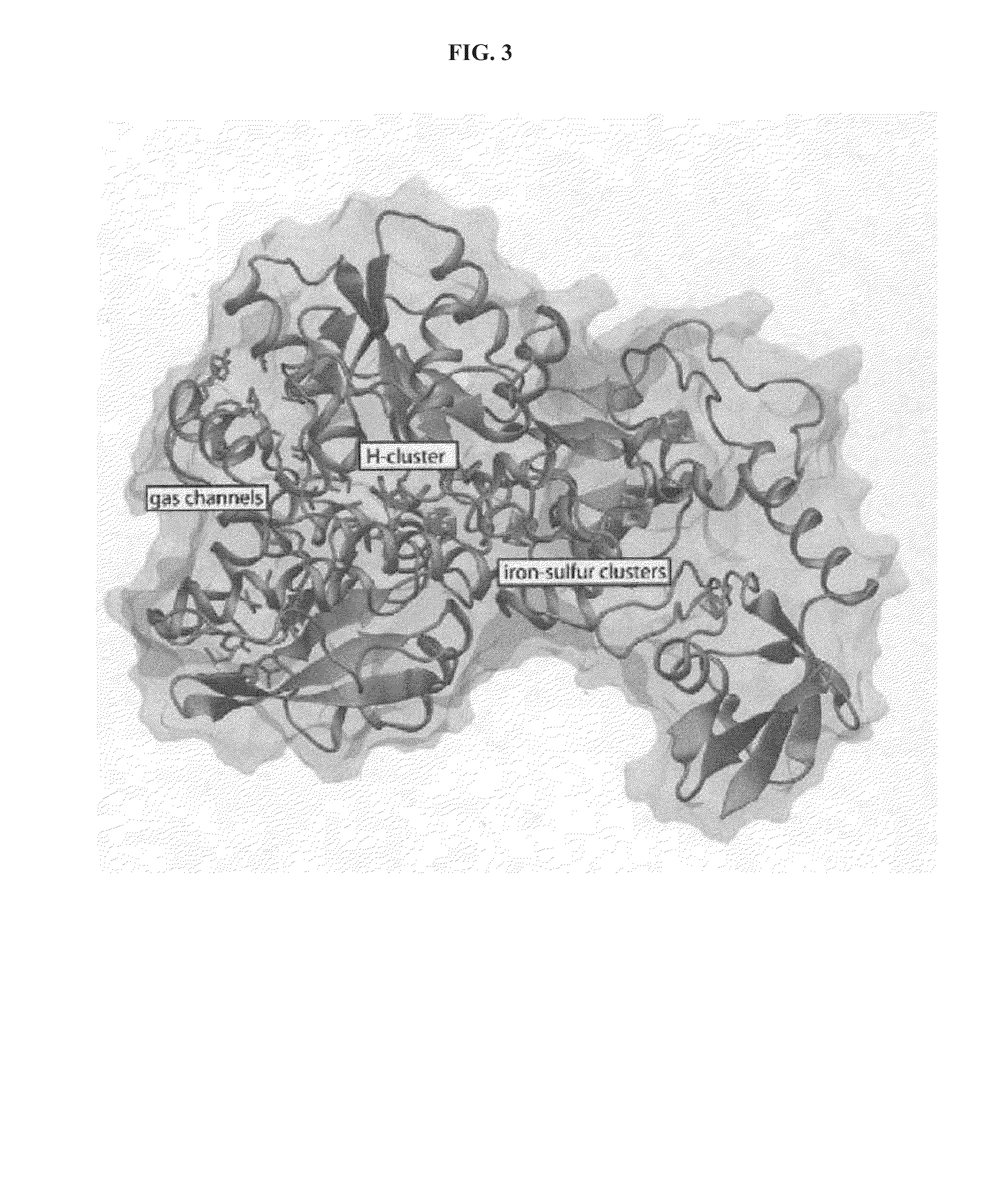
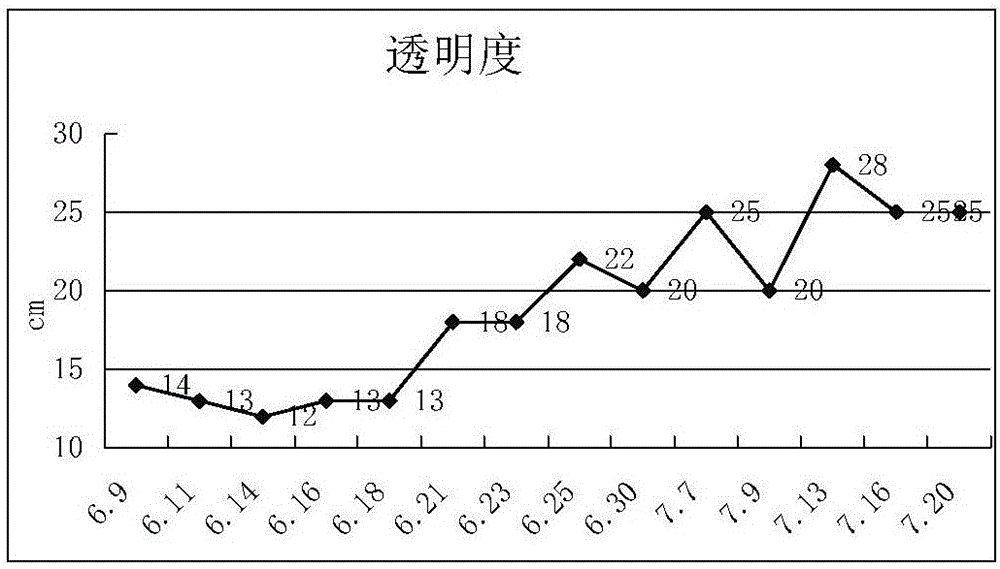
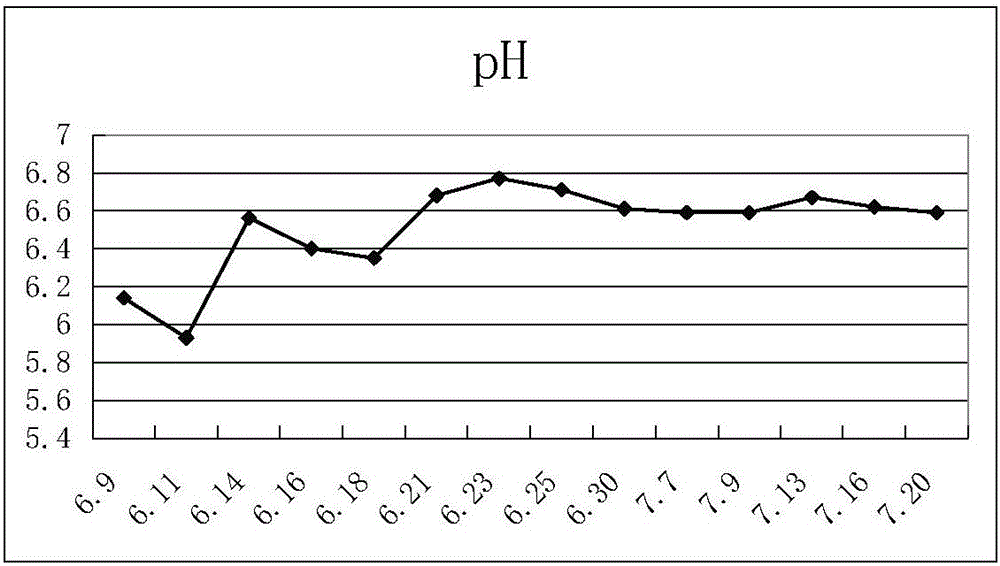
Patents
Literature
48 results about "Chlorophyta" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
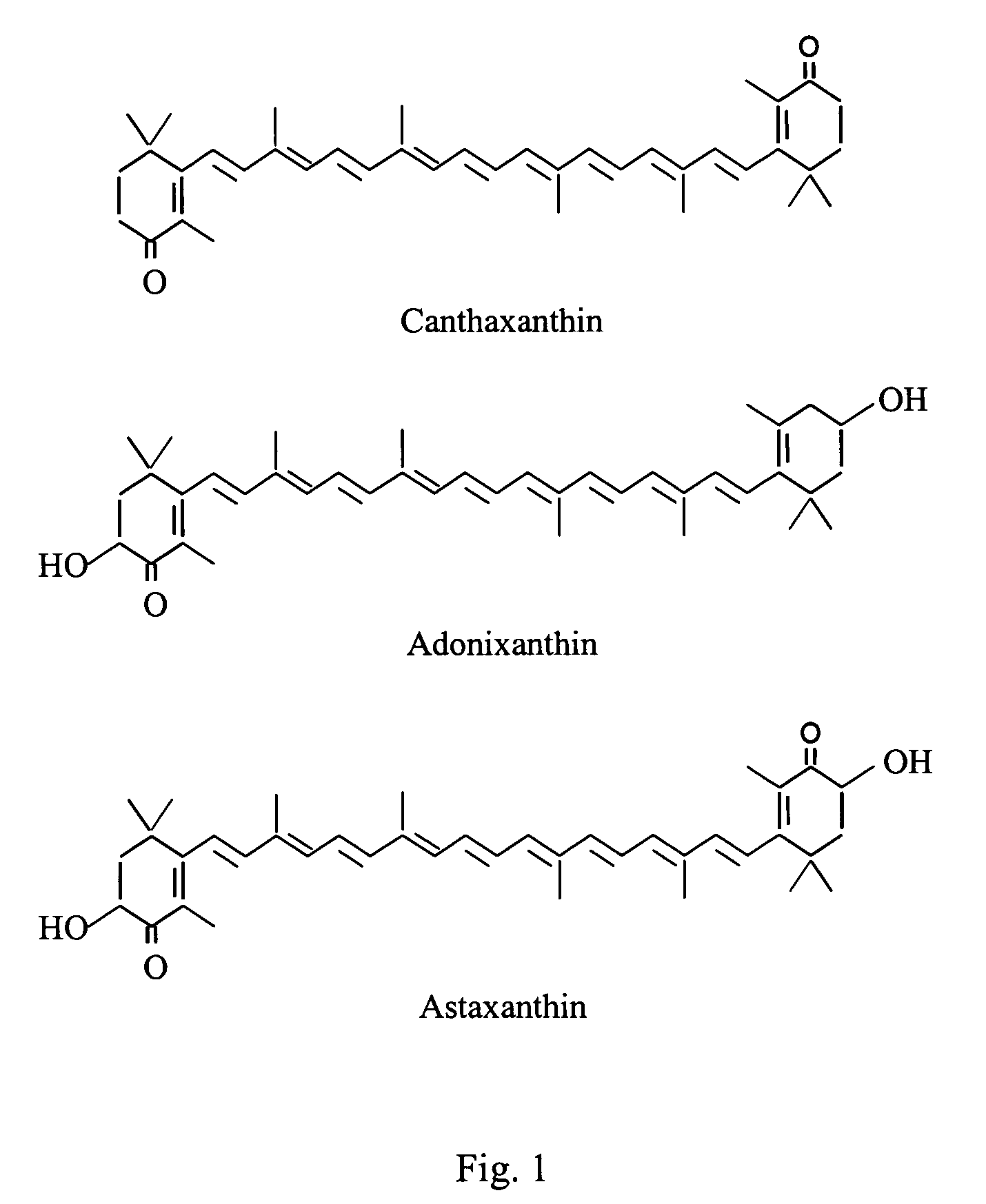
Chlorophyta or Prasinophyta is a taxon of green algae informally called chlorophytes. The name is used in two very different senses, so care is needed to determine the use by a particular author. In older classification systems, it refers to a highly paraphyletic group of all the green algae within the green plants (Viridiplantae) and thus includes about 7,000 species of mostly aquatic photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. In newer classifications, it refers to the sister of the streptophytes/charophytes. The clade Streptophyta consists of the Charophyta in which the Embryophyta emerged. In this sense the Chlorophyta includes only about 4,300 species. About 90% of all known species live in freshwater. Like the land plants (bryophytes and tracheophytes), green algae contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b and store food as starch in their plastids.
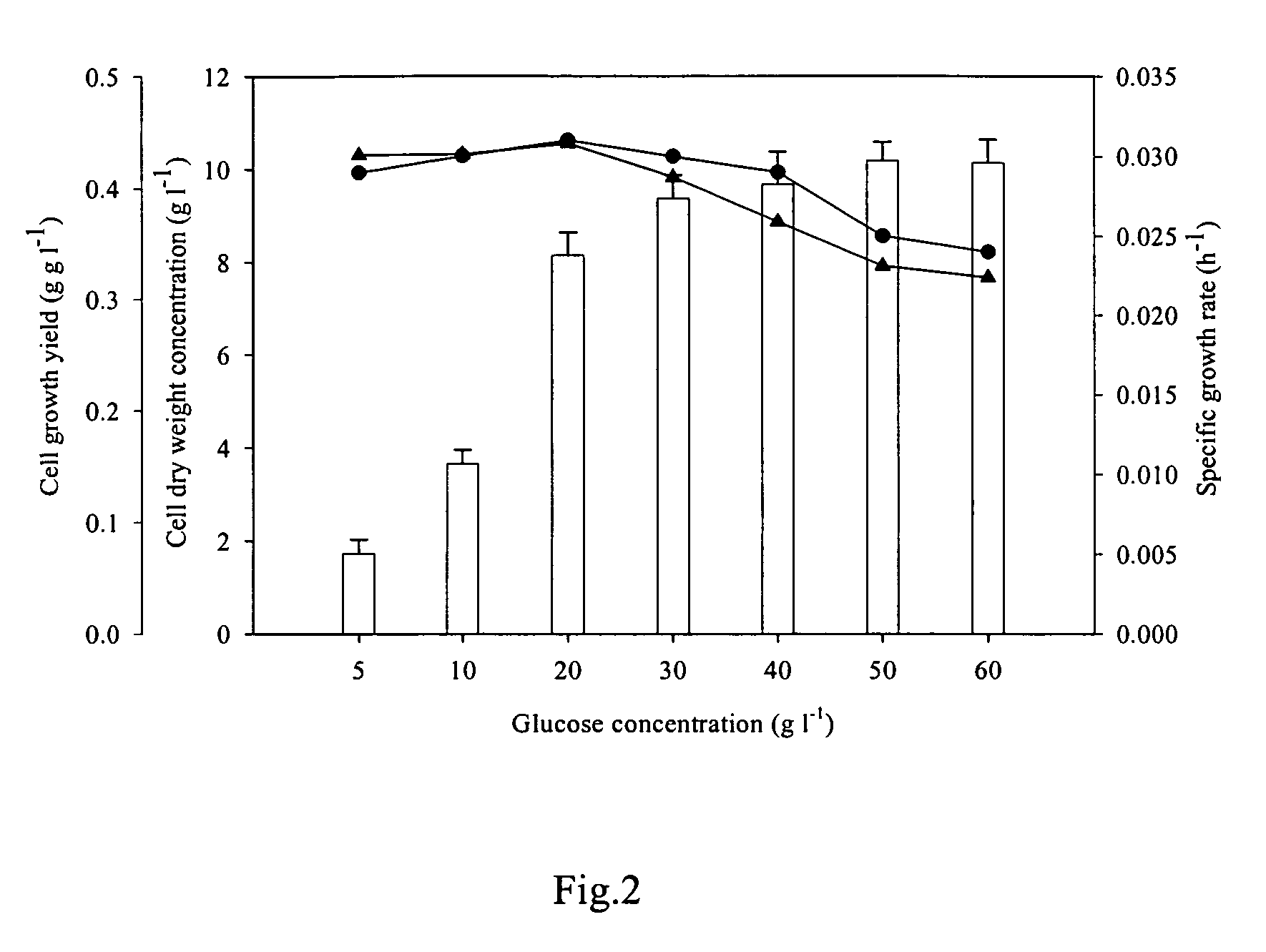
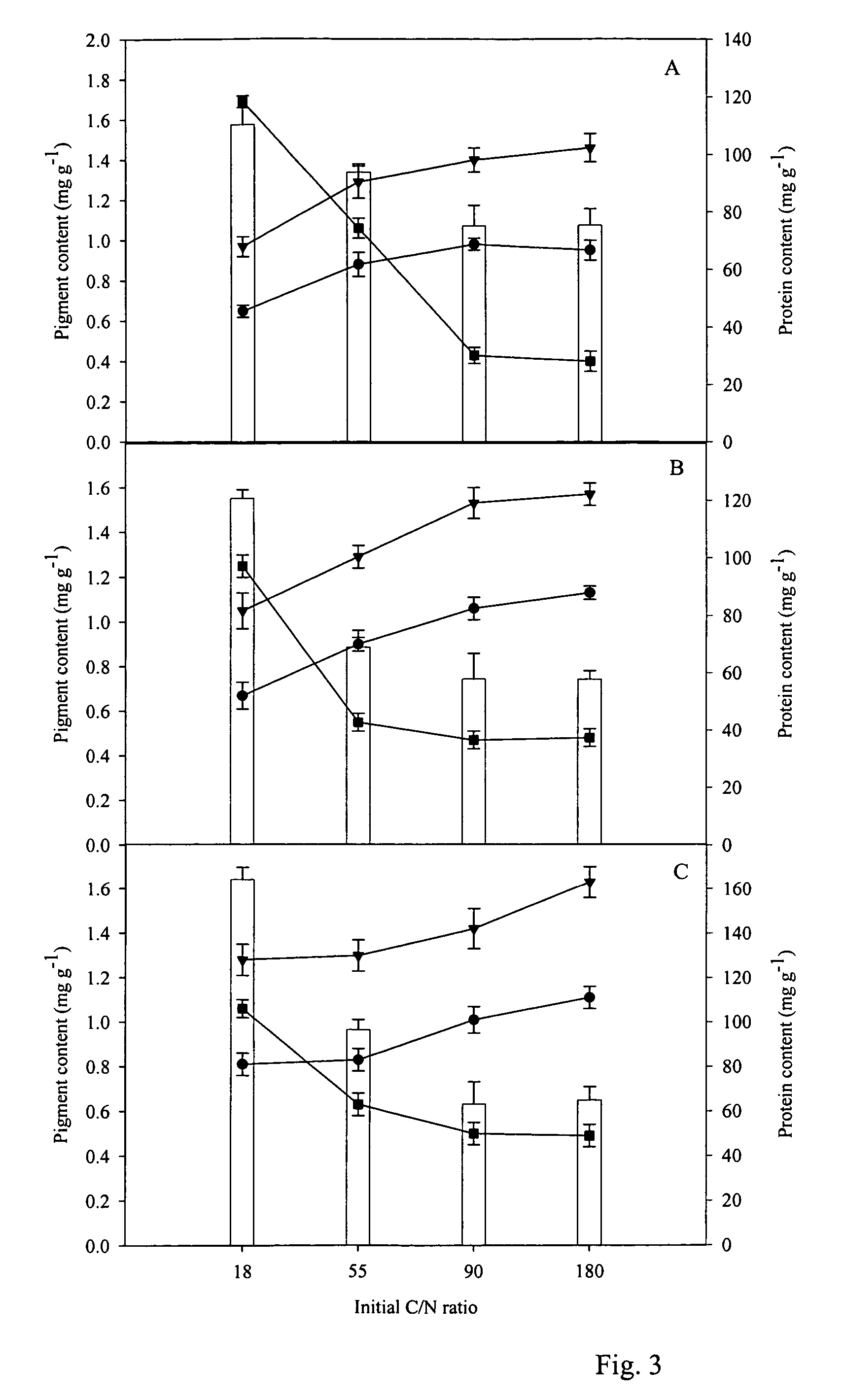
Methods for production of astaxanthin from the green microalgae Chlorella in dark-heterotrophic cultures
A method for producing the high-value ketocarotenoid astaxanthin by the green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis in dark-heterotrophic cultures shows excellent growth and high-yield astaxanthin production on glucose-supplemented media in the dark. The specific growth rate and astaxanthin yield can be as high as 0.031 h−1, and 10.3 mg l−1, respectively, which are the highest so far reported in heterotrophic algal cultures. The light-independent astaxanthin-producing ability of Chlorella zofingiensis can be employed for commercial production of astaxanthin using industrial fermenters.
Owner:HONG KONG UNIV OF
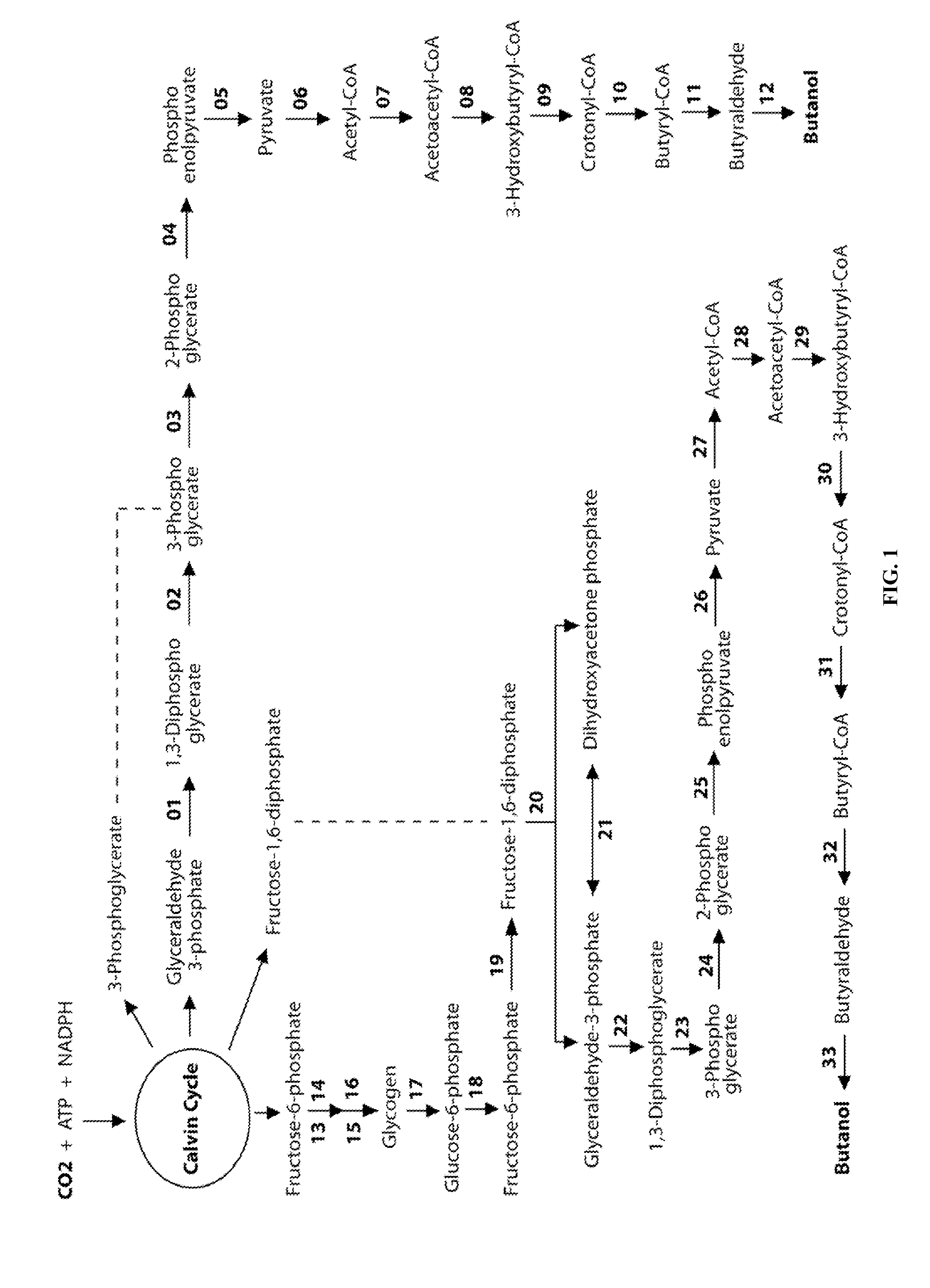
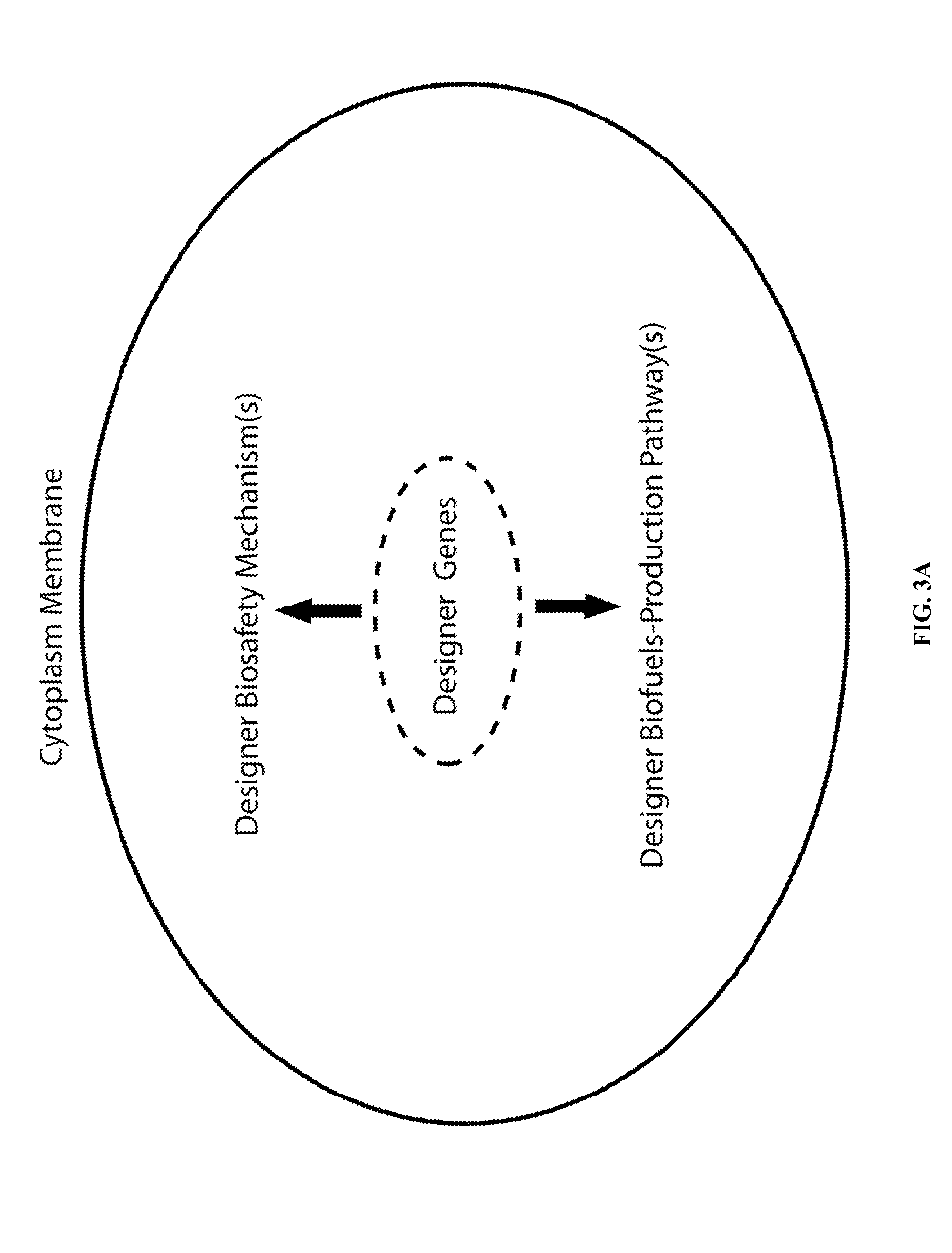
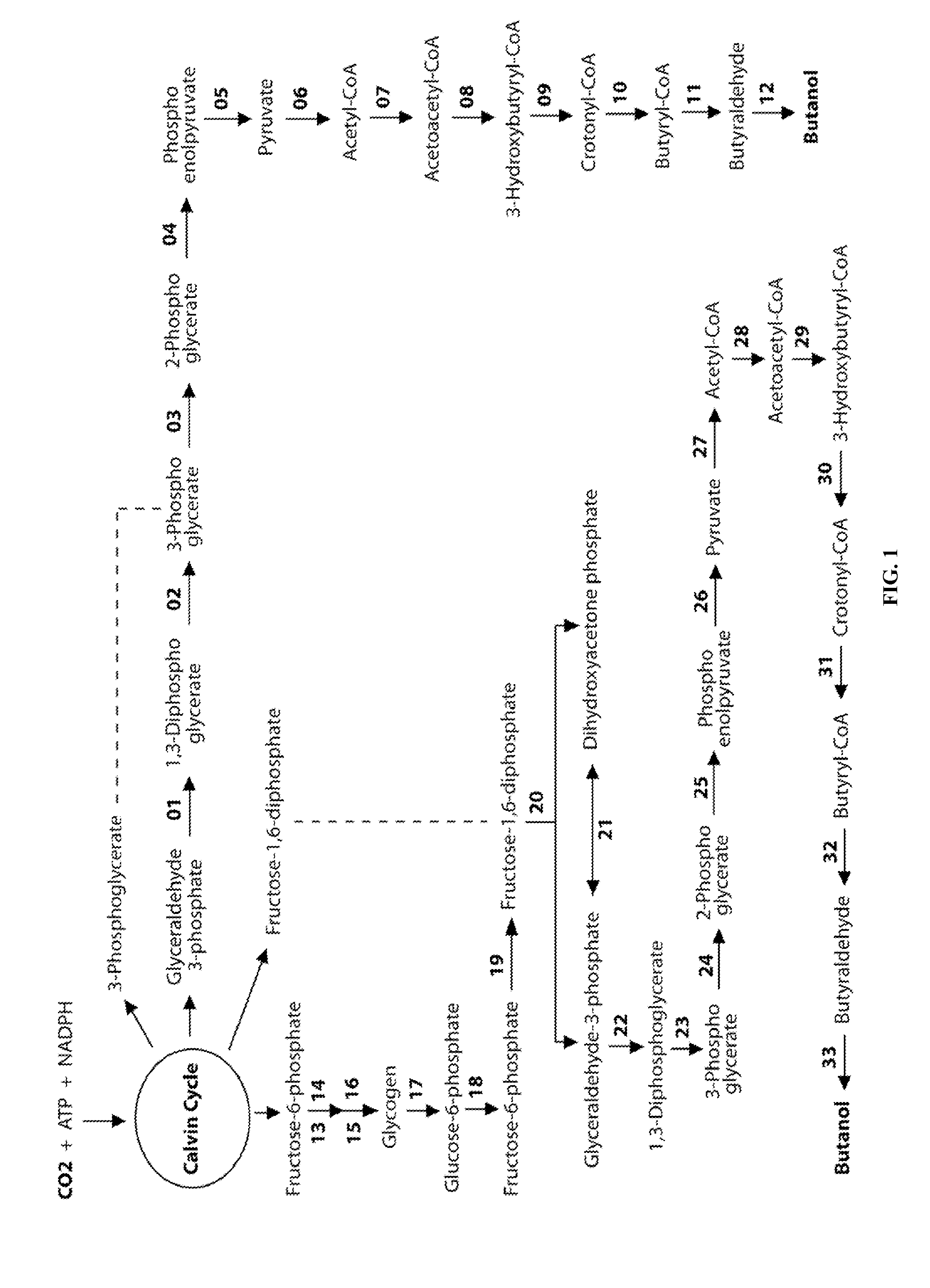
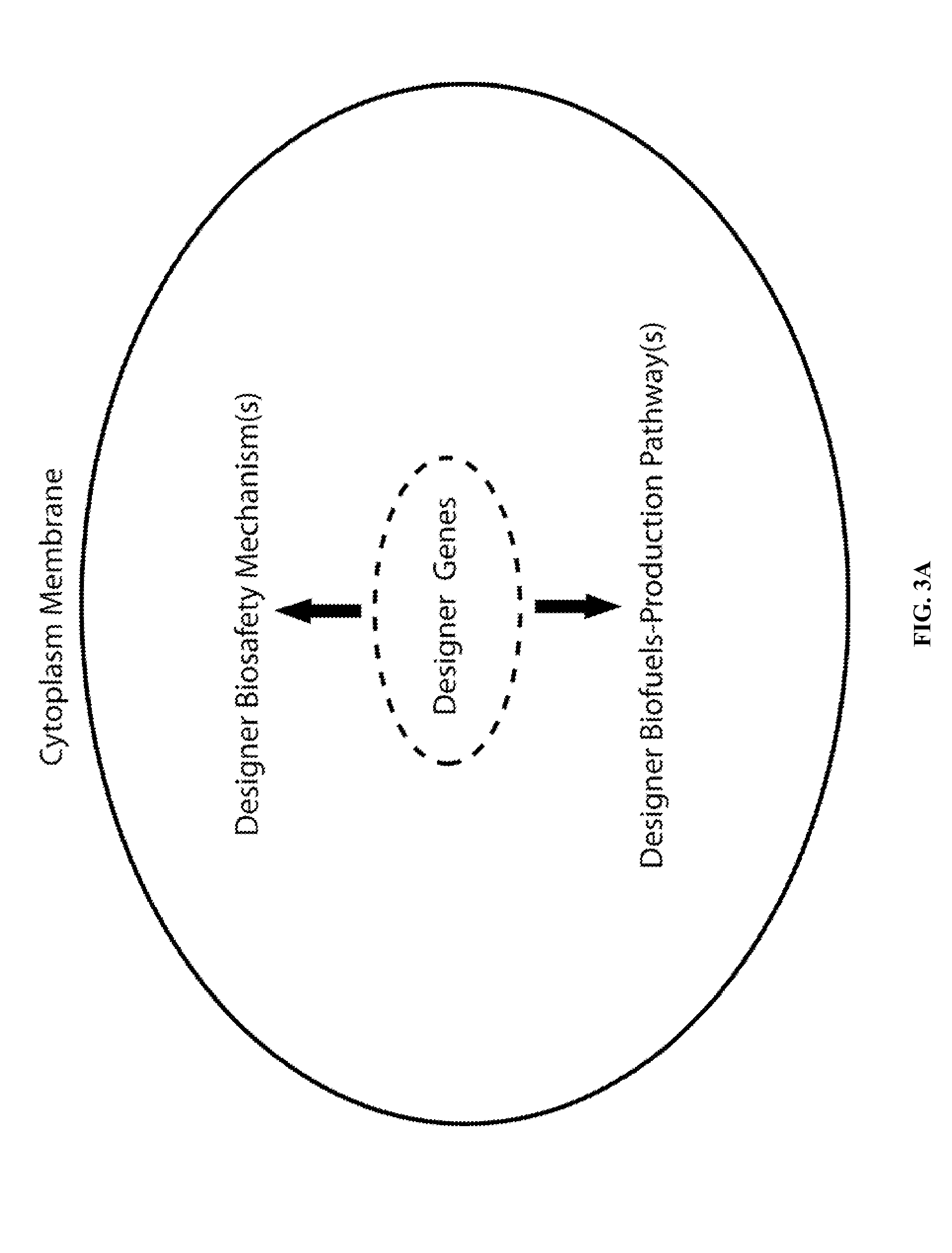
Designer Organisms for Photobiological Butanol Production from Carbon Dioxide and Water
ActiveUS20100330637A1Weaken energyReduce total powerBryophytesAlgae productsCellulosePhylum Cyanobacteria
The present invention provides a biosafety-guarded photobiological butanol production technology based on designer transgenic plants, designer algae, designer blue-green algae (cyanobacteria and oxychlorobacteria), or designer plant cells. The designer photosynthetic organisms are created such that the endogenous photobiological regulation mechanism is tamed, and the reducing power (NADPH) and energy (ATP) acquired from the photosynthetic process are used for synthesis of butanol (CH3CH2CH2CH2OH) directly from carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The butanol production methods of the present invention completely eliminate the problem of recalcitrant lignocellulosics by bypassing the bottleneck problem of the biomass technology. The photobiological butanol-production technology of the present invention is expected to have a much higher solar-to-butanol energy-conversion efficiency than the current technology and could also help protect the Earth's environment from the dangerous accumulation of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Owner:LEE JAMES WEIFU
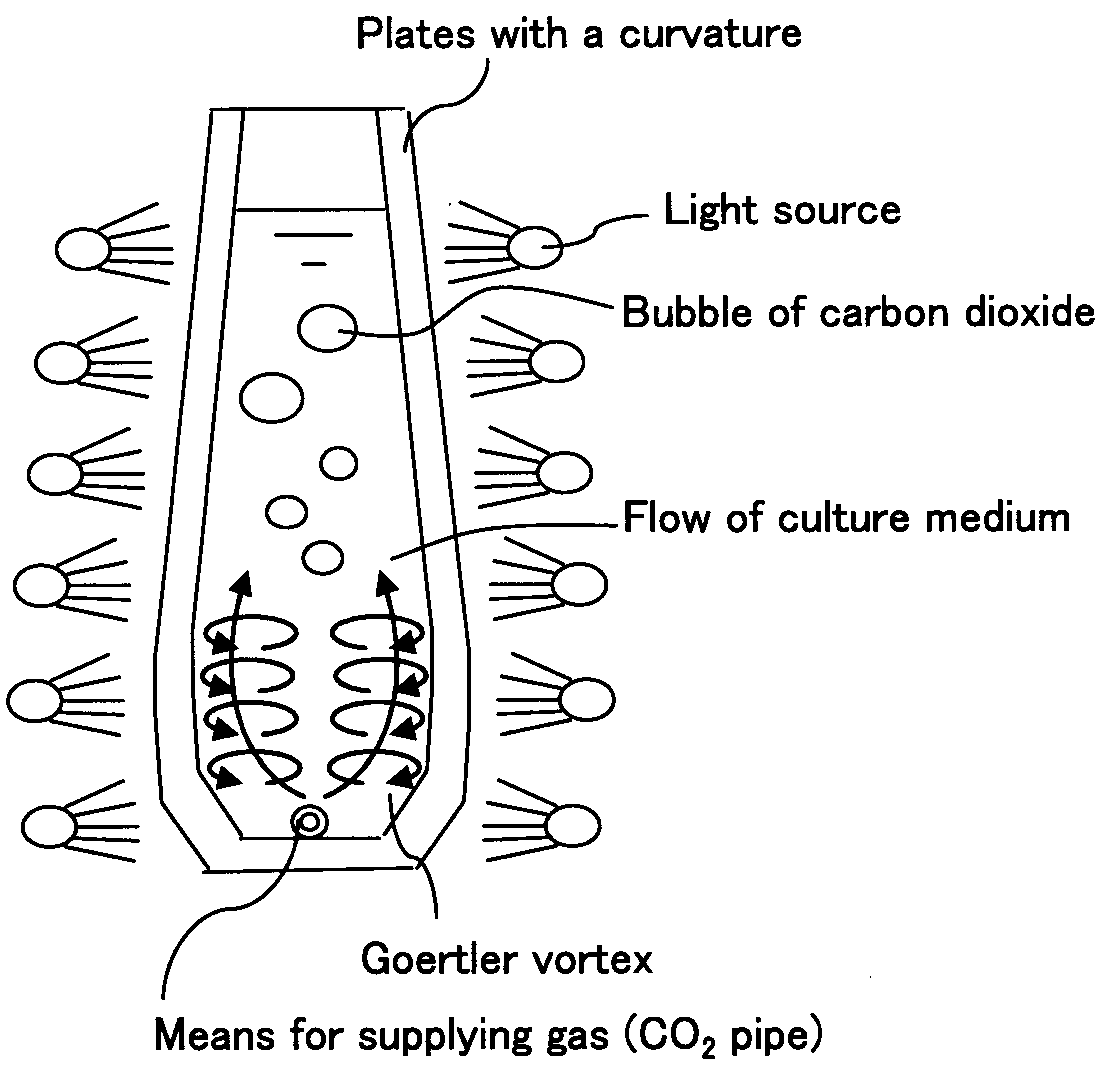
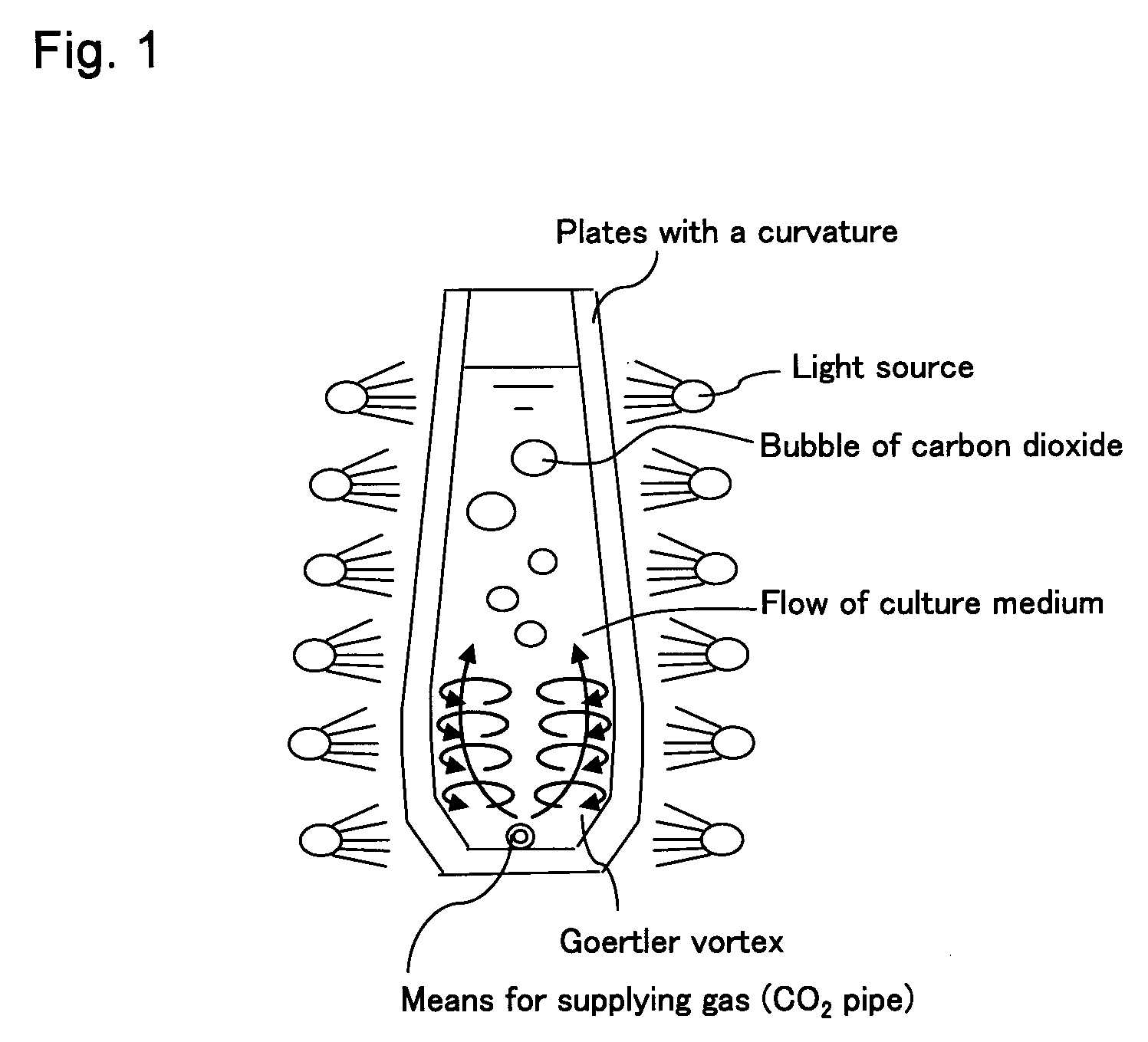
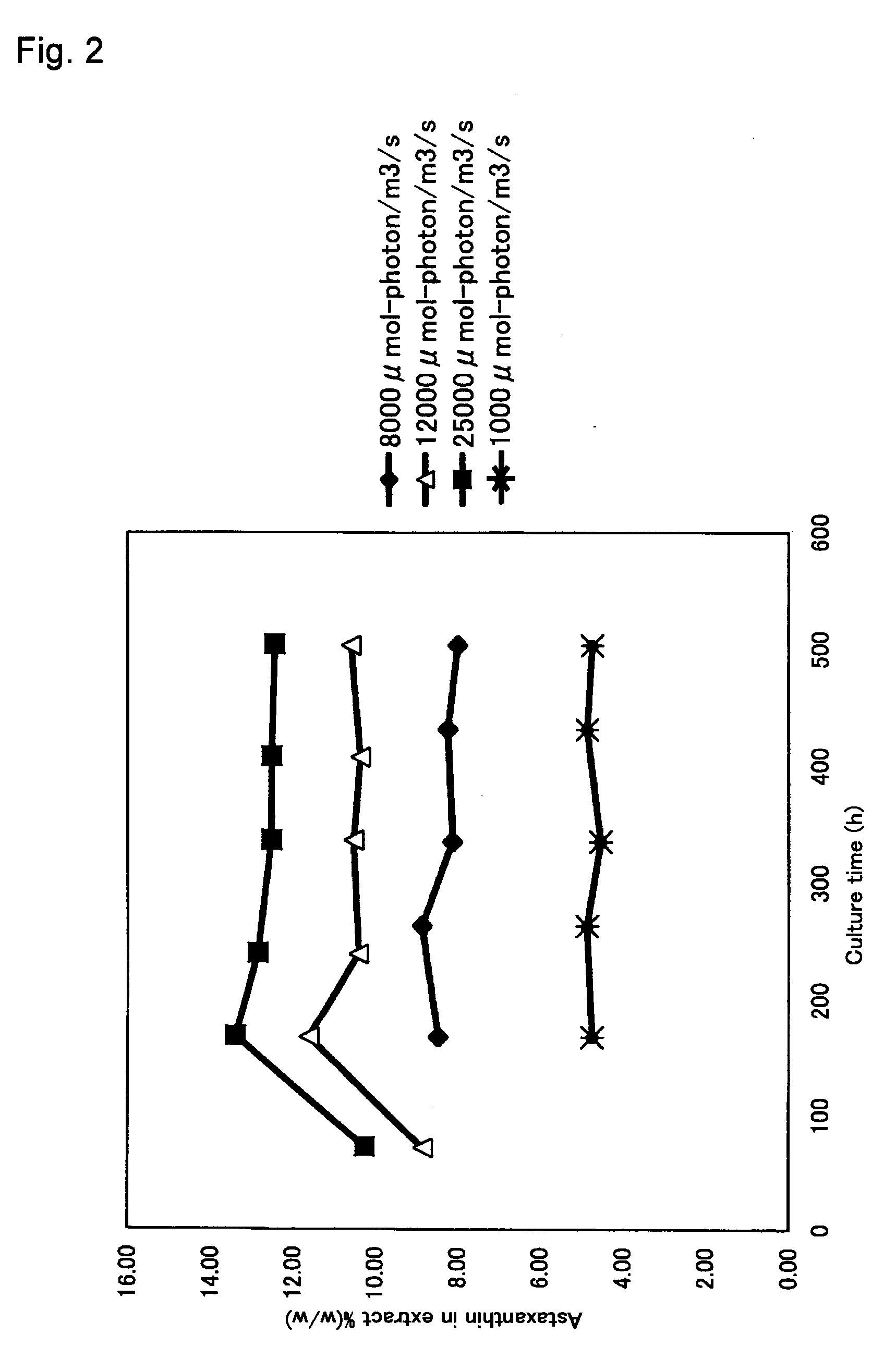
Green Alga Extract with High Astaxanthin Content and Method of Producing the Same
InactiveUS20080254056A1Increase productionIncrease concentrationBiocideCosmetic preparationsAdditive ingredientBetaxanthins
A green algal extract that contains astaxanthin at a concentration of 8 wt % or more can be obtained by cultivating an encysted green alga in a nutrient medium while supplying carbon dioxide and providing irradiation with light at a photosynthetically active photon flux input of 8000 μmol-photon / m3 / s or more, and extracting an oil component, which contains astaxanthin. A green alga that belongs to the genus Haematococcus is preferable.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
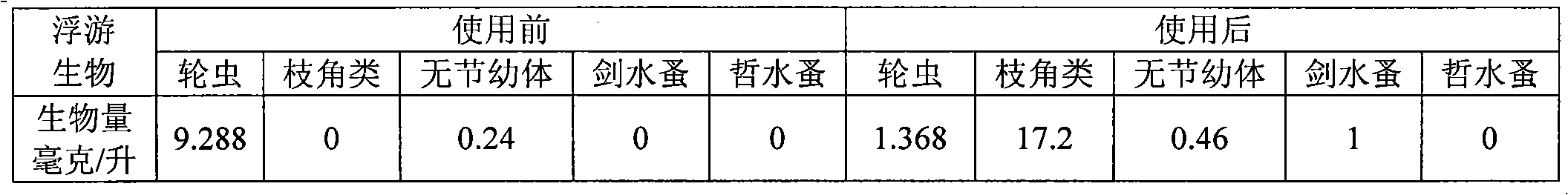
Daphnia magna breeding method for evaluating safety of transgenic rice
InactiveCN102948399AEliminate selectivityEliminate non-feedingAnimal husbandryGenetically modified riceAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a breeding method for an aquatic organism daphnia magna, and belongs to the technical field of insect breeding. The method is used for overcoming the defect in a traditional daphnia magna toxicity experiment technology, and the invention builds a method for breeding daphnia magna by utilizing rice. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a nutrient solution, preparing a rice flour solution, breeding and collecting young fleas. According to the daphnia magna breeding method disclosed by the invention, rice is used for breeding the daphnia magna, so that the defect that the daphnia magna in the conventional method selectively takes in natural goods such as green alga, but does not take in or take in a little rice is overcome. Moreover, an adverse factor that the experimental result is easily affected by uncertain nutritional ingredients of the green alga, and reliable experiment support is provided for evaluating the safety of transgenic rice.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Blue green algae growth inhibitor
InactiveCN106472599AHigh densityEliminate bloomsBiocideDead animal preservationWater qualityRare earth
The invention discloses a blue green algae growth inhibitor which comprises the following components by weight: 10%-25% of plant extract, 1.5%-5% of a blue green algae complexing agent, 1.5%-3% of blue green algae growth inhibin, 20%-35% of a synergist, 1%-10% of rare earth, 30%-40% of diatom forming soil, 2.5%-8.7% of a bio-enzyme microbial inoculums and 0.5%-10% of humic acid powder. The blue green algae growth inhibitor can be used for killing blue green algae in a long time, and can deprive compulsively blue green algae cell thylakoid pseudo telescopic function for solidifying, sinking, rigidifying and dying of blue green algae cells, eliminating of water bloom and purifying of water quality. The blue green algae growth inhibitor can effectively kill spirogyra, hydrodictyon, chaetophora and bottleneck algae and other mud moss filamentous capsules in an aquaculture pond, and can eliminate a large number of algae attached to meshes in cage culture, and after biological algae removal, beneficial algae and beneficial microorganisms are recultivated to add nutrition balance elements for reactivating the water quality.
Owner:匡新生
Method for culturing phytoplankton with predominant chlorophyta
InactiveCN102657071APromote growthGrowth restrictionUnicellular algaeClimate change adaptationCelluloseBottle
The invention relates to a culture method for phytoplankton, belonging to the field of breeding. The invention discloses a method for culturing phytoplankton with predominant chlorophyta, comprising the following steps of: (1) producing culture solution, namely selecting cleaned aquatic plants with low cellulose content at first, and then adding a proper amount of water in the aquatic plants and placing the aquatic plants in a light-tight and warm environment to rot and ferment, and finally filtering the rotted and fermented solution of the aquatic plants to obtain the culture solution rich in nutrient elements such as nitrogen and phosphorus; (2) obtaining a natural eutrophic water body in late spring and early summer; (3) filtering large zooplankton and large individuals of phytoplankton in the obtained water body by a 200-mesh plankton mesh; (4) adding the culture solution produced in the step 1 in the water body filtered by the plankton mesh; and (5) culturing the culture water body with the culture solution in a transparent glass bottle at natural temperature under natural light, thus obtaining phytoplankton with predominant chlorophyta.
Owner:FISHERY MACHINERY & INSTR RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERY SCI
Ecological cultivation mode capable of simulating river-sea migration of Yangtze coilianasus
InactiveCN103404466AIncrease flow rate stimulusPromote conversionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPrawnWater quality
The invention relates to an ecological cultivation mode capable of simulating the river-sea migration of Yangtze coilianasus. The ecological cultivation mode capable of simulating the river-sea migration of Yangtze coilianasus relates to cultivation environment, water quality and feedstuff and includes three phases of juvenile coilianasus fry cultivation phase which comprises culturing green alga, rotifer, cladocera and juvenile prawn as the feedstuff; coilianasus fry seedling cultivation phase which comprises culturing coilianasus fry seedlings in double-layer hollow greenhouses with seawater, changing the salinity of the seawater over time and culturing green alga suitable for growing in the seawater as feedstuff; adult fish gonad development phase which comprises performing fresh water cultivation and culturing green alga, rotifer, cladocera, small fish and small prawn which are suitable for fresh water cultivation as feedstuff. By manually changing salinity, water pressure, water flow, temperature and the like and enhancing water flow speed stimulation, the development of the gonad of adult coilianasus can be promoted, and nutrient substance accumulated inside the body of the coilianasus is transported towards the gonad to form nutrient substance with the unique flavor and taste of the Yangtze coilianasus through substance destruction and recombination.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGYANG GRP
Methods and compositions for growth of hydrocarbons in Botryococcus sp
Acceleration of botryococcenoids and growth by concomitant provision of appropriate light, minerals, and assimilable carbon. Specifically, methods, compositions and systems for the in vitro growth of hydrocarbons in photosynthetic organisms while maintaining a biologically exclusive monocultural environment, as for example, from Botryococcus species, is disclosed. Niche-nutrients can include about 200 ppm to about 3% nitrogen, and about 100 ppm to about 15% P205, and about 100 ppm to about 3.5% K20. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to the growth of the Chlorophyta such as Botryococcus sp. in a nutrient medium that includes up to 15% phosphates, at least 3 ppm soluble iron, and up to about 70 ppm soluble zinc. Also disclosed is a substantially pure culture of Botryococcus braunii var. Showa, strain Ninsei, having the ATCC Accession No. PTA-7441, its parts, and hydrocarbons produced therefrom.
Owner:NONOMURA ARTHUR M
Water quality conditioner for inhibiting harmful algae and use method thereof
InactiveCN101993149ASatisfy nutritionMeet ecological needsBiological water/sewage treatmentFertilizer mixturesWater qualityAquaculture
The invention discloses a water quality conditioner for inhibiting harmful algae, which mainly comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 10-60% of soluble silicon metered based on SiO2, 10-60% of calcium oxide, 1-20% of magnesium, and 1-25% of phosphorus. When the water quality conditioner is in use, the components are proportioned and uniformly mixed to form a blending agent, and the blending agent is scattered on a water surface in a dry way in the morning in a selected clear day, with 5-10kg per mu. The water quality conditioner can fully meet the nutrition and ecologicalrequirements of the bloom of beneficial algae such as microalgae so as to ensure that the microalgae beneficial to aquaculture is greatly bloomed and harmful algae such as blue-green algae is inhibited; after the water quality conditioner is applied for 3-7 days, the water body is improved, the beneficial algae such as the microalgae is bloomed while the harmful algae such as the blue-green algaeand the like are massively extincted, and the water body becomes rich, active, delicated and clear. The invention can be widely applied to various water areas such as ponds, reservoirs, lakes, coastal sea and the like and the treatment and prevention of the harmful algae in the culture of fishes, shrimps and crabs, and has no damage to human bodies and aquatic organisms.
Owner:东莞市凯得威农业科技有限公司
Designer organisms for photobiological butanol production from carbon dioxide and water
ActiveUS8735651B2Higher solar-to-butanol energy-conversion efficiencyWeaken energyBacteriaUnicellular algaeAlgaenanCellulose
Owner:LEE JAMES WEIFU
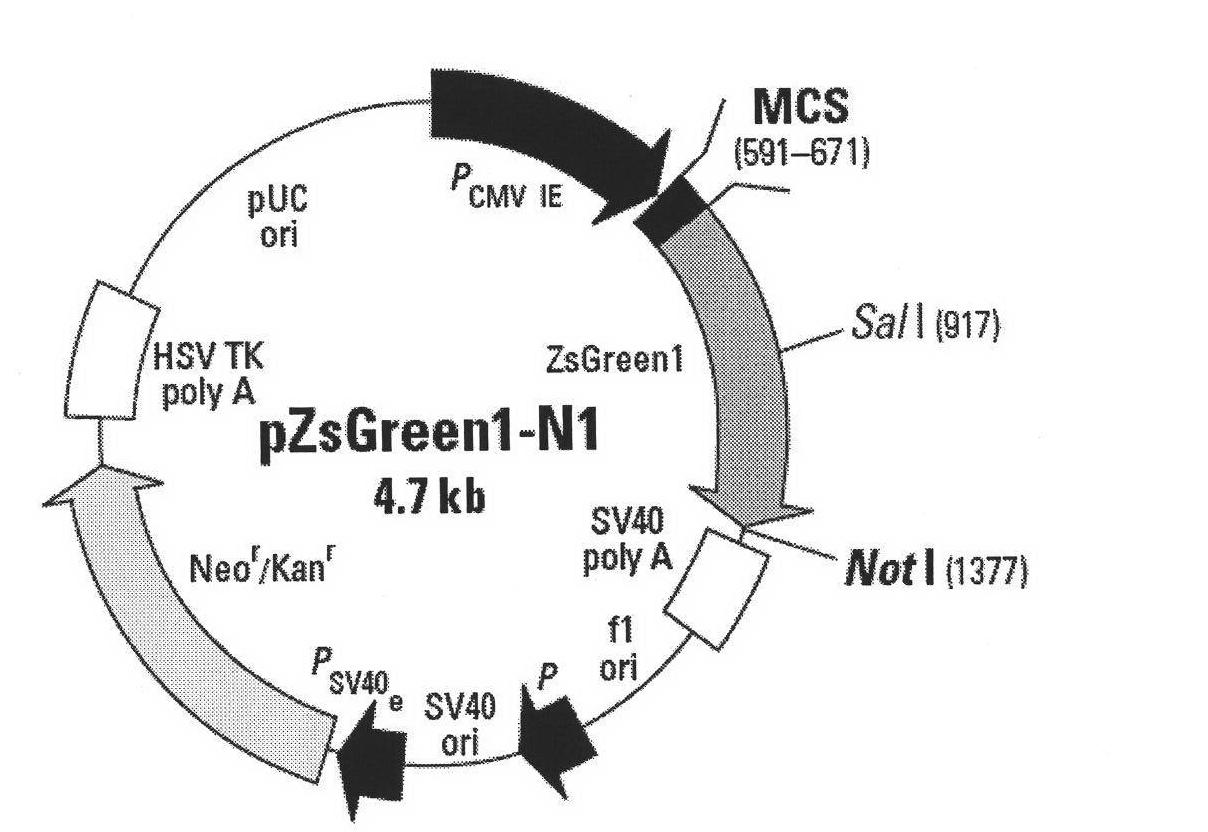
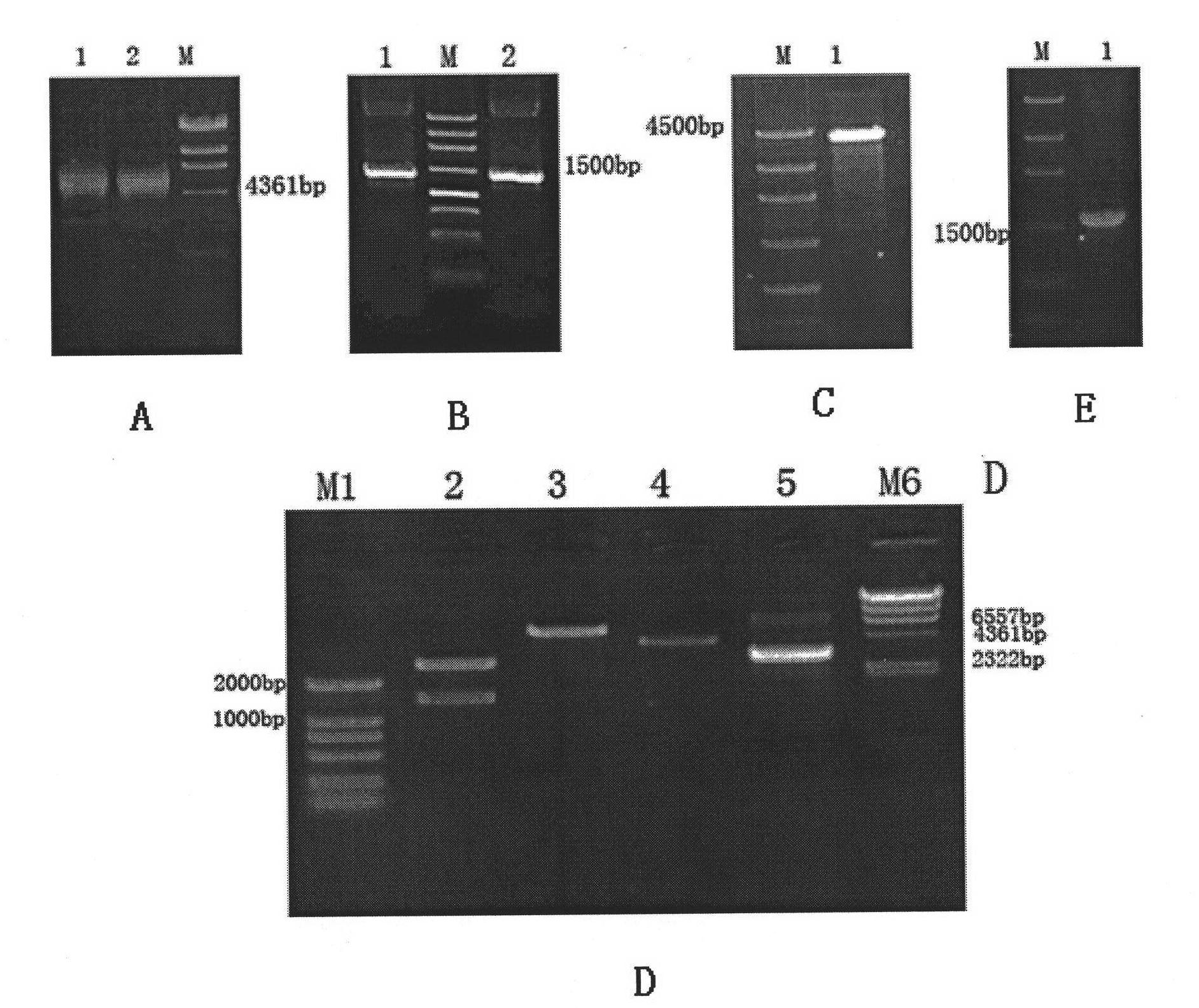
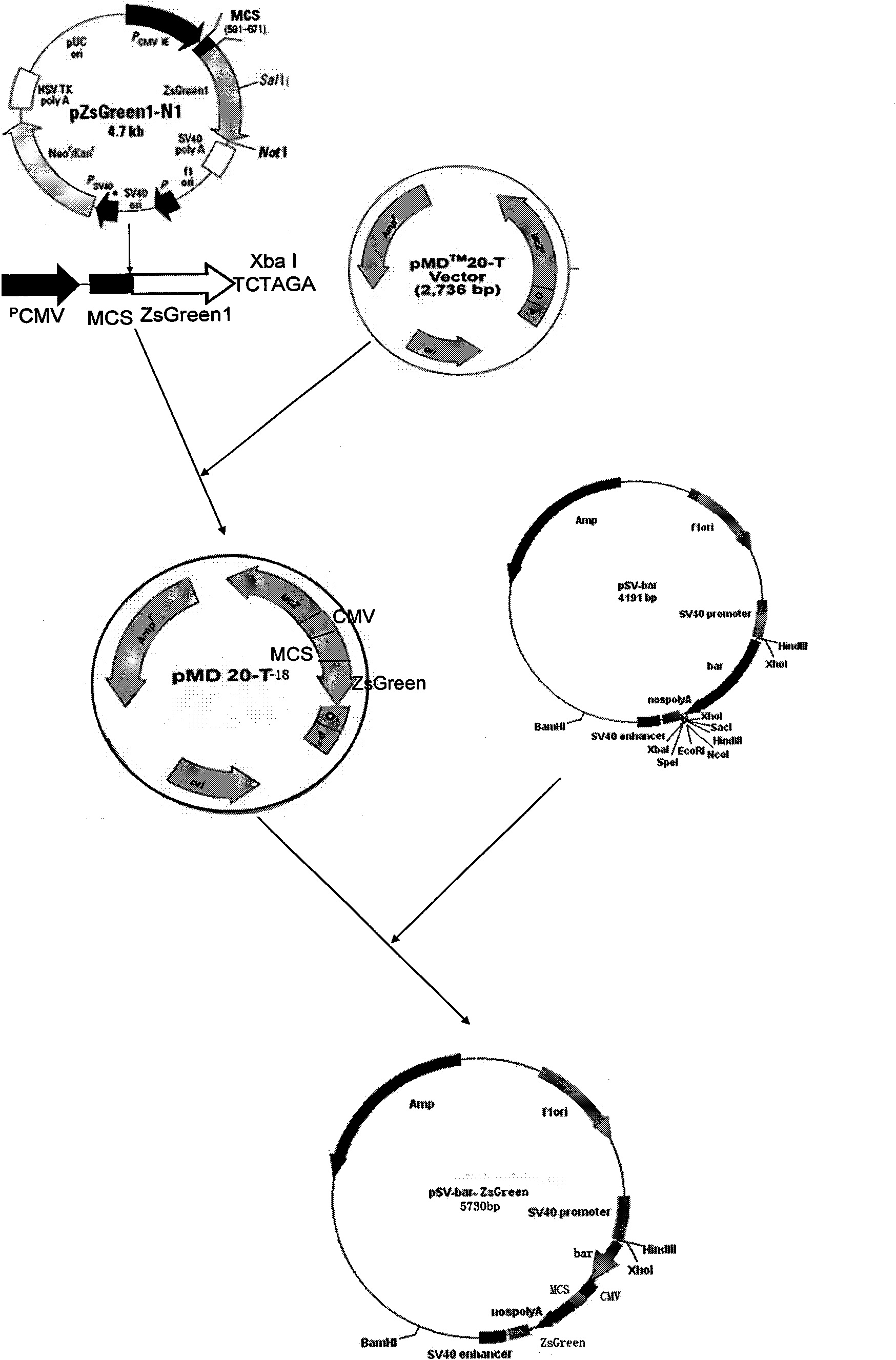
Expression vector for large green alga bioreactor and transformation method thereof
InactiveCN102102107AVersatilityAffect start-up efficiencyAlgae productsVector-based foreign material introductionResistant genesGreen fluorescent protein
The invention provides a vector capable of making an exogenous gene expressed stably and efficiently in a large green alga bioreactor and a method thereof for transformation and expression in a large green alga. In the invention, a protoplast of a large green alga is used as a receptor, the conventional vector of higher plants or a vector modified by a homologous recombination technique are fully utilized to construct a green fluorescent tracing and fusion protein gene-containing vector PSB-bar-ZsGeen for use in a large green alga bioreactor, and the vector PSB-bar-ZsGee is connected with a SV40 gene promoter, a resistance gene, a cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter and the like in turn to realize the high-efficiency and stable expression of the exogenous gene in the large green alga.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Water treatment system and treatment method for settling algae pond-phycomycetes symbiotic ecological plate slot-biofilter
InactiveCN109399798AEffluent water quality up to standardEasy to buildWater contaminantsTreatment involving filtrationParticulatesAnaerobic microorganisms
The invention relates to a water treatment system and a treatment method for settling algae pond-phycomycetes symbiotic ecological plate slot-biofilter. The water treatment system is provided with thesettling algae pond, the phycomycetes symbiotic ecological plate slot and the biofilter successively according to the water inflow direction. Silkweed grows in the settling algae pond in a floating manner for removing element such as nitrogen and phosphorus in sewage. In addition, the settling algae pond also can remove impurities such as particulates and suspended solids in water through settlement action. The phycomycetes symbiotic ecological plate slot is naturally formed by a shallow and long pond with silkweed. Algae growing in a floating manner, such as microorganisms and aquatic insects, and organic matters and part of nitrogen and phosphorus in a water body are removed primarily. Aerobiotic / anaerobic microorganisms grow on a film in a biofilter, so that organic matters in water can be further removed, and the impurities are filtered.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
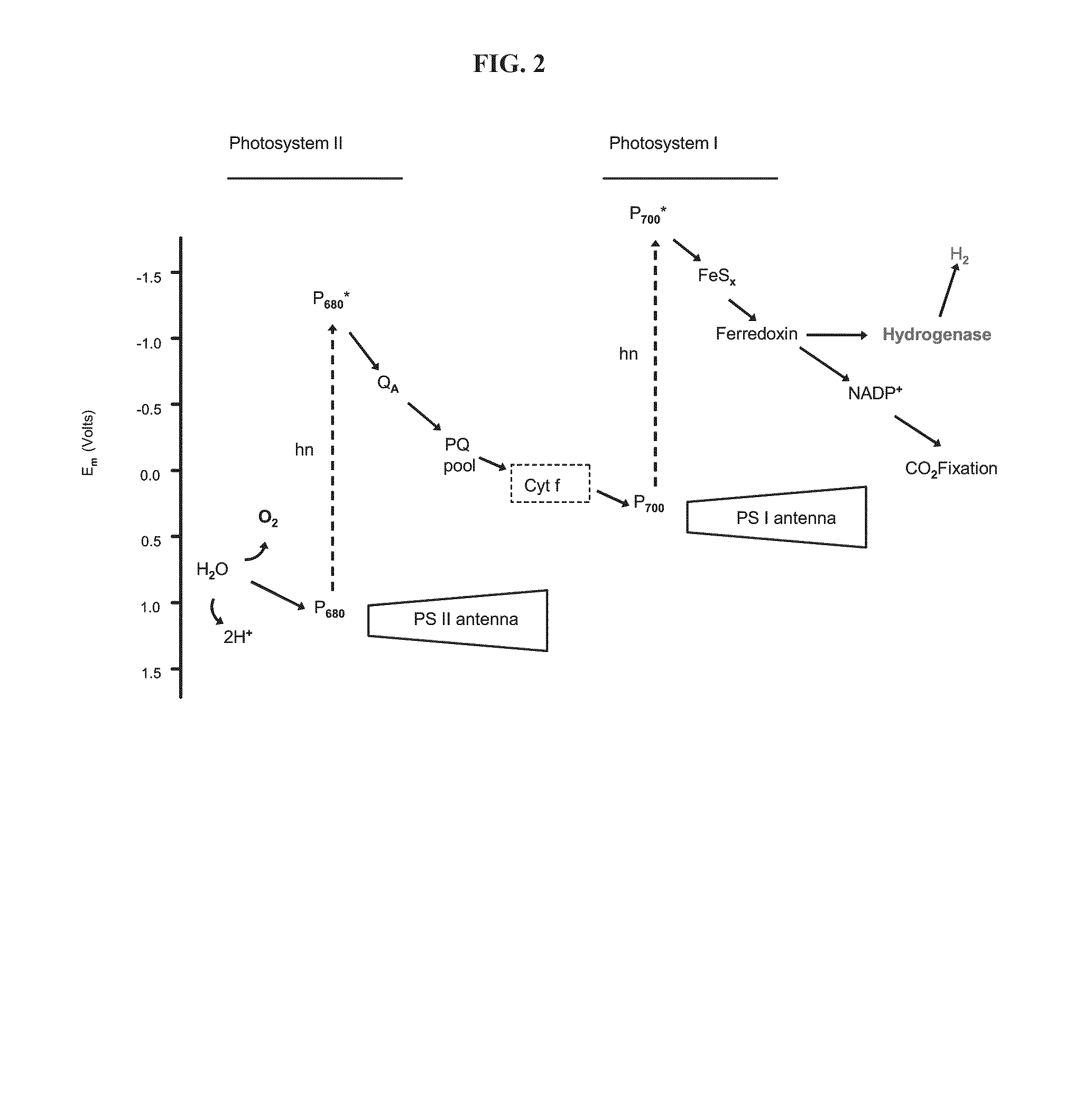
Photosynthetic hydrogen production from the green alga chlamydomonas reinhardtii
The present invention relates generally to hydrogen production for use in fuel cells, foodstuffs and chemical production, and more particularly, to biologically and photosynthetically produced hydrogen. Specifically, disclosed is a method for producing bacteria and green alga that can produce hydrogen in quantities that exceed four hundred percent of the hydrogen produced by green alga in nature; thus, producing organisms which can serve as hydrogen generators for fuel cells, chemical production and numerous other applications.
Owner:H2OPE BIOFUELS LLC
Method for removing green alga in nori cultivation process
ActiveCN103518698ANo pollution in the processChemically stableWeed killersClaviceps purpureaSolubility
The invention relates to a method for restraining green alga growth, in particular to a method for removing green alga in the nori cultivation process. Firstly, algaecide is prepared, wherein solid sodium percarbonate is dissolved in deionized water, so that sodium percarbonate treating fluid is prepared, and the pH value of the treating fluid is between 9 and 10; the prepared algaecide is directly sprayed on green alga bodies attached to a net curtain, a whole raft frame and a whole mooring rope in the nori cultivation process 2 hours before a flood tide and the algaecide is sprayed once every 1 to 3 months. According to the method for removing the green alga in the nori cultivation process, the sodium percarbonate serves as the algaecide and is free of toxin, odor and pollution, high in water solubility, convenient to prepare, free of harm to the environment and free of biological accumulation. The method for removing the green alga in the nori cultivation process is very simple and convenient to achieve, the use cost is low, rinse is not required, and the method is slightly influenced by natural conditions and can be used in a large scale. Three days later after the algaecide is sprayed, the removal rate of the green alga is 100%, and the growth of the nori is not influenced.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Outdoor breeding method for penaeus vannamei in pond
InactiveCN108541638AAvoid Poor Water ColorPromote growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseNitrite
The invention relates to an outdoor breeding method for penaeus vannamei in a pond. The method comprises the following steps: before young penaeus vannamei is thrown, salinity, pH, total alkalinity and total hardness of a culture water body are adjusted into required ranges, a carbon source is added, then the young penaeus vannamei is thrown, and management is performed. The penaeus vannamei cultured by the method provided by the invention has good growth vigor, and the breeding difficult problems that a water color is not good, ammonia nitrogen and nitrite exceed a standard for a long term, apH value is stayed at a high level or changed greatly, blue-green algae are bred, parasites are too more, a water body is turbid for a long term, pollution is serious, and diseases often occur due toimbalance of carbon and nitrogen in the water body are avoided.
Owner:广州普麟生物制品有限公司 +1
Method for breeding chlorella phytoplankton from cyanobacterial bloom
ActiveCN106754385AEasy to trainSave raw materialsUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesCyanophagesIron salts
The invention discloses a method for breeding chlorella phytoplankton from cyanobacterial bloom. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the cyanobacterial bloom from a water body in which the cyanobacterial bloom occurs and properly concentrating the cyanobacterial bloom; aerating, rotting and degrading the concentrated cyanobacterial bloom at 18-45 DEG C; then adding running water to dilute a total phosphor concentration to 5.0-15.9mg / L after the cyanobacterial bloom is degraded for 25-40 days until the water body becomes odorous and is represented in black brown or dark brown, and adding a mineral substance mixture which is composed of calcium salt, magnesium salt, iron salt and potassium salt; and conducting cultivation for several days, so that chlorella, which is high in concentration and purity, is obtained. With the application of the method, the cyanobacterial bloom can be transformed into the chlorella phytoplankton, so that innocent treatment and utilization of the cyanobacterial bloom are promoted and transformation of nutrient substances in the water body is accelerated; the method can be directly used for processing the cyanobacterial bloom; and in addition, the culture method provided by the invention is simple and convenient to implement; therefore, a good way is provided for resource utilization of the cyanobacterial bloom.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Method for constructing green alga phase in saline-alkali soil underground water shrimp industrial culture pond
ActiveCN105875395AAdaptableGuaranteed adaptabilityClimate change adaptationAgriculture gas emission reductionAlkali soilWater quality
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI +1
Culturing method for chlorophyta scenedesmus phytoplankton
InactiveCN104357329AEasy to trainRaw materials are easy to getUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesFresh water organismScenedesmus
The invention relates to a culturing method for phytoplankton, in particular to a culturing method for chlorophyta scenedesmus phytoplankton. The method comprises the following steps of performing shading treatment on the periphery and bottom of an open container by virtue of a shade, injecting water into the container, wrapping freshwater fish compound feeds and dry clay powder with a nylon filter screen to form a feed bag, and sinking the feed bag to the bottom of the container, wherein the proportion of water, the freshwater fish compound feeds to the clay powder is (0.5-4L):(1-4g):1g; rotting the feed bag under an airtight condition of 18 to 35 DEG C, and removing the feed bag when the total nitrogen content of a water body reaches 15 to 25mg / L; removing the shade from the open container, performing aeration treatment on the water body for 8 to 20 days to obtain high-density and high-purity chlorophyta scenedesmus phytoplankton. The culturing method provided by the invention is simple, convenient to implement and low in culturing cost, the raw materials are readily available, and can be continuously used for many times, and great economic benefits are created.
Owner:FISHERY MACHINERY & INSTR RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERY SCI
Special soilless culture substrate for strawberries
InactiveCN104782458AMeeting nutritional needsReduce pollutionAgriculture gas emission reductionCultivating equipmentsFragariaAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a strawberry culture substrate, in particular to a special soilless culture substrate for strawberries. The substrate is formed by mixing 15%-20% of green alga, 10%-12% of spirogyra, 15%-20% of rotten wood, 30%-40% of hyperphosphate slag, 10%-15% of beer grain, 5%-10% of apple pomace, 0.1%-0.3% of zinc ash, 0.2%-0.4% of manganese ash, 0.1%-0.3% of silica ash and 8%-10% of fresh banana skin. According to the special soilless culture substrate for the strawberries, waste is selected as substrate raw materials, natural waste resources are fully utilized, so environment pollution is reduced; the substrate has high content of microelements like zinc and manganese, so the requirements of the strawberries for microorganism elements can be satisfied; in the planting process, the phenomena that nutrients are luxuriant in the early period of strawberry planting process or nutrients are inadequate in the later period of strawberry planting process can be avoided through ceaselessly slow release of nutritional ingredients of the substrate, the requirements of the strawberries for the nutrients in a whole growing period can be met, external fertilization is not needed in the planting process, just the daily water requirement needs to be satisfied, water can flow quickly through the substrate, and germination of bacteria sources of powdery mildew, gray mold and anthracnose is avoided; accordingly, growth of roots of the strawberries is promoted, protection layers are formed on surfaces of the roots, and the disease-resistance capacity of seedlings is improved.
Owner:阜阳市王冰生态农业科技有限公司
Methods and compositions for growth of hydrocarbons in Botryococcus sp
Acceleration of botryococcenoids and growth by concomitant provision of appropriate light, minerals, and assimilable carbon. Specifically, methods, compositions and systems for the in vitro growth of hydrocarbons in photosynthetic organisms while maintaining a biologically exclusive monocultural environment, as for example, from Botryococcus species, is disclosed. Niche-nutrients can include about 200 ppm to about 3% nitrogen, and about 100 ppm to about 15% P2O5, and about 100 ppm to about 3.5% K2O. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to the growth of the Chlorophyta such as Botryococcus sp. in a nutrient medium that includes up to 15% phosphates, at least 3 ppm soluble iron, and up to about 70 ppm soluble zinc. Also disclosed is a substantially pure culture of Botryococcus braunii var. Showa, strain Ninsei, having the ATCC Accession No. PTA-7441, its parts, and hydrocarbons produced therefrom.
Owner:NONOMURA ARTHUR M
Appetite-promoting snakehead fodder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104799079AIncrease appetiteSuitable for palateFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyOyster
The invention discloses appetite-promoting snakehead fodder which comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 60-70 parts of corn flour, 30-40 parts of soybeans, 20-25 parts of lucerne meal, 10-15 parts of chestnut shell, 20-25 parts of peanut shell, 5-8 parts of soybean shell, 5-7 parts of brown sugar, 10-13 parts of preserved duck egg, 14-19 parts of pepper stem, 6-11 parts of green alga, 10-14 parts of flammulina velutipes root and base, 2-3 parts of spiced salt, 20-24 parts of arrowroot, 4-7 parts of muskmelon flower, 2-5 parts of corn stigma, 15-20 parts of mango skin, 3-4 parts of hydrocotyle asiatica, 1-2 parts of citronella, 1-2 parts of ailanthus altissima flower, 5-7 parts of sugar dreg powder, 20-25 parts of oyster shell powder, 20-25 parts of fish paste, 3-4 parts of saccharomycetes, 3-4 parts of a phagostimulant and an appropriate amount of water. The appetite-promoting snakehead fodder is good in food inducing property and meets the taste demand of snakeheads, can induce great appetite of ducks, and effectively promotes rapid growth of snakeheads; the snakeheads fed with the fodder are good in meat quality and taste and rich in nutrition, and excellent culture benefits are realized.
Owner:ANHUI PROVINCE JINTUO LAKE CRAB IND CO LTD
Seaweed and ferment rice cakes and making method thereof
InactiveCN110623202ABalanced unique nutritionBalanced Unique FlavorFood shapingFood ingredient functionsFruit juicePorphyra
The invention discloses seaweed and ferment rice cakes and a making method thereof, and relates to the technical field of food processing. The seaweed and ferment rice cakes comprise the raw materialsin parts by weight of 50-90 parts of rice, 1-30 parts of starch, 0.01-20 parts of seaweed ferment, 0.01-2 parts of brown algae dietary fiber powder, and 0.1-30 parts of fruit juice, and preferably 0.1-2 parts of probiotics, 0.1-2 parts of prebiotics and 0-5 parts of plant carbon black are added. In the selected raw materials, the seaweed ferment is prepared by fermentation of one or more of brownalgae ferment, red algae ferment and green alga ferment, the brown algae ferment is from kelp or undaria pinnitafida, and the red algae ferment is free laver. The rice cakes are used as a carrier, and the made seaweed ferment rice cakes contain the seaweed, the fruit juice, the prebiotics, the probiotics, the plant carbon black and the like, so that balanced and unique nutrients and flavor can begiven to the rice cakes, and the health value for nourishing the stomach and intestines is provided. The seaweed and ferment rice cakes have good market prospects.
Owner:QINGDAO BRIGHT MOON SEAWEED BIO HEALTH TECH GRP CO LTD
Efficient shrimp breeding pond water adjusting technology based on activity of algae
InactiveCN110467266ASimple compositionTo achieve the purpose of diverting waterWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processBiological water/sewage treatmentFresh water organismOxygen
The invention relates to the technical field of aquaculture, and discloses an efficient shrimp breeding pond water adjusting technology based on the activity of algae. The efficient shrimp breeding pond water adjusting technology comprises: 1) water fertility adjusting at the early stage of breeding, wherein complete aeration is performed by opening an aerator, a bottle of Jieduxianfeng is used inper 4-5 mu of a water body, the Jieduxianfeng is diluted, the diluted Jieduxianfeng is poured into the whole pool, the pool is refilled with new water after the Jieduxianfeng is used for 3-4 days, and 1000-2000 ml of a fresh water Chlorella solution with a concentration of 2000000 / ml is poured into per mu of the water body. According to the present invention, with the technology, by arranging Chlorella, Chlorella belongs to Chlorophyta, is a eukaryote, is a spherical single-cell algae, is one of the earliest life on earth, is an efficient photosynthetic plant, is subjected to autotrophic growth reproduction, can be conveniently and simply reproduced, has strong reproduction ability, can continuously convert solar energy into algae containing various nutrients, and can release a large amount of oxygen during proliferation, wherein the one Chlorella cell can be divided into four cells every 24-28 h by using sunlight, water and carbon dioxide.
Owner:阿尔格生命科学(江苏)有限公司
Feed for promoting growth of ancistrus fries and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a feed for promoting the growth of ancistrus fries. The feed is characterized in that the feed is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 300 to 400 parts of blue-green algae, 20 to 30 parts of saccharomyces cerevisiae, 50 to 60 parts of cooked yolk, 100 to 150 parts of spinach powder, 30 to 50 parts of garlic powder, 30 to 40 parts of haw powder, 50 to 60 parts of wheat gluten, 0.1 to 0.3 parts of sodium humate, 0.01 to 0.03 parts of protease, 10 to 20 parts of medicinal stone powder, 0.5 to 1 part of fish multivitamin and 400 to 500 parts of minced fresh shrimp. Each component of the feed is screened strictly, each component is a natural substance, nutrition is complete and balanced, palatability and attractant effect are good, the feed is easy to digest and absorb, and the growing speed of the ancistrus fries can be increased remarkably. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the feed for promoting the growth of the ancistrus fries, the steps are simple, the requirement on equipment is low, the method is easy to operate, and the cost is low.
Owner:吴磊磊
Regionally cultured aquatic miniature organism nourishing agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106745762AOptimizing Diversity StructureImprove water qualityWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsFish qualityMortality rate
The invention discloses a regionally cultured aquatic miniature organism nourishing agent and a preparation method thereof. The nourishing agent is composed of culture pond muddy water, an indigenous microorganism flora enriched culture medium, and a microorganism culture material; wherein the weight ratio of the microorganism culture material to the culture pond muddy water is 1: (0.6-1); and the indigenous microorganism flora enriched culture medium accounts for 10 to 20% of the total weight of the microorganism culture material and the culture pond muddy water. The nourishing agent can optimize the diversity of miniature organisms in a culture pond. After using the nourishing agent, the pool nutrient type alga structure is converted into medium nutrient type alga structure composed of beneficial algae communities such as green alga. Moreover, the nourishing agent can reduce the death rate of fish, and the using amount of medicine is reduced. Moreover, the fish quality is improved, the yield of each mu is increased, the feed coefficient is reduced, the fish color becomes healthier, the taste becomes better, and the fish meat does not have any fishy smell and is tight.
Owner:PEARL RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for cultivating chlorella by using food waste
ActiveCN107686815ARaw materials are readily availableEasy to implementWaste processingUnicellular algaeHigh concentrationResource utilization
The invention relates to a cultivating method for phytoplankton chlorella and in particular to a method for cultivating chlorophyta chlorella phytoplankton by using food waste. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, to obtain the food waste, and controlling the solid volume proportion in the food waste to be 5%-60%, placing in a transparent capped container, adding corresponding substances, and aeration-rotting in 18-45 DEG C of the room temperature; after 30-60 days of the rotting, and while the body of water is taupe or light brown and has the obvious ammonia smell, transferringupper rotting liquid to a transparent container, and diluting by using tap water, wherein the total phosphorus concentration in the diluted water body is 1.2-5.2 mg / L; and stirring the diluted water body, and placing for 5-10 days, to obtain the chlorella phytoplankton with the high concentration. The provided cultivating method is simple and is easily implemented, and raw materials are easily obtained and can be continuously used for many times. The cultivation cost is low. An excellent way is provided for the resource utilization of the food waste.
Owner:FISHERY MACHINERY & INSTR RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERY SCI
Biological crust restoration material for promoting ecological restoration of ionic rare earth tailing area, application and restoration method
ActiveCN113857235APromote the leaching of ammonia nitrogenIncrease contentClimate change adaptationContaminated soil reclamationChlamydomonas sajaoAmmoniacal nitrogen
The invention belongs to the technical field of ecological restoration of mines, and relates to a biological crust restoration material for promoting the ecological restoration of an ionic rare earth tailing area, application and a restoration method. The biological crust restoration material for promoting the ecological restoration of the ionic rare earth tailing area provided by the invention comprises broadleaf algae and / or indigenous soil algae; the types of the indigenous soil algae comprise cyanobacteria sphingothrix and / or chlorophyta chlamydomonas; the variety of the broadleaf algae comprises nostoc nitrogen fixing and / or microcoleus vaginatus. According to the restoration material, the culture solution of the broadleaf algae and the indigenous soil algae is applied to the soil of an ion type rare earth tailing area to be repaired, the content of organic matter in the tailing soil can be remarkably increased, the ammonia nitrogen content is reduced, the crust area of a tailing surface layer is increased, an exposed surface layer is greatly reduced, the extremely degraded ecological environment of the ionic rare earth abandoned mining area caused by abandoned tailings can be quickly improved, and the soil degradation and environmental pollution of the mining area caused by the mining of the rare earth mine can be improved.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF ECO-ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & PLANNING
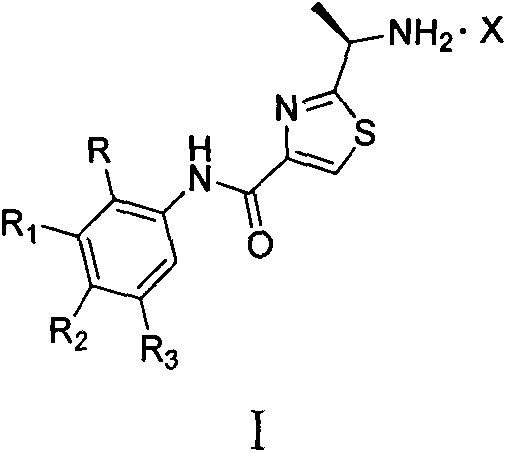
Salifying method of 2-(1-amido-ethyl)-N-phenyl thiazole-4-methanamide compound and application
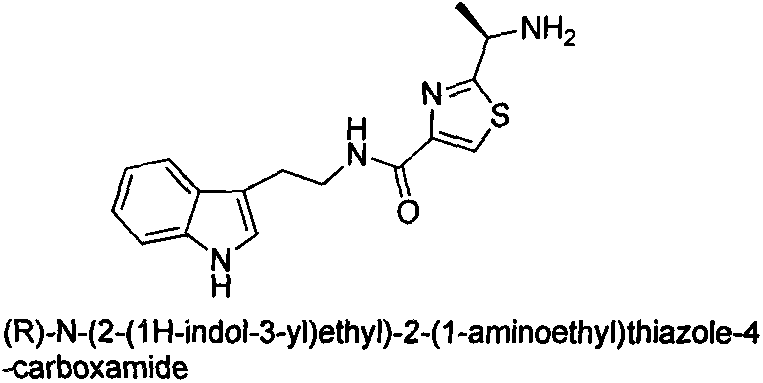
The invention relates to a salting method of a 2-(1-amido-ethyl)-N-phenyl thiazole-4-methanamide compound and a derivative thereof, and application thereof in the aspects of prevention and treatment of limnetic algae. The 2-(1-amido-ethyl)-N-phenyl thiazole-4-methanamide compound is a compound shown in a structural general formula, wherein X is HCl, H2SO4, H3PO4, maleic acid, fumaric acid, para-toluenesulfonic acid, citric acid, oxalic acid, malic acid, acetic acid, tartaric acid and the like; R, R1, R2 and R3 are H, halogens, C2-C5 alkyls, sulfo groups, alkoxy, nitryl, amino, substituted amino and the like. The salifying method of the compound is simple and convenient in process, and applicable to industrial production, and has the potential of developing an efficient algicide. The 2-(1-amido-ethyl)-N-phenyl thiazole-4-methanamide compound has excellent broad-spectrum killing algae activity on limnetic algae chlorophyta verdigris microcystin algae, scenedesmus obliquus, chlorella pyrenoidosa and the like. Compared with the traditional algicide, the 2-(1-amido-ethyl)-N-phenyl thiazole-4-methanamide compound has the characteristics of being high in activity, friendly to environment, low in toxicity on non-target organisms and the like, simple in synthetic method, and is an algicide lead compound with value.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Hybrid culturing method for bass and crucian by using ecological-floating-bed-technology-based pond
InactiveCN109197695AIncrease productionPromote healthy growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSebastesWater quality
The invention discloses a hybrid culturing method for bass and crucian by using an ecological-floating-bed-technology-based pond. On the basis of lift habits of various cultured fishes, intercroppingyellow-head catfishes only need to eat residual feeds fully and intercropping crucian plays a role in removing excrements of the bass. When the crucian and yellow-head catfishes, together with the bass, are cultured together in a pond, a phenomenon that the water quality is affected by the residual feed corruption and deterioration is prevented, the ecological balance of the pond is kept, and thecrucian and yellow-head catfish yields are increased additionally. With the biological floating bed technology, water hyacinth is transplanted and the coverage rate of the water hyacinth on the watersurface is controlled, so that nitrogen and phosphorus transformation effect is fully utilized, the dissolved oxygen content in the water is ensured, and biomass of the green alga and blue-green algaeand the like is reduced obviously. Therefore, the purification effect of the culturing pond water is realized; and thus the healthy growth of fishes is promoted effectively and the culturing yield isincreased.
Owner:王欣
Chlorophytum indoor water planting method
InactiveCN104620956AImprove viewing valueEliminate formaldehydeCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationPlantletChlorophyta
The invention discloses a chlorophytum indoor water planting method and belongs to the technical field of potting cultivation. The chlorophytum indoor water planting method overcomes the defect that the appearance of an existing water planting chlorophytum is single and further increases the ornamental value. According to the chlorophytum indoor water planting method, high-quality chlorophyta are selected, arranged and cultivated in a pipeline through water, plantlets putting forth from axils of the chlorophyta droop and extend to form a row, and the chlorophyta have very high ornamental value and can play a role in purifying air and removing formaldehyde better.
Owner:CHONGQING QIANJIANG DISTRICT QIANSHUANG TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com