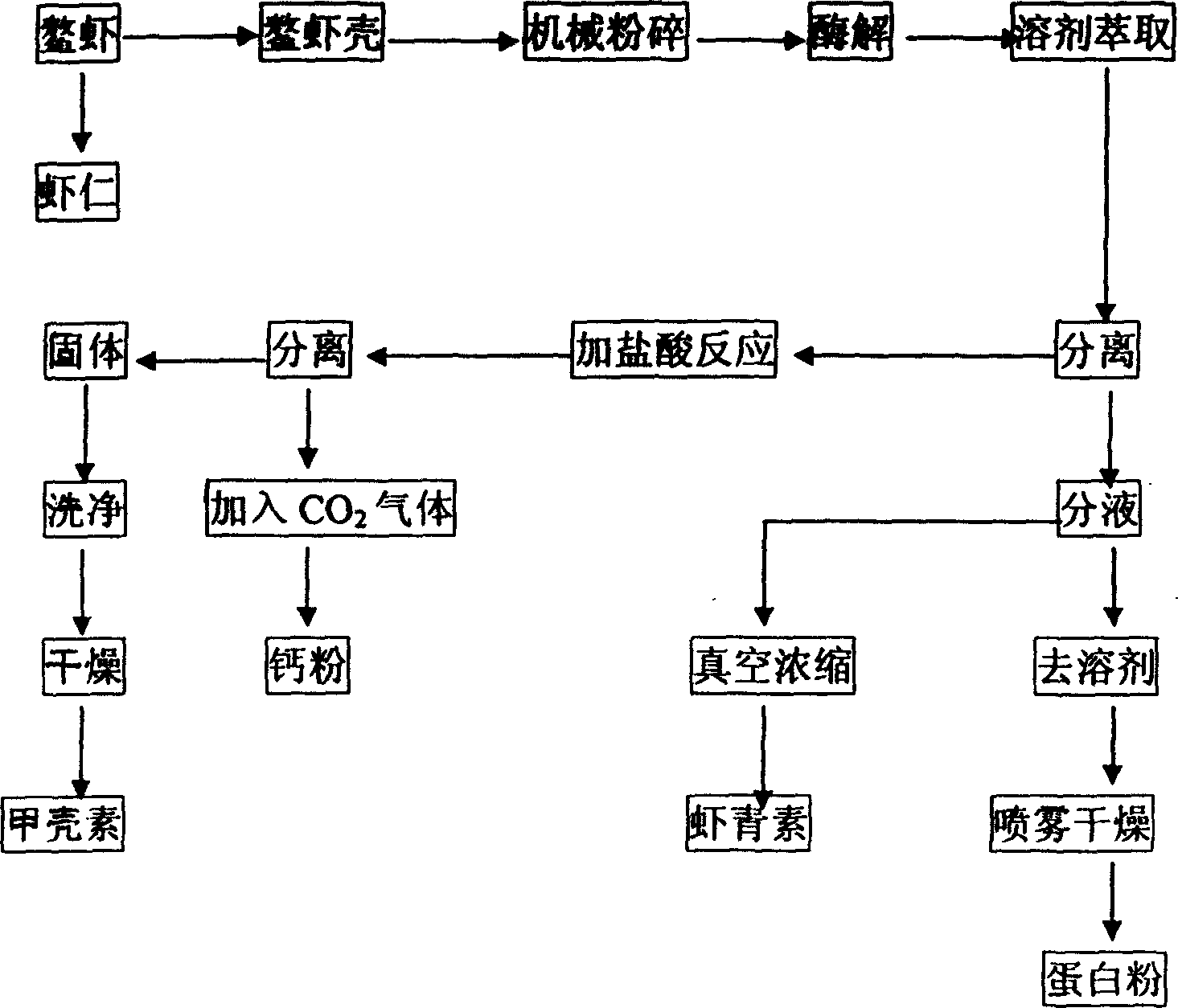
The method of producing chitin, astaxanthin, protein, calcium powder and biofertilizer with shrimp shell includes the following technological steps: crushing shrimp shell, enzymolysis with composite enzyme, extracting with organic solvent, reaction and separating liquid from solid; separating the liquid into hydrolysis liquid and organic liquid ; vacuum concentrating the organic liquid to obtain coarse astaxanthin; eliminating organic solvent from hydrolysis liquid, vacuum concentrating and spray drying to obtain protein powder; soaking the solid in 3 % concentration hydrochloric acid and rinsing to obtain chitin; introducing CO2 gas to the waste acid solution and filtering to obtain active calcium powder; ultrafiltering the coarse astaxanthin liquid to obtain astaxanthin; adding phytic acid and active oligose into the effluent to obtain nutritious liquid as biofertilizer.
Owner:林大昌
Health care food containing natural astaxanthin
InactiveCN101053409AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove immunityFood shapingFood preparationSide effectPropolis
The patent relates to health foods containing natural astaxanthin, which is made into liquid capsule containing natural astaxanthin with natural astaxanthin oil, edible oil and fat and natural antioxidant as raw materials by conventional processing; or which is made into power capsule or tables containing natural astaxanthin with natural astaxanthin, natural antioxidant and other health food as raw materials by conventional processing. In comparison with present technology, the advantage of the invention includes, (1) the health food provided in present patent takes natural astaxanthin as main raw material, has the strongest antioxidant, capable of improving human immunity and anti-aging and ranking first in terms of health foods containing natural antioxidant; (2) the health food is made from pure natural materials and without any compound materials and side-effect; (3) the natural astaxanthin of health food coordinately used with shark cartilage, glucosamine hydrochloride, chitosan, propolis and paclitaxel etc as function material, which is capable of enhancing astaxanthin function; (4) adding antioxidant of natural tea-pigment and tea polyphenols is capable of avoiding oxidation of astaxanthin, thus prolonging shelf life more than one year.
Owner:汪昔奇 +1
Composition and method to alleviate joint pain
Beneficial and synergistic effects for alleviating joint pain and symptoms of osteoarthritis and / or rheumatoid arthritis have been found with krill oil and / or marine oil in combination with other active constituents, including astaxanthin and polymeric hyaluronic acid or sodium hyaluronate (hyaluronan) in an oral dosage form.
Owner:US NUTRACEUTICALS LLC
Inflammatory Disease Treatment
InactiveUS20100291053A1Reduce negative impactBiocideHydrocarbon active ingredientsStress inducedDocosahexaenoic acid
We describe a composition comprising a source of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid, for example, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and a carotenoid, for example, astaxanthin and other nutrients for prophylactic and / or therapeutic use in the healing of trauma- and stress-induced inflammatory conditions.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONUTRITION EURO
Method for extracting astaxanthin from haematococcus pluvialis
InactiveCN101691348ASimple extraction processEasy to keepOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionOrganic solventBetaxanthins
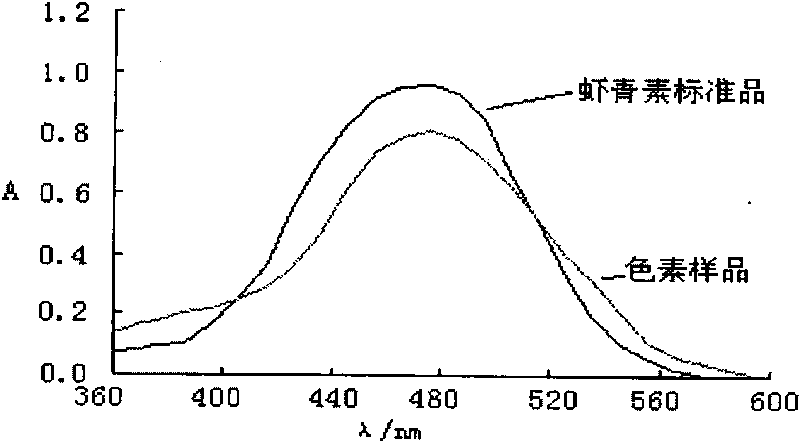
The invention provides a method for extracting astaxanthin from haematococcus pluvialis. Astaxanthin is extracted by adopting above-critical CO2 extracting process. The temperature of an extracting kettle is ranged from 30 to 50 DEG C and the pressure is ranged from 20 to 30 MPa. Flowing speed of CO2 fluid is 20 to 40 L / h and the extracting time is 2 to 4 h. The astaxanthin has strongest inoxidizability and is easy to be oxidized. The extracting method of the invention is simple, rapid and convenient to operate. CO2 is used as the extraction solvent in extraction process, so the production process is environment-friendly and the extraction has no organic solvent residue. The temperature during extraction process is low for efficiently avoiding active substance to decompose at high temperature. The acquired astaxanthin extraction is bolarious pasty substance and can be used as materials for developing health-care food or officinal component.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing astaxanthin extractive from haematococcus pluvialis powder
The invention discloses a method for preparing an astaxanthin extractive from haematococcus pluvialis powder. The method comprises the following steps: (1), weighing haematococcus pluvialis powder, adding food-grade alcohol, fully and uniformly mixing to obtain a mixture as a reaction system, and extracting the reaction system for 1 to 2 hours at a room temperature in a dark place, wherein the ratio of haematococcus pluvialis powder to food-grade alcohol is 1 g / 10-20 mL, and the food-grade alcohol adopts a food-grade alcohol solution with the volume concentration of larger than or equal to 95%; (2), centrifuging after extraction is finished to respectively obtain residue and supernatant liquor; (3) replacing the haematococcus pluvialis powder obtained from the step (1) with the residue, and repeating the step (1) and the step (2) at least once in sequence; and (4), combining the supernatant liquor obtained from the step (2) and the supernatant liquor obtained from the step (3), and recovering alcohol through vacuum concentration to obtain a dark red extract, namely the astaxanthin extractive. The astaxanthin extractive, prepared by the method, has the characteristic of high content of the astaxanthin monomer.The invention discloses a method for preparing an astaxanthin extractive from haematococcus pluvialis powder. The method comprises the following steps: (1), weighing haematococcus pluvialis powder, adding food-grade alcohol, fully and uniformly mixing to obtain a mixture as a reaction system, and extracting the reaction system for 1 to 2 hours at a room temperature in a dark place, wherein the ratio of haematococcus pluvialis powder to food-grade alcohol is 1 g / 10-20 mL, and the food-grade alcohol adopts a food-grade alcohol solution with the volume concentration of larger than or equal to 95%; (2), centrifuging after extraction is finished to respectively obtain residue and supernatant liquor; (3) replacing the haematococcus pluvialis powder obtained from the step (1) with the residue, and repeating the step (1) and the step (2) at least once in sequence; and (4), combining the supernatant liquor obtained from the step (2) and the supernatant liquor obtained from the step (3), and recovering alcohol through vacuum concentration to obtain a dark red extract, namely the astaxanthin extractive. The astaxanthin extractive, prepared by the method, has the characteristic of high content of the astaxanthin monomer.
Owner:NINGBO HONGLONG BIO TECH
Carotenoid-containing compositions and methods
The present invention is directed to carotenoid compositions and methods for inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria or for preventing or treating bacterial infections in subjects by administration of an effective amount of astaxanthin and beta-carotene.
Owner:MEAD JOHNSON NUTRITION
Astaxanthin-containing bacterial cellulose membrane product
The invention relates to an astaxanthin-containing bacterial cellulose membrane product. The unique astaxanthin-containing bacterial cellulose membrane product is obtained by uniformly dispersing astaxanthin into a fine mesh-shaped structure of bacterial cellulose. The disadvantage that the astaxanthin cannot be stored for a long time under general preservation conditions is overcome; and meanwhile, a good beauty and skin care product with anti-aging and whitening functions is also provided for consumers. The astaxanthin in the bacterial cellulose membrane product has stable properties, the structure of the astaxanthin cannot be damaged, and the astaxanthin can be slowly and durably released to the applied skin when the product is used, and achieve good effects of resisting senility, oxidization and wrinkles, whitening and protecting sunshine. Meanwhile, the membrane product also has good water supplement and moisturizing effects due to high water retention performance of the bacterial cellulose.
Owner:HAINAN GUANGYU BIOTECH
Novel method for high-efficiently producing astaxanthin by utilizing microalgae
ActiveCN103571906APromote rapid accumulationImprove qualityUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBetaxanthins
The present invention involves a new method using micro-algae for the high-efficiency production of astaxanthin, said method comprising steps including the heterotrophic culture of micro-algae, dilution, light-induced culture, harvesting of algae cells and the extraction of astaxanthin. The method of the present invention takes full advantage of the rapid growth of micro-algae in the heterotrophic culture stage and of the high accumulation of astaxanthin brought about by the light-induced culture of the great quantity of algae cells obtained through said heterotrophic culture to significantly increase the efficiency of production of astaxanthin in micro-algae and thereby achieve low-cost, high-efficiency and large scale production of astaxanthin through micro-algae. The method not only provides an important technical means to address the large-scale industrial production of astaxanthin through micro-algae but also ensures an ample source of raw material for the widespread utilization of astaxanthin.
Owner:云南保山泽元藻业健康科技有限公司
Haematococcus extract preparation, and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN101978975AEasy to operateReduce energy consumptionSenses disorderNervous disorderMedicineBetaxanthins
The invention provides a haematococcus extract preparation, and a preparation method and use thereof. A haematococcus extract soft capsule provided by the invention comprises the contents of haematococcus extract and an oleic phase, wherein the astaxanthin content of the haematococcus extract is 2 to 20 percent (w / w); and the mass-to-volume ratio (g / mL) of astaxanthin in the haematococcus extract and the oleic phase is 1-10:100. The invention also provides the method for preparing the haematococcus extract soft capsules. Experiments show that the haematococcus extract soft capsule provided by the invention has stability remarkably superior to that of the haematococcus extract and conventional products and is of great importance to the application of the astaxanthin to antioxidation, the enhancement of immunity, the suppression of tumorigenesis, the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease, the prevention of skin aging and the maintenance of health of eyes and the central nervous system.
Owner:YUNNAN GREEN A BIOLOGICAL PROJECT
Method for extracting astaxanthin from haematococcus pluvialis
ActiveCN103787941AReduce the possibility of oxidative degradationImprove extraction qualityOrganic chemistryAbnormal growthsFrond
The invention provides a method for extracting astaxanthin from haematococcus pluvialis, and belongs to the technical fields of bioprocess technology and chemical technology. The method comprises the following steps: completing the selection of raw materials through abnormal growth of cells of the selected haematococcus pluvialis, dilution of high-density algae cells and light induction, carrying out wall-breaking treatment on frond by using an ultrahigh pressure extractive technology, then extracting, eluting, concentrating, saponifying and centrifuging, thus obtaining the astaxanthin. The method has the advantages that the consumption of an organic solvent is little, an extraction agent can be circularly utilized, the environmental pollution is little, the production cost is low, the recovery rate is high, few impurities exist, the possibility of oxidative degradation of the astaxanthin is reduced, and the extraction quality of the astaxanthin is improved.
Owner:QINGDAO KEHAI BIOLOGICAL
Methods and compositions to promote ocular health
Embodiments include a composition to promote ocular health and a method of treatment for a subject exposed to a source of oxidative or visual stress to the eye or having a degradation of the eye. The composition may include amounts of vitamin A, which includes beta-carotene; vitamin C; vitamin D; vitamin E; zinc; copper; selenium; non-vitamin A carotenoids, which include lutein and zeaxanthin; omega-3 fatty acids, which include eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid; taurine; alpha lipoic acid; pine bark extract; astaxanthin; and Piper spp. extract. The method includes the step of administering to the subject a daily dose of a composition to promote ocular health.
Owner:WOOLDRIDGE CONSTR CO
Astaxanthin extraction method
InactiveCN101381337AReduce lossAvoid high temperature oxidation lossOrganic chemistryLoss rateAstaxanthin
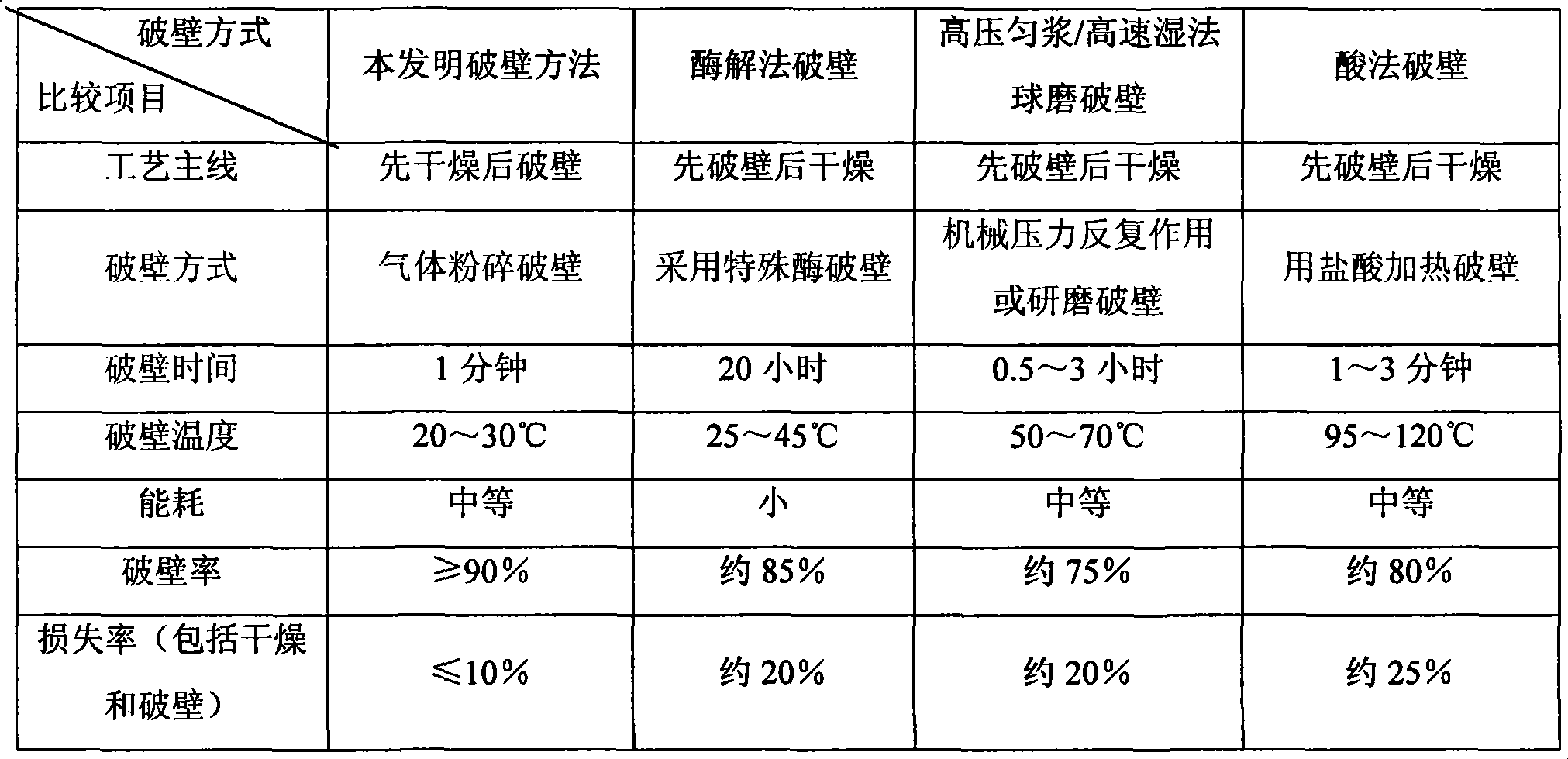
The invention discloses a method for extracting astaxanthin, which is finished by taking a rhodotorula or microalgae feed liquid containing the astaxanthin as a raw material, and performing separation, drying, crushing wall-breaking processes to the feed liquid. The method comprises the following concrete steps: the raw material is separated first to produce a mashed material with the water content less than or equal to 90 percent; the mashed material is dried to produce feed powder with the water content of between 5 and 10 percent; then an airflow crushing method is adopted to crush the feed powder to particles with diameters less than or equal to 10mu m. In the method, the drying is performed first and then the wall-breaking is performed, so the loss of the astaxanthin is reduced; the airflow crushing method is adopted, and has high wall-breaking rate and short wall-breaking time (only 1 minute or so), the temperature is between 20 and 30 DEG C during the wall-breaking process, and avoids the loss of the astaxanthin due to high-temperature oxidation; and the loss rate of the astaxanthin is less than or equal to 10 percent, and the wall-breaking rate is more than or equal to 90 percent.
Owner:陈锦猜
Method for producing astaxanthin by haematococcus pluvialis
InactiveCN103114121AIncrease temperatureIncreased efficacy of irradiationUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesPhosphatePotassium
The invention discloses a method for producing astaxanthin by haematococcus pluvialis. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, naturally culturing the haematococcus pluvialis in water of a culture pool for 6-8 days so that the haematococcus pluvialis proliferates, then adding potassium dihydrogen phosphate and sodium nitrate to the pool water, and covering the pool with a red thin film, so that algae cells of the haematococcus pluvialis rapidly grow to reach conversion state under the irradiation of 630nm-760nm light waves; transferring the algae cells at the conversion state to pool water with potassium dihydrogen phosphate, the final concentration of which is 0.02-0.05g / L, covering the pool with a blue thin film, so that the algae cells of haematococcus pluvialis are cultivated to mature under the irradiation of 430nm-490nm light waves, and thus obtaining haematococcus pluvialis, the algae cells of which are rich in astaxanthin, wherein potassium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium nitrate and red lights can enable the algae cells to rapidly grow and reach conversion state in shorter time, and the potassium dihydrogen phosphate and blue lights can enable the algae cells to rapidly grow, mature and accumulate astaxanthin. The method has the advantages of little investment, cultivation simpleness and high economic benefits.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Algae with astaxanthin production and astaxanthin production by yeast mixed culture fermentation
A process for preparing astaxanthin includes such steps as preparing special culture medium, loading it in reactor, inoculating algae including Haematococcacea able to generate astaxanthin and yeast in it, culturing and fermenting. Its advantages are low cost, and high conversion rate of saccharide, biomass and output of astaxanthin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
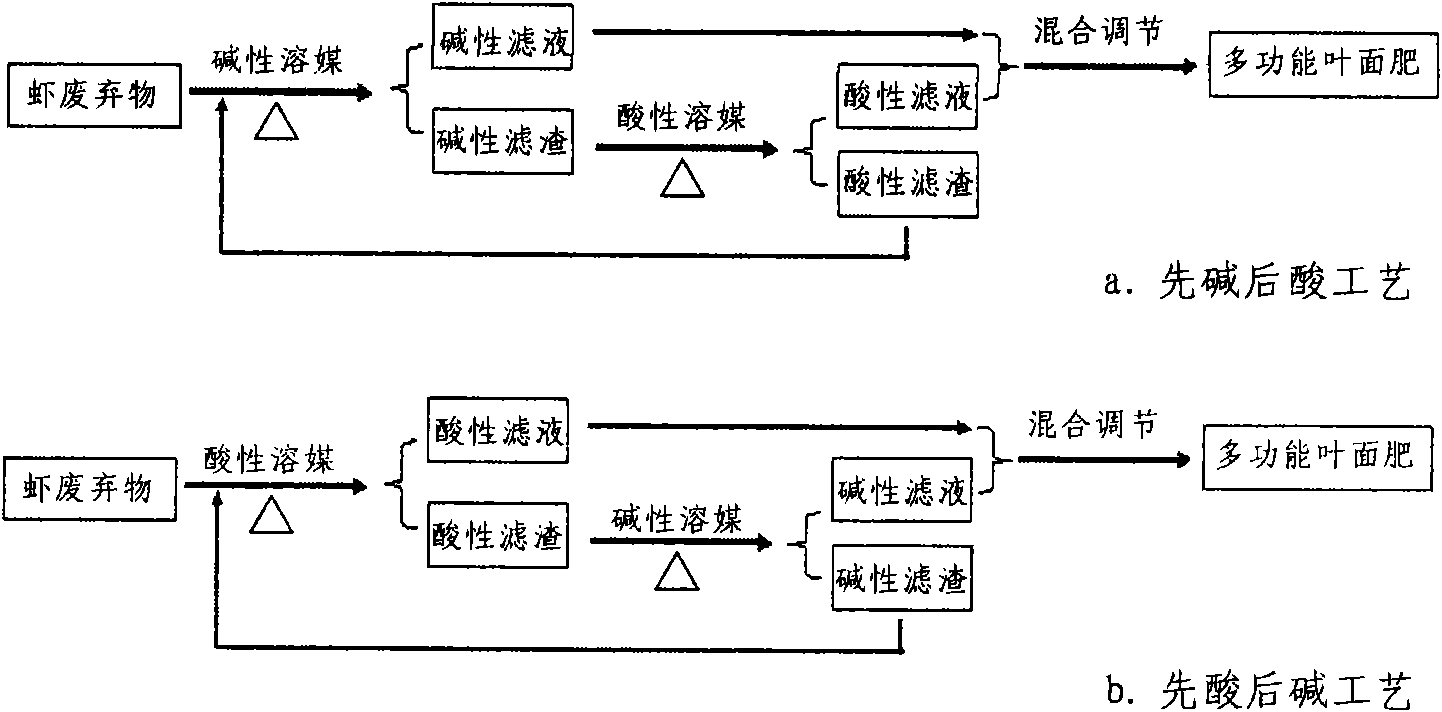
Method for preparing multifunctional leaf fertilizer by using shrimp waste
ActiveCN101591198AZero emissions possibleSimple processAnimal corpse fertilisersClimate change adaptationAdditive ingredientMagnesium salt
Owner:ZHANJIANG BOTAI BIOCHEM IND +1
Astaxanthin-producing ocean rhodotorula YS-185 and method for producing astaxanthin thereof
ActiveCN101705193AIncrease productionIncrease biomassFungiMicroorganism based processesRhodotorulaAstaxanthin
The invention relates to ocean rhodotorula YS-185 bred with high yield of astaxanthin, which is obtained from ocean, wherein the rhodotorula is preserved in CCTCC of Wuhan, China with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M207077; the invention also relates to a method for producing astaxanthin by fermenting and cultivating the ocean rhodotorula YS-185. The astaxanthin produced by the ocean rhodotorula YS-185 is natural astaxanthin and can be widely applied to high-quality cosmetics, food and feed additives.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for producing astaxanthin by inducing Haematococcus pluvialis
ActiveCN104232720AIncrease carbon dioxide levelsPlay a stirring roleMicroorganism based processesFermentationGrowth phaseBetaxanthins
Owner:BIOALGO CY CO LTD +1
Method for producing krill oil, protein peptide powder and chitosan by full utilization of Antarctic krill powder
InactiveCN106010783ARealize high-value comprehensive utilizationRealize full utilization of high valueCultivating equipmentsFatty-oils/fats productionResource utilizationAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a method for producing krill oil, protein peptide powder and chitosan by full utilization of Antarctic krill powder. The method comprises the following steps: 1. extraction of krill oil: extracting the Antarctic krill powder by adopting an organic solvent, and carrying out low-temperature decompression desolvation, extraction and concentration on the extracting solution, wherein the contents of obtained krill oil phospholipid and astaxanthin are high; 2. preparation of protein peptide powder: carrying out compound enzymolysis on degreased shrimp meal to obtain an enzymolysis solution, and refining and then spray-drying the enzymolysis solution to obtain the protein peptide powder, wherein the peptide content of the obtained protein peptide powder is greater than or equal to 85%; and 3. preparation of chitosan: decalcifying the shrimp shell meal which is degreased by the organic solvent and is subjected to deproteinization by enzymolysis by adopting microorganism fermentation, further carrying out deproteinization, carrying out oxidative decoloration, and carrying out deacetylation to obtain chitosan and byproduct organic calcium. The method really realizes high-valued full utilization of the Antarctic krill powder, can be used for extracting nutritional ingredients in the Antarctic krill powder to the maximum extent so as to improve the resource utilization ratio, can avoid generation of waste residues, and can ensure the benefit maximization of an enterprise.
Owner:青岛南极维康生物科技有限公司 +1
Method for synthesizing astaxanthin by inducing chlorella vulgaris by using plant hormones and iron ions
ActiveCN103045709ASynthesis fastEfficient accumulationMicroorganism based processesFermentationPlant hormoneAstaxanthin
The invention belongs to the field of microalgae biotechnologies, and particularly relates to a method for synthesizing astaxanthin by inducing chlorella vulgaris by using plant hormones and iron ions. The method specifically comprises the steps of: activating and culturing the chlorella vulgaris in a liquid culture medium to obtain a synchronously growing chlorella vulgaris solution for later use; and taking the chlorella vulgaris solution growing to an exponential growth phase, adding the plant hormones and the iron ions in the chlorella vulgaris solution, replenishing a carbon source and a nitrogen source for culturing, ending the culturing until the accumulation of the astaxanthin in chlorella vulgaris cells is maximum (the accumulation of the astaxanthin is determined by adopting a liquid chromatography during sampling), and harvesting cell disruption and extracting the astaxanthin. The method is simple and easy to operate and low in cost, and is capable of remarkably increasing the yield of the astaxanthin, thereby greatly increasing the efficiency of producing the astaxanthin by the chlorella vulgaris.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low energy- wasting and environment protection method for extracting chitin as well as biologically active substance thereof from shrimp shell
InactiveCN101176549AImprove freshnessIncrease profitCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesOrganic chemistryShrimpMicrowave oven
The invention relates to a low-consumption and environment-protection method for extracting chitin and bioactive substances from shrimp shell, which comprises the steps that: the fresh shrimp shell is arranged in a microwave oven for heating, then is arranged in the NaOH solution and boiled for 1 to 2 hours, then is immersed in the HCI solution for immersion; the shrimp shell is treated again with the NaOH solution, and is arranged in the sunshine and heavily sunned for decoloration after immersed in the HCI solution, thus the chitin product is obtained; when protein powder is extracted, protein is separated from the alkali treatment solution through the physical process of freezing and thawing; and when astaxanthin product is extracted, papain is adopted for degradation, then astaxanthin is obtained through ethanol extraction. The invention has the advantages of high material utilization ratio of shrimp shell, less acid and alkali consumption, less dosage of organic solvent, complete separation of various useful substances in shrimp shell, high purity of the obtained product, no discharge of waste acid, waste alkali and harmful organic solvent during reaction process, and effective use of various treatment solutions generated during reaction.
Owner:湖北东方天琪生物工程股份有限公司
Composition containing Cistanche deserticola or Herba Cynomorii and combination of chrysanthemum, taurine, lycopene, xanthophyll and beta-carotene
InactiveCN102813753AEffective nourishmentEffective protectionSenses disorderHydrocarbon active ingredientsSide effectBeta-Carotene
The invention relates to a nutritional food and a medicine, and especially relates to a composition which can alleviate the eye fatigue, improve the eyesight, reduce the blood fat and nourish the liver and the kidney, has no toxic side effects and is suitable for long-term taking. The composition comprises the following components, by weight, 100-900 parts of Cistanche deserticola or Cistanche deserticola, and one or several of 200-1000 parts of chrysanthemum, 200-2000 parts of taurine, 5-30 parts of lycopene or 5-30 parts of astaxanthin or 100-900 parts of grape pip, 2.5-15 parts of beta-carotene or a Dunaliella salina extract, and 6-30 parts of xanthophyll.
Owner:孟令刚
Method for preparing astaxanthin monomer
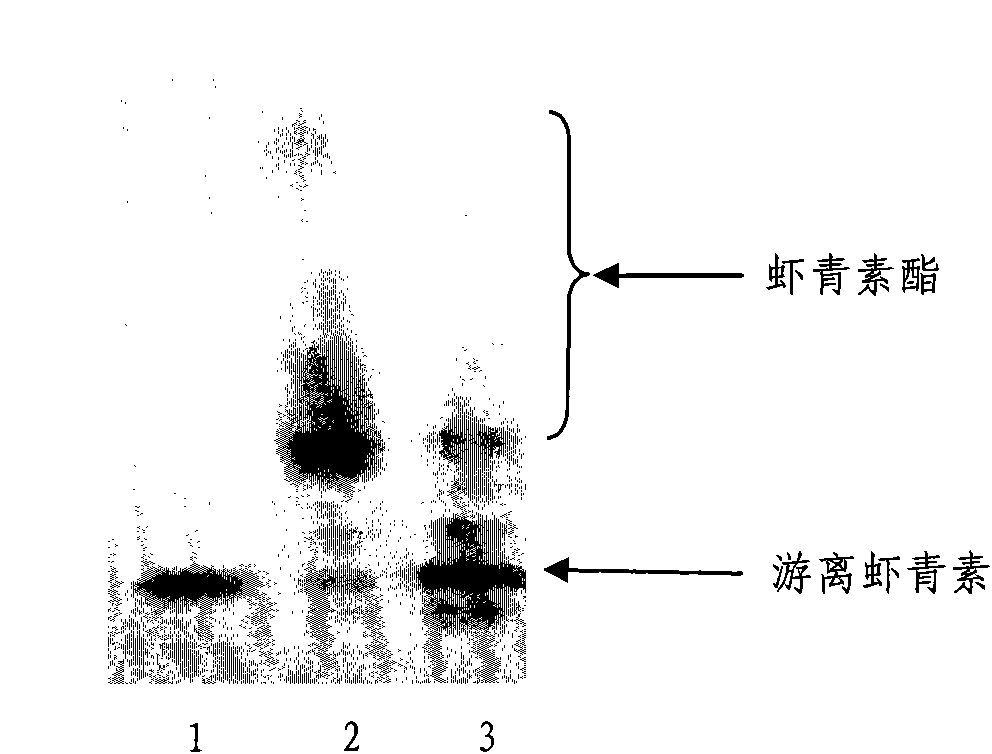
The invention provides a new method for preparing an astaxanthin monomer. In the method, a free astaxanthin monomer is obtained by hydrolyzing astaxanthin ester with lipase. The recovery rate of the astaxanthin monomer reaches 63.2 percent by using the method. The method is simple to operate, namely a desired product can be obtained by one reaction and extraction; and the method saves the energy consumption and can avoid the loss of the astaxanthin during long-term reaction to a certain extent. The method lays the foundation of the industrial application for extracting the astaxanthin monomer from crude extract of haematococcus pluvialis by an enzyme method.
Owner:秦皇岛惠恩生物技术有限公司
Simple method for culturing haematococcus pluvialis to produce astaxanthin
ActiveCN101586140AReduce purchasesPromote vegetative growthMicroorganism based processesFermentationBetaxanthinsBiology
The invention discloses a simple method for culturing haematococcus pluvialis to produce astaxanthin; the method comprises three culturing processes of narrow neck flask, plastic cask or Nylon bag, cement pit; each step passes through various physical and chemical environmental parameters, such as nitrogen and phosphorus contents, pH value, incubation temperature, illumination intensity, illumination time, exact adjusting and controlling measure of adding with halite or halogeno salt, H2O2 and FeCl2 and cell state, etc; each step has definite object, and reasonable control such that the haematococcus pluvialis has excellent vegetative growth, fast conversion of vegetative growth to non-vegetative growth, and accumulates much astaxanthin, thereby improving the efficiency and stability of culturing, converting and accumulating, and effectively preventing the pollution of mixed algae; because the invention is an open culturing and does not need closed photobioreactor, thereby greatly reducing the production cost and obviously improving the productivity, and open culturing haematococcus pluvialis to produce astaxanthin in large scale.
Owner:LIJIANG CHENGHAI BAOER BIOLOGICAL DEV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com