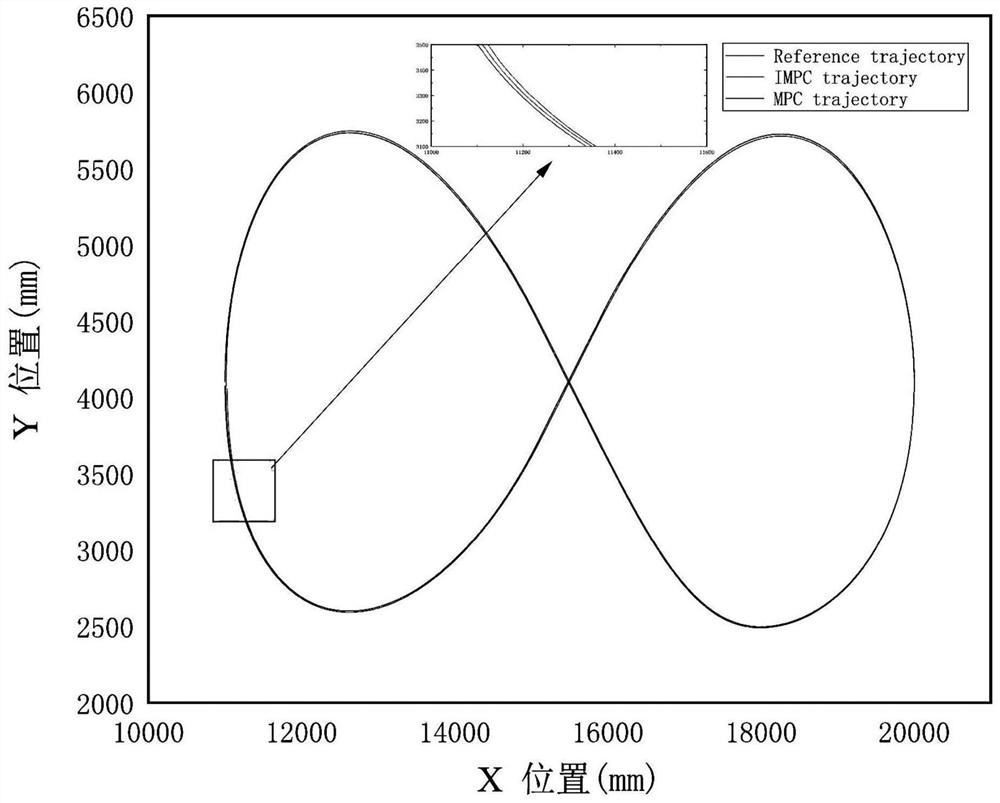
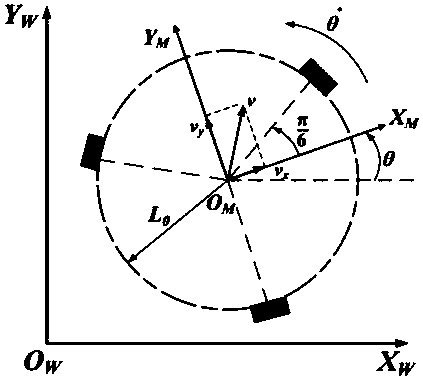
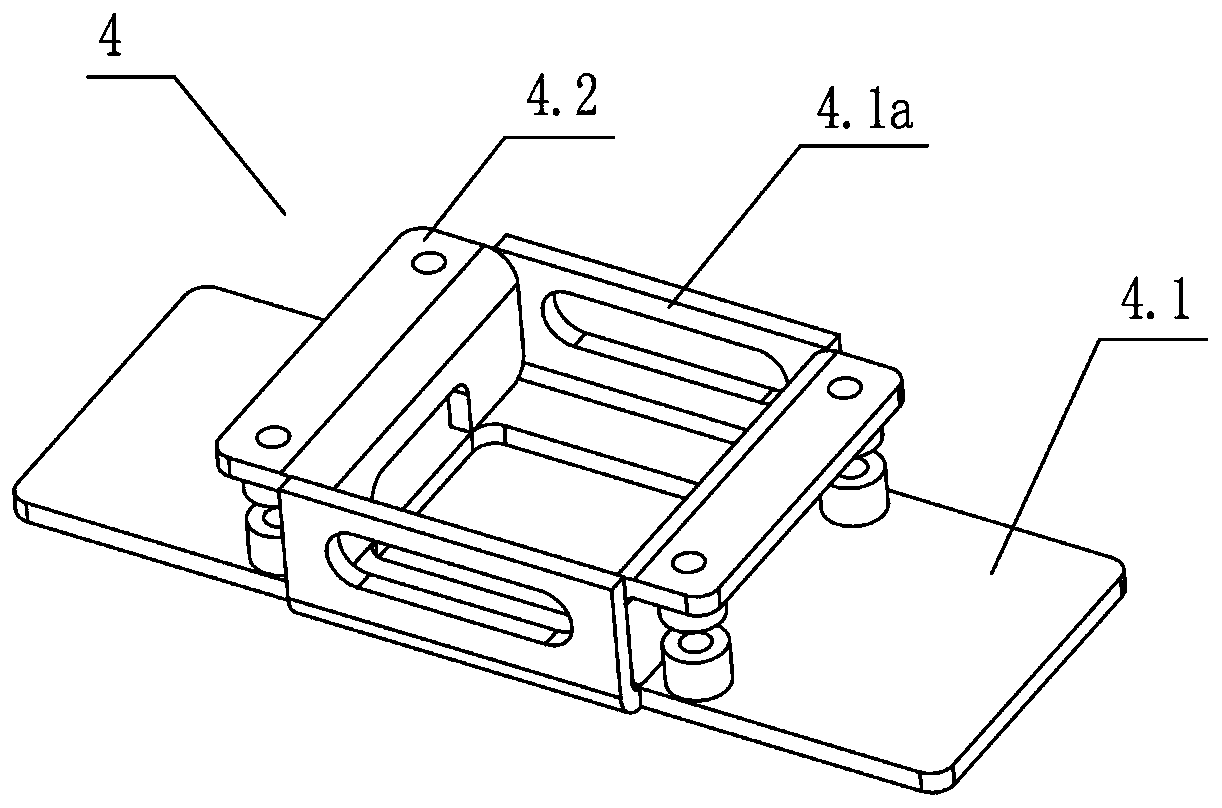
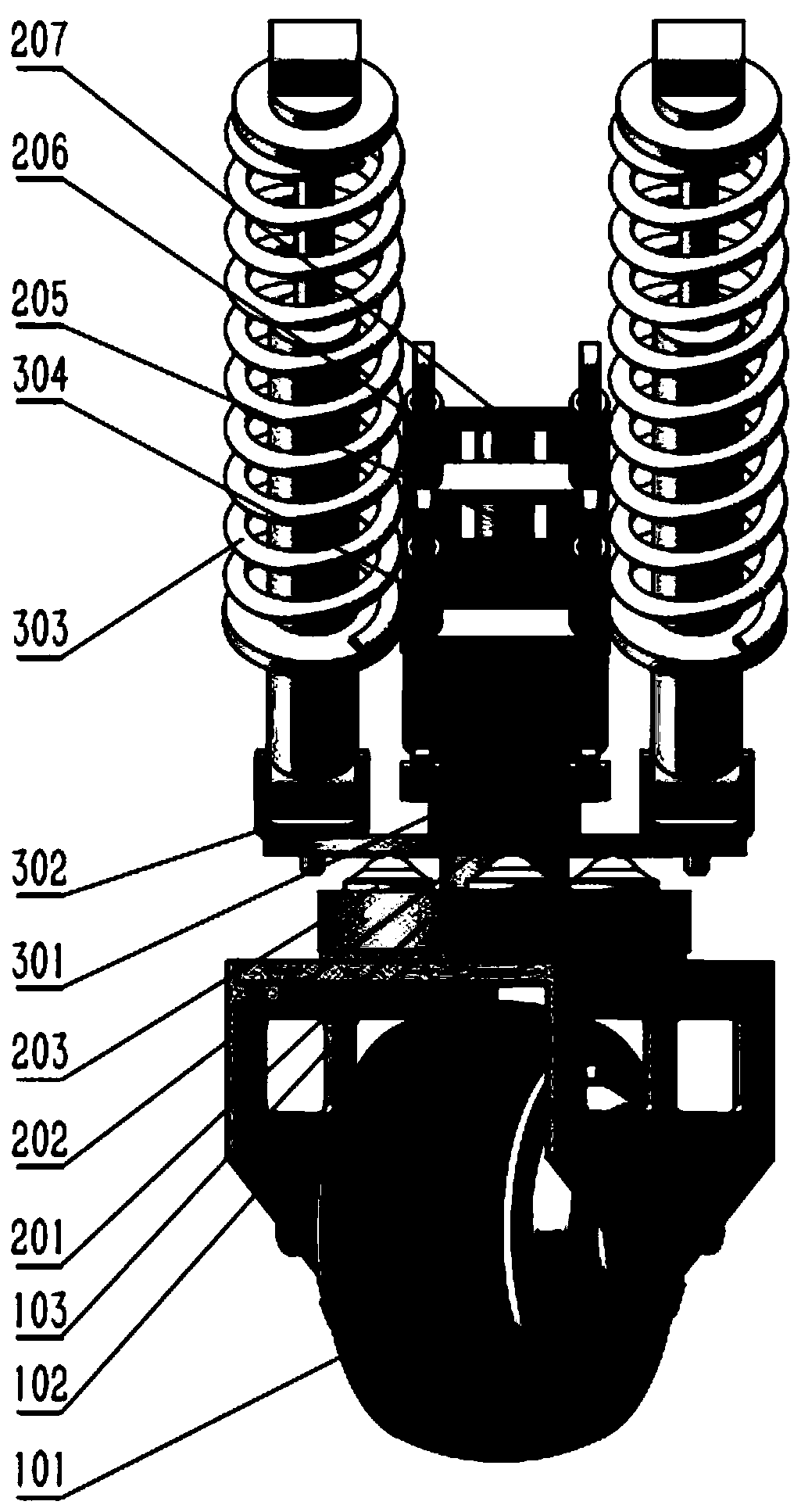
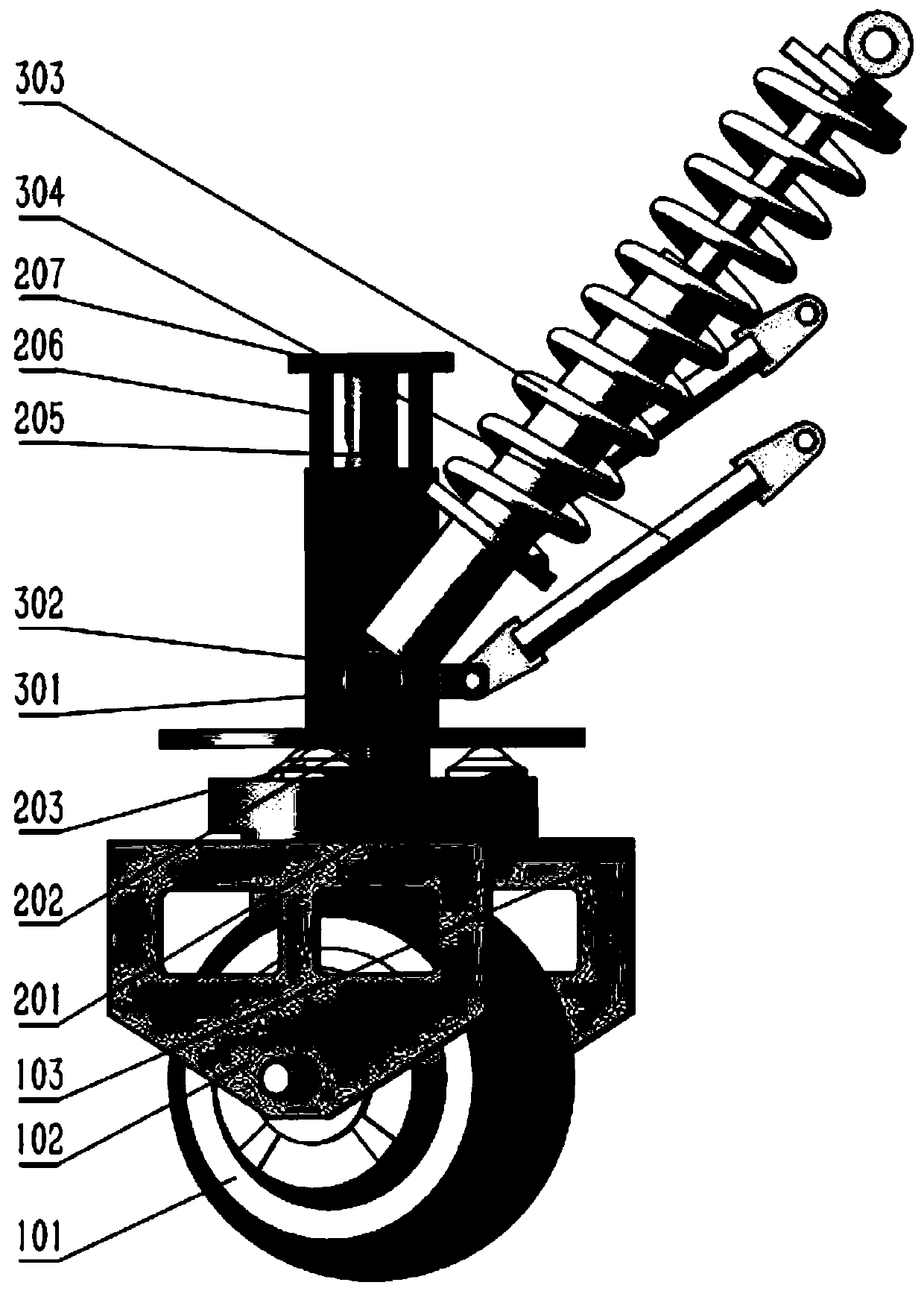
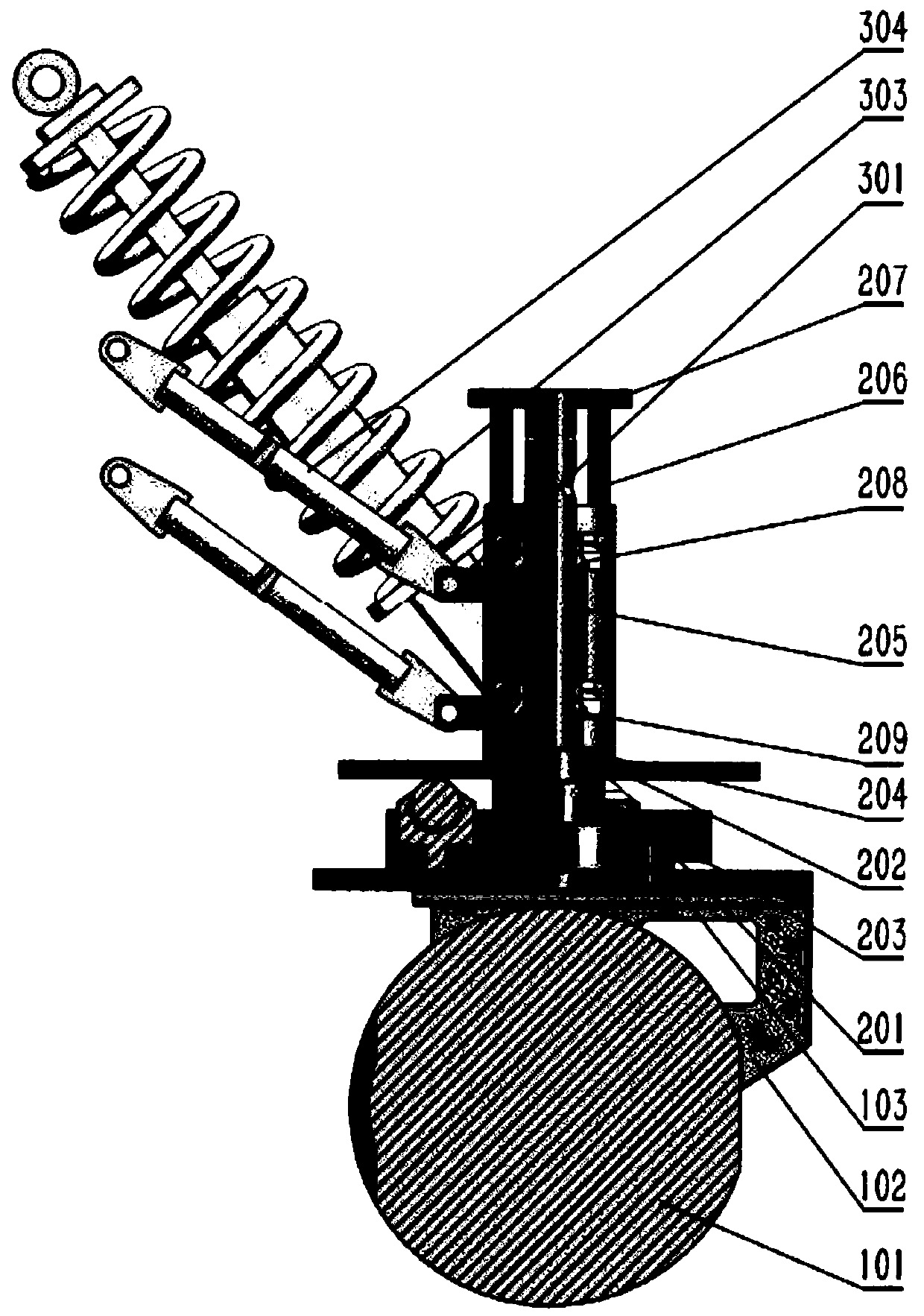
Patents
Literature
82 results about "Omnidirectional mobile robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
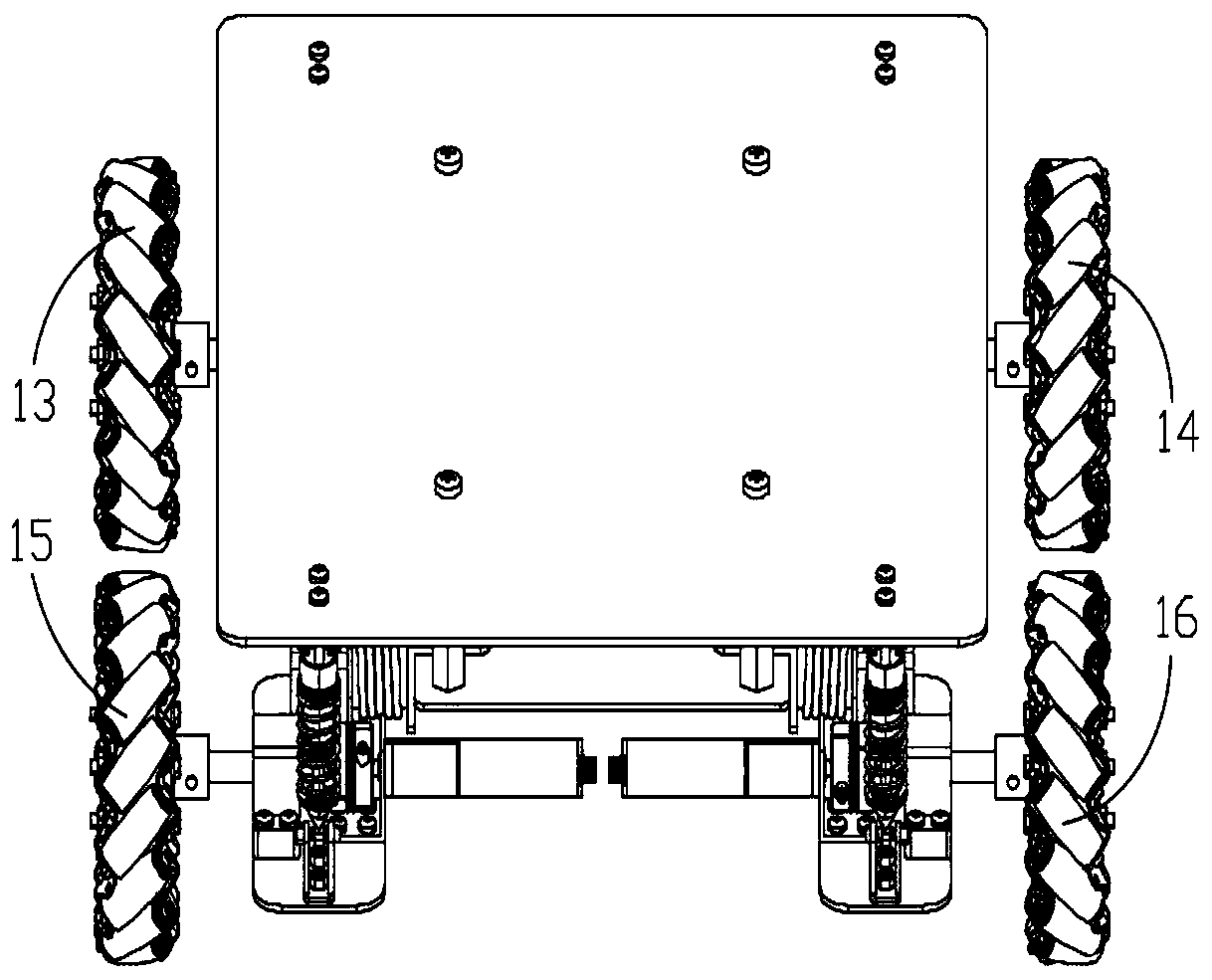
Omnidirectional mobile robot autonomous navigation apparatus and method based on laser range finder
PendingCN106406338AImprove accuracyReduce match failuresPosition/course control in three dimensionsTotal factory controlAngular velocityLaser rangefinder
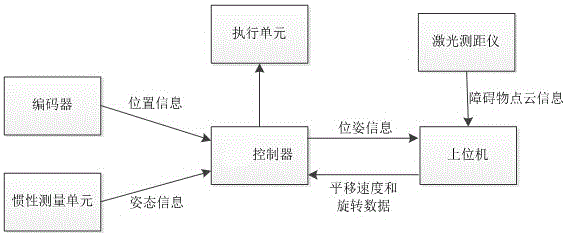
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile robot autonomous navigation and particularly relates to an omnidirectional mobile robot autonomous navigation apparatus and method based on a laser range finder. The omnidirectional mobile robot autonomous navigation apparatus based on the laser range finder comprises an encoder for measuring the movement distance of wheels of a mobile robot, and an inertia measurement unit for measuring the rotation angular velocity and the acceleration of the mobile robot. The encoder and the inertia measurement unit are connected with a controller. The omnidirectional mobile robot autonomous navigation apparatus also comprises the laser ranger finder which is connected with a host computer. The host computer is connected with the controller, and the controller is connected with an execution unit. The invention utilizes the laser range finder to position the mobile robot, establishes a two-dimensional planar map of the environment, carries out autonomous navigation according to a target task, and achieves autonomous obstacle avoidance in the movement.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
SLAM device integrating multiple vehicle-mounted sensors and control method of device
InactiveCN105783913APrecise positioningImprove mapping performanceNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSimultaneous localization and mappingMultiple sensor
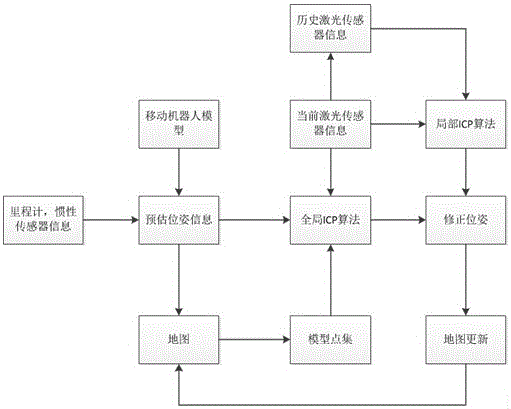
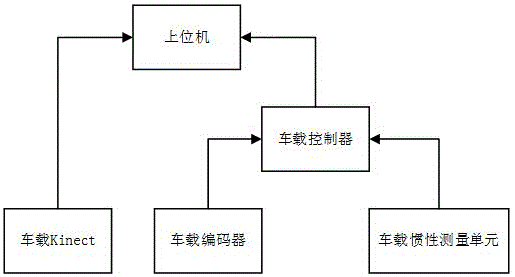
The invention relates to the technical field of simultaneous localization and mapping methods of three-wheel omnidirectional mobile robots integrating multiple vehicle-mounted sensors, and particularly relates to an SLAM device integrating the multiple vehicle-mounted sensors and a control method of the device.The SLAM device integrating the multiple vehicle-mounted sensors comprises the vehicle-mounted sensors, a vehicle-mounted encoder, a vehicle-mounted inertia measurement unit, a vehicle-mounted controller and an upper computer; the vehicle-mounted encoder and the vehicle-mounted inertia measurement unit are connected with the vehicle-mounted controller, and the vehicle-mounted controller is connected with the upper computer.The localization and mapping effects of the robots can be improved, the problem of localization and mapping errors brought by depth value deletion or characteristic point scarcity which are generated when SLAM is conducted only by relying on an RGB-D sensor is solved, and therefore the robustness and accuracy of SLAM are improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
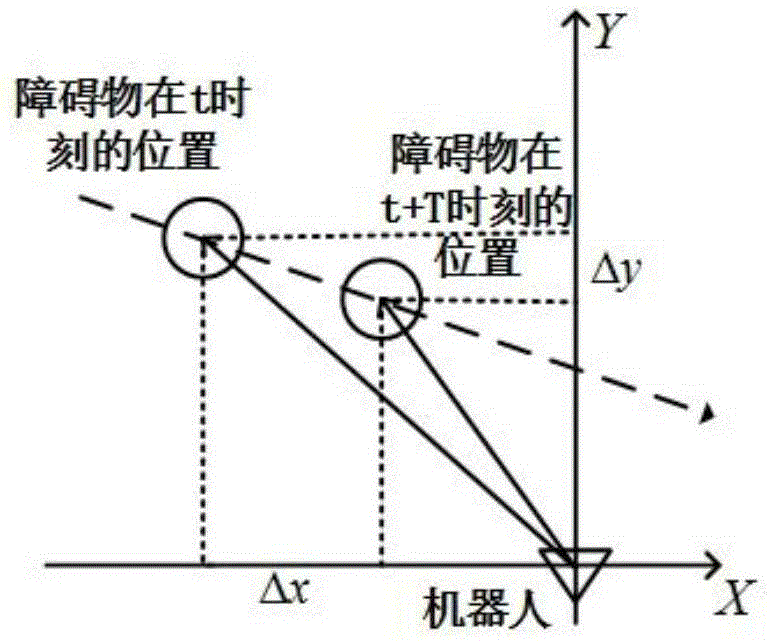
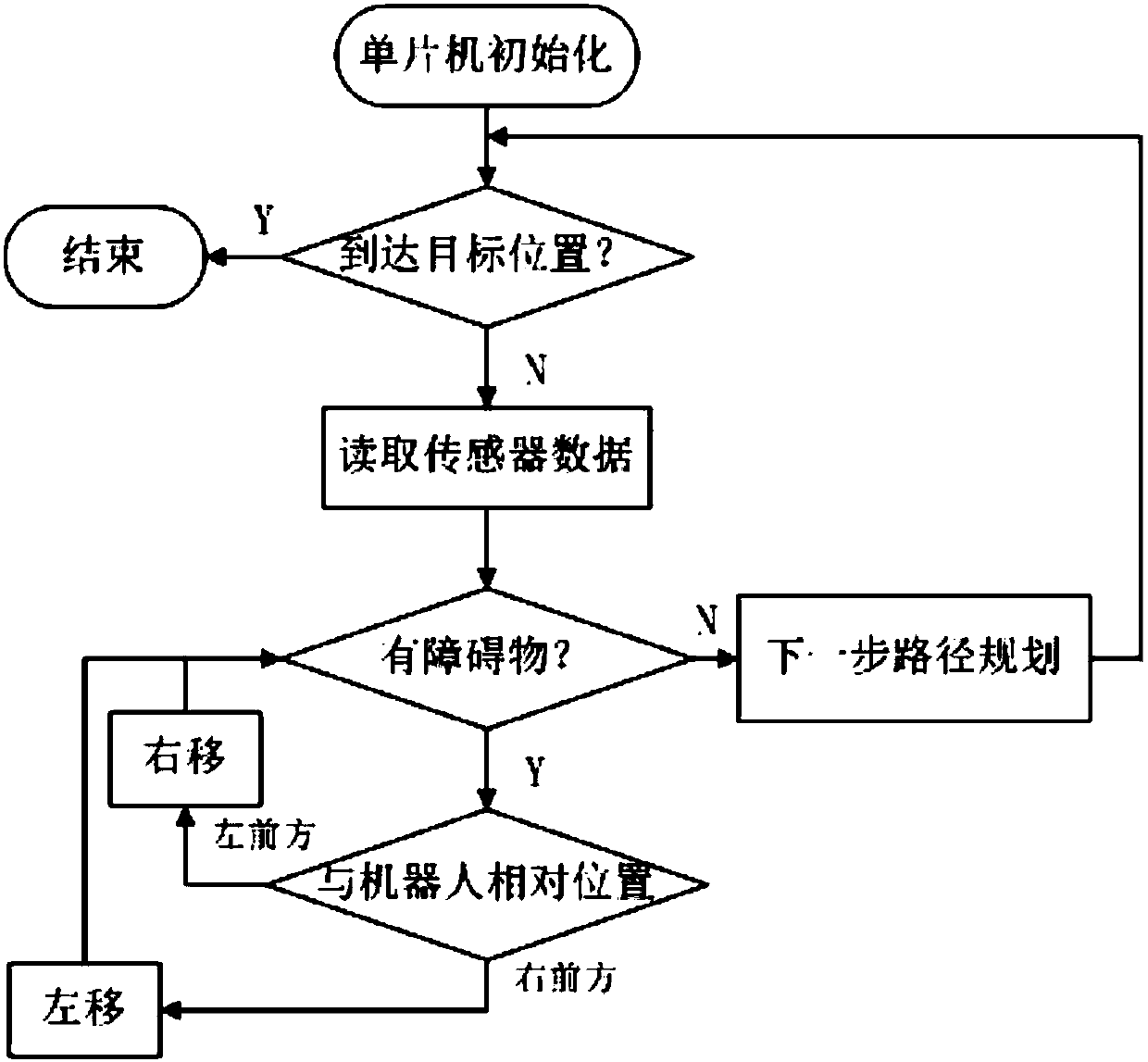
Dynamic obstacle-avoiding method of omnidirectional mobile robot
ActiveCN105223956ASmooth obstacle avoidance trajectoryPosition/course control in two dimensionsObservational errorLaser ranging
The invention provides a dynamic obstacle-avoiding method. The dynamic obstacle-avoiding method is characterized in that aimed at defects of a reciprocal speed obstacle-avoiding algorithm, an obstacle-avoiding responsibility coefficient is set, risk factors are introduced according to different obstacles, phenomena of delayed obstacle avoidance and unnecessary obstacle avoidance caused in measuring errors in the reciprocal speed obstacle-avoiding algorithm are improved, and a planned obstacle-avoiding track is smoother. In an unknown environment without an external positioning system, a vehicle-mounted laser range finder is used for detecting obstacles and estimating moving speeds of the dynamic obstacles, and based on the provided obstacle-avoiding scheme, an omnidirectional mobile robot is enabled to avoid dynamic and static obstacles in the moving range.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
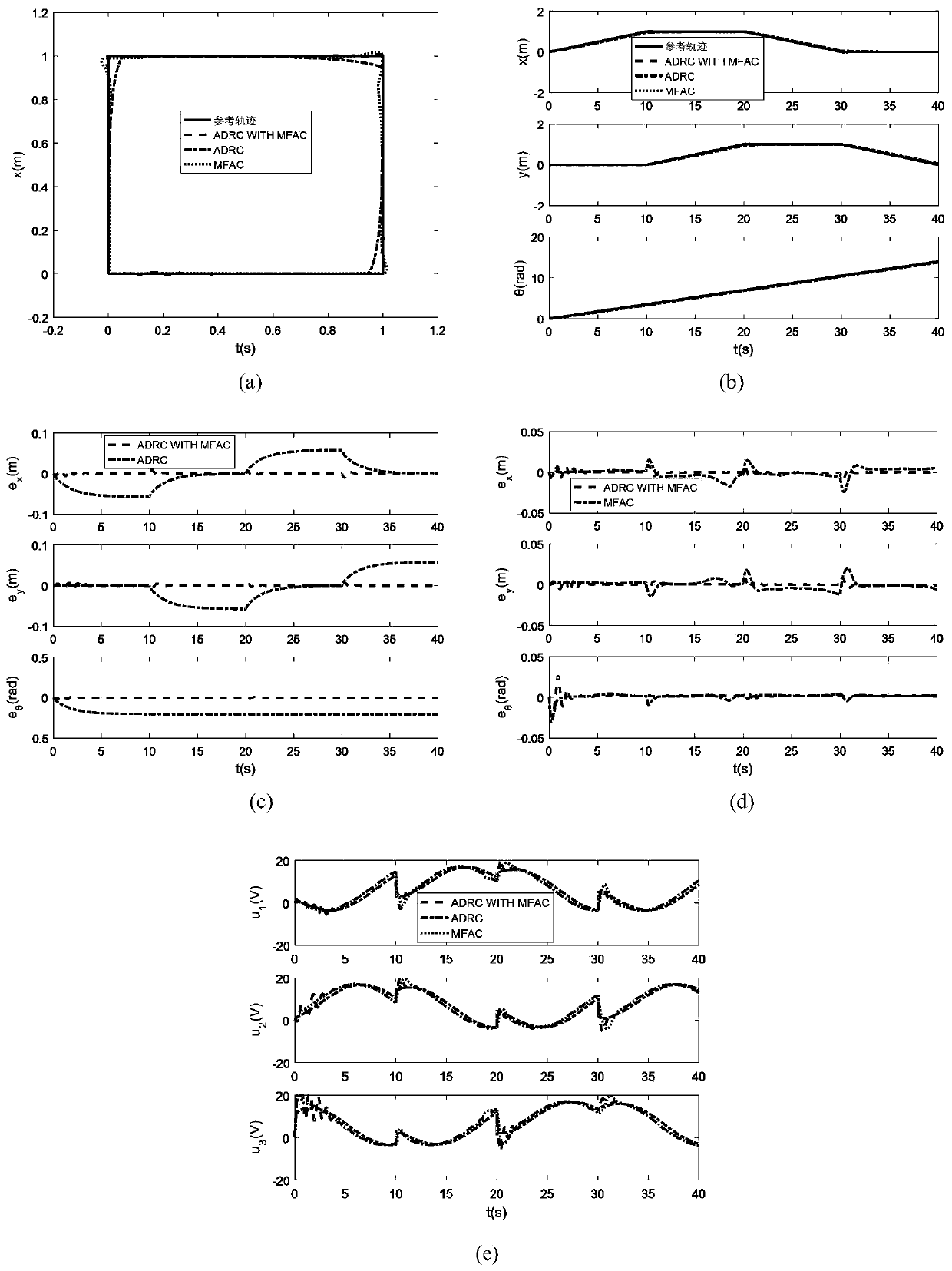
Passive omni-directional mobile robot trajectory tracking auto-disturbance rejection control method
ActiveCN108710302AReduce the need for feedbackReduce high frequency interferenceAdaptive controlRobotic systemsControl signal
The invention relates to the control of trajectory tracking of omni-directional mobile robots. In order to realize the precise control of the omni-directional mobile robot under the condition that theuncertainty of a dynamic model and the external disturbance exist simultaneously, and avoid the inversion operation, the technical solution adopted by the present invention is that: the omni-directional mobile robot trajectory tracking auto-disturbance control method uses an optimized reduced-order extended state observer to estimate the total disturbance of the omnidirectional mobile robot system, including unmodeled parts, parameter uncertainties and external disturbances, and uses a passive controller designed based on passive characteristics of the omnidirectional mobile robot system to compensate the disturbance estimated by the observer to achieve trajectory tracking control; the extended state observer actively takes the disturbance information from the input and output signals ofa controlled object to eliminate interference with control signals before the disturbance affects the system. The invention is mainly applied to the trajectory tracking and control of mobile robots.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Error model predictive control method based on kinematics modeling of omnidirectional mobile robots
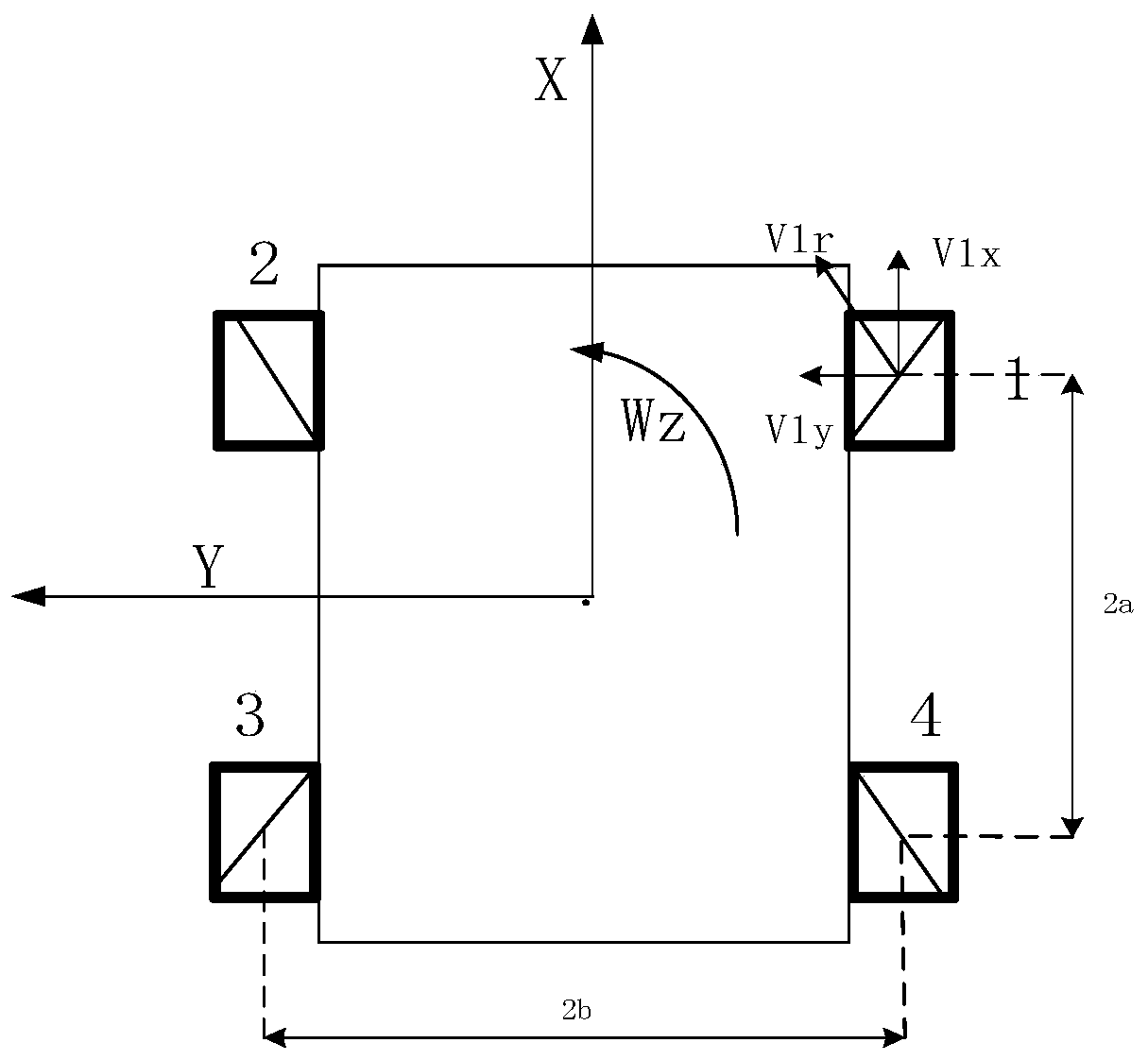
ActiveCN109885052ASolve the speed constraint problemFull rangePosition/course control in two dimensionsPosition/direction controlPredictive controllerOmnidirectional mobile robot
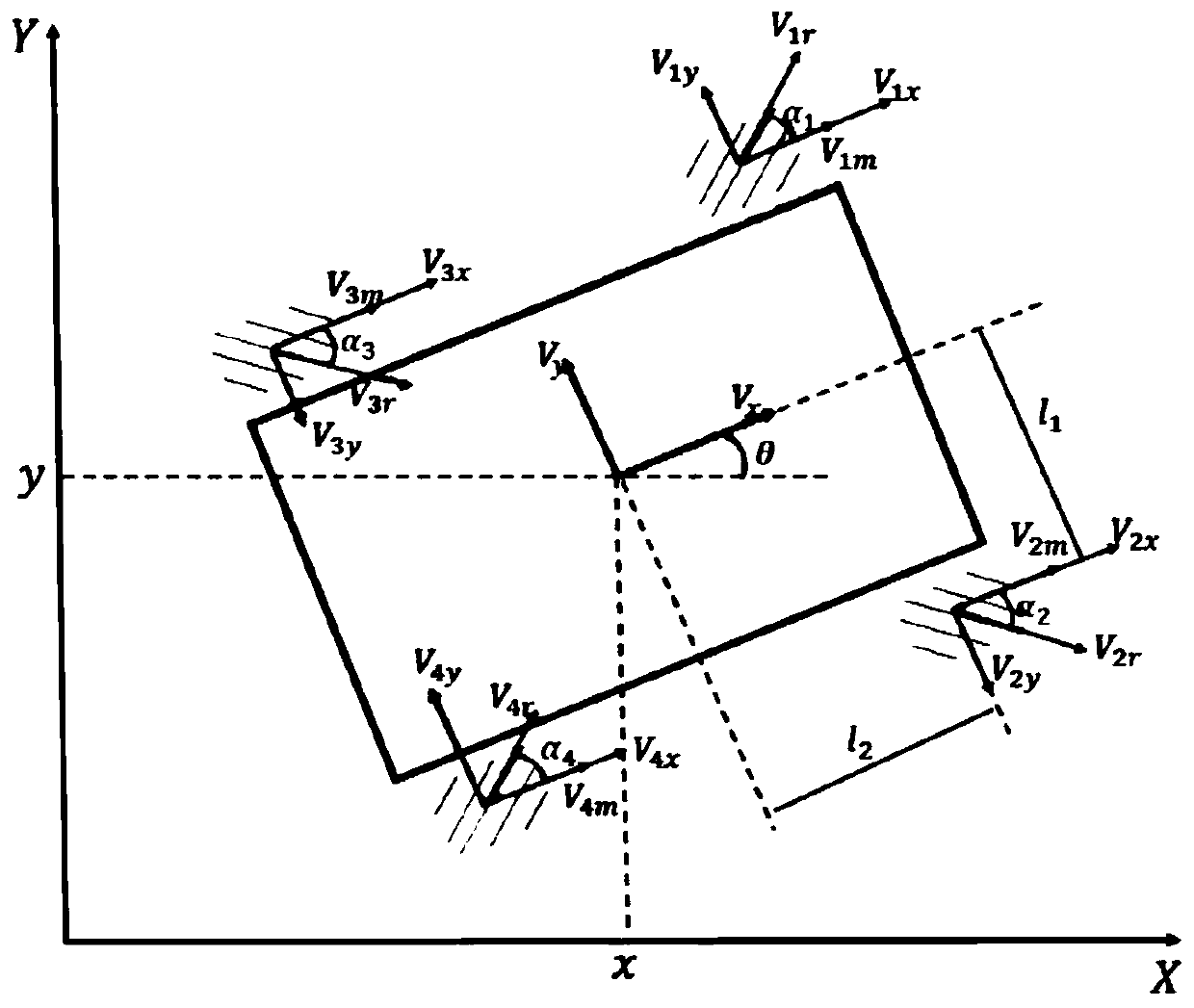
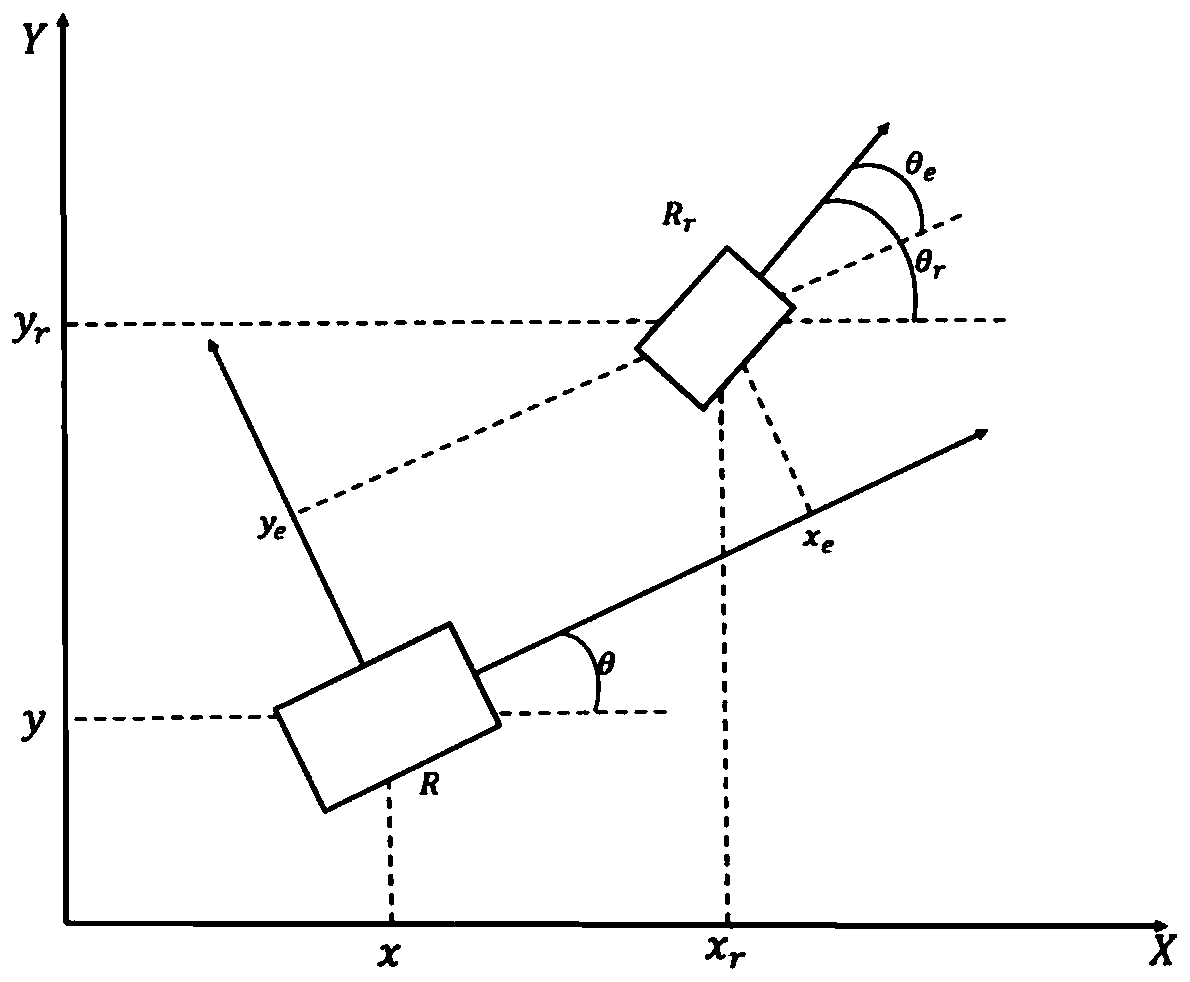
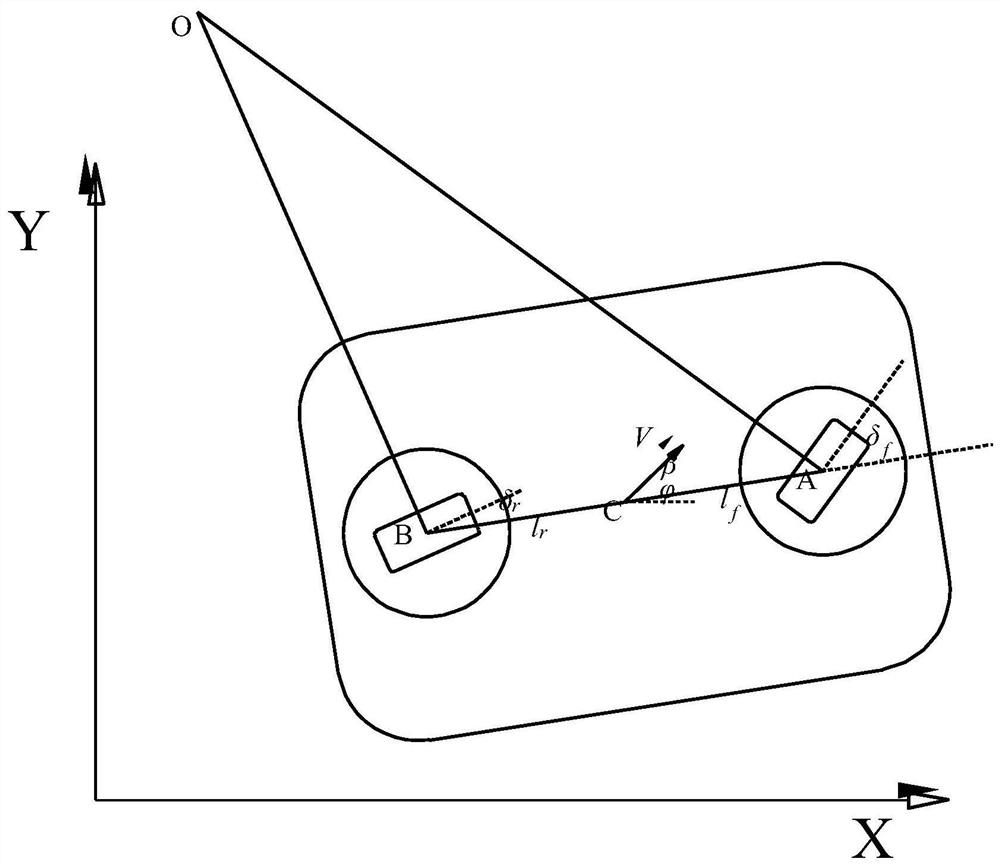
The invention discloses an error model predictive control method based on kinematics modeling of omnidirectional mobile robots. The error model predictive control method comprises the following stepsthat S11, a velocity constraint kinematics model is established between FM-OMR four Mecanum wheels; S12, a tracking error kinematics model of a FM-OMR is established; S13, aiming at the trajectory tracking problem of the FM-OMR and the tracking error kinematics model, an error model predictive controller combined with a velocity constraint equation is designed; and S14, according to the error model predictive controller, effective trajectory tracking parameters between the omnidirectional mobile robots are controlled so as to enable tracking errors between the omnidirectional mobile robots toremain unchanged. According to the error model predictive control method based on the kinematics modeling of the omnidirectional mobile robots, the error model predictive control method based on the trajectory tracking error kinematics modeling is provided aiming at the omnidirectional mobile robots with the four Mecanum wheels, the non-holonomic constraint problem of the effective trajectory tracking control is solved, and the accuracy and the validity are realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Following type lower limb motion rehabilitation omnidirectional mobile robot
ActiveCN106166370AImprove use comfort performanceAdjust left and right widthGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesEngineeringOmnidirectional mobile robot
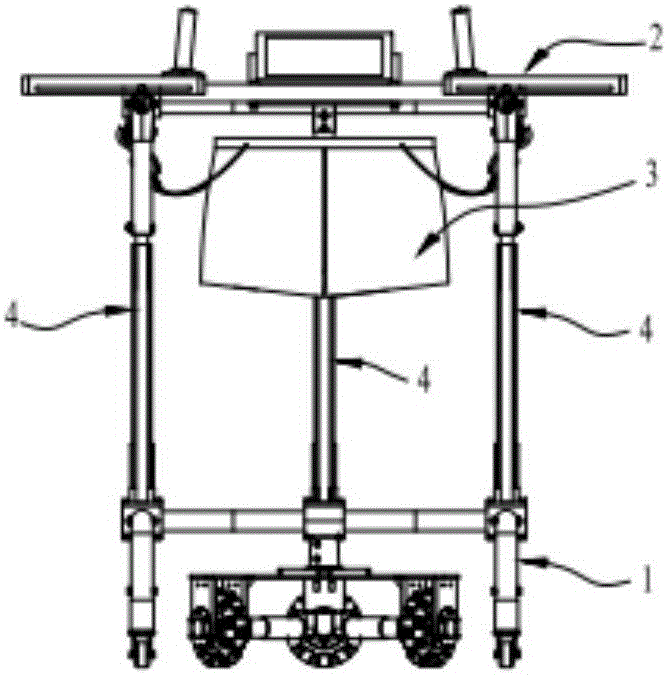
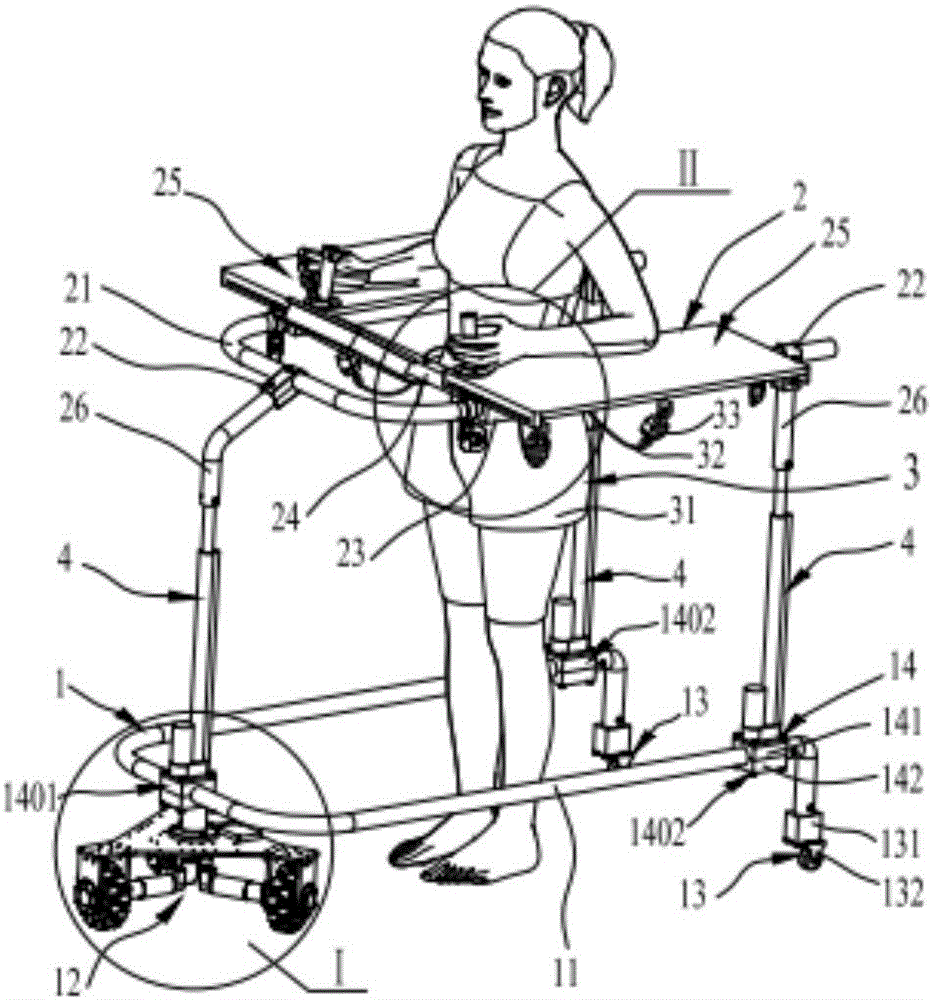
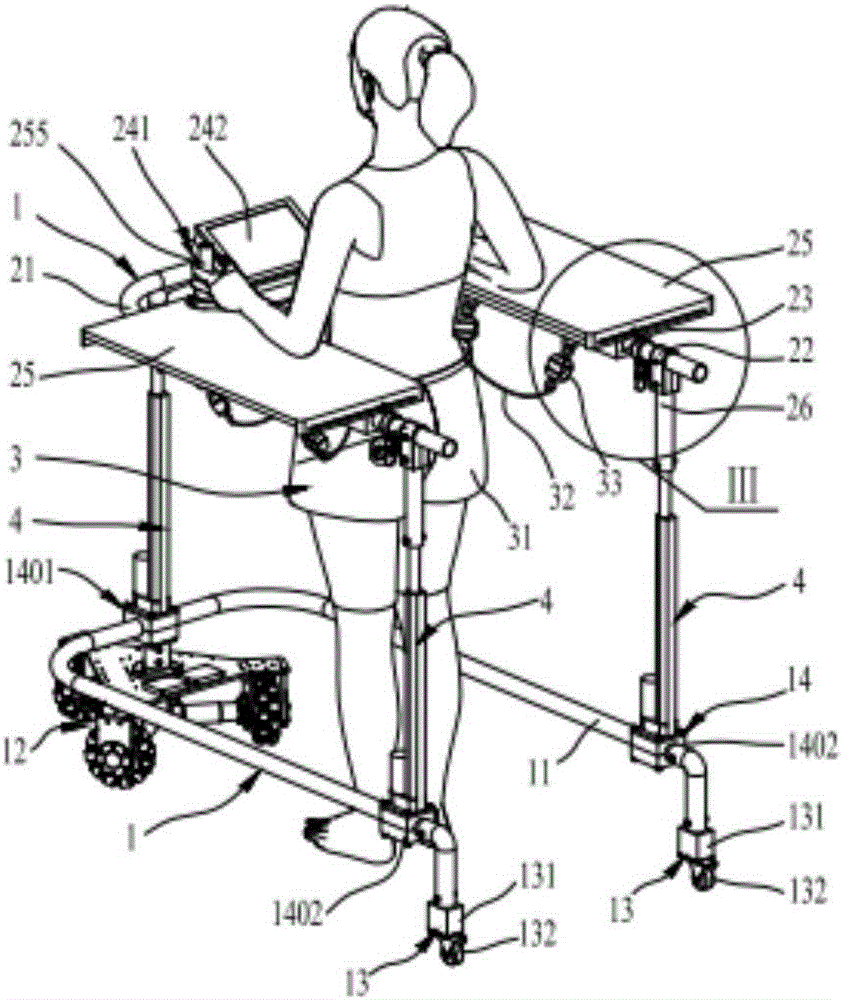
The invention discloses a following type lower limb motion rehabilitation omnidirectional mobile robot. A U-shaped moving bottom frame and an upper U-shaped protective frame are connected through a telescoping support device, an omnidirectional mobile chassis is connected under the front end bending section of the U-shaped frame of the omnidirectional mobile bottom U-shaped mobile bottom frame, the rear end is connected with two universal wheel assemblies, the omnidirectional mobile chassis includes a chassis main frame and continuous switching wheel assemblies, the chassis main frame is connected with the U-shaped frame, the three continuous switching wheel assemblies are connected to the bottom surface of the chassis main frame and are in circumference array triangular distribution, and a fall-down protector is arranged under the upper U-shaped protective frame and is connected with the upper U-shaped protective frame. A user is between the U-shaped moving bottom frame and the upper U-shaped protective frame to be protected by the fall-down protector, the walking intention of the user can be determined by a walking intention detection device, the robot is controlled to follow the user to move, protects the user from secondary injury by accidentally falling down, and assists the user to perform lower limb motion rehabilitation training.
Owner:XUZHOU UNIV OF TECH
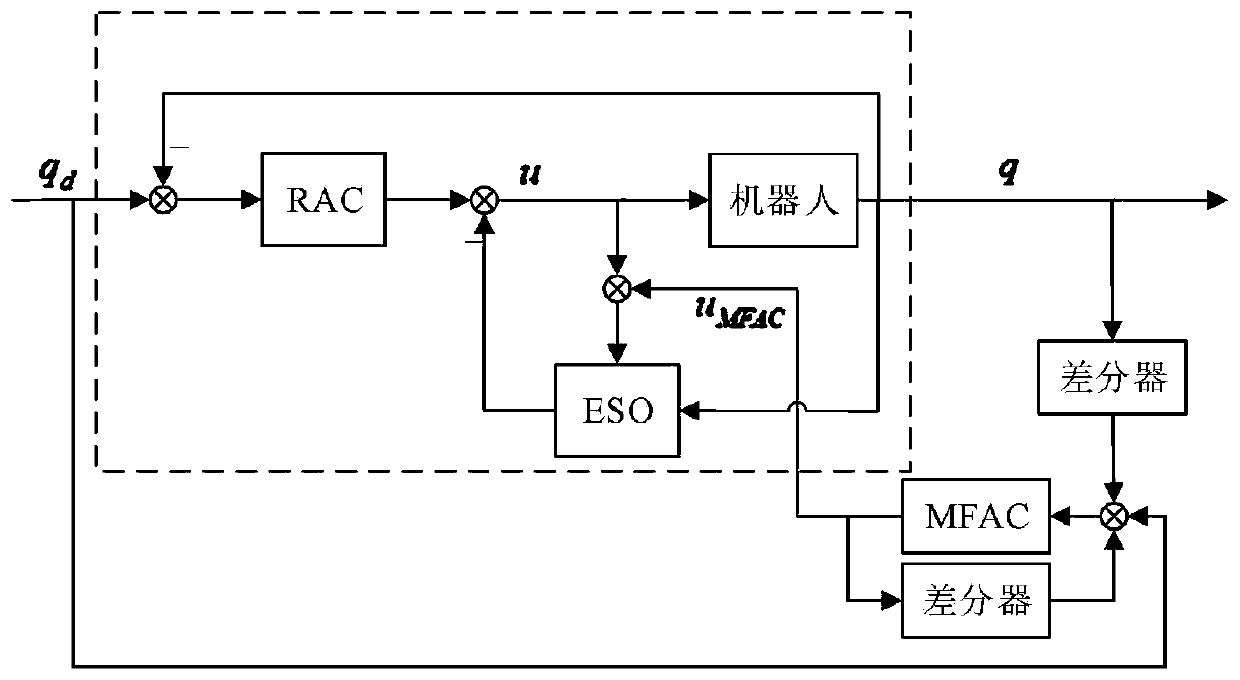
Robot trajectory tracking auto-disturbance rejection control method based on model-free outer loop compensation
The invention relates to a robot trajectory tracking auto-disturbance rejection control method based on model-free outer loop compensation. The method comprises the following steps that step 1, an omnidirectional mobile robot system dynamics model is established; step 2, an extended state observer is designed according to the dynamics model; step 3, an auto-disturbance rejection controller is designed according to an analytic acceleration control method, wherein the auto-disturbance rejection controller is composed of two parts, one part is used for compensating for the total disturbance of asystem, the other part is used for the trajectory tracking control over a robot, proportional differential feedback is introduced, and the model-free adaptive controller is obtained according to a false Jacobian matrix estimated value to add model-free adaptive control into the extended state observer.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Reverse movement navigation method in omnidirectional mobile robot channel
ActiveCN107065887ASolve the backward navigation problemEasy to implementPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesReal-time dataRadar
The present invention discloses a reverse movement navigation method in an omnidirectional mobile robot channel. The method comprises the following steps: the step 1: controlling a robot to move forwards in a channel, and estimating the current position information of the robot according to an encoder; the step 3, employing real-time data obtained by a laser radar in the robot movement process to generate a local map; the step 3, splicing the local map according to the real-time position of a dolly and the obtained local map, and obtaining the global map of the channel; the step 4: employing the least square method to fit two side boundaries of the channel according to the generated global map, and obtaining a track lime suitable for the travel of the dolly through calculation; the step 5, allowing the robot to start reverse movement, allowing the laser radar to collect real-time data to generate the local map, matching the local map and the global map, and obtaining the current position information of the dolly; and the step 6, performing pose regulation according to the deviation between the current position information of the robot and the track line to keep the robot to follow the track line.
Owner:重庆恒盛德科技有限公司
Method for robot to initiatively search and position smell source
ActiveCN106918367AFlexible moving processWide range of activitiesNavigation instrumentsLaser rangingAngular degrees
The invention discloses a method for a robot to initiatively search and position a smell source. The method comprises steps that firstly a used all-directional moving robot for searching and positioning a smell source is designed; an included angle between 90 degrees to 180 degrees is formed between a smoke plume finding stage robot and the robot runs along the upper wind direction; when the wind speed is smaller than a set threshold value, the robot carries out comprehensive searching based on the Z-shaped traversing method and changes the running direction when meeting a boundary; the smoke plume finding stage robot carries out swinging movement in variable step sizes and variable angles; by combining 360-degree all-directional rotation movement of the robot body, if gas is not detected, the robot carries out forward spiral-line movement in the clockwise direction; the robot body carries out 360-degree all-directional rotation movement; at a smell source positioning stage, a laser range finding sensor and a gas sensor carried by the robot are used for measuring gas concentration around a suspicious smell source so as to carry out gas source judgment, and finally the positioning is finished. Compared with the traditional smell source searching method, the provided method has high practicability and robustness.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Omnidirectional mobile platform
InactiveCN106143680ALow costLow application environment requirementsTyre tread bands/patternsVehiclesEngineeringOmnidirectional mobile robot
The invention belongs to the technical field of mobile platforms, in particular to an omnidirectional mobile platform. It includes wheels, a motion control unit, a motion execution unit and a platform base, wherein the motion control unit is arranged above the platform base, and four wheels are respectively installed on the bottom of the platform base through four motion execution units, and each motion execution unit is connected with The motion control unit is connected; the tire tread of the wheel is provided with twill. The twill pattern includes a plurality of slanted grooves and a plurality of slanted blocks inclined along the same direction, and the slanted grooves and slanted blocks are alternately arranged at intervals. The chute and the inclined block are parallel to each other. The invention can reduce the cost, meet the requirements of small size, reduce the requirements of the application environment, have the characteristics of simple structure, etc., and increase the achievable scope of the omnidirectional mobile platform application.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
All-directional movable double-arm robot
PendingCN110154033AIncrease operating spaceSolve the singularityProgramme-controlled manipulatorArmsUltrasonic sensorRadar
The invention discloses an all-directional movable double-arm robot. The all-directional movable double-arm robot comprises a vehicle body, a rotary hoisting platform, a laser radar, a first mechanical arm, a second mechanical arm, a camera, a plurality of ultrasonic sensor modules, a power supply system, an embedded host and an industrial control host, wherein the rotary hoisting platform can berotatably mounted on a top surface of the vehicle body; the laser radar can be rotatably mounted at the top end of the rotary hoisting platform; and the first mechanical arm and the second mechanicalarm can be mounted on the rotary hoisting platform in an up-down movement manner. The all-directional movable double-arm robot disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the robot hastwo rotating degrees of freedom and vertical degrees of freedom, so that an operation space of an all-directional movable robot can be greatly improved and a working blind region is reduced; more complicated working tasks can be carried out through the cooperation of double arms; the navigation and positioning precision is improved and the reliability and robustness of a navigation system are improved; and the obstacle-avoiding performance of the system is improved.
Owner:合肥哈工图南智控机器人有限公司
Path planning system and method based on multiple omni-directional mobile robots
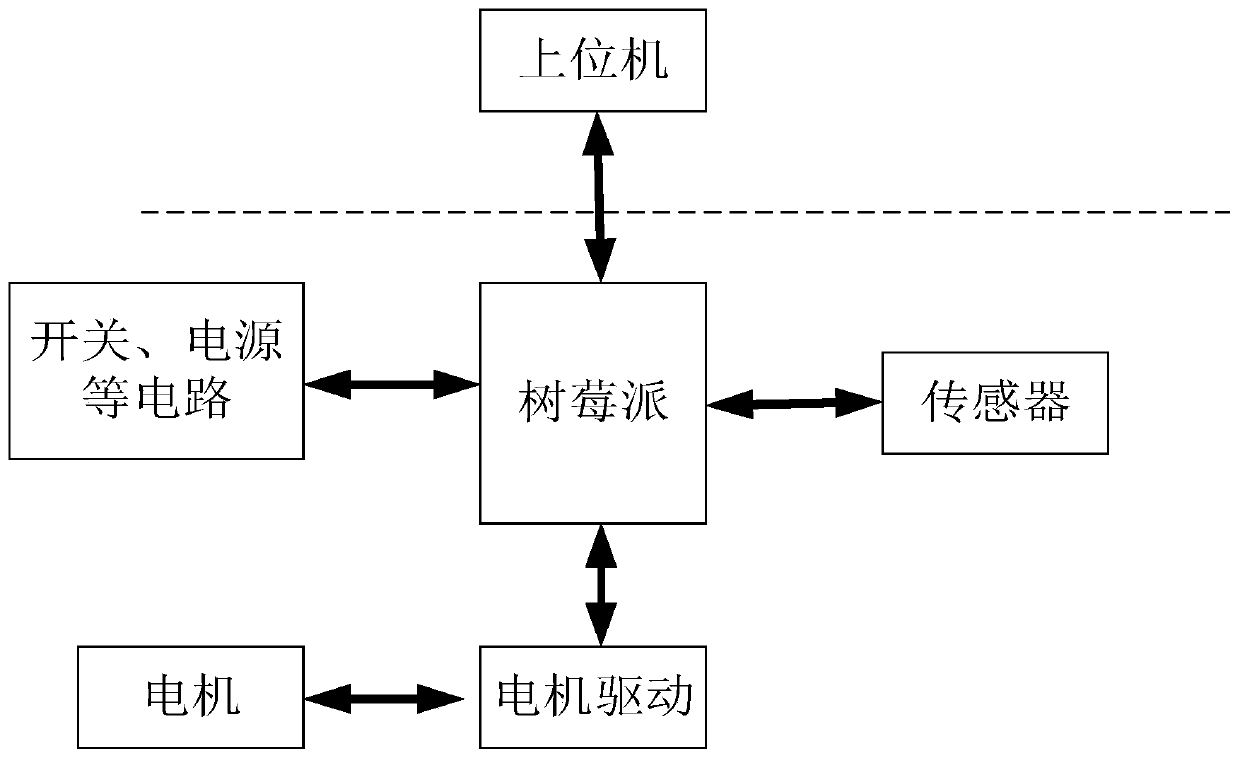
ActiveCN109978272AReduce development difficultyIncrease flexibilityForecastingPosition/course control in two dimensionsMotor driveSimulation
The invention discloses a path planning system and method based on multiple omni-directional mobile robots. The path planning system comprises a robot, an upper computer, a motor driving system and aRaspberry Pi main control bottom layer. The upper computer system is connected with the raspberry pi main control bottom layer through a wireless local area network; the Raspberry Pi main control bottom layer is connected with a sensor and a motor driving system in the robot respectively; a plurality of omni-directional mobile robots are positioned by using sensors. The path planning method comprises the following steps of (1) enabling the robot to position by using a sensor carried by the robot; (2) generating a global path by utilizing an A * algorithm according to a given target position; and (3) according to the actual environment, generating a local path by utilizing an RVO local path planning algorithm, and finishing the autonomous navigation of a plurality of robots. For the path planning of the multiple robots, the problem of the motion collision of the multiple mobile robots can be avoided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
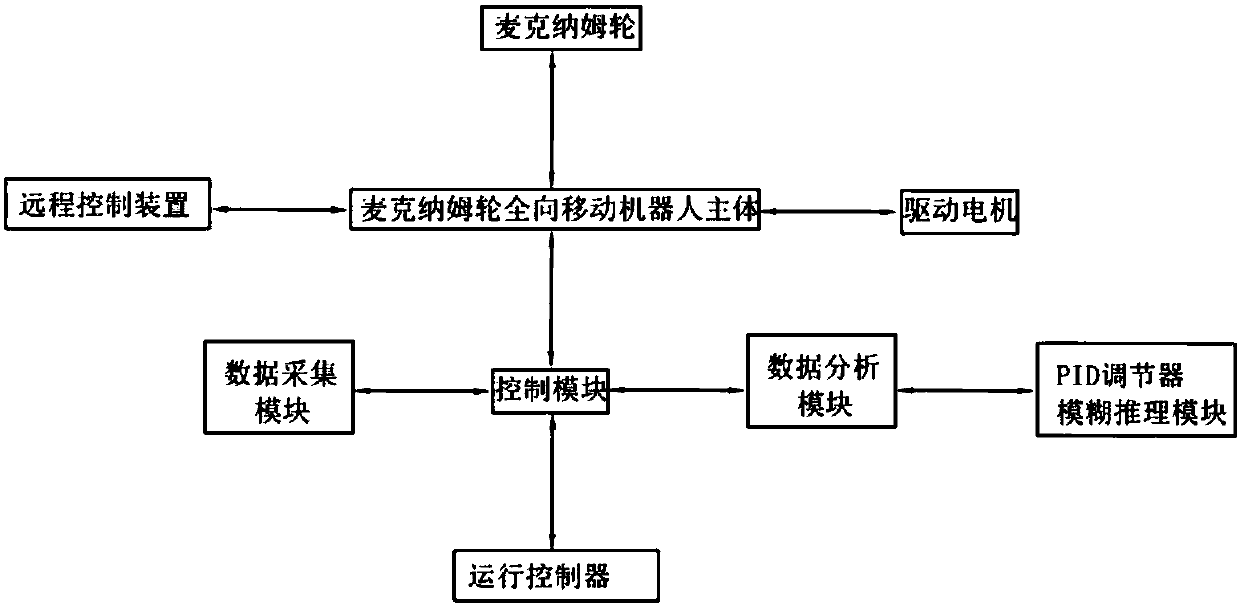
Control device for omnidirectional running of Mecanum wheels
InactiveCN107807646AImprove applicabilityIncrease flexibilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsOmnidirectional antennaFuzzy inference
The invention relates to the technical field of robot, in particular to a control device for omnidirectional running of Mecanum wheels. The control device includes a Mecanum wheel robot body and a control module. The control module includes a data acquisition module, a data analysis module and a running controller. The data acquisition module includes a plurality of sensors. The data analysis module includes a PID regulator and a fuzzy inference module. The fuzzy inference module is used for fuzzifying the signal of the data acquisition module and outputting fuzzy quantity. The PID regulator defuzzifies the fuzzy quantity and transmits the fuzzy quantity to the running controller. The running controller makes a drive motor on the Mecanum wheel omnidirectional mobile robot body move. In theinvention, a fuzzy PID control technology is adopted to combine a fuzzy algorithm with a traditional PID controller. Based on the advantages of simple control, good performance and high reliability of the conventional PID controller, the values of the parameters of the PID controller are adjusted, and thus, the applicability and flexibility of the controller are improved.
Owner:DONGGUAN HANDY INTELLIGENT ROBOT TECH CO LTD
Domestic helping omnidirectional mobile robot
PendingCN107714405AMeet the needs of useSolve the problem on your ownWalking aidsMotor speedWheelchair
The invention provides a domestic helping omnidirectional mobile robot, which relates to a robot and solves the problems that the movability of a conventional wheelchair is low, and great harm is caused on the health after people sit the wheelchair for a long period. The front side and the back side of a base plate of the mobile robot are provided with two Mecanum wheels; each Mecanum wheel is singly driven by a motor speed reducer I; a foot sole carrying plate is arranged on the base plate; one end of a long connecting rod is fixedly connected with the bottom of a seat; a hinging plate is arranged at each of the front side and the back side of an upright post; the two ends of a short connecting rod are respectively hinged to the hinging plate arranged at one side of the upright post and the other end of the long connecting rod; the two ends of a bent connecting rod are respectively hinged to the hinging plate arranged at the other side of the upright post and the long connecting rod;the upright post is fixedly connected onto the base plate; an execution mechanism I drives the short connecting rod, so that the seat can swing, and extend and retract backwards and backwards; a kneesupporting protection plate is provided with a regulating rod; a knee supporting lengthening device is fixed on the upright post, so that a regulating rod of the knee supporting protection plate is buckled on the upright post in a sleeving way. The domestic help omnidirectional mobile robot is applicable to old people, disabled people and paralyzed people inconvenient to move.
Owner:HANGZHOU ROBOCT TECH DEV CO LTD
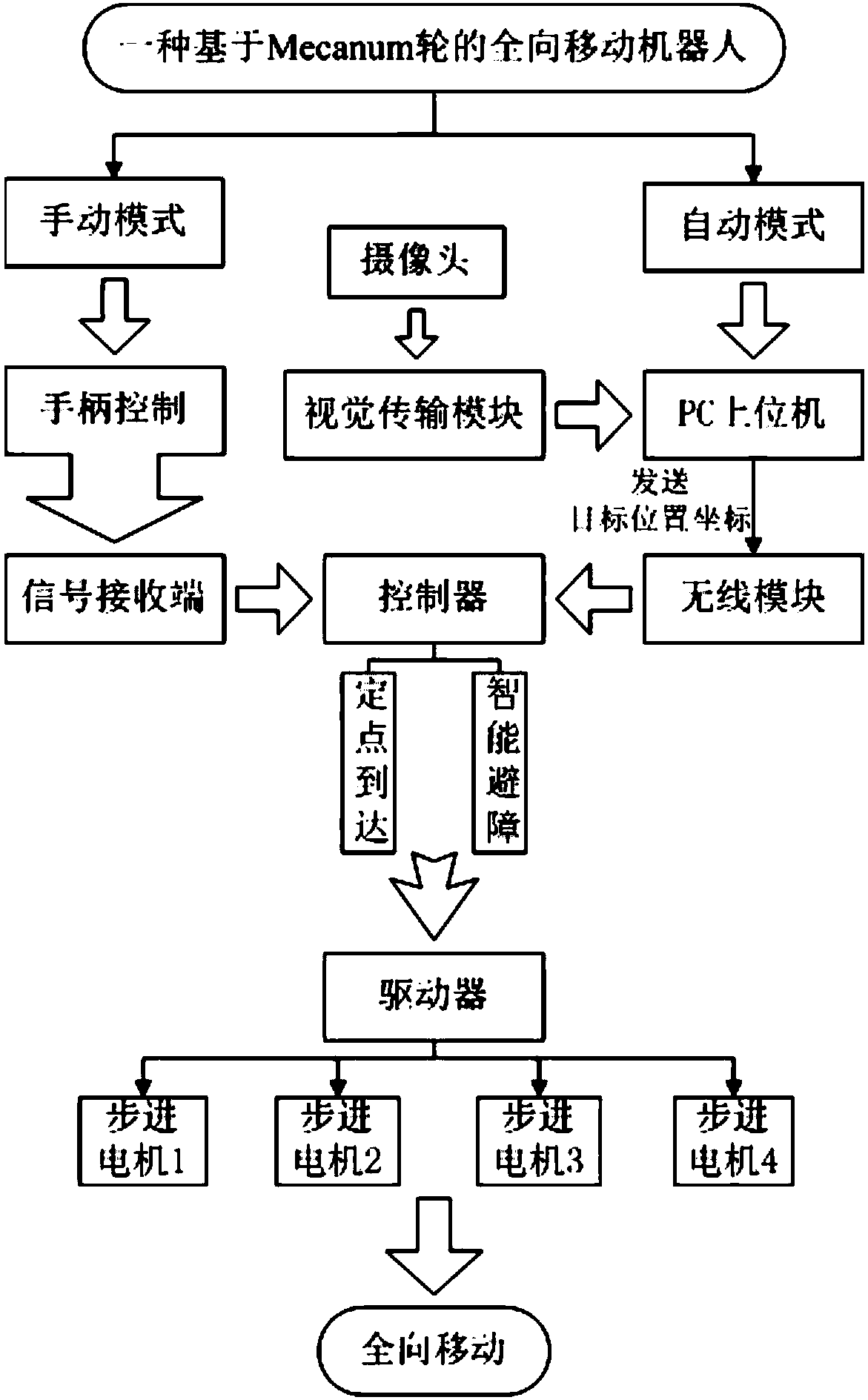
Omni-directional mobile robot based on Mecanum wheel and control method thereof
InactiveCN108544465ALinear adjustableImprove space utilizationProgramme-controlled manipulatorWireless controlCoupling
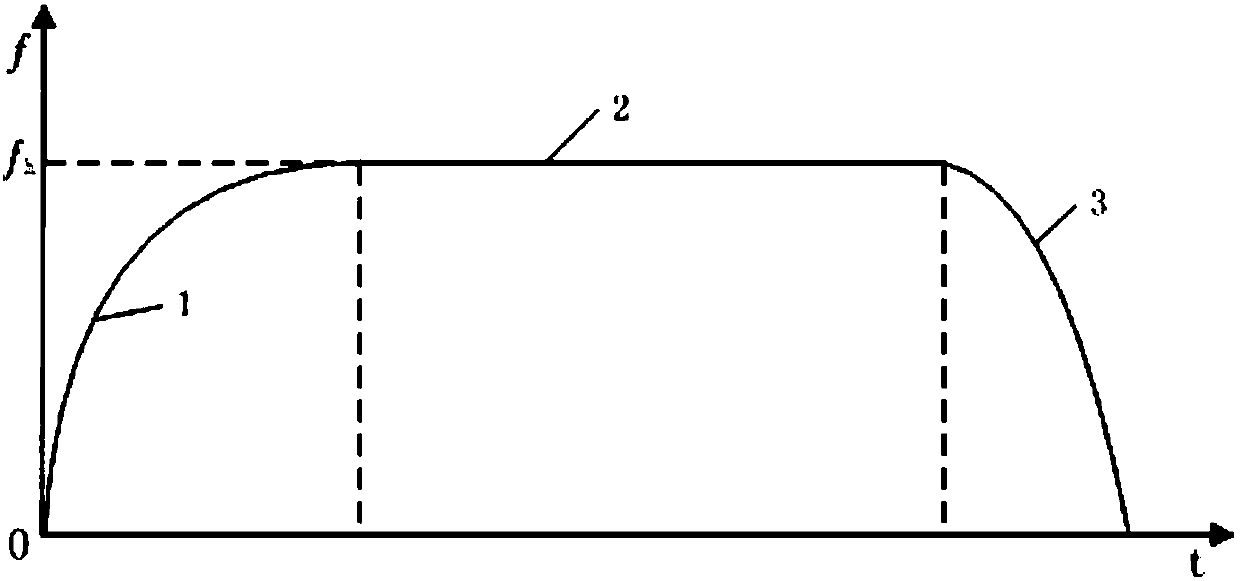
The invention discloses an omni-directional mobile robot based on a Mecanum wheel. The robot comprises a chassis, the Mecanum wheel, a driver, a controller, a wireless communication module, a detection module, a visual transmission module and a power module; the front side and the rear side of the chassis are each provided with a stepping motor, the Mecanum wheel is connected with the stepping motors through a coupler, the structure is symmetric, and the controller on the chassis is connected with the driver, the wireless control module, the detection module, the visual transmission module andthe power module through a circuit, a traditional wheel type moving mechanism is improved, more flexibility is achieved, and the omni-directional characteristics are used for providing great convenience for storage and carrying; the independently-designed programmable driver is small in self weight, small in size, and high in drive capacity, and the space utilization rate of the robot is improved, an exponential type speed model is built, adjustable PWM soft starting and soft braking can be achieved, the drive manner of the stepping motors is optimized, and in combination with the manual modeand the automatic mode, the function of the omni-directional mobile robot is enriched.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
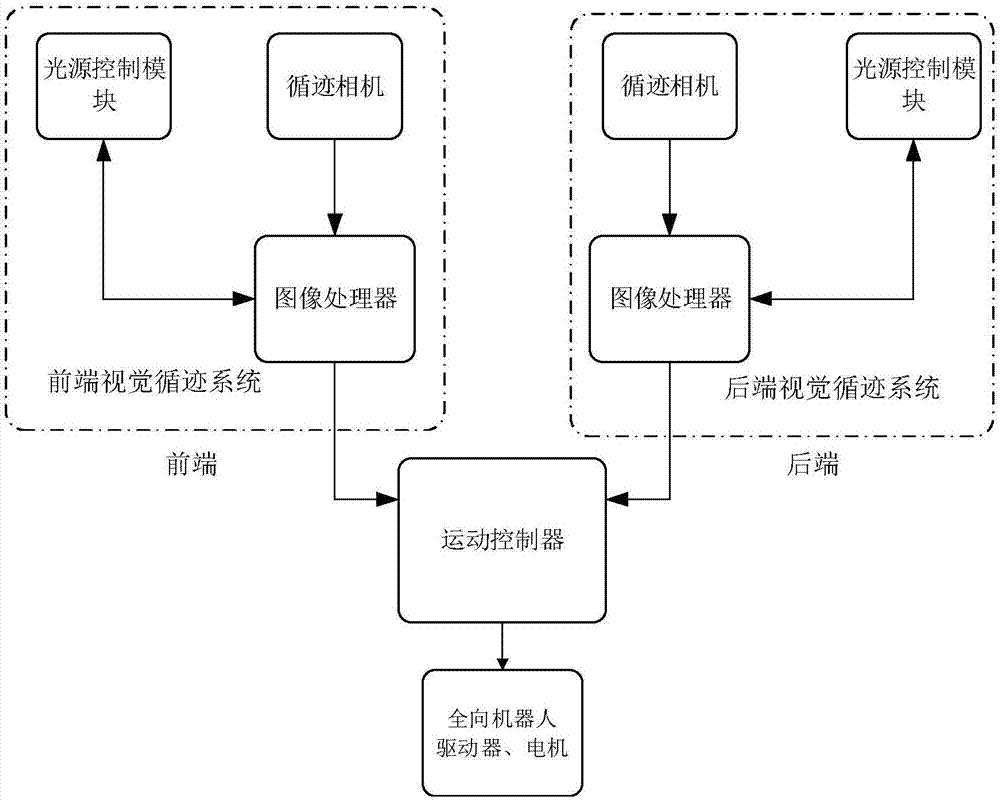
Double-vision tracking device and method used for omni-directional movement robot
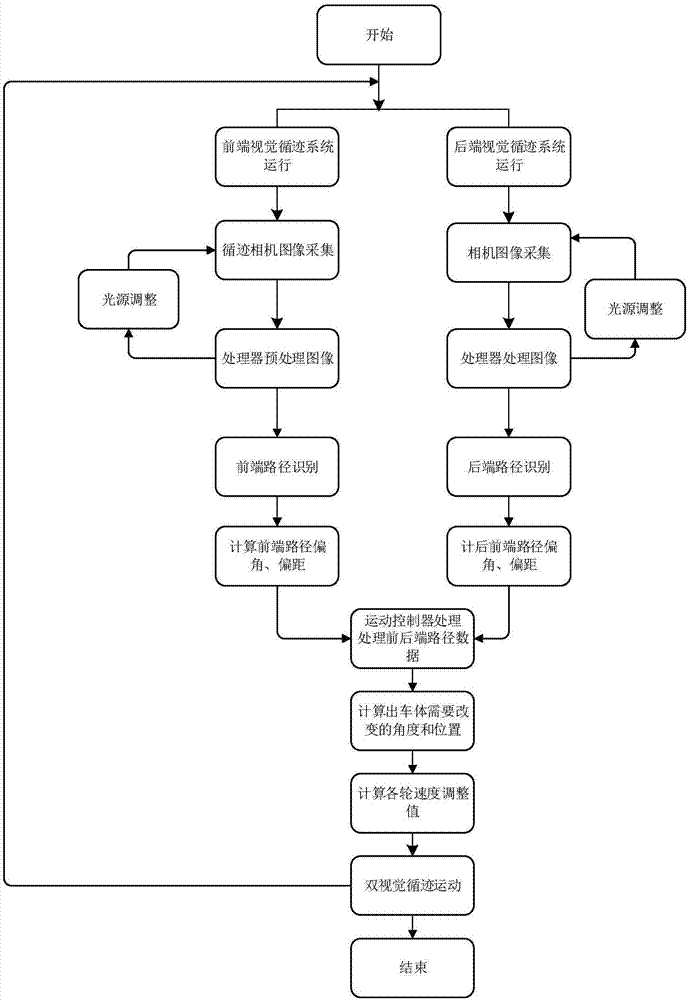
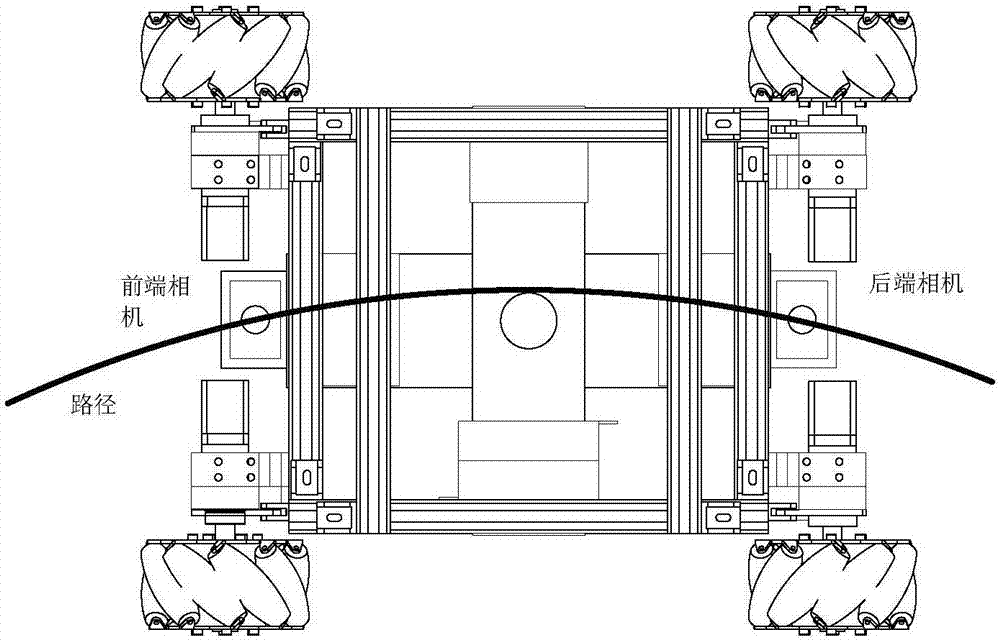
InactiveCN106985142AImprove tracking accuracyFull path informationProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringOmni directional
The invention discloses a double-vision tracking device and method used for an omni-directional movement robot. The tracking device comprises a front end vision tracking system installed at the front end of the robot, a rear end vision system installed at the rear end, and a movement controller. A vision recognition system provides the guide and judgment foundation for movement of the robot by acquiring front route images and rear route images of the robot and extracting offset distance and deflection angle information. The front end vision tracking system and the rear end vision tracking system are each in communication with the movement controller and transmit information of the deflection angle and the offset distance in real time. The movement controller calculates the optimal movement route information of the robot and then regulates the speed of each wheel of the robot so that the front end and the rear end of the robot can both move along the route. The deflection between the front end of the robot and the reference route and the deflection between the rear end of the robot and the reference route are each detected through the two-way vision recognition system, more complete route information is obtained, the control precision is improved, the tracking posture of the omni-directional movement robot is determined, and better insurance is provided for movement navigation and obstacle avoidance of the robot.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Independent suspension structure of Mecanum wheel omni-directional mobile robot
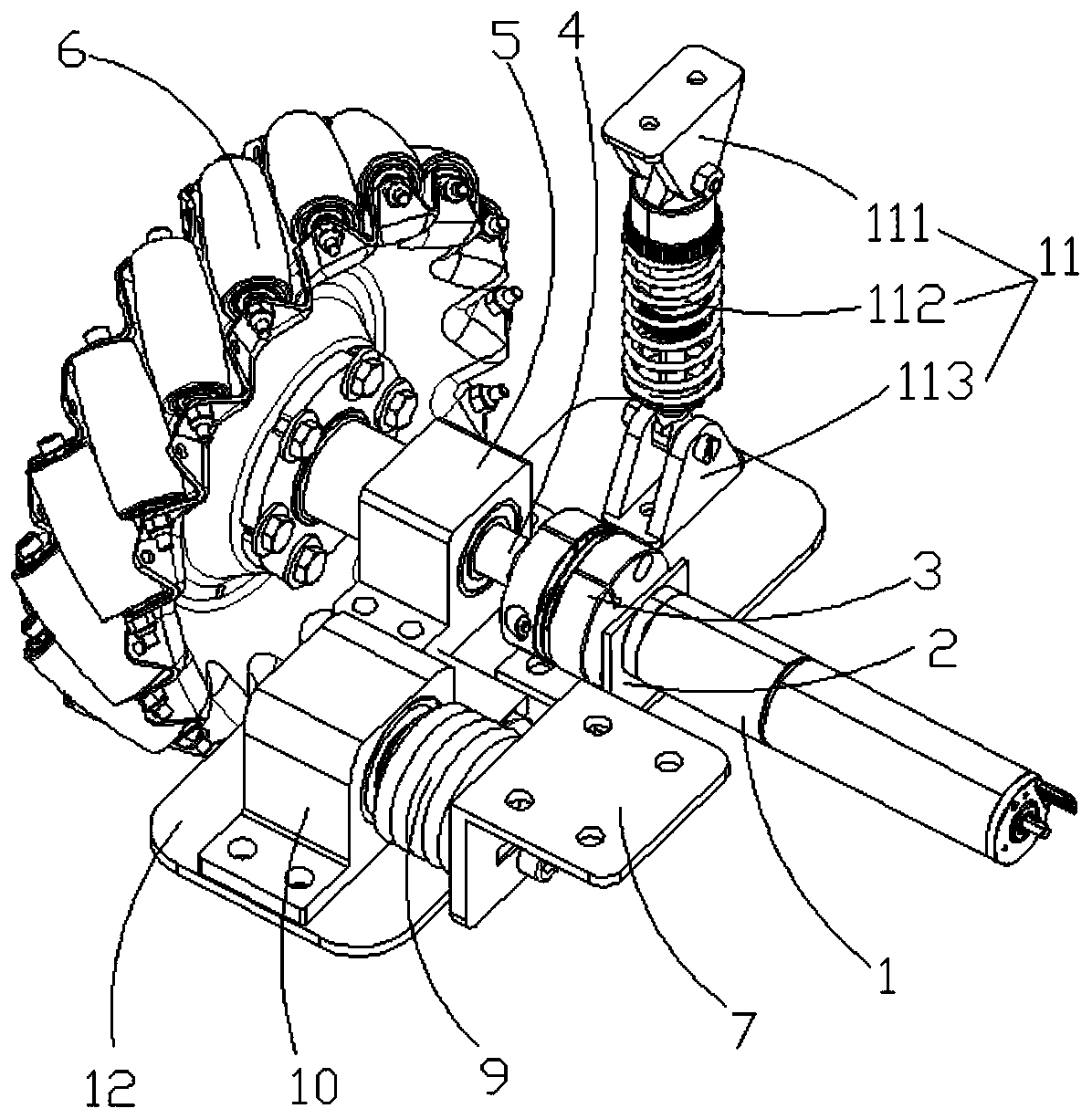
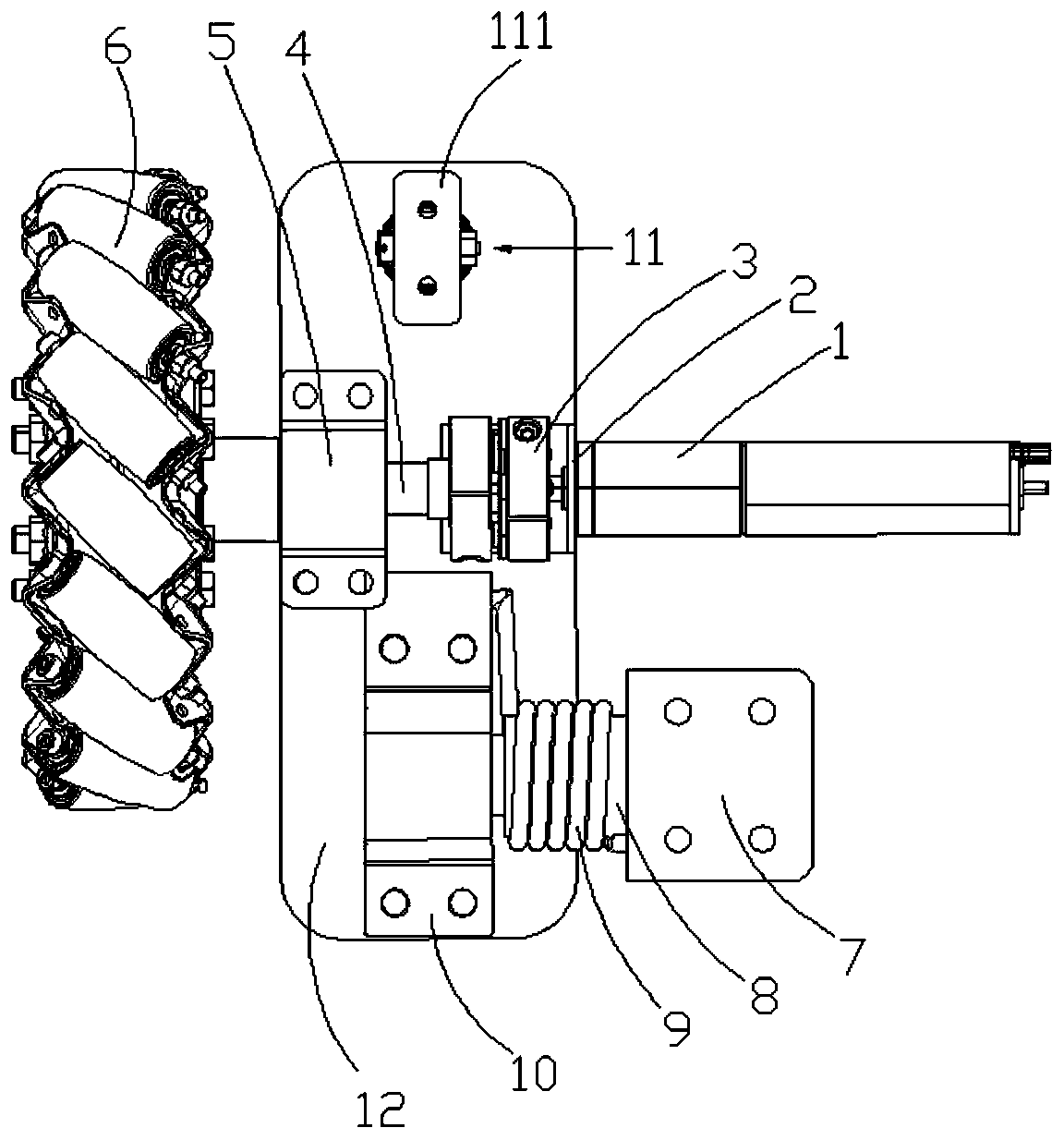
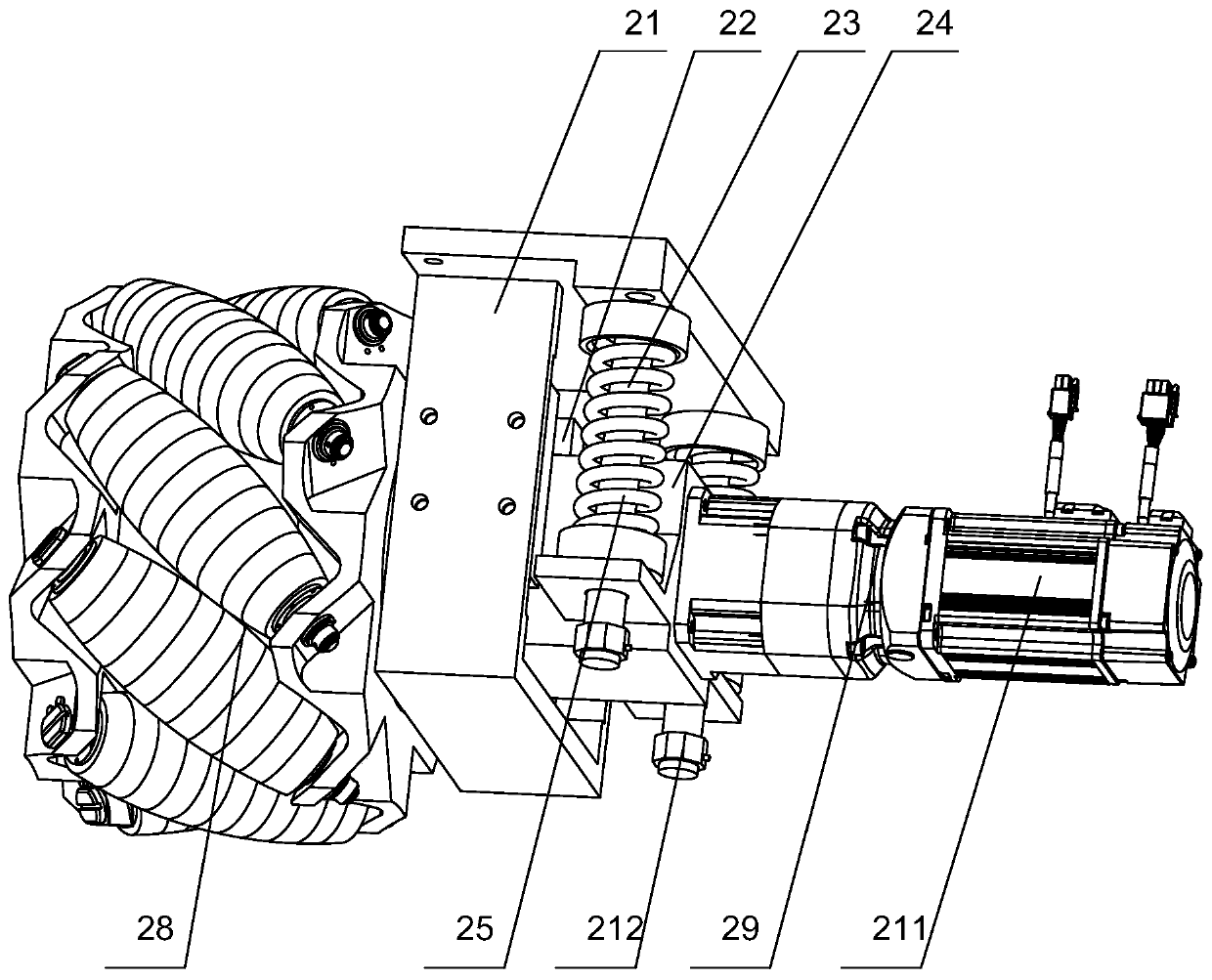
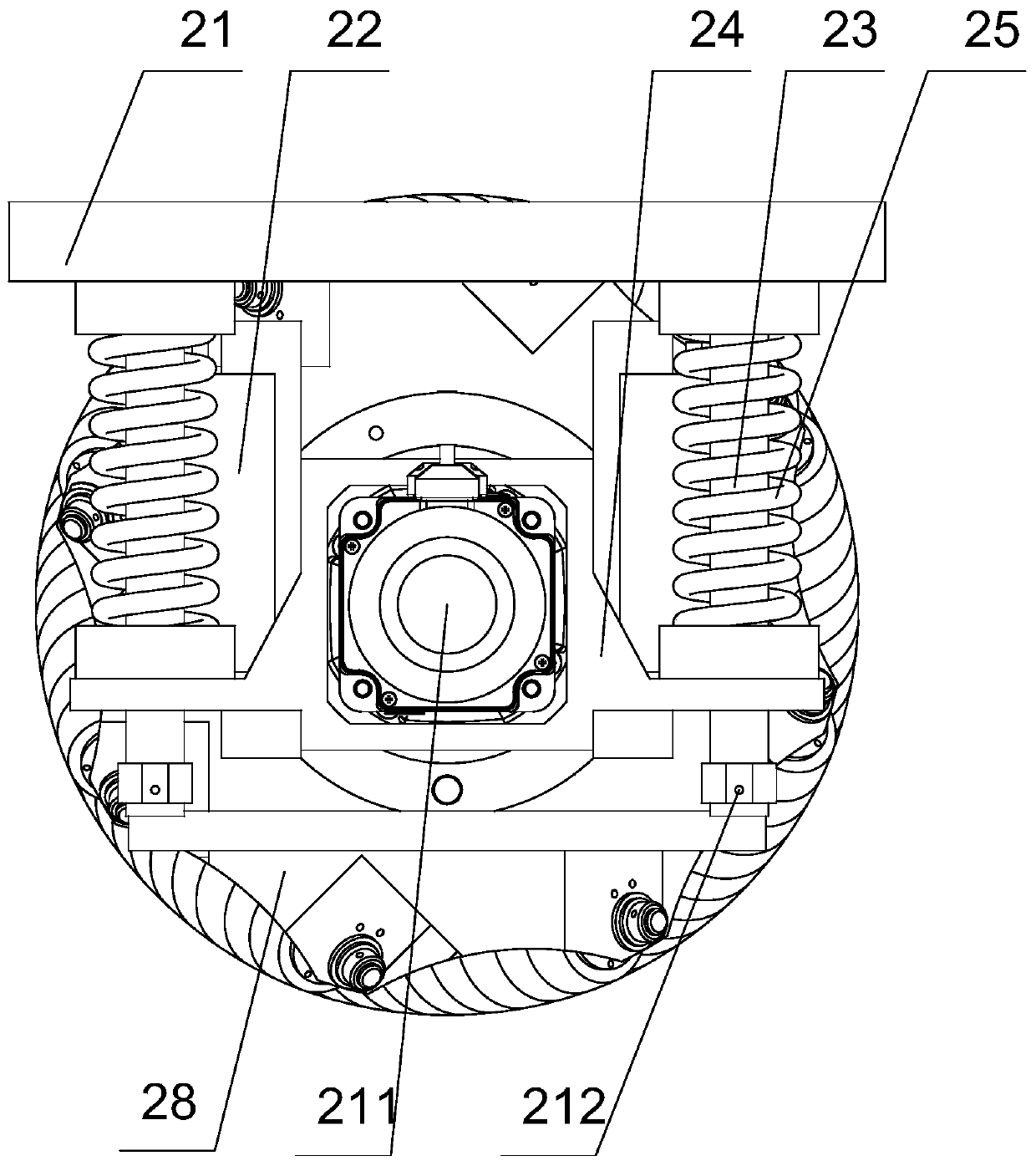
PendingCN110077184ASmooth motionReduce bouncingResilient suspensionsVehicle springsMotor speedReduction drive
The invention provides an independent suspension structure of a Mecanum wheel omni-directional mobile robot. The independent suspension structure of the Mecanum wheel omni-directional mobile robot comprises a suspension bottom plate; a motor speed reducer, an L-shaped support, a shaft coupling, an output shaft, an axle bearing seat and a shock absorbing device are mounted on the suspension bottomplate in a matched manner; the motor speed reducer is connected with one end of the output shaft through the shaft coupling; the other end of the output shaft is fixedly connected with a Mecanum wheel; the independent suspension structure of the Mecanum wheel omni-directional mobile robot further comprises a torsion spring, a torsion spring shaft, an L-shaped connecting piece and a torsion springshaft bearing seat; a torsion spring shaft bearing is mounted in the torsion spring shaft bearing seat; the axis of the torsion spring shaft bearing is parallel to the axis of an axle bearing; one endof the torsion spring shaft is fixed on a vehicle body through the L-shaped connecting piece; the other end of the torsion spring shaft is inserted into an internal ring of the torsion spring shaft bearing; the torsion spring is arranged on the torsion spring shaft in a sleeving manner; one end of the torsion spring is fixed on the L-shaped connecting piece; and the other end of the torsion spring is fixed on the suspension bottom plate. According to the independent suspension structure of the Mecanum wheel omni-directional mobile robot, a spring damping shock absorber and the torsion springare utilized to perform double shock absorption so that the shock absorbing effect is better and the robot motion is more stable.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
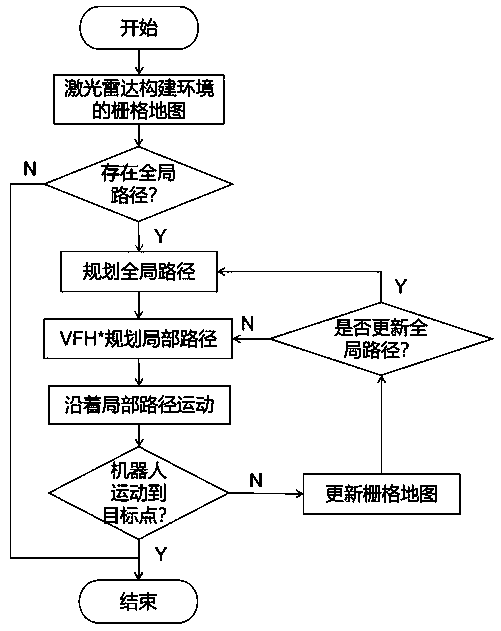
Omnidirectional mobile robot autonomous navigation system based on VFH* local path planning method
InactiveCN111142542AGood autonomous navigationComprehensive consideration of obstacle avoidancePosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesAutonomous Navigation SystemSimulation
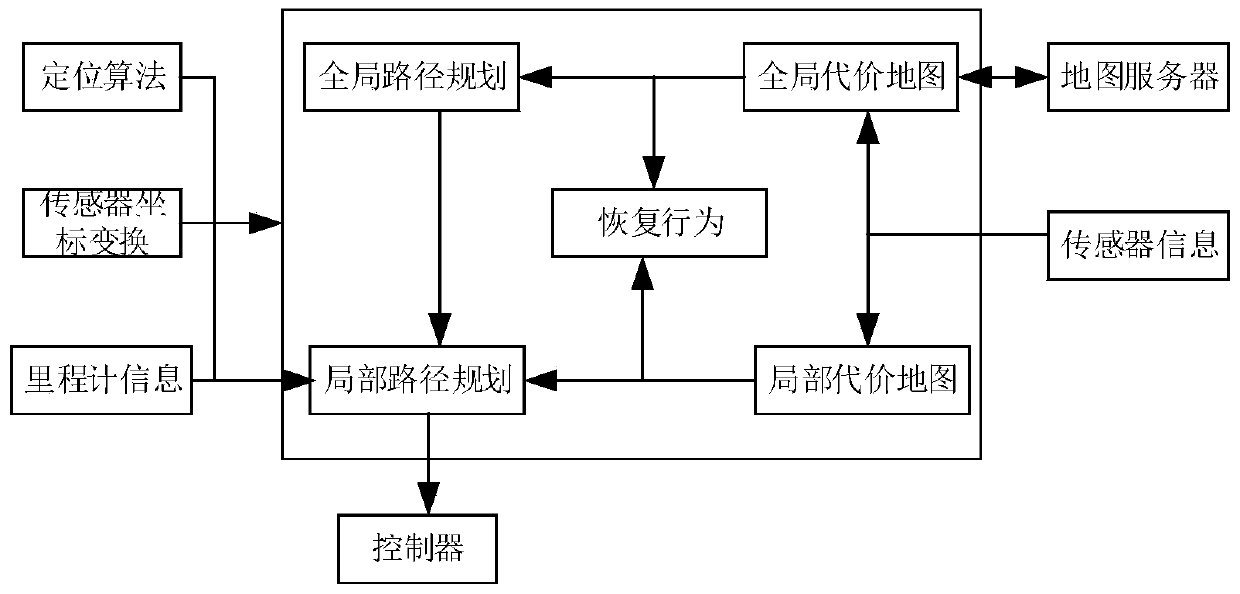
The invention provides an omnidirectional mobile robot autonomous navigation system based on a VFH* local path planning method. Firstly, a laser radar installed on a mobile robot is utilized to construct a grid map of the environment, then a global path from the current position of the mobile robot to an expected target position is planned through a global path planning method, and finally, a local target point is selected from the global path to plan a local path. According to the local path planning method, a VFH+ obstacle avoidance method is improved, so that the mobile robot can select theobstacle avoidance direction as optimal as possible, meanwhile, the situation that VFH+ can select a non-optimal obstacle avoidance direction under special conditions is eliminated in combination with the thought of A* path planning, and the planned local path is as short as possible under any condition. After the local path is planned, the mobile robot is controlled to move in the direction of the local path, and meanwhile, the local path is updated at a certain frequency so that the mobile robot can autonomously navigate in a scene with a complex and changeable environment.
Owner:苏州晨本智能科技有限公司
Wheel-track combined omnidirectional mobile robot
InactiveCN108860340AOmni-directional mobile implementationHigh speedEndless track vehiclesTerrainEngineering
The invention provides a wheel-track combined omnidirectional mobile robot comprising a chassis frame, a chassis crawler belt device and a chassis wheel device; the chassis crawler belt device and thechassis wheel device are both mounted on the chassis frame; the chassis wheel device comprises four moving wheels, wherein two moving wheels are mounted at a vertical front end of the chassis frame and are symmetrically arranged at two lateral sides of the chassis frame; the other two moving wheels are disposed at the longitudinal rear end of the chassis frame and are symmetrically disposed on the two lateral sides of the chassis frame; the chassis crawler belt device is provided with an annular crawler belt, and the annular crawler belt is placed between the moving wheels on both sides and surrounds in the longitudinal direction; a front end of the annular crawler belt extends to the front of the front moving wheels and a rear end of the annular crawler belt extends to the rear of the rear moving wheels; the bottom of the annular crawler belt is higher than the bottom of the moving wheels. The invention has strong terrain adaptability and obstacle-obstructing performance, simple structure, high mobility and omnidirectional movement.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Omnidirectional mobile robot
InactiveCN111409056AHigh degree of automationHighly integratedManipulatorOmnidirectional mobile robotElectric control
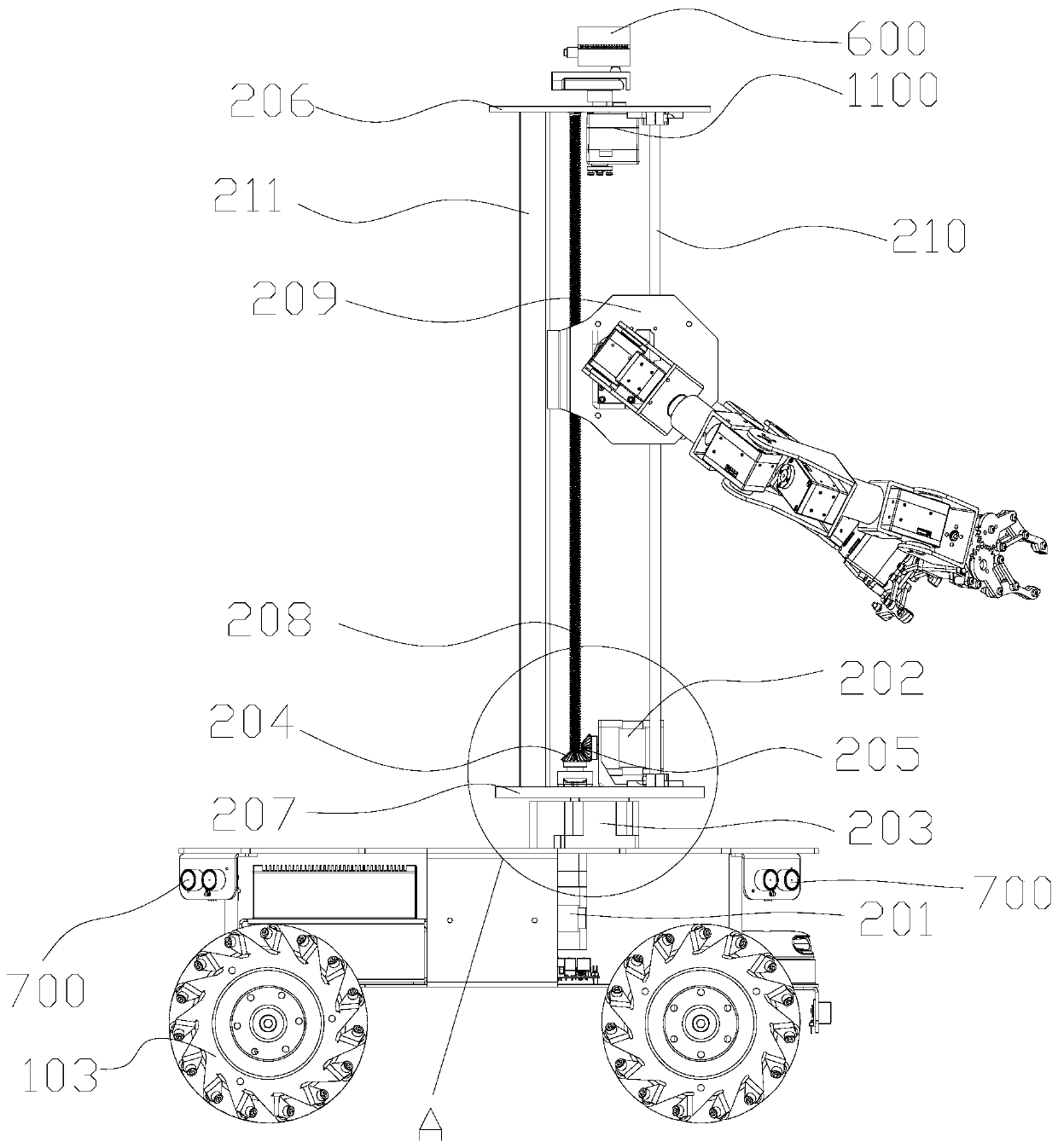
The invention provides an omnidirectional mobile robot. The robot comprises a vehicle body, Mecanum wheel components, an electric control system, a power system, a posture adjusting platform, a mechanical arm and a binocular vision system, wherein the four Mecanum wheel components are fixedly installed at the four corners of the vehicle body correspondingly, the electric control system and the power system are installed in the vehicle body, the posture adjusting platform achieving two-degree-of-freedom direction adjustment is fixedly installed on the vehicle body, the mechanical arm achievingsix-degree-of-freedom control is fixedly installed on an inclined supporting platform of the posture adjusting platform, and the binocular vision system is fixedly installed on the vehicle body. According to the robot, the structural form of an omnidirectional moving and automatic welding function is achieved through the mechanical arm, vehicle body automatic navigation and the binocular vision system, and the structure can meet the requirements of omnidirectional moving automation (welding, carrying, gluing, assembling and the like).
Owner:TIANJIN AEROSPACE ELECTROMECHANICAL EQUIP RES INST
Integral model prediction control method of omnidirectional mobile robot
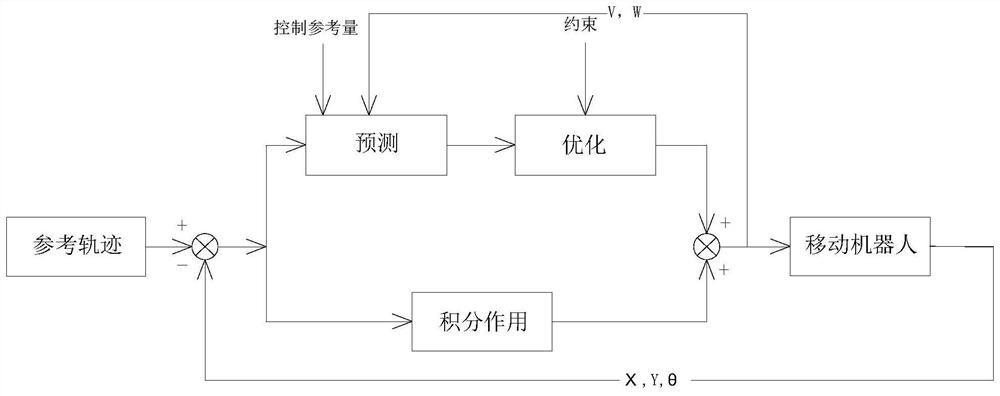
ActiveCN112025697ASimple designThe implementation process is simpleProgramme-controlled manipulatorAdaptive controlSimulationOmnidirectional mobile robot
The invention relates to the technical field of robot optimization control, in particular to an integral model prediction control method of an omnidirectional mobile robot. The integral model prediction control method comprises the following steps that 1, a kinematics model of the omnidirectional mobile robot is established; 2, a prediction model of integral model prediction control is designed; 3, a target function is designed; 4, constraint conditions are designed; and 5, aiming at steady-state errors existing in operation, an integral effect is designed to enable the mobile robot to be capable of preparing within specified time and rapidly and stably tracking a track. The mobile robot can have better track tracking capability and operation control precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Model-free auto disturbance rejection control method for omnidirectional mobile robot trajectory tracking
ActiveCN109709810AVerify validityGuaranteed accuracyAdaptive controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsControl systemState observer
The invention relates to a model-free auto disturbance rejection control method for omnidirectional mobile robot trajectory tracking. The method includes the following steps: step one, performing estimation on an inertial matrix on a general control system by utilizing a model-free adaptive pseudo Jacobian matrix (PJM), and obtaining a kinetic model of a discretized omnidirectional mobile robot; step two, designing an extended state observer according to the kinetic model; and step three, designing a controller, wherein the controller consists of three parts, the first part is an auto disturbance rejection part based on a traditional feedback control method, and the second part uses the observer to compensate the unmodeled part and disturbed part of the system; and obtaining a model-free controller.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Tunnel water seepage detection omnidirectional mobile robot based on binocular vision
PendingCN110567590AImprove detection efficiencyImprove detection accuracyOptically investigating flaws/contaminationSensing heat from liquidsWorking environmentEngineering
The invention discloses a tunnel water seepage detection omnidirectional mobile robot based on binocular vision and belongs to the field of tunnel detection robots. The robot comprises a vehicle body,omnidirectional wheel parts, a sensor unit, a control unit and an infrared detection unit. The omnidirectional wheel parts are controlled by the control unit to drive the vehicle body, and the omnidirectional movement of the robot is achieved. The position of the robot is obtained through the sensor unit for real-time positioning, infrared and optical images of a tunnel site are remotely obtainedthrough the infrared detection unit, and the remote monitoring of a tunnel by an inspector is achieved. According to the invention, the problems of high danger degree, poor working environment and heavy working task of traditional tunnel water seepage manual detection can be effectively solved, and the safety and accuracy of tunnel water seepage detection can be improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
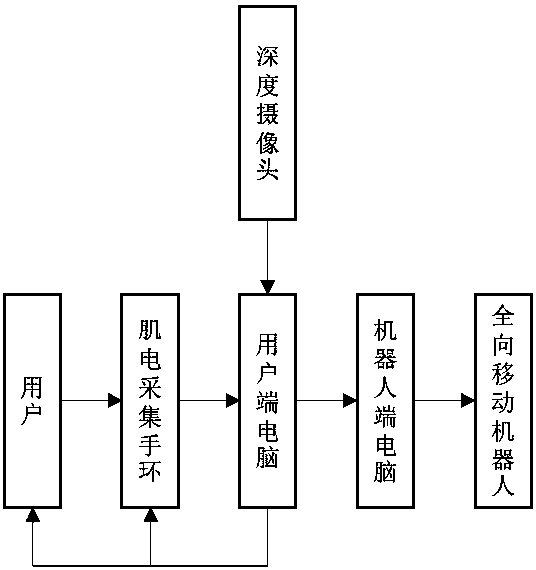
Gesture control mobile robot remote operation system with auxiliary obstacle avoidance function
PendingCN108062102AImprove efficiencyGood effectPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesObstacle avoidance algorithmPotential field
The invention discloses a gesture control mobile robot remote operation system with an auxiliary obstacle avoidance function. The system comprises a myoelectricity collection hand ring, a user side computer vision feedback device, a user side computer host, a deep camera and an omni-directional moving robot, wherein the deep camera collects image information around the omni-directional moving robot and conveys the information to the user side computer host; display is performed by the user side vision feedback device; an operator watches images on the user side computer vision feedback deviceand uses the myoelectricity collection hand ring for controlling the omni-directional moving robot; the omni-directional moving robot has the obstacle avoidance algorithm based on an artificial potential field method and performs auxiliary obstacle avoidance.
Owner:苏州晨本智能科技有限公司
Mecanum-wheel omnidirectional mobile robot
PendingCN107839787AControl trackLow costControllers with particular characteristicsManipulatorRoboticsMobile robot control
The invention relates to the technical field of robots, in particular to a Mecanum-wheel omnidirectional mobile robot. The Mecanum-wheel omnidirectional mobile robot comprises an Mecanum-wheel mobileplatform, a robot body, a control device, an operation panel, a lifting device and a power supply device, wherein the Mecanum-wheel mobile platform comprises a frame and multiple Mecanum wheels, the Mecanum wheels are installed on the bottom of the frame, each Mecanum wheel is a driving wheel, and the lifting device is installed on the upper portion of the robot body. According to the Mecanum-wheel omnidirectional mobile robot, the design of the Mecanum-wheel mobile platform is adopted, steering and rotation of the omnidirectional mobile robot can be achieved without adopting a special rotating mechanism; a programmable controller is adopted as the control device, so that programming can be conducted on the omnidirectional mobile robot to control movement of the omnidirectional mobile robot without electromagnetic force, compared with a tradition mode that the movement of the robot is controlled through magnetic lines of force, the Mecanum-wheel omnidirectional mobile robot has the advantages that the cost can be effectively lowered, and moreover, a fuzzy PID control technology is adopted, so that the track of the omnidirectional mobile robot is precisely controlled.
Owner:DONGGUAN HANDY INTELLIGENT ROBOT TECH CO LTD
Three-wheel omnidirectional moving robot platform
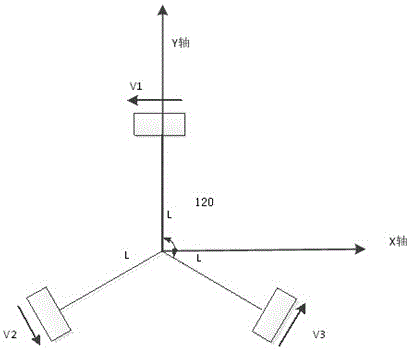
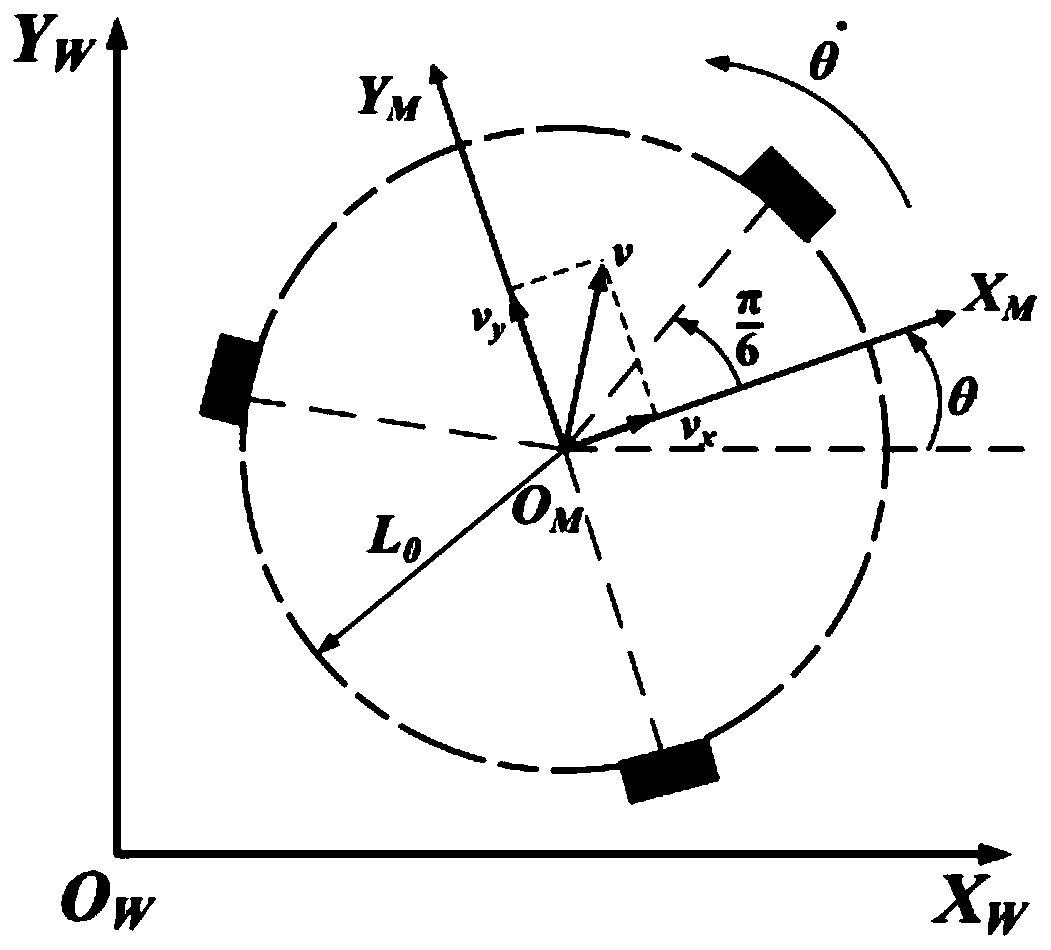
InactiveCN110614625AFlexible moving processRealize omnidirectional freedom of movementProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsCoupling
The invention relates to a three-wheel omnidirectional moving robot platform, and belongs to the field of robots. The three-wheel omnidirectional moving robot platform is formed by an omnidirectionalmoving chassis, an electric module and the like. Motor modules are fixed into the chassis through motor bases and are uniformly distributed on the circumference of the chassis at 120 degrees; omnidirectional moving is realized through kinematic control; encoders are arranged on direct-current servo motors; the direct-current servo motors are fixed onto the motor bases; forces are transmitted to connecting shafts through couplers; one ends of the connecting shafts are fixed through integrated bearing seats; and the other ends of the connecting shafts are arranged on omnidirectional wheels, so that the control on the omnidirectional wheels through the direct-current servo motors is realized. The moving platform can move on a plane toward any direction and can further rotate in situ on the plane at any angle, so that a robot can freely move omnidirectionally and can flexibly move within a narrow space. The three-wheel omnidirectional moving robot platform provided by the invention adoptsMecanum wheels as moving mechanisms and does not need a rotating device so as to be simple and reliable to control. The three-wheel omnidirectional moving robot platform provided by the invention solves the problems that most existing moving chassis is large in turning radius and less in freedom degree.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Multi-robot cooperation control system
InactiveCN104898575AOvercome lack of range of movementOvercome limitationsNumerical controlTransceiverDrive wheel
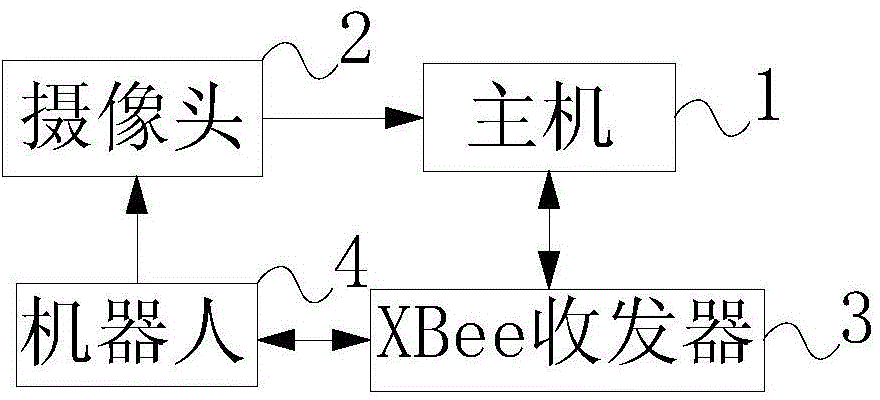
The invention discloses a multi-robot cooperation control system. The system includes a host, a camera, an XBee transceiver and multiple robots. The camera is in signal connection with the host, and is used for shooting images of all the robots. The XBee transceiver is in signal connection with the host, and also in signal connection with XBee transmit-receive modules of the robots. The four-wheel omnidirectional mobile robots, adopted by the system, have flexibly moving capabilities, overcome the problem that the moving range of differential driven wheel mobile robots is limited, and help to improve the performance of a multi-robot platform. Image processing techniques are utilized by the multi-robot cooperation control system to position the robots. Images captured by the camera are rich in information. The sampling period is short. The system is less interfered by a magnetic field and other interference factors. The restrictions of the prior art, such as mileometer, inertial navigation, GPS and other positioning technologies, are overcome.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
Mobile robot chassis and omnidirectional mobile robot
PendingCN109909980AIncrease elasticitySmooth motionProgramme-controlled manipulatorStacking articlesRadarEngineering
The invention specifically discloses a mobile robot chassis and an omnidirectional mobile robot. The mobile robot chassis comprises a protective frame, a bottom plate is fixed to the top surface of the protective frame, a supporting plate is fixed to the top surface of the bottom plate, and the left end and the right end of the bottom surface of the bottom plate are separately connected with a second connecting assembly and a first connecting assembly, wherein the first connecting assembly and the second connecting assembly are correspondingly connected with a first driving assembly and a second driving assembly; the omnidirectional mobile robot using the chassis comprises a shell, wherein a motion controller, a jacking device and a laser radar device are arranged in the shell; the motioncontroller is fixed to a supporting plate; the jacking device and the laser radar device are both fixed to the bottom plate; a plurality of ultrasonic radars are arranged at the periphery of a shell side plate and the protective frame; a voice broadcast box is embedded on the left side of the shell side plate; and two-dimensional code readers are separately arranged at the jacking end of the jacking device and the bottom of the bottom plate. The omnidirectional mobile robot has stable and reliable operation and realizes intelligent movement and automatic obstacle avoidance.
Owner:小驴机器人(武汉)有限公司
Independent steering driving wheel based on hub motor
ActiveCN109909973AAvoid entanglementSmall footprintElectrical steeringMotor depositionDrive wheelOptical axis
The invention relates to an independent steering driving wheel based on a hub motor, and belongs to the technical field of driving wheels. According to the independent steering driving wheel of an omnidirectional mobile robot, a shaft table is fixed to the center of a hub frame, hollowing is convenient for cabling of the hub motor, and a universal wheel is installed on the shaft table to reduce the friction during the relative rotation. A small flange coaxially sleeves the shaft table and is fixed, and the hollow shaft is coaxially embedded into the small flange and fixed. A sleeve coaxially sleeves the shaft table, and a sleeve disk is in contact with an upward universal wheel. A hollow shaft coaxially sleeves a lower angle contact bearing and an upper angle contact bearing, the lower angle contact bearing and the upper angle contact bearing separately and coaxially sleeve the upper end and lower end of the hollow shaft, the lower surface of the upper angle contact bearing is in contact with the hollow shaft, the upper surface of the lower angle contact bearing is in contact with the hollow shaft, and the lower surface of the lower angle contact bearing is in contact with the small flange. Optical shafts are evenly distributed and fixed to the upper part of the sleeve, and the upper ends of the optical shafts are embedded in an upper flange disc and fixed. In the process of traveling, a connected shock absorber is less bumpy and vibrated, and the stability in the process of traveling is ensured.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
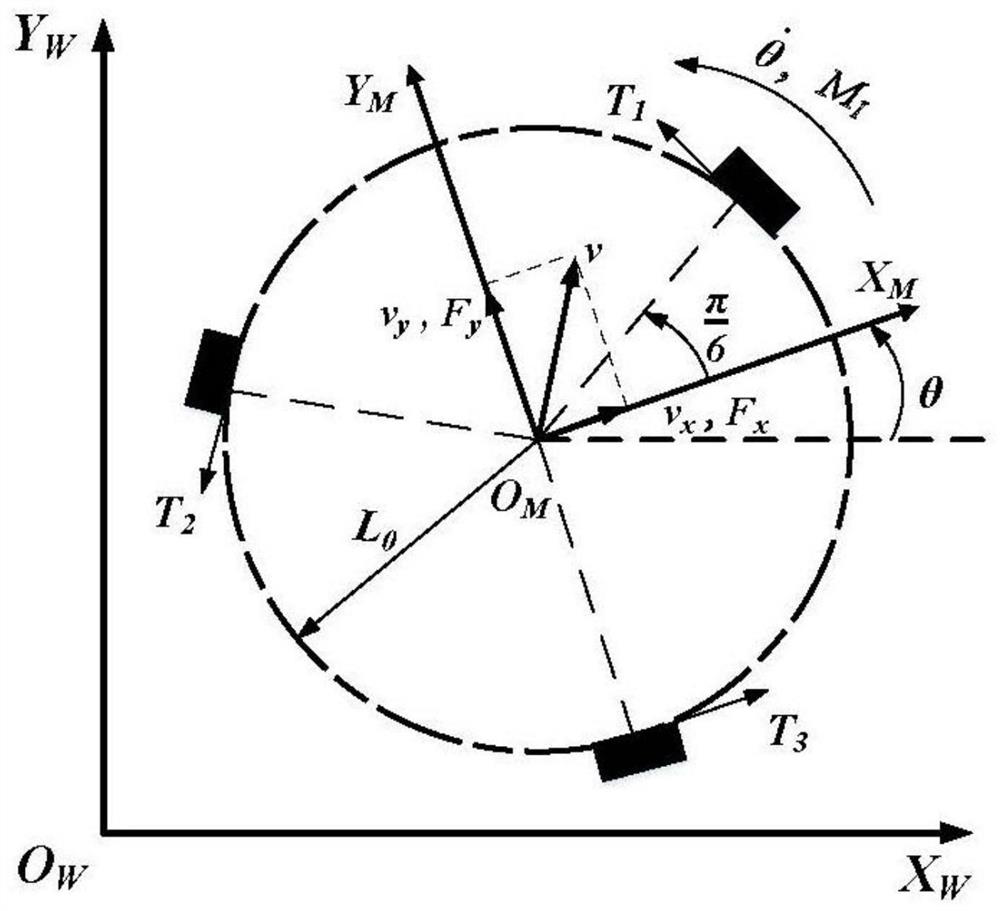
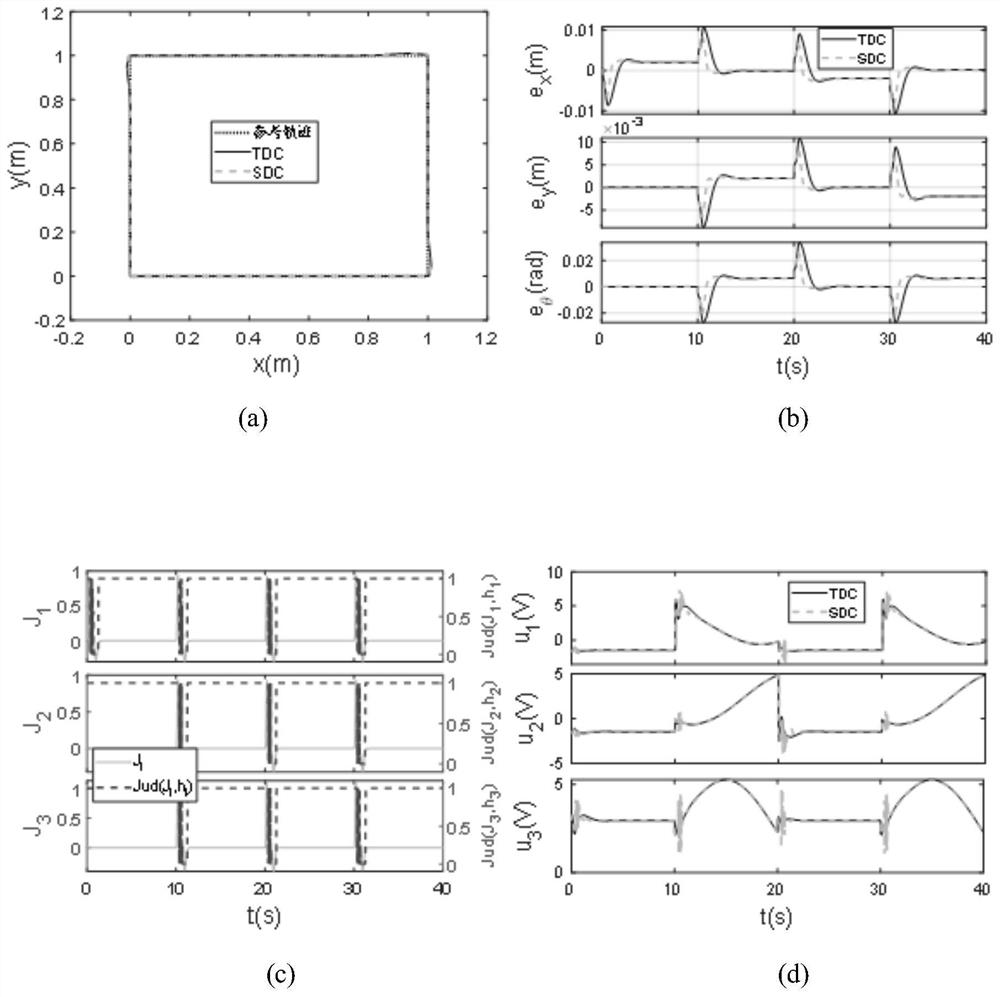
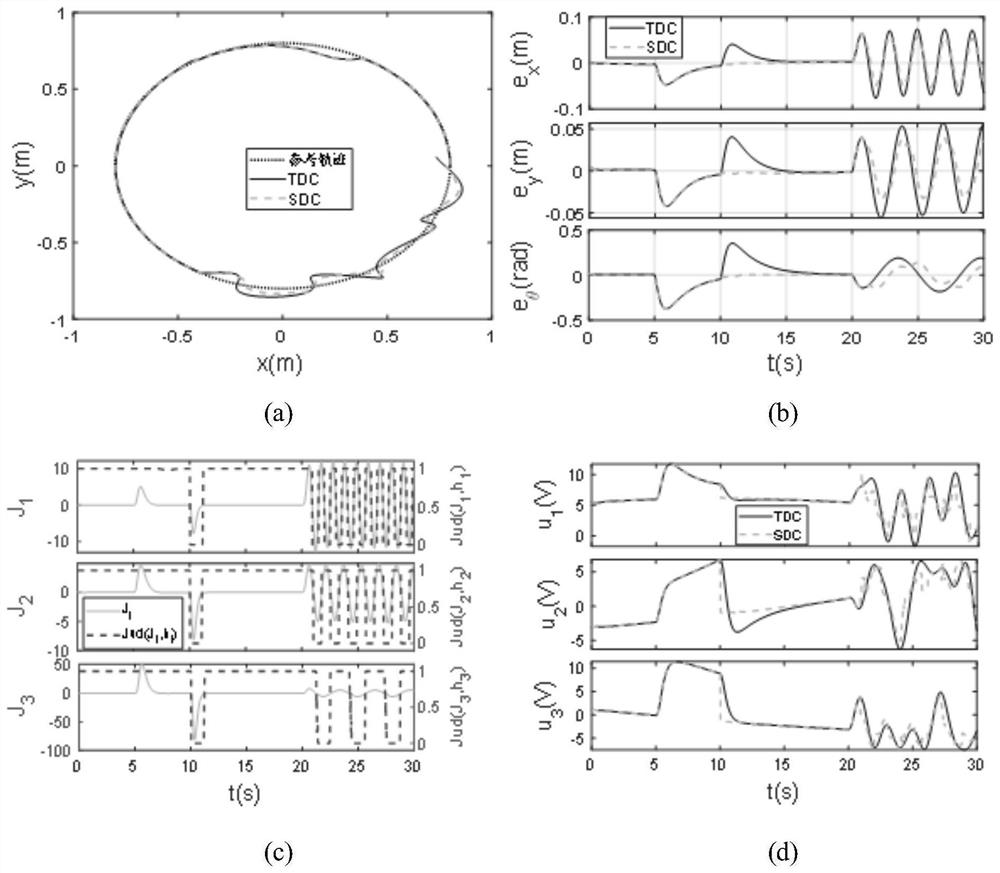
Omnidirectional mobile robot trajectory tracking control method based on selective disturbance compensation
ActiveCN112008728AHigh precisionGuaranteed stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl systemActive disturbance rejection control
The invention discloses an omnidirectional mobile robot trajectory tracking control method based on selective disturbance compensation. The omnidirectional mobile robot trajectory tracking control method comprises the following steps that an omnidirectional mobile robot system kinetic model is established; an extended state observer is designed based on the omnidirectional mobile robot kinetic model; and a selective disturbance compensation controller is designed by utilizing the total disturbance estimated by the extended state observer. According to the omnidirectional mobile robot trajectory tracking control method based on the selective disturbance compensation, the selective disturbance compensation scheme is designed, and classic full-disturbance-compensation active disturbance rejection control is improved, so that a control system distinguishes disturbance types in real time; and meanwhile, favorable disturbance is fully utilized to compensate adverse disturbance, and under thecondition that the system has various types of disturbance, high-performance trajectory tracking control over the omnidirectional mobile robot is achieved through the selective disturbance compensation.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com