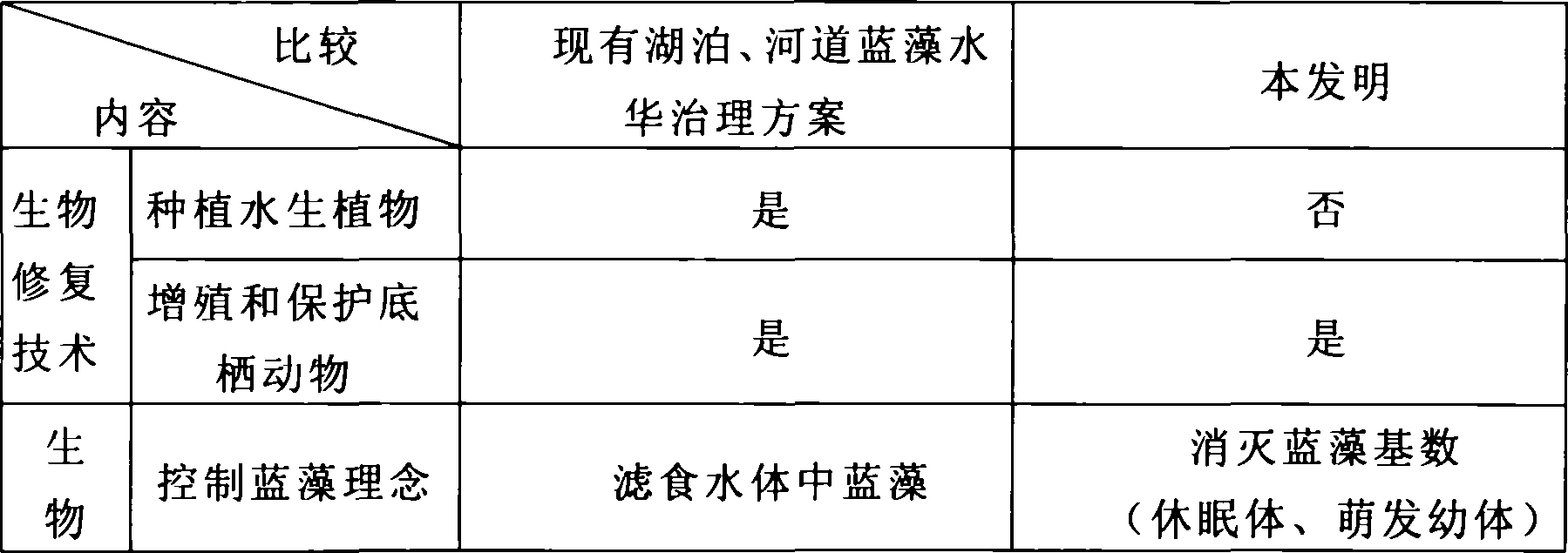
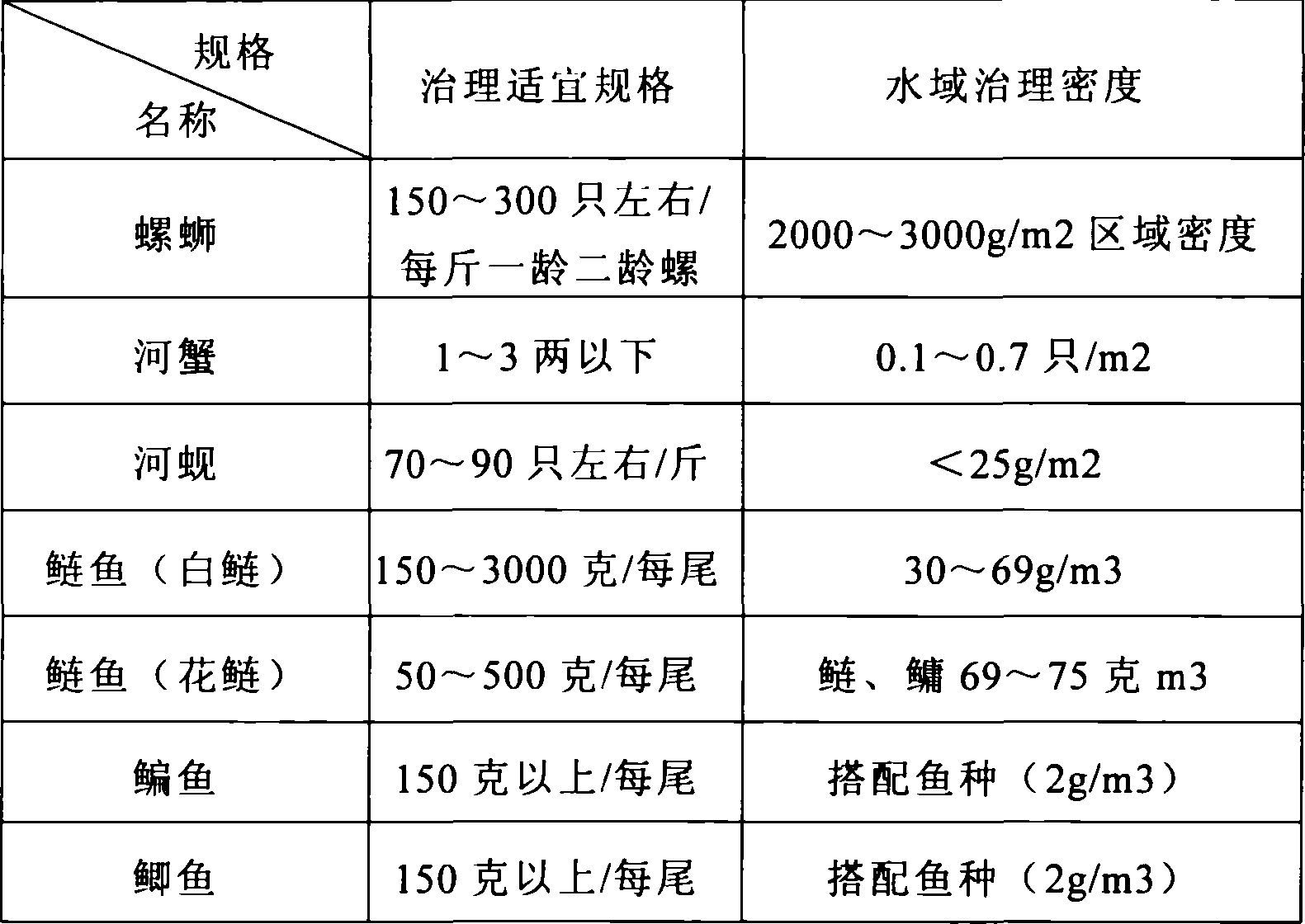
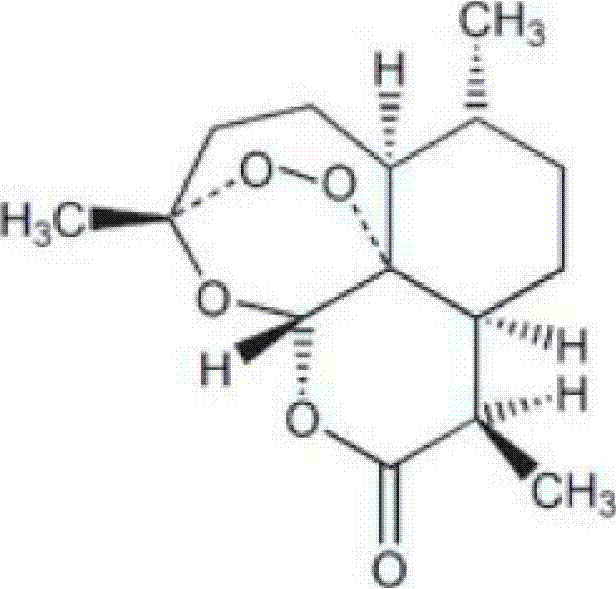
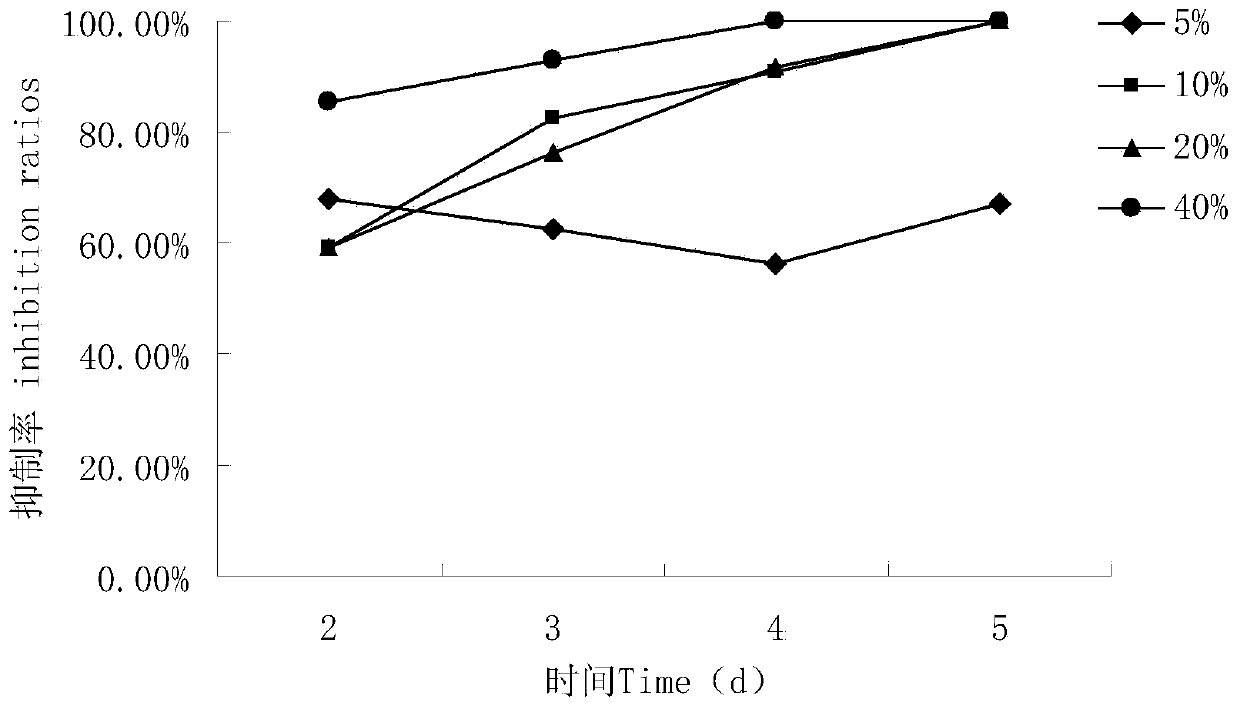
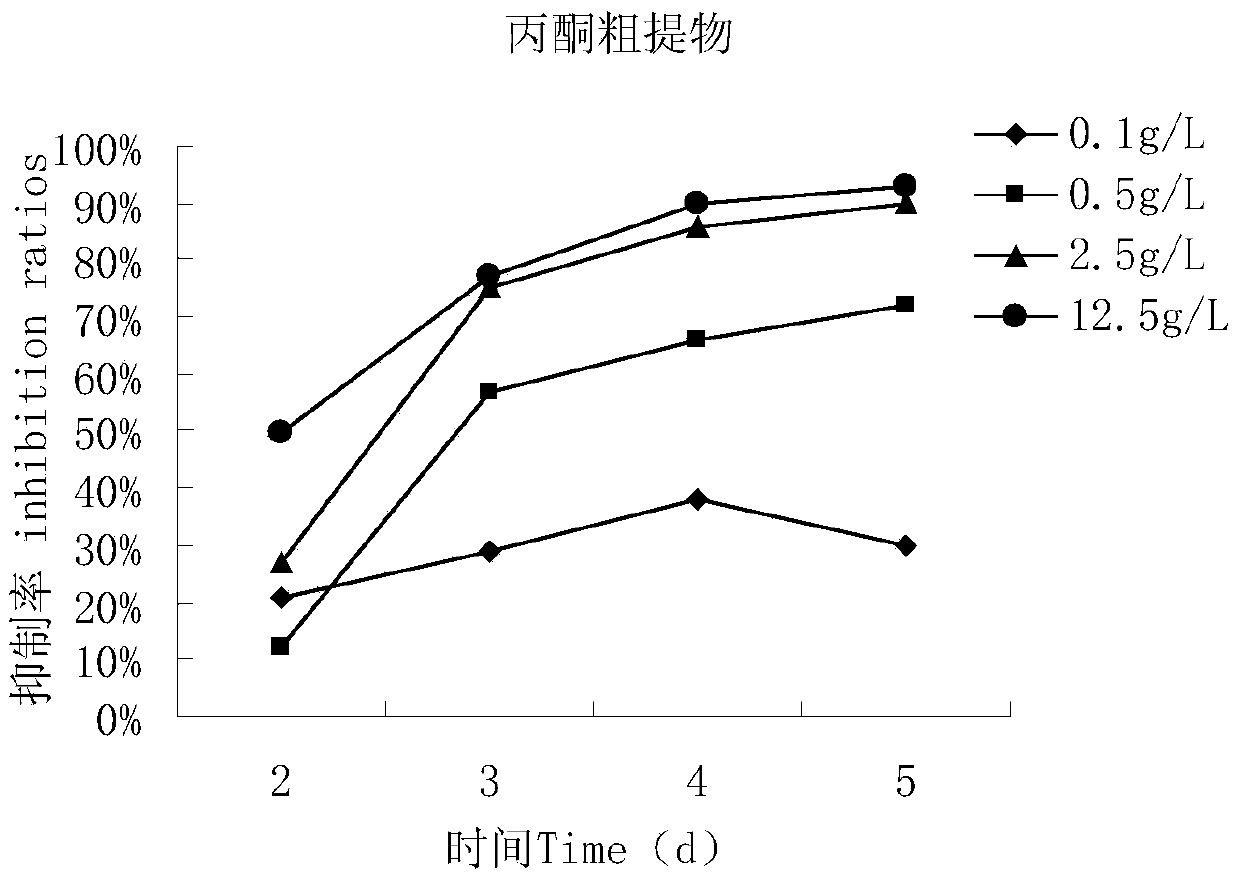
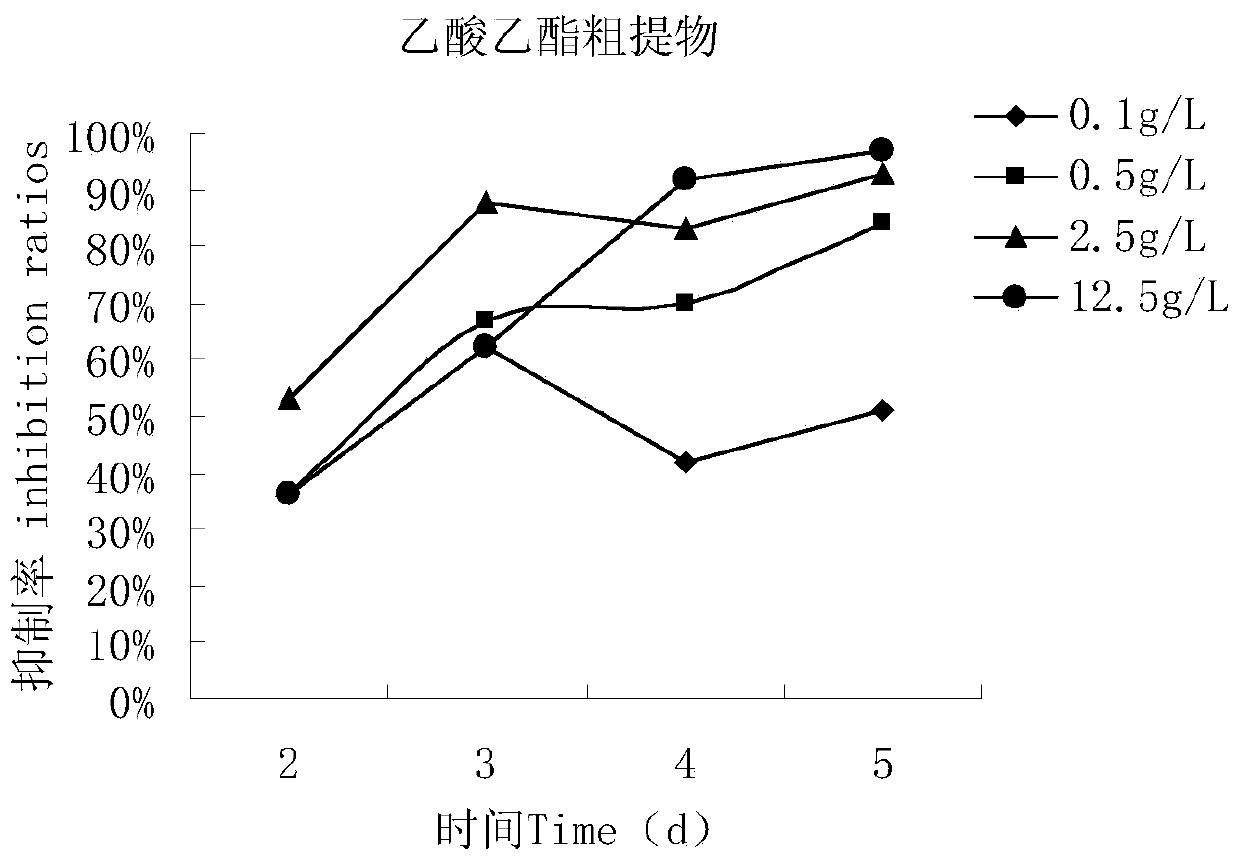
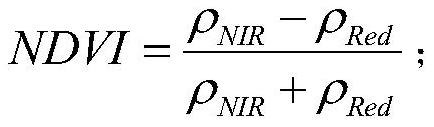Patents
Literature
293 results about "Cyanobacterial bloom" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cyanobacteria blooms form when cyanobacteria, which are normally found in the water, start to multiply very quickly. Blooms can form in warm, slow-moving waters that are rich in nutrients from sources such as fertilizer runoff or septic tank overflows.
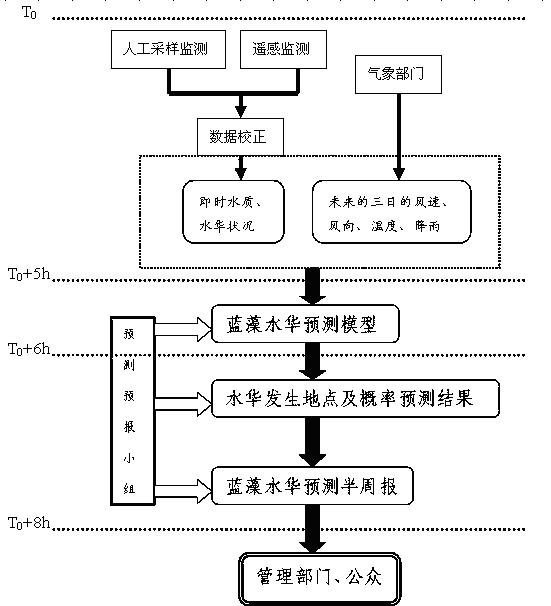
Method for forecasting blue-green algae water bloom in large-scale shallow lake within 72 hours
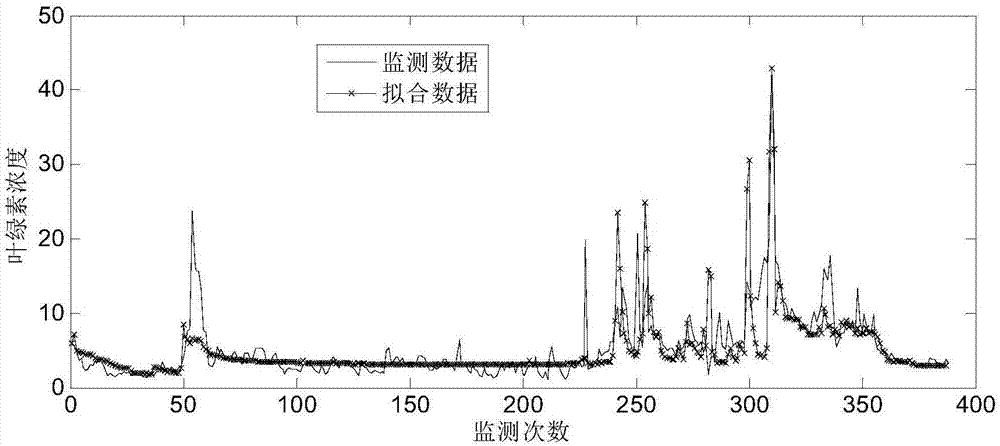
The invention discloses a method for forecasting blue-green algae water bloom in a large-scale shallow lake within 72 hours. The method comprises the following steps of: building a content forecasting model of chlorophyll a in a water body and a probability forecasting model of water bloom generation according to an in-situ growth rate and drift rate parameters of blue-green algae; analyzing instant content of the chlorophyll a in a monitoring water area; distributing and acquiring meteorological information data in a monitoring period; inputting the built models; and outputting a predicted value of the concentration of the chlorophyll a in the monitoring water area in the next 72 hours and the water area and the probability of water bloom generation. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of strong operability, easily acquired parameters used for forecasting and high timeliness, and can be used for rapidly and accurately predicting breakout of the blue-green algae water bloom and forecasting the blue-green algae water bloom in a waterhead site and a vital landscape water area.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Method for controlling water bloom of blue algae
InactiveCN1562809ACompletely curedSimple methodSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentCyanophagesCarp
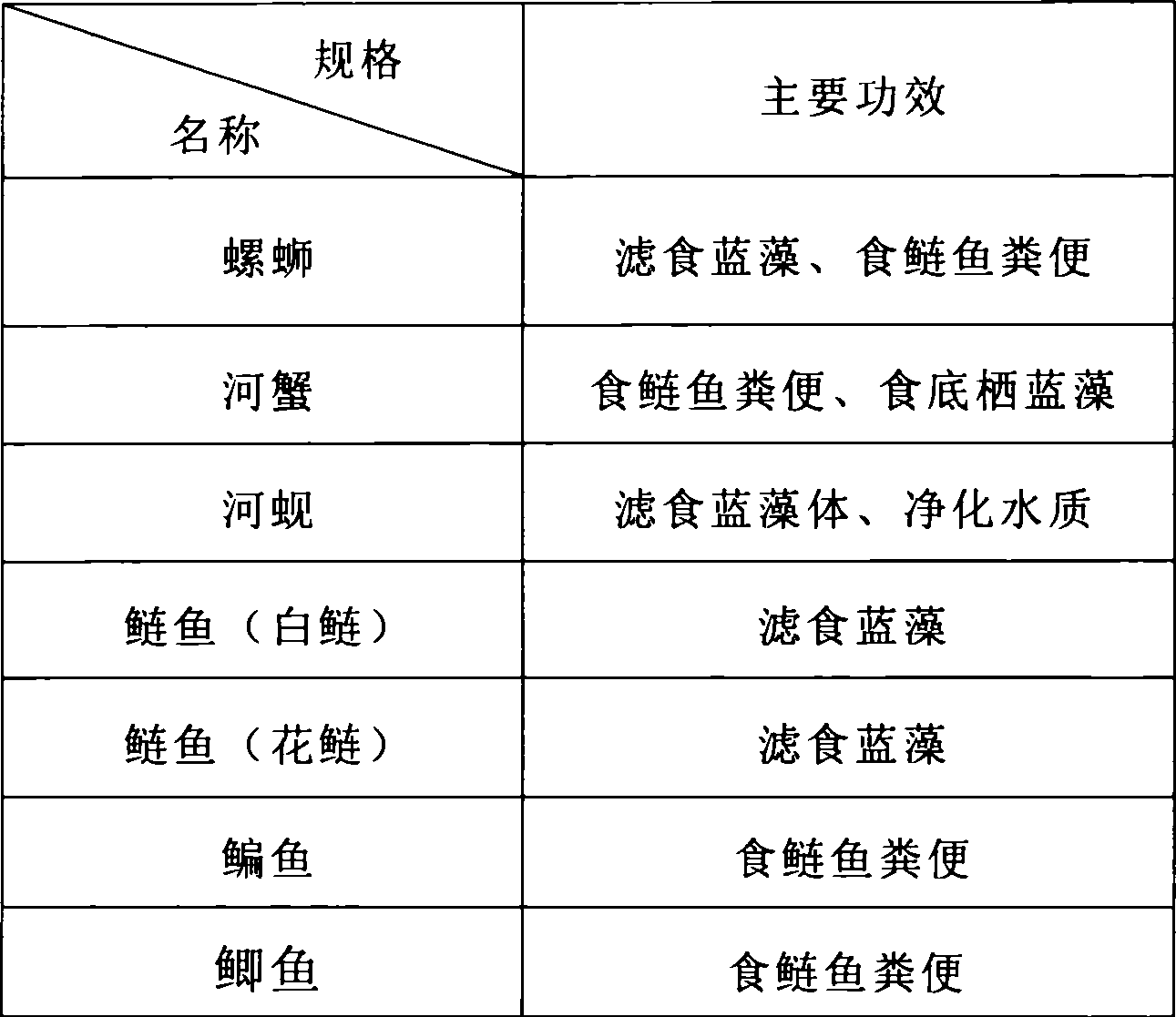
At first, breeding filter feed silver carp, carp and crucian carp in area of water bloom breakout to control algae growing; pelagian eats small algae to reduce quantity of the algae; spiral shell and clam can moves carrying roes toincrease fish spreading area; cyanophage, dissolved algae bacteria and other microbe eating algae are separated and purified from natural water, which is cultured to large quantities in laboratory then to be put in blue algae water bloom breakout orea to control algae; resumption of water plant in water bloom breakout area can control algae growing. Last is getting rid of algae by machine including fixed blue adgae water bloom removing machine and mobile blue adgae water bloom removing machine.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
High-precision monitoring method for cyanobacterial blooms in large shallow lake through MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) and satellite
ActiveCN103743700AReflect accuracyReflect its spatio-temporal distributionMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationModerate-resolution imaging spectroradiometerShallow lake
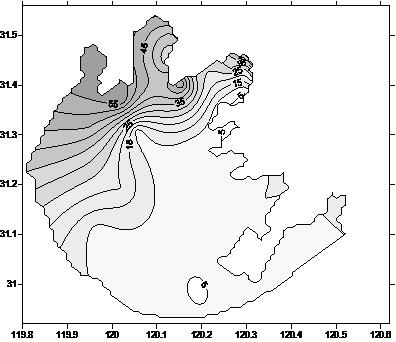
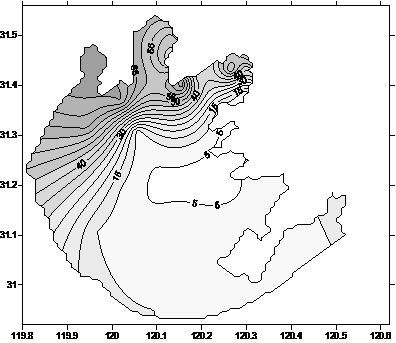
The invention discloses a high-precision monitoring method for cyanobacterial blooms in a large shallow lake through an MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) and a satellite. The high-precision monitoring method is characterized by comprising the following steps: screening recognition indexes of the cyanobacterial blooms (short for algal blooms) which are insensitive to the type and thickness of an atmospheric aerosol; combining the synchronous MODIS, LandsatTM / ETM and satellite image in 2000-2013 year and a gradient analysis result of land and water information to obtain a pure pixel index threshold value of the algal blooms; precisely calculating the area of the algal blooms in a mixed pixel (part of pixels covered by the algal blooms) of the algal blooms by using a pixel growth algorithm (APA); and furthermore, estimating the actual area of the algal blooms in the total water area of the lake and the areal distribution of the algal blooms. The high-precision monitoring method can be used for precisely obtaining the spatial and temporal distribution of the algal blooms in the shallow lake, accurately analyzing the generation and development condition and trend of the algal blooms, scientifically estimating the lake pollution control and ecological remediation effects and providing the scientific and technological support for making a scientific decision for water resource management and water environment protection of departments of water conservation, environment protection and the like.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
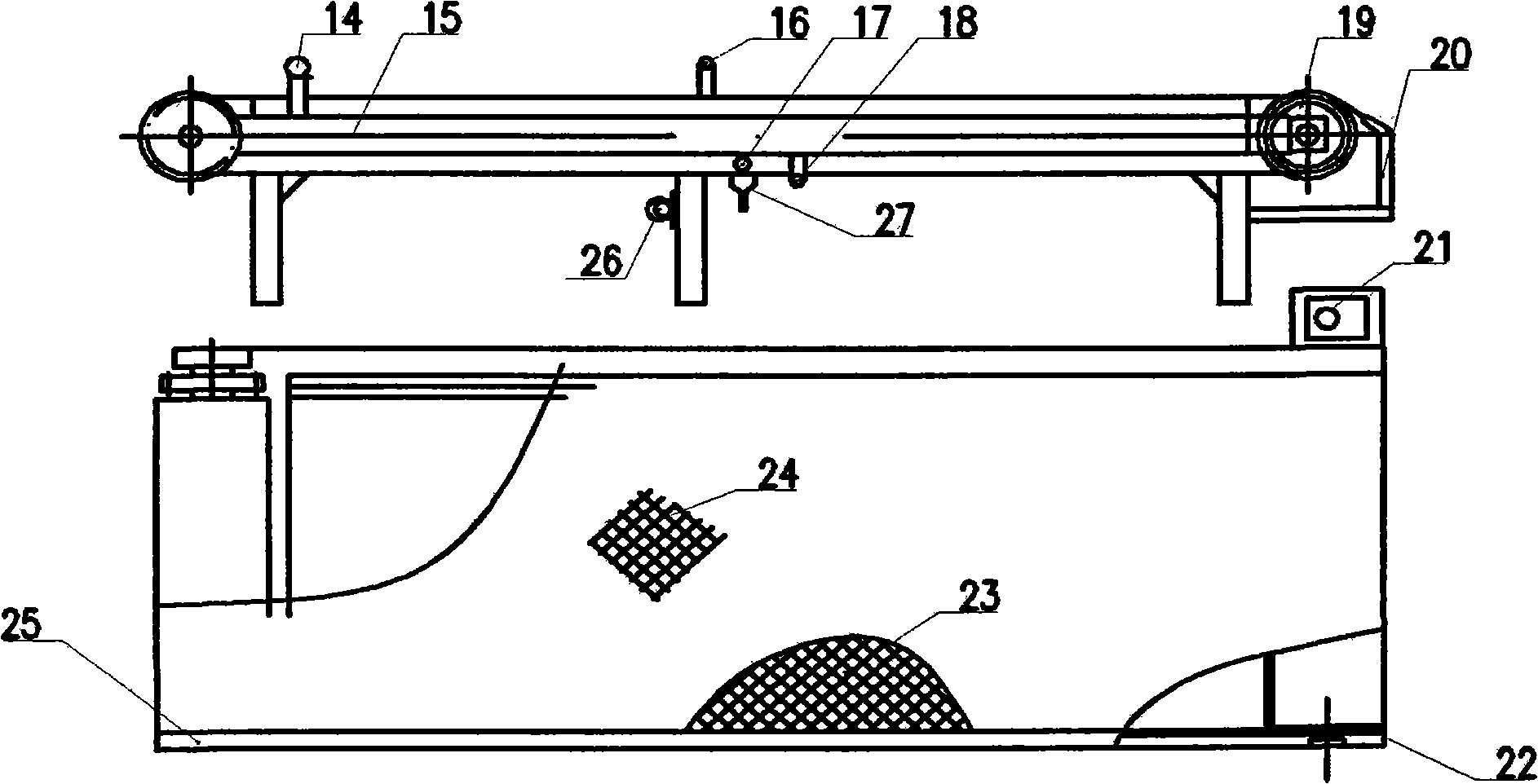
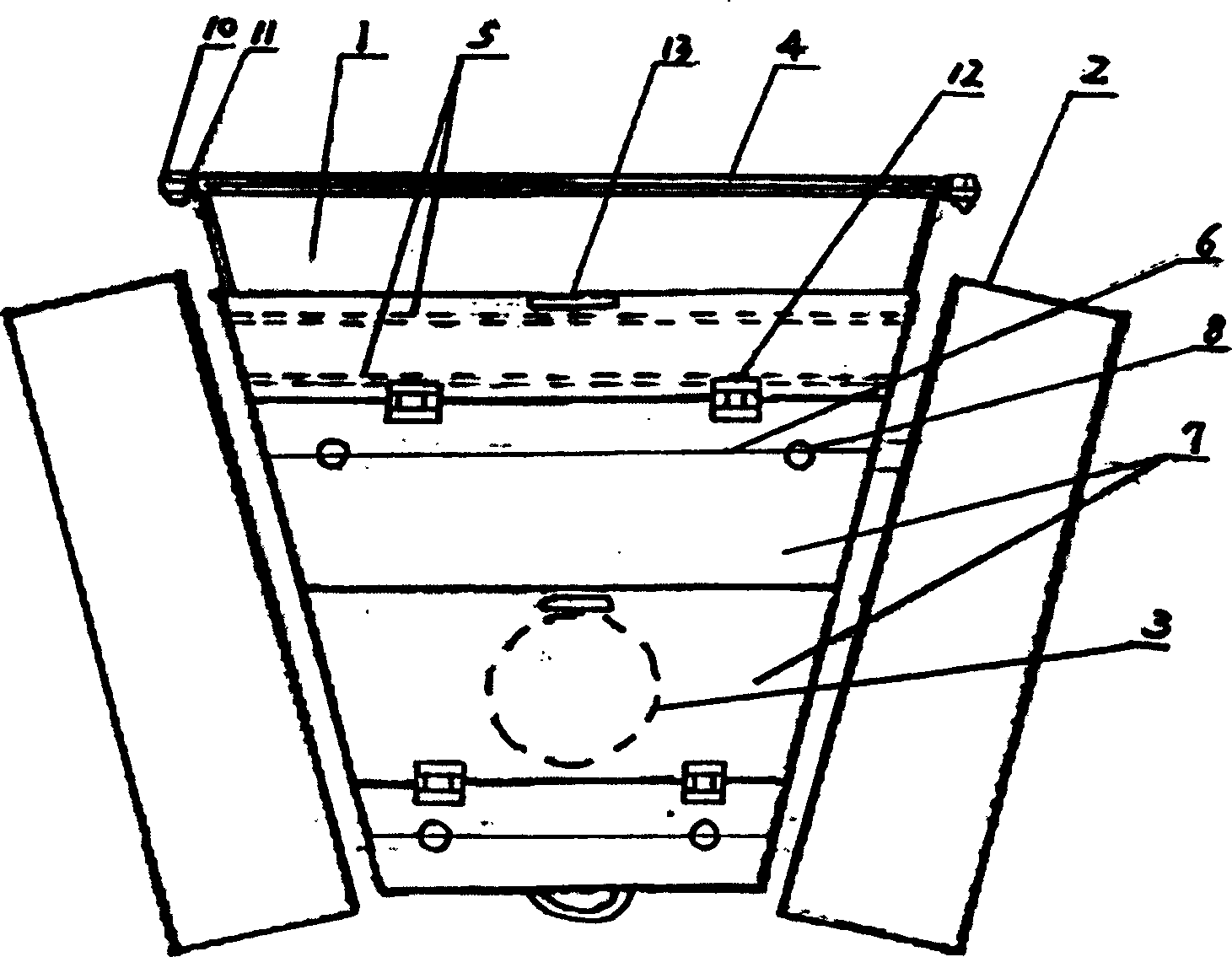
Method and apparatus for harvesting water bloom blue algae
InactiveCN101318714ASimple methodSimple and fast operationWater cleaningWater/sewage treatmentPhylum CyanobacteriaFiltration
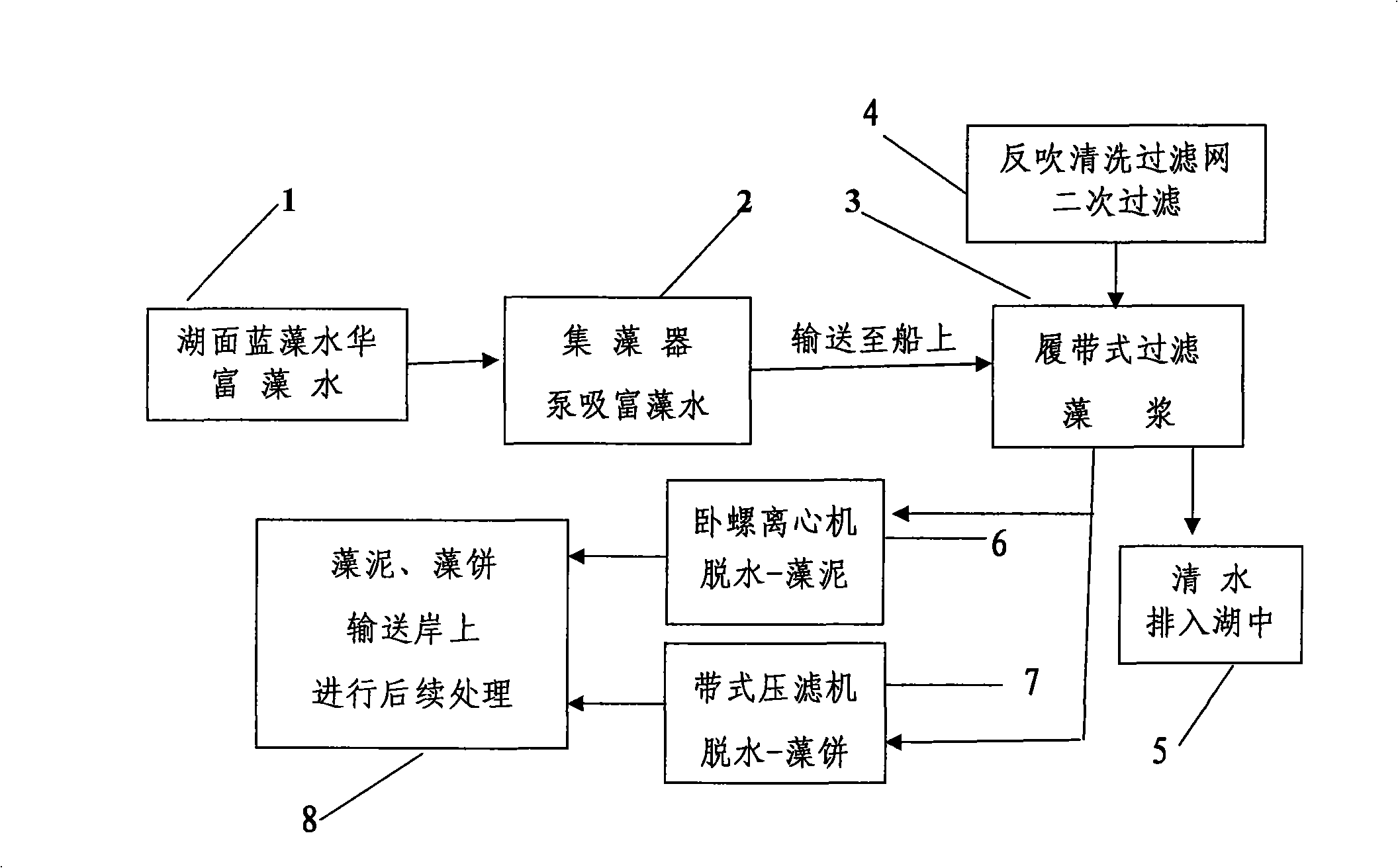
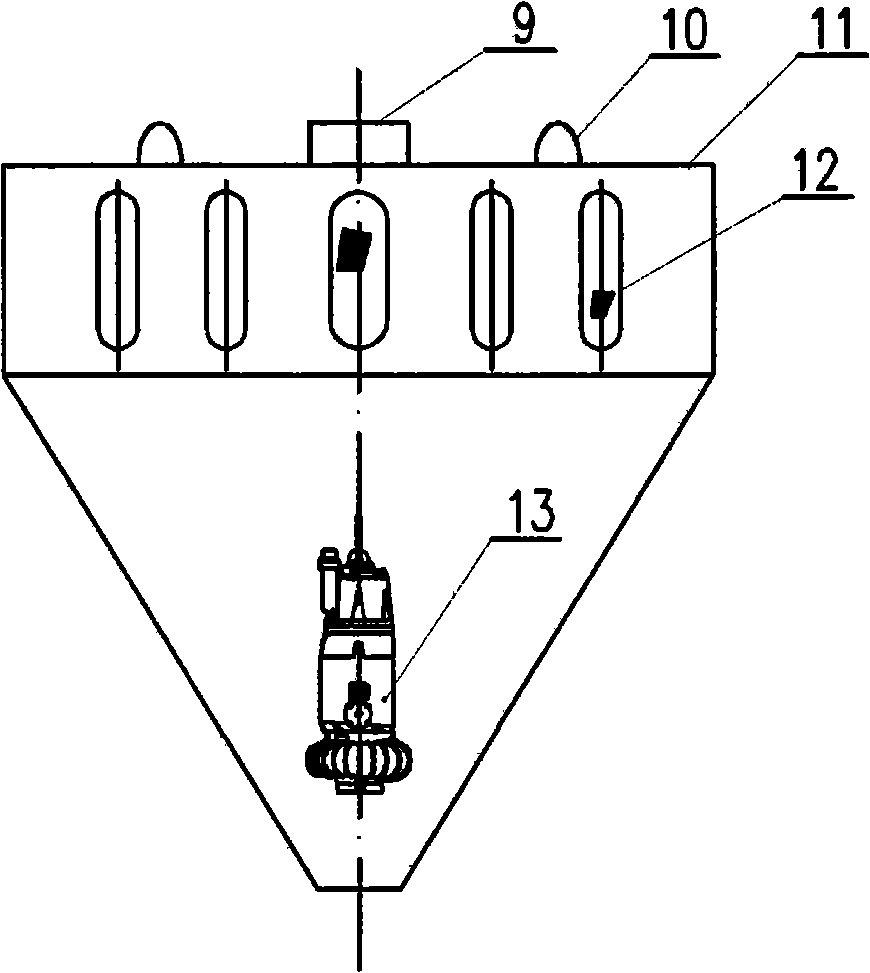
The invention discloses a method and a device for harvesting water-blooming cyanobacteria. The method comprises the following steps that: A. the water-blooming cyanobacteria is enriched into algae-rich water on water surfaces of lakes, reservoirs and riverways; B. an algae sucker pump is used to suck the algae-rich water; C. the algae-rich water is conveyed to a filtering system of a caterpillar system on a ship and is filtered into algae pulp; D. the algae pulp is subject to reverse purging and then secondary filtration; and E. the algae pulp is concentrated and dehydrated into algal biscuits or algae mud through a belt filter press or a horizontal screw decanter. The device for harvesting the water-blooming cyanobacteria comprises an algae sucker, a caterpillar algae-laden water filtering device, the belt filter press and the horizontal screw decanter, wherein, the fore of the ship is provided with the algae sucker, a non-clogging pump or a membrane pump is arranged in the algae sucker, the upper end of the algae sucker is provided with an impurity prevention net, and a cover plate is provided with a hoisting ring; and the caterpillar filtering device is fixed on a main frame body, and a stainless steel foraminous conveyer is arranged below a filter screen. The method is easy to operate, saves the energy, has low cost, a simple structure and convenient use, and effectively solves the problems of harvesting, concentration and dehydration of the water-blooming cyanobacteria accumulated in the lakes, reservoirs and riverways.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
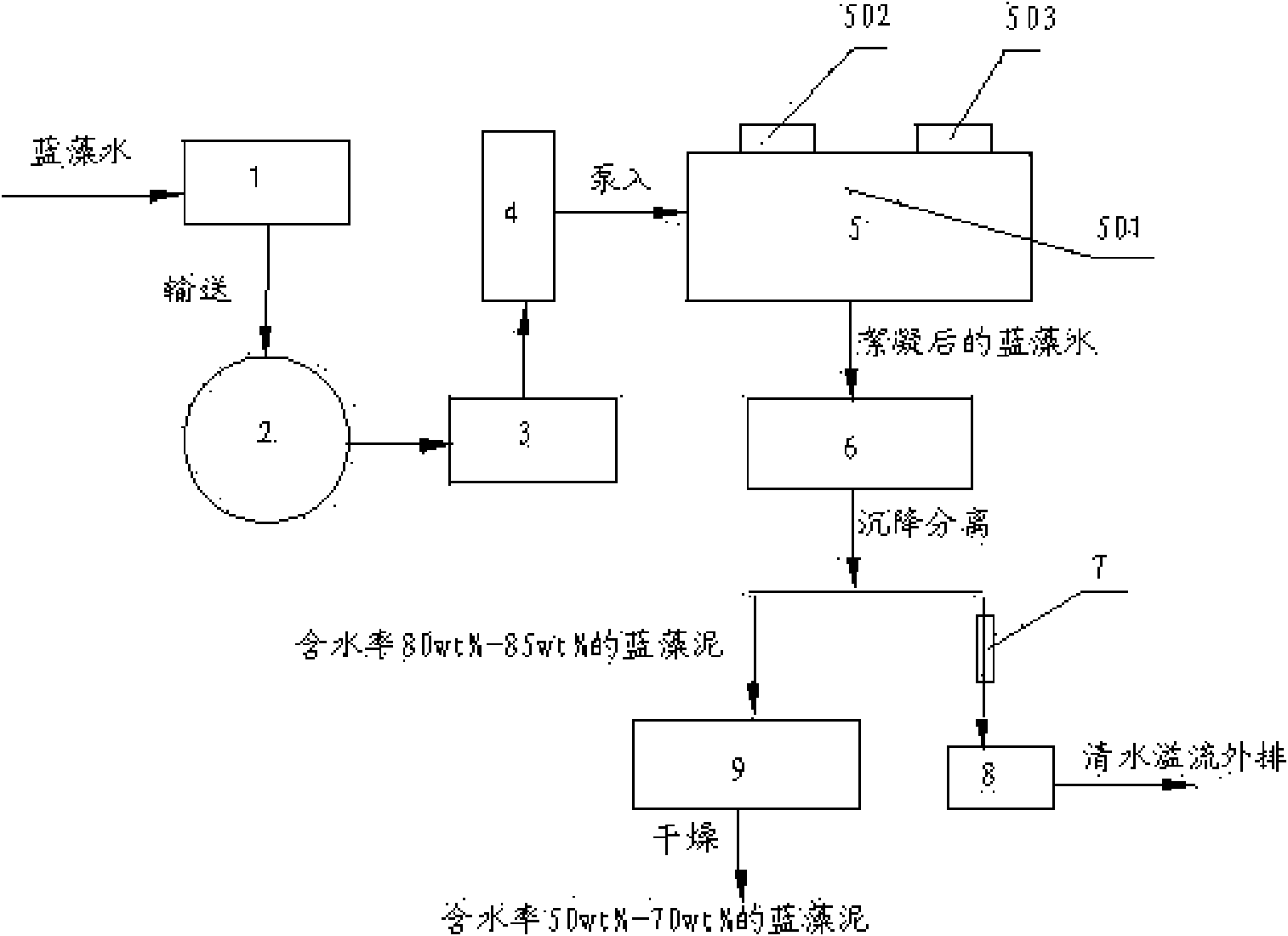
Method for controlling cyanobacteria bloom
InactiveCN101602533AImprove processing efficiencyIncreased efficiency of harvesting cyanobacteriaSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater cleaningPhylum CyanobacteriaResource utilization
The invention discloses a method for controlling cyanobacteria bloom, which belongs to the technical field of water pollution treatment. The method for controlling the cyanobacteria bloom comprises the steps of: (1) utilizing an acquisition system with a sucking disk to perform suction acquisition on cyanobacteria on the water surface of a water body; (2) pumping cyanobacteria water which is subjected to suction acquisition into a conveying pipeline through a suction pump, and conveying the cyanobacteria water to a storage tank; (3) pumping the cyanobacteria water in the storage tank into a dosing system through a screw pump, adding a flocculating agent into the cyanobacteria water, and mixing evenly to ensure that the cyanobacteria is flocculated; (4) sending the cyanobacteria water with the flocculated cyanobacteria into a settling separation system for solid-liquid separation to obtain water and cyanobacteria mud with the water content of 80 percent, sending the water obtained after the solid-liquid separation to a clear water tank for temporary storage through the settling separation system, and then draining the water into the water body through an overflow port; and (5) separating the obtained cyanobacteria mud to obtain cyanobacteria mud with the water content less than 70 percent after the drying. The method for controlling the cyanobacteria bloom has the advantages of environmental protection, low cost and convenient operation, and can realize the safe disposal and resource utilization of the cyanobacteria bloom.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
Cyanobacteria biomass spatial-temporal change monitoring and visualization method based on remote sensing image
InactiveCN103063202AImprove reliabilityImprove recognition accuracyPicture interpretationPhylum CyanobacteriaCharacteristic space
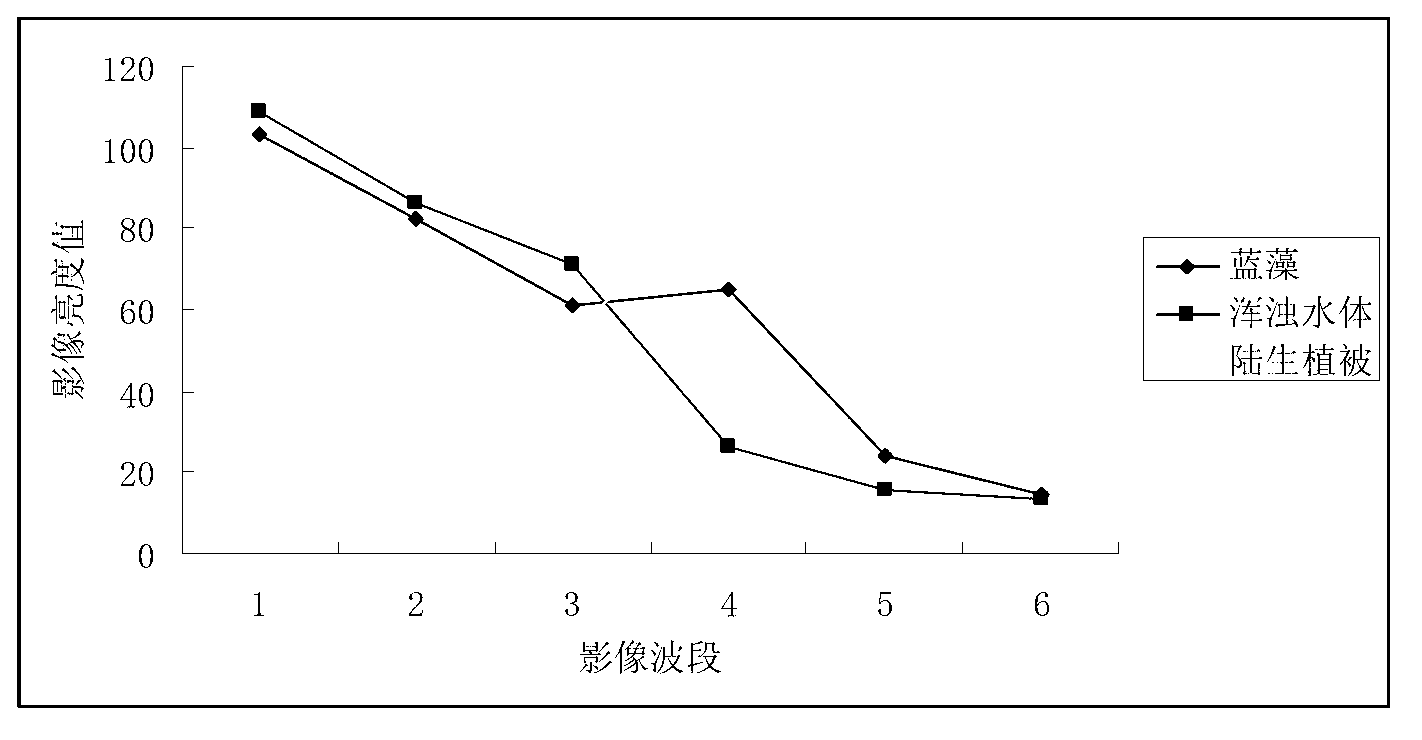
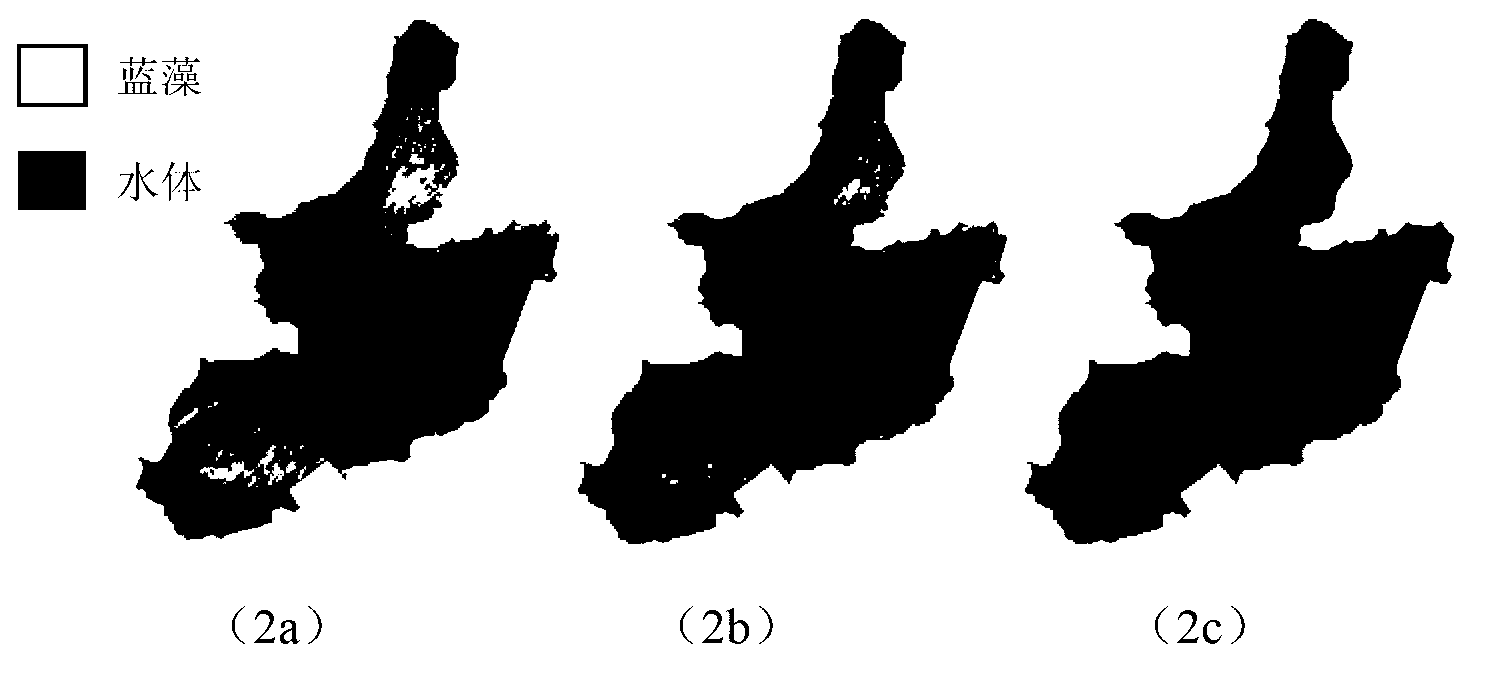
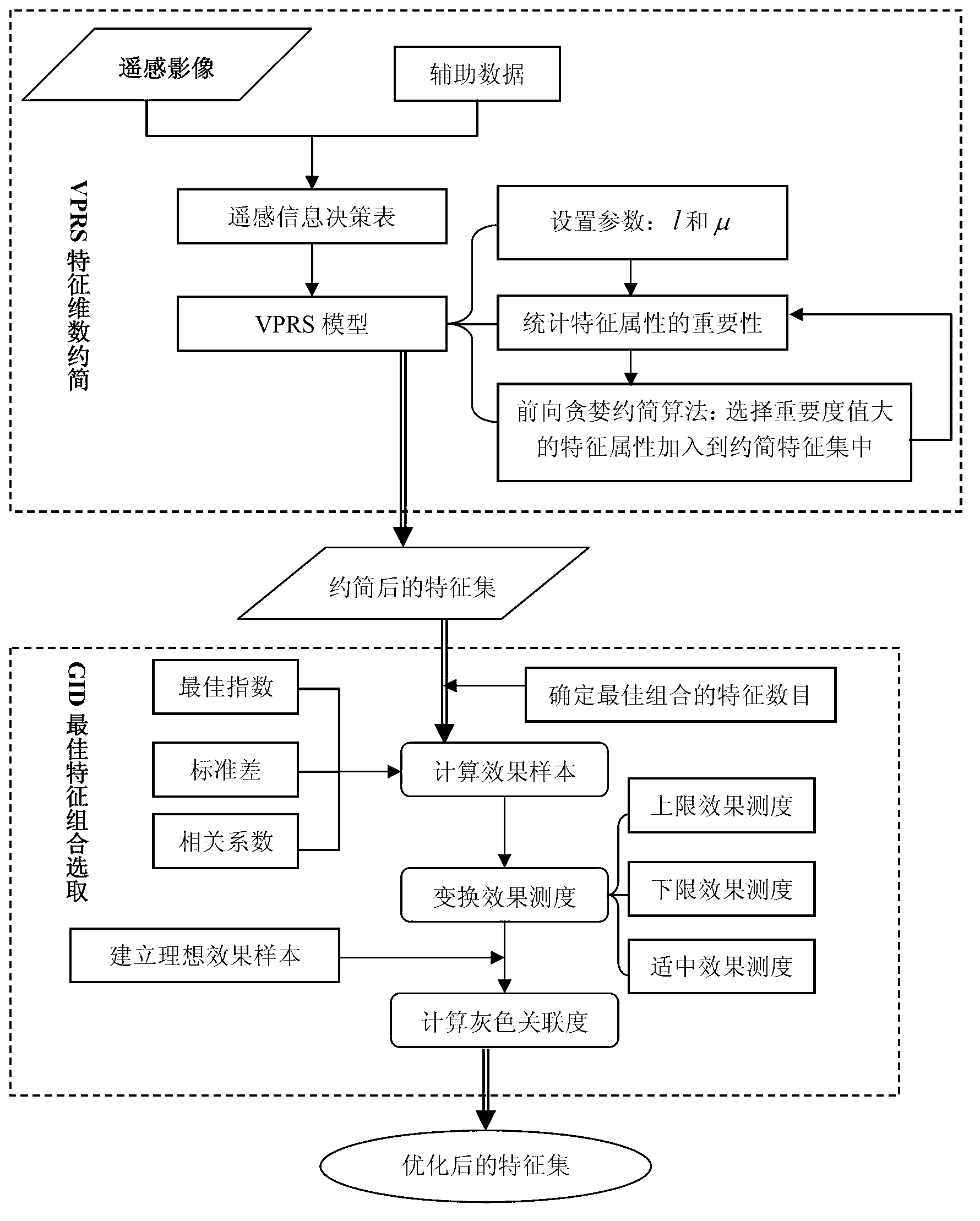
The invention relates to a cyanobacteria biomass spatial-temporal change monitoring and visualization method based on a remote sensing image. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pre-processing the remote sensing image of a research region, and constructing a normalized difference cyanobacteria bloom index (NDI-CB); (2) optimizing characteristics of the remote sensing image by using a characteristic optimization model based on VPRS (Variable Precision Rough Set)-GID (Grey Incidence Decision), and obtaining an optimized multi-characteristic space; (3) establishing a double-weighted SVM (Support Vector Machine) classification model based on a wavelet kernel according to the multi-characteristic space, performing extraction identification and change detection on the spatial distribution information of cyanobacterial bloom, and performing comprehensive verification and precision analysis by combining field observation data; and (4) performing overlapping display on the processed remote sensing image, GIS (Geographic Information System) vector data and the field observation data, thereby realizing the analog simulation of spatial-temporal change processes and rules of erupting the cyanobacterial bloom. Compared with the prior art, the cyanobacteria biomass spatial-temporal change monitoring and visualization method based on the remote sensing image has advantages of high cyanobacteria identifying precision and reliability, and the like, and is beneficial to analyzing and judging of causes and distribution changes of the cyanobacterial bloom.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
Method for controlling cyanobacterial bloom by utilizing composite strain and trace element
InactiveCN101712511AReduce eutrophicationEffective controlBiological water/sewage treatmentTrace elementAlgae
The invention relates to a method for controlling cyanobacterial bloom, which is mainly characterized by throwing composite biological strains, trace elements and filter-feeding fishes into a water body so as to rapidly construct a beneficial bacteria-algae cycling system of the water body, fundamentally lower the eutrophication degree of the water body and and achieve the goal of thoroughly controlling the cyanobacterial bloom. The invention is suitable for the ecological management of various eutrophy water bodies and has simple operation, low cost, rapid management and obvious effect.
Owner:北京普仁生态技术有限公司
Blue algae bloom activated char and preparation thereof
The invention relates to a blue algae water bloom active carbon and a preparation method thereof. The active carbon is produced by drying the blue algae water bloom alga mud at the hign temperature of 250 to 600 DEG C for 0.5 to 2 hours. The invention starts a new trail for utilizing the blue algae water bloom as a resource. The method can effectively produce active carbon with blue algae water bloom, which can not only save resources but also is favorable to protect the ecological environment and finally the purpose of treating pollution and reducing the pollution treatment cost can be realized.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Sorption algae apparatus of collecting blue algae water bloom
InactiveCN1559928AImprove harvesting efficiencyLow priceWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWater cleaningAgricultural engineeringAlgae
The invention discloses an algae absorber of collecting water blooms and blue-green alga, using a ladder type pontoon to collect water blooms and blue-green alga enriched on water surface by a absorbing pump. It is composed of ladder type tank component, bracket, cover plate, hinge and water pump pipe, where there is the ladder type tank component installed in the ladder type tank, the component, the float, a pump tube, a regulator, and a two-layer filter net fence are fixed through the bracket and the cover plate by using connecting nuts and bolts, the front end of the ladder type tank is provided with the regulator, it uses a sheet with two ends fixed with active nut and active bolt to fix a socket on two sides of the ladder type tank, and the two-layer filter net fence is inserted in the socket. It is widely applied to the harvest of water blooms and blue-green alga in lakes, riverways, reservoirs and lake bends in gardens.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
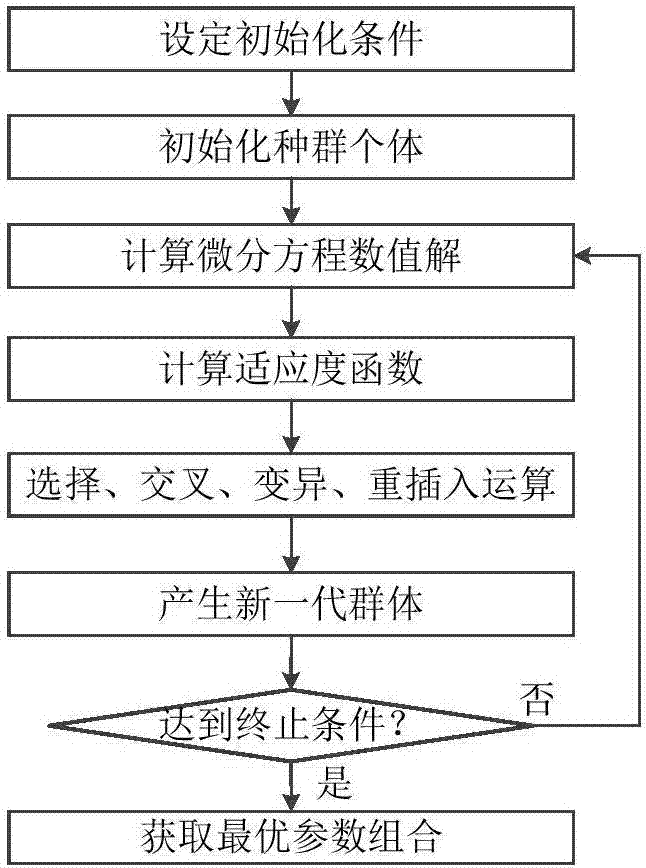
Cyanobacterial bloom predicting method based on non-linear kinetic time-series model
The invention discloses a cyanobacterial bloom predicting method based on a non-linear kinetic time-series model, which belongs to the water environment predicting field. The method comprises the following steps: using the blue algae growth rate as a time-varying parameter; creating a non-linear kinetic time-series model for the cyanobacteria growth with double nutrient salt cycling; using the combination of the numerical algorithm and the intelligent evolutionary algorithm, optimizing the constant parameters in the non-linear kinetic time-series model for the cyanobacteria growth; through setting the multivariate time-series model to realize the prediction of the time-varying parameter and the cyanobacteria biomass and through using the bifurcation theory and the central manifold theory to make a nonlinear kinetic analysis of the cyanobacteria growth time-varying system, obtaining the outbreak conditions for a cyanobacteria bloom so as to make an early warning of the bloom outbreak. The method proposed by the invention not only determines the conditions for a cyanobacteria bloom outbreak, but also improves the bloom prediction accuracy, providing an effective reference for an environmental protection department and governance decisions for water environment treatment.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Controllable fast reservior blue-green alga bloom eliminating method
ActiveCN1887742AImprove efficiencyAchieve the goal of complete algae controlBiological water/sewage treatmentFilter feederFeces
The controllable fast reservoir blue-green alga bloom eliminating method includes: raising filter feeder fishes; raising and protecting snails, crabs, calms and other water benthic fauna to degrade excrement of the fishes; and controlling water level to favor the disturbance of wind wave to bottom sludge, to ensure the ingestion of water benthic fauna to silt and the limitation of snails' ingestion area. The present invention adopts biological treatment of reservoir blue-green alga bloom without lowering eutrophic salt condition of water.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
Lysinibacillusfusiformis and method for degrading microcystis aeruginosa by using lysinibacillusfusiformis
ActiveCN102888354ALow costStrong targetingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses lysinibacillusfusiformis and a method for degrading microcystis aeruginosa by using lysinibacillusfusiformis, belongs to the technical field of environment friendliness and water treatment, provides algicidal bacteria TL which is suggested to be classified and named ysinibacillusfusiformis with the collection number CGMCC NO.6108, and also provides a method for degrading microcystis aeruginosa by using lysinibacillusfusiformis. The characteristics of the separated algae-lysing bacteria lysinibacillusfusiformis are exerted by a mode of indirectly dissolving algae by secreting extracellular non-protease algae-killing substances and a mode of directly dissolving algae by contacting algae cells, and the lysinibacillusfusiformis has high degradation rate of microcystis aeruginosa, and has wide application prospect in the aspect of preventing cyanobacterial bloom in which microcystis aeruginosa is used as preponderant algae by a microbiological method.
Owner:ANHUI HUANGHE WATER RESOURCE POLYTRON TECH INC
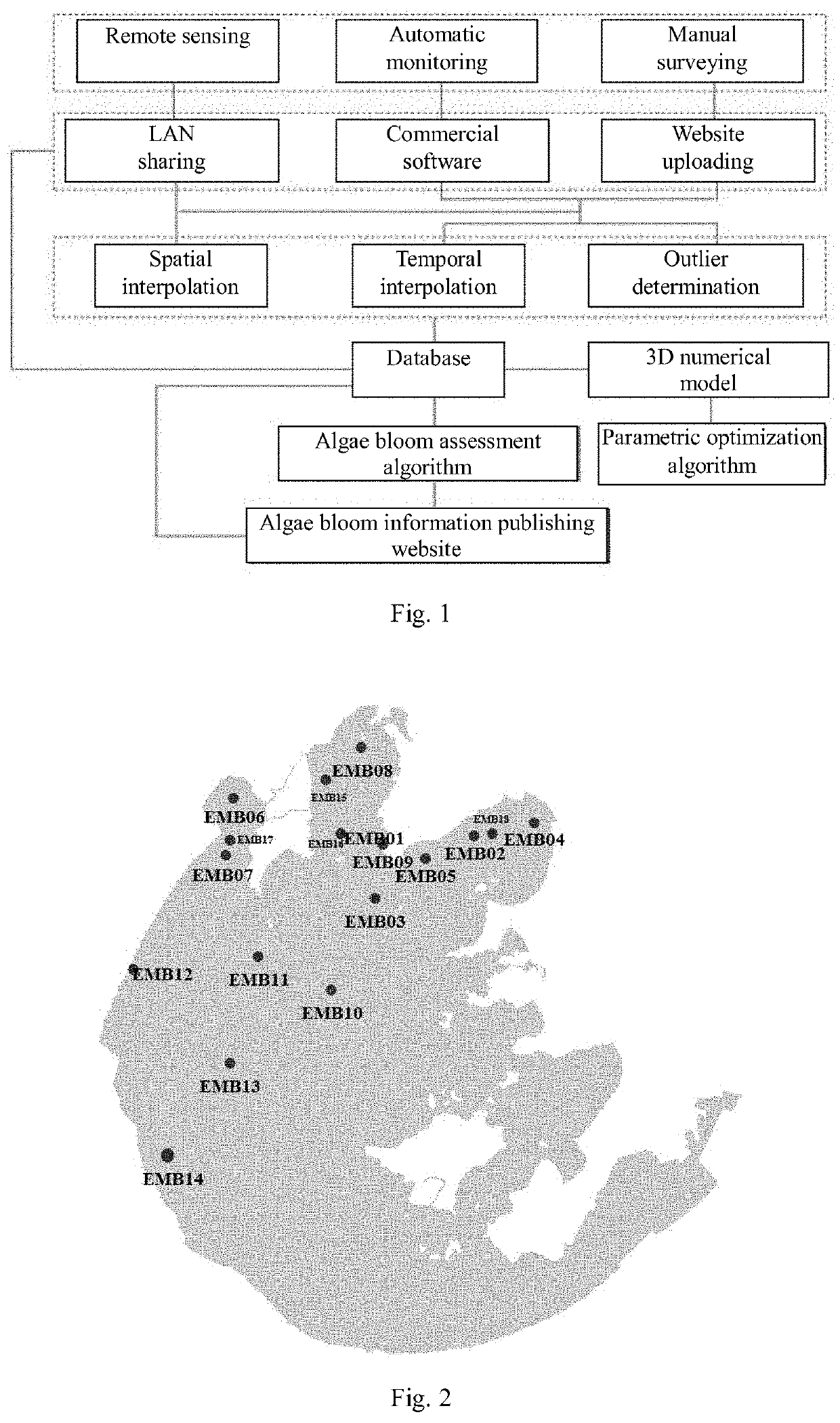
Stereoscopic monitoring and data mining system and method for harmful lake cyanobacteria bloom
ActiveUS20210293770A1Accurate responseComprehensive dataTesting waterTesting plants/treesEngineeringNumerical models
The invention relates to a comprehensive monitoring and data mining system and method for algae bloom of lake, wherein, the method comprises acquiring monitoring indicator data related to algae bloom of lake by three ways, i.e., remote sensing monitoring, automatic monitoring and manual surveying, and transmitting the acquired data to a data center by Internet; performing data backup and data preprocessing of the received data in the data center, including temporal interpolation, spatial interpolation and outlier determination and processing; transmitting the preprocessed data to a database for storage; performing computation of 3D numerical model of lake according to the data source stored in the database, assessing the risk of algae bloom of the lake to be monitored according to the simulation data of the numerical model, and displaying predictive warning information on algae bloom of the lake on a public platform.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
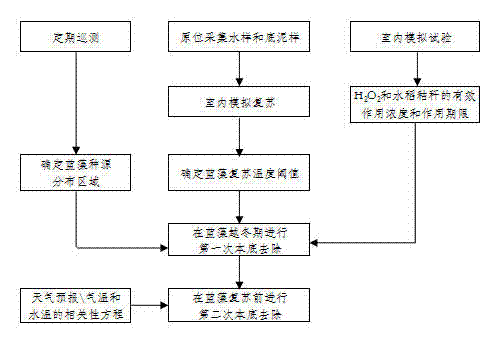
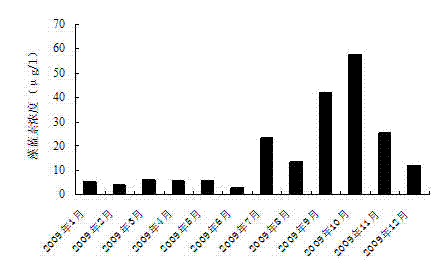
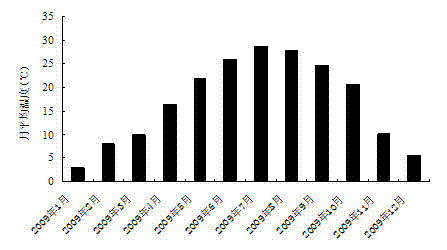
Removal of Provenance Sources of Overwintering Bloom Cyanobacteria in Large Shallow Lakes
ActiveCN102295333AImprove securityEasy to degradeWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processPhylum CyanobacteriaCyanobacteria
A removing method of overwintering water-blooming cyanobacteria provenances in large-scale shallow lakes is disclosed. In the overwintering period and the recovery period, algae-controlling agents are respectively used in distribution areas of overwintering water-blooming cyanobacteria provenances twice to perform background removal of overwintering cyanobacteria provenances in water and sediment, wherein the first background removal is performed in the overwintering period, and the second background removal is performed in the recovery period before cyanobacteria recover; and the algae-controlling agent comprises rice straw and H2O2 with effective concentrations. The invention is based on the self-growth and recovery rule of algae; environment-friendly algae-controlling agents are used for prevention and control treatment at provenance regions for cyanobacteria growth and in bottleneck periods - the overwintering and the recovery periods; overwintering water-blooming cyanobacteria provenances in large-scale shallow lakes can be effectively removed; cyanobacteria water bloom can be treated from the source; and the method is a new approach for the prevention and control of the generation of harmful algae water bloom.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
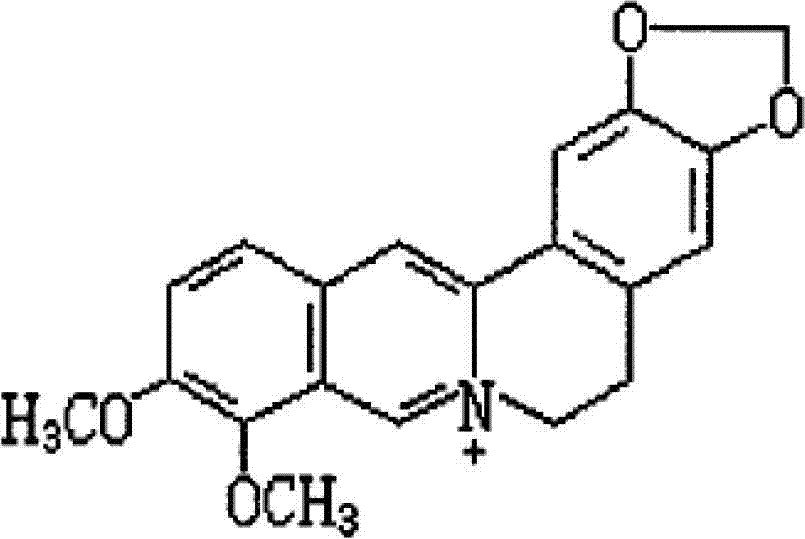
Berberine.artemisinin composite algicide
InactiveCN102771484AOvercoming defects such as high dosageWide variety of sourcesBiocideAnimal repellantsPhylum CyanobacteriaFresh water organism
The invention discloses a berberine. artemisinin composite algicide which mainly contains 600mg / L of berberine and 6-7.5mg / L of artemisinin. The algicide provided by the invention is used for controlling cyanobacterial bloom, when the net content of berberine reaches 10.0mg / L and the net content of artemisinin is more than 0.1mg / L in the pond water, the cyanobacteria amount in the water drops to the 10% of the initial density value after 10 days. The algicide provided by the invention is mainly applied to the prevention and control of harmful cyanobacterial bloom in artificial water systems, lakes, reservoirs, ponds and other freshwater bodies. The composite algicide provided by invention is botanical algicide, and has strong and durable inhibitory effect on algae, no significant impact on other aquatic organisms and no environmental pollution.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
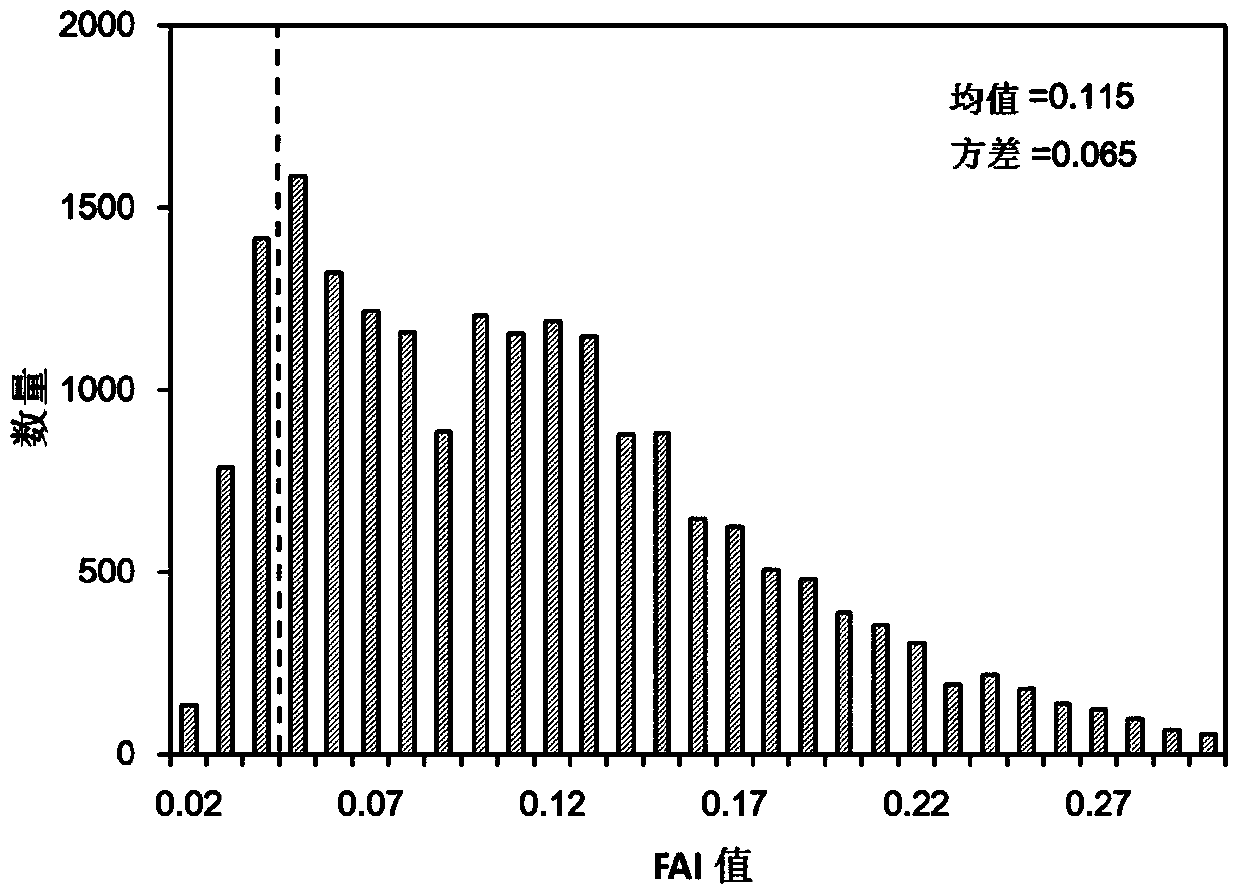
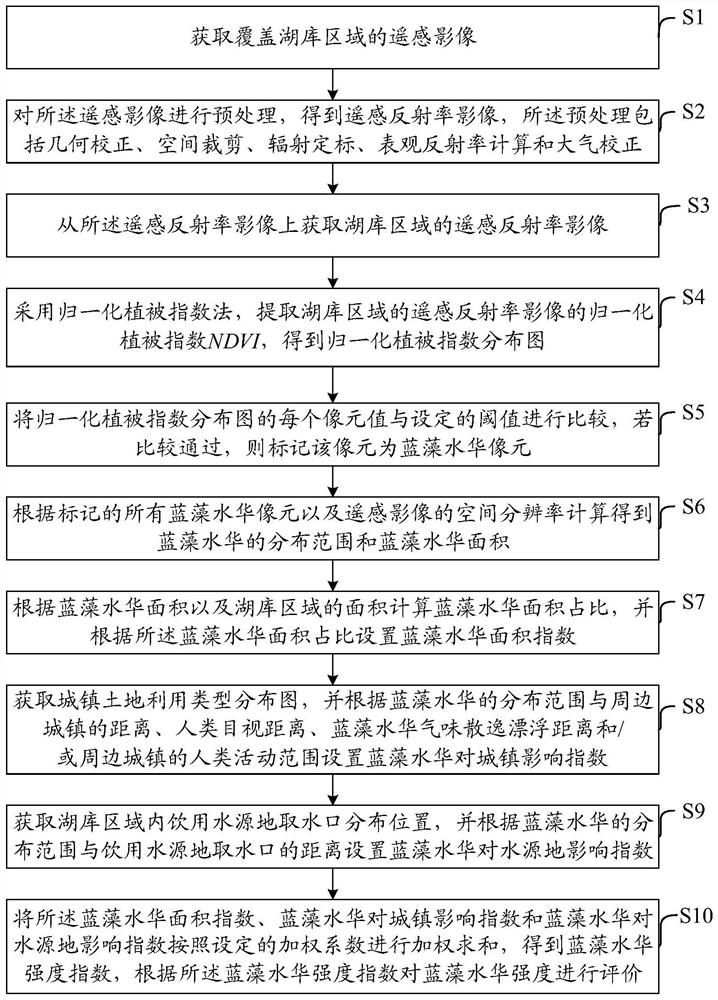
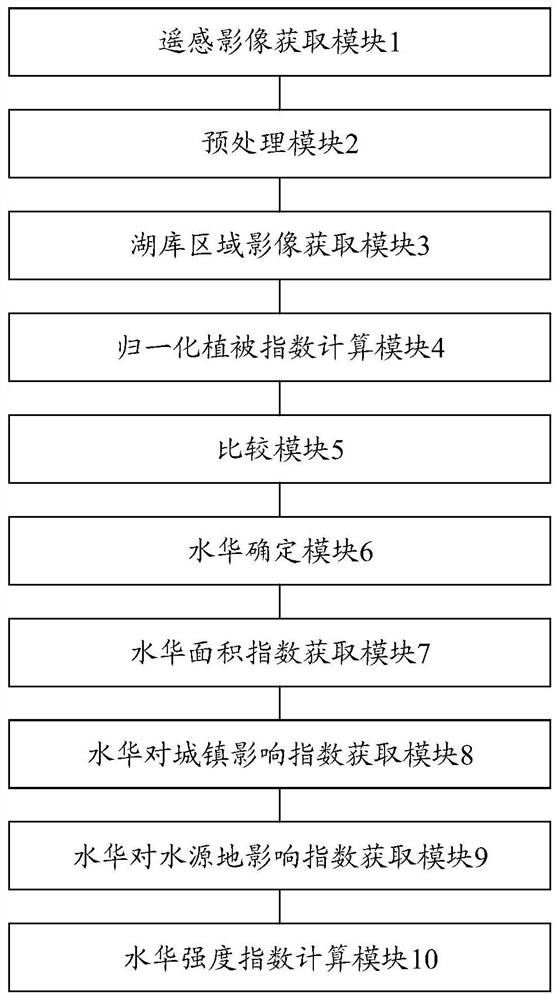
Inland lake and reservoir cyanobacterial bloom intensity evaluation method and device based on remote sensing
ActiveCN112232234AHighlight the extent of the outbreakIssues that highlight the impactImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionWater sourcePotable water
The invention discloses an inland lake and reservoir cyanobacterial bloom intensity evaluation method and device based on remote sensing, and belongs to the field of water pollution monitoring. According to the method, the distribution range and the area of the cyanobacterial bloom are obtained through the remote sensing image, and the cyanobacterial bloom intensity is evaluated according to the proportion of the area of the cyanobacterial bloom, the influence condition of cyanobacterial bloom outbreak on cities and towns and the influence condition of cyanobacterial bloom outbreak on a drinking water source water intake; the method highlights the cyanobacterial bloom outbreak degree and the influence of cyanobacterial bloom outbreak on human activity areas around lakes and reservoirs andwater intakes of water supply water sources, and provides a scientific basis for lake and reservoir water environment management.
Owner:MINISTRY OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT CENT FOR SATELLITE APPL ON ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT
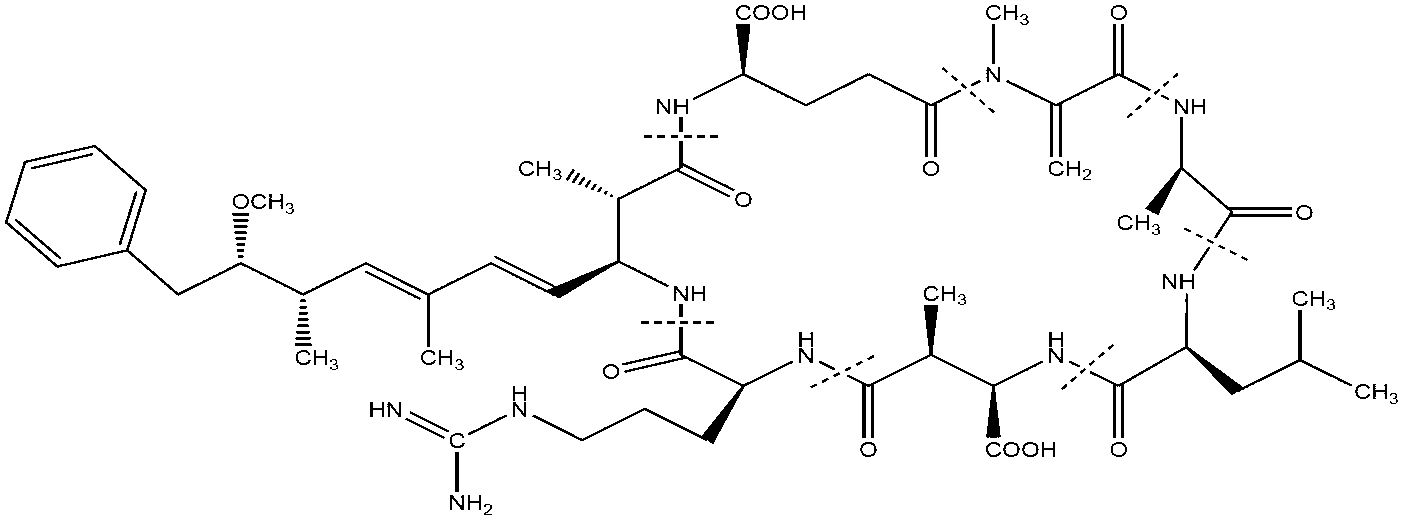
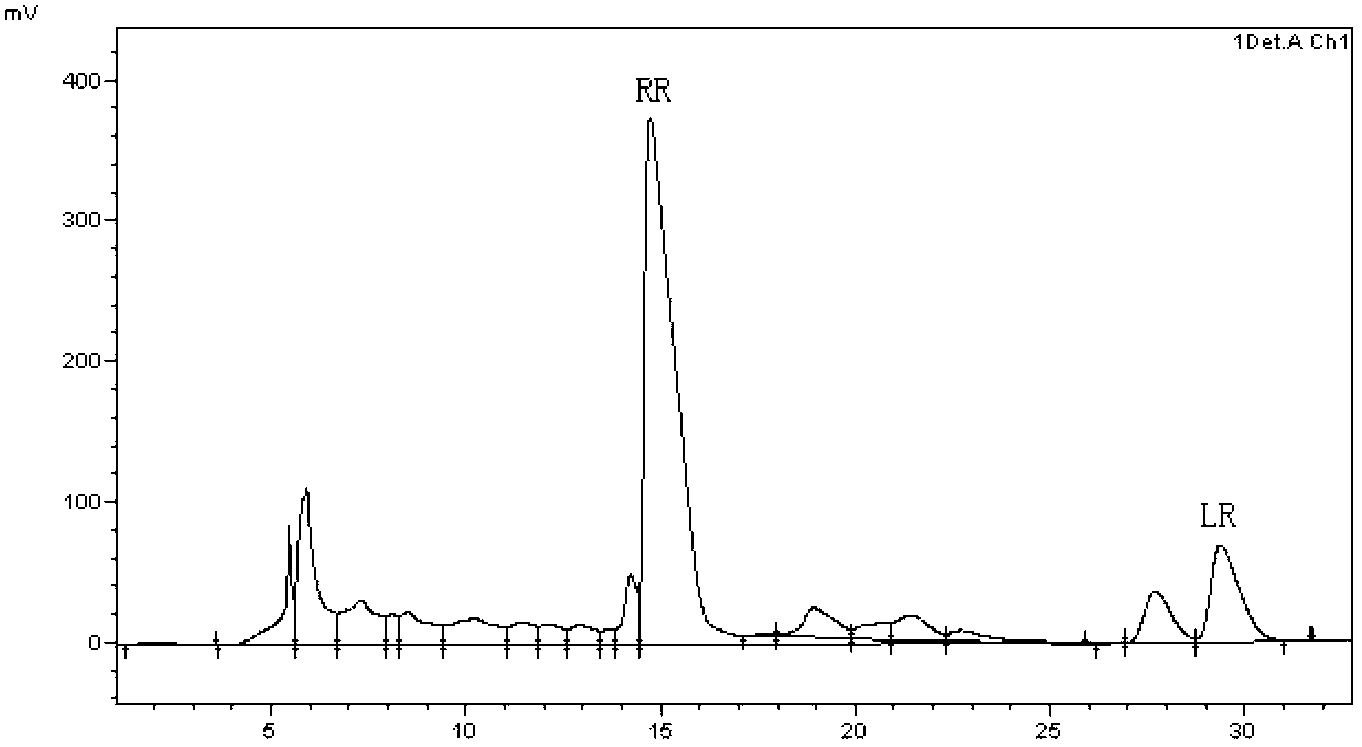
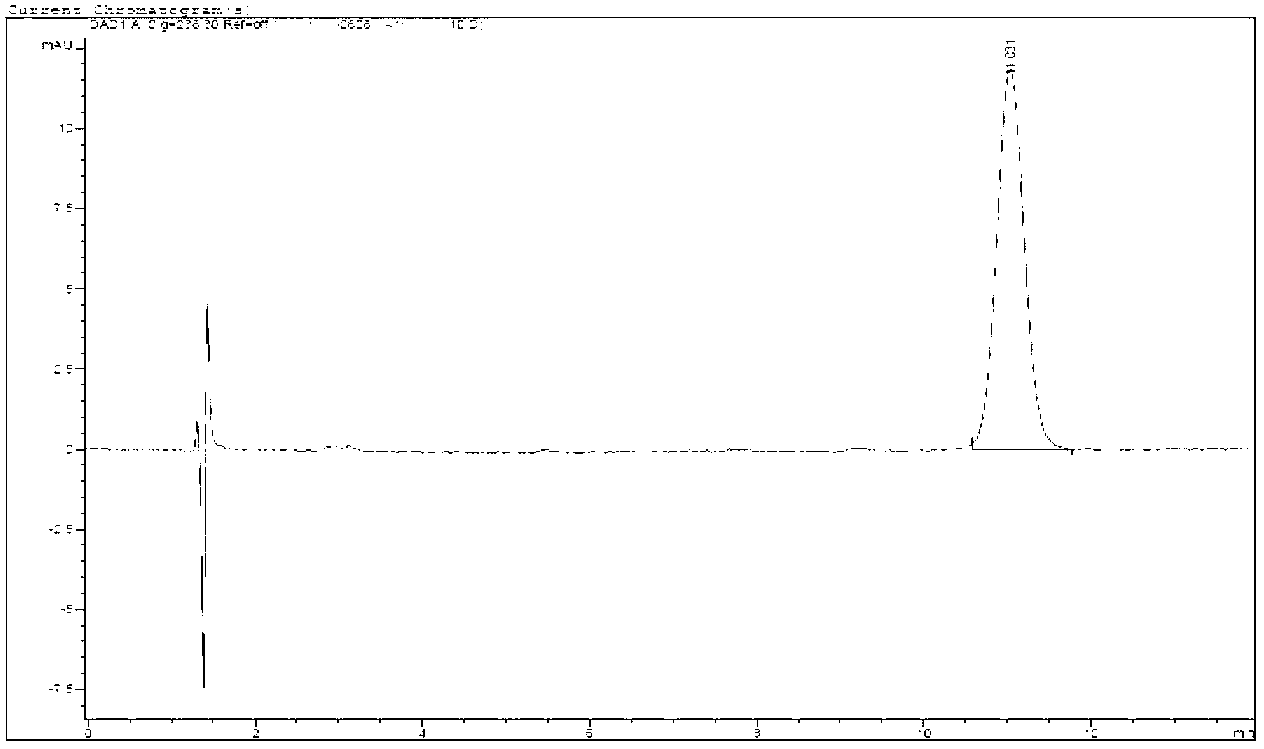
Method for extracting and purifying microcystic toxins LR and RR by taking cyanobacterial bloom in Dian Lake as raw material
ActiveCN103163001AEasy to getReduce pollutionPreparing sample for investigationRotary evaporatorCell wall
The invention provides a method for extracting and purifying microcystic toxins LR and RR by taking cyanobacterial bloom in the Dian Lake as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps of: A. fishing out cyanobacterial bloom in the Dian Lake during an outbreak period by a biological net, and filtering cyanobacterial bloom samples by a filtering sieve; B. performing multigelation treatment on the processed cyanobacterial bloom samples; C. soaking the cyanobacterial bloom samples processed in the step B in an acetic acid solution, furthermore, damaging the cell walls of the cyanobacterial bloom samples by an ultrasonoscope during the soaking process, and centrifuging the cyanobacterial bloom samples to obtain supernatant; D. activating the supernatant to obtain solid phase extraction columns; E. cleaning the solid phase extraction columns after gathering, drying the solid phase extraction columns, and eluting microcystis toxins; F. enabling an eluant from the step E to pass through a small silica gel column, eluting the small silica gel column by carbinol, and adsorbing the microcystis toxins dissolved in the carbinol; G. rotating an evaporator to concentrate an eluant in the step F; H. separating the microcystic toxins LR and RR by a high performance liquid chromatography; and I. purifying. The method can be used for preparing finished products with high purity.
Owner:云南省环境监测中心站
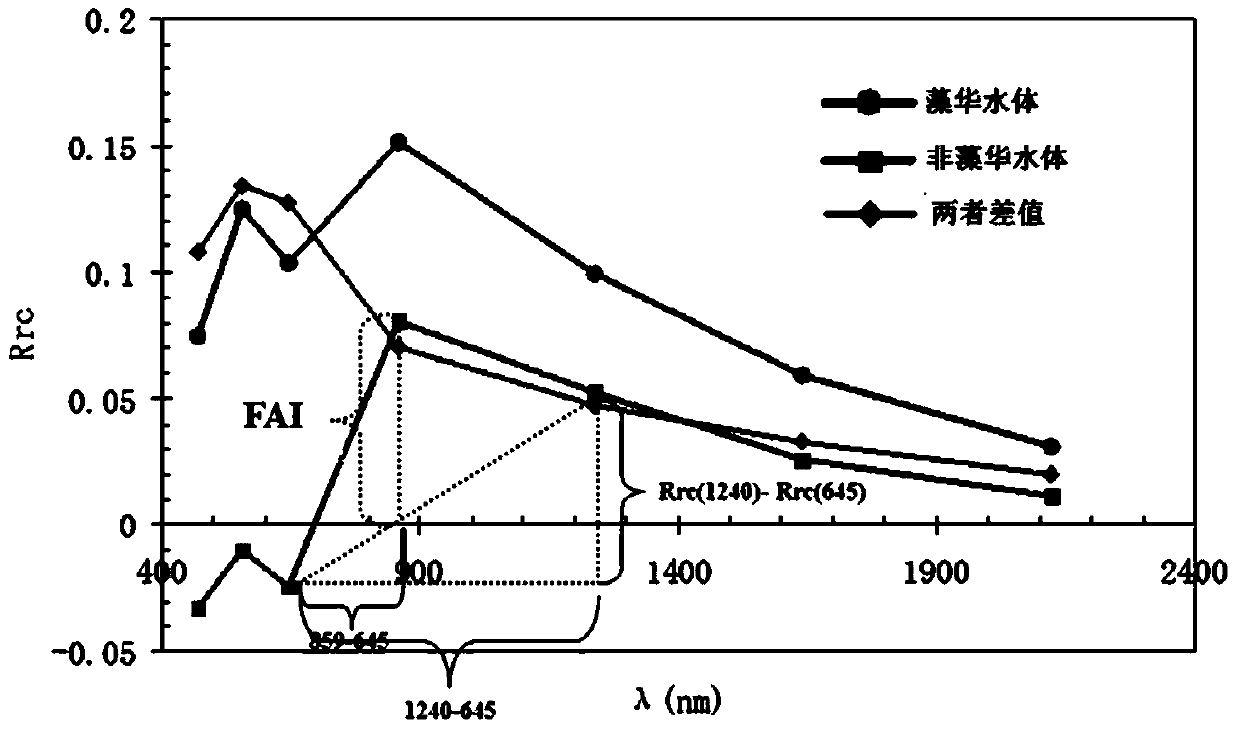
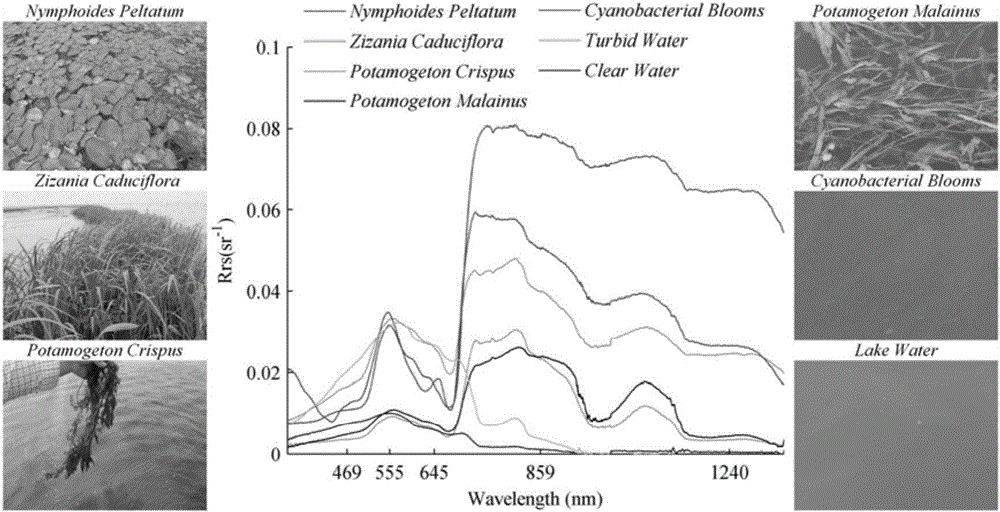
MODIS (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer) satellite synchronous monitoring method for cyanobacterial bloom and aquatic vegetation in eutrophic lakes
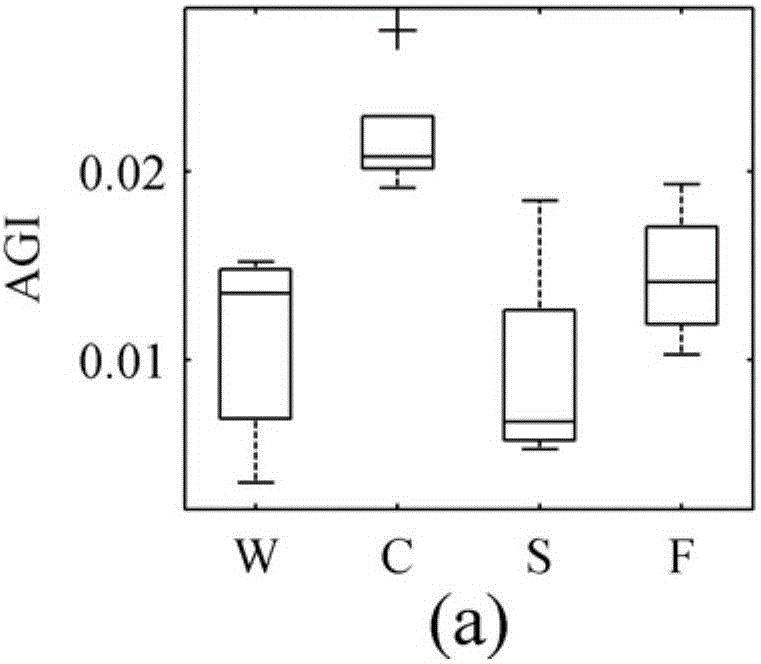
ActiveCN106315856AReflect the space-time distributionImprove forecast accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological water/sewage treatmentNatural satelliteClassification methods
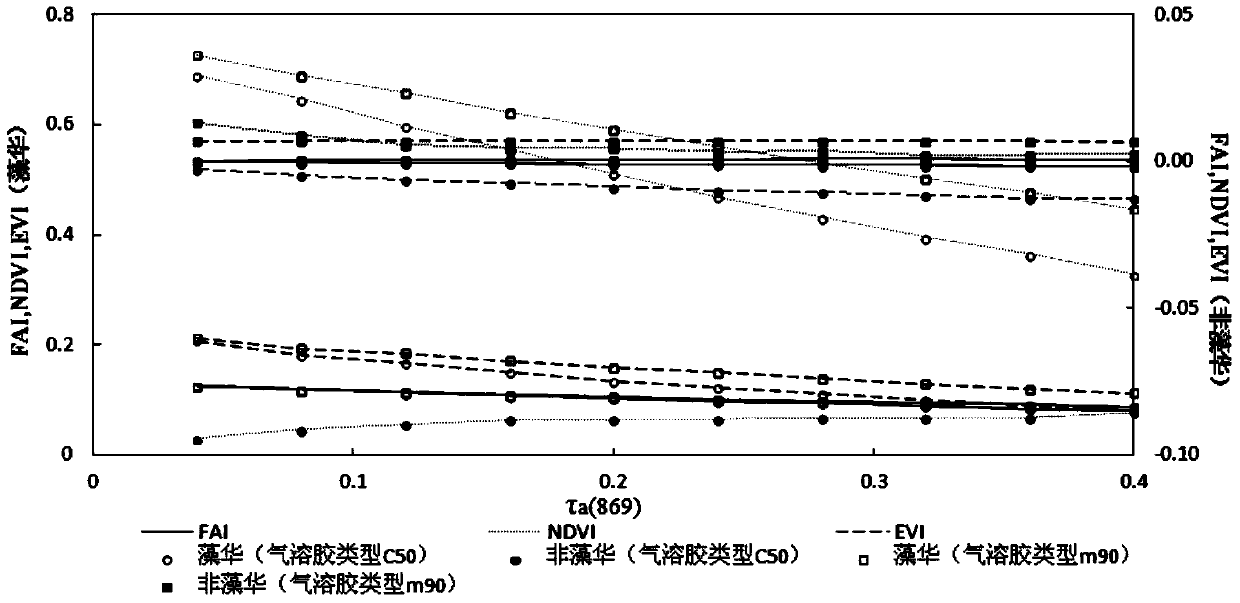
The invention provides an MODIS (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer) satellite synchronous monitoring method for cyanobacterial bloom and aquatic vegetation in eutrophic lakes. The MODIS satellite synchronous monitoring method includes combining spectral characteristics of the cyanobacterial bloom, the submerged vegetation and floating-leaf / emergent vegetation with one another on the basis of field measured spectral data and creating alga and grass indexes (AGI); combining turbid water indexes (TWI) and floating alga indexes (FAI) with one another and determining basic classification processes; determining classification thresholds for the AGI, the TWI and the FAI on the basis of historically acquired MODIS satellite data; ultimately completely constructing classification decision trees and synchronously monitoring the cyanobacterial bloom, the submerged vegetation and the floating-leaf / emergent vegetation on MODIS satellite images. Alga-containing water and grass-containing water can be separated from each other by the aid of the alga and grass indexes (AGI). High-turbidity water can be identified by the aid of the turbid water indexes (TWI), and the submerged vegetation and the floating-leaf / emergent vegetation can be differentiated from each other by the aid of the floating alga indexes (FAI). The MODIS satellite synchronous monitoring method has the advantage that interannual and inter-monthly variation laws and spatial distribution of the cyanobacterial bloom, the submerged vegetation and the floating-leaf / emergent vegetation in the eutrophic lakes can be accurately acquired on the basis of the MODIS satellite synchronous monitoring method.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Preparation method and application of immobilized algal toxin degrading bacteria
ActiveCN103436518AImprove degradation rateImprove toleranceMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsFiberPhylum Cyanobacteria
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of immobilized algal toxin degrading bacteria. The preparation method of the immobilized algal toxin degrading bacteria comprises the steps: selecting activated carbon fibers as an immobilization material, after carrying out washing, boiling, hydrochloric acid soaking, drying and other pretreatment steps of the immobilization material, adding into an LB culture medium according to a certain specific value, then inoculating a bacterial strain for degrading microcystins (MCs), and carrying out immobilized culture to obtain the immobilized algal toxin degrading bacteria. In the application of the immobilized algal toxin degrading bacteria, while the activated carbon fibers adsorb algal toxins, the algal toxin degrading bacteria immobilized on the activated carbon fibers can degrade the algal toxins, can greatly shorten the time of degradation of the MCs, and simultaneously can biologically regenerate the activated carbon fibers. The bacterial strain for degrading the MCs has the MC-LR degradation rate of up to 91% or more, and is especially suitable for degradation of the MCs generated in a process of extracting phycobiliproteins from water-blooming cyanobacteria.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Complex microbial inoculant for preventing and treating cyanobacterial bloom in aquaculture as well as preparation method and application of complex microbial inoculant
ActiveCN109593681AHas a decomposition effectPromote degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsBacillus amyloliquefaciensMicrobiology
The invention relates to a complex microbial inoculant for preventing and treating cyanobacterial bloom in aquaculture as well as a preparation method and an application of the complex microbial inoculant. The complex microbial inoculant comprises fermented Bacillus subtilis MES 810 powder and fermented Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MES812 powder in a mass ratio being 1:1. The complex microbial inoculant is prepared from the fermented Bacillus subtilis powder and the fermented Bacillus amyloliquefaciens powder by sufficient mixing in a mass ratio being 1:1, the viable count of the fermented Bacillus subtilis powder is not lower than 2.0*10<10>cfu / g, and the viable count of the fermented Bacillus amyloliquefaciens powder is not lower than 4.0*10<9>cfu / g. The prepared complex microbial inoculant for preventing and treating cyanobacterial bloom in aquaculture not only has an inhibition effect on cyanophyta algae, but also has no influence on other beneficial algae, thereby being an environment-friendly product.
Owner:天津开发区坤禾生物技术有限公司 +1
Method for inhibiting cyanophyta microcystis bloom
InactiveCN104098190ALarge particlesGrowth inhibitionBiological water/sewage treatmentAquaculture industryTotal nitrogen
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting cyanobacterial bloom, belongs to the fields of aquaculture industry and environmental science, and particularly provides a method for inhibiting cyanophyta microcystis bloom, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) monitoring the nitrogen element concentration of water in which cyanophyta microcystis bloom occurs; (2) aerating the water continuously to maintain the oxyty of the water; (3) adding carbonaceous saccharides during aeration, wherein the addition concentration depends on the total nitrogen concentration of the water; (4) adding silicon compounds into the water during addition of the saccharides; (5) ensuring that cyanobacterial bloom particles become smaller and smaller, and the water becomes more transparent after 2 to 3 days; (6) adding saccharides again in the 7th to 10th days to ensure that the cyanobacterial bloom particles become smaller and less. Through the adoption of the method, cyanobacterial bloom in the water is effectively inhibited; the transparency of the water is improved; the significances in environment protection and ecologic protection are both high.
Owner:FISHERY MACHINERY & INSTR RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERY SCI
Method capable of utilizing lake cyanobacterial blooms to culture planktonic algae
The invention relates to a method capable of utilizing lake cyanobacterial blooms to culture planktonic algae, firstly cyanobacterial bloom pulp is obtained from a lake in a season that the cyanobacterial blooms happen in the lake, then cyanobacteria pulp is aerated or stirred to guarantee a local aerobic zone to form in the cyanobacteria pulp, rotten cyanobacteria pulp is transferred into a container with tap water to dilute after the cyanobacteria pulp is treated about 10 days by being ventilated in normal temperature, and the container which is used to store mixed liquor of the tap water and the rotten cyanobacteria pulp is placed in an outdoor opening environment, and is aerated or stirred to keep dissolved oxygen in the mixed liquor above 3mg / L. The container which stores the mixed liquor of the tap water and the rotten cyanobacteria pulp can have the advantage of planktonic algae after the container is aerated or stirred about 10 days. The method capable of utilizing lake cyanobacterial blooms to culture the planktonic algae is simple in culture method, easy to obtain raw materials, convenient to carry out, low in culture cost and wide in appliance range.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Biological algae control technology and application thereof in treating blue-green algae of Lake Tai
InactiveCN101723519AOutbreak controlControl secondary pollutionBiological water/sewage treatmentWater qualityNitrogen
The invention discloses biological algae control technology and application thereof in treating blue-green algae of the Lake Tai. The technology comprises the following steps: culturing oreochromis nilotica in a region with the blue-green algae, performing effective biological control on the blue-green algae in a water body, controlling overgrowth of the blue-green algae in the water body and inhibiting the explosion of cyanobacterial bloom by using the oreochromis nilotica to directly eat the blue-green algae, and effectively remove enriched nitrogen and phosphorus in the water body to achieve the aim of removing pollutant and purifying water quality by using the oreochromis nilotica to eat the blue-green algae. Through the technology, the explosion of blue-green high-risk region of local part of the Lake Tai can be effectively inhibited, and income increase of local fishermen and farmers is promoted. The technology and the application overcome the defects of the conventional physical, chemical and biological blue-green algae prevention and control, not only avoid pollution and biological risk, but also realize biological control on the blue-green algae.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INSITUTE OF JIANGSUPROVINCE
Inhibition method of microcystis aeruginosa
The invention relates to an inhibition method of microcystis aeruginosa. A cordate houttuynia extract is used for inhibition. The inhibitor raw material of the inhibition method is rich and easy to get and environment-friendly during the treatment process of cyanobacterial bloom, and does not cause secondary pollution on water.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Compound microbial preparation capable of inhibiting and killing blue-green algae as well as preparation and application methods thereof
The invention relates to a compound microbial preparation capable of inhibiting and killing blue-green algae. The preparation is prepared from the following components by weight percent: 35%-60% of chicken manure extract, 35%-60% of rice husk powder, and 2%-5% of complex microbial inoculants, wherein the complex microbial inoculants comprise bacillus subtilis, thermoactinomyces, enterobacter aerogenes and saccharomycetes, the effective viable count of the bacillus subtilis is 1,900 million / gram, the effective viable count of the thermoactinomyces is 6 million / gram, the effective viable count of the enterobacter aerogenes is 1 million / gram, and the effective viable count of the saccharomycetes is 3-4 million / gram. The problems that a method for eliminating cyanobacterial bloom in the prior art consumes a lot of manpower and material resources and easily causes secondary pollution are solved.
Owner:WUHAN EZHENGNONG SCI & TECH
Method and system for controlling ecological sensitive area blue algae bloom of eutrophic large-size lakes and reservoirs
InactiveCN103663708AReduce pollutionDoes not increase emissionsBiological water/sewage treatmentAquatic animalWind wave
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental protection, and particularly relates to a method for controlling ecological sensitive area blue algae bloom of eutrophic large-size lakes and reservoirs. According to the invention, under the action of natural wind power and wind direction, blue algae in a large water area are diverted and converged into an artificially arranged small-range separation area to prevent further escape thereof; then, the blue algae are eaten by algae-eating animals bred at high density in a centralized manner; and when the density of the blue algae is too high, additional manual fishing removal is performed. Effective wave breaking measures are taken to reduce wind waves inside and outside the separation area, thus creating conditions for floating convergence of blue algae. The perennial control on population sources inside and outside an ecological sensitive area reduces the occurrence of blue algae bloom and creates conditions for recovery of other aquatic animals and plants, thus finally forming a benign development situation in which blue algae are less and less and other beneficial organisms are more and more.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Compound microorganism controlling cyanobacterial bloom as well as preparation method and application of compound microorganism
InactiveCN109897801AEasy to operateOperational securityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismSide effect
The invention discloses a compound microorganism controlling cyanobacterial bloom. The compound microorganism comprises components in parts by weight as follows: 10-30 parts of bacillus laterosporus and 10-30 parts of bacillus amyloliquefaciens. The compound microorganism can effectively degrade organic pollutants in water, removes nitrogen and phosphorus, controls and reduces the cyanobacterial bloom, and is free of side effects on the environment and humans. The invention further discloses a preparation method and an application of the compound microorganism.
Owner:北京天诚众合科技发展有限公司
Method for screening algicidal bacteria and removing microcystis aeruginosa from Lake Tai branch river sediment
InactiveCN103497913AStable algae lytic abilityLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyGenus Lysinibacillus
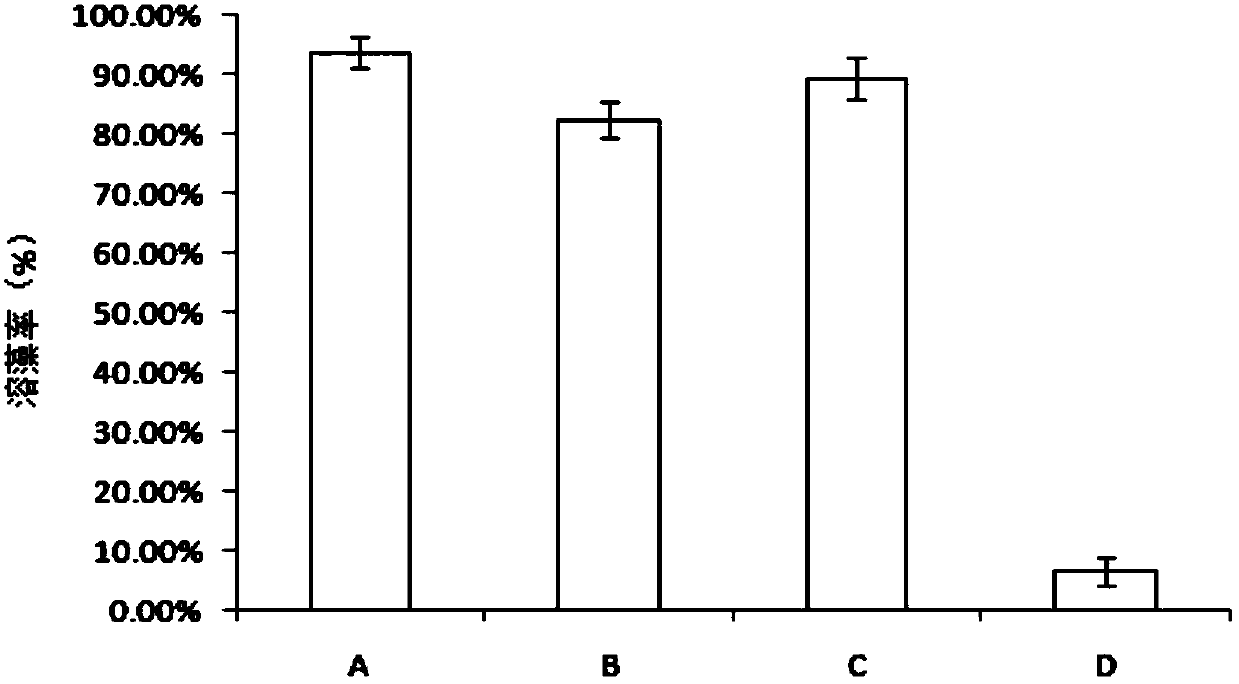
The invention relates to a method for screening algicidal bacteria and removing microcystis aeruginosa from Lake Tai branch river sediment, belonging to the technical field of environment-friendly water treatment. The invention provides Lysinibacillus fusiformis of which the collection number is CGMCC NO.7520. The invention also provides a method for screening algicidal bacteria and removing microcystis aeruginosa from Lake Tai branch river sediment. The screened algicidal bacteria has a certain dissolution action on the dominant alga strain microcystis aeruginosa in blue algae bloom, and the algicidal bacteria TR3 can be obtained by separation. Under the optimum conditions, the removal rate of the algicidal bacteria TR3 for microcystis aeruginosa within 96 hours can reach 97.18%, so the algicidal bacteria TR3 has very ideal alga dissolution effect; and thus, the algicidal bacteria TR3 can better display the alga dissolution characteristic in a natural water body, and has wider application prospects in large-area water body blue algae bloom pollution treatment.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Stenotrophomonas and applications thereof
InactiveCN103667135ASimple screening methodBroad-spectrumBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynechococcusMetabolite
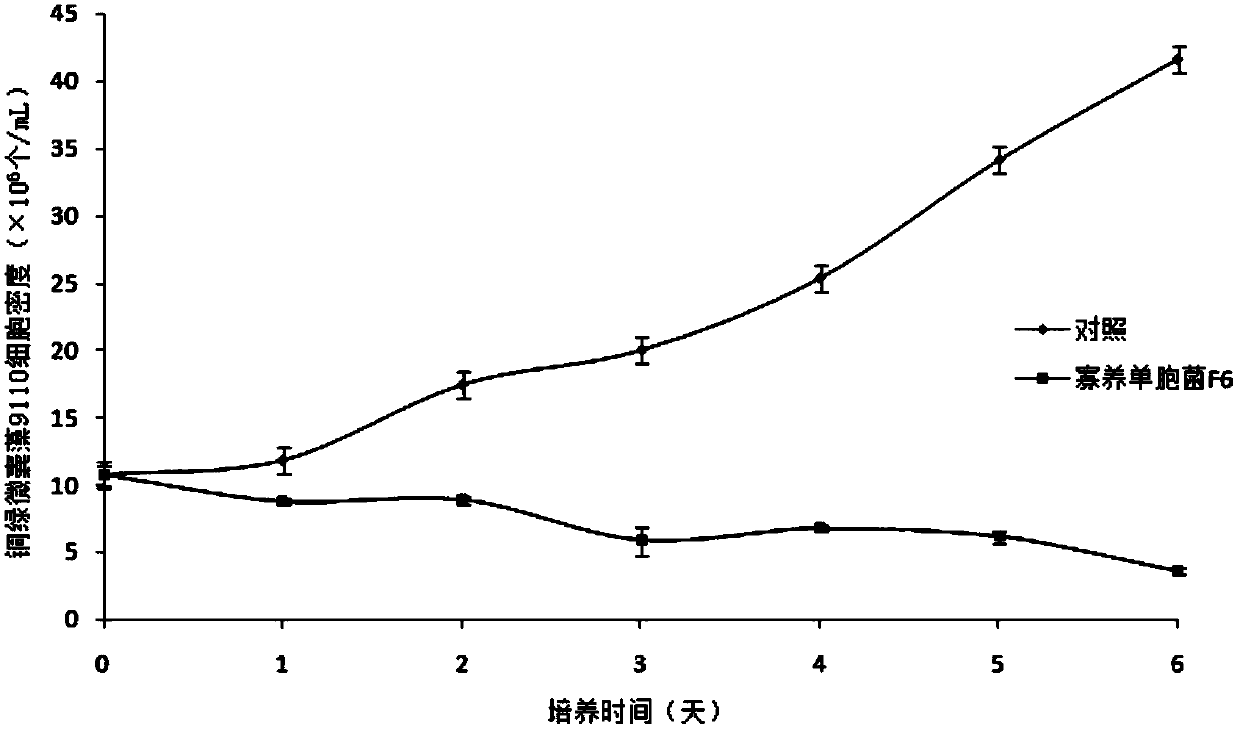
The invention provides a strain of stenotrophomonas sp., which is named as stenotrophomonas F6, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.6547. Two active algicidal substances, namely cyclo(glycine-proline) and hydroquinone, are separated from the metabolism products of the stenotrophomonas F6, and then the substances are purified and identified. The half effective concentration of the cyclo(glycine-proline) on inhibiting microcystis aeruginosa 9110 is 9.5 mg / L, and the cyclo(glycine-proline) has no inhibiting effect on synechococcus BN60. The half effective concentrations of hydroquinone on inhibiting microcystis aeruginosa 9110 and synechococcus BN60 are 0.96 mg / L and 5.6 mg / L. The stenotrophomonas F6 and the active algicidal substances (cyclo(glycine-proline) and hydroquinone) can be applied to the development and production of novel algicide, and finally are applied to the control of cyanobacterial bloom in fresh water.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cyanobacterial bloom prediction method based on multi-factor time sequence-random depth confidence network model
ActiveCN108416460AReduce usageImprove forecast accuracyForecastingNeural architecturesSequence analysisAlgorithm
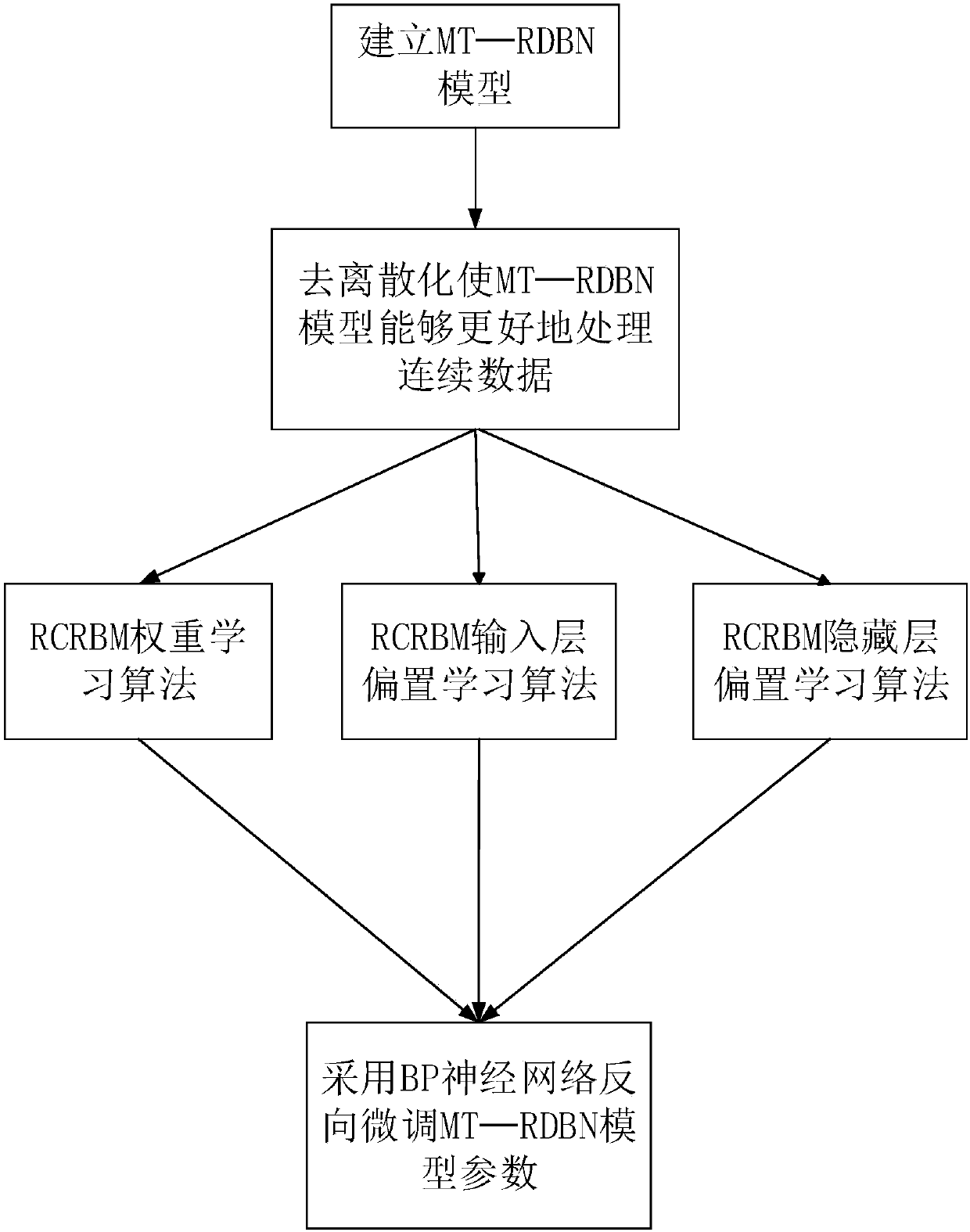
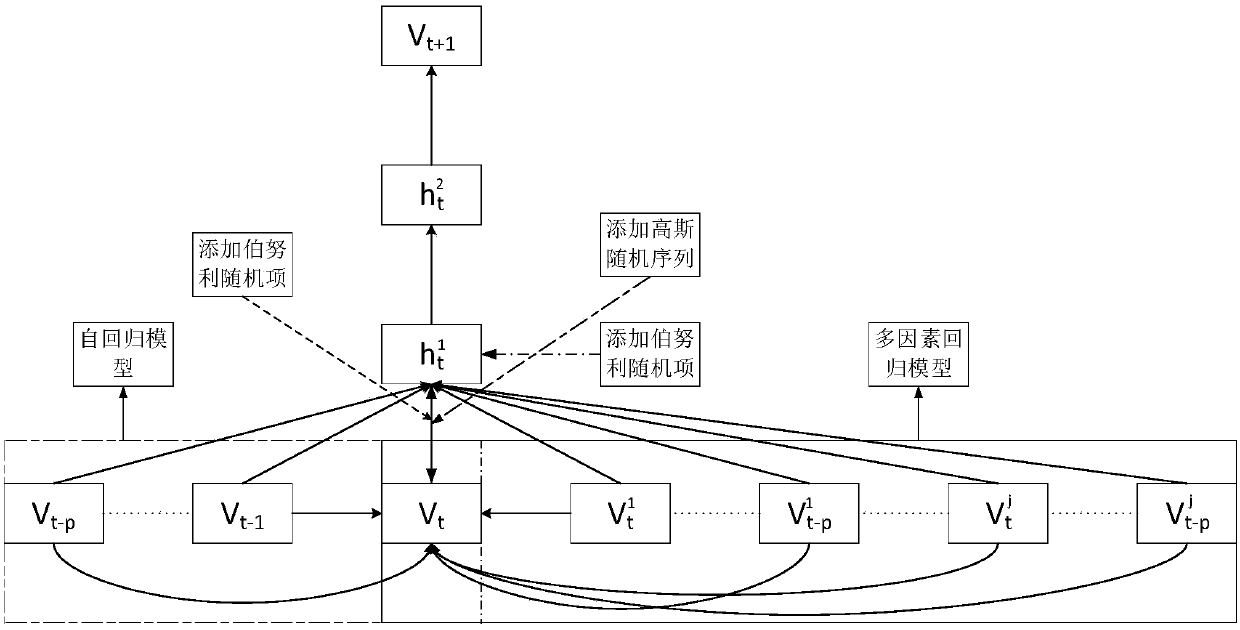
The invention discloses a cyanobacterial bloom prediction method based on a multi-factor time sequence-random depth confidence network model and belongs to the water environment prediction technologyfield. In the invention, improved depth confidence network method is combined with a multi-factor time sequence analysis method so as to construct the multi-factor time sequence-random depth confidence network model, and then, a MT-RDBN model is adopted to discretize, an RCRBM learning algorithm and MT-RDBN model parameter fine-tuning are adopted too. An autoregressive model and a multi-factor regression model in a time sequence are used when the model is established, influence factors are considered so that an MT-DBN model can predict the representation factor of a future moment through the chlorophyll concentrations and the influence factor data of a current time and a historical moments, a sample application amount is reduced and prediction precision is increased.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com