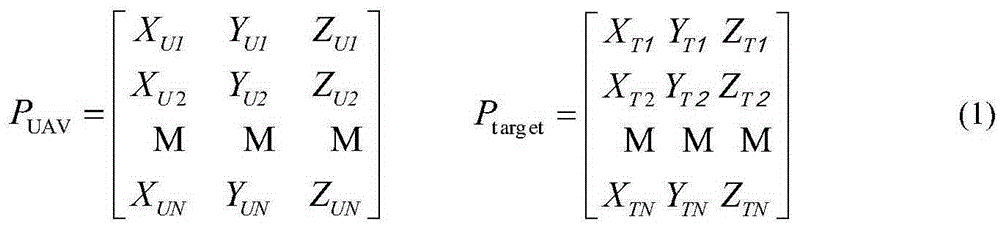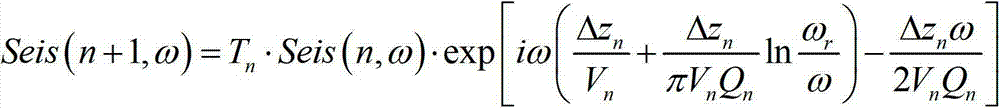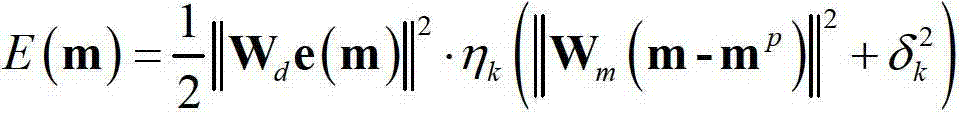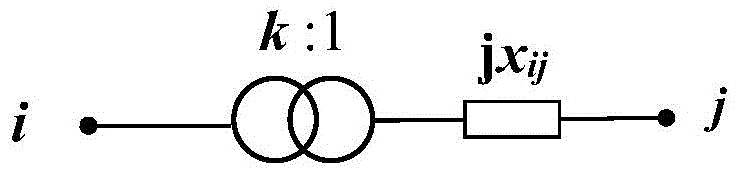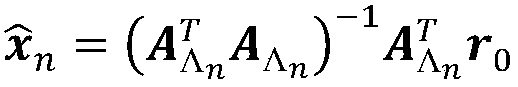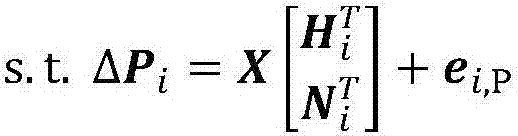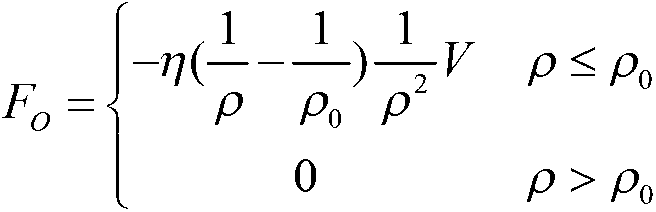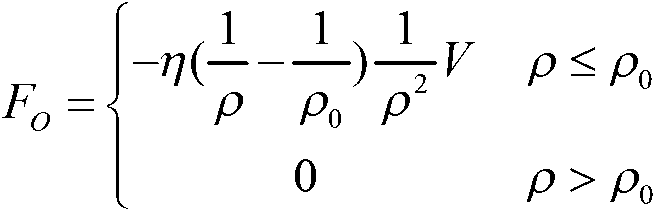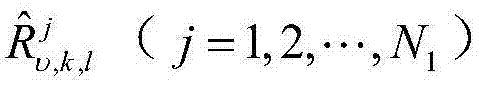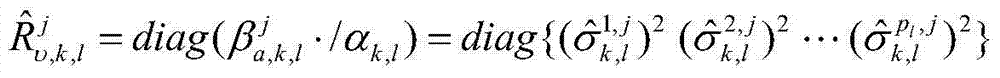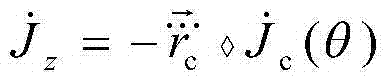Patents
Literature
264 results about "Jacobian matrix and determinant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In vector calculus, the Jacobian matrix (/dʒəˈkoʊbiən/, /dʒɪ-, jɪ-/) of a vector-valued function in several variables is the matrix of all its first-order partial derivatives. When this matrix is square, that is, when the function takes the same number of variables as input as the number of vector components of its output, both the matrix and its determinant are referred to as the Jacobian in literature.
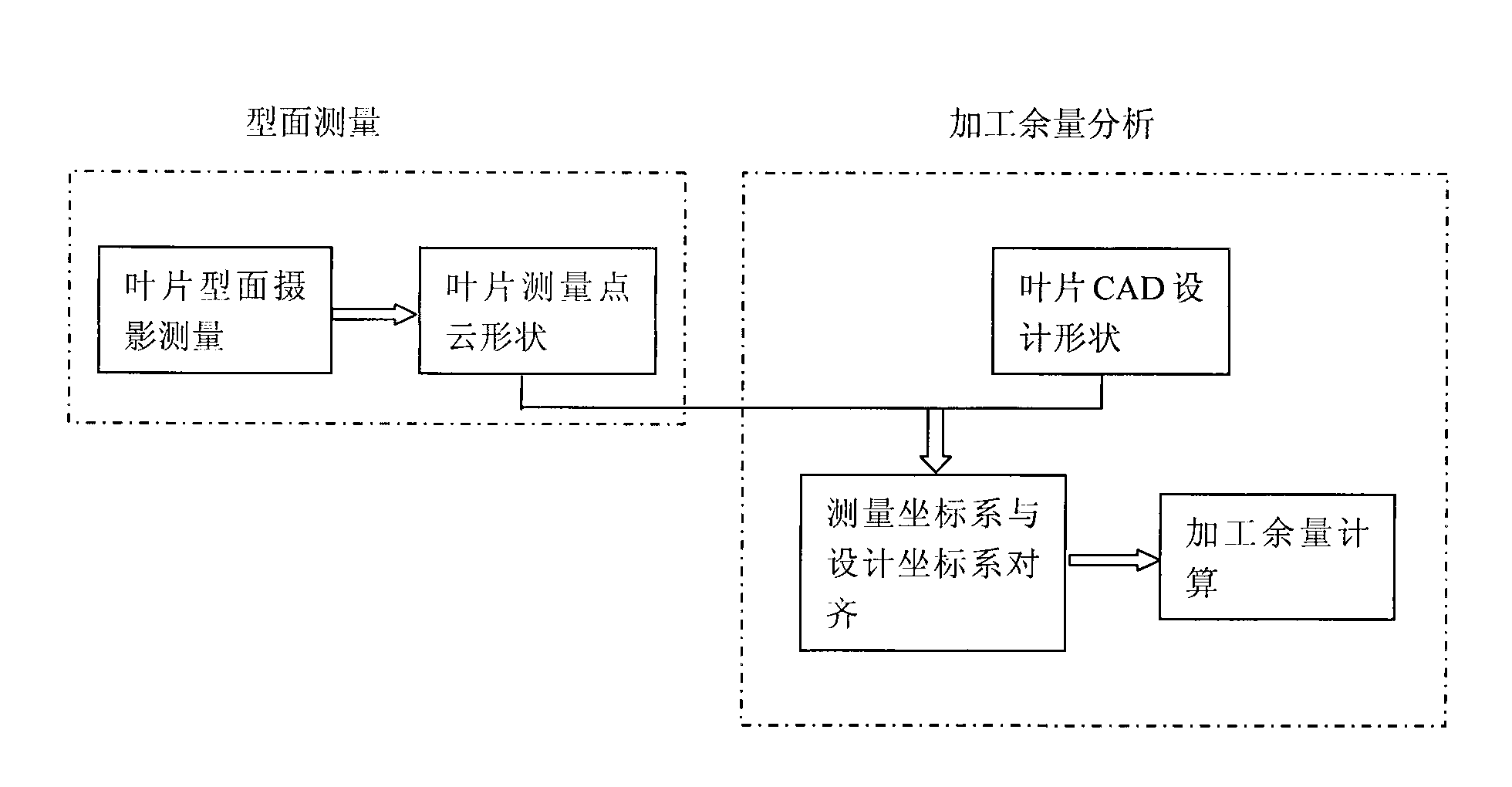
Water turbine blade blank profile measuring and machining allowance analyzing method
InactiveCN101634544AHigh speedImprove machining accuracyUsing optical meansCavitationMeasurement point
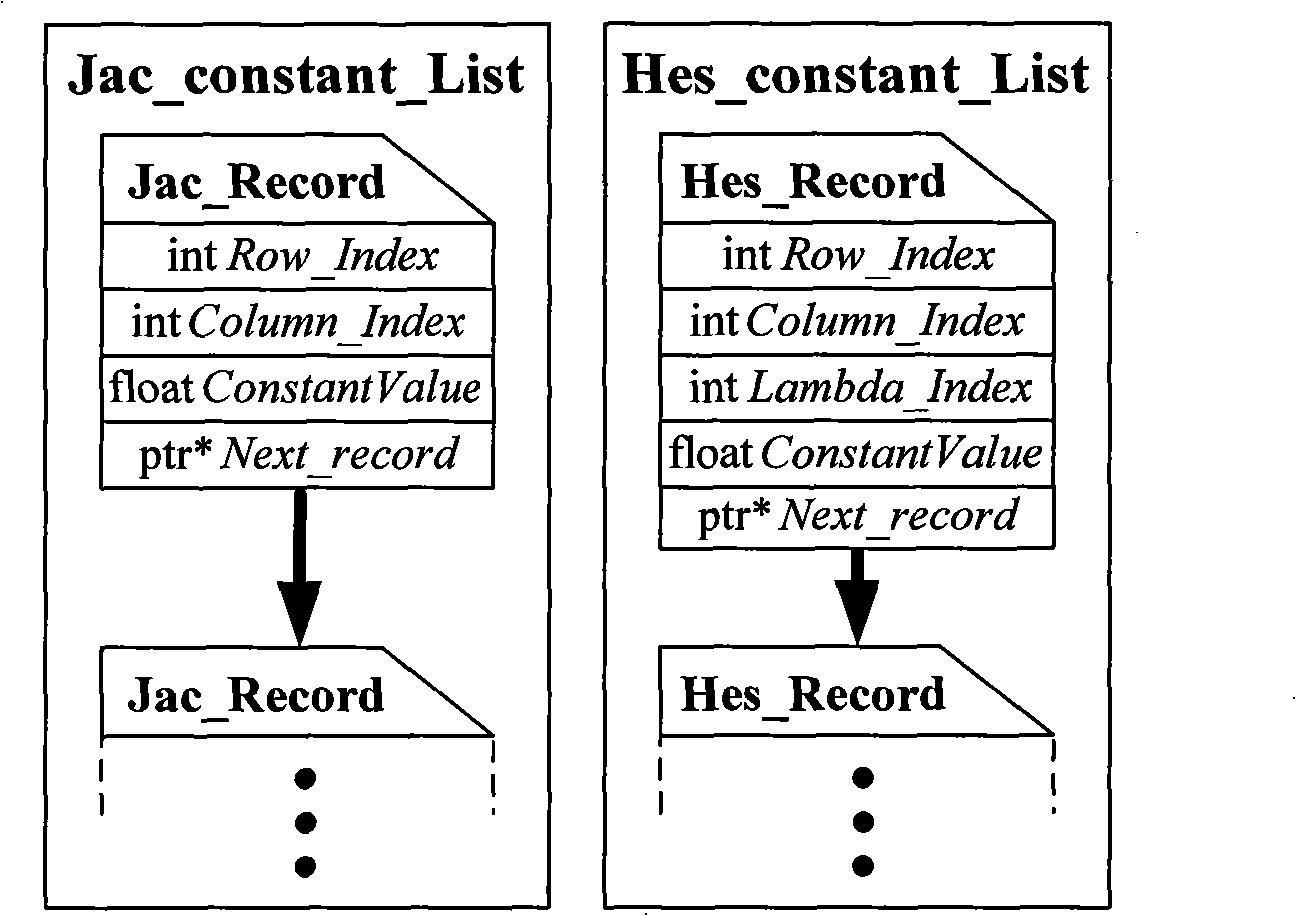
The invention relates to a water turbine blade blank profile measuring and machining allowance analyzing method capable of effectively solving the problem of water turbine blade blank profile measurement and machining allowance analysis to ensure the manufacturing quality and precision of the water turbine blades, comprising the following technical solutions: measuring the blade blanks by using a digital close range photogrammetry to obtain the measuring point cloud data shapes of the blank profiles consequently, aligning a measuring coordinate system where the measuring point clouds are located to a design coordinate system where a CAD design model is located, establishing a differential relation of free-form surface parameters with respect to rigid rotation parameters by using an analytic method derived by the multivariate of Newton iteration method to obtain a Jacobian matrix and Hessian matrix which are available for a target equation; then performing the numerical optimization calculation based on the LM method and Newton iteration method, and performing report or graphical output and print on the result. The inventive method is scientific, advanced, stable and reliable, and has high accuracy, thereby ensuring the hydraulic stability, production efficiency and cavitation property, and bringing enormous economic and social benefits.
Owner:郑州辰维科技股份有限公司
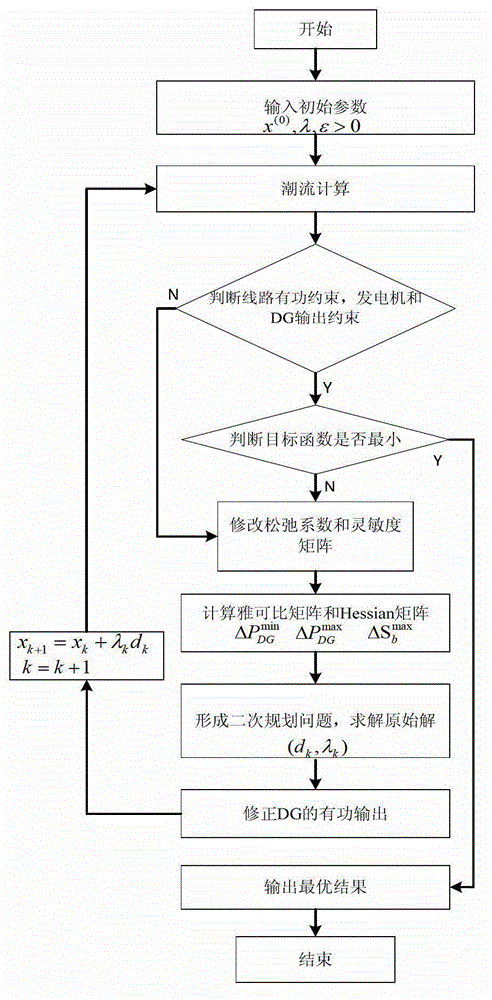
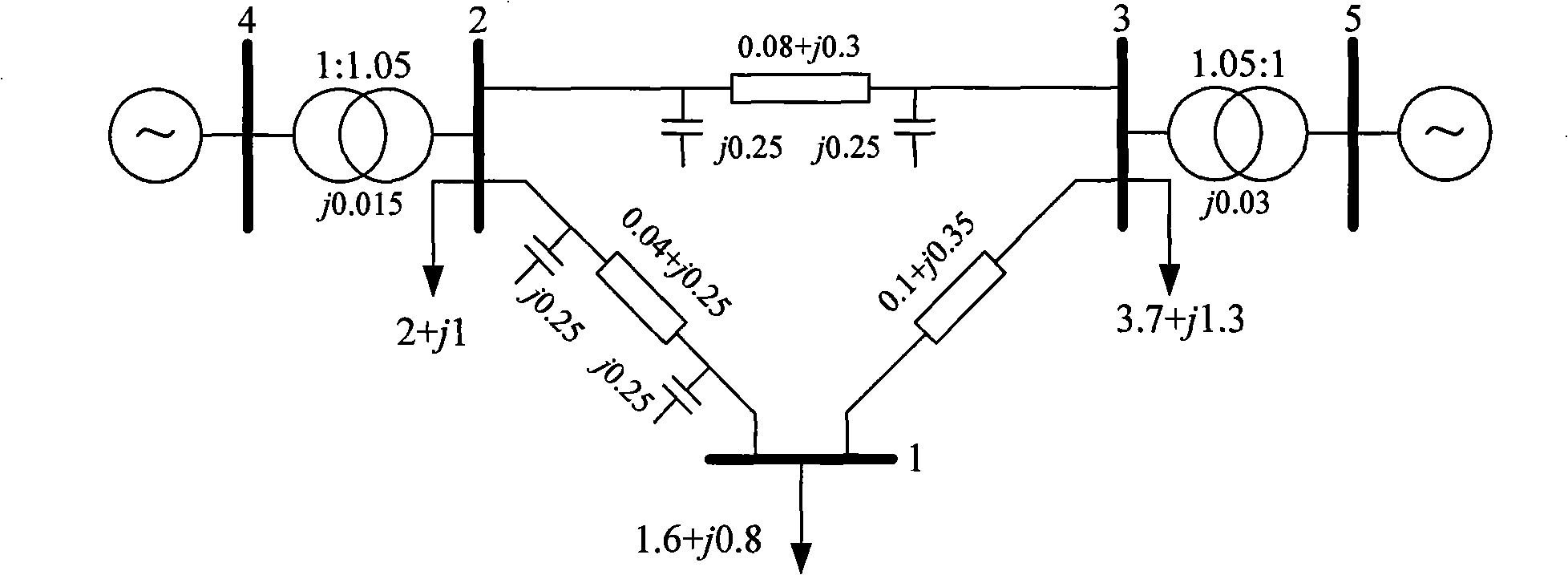
Optimal power flow optimization method of distributed power supplies
ActiveCN103150606ASimple calculationQuick calculationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsForecastingCorrelation coefficientEngineering
The invention relates to an optimal power flow optimization method of distributed power supplies. The optimal power flow optimization method of the distributed power supplies includes the following steps: A, variable in a distribution network is initialized; B, load flow calculation is carried out on the distribution network; C, lines are judged to be overloaded or not, and active output force and reactive output force of an engine and the distributed power supplies are judged to overstep the boundary or not; D, if constraint equations are all met, a step E is continued, otherwise a step F is continued; E, an objective function is judged to be the minimum or not, if the objective function is the minimum, a step J is continued, otherwise a step F is continued; F, net loss correlation coefficients are corrected; G, a Jacobean matrix and a Hessian matrix are calculated; H, a problem of sequential quadratic programming is formed and the search direction and a step size are solved; I, output force at the position of a balancing node bus and output force of each distributed power supply are corrected, and the step B is jumped to; and J, an optimal power flow result is output. The optimal power flow optimization method of the distributed power supplies provides basis of access capacity calculation for determining the distributed power supplies to be connected in a power distribution network, is simple in calculation and low in complexity, and can rapidly calculate the output force of the distributed power supplies.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Elastography imaging modalities for characterizing properties of tissue
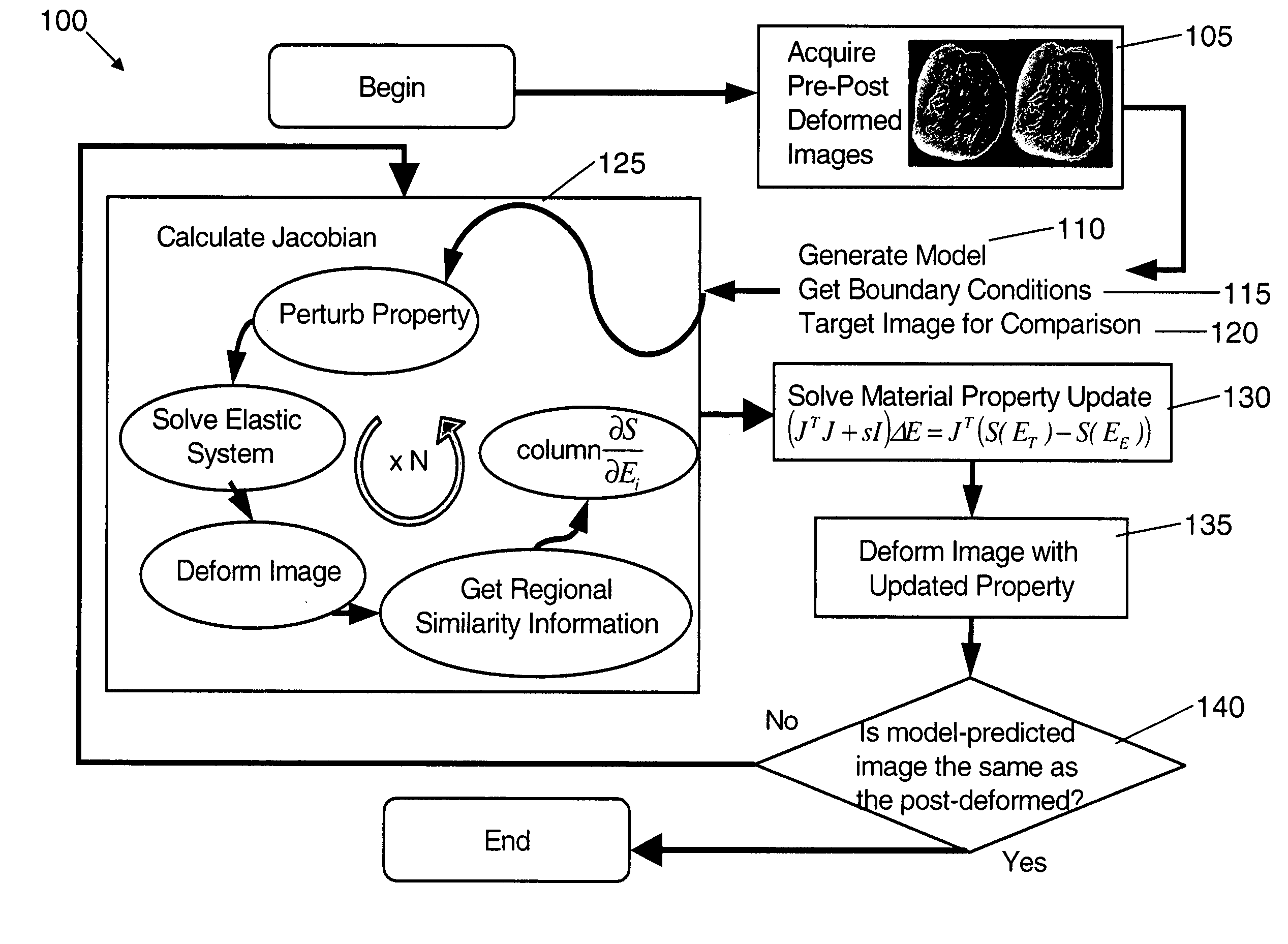
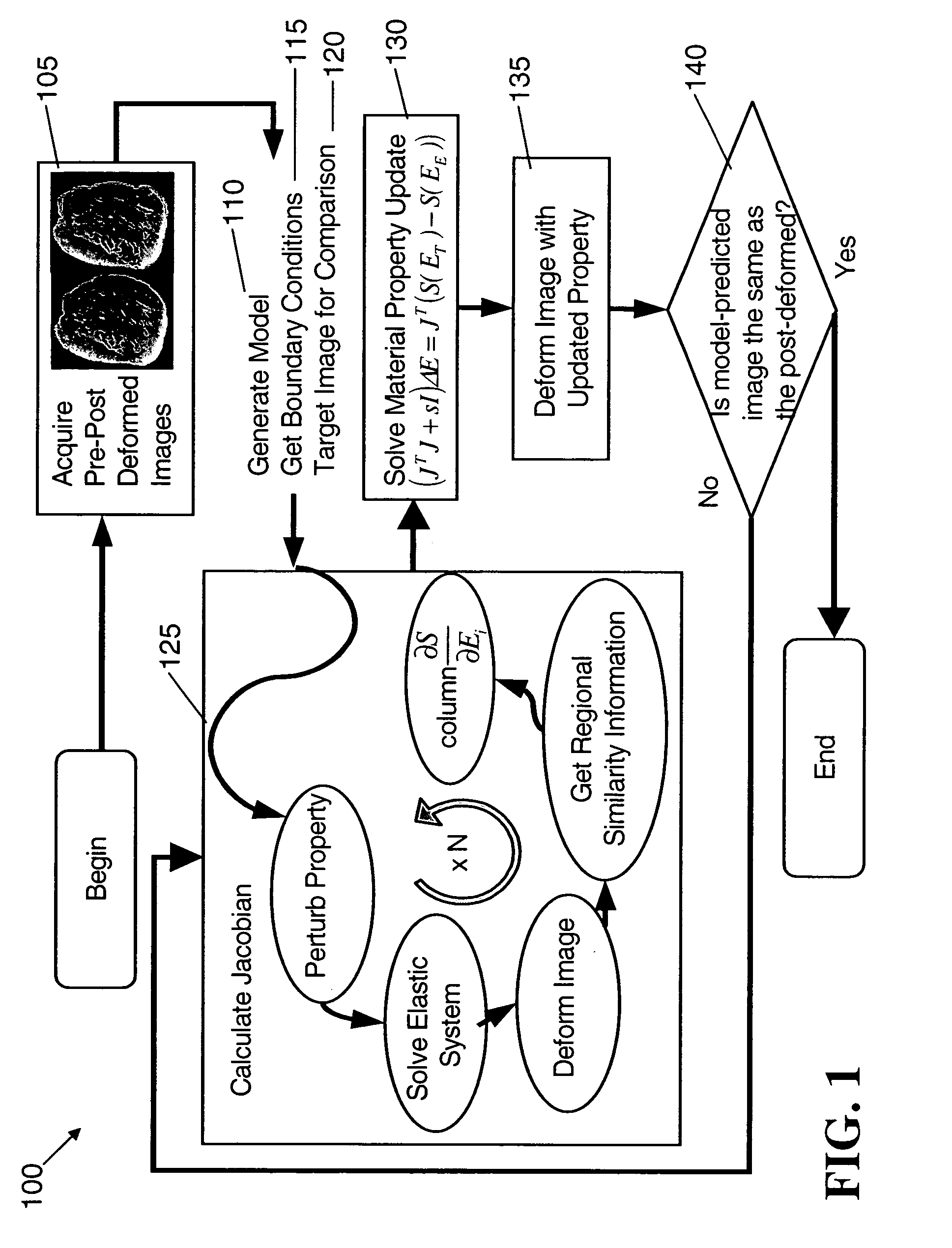
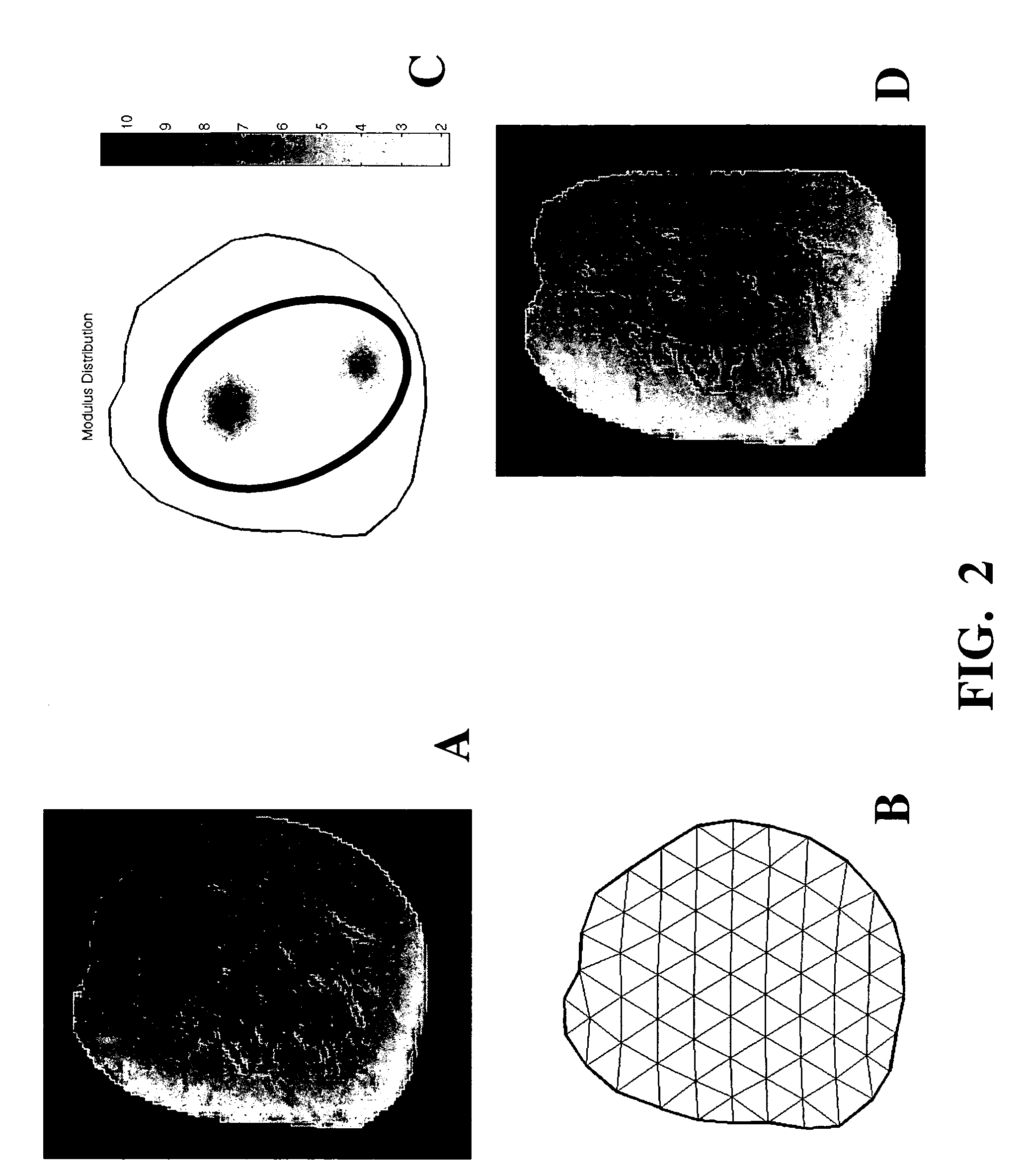
An image reconstruction algorithm begins with an initial acquisition of a preoperative imaging volume followed by a second imaging sequence subsequent to an applied deformation. A computational domain (model) is generated from the preoperative image series and boundary conditions are derived from a pre-post deformation comparison, as well as from information gathered from deformation source application (i.e., displacement and / or force). Using boundary conditions, a series of model-based image deformations is accomplished while varying model material properties. A calculation of a Jacobian matrix relating the change in regional mutual information is performed with respect to the change in material properties. Upon completion of this process, matrix regularization techniques are used to condition the system of equations and allow for inversion and subsequent delivery of model-property adjustments.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Location and environment modeling method of intelligent movable robot
The invention discloses a location and environment modeling method of an intelligent movable robot, and the method comprises the steps of firstly forming correction iteration expanded Kalman filtering algorithm and determining a number of iterations, then establishing a movement model and an observation model of the movable robot, initializing the status of the movable robot, calculating a position jacobian matrix, controlling and inputting the jacobian matrix to calculate, observing the jacobian matrix and the like; and finally solving a Kalman gain matrix, updating a status estimation equation and a covariance matrix by resolving Kalman gain matrix, and repeating partial steps. The method is centralized on the expanded Kalman filter algorithm which is widely used in the simultaneous location and environment modeling field of the movable robot, and the algorithm is improved, so that the performance of the algorithm is greatly improved, and the algorithm can better meet the application in the SLAM (simultaneous location and mapping). The method also provides powerful technical support for the autonomous navigation and completion of complicated intelligent tasks of the movable robot in an unknown environment.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
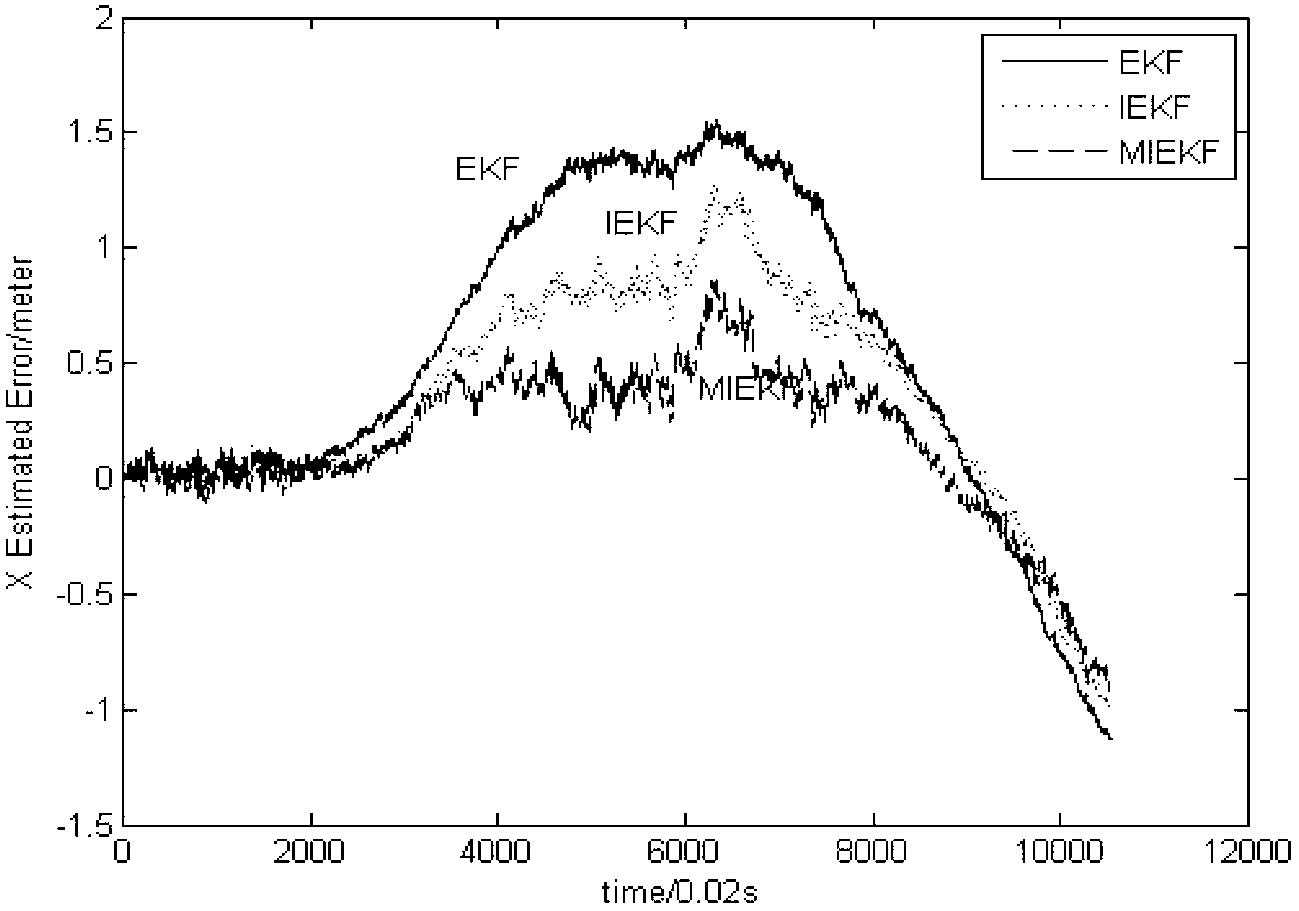
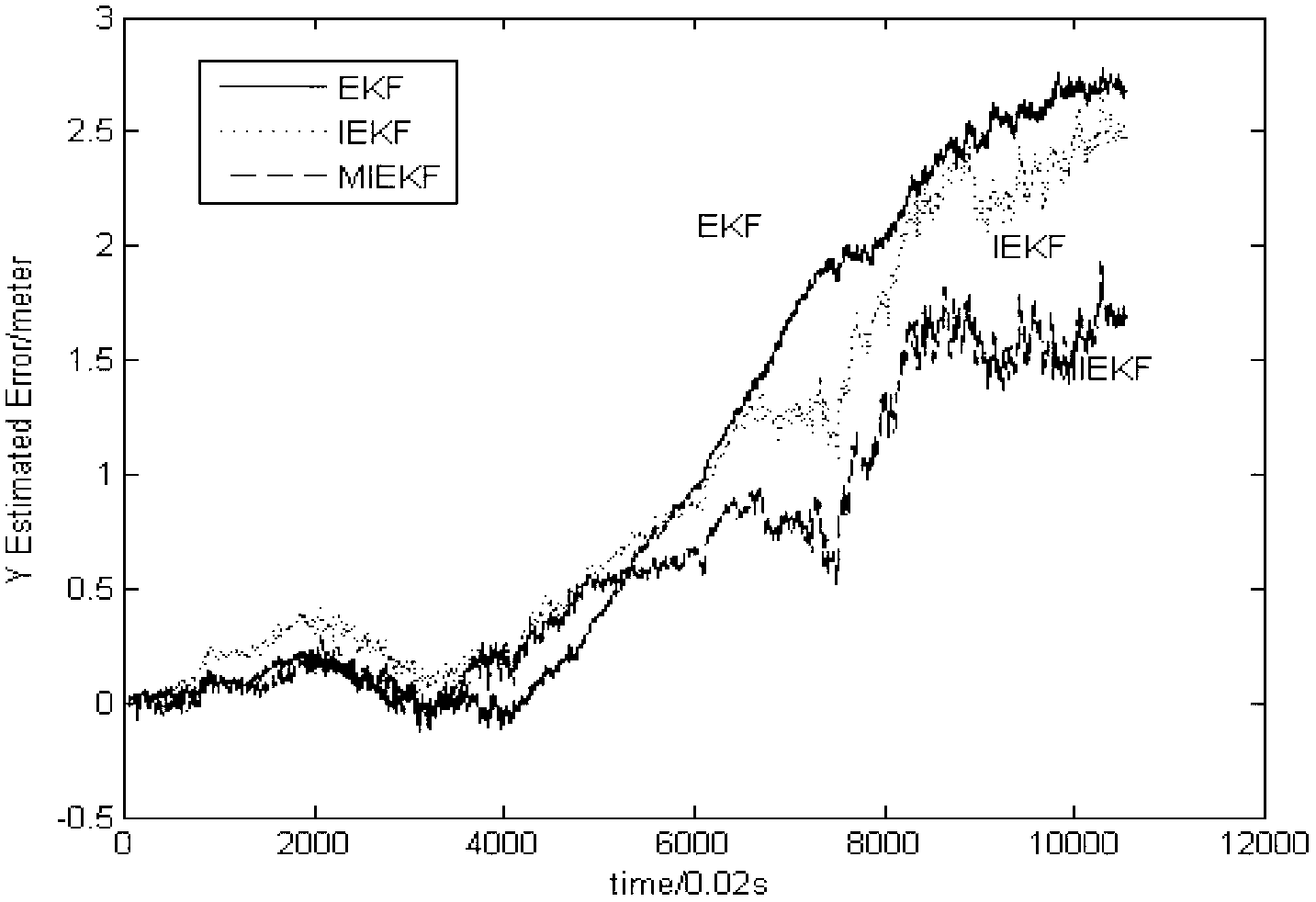
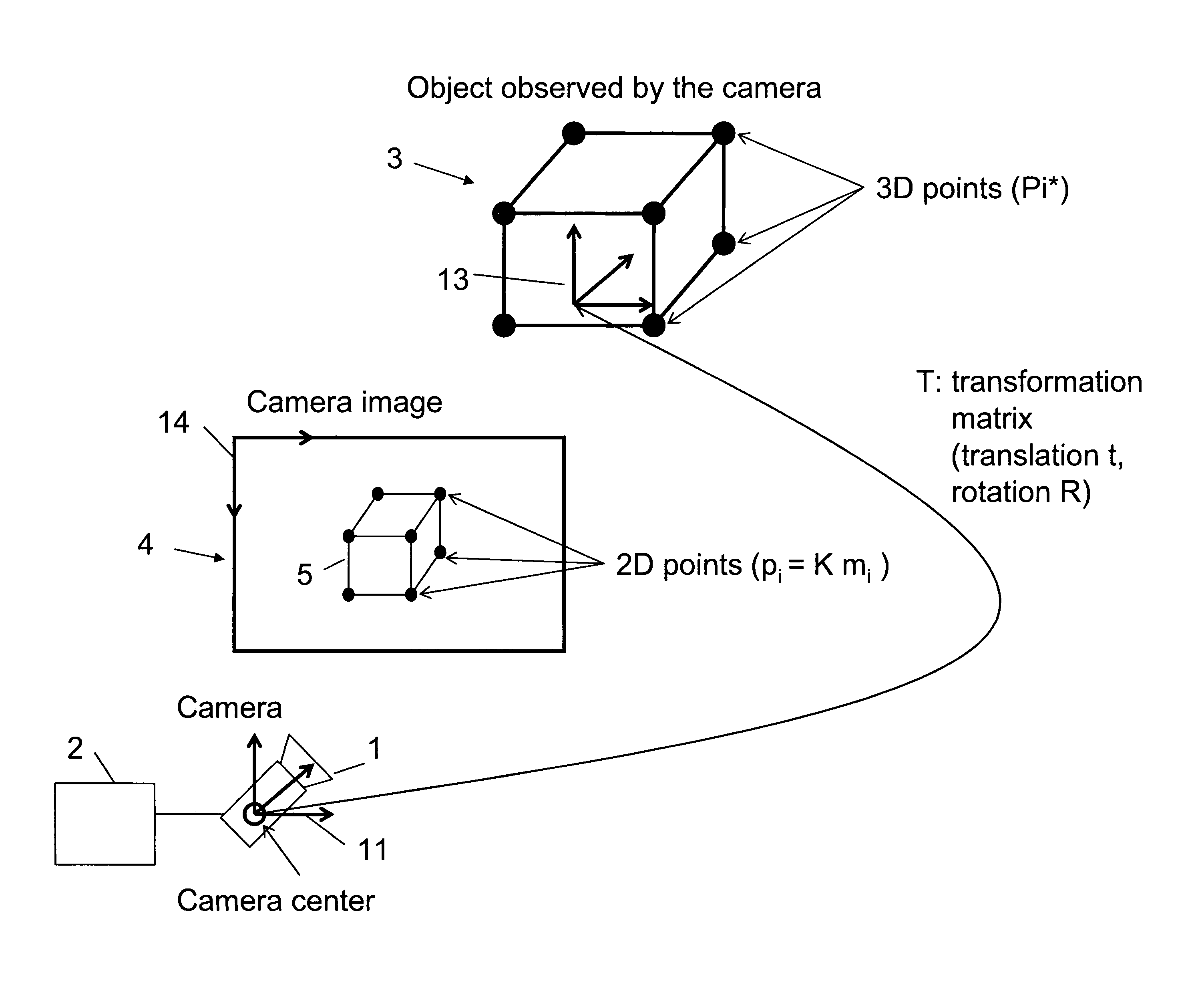
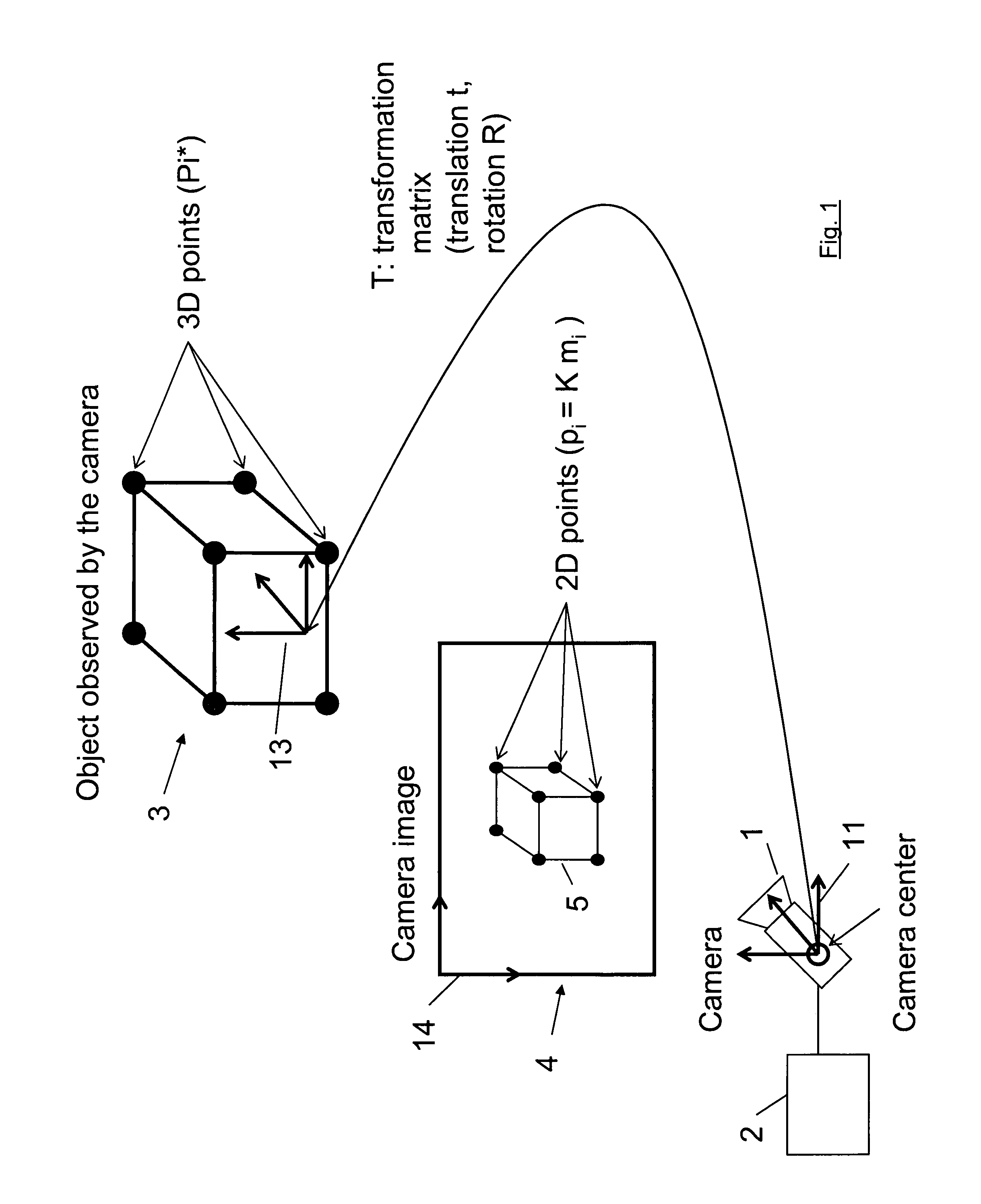
Method for determining the pose of a camera with respect to at least one real object
ActiveUS20120120199A1Reduce computing timeImage enhancementImage analysisIteration loopComputer vision
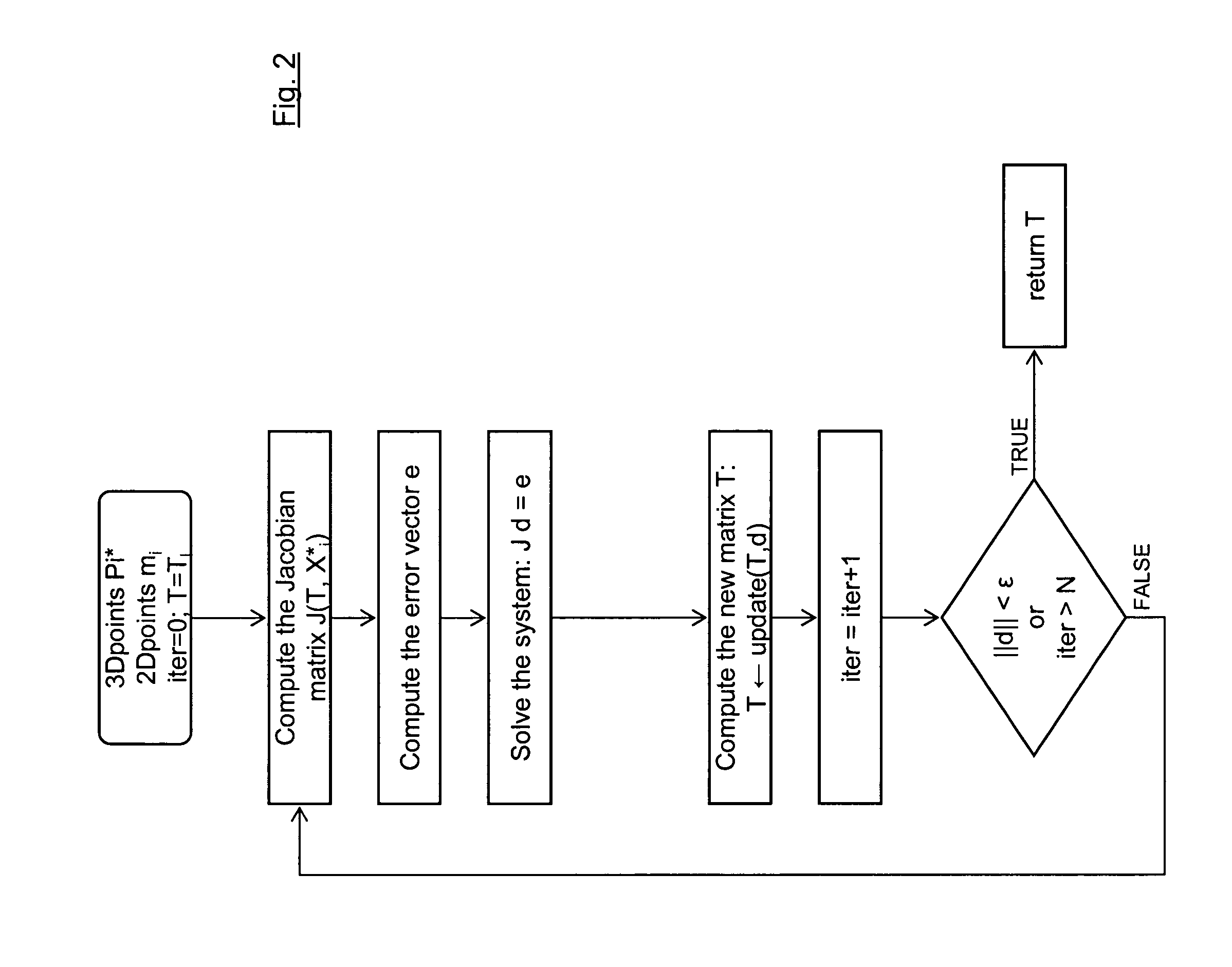
A method for determining the pose of a camera with respect to at least one real object, the method comprises the following steps: operating the camera (1) for capturing a 2-dimensional (or 3-dimensional) image (4) including at least a part of the real object (3), providing a transformation matrix (T) which includes information regarding a correspondence between 3-dimensional points (Pi*) associated with the real object (3) and corresponding 2-dimensional points (or 3-dimensional points) (p,) of the real object (5) as included in the 2-dimensional (or 3-dimensional) image (4), and determining an initial estimate of the transformation matrix (Tl) as an initial basis for an iterative minimization process used for iteratively refining the transformation matrix, determining a Jacobian matrix (J) which includes information regarding the initial estimate of the transformation matrix (Tl) and reference values of 3-dimensional points (Pi*) associated with the real object (3). Further, in the iterative minimization process, in each one of multiple iteration loops determining a respective updated version of the transformation matrix (T) based on a respective previous version of the transformation matrix (T) and based on the Jacobian matrix (J), wherein the Jacobian matrix is not updated during the iterative minimization process, and determining the pose of the camera (1) with respect to the real object (3) using the transformation matrix (T) determined at the end of the iterative minimization process. As a result, the camera pose can be calculated with rather low computational time.
Owner:APPLE INC
Model-based feature tracking in 3-D and 2-D imagery
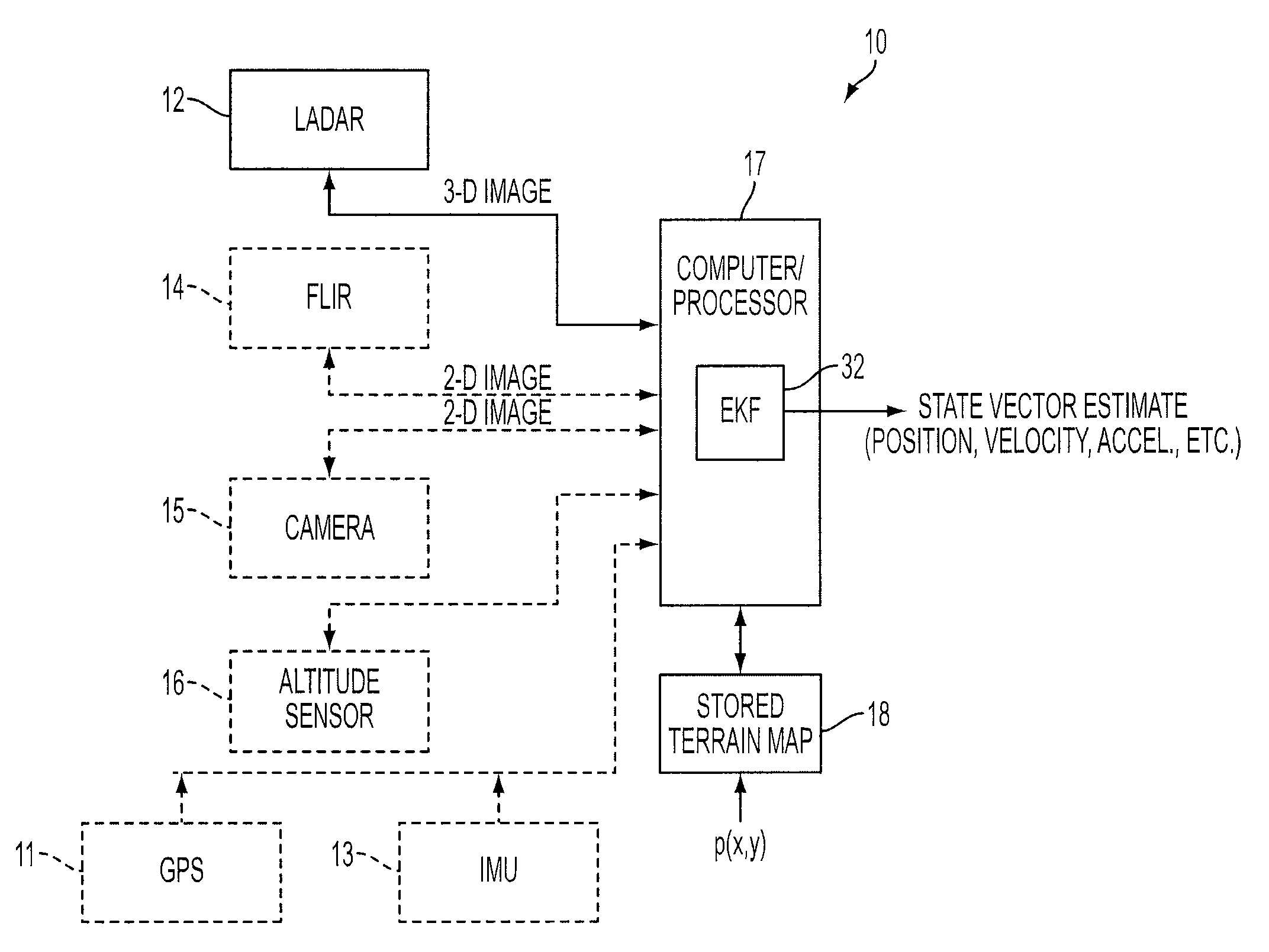
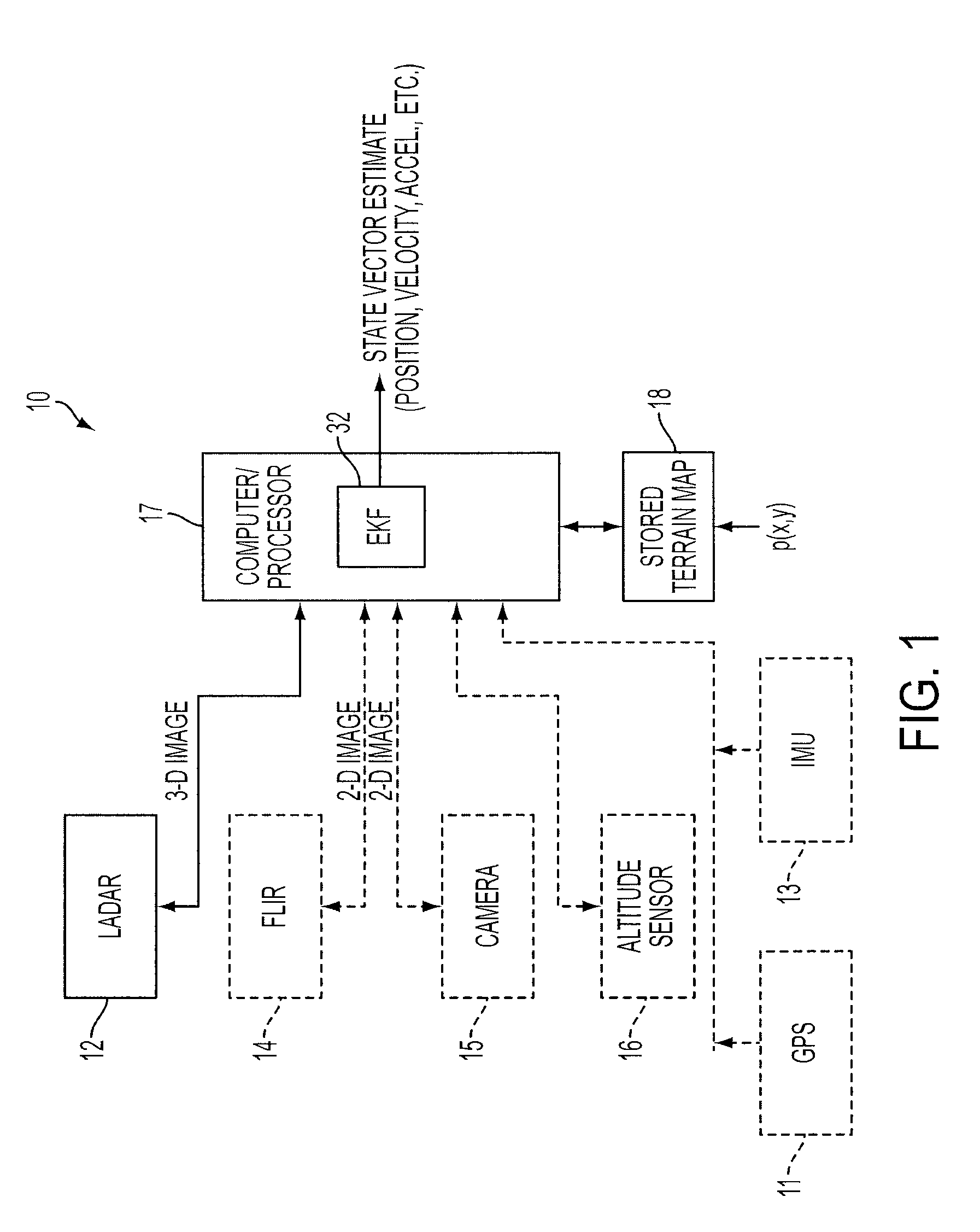
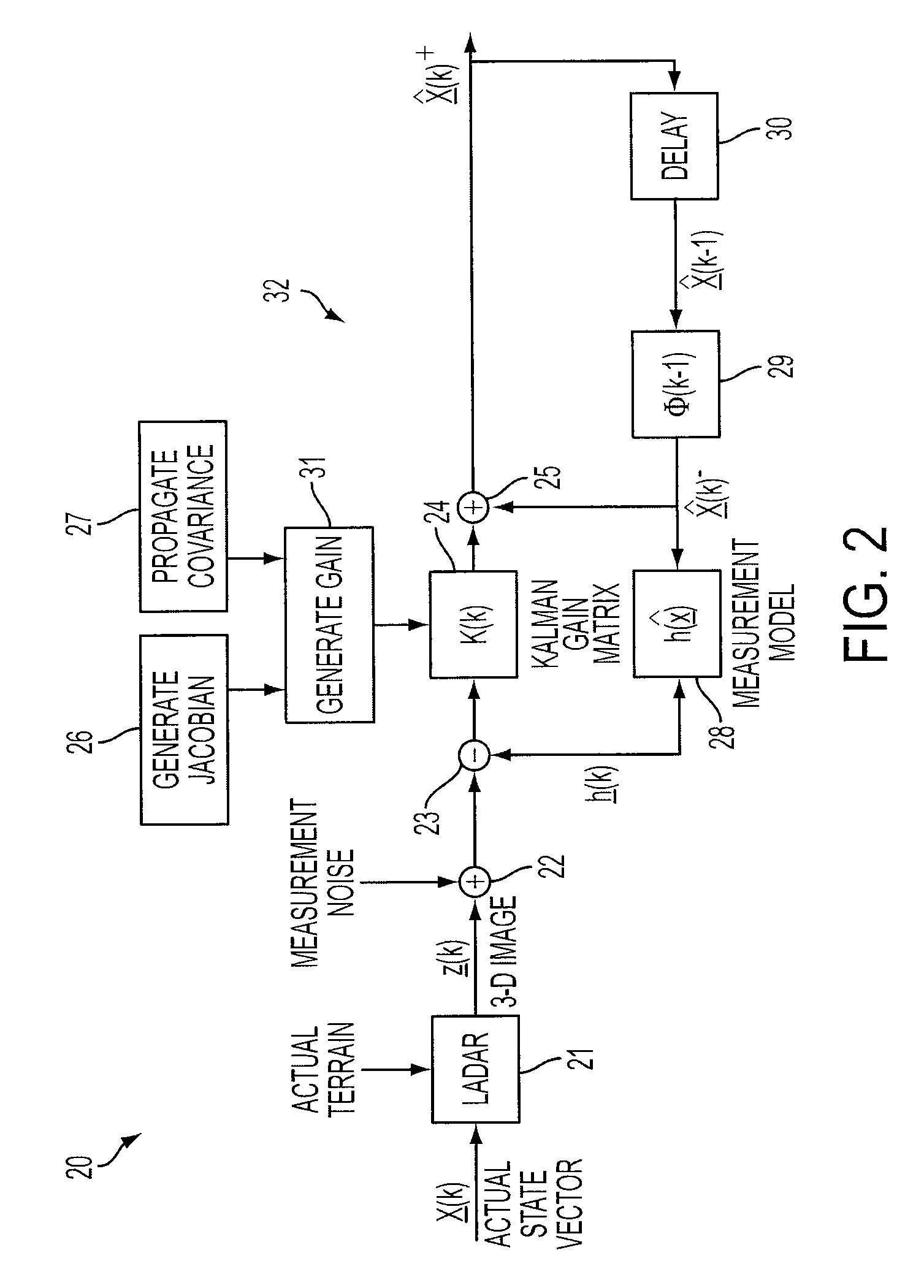
A feature tracker for tracking a target includes an imaging sensor for imaging the target and a Kalman filter for generating predicted position, velocity and acceleration of the imaging sensor with respect to the target. The Kalman filter includes a state vector estimate of the position, velocity and acceleration of the imaging sensor, and a model for characterizing the target. The model characterizes the target by using at least one bivariate Gaussian function for the target. The Kalman filter includes a Jacobian matrix defined as a partial derivative of the model with respect to the state vector estimate. The Kalman filter includes a gain matrix generated from the Jacobian matrix.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Mobile object controller and floor surface estimator
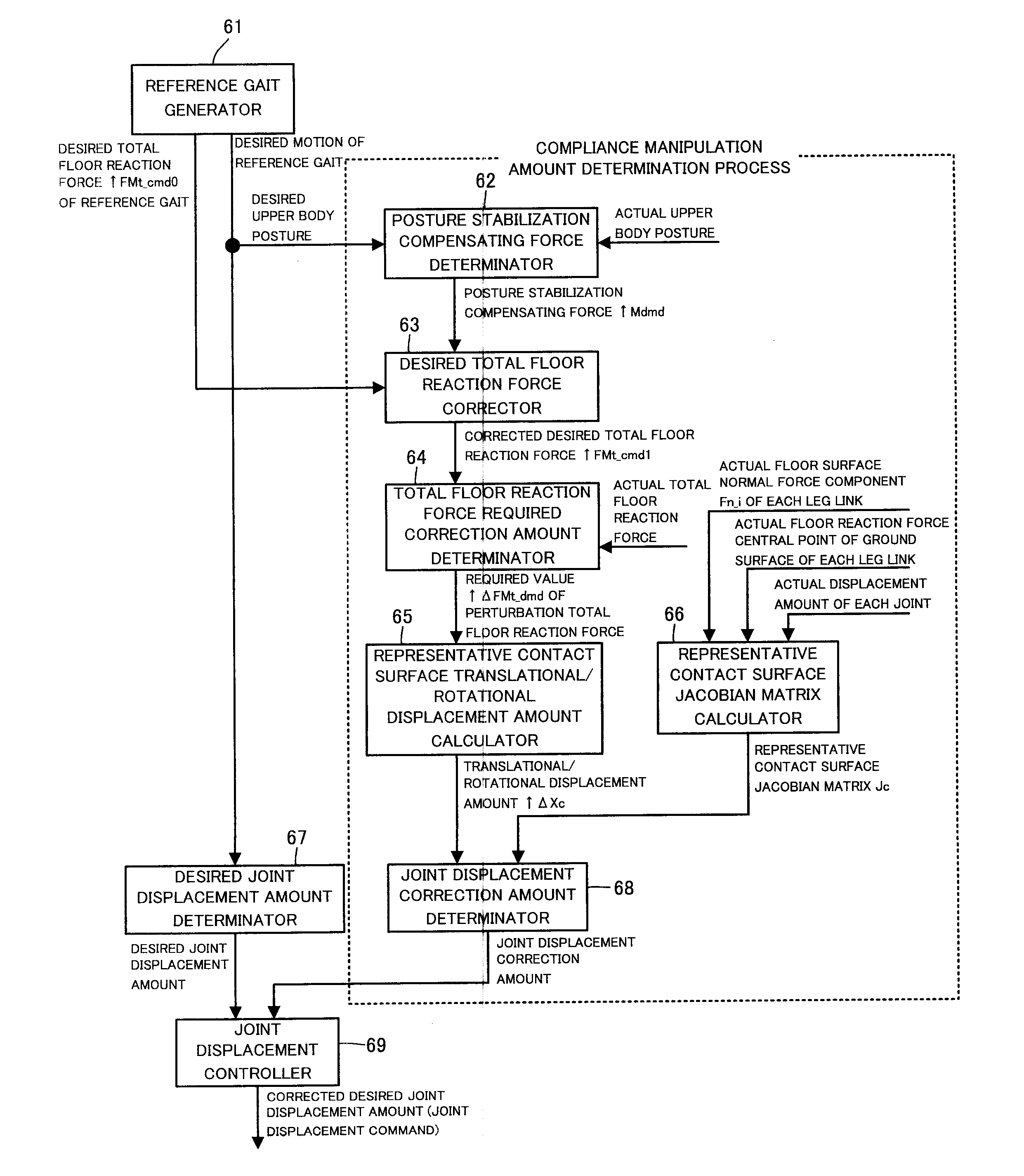
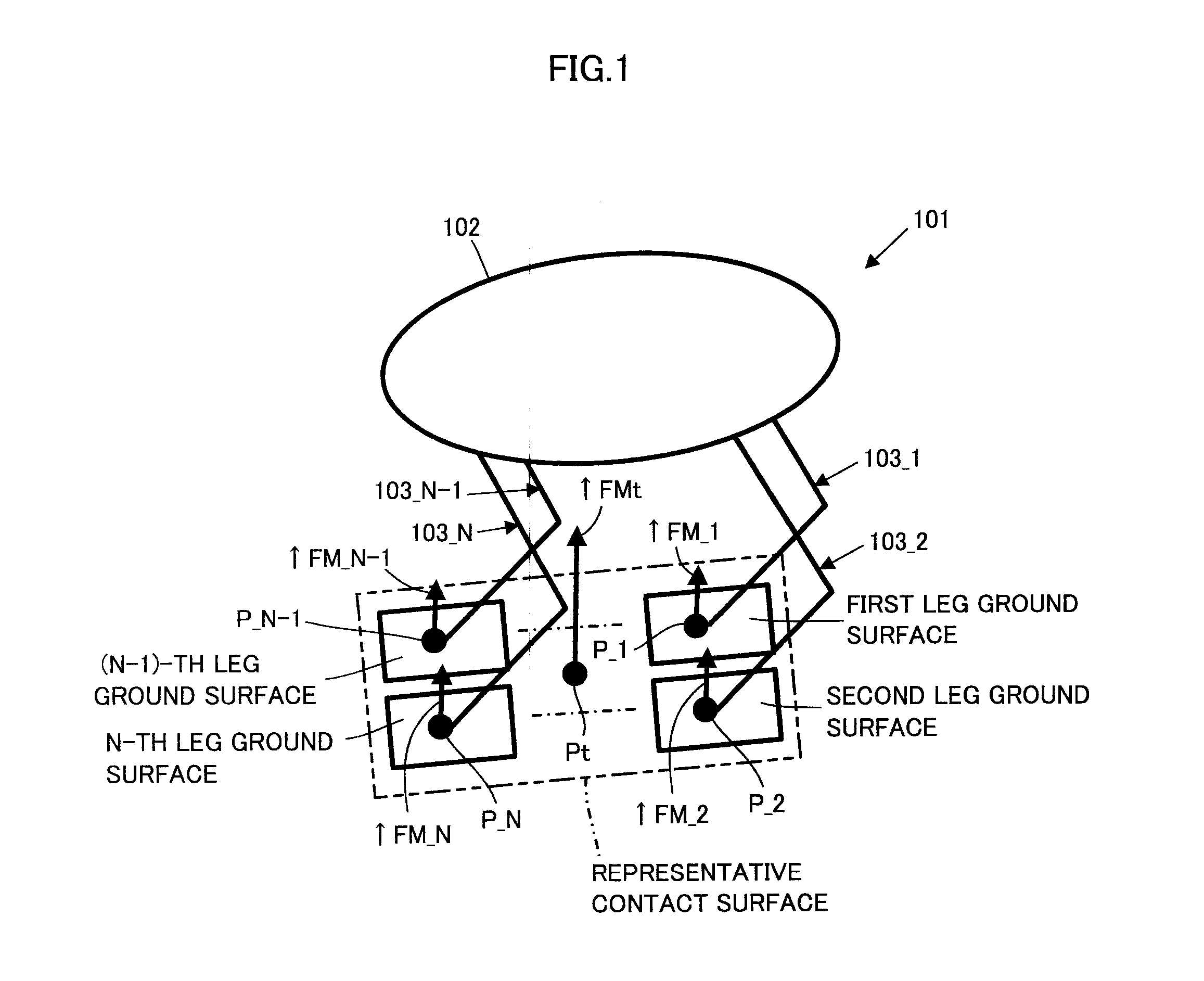
ActiveUS20120303162A1Efficiently determinedSmooth changeProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringMatrix representation
A total floor reaction force required correction amount by which an error between an observed value of a total floor reaction force acting on a mobile object 101 and a desired total floor reaction force approaches zero is converted to a spring displacement amount of a position / posture of a representative contact surface representative of ground surfaces of the mobile object 101. A correction amount of a displacement amount of each joint of the mobile object 101 is determined by multiplying the spring displacement amount by a pseudo inverse matrix of a Jacobian matrix representing a relation between a change amount of the position and posture of the representative contact surface per unit time and a change amount of a generalized variable vector per unit time. The displacement amount of each joint is controlled according to a corrected desired joint displacement amount obtained by correcting a desired joint displacement amount.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Data set inversion using source-receiver compression
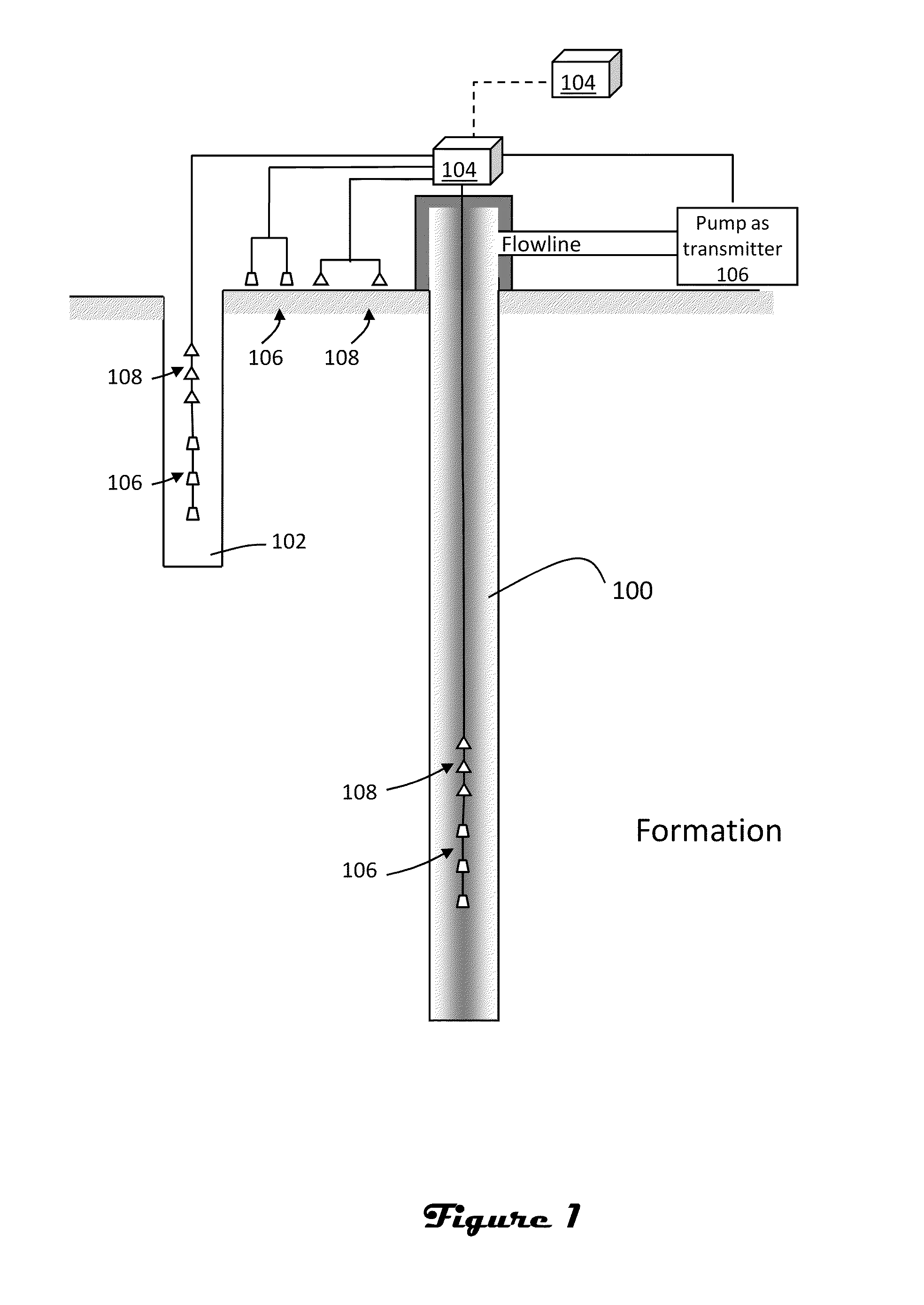
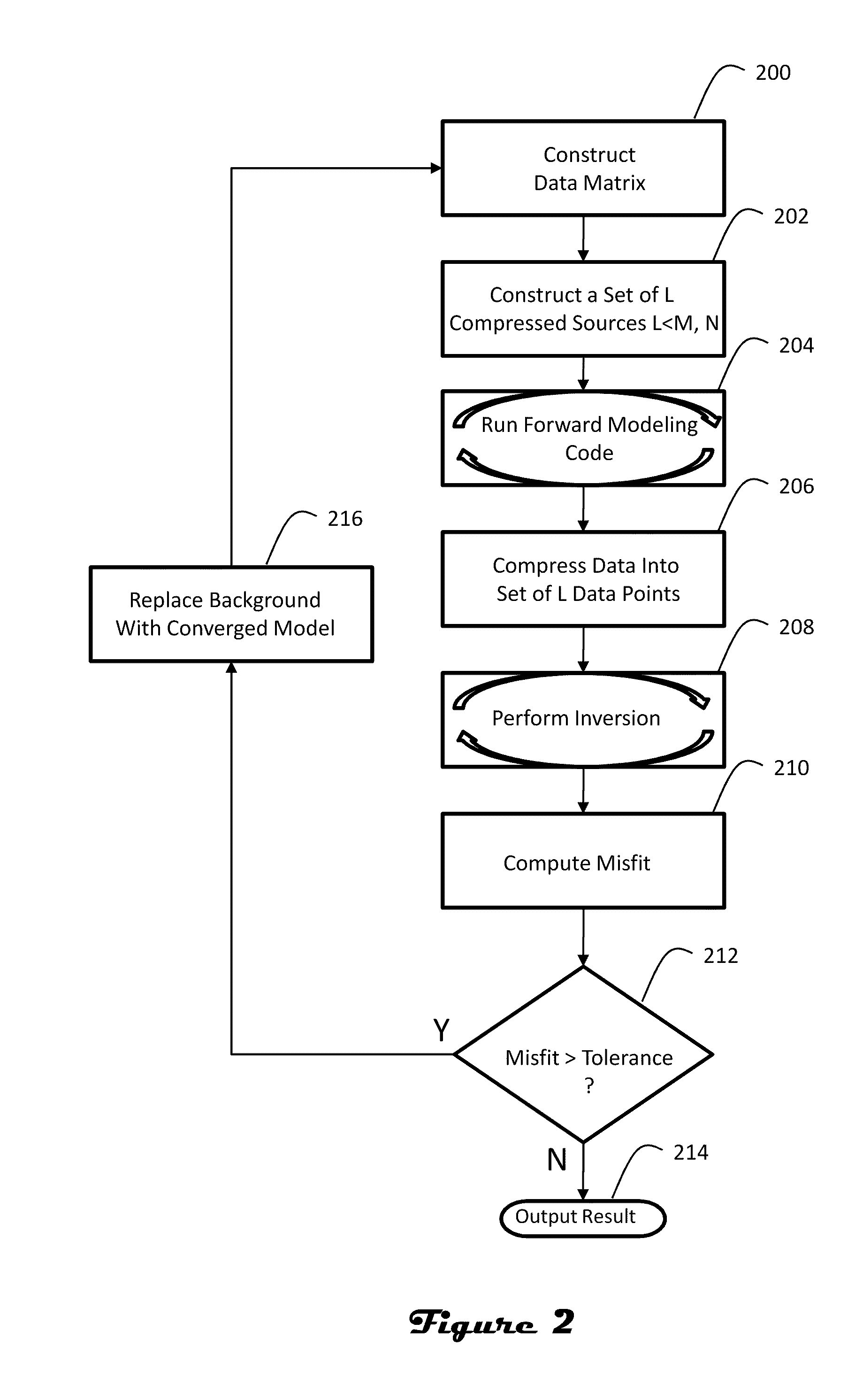
ActiveUS20110246140A1Low costReduce computing costElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationData setModel parameters
Source-receiver compression is used to help design surveys and mitigate the computational costs of data set inversion. The source-receiver compression is based on data redundancy and sensitivity. More particularly, a compressed source array is produced for minimum redundancy and maximum sensitivity to reservoir model parameters. The synthesized transmitter array has a reduced number of sources, thereby reducing the number of forward model simulations needed to carry out the inversion. Furthermore, the data collected at the receivers employed in the survey can be compressed. This has the implication of reducing the computational cost of constructing the Jacobian matrix and inverting the corresponding Hessian matrix.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP +1
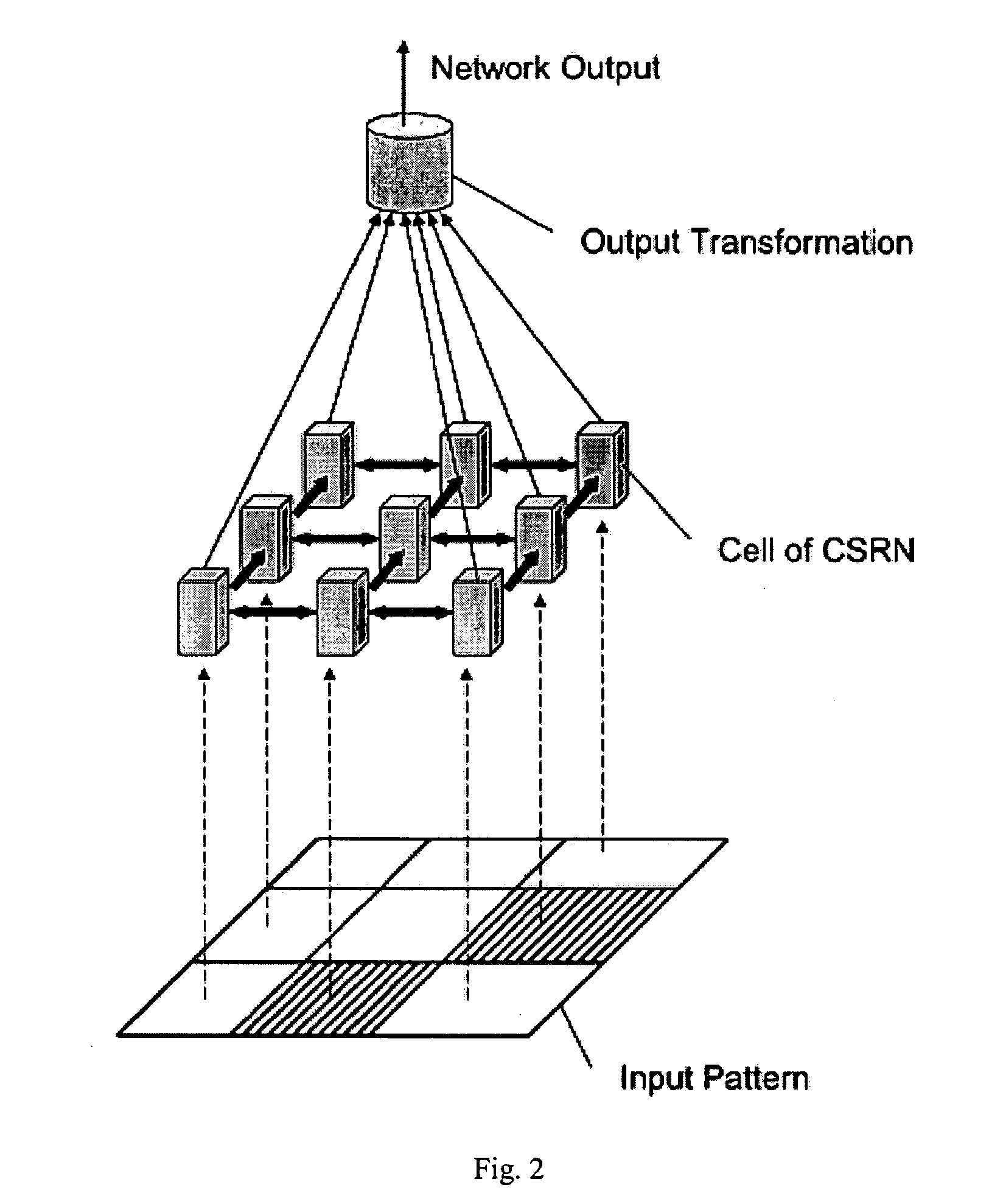
Methods of improved learning in simultaneous recurrent neural networks
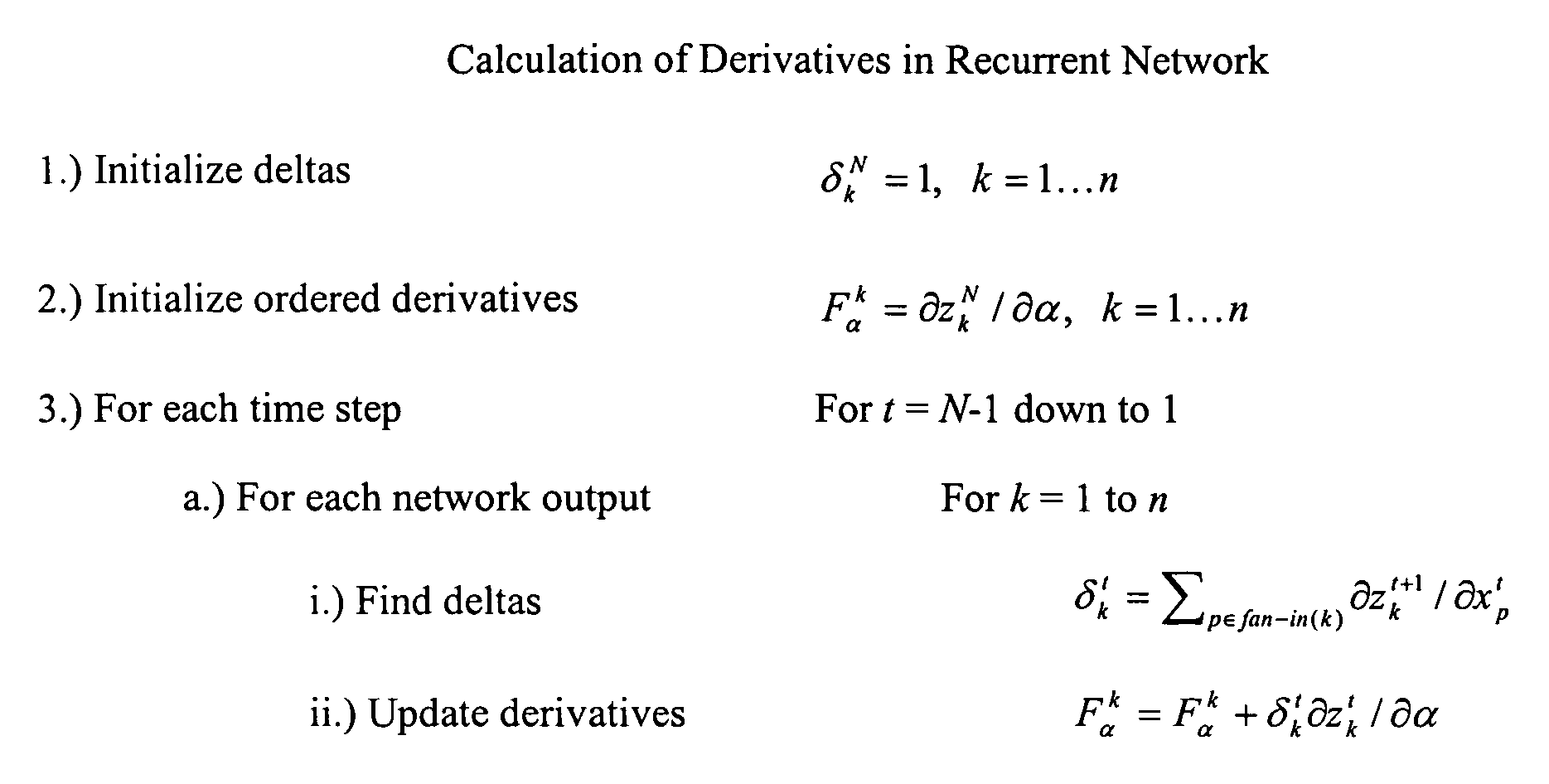
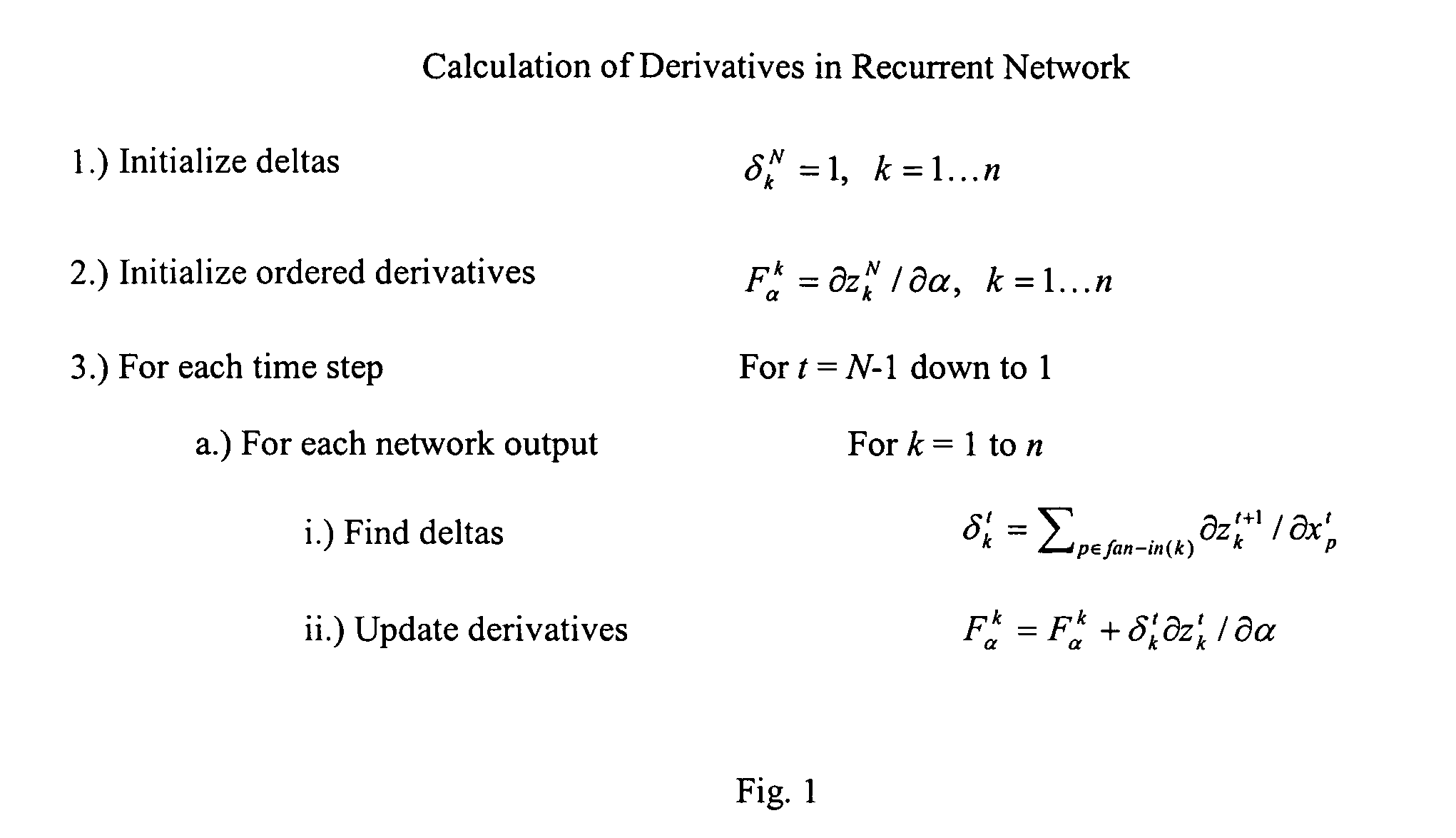
Methods, computer-readable media, and systems are provided for machine learning in a simultaneous recurrent neural network. One embodiment of the invention provides a method including initializing one or more weight in the network, initializing parameters of an extended Kalman filter, setting a Jacobian matrix to an empty matrix, augmenting the Jacobian matrix for each of a plurality of training patterns, adjusting the one or more weights using the extended Kalman filter formulas, and calculating a network output for one or more testing patterns.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MEMPHIS RESEARCH FOUNDATION
Animation creation program
InactiveUS7106334B2Simpler and easer operationEasy to operateAnimation3D-image renderingHumanoid robot naoAnimation
The present invention provides an animation creation program whereby the posture of a structure comprising a plurality of links can be determined by means of a simpler and easer operation. In accordance with the movement of one link in the structure comprising a plurality of links, the animation creation program of the present invention automatically determines the spatial positions of the other links of the structure so that the structure retains a posture that is as natural as possible. The animation creation program of the present invention uses, for example, inverse kinematics computation that is a computation method for controlling a human-type robot (humanoid) and is based on a matrix known as a Jacobian and the inverse matrix thereof which is known as the Singularity-Robust Inverse (SR-Inverse). By using this computation method in an animation creation program, in the creation of an animation of a structure comprising a plurality of links, it is possible, when moving one link of a structure displayed on a screen, to automatically determine the positions of the other links of the structure so that the posture of the structure as a whole does not become unnatural, and to create an animation of the structure comprising a plurality of links by means of a simpler and easer operation.
Owner:SEGA CORP
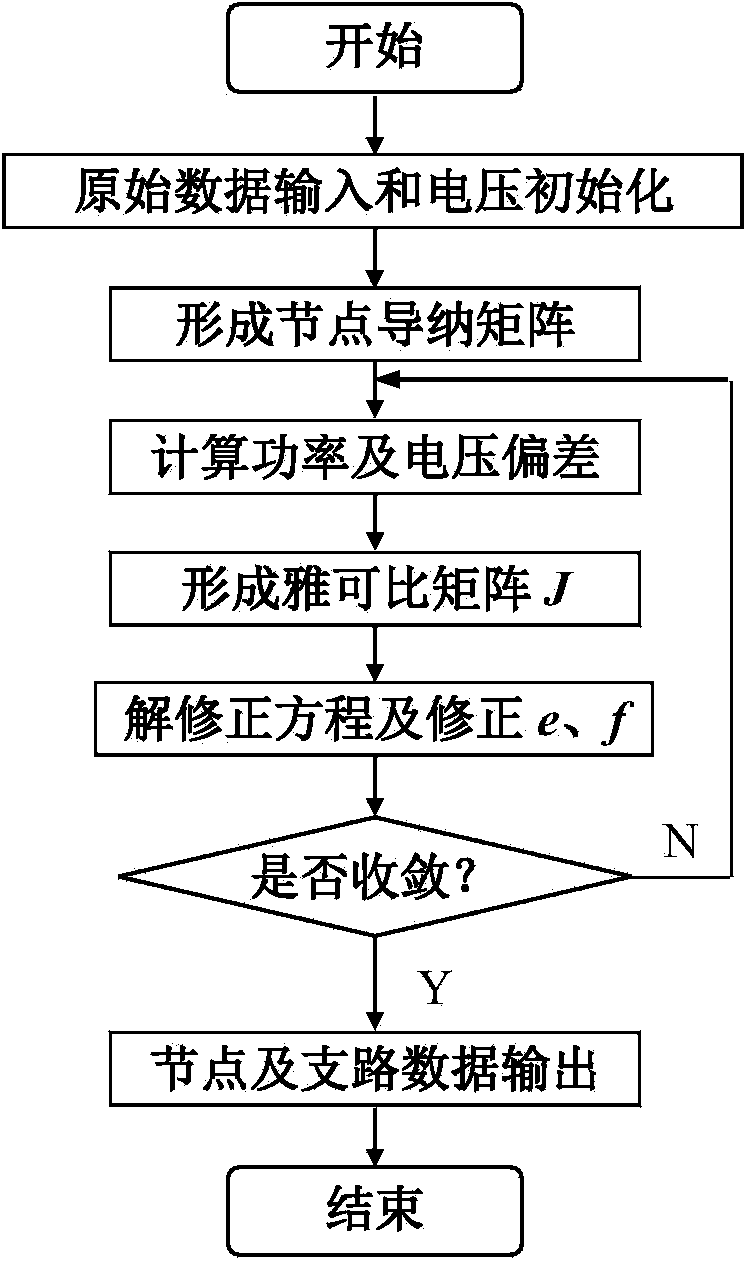
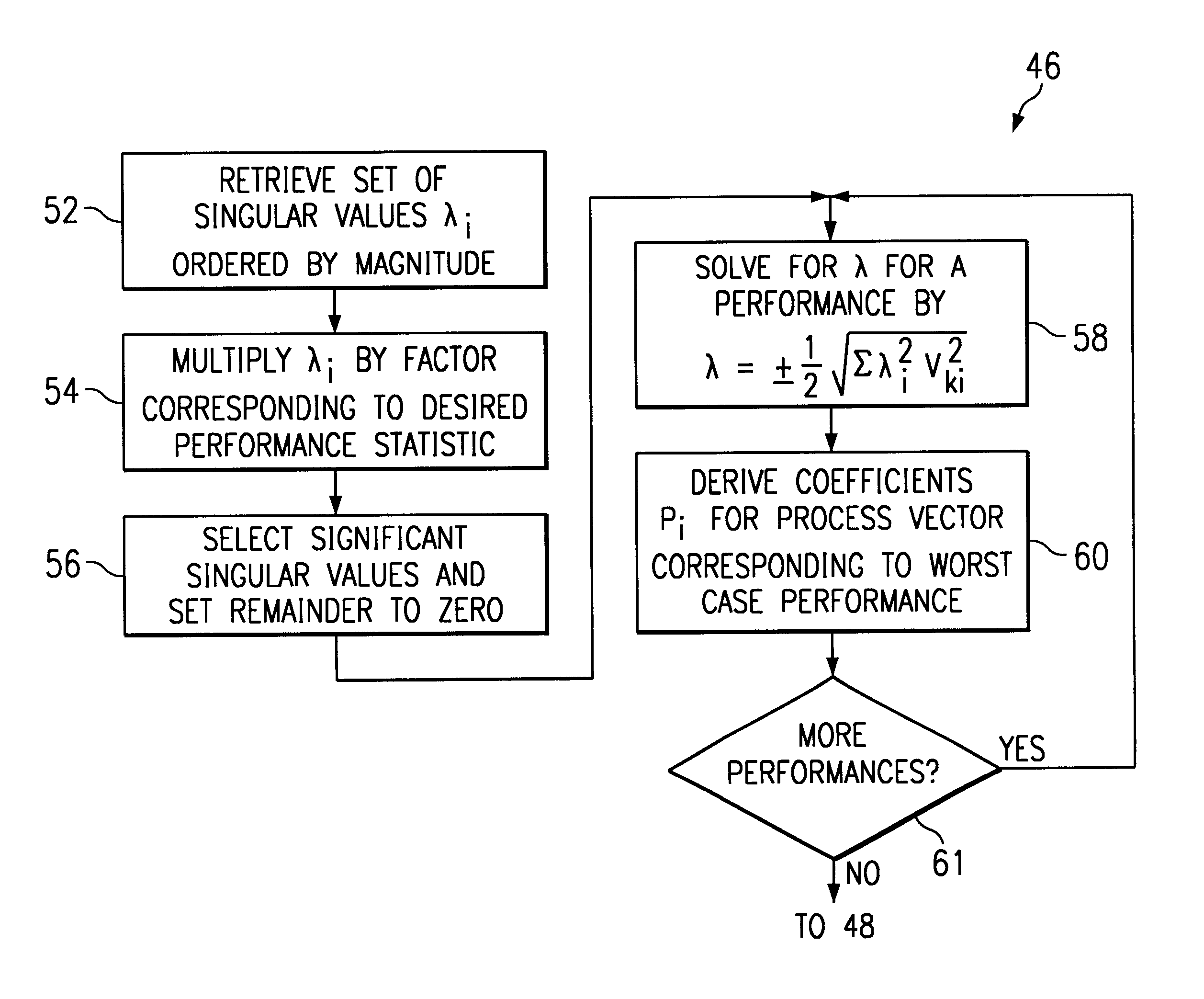
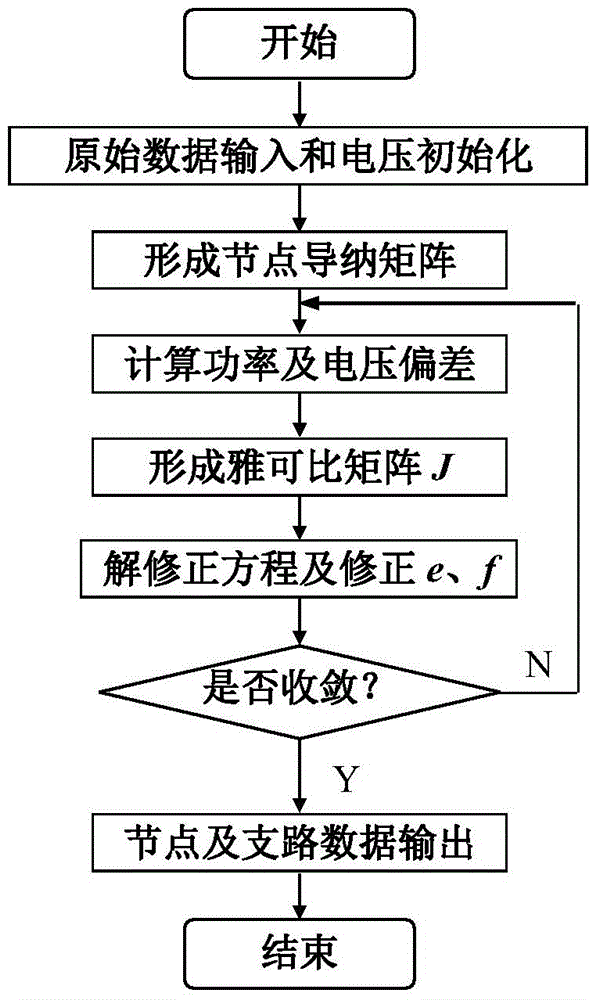
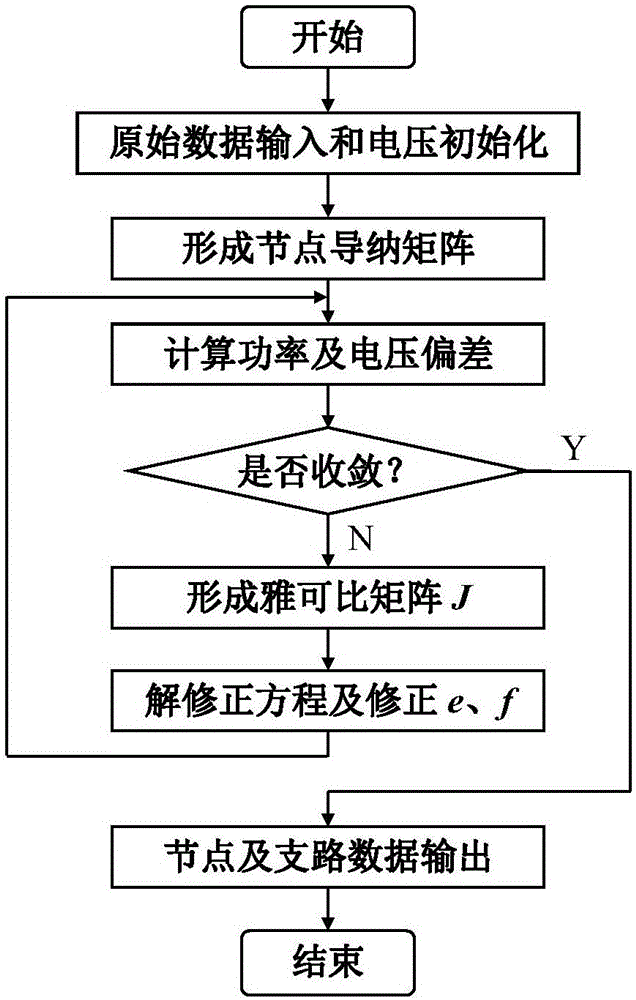
Rectangular coordinate Newton method load flow calculation method with changeable Jacobian matrix
ActiveCN104037764ASolving Convergence ProblemsConvergent and reliableAc network circuit arrangementsRectangular coordinatesOriginal data
The invention discloses a rectangular coordinate Newton method load flow calculation method with a changeable Jacobian matrix. The method includes the following steps that original data input and voltage initialization are conducted; a node admittance matrix is formed; power and voltage deviations are calculated, and the maximum amount of unbalance delta Wmax is obtained; the Jacobian matrix J is formed; a correction equation is solved and a real part e and an imaginary part f of voltage are corrected; node and circuit data are output. According to the rectangular coordinate Newton method load flow calculation method, a Jacobian matrix calculation method different from that used in the following iteration processes is adopted in the initial iteration process, and the convergence problem of rectangular coordinate Newton method load flow calculation in analyzing a system with a small-impedance branch circuit is solved. When misconvergence happens with conventional rectangular coordinate Newton method load flow calculation, the rectangular coordinate Newton method load flow calculation method with the changeable Jacobian matrix can achieve reliable convergence, and the number of iterations is fewer compared with the prior art. The rectangular coordinate Newton method load flow calculation method with the changeable Jacobian matrix can effectively solve the convergence problem of the conventional rectangular coordinate Newton method load flow calculation in analyzing the system with the small-impedance circuit branch, and meanwhile load flow calculation can be performed on normal systems, and adverse effects are avoided.
Owner:SUWEN ELECTRIC ENERGY TECH
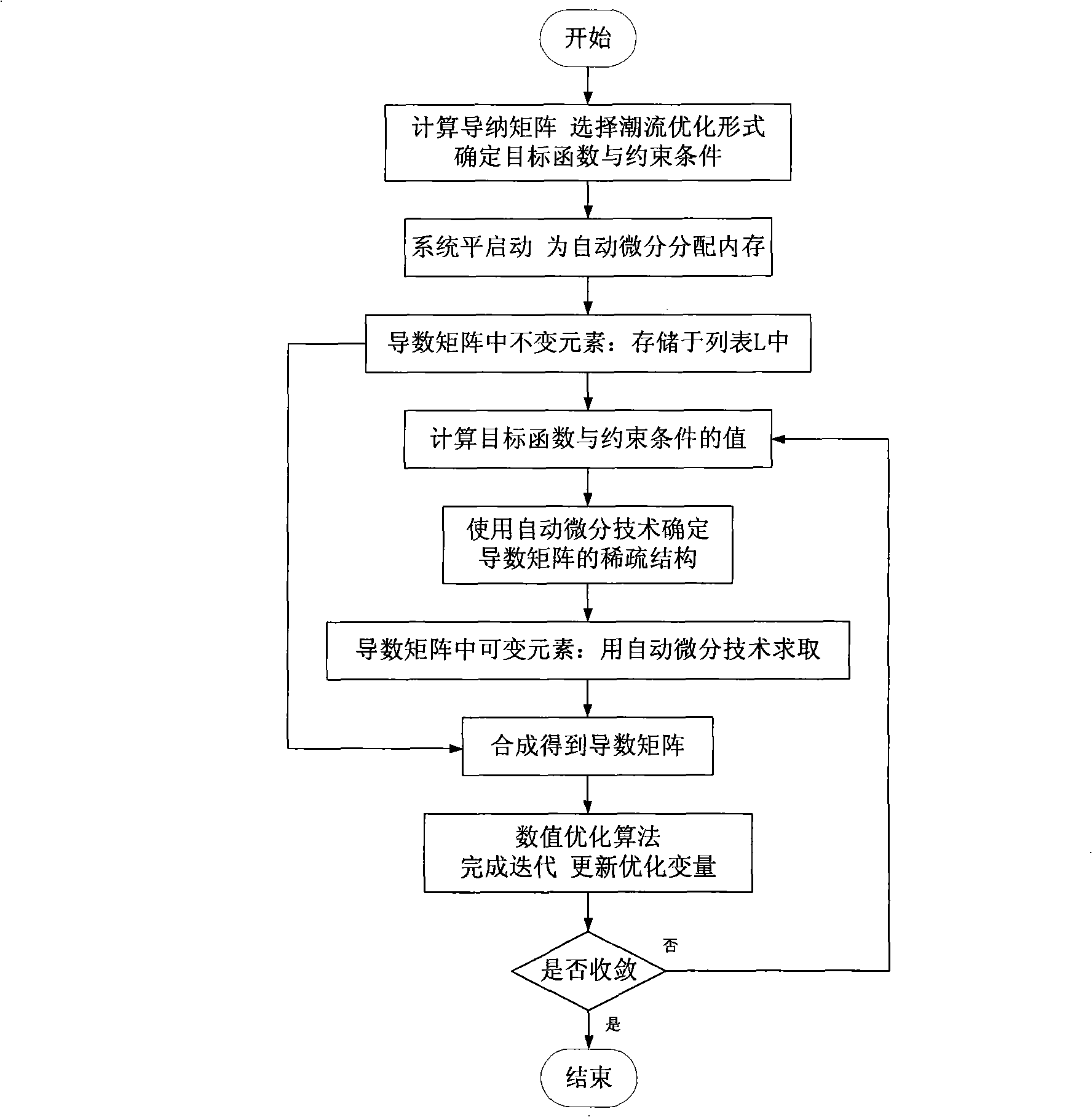
Method for optimizing electric power system tide base on part automatic differential technology
InactiveCN101409447AEfficient and flexibleEasy to calculateData processing applicationsSystems intergating technologiesMaintainabilityElectric power system
The invention discloses a tidal current optimization method of an electric power system based on partial automatic differentiation technique. Compared with the existing tidal current optimization methods based on the automatic differentiation technique, the algorithm fully utilizes the unchangeable characteristic of most elements in a Jacobian matrix and / or a Hessian matrix of an objective function and a constraint function during iteration, and is added with a function of identifying invariable elements in the Jacobian matrix and the Hessian matrix, and stores the invariable elements in a list before the first iteration; in each iteration of a numerical optimization algorithm, variable elements in the Jacobian matrix and / or the Hessian matrix can be computed only by the automatic differentiation technique. The tidal current optimization method based on the partial automatic differentiation technique can greatly reduce the burden on software developers and maintainers, improve the maintainability and the flexibility of a tidal current optimization application program, efficiently support customized models, and satisfy the analysis, running and scheduling requirements of the modern power system on the premise that the computational efficiency is not reduced substantially.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
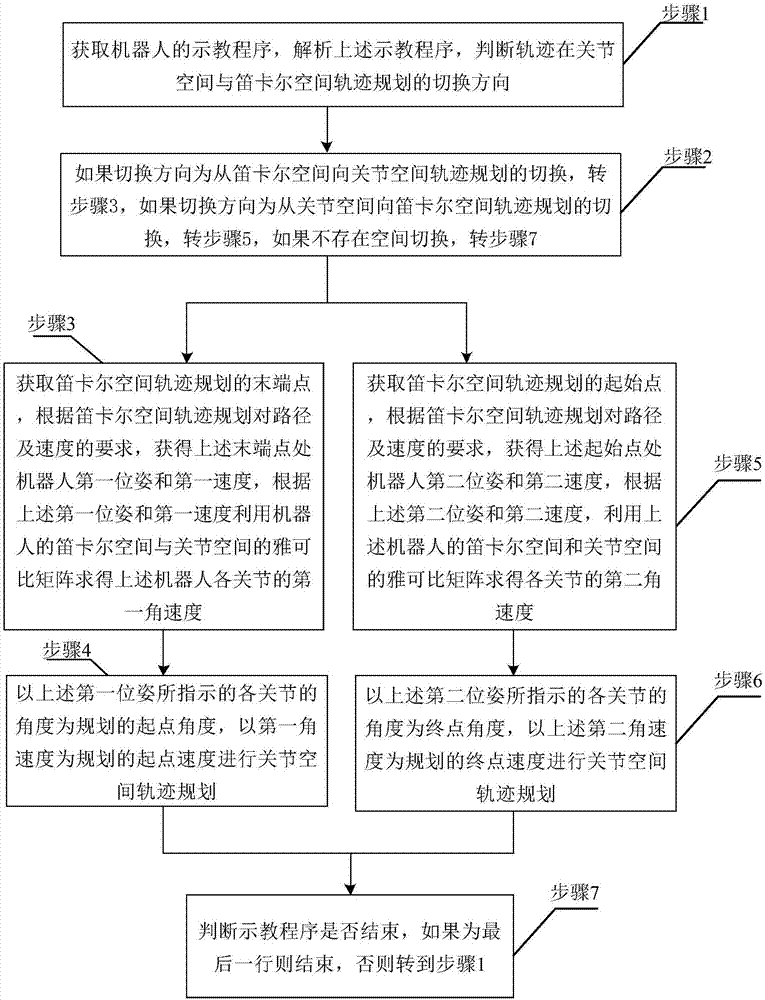
Smooth transition method of multi-space trajectory planning of teaching robot, and devices
ActiveCN107571261ASolve the stall problemImprove work efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorTeaching programAngular velocity
The invention relates to the field of robot trajectory planning, and provides a smooth transition method of multi-space trajectory planning of a teaching robot, aiming at solving the unsmooth problemin the trajectory switching process. The smooth transition method comprises the steps that a teaching program of the teaching robot is analyzed, the switching direction of the trajectory planning is judged, if the trajectory planning is that the switching direction is from cartesian space to joint space, a tail end of cartesian space trajectory planning is acquired, according to the requirements on a path and a velocity, a first posture and a first velocity at the tail end are acquired, first angular velocities of various joints are obtained by employing a jacobi matrix, and by taking an angleindicated by the first posture as a starting angle and the first angular velocities as starting velocities, joint space trajectory planning is carried out; or else, a starting point of the cartesianspace trajectory planning is acquired, a second posture at the starting point and second angular velocities of the various joints are obtained, and by taking an angle indicated by the second posture as a terminal angle and the second angular velocities as terminal velocities, the joint space trajectory planning is carried out. Smooth transition of the trajectory planning in space switching is realized.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
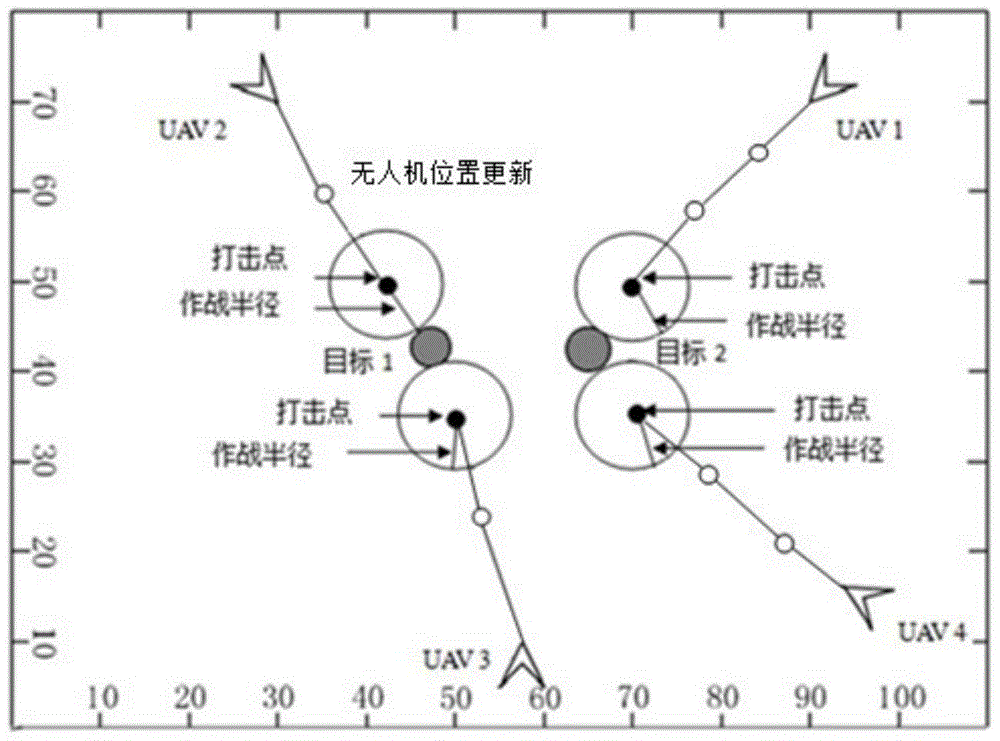
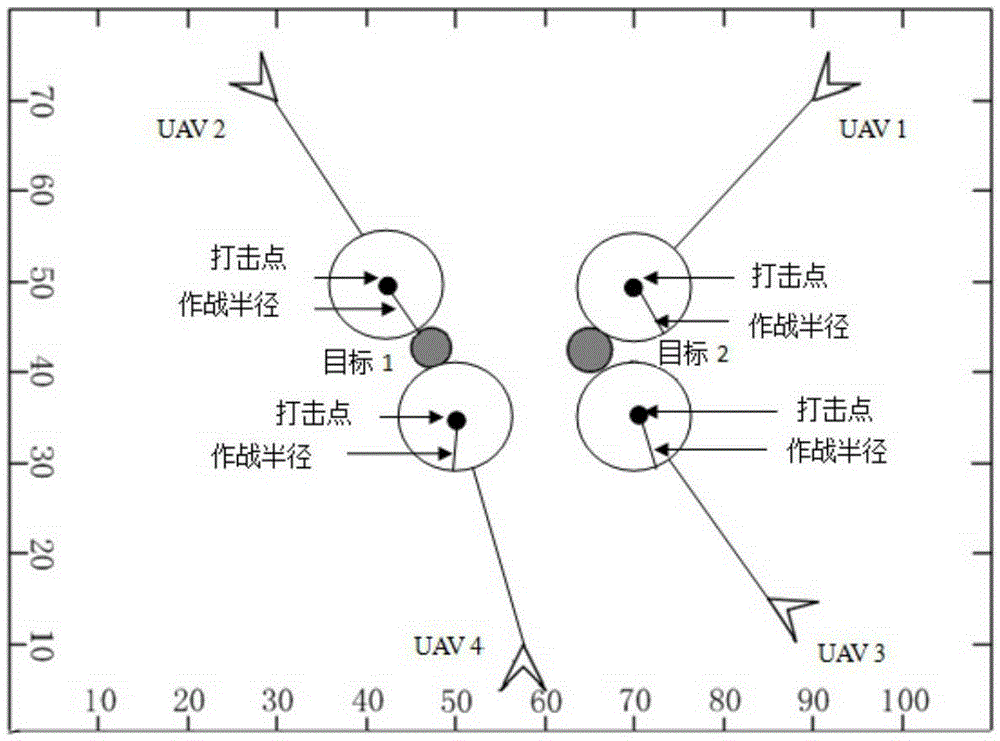
Moving horizon method-based multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative attack task allocation method
InactiveCN105739303AImprove coordinated strike capabilityAvoid the curse of dimensionalityVehicle position/course/altitude controlAdaptive controlOptimal decisionHorizon
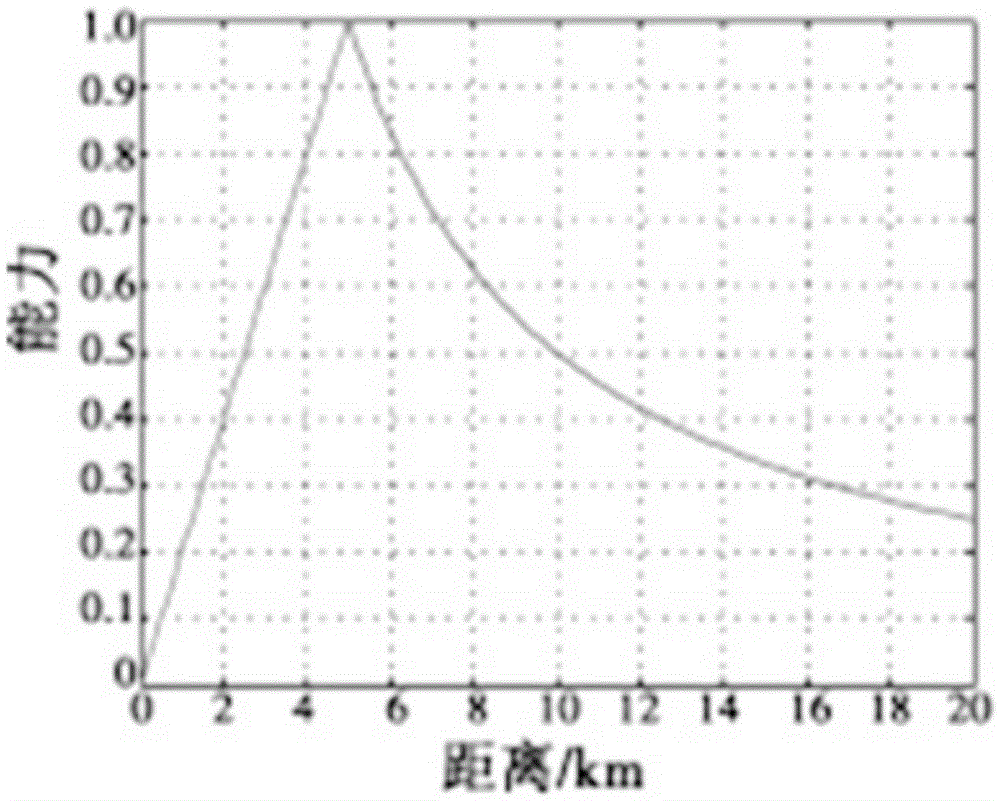
The invention relates to a moving horizon method-based multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative attack task allocation method and belongs to the multi-unmanned aerial vehicle coordinated control technical field. The method includes the following steps that: the ability function of unmanned aerial vehicles is established, a calculation method of a multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative attack position is provided through the jacobian matrix of the ability function; a unmanned aerial vehicle damage cost index function, a voyage cost index function and a multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative task assignment model are established; and a moving horizon method is utilized to model a maneuver decision-making problem into an optimized control problem, and a whole maneuver target approach process is discretized temporally and spatially, optimal maneuver strategies can be solved piecewise, and an optimal decision-making method for a multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative attack task can be provided. With the horizon method-based multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative attack task allocation method of the invention adopted, a higher target gain value and damage efficiency can be obtained, and multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative attack ability can be improved.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
Robot control apparatus
ActiveUS8155790B2Improve accuracyStable controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlRobot controlActuator
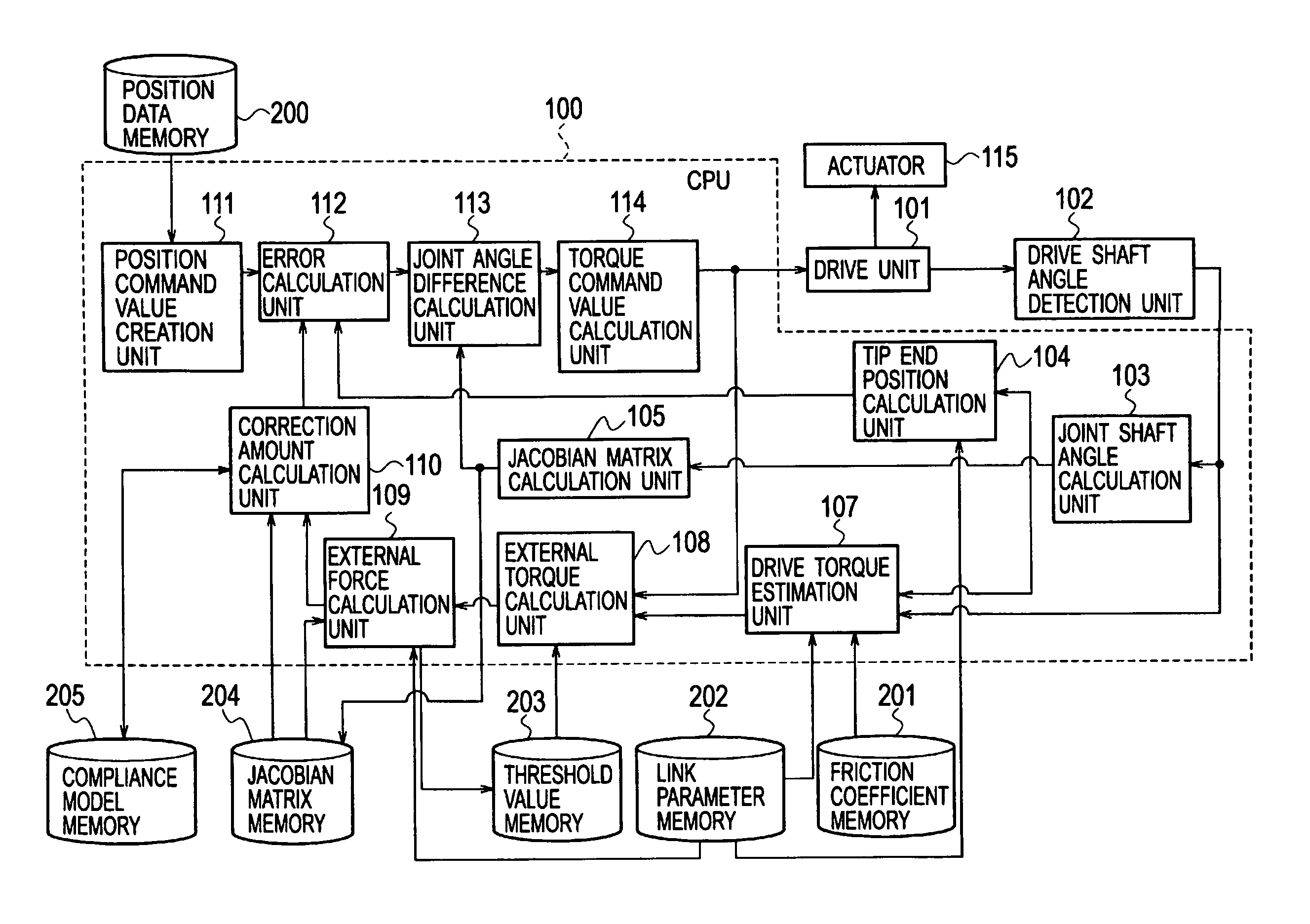
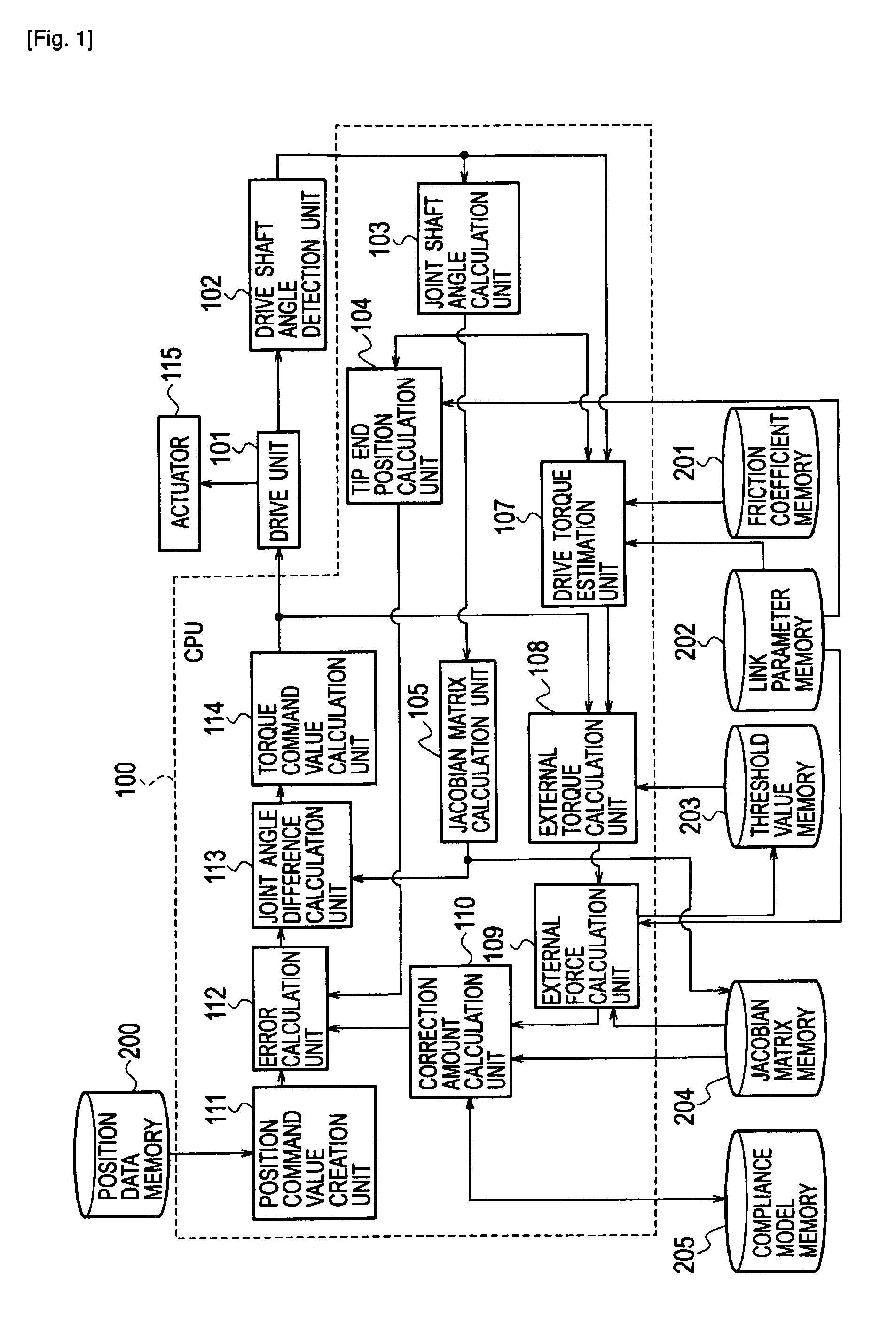
A robot control apparatus includes: a drive unit (101) driving an actuator (115) based on a torque command value; a drive torque estimation unit (107) estimating a drive torque from a joint shaft angle; an external torque calculation unit (108) calculating a difference between the estimated drive torque and the torque command value as an external torque; a Jacobian matrix calculation unit (105) calculating a Jacobian matrix based on the joint shaft angle; an external force calculation unit (109) calculating an external force from the Jacobian matrix and the external torque; and a correction amount calculation unit (110) calculating a correction amount from the external force.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Counter-attack countermeasure optimal strategy method for multi-unmanned plane cooperative strike task
InactiveCN105278542AImprove coordinated strike capabilityEstimated benefit value is largeAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsCountermeasureSimulation
The invention aims to solve the problem of a counter-attack countermeasure optimal strategy for a multi-unmanned plane cooperative strike task and belongs to the technical field of multi-unmanned plane cooperative control. The invention combines a capability function with a multi-unmanned plane cooperative strike counter-attack countermeasure model and provides a counter-attack countermeasure method for the multi-unmanned plane cooperative strike. Firstly, the capability function of an unmanned plane is established; then by means of a jacobian matrix of the capability function, a calculation method for the position of the multi-unmanned plane cooperative strike is created; and the multi-unmanned plane cooperative strike counter-attack countermeasure model is established further, and a solving method for a n-person limited strategy static counter-attack countermeasure model and the pure-strategy nash equilibrium is created. The invention achieves the counter-attack countermeasure optimal strategy for the multi-unmanned plane cooperative strike, obtains great assessment profit value and strike strike efficiency, and improves the multi-unmanned plane cooperative strike capability.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
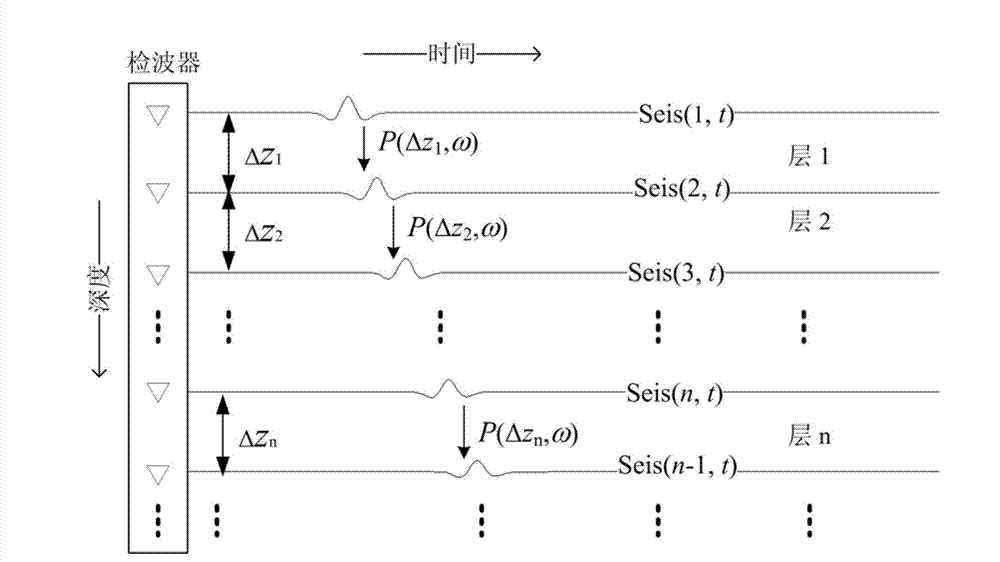
Self-adapting wave form retrieval method through utilization of zero offset vertical seismic profile (VSP) data to estimate speed and Q value
InactiveCN103163554AIncreased sensitivityHigh precisionSeismic signal processingPeak valueSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a self-adapting wave form retrieval method through utilization of zero offset vertical seismic profile (VSP) data to estimate speed and Q value. The method includes a first step of selecting undisturbed a segment of a first-motion wave in a self-adapting mode to the maximum extent according to the signal to noise ratio of the actual VSP data and the degree of a direct wave disturbed by an upward traveling wave, and fully utilizing effective information to construct an objective function, a second step of improving the sensitiveness of the objective function to changes of the Q value through proper construction of a data weighting matrix according to the feature that the Q value is more difficult to estimate than other parameters; a third step of adopting a recently developmental self-adapting multiplication regularization method to improve the ill-conditional problem of nonlinear inversion, and limiting the value range of the unknown parameters through nonlinear transformation, and a fourth step of inferring analytical expressions of elements of a jacobian matrix so as to decrease the calculated amount of inverse problems. Compared with a spectrum ratio method and a wavelet envelope peak value instantaneous frequency method, the method is relatively smaller in influence of the upward traveling wave, stronger in anti-noise performance, and higher in accuracy of inverse parameters.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Accurate linearization method of measurement equation for electric power system state estimation
ActiveCN102831315AReduce complexityEasy to solveData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsElectric power systemEngineering
The invention provides an accurate linearization method of a measurement equation for electric power system state estimation. The accurate linearization method is characterized by including steps of establishing a network model and calculating a nodal admittance matrix; selecting state vectors and measurement vectors; and forming a jacobian matrix so as to get the accurately linearized measurement equation. The accurately linearized measurement equation is obtained by selecting the state vectors and the measurement vectors, and the state vectors can be solved by means of any types of existing state estimation according to the accurately linearized measurement equation, and estimation values such as all branch power and node injection power in the network can be acquired, so that complexity of the state estimation model is reduced greatly and the equation is easy to solve.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Worst case performance modeling of analog circuits
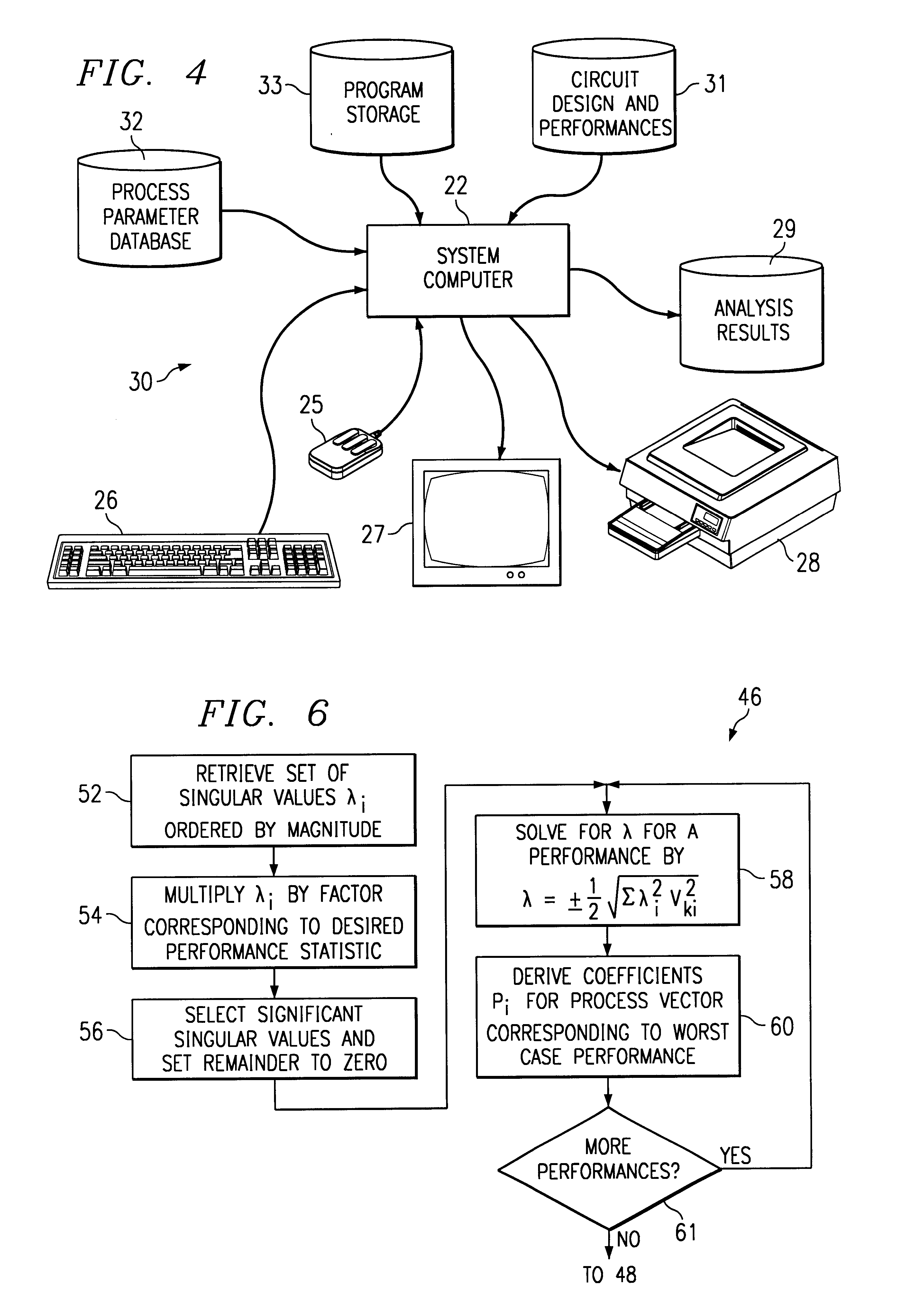
InactiveUS6850877B1Improve automationWide applicabilityDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationSingular value decompositionProgram instruction
A computer system (30) and method of operating the same to model worst case performances of an analog circuit is disclosed. The computer system (30) includes disk storage devices for storing a process parameter data base (32), design of the circuit (31), and program instructions for performing the modeling method (33). Under the control of the program instructions, the system computer (22) retrieves the process parameters and desired performances, and performs a designed experiment to determine a Jacobian matrix of the dependence of the performances upon the process parameters. Singular value decomposition of the Jacobian matrix provides a set of singular values and a rotation vector, from which the coefficients of a worst case vector of the process parameters for each of the circuit performances are then derived. The system computer (22) then applies the simulation to the worst case vectors, to evaluate the worst case performances of the designed circuit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
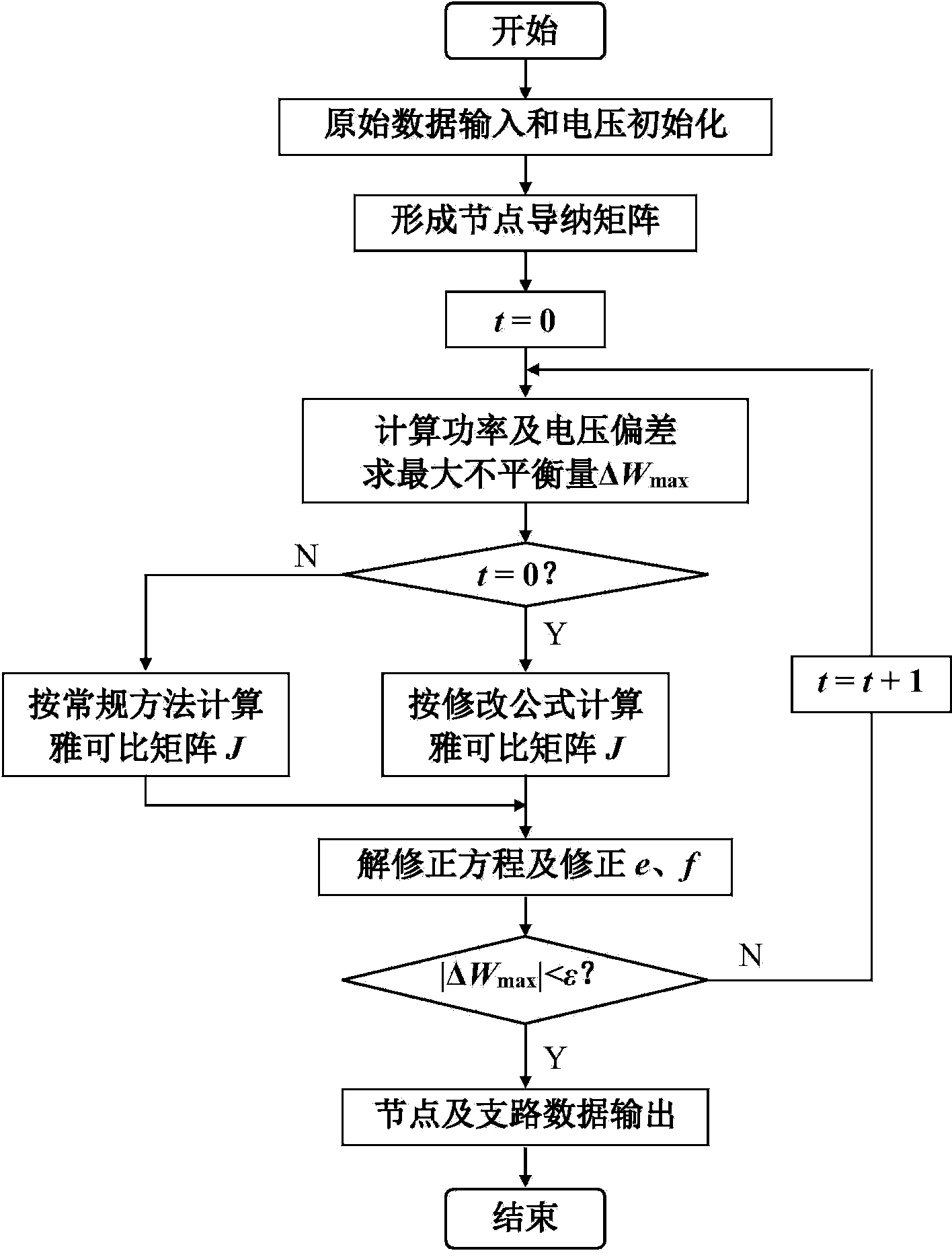
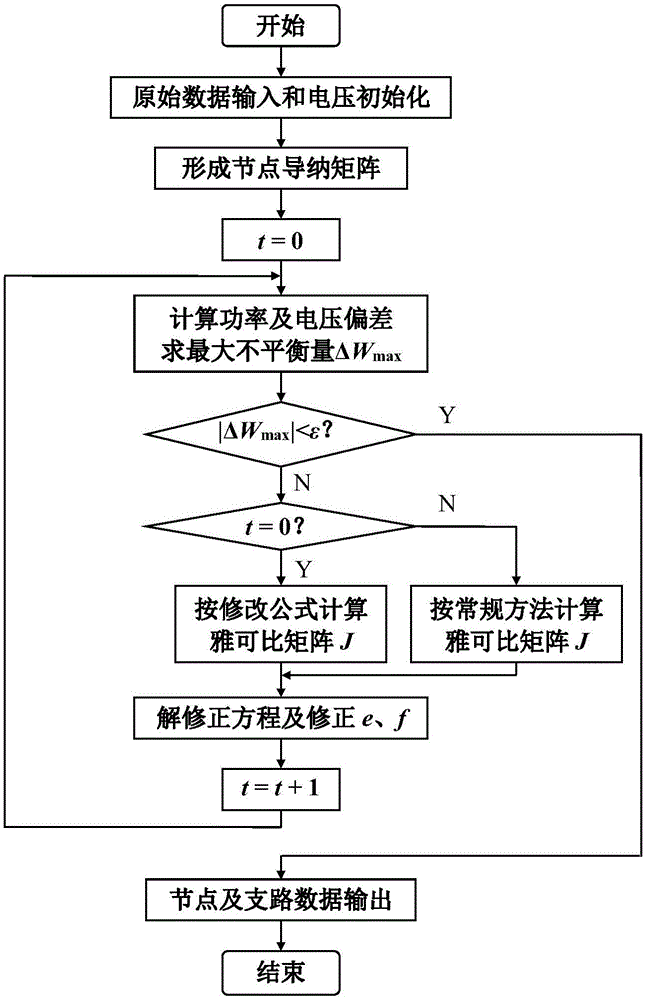
Load flow calculation method of rectangular coordinate newton method
InactiveCN104022507ASolving Convergence ProblemsConvergent and reliableAc network circuit arrangementsRectangular coordinatesOriginal data
The invention discloses a load flow calculation method of a rectangular coordinate newton method. The load flow calculation method comprises the following steps: inputting original data and initializing a voltage; forming a node admittance matrix; calculating power and a voltage deviation; forming a jacobian matrix J; solving a modified equation and modifying a real part e and an imaginary part f of the voltage; and outputting nodes and branch data. The calculation formula of partial elements (i=j) of the jacobian matrix obtained in a manner of load flow calculation by utilizing the rectangular coordinate newton method is modified and improved, so that the problem of astringency of the load flow calculation of the rectangular coordinate newton method during the analysis of branch systems containing small impedance is solved. As compared with the fact that the astringency of the small impedance branch systems cannot be realized by adopting the load flow calculation of the conventional rectangular coordinate newton method, the reliable astringency of the small impedance branch systems can be realized by utilizing the load flow calculation disclosed by the invention; and the load flow calculation to normal systems can be carried out at the same time, so that harmful effects are avoided.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
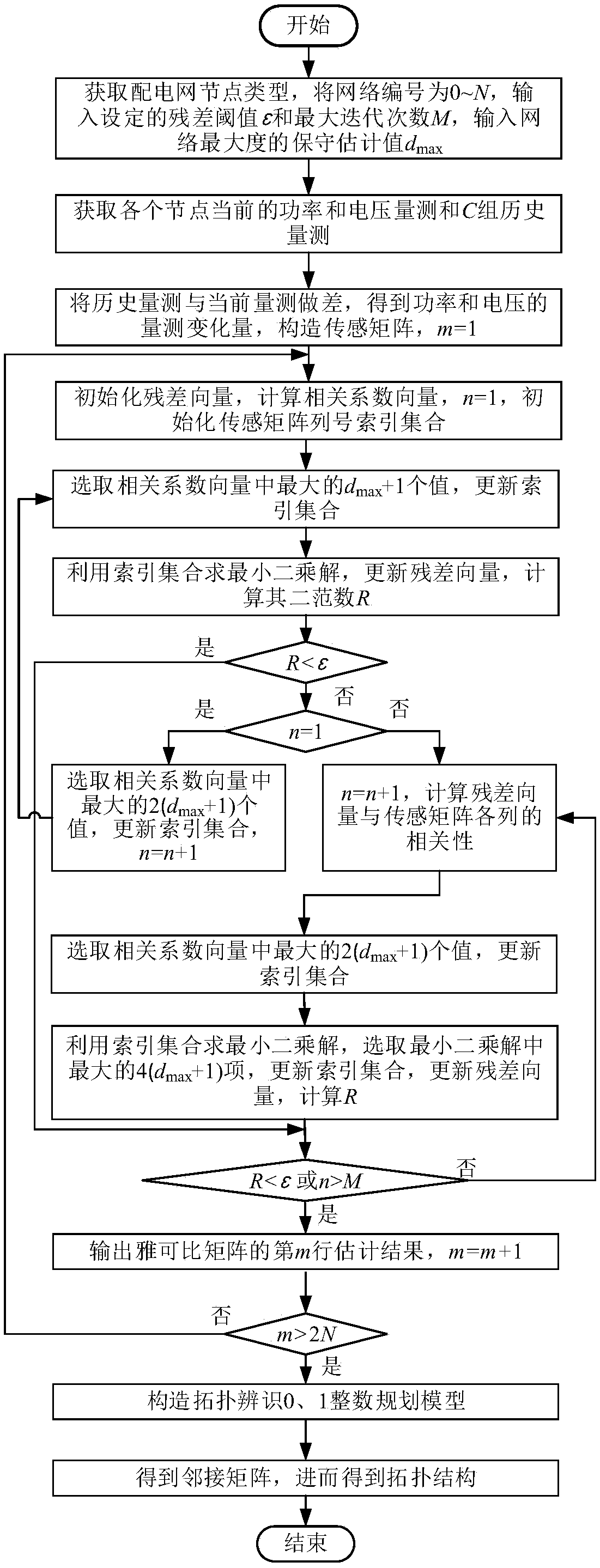
Identification method for intelligent distribution network topology based on synchronous phasor measurement
ActiveCN108199375AAvoid dependenceReduce dependenceSystems intergating technologiesInformation technology support systemNODALMeasurement device
An Identification method for intelligent distribution network topology based on synchronous phasor measurement, which comprises the following steps of: 1) acquiring node quantity and number of a powerdistribution network, and inputting a termination condition parameter; 2) acquiring the measuring data of the synchronous phasor measurement device; 3) constructing a sensing matrix so that the linenumber of the power flow Jacobin matrix m=1; 4) calculating a voltage correlation coefficient vector; 5) iteratively solving the least squares estimation problem until the termination condition is satisfied; 6) judging whether the estimation of all the rows of the Jacobin matrix is finished, if yes, then entering into the step 7), otherwise m=m+1, then returning to the step 4); 7) constructing a topological identification 0 and1 integer programming model; 8) solving 0 and 1 integer programming model to obtain the network topology of the distribution network. The invention realizes the accurateidentification of the power distribution network topology based on the measurement information completely to avoid the dependence of the estimation problem on the line parameters and effectively reduce the error identification result caused by inaccurate line parameters.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
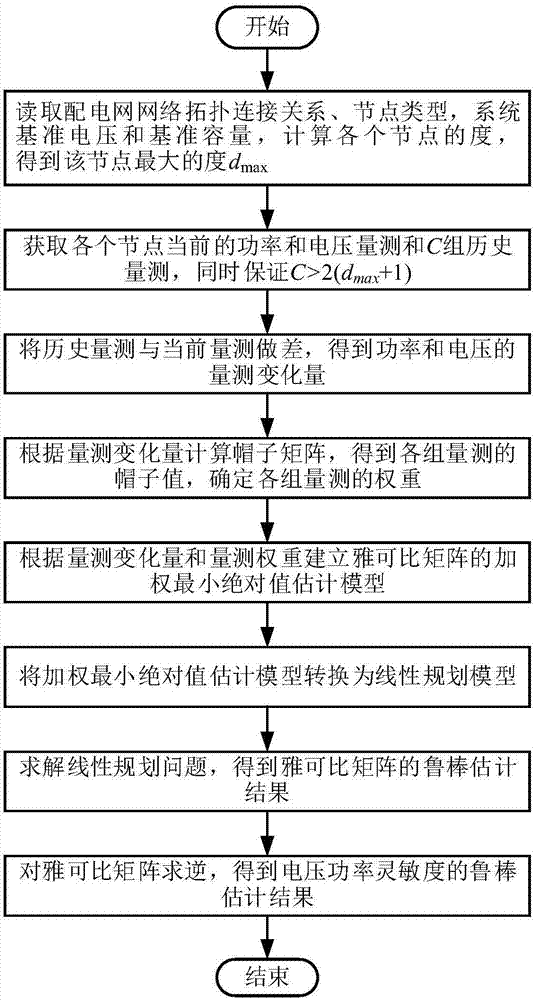
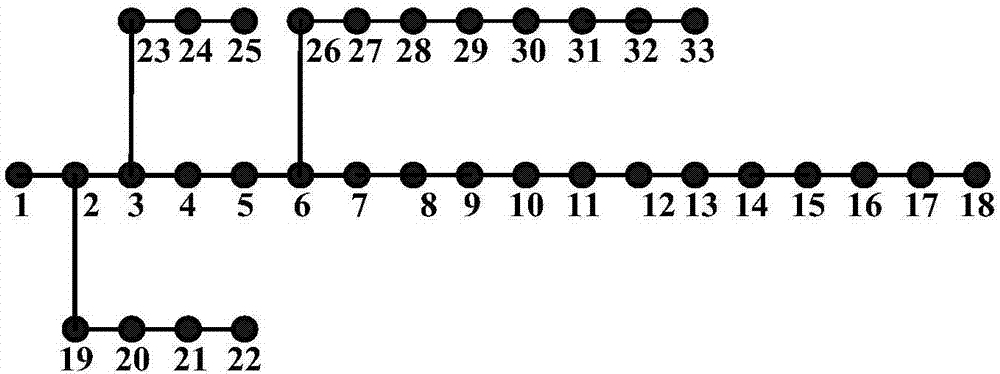
Robust estimation method based on synchronous phasor measurement for voltage power sensitivity of distribution network
ActiveCN107577870AImprove estimation accuracyImprove robustnessSystems intergating technologiesSpecial data processing applicationsVoltage amplitudeHat matrix
Disclosed is a robust estimation method based on synchronous phasor measurement for voltage power sensitivity of a distribution network. The method comprises the steps of obtaining the network topology connection relationship, node type, system reference voltage and reference capacity of the distribution network; obtaining the maximum degree of nodes according to the topology connection relationship; obtaining the measurement values of the active power, reactive power, voltage amplitude and voltage phase angle of a synchronous phasor measurement device of each node of a system at the current moment and C groups of historical measurement data of the synchronous phasor measurement device; obtaining change values of C groups of power and voltage measurement; calculating a hat matrix, obtaining the hat value of each group of measurement, and determining the weight of each group of measurement; establishing a weighted least absolute value estimating model of a Jacobian matrix; converting the weighted least absolute value estimating model into a linear programming model; solving the linear programming model, and obtaining a robust estimation result of the Jacobian matrix; calculating theinversion of the Jacobian matrix, and obtaining an estimation result of voltage power sensitivity. By means of the method, the influence of an lever effect of bad voltage measurement data on the estimation precision is avoided, and the estimation precision of an algorithm is improved.
Owner:南京首风智慧电力研究院有限公司
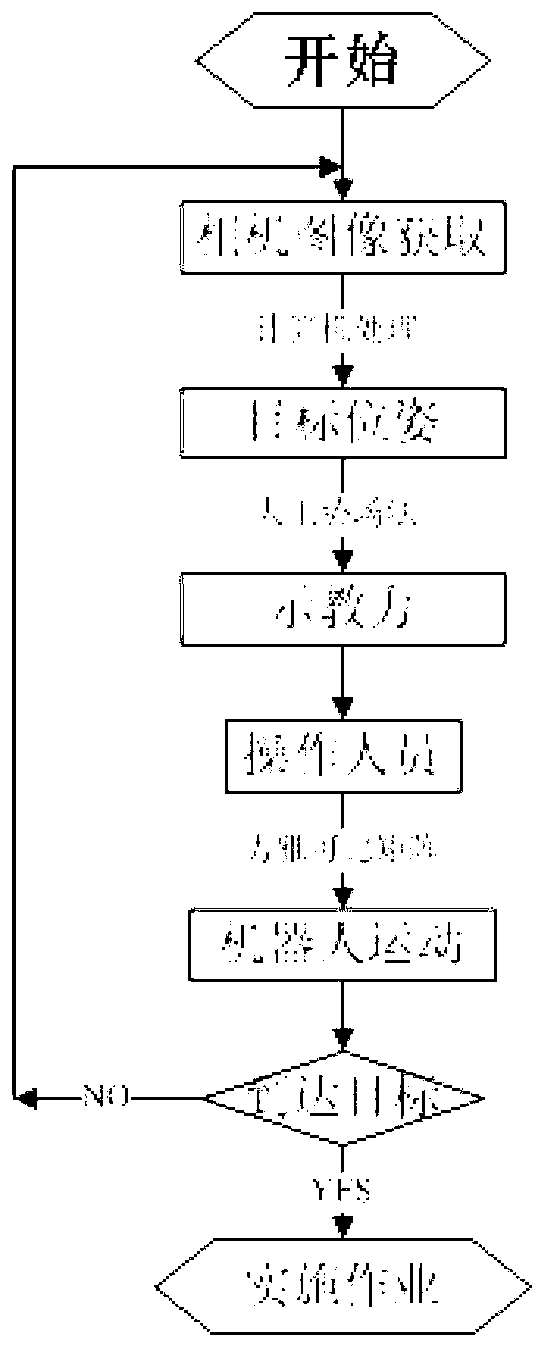
Kinesthesis teaching control method based on vision sense for remote control of robot
InactiveCN103105851ARealize kinesthetic teachingImprove work efficiencyVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlRobotic systemsRemote control
The invention provides a kinesthesis teaching control method based on vision sense for remote control of a robot. The steps comprises the steps of using stereoscopic vision technology to identify an onsite operation object and a background environment (an obstacle) and extract space information; constructing virtual attraction of the operation object to the robot by using the pose relation of the operation object and the tail end of the robot calculated through vision identification as a parameter; constructing the obstacle repulsive force exerted by the robot by using the distance of the tail end of the robot and the background environment (the obstacle) along the speed direction of the robot as a parameter; combining the virtual attraction of the operation object, the obstacle visual repulsive force and the real acting force of the robot when the robot clamps objects into the teaching force of the robot; and through the jacobian matrix between a main end system and a sub end system, feeding back the teaching force to an operation handle, and therefore kinesthesis teaching to an operator is achieved. The kinesthesis teaching control method can effectively improve the intellectuality, the safety and easy handling of a main robot system and a sub robot system.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
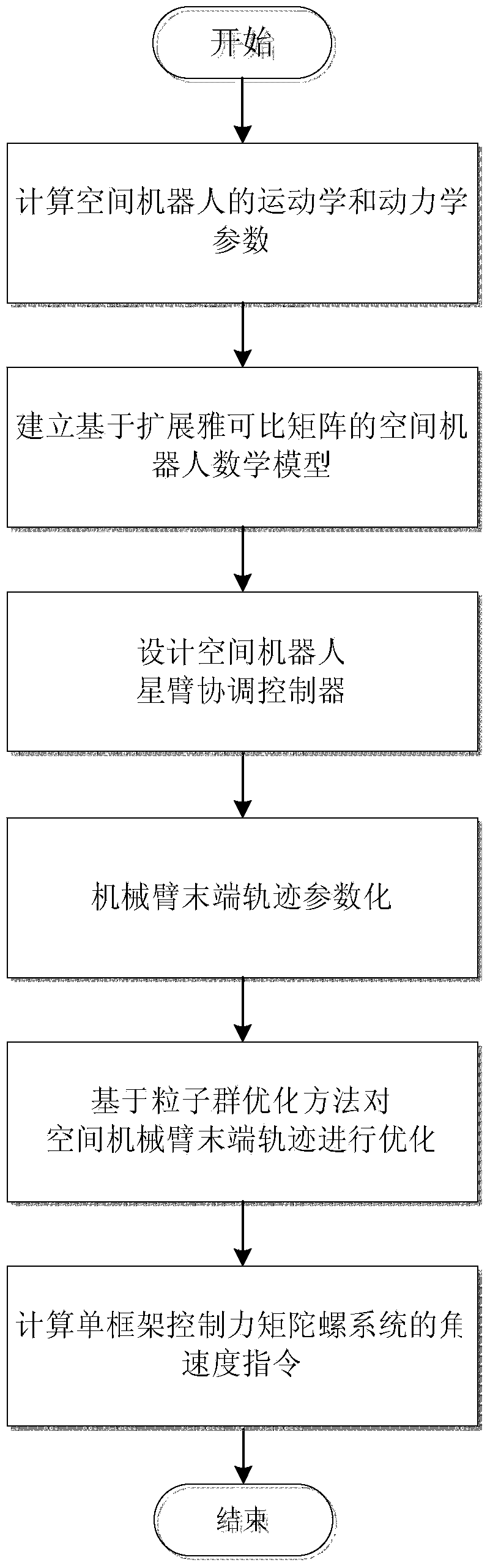
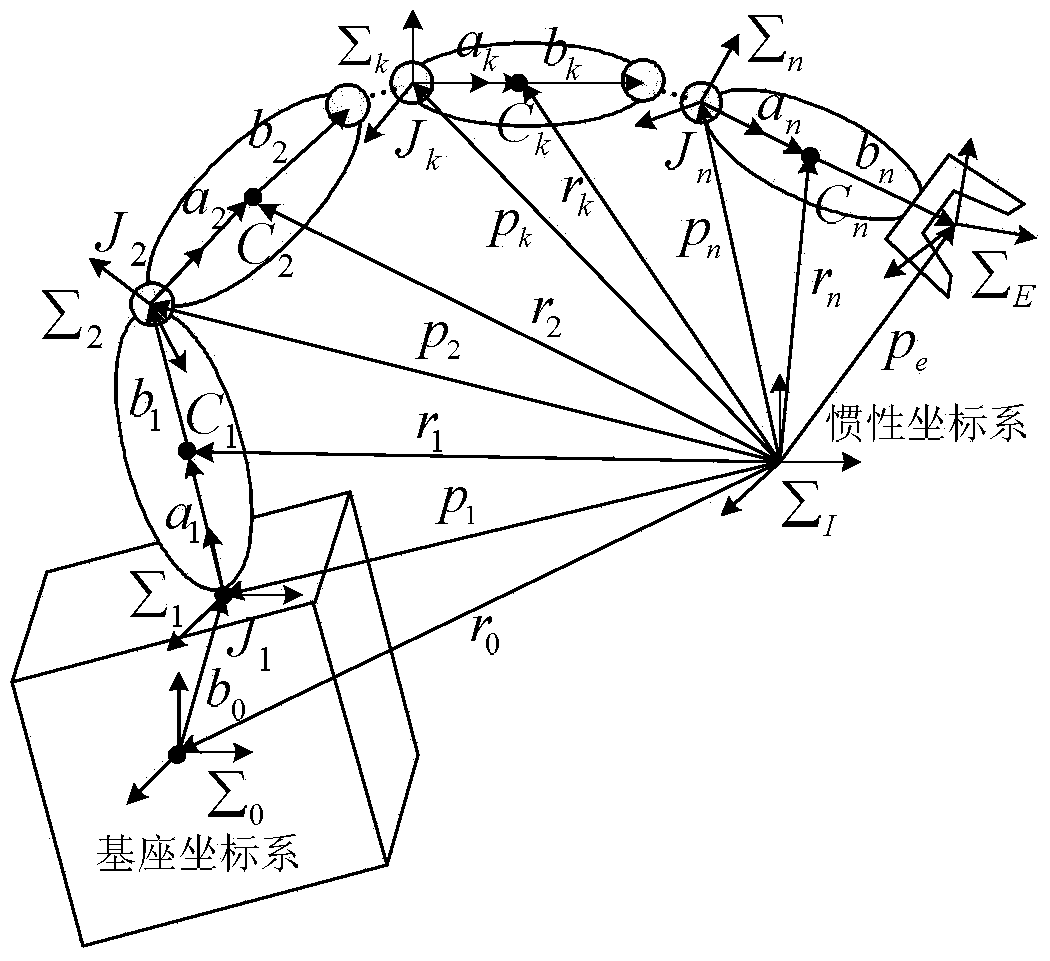
Method for coordination control over satellite arms of space robot based on expanded Jacobian matrix
InactiveCN103869704ARealize coordinated controlReduce consumptionAdaptive controlMathematical modelAngular velocity
The invention discloses a method for coordination control over satellite arms of a space robot based on an expanded Jacobian matrix. The method achieves integrated coordination control over a space manipulator operating in orbit and a base satellite. The method comprises the steps of computing kinetic parameters and dynamic parameters of the space robot, establishing a mathematical model of the space motor based on the expanded Jacobian matrix, designing a coordination controller of the satellite arms of the space robot, conducting parameterization on the trajectory of the tail end of the manipulator, optimizing the trajectory of the manipulator, and computing an angular velocity instruction of a single gimbal control moment gyro system of the space robot. According to the method, hysteretic feedback control conducted by a satellite according to attitude measurement is not needed, overall mathematical modeling is conducted on the coupled motion of the satellite arms, the angular velocity instruction of the single gimbal control moment gyro system is directly computed according to the input trajectory of the tail end of the manipulator, the single gimbal control moment gyro system is used for compensation, needed by the satellite, for manipulator motion, and then overall coordination control over the satellite arms is realized; the trajectory of the tail end of the manipulator is optimized, so that the energy consumed by a satellite state control system for compensating for the restoring torque of the manipulator is small.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
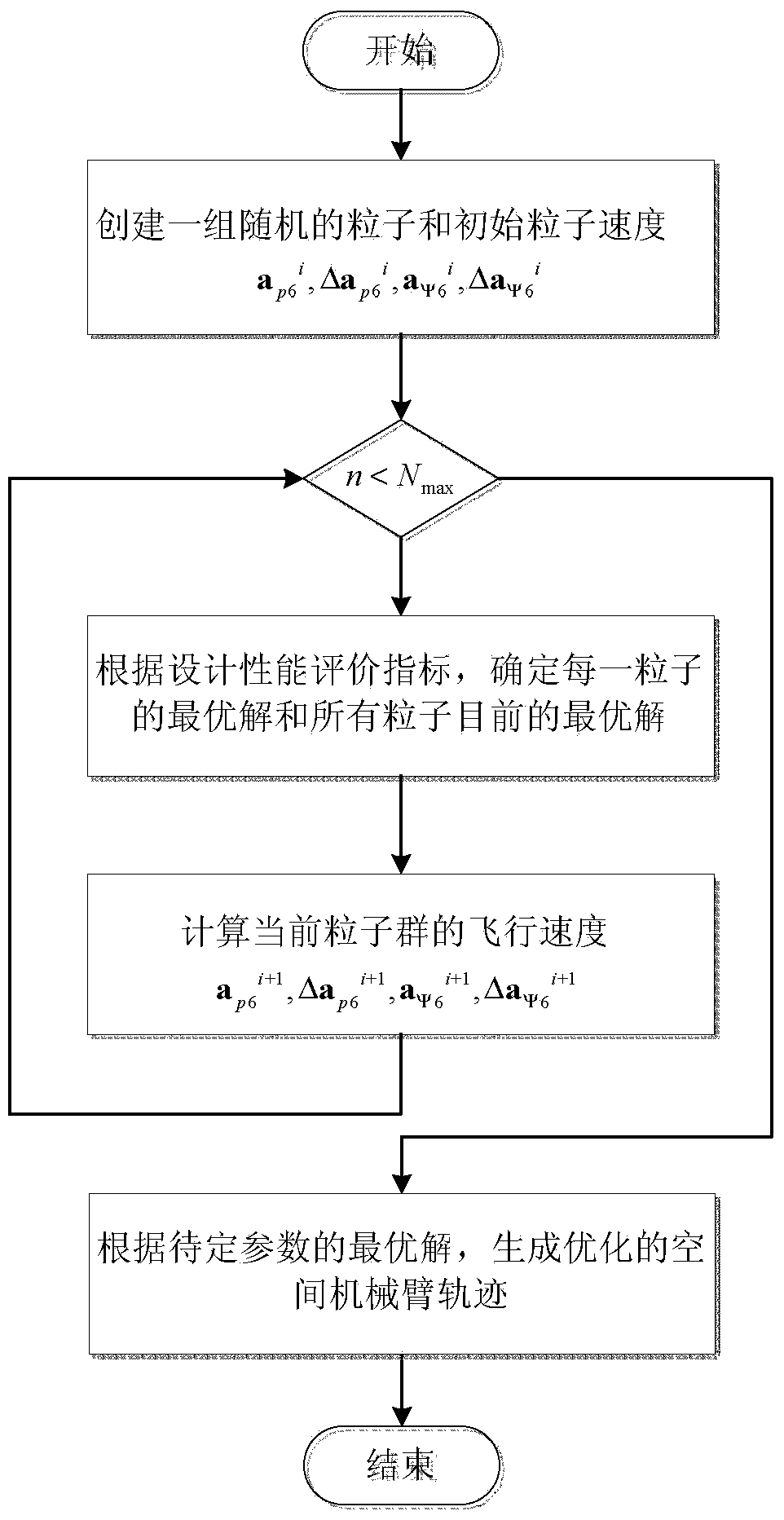
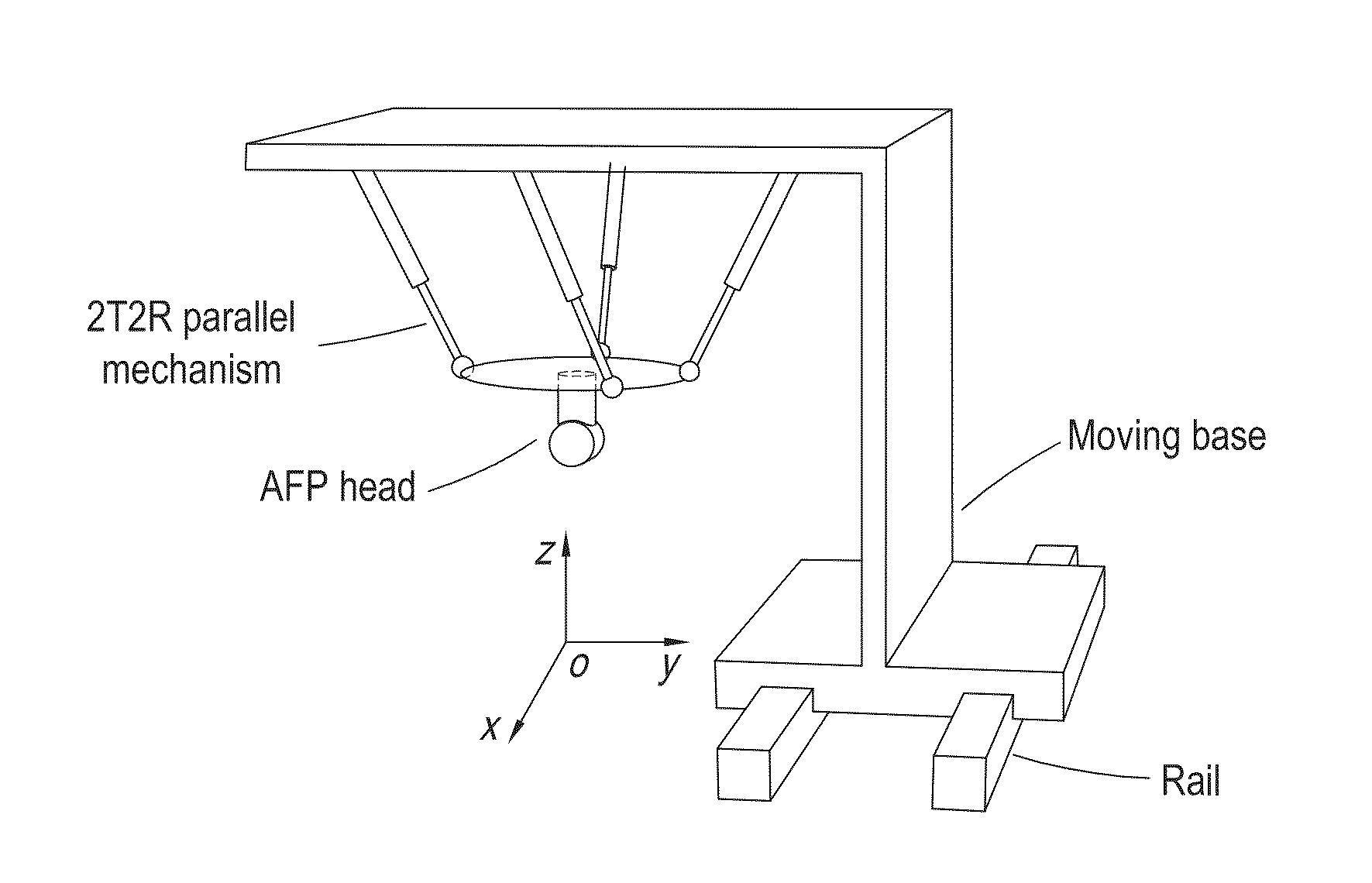
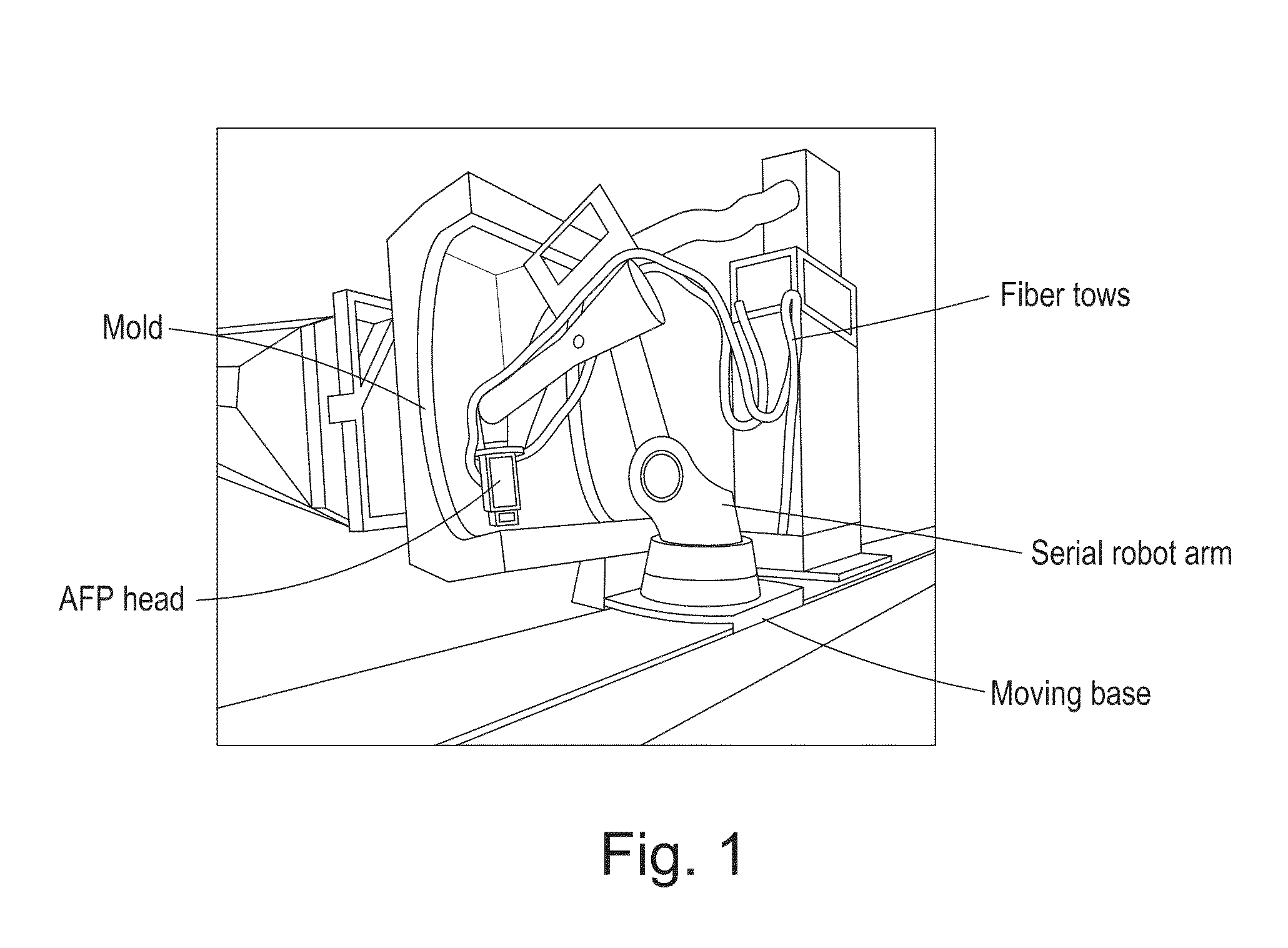
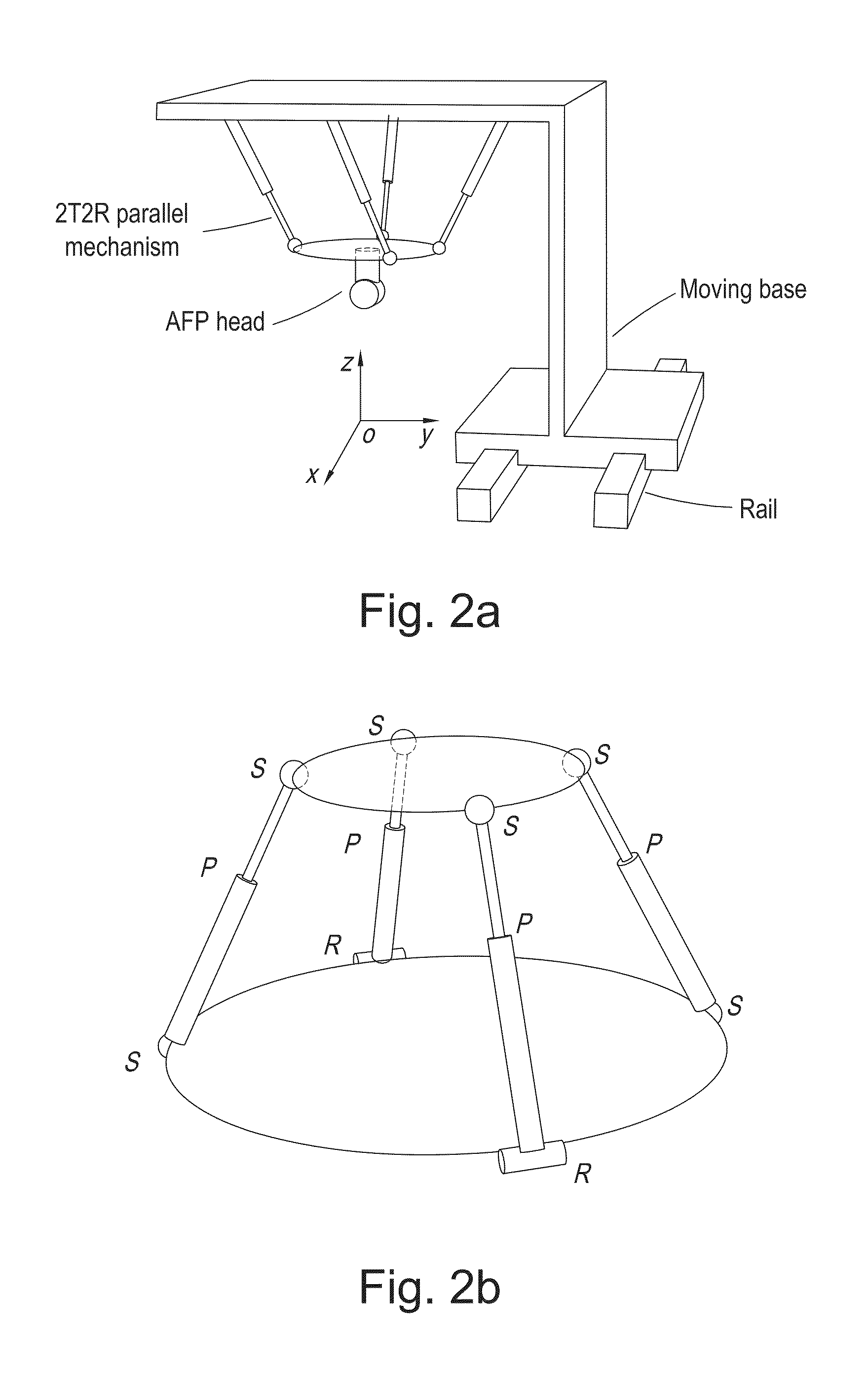
Parallel mechanism based automated fiber placement system
ActiveUS20160250749A1Good kinematic performanceOptimization mechanismProgramme-controlled manipulatorDomestic articlesAviationFiber
The present invention introduces a new concept of applying a parallel mechanism in automated fiber placement for aerospace part manufacturing. The proposed system requirements are 4DOF parallel mechanism consisting of two RPS and two UPS limbs with two rotational and two translational motions. Both inverse and forward kinematics models are obtained and solved analytically. Based on the overall Jacobian matrix in screw theory, singularity loci are presented and the singularity-free workspace is correspondingly illustrated. To maximize the singularity-free workspace, locations of the two UPS limbs with the platform and base sizes are used in the optimization which gives a new design of a 4DOF parallel mechanism. A dimensionless Jacobian matrix is also defined and its condition number is used for optimizing the kinematics performance in the optimization process. A numerical example is presented with physical constraint considerations of a test bed design for automated fiber placement.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Multi-sensor quantitative fusion target tracking method based on variational Bayesian
InactiveCN103778320AImplement adaptive functionsNavigational calculation instrumentsSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionAttenuation coefficient
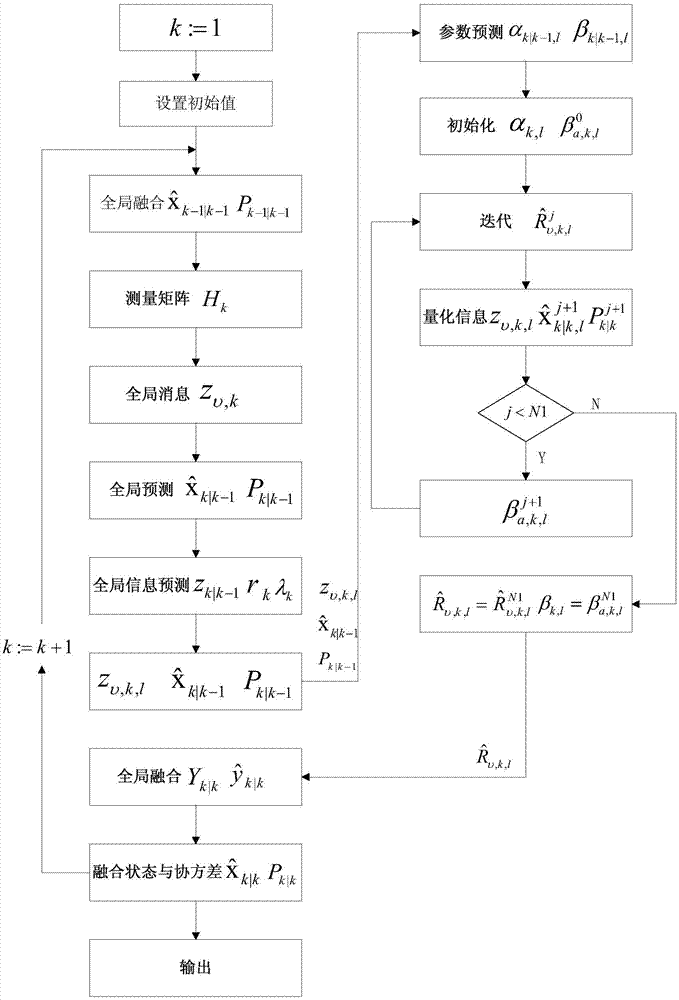
The invention relates to a multi-sensor quantitative fusion target tracking method based on a variational Bayesian method and a strong tracking information filtering method. According to the multi-sensor quantitative fusion target tracking method, a structure including a primary processor and a secondary processor are provided. In the primary processor, an enhanced measurement matrix H(k) and enhanced global information z (upsilon, k) are constructed; one-step prediction (k|k)-1) and corresponding covariance P(k|k-1) are calculated, global information predication z (k|k-1) is calculated, and a z (upsilon, k, 1), the (k|k)-1 and the P(k / k-1) are sent into the secondary processor. In the secondary processor, information noise variance is calculated, and (upsilon, k, 1) is sent to the primary processor, and in the primary processor, fusion estimation and corresponding covariance can be obtained through calculation, wherein please see the instruction for the formula of fusion estimation and corresponding covariance. Due to the fact that the variational Bayesian method and the self-adaptive strong tracking information filtering method are adopted in the multi-sensor quantitative fusion target tracking method, the high tracking capacity is achieved, unknown variance of noise can be estimated and measured, and the self-adaptive function can be achieved. Meanwhile, an attenuation coefficient can be estimated through an iterative method without calculating a jacobian matrix.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Newton method power flow calculation method which changes Jacobi matrix with iteration and node types
InactiveCN106532711ASolving Convergence ProblemsConvergent and reliableAc networks with different sources same frequencyComplex mathematical operationsRectangular coordinatesNewton's method
The invention discloses a Newton method power flow calculation method which changes a Jacobi matrix with iteration and node types. A PQ node calculates a Jacobi matrix element by using an ai value and a bi value which are calculated by given values Pis and Qis in the first-time iteration. A PV node and all nodes in the subsequent iteration calculates the Jacobi matrix element by using a conventional method. The method solves a convergence problem of a rectangular coordinate Newton method power flow calculation method in the analysis of a power system containing a low impedance branch in such a way that the PQ node adopts the Jacobi matrix calculation method in the first iteration process and which is different from that in the subsequent iteration processes. The method of the invention can be reliably converged when he conventional rectangular coordinate Newton method are not convergent, is less than the number of iterations than the prior art. The Newton method power flow calculation method can not only solve the convergence problem of the rectangular coordinate Newton method power flow calculation method in the analysis of a power system containing a low impedance branch, but also can calculate the power flow of the normal power system without any adverse effect.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
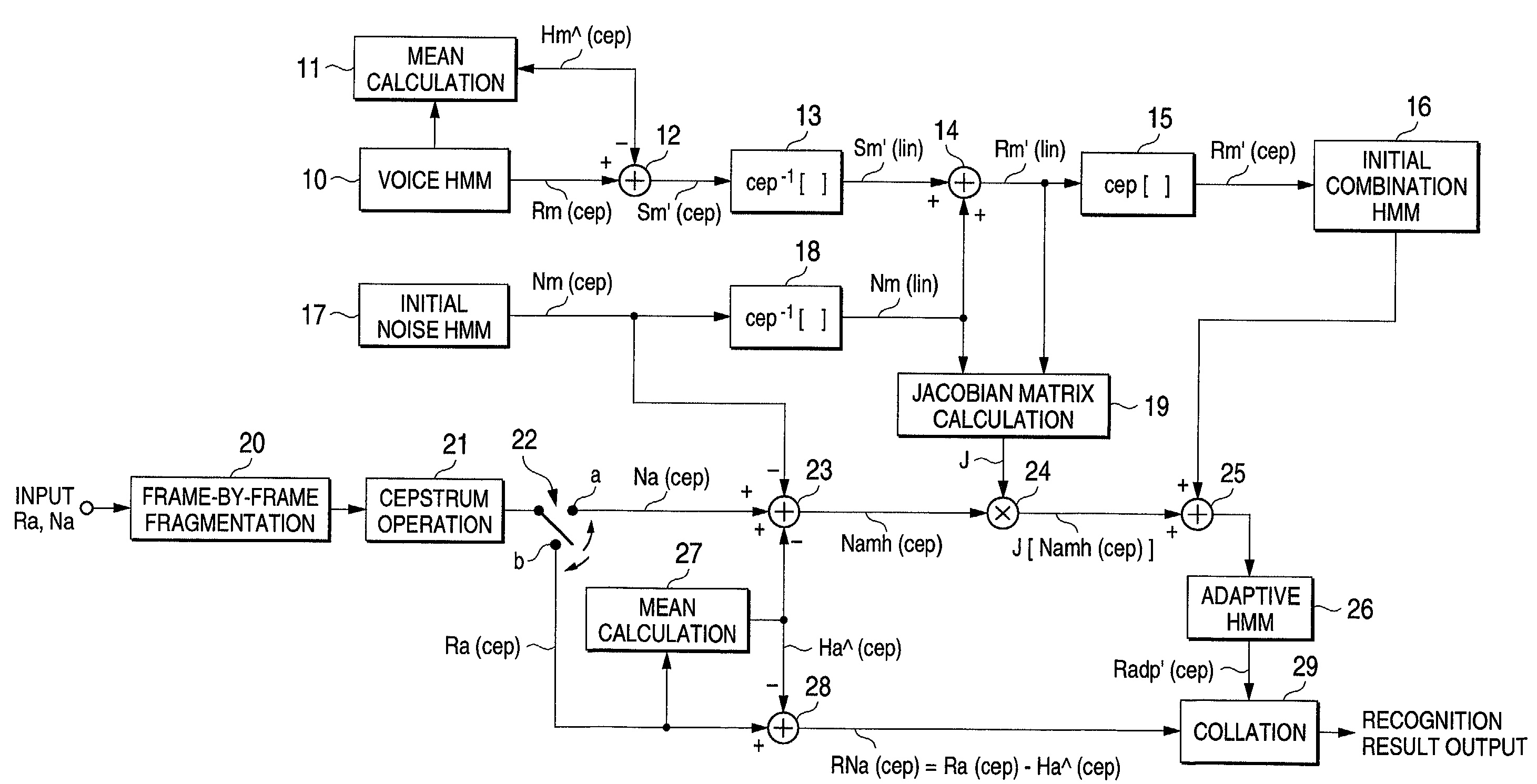
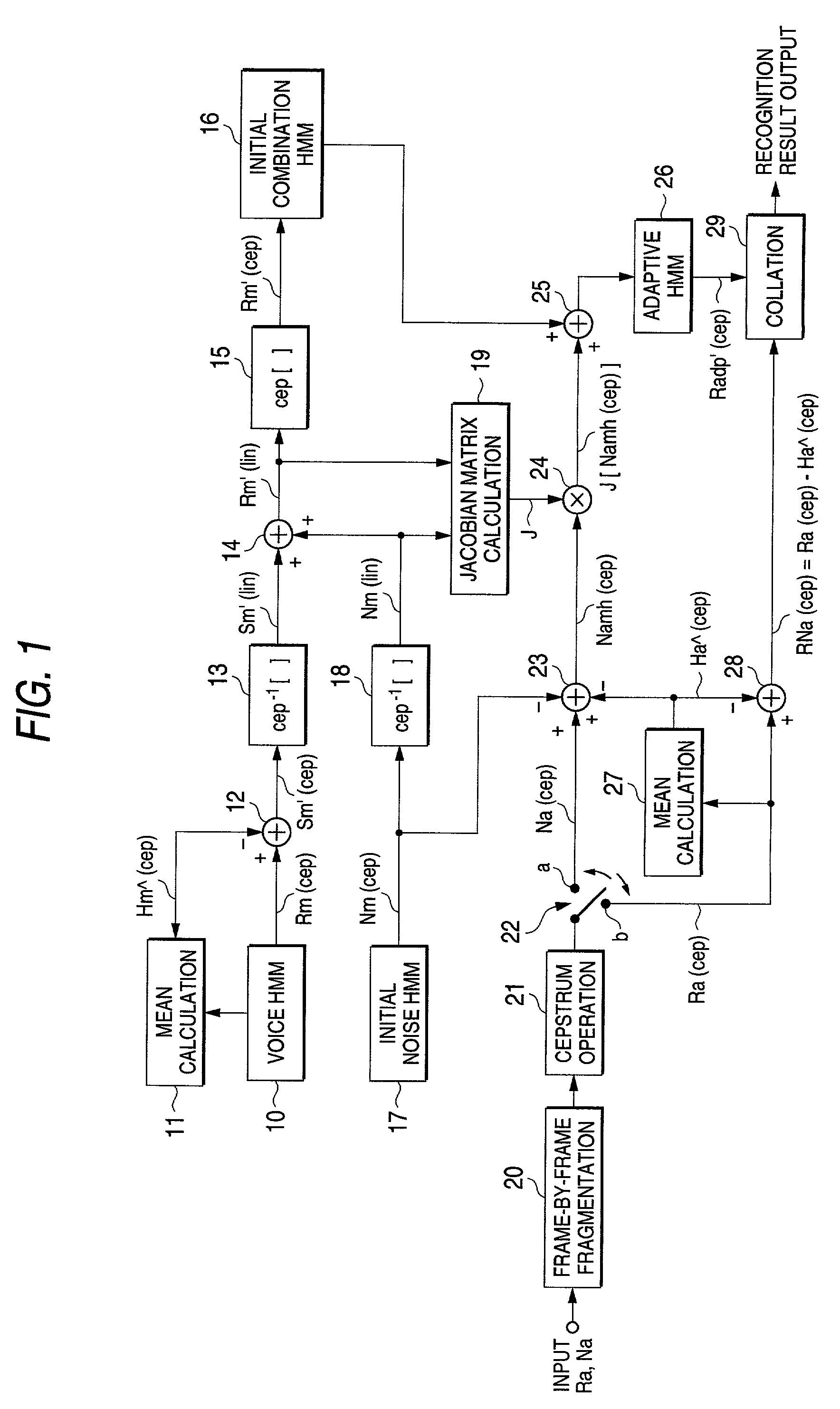
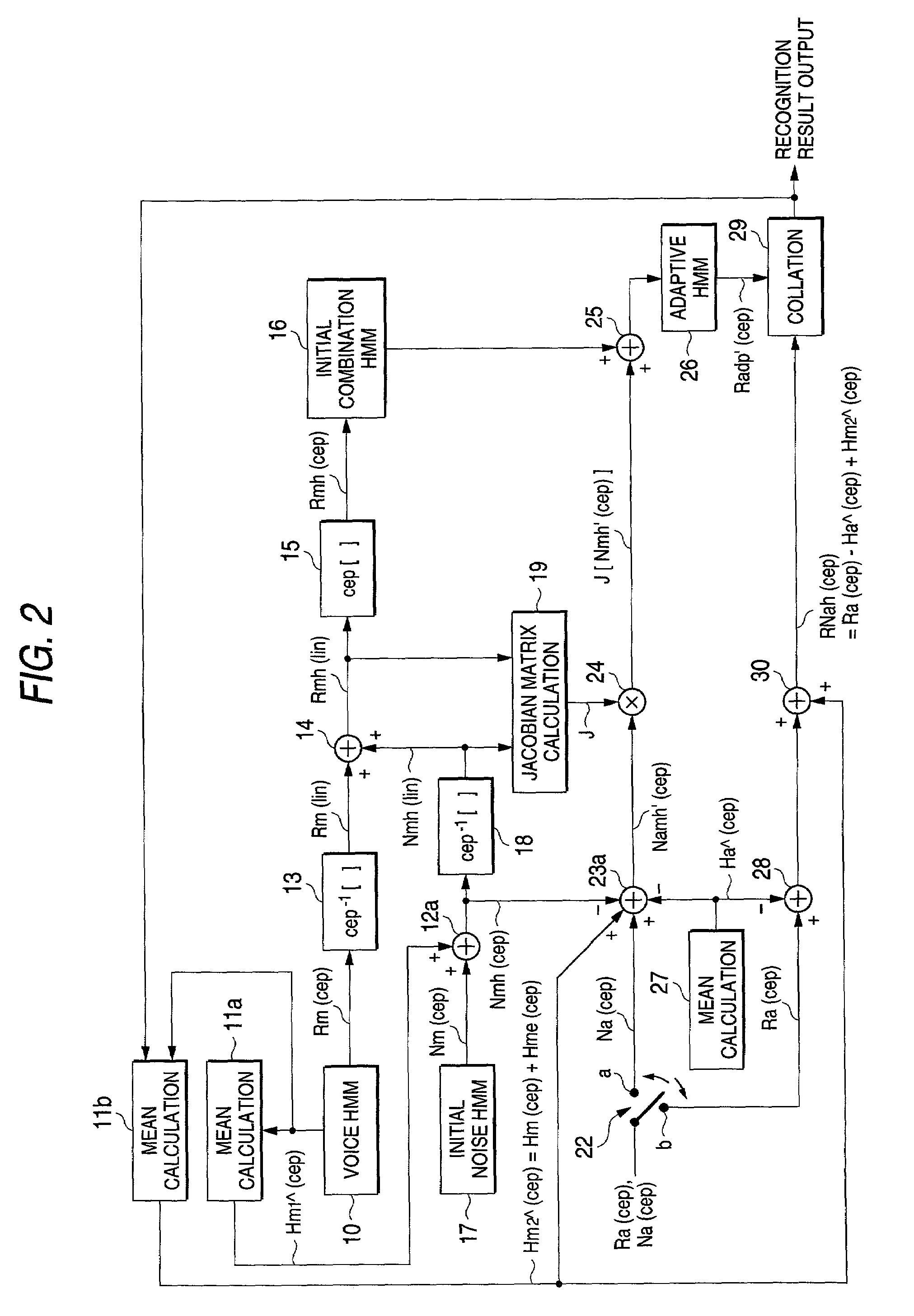
Voice recognition system
InactiveUS7016837B2Noise and distortionAdequate voice recognitionSpeech recognitionSpeech identificationSpeech sound
An initial combination HMM 16 is generated from a voice HMM 10 having multiplicative distortions and an initial noise HMM of additive noise, and at the same time, a Jacobian matrix J is calculated by a Jacobian matrix calculating section 19. Noise variation Namh (cep), in which an estimated value Ha^(cep) of the multiplicative distortions that are obtained from voice that is actually uttered, additive noise Na(cep) that is obtained in a non-utterance period, and additive noise Nm(cep) of the initial noise HMM 17 are combined, is multiplied by a Jacobian matrix, wherein the result of the multiplication and initial combination HMM 16 are combined, and an adaptive HMM 26 is generated. Thereby, an adaptive HMM 26 that is matched to the observation value series RNah(cep) generated from actual utterance voice can be generated in advance. When performing voice recognition by collating the observation value series RNah(cep) with adaptive HMM 26, influences due to the multiplicative distortions and additive distortions are counterbalanced, wherein an effect that is equivalent to a case where voice recognition is carried out with clean voice can be obtained, and a robust voice recognition system can be achieved.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
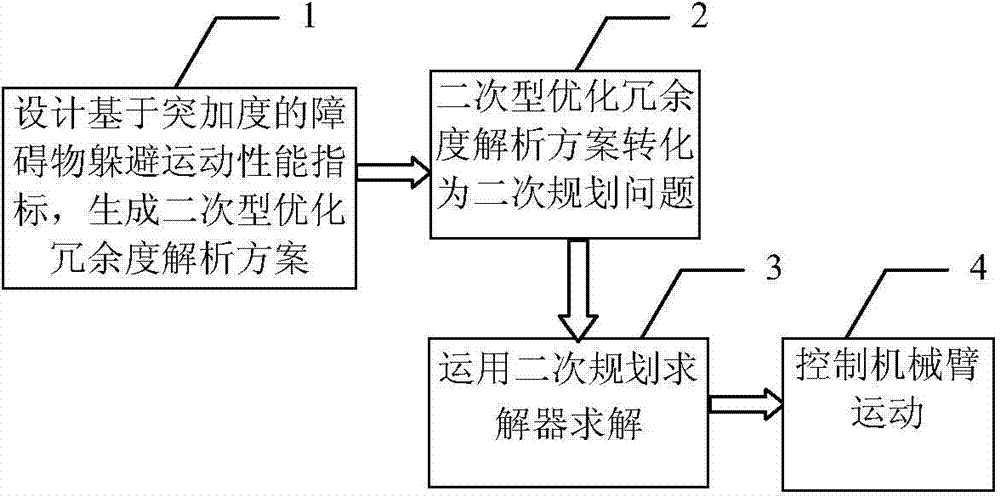
Barrier escaping motion planning method based on impact degree
The invention discloses a barrier escaping motion planning method based on an impact degree. The method comprises the steps of 1) designing barrier escaping motion performance indices based on the impact degree so that the designed motion performance indices are subject to a Jacobian matrix equation based on the impact degree, a barrier escaping inequation based on the impact degree, joint angle limitation, joint speed limitation, joint acceleration limitation and joint impact degree limitation, and generating a quadratic form optimization redundancy analysis scheme, 2) transforming the quadratic form optimization redundancy analysis scheme generated in the step 1) into a secondary planning problem, 3) solving the secondary planning problem in the step 2) by use of a secondary planning solver, and 4) transferring the solution result of the step 3) to a lower computer controller to drive a mechanical arm to move. According to the barrier escaping motion planning method, the barrier escaping motion performance indices based on the impact degree are designed, the mechanical arm is controlled to escape a barrier at an impact degree layer, and meanwhile, the mechanical arm is capable of completing a given tail end task.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
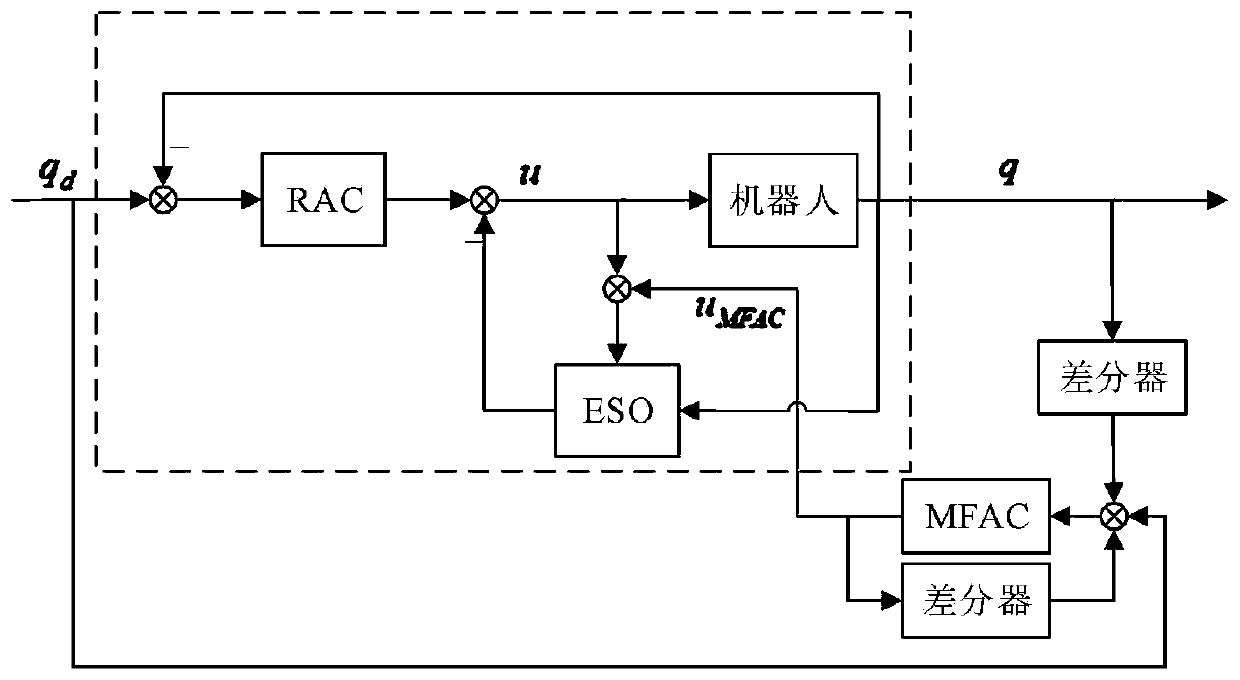
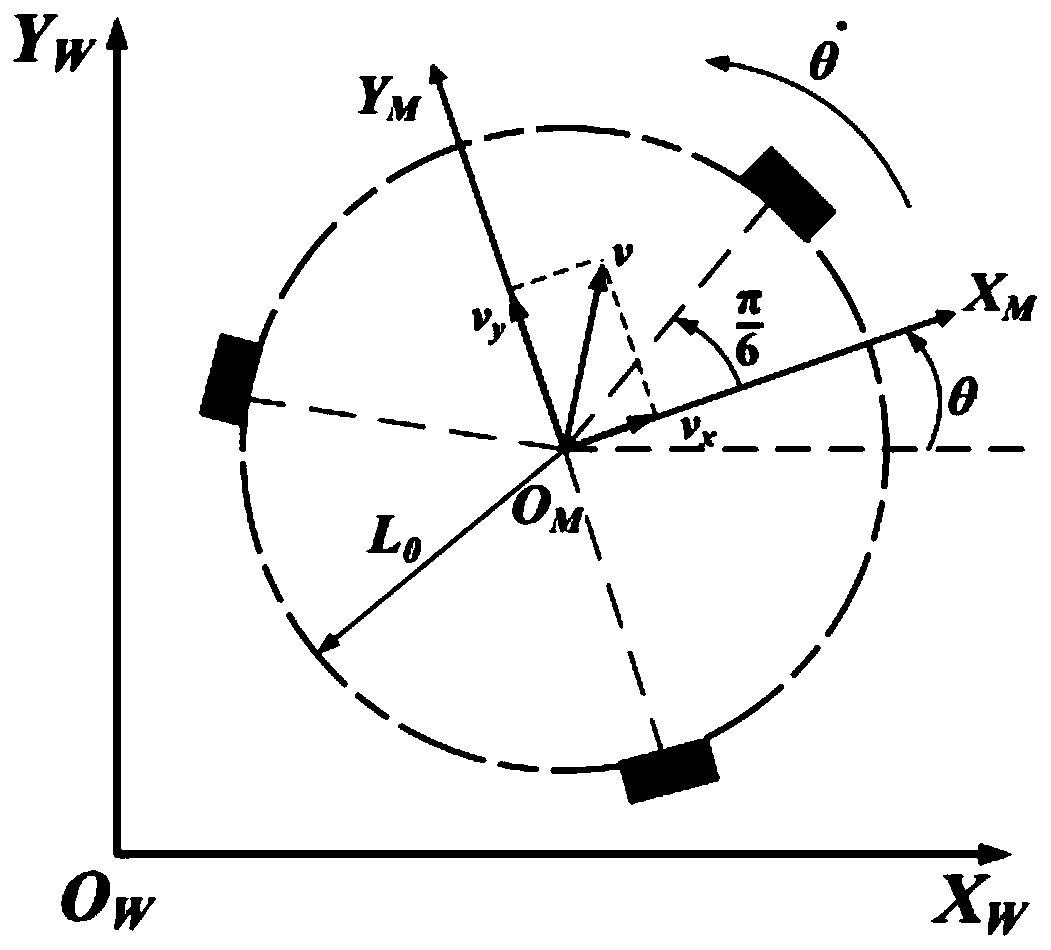
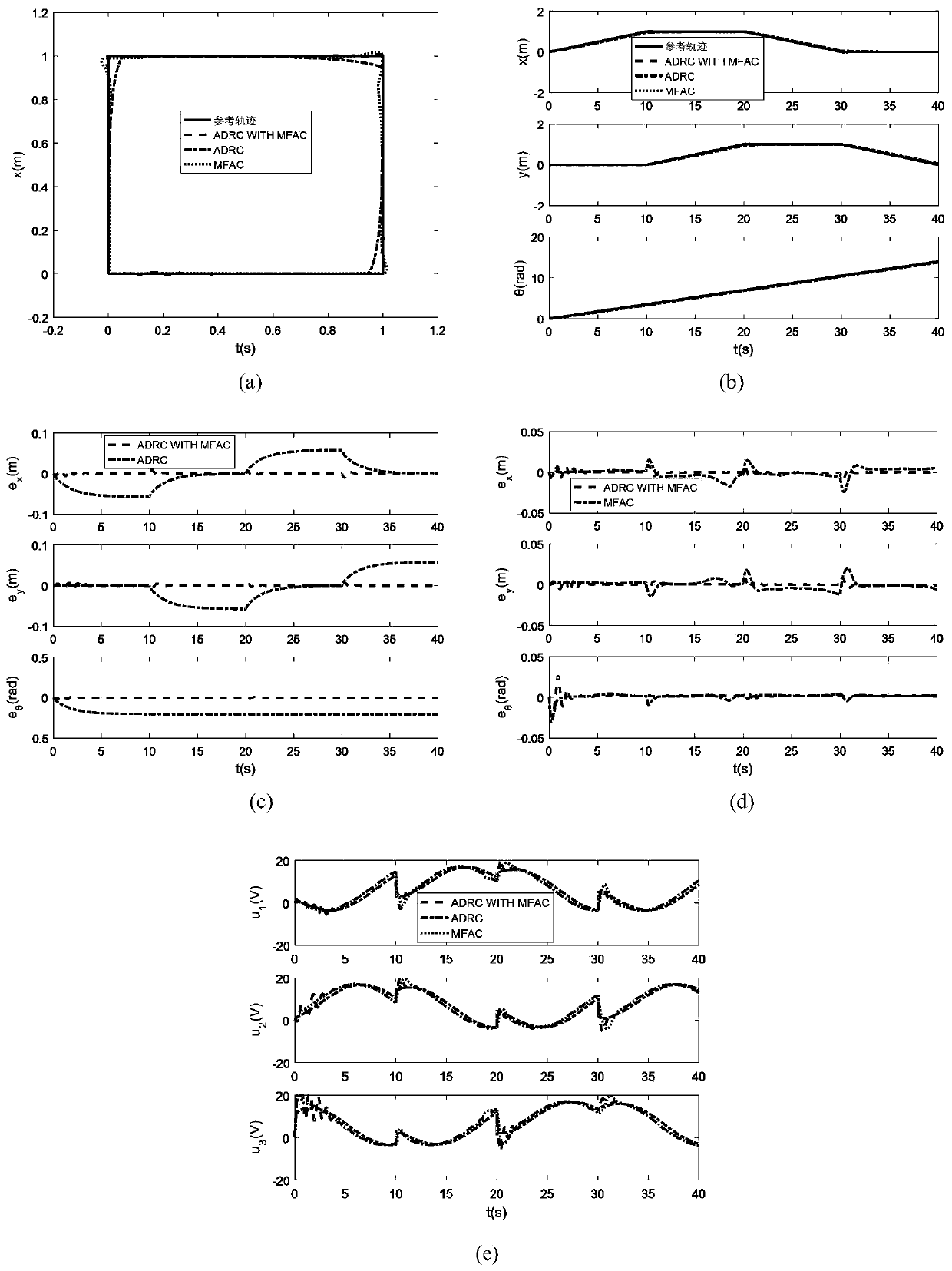
Robot trajectory tracking auto-disturbance rejection control method based on model-free outer loop compensation
The invention relates to a robot trajectory tracking auto-disturbance rejection control method based on model-free outer loop compensation. The method comprises the following steps that step 1, an omnidirectional mobile robot system dynamics model is established; step 2, an extended state observer is designed according to the dynamics model; step 3, an auto-disturbance rejection controller is designed according to an analytic acceleration control method, wherein the auto-disturbance rejection controller is composed of two parts, one part is used for compensating for the total disturbance of asystem, the other part is used for the trajectory tracking control over a robot, proportional differential feedback is introduced, and the model-free adaptive controller is obtained according to a false Jacobian matrix estimated value to add model-free adaptive control into the extended state observer.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com