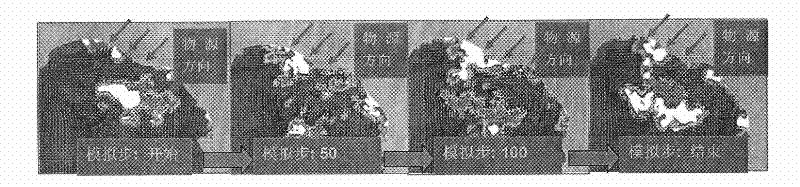
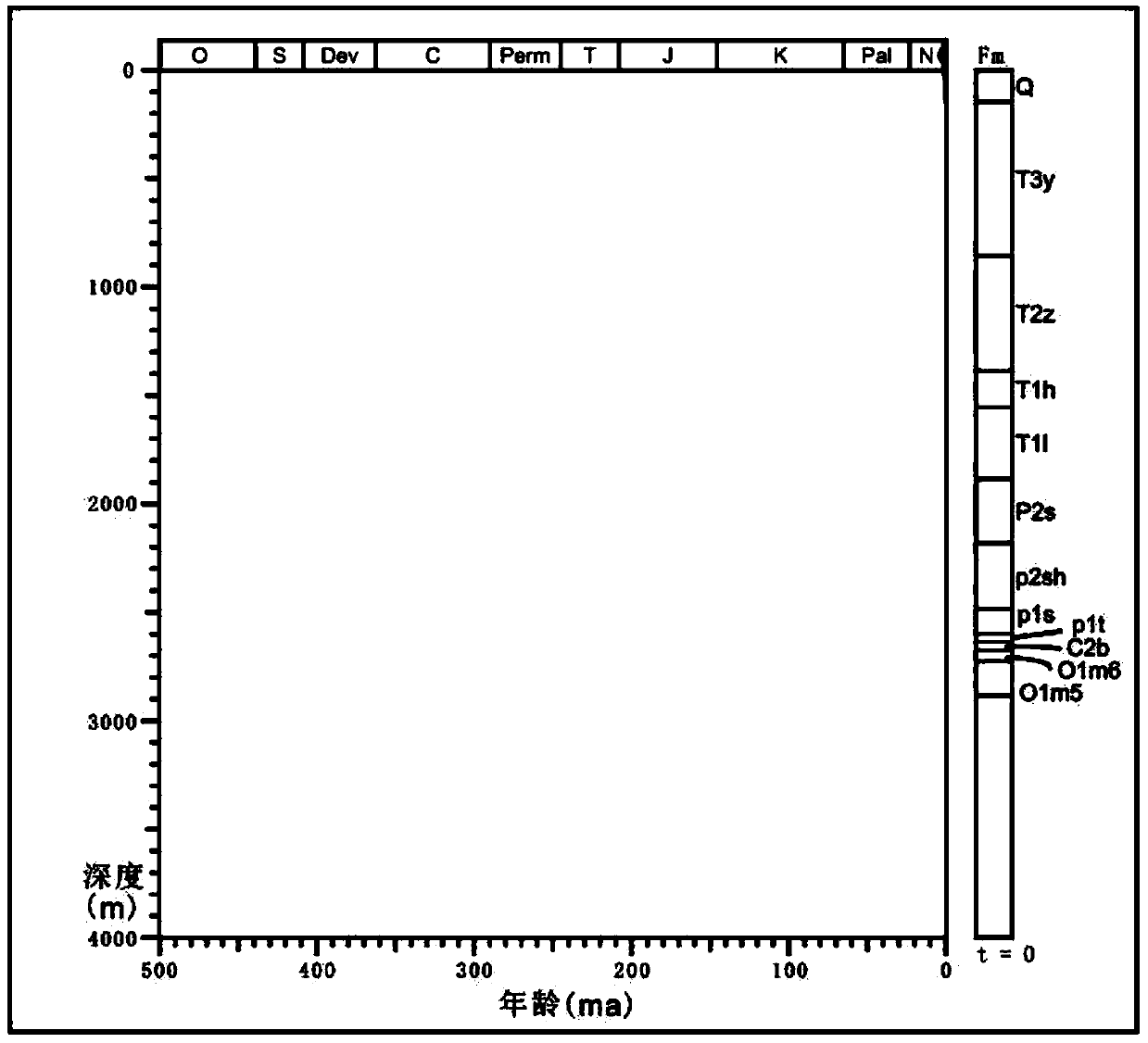
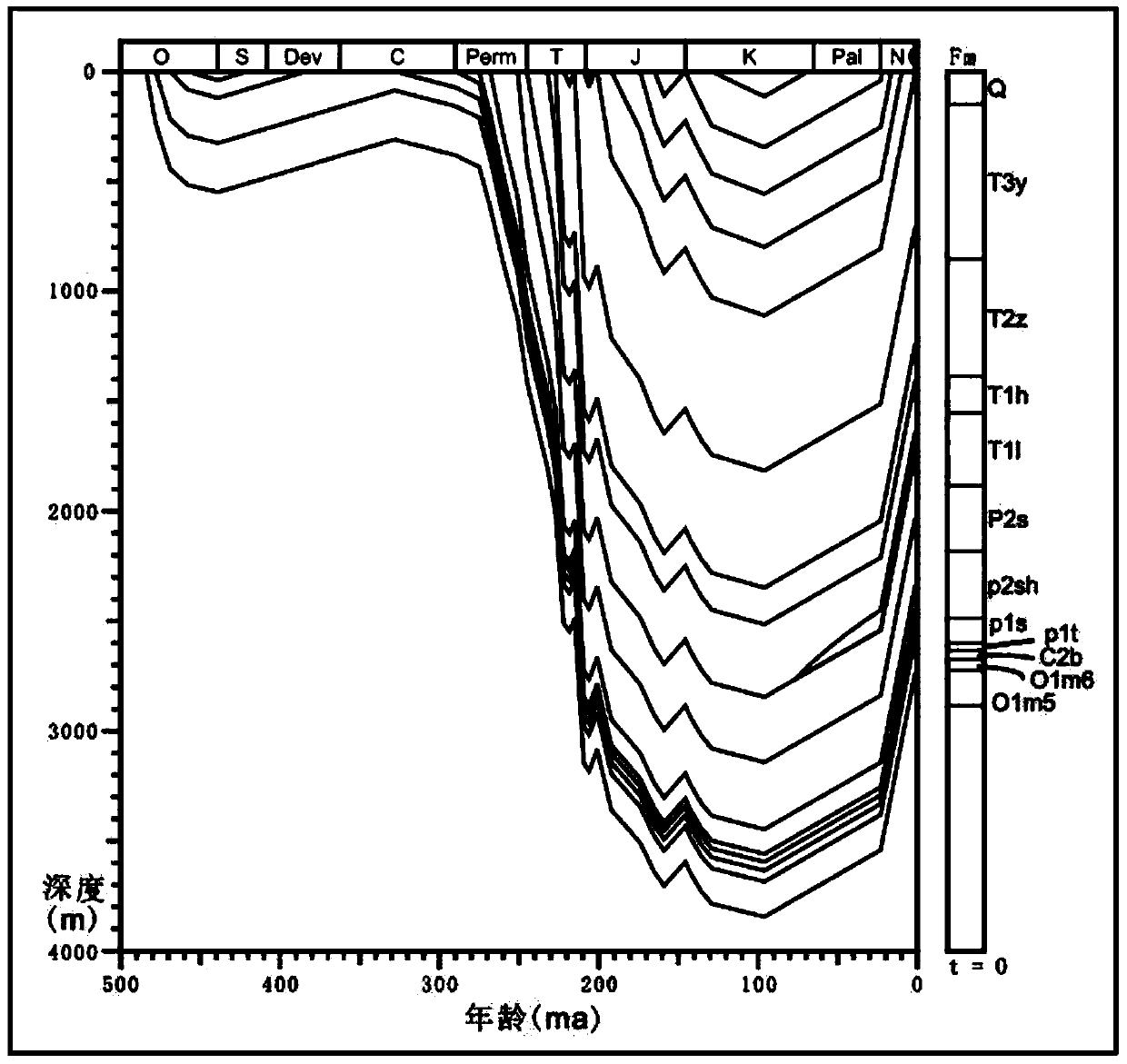
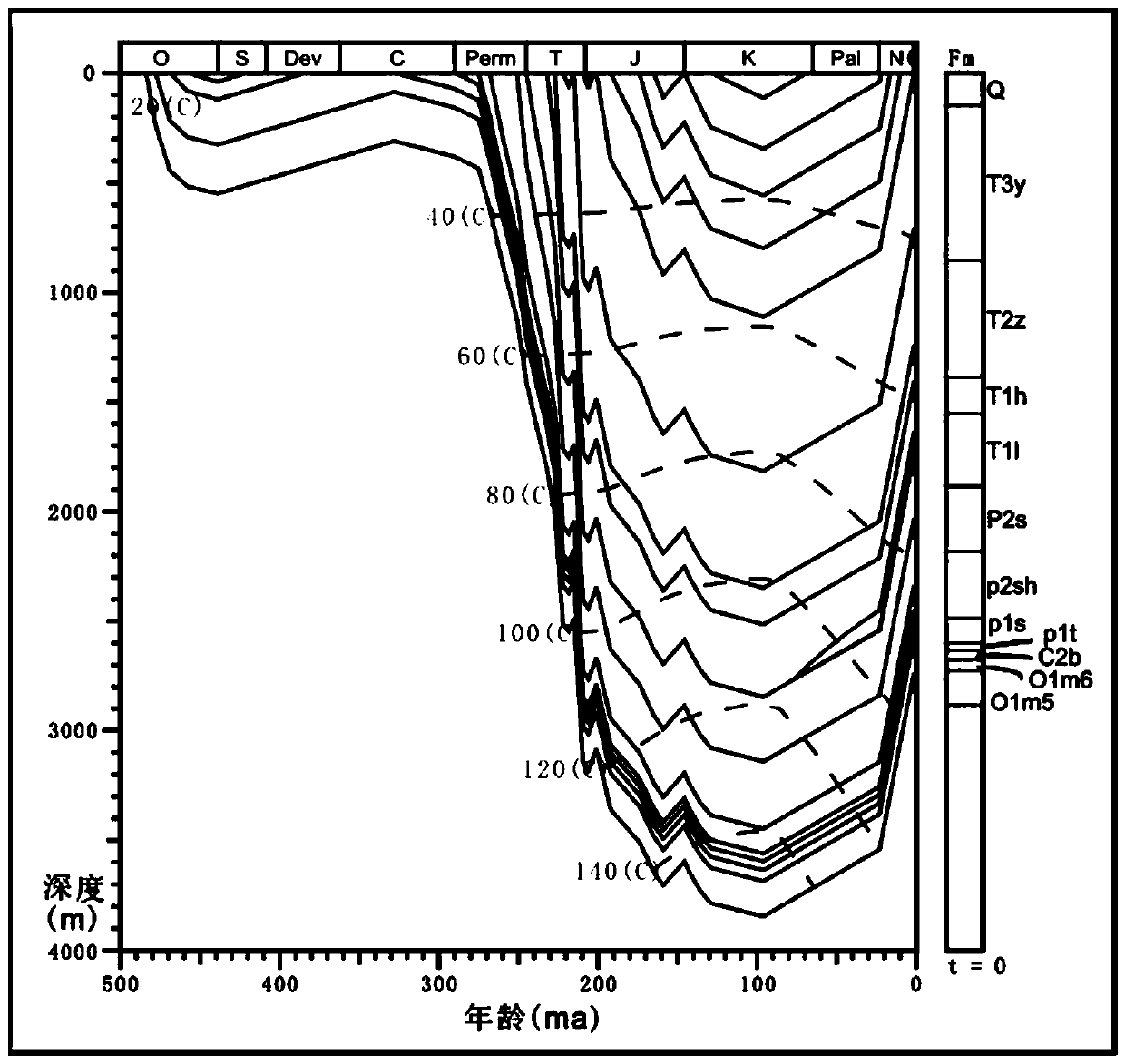
Patents
Literature
142 results about "Sedimentary basin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
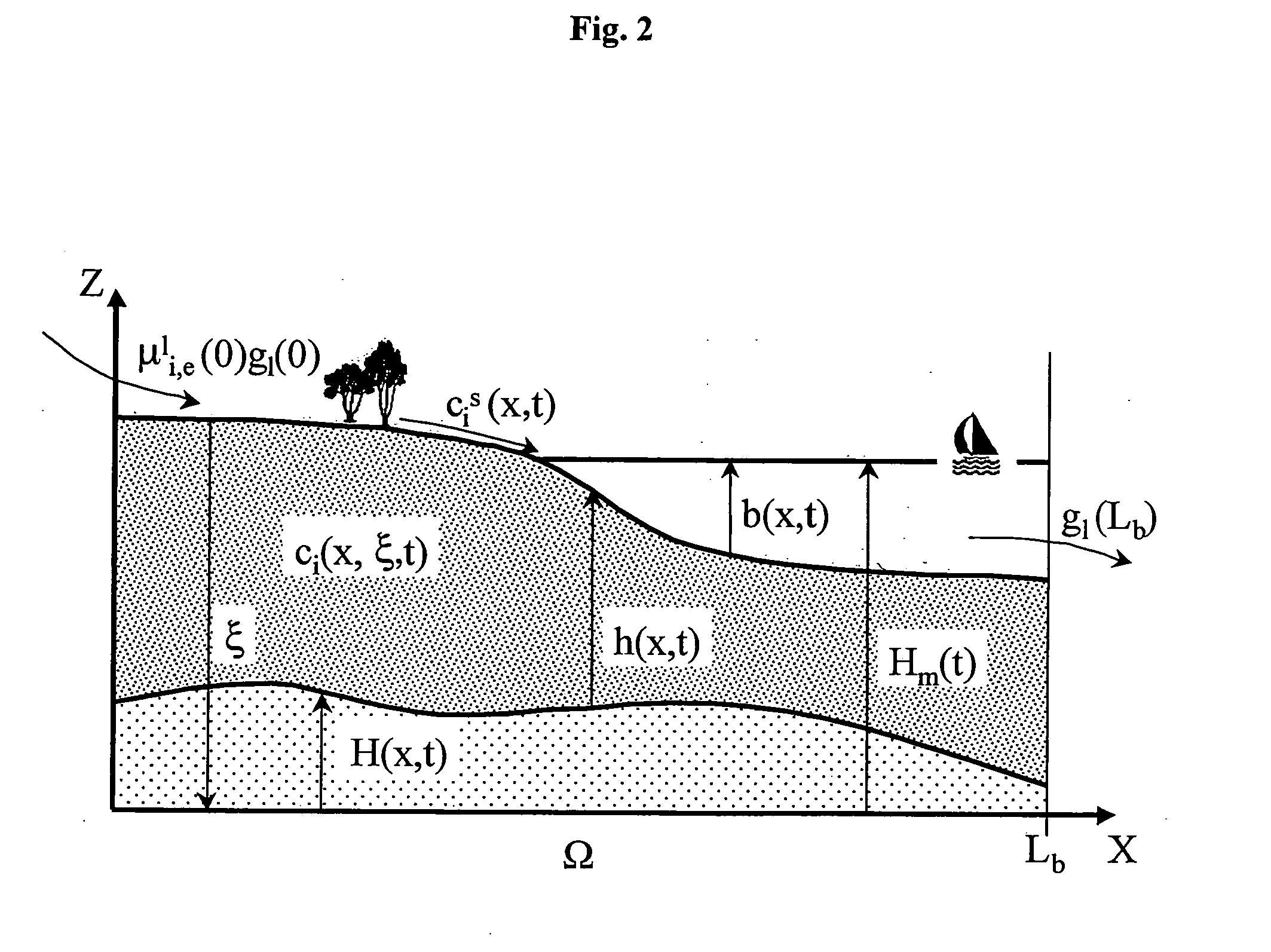
Sedimentary basins are regions of Earth of long-term subsidence creating accommodation space for infilling by sediments. The subsidence can result from a variety of causes that include: the thinning of underlying crust, sedimentary, volcanic, and tectonic loading, and changes in the thickness or density of adjacent lithosphere. Sedimentary basins occur in diverse geological settings usually associated with plate tectonic activity. Basins are classified structurally in various ways, with a primary classifications distinguishing among basins formed in various plate tectonic regime (divergent, convergent, transform, intraplate), the proximity of the basin to the active plate margins, and whether oceanic, continental or transitional crust underlies the basin. Basins formed in different plate tectonic regimes vary in their preservation potential. On oceanic crust, basins are likely to be subducted, while marginal continental basins may be partially preserved, and intracratonic basins have a high probability of preservation. As the sediments are buried, they are subjected to increasing pressure and begin the process of lithification. A number of basins formed in extensional settings can undergo inversion which has accounted for a number of the economically viable oil reserves on earth which were formerly basins.
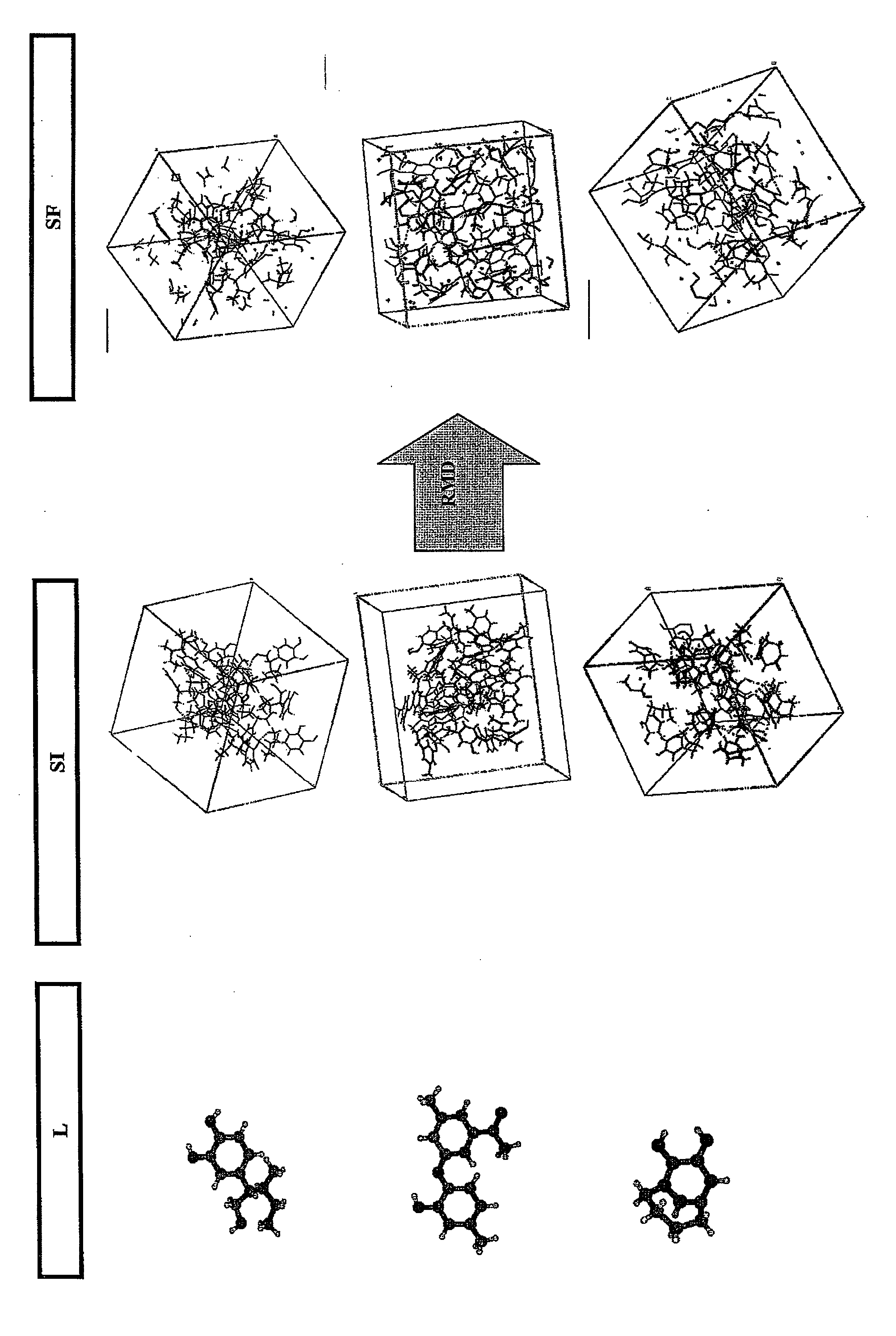
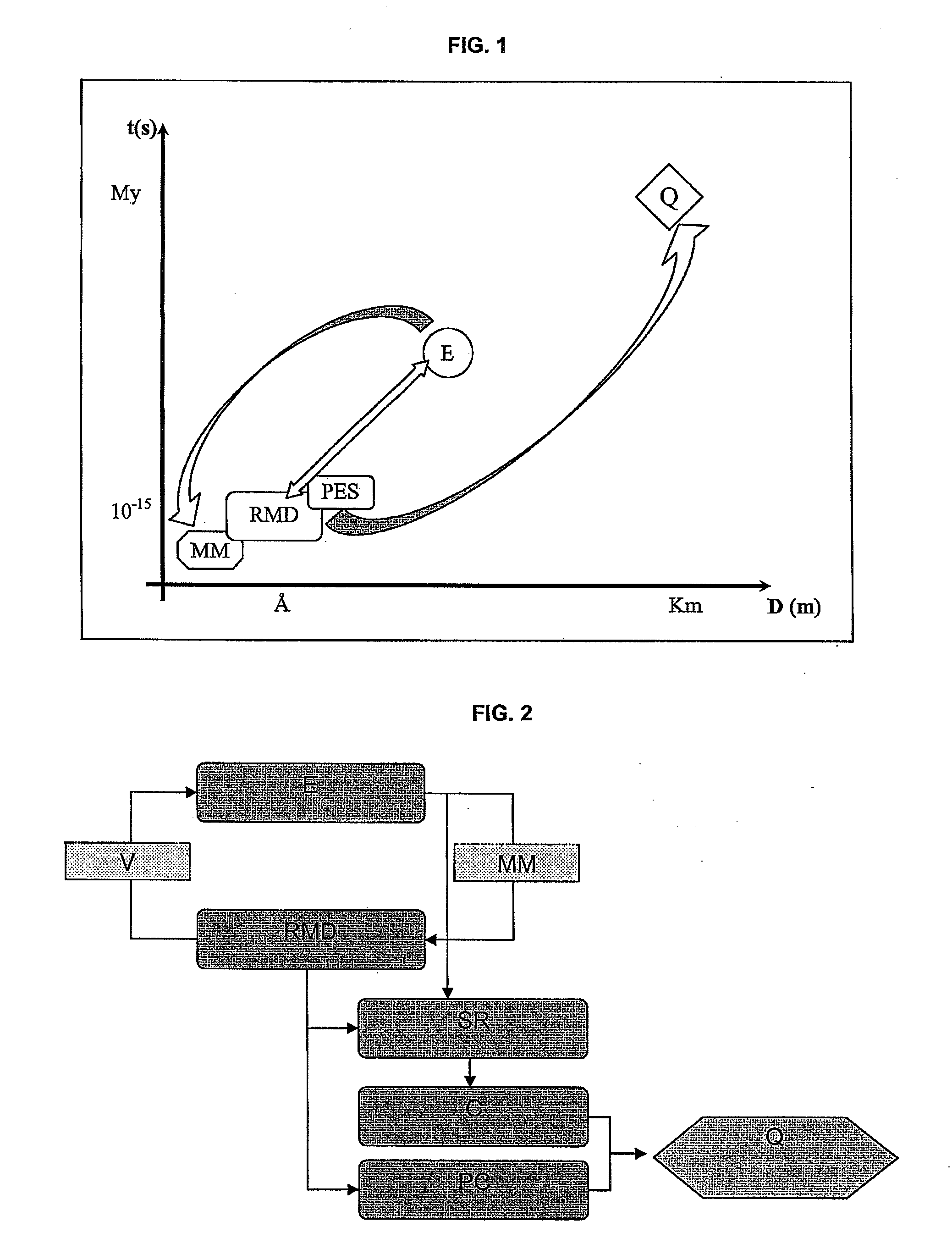
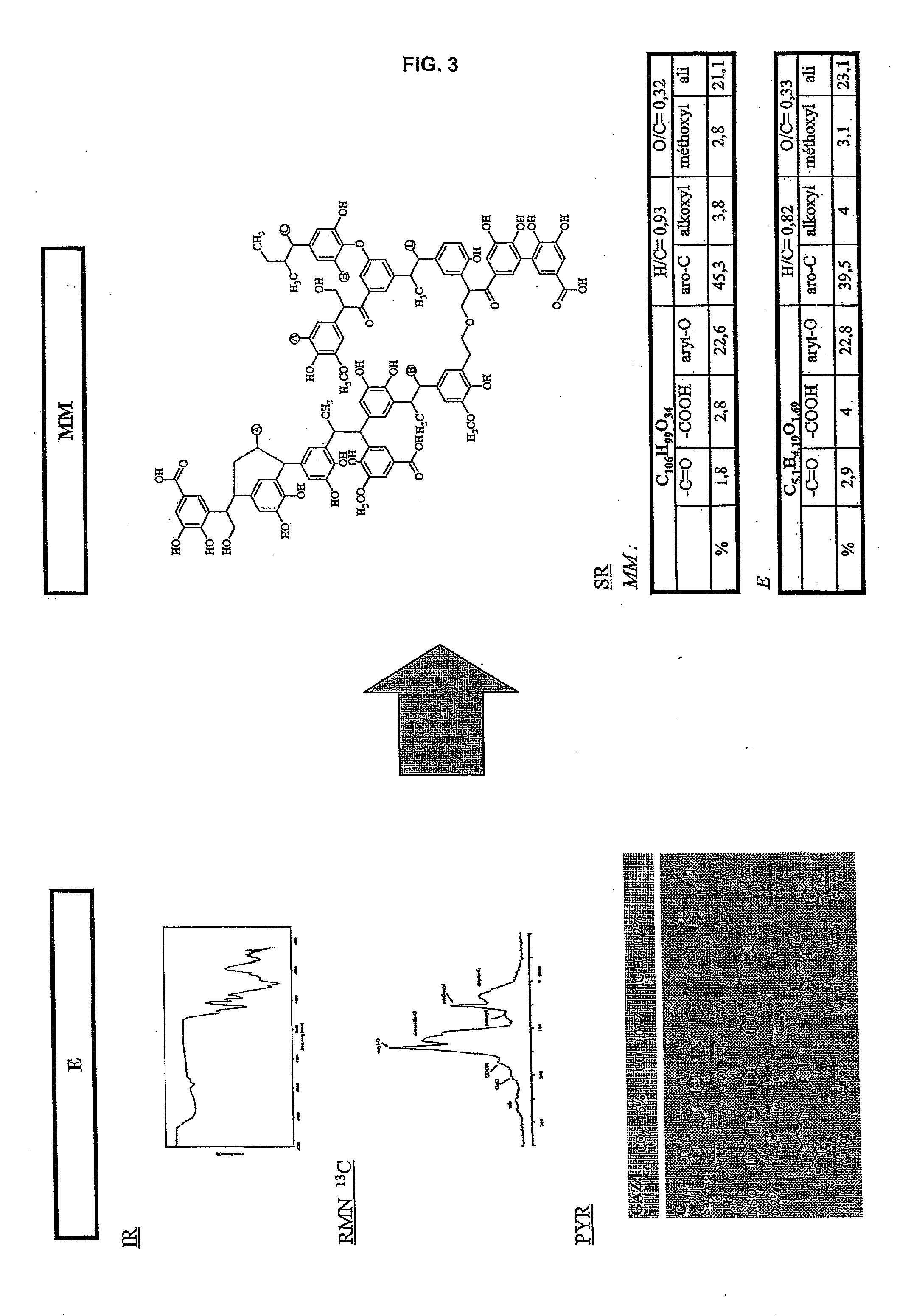
Method of quantifying hydrocarbon formation and retention in a mother rock
InactiveUS20080059140A1Analogue computers for chemical processesSeismologyHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSedimentary basin
The method according to the invention allows the formation of oil and the retention phenomenon in the mother rock to be modelled. Organic matter characterization experiments are used to establish the molecular model (MM) of the initial sample (E). The thermal cracking reaction of this molecular model is reproduced by dynamic molecular simulation computations with a reactive force field (RMD) and validated by comparison with experimental data. The reaction mechanism obtained (SR) allows to carry out a kinetic study (C) by variation of the temperature parameter. The phase equilibria (PES) of the reaction medium are determined at any time from dynamic simulation. The successive phase equilibrium assessments at various progress stages of the cracking reaction allow following the physicochemical evolution (PC) of the thermal maturation of the organic sample studied. The free hydrocarbons (liquid and gaseous) that are not retained in the solid residue can be quantified throughout numerical modelling of the sample maturation; representing, in the sedimentary basins, the hydrocarbons that are not retained in the organic matrix of the mother rock (Q). This quantity can be used as an indicator or an input value for the retention threshold in basin models.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
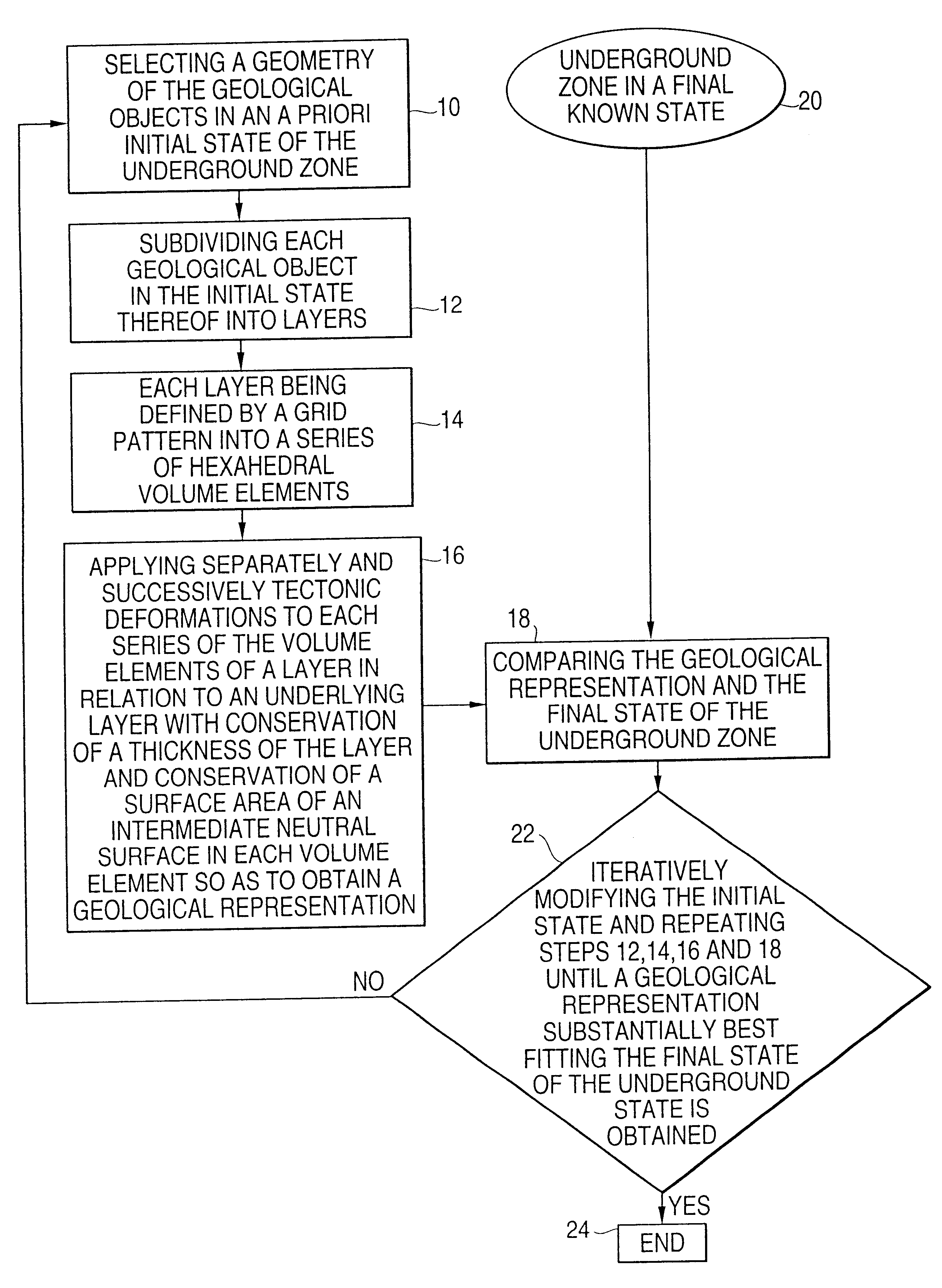
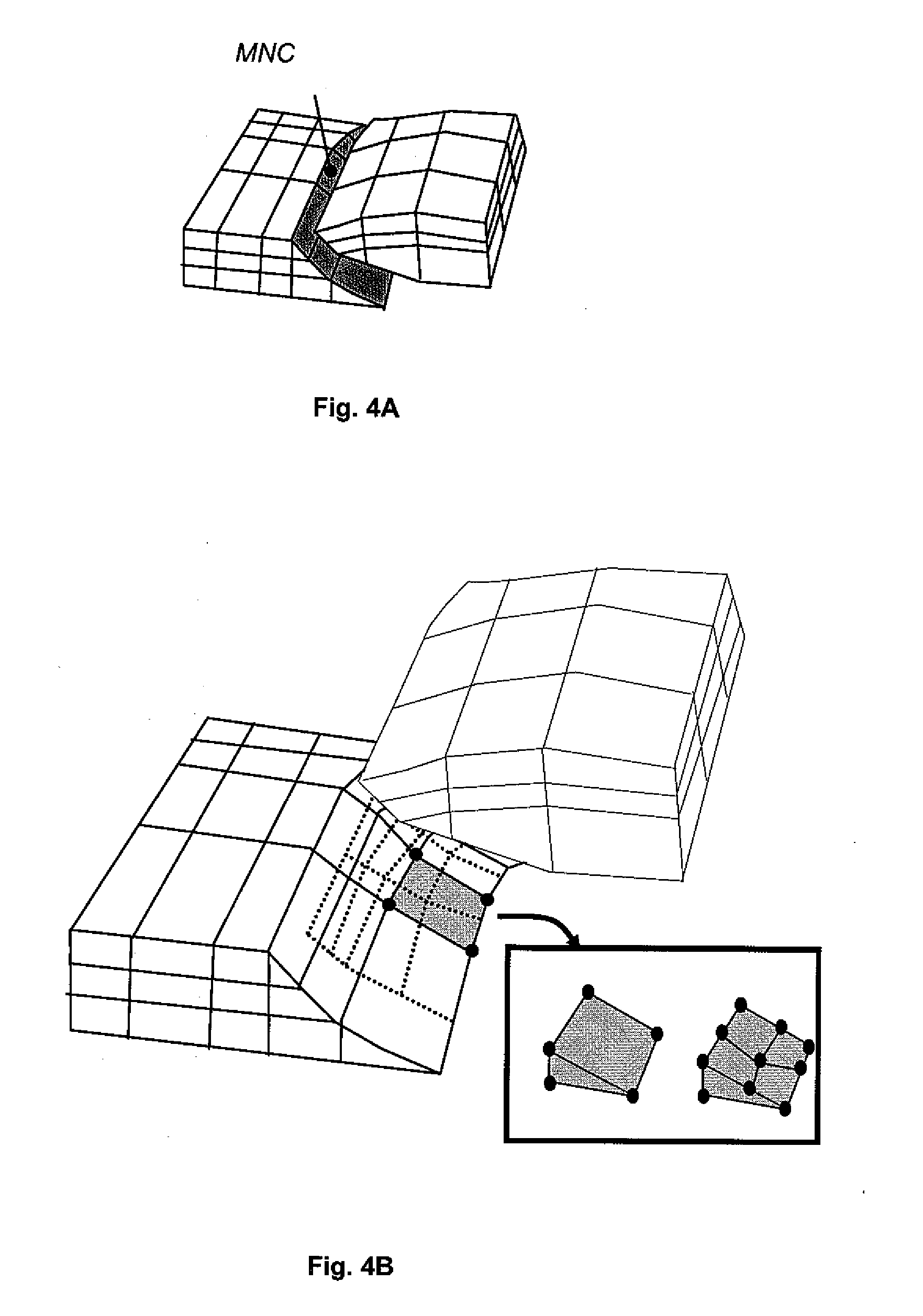
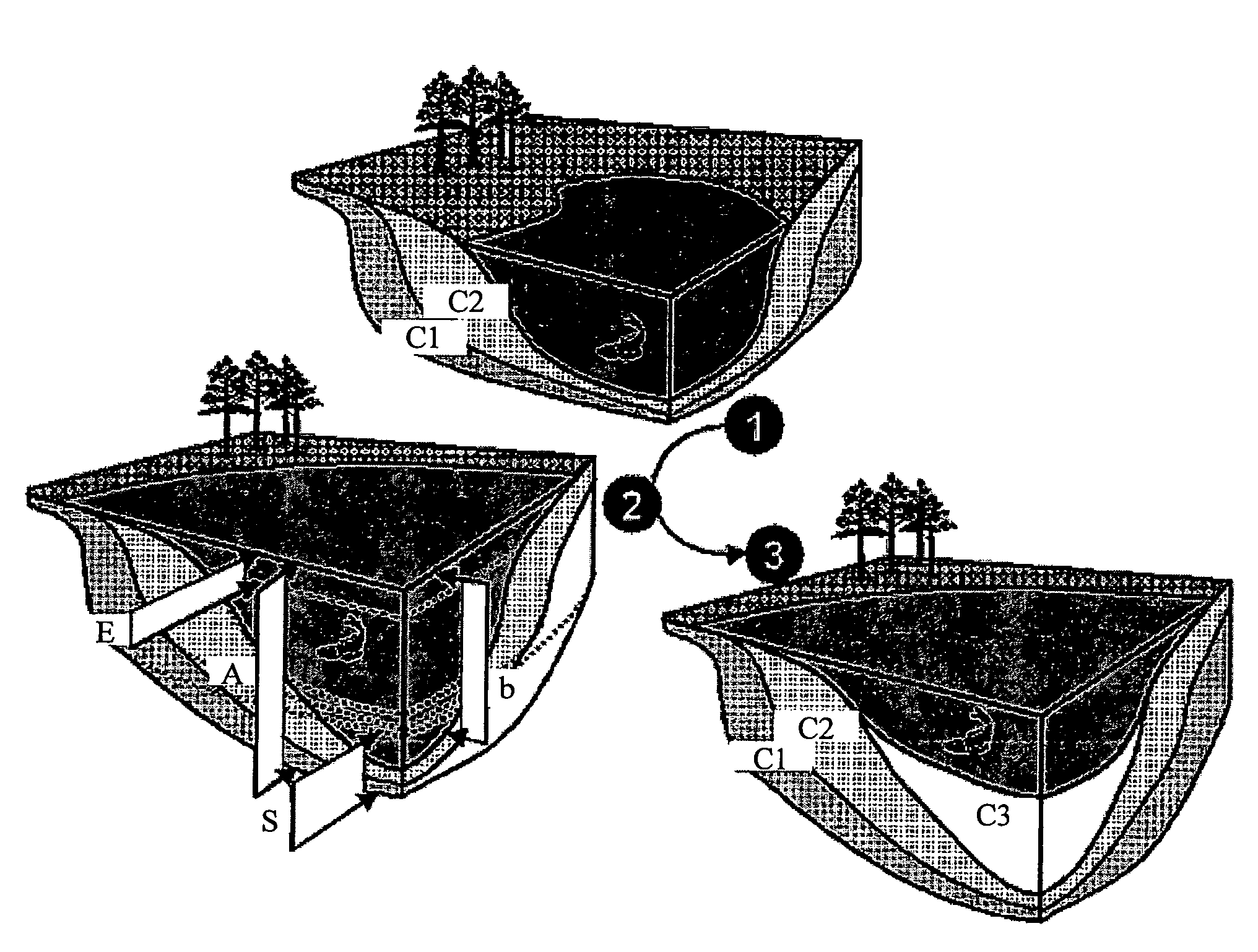
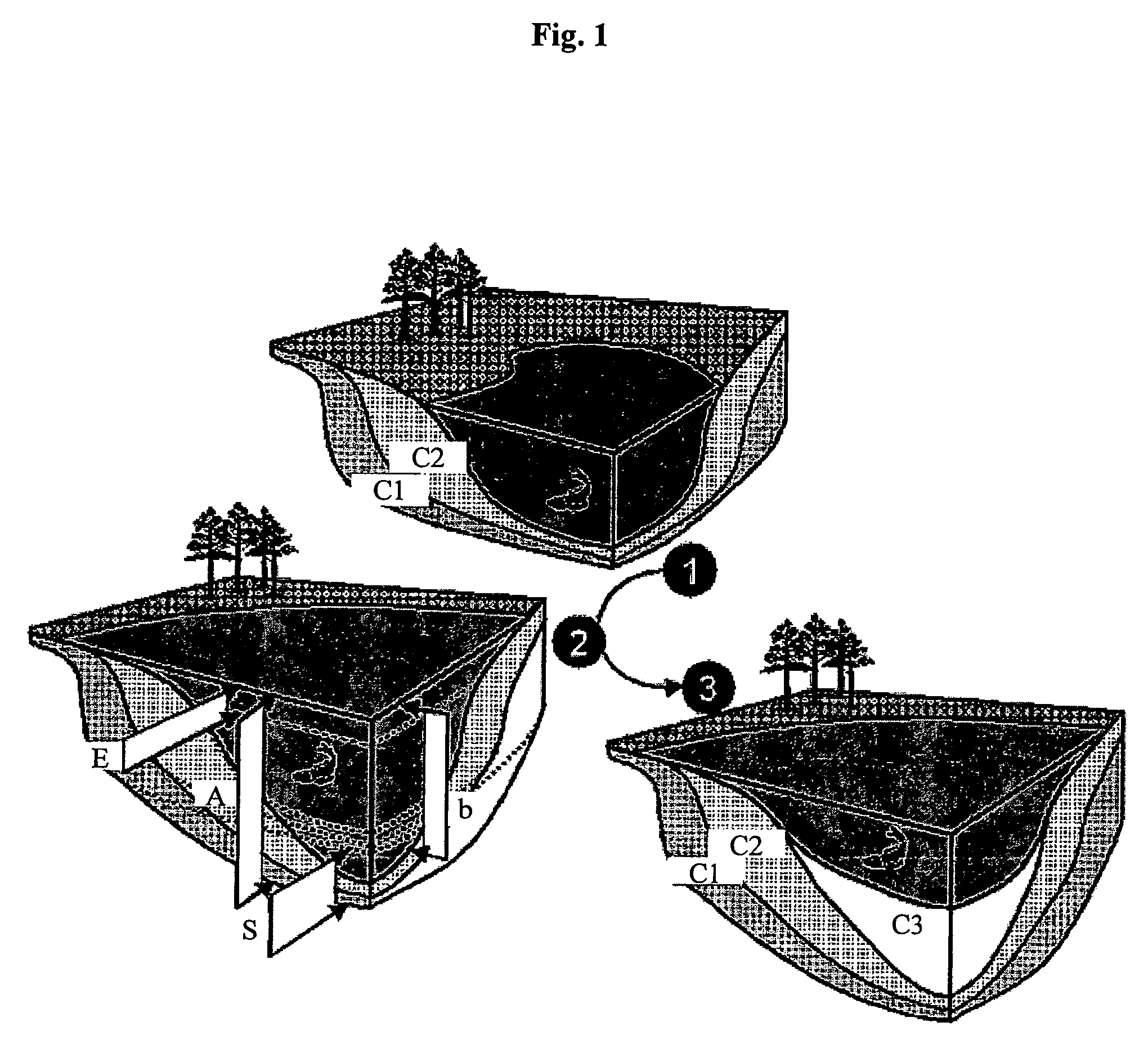
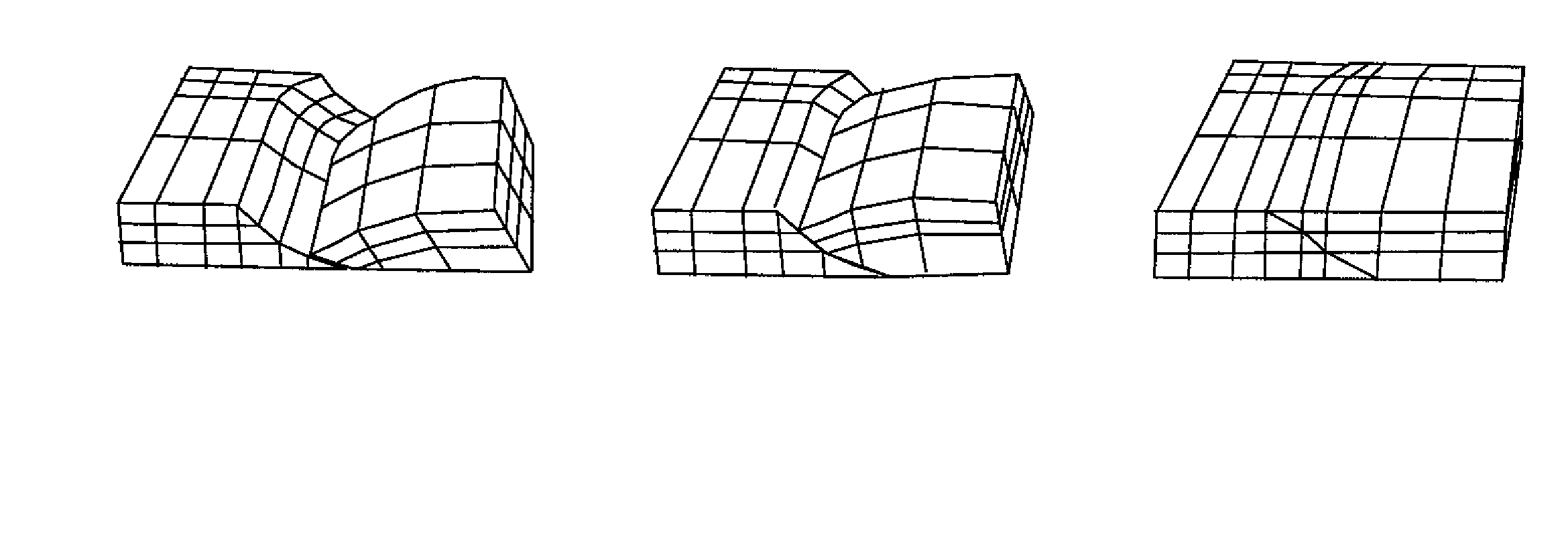
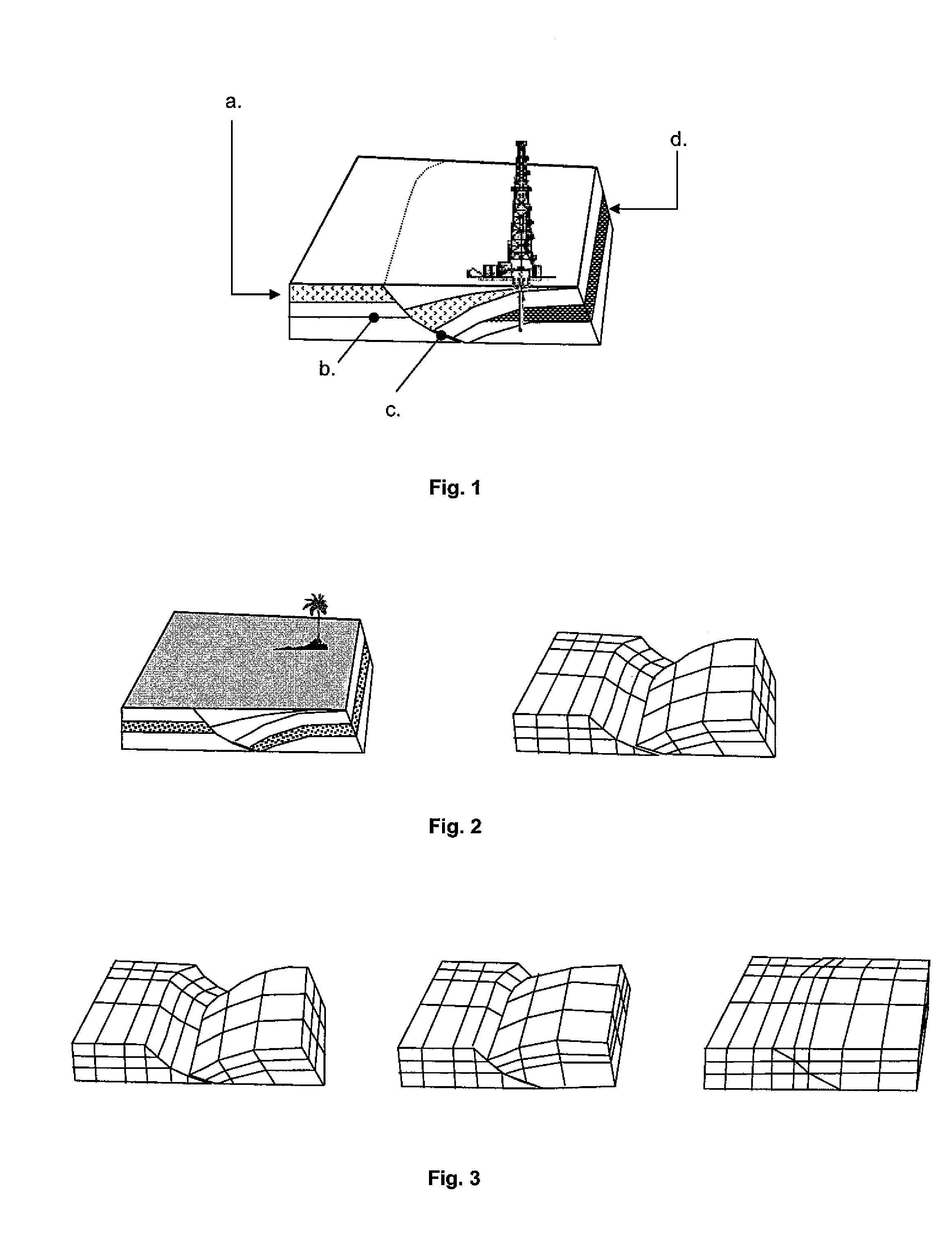
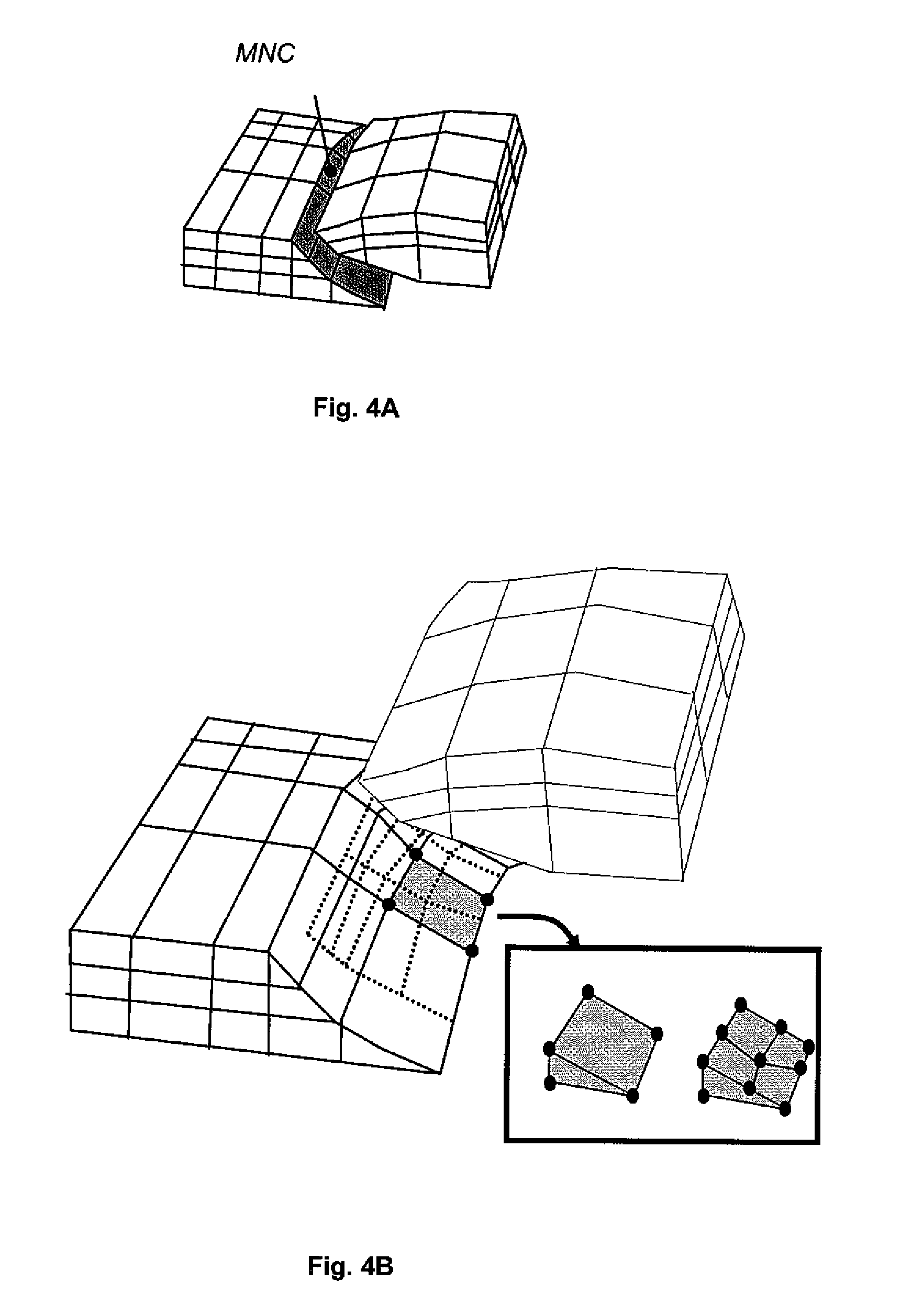
Method for forming a 3D kinematic deformation model of a sedimentary basin
InactiveUS6597995B1Easy to implementSave areaSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsGrid patternGeomorphology
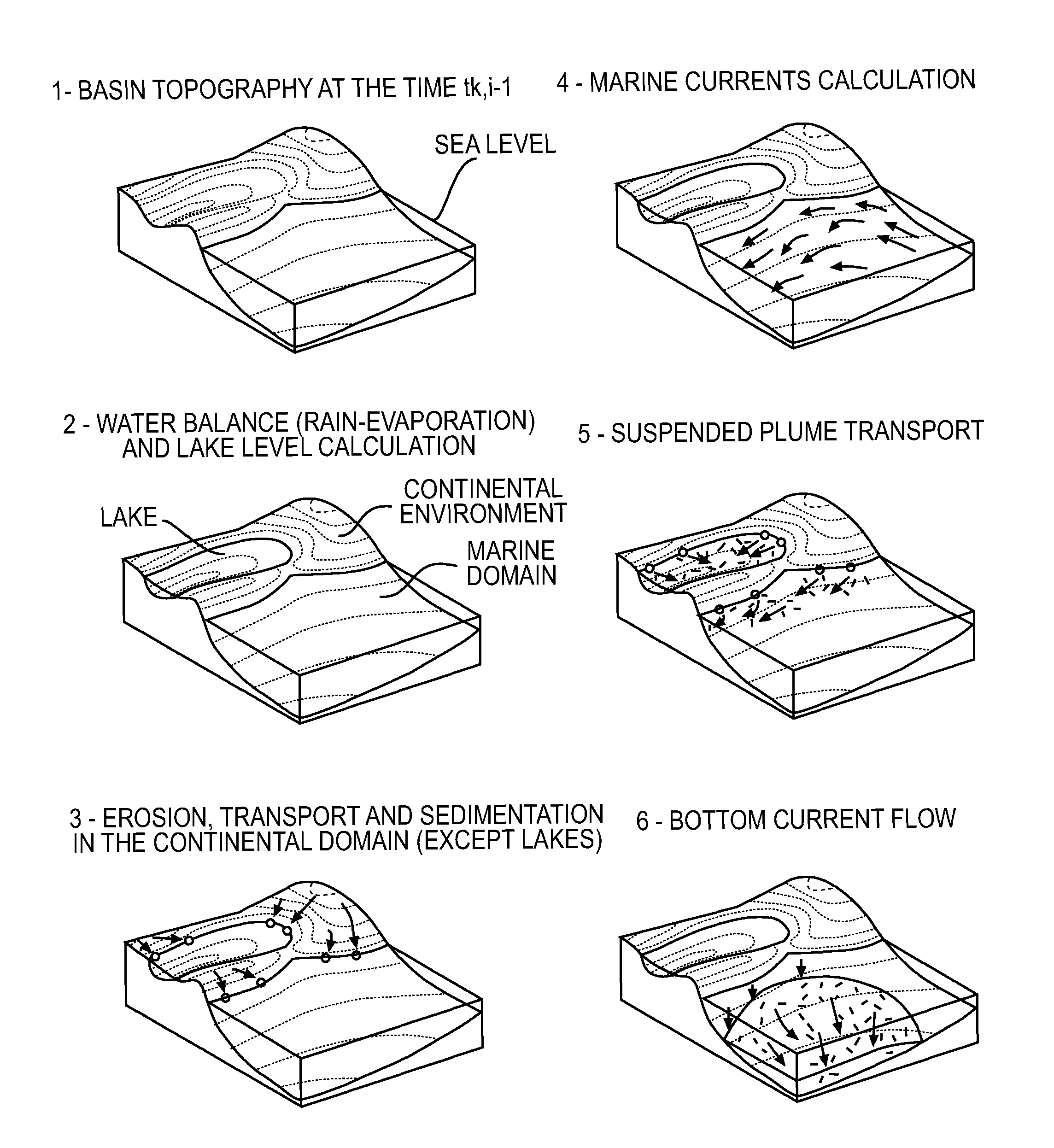
A method for forming a prograde kinematic model allowing reproduction in 3D intermediate geometries of geologic objects of an underground zone such as a sedimentary basin, from an initial state to a current state. A representation of the current geometry of the geologic objects of the zone is formed by interpretation of acquired data obtained by seismic exploration, by in-situ measurements and by observations, then each geologic object is subdivided into layers separated by deformation interfaces. Each one of the layers is defined by means of a grid pattern into a series of hexahedral volume elements. Tectonic deformations are then applied separately and successively to each series of volume elements of a layer in relation to an underlying layer while conserving the thickness and the surface area of an intermediate neutral surface in each volume element. Then the tectonic deformations are iteratively modified until a geologic representation substantially in accordance with the known final state of the underground zone is obtained.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method of seeking hydrocarbons in a geologically complex basin, by means of basin modeling
ActiveUS20090265152A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingGeomorphologyStructure of the Earth
A method for mapping a complex sedimentary basin is disclosed. A grid representative of the current architecture of the basin is constructed. A mechanical structural restoration is applied in three dimensions so as to reconstruct the past architectures of the basin from the current time up to a geological time t. A simulation of the geological and geochemical processes that govern the formation of a petroleum reservoir is then carried out, directly in the grids obtained from the restoration, from the geological time t to the current one. This simulation is thereafter used for mapping the sedimentary basin so as to identify zones of the basin where hydrocarbons may have accumulated.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
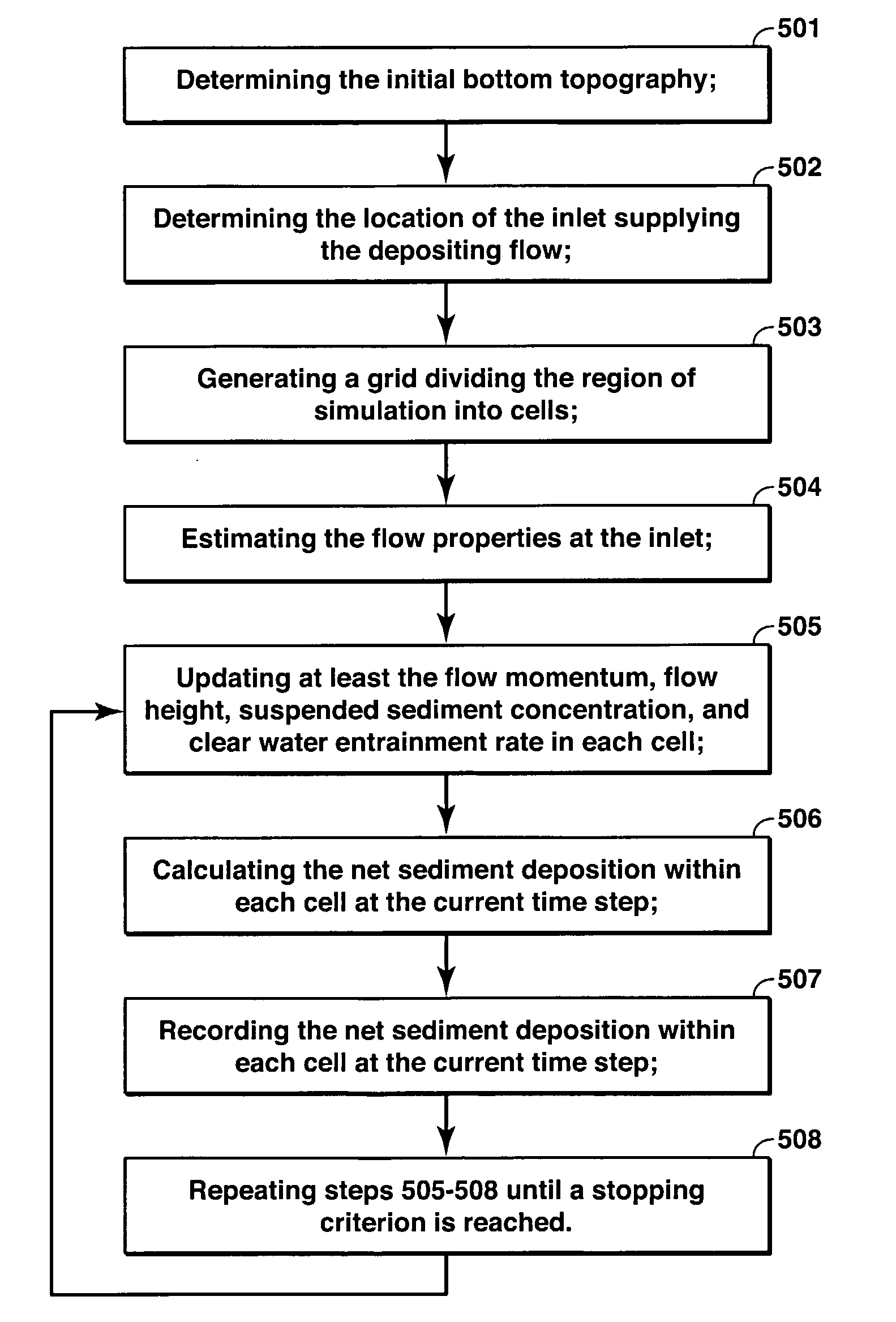
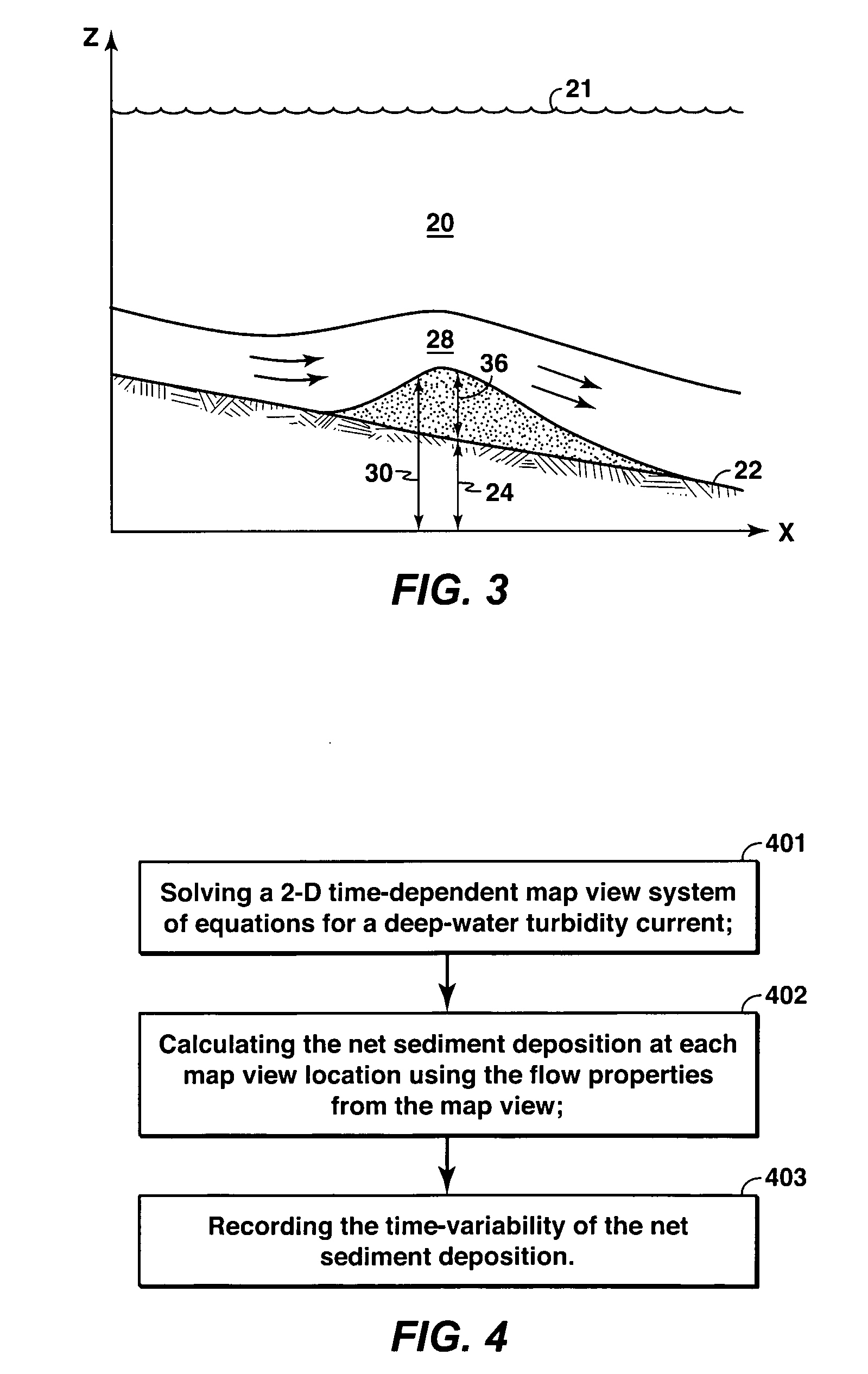
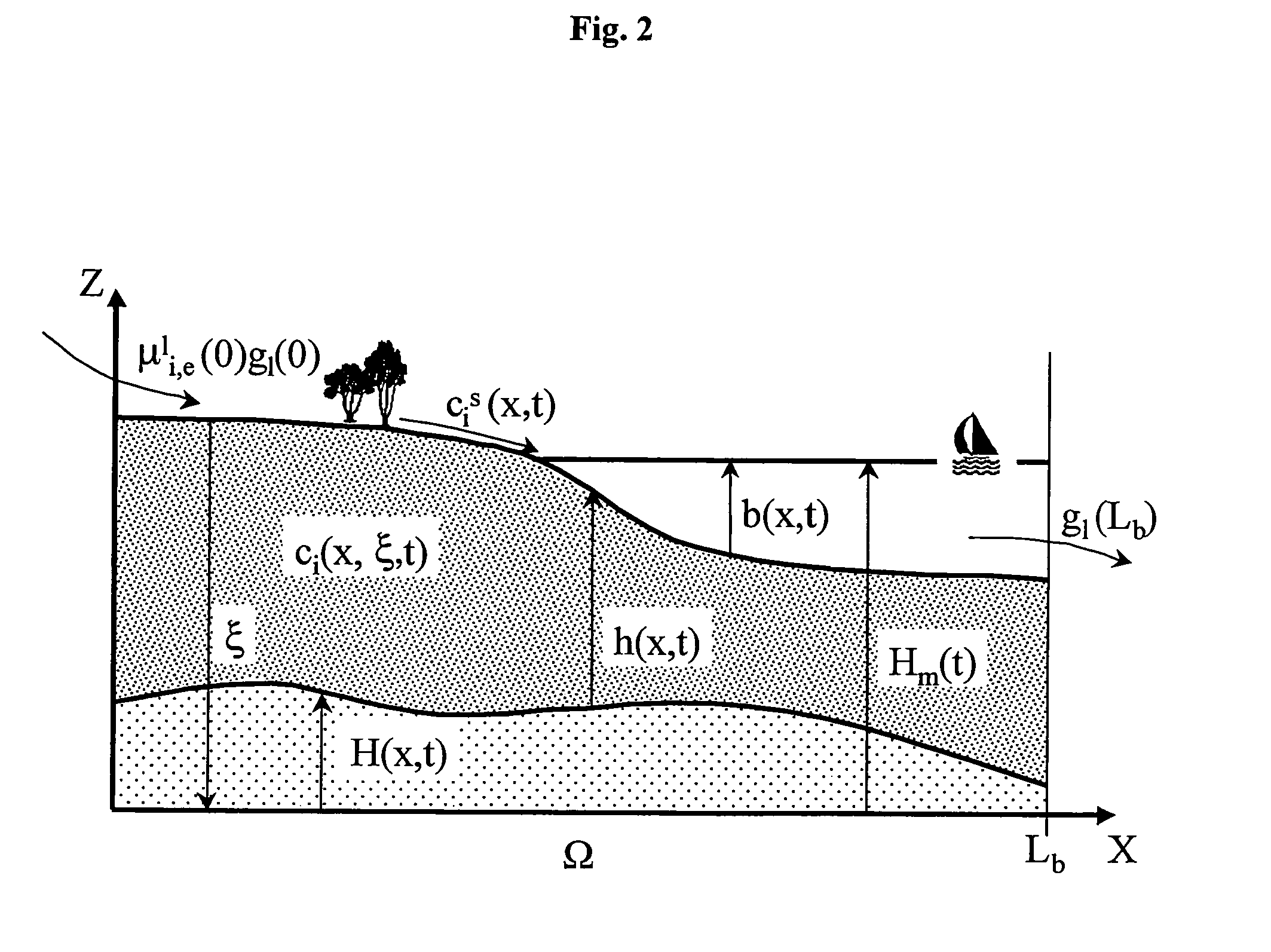
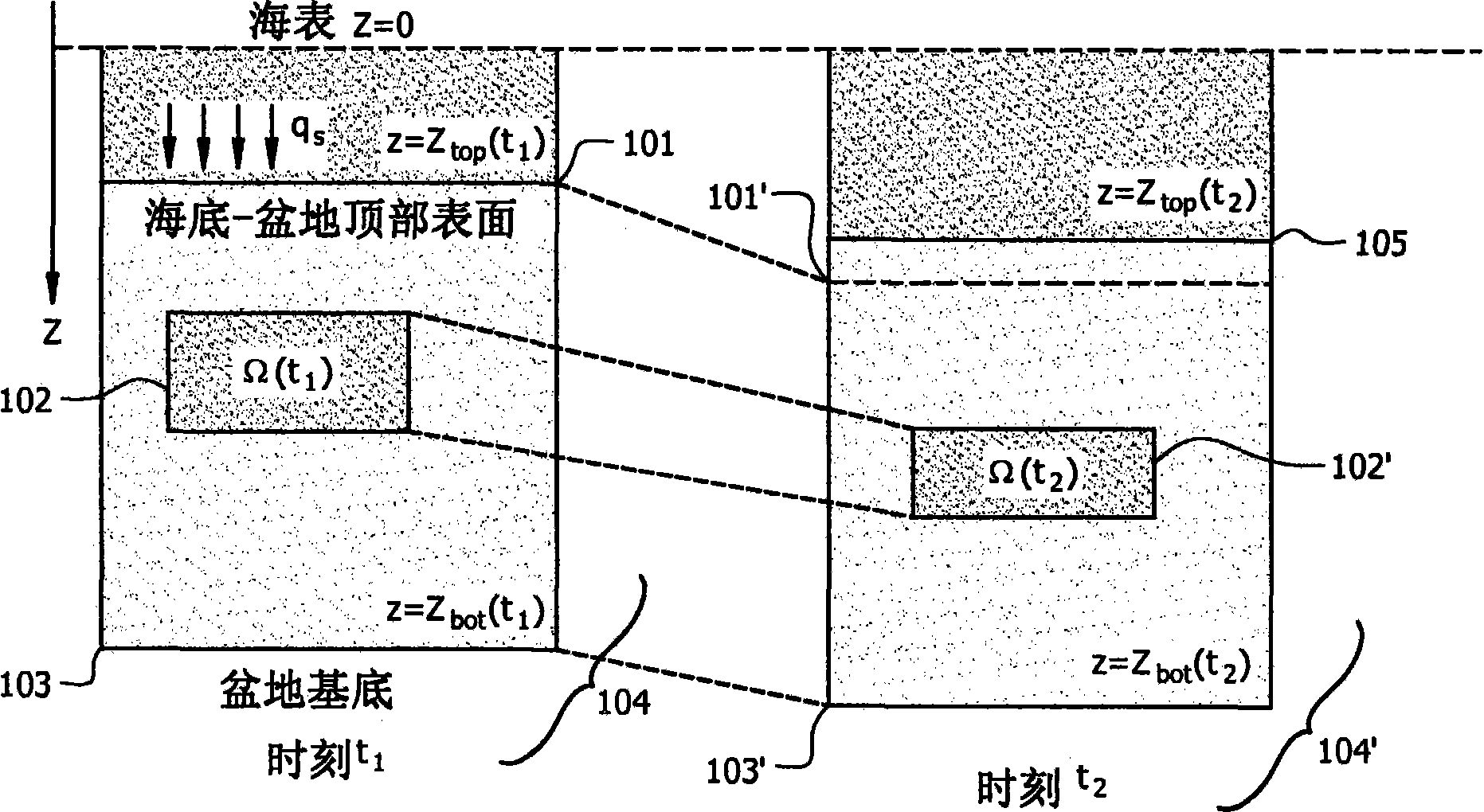
Method For Evaluating Sedimentary Basin Properties By Numerical Modeling Of Sedimentation Processes
ActiveUS20070219725A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationMomentumSedimentary basin
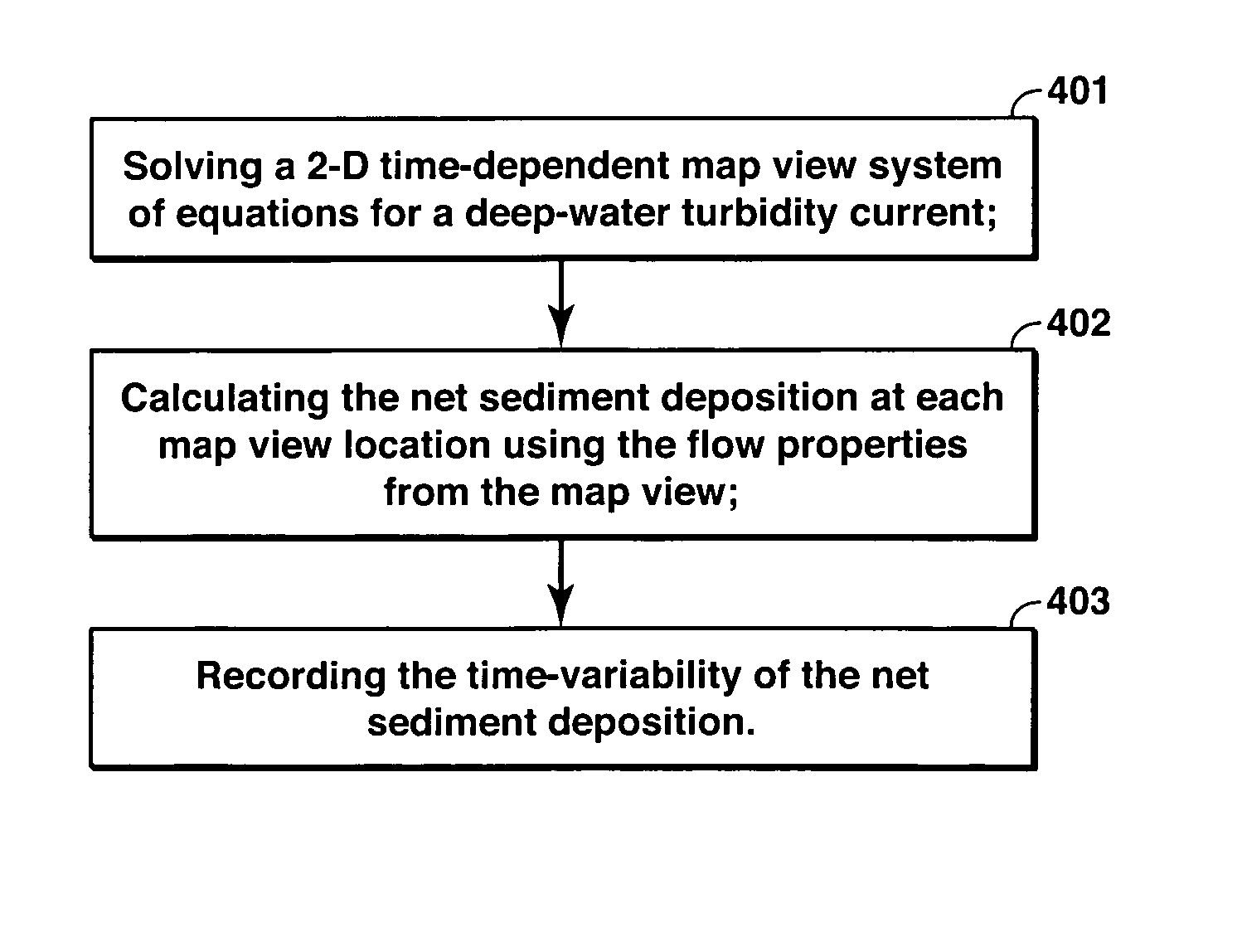
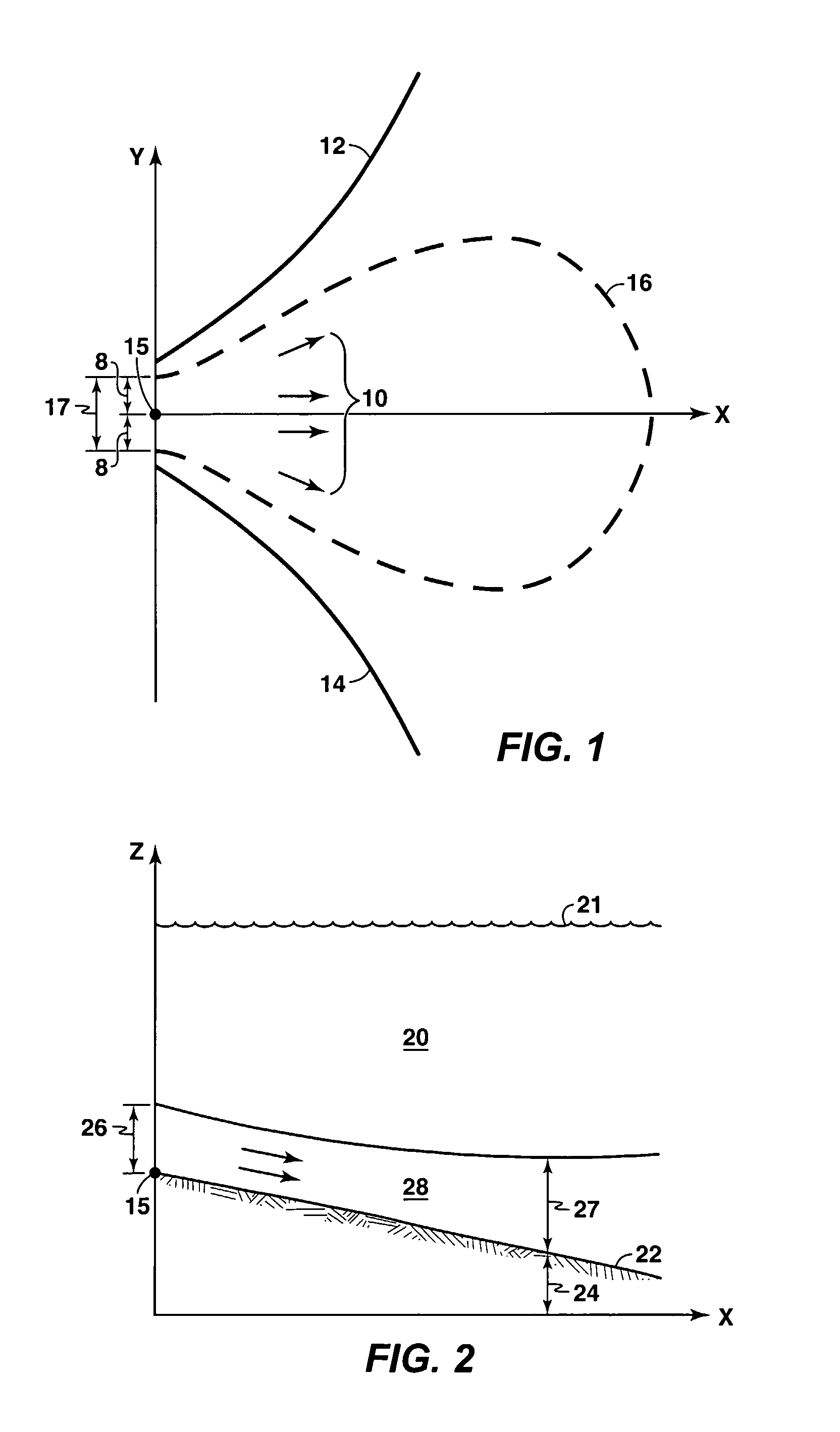
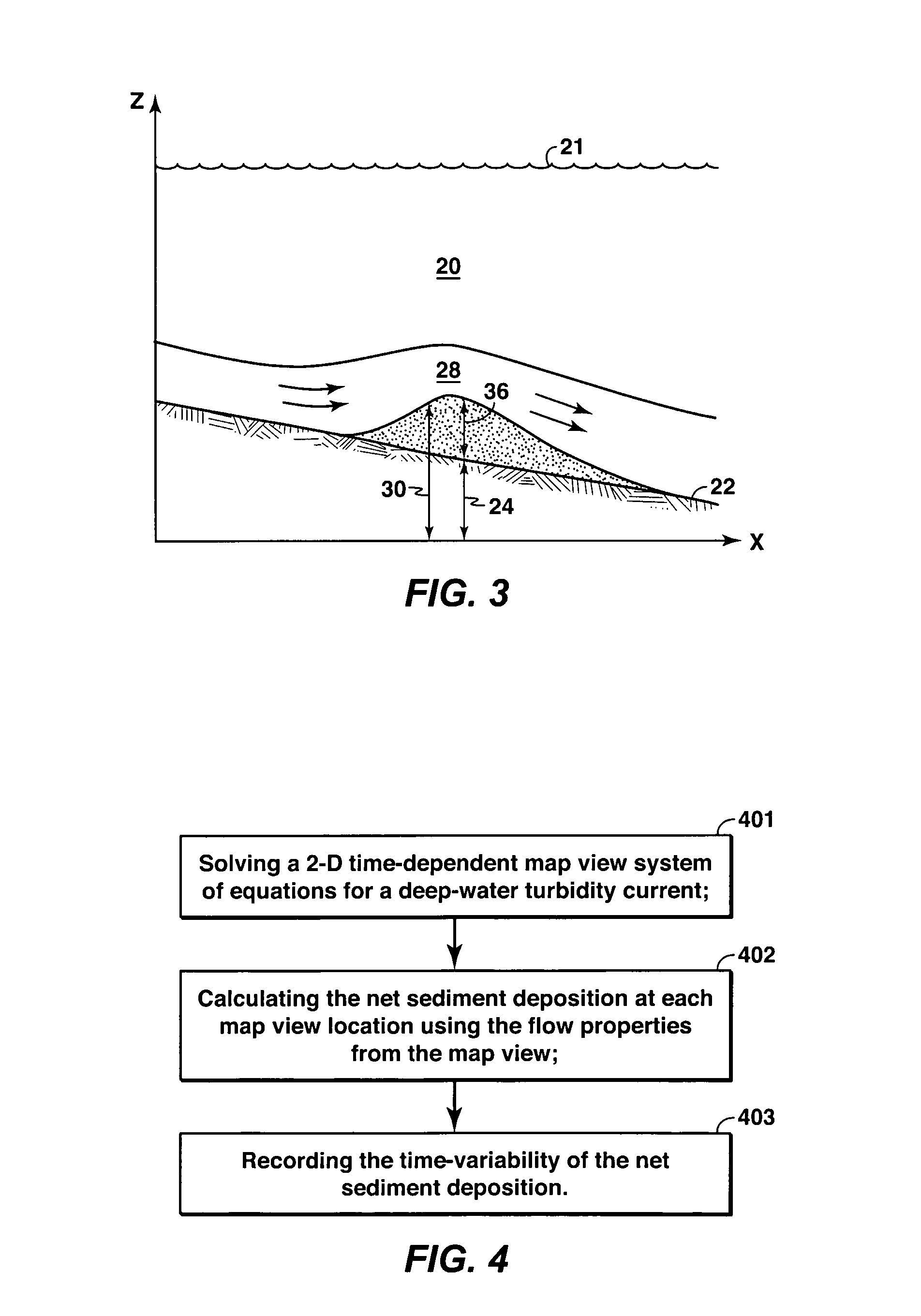
A method is disclosed for simulating the formation of sedimentary deposits. In one embodiment, this method involves, (a) solving a two-dimensional time-dependent map view system of equations for at least flow momentum, flow height, suspended sediment concentration, and entrainment of overlying water, (b) calculating net sediment deposition at each map view location using the flow properties, (c) recording the time-variability of the net sediment deposition.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
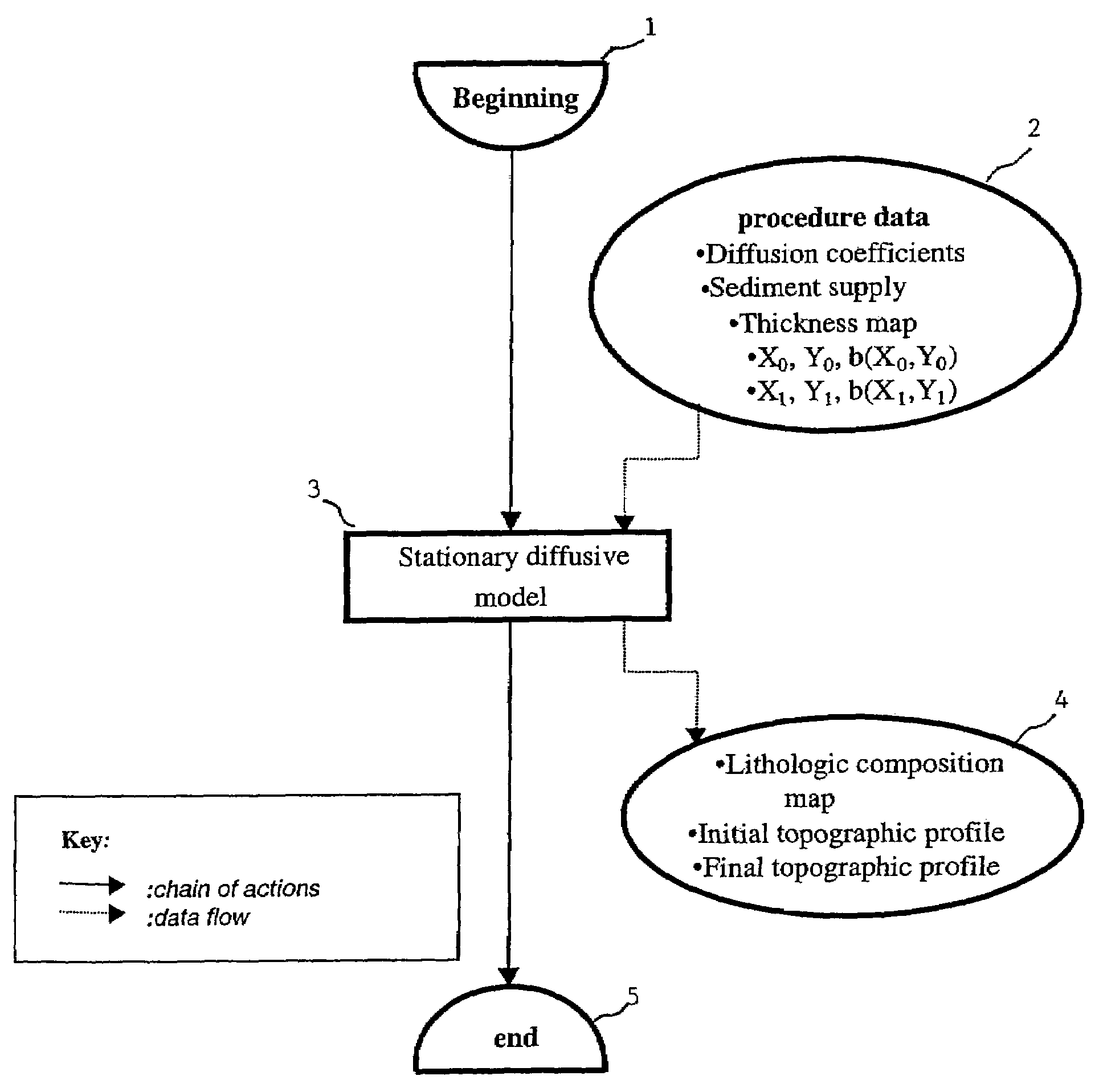
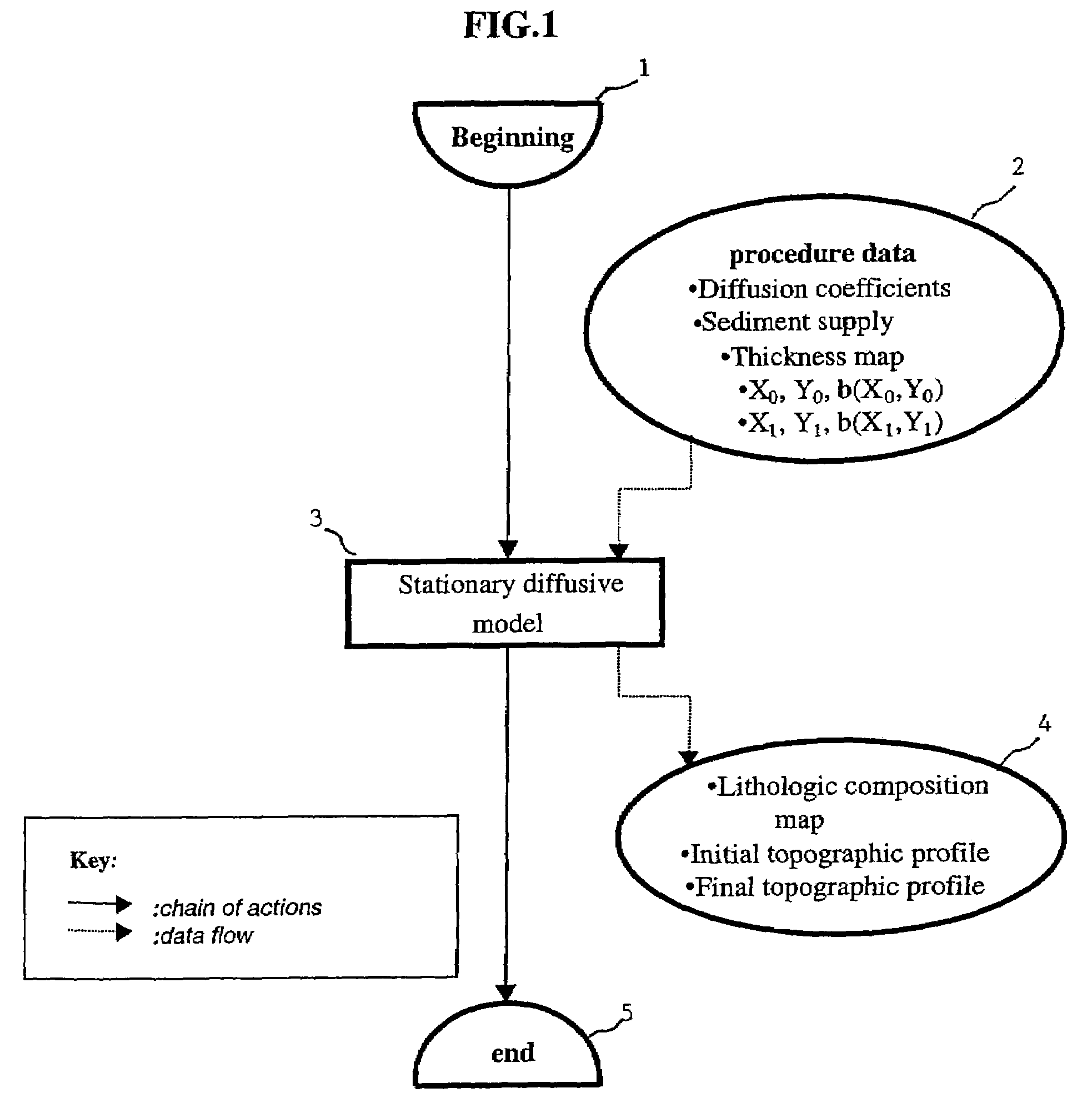
Method of simulating the sedimentary deposition in a basin respecting the thicknesses of the sedimentary sequences
ActiveUS7337069B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsLithologyFixed point algorithm
The method of the invention allows, by means of an iterative inversion algorithm, prediction of the spatial distribution of the lithologic composition of sediments deposited in a sedimentary basin during a geologic time interval, and the temporal evolution of the depositional profile throughout filling of the basin, while respecting exactly the thicknesses of the sedimentary sequences measured otherwise which is useful for locating hydrocarbon reservoirs. Input data of thickness maps of the sedimentary layer, location and composition of the sediment supply at the boundaries of the sedimentary basin, and physical parameters characterizing transport of the sediments during the period of consideration are applied to an iterative inversion loop initialized by the accommodation provided by a stationary multilithologic diffusive model which works as a fixed-point algorithm correcting the accommodations by means of a preconditioning of the residue on the sequence thicknesses obtained by an instationary model.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method of seeking hydrocarbons in a geologically complex basin, by means of basin modeling
ActiveUS8150669B2Analogue computers for chemical processesSeismologyGeomorphologyStructure of the Earth
A method for mapping a complex sedimentary basin is disclosed. A grid representative of the current architecture of the basin is constructed. A mechanical structural restoration is applied in three dimensions so as to reconstruct the past architectures of the basin from the current time up to a geological time t. A simulation of the geological and geochemical processes that govern the formation of a petroleum reservoir is then carried out, directly in the grids obtained from the restoration, from the geological time t to the current one. This simulation is thereafter used for mapping the sedimentary basin so as to identify zones of the basin where hydrocarbons may have accumulated.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Modeling In Sedimentary Basins
InactiveUS20100223039A1Simplify compactionEfficient productionComputation using non-denominational number representationGeological measurementsHydrostatic pressureEngineering
Embodiments of the invention operate to produce basin models that describe the basin in terms of compaction and fluid flow. The equations used to define compaction and fluid flow may be solved simultaneously. Embodiments of the invention use equations that define a set of unknowns that are consistent over the basis. The equations may define total pressure, hydrostatic pressure, thicknesses, and effective stress.
Owner:MALIASSOV SERGUEI
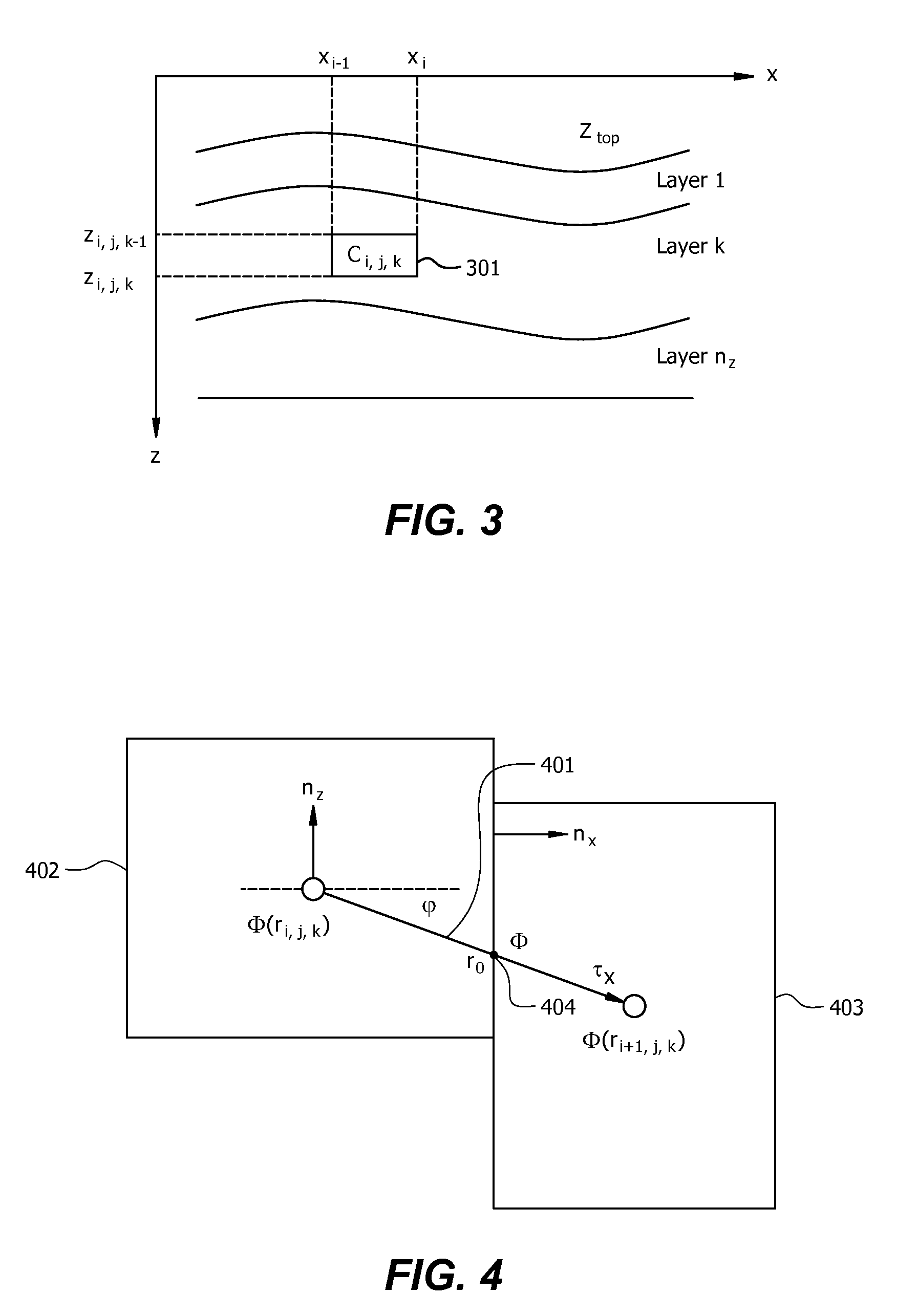
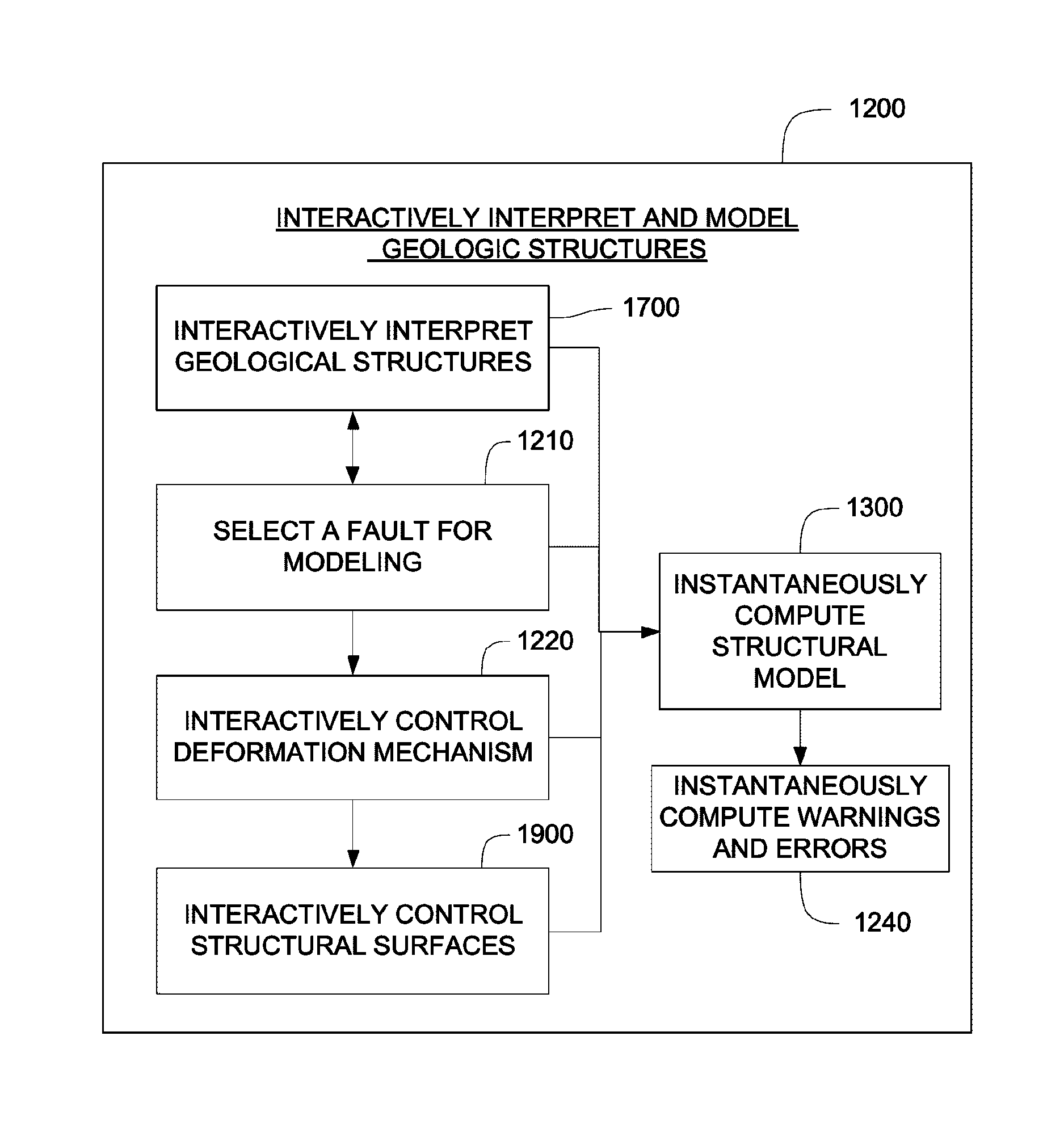
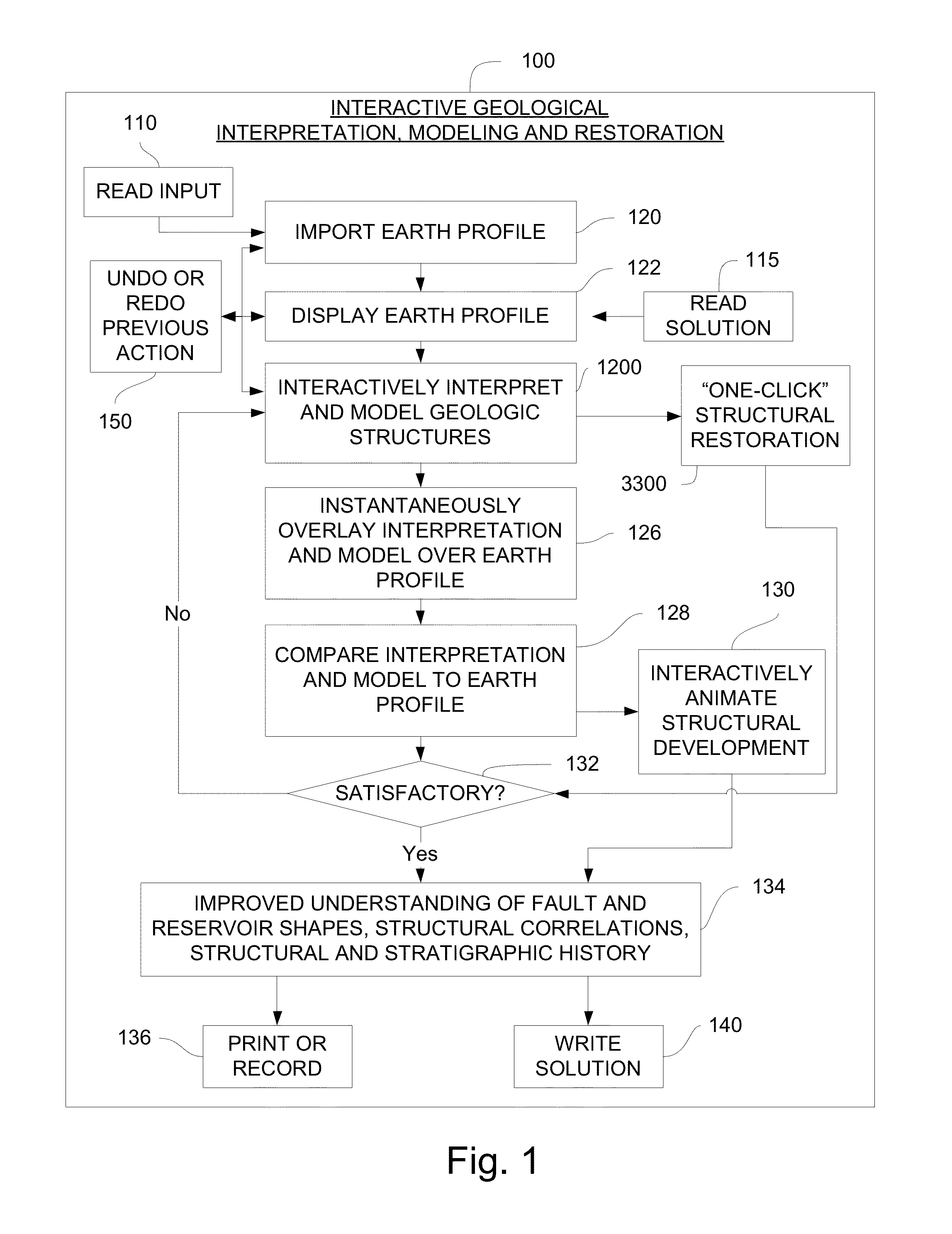
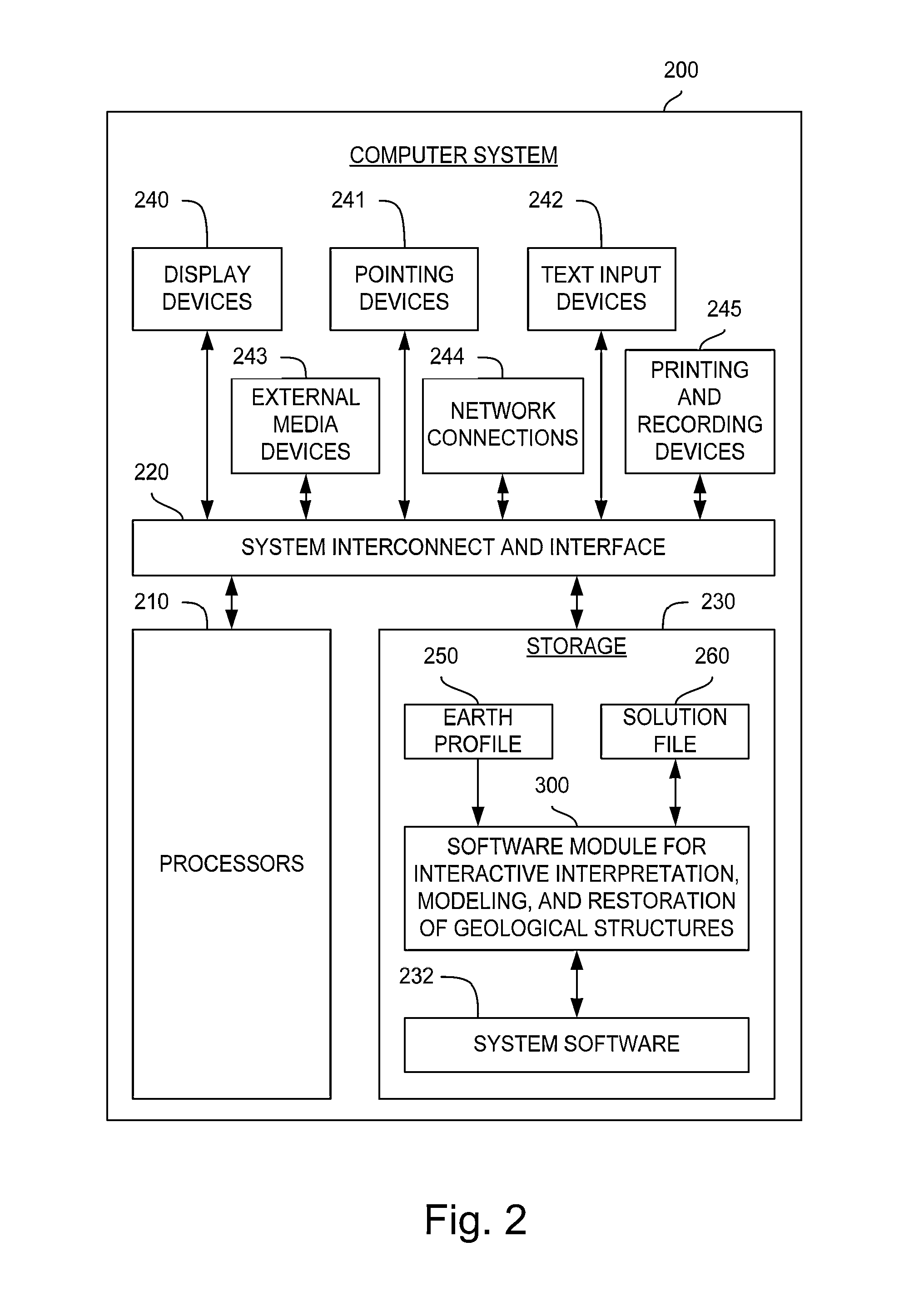
Method and system for interactive geological interpretation, modeling and restoration
ActiveUS8798974B1Quality improvementComputation using non-contact making devicesGeomodellingGeological scientistSimulation
The present invention comprises a computer-implemented method for interactive geological interpretation, structural modeling and structural restoration, in which instantaneous feedback is provided to an interpreter. A software module is loaded into and executed by the computer system to implement the method of the invention. The method and system are employed by a technician or scientist, such as an earth scientist, geologist or geophysicist, hereinafter called an “interpreter”. Using the method and system, the interpreter can make skilled qualitative and quantitative appraisals of geologic structures that occur within the upper parts of the earth's crust, including both the current state of such structures and their kinematic development through time. One use of such appraisals is to evaluate resources found in structures within sedimentary basins, including but not limited to oil and gas resources. The method and system can be used to train novice and advanced interpreters to improve their understanding.
Owner:NUNNS ALAN GORDON
Method of predicting the amount and the composition of fluids produced by mineral reactions operating within a sedimentary basin
InactiveUS20140377872A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEarth material testingMineral reactionsPorosity
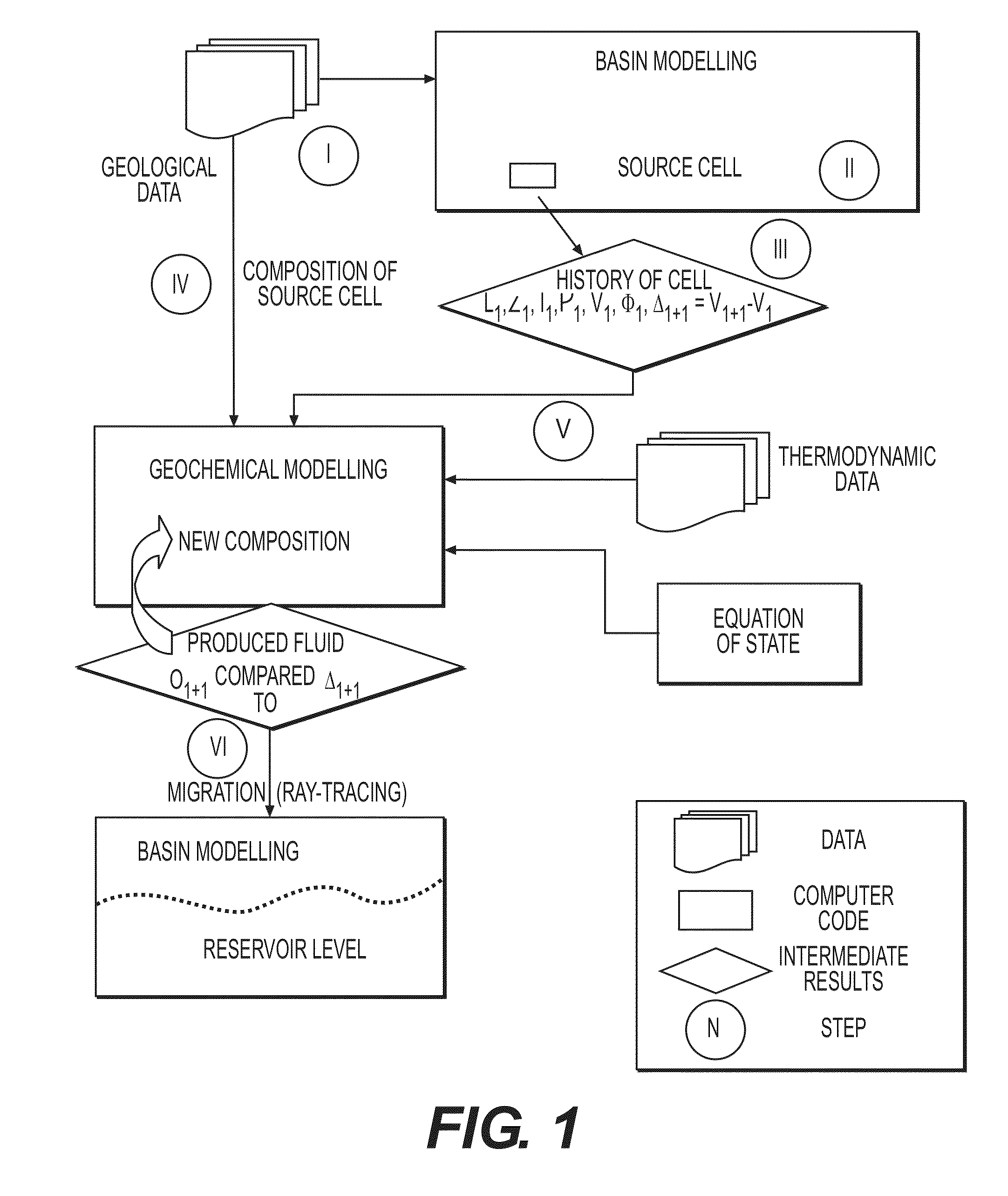
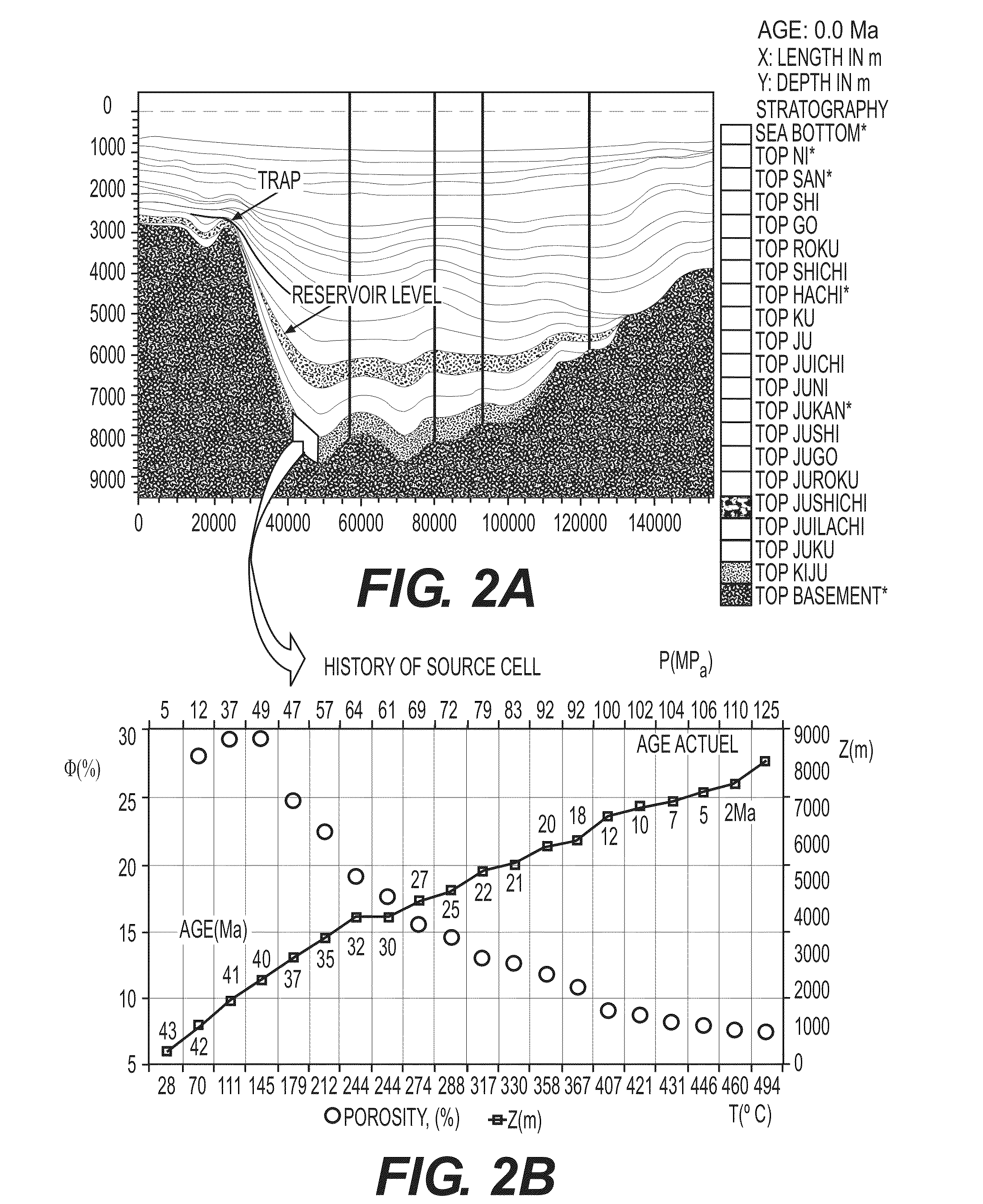
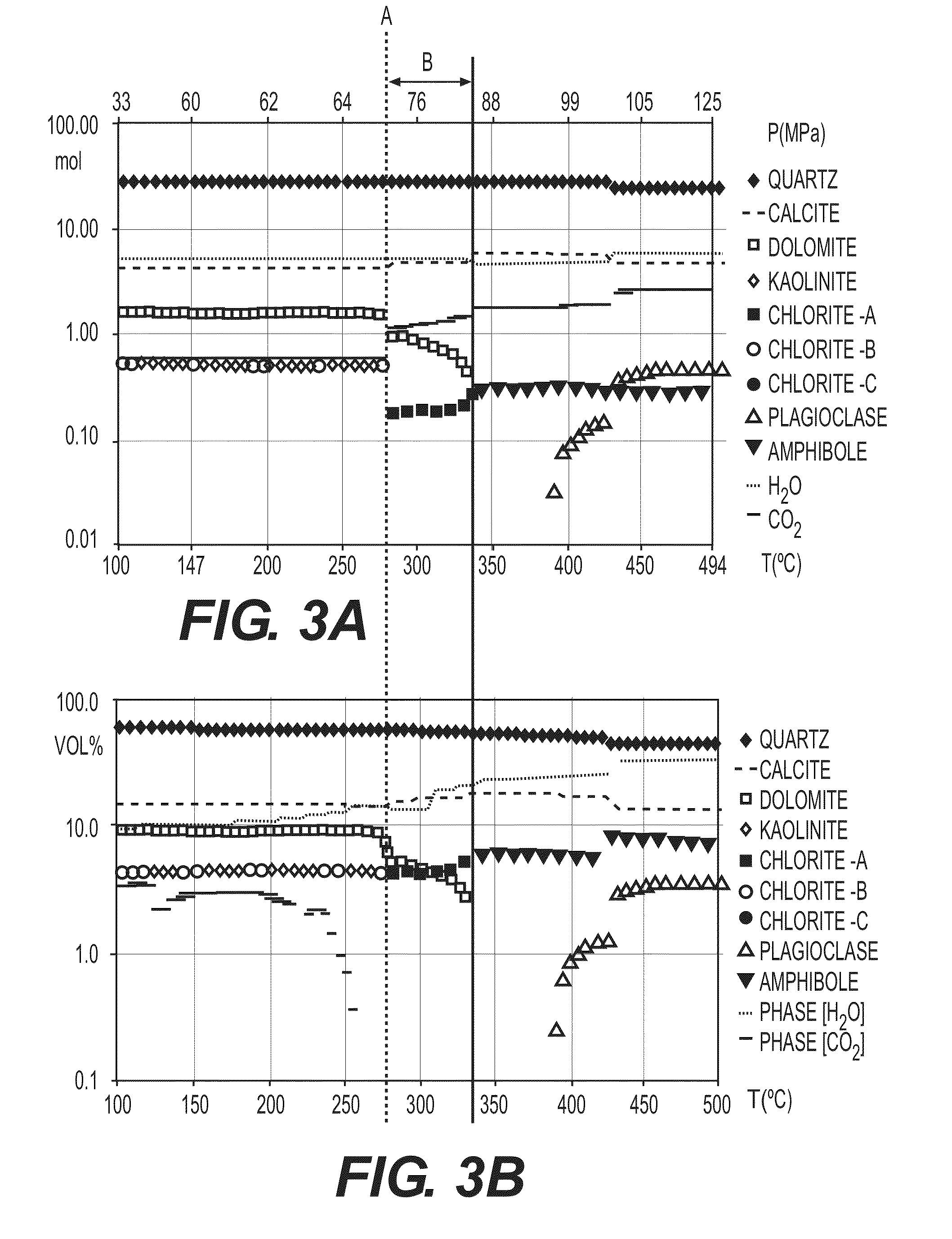
The invention is a method of predicting the amount and the composition of fluids produced by mineral reactions operating within a sedimentary basin and trapped with hydrocarbons in reservoirs. Geological data characteristic of the basin are acquired and a representation of the basin by a grid is constructed. The evolution of a depth of burial (z), a temperature (T), a pore pressure (P), a volume (V) and a porosity φ at successive ages (ti) representative of the geological history of the basin is then calculated for at least one set of cells of the grid, using a basin model and the geological data. A mineralogical or chemical rock composition is determined in each cell of the set of cells from the geological data of the basin. The amount and the composition of fluids of mineral origin is determined within the set of cells using a geochemical model and an equation of state, from the parameters, the composition and a thermodynamic database.
Owner:TOTAL PUTEAUX FR +1
Method for evaluating sedimentary basin properties by numerical modeling of sedimentation processes
ActiveUS8117019B2SeismologyComputation using non-denominational number representationMomentumTemporal change
A method is disclosed for simulating the formation of sedimentary deposits. In one embodiment, this method involves, (a) solving a two-dimensional time-dependent map view system of equations for at least flow momentum, flow height, suspended sediment concentration, and entrainment of overlying water, (b) calculating net sediment deposition at each map view location using the flow properties, (c) recording the time-variability of the net sediment deposition.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method of developing a sedimentary basin from a stratigraphic simulation of multilithologic filling taking account of fine sediment transport
The invention is a method of developing a sedimentary basin from a stratigraphic simulation of multilithologic filling accounting for fine sediment transport. The sedimentary basin is broken up into geologic layers with each geologic layer being subdivided into a series of climatic layers. Each climatic layer is associated with at least one constant climatic parameter. A stratigraphic simulation is performed within each climatic layer using a stratigraphic model. The sediment transport in the continental domain and sediment bottom layer transport in the marine and lacustrine domains are modelled using nonlinear diffusion equations under maximum erosion rate constraint. Suspended sediment transport in the marine and lacustrine domain is modeled using an advection-diffusion equation accounting for a particle fall rate and of a marine and lacustrine current velocity. The climatic layers belonging to a single geologic layer are then homogenized and the basin is developed according to the stratigraphic simulation results.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method for exploitation of hydrocarbons from a sedimentary basin by means of a basin simulation taking account of geomechanical effects
ActiveUS20170177764A1Increase success rateFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSedimentary basin
Method for exploitation of a sedimentary basin containing hydrocarbons by means of a basin simulation.On the basis of a reconstitution of the formation of the first of the layers of the basin, for at least one of the layers underlying the first layer, a conjoint basin simulation of the layer concerned and at least one underlying layer is carried out. A conjoint geomechanical simulation of the layer concerned and at least one underlying layer is then carried out. If the deviation between some of the parameters from the geomechanical simulation and those from the basin simulation is above a predefined threshold the previous steps are repeated applying a correction to the basin simulation. The basin is then exploited as a function of the results of the basin simulation.Application in particular to the exploration and exploitation of hydrocarbon deposits.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method for simulating the deposition of a sedimentary sequence in a basin
ActiveUS7117091B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusSeismic signal processingSeismic surveyHydrocotyle bowlesioides
The invention is a method relating to the formation by simulation of a reference map of the spatial distribution of the sediment supply, according to the composition thereof, in a sedimentary basin during a sedimentary deposition sequence (during a given geologic time interval) and also allows obtaining the topography of the land surface of the basin at the beginning and at the end of this period. The available input data are a map of the thickness of the sedimentary layer studied, known by interpretation of seismic survey results, data relative to the location and to the composition of the sediment supply at the boundaries of the sedimentary basin being studied, obtained by interpretation of seismic surveys, measurements and observations, and physical parameters characterizing transportation of the sediments (diffusion coefficients in the marine environment and in the continental environment) during the period considered. An application is locating hydrocarbon reservoirs.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
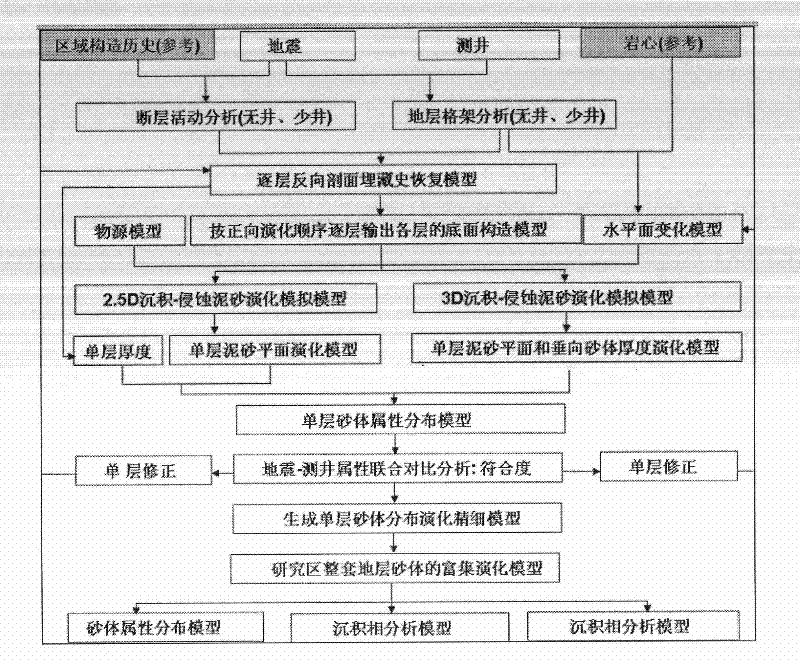
Method for analyzing sand bodies in reservoirs based on inversion technique of sedimentary dynamics
InactiveCN102243678AImplement distribution evolution analysisSpecial data processing applications3D modellingTerrainWell logging
The invention discloses a method for analyzing sand bodies in reservoirs based on an inversion technique of the sedimentary dynamics under the condition of sparse wells. The method is characterized in that through building a sand-body inversion model of sedimentary dynamics based on a principle of three-dimensional sedimentary transport geology and considering the control action of fluid velocity on sedimentary evolution and the reconstructive function of tectonic movements, the analysis on the distribution evolution of sand bodies in complex sedimentary basins under the condition of sparse wells can be realized. The method is implemented through the following steps: re-simulating the relationship between the three-dimensional attribute distribution data of a single sand layer of a reservoir and the time variation; carrying out variance making on the pre-simulated results and the results obtained by simulating well-point data as well as well logging interpretation and bore-hole data of the reservoir; according to the concept of a negative gradient search algorithm, modifying the terrain, flow field and source distribution of the reservoir; and operating the steps until the accuracy conditions of reservoir modeling are satisfied. The method disclosed by the invention provides a basis for the development of analysis on sand bodies in basin reservoirs under the condition of sparse wells, and is especially suitable for being applied to the research on sand bodies in sea basins with less drill holes.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Strata denudation amount recovery method
ActiveCN105204069AErosion RecoveryEasy accessSeismic signal processingRecovery methodData acquisition
The invention discloses a strata denudation amount recovery method. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out a data acquisition step: acquiring a strata thickness and a strata age of each layer system of a position to be analyzed; carrying out a settlement model establishment step: constructing a settlement model of the position to be analyzed according to the strata thickness and the strata age; carrying out a denudation amount recovery step: calculating an accumulative deposition thickness of the position to be analyzed according to the settlement model and the strata age, and calculating the strata denudation amount of the position to be analyzed according to an accumulation thickness and a strata thickness. The method is suitable for a multi-period settlement-uplifting and multi-period burying-denudation long-term development evolution deposition basin, excessive analysis and test cost does not need to be spent, and the method is not limited by a sample rock type and a stratigraphic buried depth and possesses good enforceability, objectivity and reliability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
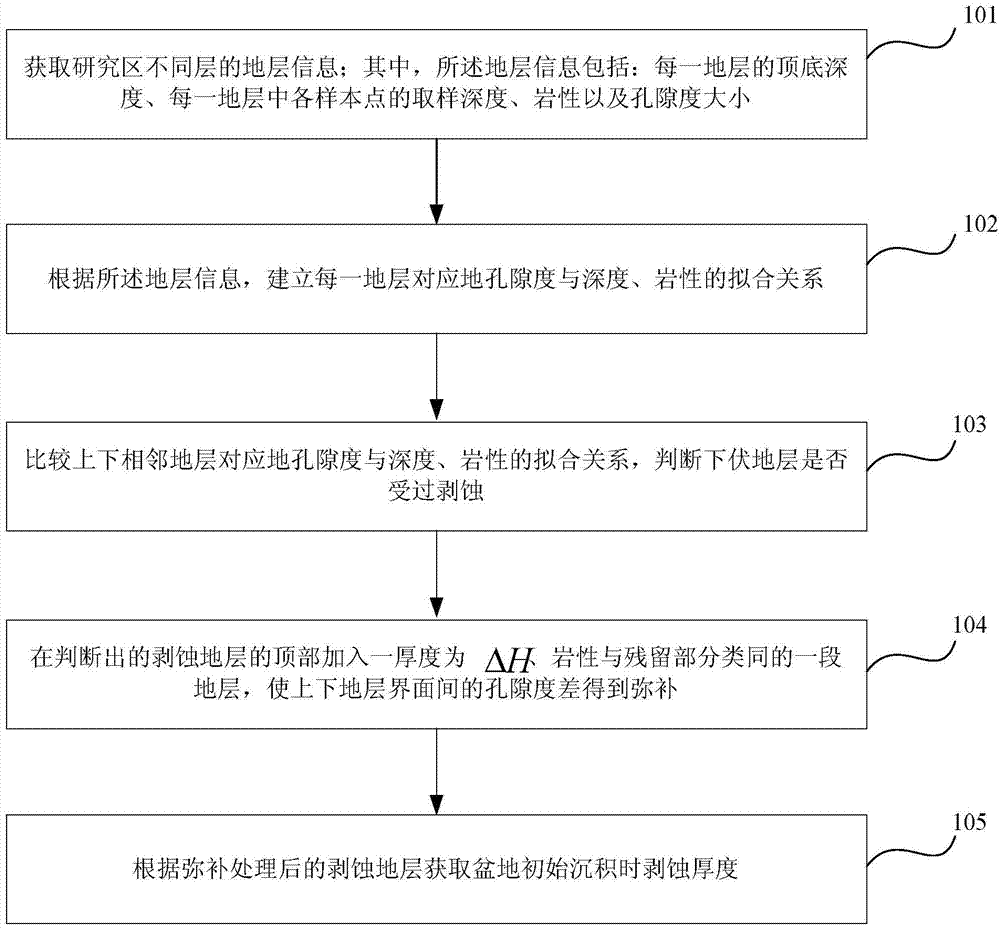
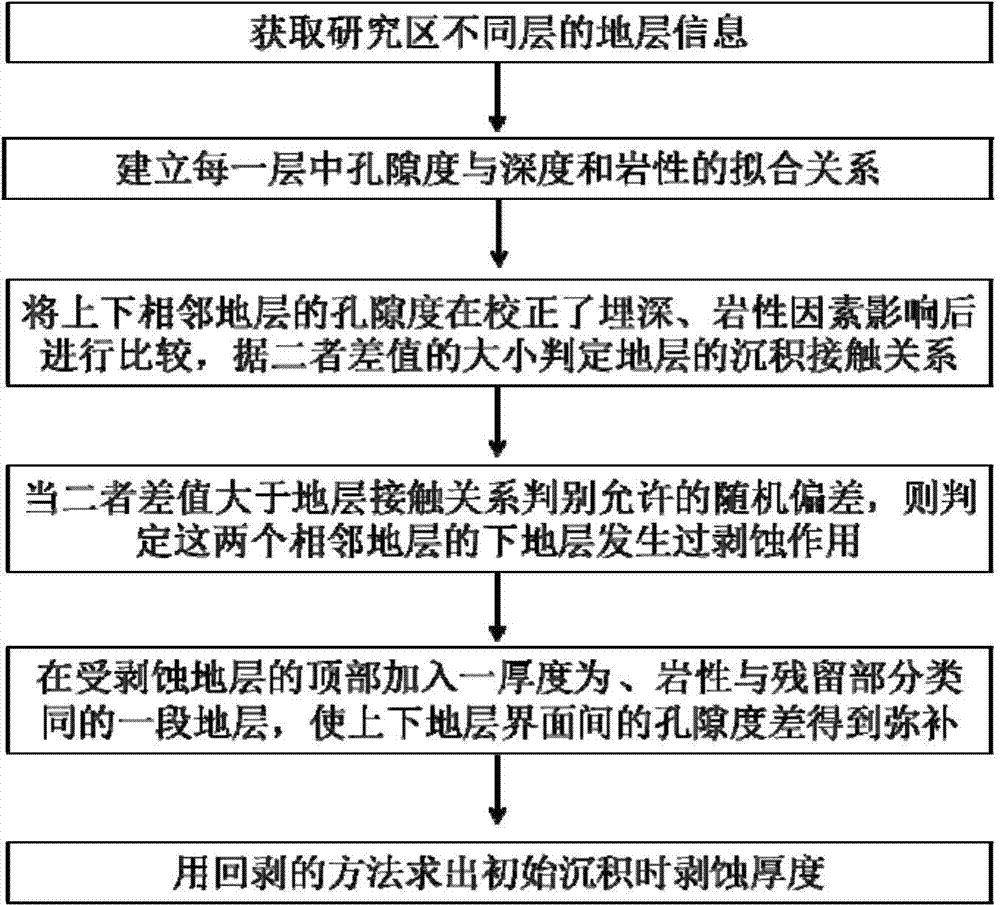
Method and device for acquiring erosion thickness of sedimentary basin
The invention relates to a method and device for acquiring erosion thickness of a sedimentary basin. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring information of different stratums in a researched area, wherein the information includes top-to-bottom depth of each stratum, sampling depth of each sample point of each stratum, lithology and porosity; building a fitting relationship between the corresponding porosity, depth and lithology of each stratum according to the stratum information; comparing the fitting relationships of the corresponding porosity, depth and lithology of upper and lower adjacent stratums to determine the erosion of the lower one of the two upper and lower adjacent layers; adding a stratum of which the thickness is shown as delta H and the lithology is similar to the that of the residual part to the top part of the determined erosion stratum, in order to compensate porosity difference between the upper and lower stratum interfaces; acquiring the erosion thickness H0 of the basin under initial deposition according to the compensated erosion stratum. According to the technical scheme, the method shows high applicability and effectiveness in complex geological conditions.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
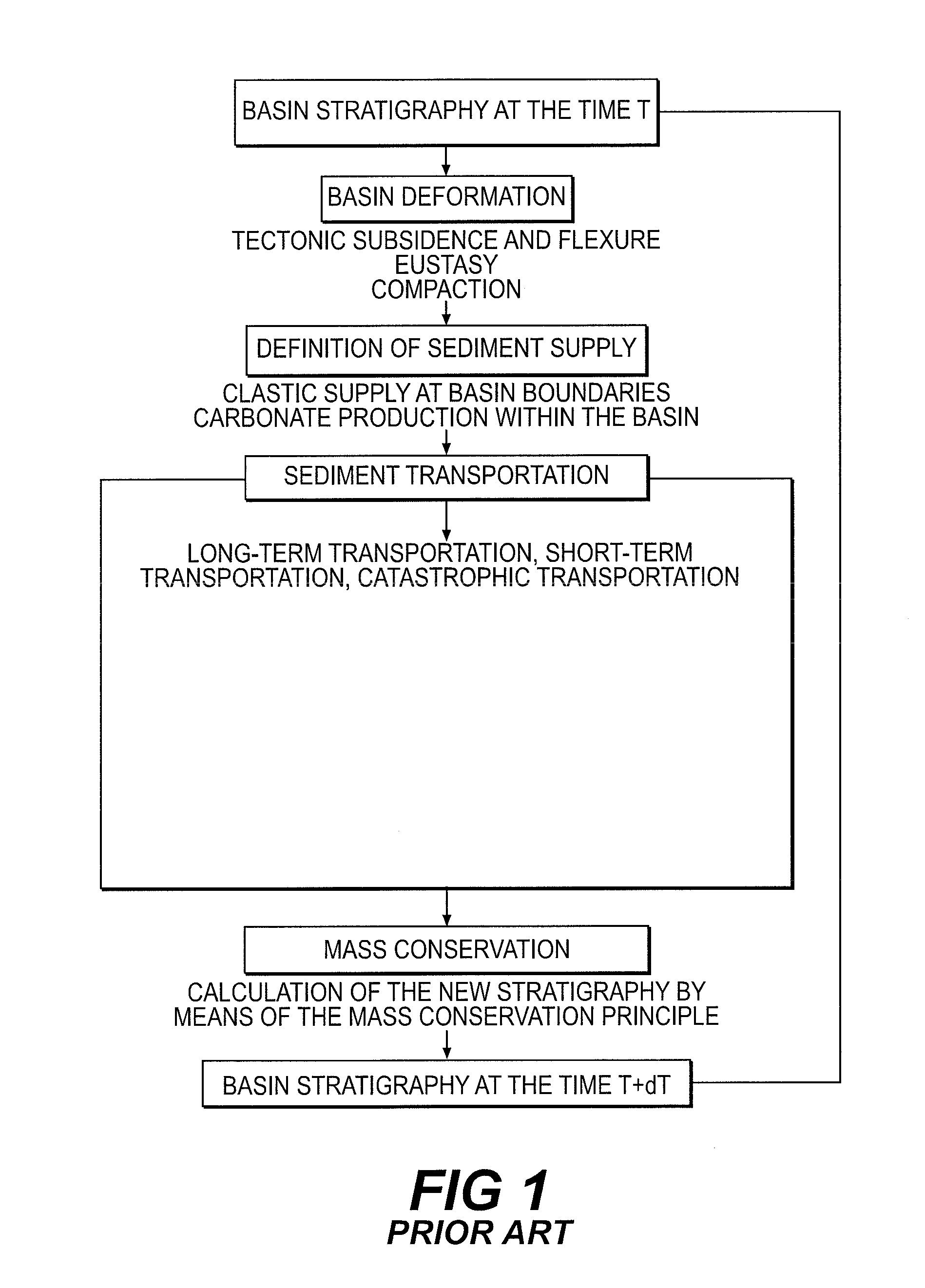
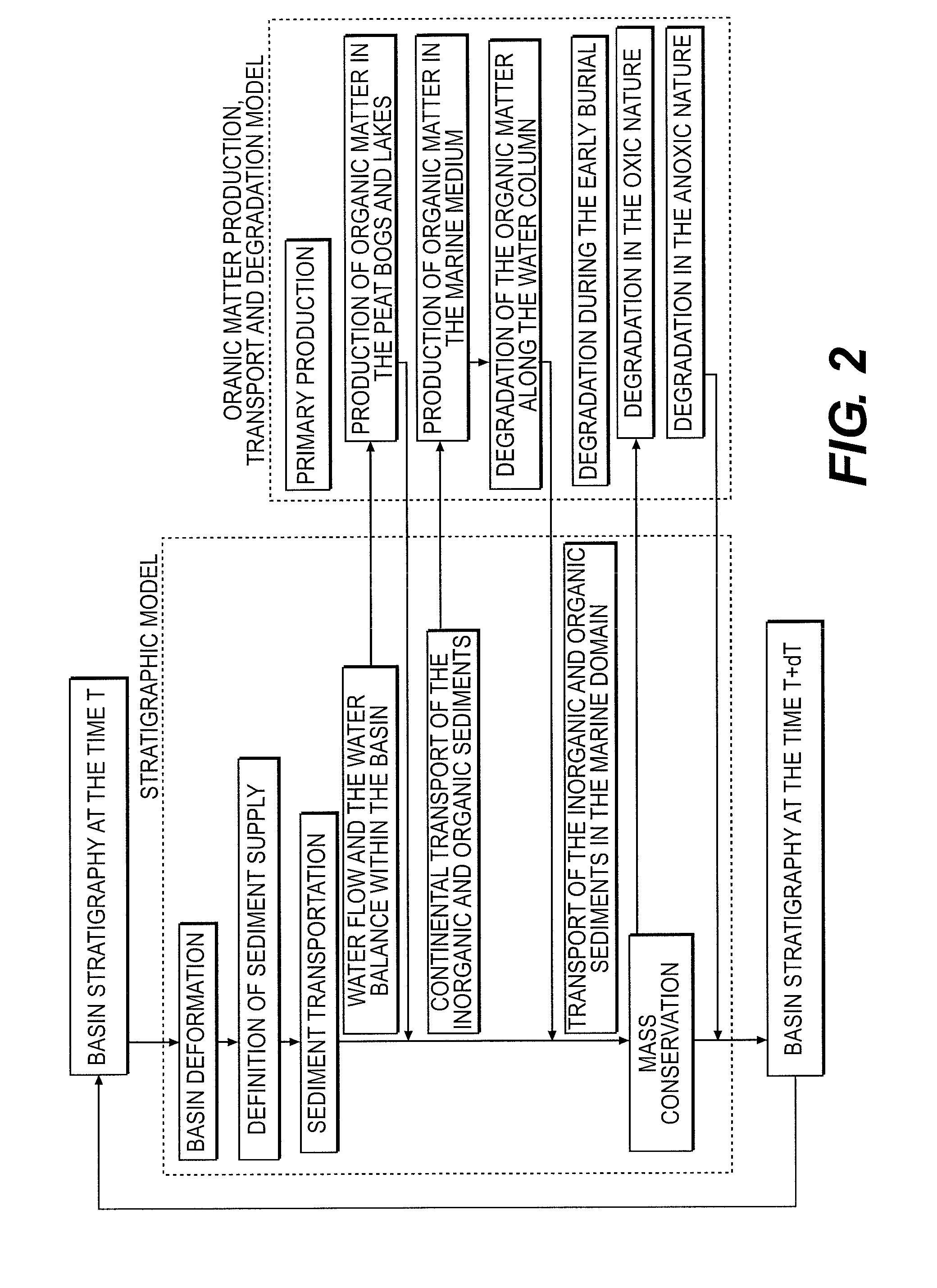
Sedimentary basin development method using stratigraphic simulation coupled with an organic matter production and degradation model
The invention is a method of developing a sedimentary basin wherein the distribution and the quality of the organic matter in the sedimentary basin are determined using stratigraphic modelling representing the evolution of the sedimentary basin. The method is based on the coupling of a stratigraphic model with an organic matter production, transport and degradation model. The sedimentary basin is then developed according to the distribution and the quality of the organic matter.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
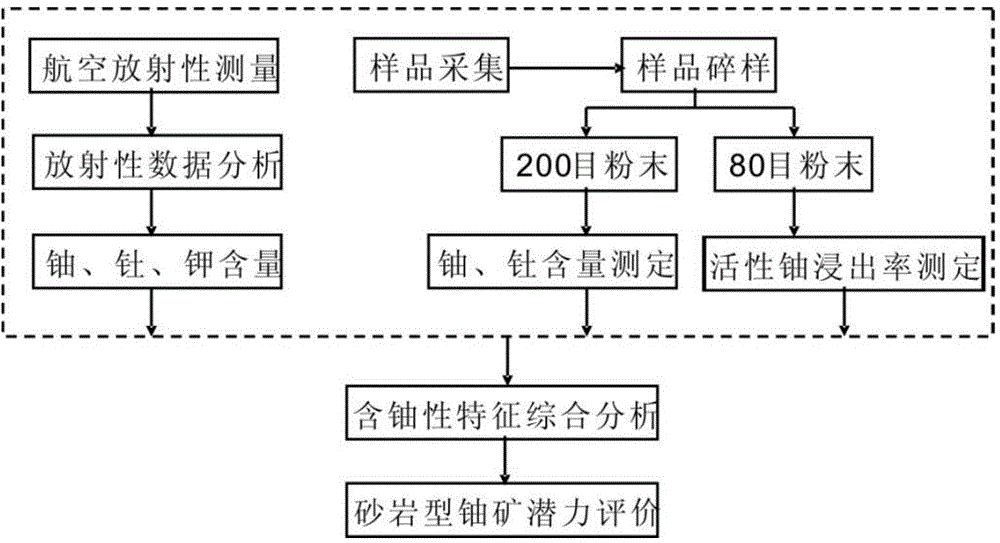
Sedimentary basin base uranium fertility and sandstone-type uranium deposit mineralization potentiality evaluation method
InactiveCN105807327AAnalytical testing requirements are clearEasy to operateNuclear radiation detectionGamma energySedimentary basin
The invention belongs to the technical field of uranium mines, and specifically discloses a sedimentary basin base uranium fertility and sandstone-type uranium deposit mineralization potentiality evaluation method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, comprehensively measuring aerial gamma energy spectra in a base provenance area; S2, collecting a medium acidic igneous rock sample in an aerial radioactivity measurement work area, and performing 80-mesh and 200-mesh pollution-free crushing on the sample; S3, measuring the quantity of ferrous oxide and major and minor components in the 200-mesh pollution-free powder; S4, measuring the share of active uranium in the 80-mesh pollution-free powder; S5, analyzing and arranging data about the content of uranium and thorium, the thorium-uranium ratio and the leaching rate of the active uranium; and S6, analyzing the base rock uranium fertility and evaluating the sandstone-type uranium deposit mineralization potentiality in combination with the data results of S1 and S4. The method is used for judging the uranium fertility of large sedimentary basin margin erosion source areas, and providing basis for large sedimentary basin sandstone-type uranium deposit mineralization potentiality evaluation.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
Comprehensive geophysical method for sedimentary basin uranium resource exploration
ActiveCN103675944AReduce economic riskShorten the exploration cycleGeological measurementsBasementDistribution characteristic
The invention belongs to the field of geophysical exploration methods, and particularly relates to a comprehensive geophysical method for sedimentary basin uranium resource exploration. The method includes the following steps: in a sedimentary basin for uranium resource exploration, utilizing gravity data to delineate basement relief and determine a depression area; in the depression area, performing aeromagnetic measuring to determine favorable uranium mineralization regions; on the basis of the favorable uranium mineralization regions, carrying out three-dimensional seismic exploration, and delineating distribution characteristics, structural characteristics and inversion-series physical parameters of layers containing mine meshes. By the method, a technical means is provided for sedimentary basin uranium resource evaluation, economic risk of sedimentary basin uranium resource exploration is lowered, and exploration cycle is shortened.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
Sedimentary facies prediction method based on hydrodynamics
InactiveCN106960076AMeet needsLess affected by human factorsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSedimentary basinComputer science
The invention discloses a sedimentary facies prediction method based on hydrodynamics. The method comprises the following steps: determining main sand control geological factors; utilizing the stratigraphic burial history for basin reconstruction; classifying sediments into two types according to different particle transportation modes; calculating a sedimentary amount of the sediments according to simulated characteristics of sedimentary components, and repeating simulation until the simulation is complete; selecting plane data of 1-4,400 moments, selecting a profile for analysis, and determining the sedimentary facies of the profile; randomly selecting a profile in the source direction or in the direction vertical to the source direction, selecting and extracting profile data, and determining the sedimentary facies of the profile based on characteristics of graphs; determining a corresponding relationship between a proportional relationship among profile components and the sedimentary facies; analyzing a corresponding relationship between a sand-mud proportion in the profile and the sedimentary facies according to the selected profile and the determined sedimentary facies of the profile; and determining the sedimentary facies of a plane. The method has the advantage that quantitative descriptions of the sedimentary facies of a sediment area can be achieved.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
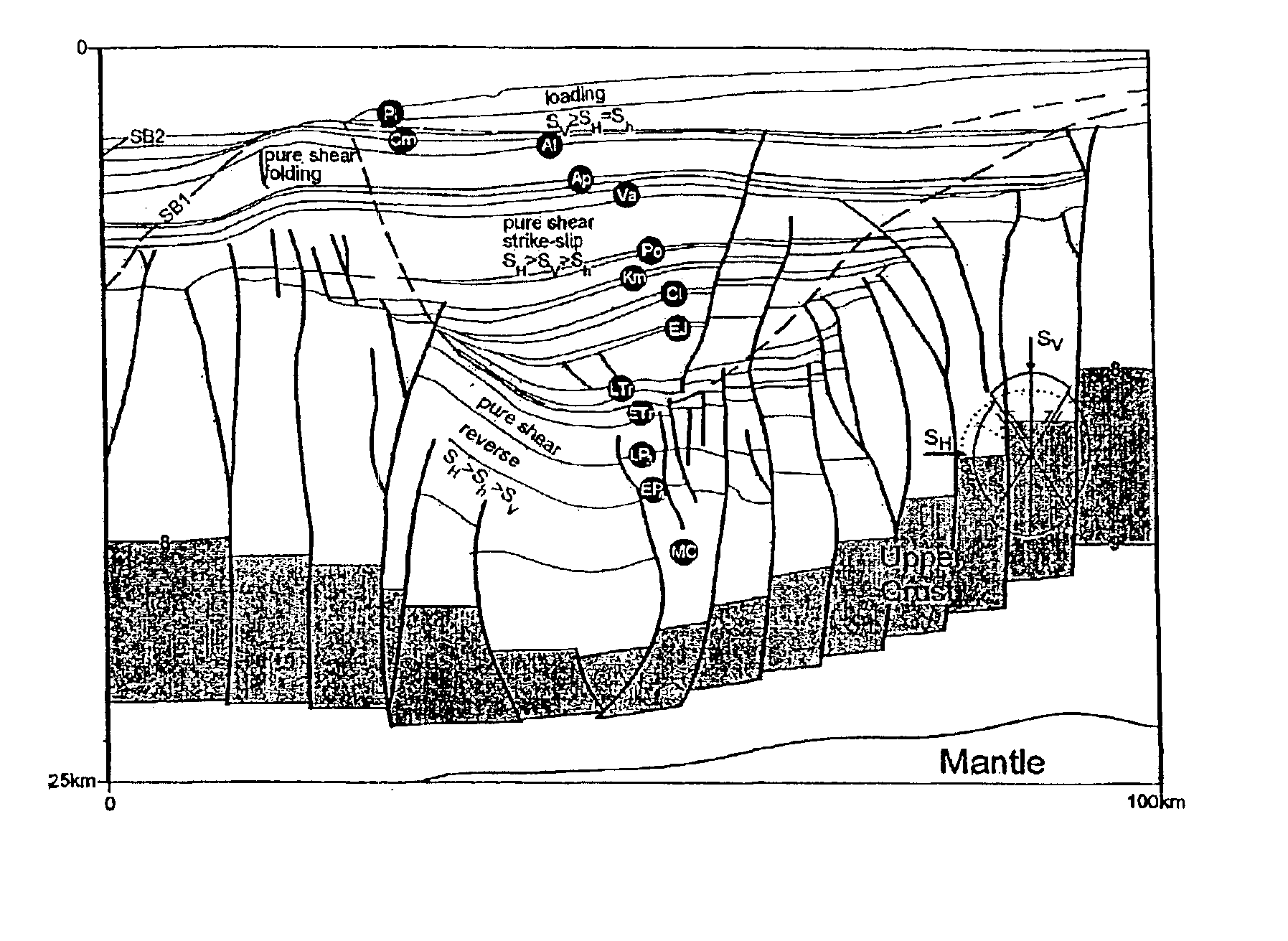
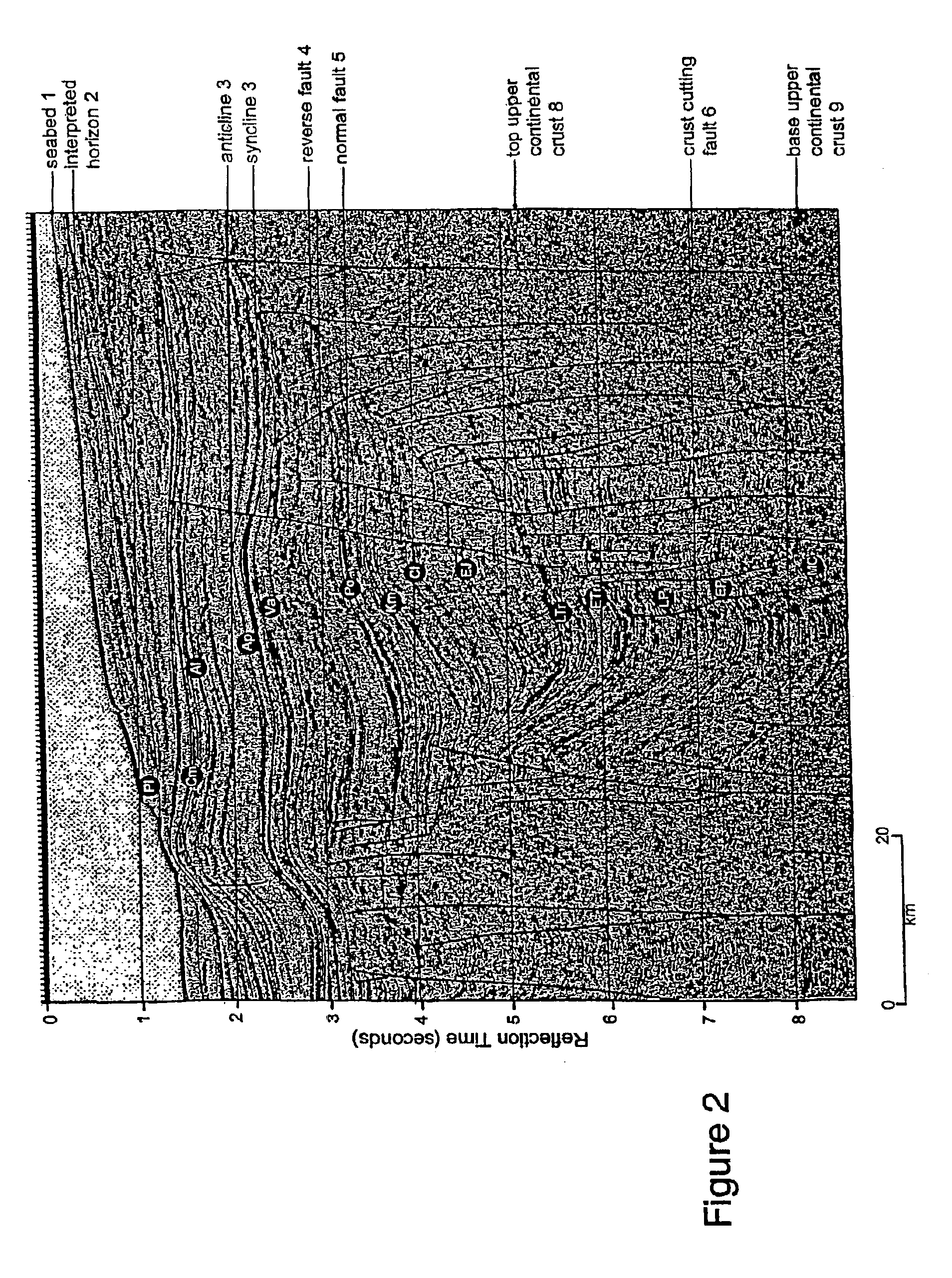
Method for detecting direction and relative magnitude of maximum horizontal stress in earth's crust
InactiveUS6885944B2Collapse problemIncrease pressureSeismic signal processingAnalogue computers for heat flowRelative magnitudeHorizontal stress
This invention relates to a method for determining direction and relative magnitude of maximum horizontal stress in sedimentary basins within Earth's crust. In particular the method uses seismic reflection data in determining the direction and magnitude of stresses. The method involves identifying from seismic data faults which cut the upper continental crust and uses those faults in conjunction with globally simultaneous compressional structures such as anticline to map the horizontal stresses. The invention has a particular application in the hydrocarbon exploration and production industry and has the advantage of providing the results pre-drill.
Owner:STOCHASTIC SIMULATION
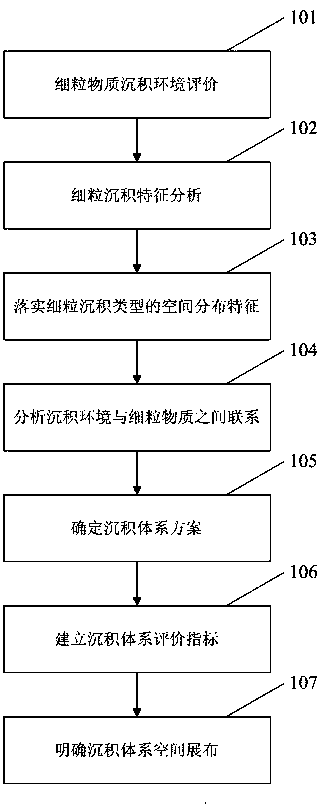
Continental lacustrine basin shale sedimentary system division method
InactiveCN109190953AIdentify developmental featuresPerfecting the Sedimentation TheoryResourcesEnvironment of AlbaniaSedimentology
A continental lacustrine basin shale sedimentary system division method includes: 1, evaluating sedimentary environment of fine-grained matter to divide sedimentary system or sedimentary facies; 2, analyzing that fine particle sedimentary characteristics; 3, carrying out the spatial distribution characteristics of the fine grain sedimentary type; 4, analyzing the internal relationship between thesedimentary environment and the fine-grained matter to determine the sedimentary mechanism of the fine-grained matter; 5, determining a sedimentary system scheme; 6, establishing an evaluation index of the sedimentary system; 7, defining the spatial distribution of the sedimentary system. The continental lacustrine basin shale sedimentary system division method provides the direction for shale oilexploration, provides related theoretical support for deep research of hydrocarbon generation-reservoir forming-accumulation of for lacustrine facies shale and is of great theoretical significance tothe development of sedimentology and reservoir geology.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
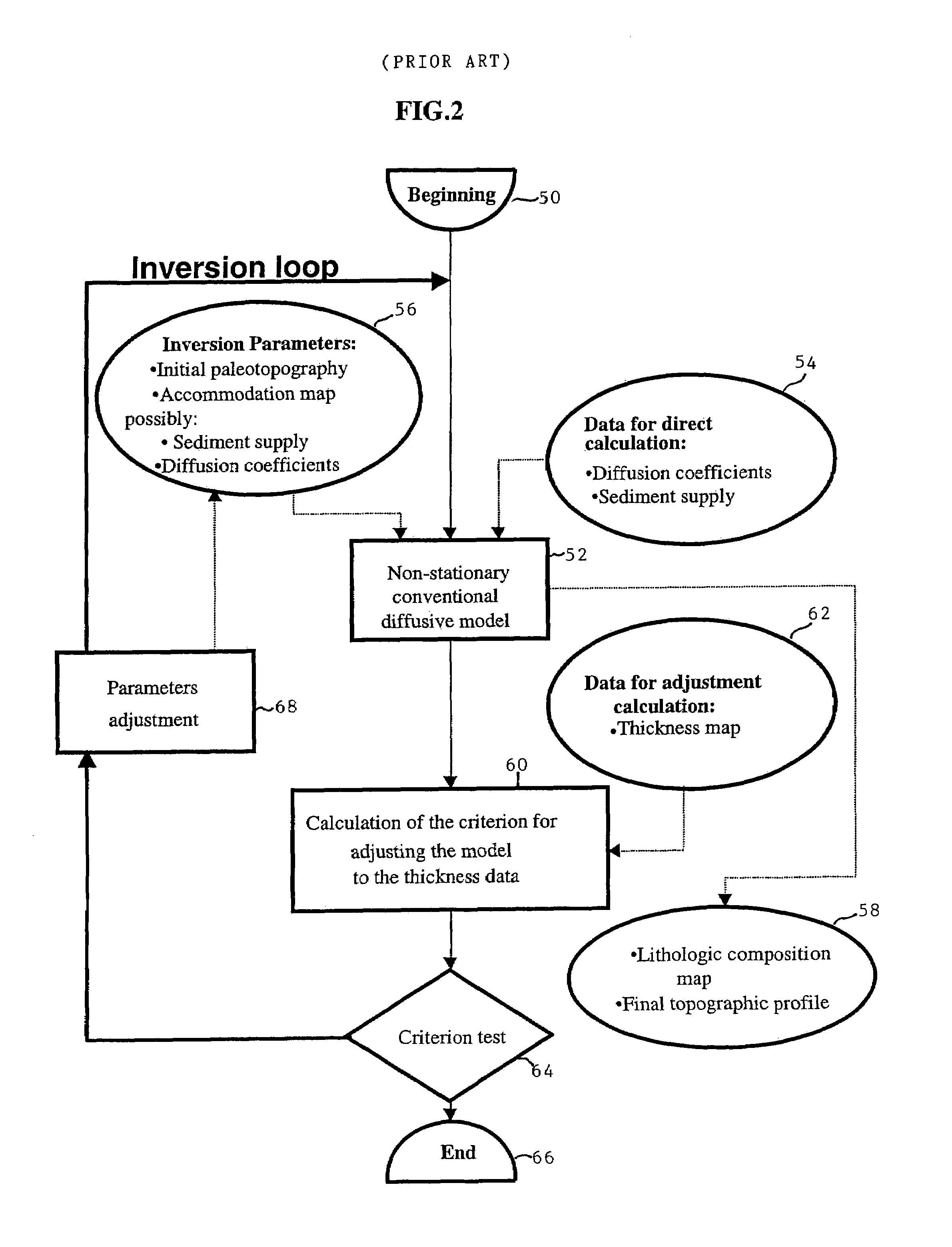
Method of simulating the sedimentary deposition in a basin respecting the thicknesses of the sedimentary sequences
ActiveUS20060015260A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsLithologySeismic survey
The method allows, by means of an iterative inversion algorithm, to predict the spatial distribution of the lithologic composition of sediments deposited in a sedimentary basin during a geologic time interval, and the temporal evolution of the depositional profile throughout filling of the basin, while respecting exactly the thicknesses of the sedimentary sequences measured otherwise. The input data consist of the thickness maps of the sedimentary layer studied, data relative to the location and to the composition of the sediment supply at the boundaries of the sedimentary basin studied, and physical parameters characterizing transport of the sediments during the period considered. These data are determined by interpretation of seismic surveys, by measurements and observations. This set of data is applied to an iterative inversion loop initialized by the accommodation provided by a stationary multilithologic diffusive model. This loop then works as a fixed-point algorithm correcting the accommodations by means of a preconditioning of the residue on the sequence thicknesses obtained by an instationary model. This preconditioning is obtained by applying the tangent application of the stationary multilithologic model to the residue on the thicknesses. At the output, we obtain the accommodation at the end of the sequence considered, as well as the bathymetry and surface composition solutions at any time of the sequences of the instationary model calibrated to the layer thicknesses. Application: location of hydrocarbon reservoirs notably.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
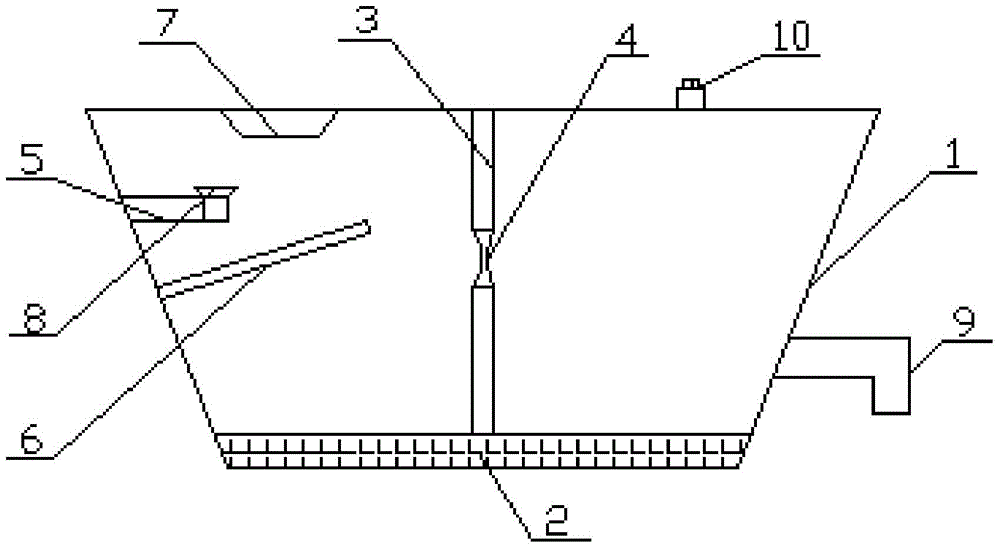
Multifunctional sedimentary water tank experiment device and method
ActiveCN107219061AImplement the spread featureHigh degree of automationHydrodynamic testingMaterial analysisOcean bottomControl system
The invention relates to a multifunctional sedimentary water tank experiment device and method. The technical scheme is that the device comprises four parts of a water tank external wall, a variable-gradient slope system, a seabed or lakebed system and a power and control system. The power and control system supplies power to other parts. The variable-gradient slope system comprises a sedimentary slope, elevating columns, a column house and a cylinder. The lower side of the sedimentary slope realizes elevating through the elevating columns and the column house, and scaling and shortening of the sedimentary slope are realized through the cylinder. The seabed or lakebed system is provided with a volcano model, an inclined plane I and an inclined plane II. The water tank external wall comprises a baffle plate having a notch and a transparent baffle plate. The beneficial effects are that the sedimentary environments of the simulation sea, lake and desert are integrated, the slope toe of the sedimentary basin can be freely changed, the sedimentary base can automatically elevate and sedimentation of earthquake, volcano and other special events can be simulated so that the degree of automation is high.
Owner:山东石油化工学院
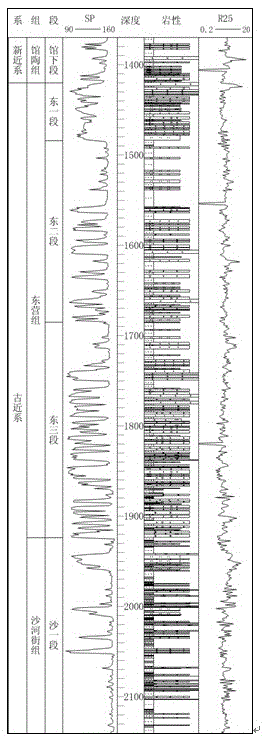
Method for establishing burial-thermal evolution history map of shale gas reservoir
InactiveCN110517794AImprove accuracyAccuracy of high thermal evolution historyInformaticsInstrumentsGround temperatureLithology
The invention provides a method for establishing a burial-thermal evolution history map of a shale gas reservoir. The method comprises the steps of acquiring layering data of a current stratum and static temperature measurement data of the current stratum; establishing a stratum lithology model of an interval for research; acquiring various burial history parameters; calculating the paleo-thickness and the buried depth of each stratum in each period; determining the ground temperature gradient, the heat conductivity, the heat generation rate and the ground heat flow value characteristics of the current ground temperature field; analyzing a formation mechanism and an evolution rule of the paleo-geothermal field; determining the maximum paleo-ground temperature experienced by the stratum towhich the sample belongs in the geological evolution process by using vitrinite reflectivity data; moreover, determining the paleo-geothermal gradient at the moment jointly by utilizing the Ro data ofthe multiple samples at different depths; determining a paleo-temperature evolution process of the sample, restoring a paleo-geothermal gradient evolution history, and drawing a burial history map ofthe paleo-geothermal field of the research area; calculating hydrocarbon source rock maturity evolution history; establishing and drawing a burial-thermal evolution history map of a sedimentary basin. According to the invention, high thermal performance history precision can be obtained.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Sedimentation basin
InactiveCN105129907AEasy to useEasy to operateWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSedimentary basinPrecipitation
The invention discloses a sedimentation basin. The sedimentation basin comprises a sedimentation basin body; the interior bottom end surface of the sedimentation basin body is provided with an active carbon adsorption layer; the interior of the sedimentation basin body is divided into a sedimentation zone and a water purification zone through a separator plate; the middle-upper part of the separator plate is provided with an overflow outlet; two sides of the sedimentation basin body are respectively provided with a water inlet pipe and a water outlet pipe, wherein the water inlet pipe is located in the sedimentation zone and the water outlet pipe is located in the water purification zone; an obliquely arranged flow deflector is installed below the water inlet pipe; and an ultraviolet sterilizer is arranged over the flow deflector. The sedimentation basin provided by the invention has good natural sedimentation effect, can exert bactericidal effect and reduce manual operation interfaces and is convenient to use.
Owner:合肥科启环保科技有限公司
Pseudo logs to improve stratigraphic correlation between sedimentary basins
InactiveUS20100094559A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsGeomorphologySedimentary basin
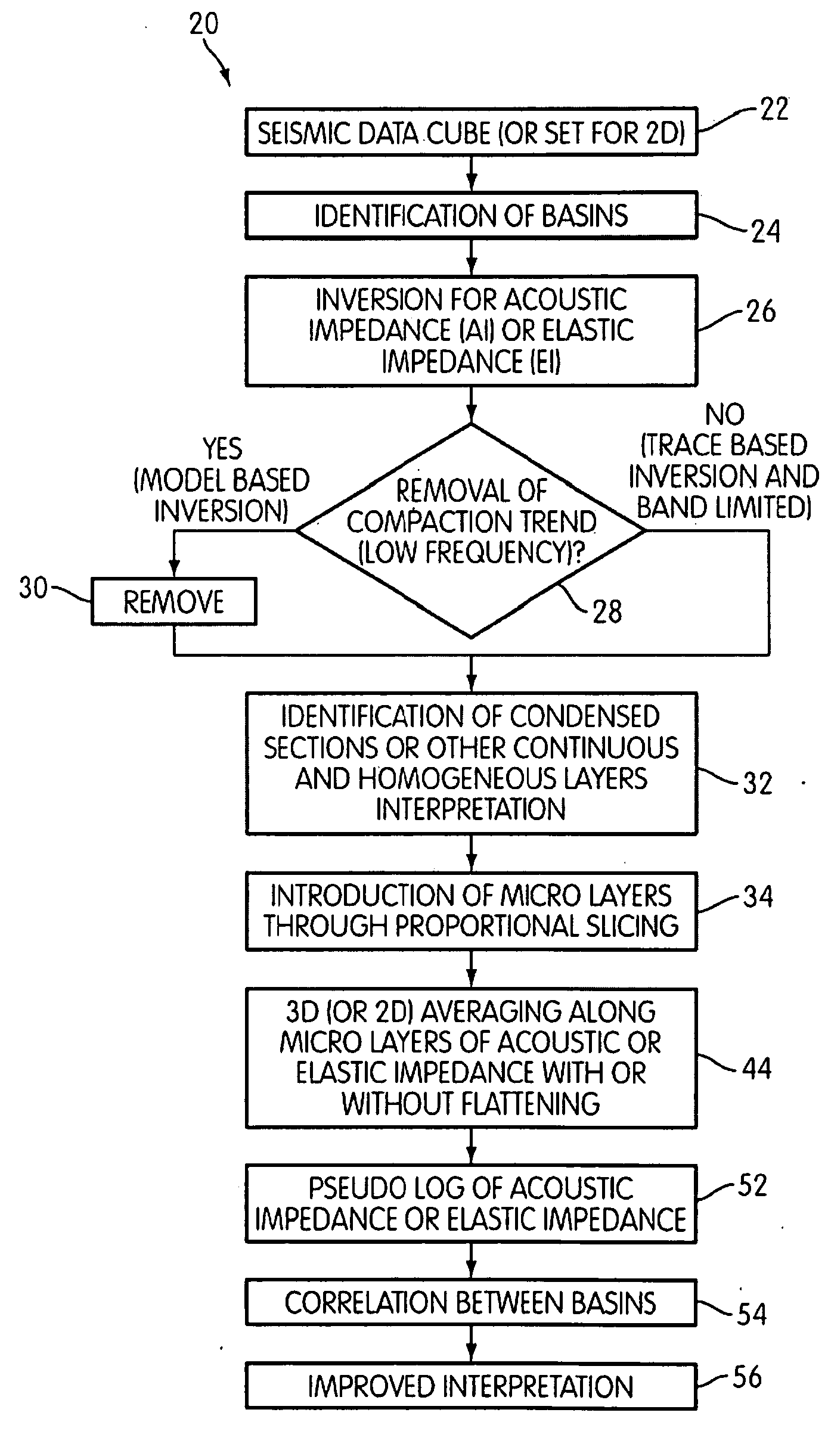
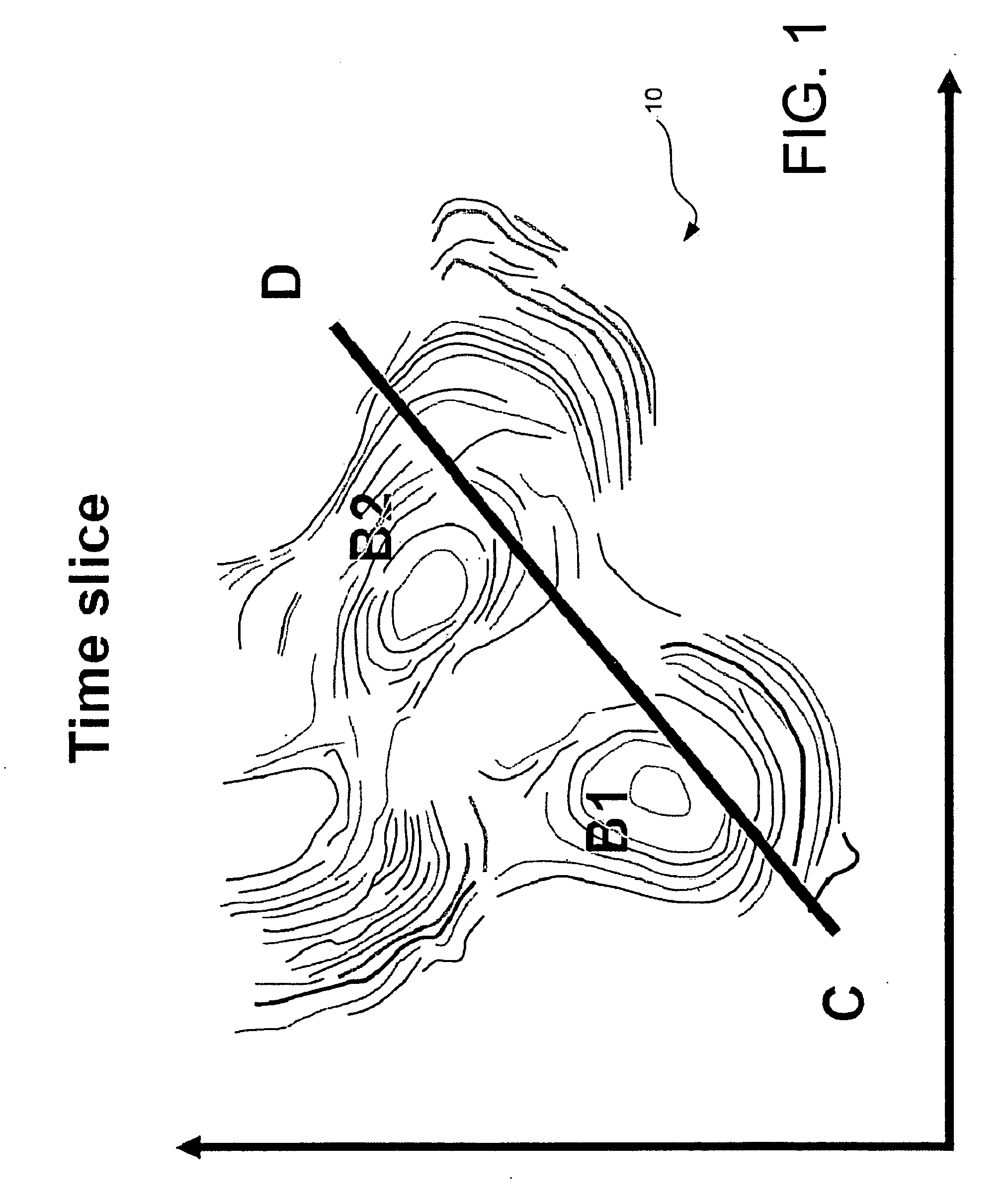
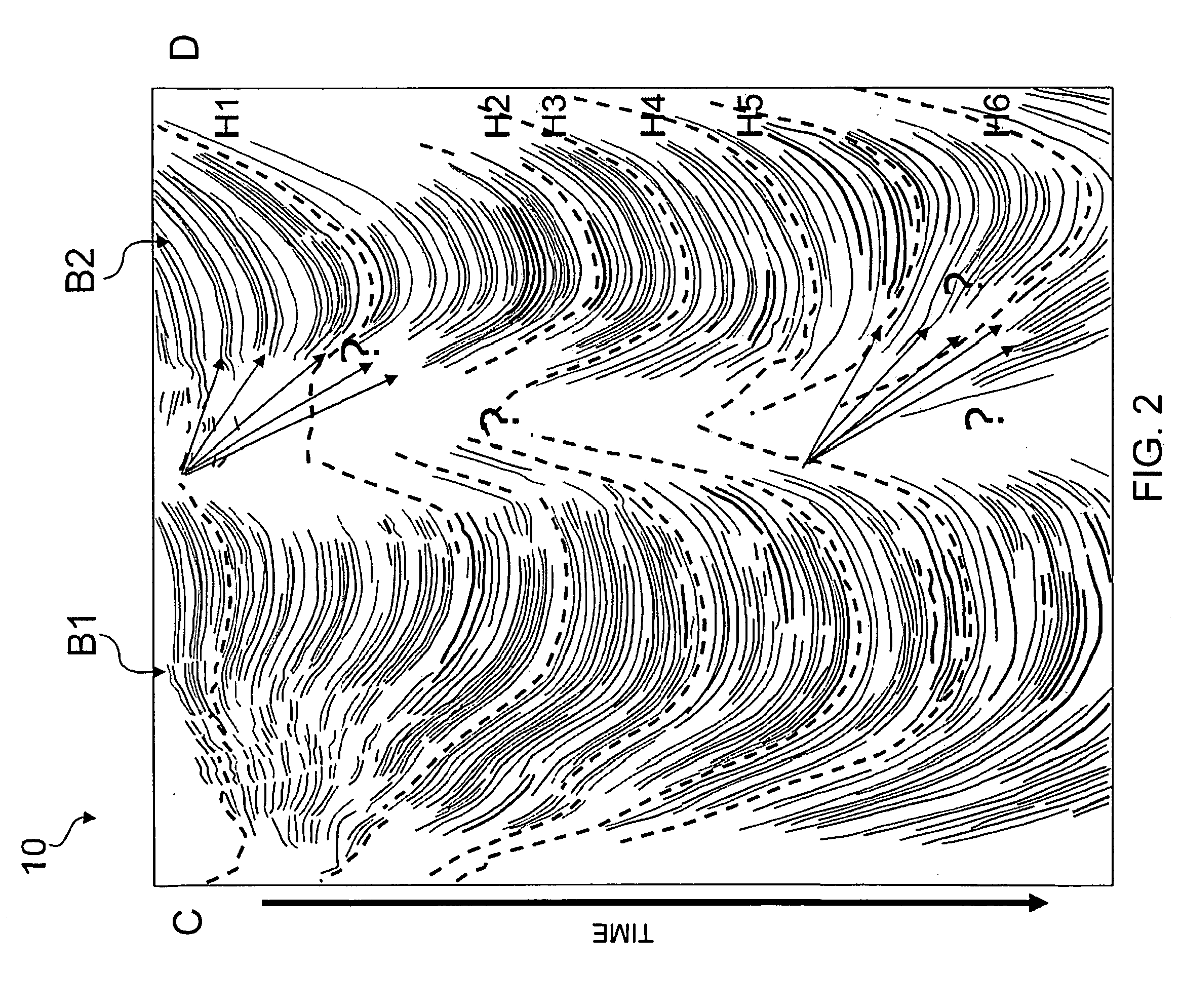
In order to improve the tie between depositionally equivalent beds relative to two or more basins detected within a multi dimensional seismic volume of interest, pseudo logs based on the average of attributes derived from seismic impedance where the compaction trend is not present are created for each basin. The mean is taken over all available azimuths, following the structural variations of introduced micro layers. The correlation between the pseudo log relative to each basin enable a more reliable interpretation between the different basins from which sound exploration decision can be made. Such a process has been successfully applied to seismic data acquired in deep water environment.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Modeling in sedimentary basins
InactiveCN101903805AShorten the timeSolve liquidity problemsSeismology for water-loggingHydrostatic pressureSedimentary basin
Embodiments of the invention operate to produce basin models that describe the basin in terms of compaction and fluid flow. The equations used to define compaction and fluid flow may be solved simultaneously. Embodiments of the invention use equations that define a set of unknowns that are consistent over the basis. The equations may define total pressure, hydrostatic pressure, thicknesses, and effective stress.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
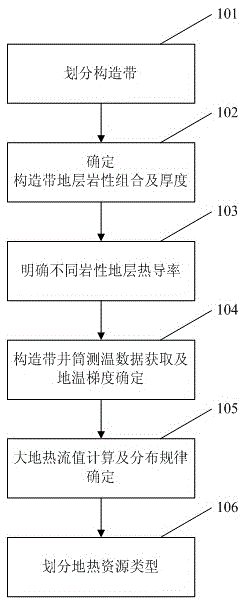
Sedimentary basin type underground heat resource classification method
ActiveCN105487135AOvercoming intractable difficultiesOvercoming the problem of low division accuracySeismologyLithologyGround temperature
The invention provides a sedimentary basin type underground heat resource classification method. The method comprises the steps that 1) tectonic zones of a sedimentary basin are divided by utilizing well drilling, logging, well logging and earthquake data and the like; 2) lithological combination and thickness of the stratum are determined for different tectonic zones; 3) the thermal conductivities of different lithological stratums are made clear via rock core sampling test; 4) shaft temperature measuring data of the tectonic zones is obtained, and distribution of the ground temperature gradient is determined according to the shaft temperature measuring data; 5) the ground heat flow value is calculated by utilizing the thermal conductivities of different lithological stratums and the ground temperature gradient comprehensively via a geothermic formula, and the planar distribution rule of the ground heat flow value is made clear; and 6) sedimentary basin type underground heat resource is classified according to the planar ground heat flow value. The method is highly operable, and can be used to provide more accurate methods and materials for research on geothermal reservoir reasons, evaluation of underground heat resource amount and research on development and utilization area selection of the underground heat resource.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Comprehensive evaluation method for single well oil gas geology
The invention relates to a comprehensive evaluation method for single well petroleum geology. The method comprises the following steps: 1, source rock evaluation; 2, reservoir stratum evaluation; 3, overlying stratum evaluation; 4, entrapment evaluation; 5, oil gas source comparison. According to the comprehensive evaluation method for the single well oil gas geology, the sequence stratigraphy theory serves as guidance, systematic observation of rock debris and the core and sample analysis serve as the bases, physical geography materials such as logging are combined, system partitioned strata are compared with adjoining wells, target stratum series sedimentary facies markers, sedimentary facies types and characteristics, stratigraphic sequence characteristics and sedimentary cycles, structures and structural characteristics are researched, sedimentary facies, cored interval sedimentary microfacies and comprehensive logging interval sedimentary microfacies are partitioned, sedimentary environment analysis is conducted, a single well facies model and whole well sedimentary facies sections are established, the mutual relations between the sedimentary facies and a crude stratum, a reservoir stratum and an overlying stratum are defined, and outlining basis is provided for conducting single well oil gas geology basic element analysis.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com