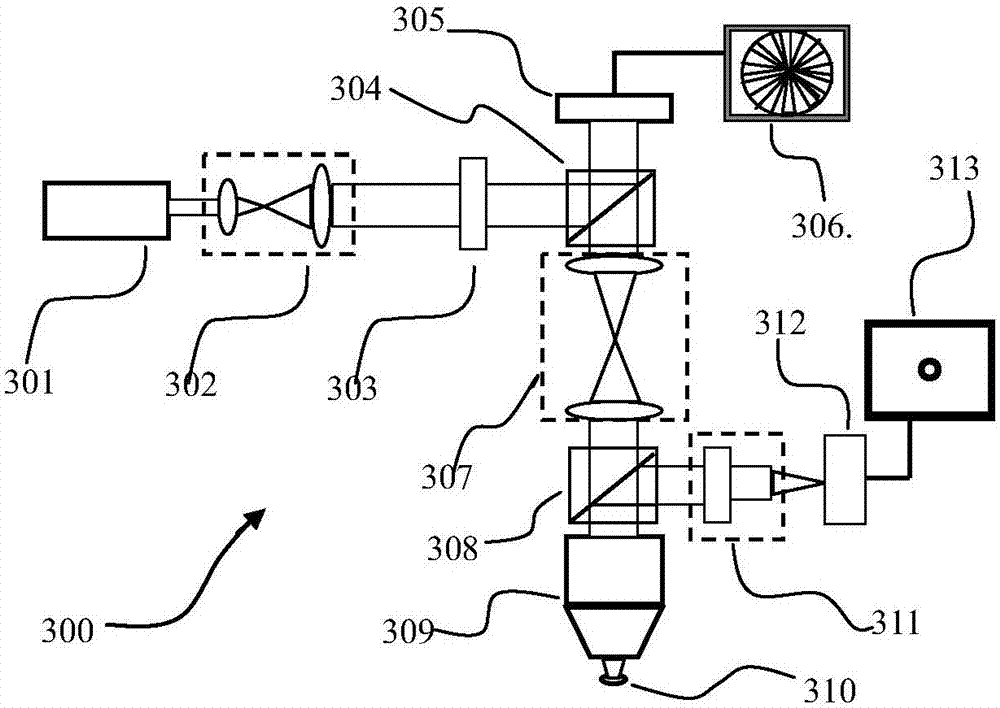
Patents
Literature
131 results about "Phase map" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
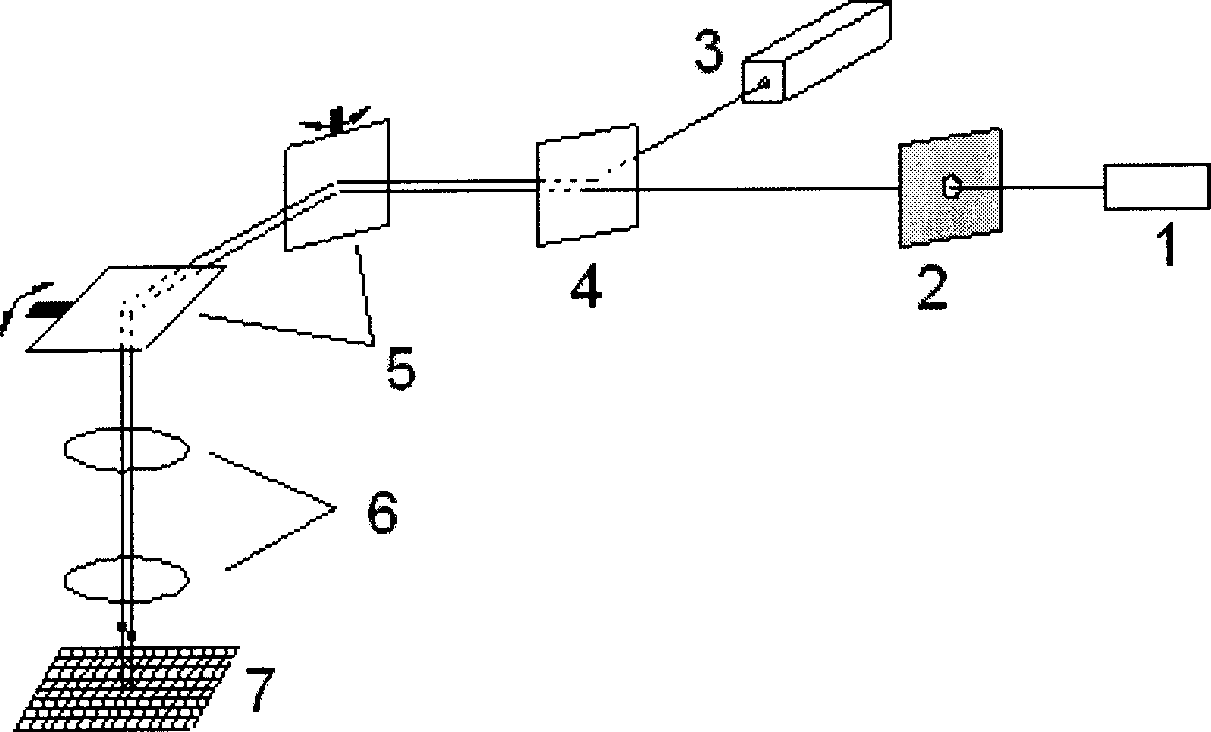
Hybrid method for 3D shape measurement
InactiveUS20110080471A1Provide imageMeasurement speedImage enhancementImage analysis3d shapesHybrid approach
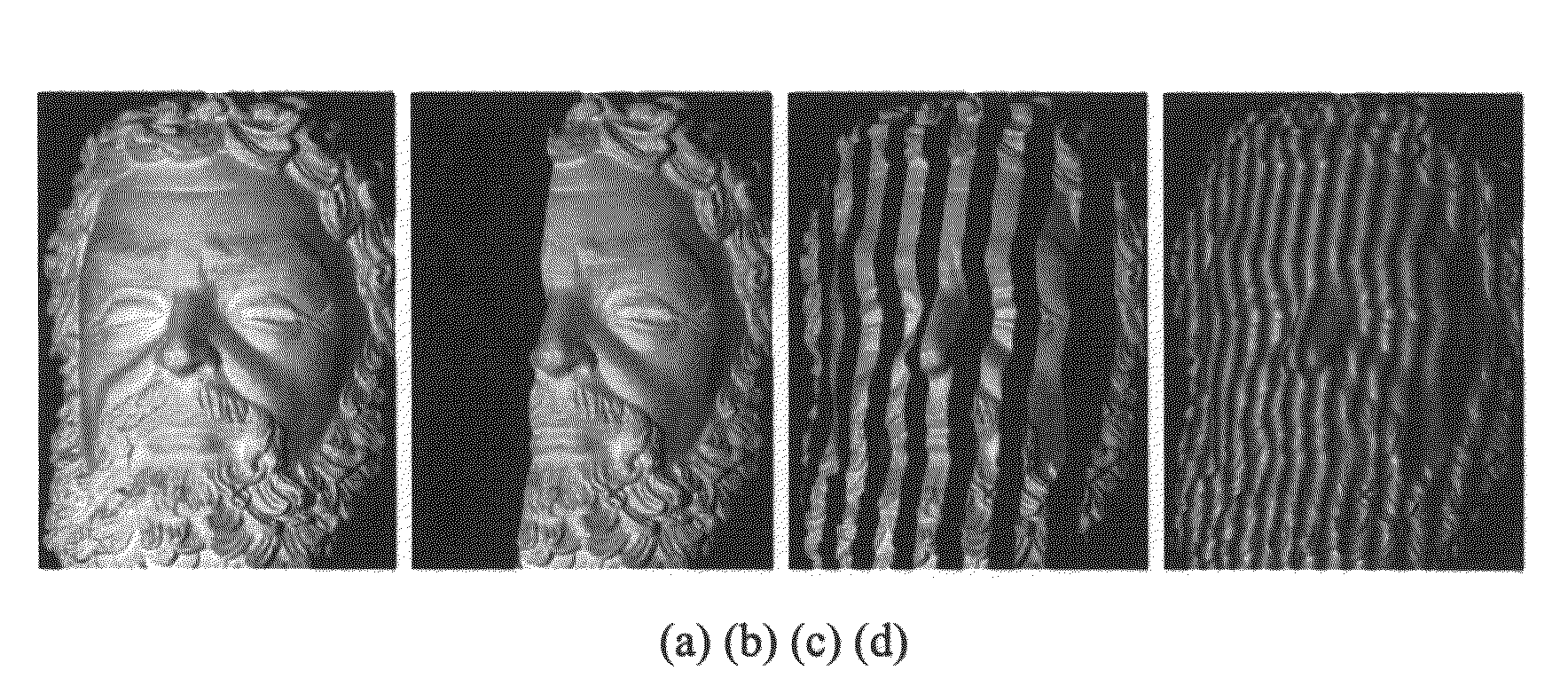
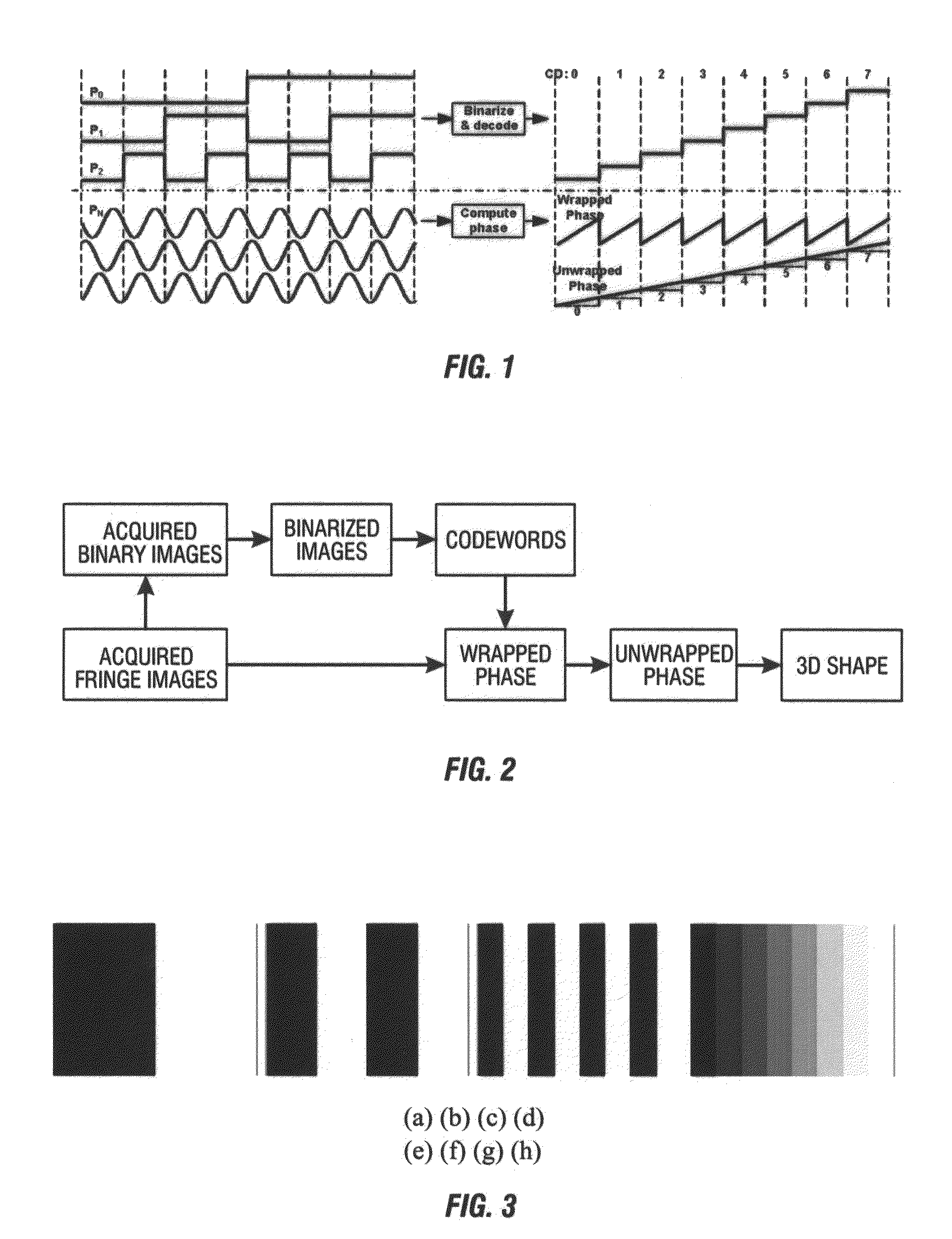
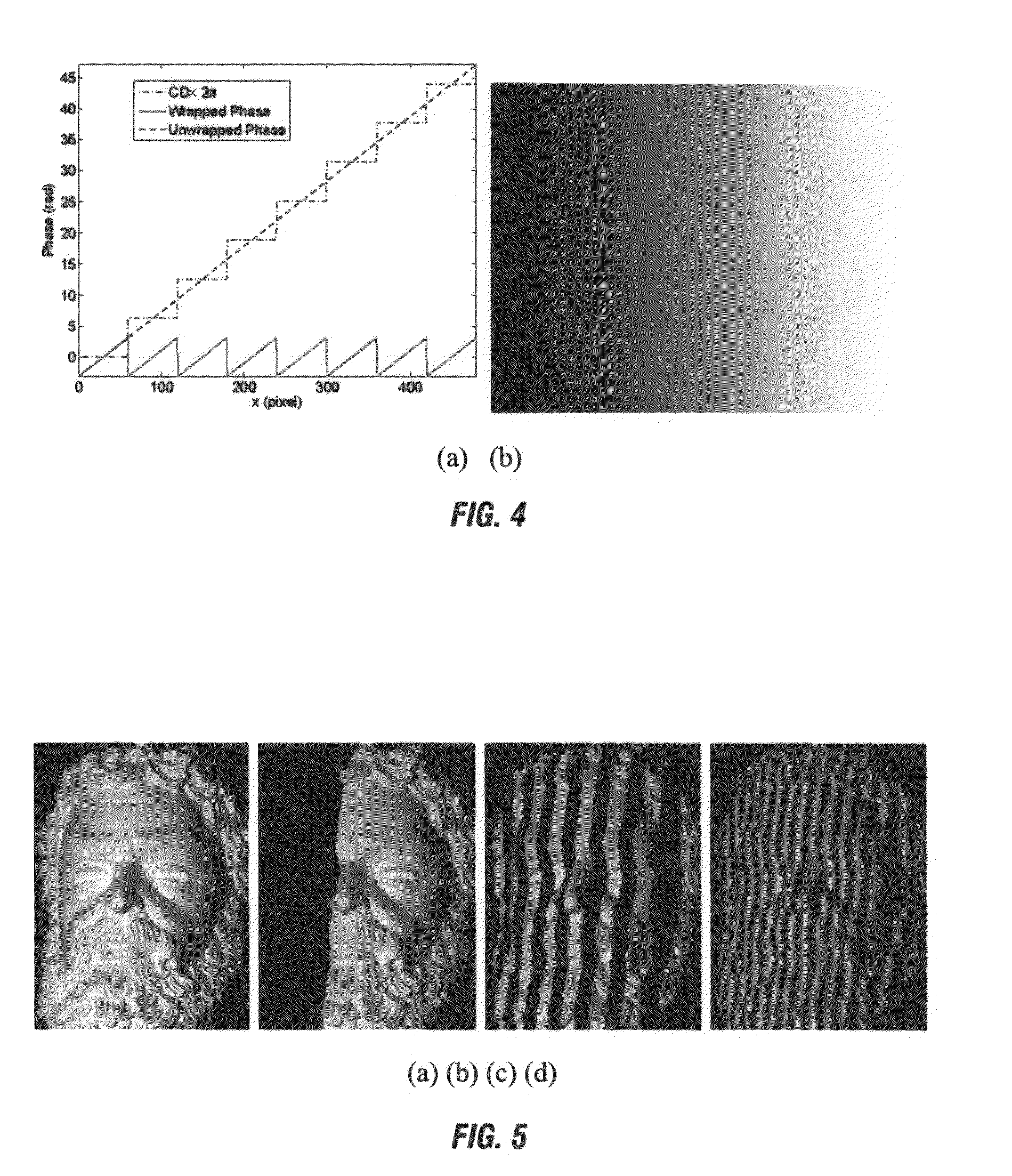
A method for three-dimensional shape measurement provides for generating sinusoidal fringe patterns by defocusing binary patterns. A method for three-dimensional shape measurement may include (a) projecting a plurality of binary patterns onto at least one object; (b) projecting three phase-shifted fringe patterns onto the at least one object; (c) capturing images of the at least one object with the binary patterns and the phase-shifted fringe patterns; (d) obtaining codewords from the binary patterns; (e) calculating a wrapped phase map from the phase-shifted fringe patterns; (f) applying the codewords to the wrapped phase map to produce an unwrapped phase map; and (g) computing coordinates using the unwrapped phase map for use in the three-dimensional shape measurement of the at least one object. A system for performing the method is also provided. The high-speed real-time 3D shape measurement may be used in numerous applications including medical science, biometrics, and entertainment.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method and apparatus for determining object characteristics
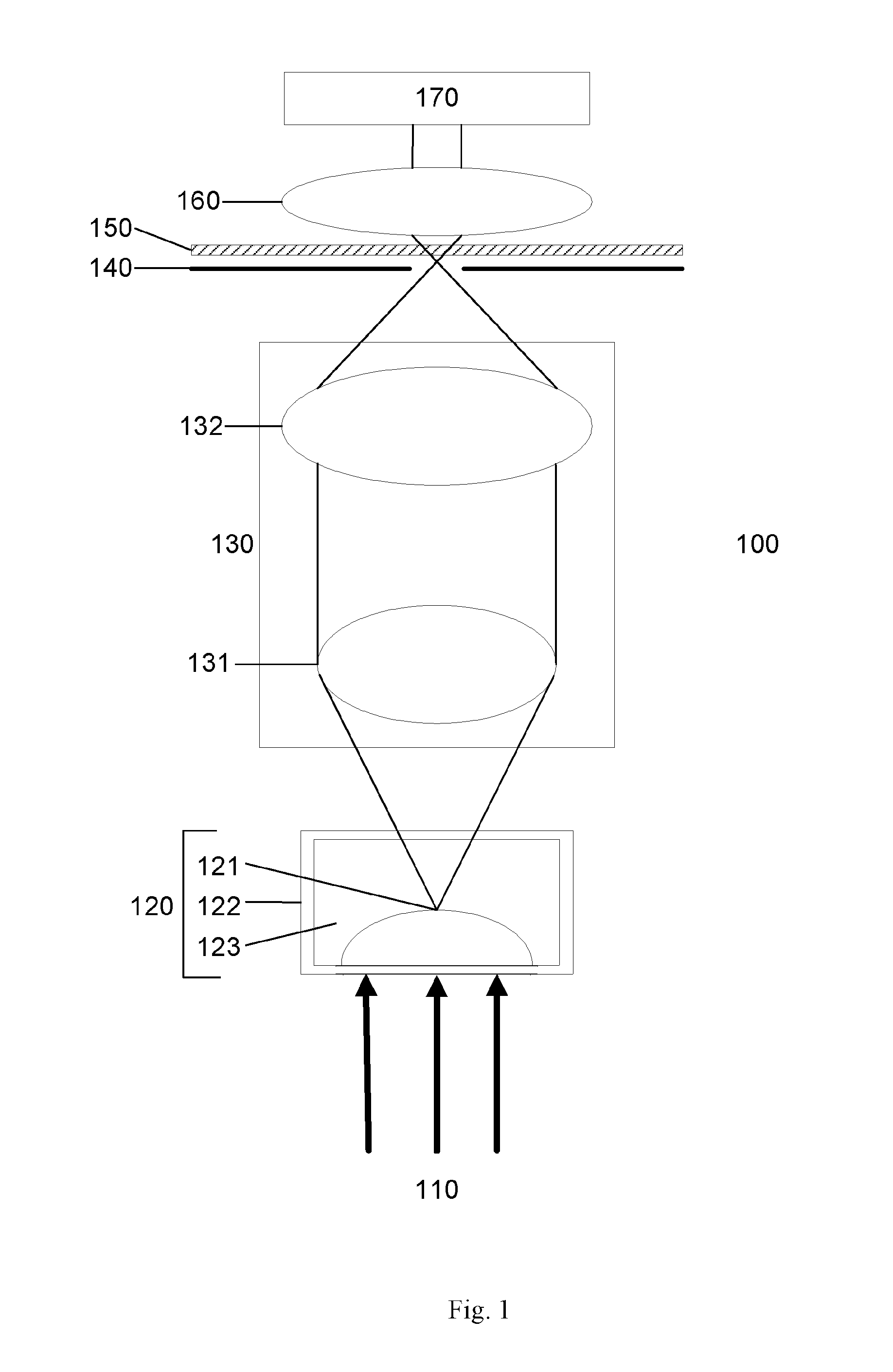
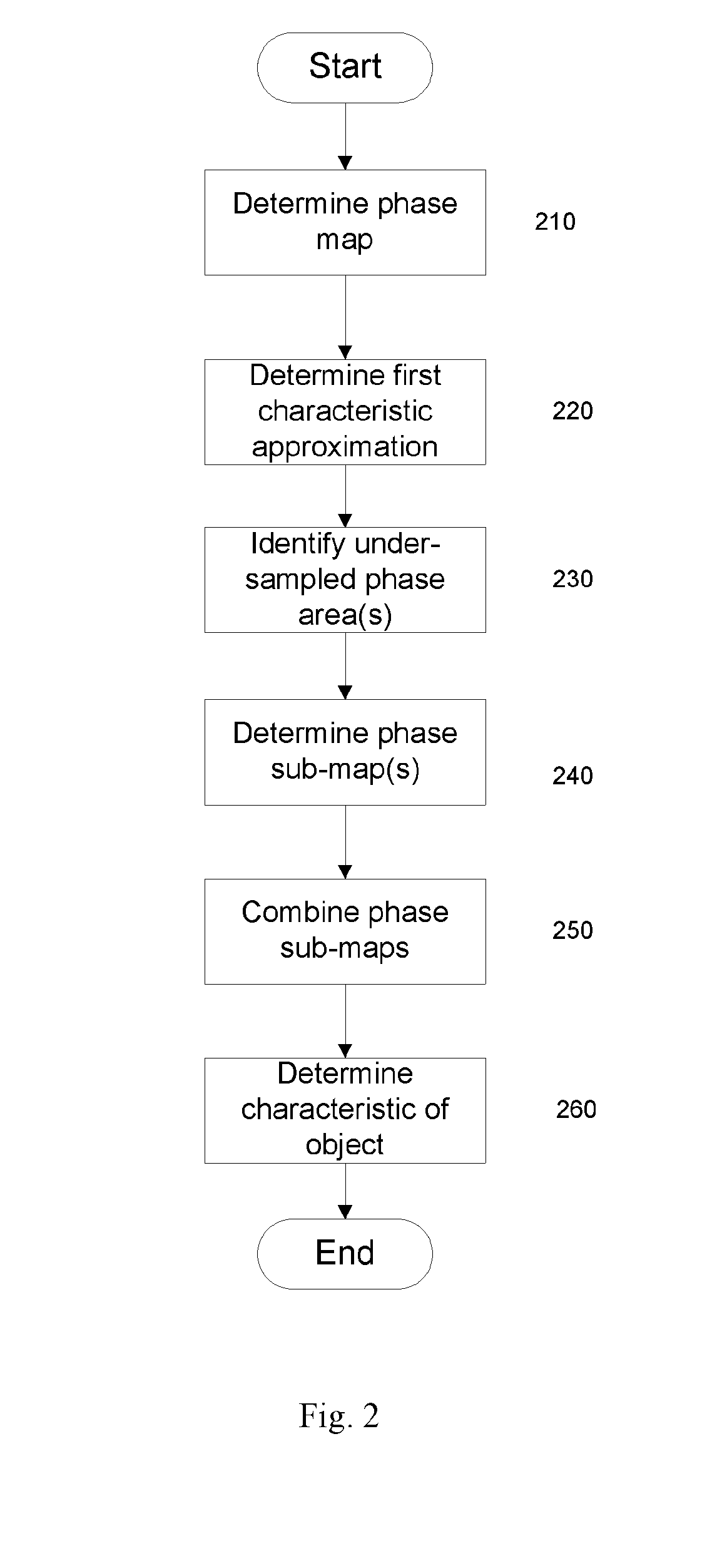
Embodiments of the invention provide a method of determining one or more characteristics of a target object, comprising determining a first phase map for at least a region of a target object based on radiation directed toward the target object, determining one or more further phase maps for a sub-region of the region of the target object, determining a number of phase wraps for the sub-region based on a plurality of phase maps for the sub-region, and determining a characteristic of the region of the target object based on the number of phase wraps for sub-region and the first phase map. Embodiments of the invention also relate to a method of determining one or more characteristics of a target object, comprising determining a phase map for at least a region of a target object based on one or more diffraction patterns, determining a wavefront at a plane of the object based upon the phase map, and determining a refractive property of the object based on the wavefront.
Owner:PHASE FOCUS
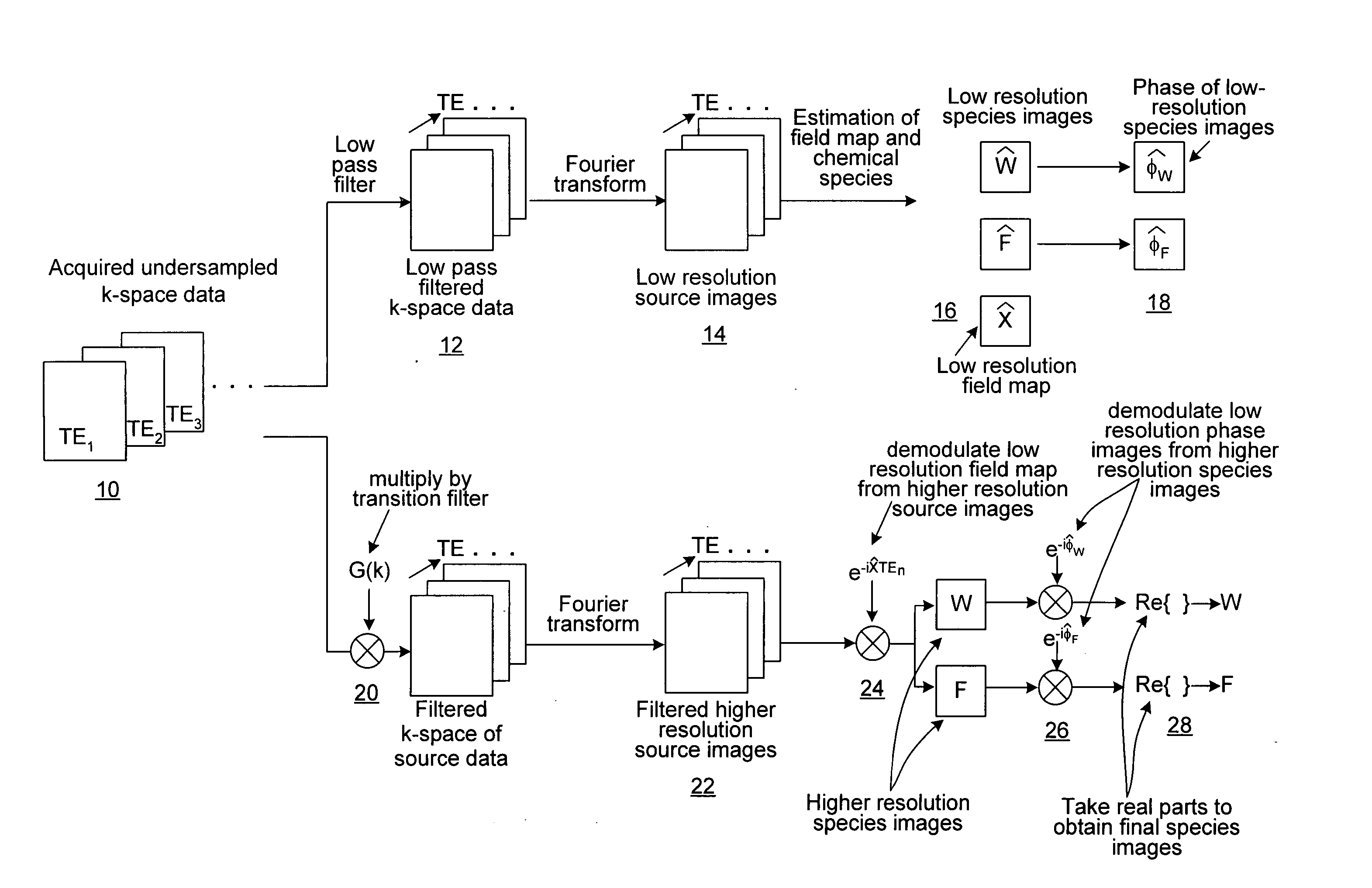
Homodyne reconstruction of water and fat images based on iterative decomposition of MRI signals
ActiveUS7298144B2Maximize resolutionMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionImage resolutionDecomposition
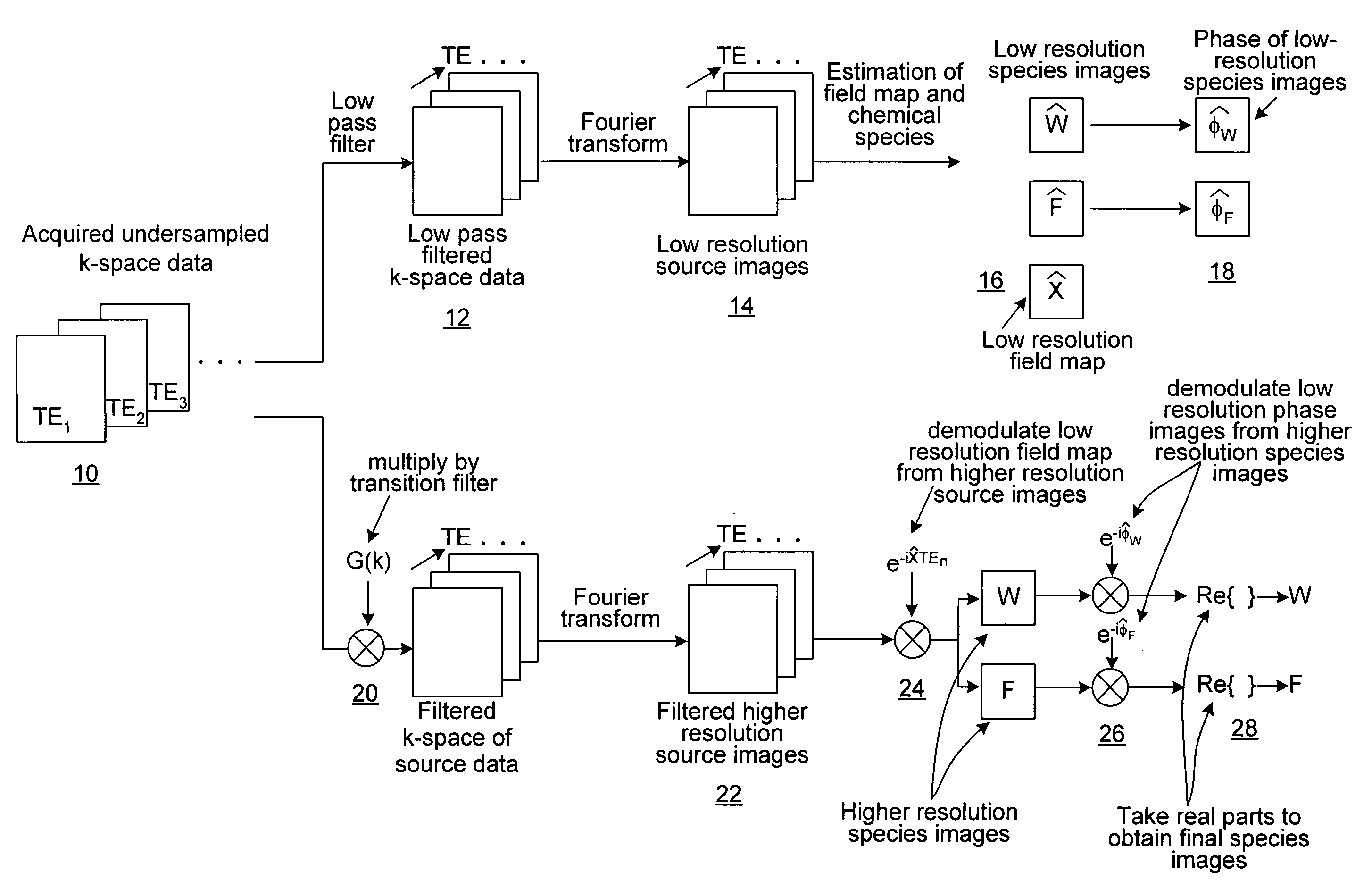
Homodyne image reconstruction is combined with an iterative decomposition of water and fat from MR signals obtained from a partial k-space signal acquisition in order to maximize the resolution of calculated water and fat images. The method includes asymmetrical acquisition of under-sampled MRI data, obtaining low resolution images, and then estimating a magnetic field map and phase maps of water and fat image signals from the low resolution images. The acquired data is again filtered and Fourier transformed to obtain an estimate of combined fat and water signals using the estimated magnetic field map and phase maps. Water and fat images are then estimated from which phases of the water and fat images are determined. The real parts of the water and fat images are then used in calculating water and fat images using a homodyne process.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Polarization interference synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging method based on polarization data amalgamation
InactiveCN101369019AReduce computing timeShorten the timeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarDecomposition
Disclosed is a three-dimensional imaging method for a Polarimetric Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (Pol-In-SAR) based on the polarimetric data integration, which belongs to the Polarimetric radar Interferometric measurement data processing technology field. The data is read in and two scattering vectors k1 and k2 are structured to each scattering unit; eigenvalue decomposition is performed on the matrix K1 K1-K2 K2 and three eigenvalues are obtained: Lambada1>0, Lambada1>0 and Lambada3=0; values of formula(1) can be respectively calculated so as to determine which condition the value belongs to; if in condition 1, w=w<(1)> can be calculated according to formula (6); if in condition 2, w=w<(2)> can be calculated according to formula (14); and then Phi[s]=arg(wk1k2w)can be calculated. An enhanced complex image can be obtained according to formula 3); the matrix Omega12=> is calculated; and then Phi[m]=arg(w[Omega12]w) can be calculated according to formula 22). The flat-earth effect is removed on the obtained whole phase map (single view or multi-view); and phase unwrapping is performed by using branch-cut algorithm. The invention has wide application range, and the calculating time is smaller than that of the interference optimization method; and the integrated phase quality is better than that of interference optimization method, the phase quality can be always enhanced despite the original signal level, thereby establishing a fine basis for generating accurate digital elevation model (DEM) in the future.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Homodyne reconstruction of water and fat images based on iterative decomposition of MRI signals
ActiveUS20060250132A1Maximize resolutionMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionImage resolutionDecomposition
Homodyne image reconstruction is combined with an iterative decomposition of water and fat from MR signals obtained from a partial k-space signal acquisition in order to maximize the resolution of calculated water and fat images. The method includes asymmetrical acquisition of under-sampled MRI data, obtaining low resolution images, and then estimating a magnetic field map and phase maps of water and fat image signals from the low resolution images. The acquired data is again filtered and Fourier transformed to obtain an estimate of combined fat and water signals using the estimated magnetic field map and phase maps. Water and fat images are then estimated from which phases of the water and fat images are determined. The real parts of the water and fat images are then used in calculating water and fat images using a homodyne process.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Spatial Light Interference Microscopy and Fourier Transform Light Scattering for Cell and Tissue Characterization
ActiveUS20120105858A1Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFourier opticsFourier transform on finite groups
Methods and apparatus for rendering quantitative phase maps across and through transparent samples. A broadband source is employed in conjunction with an objective, Fourier optics, and a programmable two-dimensional phase modulator to obtain amplitude and phase information in an image plane. Methods, referred to as Fourier transform light scattering (FTLS), measure the angular scattering spectrum of the sample. FTLS combines optical microscopy and light scattering for studying inhomogeneous and dynamic media. FTLS relies on quantifying the optical phase and amplitude associated with a coherent image field and propagating it numerically to the scattering plane. Full angular information, limited only by the microscope objective, is obtained from extremely weak scatterers, such as a single micron-sized particle. A flow cytometer may employ FTLS sorting.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
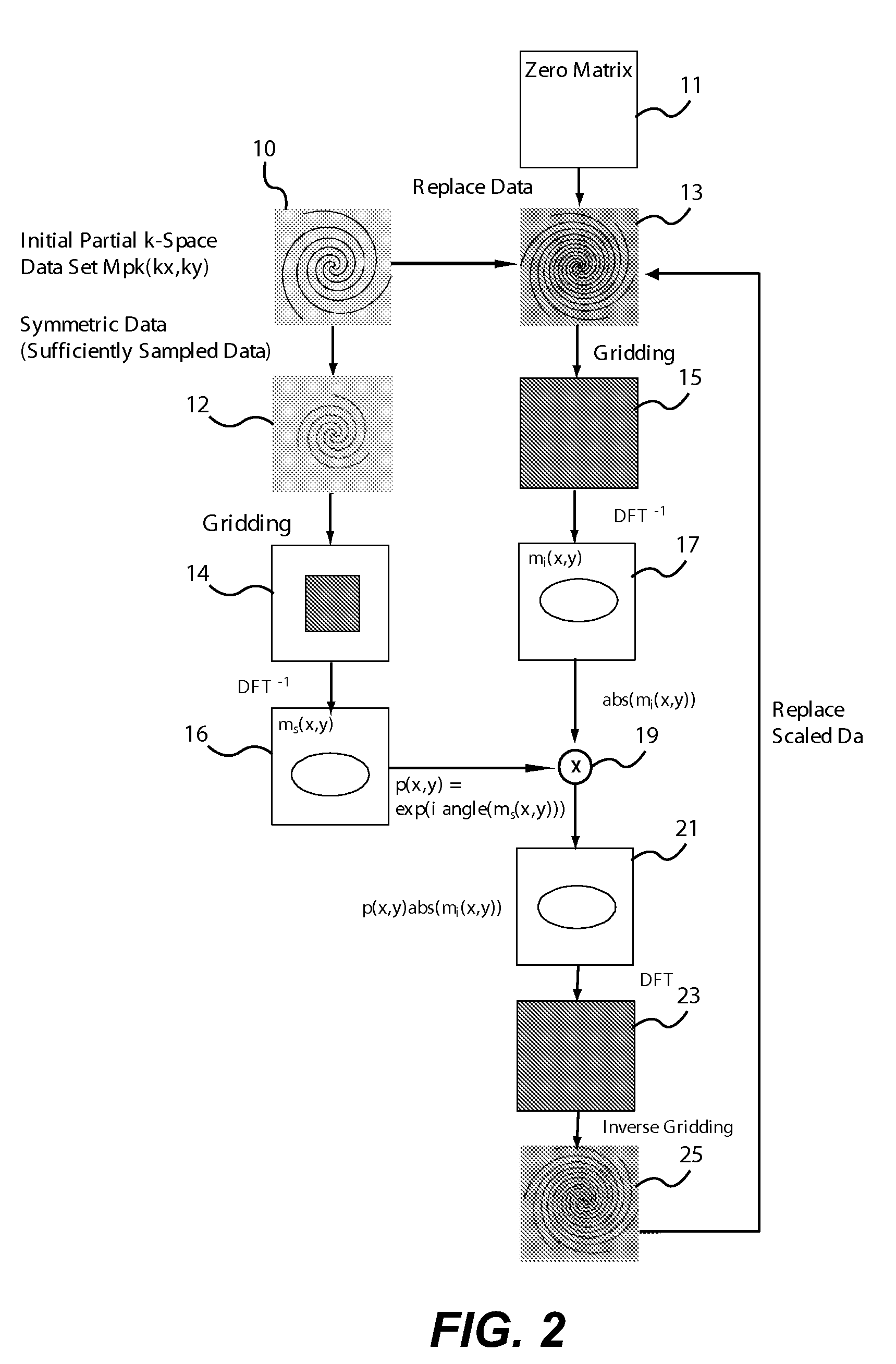
Efficient methods for reconstruction and deblurring of magnetic resonance images
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Efficient methods for reconstruction and deblurring of magnetic resonance images
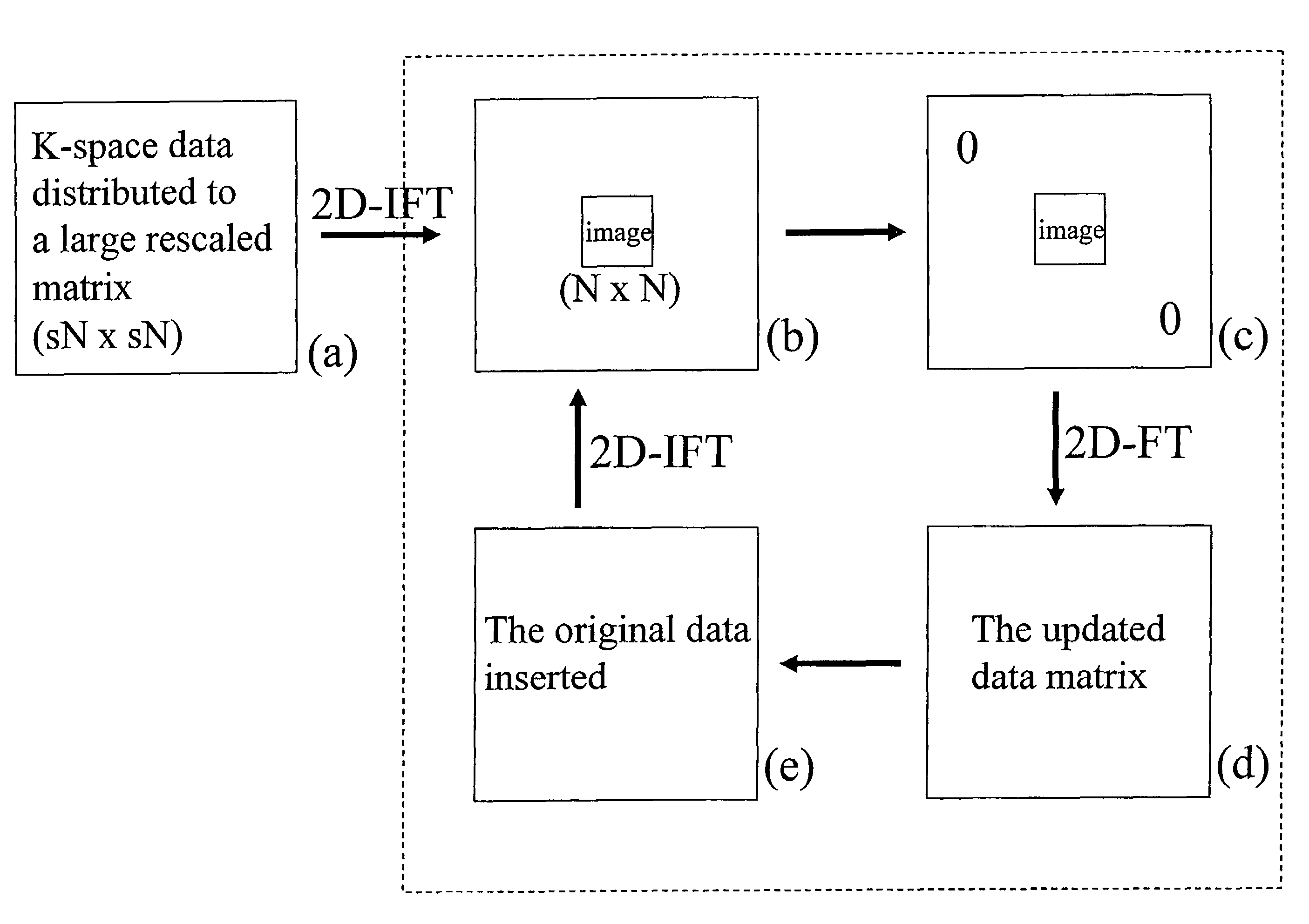
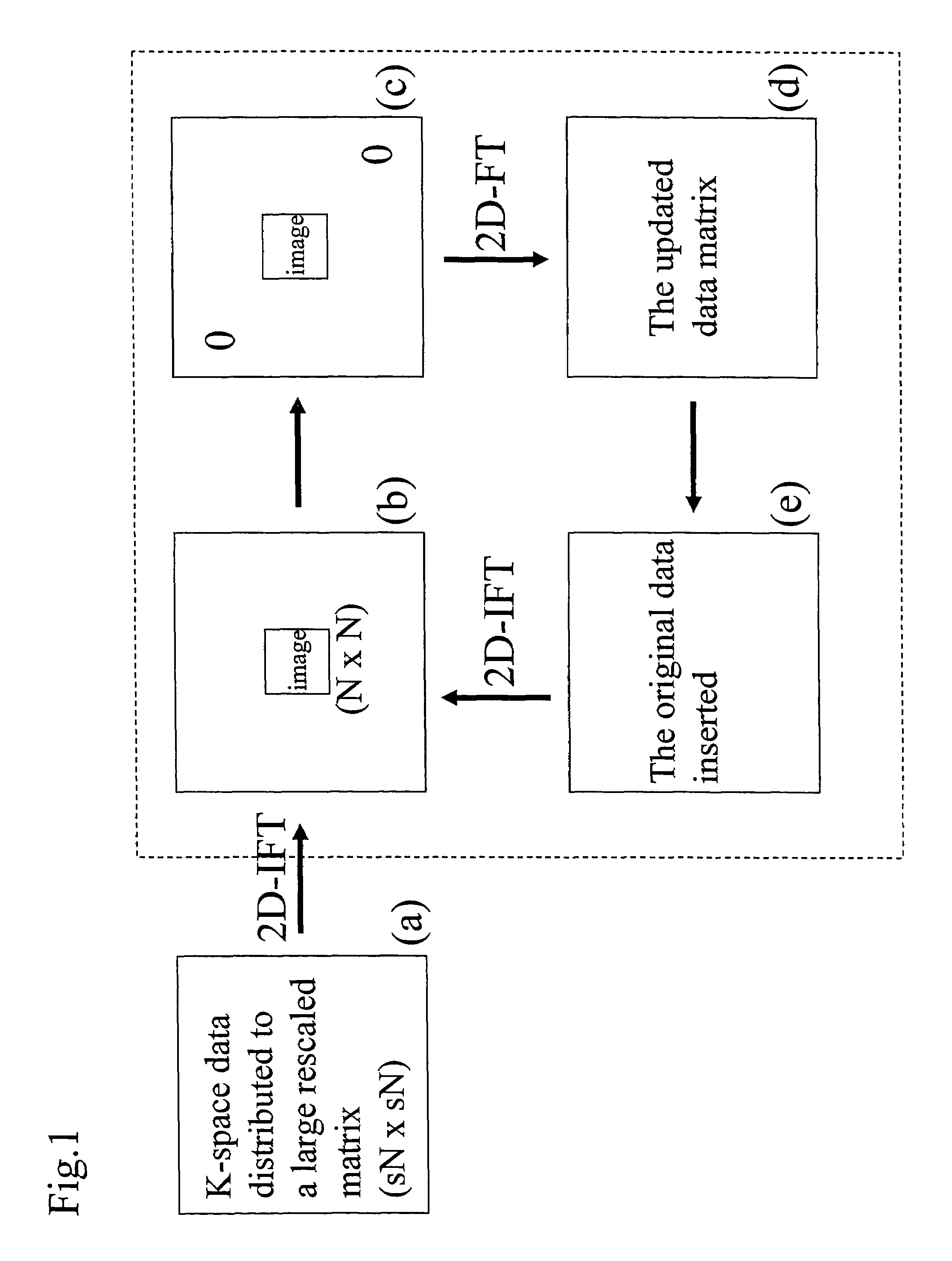
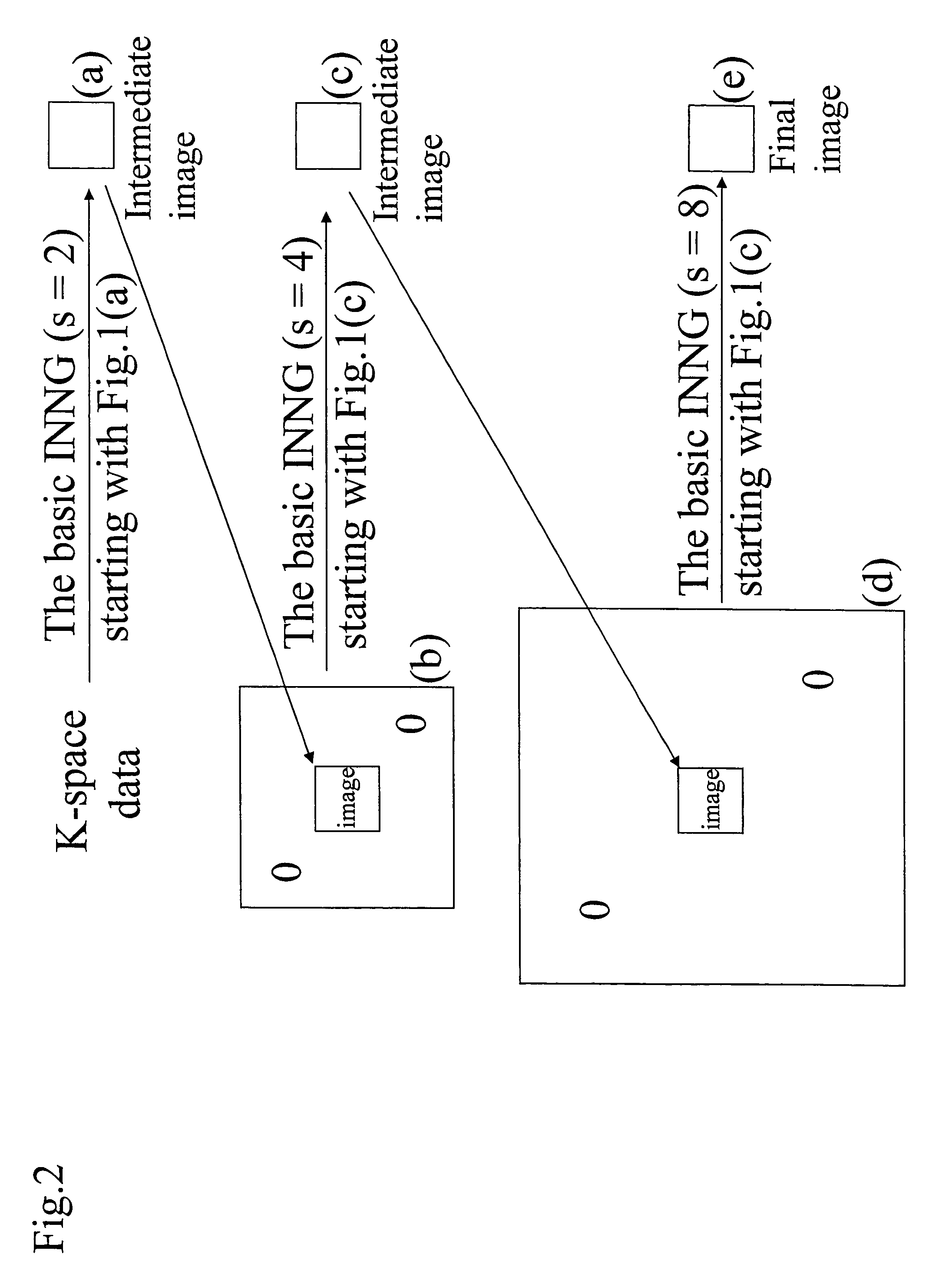
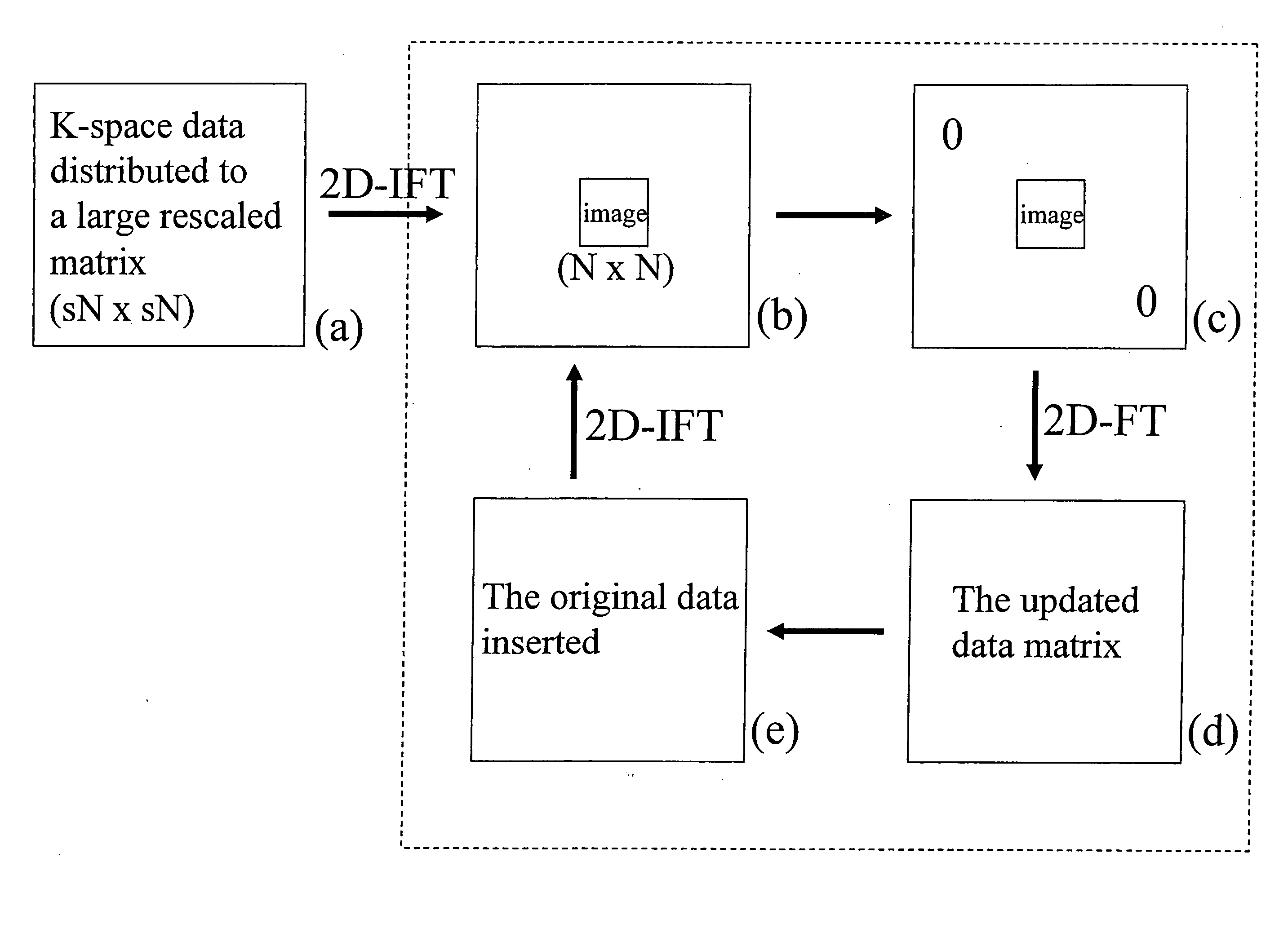
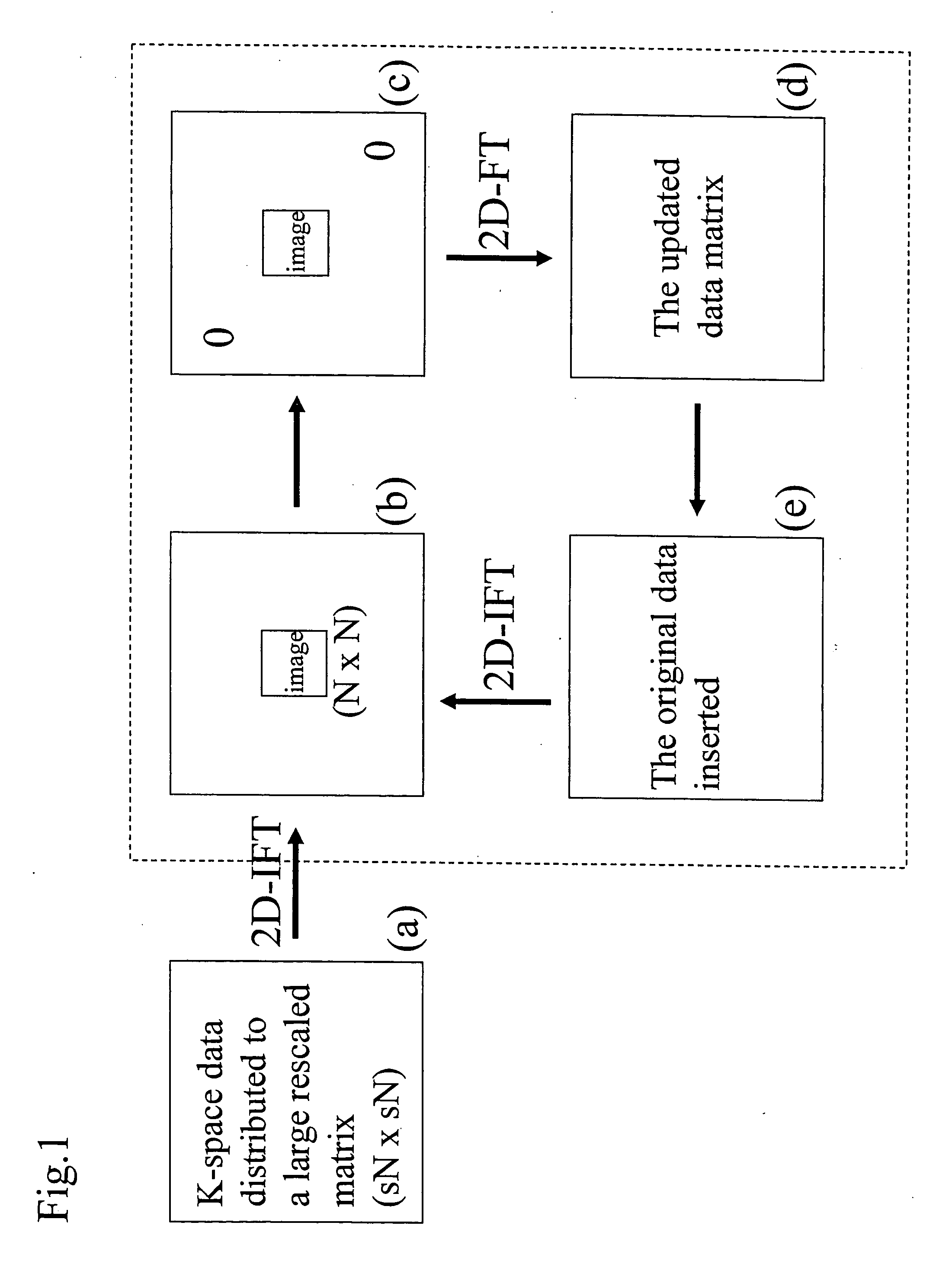
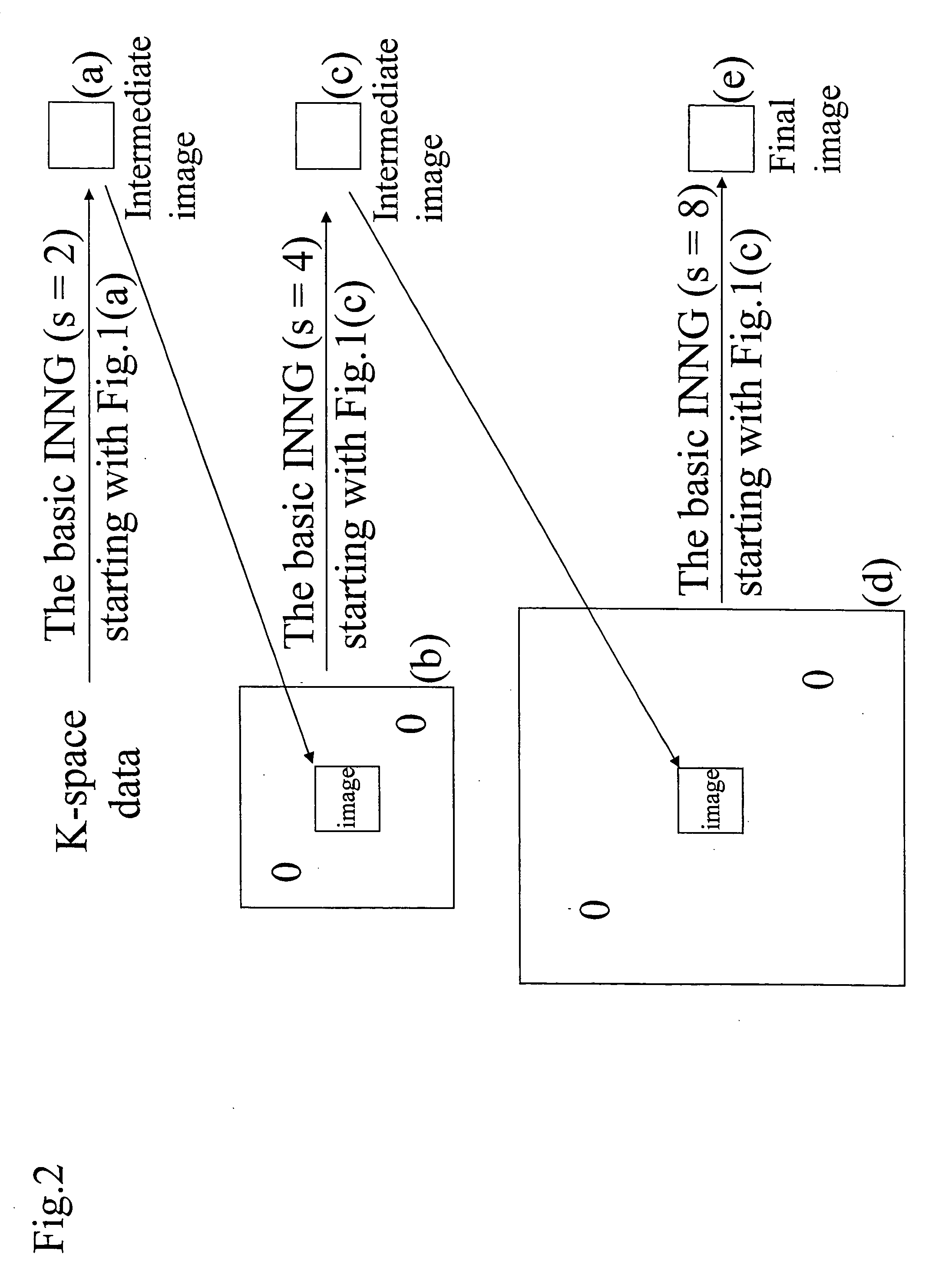
Methods are described for efficient reconstruction of MRI data. In one practice, new reconstruction algorithms for non-uniformly sampled k-space data are presented. In the disclosed algorithms, Iterative Next-Neighbor re-Gridding (INNG) and Block INNG (BINNG), iterative procedures are performed using larger rescaled matrices than the target grid matrix In BINNG algorithm, the sampled k-space region is partitioned into several blocks and the INNG algorithm is applied to each block. In another practice, a novel partial spiral reconstruction (PFSR) uses an estimated phase map from a low-resolution image reconstructed from the central k-space data and performs iterations, similar to the iterative procedures with INNG, with an imposed phase constraint. According to yet another practice, an off-resonance correction is performed on matrices that are smaller than the full image matrix. All these methods reduce the computational costs while rendering high-quality reconstructed images.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Annular focusing light spot realization method and realization device thereof
ActiveCN106950705APrecise position controlPrecise size controlOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorLight spot
The invention discloses an annular focusing light spot realization method. The method includes that a laser beam is expanded and collimated and then the expanded and collimated laser beam is converted into a linearly polarized laser beam; the laser beam phase modulation is carried out on the linearly polarized laser beam after the collimation and expansion by means of a reflective pure phase spatial light modulator; the linearly polarized light is imaged after the phase modulation to the rear aperture plane of a focusing object lens via a 4F imaging system; the object lens is used to focus the phase-modulated incident linearly polarized laser beam, a plurality of focal points are generated on the circumference in the focal plane area, and the azimuthal spacing between the focal points equal is equal; an annular light spot is generated when the circumference radius is reduced to a wavelength lambda, and the size of the annular light spot is continuously decreased when the circumference radius r changes until a solid light spot is formed; and when a plurality of phase modulation graphs are calculated, the change in the corresponding position movement of each graph is small, and the phase map of the spatial light modulator is updated so that the annular light spot moves continuously. The annular focusing light spot realization method realizes the non-vortex plane linearly polarized light focusing to generate the dynamic annular light spot which is accurate in position and size control.
Owner:唐山斯腾光电科技有限公司
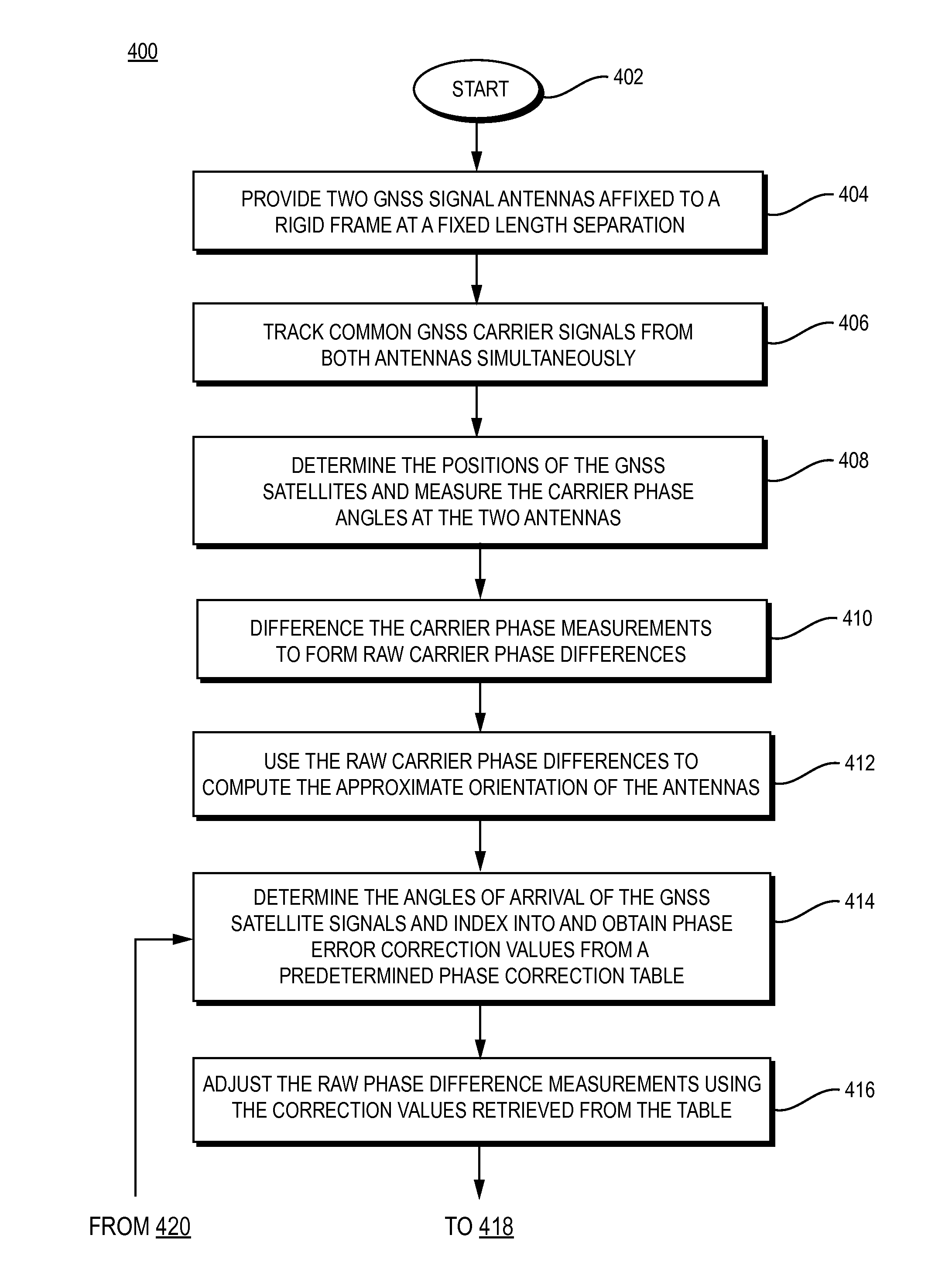
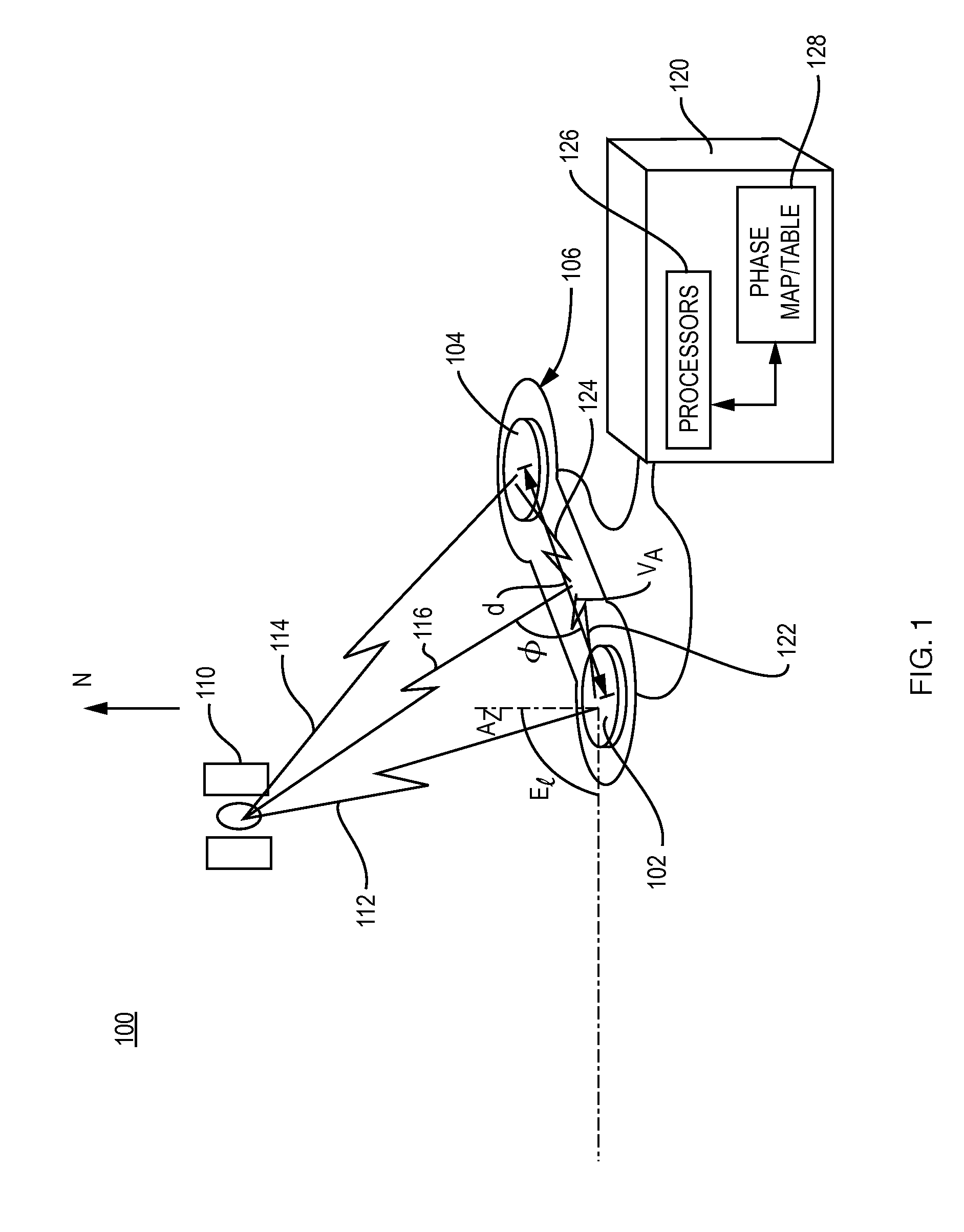
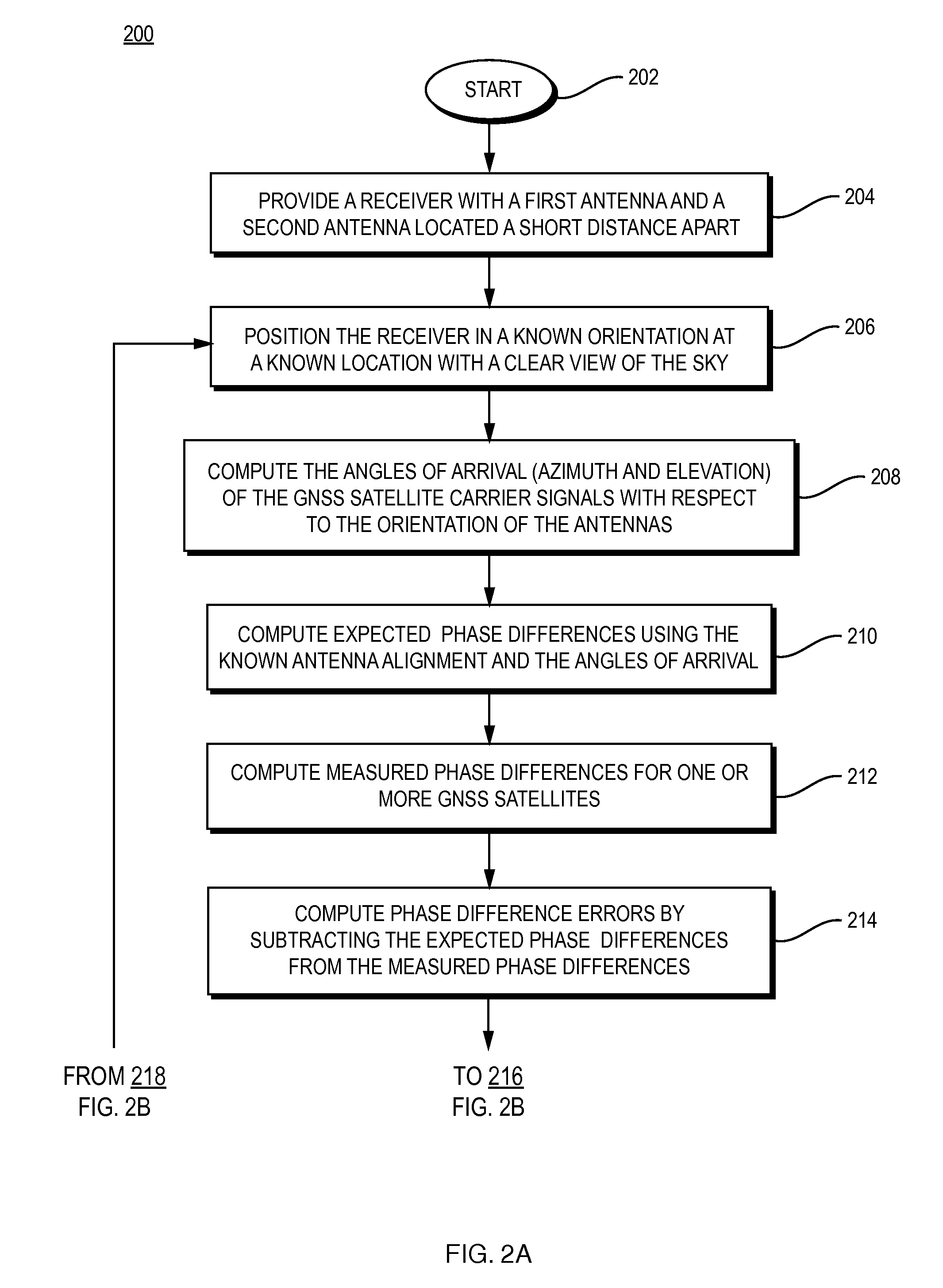
Short and ultra-short baseline phase maps
ActiveUS20110090113A1Correction of phase differenceImprove accuracySatellite radio beaconingAngle of incidenceError map
A system for generating and utilizing a look-up mechanism consisting of one or more phase difference error maps, tables and / or mathematical models calculates the respective maps, tables and / or models by placing a short baseline or ultra-short baseline antenna array in a known location and known orientation, determining angles of incidence of incoming GNSS satellite signals with respect the antenna array and calculating expected carrier phase differences between respective pairs of antennas, calculating measured carrier phase differences between the respective pairs of antennas, and determining carrier phase difference errors using the expected and measured carrier phase differences. The carrier phase difference errors are then recorded in the look-up mechanism, with the maps and, as appropriate, look-up tables for the respective pairs of antennas being indexed by angles of incidence. Thereafter, the system utilizes the look-up mechanism when determining the unknown orientation of the antenna structure. For respective pairs of antennas, the system enters the look-up mechanism based on angles of incidence determined from a calculated orientation, and uses the retrieved values in the calculation of a corrected orientation, to compensate for phase distortion.
Owner:NOVATEL INC
Incorporation of a phase map into fast model-based optical proximity correction simulation kernels to account for near and mid-range flare
InactiveUS20050091013A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFast Fourier transformReal arithmetic
A first method to compute a phase map within an optical proximity correction simulation kernel utilizes simulated wavefront information from randomly generated data. A second method uses measured data from optical tools. A phase map is created by analytically embedding a randomly generated two-dimensional array of complex numbers of wavefront information, and performing an inverse Fourier Transform on the resultant array. A filtering function requires the amplitude of each element of the array to be multiplied by a Gaussian function. A power law is then applied to the array. The elements of the array are shuffled, and converted from the phasor form to real / imaginary form. A two-dimensional Fast Fourier Transform is applied. The array is then unshuffled, and converted back to phasor form.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
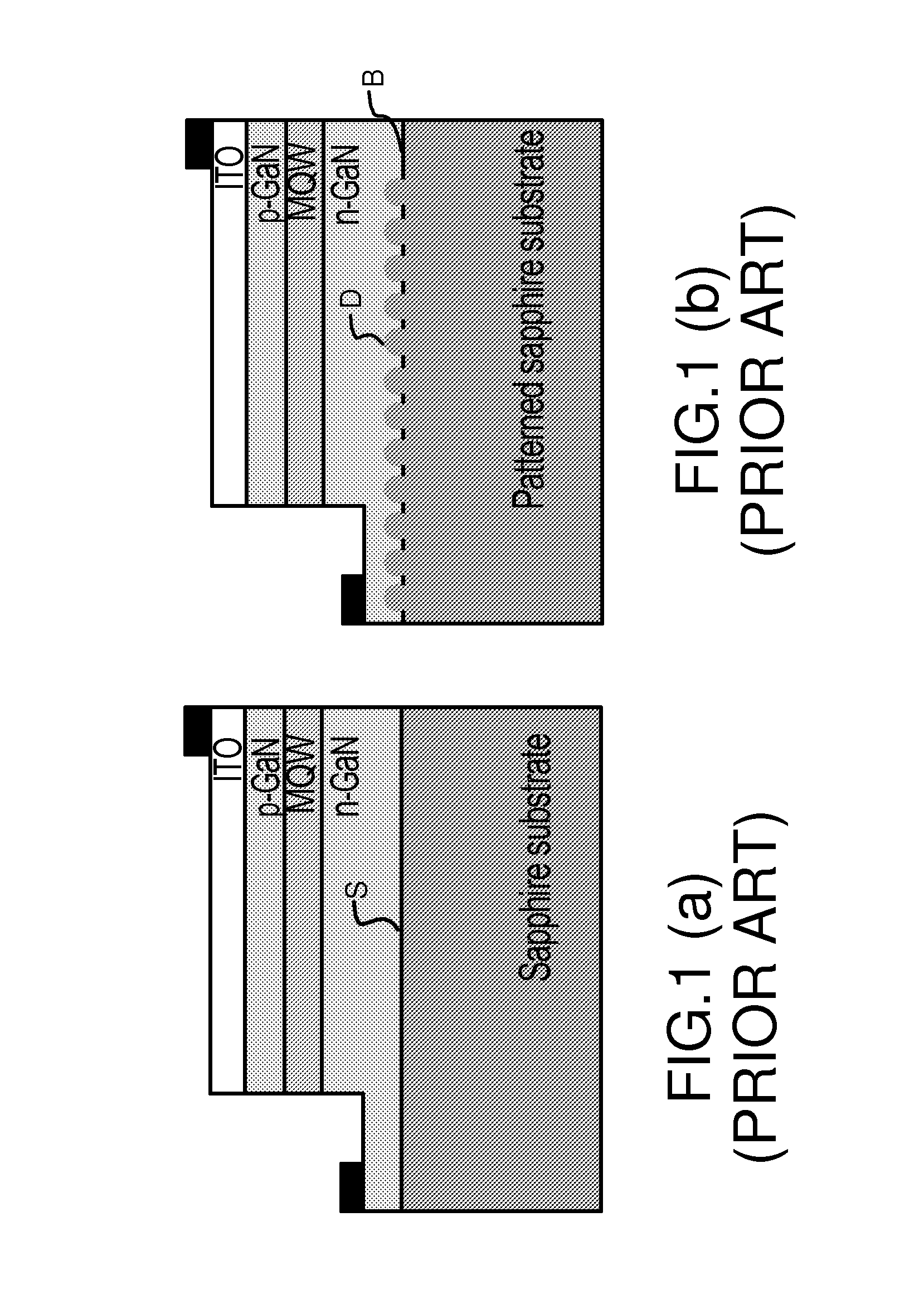
Interferometric technique for measuring patterned sapphire substrates
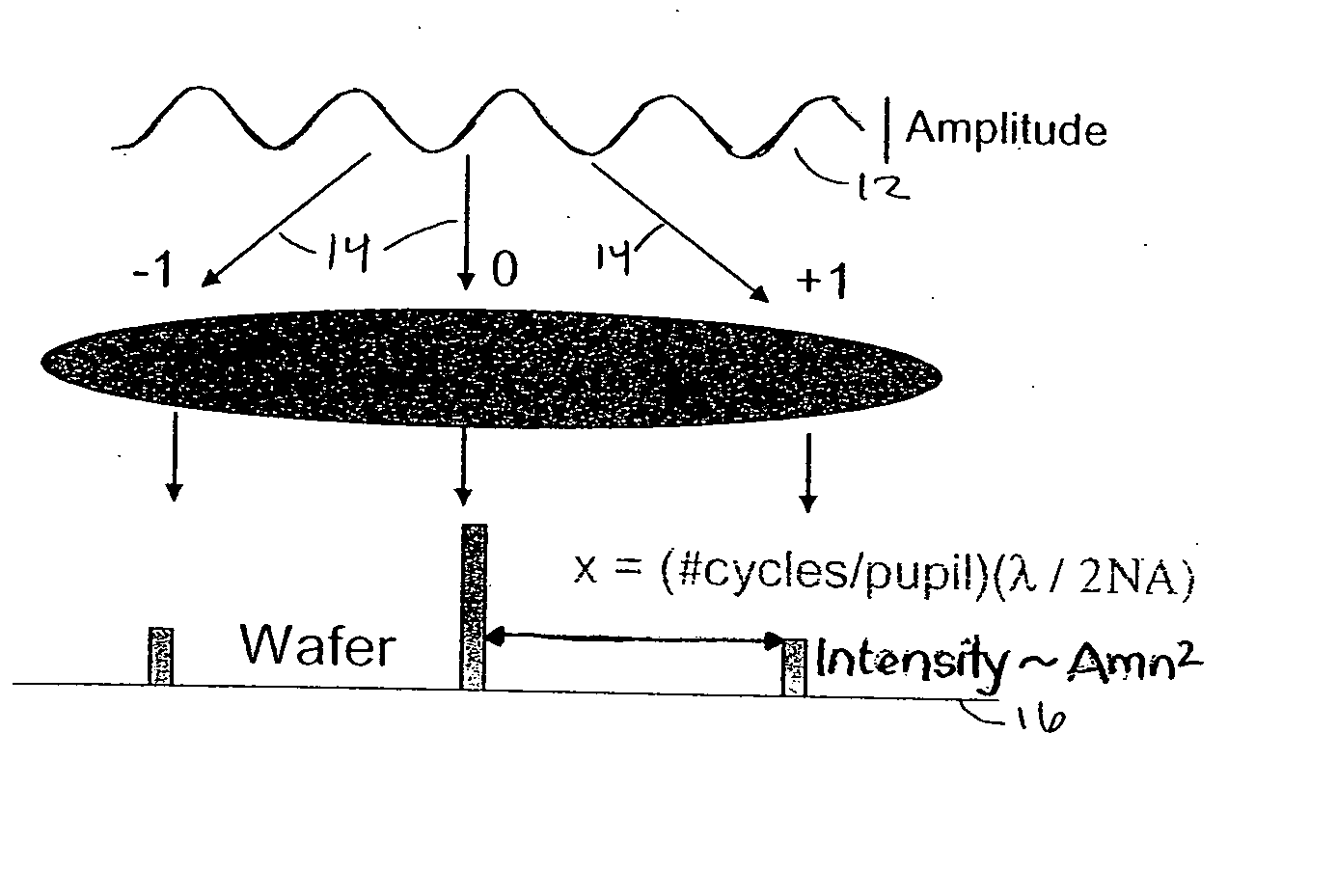
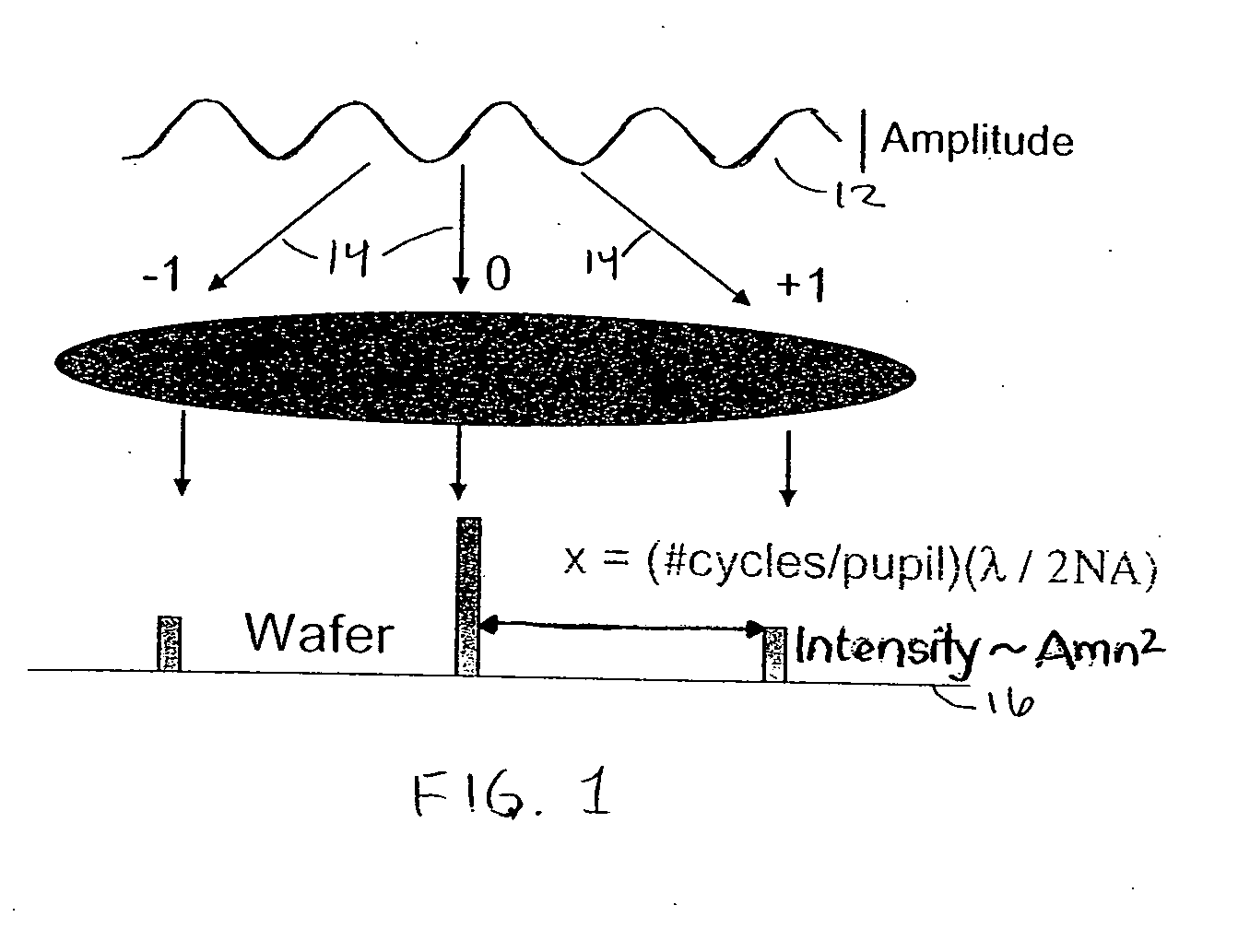
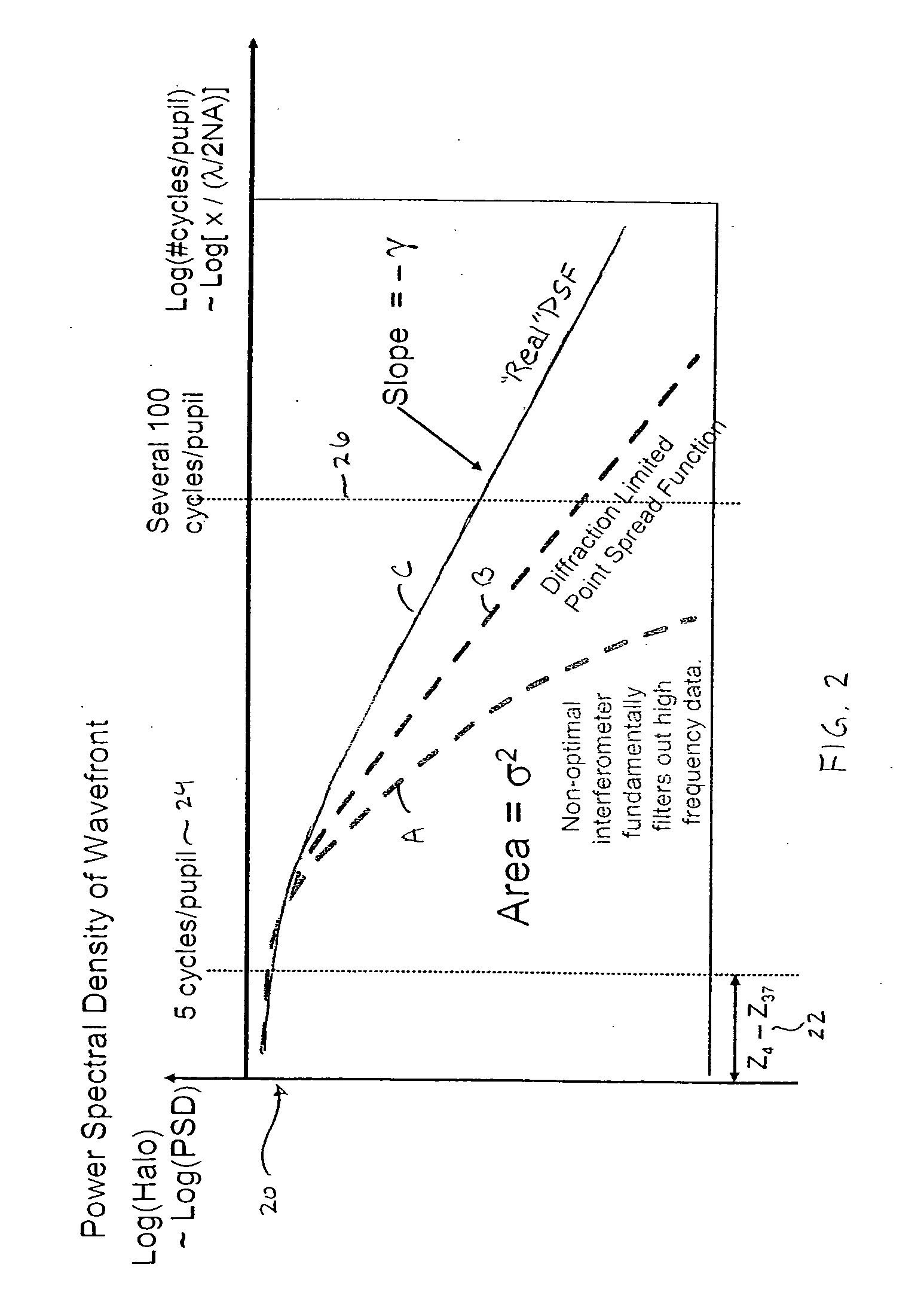
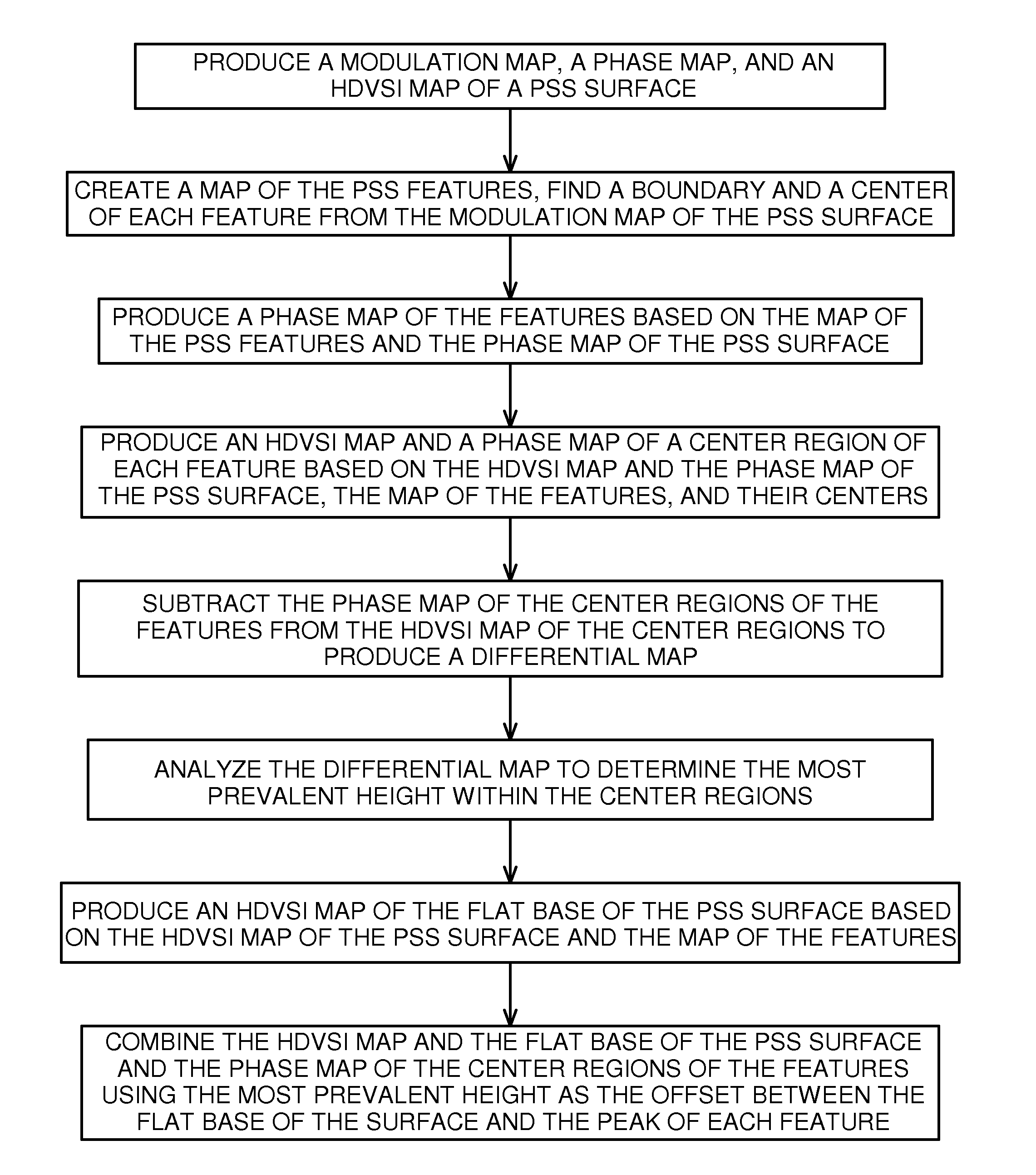
A patterned sapphire substrate is measured from a fine phase map and a coarser height map of the sample. The boundaries of the PSS features are identified by finding the locations of minimum contrast in the modulation map of the substrate and are used to produce a height map of the substrate base and a phase map of center regions of the features. A fringe-order map of the features with respect to the base is used to identify the most prevalent fringe order of pixels in the center-regions of the features. That fringe order is adopted as the correct offset between corresponding pixels in the phase map of the center regions of the features and the base of the substrate. A complete map of the substrate is thus obtained by combining the phase map of the features with the height map of the substrate with an offset equal to the fringe order produced by the invention.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
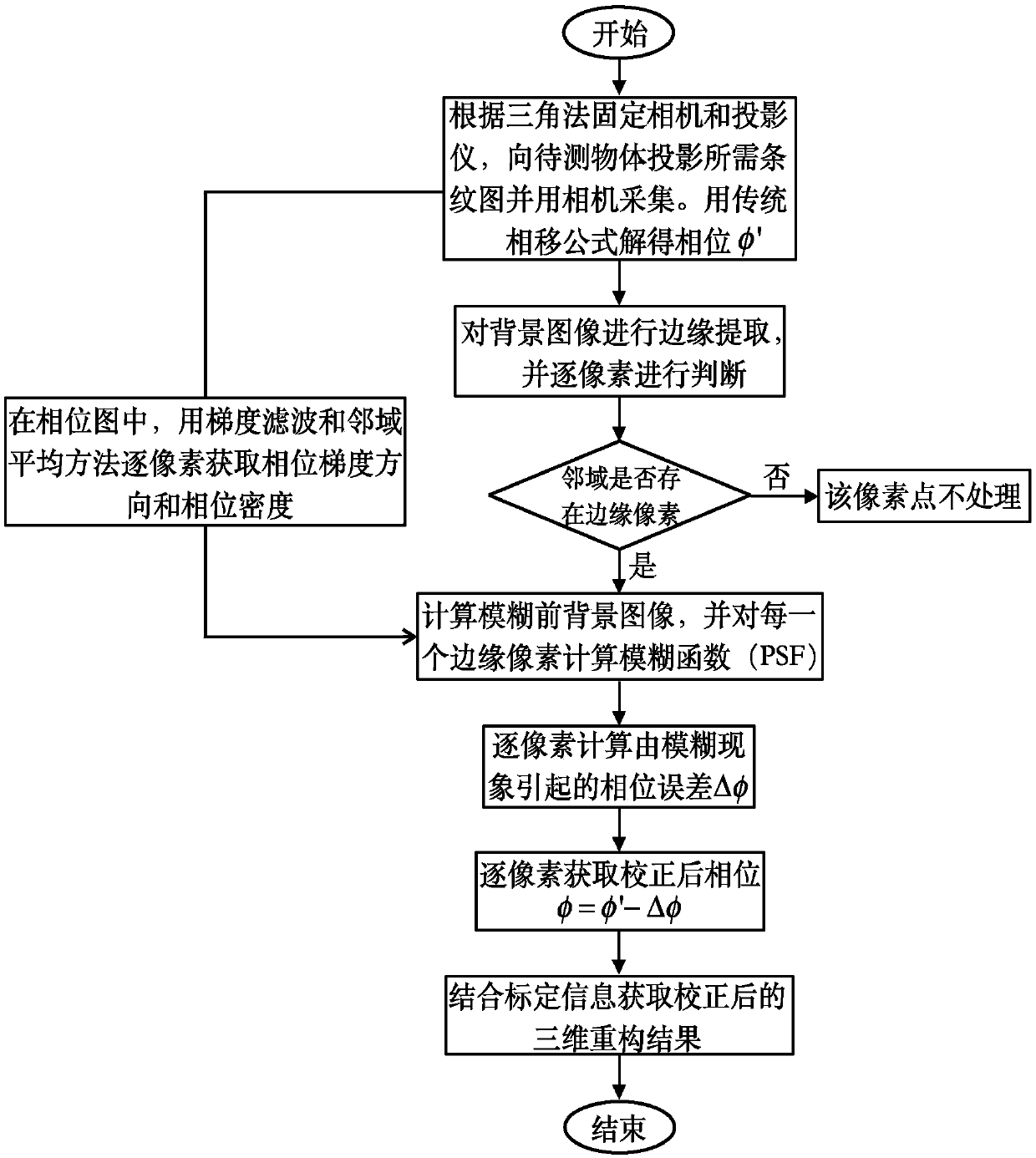
Phase error correction method for out-of-focus phenomenon of fringe projection three-dimensional measuring system
ActiveCN108168464AEasy to implementAccurate solutionUsing optical meansDiffusion functionThree dimensional measurement
The invention discloses a phase error correction method for an out-of-focus phenomenon of a fringe projection three-dimensional measuring system. The method comprises: a computer generates a phase-shifted fringe image and the image is collected by a camera; for the collected image, a background image I' and a phase phi' containing an error are calculated and edge extraction is carried out on the background image I'; a point spread function (PSF) of each edge pixel is calculated after edge map obtaining; a phase gradient direction and a phase density of each to-be-processed pixel are calculatedby using gradient filtering and neighborhood averaging methods in the phase map phi'; and then for the to-be-processed pixels, phase errors delta phi caused by the out of focus of the camera are calculated pixel by pixel, so that a finally corrected phase phi is obtained and the phi meets a formula: phi=phi'-delta phi. The corrected phase information can be converted into three-dimensional information of a to-be-measured object by a phase-height mapping relationship.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Real-virtual relating method for generating interference phase pattern of synthetic aperture radar without interference spots
InactiveCN1680826AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisCorrelation coefficientSynthetic aperture radar
A correlation method of real part and imaginary part in interference phase map includes using isoline window in size of m x n to carry out correlation operation for real part and imaginary part data of two complex maps for deriving out correlation coefficient C1, utilizing the same manner to drive out C2 by carrying out correlation operation for real part of the first complex map data and for imaginary part of the second complex map data, deriving out arc tangent for obtaining interference phase map by utilizing ratio of C1 and C2; using two accurate complex maps to generate interference phase map being free from coherent speckle noise.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
In situ determination of pixel mapping in interferometry
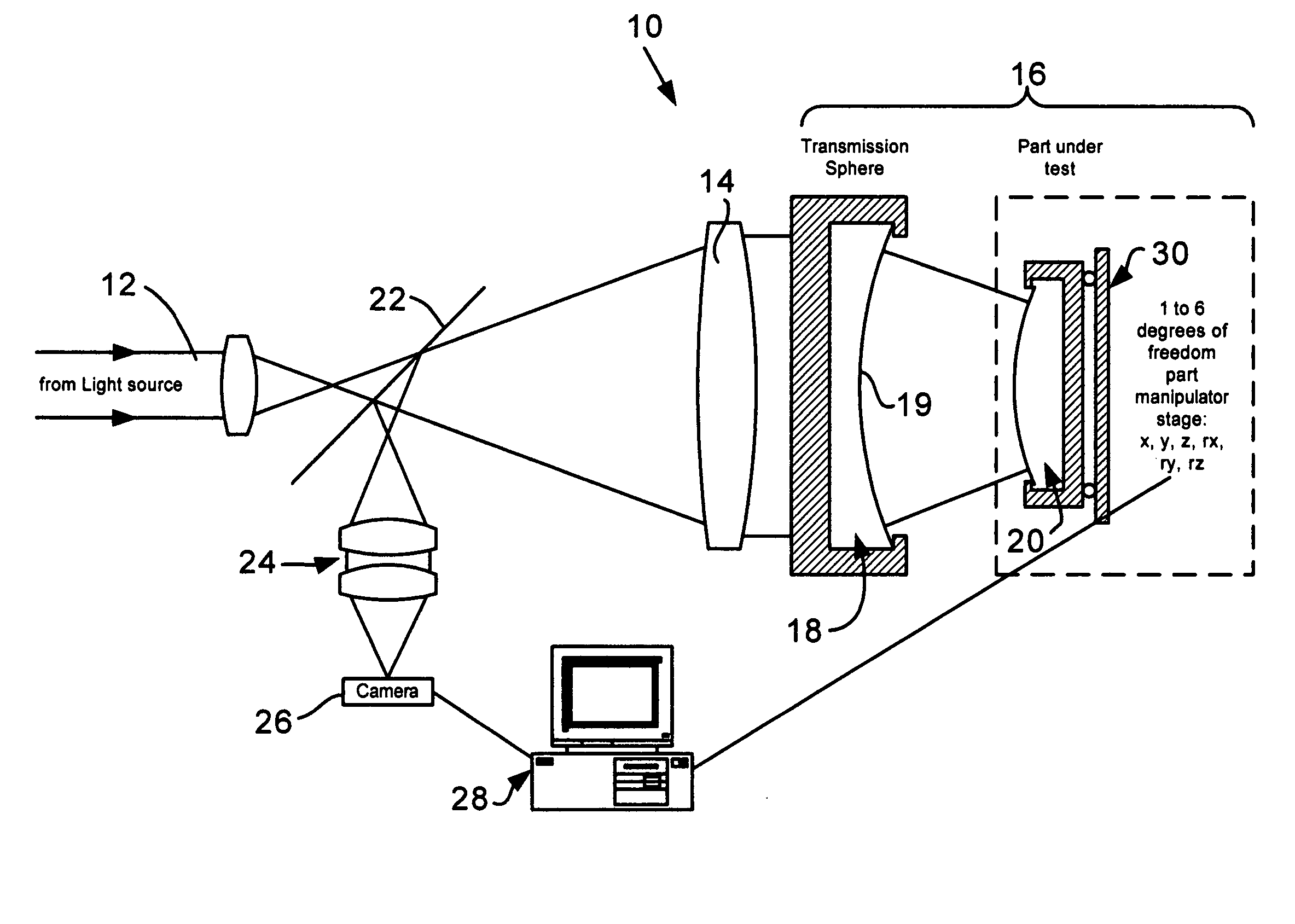
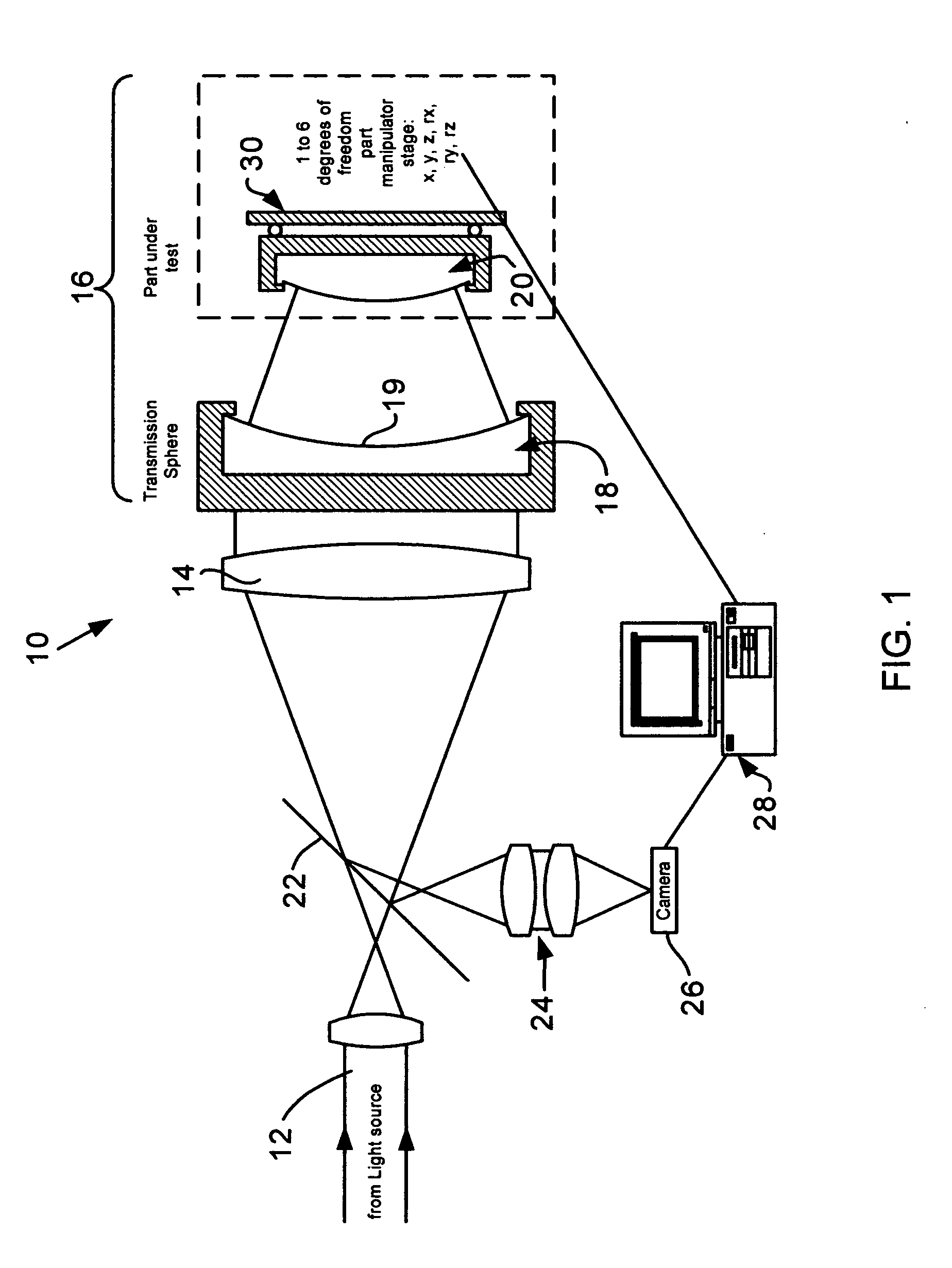
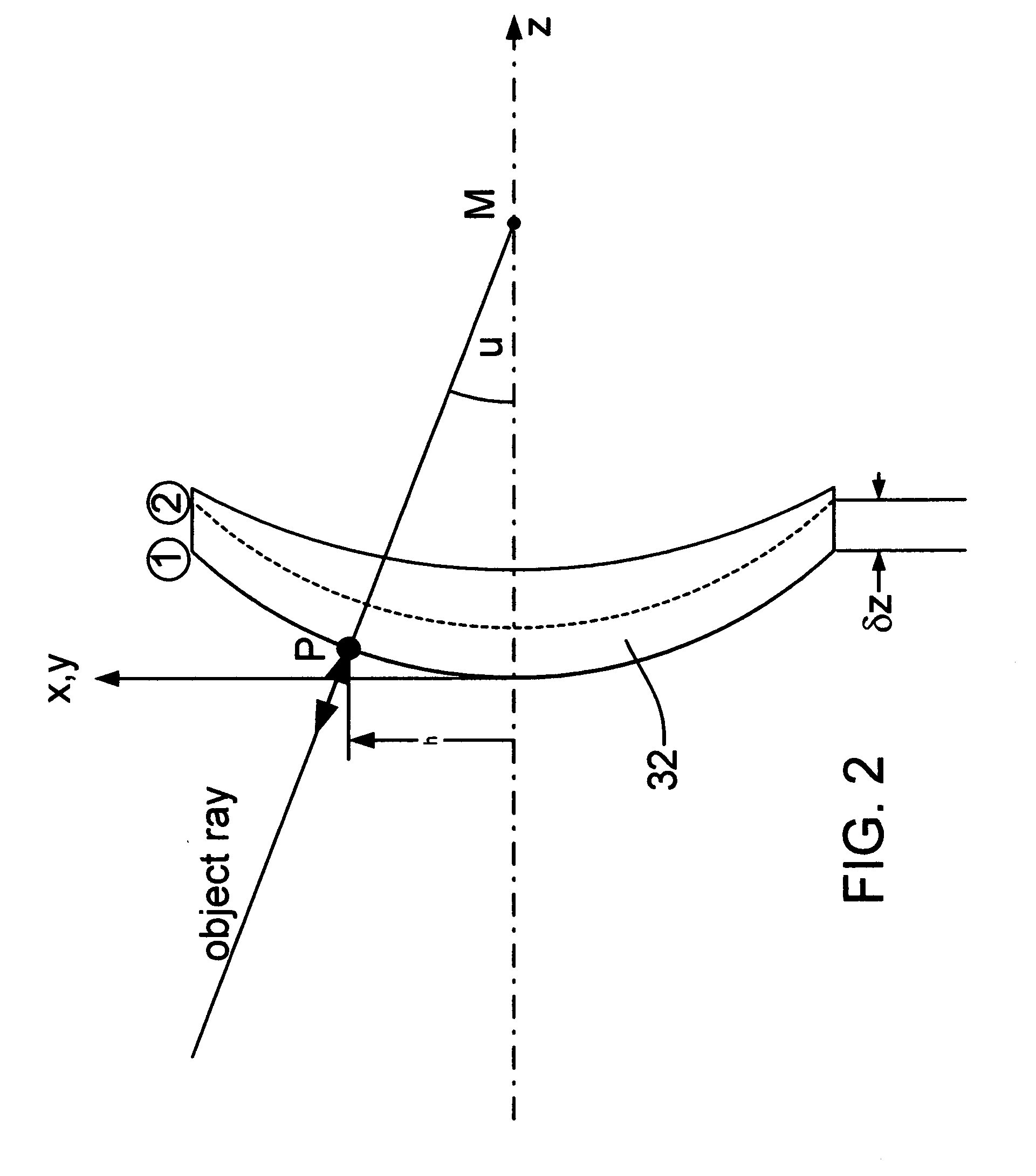
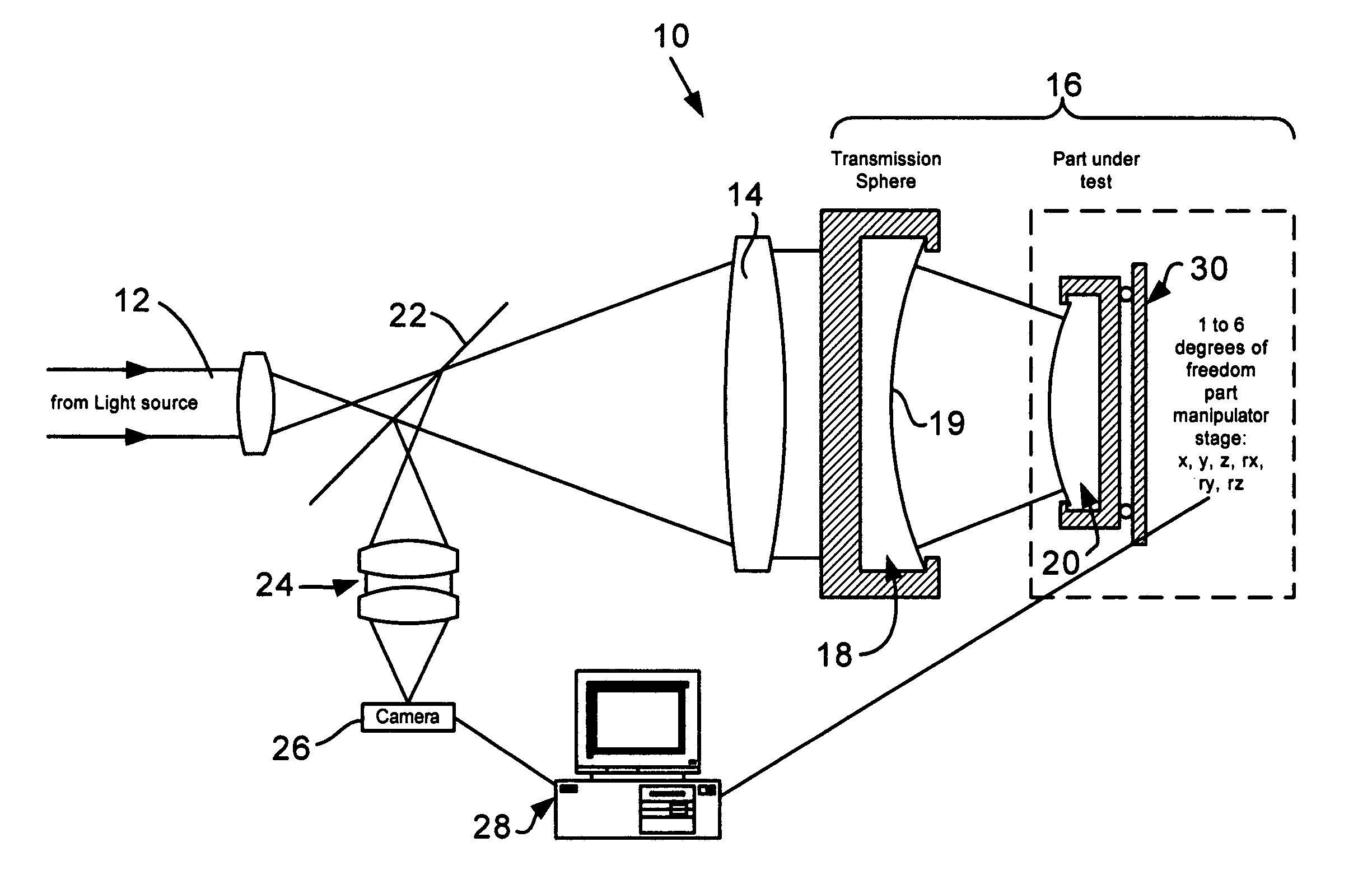
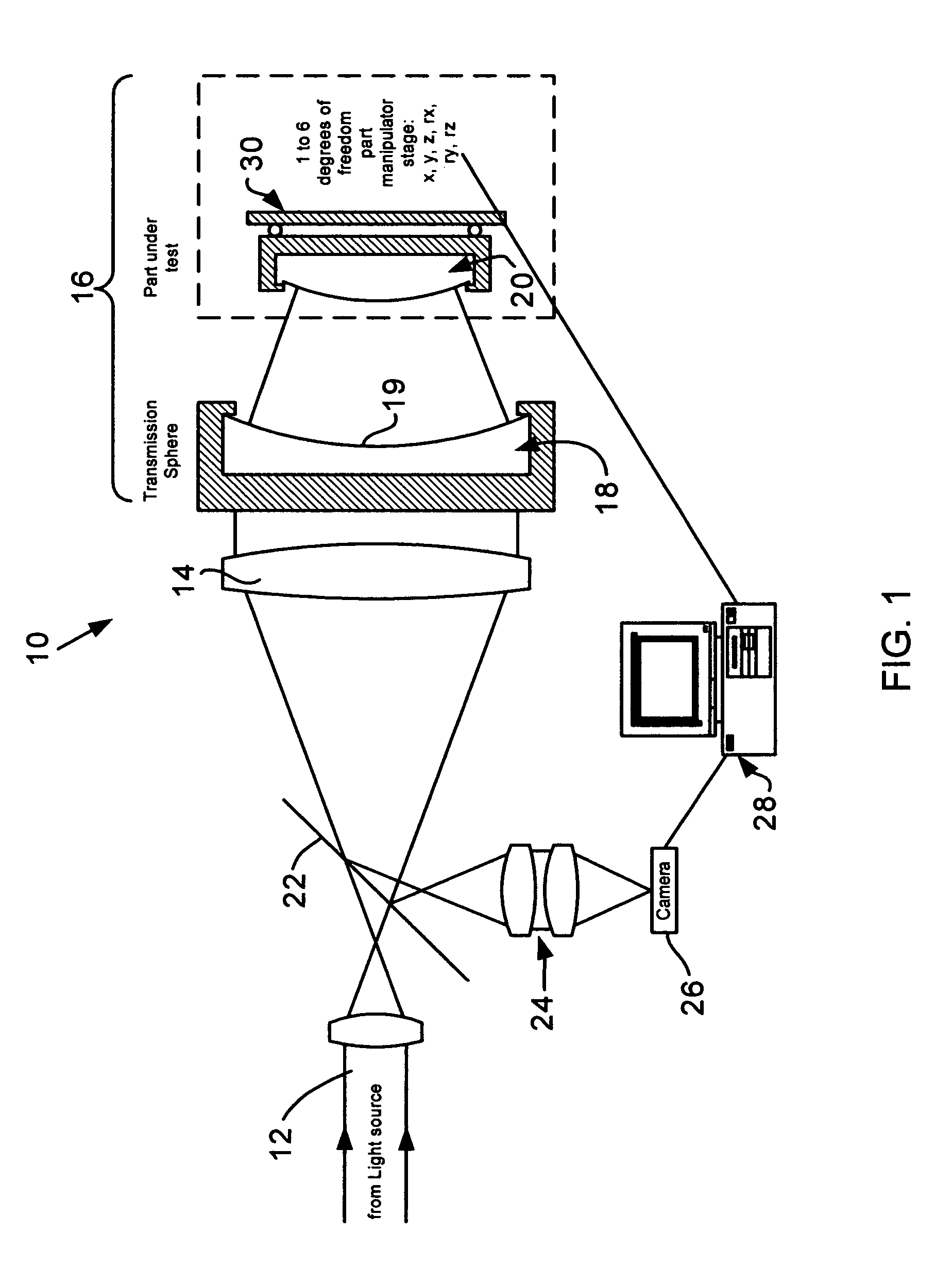
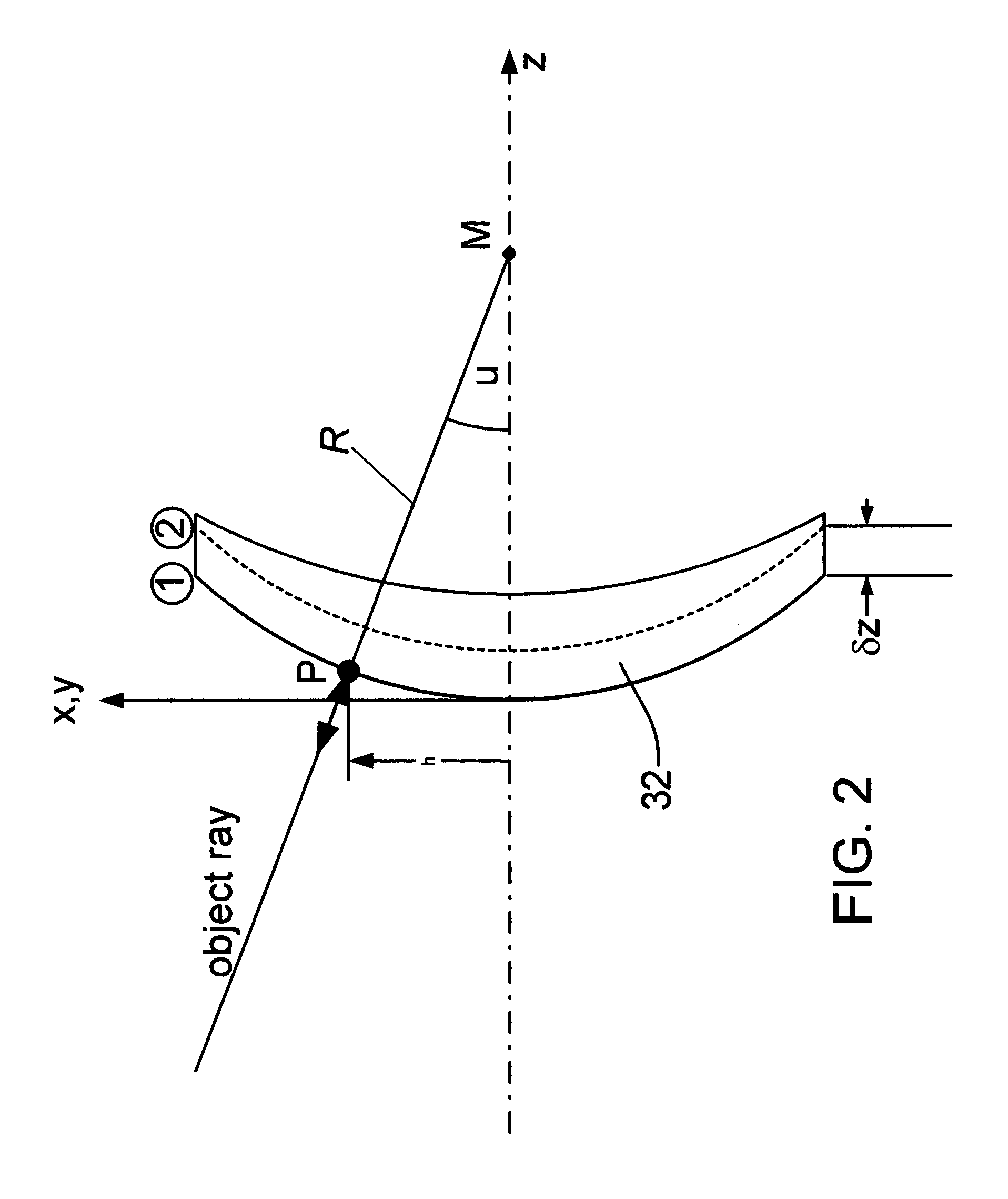
Interferometric methods and apparatus by which the map between pixel positions and corresponding part locations are determined in situ. The part under test, which is assumed to be a rigid body, is precisely moved from a base position to at least one other position in one to six degrees of freedom in three-dimensional space. Then, the actual displacements are obtained. The base position is defined as the position with the smallest fringe density. Measurements for the base and all subsequent positions are stored. After having collected at least one measurement for each degree of freedom under consideration, the part coordinates are calculated using the differences of the various phase maps with respect to the base position. The part coordinates are then correlated with the pixel coordinates and stored.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
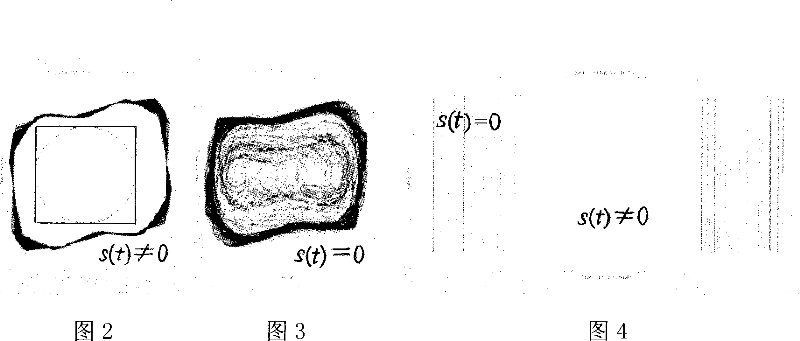
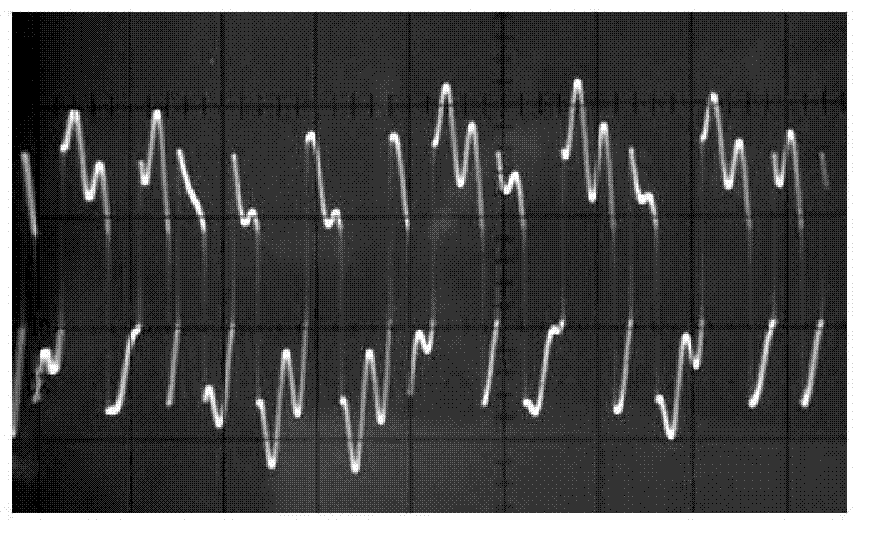
Segmenting detecting method for pattern domain of Duffing vibrator phase diagram
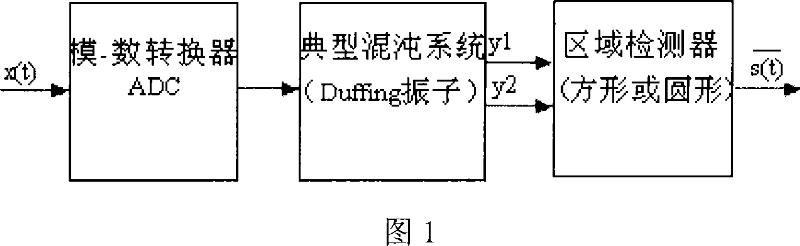
The present invention provides an image area cutting method of the Duffing vibration generator phase map. 1. Selecting a typical Duffing vibration generator normalized equation. 2. Inserting an A / D converter in front of the typical Duffing vibration generator, inserting an area cutter in back. 3. Inputting the signals having noise to be detected into the A / D converter. 4. A quarter to a tenth of a circle of the signals to be detected is used as the converting circle of the A / D converter and is used together with a Duffing vibration generator equation to figure out the step length. 5. The result is calculated out by the Duffing vibration generator by using a fourth order Runge-Kutta algorithm and is sent to the area cutter. 6. The result is judged by the area cutter which then outputs the detected signals carrying the information of the data to be detected. In the present invention the identifying problem of two-dimensional chaos vibration generator phase map is transformed into a problem of one-dimensional detecting, and the problem that the phase map analyzing method can not be directly used for detecting the communication signals currently is solved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
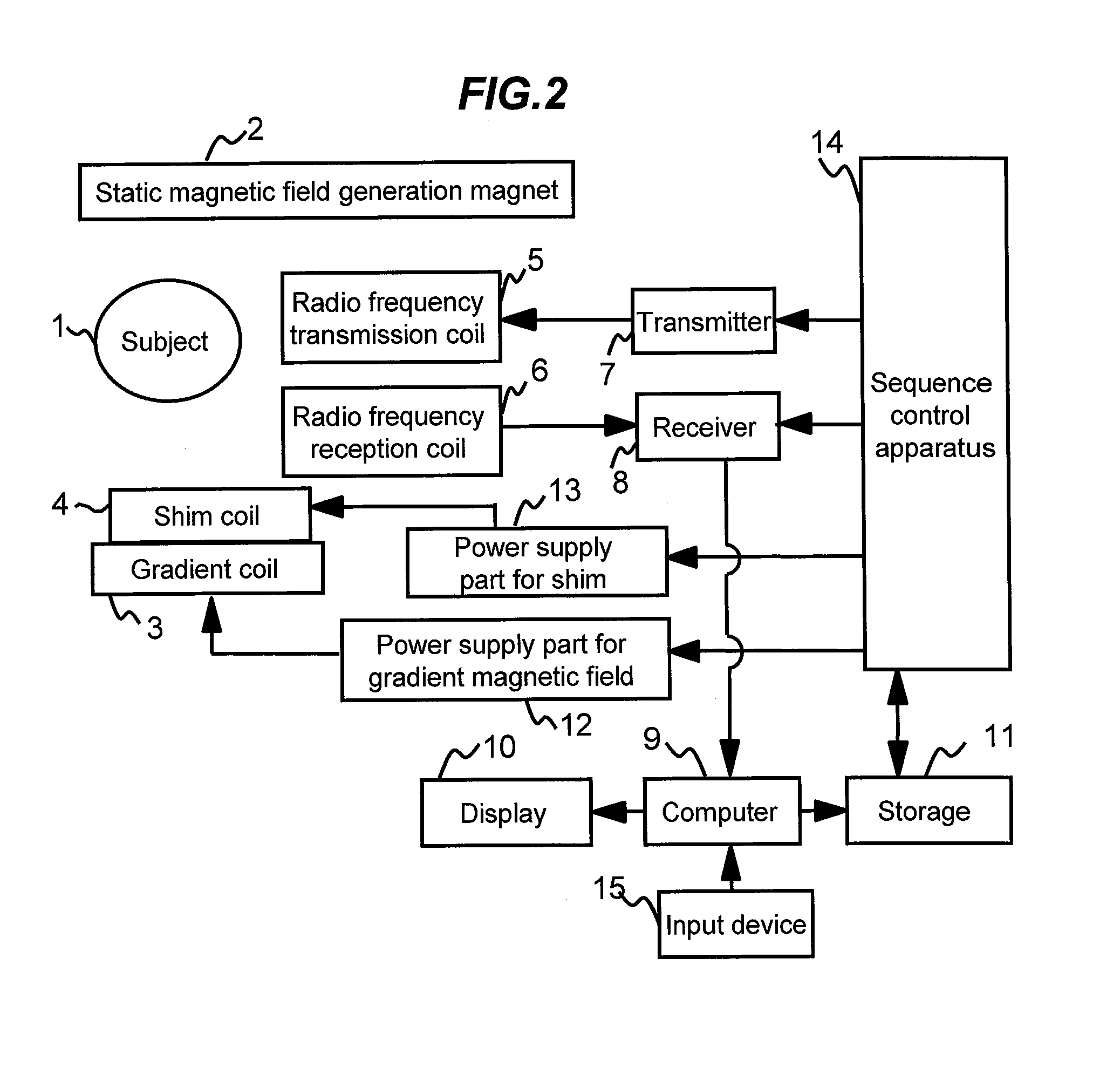
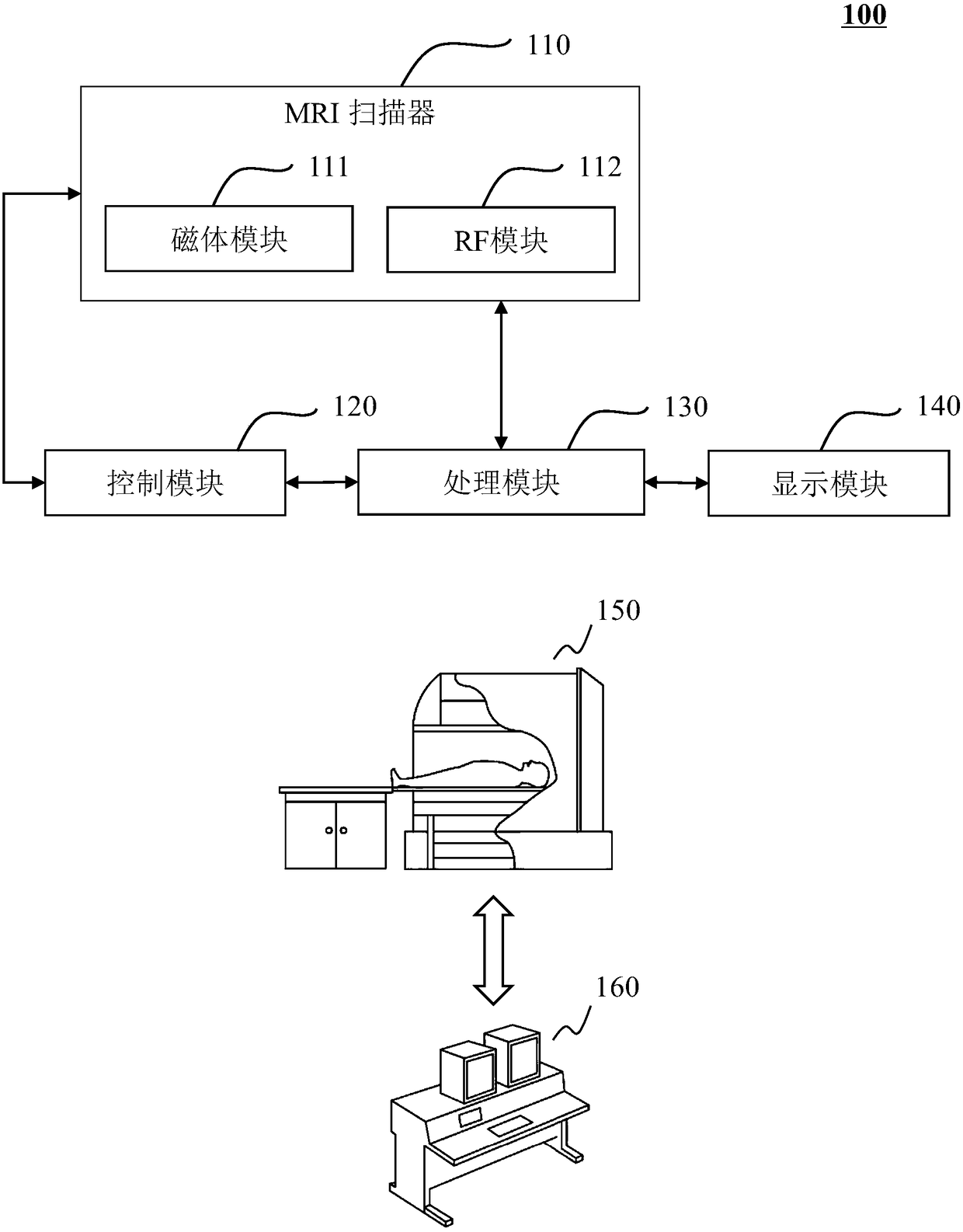
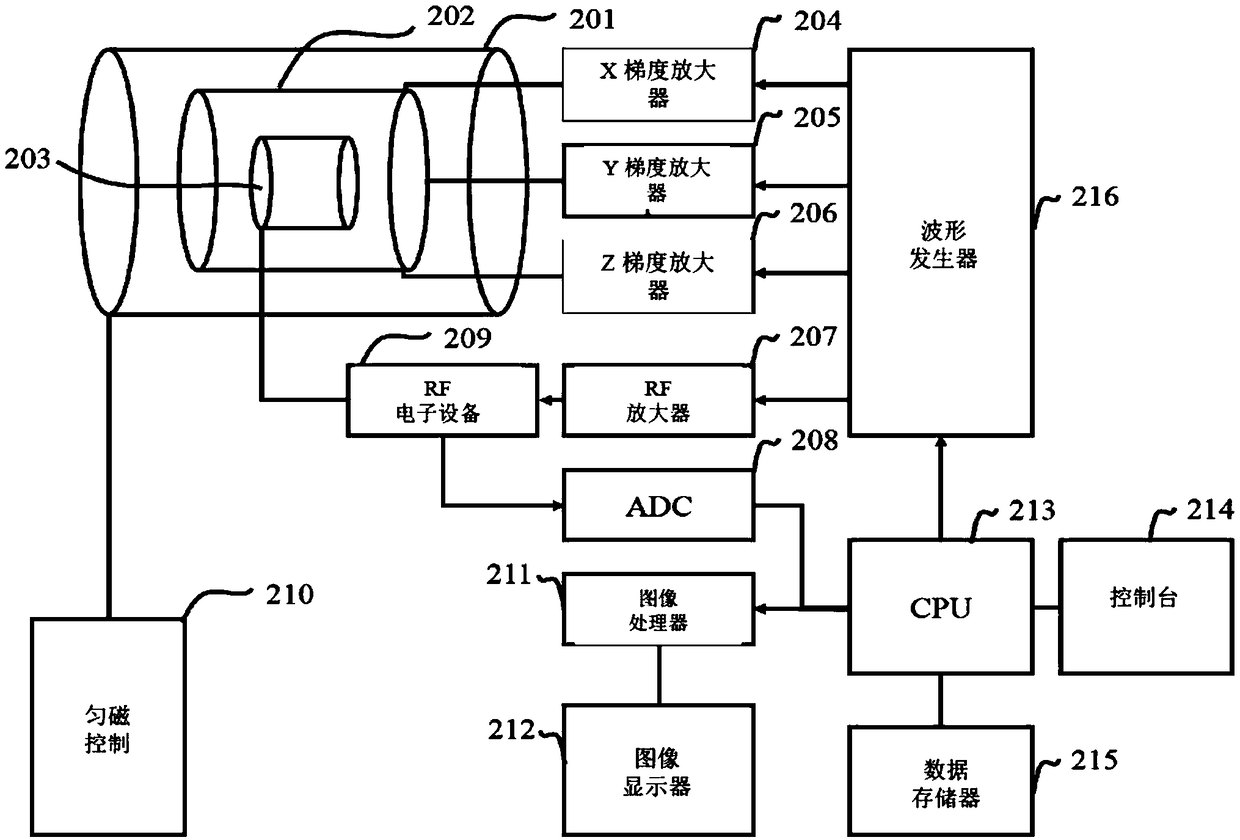
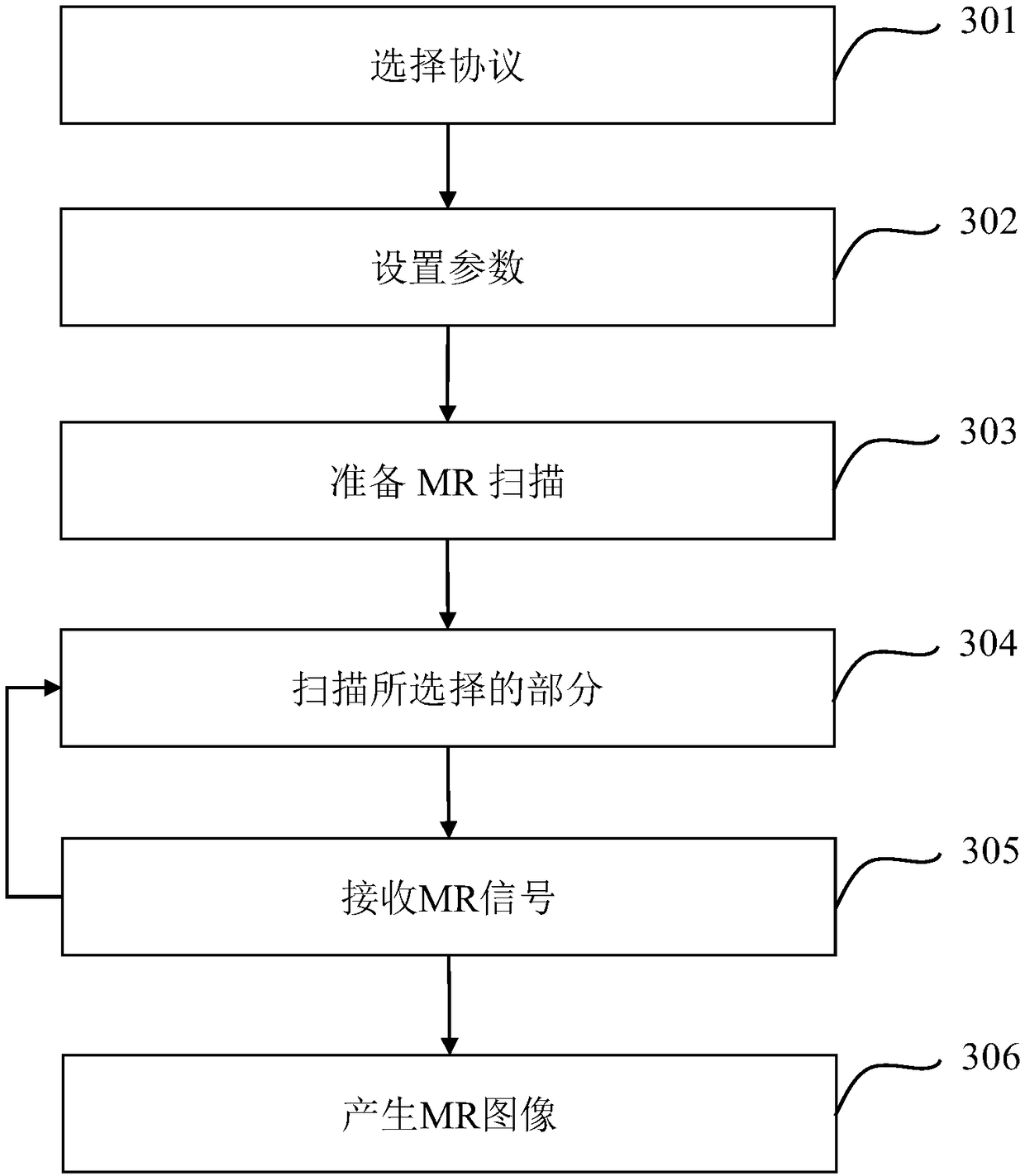
Magnetic resonance imaging device
ActiveUS20120301007A1Measurement is limitedEasy to separateMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionPhase correctionDifference-map algorithm
Water / fat separation imaging is performed by an MRI device, even if the measurement is not performed with such echo times that the phases of water and fat signals become in-phase or out-of-phase. A determination is made as to which of two obtained separation images is a water image or a fat image. Two water / fat ratio maps are calculated from two original images obtained with such two echo times that phase differences of water and fat signals do not become positive and negative values, and do not becomes integral multiples of π. Two phase maps are calculated from the two water / fat ratio maps and are combined to calculate two minimum phase difference maps showing minimum spatial phase difference. From dispersion in differential maps obtained by spatially differentiating the minimum phase difference maps, a correct minimum phase difference map is determined, and is used to perform phase correction of the original image.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
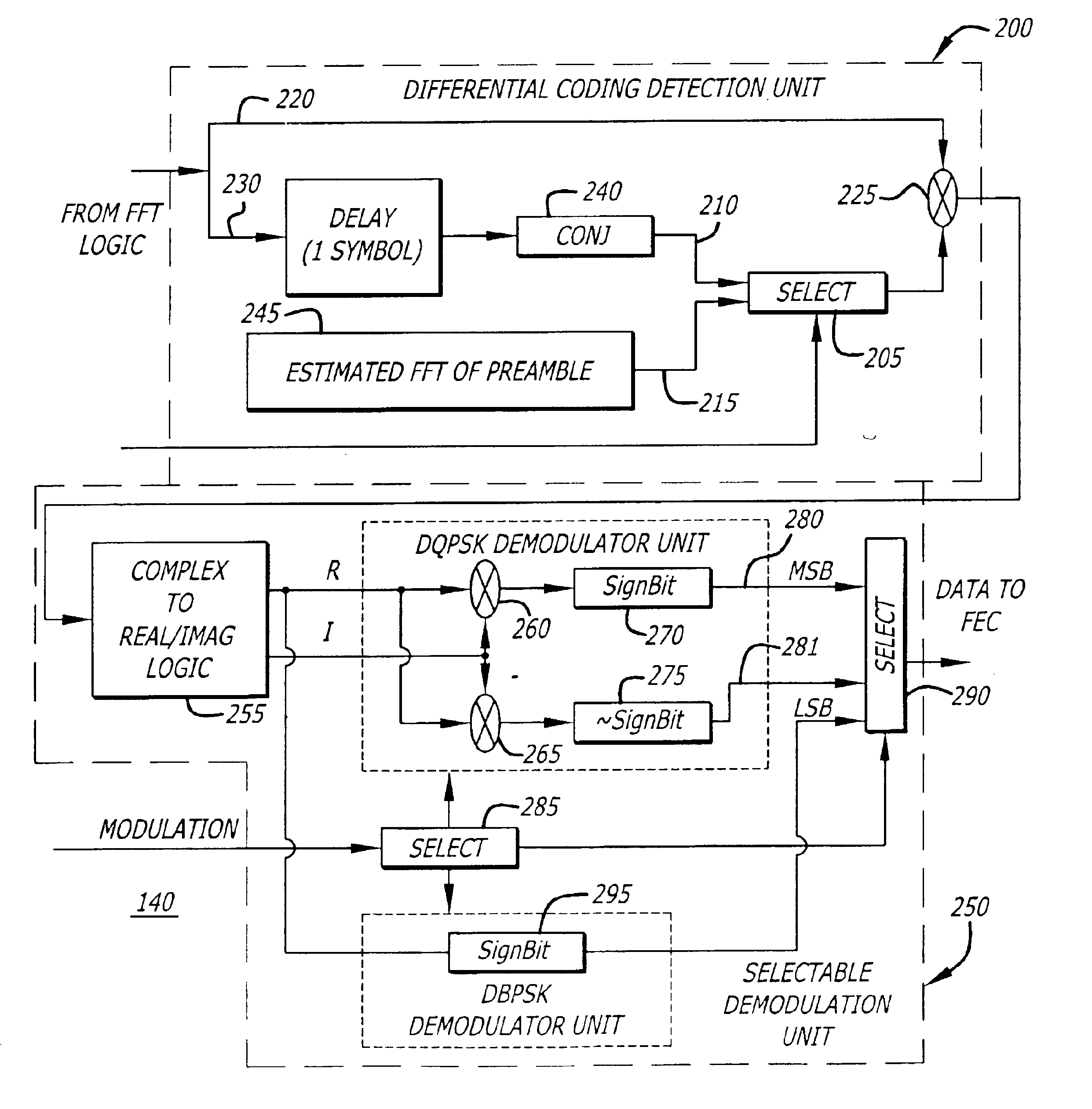
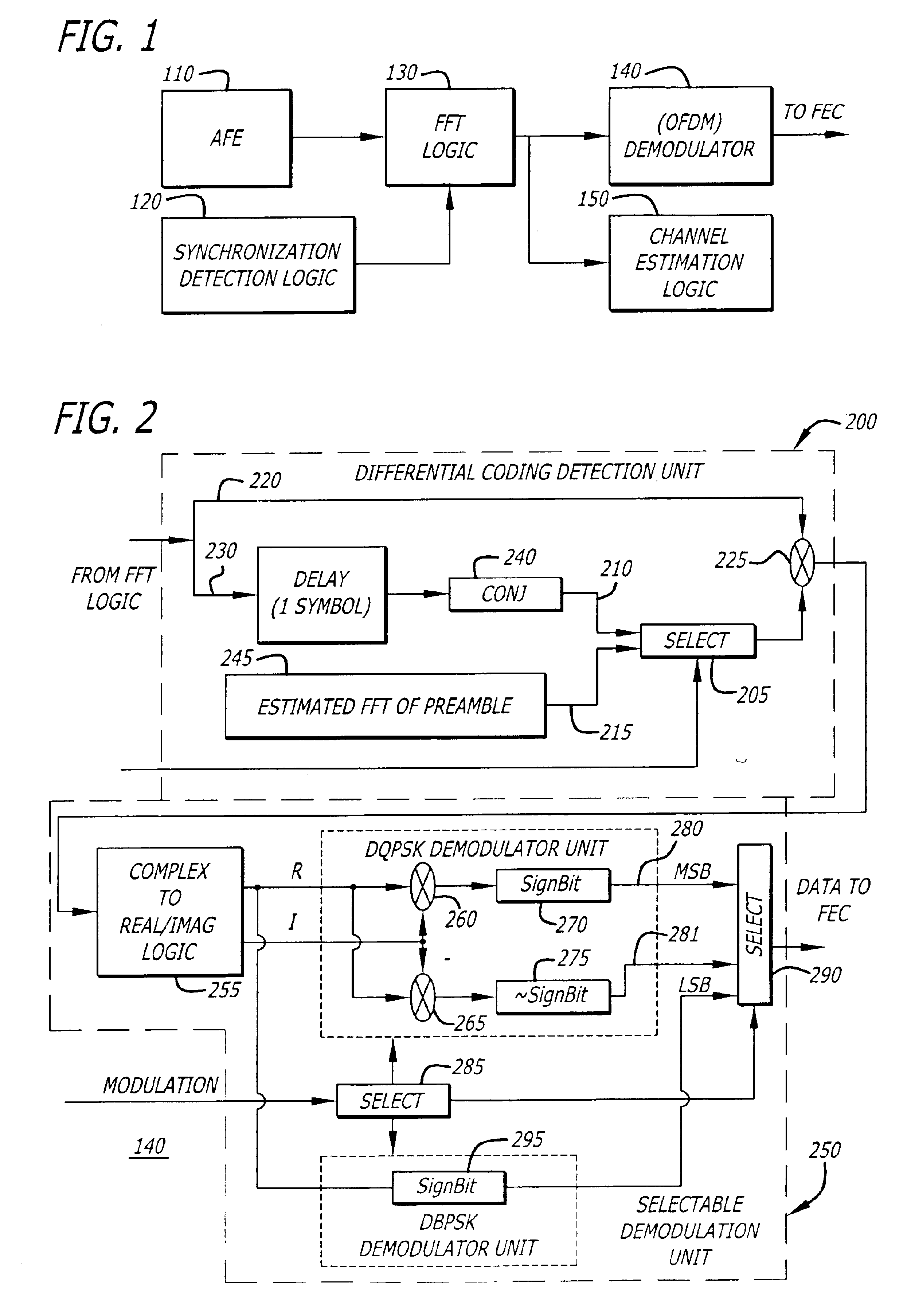
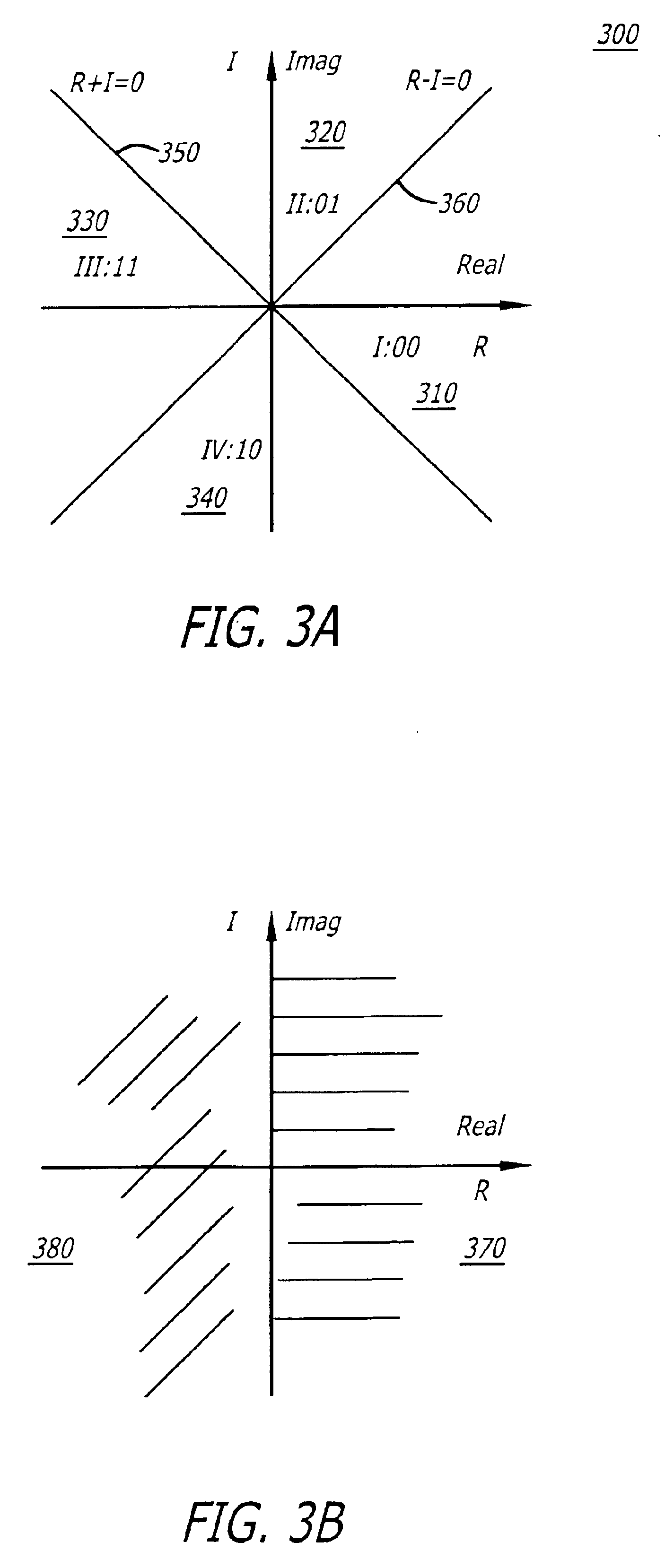
Blind channel estimation and data detection for PSK OFDM-based receivers
InactiveUS6983029B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorSecret communicationPhase differenceAlgorithm
In general, one embodiment of the invention relates to a method for detecting data bits and estimating the channel reliability of each carrier. The detection method comprises (i) computing a complex phase difference between a current symbol and a previous symbol, (ii) separating a real value component (R) from a corresponding imaginary value component (I) forming the complex phase difference, (iii) determining at least one boundary constraint line of a complex phase map for a selected demodulation scheme, and computing an arithmetic combination of the real value component and the corresponding imaginary value component to detect whether a series of bits falls within a selected region of the complex phase map defined by the at least one boundary constraint line. Over N symbols propagating over a carrier, including the current symbol and the previous symbol, the channel estimation counts a number of symbols (less than N but greater than a threshold) that fall within an estimated area of the complex phase map. The estimated area is bound by boundary constraint lines based on a parameterized real value component.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Full-fiedl correction method for laser scanning cofocal microscope scanning distortion phenomenon
The present invention adopts standard raster specimen, using LSCM scanning moire method to obtain scanning moire image, to proceed four steps phase shift processing to originality image though moire phase shift technology to obtain phase shift moire image, according to moire phase shift theory to obtain phase map, after unpackaging to obtain originality phase map, according to phase and displacement field relation to obtain scanning perturbed field, thereby reaching correction target. Compared with current method, the present invention can directly measure scan line perturbed field resulted from scanning control unit distortion phenomena through scanning moire and moire phase shift technology , with high precision, simple operation, and real time and all field measurement.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
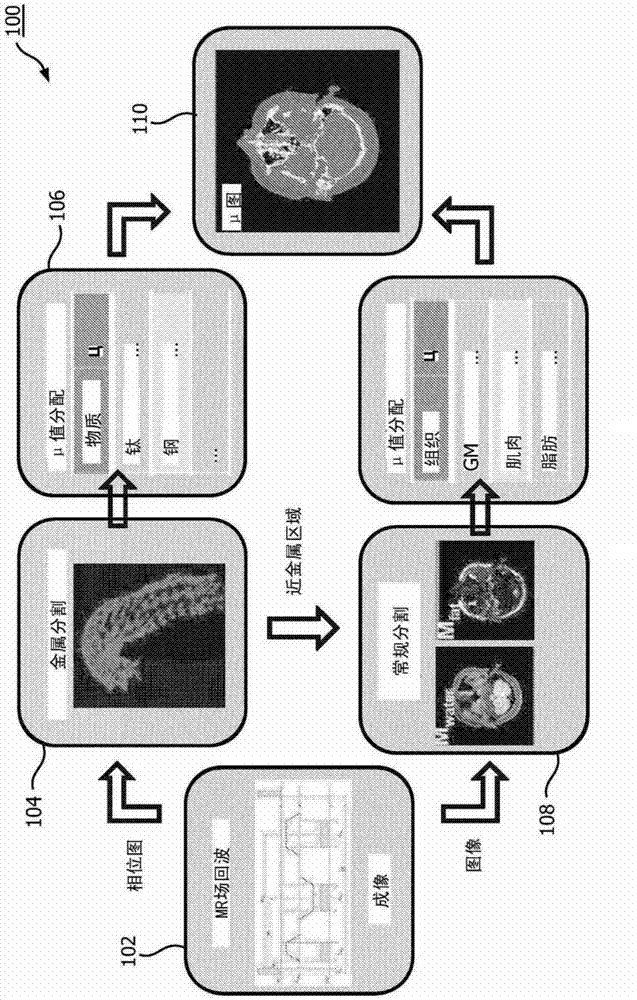
System and method for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN109477877AReconstruction from projectionMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonancePhase maskPhase unwrapping
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
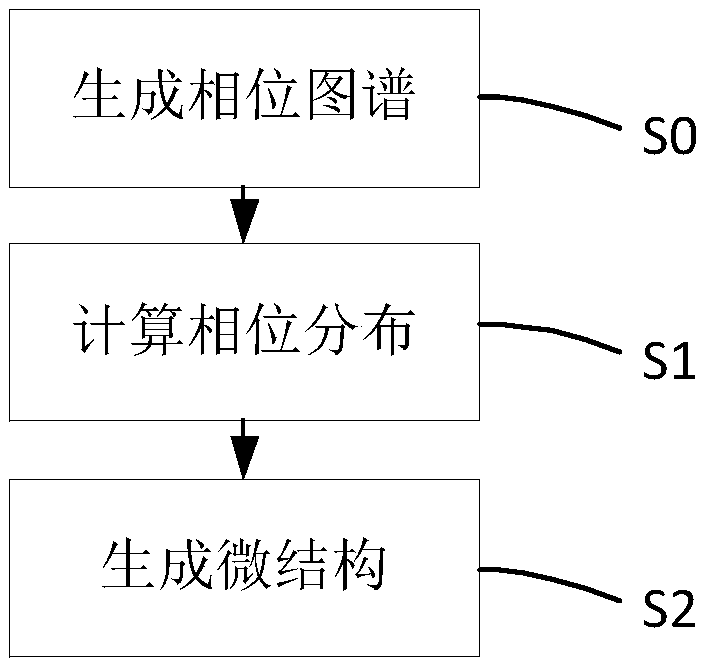
Super-lens microstructure generation method and micro two-photon microscope system based on super lens
ActiveCN109507765AReduce the impactSpeed up progressPhotomechanical apparatusMicroscopesIn vivoImaging equipment
The invention provides a super-lens microstructure generation method. The method includes the following steps of generating phase maps, calculating phase distribution and generating microstructures. The invention further relates to a micro biphoton microscopy system based on the super-lens. A super-surface lens is introduced into the field of biphoton microscopy, medium numerical aperture focusingis achieved under full field of view, the structure of a microscope is greatly simplified, the weight of the overall equipment is largely reduced, and lighter load animal experiments can be achieved.The reliability of in vivo biphoton microscopy experimental data is improved, and the method has high scientific value for micro biphoton, especially in vivo microscopic imaging; the influence of a backpack type micro microscope system on observed objects (such as mice) is further reduced. According to the system, from simulation design to processing to experiments, a super-surface lens is introduced into the biphoton microscopy imaging system, and a new generation of imaging equipment is provided for brain imaging of living animals. The progress in brain and Neuroscience research is promoted.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Digital imaging assembly and methods thereof
InactiveUS7282716B2Eliminate effectiveEasy to seeRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesDigital imagingCoherent wave
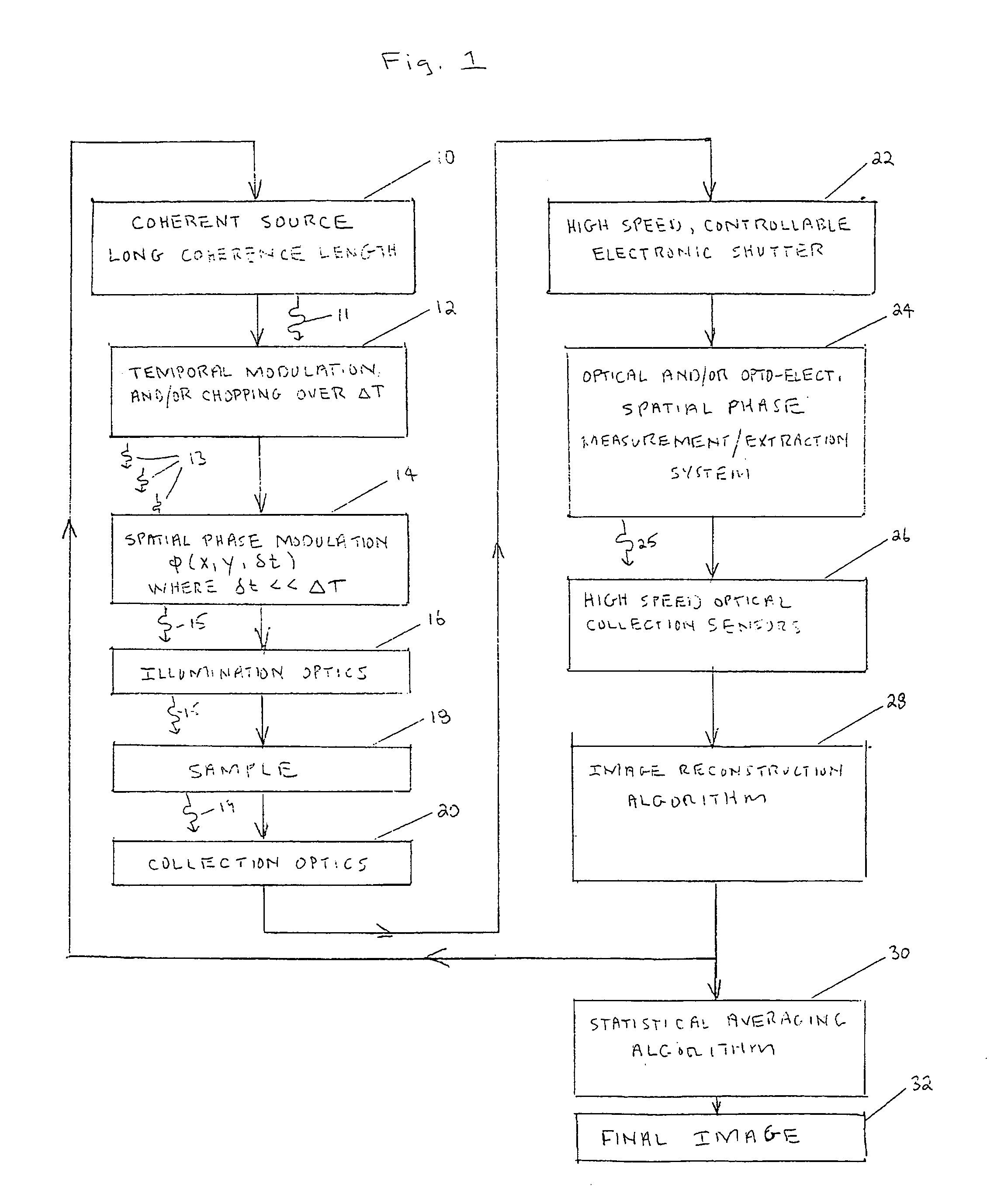
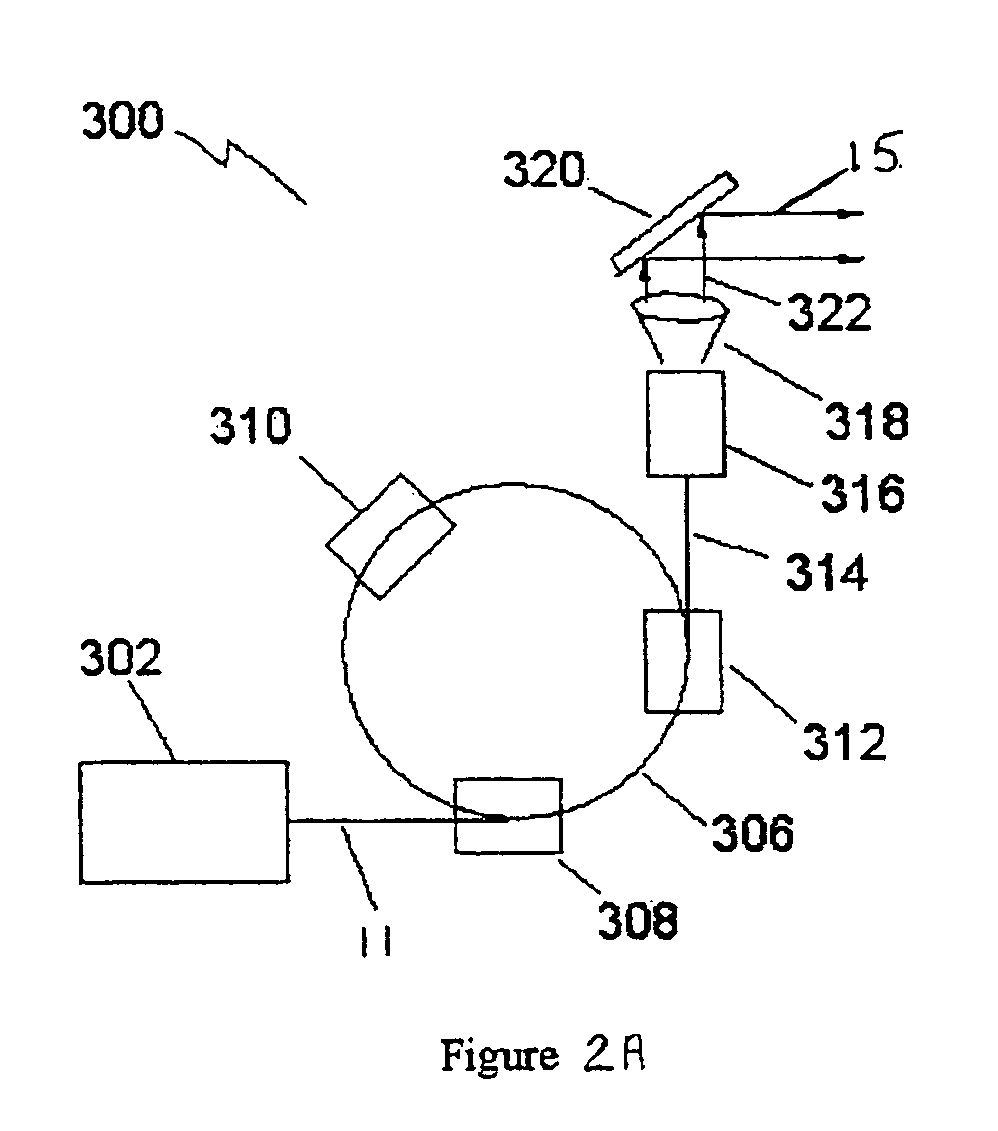
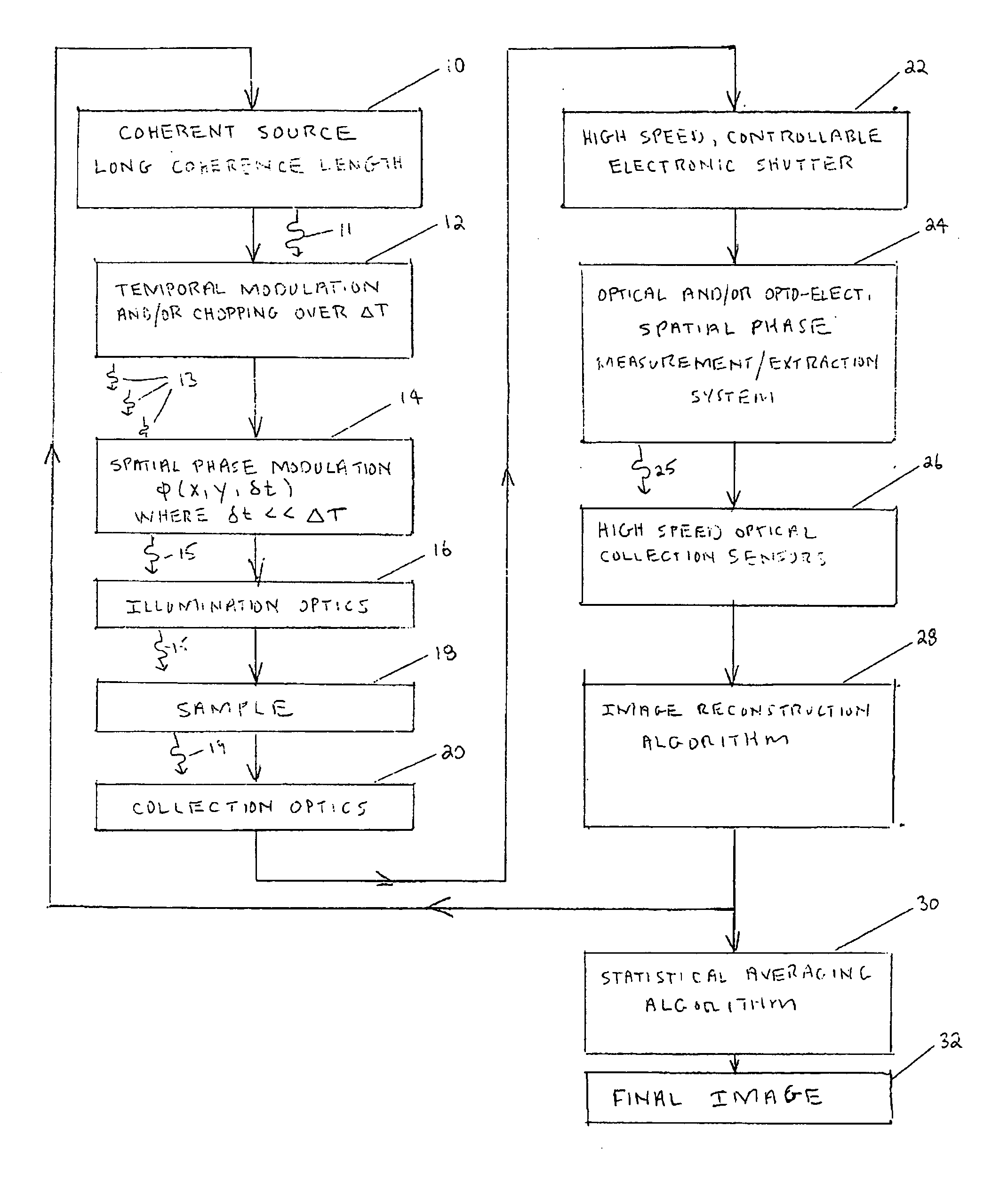
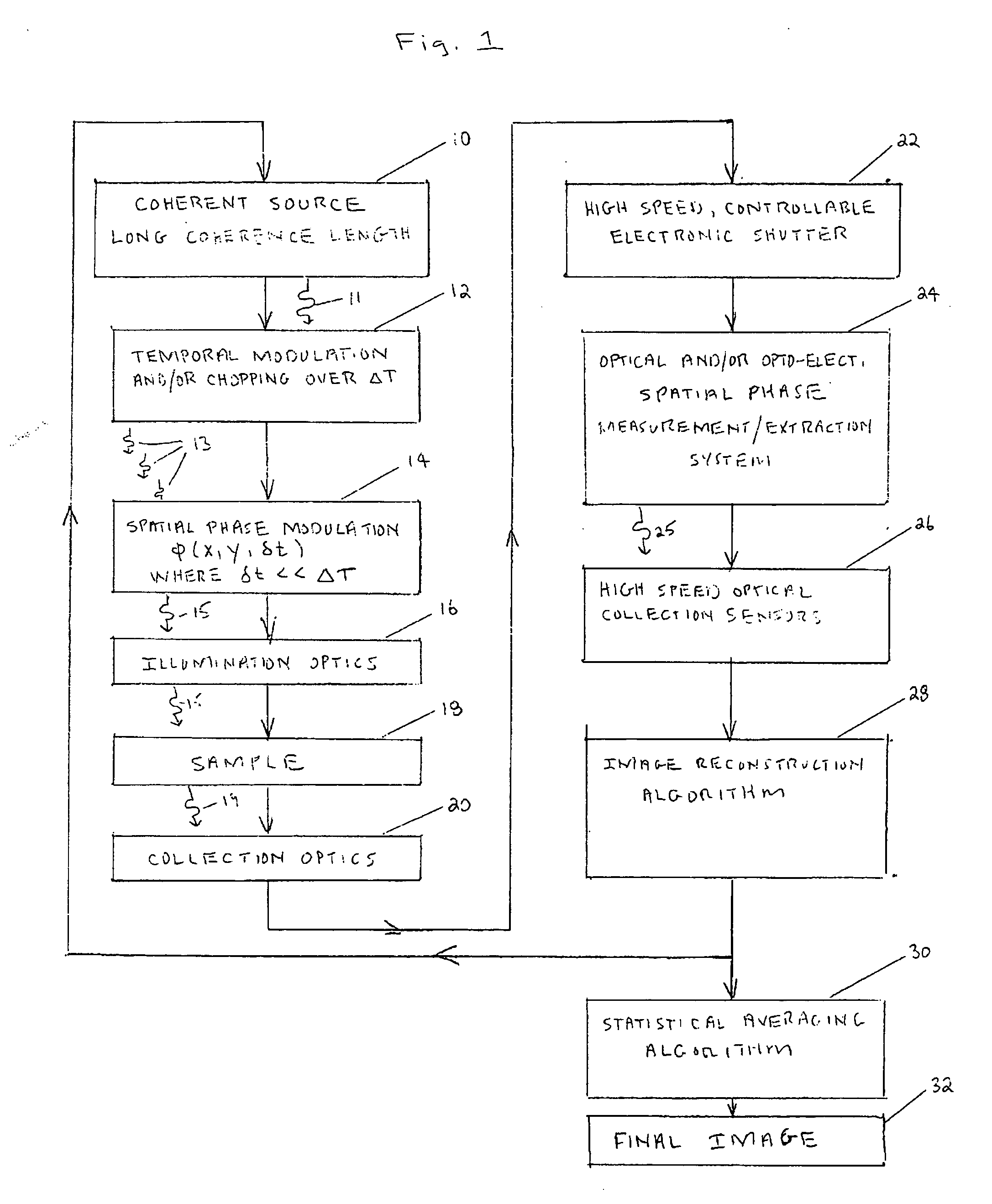
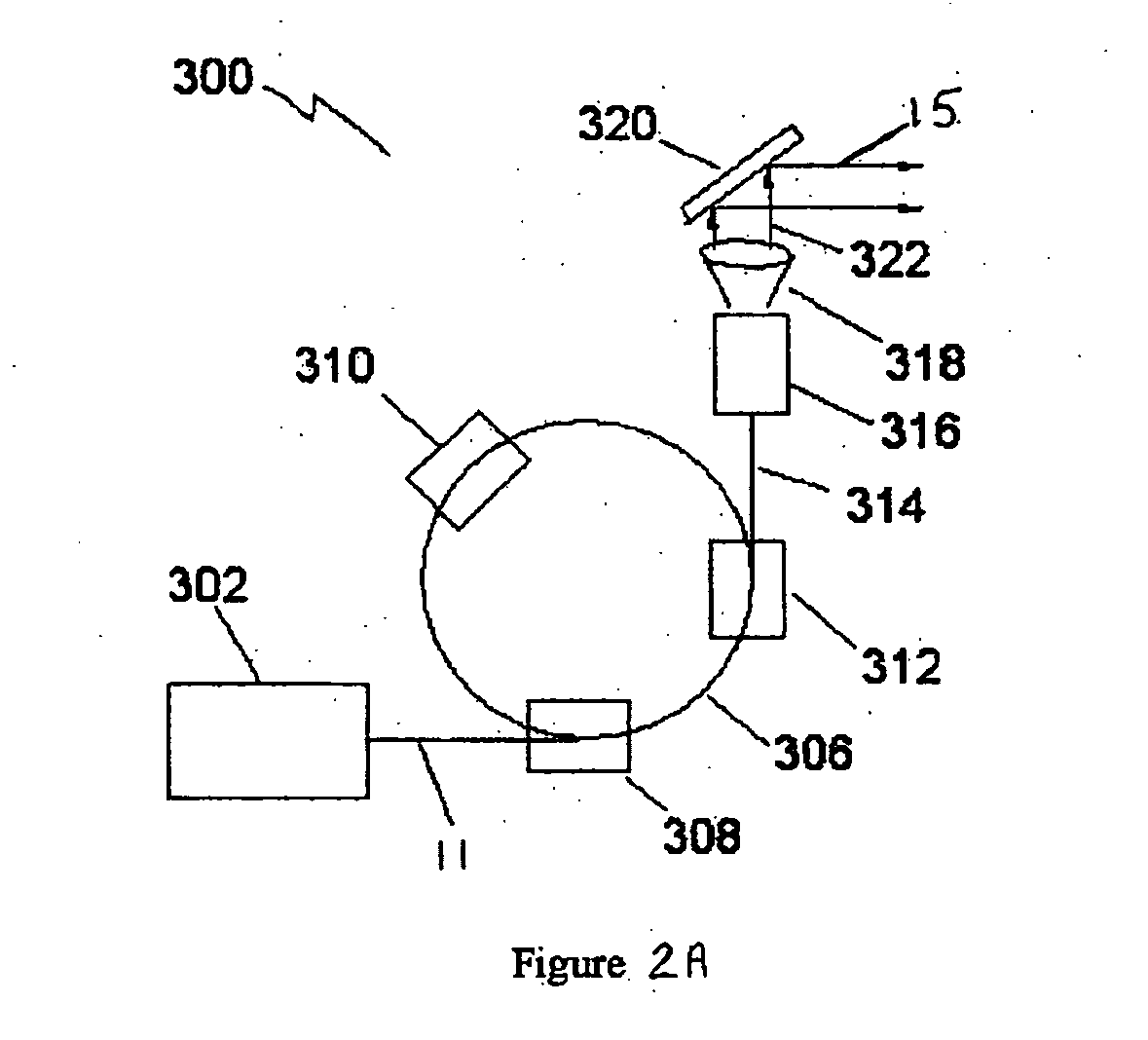
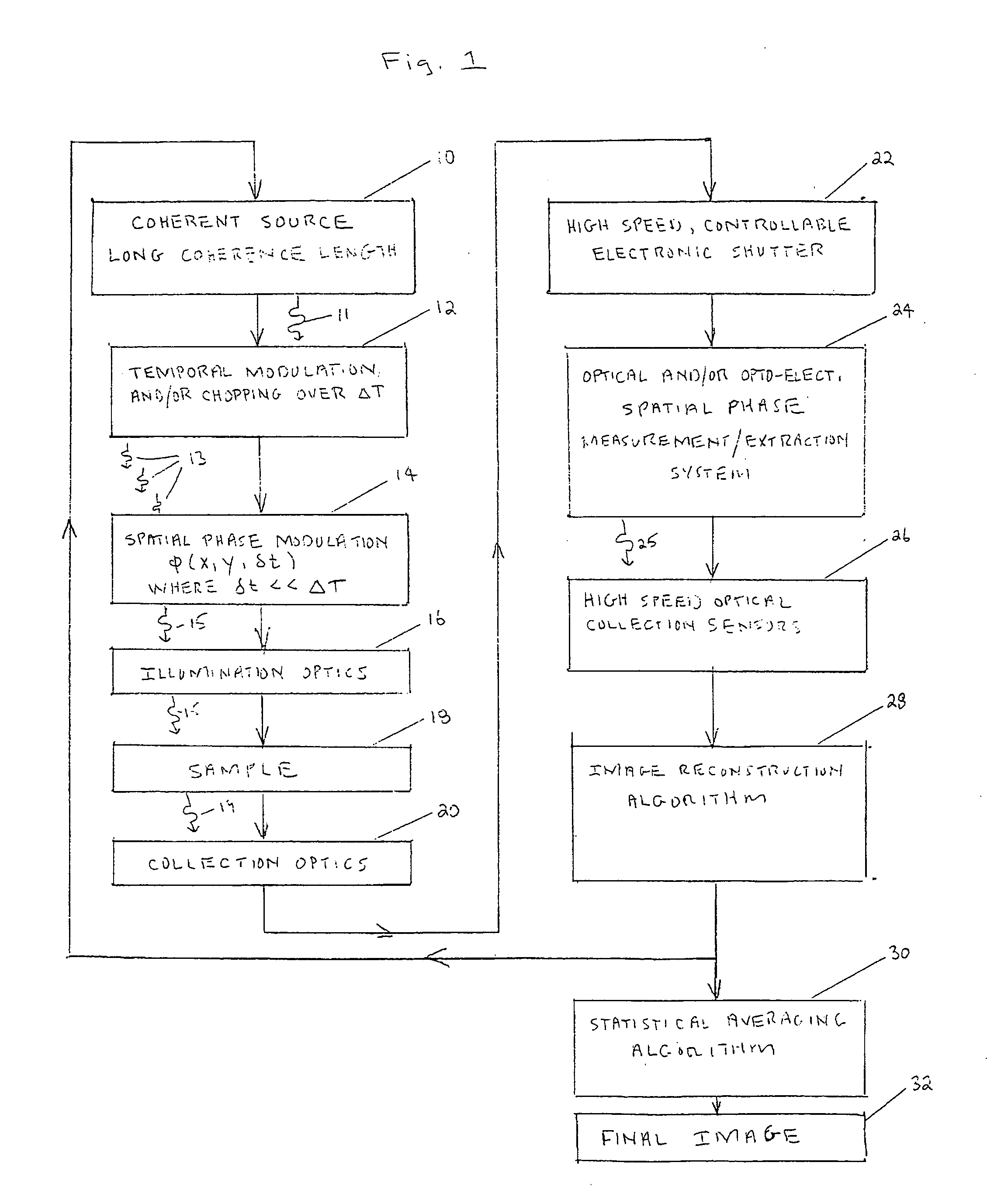
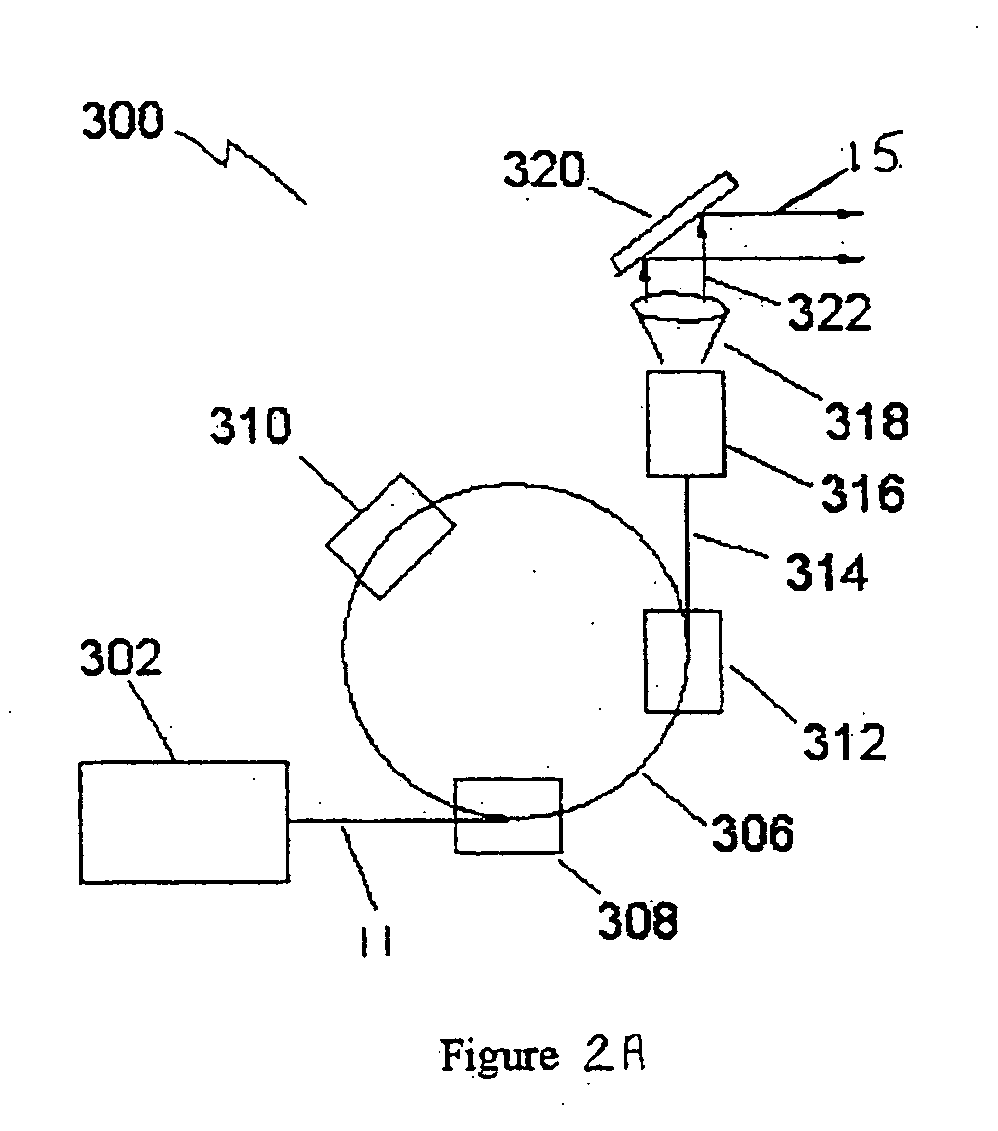
A coherent radiation imaging system that produces digital images with a reduced amount of speckle. Radiation from a long coherence length source is used to form an image of a sample. The output coherent wave is temporally divided into a plurality of wavelets. The spatial phase of each wavelet is then modulated a known and different amount. Each phase modulated wavelet illuminates the sample and is perturbed by its interaction with the sample. A spatial phase map of each perturbed wavelet is then created and converted to a sample image with an image reconstruction program. The plurality of sample images thus formed is statistically averaged to form a final averaged image. The high frequency speckle that is not optically resolvable tends to average to zero with continual statistical averaging, leaving only the optically resolvable lower frequency phase information.
Owner:WAVEFRONT ANALYSIS +1
Novel four-order neural network hyperchaotic circuit
InactiveCN103049790AChange Chaos CharacteristicsPhysical realisationAudio power amplifierCommunications system
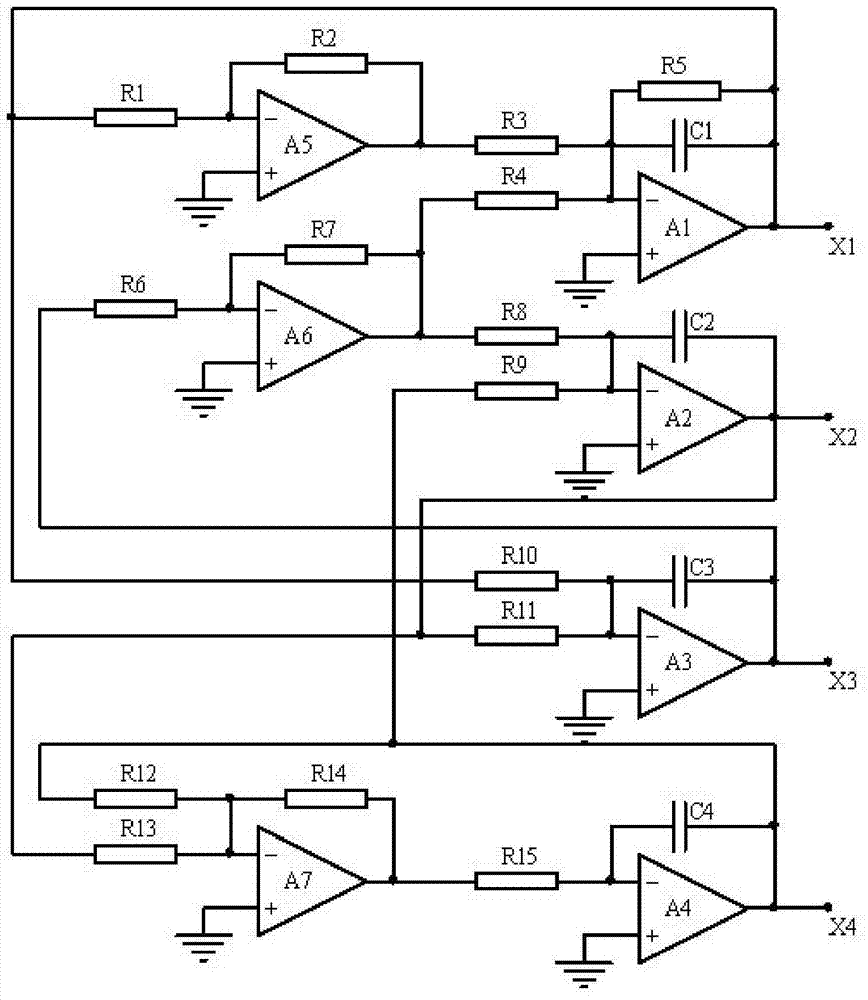
The invention discloses a novel four-order neural network hyperchaotic circuit. First, second, third and fourth operational amplifiers A1, A2, A3 and A4 construct a linear inverting integrator; the output ends of the first, second, third and fourth operational amplifiers are chaotic signal output ends X1, X2, X3 and X4 respectively; a fifth operational amplifier A5 constructs a nonlinear inverting limiting amplifier; sixth and seventh operational amplifiers A6 and A7 construct a linear inverting amplifier; an inverting integrator A1 is connected with a limiting amplifier A5 and an amplifier A3 respectively; an inverting integrator A2 is connected with an integrator A3 and an amplifier A7 respectively; an inverting integrator A3 is connected with an amplifier A6; and an inverting integrator A4 is connected with an integrator A2 and an integrator A7 respectively. Due to the adoption of the four-order neural network hyperchaotic circuit, various waveforms, phase maps and chaotic evolvement curves can be output, and a hyperchaotic secret communication system can be constructed.
Owner:SHANDONG FOREIGN LANGUAGES VOCATIONAL COLLEGE
Digital imaging assembly & methods thereof
InactiveUS20060043302A1Easy to seeMore sensitive and less imposing wayRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansDigital imagingCoherent wave
Owner:TECH INNOVATIONS LLC +1
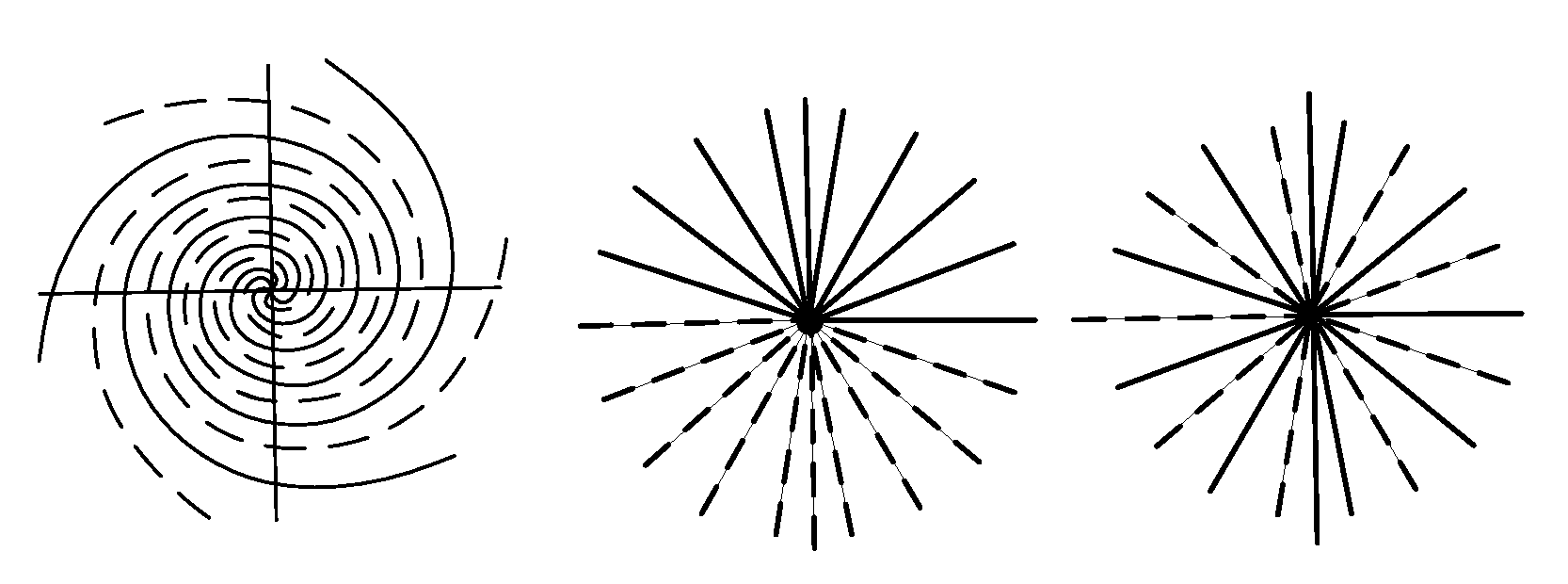
Partial k-space reconstruction for radial k-space trajectories in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7277597B2Minimal aliasing artifactAccurate compensationMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmK space trajectory
A modified projection on convex sets (POCS) algorithm and method for partial k-space reconstruction using low resolution phase maps for scaling full sets of reconstructed k-space data. The algorithm can be used with partial k-space trajectories in which the trajectories share a common point such as the origin of k-space, including variable-density spiral trajectories, projection reconstruction trajectories with a semicircle region acquisition, and projection reconstruction trajectories with every other spike acquired.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Digital imaging assembly and methods thereof
InactiveUS20050167595A1Remove speckle noiseEliminate effectiveRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesDigital imagingRadiation imaging
A coherent radiation imaging system that produces digital images with a reduced amount of speckle. Radiation from a long coherence length source is used to form an image of a sample. The output coherent wave is temporally divided into a plurality of wavelets. The spatial phase of each wavelet is then modulated a known and different amount. Each phase modulated wavelet illuminates the sample and is perturbed by its interaction with the sample. A spatial phase map of each perturbed wavelet is then created and converted to a sample image with an image reconstruction program. The plurality of sample images thus formed is statistically averaged to form a final averaged image. The high frequency speckle that is not optically resolvable tends to average to zero with continual statistical averaging, leaving only the optically resolvable lower frequency phase information.
Owner:WAVEFRONT ANALYSIS +1
Method for detecting field water obstacle detection based on polarizing information
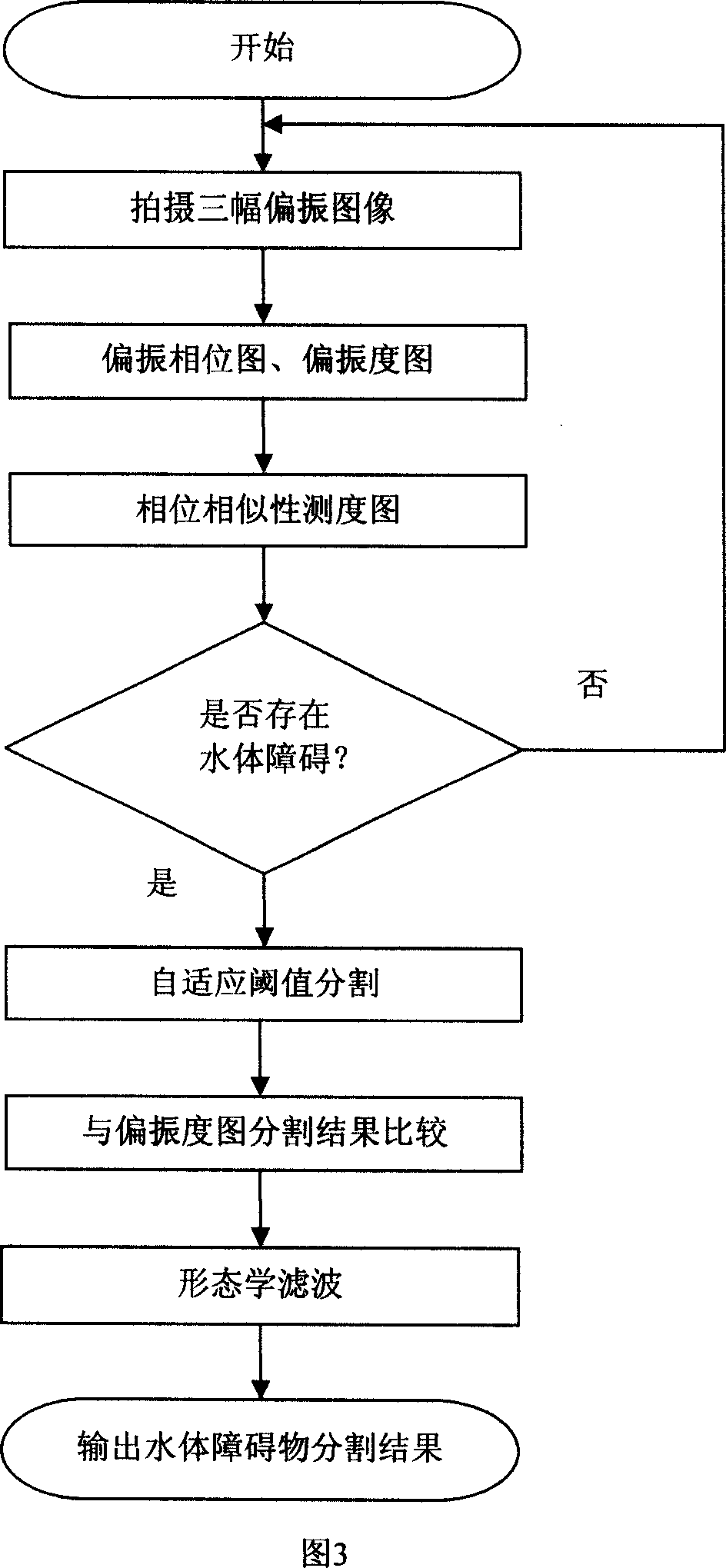
InactiveCN101033961AQuick checkEasy to identifyPicture interpretationImage segmentation algorithmSelf adaptive
This invention relates to a method of detecting outdoors water substance impediment base on polarization information, the process is: fix polarizationlum filter at camera front; pick three pieces different polarization physic images in identity region; count the polarization degree chart, polarization phase map and phase similarity measure chart of this region, and at the phase similarity measure chart verdict whether water substance impediment existing; if existing, then through self-adapting threshold partition algorithm to line out possible range of water substance impediment, at last combine polarization degree chart to definite true water substance impediment region. This device by detecting polarization characteristic of water-reflected light, could detect rounded water surface region, especially possess favorable identify effect to state of water surface existing reflection .This invention adopt relatively simple image segmentation algorithm, small calculated amount, quickly, high accuracy rating, and wide detecting celerity, wide applicability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
In situ determination of pixel mapping in interferometry
Interferometric methods and apparatus by which the map between pixel positions and corresponding part locations are determined in situ. The part under test, which is assumed to be a rigid body, is precisely moved from a base position to at least one other position in one to six degrees of freedom in three-dimensional space. Then, the actual displacements are obtained. The base position is defined as the position with the smallest fringe density. Measurements for the base and all subsequent positions are stored. After having collected at least one measurement for each degree of freedom under consideration, the part coordinates are calculated using the differences of the various phase maps with respect to the base position. The part coordinates are then correlated with the pixel coordinates and stored.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
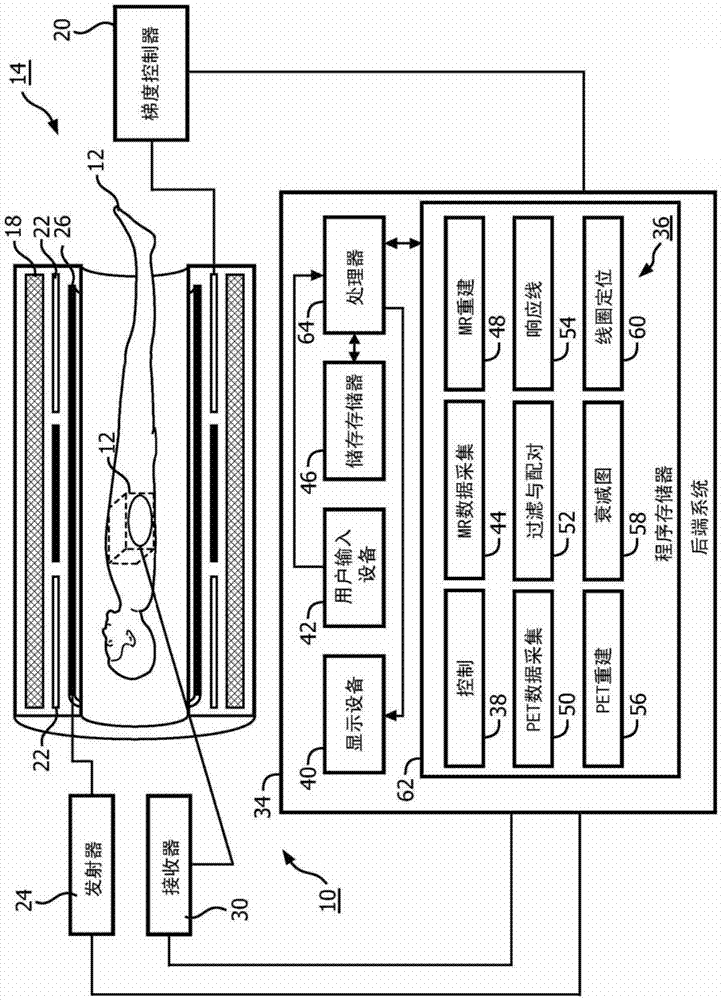
MR receive coil localization and MR-based attenuation correction
ActiveCN104736062AImprove image qualityComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
A system (10) and method generate one or more MR data sets of an imaging volume (16) using an MR scanner (14). The imaging volume (16) includes one or more of a region of interest (ROI), the ROI including a metal element, and a local receive coil (18) of the MR scanner (14). At least one of an attenuation, confidence or density map accounting for the metal element is generated and the location of the local receive coil (18) within the imaging volume (16) is determined. The generating includes identification of the metal element within the ROI based on a phase map of the ROI generated from the MR data sets. The determining includes registering a known sensitivity profile of the local receive coil (18) to a sensitivity map of the local receive coil (18) generated from the MR data sets.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
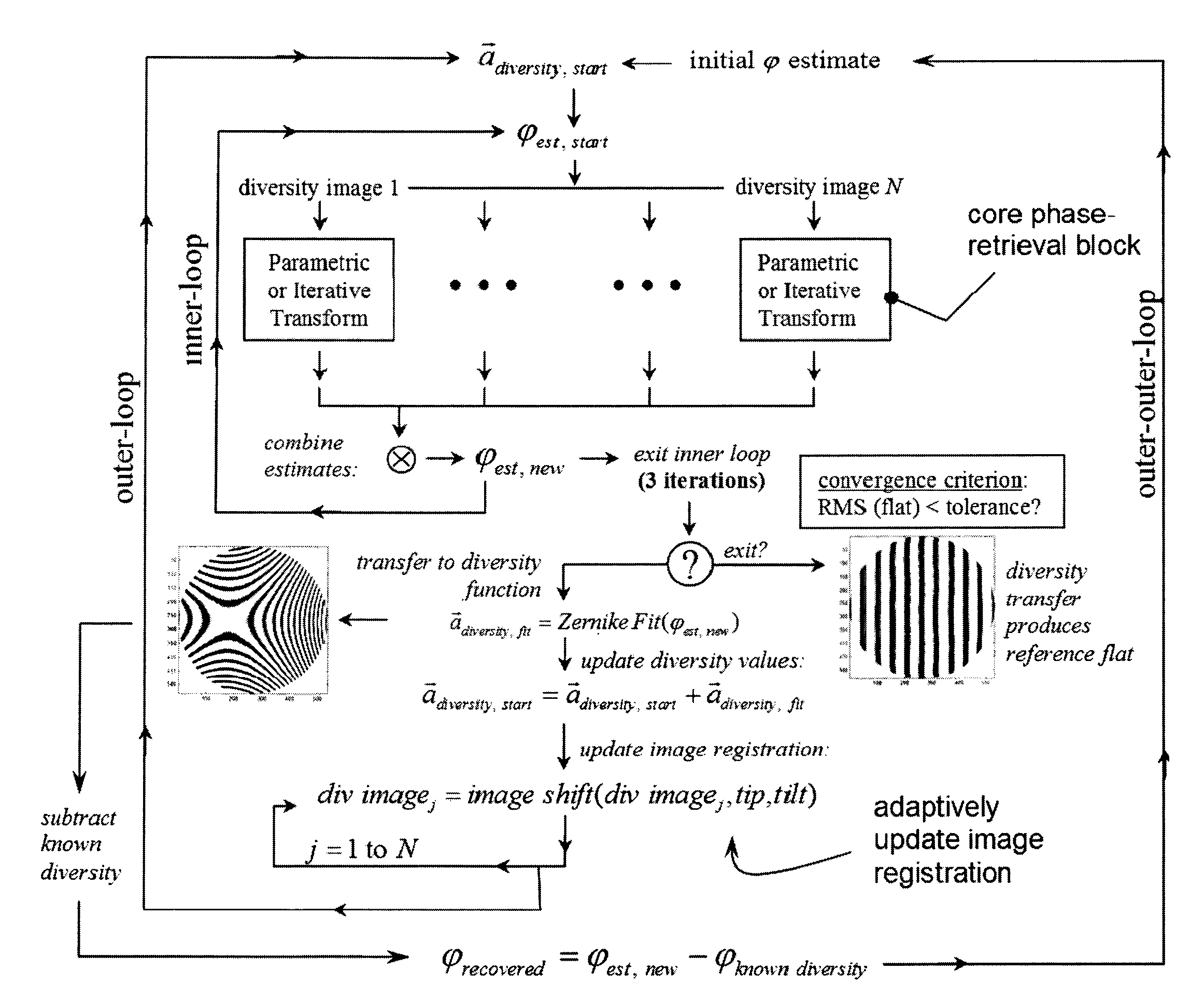
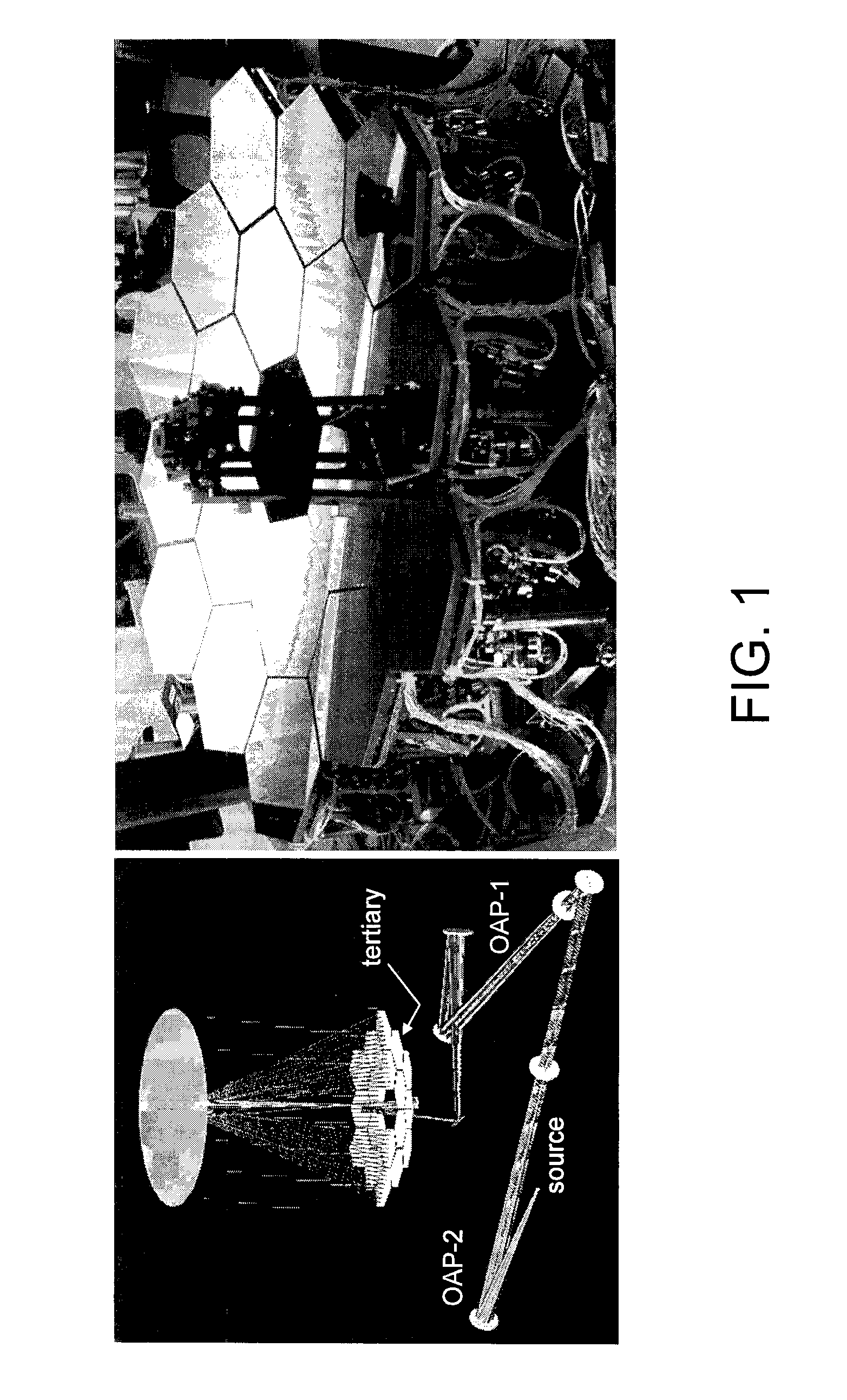
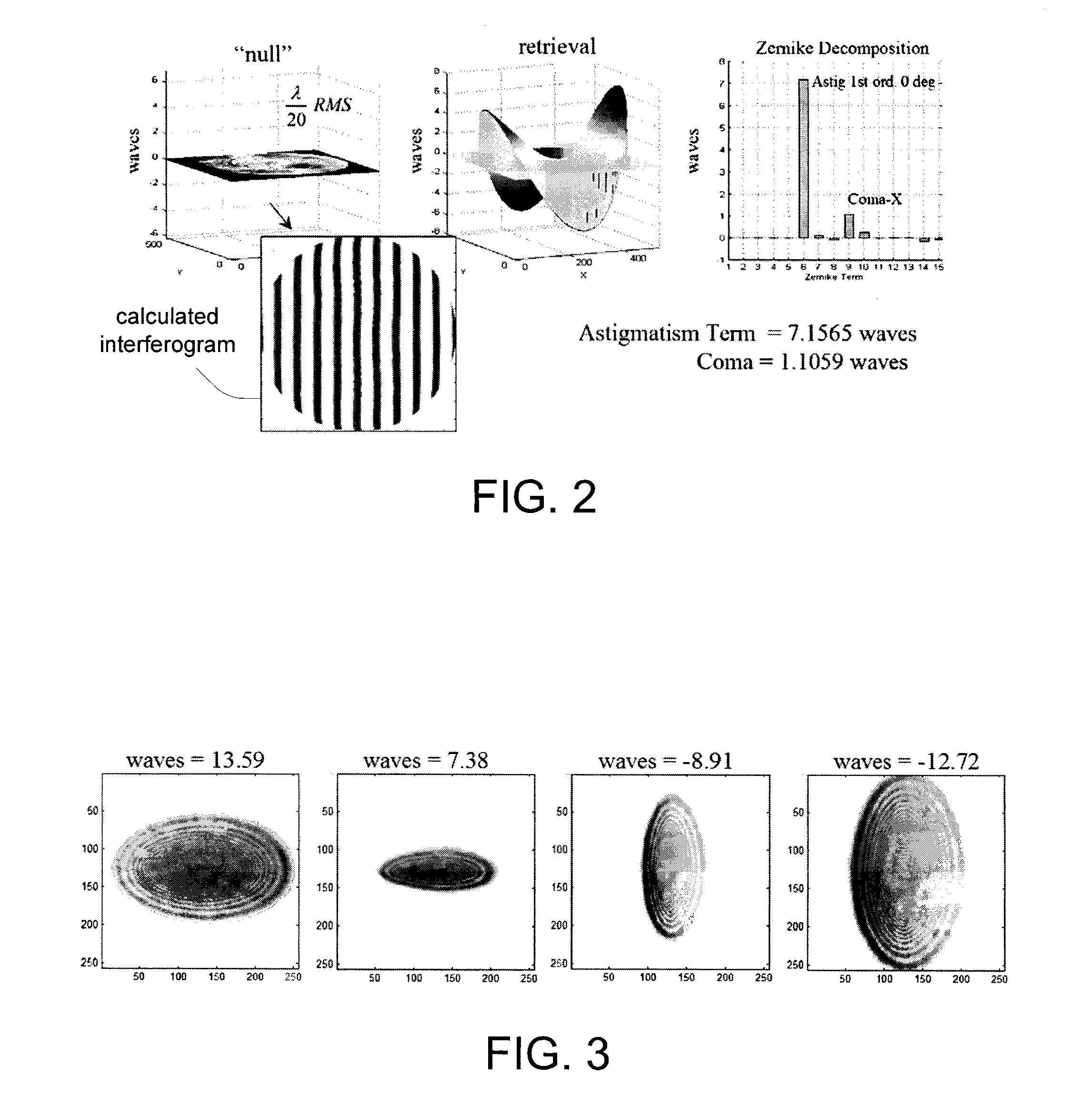
Hybrid diversity method utilizing adaptive diversity function for recovering unknown aberrations in an optical system
A method of recovering unknown aberrations in an optical system includes collecting intensity data produced by the optical system, generating an initial estimate of a phase of the optical system, iteratively performing a phase retrieval on the intensity data to generate a phase estimate using an initial diversity function corresponding to the intensity data, generating a phase map from the phase retrieval phase estimate, decomposing the phase map to generate a decomposition vector, generating an updated diversity function by combining the initial diversity function with the decomposition vector, generating an updated estimate of the phase of the optical system by removing the initial diversity function from the phase map. The method may further include repeating the process beginning with iteratively performing a phase retrieval on the intensity data using the updated estimate of the phase of the optical system in place of the initial estimate of the phase of the optical system, and using the updated diversity function in place of the initial diversity function, until a predetermined convergence is achieved.
Owner:NASA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com