Method of quantifying hydrocarbon formation and retention in a mother rock
a hydrocarbon and mother rock technology, applied in the field of methods of quantifying hydrocarbon formation and retention in mother rock, can solve the problems of kinetic parameters lag, uncertainty in the estimation of oil window, and difficulty in elaborating the reaction mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0067] The method according to the invention numerically models the thermal maturation of the organic matter of the mother rock or of any other macromolecular system, and the retention of the products from this reaction in the residual organic matrix, and to possibly extrapolate the results to the basin scale.
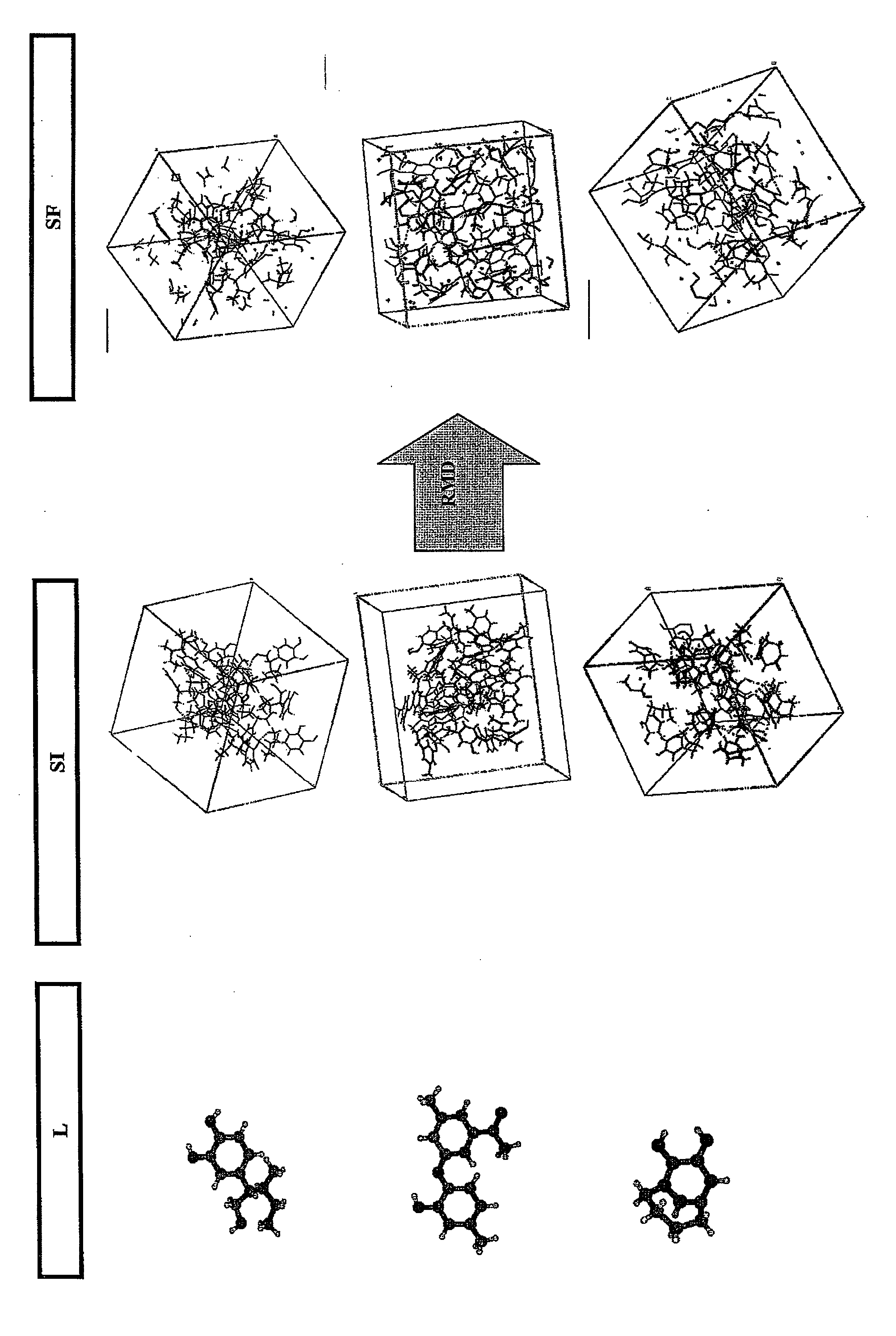
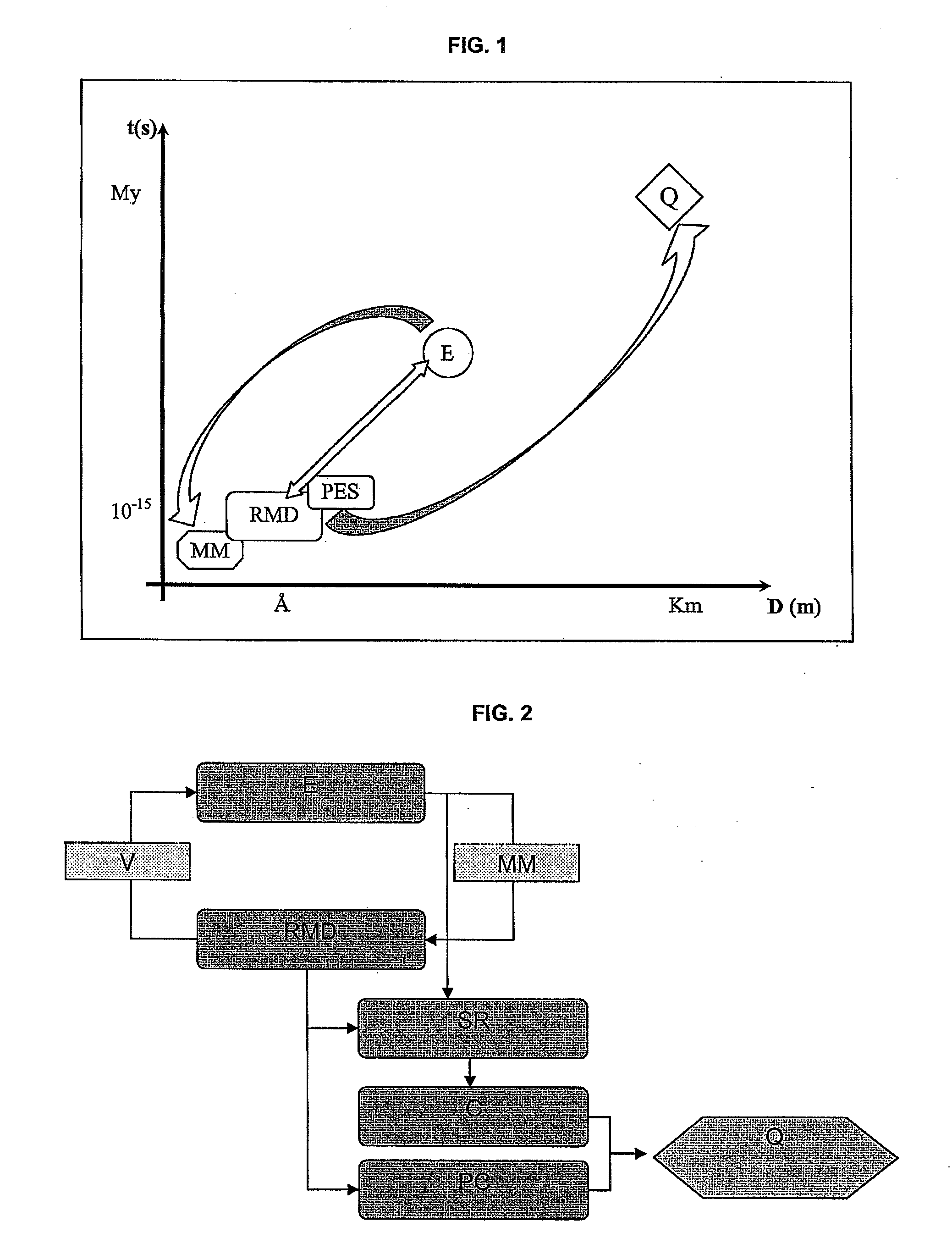
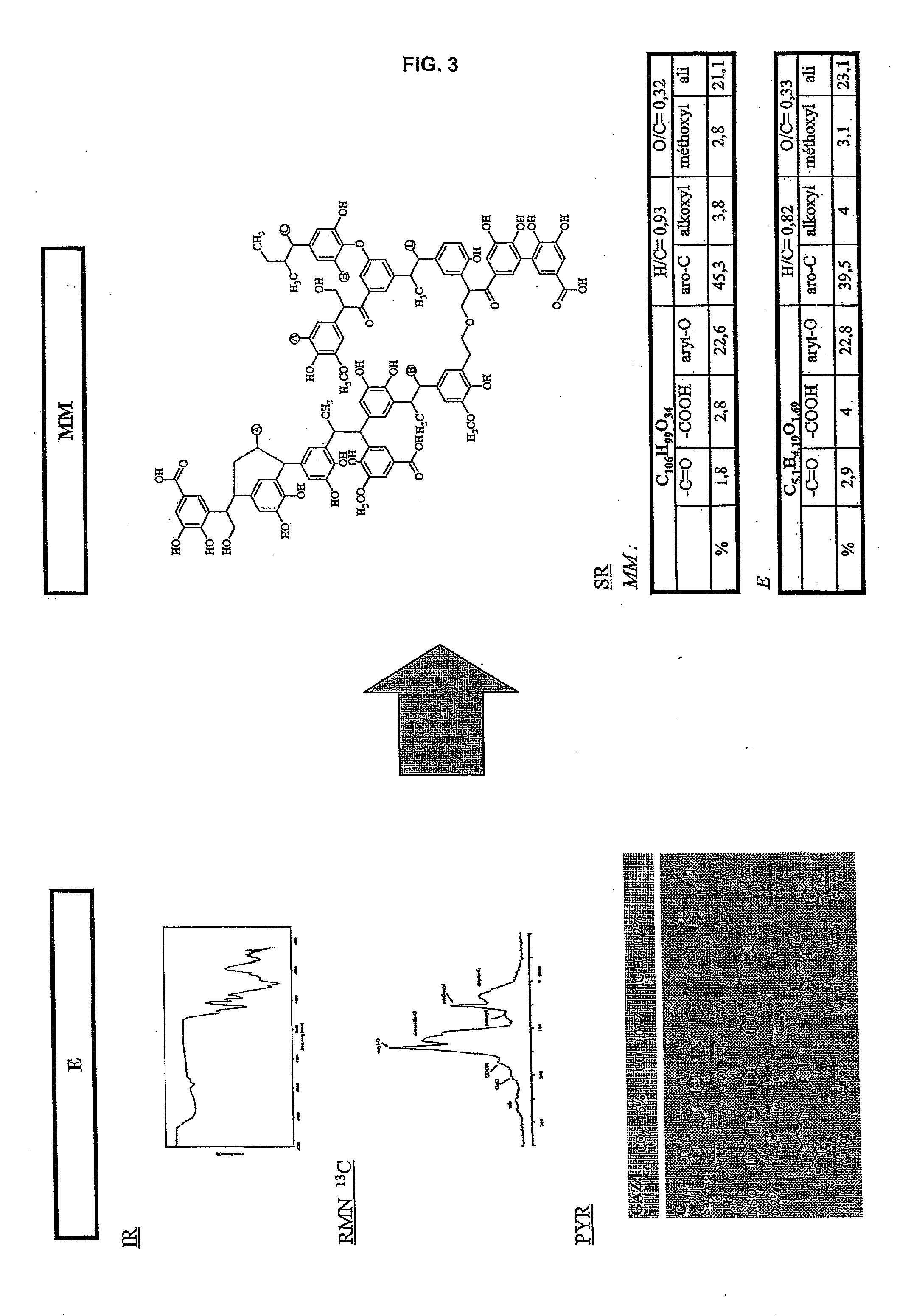
[0068]FIG. 1 shows the principle of the method as a function of the various space scales (D(m): Distance in meter) and time scales (t(s): time in second). The initial kerogen (or any other macromolecular structure) sample (E) is experimentally characterized, which allows determination of a molecular model of the structure (MM (Å, 10−15 s)). This molecular model is the input datum of the dynamic simulations coupled with a reactive force field (RMD (Å, 10−15 s)). These simulations model the thermal cracking reaction of the molecular model under the given conditions, and they are validated by comparison with the experimental thermal maturation data. At several stages of the simul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com