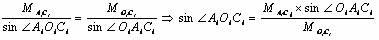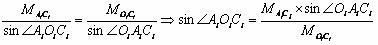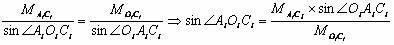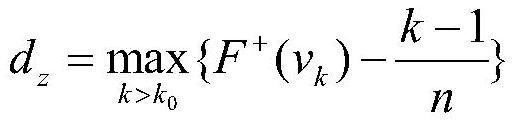Patents
Literature
42 results about "Bathymetry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bathymetry (/bəˈθɪmətriː/) is the study of underwater depth of lake or ocean floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The name comes from Greek βαθύς (bathus), "deep", and μέτρον (metron), "measure". Bathymetric (or hydrographic) charts are typically produced to support safety of surface or sub-surface navigation, and usually show seafloor relief or terrain as contour lines (called depth contours or isobaths) and selected depths (soundings), and typically also provide surface navigational information. Bathymetric maps (a more general term where navigational safety is not a concern) may also use a Digital Terrain Model and artificial illumination techniques to illustrate the depths being portrayed. The global bathymetry is sometimes combined with topography data to yield a Global Relief Model. Paleobathymetry is the study of past underwater depths.
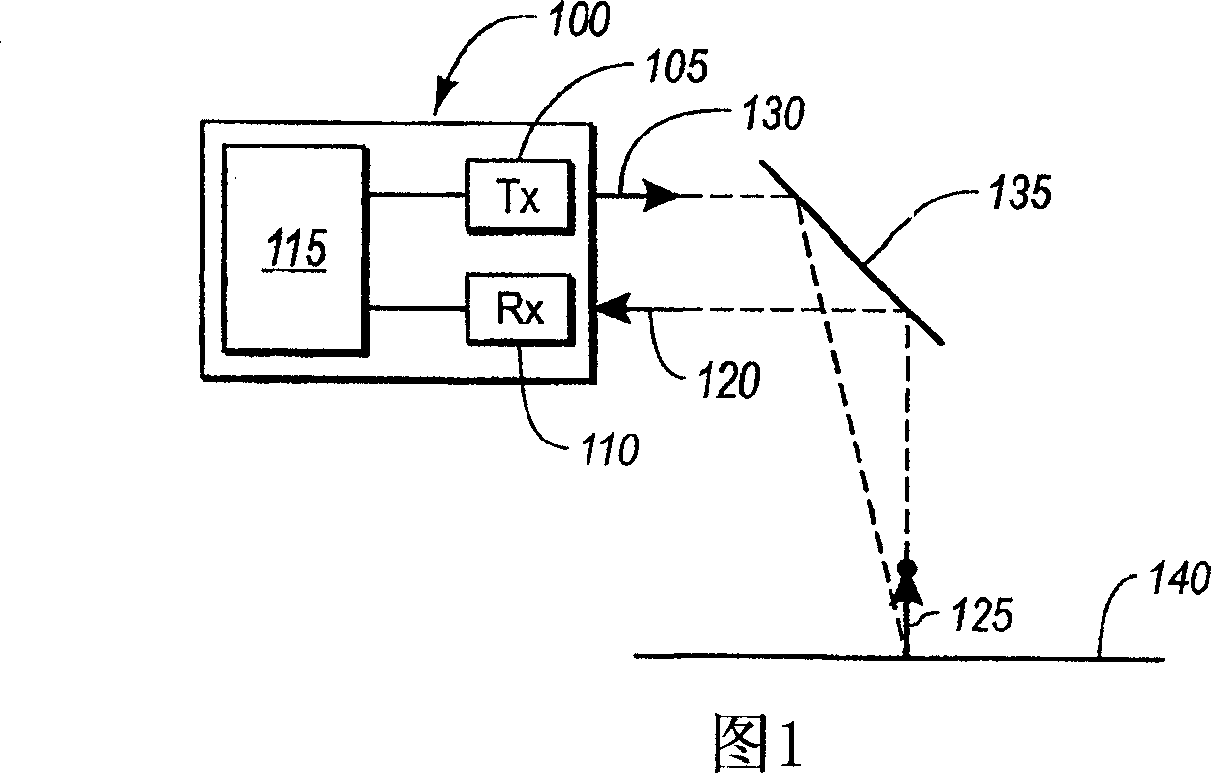
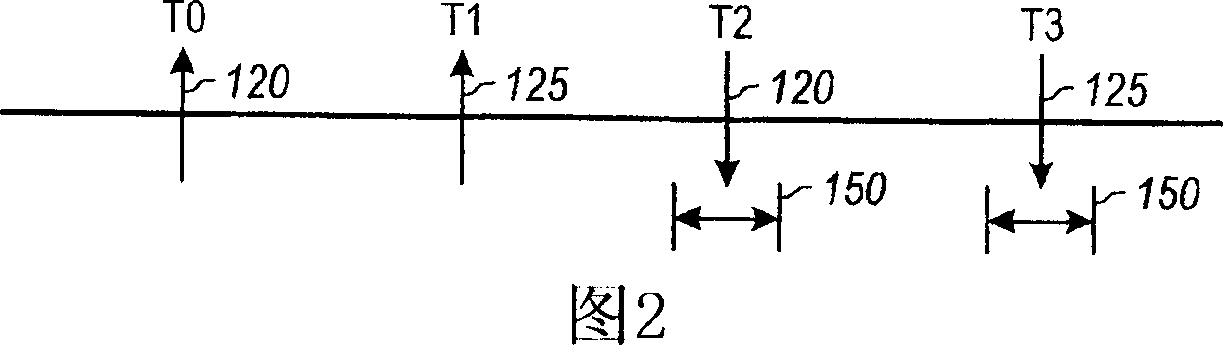
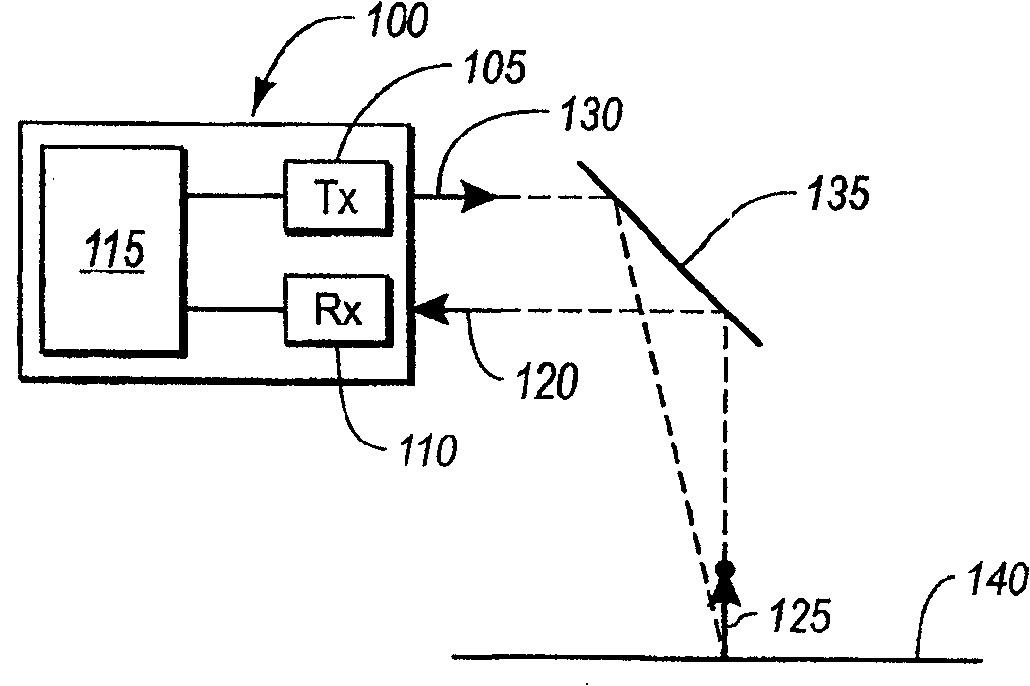
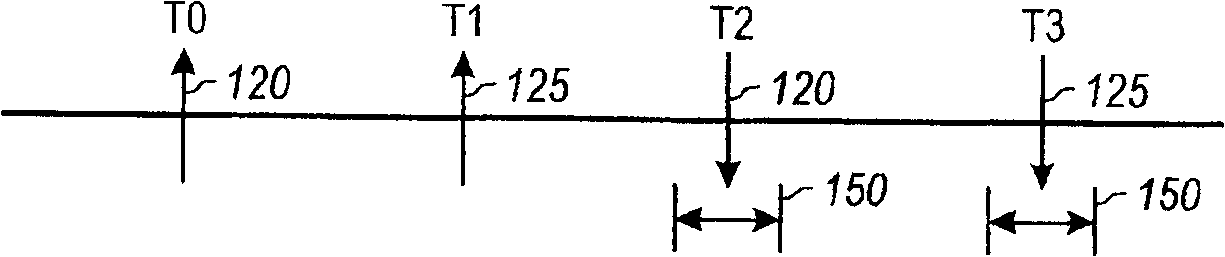
Increasing measurement rate in time of flight measurement apparatuses
An apparatus for measuring distance to a surface is disclosed. The apparatus transmits at least one subsequent pulse of light prior to receiving a reflection of a previously sent pulse of light. Thus, multiple pulses of light are in-flight at a given time. The embodiments are applicable to terrain mapping, bathymetry, seismology, detecting faults, biomass measurement, wind speed measurement, temperature calculation, traffic speed measurement, military target identification, surface to air rangefinding, high definition survey, close range photogrammetry, atmospheric composition, meteorology, distance measurement, as well as many other applications. Examples of such apparatuses include laser ranging systems, such as light detection and ranging (LIDAR) systems, and laser scanners. Data received from the apparatus by a data processing unit can be used to create a data model, such as a point cloud, digital surface model or digital terrain model describing the surface, terrain, and / or objects.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
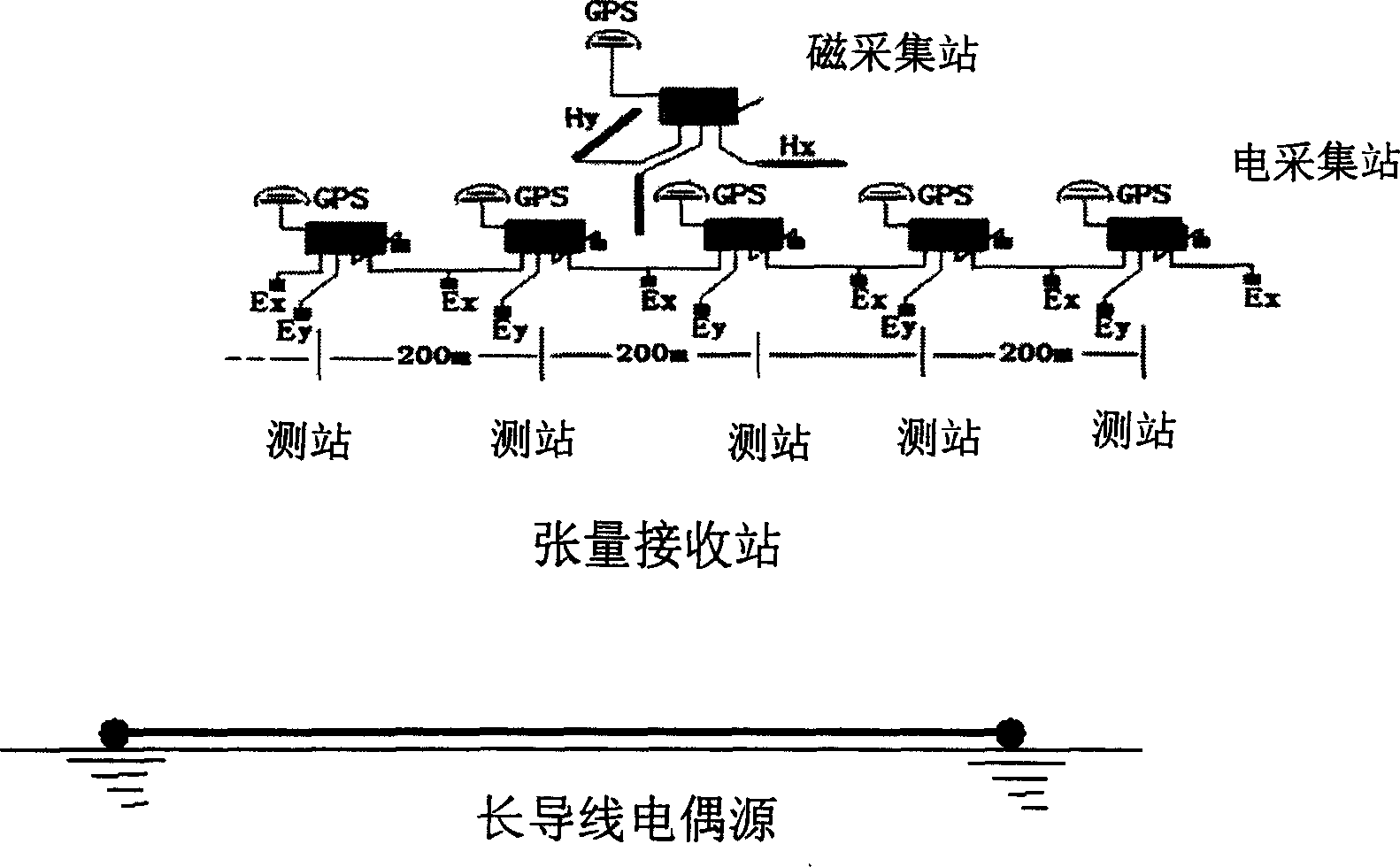
Artificial source time frequency electro magnetic bathymetry
The present invention can implement the utilization of electromagnetic depth-measuring exploration method in frequency-domain method and time-domain method. Said invention utilizes that exciting and receiving a series of frequency (period) pulses to research the law of whole spectrum, at the same time, research the signal attenuation law of every frequency (period), from short period to long period, the reflected underground informations can be progressively deepened, the superposition of these informations can raise exploration accuracy, and the time-domain and frequency-domain boty can be used for making mutual check by means of time-frequency conversion so as to greatly raise exploration accuracy. Said invention can be mainly used for making exploration of oil, gas, mineral resources and geothermal resource.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
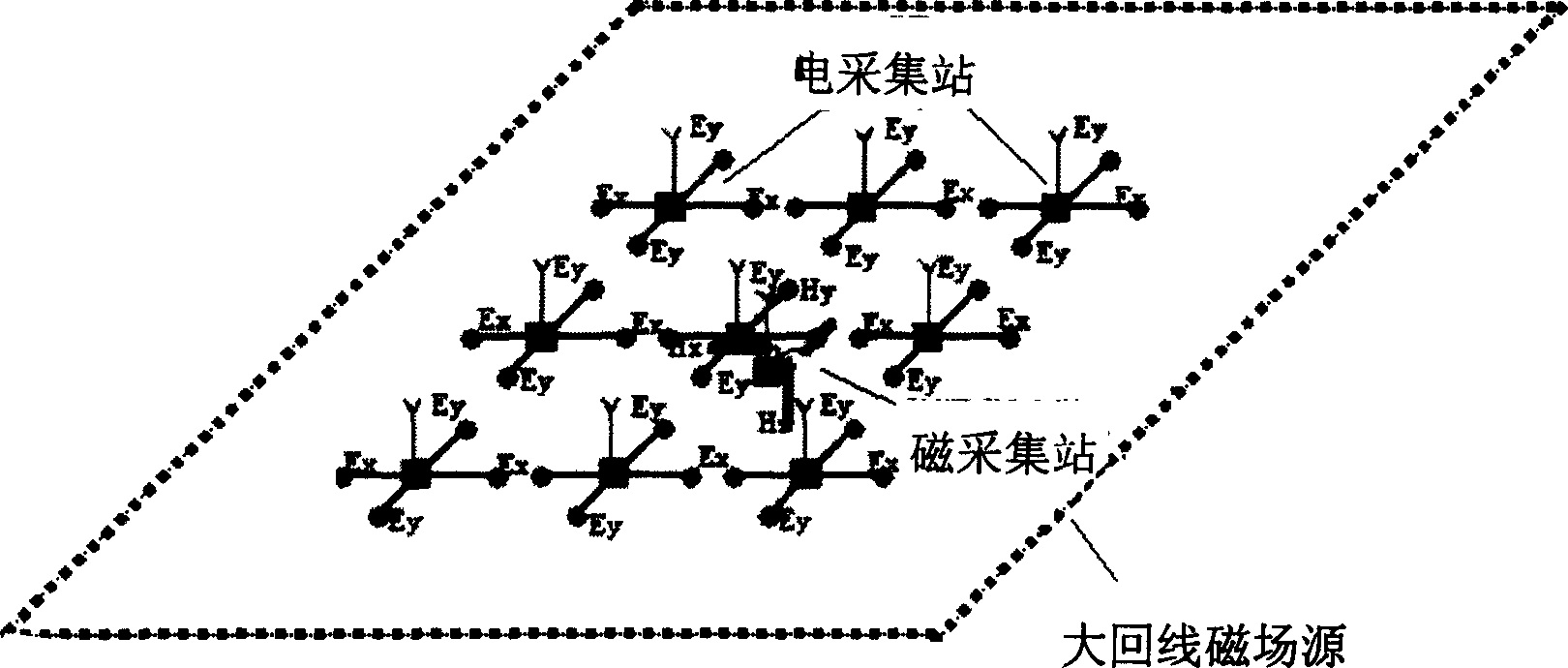
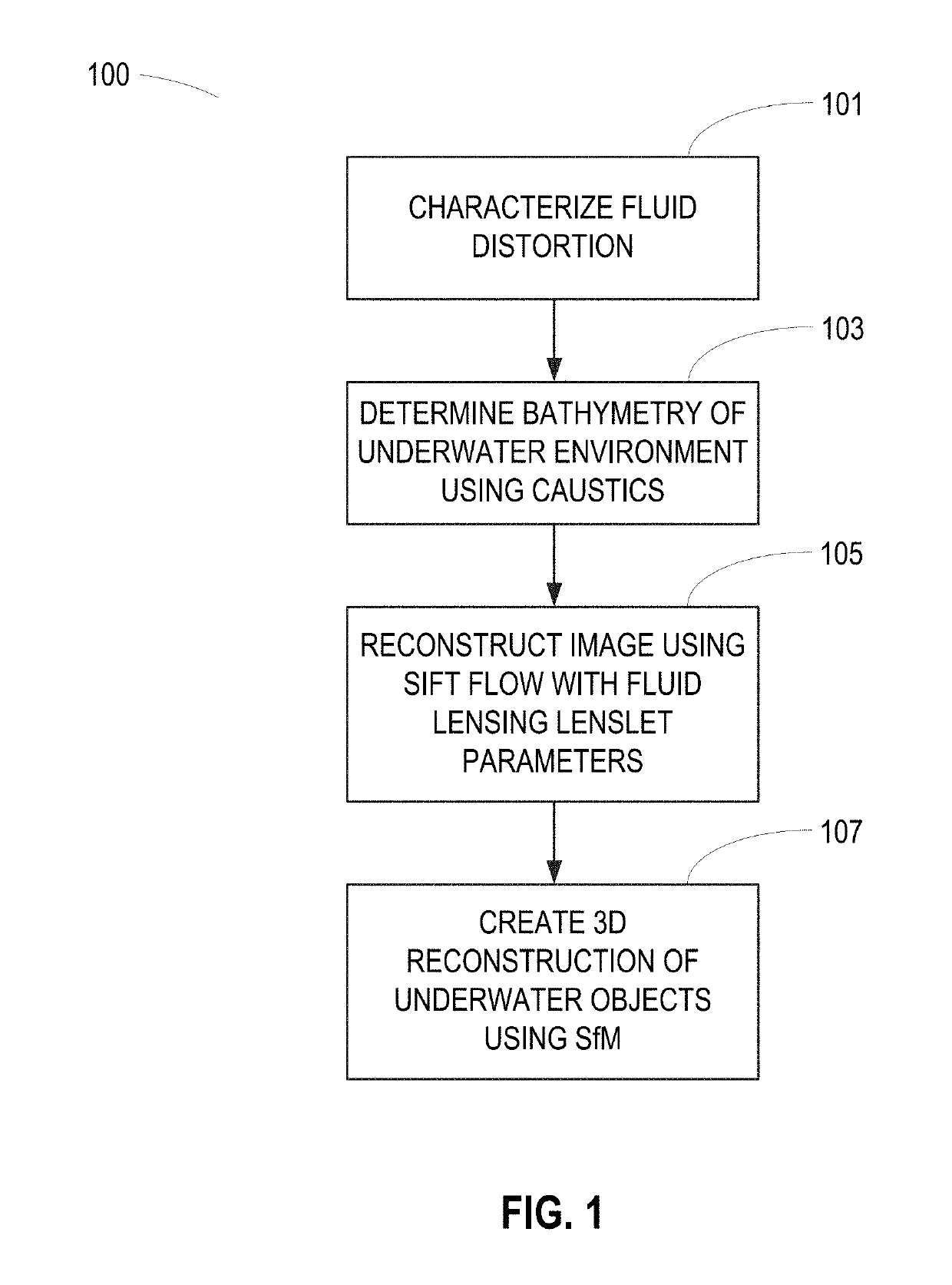
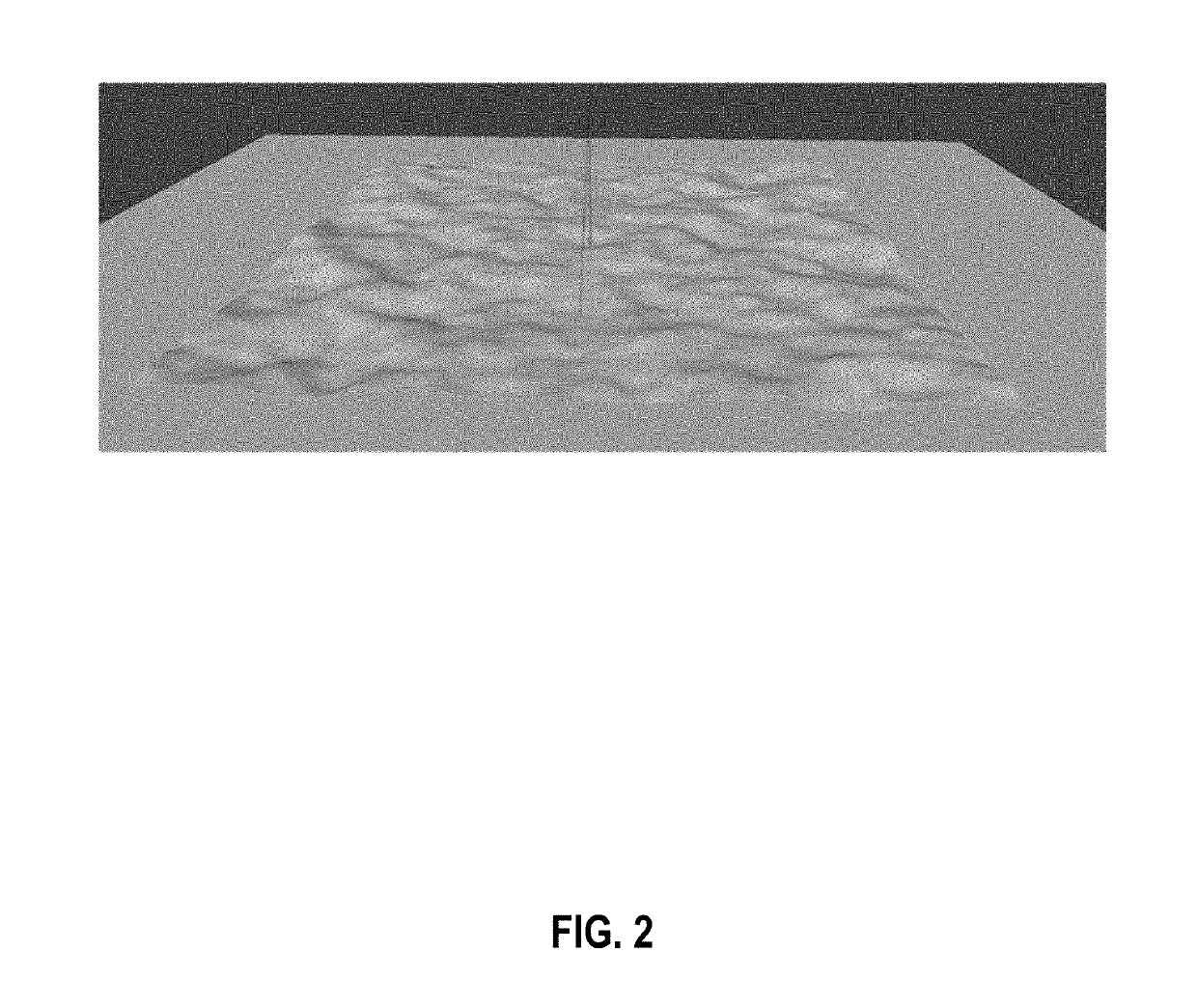
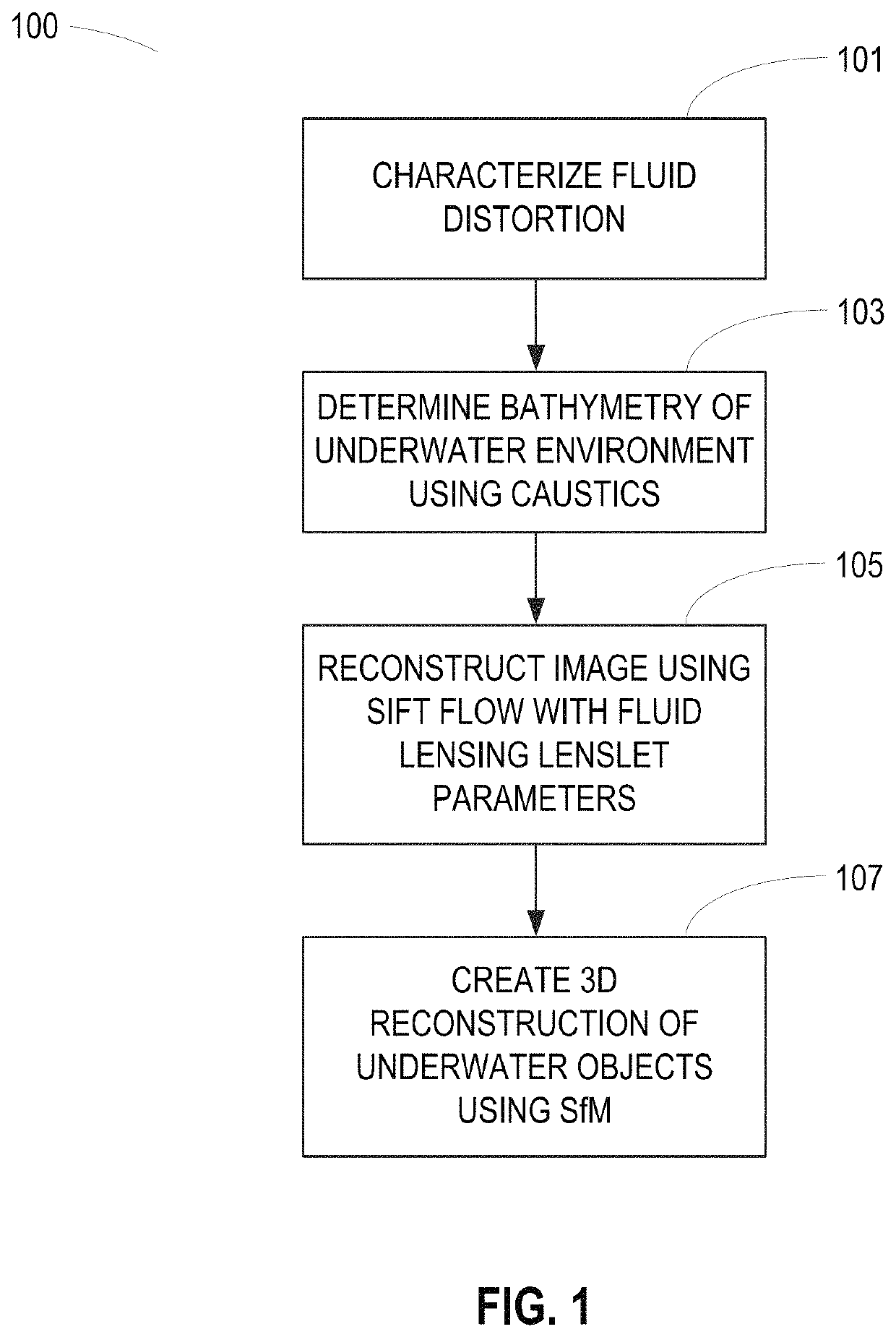
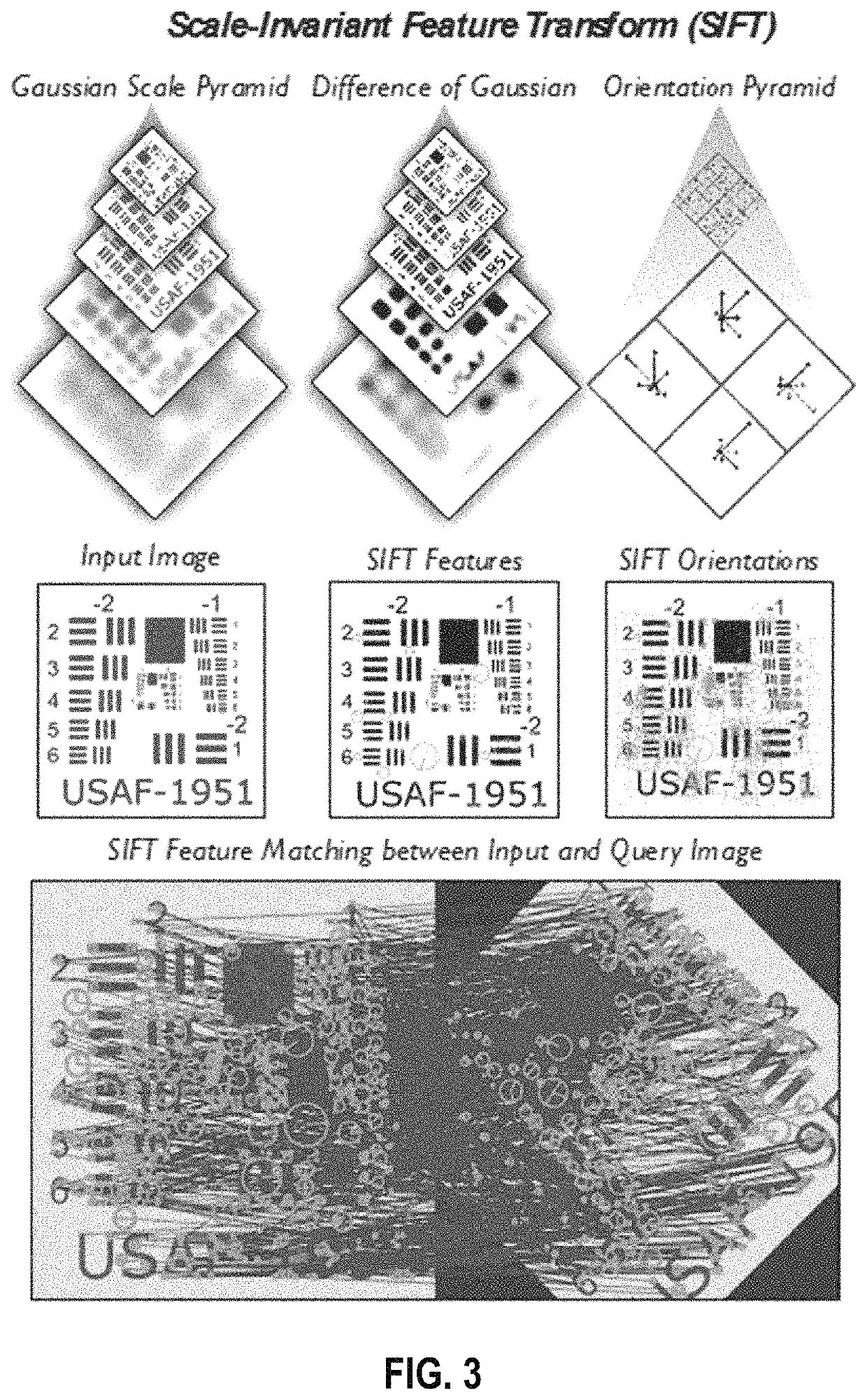
System and method for imaging underwater environments using fluid lensing
ActiveUS20190266712A1Improve propertiesImprove resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisHigh frame rateBathymetry
Systems and methods are described for correcting distorted images captured of underwater environments. Caustics are used to provide additional illumination to underwater objects, and lenslets from ocean wave fluid lensing are used to magnify a benthic scene for enhancing the effective resolution of the images. The process introduces a fluid distortion characterization methodology, caustic bathymetry concepts, fluid lensing lenslet homography technique, two dimensional image reconstruction process, and three dimensional airborne fluid lensing process for characterizing the aquatic surface wave field, modelling bathymetry using caustic phenomena, and robust high-resolution aquatic remote sensing. Performing remote sensing using fluid lensing, also referred to as the fluid lensing process, utilizes high-frame-rate multispectral remote sensing data to remove ocean wave distortions from an image, to enhance the resolution of an image by exploiting ocean waves, and to enhance the signal strength of an image otherwise impaired by optical absorption in the water column.
Owner:NASA
Method of simulating the sedimentary deposition in a basin respecting the thicknesses of the sedimentary sequences
ActiveUS20060015260A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsLithologySeismic survey
The method allows, by means of an iterative inversion algorithm, to predict the spatial distribution of the lithologic composition of sediments deposited in a sedimentary basin during a geologic time interval, and the temporal evolution of the depositional profile throughout filling of the basin, while respecting exactly the thicknesses of the sedimentary sequences measured otherwise. The input data consist of the thickness maps of the sedimentary layer studied, data relative to the location and to the composition of the sediment supply at the boundaries of the sedimentary basin studied, and physical parameters characterizing transport of the sediments during the period considered. These data are determined by interpretation of seismic surveys, by measurements and observations. This set of data is applied to an iterative inversion loop initialized by the accommodation provided by a stationary multilithologic diffusive model. This loop then works as a fixed-point algorithm correcting the accommodations by means of a preconditioning of the residue on the sequence thicknesses obtained by an instationary model. This preconditioning is obtained by applying the tangent application of the stationary multilithologic model to the residue on the thicknesses. At the output, we obtain the accommodation at the end of the sequence considered, as well as the bathymetry and surface composition solutions at any time of the sequences of the instationary model calibrated to the layer thicknesses. Application: location of hydrocarbon reservoirs notably.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
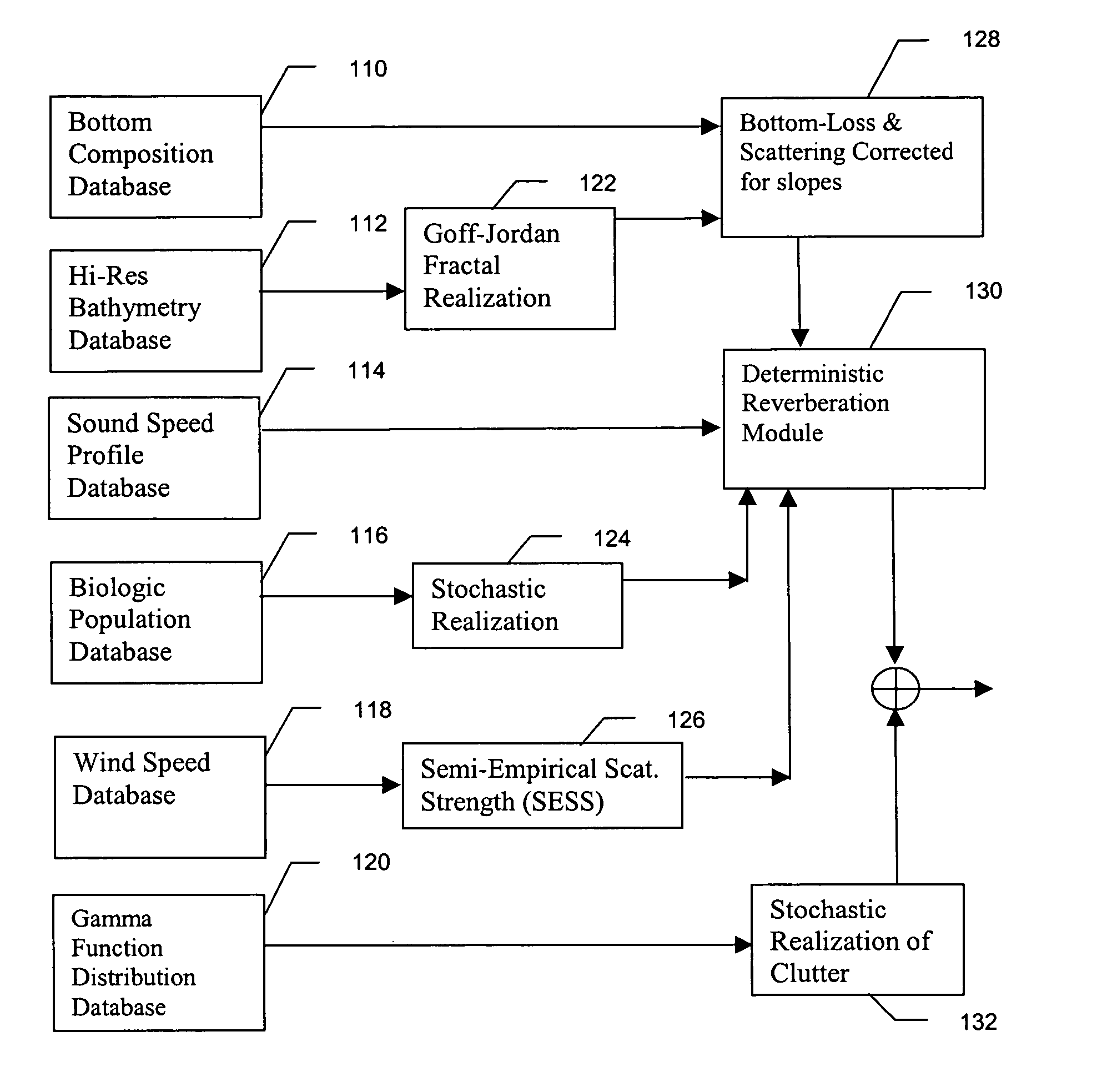
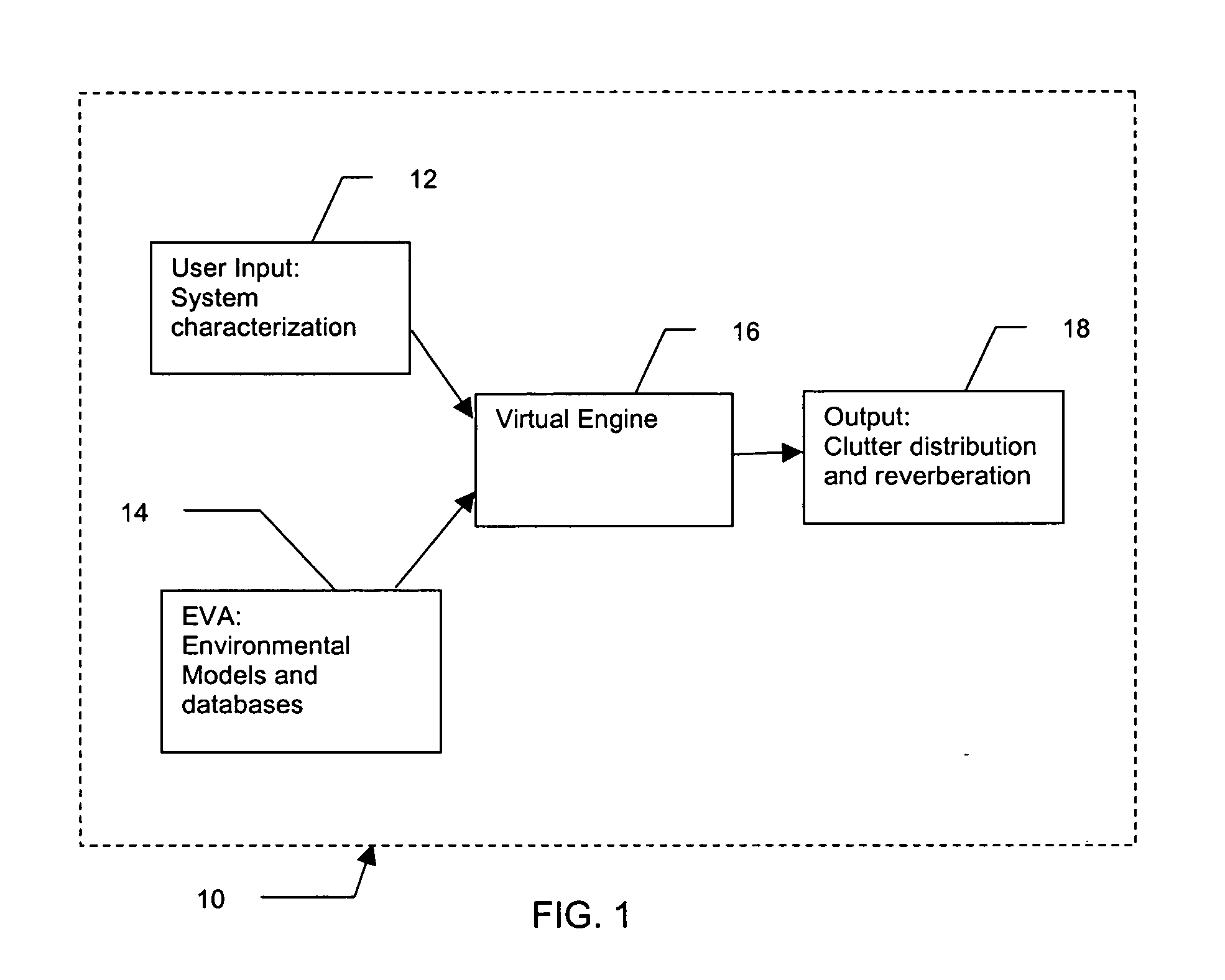
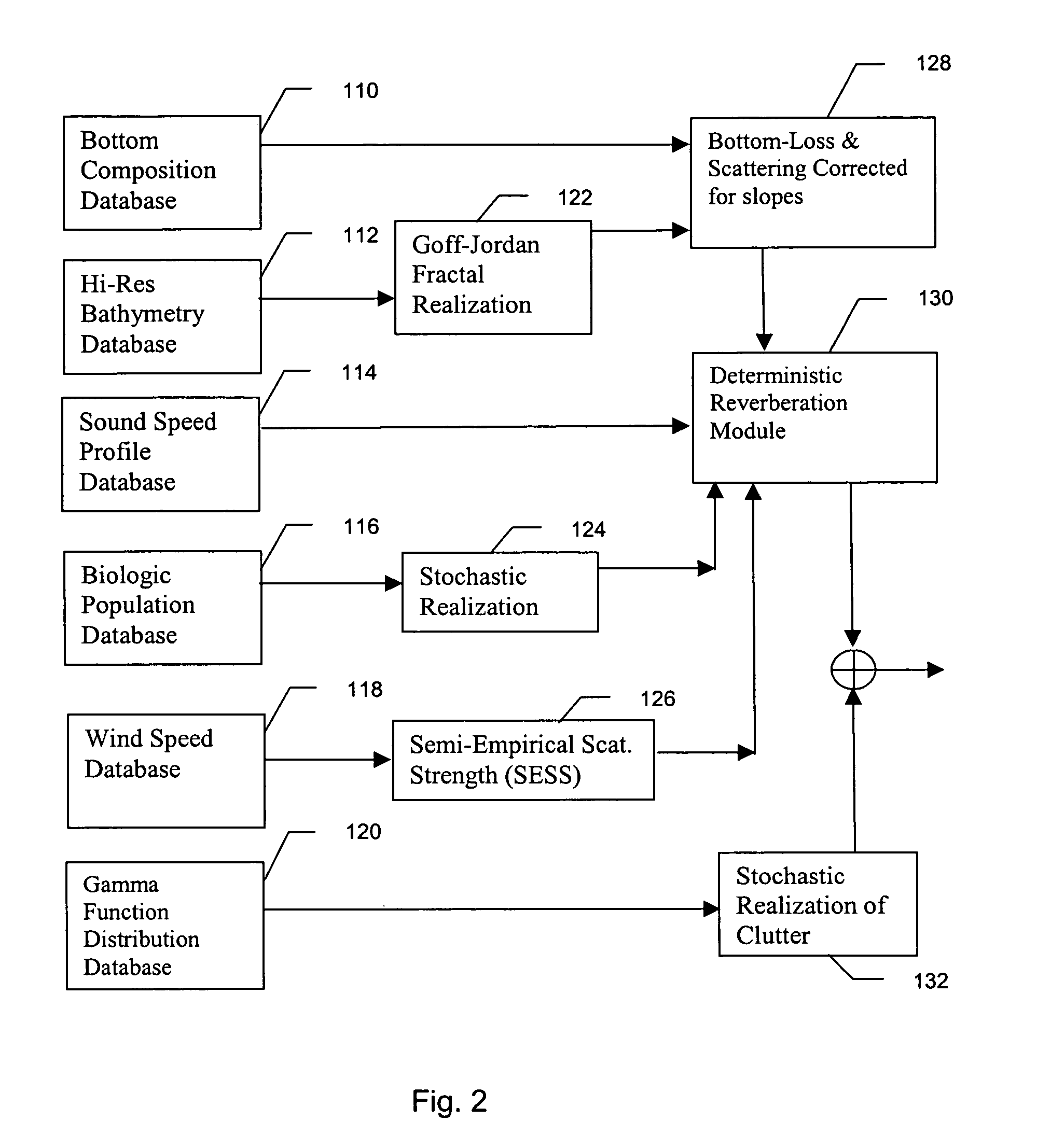
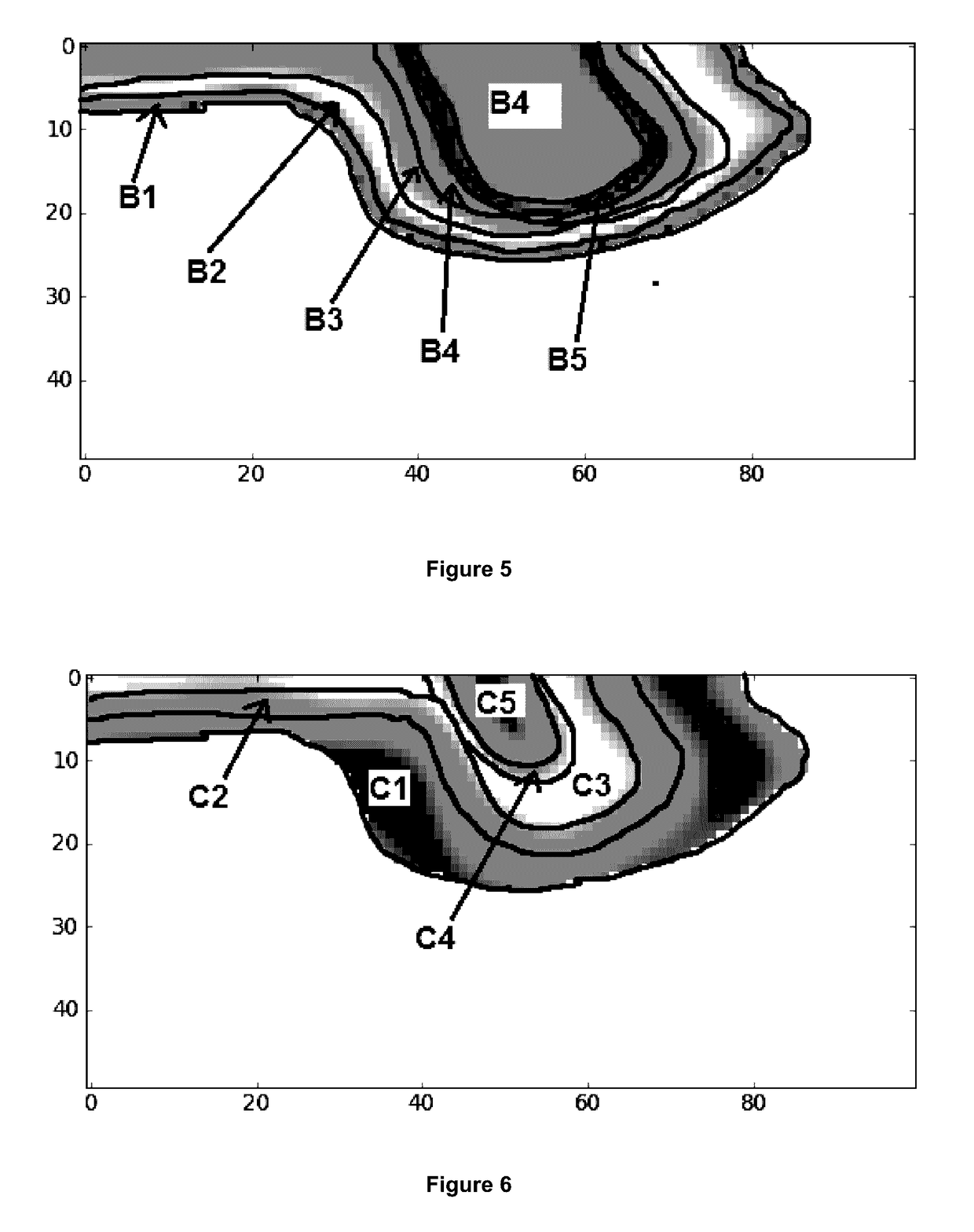
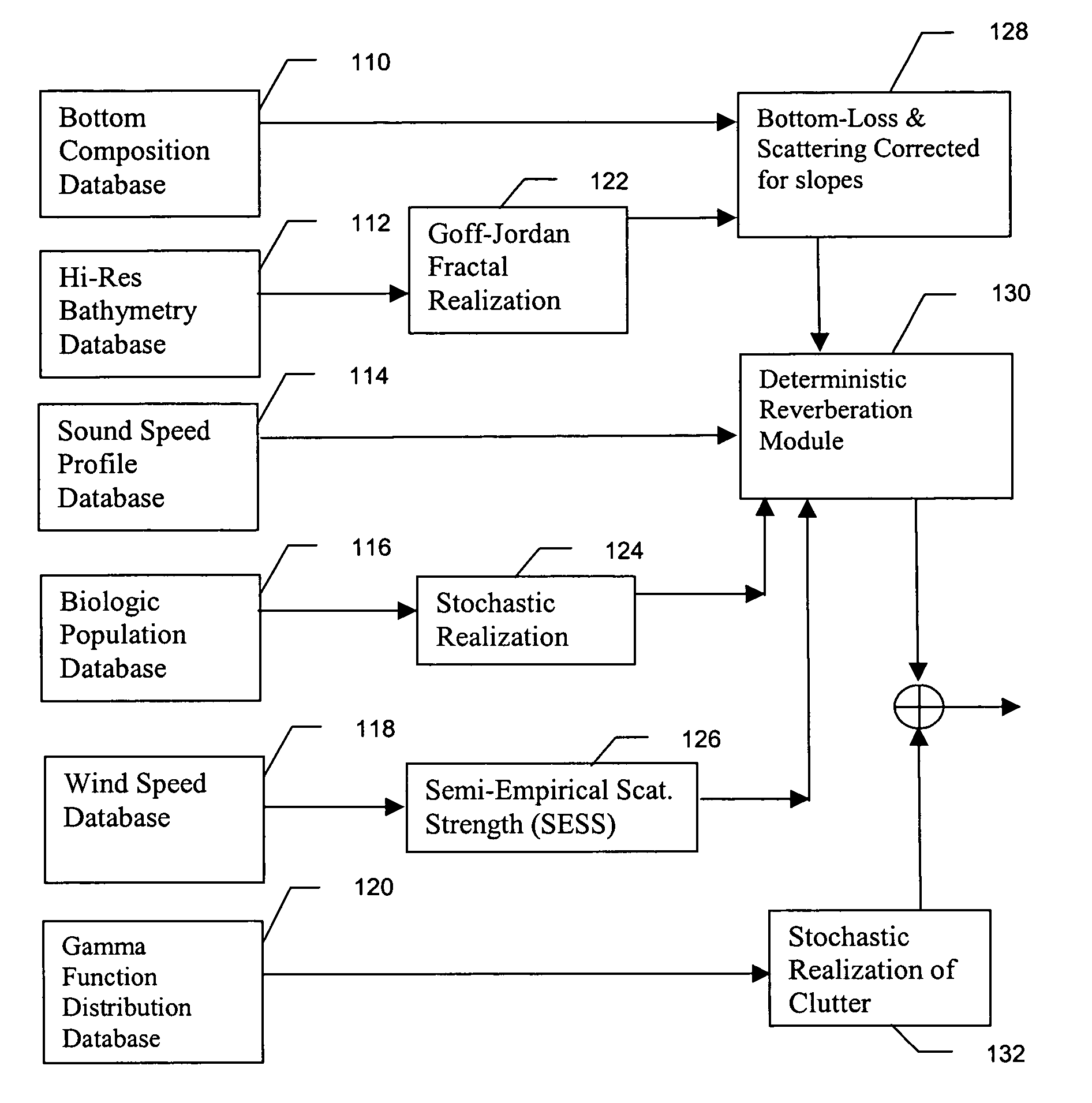
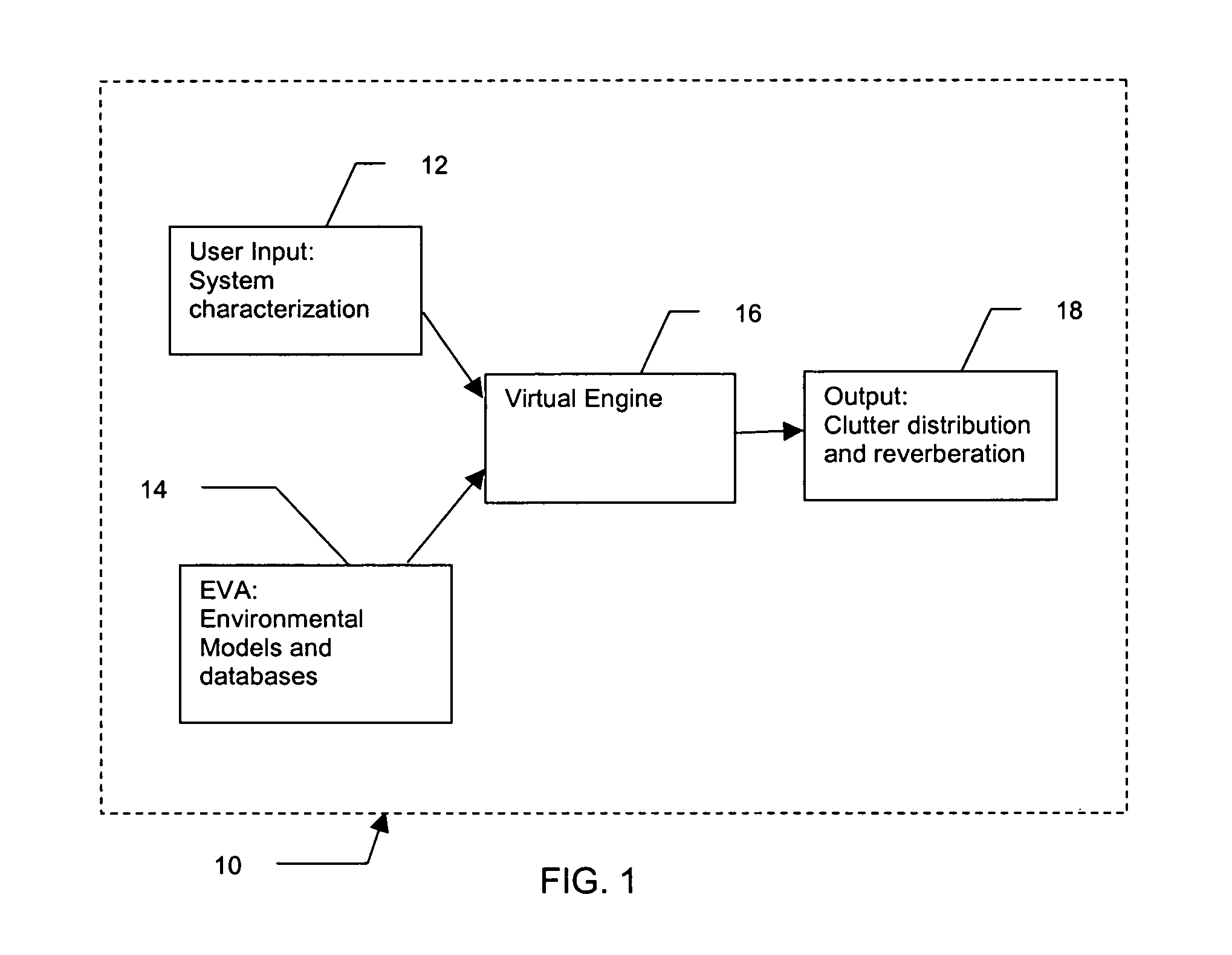
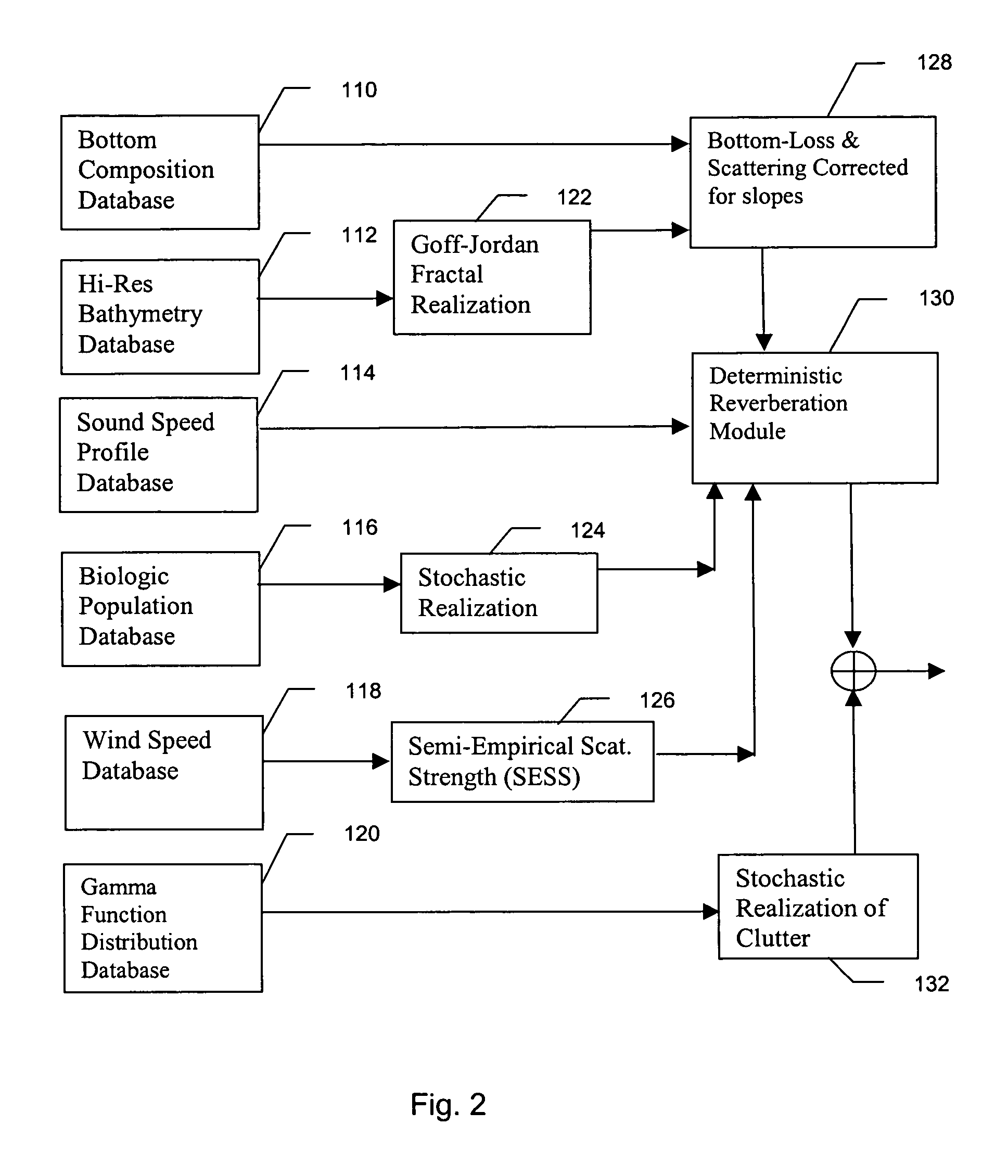
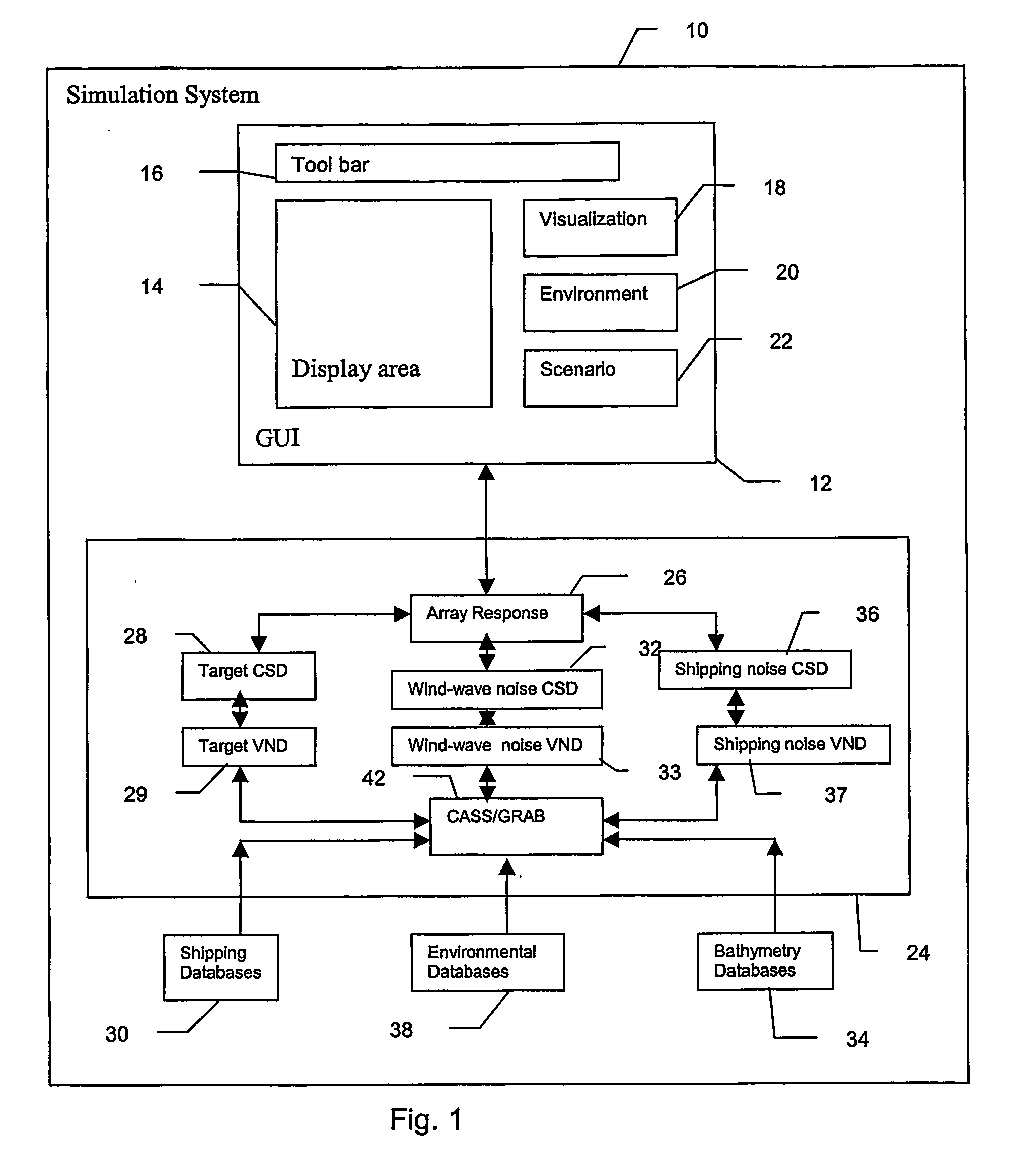
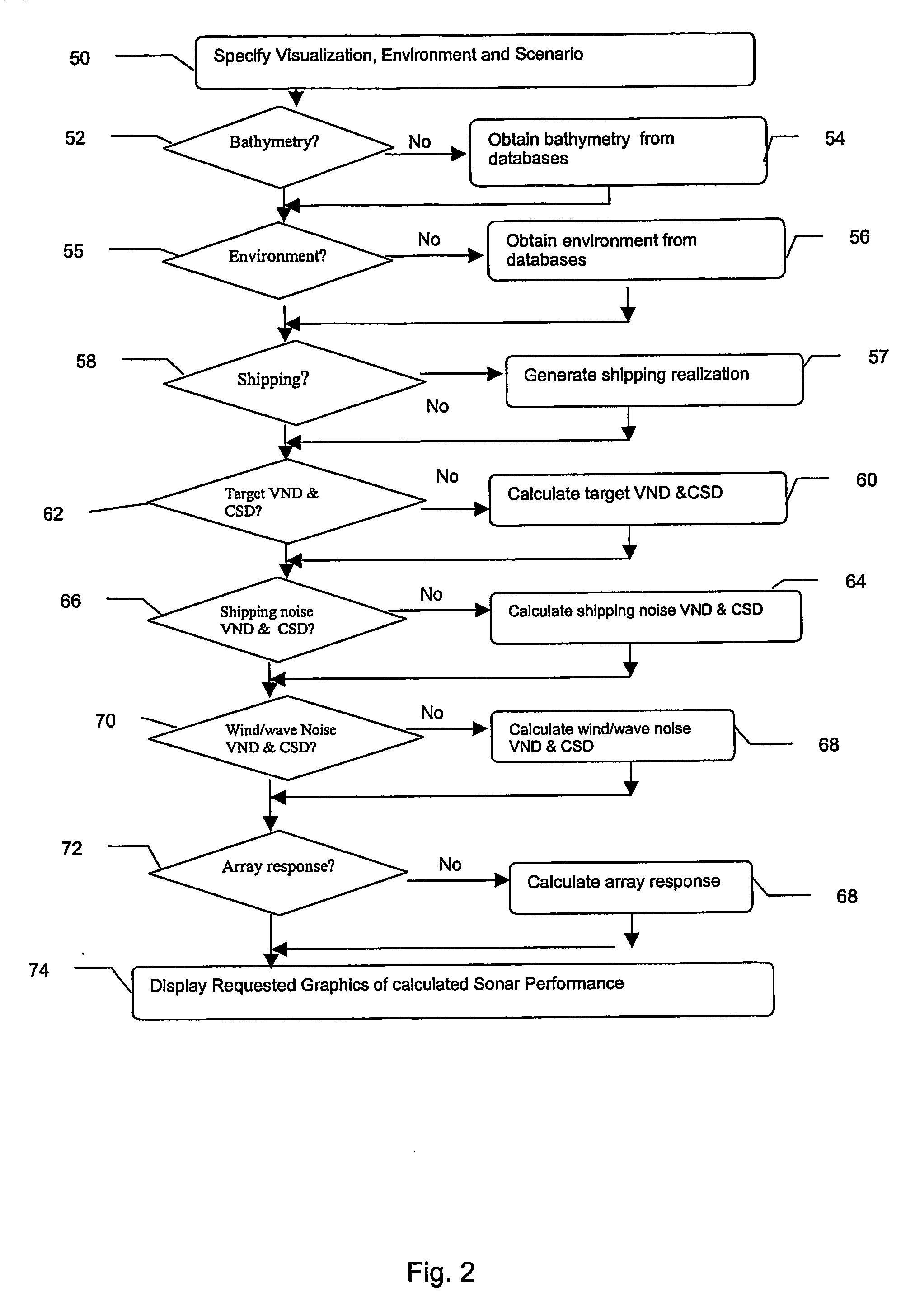
Method and apparatus for active sonar performance prediction
InactiveUS20050286345A1Wave based measurement systemsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionMathematical modelSound speed profile
A system and method for predicting active, low-frequency sonar array performance in shallow, littoral waters using a physics-based modeling of acoustic reverberation. An operator characterizes the active sonar's acoustic transmitter and receiver, the environment it is operating in and the targets to be detected. The operator selects appropriate bathymetry, bottom composition and sound-speed profile. The spatial resolution of the bathymetry database is enhanced using fractal interpolation and a bottom-loss-and-scattering corrected-for-slope is calculated. A semi-empirical scattering strength is derived from a wind-speed data base and a stochastic biologic realization is derived from a biologic population database. These are then used to calculate a deterministic component of bottom, surface and volume reverberation using a normal mode mathematical model of acoustic wave propagation. A stochastic realization of clutter is calculated using a Generalized Gamma distribution database, and combined with the deterministic components of reverberation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
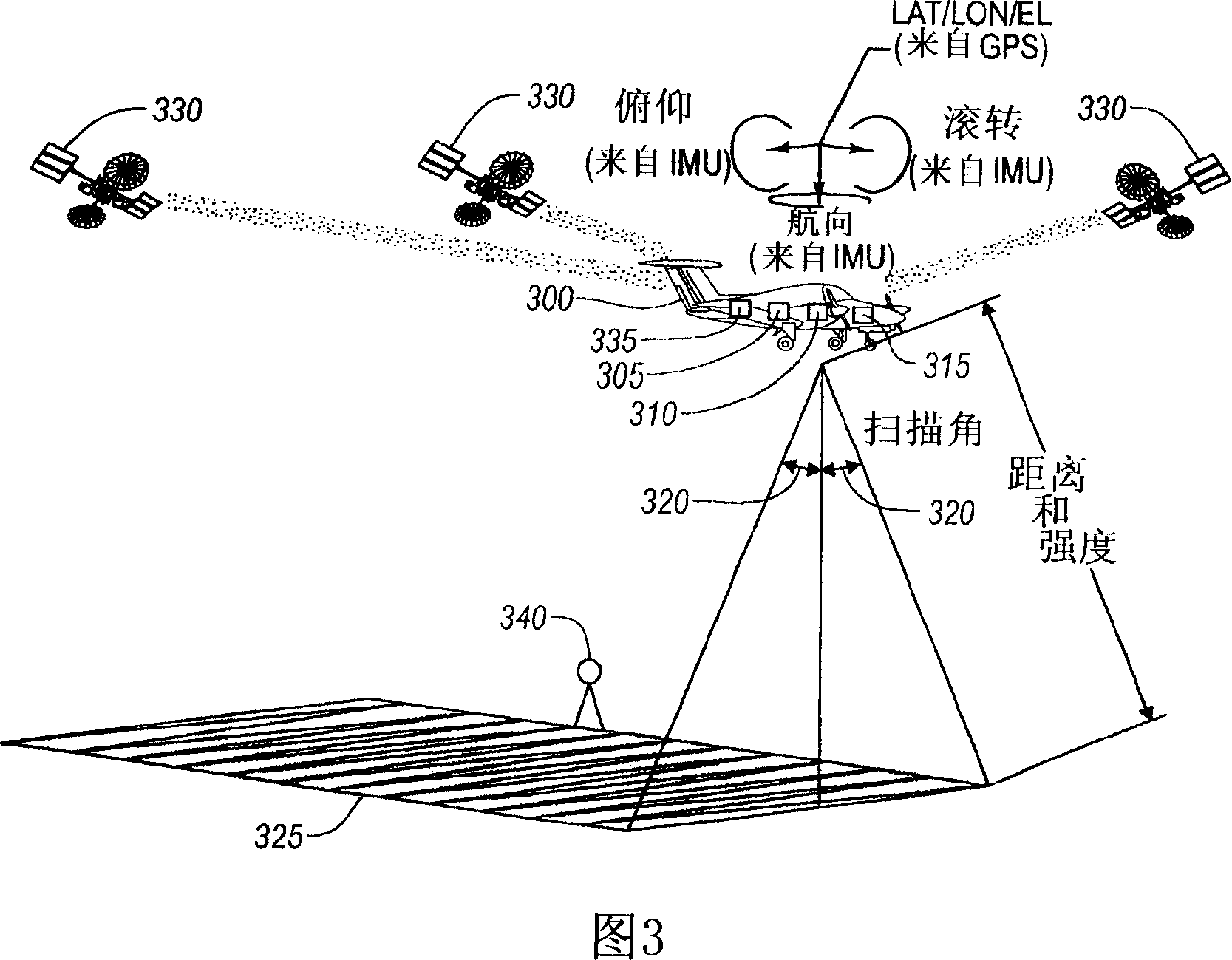
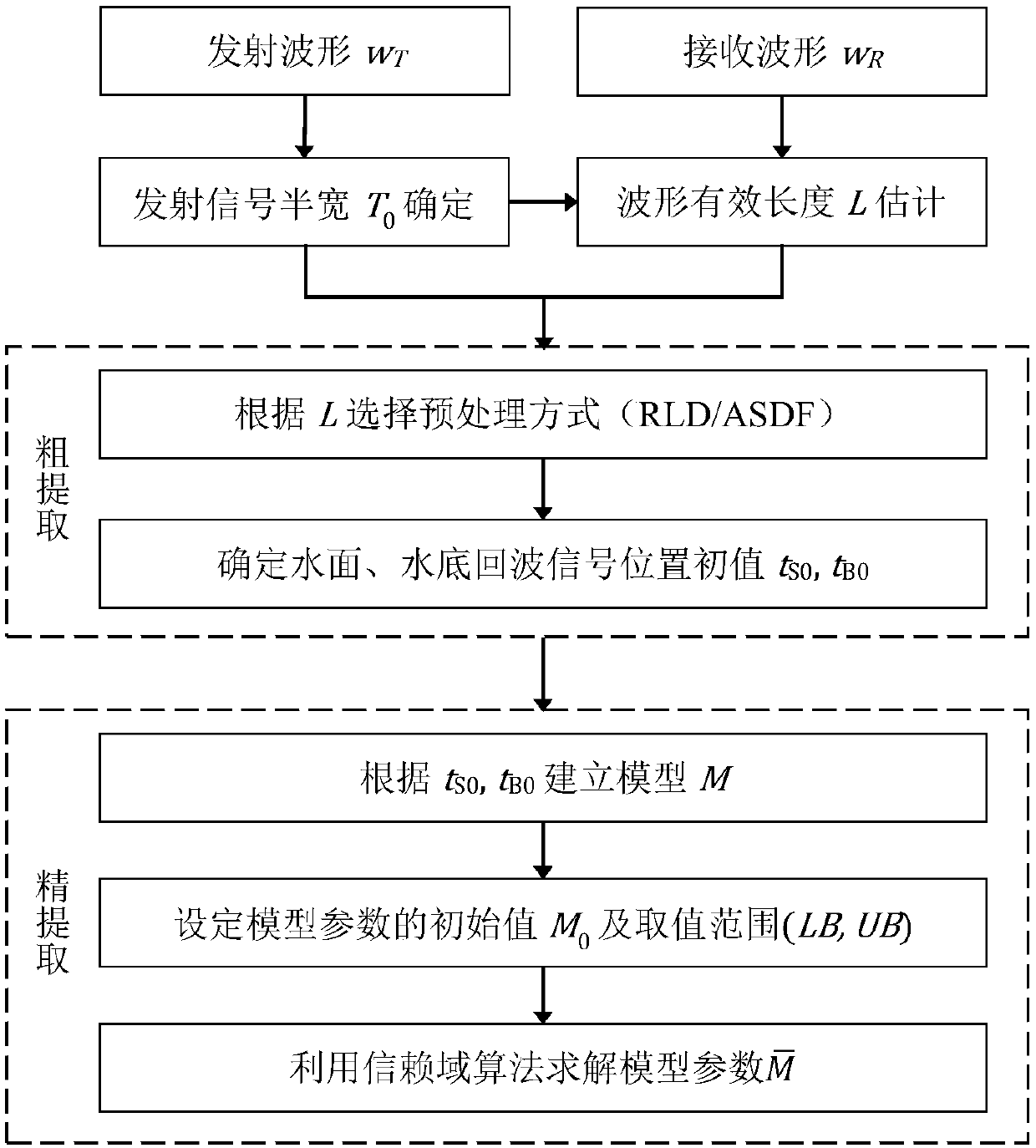
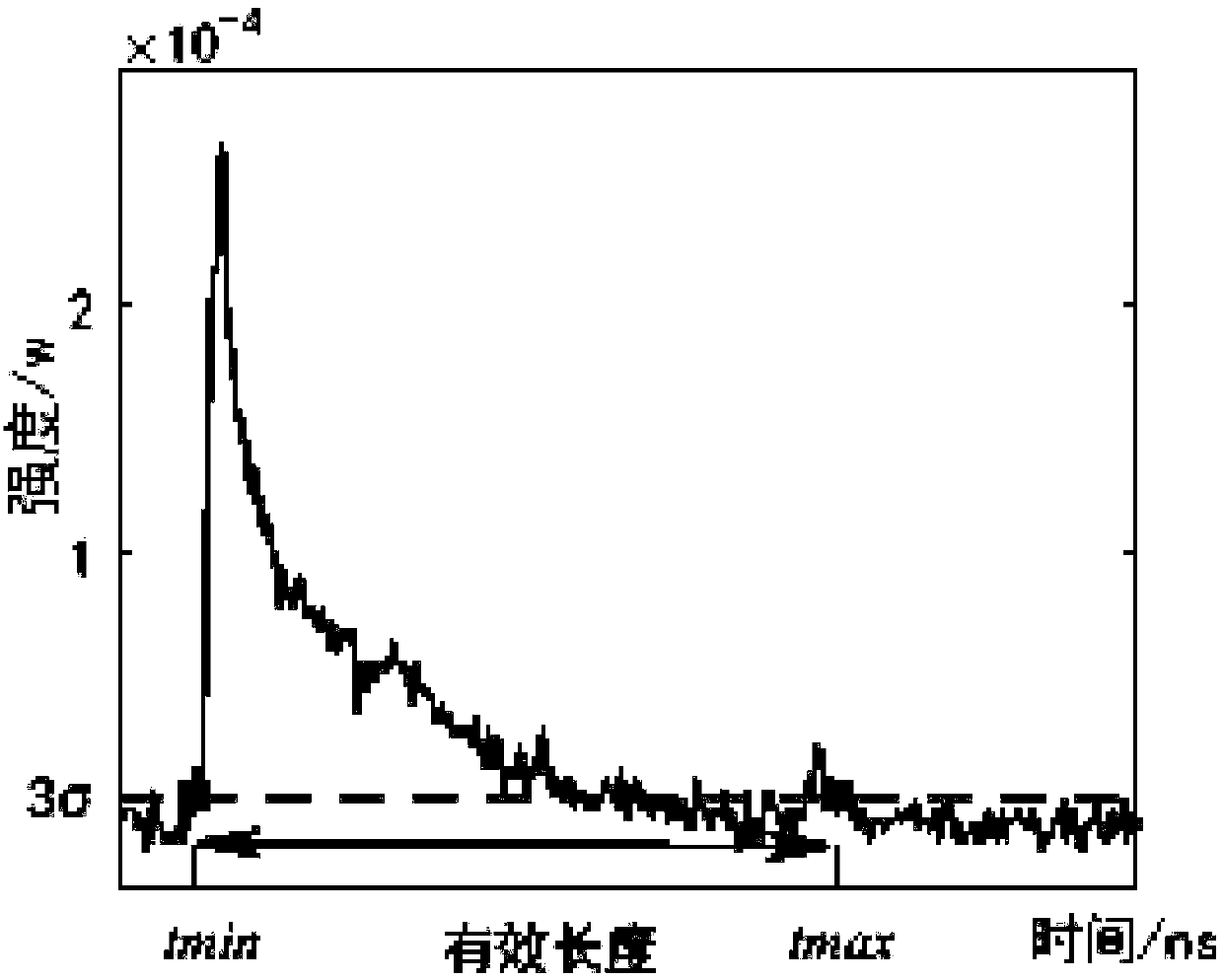
Method and system for determining initial value of effective signal of airborne lidar bathymetry received waveform
The invention relates to a method and a system for determining an initial value of an effective signal of an airborne lidar bathymetry received waveform. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining awaveform to be processed, and taking the global maximum value point of the waveform as an initial value tS0 of a water surface echo signal position; and taking the maximum value in a set range near the extreme point of the first derivative of the waveform as the initial value tB0 of the water bottom echo signal position. According to the scheme, the maximum value detection is combined with the finding that the first derivative extreme value is always associated near the effective signal, so that the accuracy of determining the effective signal is improved. Meanwhile, the intensity of atmospheric scattering and water body backscattering is far less than that of water surface reflection, so that a waveform global maximum value point can be considered as an initial value of the water surfaceecho signal position.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Method for exploitation of a sedimentary basin by means of maps of total organic carbon and hydrogen index
ActiveUS20170167230A1More dataMany timesFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationHydrogenHydrogen index
The present invention relates to a method for exploitation of a sedimentary basin. Exploitation of the sedimentary basin is permitted by the choice of zones of interest within the basin, the zones being determined by means of maps of total organic carbon TOC and of hydrogen index HI of at least one sedimentary layer. According to the invention, the maps of total organic carbon TOC and of hydrogen index HI are obtained taking into account the current values of TOCA(W) and HIA(W) at the level of the well and taking into account the maps of bathymetry BM and of sedimentation rate SM.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Automatic water-quality layering and sampling system
PendingCN106769212AAccurately determineExact stratified samplingWithdrawing sample devicesPeristaltic pumpBathymetry
The invention relates to an automatic water-quality layering and sampling system which comprises an unmanned ship and a sampling module, wherein the unmanned ship has an autonomous navigation function, and the sampling module is mounted on the unmanned ship. The sampling module comprises a peristaltic pump, a sampling water distributor, a servo reel pipe, a single-beam bathymetry sensor, a water depth pressure sensor, a plurality sampling bottles, a water absorption tube and a PLC (programmable logic controller) control system, the peristaltic pump absorbs sampling water and is connected with the sampling water distributor through the water absorption tube, the sampling water distributor is connected with the sampling bottles, the water depth pressure sensor is mounted is mounted at one end of a winding line on the servo reel pipe and positioned in the front of the unmanned ship, the single-beam bathymetry sensor is mounted at the bottom of the unmanned ship, and the single-beam bathymetry sensor, the water depth pressure sensor, the peristaltic pump and a servo motor of the servo reel pipe is connected with the PLC control system.
Owner:天津弘盛科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for active sonar performance prediction
InactiveUS7002877B2Wave based measurement systemsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionWater useMathematical model
A system and method for predicting active, low-frequency sonar array performance in shallow, littoral waters using a physics-based modeling of acoustic reverberation. An operator characterizes the active sonar's acoustic transmitter and receiver, the environment it is operating in and the targets to be detected. The operator selects appropriate bathymetry, bottom composition and sound-speed profile. The spatial resolution of the bathymetry database is enhanced using fractal interpolation and a bottom-loss-and-scattering corrected-for-slope is calculated. A semi-empirical scattering strength is derived from a wind-speed data base and a stochastic biologic realization is derived from a biologic population database. These are then used to calculate a deterministic component of bottom, surface and volume reverberation using a normal mode mathematical model of acoustic wave propagation. A stochastic realization of clutter is calculated using a Generalized Gamma distribution database, and combined with the deterministic components of reverberation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
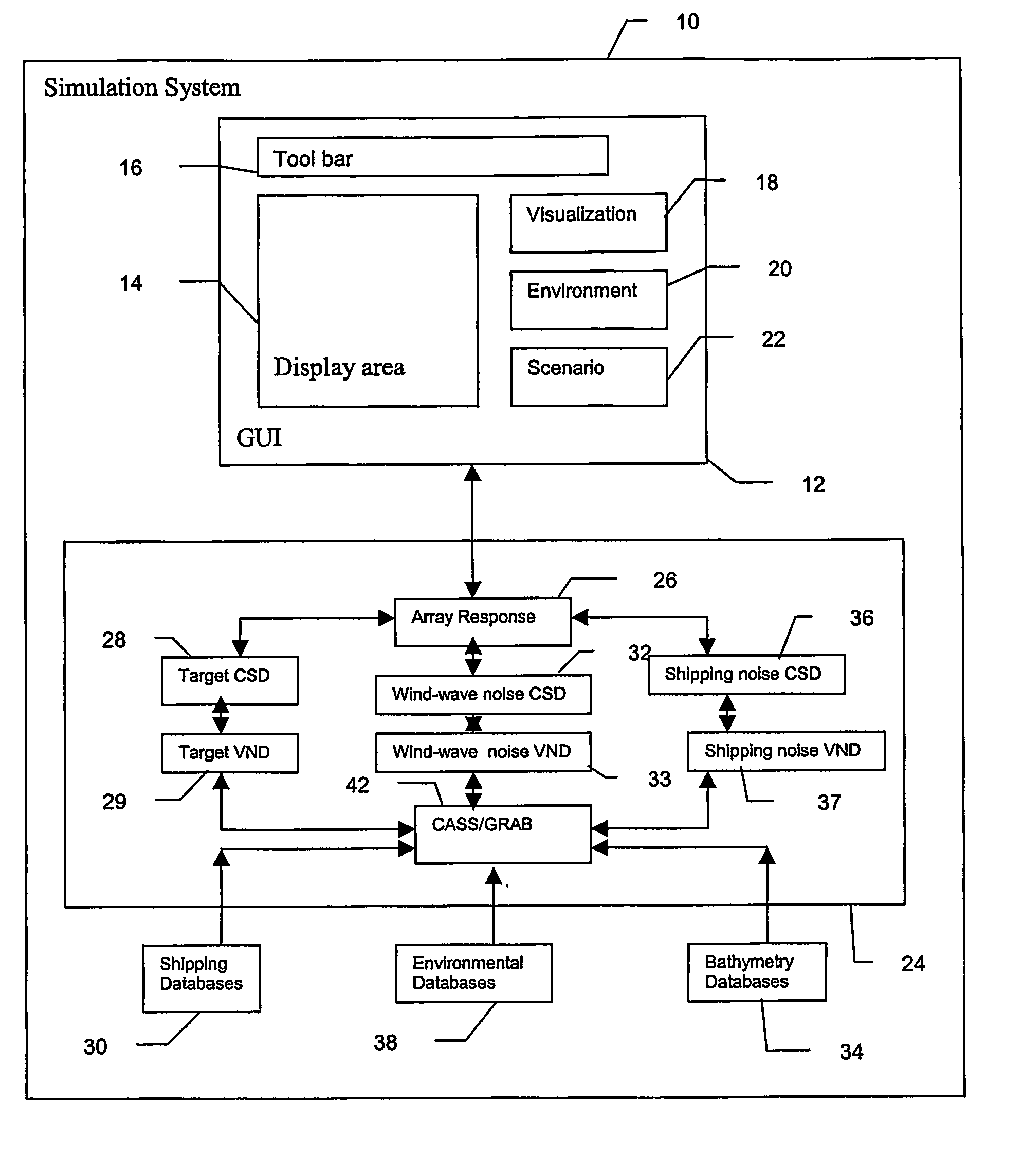
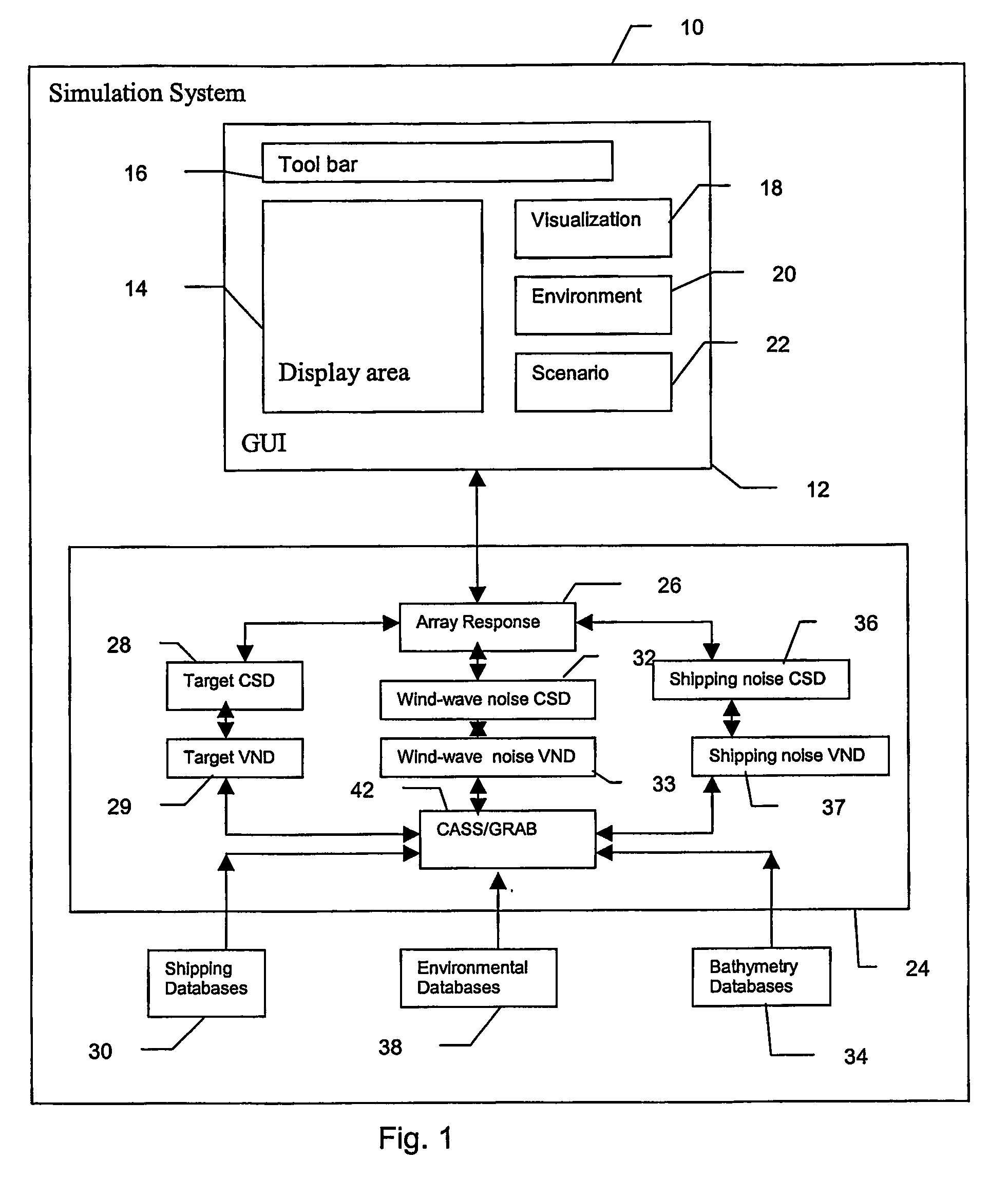
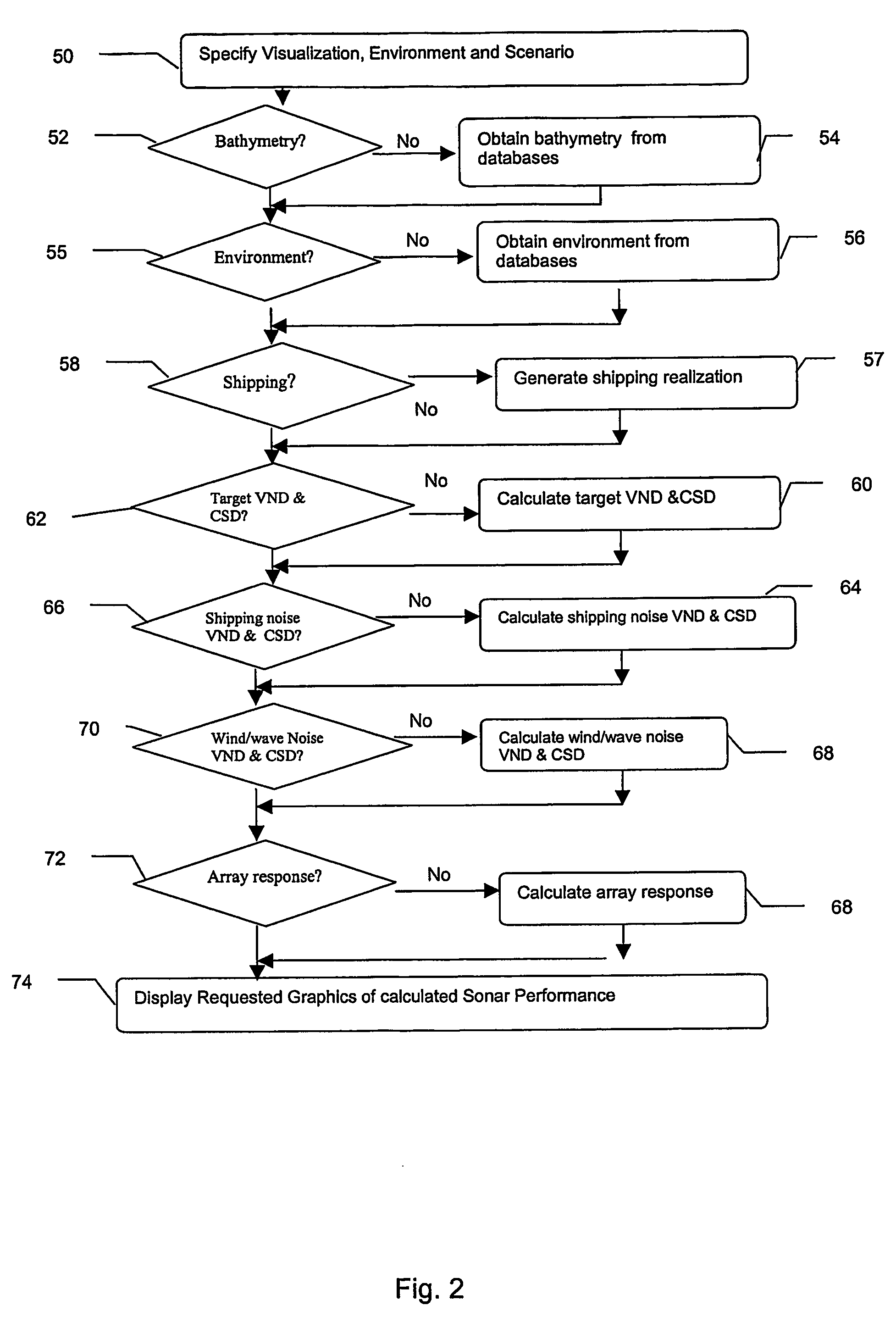
Method and apparatus for high-frequency passive sonar performance prediction
InactiveUS7187619B2Cosmonautic condition simulationsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionBathymetryGeolocation
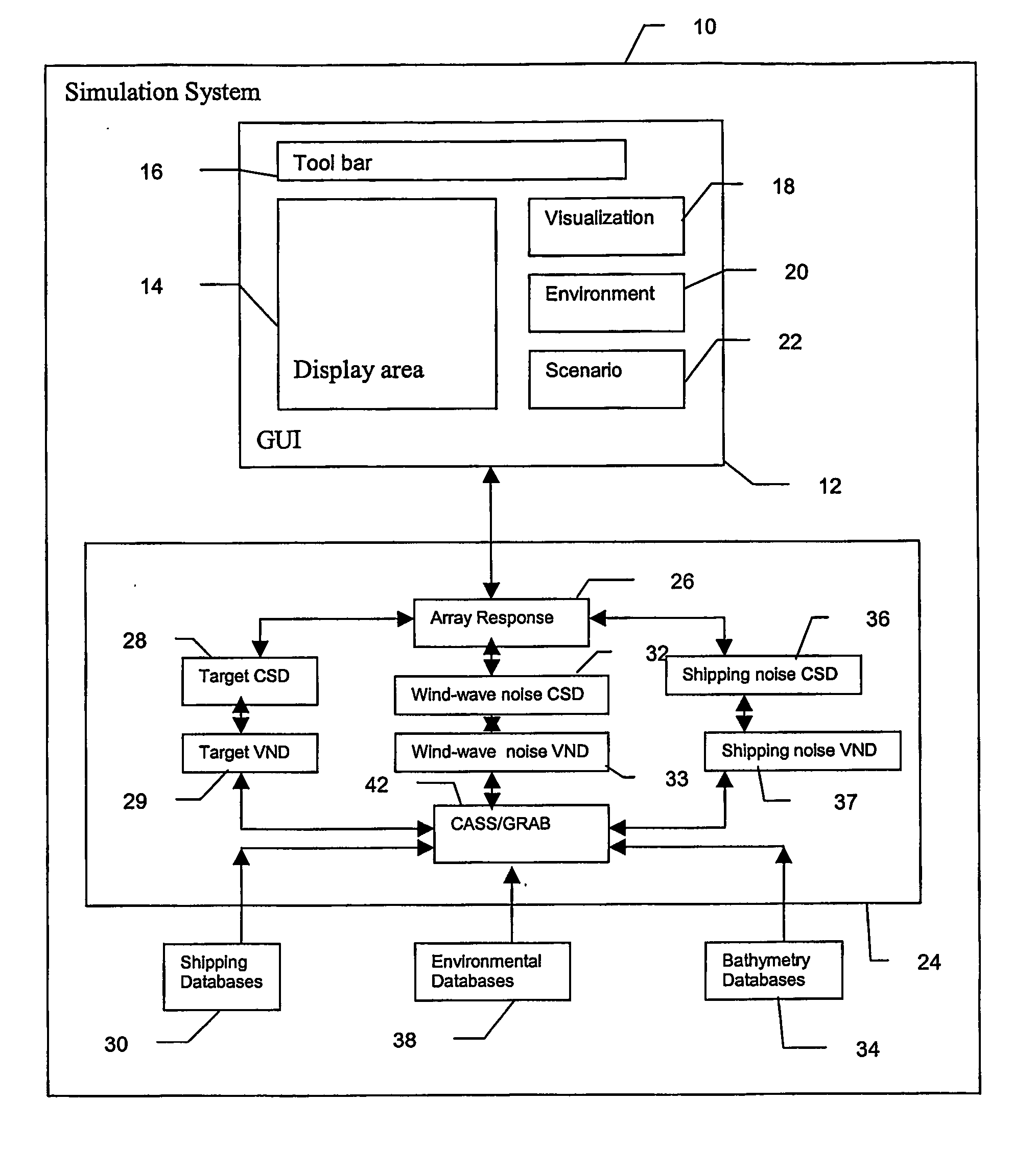
A system and method for predicting passive, high-frequency sonar array performance at any underwater location, implemented as a software package running on a computer. An operator selects an arbitrary geographical location, specifies a sonar array and defines a target. The necessary bathymetry, and associated oceanographic, environmental and meteorological data are automatically acquired or generated, along with appropriate models for ocean surface and bottom reflectivity, and vertical noise directionality. A Comprehensive Acoustic System Simulation (CASS) software module performs appropriate ray tracing, which is used to produce Cross-Spectral Density (CSD) matrices for the target and the anisotropic ambient noise. These are used to generate graphic and numeric representations of the array's performance at the selected location. A time of year may also be specified and the appropriate anisotropic noise field for conditions expected at that location at that time of year will be generated. Shipping realizations may be incorporated.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for drawing isobath of lake
InactiveCN102506831ASimple methodLow costOpen water surveyWater resource assessmentTerrainEnvironmental resource management
The invention discloses a method for drawing an isobath of a lake and belongs to the technical field of analysis and measurement control. The method comprises the following steps of: utilizing a simple and convenient operating instrument, such as, a ground DE2A electronic theodolite, a ruler, a bathymetry rod, a compass, a ship, and the like, to measure a complex terrain condition, and then calculating according to a sine and cosine theorem and applying CAD (Computer-Aided Design) to draw an isobath chart close to a point in the lake and draw the terrain appearance of the lake. The method has the advantages of simpleness and easiness in operation, time-saving and labor-saving property, cost-saving property, accurate measuring and calculating result, and is suitable for the preparation work performed by a surveying and mapping non-professional person before the engineering design is performed.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for high-frequency passive sonar performance prediction
InactiveUS20060193202A1Cosmonautic condition simulationsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionBathymetrySoftware modules
A system and method for predicting passive, high-frequency sonar array performance at any underwater location, implemented as a software package running on a computer. An operator selects an arbitrary geographical location, specifies a sonar array and defines a target. The necessary bathymetry, and associated oceanographic, environmental and meteorological data are automatically acquired or generated, along with appropriate models for ocean surface and bottom reflectivity, and vertical noise directionality. A Comprehensive Acoustic System Simulation (CASS) software module performs appropriate ray tracing, which is used to produce Cross-Spectral Density (CSD) matrices for the target and the anisotropic ambient noise. These are used to generate graphic and numeric representations of the array's performance at the selected location. A time of year may also be specified and the appropriate anisotropic noise field for conditions expected at that location at that time of year will be generated. Shipping realizations may be incorporated.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Artificial source time frequency electro magnetic bathymetry
The present invention can implement the utilization of electromagnetic depth-measuring exploration method in frequency-domain method and time-domain method. Said invention utilizes that exciting and receiving a series of frequency (period) pulses to research the law of whole spectrum, at the same time, research the signal attenuation law of every frequency (period), from short period to long period, the reflected underground informations can be progressively deepened, the superposition of these informations can raise exploration accuracy, and the time-domain and frequency-domain boty can be used for making mutual check by means of time-frequency conversion so as to greatly raise exploration accuracy. Said invention can be mainly used for making exploration of oil, gas, mineral resources and geothermal resource.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Adaptive filtering method of photon counting lidar for bathymetry
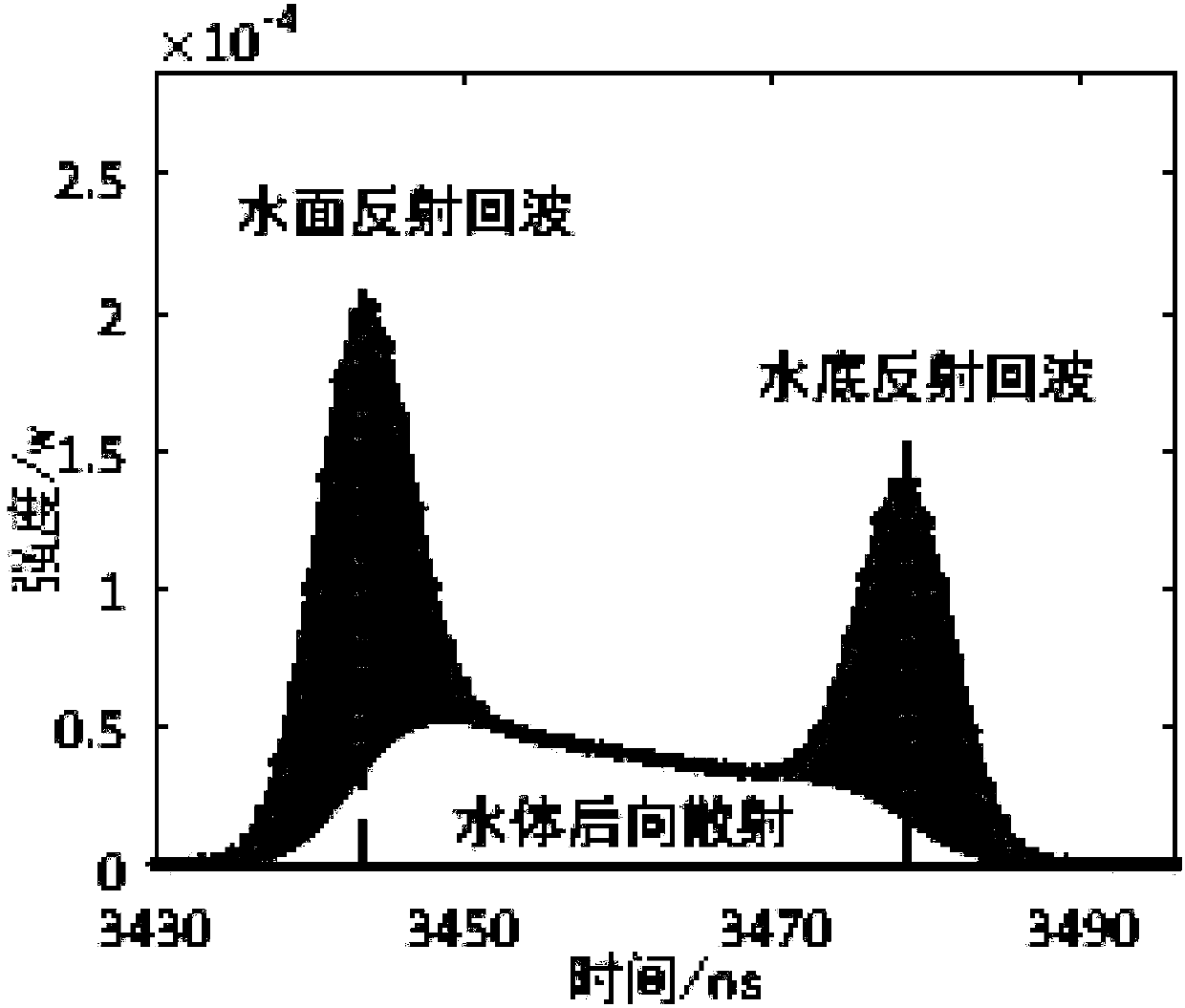
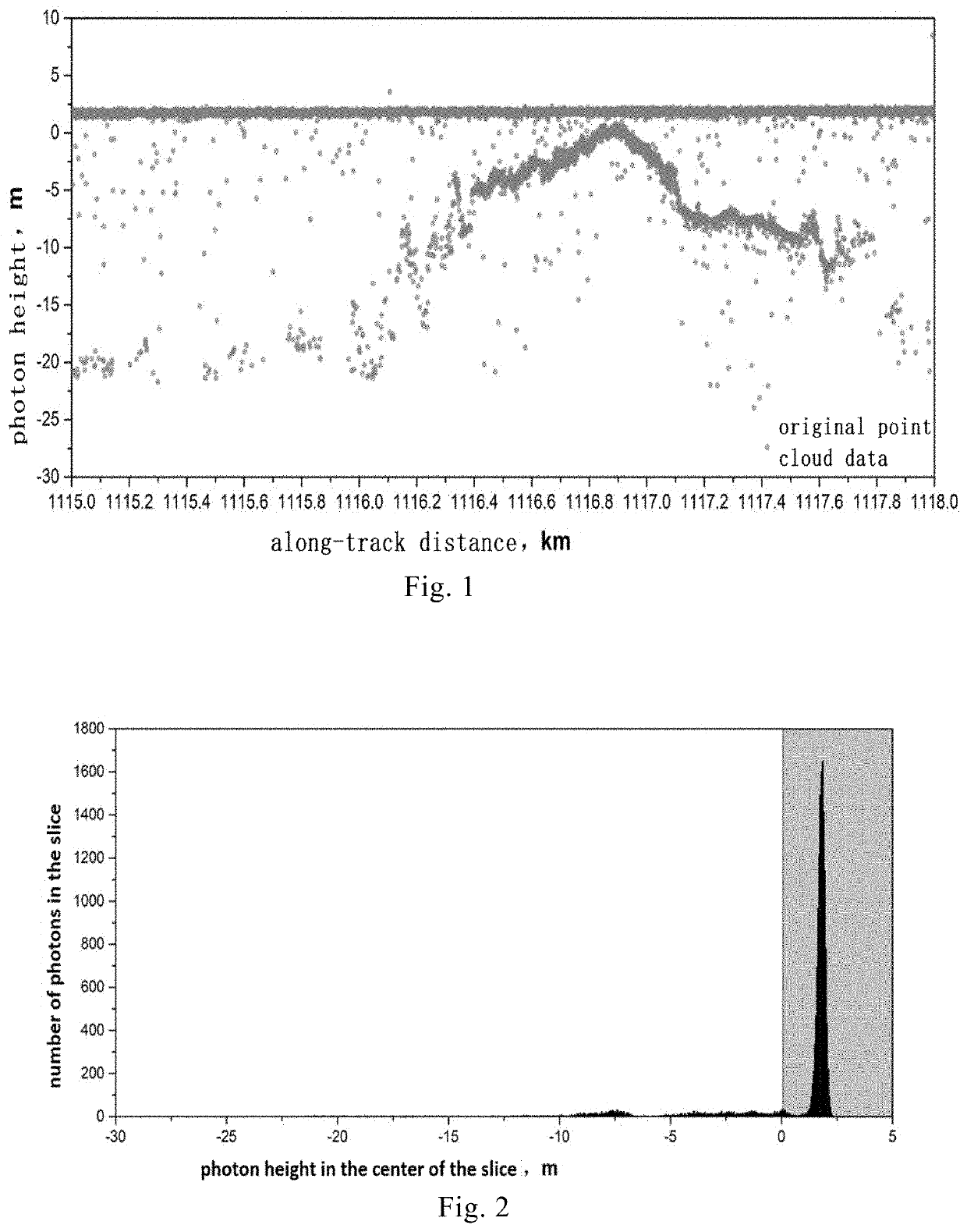
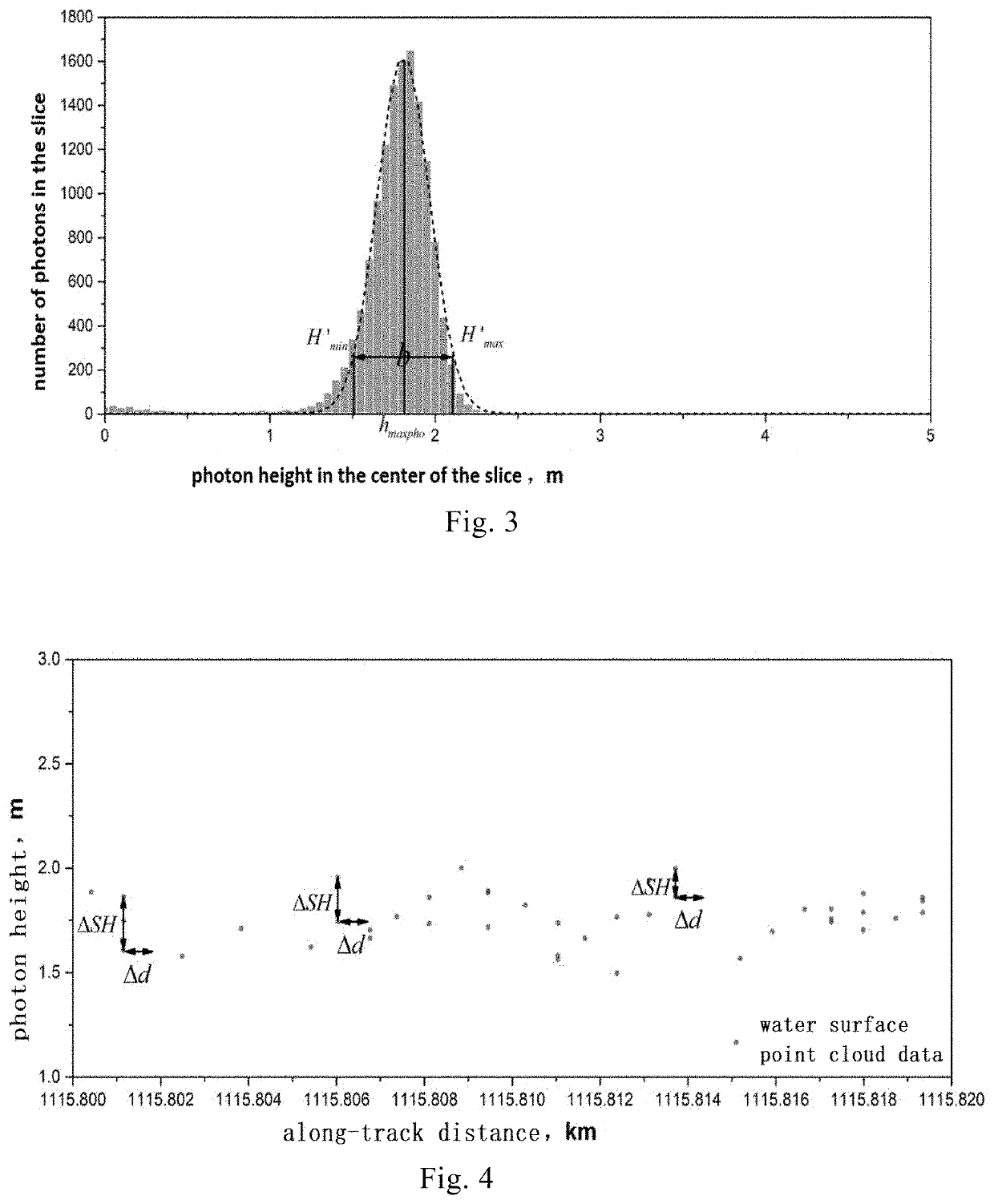
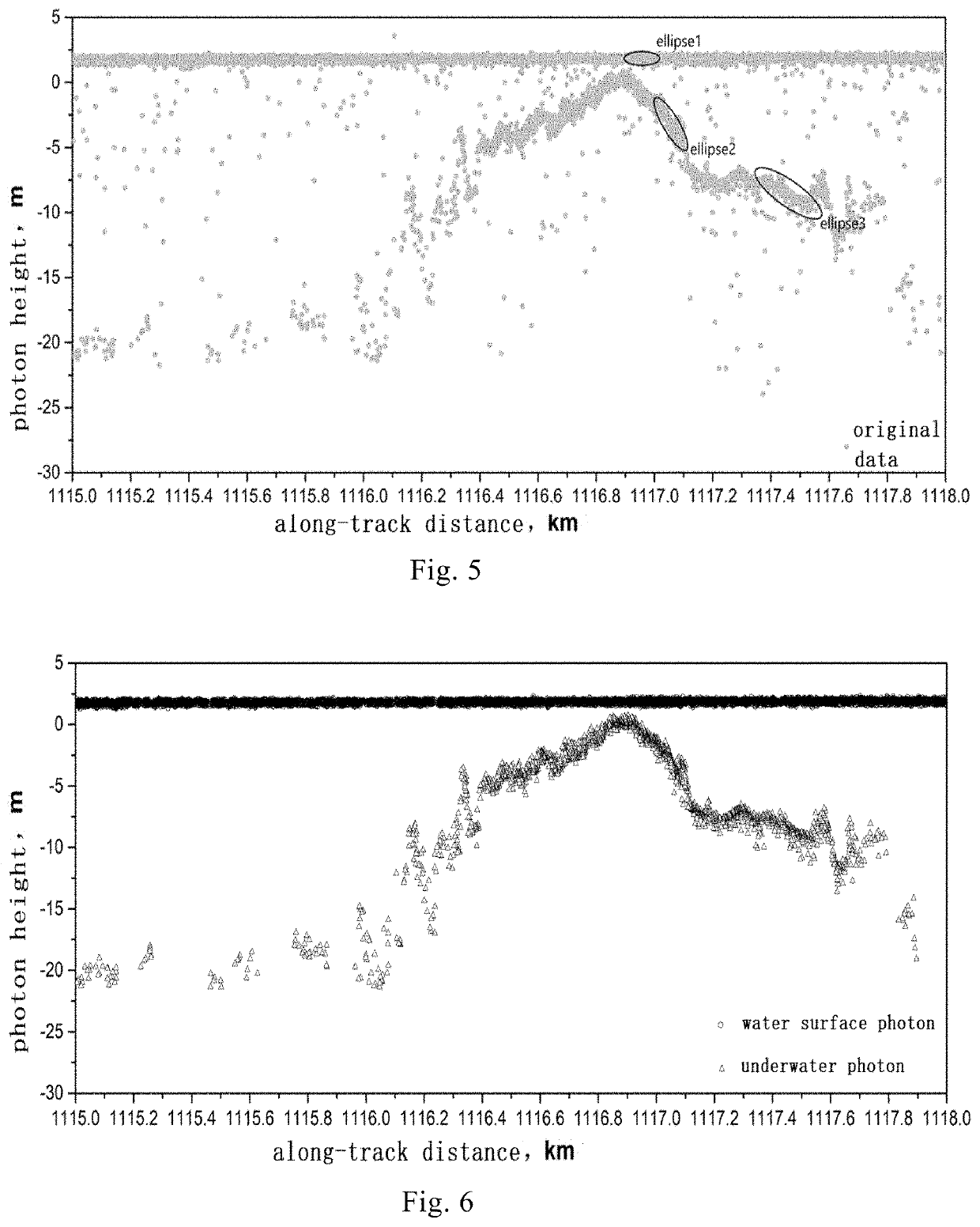
ActiveUS11448765B2Automatically and efficiently extractValid choiceAdaptive networkMeasuring open water depthUnderwaterBathymetry
An adaptive filtering method of photon counting Lidar for bathymetry is provided in this invention, which includes steps: step S1: adaptively acquiring parameters of elliptic filtering for water surface photon signals; step S2: determining a relationship between filter parameters and elevation of underwater photon signals, and obtaining parameters of the elliptic filtering for photon signal in water column; and step S3: filtering and fitting the water surface photon signals and the underwater photon signals to acquire continuous bathymetry results.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Flight time measurement apparatus and method for increasing measurement rate
An apparatus for measuring distance to a surface is disclosed. The apparatus transmits at least one subsequent pulse of light prior to receiving a reflection of a previously sent pulse of light. Thus, multiple pulses of light are in-flight at a given time. The embodiments are applicable to terrain mapping, bathymetry, seismology, detecting faults, biomass measurement, wind speed measurement, temperature calculation, traffic speed measurement, military target identification, surface to air rangefinding, high definition survey, close range photogrammetry, atmospheric composition, meteorology, distance measurement, as well as many other applications. Examples of such apparatuses include laser ranging systems, such as light detection and ranging (LIDAR) systems, and laser scanners. Data received from the apparatus by a data processing unit can be used to create a data model, such as a point cloud, digital surface model or digital terrain model describing the surface, terrain, and / or objects.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
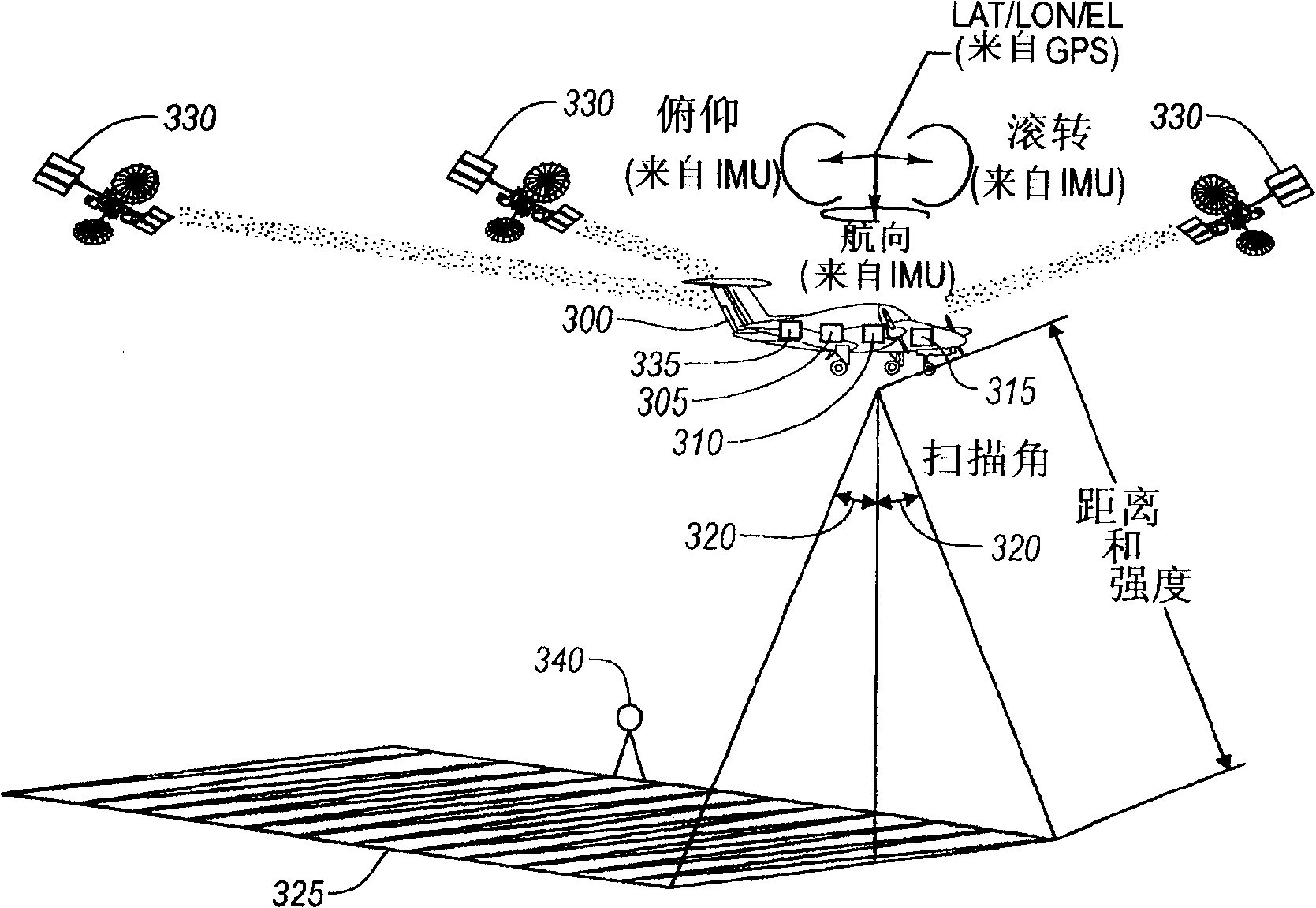
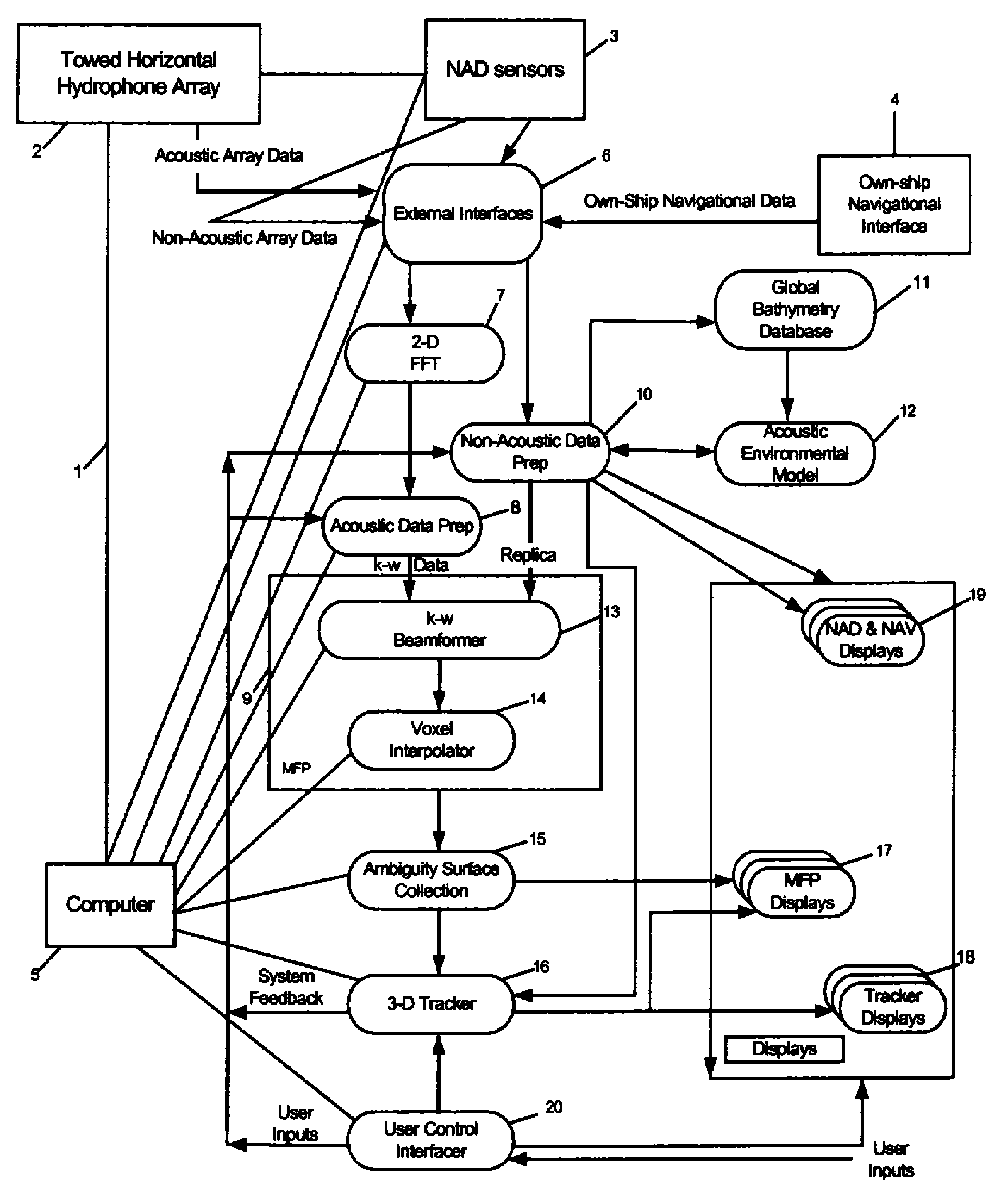
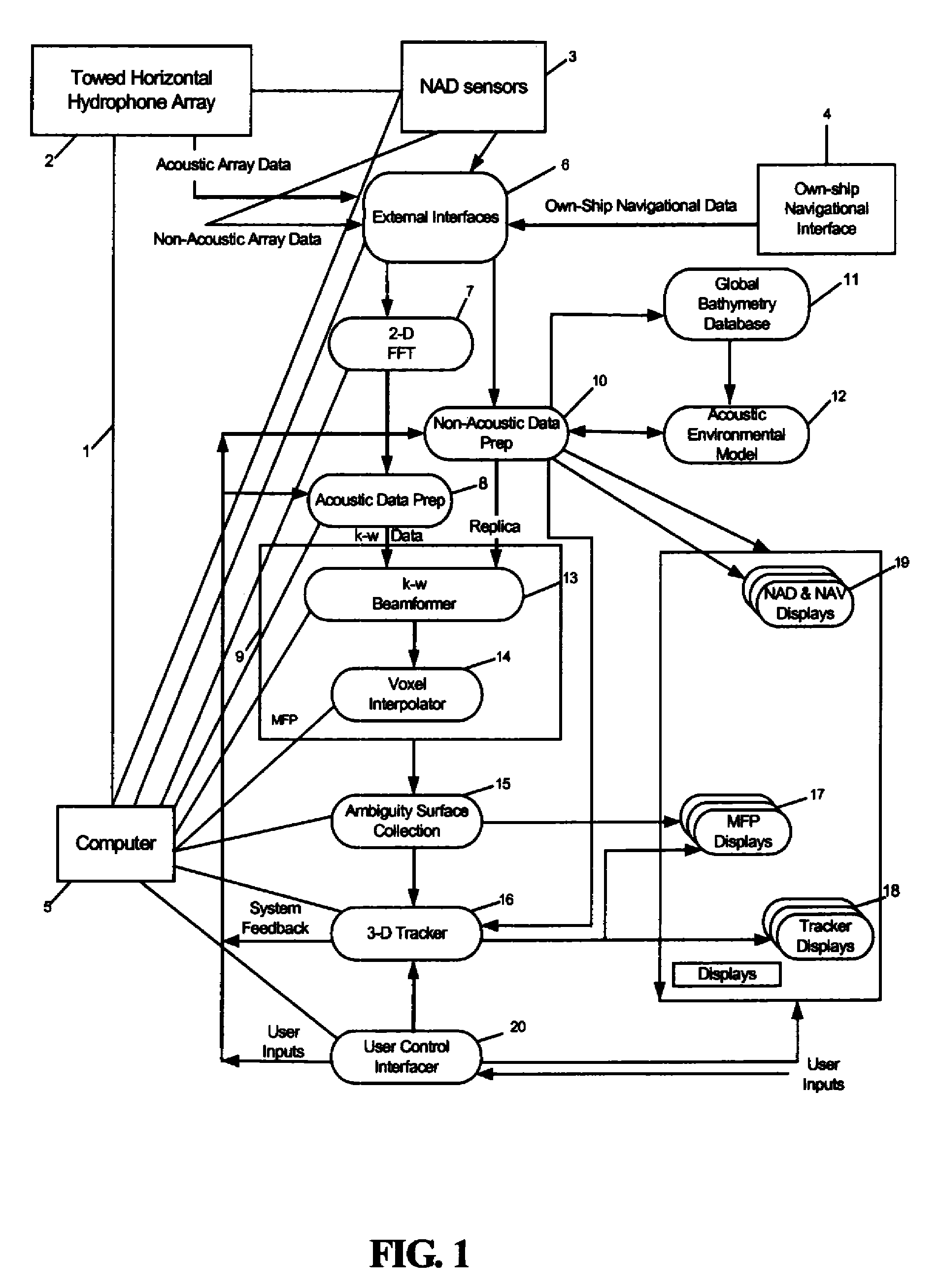
Point source localization sonar system and method
InactiveUS7639565B2Minimal space requirementLow costSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionDirection findersSurface displayAcoustic array
A matched-field based sonar system and method of use that supports real-time, three-dimensional acoustic source localization using a mobile, horizontal array. The system receives and processes acoustic array, non-acoustic array, and own-ship navigational data in the matched-field process (MFP). Driven by own-ship and array status, a global bathymetry database and an acoustic environmental model are used to generate replicas for the MFP. If a three-dimensional tracker is assigned, then the tracker will steer the search region to maintain contact on the target of interest. Displays are provided to the user including tracker displays (which provide tracker information), MFP ambiguity surface displays (which support contact localization), and non-acoustic and navigational displays. A control interface allows a user to control the search region in bearing, range, depth, and frequency; assign the three-dimensional tracker function; and control display processing.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
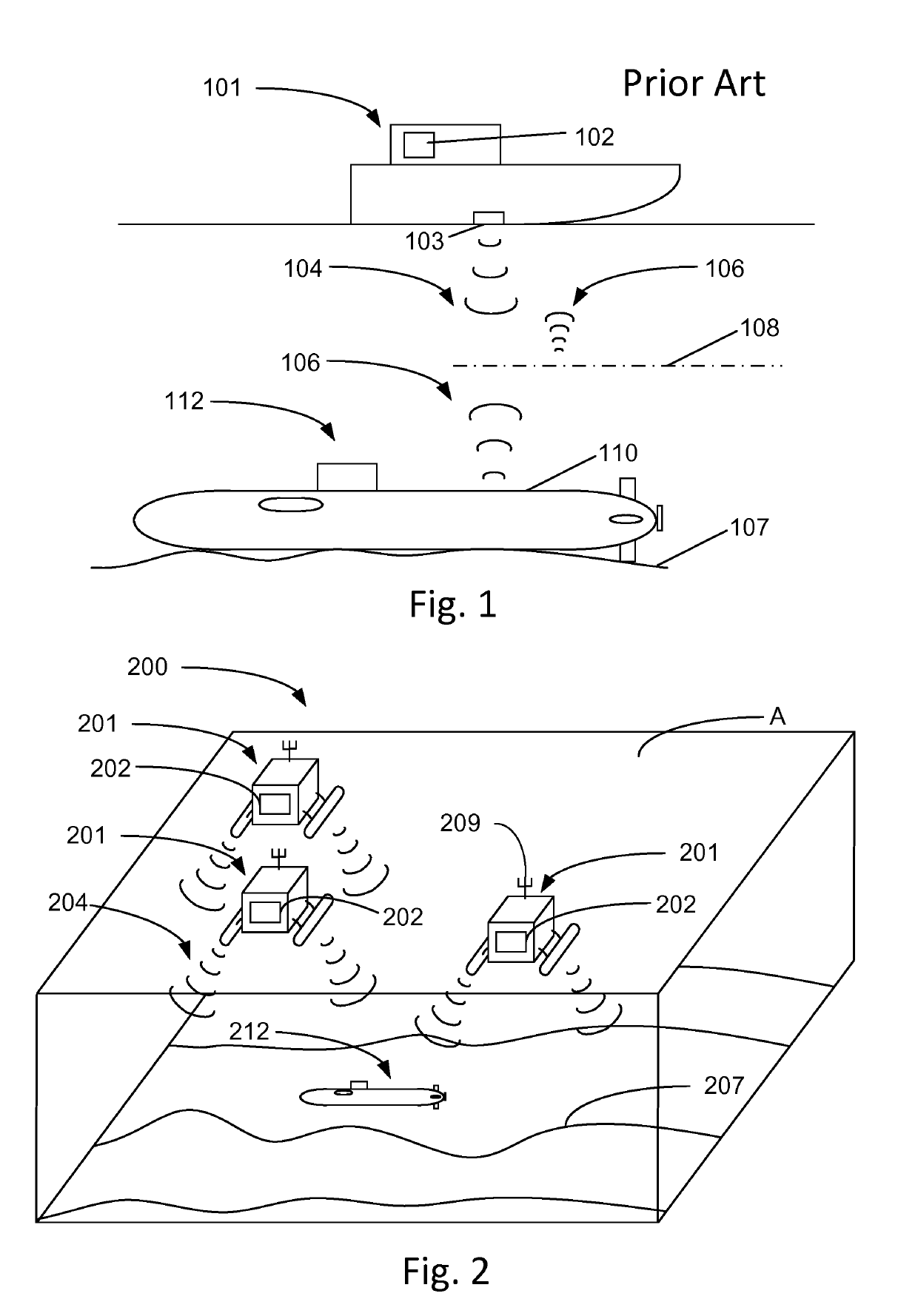
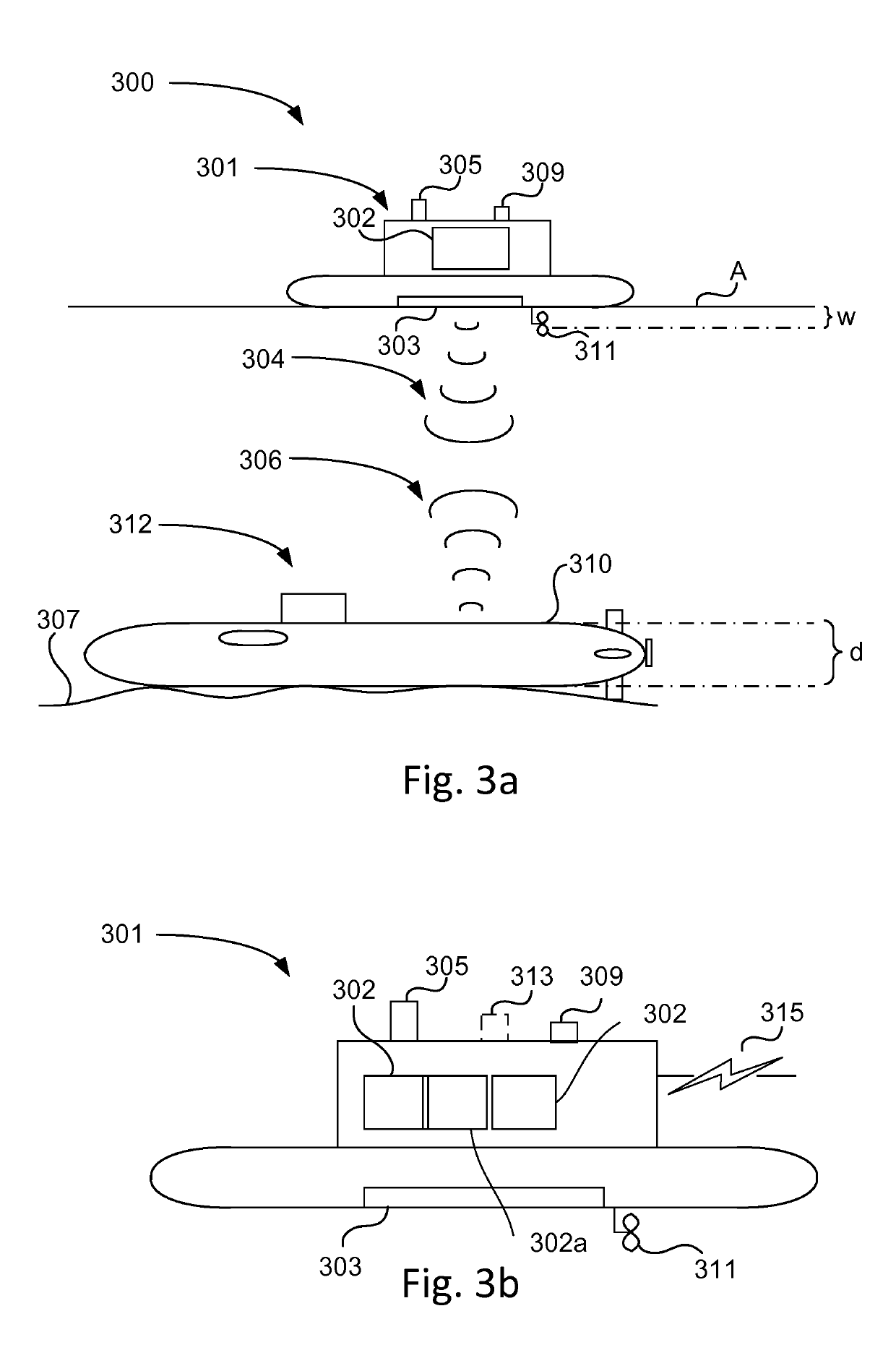
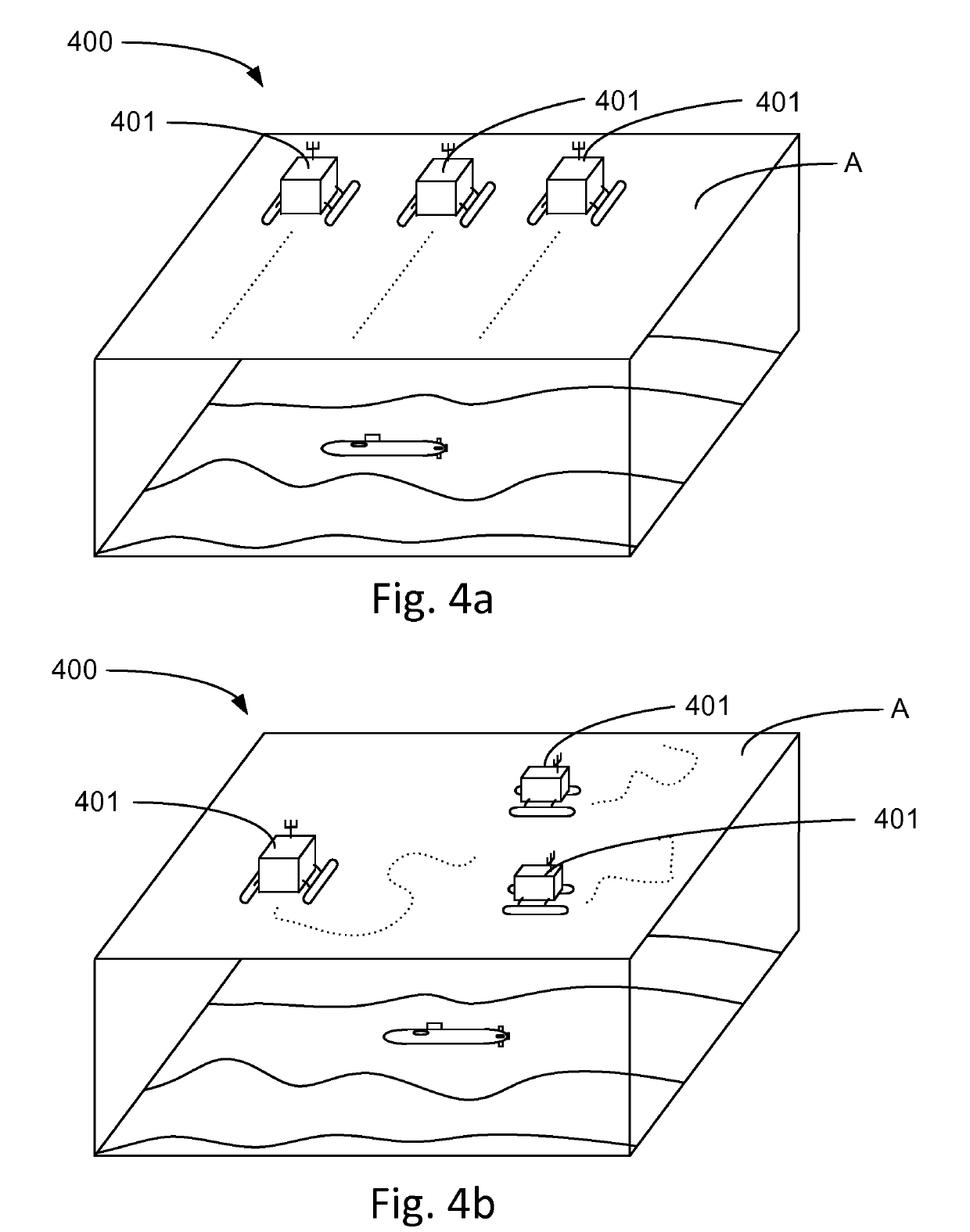
System for detecting subsurface objects and unmanned surface vessel
ActiveUS10502828B2Shorten the timeIncrease in sizeSeismology for water-covered areasAcoustic wave reradiationMarine engineeringBathymetry
The present disclosure relates to a system (300) for detecting subsurface objects within a confined sea area. The system comprises one or more surface vessels (301) and at least one control unit (302). Each surface vessel (301) comprises positioning means and is arranged to gather bathymetry measurements during controlled motion in a path within the confined sea area and to transmit the bathymetry measurements to the at least one control unit (302). The control unit (302) is arranged to receive bathymetry measurements from the one or more surface vessels (301). Each surface vessel (301) is unmanned and arranged to operate in an autonomous or remotely controlled state when gathering bathymetry measurements. The control unit (302) is arranged to retrieve bathymetry data representing said path from a memory in the control unit. The control unit (302) is further arranged to compare the received bathymetry measurements to the retrieved bathymetry data and to indicate a presence of a subsurface object upon determination of a deviation between received bathymetry measurements and retrieved bathymetry data for at least one geographical position along said path. The disclosure also relates to an unmanned surface vessel adapted to detect subsurface objects.
Owner:KRONANDER TORBJOERN +1
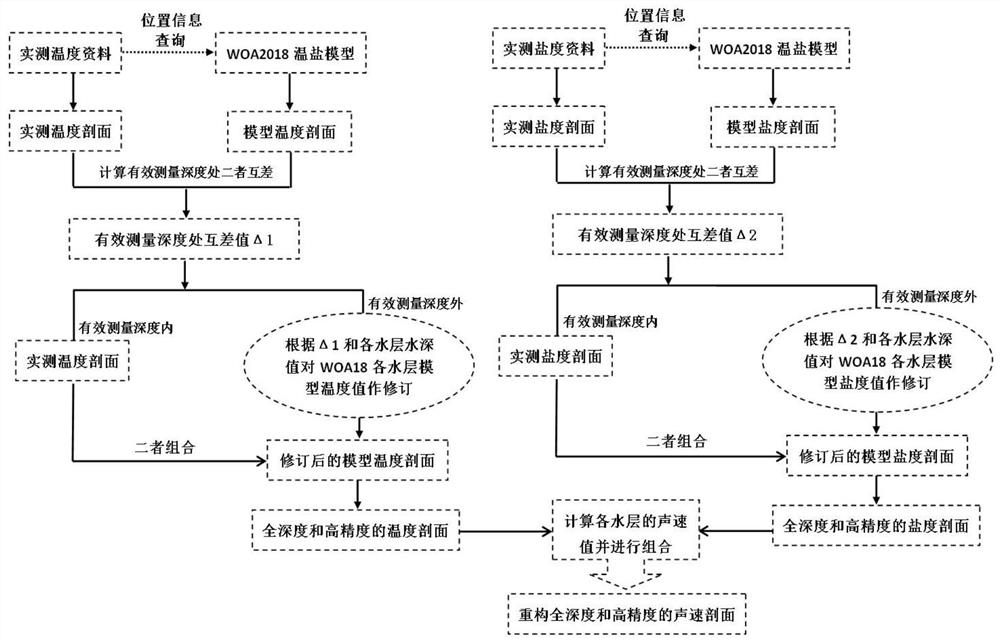
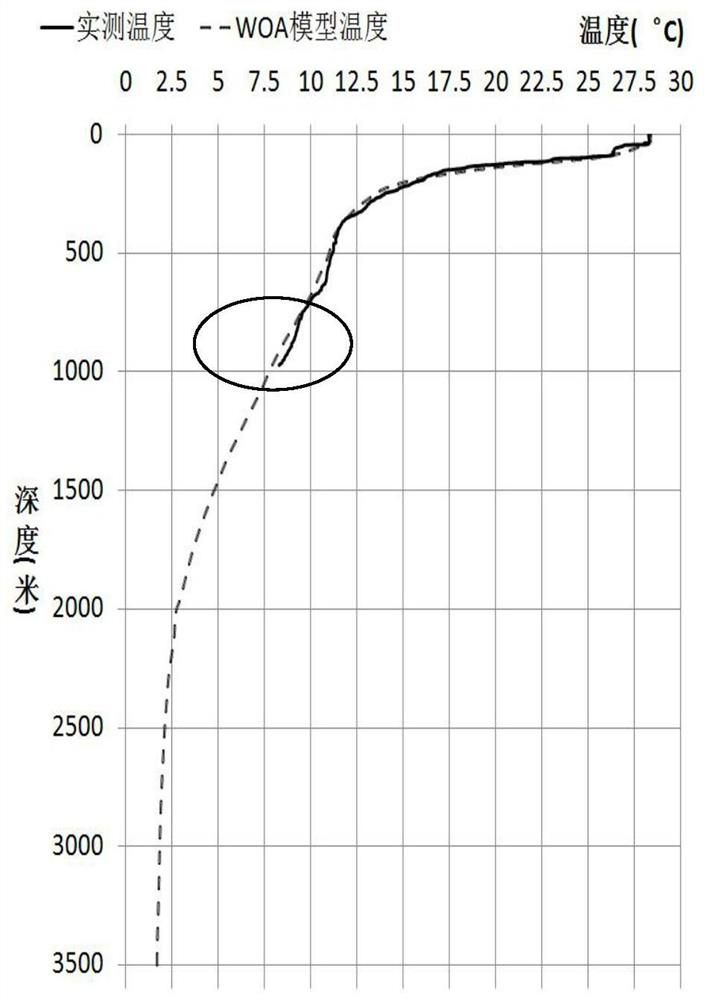
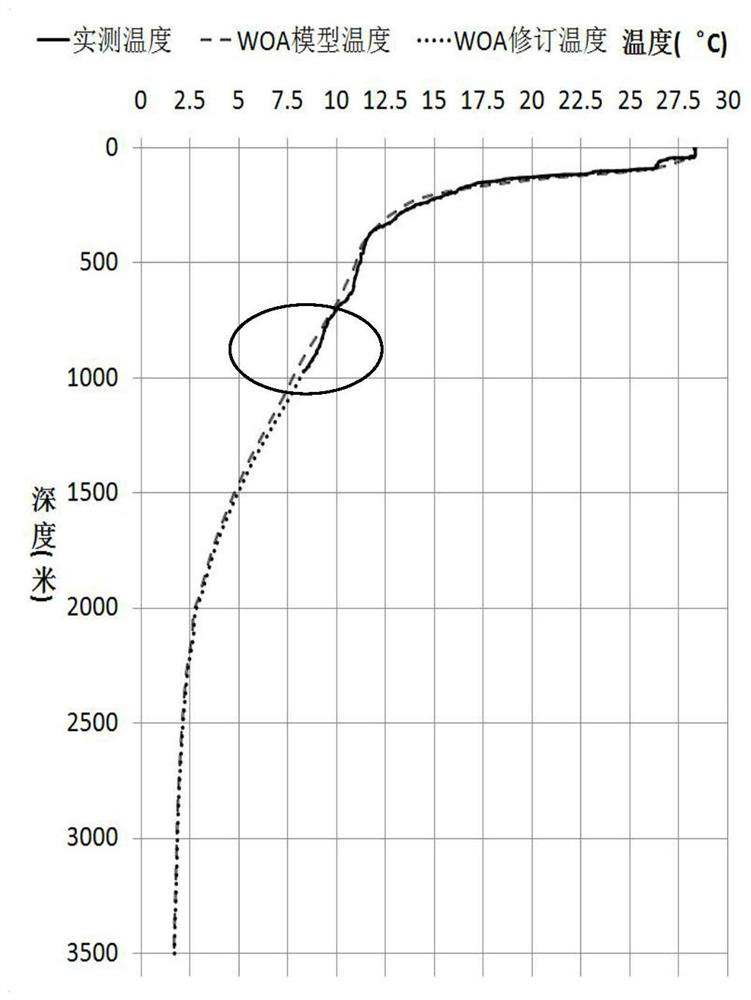
Combined with woa2018 model and measured temperature and salinity data to reconstruct full-depth sound velocity profile method
ActiveCN111523200BEfficient measurementSolve quality problemsMeasurement devicesDesign optimisation/simulationSound speed profileBathymetry
Owner:THE CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY 92859 TROOPS
System and method for imaging underwater environments using fluid lensing
ActiveUS10929966B2Improve propertiesImprove resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisSensing dataSea waves
Systems and methods are described for correcting distorted images captured of underwater environments. Caustics are used to provide additional illumination to underwater objects, and lenslets from ocean wave fluid lensing are used to magnify a benthic scene for enhancing the effective resolution of the images. The process introduces a fluid distortion characterization methodology, caustic bathymetry concepts, fluid lensing lenslet homography technique, two dimensional image reconstruction process, and three dimensional airborne fluid lensing process for characterizing the aquatic surface wave field, modelling bathymetry using caustic phenomena, and robust high-resolution aquatic remote sensing. Performing remote sensing using fluid lensing, also referred to as the fluid lensing process, utilizes high-frame-rate multispectral remote sensing data to remove ocean wave distortions from an image, to enhance the resolution of an image by exploiting ocean waves, and to enhance the signal strength of an image otherwise impaired by optical absorption in the water column.
Owner:NASA
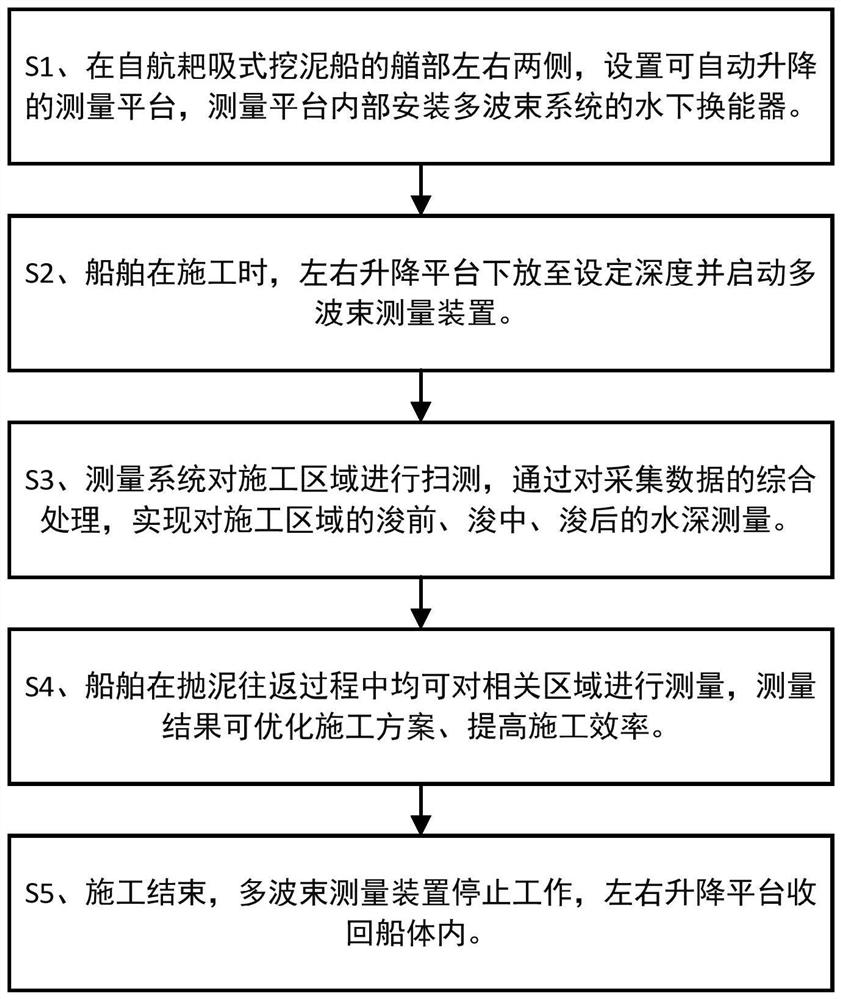
A dredging-measuring integrated water depth measurement method for a self-propelled trailing suction dredger
ActiveCN109386016BReduce operating costsMeet construction measurement requirementsMechanical machines/dredgersTerrainMarine engineering
The invention provides a dredging-measuring integrated water depth measurement method for a self-propelled trailing suction dredger, which is used to solve the problems of high cost, limited sea conditions, and poor timeliness of data caused by traditional measurement methods. The invention makes full use of the construction characteristics of the self-propelled trailing suction dredger to provide an integrated method of dredging and measuring while dredging construction and measuring, and completes the scanning and surveying of the underwater terrain of the corresponding construction area during the ship construction process, thereby realizing Bathymetry in construction areas. The invention effectively improves the timeliness of measurement before, during and after dredging, and guides the self-propelled trailing suction dredger to sweep shallows in time through real-time measurement, thereby improving the construction efficiency and quality of dredging, and saving the operating cost of measurement work.
Owner:WUHAN DEERDA TECH CO LTD
Determination and Elimination Method of Delay Between Unmanned Ship Sounding Data and Positioning Data
ActiveCN112902931BEliminate sounding delayEliminate propagation timeSynchronisation arrangementMeasuring open water depthTimestampPropagation time
Owner:SHANGHAI HUACE NAVIGATION TECH
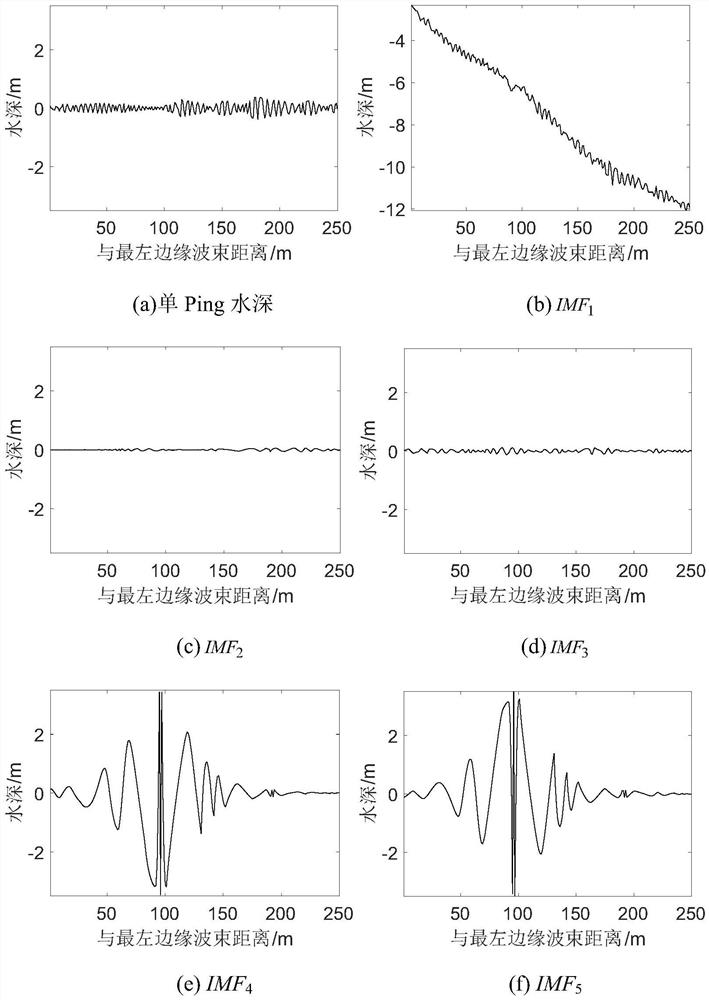
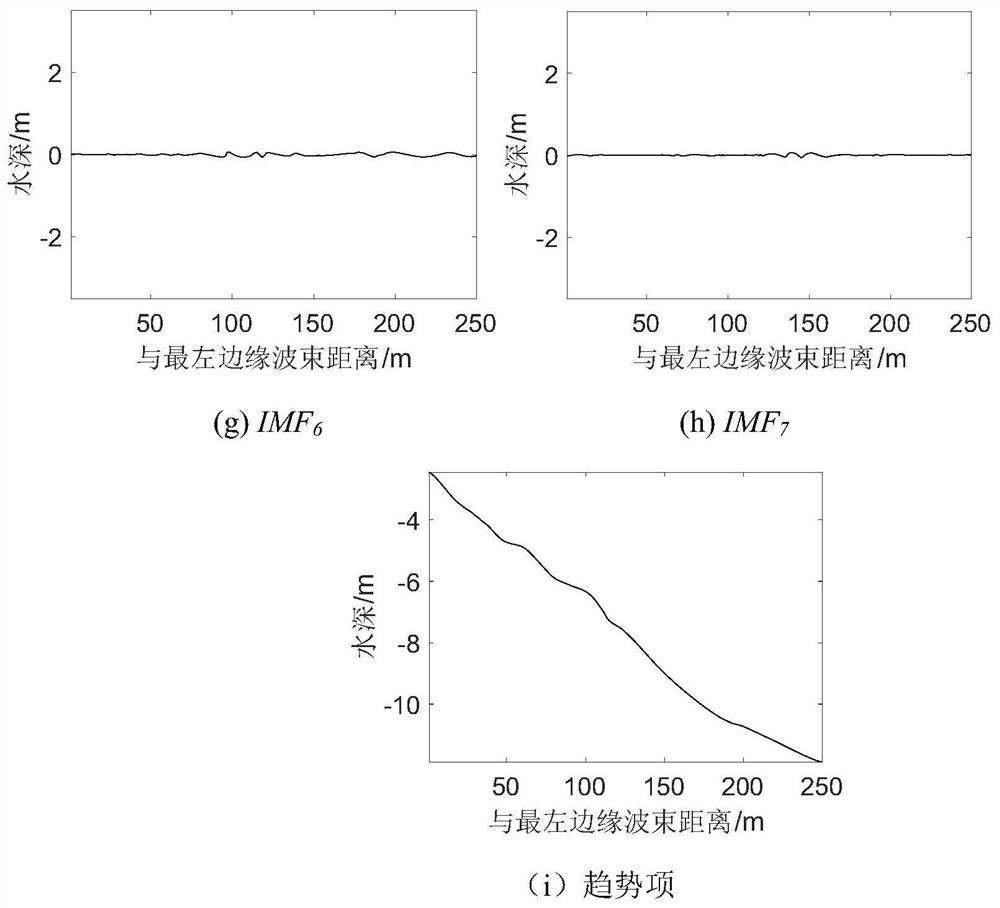
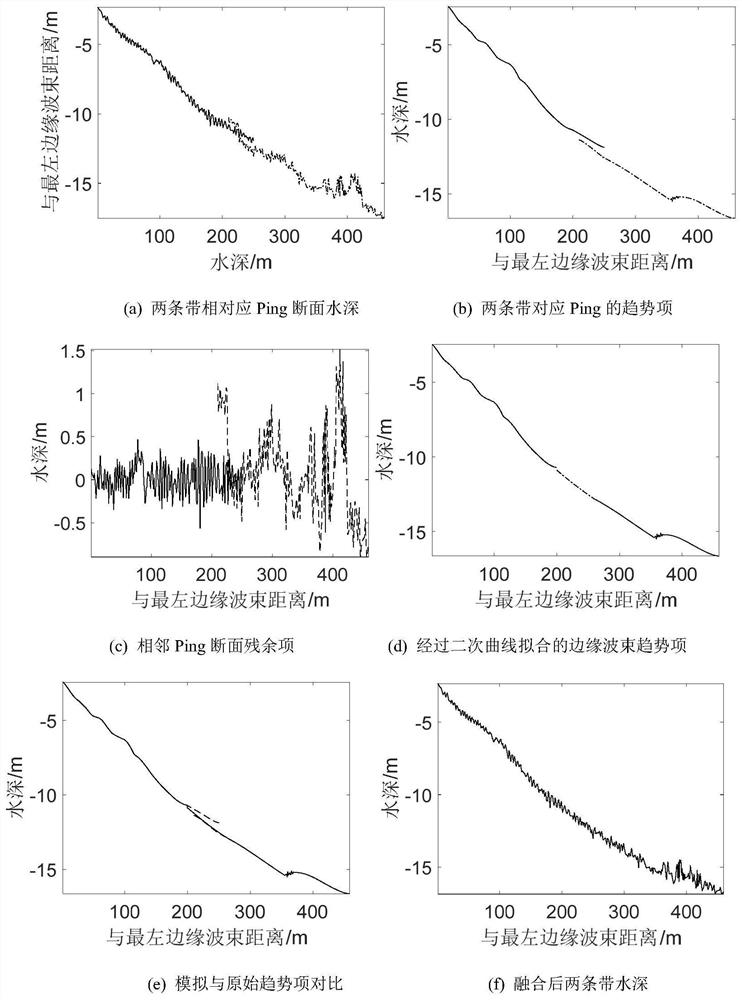
A Method of Improving emd to Attenuate Multi-beam Residual Errors
The invention discloses a method for improving EMD to weaken multi-beam residual errors, belonging to the technical field of marine resource detection, comprising the following steps: using the minimum distance method to find the same Ping section of adjacent strips; using the cubic Bessel interpolation method to Re-interpolate the extreme points; use the cubic Bessel interpolation method to perform empirical mode decomposition on the multi-beam water depth data to obtain the trend item and residual item of the seabed change; construct a new edge beam trend item; construct the overall seabed trend item; construct Seabed bathymetry strip data. The method of the present invention has universal characteristics, not only considering the superior adaptability of EMD, but also combining the accuracy of screening extreme points of the cubic Bessel interpolation method, and can better screen out the extreme value of the envelope, It is an effective method to reduce the multi-beam residual error.
Owner:江苏华瀚耀星海洋科技有限公司
A trend surface filtering method and system for multi-beam bathymetry data
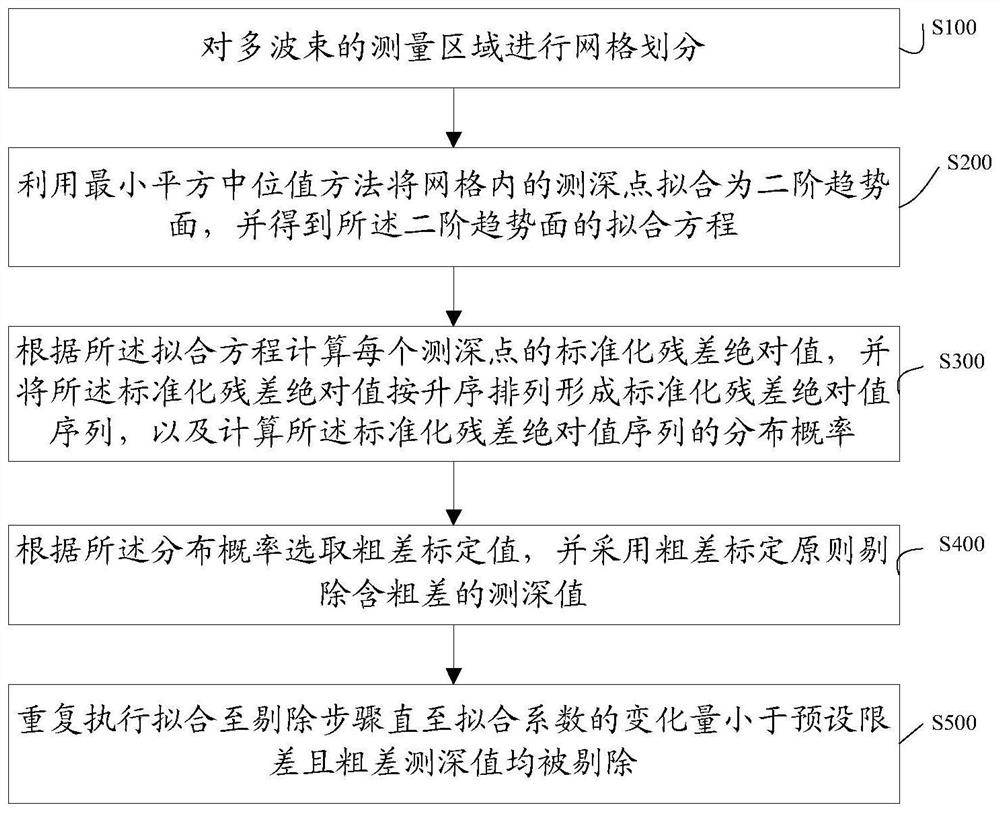
ActiveCN107229594BReduce false alarm rateImprove effectivenessComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmBathymetry
The invention discloses a multi-beam sounding data trend surface filtering method and system. The method comprises the steps that mesh generation is conducted on a multi-beam measurement area; sounding points in meshes are fitted into a second-order trend surface through a least square median method, and a fitting equation of the second-order trend surface is obtained; standardized residual absolute values of all the sounding points are calculated according to the fitting square, and the distribution probability of the standardized residual absolute values is calculated; a gross calibration value is selected according to the distribution probability, and sounding values containing gross errors are removed by adopting a gross error calibration principle; and fitting is repeatedly executed to the removing step until the variation of a fitting coefficient is smaller than preset tolerance and all the gross error sounding values are removed. According to the method, by improving the gross error calibration principle, reasonable sounding values with high observation noise are accepted, the false alarm rate of the trend surface filtering method is decreased, and the quality of data obtained after filtering processing is improved.
Owner:深圳市建设综合勘察设计院有限公司
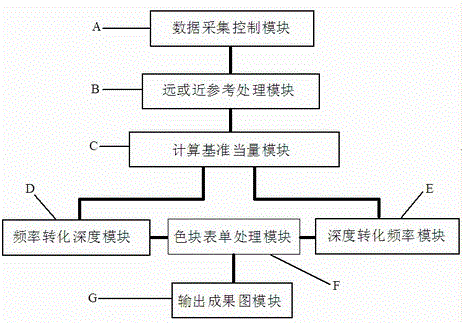
Ground geomagnetic data intuitive color block processing method based on reference equivalent weight
The present invention discloses a ground geomagnetic data intuitive color block processing method based on a reference equivalent weight. The method is applied in the technical field of ground geomagnetic bathymetry data processing. The method aims to overcome the defects in the existing ground geomagnetic bathymetry data inversion processing. The method can dynamically establish a reference equivalent weight to process the original data, and convert the data into different color blocks to visually display geological information including geological profile, fault structure, mineral location form or stratum information.
Owner:王玉喜
MF method for automatic fusion of multi-source heterogeneous bathymetric data to construct high-resolution dbm
ActiveCN109544691BHigh precisionHigh resolutionGeometric image transformationVisual data miningAlgorithmBathymetry
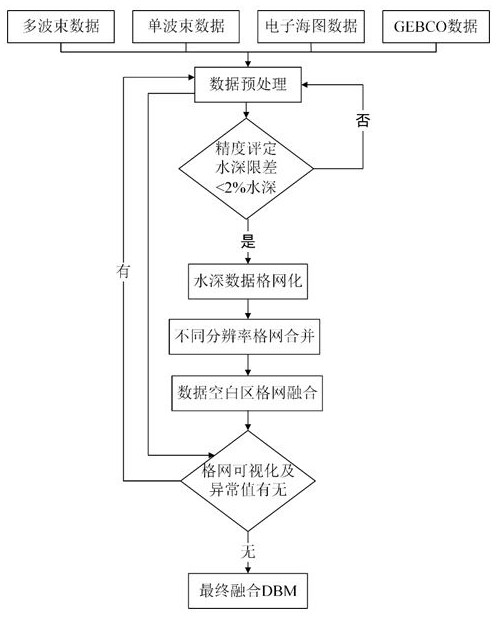
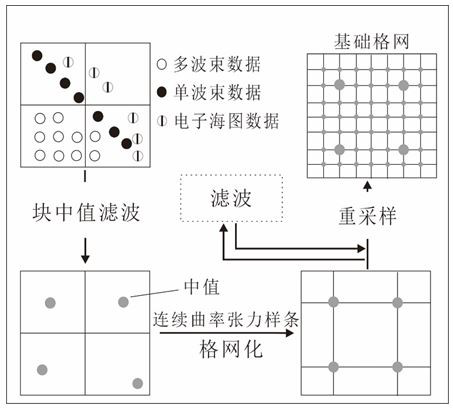
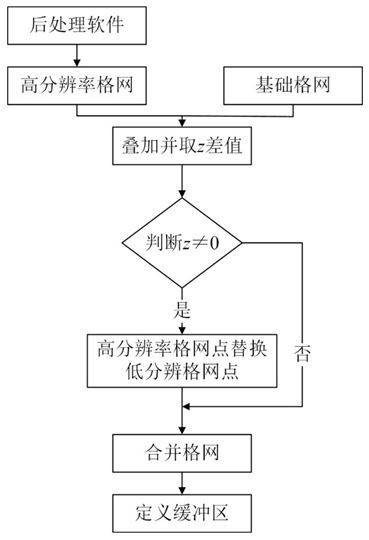
The invention discloses an MF method for automatically fusing multi-source heterogeneous water depth data to construct a high-resolution DBM. This method organically integrates multi-beam, single-beam, electronic chart data and global ocean topography data through the technical process of merging-fusion, so as to solve the problem of complex sources of global bathymetric data, large differences in accuracy, and difficulty in integrating and constructing high-level data. Problems with precision digital bathymetry models. The method includes the following steps: preprocessing data, evaluating accuracy, gridding, grid merging, fusion, visual comparison analysis and cleaning abnormal points, and completing the fusion of multi-source water depth data. The fused DBM can better reflect fine topographic feature information, while retaining high-resolution topographic details, it fills in data gaps, and can be extended and applied to the management and utilization of multi-source heterogeneous bathymetric data. , marine geographic information system, seabed topography and landform mapping, marine scientific research and other aspects have important practical application value.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
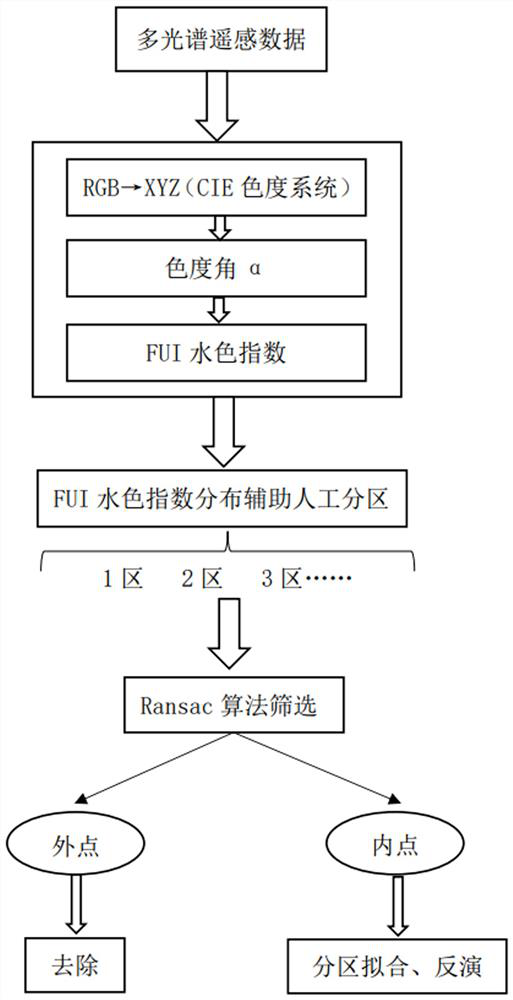
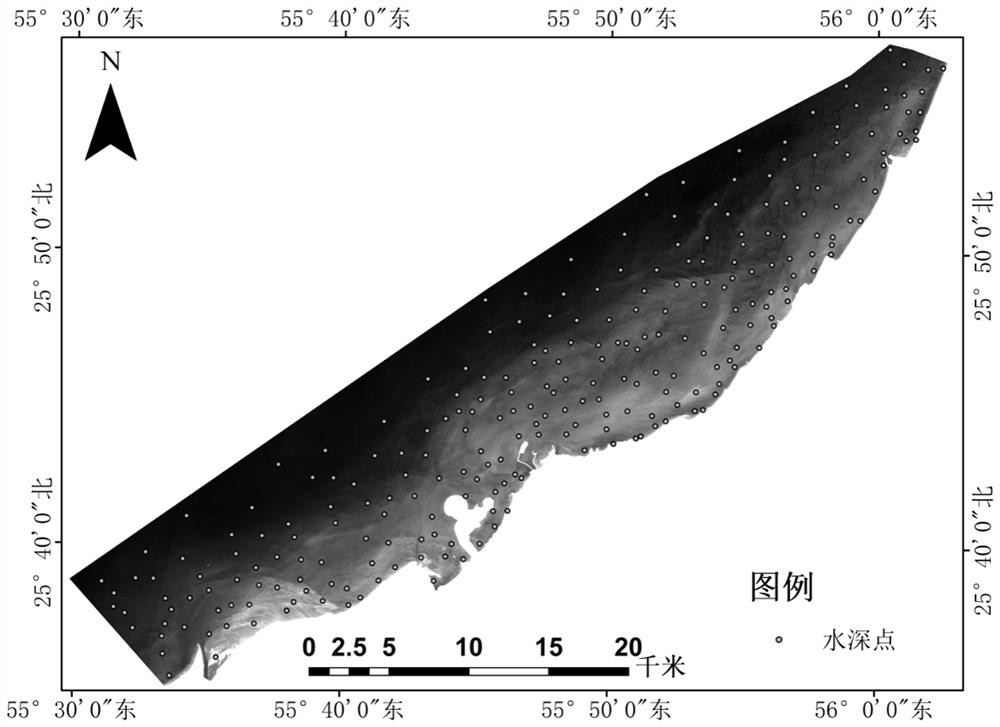
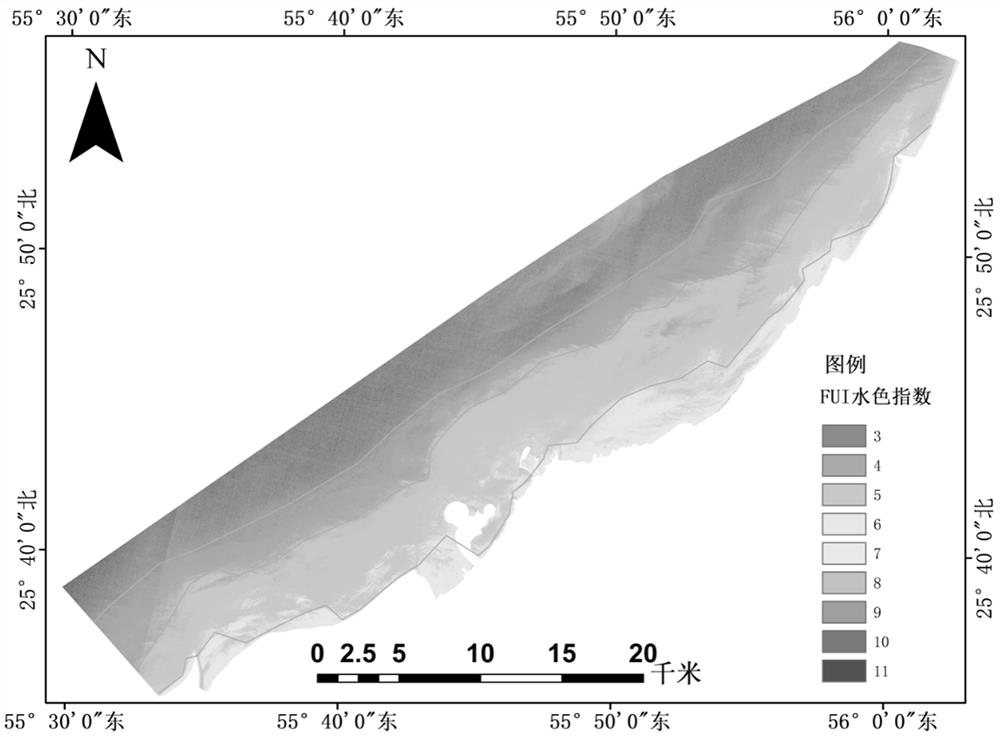
Shallow Sea Remote Sensing Water Depth Inversion Method Based on Fui Partition and Ransac
ActiveCN113255144BFully account for spatial heterogeneityGood anti-gross performanceDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsSensing dataData set
The present invention relates to a shallow sea remote sensing water depth inversion method based on FUI partition and Ransac. The present invention first uses multi-spectral remote sensing data to calculate the FUI water color index, and based on the distribution of the FUI water color index, combined with manual visual interpretation, the shallow sea area Partition; then use the Ransac algorithm to filter the data set of field sounding points in each partition (the sounding value of the field sounding point and its corresponding reflectance on the R, G, and B bands), retain the correct data, and remove the existing Data with large errors; finally, use the preserved field sounding point data set for partition inversion. The invention organically combines the idea of partitioning with the idea of robust estimation, and improves the inversion precision to a certain extent. The invention can be widely applied to the field of shallow sea multispectral remote sensing water depth inversion.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
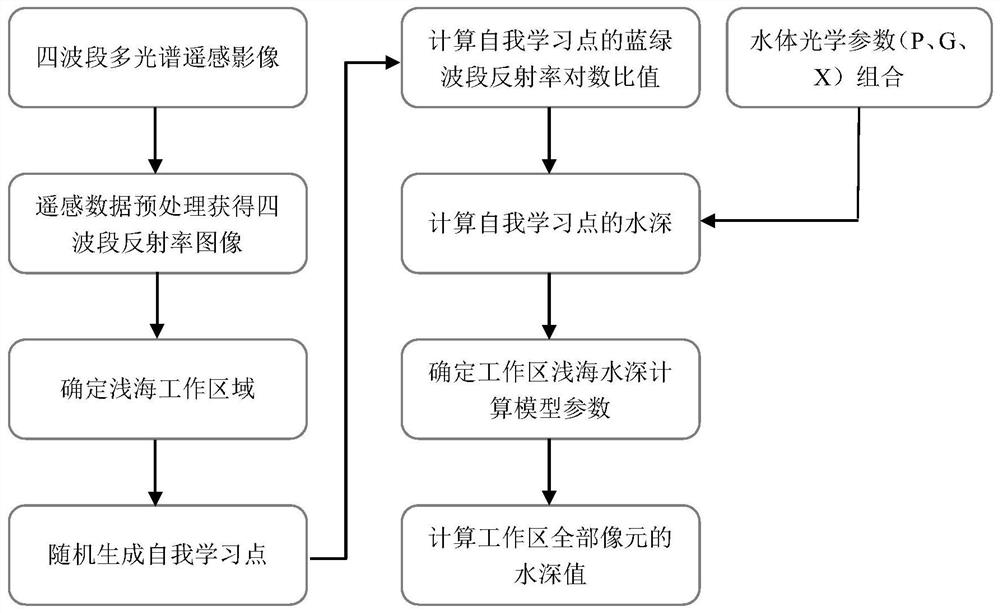
An Uncontrolled Extraction Method of Shallow Sea Depth Based on Four-Band Multispectral Remote Sensing Images
ActiveCN111561916BWide range of usesSolve the problem of water depth extraction in four-band multi-spectral remote sensingMeasuring open water depthMachines/enginesAnalytic modelMacroscopic scale
The invention provides an uncontrolled extraction method of shallow water depth based on four-band multi-spectral remote sensing images, aiming at the measurement requirements of oceanic islands and reefs, combining the existing logarithmic ratio model and semi-analytical model, using the logarithmic ratio model blue The strong linear relationship between the logarithmic ratio of the reflectance of the green band and the water depth, the macroscopic constraints on the optical parameters of the regional water body, and the realization of shallow water depth extraction based on four-band multi-spectral remote sensing images without the support of actual measurement data will greatly improve the historical accumulation time. The application efficiency of the four-band multi-spectral remote sensing images with the most abundant and widely used remote sensing platforms is an innovation in the application of remote sensing information technology, a beneficial supplement to shallow water bathymetry on islands and reefs, and has great practical value .
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
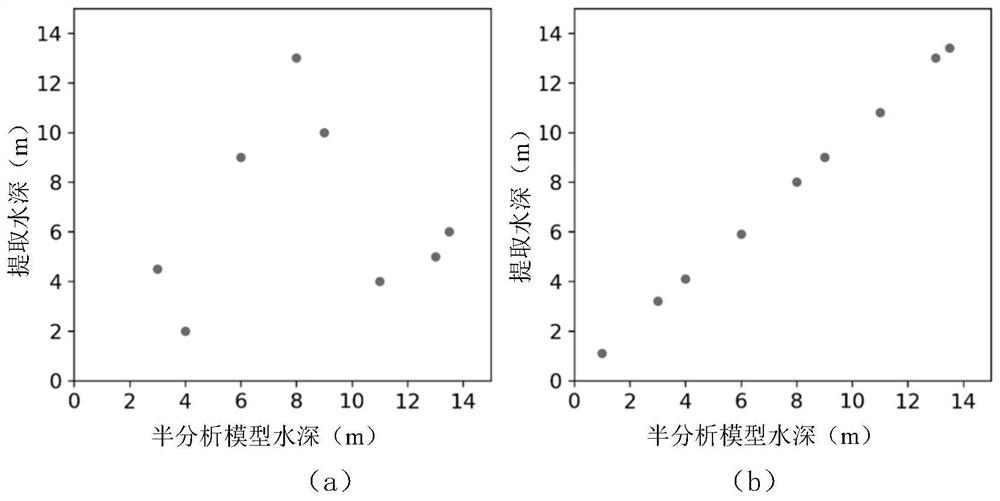
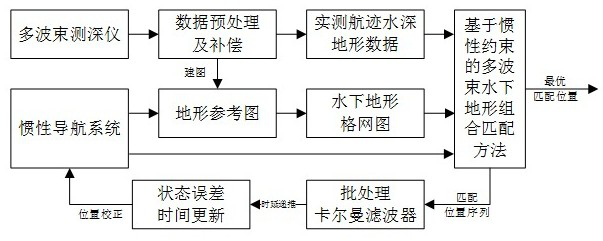
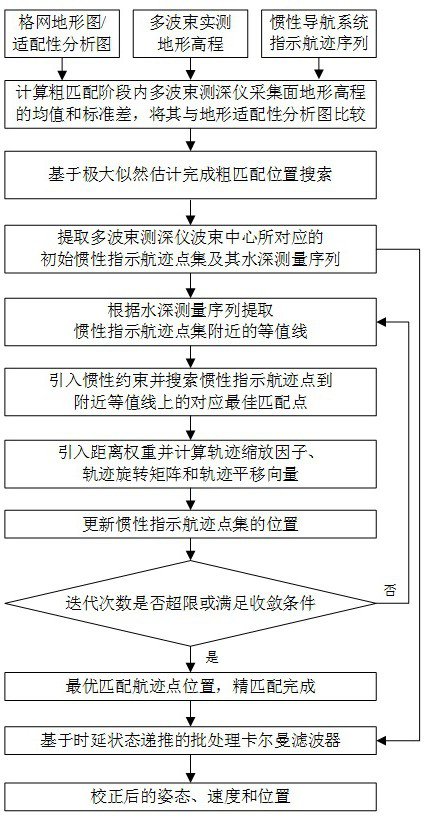
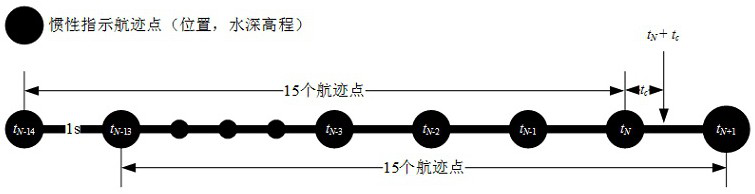
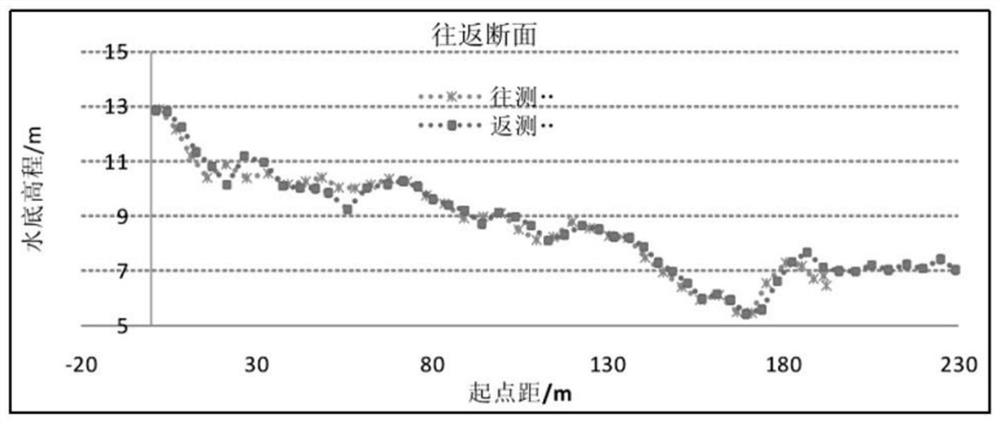
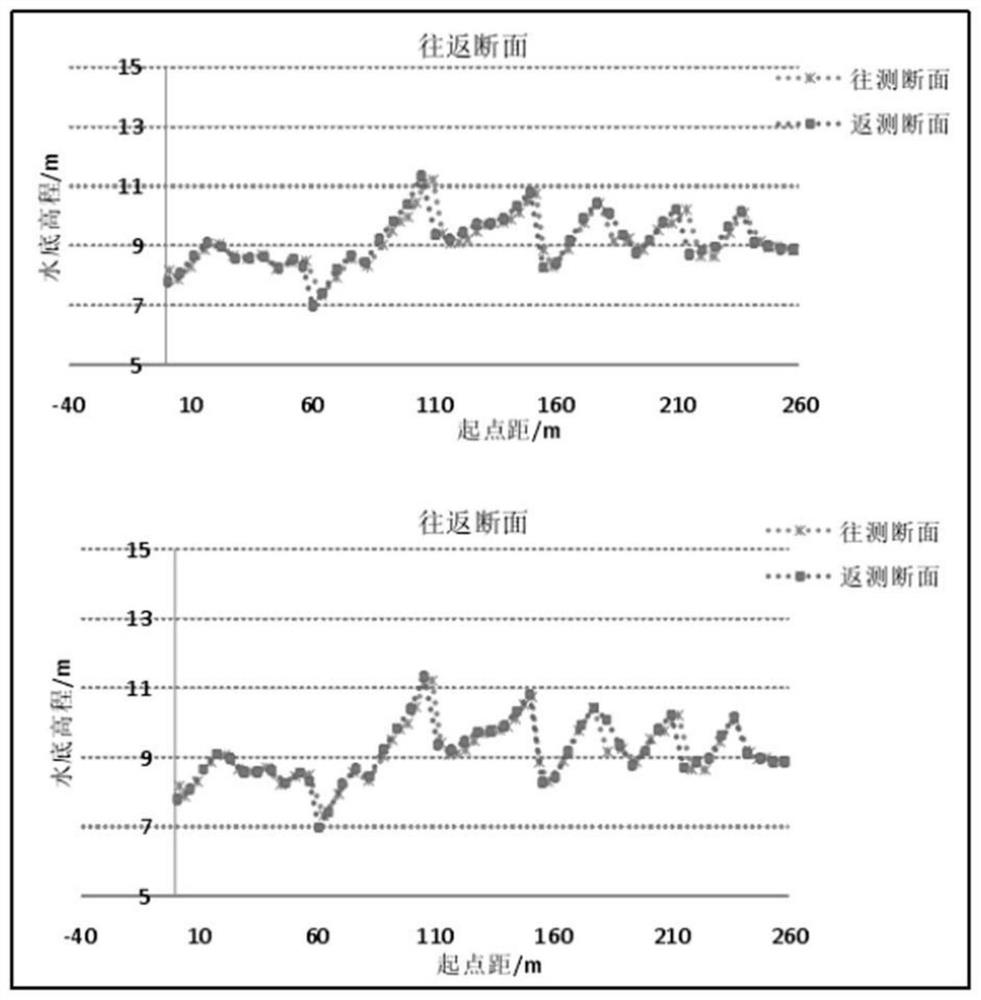
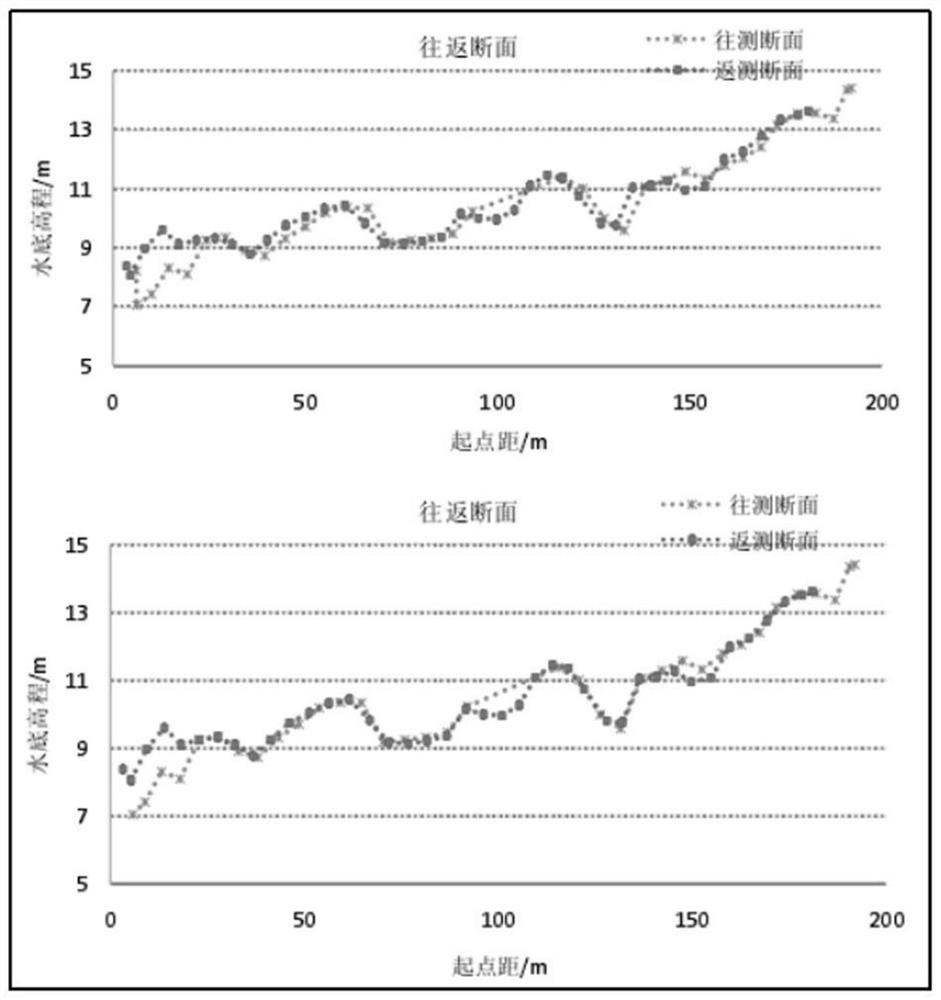
Multi-beam underwater terrain combination matching method based on inertial constraints
ActiveCN114623822BSolve the problem of easy to fall into local optimal matchingSolve the errorNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsTerrainKaiman filter
The invention discloses a multi-beam underwater terrain combination matching method based on inertial constraints, which belongs to the field of terrain-assisted inertial navigation. The method of the present invention: firstly, based on the bathymetry sequence and the initial position provided by the inertial navigation system, using terrain adaptation parameters and maximum likelihood estimation to achieve fast rough matching; then, introducing inertial constraints and distance weights to reduce mismatched points The influence of , and an accurate numerical solution for calculating the trajectory scaling factor is given. The precision matching is achieved by sequentially scaling, rotating and translating the inertial indicated track; finally, the position sequence obtained by the two-step matching is compared with the inertial track The difference between the indicated position sequences of the navigation system is used as the observation value of the Kalman filter based on the time-delay error correction based on state recursion to correct the attitude, velocity and position of the inertial navigation system and improve the positioning accuracy of the integrated navigation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Underwater topographic survey method suitable for shallow sea area of radiant sand ridge group
ActiveCN108469620BImprove work efficiencyHigh measurement accuracyMeasuring open water depthSatellite radio beaconingTerrainBathymetry
The invention relates to an underwater terrain measurement method suitable for shallow sea areas of radiant sand ridge groups, in which a sounding platform, a PPK reference station and a mobile station are set; positioning and navigation data are collected, as well as the sounding data and sounding data measured by the sounder Antenna height data measured by the GNSS receiver; basic processing and data fine processing of the acquired data; using feature point matching scheme or section overall translation scheme to correct the influence of time delay; corresponding time points for bathymetry data and GNSS receiver The antenna height data is matched to obtain the topographic ellipsoid height data of the sea area; the topographic water depth data of the sea area are obtained through datum conversion. This method is applied to the measurement environment with wide shallow water, avoids dependence on tidal data, and has high measurement accuracy and efficiency.
Owner:江苏省有色金属华东地质勘查局地球化学勘查与海洋地质调查研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com