Patents
Literature
199 results about "Feature tracking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
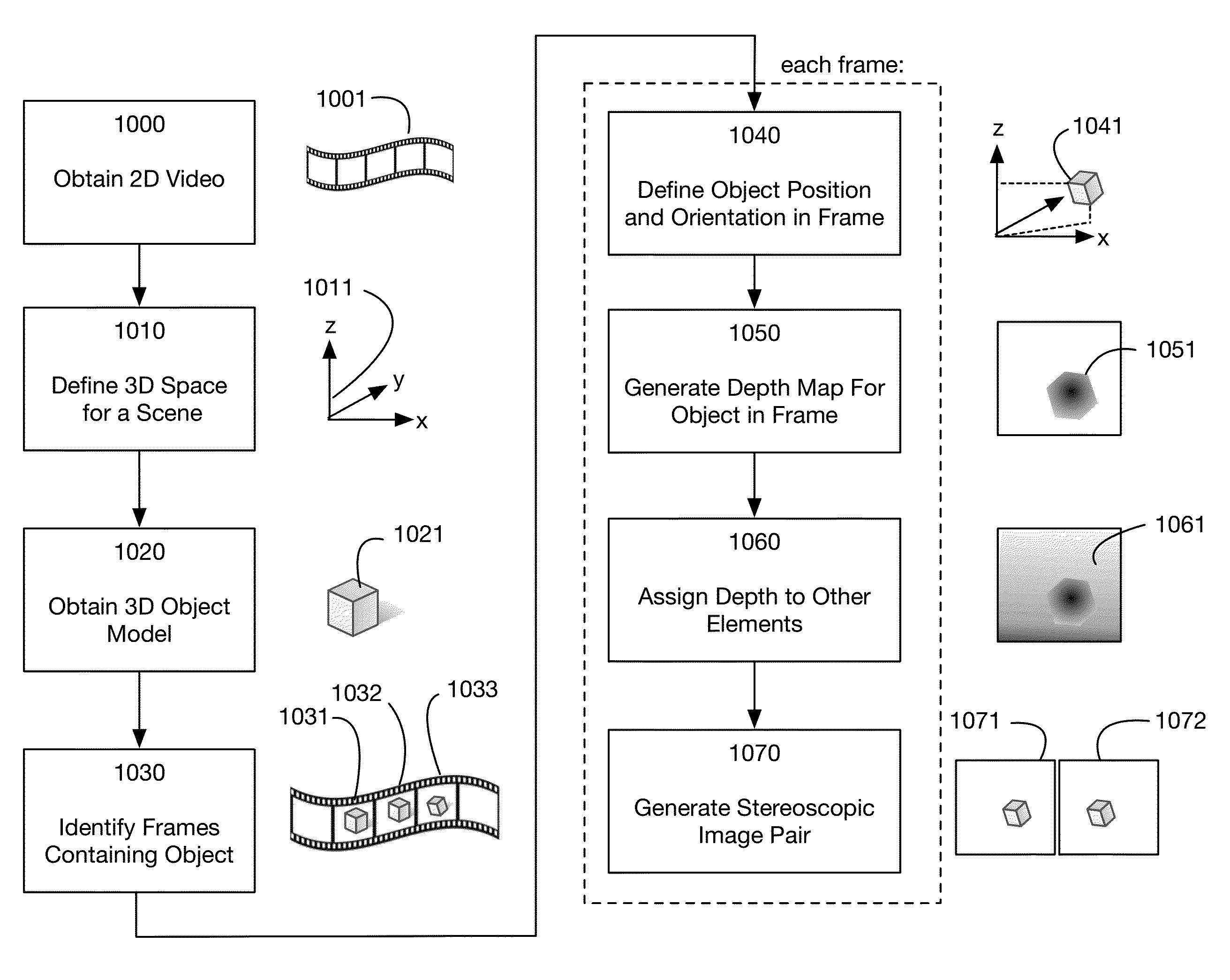
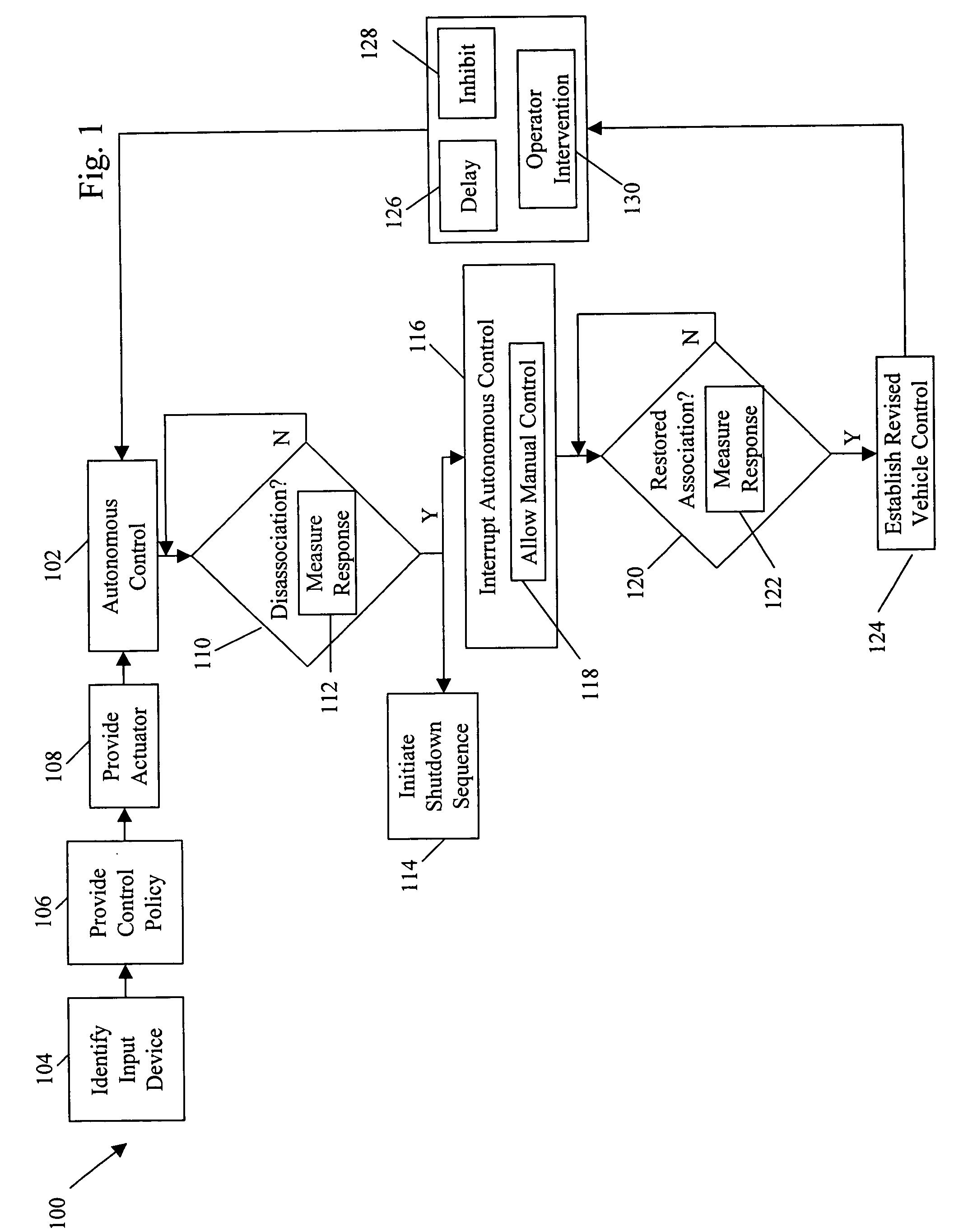
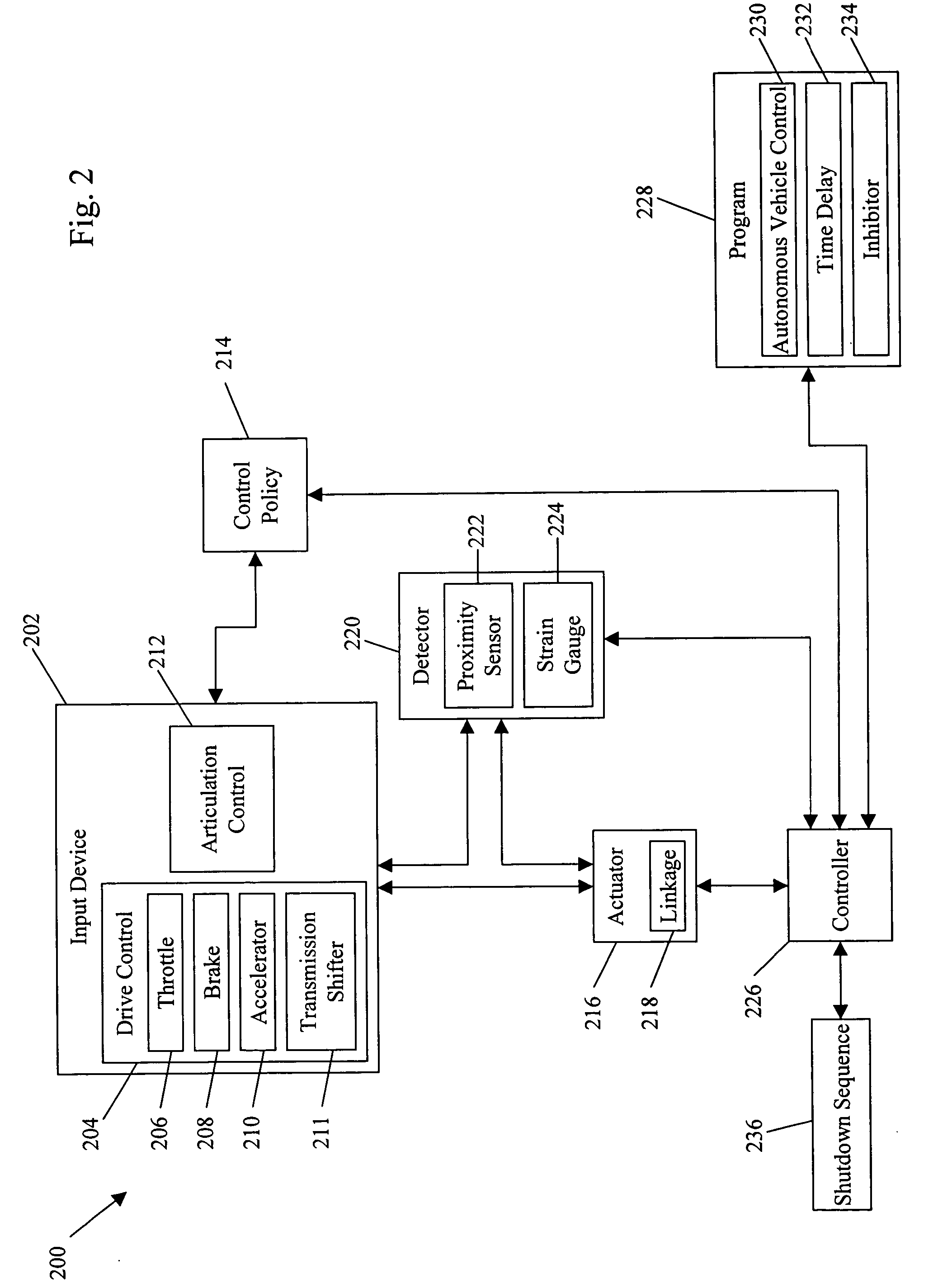
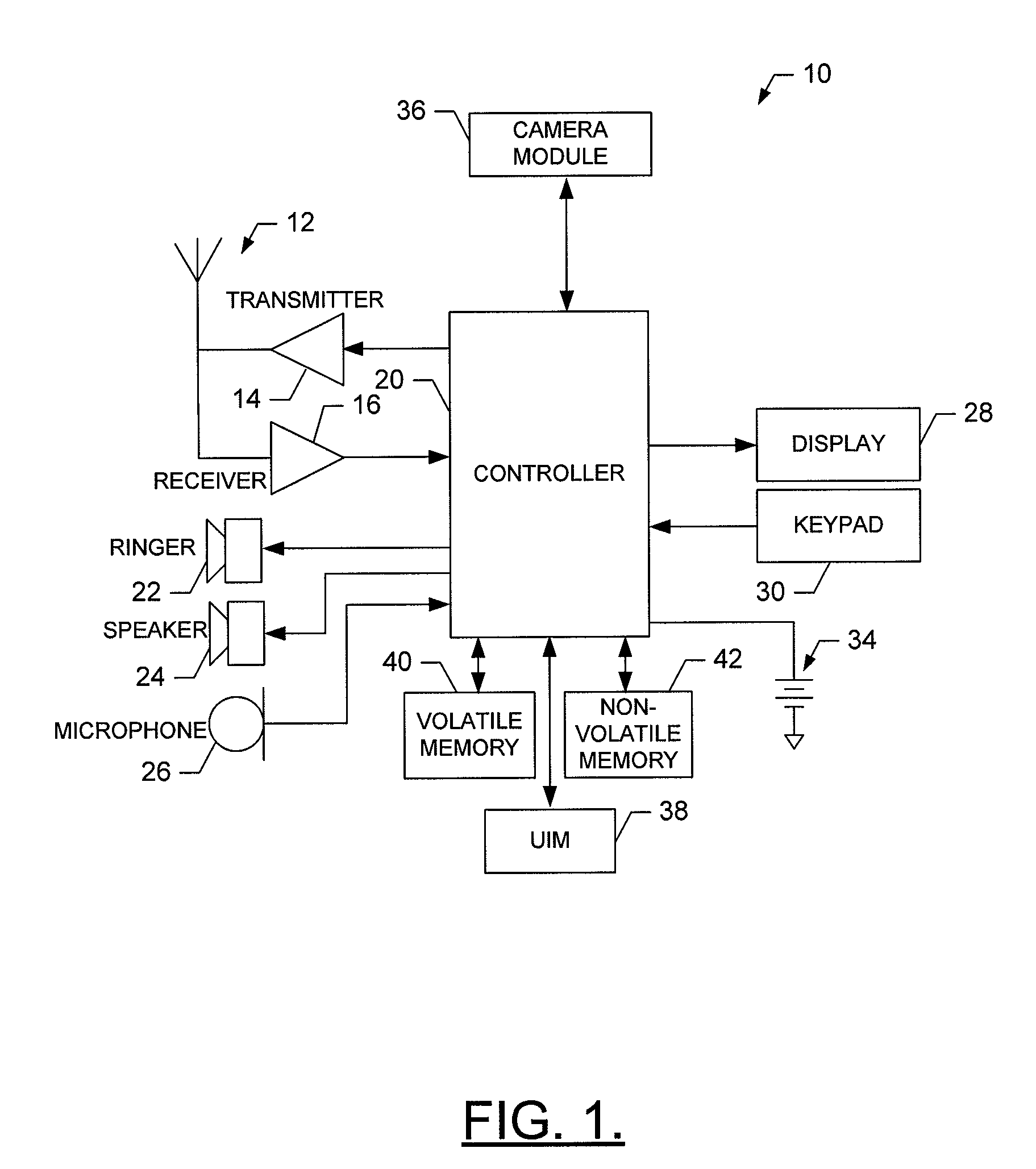
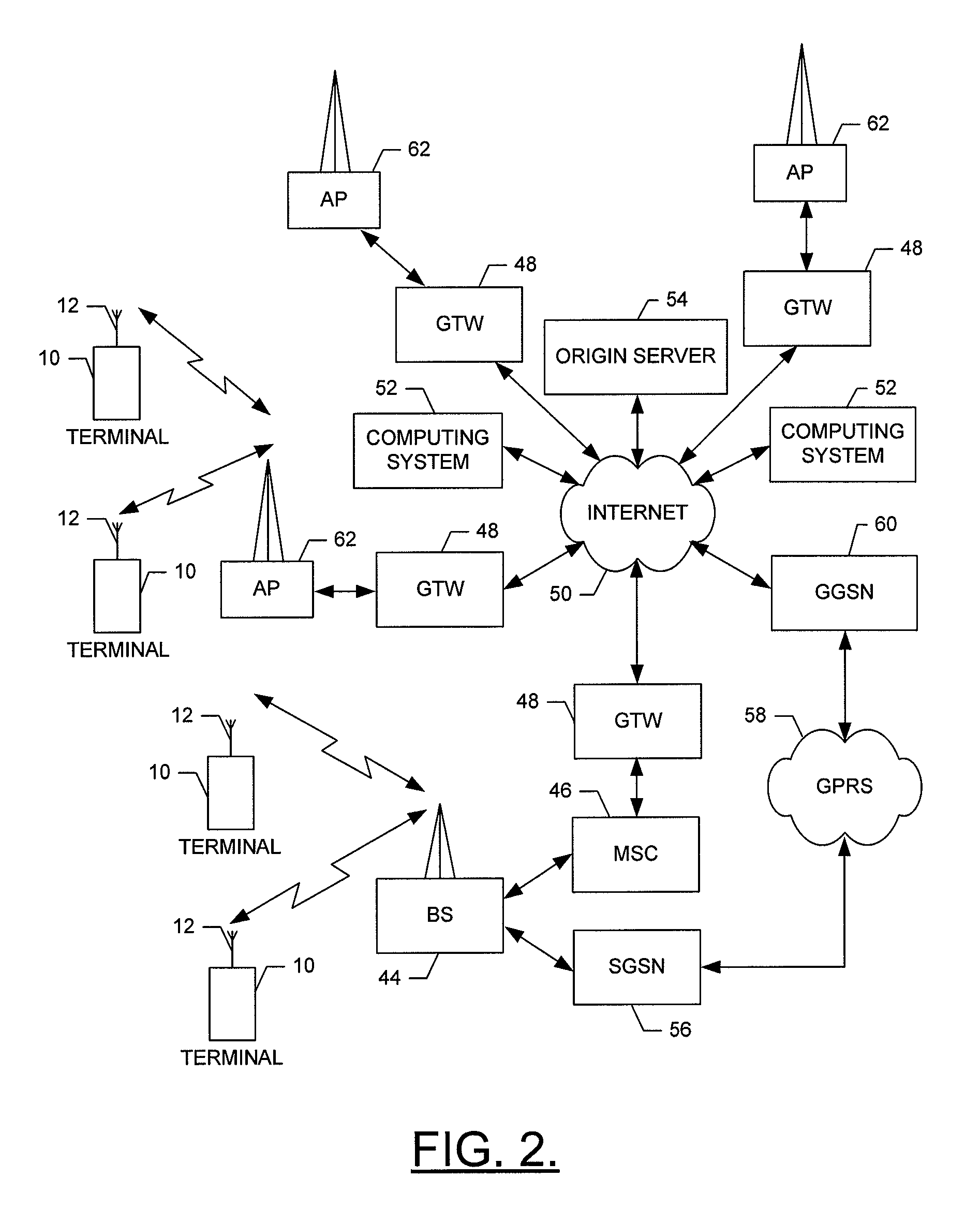
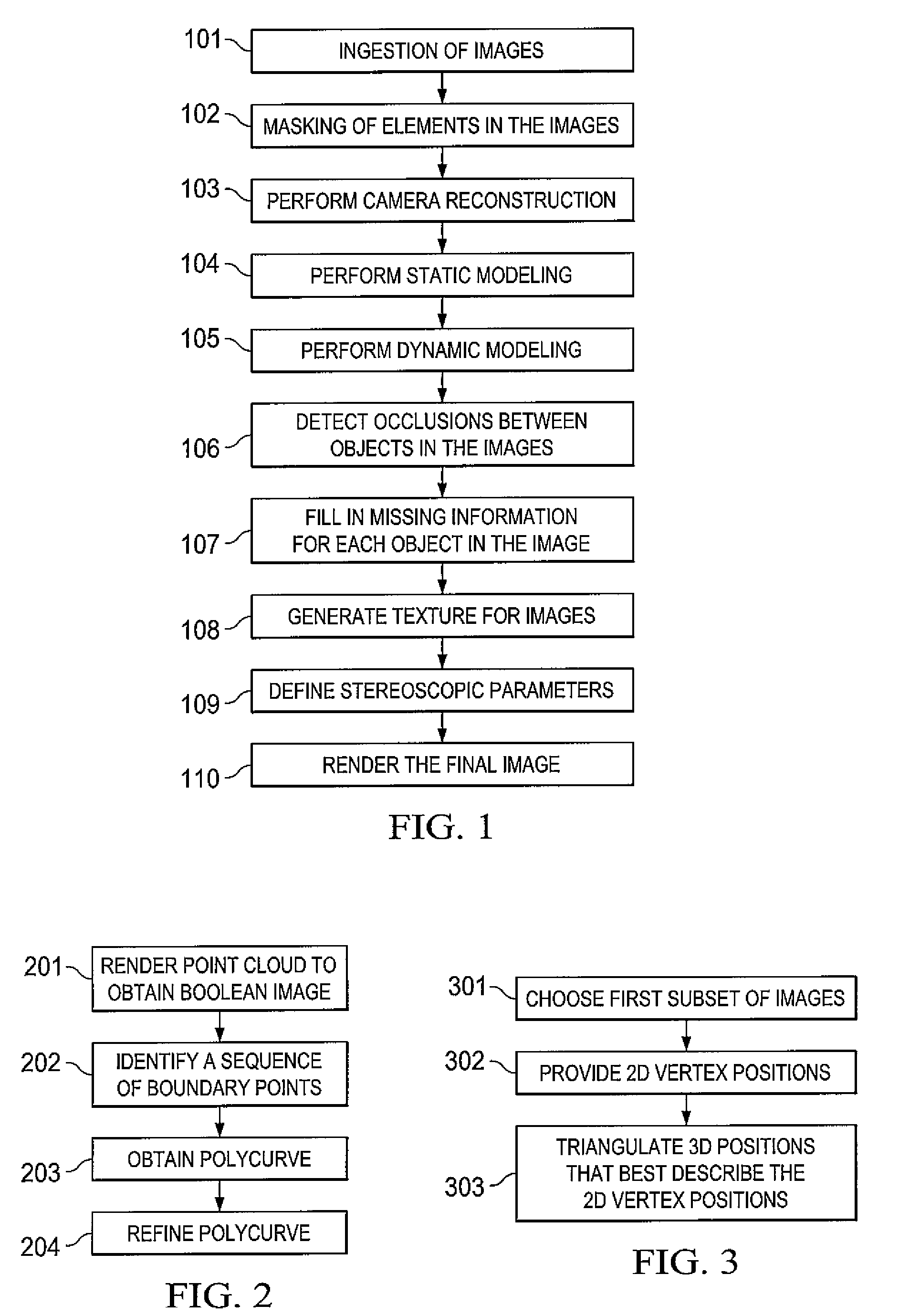
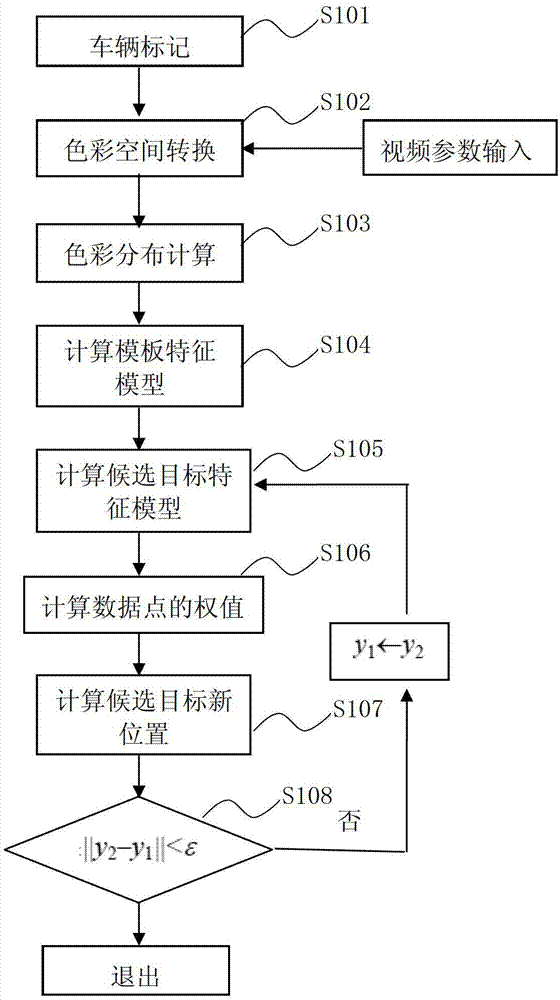
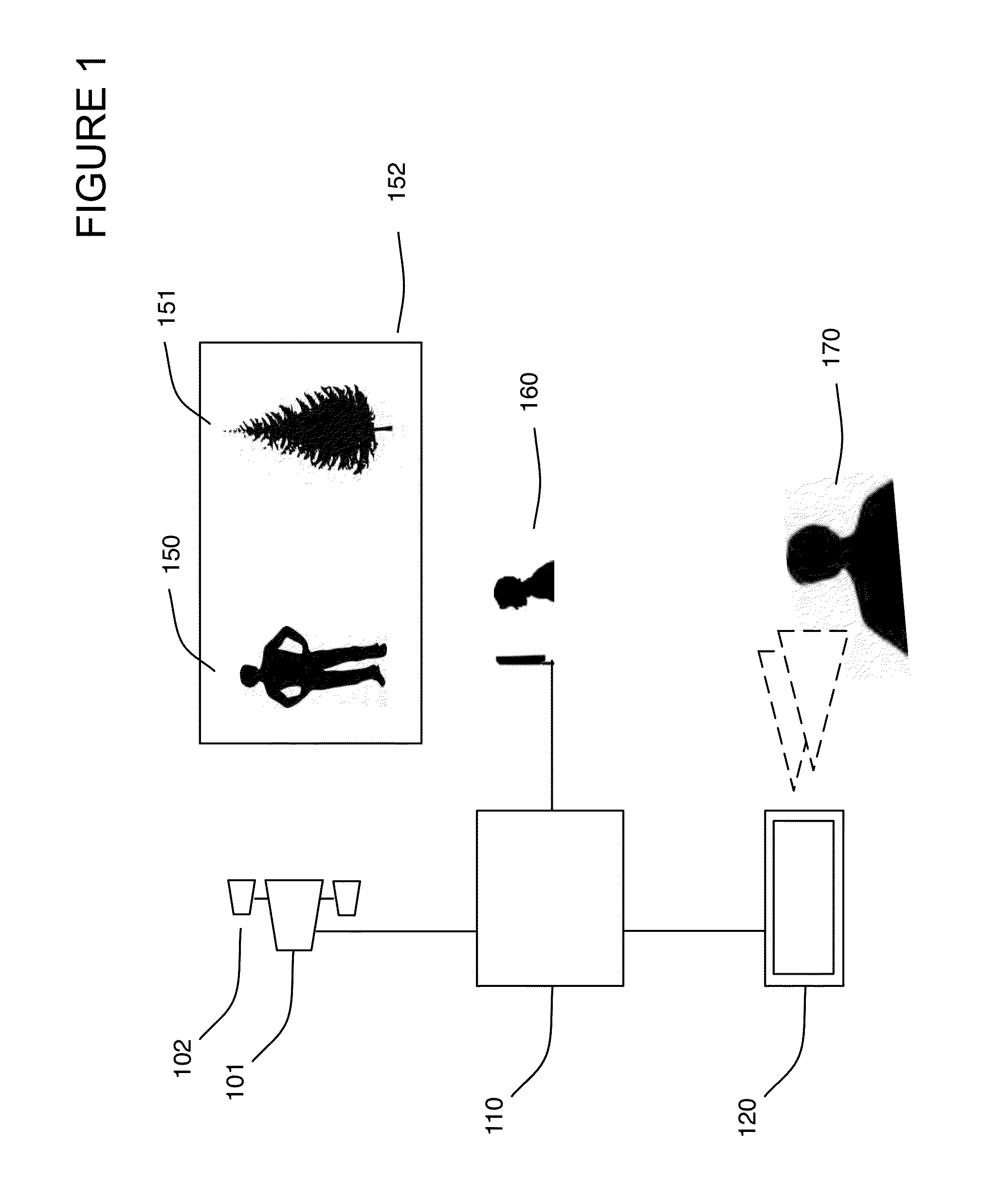
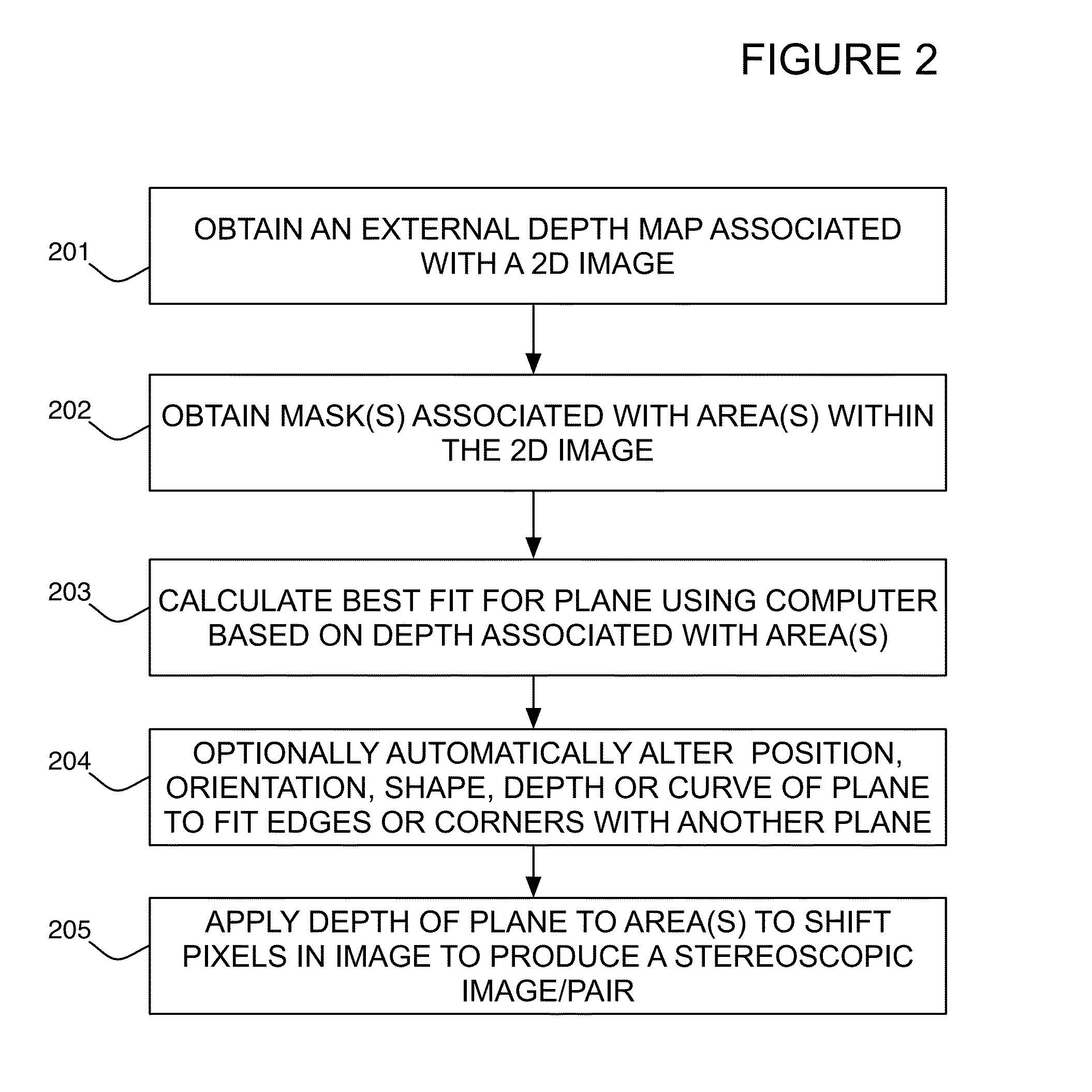
Method of converting 2D video to 3D video using 3D object models
InactiveUS9438878B2Quick conversionIncrease flexibilityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature trackingDegrees of freedom
Method for converting 2D video to 3D video using 3D object models. Embodiments of the invention obtain a 3D object model for one or more objects in a 2D video scene, such as a character. Object models may for example be derived from 3D scanner data; planes, polygons, or surfaces may be fit to this data to generate a 3D model. In each frame in which a modeled object appears, the location and orientation of the 3D model may be determined in the frame, and a depth map for the object may be generated from the model. 3D video may be generated using the depth map. Embodiments may use feature tracking to automatically determine object location and orientation. Embodiments may use rigged 3D models with degrees of freedom to model objects with parts that move relative to one another.
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
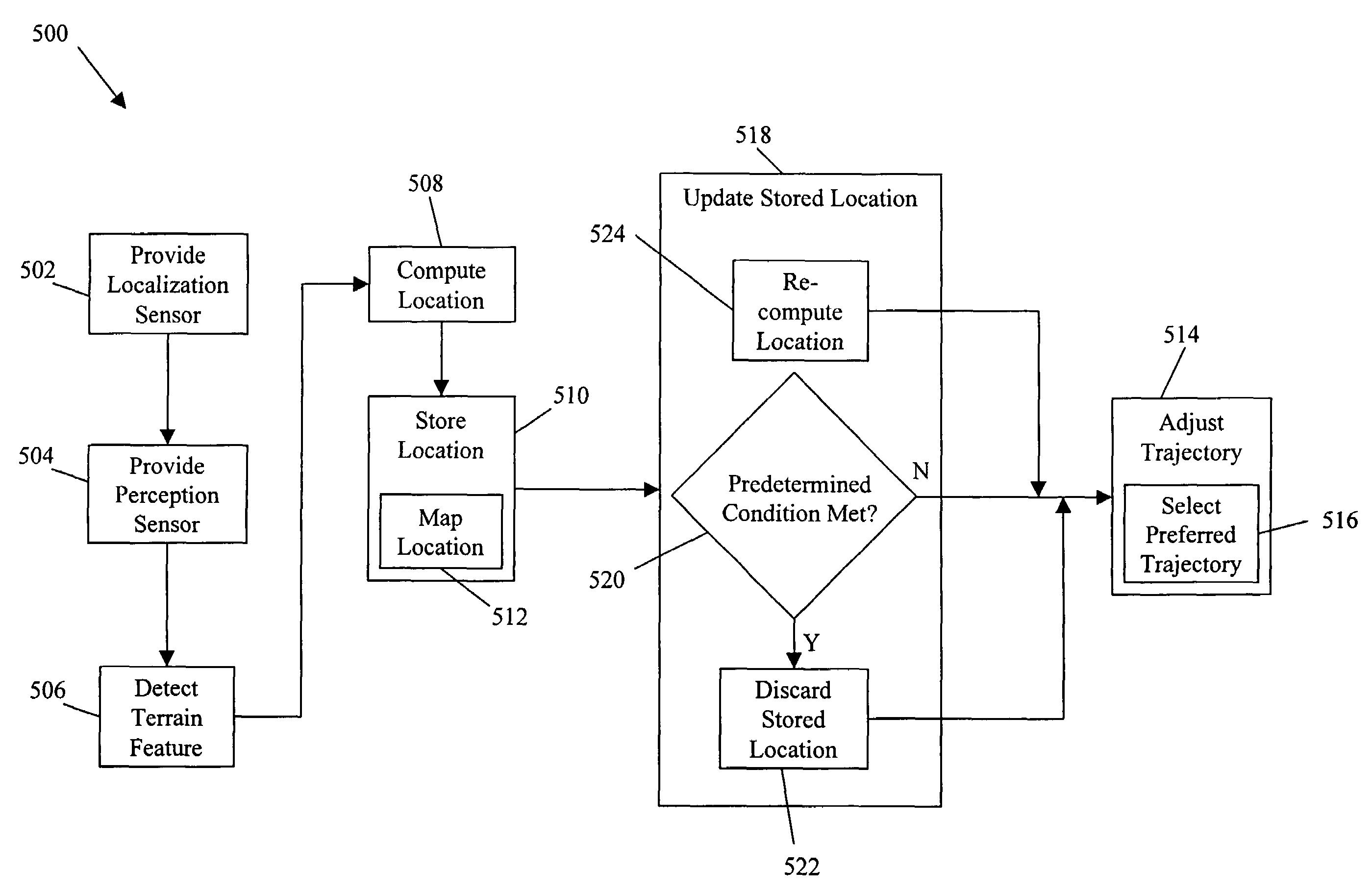
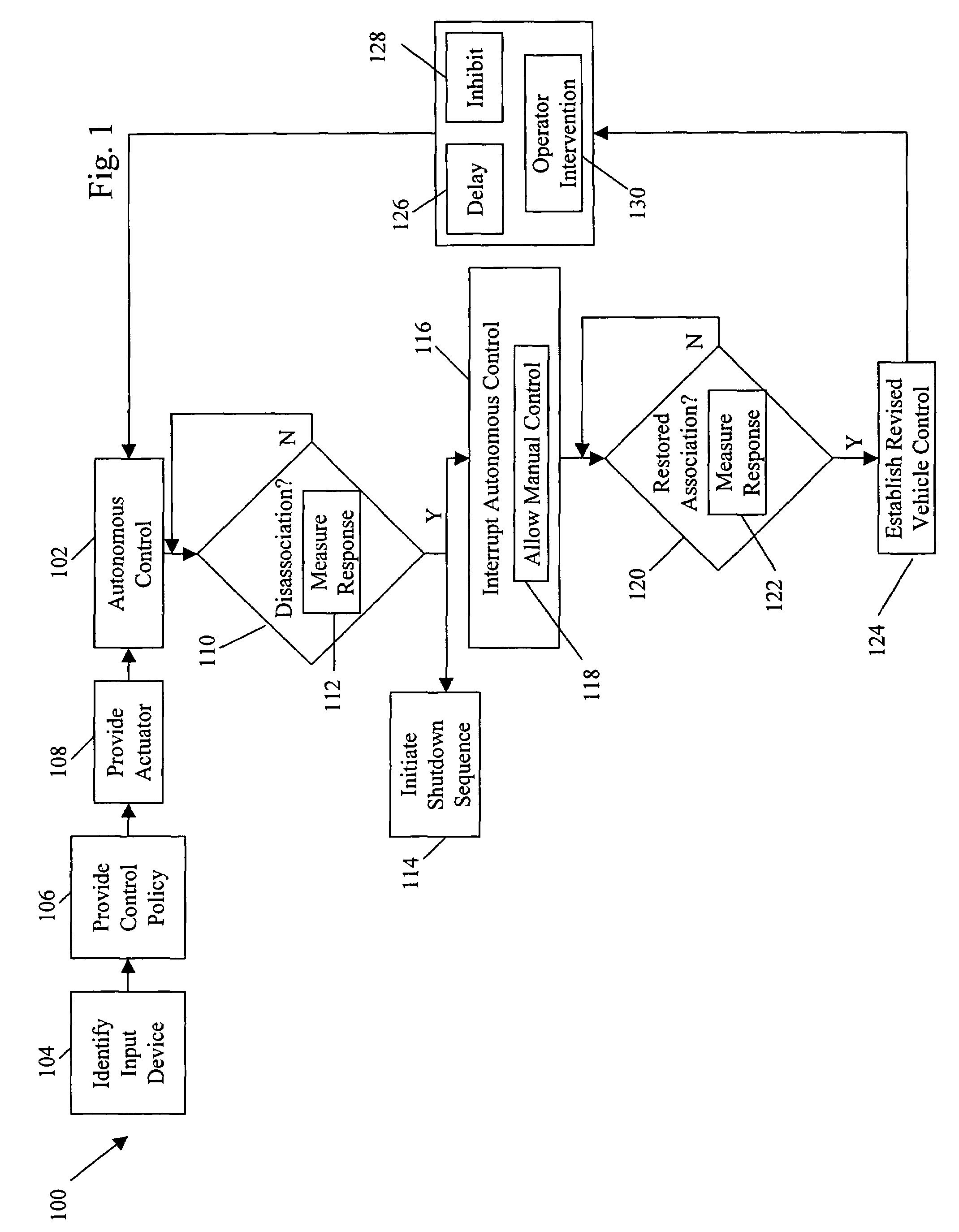
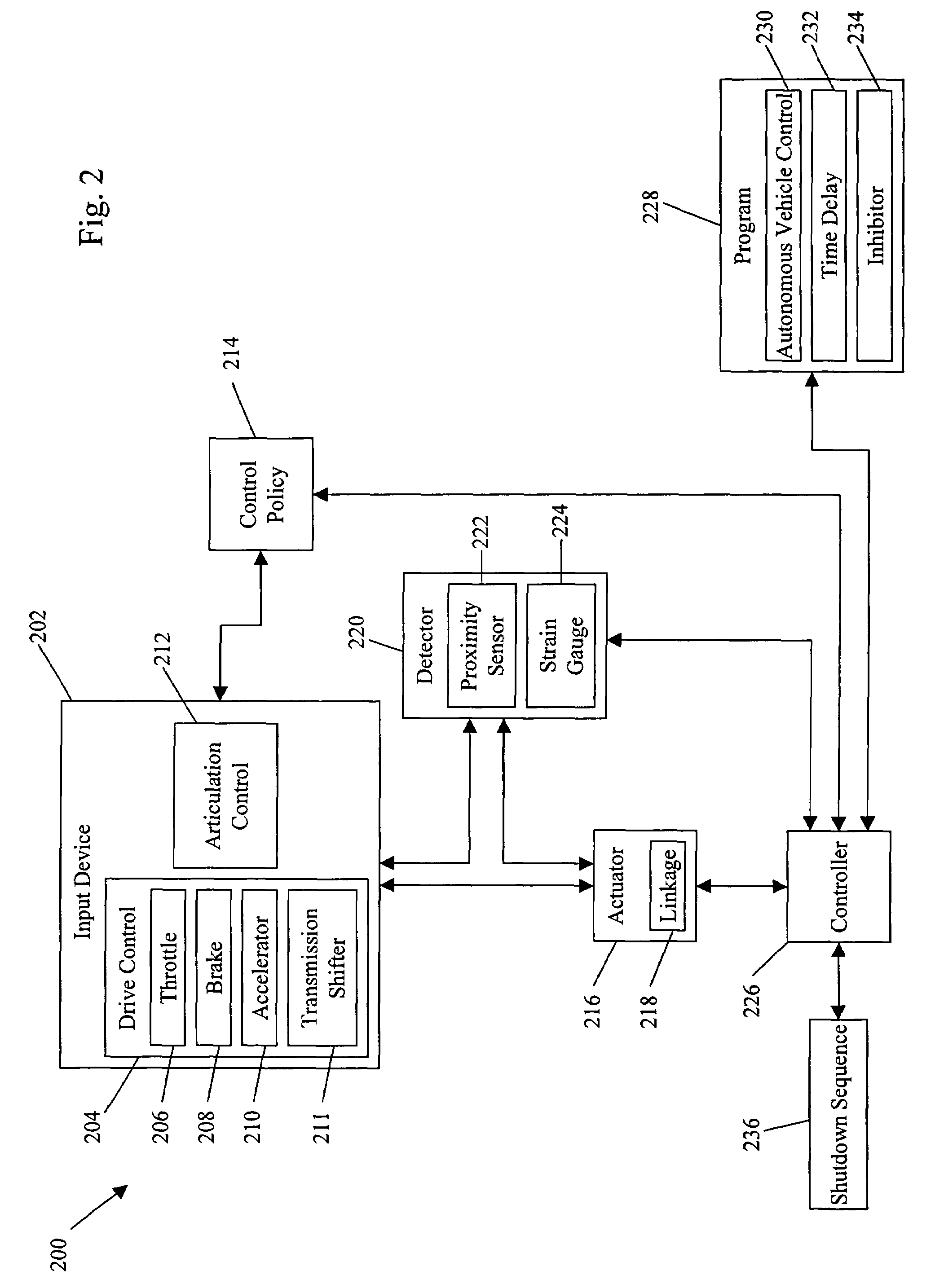
System and method for terrain feature tracking
InactiveUS20060089764A1Digital data processing detailsVehicle position/course/altitude controlTerrainPattern perception
System and method for tracking obstacles by an autonomous vehicle. Localization sensors (i.e., sensors to measure pitch, roll, and yaw, and systems including an inertial navigation system, a compass, a global positioning system, or an odometer) detect the position of the vehicle. Perception sensors (e.g., LIDAR, stereo vision, infrared vision, radar, or sonar) assess the environment about the vehicle. Using these sensors, locations of terrain features relative to the vehicle are computed and kept up-to-date. The vehicle trajectory is adjusted to avoid terrain features that are obstacles in the path of the vehicle.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
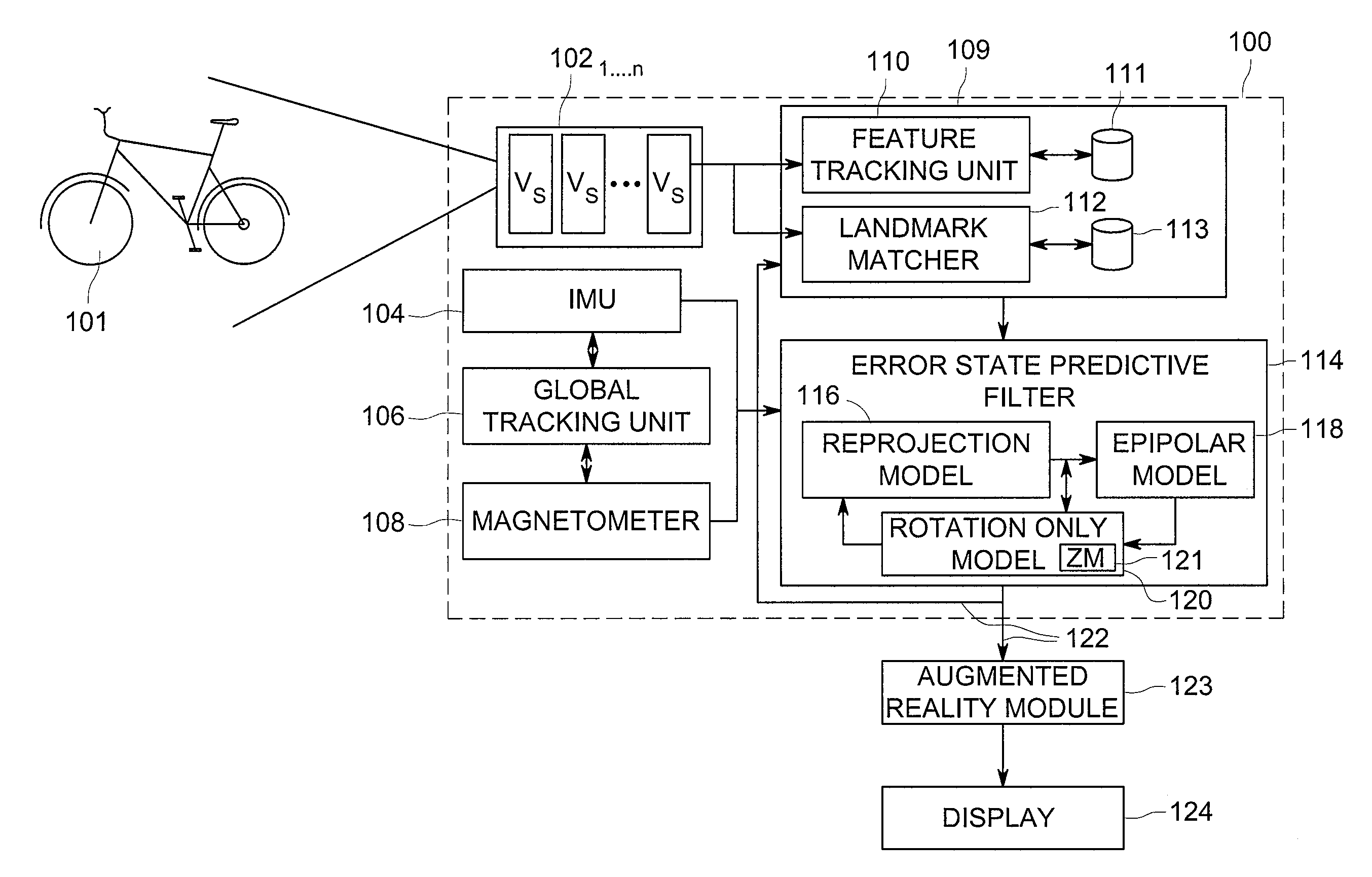
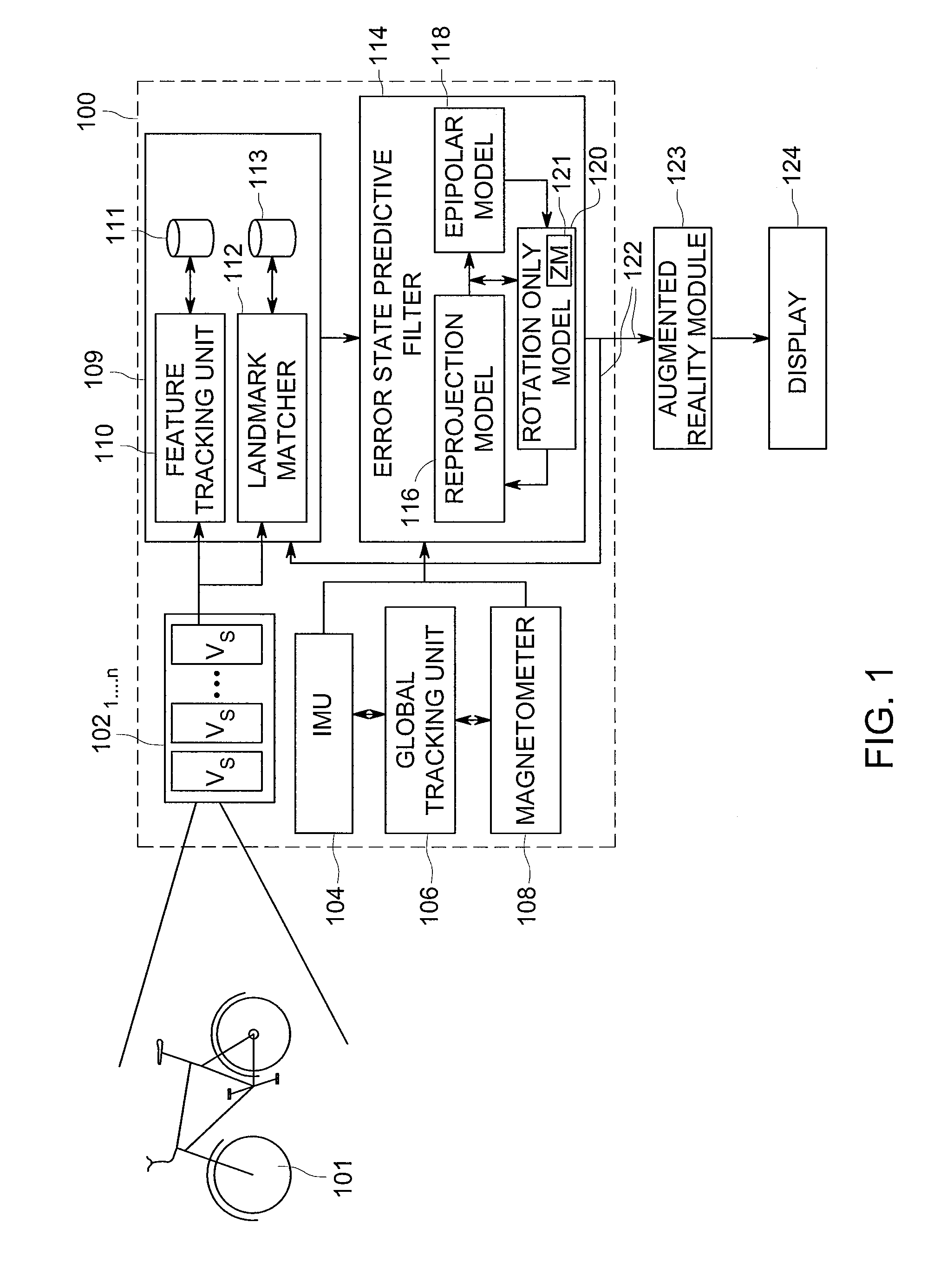
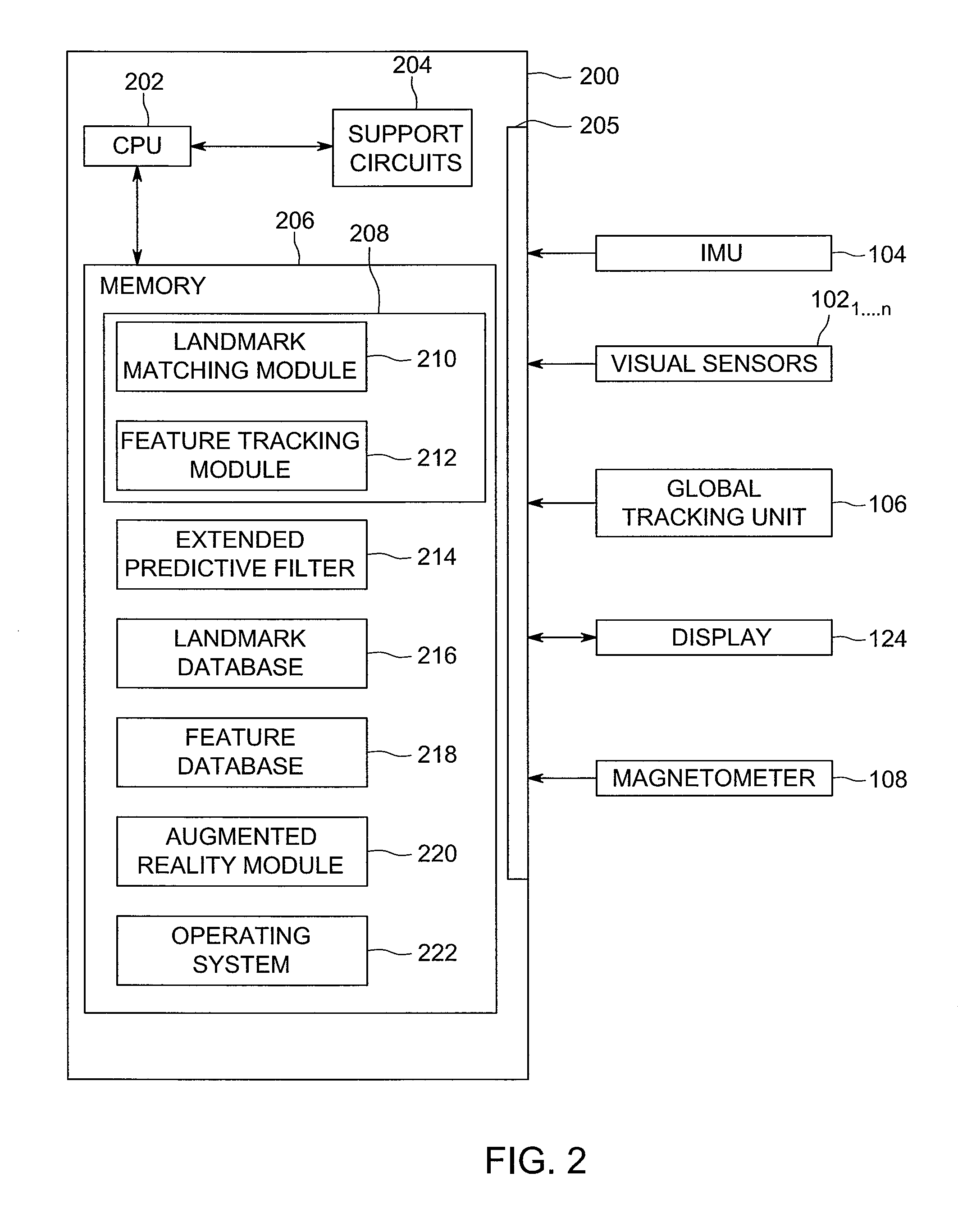
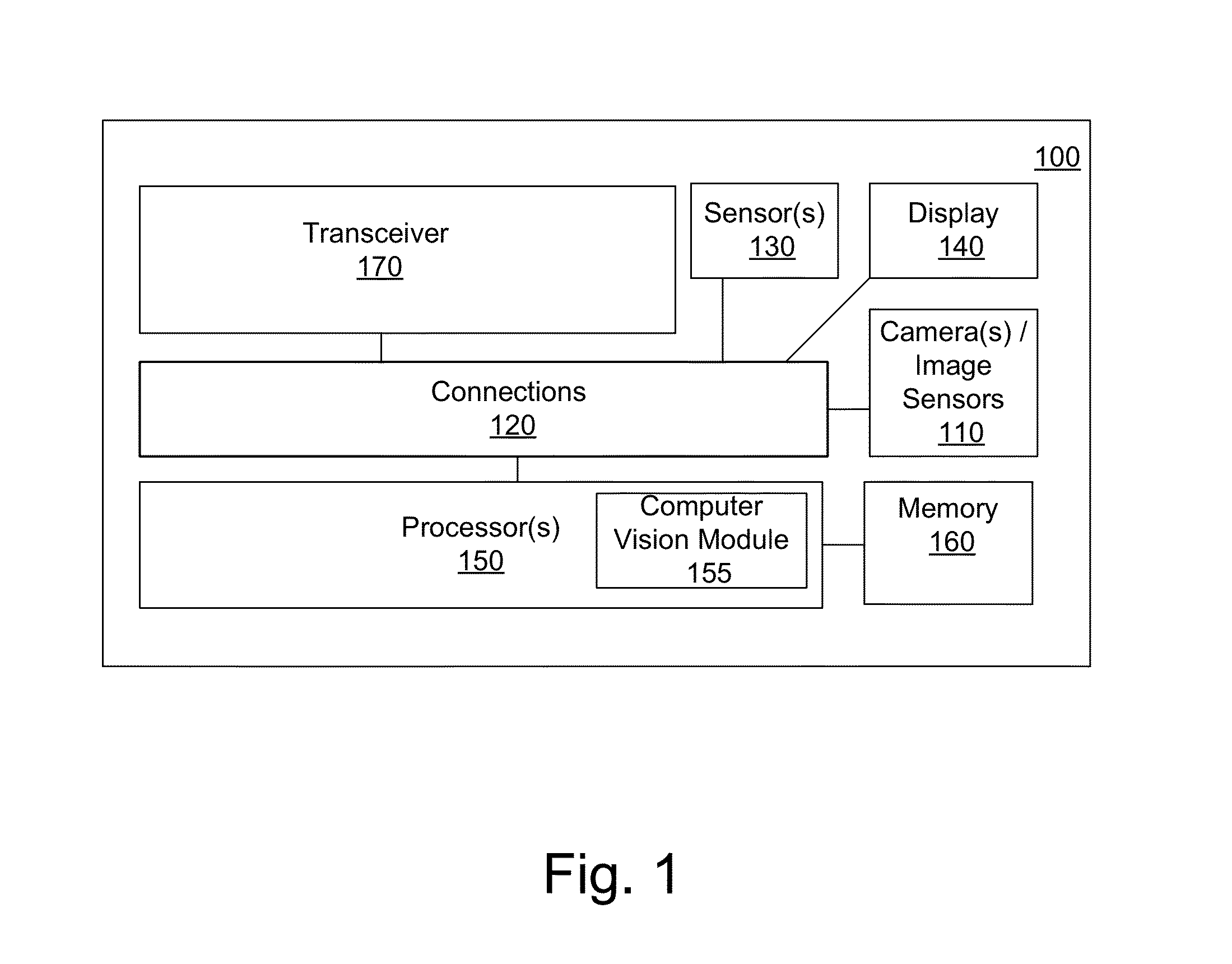
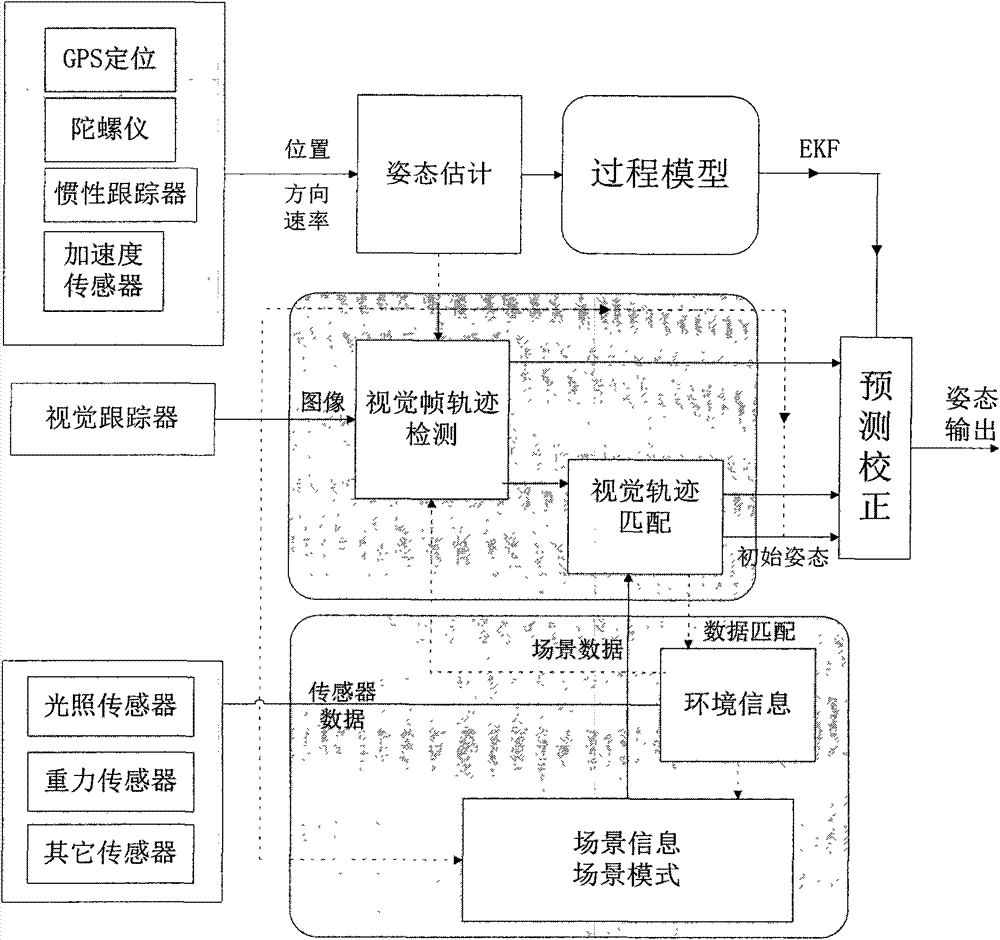
Method and apparatus for generating three-dimensional pose using monocular visual sensor and inertial measurement unit
ActiveUS8761439B1Accurate informationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionGyroscopeFeature tracking
An apparatus for providing three-dimensional pose comprising monocular visual sensors for providing images of an environment surrounding the apparatus, an inertial measurement unit (IMU) for providing gyroscope, acceleration and velocity information, collectively IMU information, a feature tracking module for generating feature tracking information for the images, and an error-state filter, coupled to the feature track module, the IMU and the one or more visual sensors, for correcting IMU information and producing a pose estimation based on at least one error-state model chosen according to the sensed images, the IMU information and the feature tracking information.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
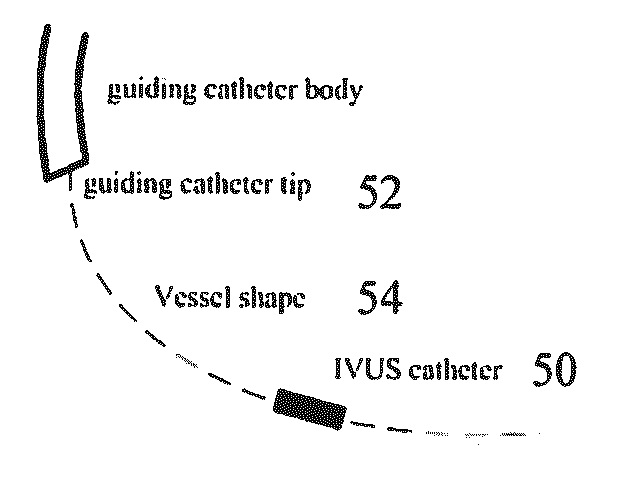
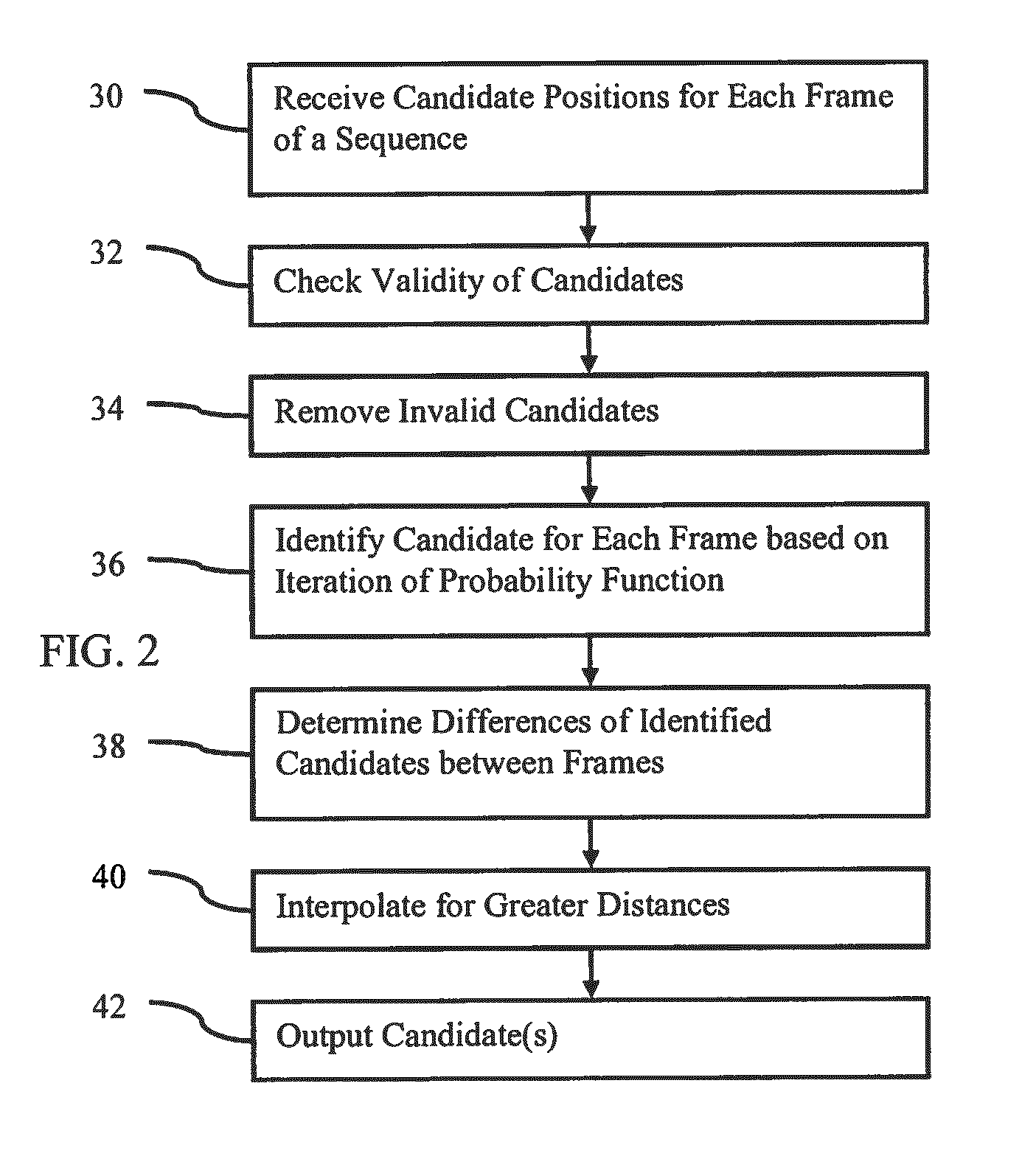
Optimization of multiple candidates in medical device or feature tracking
Multiple candidates are optimized in medical device or feature tracking. Possible locations of medical devices or features for each of a plurality of different times are received. The possible locations of devices are modeled using a probability function. An iterative solution to obtain the maximum of the probability function determines the possible locations to be used as the locations of the medical devices or features for each time. Where two or more medical devices or features are provided with a geometric relationship, such as being connected by a detected guide wire, the probability function may account for the geometric relationship, such as a geodesic distance between the possible locations for the two medical devices.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
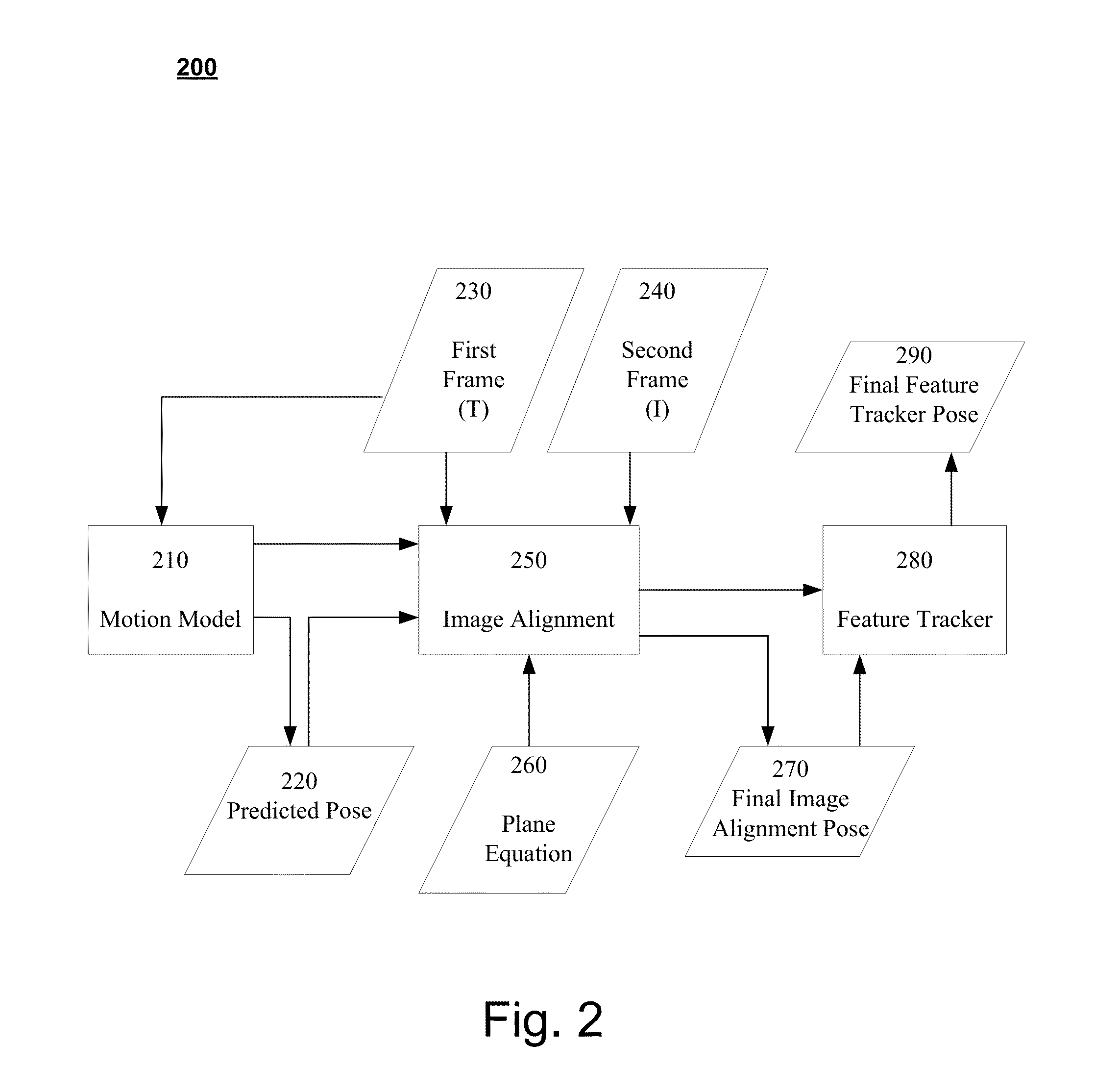
Systems and Methods for Feature-Based Tracking
Disclosed embodiments pertain to feature based tracking. In some embodiments, a camera pose may be obtained relative to a tracked object in a first image and a predicted camera pose relative to the tracked object may be determined for a second image subsequent to the first image based, in part, on a motion model of the tracked object. An updated SE(3) camera pose may then be obtained based, in part on the predicted camera pose, by estimating a plane induced homography using an equation of a dominant plane of the tracked object, wherein the plane induced homography is used to align a first lower resolution version of the first image and a first lower resolution version of the second image by minimizing the sum of their squared intensity differences. A feature tracker may be initialized with the updated SE(3) camera pose.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
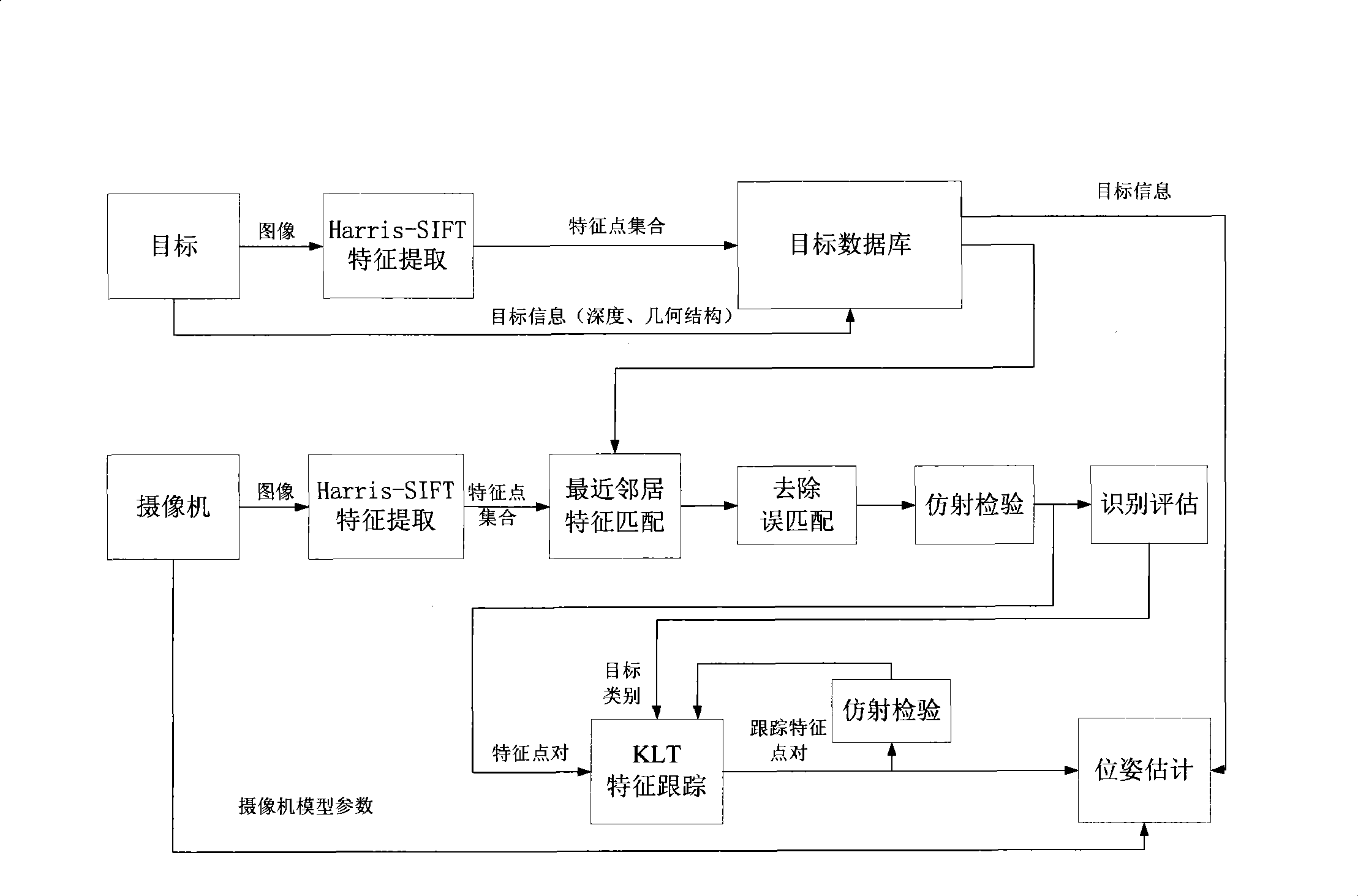
Real time vision positioning method of monocular camera
InactiveCN101441769AReduce complexityLow costTelevision system detailsImage analysisModel parametersVisual positioning
The invention relates to a method for real-time vision positioning for a monocular camera, which belongs to the field of computer vision. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring an object image characteristic point set to establish an object image database and perform real-time trainings; secondly, modeling the camera to acquire model parameters of the camera; and thirdly, extracting a real-time image characteristic point set by the camera, matching real-time image characteristic points with the characteristic point set in the object database, and removing error matching and performing an affine inspection to acquire characteristic point pairs and object type information. The characteristic point pairs and the object type information are used to perform characteristic tracking, and accurate tracking characteristic points of the object image are combined with the model parameters of the camera so as to acquire three-dimensional poses of the camera. The method can achieve the functions of self-positioning and navigation by using a single camera only, thus the system complexity and the cost are reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
System and method for terrain feature tracking
System and method for tracking obstacles by an autonomous vehicle. Localization sensors (i.e., sensors to measure pitch, roll, and yaw, and systems including an inertial navigation system, a compass, a global positioning system, or an odometer) detect the position of the vehicle. Perception sensors (e.g., LIDAR, stereo vision, infrared vision, radar, or sonar) assess the environment about the vehicle. Using these sensors, locations of terrain features relative to the vehicle are computed and kept up-to-date. The vehicle trajectory is adjusted to avoid terrain features that are obstacles in the path of the vehicle.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
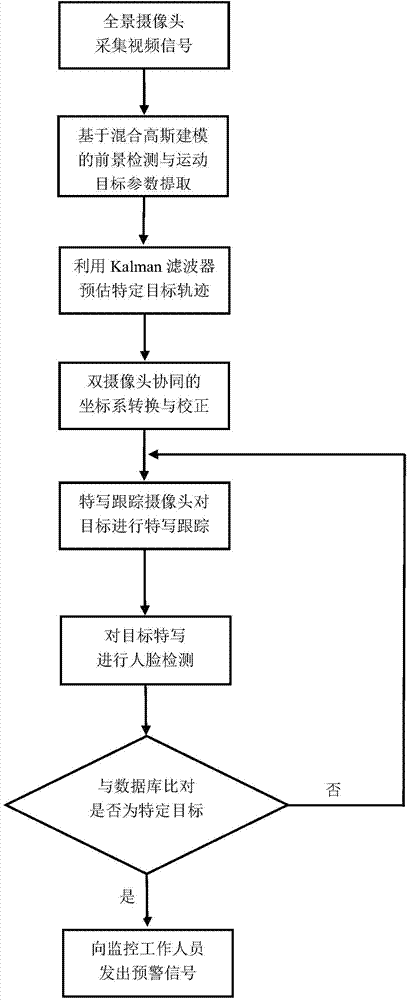
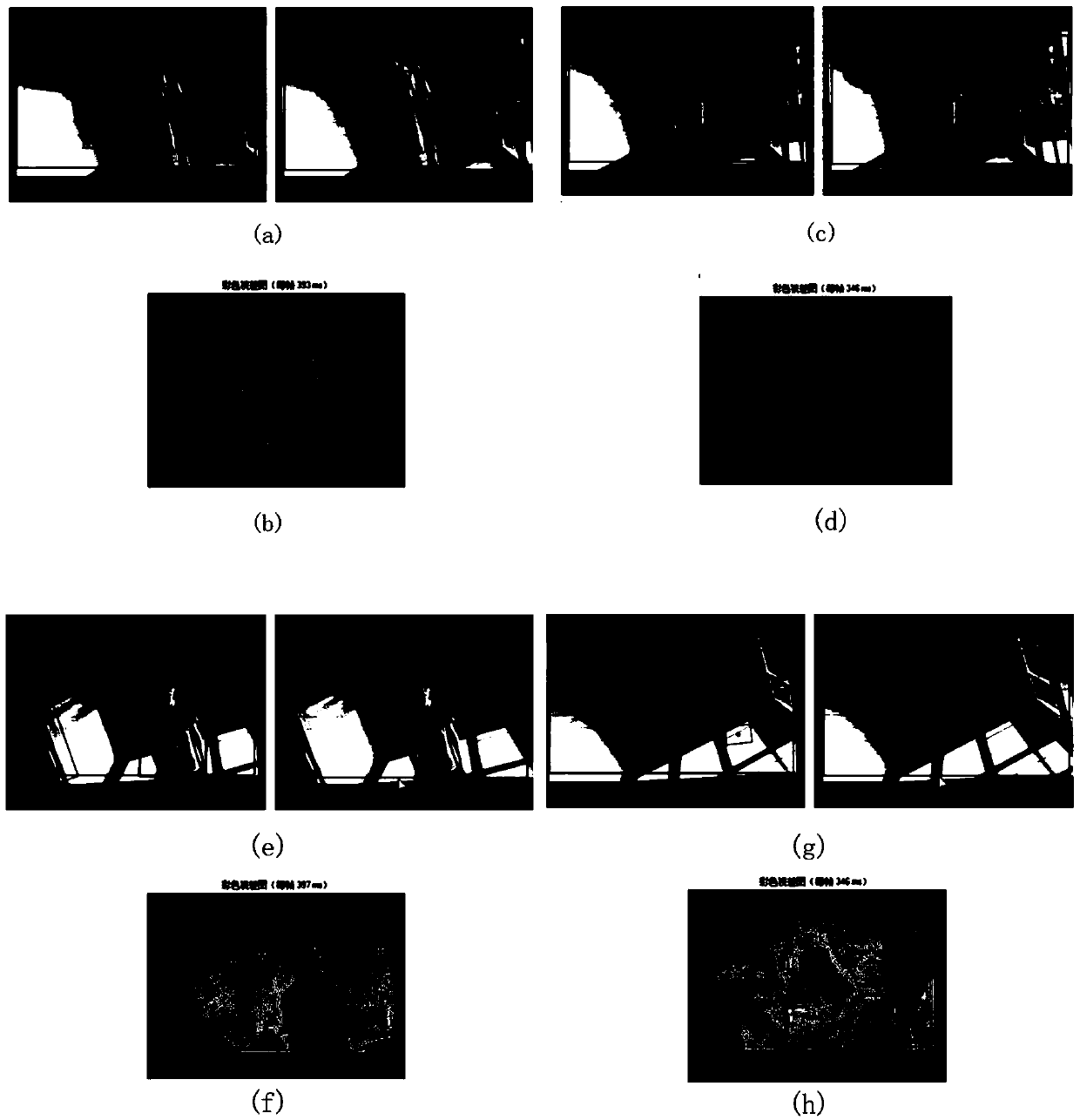
Suspicious target detection tracking and recognition method based on dual-camera cooperation
InactiveCN104301669AQuick identificationEasy accessTelevision system detailsImage analysisPattern recognitionGoal recognition
The invention discloses a suspicious target detection tracking and recognition method based on dual-camera cooperation, and belongs to the technical field of video image processing. The method comprises the steps that a panoramic surveillance camera is utilized for collecting a panoramic image, the improved Gaussian mixture modeling method is adopted for carrying out foreground detection, basic parameters of moving targets are extracted, a Kalman filter is utilized for estimating a movement locus of a specific target, the specific target is recognized according to velocity analysis, the dual-camera cooperation strategy is adopted, a feature tracking camera is controlled to carry out feature tracking on the moving targets, a suspicious target is locked, the face of the suspicious target is detected, face recognition is carried out, face data are compared with a database, and an alarm is given if abnormities exist. According to the suspicious target detection tracking and recognition method, the dual-camera cooperation tracking surveillance strategy is adopted, defects of a single surveillance camera on a specific scene are overcome, and the added face recognition function can assist workers in identifying the specific target to a greater degree; in addition, the tracking algorithm adopted in the method is good in real-time performance, target recognition and judgment standards are simple and reliable, and the operation process is fast and accurate.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
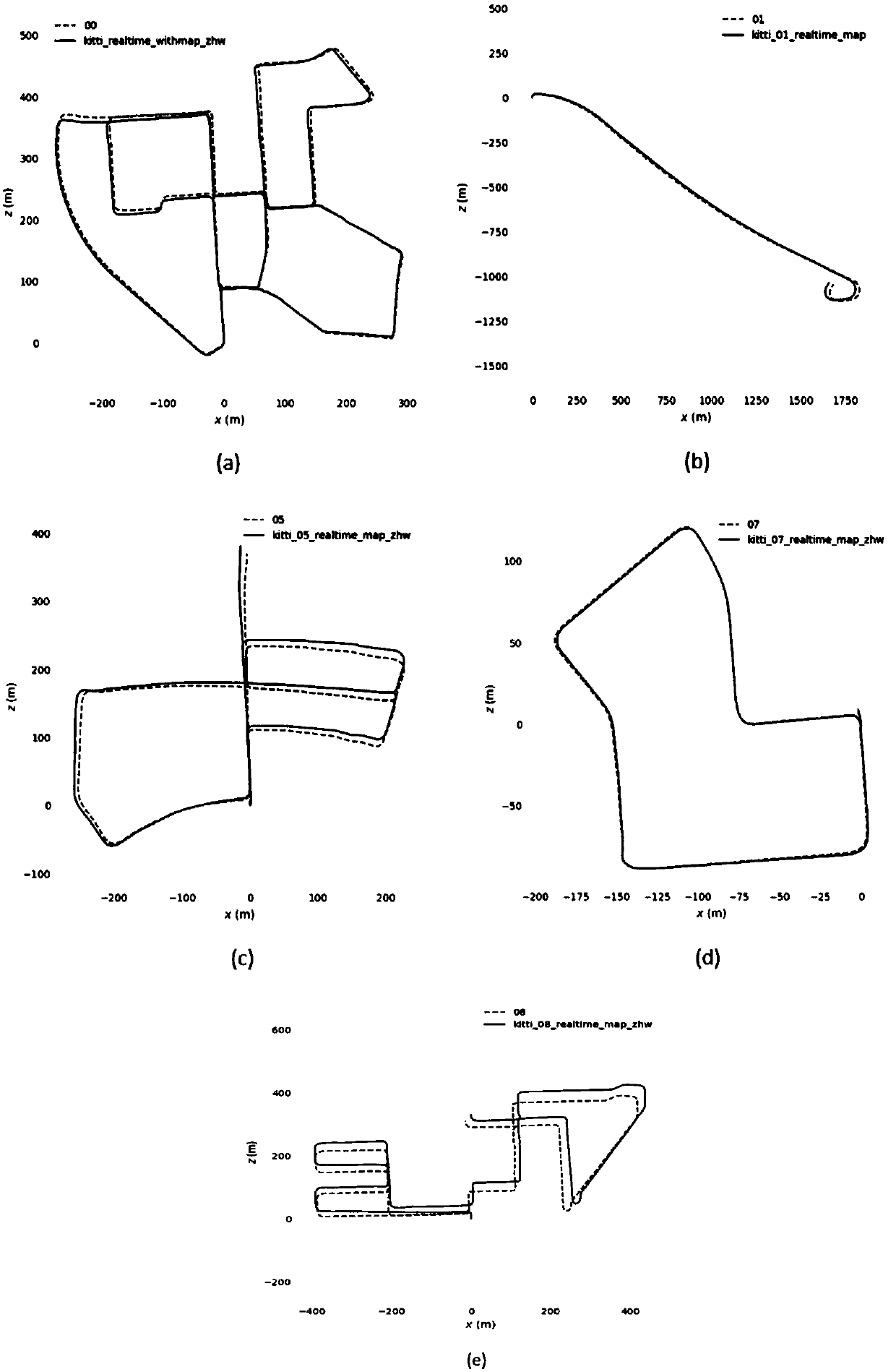
ORB-SLAM based high-precision vehicle positioning method
ActiveCN109631855ALow costPositioning appliesInstruments for road network navigationPicture interpretationPattern recognitionClosed loop
The invention discloses an ORB-SLAM based high-precision vehicle positioning method, which mainly solves a problem of low accuracy of the positioning result of the current ORB-SLAM classical positioning algorithm. The implementation of the method comprises the steps of selecting a calibration board to calibrate a binocular camera, and carrying out stereo correction on a captured image; detecting ORB feature points in the corrected image, and completing the feature point extraction; matching the extracted feature points by using a binocular sparse feature matching method, then acquiring the current camera pose information by using an adjacent frame feature tracking method, and constructing a local map; carrying out closed-loop detection and global optimization on the constructed local map so as to complete the establishment of a visual map, and preserving the visual map; and selecting a vehicle positioning scheme according to the number of matched feature points in the image, and determining the final position of the target vehicle through reading the visual map. The method disclosed by the invention can improve the vehicle positioning accuracy and robustness, and can be used for artificial intelligence management and safety disposal of unmanned automobiles.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
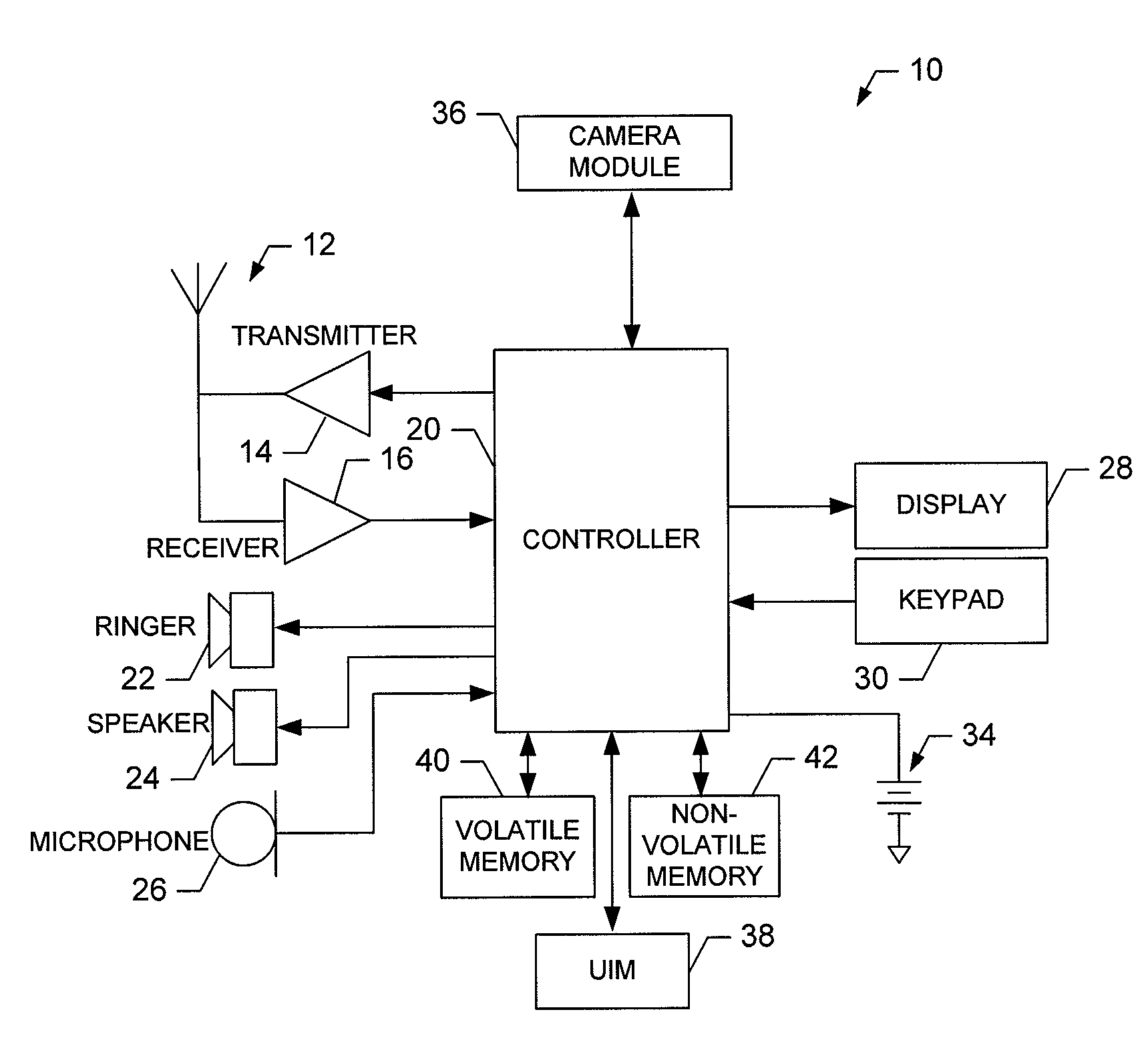
Method, Device, Mobile Terminal and Computer Program Product for a Camera Motion Detection Based Scheme for Improving Camera Input User Interface Functionalities
ActiveUS20080007620A1Easy to optimizeMinimizing image blurTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionComputer module
A device for utilizing camera motion detection for a camera input interface includes a feature extractor, a feature tracker and a capture module. The feature extractor is configured to determine at least one obvious feature in an image frame. The feature tracker is in communication with the feature extractor. The feature tracker is configured to determine an amount of movement of the at least one obvious feature in a subsequent image frame and compare the amount of movement to a threshold. The capture module is in communication with the feature tracker. The capture module is configured to capture an image in response to the comparison of the amount of movement to the threshold.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
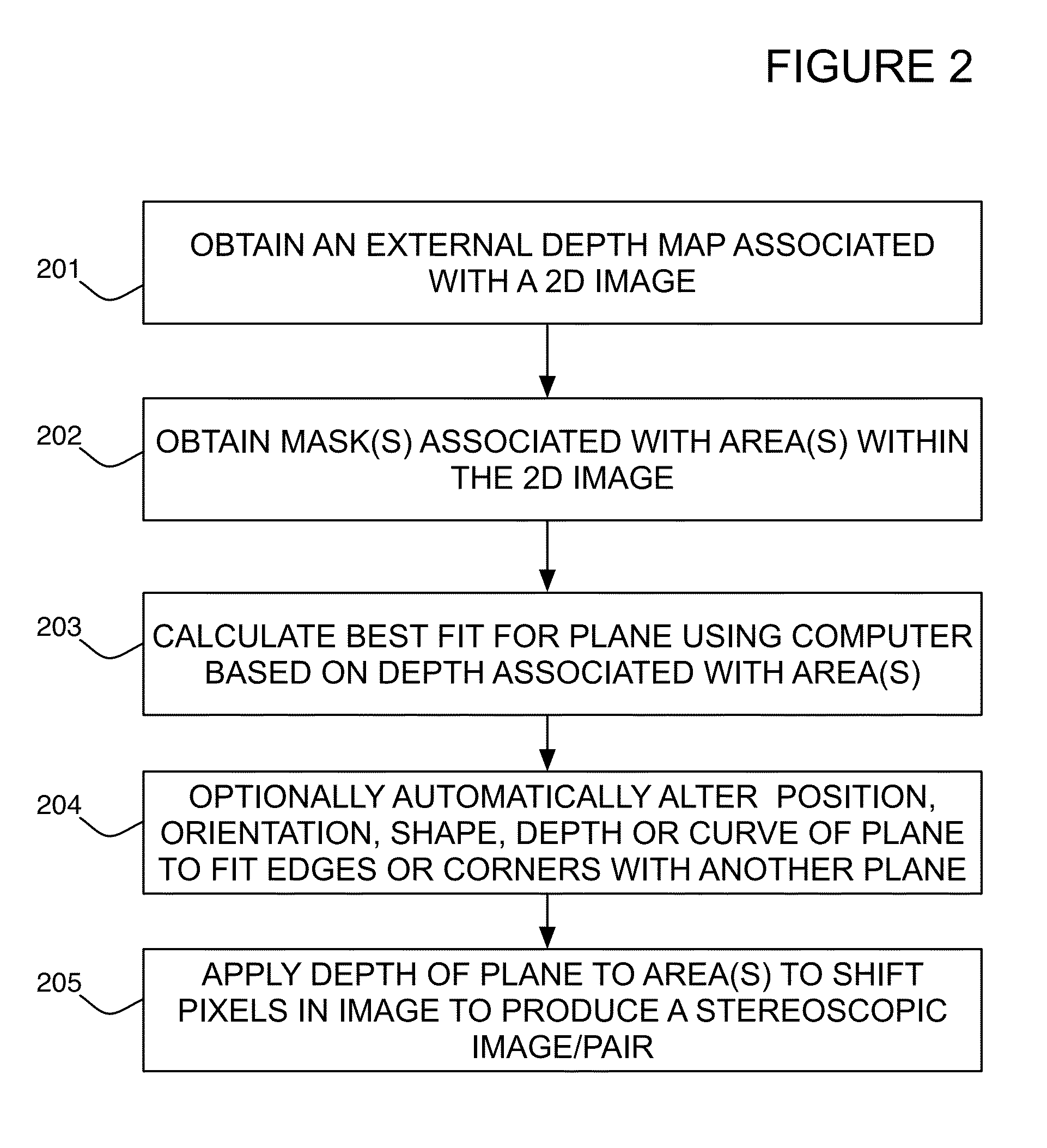
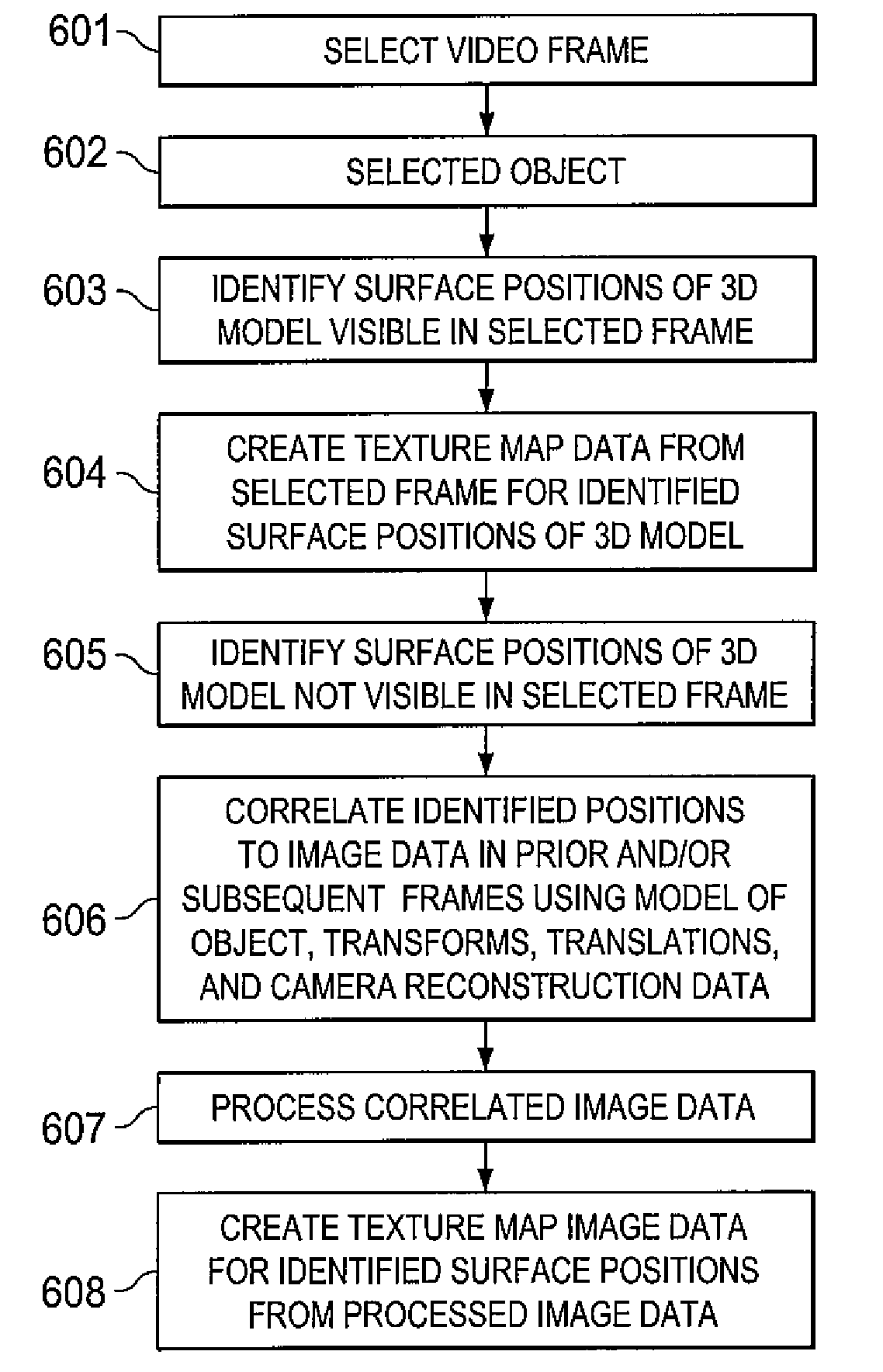
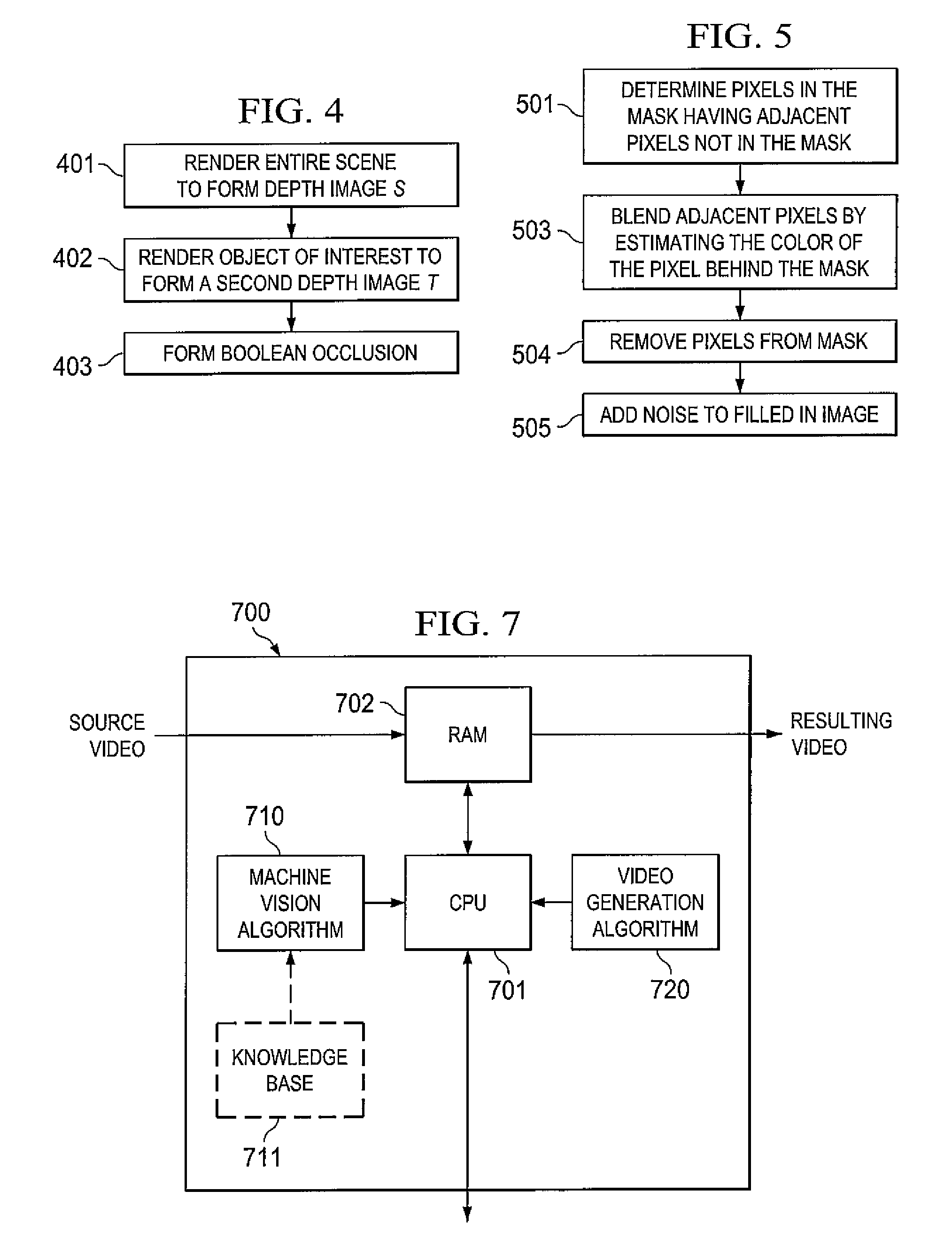
System and method for using feature tracking techniques for the generation of masks in the conversion of two-dimensional images to three-dimensional images
The present invention is directed to systems and methods for controlling 2-D to 3-D image conversion and / or generation. The methods and systems use auto-fitting techniques to create a mask based upon tracking features from frame to frame. When features are determined to be missing they are added prior to auto-fitting the mask.
Owner:CONVERSION WORKS
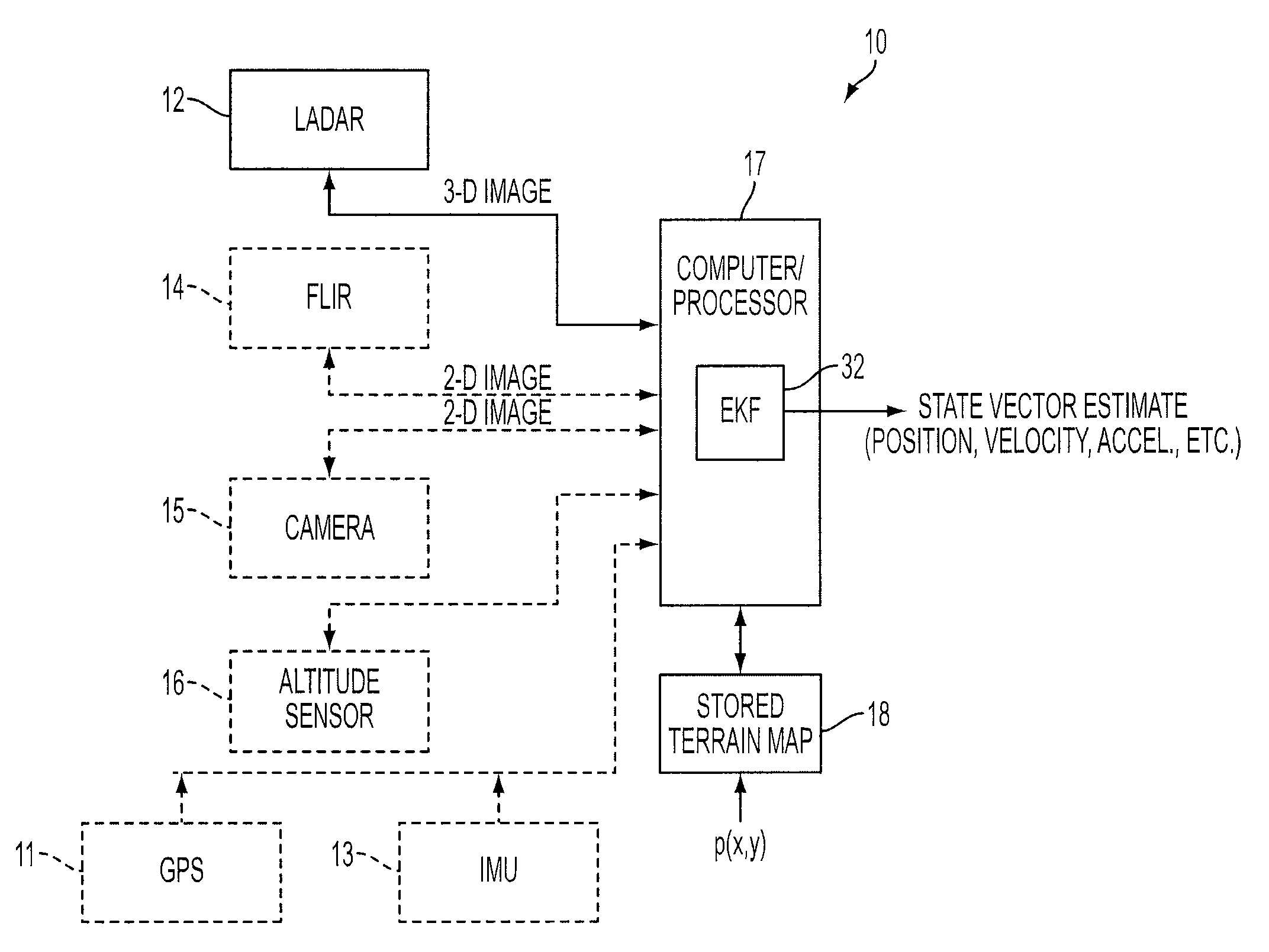
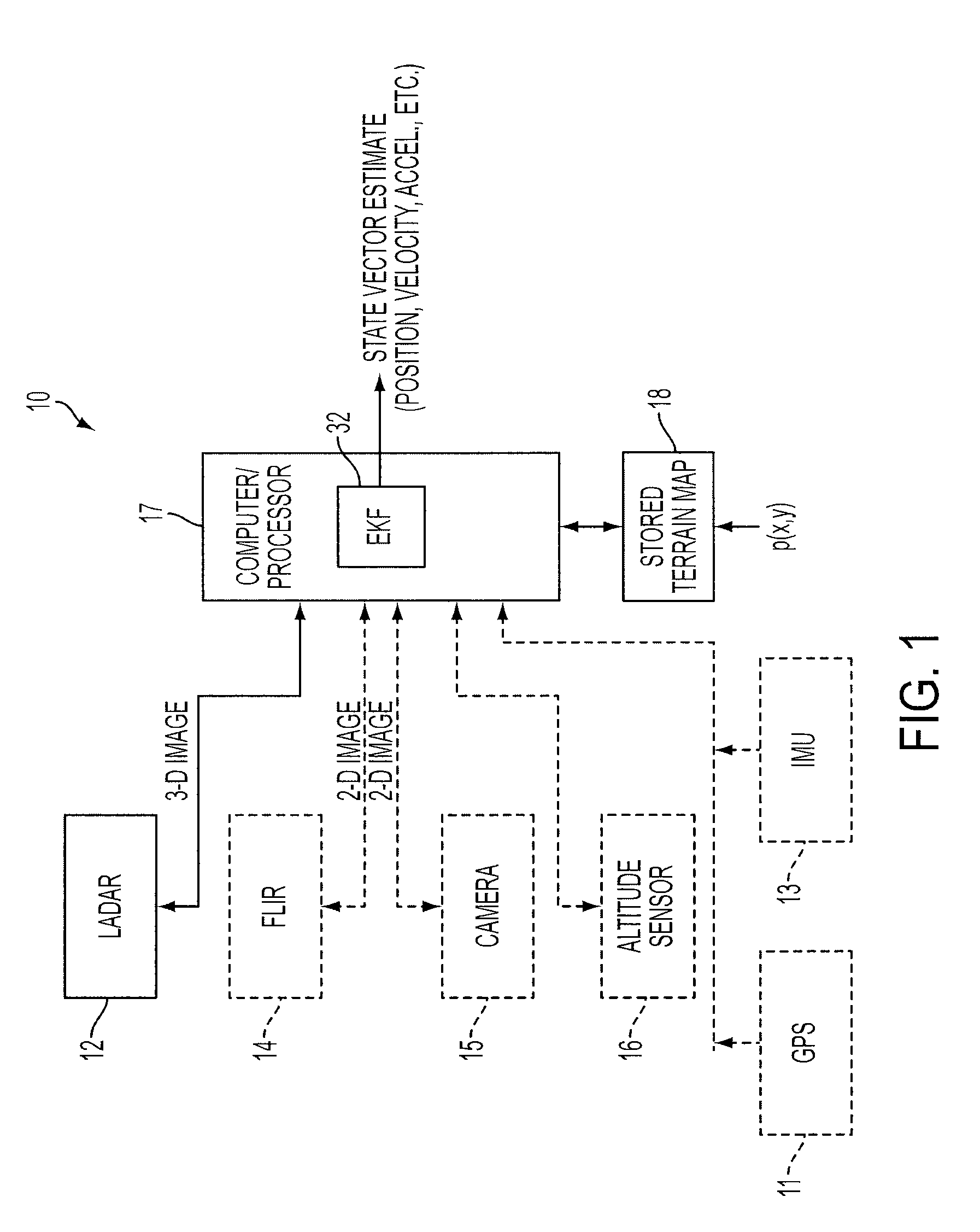
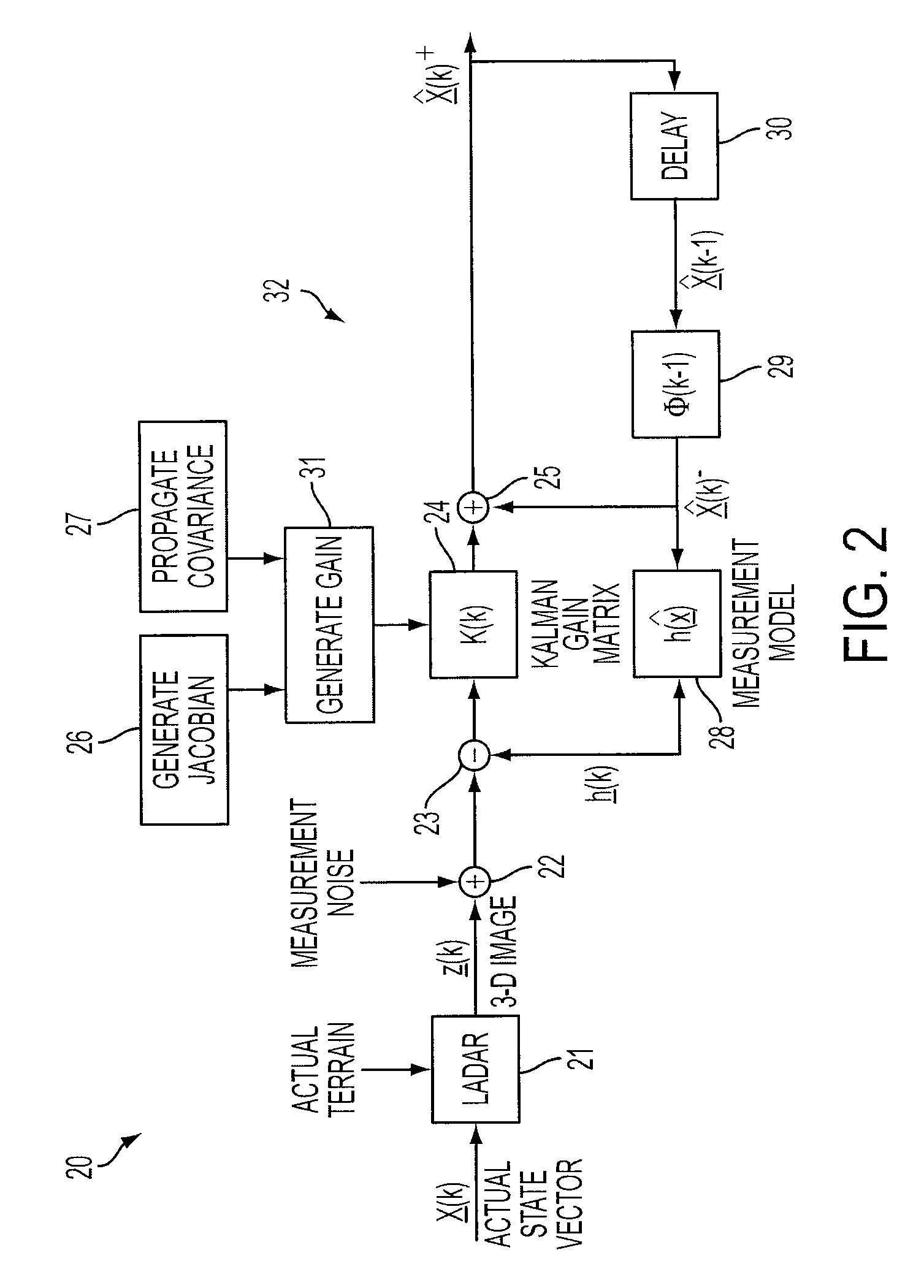
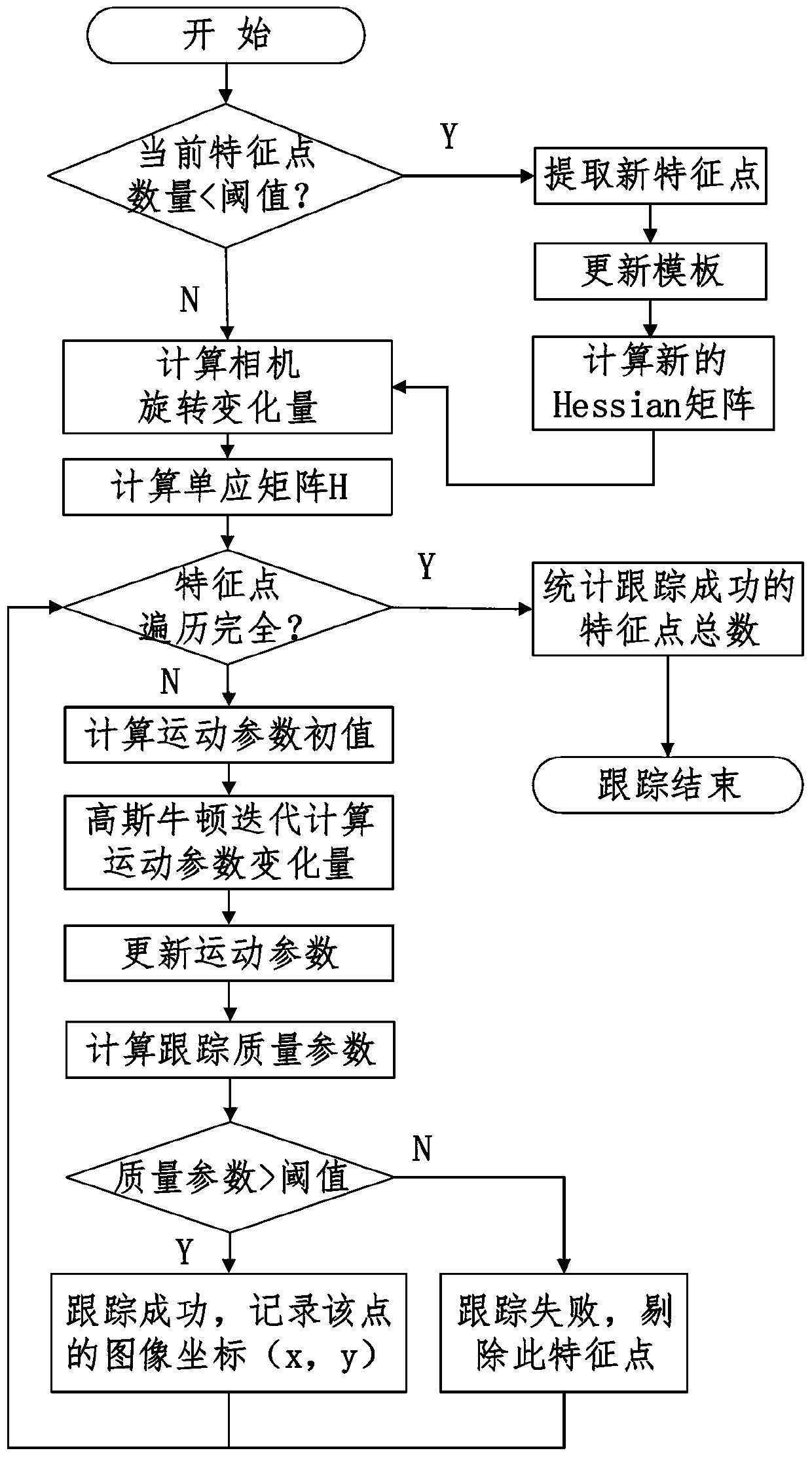
Model-based feature tracking in 3-D and 2-D imagery
A feature tracker for tracking a target includes an imaging sensor for imaging the target and a Kalman filter for generating predicted position, velocity and acceleration of the imaging sensor with respect to the target. The Kalman filter includes a state vector estimate of the position, velocity and acceleration of the imaging sensor, and a model for characterizing the target. The model characterizes the target by using at least one bivariate Gaussian function for the target. The Kalman filter includes a Jacobian matrix defined as a partial derivative of the model with respect to the state vector estimate. The Kalman filter includes a gain matrix generated from the Jacobian matrix.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
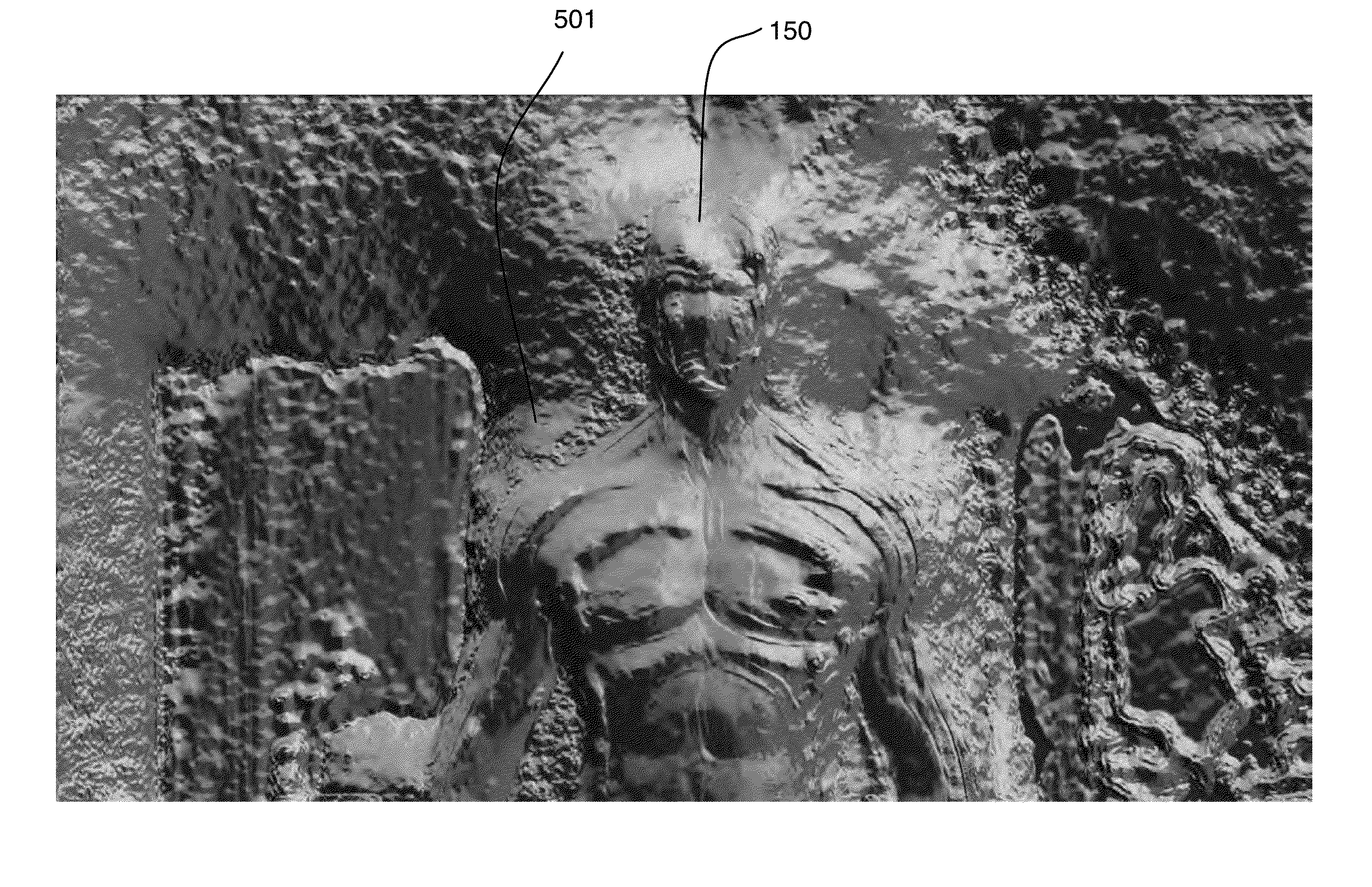
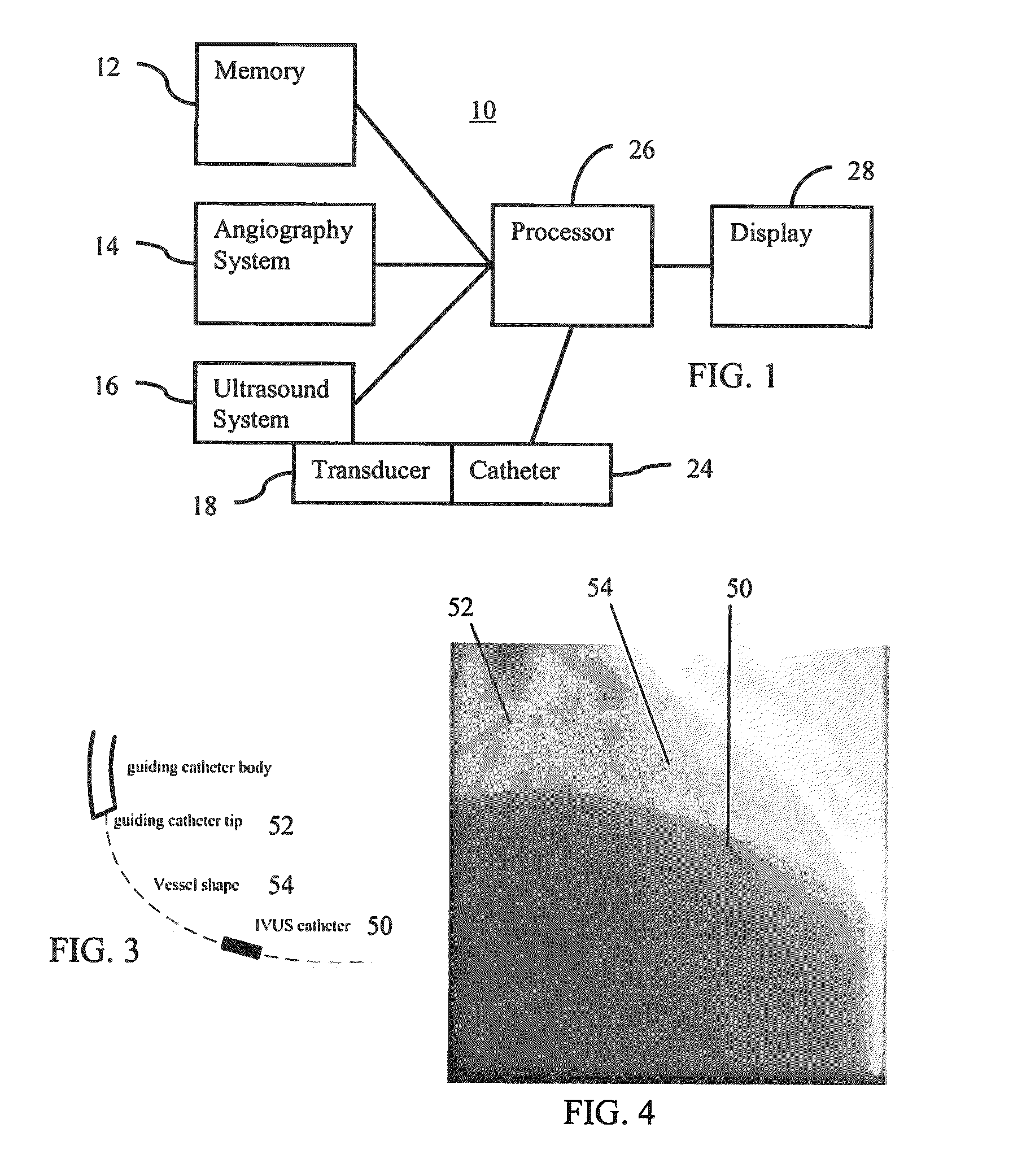
Feature Tracking Using Ultrasound
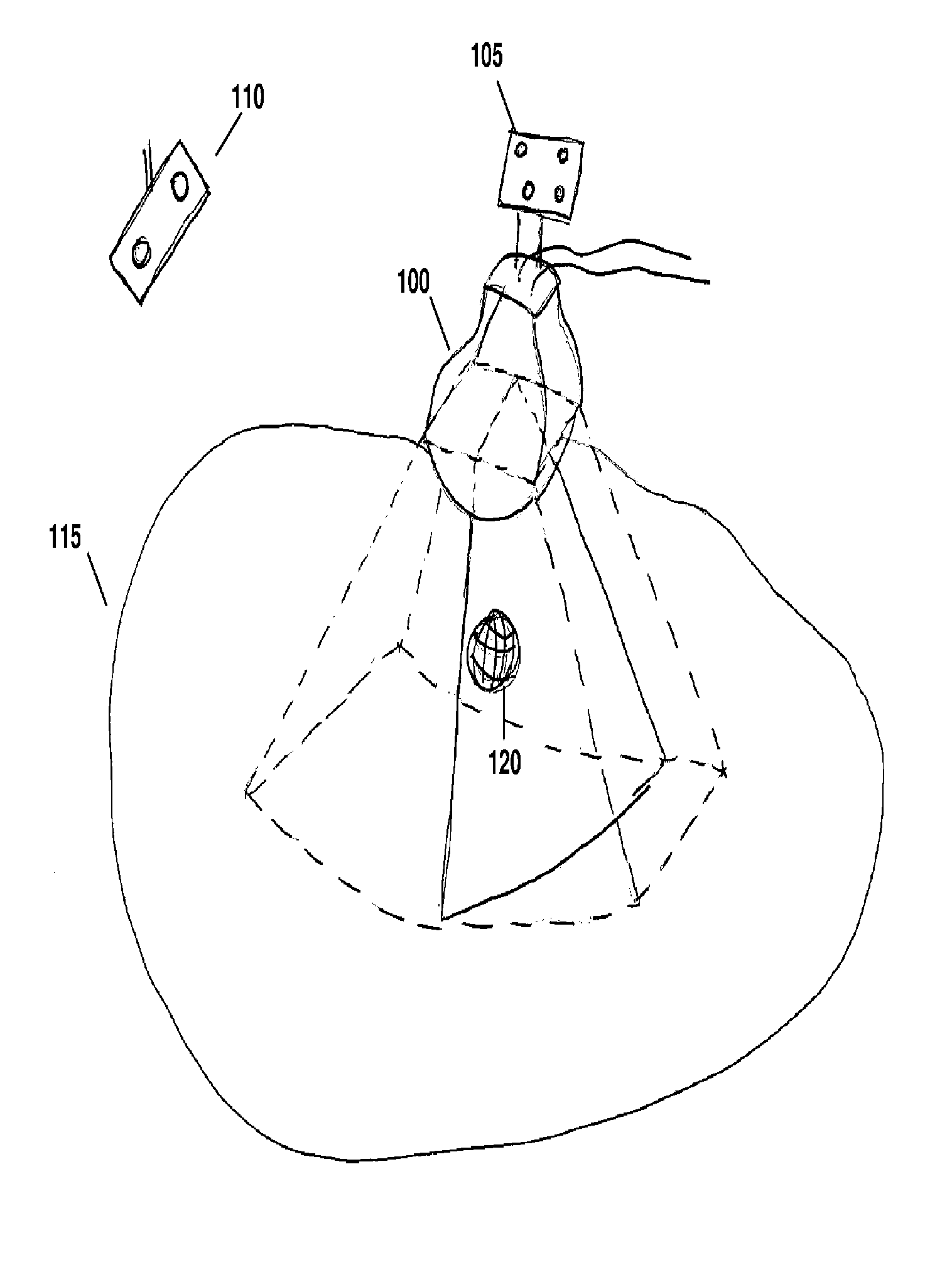
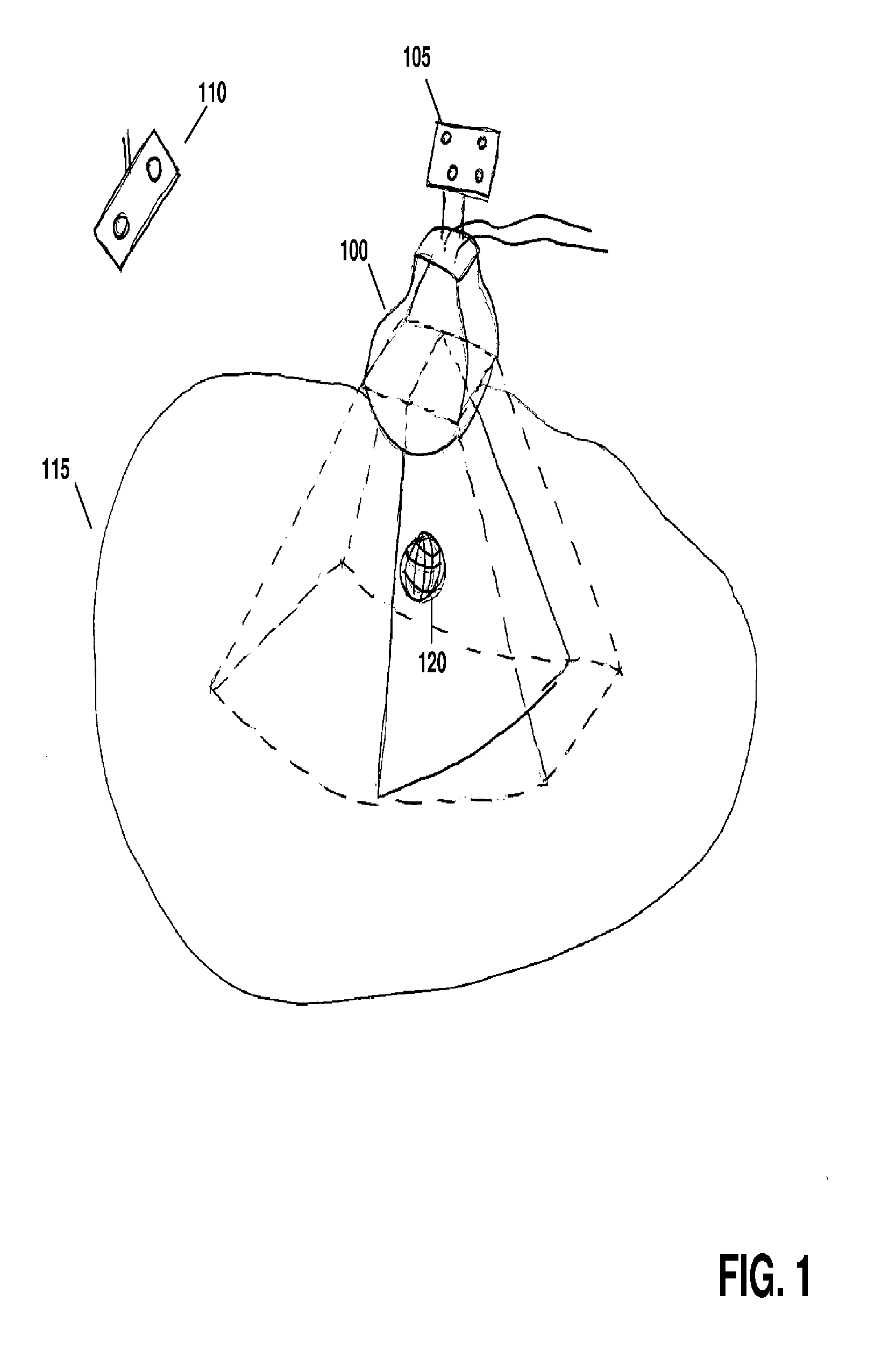
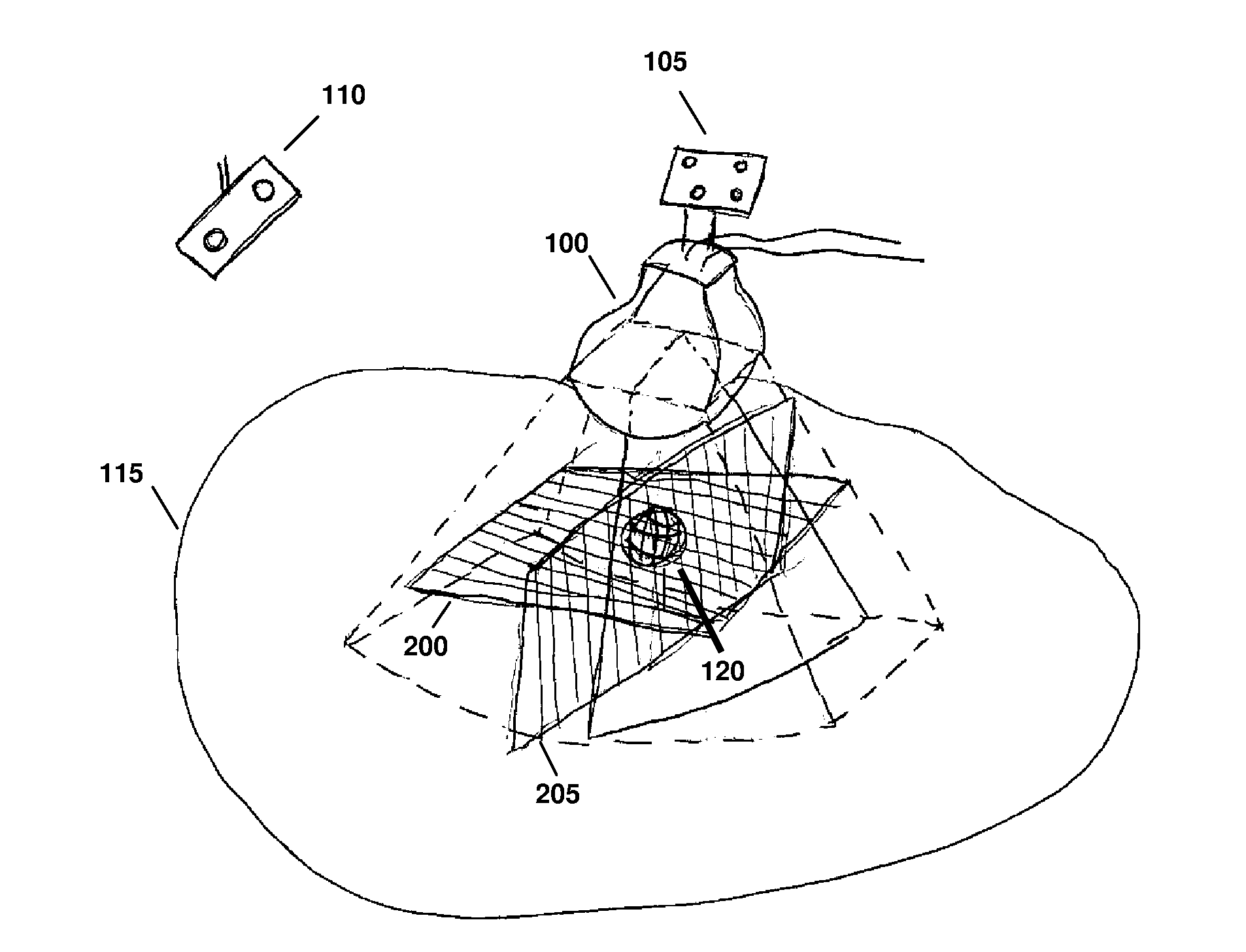
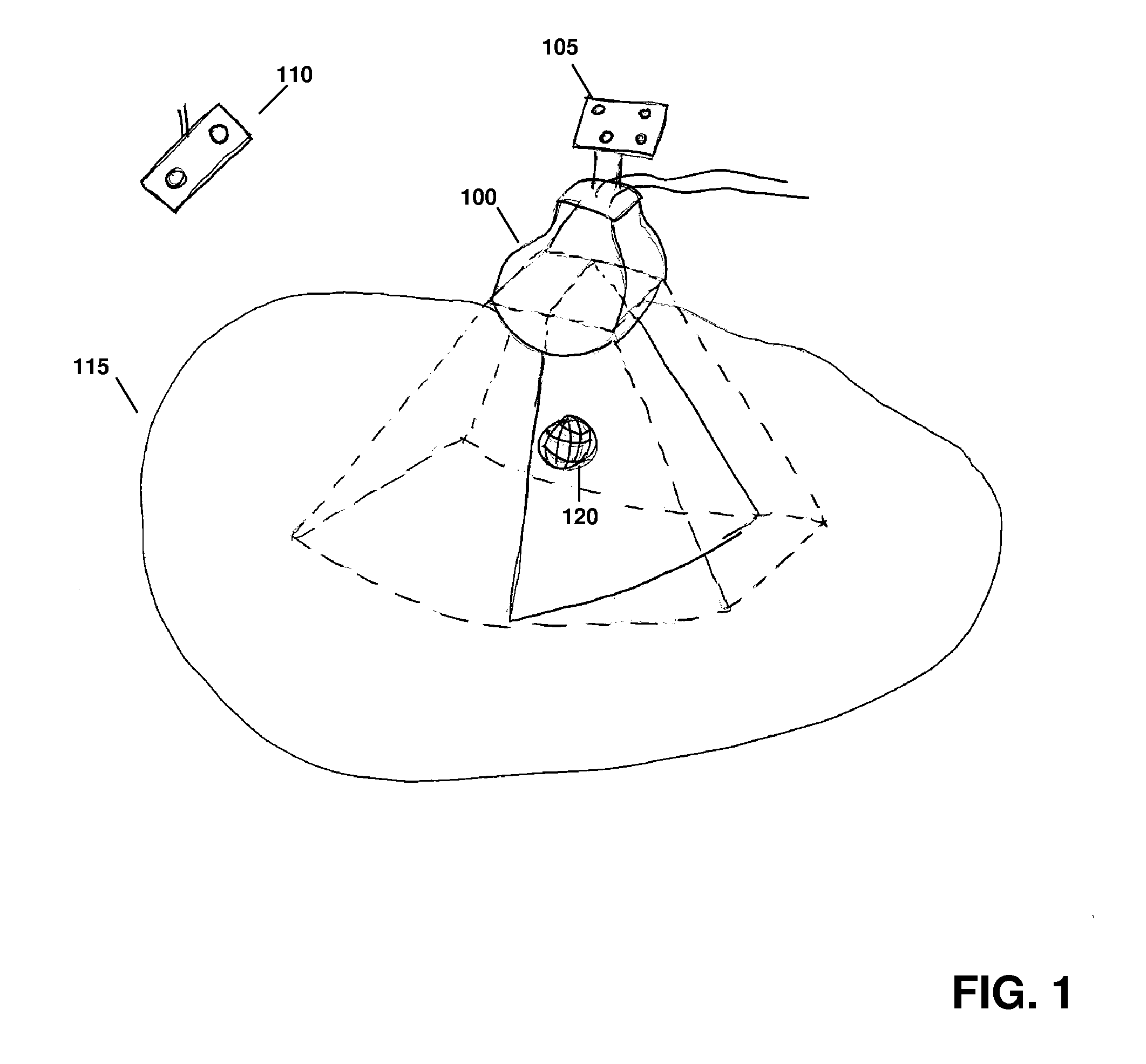
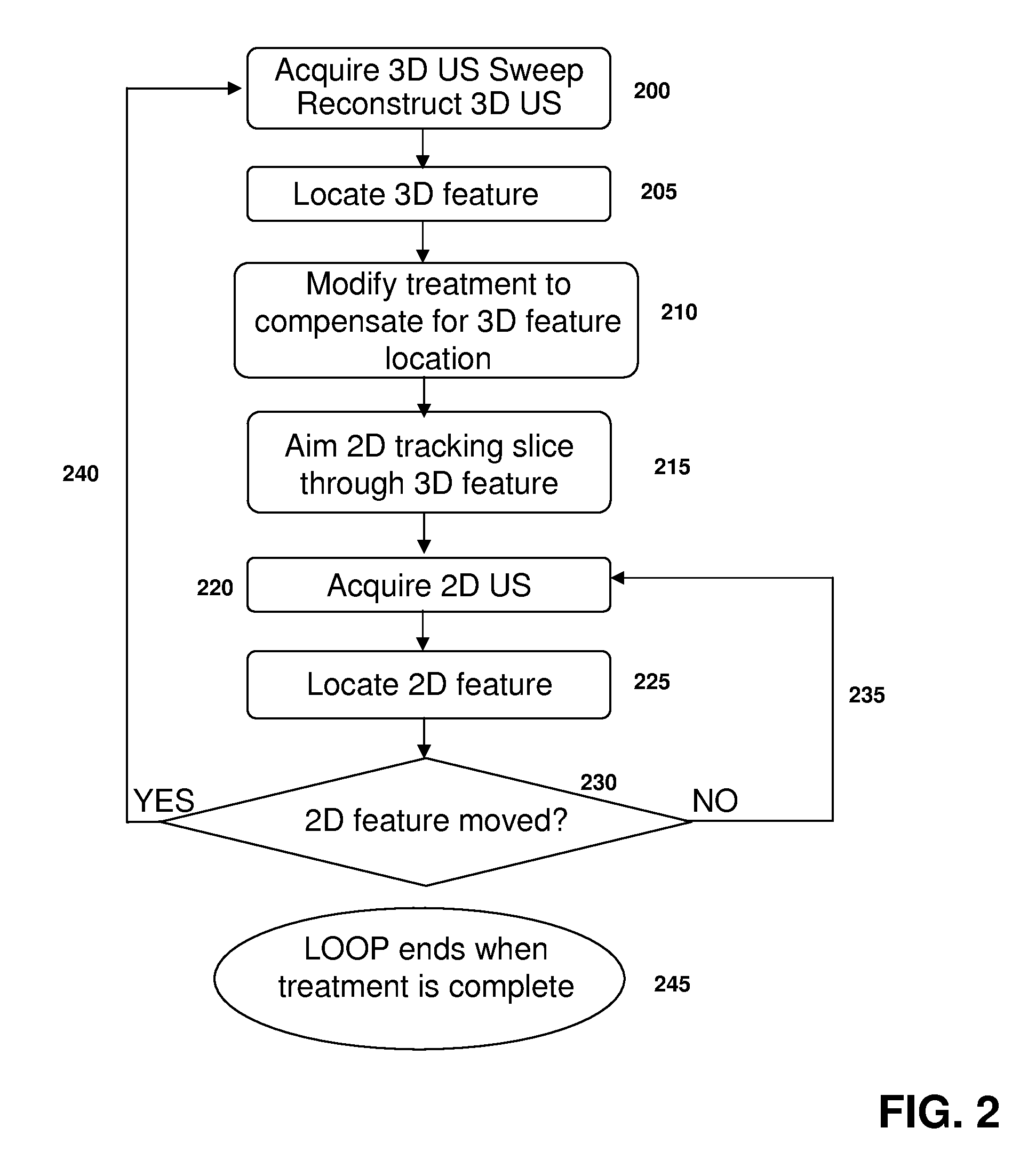
ActiveUS20120071758A1Reduce the burden onGood periodicityImage enhancementImage analysisSupporting systemSonification
Various implementations of the invention provide techniques and supporting systems that facilitate real-time or near-real-time ultrasound tracking for the purpose of calculating changes in anatomical features during a medical procedure. More specifically, anatomical features within a patient undergoing a medical procedure are tracked by obtaining temporally-distinct three dimensional ultrasound images that include the feature of interest and obtaining a targeted subset of ultrasound images focused on the feature. Based on the targeted subset of ultrasound images, a displacement of the feature is determined and image parameters used to obtain the targeted subset of ultrasound images are adjusted based on the displacement. This results in a time-based sequence of three dimensional images and targeted ultrasound images of the feature that identify changes in the position, size, location, and / or shape of the feature.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
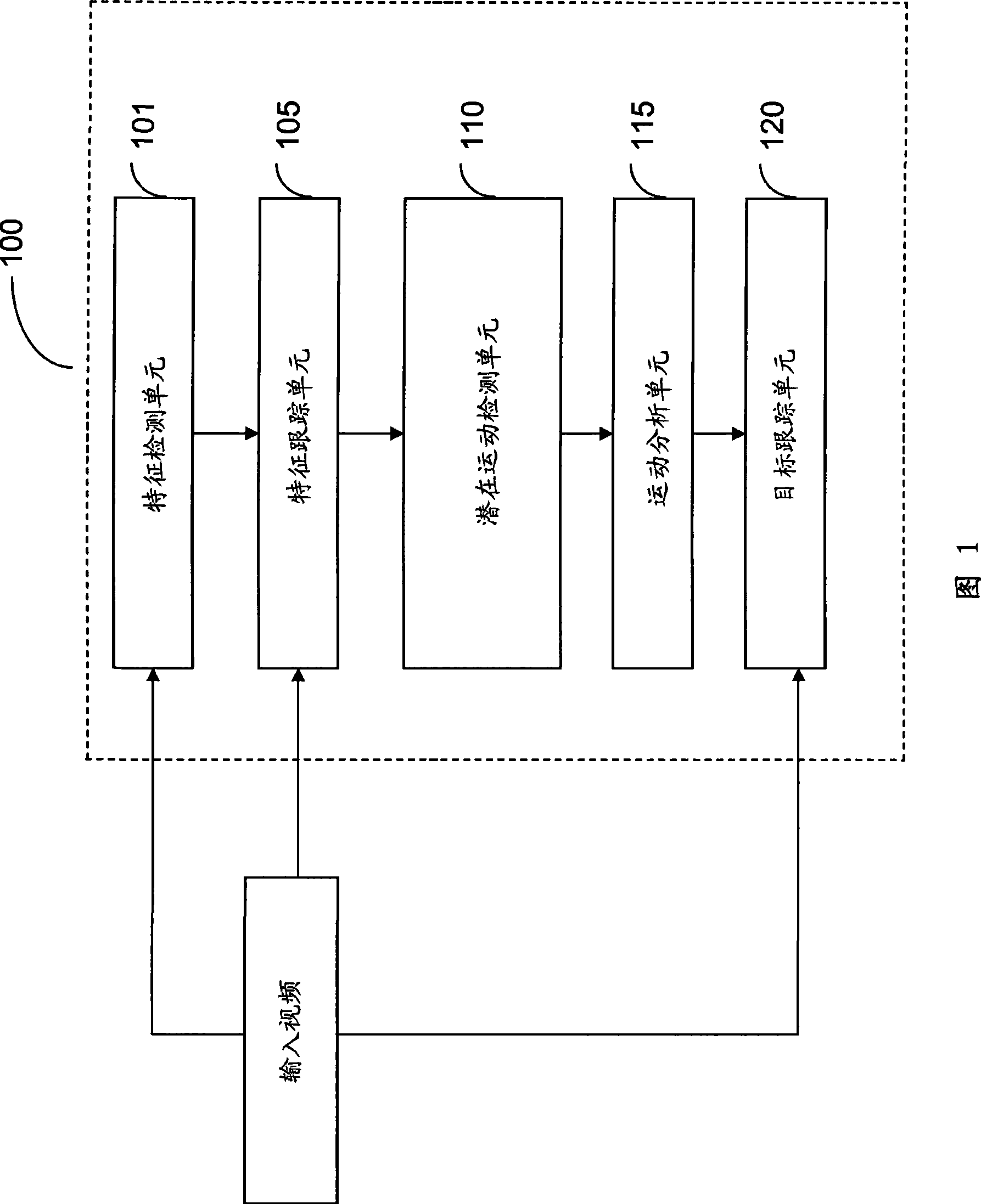
System, device and method for moving target detection and tracking based on moving camera
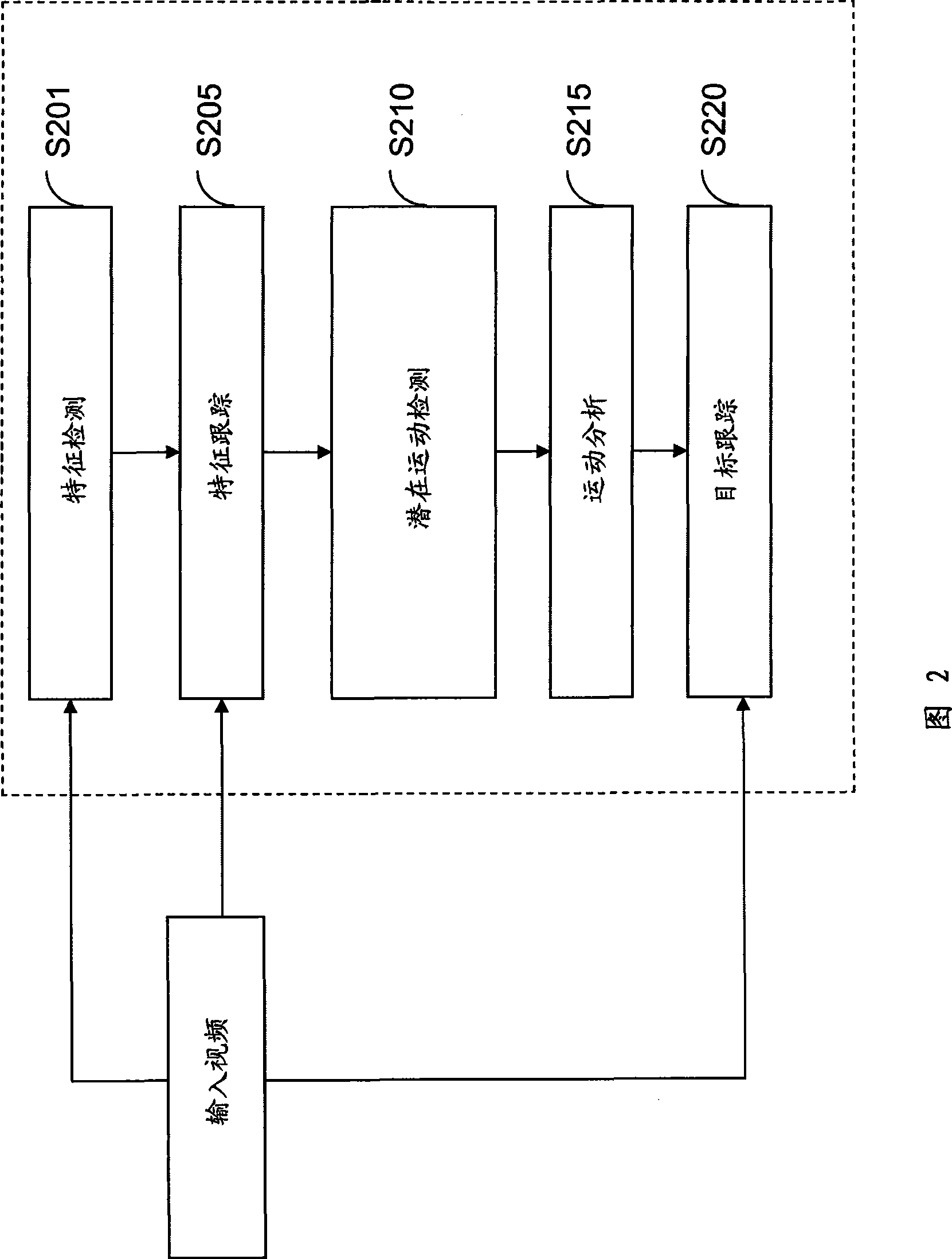
A detection and tracking device for moving target based on movement camera comprises a characteristic detection unit, finding characteristic point in a first frame of inputted video frequency; characteristic tracking unit, tracking characteristic point found by characteristic detection unit in following frame; latent movement detection unit, finding latent movement point from characteristic point tracked by characteristic tracking unit; movement analysis unit, determining movement point from latent movement point found by latent movement detection unit; target tracking unit, tracking movement target area from inputted video frequency according to given initial position. The inventive movement target detection and tracking system, device and method provide movement target position for 3A imaging at moving platform.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Visual positioning method based on robust feature tracking
InactiveCN103345751AImprove convergence rateImprove feature tracking performanceImage analysisFeature extraction algorithmVisual positioning
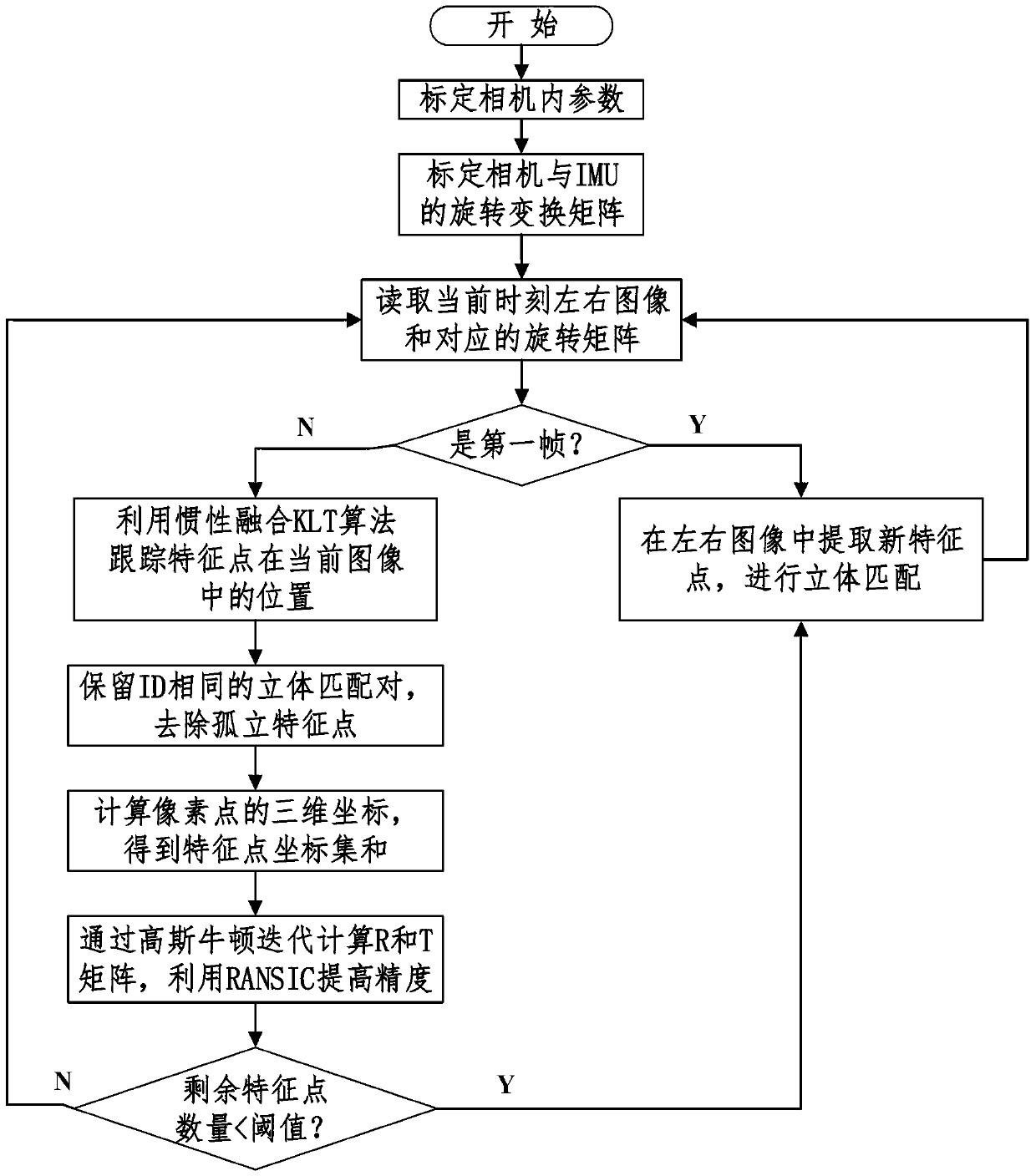
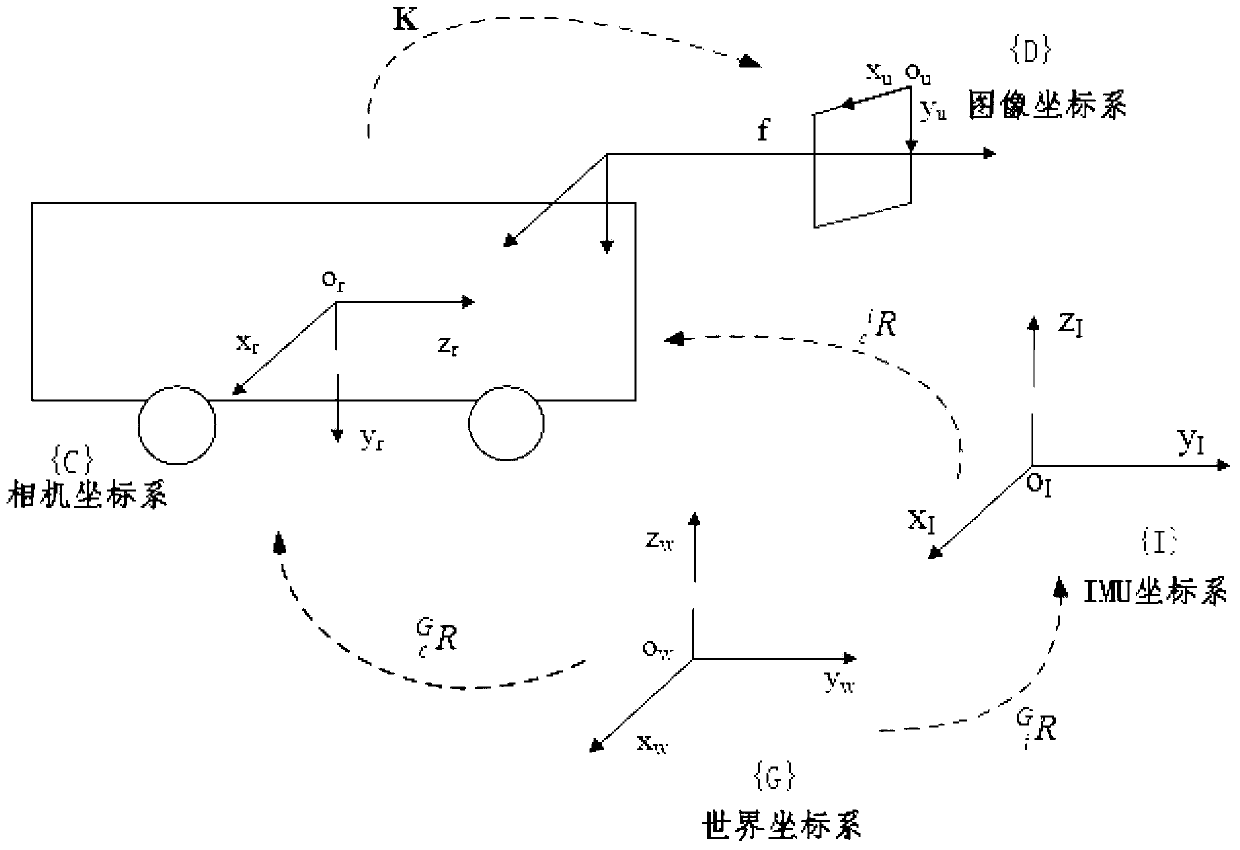
The method discloses a robust feature tracking and stereoscopic vision positioning technology based on image processing and machine vision. The technology can integrate inertial information and visual information and achieve reliable stereoscopic vision positioning under camera waggling conditions and outdoor light conditions. Images are collected through a binocular video camera in real time, and rotation information of the camera is collected with an inertial measurement unit. Feature points in the images are extracted with a feature extraction algorithm, and the feature points of the left image and the feature points of the right images are matched stereoscopically. The inertial information is combined and the inertia and the KLT algorithm are integrated to track the feature points, so that the reliability of the feature tracking is promoted. Three-dimensional information of the feature points is restored according to the double vision geometric principle. Motion parameters of the camera are obtained through position information of the feature points with the Gaussian and Newton iteration method. The accuracy of visual positioning is further promoted with the RANSIC algorithm. The whole process is iterated continuously, and thus real-time calculation of the posture and the position of the camera is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Feature Tracking Using Ultrasound
InactiveUS20110172526A1Reduce the burden onGood periodicityImage enhancementImage analysisSupporting systemSonification
Various implementations of the invention provide techniques and supporting systems that facilitate real-time or near-real-time ultrasound tracking for the purpose of calculating changes in anatomical features during a medical procedure. More specifically, anatomical features within a patient undergoing a medical procedure are tracked by obtaining temporally-distinct three dimensional ultrasound images that include the feature of interest and obtaining a targeted subset of ultrasound images focused on the feature. Based on the targeted subset of ultrasound images, a displacement of the feature is determined and image parameters used to obtain the targeted subset of ultrasound images are adjusted based on the displacement. This results in a time-based sequence of three dimensional images and targeted ultrasound images of the feature that identify changes in the position, size, location, and / or shape of the feature.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
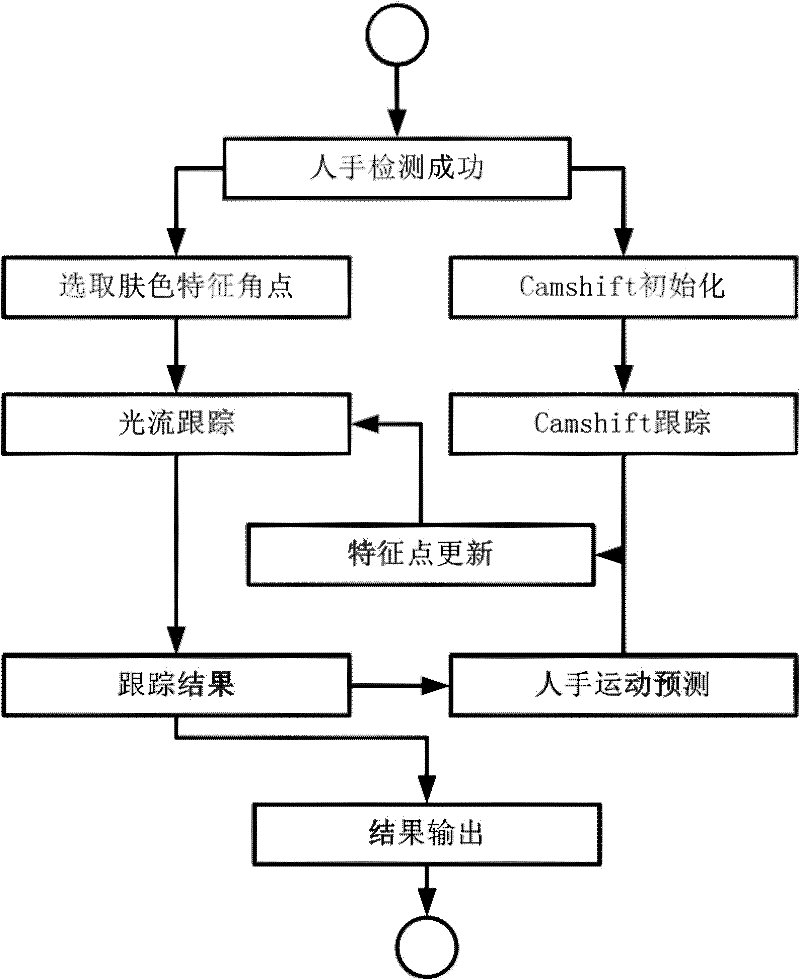
Method of Tracking Morphing Gesture Based on Video Stream
InactiveCN102270348ARemove background changesEliminate distractionsImage analysisSkin complexionMean-shift
The invention discloses a method for tracking deformable hand gesture based on video streaming, comprising the steps of: obtaining a frame image, and extracting a sub-image containing a human hand from the obtained frame image; selecting feature tracking points from the sub-image containing the human hand, and initializing a continuously self-adaptive mean shift tracker by the sub-image containing the human hand; performing optical flow calculation on the selected feature tracking points to serve as a local tracking result, and synchronously overall tracking the human hand by the continuouslyself-adaptive mean shift tracker to obtain a global tracking result; updating the feature tracking points; and adopting the result of the optical flow tracking as the final output result of the deformable hand gesture. The method for tracking the deformable hand gesture based on video streaming can be used for tracking the human hand with randomly deformable hand gesture and enabling human-computer gesture interaction to operate in a more comfortable manner. According to the invention, the tracking can be performed aiming at the randomly deformable hand gesture, the interference from change of a background and a large area of complexion is eliminated, and the real-time robust hand gesture tracking is achieved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
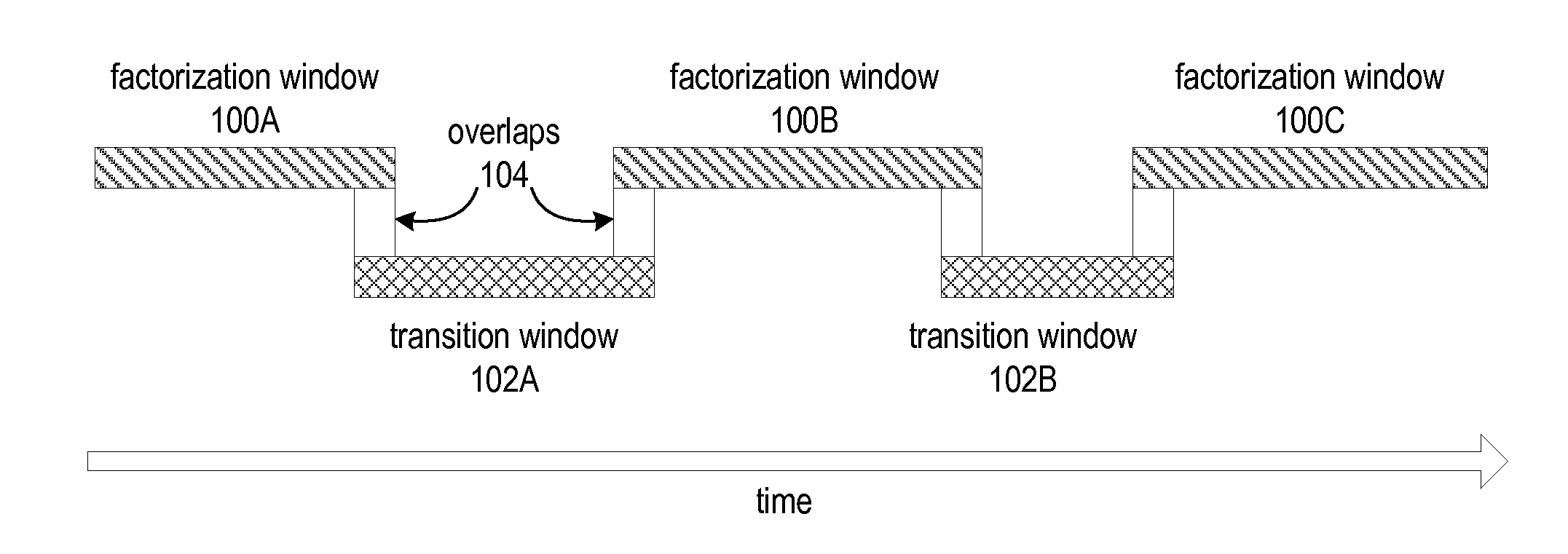
Methods and Apparatus for Robust Video Stabilization
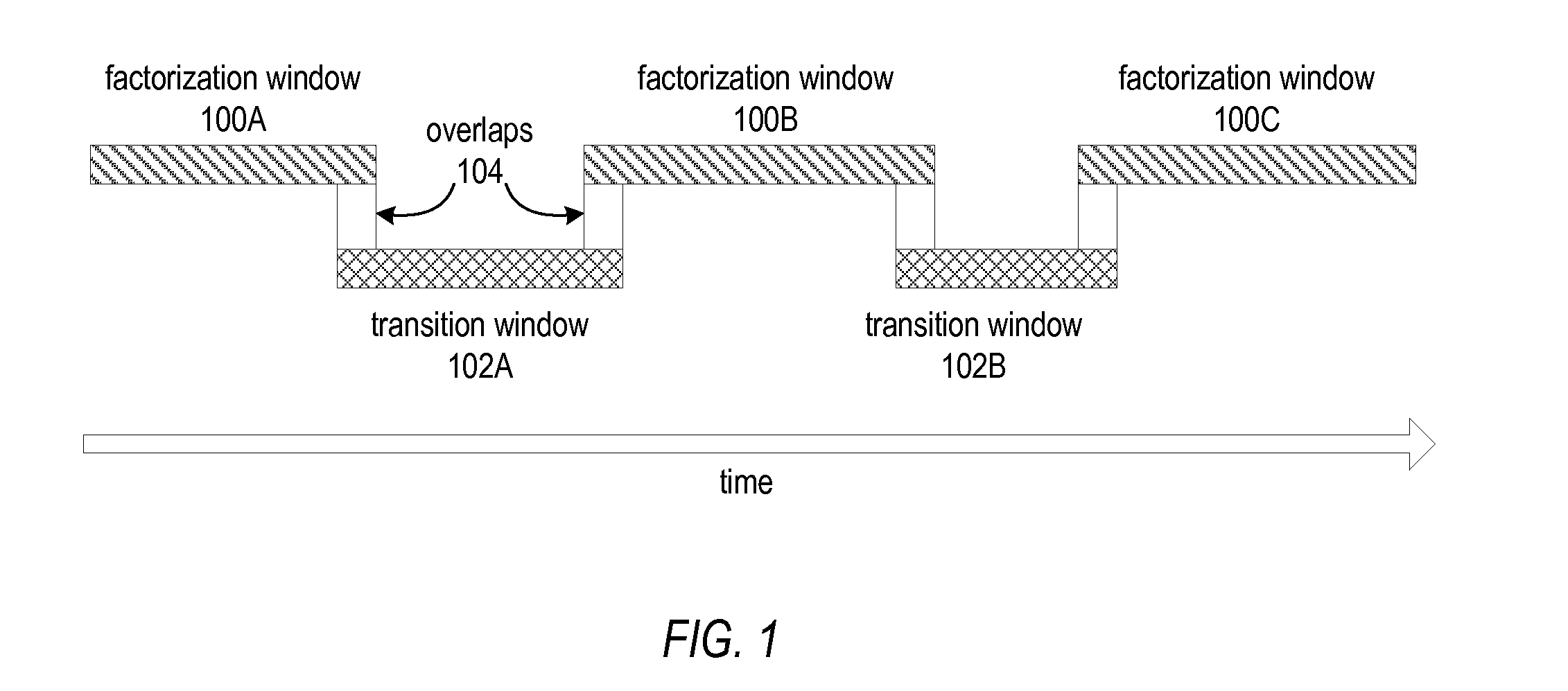
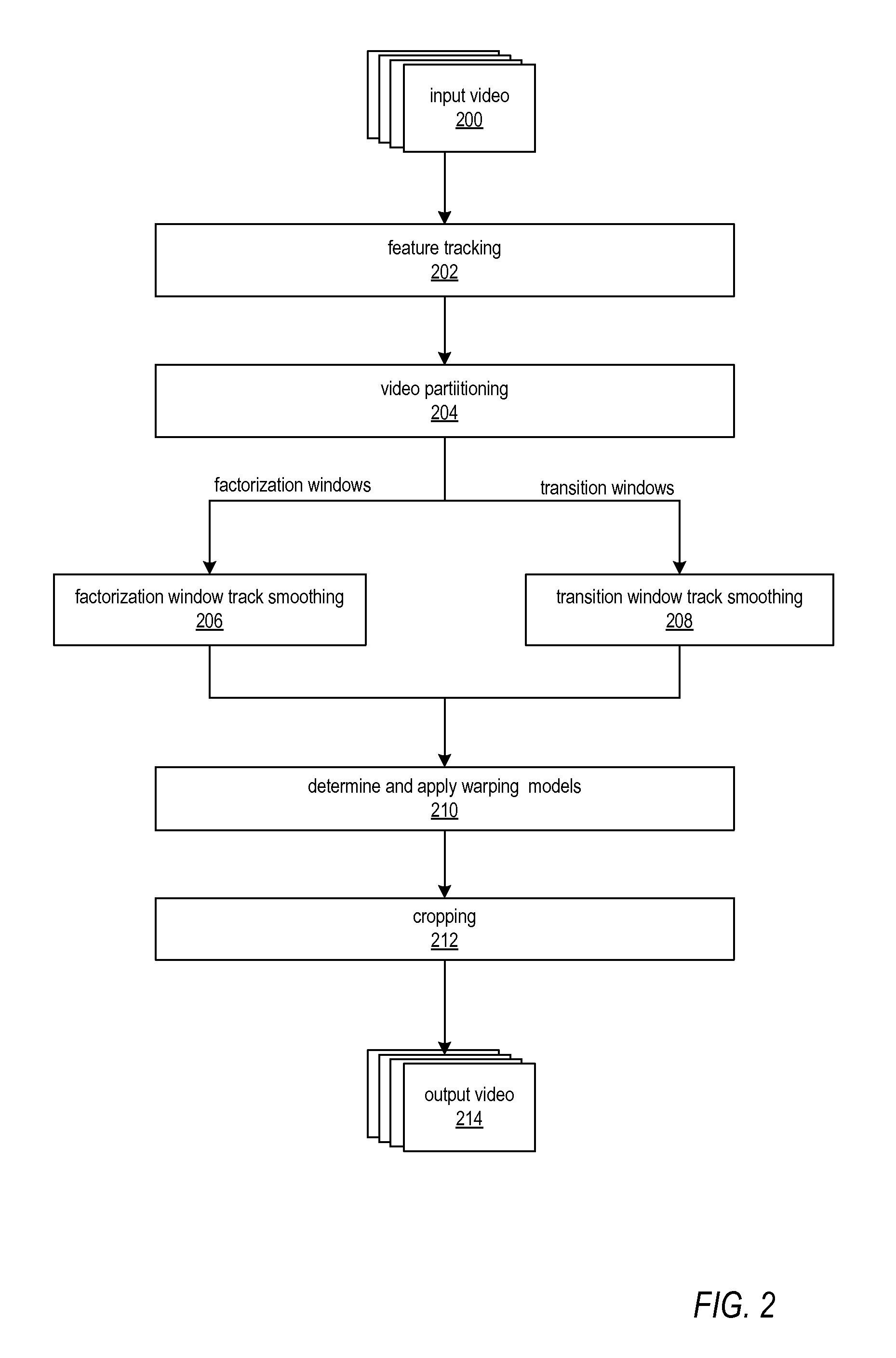
ActiveUS20130128066A1Smoother trajectorySmooth transitionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionFeature tracking
Methods and apparatus for robust video stabilization. A video stabilization technique applies a feature tracking technique to an input video sequence to generate feature trajectories. The technique applies a video partitioning technique to segment the input video sequence into factorization windows and transition windows. The technique smoothes the trajectories in each of the windows, in sequence. For factorization windows, a subspace-based optimization technique may be used. For transition windows, a direct track optimization technique that uses a similarity motion model may be used. The technique then determines and applies warping models to the frames in the video sequence. In at least some embodiments, the warping models may include a content-preserving warping model, a homography model, a similarity transform model, and a whole-frame translation model. The warped frames may then be cropped according to a cropping technique.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Method and system for detecting illegal left-and-right steering of vehicle at traffic intersection
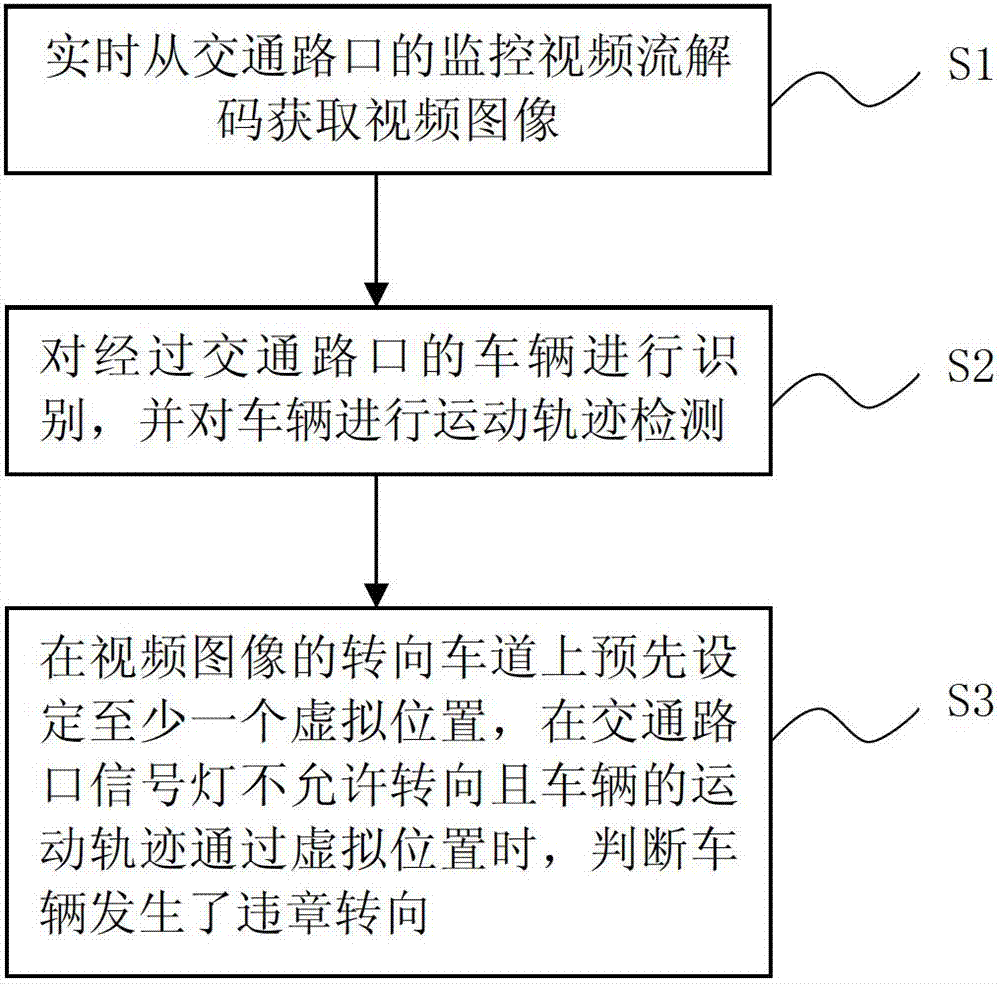
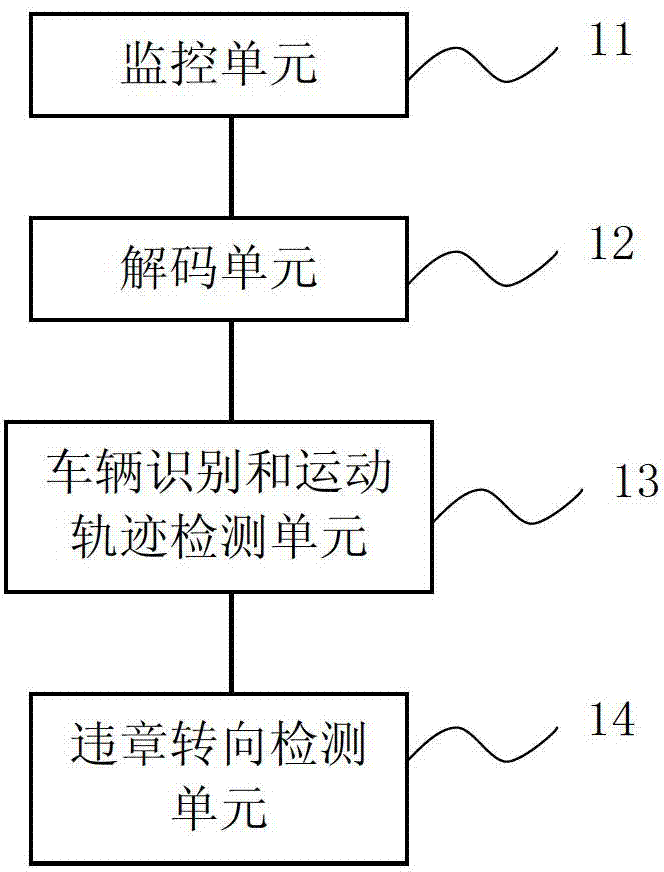
ActiveCN102903239AReduce workloadWays to Avoid Landfilling Induction CoilsDetection of traffic movementFeature trackingVirtual position
The invention provides a method and a system for detecting illegal left-and-right steering of a vehicle at traffic intersection. The method comprises the following steps of: decoding monitoring video streaming in real time from the traffic intersection so as to obtain a video image; distinguishing vehicles passing through the traffic intersection and detecting the moving trails of the vehicles; and presetting at least one virtual position on a steering lane of the video image so as to judge that the vehicle has illegal steering when the steering is not allowed by a signal lamp at the traffic intersection and the moving trail of the vehicle passes through the virtual position. According to the invention, by adopting the method for intelligently analyzing the video, the virtual loop is drawn on the monitoring video, the moving trail of the vehicle is tracked and analyzed through characteristics, and whether the vehicle has illegal steering is judged through the preset virtual loop so as to reduce the workload of manual check and control; and simultaneously, as the touch capture is achieved through the video virtual loop, the way that an induction loop is embedded in a pavement in the traditional technology is avoided, and the pavement does not need to be dig.
Owner:JIANGSU CHINA SCI INTELLIGENT ENG
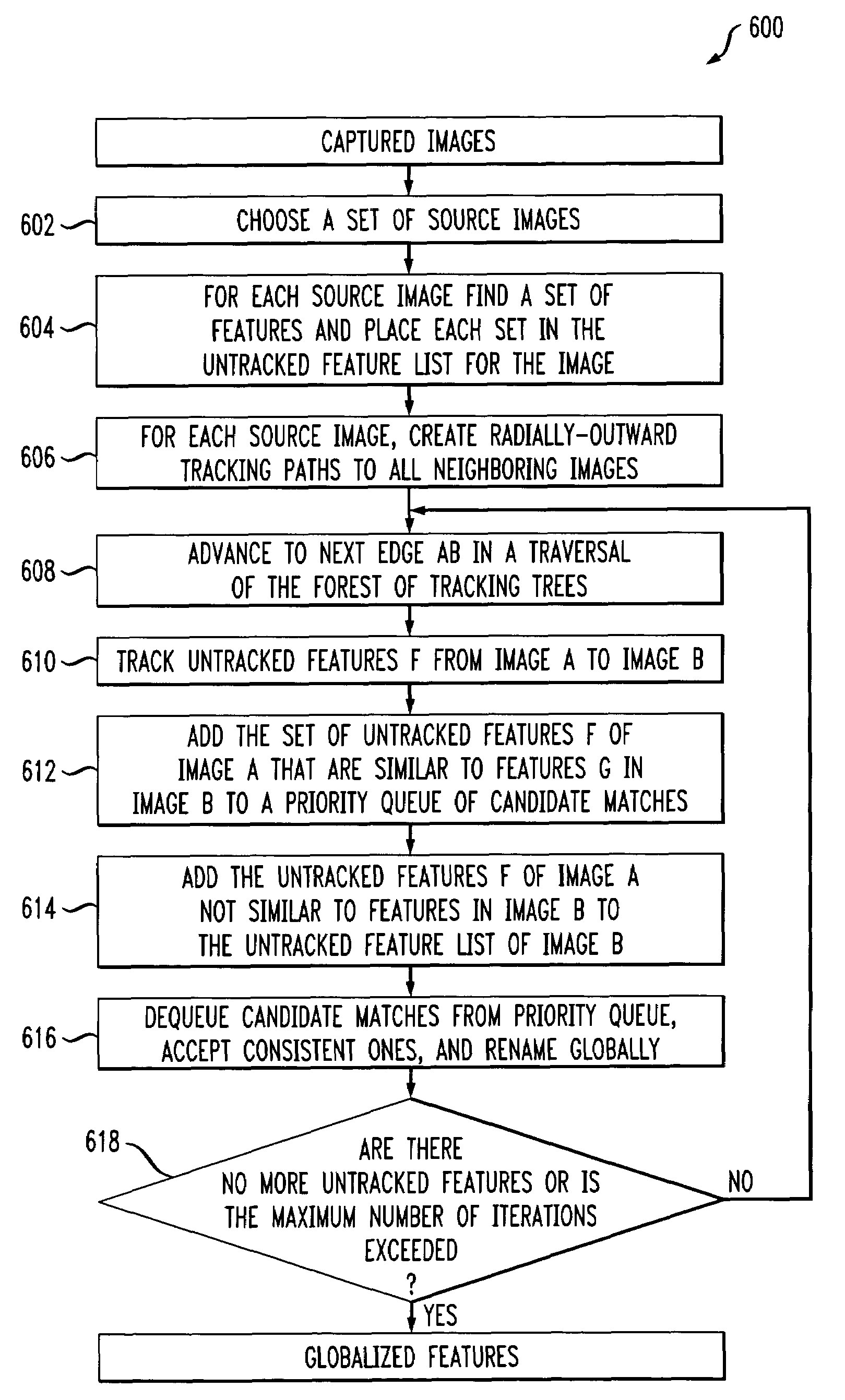
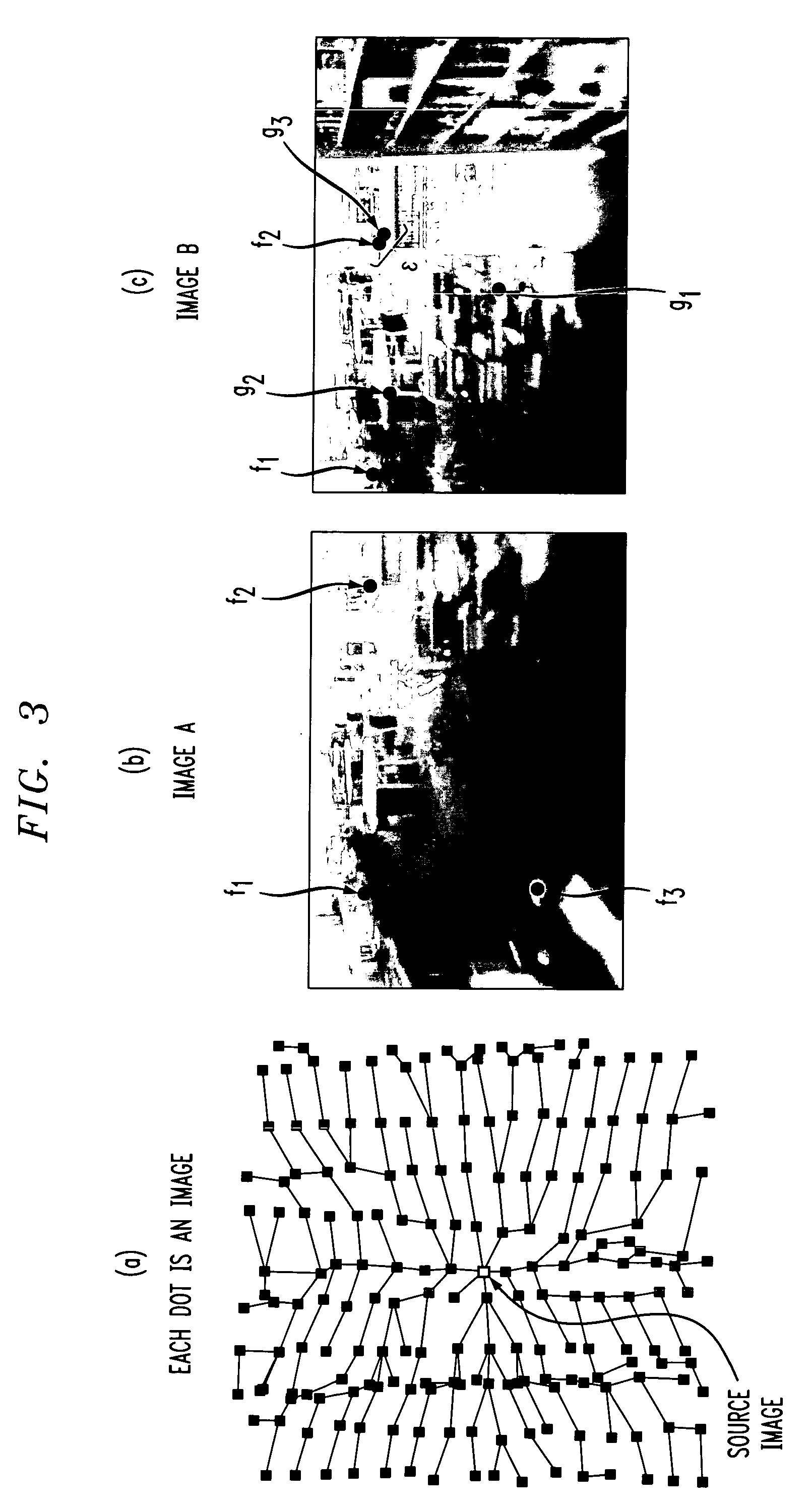
Method and apparatus for finding feature correspondences between images captured in real-world environments
InactiveUS7356164B2Improved arbitrary viewpoint renderingImage analysisVisual representation by matrix printersPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
Techniques for computing a globally consistent set of image feature correspondences across a wide range of viewpoints suitable for interactive walkthroughs and visualizations. The inventive approach takes advantage of the redundancy inherent in a dense set of images captured in a plane (or in higher dimensions, e.g., images captured in a volume, images captured over time, etc). The technique may detect features in a set of source images and track the features to neighboring images. When features track to the same position in the same image, they are flagged as potential correspondences. Among the potential correspondences, the technique selects the maximal set using a greedy graph-labeling algorithm (e.g., best-first order). Only correspondences that produce a globally consistent labeling are selected. After globalization is done, a set of features common to a group of images can be quickly found and used to warp and combine the images to produce an interpolated novel view of the environment.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
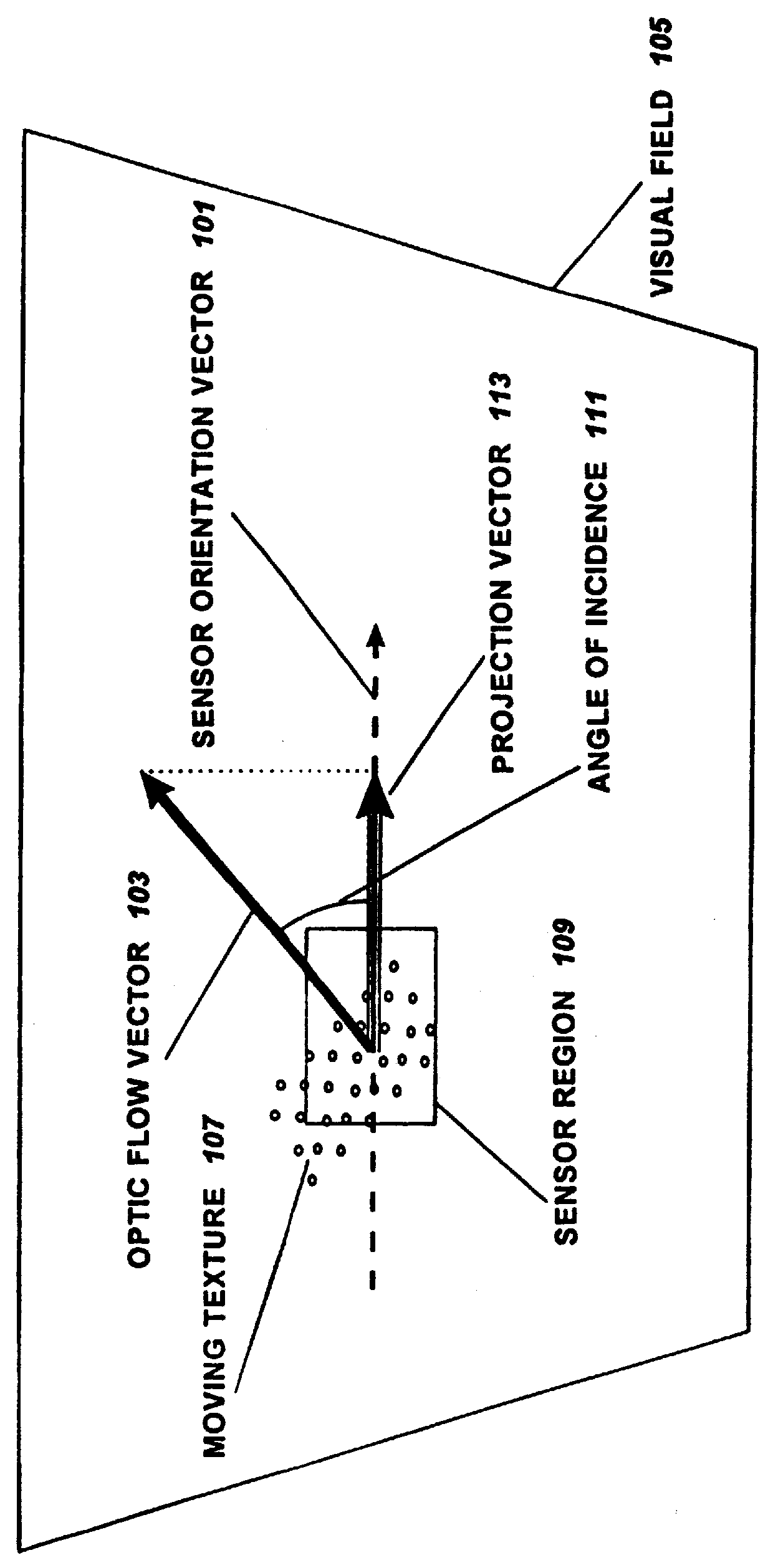
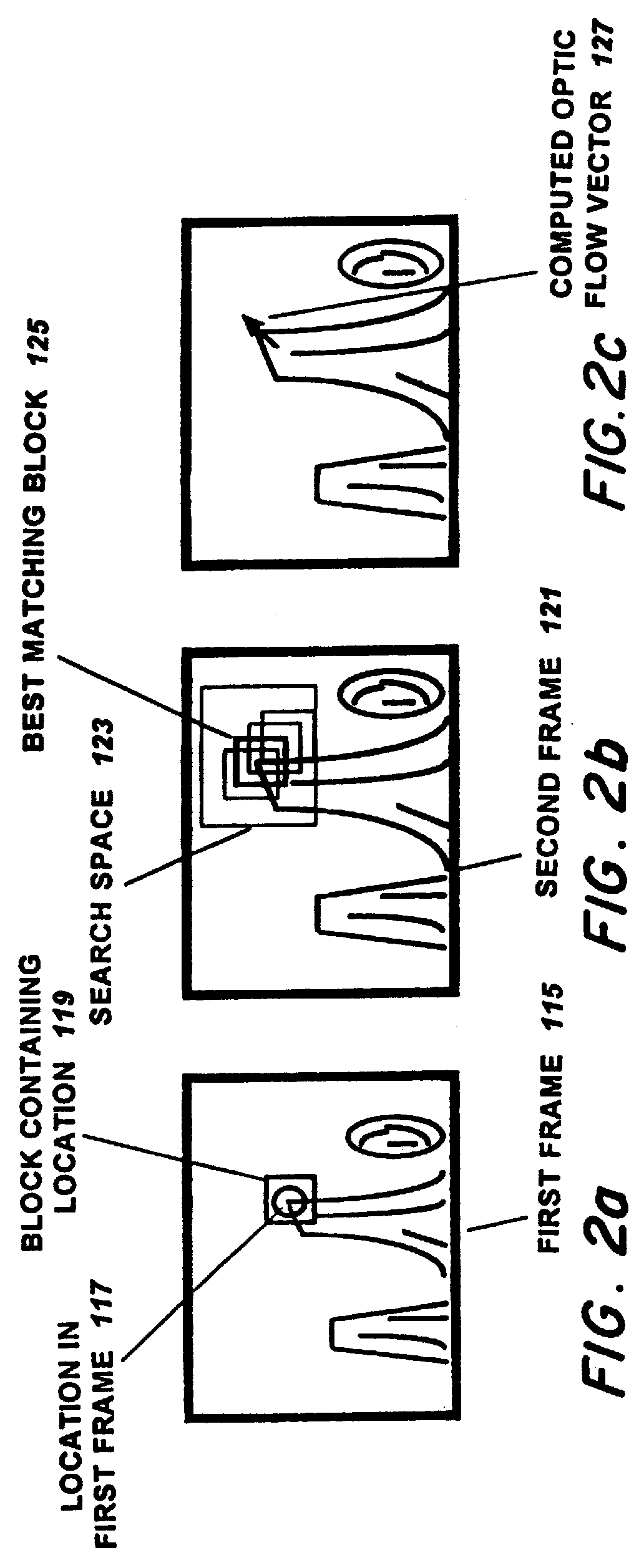
Feature tracking linear optic flow sensor
InactiveUS6020953AInhibition transitionSpeed up the flowImage analysisSpeed measurement using accelerationMotion detectorOptical flow
This invention is a one-dimensional elementary motion detector that measures the linear optical flow in a small subsection of the visual field. This sensor measures motion by tracking the movement of a feature across the visual field and measuring the time required to move from one location to the next. First a one-dimensional image is sampled from the visual field using a linear photoreceptor array. Feature detectors, such as edge detectors, are created with simple circuitry that performs simple computations on photoreceptor outputs. The detection of the feature's location is performed using a winner-take-all (WTA) mechanism on feature detector outputs. Motion detection is the performed by monitoring the location of the high WTA output in time to detect transitions corresponding to motion. The correspondence problem is solved by ignoring transitions to and from the end lines of the WTA output bus. Speed measurement is performed by measuring the time between WTA output transitions. This invention operates in a one-dimensional subspace of the two-dimensional visual field. The conversion of a two-dimensional image section to a one-dimensional image is performed by a specially shaped photoreceptor array which preserves image information in one direction but filters out image information in the perpendicular direction. Thus this sensor measures the projection of the 2-D optical flow vector onto the vector representing the sensor's orientation. By placing several of these sensors in different orientations and using vector arithmetic, the 2-D optical flow vector can be determined.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
Landmark-free tracking registering method
InactiveCN104077596AEnhance expressive abilityImprove adaptabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionState of artFeature tracking
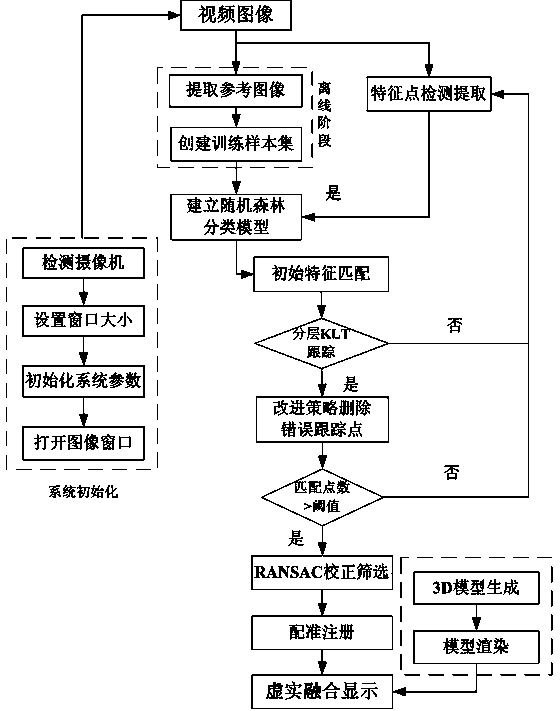
The invention discloses a landmark-free tracking registering method, and belongs to the technical field of augmented reality. In order to overcome the defects in the prior art, a random forest classification model is constructed, feature points extracted through the CenSurE algorithm are rapidly and initially matched, and the matching feature points are continuously tracked through an existing feature point continuous tracking technology, and therefore the calculation required for feature matching is greatly reduced, and the stability of feature point selection is improved; a light flow feature tracking method is further improved, fault tracking points are screened out, accuracy and efficiency of tracking registering are improved, and the real-time performance of an augmented reality system is improved. Compared with the prior art, the accuracy and the efficiency of tracking registering can be effectively improved, and then the real-time performance of the augmented reality system is improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Self-adaptive feature fusion-based multi-scale correlation filtering visual tracking method
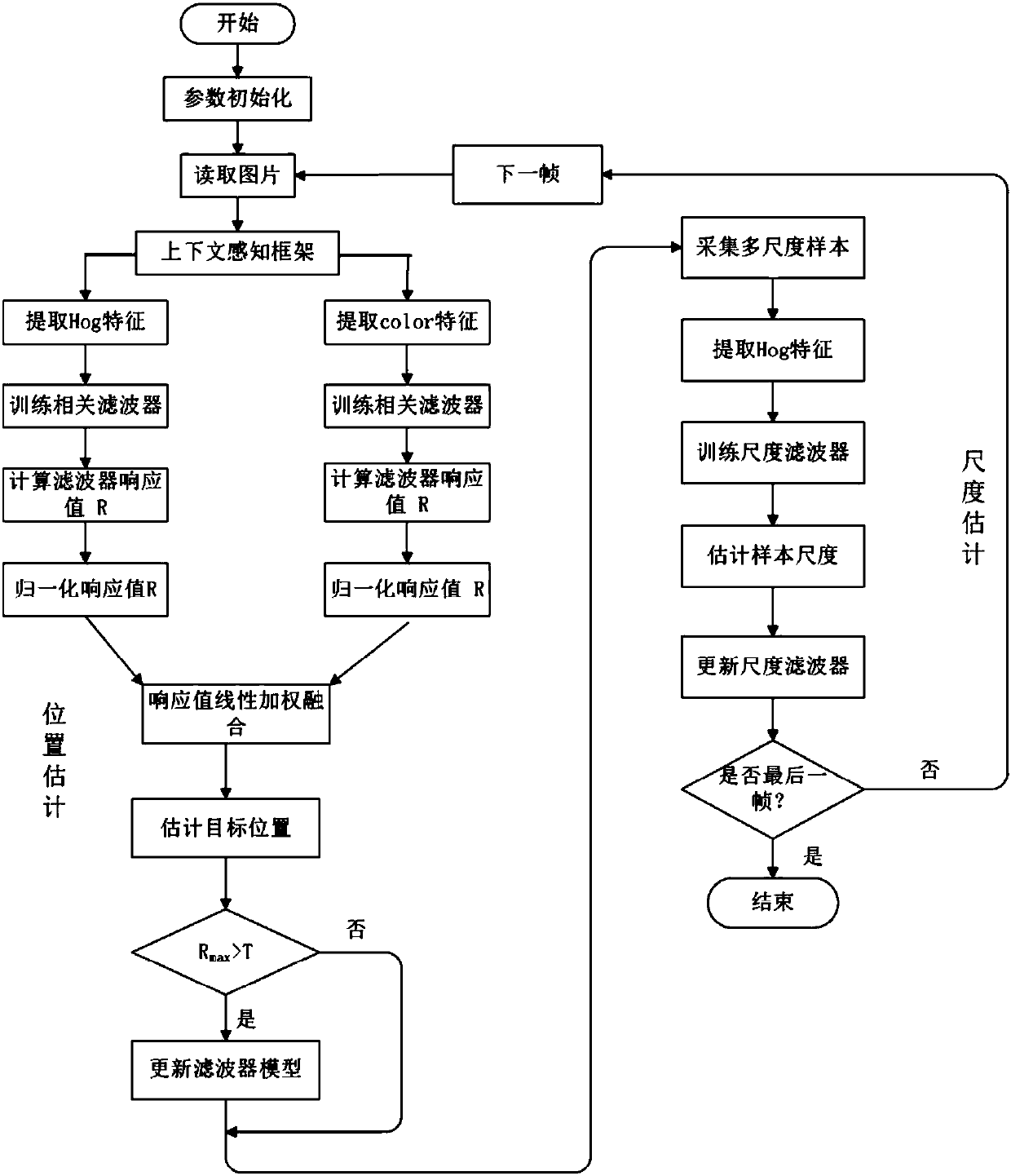
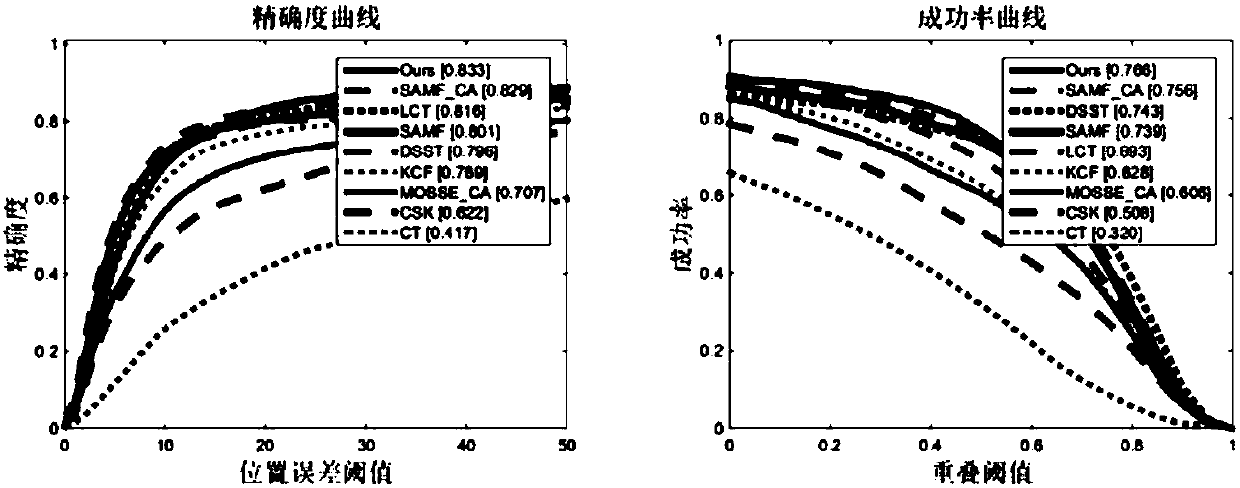
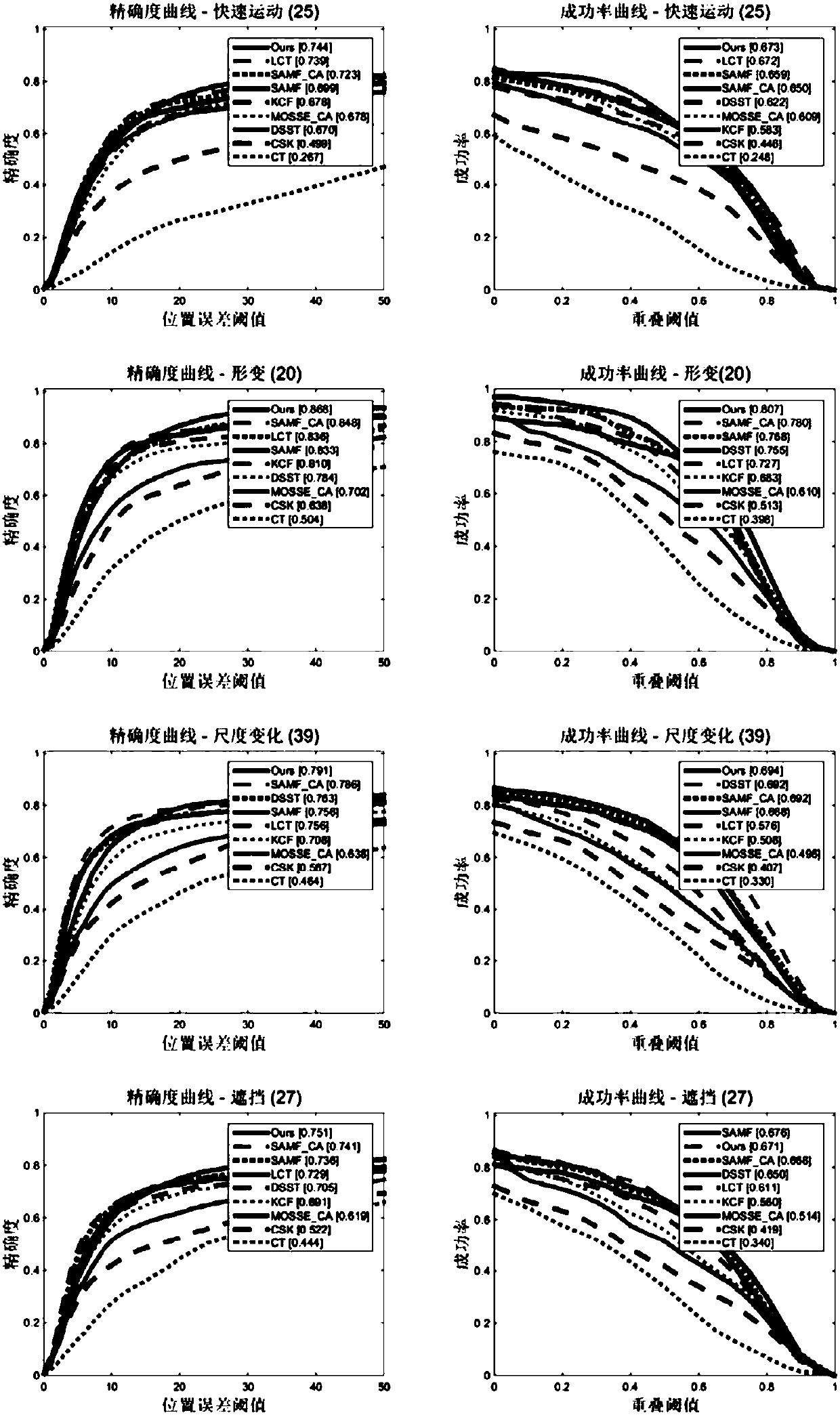
ActiveCN108549839AImprove performanceAvoid the problem of limited expression of a single featureImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionScale estimationPhase correlation
The invention discloses a self-adaptive feature fusion-based multi-scale correlation filtering visual tracking method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the correlation filtering is carried out on a target HOG feature and a target color feature respectively by using a context-aware correlation filtering framework; the response values under the two features are normalized; weightsare distributed according to the proportion of the response values and then are subjected to linear weighted fusion, so that a final response graph after fusion is obtained; the final response graph is compared with a pre-defined response threshold value to judge whether the filtering model is updated or not; finally, a scale correlation filter is introduced in the tracking process, so that the scale adaptability of the algorithm is improved. The method can be used for tracking various features. The performance advantages of the features are brought into play, and a model self-adaptive updating method is designed. In addition, a precise scale estimation mechanism is further introduced. According to the invention, the updating quality and the tracking precision of the model can be effectively improved, and the model can be changed in scale. The method is good in robustness under complex scenes such as rapid movement, deformation, shielding and the like.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY +1
Method of converting 2d video to 3D video using 3D object models
InactiveUS20160005228A1Increased artisticIncreased technical flexibilityImage analysisSteroscopic systemsFeature trackingDegrees of freedom
Method for converting 2D video to 3D video using 3D object models. Embodiments of the invention obtain a 3D object model for one or more objects in a 2D video scene, such as a character. Object models may for example be derived from 3D scanner data; planes, polygons, or surfaces may be fit to this data to generate a 3D model. In each frame in which a modeled object appears, the location and orientation of the 3D model may be determined in the frame, and a depth map for the object may be generated from the model. 3D video may be generated using the depth map. Embodiments may use feature tracking to automatically determine object location and orientation. Embodiments may use rigged 3D models with degrees of freedom to model objects with parts that move relative to one another.
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
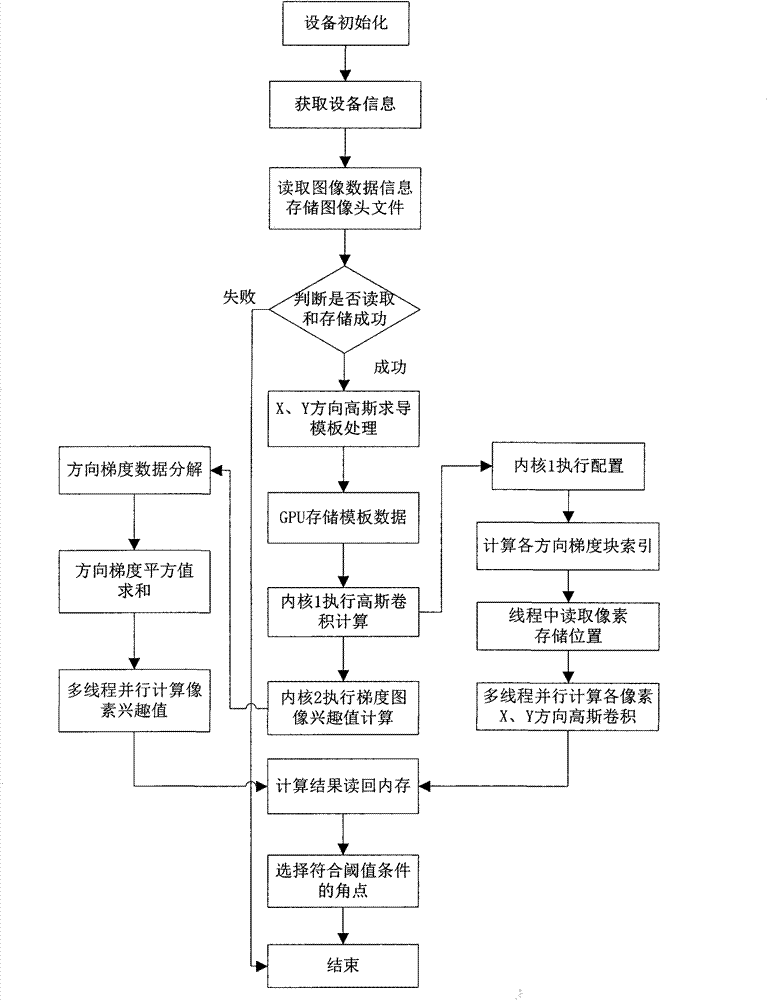
Tracking and matching parallel computing method for wearable device
InactiveCN103927745AOvercoming low synchronicityOvercome speedImage analysisProcessor architectures/configurationFeature extractionMultiple sensor
The invention discloses a tracking and matching parallel computing method for a wearable device so as to achieve augmented reality tracking and matching. According to the tracking and matching parallel computing method, the SCAAT-EKF feature tracking technology is adopted, complementary fusion data acquisition is conducted on multiple sensors in the wearable device, and data collision can be effectively avoided; the operation strategy based on the double kernal CPU+GPU group kernel multi-channel is utilized, corner detection and extraction based on the Harris algorithm are conducted in the GPU, the double kernal CPU is used for conducting P-KLT tracking and matching calculation, and therefore algorithm fast parallel processing is achieved. The tracking and matching parallel computing method mainly comprises the steps of hybrid tracking and feature extraction for the wearable device, accurate extraction of feature points of target natural features without marks, Harris corner point detection achieved based on a GPU parallel processing mechanism, the CPU-based P-KLT parallel feature tracking algorithm and the secondary matching optimization algorithm. The tracking and matching parallel computing method for the wearable device achieves combination of the sensors of the wearable device and visual tracking and matching, and has the wide prospect in the augmented reality three-dimensional registration aspect.
Owner:北京中海新图科技有限公司 +1
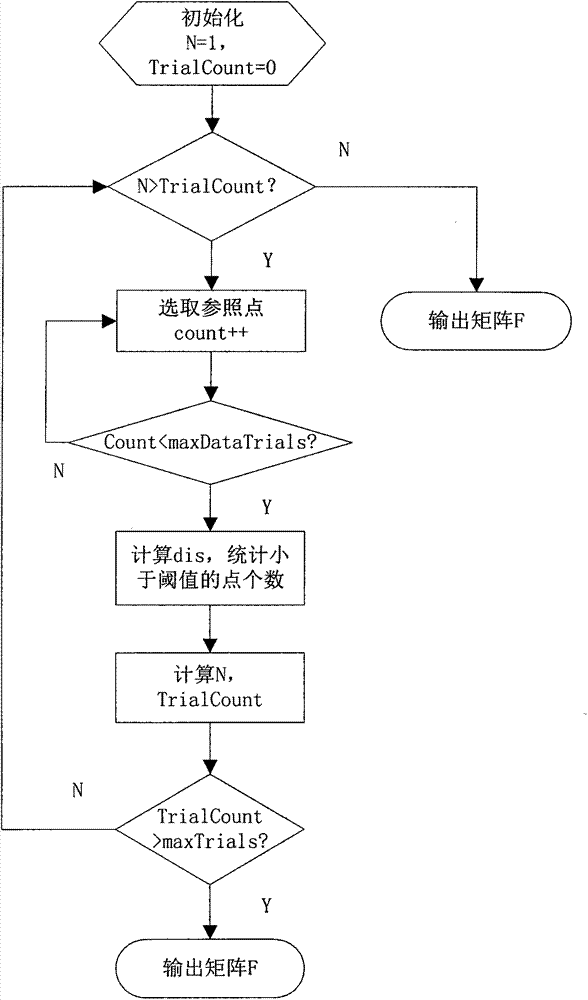
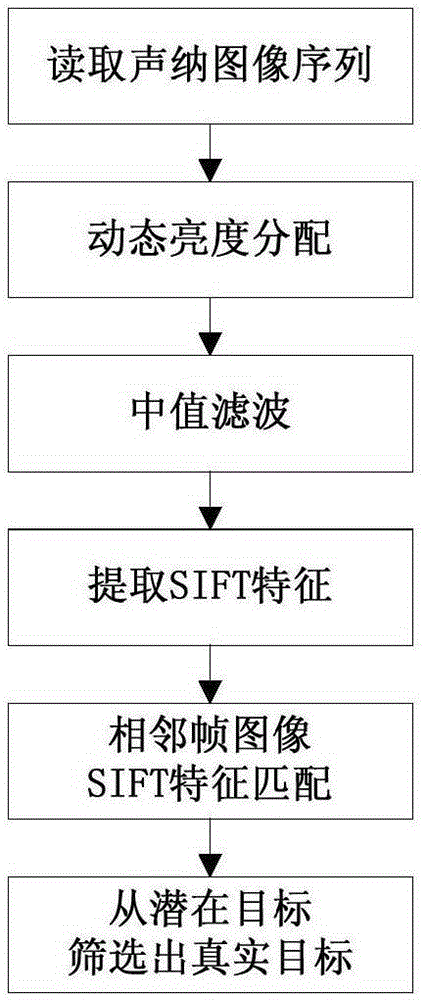
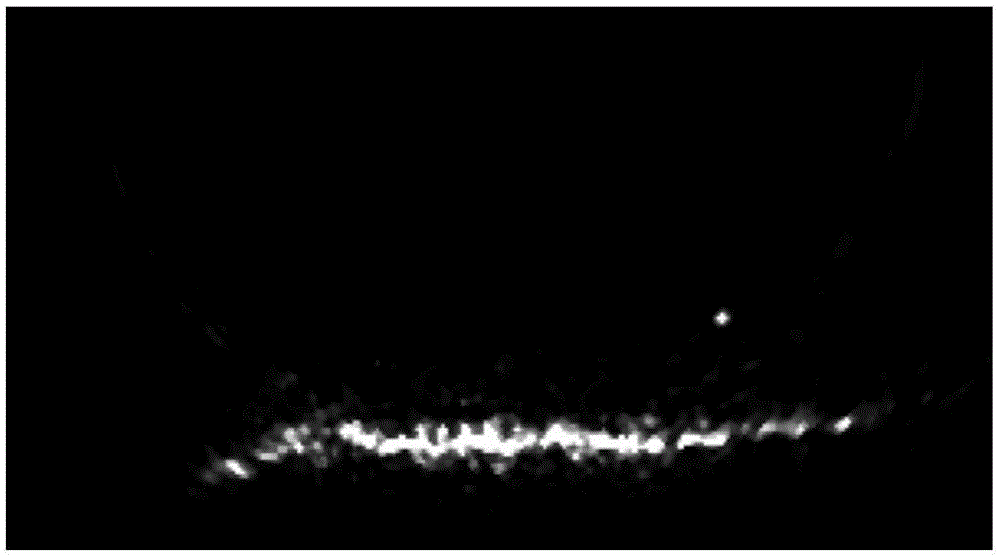
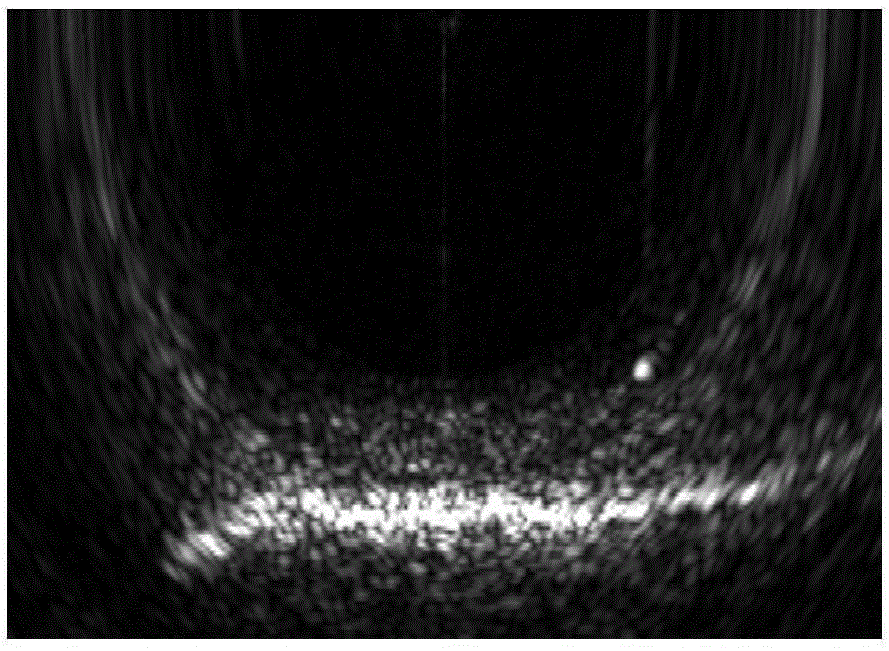
Multi-beam sonar target detection method by applying feature tracking
ActiveCN105182350AImprove image qualityImprove robustnessAcoustic wave reradiationPattern recognitionScale-invariant feature transform
The invention provides a multi-beam sonar target detection method by applying feature tracking. The method comprises steps: (1) data are acquired through a sonar system, sonar images are formed through imaging, and the continuous sonar images form a sonar image sequence; (2) pretreatment is carried out; (3) scale invariant feature transform features of each frame of sonar image after pretreatment are extracted; (4) feature matching is carried out on former two frames in the sonar image sequence, features which are successfully matched are marked as potential targets, and features which are not matched successfully are discarded; and (5) features presenting the potential targets are tracked in subsequent frames in the sonar image sequence, real targets are screened in the potential targets after the image sequence is traversed, and a feature locus for the real targets can be obtained. The method is used in a single frame of image to judge whether the target exists or not, multiple target features are tracked at the same in the sonar image sequence, the real targets are screened in the potential targets, and the method is wide in applicability.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
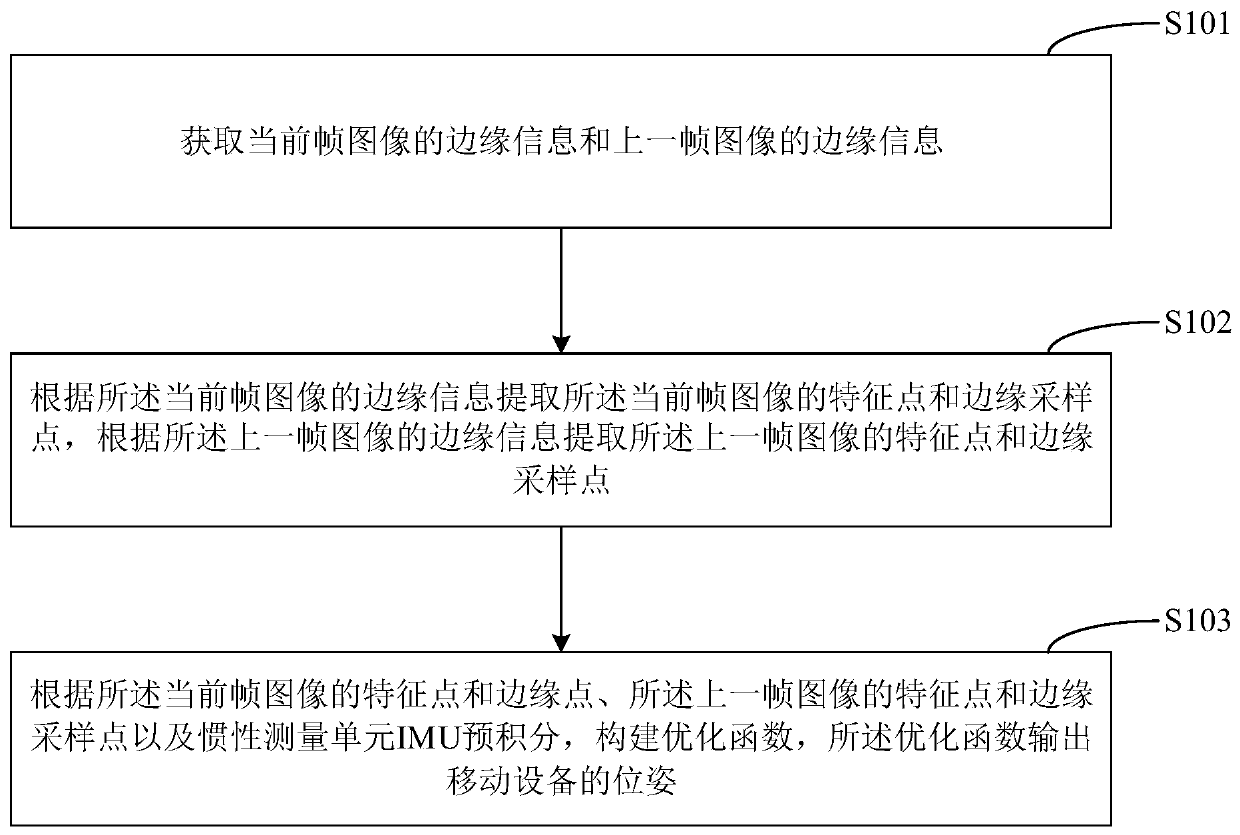
Visual inertia speedometer method, visual inertia speedometer device and mobile equipment
ActiveCN110246147AImprove accuracyReduce the chance of lossImage analysisInternal combustion piston enginesFeature trackingMobile device
The invention is applicable to the technical field of SLAM, and provides a visual inertial speedometer method, a visual inertial speedometer device, mobile equipment and a computer readable storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining the edge information of a current frame image and the edge information of a previous frame image; extracting feature points and edge sampling points of the current frame of image according to the edge information of the current frame of image, and extracting feature points and edge sampling points of the previous frame of image according to the edge information of the previous frame of image; and constructing an optimization function according to the feature point and the edge point of the current frame of image, the feature point and the edge sampling point of the previous frame of image and the IMU pre-integration, and outputting the pose of the mobile device by the optimization function. According to the invention, the feature matching rate can be improved, the feature tracking loss probability is reduced, and the pose estimation accuracy is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method to determine a direction and amplitude of a current velocity estimate of a moving device
InactiveUS20150293138A1Adequate motionSpeed measurement using accelerationAverage speed measurementCurrent velocityFeature tracking
A new method for the estimation of ego-motion (the direction and amplitude of the velocity) of a mobile device comprising optic-flow and inertial sensors (hereinafter the apparatus). The velocity is expressed in the apparatus's reference frame, which is moving with the apparatus. The method relies on short-term inertial navigation and the direction of the translational optic-flow in order to estimate ego-motion, defined as the velocity estimate (that describes the speed amplitude and the direction of motion). A key characteristic of the invention is the use of optic-flow without the need for any kind of feature tracking. Moreover, the algorithm uses the direction of the optic-flow and does not need the amplitude, thanks to the fact that the scale of the velocity is solved by the use of inertial navigation and changes in direction of the apparatus.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
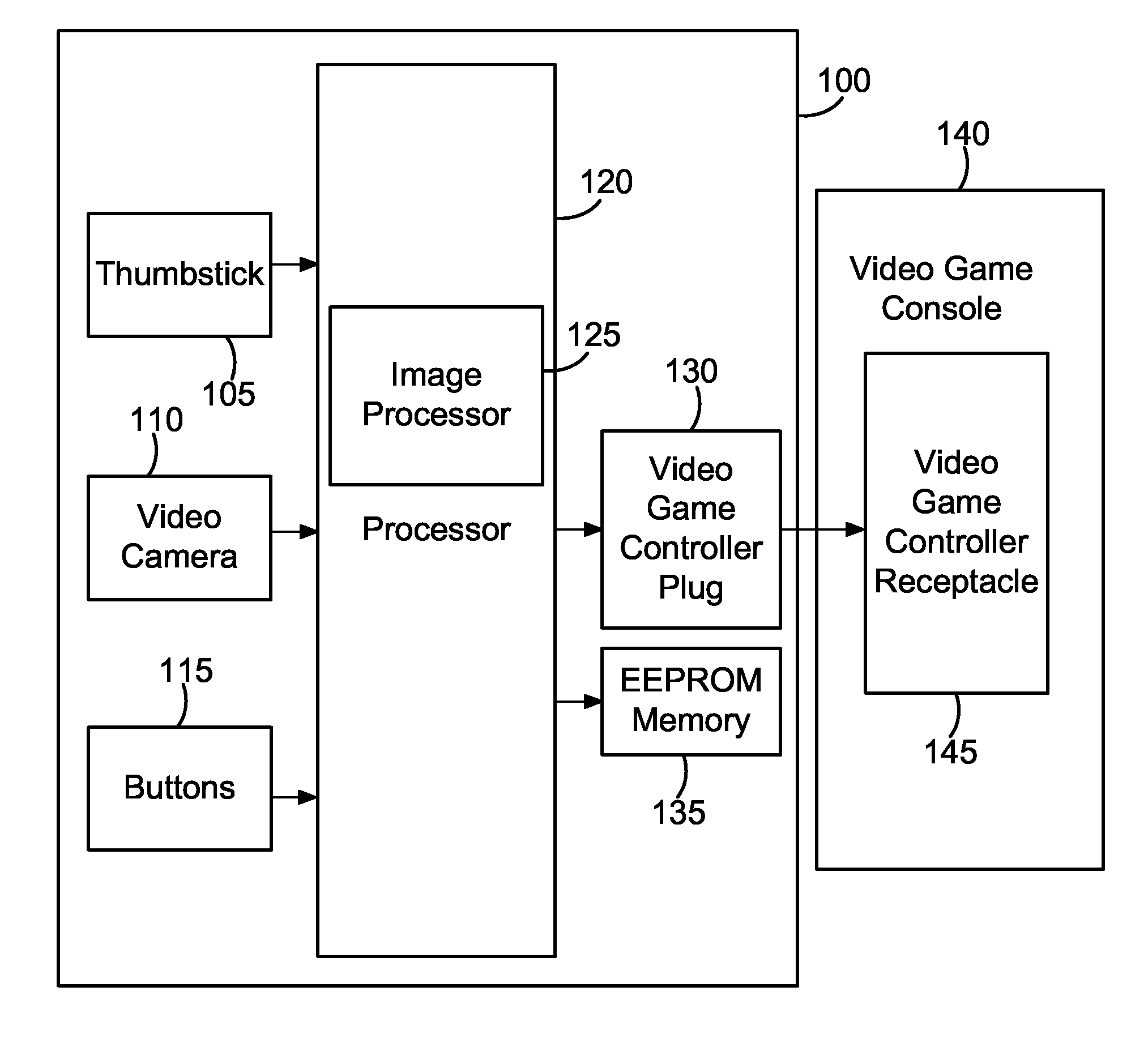
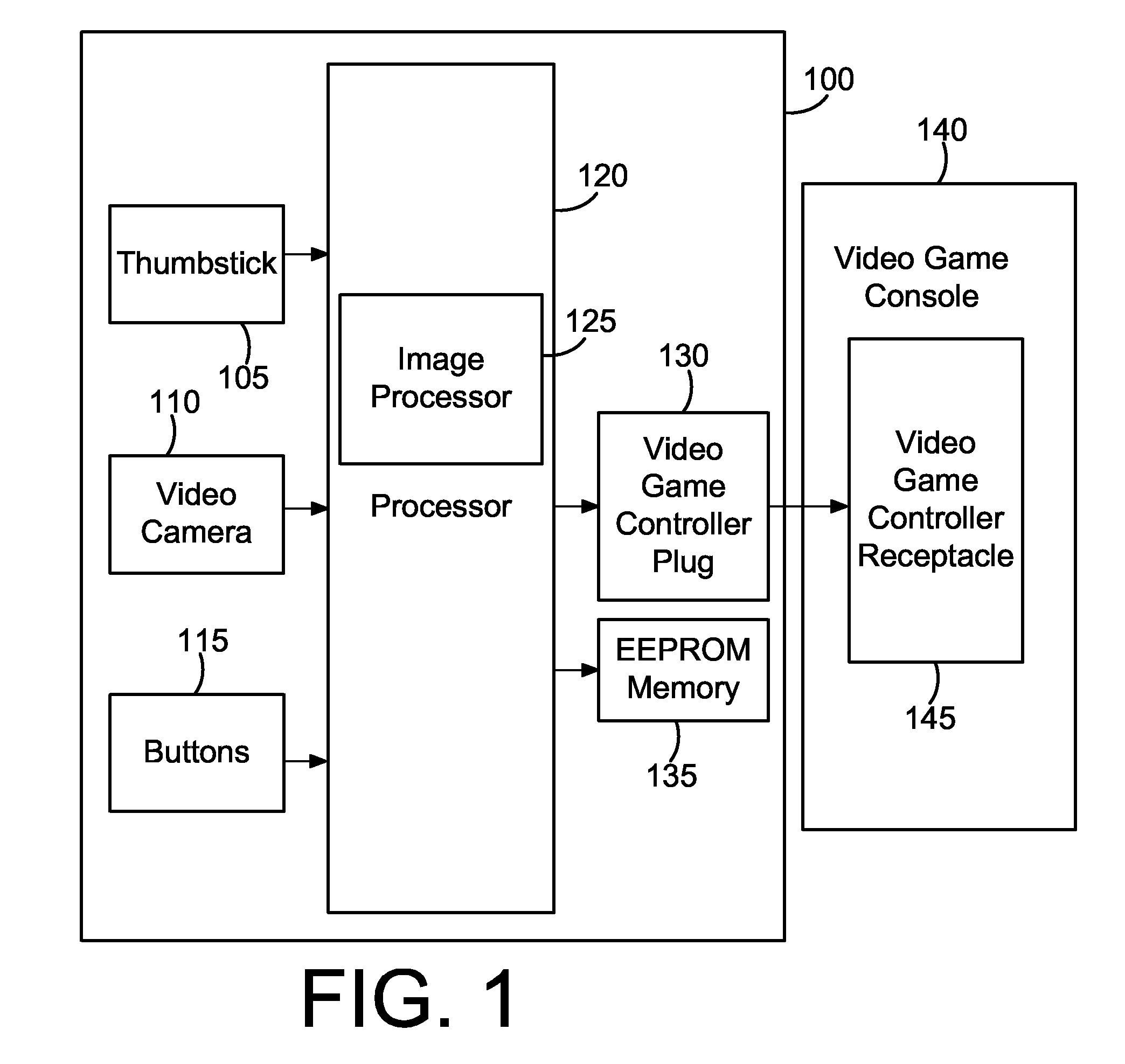
Method and apparatus for providing realistic gun motion input to a video game
InactiveUS20070117628A1Improve precisionImprove realismVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsMicrocontrollerComputer graphics (images)
A method and apparatus for providing realistic gun motion input to a video game. In one embodiment, a plastic enclosure houses a video camera, PCB, microcontroller processor, and many buttons for controlling various aspects of a video game. The processor examines images from the video camera using various feature tracking algorithms and determines the direction and magnitude of motion of the video camera, and hence the motion of plastic gun shaped enclosure in which the video camera is mounted, and that the game player is wielding. This motion data is translated into motion data that a video game running on a video game console can understand, and transmitted to the video game console. The end result is that a user pointing and moving the plastic gun will cause the in game character of the video game to move and point its gun in concert with the game player, thereby providing an intuitive and fun aiming mechanism for playing video games. The button presses that the game player initiates on the apparatus are also reported to the video game and also affect various actions therein.
Owner:STANLEY MARK JOSEPH
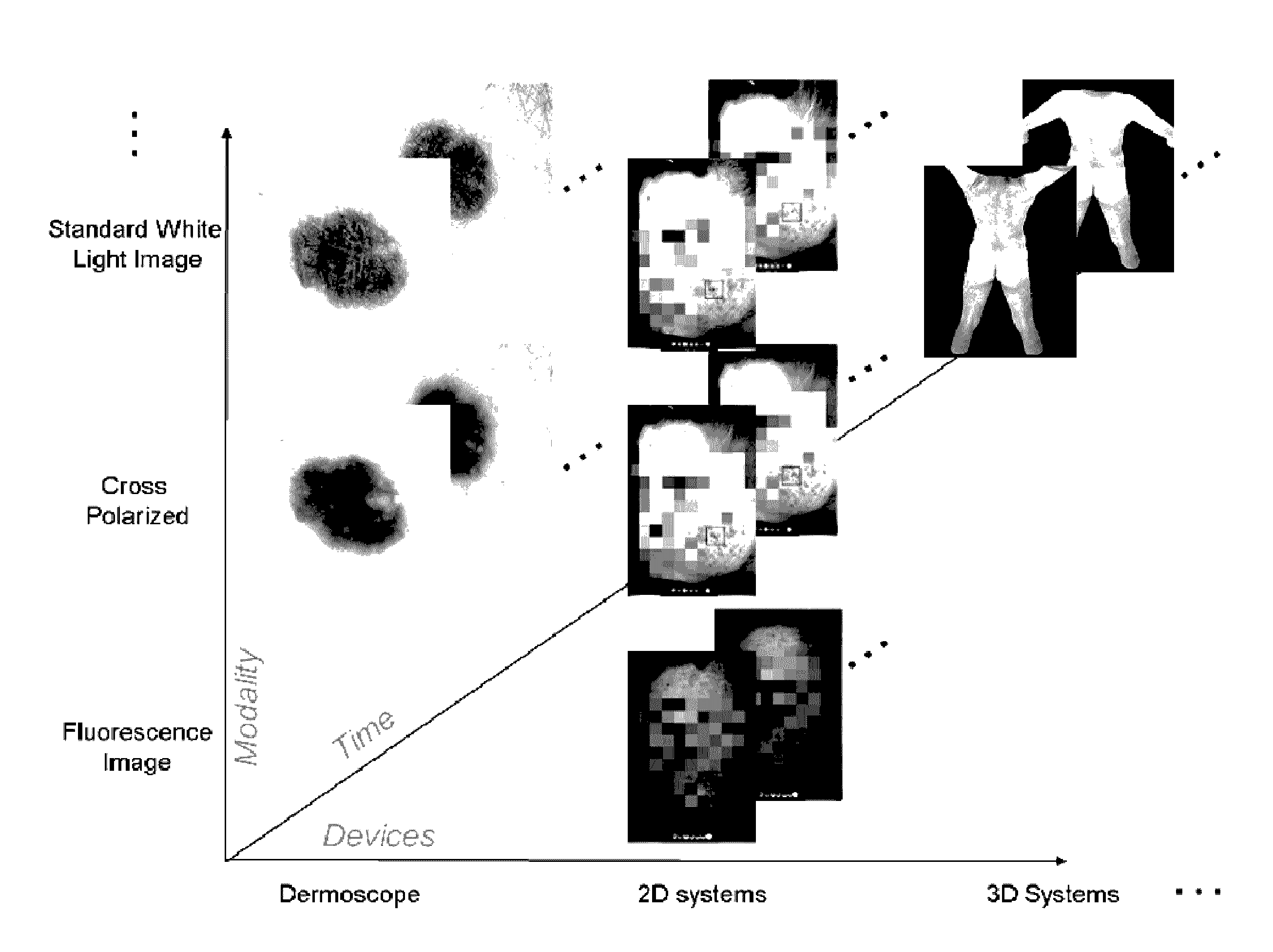
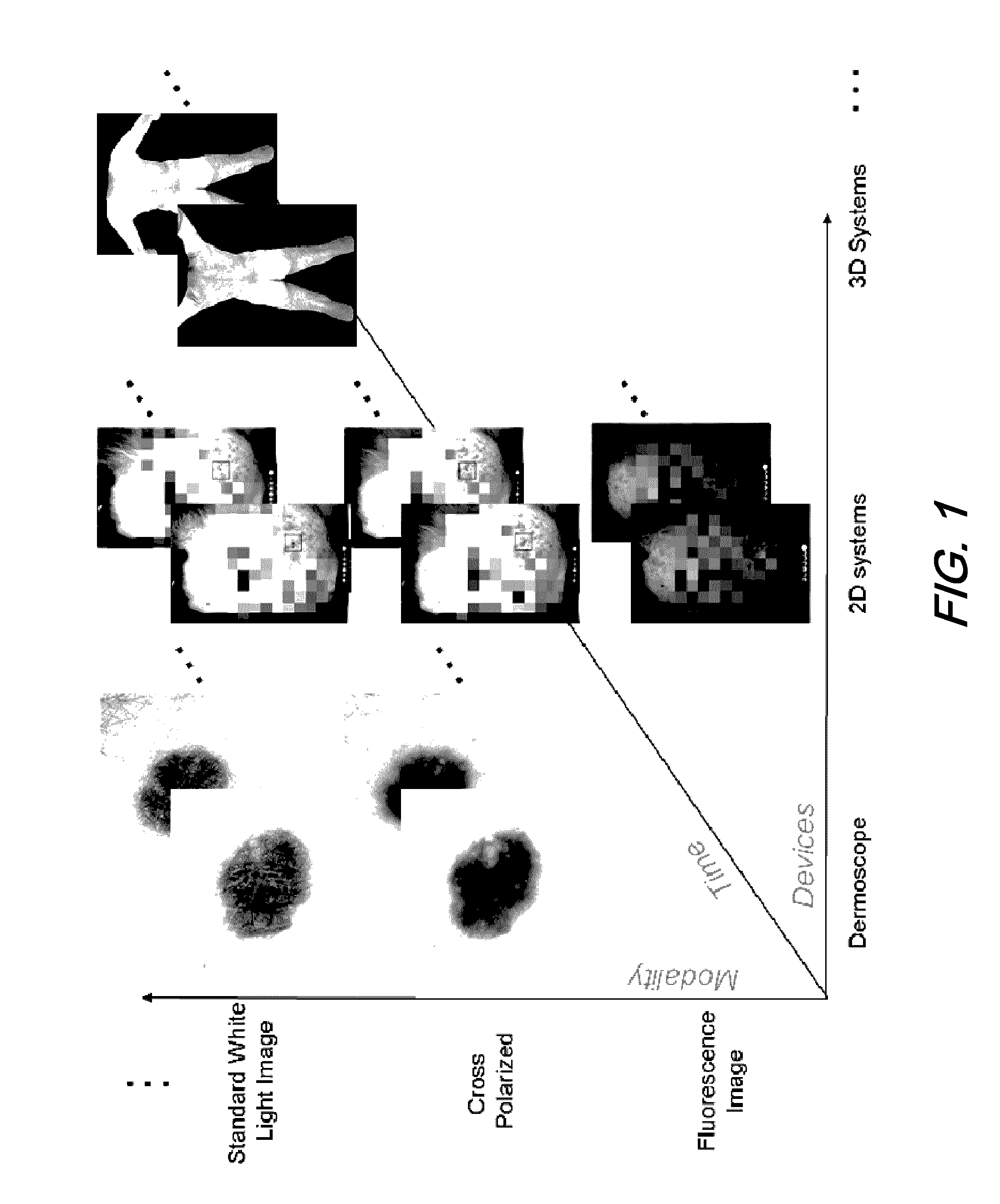
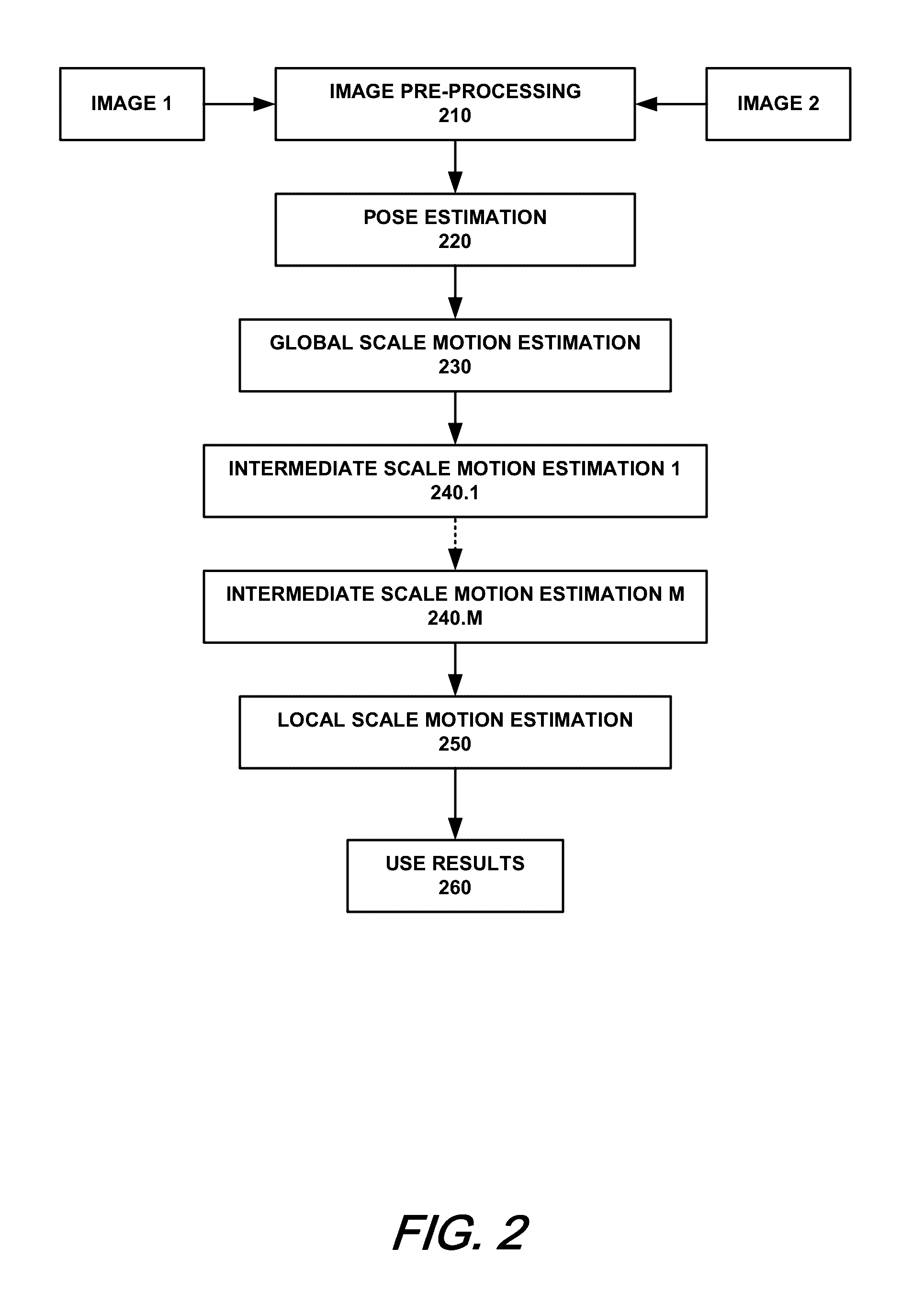
Dermatological feature tracking over multiple images
Methods and apparatus are disclosed that assist a user such as a doctor to track changes that occur in features of a subject's skin as the skin features evolve over time. Such a tracking can be done for images captured under different imaging / lighting modalities, by different image capture devices, and / or at different points in time. Methods and apparatus to automatically identify and track the unconstrained appearance / disappearance of skin features are disclosed.
Owner:CANFIELD SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com