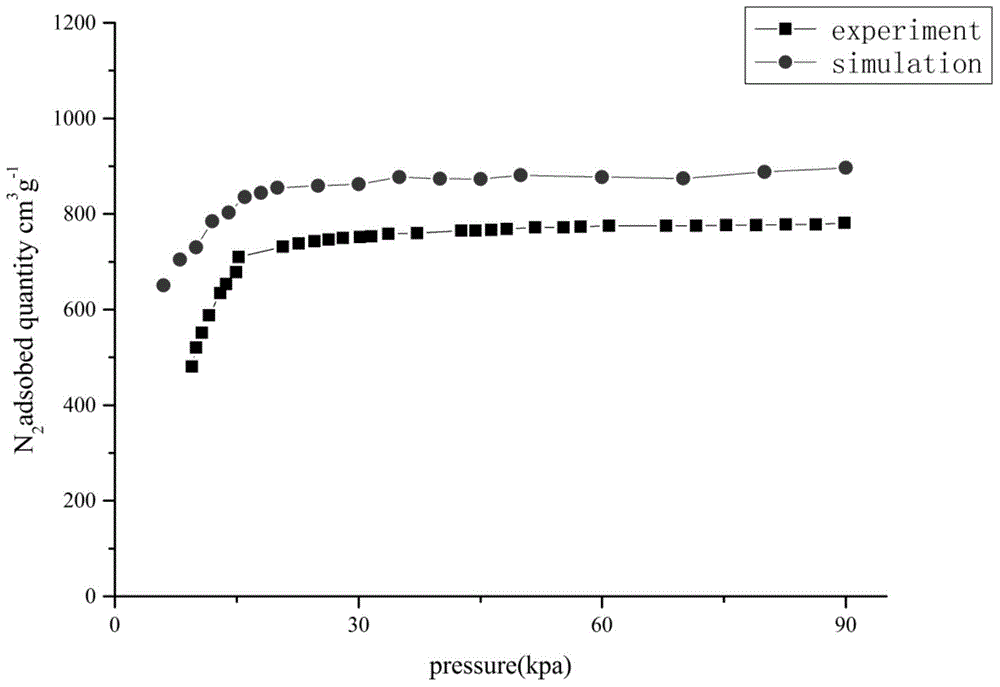
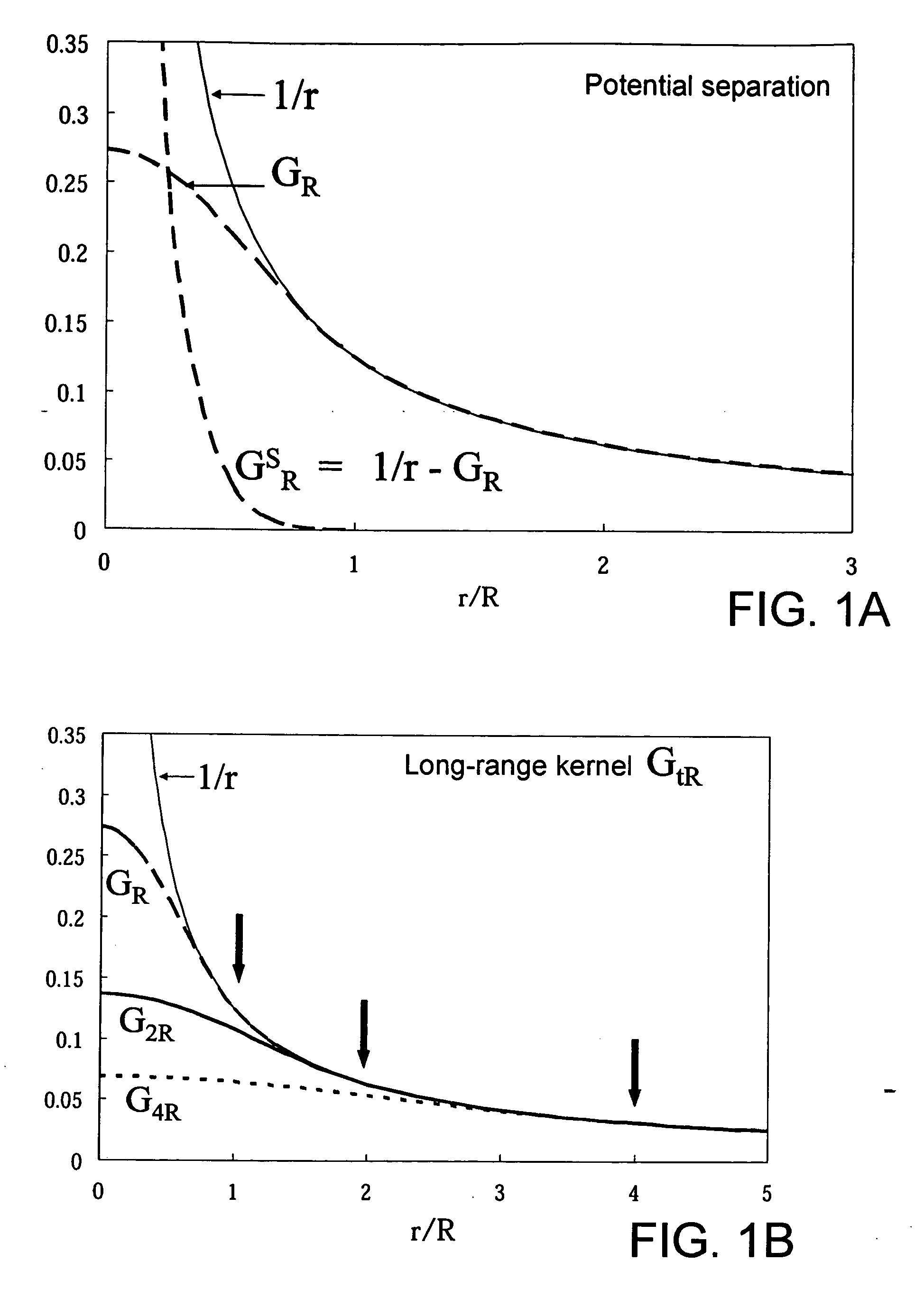
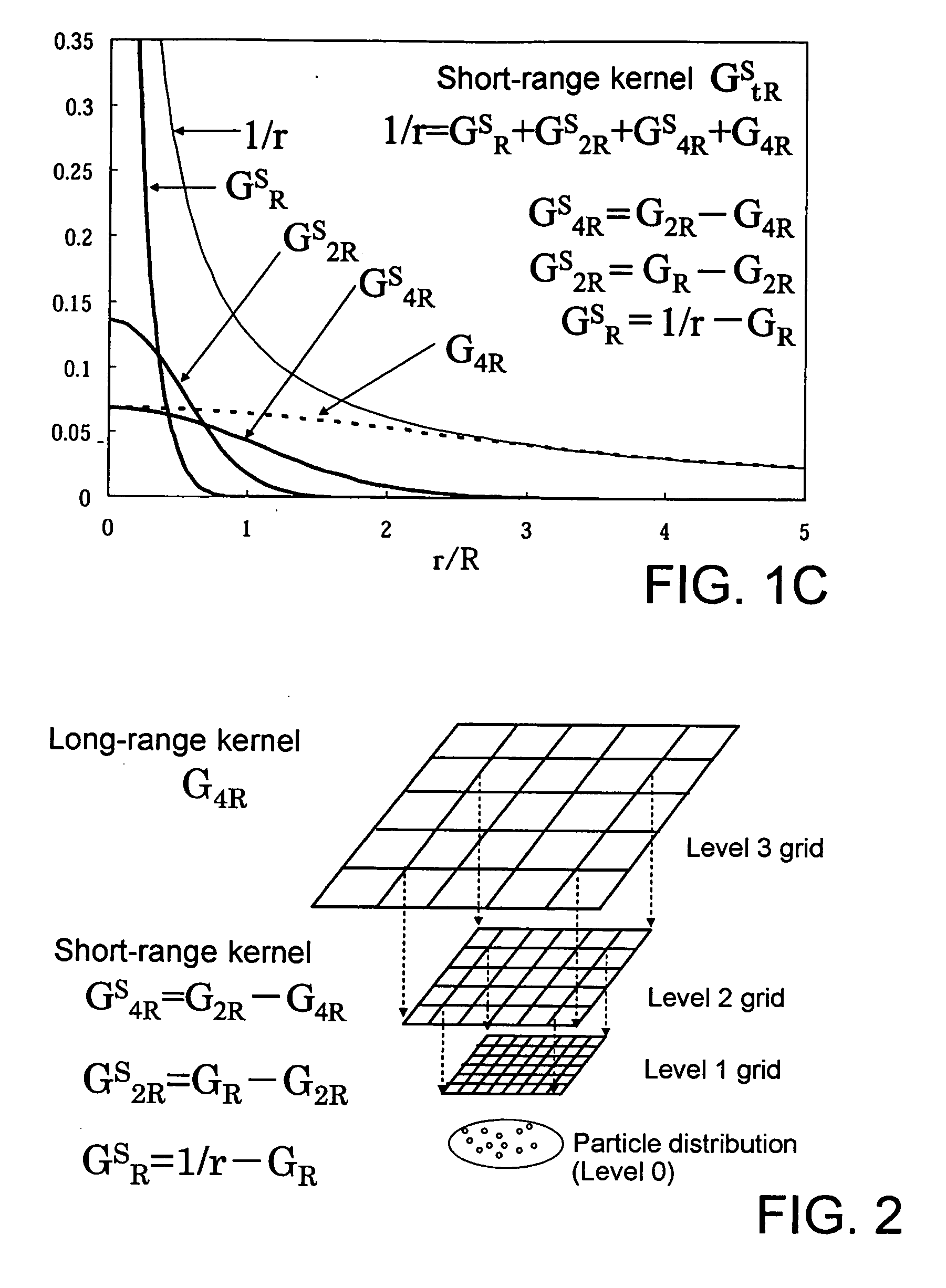
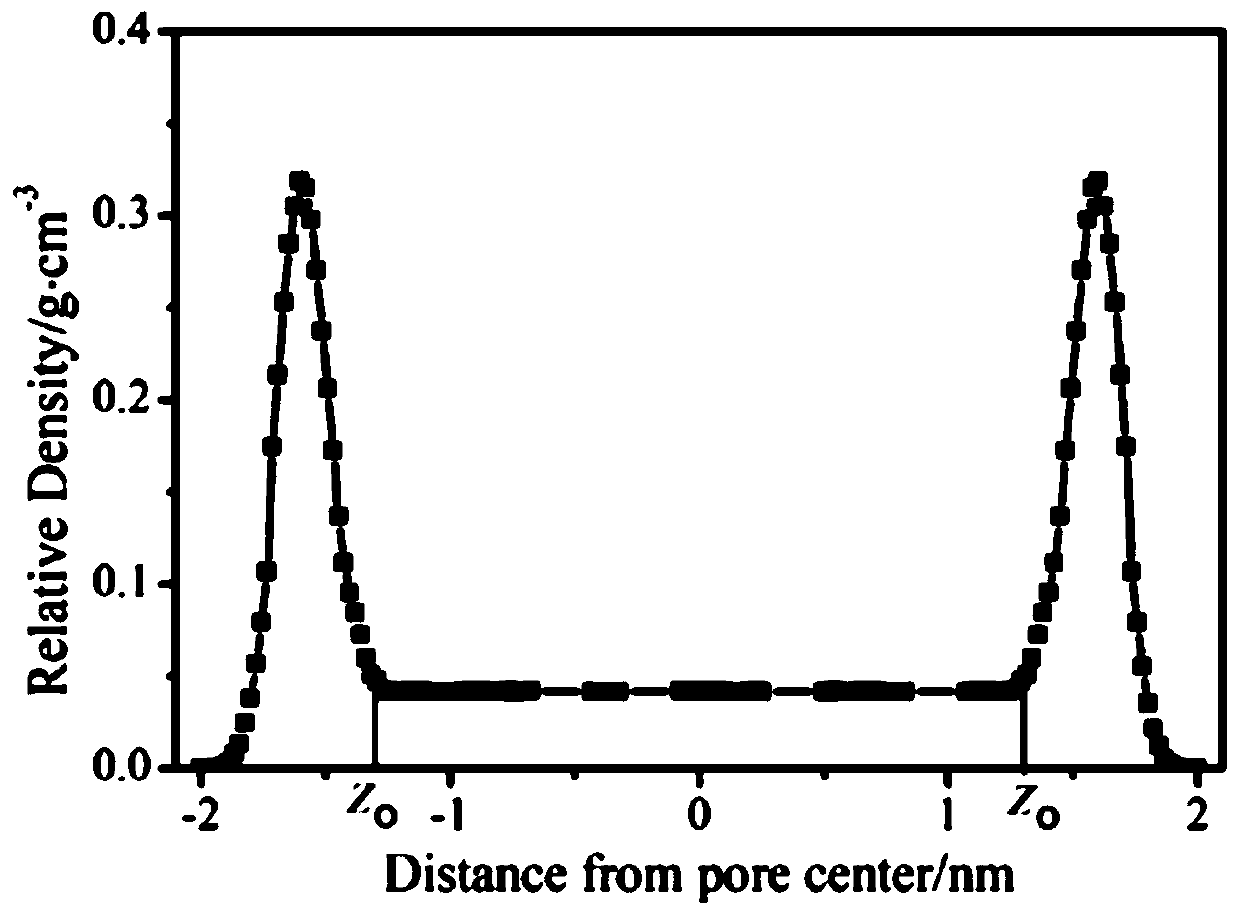
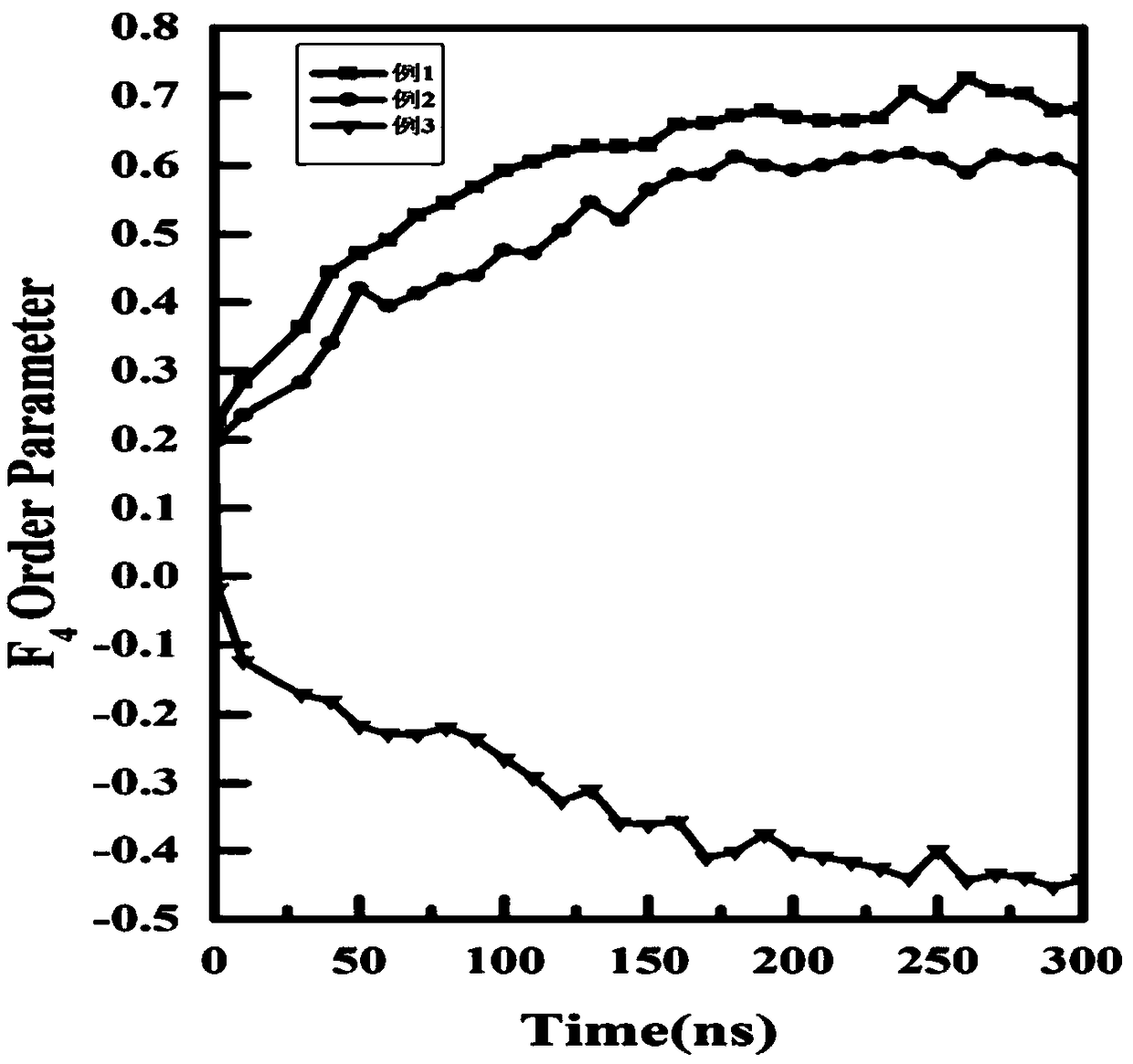
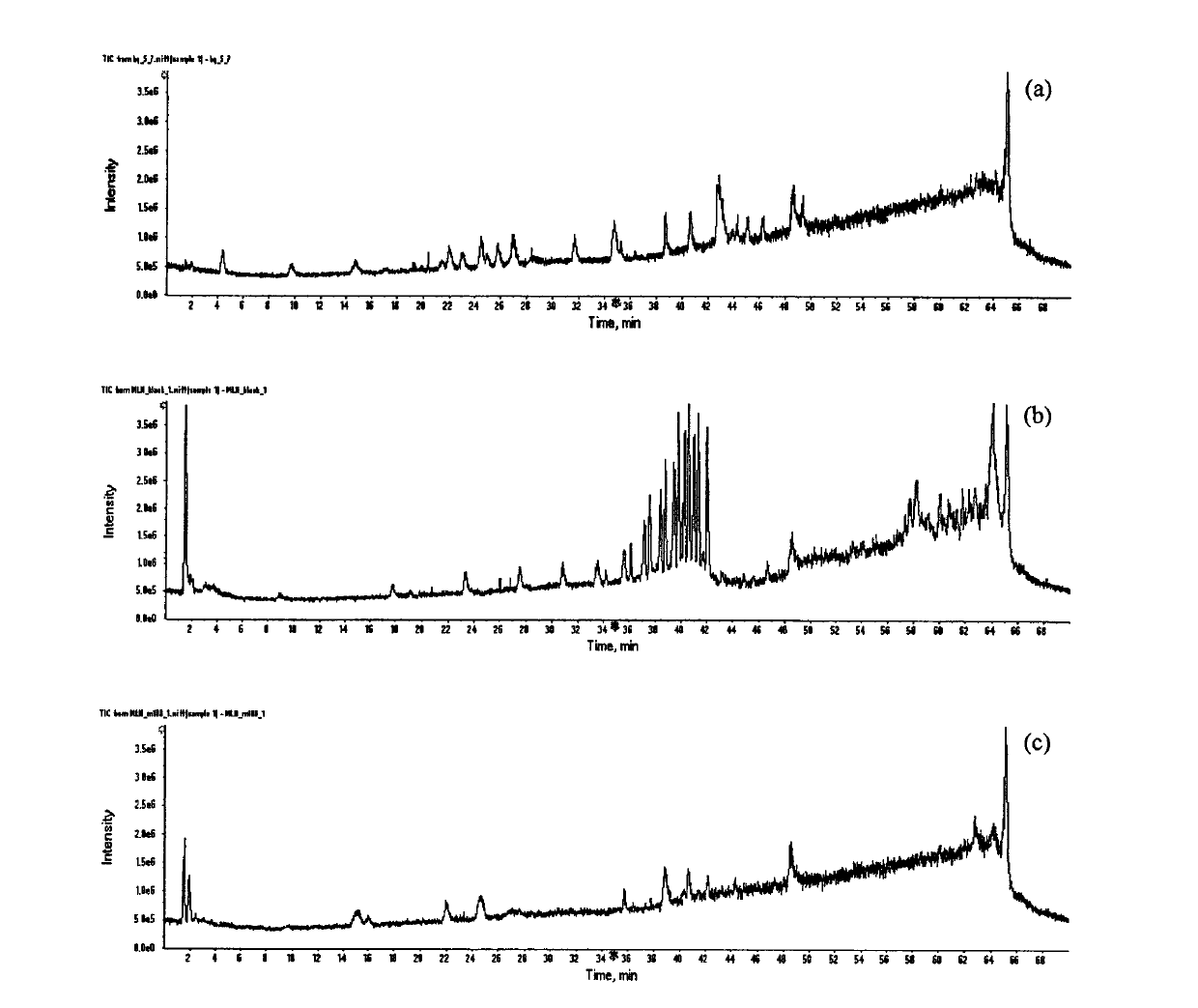
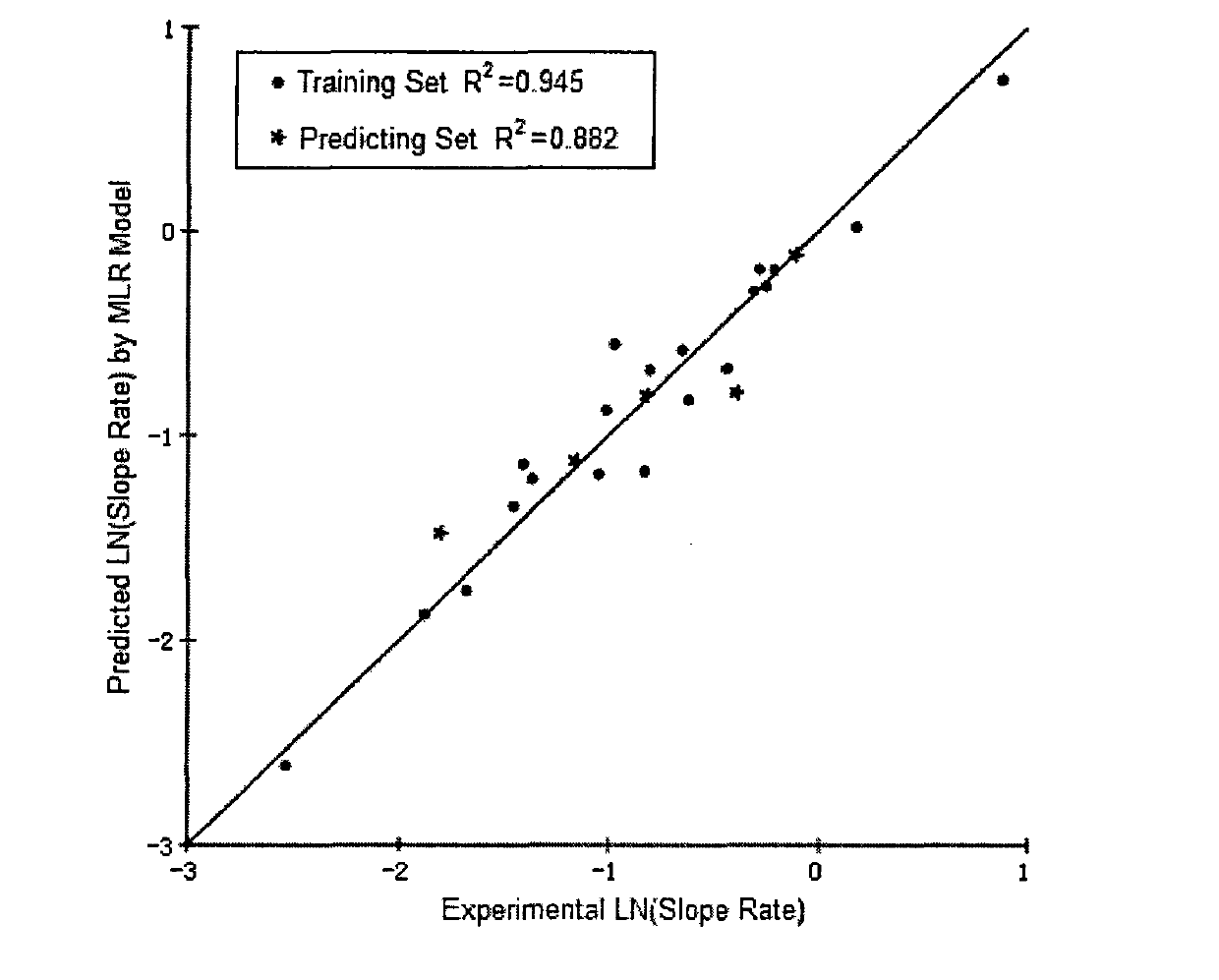
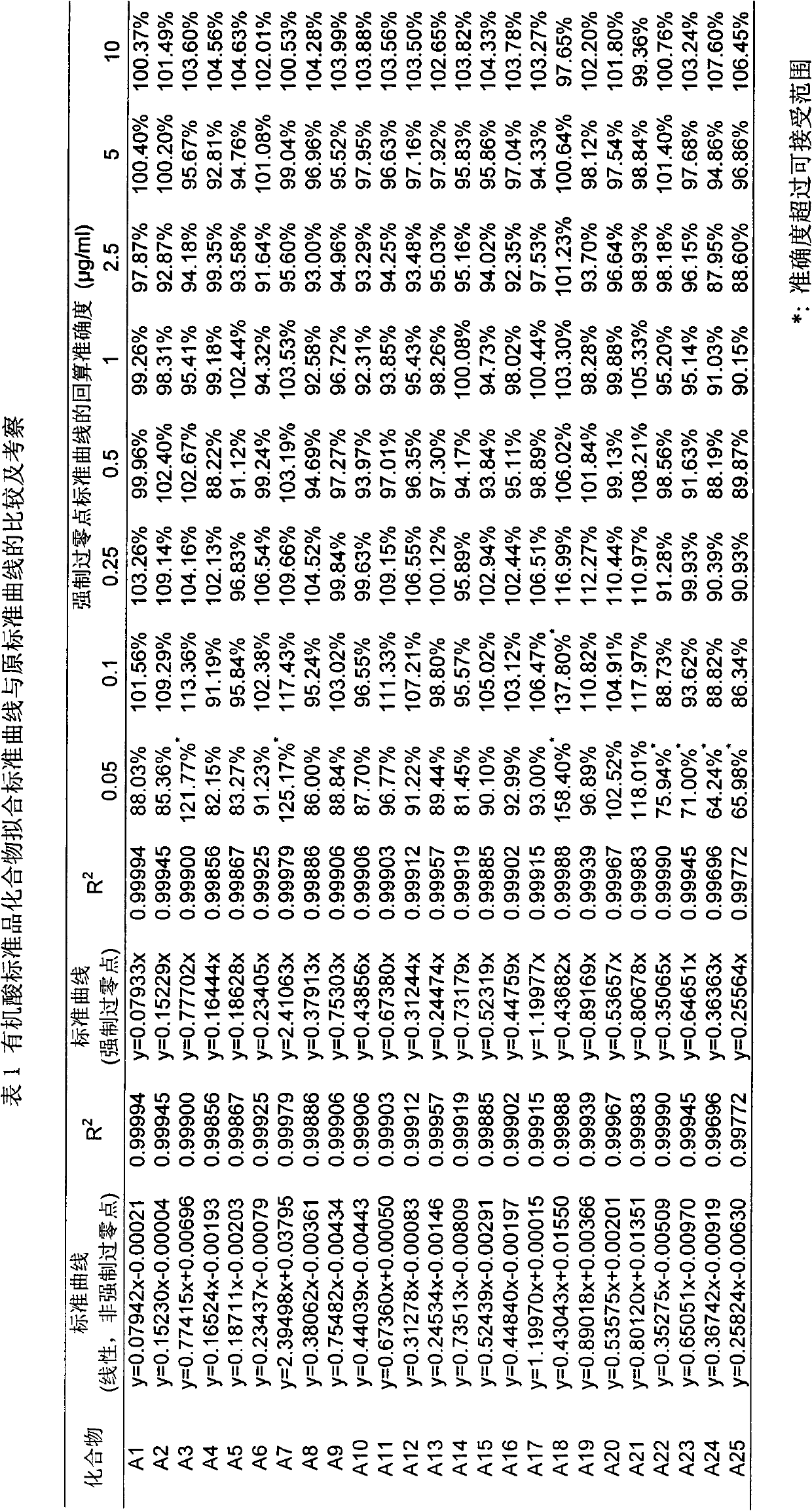
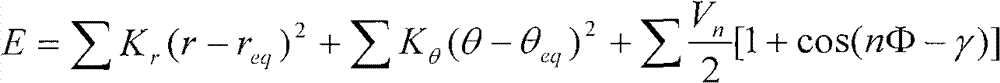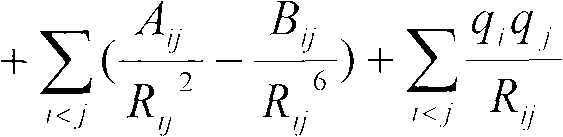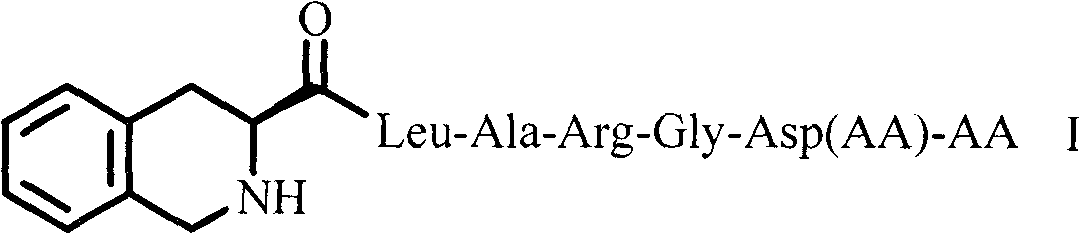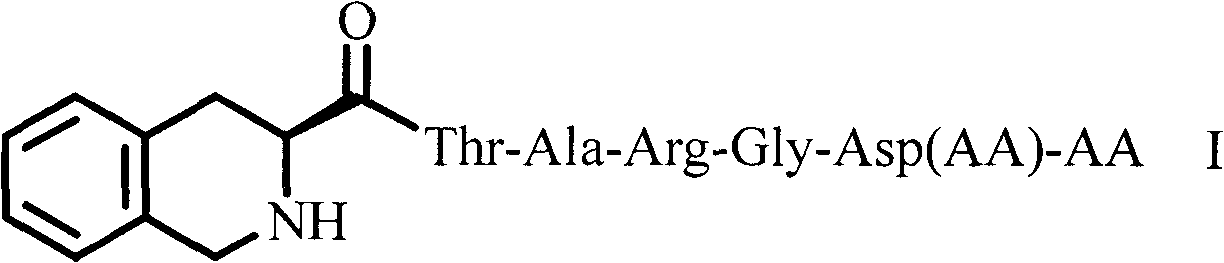Patents
Literature
156 results about "Molecular simulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of quantifying hydrocarbon formation and retention in a mother rock
InactiveUS20080059140A1Analogue computers for chemical processesSeismologyHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSedimentary basin
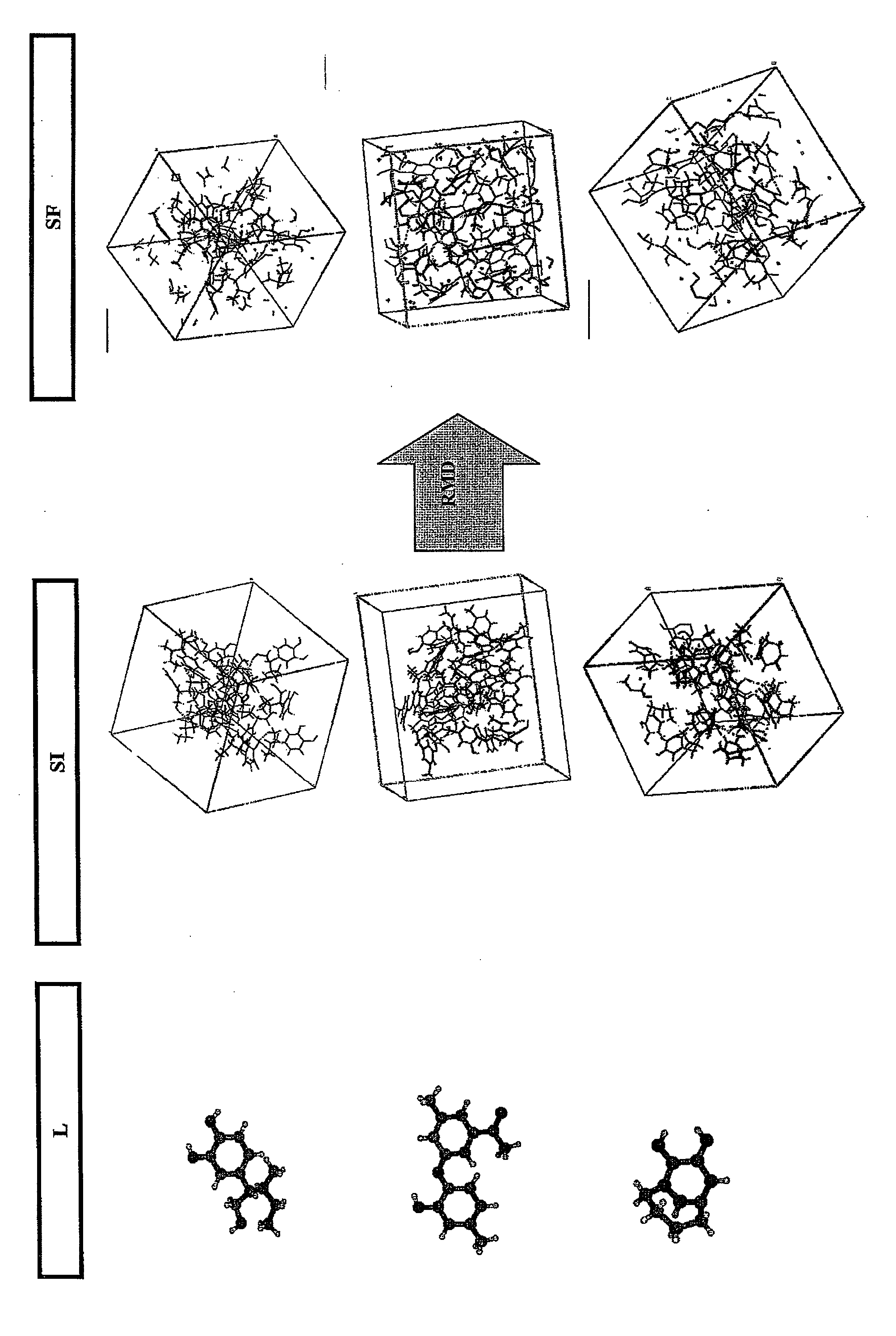
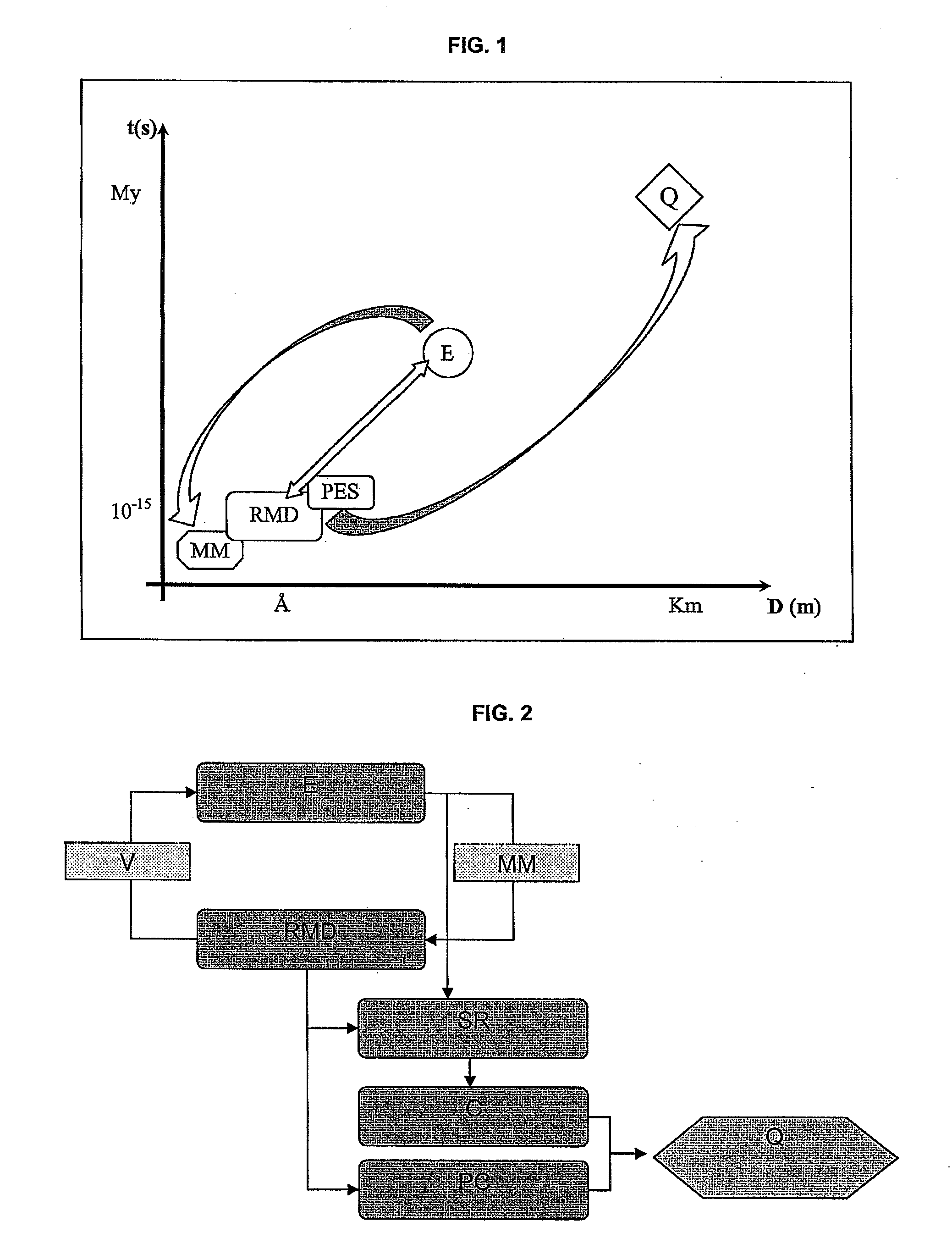
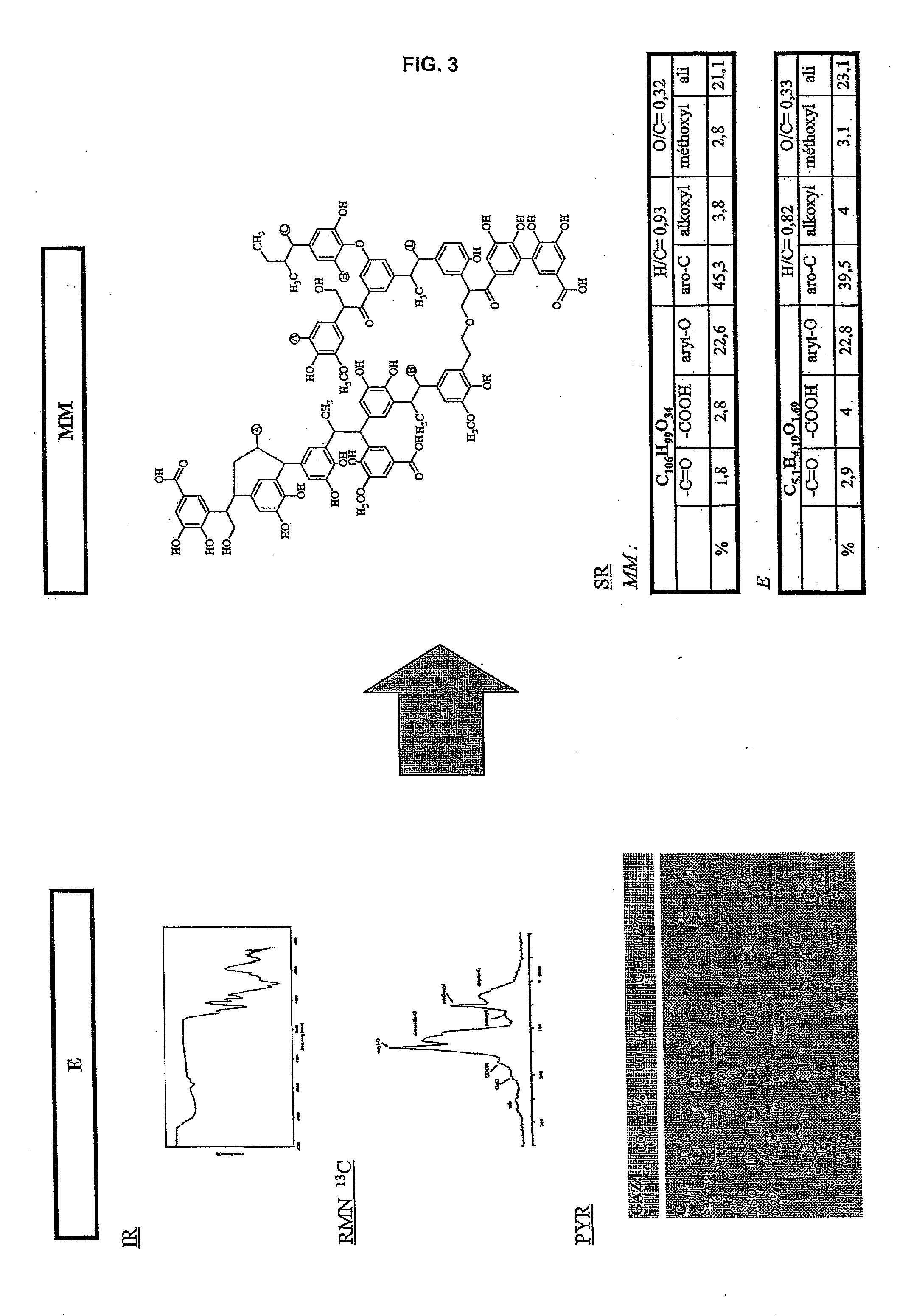
The method according to the invention allows the formation of oil and the retention phenomenon in the mother rock to be modelled. Organic matter characterization experiments are used to establish the molecular model (MM) of the initial sample (E). The thermal cracking reaction of this molecular model is reproduced by dynamic molecular simulation computations with a reactive force field (RMD) and validated by comparison with experimental data. The reaction mechanism obtained (SR) allows to carry out a kinetic study (C) by variation of the temperature parameter. The phase equilibria (PES) of the reaction medium are determined at any time from dynamic simulation. The successive phase equilibrium assessments at various progress stages of the cracking reaction allow following the physicochemical evolution (PC) of the thermal maturation of the organic sample studied. The free hydrocarbons (liquid and gaseous) that are not retained in the solid residue can be quantified throughout numerical modelling of the sample maturation; representing, in the sedimentary basins, the hydrocarbons that are not retained in the organic matrix of the mother rock (Q). This quantity can be used as an indicator or an input value for the retention threshold in basin models.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
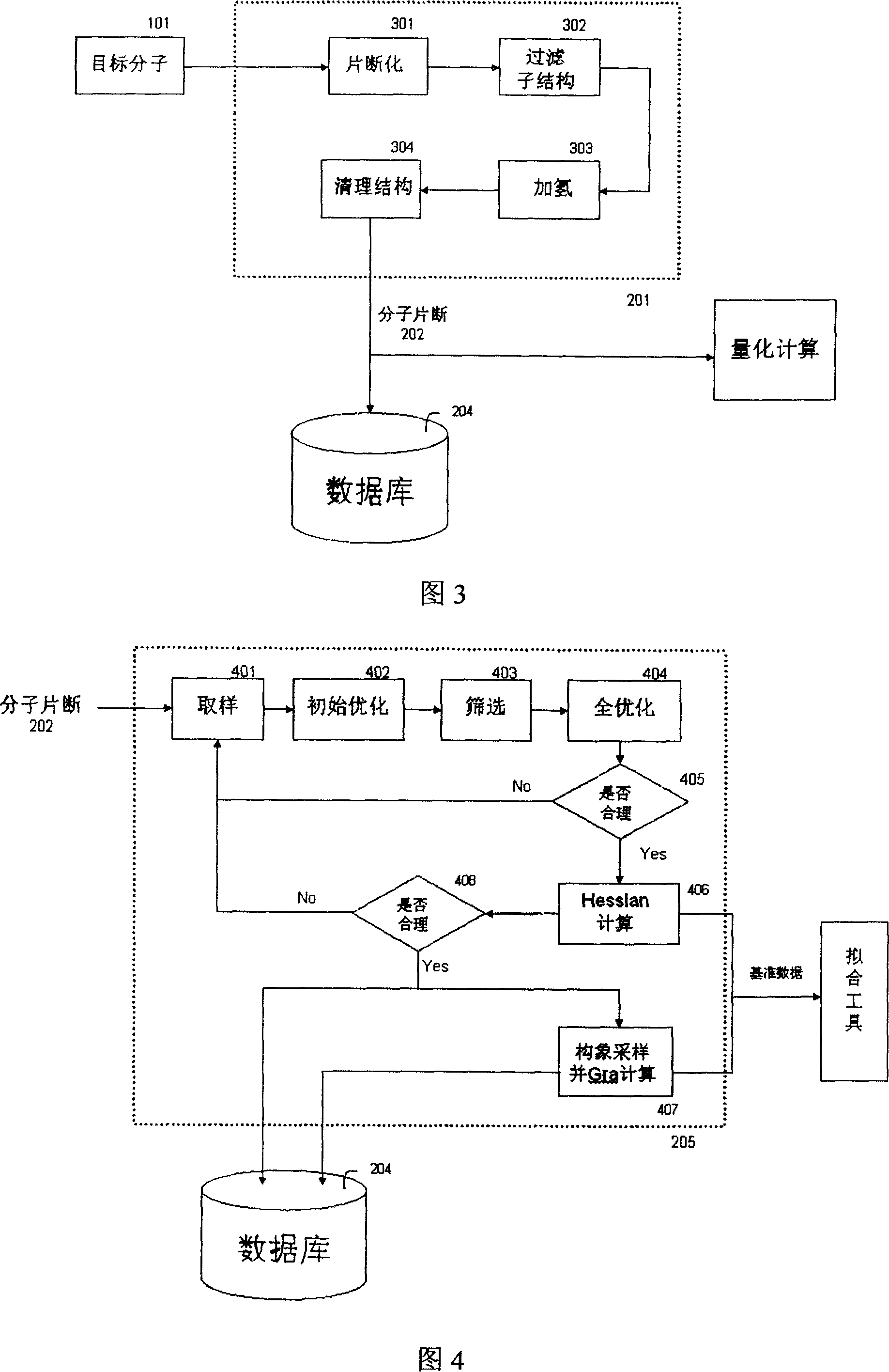
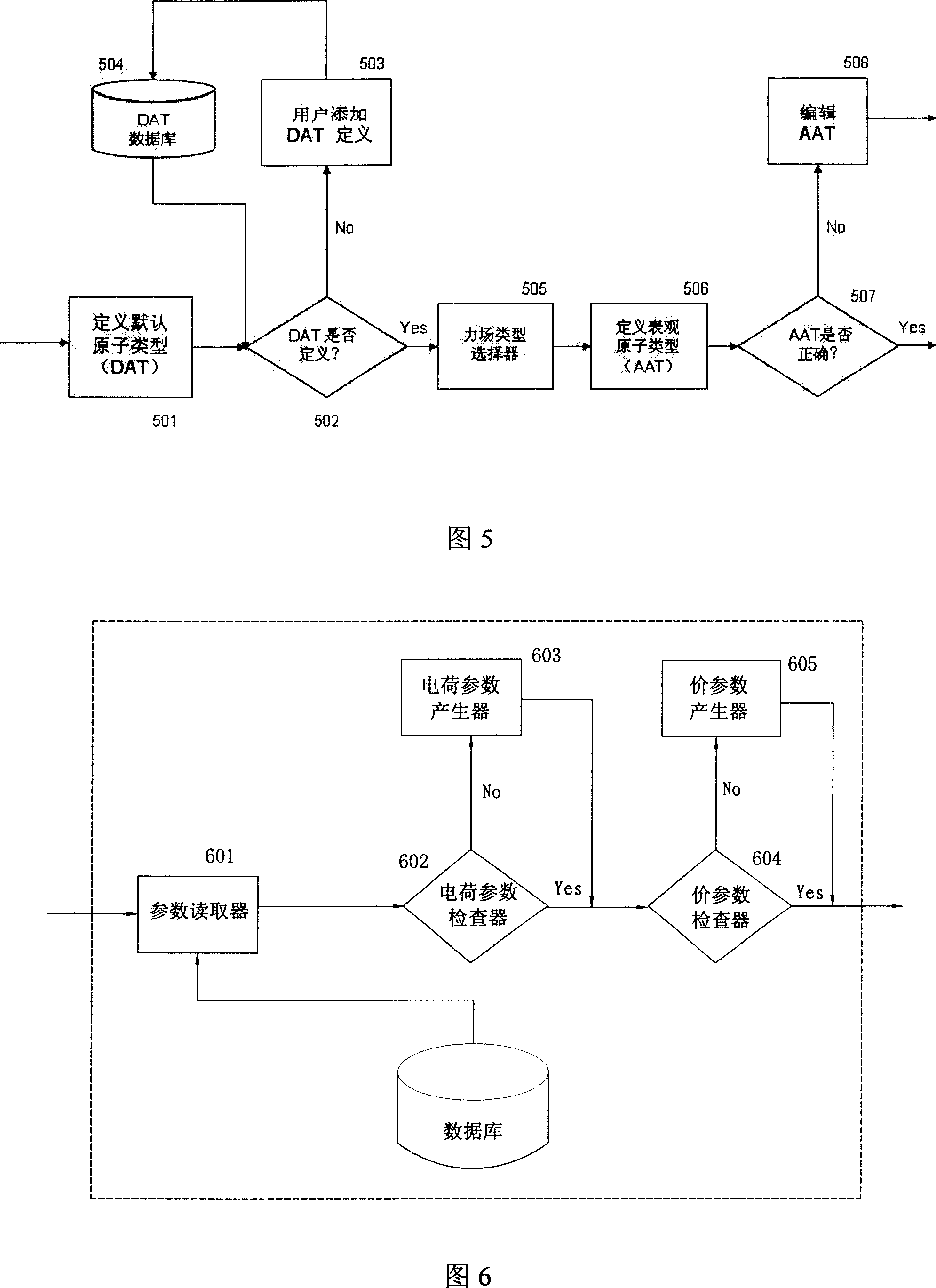
Automatic generating method for force field parameter of molecular mechanics
InactiveCN101131707AAccurate derivationAutomatic derivationComputational theoretical chemistrySpecial data processing applicationsChemical industryBasic research
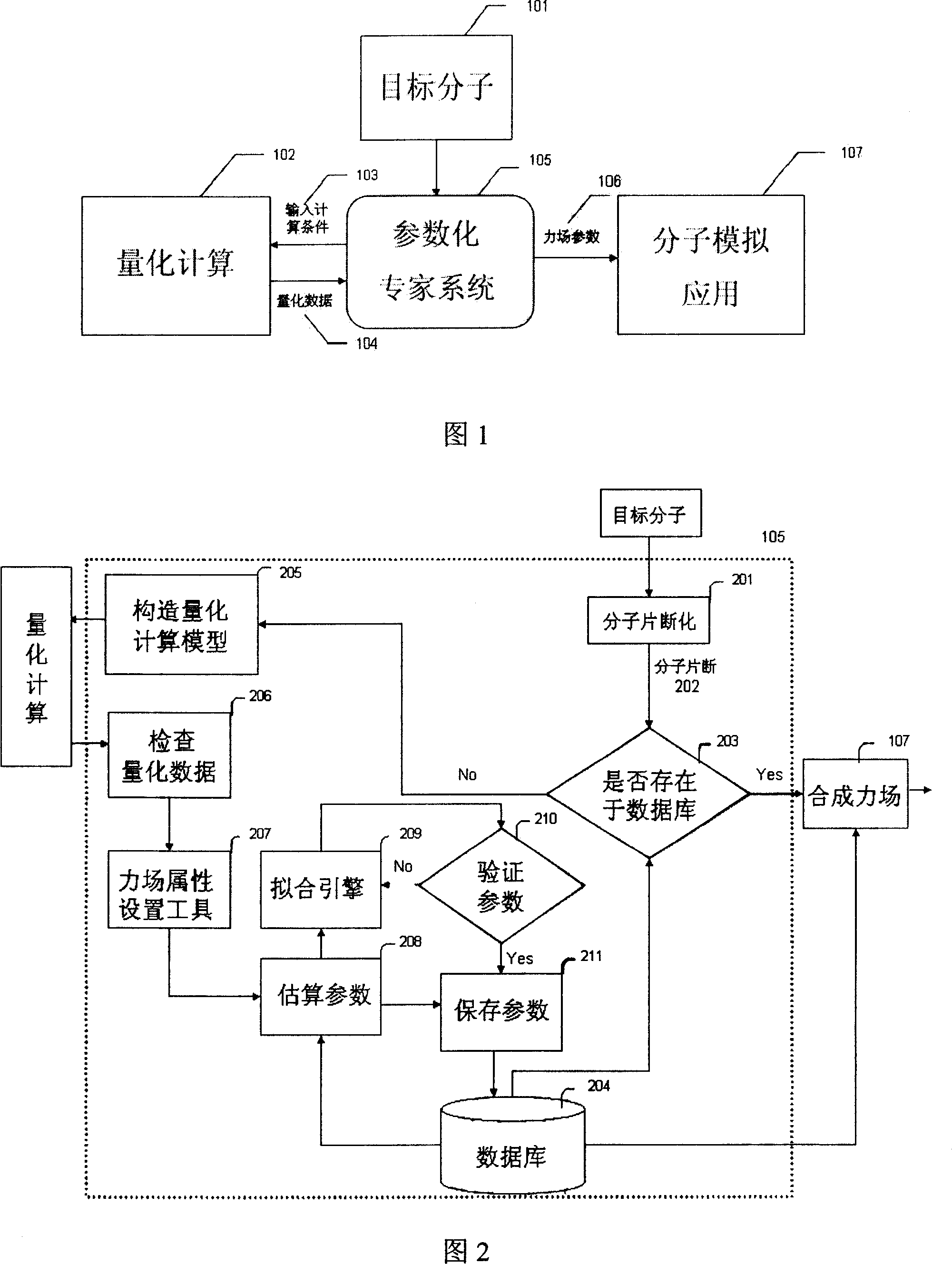
The invention relates to the automatic generating method of the molecular mechanic field's parameter, including the method to generate automatically the parameter of the molecular mechanic that is required in molecular simulation, and it can be used for basic research such as the materials science, life sciences, medication science, and chemical industry and so on. The main content of the invention are: searching the only molecular-model collection which can be used for generating the molecular field's parameter for the goal molecular; carrying quantum-mechanical calculation on the molecular-model collection to get the reference data that can be used for fitting the molecular mechanics field; fitting automatically a lot of nonlinear data; verifying automatically the fitting results; storing and managing the data and fitting results referred above with database. The invention can solve the bottle-neck problem that lacking perfect and precise force-field in the use of the molecular simulation technique abroad at present. The invention provides a new systematic method which can deduce molecular force field quickly, exactly and automatically.
Owner:YIANG COMPUTATIONAL CHEM SOFTWARE SHANGHAICO
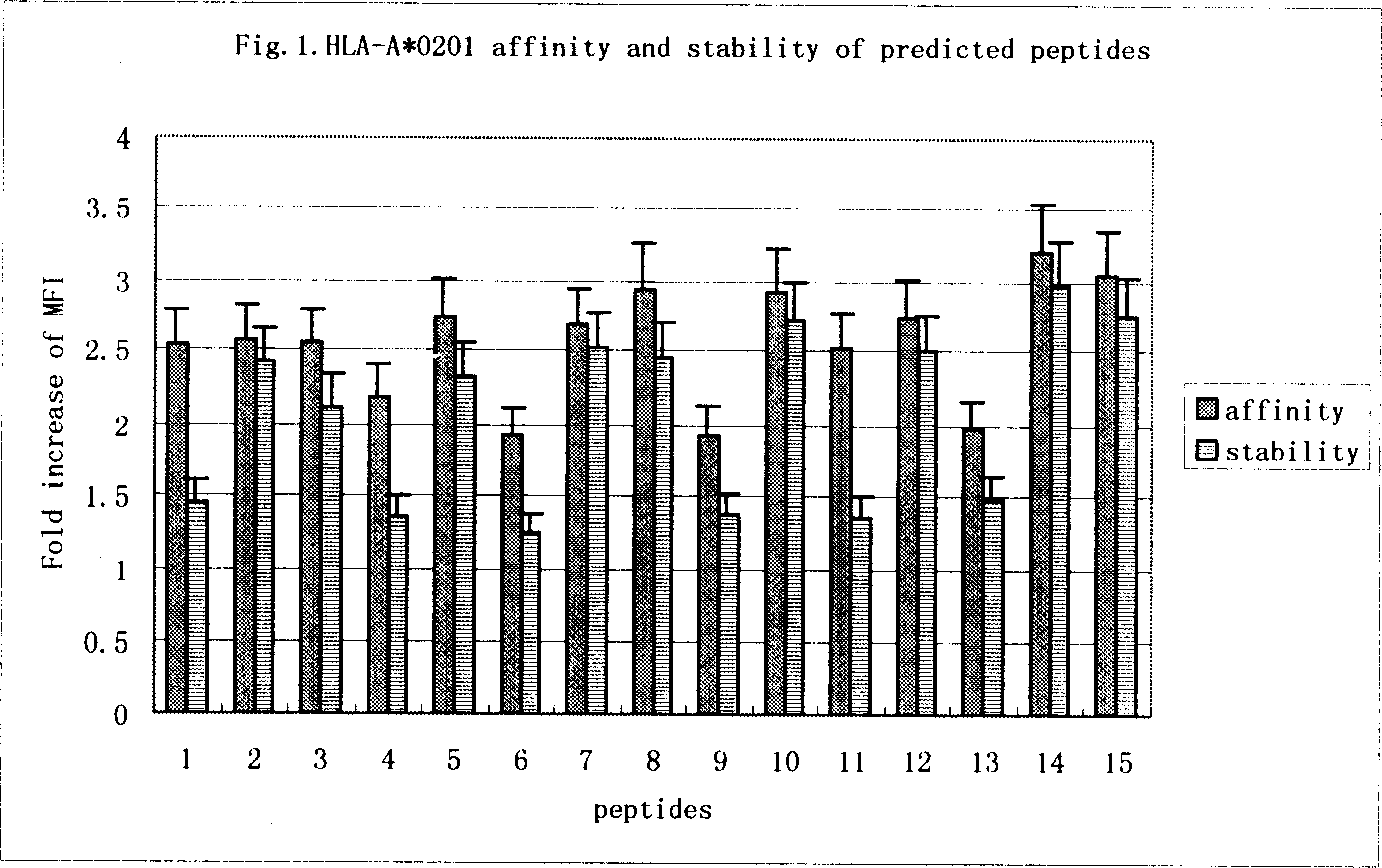
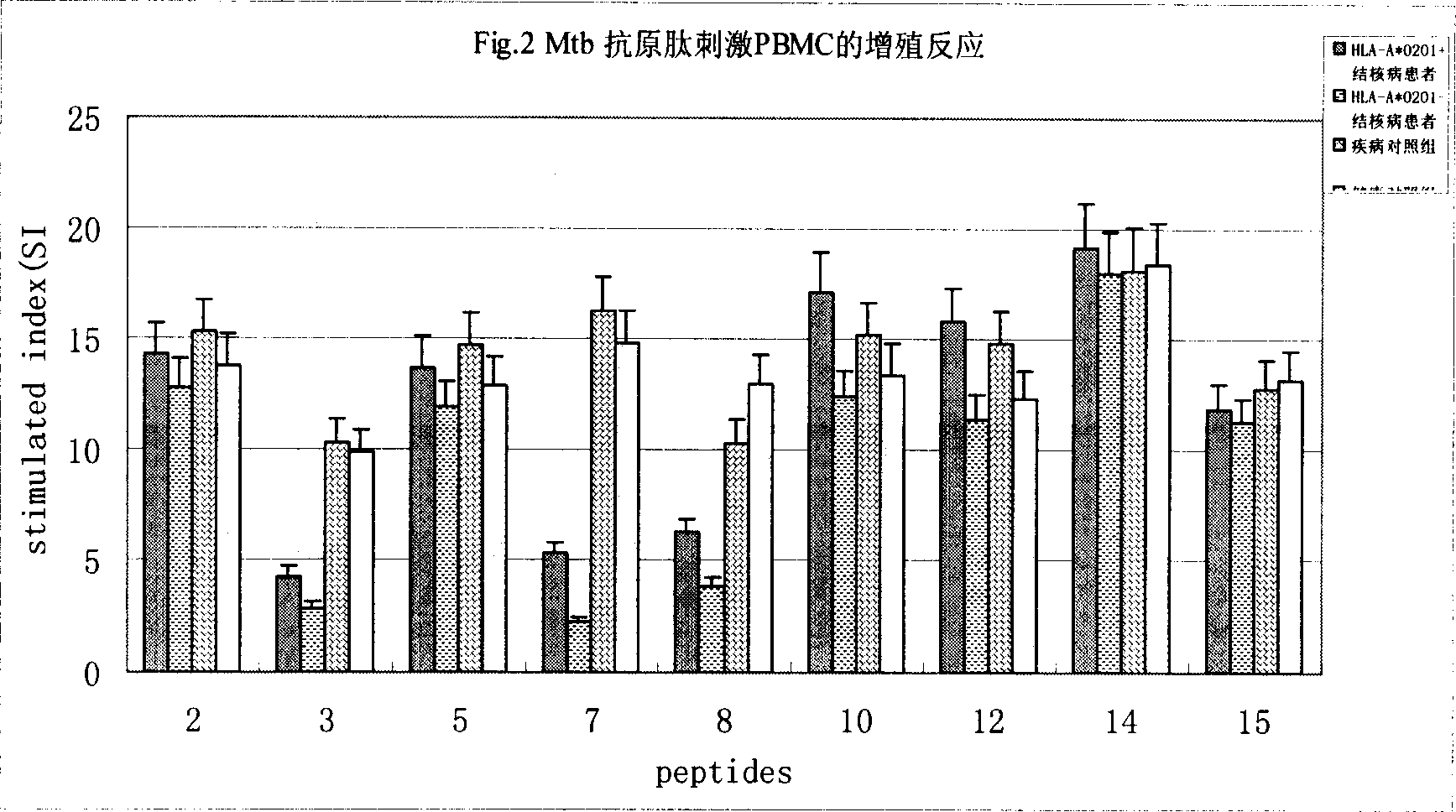
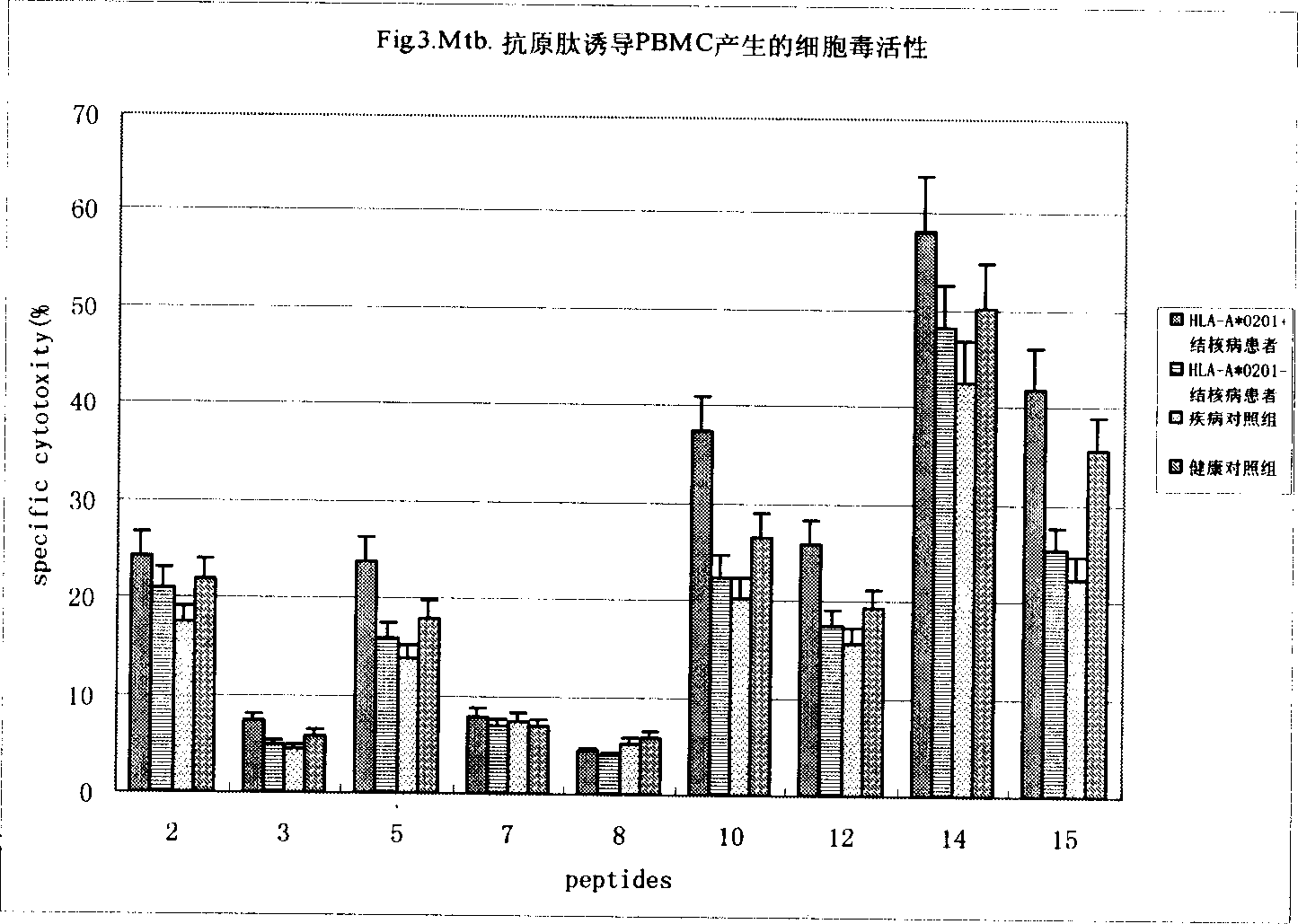
Antigen epitope for exciting human anti-tubercle bacillus protective immunoreaction and its use
InactiveCN1858059AHelp preventAids in healingAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMolecular ImmunologyBCG vaccine
The present invention relates to molecular immunology technology, and aims at screening out antigen epitope molecular simulation peptide capable of exciting human body's protective immunoreaction against tubercle bacillus, researching protective immunoreaction mechanism against tuberculosis, and further developing new type of concatenate polyepitope tuberculosis vaccine. The present invention provides one kind of antigen epitope molecular simulation peptide capable of exciting human body's protective immunoreaction against tubercle bacillus, and the peptide contains the amino acid sequence selected from SEQ ID Nos. 2, 5, 10, 12, 14 and 15. The present invention also provides the screening process and use of the peptide. The present invention may be used in preventing and controlling tuberculosis.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
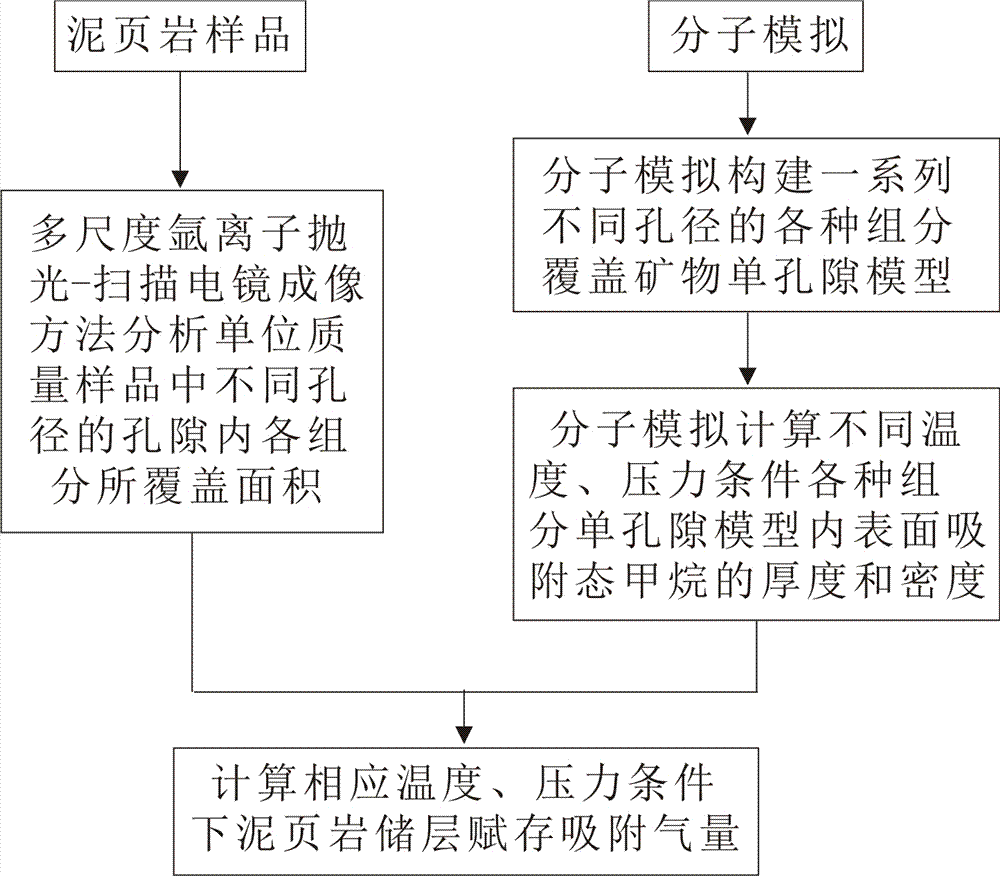
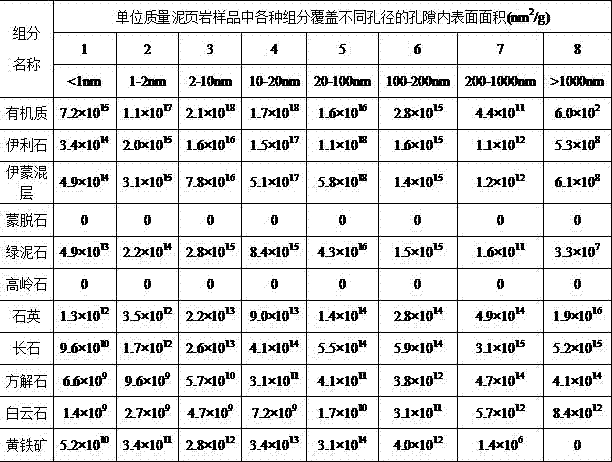
Method for evaluating shale reservoir stratum occurrence gas absorption quantity
ActiveCN106940279ARealize quantitative evaluationEasy to operateMaterial analysisScanning electron microscopePore diameter
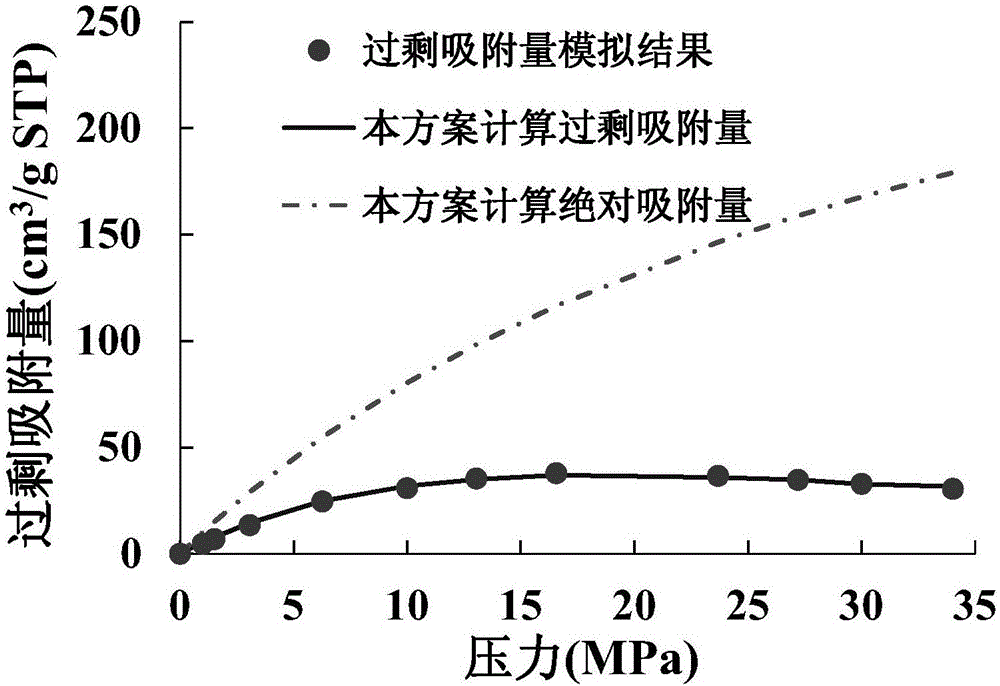
A method for evaluating shale reservoir stratum occurrence gas absorption quantity belongs to the technical field of petroleum exploration and development. The method can evaluate the shale reservoir stratum occurrence gas absorption quantity at different temperatures and pressures, so that the problem the cost for an on-site core analysis and isothermal adsorption experiment is high is overcome. The method comprises the following steps: 1) analyzing the component covered area of holes having different diameters in a shale sample per unit mass through a multiscale argon ion polishing and scanning electron microscope imagining method; 2) establishing a series of single-hole models of inner surfaces of holes which are covered with components and having different diameters through molecular simulation; 3) calculating the thickness and density of adsorbed-state methane located at the inner surfaces of mineral single-hole models in different temperature and pressures through molecular simulation; and 4) according to the component covered area of holes having different diameters and the thickness and density of adsorbed-state methane located at the inner surfaces of mineral single-hole models in different temperature and pressures in the shale sample, calculating the shale reservoir stratum occurrence gas absorption quantity at corresponding temperature and pressure.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
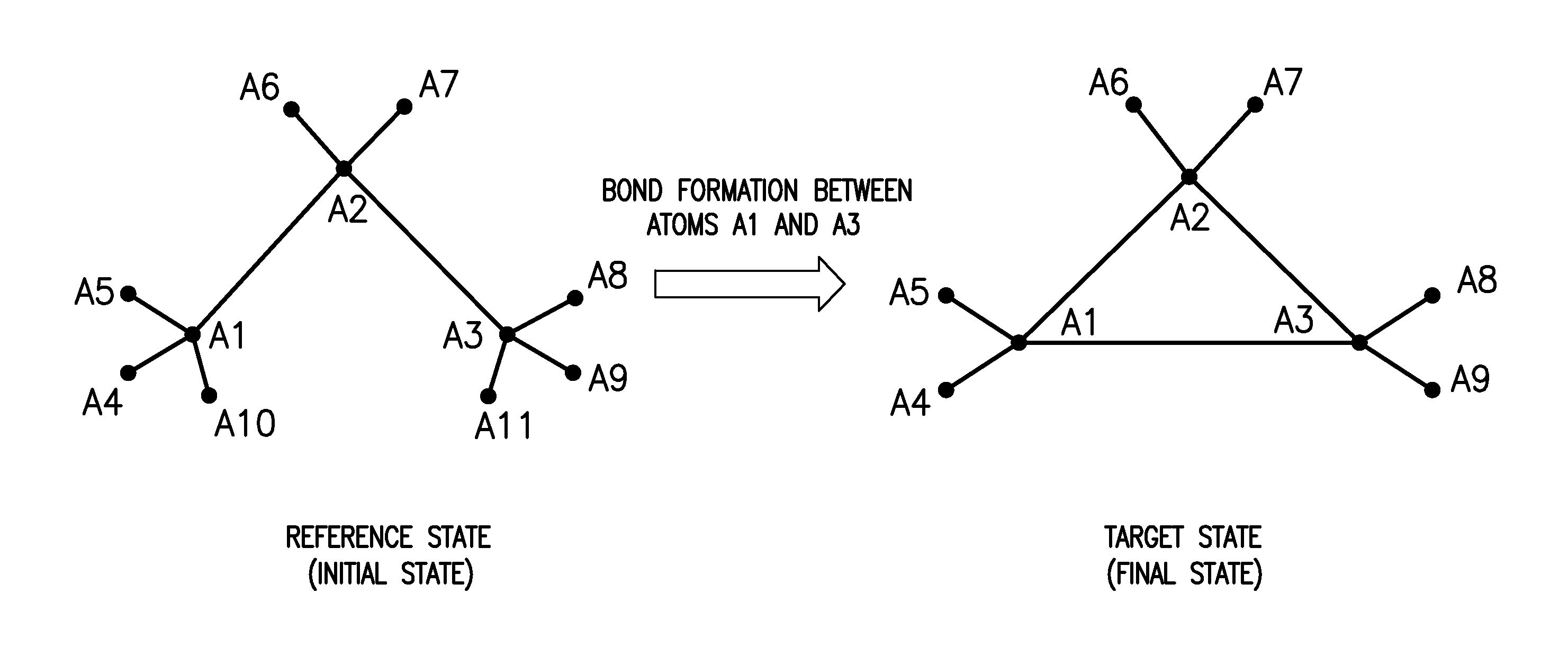
Methods and systems for calculating free energy differences using a modified bond stretch potential
InactiveUS20150178442A1Chemical property predictionAnalogue computers for chemical processesHarmonic potentialFree energies
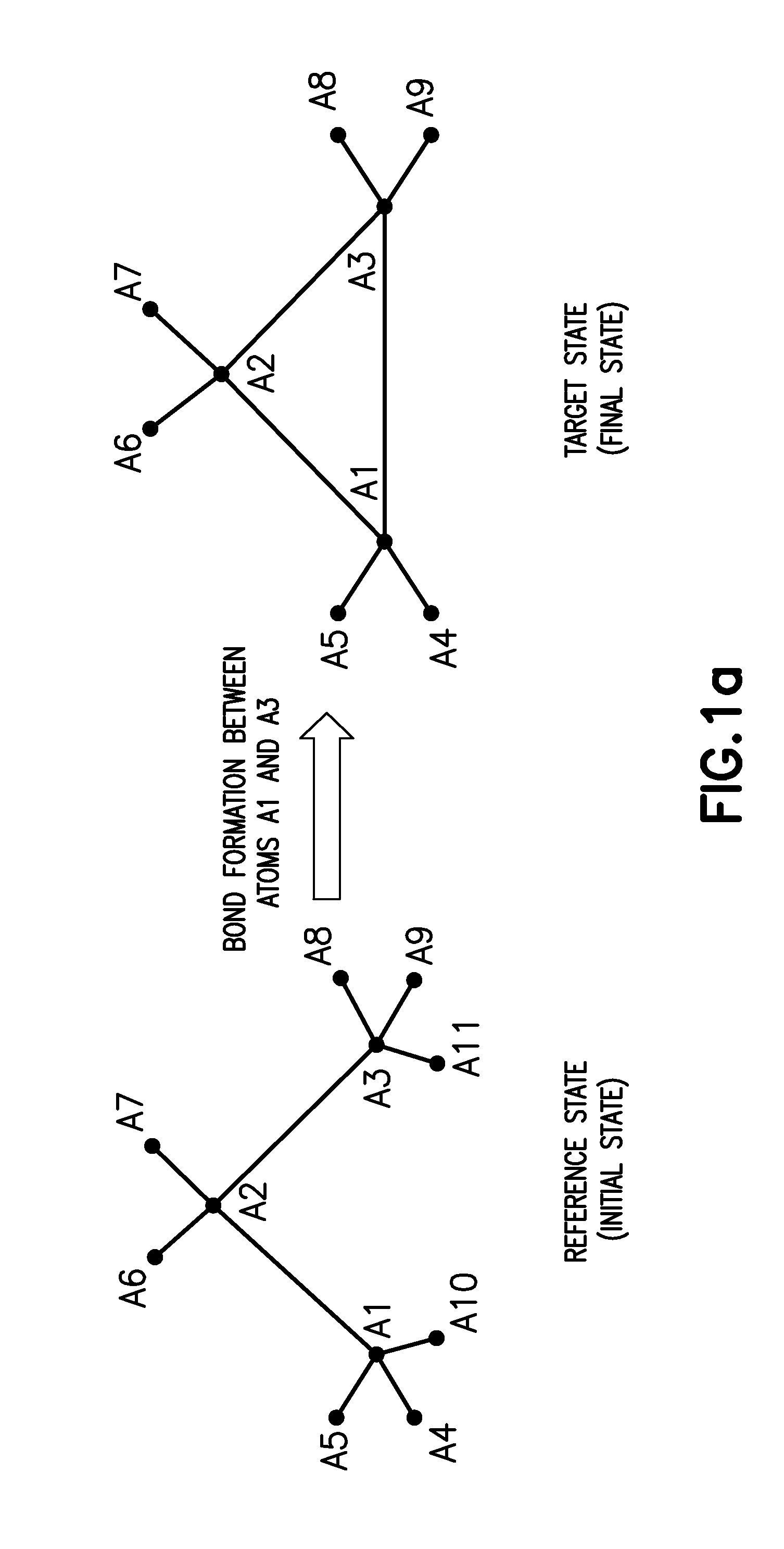
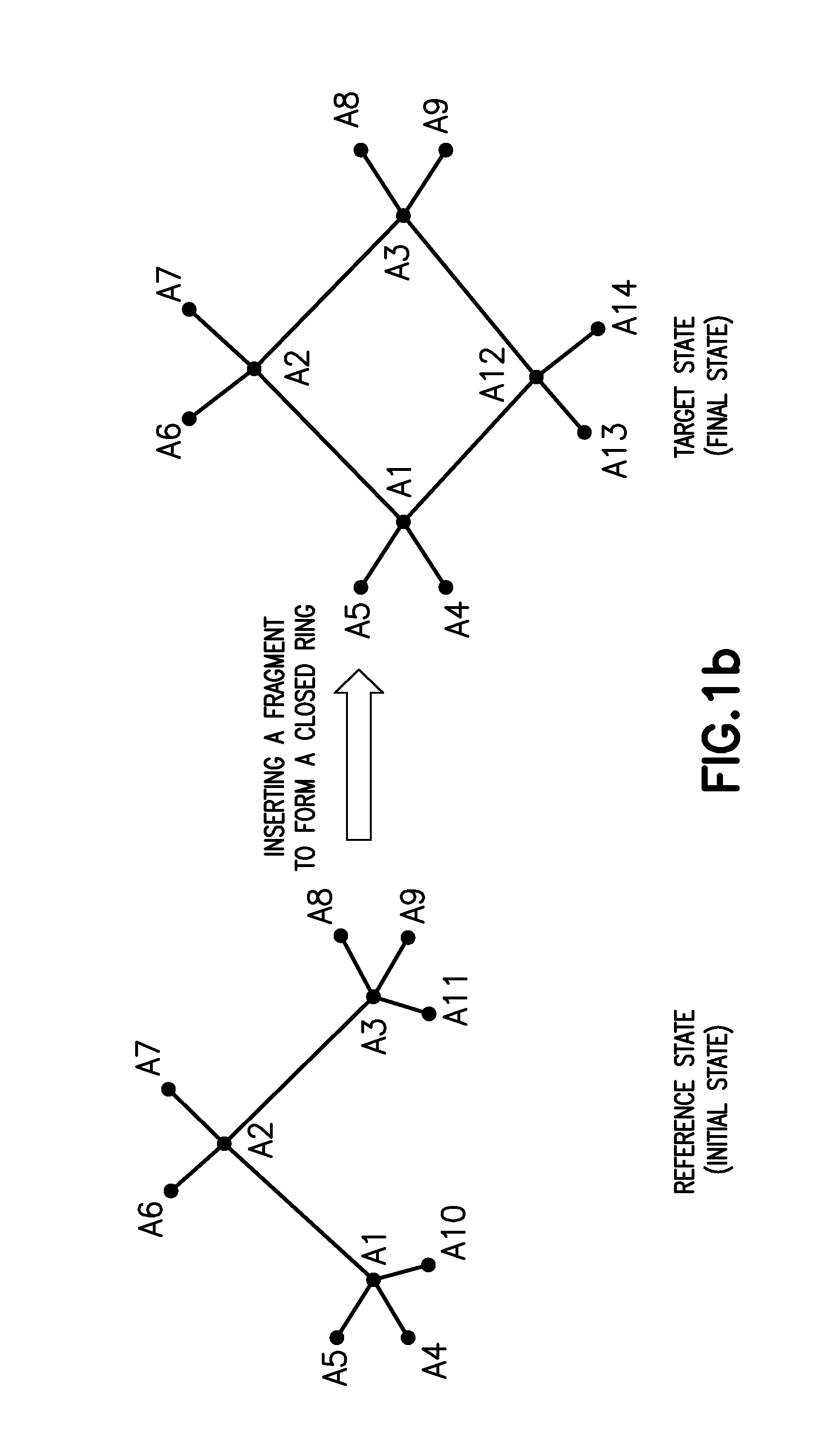
A method and system for calculating the free energy difference between a target state and a reference state. The method includes determining one or more intermediate states using a coupling parameter, performing molecular simulations to obtain ensembles of micro-states for each of the system states, and calculating the free energy difference by an analysis of the ensembles of micro-states of the system states. The method can be particularly suited for calculating physical or non-physical transformation of molecular systems such as ring-opening, ring-closing, and other transformations involving bond breaking and / or formation. A soft bond potential dependent on a bond stretching component of the coupling parameter and different from the conventional harmonic potential is used in the molecular simulations of the system states for the bond being broken or formed during the transformation.
Owner:SCHRODINGER INC
Method for measuring adsorption phase density of adsorbate gas on adsorbate
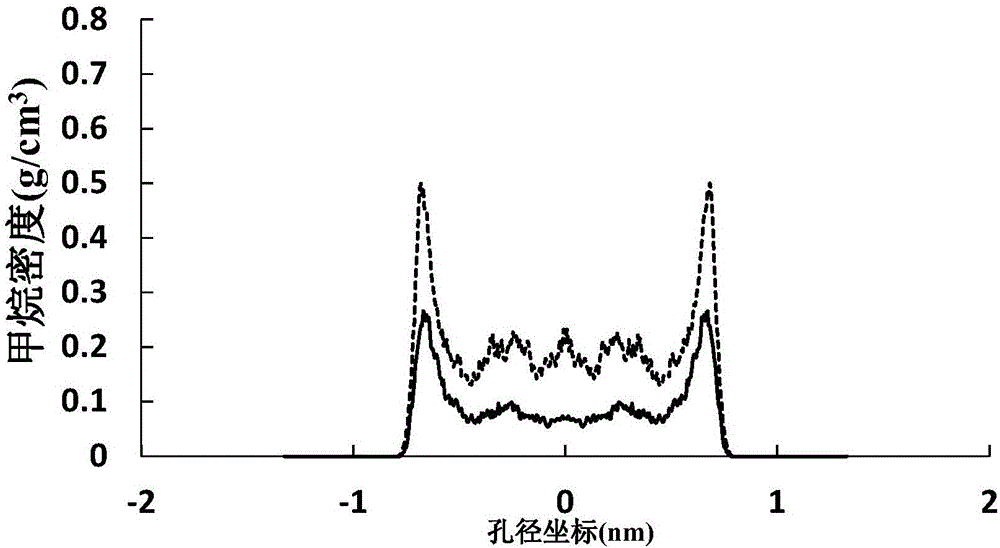
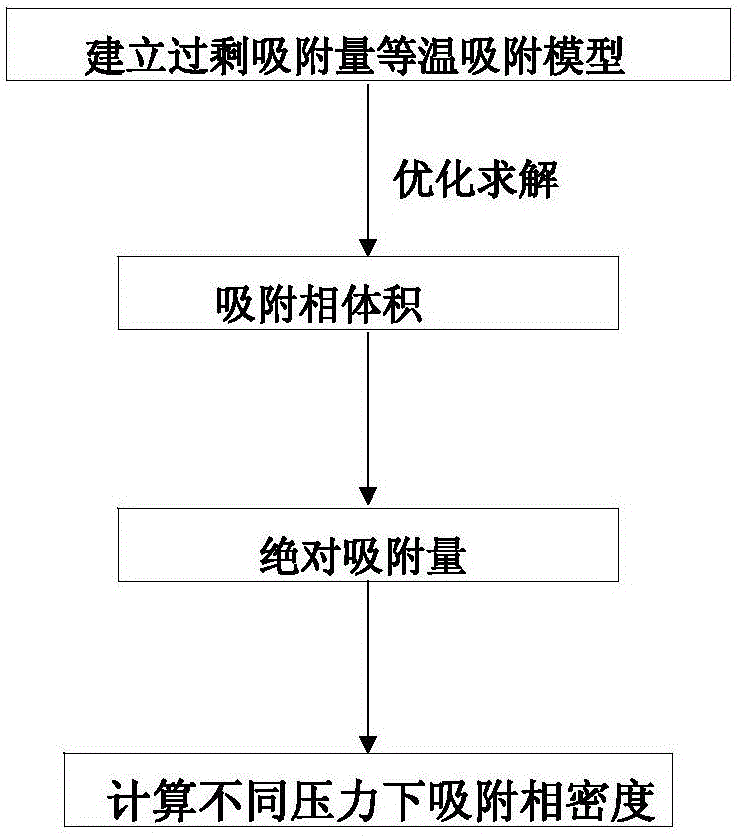
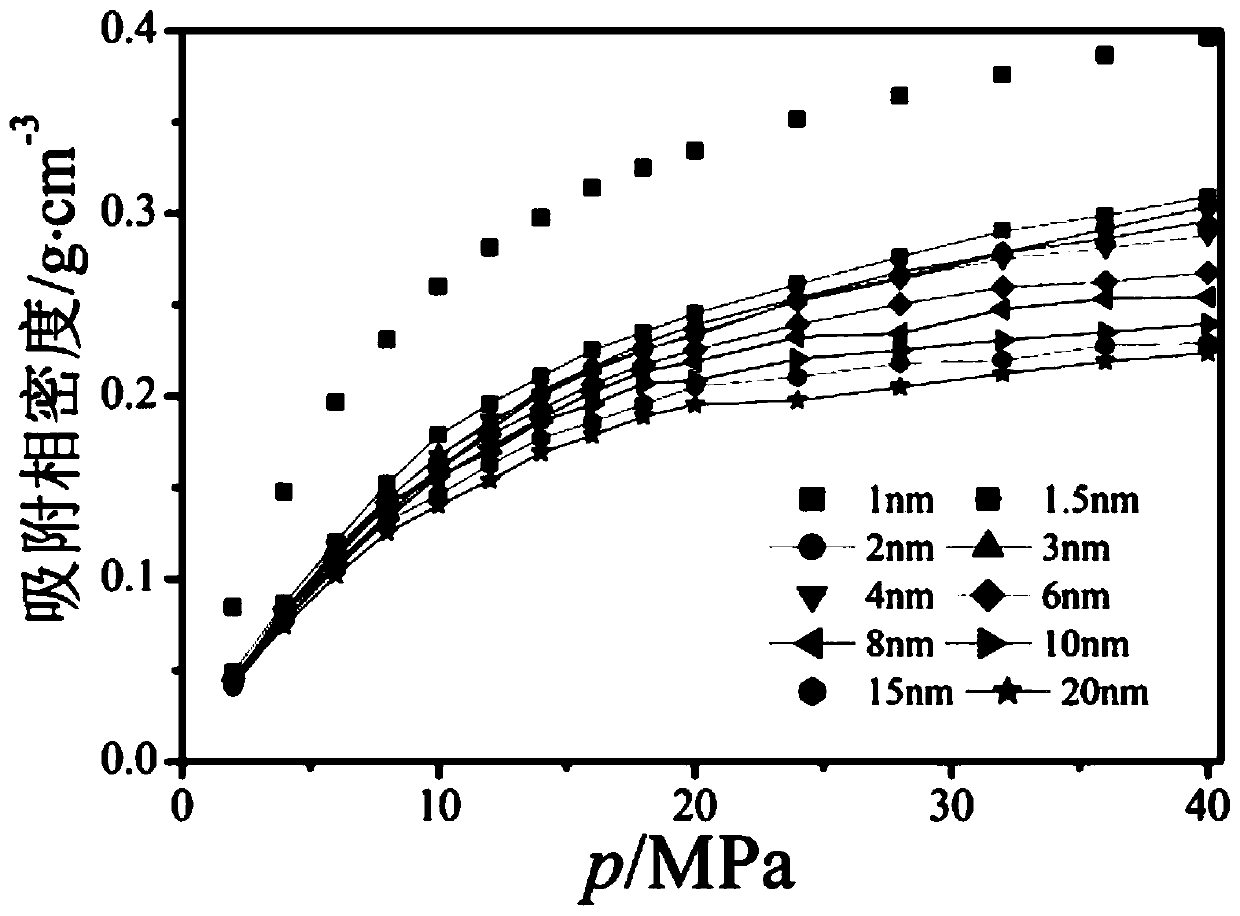
ActiveCN106290061AReasonable assumptionsReasonableSpecific gravity measurementPhysical chemistryPhase volume
The invention discloses a method for measuring the adsorption phase density of adsorbate gas on adsorbate. The method includes the steps: 1) measuring the excess adsorption quantity and the body phase density of the adsorbate gas under at least three different types of pressure; 2) acquiring adsorbed phase volume according to a corrected isothermal adsorption model and the excess adsorption quantity and the body phase density measured in the step 1); 3) acquiring the absolute adsorption quantity of the adsorbate gas on the adsorbate according to the corrected isothermal adsorption model and an isothermal adsorption model; 4) acquiring the adsorbed phase density of the adsorbate gas on the adsorbate according to a formula (1), and denoting the adsorbed phase density as rho adsorption phase with the unit g / cm<3>. The method is directly implemented based on original isothermal adsorption test data, simple, practicable and easy to popularize. According to research of adsorption behaviors by molecular simulation, assumed conditions of the method are more reasonable, and reasonableness is obviously superior to that of a traditional optimization scheme.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Coarse-grained molecular dynamic method for analyzing graphene assembly
InactiveCN106934137AEasy constructionPredicting Self-Assembly BehaviorDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic methodSingle layer graphene
The invention discloses a coarse-grained molecular dynamic method for analyzing a graphene assembly and belongs to the field of computer molecular simulation technology. The method comprises the steps that (a) a coarse-grained model of single-layer graphene is constructed; (b) a coarse-grained model of the graphene assembly is constructed according to the assembling form; (c) an interaction between coarse grains is set; and (d) coarse-grained simulation calculation is performed. Through the method, a calculation model of the graphene assembly can be easily constructed, and an actual assembly model is accurately obtained in a relaxation process. Adopted Tersoff potential function and Lennard-Jones potential function can well represent breakage and formation of chemical bonds in the assembly and accurately predict a self-assembling behavior of graphene. The adopted Tersoff potential function and Lennard-Jones potential function can accurately predict a mechanical behavior of the graphene assembly.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Machine Learning and Molecular Simulation Based Methods for Enhancing Binding and Activity Prediction
PendingUS20190272887A1Chemical property predictionEnsemble learningPrediction systemComputer science
Systems and methods for molecular simulation in accordance with embodiments of the invention are illustrated. One embodiment includes a method for predicting a relationship between a ligand and a receptor. The method includes steps for identifying a plurality of conformations of a receptor, computing docking scores for each of the plurality of conformations and a set of one or more ligands, and predicting a relationship between the set of one or more ligands and the plurality of conformations of the receptor.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
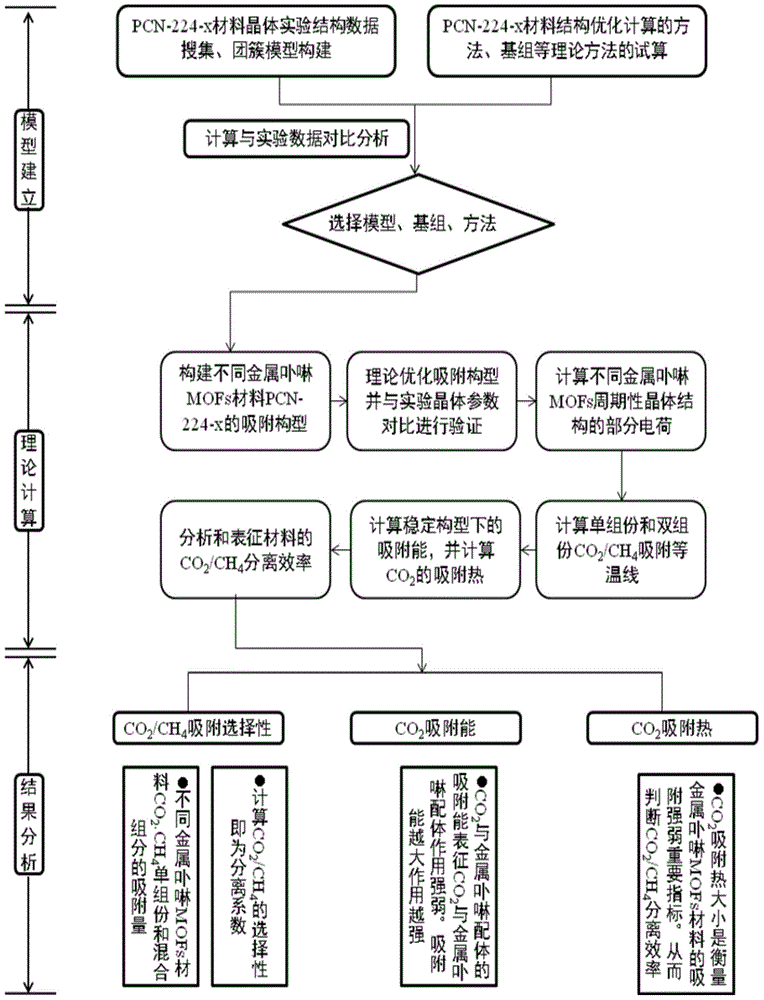
Method for quantitatively analyzing efficiency of metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2/CH4
InactiveCN104899356AAvoid complexityOvercome stabilityAdsorption purification/separationSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular sievePartial charge
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively analyzing efficiency of metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4. According to the method of the invention, the efficiency of the metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4 is quantitatively analyzed based on density functional theory calculation of auantum chemistry and Monte Carlo molecular simulation. By determining interaction energy between probe molecules and different metalloporphyrin ligands and adsorption heat, interaction between CO2 and metalloporphyrin MOFs materials is quantitatively analyzed, and finally calculation of selectivity in adsorption of CO2 / CH4 is used to characterize efficiency and features of different metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4. The method comprises steps of: construction of a cluster model; structural optimization of a stable structure and calculation of partial charges; calculation of a CO2 / CH4 separation coefficient; calculation of adsorption energy and adsorption heat; and analysis and characterization of efficiency in separating CO2 / CH4. According to the method of the invention, efficiency of metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4 can be quantitatively characterized without any actual experiment. The method of the invention can be further extended for analysis of efficiency of other porous molecular sieves of known crystal structures and MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
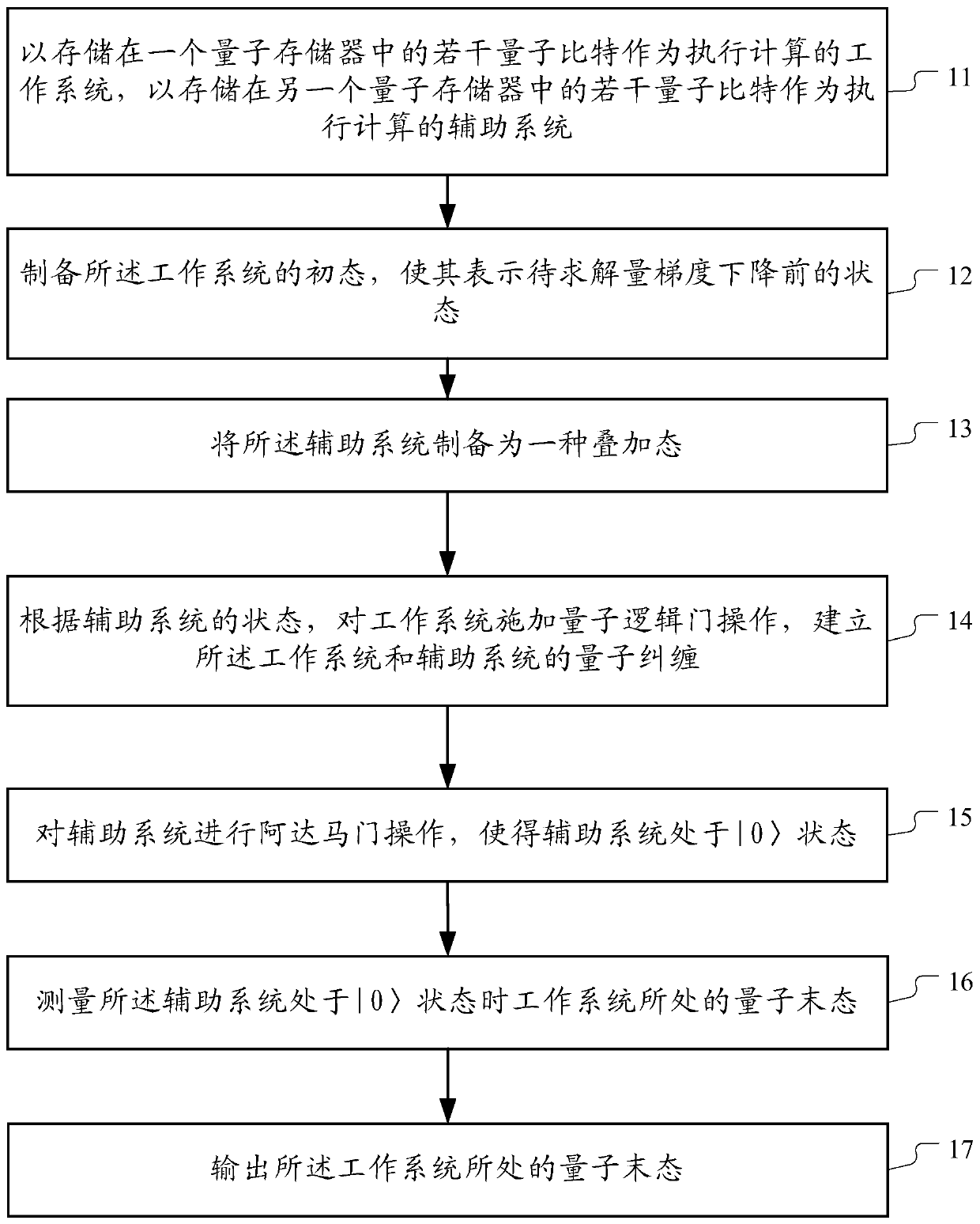
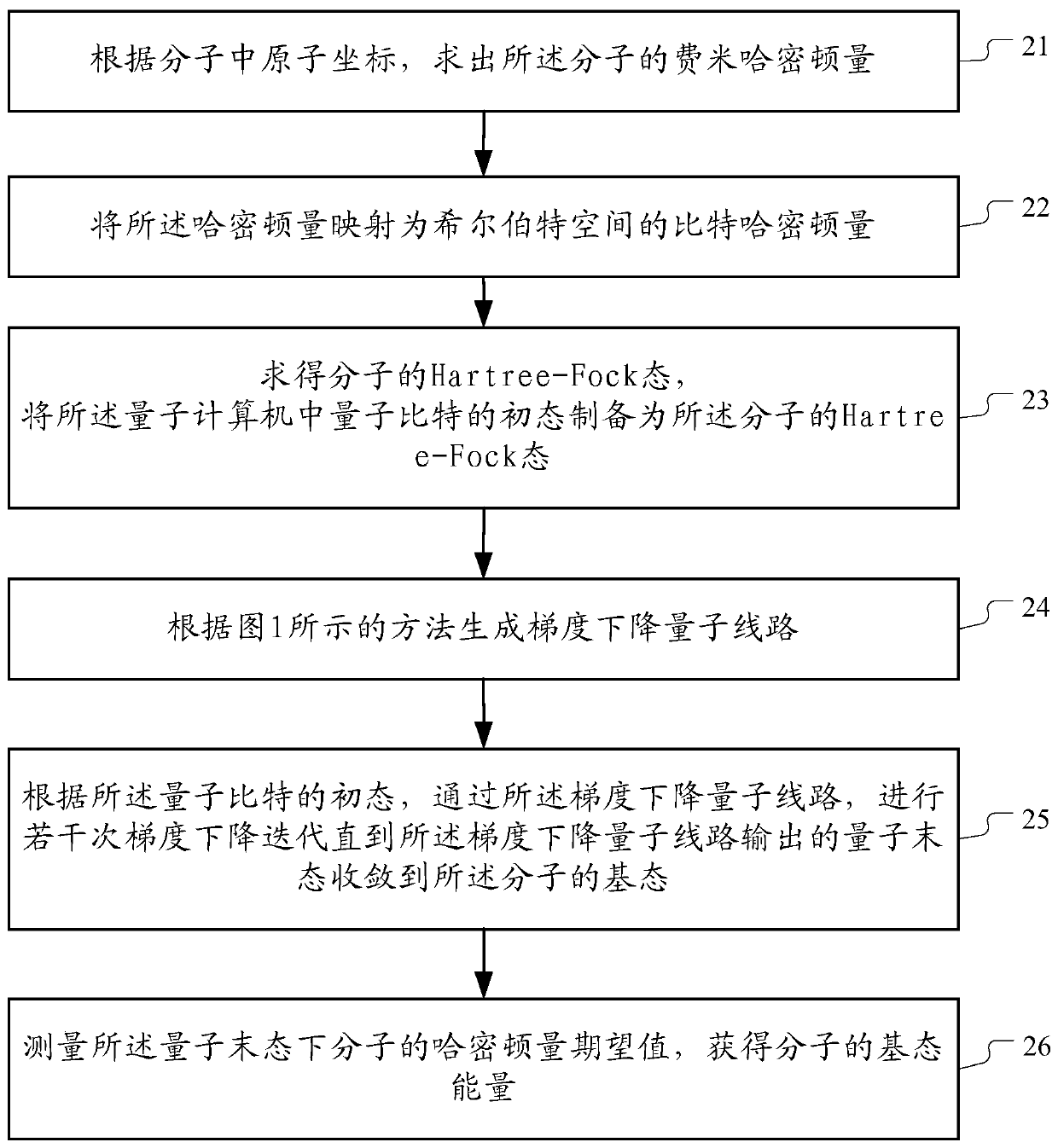
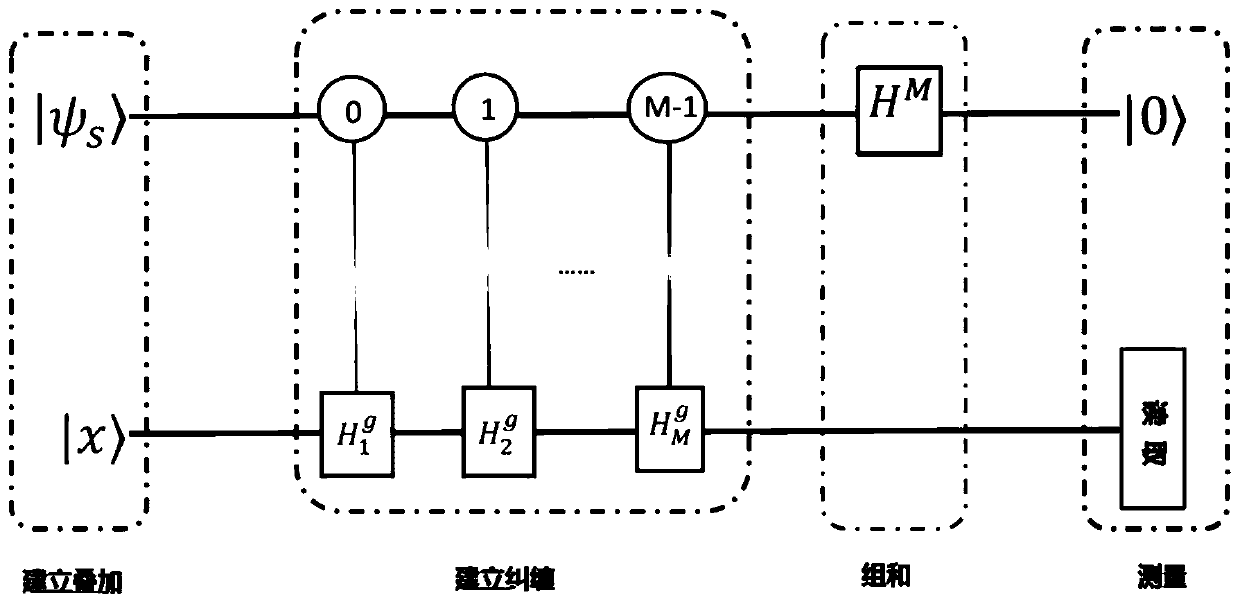
Full-quantum molecular simulation method based on quantum computer
The embodiment of the invention provides a full-quantum molecular simulation method based on a quantum computer. The method comprises the following steps: giving geometric coordinates of atoms in a molecule, calculating a molecular Hamiltonian quantity, and preprocessing the molecular Hamiltonian quantity into a bit Hamiltonian quantity of a Hilbert space; constructing a quantum circuit by utilizing a quantum gradient descent algorithm, executing a quantum circuit diagram on a quantum computer, and obtaining a quantum final state when the initial quantum state passes through the quantum circuit; and the quantum tail state approaching to the ground state of the Hamiltonian quantity, carrying out iteration continuously to obtain the ground state and ground state energy of the bit Hamiltonianquantity which can determine most properties of molecules.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
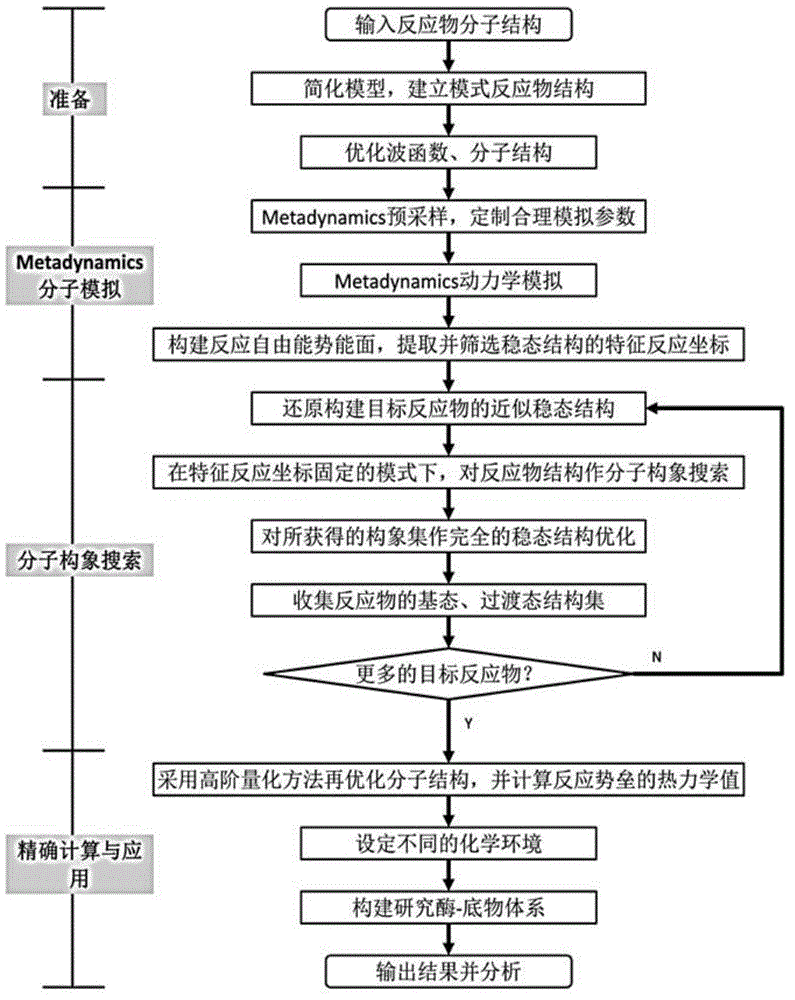
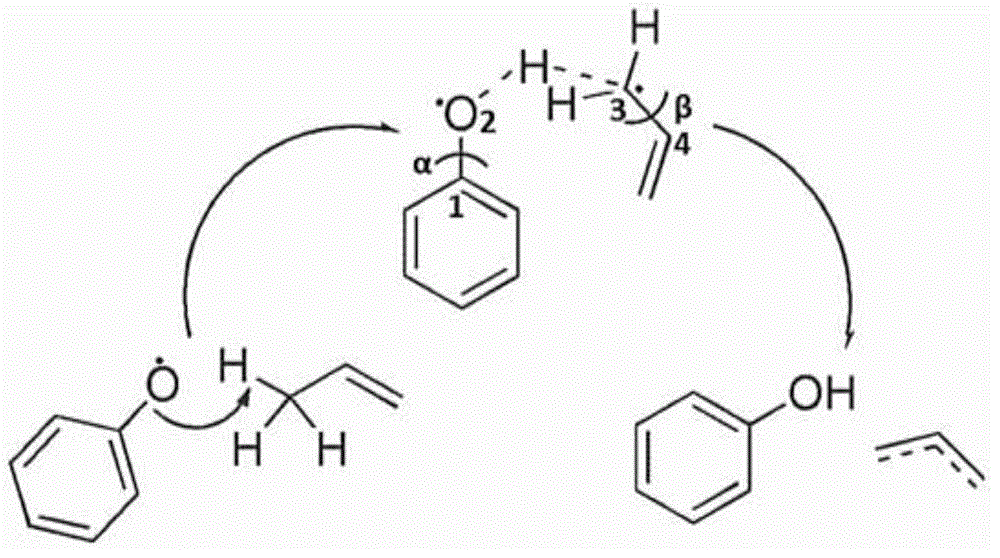
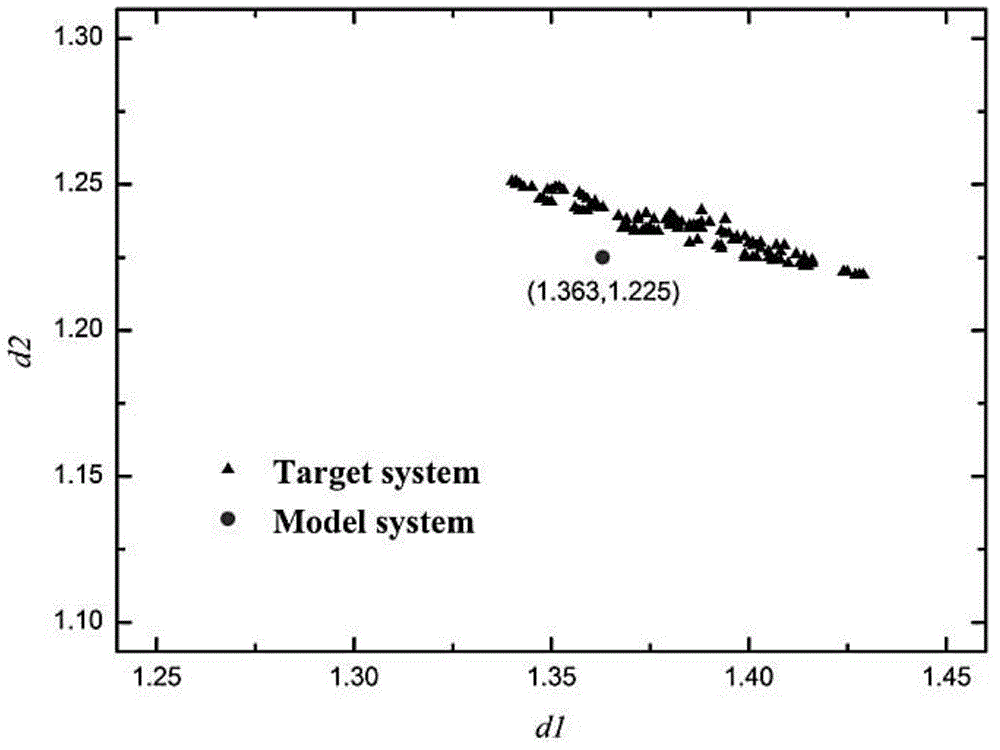
Complex system reaction access calculating system and implementing method thereof
ActiveCN104021265AIncrease productivityImprove responseSpecial data processing applicationsReaction coordinateCritical structure
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical and molecular structure information, and provides a complex system reaction access calculating system and an implementing method thereof. The calculating system comprises a molecular simulation and quantum chemistry calculating module, a molecular conformation searching module and a refined calculation and application module. A molecular structure simplified pattern reaction system is constructed, a characteristic reaction path is analyzed, and relevant key structures comprising ground states and transient states of reactions of a target reaction system are searched for. Based on a low-dimensional characteristic potential energy surface in a pattern system, a reaction network access is set up, and reaction coordinates of local minimum points and saddle points of a potential energy surface in a network are recorded; based on information of the reaction coordinates, molecule grafting restoring the pattern system (simple) to the target system (complex) is achieved. Through the molecular conformation searching technology, under the condition of characteristic coordinate restraint, a conformation set of reaction objects of the target system is searched for, and molecules in the conformation set are structurally optimized; effective ground state and transient state molecular structures of the reaction objects are collected according to the reaction characteristics of the characteristic coordinates on the reaction path.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
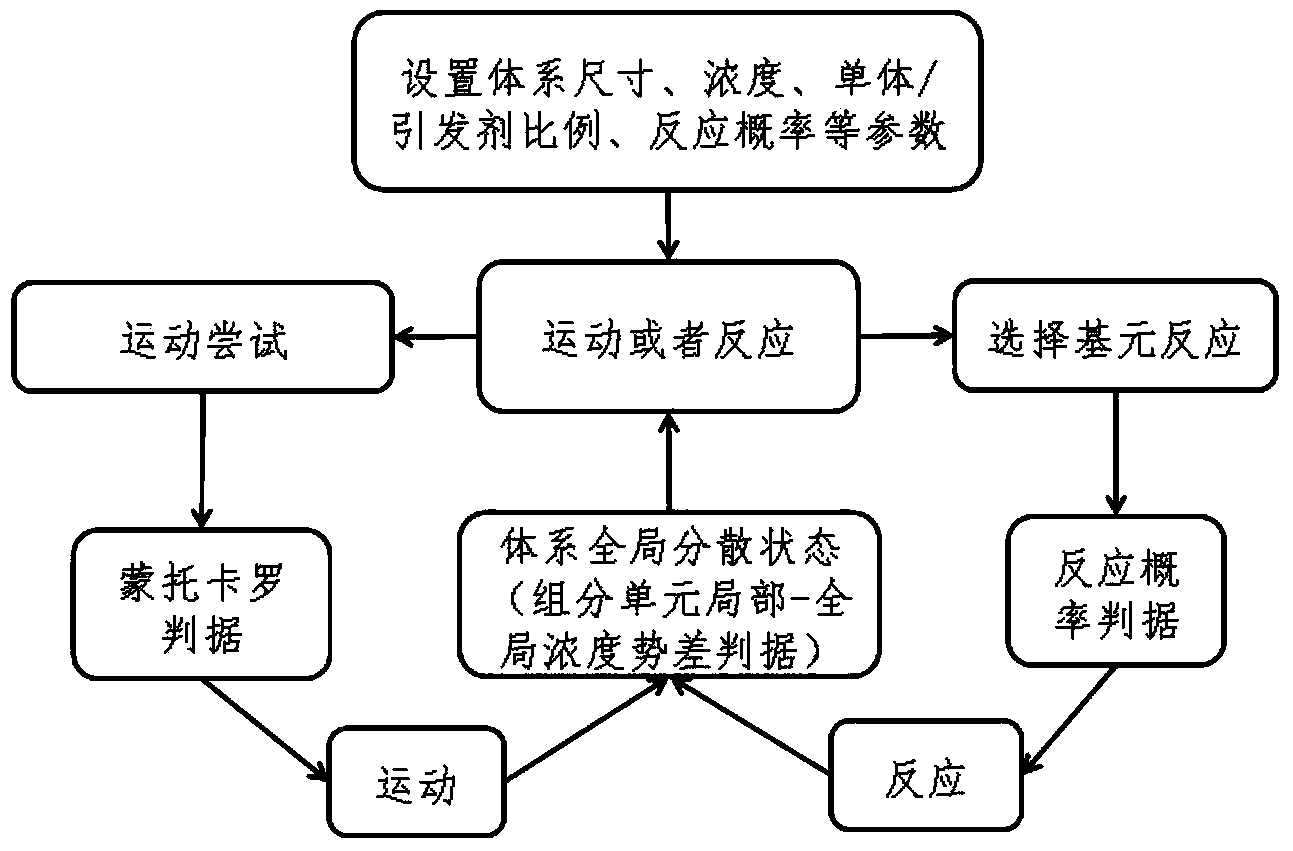
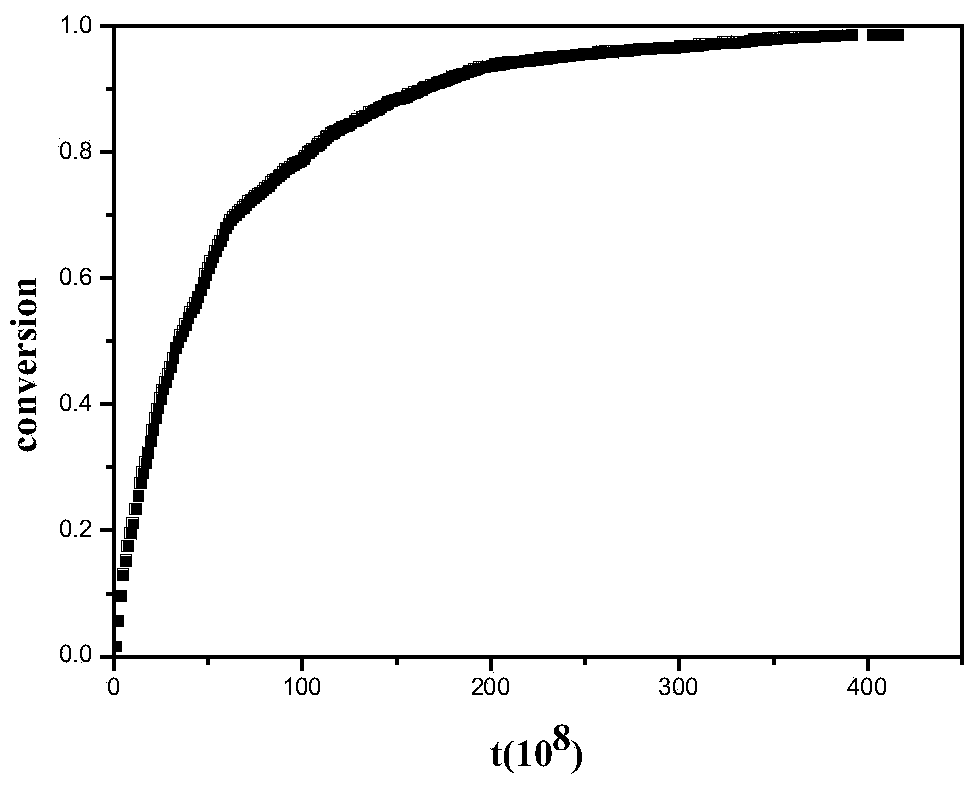
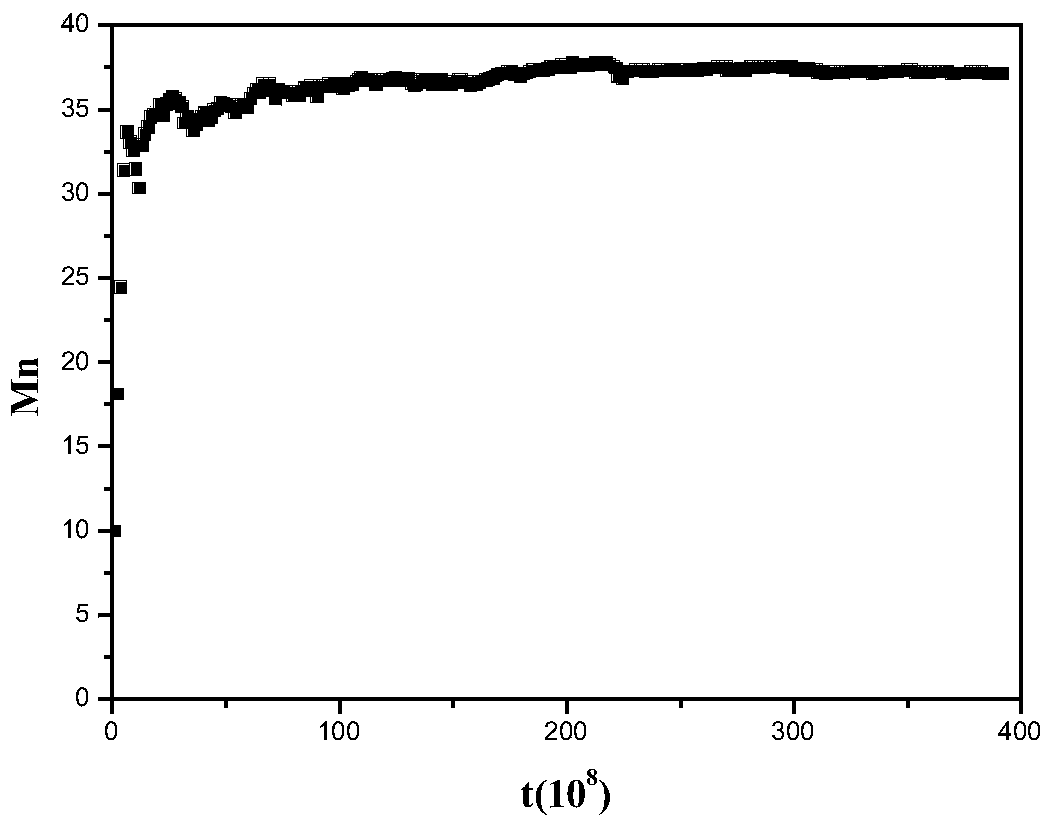
Monte carlo molecular simulation research method for kinetic process of polymerization reaction
InactiveCN104268405AWith concentration diffusion effectImproved Energy CriterionSpecial data processing applicationsStudy methodsMonomer
The invention relates to a monte carlo molecular simulation research method for the kinetic process of polymerization reaction. The method comprises the step that the polymerization reaction simulation process is divided into two parts, namely, a systemic movement part and a polymerization reaction part; when in the polymerization reaction part, the occurrence probability of triggering, chain growth, chain transfer, chain termination and other elementary reactions are controlled through different reaction probability; when in the systemic movement part, a local-global concentration potential difference which shows the difference of the local concentration and the global concentration of components is introduced to determine the concentration distribution state of each unit component in the system, in order to realize the balanced distributing state of the component unit in the polymerization reaction process; the monte carlo energy criterion for controlling unit particle movement involves a chemical key part and a non-key part. The method is simple and efficient; the problem of non-uniform distribution of the component unit in the simulation system caused by the consumption of an initiator and a monomer under the polymerization reaction can be avoided, and the kinetic process of the experiment system can be really reflected by being compared with the traditional molecular simulation method.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Method for establishing molecular simulation force filed of protein system
InactiveCN102779239AComputational workload is reasonableSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular simulationSingle point
The invention relates to a method for establishing a molecular simulation force field of a protein system. For establishing the force field, a tetrapeptide structure of amino acid is taken as a model, five representative structures are selected, and the configuration of the model molecules is as follows: firstly optimizing a gaseous 6-31G**base group, then conducting single-point correcting on gaseous 6-31G**, 6-311++G** and a cc-pVTZ base group, and conducting single-point energy calculation by using the configuration optimized by M052x / 6-31G** through an MP2 / cc-pVTZ method. A water solvent model adopted by liquid-state calculation is IEFPCM, and when a hole is constructed, a UAKS united-atom topology model is selected. The force field is obtained by the method, the accuracy is improved greatly, the calculated RMS (Root Mean Square) value is obviously smaller than that of other force fields, and approaches to the M052x result of a QM method, the calculated RMS-C value indicates that the new force field method overcomes the defect of conformation deviation in the original force field.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS
Molecular simulation method and apparatus
InactiveUS20070061119A1Increase computing speedLeveling precisionOrganic chemistry methodsAnalogue computers for chemical processesMolecular simulationMesh grid
In molecular simulation including the step of calculating non-bonding interactions in a system having particles with electric charges, using a multigrid method, upon determining the electric charges at grid points in a coarser grid of a higher level that is one step higher than the level to be observed, when a pair of grid points in the observed level, or a pair of particles in the observed level, both coincide with the grid points of the grid of the higher level, the charges at the grid points of the higher level are determined so that the energy of the pair in the higher level becomes equal to the correct energy value in the observed level.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for constructing shale adsorption gas adsorption phase density model and calculating absolute adsorption capacity
The invention discloses a method for constructing a shale adsorption gas adsorption phase density model and calculating absolute adsorption capacity. The method comprises the following steps: regressing gas phase density into a polynomial function related to pressure; constructing a slit pore structure model of the adsorbent, and obtaining excess adsorption capacity, adsorption phase volume and absolute adsorption capacity of adsorbate in shale at different temperatures, different pressures and different pore diameters through a molecular simulation means; constructing an excess adsorption capacity model; obtaining the contribution rate of the adsorbing capacity of the adsorbate in the graphite pores to the adsorbing capacity of the shale sample under different pressure points; obtaining an adsorption phase density model of the adsorbate in the graphite slit holes and an adsorption phase density model of the adsorbate in the illite holes under different temperatures, different pressures and different hole diameters; and constructing a calculation model of the adsorbate adsorption phase density in the shale. The model is based on contribution rate, pressure, temperature and aperturedata, and the adsorption phase density calculated by the model is high in accuracy, so that the calculation accuracy of the absolute adsorption capacity is improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
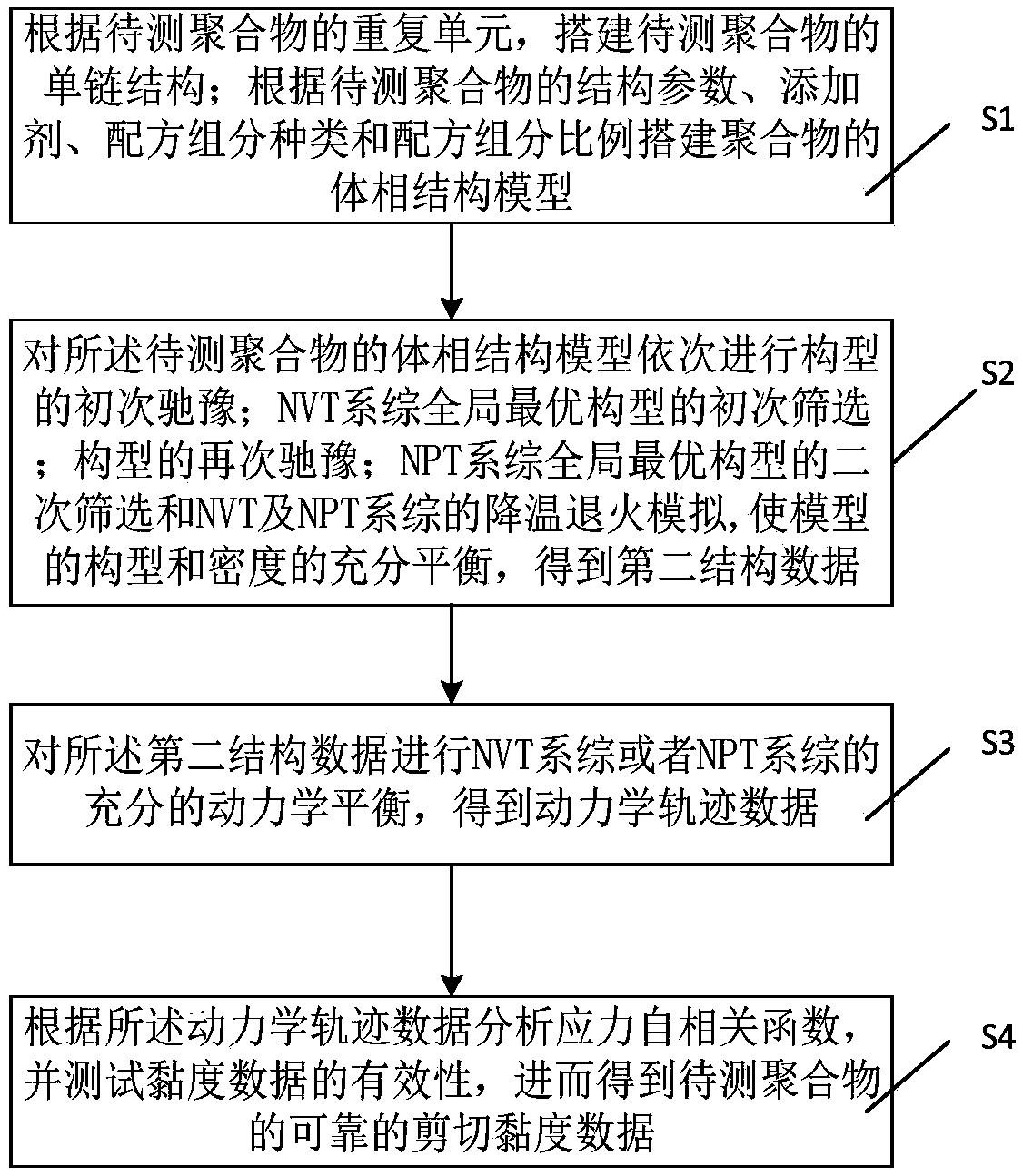
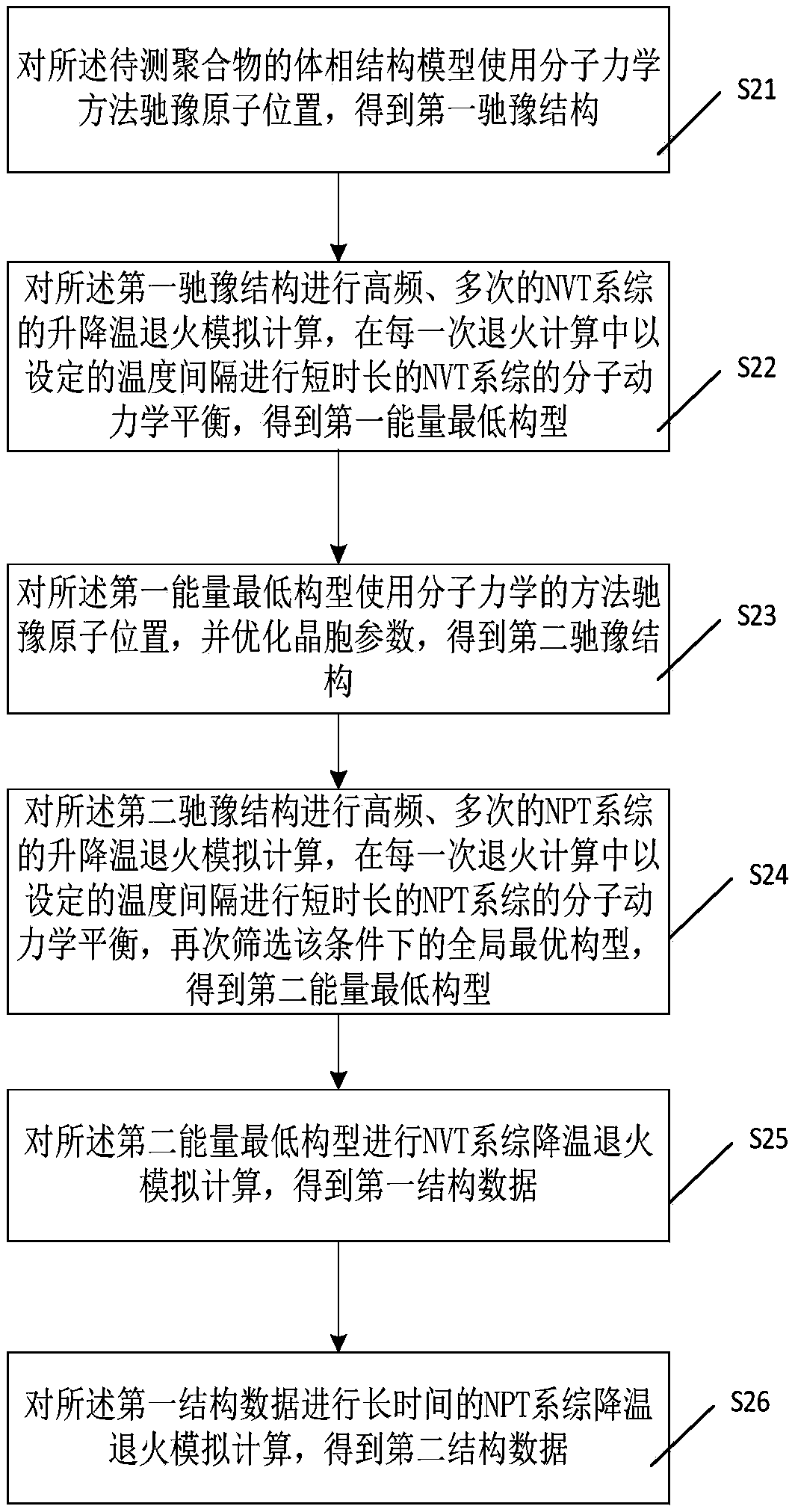
Method and system for evaluating the flowability of polymer materials by molecular simulation
ActiveCN108959844AGuaranteed reasonablenessGuaranteed repeatabilitySpecial data processing applicationsShear viscosityGlobal optimum
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the flowability of a polymer material by adopting a molecular simulation method. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a single chain structure of the polymer to be tested according to a repeating unit of the polymer to be tested; establishing a bulk structure model of the polymer according to the structure parameters and ingredientsof the polymer; carrying out the first relaxation of the bulk structure model, the first selection of the global optimum configuration of the NVT ensemble, the second relaxation of the configuration,the second selection of the global optimum configuration of the NPT ensemble, and the cooling annealing simulation of the NVT and NPT ensembles in order to make the configuration and density of the model fully balanced, and obtaining the second structure data; carrying out sufficient dynamic equilibrium on the second structural data to obtain the dynamic trajectory data; testing the validity of the viscosity data was tested by the stress autocorrelation function analysis of the kinetic trajectory data, and obtaining the reliable shear viscosity data of the polymer . The method of the invention can quickly, efficiently and accurately calculate the shear viscosity data of the polymer material.
Owner:苏州创腾软件有限公司 +1
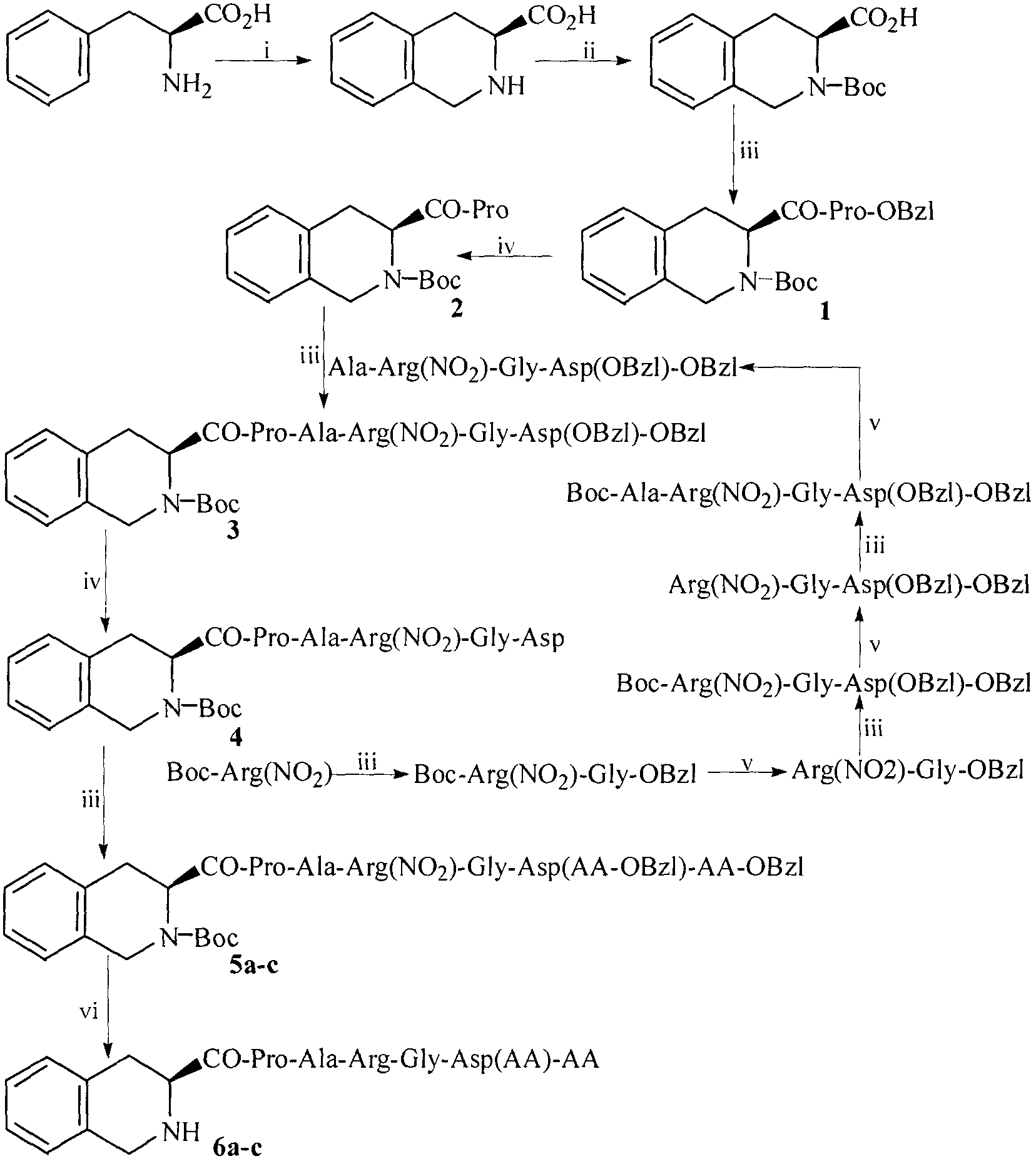
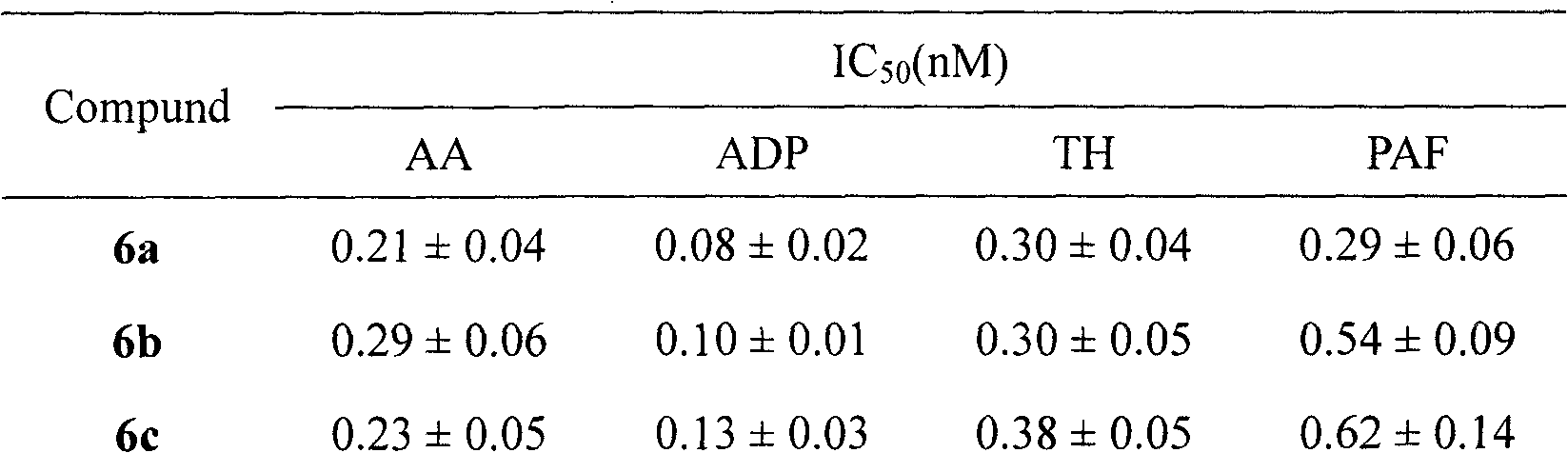
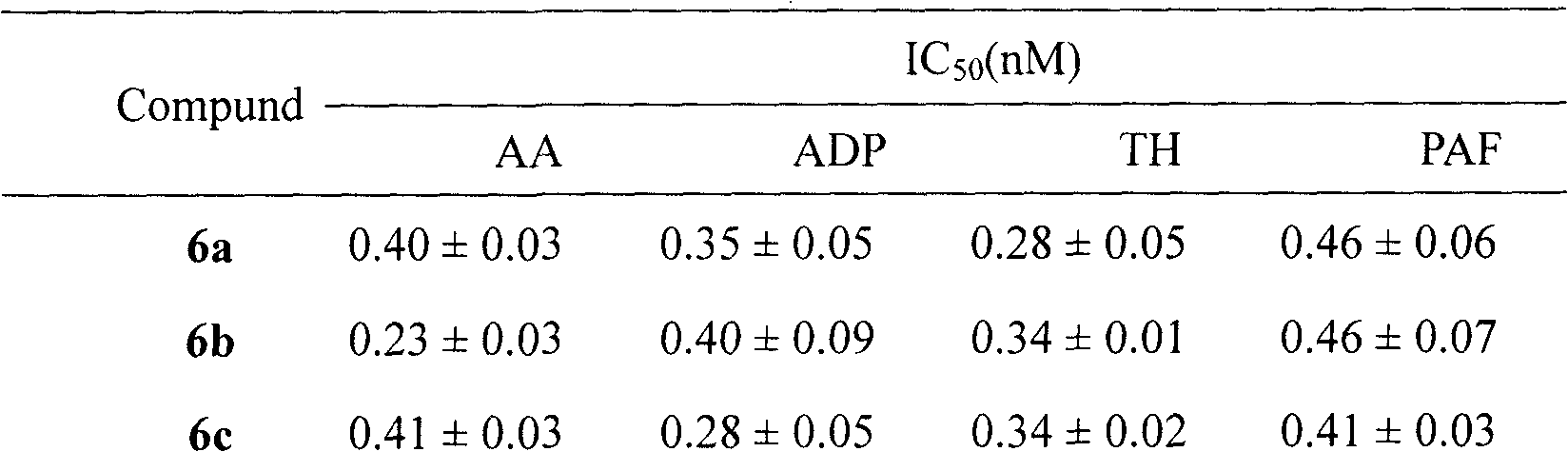
Tetrahydroisoquinolinyl-3-carboxylic acid modified PARGD heptapeptides, and synthesis, antithrombotic activity and application thereof
InactiveCN103450342APeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsAntithrombotic AgentP-selectin
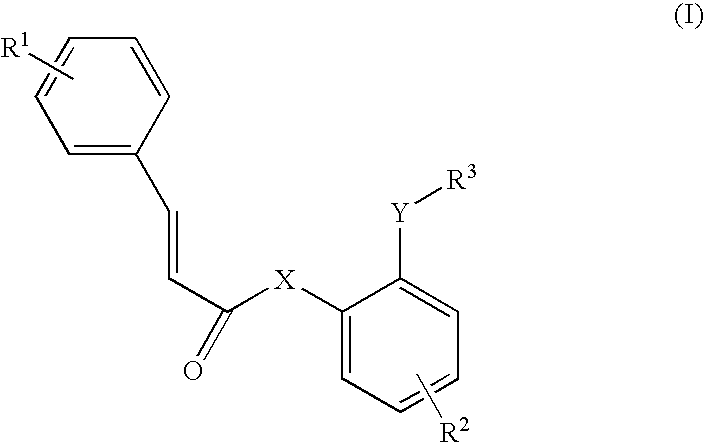
The invention provides 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides disclosed as general formula I, a molecular simulation method of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides, a preparation method of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides, inhibiting action of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides on expression of glycoprotein IIb / IIIa and P-lectin, anti-thrombocyte aggregation action of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides, and antithrombotic action of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides on a rat thrombosis model. Therefore, the invention provides clinical application prospects of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides disclosed as general formula I as an antithrombotic agent. In the general formula I, AA represents Ser or Val or Phe residue.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Pyrethroid hapten design based on computer molecular simulation technique and application
ActiveCN102901811AGood forecastShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsMaterial analysisSynthetic ImmunogensImmunologic function
The invention relates to pyrethroid hapten design based on a computer molecular simulation technique and an application, which belongs to the technical field of pyrethroid pesticide detection. Six kinds of available hapten are designed by using the pyrethroid hapten design. Gaussian software is utilized to calculate charge distribution of the hapten and a target object, and Discovery Studio 2.5 software is utilized to establish spatial conformation of the hapten and the target object. By comparison, the hapten with the highest degree of structure similarity is selected as immune hapten (hapten 1), the hapten is predicted to generate a good immune effect, and the hapten with higher structure difference is selected as coated hapten (hapten 5). The computer molecular simulation software is successfully used by the method to design the hapten of a pyrethroid pesticide; a mass selection antibody which is used for identifying the pyrethroid pesticide is prepared through synthesis of immunogen and immunity, serum screening, fusion, screening and acrylics; the method is proven to have strong predictive ability, and time and funds are saved; and a new method is provided for later analyzing and researching immunology.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
3D-Structure model of SARS coronavirus 3CL protease and anti-SARS drugs
The present invention discloses 3D-structure of SARS-CoV Viral 3CL Protease obtained through molecular simulation. The 3D-structure is used as a drug target for screening the existing medical database CMC (Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry, MDL Information System, Inc.), and a group of compounds which have the activity of inhibiting SARS-CoV virus 3CL Protease are found. Cinanserin was tested at molecular and viral levels, and it was found to be able to inhibit the SARS-CoV viral 3CL protease and SARS-CoV viruses. Cinanserin analogs were synthesized and tested at molecular and viral levels, they were found to be able to inhibit the SARS-CoV virus 3CL Protease and SARS-CoV viruses, and may be used for treating and / or preventing SARS-CoV virus infection.
Owner:SHANGHAI LEAD DISCOVERY PHARMA +1
Molecular design of porcine parvovirus-like particle B cell epitope insertion site
InactiveCN102417912ANon-pathogenicImprove replication efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesVaccinationDelta-v
The invention relates to a molecular design of porcine parvovirus-like particle B cell epitope insertion site and belongs to the field of genetic engineering vaccine. Structure modeling of porcine parvovirus (PPV) capsid protein VP2 is performed by using bioinformatics software and the location of four extrusive Loop structures is determined by three-dimensional structure analysis. Firstly, on the basis of molecular simulation and literature support, we infer that loop 2,4 region can act as insertion sites of exogenous epitope gene. As is shown through experiments, after respective deletion of corresponding genes in PPV VP2 Loop2 (212aa-245aa), Loop (413aa-424aa) and then expression by adenovirus expression system, all recombinant virus with deletion mutations of Loop 2,4 can assemble regular virus-like particles [PPV: delta V LPs]. The invention also relates to an application of recombinant PPV delta V P2 virus-like particles of exogenous gene expressed by the recombinant virus in vaccination and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
A method for simulating the effect of an applied electric field on the formation and decomposition of methane hydrate
ActiveCN109271679AReduce usageReduce pollutionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionCrystal cell
A method for simulating the effect of an applied electric field on the formation and decomposition of methane hydrate. A methane hydrate crystal cell is established by modeling with computer simulation software, the methane hydrate crystal cell is melted at a high temperature to obtain a gas-liquid mixed phase, and then the methane hydrate crystal cell and the gas-liquid mixed phase are superposedto obtain an initial configuration; By setting simulation parameters, the stable configuration was obtained through energy minimization and pre-equilibrium simulation, and the molecular simulation was carried out by applying electric fields with different intensities and frequencies. Molecular trajectory coordinates were obtained by molecular dynamics calculation, and the molecular trajectory coordinates were analyzed by image analysis and computation. From the molecular point of view, the real-time observation of the effects of applied electric fields with different intensities and frequencies on the formation and decomposition of methane hydrate provides theoretical guidance for the practical application of electric fields in various fields of methane hydrate. The new technology can reduce the use of chemical accelerators and inhibitors of hydrate which will pollute the environment by controlling the hydrate formation and decomposition with an applied electric field.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Novel non-standard-dependence quantitative analysis method based on study on homologous/similar compound structure-mass-spectrum response relationship
InactiveCN103018317AMass Spec Response High and LowQuantitatively accurateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMethodological researchCompound structure
The invention belongs to the field of analysis, relates to a quantitative analysis method for homologous / similar compounds, and particularly relates to a quantitative compound analysis method for a complicated matrix sample which does not contain a standard substance. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting a series of homologous / similar compounds, and carrying out mass-spectrum quantitative methodological study and textual research on the homologous / similar compounds; (2) carrying out zero-intercept linear fitting according to established standard curves of all the compounds; (3) carrying out structural optimization on the compounds by using molecular simulation software, and calculating related molecular descriptors; (4) carrying out establishment and verification on the relationship between the structures and mass-spectrum responses of the compounds by using the molecular simulation software; (5) carrying out qualitative analysis on the complicated matrix sample by employing related mass spectrometry technologies; (6) calculating the slope coefficients of linear fit standard curves of the verified series compounds according to a structure-mass-spectrum response relationship equation established previously; and (7) obtaining the concentrations of the compounds in the complicated matrix sample by using the fit standard curves of the series compounds. Thus, the non-standard-dependence quantitative analysis is realized.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
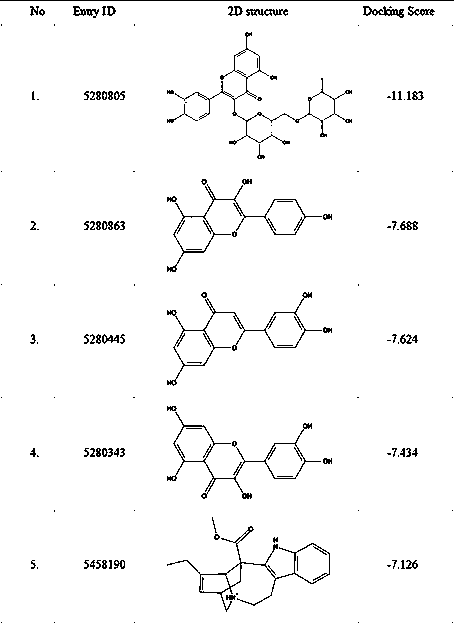
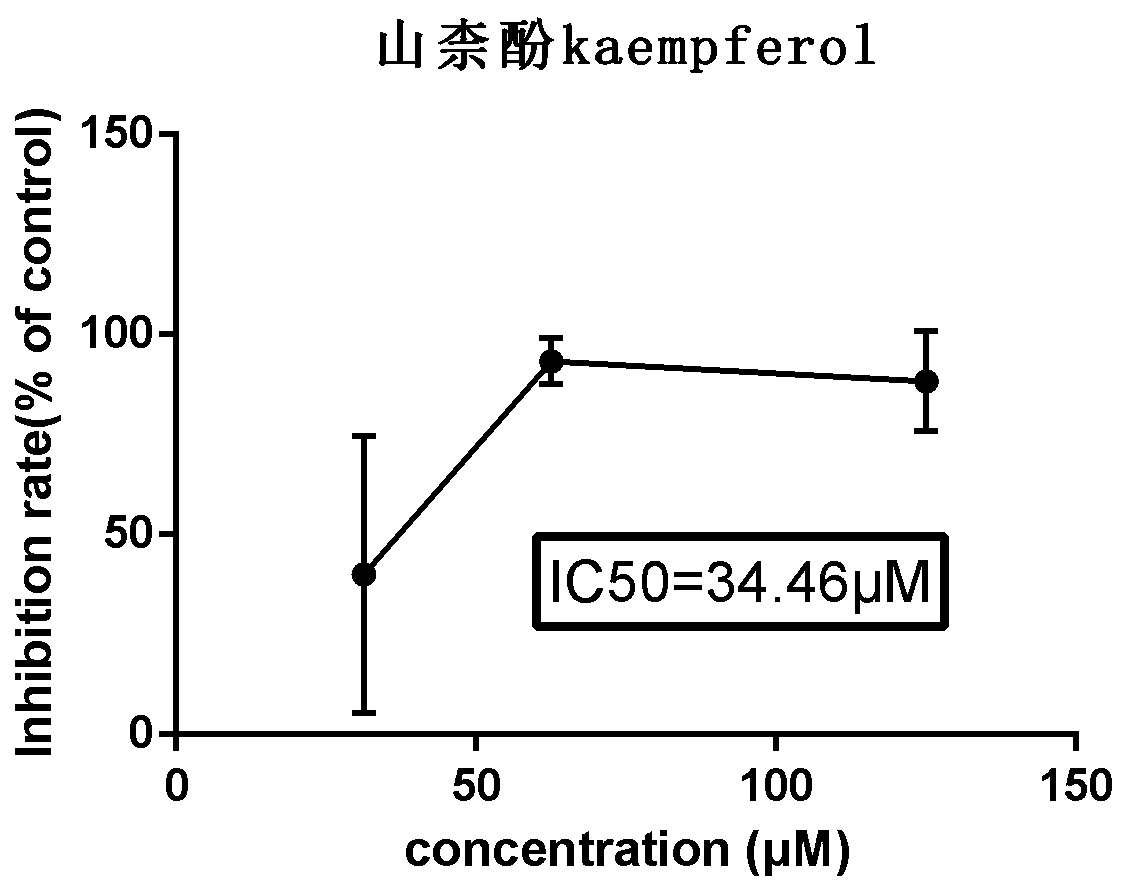
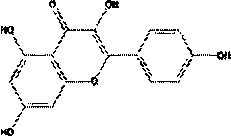
Discovery of novel application of kaempferol in inhibition of COVID-19 viruses based on molecular simulation
PendingCN111402968AGood inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectMolecular designMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein targetChinese herbology
The invention relates to discovery of novel application of kaempferol in inhibition of COVID-19 viruses based on molecular simulation. According to the invention, 3CL main protease of COVID-19 virusesis used as a target protein, the compound kaempferol is virtually screened out from a database containing 57278 traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) small molecules; results of anti-COVID-19 coronavirus experiments of kaempferol at a cellular level prove that kaempferol has a remarkable inhibition effect on cytopathy caused by infection of Vero E6 cells with the novel coronaviruses in a concentration range of 62.50 to 125.00 [mu]g / ml; and the discovery provides evidences for scientificity and potential curative effect of traditional Chinese medicines against the novel coronaviruses from the perspective of treatment target analysis.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
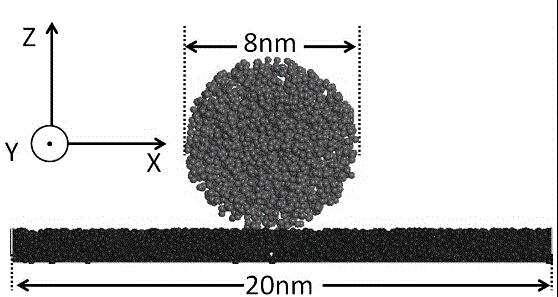
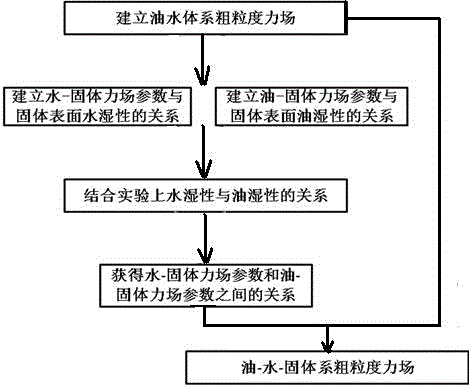
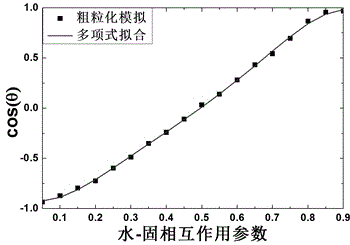
Oil-water-solid three-phase system coarse graining force field development method
InactiveCN104573223ADevelop method extensionsHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsBasic researchOil water
The invention provides an oil-water-solid three-phase system coarse graining force field development method, and belongs to the technical field of molecular simulation. The method can be applied to basic research related to a multi-phase system and includes the steps: 1) building an oil-water system coarse graining force field; 2) building a coarse graining solid surface through Materials Studios software, and adjusting interaction parameters of water and solid or oil and solid to obtain the relationship among the water-solid interaction parameters and the water wetness of the solid surface and the relationship among the oil-solid interaction parameters and the oil wetness of the solid surface; 3) associating the water-solid interaction parameters with the oil-solid interaction parameters based on theoretical interrelation of the water wetness and the oil wetness. The coarse graining force field is built through the relationship between the water wetness and the oil wetness by the aid of computer simulation technology, precision of the coarse graining force field is improved, development of the coarse graining force field is promoted, and the method has an important guiding significance for researching the multi-phase system.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Tetrahydroisoquinolinyl-3-carboxylic acid modified LARGD heptapeptides, and synthesis, antithrombotic activity and application thereof
InactiveCN103450344APeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsAntithrombotic AgentP-selectin
The invention provides 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides disclosed as general formula I, a molecular simulation method of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides, a preparation method of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides, inhibiting action of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides on expression of glycoprotein IIb / IIIa and P-lectin, anti-thrombocyte aggregation action of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides, and antithrombotic action of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides on a rat thrombosis model. Therefore, the invention provides clinical application prospects of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides disclosed as general formula I as an antithrombotic agent. In the general formula I, AA represents Ser or Val or Phe residue.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Antiviral drug virtual screening method using tobacco mosaic virus RNA helicase as target
InactiveCN104504301ASpeed up screeningSpecial data processing applicationsIn silico combinatorial chemistryTobacco mosaic virusHelicase
The invention discloses an antiviral drug virtual screening method using tobacco mosaic virus RNA helicase as a target. The method is that the molecular modeling software is utilized for determining a virtual screening three-dimensional structure of virtual screened active conformation under the condition that helicase binds with ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). The method can be used for quickly screening a compound with activity for preventing and controlling tobacco mosaic virus.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Method for analyzing surface hydrophobicity of fluorinated polyurethane
InactiveCN106096258AEliminate distractionsReliable resultsChemical property predictionComputational theoretical chemistryExperimental researchChemical physics
The invention discloses a method for analyzing surface hydrophobicity of fluorinated polyurethane. Materials Studio software is utilized to establish a surface structure model containing fluorinated polyurethane, water clusters are placed above a float point unit (FPU) surface model, and FPU surface hydrophobicity is analyzed through a molecular dynamics calculation method. Since the molecular simulation calculation process is performed in an ideal environment, interference of all external factors is excluded. The method for analyzing surface hydrophobicity of fluorinated polyurethane is more effective, results are more reliable, and the theoretical basis and guidance are provided for experimental research.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Preparation method of molecularly imprinted polymer capable of simultaneously adsorbing multiple nitrides
InactiveCN104877071AUniform particlesLarge specific surface areaWaste minimisationFunctional monomer
The invention provides a molecularly imprinted polymer capable of simultaneously adsorbing multiple nitrides and a preparation method of the molecularly imprinted polymer, and belongs to the technical field of environmental pollution control chemistry. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly simulating an imprinting preassembly system based on a density functional theory by using a molecular simulation technology, screening out an optimal functional monomer, and preparing a molecularly imprinted adsorption material based on simulation results by virtue of seeded emulsion polymerization. An adsorbing agent synthesized by using the method provided by the invention is uniform in particle, large in specific surface area and good in adsorption kinetics; and compared with a conventional single template imprinting adsorption material, the molecularly imprinted polymer provided by the invention ensures that multiple imprinted binding sites are successfully formed, and has greater practical values.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Tetrahydroisoquinolinyl-3-carboxylic acid modified TARGD heptapeptides, and synthesis, antithrombotic activity and application thereof
InactiveCN103450343APeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsAntithrombotic AgentP-selectin
The invention provides 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides disclosed as a general formula I, a molecular simulation method of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides, a preparation method of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides, inhibiting action of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides on expression of glycoprotein IIb / IIIa and P-lectin, anti-thrombocyte aggregation action of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides, and antithrombotic action of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides on a rat thrombosis model. Therefore, the invention provides clinical application prospects of the 3 novel antithrombotic quasi-peptides disclosed as the general formula I as an antithrombotic agent. In the general formula I, AA represents Ser or Val or Phe residue.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
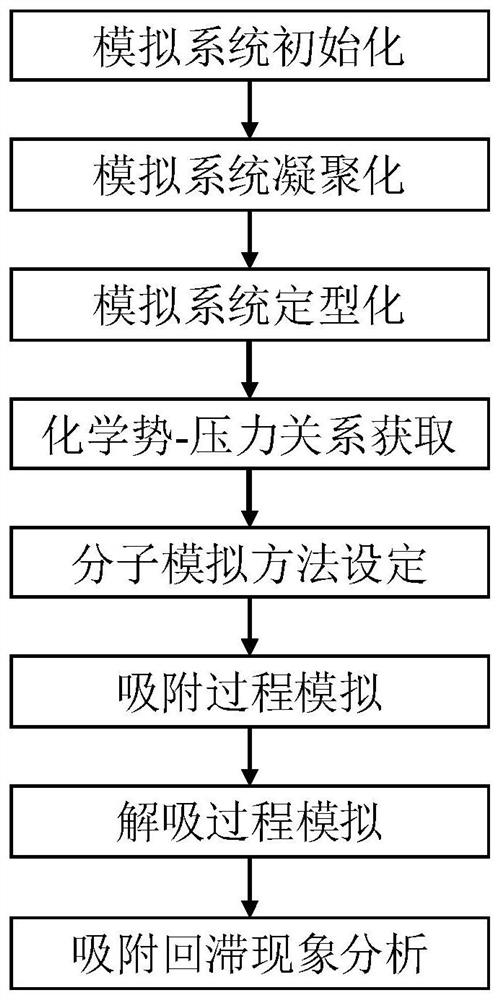
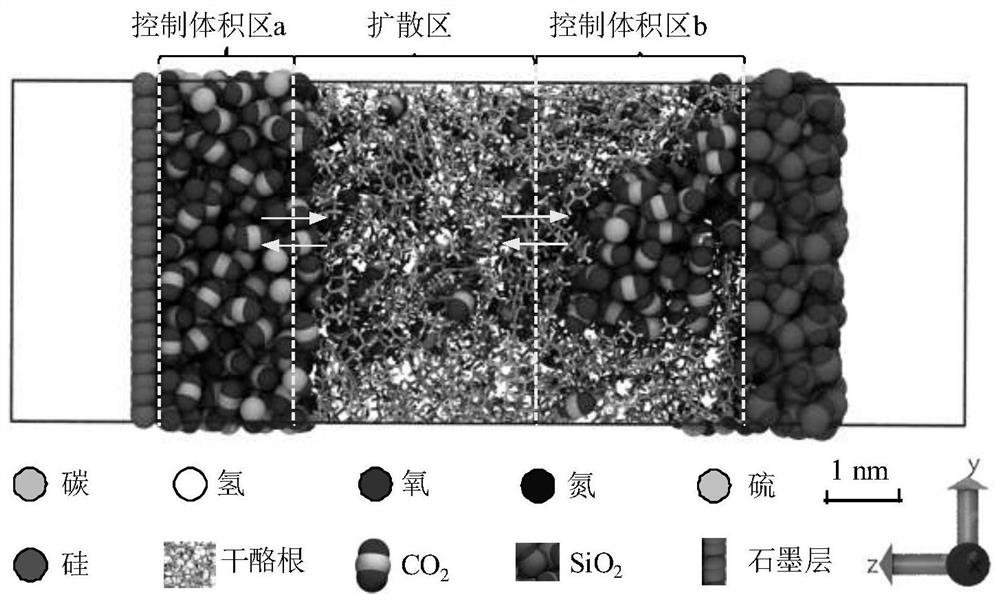
Molecular simulation method for shale gas adsorption hysteresis phenomenon
ActiveCN112414891AFacilitate understanding of deposit behaviorFacilitate understanding of the desorption mechanismMaterial analysisExperimental testingChemical physics
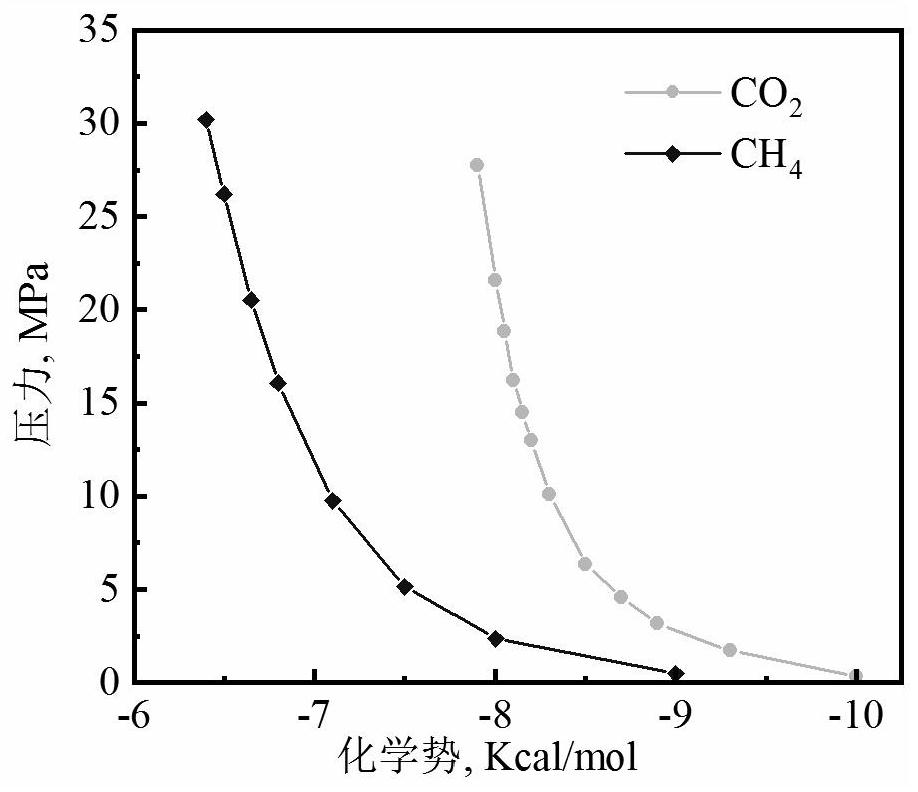
The invention provides a molecular simulation method for a shale gas adsorption hysteresis phenomenon. The method comprises the following steps: S1, initializing a simulation system; S2, coagulating the simulation system; S3, modeling the simulation system; S4, obtaining the relationship between the shale gas chemical potential and the pressure; S5, setting a gas adsorption / desorption molecular simulation method; S6, simulating a shale gas adsorption process; S7, simulating a shale gas desorption process; and S8, performing shale gas adsorption hysteresis phenomenon analysis. By constructing the gas adsorption simulation device and combining with the proposed DCV-GCMD-F simulation method, the adsorption and desorption physical process of the reducing gas in the complex nano-pore structureof the shale can be maximized on the molecular scale, the adsorption hysteresis phenomenon of the supercritical gas obtained by experimental testing is reproduced, and the micromechanism of adsorptionhysteresis is explained. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the occurrence behavior and the desorption mechanism of the supercritical gas in the complex nano-pores of the shale can be found out, so that a theoretical basis is laid for the productivity potential tapping of the shale gas and the design of targeted production increasing measures.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com