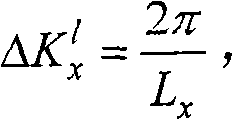Patents
Literature
262 results about "Interferometric synthetic aperture radar" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
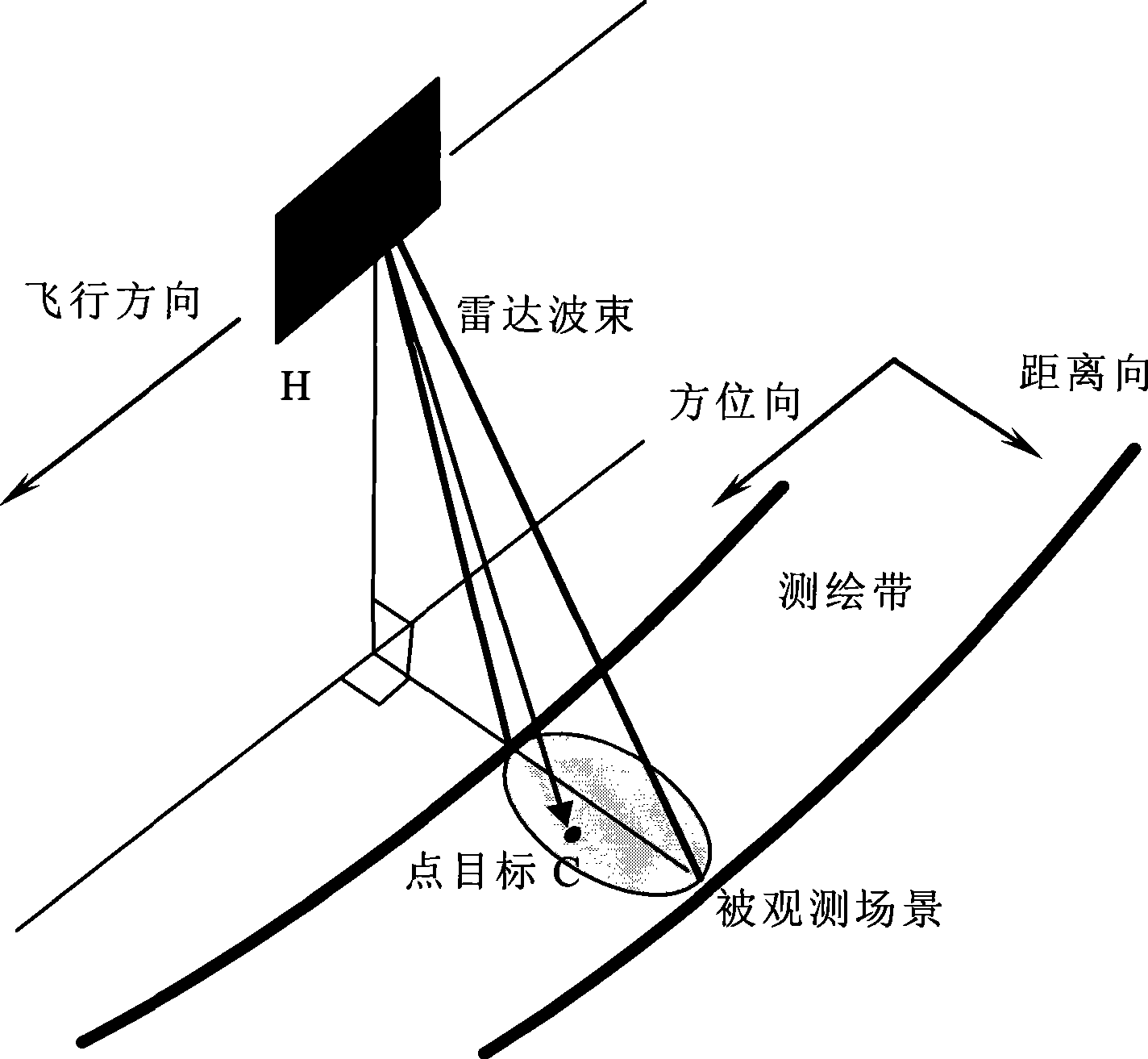
Interferometric synthetic aperture radar, abbreviated InSAR (or deprecated IfSAR), is a radar technique used in geodesy and remote sensing. This geodetic method uses two or more synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images to generate maps of surface deformation or digital elevation, using differences in the phase of the waves returning to the satellite or aircraft. The technique can potentially measure millimetre-scale changes in deformation over spans of days to years. It has applications for geophysical monitoring of natural hazards, for example earthquakes, volcanoes and landslides, and in structural engineering, in particular monitoring of subsidence and structural stability.
Method for improving earth surface shape change monitoring precision of InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) technology based on high-precision DEM (Digital Elevation Model)
InactiveCN103675790AError Phase CancellationHigh precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionShape changeInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
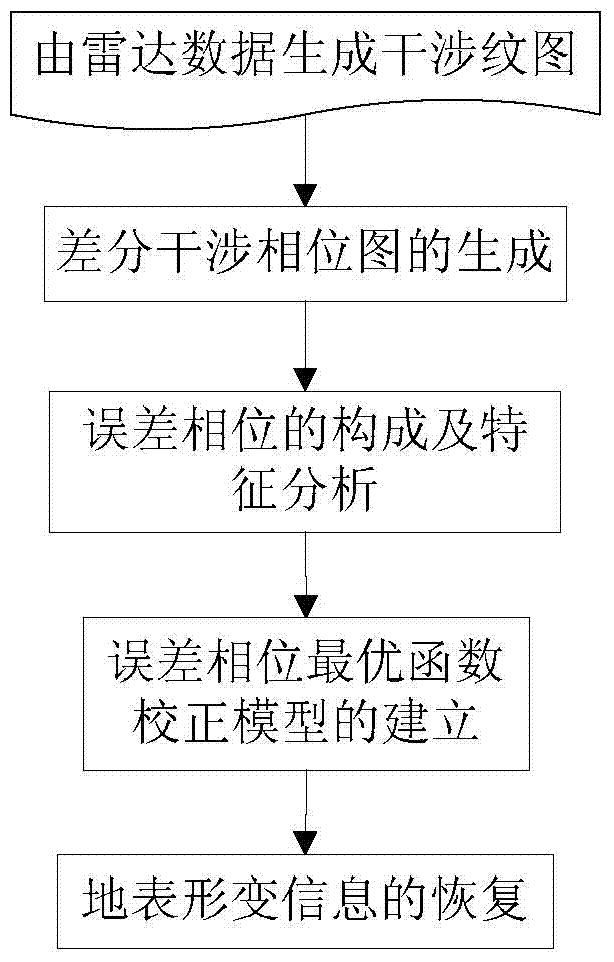
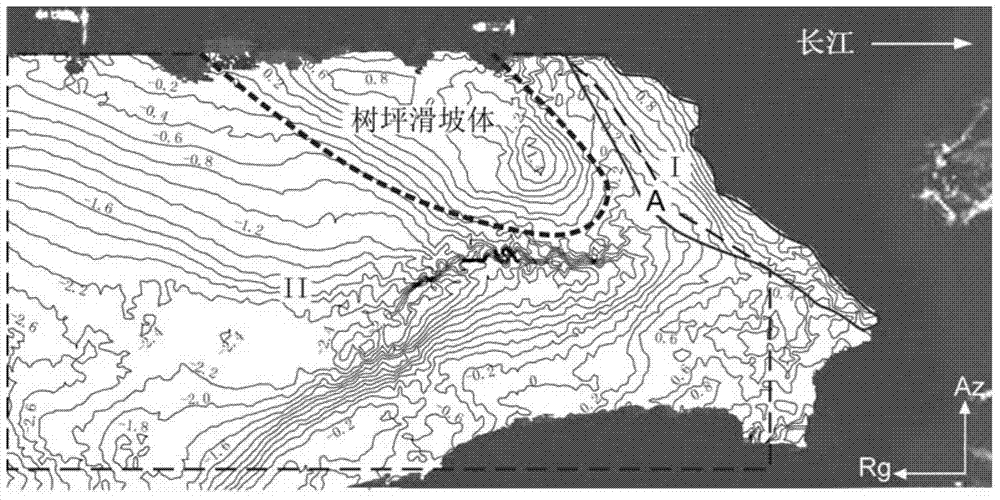
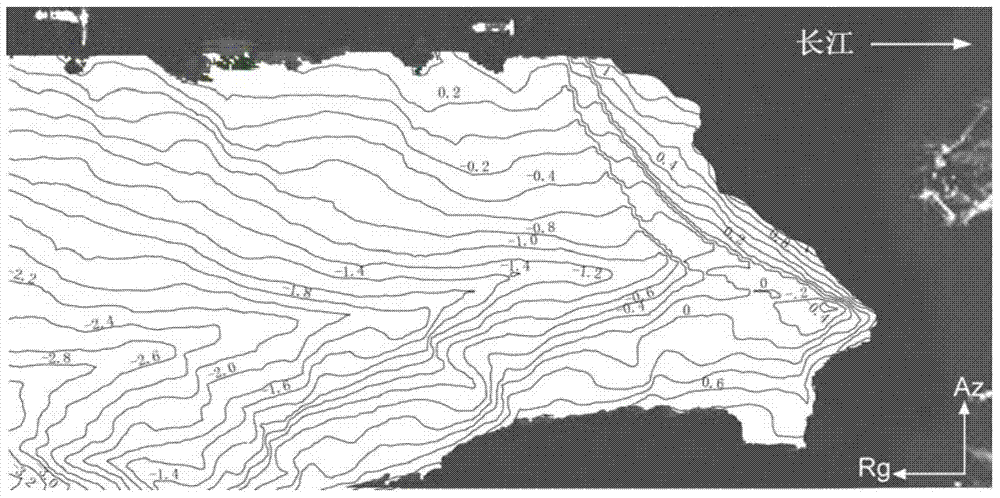
The invention discloses a method for improving earth surface shape change monitoring precision of an InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) technology based on a high-precision DEM (Digital Elevation Model). The method comprises five steps below: step 1, generating an interferogram by using radar data; step 2, generating a differential interference phase diagram; step 3, establishing error phases and performing feature analysis; step 4, establishing an error phase optimal function calibration model; step 5, recovering earth surface shape change information of a monitoring region based on results of steps 2 and 4. According to the invention, the error phases and elevation values or the error phases, the elevations and coordinate values along a distance / azimuth of different regions of a research region are extracted, the optimal function calibration models of the error phases of corresponding regions are established respectively based on a least square method, and a simulative error phase is finally removed from the differential interference phase diagram to further recover shape change information along a direction of a sight line of a radar in the monitoring region. The method for improving the earth surface shape change monitoring precision of the InSAR technology based on the high-precision DEM has practical value and wide application foreground in the application field of a satellite borne synthetic aperture radar monitoring technology for earth surface shape change.
Owner:CHINA AERO GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY & REMOTE SENSING CENT FOR LAND & RESOURCES
3D terrain imaging system of interferometric synthetic aperture radar and elevation mapping method thereof
InactiveCN101551455AReal-time quick-look observationAchieve observationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
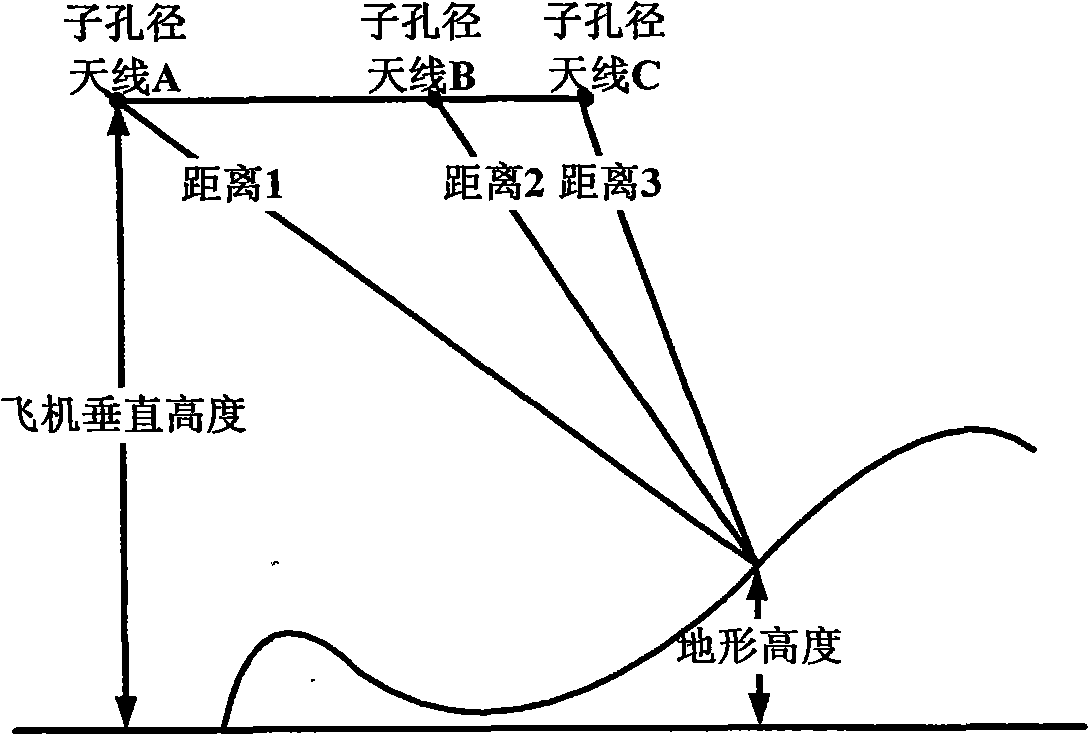
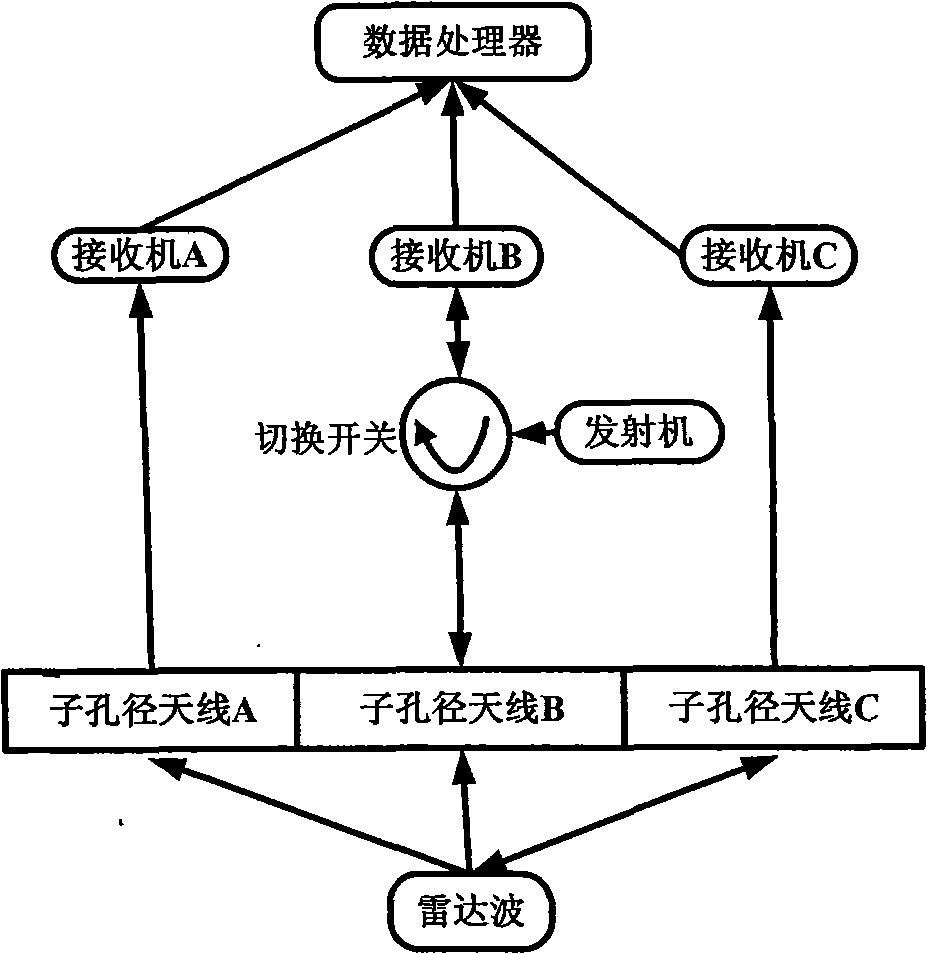
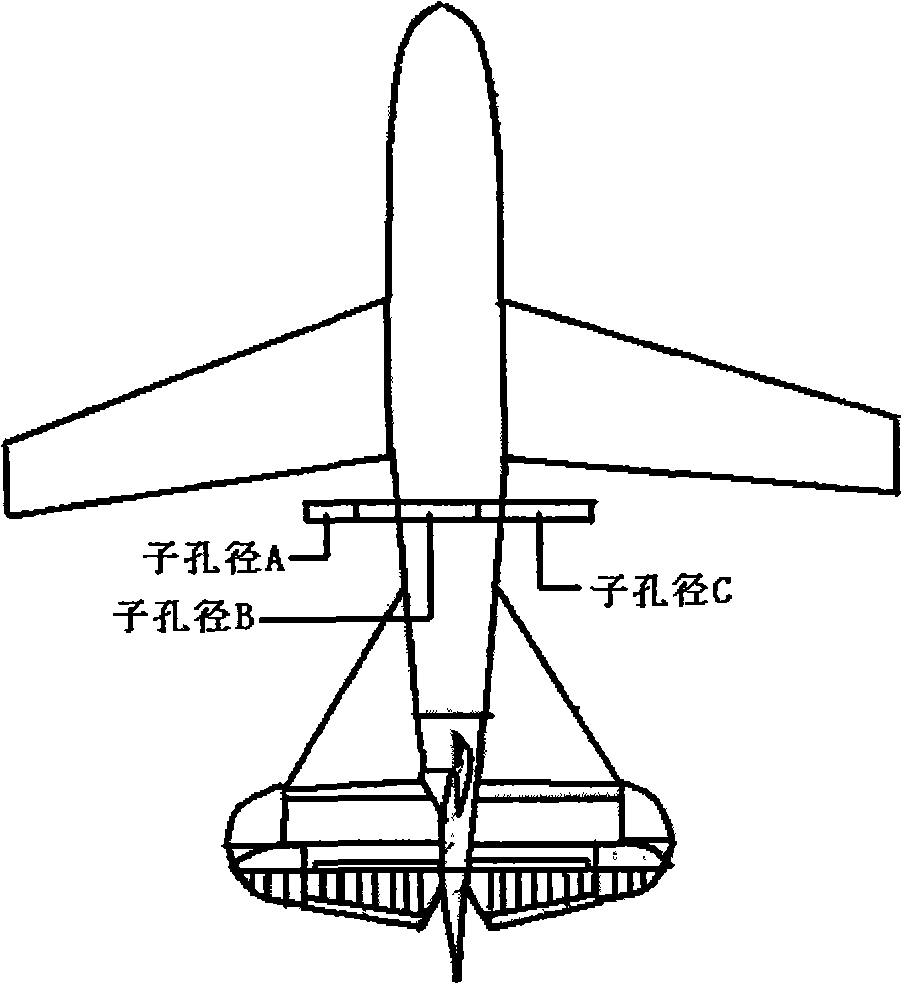
The invention discloses a 3D terrain imaging system of the interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) and an elevation mapping method thereof, which mainly solve the problems that the existing InSAR has bad imaging pragmaticality and can not implement 3D elevation mapping on the fast-changing terrain and the transilient terrain. The system comprises three sub-aperture antennas, a radar transmitter, a radar receiver and an imaging data processor; the imaging signal processor comprises a SAR image processing unit and an InSAR image processing unit. The invention receives radar echo through the three sub-apertures, then conducts SAR imaging process on the radar echo respectively received by the three sub-apertures, and then conducts InSAR imaging process on the obtained SAR complex pattern, wherein the InSAR imaging process comprises image registration, phase filtering and phase unfolding based on cluster analysis. The processed InSAR phase unfolded image is processed with an elevation inversion to recover a three dimensional digital elevation map. The invention has the advantages of wide adaptability to mapped terrains, and high imaging effectiveness, therefore, the invention can be used in the mapping of the 3D terrain.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Ground surface deformation high-resolution interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) monitoring method along high speed railway
InactiveCN104111456AHigh precisionImprove the level of fine monitoringRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarSubsidence
Disclosed is a ground surface deformation high-resolution interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) monitoring method along a high speed railway. The method includes four steps of (1) selection of high-resolution SAR data, (2) a high-resolution InSAR high speed railway area deformation information extraction method, (3) a multi-track deformation rate result integrating method and (4) a high speed railway target recognition and deformation extraction method. By means of the ground surface deformation high-resolution InSAR monitoring method along the high speed railway, the high speed railway can be completely covered and monitored by a high-resolution InSAR, recognition and separation of high speed railway subgrade settlement and area surface subsidence can be effectively achieved, and InSAR accurate monitoring level of high speed railway ground surface deformation in China can be greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA AERO GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY & REMOTE SENSING CENT FOR LAND & RESOURCES
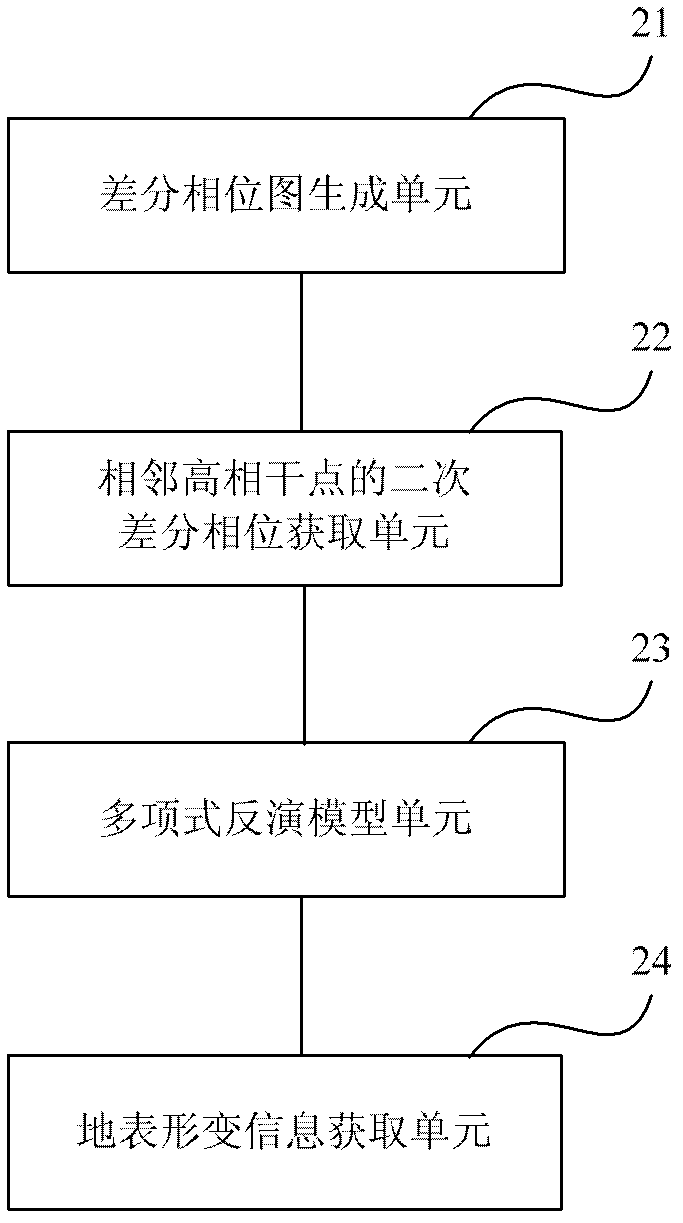
Time sequence InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) deformation monitoring method and device based on polynomial inversion model
InactiveCN102608584AFit closelyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionResidual deformationInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
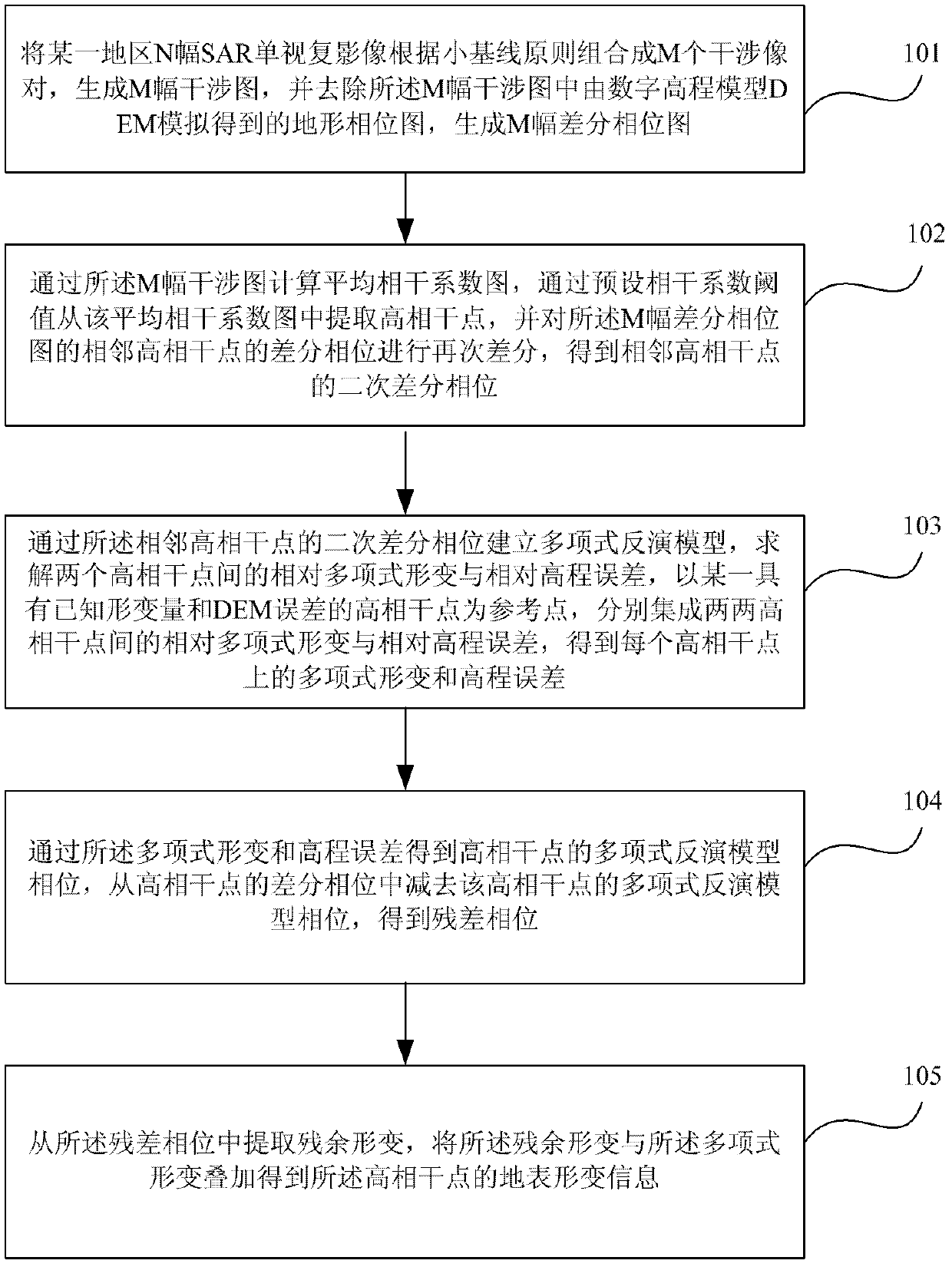
The invention provides a time sequence InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) deformation monitoring method and a device based on a polynomial inversion model. The method comprises the following steps of: combining N SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) single look complexes of a certain region to generate M interference pictures and generate M differential phase pictures; calculating an average coherent coefficient picture and extracting high coherent points; establishing a polynomial inversion model by carrying out difference again on a differential phase of the two adjacent high coherent points; solving relative polynomial deformation and a relative elevation error of the adjacent points respectively integrating by taking a certain high coherent point provided with known deformation amount and a DEM (Dynamic Effect Model) error as a reference point to obtain the polynomial deformation and the elevation error of each high coherent point; after a phase of the polynomial inversion model is obtained, subtracting the phase of the polynomial inversion model from the differential phase of the high coherent points to obtain a residual phase; and extracting residual deformation from the differential phase to be overlapped with the polynomial deformation to obtain ground surface deformation information of the high coherent points. The method provides a solution for highly-precisely monitoring the ground surface deformation.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
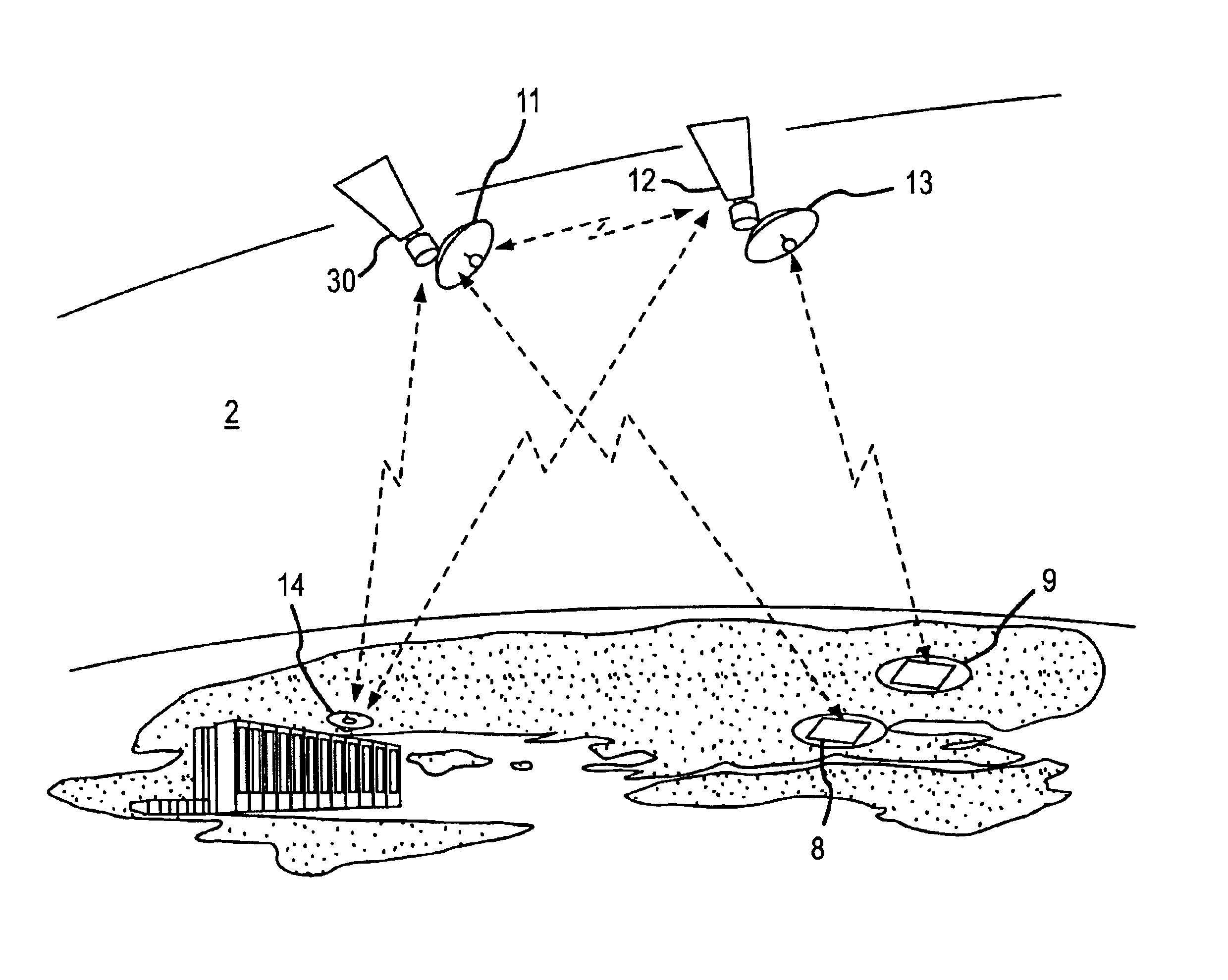
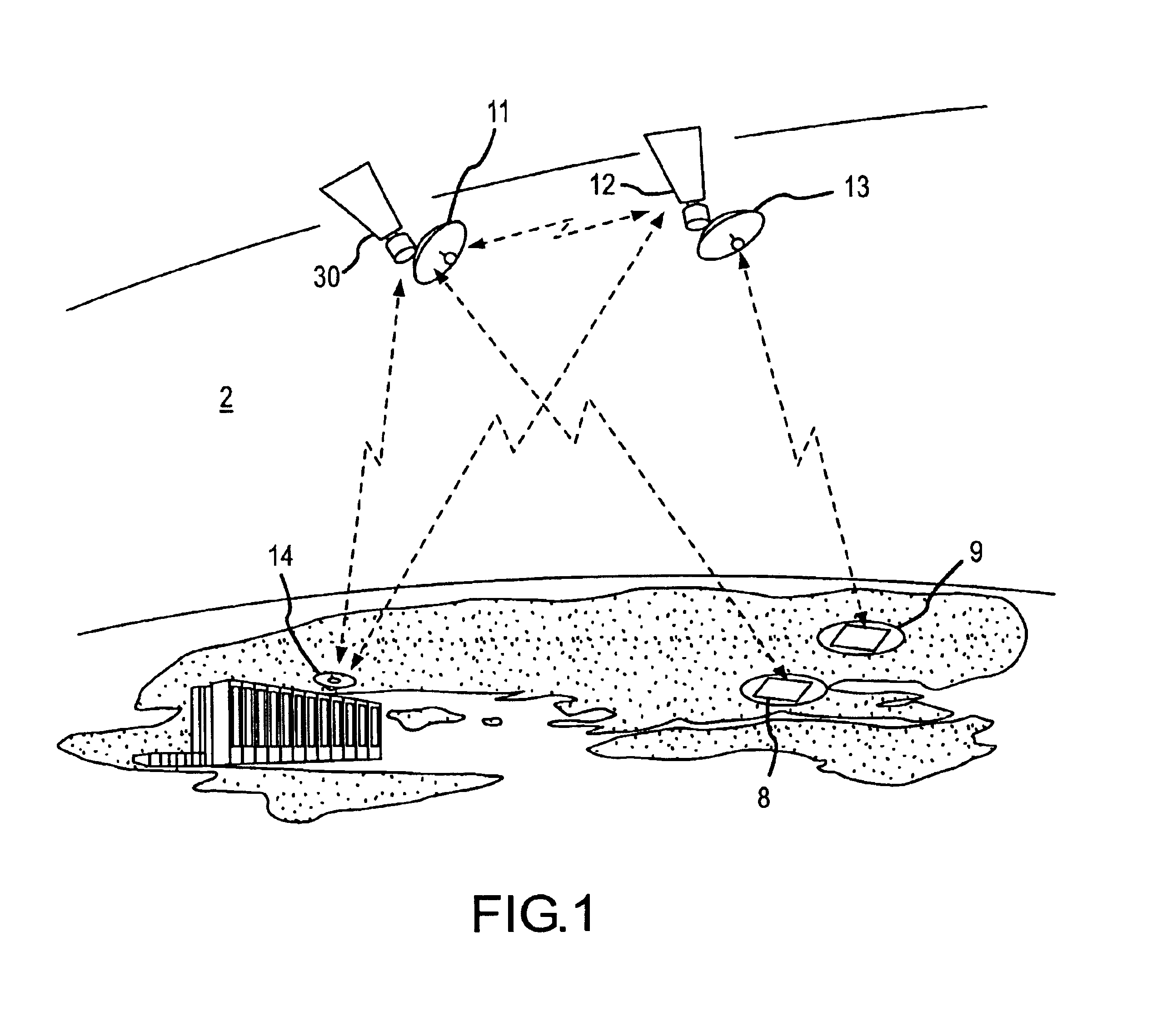
Method and apparatus for collection and processing of interferometric synthetic aperture radar data
InactiveUS6864828B1Minimize decorrelation effectAvoid interferenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarImaging processing
A system and method provide for the collection of interferometric synthetic aperture radar (IFSAR) data. In the system, a first space vehicle configured for emitting electro-magnetic energy and collecting the reflection from a region of interest (ROI), may be directed along a first orbital track. The collected image data may be stored and later provided to a ground station for image and interferometric processing. A second space vehicle may also be configured for emission and collection of electro-magnetic energy reflected from the plurality of ROI's. The second space vehicle is positioned in an aligned orbit with respect to the first space vehicle where the separation between the vehicles is known. In order to minimize decorrelation of the ROI during image processing, the lead and trail satellite are configured to substantially simultaneously emit electromagnetic pulses image data collection. In order to avoid interference in the collection of this image data, each system is configured to control the emission of pulses such that the receipt of direct and bistatic pulses by the other vehicles does not interfere with data collection.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
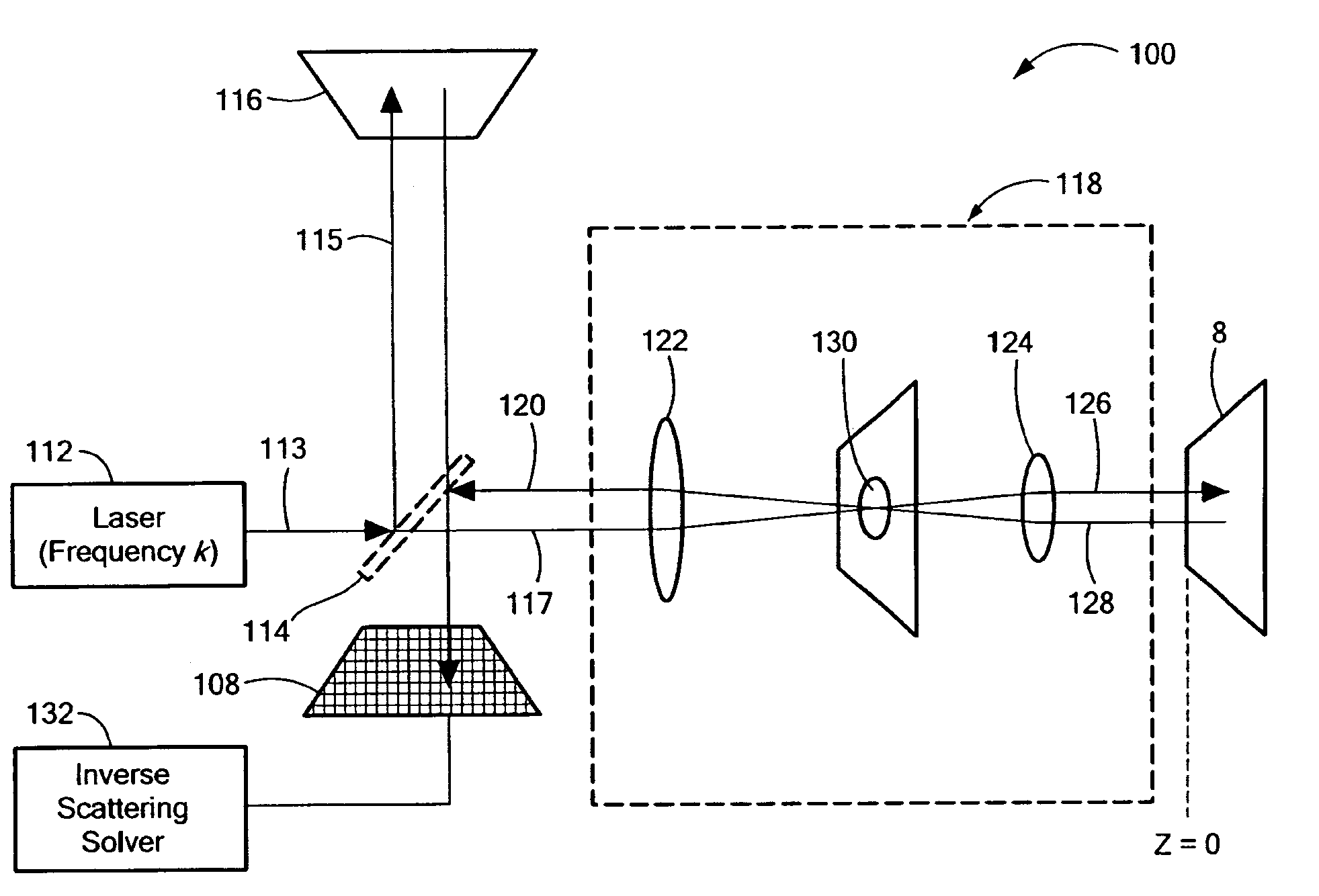
Interferometric synthetic aperture microscopy
ActiveUS7602501B2Digital computer detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansInterferometric synthetic aperture radarMicroscopy
Methods and apparatus for three-dimensional imaging of a sample. A source is provided of a beam of substantially collimated light characterized by a temporally dependent spectrum. The beam is focused in a plane characterized by a fixed displacement along the propagation axis of the beam, and scattered light from the sample is superposed with a reference beam derived from the substantially collimated source onto a focal plane detector array to provide an interference signal. A forward scattering model is derived relating measured data to structure of an object to allow solution of an inverse scattering problem based upon the interference signal so that a three-dimensional structure of the sample may be inferred in near real time.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Spectrometric synthetic aperture radar
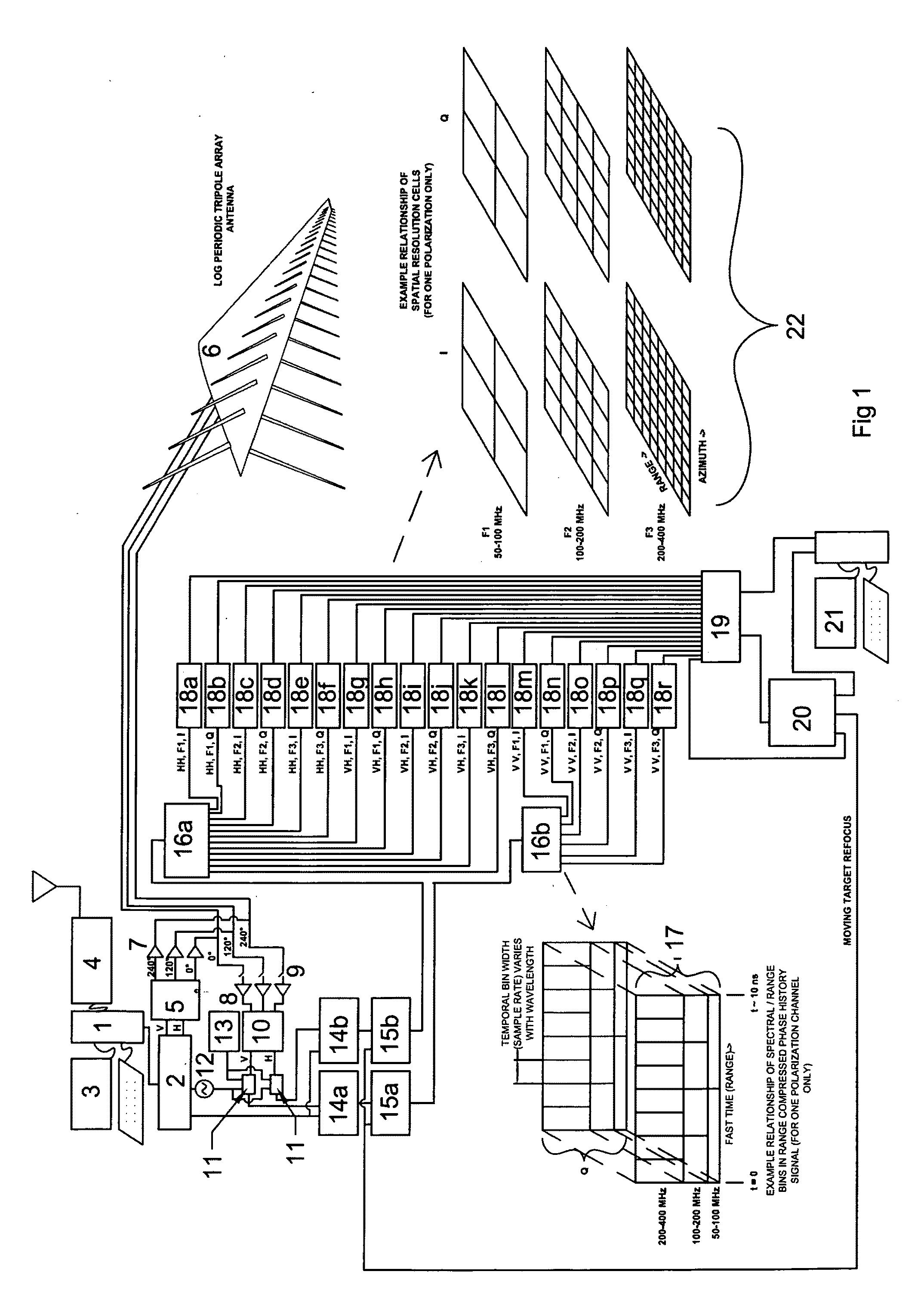
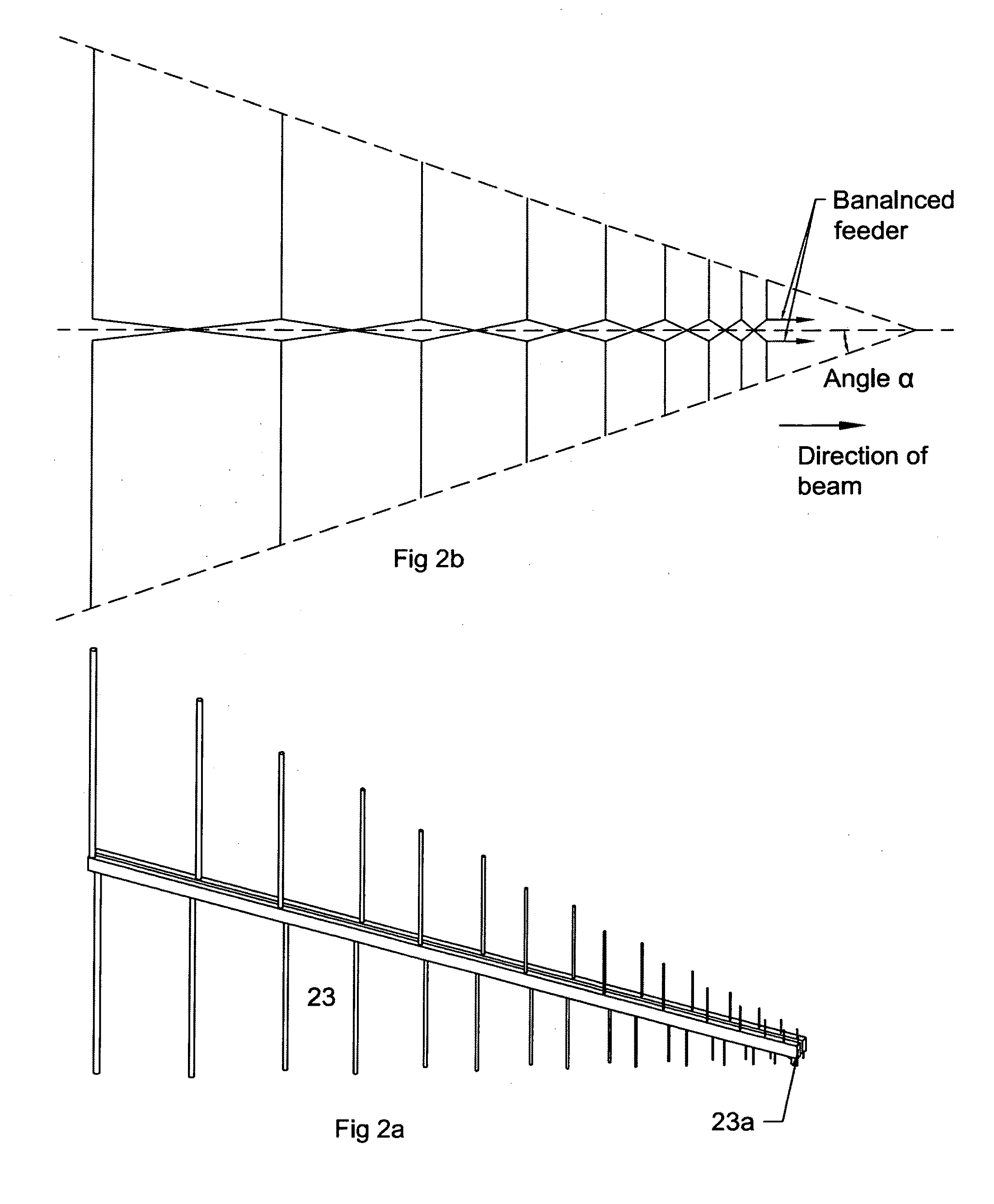
ActiveUS20090102705A1Generate efficientlyImprove electricity efficiencyLogperiodic antennasAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesUltra-widebandFrequency spectrum
This invention relates to improved ultra-wideband synthetic aperture radar and inverse synthetic aperture radar, capable of simultaneously and independently imaging a plurality of spectral and polarimetric channels covering multiple radio frequency octaves. Advances in technologies relating to signal processing, graphical user interfaces, color representations of multi-spectral radar images, low aerodynamic drag polarimetric SAR antenna systems, and synthetic aperture radar aircraft platforms are some of the advancements disclosed herein.
Owner:OBERMEYER HENRY K
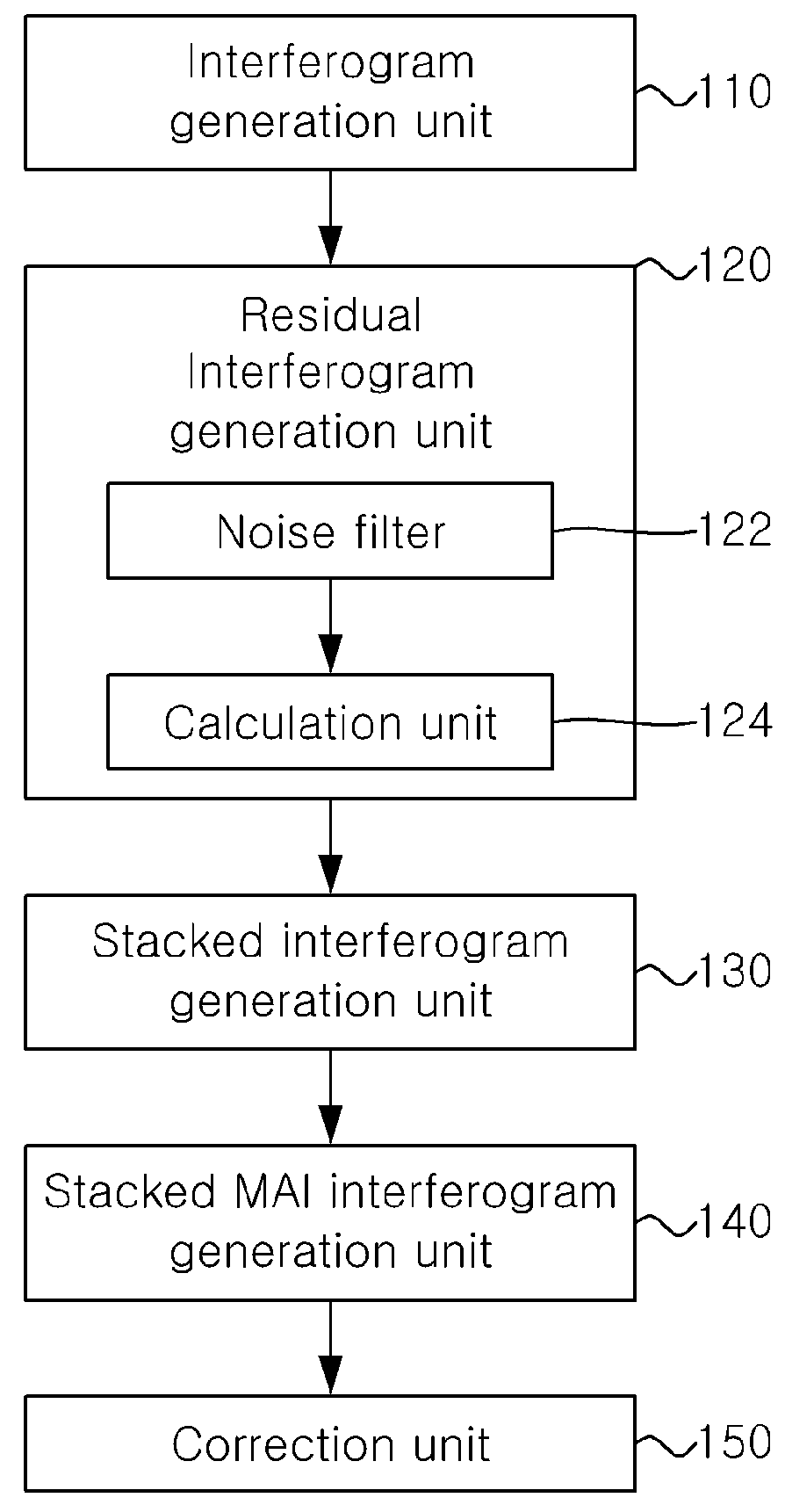
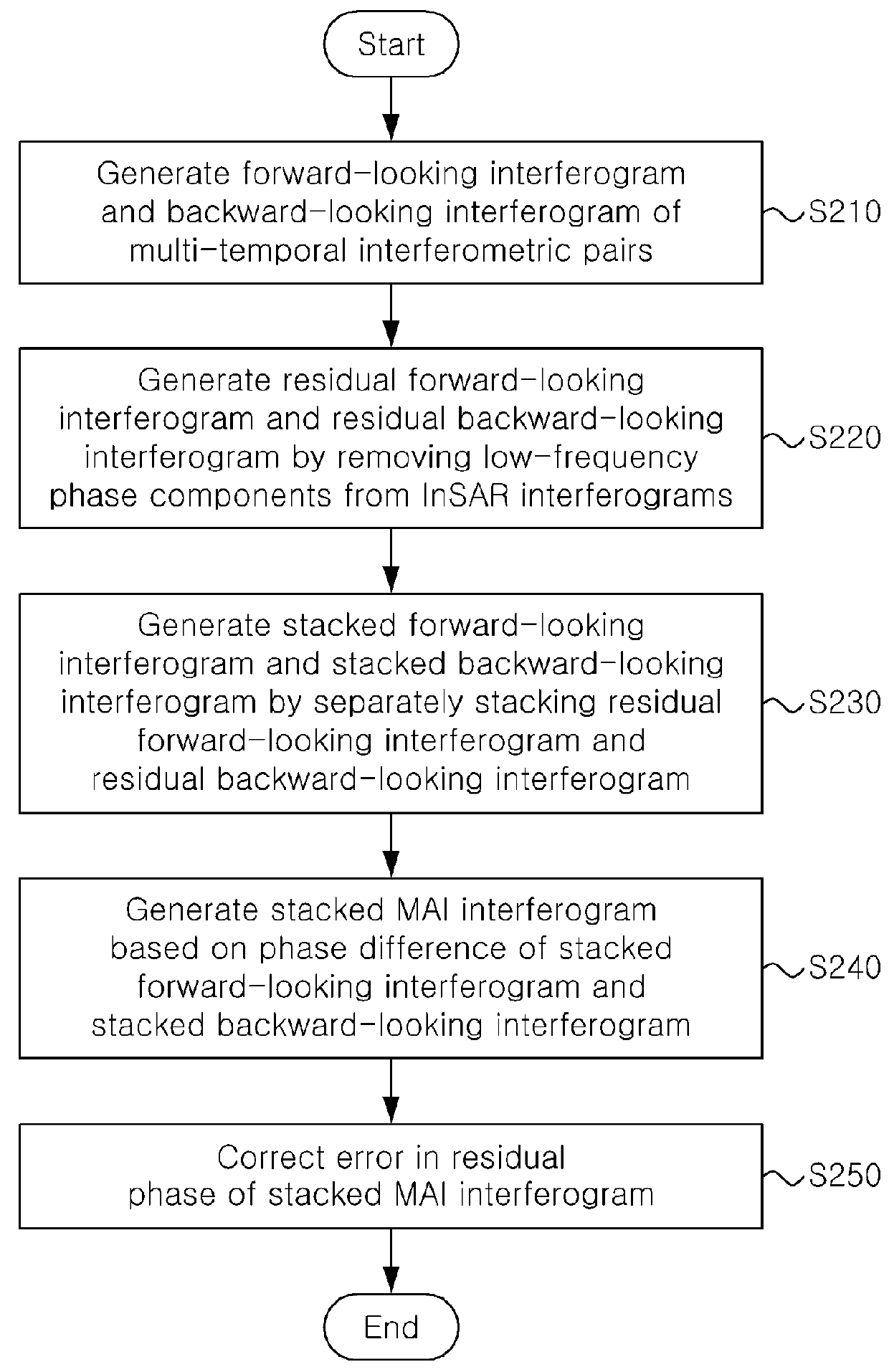
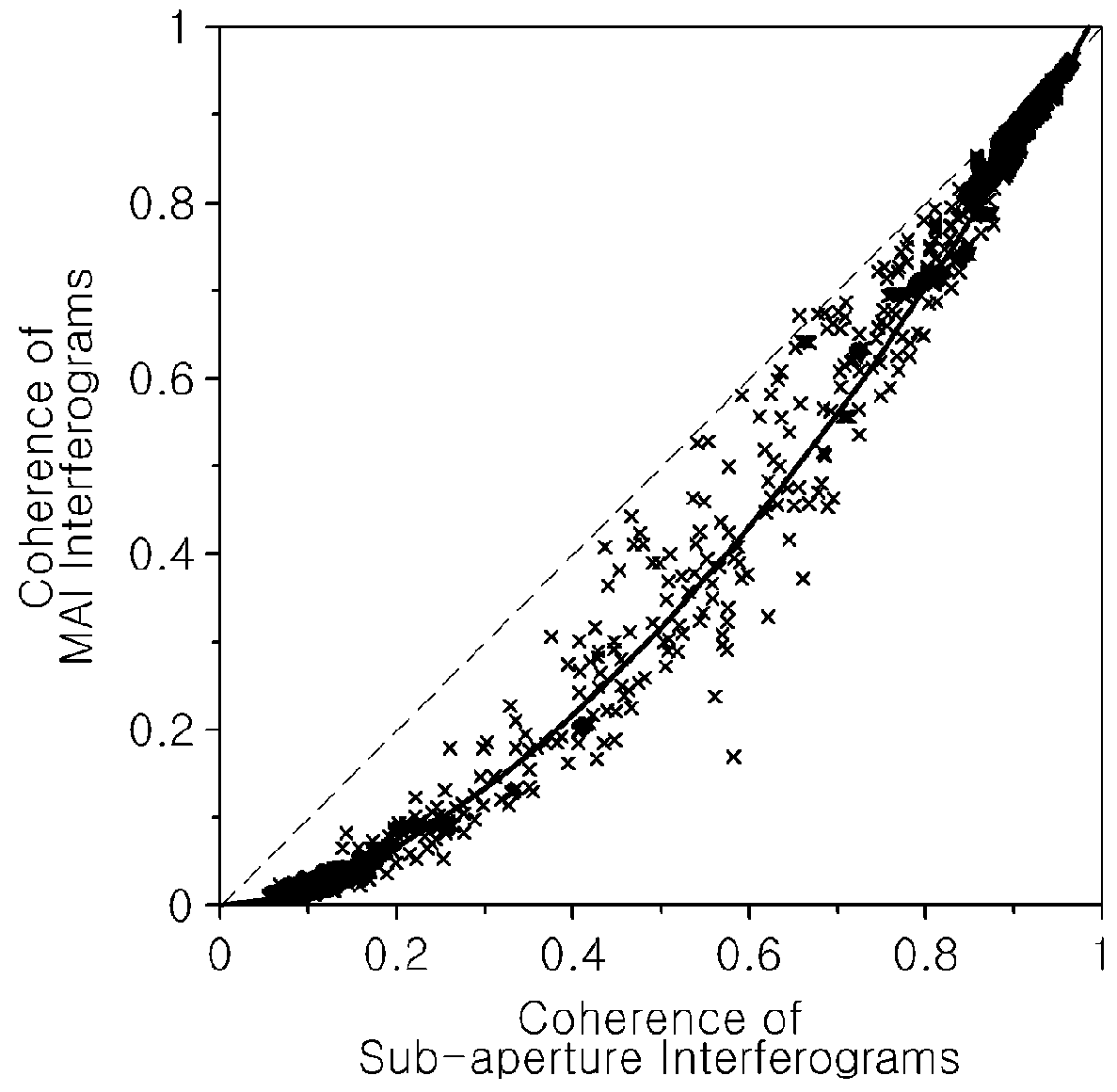
Method and apparatus for stacking multi-temporal mai interferograms
ActiveUS20160033639A1High precisionAccurate observationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarPhase difference
An apparatus and method for stacking multi-temporal MAI interferograms Disclosed are disclosed herein. The apparatus includes a processor configured to: generate a forward-looking InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) interferogram and a backward-looking InSAR interferogram of multi-temporal interferometric pairs; generate a residual forward-looking interferogram and a residual backward-looking interferogram by removing low-frequency phase components from the forward-looking InSAR interferogram and the backward-looking InSAR interferogram; generate a stacked forward-looking interferogram and a stacked backward-looking interferogram by separately stacking the residual forward-looking interferogram and the residual backward-looking interferogram; and generate a stacked MAI interferogram based on a phase difference between the stacked forward-looking interferogram and the stacked backward-looking interferogram.
Owner:UNIV OF SEOUL IND COOP FOUND
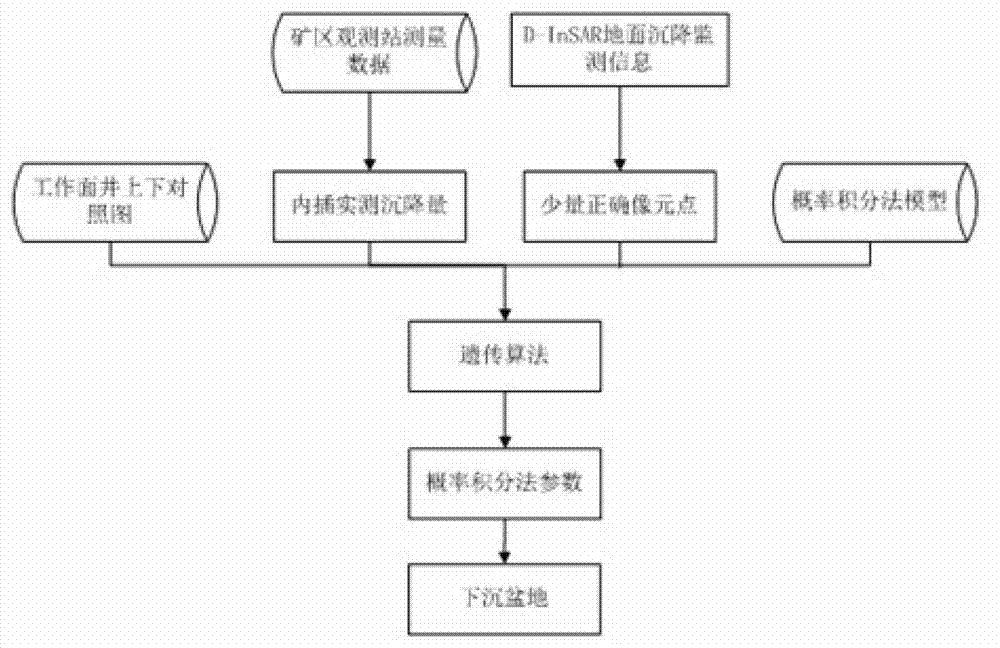
Mining area surface subsidence synthetic aperture radar interferometry monitoring and calculating method
InactiveCN103091676AAddresses issues requiring more surface control pointsClear process structureRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTerrainInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
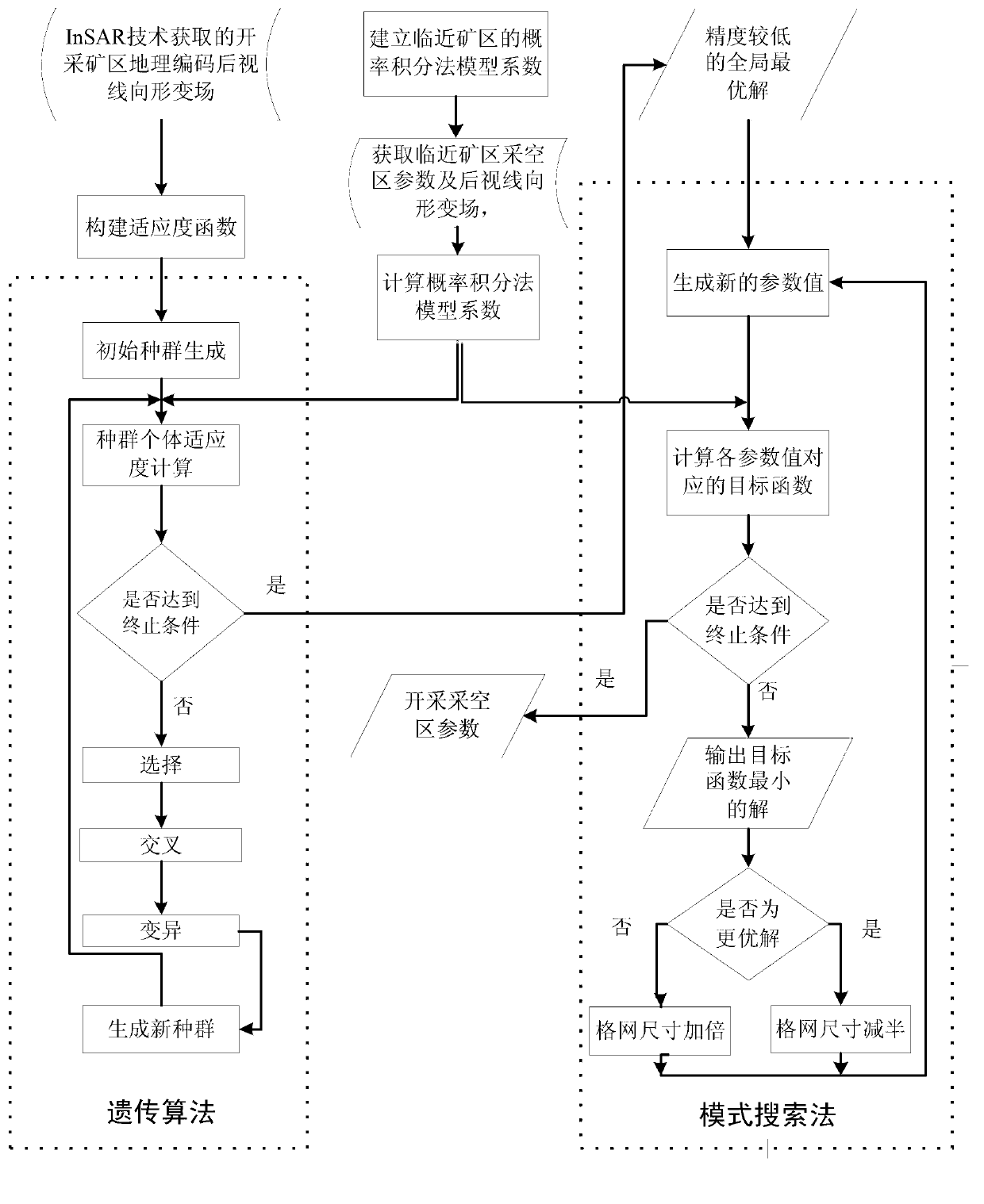
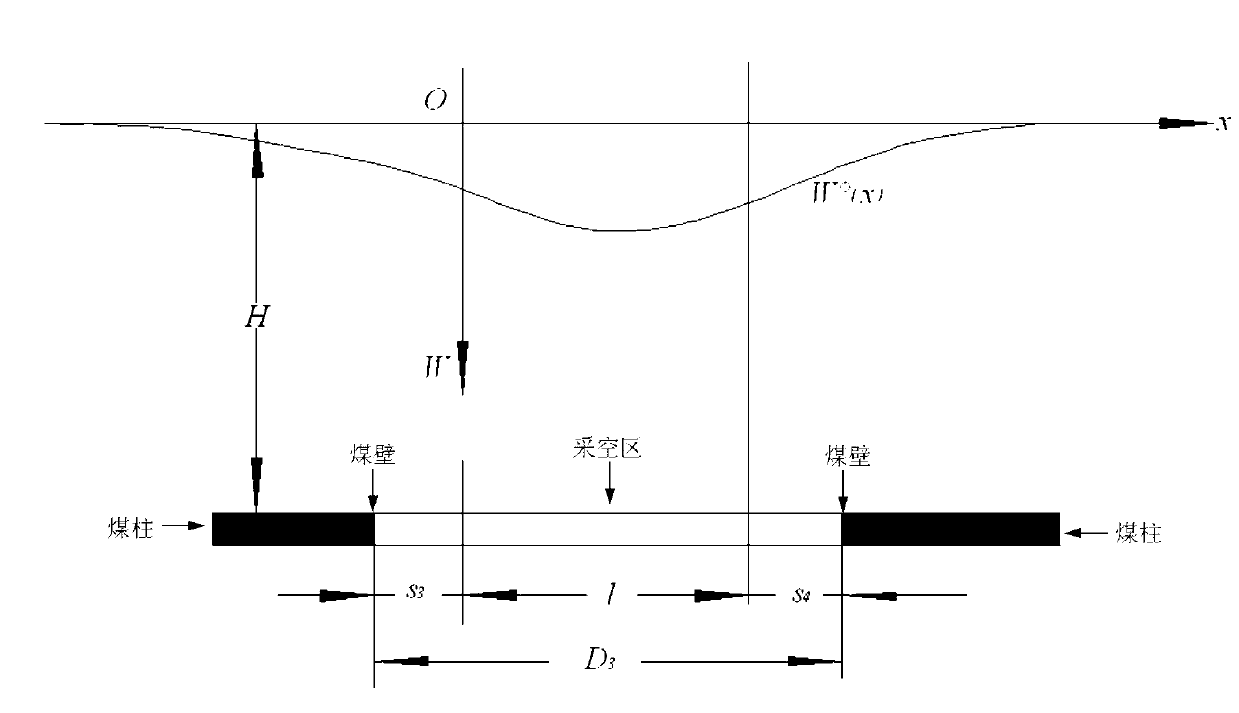
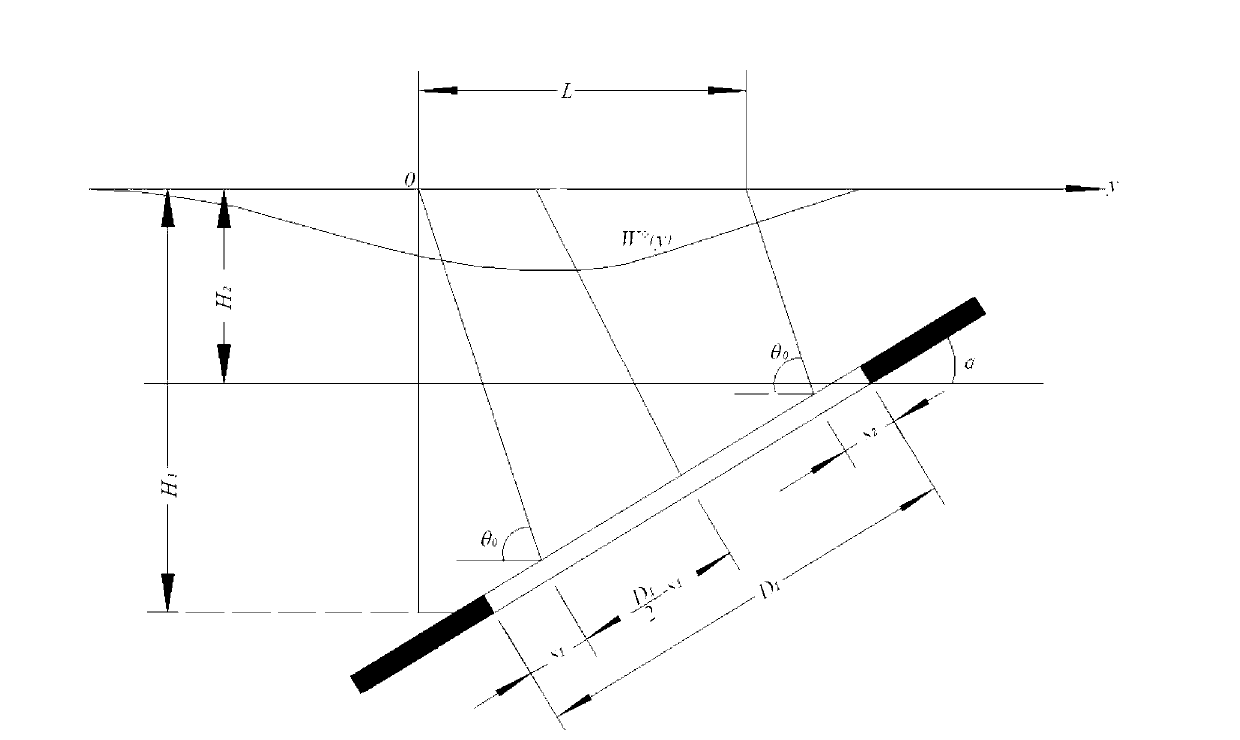
A mining area surface subsidence synthetic aperture radar interferometry monitoring and calculating method belongs to mining area surface subsidence monitoring and calculating method. The method comprises the following steps: having format conversion, calibration, pre-filtering and interference to interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) data to obtain an InSAR interference phase, eliminating flat ground effect, an terrain phase and orbit errors of the interference phase by means of precise orbit data and an external dynamic effect model (DEM), obtaining phase values which only contain deformation information of a ground surface after filtering to residual phases, on the condition of large deformation gradient, through phase unwrapping, obtaining deflection of the edge of a mining subsidence basin, fusing the deflection with a few ground measured data, reversely deducing probability integral method parameters of the subsidence basin through a genetic algorithm, calculating sinking values of an arbitrary point of the whole surface subsidence basin through required probability integral method parameters and geological mining data, and therefore mining subsidence deformation field is produced. The mining area surface subsidence synthetic aperture radar interferometry monitoring and calculating method has the advantages of being high in monitoring accuracy, large in monitoring range, convenient to operate, low in cost and large in technical content.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
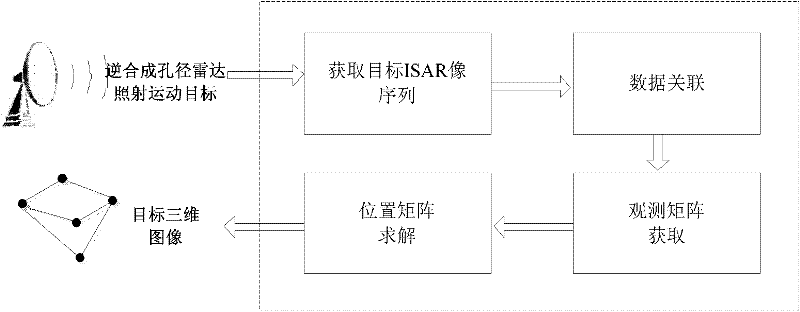
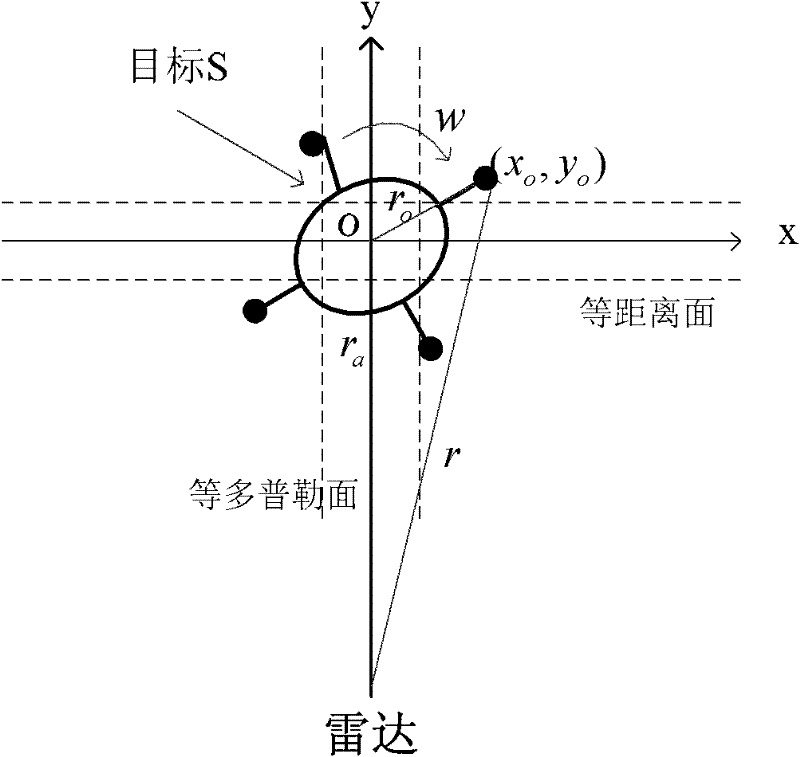
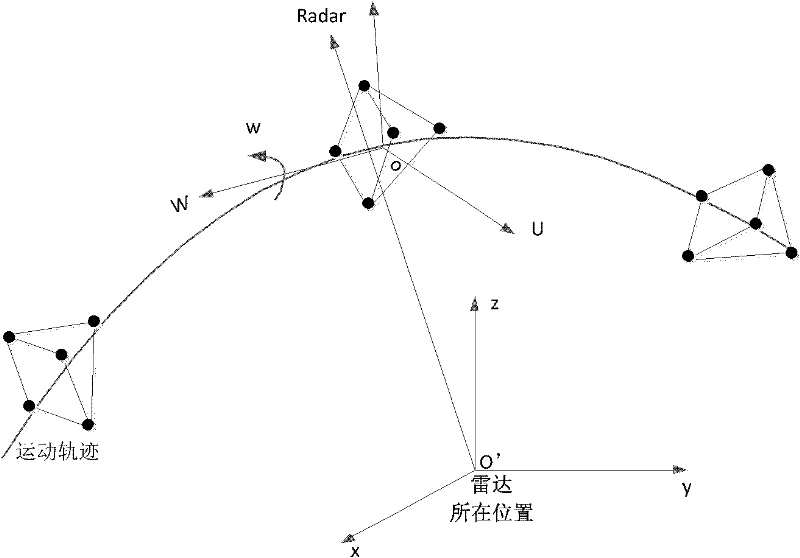
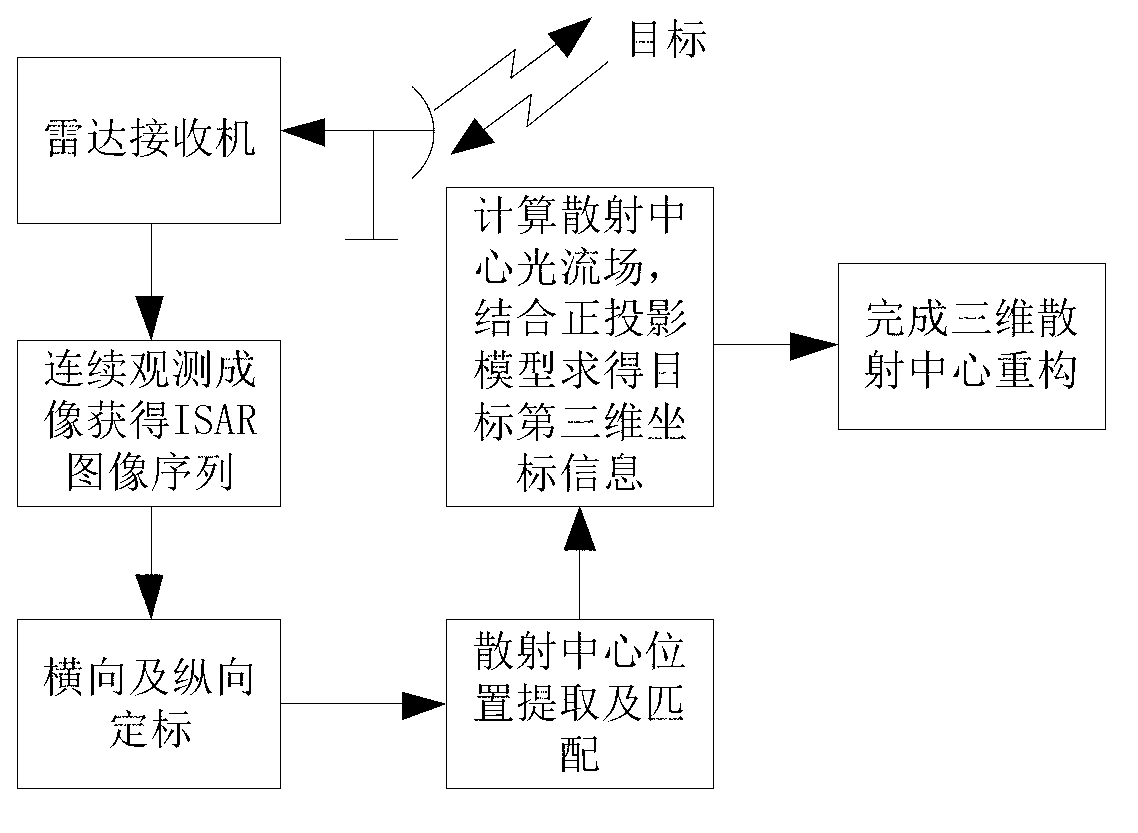
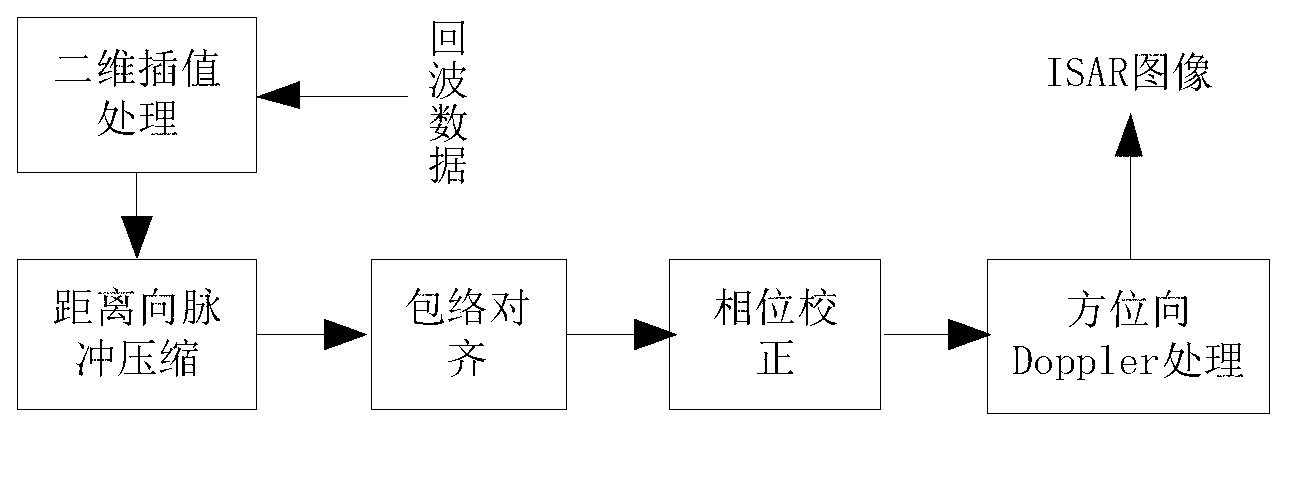
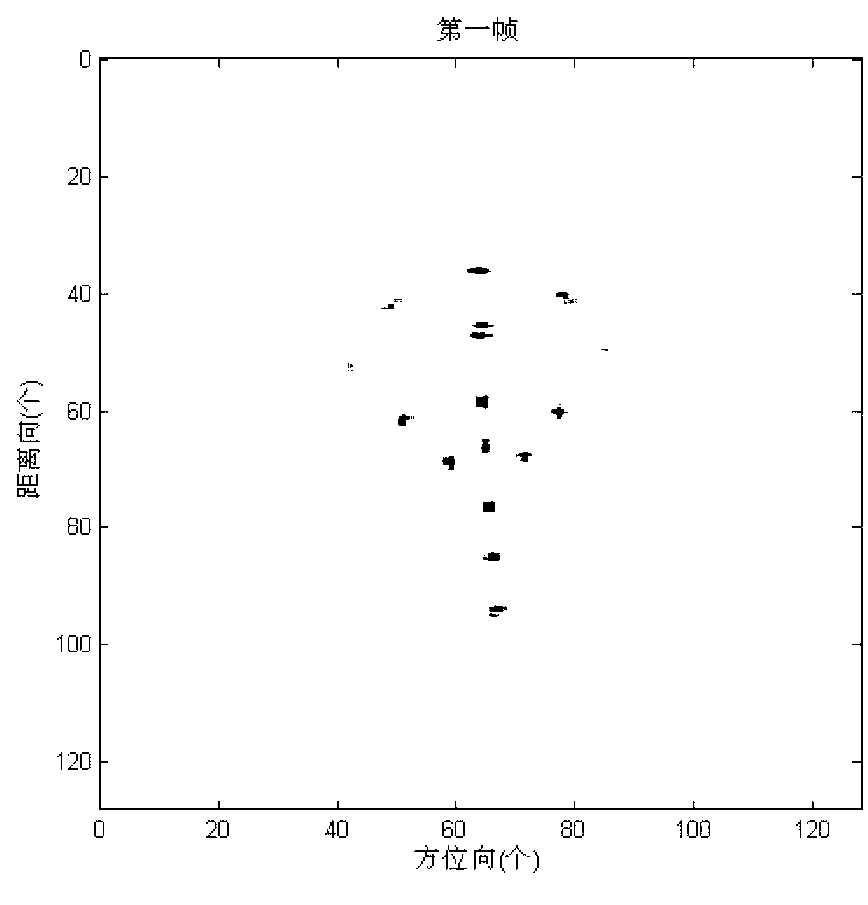
Three-dimensional position reconstructing method based on ISAR (inverse synthetic aperture radar) image sequence for scattering point
InactiveCN102353945ASolve the unknownSolve the problem that the viewing angle parameters are difficult to obtainRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSingular value decompositionInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a three-dimensional position reconstructing method based on an ISAR (inverse synthetic aperture radar) image sequence for a scattering point, which comprises the following four links: a target ISAR image gives the distribution information of a target strong scattering point in a radial direction and a transverse direction based on a distance-Doppler high resolution basic principle; data correlation gives a corresponding relationship between two-dimensional projection points in the ISAR image sequence and is realized by utilizing a flight path initialization method through extracting the one-dimensional radial distance information of all the scattering points in an image sequence; an observing matrix is obtained through the following steps: obtaining a target ISAR image sequence through a period of time of sampling, and after the data correlation, and combining the two-dimensional position coordinates of all the corresponding projection points in a sequence to form the observing matrix, so as to form three-dimensional reconstructed known information; and a position matrix is solved through the following step: solving the optimal estimation of a three-dimensional position matrix of a target scattering point from a subspace through carrying out singular value decomposition on the observing matrix and by utilizing a rank theory and using the orthogonality of a projection space as a constraint condition, so as to obtain a target three-dimensional reconstructed image.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
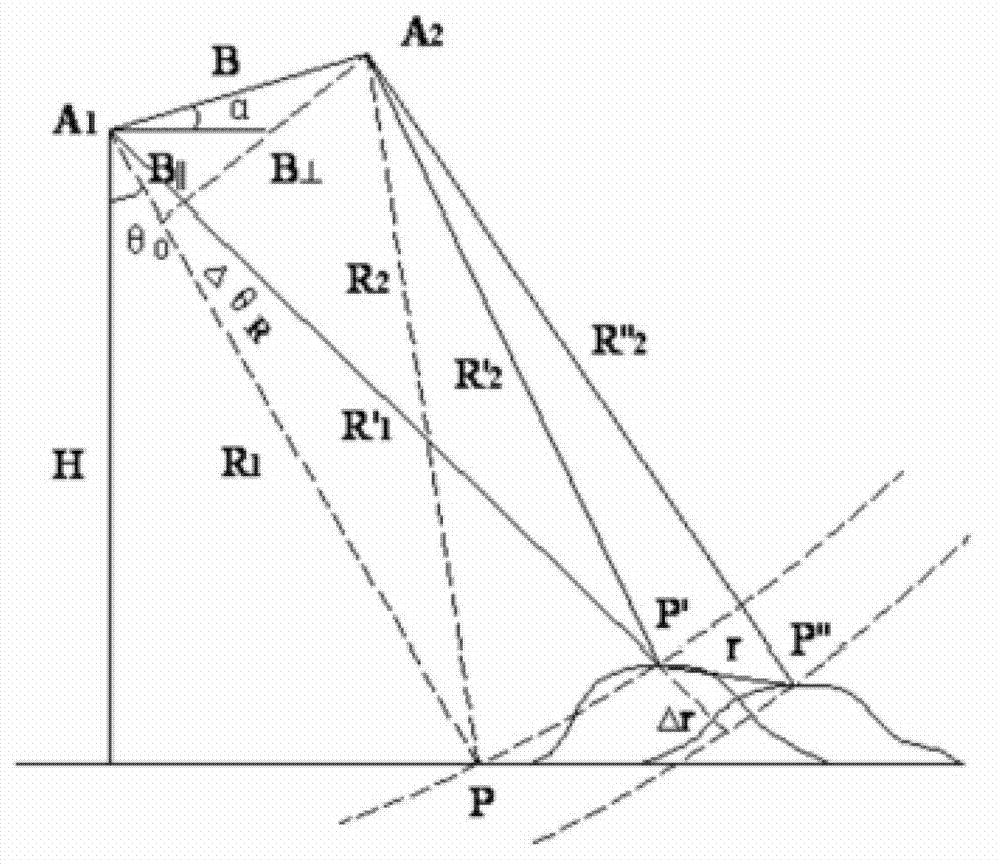
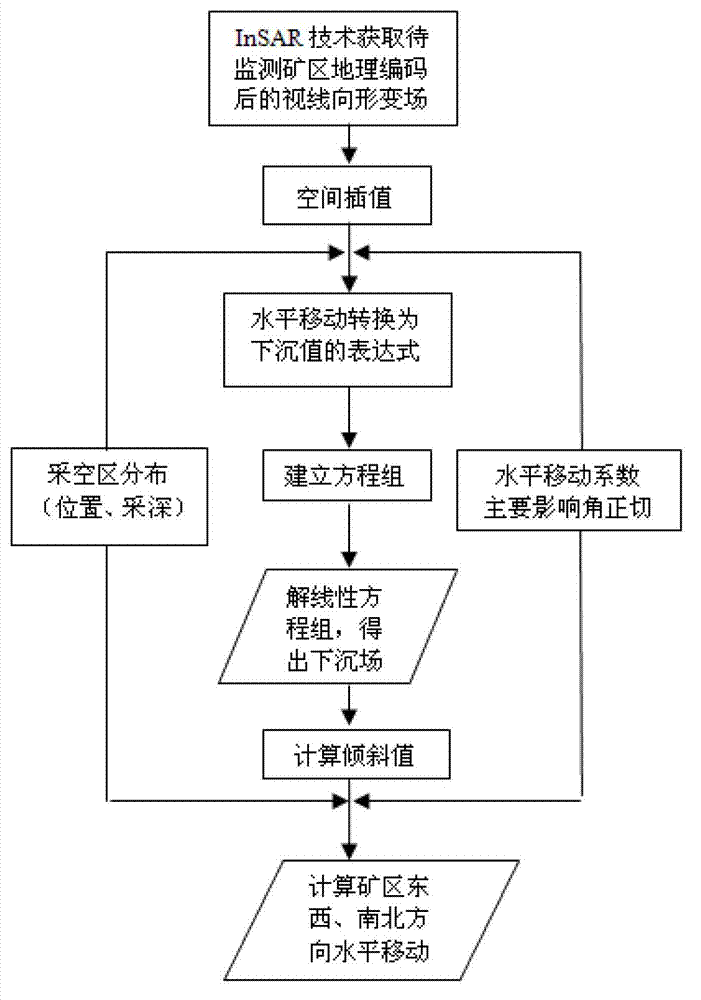
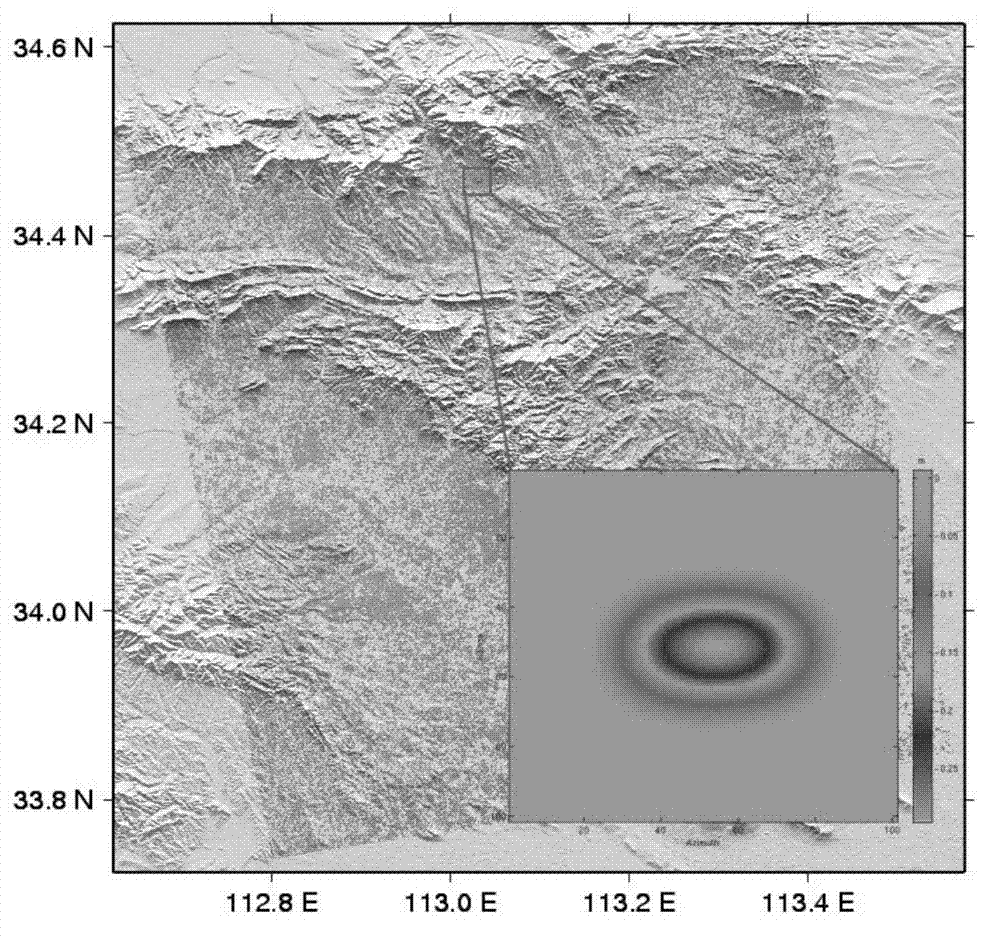
Method for obtaining mining area earth surface three-dimensional deformation fields through single interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) interference pair
ActiveCN102927934AHigh precisionBreak through the strict requirementsUsing wave/particle radiation meansEffective radiusInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a method for obtaining mining area earth surface three-dimensional deformation fields through a single interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) interference pair. The method includes that a mining field radar sight deformation field is obtained through an InSAR technology, pixels with coherence which is lower than an unwrapping threshold value in the sight deformation field is subjected to spatial interpolation to obtain a spatial continuous deformation field, main effective radius of each pixel is calculated through mining area working face distribution and main effective angles, after mining area horizontal shifting coefficients are obtained, the mining area earth surface horizontal shifting is converted to an expression of a sinking value, an equation set is formed according to the radar imaging principle, the equation set is solved to obtain a solution of the earth surface sinking value, according to the sinking value, tilting values of east, west, south and north directions are calculated, and the deformation fields of the east, west, south and north directions are calculated according to a proportional relation among the tilting values of the east, west, south and north directions and the horizontal shifting. The method has the advantages that the restrictions that when the three-dimensional deformation field is solved by the aid of the InSAR, the requirements for data are strict, the monitoring cost is high and the like are broken, and the application space of the InSAR technology in the mining area is greatly widened.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
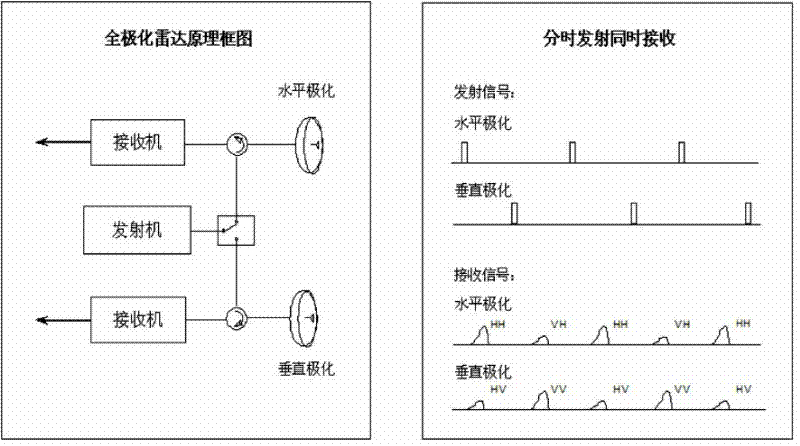
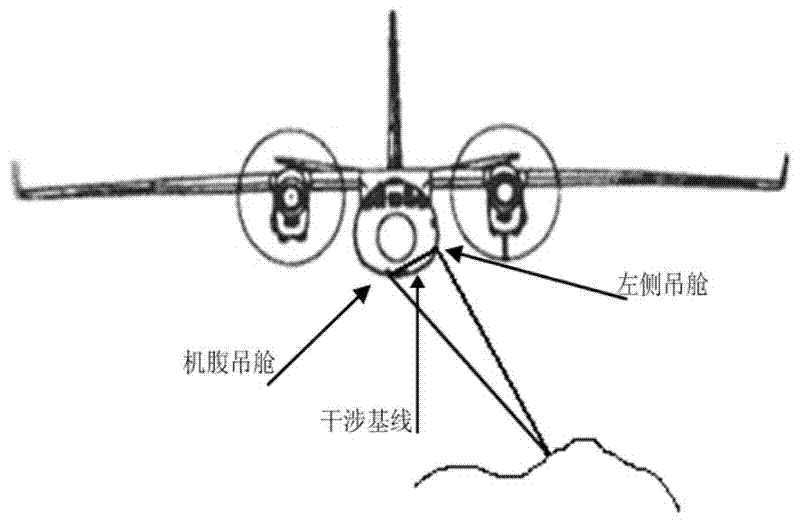
Single-pass full-polarization interferometric synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
ActiveCN102331575ARadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radar3d topography
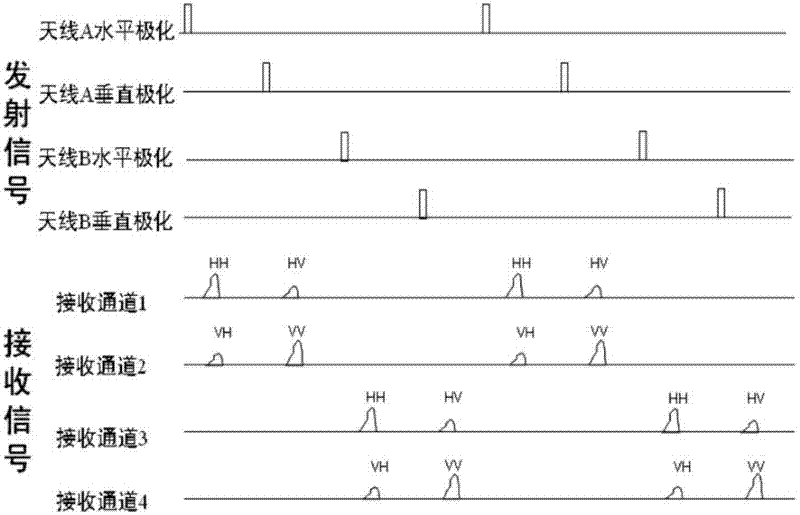
The invention relates to a single-pass full-polarization interferometric synthetic aperture radar (SAR) which combines a polarization technology and an interferometric technology. The single-pass full-polarization interferometric SAR comprises a dual-polarization active phased-array antenna, a receiving sub-machine, a calibration and acquisition sub-machine, a monitoring sub-machine, a distribution sub-machine and a recorder. By adoption of the single-pass full-polarization interferometric SAR, the polarization interferometric SAR data of eight channels can be simultaneously obtained, and a three-dimensional topographic map of a target scene can be obtained through interferometry. The obtained polarization interferometric SAR data can be applied to vegetation parameter inversion in forestry and agriculture and can be also applied to detection of surface deformation in an earthquake disaster and large-area three-dimensional topographic mapping.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Mining lot exploiting and monitoring method based on interferometric synthetic aperature radar (InSAR) technology
ActiveCN103091675AExpand application spaceLow costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarRadar
The invention provides a mining lot exploiting and monitoring method based on interferometric synthetic aperature radar (InSAR) technology. The method includes the steps of obtaining a probability integral method model coefficient of a mining area adjacent to a mining area to be detected, using a radar sight line directional deformation field, obtained through the InSAR technology, of a mining lot to be detected, using the length, the width, the thickness, an exploiting depth, a trend azimuthal angle and a central point coordinate of a working face of the mining area to be detected as unknown numbers, and enabling the unknown numbers and a probability integral method model coefficient of the mining area adjacent to the mining area to be detected to be brought in the probability integral method model, then using a genetic algorithm to search and obtain a parameter value of the working face of the mining area to be detected, finally, using the working face parameter value obtained through the genetic algorithm as an initial value of a mode searching method, and obtaining the accurate working face parameter value of the mining area to be detected through iterative search. The mining lot exploiting and monitoring method overcomes the defects in the prior art that only an approximate exploiting location can be obtained in the process of exploiting monitoring to the mining area, and underground goaf detailed parameter information can not be obtained accurately, greatly expands the application space of the InSAR technology in the mining area, and provides a mining area exploiting fine monitoring method which is low in cost and large-scale.
Owner:经通空间技术(河源)有限公司
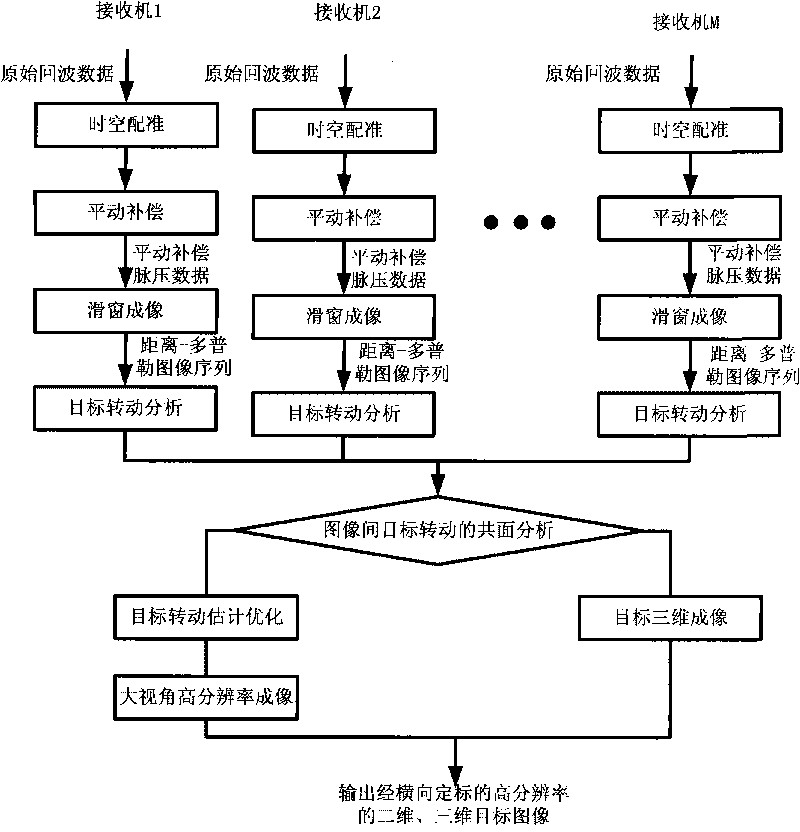
Method for estimating target rotation of inverse synthetic aperture radar based on time-space image sequence
InactiveCN101738614AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed stabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarHigh resolution imaging
The invention discloses a method for estimating target rotation of an inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) based on time-space image sequence, which comprises the following steps: acquiring a time-dimensional RD image sequence of the ISAR according to the received echo data; and analyzing and estimating the rotation of a target by tracking attitude change between images caused by the rotation of the target; judging whether the rotation planes of the target in any two RD images are coplanar according to a time-space two-dimensional image sequence acquired by a single receiver or a plurality of receivers; when the rotation planes are coplanar, further improving the estimation precision of a rotation parameter through a dominant point method or a rotation related method; moreover, realizing large-angle high-resolution imaging by PFA or CBP algorithm; and when the rotation planes are non-coplanar, estimating the azimuth and pitching rotation information of the target so as to realize three-dimensional imaging of the target. The method ensures the target rotation estimation precision and stability, and meanwhile can improve the performance of the ISAR imaging in the three aspects of transverse calibration, large-angle high-resolution imaging and three-dimensional imaging. Moreover, compared with the conventional target rotation estimation method, the method has high precision, and is easy in engineering realization.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Polarization interference synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging method based on polarization data amalgamation
InactiveCN101369019AReduce computing timeShorten the timeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarDecomposition
Disclosed is a three-dimensional imaging method for a Polarimetric Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (Pol-In-SAR) based on the polarimetric data integration, which belongs to the Polarimetric radar Interferometric measurement data processing technology field. The data is read in and two scattering vectors k1 and k2 are structured to each scattering unit; eigenvalue decomposition is performed on the matrix K1 K1-K2 K2 and three eigenvalues are obtained: Lambada1>0, Lambada1>0 and Lambada3=0; values of formula(1) can be respectively calculated so as to determine which condition the value belongs to; if in condition 1, w=w<(1)> can be calculated according to formula (6); if in condition 2, w=w<(2)> can be calculated according to formula (14); and then Phi[s]=arg(wk1k2w)can be calculated. An enhanced complex image can be obtained according to formula 3); the matrix Omega12=> is calculated; and then Phi[m]=arg(w[Omega12]w) can be calculated according to formula 22). The flat-earth effect is removed on the obtained whole phase map (single view or multi-view); and phase unwrapping is performed by using branch-cut algorithm. The invention has wide application range, and the calculating time is smaller than that of the interference optimization method; and the integrated phase quality is better than that of interference optimization method, the phase quality can be always enhanced despite the original signal level, thereby establishing a fine basis for generating accurate digital elevation model (DEM) in the future.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for compensating relative motion of mobile multiple objective for reverse synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN1727913ARemove lateral distance blurEliminate false targetsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDiffusionInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
A method for compensating relative motion of ISAR mobile multiobject gives motion compensation to subecho by picking up subecho of relative motion object from echo data being compensated primarily of mobile multiobject to overcome influence of Dopple diffusion caused by motion to object imaging ; then carrys out motion compensation secondarily to total echo to eliminate compensation error caused primary compensation for obtaining clear space two ¿C dimensional distrubution map of high speed multiobject .
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi- baseline interference synthetic aperture radar interference phase unwrapping method
InactiveCN101339245AAccurate Dimension EstimationPrecise expansionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTerrainInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
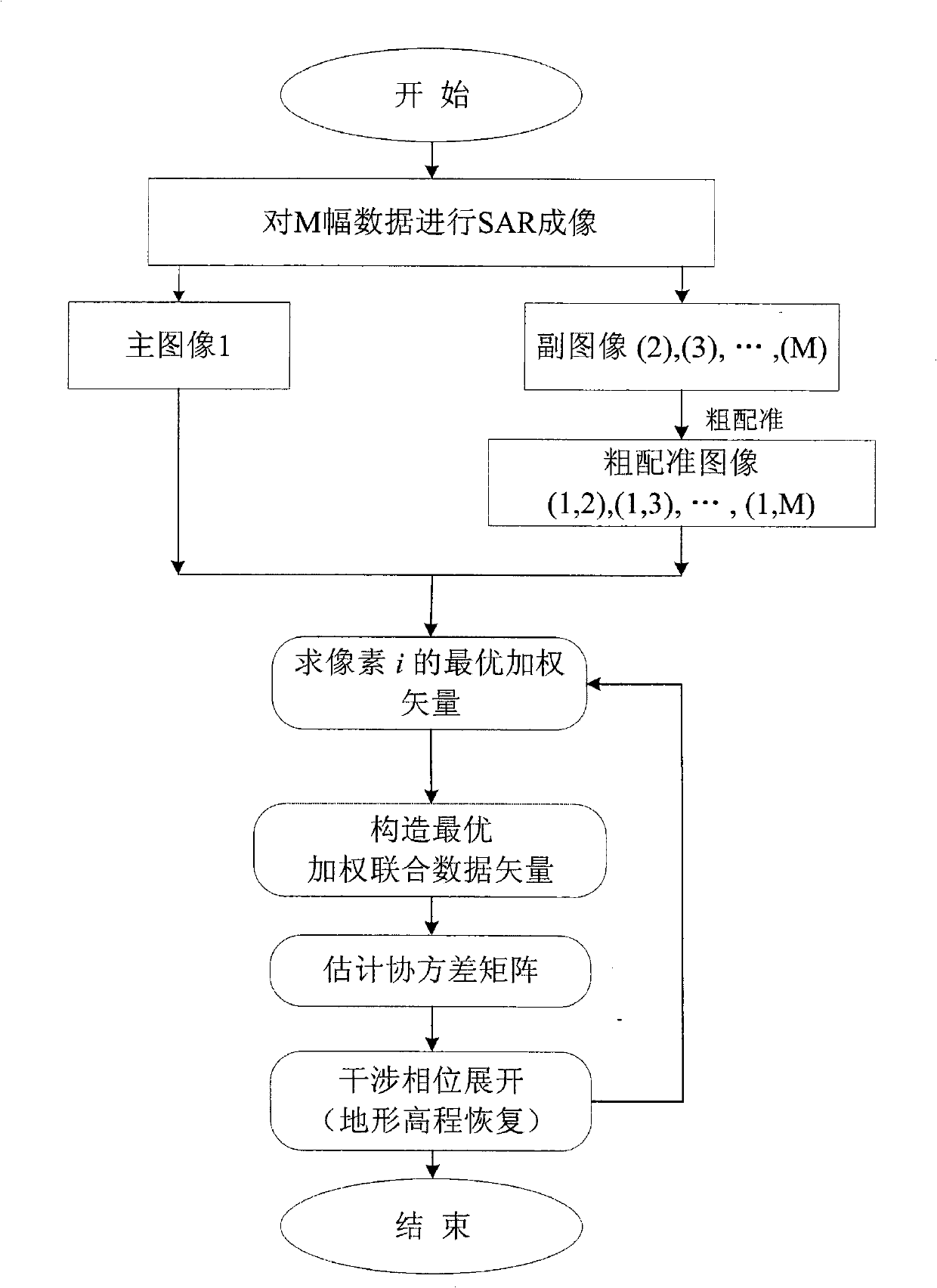
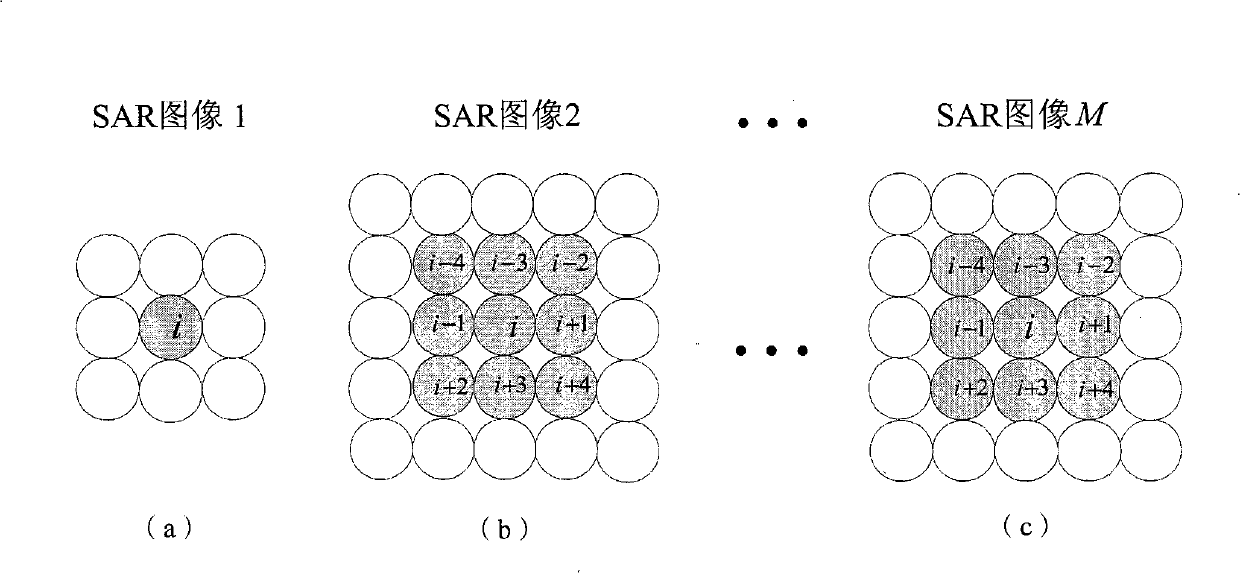
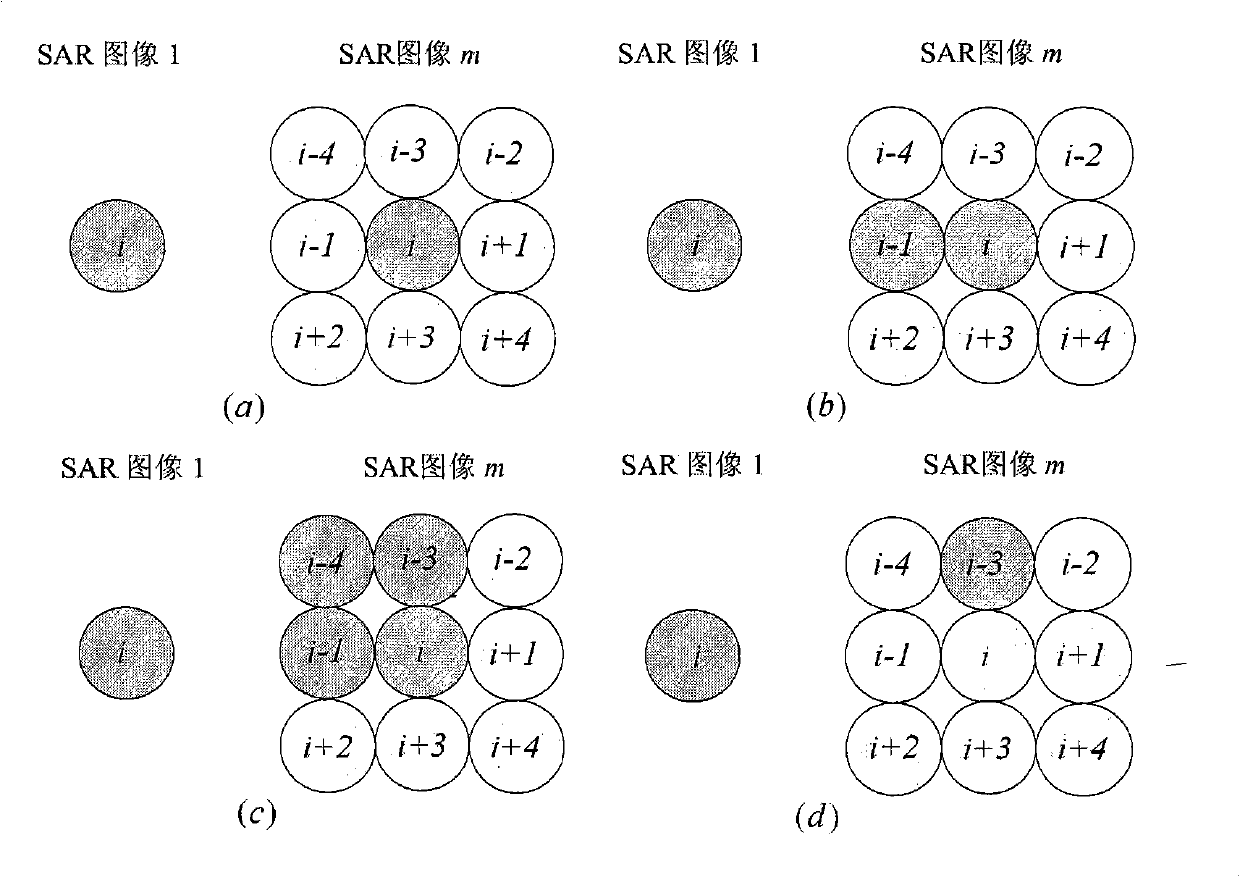
The invention discloses an expansion method of an interference phase of multi-baseline interference synthetic aperture radar. The process is that a SAR imaging processing is carried out respectively to M echo data received by a satellite; any one of the images after the SAR imaging processing is selected as a main image; by using the main image as a reference, a rough registration is carried out respectively to other images through a correlation method so as to obtain M-1 roughly-registered SAR images; A roughly-registered SAR image is used for constructing an optimum weighted joint data vector jx (i, w); a covariance matrix Cov (i, w) is estimated according to the optimum weighted joint data vector and resolved characteristically so as to obtain a cost function; the interference phase phi corresponding to the minimum value of the output power of the cost function is used as the deployment result of the interference phase; the above-mentioned relevant process is repeated respectively to each of pixels to obtain the expansion result of the interference phase of the entire image. The expansion method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of small calculating amount and accurate expansion of the interference phase when the SAR image registration accuracy is bad, thereby being used for the reconstruction of a ground three-dimensional terrain with high resolution and high precision and the detection of a ground moving target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Target rotation angle estimating and transverse locating method for inverse synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN101498788AAvoid blindnessGuaranteed accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
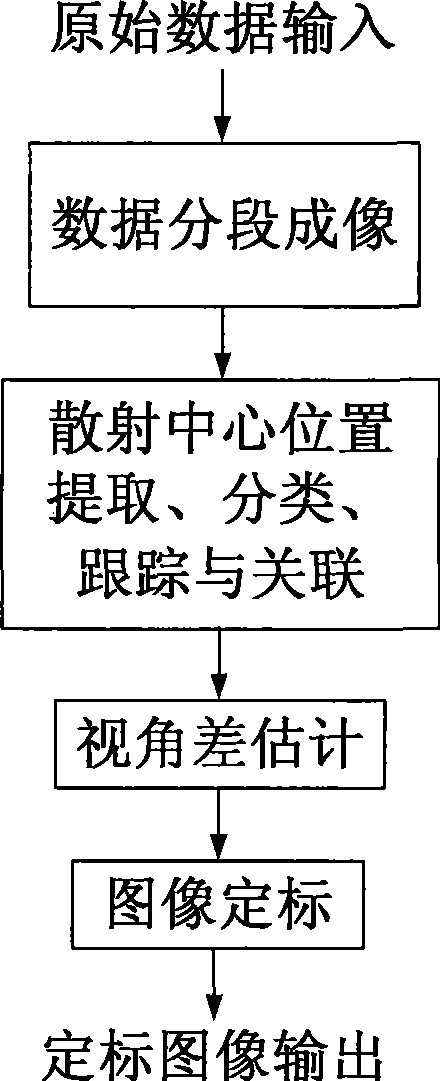
The invention discloses a rotating angle estimating and transverse picketage method for an inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) object. Firstly, ISAR data is imaged section by section; the position information of a scattering center in each image is extracted, and the scattering centers of all images are associated; the scattering centers are classified according to the position information of the scattering centers; the scattering centers are combined in an optimizing mode according to the classification result; a visual angle difference between images formed twice is estimated; the rotating speed of the object with respect to a radar is estimated combining the interval of the images formed twice; and a concerned rotating angle is obtained according to pulse count accumulated by the ISAR images so as to determine the transverse size of the images. The invention does not need to suppose a point scattering model and can restrain the influence of migratory motion of an exceeding resolution element. The treatment for an image field is suitable to select the scattering centers and optimize the estimating result. Compared with a picketage method of a time domain, the invention reduces the amount of calculation the picketage and improves the reliability of the picketage.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
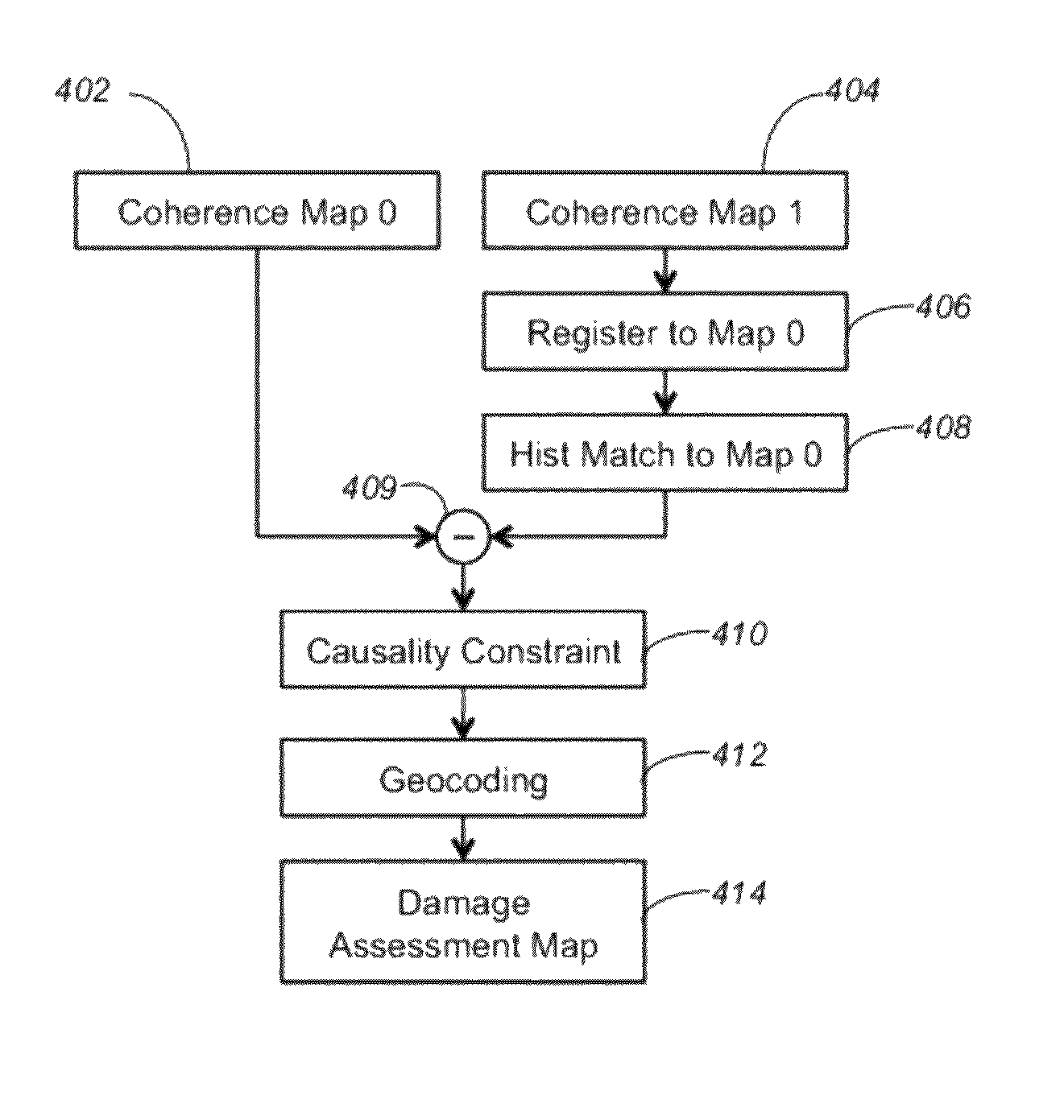
Damage proxy map from interferometric synthetic aperture radar coherence
ActiveUS20120319893A1Durable damageEasy to explainRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarRadar
A method, apparatus, and article of manufacture provide the ability to generate a damage proxy map. A master coherence map and a slave coherence map, for an area prior and subsequent to (including) a damage event are obtained. The slave coherence map is registered to the master coherence map. Pixel values of the slave coherence map are modified using histogram matching to provide a first histogram of the master coherence map that exactly matches a second histogram of the slave coherence map. A coherence difference between the slave coherence map and the master coherence map is computed to produce a damage proxy map. The damage proxy map is displayed with the coherence difference displayed in a visually distinguishable manner.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
External calibration method of satellite-borne interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) system
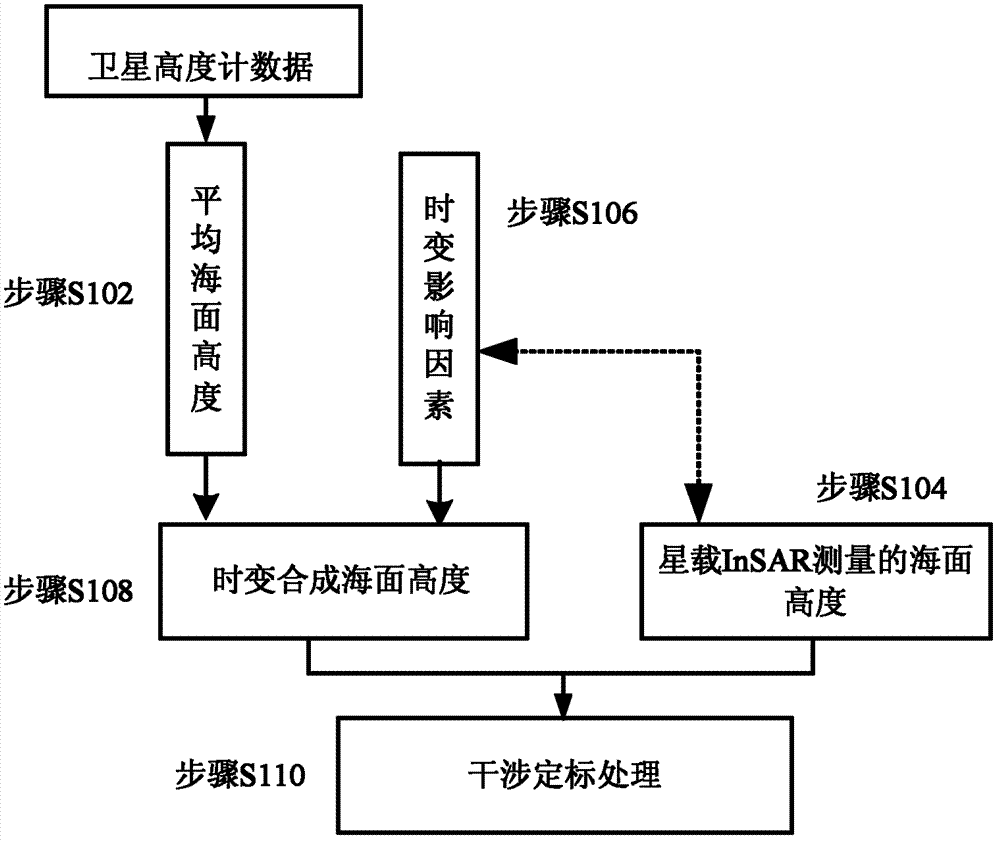
ActiveCN103364766ASolve the shortcomings of difficult long-term dynamic monitoringAvoid Design Implementation DifficultiesWave based measurement systemsNatural satelliteInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses an external calibration method of a satellite-borne interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) system. The external calibration method comprises that sea surface height data is measured by a satellite height gauge, and average sea surface height data is acquired after time varying influence factors are removed; sea surface height data measured by the satellite-borne InSAR system is acquired through sea images and uncalibrated interference parameters of preset time and space distribution acquired by the satellite-borne InSAR system; sea height variation brought about by the time varying influence factors except for the spreading effect under the condition of the preset time and space distribution is calculated in a simulation mode; time varying synthesized sea surface height data is acquired by the average sea surface height and the sea surface height variation brought about by time varying influence factors except for the spreading effect; and the sea surface height data measured by the satellite-borne InSAR system is corrected by taking the time varying synthesized sea surface height data as standard data, thereby realizing calibration of the satellite-borne InSAR system. According to the invention, an external calibration method based on a sea field is adopted, thereby being capable of carrying out long-term dynamic monitoring on slow variation elements in error of the satellite-borne InSAR system.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Computer emulation method for sea-surface imaging of bistatic synthetic aperture radar
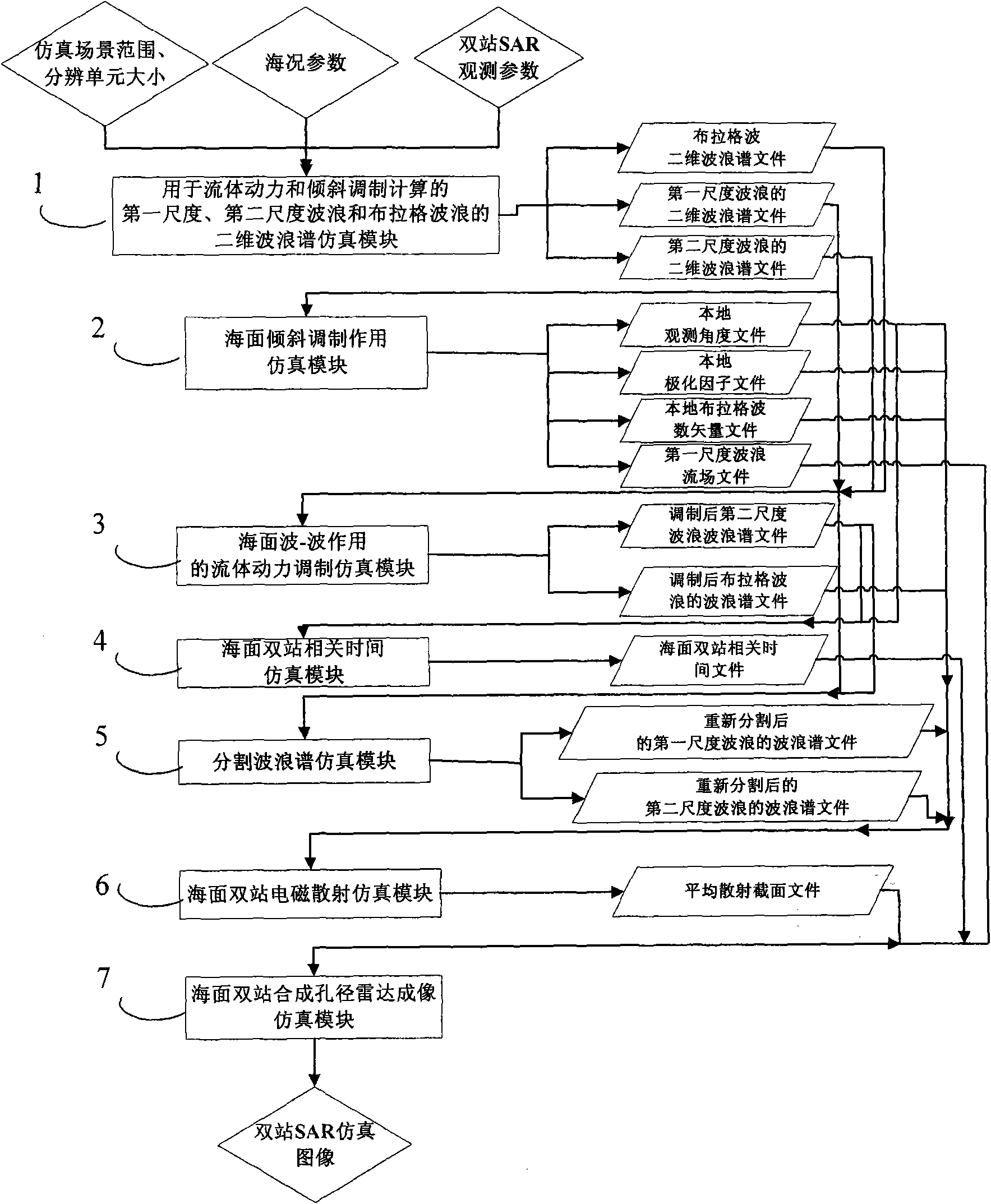
ActiveCN101587500AGood application effectImprove the level ofSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarRadar
The invention provides a computer emulation method for sea-surface imaging of a bistatic synthetic aperture radar, and relates to the technical field of synthetic aperture radar imaging and the field of oceanography. The method simplifies and decomposes emulated true scenes into seven suitable computer emulations in an approximation degree, namely, emulation of sea-surface waves, emulation of tilt modulation generated by wave surfaces of first-scale waves, emulation of fluid power modulation generated by interaction between sea-surface waves, sea-surface bistatic correlation time simulation, divided wave spectrum emulation, sea-surface bistatic electromagnetic scattering emulation, and sea-surface synthetic aperture radar image emulation, and develops software to solve the problems one by one to generate a final emulated bistatic synthetic aperture radar sea-surface image. The method takes files as ports, integrates emulation problems of several subjects, and not only meets the requirement of final emulation, but also facilitates the development of software modules.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
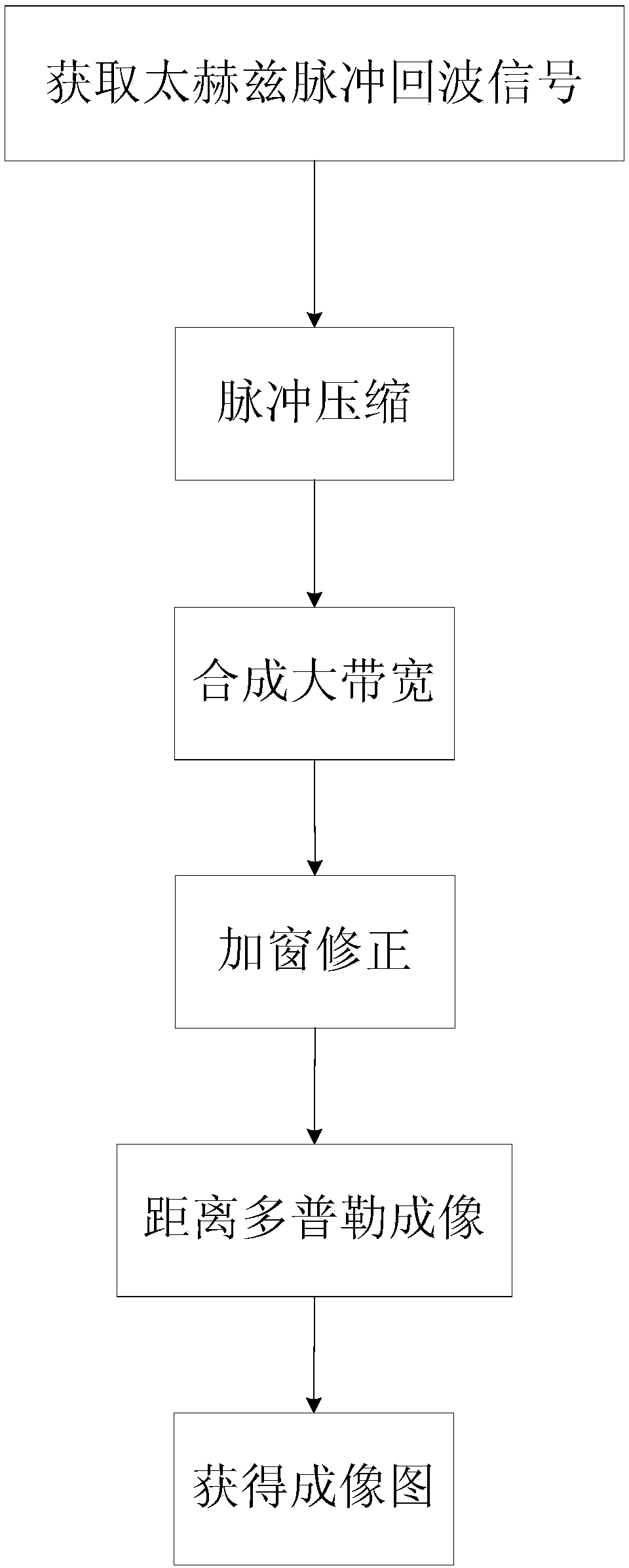
Terahertz inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on frequency modulation step frequency
ActiveCN103454637AAzimuth Resolution RealizationOvercoming the problem of low resolution in the range directionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarTerahertz gap
The invention discloses a terahertz inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on a frequency modulation step frequency to solve the problem that in the prior art, the range resolution and the direction resolution of inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging in the microwave band are not high. The method includes the steps of firstly, obtaining a terahertz pulse echo signal; secondly, conducting pulse compression; thirdly, synthesizing a broadband; fourthly, conducting windowing and correcting; fifthly, conducting distance Doppler imaging; sixthly, obtaining an imaged picture. According to the method, the characteristic that the terahertz wave has the high frequency and the broadband is combined with the frequency modulation step frequency system so that the high-resolution terahertz inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging can be achieved through the method of synthesizing the broadband.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
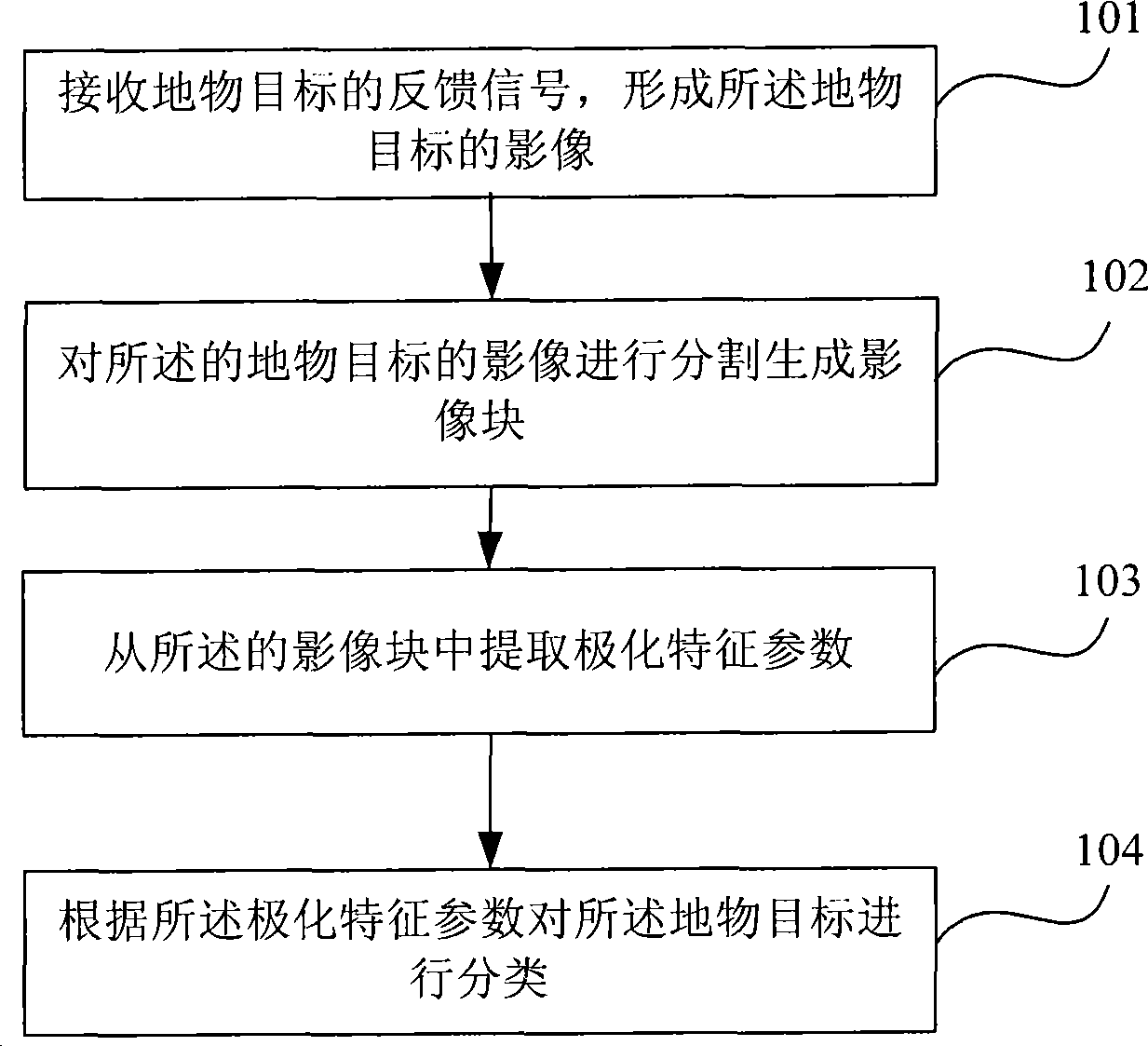
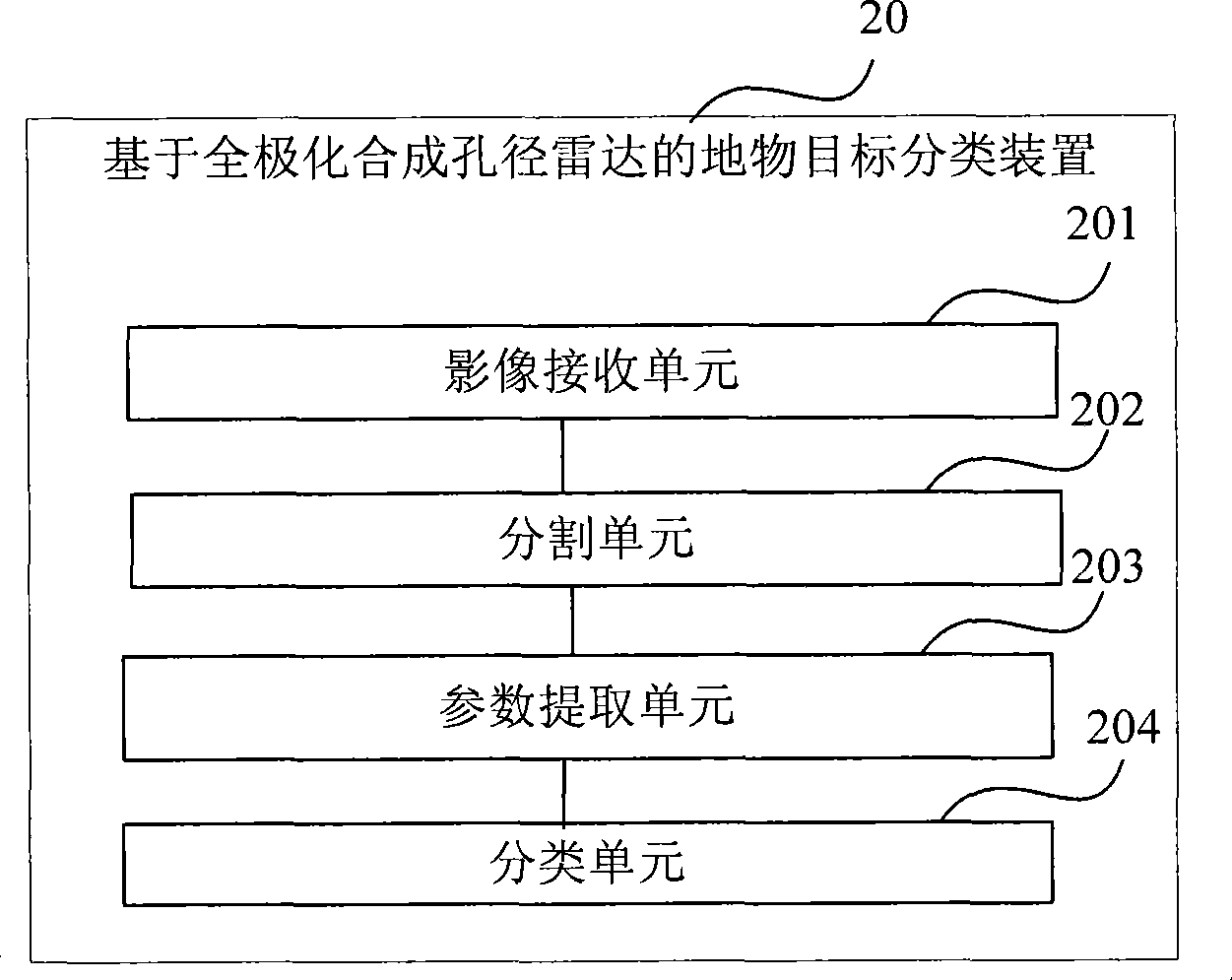
Ground object target classification method and apparatus based on polarimetric synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN101498789ARadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarPolarimetric synthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a ground object target classification method and a device based on a full-polarization synthetic aperture radar (SAR). The method comprises the steps of receiving the feedback signal of a ground object target to form an image of the ground object target, partitioning the image of the ground object target to form image blocks, extracting polarization characteristic parameters from the image blocks and classifying the ground object target according to the polarization characteristic parameters. The device comprises an image receiving unit, a partitioning unit, a parameter extracting unit and a classifying unit, wherein the image receiving unit is used for receiving the feedback signal of the ground object target so as to form the image of the ground object target; the partitioning part is used for partitioning the image of the ground object target so as to form the image blocks; the parameter extracting unit is used for extracting the polarization characteristic parameters from the image blocks; and the classifying unit is used for classifying the ground object target according to the polarization characteristic parameters. The invention provides a solution for realizing high-precision classification of the ground object target with full-polarization SAR image.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
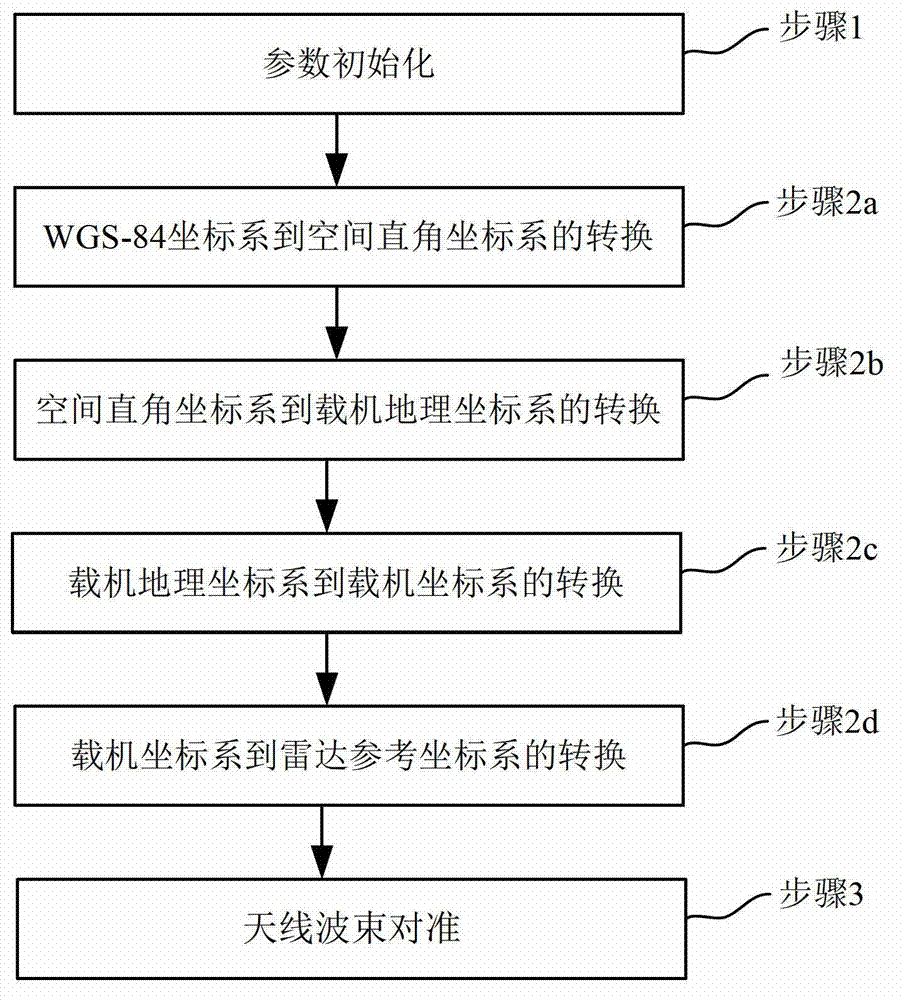
Spatial synchronization method of bistatic synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
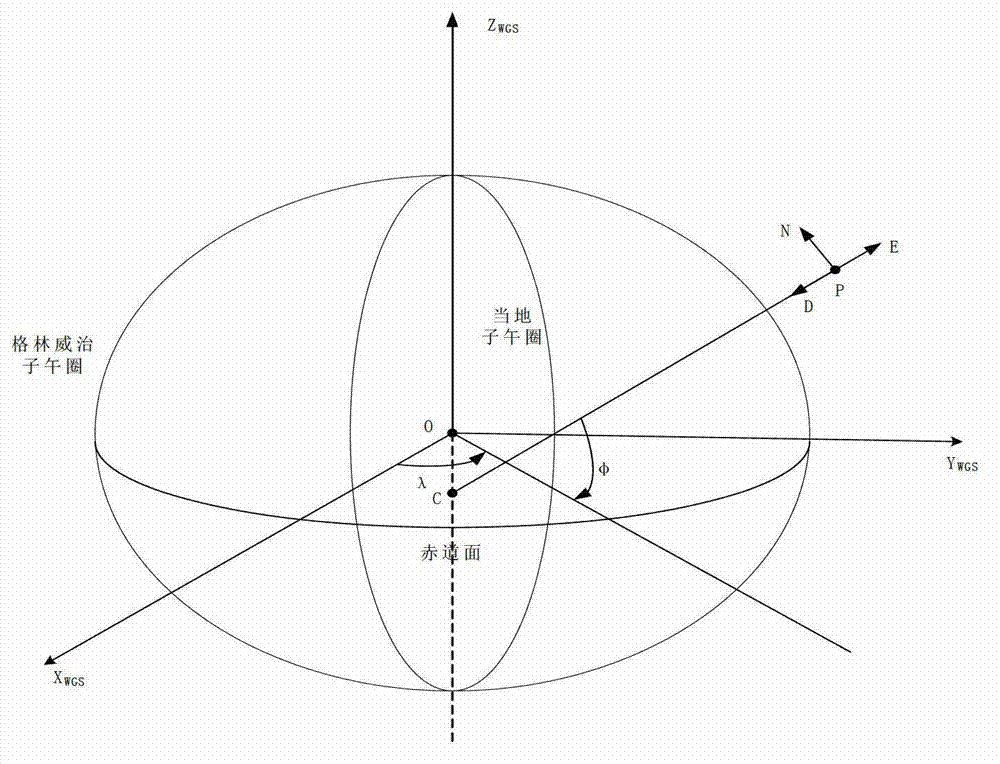
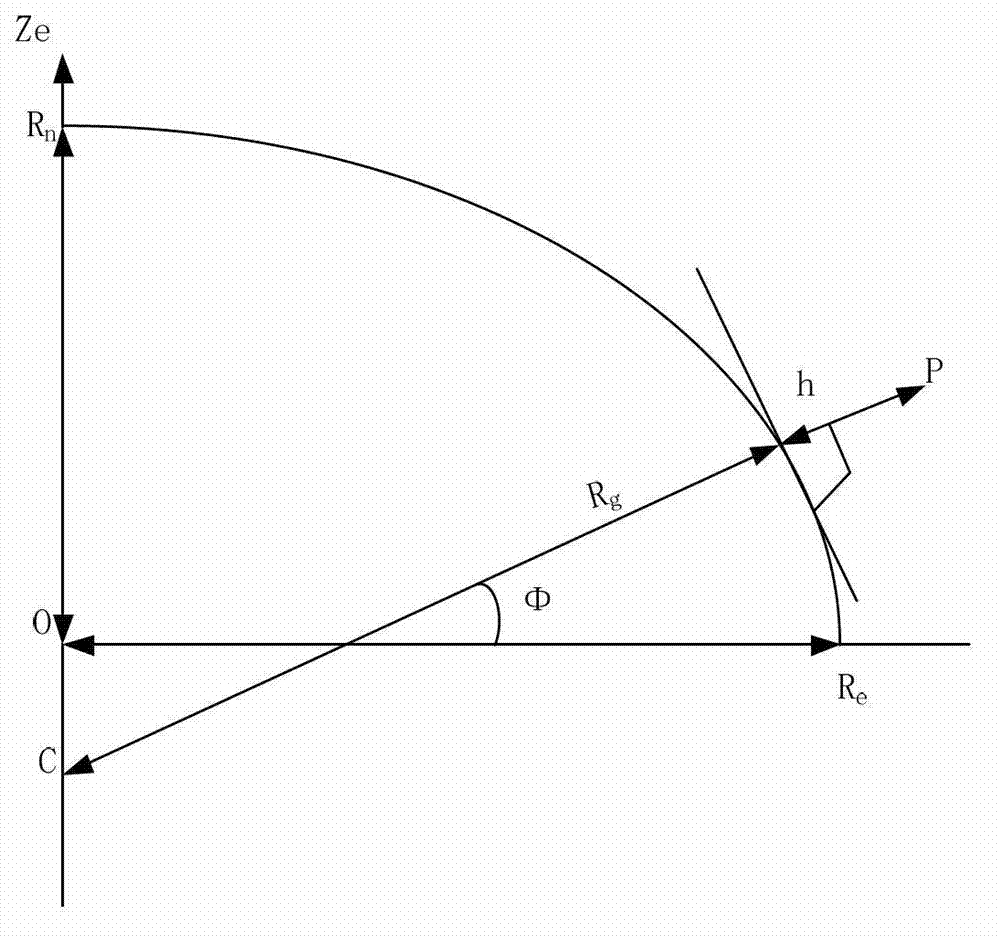
ActiveCN102967851AGuaranteed accuracyPrecise alignmentWave based measurement systemsInterferometric synthetic aperture radarRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses a spatial synchronization method of bistatic synthetic aperture radar (SAR). The method comprises steps of initializing parameters and converting a World Geodetic System (WGS)-84 coordinate system to a spatial rectangular coordinate system; converting the spatial rectangular coordinate system to an aerial carrier geographic coordinate system; converting the aerial carrier geographic coordinate system to an aerial carrier coordinate system; converting the aerial carrier coordinate system to a radar reference coordinate system; and aligning antenna beams. Global positioning system (GPS) special coordinate information and attitude information of an aerial carrier platform are used, the coordinate conversion is conducted in accordance with the sequence of the WGS-84 coordinate system, the spatial rectangular coordinate system, the aerial carrier geographic coordinate system, the aerial carrier coordinate system and the radar reference coordinate system, the accuracy of antenna pointing control parameters which are obtained finally can be guaranteed, the GPS special coordinate information and the attitude information of the aerial carrier platform are used, airborne bistatic SAR antenna pointing control parameters can be exported through the conversion of multi-coordinate systems, and the antenna beam pointing for receiving and transmitting the aerial carrier can be aligned through antenna pointing control parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for processing complex interferometric SAR data
ActiveUS20080231504A1Improves subsidence measurementImprove boundary qualityImage enhancementComputer controlData setInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
A computer system for processing interferometric synthetic aperture radar (SAP) images includes a database for storing SAR images to be processed, and a processor for processing interferometric SAR images from the database. The processing includes receiving first and second complex SAR data sets of a same scene, with the second complex SAR data set being offset in phase with respect to the first complex SAR data set. Each complex SAR data set includes a plurality of pixels. An interferogram is formed based on the first and second complex SAR data sets for providing a phase difference therebetween. A complex anisotropic diffusion algorithm is applied to the interferogram. The interferogram includes a real and an imaginary part for each pixel. A shock filter is applied to the interferogram. The processing further includes performing a two-dimensional variational phase unwrapping on the interferogram after application of the shock filter.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Method for reconstructing target three-dimensional scattering center of inverse synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN103217674AResolve mismatchSmall amount of calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a method for reconstructing target three-dimensional scattering center inverse synthetic aperture radar. The method for reconstructing the target three-dimensional scattering center of the inverse synthetic aperture radar comprises the following steps: conducting continuous image formation on echo data after motion compensation so as to obtain an ISAR two-dimensional image sequence; respectively conducting horizontal scaling and vertical scaling on the information storage and retrieval (ISAR) two-dimensional image sequence so as to obtain a position coordinate of the scattering center; and respectively extracting a position coordinate of the scattering center in an ISAR two-dimensional image of each frame, calculating a displacement velocity field of every two adjacent frames of the scattering center of the ISAR two-dimensional image, combining projection equation and target motion equation of an orthographic projection model so as to obtain estimated values of a third dimension coordinate by combining a projection equation and a target motion equation of an orthographic projection model, and averaging multiple estimated values to obtain the final third dimension coordinate. Therefore, reconstruction of the target three-dimensional scattering center is completed directly. The method for reconstructing the target three-dimensional scattering center of the inverse synthetic aperture radar does not need cost of extra system hardware, can distinguish scattering centers with different heights in the same distance and position resolution unit, does not need to utilize prior information such as observation perspective of the radar, and has relatively small calculating amount.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Polarimetric calibration technique based on natural distribution scenes and rare calibrator
ActiveCN102393513AAvoid layingPreserve polarized scattering featuresWave based measurement systemsChannel dataInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
The present invention relates to a polarimetric calibration technique based on natural distribution scenes and a rare calibrator, which is used for the calibration and correction of distorted polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data. The present invention breaks the calibration bottleneck of domestic machine-borne polarimetric SAR data, and develops a technique which utilizes widely distributed natural ground objects for the crosstalk calibration of polarimetric data without the help of an artificial corner reflector and needs only one or a small amount of triple-sided corner reflectors for the calibration of the imbalance of polarimetric receiving channels. In addition, the technique uses the strength change of natural ground object scenes with wide similar radar backward scattering properties in the distance direction to fit out an antenna directional pattern, and fully utilizes polarimetric ground object information to correct all the polarimetric SAR channel data with the same antenna directional pattern, thereby retaining the polarimetric scattering characteristics of ground object targets before and after correction.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
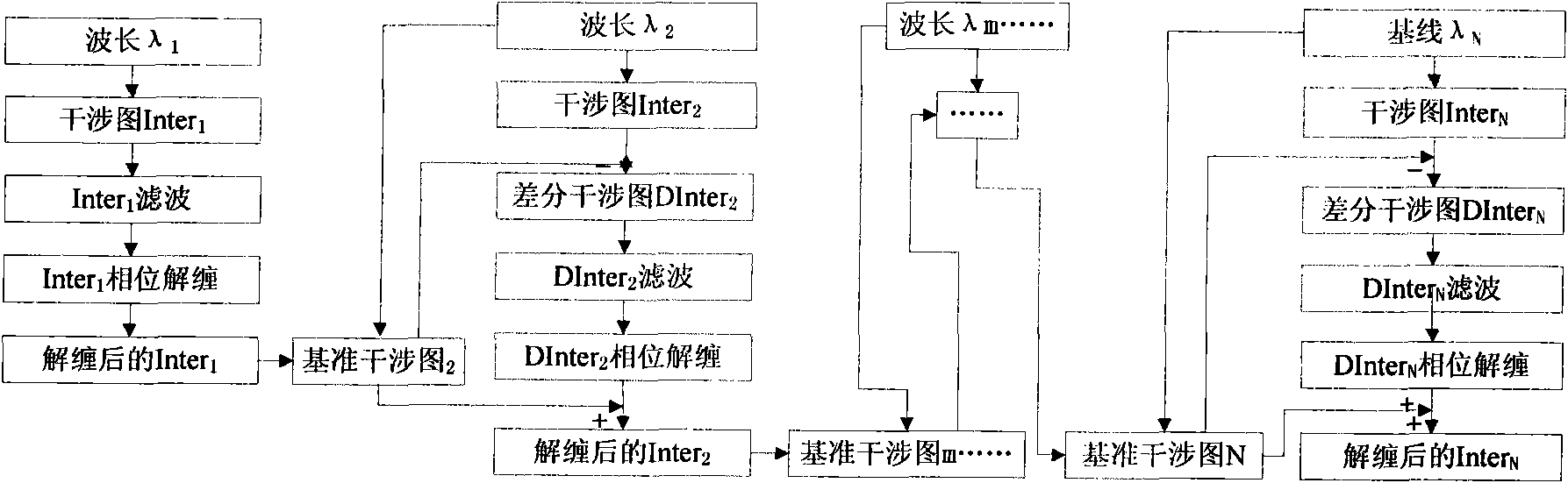
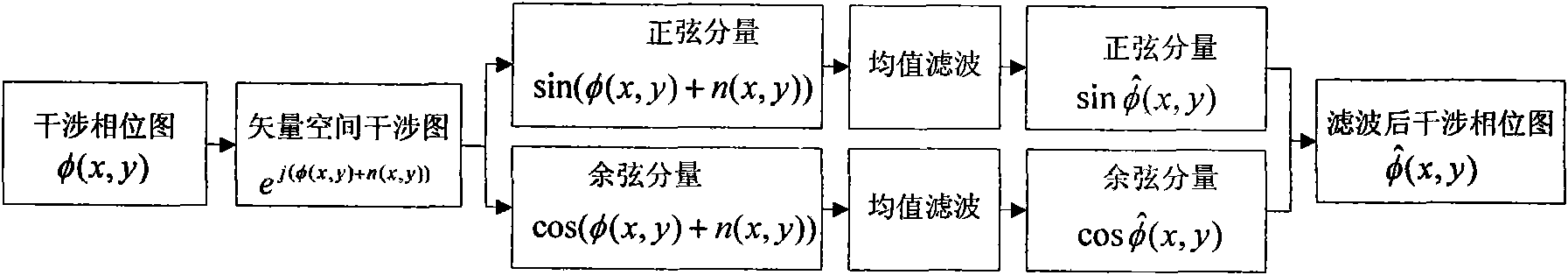
Multiband InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) phase unwrapping method based on differential filtration
InactiveCN101881831ASolving the phase unentanglement puzzleHigh frequencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarFiltration
The invention relates to a Multiband InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) phase unwrapping method based on differential filtration. The method comprises the following steps of: from the beginning of interference data with the longest wavelength and on the basis of carrying out effective unwrapping on a long-wavelength and low-frequency interferogram, generating a short-wavelength and high-frequency reference interferogram from an unwrapped low-frequency interferogram according to a proportional relation among wavelengths, and then carrying out differential filtration on the short-wavelength and high-frequency interferogram and the reference interferogram to obtain a differential interferogram, thereby reducing the fringe frequency of the short-wavelength and high-frequency interferogram; carrying out filtration and phase unwrapping on the differential interferogram, and then obtaining an unwrapping result of the short-wavelength and high-frequency interferogram according to the unwrapping results of the reference interferogram and the differential interferogram; and accordingly, continuously carrying out unwrapping till the lowest-wavelength interferogram. The invention effectively solves the phase unwrapping difficulty of aliasing interference fringes at steep areas under the condition of shorter-wavelength and improves the phase unwrapping solvability and the unwrapping accuracy.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
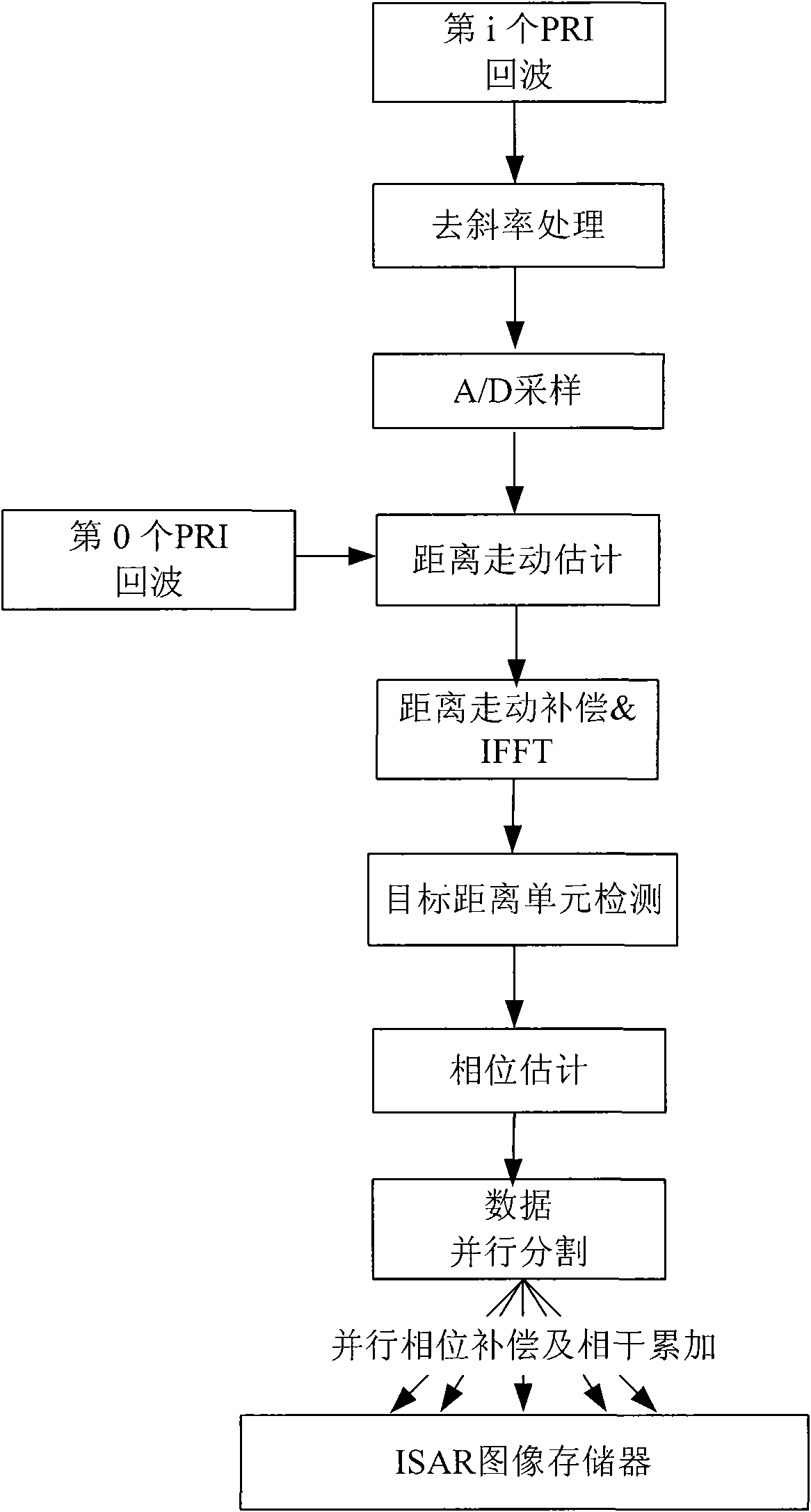
Parallel real-time imaging processing method for inverse synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN101592733AImprove computing efficiencyTo achieve the purpose of real-time imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarDecomposition
The invention provides a parallel imaging processing method for real-time imaging of an inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR). Aiming at the real-time requirement of the ISAR on the imaging of a high-speed moving target, the method adopts parallel processing technology, designs a parallel processing system structure aiming at ISAR imaging, and performs corresponding parallel decomposition on an ISAR algorithm. The method realizes an ISAR imaging algorithm having causality relative to slow time through a reasonable algorithm design to make data acquisition and imaging processing simultaneously performed; and compared with the conventional ISAR imaging serial processing algorithm, the method can greatly improve the operating efficiency of the ISAR imaging so as to realize real real-time processing to facilitate practical application of the ISAR in projects.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
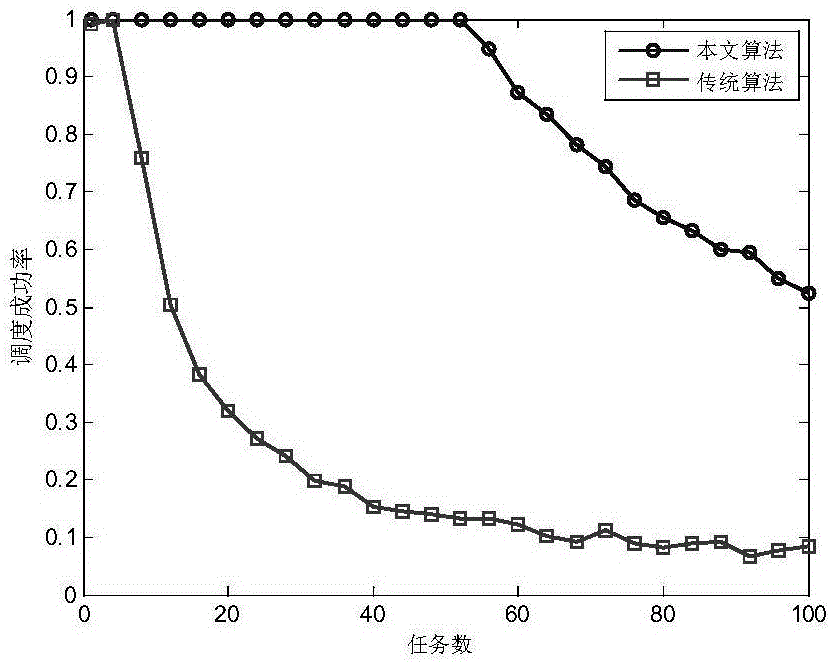
Pulse interlacing-based inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) imaging self-adaptive radar resource scheduling method
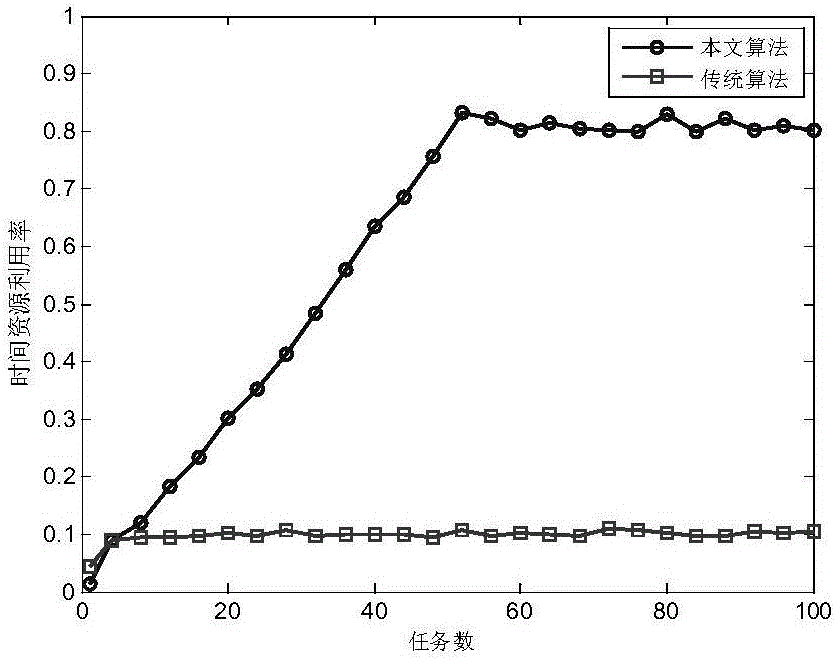
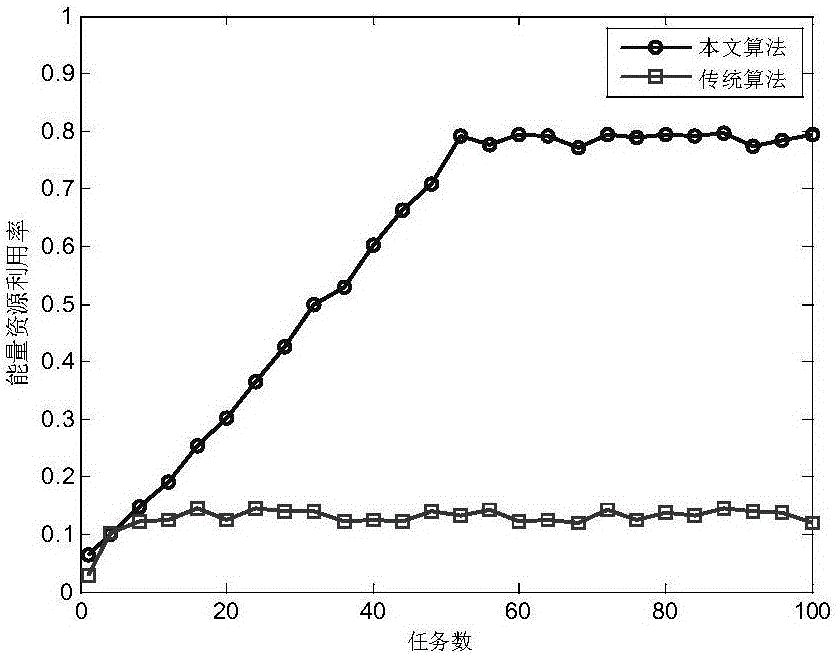
ActiveCN106777679AImprove power utilizationImprove resource utilizationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsInterferometric synthetic aperture radarResource utilization
The invention provides a pulse interlacing-based inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) imaging self-adaptive radar resource scheduling method. The method comprises the steps of 1, sending a small amount of pulse for recognizing target characteristics; 2, calculating parameters such as observation dimension by using recognized results; 3, scheduling all radar imaging tasks by utilizing a pulse interlacing technology under the premise of meeting resource constraint; 4, carrying out sparse aperture observation imaging on the successfully scheduled takes. The method greatly improves the scheduling success rate and resource utilization rate of a system. After the imaging target characteristics are recognized, the saturation capacity of the system can be concluded by means of a changing curve of an average interlacing degree, so that the scheduling method is more effective.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com