MODIS (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer) satellite synchronous monitoring method for cyanobacterial bloom and aquatic vegetation in eutrophic lakes
A technology for cyanobacterial blooms and eutrophication, applied in the field of remote sensing, can solve problems such as affecting the accuracy of daily remote sensing monitoring of cyanobacterial blooms and being unable to adapt to the temporal and spatial changes of aquatic plants.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045] In order to better understand the technical content of the present invention, specific embodiments are given together with the attached drawings for description as follows.
[0046] Aspects of the invention are described in this disclosure with reference to the accompanying drawings, which show a number of illustrated embodiments. Embodiments of the present disclosure are not necessarily intended to include all aspects of the invention. It should be understood that the various concepts and embodiments described above, as well as those concepts and embodiments described in more detail below, can be implemented in any of a number of ways, which should be the concepts and embodiments disclosed by the present invention and not Not limited to any implementation. In addition, some aspects of the present disclosure may be used alone or in any suitable combination with other aspects of the present disclosure.
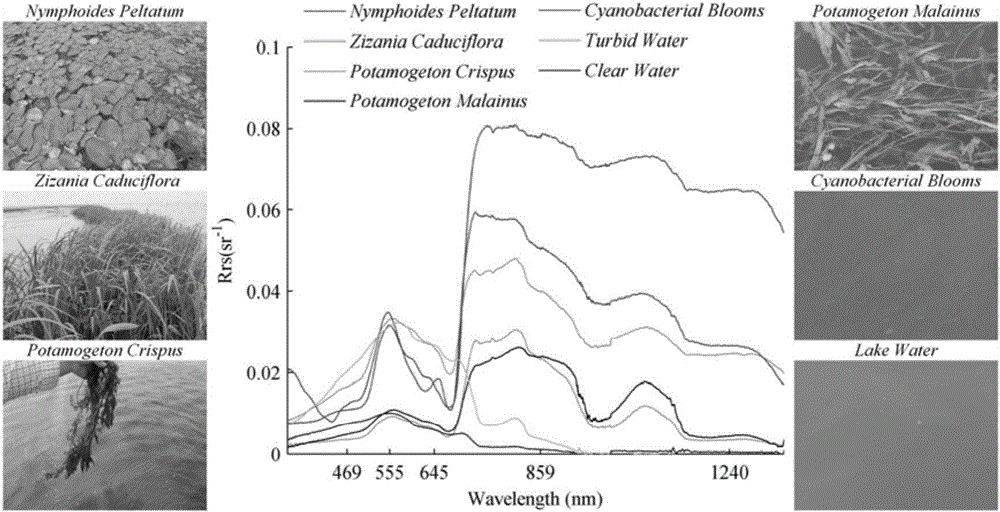
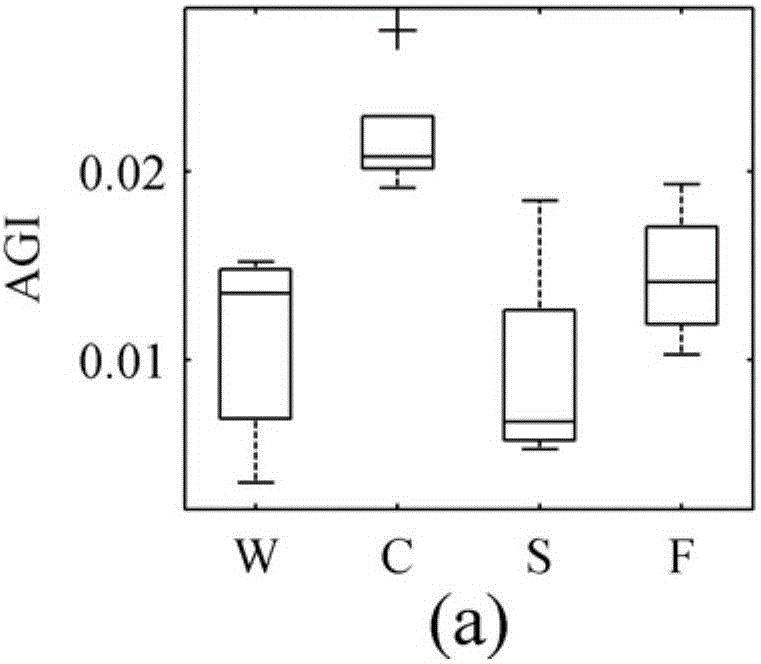
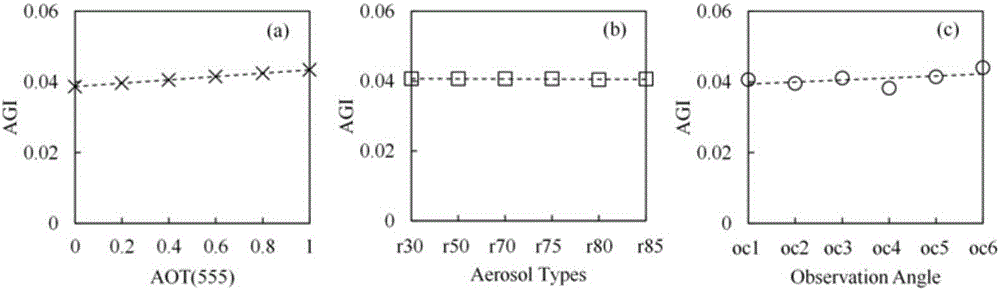
[0047] This embodiment takes Taihu Lake as an example to further ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com