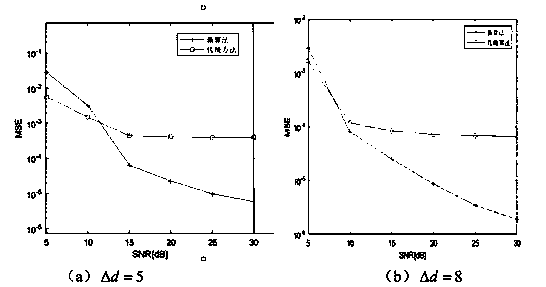
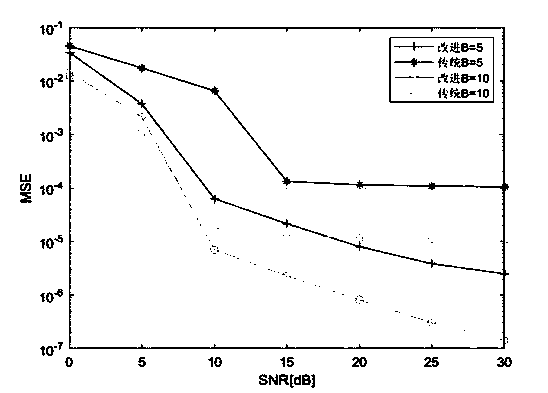
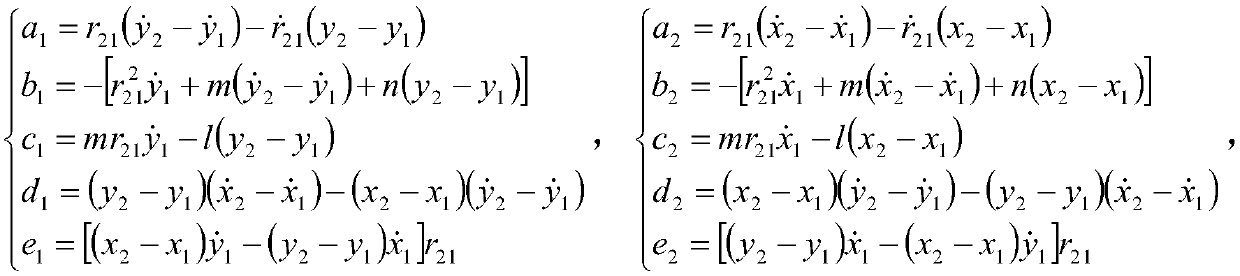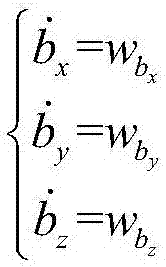Patents
Literature
50results about How to "Achieving High-Precision Estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Combined positioning method for moving multi-station passive time difference and frequency difference
ActiveCN107526073ARealize high-precision positioningAchieving High-Precision EstimationUsing reradiationObservation matrixGlobal optimal
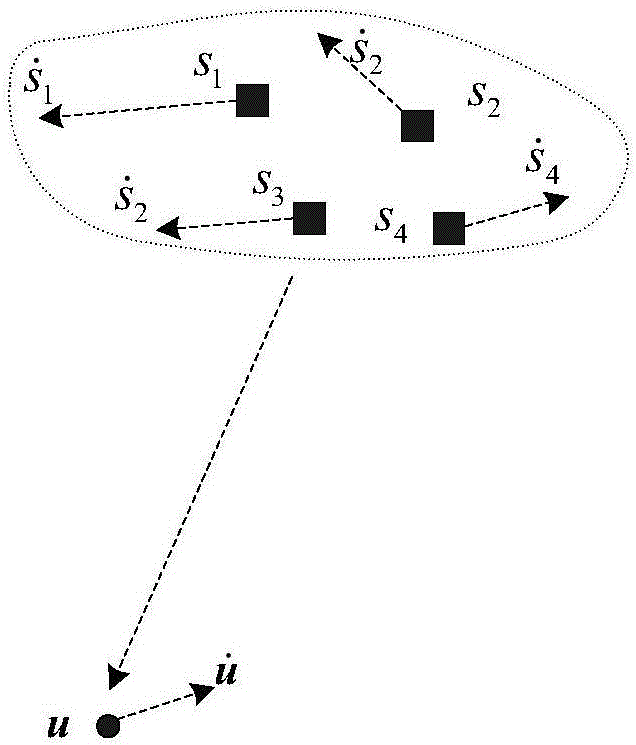
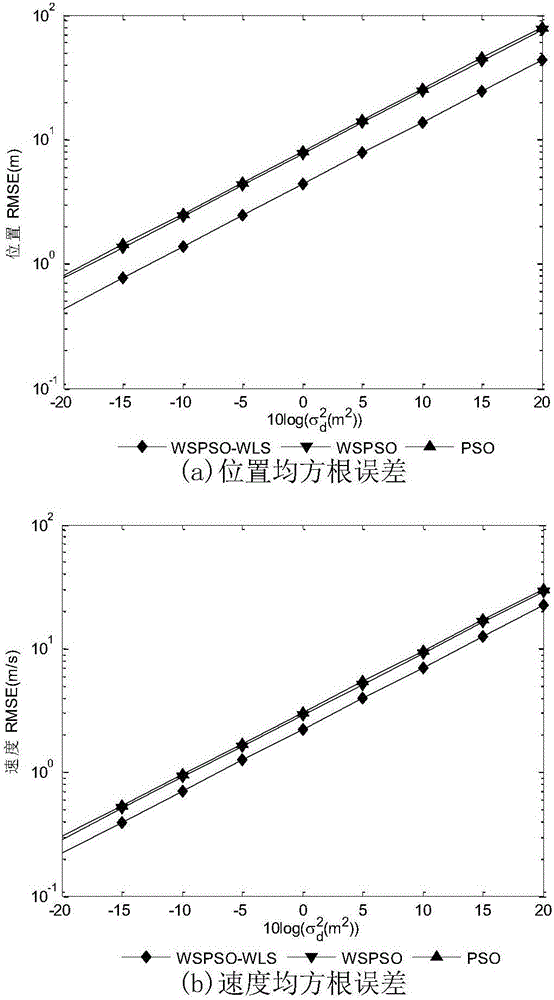
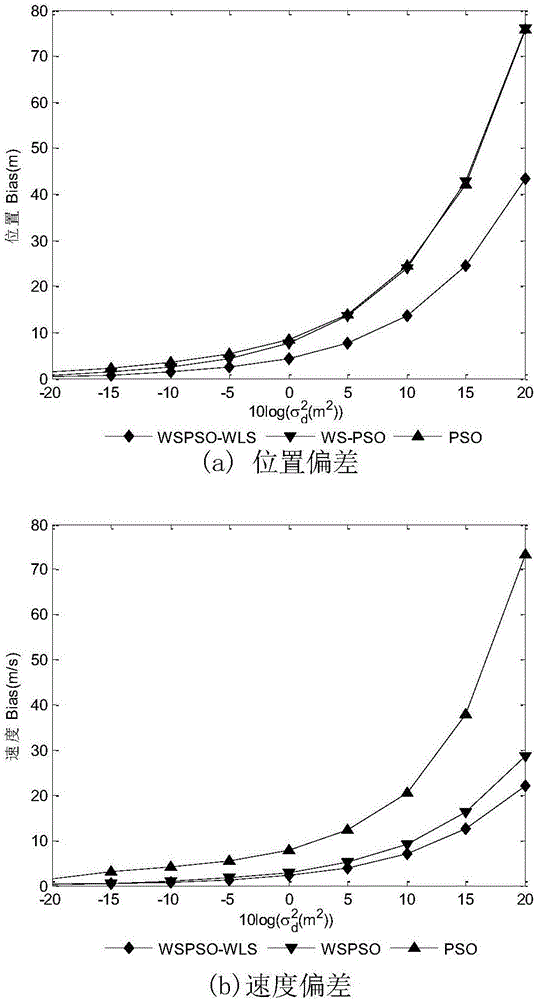
The invention discloses a combined positioning method for moving multi-station passive time difference and frequency difference, wherein the method belongs to the field of passive positioning technology. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a time different positioning model; establishing a frequency different positioning model; constructing a time difference and frequency difference observation matrix epsilicon1, and designing a fitness function; initiating a group and various parameters; evaluating the fitness function value of each particle; sequencing all particles; when the algorithm satisfies a terminating condition, outputting a current global optimal value; reconstructing the time difference and frequency difference matrix epsilicon2; obtaining a weighted least square solution theta2 and a covariance matrix cov(theta2); and calculating position and speed of a radiation source. The combined positioning method has advantages of performing optimal value solving on the fitness function which is obtained from the time difference and frequency difference observation matrix, combining a particle swarm optimization algorithm with a least square algorithm, and realizing high-precision target position on the condition of four base stations, and furthermore calculating speed information of the target. The combined positioning method can realize high-precision estimation to the position of the radiation source and is not limited by a station site layout. Furthermore relatively high positioning estimation precision is realized.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
MODIS satellite high-precision monitoring method for chlorophyll-a in eutrophic lake water body
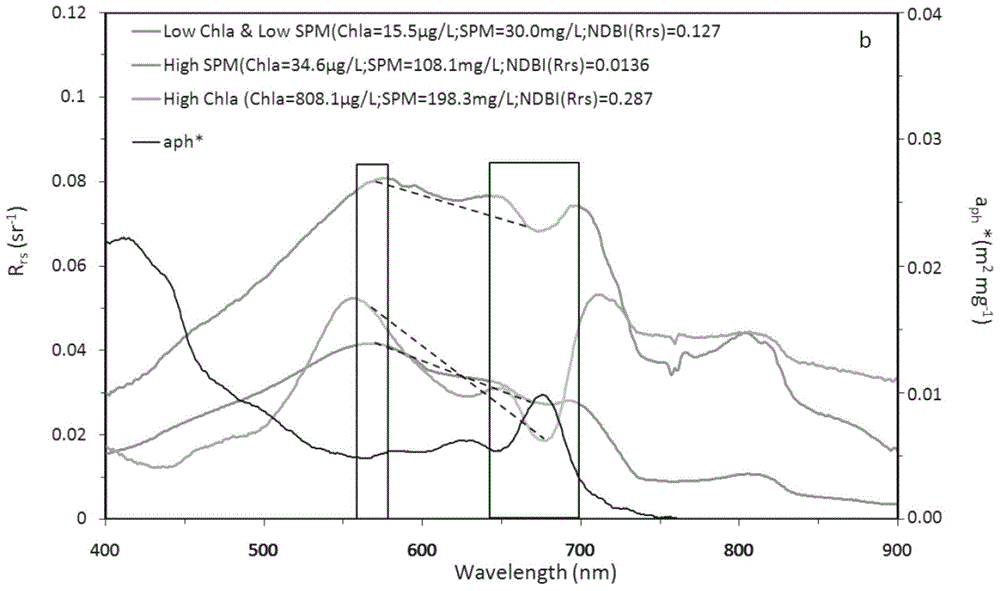
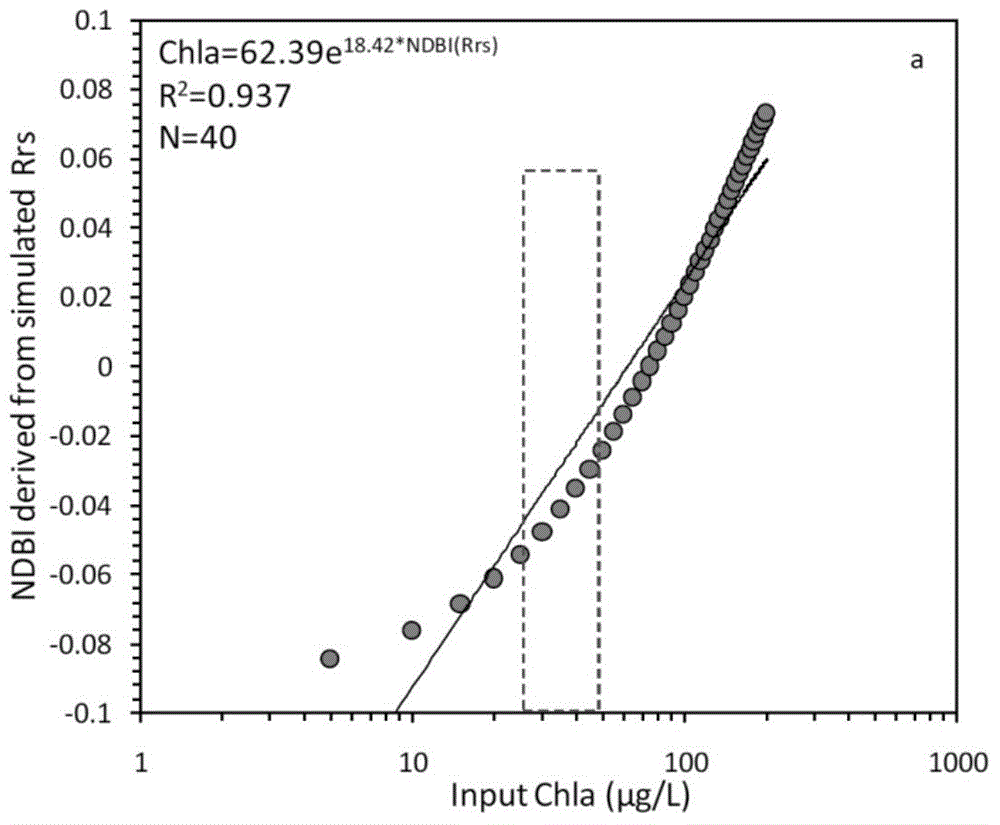
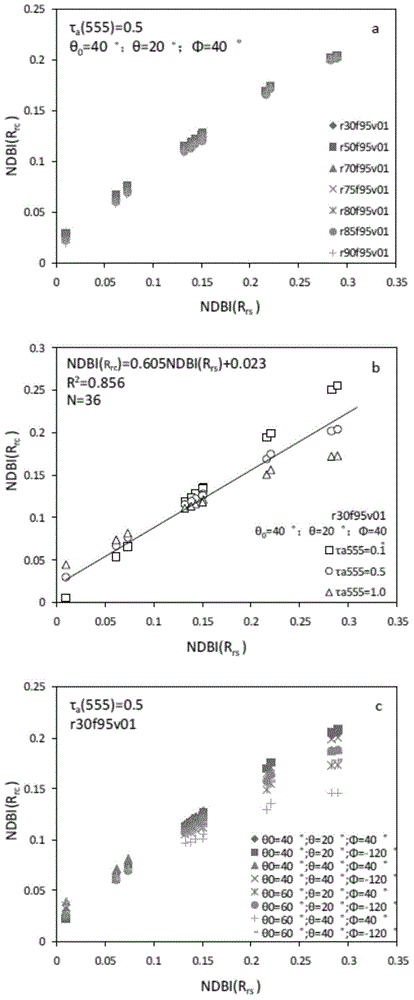
ActiveCN104820224AAchieving High-Precision EstimationReflect the space-time distributionElectromagnetic wave reradiationRayleigh scatteringEutrophication
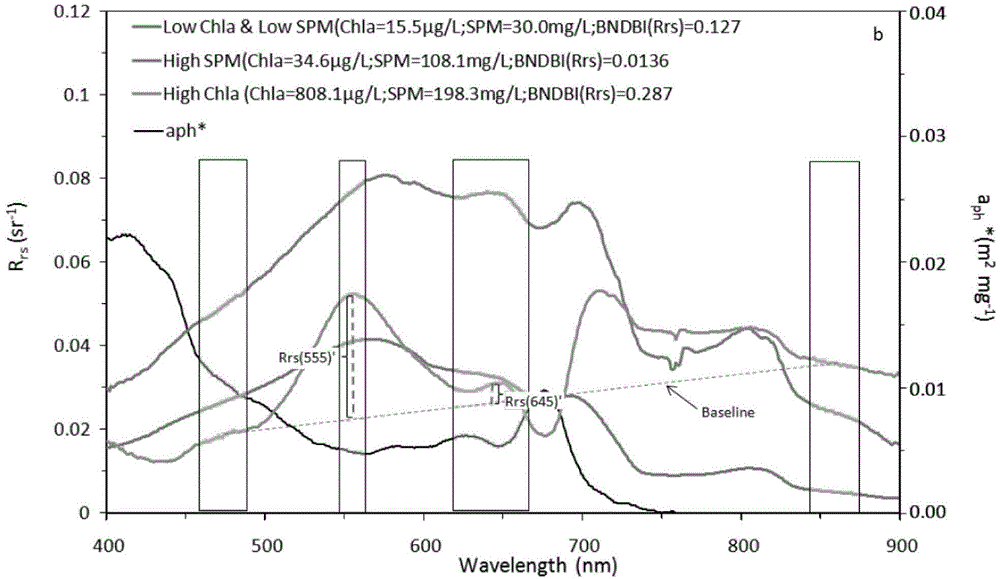
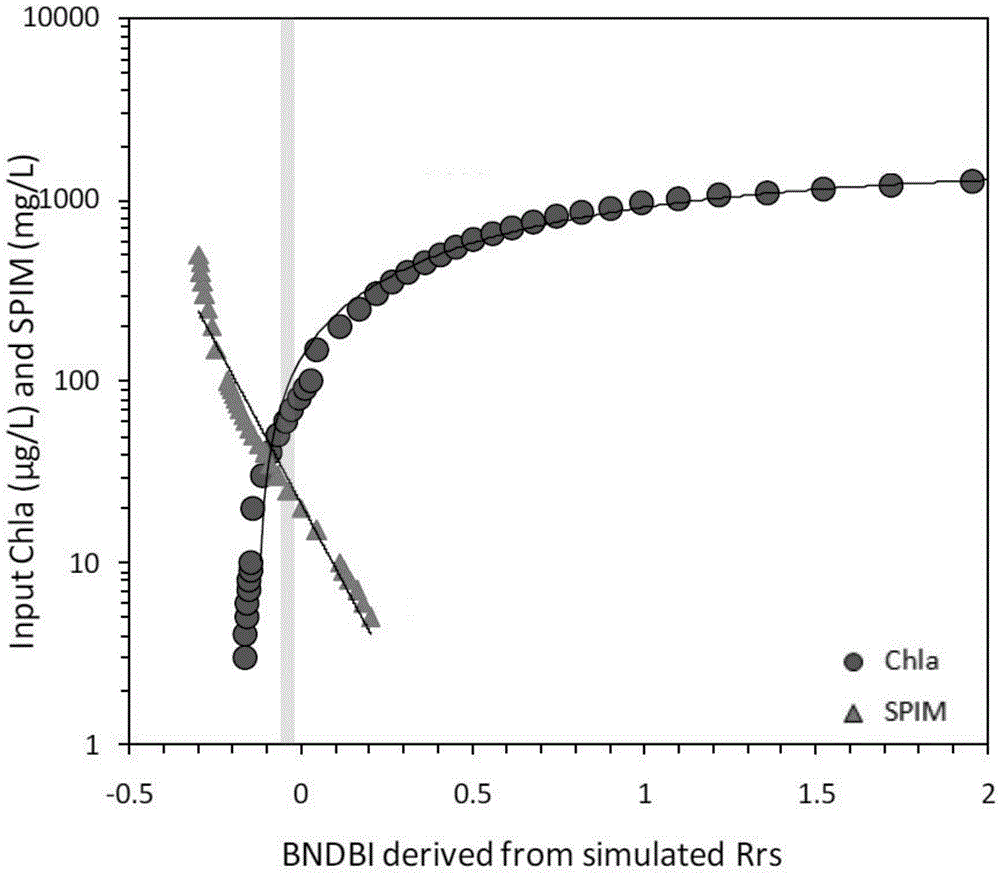
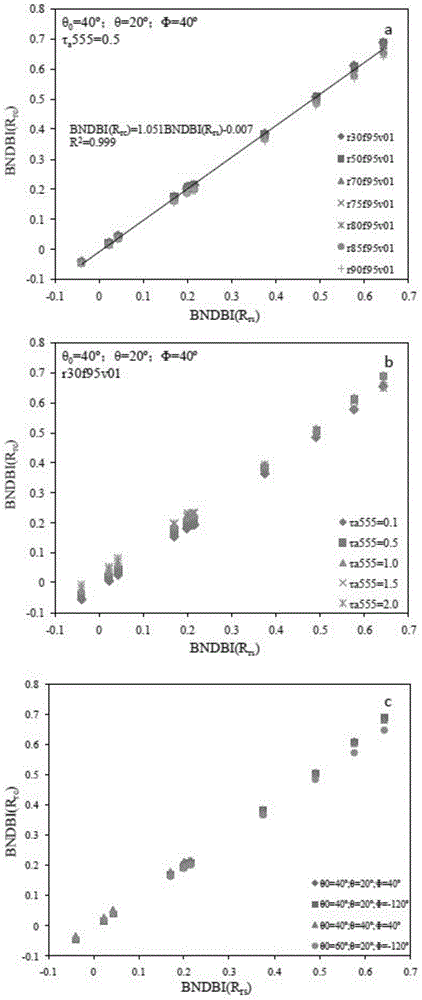
The invention provides an MODIS satellite high-precision monitoring method for chlorophyll-a in a eutrophic lake water body. The method comprises the following steps: screening a chlorophyll-a evaluation index (BNDBI) which is sensitive to the concentration change of chlorophyll-a and not affected by highly suspended matters, thin cloud and solar flares; acquiring the quantitative relationship between BNDBI and the concentration of chlorophyll-a on the basis of biological optical model simulation; acquiring a chlorophyll-a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectrum (Rrs) and BNDBI by referring to water body spectral information and corresponding water body chlorophyll-a concentration of 2013-2014 lake field monitoring; acquiring the quantitative relationship between the ground monitoring and remote sensing reflectance ratio (Rrs) and Rrc after simulated Rayleigh scattering correction by simulating different aerosol types and thicknesses and different solar elevation angles, satellite observation angles and azimuth angles; and extending the chlorophyll-a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectrum data to satellite image data after Rayleigh scattering correction. Based on the method, inter-annual and inter-monthly change rules and spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a in a eutrophic lake can be acquired accurately.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
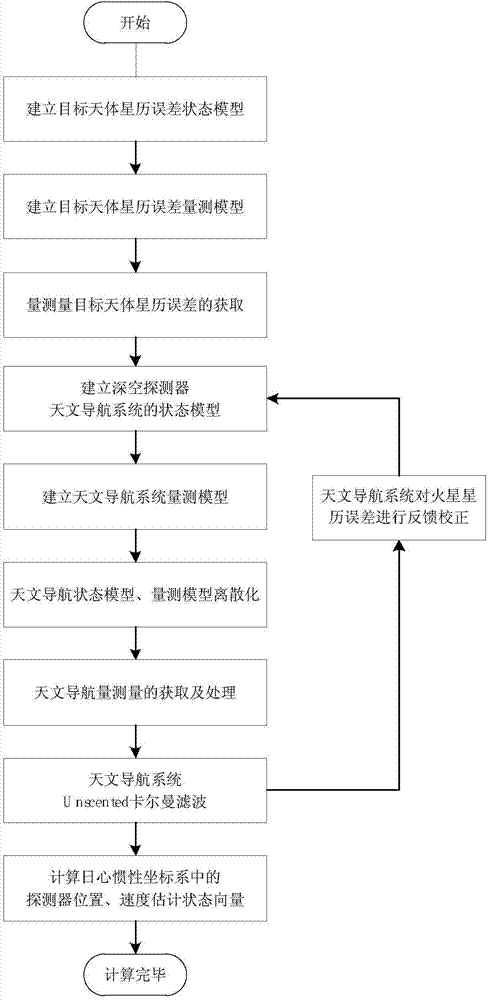
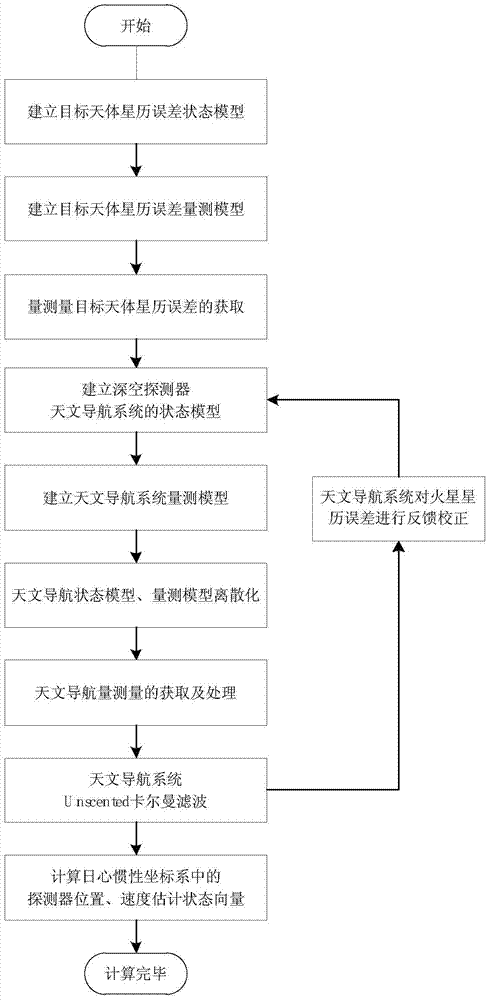
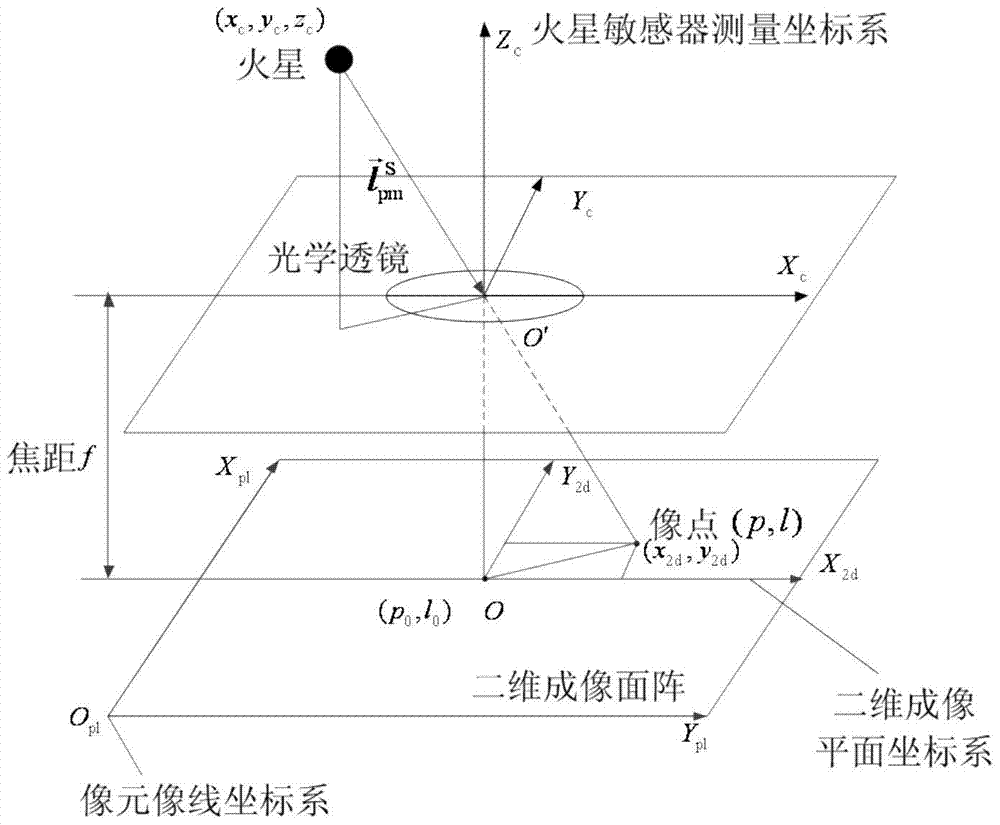
Deep space detector astronomy/radio combination navigation method based on ephemeris correction
ActiveCN103063217AAchieving High-Precision EstimationLittle impact on accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation systemSpaceflight
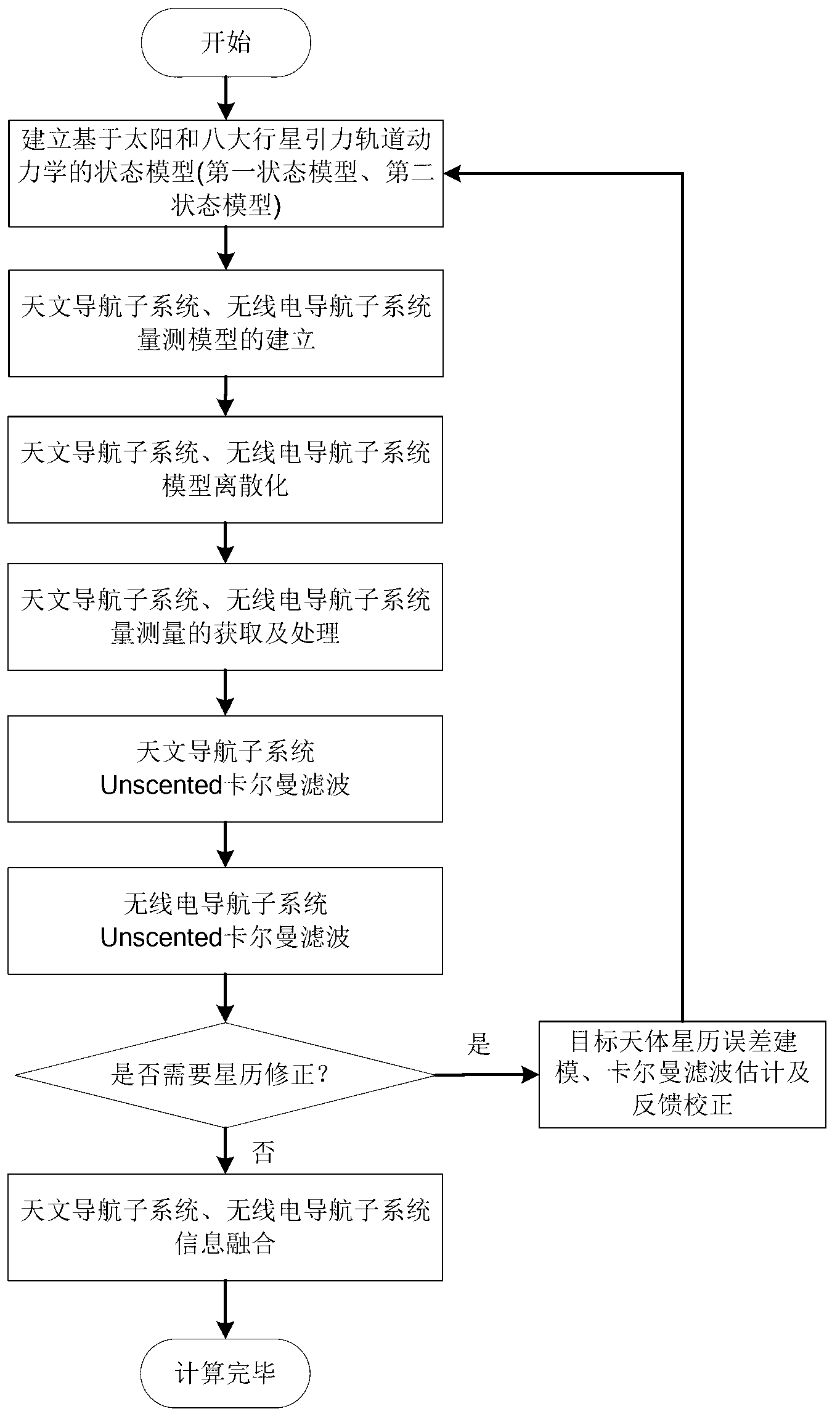
The invention relates to a deep space detector astronomy / radio combination navigation method based on ephemeris correction. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a Mars detector state model and astronomy astronomy navigation and radio navigation subsystem measurement models, acquiring the measured values of astronomy and radio navigation subsystems, and carrying out filtering estimation to obtain the position of the detector in an inertia coordinate system treating a target heavenly body as a center and the speed of the detector; and establishing the ephemeris error state model and the measurement model of the target heavenly body based on the position and the speed, obtaining the ephemeris error measurement value of the target heavenly body according to the estimation states of the two astronomy and radio navigation subsystems, utilizing a Kalman filtering method estimate the ephemeris error of the target heavenly body, feeding back to a navigation system model, and carrying out information fusion. The deep space detector astronomy / radio combination navigation method belongs to the technical field of spaceflight and navigation, can realize the online estimation of the heavenly body ephemeris error and the correction of the navigation system model error, and is suitable for the capture segment of a detector.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
High-precision satellite MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) monitoring method for chlorophyll a of eutrophic lake water body
ActiveCN104390917AAchieving High-Precision EstimationReflect the space-time distributionColor/spectral properties measurementsRayleigh scatteringEutrophication
The invention provides a high-precision satellite MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) monitoring method for chlorophyll a of a eutrophic lake water body. The method comprises the following steps: screening a chlorophyll a evaluation index (NDBI) which is sensitive to the concentration change of the chlorophyll a and is not influenced by high suspended solids; obtaining a quantitative relation between the NDBI and the concentration of the chlorophyll a on the basis of biological optical model simulation; combining spectral information of the water body and the corresponding concentration of the chlorophyll a of the water body monitored in the field in Chaohu Lake in year 2013-2014, so as to obtain a chlorophyll a inversion algorithm based on a ground measured spectrum (Rrs) and the NDBI; simulating different aerosol types and thicknesses, different solar altitudes, satellite observation angles and azimuth angles, so as to obtain a quantitative relation between the ground monitored remote sensing reflectance (Rrs) and simulated Rrc subjected to Rayleigh scattering correction; and further extending the chlorophyll a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectral data to satellite image data subjected to the Rayleigh scattering correction. According to the method, the inter-annual and inter-monthly change rules and space distribution of the rules of the concentration of the chlorophyll a of a eutrophic lake can be accurately obtained.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Deep space explorer acquisition phase celestial navigation method based on target object ephemeris correction
ActiveCN105203101AAchieving High-Precision EstimationLittle impact on accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by astronomical meansEuclidean vectorInertial coordinate system
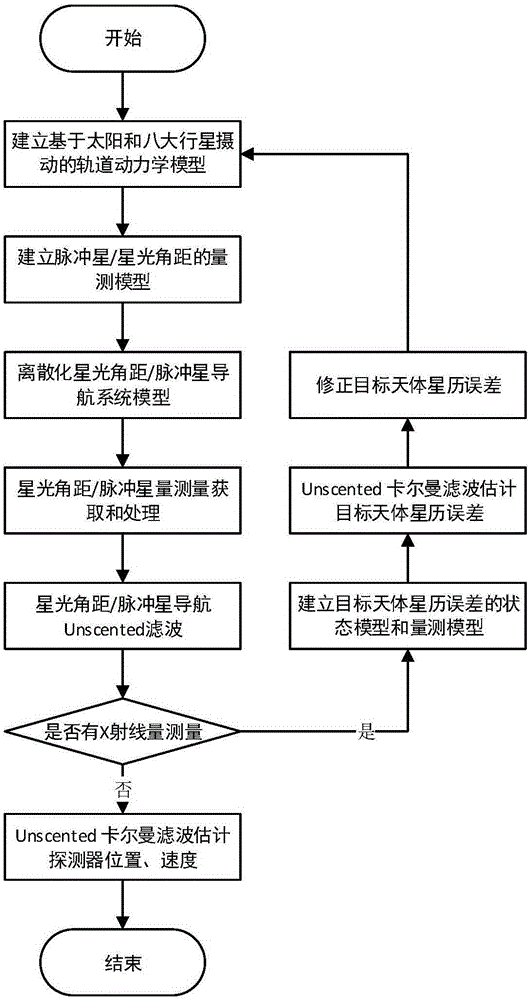
The invention relates to a deep space explorer acquisition phase celestial navigation method based on target object ephemeris correction. According to the method, firstly, a Martian explorer state model, a startlight angle navigation sub system measuring model and an X-ray pulsar navigation sub system measuring model are built; then, the startlight angle and the X-ray pulsar quantity measurements are respectively obtained; filtering estimation is performed to obtain the position and the speed of a detector in a heliocentric inertia coordinate system and a target object center inertia coordinate system; on the basis, a state model and a measuring model of target object ephemeris error are built; the quantity measurement about the target object ephemeris error is obtained through estimation state vectors of the startlight angle navigation sub system and the X-ray pulsar navigation sub system; a Kalman filtering method is used for estimating the target object ephemeris error; the target object ephemeris error is fed back into a navigation system model; the position of a target object in the navigation model is corrected. The deep space explorer acquisition phase celestial navigation method belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation, can be used for estimating the object ephemeris error and correcting the model error of the navigation system on line, and is applicable to the explorer acquisition phase.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
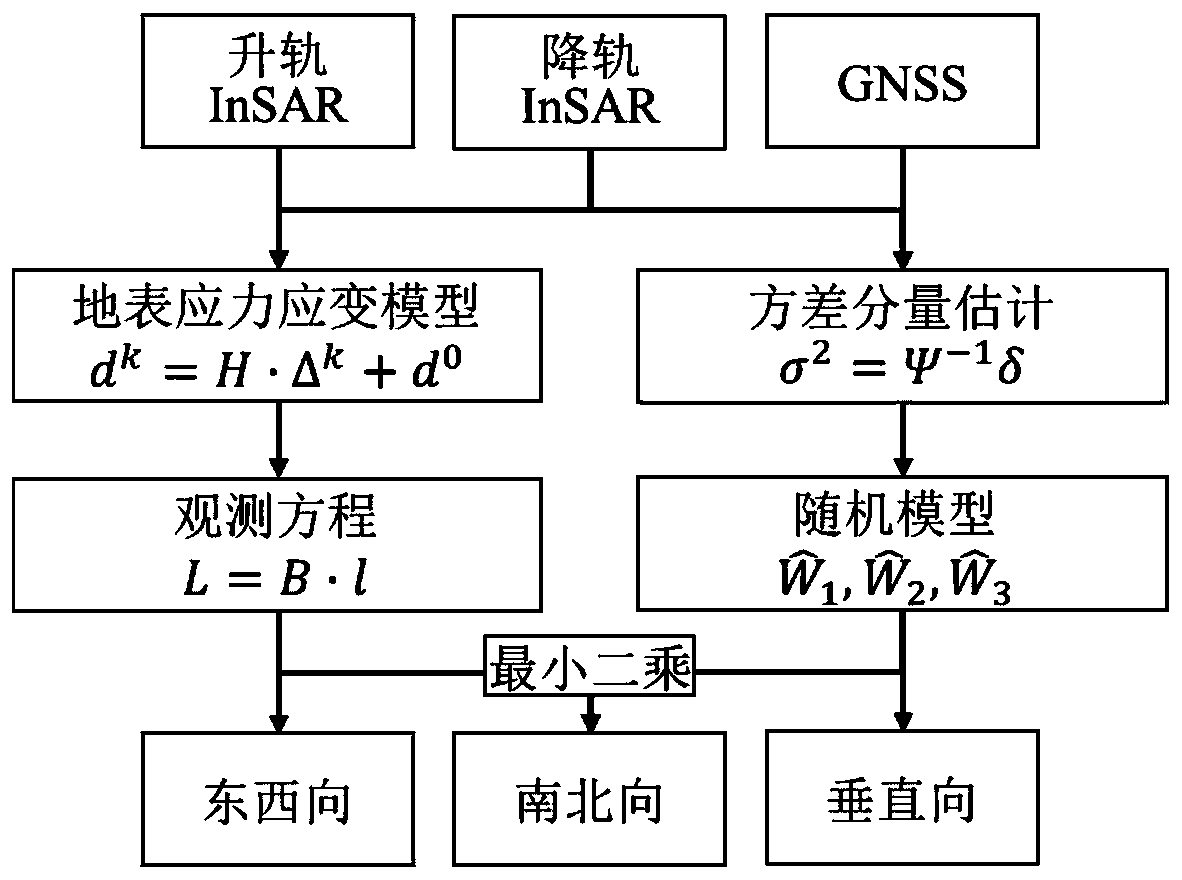
Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) and global navigation satellite system (GNSS) weight determining method aiming at three-dimensional ground surface deformation estimation
ActiveCN110058236AAchieving High-Precision EstimationExact weight ratioSatellite radio beaconingUsing wave/particle radiation meansSurface stressGeomorphology
The invention discloses an interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) and global navigation satellite system (GNSS) weight determining method aiming at three-dimensional ground surface deformation estimation. The InSAR and GNSS weight determining method comprises the steps that 1, by utilizing ascending rail InSAR data and descending rail InSAR data of a to-be-monitored area and GNSS data ofthe to-be-monitored area, the function relationship between three-dimensional deformation d<0> of an unknown point and a certain quantity of the InSAR / GNSS data L of surrounding points is established based on a ground surface stress strain model and observed value imaging geometry; 2, K observed data in the ascending rail InSAR, descending rail InSAR and GNSS observed values L are subjected to relative weight determining, and an initial weight matrix W of all kinds of observed values of InSAR / GNSS is determined; 3, a precise weight matrix hat{W} between all kinds of observed values of InSAR / GNSS is estimated and determined through variance components, and high-precision three-dimensional deformation d<0> is solved based on the least squares criterion; and 4, as for each ground surface point, InSAR and GNSS fusion estimation of a high-precision three-dimensional ground surface deformation field is achieved through the step 1 to the step 3.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
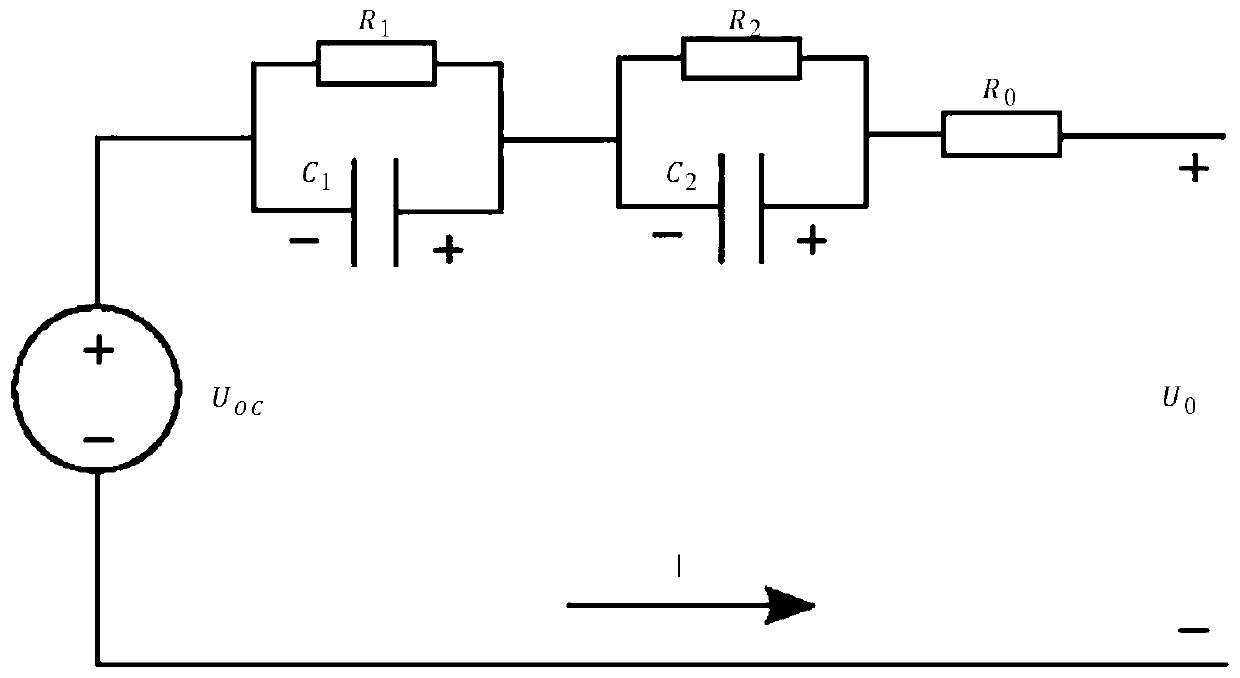
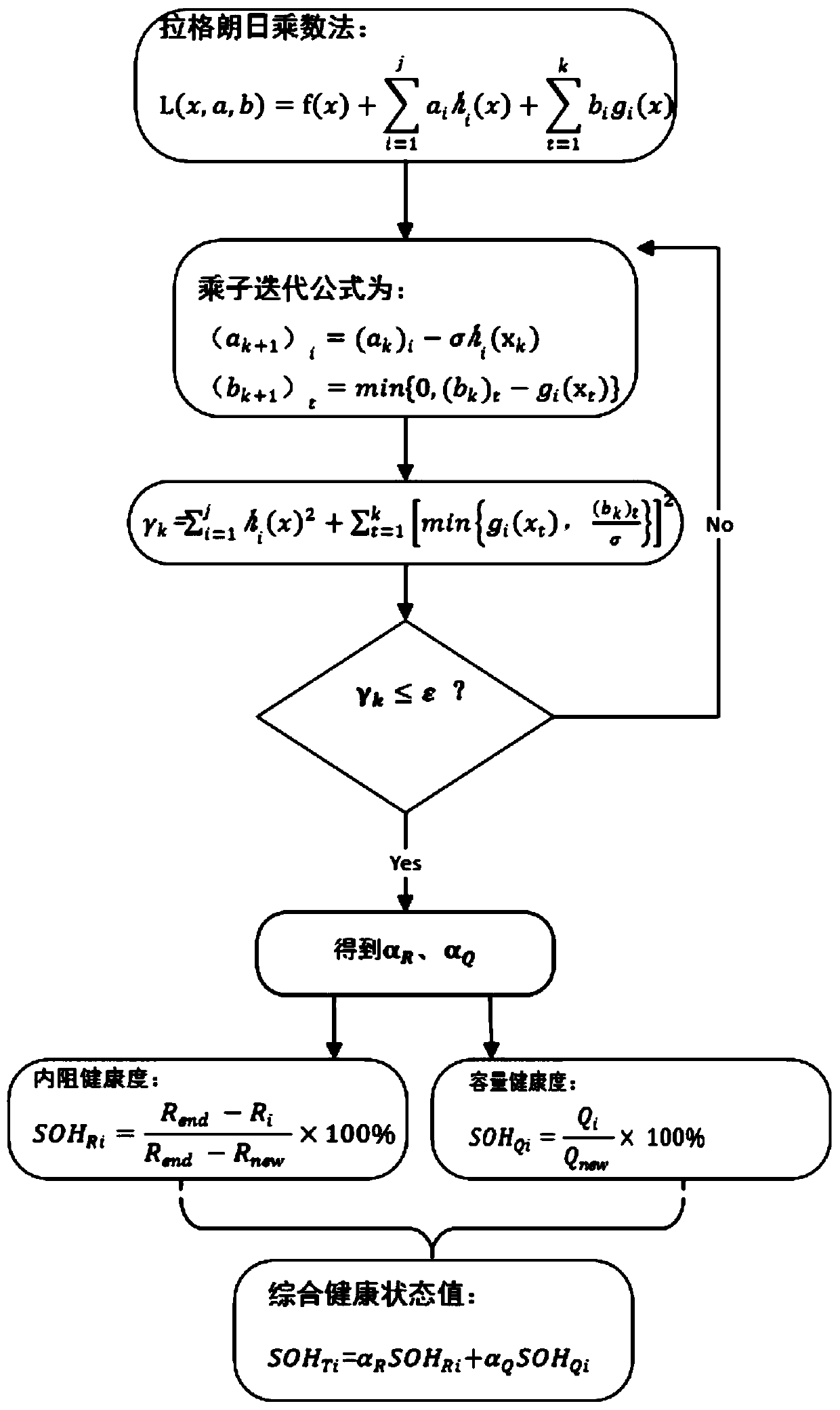
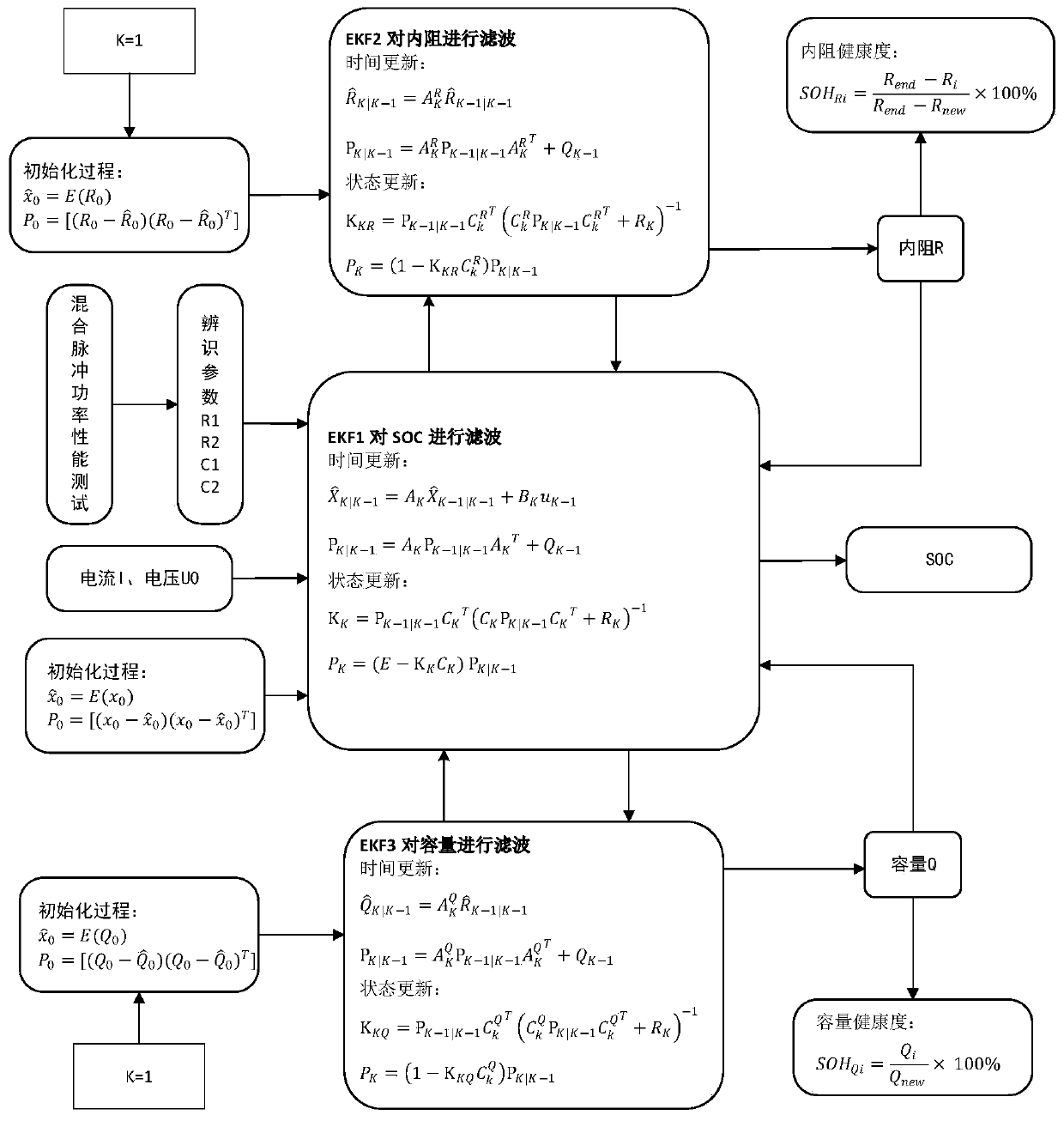
Power battery multi-dimensional fusion SOC and SOH online joint estimation method
ActiveCN111337832AReduce complexityAchieving High-Precision EstimationElectrical testingVehicular energy storagePower batteryInternal resistance
The invention relates to a power battery multi-dimensional fusion SOC and SOH online joint estimation method. According to the invention, the method comprises the steps: selecting a dual extended Kalman filter (Dual-EKF) method and a multi-dimensional fusion estimation method to solve the problems of large workload, low estimation precision and the like of separately designing SOC and SOH estimation systems; obtaining related data through a mixed pulse power performance test, and establishing second-order RC equivalent circuit model identification model parameter values R1, R2, C1 and C2; performing online accurate estimation on three state parameters of SOC, internal resistance and rated capacity by using a Dual-EKF method so as to determine SOHRi and SOHQi; and finally, calculating health state weight coefficients alpha R and alpha Q of two dimensions by using a normalized least square method, and performing fusing to obtain a comprehensive health state value SOHTi; finally, accurately estimating the SOH value of the power battery, achieving the SOC and SOH combined online estimation, and improving the estimation precision of the SOC and SOH values. Therefore, the applicability of the method to an embedded power battery management system is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Ephemeris correction-based autonomous celestial navigation method for deep space probe in capturing stage
ActiveCN104764449ALittle impact on accuracyAchieving High-Precision EstimationNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by astronomical meansAngular distanceDynamic models
The invention discloses an ephemeris correction-based autonomous celestial navigation method for a deep space probe in a capturing stage. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing an ephemeris error state model and an ephemeris error measurement model of a target celestial body, and measuring ephemeris error according to a position difference between a predicted celestial body image and an actual celestial body image; secondly, simultaneously taking the ephemeris error state model and an orbital dynamic model as a celestial navigation system state model, taking the ephemeris error measurement model and a starlight angular distance measurement model as measurement models of a celestial navigation system, estimating the position and speed of the probe and the ephemeris error of the target celestial body by a Unscented Kalman filtering method, feeding back the estimated ephemeris error to the state model, and correcting the ephemeris data of the target celestial body, thereby obtaining the position and speed of the probe, relative to the target celestial body and the heliocenter, after autonomously correcting the ephemeris error. The method provided by the invention belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation, can perform on-line estimation on ephemeris error of celestial bodies and correct model error of the navigation system, and is suitable for the probe capturing stage.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
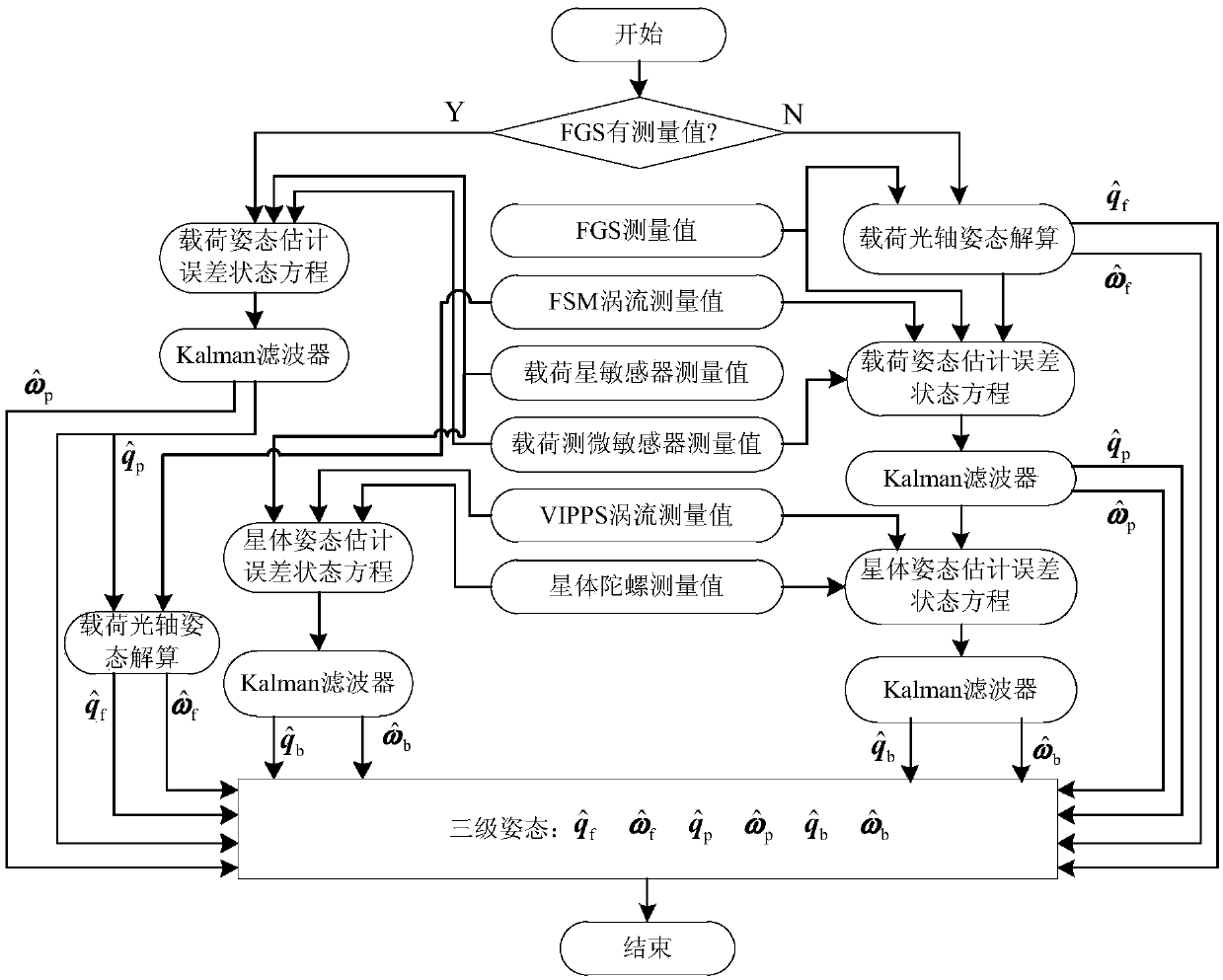
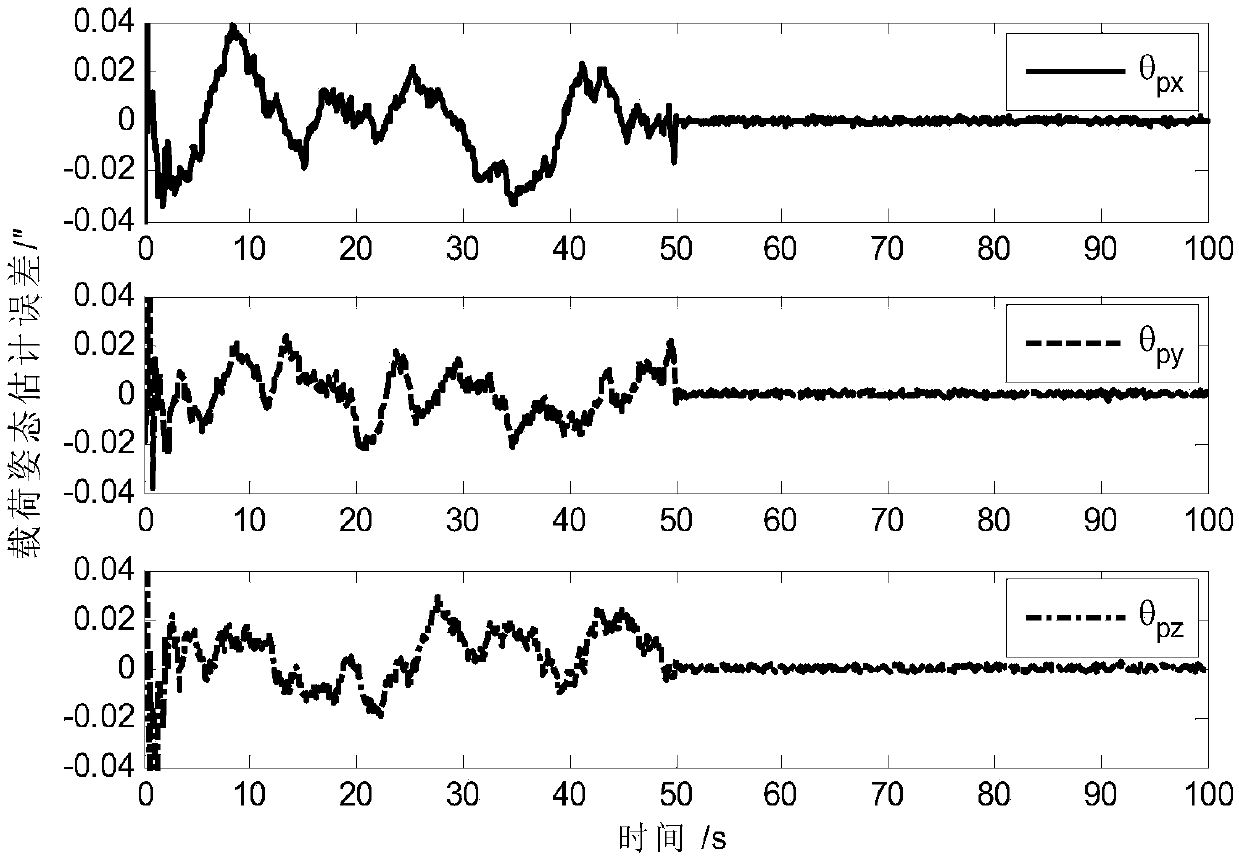
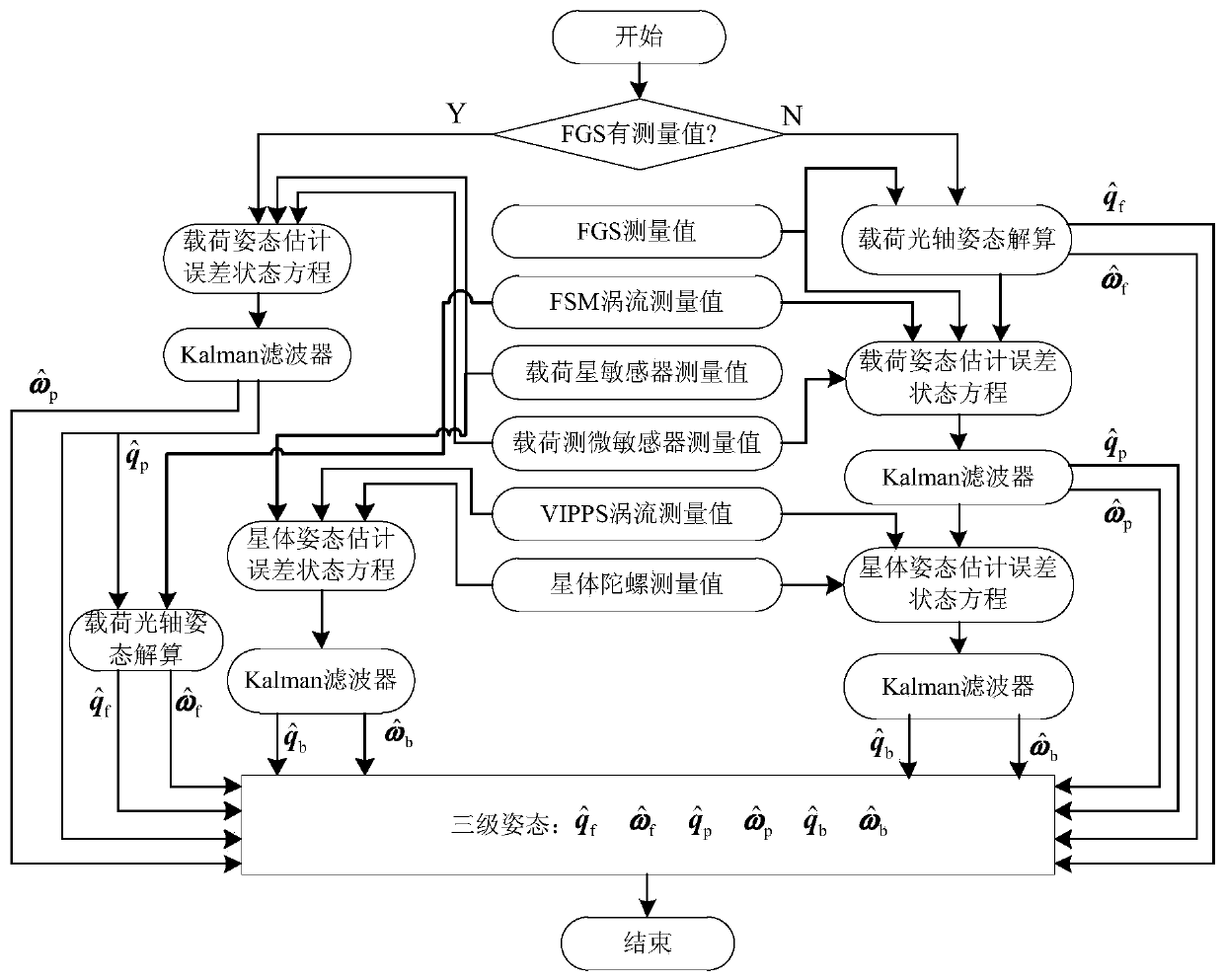
Determining method for ultrahigh-accuracy attitude of spacecraft multi-stage compound control system
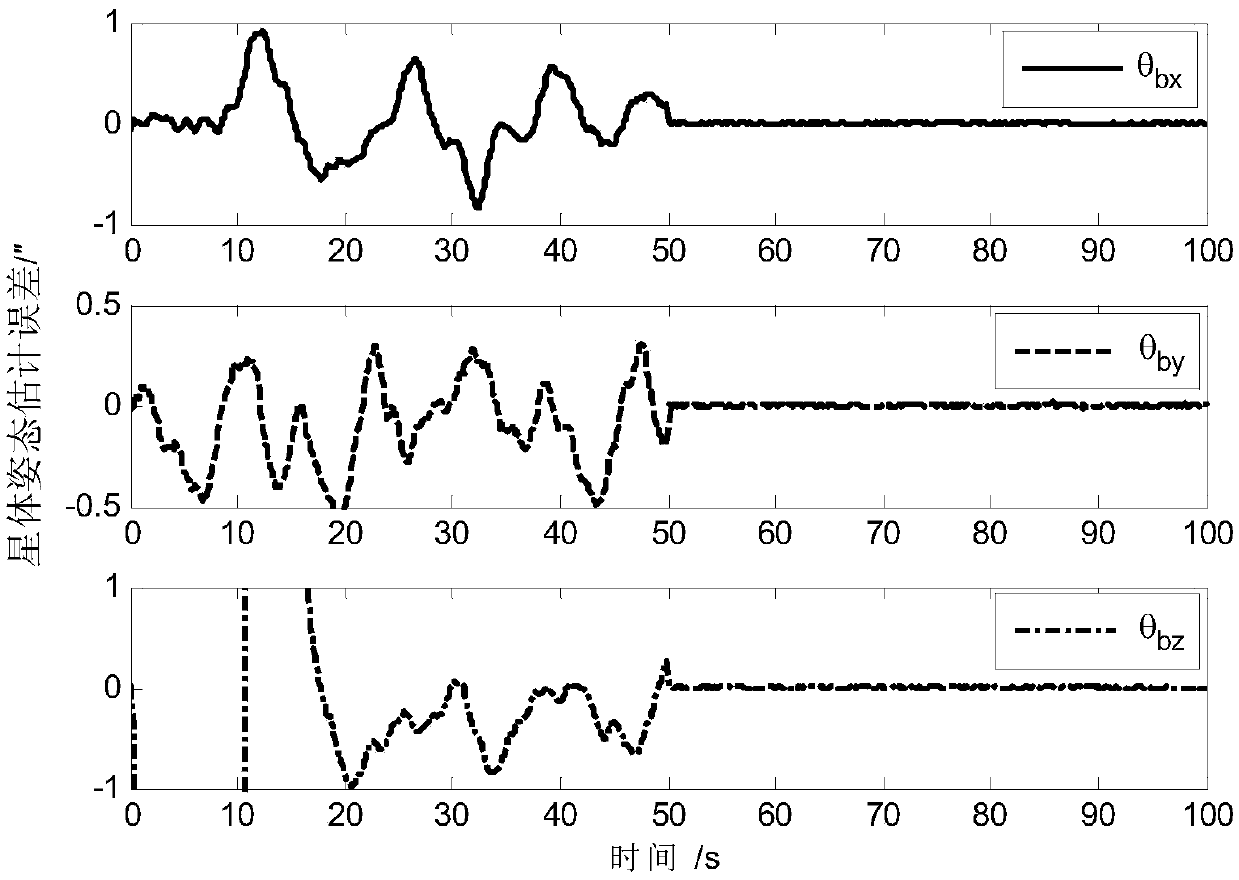
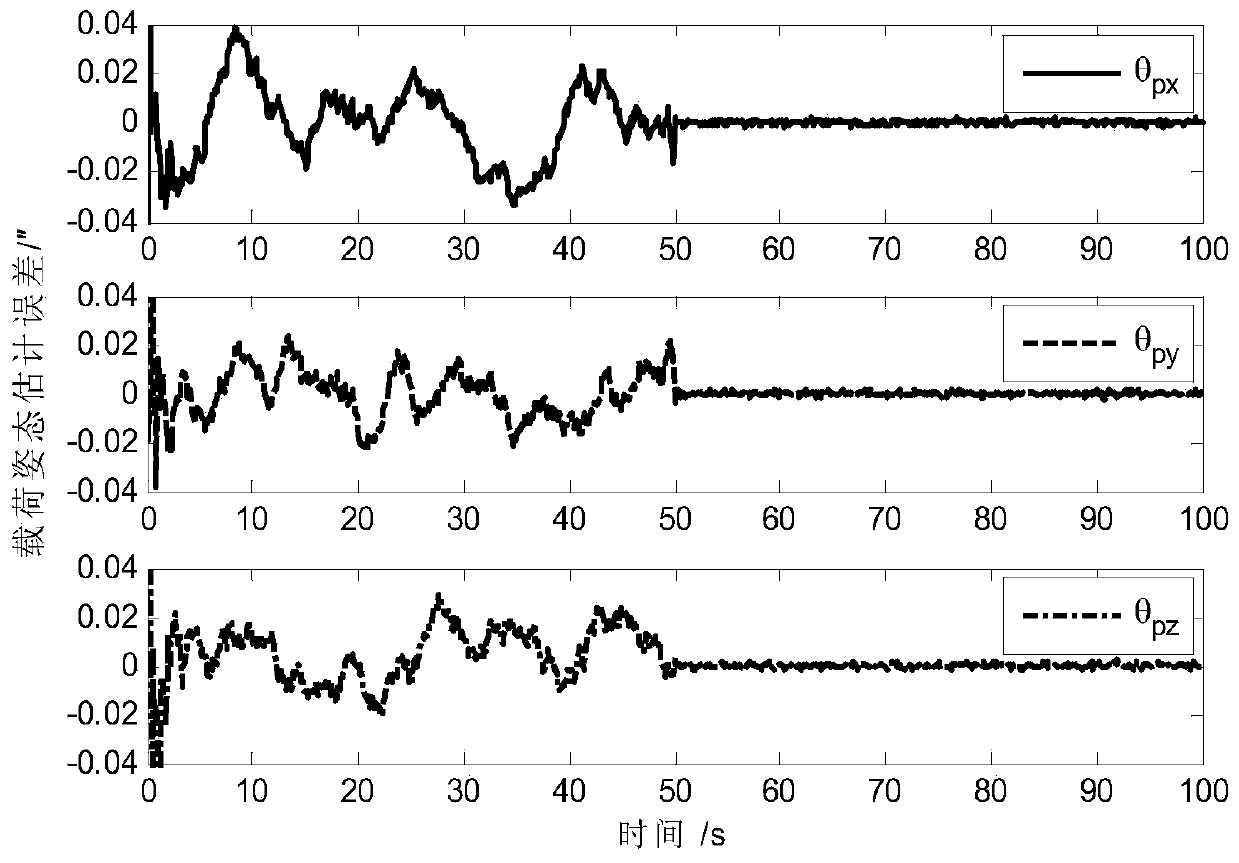
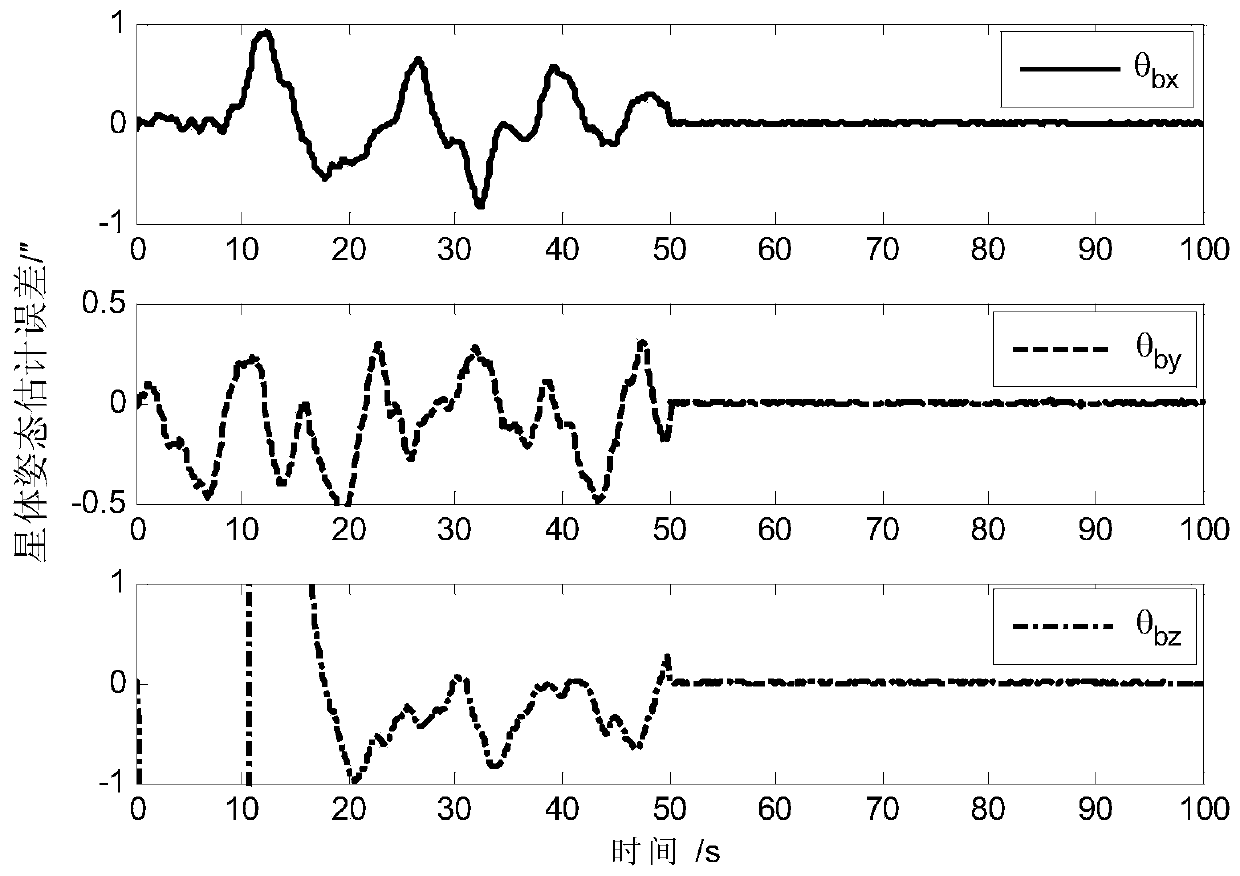
ActiveCN108801270AAchieving High-Precision EstimationImplementing Relative Pose EstimationCosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationQuaternionControl system
A determining method for ultrahigh-accuracy attitude of a spacecraft multi-stage compound control system. The determining method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing an attitude constraintmodel between a star and a load as well as between the load and a fast reflective mirror of the spacecraft multi-stage compound control system; (2) establishing a relative attitude quaternion model between the star and the load as well as between the load and the fast reflective mirror; (3) judging whether a star guiding sensor has a measured value or not; (4) establishing a load attitude estimation error state equation if the star guiding sensor has no the measured value, estimating a load attitude by adopting a Kalman filtering method, and realizing determination on high accuracy of the loadattitude; (5) establishing a star attitude estimation error state equation, and realizing determination on high accuracy of a star attitude by adopting the Kalman filtering method; (6) estimating a load sight attitude by adopting a measured value qfm of the star guiding sensor if the star guiding sensor has the measured value; (7) establishing the load attitude estimation error state equation, estimating the load attitude by adopting the Kalman filtering method, and realizing the determination on high accuracy of the load attitude; (8) establishing the star attitude estimation error state equation.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Geosynchronous orbit determination and parameter determination method based on differential algebra
ActiveCN109032176AAvoid singularitiesImprove estimation accuracyPosition/course control in three dimensionsSynchronous orbitGeosynchronous satellite
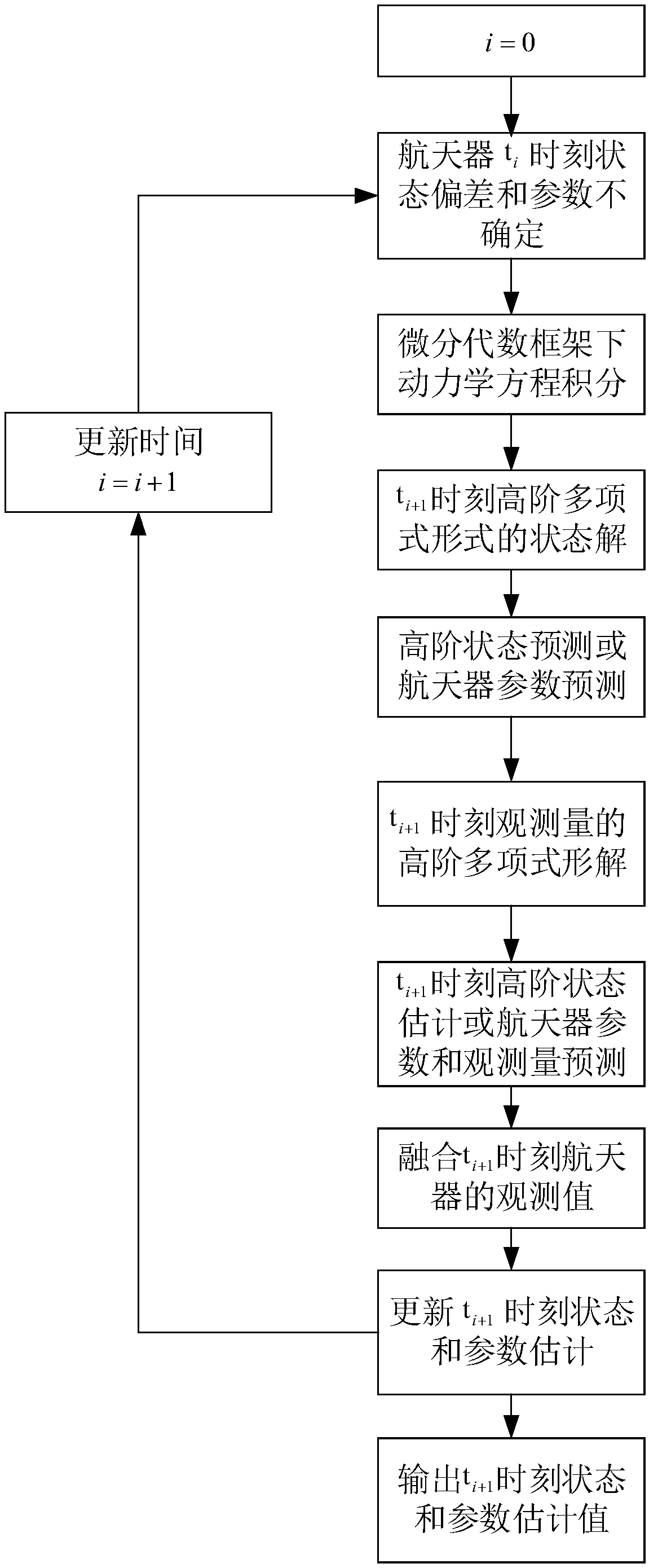
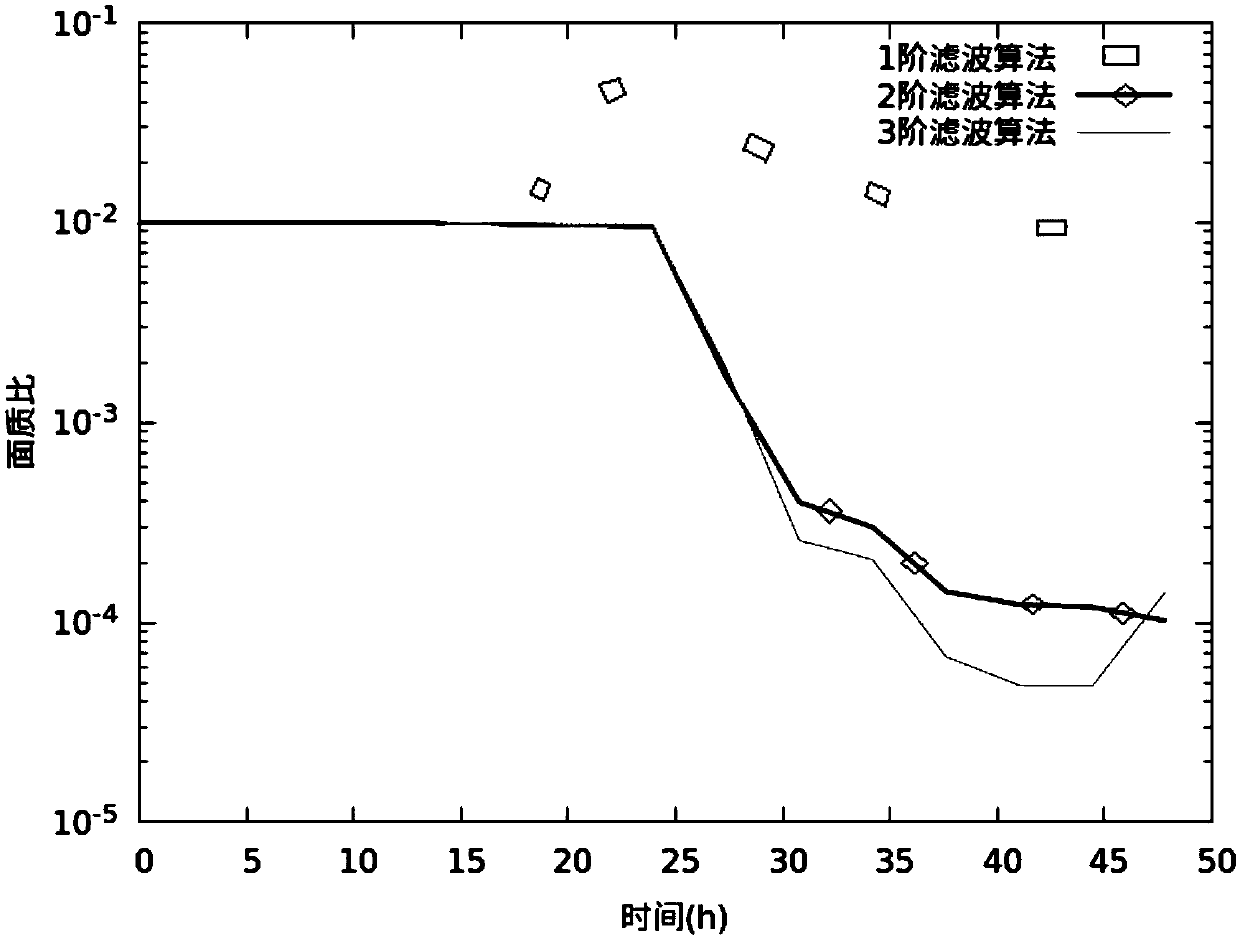
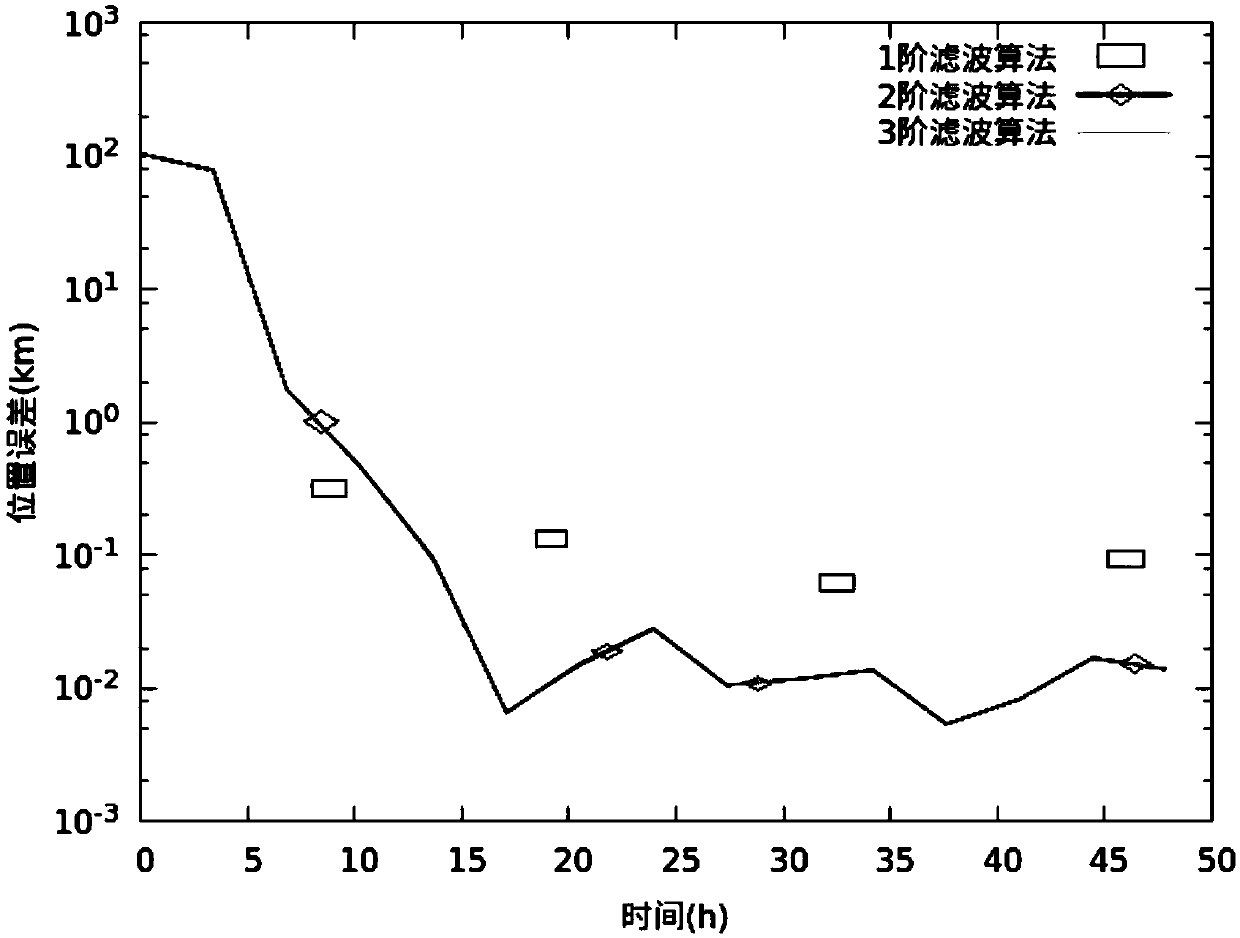
The invention discloses a geosynchronous orbit determination and parameter determination method based on differential algebra. A kinetic model described based on geosynchronous satellite orbit elements is selected and used, use of a relatively greater integration step in a numerical integration process is avoided and appearance of singular points is avoided for the kinetic model, moreover, a perturbative force item is added in the kinetic model, polynomial form integration is executed, thus, obit statuses and spacecraft parameters are obtained, high-order prediction is executed for the obtained parameters, and meanwhile, high-order prediction of observed quantity is executed; by means of nonlinear information of the kinetic model and an observation model, estimation accuracy is improved; in combination with actual observed values of a spacecraft, high-order prediction values of the obit status and the spacecraft parameters are updated and high-order estimated values as initial values are obtained; and by repeating the implementation process above, geosynchronous orbit determination and parameter determination can be completed. The method provided by the invention not only can improve accuracy of obit estimation and realize high-precision estimation of the parameters, but also can greatly reduce calculation cost.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Arrival angle estimation method based on sparse Bayesian theory in existence of cross coupling
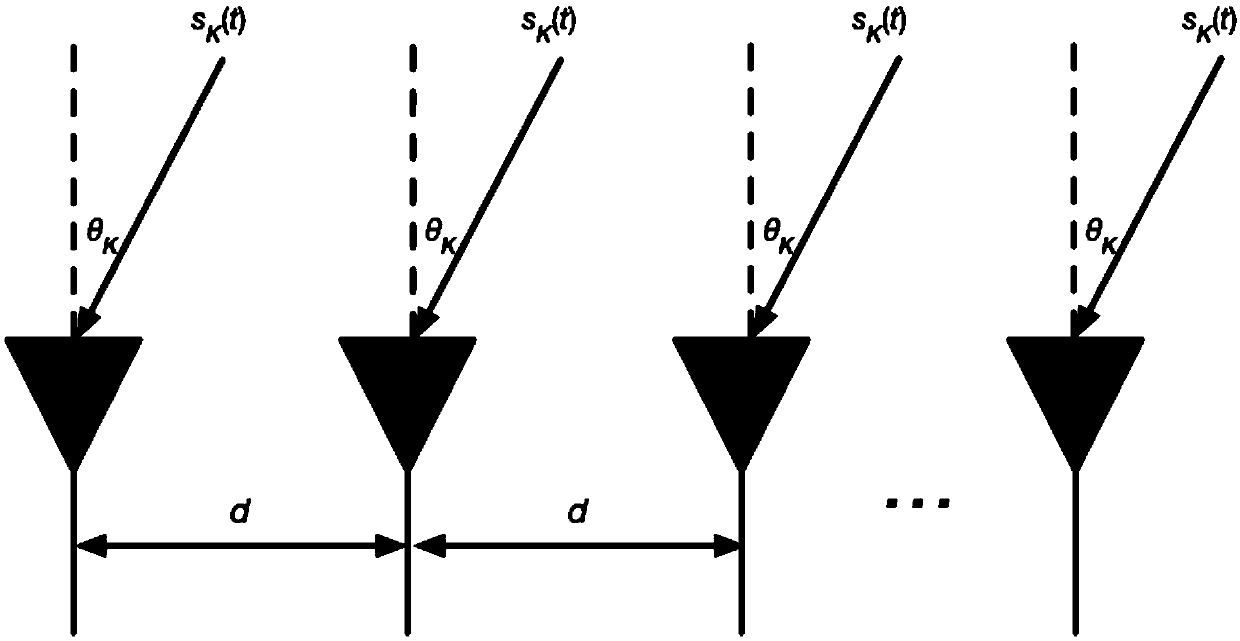
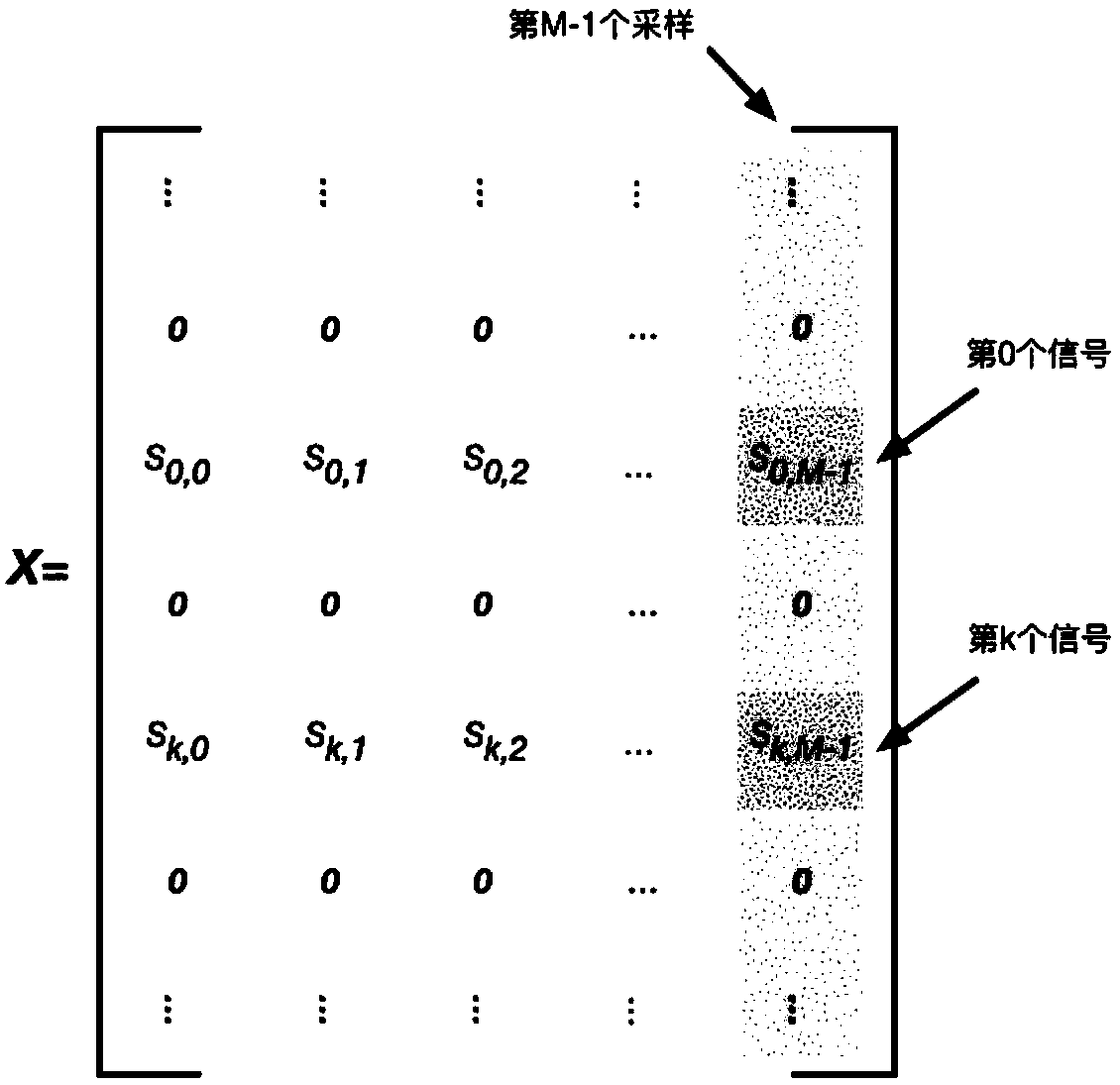
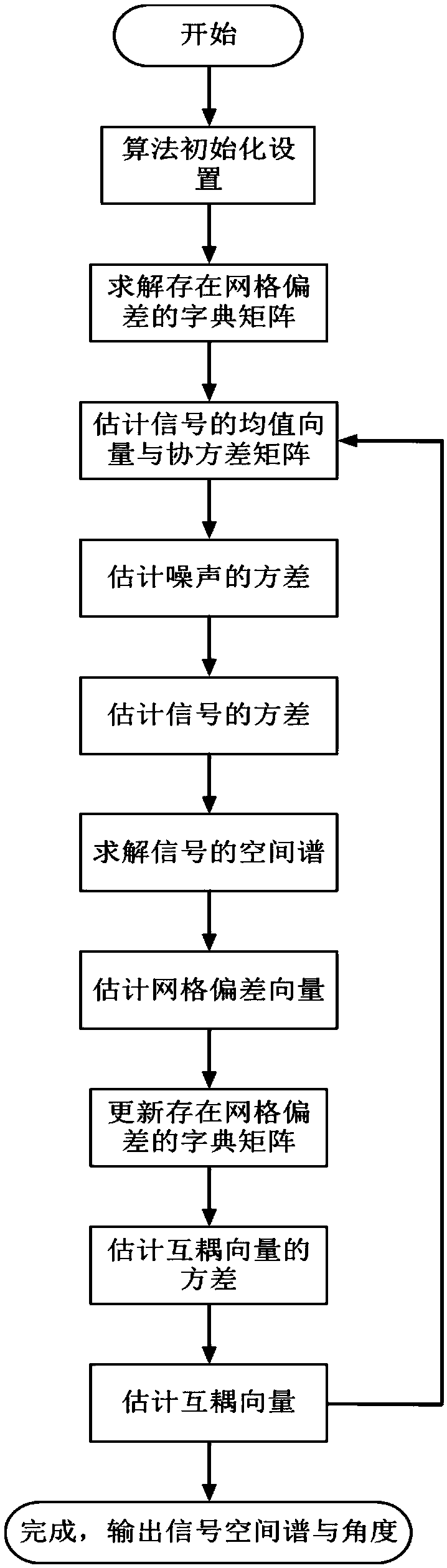
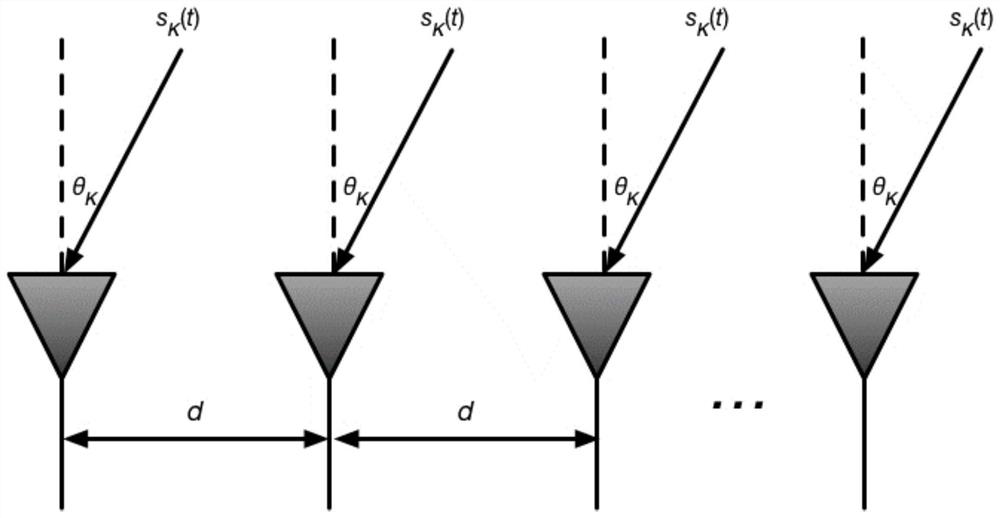
ActiveCN108957390AImproving Angle of Arrival Estimation PerformanceSolve the signal angle of arrival estimation problemRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsCouplingEstimation methods
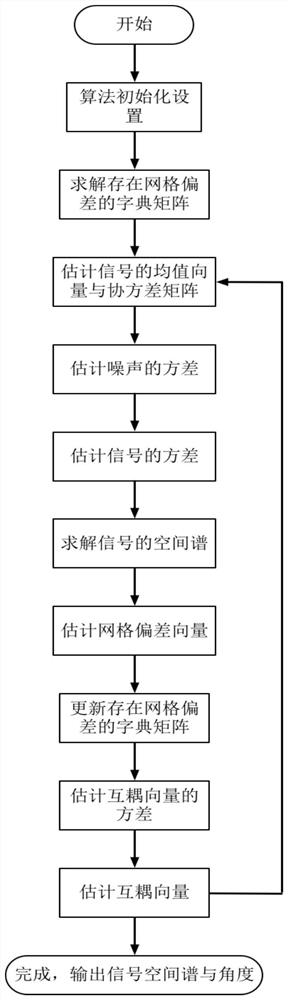
The present invention discloses an arrival angle estimation method based on the sparse Bayesian theory in existence of cross coupling. The method comprises the steps of: constructing a sparse signal model in the existence of antenna array cross coupling and arrival angle grid deviation; initializing unknown parameters in the sparse signal model; according to the current unknown parameter values, solving a joint probability distribution function based on the Bayesian theory, and estimating a receiving signal mean value and a covariance matrix; through adoption of the maximization likelihood function, estimating the variance of noise and variance of the receiving signals; calculating and obtaining a spatial spectrum of the receiving signals; through adoption of the maximization likelihood function, estimating the arrival angle grid deviation, and updating a dictionary matrix in the existence of the grid deviation; estimating the variance of the array antenna cross coupling vector and thecross coupling vector of the array antenna; and performing iteration calculation until reaching the set number of times of iteration, finishing the iteration, and outputting the spatial spectrum of the receiving signals and the solved receiving signal arrival angle. The arrival angle estimation method based on the sparse Bayesian theory in existence of cross coupling improves the arrival angle estimation performance and achieves the high-precision estimation of the signal arrival angle.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
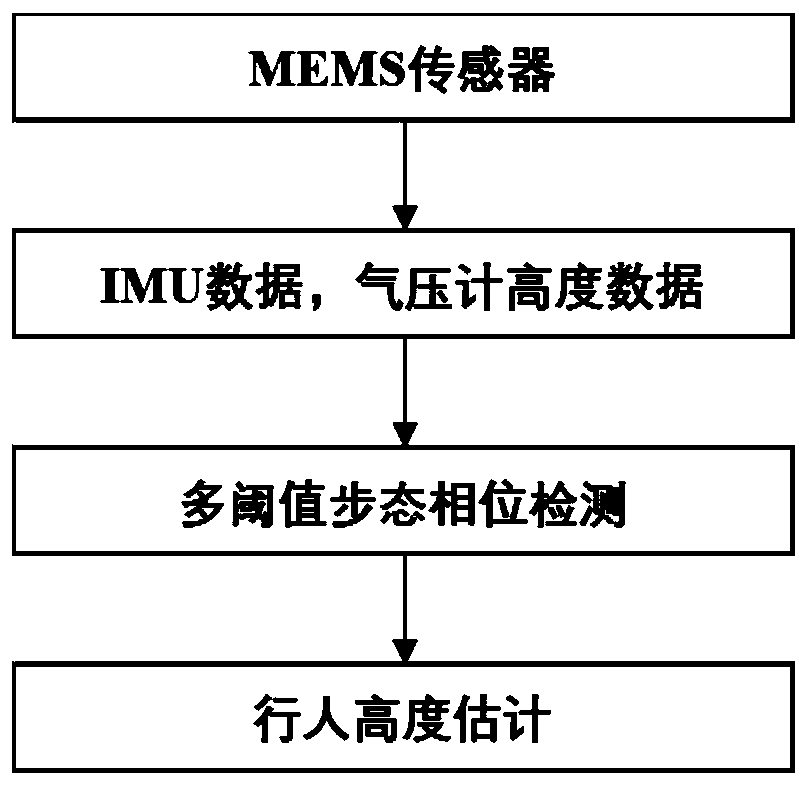
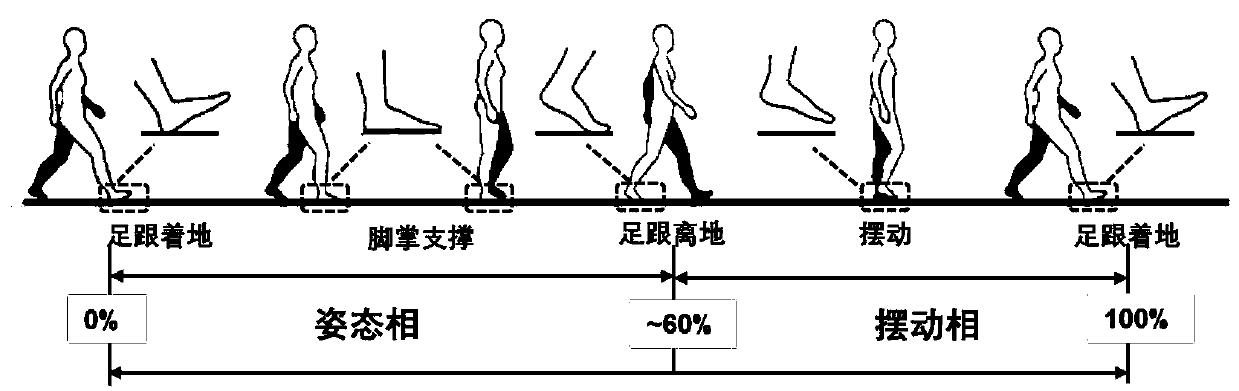
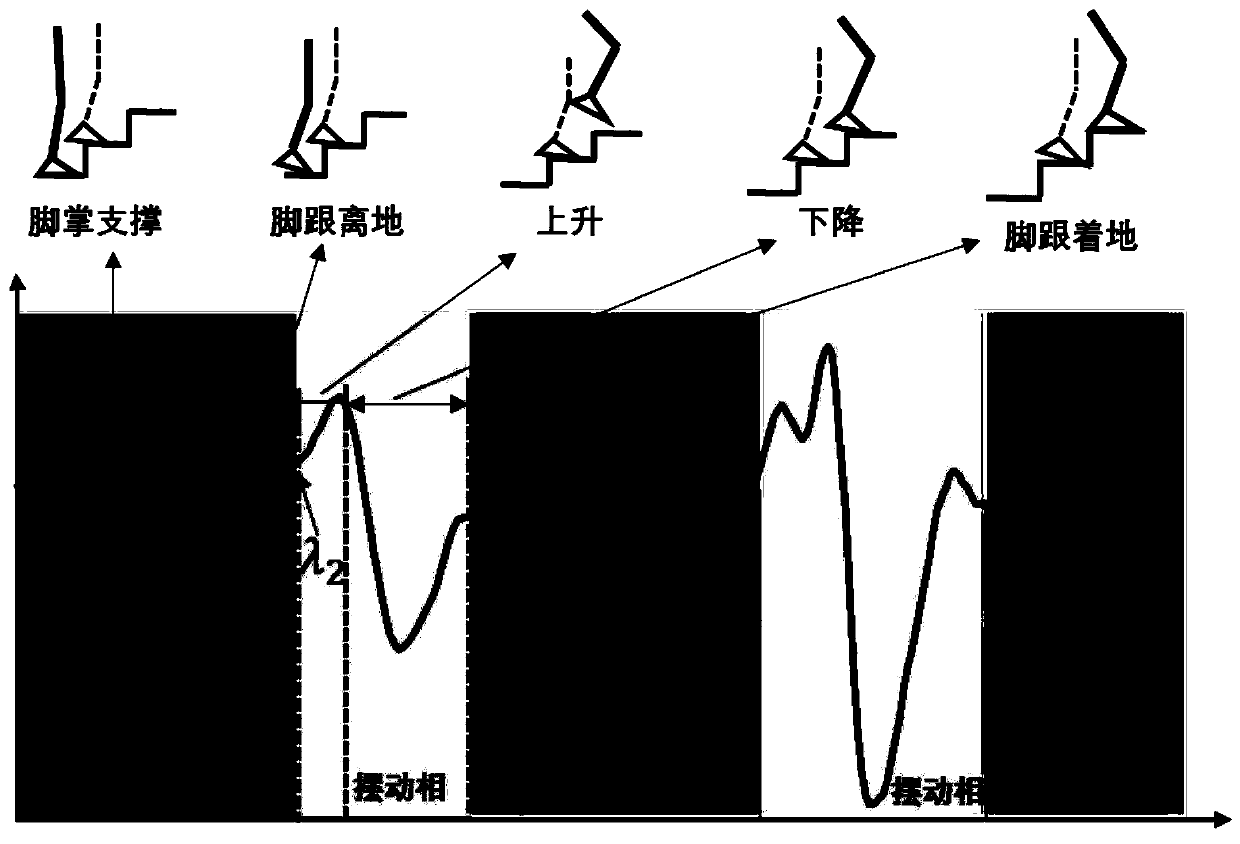
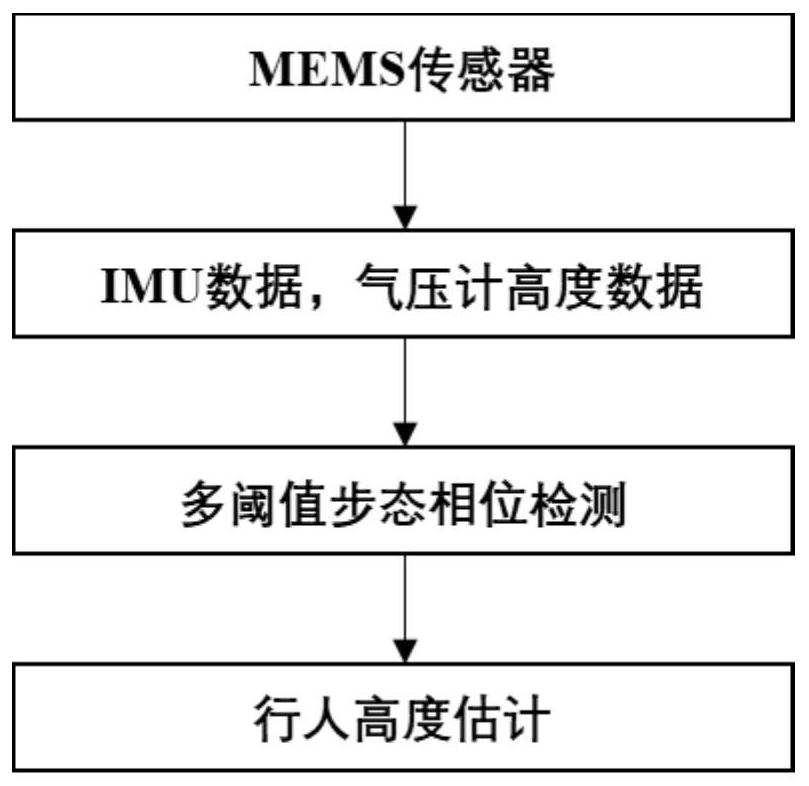
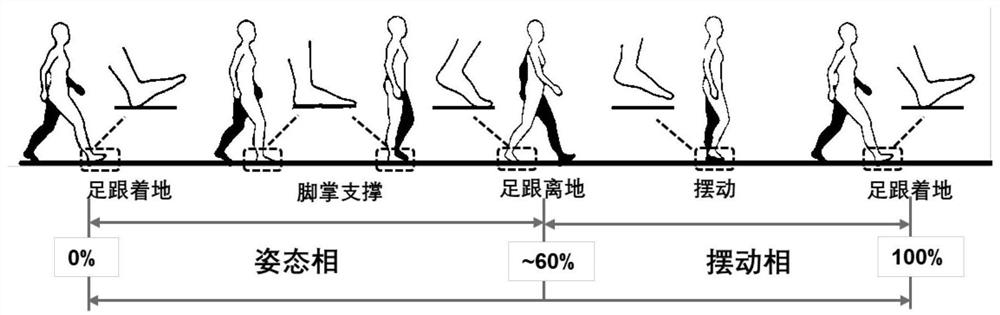
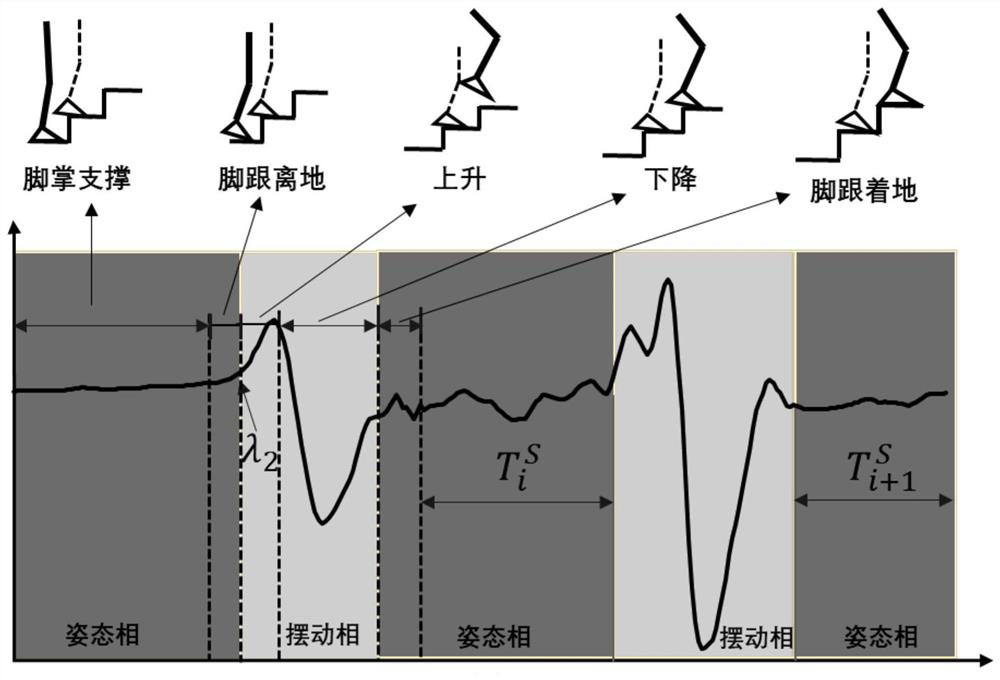
Method for estimating pedestrian height position in multi-story building based on MEMS sensor
ActiveCN109827568ASimplify the state of motionRealize high-precision correctionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAngular velocityEngineering
The invention discloses a method for estimating a pedestrian height position in a multi-story building based on an MEMS sensor. The method comprises the steps of: fixing an MEMS integrated sensing device on a pedestrian's lower limb; employing the MEMS integrated sensing device to collect acceleration data, angular velocity data and pedestrian height data in the process that the pedestrian walks astaircase; employing a multi-threshold detection method to determine an attitude phase and the swing phase of the pedestrian gait movement; performing correction of the accelerations of the attitudephase and the swing phase in the vertical direction, updating the speed of the attitude phase to be 0, and performing secondary integration for the corrected acceleration in the vertical direction toobtain the estimated heights of the attitude phase and the swing phase of the pedestrian; and determining whether there is deviation between the estimated height data obtained by the attitude phase and the target height data measured by a micro manometer or not, if yes, performing error linear compensation for the estimated height obtained by the swing phase and finally obtaining the updated pedestrian positioning data. The accurate estimation of the pedestrian height position is achieved based on one sensor node.
Owner:东北大学秦皇岛分校
Dual parallel antenna array-based coherent distributed non-circular signal DOA estimation method
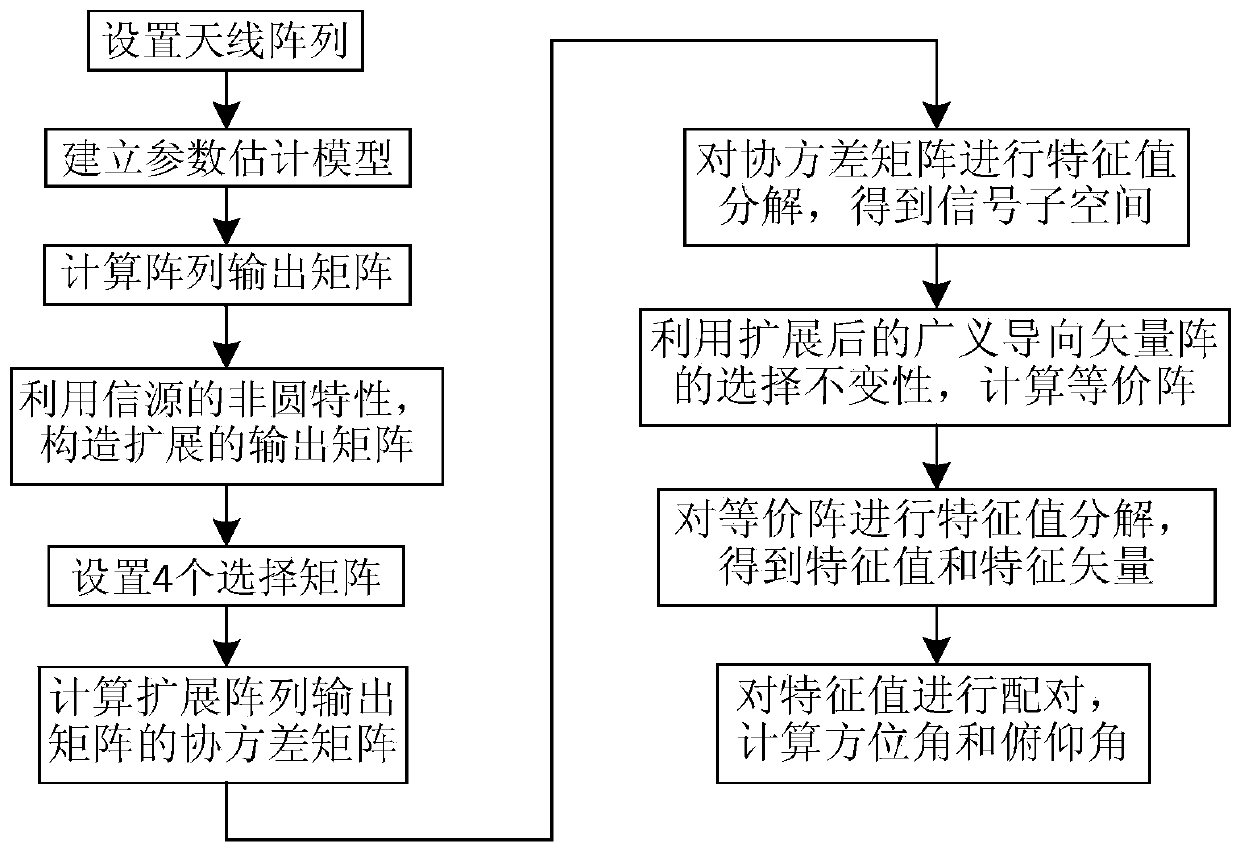
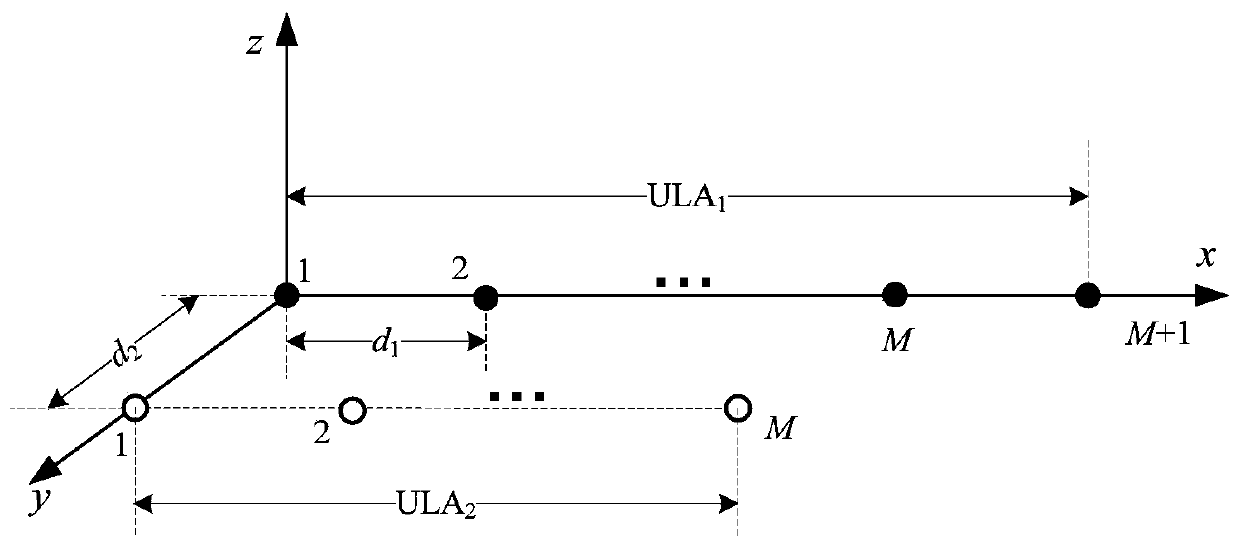
InactiveCN109782218AExtended output matrixImprove estimation performanceDirection findersComplex mathematical operationsDecompositionEstimation methods
The invention relates to a dual parallel antenna array-based coherent distributed non-circular signal DOA estimation method, which belongs to the field of array signal processing. The two-dimensionalDOA estimation method for coherent distributed non-circular signals comprises steps: an array output matrix is calculated by using two parallel uniform linear arrays; by using the non-circular characteristics of a source, an extended output matrix is constructed; four selection matrices are set, and an extended steering vector array has rotational invariance; the covariance matrix of an extended array output matrix is calculated; the covariance matrix is subjected to eigenvalue decomposition to obtain signal subspace; an equivalent matrix is calculated, the equivalent matrix is subjected to eigenvalue decomposition respectively, eigenvalues are paired, and estimation on an azimuth angle and a pitch angle are realized. By using the non-circular characteristic of the signal, the number of array elements is extended virtually, and the estimation performance is improved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
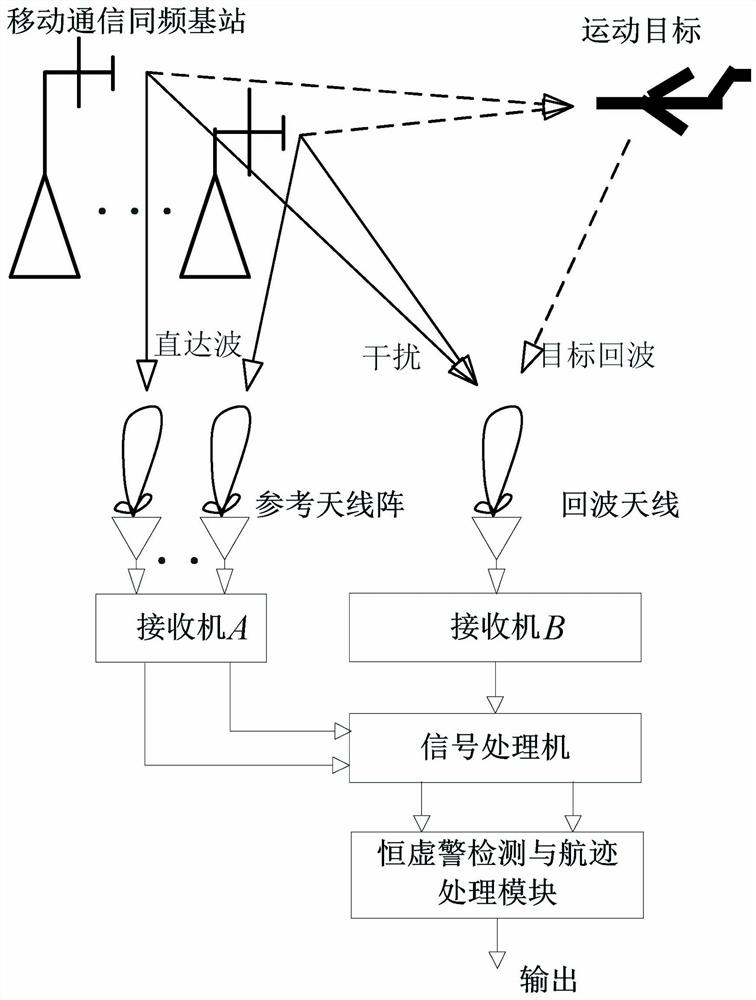
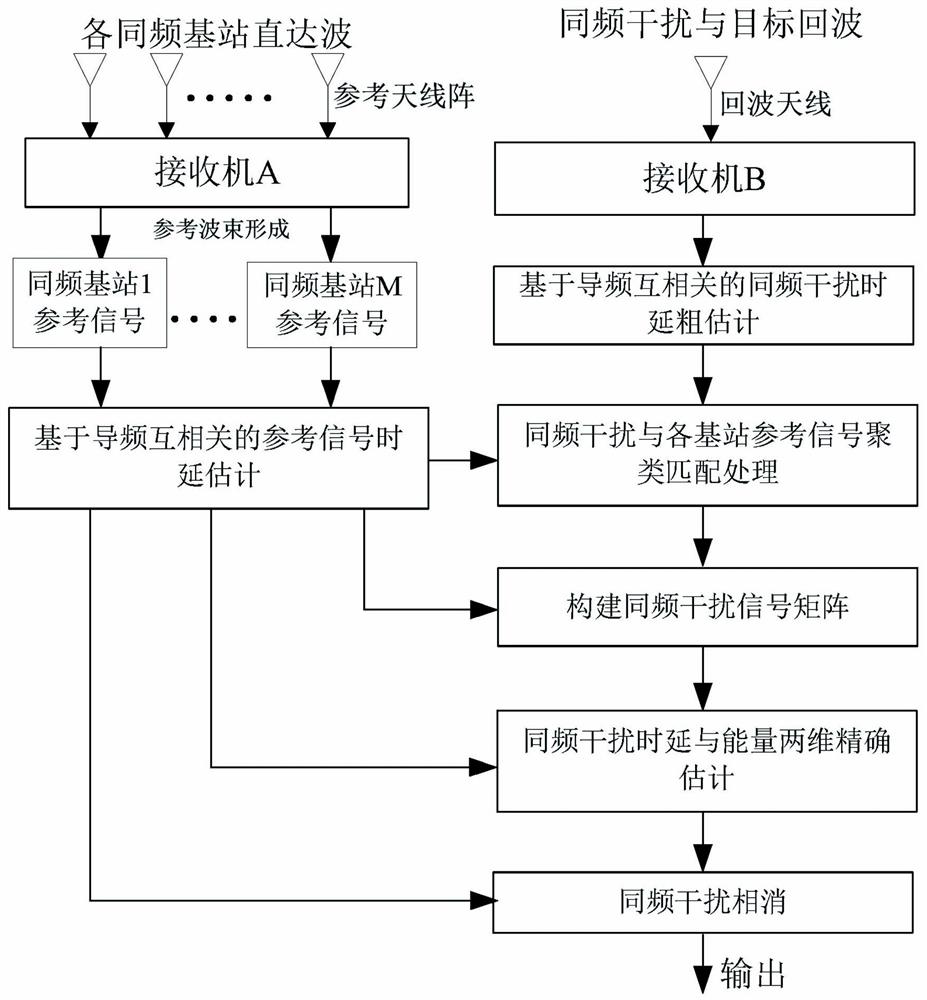
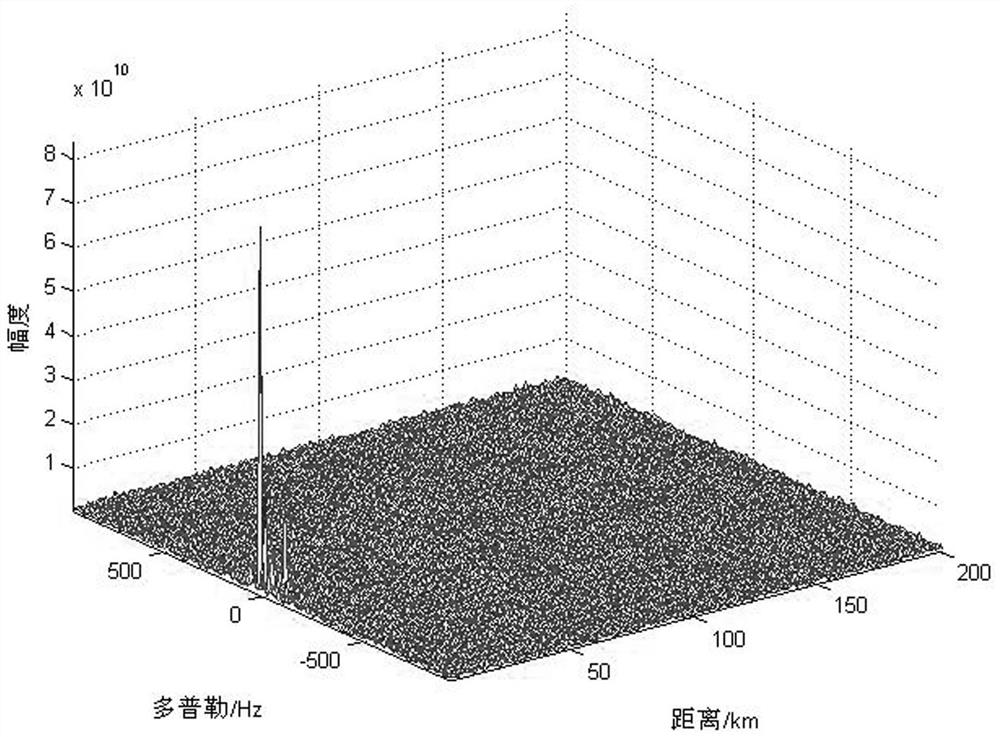
External radiation source radar same-frequency interference time delay and energy rapid estimation system and method
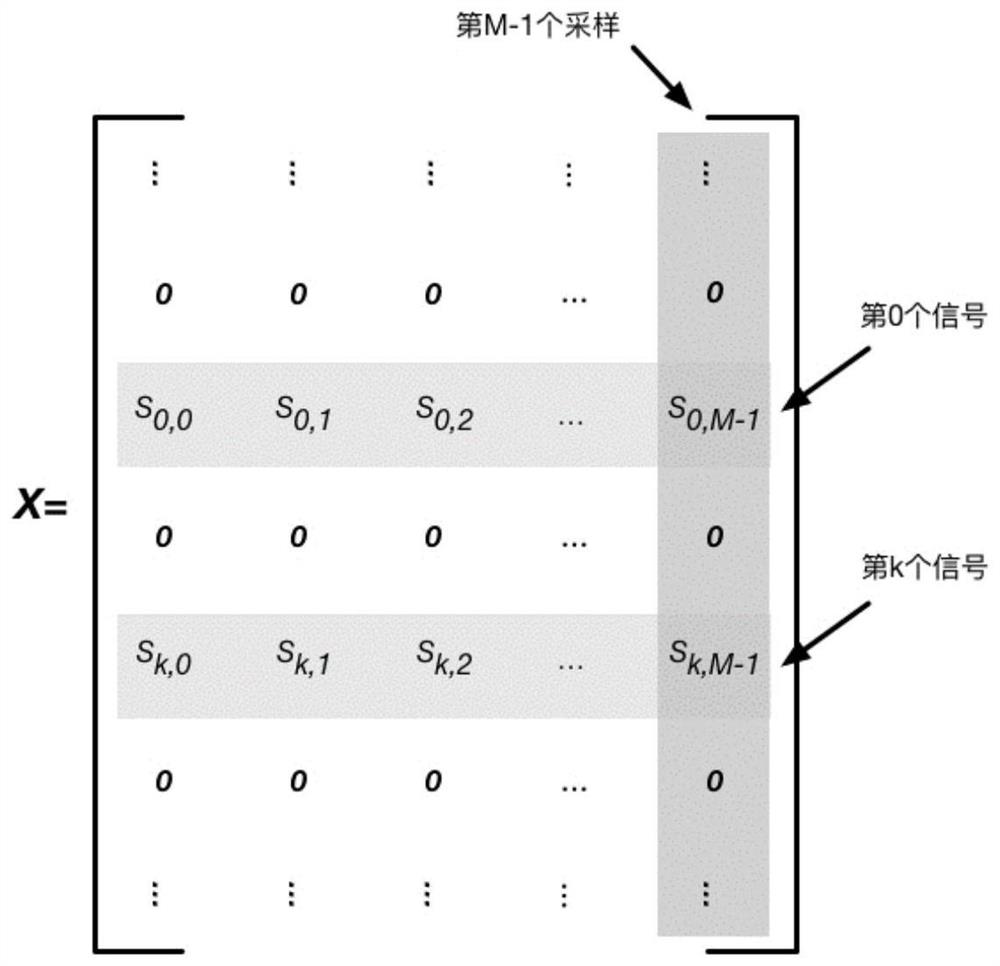
ActiveCN111650563ALow method complexityEasy to implementWave based measurement systemsICT adaptationInterference (communication)Reference antenna
The invention discloses an external radiation source radar same-frequency interference time delay and energy rapid estimation system and method. The method comprises the following steps that the reference antenna obtains reference signals directly reached by the same-frequency interference base stations through beam forming; the echo antenna receives echo signals containing same-frequency interference and target echoes; a pilot cross-correlation algorithm is usedto obtain coarse time delay parameters of reference signals and same-frequency interference signals, clustering matching processing is performed on the reference signals and the same-frequency interference of each base station, then a same-frequency interference signal matrix is constructed, and a subspace projection method is utilized to obtain two-dimensional accurate estimation of same-frequency interference time delay and energy. The method can achieve the precise estimation of the same-frequency interference time delay andenergy from different radiation sources under the condition of the same-frequency interference of a plurality of radiation sources of the mobile communication external radiation source radar, and further achieves effective inhibition. The invention also discloses an external radiation source radar same-frequency interference time delay and energy rapid estimation system. The system is low in costand convenient in networking.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Dual-station time difference frequency difference joint positioning method for fixed radiation source
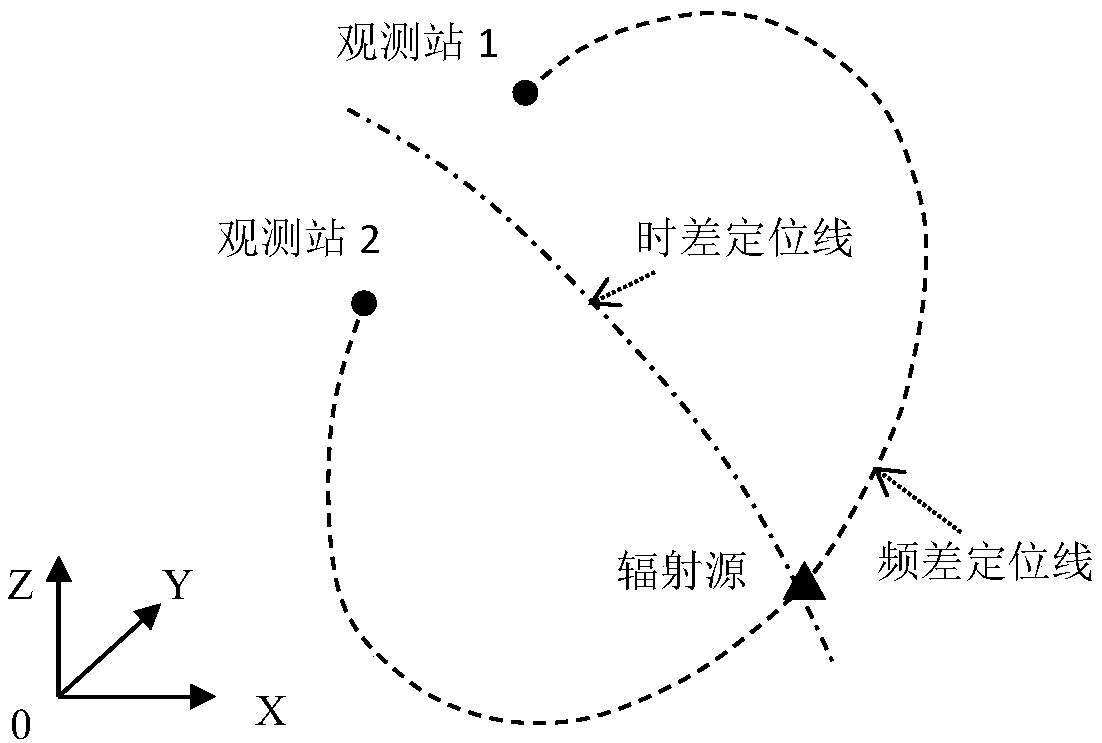
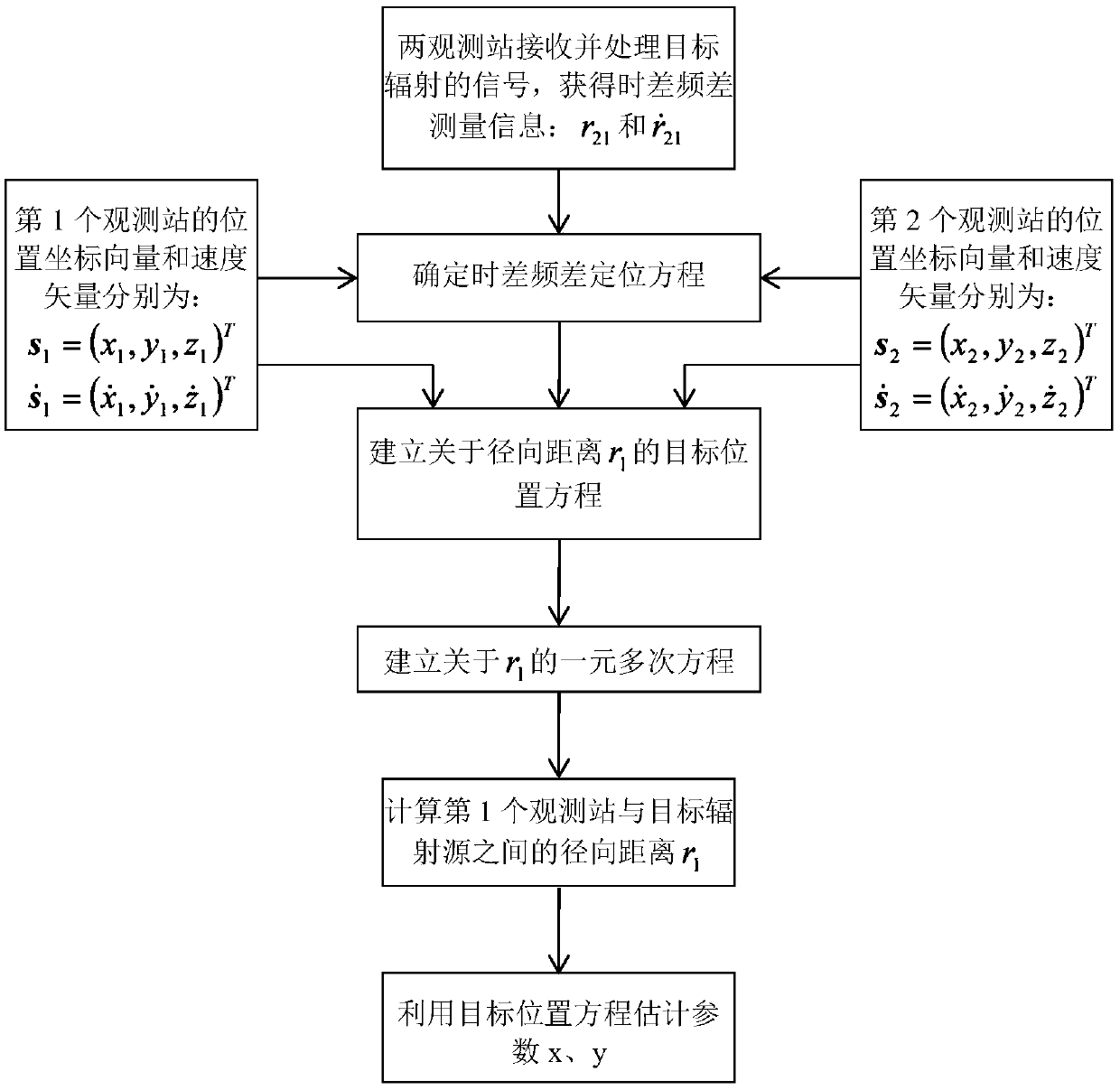
InactiveCN108761387AAchieving High-Precision EstimationEffective strikePosition fixationNonlinear systems of equationsClassical mechanics
A dual-station time difference frequency difference joint positioning method for a fixed radiation source includes the following steps: two observation stations receive electromagnetic wave signals emitted by a target radiation source to obtain time difference frequency difference measurement information; time difference frequency difference positioning equations as described in the specificationare determined; target position equations as described in the specification are established; a radial distance equation: k6r16+k5r15+k4r14+k3r13+k2r12+k1r1+k0=0 is established; the radial distance equation is solved to obtain the radial distance between the first observing station and the target radiation source; and according to the radial distance r1 between the first observation station and thetarget radiation source, the target position equation is used to calculate the target position parameter, and the positioning of the target radiation source is completed. The invention adopts the time difference frequency difference joint positioning method and converts the nonlinear equations into linear equations by using the radial distance, the calculation is simple, the positioning speed isfast, and the high-precision estimation of the fixed radiation source position of a given plane can be realized.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Interference cancellation interleaving OFDMA uplink CFO estimation method
InactiveCN110247873AReduce complexityEliminate distractionsSynchronisation arrangementMulti-frequency code systemsMulti user interferenceCarrier signal
The invention relates to an interleaved OFDMA uplink carrier frequency deviation CFO estimation method for iterative multi-user interference cancellation. The CFO of the OFDMA can damage the orthogonality between subcarriers, serious inter-carrier interference ICI is generated, and multiple access interference MAI can also be brought. In the scheme of the invention, the method comprises the following steps: the base station sorts the users according to the received signal intensities; the base station estimates from the user with the strongest receiving power to the user with the lowest power; feedback signals of the estimated users with the higher receiving power and feedback signals of the weak users estimated in the last iteration are all subtracted from the receiving signals, interference of frequency deviation of other users on pilot frequency point signals of the users is eliminated and then multiplied by a phase compensation factor, and the CFO of the current user is obtained by maximizing the power of the pilot frequency point. And the next iteration is entered until the CFO of the user with the weakest receiving power is estimated. The estimation method has the advantages that the estimation precision is high, the convergence speed is high, a small number of pilots are inserted into data sent by a user, and a large number of frequency bands do not need to be occupied.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
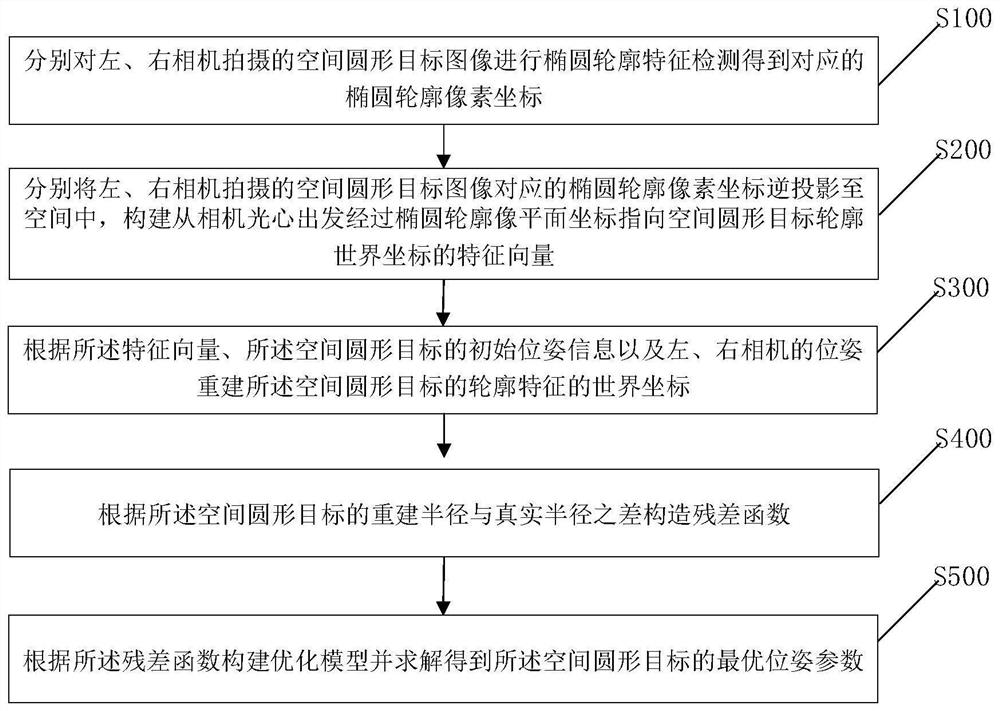
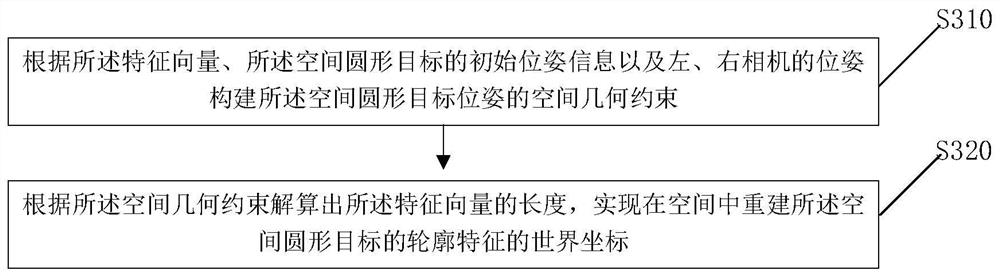
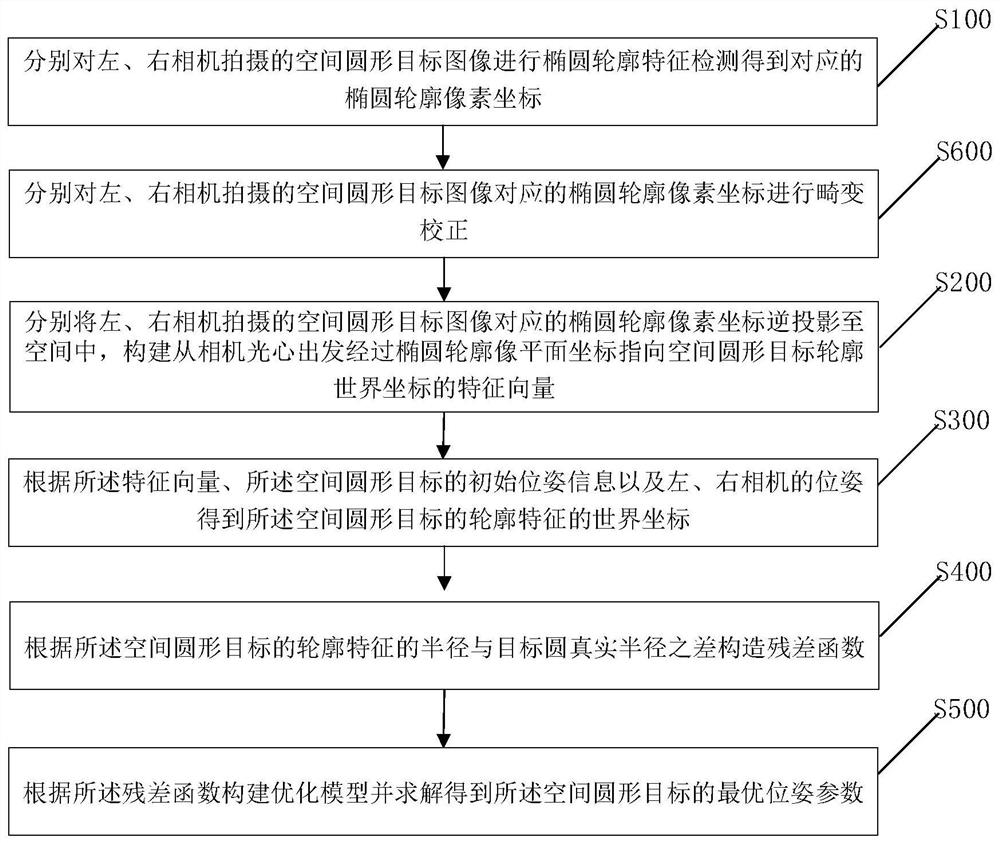
Circular target pose measurement method and device based on binocular inverse projection transformation
ActiveCN113052905AAchieving High-Precision EstimationImage analysisUsing optical meansPhysicsNuclear medicine
The invention provides a circular target pose measurement method and device based on binocular inverse projection transformation. The method comprises the following steps: respectively carrying out elliptic contour feature detection on spatial circular target images shot by a left camera and a right camera to obtain corresponding elliptic contour pixel coordinates; inversely projecting the elliptic contour pixel coordinates corresponding to spatial circular target images shot by the left camera and the right camera into the space, and constructing a feature vector which starts from the optical center of the camera, passes through elliptic contour image plane coordinates and points to contour world coordinates of the spatial circular target ; according to the feature vectors, the initial pose information of the spatial circular target and the poses of the left camera and the right camera, acquiring world coordinates of the contour features of the reconstructed spatial circular target; constructing a residual function according to the difference between the radius of the reconstructed spatial circular target contour and the real radius of the circular target; and constructing an optimization model according to the residual function, and solving to obtain an optimal pose parameter of the space circular target, thereby realizing high-precision estimation of the pose of the long-distance small-size space circular target.
Owner:中国人民解放军63920部队
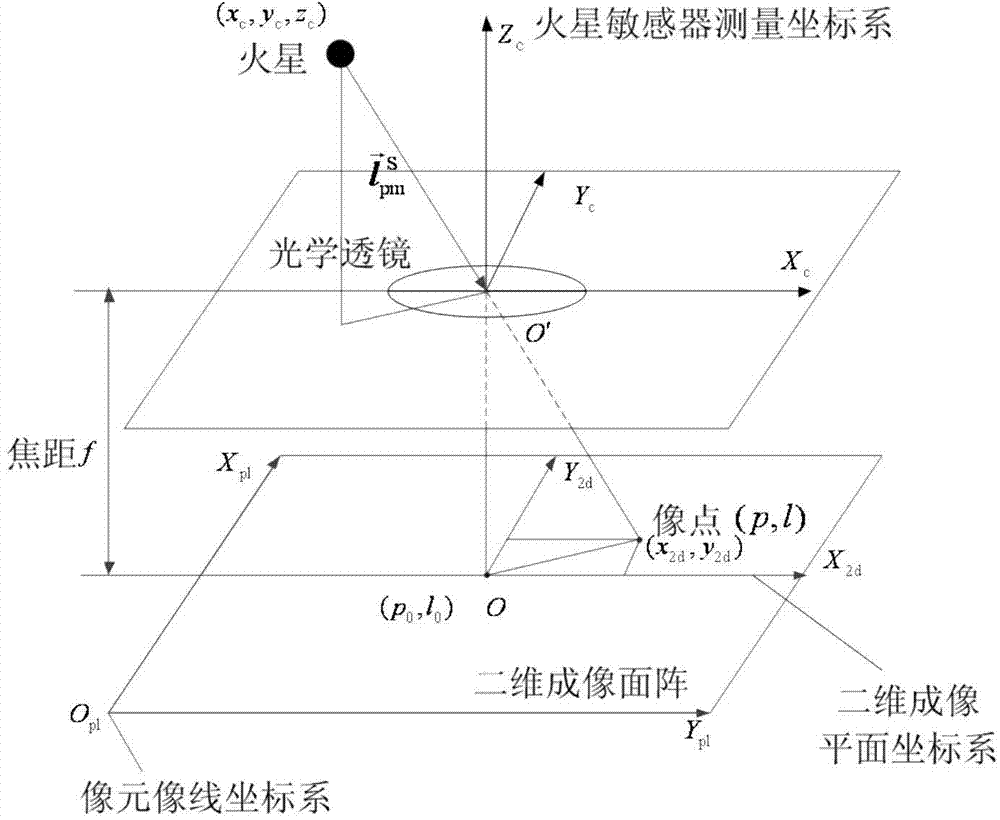
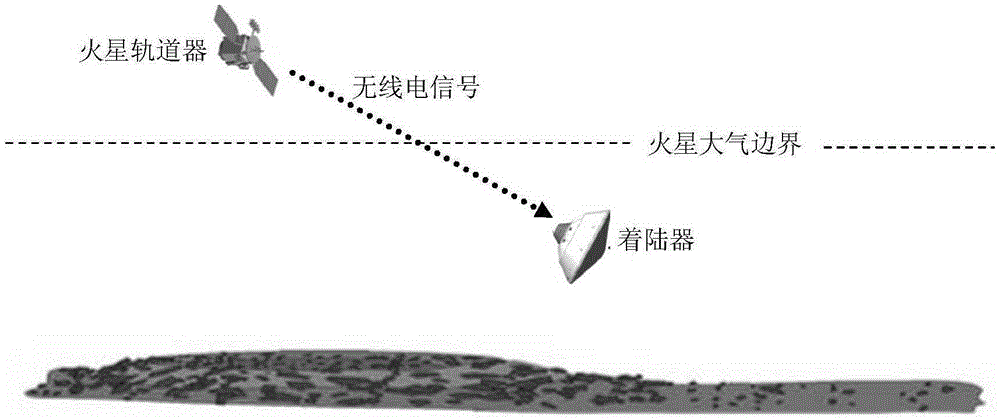
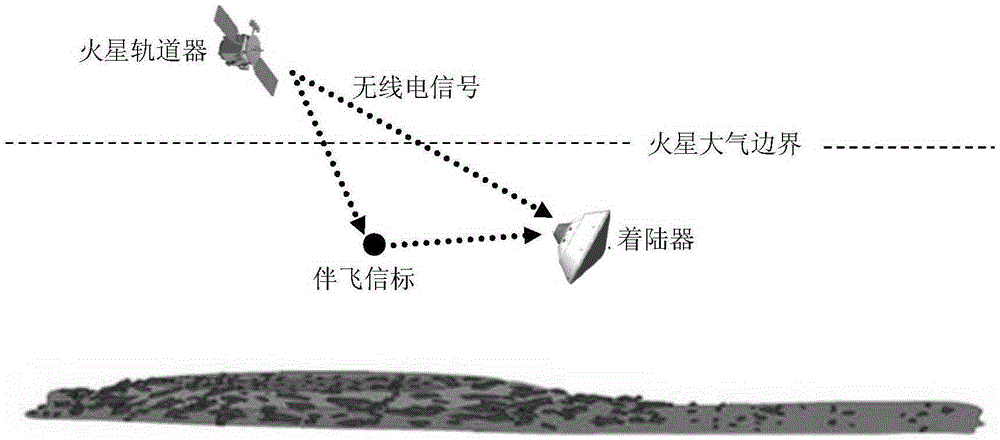
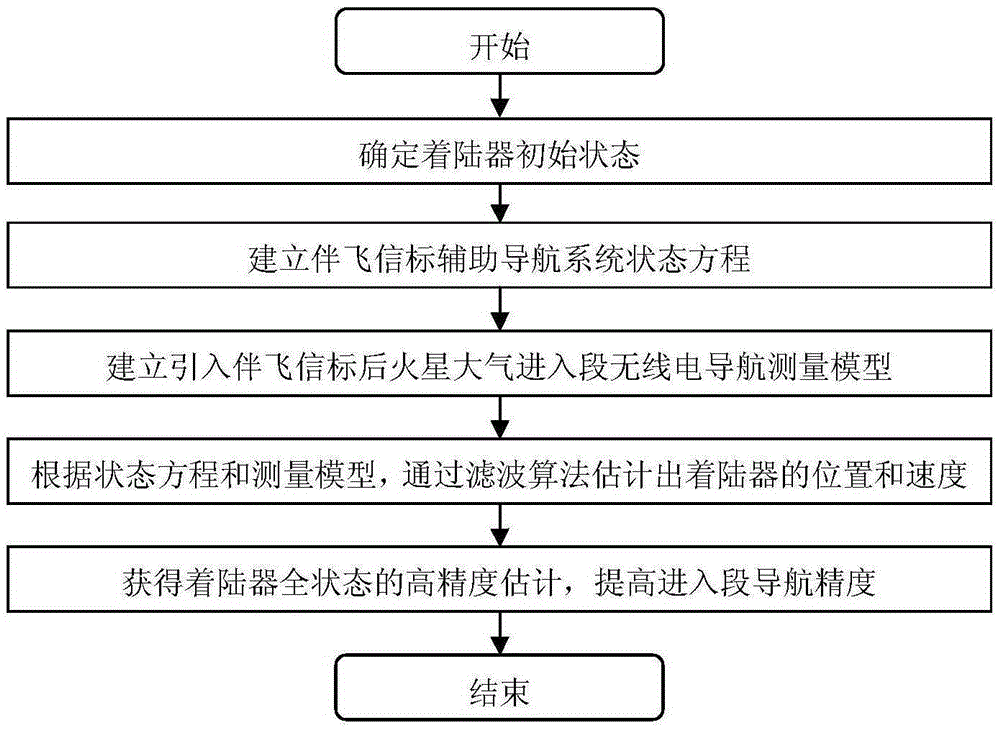
Mars atmosphere entry section accompanying flight beacon auxiliary navigation method
InactiveCN105203112AOptimize geometryAchieving High-Precision EstimationInstruments for comonautical navigationDeep space explorationSpeed measurement
The invention discloses a Mars atmosphere entry section accompanying flight beacon auxiliary navigation method, relates to a beacon auxiliary navigation method, and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. According to the method, on the basis of the Mars atmosphere entry section inertial navigation, an accompanying flight beacon is introduced; by adding the radio distance measurement and speed measurement among a landing device, a rail device and the accompanying flight beacon as a measuring quantity, an initial state deviation is corrected; a geometrical configuration during the radio navigation of the landing device and the rail device is improved; the entry section navigation precision is further improved. The Mars atmosphere entry section accompanying flight beacon auxiliary navigation method disclosed by the invention can solve the problems of the inertial navigation that the initial state deviation cannot be corrected during inertial navigation, and the measurement errors are accumulated along with time. The geometrical configuration of the radio navigation can be improved; the high-precision estimation of a full state of the landing device is obtained; the entry section navigation precision is further improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
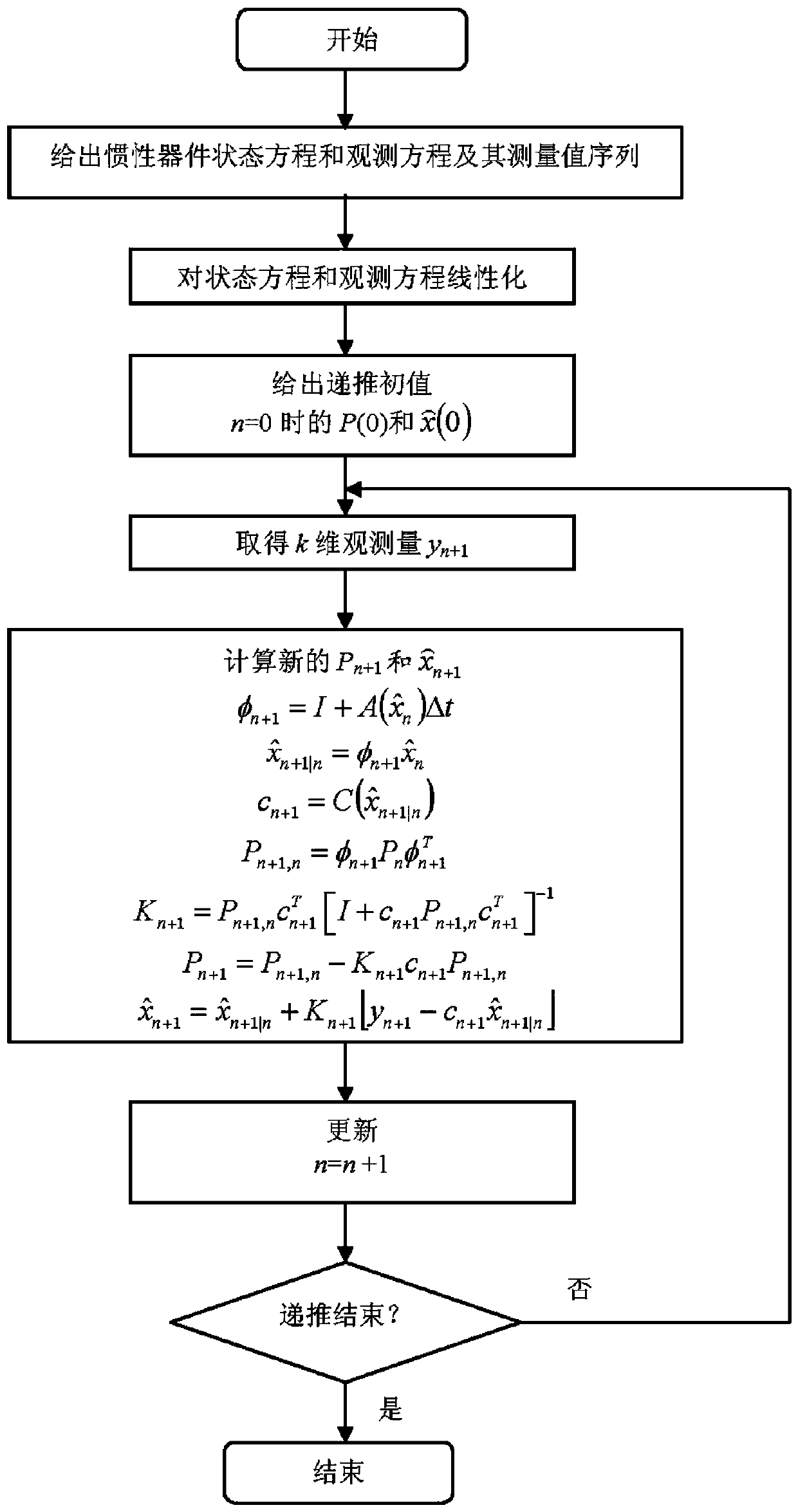
Method for determining error coefficient of inertial device
ActiveCN110186479AOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to handle nonlinear equationsWide applicabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterError coefficient
The invention relates to a method for determining an error coefficient of an inertial device, in order to overcome the deficiency that the estimated value of the existing kalman filter is not unique by performing linear processing on a nonlinear state equation and a nonlinear observation equation and by calculating the error coefficient of the inertial device by using an extended recursive least square method. The method can adapt to the situation when the state equation and the observation equation are nonlinear functions, and can also meet the situation when the state equation and the observation equation are linear functions. The method can be used for realizing real-time calculation, is easy to implement and has a value of engineering practical application.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
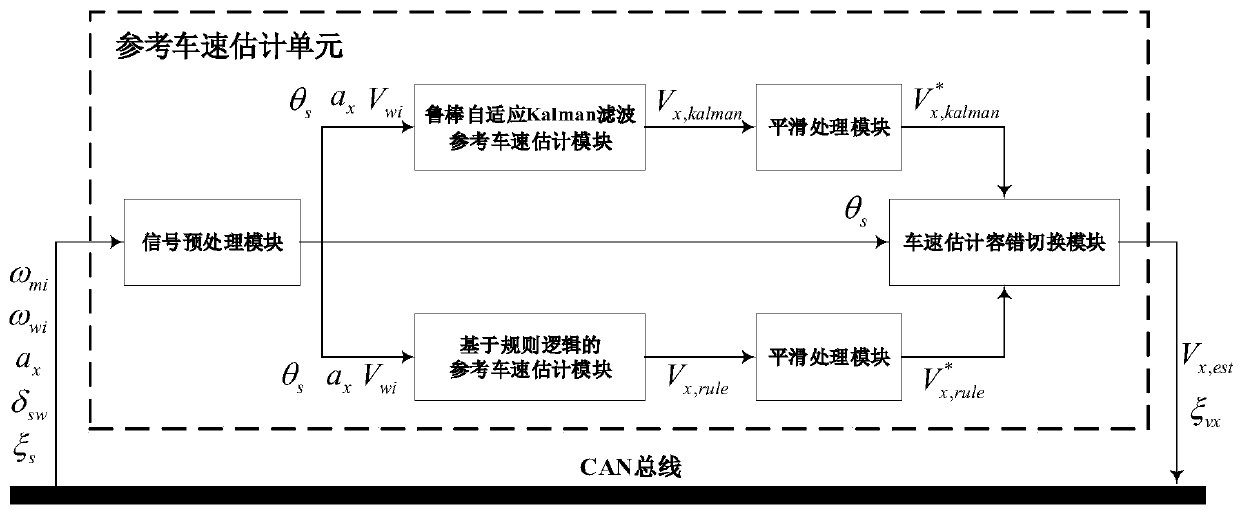
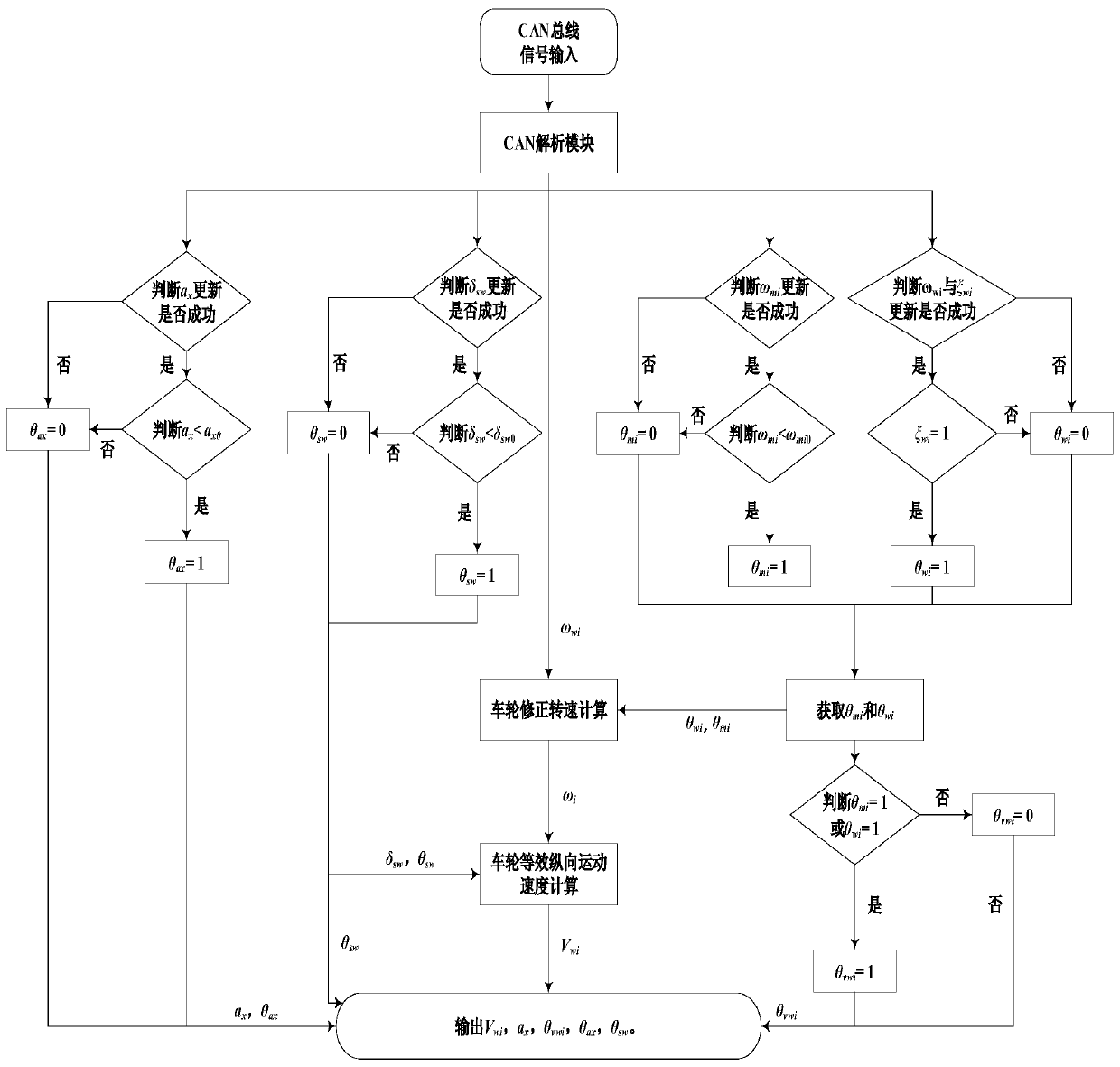
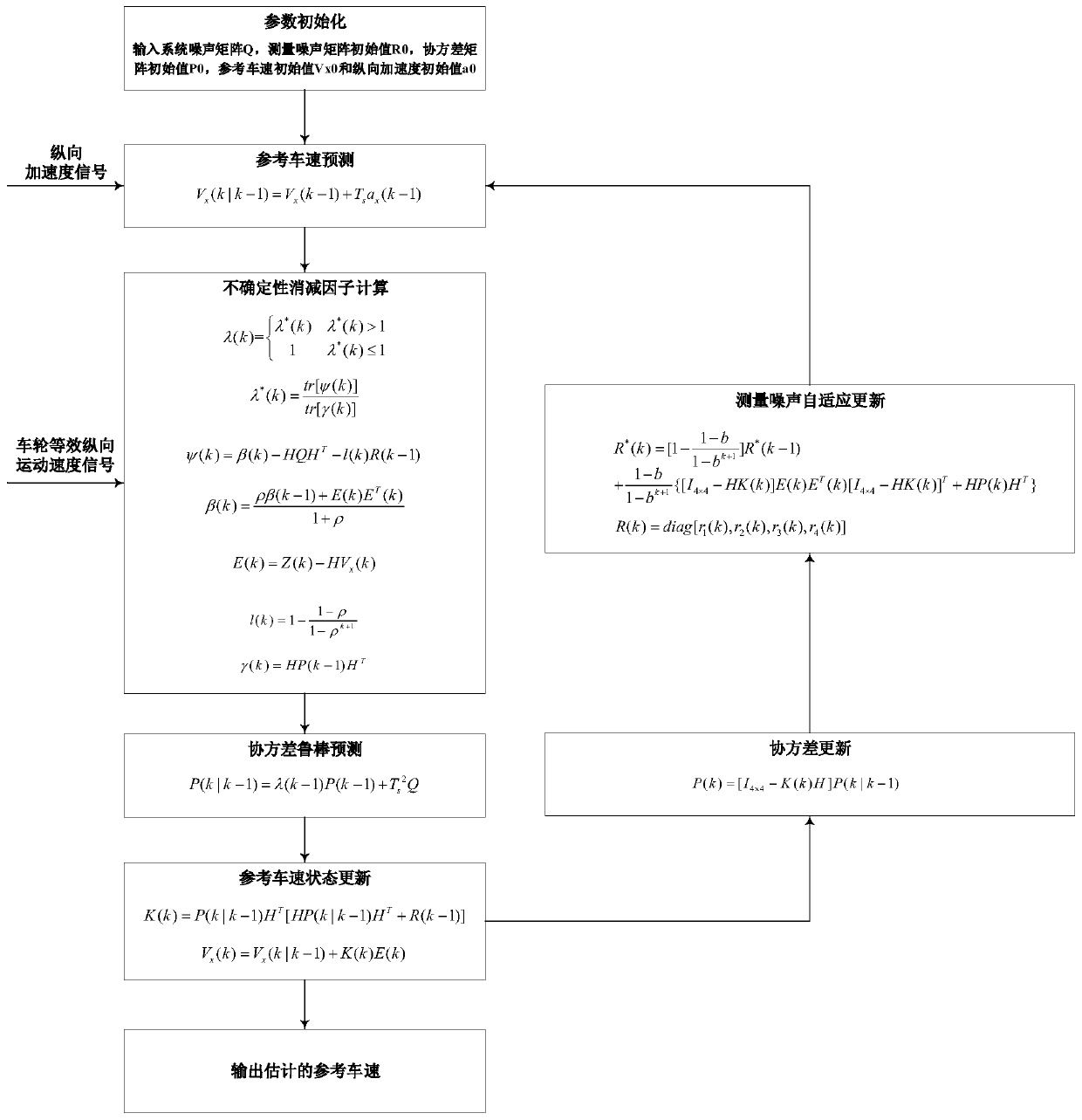
Four-wheel independent drive electric vehicle reference vehicle speed fault-tolerant adaptive estimation method
ActiveCN111062088AAchieving High-Precision EstimationNo additional costGeometric CADElectric energy managementControl engineeringAutomotive control systems
The invention relates to a four-wheel independent drive electric vehicle reference vehicle speed fault-tolerant adaptive estimation method. A robust adaptive Kalman filtering reference vehicle speed estimation module and a reference vehicle speed estimation module based on rule logic are selected for estimation, wherein the reference vehicle speed estimation module based on the rule logic is usedas a backup of the robust adaptive Kalman filtering reference vehicle speed estimation module, and when Kalman filtering diverges, Kalman filtering can be replaced by a method based on the rule logicto be output; the method is small in dependence on preset parameters, high in estimation precision, good in working condition adaptability and high in fault-tolerant capability, vehicle speed estimation under various complex working conditions such as wheel locking, slipping, ramp driving and steering driving can be achieved, the function safety requirement of automobile control system software design is met, and reliability is effectively guaranteed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
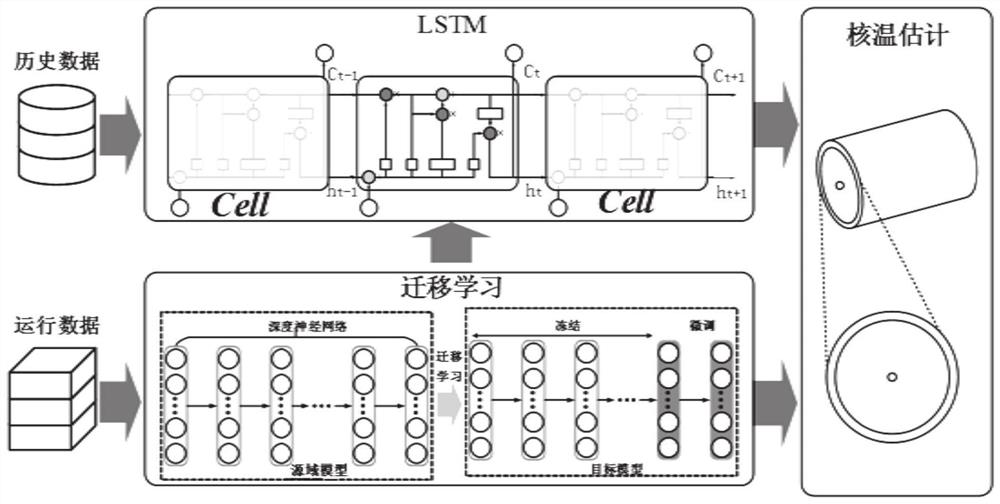
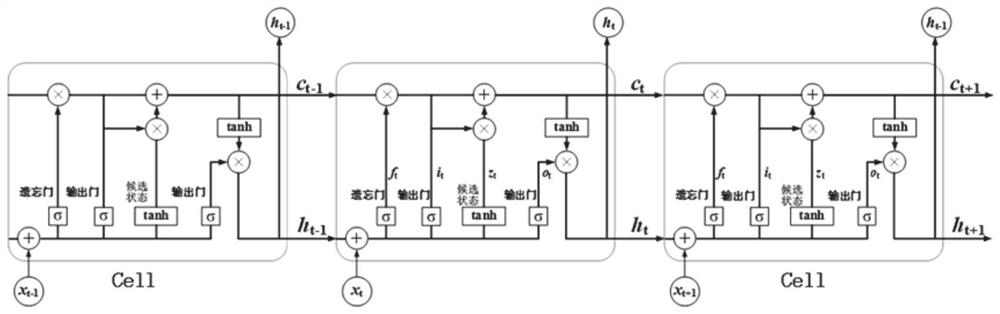
Lithium battery nuclear temperature evaluation method and system based on transfer learning
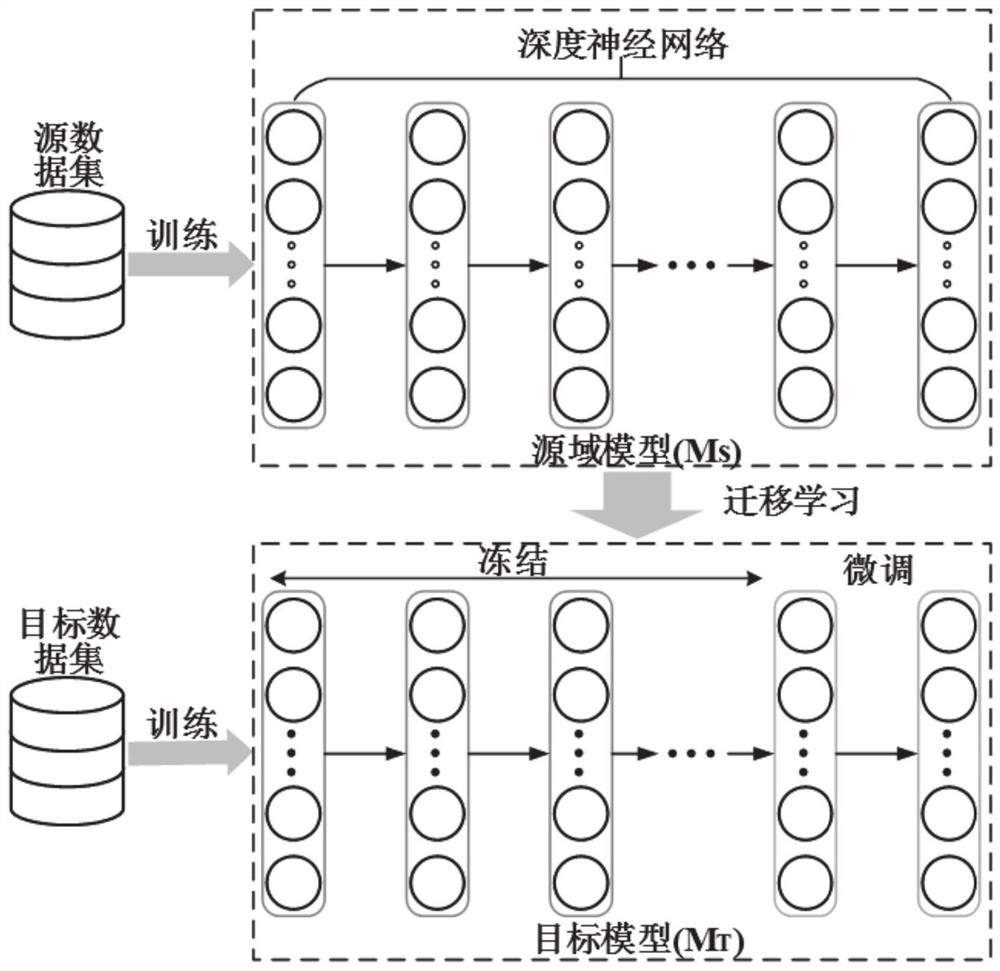
PendingCN113962154ASpeed up training progressImprove training efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesDomain modelSimulation
The invention provides a lithium battery nuclear temperature evaluation method and system based on transfer learning. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring target domain lithium battery parameter data; obtaining a lithium battery nuclear temperature evaluation result according to the obtained lithium battery parameter data and a target domain neural network model, wherein the target domain neural network is obtained by training according to historical data of a source domain lithium battery to obtain a source domain neural network model, and retraining a full connection layer of the source domain neural network model according to target domain data. According to the invention, transfer learning is adopted, and the established source domain model is transferred to the target domain lithium battery, and the nuclear temperature of other lithium batteries in the target domain can be accurately estimated with only a small amount of information of the target domain being used as training data, so that the model training progress is accelerated, and the training efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Rice planting distribution extraction method based on wind cloud satellite data
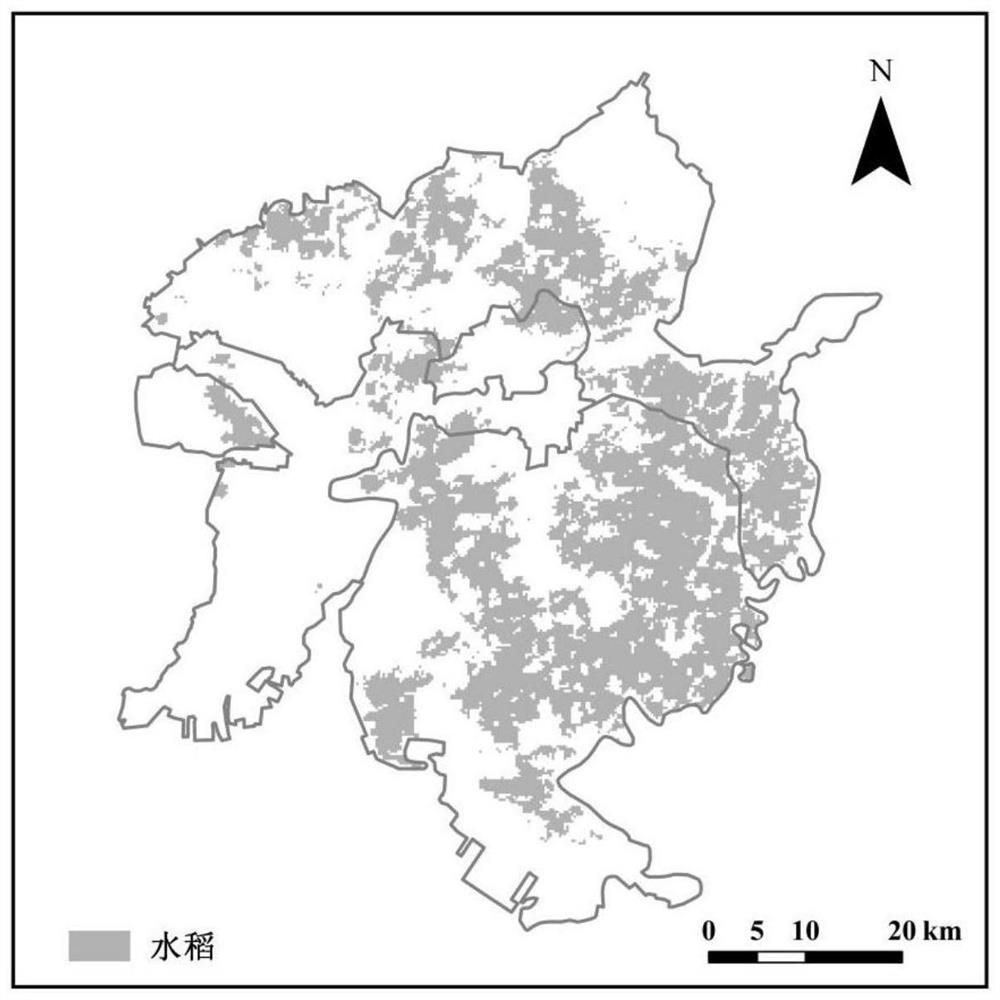
InactiveCN113723319AMake up for technical gapsAchieving High-Precision EstimationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSatellite dataSoil science
The invention discloses a rice planting distribution extraction method based on wind cloud satellite data. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring remote sensing indexes of rice in different phenological periods in a research area based on wind cloud satellite image data, wherein the remote sensing indexes comprise a normalized water body index, a normalized vegetation index, a ratio vegetation index and a difference value between the normalized water body index and the normalized vegetation index; according to a threshold value of a difference value between the normalized water body index and the normalized vegetation index, extracting a rice potential planting distribution area; performing pixel elimination on the wind cloud satellite image data of the potential rice planting distribution area according to thresholds of the normalized water body index, the normalized vegetation index and the ratio vegetation index of the rice in different phenological periods in the research area to obtain an actual rice planting distribution map in the research area; and obtaining the rice planting area of the research region based on the actual rice planting distribution diagram of the research region. The technical blank of rice planting distribution information extraction based on wind cloud satellite data is filled, and high-precision extraction of rice planting distribution is realized.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF METEOROLOGICAL SCI
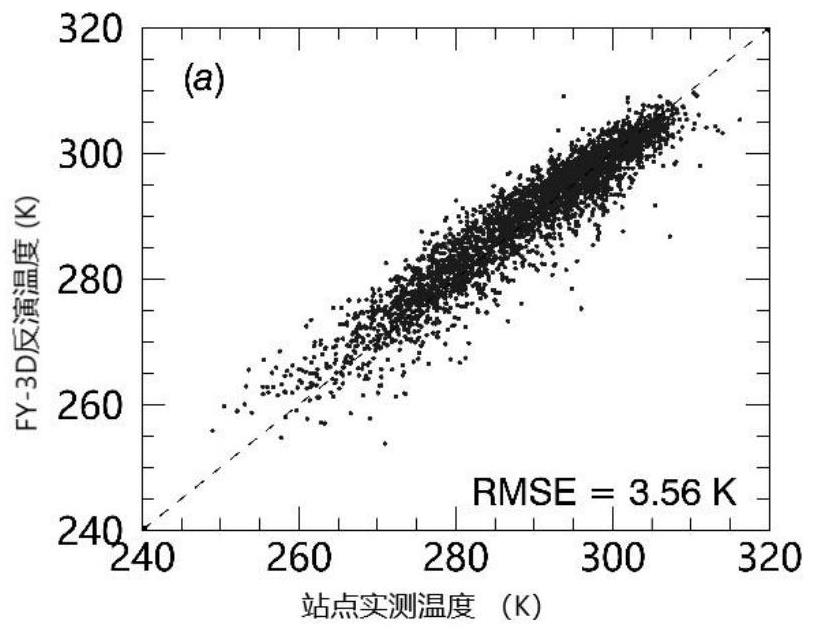
FY-3D passive microwave data under-cloud surface temperature inversion and verification method
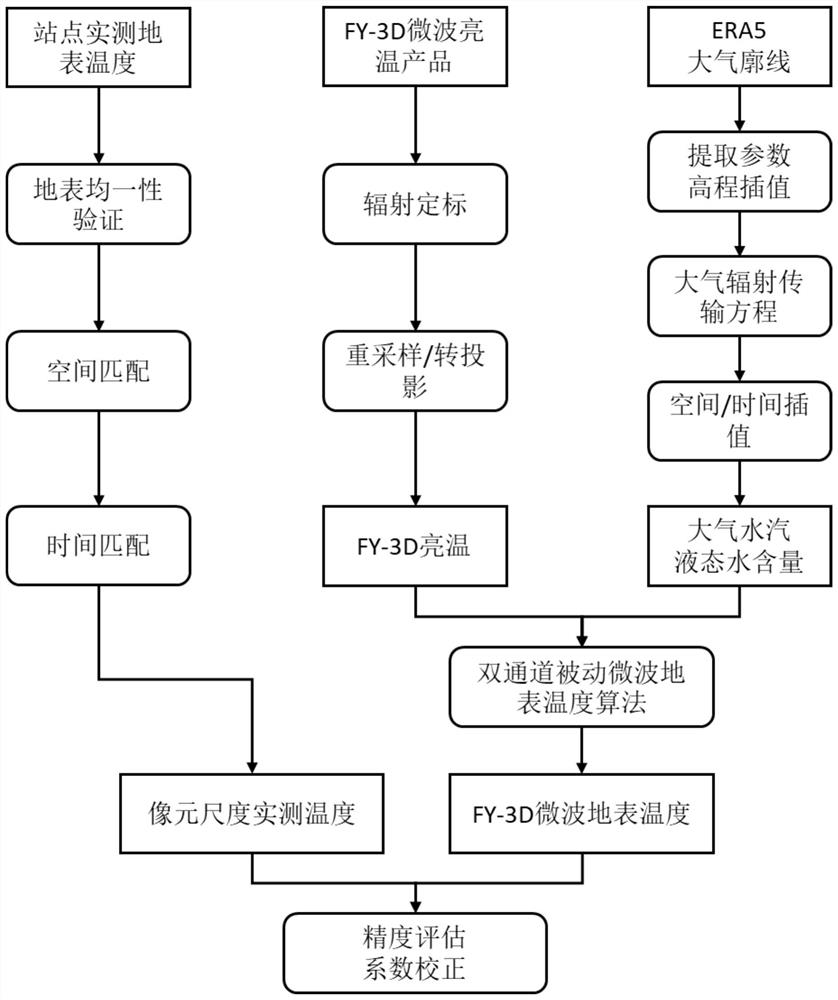
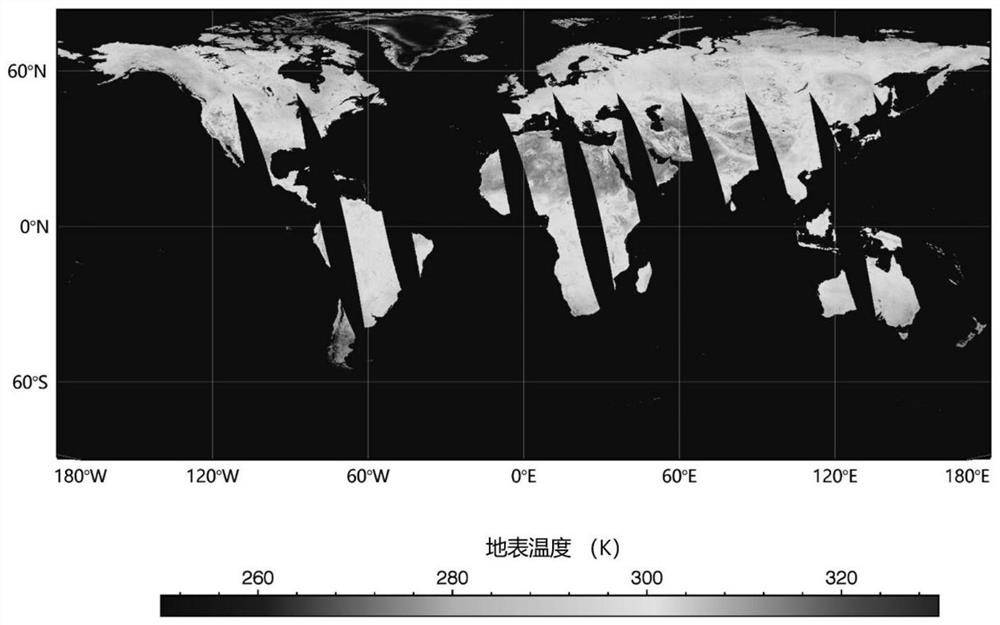
PendingCN114722350AAchieving High-Precision EstimationRealize accuracy comparison verificationRadiation pyrometryComplex mathematical operationsBrightness temperaturePerpendicular polarization
The invention provides an FY-3D passive microwave data under-cloud surface temperature inversion and verification method, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining FY-3D passive microwave data, carrying out the data preprocessing, and extracting the dual-channel brightness temperature of 18.7 GHz and 23.8 GHz vertical polarization channels; eRA5 atmosphere profile data are obtained, and data processing is carried out to extract the content of atmosphere water vapor and liquid water; based on the dual-channel brightness temperature of the 18.7 GHz and 23.8 GHz vertical polarization channels, combining the corresponding atmospheric water vapor and liquid water content data, and adopting a dual-channel physical algorithm to estimate the surface temperature under the clouded condition; and verifying and correcting the estimated surface temperature by using the surface temperature data under the cloud measured by the site. According to the method, the influence of the atmospheric water vapor and the liquid water content in the cloud on passive microwave radiation is quantified, the estimation precision of the under-cloud surface temperature is improved, and the precision comparison verification of the under-cloud surface temperature of the ground point data and the FY-3D passive microwave data is realized.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
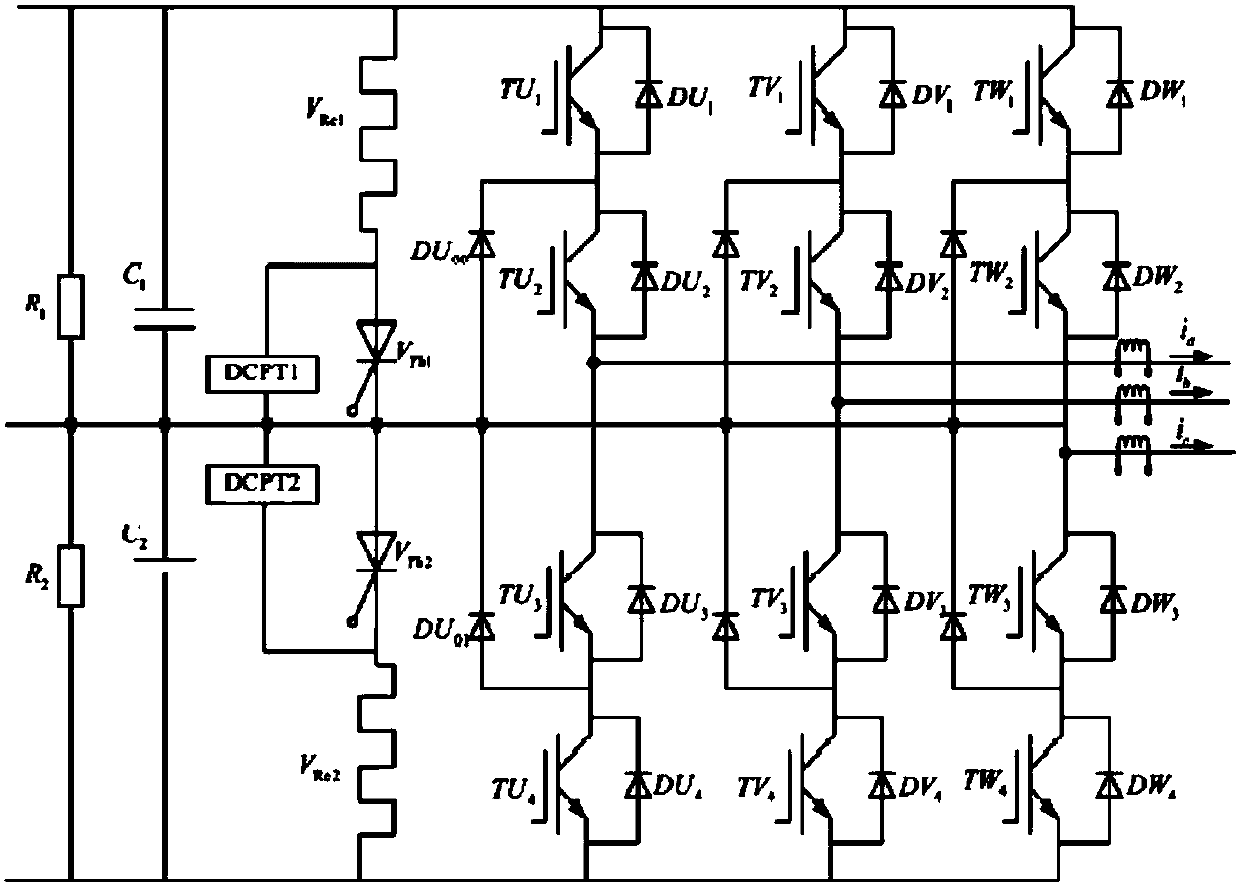
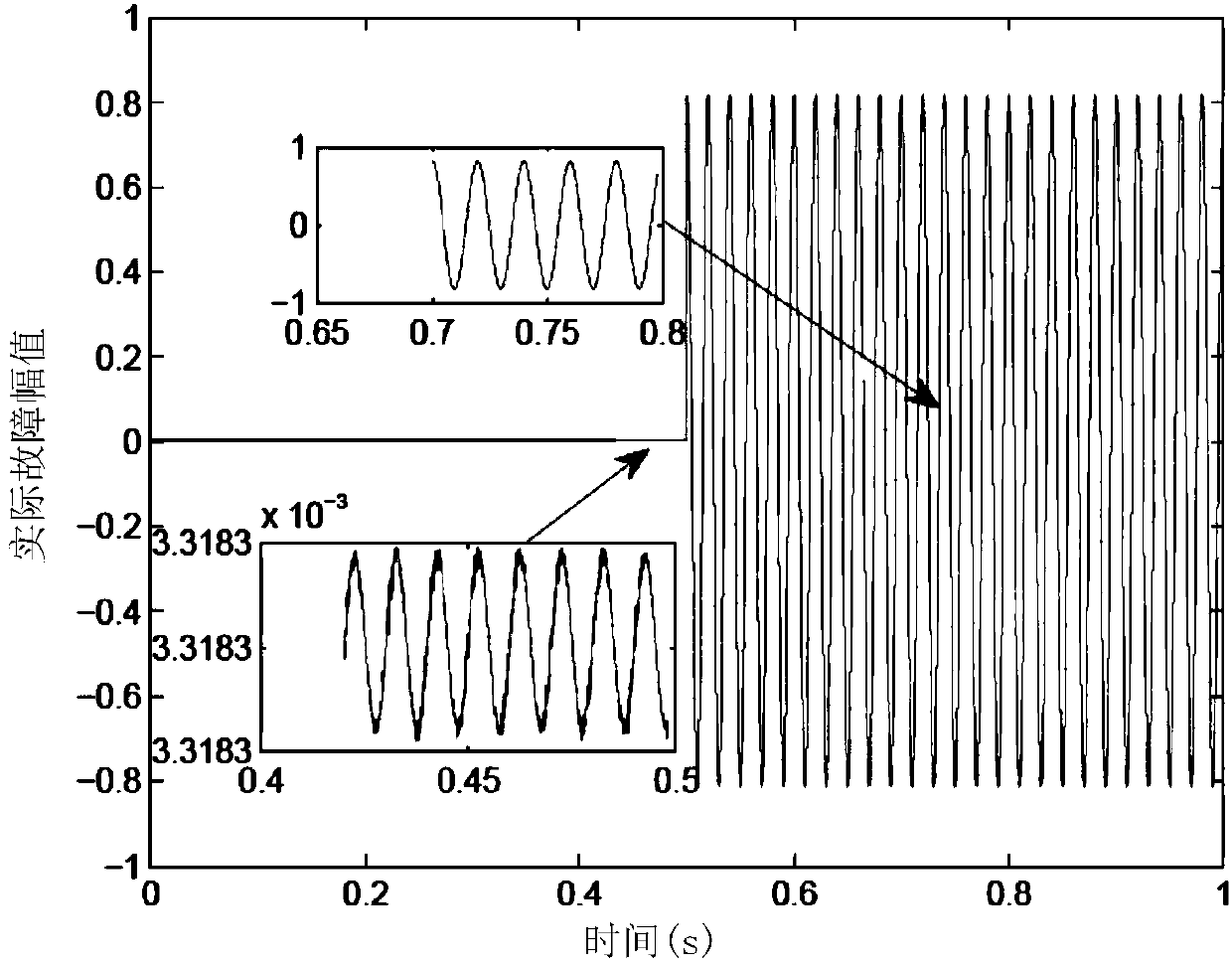
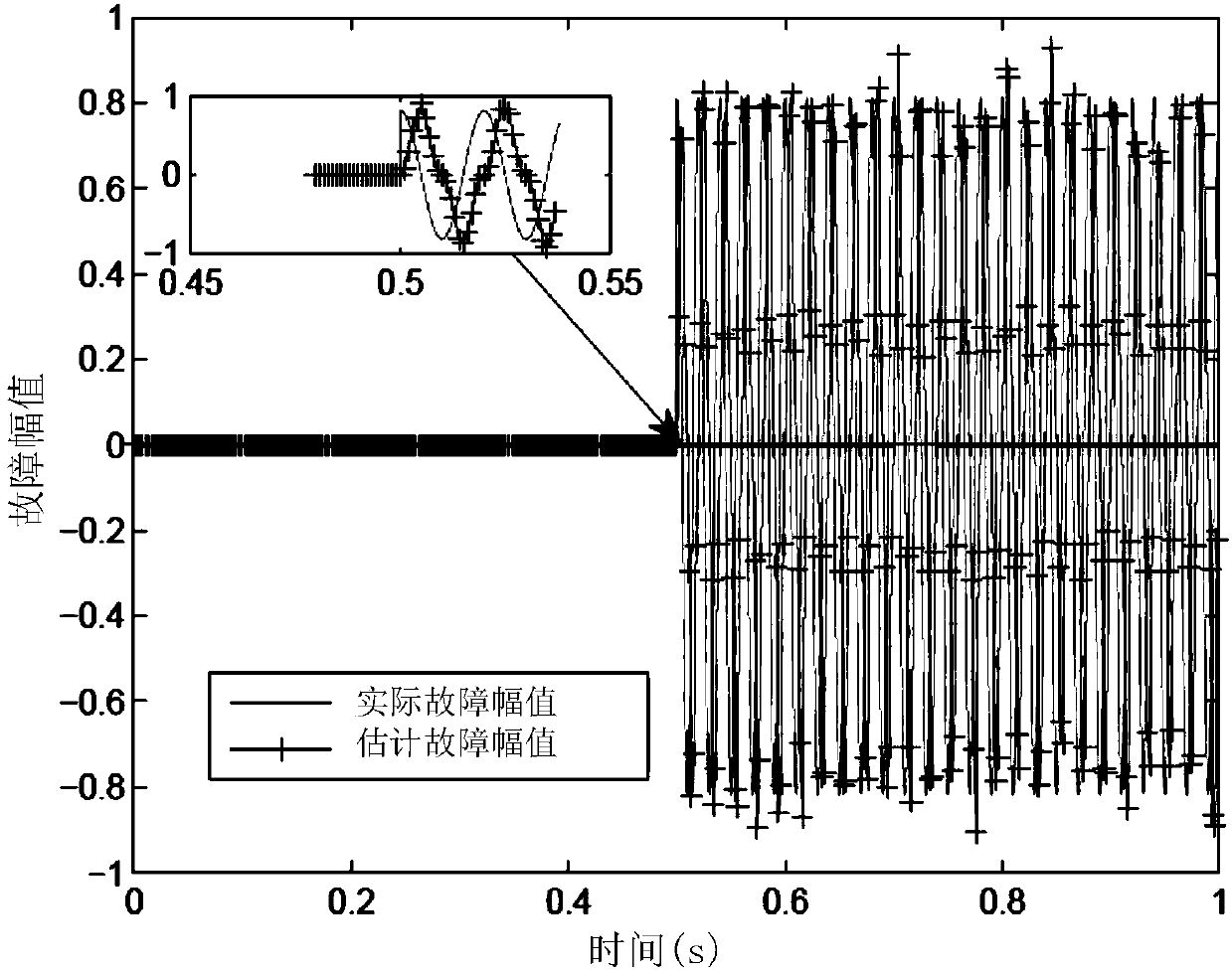
Design method of tiny fault estimation system used for CRH2 high-speed railway inverter
InactiveCN108595783AHigh sensitivityMovableGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationData modelHigh speed train
The invention discloses a design method of a tiny fault estimation system used for a CRH2 high-speed railway inverter, and belongs to the field of fault diagnosis and fault estimation. The method specifically comprises the following steps of in a first stage, building an offline data model: 1) collecting steady state running data of a high-speed train and preprocessing offline data; 2) calculatinga score matrix of a rotation subspace where the preprocessed data is located; and 3) determining a nonlinear relationship between a fault estimation value and a fault magnitude, thereby performing online estimation; and in a second stage, performing online fault estimation: 4) processing online data; 5) calculating online score vectors; and 6) estimating the existent fault magnitude by utilizinga fault estimator. The invention designs a multivariate statistical analysis-based estimation method. The method combines Kullback Leibler divergence and a neural network approximation method, can realize relatively accurate fault estimation, and has a certain advantage in sensitivity to tiny fault estimation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
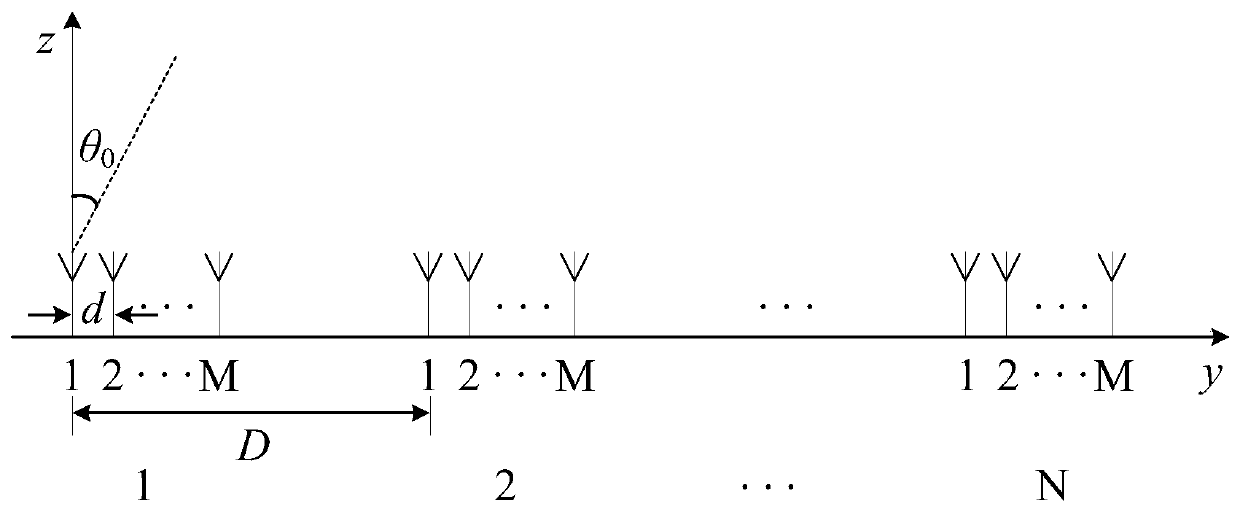
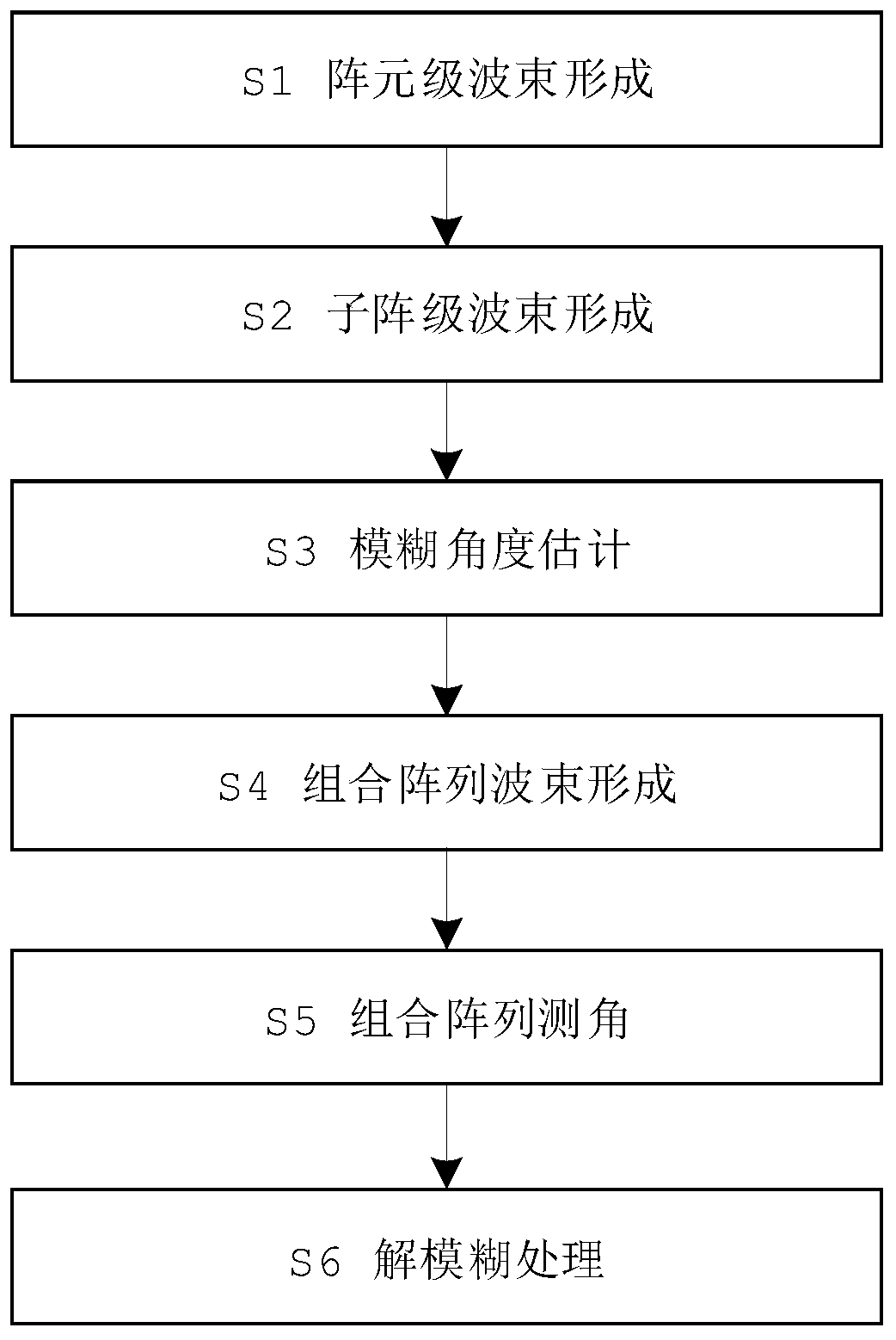
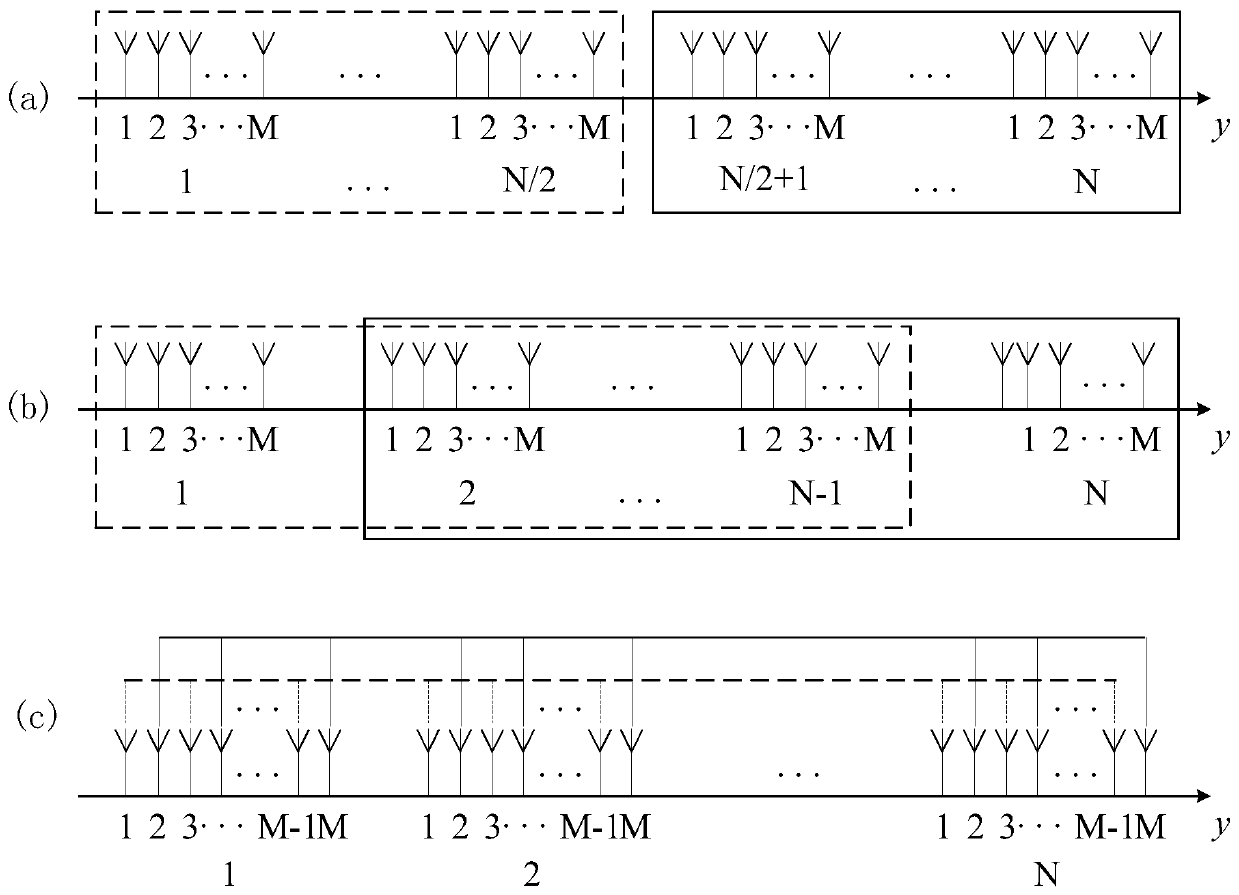
Distributed coherent radar angle measurement method
ActiveCN110988835AAchieving High-Precision EstimationUnambiguous angle measurementWave based measurement systemsGrating lobeEngineering
Owner:THE 724TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
An autonomous celestial navigation method for deep space probes in the capture segment based on ephemeris correction
ActiveCN104764449BLittle impact on accuracyAchieving High-Precision EstimationNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by astronomical meansDynamic modelsAngular distance
The invention discloses an ephemeris correction-based autonomous celestial navigation method for a deep space probe in a capturing stage. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing an ephemeris error state model and an ephemeris error measurement model of a target celestial body, and measuring ephemeris error according to a position difference between a predicted celestial body image and an actual celestial body image; secondly, simultaneously taking the ephemeris error state model and an orbital dynamic model as a celestial navigation system state model, taking the ephemeris error measurement model and a starlight angular distance measurement model as measurement models of a celestial navigation system, estimating the position and speed of the probe and the ephemeris error of the target celestial body by a Unscented Kalman filtering method, feeding back the estimated ephemeris error to the state model, and correcting the ephemeris data of the target celestial body, thereby obtaining the position and speed of the probe, relative to the target celestial body and the heliocenter, after autonomously correcting the ephemeris error. The method provided by the invention belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation, can perform on-line estimation on ephemeris error of celestial bodies and correct model error of the navigation system, and is suitable for the probe capturing stage.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Estimation method of pedestrian height and position in multi-storey building based on mems sensor
ActiveCN109827568BAccurate and reliable vertical height estimationSolve the problem of low positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSimulationMems sensors
The invention discloses a method for estimating the height and position of pedestrians in a multi-storey building based on a MEMS sensor, comprising: fixing a MEMS integrated sensing device on the pedestrian's lower limbs; the MEMS integrated sensing device collects acceleration data, angular velocity data and Pedestrian height data; multi-threshold detection method is used to determine the posture phase and swing phase of pedestrian gait motion; the vertical acceleration of the posture phase and swing phase is respectively corrected, and the speed of the posture phase is updated to zero, and the The corrected vertical acceleration is quadratically integrated to obtain the estimated height of the pedestrian's attitude phase and swing phase; it is judged whether there is a deviation between the estimated height data obtained by the attitude phase and the target height data measured by the microbarometer. If it is, the error linear compensation is performed on the estimated height obtained by the swing phase, and finally the updated pedestrian positioning data is obtained. The invention realizes the accurate estimation of pedestrian's height position based on one sensor node.
Owner:东北大学秦皇岛分校
A Robust Estimation Method for Rational Function Model Parameters of Satellite Remote Sensing Imagery
InactiveCN104123457BReduce morbidityRobust and unbiased solutionSpecial data processing applicationsCheck pointModel parameters
The invention belongs to the technical field of surveying science, and particularly discloses a steady parameter estimation method of a rational function model of a satellite remote sensing image. The method comprises the steps that a control point grid and a check point grid are established in the image coverage range by using a strict imaging geometric model and a global DEM; linearization is conducted on the RFM with parameters of the RFM serving as unknown numbers to obtain an error equation coefficient matrix, QR decomposition is conducted on the error equation coefficient matrix through the Householder conversion method, and a new parameter resolving equation is established; parameter resolving is conducted on the equation through the Levenberg-Marquardt method to obtain the needed parameters of the RFM; image coordinates corresponding to object space coordinates of the check point grid are calculated through the resolved RFM, the image coordinates are compared with original image coordinates in the check point grid, maximum errors, minimum errors and mean square errors in the row direction and the list direction of the image are counted, and the fitting precision of the model is estimated. By means of the method, the fitting precision which is superior to that obtained through the ridge estimation algorithm can be achieved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
An ultra-high-precision attitude determination method for multi-stage composite control of spacecraft
ActiveCN108801270BAchieving High-Precision EstimationImplementing Relative Pose EstimationCosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationQuaternionControl system
A determining method for ultrahigh-accuracy attitude of a spacecraft multi-stage compound control system. The determining method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing an attitude constraintmodel between a star and a load as well as between the load and a fast reflective mirror of the spacecraft multi-stage compound control system; (2) establishing a relative attitude quaternion model between the star and the load as well as between the load and the fast reflective mirror; (3) judging whether a star guiding sensor has a measured value or not; (4) establishing a load attitude estimation error state equation if the star guiding sensor has no the measured value, estimating a load attitude by adopting a Kalman filtering method, and realizing determination on high accuracy of the loadattitude; (5) establishing a star attitude estimation error state equation, and realizing determination on high accuracy of a star attitude by adopting the Kalman filtering method; (6) estimating a load sight attitude by adopting a measured value qfm of the star guiding sensor if the star guiding sensor has the measured value; (7) establishing the load attitude estimation error state equation, estimating the load attitude by adopting the Kalman filtering method, and realizing the determination on high accuracy of the load attitude; (8) establishing the star attitude estimation error state equation.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
A Method of Arrival Angle Estimation Based on Sparse Bayesian Theory in the Existence of Mutual Coupling
ActiveCN108957390BImproving Angle of Arrival Estimation PerformanceSolve the signal angle of arrival estimation problemRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsCovarianceSpatial spectrum
The invention discloses a method for estimating the angle of arrival based on sparse Bayesian theory in the presence of mutual coupling, comprising: constructing a sparse signal model when there is mutual coupling of antenna arrays and a grid deviation of the arrival angle; initializing unknown parameters in the sparse signal model ;According to the current unknown parameter value, the joint probability distribution function is solved based on Bayesian theory, and the mean value and covariance matrix of the received signal are estimated; By maximizing the likelihood function, the variance of the noise and the variance of the received signal are estimated; the calculated The spatial spectrum of the received signal; by maximizing the likelihood function, estimating the grid deviation of the arrival angle, and updating the dictionary matrix when there is a grid deviation; estimating the variance of the mutual coupling vector of the array antenna and the mutual coupling vector of the array antenna; iteration The calculation stops until the set number of iterations is reached, and the spatial spectrum of the received signal and the solved angle of arrival of the received signal are output. The invention improves the performance of estimating the angle of arrival and realizes the high-precision estimation of the angle of arrival of the signal.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com