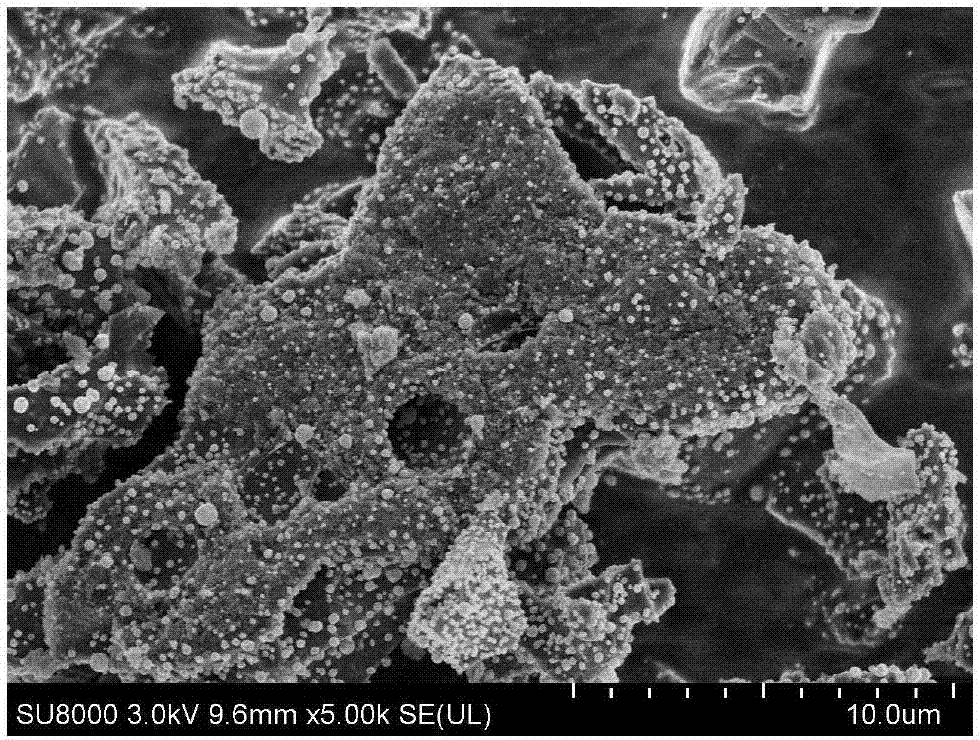
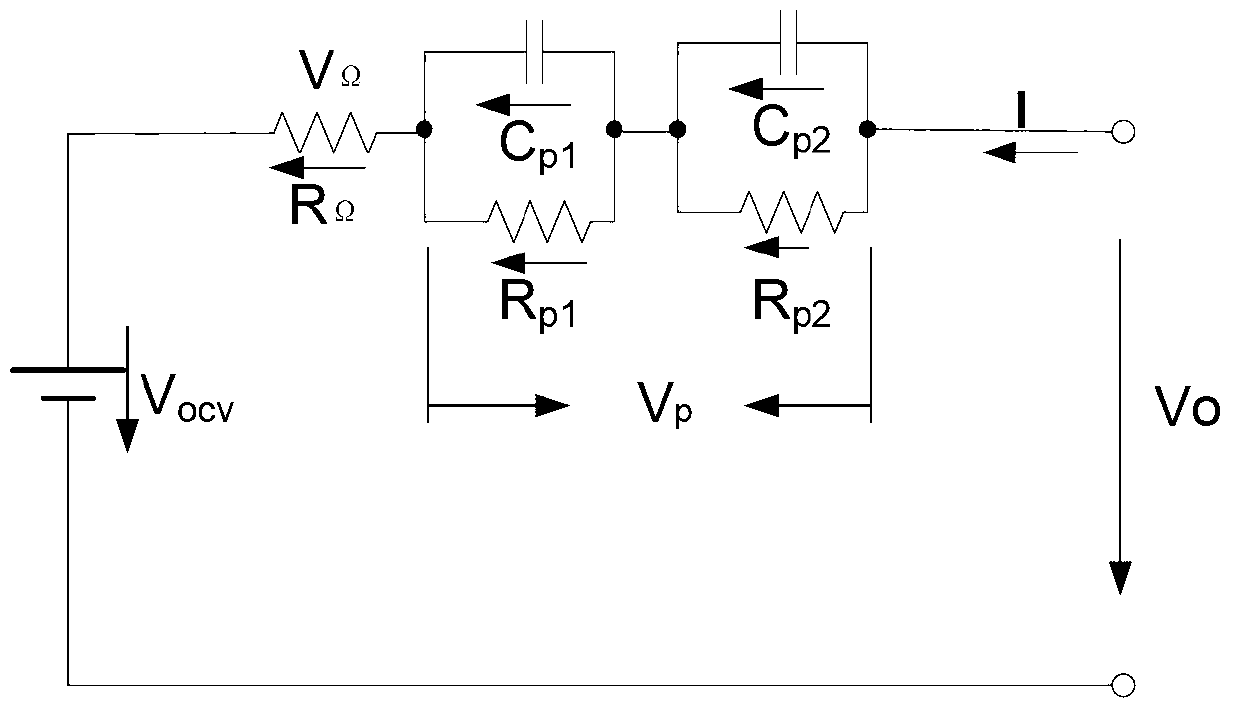
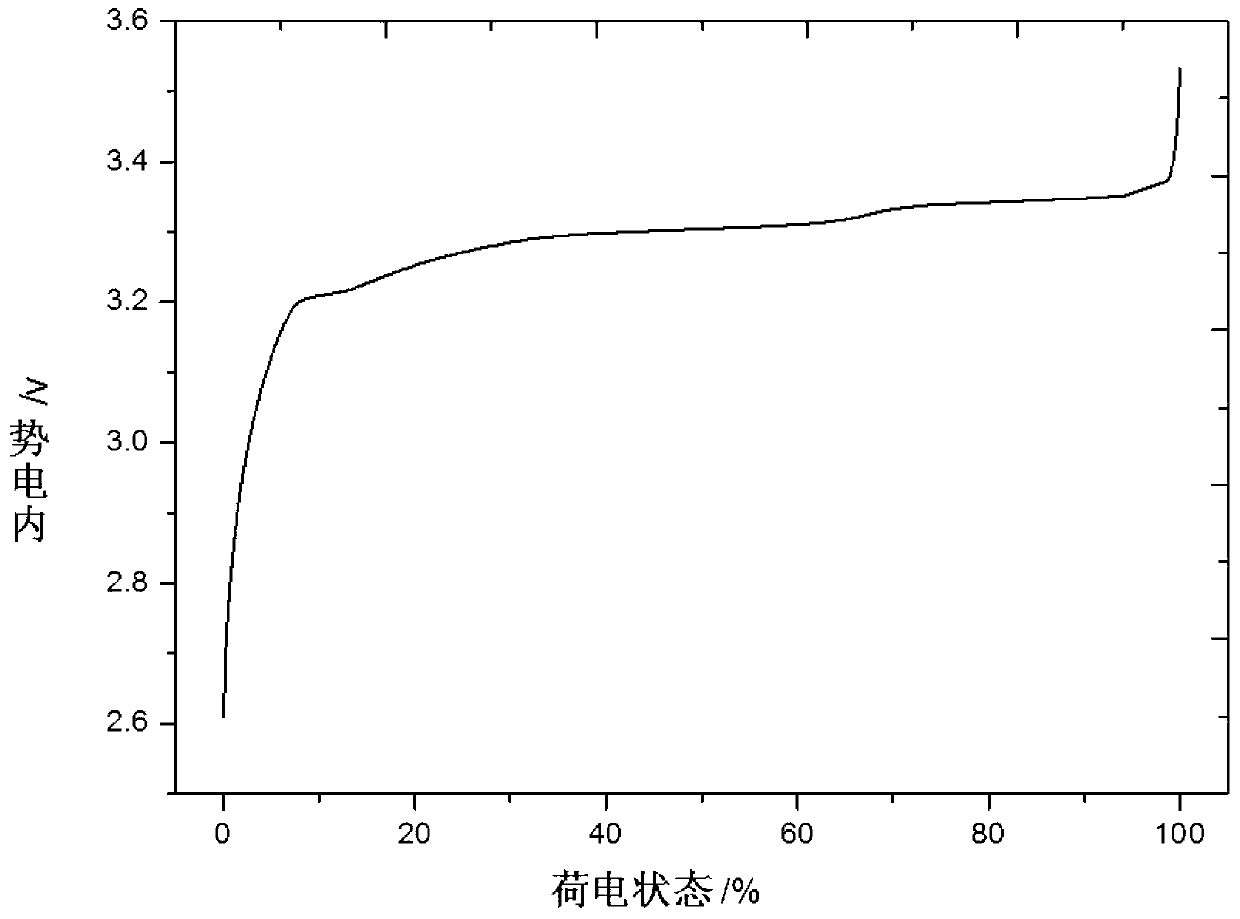
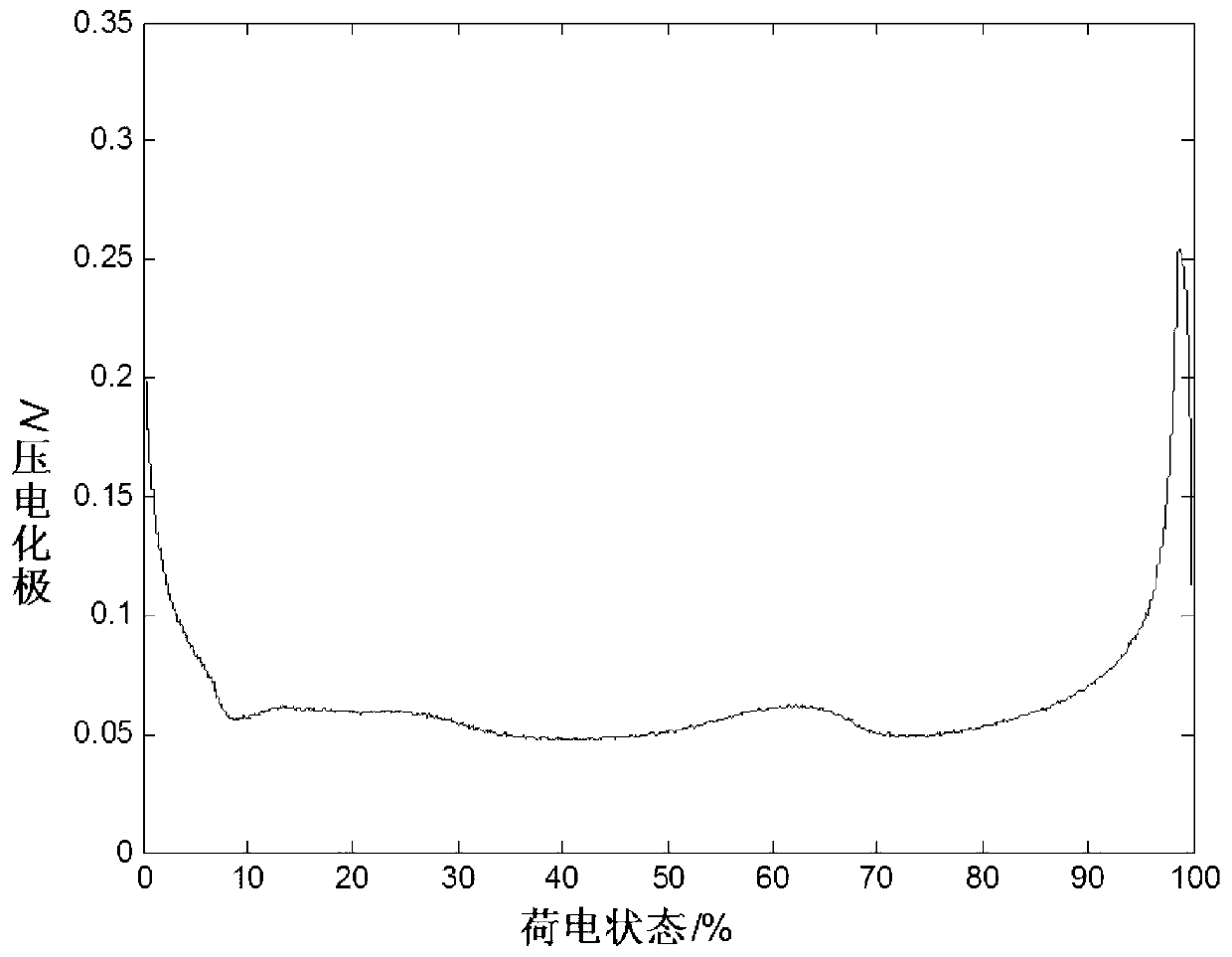
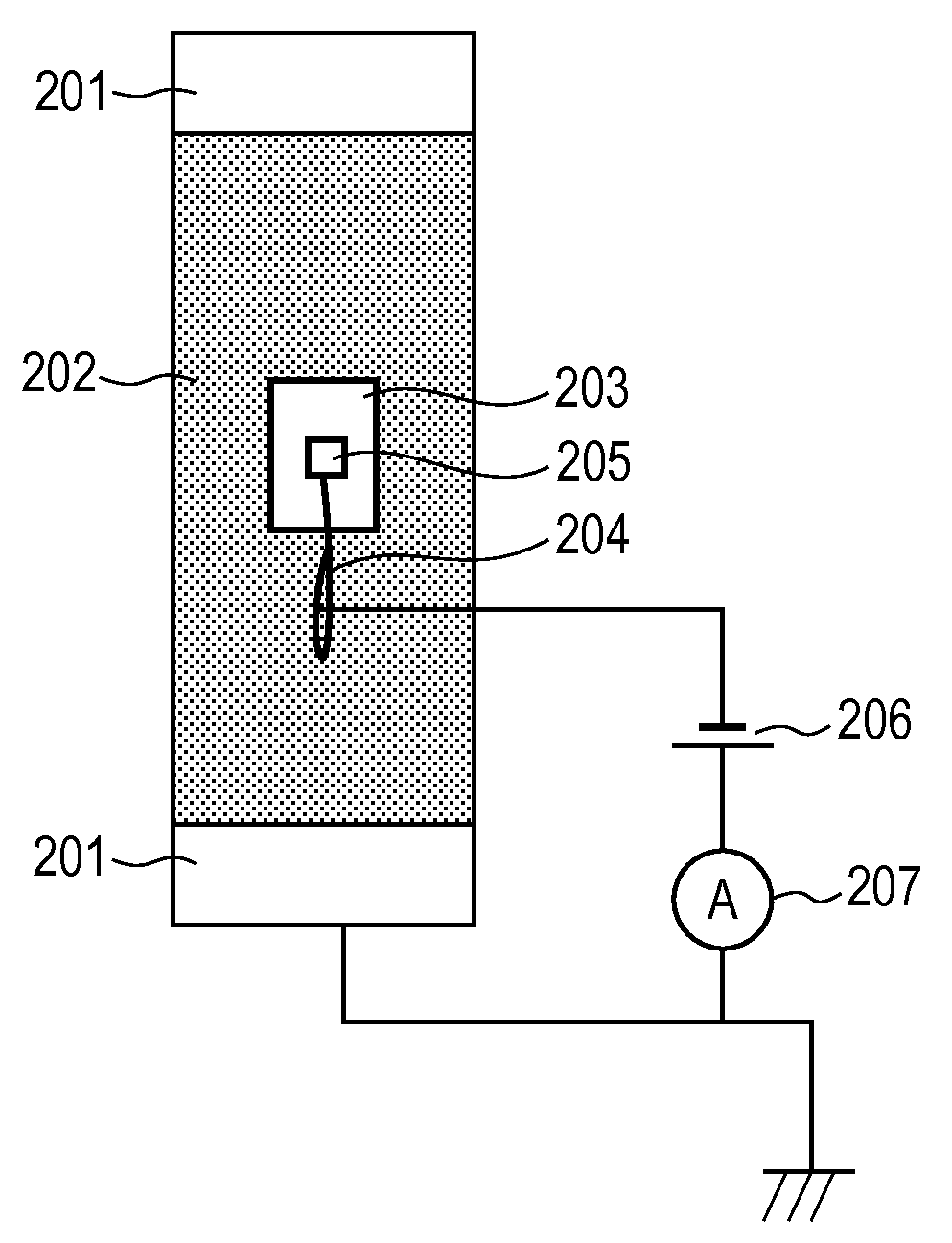
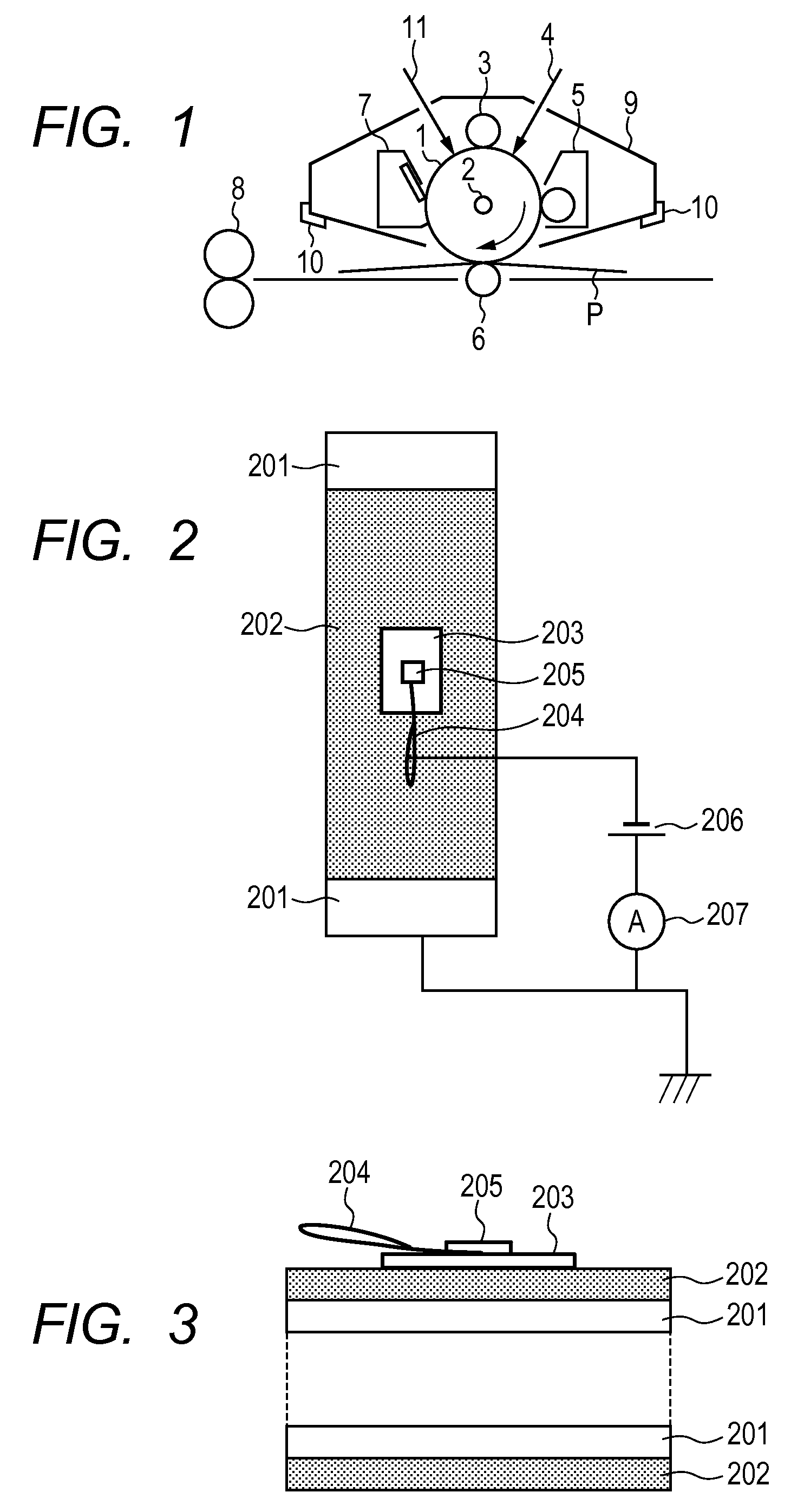
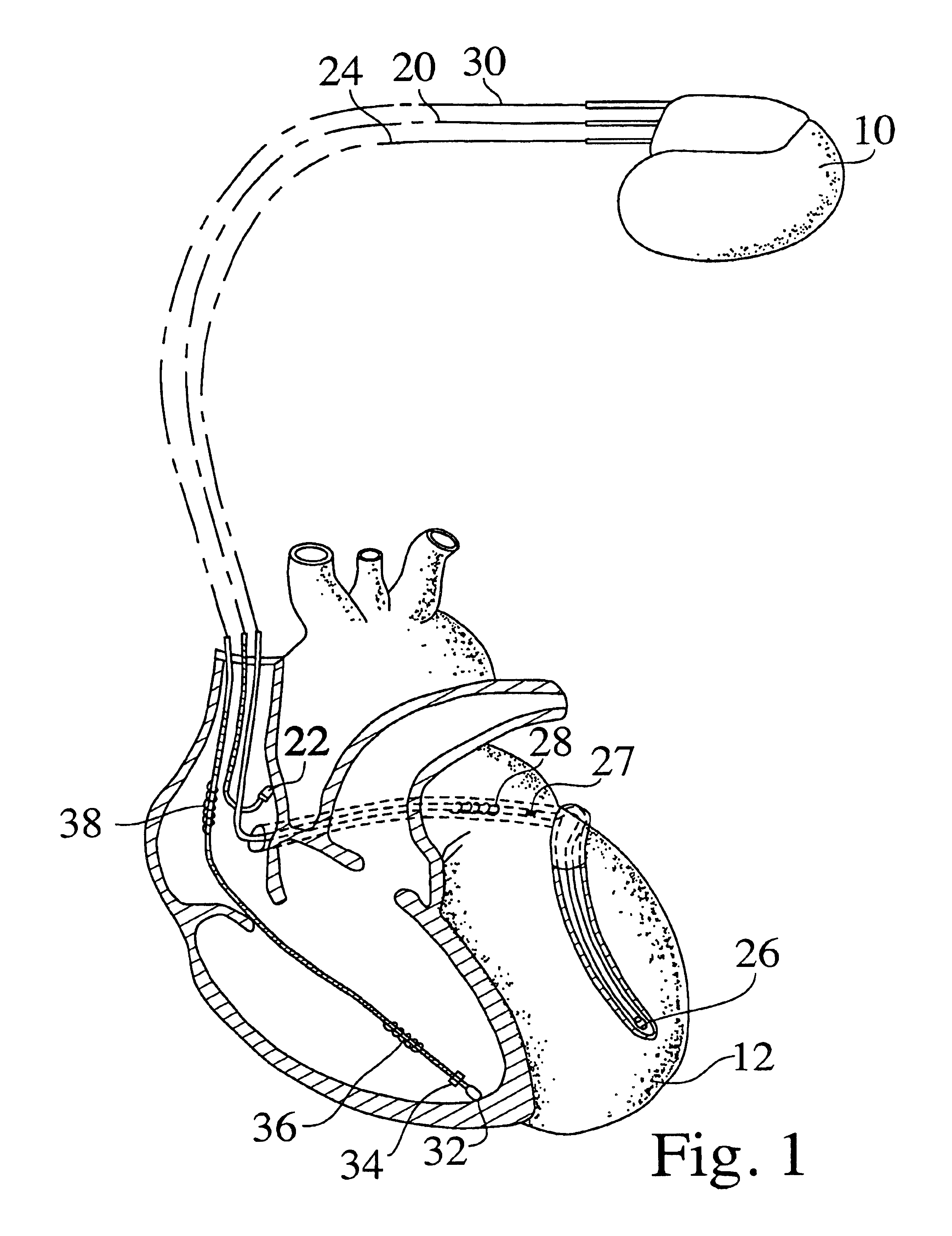
Patents
Literature
71 results about "Partial charge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A partial charge is a non-integer charge value when measured in elementary charge units. Partial charge is more commonly called net atomic charge. It is represented by the Greek lowercase letter δ, namely δ− or δ+.
Lithium battery cycle life quick testing method
ActiveCN103344917AReduce designShorten the development cycleElectrical testingElectricityTest battery
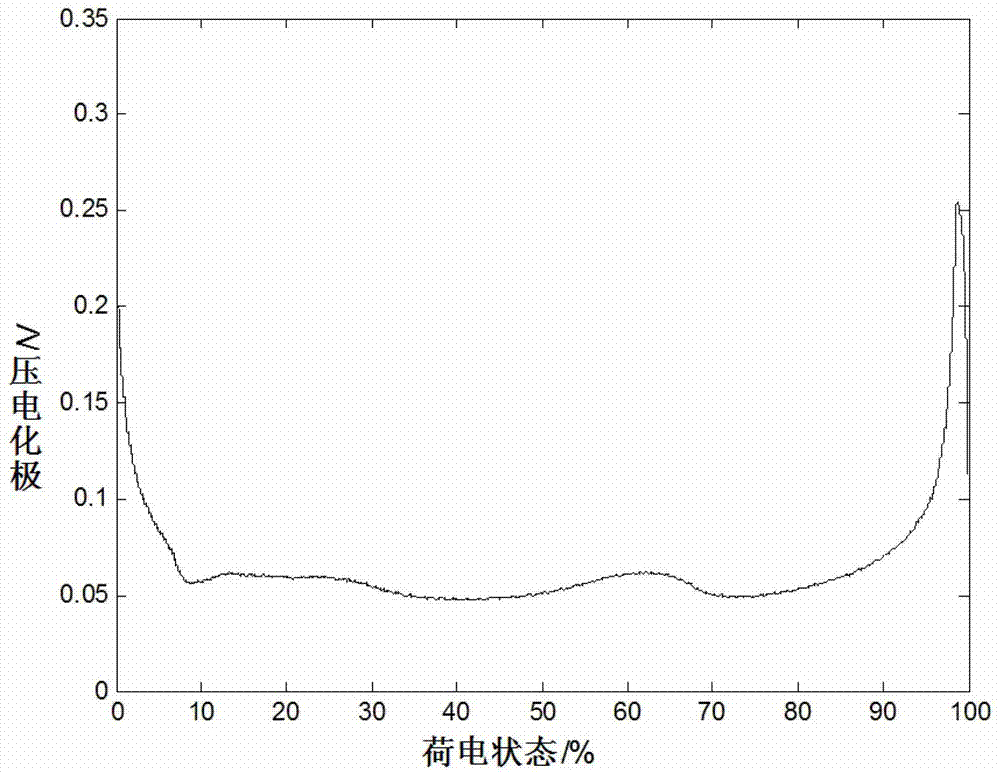
The invention relates to the technical field of lithium battery parameter determination methods, in particular to a lithium battery cycle life quick testing method. The method includes the steps of step 1, determining charge state interval for cycle life quick testing according to polarization voltage characteristics of a battery sample, step 2, carrying out a battery cycle life quick test to obtain cycle life test experimental data, step 3, carrying out cycle life mathematic model deduction in partial charge interval, step 4, establishing cycle life deduction mathematic models in 0-100% charge interval, step 5, obtaining a cycle life formula of a battery in the 0-100% charge interval, and step 6, estimating the cycle life of the tested battery. The lithium battery cycle life quick testing method overcomes the defects that time for conventional testing is long, and difference between an accelerated cycle life testing method and the reality is large, and shortens design, development and testing periods of batteries.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV +2
Method for fast detecting cycle life of lead-acid accumulator
InactiveCN102012485AQuick detection of cycle lifeReal dataCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical testingPartial chargePower flow
The invention discloses a method of fast detecting the cycle life of a lead-acid accumulator, which comprises the following steps of detecting real release capacity at first; then determining charge and discharge voltage of partial charge state of the accumulator; determining the charge voltage of the partial charge state; determining the discharge voltage of partial charge state so as to ensure that the accumulator circularly works at the charge and discharge voltage U1 and U2, is charged to U1 / each accumulator at the limited current of 0.2 to 2C, and is discharged to U2 / each accumulator as one cycle at the 2 to 4C-time large current; detecting the capacity after a plurality of times of cycle; comparing the measured discharge capacity with the actual capacity; and judging that the accumulator fails if the measured capacity is lower than 80% of the actual capacity. The invention has the advantages of actually reflecting the failure mode of the lead-acid accumulator for a power-driven automobile during operation, obviously shortening the detection time, and greatly saving the cost and energy sources.
Owner:张天任
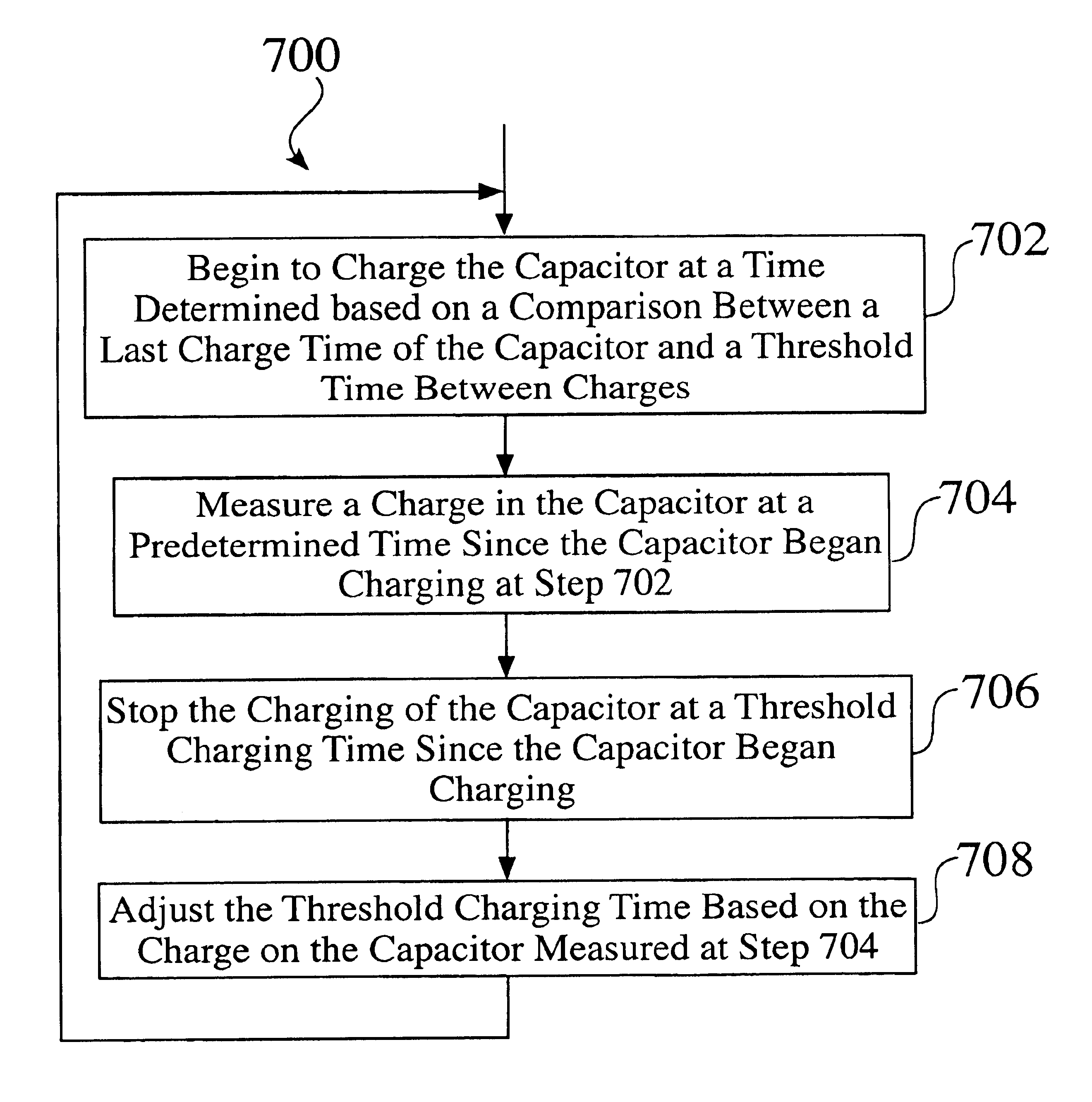
Methods and devices for inhibiting battery voltage delays in an implantable cardiac device
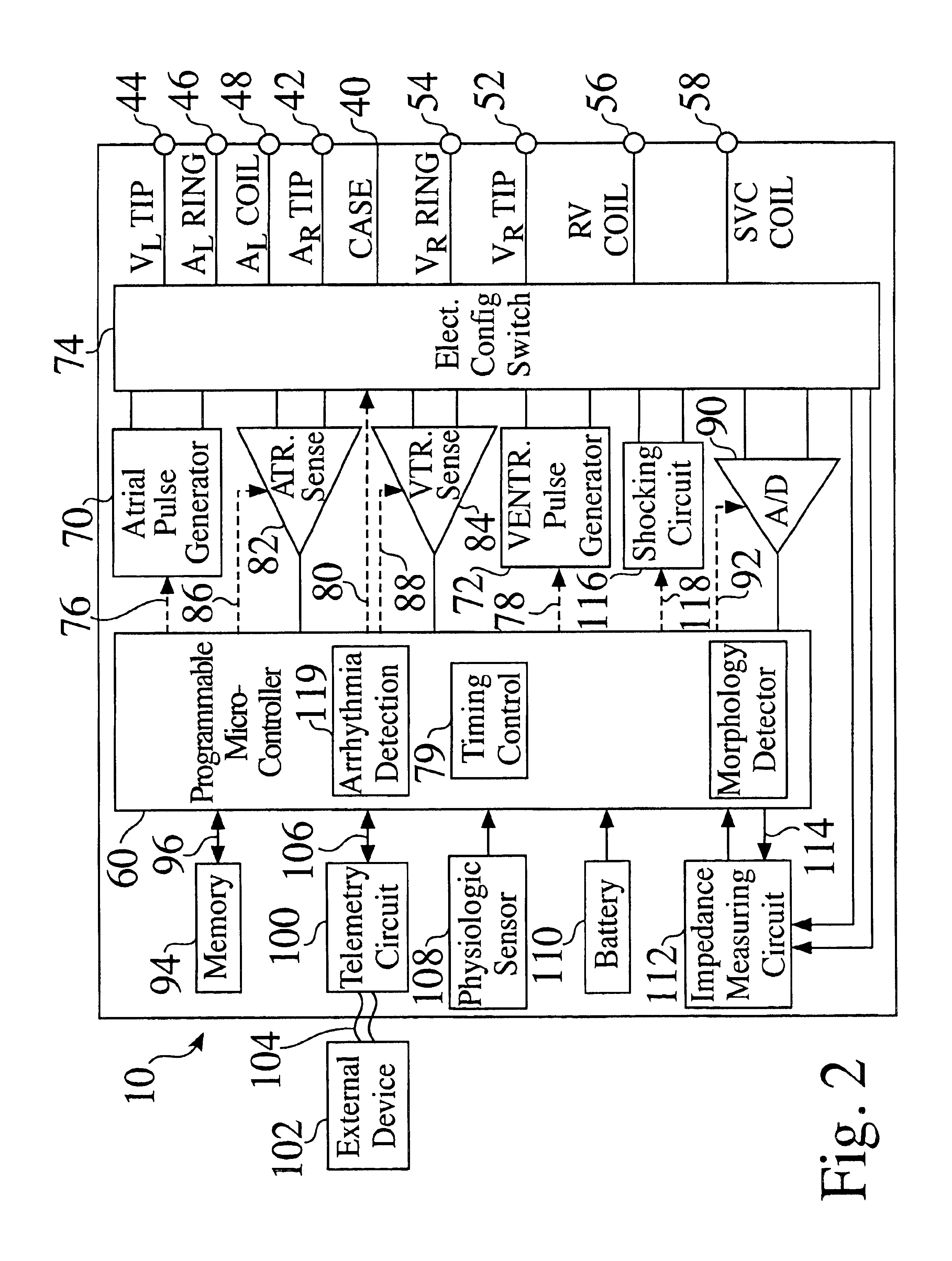
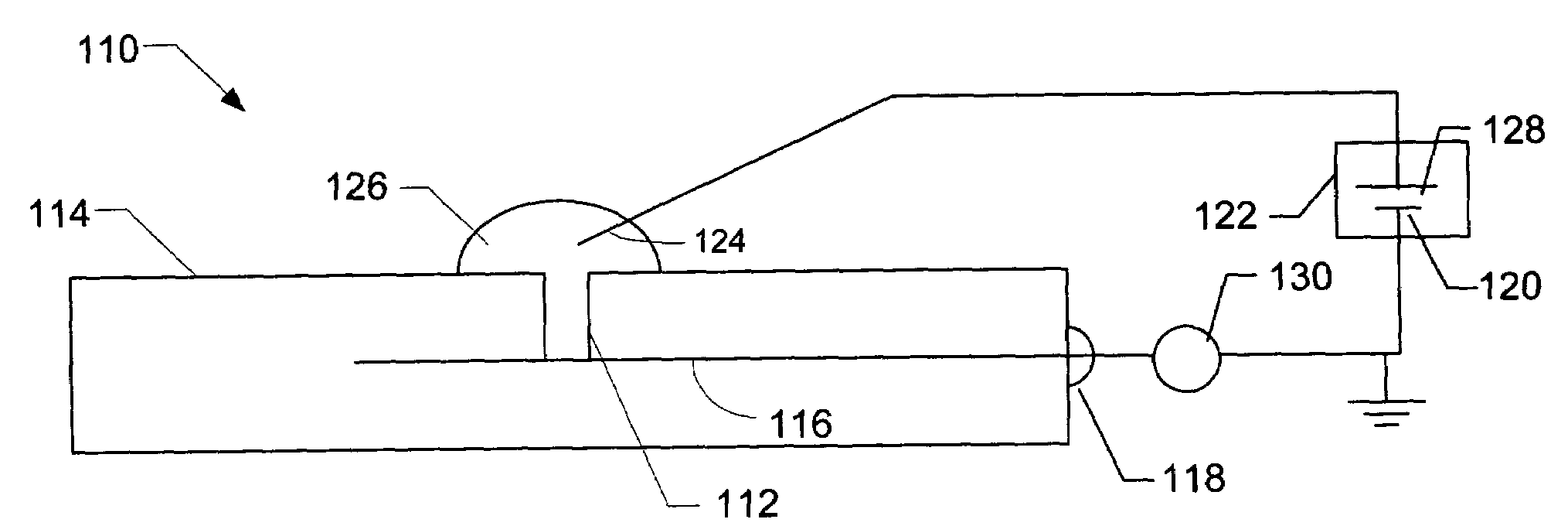
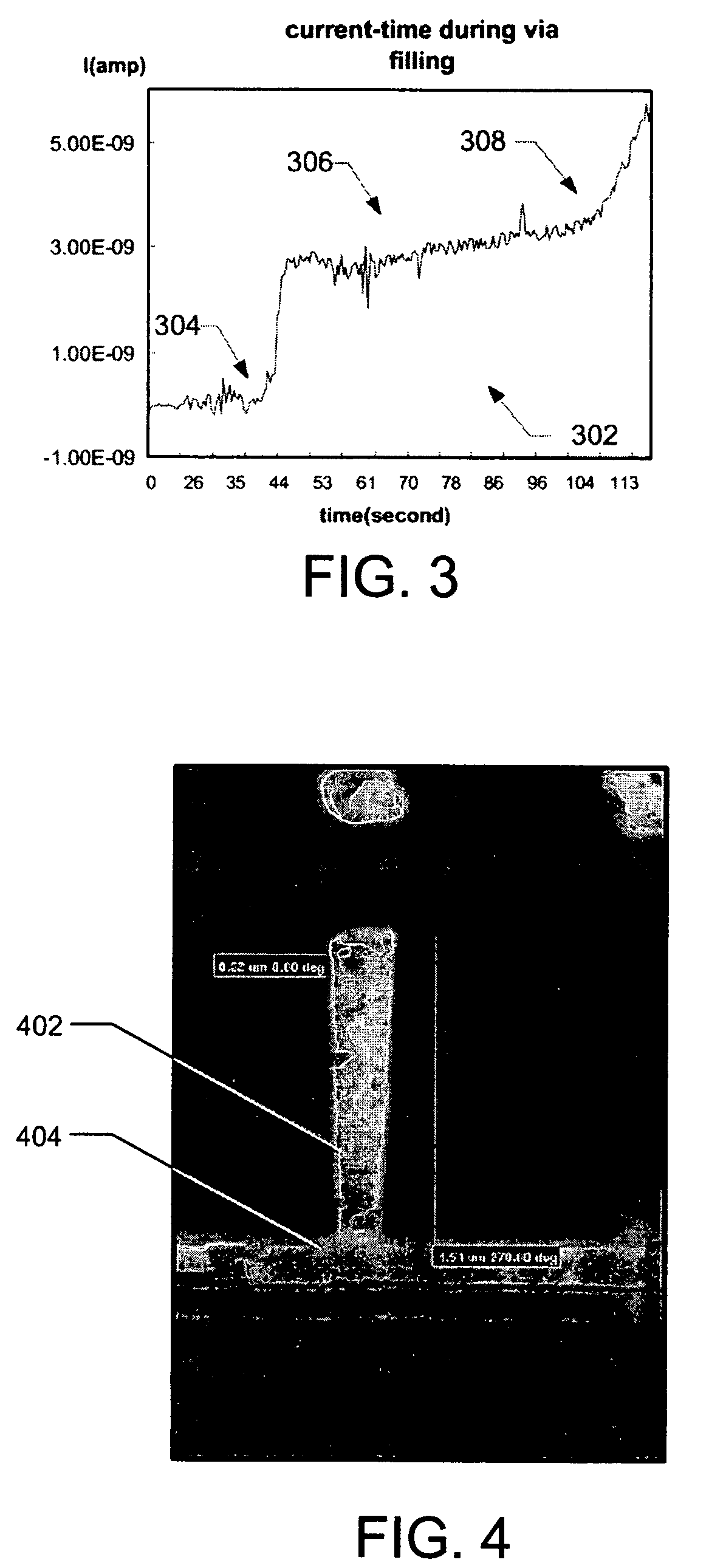
A battery of a cardiac stimulation device may experience voltage delay problems caused by a passivation layer that forms on the anode of the battery. To inhibit voltage delay, the battery is periodically used to charge the capacitor to a partial charge. Both the charge time and the interval between charges can be adjusted to reduce the power consumption required to inhibit battery voltage delay.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System for modifying small structures using localized charge transfer mechanism to remove or deposit material
ActiveUS7674706B2Rapidly precisely depositLow resistance metal conductorsFinanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPartial chargeEngineering
A charge transfer mechanism is used to locally deposit or remove material for a small structure. A local electrochemical cell is created without having to immerse the entire work piece in a bath. The charge transfer mechanism can be used together with a charged particle beam or laser system to modify small structures, such as integrated circuits or micro-electromechanical system. The charge transfer process can be performed in air or, in some embodiments, in a vacuum chamber.
Owner:FEI CO
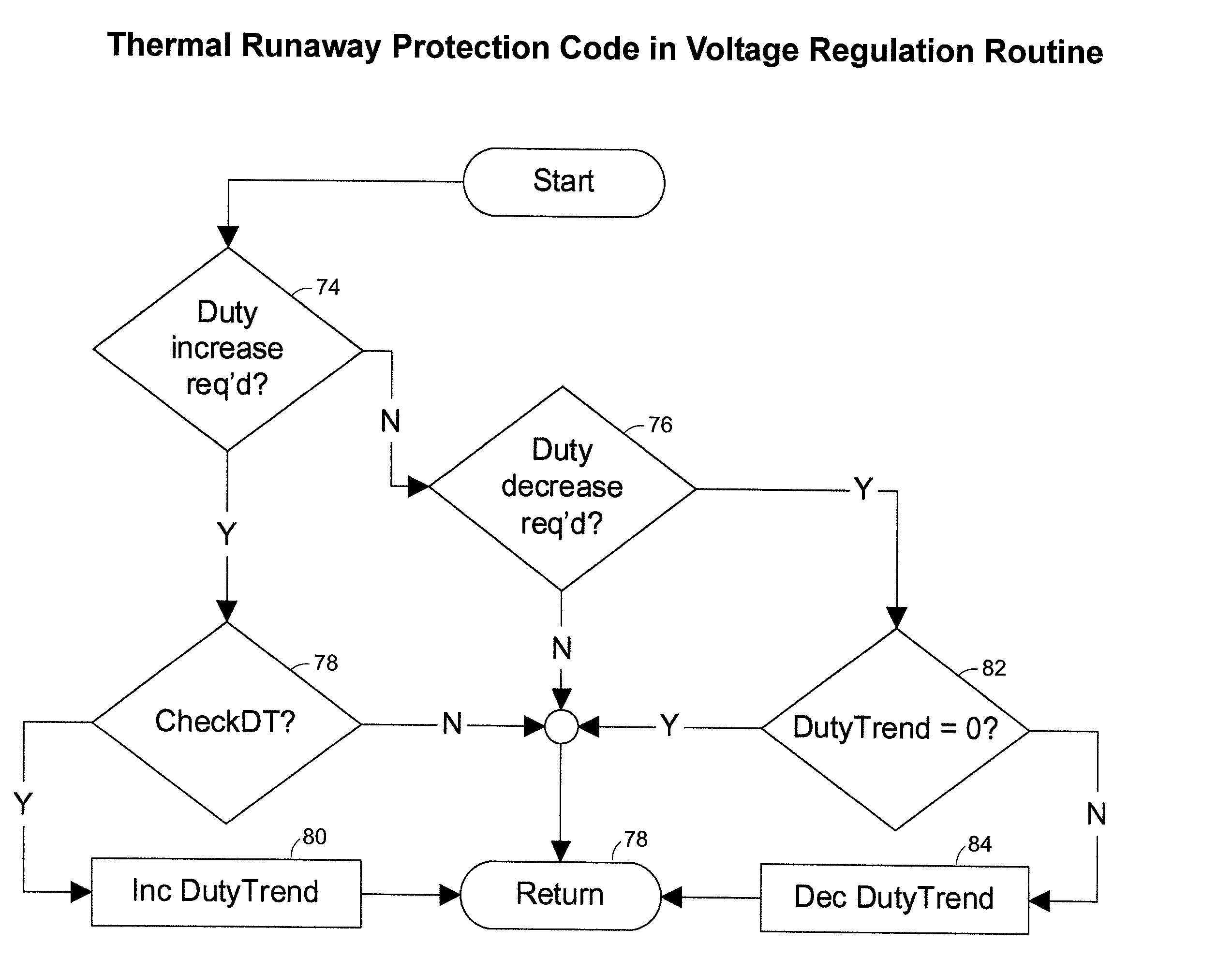
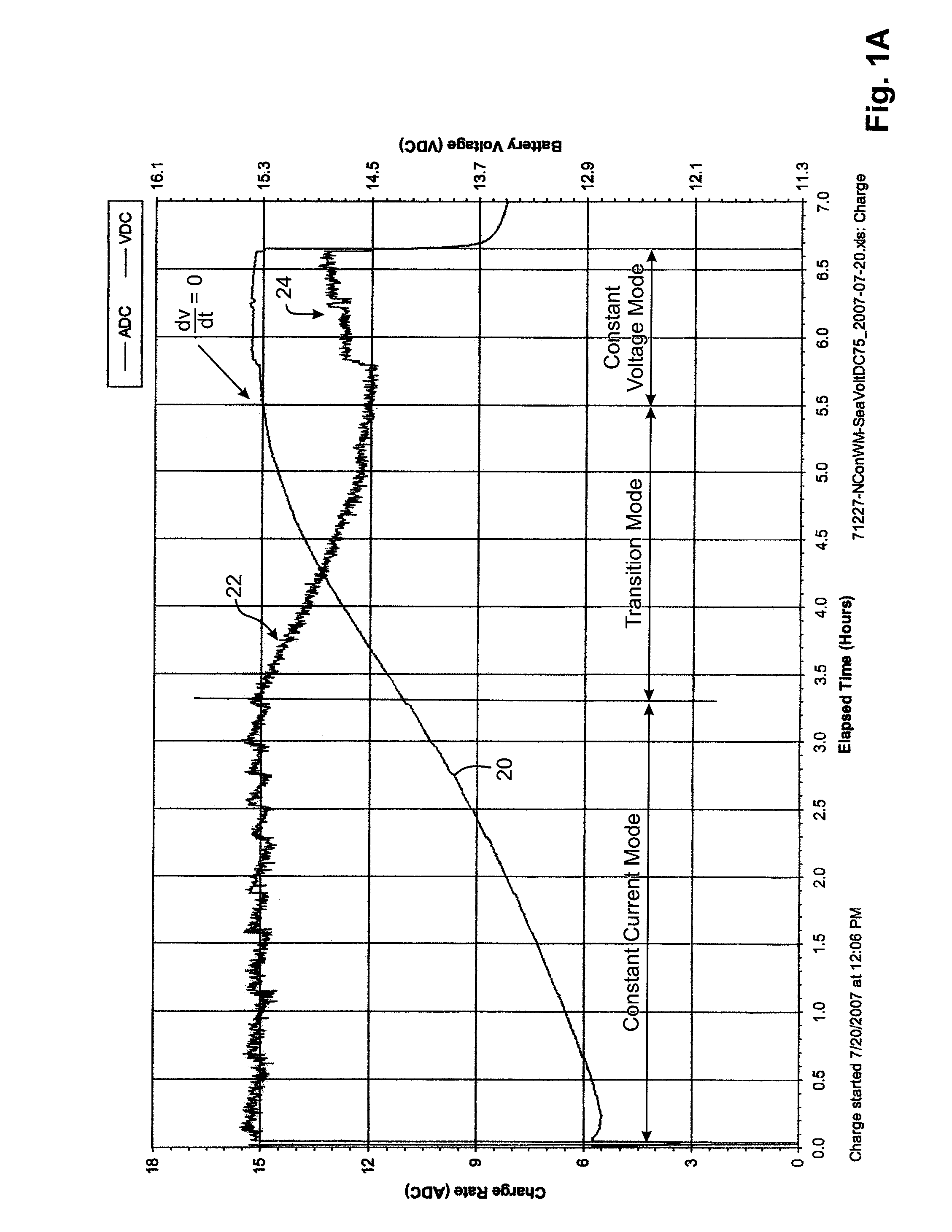
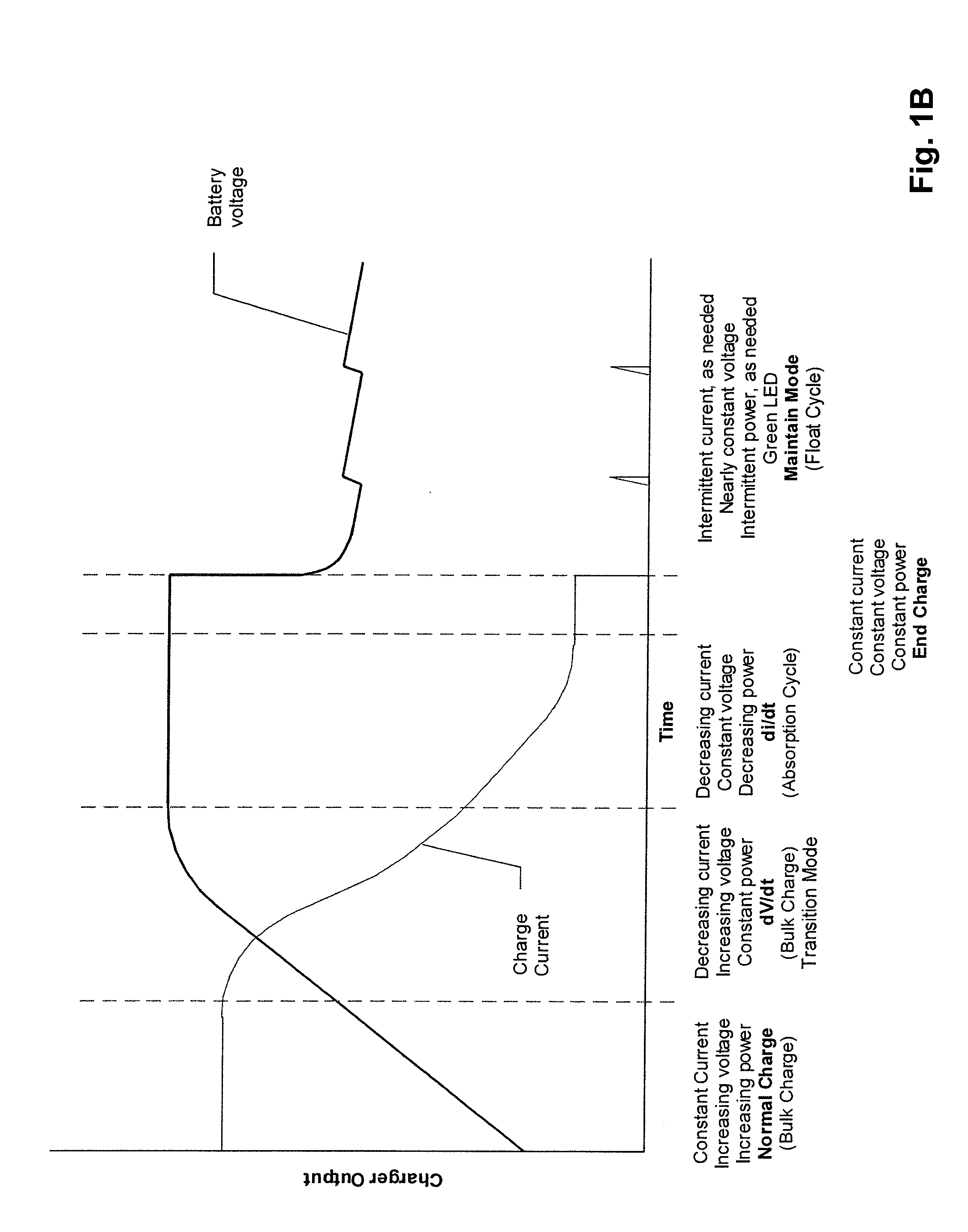
Thermal Runaway Protection System for a Battery Charger
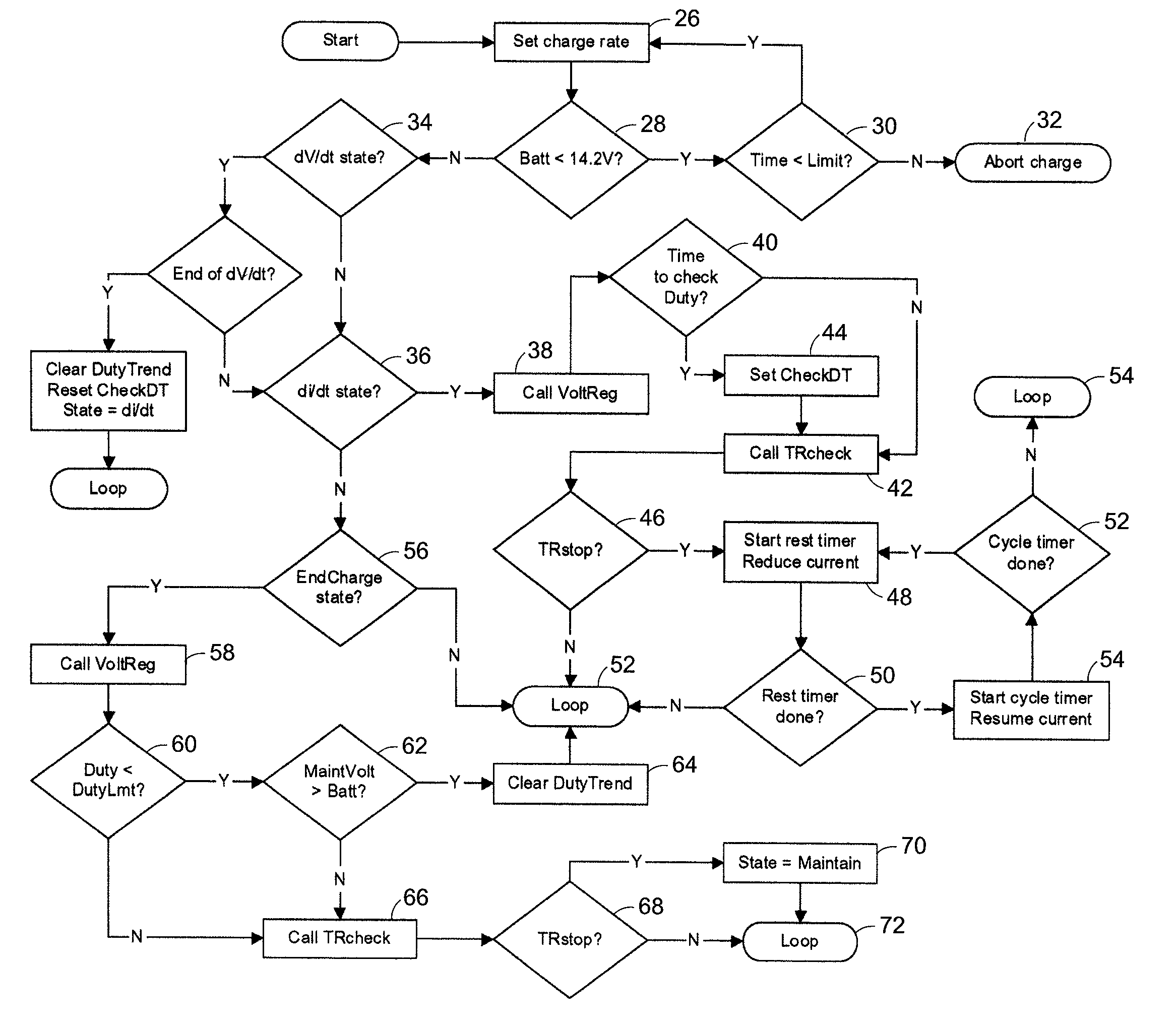
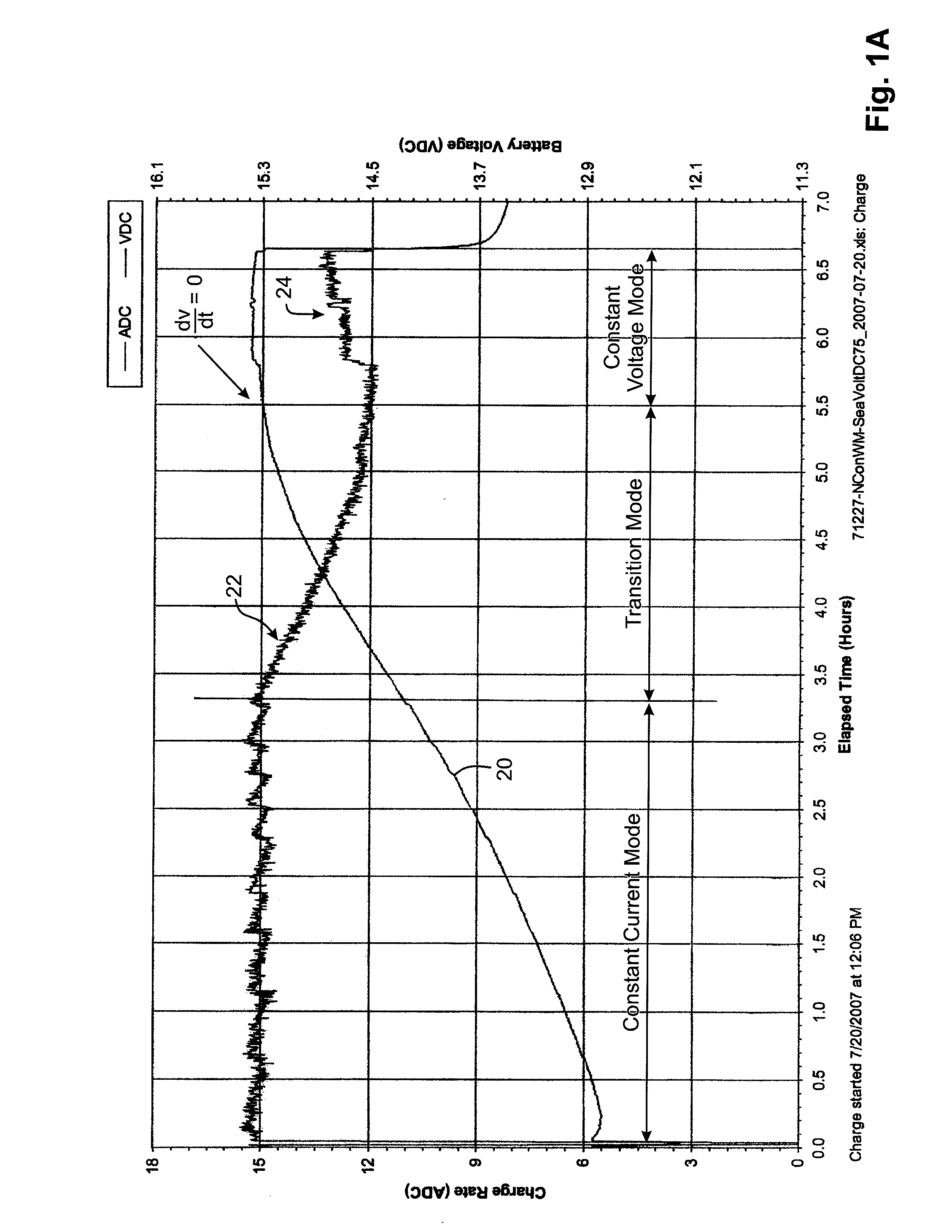
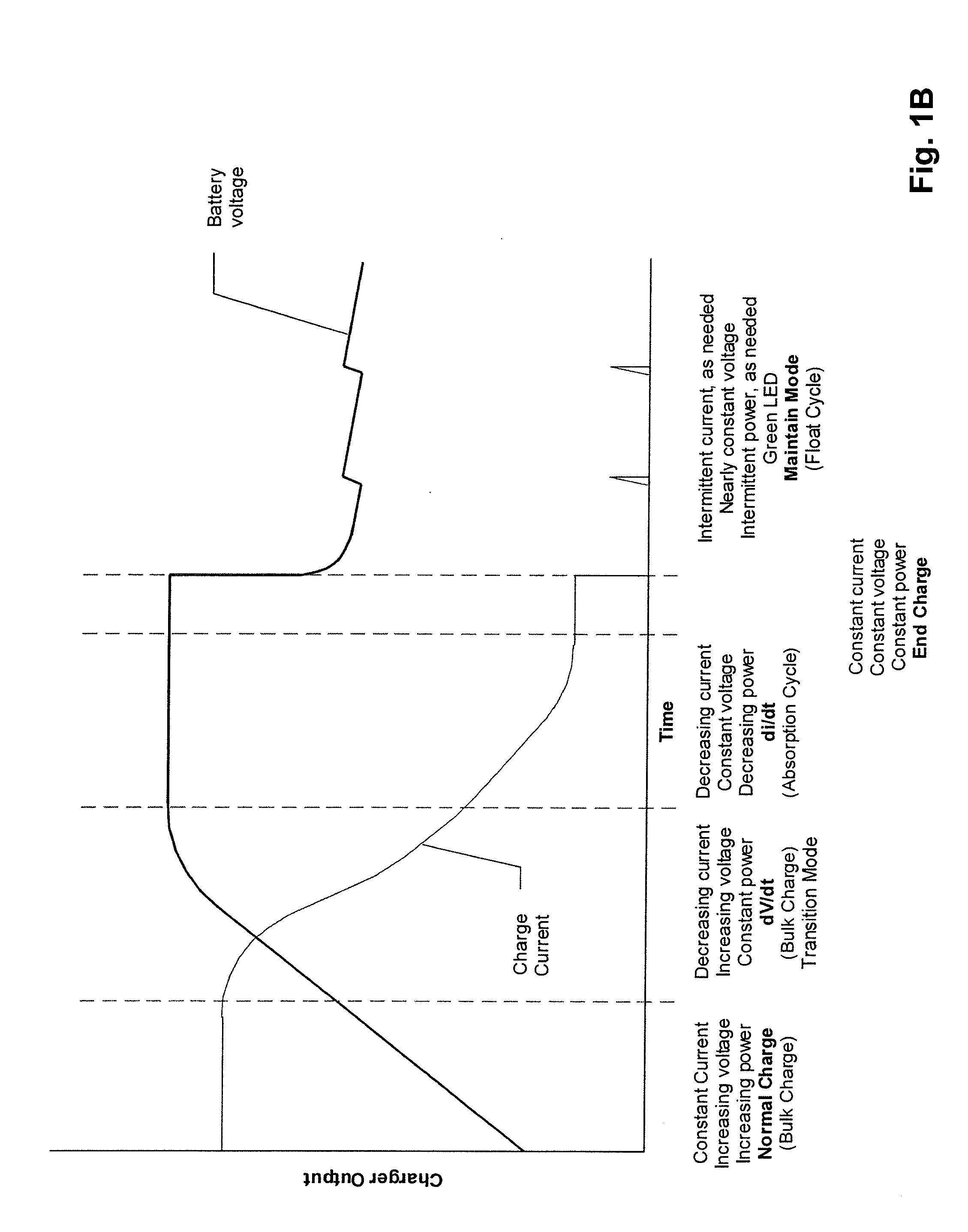
A protection system and method for a battery charger is disclosed for detecting a thermal runaway condition in a battery during charging in order to protect the battery when such a thermal runaway condition has been detected. The protection system in accordance with the present invention does not require external temperature sensors nor does it rely on actions by the technician or user. Briefly, the protection system includes one or more electrical sensors normally provided with conventional battery chargers for sensing one or more electrical parameters during charging and providing an indication of a possible thermal runaway condition based upon the trend of the electrical charging parameters. In general, the protection system monitors the charging characteristics of a battery for a complete or partial charging cycle. If the charging characteristics deviate from a normal or otherwise indicate an anomaly, as determined by software, the system assumes there may be a thermal runaway condition and executes a protection measure, such as terminating charging of the battery. Even though the anomaly may not be the result of a thermal runaway condition, the protection system in accordance with the present invention treats the anomaly as an indication of a thermal runaway condition even though some other problem is the reason for the anomaly. For example, when the anomaly is the result of a bad cell, battery charging is terminated to prevent a thermal runaway condition and not because a thermal runaway condition is detected.
Owner:SCHUMACHER ELECTRIC CORP
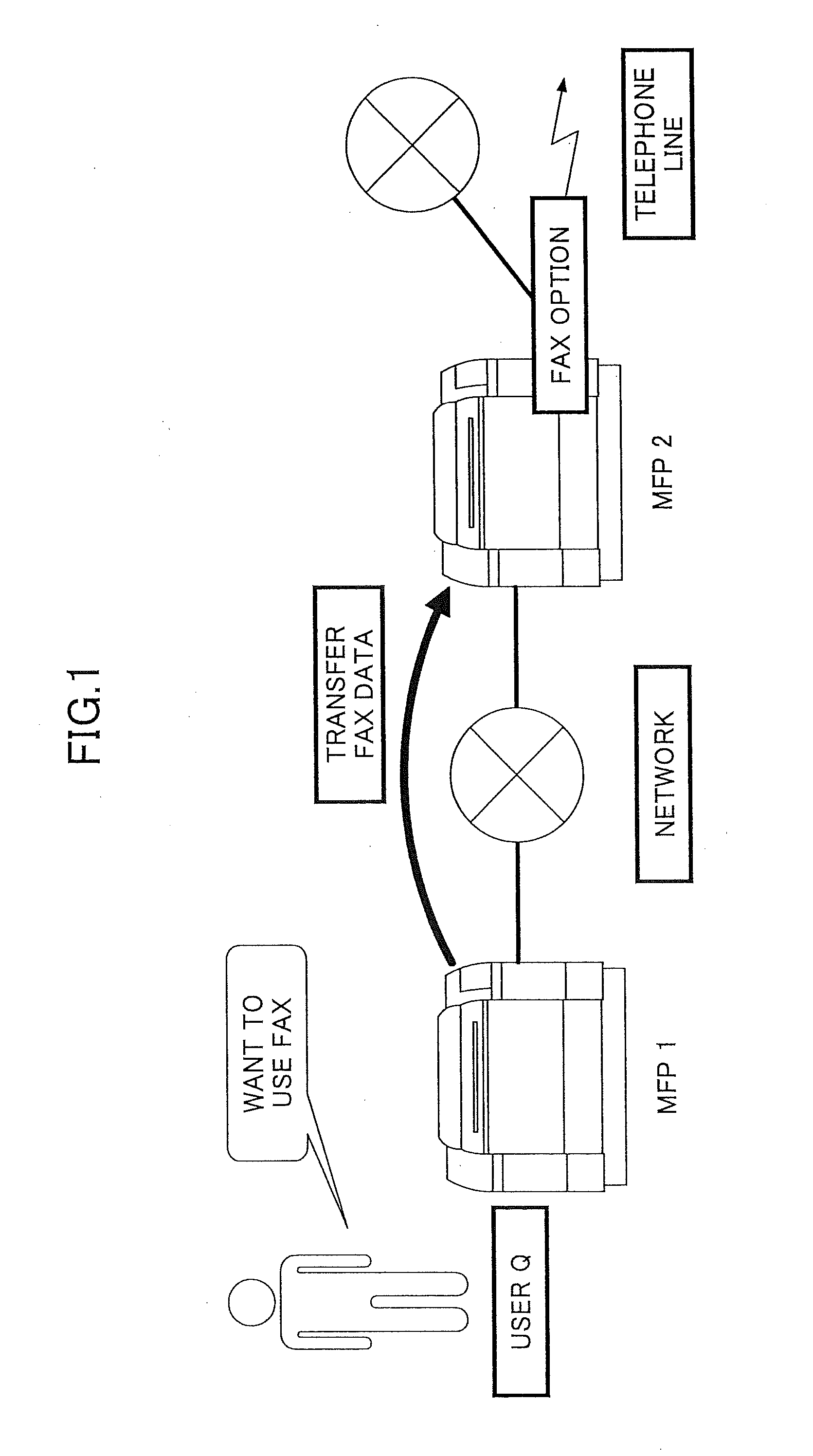
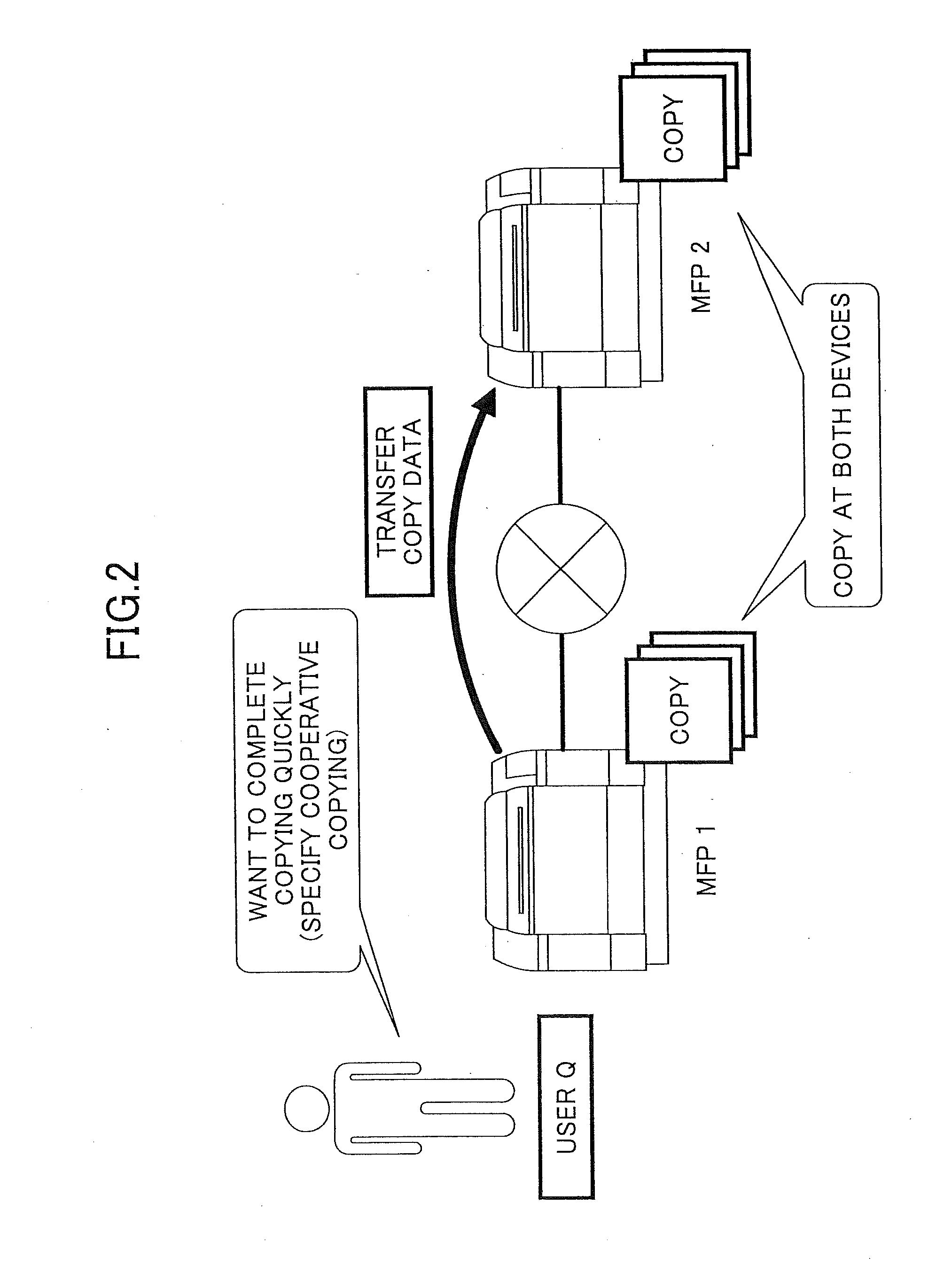
Device cooperation system, image forming apparatus, and function providing method
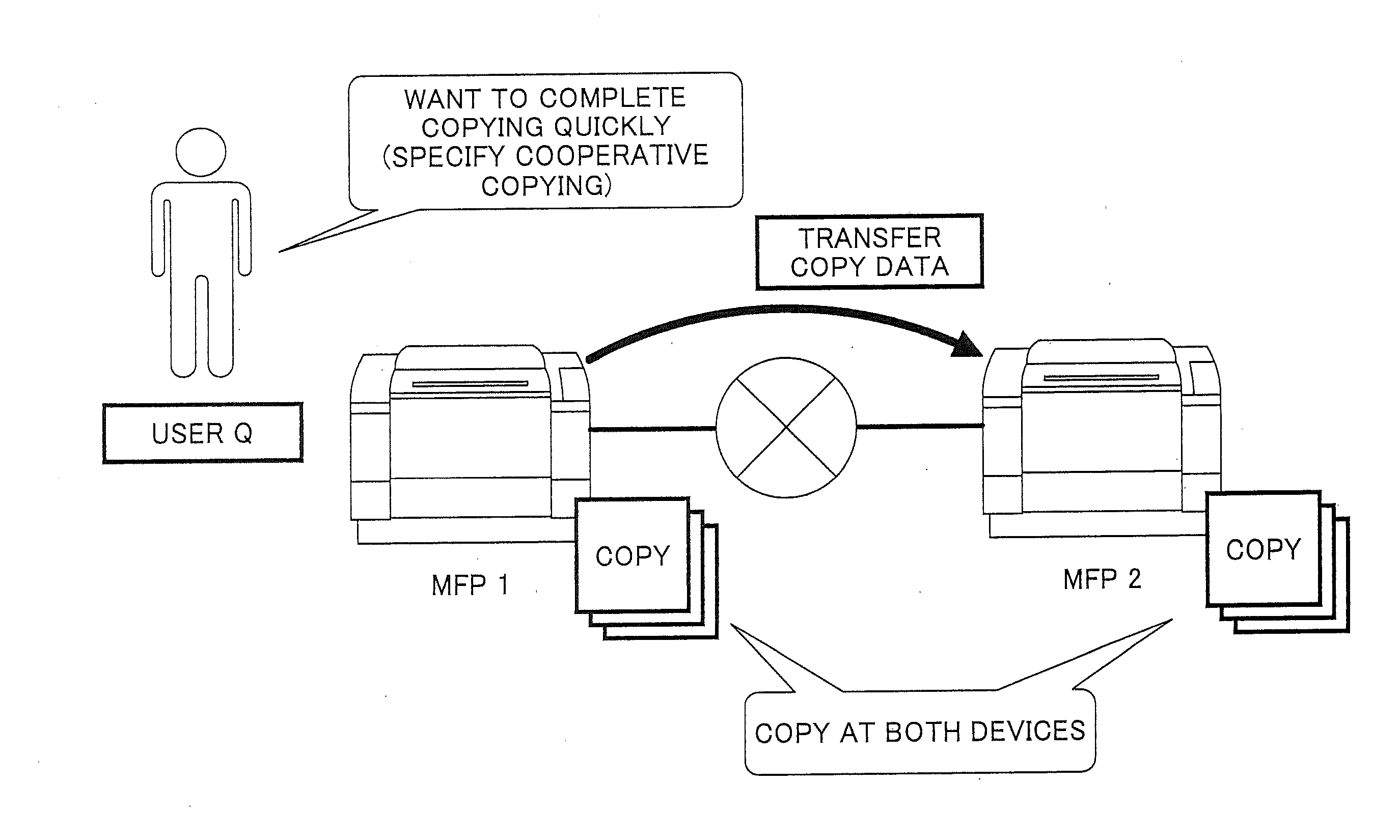
InactiveUS20130057882A1Eliminate disadvantagesEnergy efficient ICTDigitally marking record carriersPartial chargeNetwork connection
In a device cooperation system, devices connected via a network take partial charge of providing a function. A first device acquires image data to be output; receives a condition used when the first device and a second device output the image data; stores a possible output amount that can be output by the first device; determines whether a total page number, which is obtained from the condition and a number of pages of the acquired image data, is less than or equal to the possible output amount; determines first and second output numbers to be respectively allocated to the first and second devices; sends the image data and the second output number to the second device; and updates the possible output amount according to a number output by the first and second devices.
Owner:PIXTRONIX INC +1
Super capacitance storage battery
InactiveCN101719420AExtended service lifeIncrease profitElectrolytic capacitorsCapacitanceActivated carbon
The invention discloses a super capacitance storage battery comprising a positive plate, a negative plate, a clapboard and electrolyte. The super capacitance storage battery is characterized in that the positive plate is a lead storage battery positive plate and at least one of the negative plates is a compound negative plate which is formed by adding a granular capacitance electrode material in a common lead storage battery negative plate diachylum formula. In the invention, the granular capacitance electrode material is added in the negative plate diachylum formula and formed by coating an active carbon material through a conductive material and has excellent conductivity; in addition, the material has improved density after prepared into granules by milling, can form a conductive network which has wide addition proportion range and strengthens active substances of the negative plate, reduce the internal resistance, improve the output power and improve the utilization rate of the active substance of the negative plate while fully playing the capacitance performance without changing the basic structure of the active substance of the negative plate, thereby prolonging the service life of the battery under the condition of high-rate partial charge (HRPSoC).
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
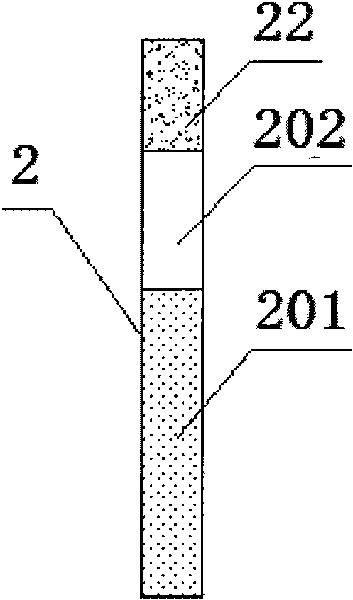
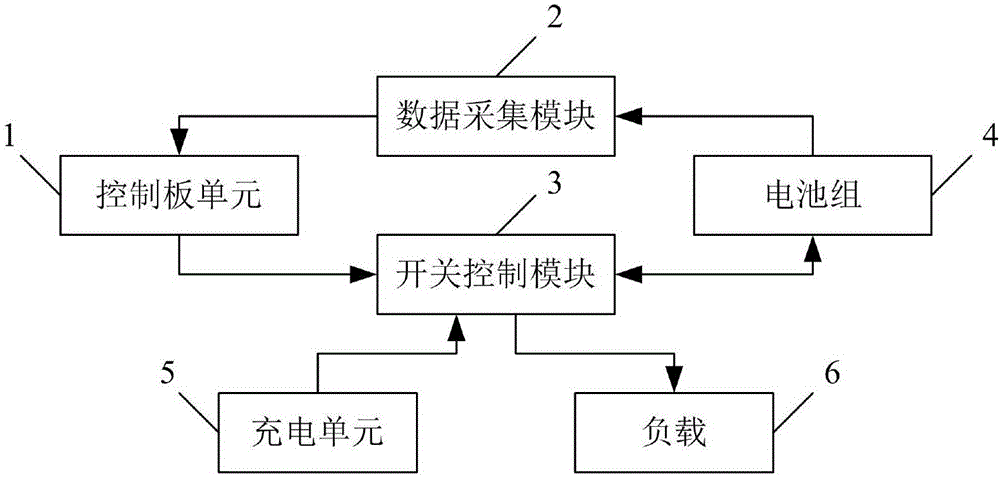
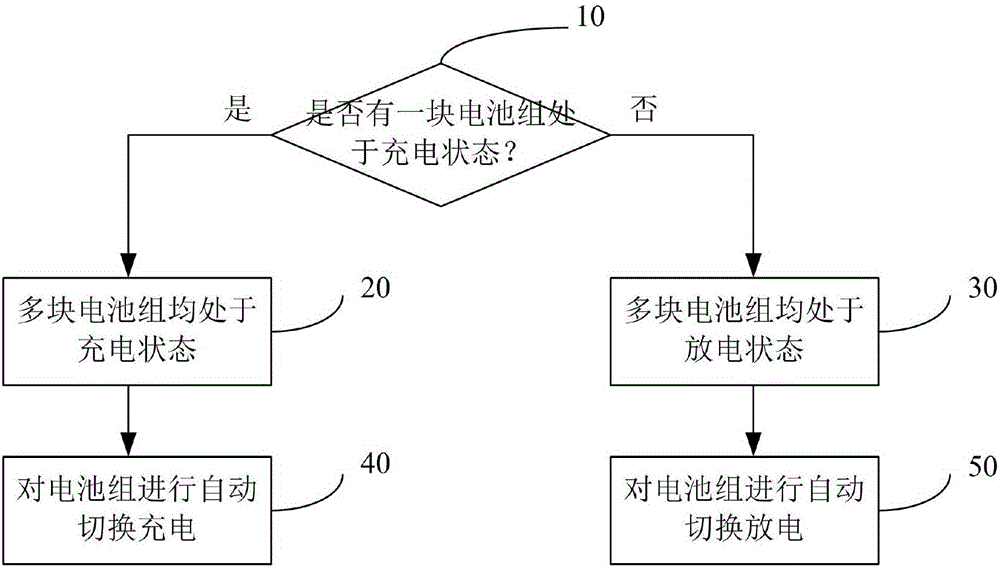
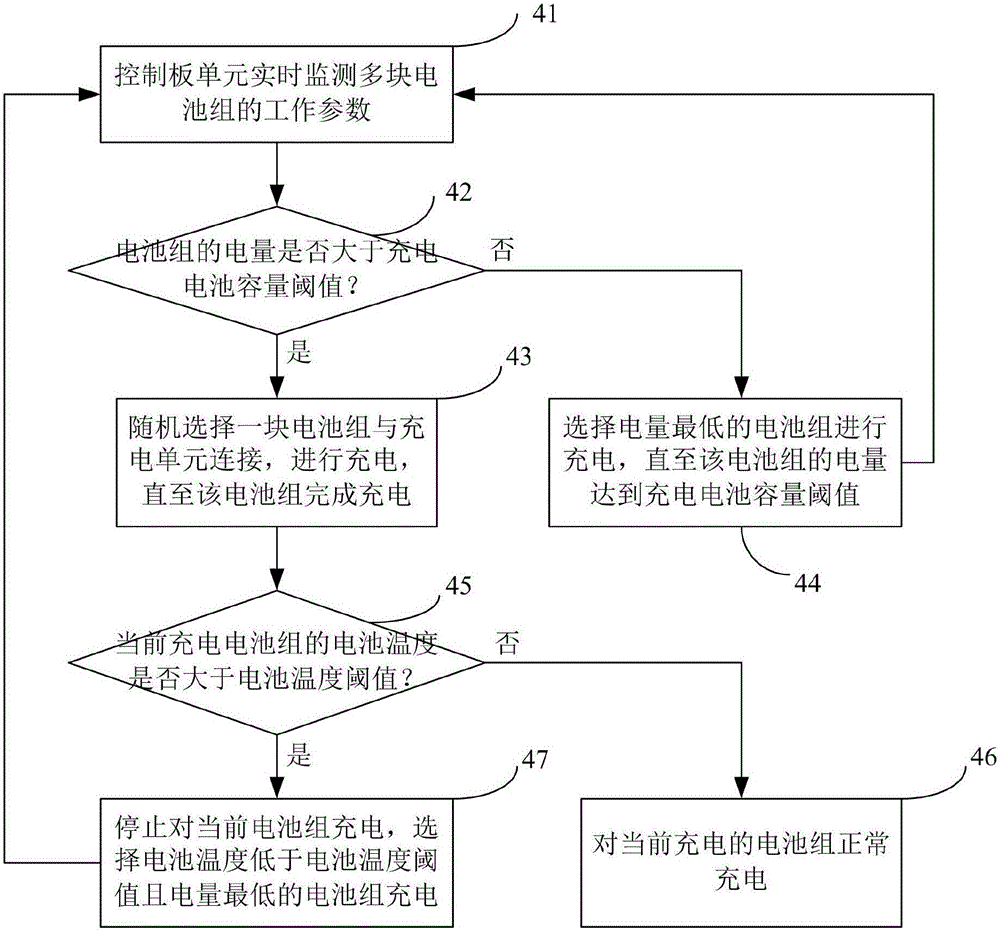
Method and system for achieving automatic switching of multiple electric car battery packs
PendingCN106849232AImprove securityExtended service lifeCharge equalisation circuitSecondary cellsPartial chargeElectrical battery
The invention relates to a method and system for achieving automatic switching of multiple electric car battery packs. The method comprises the steps that a control panel unit monitors charging and discharging parameters of the multiple battery packs in real time and judges the working states of the battery packs; if one battery pack is in the charging state, it is determined that the multiple battery packs are in the charging state, and if not, the multiple battery packs are in the discharging state; in the charging state, the battery packs are automatically switched and charged; in the discharging state, the battery packs are automatically switched and discharged. The method and system for achieving automatic switching of the multiple electric car battery packs are simple in structure and reasonable in scheme design; when the multiple battery packs are set, the single battery pack does not need to be designed to be excessively large, the occupied space is reduced, and the control panel unit controls the single cell pack charging and discharging choices by collecting the working state and the battery capacity, the battery temperature and the like of the battery packs, so that it is ensured that the batteries are in the partial charging and discharging state, the safety of the batteries is ensured, and the service life is prolonged.
Owner:GUANG DONG GREENWAY TECH CO LTD
Thermal runaway protection system for a battery charger
A protection system and method for a battery charger is disclosed for detecting a thermal runaway condition in a battery during charging in order to protect the battery when such a thermal runaway condition has been detected. The protection system in accordance with the present invention does not require external temperature sensors nor does it rely on actions by the technician or user. Briefly, the protection system includes one or more electrical sensors normally provided with conventional battery chargers for sensing one or more electrical parameters during charging and providing an indication of a possible thermal runaway condition based upon the trend of the electrical charging parameters. In general, the protection system monitors the charging characteristics of a battery for a complete or partial charging cycle. If the charging characteristics deviate from a normal or otherwise indicate an anomaly, as determined by software, the system assumes there may be a thermal runaway condition and executes a protection measure, such as terminating charging of the battery. Even though the anomaly may not be the result of a thermal runaway condition, the protection system in accordance with the present invention treats the anomaly as an indication of a thermal runaway condition even though some other problem is the reason for the anomaly. For example, when the anomaly is the result of a bad cell, battery charging is terminated to prevent a thermal runaway condition and not because a thermal runaway condition is detected.
Owner:SCHUMACHER ELECTRIC CORP
Tracking aging effect on battery impedance and tracking battery state of health
InactiveUS20140306712A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical testingState dependentPartial charge
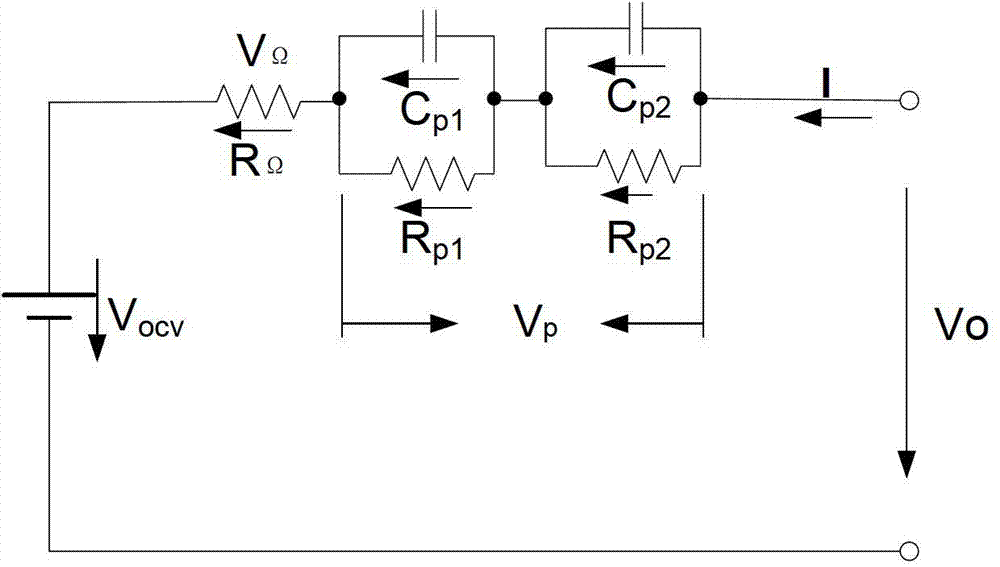
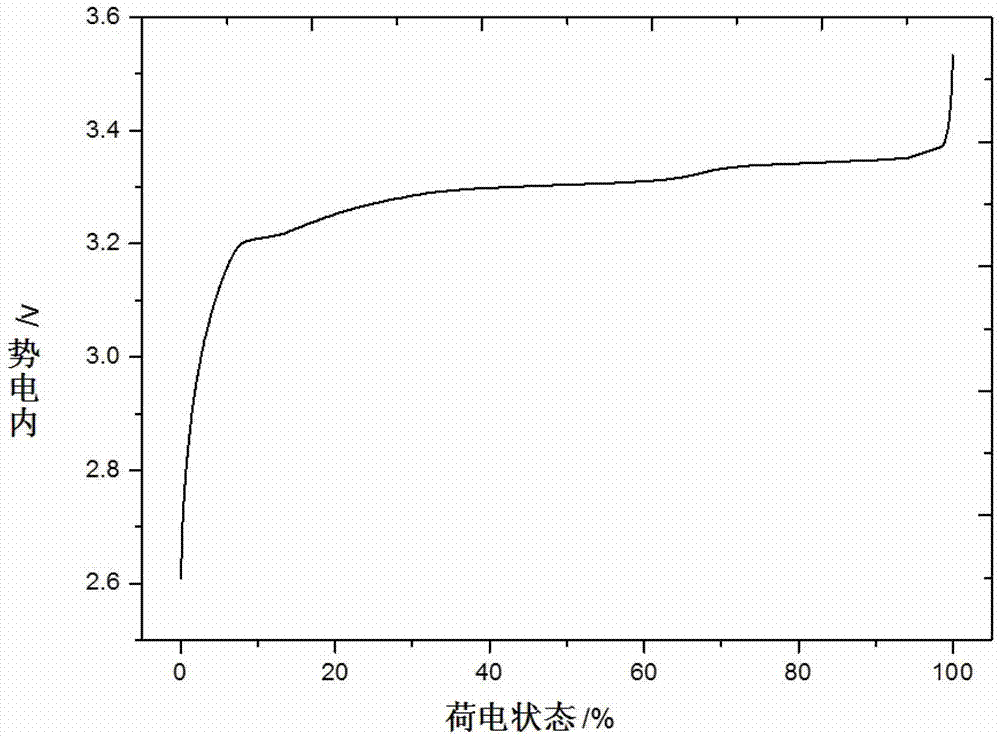
Methods and systems for tracking aging effect on battery impedance are provided. A first voltage associated with a first state of a battery, a second voltage associated with a second state of the battery, and an impedance of the battery are determined. A battery impedance table that is used for calculating a state of charge of the battery is updated using the determined impedance. Methods and systems for tracking state of health of a battery are also provided. Partial charge cycles of a received battery are counted between a first charge event and a second charge event of the battery. State of health data of the batter is tracked, and a new state of health estimation is calculated based on the state of health data if the counted partial charge cycles of the battery has a count value that has a predetermined relationship with a predetermined count threshold.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
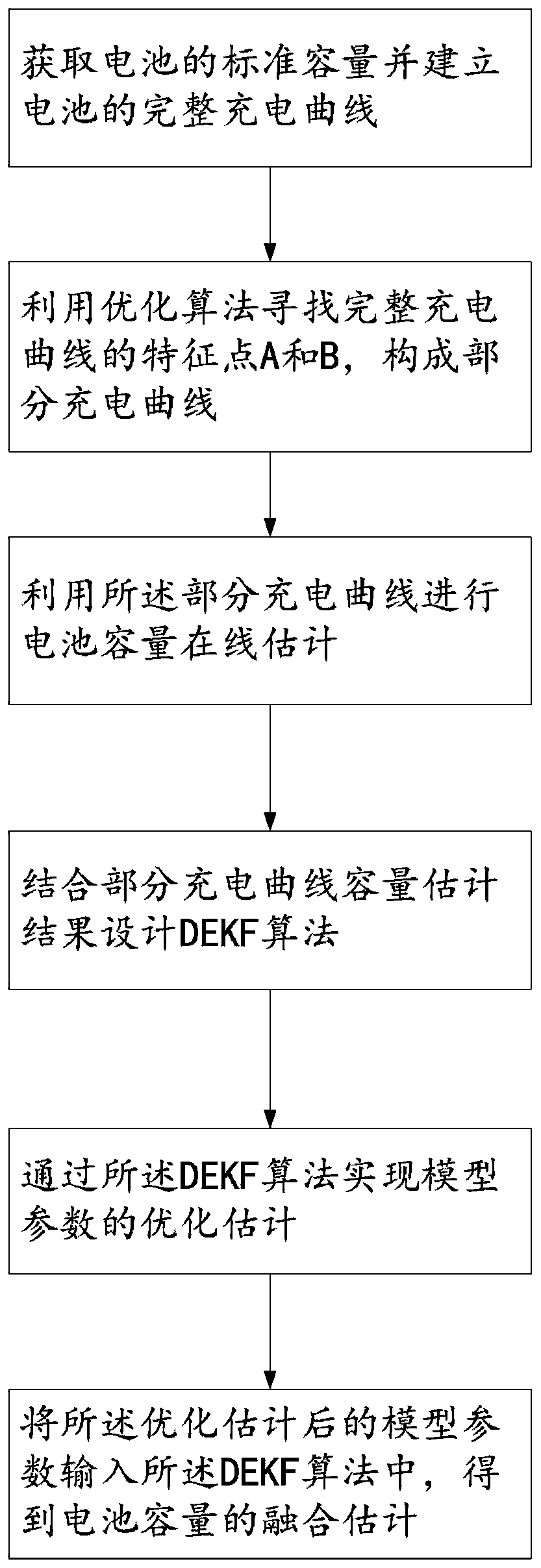
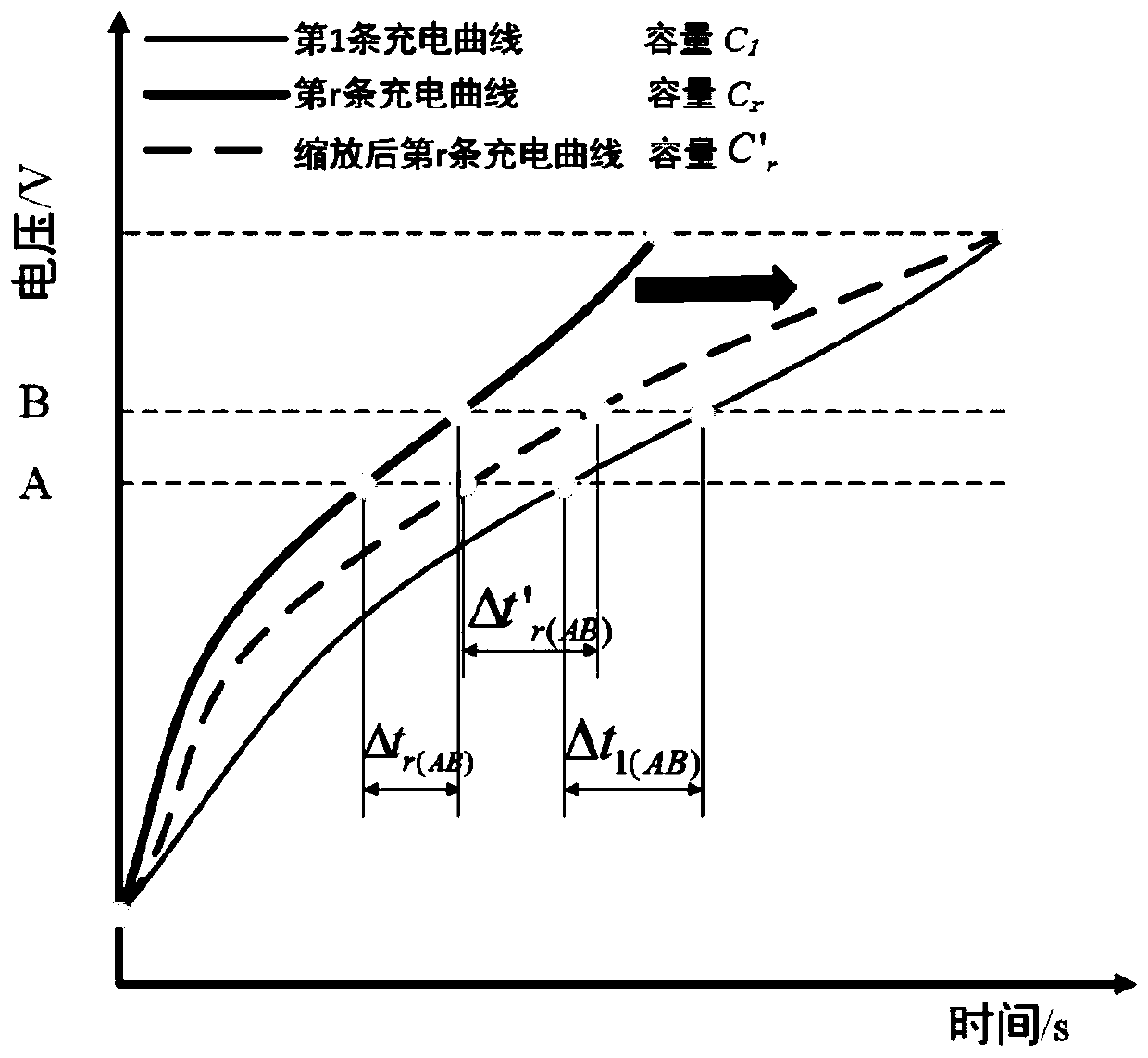
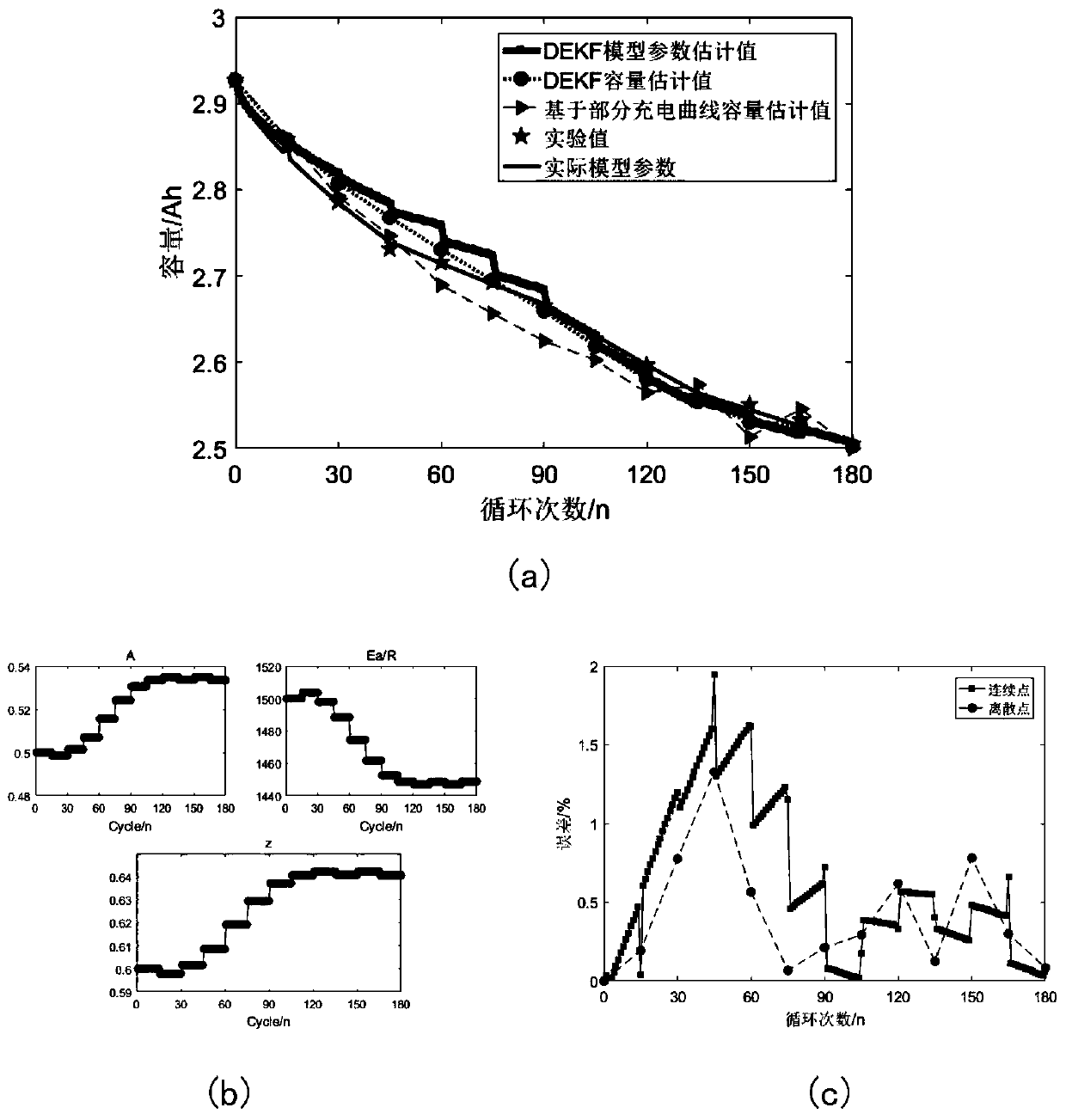
Lithium ion battery dual Kalman filtering capacity estimation method
InactiveCN109814041AAccurate timingCapacity estimation real-timeElectrical testingSimulationModel parameters
The invention provides a lithium ion battery dual Kalman filtering capacity estimation method based on the combination of partial charge curves and a semi-empirical life model. The method effectivelycombines the respective advantages of a data driving method and an empirical model method for battery capacity estimation, for the situation that complete charging is rare in the actual use process ofan electric automobile, a method based on the capacity online estimation of the partial charge curves is studied, by monitoring constant current charging data between two static voltage characteristic points, the battery capacity is estimated online, it is considered that an actual charging process may not be in accordance with the conditions required by the estimation method, the method only canintermittently obtain capacity estimation results, the Arrhenius life model is further adopted for real-time capacity estimation, while parameters of the Arrhenius life model may have a mismatching problem, by designing a DEKF algorithm, the real-time update of the model parameters is achieved, and the battery capacity is also estimated online.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
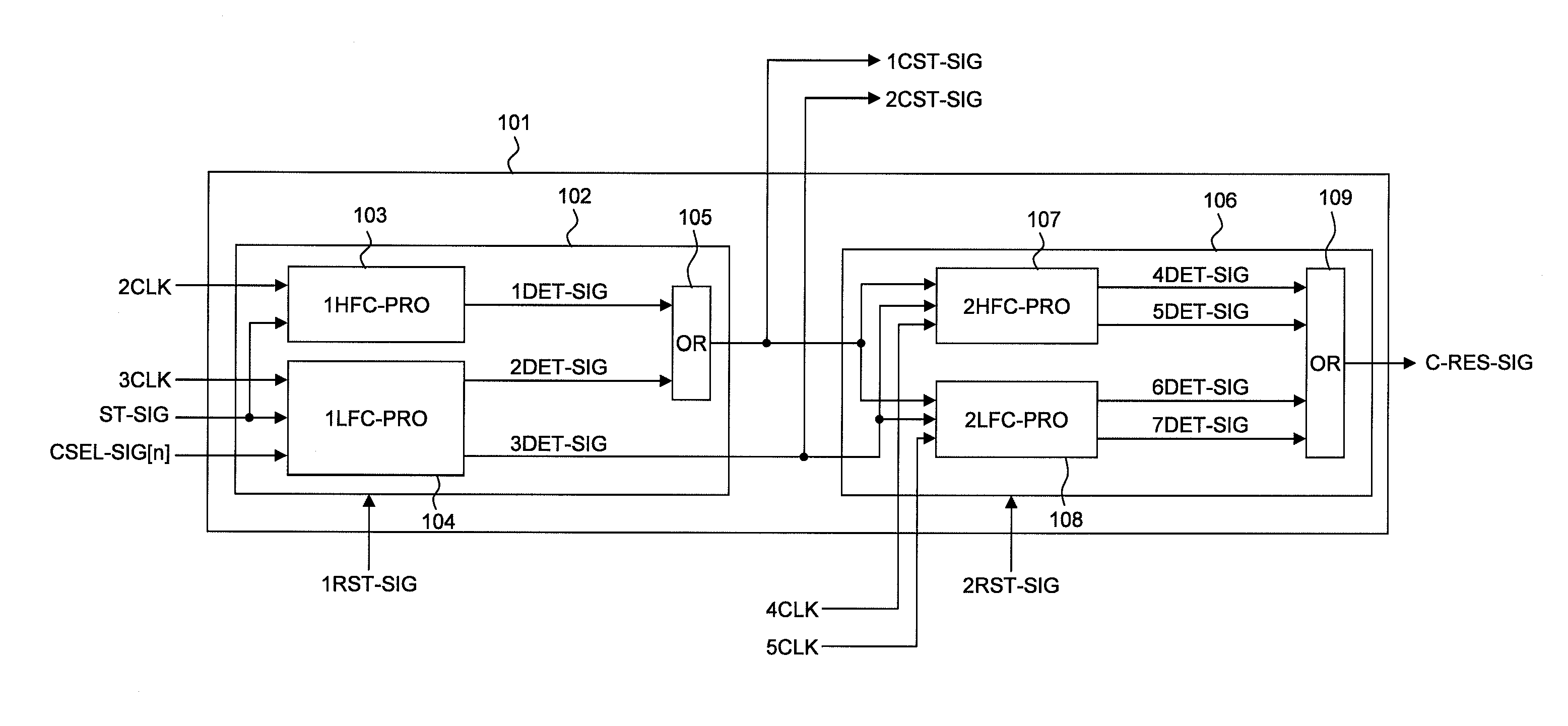
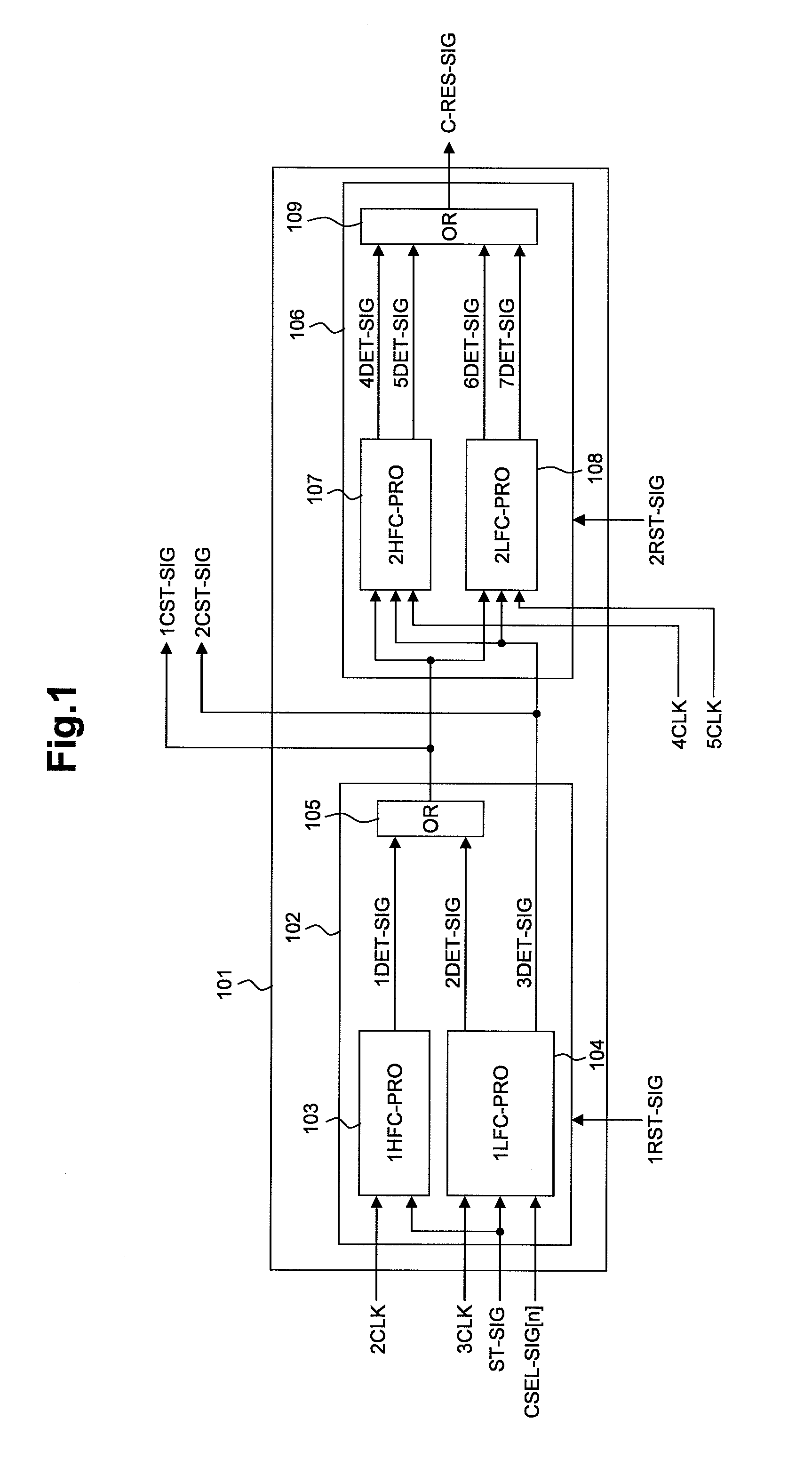
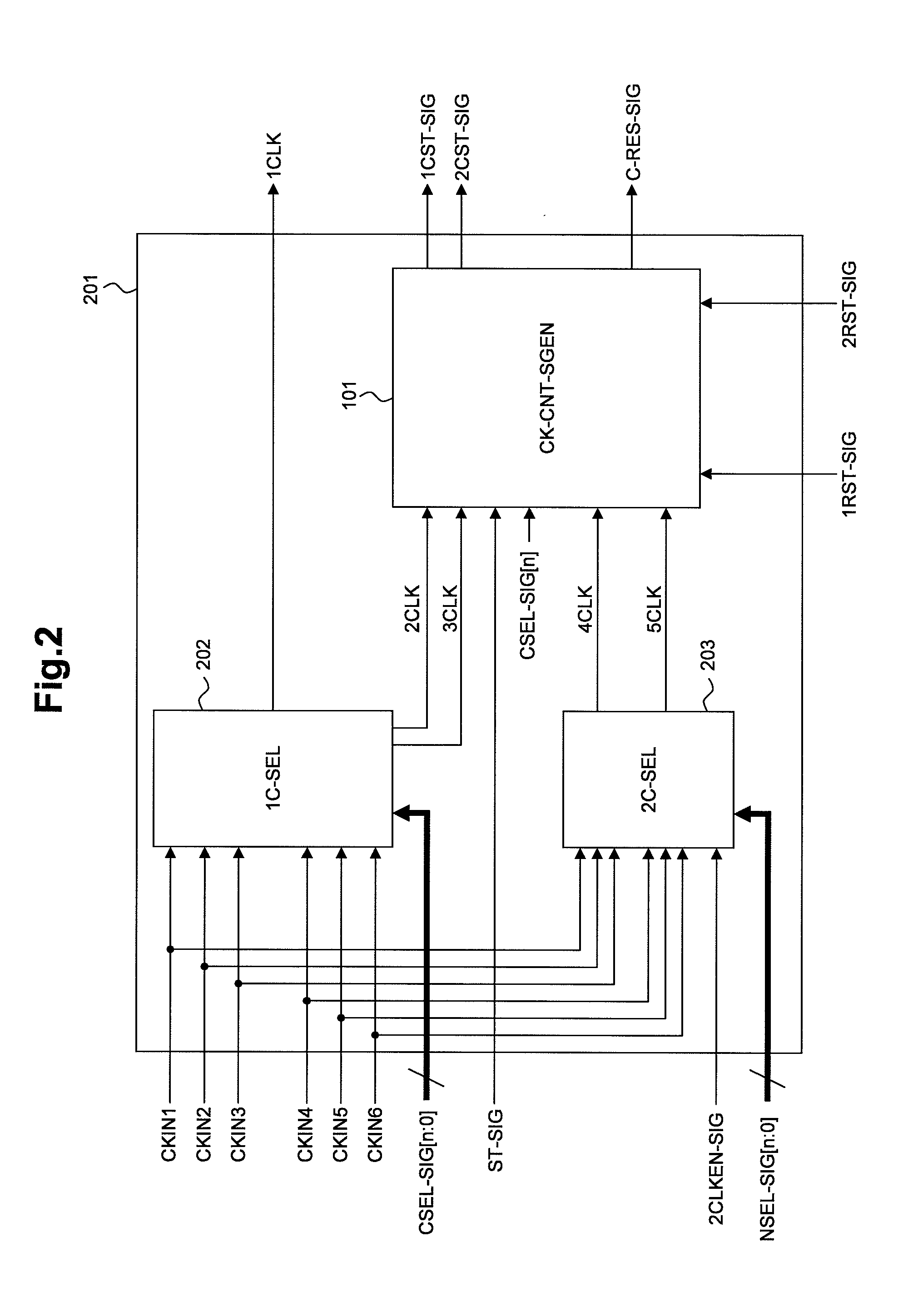
Clock control signal generation circuit, clock selector, and data processing device
InactiveUS8375239B2Reduce power consumptionLong operating timeElectronic circuit testingPulse duration/width modulationPartial chargeControl signal
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
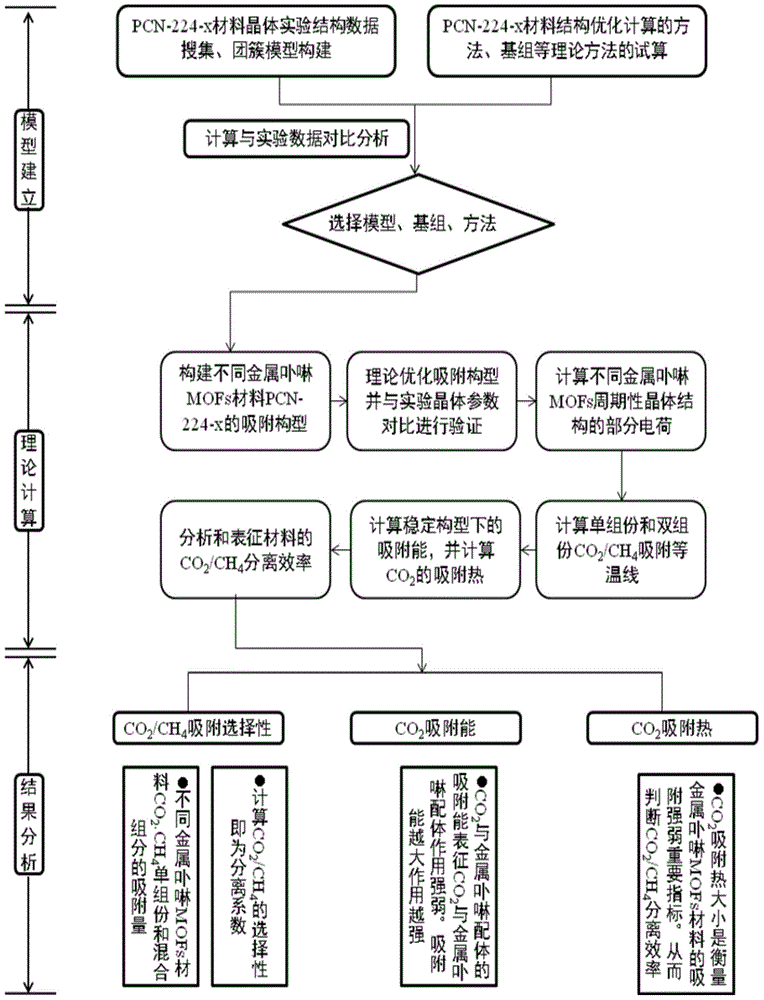
Method for quantitatively analyzing efficiency of metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2/CH4
InactiveCN104899356AAvoid complexityOvercome stabilityAdsorption purification/separationSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular sievePartial charge
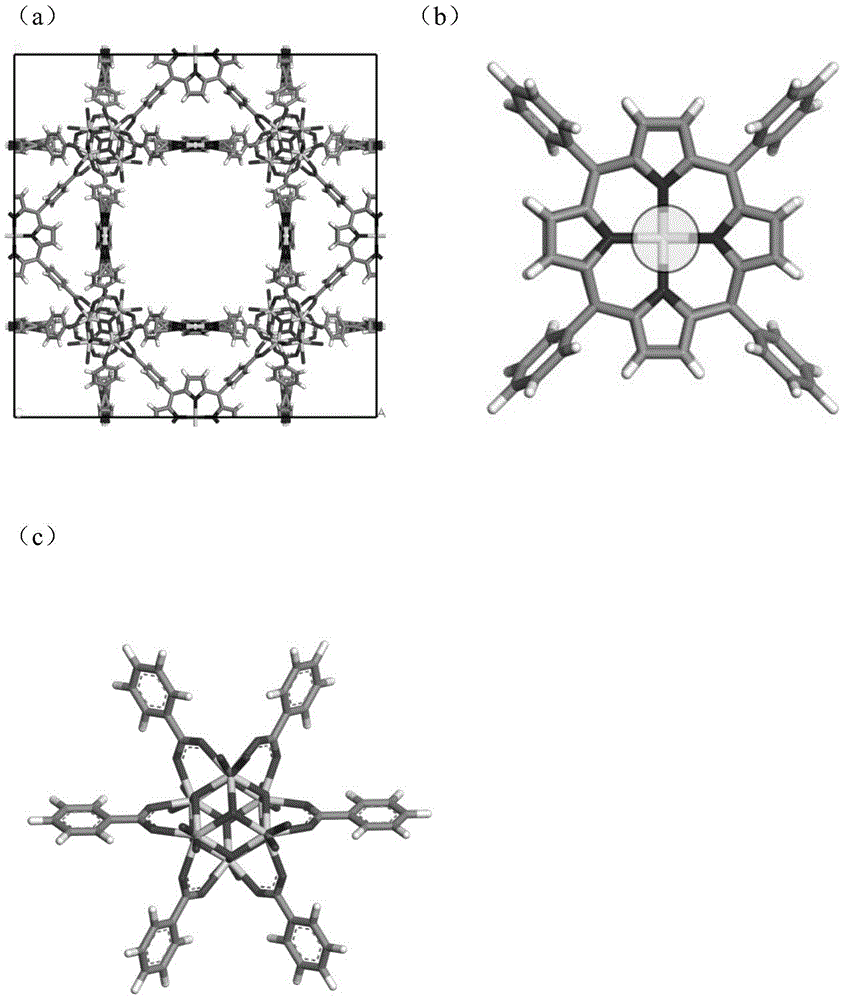
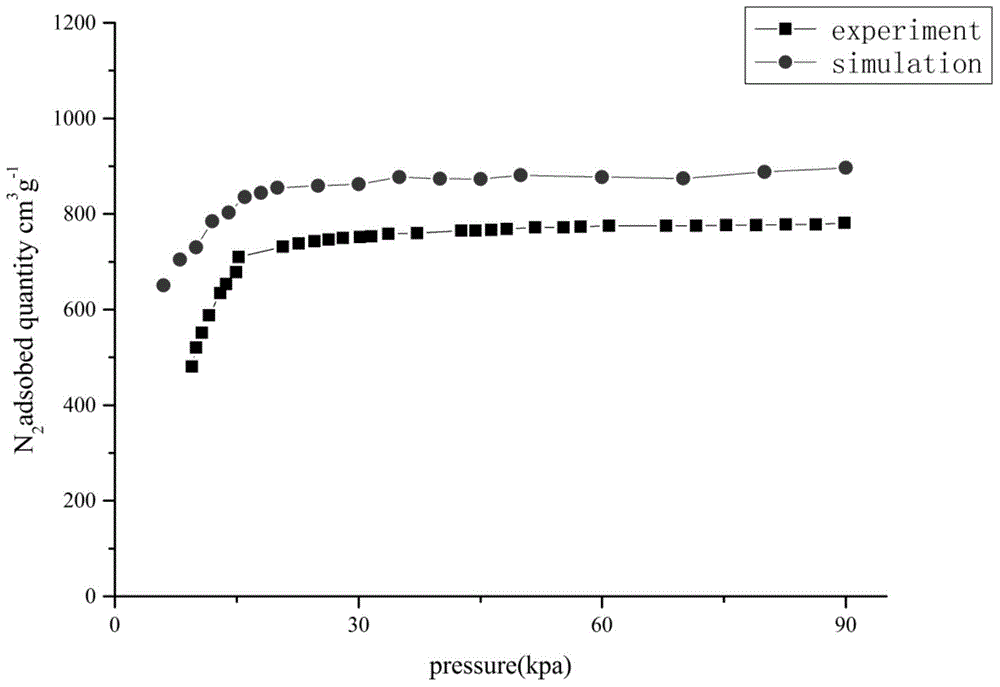
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively analyzing efficiency of metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4. According to the method of the invention, the efficiency of the metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4 is quantitatively analyzed based on density functional theory calculation of auantum chemistry and Monte Carlo molecular simulation. By determining interaction energy between probe molecules and different metalloporphyrin ligands and adsorption heat, interaction between CO2 and metalloporphyrin MOFs materials is quantitatively analyzed, and finally calculation of selectivity in adsorption of CO2 / CH4 is used to characterize efficiency and features of different metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4. The method comprises steps of: construction of a cluster model; structural optimization of a stable structure and calculation of partial charges; calculation of a CO2 / CH4 separation coefficient; calculation of adsorption energy and adsorption heat; and analysis and characterization of efficiency in separating CO2 / CH4. According to the method of the invention, efficiency of metalloporphyrin MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4 can be quantitatively characterized without any actual experiment. The method of the invention can be further extended for analysis of efficiency of other porous molecular sieves of known crystal structures and MOFs materials in separating CO2 / CH4.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Lead-acid storage battery negative electrode lead paste and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104167545AReduce contact resistanceImprove conductivityLead-acid accumulatorsCell electrodesActivated carbonPartial charge
The invention discloses a lead-acid storage battery negative electrode lead paste and a preparation method thereof, and the improvement lies in that activated carbon black and fumed silica are added in the negative electrode lead paste, components have a scientific and reasonable proportion, and the preparation method has operation steps and process parameters more normative and perfect. A lead-acid storage battery prepared from the negative electrode lead paste prepared by the method has higher utilization rate of active substances and higher induction current efficiency, and the number of the charge / discharge cycles in a partial charge state is more than 600 times and is significantly superior to that of conventional batteries.
Owner:SHUANGDENG GRP
System and method to increase lithium battery charging temperatures
ActiveUS20100188053A1Shorten charging timeExcessive degradationBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringBattery capacity
A battery charging apparatus and method adapted to reduce battery capacity as a function of increased temperature thereby permitting partial charges at temperatures in excess of manufacturer's recommendations. The method includes steps of reducing charging current and charging voltage as a function of battery temperature thereby averting chemical instability within the battery. The apparatus detects battery temperature and includes a controller that will control charger voltage and current as a function of temperature and determine a suitable charging capacity.
Owner:STRYTEN ENERGY LLC +1
Fast formation cycling for rechargeable batteries
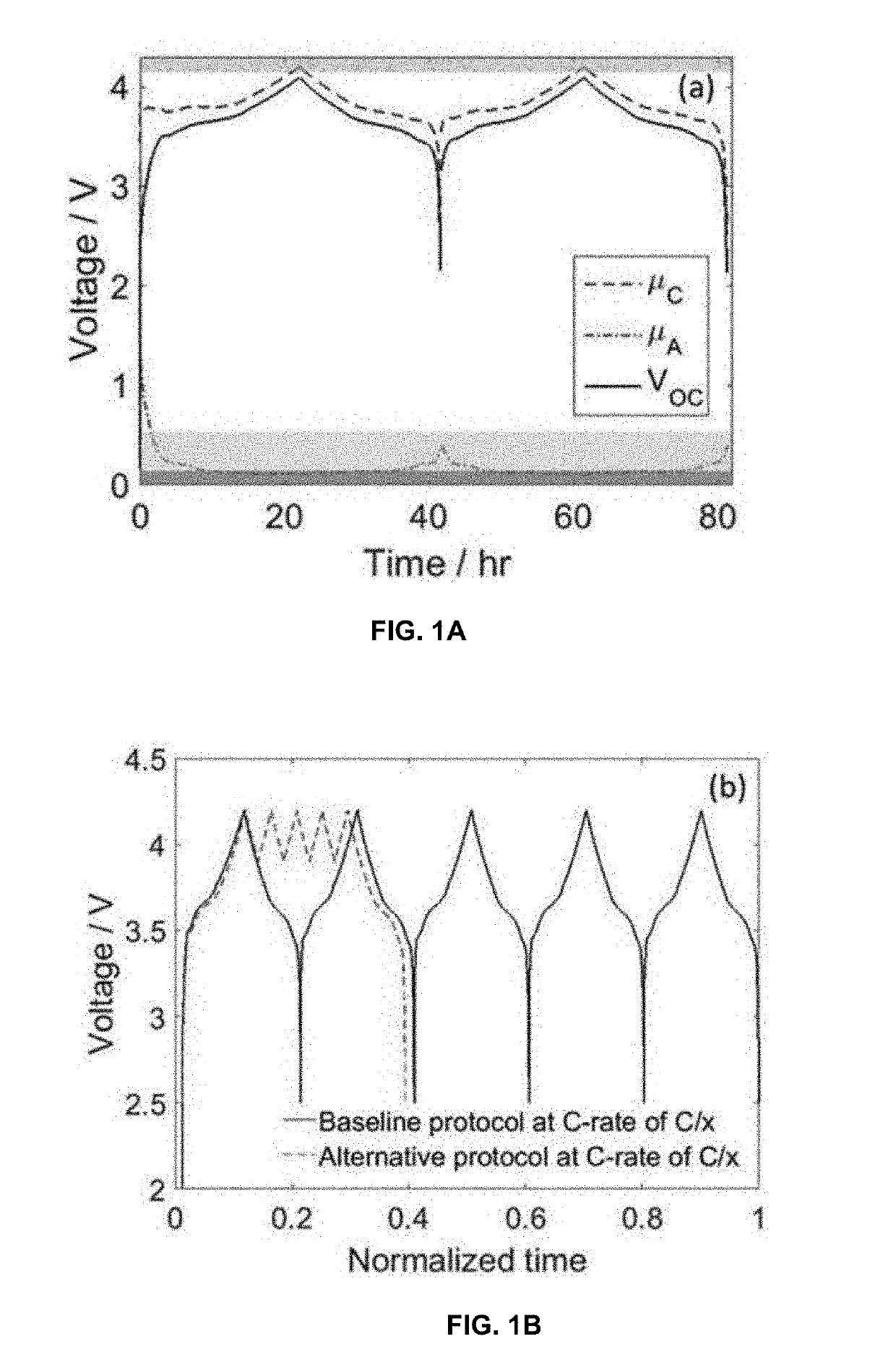
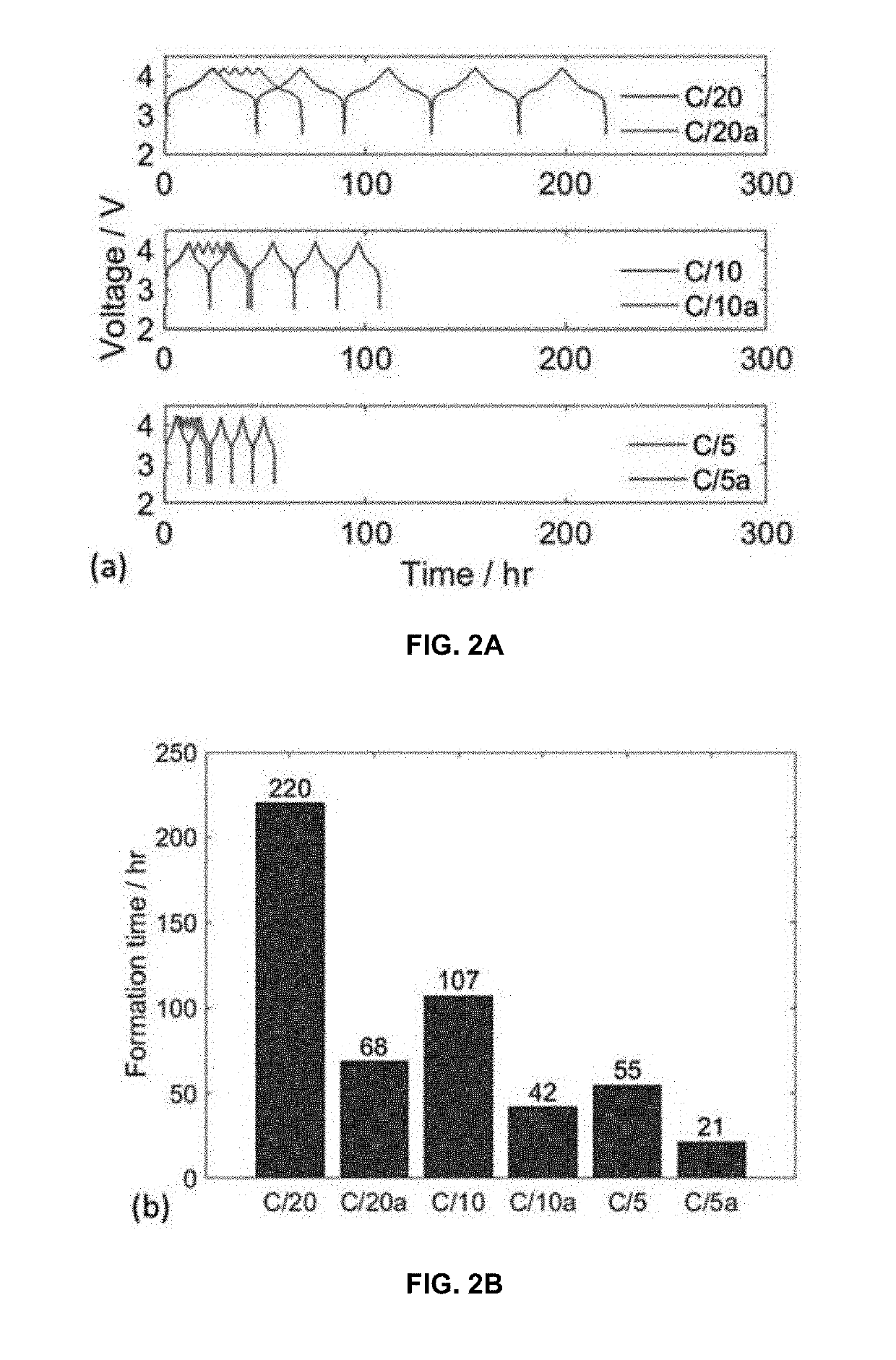
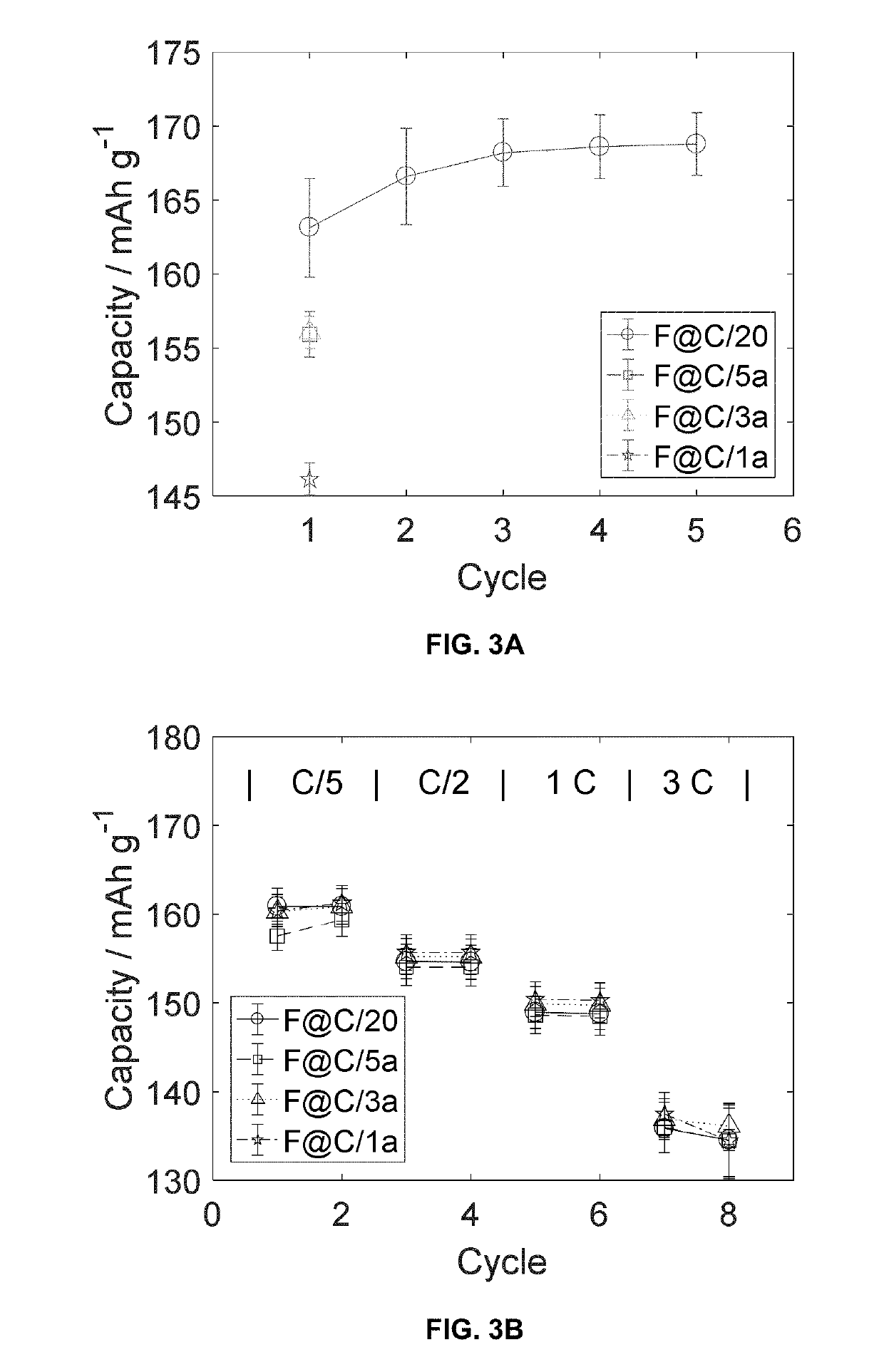
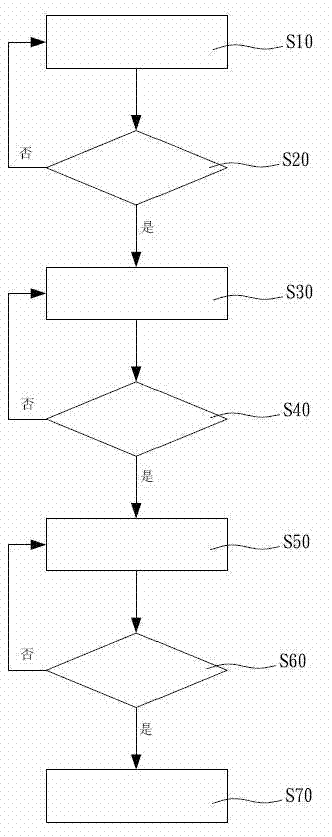
ActiveUS20190198856A1Electrode manufacturing processesSecondary cells charging/dischargingPartial chargeRechargeable cell
A method for fast formation cycling for rechargeable batteries comprising the steps of: step 1 (First Partial Charge)—charge cell from open-circuit voltage (OVC) up to 80-90% of an upper cutoff voltage (UCV) of from 4-5 V at a C rate not less than 0.5 and not more than 1.5; step 2 (First Shallow Charge)—charge cell from 80-90% of UCV to 97-100% of UCV at a C rate of not less than 0.2 and not more than 0.5; step 3 (First Shallow Discharge)—discharge cell from 97-100% of UCV to 80-90% of UCV at a C rate of not less than 0.2 and not more than 0.5; and step 4 (Subsequent Charge / Discharge Cycles)—repeat steps 2-3 up to 2-10 times where the charging and discharging rates are progressively increased by 25-75%. A battery made according to the method of the invention is also disclosed.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC +1
Multi-stage battery module charging method and charging apparatus
A multi-stage battery module charging method and a charging apparatus are discloses. The method comprises the following steps of: a, perform first-stage charge on a battery module with a first preset electric current; b, judging if the battery module achieves a preset voltage through a judgement unit; c, performing second-stage charge on the battery module with a second preset electric current, if the preset voltage is judged to be achieved; d, if the preset voltage is judged to be achieved again and a preset voltage difference among batteries or one of the batteries exceeds the preset voltage, performing third-stage charge with a third preset electric current aiming at the batteries with lower voltage; e, if the preset voltage is judged to be achieved again, performing constant-voltage charge on the battery module with the preset voltage and using the second preset electric current as an initial charging current till the battery module is charged full. By using the method, states of over-charge or partial-charge of parts of the batteries can be prevented during charge of the battery module, i.e., voltage can be stabilized, charging efficiency of the batteries can be promoted, and service life of the batteries can be prolonged.
Owner:GALLOPWIRE ENTERPRISE
Preparation method of carbon-based composite material for cathode of lead-carbon battery
The invention relates to a preparation method of a carbon-based composite material for a cathode of a lead-carbon battery, which can prepare a carbon-based lead compound composite material with a controllable proportion, wherein the lead compound uniformly distributes on the surface of carbon material and maintains the original structure character of the carbon material. The preparation method isas follows: the carbon material and a lead ion solution are uniformly mixed in a reaction vessel, a precipitant is slowly dropped, the lead ions are completely deposited on the surface of the carbon material, then filtered, washed and dried to obtain a precursor, and the composite material is obtained through high temperature treatment, and mass ratio of lead compounds is between 1% to 90%. The composite material and the active substances of cathode of lead-acid battery can be better combined by the lead oxide particles on the surface, while the cathode capacity of the cathode of the battery prepared by using the composite material additive is obviously increased, the hydrogen evolution of the cathode is reduced, cathode active material utilization rate is also greatly improved, and the cycle life of high-rate charge-discharge of partial charge state of the cathode is significantly prolonged.
Owner:吉林省凯禹电化学储能技术发展有限公司
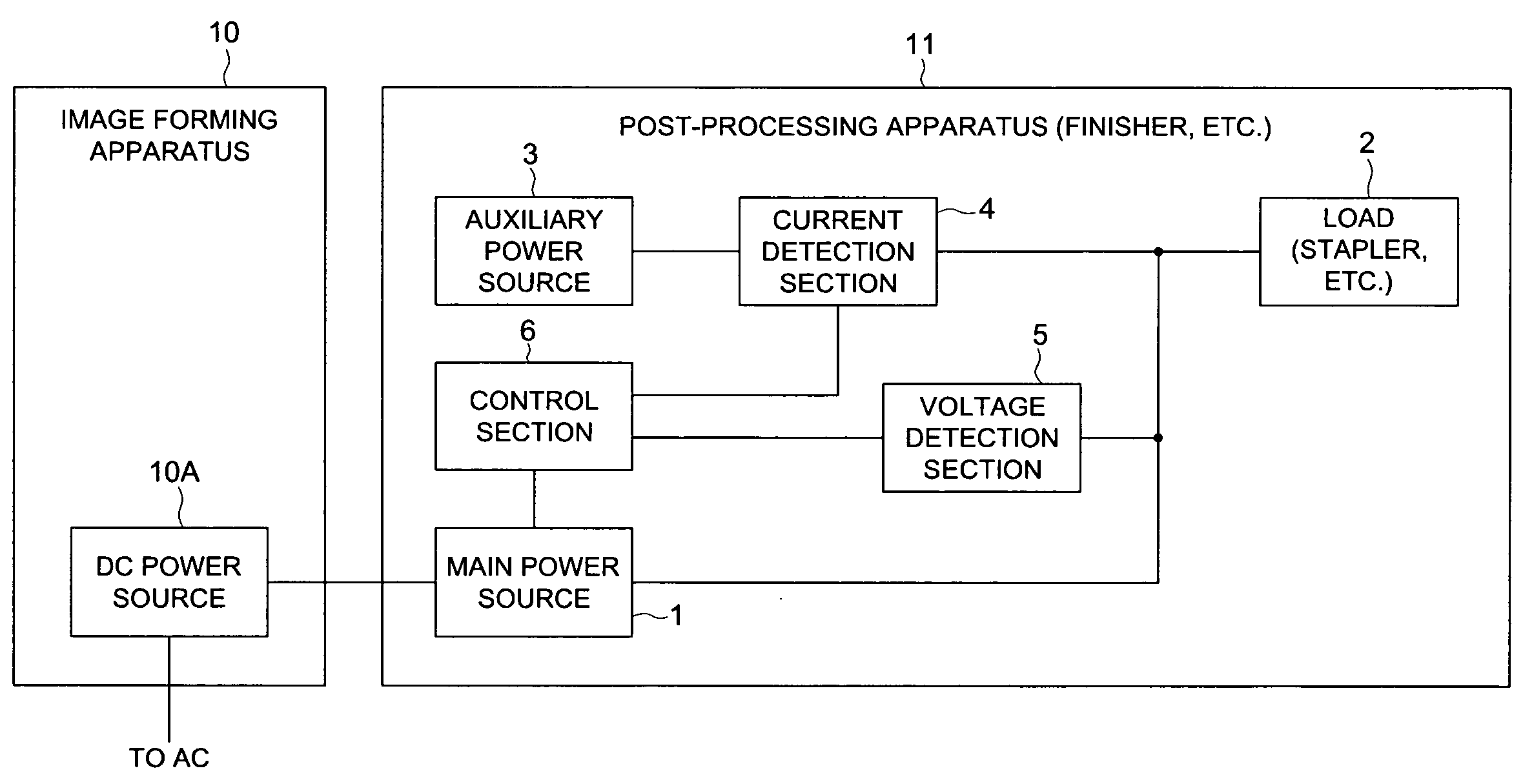
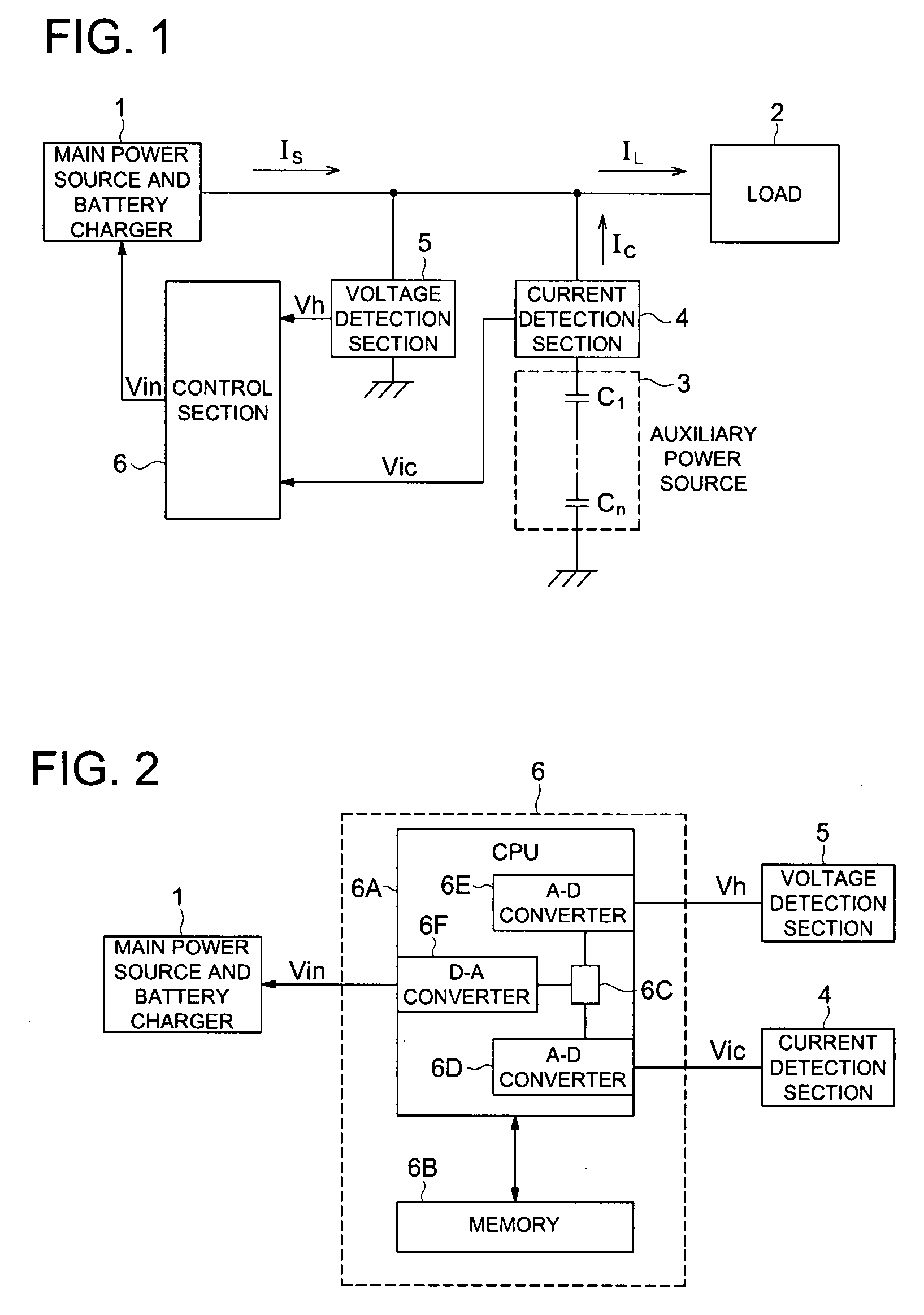
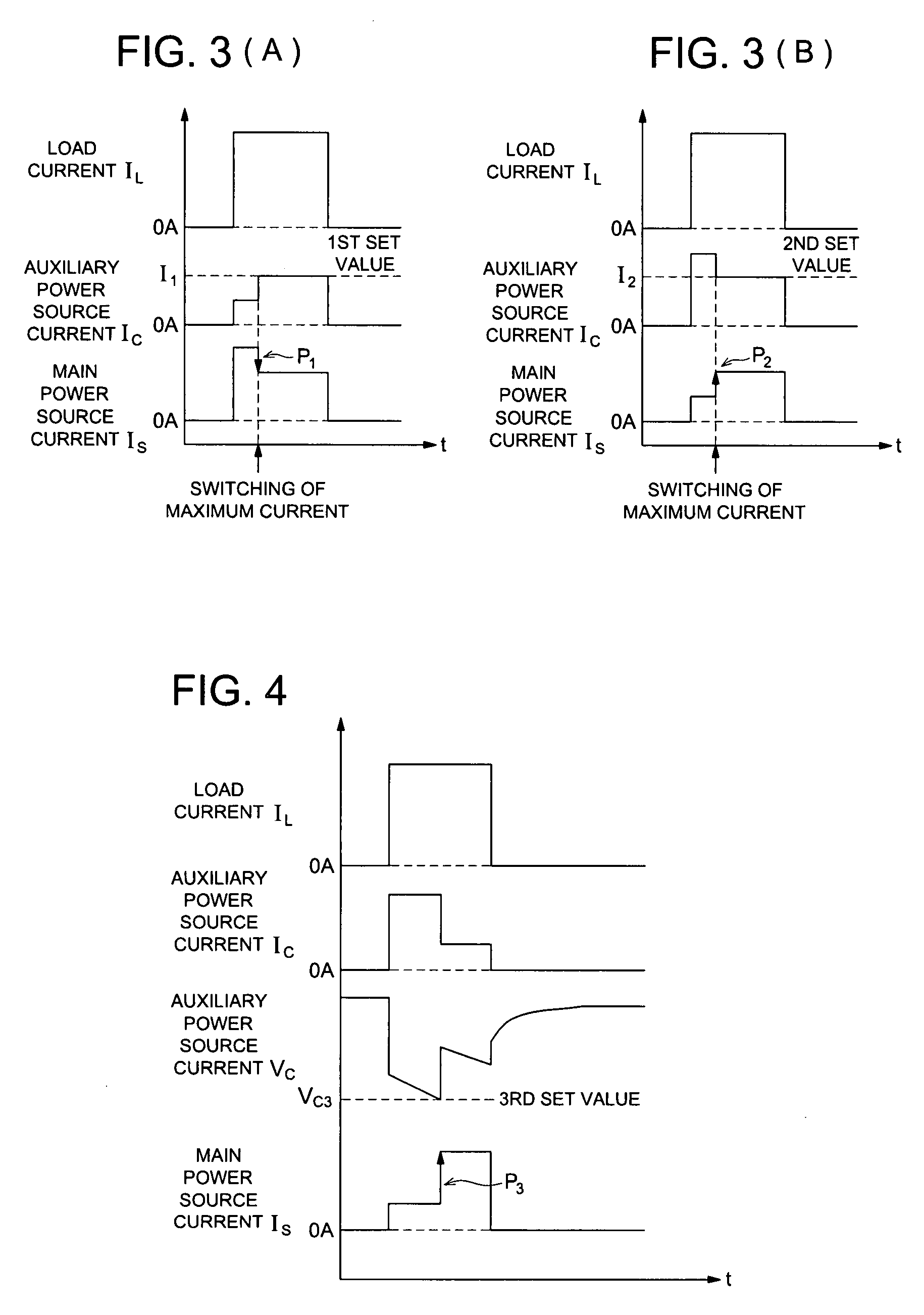
Power unit and image forming system
InactiveUS20080031651A1Switch power arrangementsElectrographic process apparatusPartial chargePeak value
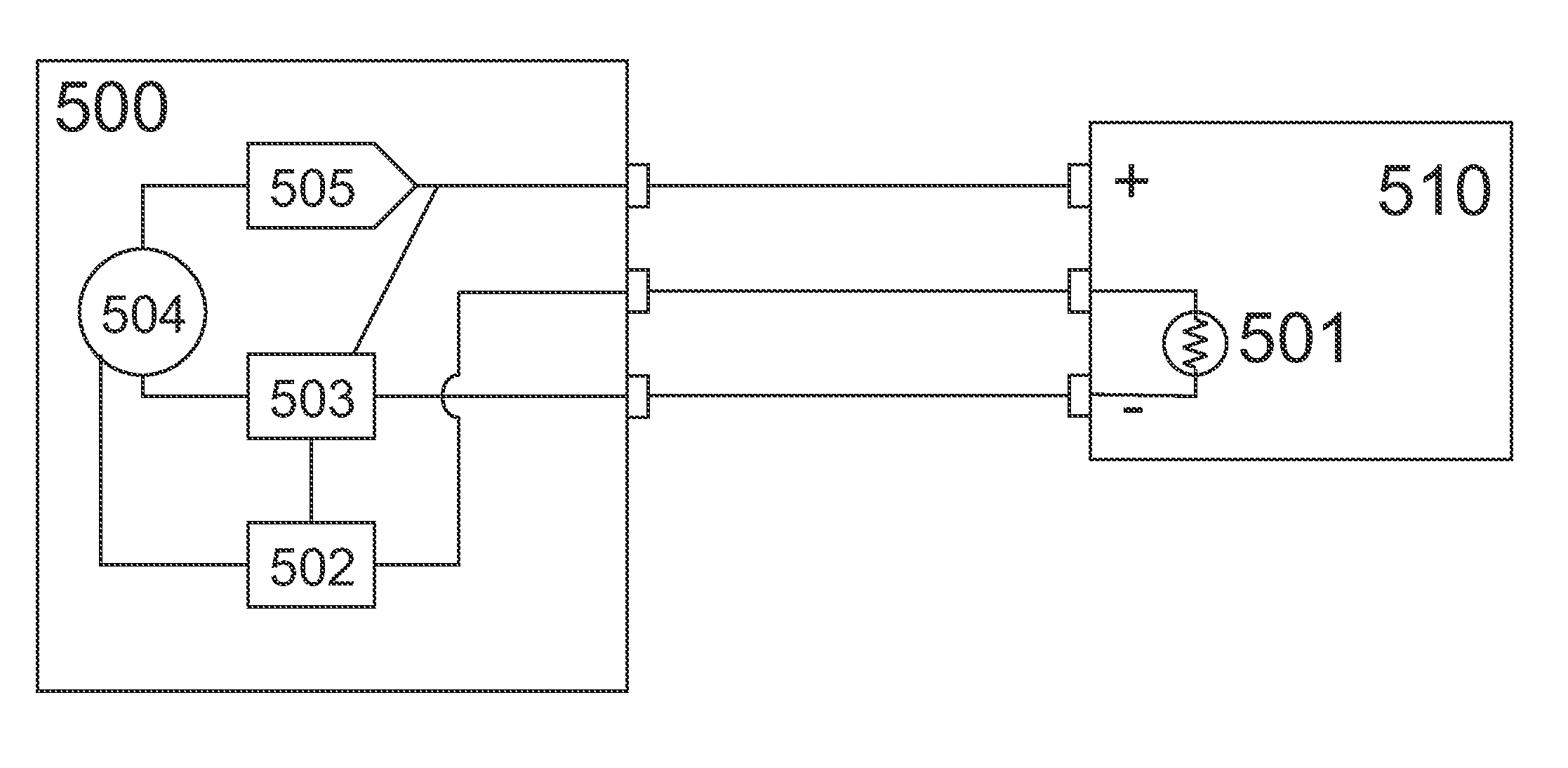
Present invention uses the main power source and auxiliary power source to supply power to a load, makes them take partial charge of power supply, and when the load current reaches its peak, detects a current and a voltage generated by the auxiliary power source, and when the detected values are larger than set values or lower than the set values, controls the output current of the main power source.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
External-applying lead carbon battery negative electrode preparation method
InactiveCN110400907AFirmly connectedDense appearanceLead-acid accumulatorsLead-acid accumulator electrodesCarbon layerFiber
The invention discloses an external-applying lead carbon battery negative electrode preparation method. The negative electrode comprises an external-applying activated carbon layer and a gel electrolyte layer for protecting the carbon layer. The plate is composed of a lead paste (lead powder, humic acid, short fiber, barium sulfate, sodium lignosulfonate, acetylene black, sulfuric acid, and pure water) and a carbon layer. Through adding a suitable binder to the carbon layer preparation and laminating the carbon layer on the surface of the plate with suitable pressure, the physical connection between the carbon phase and the lead phase and the charge transport ability on the lead-carbon interface are enhanced. Through applying the gel electrolyte on the surface of the plate containing the carbon layer, the purposes of protecting the carbon layer from falling off and suppressing hydrogen evolution from the carbon layer can be achieved. The plate formed by the carbon layer can improve thecharging acceptance of the negative electrode and the effective utilization rate of the activated material, the negative electrode sulfation phenomenon under a high-rate partial charge state can be alleviated, and the whole power density and the cycle life of the battery are improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
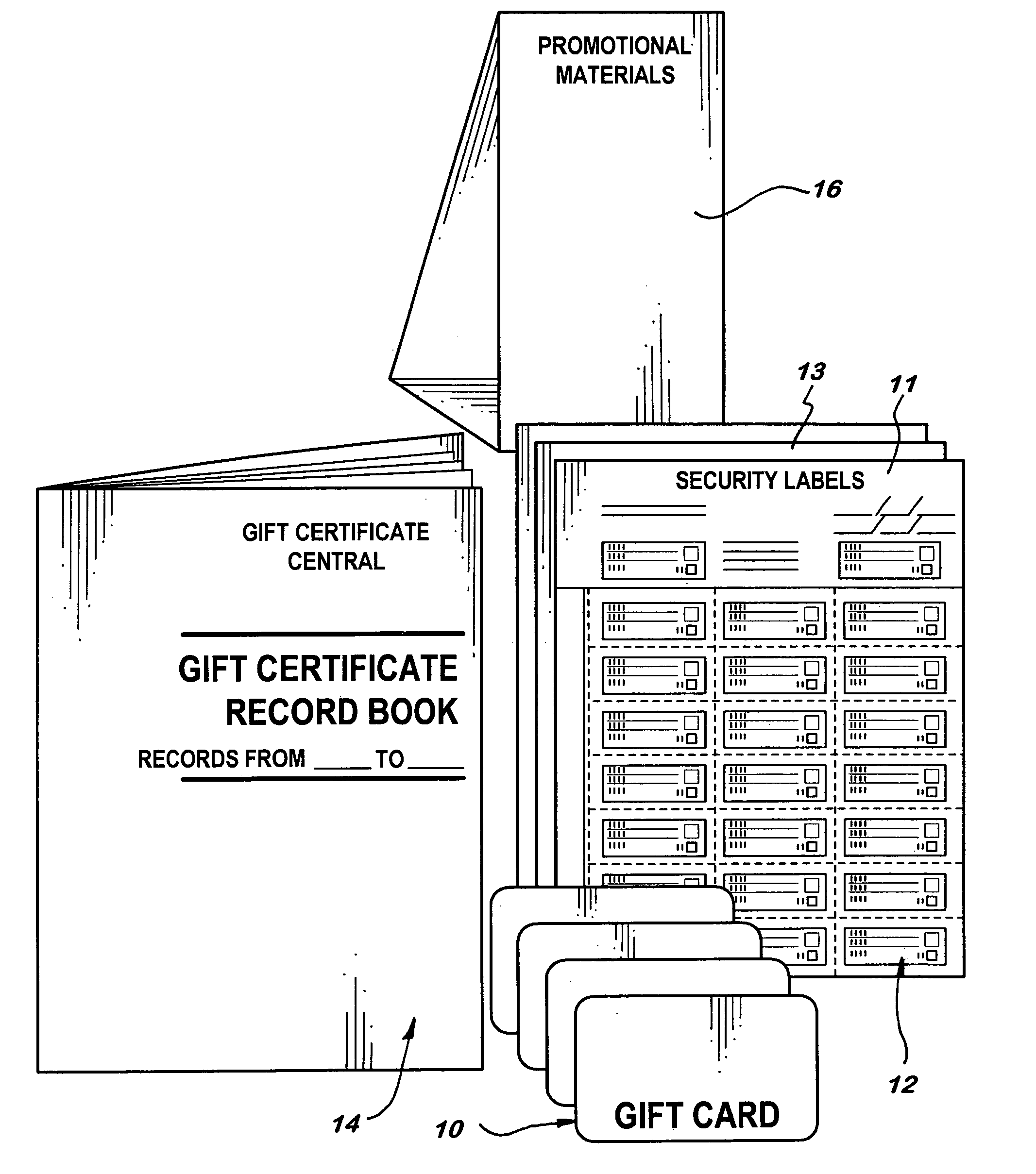
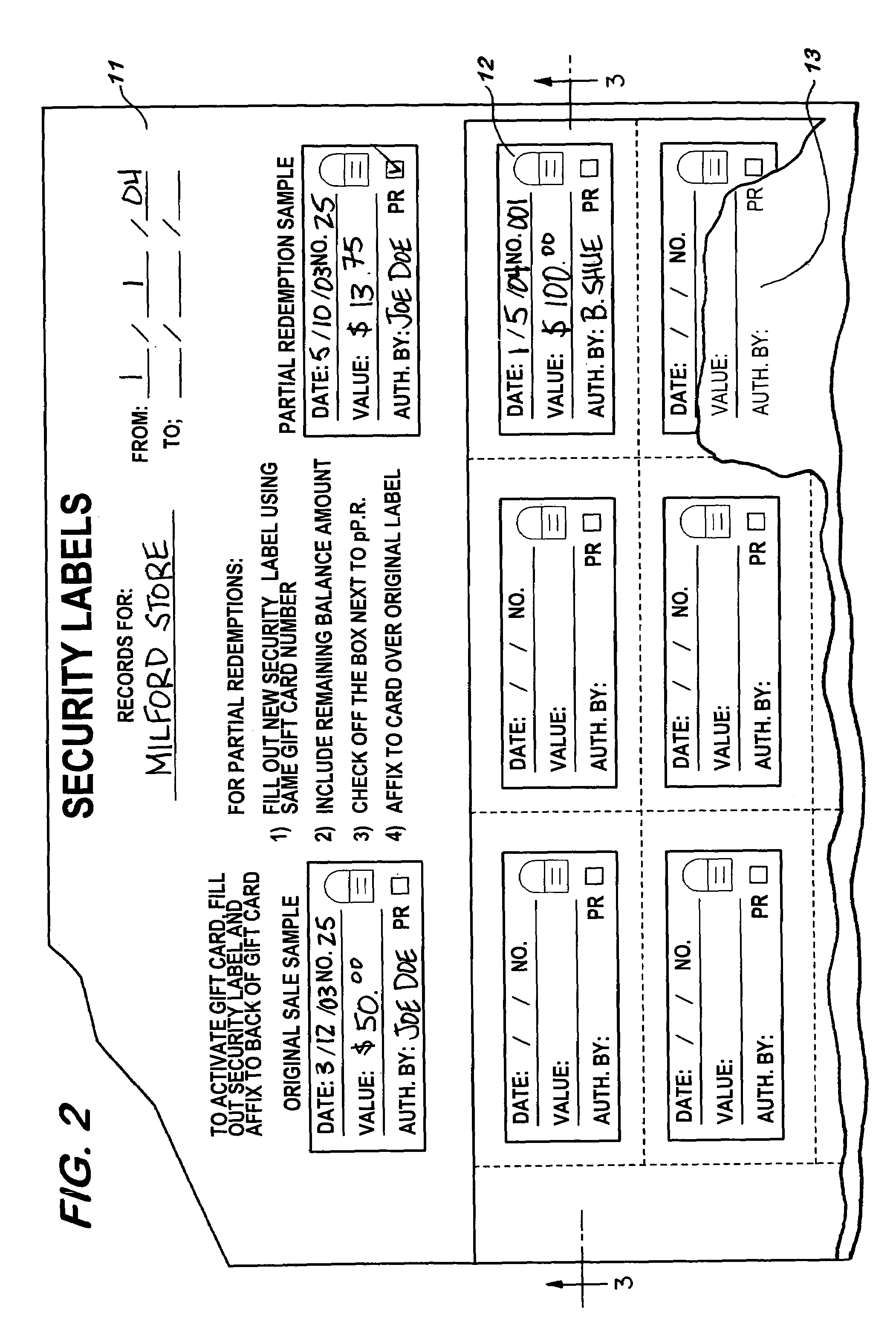
Gift card assembly and method
InactiveUS7007853B2Other printing matterRecord carriers used with machinesComputer hardwarePartial charge
A gift card system includes a gift card imprinted with indicia identifying the issuer, an adhesively coated security label permanently adhered to the card and imprinted on one surface with the value of the gift, and a gift record for recording information concerning the gift including the date of issuance and the value thereof. A recording sheet providing the gift record and the opposite surface of the substrate and the face of the recording sheet have cooperating interactive coatings thereon to imprint the recording sheet. A second security label is substantially permanently adhered on the first security label and imprinted with a reduced value to reflect a partial charge against the value on the first mentioned security label.
Owner:CORCORAN SUZANNE D +2
lead battery
InactiveCN102265448AImprove charge acceptanceSuppress coarseningCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersFinal product manufacturePartial chargeElectrical battery
In a liquid lead-acid storage battery that performs short-term intermittent charging and high-efficiency discharge to the load in a partially charged state, a positive electrode plate with a utilization rate of the positive electrode active material set in the range of 50 to 65% and carbon added to the negative electrode active material are used. A negative electrode plate that improves charge acceptance performance and life performance by using a high-quality conductive material and bisphenol-aminobenzenesulfonic acid-formaldehyde condensate, and uses a non-woven fabric formed of a material selected from glass, pulp, and polyolefin as a separator. The separator on the surface facing the negative electrode plate can further improve the charge acceptance performance and life characteristics at PSOC than conventional batteries.
Owner:SHIN KOBE ELECTRIC MASCH CO LTD
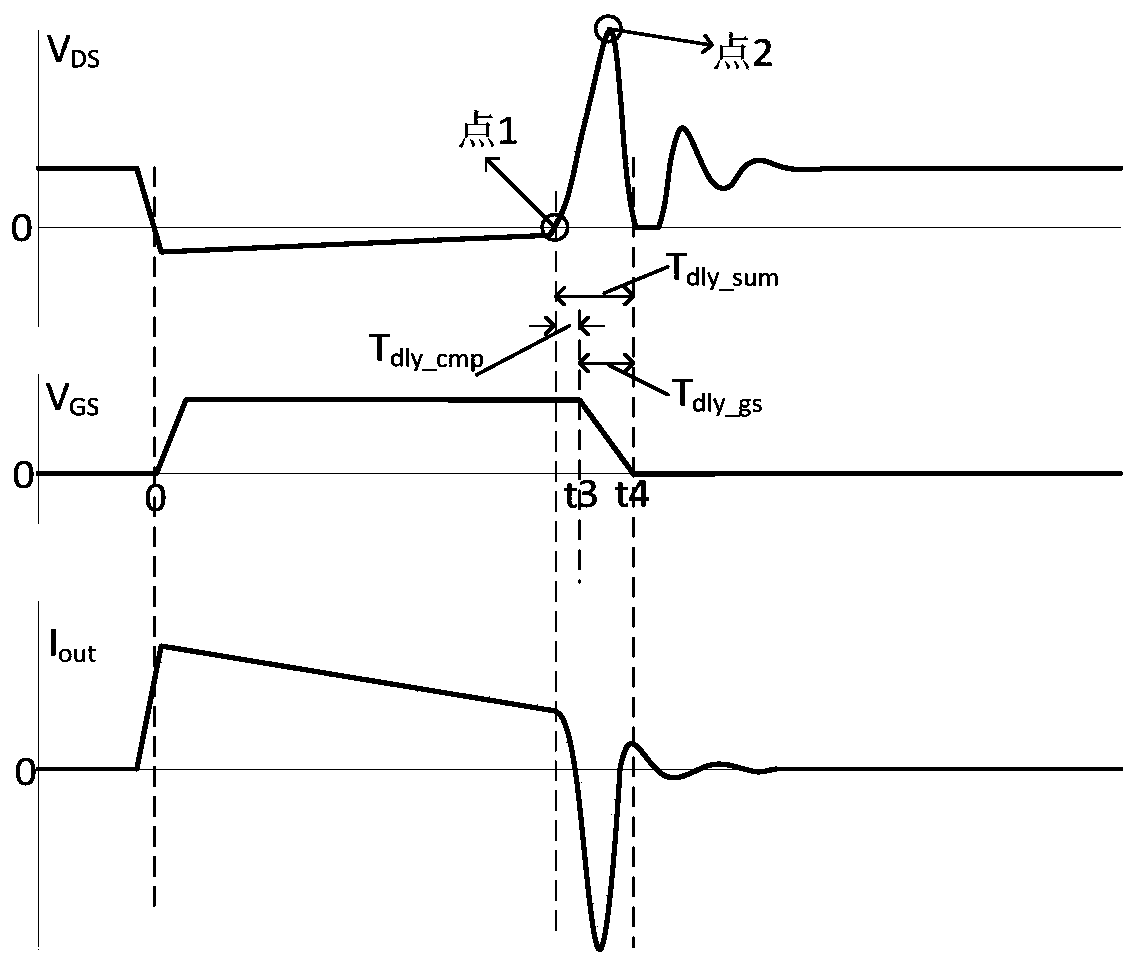
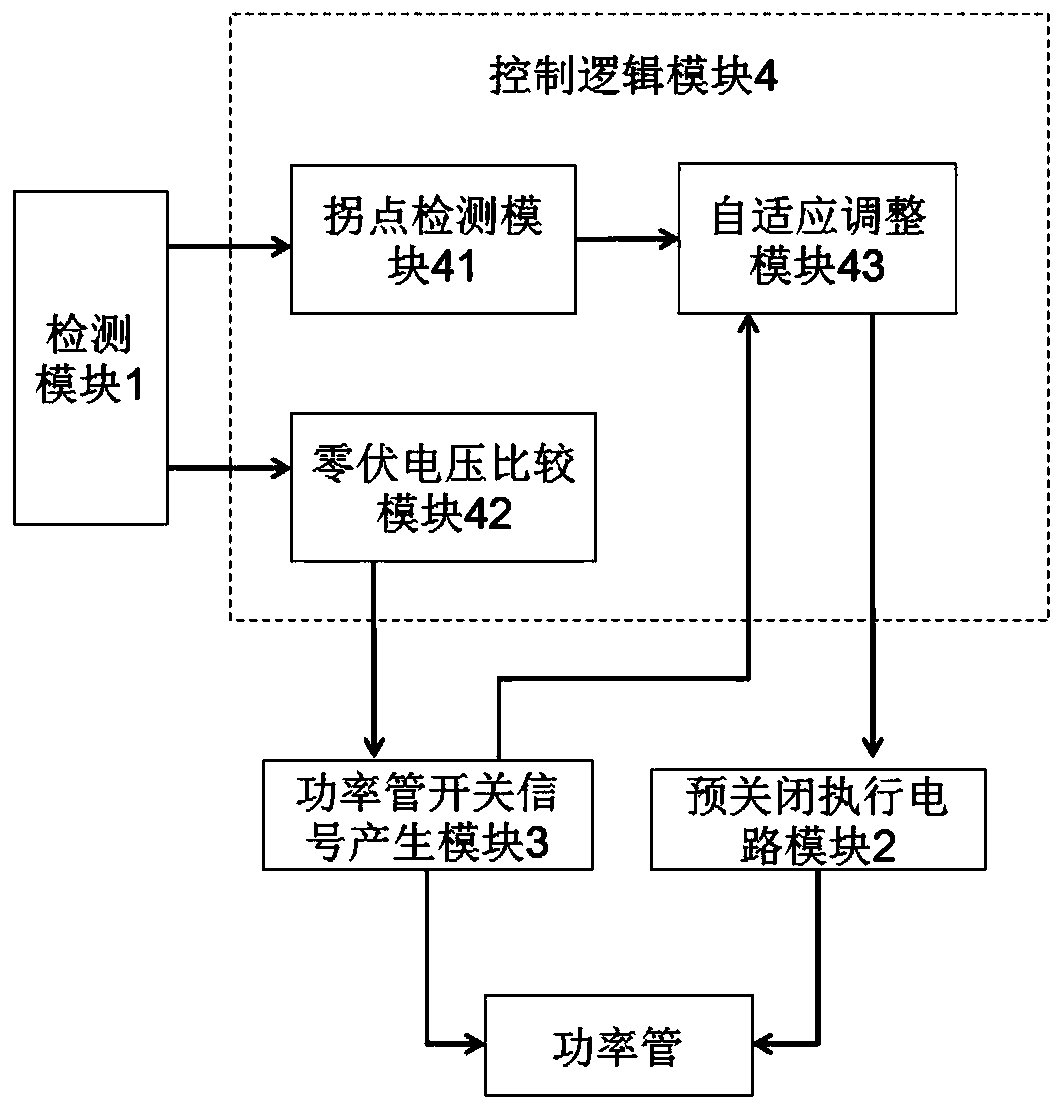
Power tube driving circuit and driving method
The invention provides a power tube driving circuit and a driving method, and relates to the field of power electronic conversion. Before the power tube is turned off, partial charges of a grid electrode of the power tube are discharged in advance through a pre-closing process, so that the power tube is turned off, wherein the starting moment of the pre-closing in the next period is adaptively adjusted through the time interval between the ending moment of the pre-closing in the current period and the turning-off moment of the power tube. Smooth starting and ending of pre-closing can be effectively guaranteed by adjusting the starting moment of pre-closing in a self-adaptive mode, especially when the method is applied to driving of a synchronous rectification power tube, it can be guaranteed that the starting moment and the ending moment of pre-closing can be adjusted in the self-adaptive mode at DCM, CCM and even depth CCM, and smooth starting and ending of pre-closing are guaranteed.
Owner:ANHUI DONGKE SEMICON CO LTD
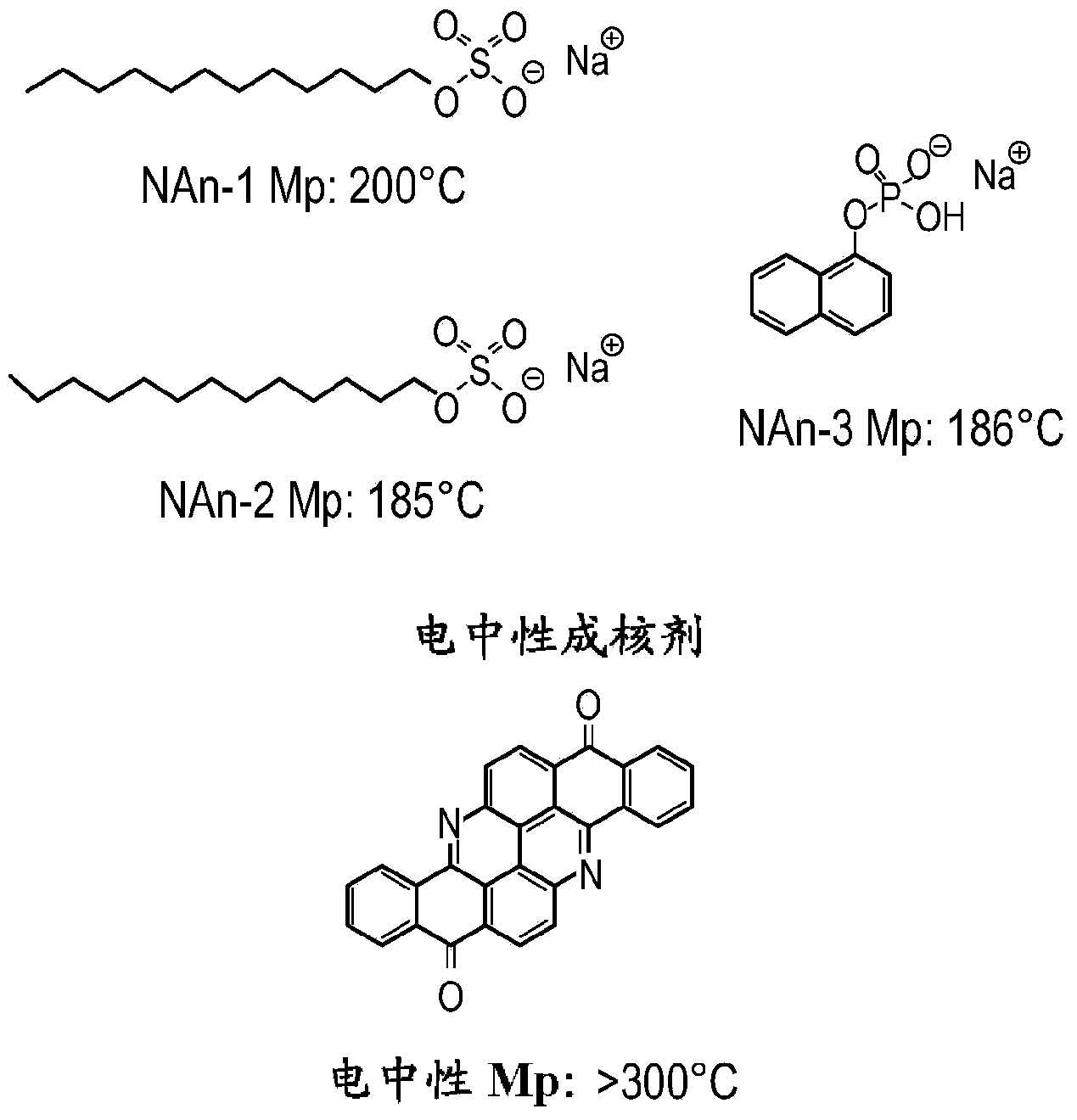
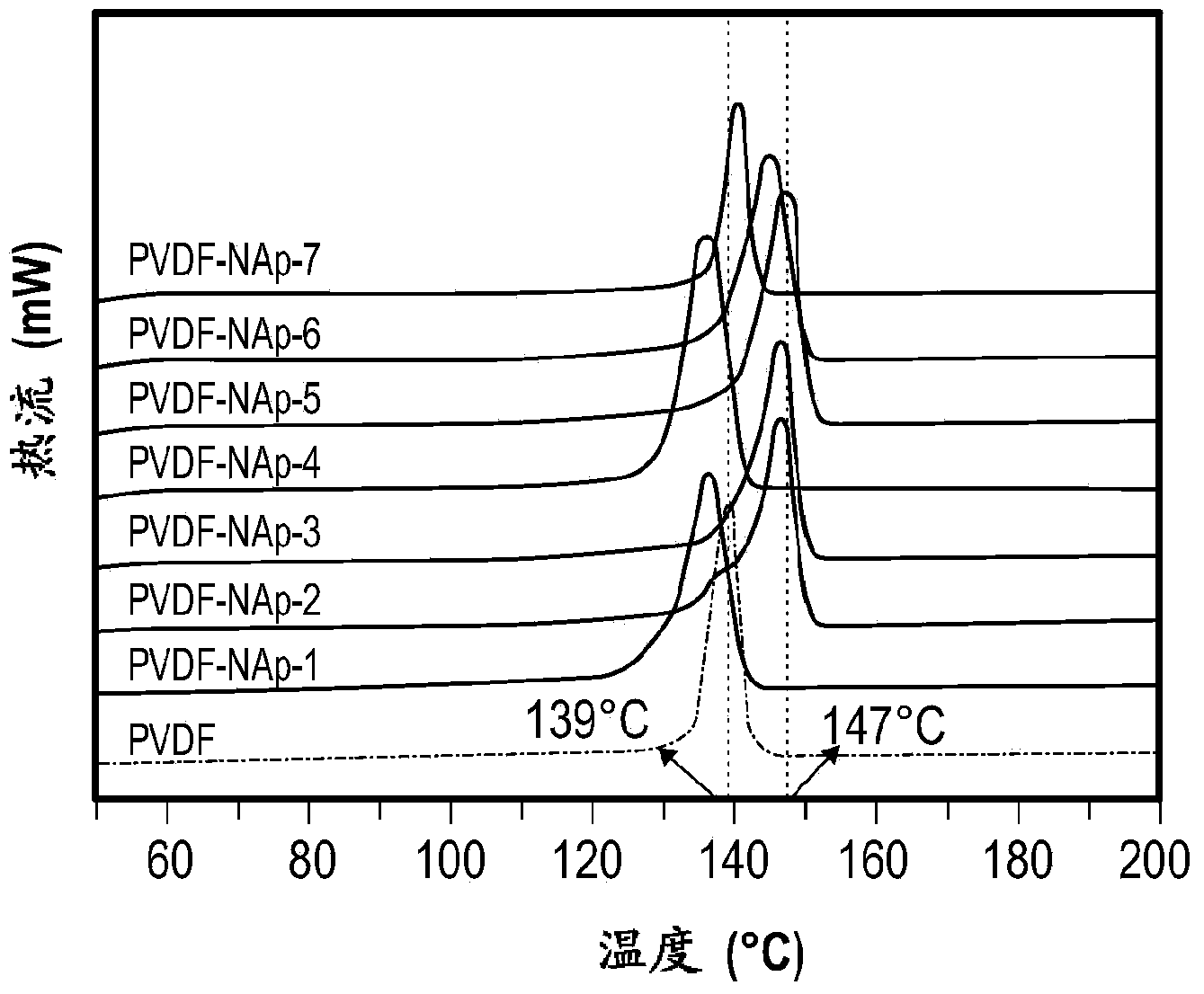
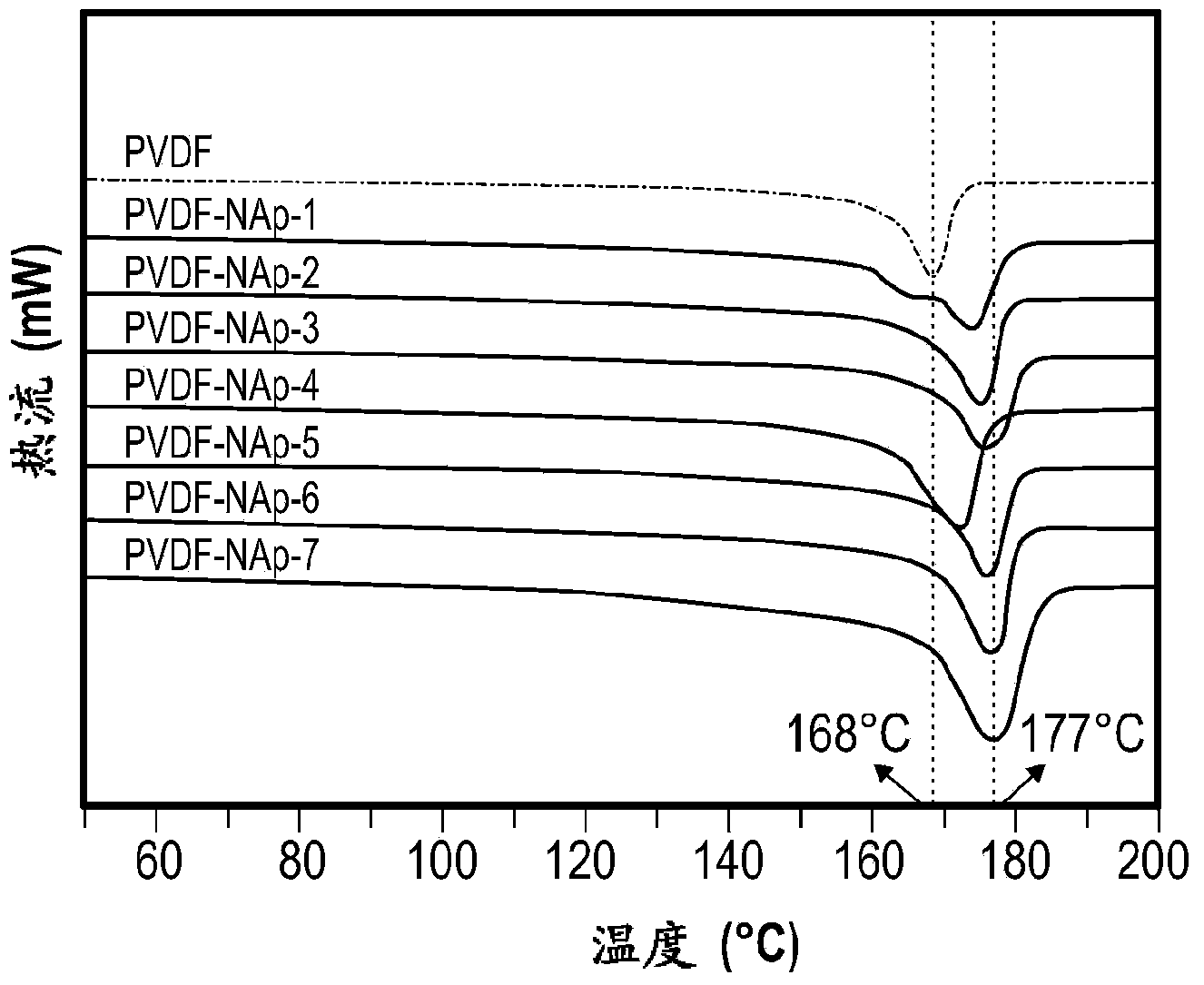
A melt processable composition and method of making
A composition includes a) a melt processable polymer including at least one chemical moiety having a partial charge; and b) a nucleating agent having a surface charge that is opposite the partial charge of the chemical moiety of the polymer, wherein the nucleating agent accelerates the rate of crystallization of the melt processable polymer; wherein the nucleating agent has a melting point greater than the melting point of the melt processable polymer. In an embodiment, a method of making the composition is also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Bipolar asymmetric supercapacitor energy storage apparatus and bipolar assembly thereof
InactiveCN108199094AIncrease specific energyIncrease powerAccumulators with bipolar electrodesBatteriesElectricityPartial charge
The invention discloses a bipolar assembly for a bipolar asymmetric supercapacitor energy storage apparatus. The bipolar assembly comprises: a substrate, wherein the substrate is insulated, and comprises two opposite surfaces; a positive electrode, wherein the positive electrode comprises a lead-containing active material and is positioned on one surface of the substrate; and a negative electrodepositioned on the other surface of the substrate, wherein the substrate has an electrical connection circuit so as to form electrical connection between the positive electrode and the negative electrode, and the negative electrode comprises a carbon-containing active material. According to the present invention, the carbon-lead battery technology and the bipolar battery technology are successfullycombined so as to effectively improve the performance of the energy storage device during the bidirectional high-power and high-frequency partial charging and discharging.
Owner:LCB INT
Method and device for controlling a capacitive load
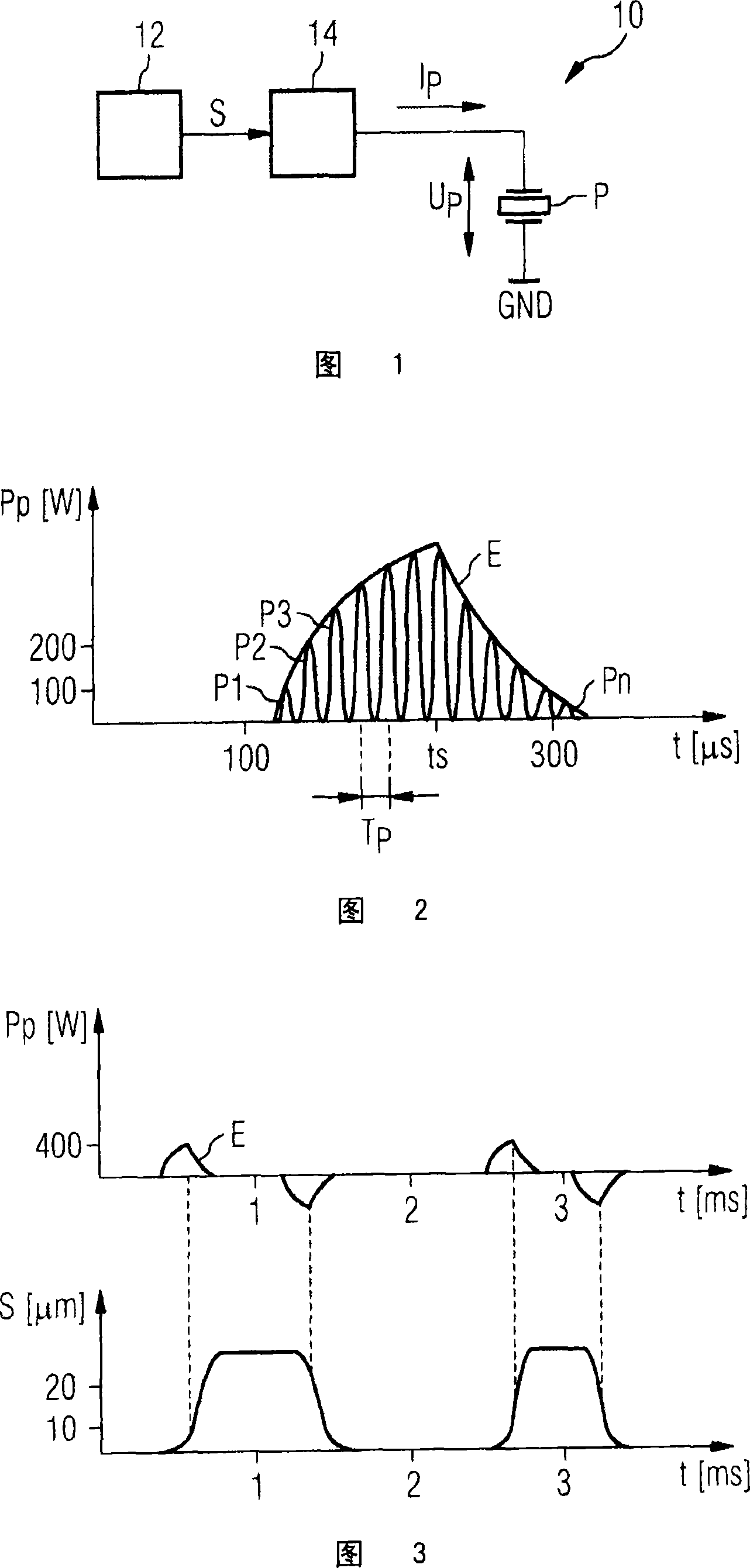
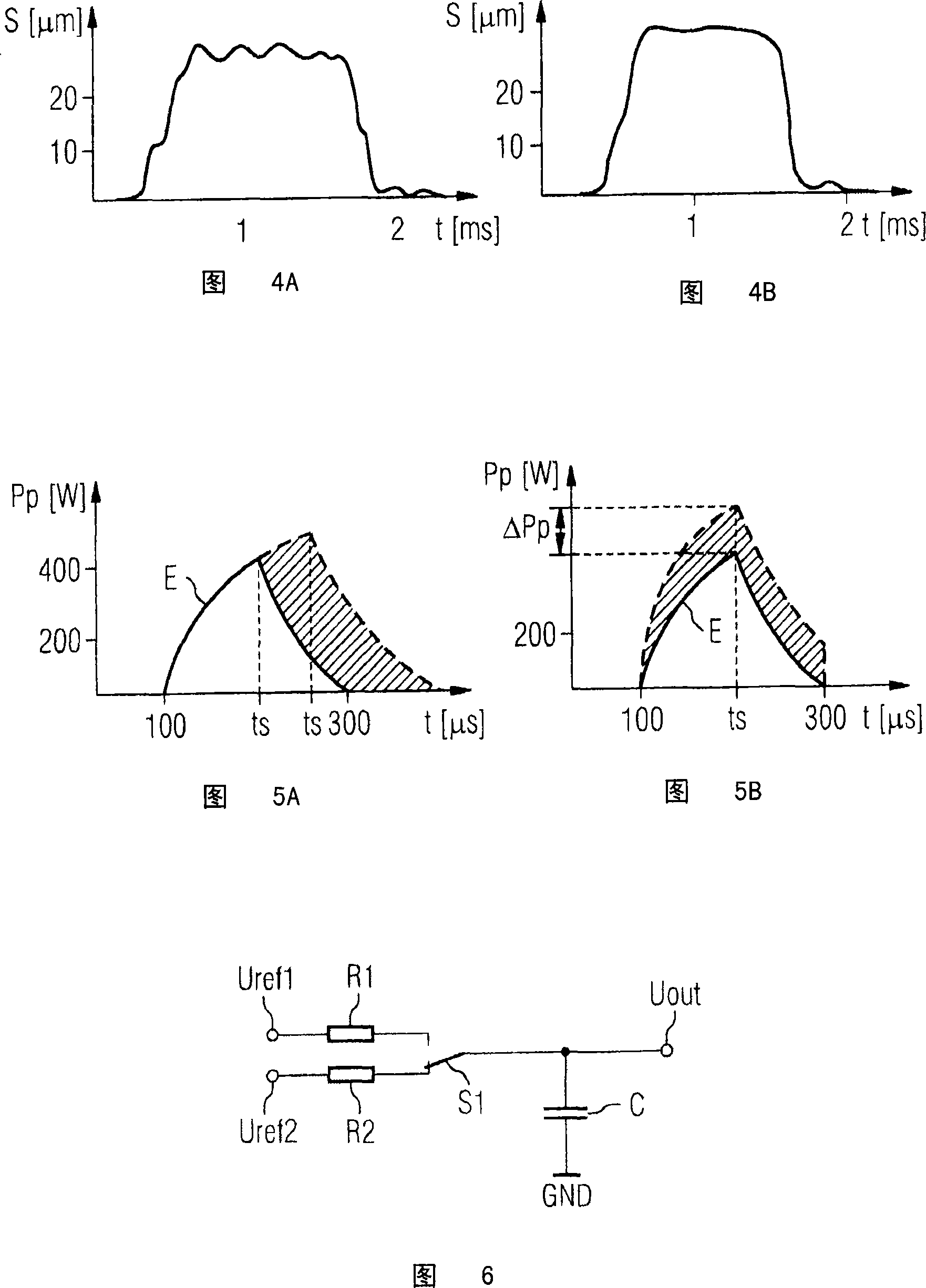
ActiveCN101253319AMonotonically decreasing slopeReduce slopeElectrical controlPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCharge currentPartial charge
The aim of the invention is to avoid a tendency of the controlled load to oscillate when controlling a capacitive load, in particular, of a piezo actuator for an injection valve of an internal combustion engine, having charging and discharging processes for charging and discharging the capacitive load by means of a load current, each loading process being effected by chronological partial load current pulses according to chronological partial charging capacity pulses (p1, p2, ... pn). To this end, the invention provides that the envelope (E) of the partial charging capacity pulses (p1, p2, ... pn), during the loading process, increases in a strictly monotonous manner in an initial phase, and the slope of the envelope decreases in a monotonous manner.
Owner:VTESCO TECH GMBH
A rapid test method for cycle life of lithium battery
ActiveCN103344917BReduce designShorten the development cycleElectrical testingElectricityTest battery
The invention relates to the technical field of lithium battery parameter determination methods, in particular to a lithium battery cycle life quick testing method. The method includes the steps of step 1, determining charge state interval for cycle life quick testing according to polarization voltage characteristics of a battery sample, step 2, carrying out a battery cycle life quick test to obtain cycle life test experimental data, step 3, carrying out cycle life mathematic model deduction in partial charge interval, step 4, establishing cycle life deduction mathematic models in 0-100% charge interval, step 5, obtaining a cycle life formula of a battery in the 0-100% charge interval, and step 6, estimating the cycle life of the tested battery. The lithium battery cycle life quick testing method overcomes the defects that time for conventional testing is long, and difference between an accelerated cycle life testing method and the reality is large, and shortens design, development and testing periods of batteries.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV +2
Antibody production method
InactiveCN107805650AImproved charge heterogeneityMaintain or increase expressionImmunoglobulinsFermentationBiotechnologyAntibody expression
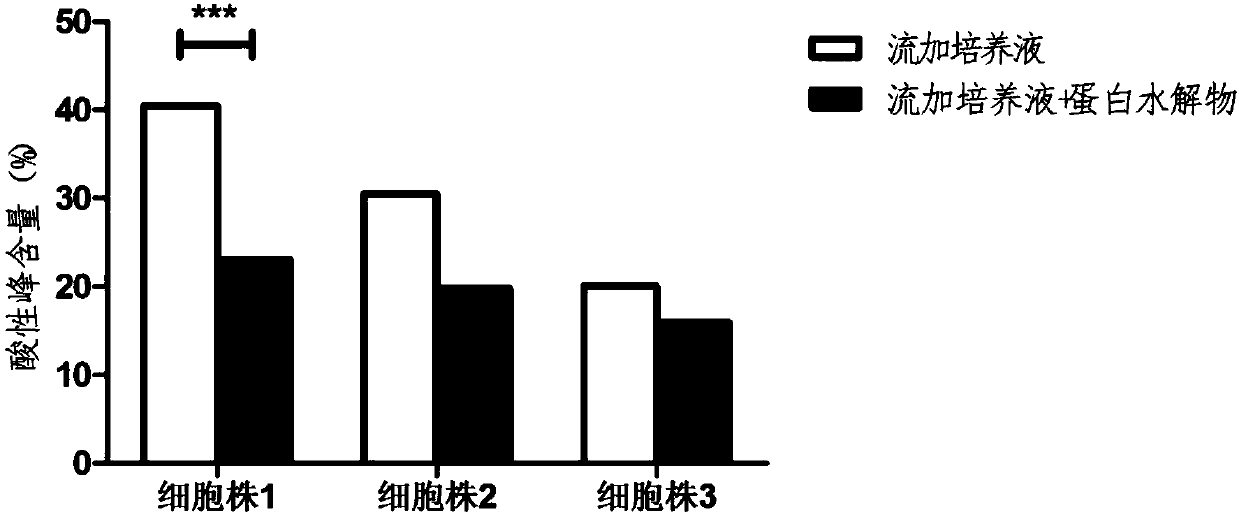
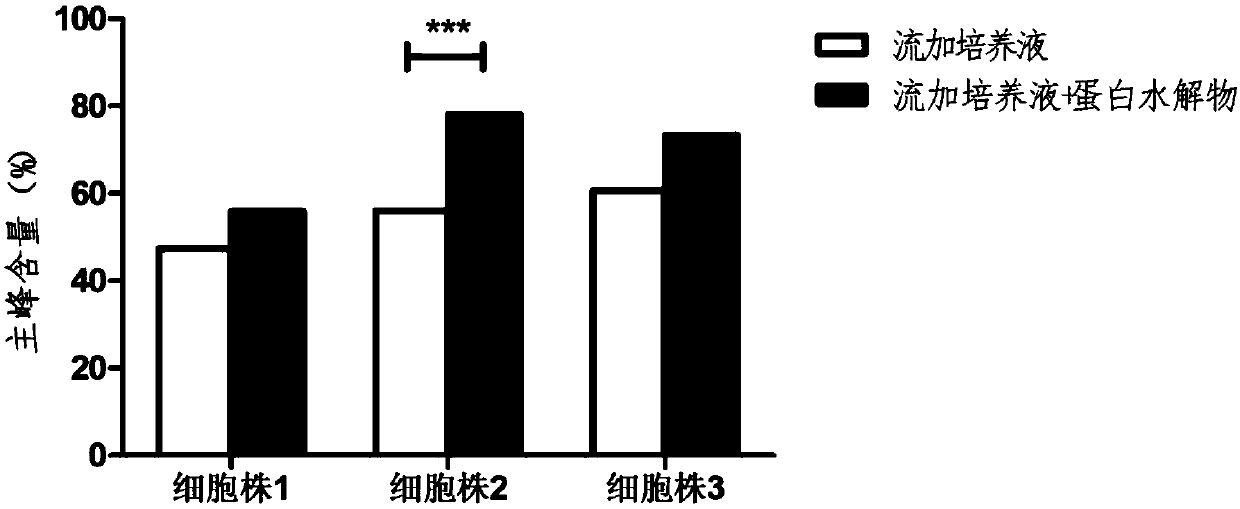
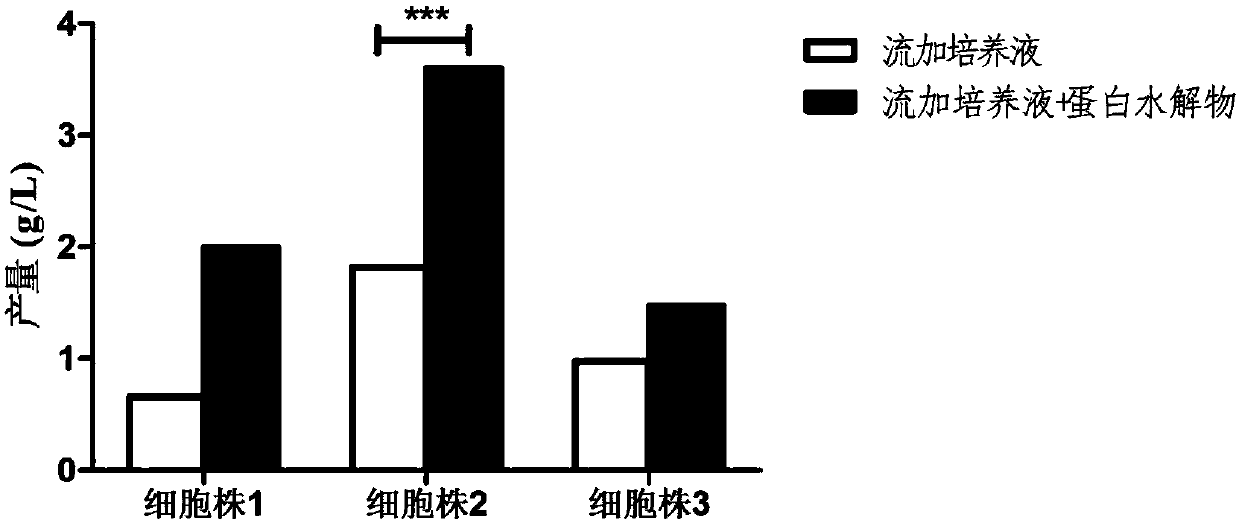
The invention discloses an antibody production method. The method starts from the metabolic process of cell culture, a protein hydrolysate is added into a fed-batch culture solution to achieve adequate nutrition and an inhibition and prevention effect on modification and degradation of partial charge heterogeneity in the expression process, thereby stably and effectively improving the charge heterogeneity of the antibody product and increasing the antibody expression. The method can effectively solve the charge heterogeneity problem in antibody production, and can maintain or improve the yield.
Owner:上海泰因生物技术有限公司
System and method of limiting degradation of the battery by prohibiting over-charge with measured temperatures
ActiveUS8237408B2Reducing unwanted side reactionShorten charging timeBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerElectrical batteryEngineering
A battery charging apparatus and method adapted to reduce battery capacity as a function of increased temperature thereby permitting partial charges at temperatures in excess of manufacturer's recommendations. The method includes steps of reducing charging current and charging voltage as a function of battery temperature thereby averting chemical instability within the battery. The apparatus detects battery temperature and includes a controller that will control charger voltage and current as a function of temperature and determine a suitable charging capacity.
Owner:STRYTEN ENERGY LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com