Increasing measurement rate in time of flight measurement apparatuses
A time-of-flight and measuring equipment technology, applied in photogrammetry/video metrology, measuring instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as light pulse rate limitation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] The principles of the embodiments described herein describe the structure and operation of several examples that illustrate the invention. It is to be understood that the drawings are diagrammatic and schematic representations of such exemplary embodiments, and therefore do not limit the scope of the invention, nor are they necessarily drawn to scale. Well-known devices and procedures are excluded to avoid overwhelming the discussion with details well known to those skilled in the art.
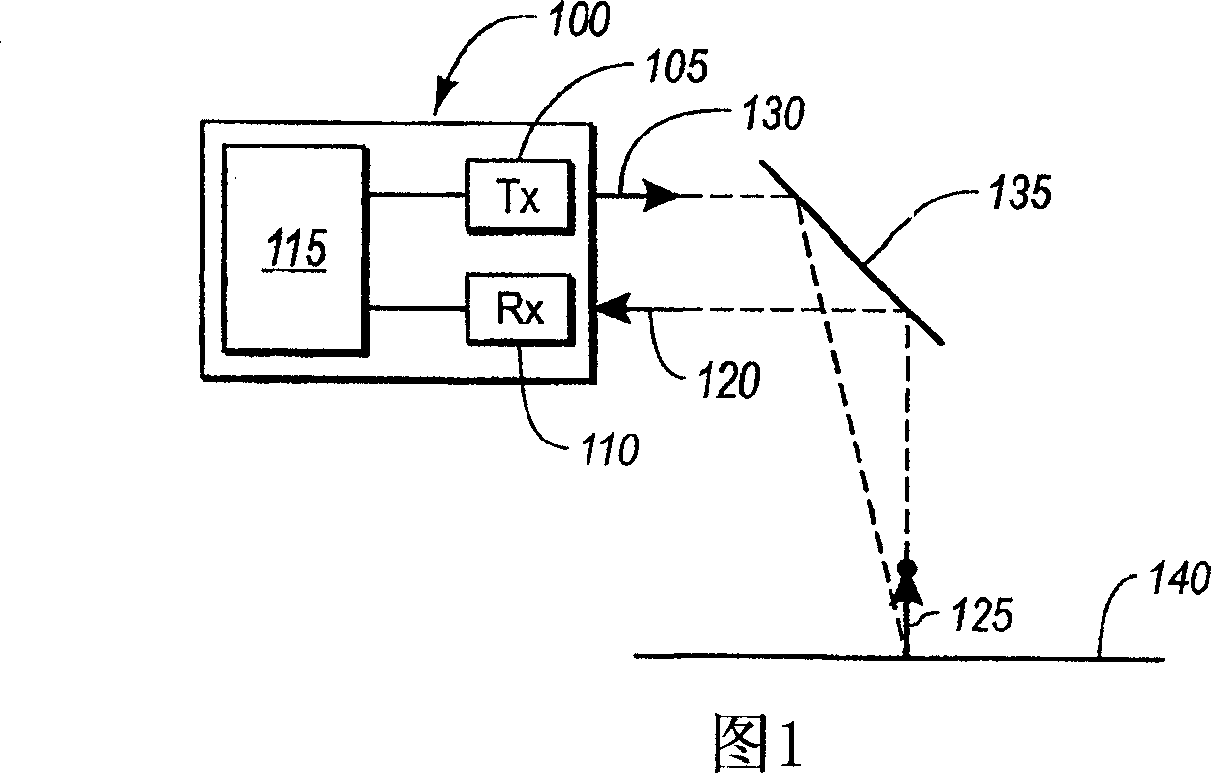
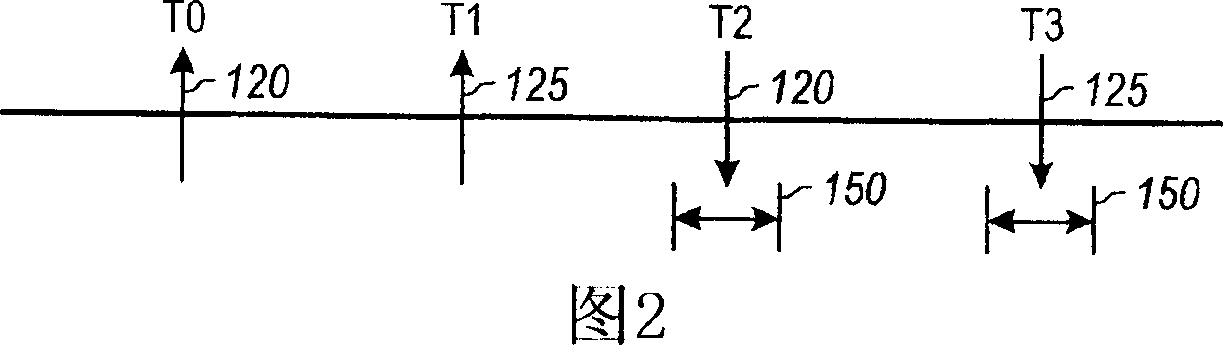
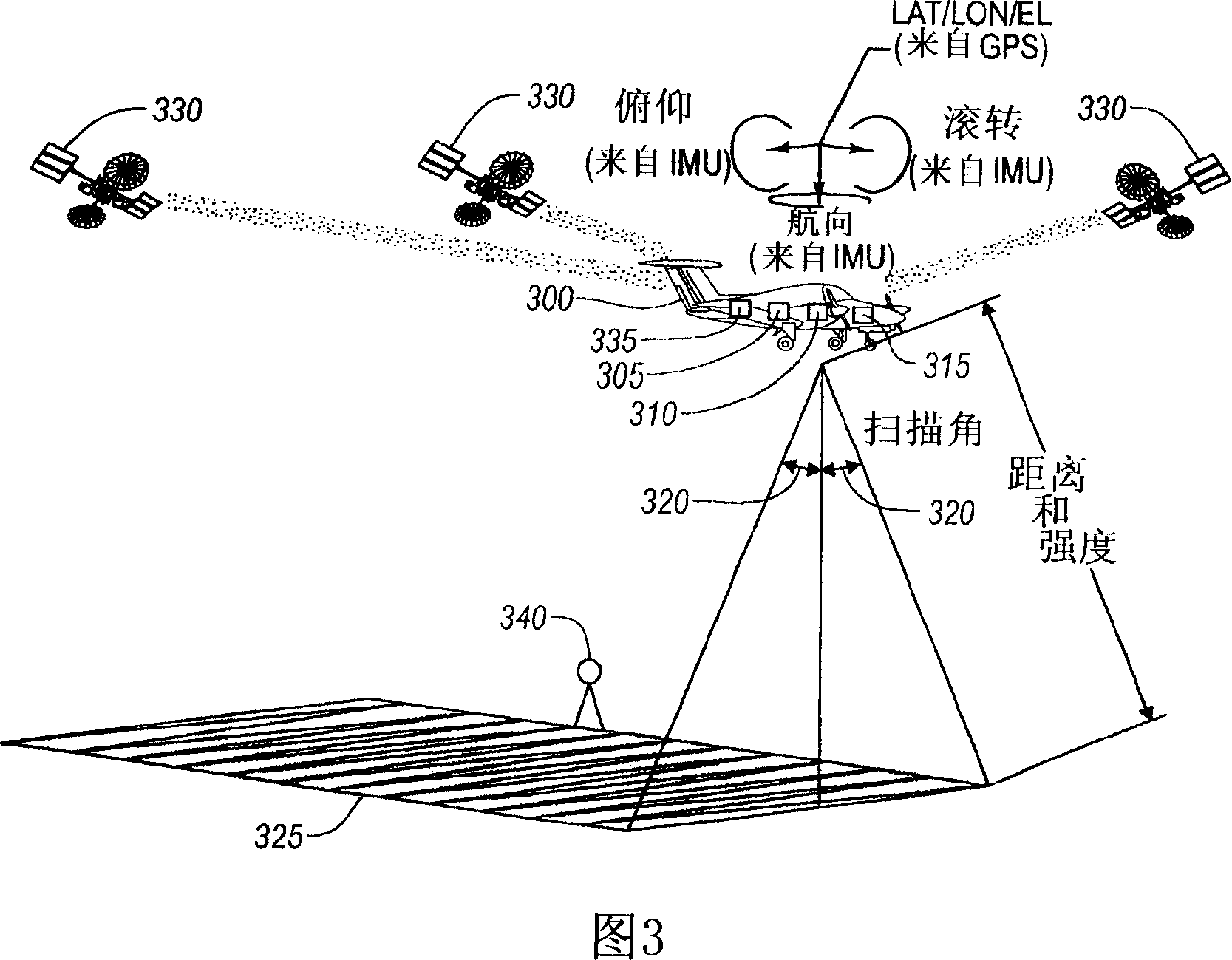
[0017] Referring to FIG. 1 , a time-of-flight measurement device 100 , such as a laser scanning or LIDAR system, is illustrated. The time-of-flight measurement device 100 includes an optical transmitter 105, such as a laser, and an optical receiver 110, such as a photodiode. Optical transmitter 105 and optical receiver 110 are electrically coupled to circuitry 115 . The first light pulse 120 is emitted by the light emitter, reflected off the surface 140, and received by the light rece...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com