Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) and global navigation satellite system (GNSS) weight determining method aiming at three-dimensional ground surface deformation estimation
A surface deformation, three-dimensional technology, applied in the reflection/re-radiation of radio waves, satellite radio beacon positioning systems, and the use of re-radiation, etc. and other problems to achieve the effect of improving accuracy and universality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
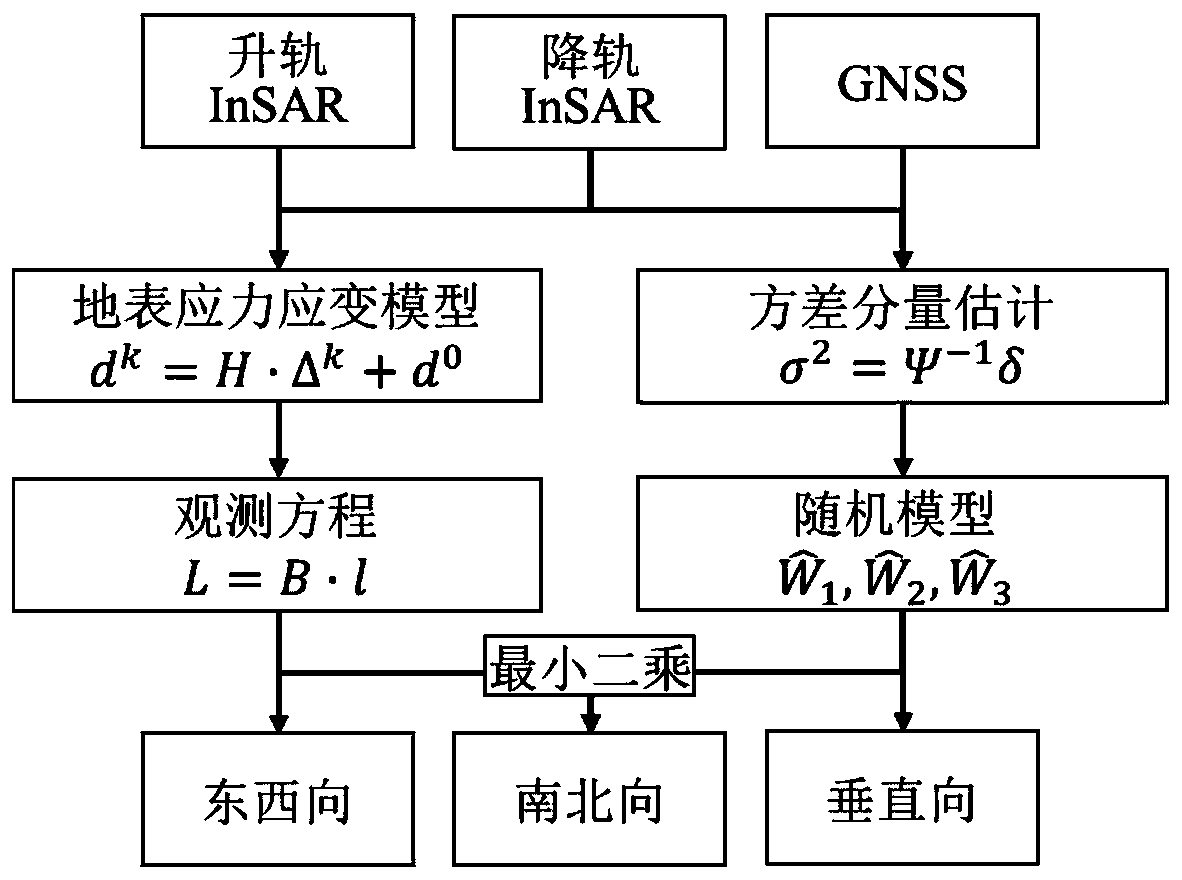
[0062] like figure 1 As shown, the specific implementation of this embodiment is as follows:
[0063] Step 1: Using the orbit-raising and descending InSAR data of the area to be monitored and the GNSS data of the area, based on the surface stress and strain model (Strain Model, SM), establish the three-dimensional surface deformation of the unknown point and a certain number of InSAR / GNSS around the point. functional relationship between data;
[0064] How to determine the amount of InSAR / GNSS data used to build the functional relationship is described in step 2.
[0065] Suppose the unknown point P 0 The three-dimensional coordinates and three-dimensional deformation of around a little P k The three-dimensional coordinates and three-dimensional deformation of Then according to the surface stress-strain model, there is the following formula:
[0066] d k =H.Δ k +d 0 (1)
[0067] in H represents the unknown parameter matrix of the stress-strain model, which c...
Embodiment 2
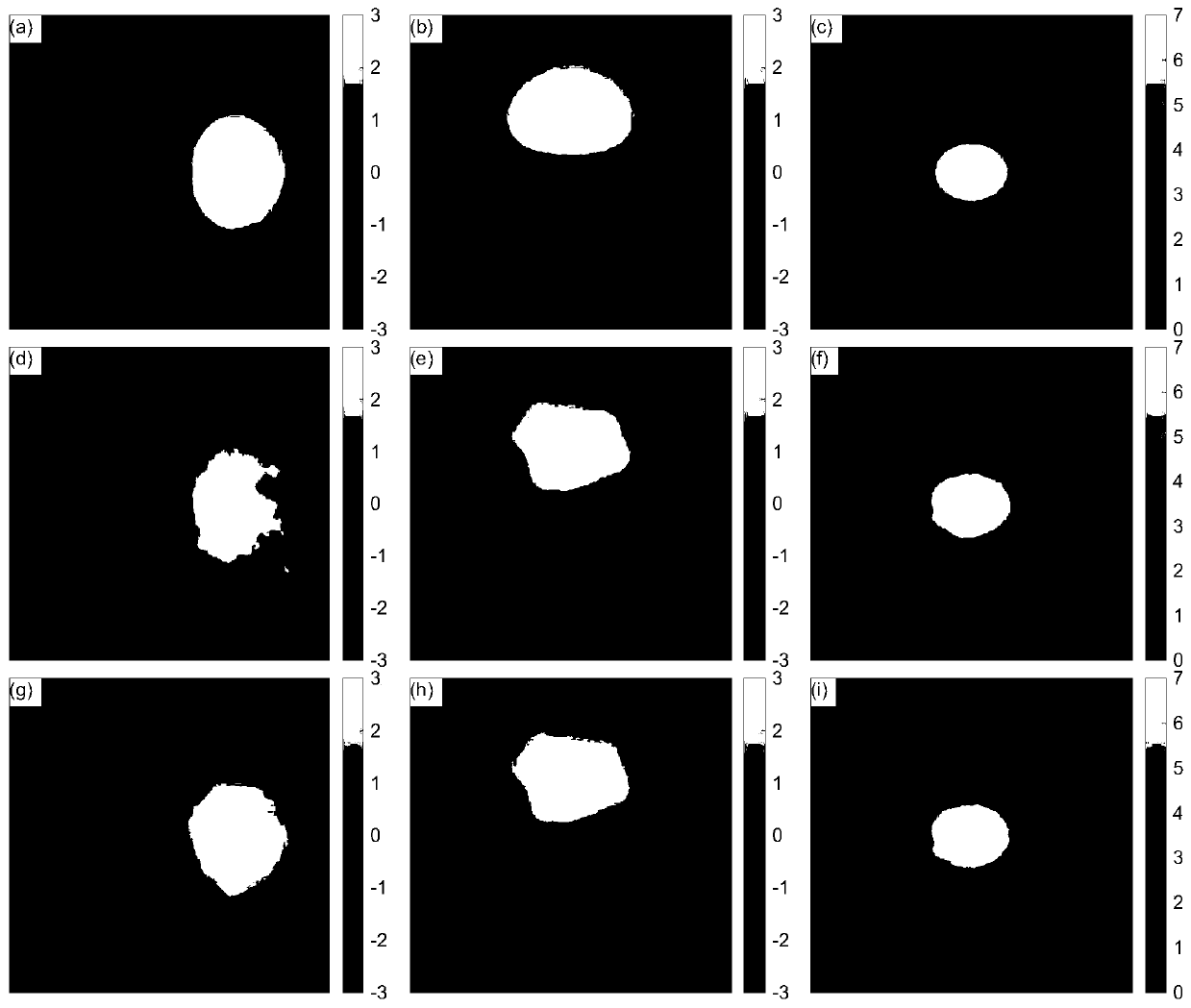
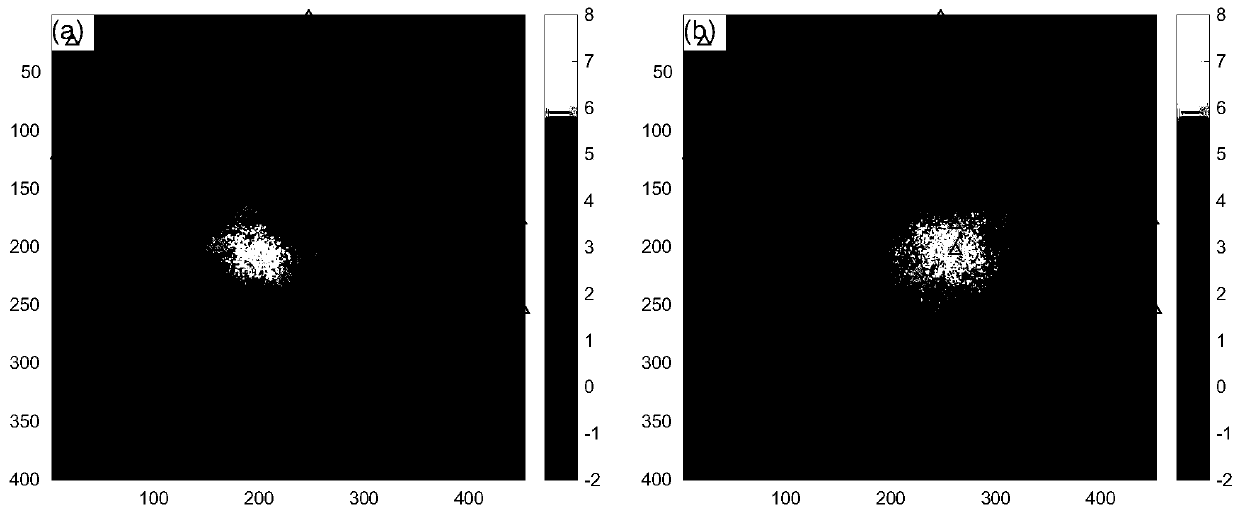
[0121] This implementation verifies the present invention through experiments, such as Figure 2-3 shown, where, figure 2 (a)-(c) are the original simulated east-west, north-south and vertical deformation data in turn, figure 2 (d)-(f) are the east-west, north-south and vertical deformation data obtained by the traditional method in turn, figure 2 (g)-(i) are the east-west, north-south and vertical deformation data obtained by the method of the present invention in turn (unit: cm); image 3 (a) is the orbit-raising InSAR data, image 3 (b) is the down-orbit InSAR data, the triangles in the figure represent the location distribution of GNSS stations (unit: cm).
[0122] Description of simulated data: ① Simulate east-west, north-south and vertical three-dimensional deformation fields in a certain area (image size 400×450) (such as figure 2 (a)-(c)); ② Combined with the imaging geometry of Sentinel-1A / B satellite data, calculate the InSAR deformation results of orbit up a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com