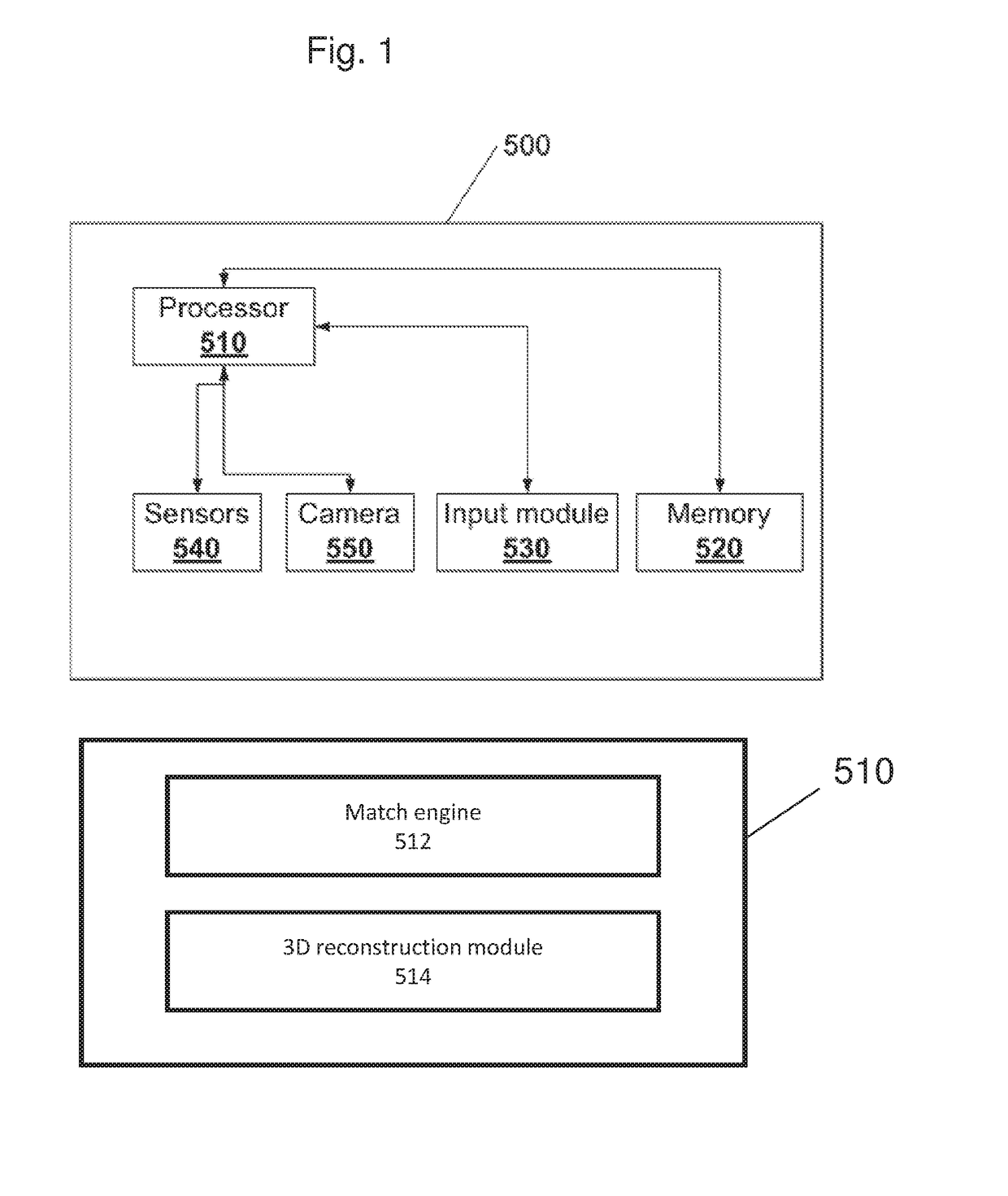
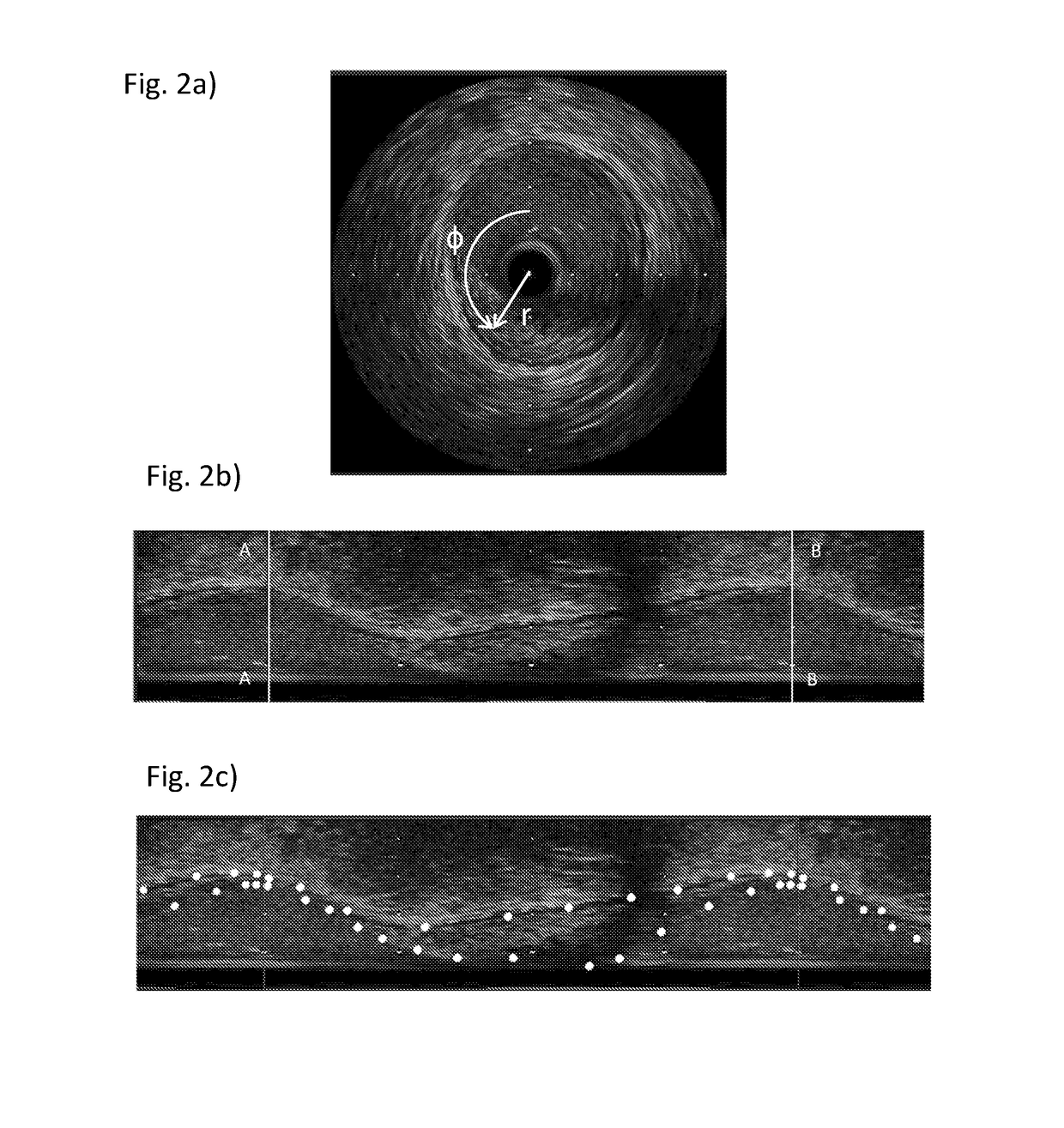
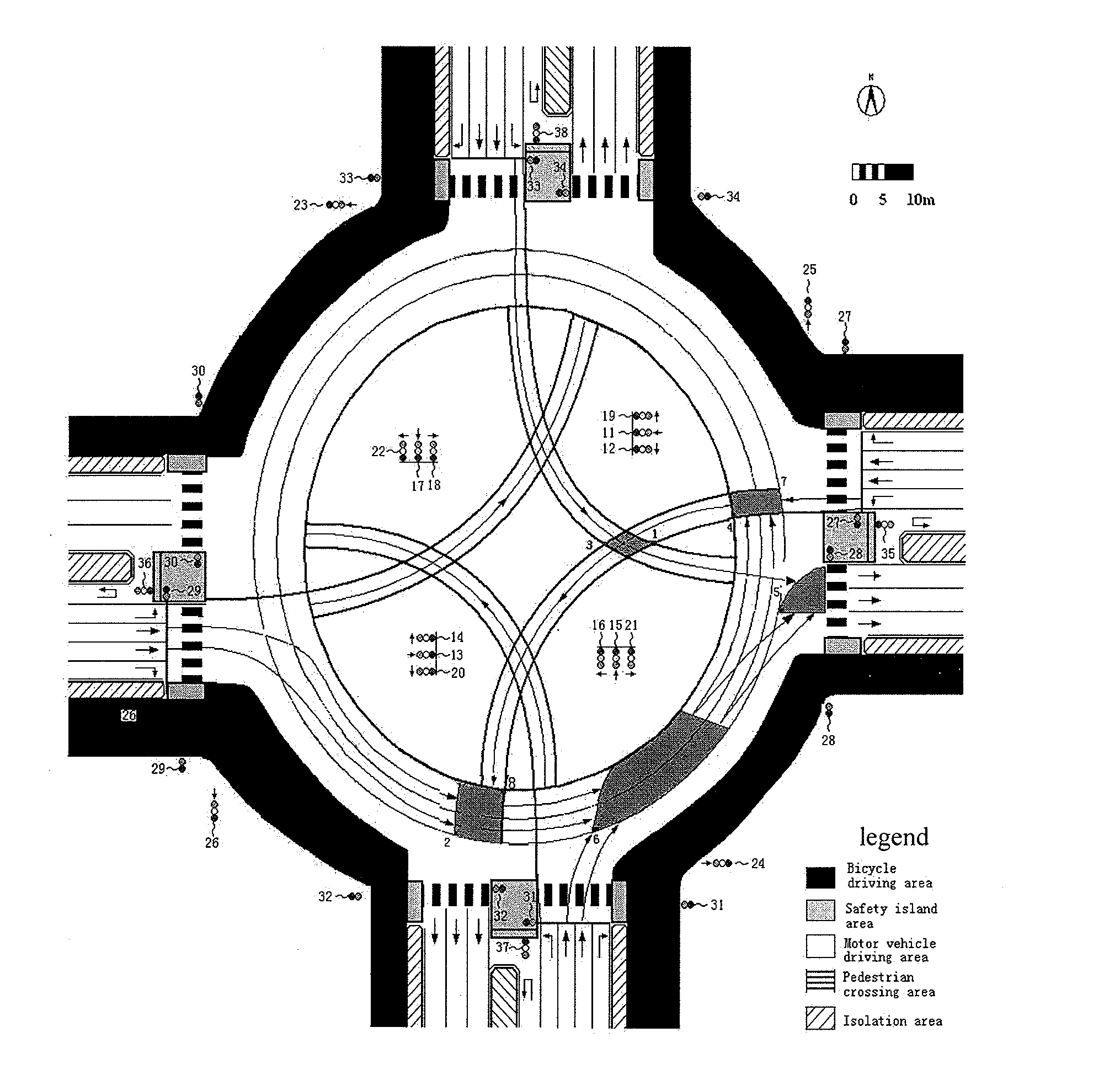
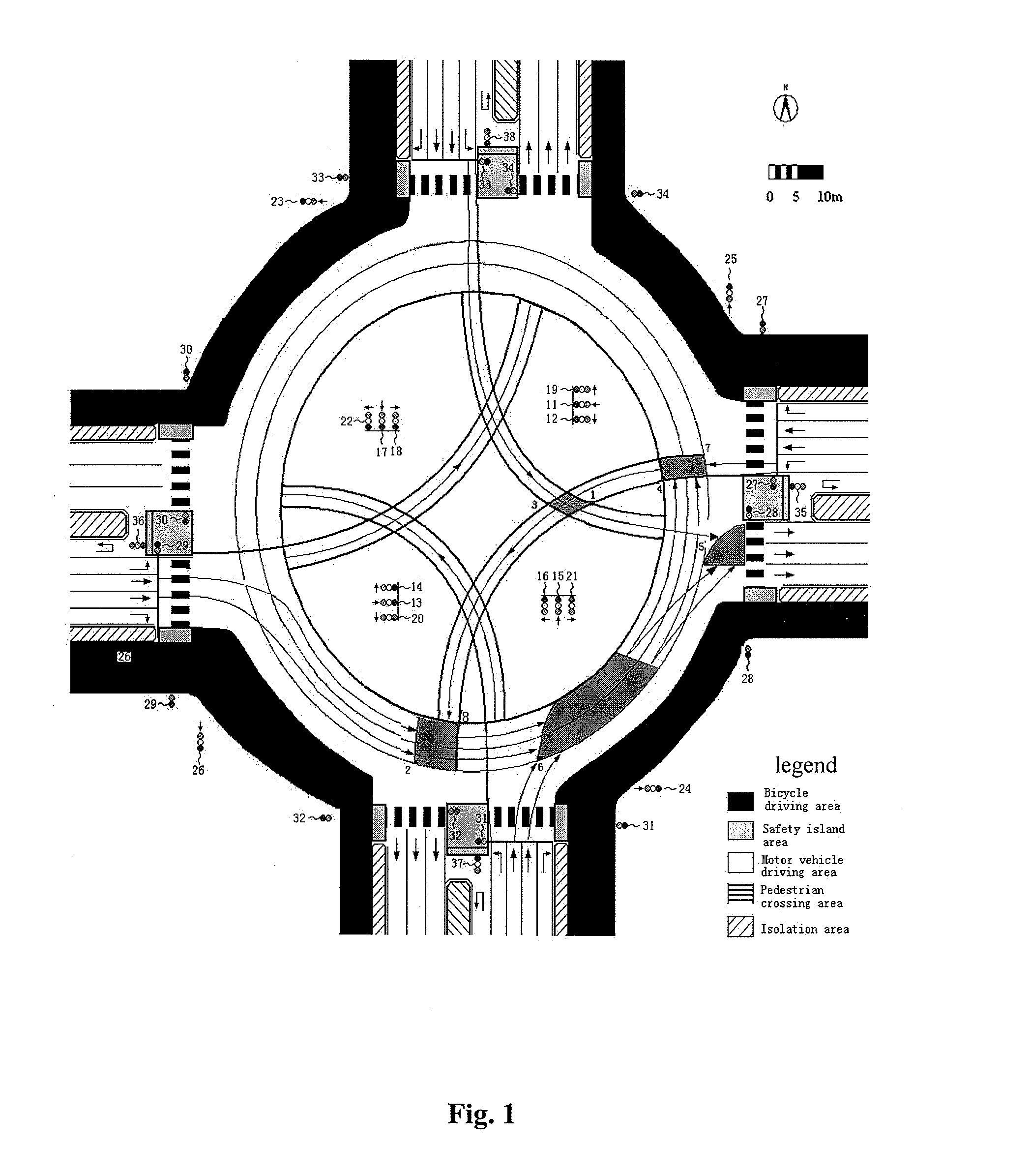
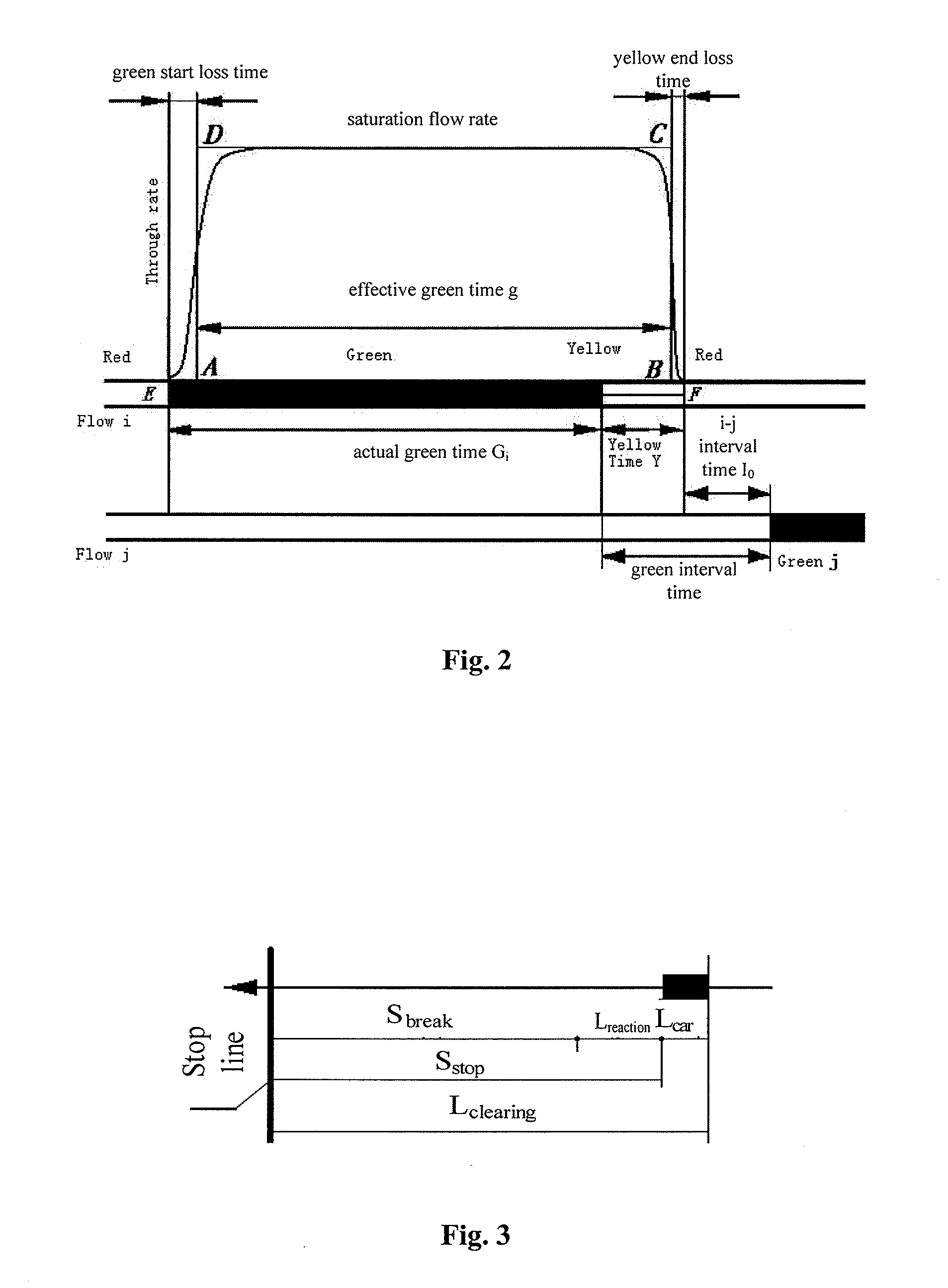
Patents
Literature
150results about How to "Minimize sum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
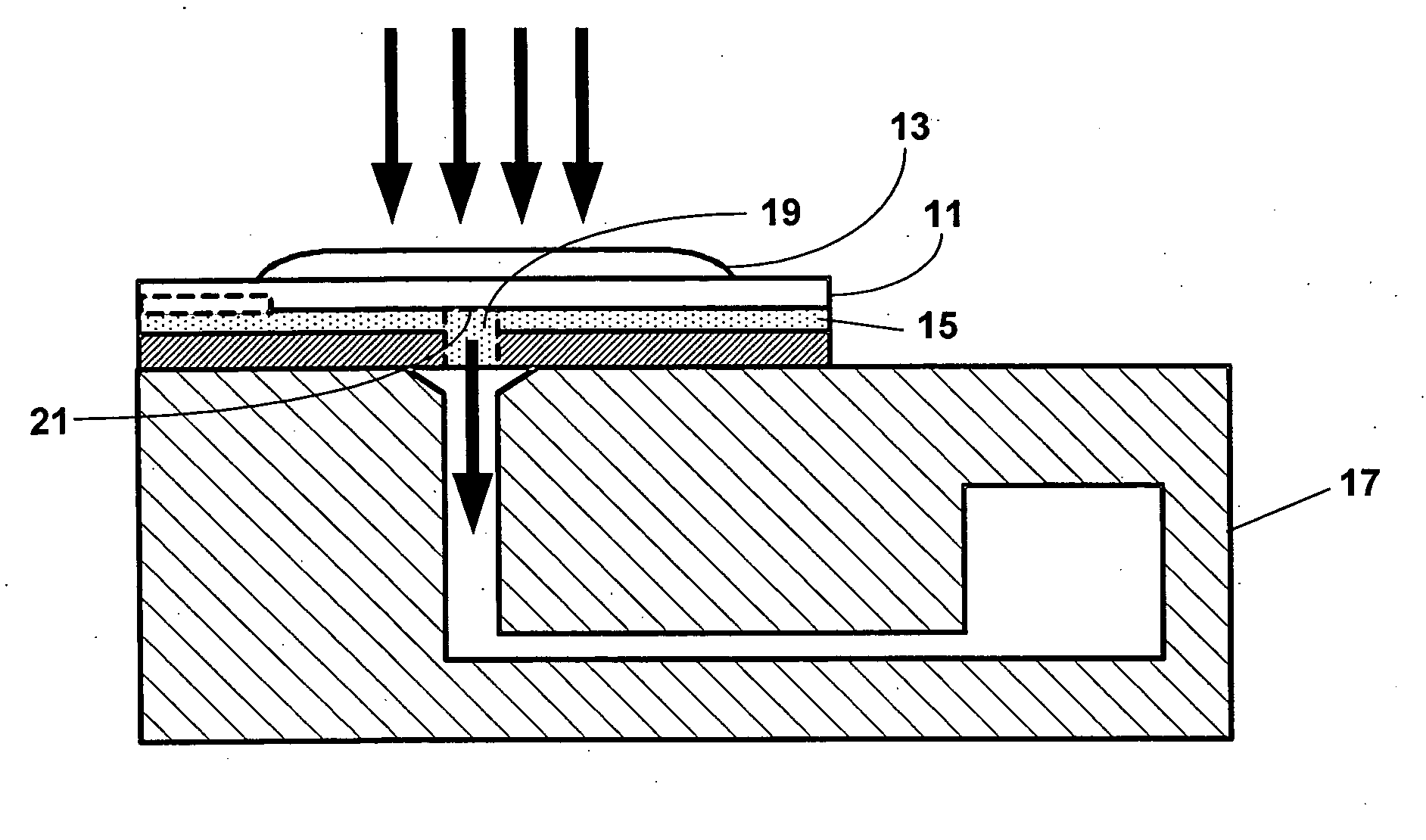
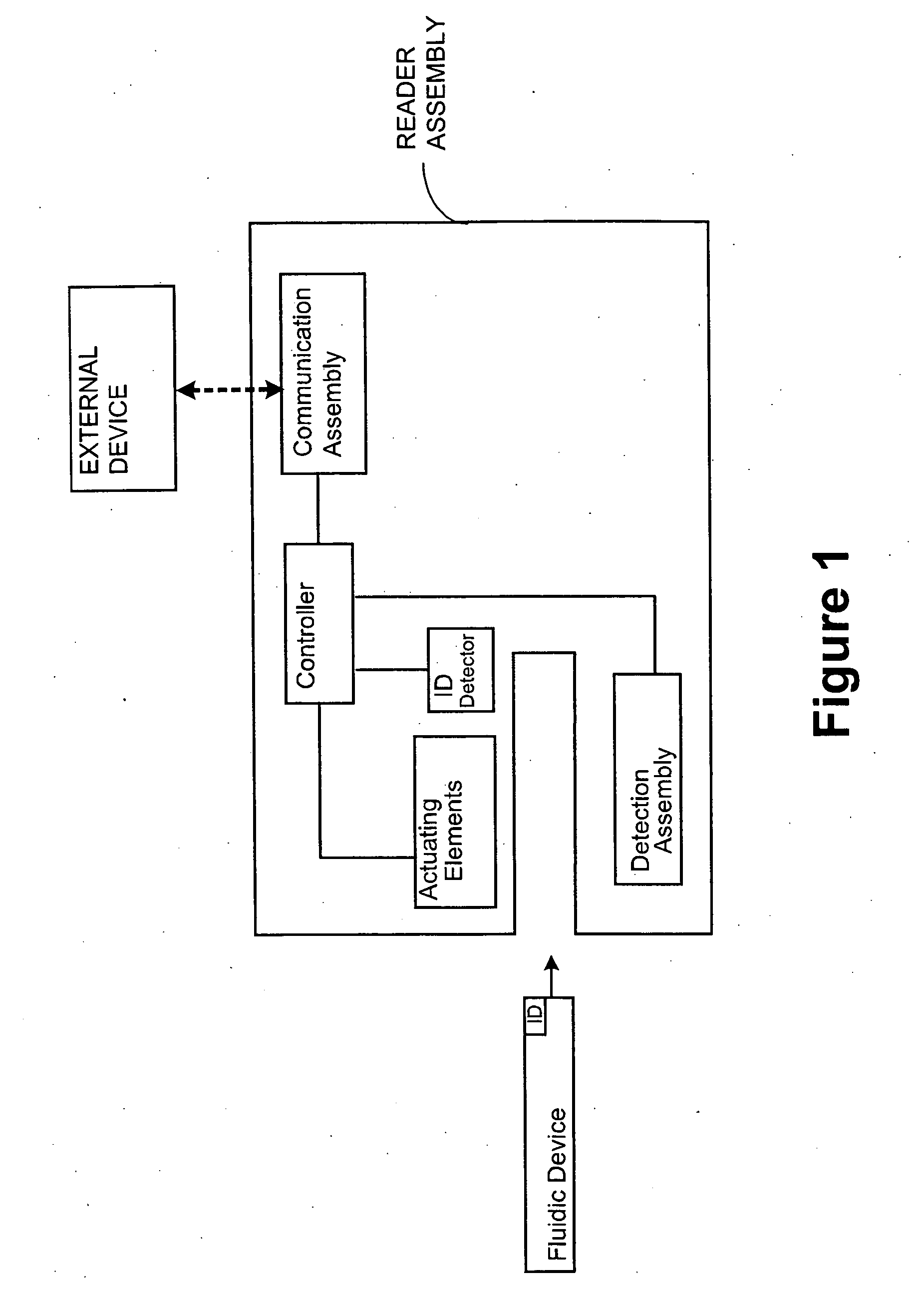
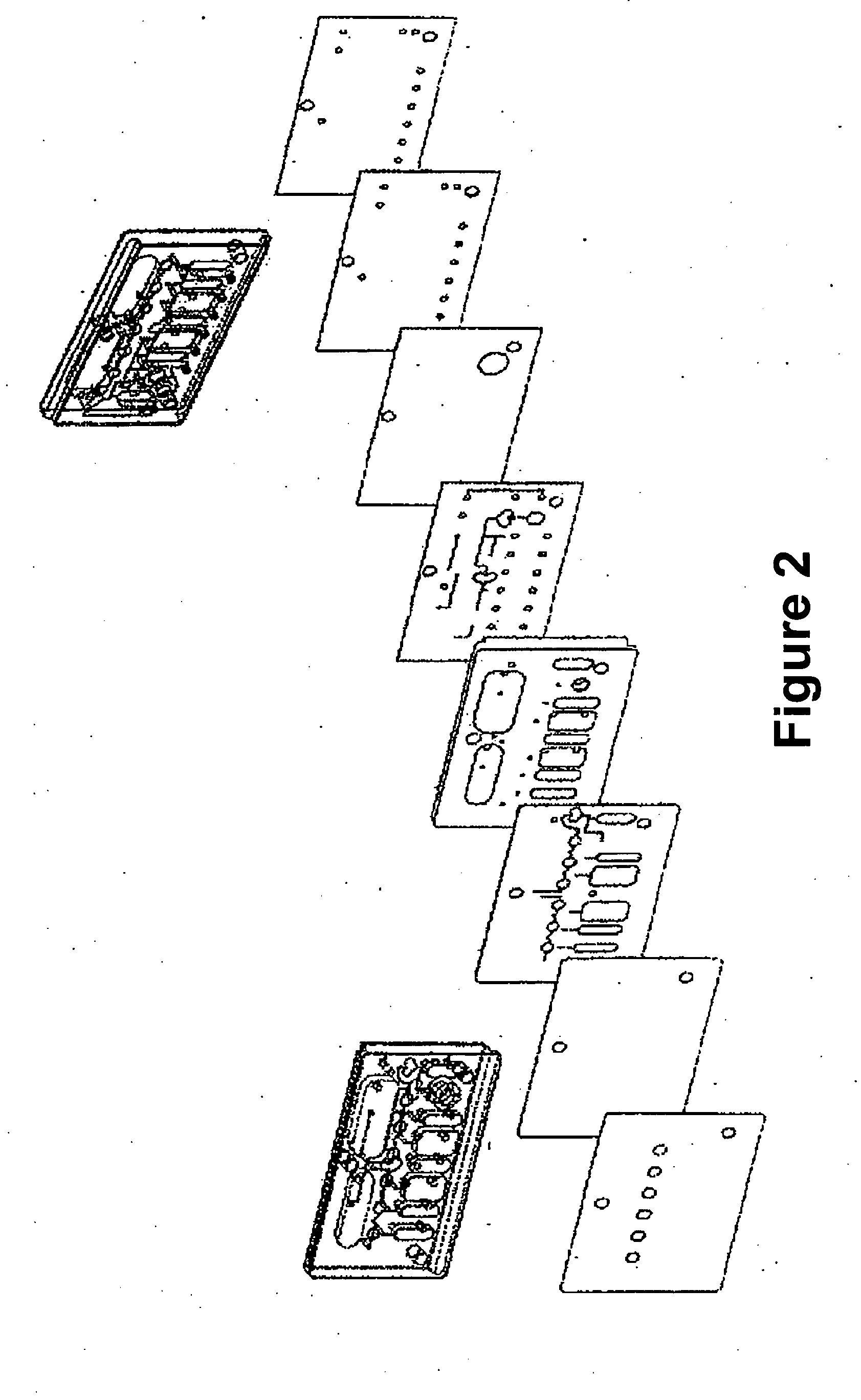
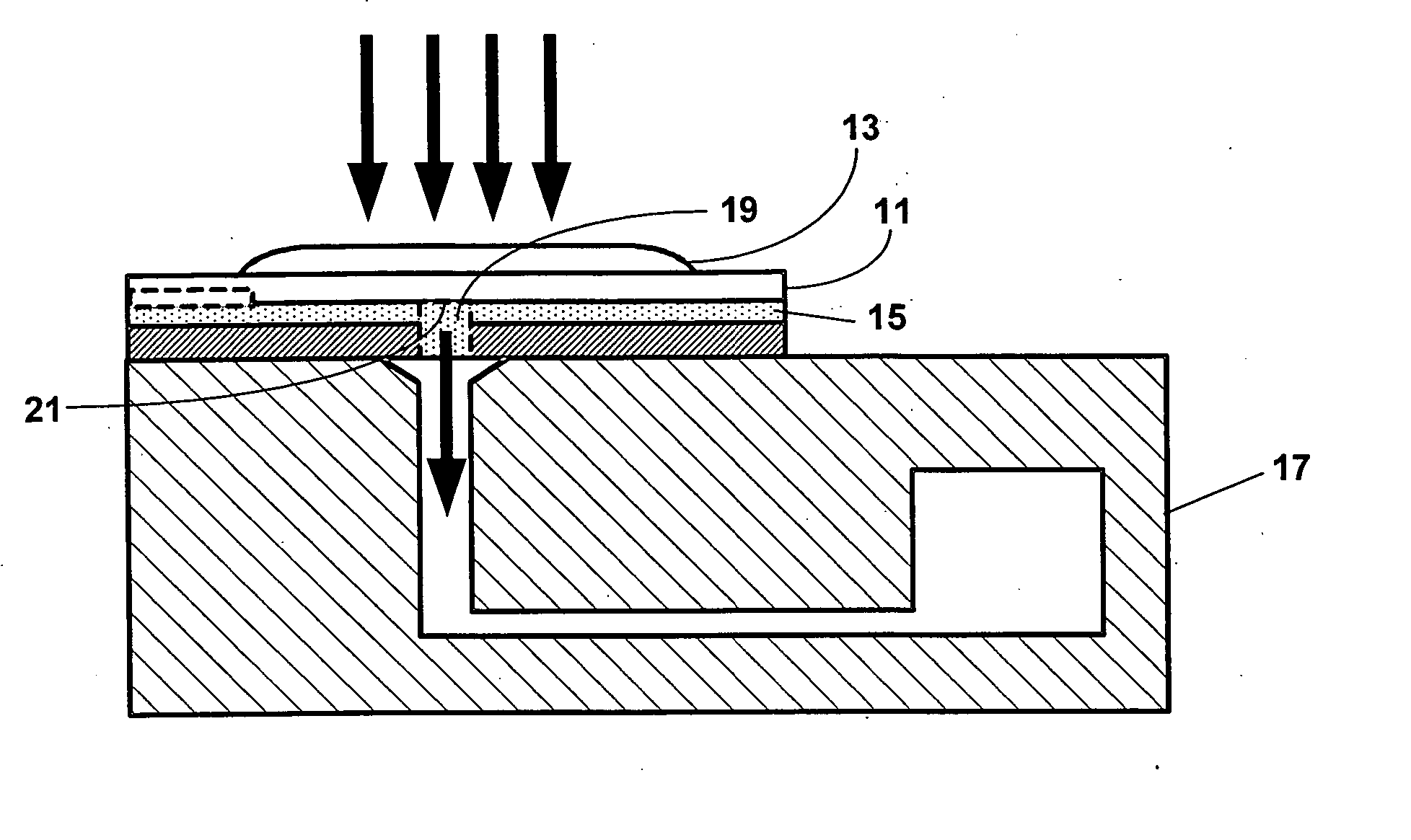
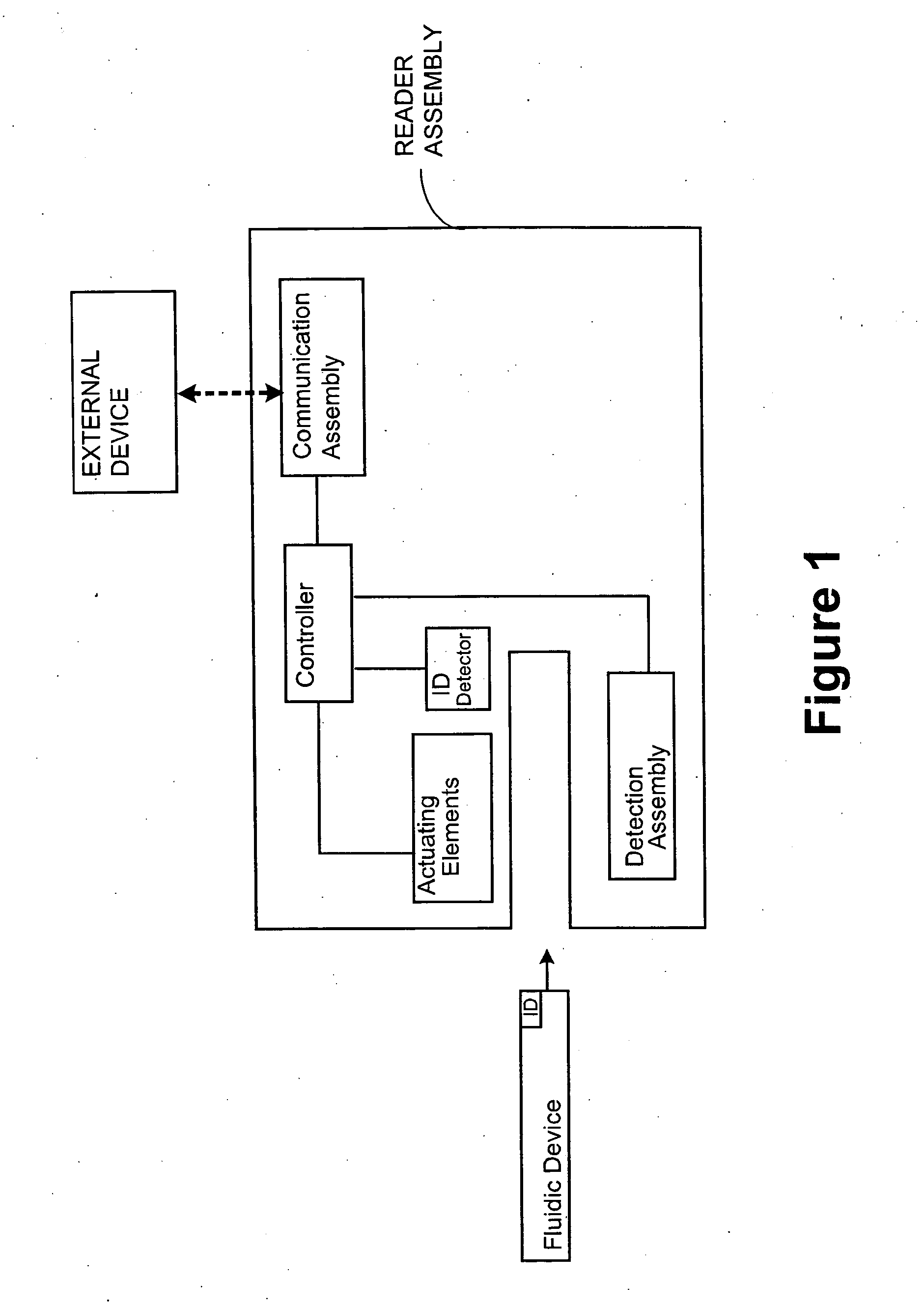
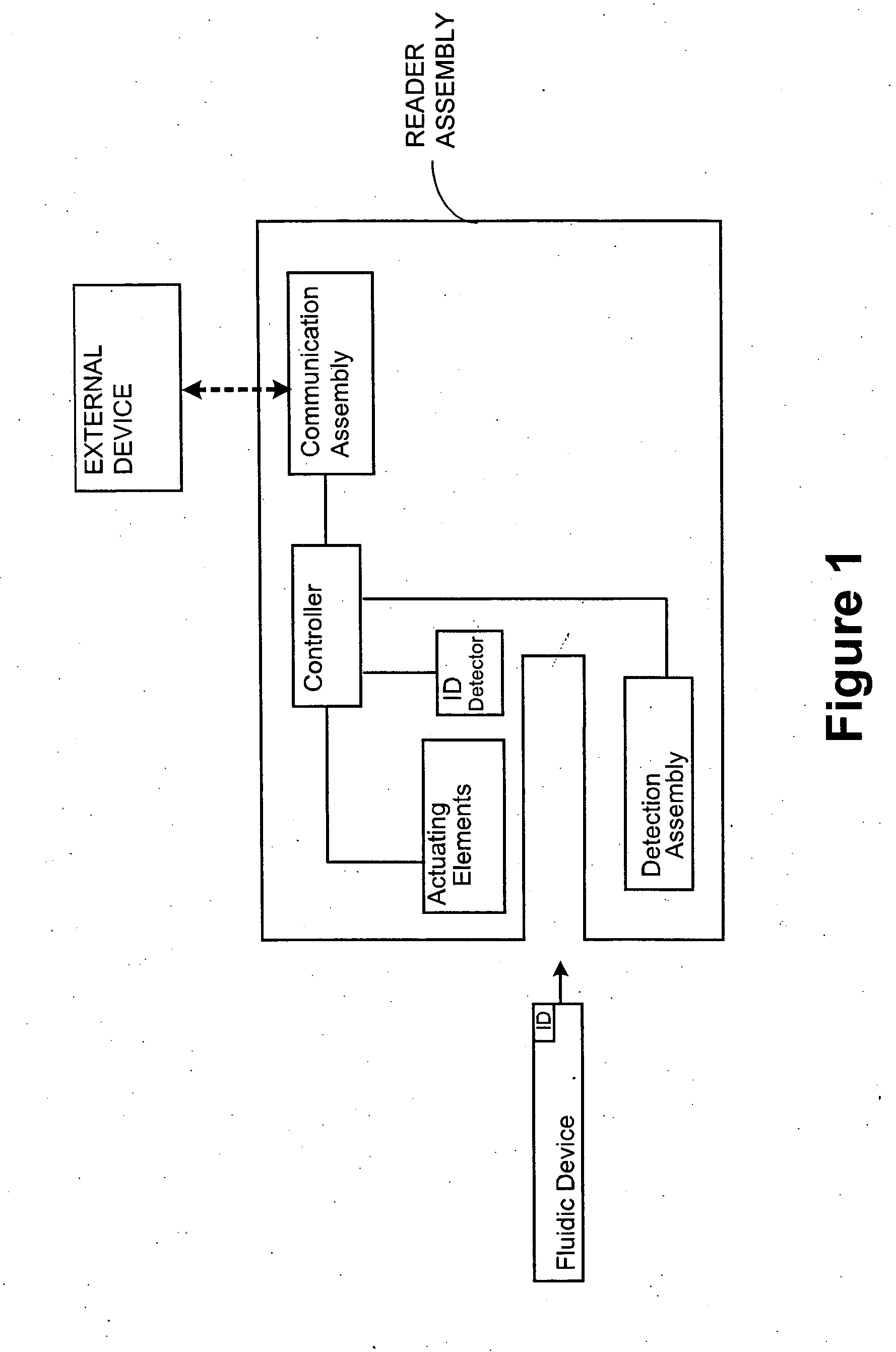
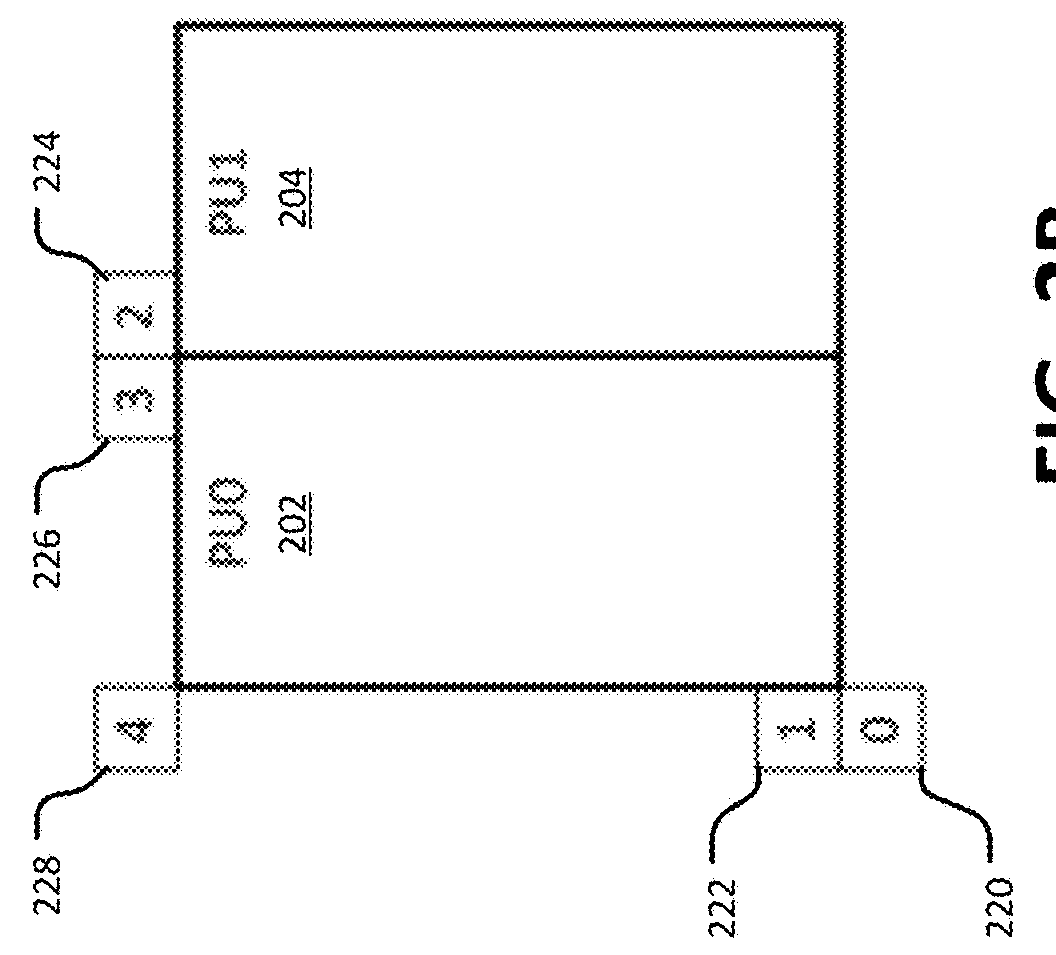
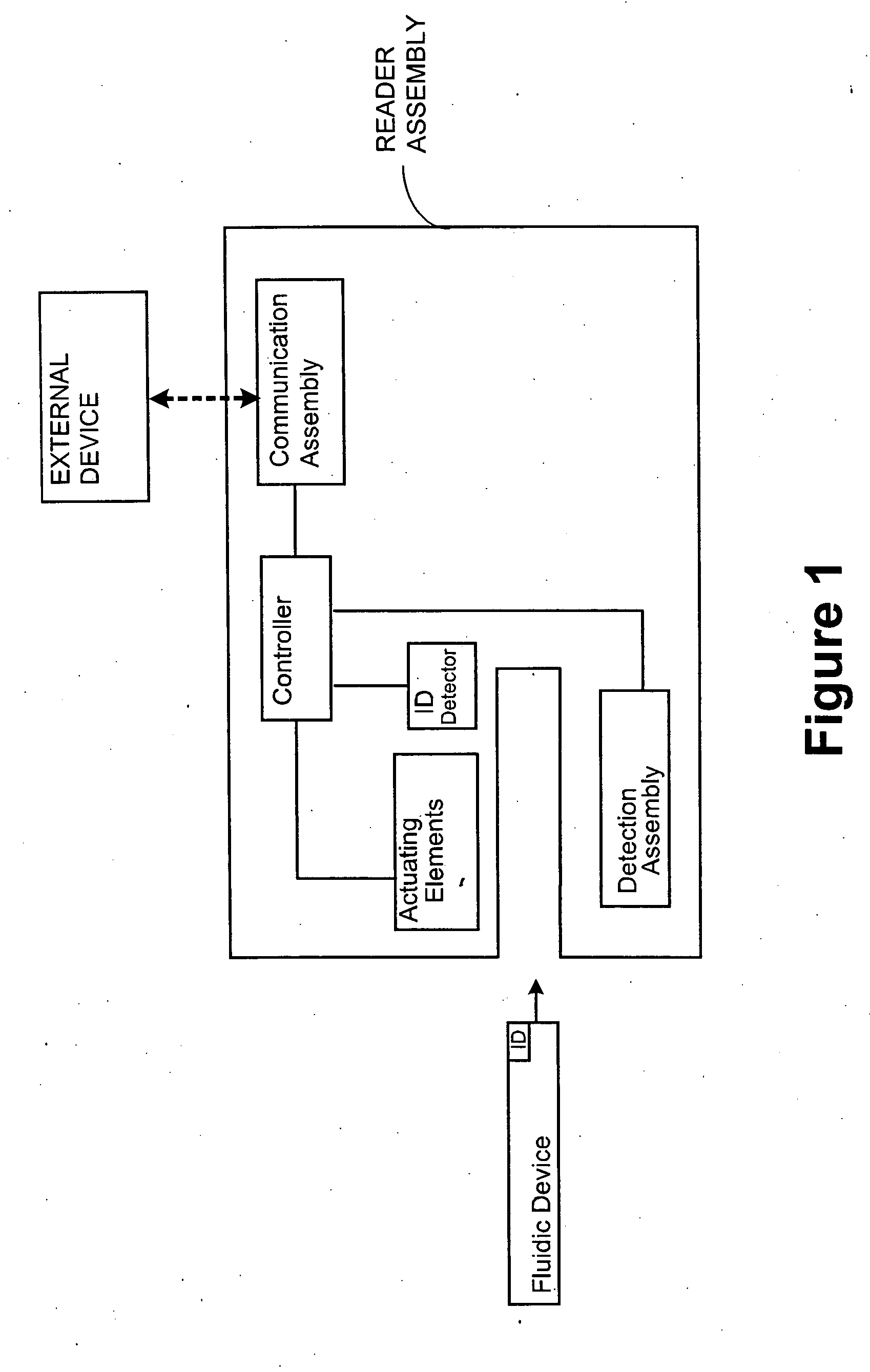
Point-of-care fluidic systems and uses thereof
ActiveUS20060264782A1Simplify laborFacilitate high throughput point-of-care testingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careBiological fluid
This invention is in the field of medical devices. Specifically, the present invention provides portable medical devices that allow real-time detection of analytes from a biological fluid. The methods and devices are particularly useful for providing point-of-care testing for a variety of medical applications.
Owner:LABRADOR DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Systems and methods for monitoring pharmacological parameters
InactiveUS20060264783A1Simplify laborUseful in detectionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAnalyteMedicine
This invention is in the field of medical devices. Specifically, the present invention provides portable medical devices that allow real-time detection of analytes from a biological fluid. The methods and devices are particularly useful for providing point-of-care testing for a variety of medical applications.
Owner:THERANOS +2
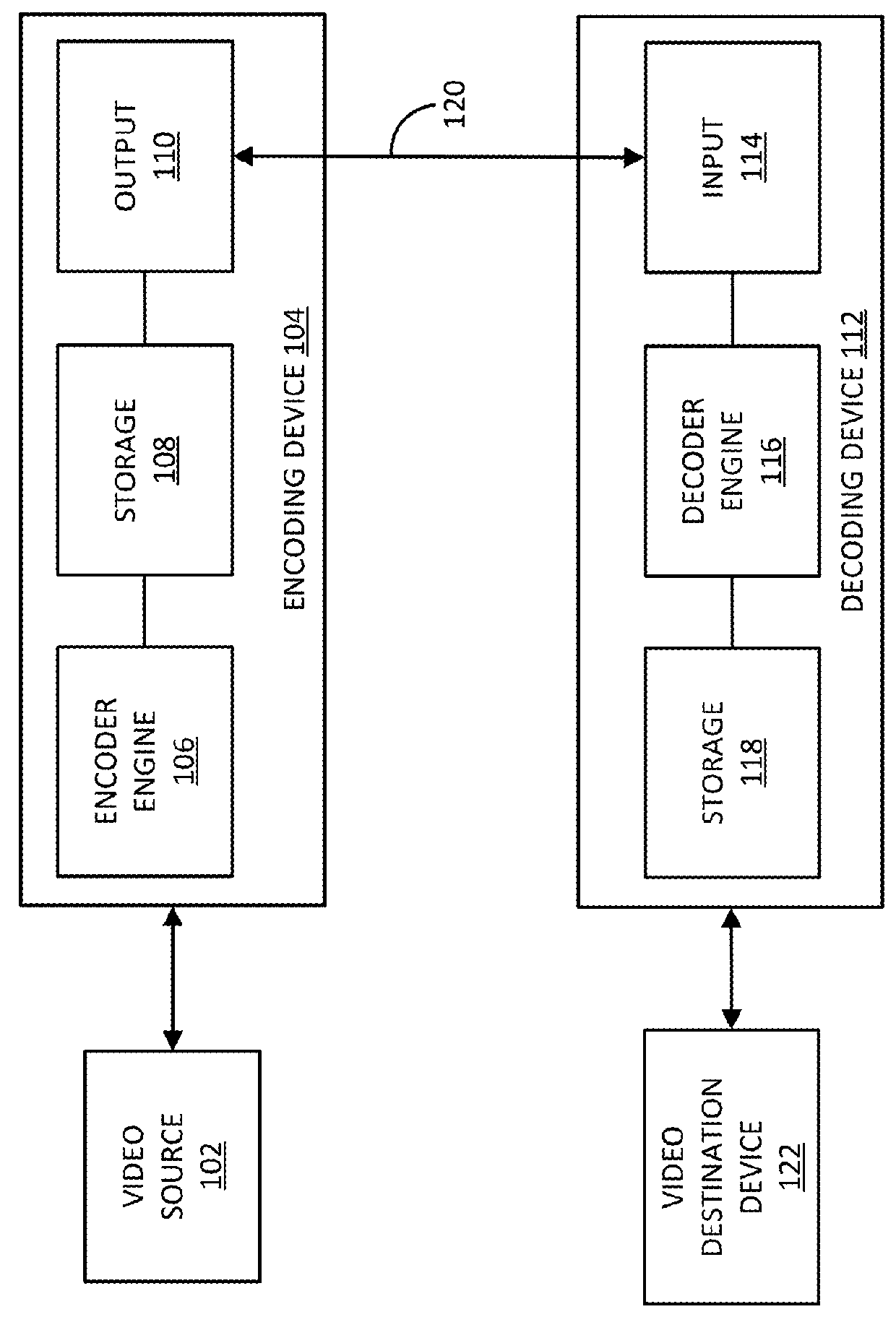
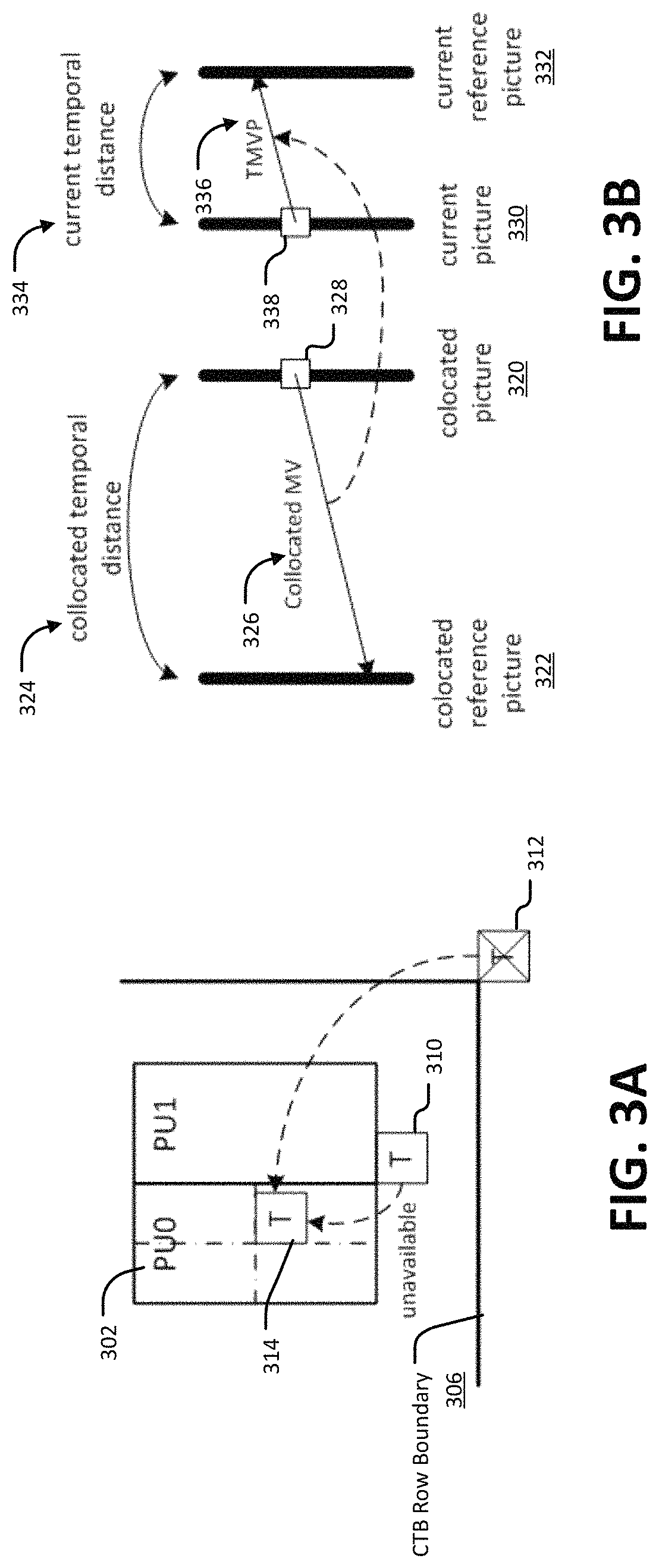
Frame rate up-conversion coding mode
ActiveUS20180098087A1Promote resultsHigh computational complexityDigital video signal modificationComputer scienceLocal illumination
Methods, apparatuses, and computer-readable medium are provided for a frame rate up-conversion coding mode, where a bilateral matching mode can be used to determine motion information. In various implementations, local illumination compensation is disallowed from being used for a block when a bilateral matching mode is used for the block. In various implementations, a bilateral matching mode is disallowed from being used when local illumination compensation is used for the block.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method And System For Fluid Flow Control In A Fluid Network System
ActiveUS20140094105A1Easy to identifyMinimize consumptionFlow control using electric meansPipeline systemsEngineeringStreamflow
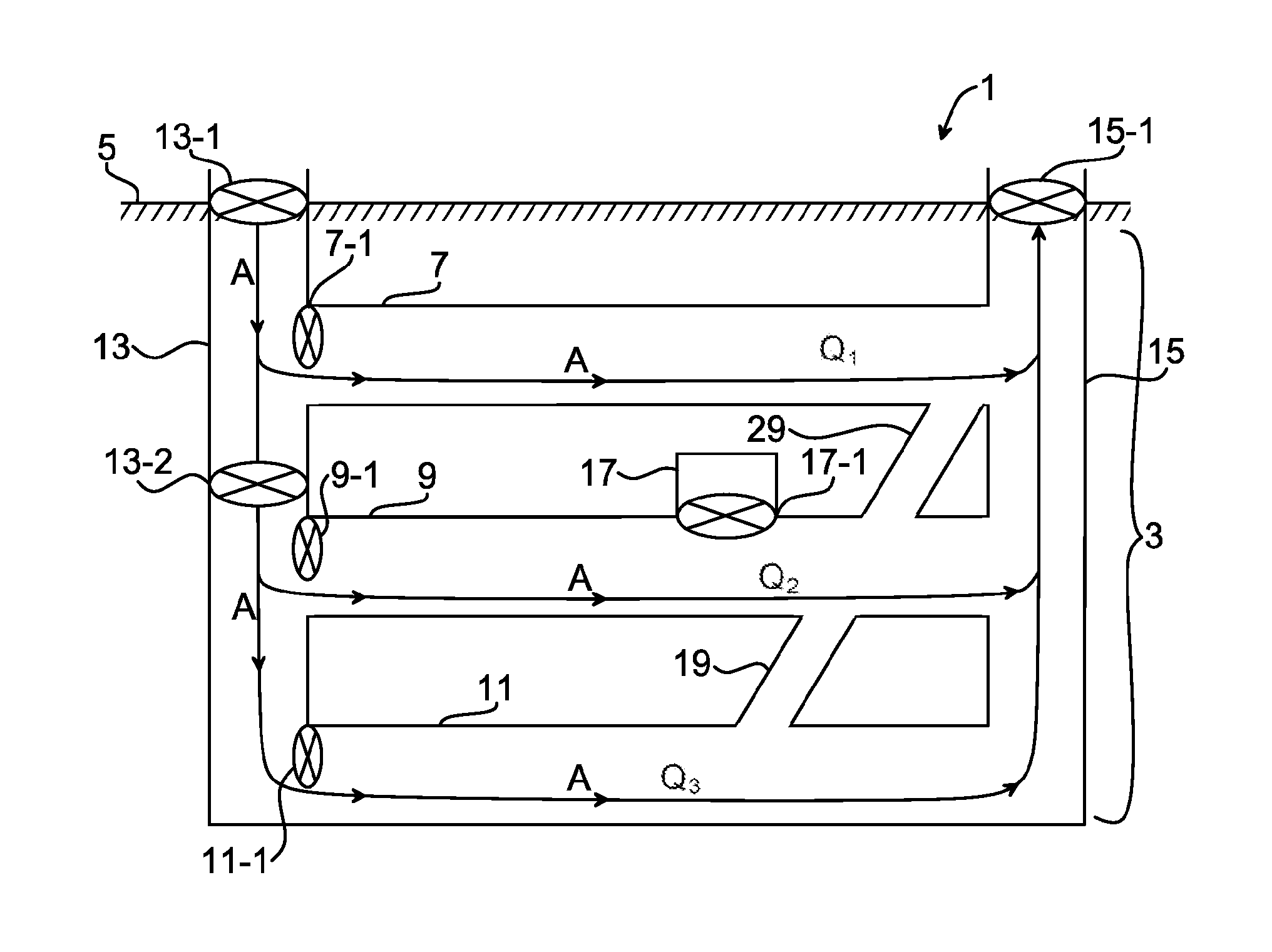
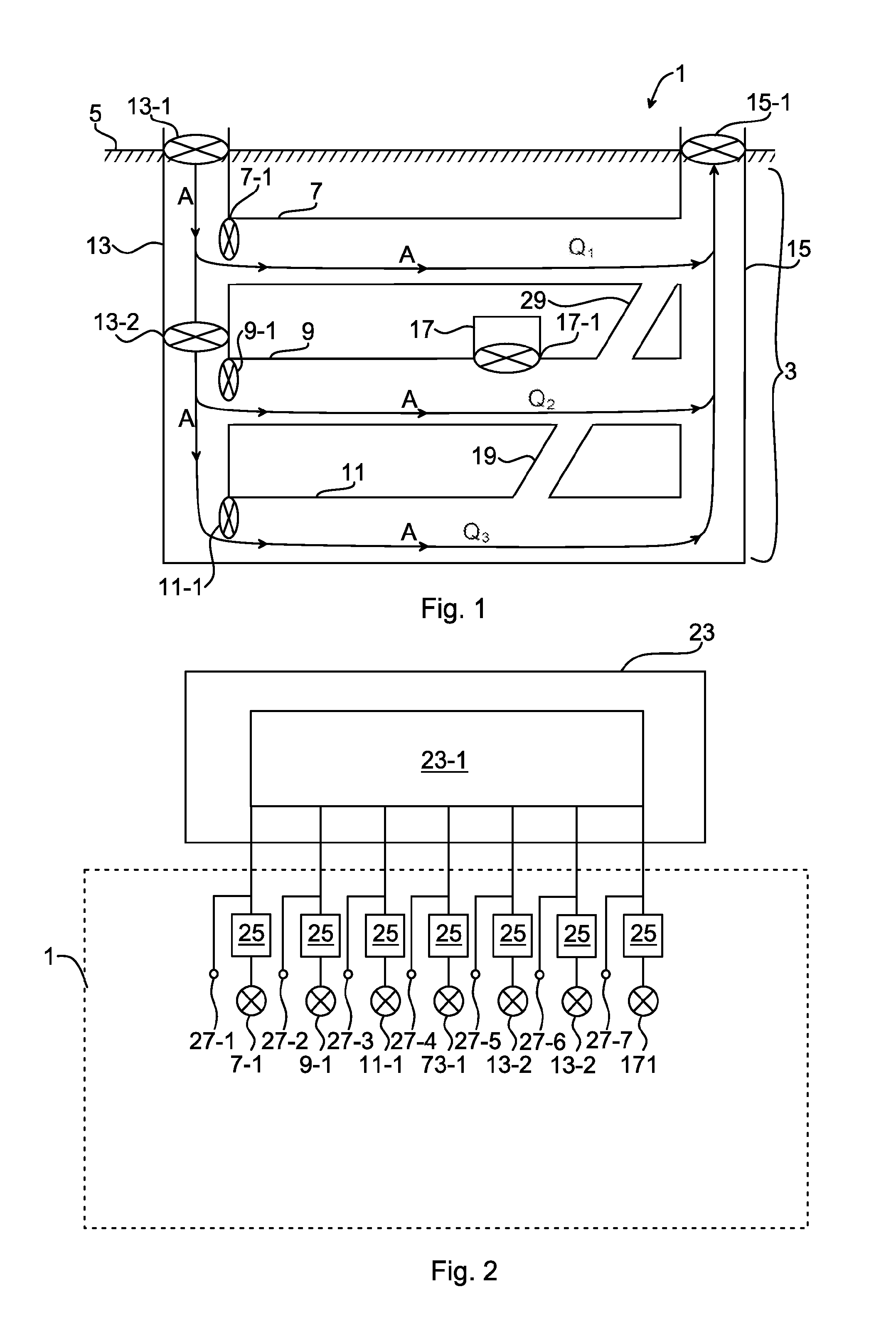
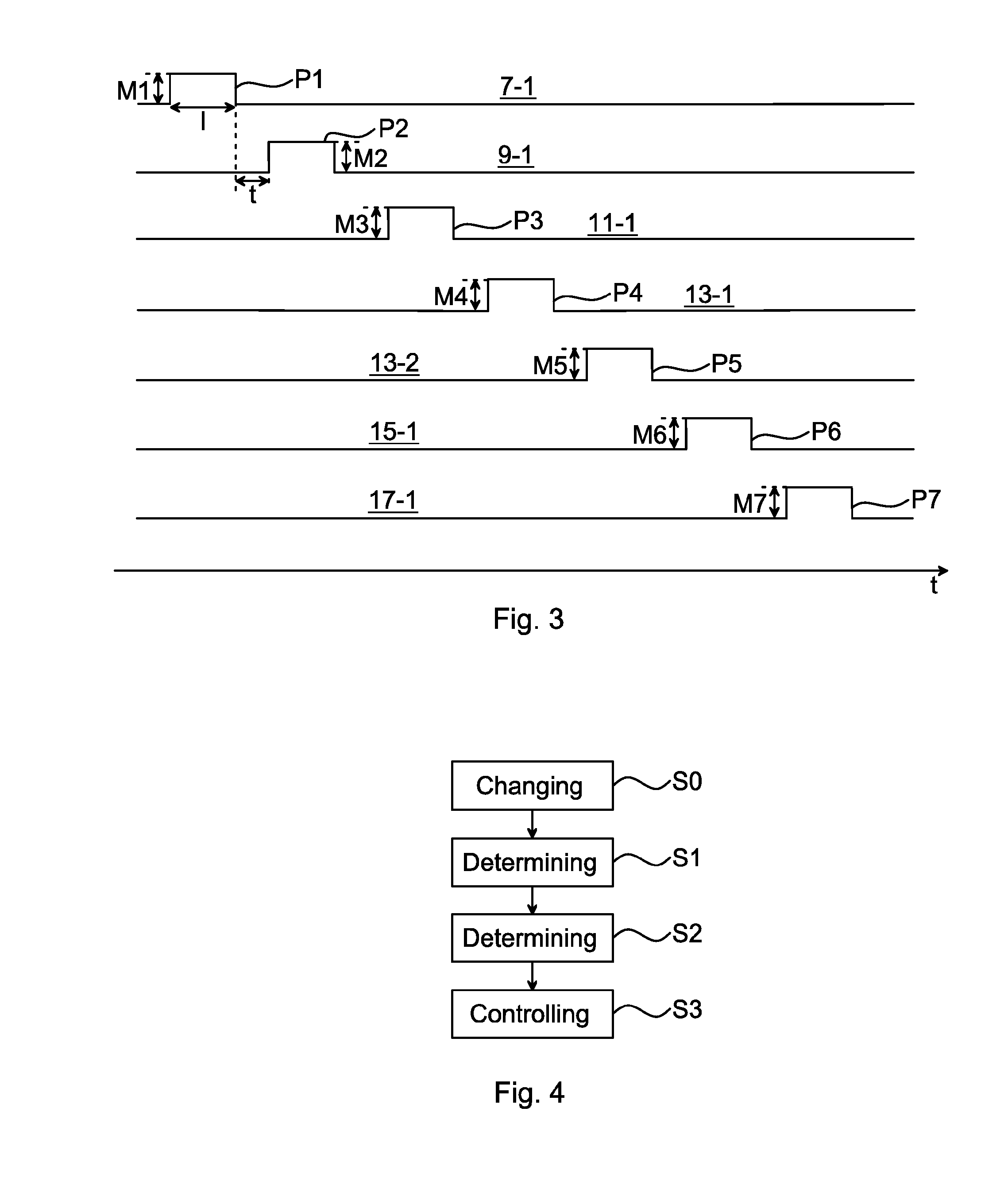
A method of controlling fluid flow in a fluid network system by means of a plurality of fluid machines. The disclosure provides a simple empirical method of identifying network characteristics of the fluid network system used for providing the required fluid flow rate in the fluid network system utilizing minimal fluid machine power. The method includes the steps of determining a relation between a change in fluid machine speed and a corresponding change in fluid flow rate for each of the plurality of fluid machines empirically; determining a minimum total fluid machine power which provides a minimum required flow rate in the fluid network system based on a constraint involving the relation between the fluid flow rate and the corresponding fluid machine speed, and controlling a speed of the plurality of fluid machines such that the minimum total fluid machine power in the fluid network system is attained.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Using topological structure for path planning in semi-structured environments
ActiveUS8392117B2Low costMinimize sumInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsEngineeringAngular orientation
A method of creating a lane network of a semi-structured environment for a vehicle, assigning a corresponding cost function to each of a plurality of coordinates of the semi-structured environment using the lane network and a state of the vehicle, the state of the vehicle corresponding to a coordinate location of the vehicle and an angular orientation of the vehicle, and determining an obstacle-free path on the semi-structured environment using the cost function of each of the plurality of coordinates.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
Systems and methods for conducting animal studies
ActiveUS20060264780A1Simplify laborFacilitate high throughput point-of-care testingCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAnalytePoint-of-care testing
This invention is in the field of medical devices. Specifically, the present invention provides portable medical devices that allow real-time detection of analytes from a biological fluid. The methods and devices are particularly useful for providing point-of-care testing for a variety of medical applications.
Owner:GOLDEN DIAGNOSTICS CORP
Frame rate up-conversion coding mode with affine motion model
ActiveUS10778999B2Promote resultsIncreased complexityTelevision signal transmission by single/parallel channelsDigital video signal modificationAffine motionReference map
Methods, apparatuses, and computer-readable medium are provided for a frame rate up-conversion coding mode, in which an affine motion model is applied when conducting bilateral matching. The frame rate up-conversion coding mode can include generated additional frames from frames provided in a bitstream. In various implementations, bilateral matching includes, for a current block in a frame that is being generated, identifying a first block in a first reference picture a second block in a second reference picture. Affine (e.g., non-linear) motion information can be determined as between the first block and the second block. The current block can be predicted using the affine motion information.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
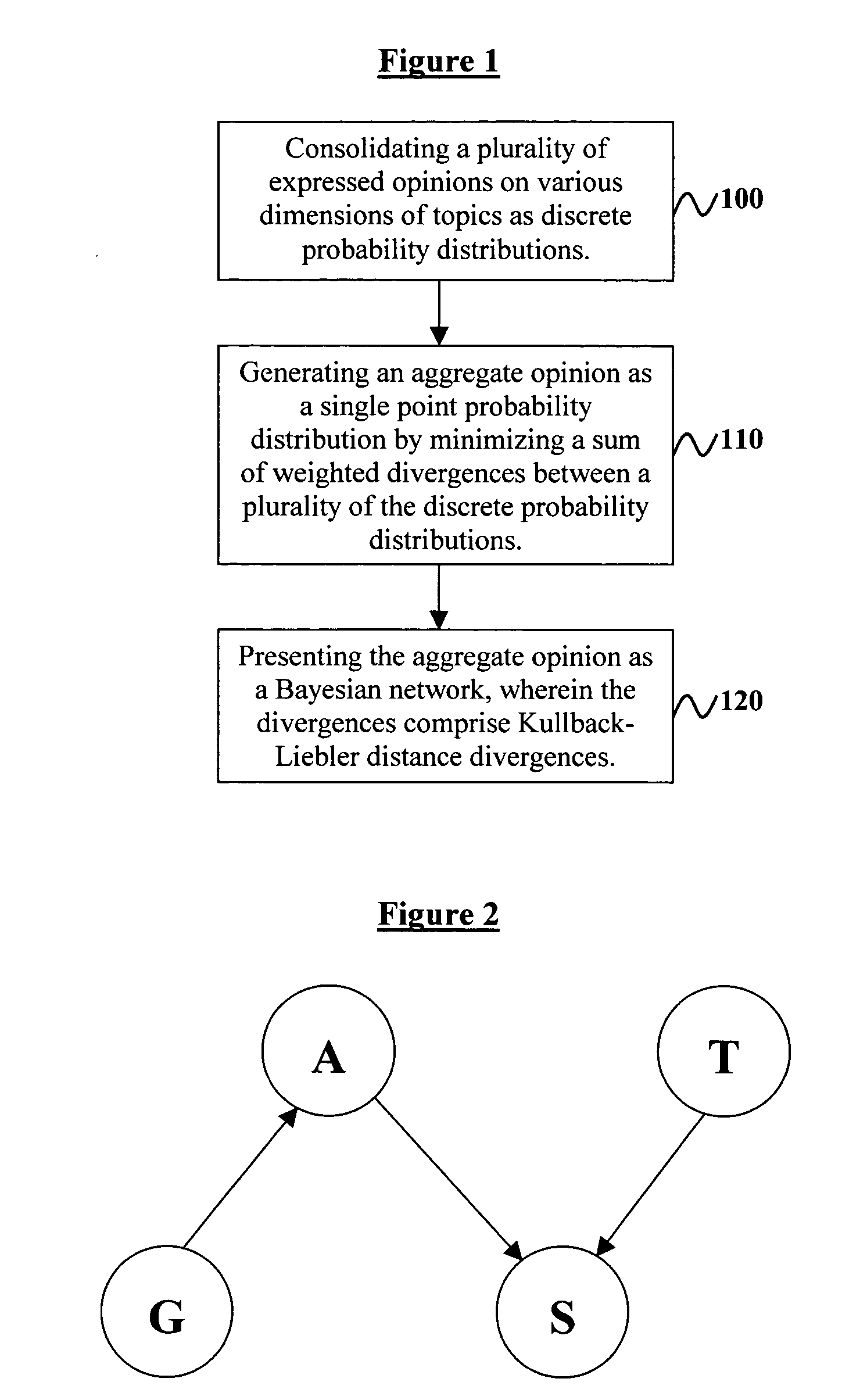
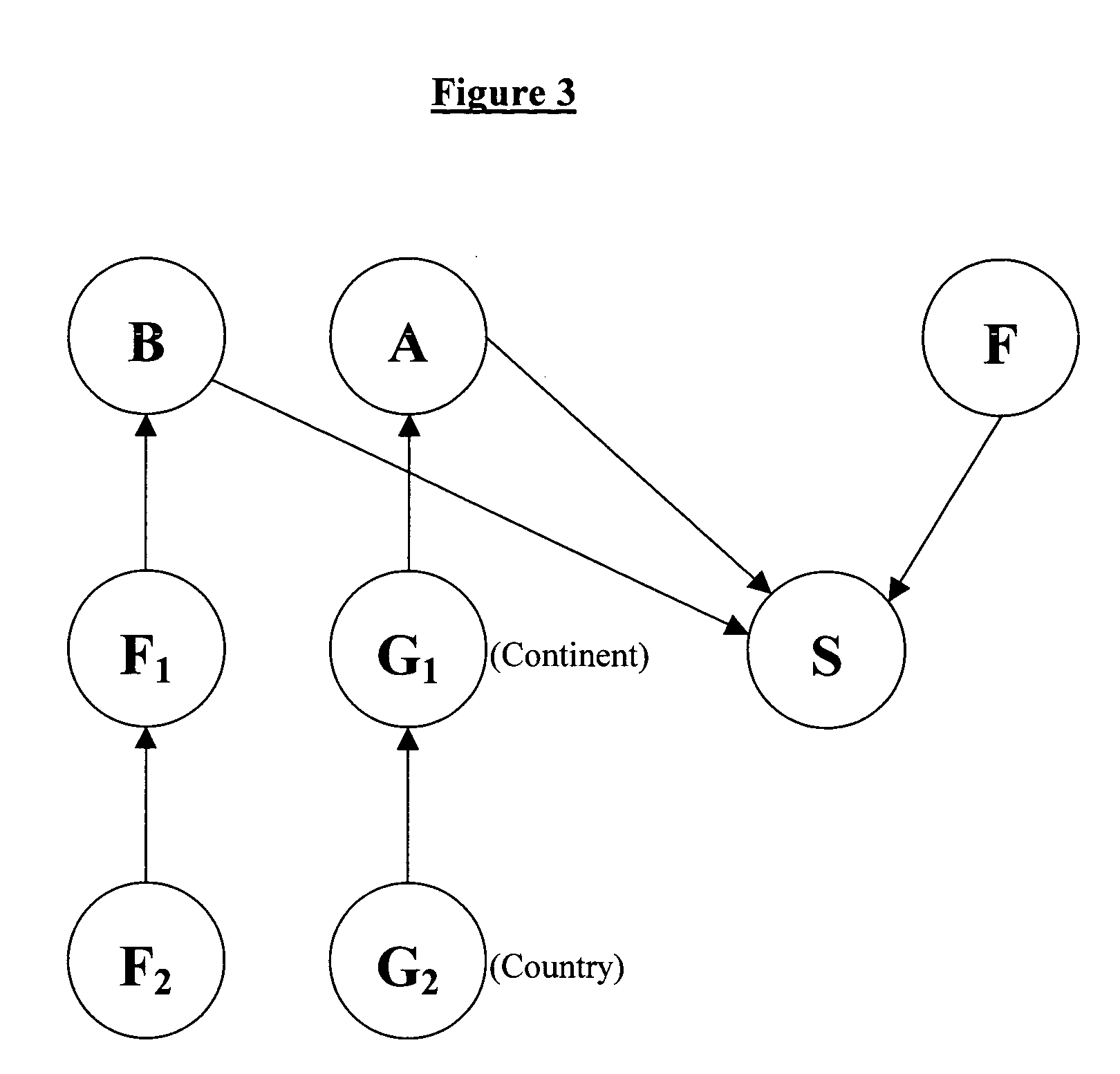
Method to hierarchical pooling of opinions from multiple sources
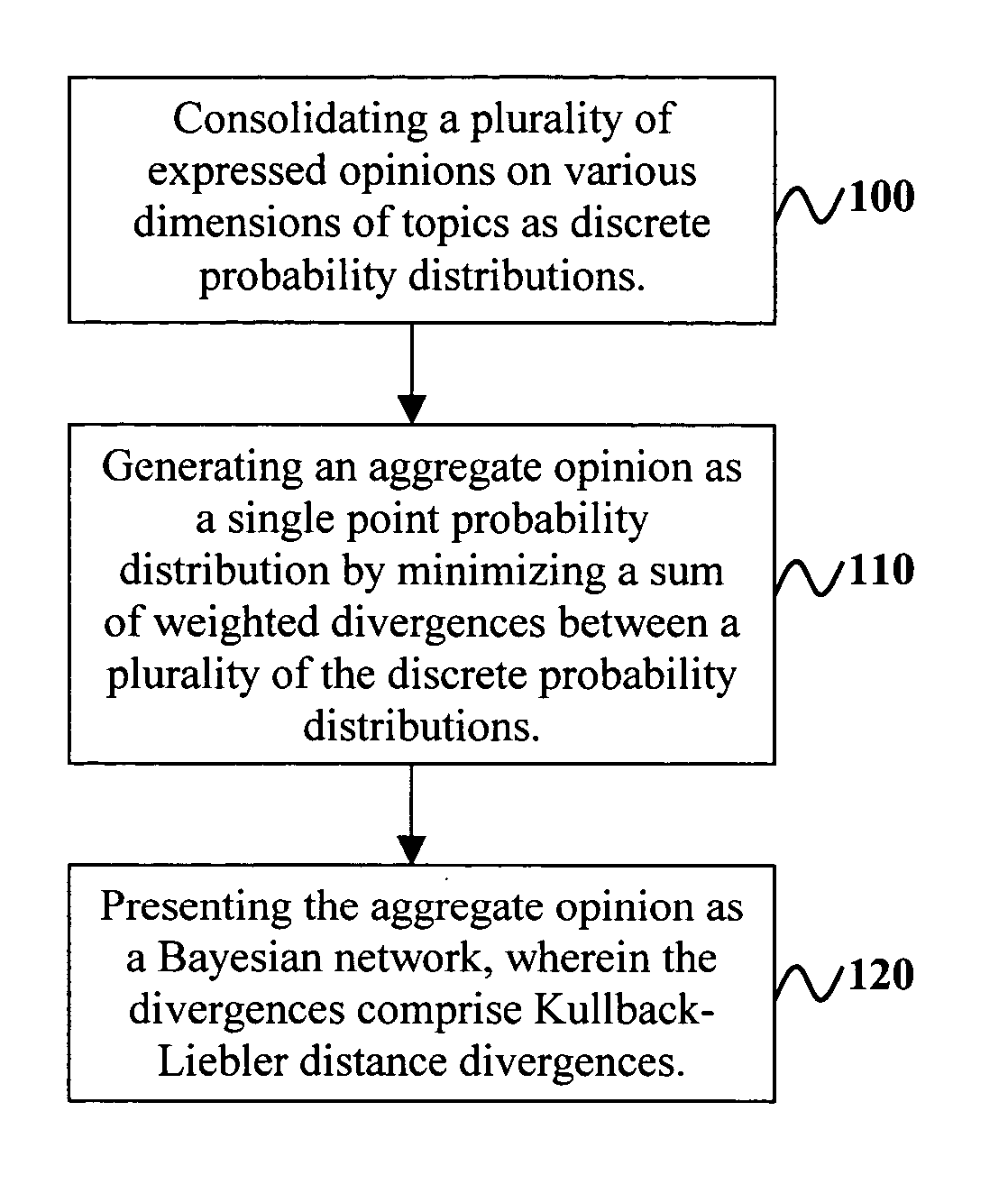
InactiveUS7130777B2Minimize sumInherent uncertaintyComputation using non-denominational number representationFuzzy logic based systemsBayesian networkData science
Disclosed is a system, method, and program storage device of aggregating opinions comprising consolidating a plurality of expressed opinions on various dimensions of topics as discrete probability distributions, generating an aggregate opinion as a single point probability distribution by minimizing a sum of weighted divergences between a plurality of the discrete probability distributions, and presenting the aggregate opinion as a Bayesian network, wherein the divergences comprise Kullback-Liebler distance divergences, and wherein the expressed opinions are generated by experts and comprise opinions on sentiments of products and services. Moreover, the aggregate opinion predicts success of the products and services. Furthermore, the experts are arranged in a hierarchy of knowledge, wherein the knowledge comprises the various dimensions of topics for which opinions may be expressed upon.
Owner:LINKEDIN
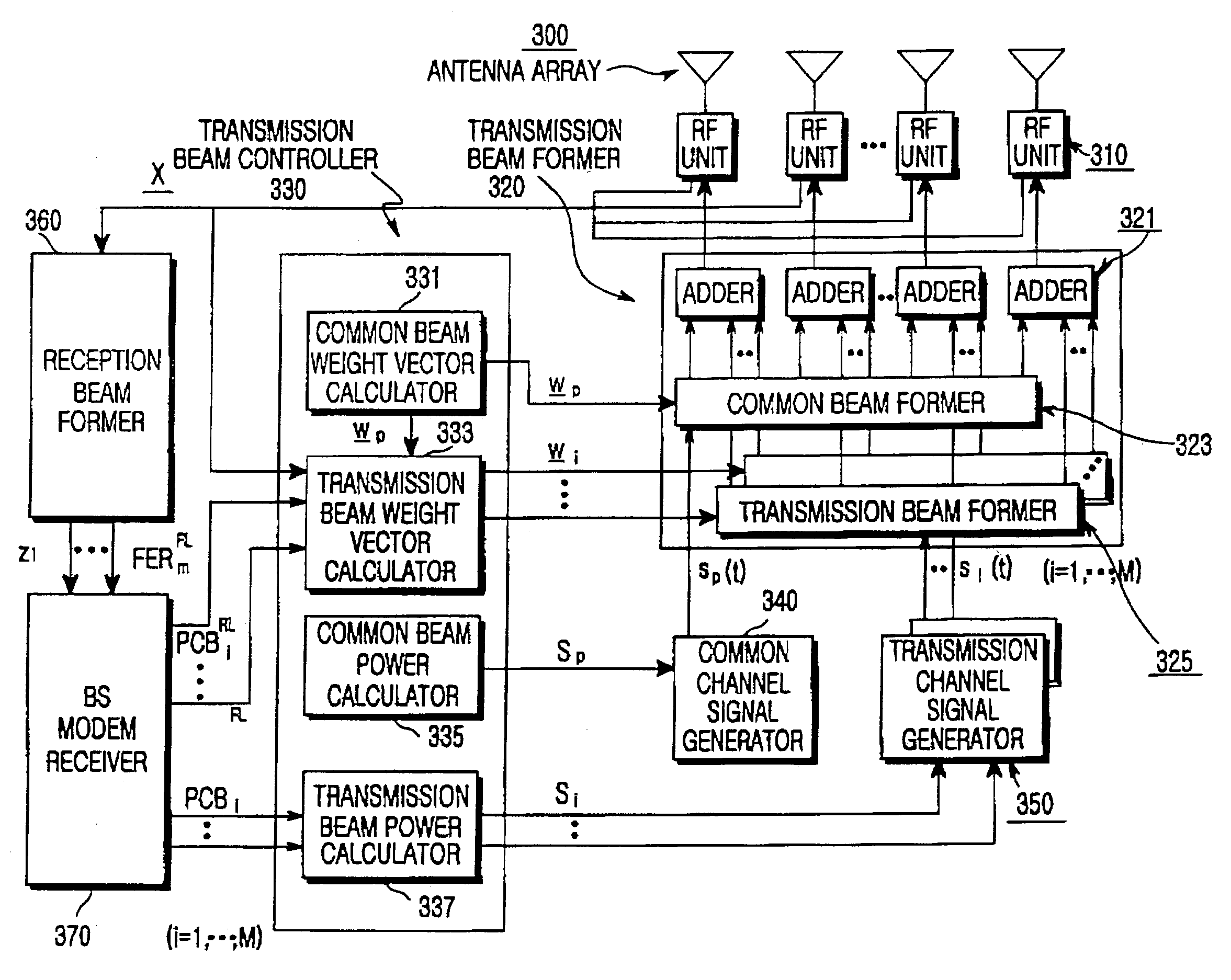
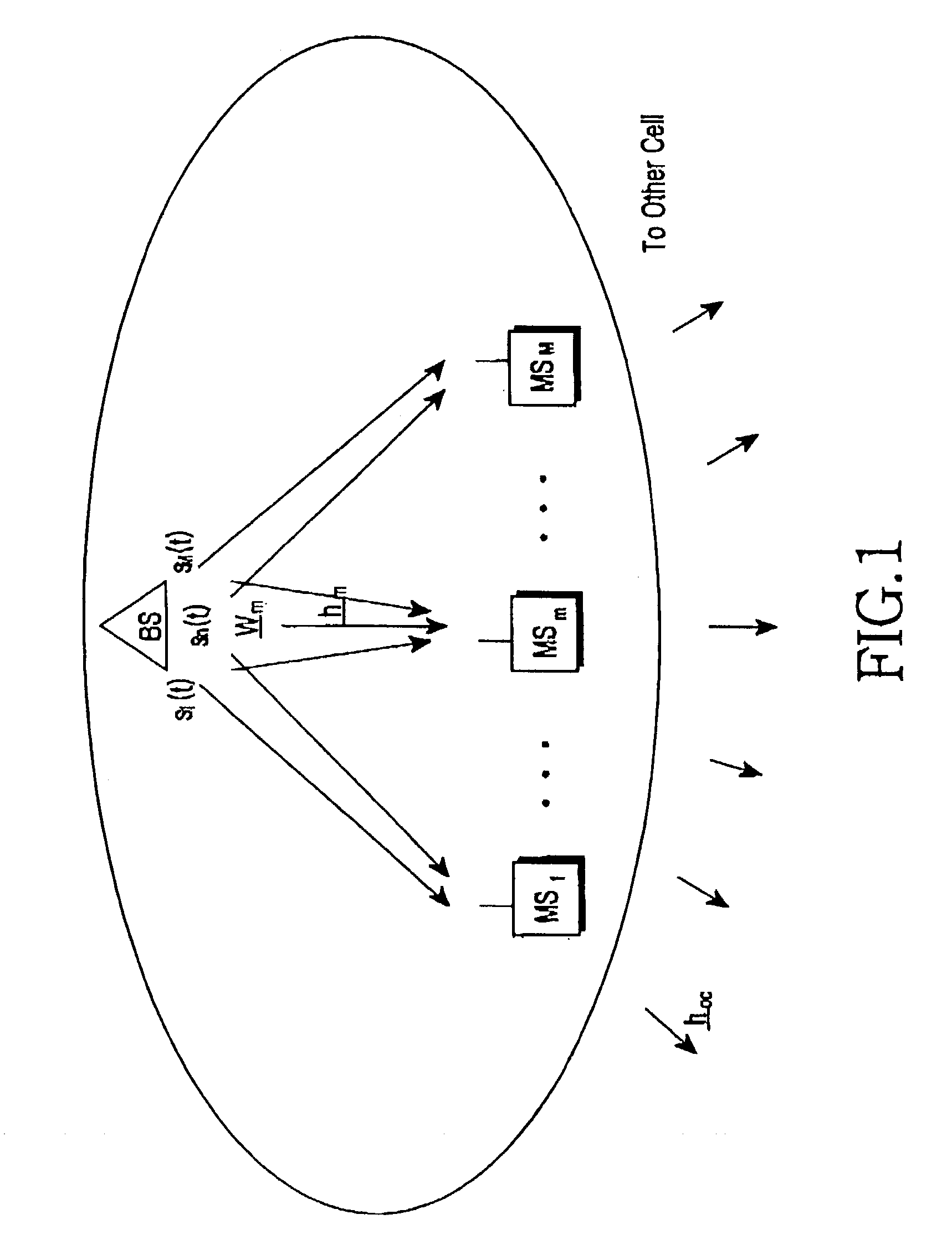
Apparatus and method for forming a forward link transmission beam of a smart antenna in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS7103384B2Power maximizationMinimize sumRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial transmit diversitySmart antennaTransmission channel
A method and apparatus for a base station including an antenna array calculates a direction of a weight vector of a transmission beam to maximize in-phase component power for a common channel signal in a transmission channel signal for transmission to a mobile station and to minimize a sum of quadrature-phase power component and interference power for other mobile stations inside and outside a cell due to a transmission channel signal for the mobile station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
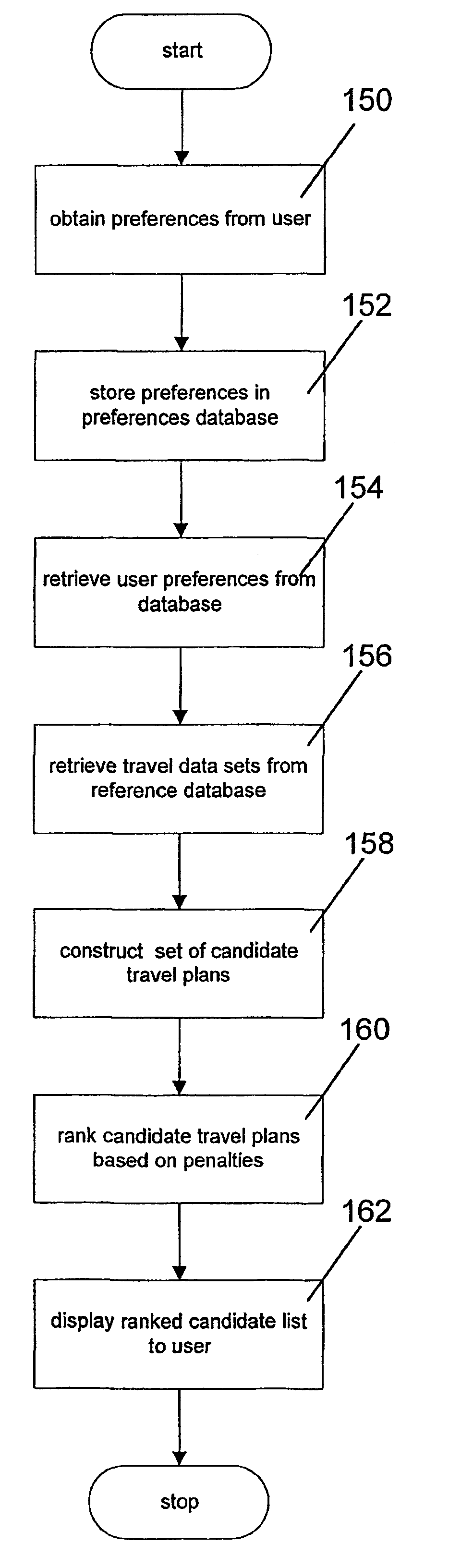
Travel route planner system and method
InactiveUS6622084B2Minimize sumInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlReference databaseData set
Owner:BALLY TECHNOLOGIES
Delay-constrained and energy-efficient online routing for asynchronous sensor networks
ActiveUS20120218926A1Life maximizationReduce the burden onPower managementEnergy efficient ICTSource to sinkWireless sensor networking
The described method and system provide an efficient routing of data packets protocol in an event-driven and delay-constrained WSN (wireless sensor network) that optimizes the sleep / wake schedule of nodes to maximize the lifetime of the WSM, subject to a constraint on the source-to-sink delay. Online forwarding techniques may be used to transfer data reports from monitoring nodes to the sink. A delay-constrained and energy-efficient routing protocol (DCEER) for asynchronous WSNs may be used to maximize the lifetime of the WSN while remaining within the maximum allowable delay requirements. With DCEER, each node may maintain the historical cost of forwarding a packet from itself to the sink as its virtual coordinate, and packets are forwarded in the direction of descending coordinates. The cost-based coordinates may change dynamically with a time-varying channel or topology. Nodes may apply a relay-selection scheme to choose a next-hop relay from a set of multiple potential relay candidates, based on a tradeoff between forwarding energy consumption (FEC) and waiting costs. The optimal stopping time for the relay-selection process may be determined based on expected forwarding and waiting costs, and the nodes may operate according to an optimal sleep / wake schedule based on waiting costs and expected traffic flow.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
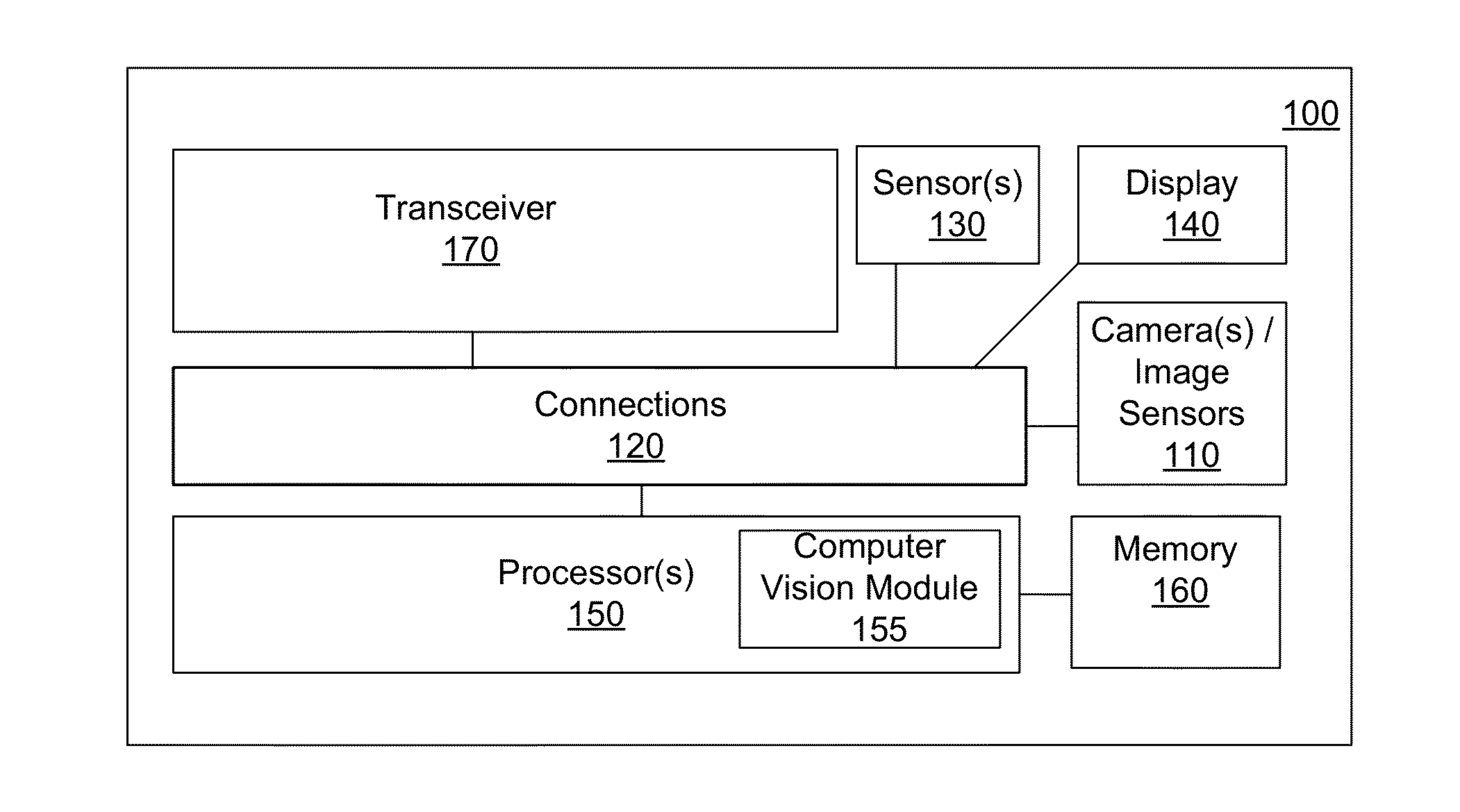
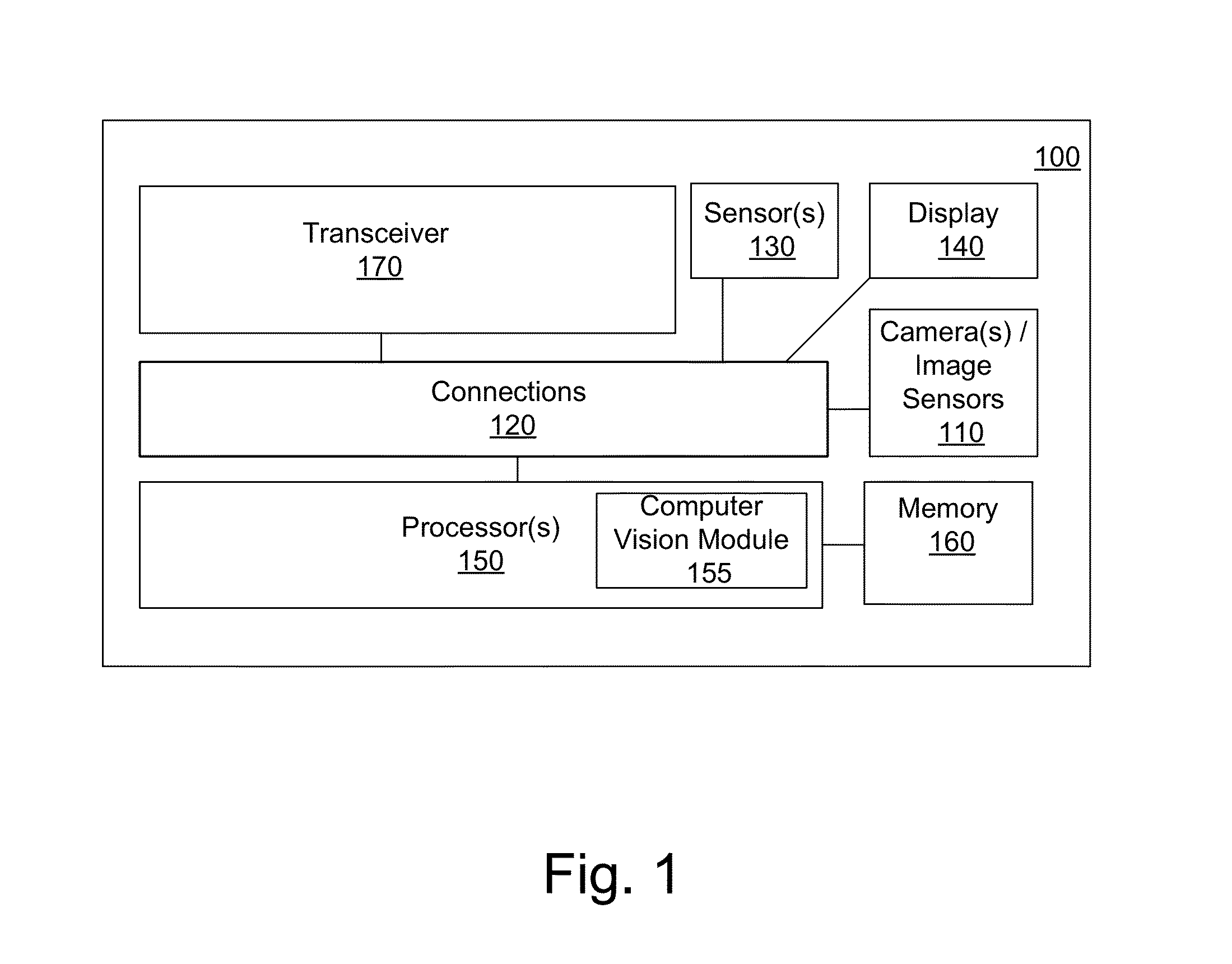
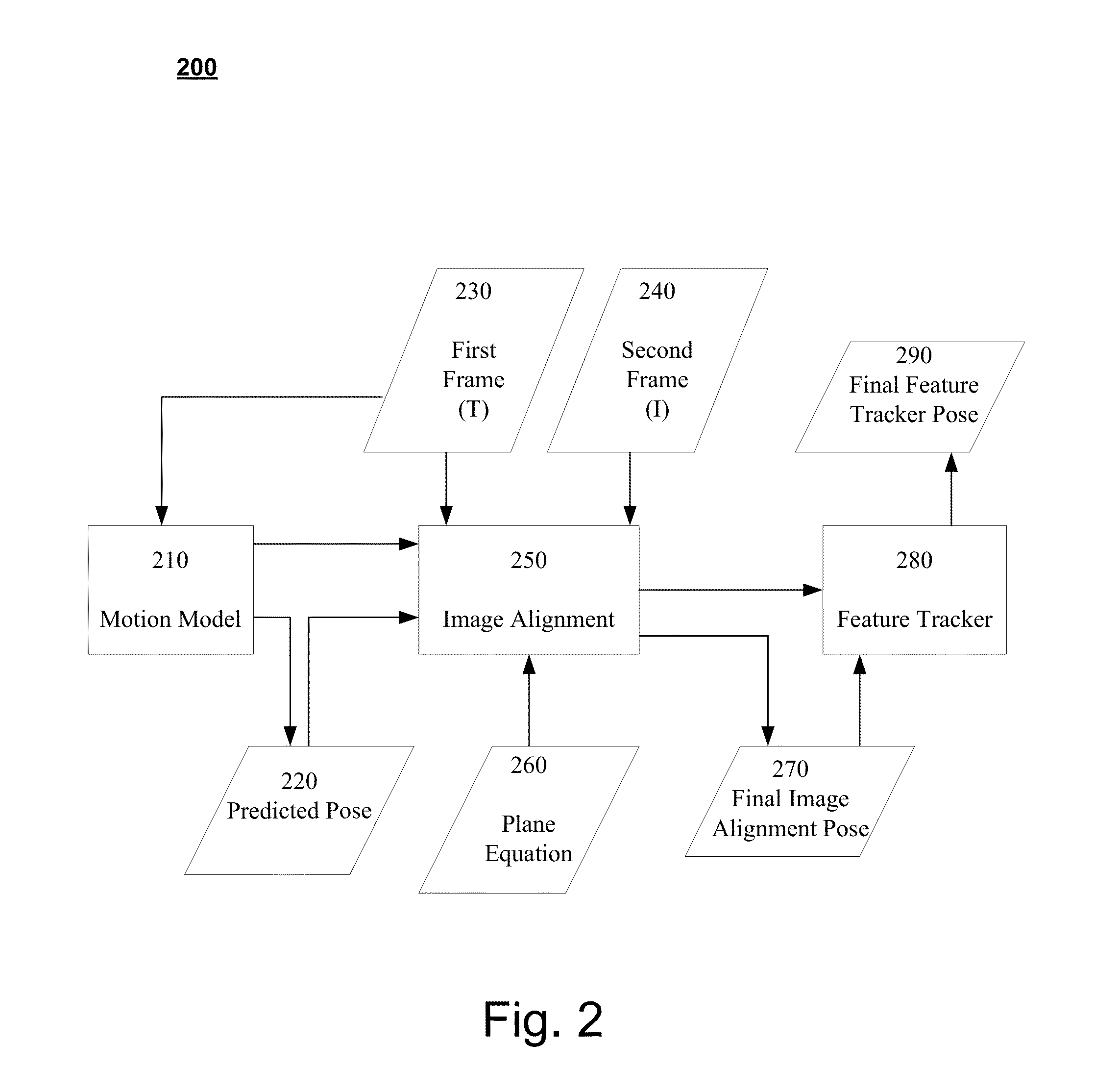
Systems and Methods for Feature-Based Tracking
Disclosed embodiments pertain to feature based tracking. In some embodiments, a camera pose may be obtained relative to a tracked object in a first image and a predicted camera pose relative to the tracked object may be determined for a second image subsequent to the first image based, in part, on a motion model of the tracked object. An updated SE(3) camera pose may then be obtained based, in part on the predicted camera pose, by estimating a plane induced homography using an equation of a dominant plane of the tracked object, wherein the plane induced homography is used to align a first lower resolution version of the first image and a first lower resolution version of the second image by minimizing the sum of their squared intensity differences. A feature tracker may be initialized with the updated SE(3) camera pose.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
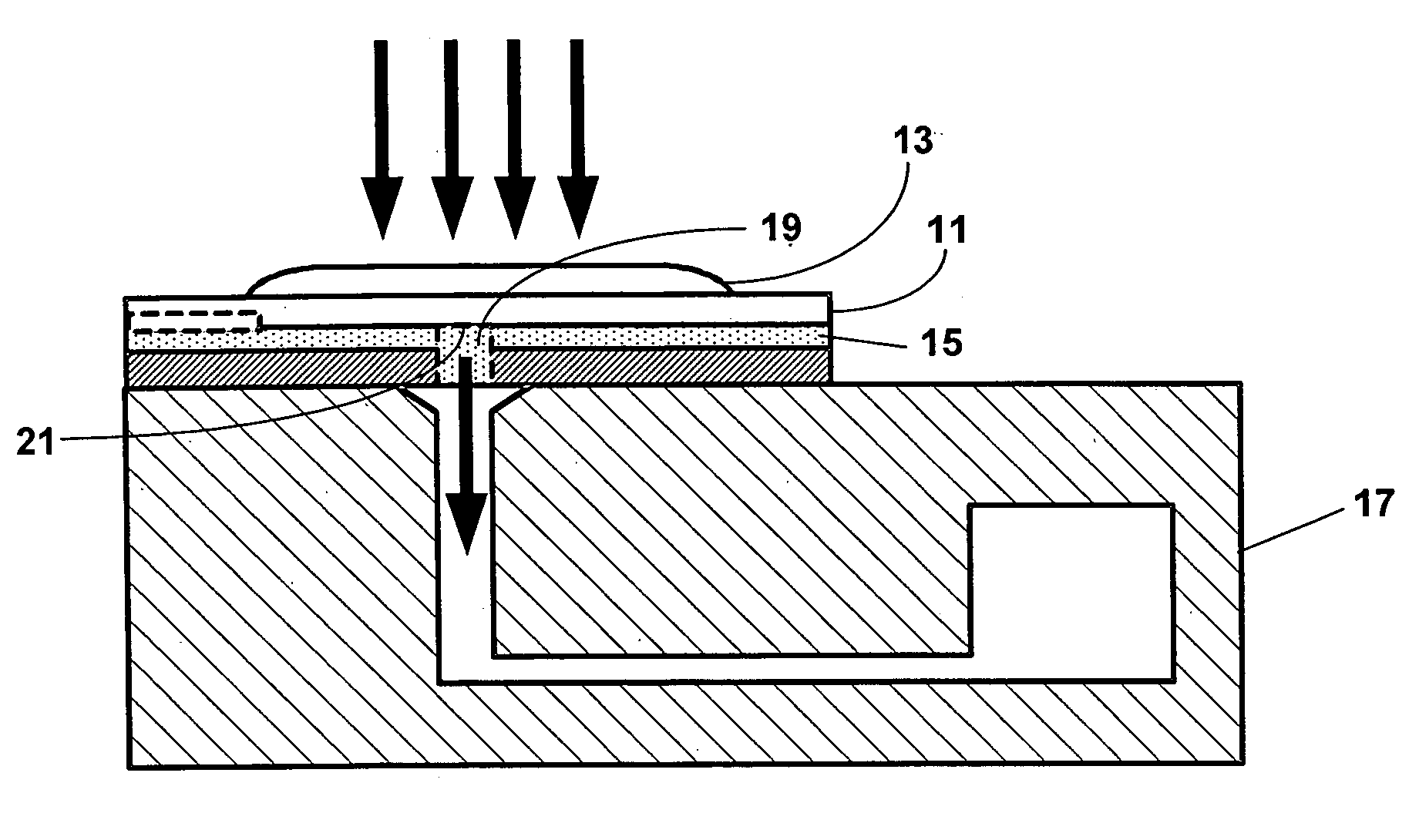
Automated detection and repositioning of micro-objects in microfluidic devices
Owner:BERKELEY LIGHTS
Frame rate up-conversion coding mode
ActiveUS20180098062A1Promote resultsIncreased complexityDigital video signal modificationAffine motionComputer science
Methods, apparatuses, and computer-readable medium are provided for a frame rate up-conversion coding mode, in which an affine motion model is applied when conducting bilateral matching. The frame rate up-conversion coding mode can include generated additional frames from frames provided in a bitstream. In various implementations, bilateral matching includes, for a current block in a frame that is being generated, identifying a first block in a first reference picture a second block in a second reference picture. Affine (e.g., non-linear) motion information can be determined as between the first block and the second block. The current block can be predicted using the affine motion information.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Systems and methods for improving medical treatments
ActiveUS20080009766A1Simplify laborFacilitate high throughput point-of-care testingCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAnalytePoint-of-care testing
This invention is in the field of medical devices. Specifically, the present invention provides portable medical devices that allow real-time detection of analytes from a biological fluid. The methods and devices are particularly useful for providing point-of-care testing for a variety of medical applications.
Owner:GOLDEN DIAGNOSTICS CORP
Method to hierarchical pooling of opinions from multiple sources
InactiveUS20050114161A1Minimize sumGood estimateComputation using non-denominational number representationFuzzy logic based systemsSubject matterSystems approaches
Disclosed is a system, method, and program storage device of aggregating opinions comprising consolidating a plurality of expressed opinions on various dimensions of topics as discrete probability distributions, generating an aggregate opinion as a single point probability distribution by minimizing a sum of weighted divergences between a plurality of the discrete probability distributions, and presenting the aggregate opinion as a Bayesian network, wherein the divergences comprise Kullback-Liebler distance divergences, and wherein the expressed opinions are generated by experts and comprise opinions on sentiments of products and services. Moreover, the aggregate opinion predicts success of the products and services. Furthermore, the experts are arranged in a hierarchy of knowledge, wherein the knowledge comprises the various dimensions of topics for which opinions may be expressed upon.
Owner:LINKEDIN
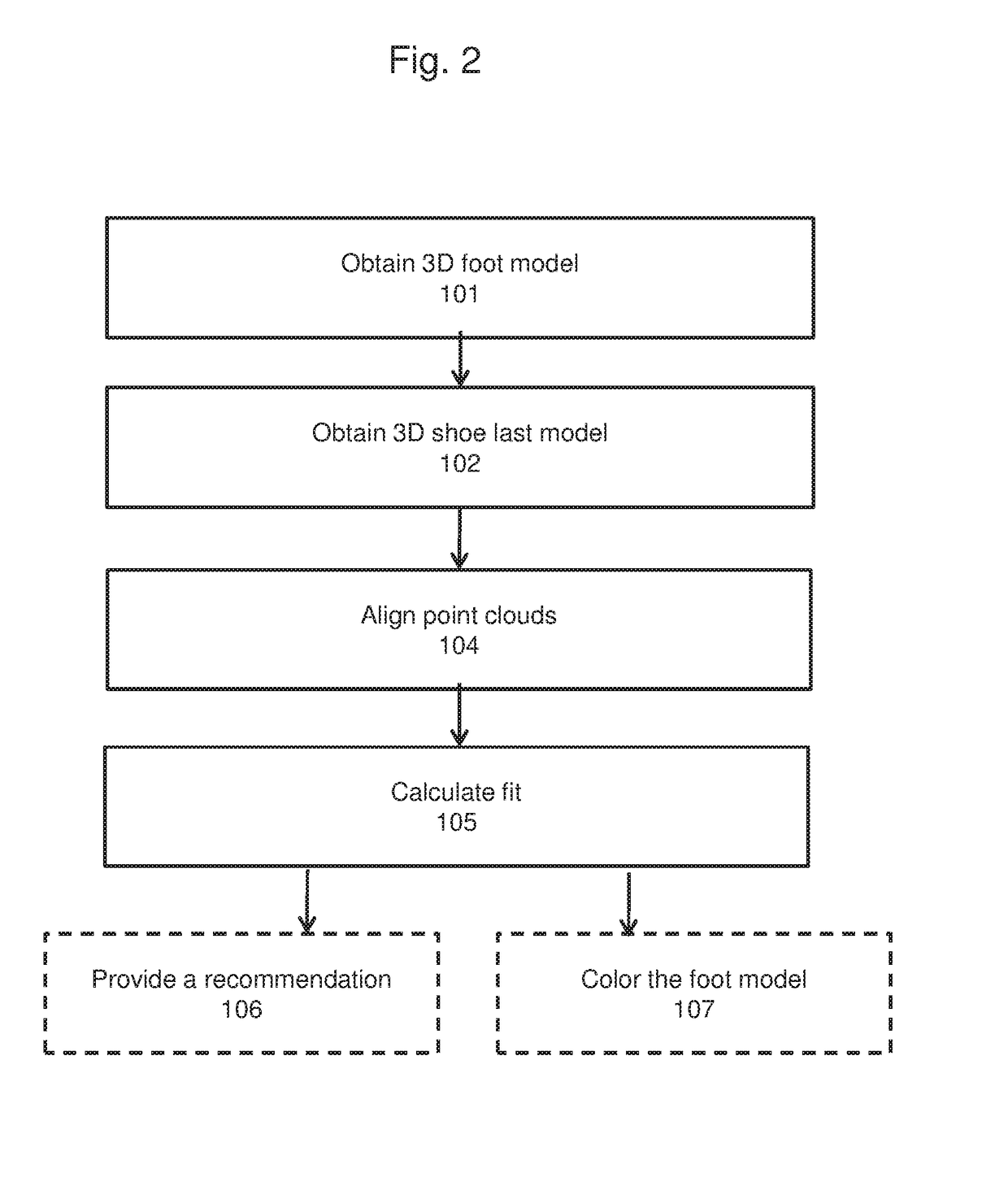
System and method of 3D modeling and virtual fitting of 3D objects
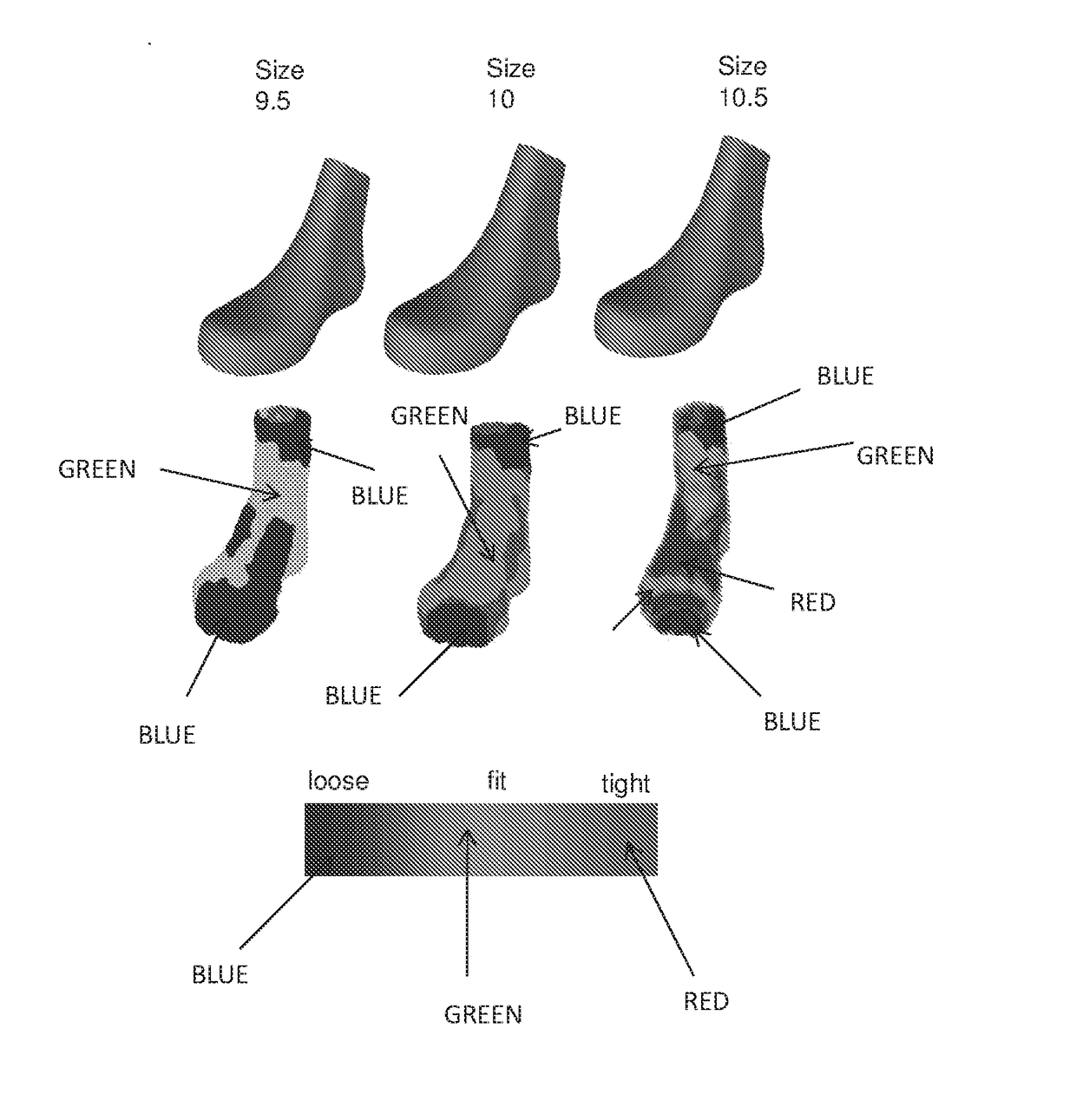
Method and system of virtual fitting a foot with a shoe by obtaining a first and second 3D model associated with the surface of the foot and interior cavity of the shoe, respectively, each 3D model comprising a point cloud; aligning the point clouds such that the heel extreme point of the two point clouds align and the ankle back extreme point of the first point cloud aligns with the top back point of the second point cloud; calculating for at least one point p in the first point cloud a value of at least one fit indicator determined based on a distance between p and a corresponding point q in the aligned second point cloud; and outputting, to a display device, a graphical representation of the first 3D model colored in accordance with the fit calculated at p.
Owner:FITFULLY LTD
A method of mapping images of human disease and of designing or selecting a medical device using a surrogate model
ActiveUS20170076014A1Maximize functionalityMinimize sumCatheterAngiographySurrogate modelMedical device
A method of designing or selecting an implantable medical device comprises the steps of: i) obtaining a plurality of measured data points of a characteristic of an anatomical feature of an individual; ii) using said data points to construct a surrogate model of said characteristic, the surrogate model being constructed by interpolating or regressing measured data points of the characteristic, and using said surrogate model to obtain predicted values of said characteristic at a plurality of locations; iii) using said predicted values to determine or select at least one value of a design parameter of the implantable medical device. There is further disclosed a method of monitoring or diagnosing a disease or disorder.
Owner:BRESSLOFF PROFESSOR NEIL +1
Traffic Signal Control System, Design Method and Special Equipment
InactiveUS20130027224A1Reduce loss timeReduce minimum green intervalControlling traffic signalsTraffic volumeEngineering
A traffic signal control method comprises confirming the shortest green light interval; confirming the conflict area of the different traffic flow and the key conflict point position according to the engineering design for road canalization; confirming the longest clear distance si(m) of the traffic tail unit of green light i and the shortest entry distance sj(m) of the traffic head unit of green light j in conflict with green light i; calculating the longest clear time Max{ti} of the traffic tail unit of green light i and the shortest entry time Min{tj} of the traffic head unit of green light j; calculating the shortest green light interval Iij=A+Max{ti}−Min{tj}; confirming the control scheme for the crossing according to the shortest green light interval and sending the control instruction to the traffic signal display device for displaying in real time according to the control scheme. A traffic signal control system and special equipment are also provided.
Owner:HWYL HUBBL TECH DEV CO LTD IN BEIJING
Method, apparatus, signals and media, for selecting operating conditions of a genset
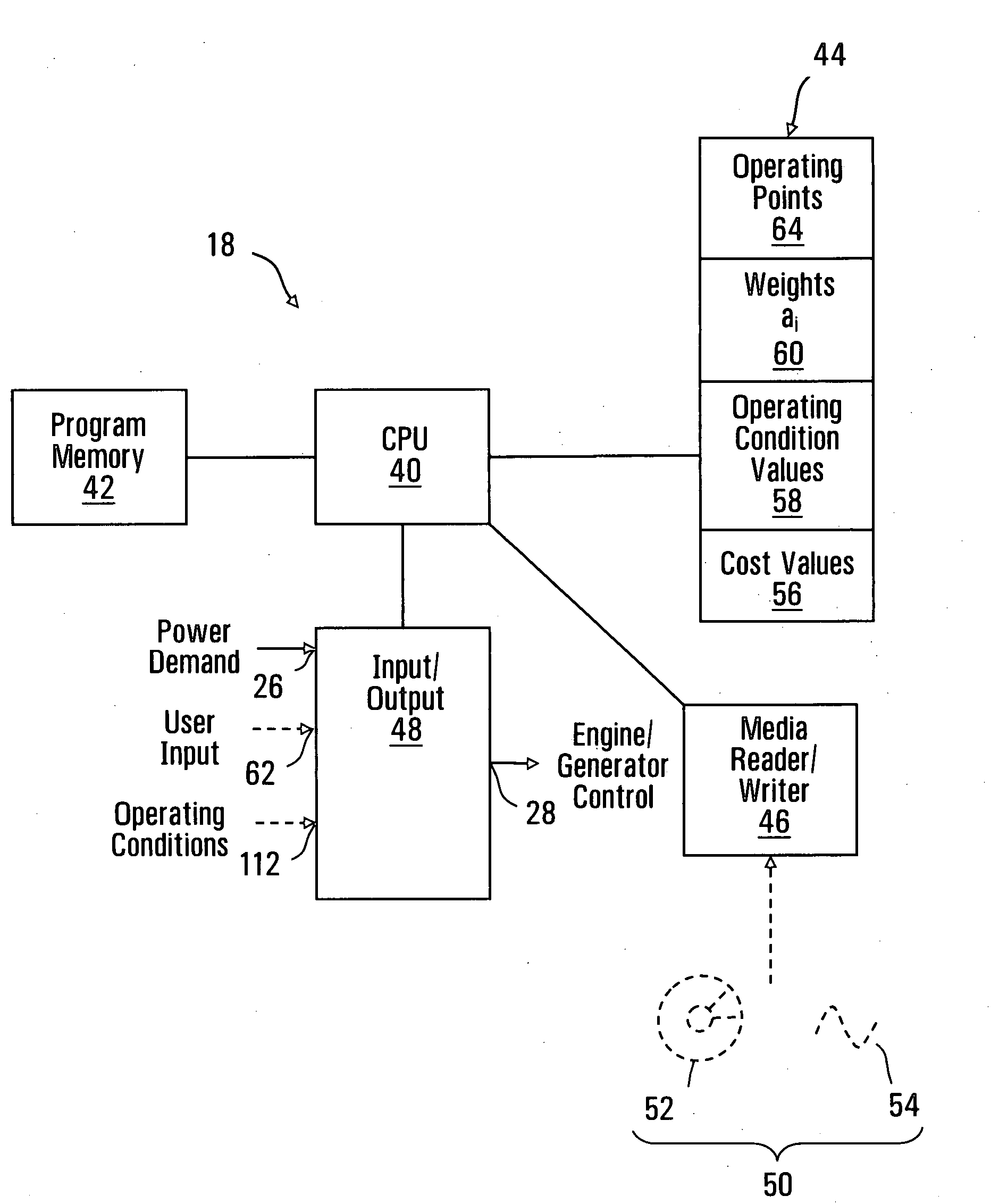
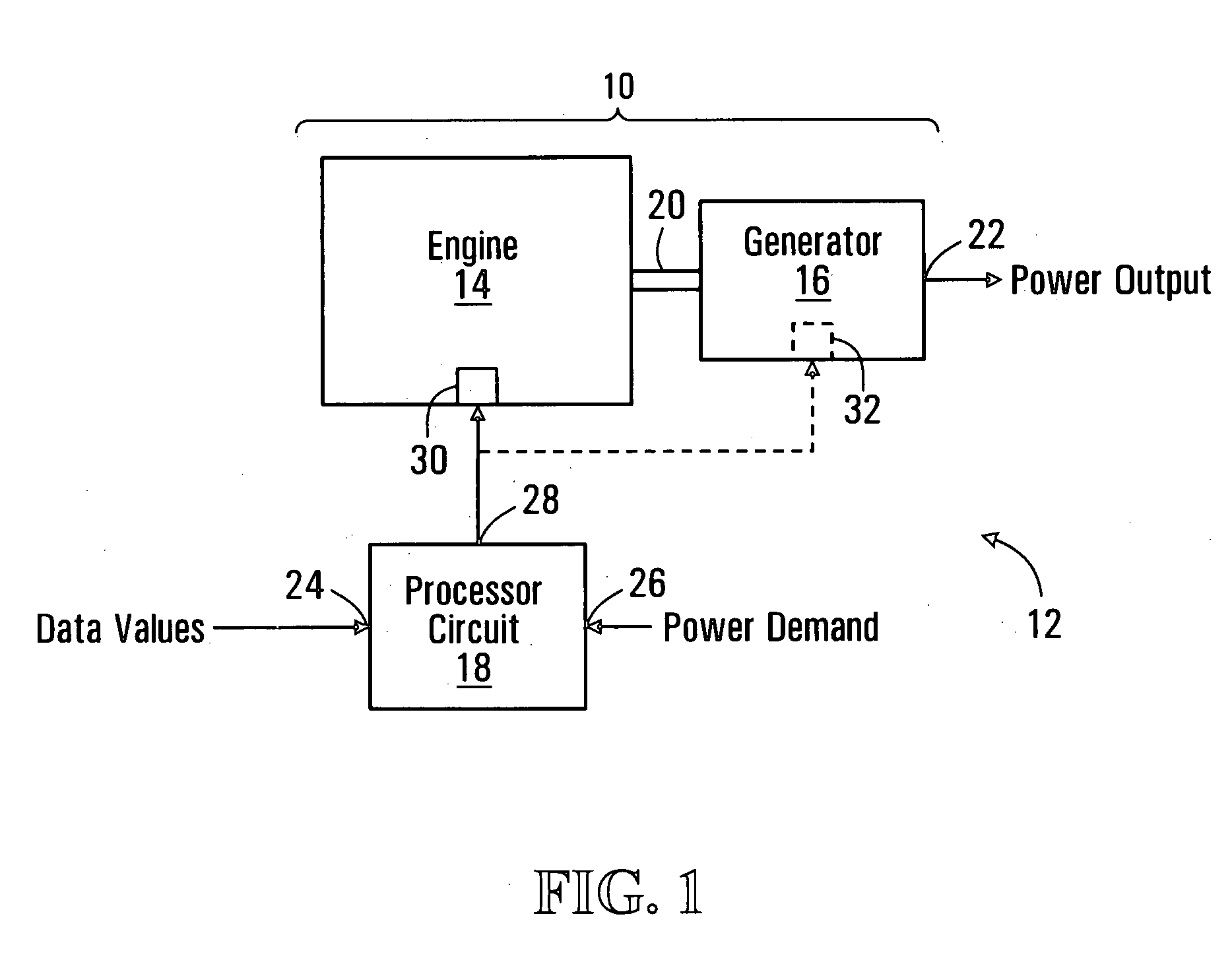
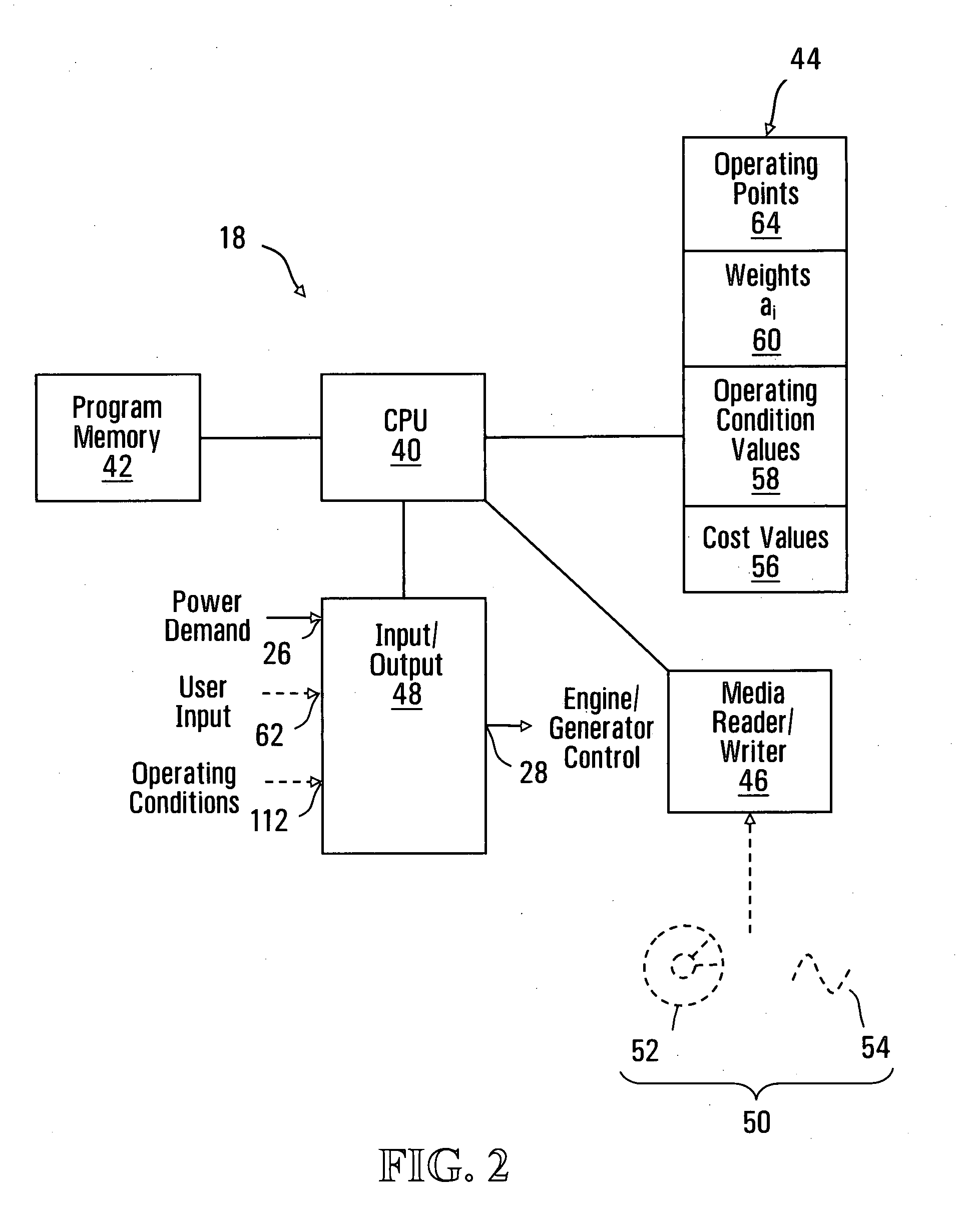
ActiveUS20080122228A1Weight optimizationEasy transferLevel controlInternal combustion piston enginesOperating pointEngineering
A method and apparatus for selecting optimal operating conditions of a genset is disclosed. The genset includes an engine coupled to an electrical power generator, the genset having a plurality of operating points each including an engine speed value and a generator electrical power output value, and having a plurality of cost values associated with operating the genset at respective operating points. The method involves selecting a set of operating points from the plurality of operating points such that a sum of cost values associated with operating points in the set is minimized and such that the engine speed and generator electrical power output values of the operating points in the set increase or decrease monotonically.
Owner:GE HYBRID TECH
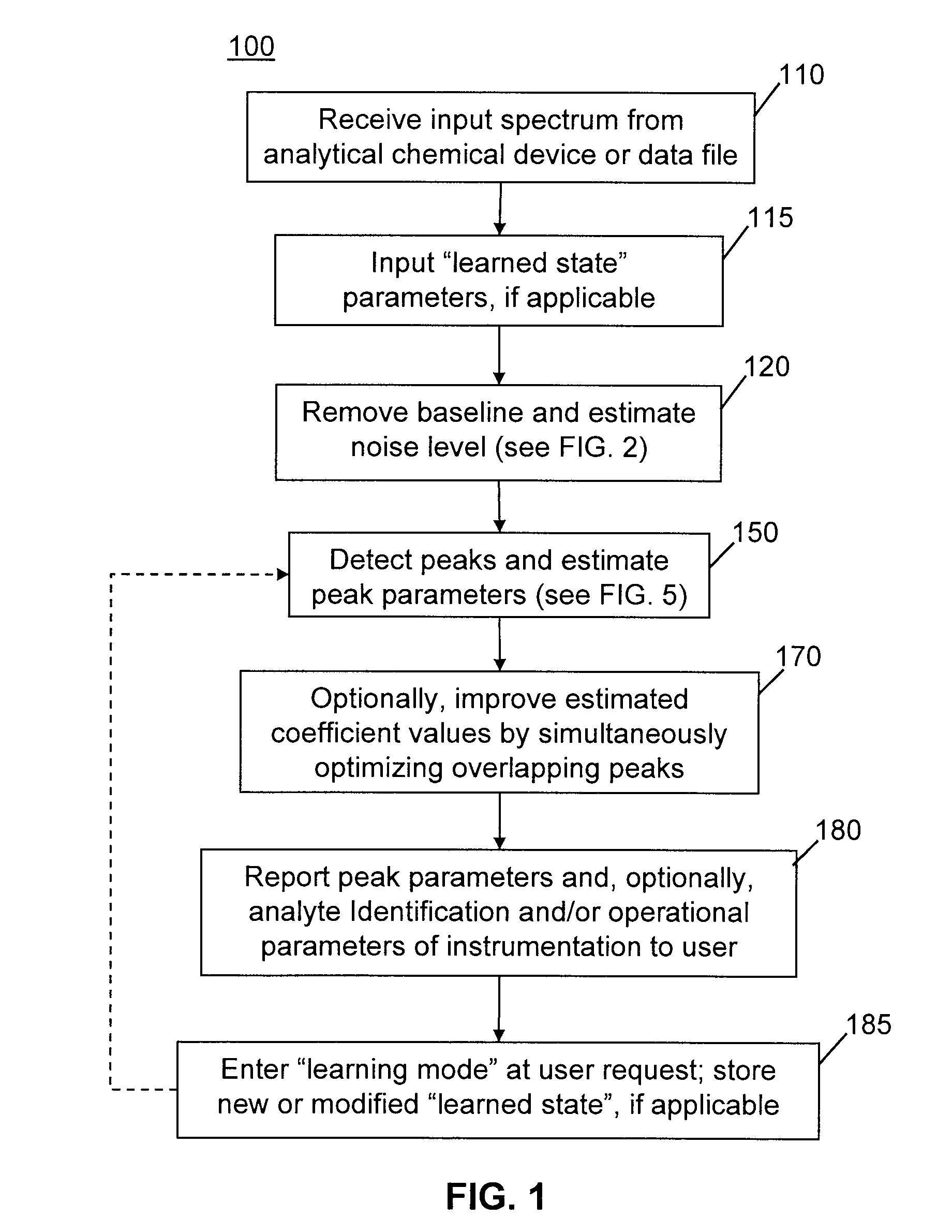
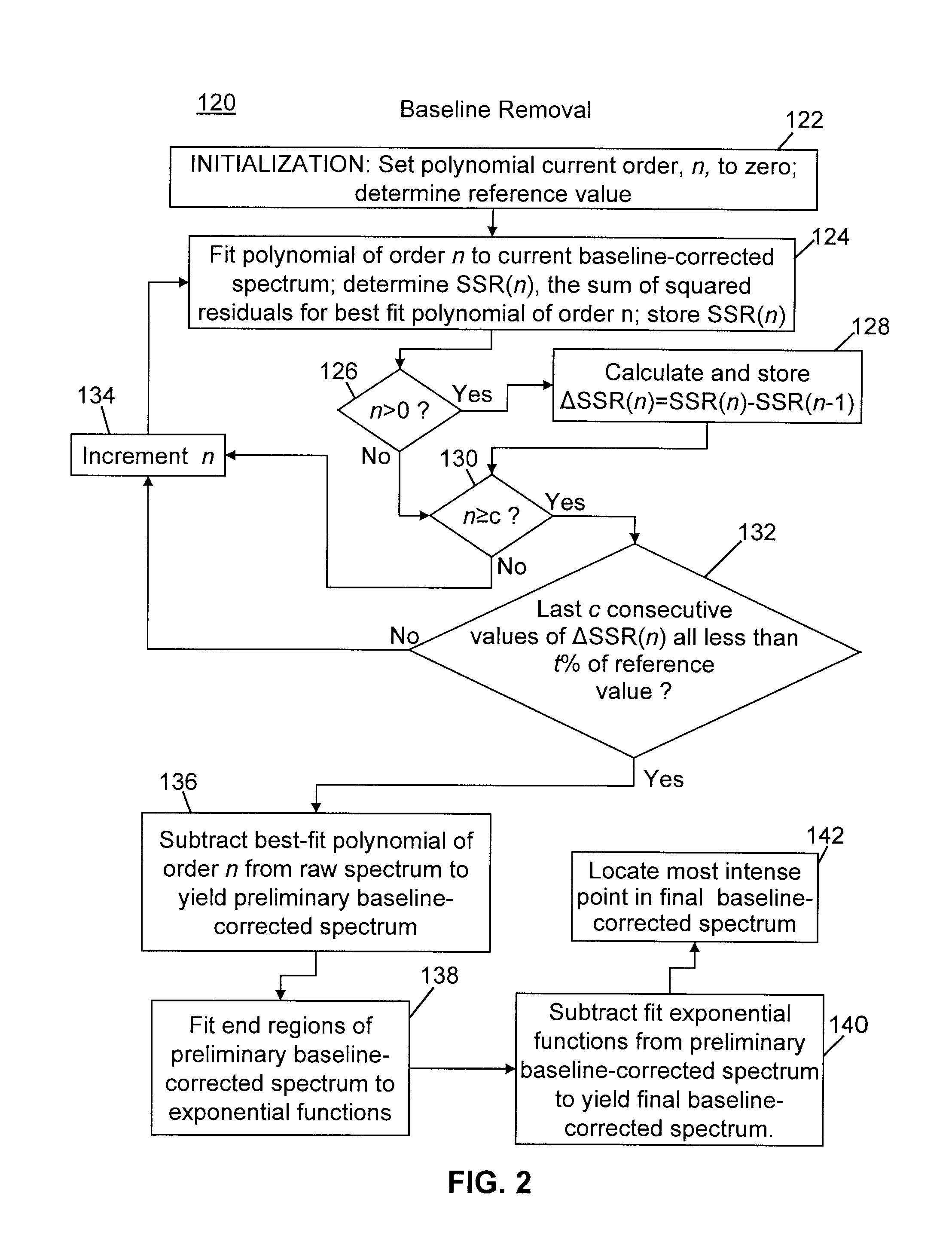
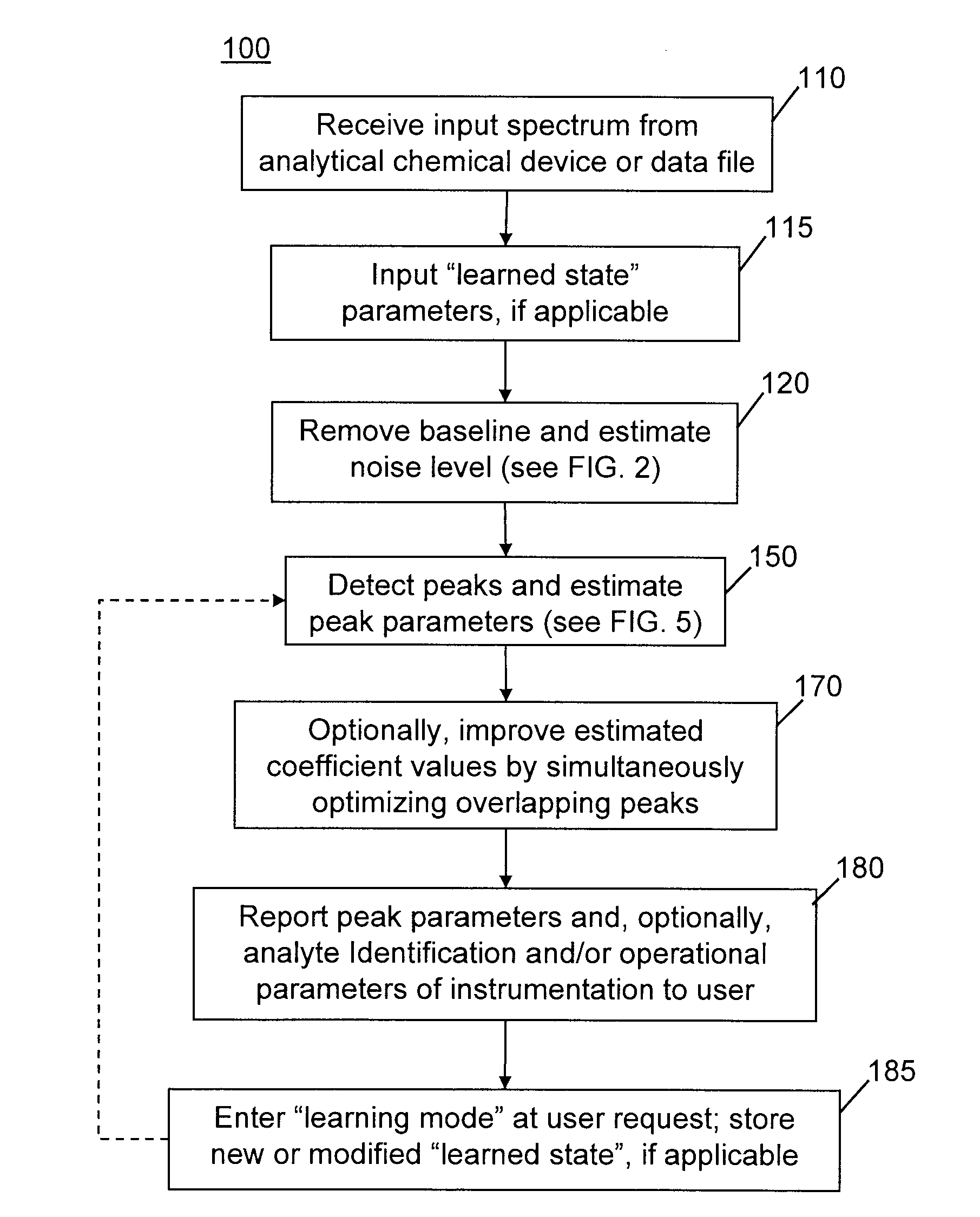
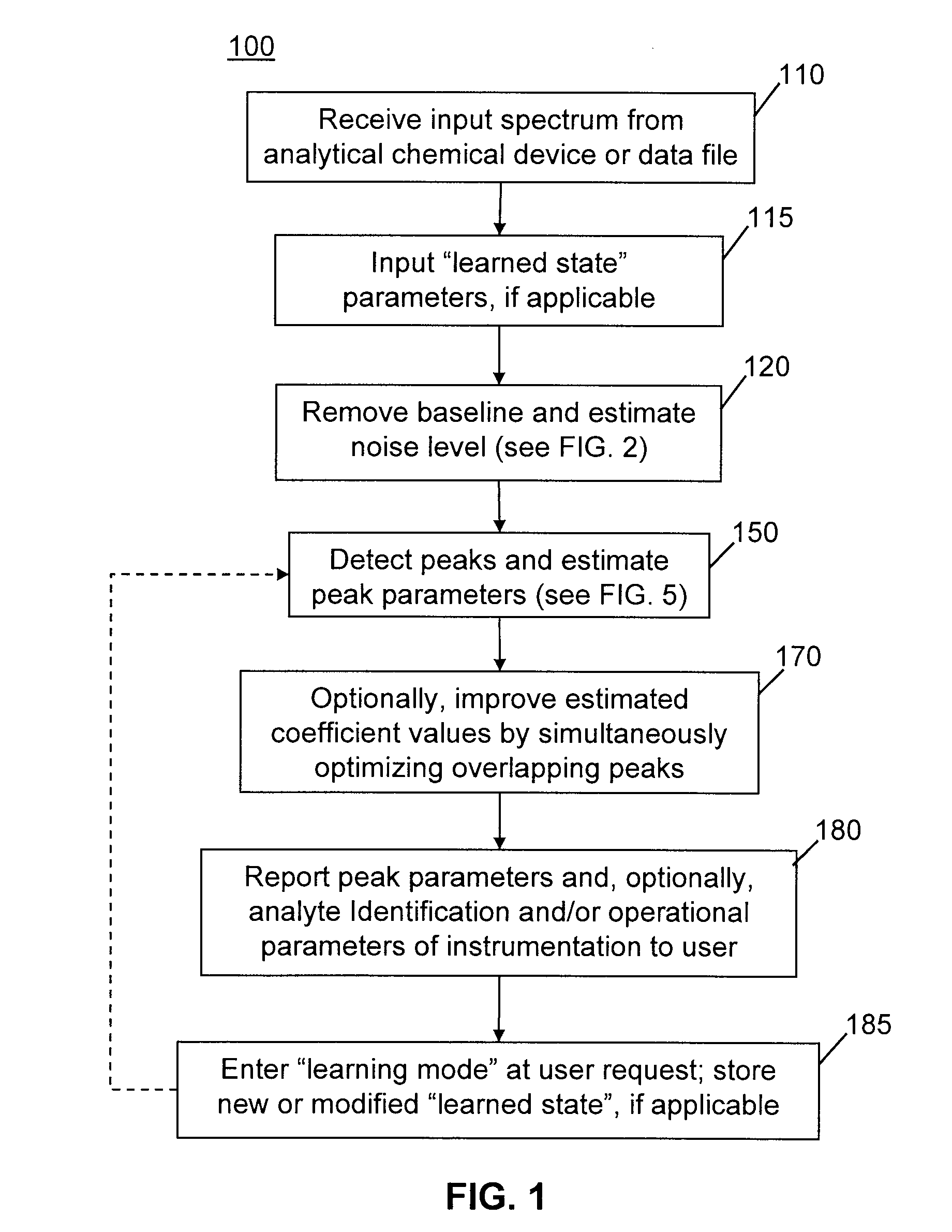
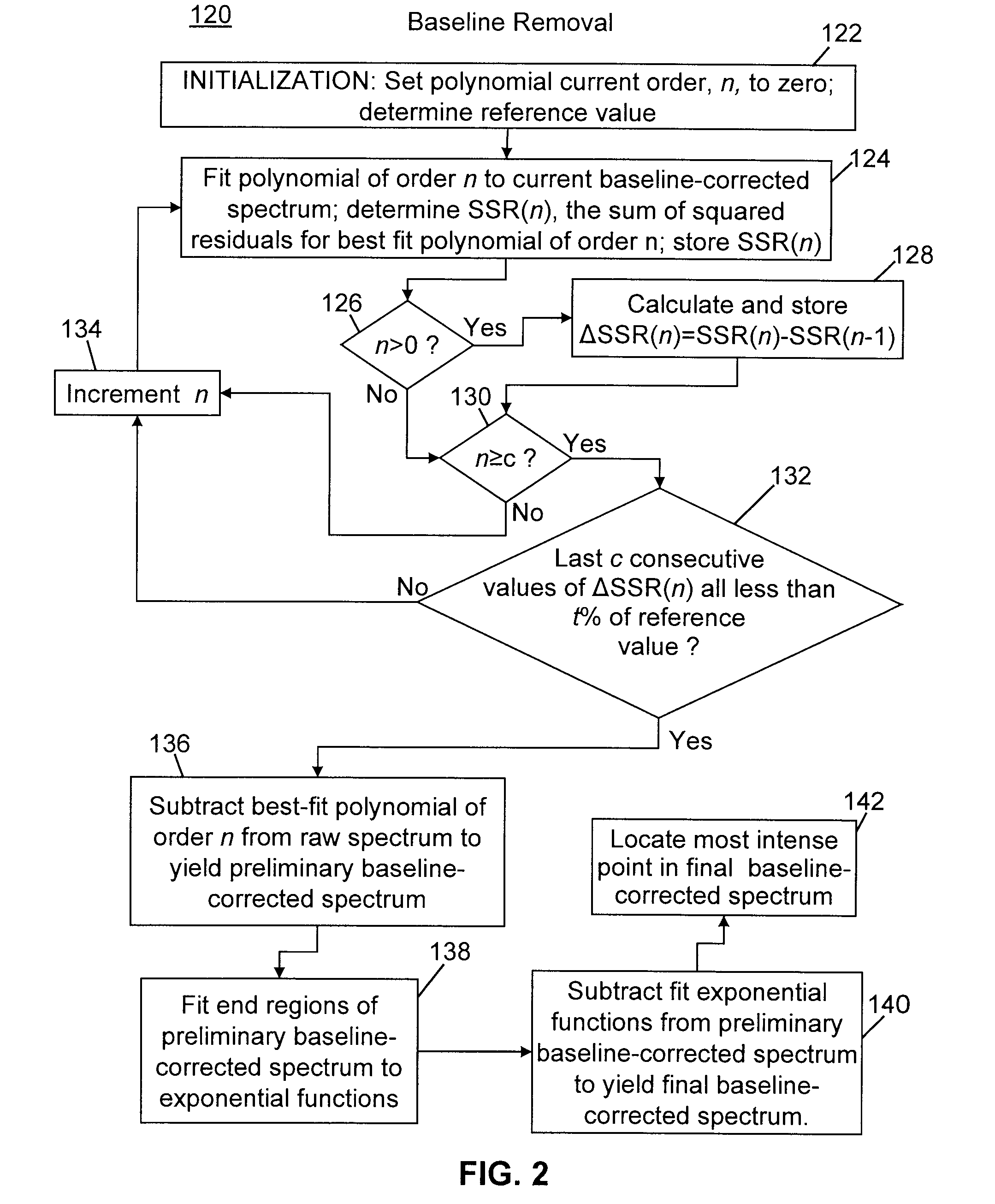
Methods of automated spectral peak detection and quantification having learning mode
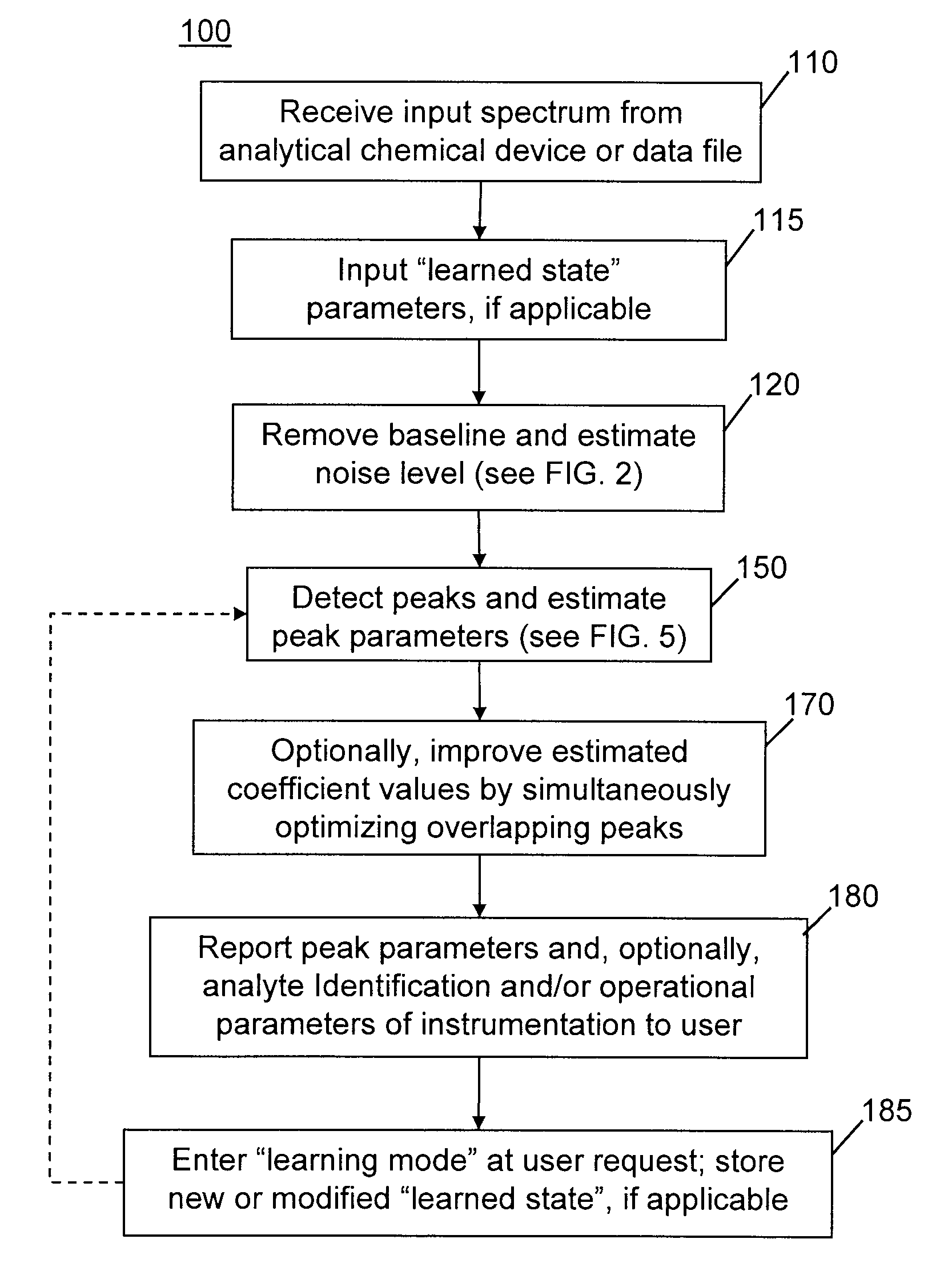
InactiveUS8428889B2Easy to handleImprove accuracyMolecular entity identificationParticle separator tubesFrequency spectrumPeak value
There is provided a method of automatically identifying and characterizing spectral peaks of a spectrum generated by an analytical apparatus comprising the steps of: receiving the spectrum generated by the analytical apparatus; automatically subtracting a baseline from the spectrum so as to generate a baseline-corrected spectrum; automatically detecting and characterizing the spectral peaks in the baseline-corrected spectrum; reporting the detected and characterized spectral peaks to a user; receiving a list of adjustments to be made to the detecting and characterizing step from the user; and adjusting exit values used in the detecting and characterizing step, based on the list of adjustments.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
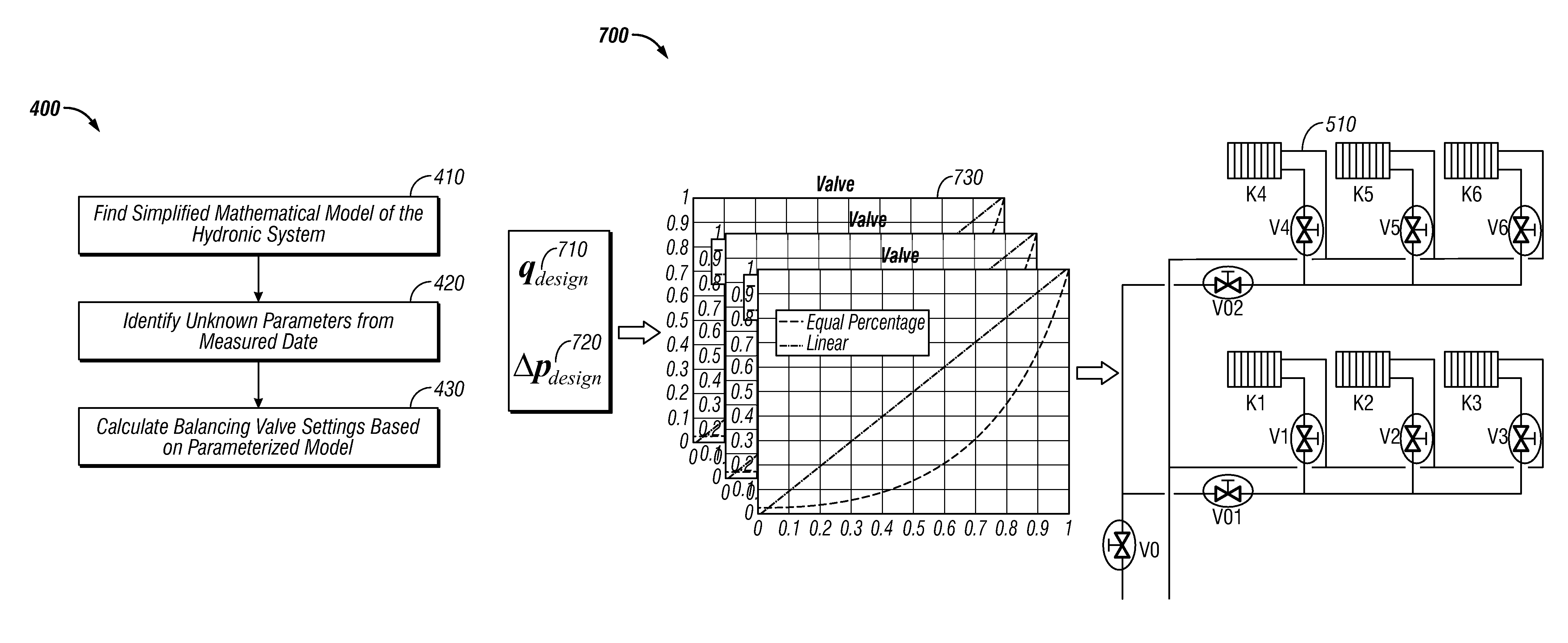
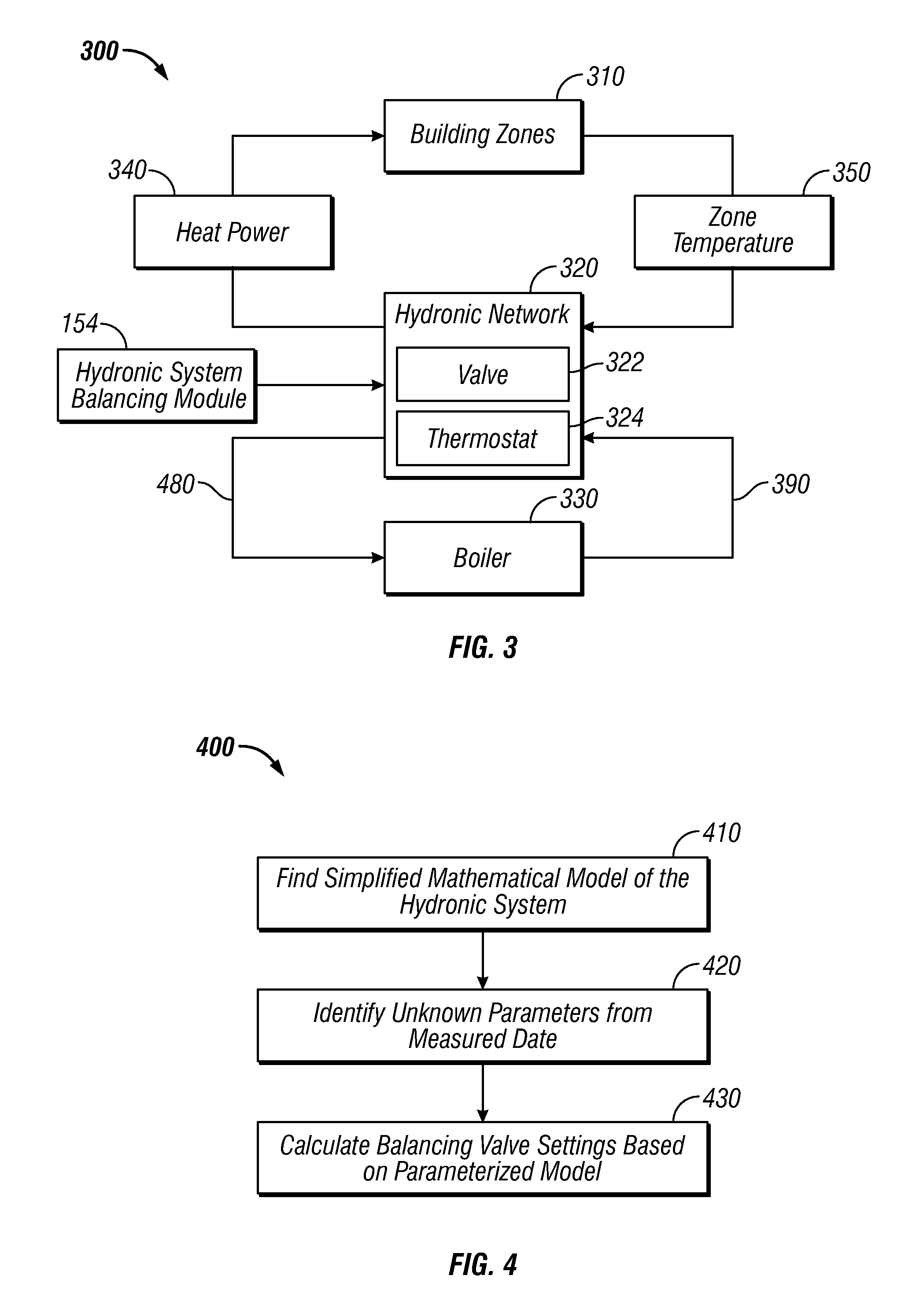
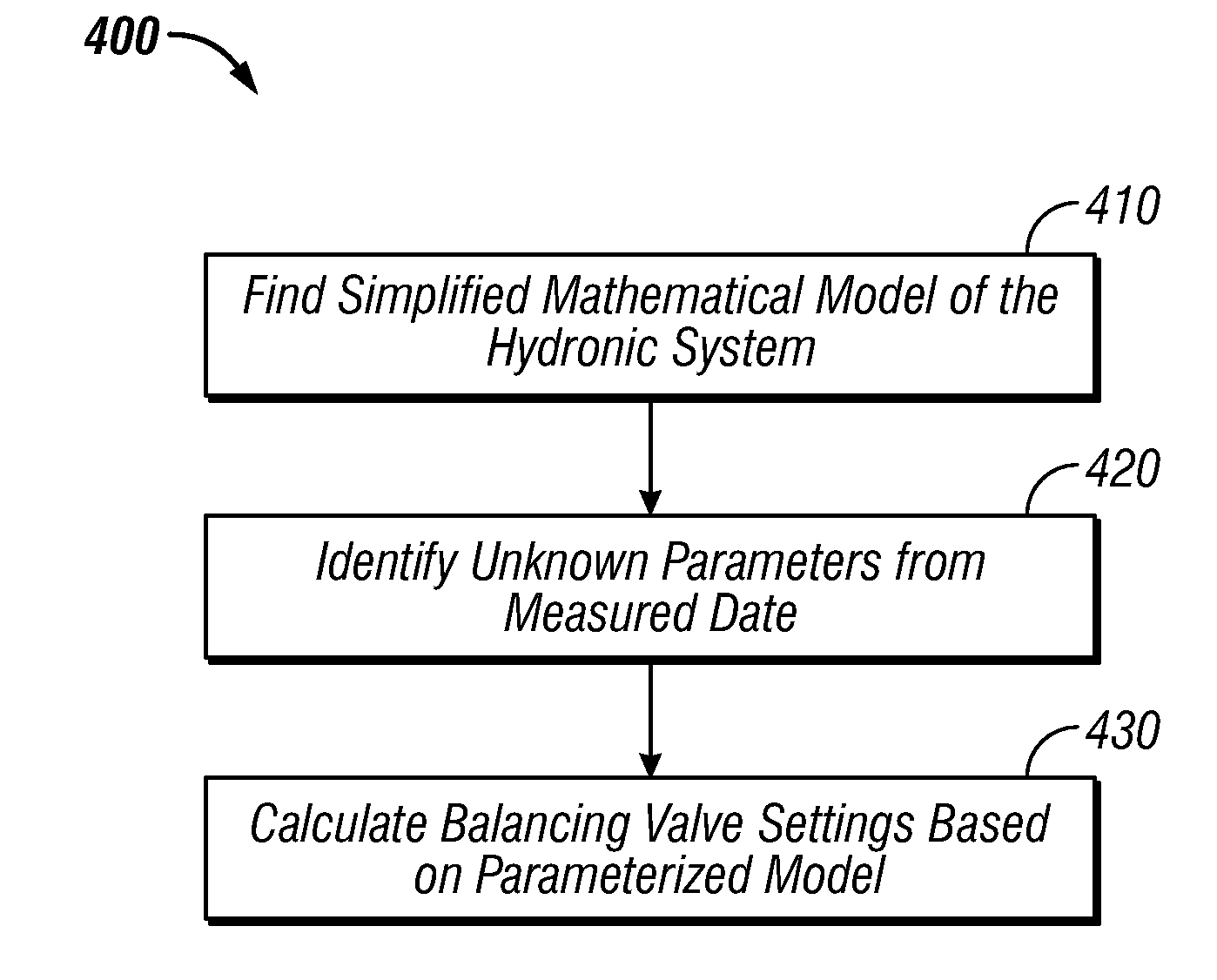
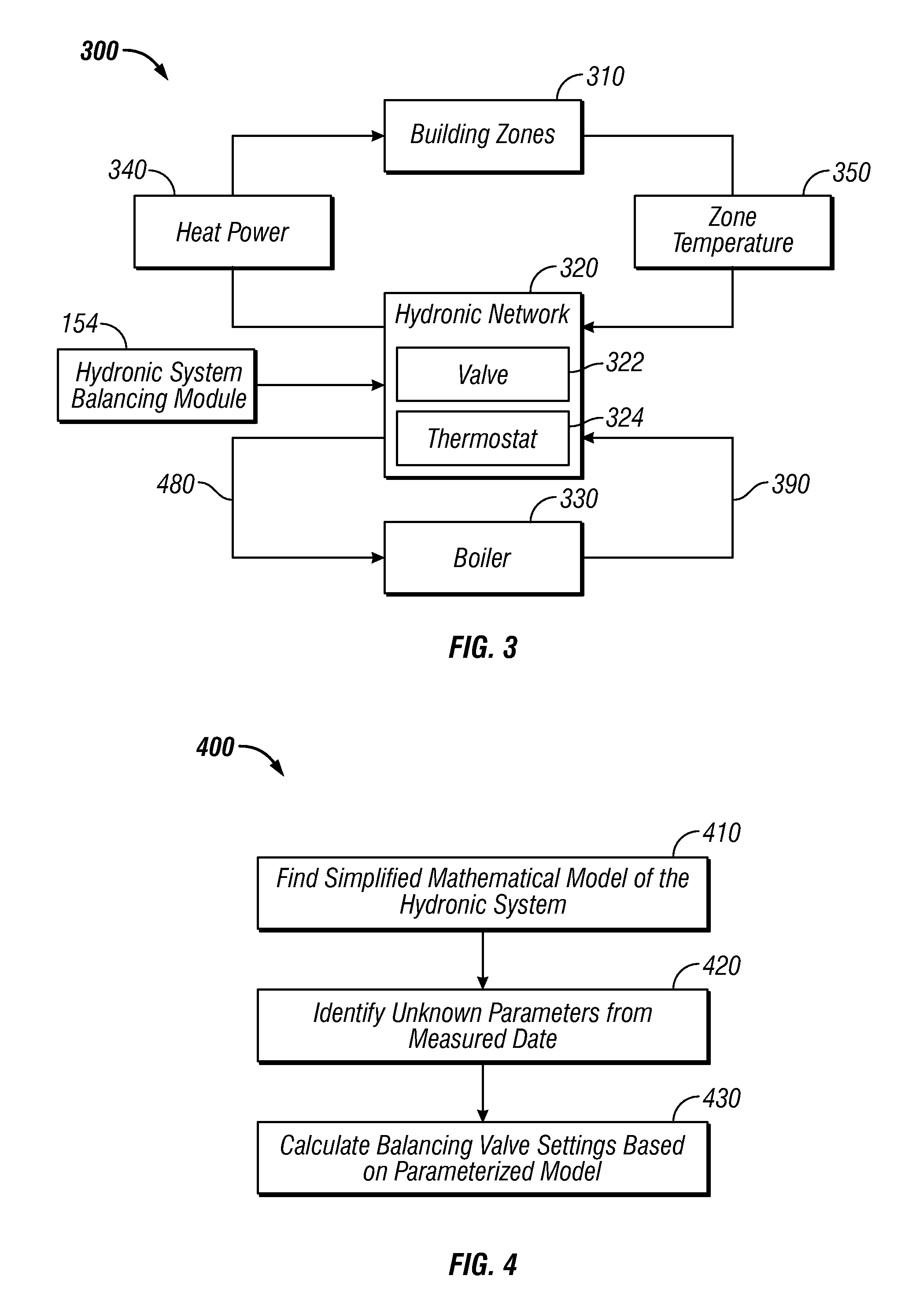
Method and system for model-based multivariable balancing for distributed hydronic networks
ActiveUS8024161B2Fast and accurate balancingMinimized pressure dropLevel controlLighting and heating apparatusMeasurement deviceMathematical model
A method and system for optimal model-based multivariable balancing for distributed hydronic networks based on global differential pressure / flow rate information. A simplified mathematical model of a hydronic system can be determined utilizing an analogy between hydronic systems and electrical circuits. Thereafter, unknown parameters can be identified utilizing the simplified mathematical model and a set of available measurements. Next, balancing valve settings can be calculated by reformulating the simplified mathematical model based on the parameterized model. The sum of pressure drops across selected balancing valves can be then minimized to achieve optimal economic performances of the system. The data can be collected and transferred to a central unit either by wireless communication or manually by reading the local measurement devices. Such a multivariable balancing approach provides a fast and accurate balancing of distributed hydronic heating systems based on a centralized and non-iterative approach.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
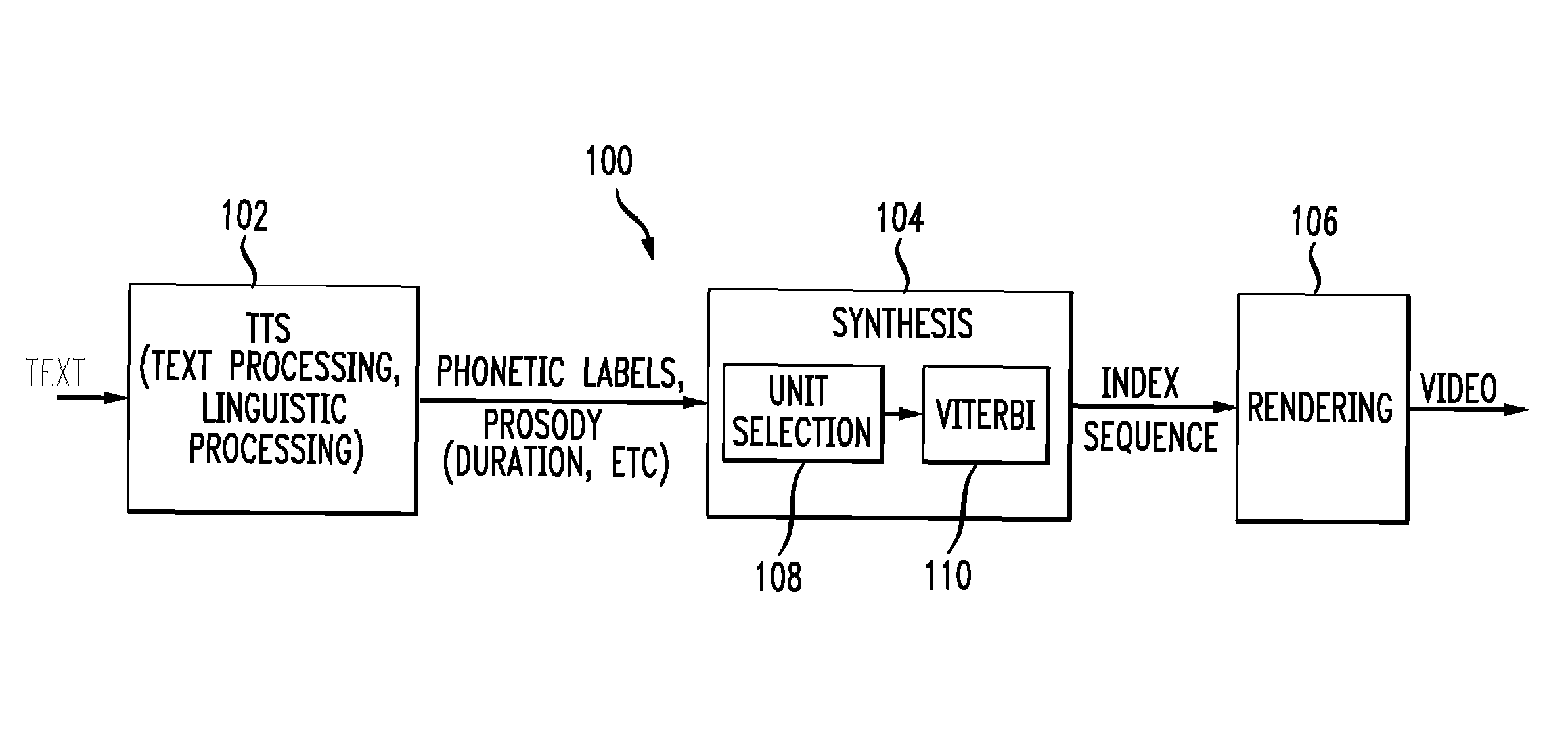
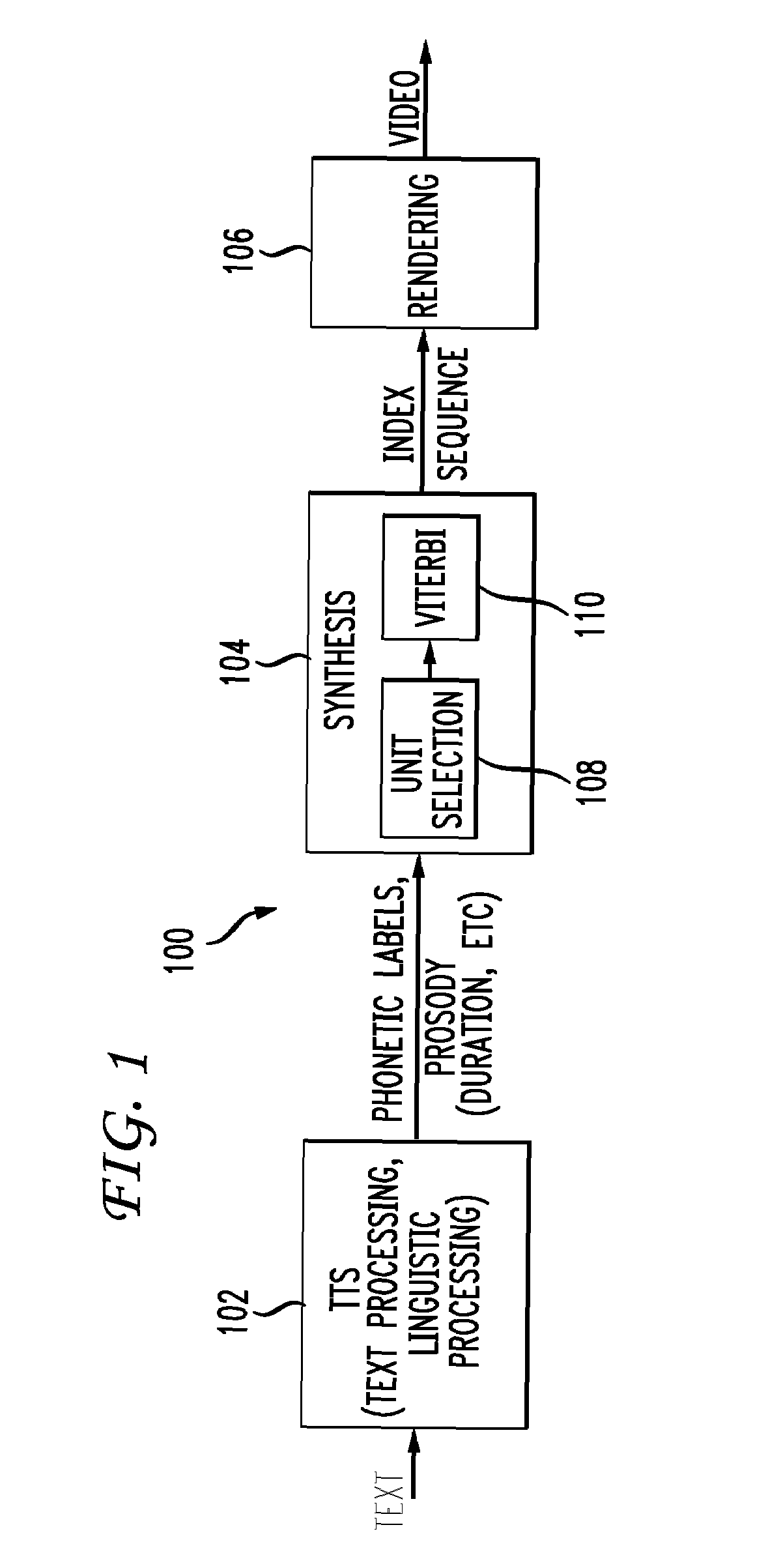
System and method for triphone-based unit selection for visual speech synthesis
ActiveUS7209882B1Quickly and efficiently selectedMinimize sumAnimationSpeech recognitionSystem usageCoarticulation
A system and method for generating a video sequence having mouth movements synchronized with speech sounds are disclosed. The system utilizes a database of n-phones as the smallest selectable unit, wherein n is larger than 1 and preferably 3. The system calculates a target cost for each candidate n-phone for a target frame using a phonetic distance, coarticulation parameter, and speech rate. For each n-phone in a target sequence, the system searches for candidate n-phones that are visually similar according to the target cost. The system samples each candidate n-phone to get a same number of frames as in the target sequence and builds a video frame lattice of candidate video frames. The system assigns a joint cost to each pair of adjacent frames and searches the video frame lattice to construct the video sequence by finding the optimal path through the lattice according to the minimum of the sum of the target cost and the joint cost over the sequence.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
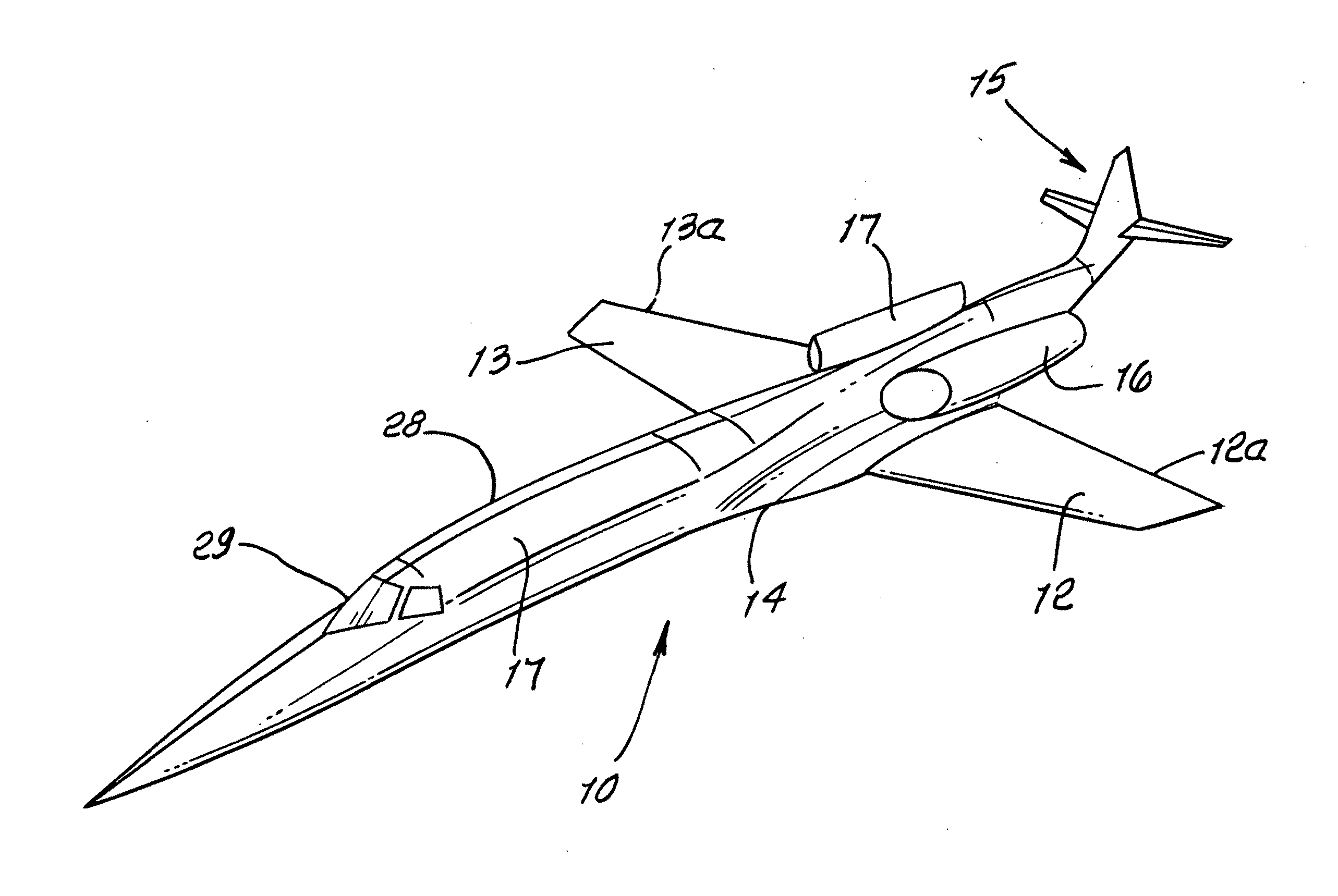
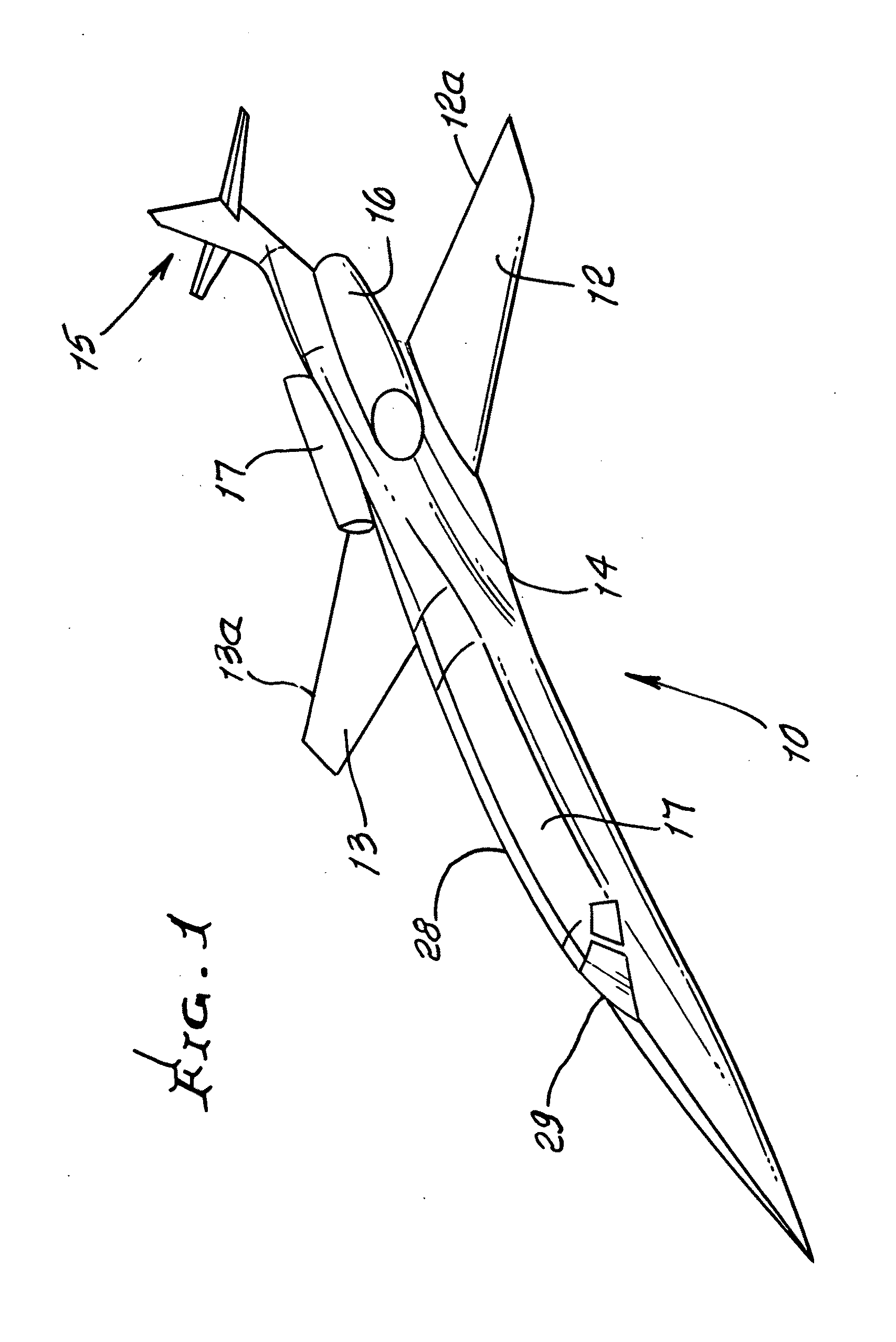
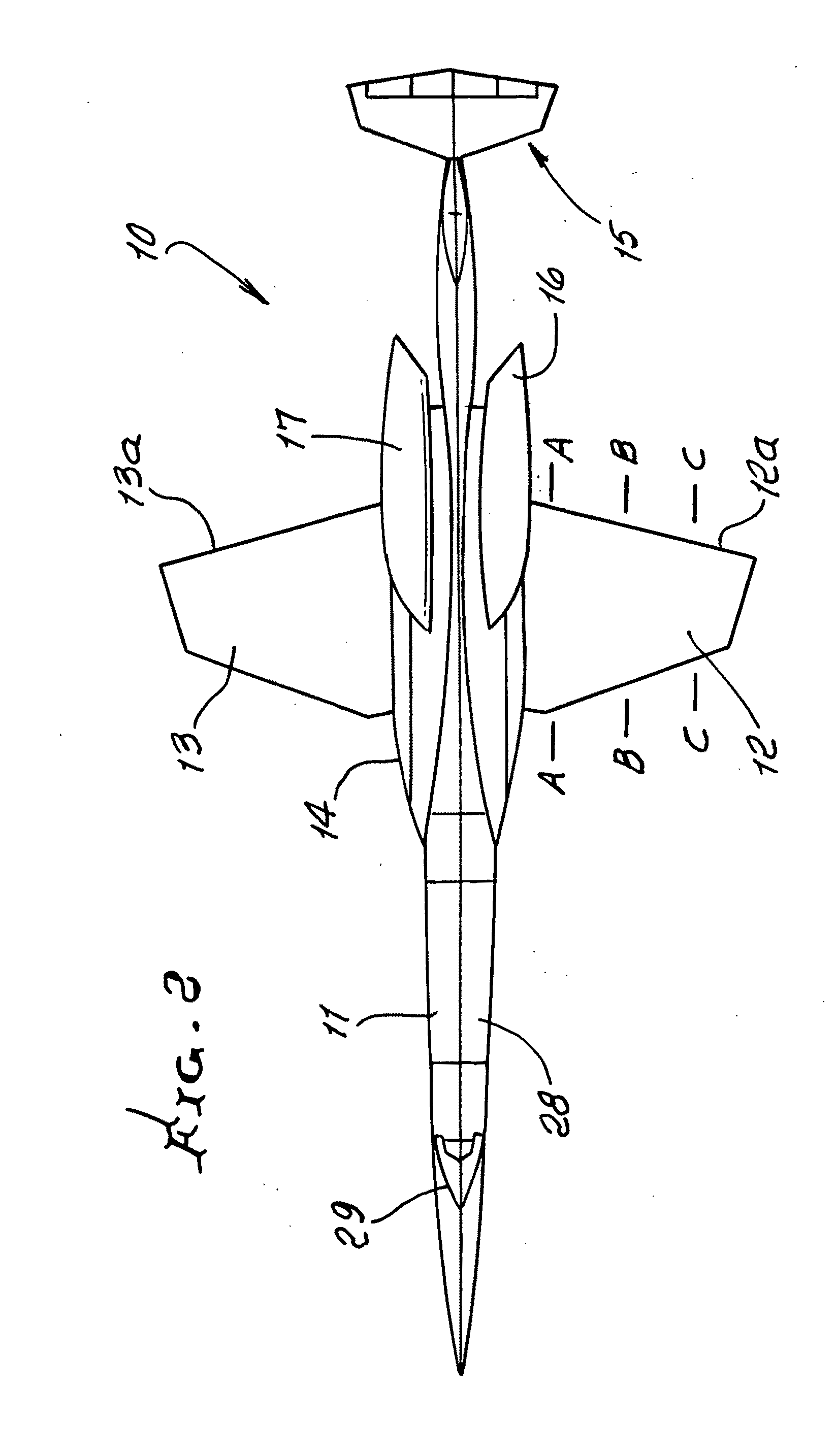
Laminar flow wing optimized for supersonic cruise aircraft
ActiveUS20110095137A1Improve completenessLower the volumeWing shapesAll-wing aircraftLeading edgeFuselage
A method of providing an aircraft having a fuselage and a wing configured for extensive laminar flow at design cruise conditions, the method characterized by a) providing wing biconvex-type airfoils having values of thickness, chord and shape along the wing span which provide substantially optimal aircraft range at design cruise conditions, considering the influences of wing drag and wing weight; b) providing wing leading edges, which are configured to effect laminar flow; c) providing fuselage and wing contours which, in combination, produce reduced total wave drag and produce extensive areas of laminar boundary layer flow on the wing; and d) providing wing sweep angularity that facilitates provision of a), b) and c).
Owner:AERION INTPROP MANAGEMENT CORP
Method and system for model-based multivariable balancing for distributed hydronic networks
ActiveUS20100049480A1Reduce effortShorten the timeLighting and heating apparatusSpace heating and ventilation detailsMeasurement deviceMathematical model
A method and system for optimal model-based multivariable balancing for distributed hydronic networks based on global differential pressure / flow rate information. A simplified mathematical model of a hydronic system can be determined utilizing an analogy between hydronic systems and electrical circuits. Thereafter, unknown parameters can be identified utilizing the simplified mathematical model and a set of available measurements. Next, balancing valve settings can be calculated by reformulating the simplified mathematical model based on the parameterized model. The sum of pressure drops across selected balancing valves can be then minimized to achieve optimal economic performances of the system. The data can be collected and transferred to a central unit either by wireless communication or manually by reading the local measurement devices. Such a multivariable balancing approach provides a fast and accurate balancing of distributed hydronic heating systems based on a centralized and non-iterative approach.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Determining a relevance function based on a query error derived using a structured output learning technique
InactiveUS8005774B2Improve efficiencyMinimize sumDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPredictor variableAlgorithm
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for generating relevance functions for ranking documents obtained in searches are provided. One or more features to be used as predictor variables in the construction of a relevance function are determined. The relevance function is parameterized by one or more coefficients. An ideal query error is defined that measures, for a given query, a difference between a ranking generated by the relevance function and a ranking based on a training set. According to a structured output learning framework, values for the coefficients of the relevance function are determined to substantially minimize an objective function that depends on a continuous upper bound of the defined ideal query error. The query error is determined using a structured output learning technique. The query error is defined as a maximum over a set of permutations.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
System and method for using texture landmarks for improved markerless tracking in augmented reality applications
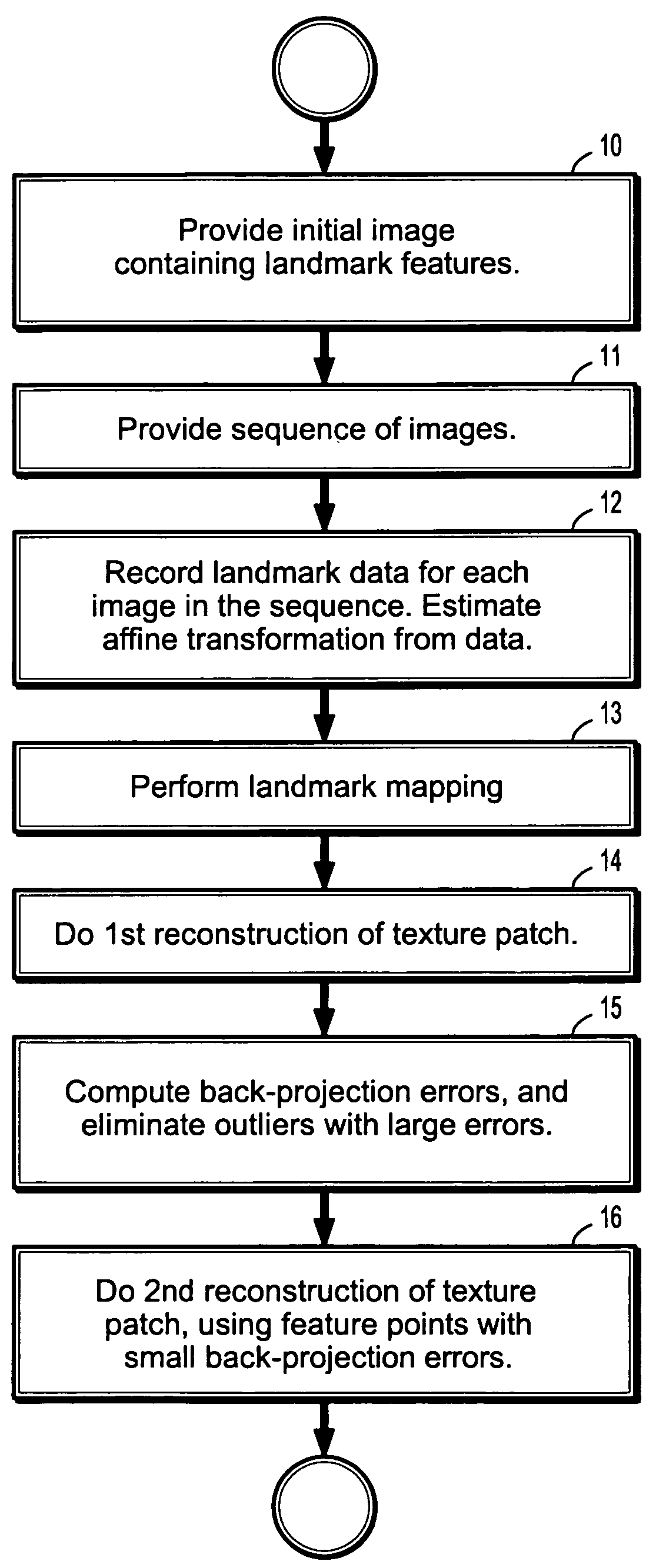
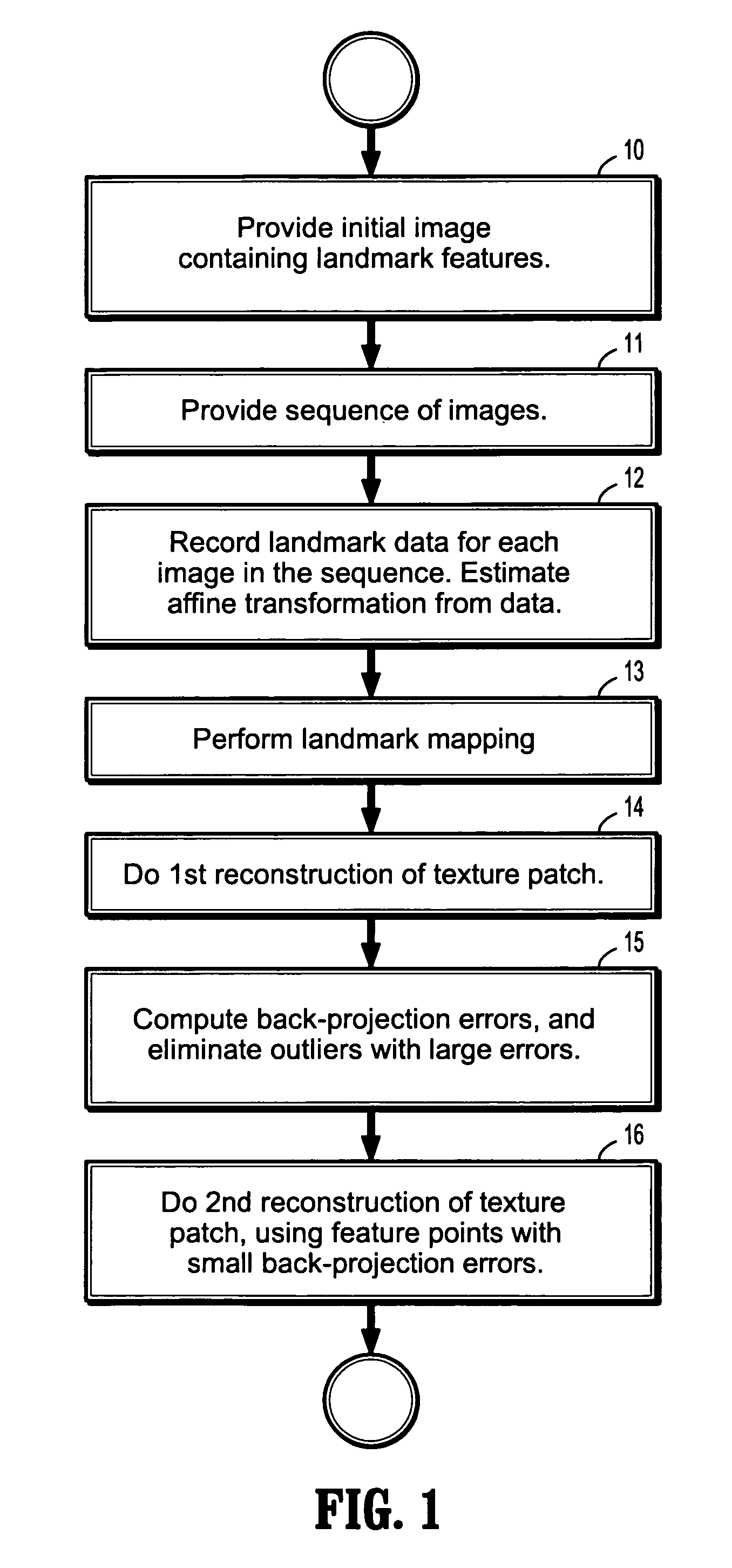
InactiveUS7616807B2Promote reconstructionAvoid driftingImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionTriangulationBack projection
A method of tracking a pose of a moving camera includes receiving a first image from a camera, receiving a sequence of digitized images from said camera, recording, for each of said sequence of digitized images, the pose and 2D correspondences of landmarks, reconstructing a location and appearance of a 2-dimensional texture patch from 2D correspondences of the landmarks by triangulation and optimization, computing back-projection errors by comparing said reconstructed texture patch with said first received image; and reconstructing said location and appearance of said 2-dimensional texture patch from the 2D correspondences of the landmarks of said sequence of digitized images by triangulation and optimization after eliminating those landmarks with large back-projection errors.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
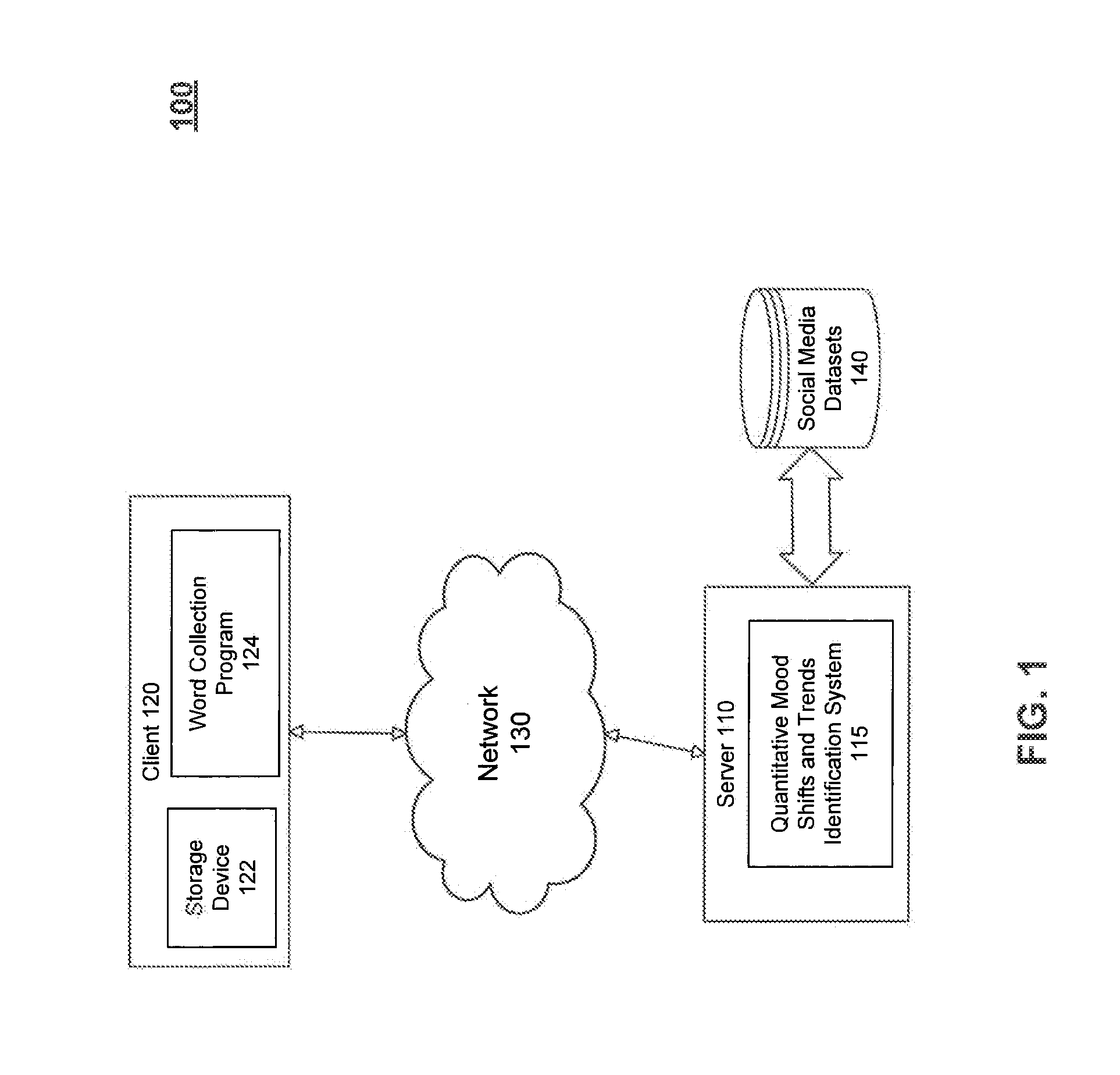
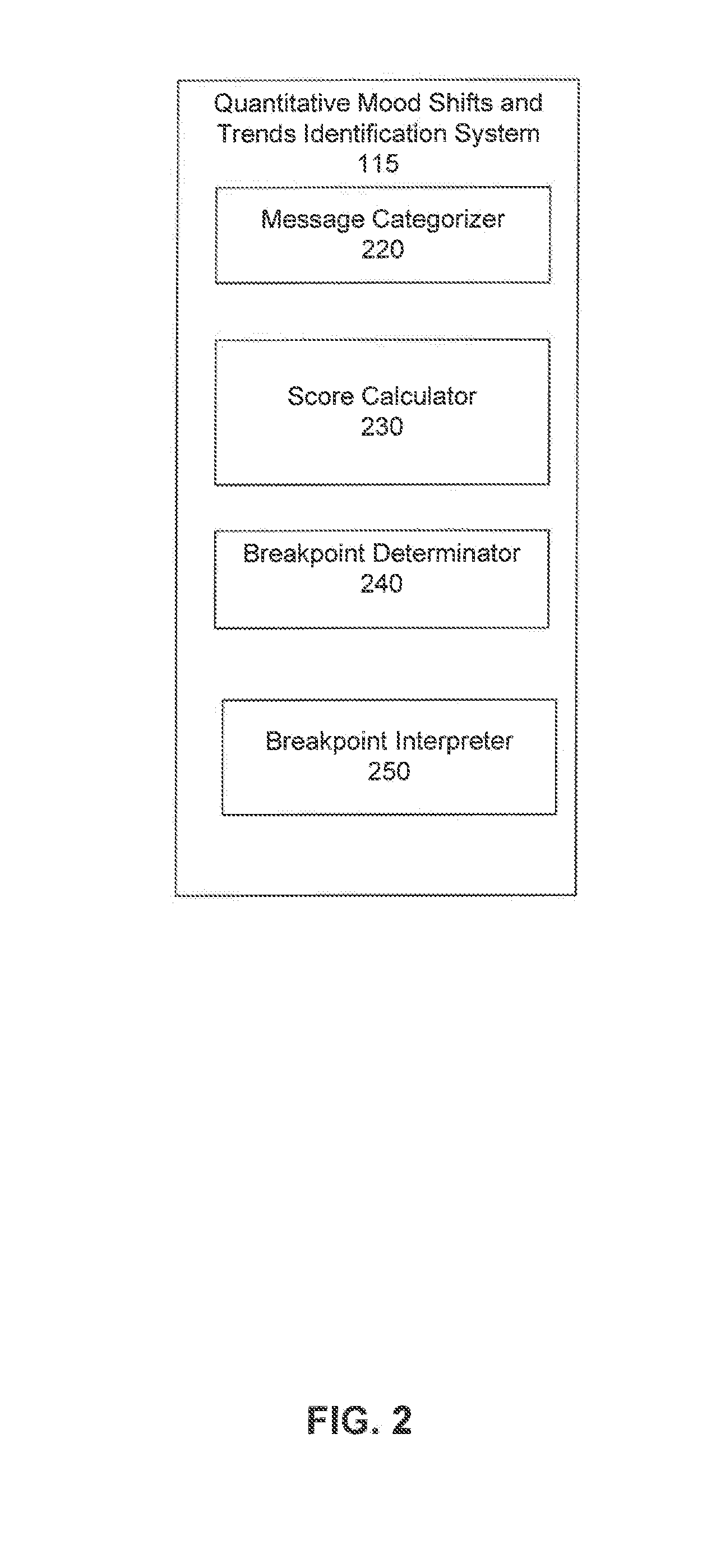
Identifying and Forecasting Shifts in the Mood of Social Media Users
ActiveUS20130275352A1Minimize sumDigital computer detailsNatural language data processingSocial mediaComputer science
Quantitatively identifying and forecasting shifts in a mood of social media users is described. An example method includes categorizing the textual messages generated from the social media users over a selected period of time into a plurality of word categories, with each word category containing a set of words associated with the mood of social media users. A score indicating an intensity of the mood of the social media users is calculated for each word category, wherein a value of the score and its corresponding time point define a data point for the word category. Subsequently, breakpoints in the mood of social media users are determined so that the breakpoints minimize a sum of square errors representing a measurement of a consistency of all data points from inferred values of the scores of the data points derived using the breakpoints over the selected period of time. Further, space of all possible breakpoints for the word categories are searched to identify a defined number and locations of the breakpoints. Finally the breakpoints over the selected period of time are interpreted to identify the shifts in the mood of social media users and trends between breakpoints.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
Methods of Automated Spectral Peak Detection and Quantification Having Learning Mode
InactiveUS20120089344A1Easy to handleAvoid problemsParticle separator tubesMolecular entity identificationFrequency spectrumPeak value
There is provided a method of automatically identifying and characterizing spectral peaks of a spectrum generated by an analytical apparatus comprising the steps of: receiving the spectrum generated by the analytical apparatus; automatically subtracting a baseline from the spectrum so as to generate a baseline-corrected spectrum; automatically detecting and characterizing the spectral peaks in the baseline-corrected spectrum; reporting the detected and characterized spectral peaks to a user; receiving a list of adjustments to be made to the detecting and characterizing step from the user; and adjusting exit values used in the detecting and characterizing step, based on the list of adjustments.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
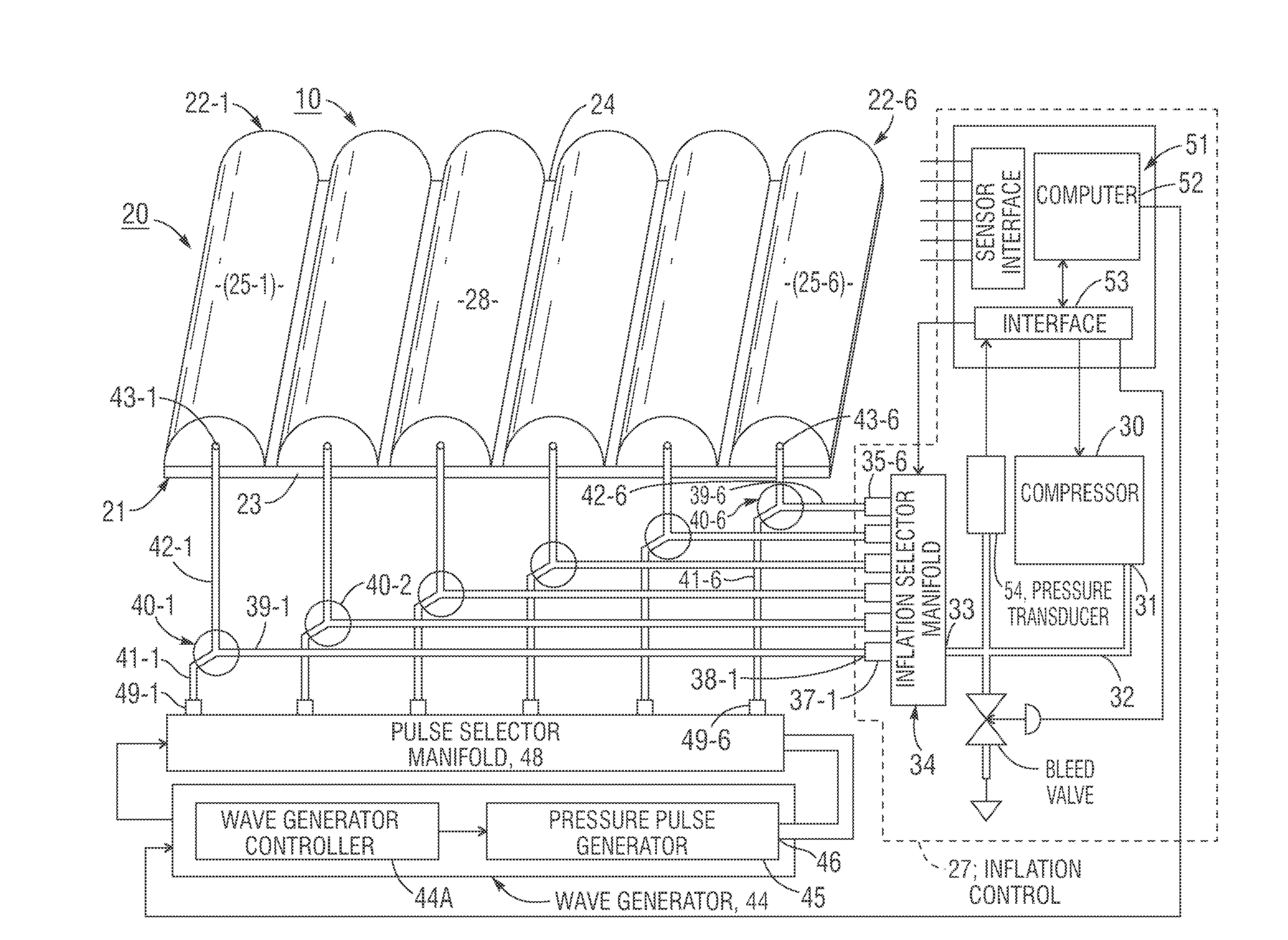
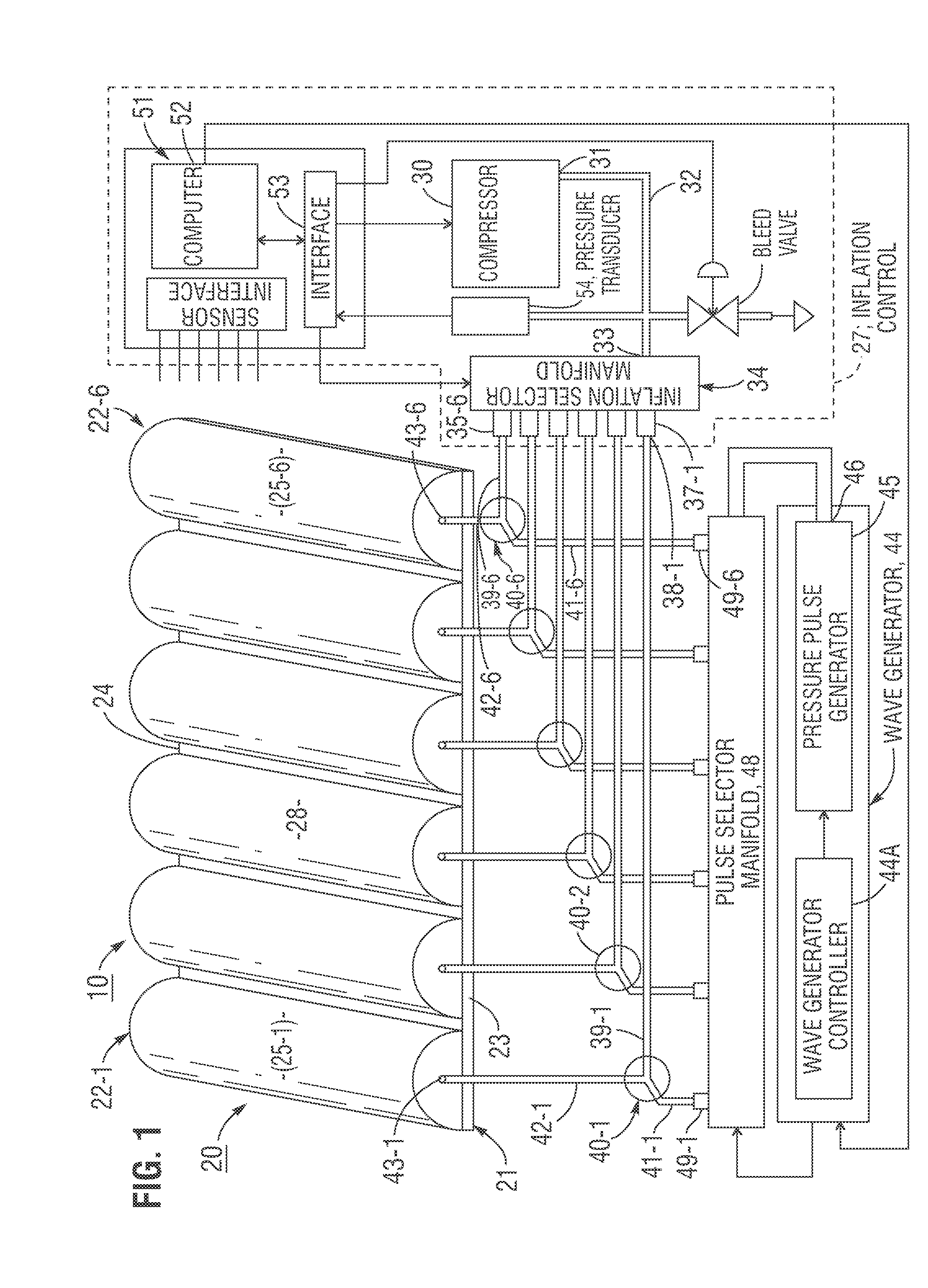
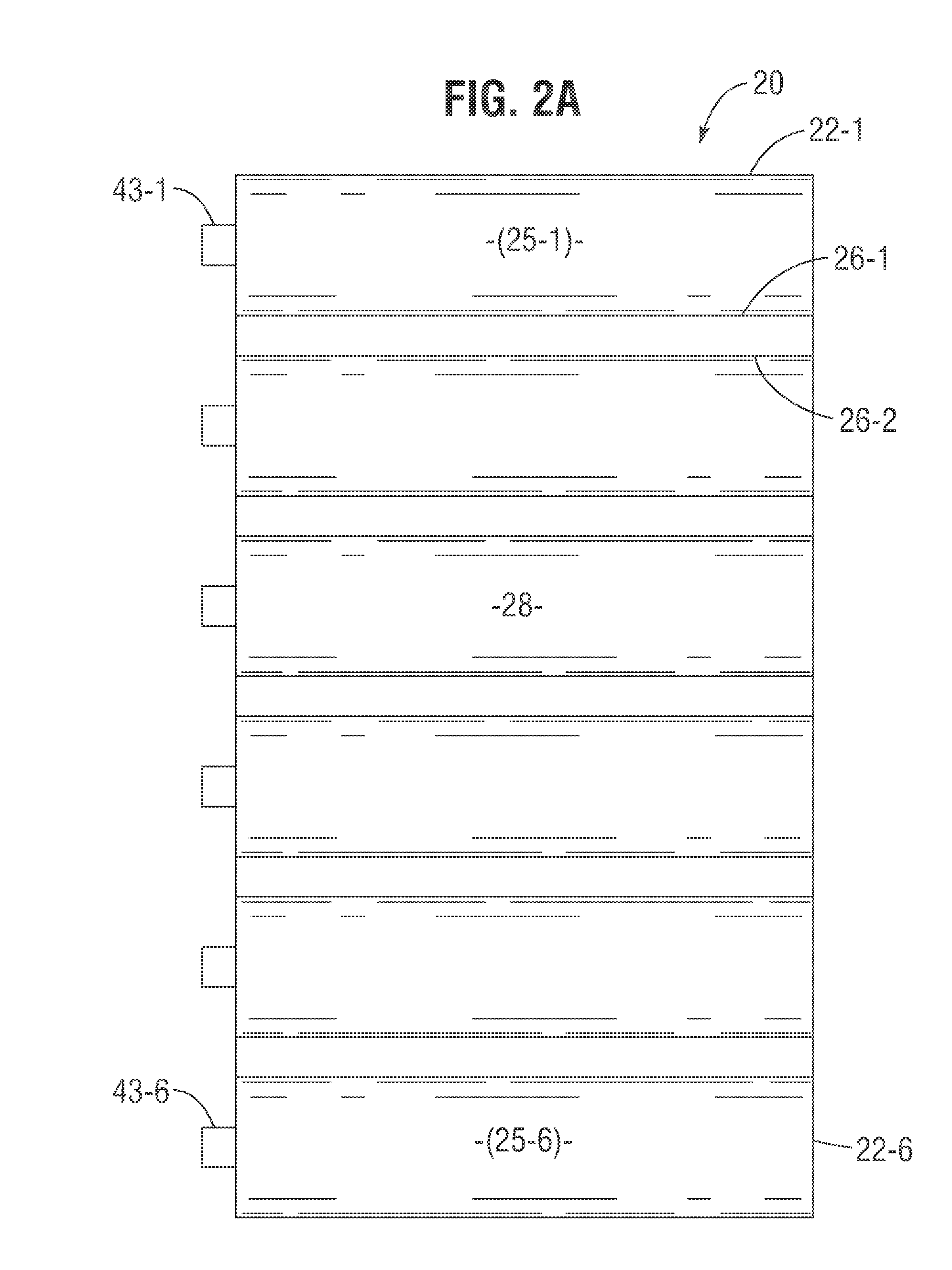
Soliton Traveling Wave Air Mattresses
InactiveUS20170056264A1Reduce formationReduce pressureFluid mattressesNursing bedsHuman bodyEngineering
A soliton air mattress includes an array of air bladder cells that are individually inflatable to quiescent pressure levels which provide comfortable support for a human body, and a soliton wave generator including an air pressure-pulse generator controlled by a wave sequence generator for introducing into ordered sequences of air bladder cells a wave-like time sequence of air pressure pulses which vary quiescent pressure levels in the cells, the pressure wave resulting in a soliton traveling wave of body support force reduction which traverses surfaces of the air bladder cells, thus reducing normal forces exerted on a body and minimizing the occurrence rate of shear forces exerted on the body, thereby inhibiting formation of bedsores. The soliton wave patterns may optionally simulate water waves and / or rocking motions of a boat to produce relaxing effects.
Owner:CHAPIN WILLIAM LAWRENCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com