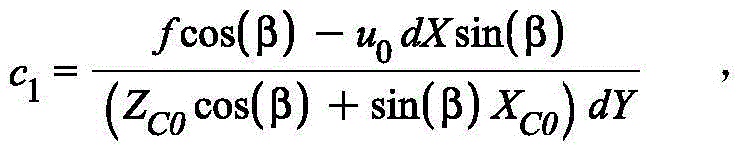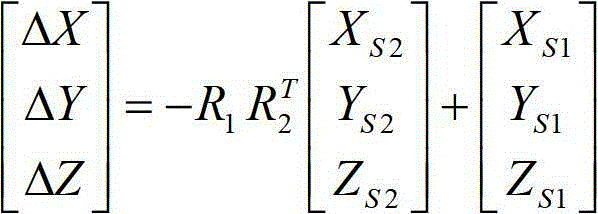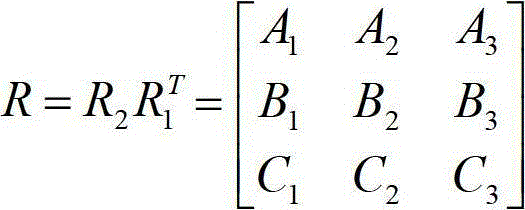Patents
Literature
95 results about "Close range photogrammetry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
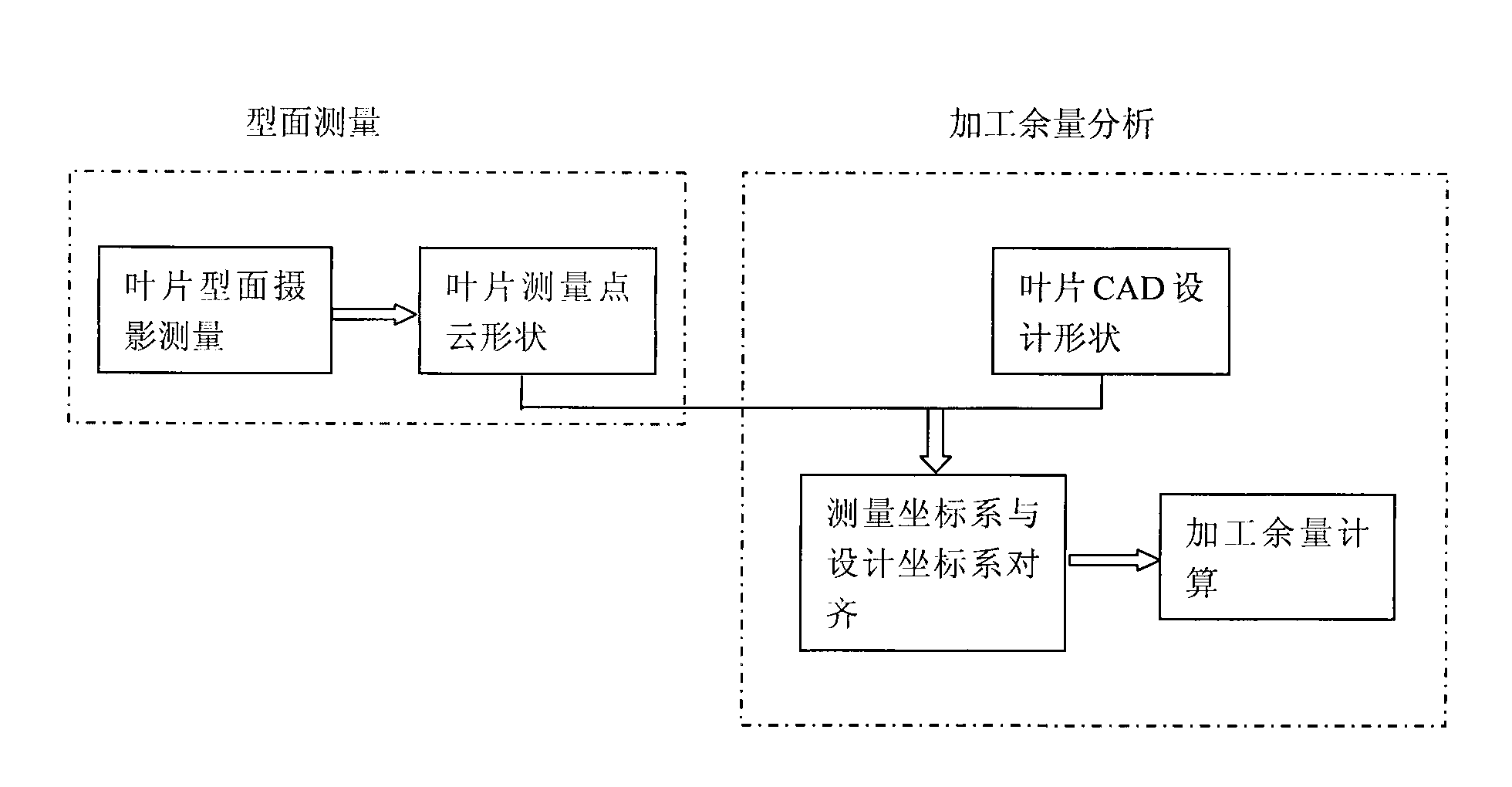
Water turbine blade blank profile measuring and machining allowance analyzing method
InactiveCN101634544AHigh speedImprove machining accuracyUsing optical meansCavitationMeasurement point
The invention relates to a water turbine blade blank profile measuring and machining allowance analyzing method capable of effectively solving the problem of water turbine blade blank profile measurement and machining allowance analysis to ensure the manufacturing quality and precision of the water turbine blades, comprising the following technical solutions: measuring the blade blanks by using a digital close range photogrammetry to obtain the measuring point cloud data shapes of the blank profiles consequently, aligning a measuring coordinate system where the measuring point clouds are located to a design coordinate system where a CAD design model is located, establishing a differential relation of free-form surface parameters with respect to rigid rotation parameters by using an analytic method derived by the multivariate of Newton iteration method to obtain a Jacobian matrix and Hessian matrix which are available for a target equation; then performing the numerical optimization calculation based on the LM method and Newton iteration method, and performing report or graphical output and print on the result. The inventive method is scientific, advanced, stable and reliable, and has high accuracy, thereby ensuring the hydraulic stability, production efficiency and cavitation property, and bringing enormous economic and social benefits.
Owner:郑州辰维科技股份有限公司
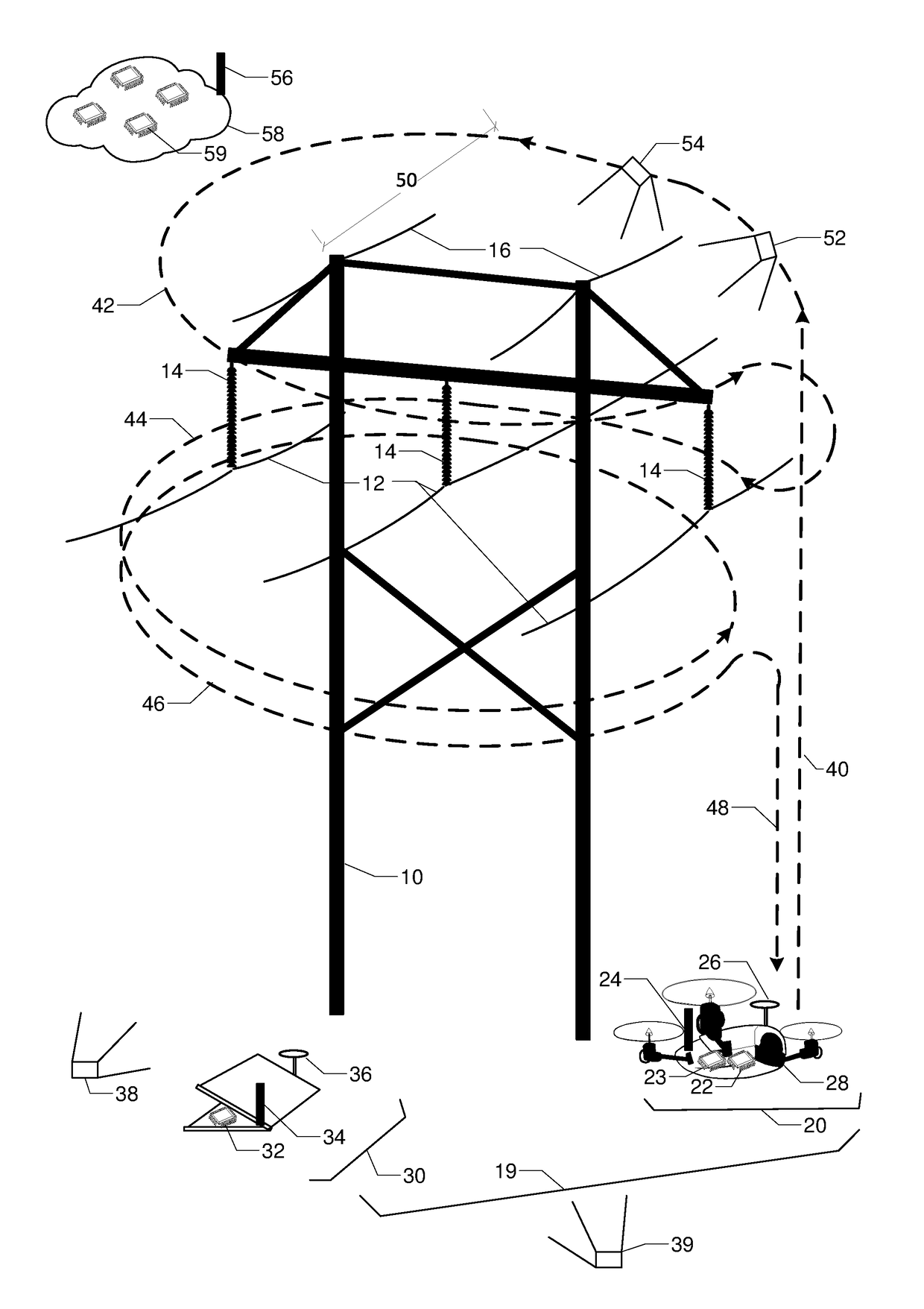
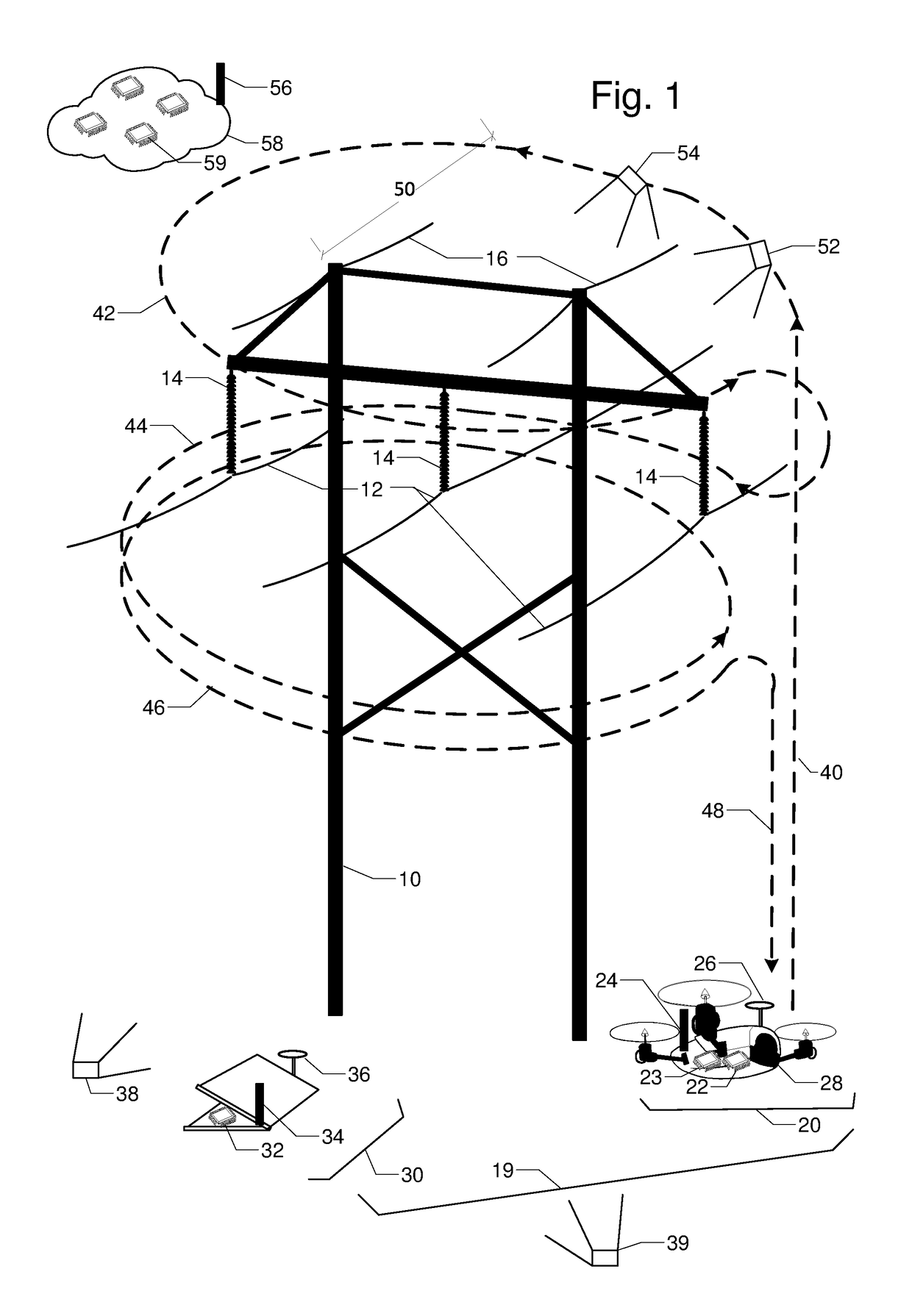
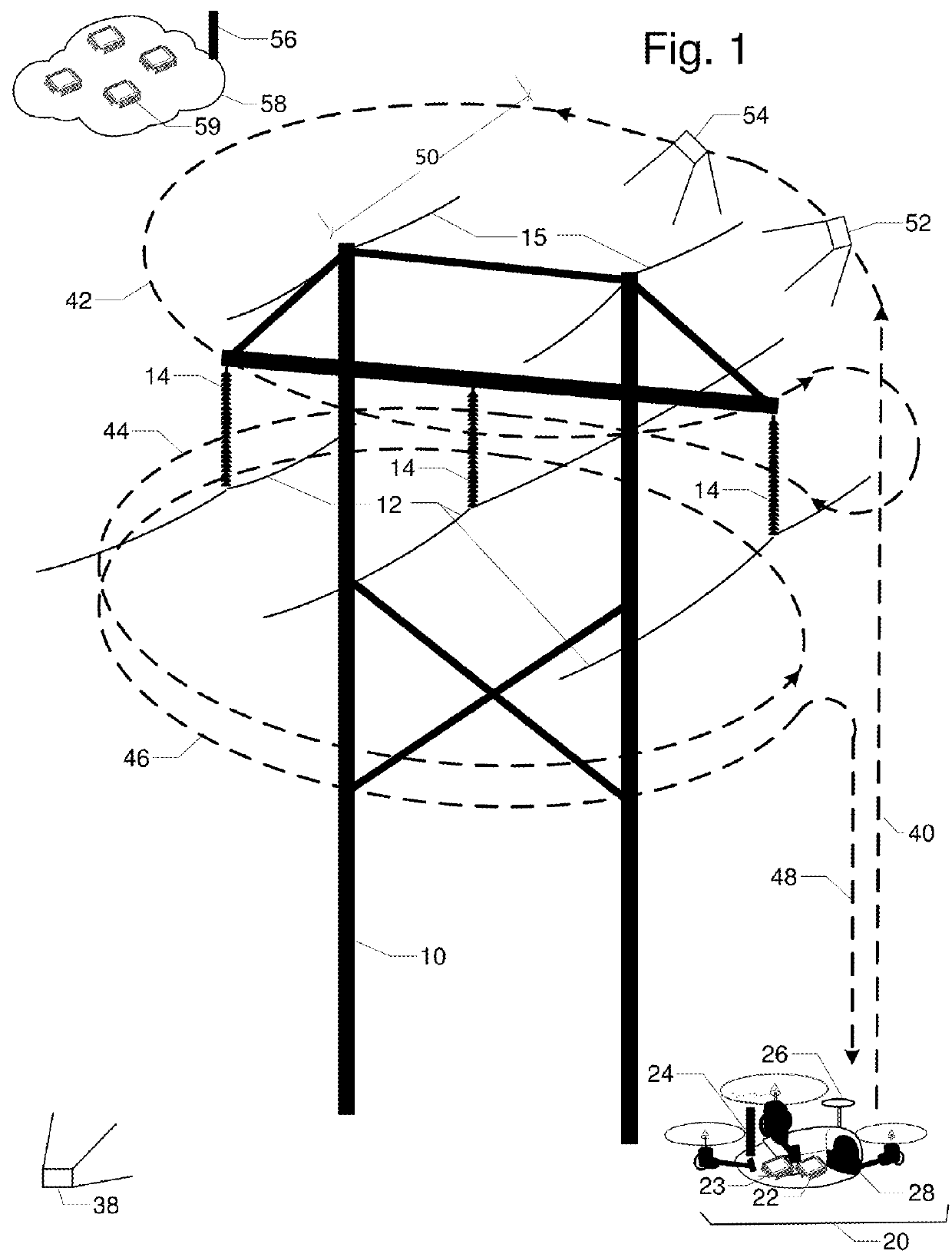
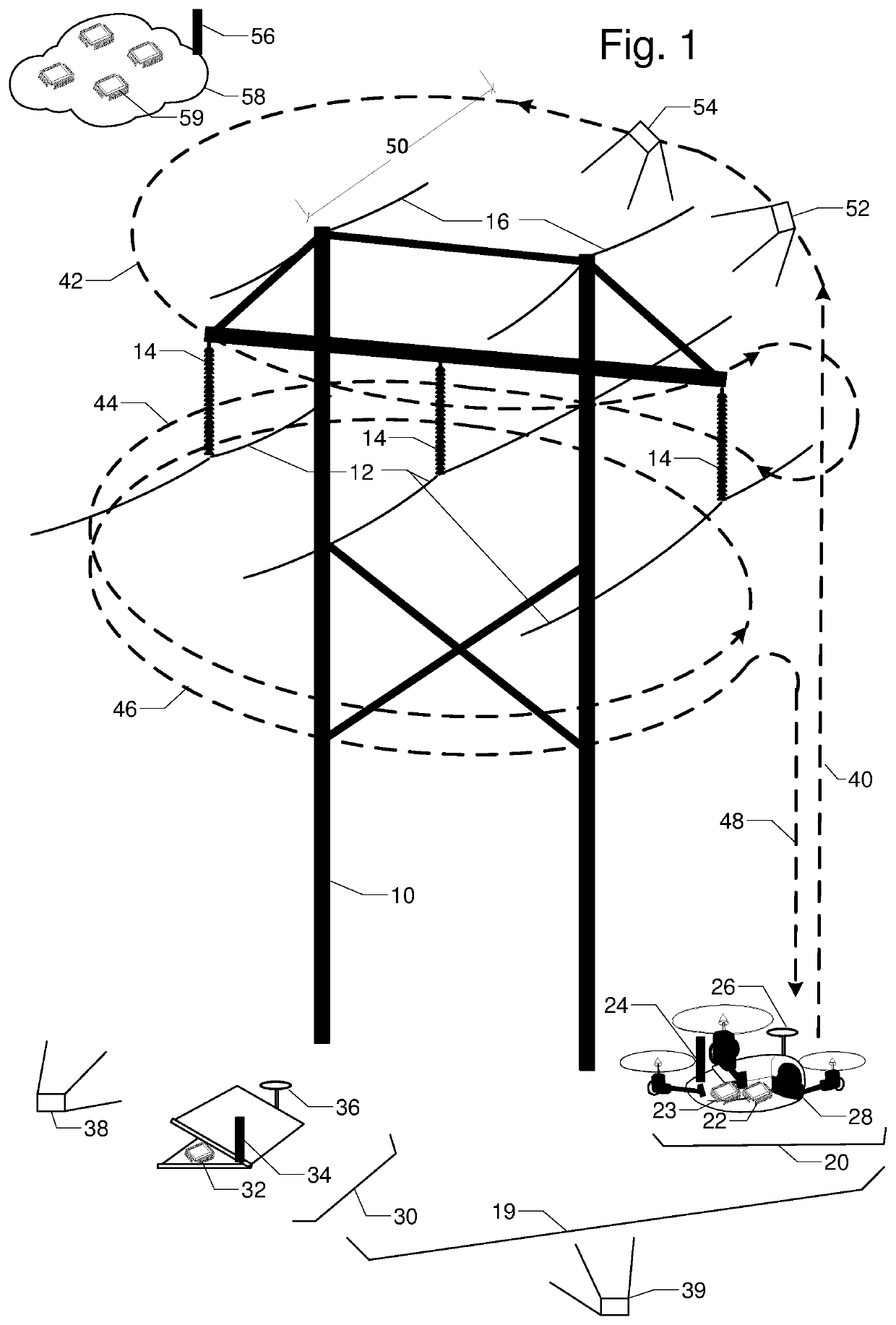
Flight planning for unmanned aerial tower inspection
ActiveUS20180032088A1Accurate calculationFull coverageAircraft componentsUnmanned aerial vehiclesTransmission towerClose range photogrammetry
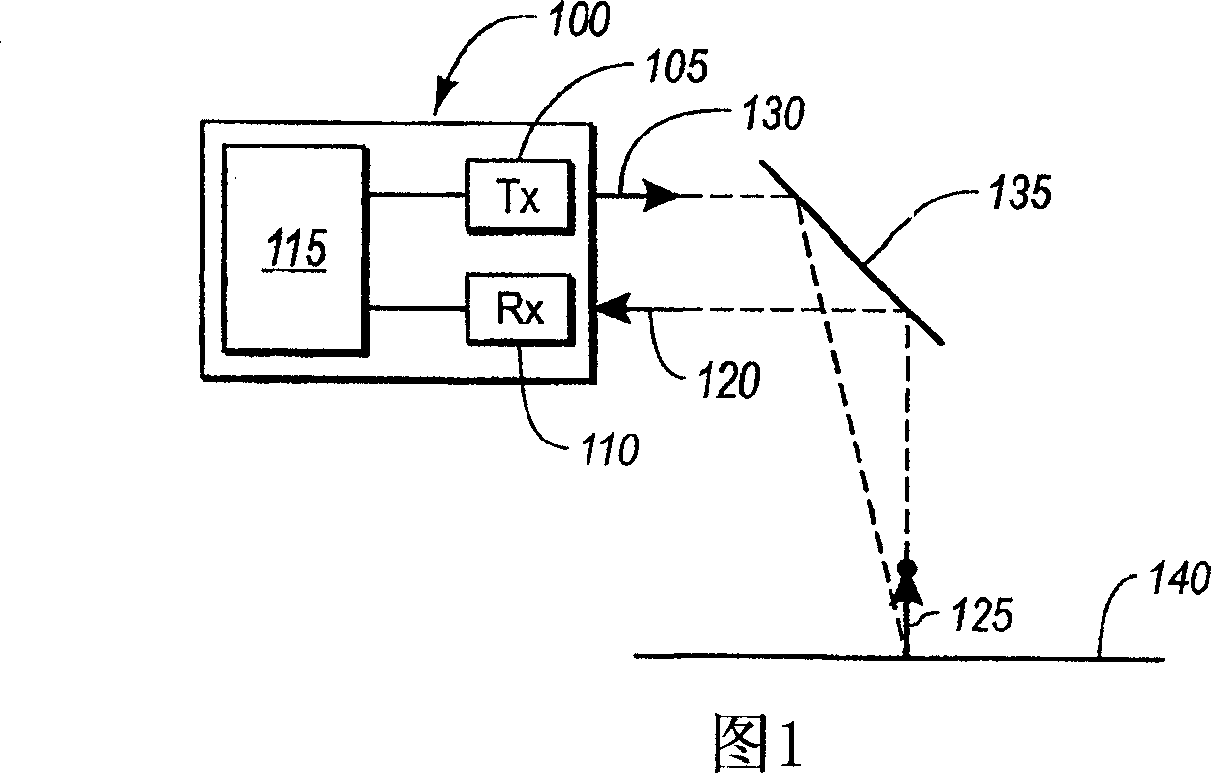
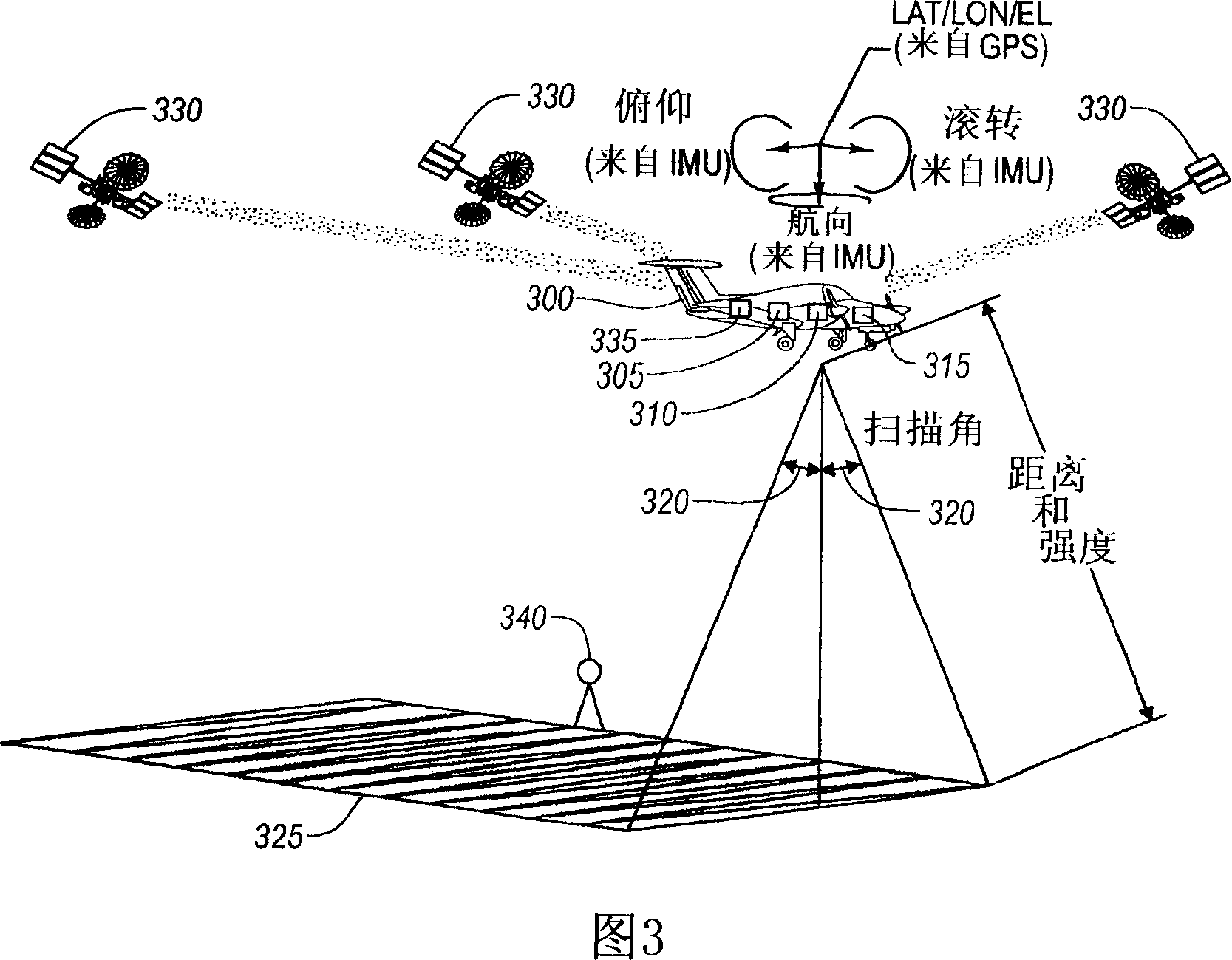
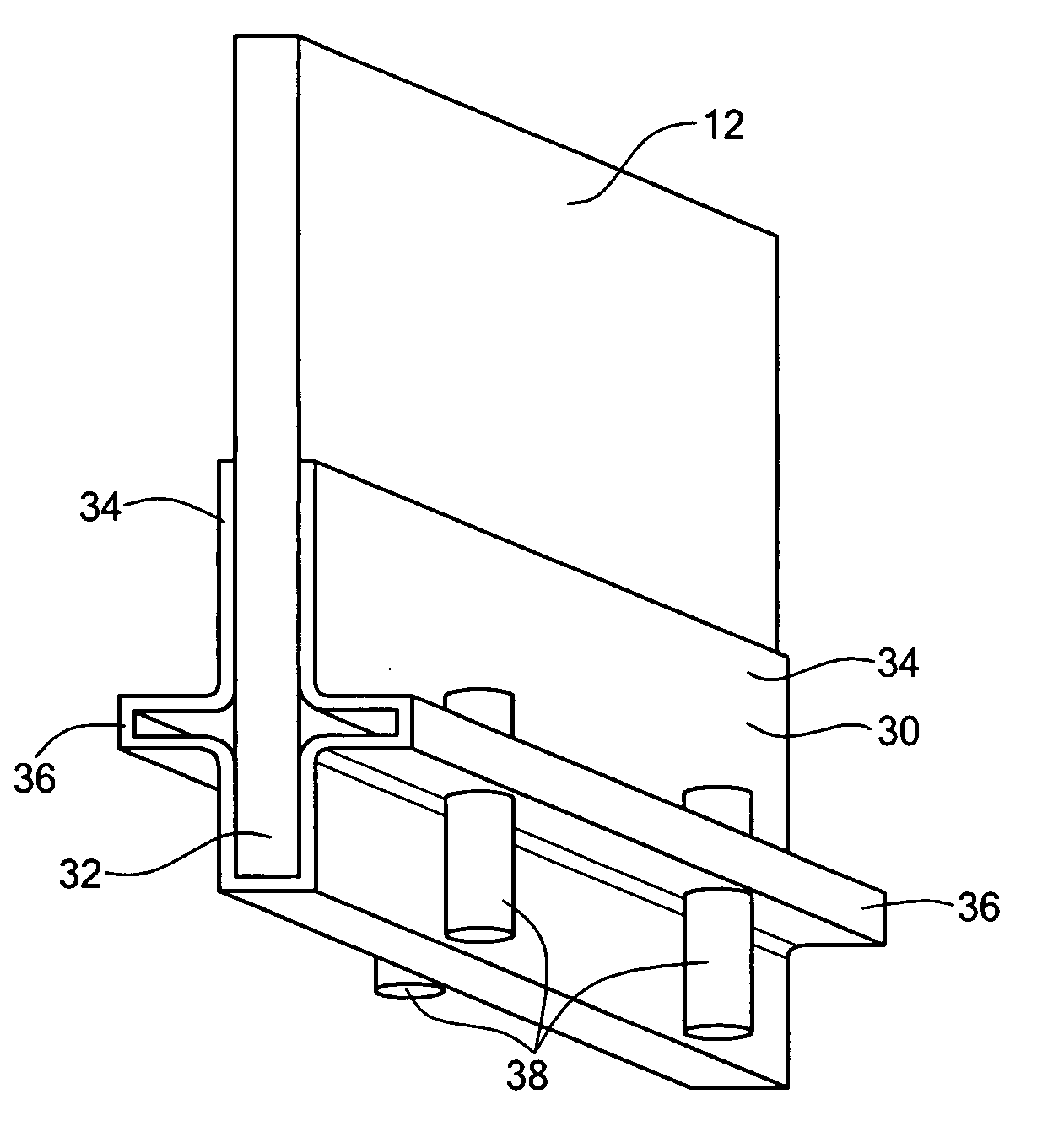
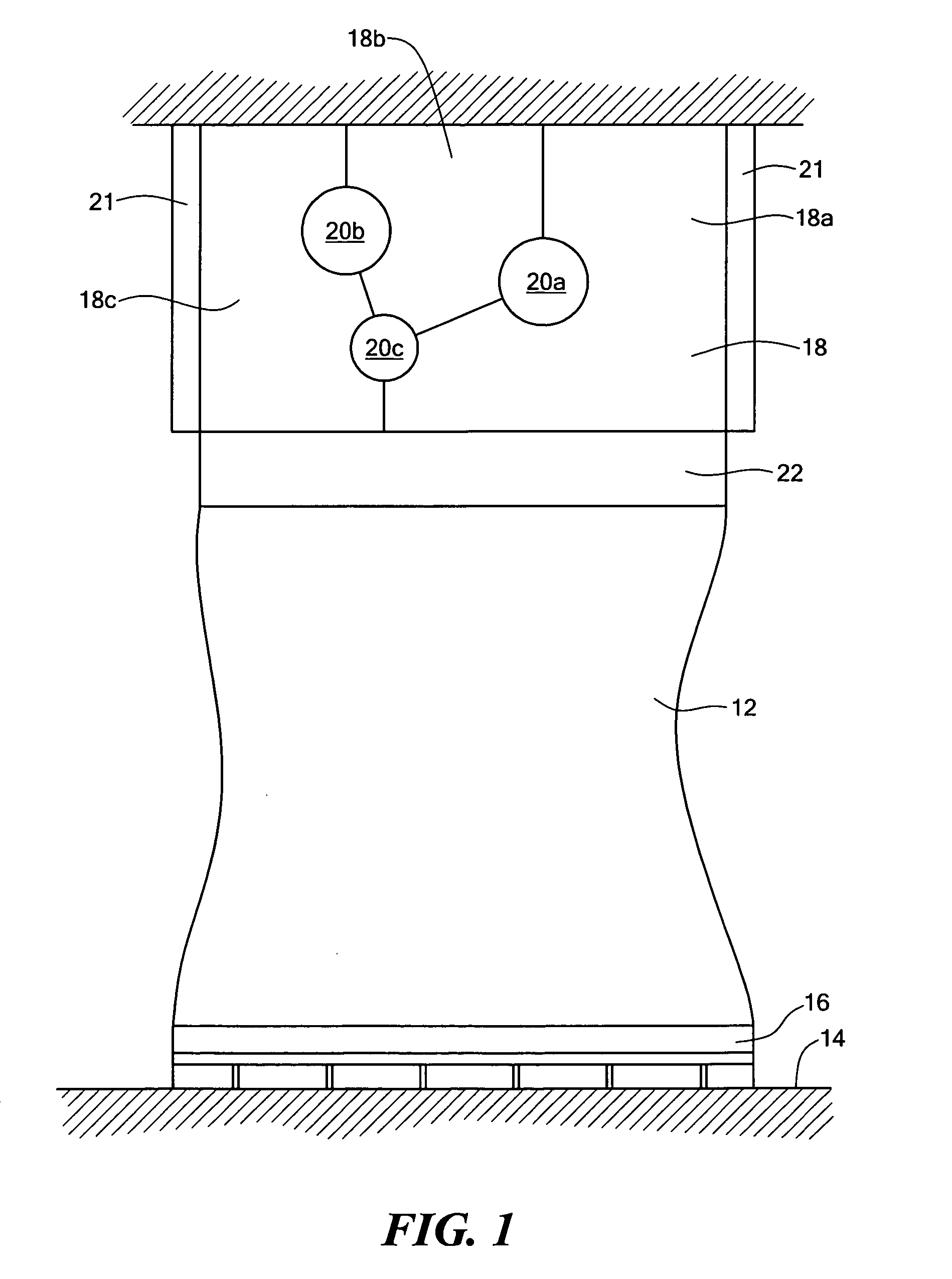
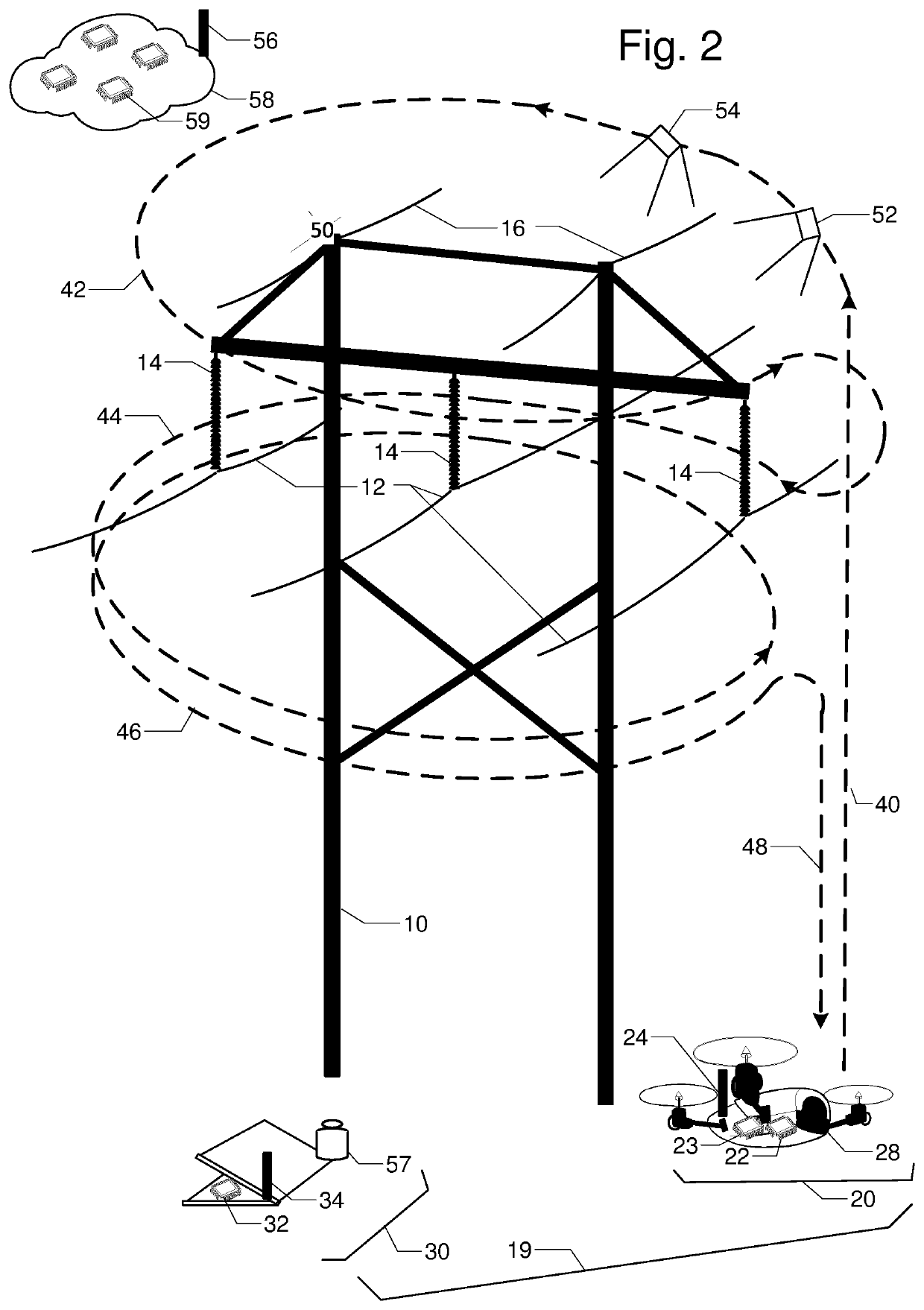
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of transmission tower 10, phase conductors 12, insulators 14, and shield wires 16. They are to be inspected by unmanned aerial vehicle UAV 20 with embedded processor and memory 22, radio 24, location rover 26, and camera 28. Base station 30 has processor and memory 32, radio 34, and location base 36. The relative location between UAV 20 and base station 30 can be accurately calculated by location base 36 and location rover 26 communicating over radios 24 and 34. Camera 28 on UAV 20 is first used to capture two or more orientation images 38 and 39 of tower 10; lines 12 and 16; and insulators 14 from different vantage points. Terrestrial or close-range photogrammetry techniques are used create a three dimensional model of tower 10; lines 12 and 16; and insulators 14. Based on inspection resolution and safety objectives, a standoff distance 50 is determined. Then a flight path with segments for ascent 40, one or more loops 42, 44, 46, and a descent 48 is designed to ensure full inspection coverage via inspection images like 52 and 54.
Owner:VAN CRUYNINGEN IZAK JAN
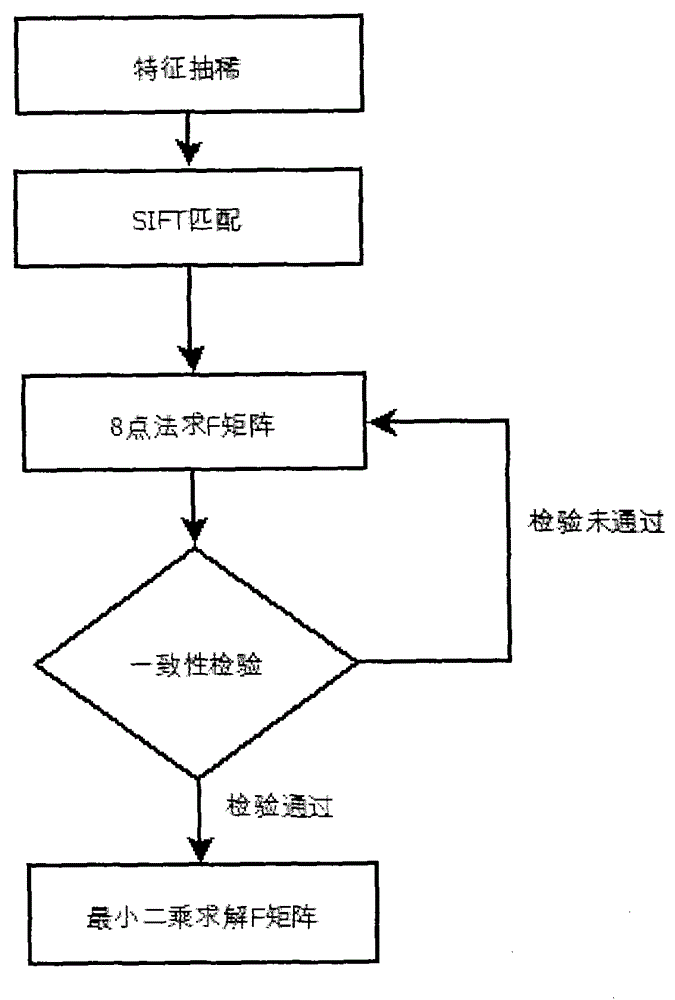
Detecting and identifying method for annular coding mark point
InactiveCN103310215AImprove recognition rateReduce the impact of recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionOptical axis
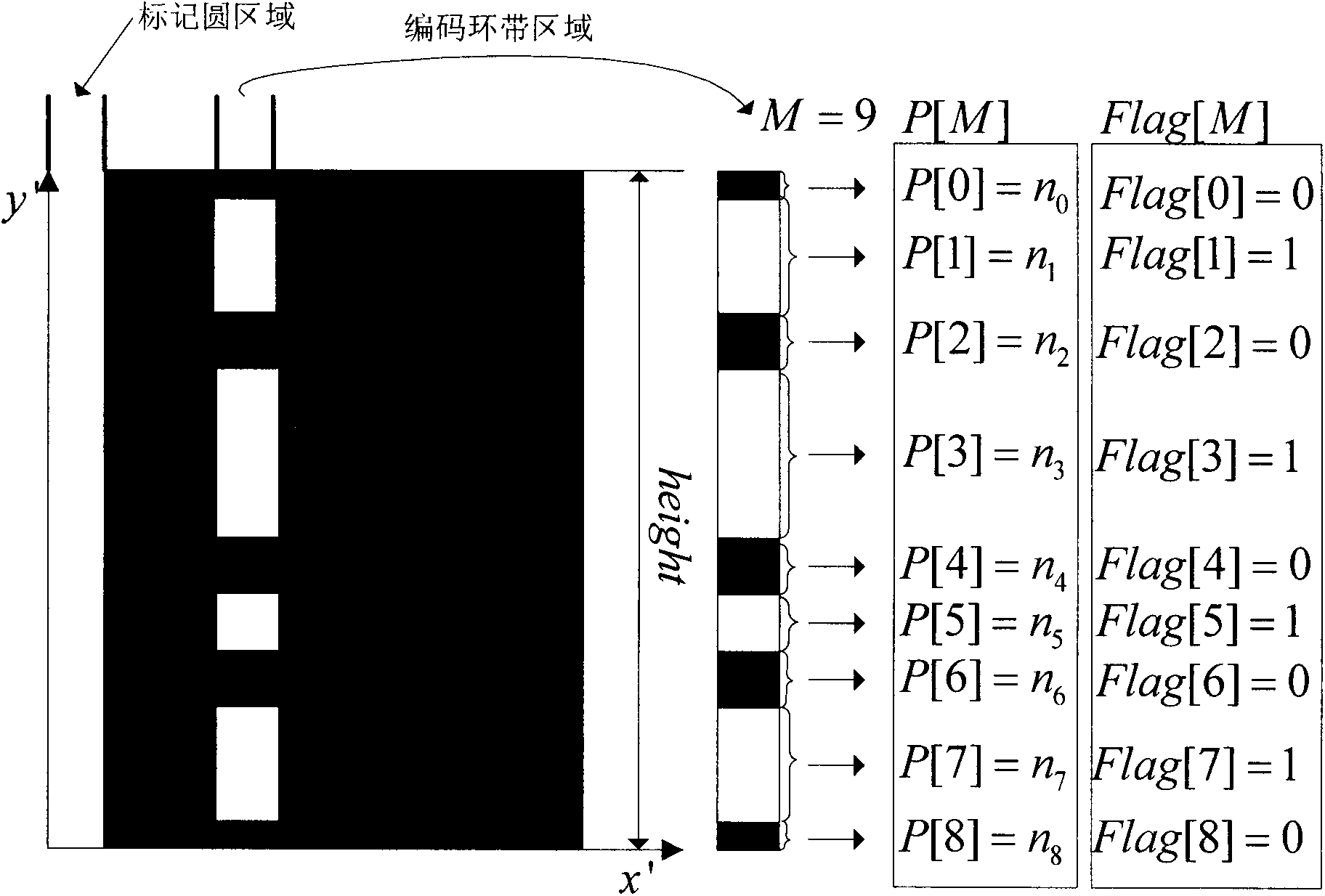
The invention belongs to the field of close-range photogrammetry and relates to a detecting and identifying method for an annular coding mark point. The method includes that first, canny edge detection is conducted on a collected image, an outline centroid is closed through a series of limiting conditions and calculation, and noise and non-coding mark points are filtered; then least square ellipse fitting is adopted, coding mark point location is conducted, an ellipse fitting error is combined to judge a partition coding mark point outline, and the outline is filled; finally, ALPC transformation for transforming a local concentric ellipse into parallel straight lines is provided, the ALPC transformation is conducted on the partitioned coding mark point, and transformed image characteristics are used for decoding. By means of the detecting and identifying method, location of the coding mark point can reach a sub pixel level, local shape characteristics of a concentric ellipse are transformed into shape characteristics of parallel straight lines which are easy to detect and calculate, coding mark point identifying speed is improved, and effects of an included angle of a camera optical axis and a coding mark point normal on the coding mark point identifying accuracy can be reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Increasing measurement rate in time of flight measurement apparatuses
An apparatus for measuring distance to a surface is disclosed. The apparatus transmits at least one subsequent pulse of light prior to receiving a reflection of a previously sent pulse of light. Thus, multiple pulses of light are in-flight at a given time. The embodiments are applicable to terrain mapping, bathymetry, seismology, detecting faults, biomass measurement, wind speed measurement, temperature calculation, traffic speed measurement, military target identification, surface to air rangefinding, high definition survey, close range photogrammetry, atmospheric composition, meteorology, distance measurement, as well as many other applications. Examples of such apparatuses include laser ranging systems, such as light detection and ranging (LIDAR) systems, and laser scanners. Data received from the apparatus by a data processing unit can be used to create a data model, such as a point cloud, digital surface model or digital terrain model describing the surface, terrain, and / or objects.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
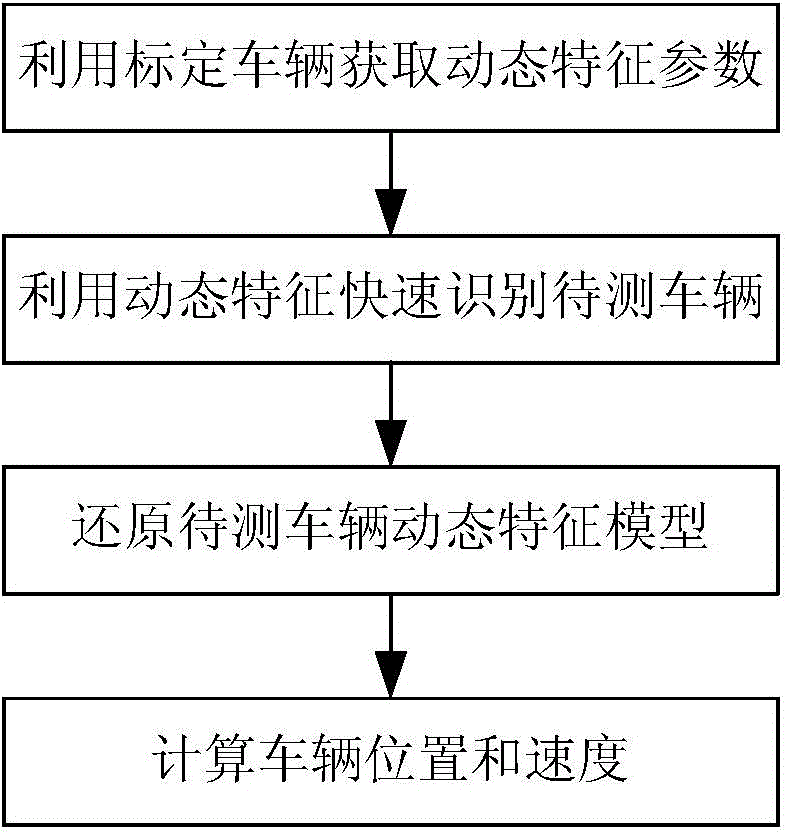
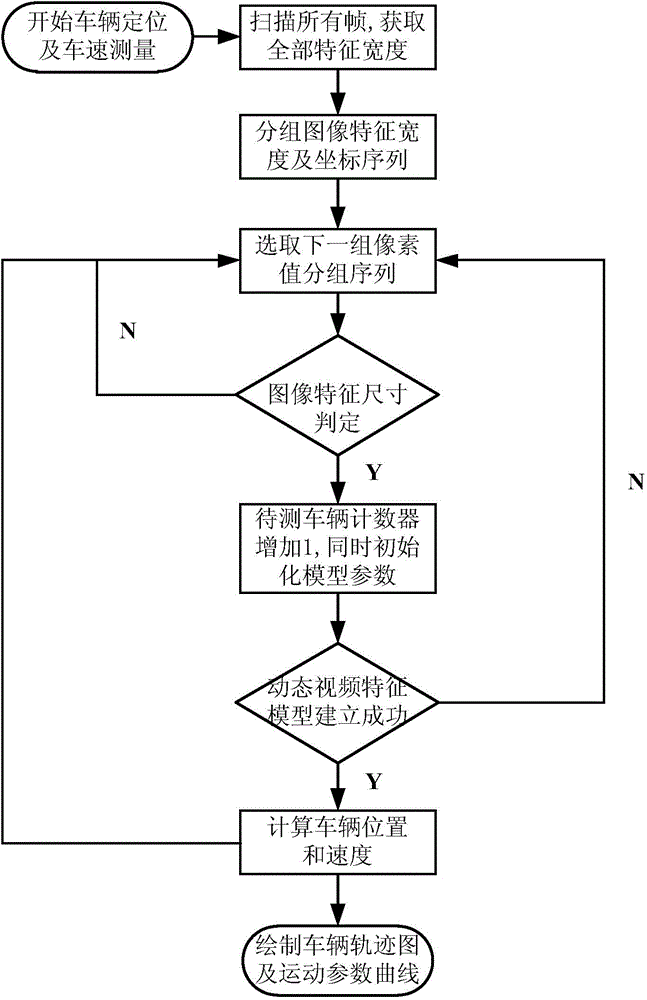
Vehicle positioning and speed measuring method based on dynamic video feature of vehicle
InactiveCN104021676AWide speed rangeA large amount of detection informationImage analysisDetection of traffic movementVideo monitoringVehicle dynamics
The invention relates to a vehicle positioning and speed measuring method based on the dynamic video feature of a vehicle, belonging to the technical field of intelligent transportation and close-range photogrammetry. The vehicle positioning and speed measuring method comprises the following steps: judging the vehicle dynamic video feature size in a video image within any time quantum in one video monitoring system according to vehicle dynamic feature parameters extracted from the video image which calibrates a vehicle traveling process, and reconstructing and reducing a dynamic video feature model of a to-be-measured vehicle traveling process corresponding to each image frame; and calculating an actual position and a vehicle speed value sequence corresponding to each image frame in the to-be-measured vehicle traveling process according to a mapping relation between the dynamic variation characteristic of the image feature size of a vehicle to be measured and the actual vehicle movement parameters, and thus acquiring the actual position and traveling speed information of the vehicle. The vehicle positioning and speed measuring method is easy to realize and high in accuracy, and is applicable to the demands of various vehicles on speed measurement in a road traffic video monitoring system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
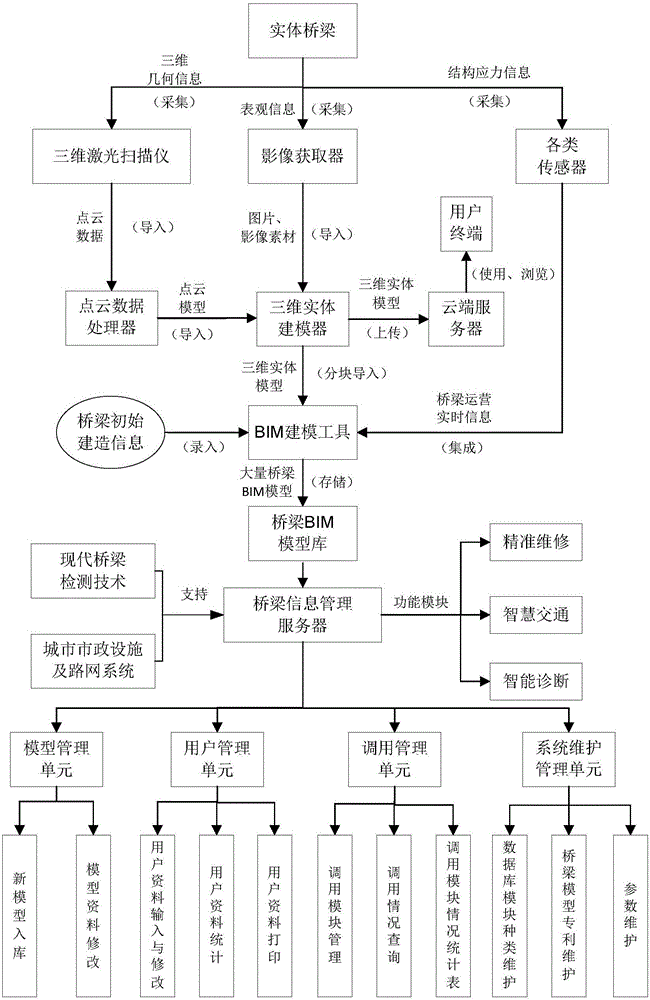
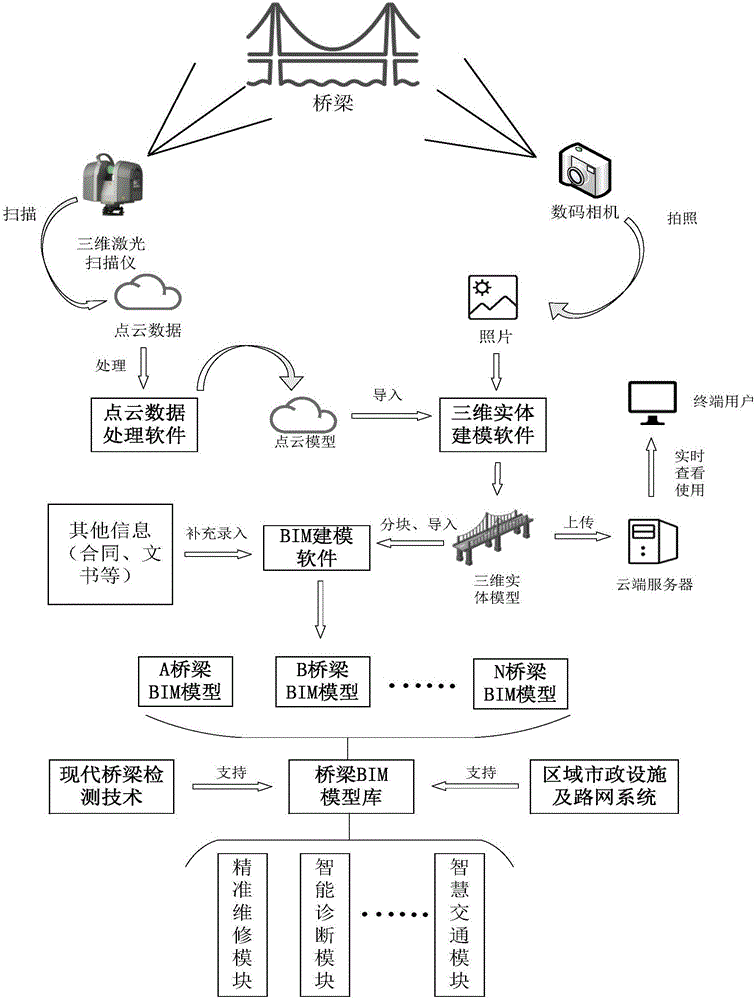
Existing bridge quick BIM modeling system and method
PendingCN106777680AOvercome limitationsImprove efficiencyGeometric CADImage data processingPoint cloudModeling software
The invention discloses an existing bridge quick BIM modeling system and method. The three-dimensional laser scanning technology serves as a bridge three-dimensional geometric data acquisition tool, and the limitation of passive ranging in traditional close-range photogrammetry, namely limitation of natural light conditions, is overcome. In actual application examples, by comparing a BIM model built through three-dimensional scanning and an actual building, it is found that the similarity between the BIM model and the actual building can reach 90% or above. A full-color-point cloud model is obtained through the three-dimensional scanning technology, a vivid and fine virtual model can be generated through three-dimensional entity modeling software processing, the method can be used for webpage real-time publish and sharing, and the cooperative work efficiency is improved. The whole BIM modeling process is convenient, quick and precise, as for small-and-medium-sized bridges, it takes a few hours from field work scanning to building of the whole BIM model, and model errors can be controlled at the millimeter level.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
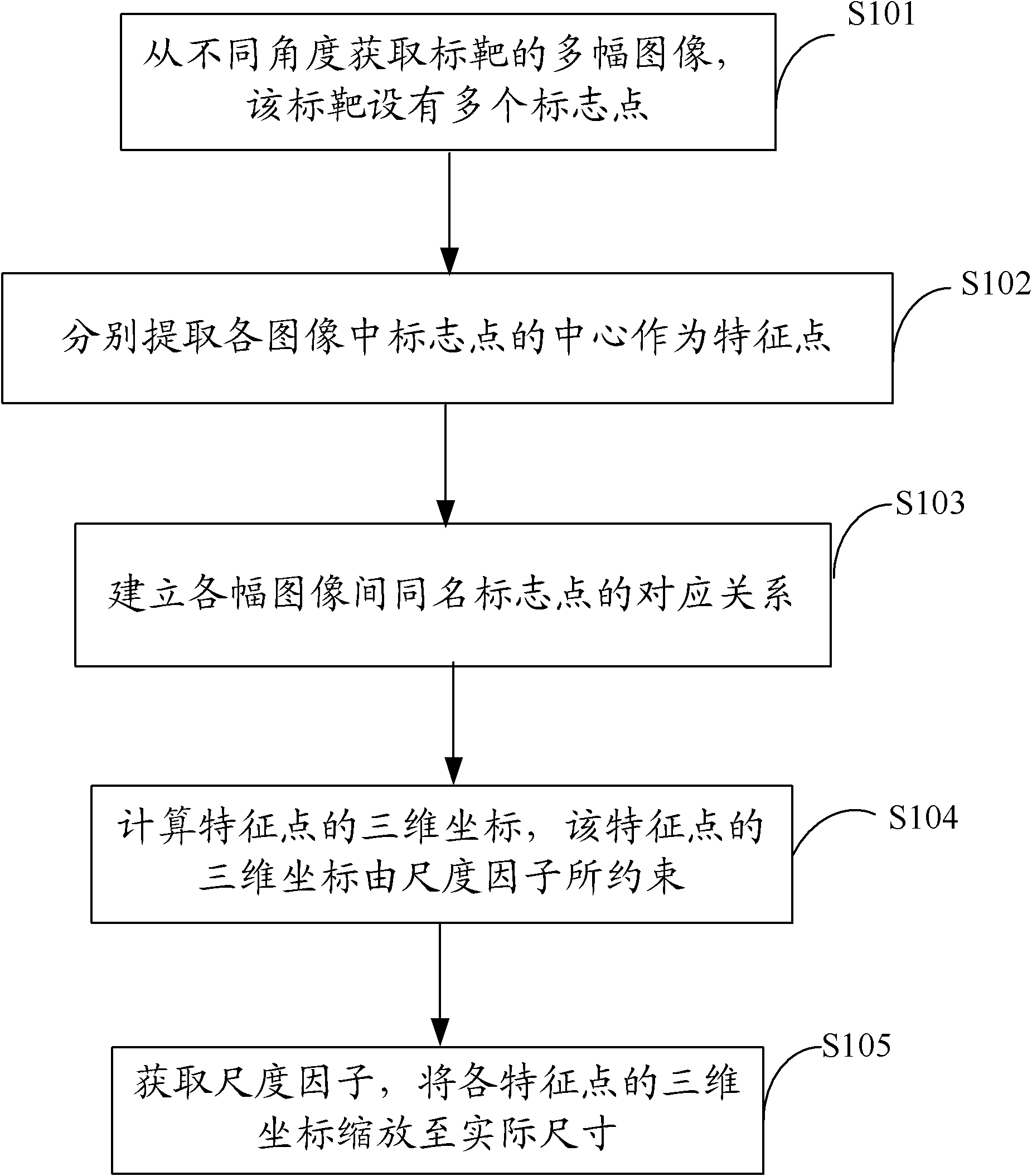
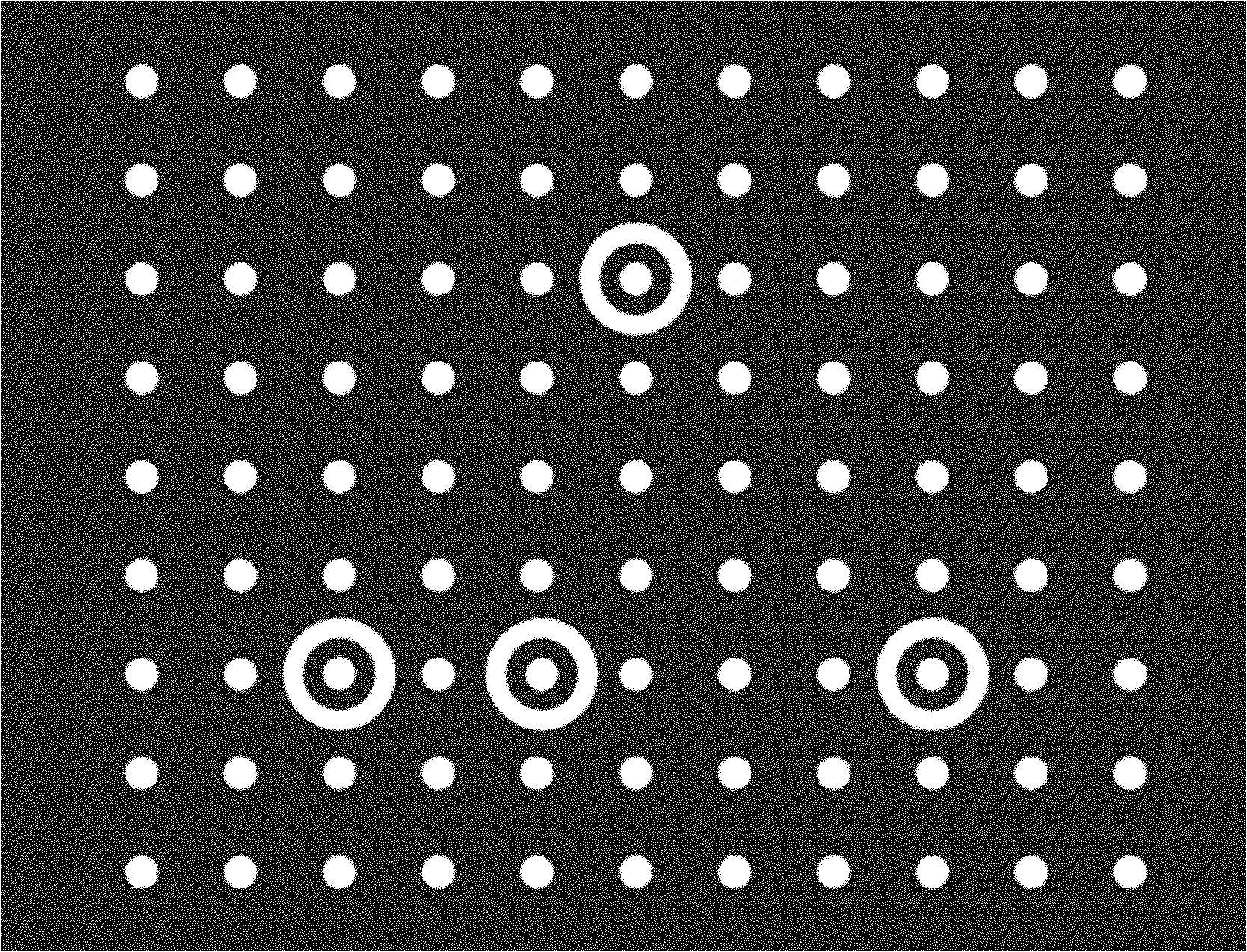
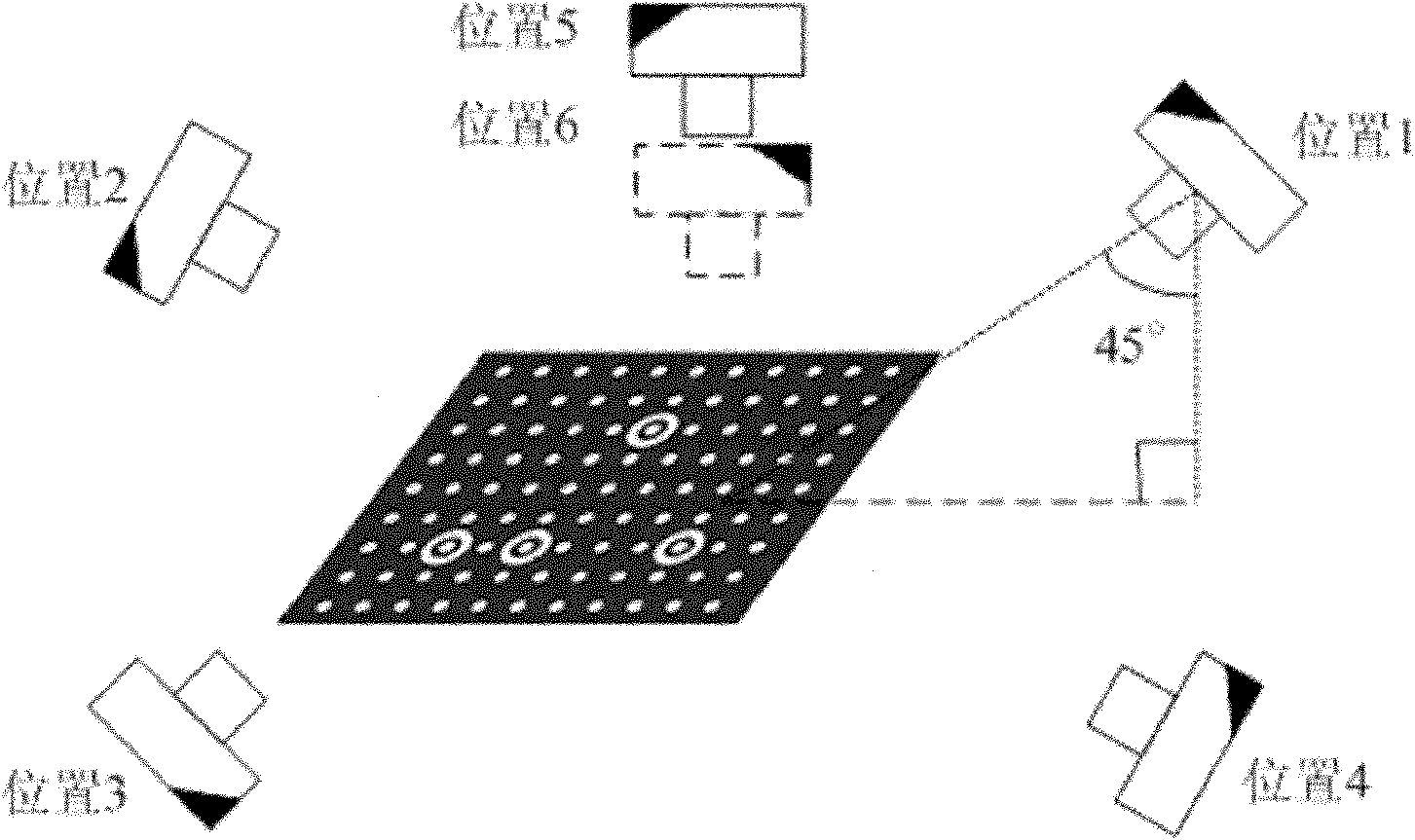
Target correction method and system
The invention is applicable to the field of machine visual and three-dimensional measurement and provides a target correction method and system. The embodiment of the invention provides the target correction method, comprising the following steps of: photographing a target from different angles to obtain a plurality of images; respectively extracting the center of a marking point in each image as a characteristic point and establishing a corresponding relation of the marking points with the same name between the images; combining a close-range photogrammetry technology to calculate a three-dimensional coordinate of the characteristic point, wherein the three-dimensional coordinate is restrained by a scale factor; finally obtaining the scale factor and zooming the three-dimensional coordinate of each characteristic point to an actual size. The target manufactured and corrected by the method has the advantages of higher precision, easiness for operation and low cost. Meanwhile, the scale factor is obtained by adopting a fringe projection measurement system and a standard ball, the correction precision is higher and the relative precision (absolute precision / target size) can reach 1:1000. Therefore, the method and the system provided by the invention can be widely applied to the vision measurement and the system calibration.
Owner:SHENZHEN ESUN DISPLAY
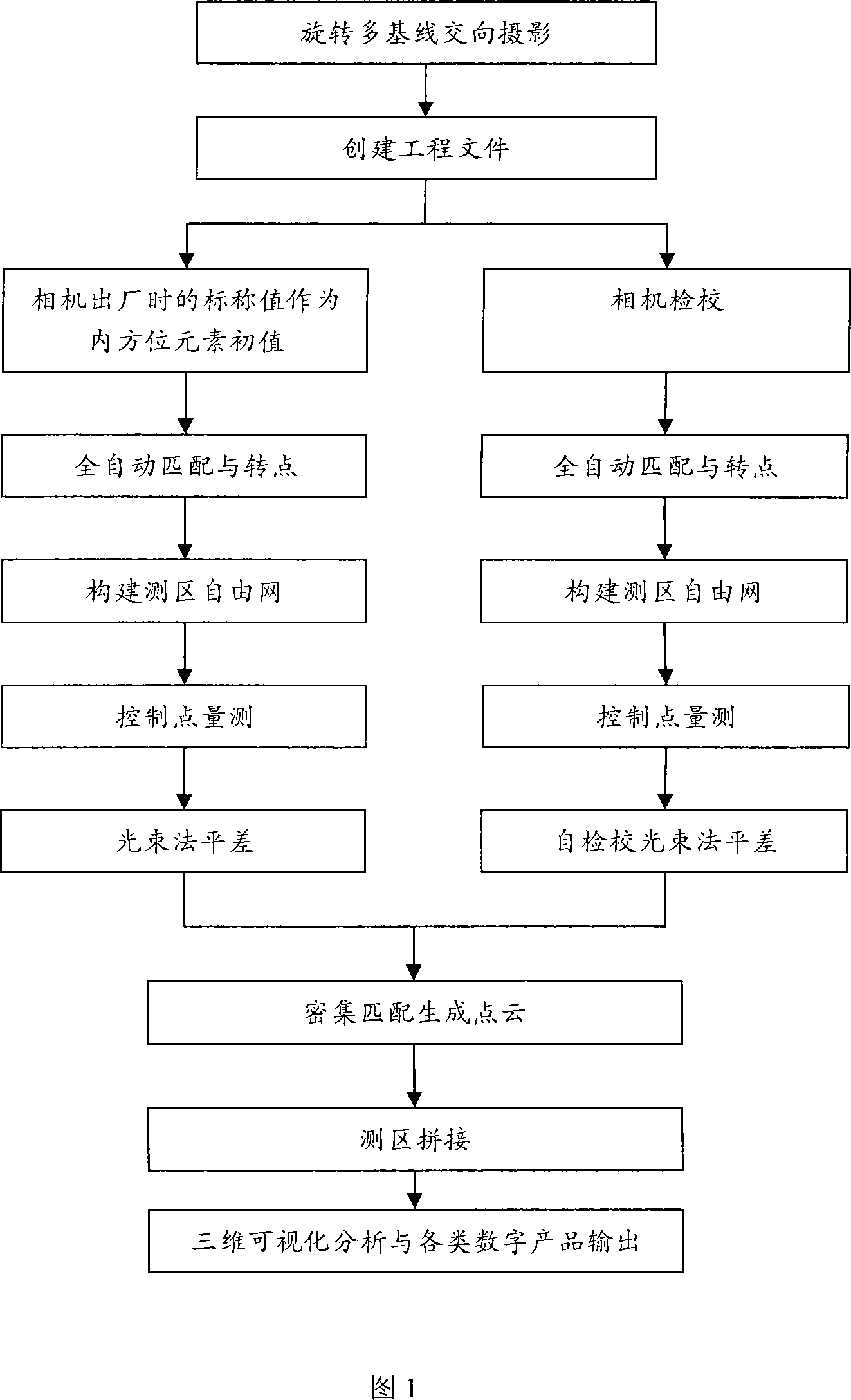
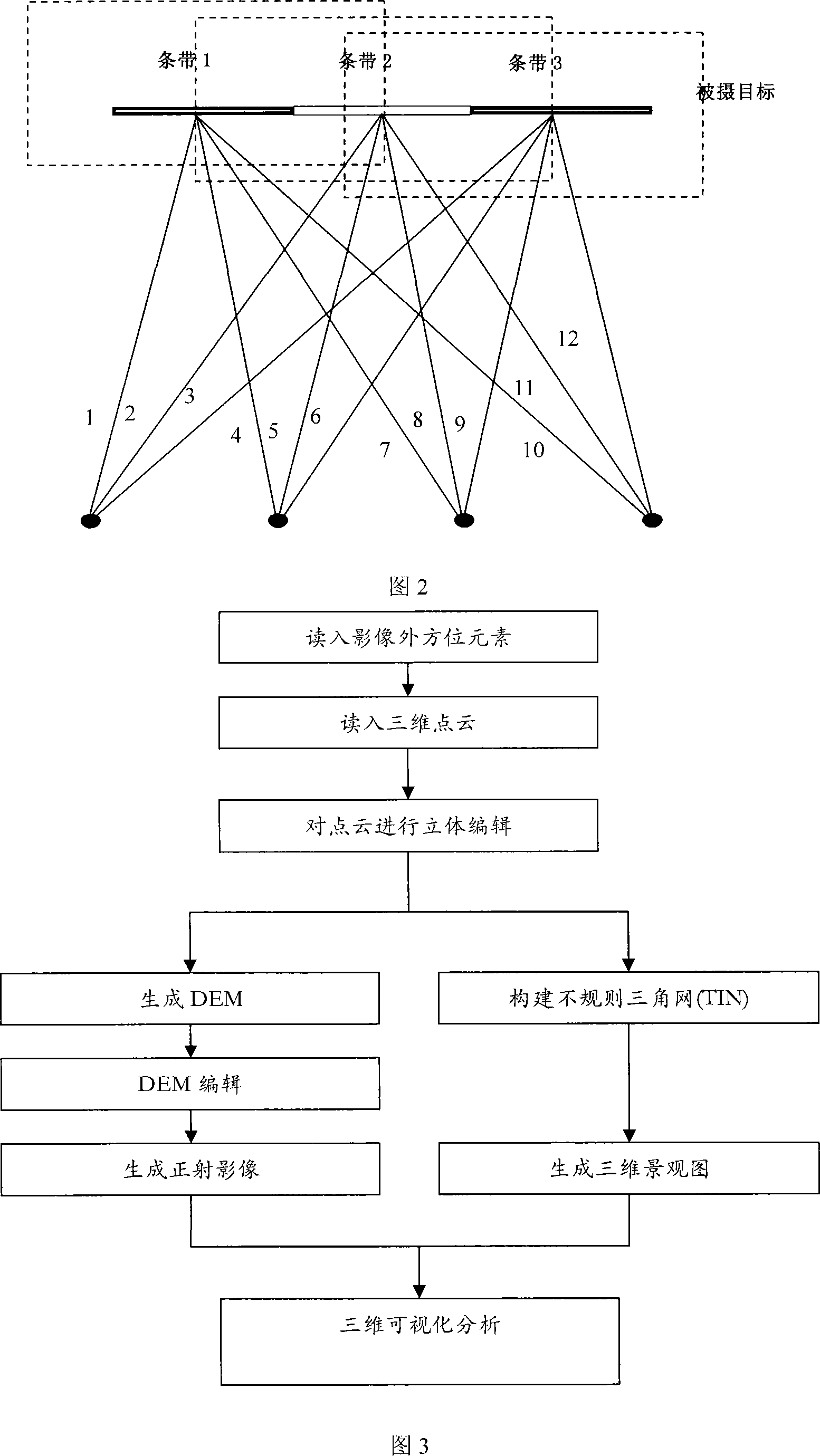
Digital close range photogrammetry method
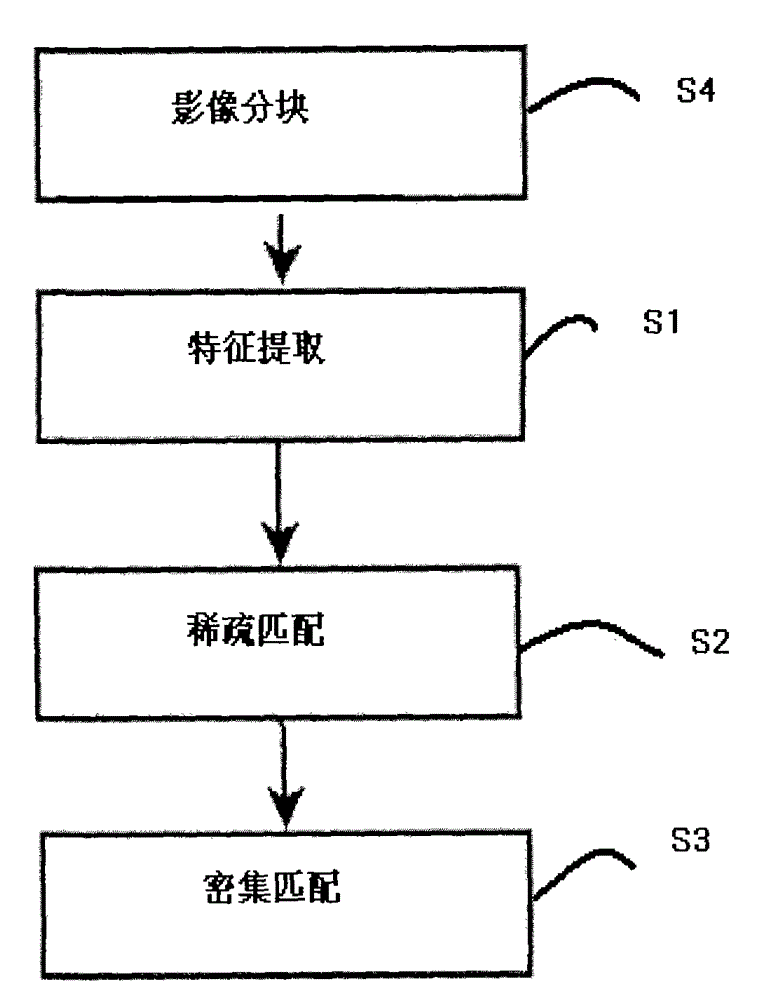
InactiveCN101226057AImprove matching accuracyImprove matching speedPicture interpretationPoint cloudClose range photogrammetry
The invention belongs to the photography measurement field, in particular to a digital close-range photogrammetry, which comprises the steps: a rotary multiple reference line convergent photography can be implemented by a camera; the close-range shooting data can be processed so as to obtain precision data, which comprises the steps: the inner orientation element initial value is obtained; the matching and turning point is in full automatic; the matching method is that the inner image strip matching is implemented with the adjacent image strip matching crossways; a measuring area free net is built; the point measurement is controlled; the beam method balancing or self-checking beam method balancing is implemented; a dense matching can be implemented according to the precision close shot data so as to generate the three-dimensional point cloud; the three-dimensional visualization measurement analysis can be implemented based on the three-dimensional point cloud. The digital close-range photogrammetry has the advantages that: the field reference point quantity can be reduced and the field workload can be lowered by taking the obtained image from the rotary multiple reference line convergent photography as a whole to implement balancing; the matching precision and speed can be improved through the rotary multiple reference line convergent photography and corresponding matching craft, furthermore, the digital close-range photogrammetry can support full automatic process to the close-range image.
Owner:WUHAN LENSOFT
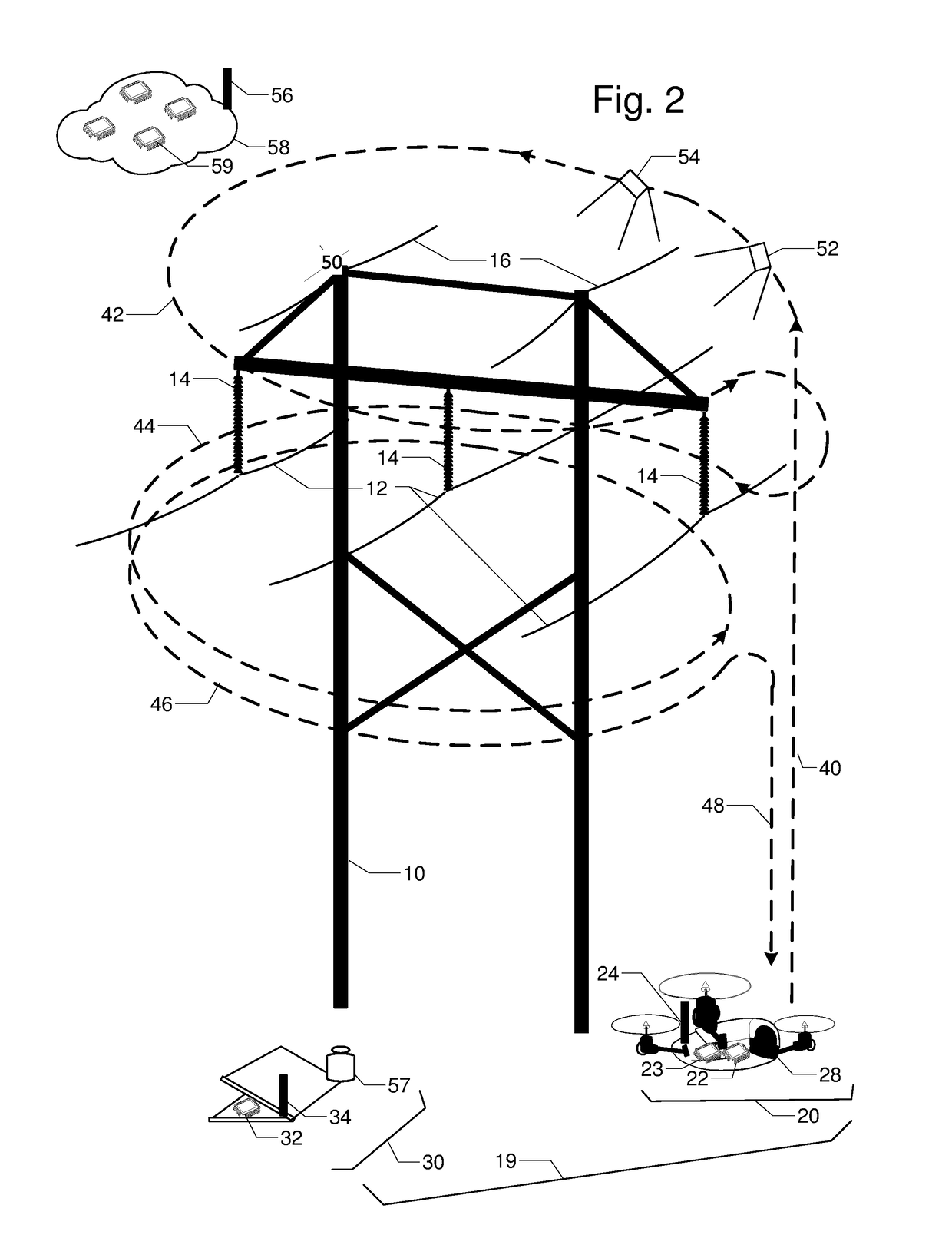
Flight Planning for Unmanned Aerial Tower Inspection with Long Baseline Positioning
ActiveUS20180095478A1Accurate calculationFull coverageSatellite radio beaconingElectromagnetic wave reradiationTransmission towerRadio equipment
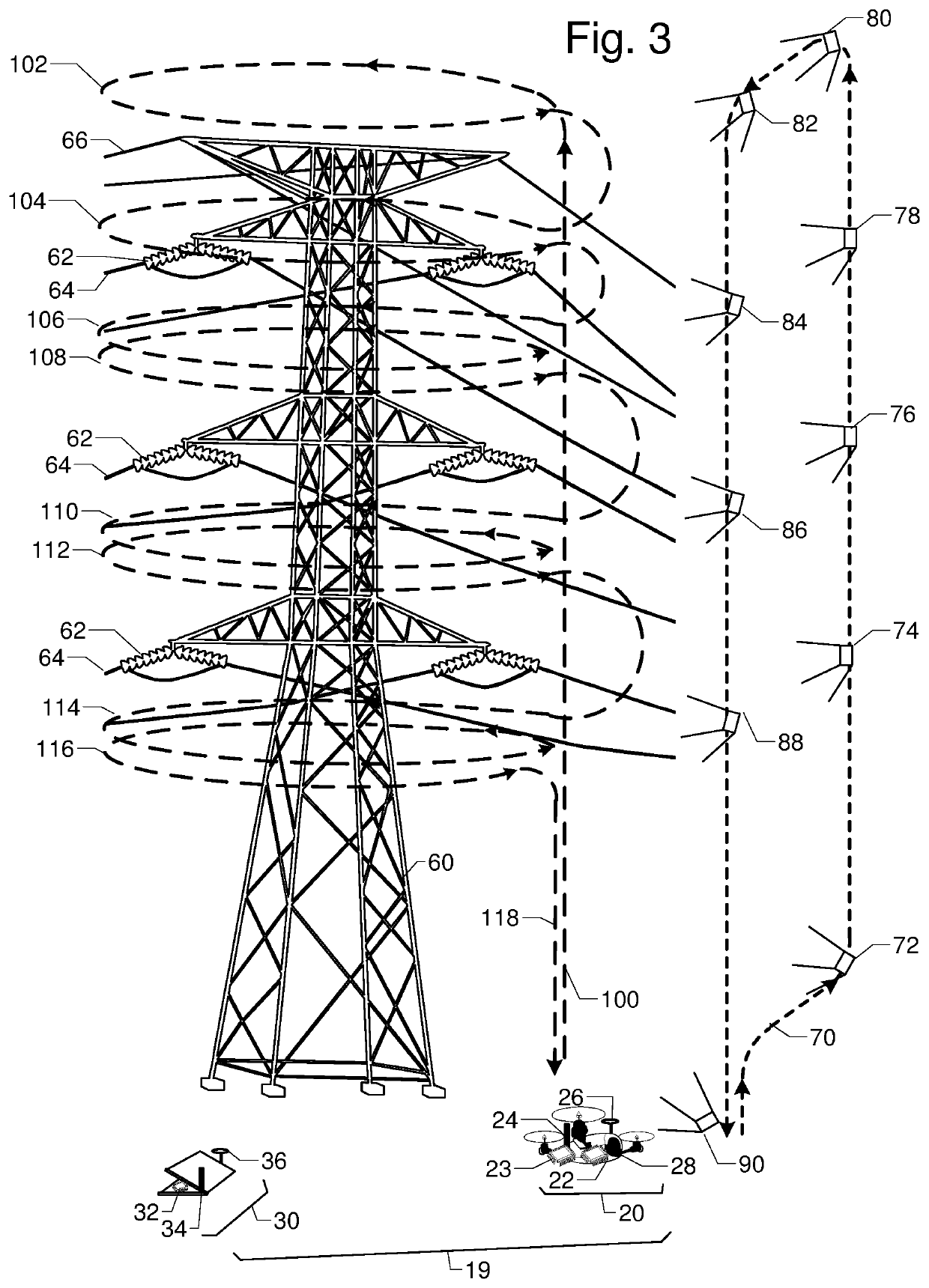
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of transmission tower 10, phase conductors 12, insulators 14, and shield wires 15. They are to be inspected by unmanned aerial vehicle UAV 20 with embedded processor and memory 22, radio 24, location rover 26, and camera 28. Continuously operating reference station 16 has GNSS antenna 17, GNSS receiver 19, and radio 18. The relative location between UAV 20 and reference station 16 can be accurately calculated using location corrections sent by radio 18 to radio 24. Camera 28 on UAV 20 is first used to capture two or more orientation images 38 and 39 of tower 10; lines 12 and 15; and insulators 14 from different vantage points. Terrestrial or close-range photogrammetry techniques are used create a three dimensional model of tower 10; lines 12 and 15; and insulators 14. Based on inspection resolution and safety objectives, a standoff distance 50 is determined. Then a flight path with segments for ascent 40, one or more loops 42, 44, 46, and a descent 48 is designed to ensure full inspection coverage via inspection images like 52 and 54.
Owner:VAN CRUYNINGEN IZAK
Architecture physical data rapid three-dimensional sampling method
InactiveCN101290237AReduce the impactGuaranteed isochronismPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryGas compositionData recording
The present invention discloses a quick three-dimensional sampling method for physical data of a building. The present invention adopts a miniature unmanned aircraft to load corresponding types of sensing devices, data recording devices and information returning devices, etc., so as to acquire the physical data (intensity of sound, audio, temperature, humidity, illuminance, light color, gas components, electromagnetic field intensity, air-ion concentration, radiation strength, etc.) and carry out round trip flight in space and continuously acquire the physical data at each point of the path, and position the miniature aircraft by a photogrametry technology. The method concretely comprises the steps of: selection of the miniature unmanned aircraft for indoor flight, selection of sensing devices or sensors for sampling the physical data of the building, establishment of a system synchronous clock, sampling of the physical data of the building and accurate spatial positioning for the sampling points by a close-range photogrammetry method. Since the aircraft is fast in moving speed and is not restricted by the ground movement condition, the isochronism of the data can be ensured even if the number of the spatial sampling is largely increased than that of the ground operations.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
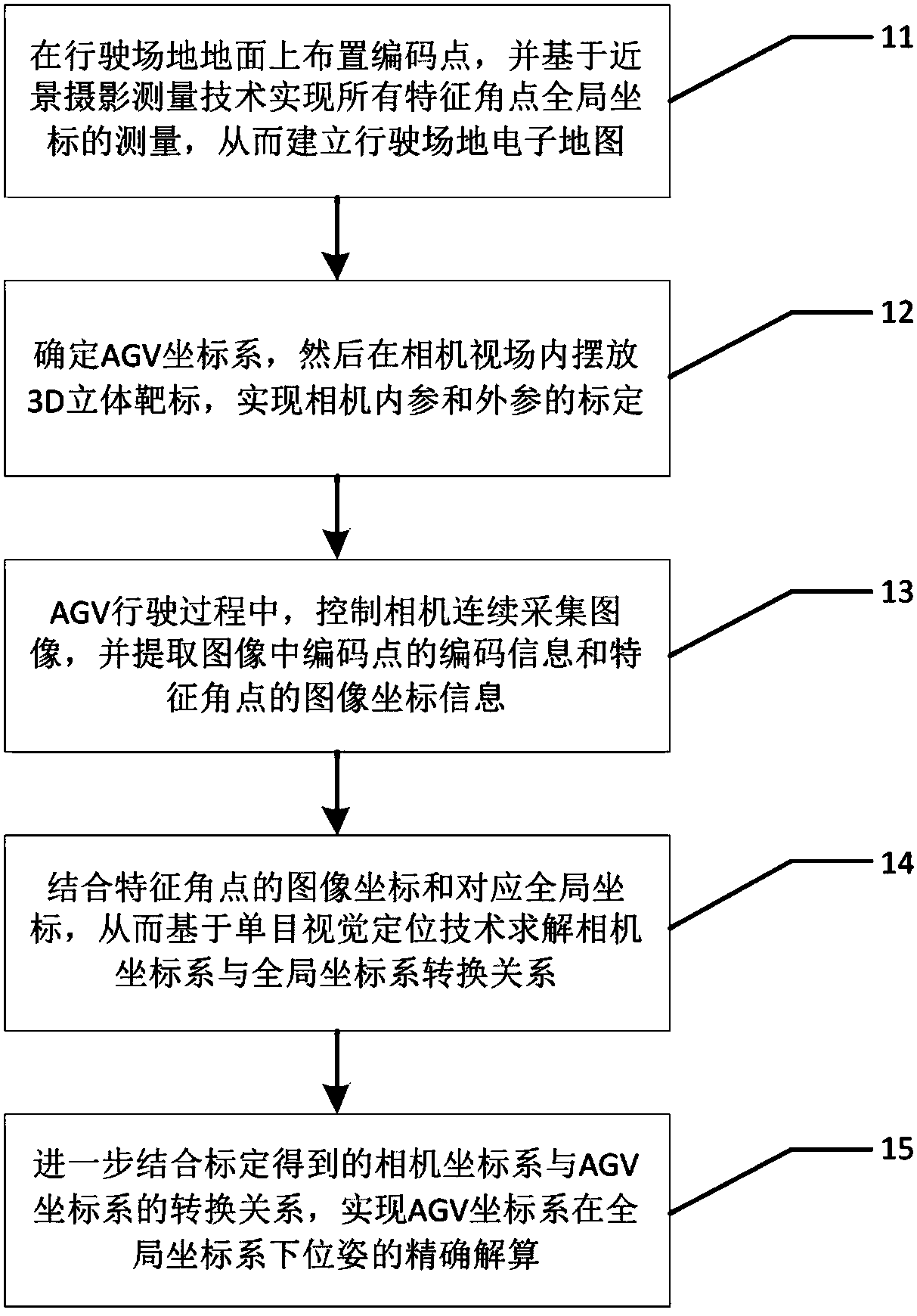
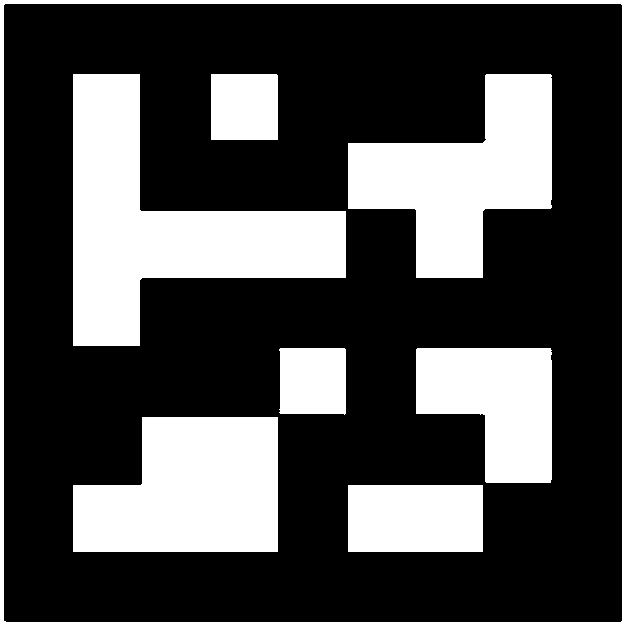
AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) visual positioning system and method
ActiveCN108571971AGuaranteed flexibilityGuaranteed real-timeNavigational calculation instrumentsAngular pointAutomated guided vehicle
The invention relates to an AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) visual positioning system and method. The system is formed by encoded points on the ground and a camera, a light source and an industrial personal computer which are on an AGV body, wherein each encoded point on the ground not only can provide unique encoded identification information and meanwhile, also provide information of global coordinates of a plurality of characteristic angular points; the global coordinates are acquired by a close range photogrammetry technology and are used for establishing a driving field electronic map so as to provide bases for AGV visual positioning; by calibrating a position and posture relationship between a camera coordinate system and an AGV coordinate system, accurate solution of a position and aposture of the AGV coordinate system under a global coordinate system can be implemented in the driving process on the basis of the characteristic information of the encoded points in a view field and a monocular visual positioning technology. The AGV visual positioning system and method provided by the invention have the characteristics of high flexibility, high accuracy, good real-time performance, high robustness and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
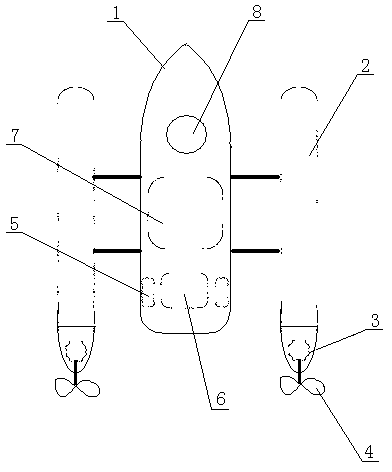
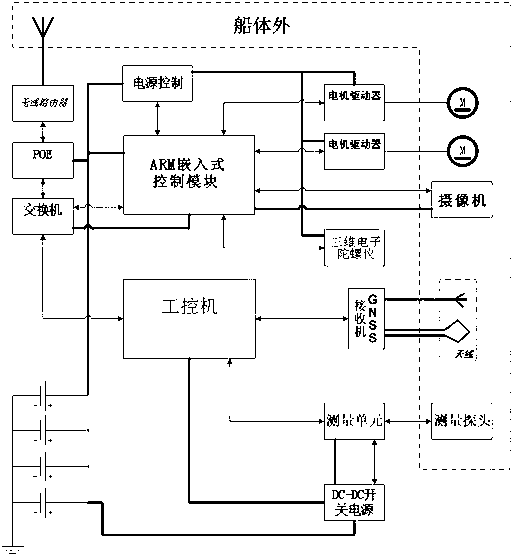
Rudderless unmanned ship capable of automatically sailing
ActiveCN103303452AReduce usageSimple structurePropulsion power plantsPropulsive elementsTerrainCommunication unit
The invention relates to the technical field of unmanned remote control measurement, and provides a rudderless unmanned ship capable of automatically sailing, which comprises a ship body, pontoons on the two sides, a communication unit, a navigation and positioning unit, a measuring unit, a power and driving unit, a ship body gesture measuring unit, an industrial personal computer, and a battery providing a working power supply for the other parts. According to the invention, the advancement, backing and turning of the unmanned ship can be realized through controlling the turning and speed difference of the power equipment mounted on the two sides of the ship body; the unmanned ship can complete planned sailing lines to perform measuring tasks such as underwater terrain plotting, flow velocity and flow rate measurement, and close-range photogrammetry; the automatic voyage of the unmanned ship at the rudderless state can be realized; the flexibility of the unmanned ship is improved; and the measuring working efficiency is greatly improved and the cost is reduced.
Owner:WUHAN CHUHANG SURVEYING SCI&TECH
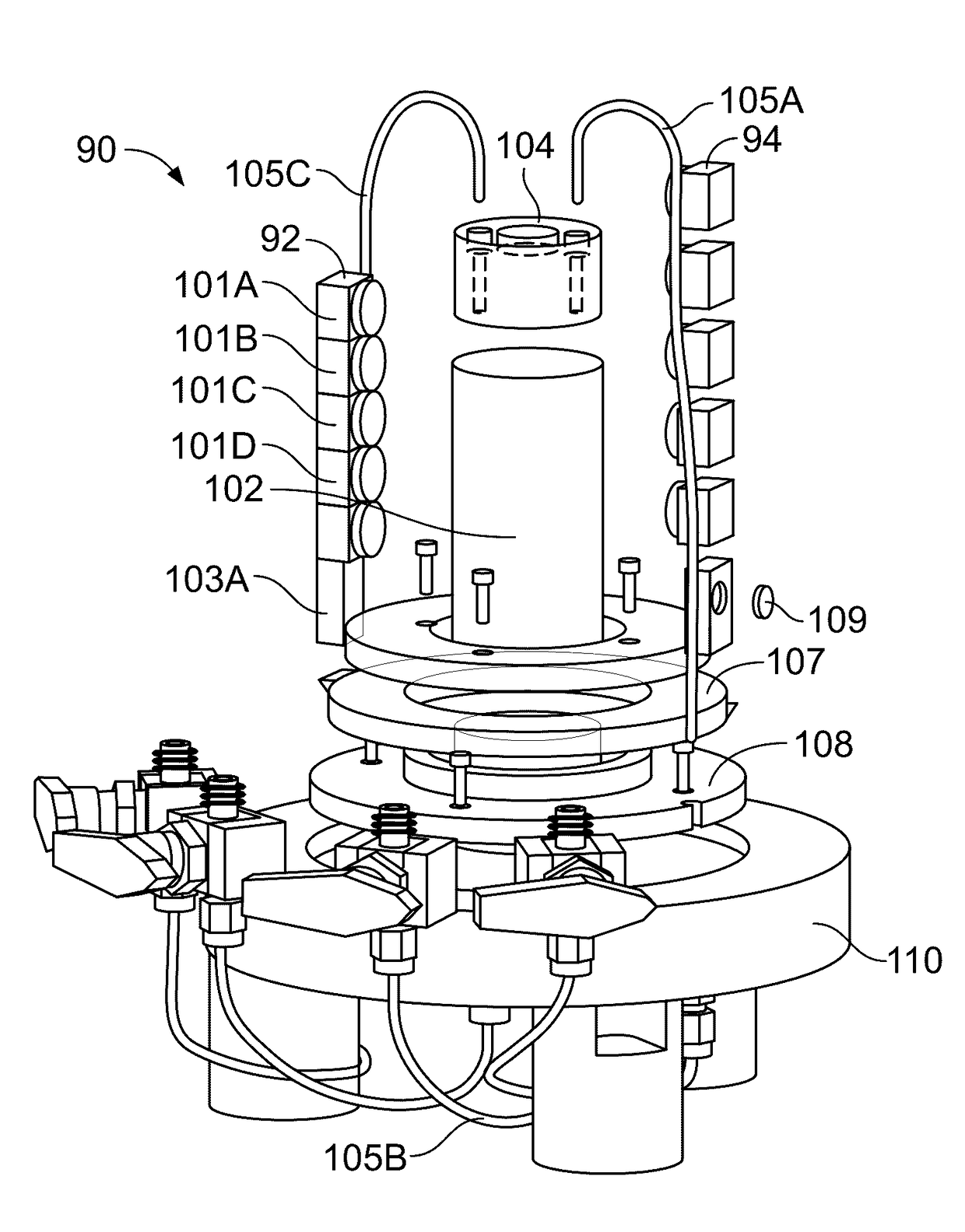
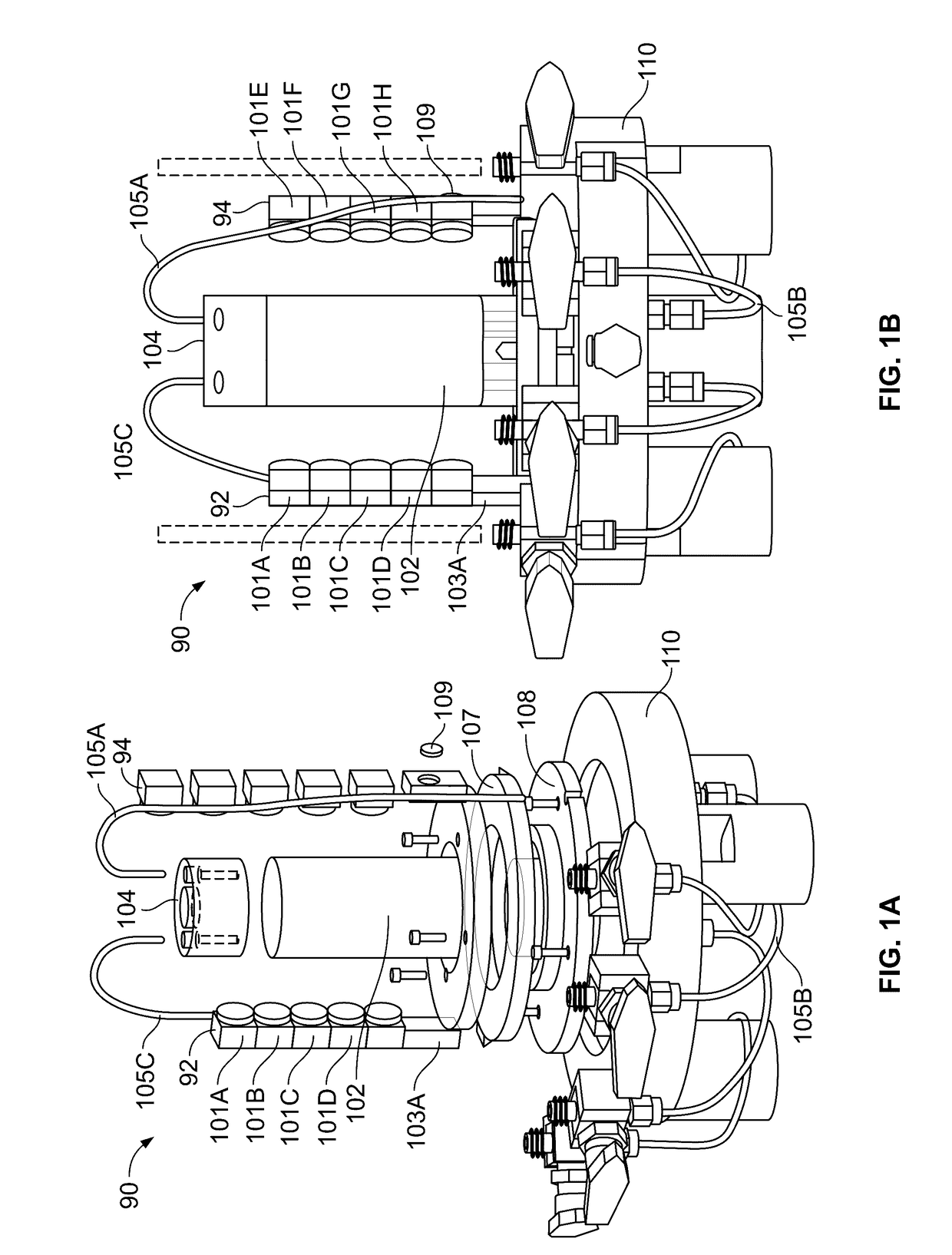
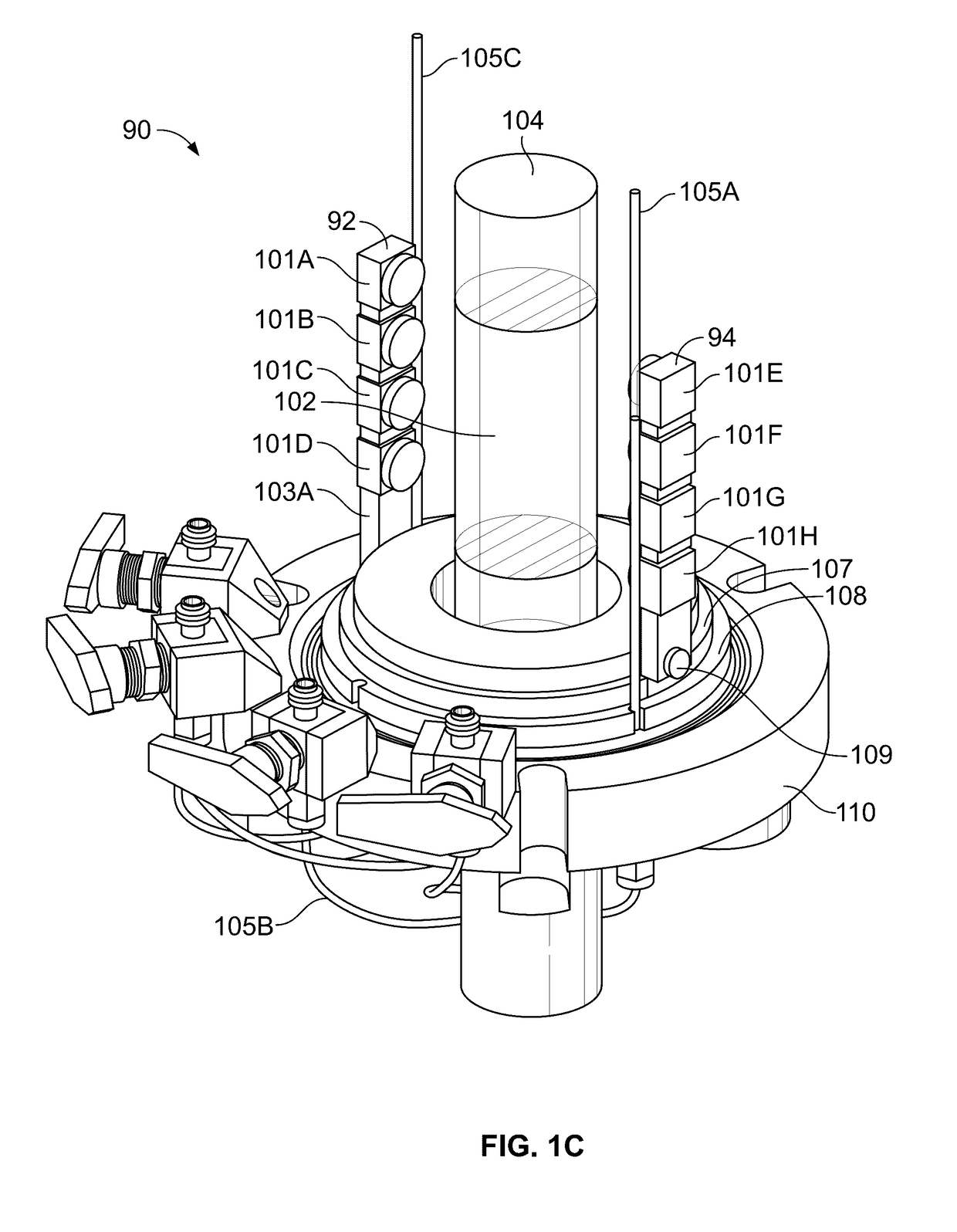
Pressurized Fluid-Submerged, Internal, Close-Range Photogrammetry System for Laboratory Testing
ActiveUS20170150015A1High quality imagingTelevision system detailsEarth material testingClose range photogrammetryEngineering
A device for measuring strain and volume of a soil sample including an enclosure adapted to receive a soil sample within another enclosure. A base adapted to hold the sample enclosure. The device also has a plurality of moveable arms located between the enclosures which may be a spaced distance apart and adapted to move around the sample. Cameras as included on the arms.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Non local stereopair dense matching method based on image gray scale guiding
InactiveCN106530337AGuaranteed matching accuracyGuaranteed matching robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxPattern recognition
The invention relates to a non local stereopair dense matching method based on image gray scale guiding. The non local stereopair dense matching method based on image gray scale guiding includes the steps: performing cost computation: taking an improved HOG operator as a cost measure, computing the cost between homonymous pixels, taking the cost as the means of describing the similarity between the homonymous pixels, and establishing a cost matrix; performing cost accumulation based on image gray scale guiding, and obtaining a stable cost accumulation result; according to a WTA strategy, obtaining an initial disparity image, rejecting a mis-matching point and an occulsion point, and obtaining a refined disparity image; and finally according to the disparity image, generating a dense high-precision three dimensional point cloud. The non local stereopair dense matching method based on image gray scale guiding fully considers the edge gray scale characteristics, has relatively high matching precision on the disparity edge, uses an eight-direction iterative cost accumulation mode so as to increase the matching robustness of a texture lacking area, and can quickly obtain a dense high-precision three dimensional point cloud, thus having great application prospect in the field of aerospace photogrammetry, low altitude photogrammetry and close-range photogrammetry, automatic driving of unmanned vehicle.
Owner:WUHAN ENG SCI & TECH RESINST
Complex multi-pipeline system detection method
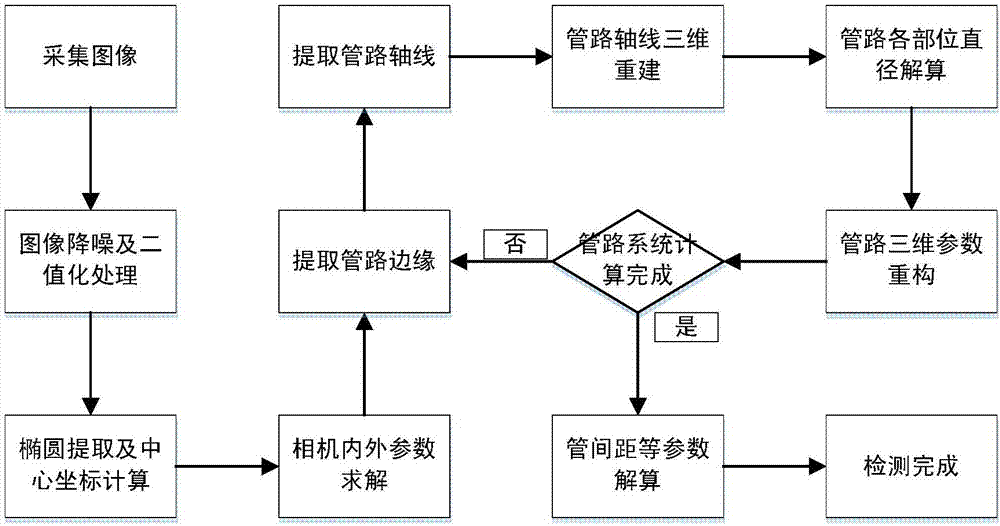
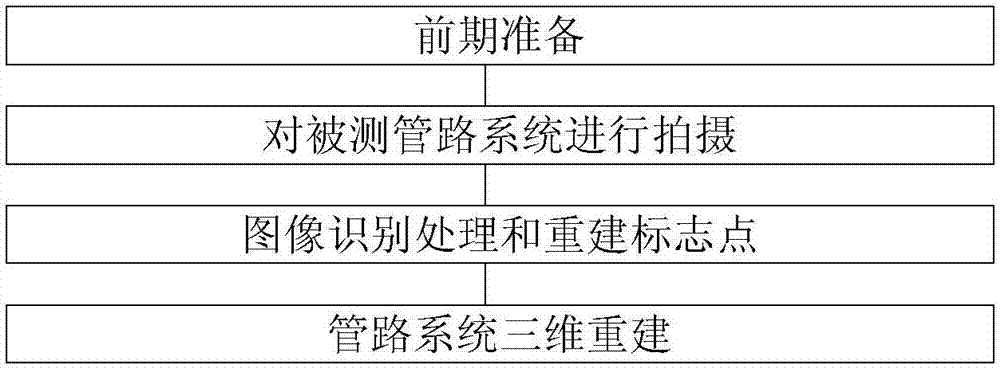
ActiveCN107218928AImprove the status quo of manual inspectionImprove measurement efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansImaging processingOptical measurements
The invention relates to a complex multi-pipeline system detection method. Mark points adhered to the surfaces of attachments in a to-be-detected pipeline system are used as the basis of industrial photogrammetry solution for later solution of inner and outer parameters of a digital camera; scales placed at the edges of the pipeline system or in other adjacent pipeline systems are used for carrying out corresponding solution on a pixel size of a camera and an actual length size of the camera in a physical coordinate system. According to the complex multi-pipeline system detection method disclosed by the invention, an optical measurement means is used; by image processing, two-dimensional pipeline identification is carried out; based on an industrial close-range photogrammetry principle, reconstruction of a three-dimensional pipeline is carried out. An image is used for carrying out data processing and the industrial photogrammetry principle is very high in three-dimensional reconstruction accuracy, and thus, only images at different angles need to be shot for complex pipelines; the complex multi-pipeline system detection method is simple and convenient to operate, and accuracy of pipeline detection is ensured.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Joiner panel system
InactiveUS20050072087A1Easy to installReduce the time required for installationRoof covering using tiles/slatesLaminationFiberMicrosphere
A joiner panel system is formed from a composite material and includes a panel attached to a deck by a coaming or shoe and attached at its upper edge by a curtain plate that fits around obstructions at the ceiling area. The shoe can be readily installed to an uneven steel deck by stud welding to reduce installation time or attached to a composite material deck. A curtain plate fabrication method uses a laser scan or close range photogrammetry of the overhead area to optimize and automate the cutting of curtain plate sections. The curtain plate sections can then be readily installed in the overhead area. A composite material panel to provide good flame, smoke and toxicity properties and good mechanical properties is formed from a phenolic resin foam material, micro-balloons to reduce the weight and density, and reinforcing fibers and powder material to improve the mechanical properties. The panel can be formed by a method in which the core and face skins are co-cured to provide a good bond.
Owner:KAZAK COMPOSITES
Absolute non-interfering precision measuring method facing ultra-large spatial complex curved surface
ActiveCN101706262ATroubleshoot initial orientation issuesSolve measurement problemsUsing optical meansMeasurement pointPhysical Marking
The invention discloses an absolute non-interfering precision measuring method facing ultra-large spatial complex curved surface. In the invention, an optical project method is utilized to set global control point and measuring point; the directed camera combined control point technology is utilized to realize the initial orientation of the measuring camera under each measuring station; the global control point is utilized to realize the splicing of each measuring point region and the measuring point is utilized to serve as public point to realize the splicing of global control point region. The invention solves the detection problem of the realization of ultra-large spatial curved surface by adopting the close-range photogrammetry method in the case of not utilizing coded marking; and no physical marking needs to be set on the surface of the detected object, and the surface appearance of the detected object is not slightly interfered.
Owner:ISVISION (TIANJIN) TECH CO LTD
EEG electrode space positioning method based on up shot measure
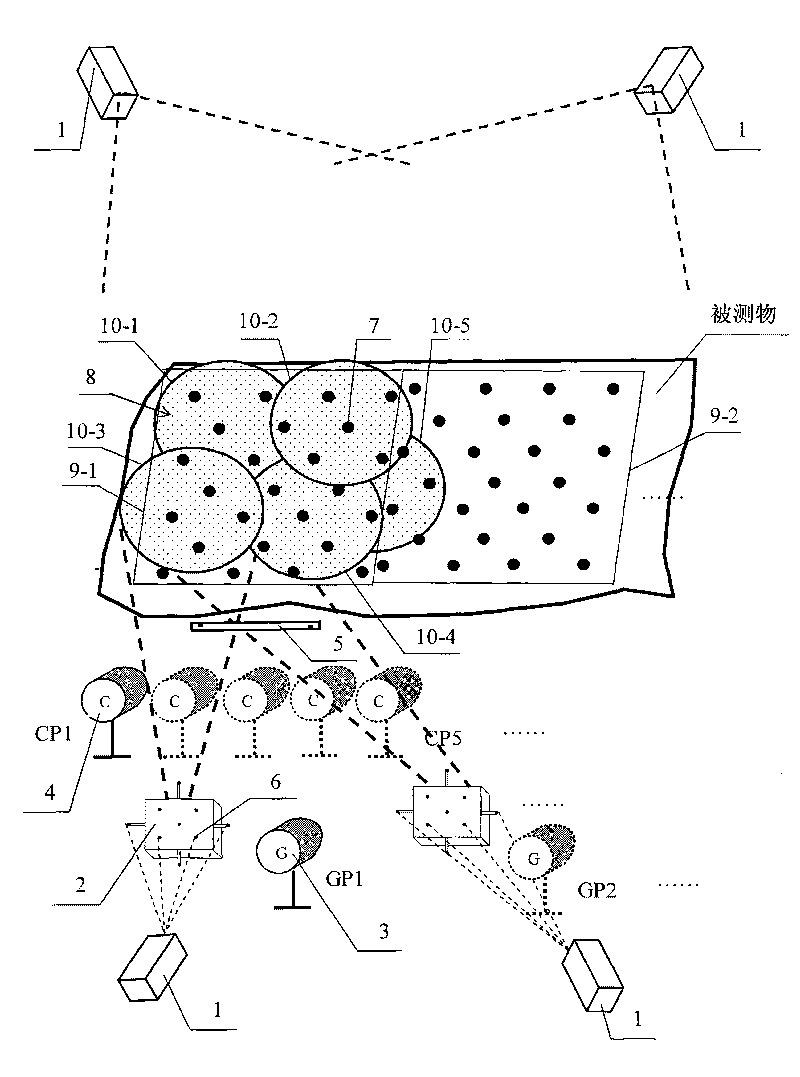
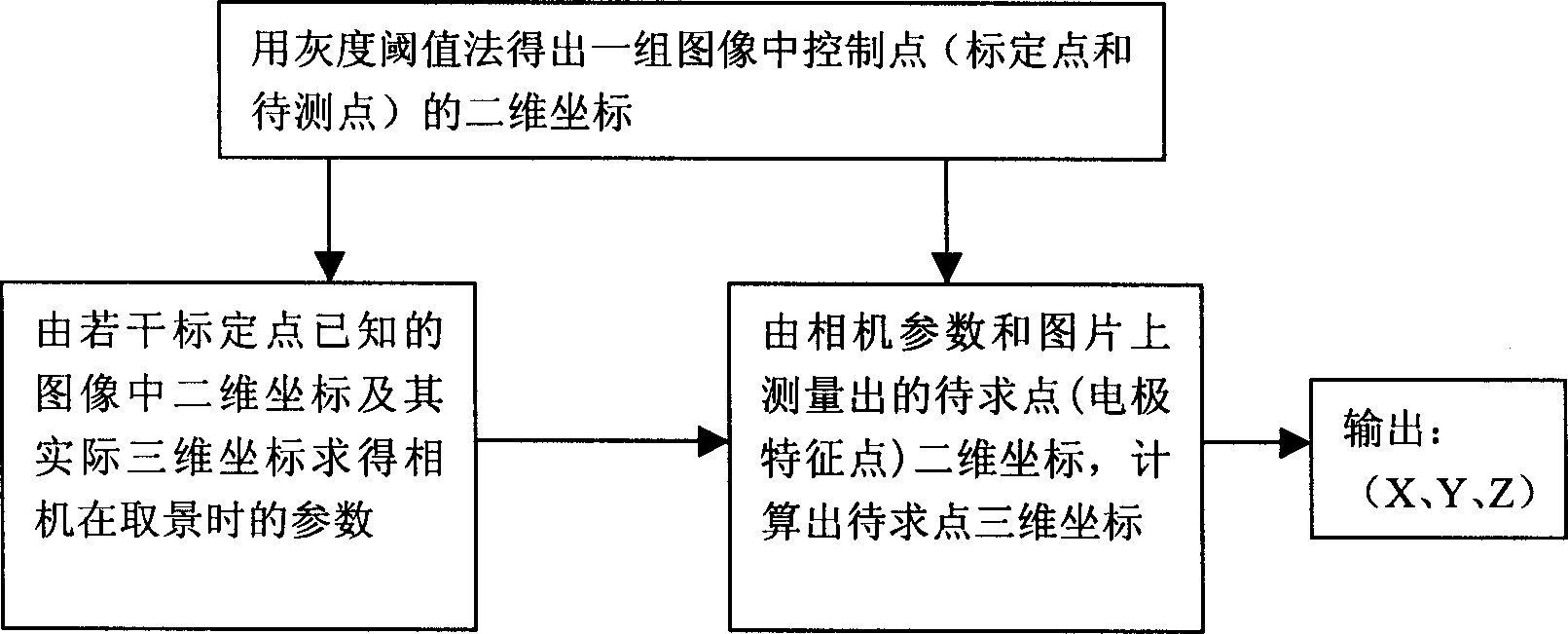
InactiveCN1405736AAchieve the expected purpose2D-image generationCamerasComputer graphics (images)Three-dimensional space
The invention belongs to the technique area of the 3D space orientation, including following steps. The system is composed of the some calibrated objects with the aiming points, the electrode cap having the fixed space positions with calibrated objects, the non-measuring camera, the image processor and the computer. The space coordinate measure of the electrode is completed through the following three steps. The 2D coordinates of the control points (the aiming points and the points to be measured) in the group of image are obtained by using the image recognition method (such as gray scale threshold method). The parameter of the camera at the shooting time can be solved inversely by the collinearity equation in the close-range photogrammetry from the 2D coordinates of the aiming points in the image and its actual 3D coordinates.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fast dense matching method based on close-range photogrammetry
InactiveCN104134203AReduce memory allocationFast extractionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionParallaxDensity reduction
The invention relates to a fast dense matching method based on close-range photogrammetry. The fast dense matching method comprises the following steps of: feature extraction: an image pyramid is built for an original image, an HARRIS corner point response value is calculated for each layer of the image in the image pyramid, and the feature point direction is determined for generating feature point description; sparse matching: density reduction is carried out by aiming at feature points for forming strong feature points, and SIFT matching is carried out on the strong feature points; and dense matching: for consistent points generated by the SIFT matching, an interpolation parallax method on a plane triangular net is adopted for solving initial left and right parallax and left and right image initial matching coordinates, left image feature points are traversed for finding matching points on right images, then, right image feature points are traversed for finding matching points on left images, and the least square template matching is adopted in the matching method. When the fast dense matching method is adopted, the fast, automatic, precise and complete dense matching can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI ROCKYSOFT
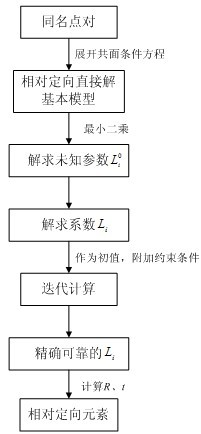
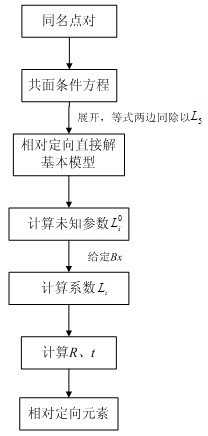
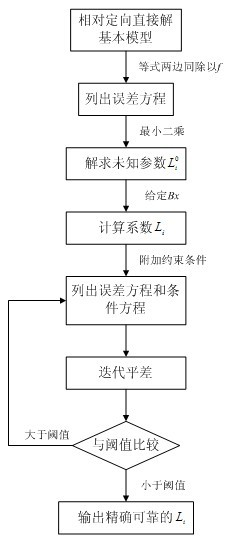
Stereo image pair automatic relative orientation method with additional non-linear constraint condition
The invention relates to a stereo image pair automatic relative orientation method with additional non-linear constraint conditions. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: firstly expanding a coplanar condition equation to obtain a basic model of a relative orientation direct solution; solving 8 unknown parameters of the relative orientation direct solution basic model by using several pairs of corresponding image points; giving a baseline component Bx, further solving 9 coefficients of the coplanar condition equation expansion; performing adjustment calculation by using the solved 9 coefficients as initial values of the adjustment and combining with the additional constraint conditions; solving the coefficients by stepwise iteration, after exact values of the coefficients are solved by iteration, performing factorization based on traditional formulae related to the relative orientation direct solution to obtain relative orientation elements. The advantages of the invention are that: no initial value is required for the calculation process of the relative orientation elements; the invention is applicable to aerial photographic images with large dip angles or images from non-metric cameras, and has good application prospects in fields of low-altitude photogrammetry and close-range photogrammetry.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Rapid registering method of multiple images and three-dimensional model
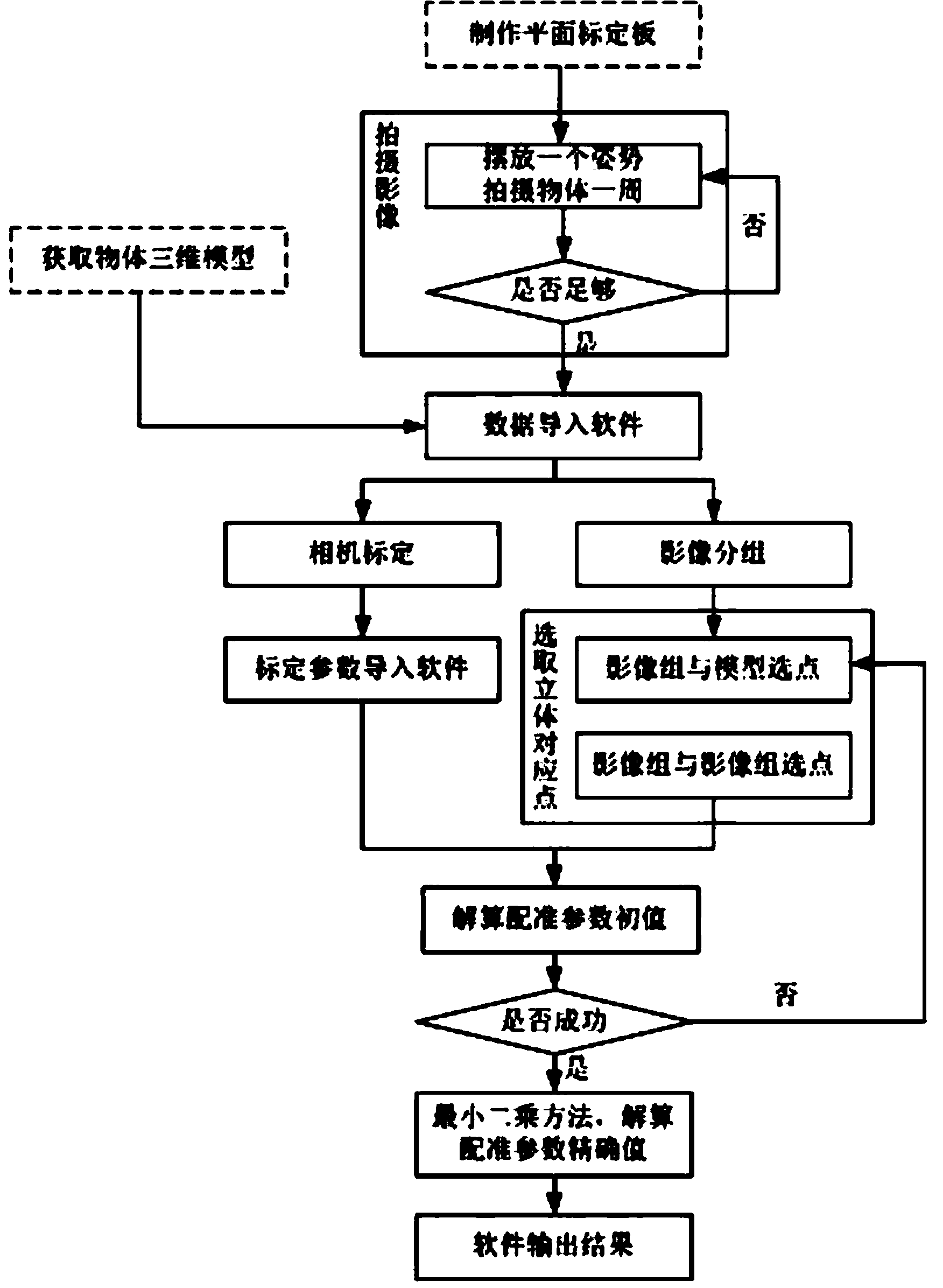
ActiveCN104048649AMeet the higher requirements of qualityHigh precisionUsing optical meansPicture interpretationRelational graphClose range photogrammetry
The invention belongs to the field of close-range photogrammetry and relates to a rapid registering method of multiple images and a three-dimensional model. The method comprises steps of image shooting, three-dimensional corresponding point selection, relational graph establishment, calculation of initial value of registering parameter, registering parameter optimization according to least square method to obtain accurate registering parameter and the like. In allusion to the defect that practicability of methods in the prior art is greatly limited by time efficiency and body surface texture, the rapid registering method of the multiple images and the three-dimensional model in the invention is improved, and revolutionary innovation is achieved. By the method, rapid registering between the multiple images and the three-dimensional model can be realized. Registering accuracy directly influences quality of texture mappings, and accuracy is high. Thus, textures are clear, the visual effect is greatly raised, and higher requirements of people on the quality of a three-dimensional model are met. The method has a good application prospect in the field of close-range photogrammetry.
Owner:ZG TECH CO LTD
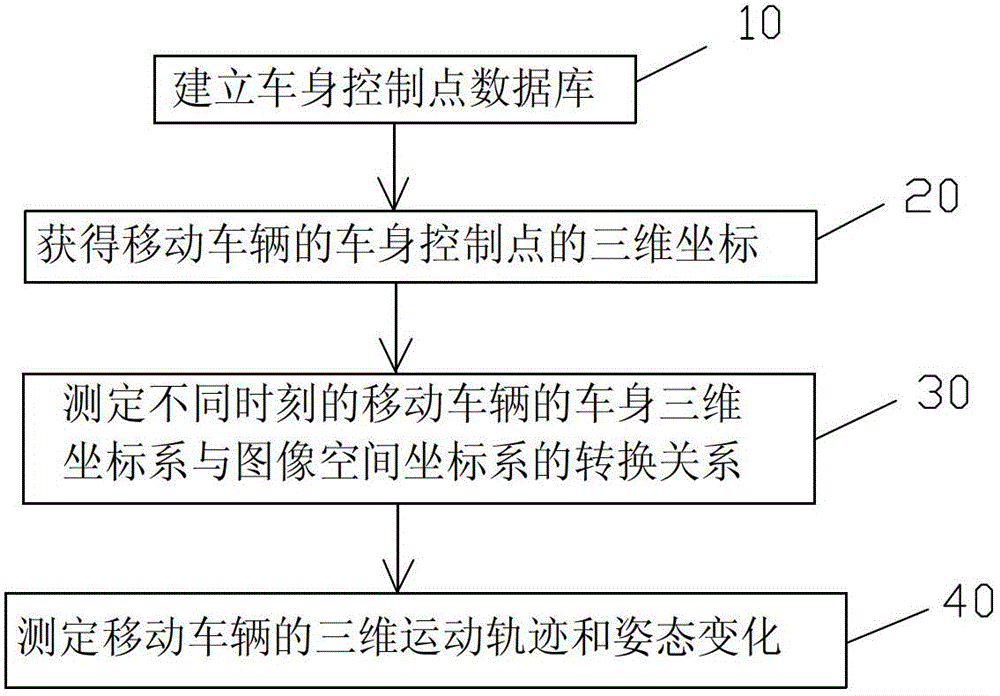
Measuring method of three-dimensional movement track of moving vehicle based on vehicle body control point
InactiveCN102721409AAccurate measurementRealize accurate calculationPicture interpretationMobile vehicleClose range photogrammetry
The invention discloses a measuring method of a three-dimensional movement track of a moving vehicle based on a vehicle body control point. The measuring method comprises the following steps of: 10, building a vehicle body control point database; 20, acquiring the three-dimensional coordinate of the vehicle body control point of the moving vehicle; 30, measuring a transformational relation between the three-dimensional coordinate systems of the vehicle body of the moving vehicle at different moments and an image space coordinate system; and 40, measuring the three-dimensional movement track and the gesture change of the moving vehicle. According to the measuring method, the moving vehicle is subjected to close-range photogrammetry by fixed photography equipment based on the vehicle body control point on the moving vehicle, so the accurate measurement of the vehicle speed and the gesture of the vehicle in a driving process can be conveniently achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Ship steel plate curved surface dimension on-line measurement system and method
InactiveCN105783774ARealize online automatic measurementReduce manual interventionUsing optical meansSheet steelCrucial point
The present invention discloses a ship steel plate curved surface dimension on-line measurement system and method. A method of combining total station automatic measurement and CCD close-range photogrammetry measurement is employed to perform three-dimensional precision measurement of key points. Besides, the CCD close-range photogrammetry measurement is employed to perform the segment measurement of three-dimensional precision of curved surface encoding mark points and non-encoding mark points and perform segment measurement of three-dimensional precision of the curved surface points, the curved surface fitting of the curved surface segment measurement is performed, the three-dimensional model of the curved surface plate is generated, and the three-dimensional model of the curved surface plate is compared with a designed three-dimensional model and is analyzed. According to the invention, the problems are overcome that the method based on the total station only can complete the measurement of data of dozens of key points and a lot of work has to be done by manpower, the precision detection analysis of the coordinates of the key points on the curve surface segment is realized, the problems are solved that the fitting and the detection of the curved surface cannot be completed and there is no online detection function.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
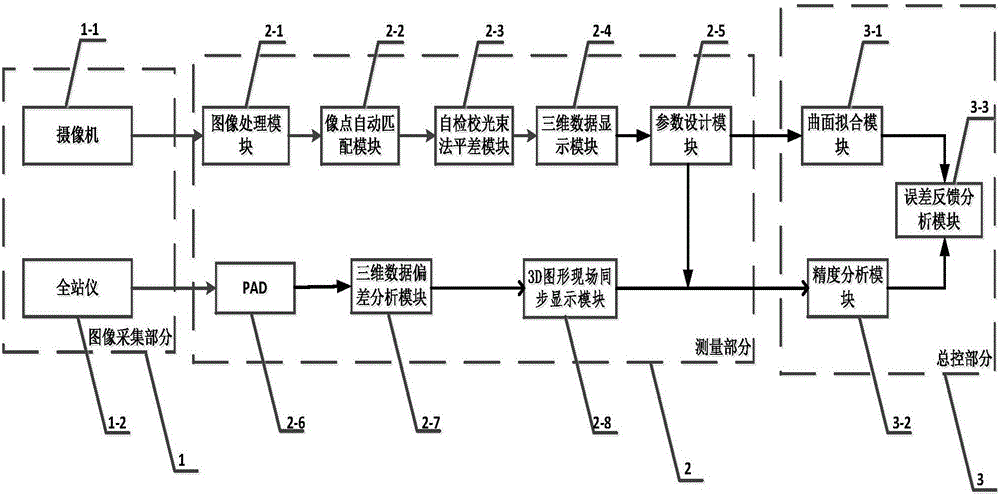
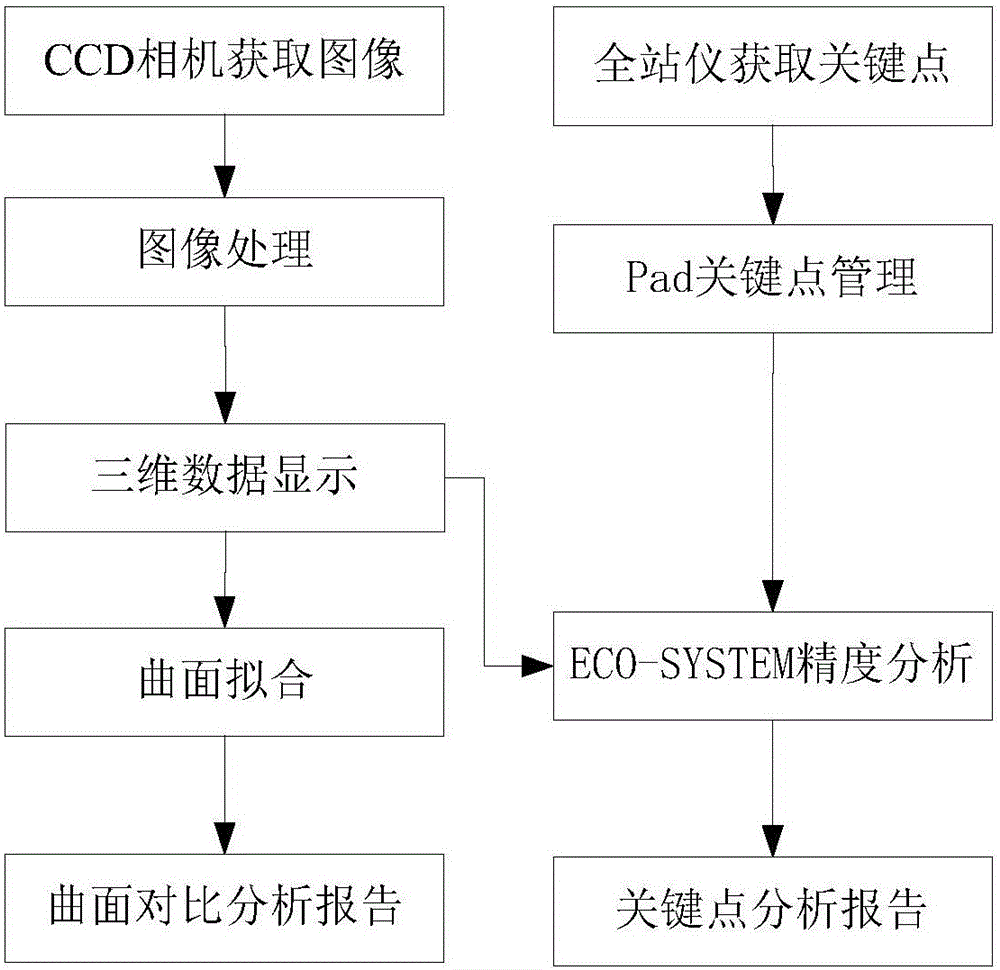
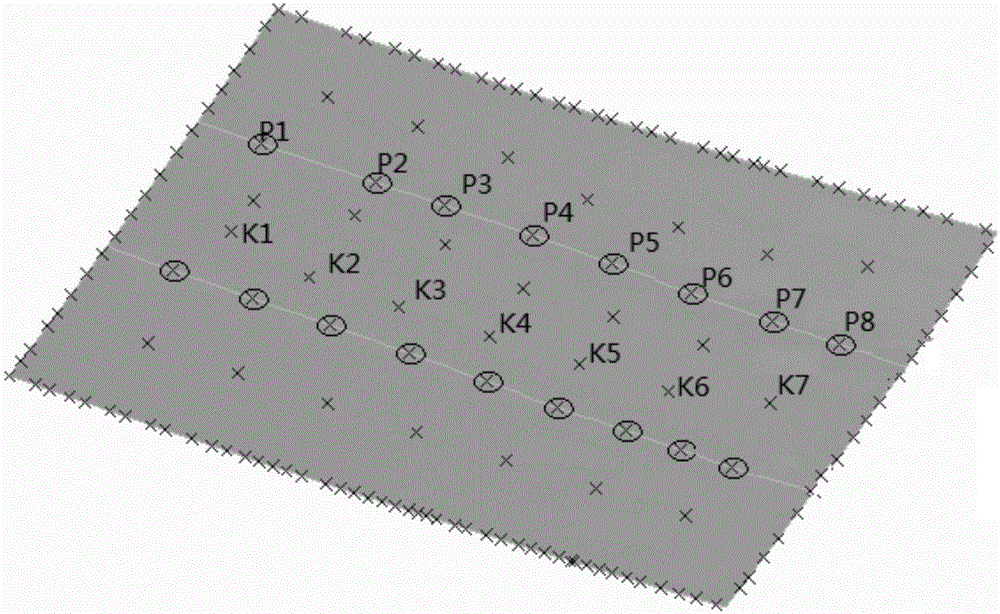
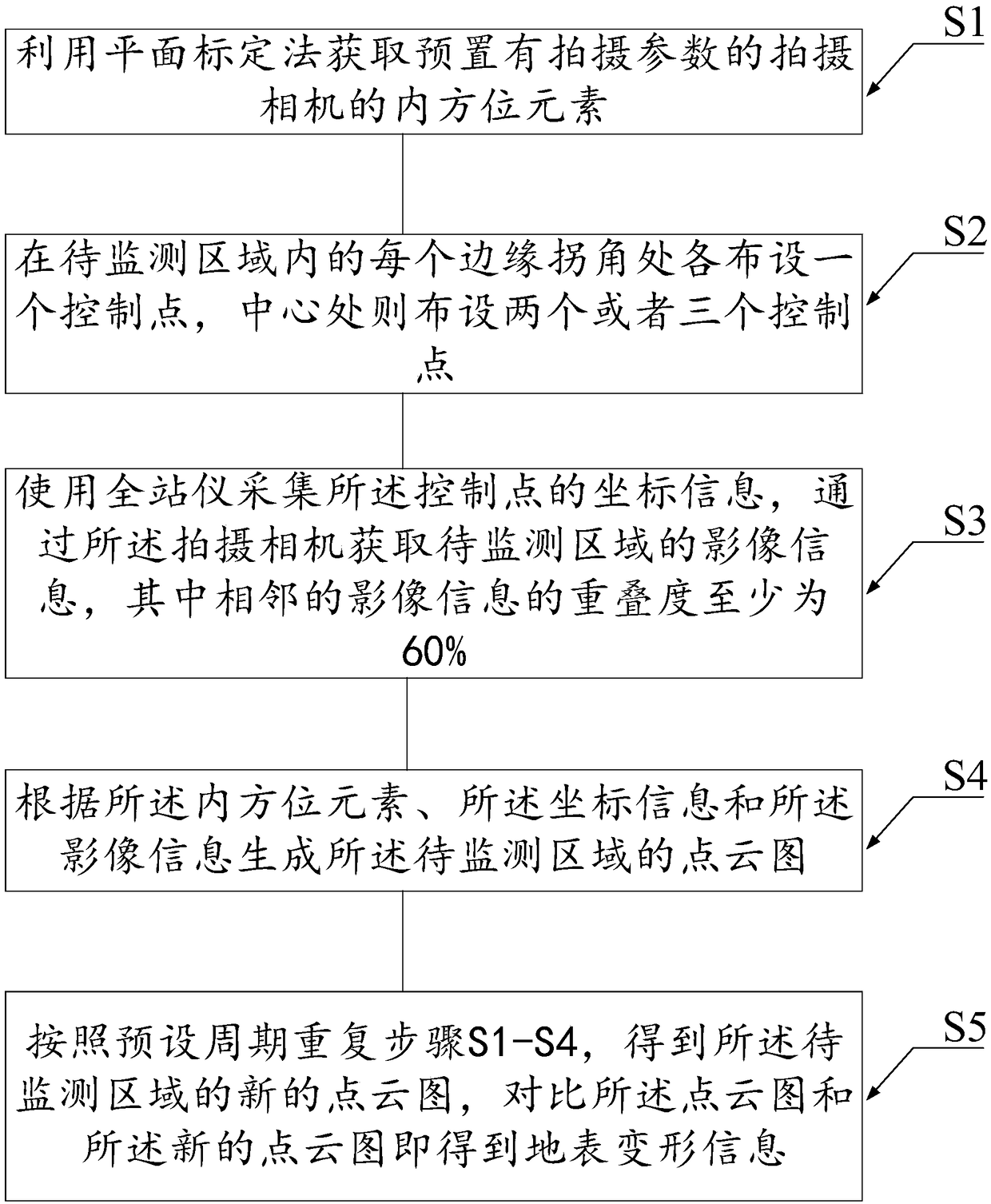
Shield subway construction ground surface deformation monitoring method based on close-range photogrammetry
The invention discloses a shield subway construction ground surface deformation monitoring method based on close-range photogrammetry, and aims to look for a more effective implementation scheme for shield subway construction monitoring. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining elements of interior orientation of a photographing camera; arranging one control point in each edge corner inan area to be monitored, and two or three control points at the center; using a total station to collect coordinate information of the control points, and obtaining image information of the area to be monitored through the photographing camera with photographing parameters preset; generating a point cloud map of the area to be monitored according to the elements of interior orientation, coordinate information and image information; and obtaining a new point cloud map of the area to be monitored, and obtaining ground surface deformation information by comparing the point cloud map with the newpoint cloud map. The shield subway construction ground surface deformation monitoring method based on close-range photogrammetry realizes multi-point monitoring through a close-range photogrammetry technology, solves the problem that the deformation condition of a monitoring point-free area is difficult to discover in existing single-point monitoring, and saves manpower.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
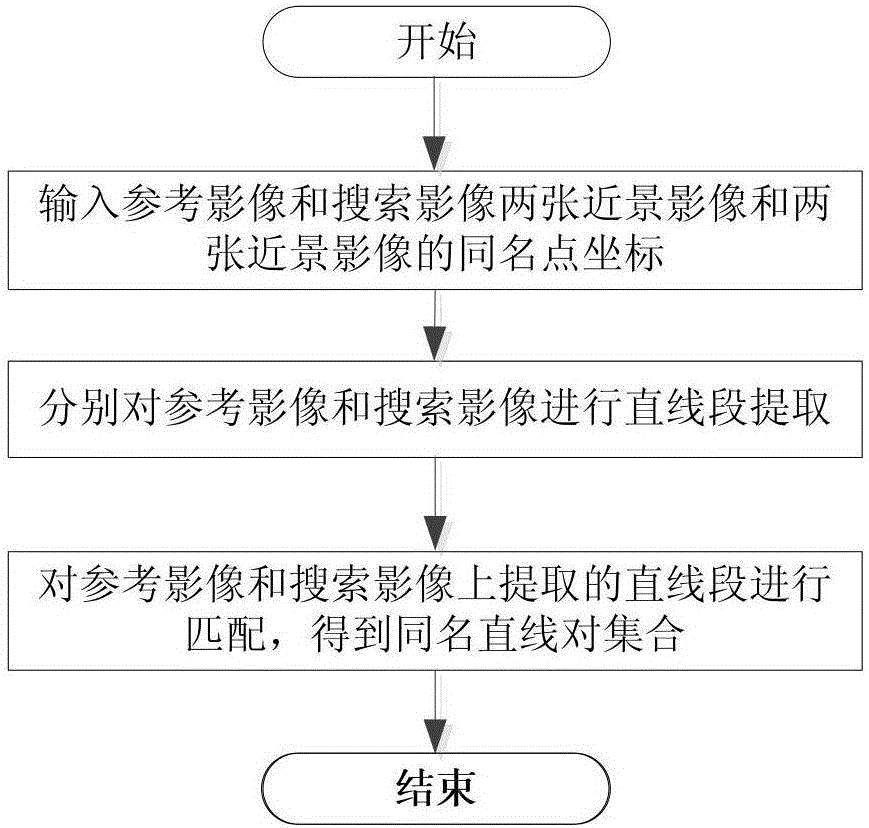
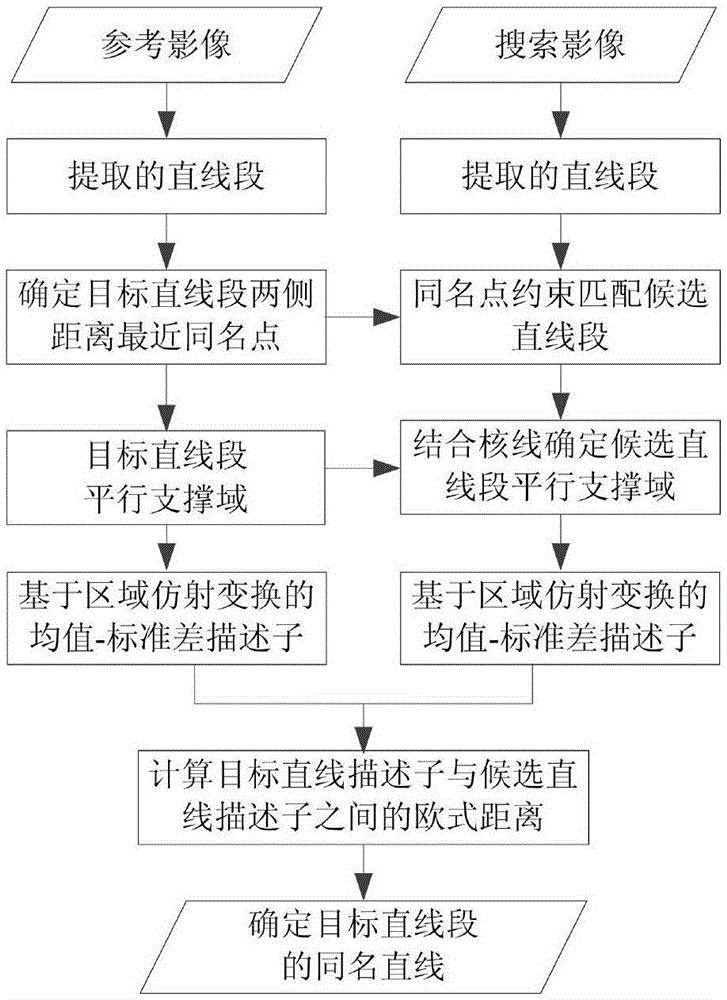
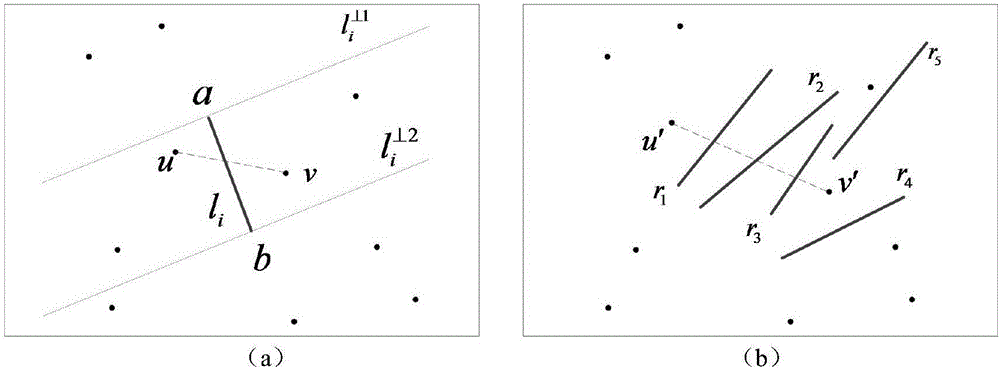
Close-range image straight-line segment matching method
ActiveCN106709870AImprove effectivenessImprove limitationsImage enhancementImage analysisReference imageClose range photogrammetry
The invention provides a close-range image straight-line segment matching method, which belongs to the technical field of close-range photogrammetry and computer vision. The close-range image straight-line segment matching method comprises the steps of: extracting straight-line segments; determining a candidate straight-line segment set of a target straight-line segment; establishing a parallel supporting domain of the target straight-line segment, and establishing a candidate straight-line segment plane supporting domain based on the parallel supporting domain of the target straight-line segment; calculating an Euclidean distance between a target straight-line segment feature descriptor and a candidate straight-line segment feature descriptor; and determining a homonymous straight-line segment of the target straight-line segment according to the Euclidean distance, so as to obtain a homonymous straight-line pair set of a reference image and a searched image. The close-range image straight-line segment matching method determines the candidate straight-line segment plane supporting domain by utilizing an epipolar constraint, constructs the descriptors based on the candidate straight-line segment plane supporting domain, enhances the effectiveness of the descriptors, performs regional affine transformation on the parallel supporting domains of the target straight-line segment and the candidate straight-line segments, realizes reliable matching of image straight-line segments of different sales, improve the limitation of the existing descriptors, and is suitable for close-range image straight-line segment matching of different types such as translation, rotation, blur and illumination.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
Flight planning for unmanned aerial tower inspection
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of transmission tower 10, phase conductors 12, insulators 14, and shield wires 16. They are to be inspected by unmanned aerial vehicle UAV 20 with embedded processor and memory 22, radio 24, location rover 26, and camera 28. Base station 30 has processor and memory 32, radio 34, and location base 36. The relative location between UAV 20 and base station 30 can be accurately calculated by location base 36 and location rover 26 communicating over radios 24 and 34. Camera 28 on UAV 20 is first used to capture two or more orientation images 38 and 39 of tower 10; lines 12 and 16; and insulators 14 from different vantage points. Terrestrial or close-range photogrammetry techniques are used create a three dimensional model of tower 10; lines 12 and 16; and insulators 14. Based on inspection resolution and safety objectives, a standoff distance 50 is determined. Then a flight path with segments for ascent 40, one or more loops 42, 44, 46, and a descent 48 is designed to ensure full inspection coverage via inspection images like 52 and 54.
Owner:VAN CRUYNINGEN IZAK JAN
Making method for grotto digital line graph based on digital close-range photogrammetry
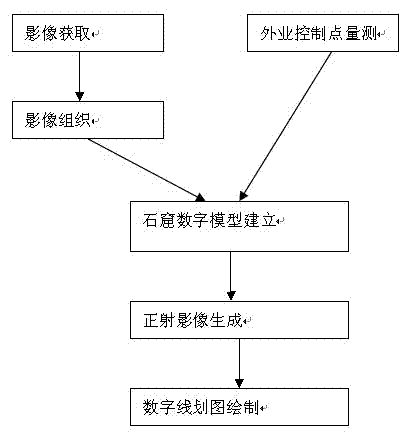
The present invention provides a making method for a grotto digital line graph based on digital close-range photogrammetry. The method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring field data: comprising image acquisition and field work control point coordinate measuring; 2, organizing the images: importing image data and camera parameters, inputting the strip parameter, and carrying out strip grouping on the images; 3, establishing a grotto digital model: carrying out aerial triangulation matching, free network bundle adjustment and encryption matching to generate an accurate grotto digital model; 4, generating an orthophoto image: carrying out accurate correcting, inlaying and merging with a software according to the digital model generated in the step 3 to generate an orthophoto image of the subject to be detected; and 5, drawing a digital line graph: drawing a digital line graph having the accurate geometric position relationship based on the orthophoto image according to the requirements of cultural relics department. The method of the present invention has characteristics of low working environment requirements, no damage on the grotto, high precision, and rapid speed.
Owner:武汉华宇世纪科技发展有限公司
Method for measuring deformation of geotechnical sample through photogrammetry
InactiveCN109931876AAvoid errorsEasy accessMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEarth material testingBoundary changeImage processing software
The invention relates to a method for measuring the deformation of a geotechnical sample through photogrammetry. According to the method of the invention, as for a geotechnical test for measuring thedeformation property of a soil body by using air as a medium, an industrial camera can be arranged at a certain distance from the main deformation surface of a soil sample before the test so as to record the change process of the soil sample; obtained photos are imported into image processing software; the software can extract the contour of the soil sample from the photos through color comparison, and obtain the pixel value of an area occupied by the soil sample before the change of the soil sample and the pixel value of an area occupied by the soil sample after the change of the soil sample;and therefore, the deformation amount of the boundary change of the soil sample is calculated; and the height or area of the deformed soil sample can be obtained through conversion calculation. A modern close-range photogrammetry technology is applied to a geotechnical test, and therefore, the deformation of the soil sample can be measured more accurately, and the efficiency of basic testers andthe accuracy of test data can be improved.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
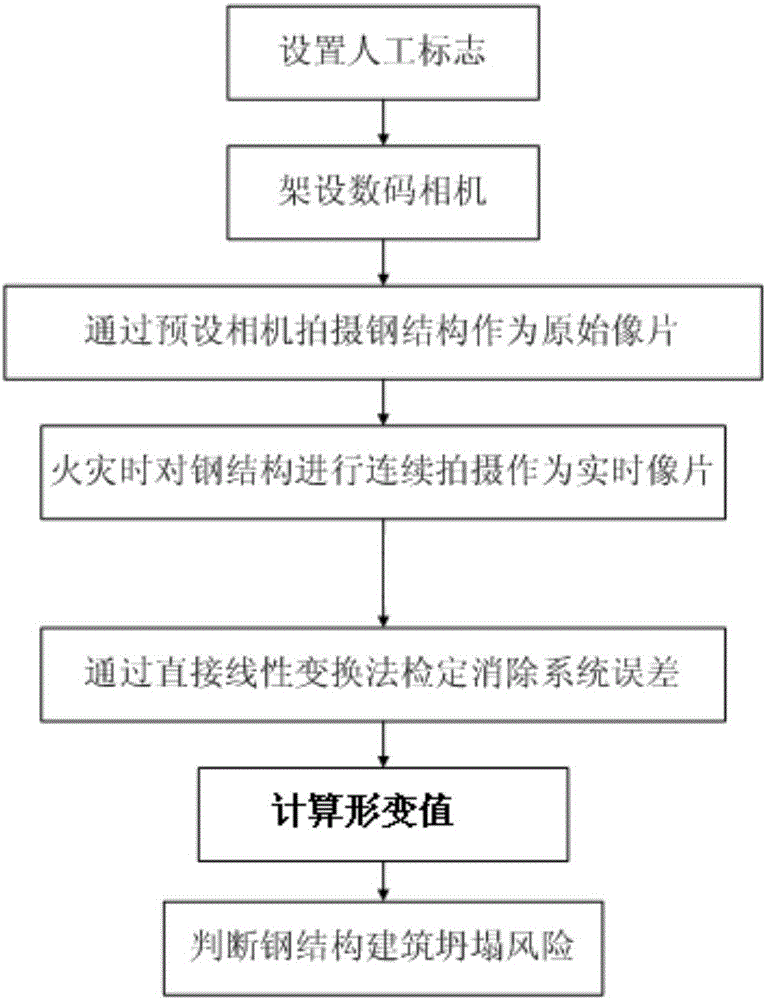
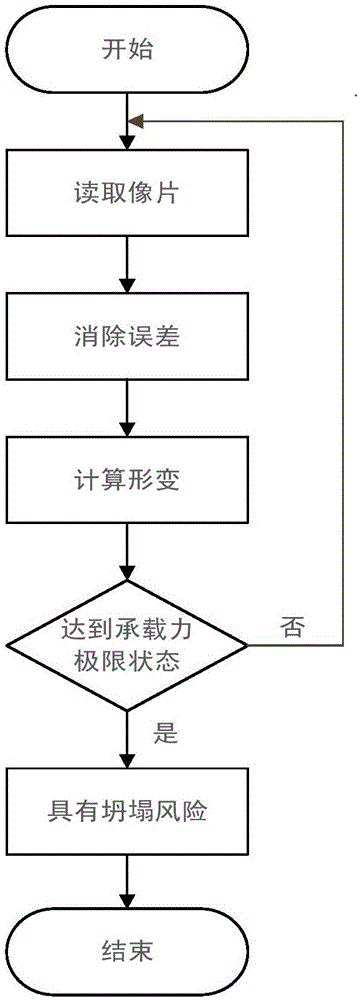
Method of monitoring collapse risk of steel-structured building in fire
ActiveCN106767718AWith economyAccuracyUsing optical meansPicture interpretationClose range photogrammetryRisk area
The invention discloses a method of monitoring collapse risk of a steel-structured building in a fire; taking pre-fire and post-fire photos of a site by means of digital close-range photogrammetry, processing the pre-fire and post-fire photos to obtain their spatial coordinates, comparing, calculating deformation of a steel structure, and determining a building has collapse risk if the deformation is greater than the bearing capacity limit of the steel structure. The technical blank in the field of collapse risk of steel-structured buildings is filled, and the method has the advantages of good economy, high performance and good accuracy, and is highly applicable and suitable for various steel-structured buildings, including the various buildings such as plants, workshops, residential buildings, integrated commercial centers and the like.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
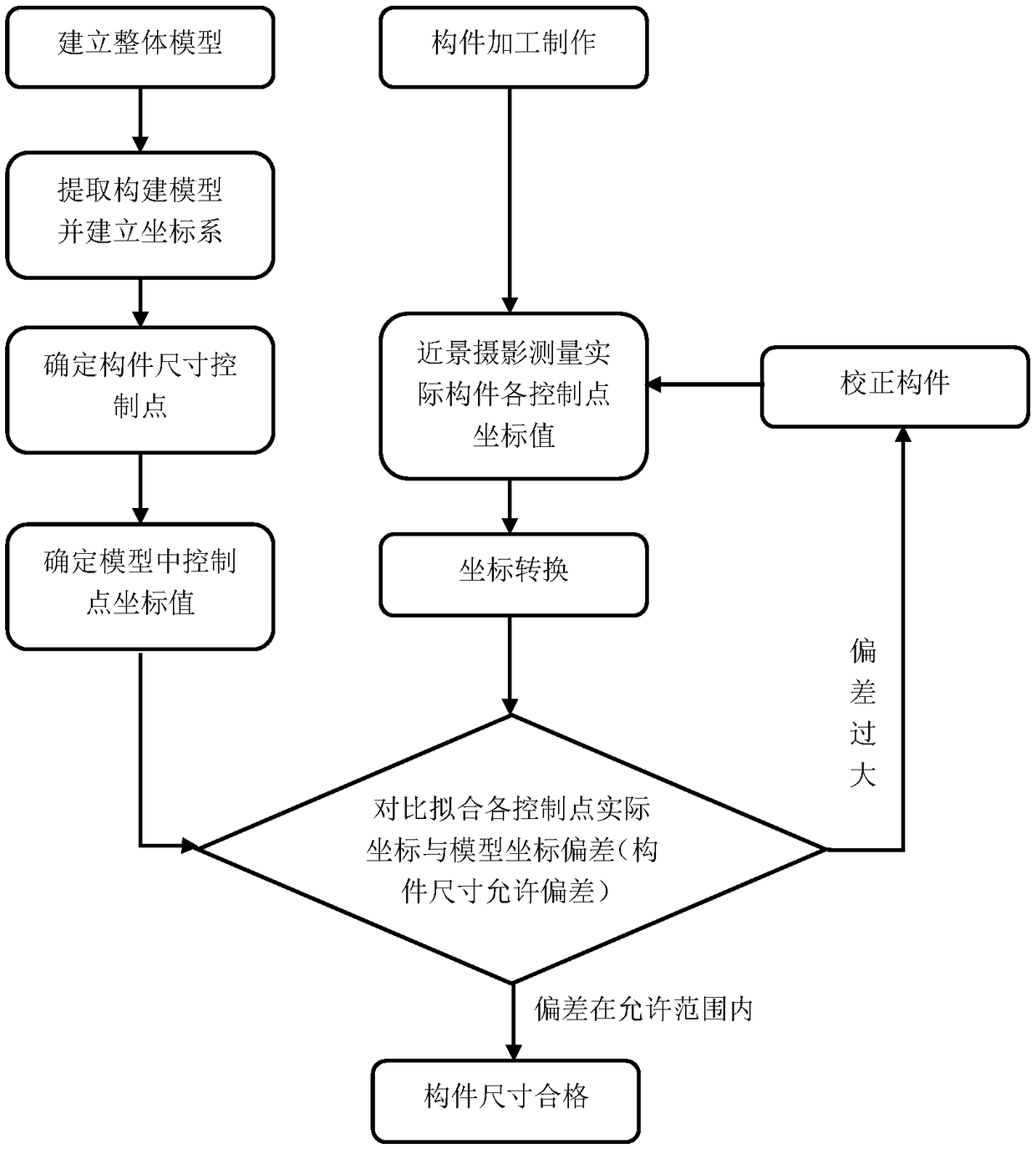
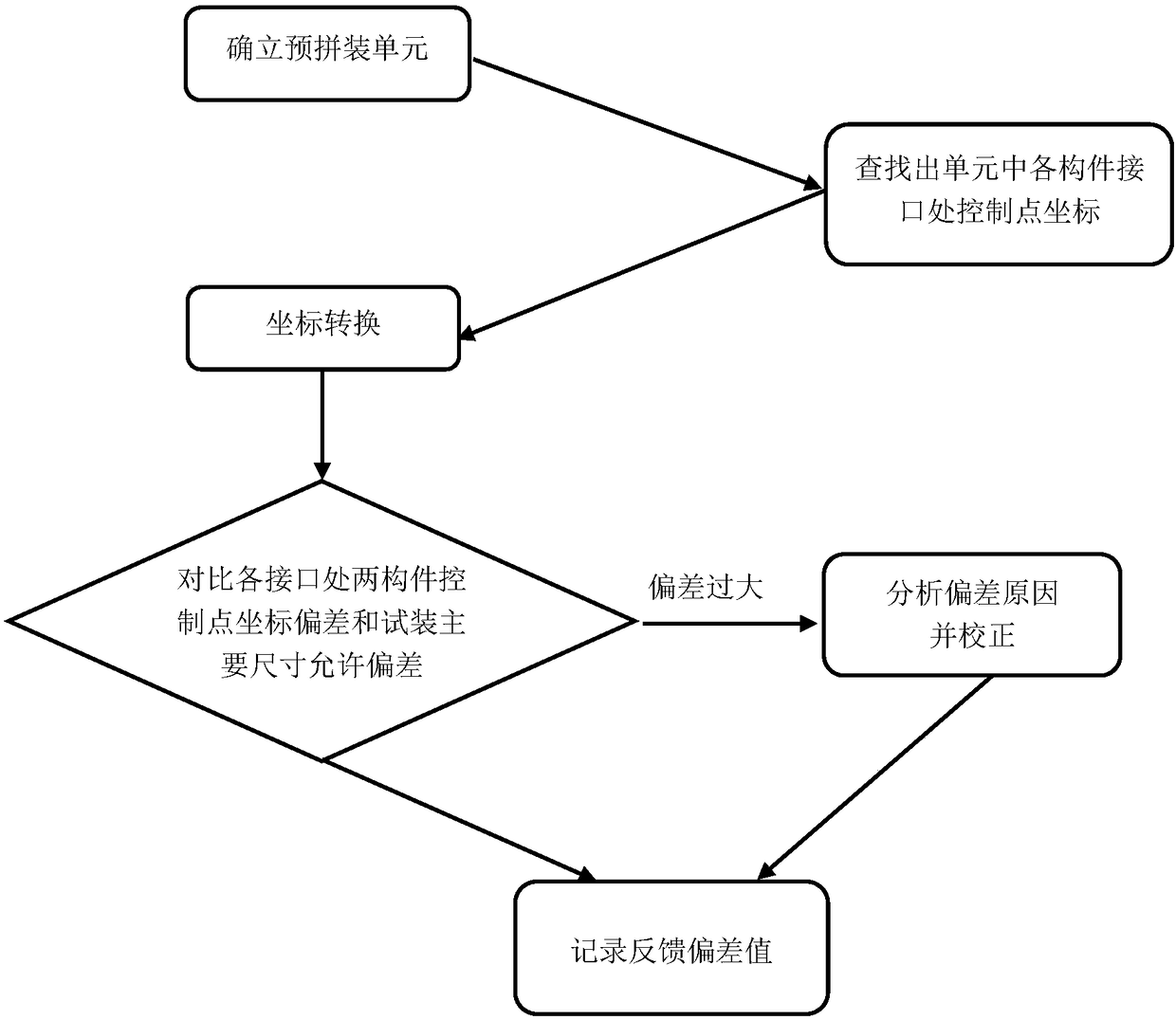
Steel structure virtual pre-assembly method
InactiveCN108563860AFully reflect the position statusSimple methodGeometric CADImage data processingEngineeringClose range photogrammetry
The invention discloses a steel structure virtual pre-assembly method, which is used for virtual pre-assembly between steel structure parts connected by bolt holes. At least one group of connecting holes is formed in a joint of each steel structure part; digital close-range photogrammetry systems are arranged on four corner points of each group of the connecting holes; two adjacent steel structureparts are connected through the connecting hole groups; central coordinates of the bolt holes on the four corner points of each connecting hole group of the steel structure parts are obtained by utilizing the digital close-range photogrammetry systems before the virtual pre-assembly; the two adjacent steel structure parts are assembled by utilizing the central coordinates of the bolt holes in thevirtual pre-assembly process; deviation values of the central coordinates of the bolt holes in the two adjacent steel structure parts are compared and analyzed; and the positions of the connecting hole groups in the steel structure parts are corrected through the deviation values. The virtual pre-assembly method is simple; and compared with an entity pre-assembly method, the virtual pre-assemblymethod can greatly reduce the cost and shorten the construction period, especially for large complex projects and projects in poor construction conditions.
Owner:CCCC SECOND HARBOR ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com