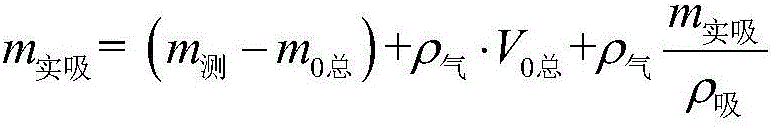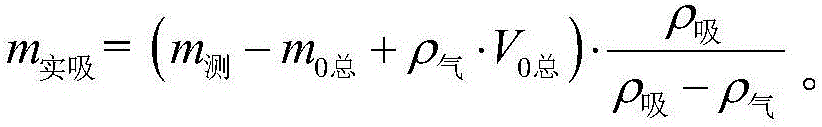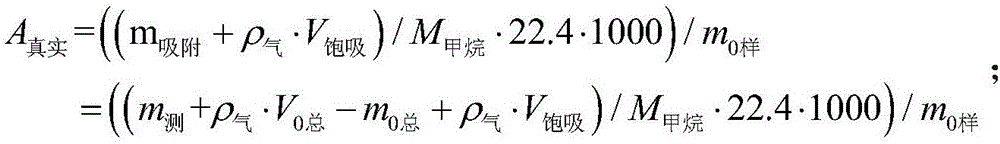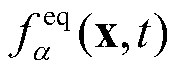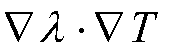Patents
Literature
52 results about "Phase density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Two phase density = (weigh of liquid + weight of vapor)/[weight of liquid/liquid density + weight of vapor/vapor density] to another formula as following. two phase density = [100/(100-%flash)]/Liquid density + %flash/vapor density.
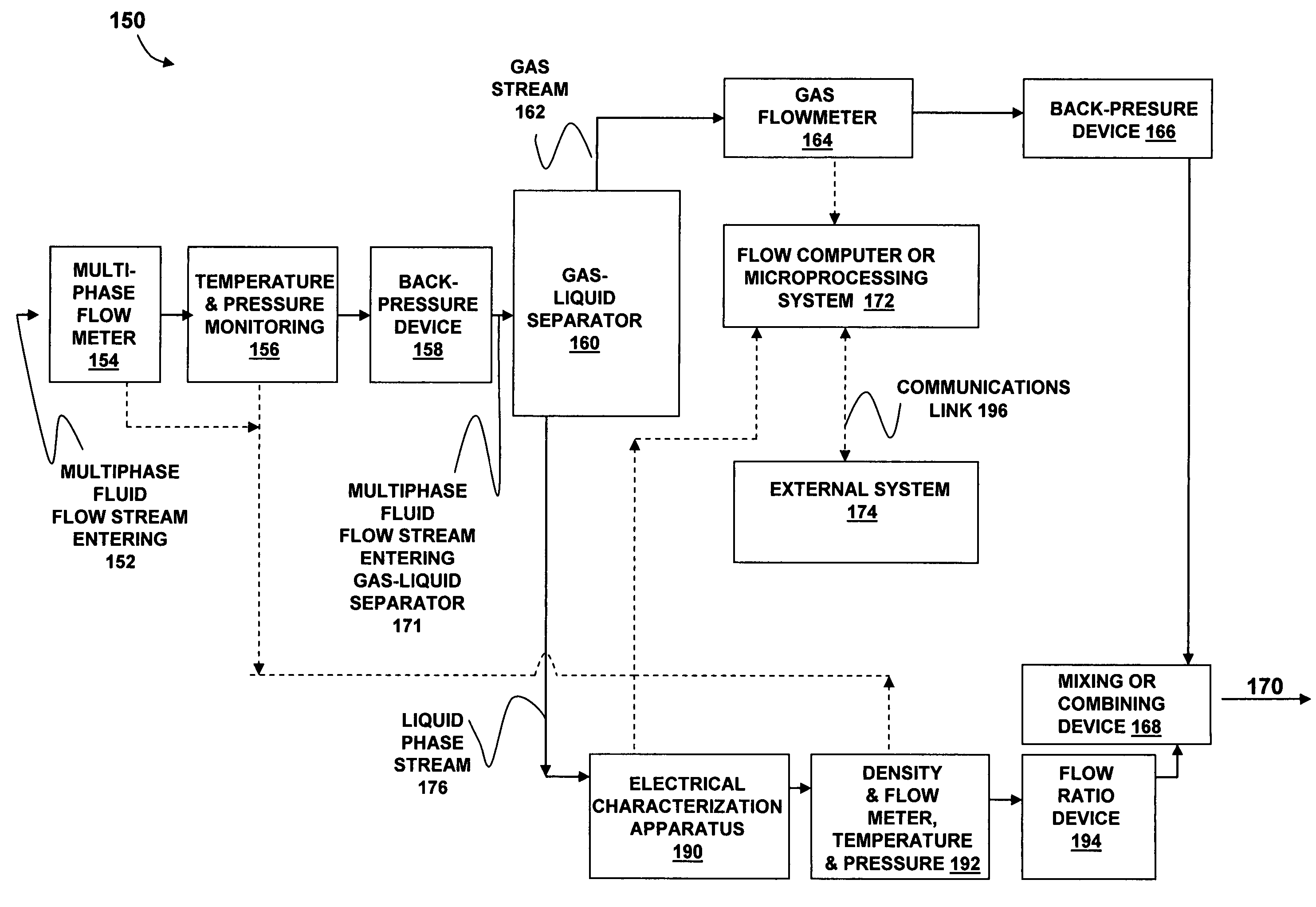
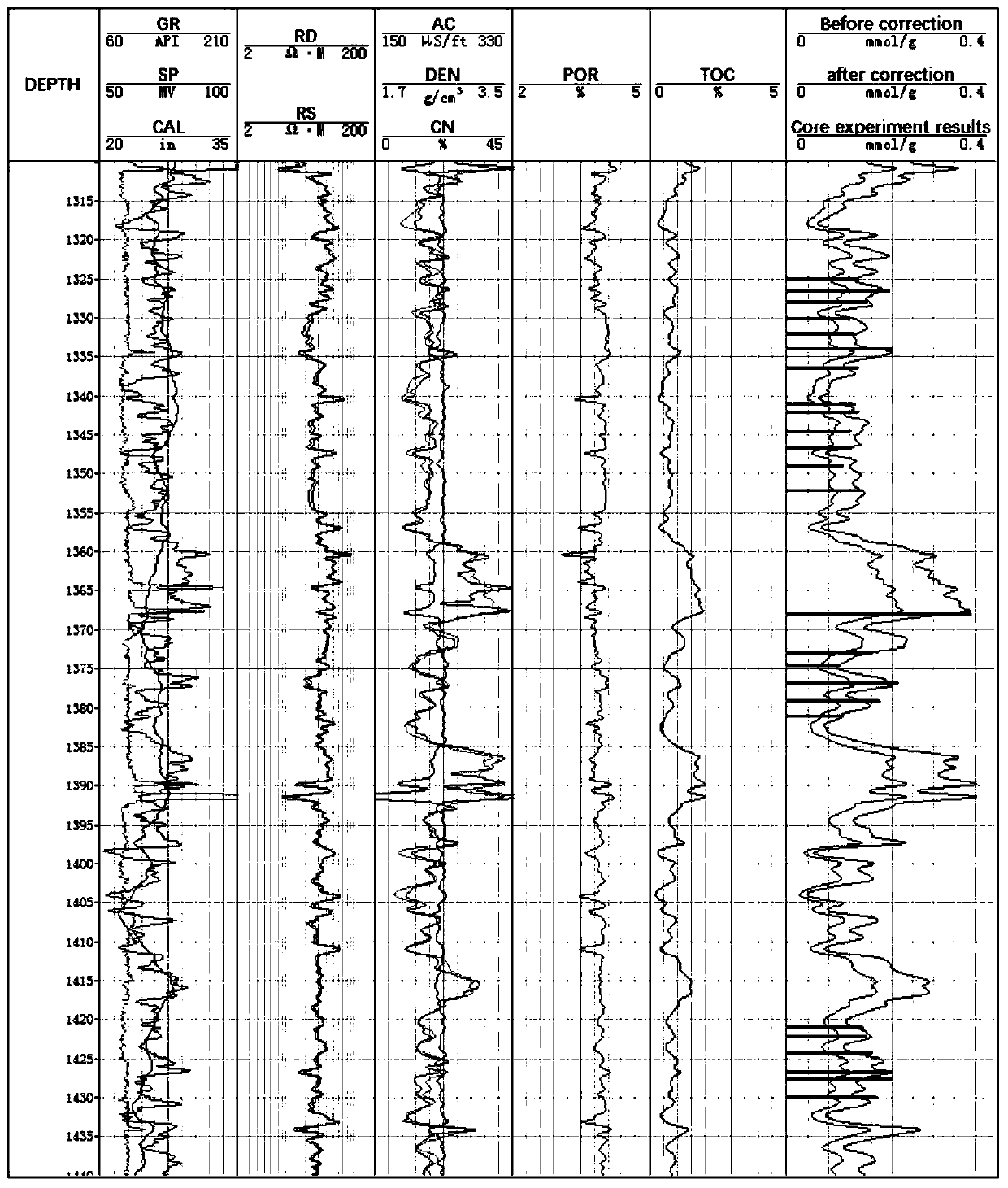
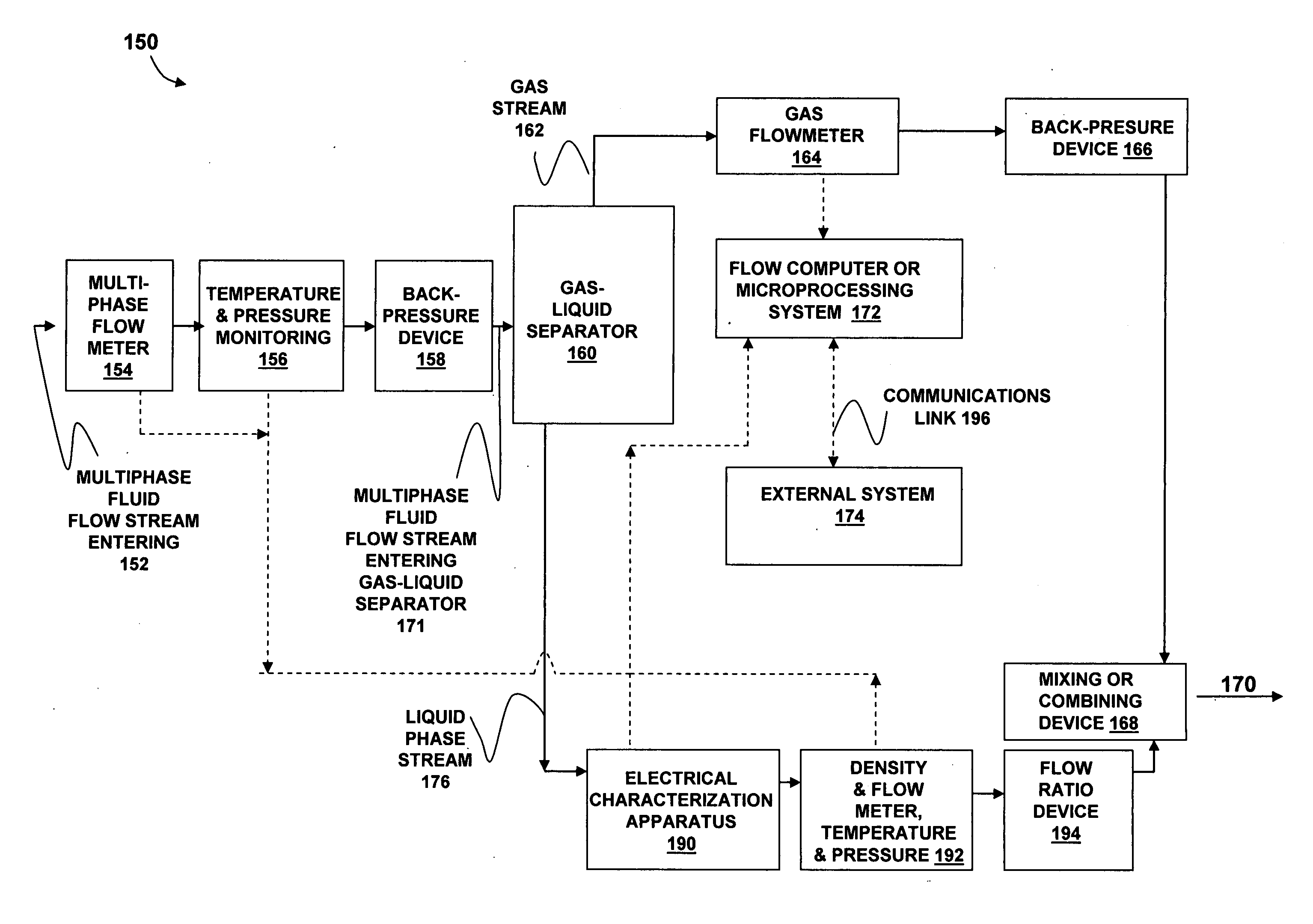
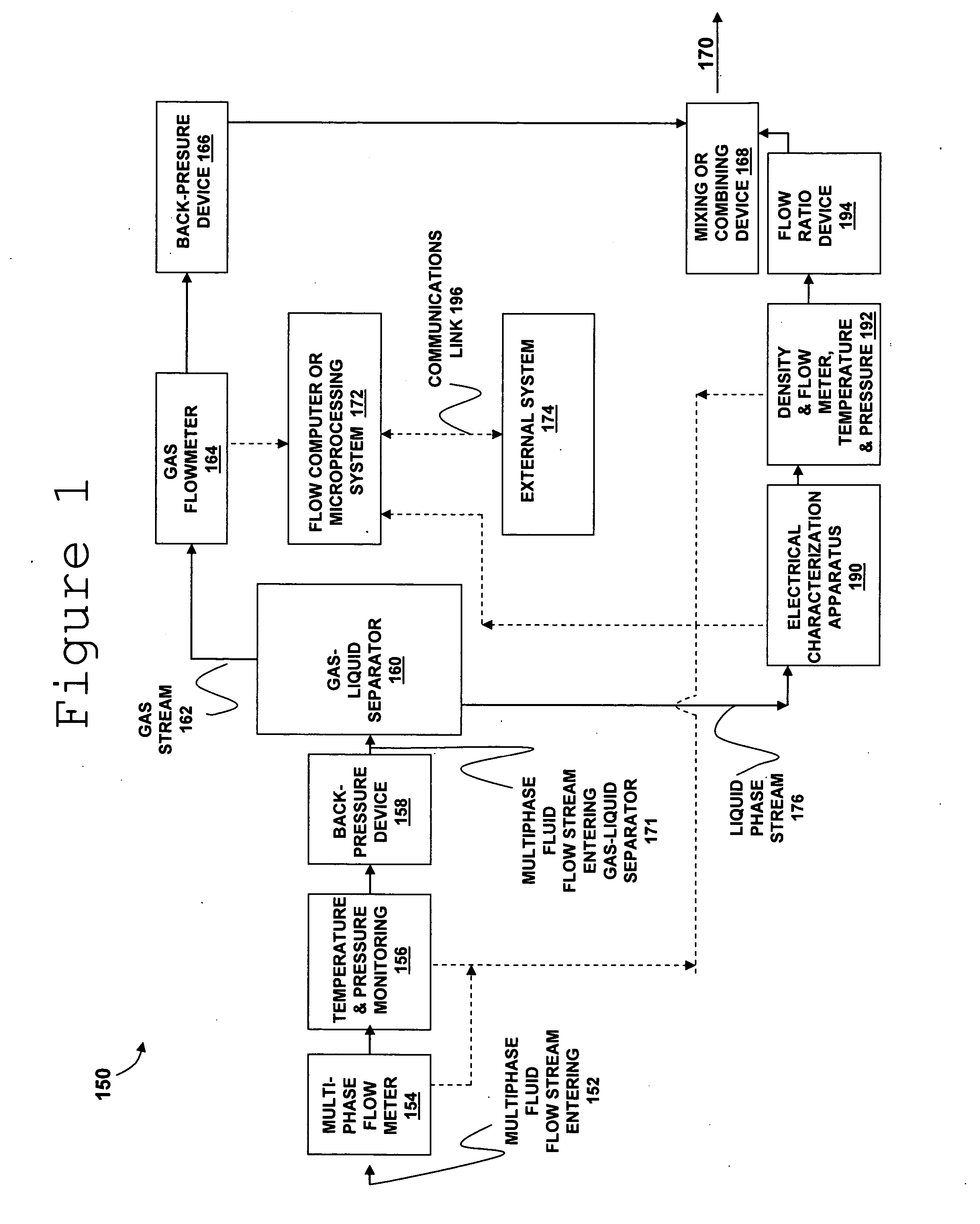
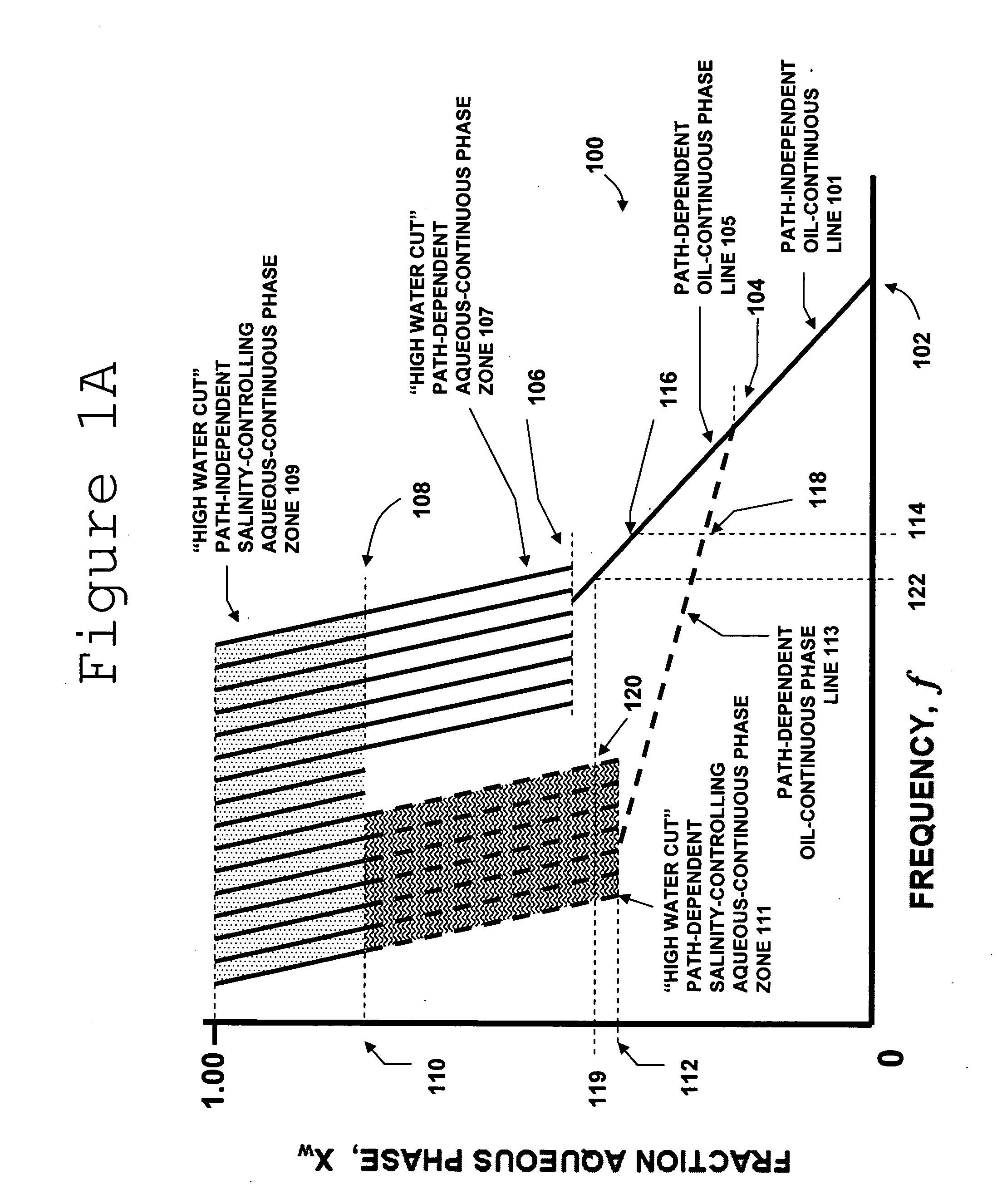
Multiphase fluid characterization
ActiveUS7523647B2Accurate measurementGreat advantageMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpecific gravity using flow propertiesPermittivityPetroleum oil
Methods for determining and validating a first phase fraction of a gravitationally-separated multiphase fluid by conducting physical and electrical property measurements on samples of the fluid. The water content of crude petroleum oil is determined after the oil and water have begun to separate into phase layers such as occurs during un-agitated holding of the crude petroleum oil. A series of measurements of electrical properties such as permittivity and physical properties such as density is collected. The density minima can be used to generate hindsight determinations of average properties, such as the dry oil phase density, which in turn can be used to increase the accuracy of the water percentage in the oil determined by the permittivity and density methods. Flow weighted averages of water percentages by each method can be used to determine and validate the water content of the crude petroleum oil.
Owner:PHASE DYNAMICS
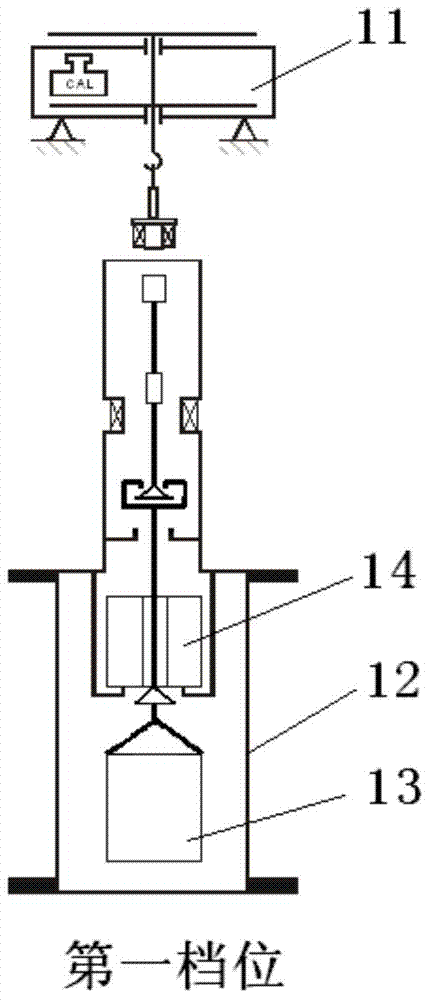
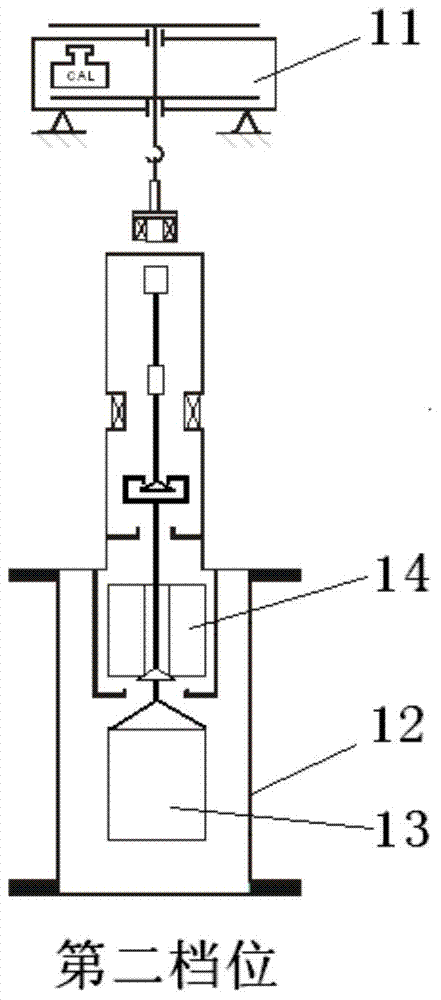
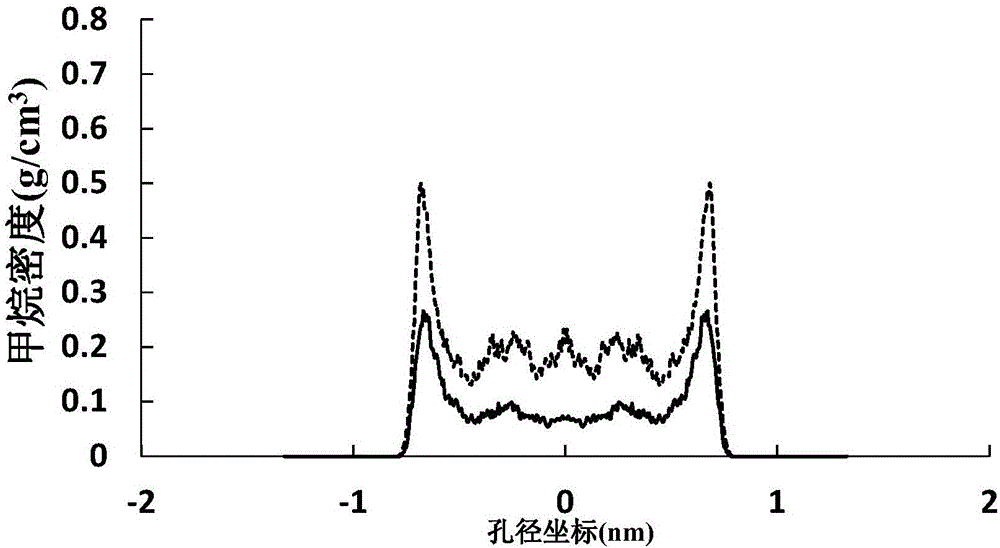
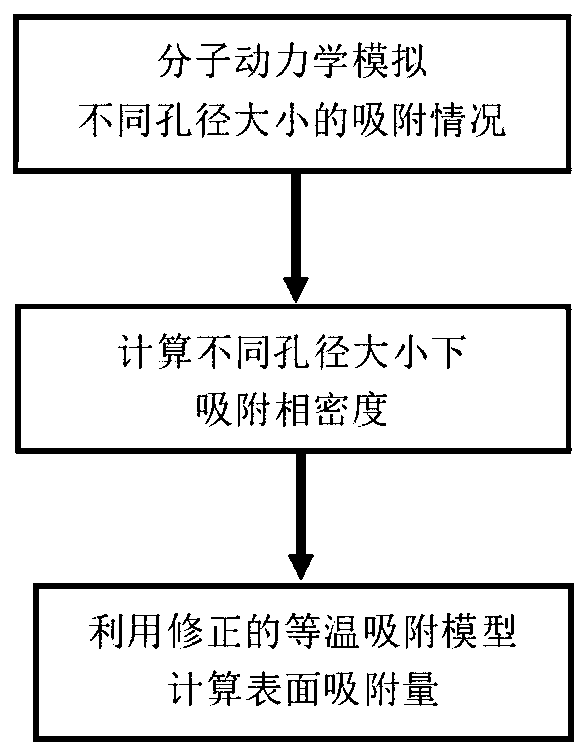
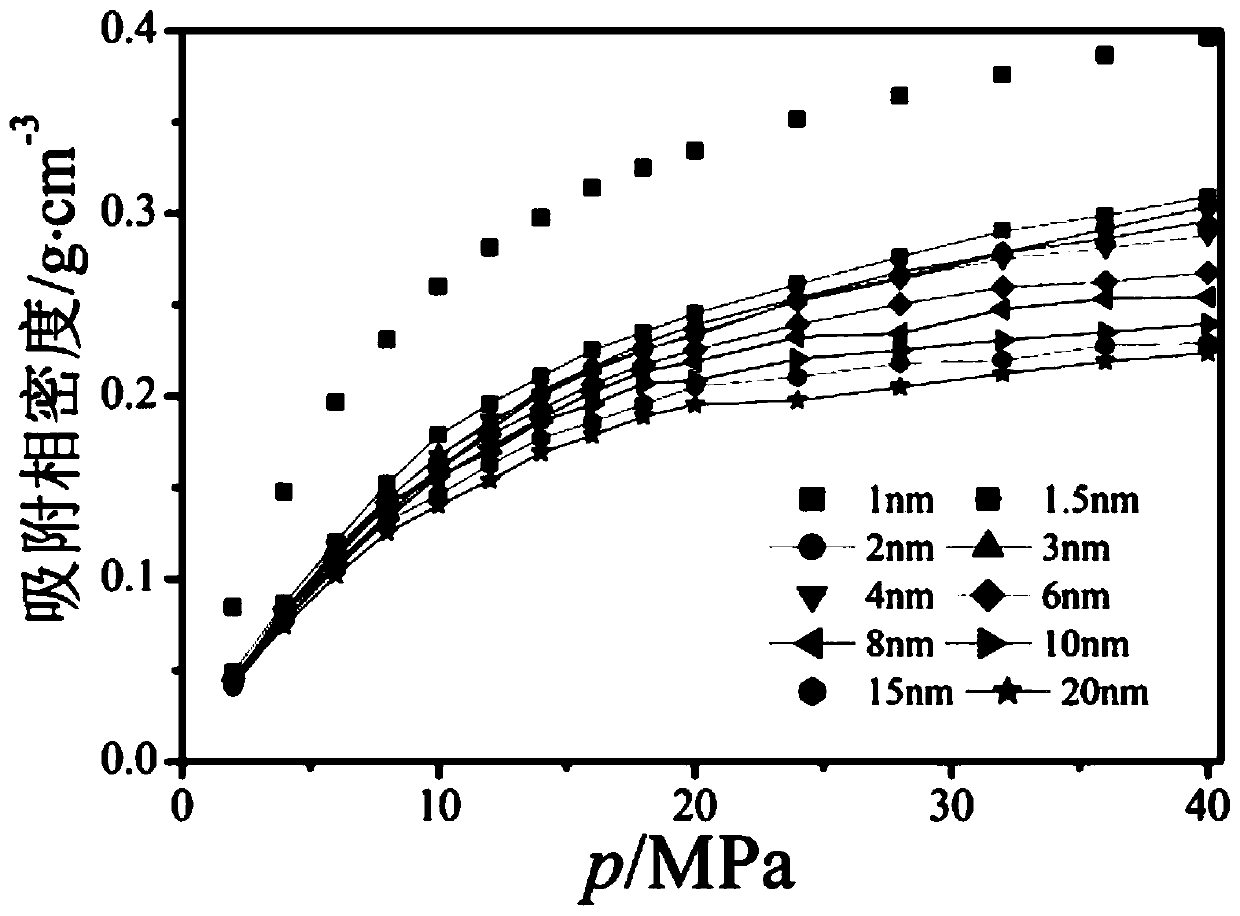
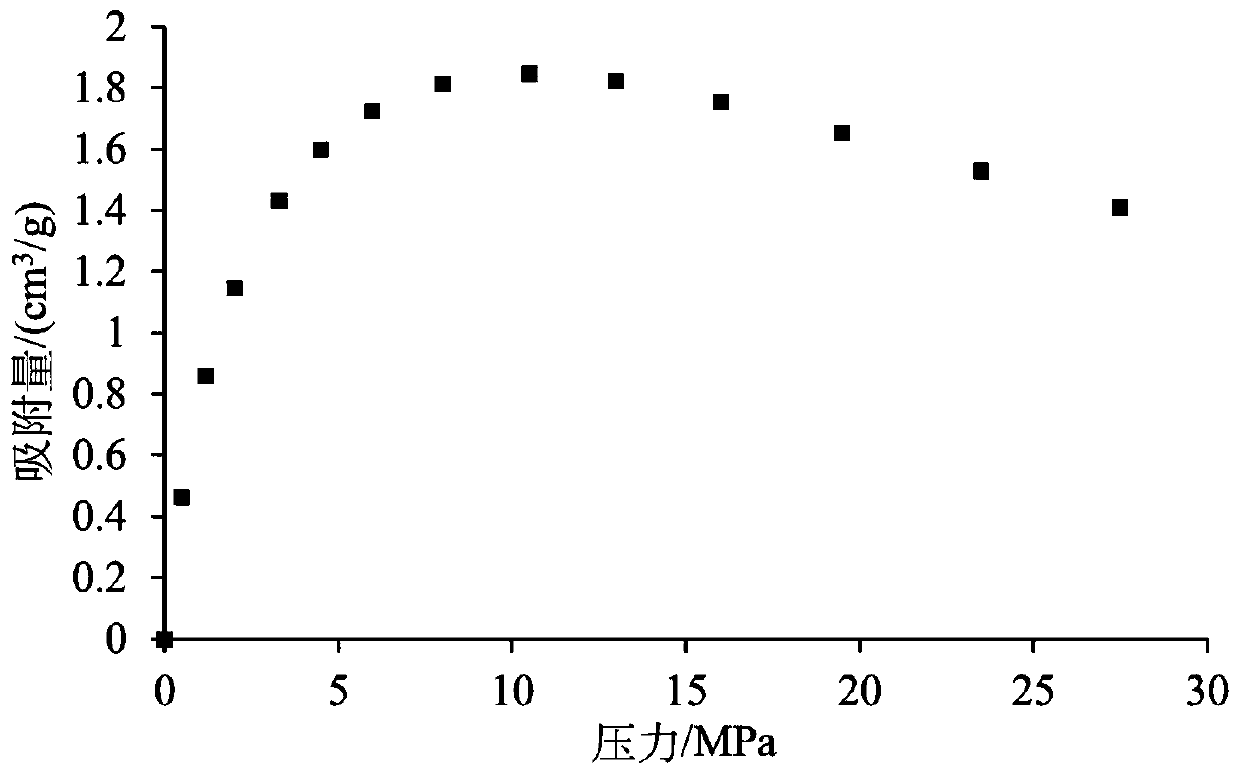
Method for accurately measuring absorbed phase density of methane on shale
InactiveCN104713803AThe result is accurateImprove applicabilitySpecific gravity measurementSubstance amountPhase volume
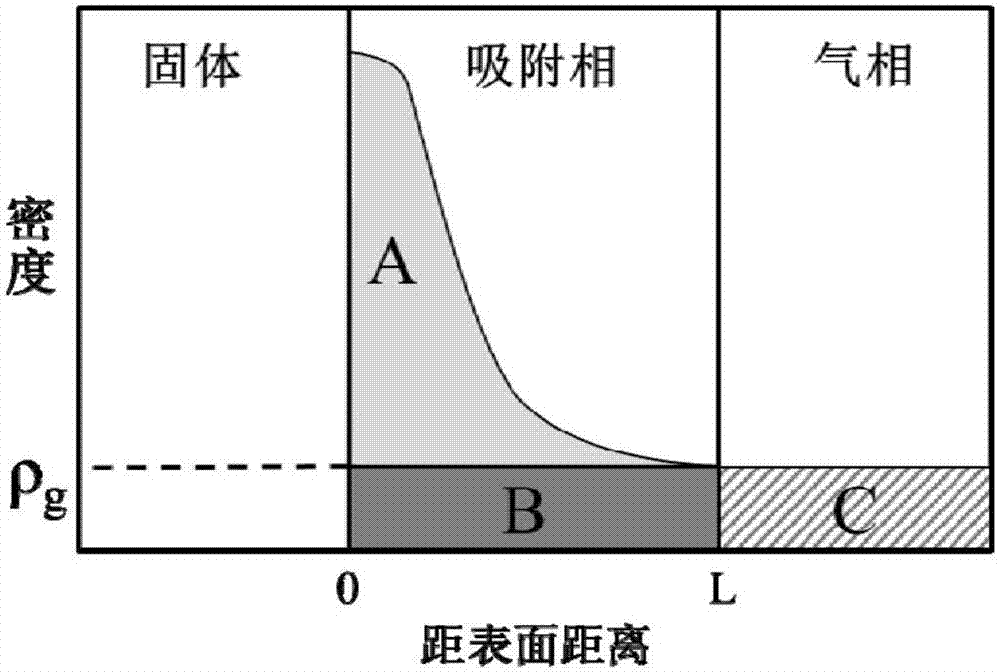
The invention relates to a method for accurately measuring absorbed phase density of methane on shale. The method comprises the following steps: 1) smashing a piece of shale sample to be 60-80 meshes, and dividing the powder into two; 2) performing a volumetric method isothermal adsorption experiment on the first shale sample, and obtaining a calculation model of the amount n, adsorbing CH4, of the adsorbed state methane substance; 3) performing a weight method isothermal adsorption experiment on the second shale sample, and obtaining a calculation model of the mass m, adsorbing CH4, of the adsorbed state methane; 4) performing adsorbed phase volume correction on the calculation model of the amount n, adsorbing CH4, of the adsorbed state methane substance, obtained in the step 2) and the calculation model of the mass m, adsorbing CH4, of the adsorbed state methane, obtained in the step 3), so as to obtain the corrected substance amount calculation model and the corrected mass calculation model of the adsorbed state methane; 5) according to a definition formula of the amount of substance, combining with the two calculation models in the step 4), and determining the mass m, adsorbing CH4, and the volume V adsorption of the adsorbed state methane; 6) according to the definition of the density, determining an exact adsorption value of the adsorbed phase density rho of methane on the shale.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for accurately calculating real adsorption quantity of methane on shale
ActiveCN106198297AAccurate measurement of excess adsorptionImprove applicabilityPreparing sample for investigationWeighing by absorbing componentThermostatHigh pressure
The invention provides a method for accurately calculating the real adsorption quantity of methane on shale. The method comprises the following steps: crushing muddy shale samples; drying in a thermostat; obtaining the change data of quality of the muddy shale samples along the gas pressure, and calculating the initial volume and quality of samples and a sample cylinder; calculating the excessive adsorption quantity of the samples under different pressures; making a plot of the quality and gas density of measured samples at high-pressure section in a rectangular Cartesian coordinate system, and fitting to obtain an analytic expression, requiring fitting R<2>=1; calculating the saturated adsorption quality and saturated adsorption phase volume of the samples, wherein the ratio of the two is density value of an adsorption phase; and correcting the excessive adsorption quantity of saturated adsorption points on an absolute line through the adsorption phase volume, and correcting the excessive adsorption quantity on front other points through adsorption phase density, thus obtaining the true adsorption quantity of methane on shale.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Method for quantitative evaluation of shale gas resource quantity of shale and characterization of adsorption gas and free gas transformation rule
The invention discloses a method for quantitative evaluation of shale gas resource quantity of shale and characterization of adsorption gas and free gas transformation rules. According to the method, influence of organic matter content, maturity, type, mineral composition and temperature and pressure conditions on shale gas absorption quantity can be analyzed, and on the basis of the influence, an adsorption model is established by combination of adsorption potential theory, supercritical adsorption experiment phenomena and computer simulation, and the core connotation is as follows: the adsorption quantity is equal to product of adsorption space and adsorption phase density, when adsorbate (shale) is determined, the adsorption space is the self attribute of the adsorbate, the adsorption space is irrelevant to the outside temperature and pressure conditions; and the adsorption phase density is a result of interaction of temperature and pressure and adsorbate pore structures.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
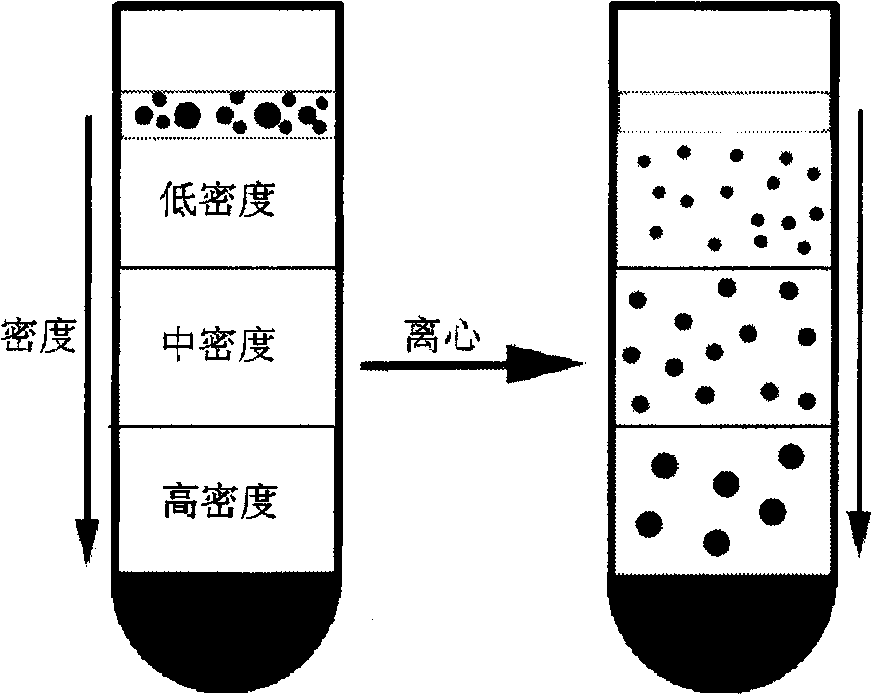
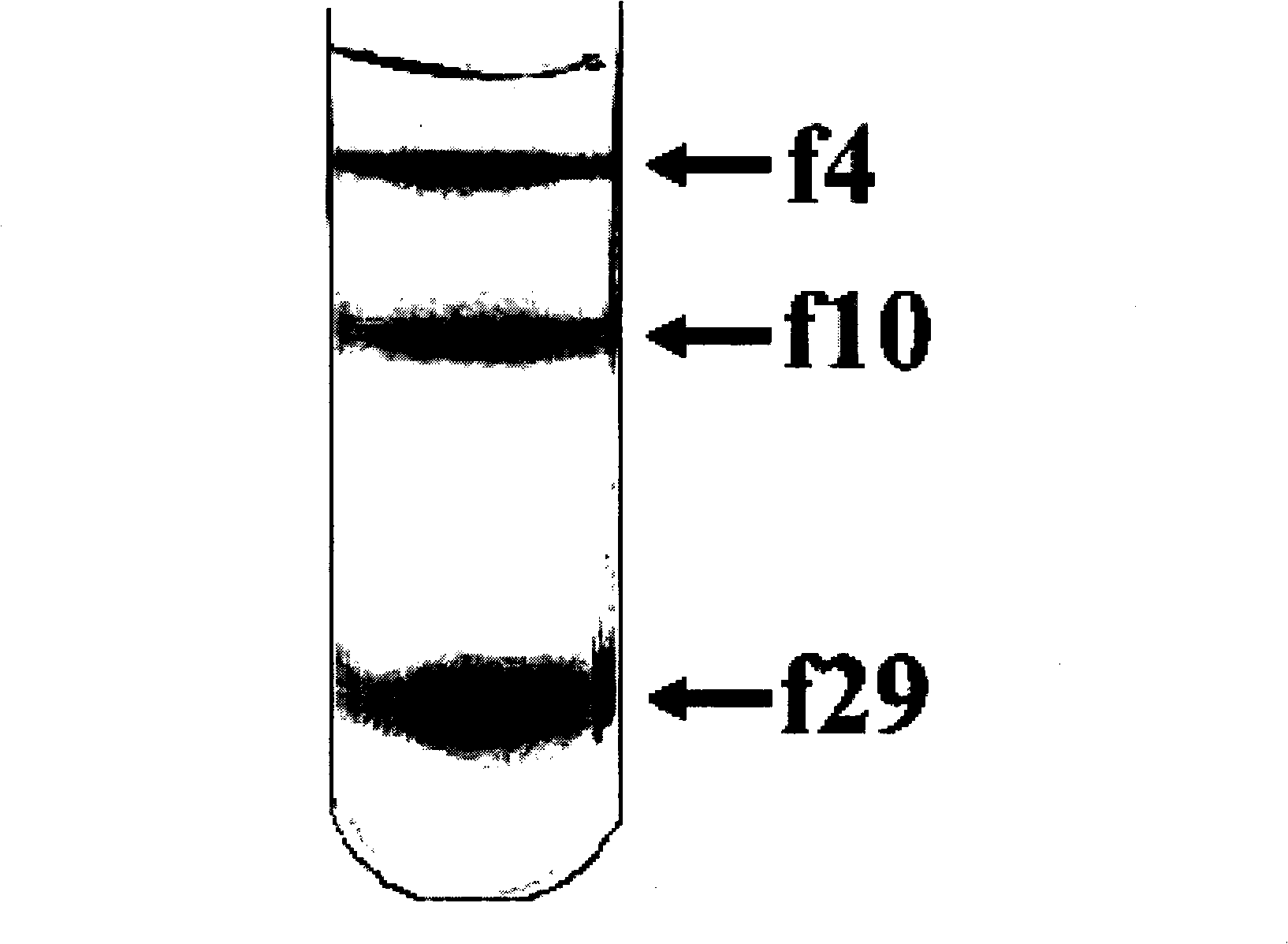
Method for separating nano-particles at water-phase density gradient centrifugation rate
InactiveCN101559401AEasy to separateWide range of separation sizesWet separationGradient centrifugationColloidal nanoparticles
The invention relates to a method for separating nano-particles at a water-phase density gradient centrifugation rate, which mainly comprises the following steps: 1) preparing the nano-particles into a homogeneous transparent colloid nano-particle solution by means of ultrasound, stirring and the like; 2) preparing density gradient solutions with different mass percentage concentrations respectively; 3) adding certain amount of density gradient medium solutions with different concentrations into a centrifuge tube in turn to prepare a step-like or linear density gradient solution; and 4) adding the solution containing colloid nano-particles to the liquid surface of the density gradient solution slowly, and performing centrifugalization under certain condition. Because the colloid nano-particles with different sizes have different sedimentation rates in the density gradient solution and can be detained at different positions in the density gradient solution so as to achieve the effect of separation. The method has the advantages of simple method, quick separation, low cost, small influence on the stability and the purity of a sample, and the separation effect of certain section can be enhanced selectively by adjusting and controlling centrifugal parameters.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
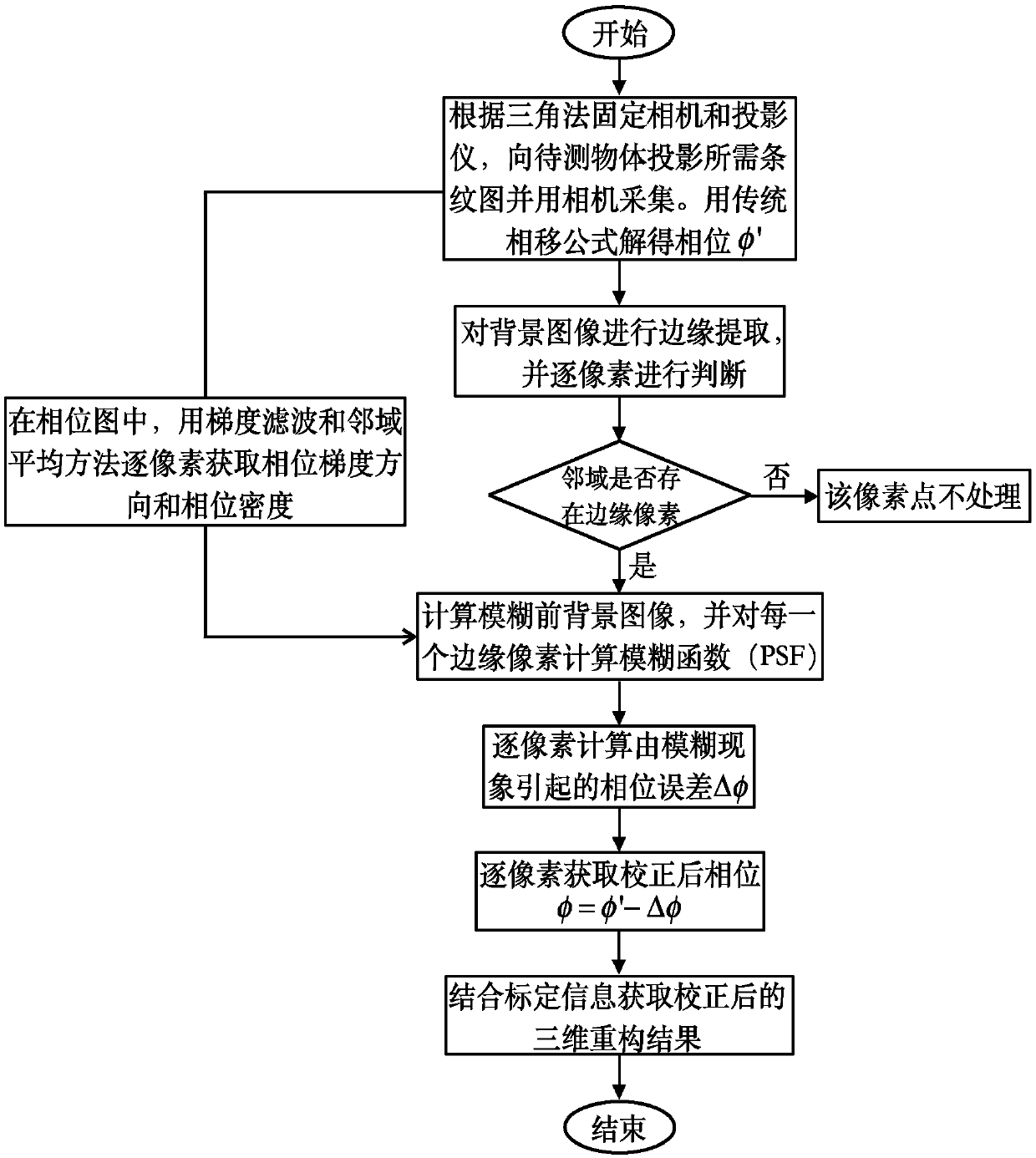
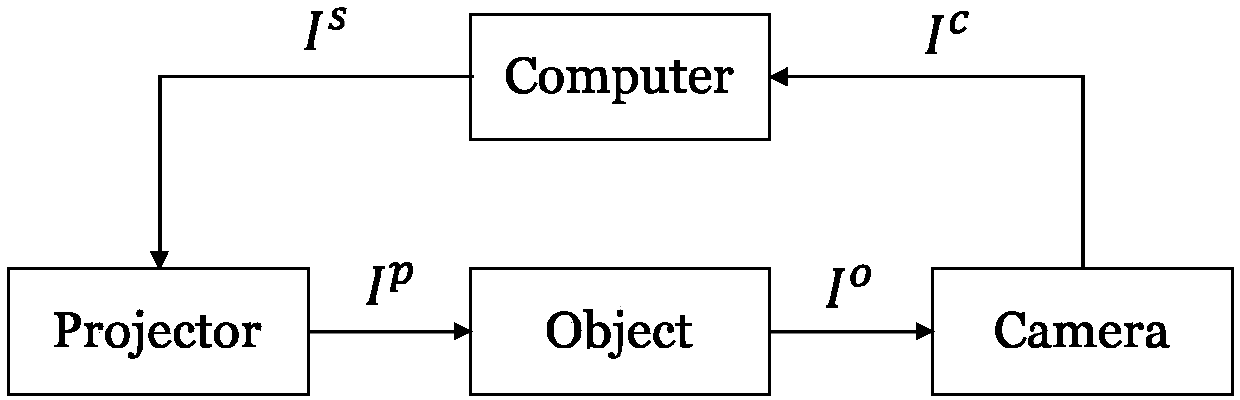
Phase error correction method for out-of-focus phenomenon of fringe projection three-dimensional measuring system
ActiveCN108168464AEasy to implementAccurate solutionUsing optical meansDiffusion functionThree dimensional measurement
The invention discloses a phase error correction method for an out-of-focus phenomenon of a fringe projection three-dimensional measuring system. The method comprises: a computer generates a phase-shifted fringe image and the image is collected by a camera; for the collected image, a background image I' and a phase phi' containing an error are calculated and edge extraction is carried out on the background image I'; a point spread function (PSF) of each edge pixel is calculated after edge map obtaining; a phase gradient direction and a phase density of each to-be-processed pixel are calculatedby using gradient filtering and neighborhood averaging methods in the phase map phi'; and then for the to-be-processed pixels, phase errors delta phi caused by the out of focus of the camera are calculated pixel by pixel, so that a finally corrected phase phi is obtained and the phi meets a formula: phi=phi'-delta phi. The corrected phase information can be converted into three-dimensional information of a to-be-measured object by a phase-height mapping relationship.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Preparation method of high-solid-content butadiene-styrene latex
ActiveCN103159893AMake up for the lack of limited sizeSatisfy processabilityInorganic saltsPotassium
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high-solid-content butadiene-styrene latex for a latex product, and provides a preparation method of a high-solid-content butadiene-styrene latex. The method comprises the following procedures: by taking butadiene and styrene as main monomers, using composite emulsifier which at least contains one surfactant containing potassium or sodium carboxylate groups, and taking small-molecule organic ammonium polycarboxylate as agglomerant and alkali metal inorganic salt as water-phase density regulator, polymerizing, removing the residual monomers, agglomerating, centrifuging, and thickening to obtain 60-65% high-solid-content butadiene-styrene latex. The preparation method of a high-solid-content butadiene-styrene latex, provided by the invention, is simple, feasible, economic, friendly to environment and high in production efficiency; and the high-solid-content butadiene-styrene latex prepared by the method can meet the requirements for production processing and service performance of products such as latex mattresses, foamed carpets and the like.
Owner:CHANGZHOU LINGDA CHEM
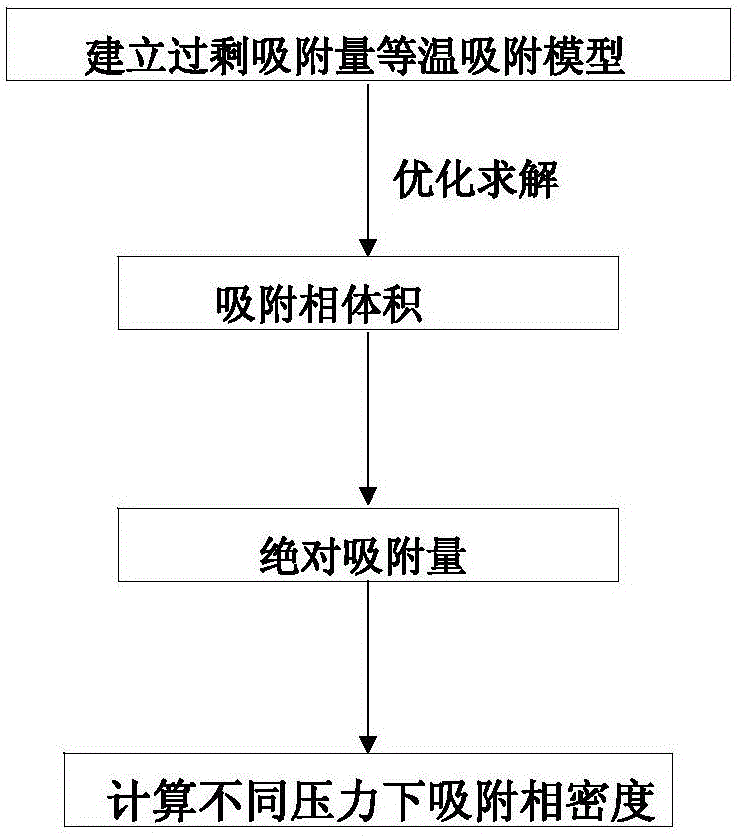
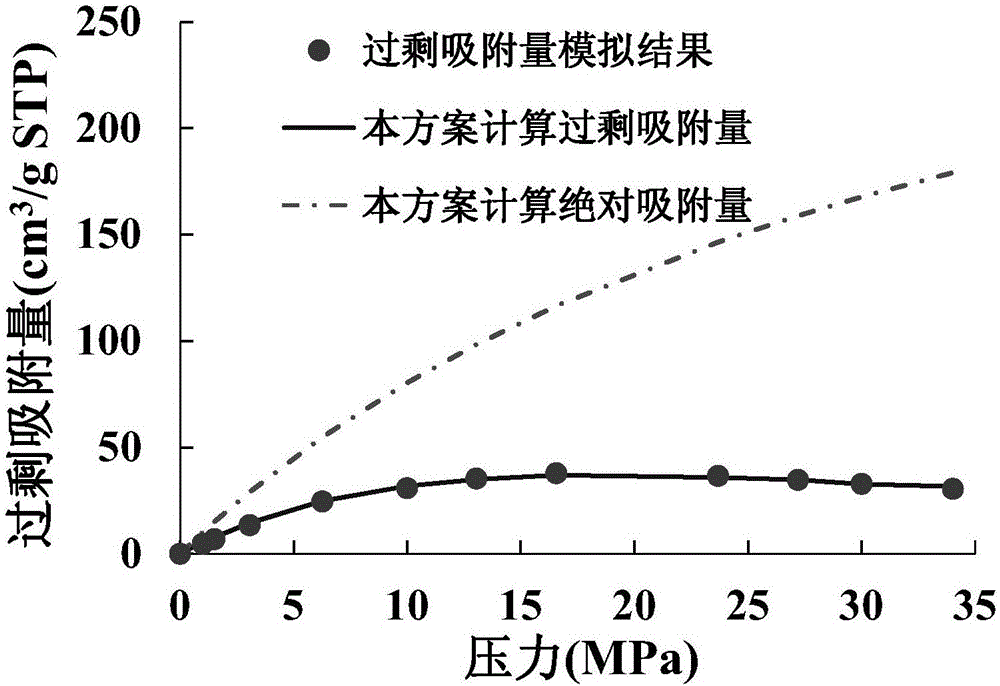
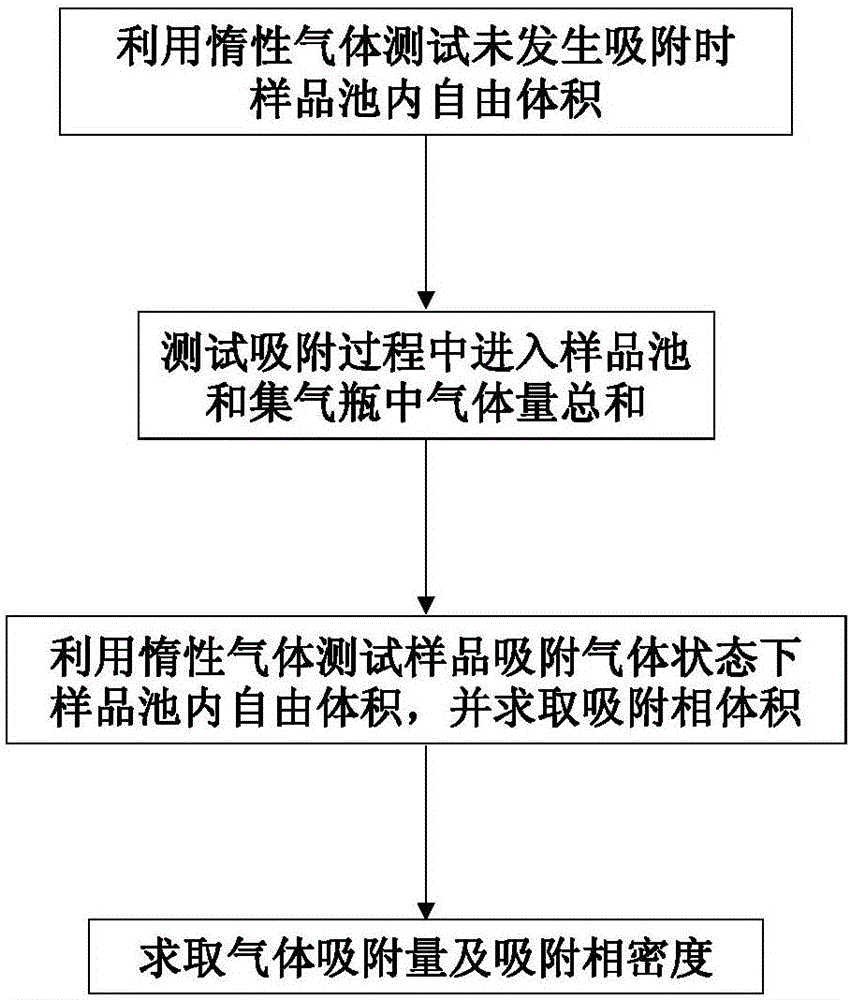
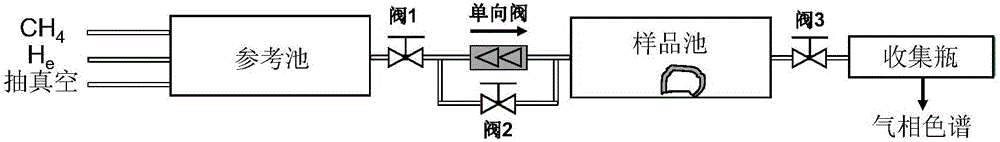
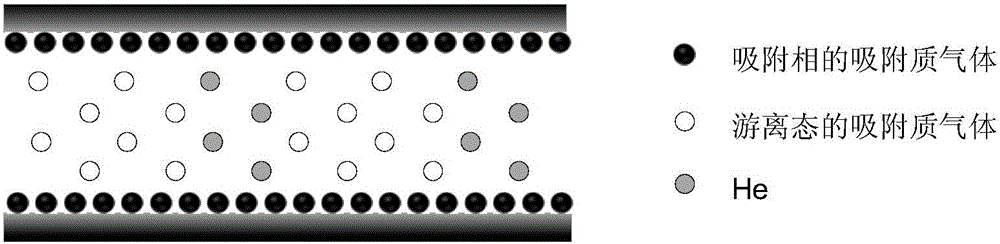
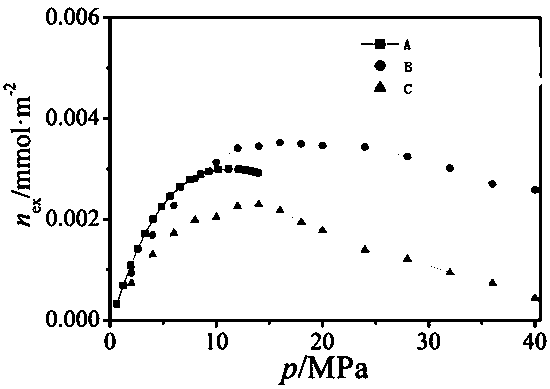
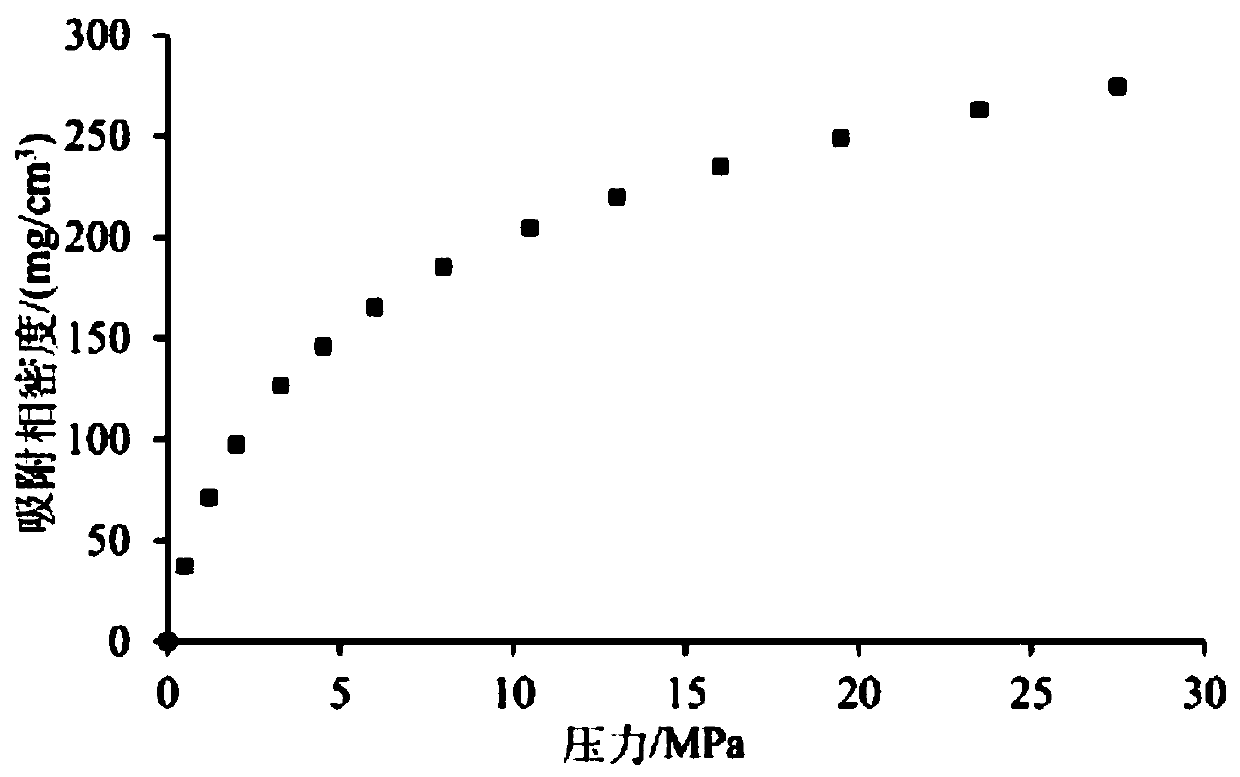
Method for measuring adsorption phase density of adsorbate gas on adsorbate
ActiveCN106290061AReasonable assumptionsReasonableSpecific gravity measurementPhysical chemistryPhase volume
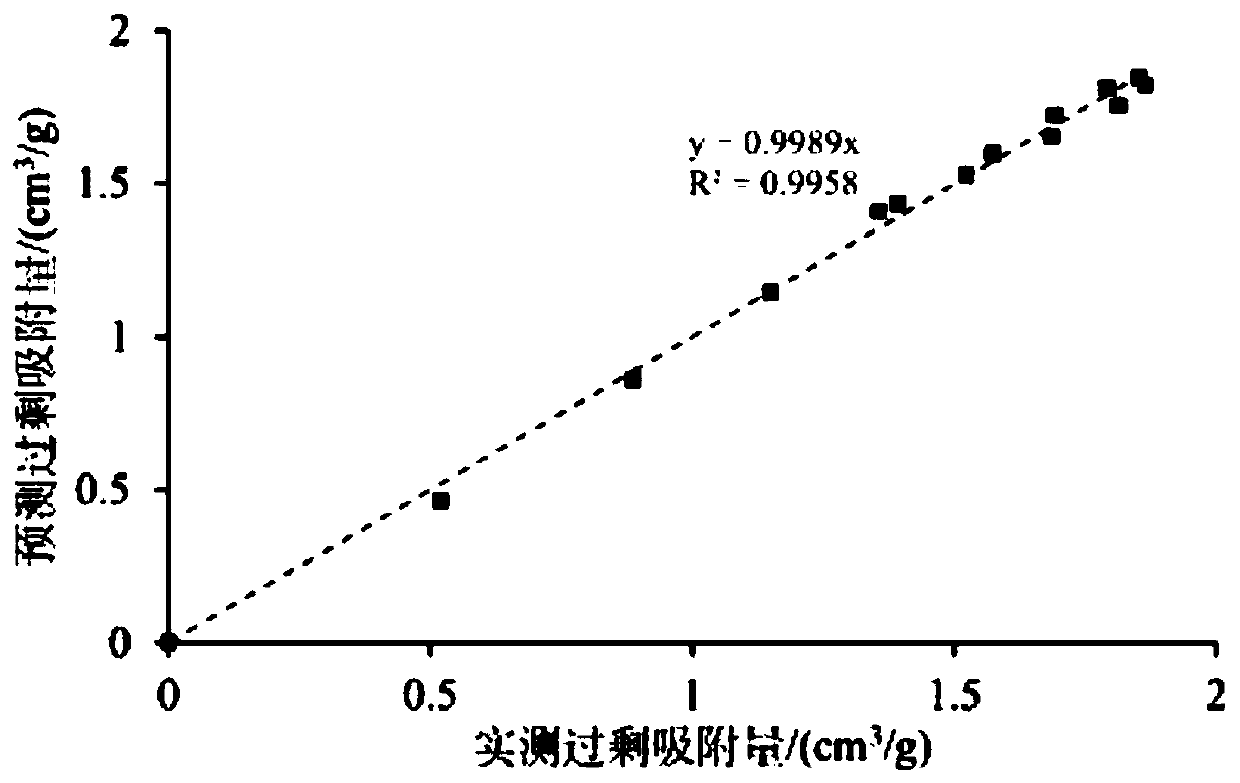
The invention discloses a method for measuring the adsorption phase density of adsorbate gas on adsorbate. The method includes the steps: 1) measuring the excess adsorption quantity and the body phase density of the adsorbate gas under at least three different types of pressure; 2) acquiring adsorbed phase volume according to a corrected isothermal adsorption model and the excess adsorption quantity and the body phase density measured in the step 1); 3) acquiring the absolute adsorption quantity of the adsorbate gas on the adsorbate according to the corrected isothermal adsorption model and an isothermal adsorption model; 4) acquiring the adsorbed phase density of the adsorbate gas on the adsorbate according to a formula (1), and denoting the adsorbed phase density as rho adsorption phase with the unit g / cm<3>. The method is directly implemented based on original isothermal adsorption test data, simple, practicable and easy to popularize. According to research of adsorption behaviors by molecular simulation, assumed conditions of the method are more reasonable, and reasonableness is obviously superior to that of a traditional optimization scheme.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
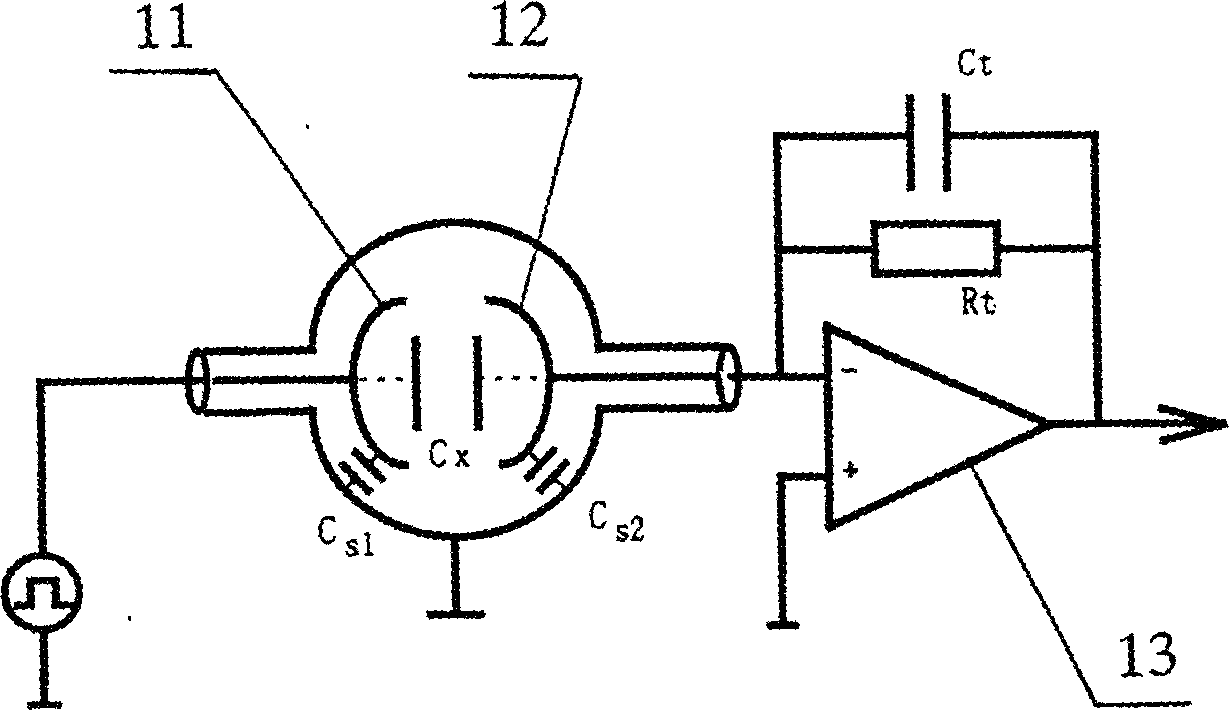
Two-phase gas-liquid flow capacitive sensor
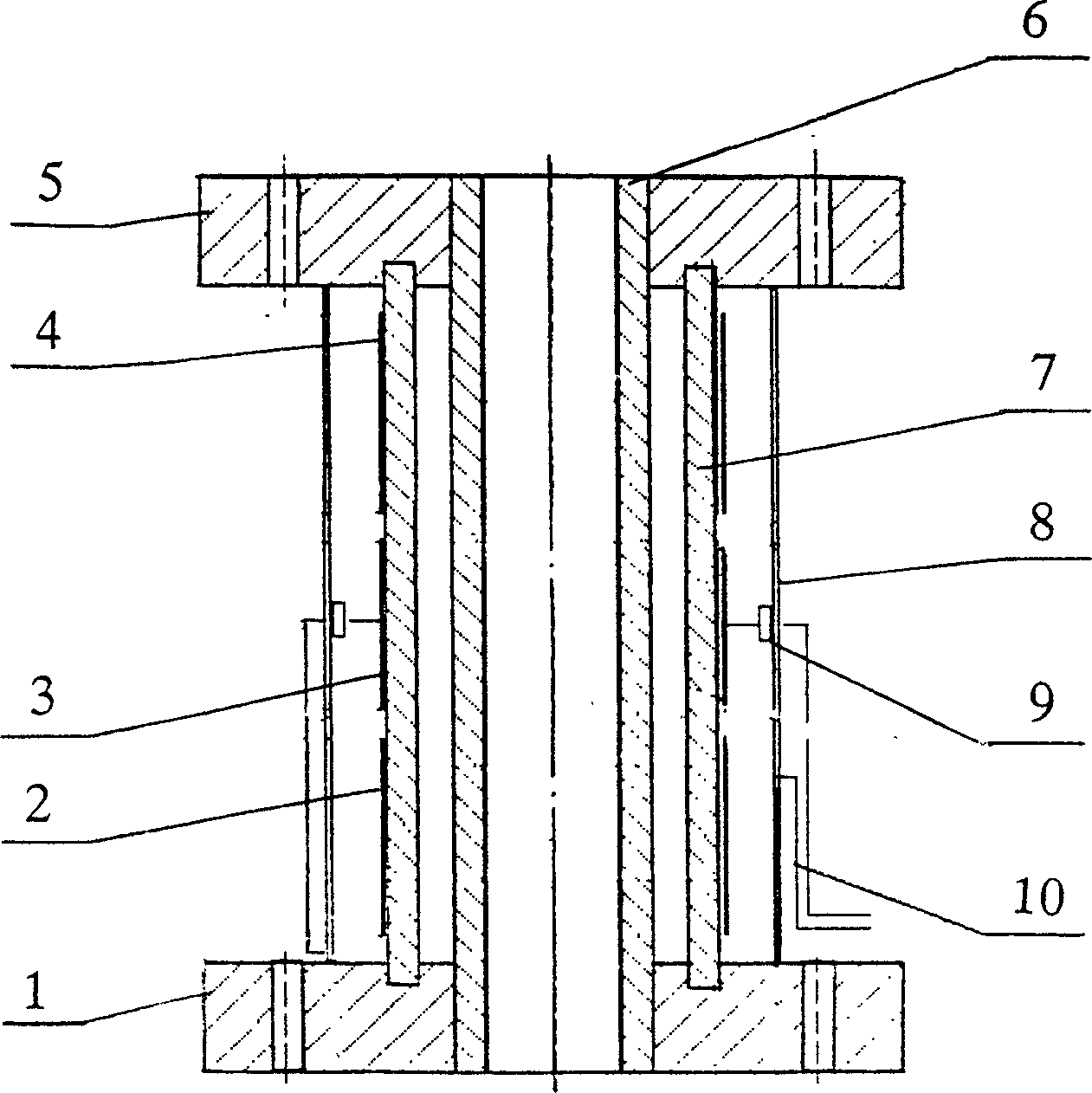
InactiveCN1487289AAccurate measurementSimple structureVolume/mass flow by electric/magnetic effectsMaterial capacitanceEngineeringCapacitance transducer
The two-phase gas-liquid flow capacitive sensor includes flange, protecting plate, capacitive plate, connecting pipe, plate pipe, shielding hood and stray capacitance filter circuit. The flanges are fixed to ends of connecting pipe, the plate and the shielding hood are fixed between two flanges, the capacitive plate is set outside the plate pipe, the protecting plate is set outside and the capacitive plate and the shielding hood are connected with lead separately. The protecting plate and the capacitive plate are in some optimal length, the angle of the arced pole plate is 120-140 deg and the radius of the shielding hood is in its optimal value. The present invention has simple structure, low cost, long life, high sensitivity and capacity of measuring flow rate, phase density and sliding ratio, and other advantages. The present invention is suitable for non-invasion measurement of two -phase gas-liquid flow in oil pipeline.
Owner:沈阳工业学院
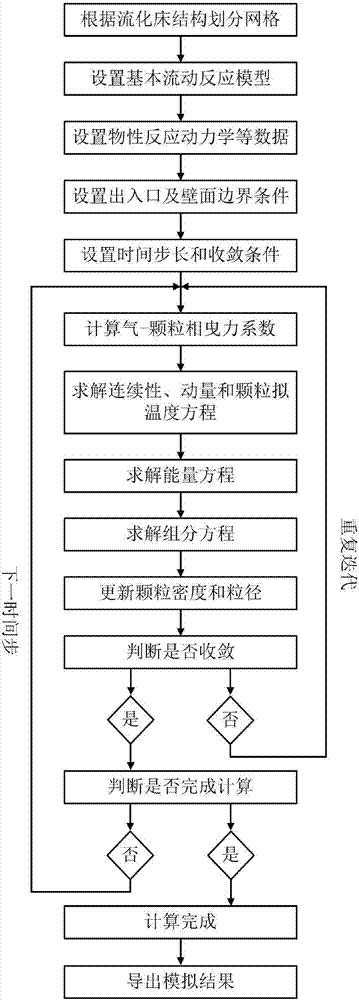
Method for simulating fluidized bed with dynamic changes of grain density and particle size
ActiveCN107132156APredicting Flow Response PropertiesSave human effortFlow propertiesDesign optimisation/simulationExperimental researchMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for simulating a fluidized bed with dynamic changes of grain density and particle size. The method comprises the following steps: 1, establishing a basic flow reaction model in the fluidized bed; 2, establishing a mathematical model for describing a change rule of the grain phase density and particle size; 3, establishing a particle type sectioned drag model; and 4, predicting flow reaction characteristics in the fluidized bed. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the fluidized bed with dynamic changes of grain density and particle size is subjected to simulation study by adopting a computational fluid mechanics method, the mathematical model for describing a change rule of the grain phase density and particle size is combined to perform real-time correction on the density and particle size of the particles, and the acting force between gas-particle phases in a coexisting system of multiple particle types through the particle type sectioned drag model, so that the flow reaction characteristics in the fluidized bed with the dynamic changes of grain density and particle size are accurately predicted. According to the method, lots of complicated and expensive experiment researches are not needed, and lots of manpower and material resources and time cost can be saved.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Molten steel refining slag composition design method
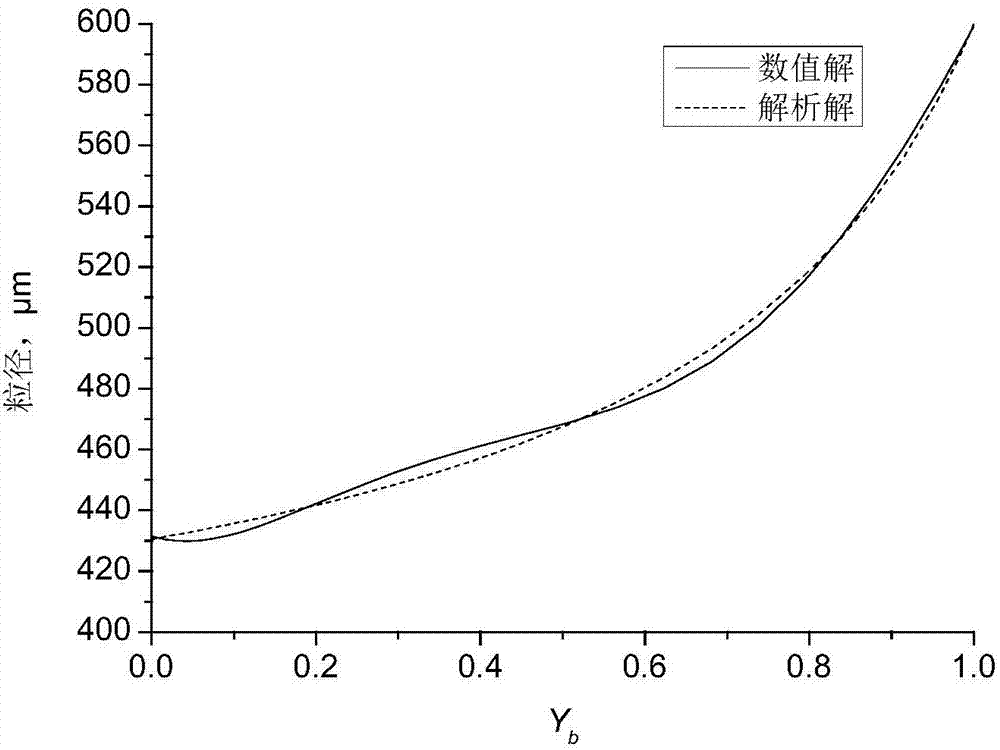
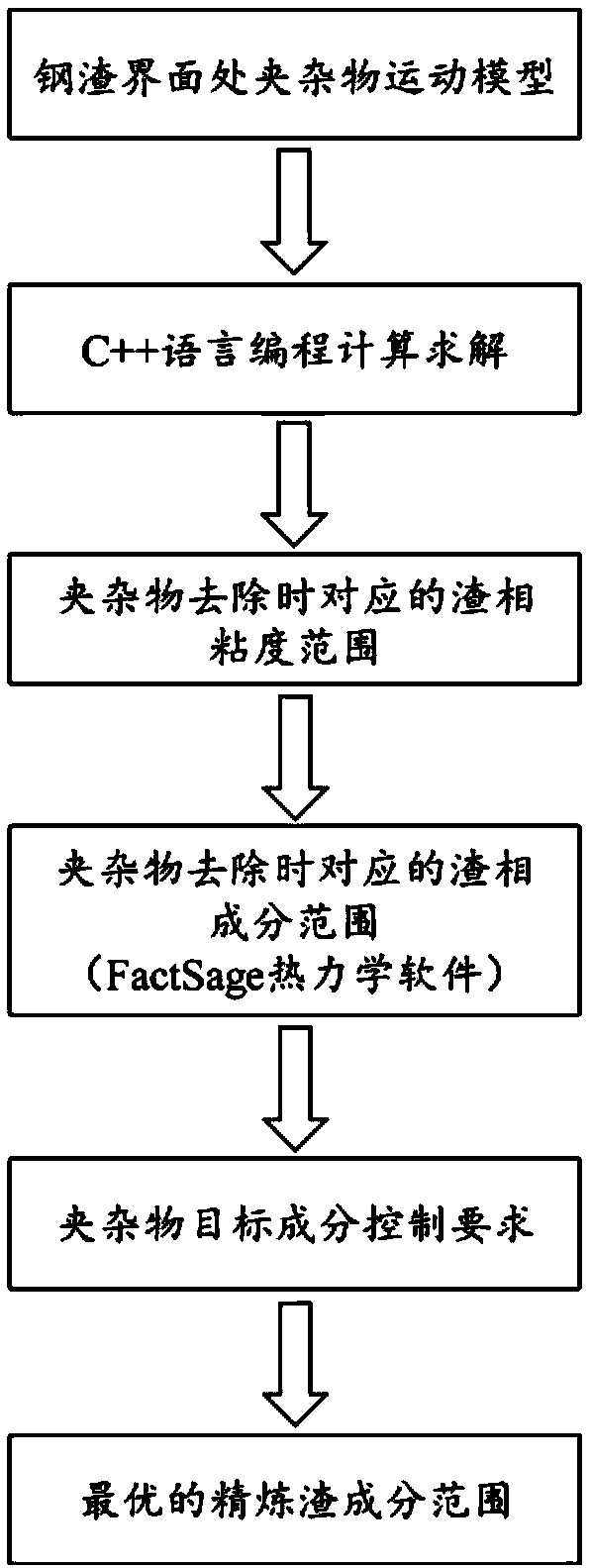
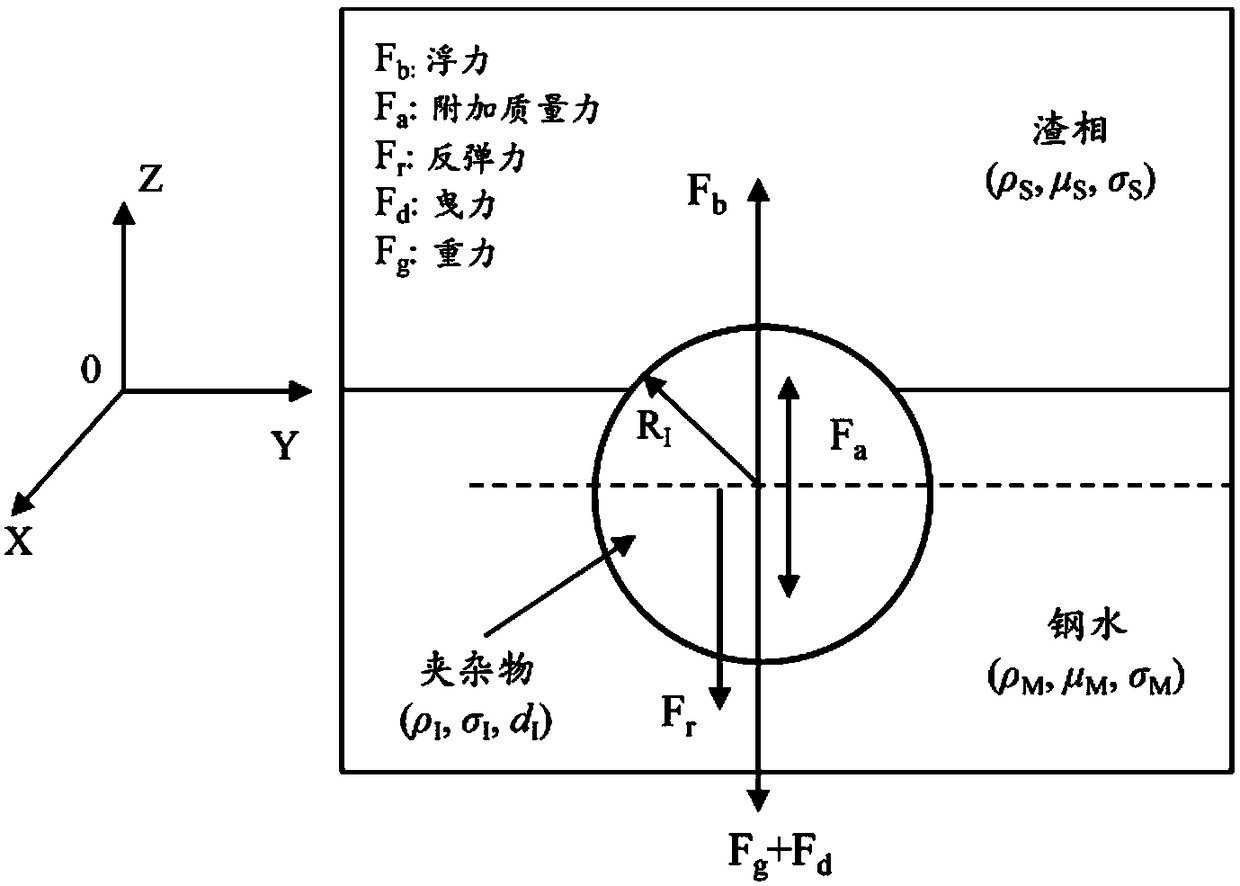
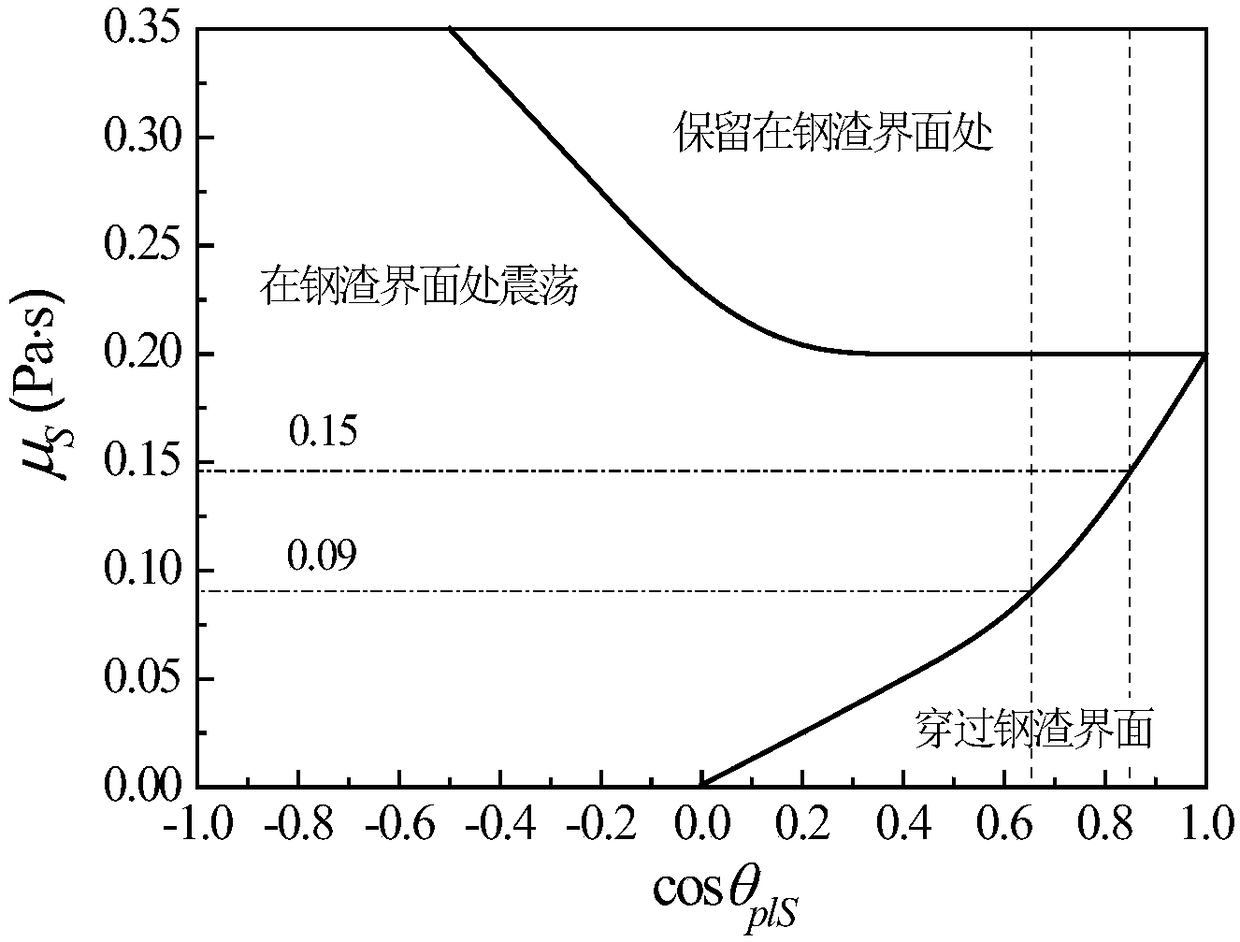
InactiveCN108875285AMeet control requirementsEasy to useDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSlagMolten steel
The invention provides a molten steel refining slag composition design method and belongs to the technical field of clean steel smelting. The method includes: building and solving a steel slag interface inclusion motion model, quantitatively evaluating the influence of inclusion size, inclusion density, slag phase density, slag phase viscosity, molten steel density, molten steel viscosity and thewettability of inclusion at the steel slag interface on the motion removing process of the inclusion at the steel slag interface, determining the slag phase viscosity range and slag phase compositionrange when the inclusion can be removed, and determining the optimal refining slag composition range according to the target composition control requirement of the inclusion in steel. The method has the advantages that the defect that the prior art cannot give consideration to both inclusion target composition control and inclusion quantity reduction is overcome, the required refining slag composition suitable for the production of different types of steel can be determined in advance, enterprise production cost can be lowered favorably, and steel product quality can be increased favorably.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for predicting density and particle size distribution of particles in fluidized bed based on computational fluid mechanics
ActiveCN104634708ASave human effortSave time and costParticle size analysisFluidized bedMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for predicting density and particle size distribution of particles in a fluidized bed based on computational fluid mechanics. The method comprises the following steps: 1, building a basic flow reaction model in the fluidized bed; 2, building a mathematic model for describing the particle phase density and particle size change rule; and 3, predicting the density and particle size distribution states in the fluidized bed. According to the method, simulation study is carried out on the fluidized bed by a computational fluid mechanics method; real-time correction is carried out on the density and the particle sizes of the particles by combining the mathematic model for describing the particle phase density and particle size change rule, so that a theoretical basis is provided for accurate prediction of the density and particle size distribution states of the particles in the fluidized bed, and performance prediction, optimal control and design enlargement of the fluidized bed. According to the method, the density and particle size distribution states of the particles in the fluidized bed are obtained by the computational fluid mechanics method, and complicated sampling analysis on the actually running fluidized bed is not needed, so that a lot of manpower, material resources and time cost are reduced; and the method disclosed by the invention is a novel method for obtaining the density and particle size distribution states of the particles in the fluidized bed.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
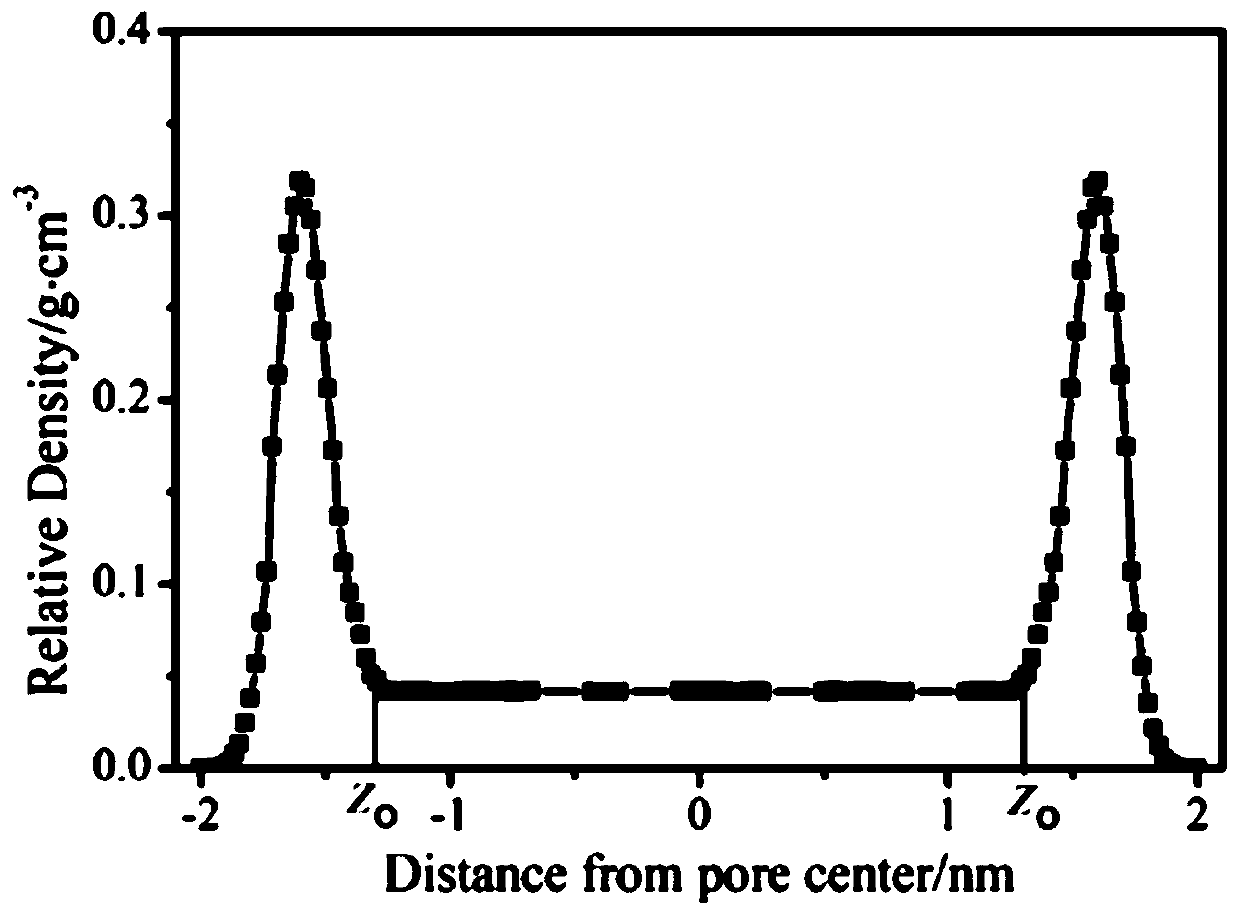
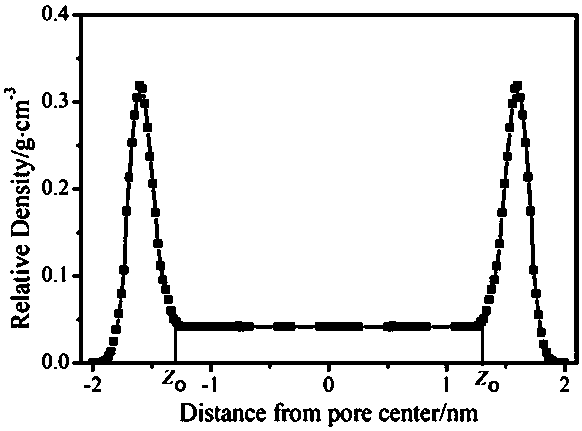
Method for calculating adsorption quantities of different aperture surfaces of shale organic matter
InactiveCN110223736ASolve the problem of real adsorption situationSolve the problem that the real adsorption of methane cannot be well reflectedMolecular entity identificationDesign optimisation/simulationVolumetric Mass DensityFluid density
The invention discloses a method for calculating adsorption quantities of different aperture surfaces of a shale organic matter. The method comprises the steps of (1), constructing an interlayer structure of graphene by means of graphite for establishing an organic matter model, and introducing a methane configuration into the established organic matter model; (2), performing adsorption simulation, performing energy minimizing on a molecule system, and obtaining an initial stable configuration through adjusting an atom position change; (3), calculating the number of methane molecules which arefilled in the organic matter aperture, determining a preferable adsorption position, utilizing a COMPASS force field in a full calculating process, calculating an intermolecular van der Waals attractive force, and an electrostatic potential energy between the methane and a skeleton; (4), dividing nano-holes into K units in a direction which is parallel with a hole wall surface, performing statistics on the kinds and number of the atoms in each box, and calculating a fluid density average value; and (5), calculating a Gibbs adsorption quantity. The method of the invention realizes better fitting between adsorption phase density calculation and an actual condition, thereby realizing higher precision.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
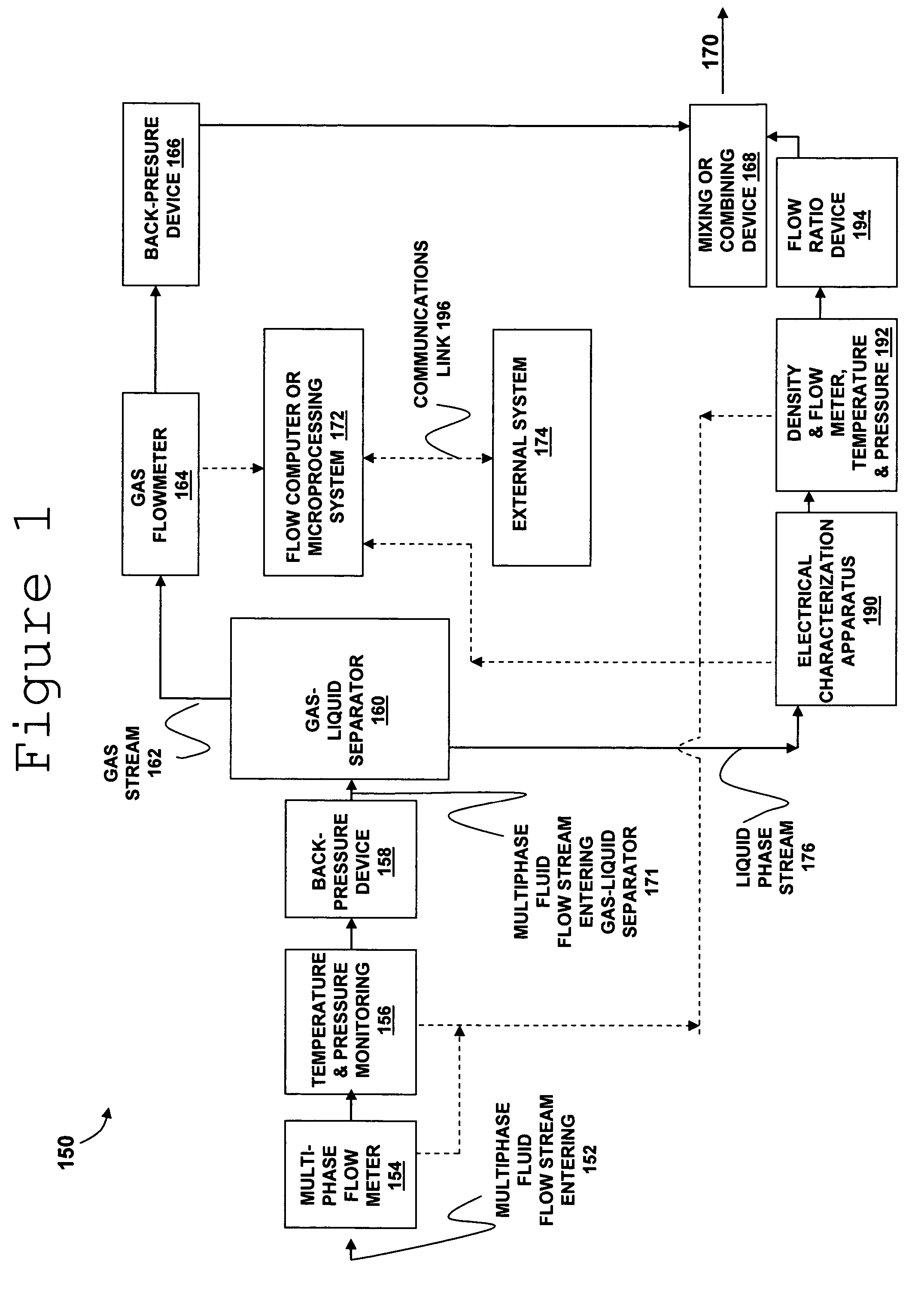
Multiphase fluid characterization
ActiveUS20070157708A1Accurately determineReduce uncertaintyTesting/calibration apparatusMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPermittivityVolumetric Mass Density
Methods for determining and validating a first phase fraction of a gravitationally-separated multiphase fluid by conducting physical and electrical property measurements on samples of the fluid. The water content of crude petroleum oil is determined after the oil and water have begun to separate into phase layers such as occurs during un-agitated holding of the crude petroleum oil. A series of measurements of electrical properties such as permittivity and physical properties such as density is collected. The density minima can be used to generate hindsight determinations of average properties, such as the dry oil phase density, which in turn can be used to increase the accuracy of the water percentage in the oil determined by the permittivity and density methods. Flow weighted averages of water percentages by each method can be used to determine and validate the water content of the crude petroleum oil.
Owner:PHASE DYNAMICS
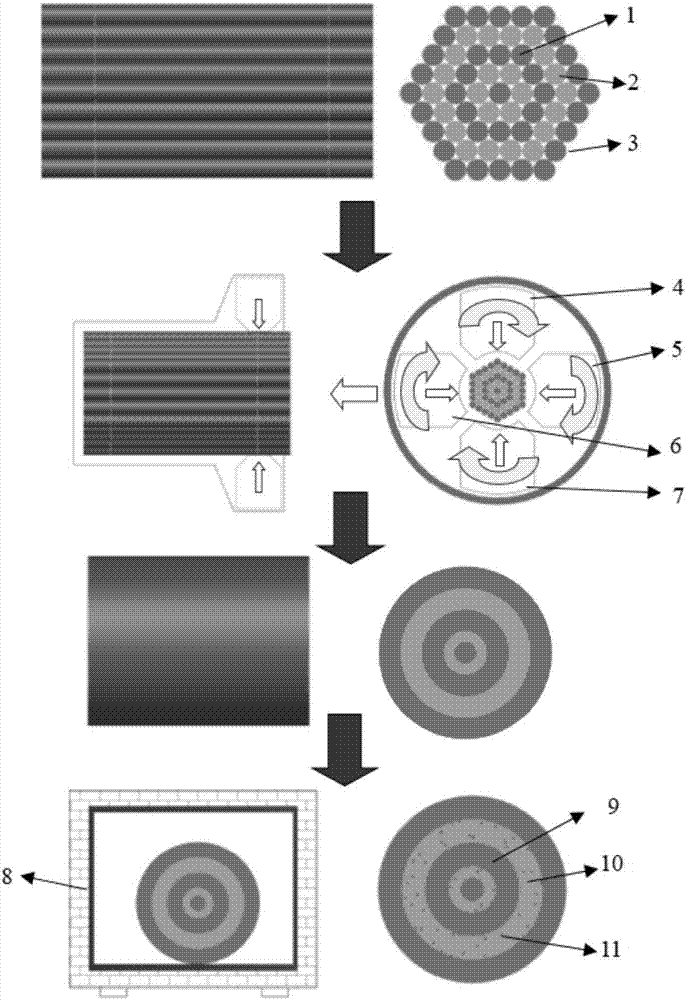
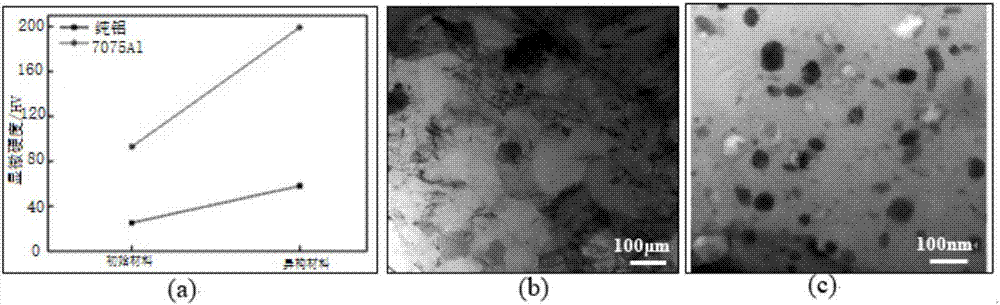
Preparation method for multi-scale precipitation of heterogeneous aluminum alloy bars
The invention provides a preparation method for multi-scale precipitation of heterogeneous aluminum alloy bars. According to the preparation method, a plurality of pure aluminum and 7075 aluminum alloy metal bars with the same length are mixed and bound, and then undergo rotating forging plastic deformation and multi-pass high-strain rotary forging deformation, so that the interfaces of initial aluminum alloy fine bars are combined to prepare pure aluminum and 7075 aluminum alloy mixed bar blanks, then multi-scale precipitation heat treatment on the bars is carried out by utilizing different age hardening behaviors of the pure aluminum and the 7075 aluminum alloy, and the heterogeneous Al and 7075 aluminum alloy bars with multi-scale precipitation phase density are finally obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
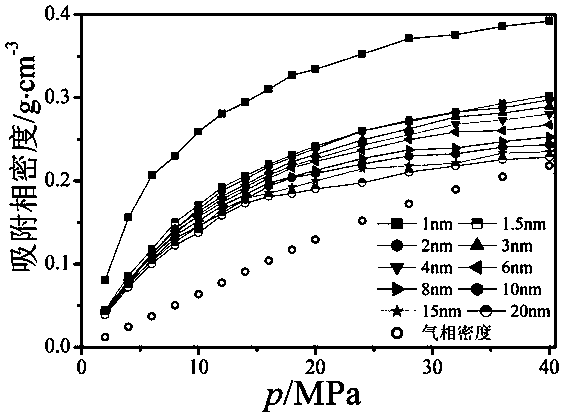
Method for constructing shale adsorption gas adsorption phase density model and calculating absolute adsorption capacity
The invention discloses a method for constructing a shale adsorption gas adsorption phase density model and calculating absolute adsorption capacity. The method comprises the following steps: regressing gas phase density into a polynomial function related to pressure; constructing a slit pore structure model of the adsorbent, and obtaining excess adsorption capacity, adsorption phase volume and absolute adsorption capacity of adsorbate in shale at different temperatures, different pressures and different pore diameters through a molecular simulation means; constructing an excess adsorption capacity model; obtaining the contribution rate of the adsorbing capacity of the adsorbate in the graphite pores to the adsorbing capacity of the shale sample under different pressure points; obtaining an adsorption phase density model of the adsorbate in the graphite slit holes and an adsorption phase density model of the adsorbate in the illite holes under different temperatures, different pressures and different hole diameters; and constructing a calculation model of the adsorbate adsorption phase density in the shale. The model is based on contribution rate, pressure, temperature and aperturedata, and the adsorption phase density calculated by the model is high in accuracy, so that the calculation accuracy of the absolute adsorption capacity is improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Method for determining adsorption phase density of adsorbate gas on adsorbate
ActiveCN106198306AThe measurement results are objective and reliableMaterial analysisPhase volumeTemperature and pressure
The invention discloses a method for determining the adsorption phase density of adsorbate gas on an adsorbate. The method disclosed by the invention is used for determining the adsorption phase volume and the adsorption phase density from the point of view of an experiment, not for optimizing and gaining the parameters from the point of view of mathematical optimization. In the conventional optimization method, a certain assumption on the adsorption phase volume or adsorption phase density is required to be made or an assumption that the adsorption phase volume does not vary with temperature and pressure or the adsorption phase density does not vary with temperature and pressure is made. In the method disclosed by the invention, the assumption on the adsorption phase volume or adsorption phase density is not required to be made, and the adsorption phase volume and adsorption phase density are directly determined from the point of view of the experiment, therefore, results determined by adopting the method are more objective and reliable than those determined by adopting the optimization method.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
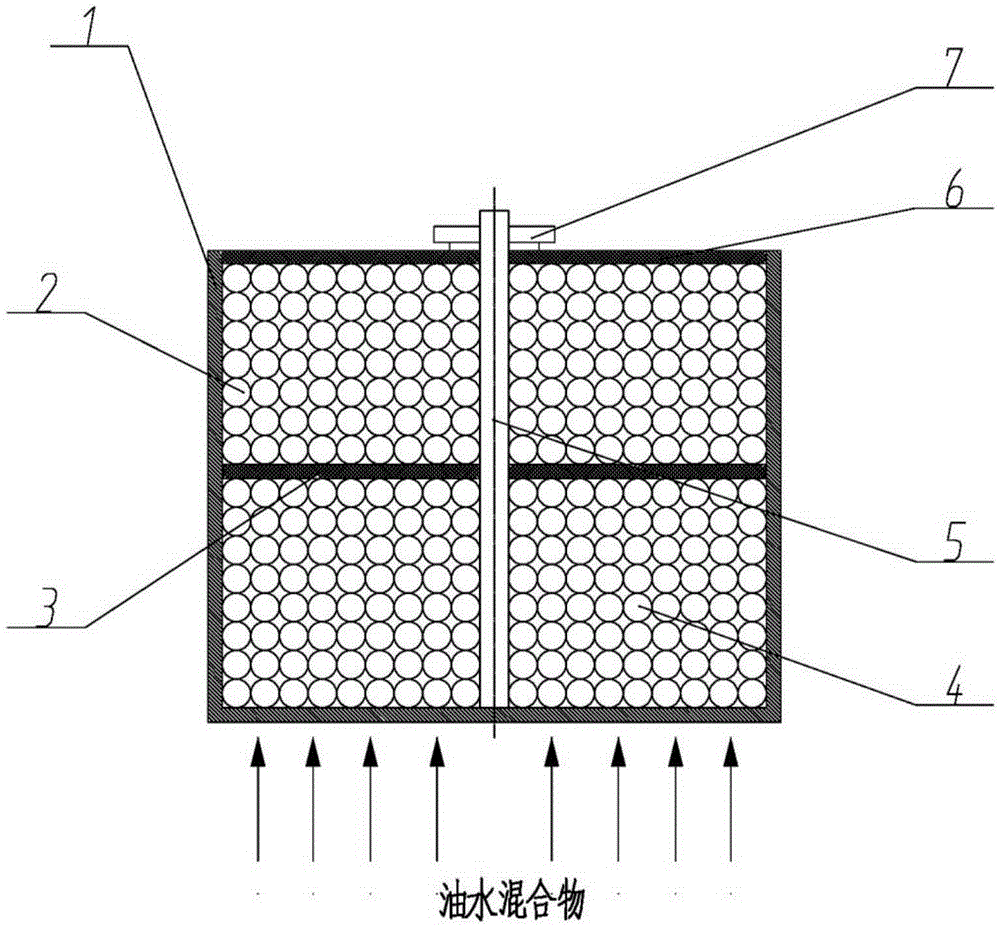
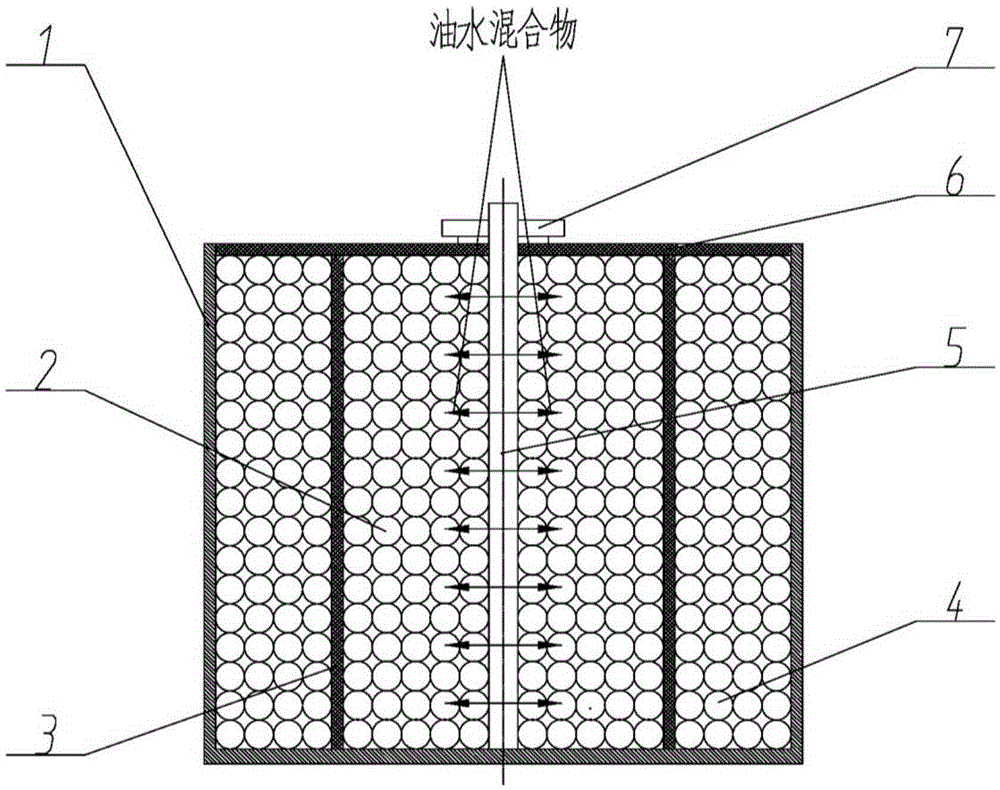
Preparation method for structured packing for oil-water separation
ActiveCN105417628AFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesLiquid separationEngineeringPetrochemical
The invention relates to a preparation method for structured packing for oil-water separation. The preparation method is applicable to separators or packed towers and other devices for oil-water two-phase separation by use of structured packing in the fields of petrochemical engineering, water pollution treatment, hydraulic system pollution control and the like. The structured packing comprises a holding frame, particles I, a partition, particles II, a shaft, a covering plate and a fastener. The structured packing has the advantages that through modification on the surfaces of the particles I and the particles II, the particles I have super-oleophylic and super-hydrophobic properties, and the particles II have super-hydrophilic and super-oleophobic properties, so that oil-water two-phase separation can be realized by use of the oil-water two-phase density difference. The preparation method is simple to realize, convenient for processing, wide in application scope and high in oil-water separation efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A high-density-ratio gas-liquid phase change mixed LBM numerical model and application
ActiveCN109766587ASimulated Density Ratio ImprovementSatisfy the accuracy requirements of boiling phase transition simulationSpecial data processing applicationsBoiling processEvaporation
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer simulation, and discloses a high-density-ratio gas-liquid phase change mixed LBM numerical model and application. In order to overcome the defects that interface parameters of a traditional single-component pseudo potential phase change model cannot be independently adjusted and controlled in phase change simulation, and the superheat degreein bubbles in the boiling process cannot be correctly reflected, on the basis of a single-component multi-relaxation pseudo potential grid Boltzmann model, a gas-liquid phase change model is established by adopting an interface pressure driving phase change mode to couple a heat transfer equation. By simulating the liquid level evaporation phenomenon, the correctness and the simulation precisionof the model are verified. The model is adopted to simulate the temperature distribution and the interface change in a single bubble growth process. Compared with an existing phase-change boiling model, the simulated gas-liquid two-phase density ratio is greatly improved, the two-phase interface parameters can be independently controlled by adopting the model, the change of the superheat degree inthe bubbles in the growth process of the bubbles can be reflected, and the phase-change boiling model is more consistent with the bubble dynamics theory.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Combined annular mist flow phase-splitting flow measuring method
ActiveCN109870201AReal-time online measurementVolume/mass flow by electric/magnetic effectsVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectPhase splittingGas phase
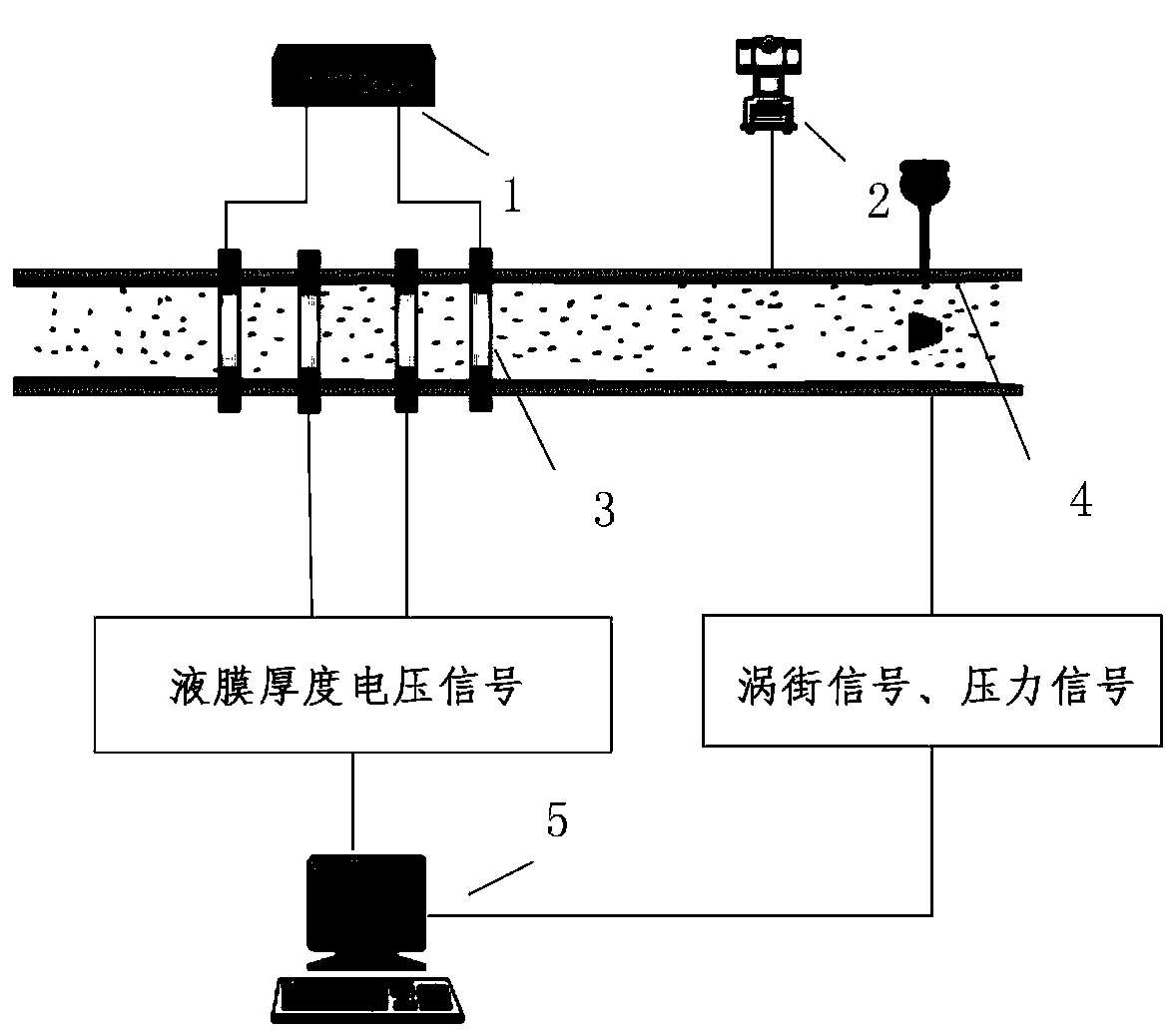
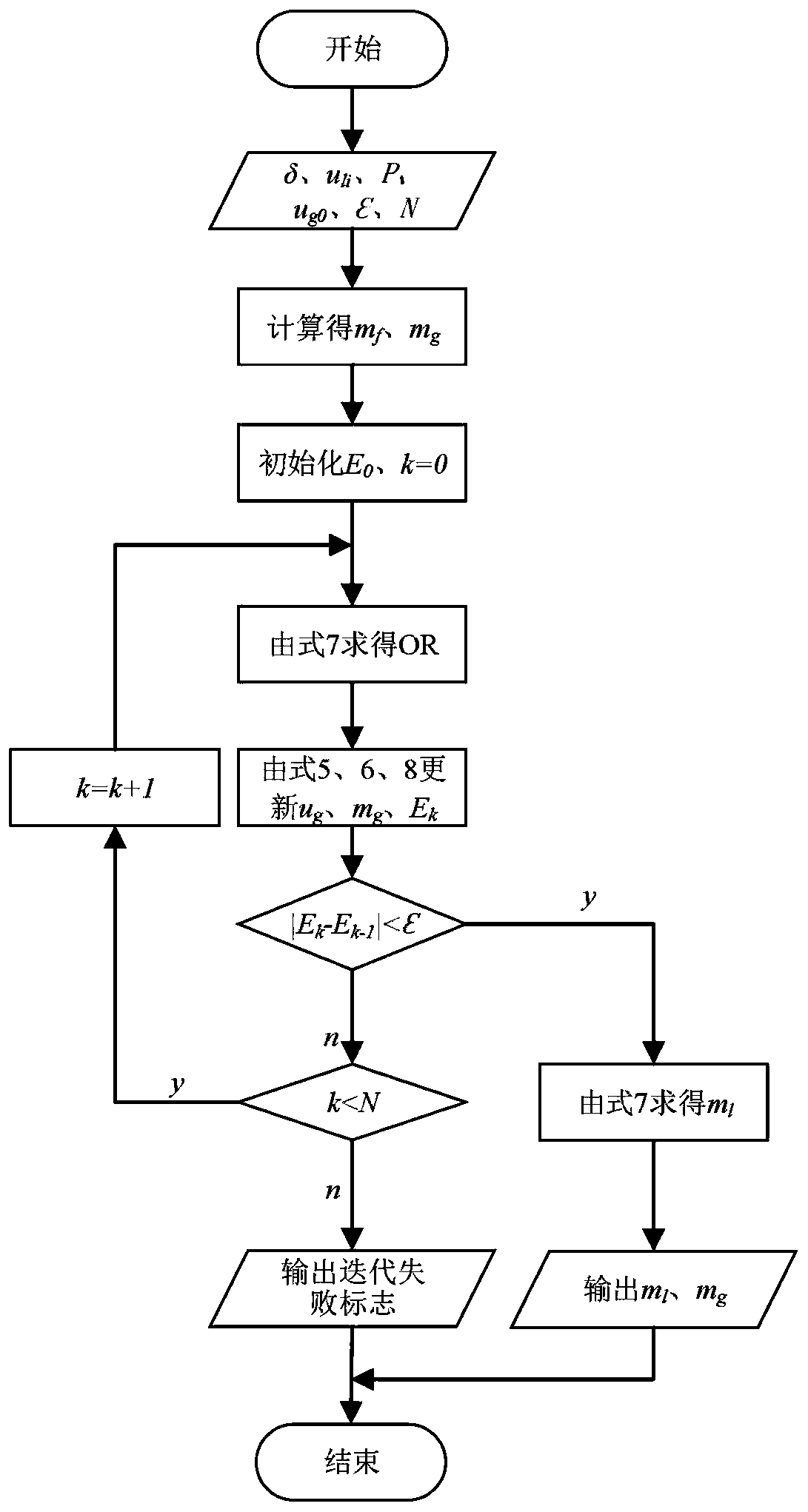
The invention relates to a combined annular mist flow phase-splitting flow measuring method. The combined annular mist flow phase-splitting flow measuring method comprises the following steps: measuring an average liquid membrane thickness of an annular mist flow in real time by using two pairs of electric conductive annular wall-attached sensors; performing relevant analysis on signals measured by the two pairs of front and back annular electric conductive sensors according to a relevant speed measuring method to obtain an average liquid membrane interface flow rate, and solving a mass flow of a liquid membrane according to the average liquid membrane thickness and the liquid membrane interface flow rate; acquiring gaseous phase density by using a vortex sensor; obtaining a read gaseous phase flow through calculation; and using the measured liquid membrane flow, the read gaseous phase flow rate and the read gaseous phase flow as known quantities, performing the iterative solution on an entrainment rate E and a reading coefficient OR by using a formula until the entrainment rate is converged, and finally calculating a total liquid phase flow according to the entrainment rate, so that the measurement objective of the annular mist flow phase-splitting flow can be achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Oil fog concentration measuring apparatus
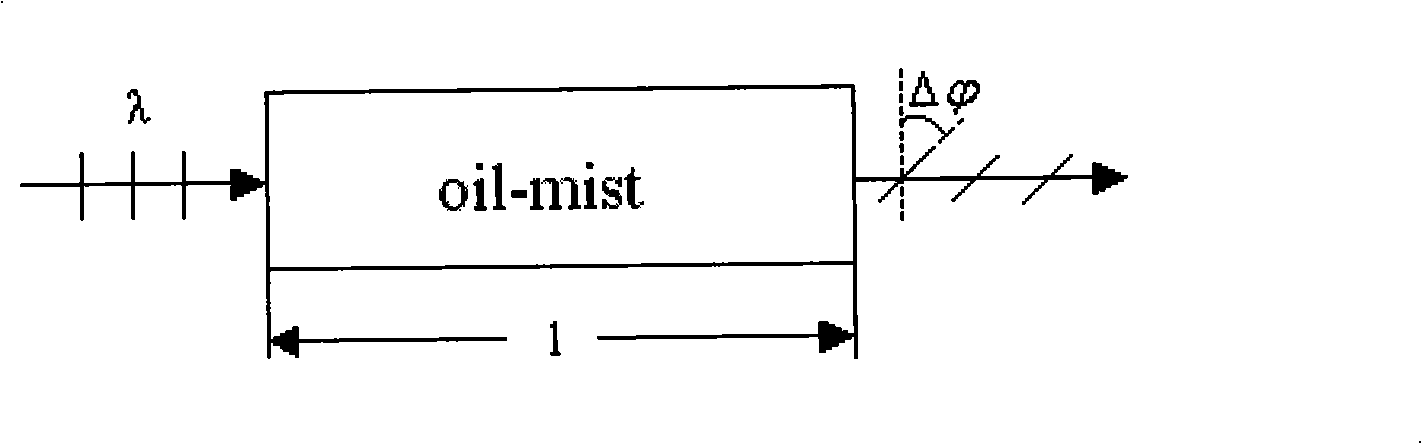
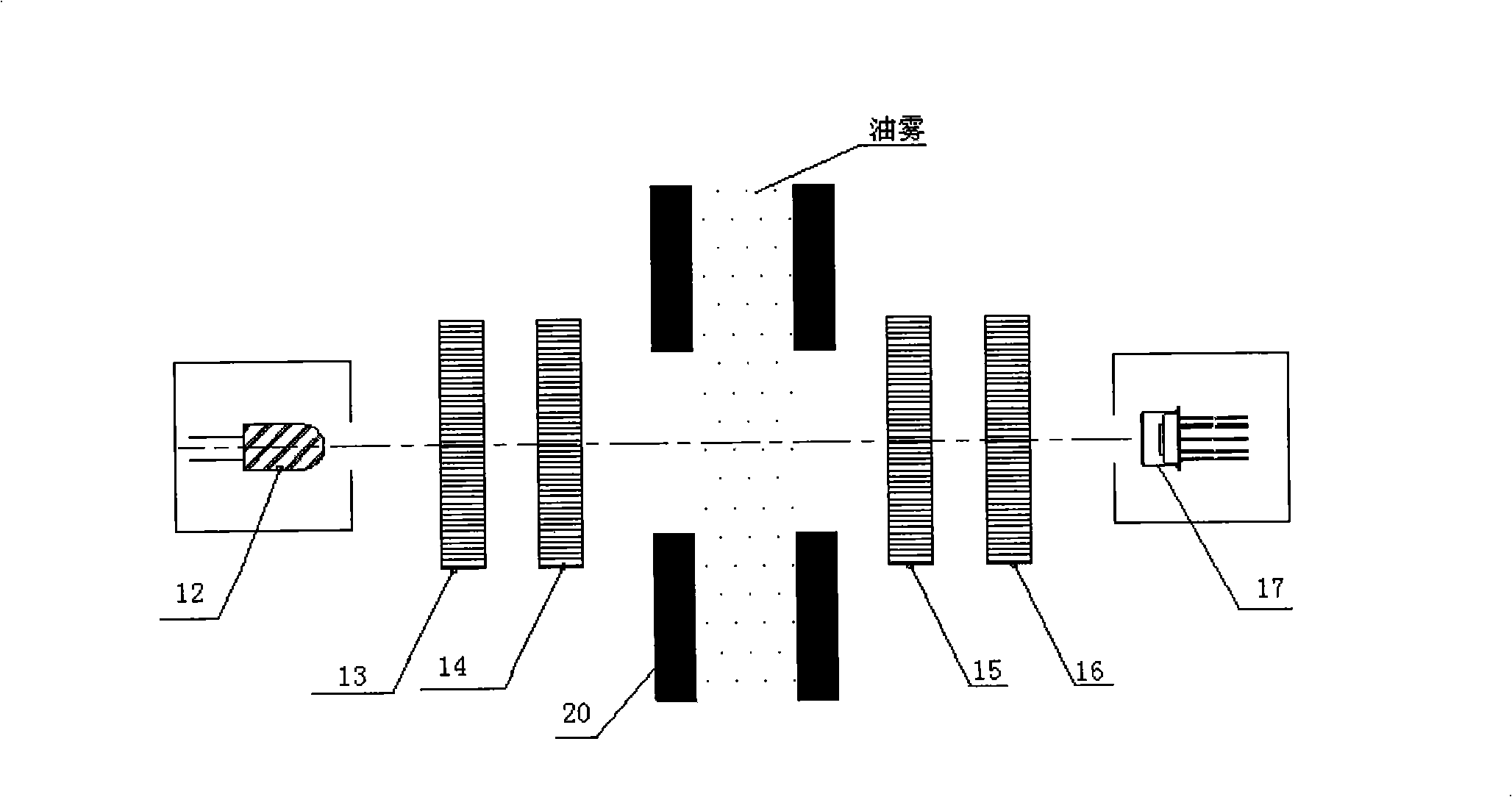
InactiveCN101334357AEasy to operateAccurate measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesMeasuring instrumentPolarizer
The invention discloses a measuring instrument of oil mist density, which belongs to the technical field of the dispersed-phase density measurement of multiphase flow, and comprises a light emitter, a polarizer, a safety spectacle, a mist chamber, a polarization analyzer and a light receiver. Parallel lights emitted from the light emitter form planar polarized lights through the polarizer; the planar polarized lights react with tiny oil mist particles in the mist chamber then oscillating planes thereof deflect, and the transmitted lights passing through the polarization analyzer are received by the light receiver which detects the optical intensity change of the planar polarized lights in situations with different oil mist densities, realizes photoelectric conversion and outputs direct current voltage, and the oil mist density is obtained directly by a voltage-density exchange table. The measuring instrument of oil mist density of the invention can implement online measurement and quantitative measurement, and has simple operations and accurate measuring results.
Owner:沈阳佳益油雾技术有限公司
Vibratory flow meter and method for correcting for an entrained phase in a two-phase flow of a flow material
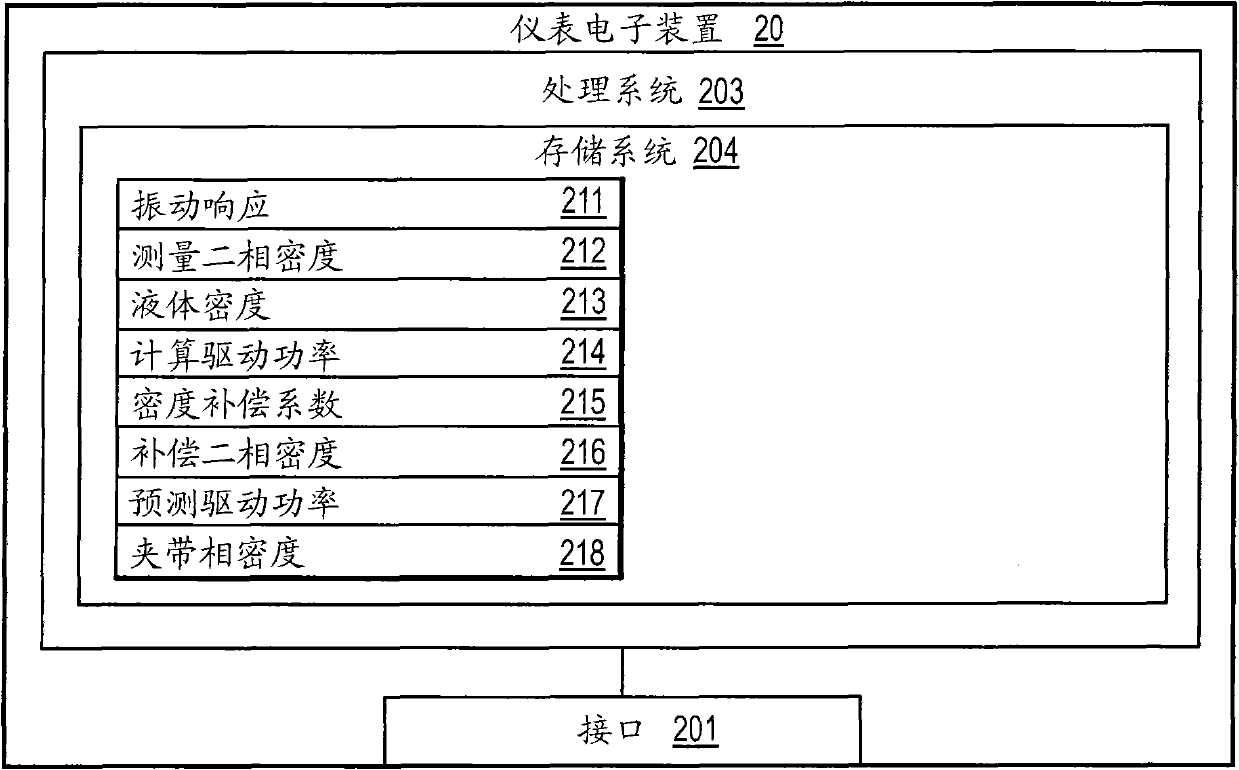
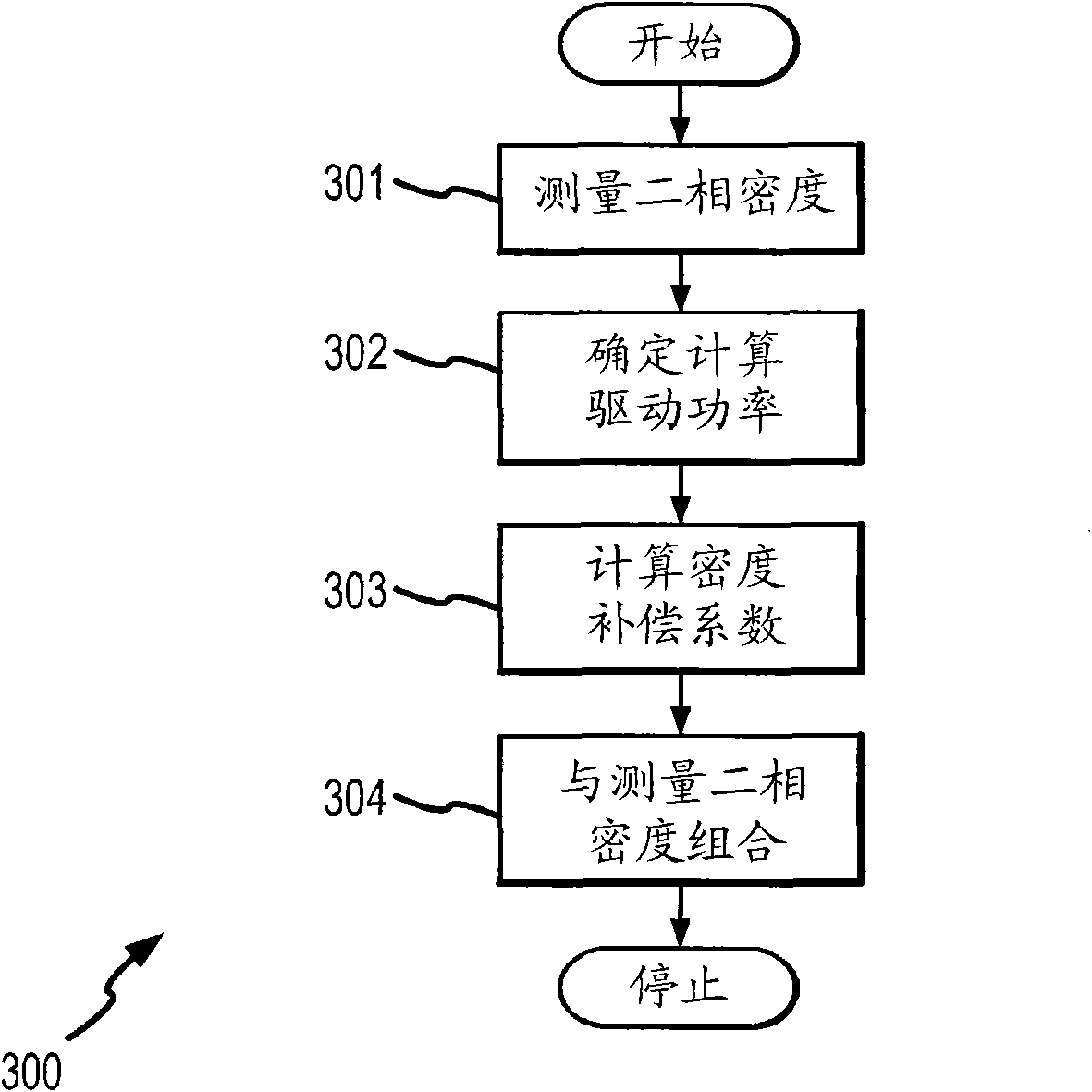
A vibratory flow meter (100) for correcting for an entrained phase in a two-phase flow of a flow material is provided. The vibratory flow meter (100) includes a flow meter assembly (10) including a driver (104) and with the vibratory flow meter (100) being configured to generate a vibrational response for the flow material. The vibratory flow meter (100) further includes and meter electronics (20) coupled to the flow meter assembly (10) and receiving the vibrational response. The meter electronics (20) is configured to generate a measured two-phase density of the two-phase flow using the vibrational response, determine the computed drive power needed by a driver (104) of the flow meter assembly (10), and calculate a density compensation factor using a liquid density of a liquid component of the two-phase flow, an entrained phase density of an entrained phase component, the measured two-phase density, and the computed drive power.
Owner:MICRO MOTION INC
Quenching oil for gear shift connection rod
InactiveCN105821186AEnhance crystal densityHigh strengthFurnace typesQuenching agentsTangential stressPhenol
The invention discloses quenching oil for a gear shift connection rod. The quenching oil is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 65-75 parts of 150N Group II base oil, 2-5 parts of high molecular weight succinimide, 10-15 parts of palm wax, 35-40 parts of refined paraffin base mineral oil, 2-3 parts of sulfide base phenol, 2-3 parts of dimethylmethane petroleum asphalt resin, 4-5 parts of epoxidation castor oil, 1-2 parts of alkylene polyether and 3-8 parts of modified antioxygen. By adopting the quenching oil, the internal crystalline phase density of metal can be reinforced, and lattice deformation torsion resistance is improved, so that metal strength is obviously improved; the tensile property and tangential stress resistance of the manufactured gear shift connection rod are greatly improved; and the service life of the connection rod is greatly prolonged.
Owner:CHANGLI FORGING
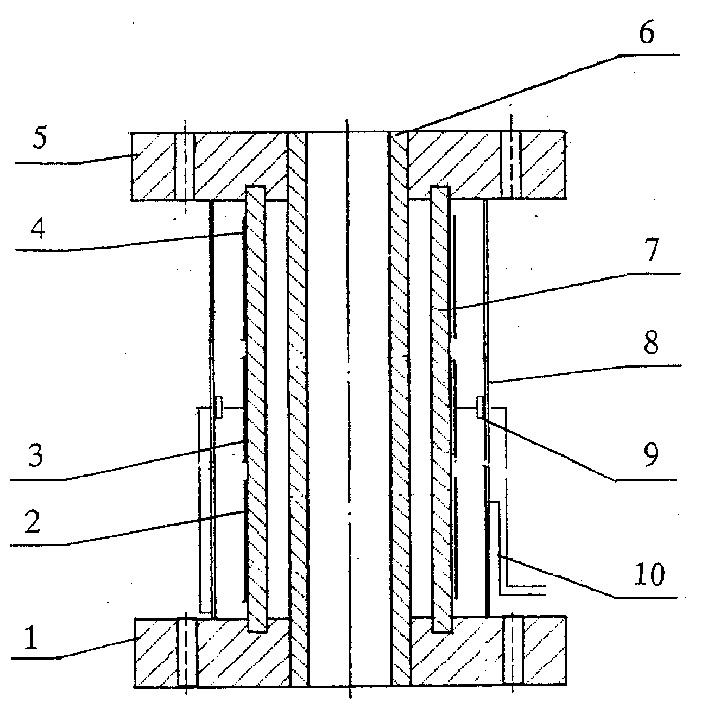
Solution to edge effect of two-phase gas-liquid flow capacitive sensor
InactiveCN1487288AAccurate measurementSimple structureMaterial capacitanceFinite element algorithmEdge effects
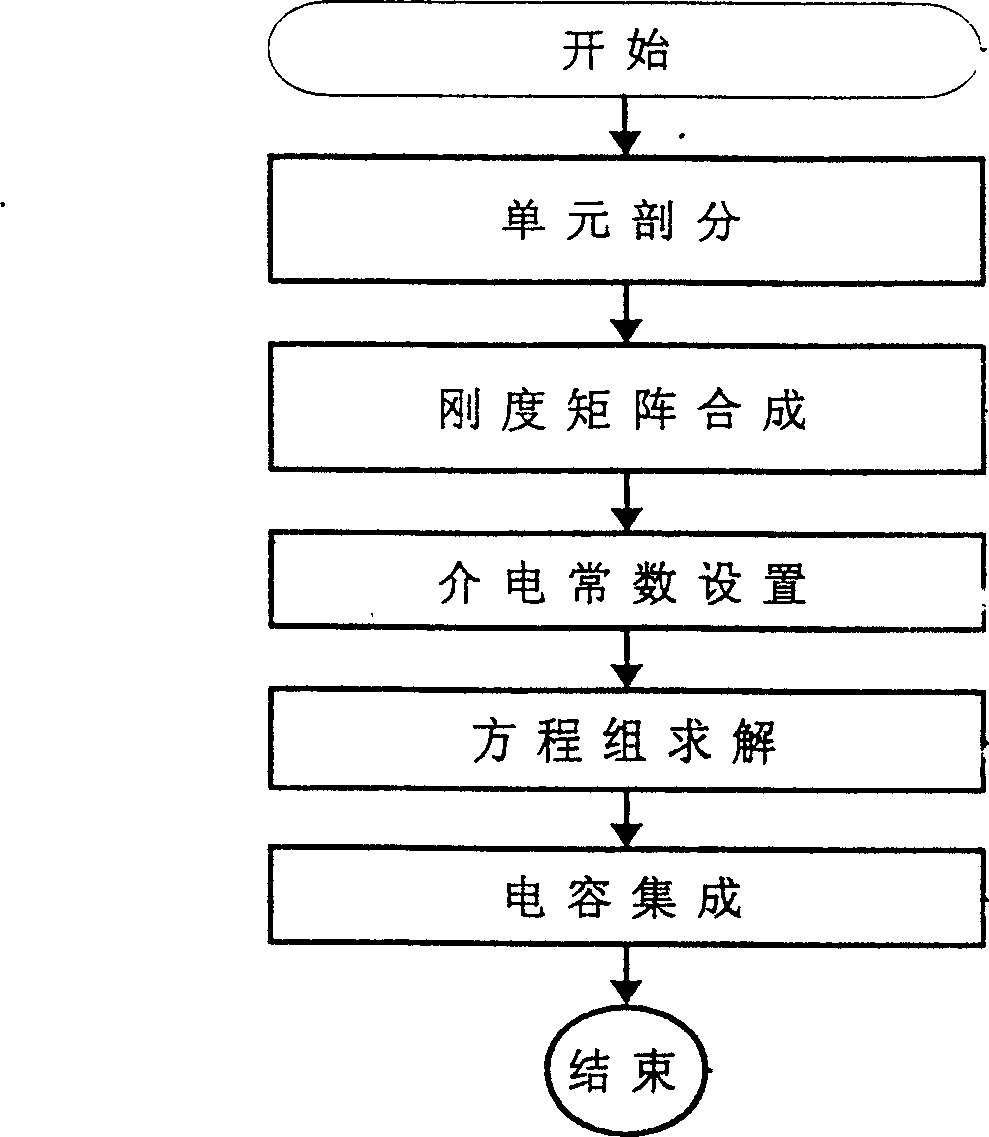
The present invention is solution to edge effect of two-phase gas-liquid flow capacitive sensor. The two-phase gas-liquid flow capactitive sensor is provided with protecting pole plates of optimal length L. The increase of length results in decreased influence of the edge effect but increased volume of the sensor, and the angle of the arced pole plate is 120-140 deg. The protecting plate length L and the angle of the arced pole plate, as the main parameters, are obtained via 3D electromagnetic field equi-parameter finite element algorithm including the steps of: start, unit separating, dielectric constant setting, rigid matrix synthesis, solving coupled equations and capacitor integration. The method of the present invention has simple structure, low cost, long life, high sensitivity and capacity of measuring flow rate, phase density and sliding ratio, and other advantages. The present invention is suitable for non-invasion measurement of two-phase gas-liquid flow in oil pipeline.
Owner:沈阳工业学院
Mixed liquor continuous separation device
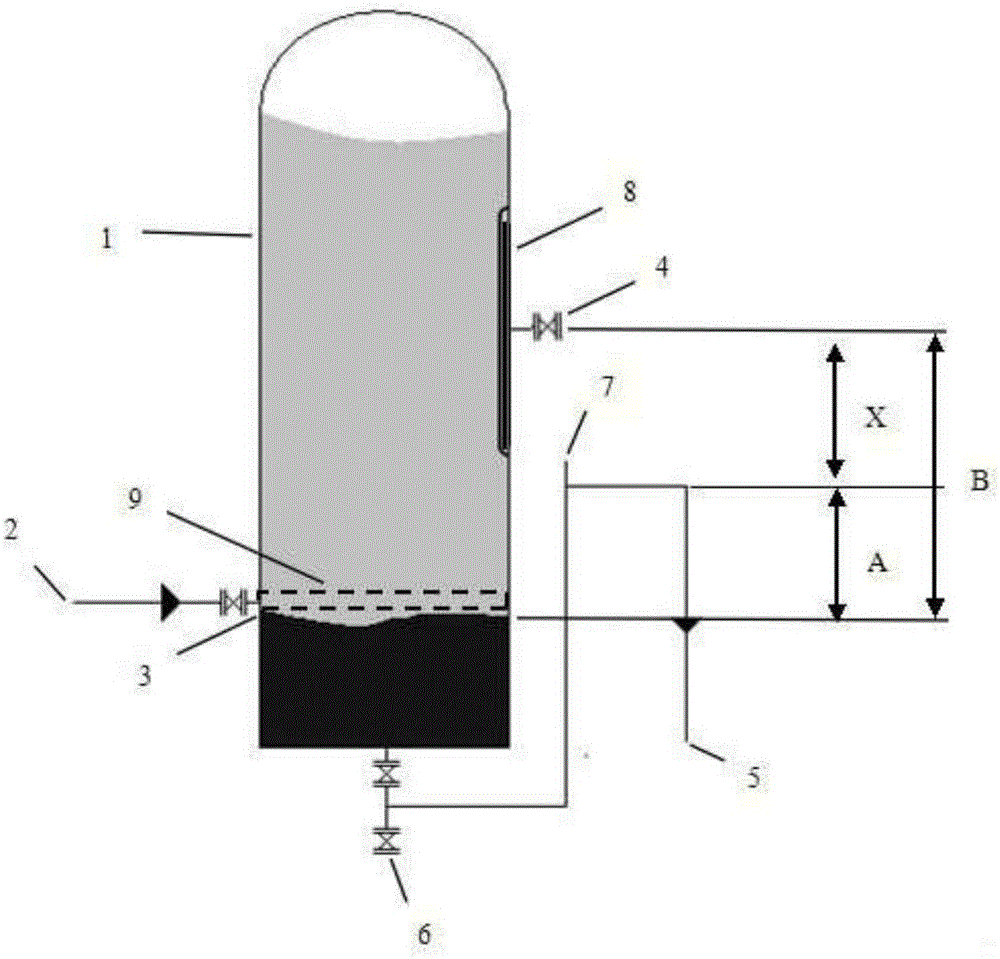
ActiveCN105031972AKeep height B constantHighly simple controlNon-miscible liquid separationOrganic fluidHeight difference
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical equipment and provides a mixed liquor continuous separation device. The device comprises a mixed liquor water diversion container (1), a mixed liquor inlet (2), a water diversion interface (3), an organic liquid overflow port (4), an aqueous phase overflow port (5), a thorough discharge port (6) and a venting port (7). With the water diversion interface (3) as the reference surface, the height of the organic liquid overflow port (4) is B, the height of the aqueous phase overflow port (5) is A, the height difference between the organic liquid overflow port (4) and the aqueous phase overflow port (5) is X=B-A, B*rho 1=A*rho 2, rho 1 represents organic phase density, and rho 2 represents aqueous phase density. By means of the density difference between two kinds of immiscible liquid, the positions of the organic liquid outflow port and the aqueous phase overflow port are reasonably designed, and automatic separation of the two kinds of immiscible liquid can be achieved through the equipment.
Owner:JIANGSU CHANGJILI NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Adsorbate gas adsorption phase density model construction and absolute adsorption capacity calculation method
ActiveCN110534161AImprove accuracyComputational theoretical chemistryChemical machine learningChemical physicsGas phase
The invention discloses an adsorbate gas adsorption phase density model construction and absolute adsorption capacity calculation method, and the method comprises the following steps: acquiring gas phase densities of adsorbate gases with different pressures at a temperature T1, and regressing the gas phase densities into a pressure-related polynomial function; constructing a pore structure of theadsorbent, and obtaining excess adsorption quantity and adsorption phase volume of adsorbate gas in an adsorption system under different temperatures, different pressures and different pore diametersthrough a molecular simulation means; calculating the absolute adsorption capacity; calculating the adsorption phase density of adsorbate gas in the adsorption system under different temperatures, different pressures and different pore diameters; taking the adsorption phase density as a target function, taking the aperture r, the temperature T and the pressure p as dependent variables, and constructing an adsorption phase density calculation model by applying a least square method. The brand-new adsorption phase density calculation method is provided, and the method is based on the basis of pressure, temperature and aperture data, considers the influence of pressure, temperature and aperture on the adsorption phase density, and improves the calculation accuracy of the adsorption phase density.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Mud shale supercritical methane isothermal adsorption model based on variable density
PendingCN110364227AIsothermal adsorption mechanismAccurate recovery of absolute adsorption capacityComputational theoretical chemistryMaterial analysisPorous mediumPhase volume
The invention discloses a mud shale supercritical methane isothermal adsorption model based on variable density. The method comprises the following steps of S1, determining an adsorption phase methanedensity change rule in an adsorption process; S2, determining an adsorption phase volume change rule in a methane isothermal adsorption process; S3, establishing a variable-density supercritical methane isothermal adsorption model nex=rhoabs*Va-rhog*Va=(rhof*ln(d*p-1)-rhog)*Va; S4, measuring isothermal adsorption data of a porous medium by means of a weight method or a capacity method, fitting the experiment data by means of the model, and obtaining the adsorption phase density, the absorption phase volume and the methane absolute absorption quantity at different pressure points. The mud shale supercritical methane isothermal adsorption model is suitable for fitting isothermal adsorption experiment data of supercritical methane of the porous mediums such as mud shale, and the model can realize more accurate fitting of the isothermal adsorption data. The mud shale supercritical methane isothermal adsorption model can accurately calculate the adsorption phase density change in an isothermal adsorption process and realizes more reasonable prediction for the adsorption phase volume and the absolute adsorption quantity.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method of continuous inkjet printing
InactiveUS20100188462A1Rule out the possibilityIncrease temperatureOpening closed containersBottle/container closureLiquid jetActive component
A liquid jet is ejected out of a nozzle, the liquid comprising one or more components, the flow of one or more of said components, the active components, being separated such that the liquid that flows within a boundary layer thickness δ, of the nozzle wall is substantially comprised of a liquid without the active components, the continuous phase, and the said active components flow substantially outside said boundary layer where δ is defined by formula (I): where μ is the continuous phase viscosity in Pa·s, U is the jet velocity in m / s ρ is the continuous phase density in kg / m3 and x is the length of the nozzle in m in the direction of flow.δ=μxρU(I)
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
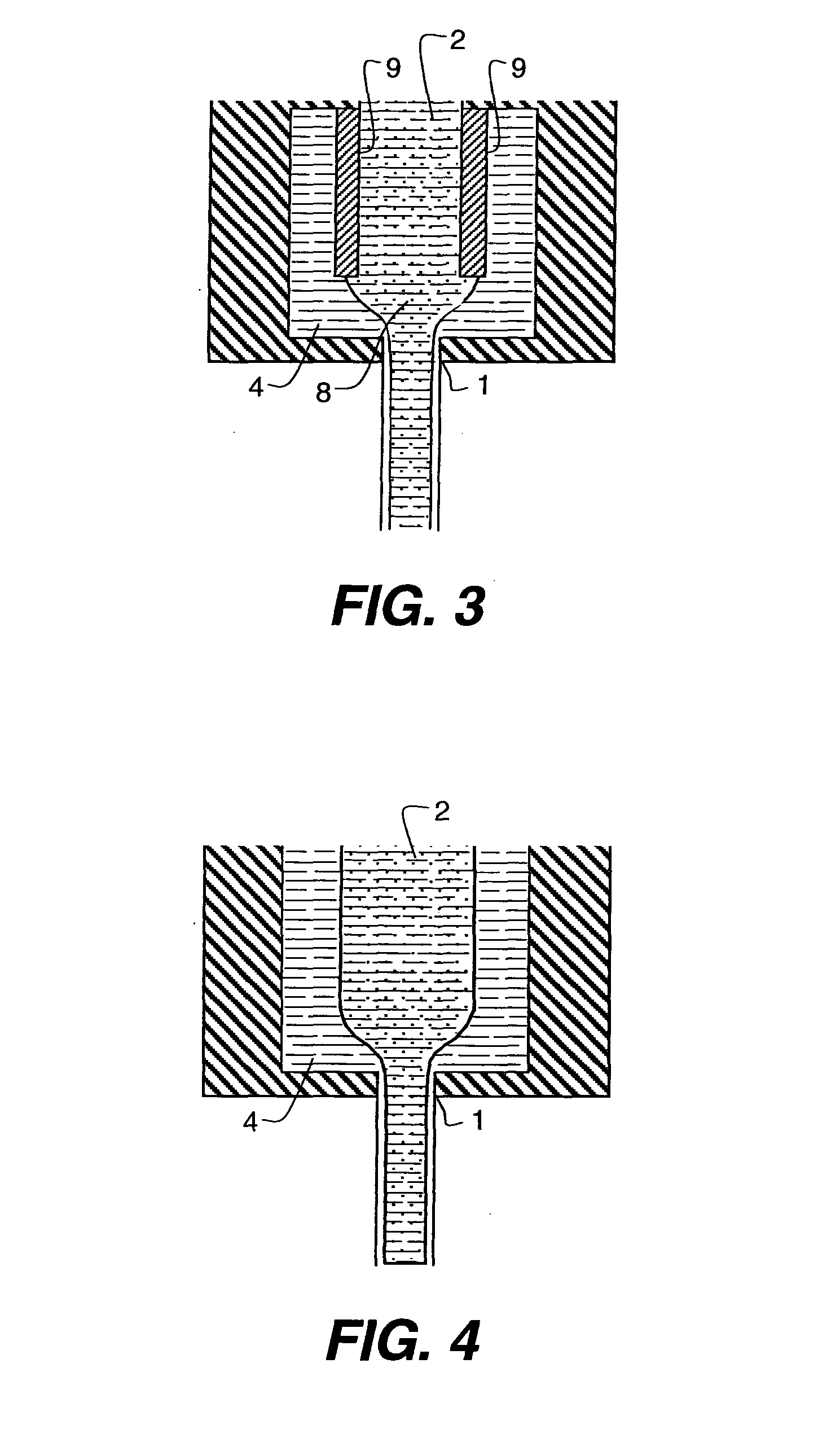
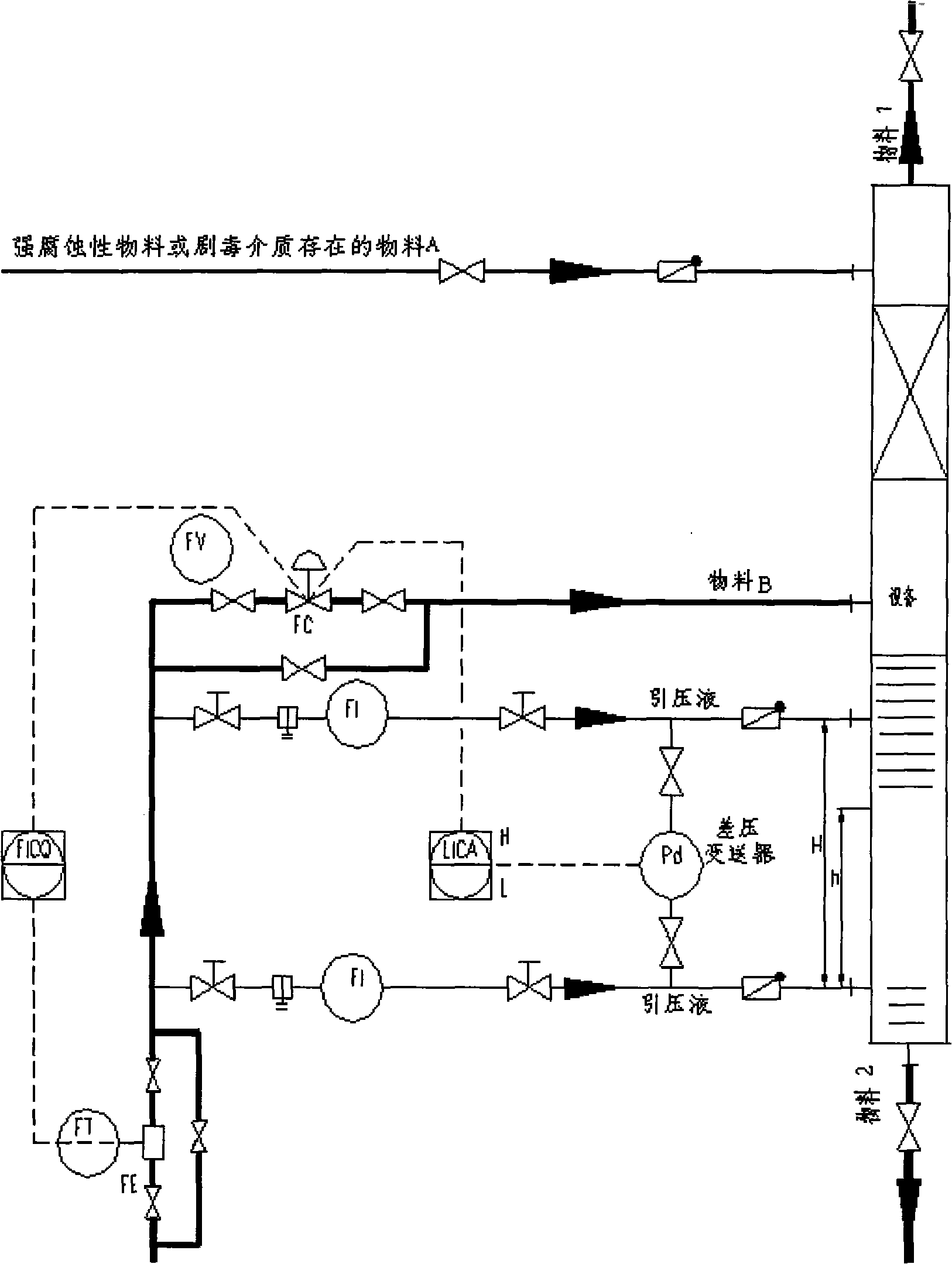
Strong corrosivity medium phase interface measurement method
InactiveCN101493353ALow costEasy to measureLevel indicators by pressure measurementEngineeringPressure difference
The invention relates to a phase interface measuring method. The method comprises the following steps: pressure liquid is pressed into a phase to be measured from an upper pressure opening and a lower pressure opening at the same flow, pressure of the pressure openings is measured, and phase interface height h (h=(deltaP-rho1*g*H) / (rho2-rho1) / g) is computed according to pressure difference deltaP between the upper pressure opening and the lower pressure opening, the height H of the upper pressure opening as well as upper phase density rho1 and lower phase density rho2 of two phases in the phase to be measured. In the measuring method, a common instrument can measure the phase interface height of highly corrosive media, which has the advantages of low cost, simple measuring method and wide application; and the measuring method can be used for measuring liquid level, the phase interface height between media with similar density and each phase interface height of a multi-phase mixture besides being especially suitable for measuring the phase interface height of the highly corrosive media.
Owner:ZHONGHAO CHENGUANG RES INST OF CHEMICALINDUSTRY CO LTD
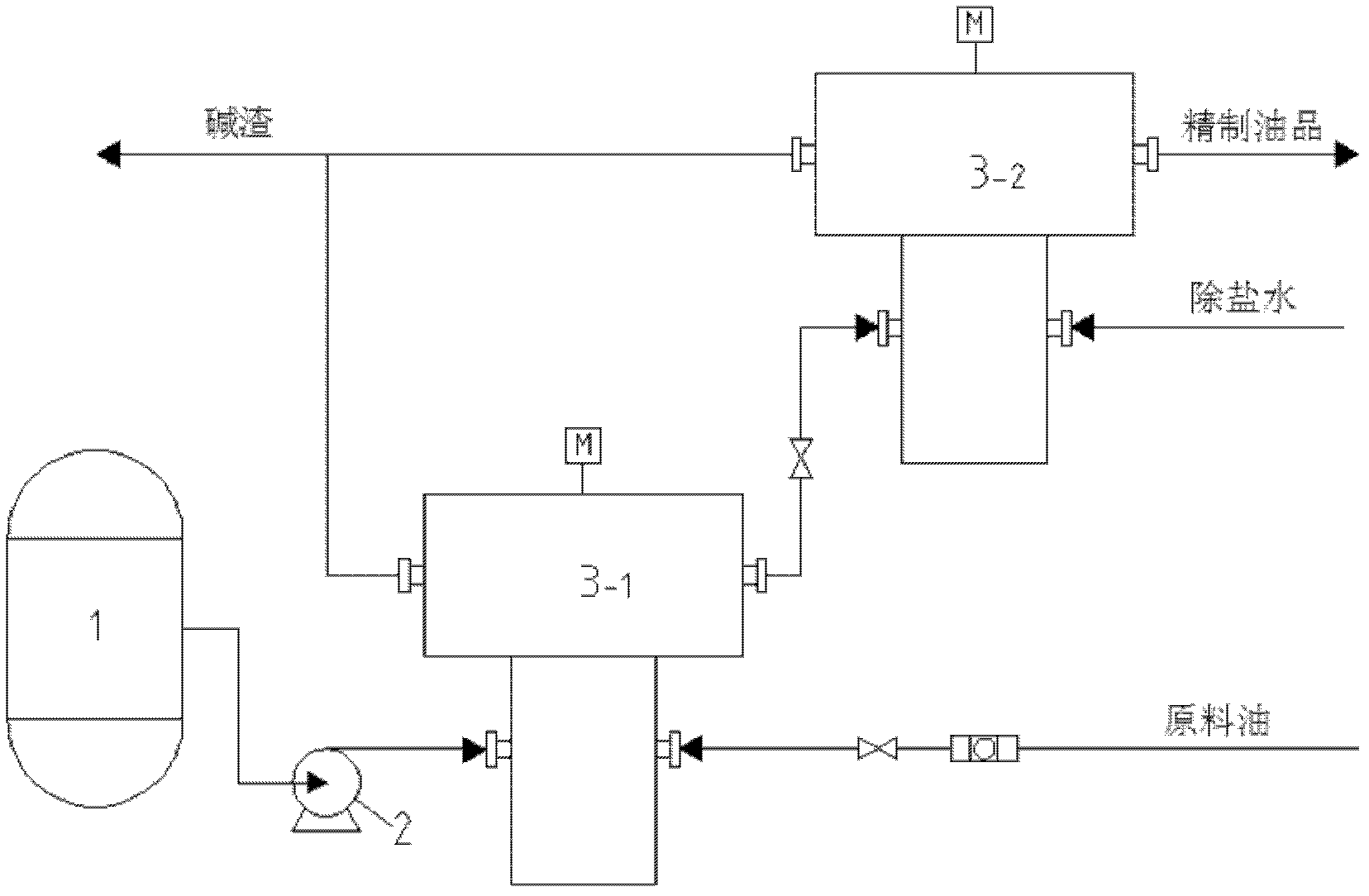
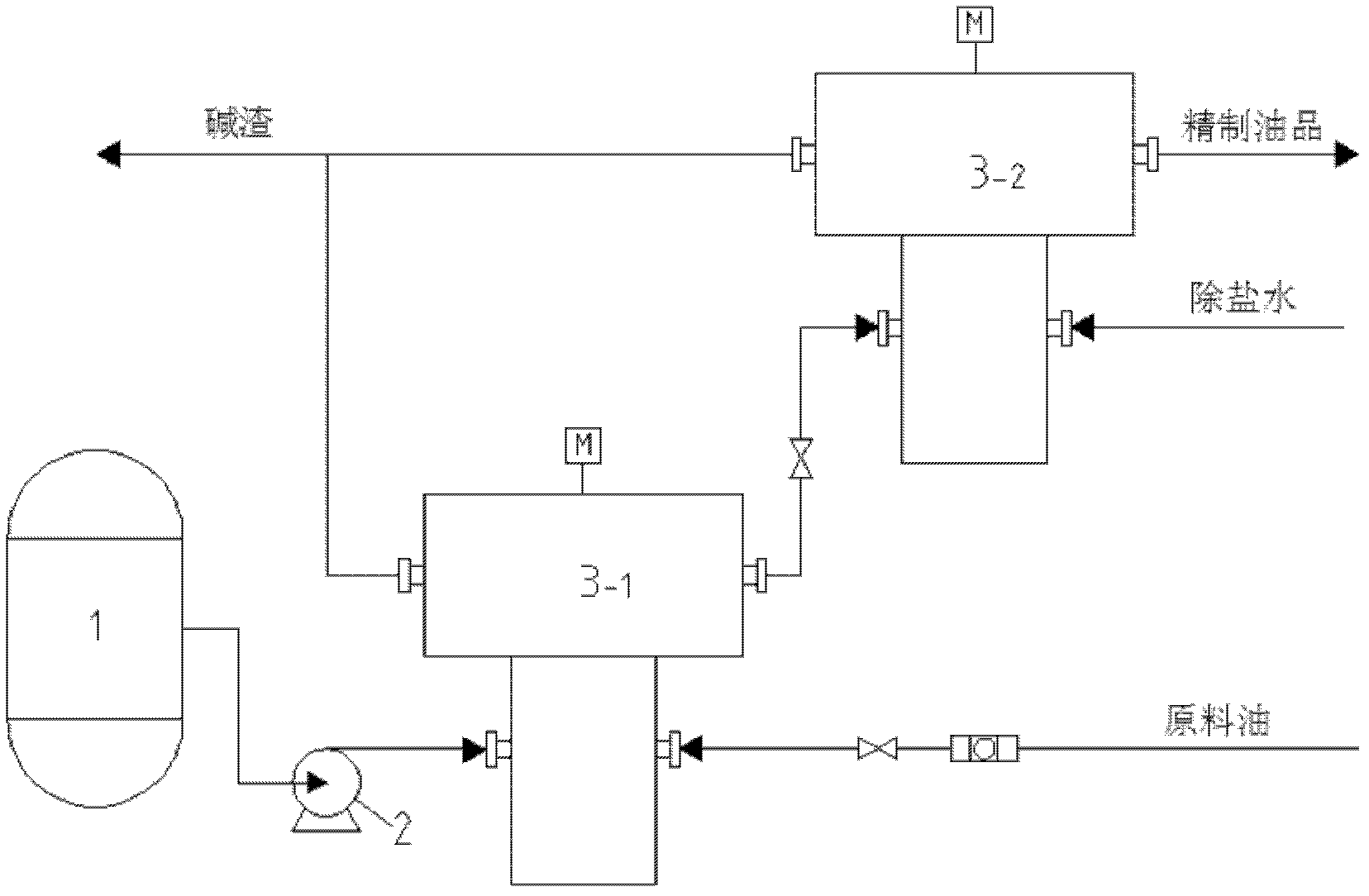
Straight-run diesel oil deacidification method and device for achieving same
InactiveCN102304385AReduce usageOvercome the shortcomings of incomplete separationTreatment with plural serial refining stagesSlagPetrochemical
The invention provides a novel straight-run diesel oil deacidification method. The method comprises the step of carrying out extraction separation on diesel oil in an alkali washing and deacidification process by utilizing a centrifugal extraction separator so that the acidity of the diesel oil is less than 1.5mg / (100ml), and the mass fraction of oil in alkali slag is less than 2%. The invention also provides a straight-run diesel oil deacidification device. By the method and device provided by the invention, the separation efficiencies of alkali washing and water washing in the diesel oil deacidification process are improved, separation time is reduced, investment is small, and applicability is strong. The method and device provided by the invention are suitable for extraction separation occasions which have the requirements of small two-phase density difference, large viscosity, short separation time and the like in a petrochemical industry.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com