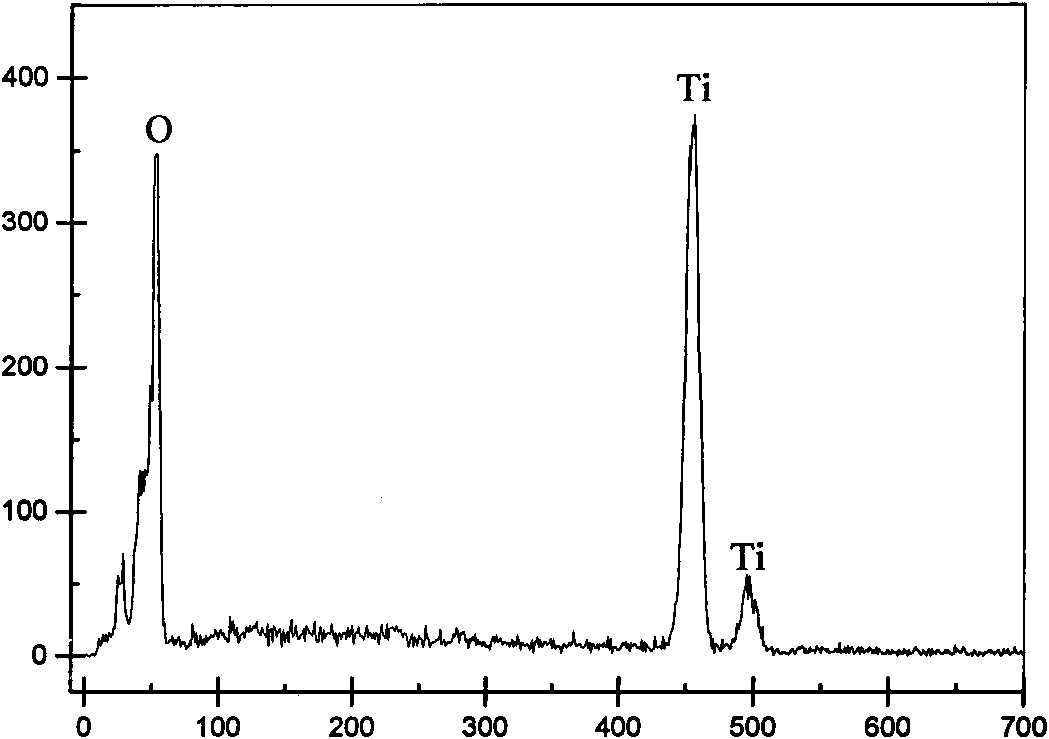
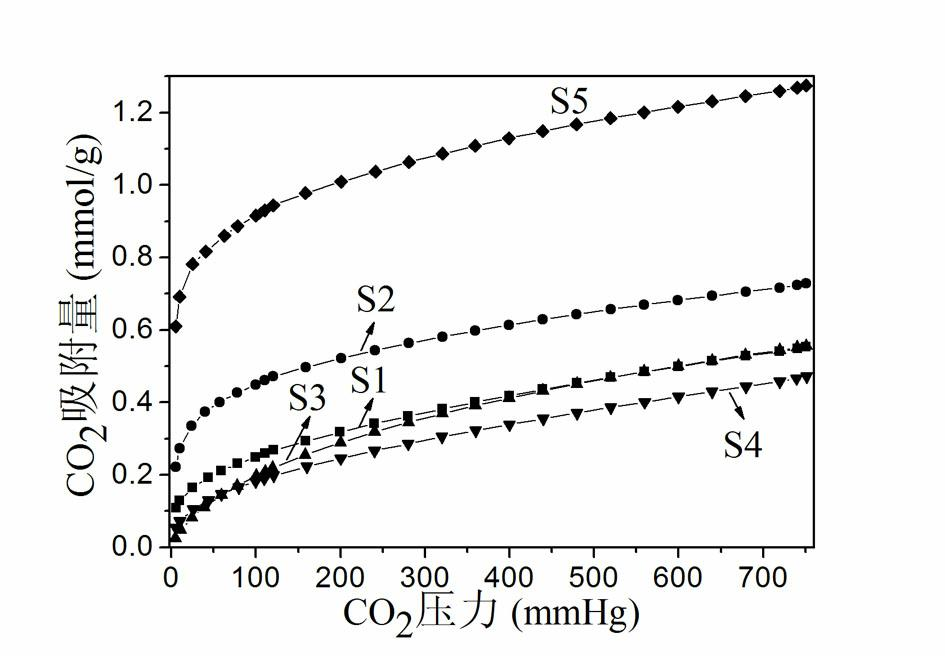
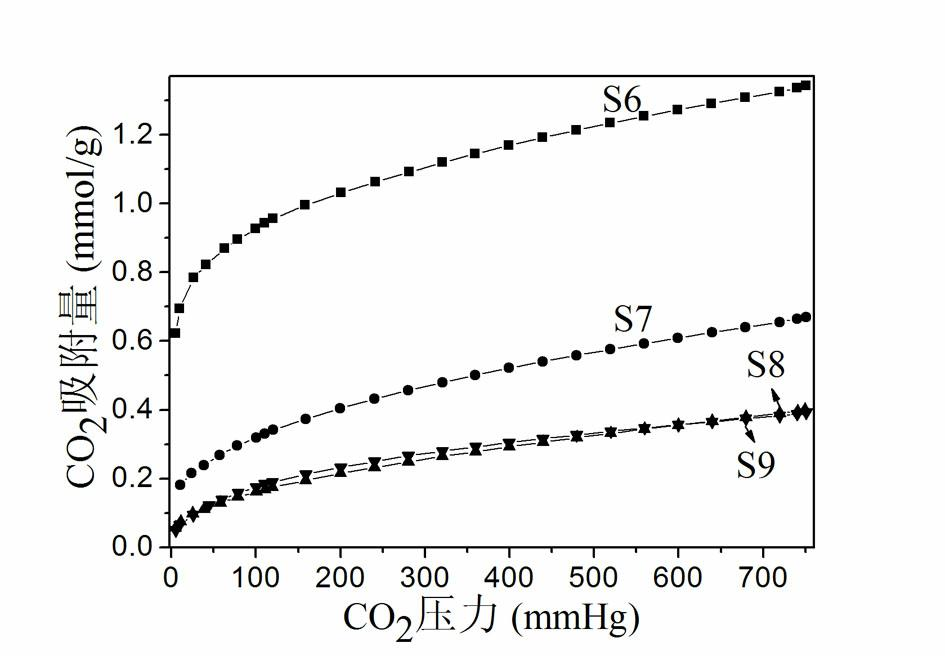
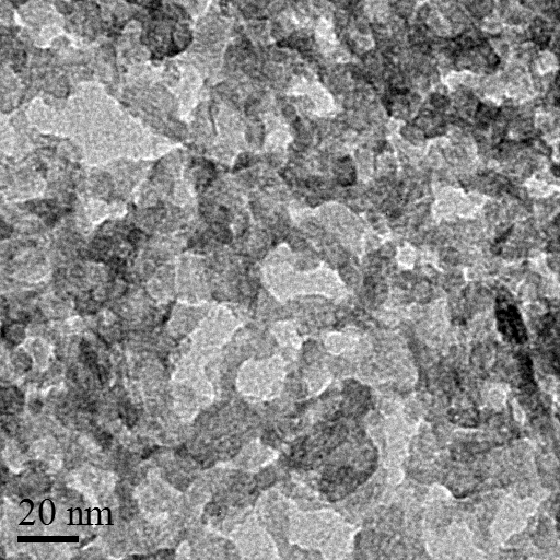
Patents
Literature
580 results about "Adsorption energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Adsorption plays an important role in energy transfer between gases, liquids, and solids. For example, gas molecules becoming adsorbed on a hot surface acquire energy corresponding to the temperature of the surface and after desorption transfer that energy to other gas molecules, thereby heating up the gas.
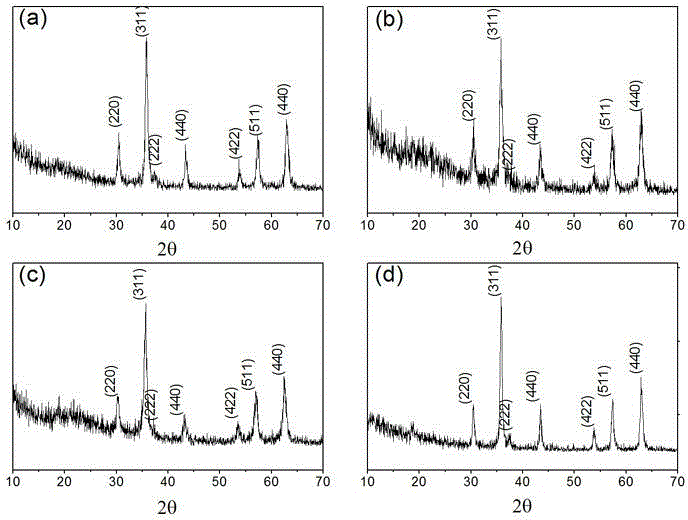
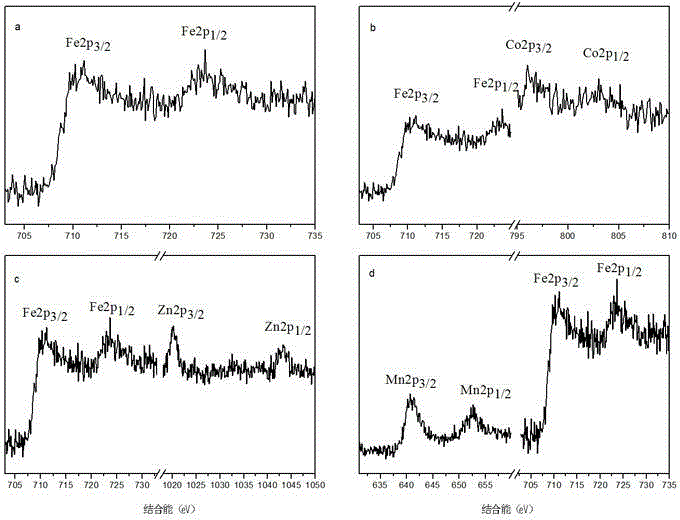
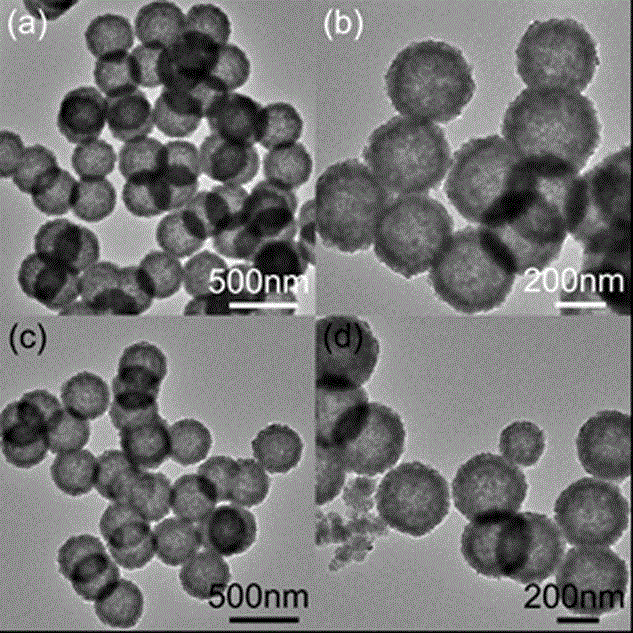
Heavy metal ion adsorbent ferrite hollow spheres MFe2O4
InactiveCN104150540AImprove adsorption capacityWide variety of sourcesOther chemical processesFerroso-ferric oxidesSorbentPollution
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental protection and environmental water treatment and in particular relates to a heavy metal ion adsorbent ferrite hollow spheres MFe2O4 (M=Fe, Co, Mn or Zn) and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the ferrite hollow spheres MFe2O4 belongs to a hydrothermal synthesis method, and the prepared ferrite hollow spheres are 180nm-380nm in diameter and 20nm-45nm in shell layer thickness and are used for adsorbing heavy metal ions As (V) and / or Cr (VI). The preparation method provided by the invention is simple and feasible, environment-friendly, pollution-free, low in equipment requirement and high in controllable degree; the raw material source is wide and the production cost is low; compared with a compound prepared in the prior art, the prepared heavy metal ion adsorbent is relatively high in adsorption capacity, and the adsorption capacity aiming at arsenic and chromium heavy metal ions reaches up to 340mg / g and is far beyond that in the prior art, so that the heavy metal ion adsorbent has relatively good application and promotion values.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
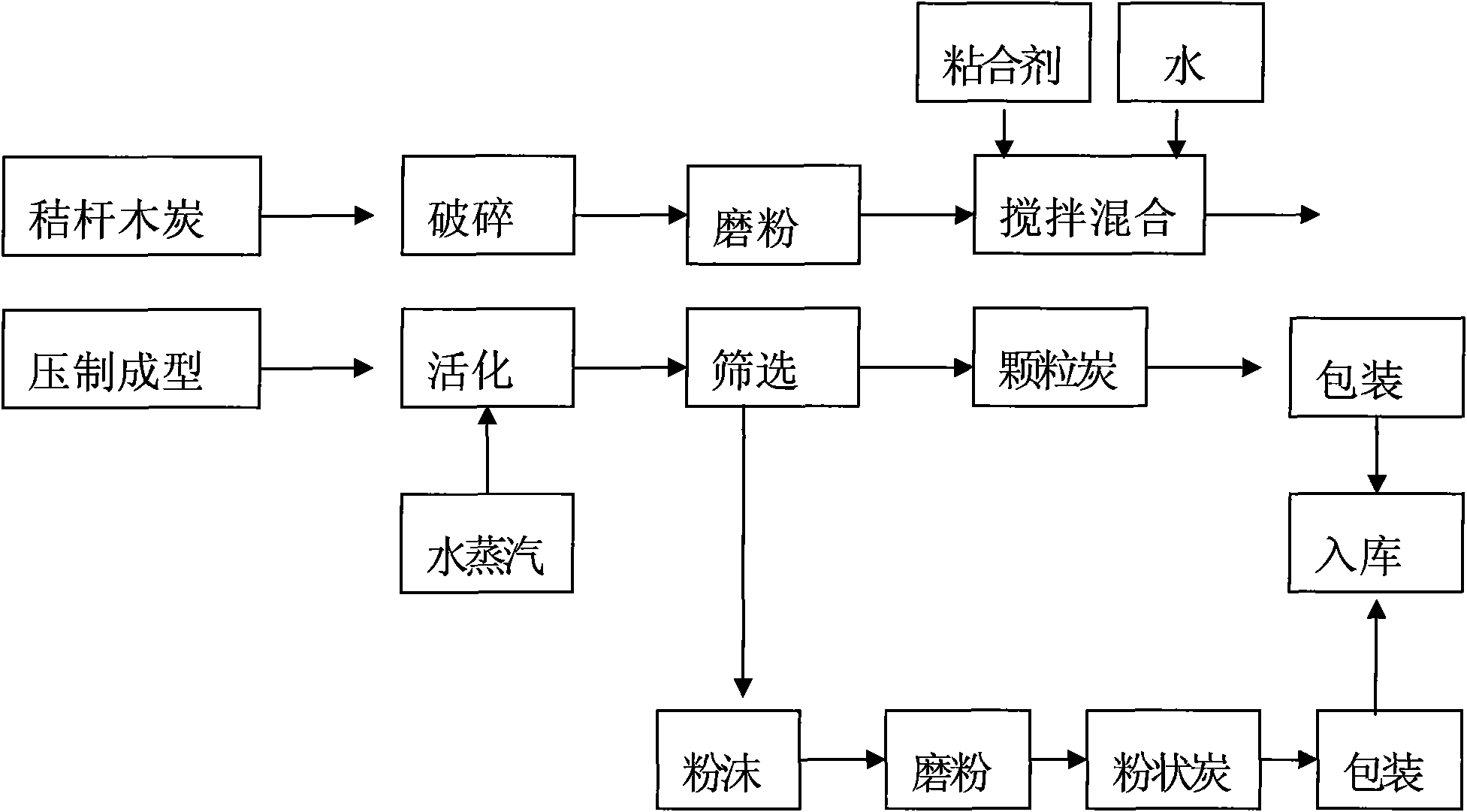
Process for producing activated carbon by physical activation method
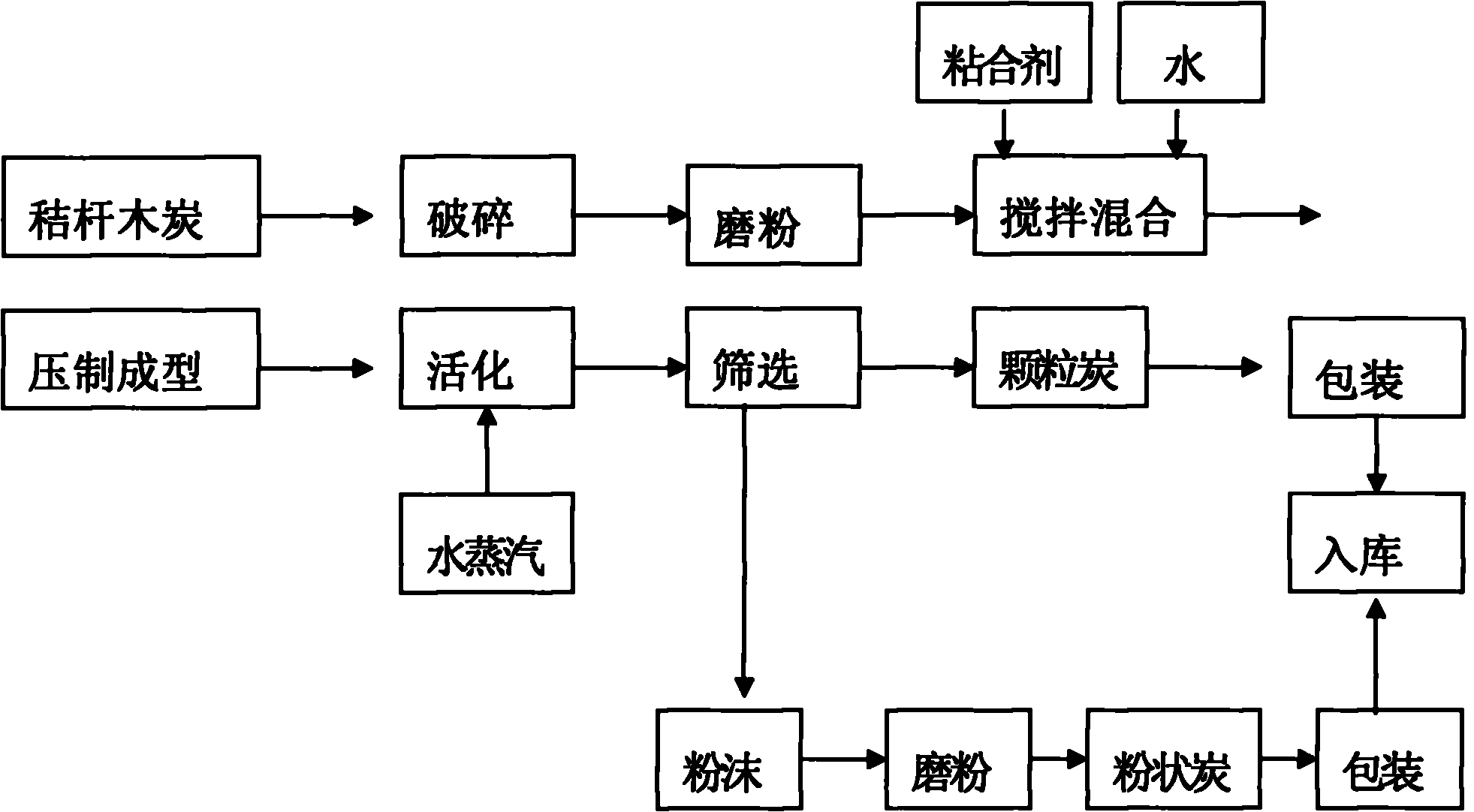
The invention discloses a process for producing activated carbon by a physical activation method. The process is characterized in that an activation process is added on the basis of machine-made straw charcoal, and comprises the following steps of: crushing and grinding the straw charcoal into powder and pressing the powder again to form grains; and feeding the grains into a special externally heated rotary activating furnace and performing activation by taking a gas as an active agent to obtain a finished product. The activation principle of the process is that: the activated carbon has strong adsorption capacity due to a special microcrystalline structure, well-developed micropores and great specific surface area thereof, and is produced by making the carbon form the porous microcrystalline structure and the straw carbon have a well-developed specific surface area. The machine-made straw charcoal produced by the process has high quality and high adsorption capacity, can be used for the production of firecrackers and fireworks, also can be widely used for the water purification for drinking water, alcoholic beverages and various cooling beverages and the advanced purification of industrial waste sewage and domestic sewage, and is also suitable for the purification of indoor air.
Owner:卞奎友
Method for removing mercury ions in water and regeneration method of adsorbent used in same
InactiveCN102432085ANanostructure, large specific surface areaLarge specific surface areaOther chemical processesCombustible gas purificationSorbentModified carbon
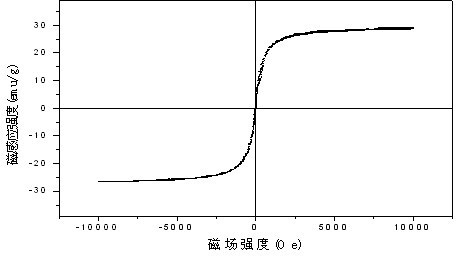
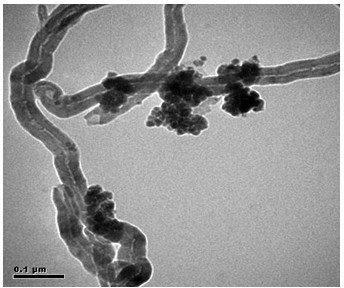
The invention relates to a method for removing mercury ions in water and a regeneration method of an adsorbent used in the same. An adsorbent is put in water to be treated to adsorb mercury ions in the water. The adsorbent is a palladium nanoparticle supported / iron oxide magnetic modified carbon nanotube composite material. The carbon nanotube composite material provided by the invention has nanostructure and large specific area; and after the carbon nanotube composite material is oxidized and activated, carboxyl group, hydroxyl group and other active functional groups are formed on the surface of the carbon nanotube composite material, thereby enhancing the hydrophilic property and the adsorptive capacity for positively charged metallic ions. The iron oxide is coated on the surface of the activated carbon nanotube composite material, and therefore, the activated carbon nanotube composite material has strong soft magnet property, and can easily implement solid-liquid separation of the adsorbent and the polluted water body under the action of an external magnetic field. The palladium modification strengthens the affinity of the composite material with mercury ions, and greatly enhances the adsorption capacity and selectivity of the original carbon nanotube composite material for mercury ions (the maximum adsorption capacity is 55.3mg / g).
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Activated carbon-metal organic framework composite materials with enhanced gas adsorption capacity and process for the preparation thereof
ActiveUS20140018238A1Enhanced methane adsorption capacityIncrease capacityOther chemical processesOrganic compound preparationActivated carbonMetal-organic framework
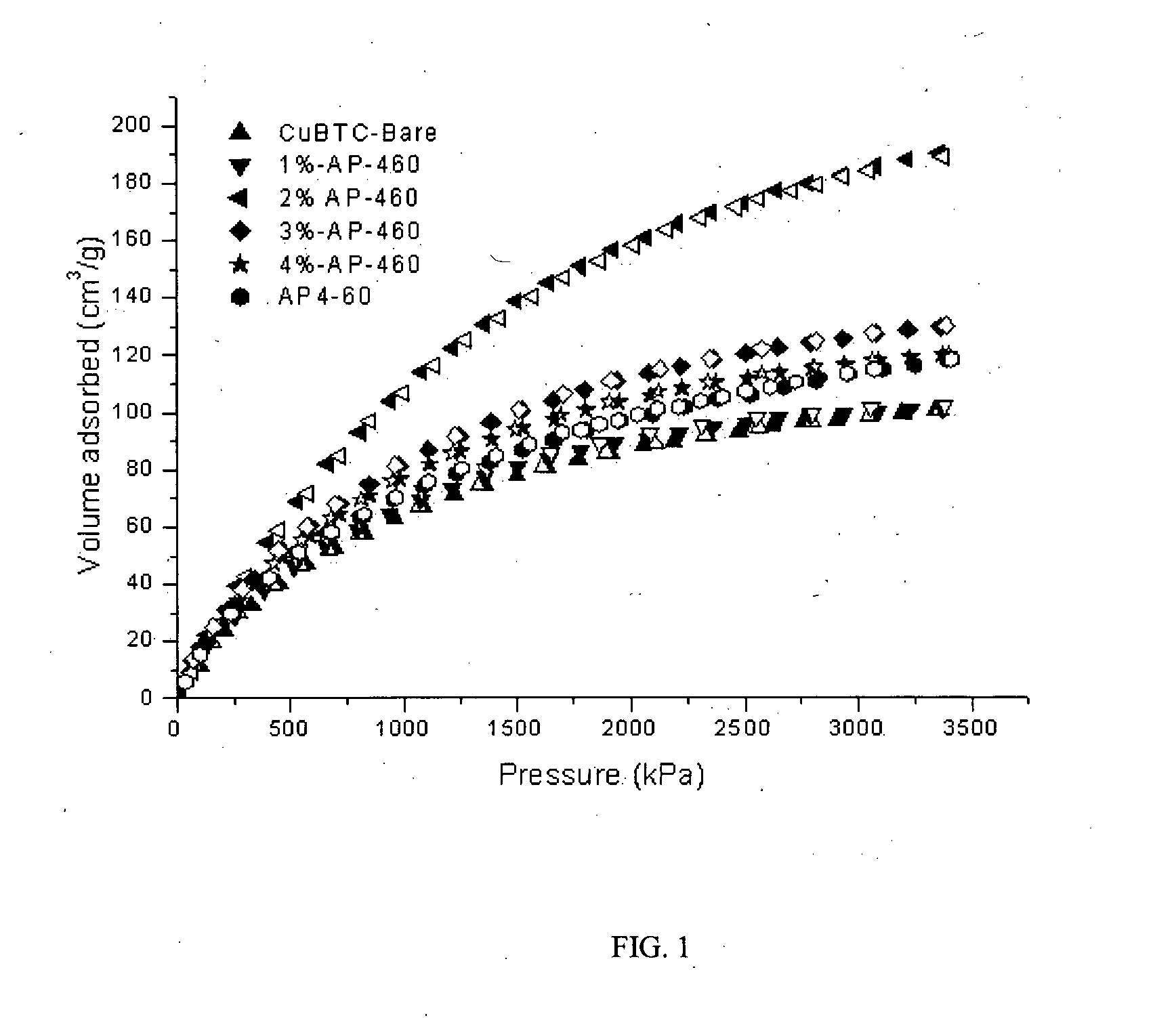
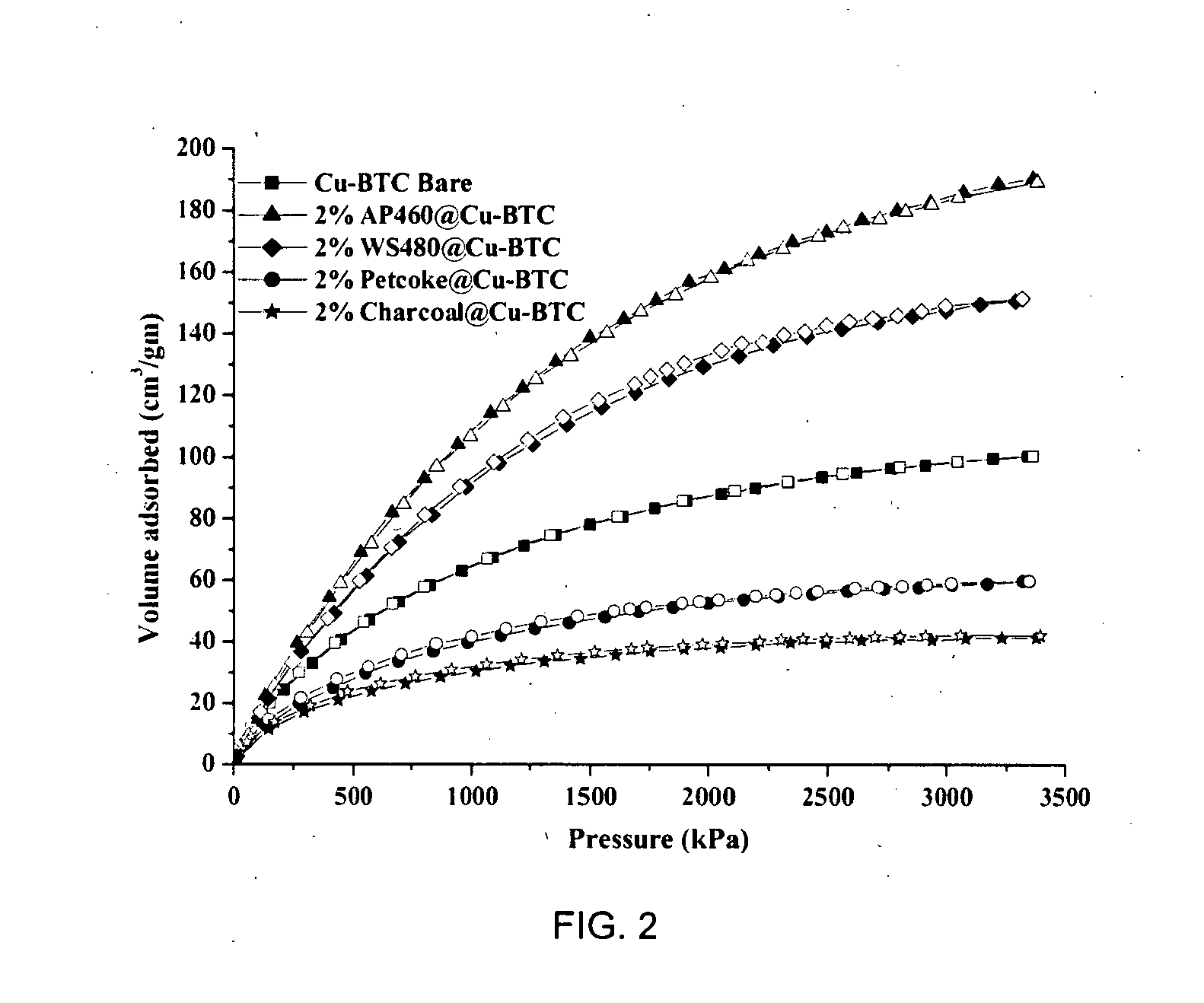
The present invention discloses activated carbon-metal organic framework composite materials (AC@MOF) with enhanced gas adsorption capacity. The present invention also discloses a process for the preparation of carbon-metal organic framework composite materials (AC@MOF). The present invention involves the use of “void space filling method” in metal organic frameworks (MOFs), which have been accomplished by in-situ addition of selected type and appropriate amount of activated carbon during the synthesis of MOF such as Cu-BTC, in the storage of gases such as methane. The gas adsorption capacity of these AC@MOF composite materials is significantly increased through this method.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES +1
Method for manufacturing magnetoresistance element and apparatus for manufacturing magnetoresistance element
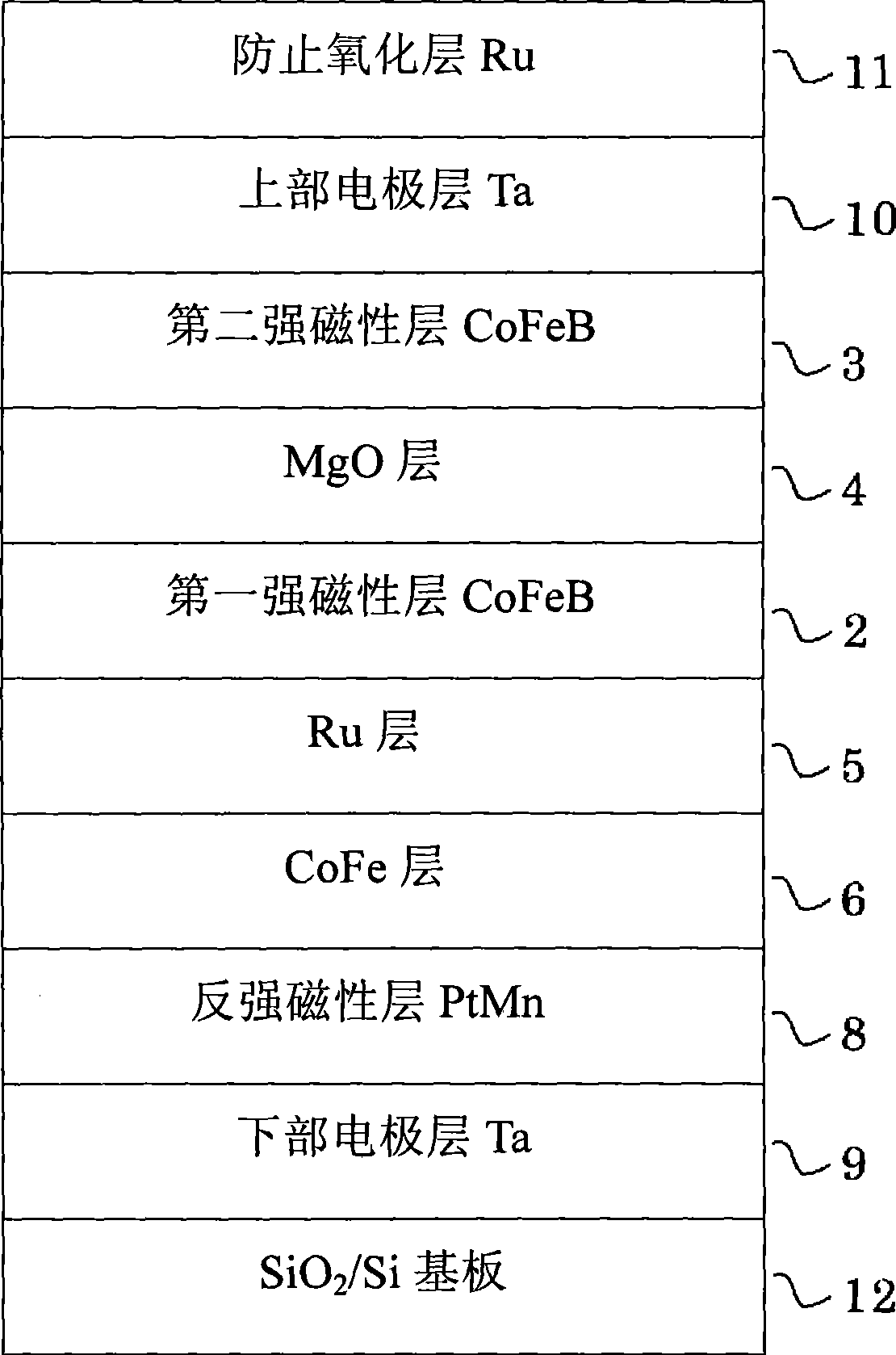
InactiveCN101395732AMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic device manufacture/treatmentTantalumAdsorption energy
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Gas and water flow condition and effect simulation device of coal bed gas well discharging and mining process
The invention discloses a gas and water flow condition and effect simulation device of a coal bed gas well discharging and mining process. The simulation device comprises a closed cylinder, a grid-shaped fracture simulation pipeline for simulating coal reservoir fracture grids is arranged in the cylinder, the front end of the fracture simulation pipeline is connected with a delivery pipeline for delivering gas and / or liquid to the fracture simulation pipeline, the fracture simulation pipeline is further connected with an air pressure blocking pipeline, a piston is arranged on one end of the air pressure blocking pipeline connected with the fracture simulation pipeline, the back end of the fracture simulation pipeline is connected with an evacuating device for simulating discharging and mining control, and the cylinder is connected with a high pressure gas delivery pipeline used for providing pressure for the fracture simulation pipeline. Positive effects and negative effect of fracture compression and expanding are caused by gas and water flow conditions, and the simulation device can simulate the gas and water flow conditions, flowing paths and positive effects and negative effect of fracture compression and expanding caused by gas and water flow conditions during discharging and mining under different fracture grid combinations, different outer differential pressures and different coal reservoir adsorption energies.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Domestic air cleaner
InactiveCN103216889AImprove cleanlinessImprove adsorption capacityLighting and heating apparatusAir conditioning systemsFiltrationUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to a domestic air cleaner which comprises a machine box, an air blower, a filter assembly, a plurality of grid-shaped air guide ceramic plates, at least one ultraviolet irradiation lamp and an ion generator, wherein the machine box is provided with an air inlet and an air outlet; and the air blower is arranged in the machine box. The domestic air cleaner disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the filter assembly is high in adsorption capacity and filter capacity and can be generally continuously used for several months, only the filter assembly needs to be disassembled for desorption when the adsorption filtration and adsorption capacity of the filter assembly are obviously lowered, and filtered air is further degraded through an ultraviolet light catalyst and sterilized through ions, thereby ensuring that the exhausted air is clean without containing harmful gases and bacteria.
Owner:佛山卢国辉电器实业有限公司
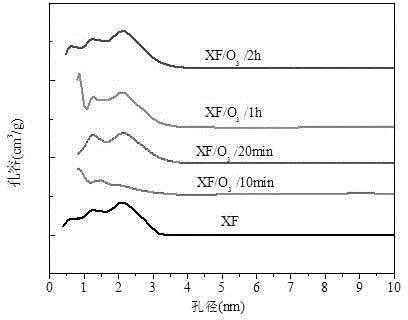
Method for modifying tobacco activated carbon by virtue of ozone and application of modified activated carbon
InactiveCN104587955AHigh retention rateSimple methodOther chemical processesControlled releaseActivated carbon
The invention discloses a method for modifying tobacco activated carbon by virtue of ozone and application of modified activated carbon. An adsorption material activated carbon for a tobacco flavor is modified with 2mol / L sulfuric acid under the condition that ozone is introduced. The specific surface area and pore volume of the modified activated carbon are both increased, the species of surface total acid groups are increased, the increases of both specific surface area and pore volume, the content of the surface total acid groups and the desorption activation energy are all associated with the sulfuric acid modification process conditions, the method provides the technical basis for improving the adsorption capacity of activated carbon on the tobacco flavor, and the tobacco activated carbon obtained by modification can be applied as an adsorbent material and / or a sustained release material and / or a controlled release material for the tobacco flavor.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGDONG IND
An Ag3VO4/TiO2 compound nano-wire having visible light activity, a preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN103285861AImprove visible light absorptionSimple processDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNanoparticleHydrothermal reaction
The present invention relates to a preparation method for an Ag3VO4 / TiO2 compound nano-wire having visible light activity, belonging to the technical field of environmental pollution control. The preparation method comprises steps for preparing Ag3VO4 / TiO2 compound nano-wire, and specifically the steps are as follows: Ag3VO4 / TiO2 compound nano-particles are added to an alkaline solution and dispersed, and is subjected to a hydrothermal reaction at a temperature of 120 ~ 250 DEG C for 24 ~ 56h, and after the reaction is completed, obtained precipitate is washed and dried, and is calcined at 100 ~ 800 DEG C for 3 ~ 8h. According to the present invention, the Ag3VO4 / TiO2 compound nano-wire has beneficial effects of a large specific surface area and a large adsorption capacity.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
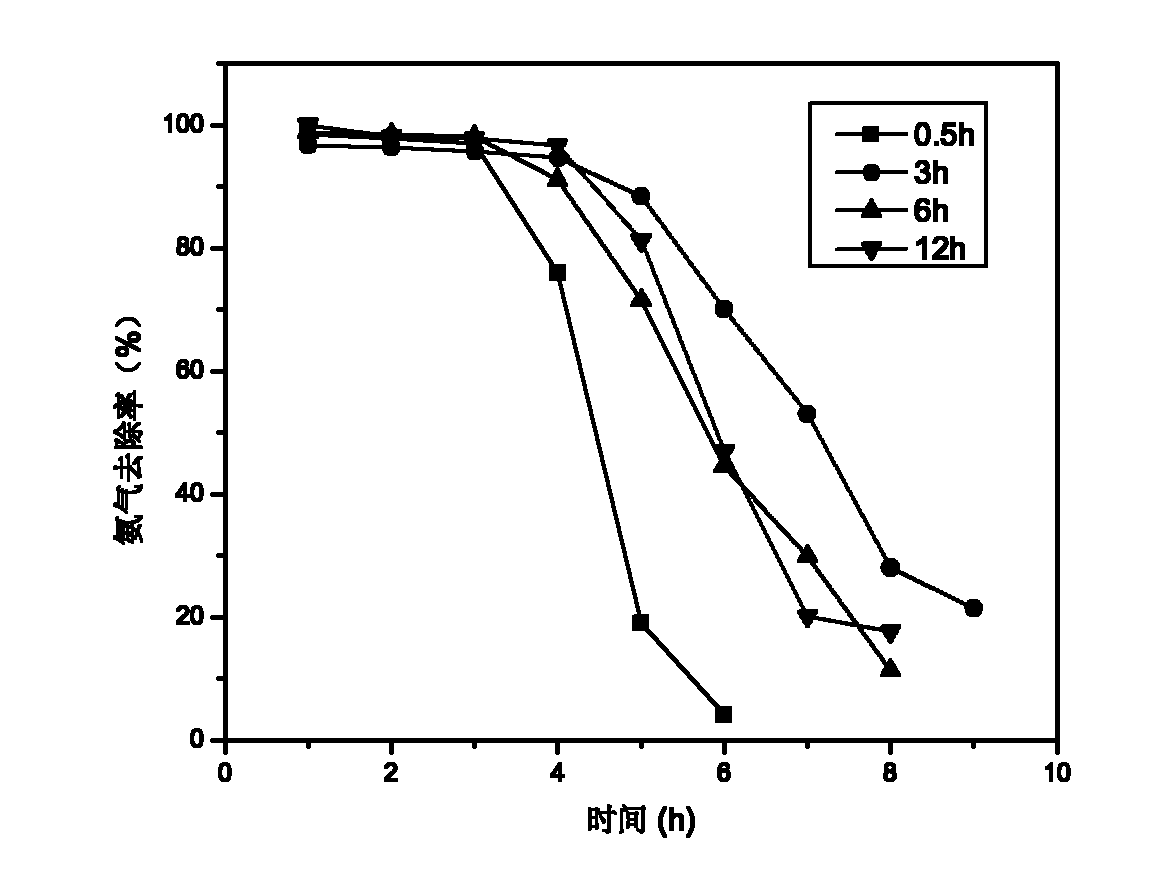
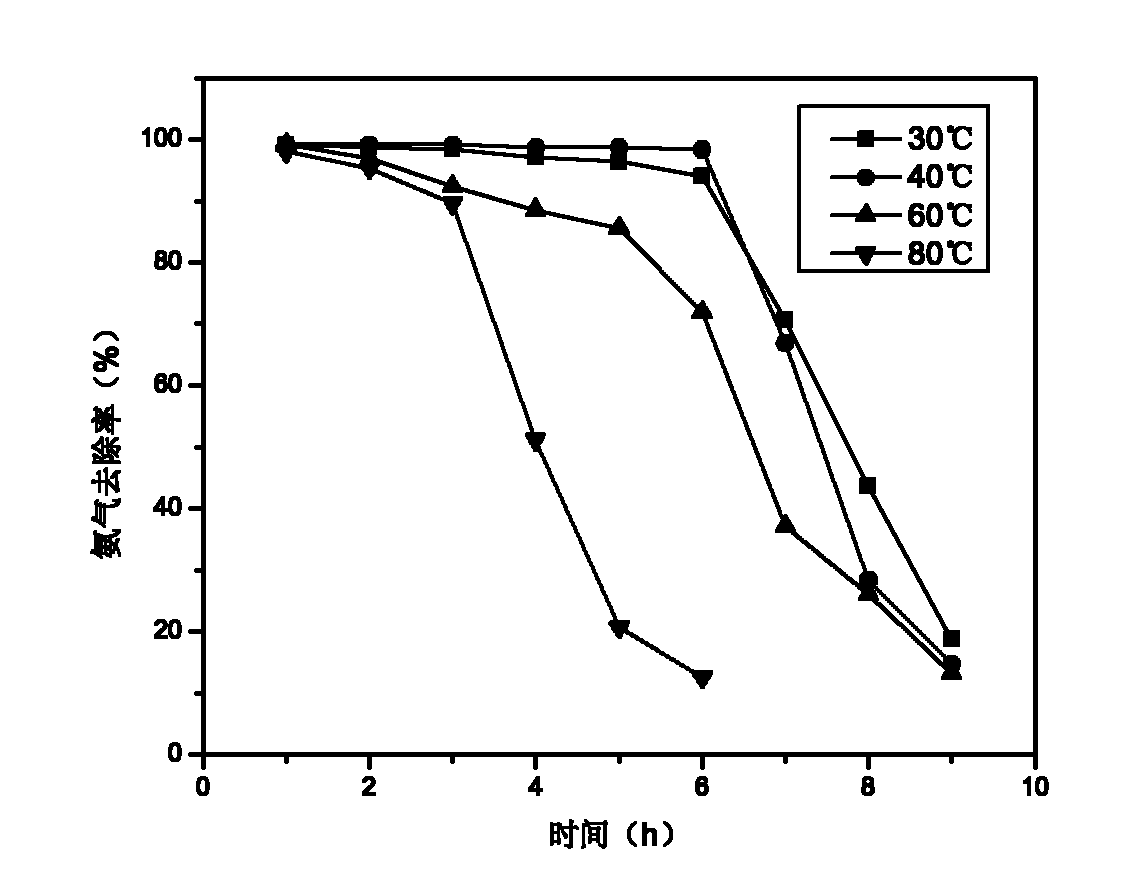
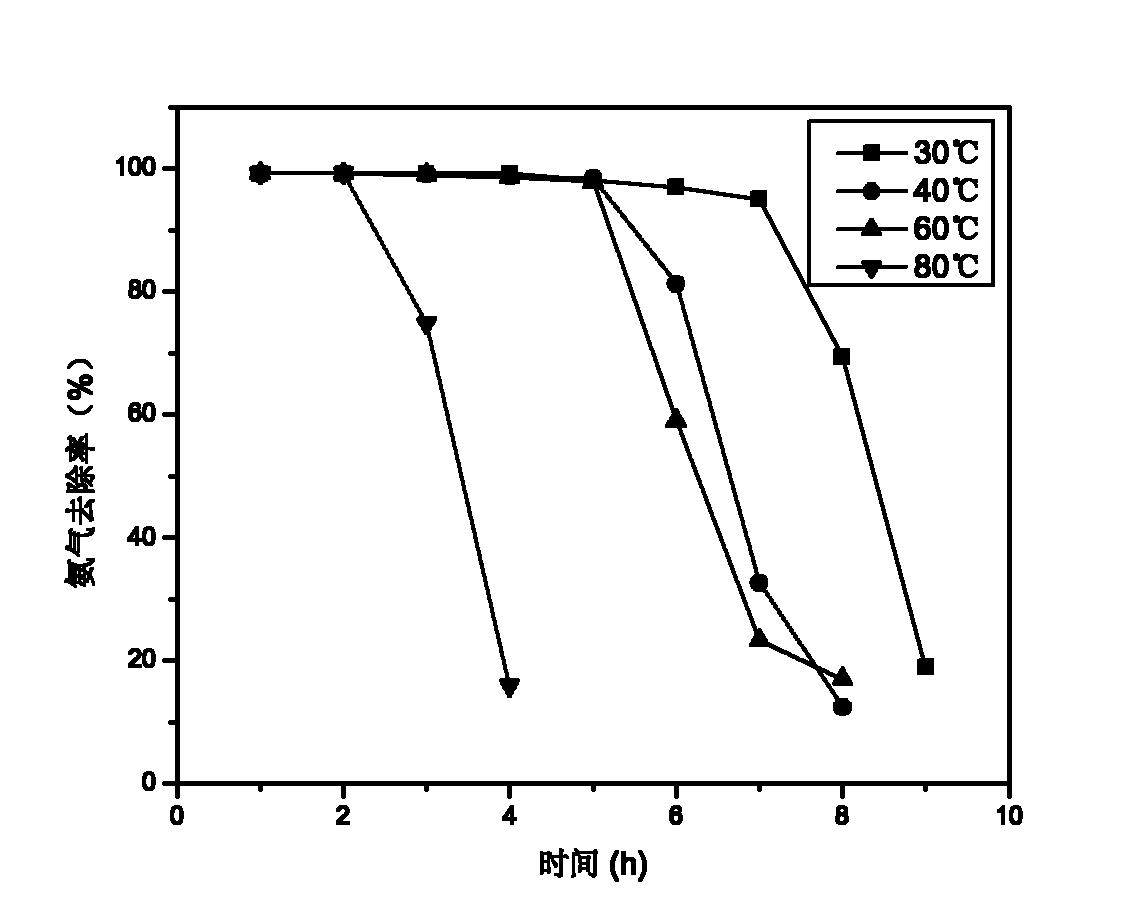
Modified active carbon and method for removing ammonia gas in intensive livestock farm
InactiveCN102627277ALarge adsorption capacityReduce concentrationOther chemical processesCarbon compoundsActivated carbonHigh pressure
The invention relates to modified active carbon and a method for removing ammonia gas in an intensive livestock farm. In the method, columnar active carbon is taken as a carrier. The active carbon is modified by adopting a high-pressure hydrothermal chemical method and an isometric solution soaking modification method to enhance the removal of ammonia gas, the volume of selected active carbon is 20ml, the adsorption temperature is 30-80 DEG C, the air speed is 300-1,200 h<-1>, and the ammonia gas concentration is 350-1,050 mg / m<3>. The modified active carbon has high adsorption capability on ammonia gas, contributes to greatly increasing the volume of adsorbed ammonia gas, and can be applied to treatment of ammonia gas in the intensive livestock farm.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
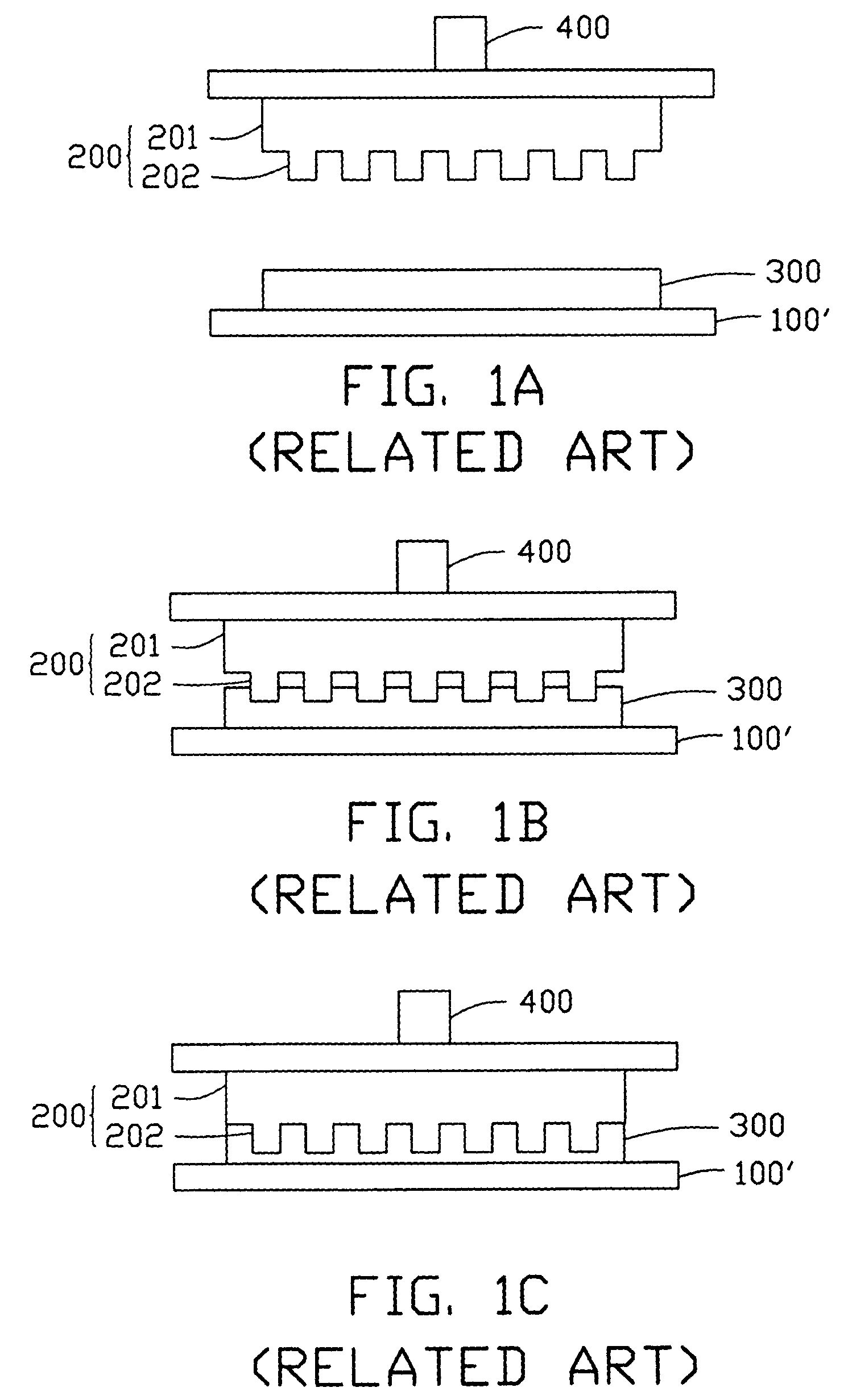
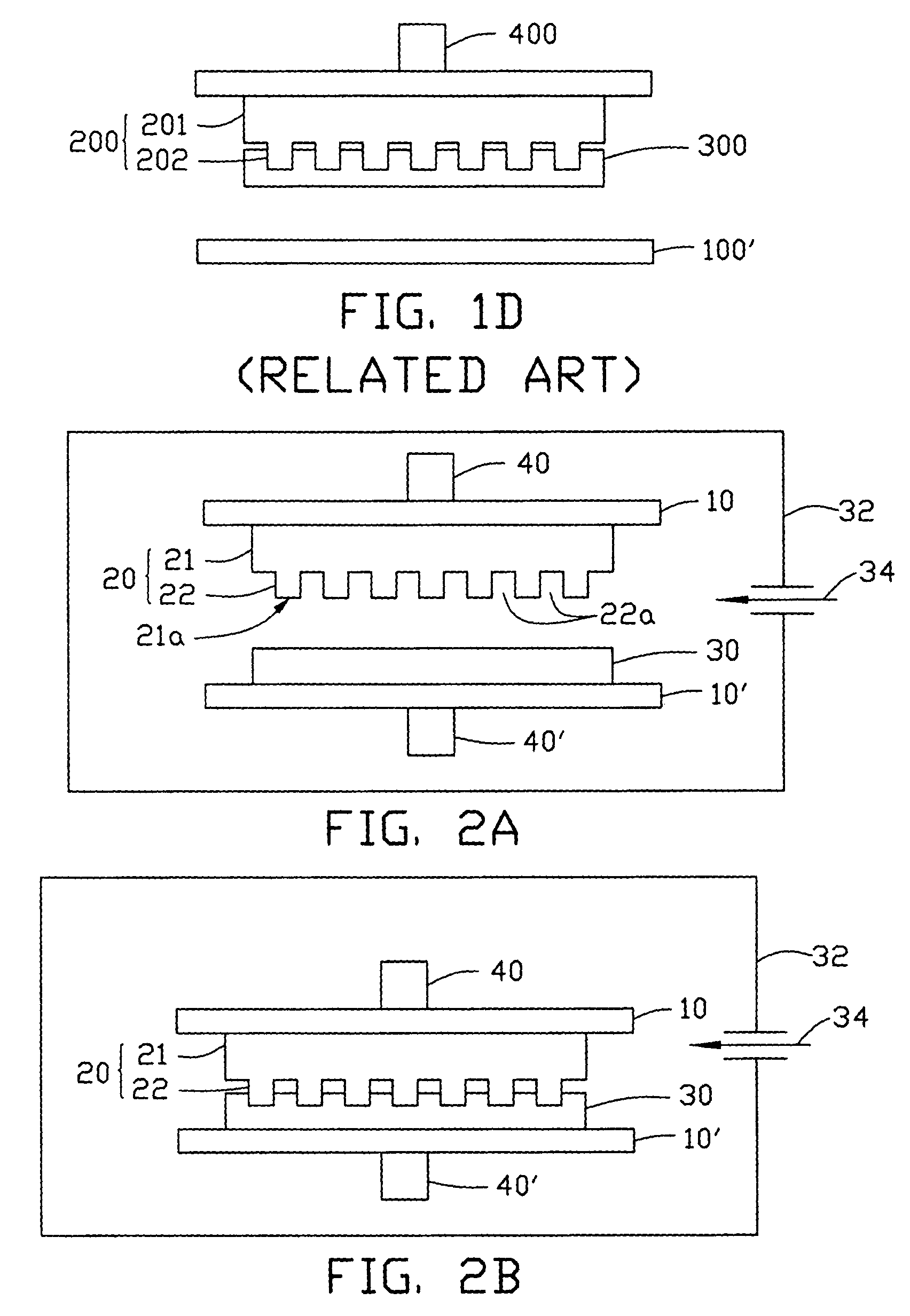
Hot embossing lithography method
InactiveUS7625513B2Lower adsorption energySoftening the polymer thin filmNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesVitrificationPolymer science
A hot embossing lithography method includes the steps of: providing a press mold (20) having a press surface, the press surface having a pattern defined therein; providing a substrate (10′) having a polymer thin film (30) formed thereon; aligning the press mold with the polymer thin film; introducing a vapor to moisten the press surface for lowering a surface adsorption energy of the press surface; heating the polymer thin film to a temperature above a glass transition temperature of the polymer thin film, thereby softening the polymer thin film; pressing the press mold into the softened polymer thin film to transfer the pattern of the press mold into the polymer thin film; cooling the polymer thin film and the press mold to a temperature near the glass transition temperature of the polymer thin film; and separating the press mold from the polymer thin film.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Modified montmorillonite filter additive containing iron oxide or/and hydroxy iron and application
InactiveCN103212371AReduce contentAluminium silicatesTobacco smoke filtersChemical adsorptionIon exchange
The invention relates to a modified montmorillonite filter additive containing iron oxide or hydroxy iron and application. Montmorillonite and the iron element are combined, and hydroxy iron ions are inserted among 001 crystal plane layers of montmorillonite by way of ion exchange and are distributed in a nanoscale state. Through the scanning electron microscope, physical adsorption, ammonia chemical adsorption and cigarette addition experimental test, the results indicate that the specific surface area of pillared montmorillonite is enlarged and the capacity of adsorbing ammonia and smoke particulate matters is improved. The hydroxy iron modified montmorillonite filter additive has a certain selective adsorption effect on benzo[a]pyrene in the cigarette smoke. The filter additive has the advantages of strong plasticity, good adsorption effect, safety and no toxicity, is low in price and is applicable and efficient.
Owner:YUNNAN RES INST OF TOBACCO SCI
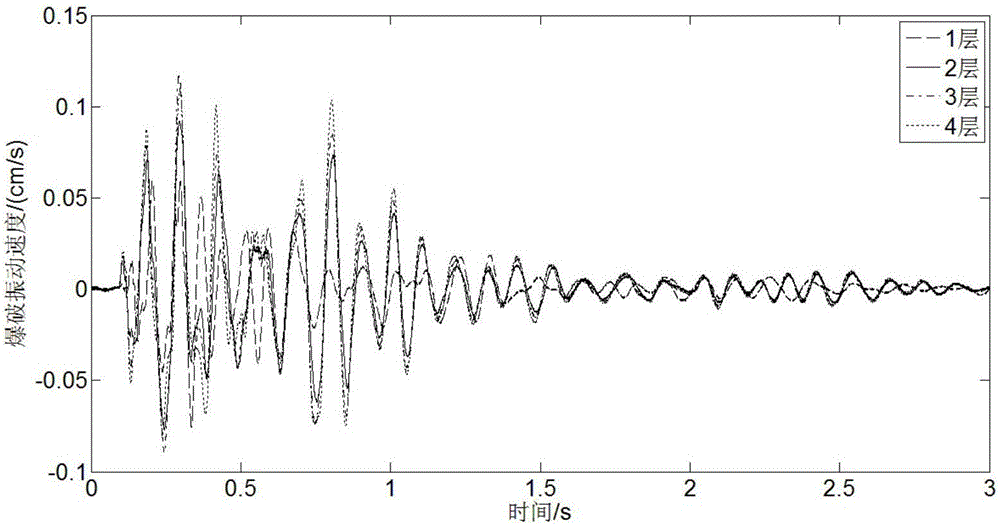
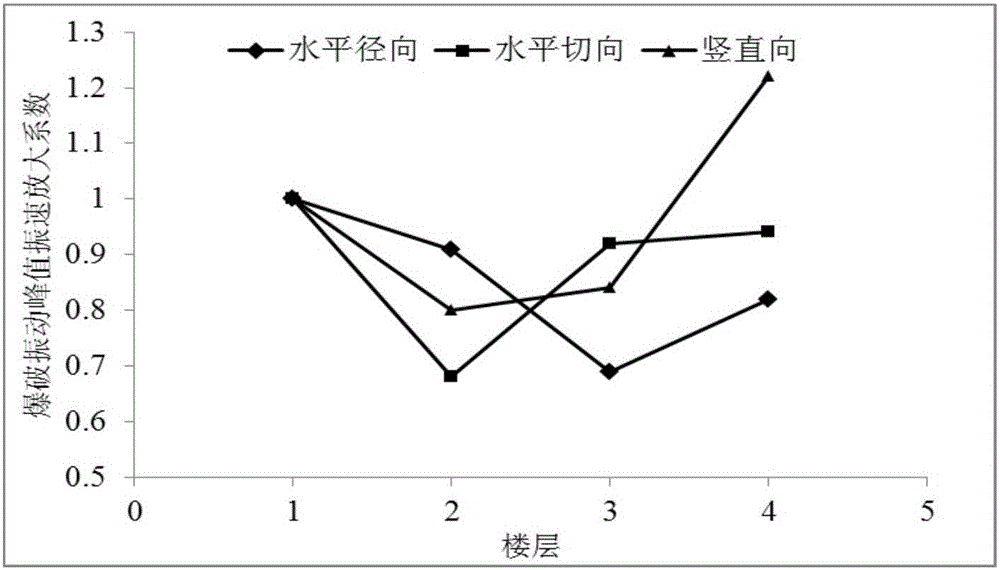
Absorbed blasting vibration energy comfort evaluation method of multistorey building
The invention discloses an absorbed blasting vibration energy comfort evaluation method of a multistorey building. The absorbed blasting vibration energy comfort evaluation method comprises the following steps: establishing an absorbed blasting vibration energy index, evaluating human body vibration characteristics by energy transfer and conversion, and analyzing blasting vibration energy frequency band representation by a power spectrum density value to obtain blasting vibration adsorption energy values in different frequency band ranges; analyzing the dynamic response characteristics of a building; obtaining the displacement amplification coefficient of a structural body; according to influence on the building by blasting vibration energy composition and different pieces of frequency band energy, carrying out frequency weighting on the vibration energy, and calling an energy weighting value as the absorbed blasting vibration energy of building frequency weighting; and multiplying each piece of frequency band energy by a human body vibration response weighting coefficient to obtain the absorbed blasting vibration energy of human body frequency weighting. By use of the absorbed blasting vibration energy comfort evaluation method, the magnitude and the frequency composition of total blasting vibration energy received by the human bodies in different floors of the building can be accurately calculated so as to achieve a purpose that blasting vibration energy comfort is accurately and objectively evaluated.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation method for modified kieselguhr composite adsorbing material
InactiveCN102641720ALarge specific surface areaImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionCongo redEngineering
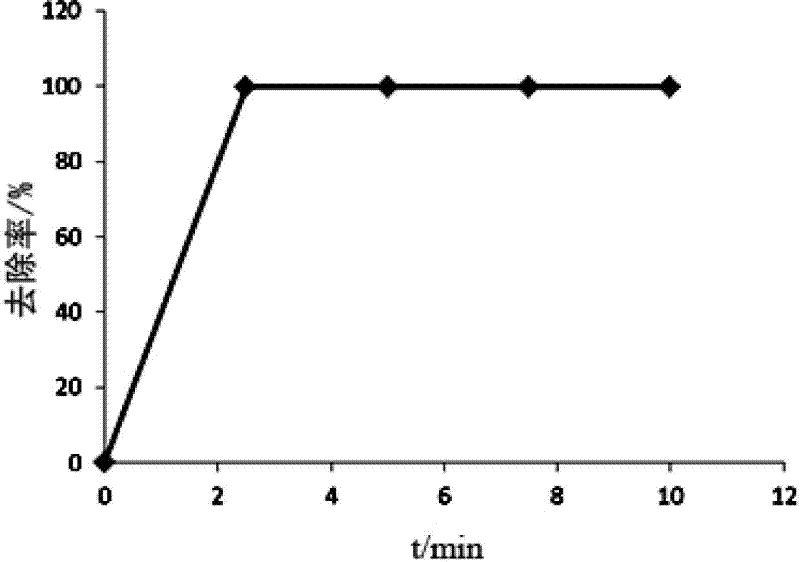
The invention discloses a preparation method for a modified kieselguhr composite adsorbing material. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) dissolving chitosan in the solution of a trivalent ferric salt, adding kieselguhr into the solution, and uniformly mixing the materials; 2) adding ethanol into the mixture to obtain a sediment, and filtering, washing and drying the sediment; and 3) adding the product obtained in the step 2) into the solution of ethanol of glutaraldehyde to be subjected to cross-linking reaction, and filtering, washing and drying the sediment. The preparation method has the beneficial effect that the kieselguhr prepared by the method is large in specific surface area and high in adsorption capacity. A dynamic absorbing experiment on Congo red shows that the highest adsorbing capacity of a composite material can be up to 1,250mg / g and the time for the balance of adsorption is not more than 10min.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
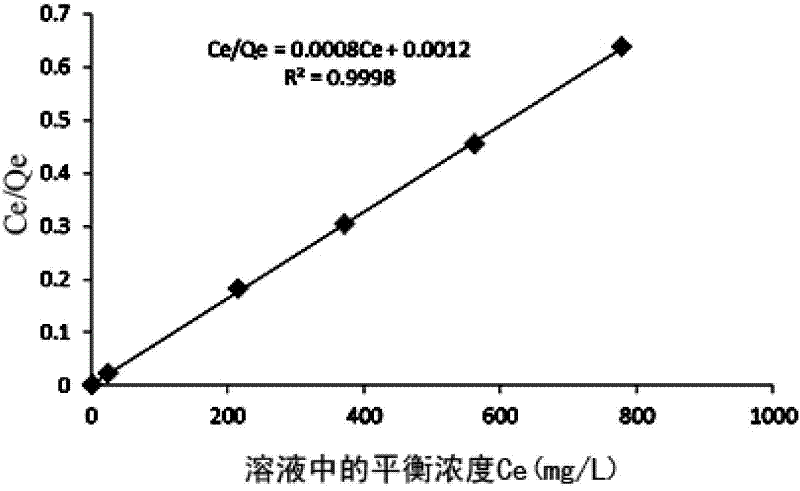
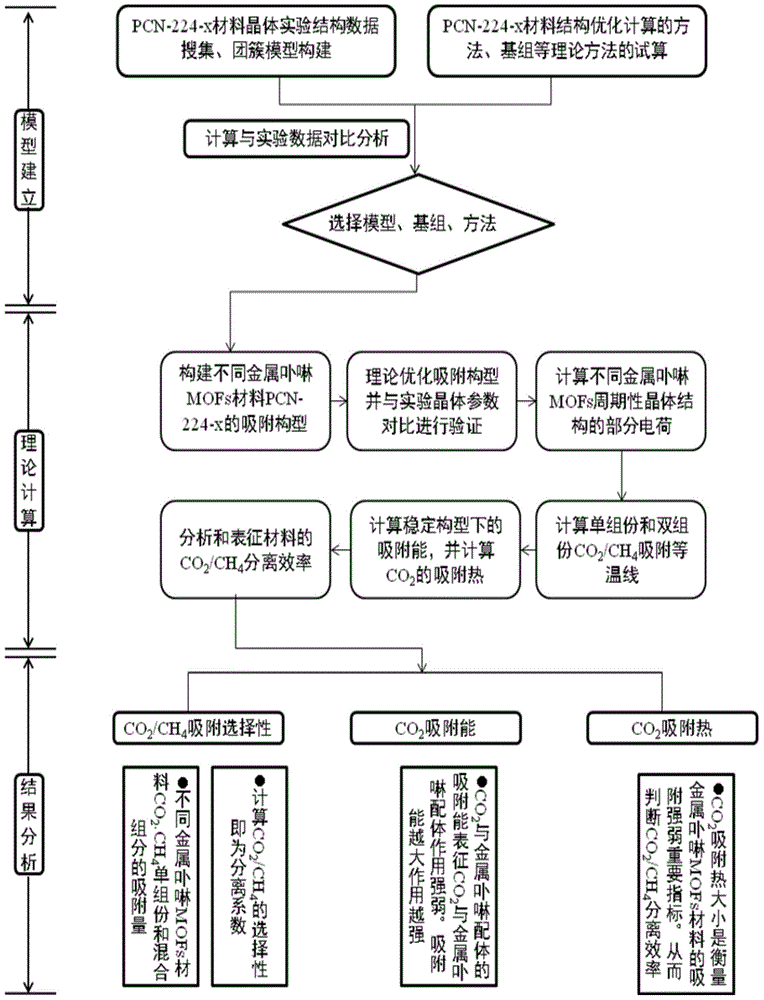
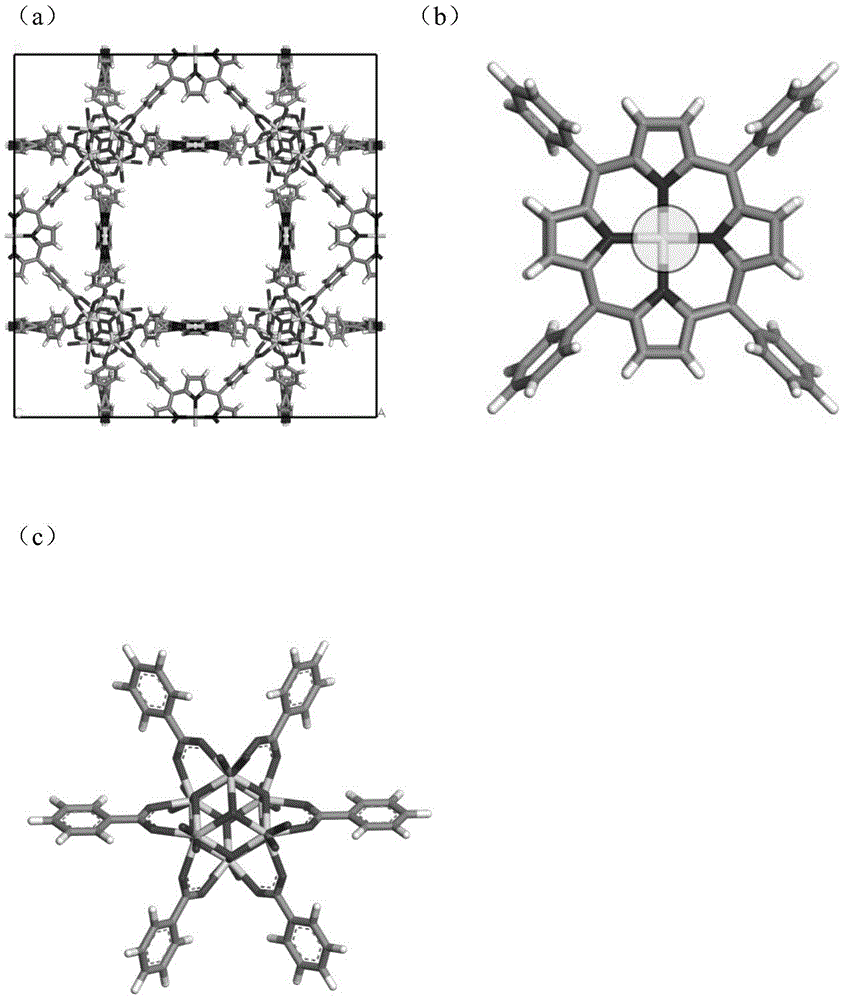
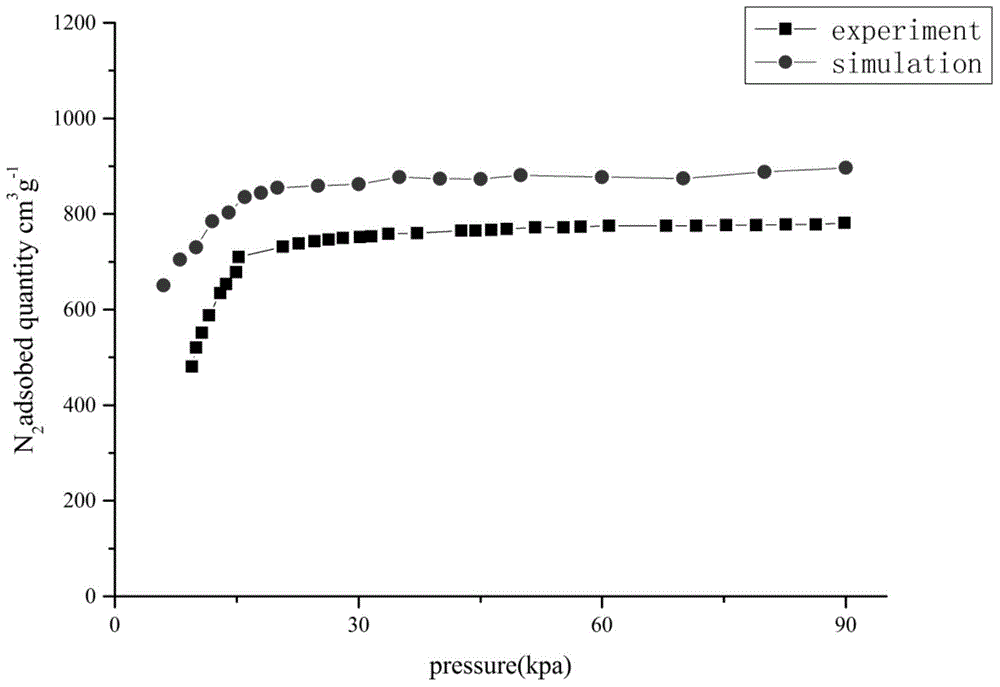
Method for quantitatively analyzing efficiency of metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2/CH4
InactiveCN104899356AAvoid complexityOvercome stabilityAdsorption purification/separationSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular sievePartial charge
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively analyzing efficiency of metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4. According to the method of the invention, the efficiency of the metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4 is quantitatively analyzed based on density functional theory calculation of auantum chemistry and Monte Carlo molecular simulation. By determining interaction energy between probe molecules and different metalloporphyrin ligands and adsorption heat, interaction between CO2 and metalloporphyrin MOFs materials is quantitatively analyzed, and finally calculation of selectivity in adsorption of CO2 / CH4 is used to characterize efficiency and features of different metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4. The method comprises steps of: construction of a cluster model; structural optimization of a stable structure and calculation of partial charges; calculation of a CO2 / CH4 separation coefficient; calculation of adsorption energy and adsorption heat; and analysis and characterization of efficiency in separating CO2 / CH4. According to the method of the invention, efficiency of metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4 can be quantitatively characterized without any actual experiment. The method of the invention can be further extended for analysis of efficiency of other porous molecular sieves of known crystal structures and MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
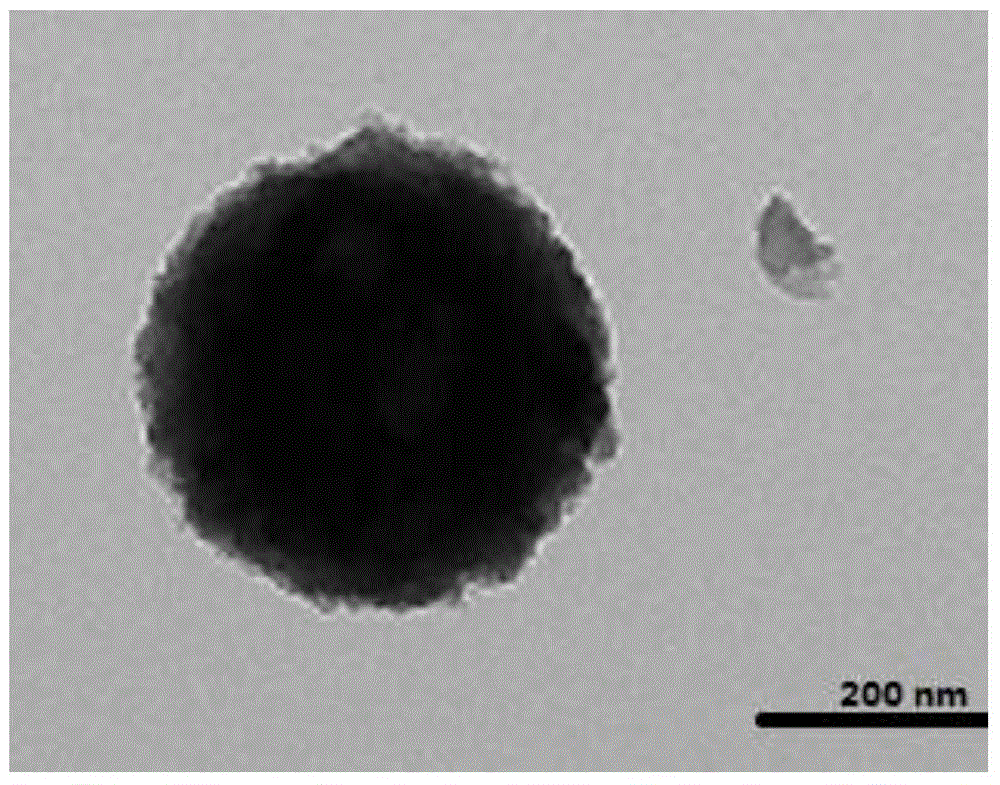
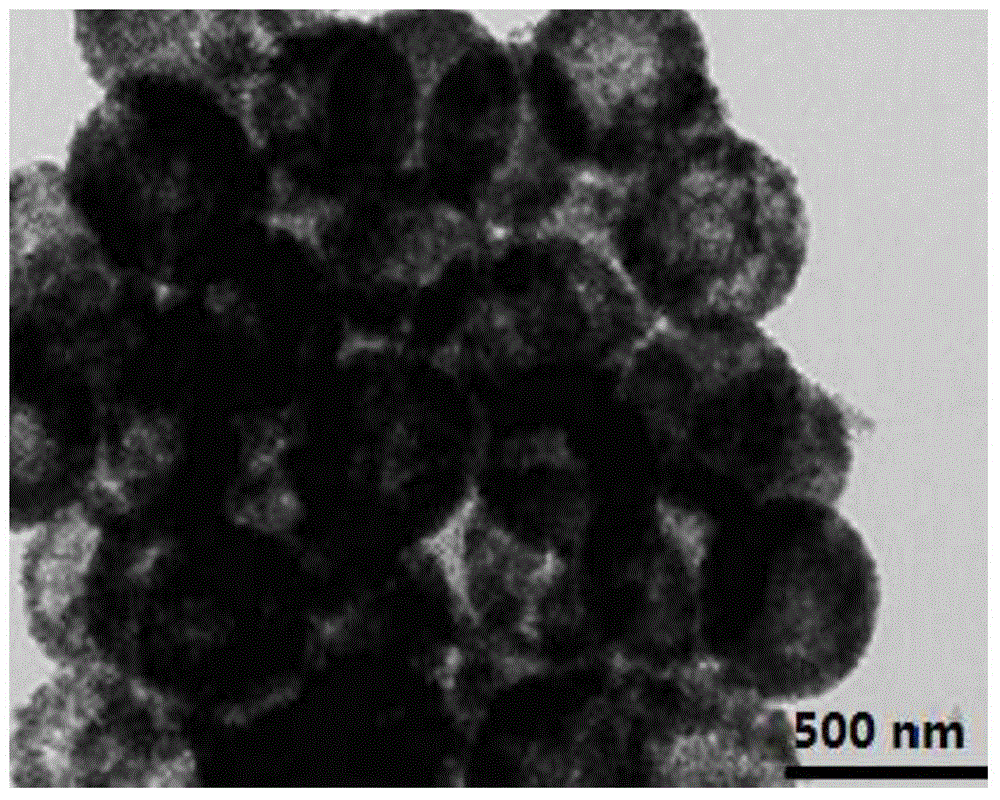
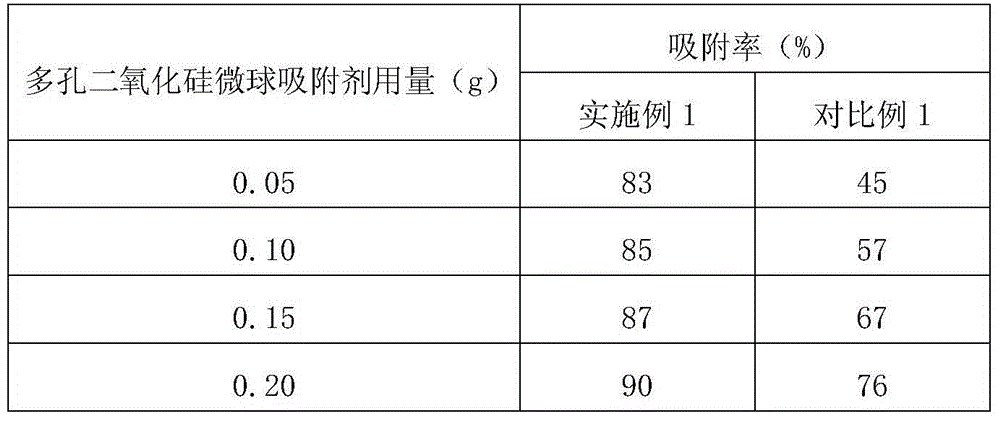
Preparation method and application of porous silicon dioxide microsphere adsorbent
InactiveCN104399427AHigh mechanical strengthImprove liquidityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsMicrosphereSorbent
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a porous silicon dioxide microsphere adsorbent. TEOS (tetraethyl orthosilicate) is used as a silicon source, ammonia water is used as a catalyst, isopropanol is used as a solvent, silicon dioxide microspheres are obtained through a hydrolysis-condensation polymerization reaction, and then the porous silicon dioxide microsphere adsorbent is obtained through a series of reactions. The synthesized porous silicon dioxide microspheres are high in mechanical strength, good in mobility and porous, have the larger specific surface area and the higher adsorption capacity and can be applied to wastewater treatment, particularly to treatment of wastewater containing high-toxicity organic pollutants and heavy metal pollutants. The preparation method has characteristics of simple technology, low cost, mild condition, economy, applicability, practicability and the like, meets actual production requirements and can be popularized and applied on a large scale.
Owner:PUTIAN UNIV
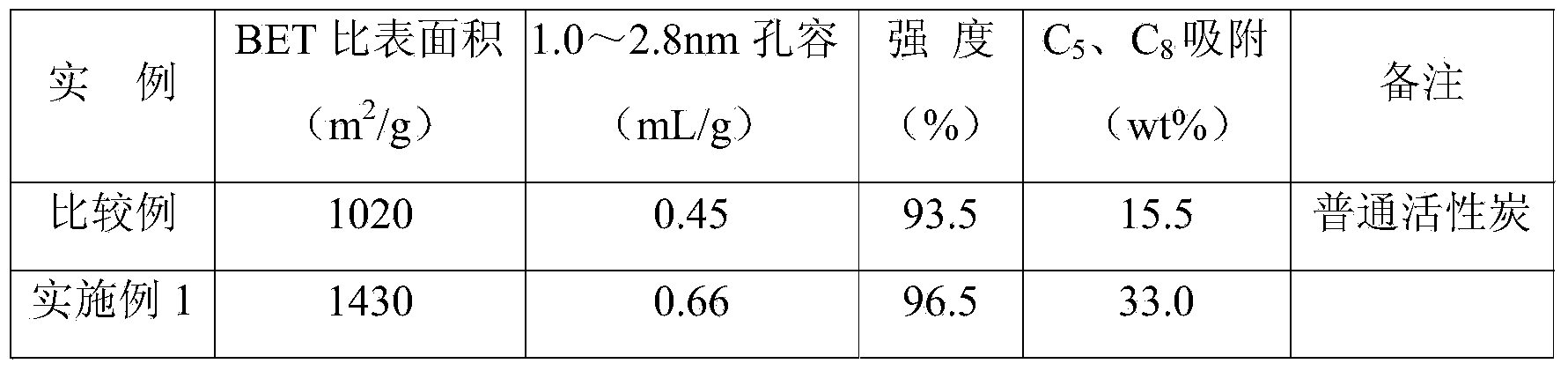
Preparation method of activated carbon adsorbent special for removing heavy hydrocarbon
ActiveCN103979535AImprove adsorption capacityHigh mechanical strengthCarbon compoundsActivated carbonSorbent
The invention discloses a preparation method of an activated carbon adsorbent special for removing heavy hydrocarbon. The method comprises the steps of performing treatment on raw materials containing carbon until the ash content is less than 3wt%, performing powder grinding, adding a binding agent and a pore regulation agent, and performing kneading molding, carbonization and activation to prepare the activated carbon adsorbent, wherein the BET (Brunauer, Emmett and Teller) method specific surface area of the obtained activated carbon adsorbent is 1200-1600m<2> / g; a Cranston-Inkley method measures that the volume of tiny pores of the activated carbon adsorbent of which the aperture is in the range of 1.0-2.8 nanometers is more than or equal to 0.6mL / g, the total pore volume is more than or equal to 0.8mL / g, and the mechanical strength is more than or equal to 95%. A product disclosed by the invention is excellent in adsorption performance, has a much higher heavy hydrocarbon adsorption capacity than that of normal activated carbon, has an adsorbing capacity of more than or equal to 32wt%, and can be recycled.
Owner:南京正森环保科技有限公司
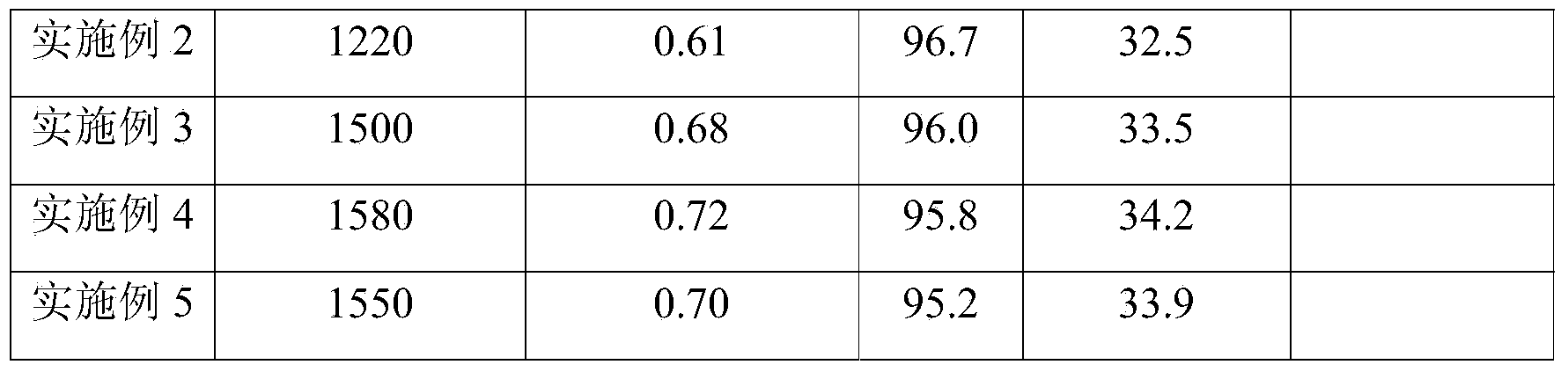
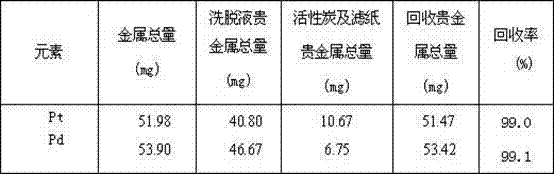
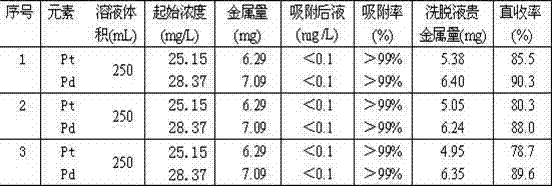
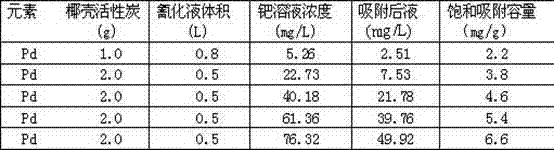
Method for enriching platinum and palladium from pressurized cyanating solution
InactiveCN102808084ASimple and fast operationPromote environmental protectionProcess efficiency improvementActivated carbonPlatinum
The invention discloses a method for enriching platinum and palladium from a pressurized cyanating solution, and belongs to a process for extracting platinum and palladium from a basic cyanating solution. The method comprises the steps as follows: enriching [Pt(CN)4]2- and [Pd(CN)4]2- from the pressurized cyanating solution of a platine group metal concentrate by cocoanut active charcoal; using a basic ethanol solution as a stripping solution for stripping the [Pt(CN)4]2- and the [Pd(CN)4]2- adsorbed on the surface of the cocoanut active charcoal; adsorbing and stripping for multiple times; burning the cocoanut active charcoal free of adsorption capacity; dissolving by acid; recovering platinum and palladium; and combining with platinum and palladium in the stripping solution. The method is easy and convenient to operate; the cocoanut active charcoal can be purchased in the market and is repeatedly utilized when in use; and the recovery rates of platinum and palladium are larger than 99%.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Environment-friendly aqueous road paint and manufacturing method thereof
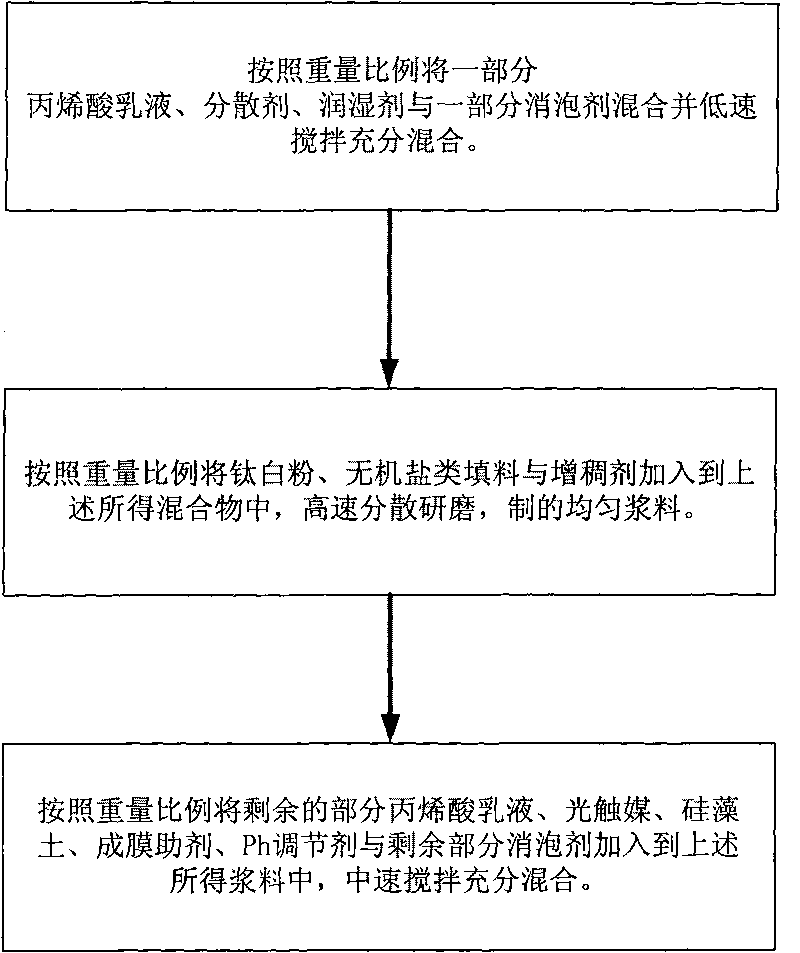
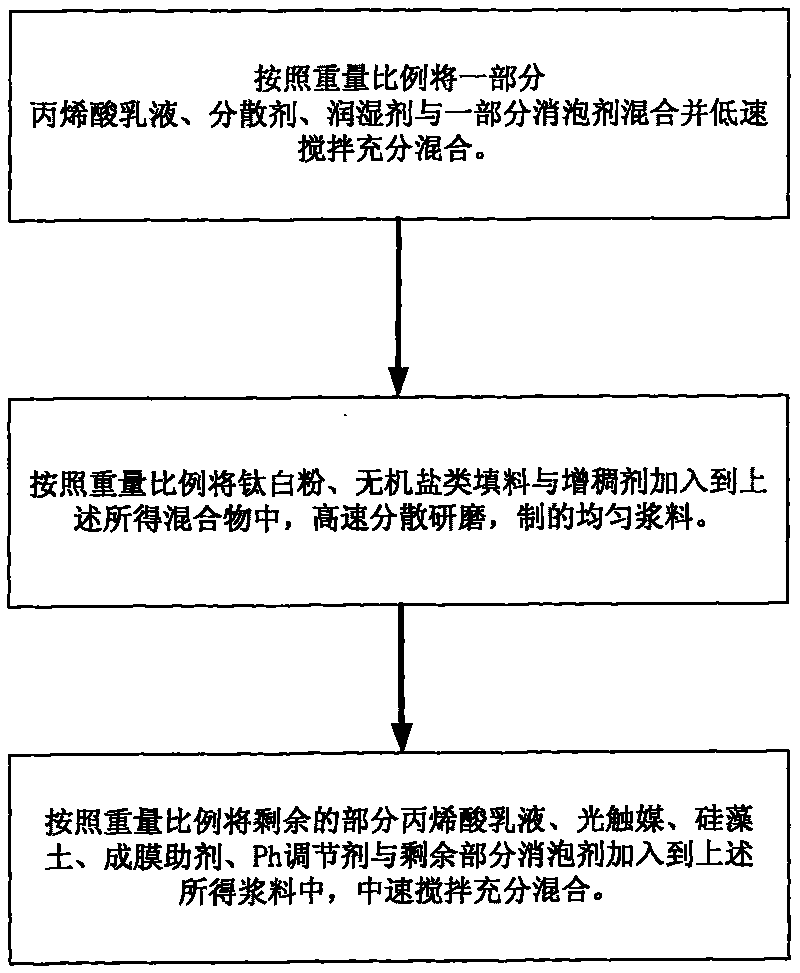
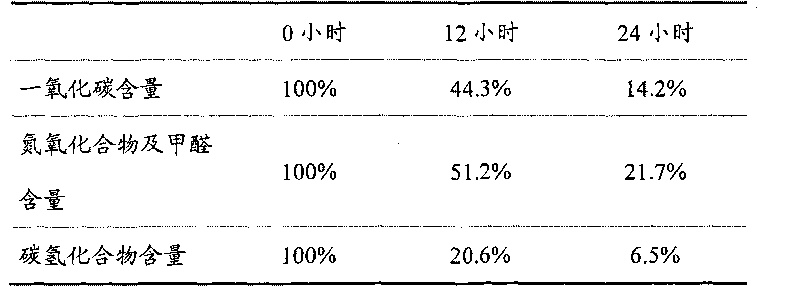
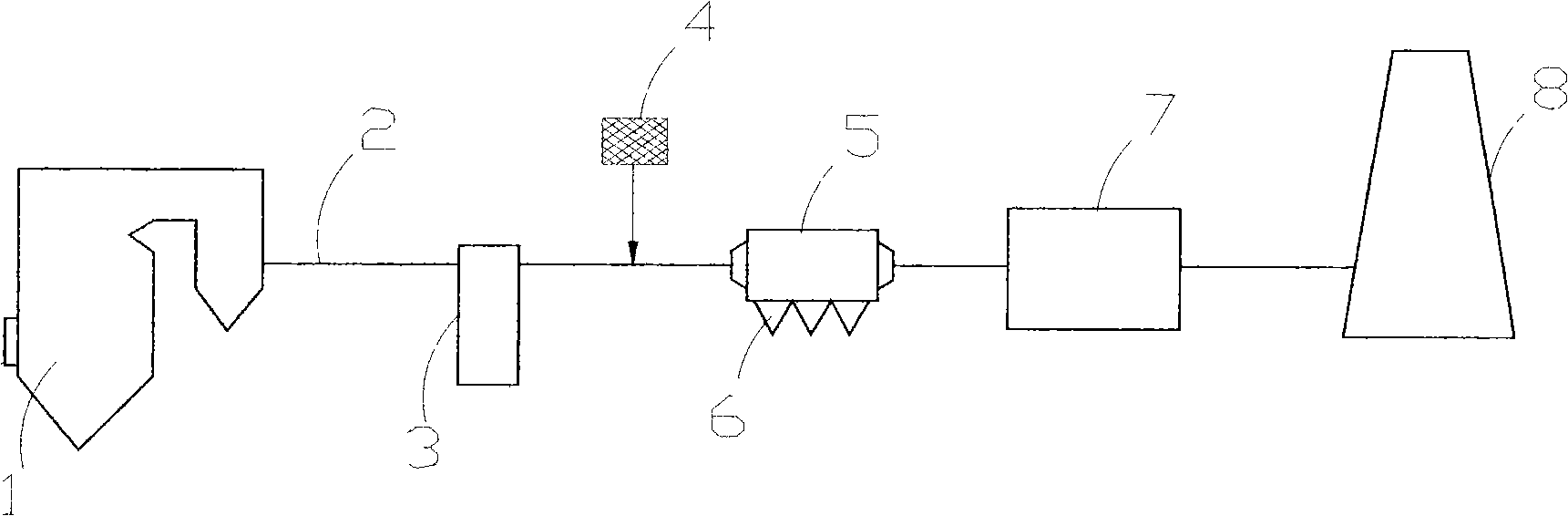
The invention discloses environment-friendly aqueous road paint and manufacturing method thereof. Components such as water, a dispersing agent, inorganic salt fillers, diatomite, a wetting agent, rutile type titanium white powder, photocatalyst, acrylic emulsion, a pH regulating agent, a defoaming agent, a thickening agent, a film forming aid, and the like are sufficiently mixed according to a certain process flow. By utilizing the strong adsorptive capacity of the diatomite, harmful substances in vehicle exhausts are absorbed in a coating containing the photocatalyst, and the photocatalyst absorbs optical energy amount to below bandgap energy under the irradiation of light so as to ensure that electrons of the photocatalyst obtain certain energy to separate from the constraints of atomic nucleuses and electron orbits and become free electrons, thus various harmful gases in the vehicle exhausts, such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, nitric oxides and the like can be oxidized and decomposed to finally form carbon dioxide, water and other innocuous substances having no harm to the human body so as to achieve the purpose of degrading the vehicle exhausts, thereby reducing photochemical smog phenomena.
Owner:CHINA PAINT MFG CO SHENZHEN
Agent for absorbing fire coal flue gas mercury pollutant and preparation and use thereof
ActiveCN101301603AConvenient sourceAchieve combinatorial optimizationOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationSpecific adsorptionSorbent
The present invention discloses an adsorbent for mercury pollution in coom smoke gas, a modified adsorbent thereof, and the preparation and application thereof. By employing the dewatered sludge from the city sewage processing factory as material, the adsorbent for mercury pollution in coom smoke gas is obtained after steps of dipping in chemical medicament, stirring and placing, pyrolysis and charring, and washing and drying. Furthermore, the modified adsorbent obtained by filtering modified element in the surface of the adsorbent can enhance the specific adsorption and the adsorption capability of the mercury of the material, and reduce the used amount of the absorption material. The adsorbent, the modified adsorbent and the compound prepared by the present invention can be used in treatment of the mercury pollution in coom smoke gas in different general operating manners. The adsorbent and the modified adsorbent prepared by the present invention have convenient material source, low production cost, facility application, and remarkable circumstance and economy benefit.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MEP
Preparation method and applications of magnetic recyclable lanthanum oxycarbonate phosphorus-removal adsorbent
ActiveCN110694583AGood magnetic separation performanceEfficient removalOther chemical processesWater contaminantsIndustrial waste waterSorbent
The invention discloses a preparation method and applications of a magnetic recyclable lanthanum oxycarbonate phosphorus-removal adsorbent. The method comprises: 1, synthesizing a lanthanum / iron composite metal organic framework precursor; 2, carrying out primary calcination; and 3, carrying out secondary calcination. According to the invention, the prepared magnetic recyclable lanthanum oxycarbonate phosphorus-removal adsorbent is a red brown powder solid in appearance, the microstructure is an obvious rod-shaped and amorphous mixed structure, the surface of the adsorbent is rough and porous,and the adsorbent integrates strong adsorption capacity of a nanometer material and good magnetic separation capacity of a magnetic material; the prepared magnetic recyclable lanthanum oxycarbonate phosphorus-removal adsorbent can remove medium-high concentration phosphorus from industrial wastewater, domestic sewage and the like and medium-low concentration phosphorus from surface water, secondary sedimentation tank effluent and the like; and the preparation method has characteristics of simple preparation process, good reproducibility, short preparation period and the like, and has good application prospect.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Synthesis method and application of nano-titanium dioxide for adsorption of heavy metals
The invention provides a synthesis method and application of nano-titanium dioxide for adsorption of heavy metals. Titanyl sulfate is put in a certain amount of water for dissolving, diluting, regulating pH value and washing so as to obtain the metatitanic precipitation. After the solid-liquid separation, the precipitation is dried at a certain temperature, grounded, sifted to get the titanium dioxide adsorbent. The adsorption experiments show that the adsorbent has a strong adsorption capacity in solution of Pb2 +, Cd2 +, Cu2 +,AsO43- and other heavy metal ions and the synthesis method can be used for purifying waste water containing high concentrations of heavy metals.
Owner:XIAN ENVIROMENTAL PROTECTION IND TRADE
Preparation method of highly-dispersed meso pore gamma-Al2O3 base alkali (soil) metal composite adsorbent
InactiveCN102658080ASimple processMild conditionsOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationSolvent evaporationSorbent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a highly-dispersed meso pore gamma-Al2O3 base alkali (soil) metal composite adsorbent, specifically comprising the following steps of: dispergating an aluminium source by the use of acid, mixing the obtained sol with a Pluronic triblock copolymer solution, adding alkali (soil) metal precursor salt according to the mol ratio of alkali (soil) metal to aluminium being less than or equal to 12%, fully stirring and uniformly mixing; and carrying out solvent evaporation-induced drying, vacuum drying and calcining on the obtained mixture or carrying out solvent evaporation-induced drying, vacuum drying and calcining after treating the obtained mixture under the hydro-thermal condition, so as to prepare the alkali (soil) metal composite adsorbent. The invention has the following advantages: the technology is simple; the condition is mild; the method is easy to control; the raw materials are cheap; and the alkali (soil) metal component and a carrier component are introduced by an in-situ one-pot method. The prepared highly-dispersed meso pore gamma-Al2O3 base alkali (soil) metal composite adsorbent has a good adsorption capability of a greenhouse gas CO2.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
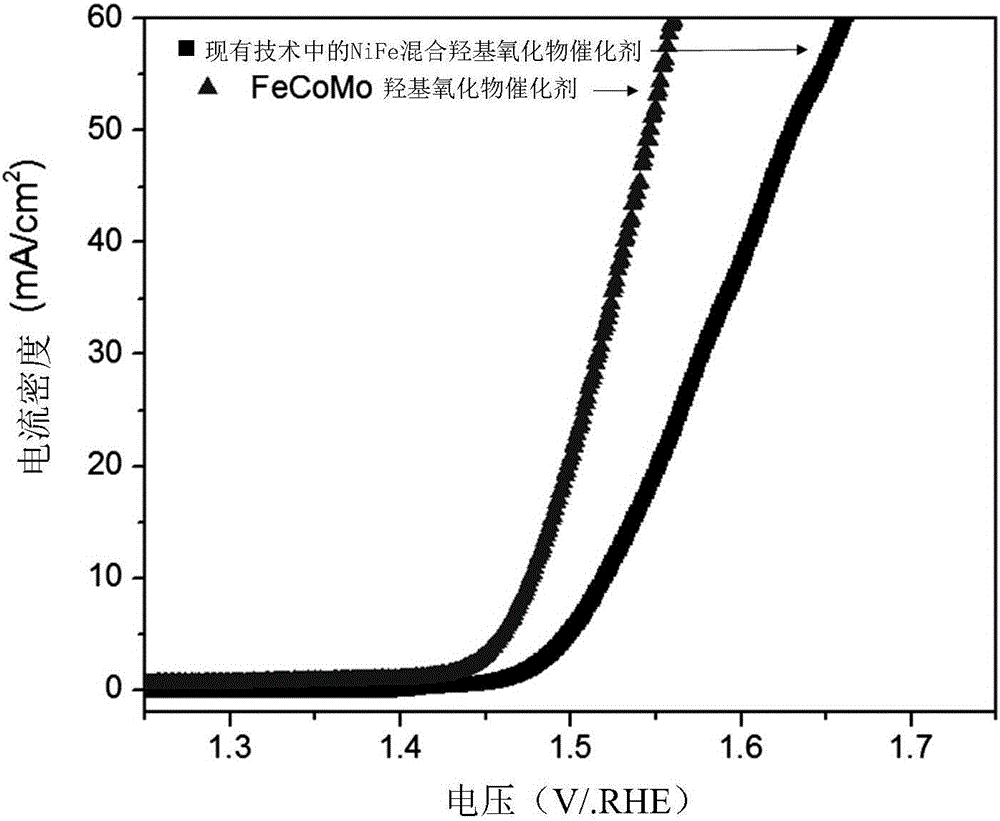
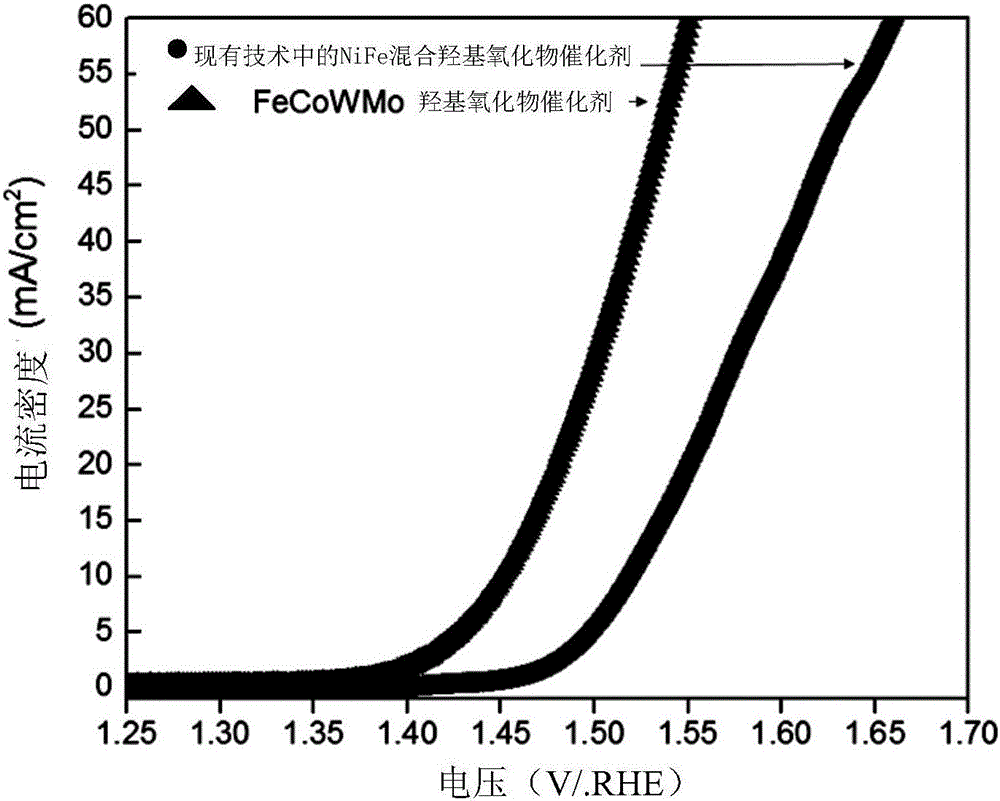
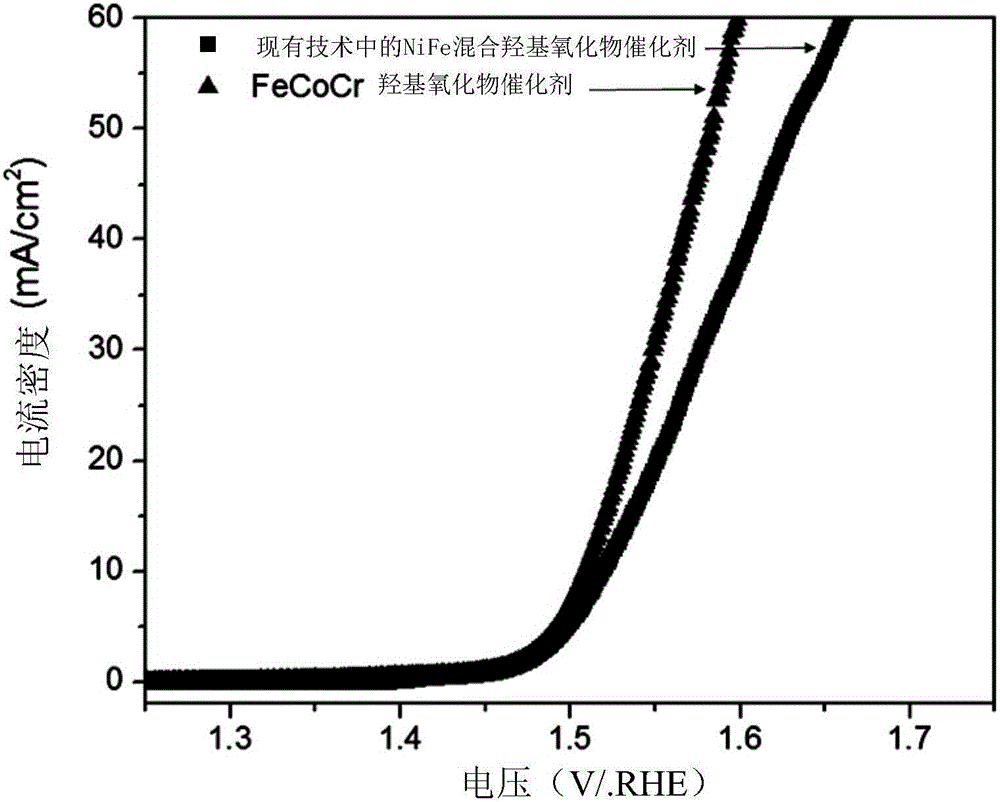
Metal oxyhydroxide catalyst, electrode, preparation methods of catalyst and electrode and electrochemical electrolysis unit
InactiveCN106693978AImprove efficiencyRich reservesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectrodesElectrolysisHydrogen
The invention provides a metal oxyhydroxide catalyst, an electrode, preparation methods of the catalyst and the electrode and an electrochemical electrolysis unit. In addition to oxygen and hydrogen, the metal oxyhydroxide further comprises two or more than two 3d transition metal elements and at least one regulator element, wherein the atoms of the 3d transition metal elements and atoms of the regulator elements are distributed in a common oxyhydroxide skeleton, and are connected onto the atoms of the regulator elements through bridging oxygen or bridging hydroxyl, and homogeneous phase distribution is realized on the atomic level; and moreover, according to the interaction among the adjacent 3d transition metal atoms and the interaction between the adjacent 3d transition metal atoms and the regulator element atoms, the adsorption energy of an intermediate in an oxygen evolution reaction can be regulated. The metal oxyhydroxide catalyst is different from a mixed metal oxide catalyst crystallized in the prior art, so that the efficiency of carrying out the oxygen evolution reaction through electrolytic water can be improved. Meanwhile, the 3d transition metal atoms have rich reserves on the earth, so that the catalytic cost can be reduced.
Owner:王艳
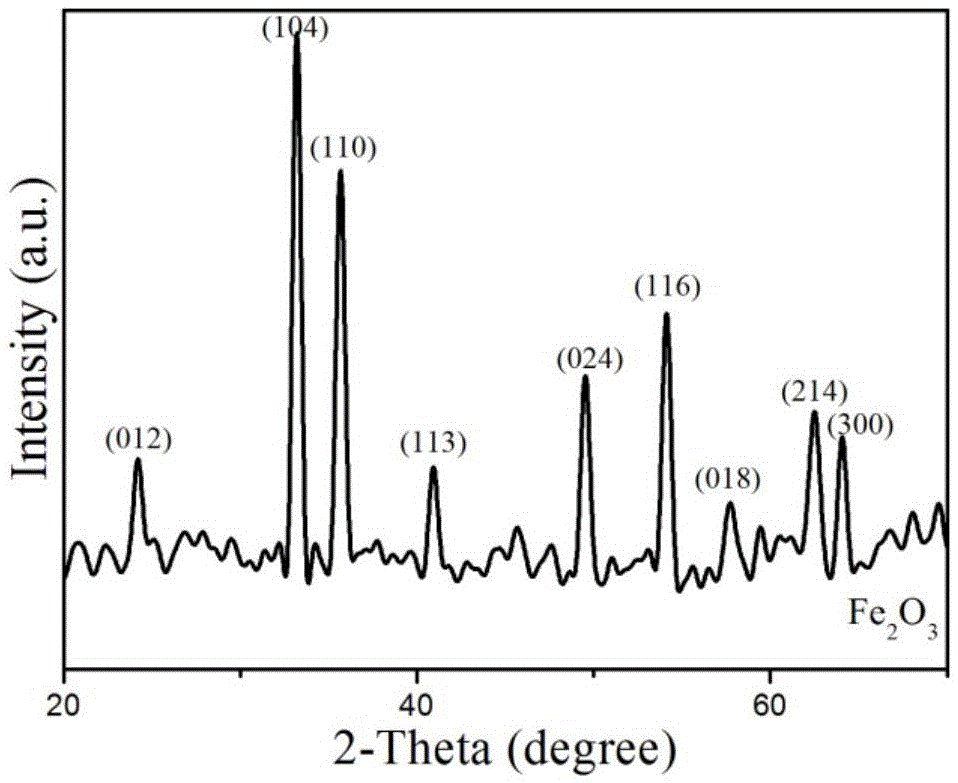
Spherical mesoporous iron oxide and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a spherical mesoporous iron oxide and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: adding certain amounts of CTAB and DDAB to water, dissolving the CTAB and the DDAB, adding a small amount of ammonia water, stirring, adding FeCl3.6H2O, continuously stirring to obtain a solution with a reddish brown precipitate, transferring the solution to a reaction kettle, placing the reaction kettle in a thermotank, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction, centrifuging the obtained product, washing the centrifuged product, drying the washed product, grinding the dried product, and calcining the ground product to obtain the mesoporous spherical iron oxide. The spherical mesoporous iron oxide with the surface having uniformly-distributed mesopores and with the inside being honeycomb is obtained by using a monocationic / dicationic surfactant as a composite template, the aperture is about 2-4nm, and the particle size is 200-250nm. The mesoporous spherical iron oxide prepared through the method has large adsorption ability to arsenic ions, lead ions and other ions, so the mesoporous spherical iron oxide is of great practical significance to develop efficient arsenic and lead removal adsorption materials.
Owner:海门市创豪工业设计有限公司
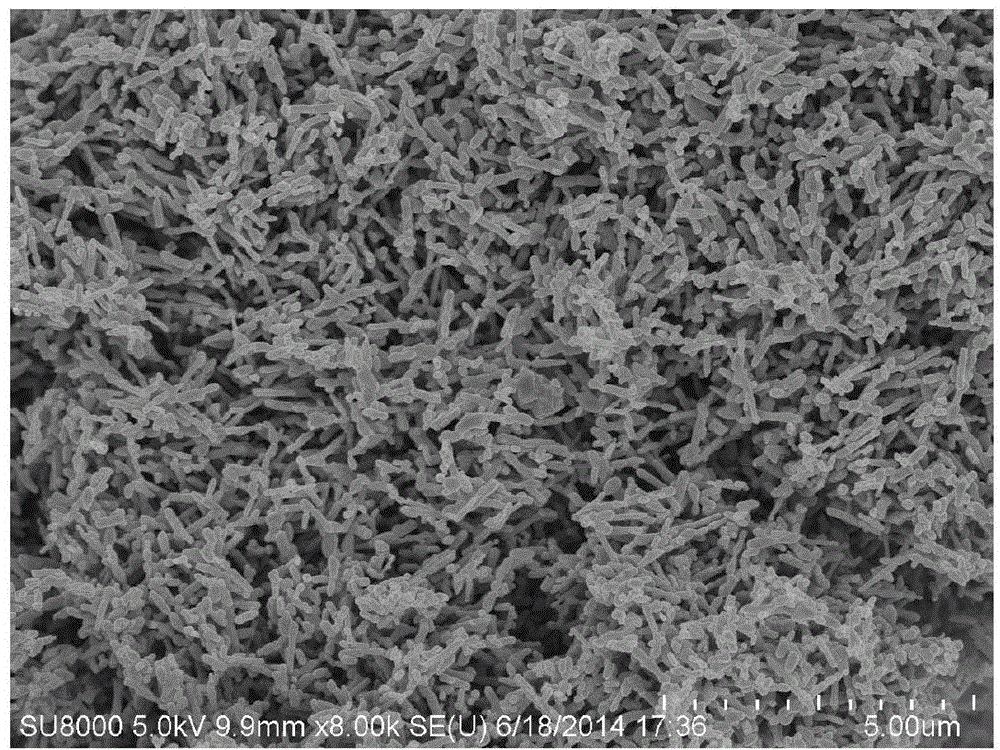
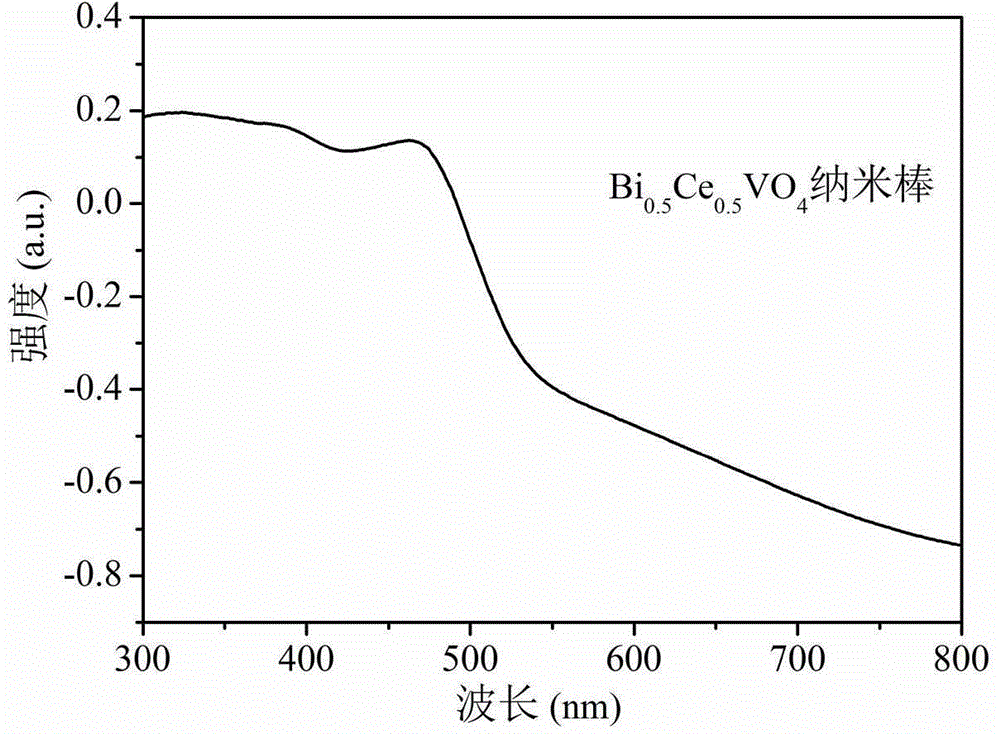
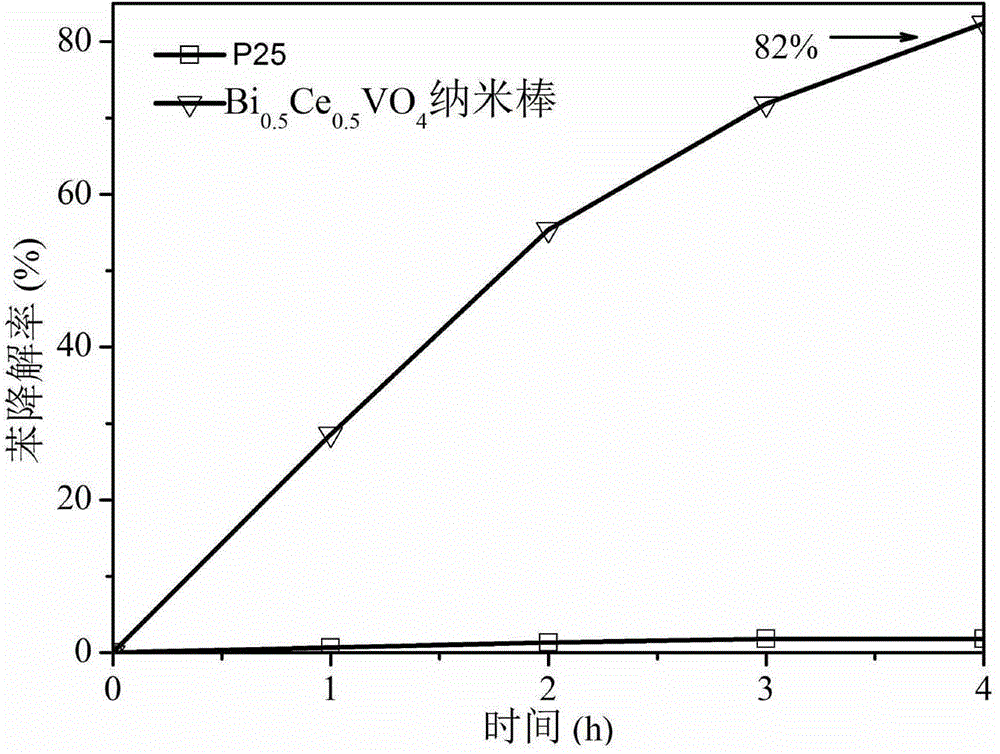
BixCel-xVO4 nanorod with visible-light activity and preparation method
InactiveCN104923212AImprove separation efficiencyLarge specific surface areaDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPollutantMicrostructure
A BixCel-xVO4 nanorod with visible-light activity is a nanoscale compound having a rod-like light-yellow microstructure and obtained by hydrothermal reaction of Bi(NO3)3.5H2O, Ce(NO3)3.6H2O and NH4VO3 at a molar ratio of x to 1-x to 1 (x is more than 0 and less than 1). A preparation method for the BixCel-xVO4 nanorod mainly comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing Bi(NO3)3.5H2O, Ce(NO3)3.6H2O and water to obtain a solution A; adding water into the NH4VO3 and dissolving a mixture in water bath with the temperature of 60 DEG C to obtain a solution B; dropwise adding the solution A into the solution B, performing hydrothermal reaction at 120 to 200 DEG C for 1 to 6 hours, cleaning precipitates, drying, and then calcining at 300 to 800 DEG C for 12 to 48 hours to obtain a light-yellow powdery substance, namely the BixCel-xVO4 nanorod. The BixCel-xVO4 nanorod is large in specific surface area and strong in adsorption capacity, has better visible-light absorption performance and greatly improves photocatalytic oxidation degradation of organic pollutants; and the preparation method for the BixCel-xVO4 nanorod is relatively simple and easy to operate.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
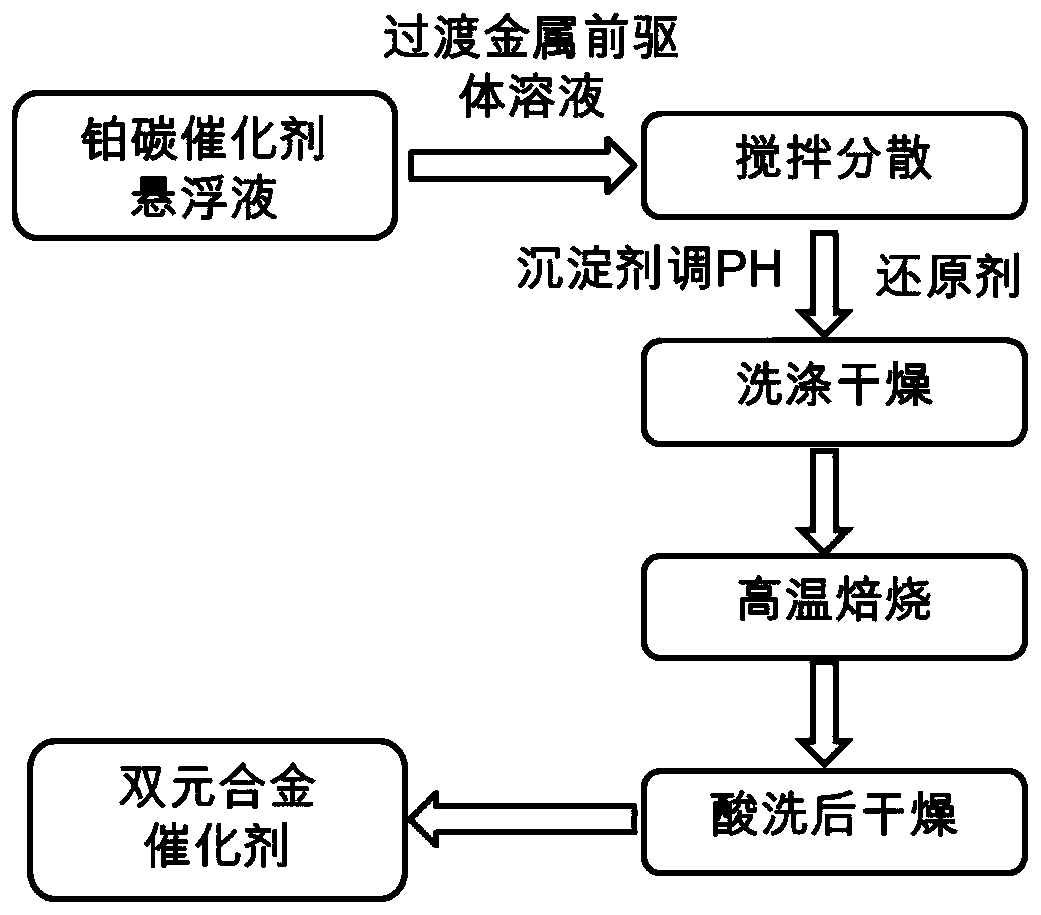
High-temperature preparation method of proton exchange membrane fuel cell binary alloy catalyst
PendingCN111589454ALow priceReduce dosageCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystMetallurgy
The invention belongs to the technical field of new energy materials and application, and particularly relates to a high-temperature preparation method of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell binary alloy catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing and stirring a transition metal precursor solution and a platinum-carbon catalyst suspension to fully disperse; (2) adding a precipitant solution and a reducing agent solution into a mixed solution dispersed in step (1), adjusting the pH value of the mixed solution to 9-13, centrifuging or filter-pressing and washing for multiple times after complete precipitation, and fully drying to obtain catalyst precursor powder; and (3) roasting the catalyst precursor powder at high temperature, cooling, pickling, and dryingto obtain catalyst powder. The transition metal element and the platinum catalyst are used for forming the binary alloy catalyst, the cost of the catalyst can be reduced, after the transition metal and platinum form an alloy, crystal lattices of platinum shrink, and the adsorption energy of the surface to oxygen is reduced, so the catalytic activity of the oxygen reduction reaction is improved.
Owner:WUXI WEIFU HIGH TECH CO LTD
Method for removing mercury ions from water by using silver-modified magnetic carbon nanotube and regeneration method
InactiveCN102553526AStrong specificityEasy to separateOther chemical processesCombustible gas purificationSorbentNanotube
The invention discloses a method for removing mercury ions from water by using silver-modified magnetic carbon nanotubes and a regeneration method thereof. A trace amount of mercury ions (Hg2+) in a polluted water body are adsorbed by silver nanoparticle-loaded / iron oxide magnetic carbon nanotubes as adsorbent under the conditions that the temperature is 20 DEG C to 60 DEG C and the pH value is 3 to 8; and the adsorbent is recycled and regenerated by thermal desorption. The silver nanoparticle-loaded / iron oxide magnetic carbon nanotube has powerful capability and specificity of adsorbing mercury ions in water. With magnetic separation techniques, the process of separating the adsorbent from the water solution is greatly simplified, the probability of secondary pollution is reduced to the greatest extent, and the environmental benefit is improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
System for exhaust gas purification
InactiveUS6350416B2Combination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesPtru catalystHydrocotyle bowlesioides
A system for exhaust gas purification disposed in the exhaust pipe of an internal combustion engine, includes an adsorbent formed by loading, on a monolithic carrier, (1) a zeolite containing at least one kind of ion of an element having an electronegativity of 1.40 or more and (2) a catalyst material formed by loading at least one kind of noble metal selected from Pt, Pd and Rh on a heat-resistant inorganic oxide, and at least one loaded carrier formed by loading, on a monolithic carrier, a catalyst component having a purifiability for the harmful substances present in the exhaust gas emitted from the engine and / or an adsorbent component having an adsorptivity for the hydrocarbons also present in the exhaust gas, the loaded carrier being provided upstream of the adsorbent in the flow direction of the exhaust gas and having a total volume of 0.6 l or more. In this system for exhaust gas purification, the thermal deterioration of the adsorbent is reduced because there is used an adsorbent of higher HC desorption start temperature and because the thermal load applied to the adsorbent is decreased by the use of a particular means.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Preparing method and application of novel compound boron nitride adsorbing material
ActiveCN109706549AHigh adsorption activityAddress limitationsOther chemical processesInorganic material artificial filamentsSorbentFine particulate
The invention provides a preparing method of a novel compound porous boron nitride material which has a high adsorption capacity for heavy metal and fine particulate matter in high-temperature flue gas. The preparing method is environmentally friendly and can achieve recycling. The preparing method comprises three synthesis steps that 1, melamine (a nitrogen source), boric acid (a nitrogen source)and an additive are utilized for synthesizing a precursor of porous boron nitride; 2, the compound precursor obtained in step 1 and a pore-forming agent are doped and mixed under protective atmosphere, and high-temperature thermal cracking is conducted; 3, an obtained cracking product is put into a solution containing a surfactant for washing and drying to obtain the novel compound boron nitrideadsorbing material with a high specific surface area and a high activity. By means of the method, the defect that an existing adsorbent cannot be utilized under high-temperature and special extreme conditions is overcome, and the preparing method has a good application prospect in the field of high-temperature adsorption.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com