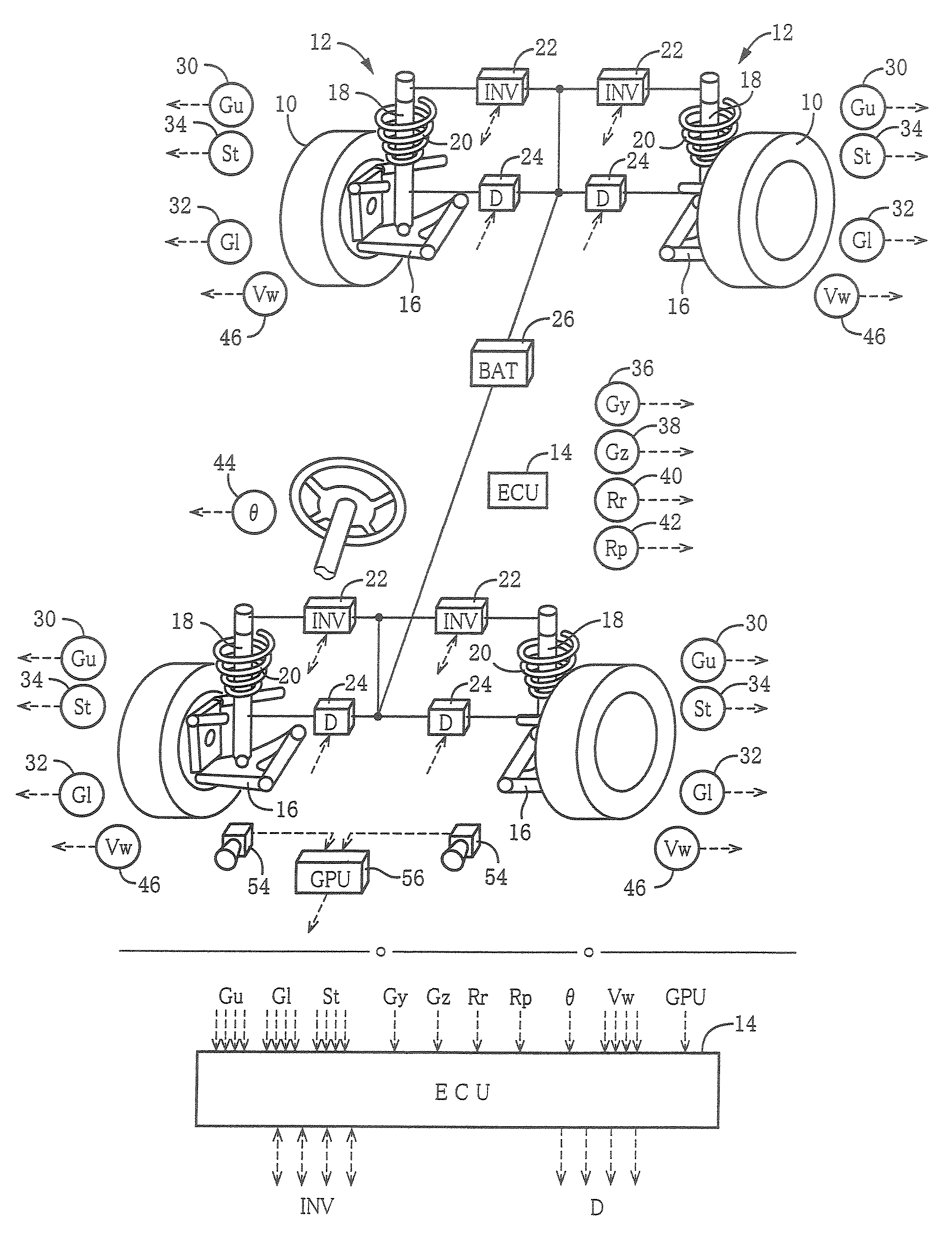
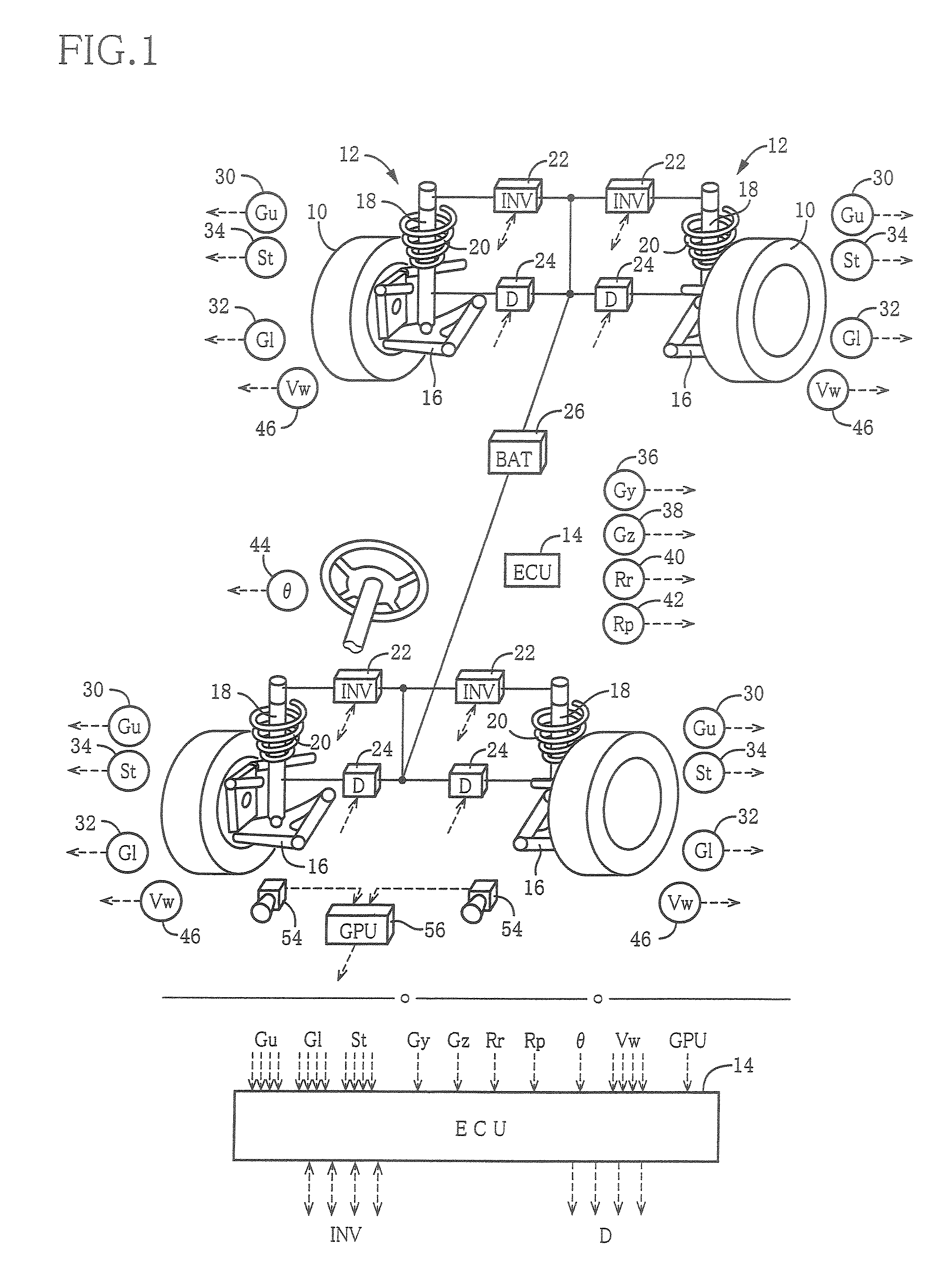
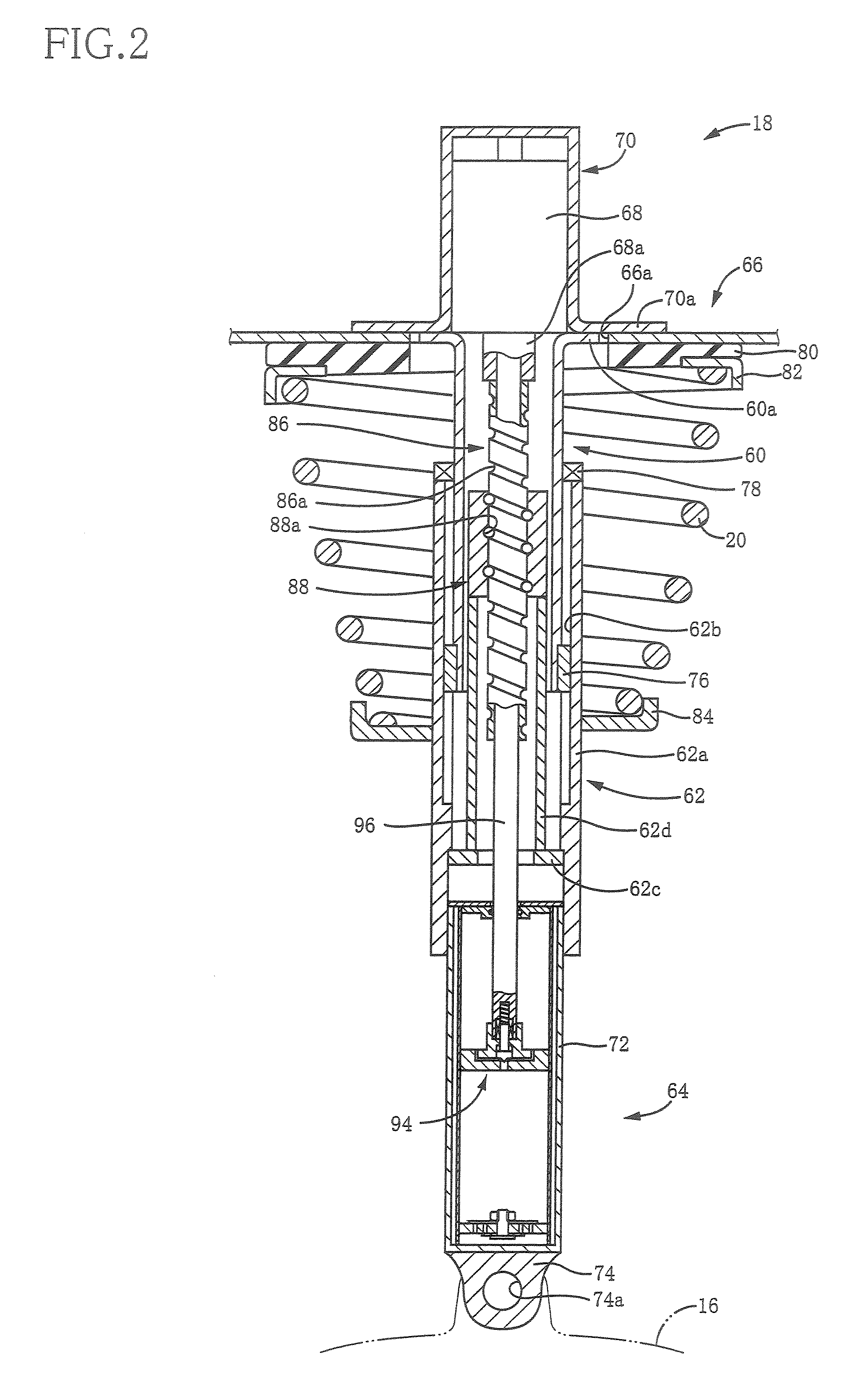
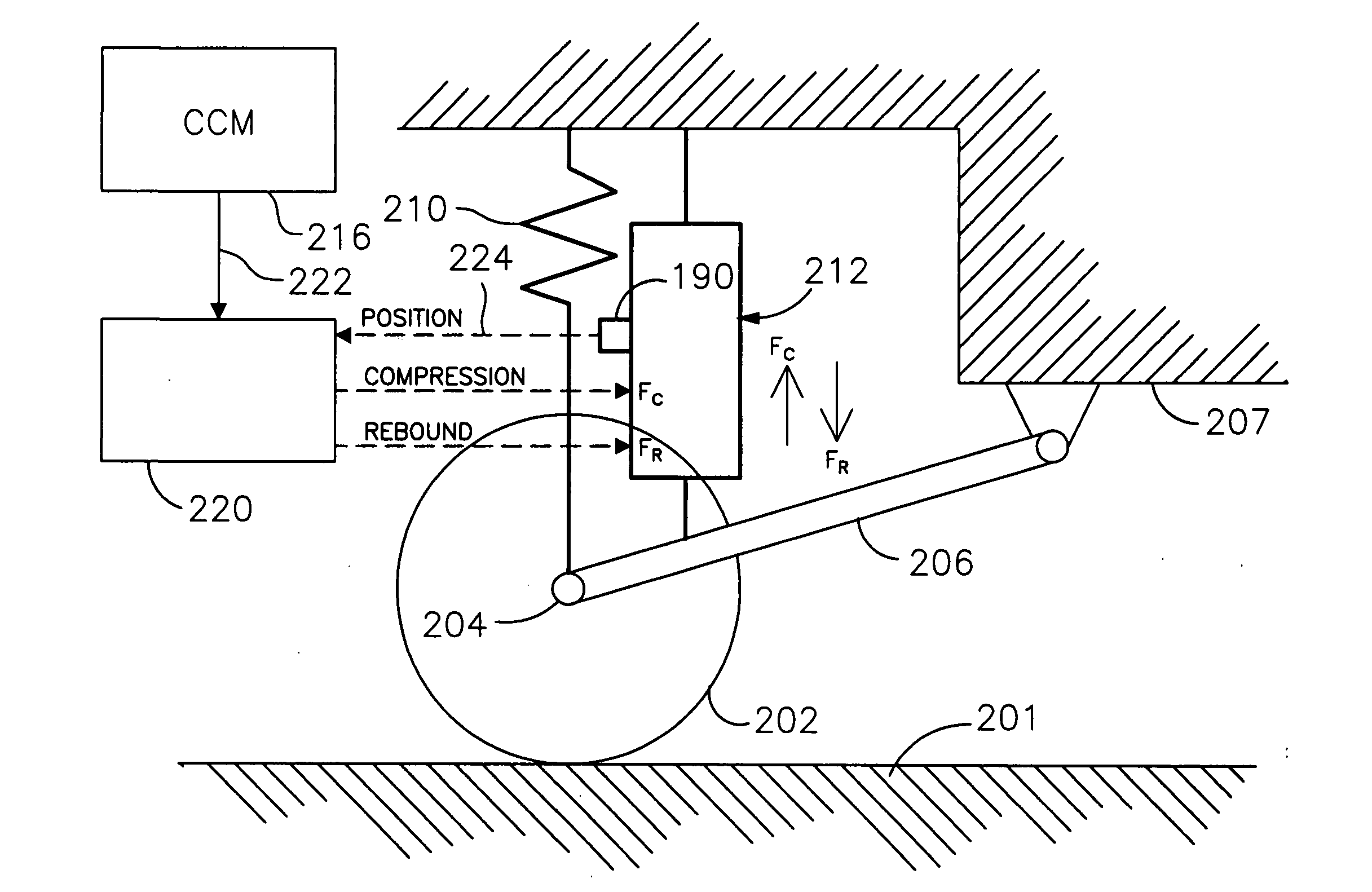
Patents
Literature
5266results about "Vehicle springs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Variable stiffness electroactive polymer systems
InactiveUS6882086B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesResilient suspensionsActive polymerPolymer science
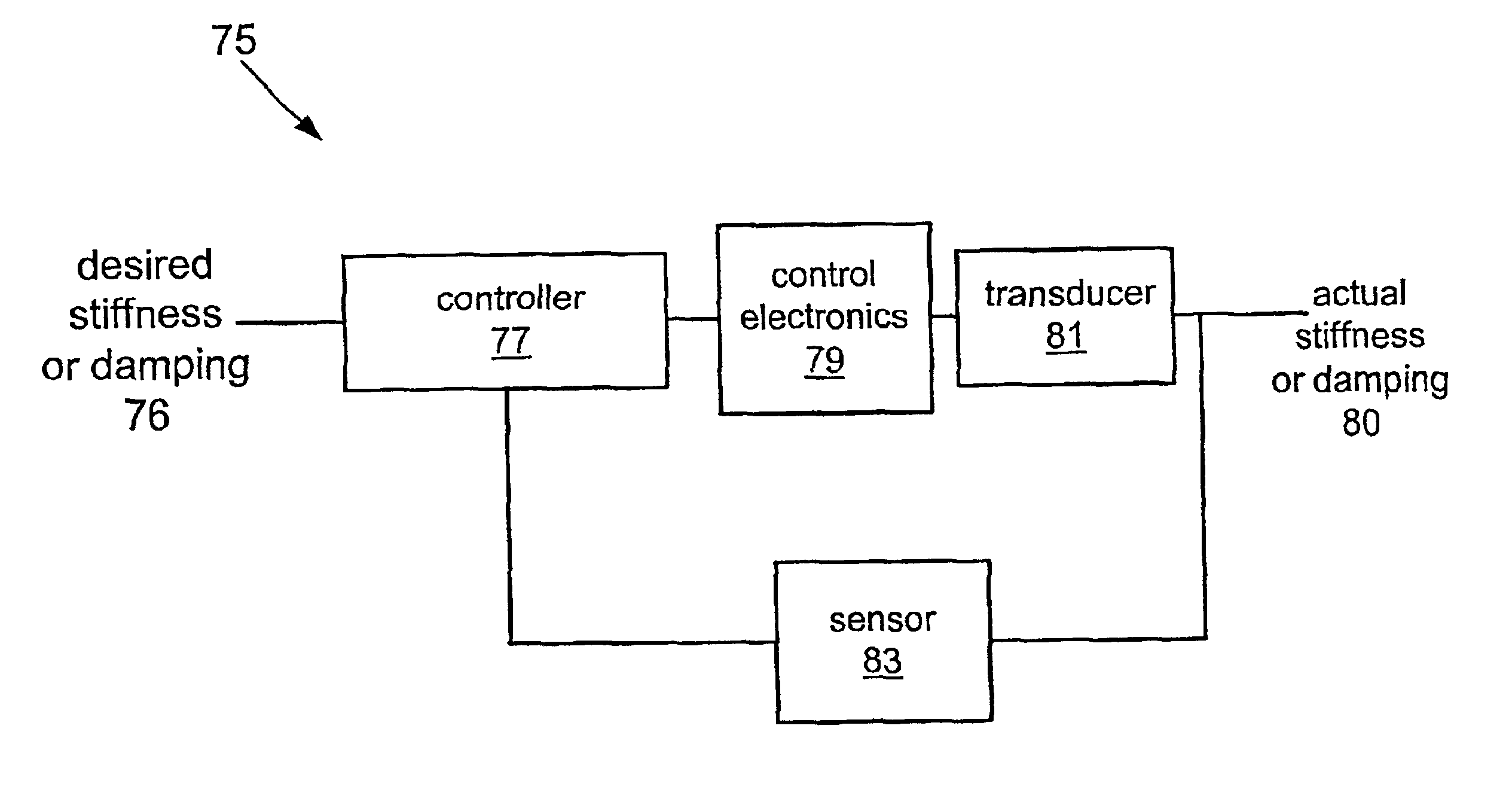
The invention relates to systems that provide variable stiffness and / or variable damping using an electroactive polymer transducer. Systems described herein offer several techniques that provide variable and controlled stiffness and / or damping. A transducer may be implemented using open loop control, thereby providing simple systems that inactively deliver a desired stiffness and / or damping performance. Alternately, closed loop control techniques permit electroactive polymer transducer designs that actively adapt the stiffness and / or damping performance of a system. Further, transducers may be implemented in a device whose stiffness changes with deflection of the polymer.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Electromagnetic linear generator and shock absorber
InactiveUS6952060B2Maximizing magnetic flux densityMaximize power generationNon-rotating vibration suppressionMechanical energy handlingElectromagnetic generatorFuel efficiency
An electromagnetic linear generator and regenerative electromagnetic shock absorber is disclosed which converts variable frequency, repetitive intermittent linear displacement motion to useful electrical power. The innovative device provides for superposition of radial components of the magnetic flux density from a plurality of adjacent magnets to produce a maximum average radial magnetic flux density within a coil winding array. Due to the vector superposition of the magnetic fields and magnetic flux from a plurality of magnets, a nearly four-fold increase in magnetic flux density is achieved over conventional electromagnetic generator designs with a potential sixteen-fold increase in power generating capacity. As a regenerative shock absorber, the disclosed device is capable of converting parasitic displacement motion and vibrations encountered under normal urban driving conditions to a useful electrical energy for powering vehicles and accessories or charging batteries in electric and fossil fuel powered vehicles. The disclosed device is capable of high power generation capacity and energy conversion efficiency with minimal weight penalty for improved fuel efficiency.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
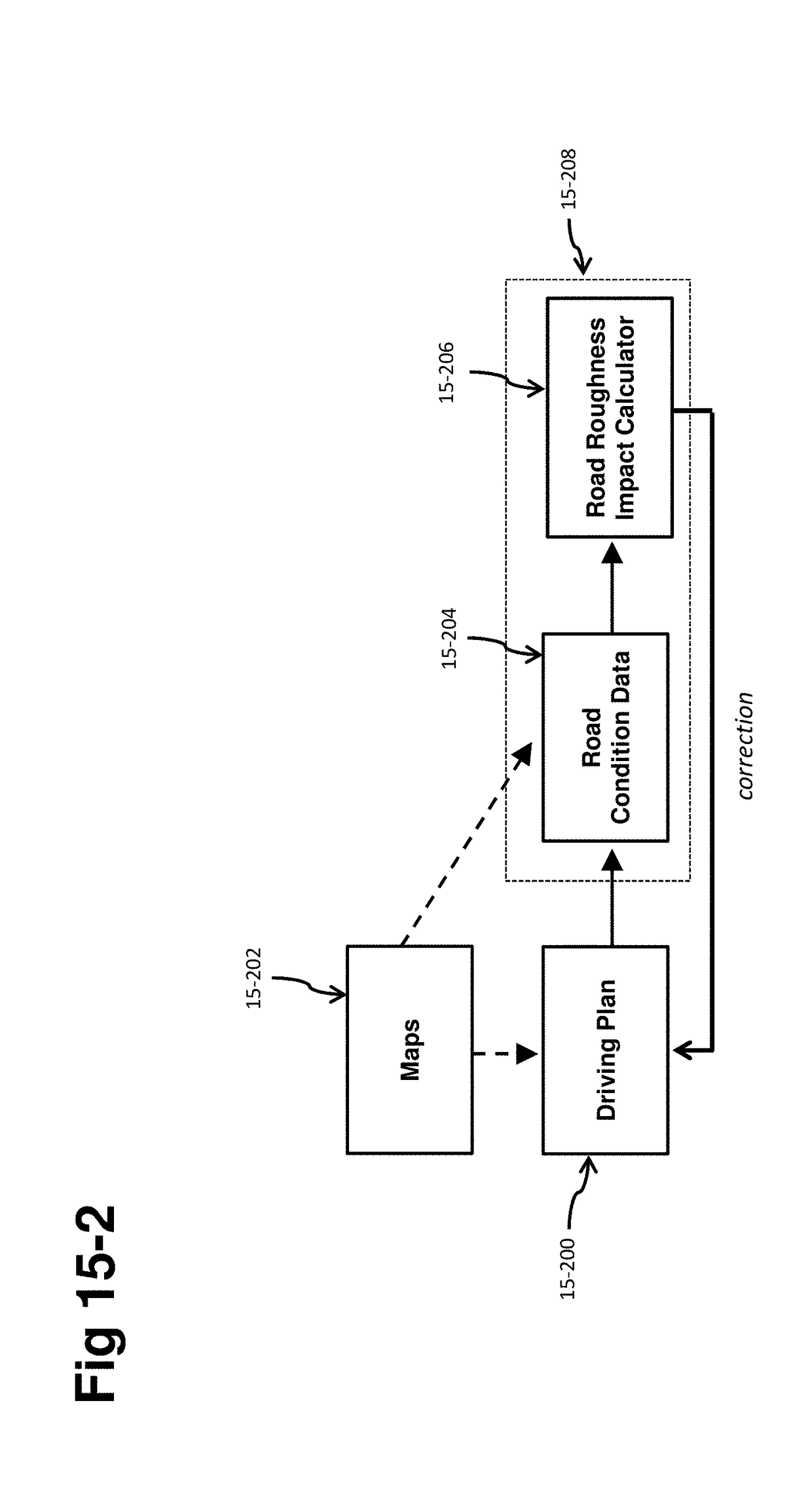
Self-driving vehicle with integrated active suspension
ActiveUS20180154723A1Improve ride comfort performanceActive suspension technologiesAssociation with control/drive circuitsSpringsEngineeringRoad surface
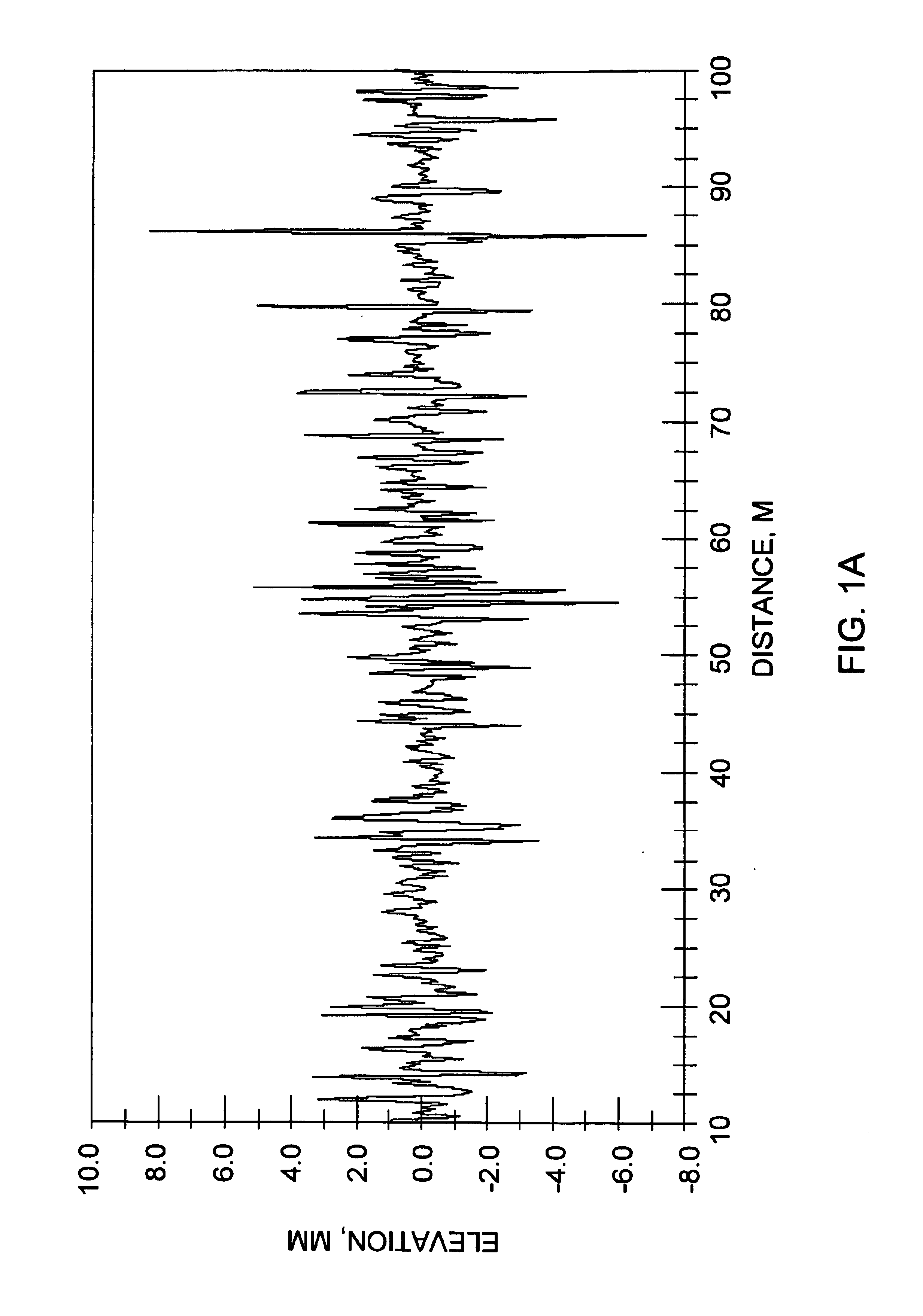
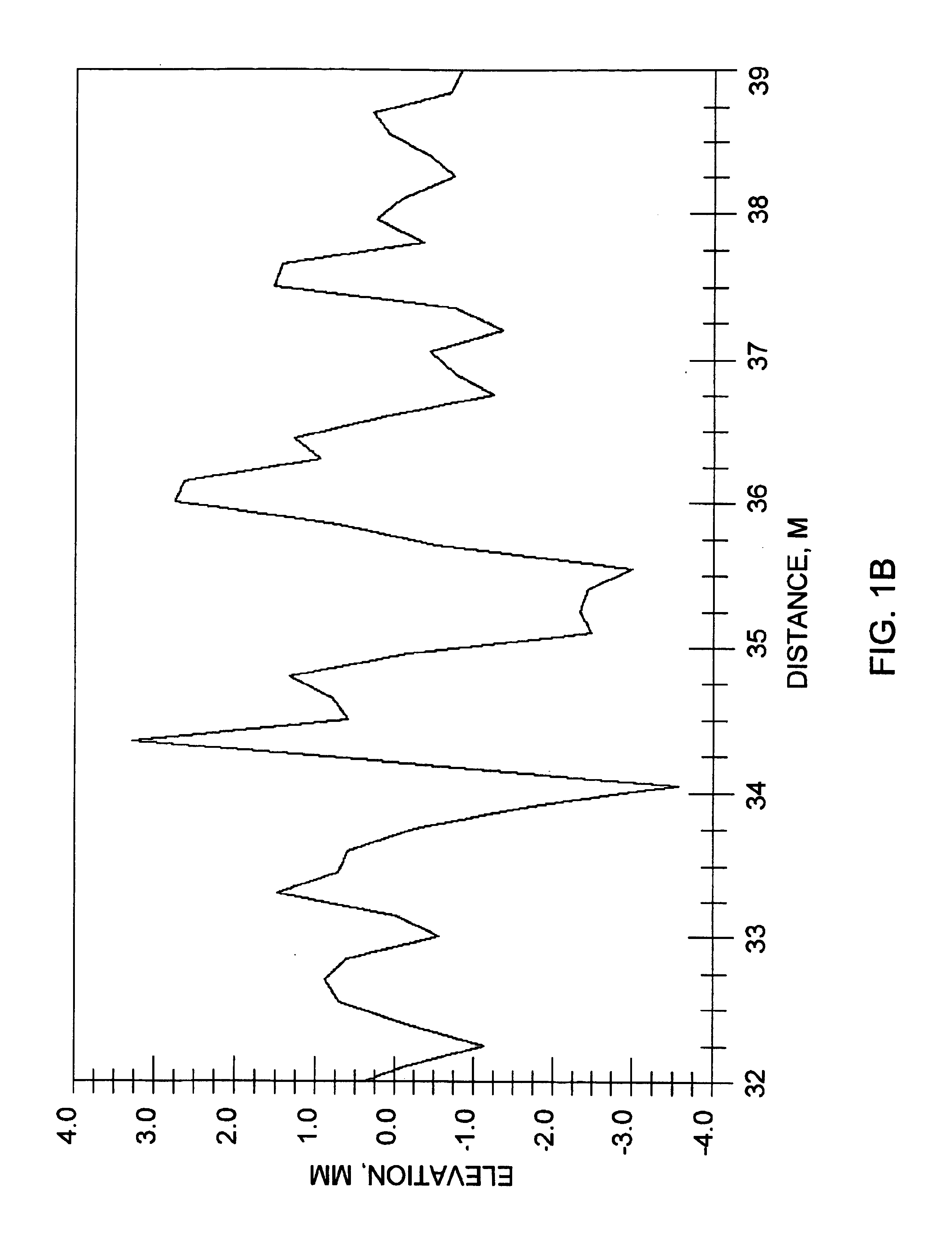
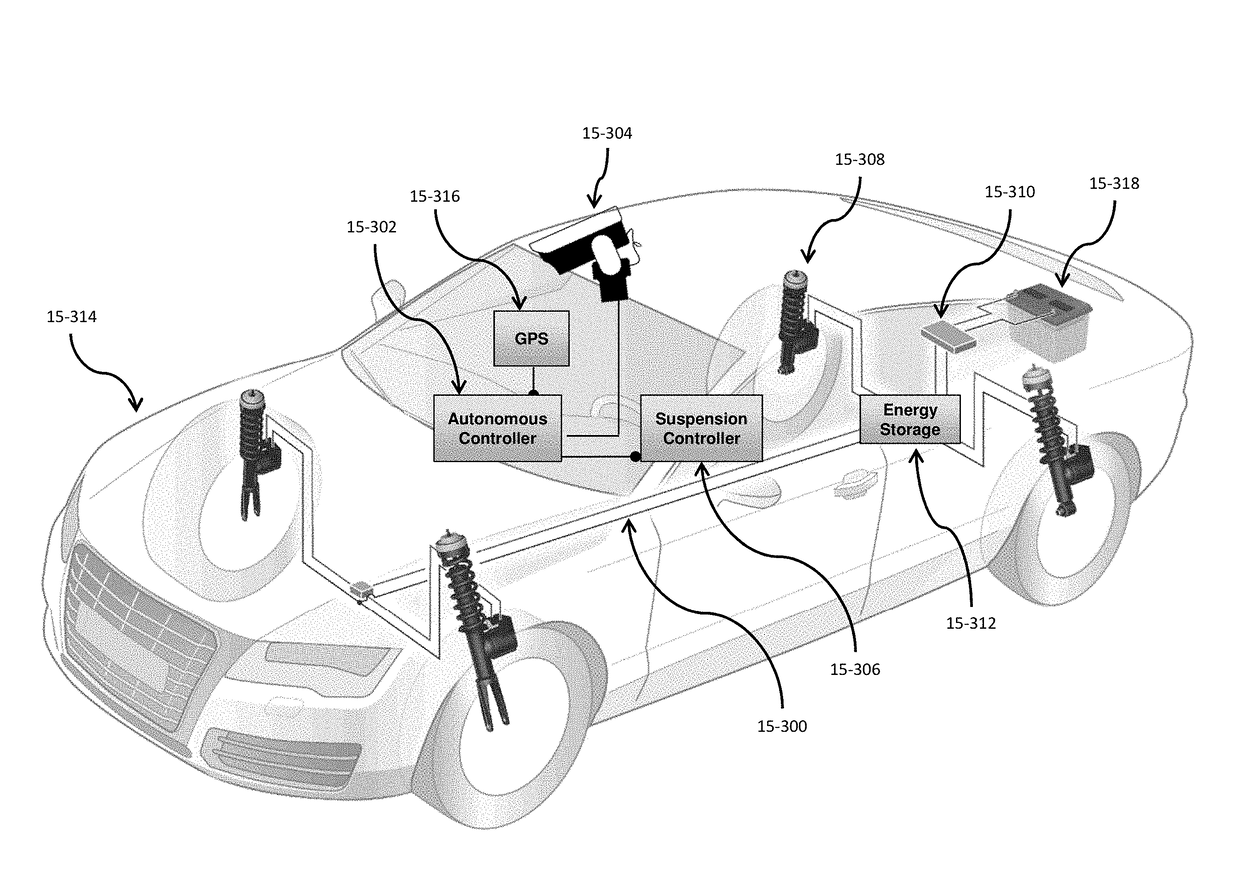
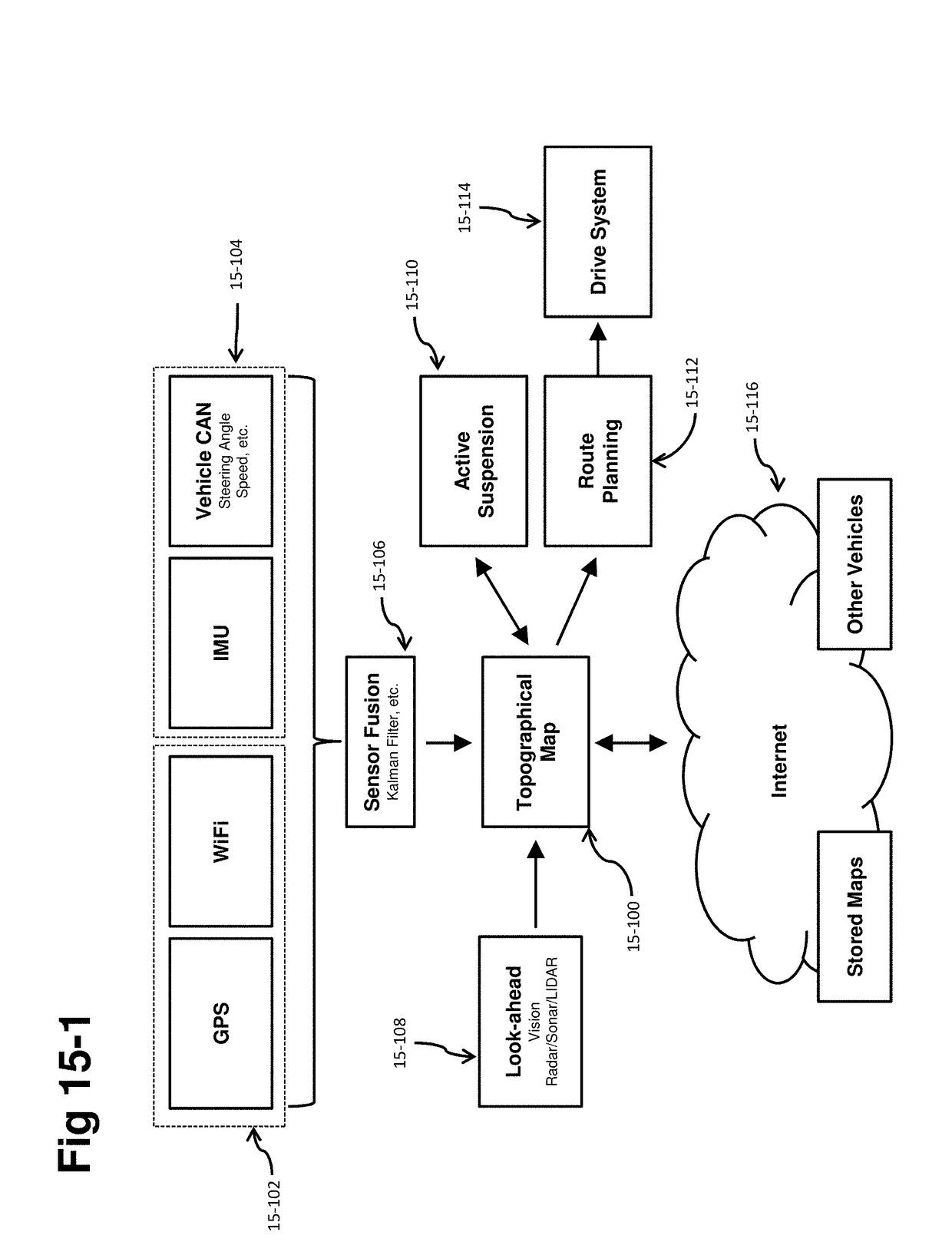
A self-driving vehicle with an integrated fully-active suspension system. The fully-active suspension utilizes data from one or more sensors used for autonomous driving (e.g. vision, LIDAR, GPS) in order to anticipate road conditions in advance. The system builds a topographical map of the road surface. Suspension and road data is delivered back to the vehicle in order to change autonomous driving behavior including route planning. Energy storage is regulated based on a planned route. Forward and lateral acceleration feel is mitigated through active pitch and tilt compensation. The fully-active suspension pushes and pulls the suspension in three or more operational quadrants in order to deliver superior ride comfort, handling, and / safety of the vehicle.
Owner:CLEARMOTION INC
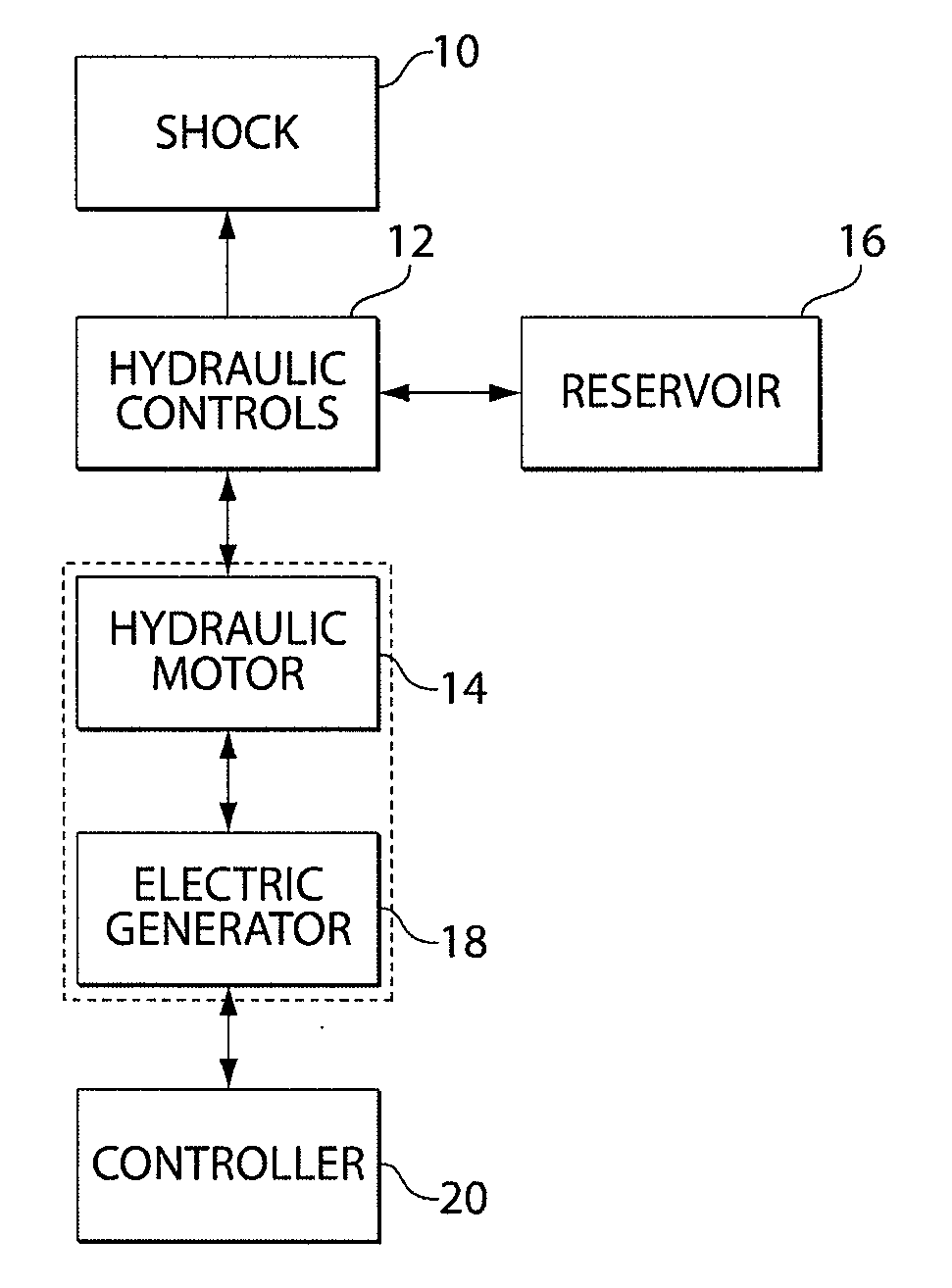
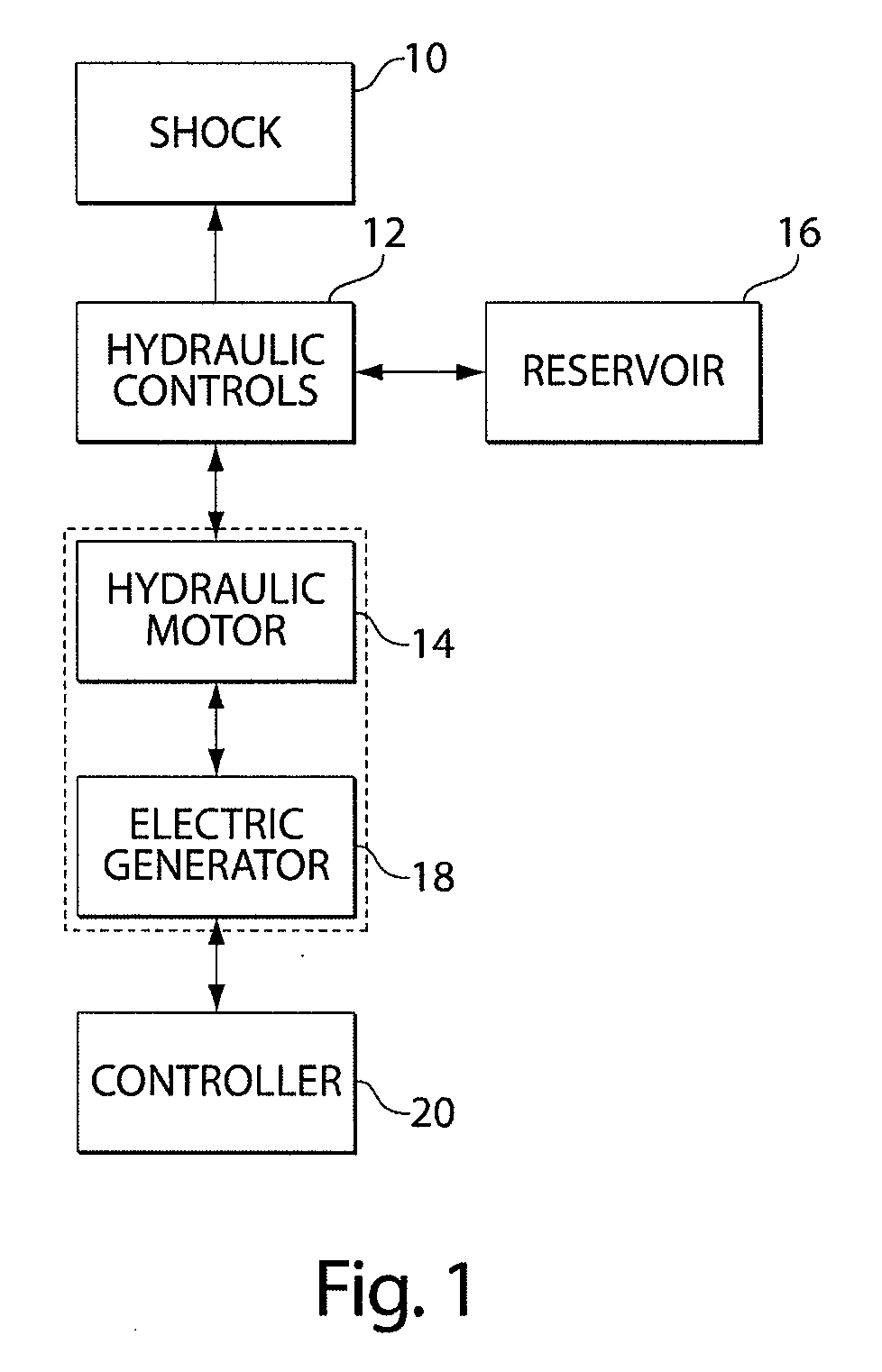
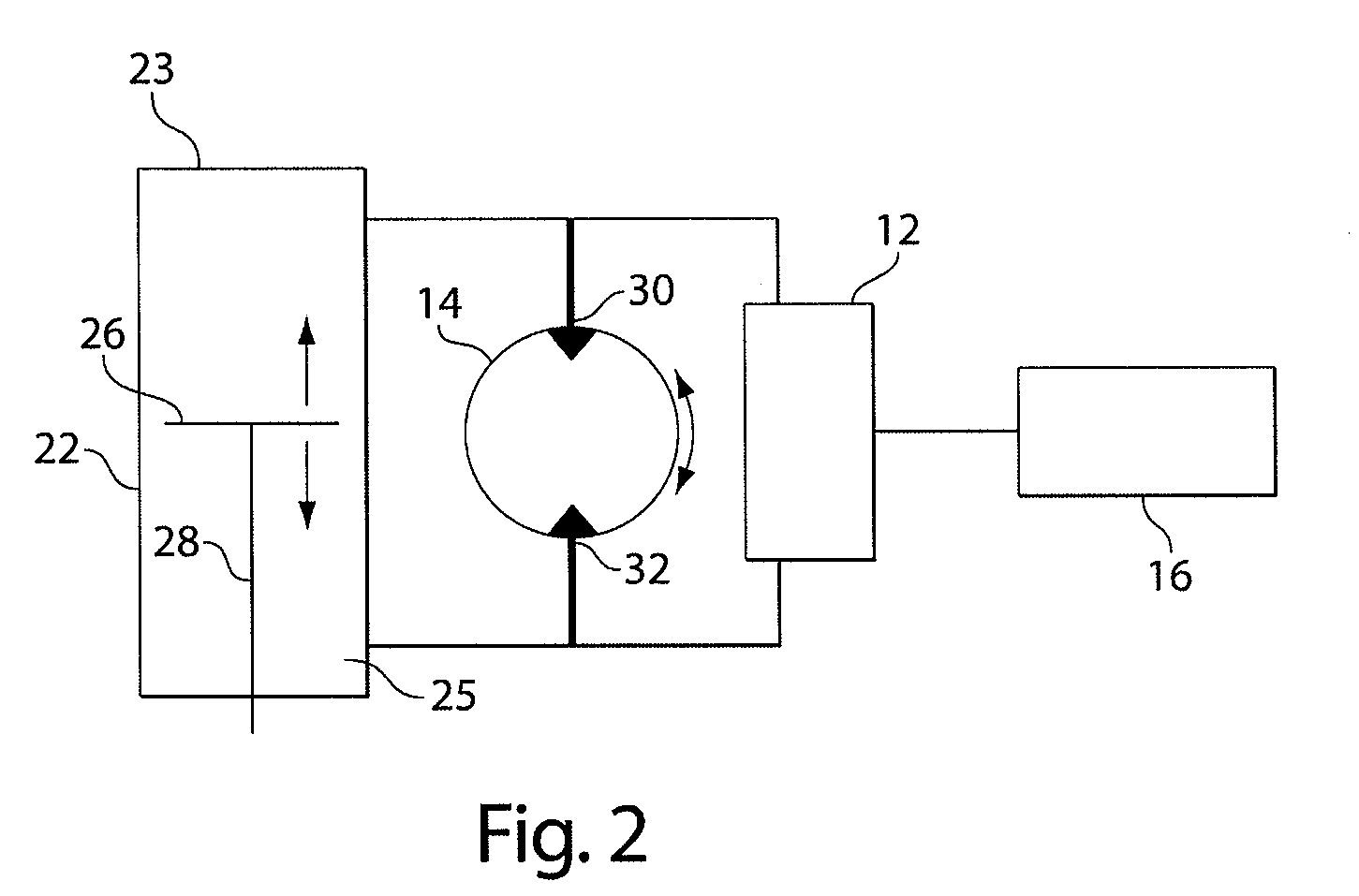
Regenerative shock absorber system
A regenerative shock absorber that include a housing and a piston that moves at least partially through the housing when the shock is compressed or extended from a rest position. When the piston moves, hydraulic fluid is pressurized and drives a hydraulic motor. The hydraulic motor, in turn, drives an electric generator that produced electric energy. The electric energy may be provided to a vehicle, among other things. The regenerative shock absorber may also provide ride performance that comparable to or exceeds that of conventional shock absorbers.
Owner:CLEARMOTION INC
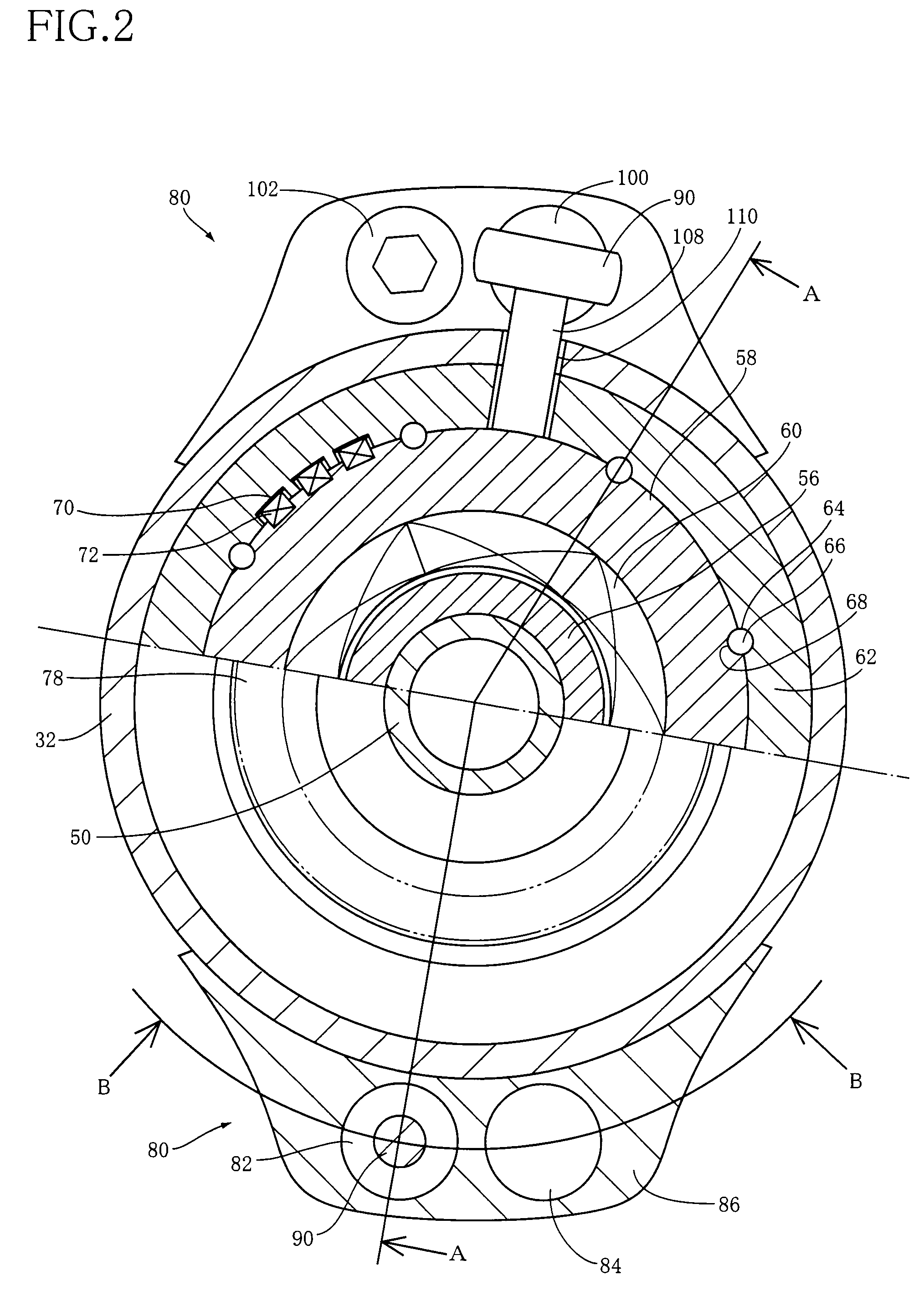
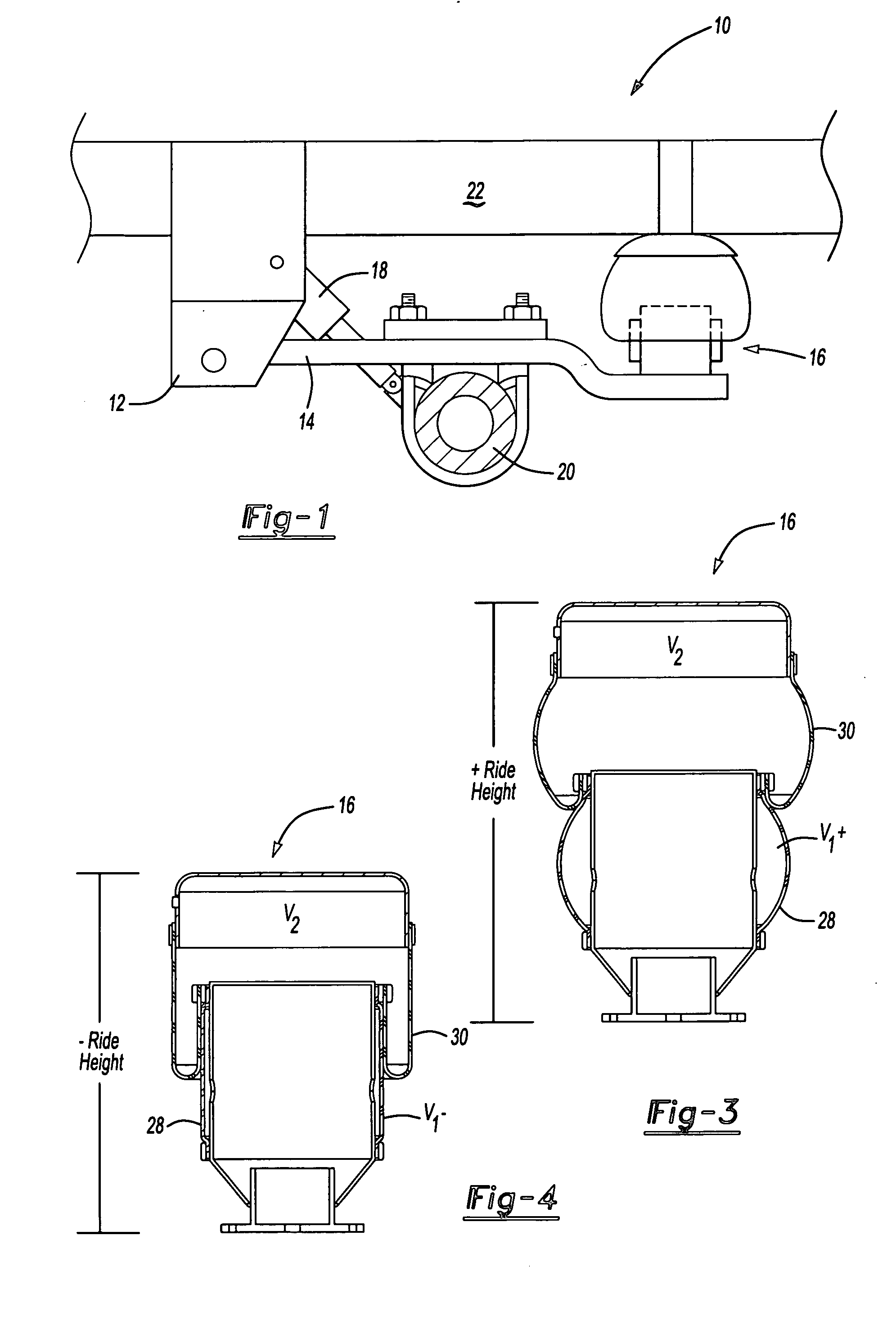
Integrated suspension system for vehicle
InactiveUS20060049013A1Easy to controlMaximize productivitySpringsLiquid based dampersCircular discDrive shaft
An integrated suspension system includes a cylinder that hermetically contains gas therein and is fixed to a vehicle body; a piston that has a motor at an upper portion thereof, is configured to support a road wheel and is guided within the cylinder to move vertically; a disk unit including a second disk that has a plurality of passage holes formed there through and a bottom surface coupled to a driving shaft of the motor to rotate while moving vertically integrally along with the piston, and a first disk that has a plurality of passage holes and is stacked on and connected via a hinge to the center of a top surface of the second disk to move vertically within the cylinder integrally along with the second disk without any rotation; and a control unit that controls an opening degree established through overlap of the passage holes formed in the first and second disks by changing power supplied to the motor to control a rotational angle of the second disk.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
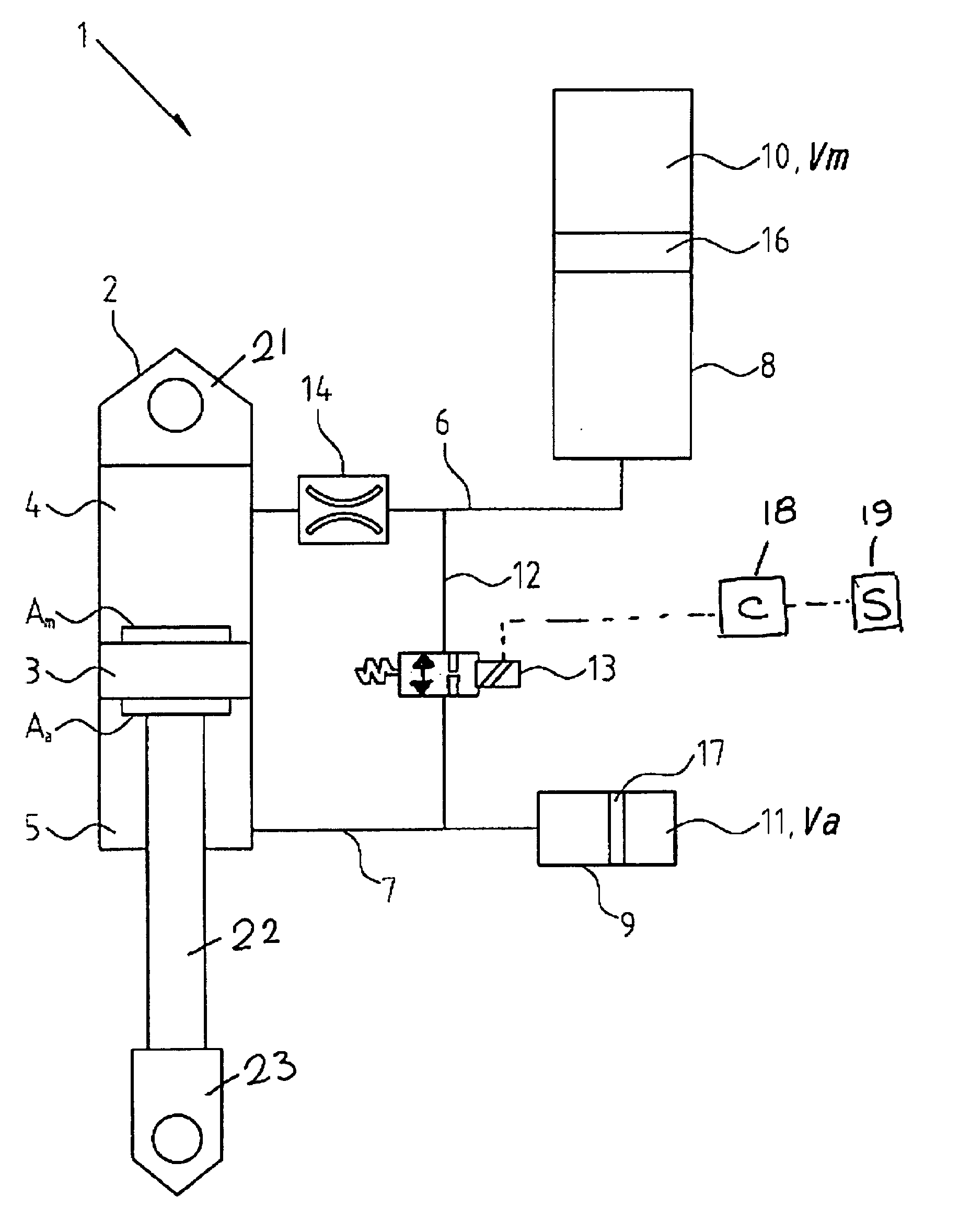
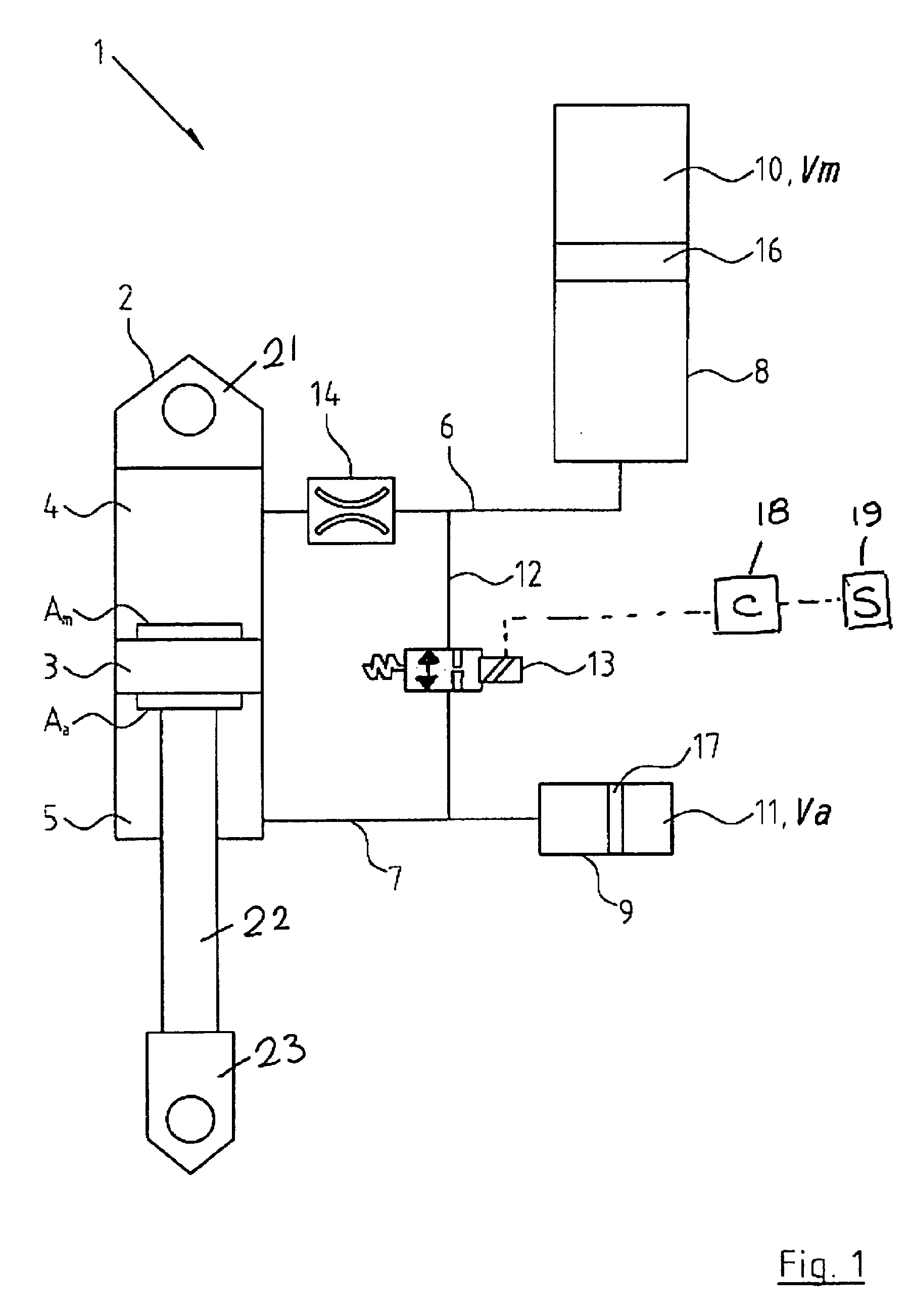
Methods and apparatus for combined variable damping and variable spring rate suspension
Pressure-sensitive vales are incorporated within a dampening system to permit user-adjustable tuning of a shock absorber. In one embodiment, a pressure-sensitive valve includes an isolated gas chamber having a pressure therein that is settable by a user.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Mounting assembly for a vehicle suspension arm
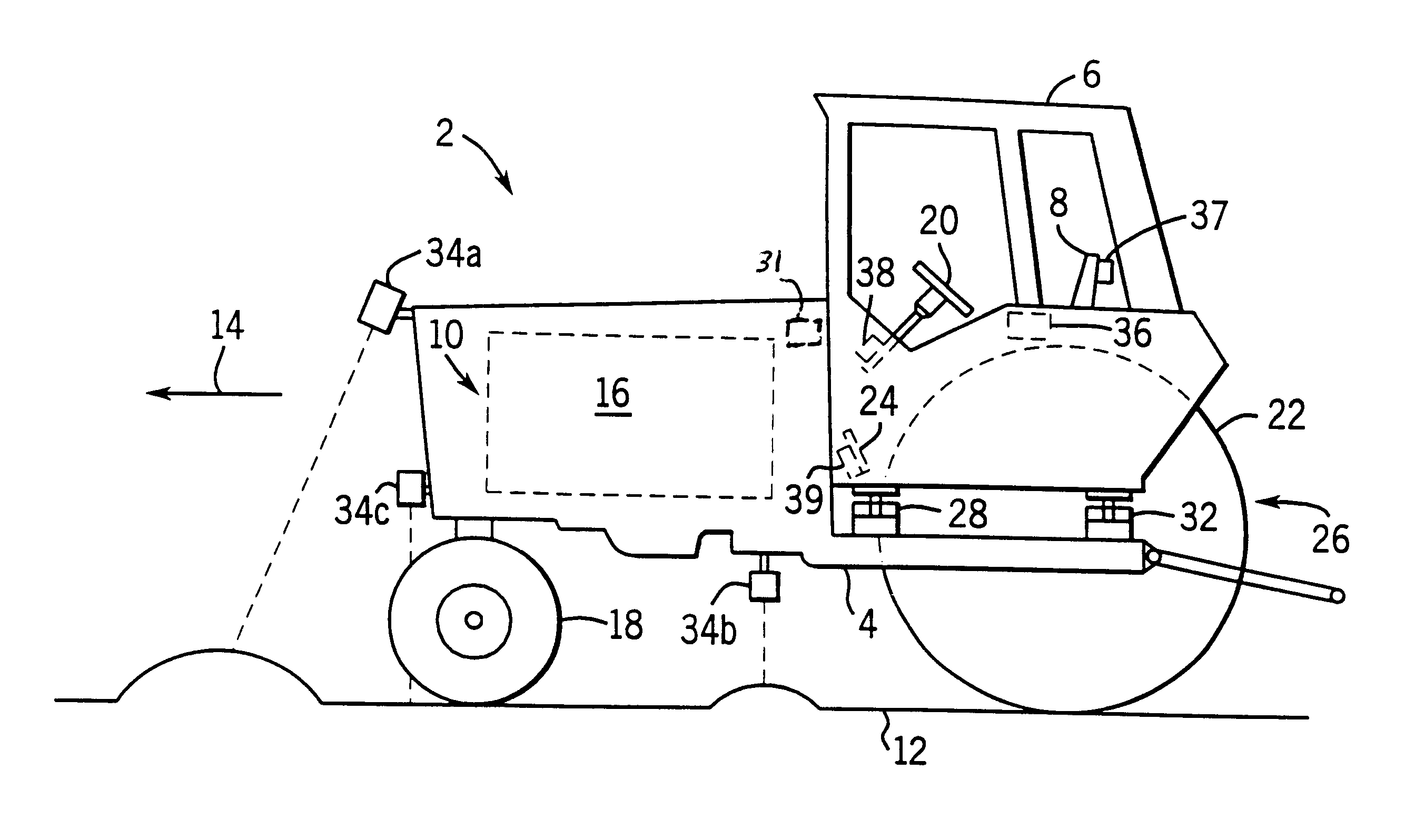
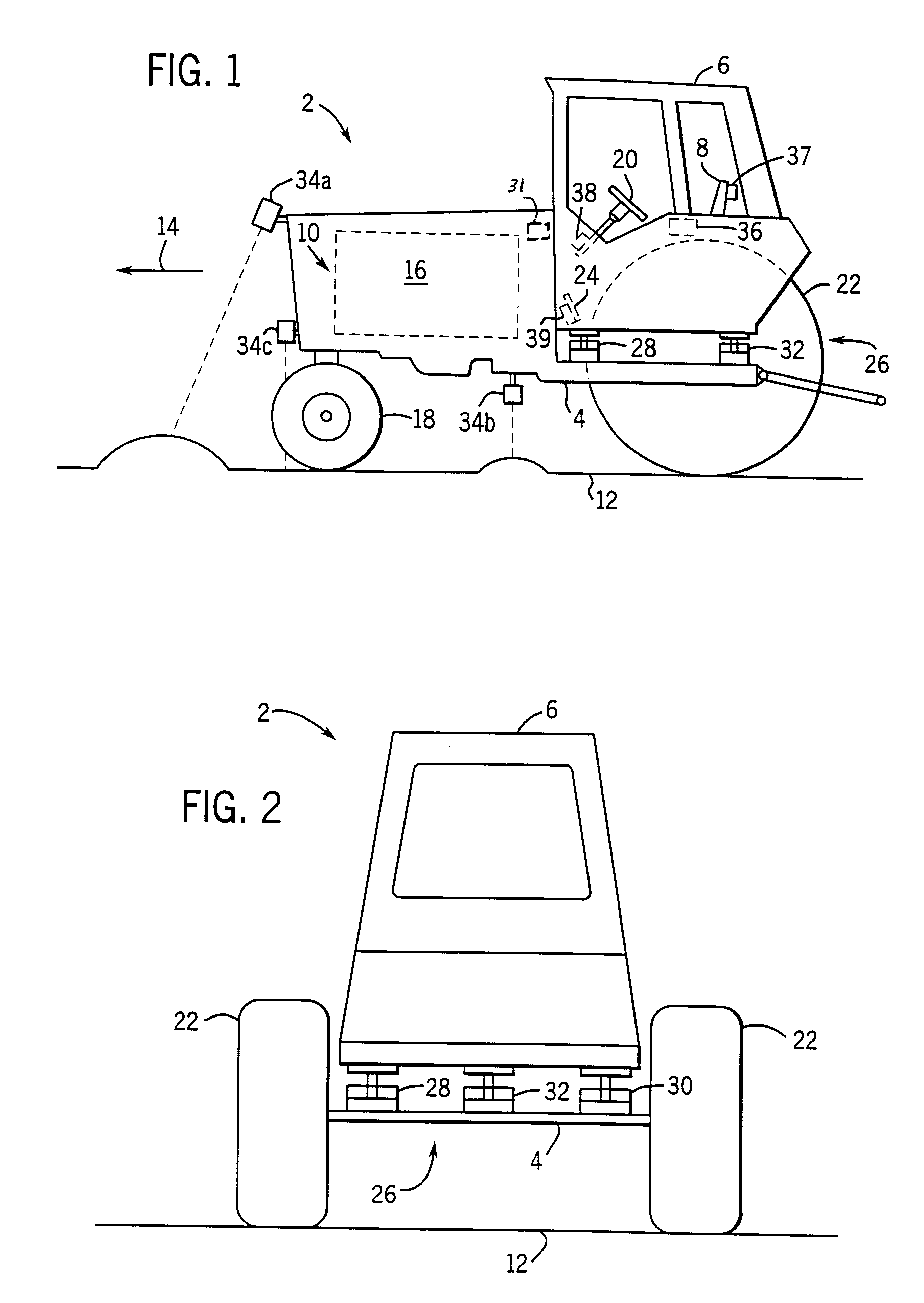
A mounting assembly for use with a mounting surface includes an arm, a pin, a pair of clamping blocks and a fastener. The arm has a cylindrical bore at one end. The pin extends through the bore. Each block of the pair of clamping blocks includes a central opening and is circumferentially discontinuous about the central opening. Each clamping block further includes a slot defined by portions of the block. The slot is dimensioned to allow the pin to pass through the slot when the block is in an unclamped position and to tightly grip the pin when the block is in a clamped position. The fasteners extend across the slots and are configured to engage the mounting surface to mount the blocks to the mounting surface.
Owner:OSHKOSH CORPORATION
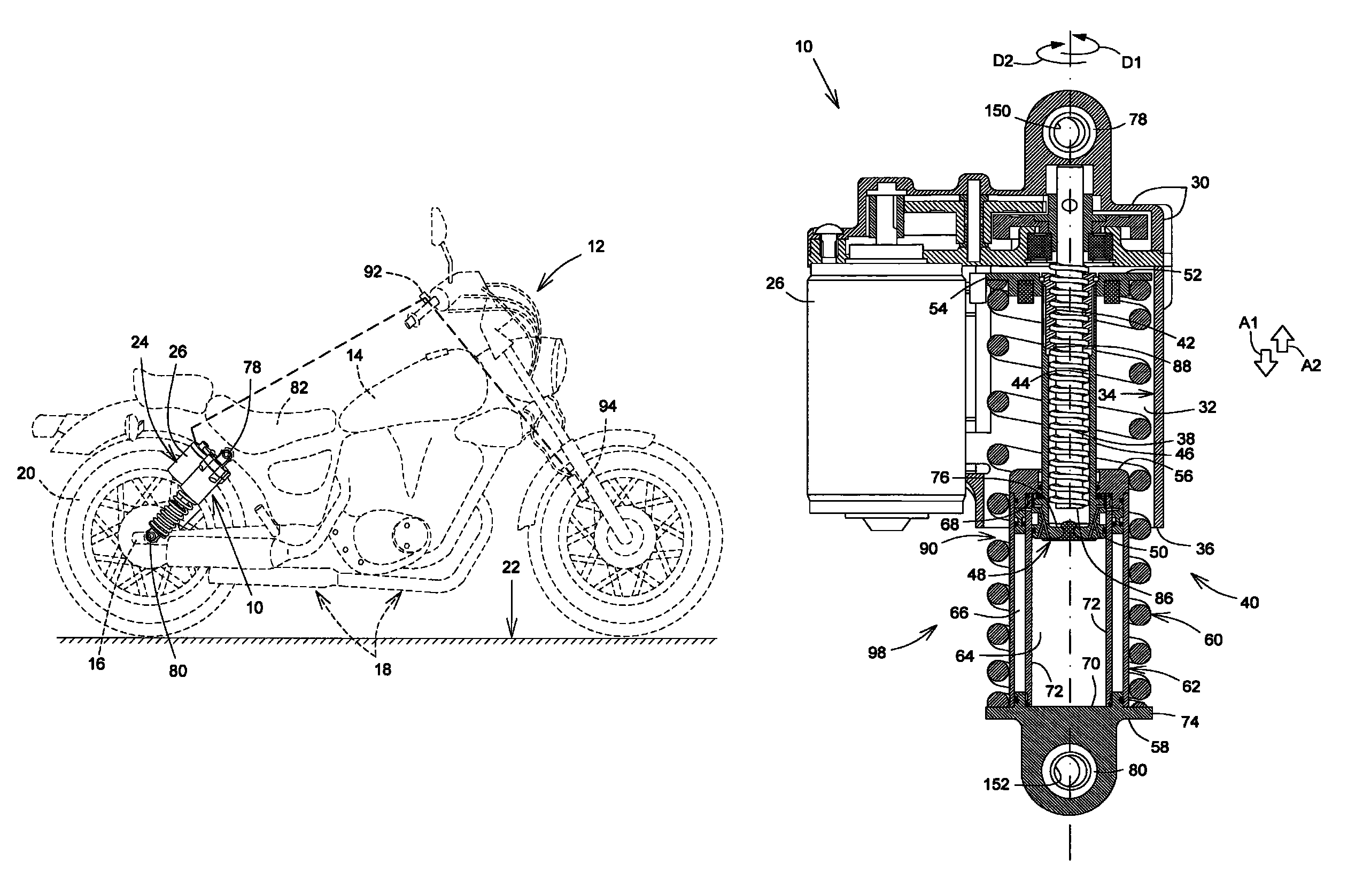
Leaning vehicle with tilting front wheels and suspension therefor
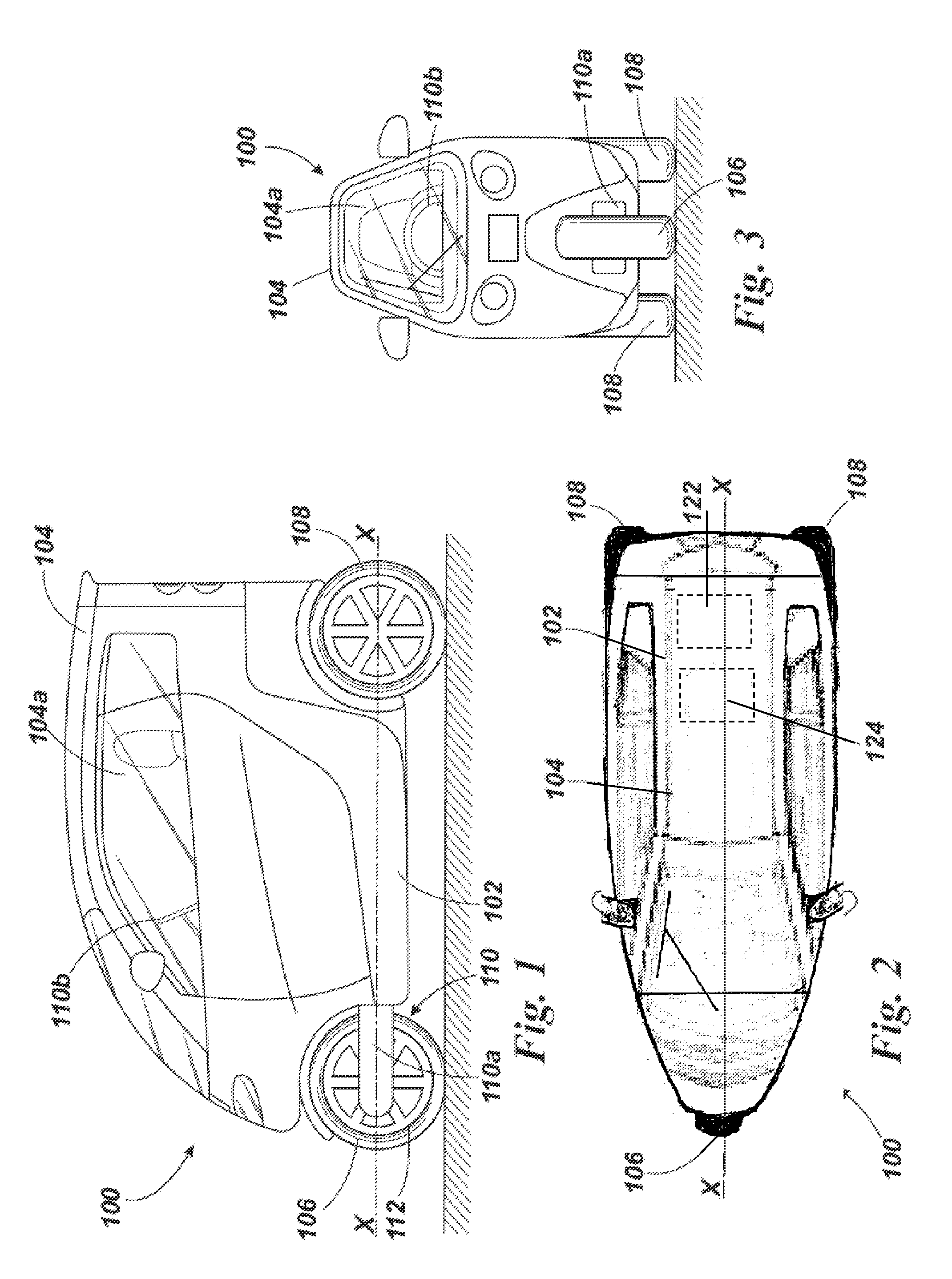
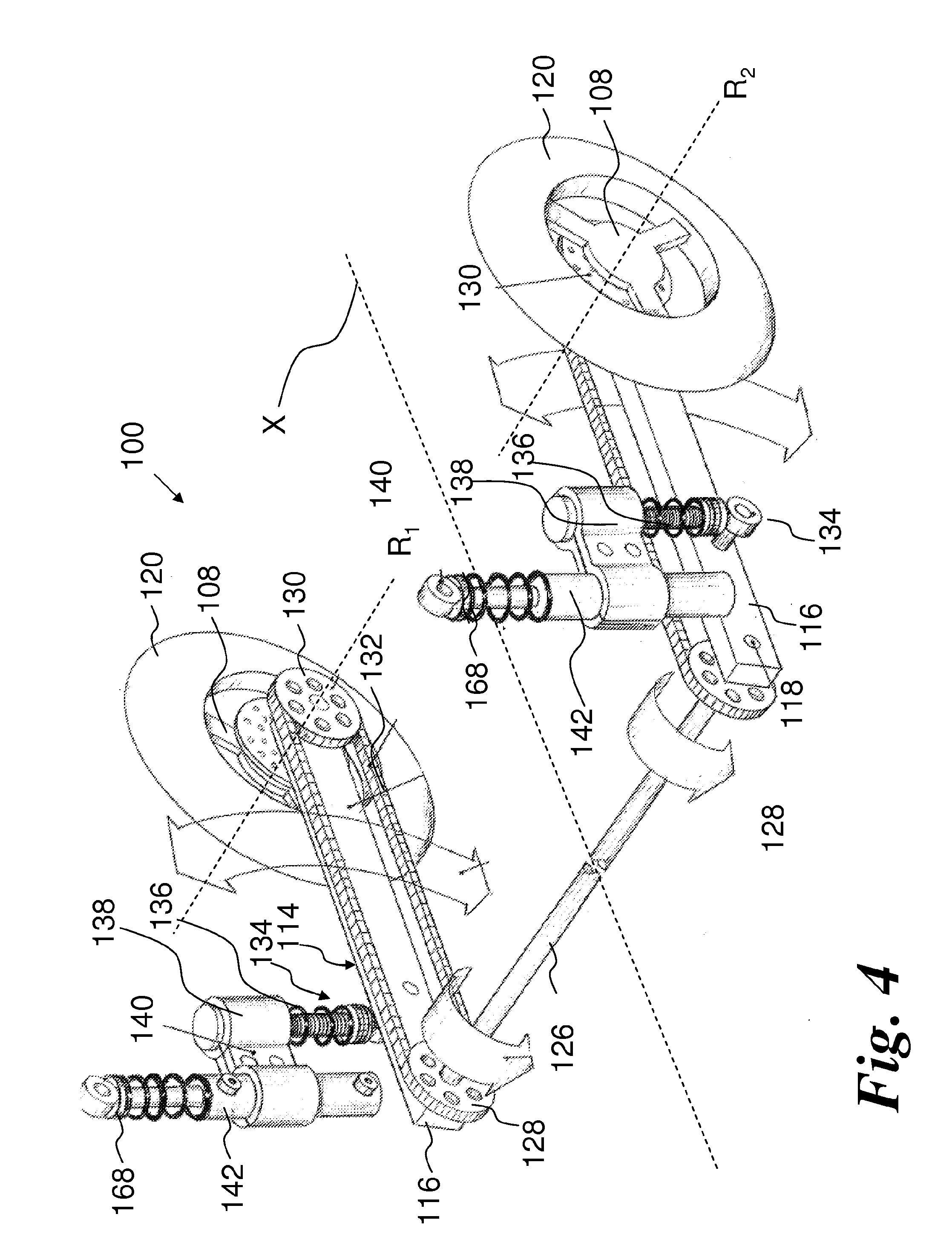
A leaning vehicle has a frame pivotally connected to the lower end of a shock tower, the pivotal connection defining a frame leaning axis wherein the frame is adapted to lean to a right side and to a left side relative to the shock tower about the frame leaning axis. The leaning vehicle includes an actuator operatively connected to the frame and to the shock tower which is adapted to impart a leaning motion to the frame relative to the shock tower about the frame leaning axis.
Owner:BOMBARDIER RECREATIONAL PROD INC
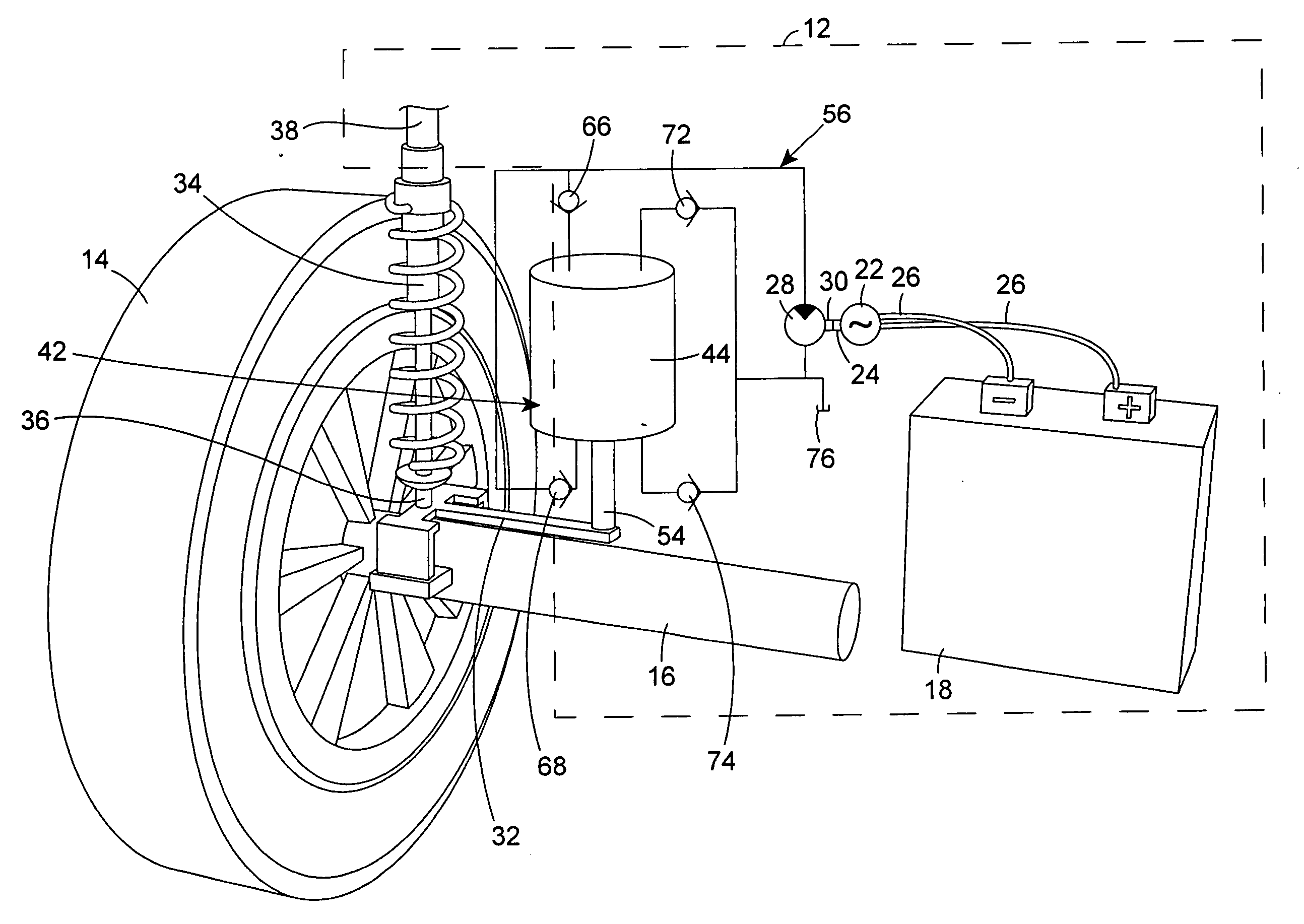
Apparatus and method for hydraulically converting movement of a vehicle wheel to electricity for charging a vehicle battery
An apparatus and its method of operation hydraulically convert the relative movements between a vehicle wheel and a body of the vehicle to electricity, and use the electricity to recharge a battery of the vehicle. A generator is provided on the vehicle and a hydraulic motor is provided on the vehicle to rotate an input shaft of the generator. A double acting piston and cylinder assembly is operatively connected to each wheel of the vehicle, and each double acting piston and cylinder assembly is connected through a hydraulic circuit to the hydraulic motor. Movements of the vehicle wheels during operation of the vehicle cause reciprocating movements of each piston in each double acting piston and cylinder assembly. The reciprocating movements of the pistons pump liquid to the hydraulic motor and draw liquid from the hydraulic motor to cause operation of the hydraulic motor. The operation of the hydraulic motor drives the generator input shaft, which in turn produces electricity that is supplied to the vehicle battery to recharge the vehicle battery.
Owner:TOWERTECH RES GROUP
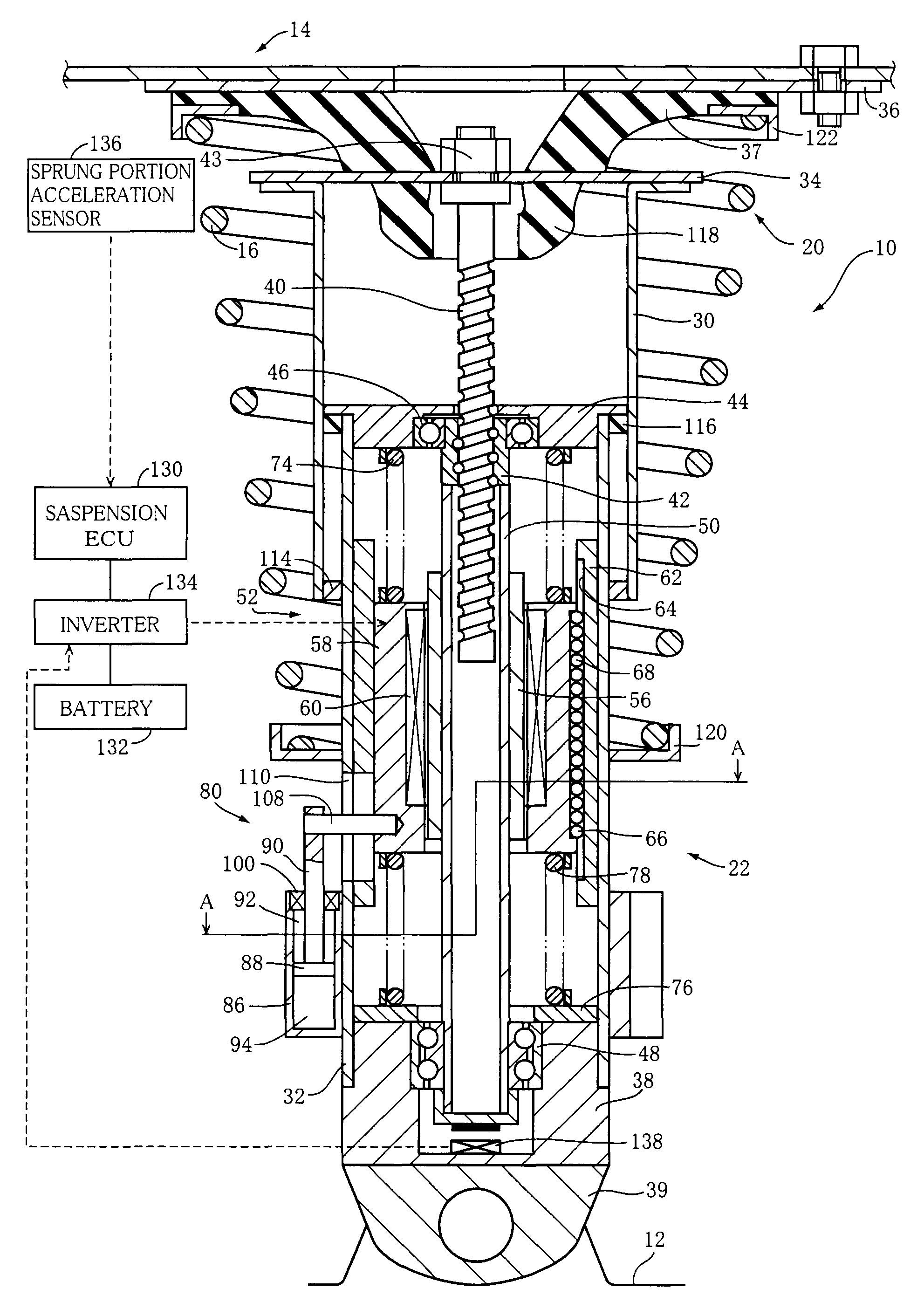
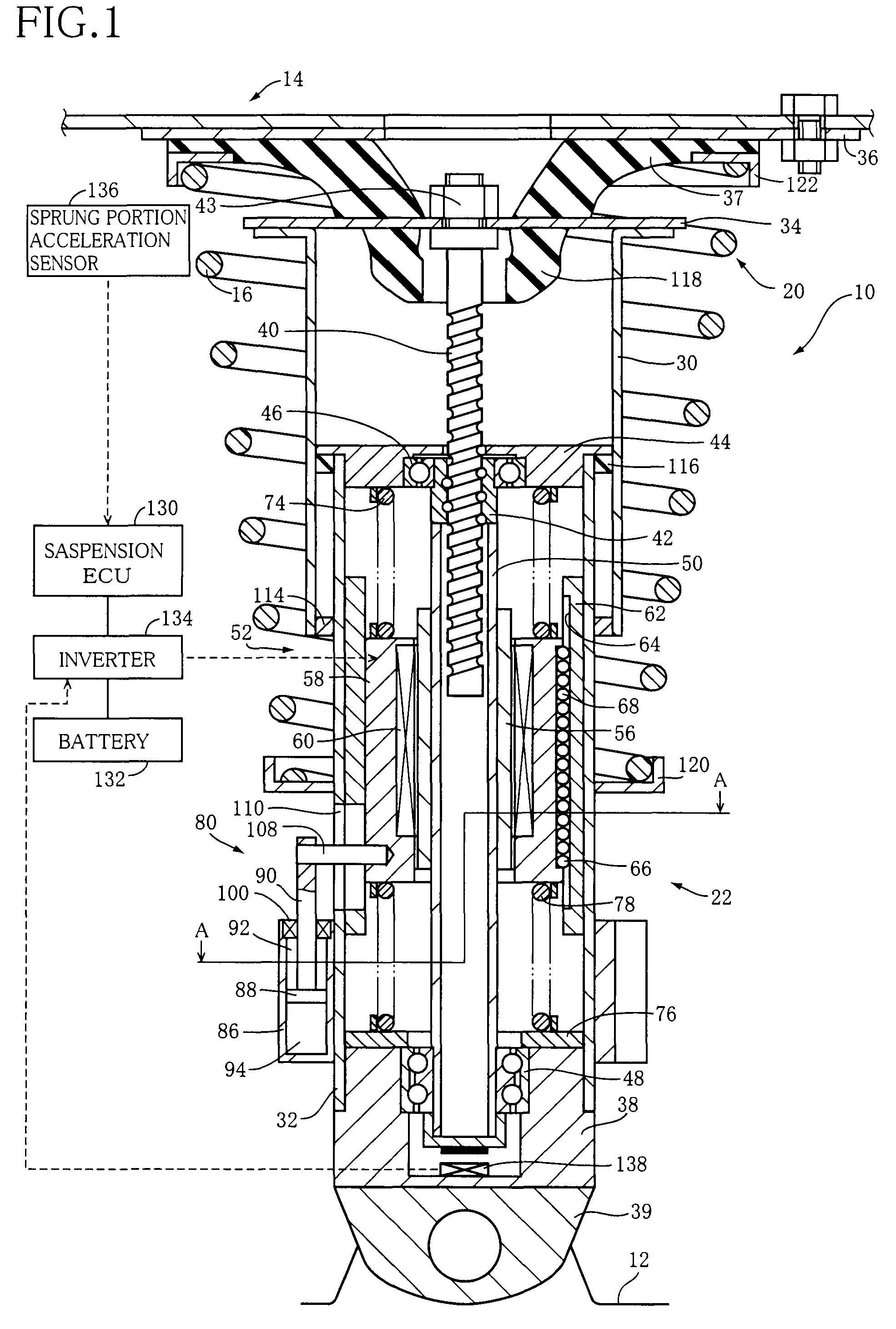
Electromagnetic shock absorber for vehicle
ActiveUS8127900B2Cope with vibrationPrevent lockMachine framesNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringShock absorber
An electromagnetic shock absorber including: (a) a wheel-side member; (b) a body-side member movable relative to the wheel-side member; and (c) a damping force generator with an electromagnetic motor including stationary and movable elements movable relative to each other. The damping force generator can generate, based on a force generated by the motor, a damping force acting against a relative movement of the wheel-side member and the body-side member. The motor has an axis extending in a both-members-relative-movement direction as a direction of the above-described relative movement. The stationary element is supported by the wheel-side member via an elastic body, to be movable relative to the wheel-side member in the both-members-relative-movement direction. The electromagnetic motor allows relative movement of the stationary element and the movable element upon movement of the stationary element relative to the wheel-side member.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
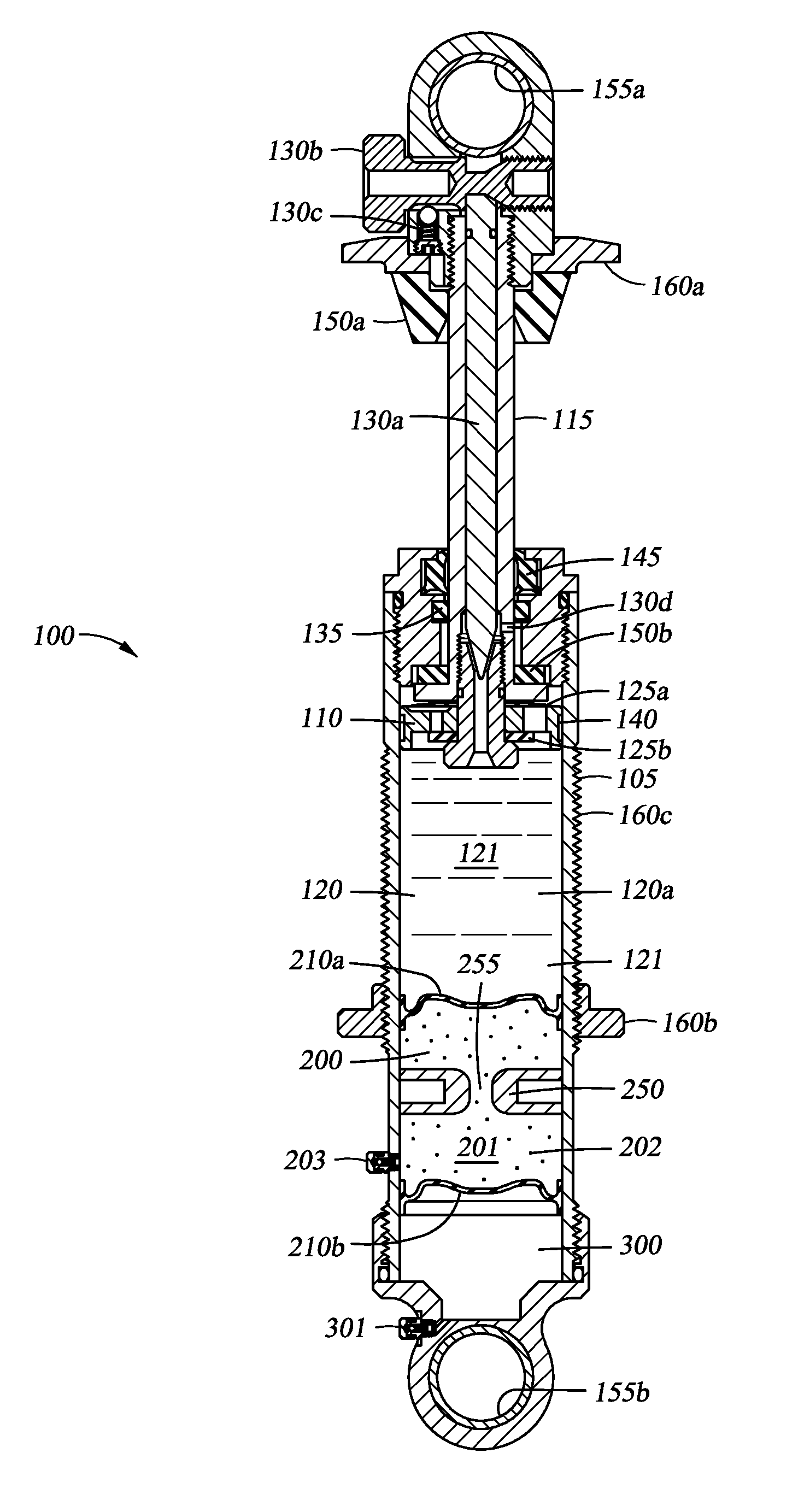
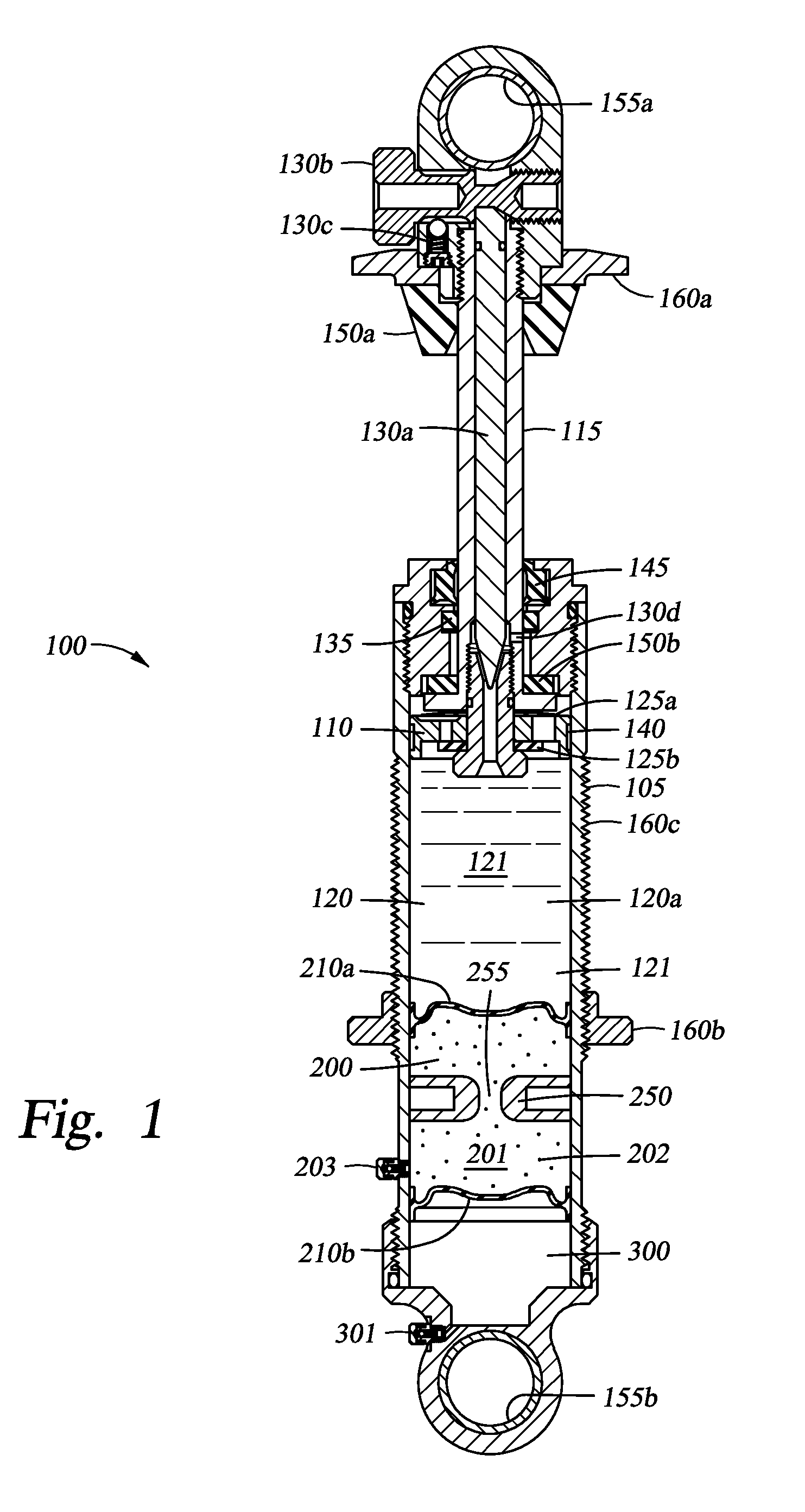
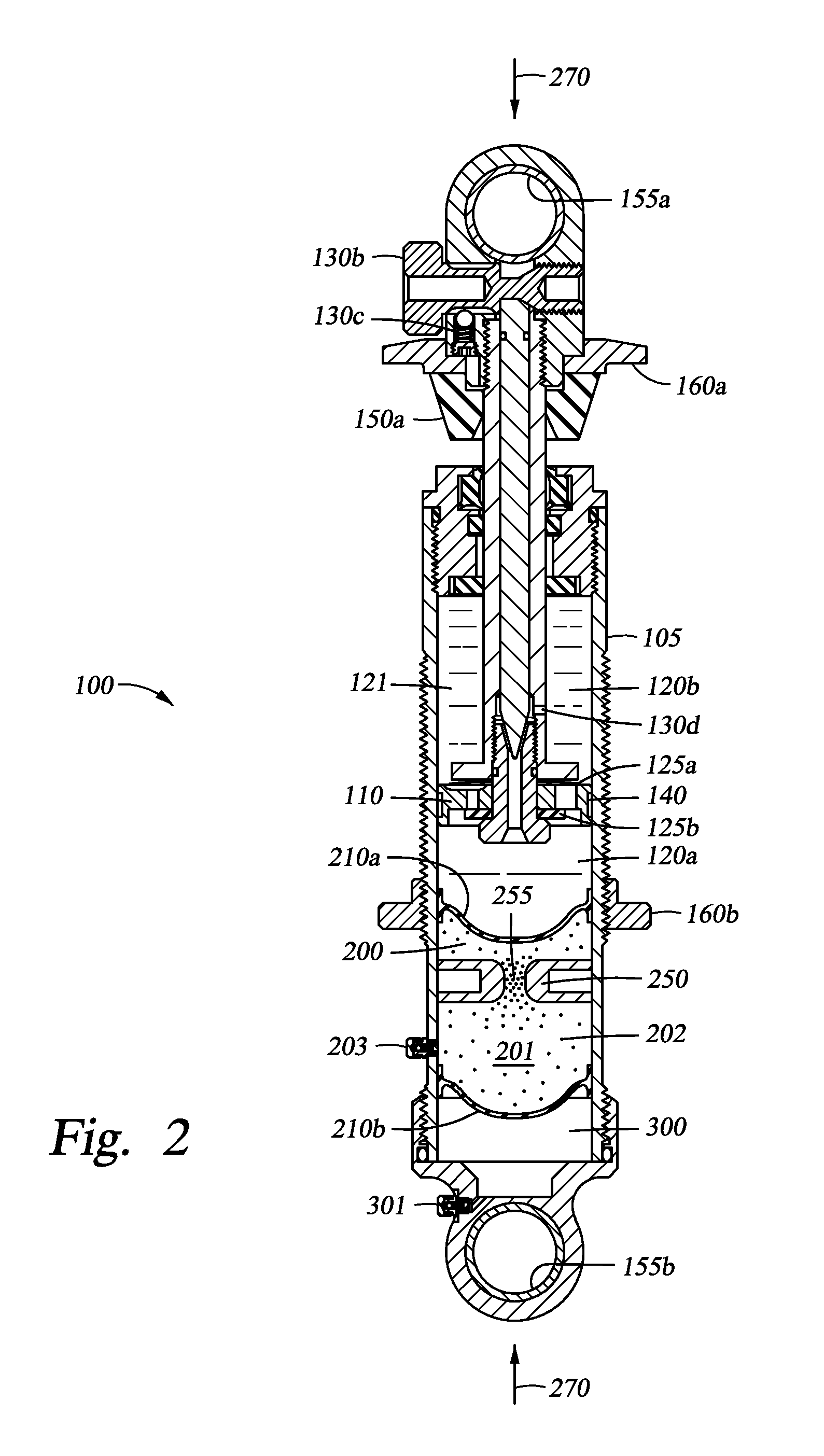
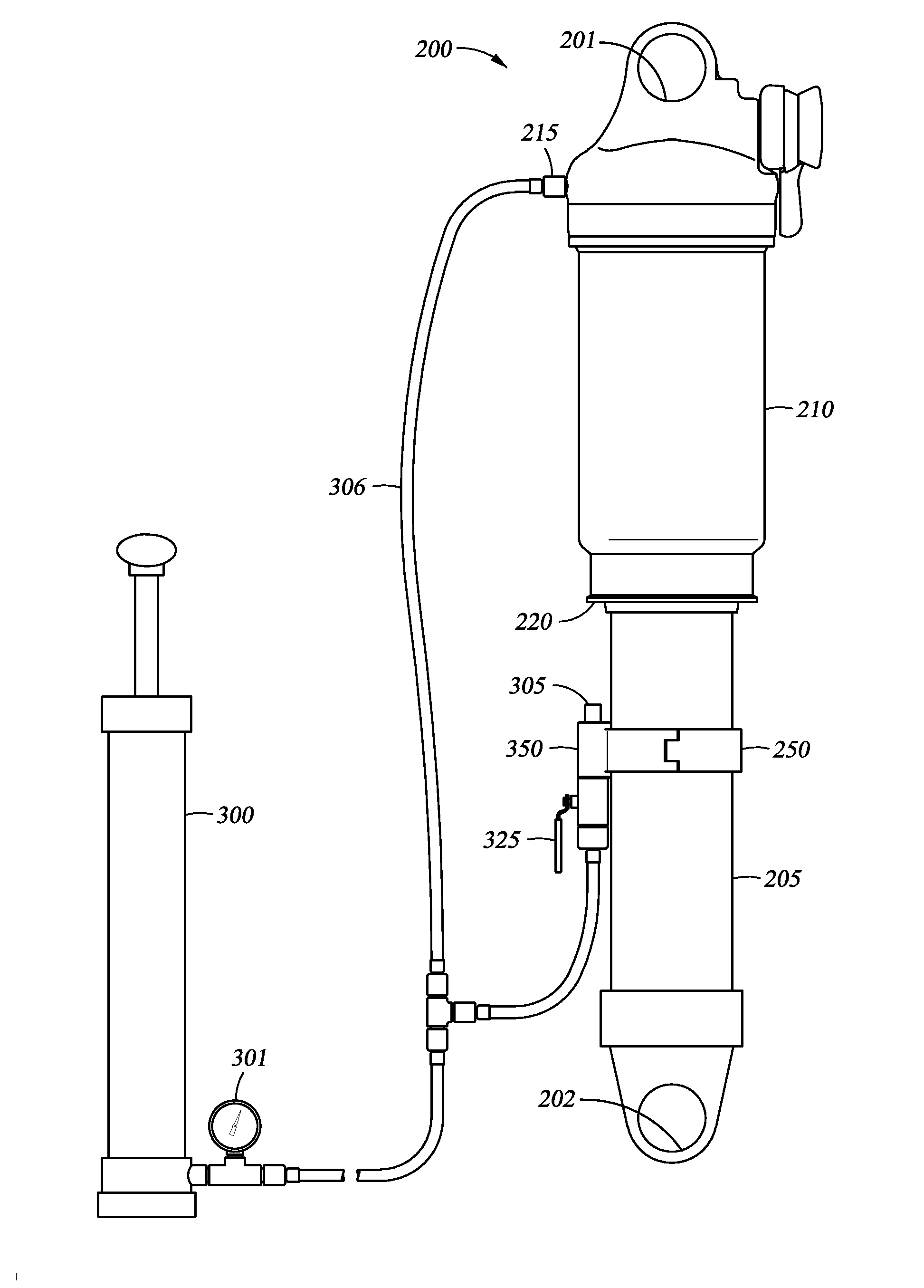
Adjustable Monotube Shock Absorber
A monotube shock absorber that can be adjusted remotely or otherwise, and a corresponding system are provided. The monotube shock absorber includes a body tube that houses a working piston therein and a bypass tube that is attached to but external with respect to the body tube. A control valve influences flow volume and rate of oil that passes through the bypass tube in a manner that correspondingly influences damping and / or other characteristics of the monotube shock absorber. The monotube shock absorber can include a floating piston separating a volume of gas from a volume of oil. The volumes of gas and oil may be entirely housed in the body tube or may be at least partially housed in an external reservoir that can include an anti-cavitation valve.
Owner:FURRER FREDRICK J
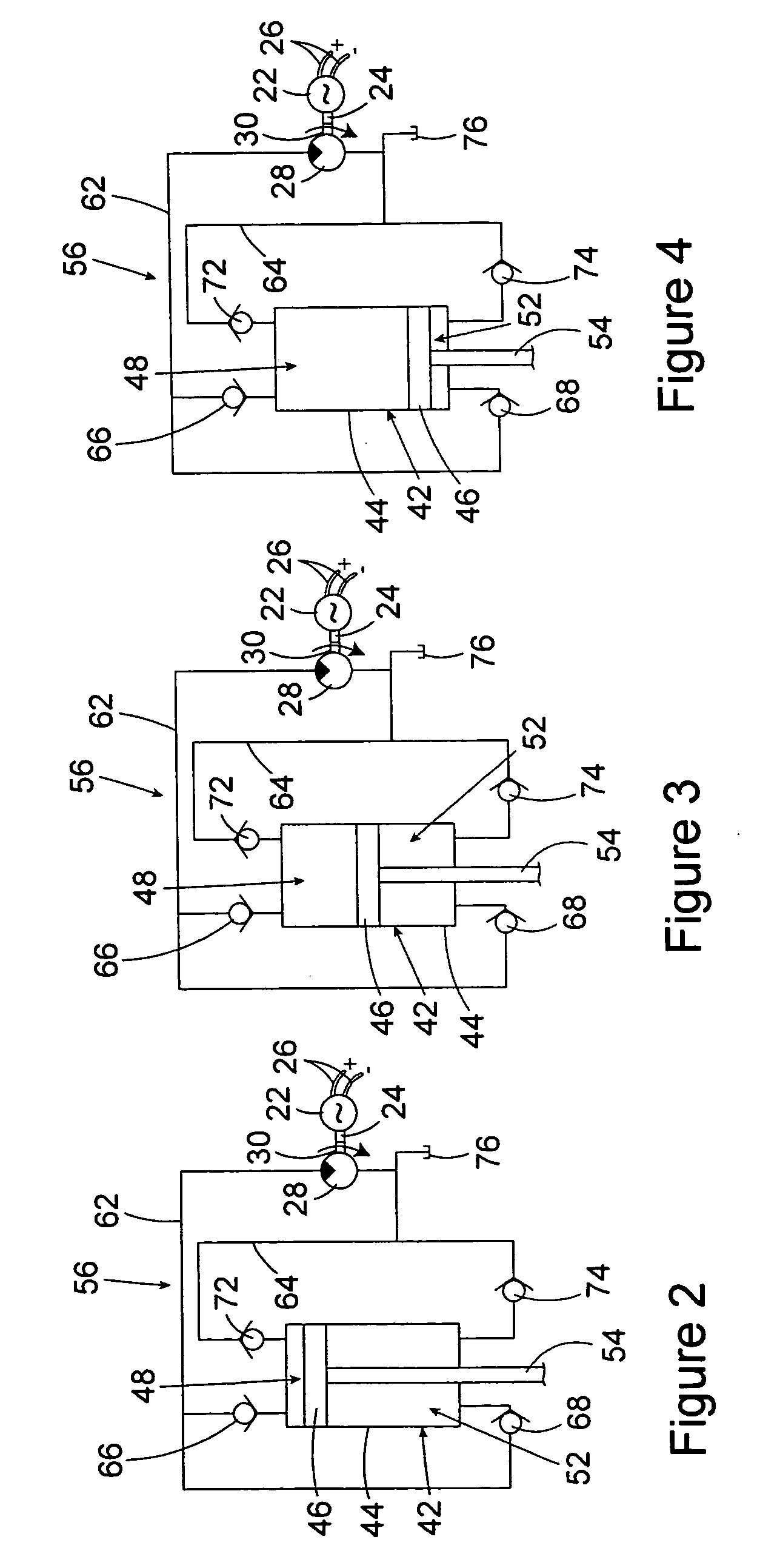
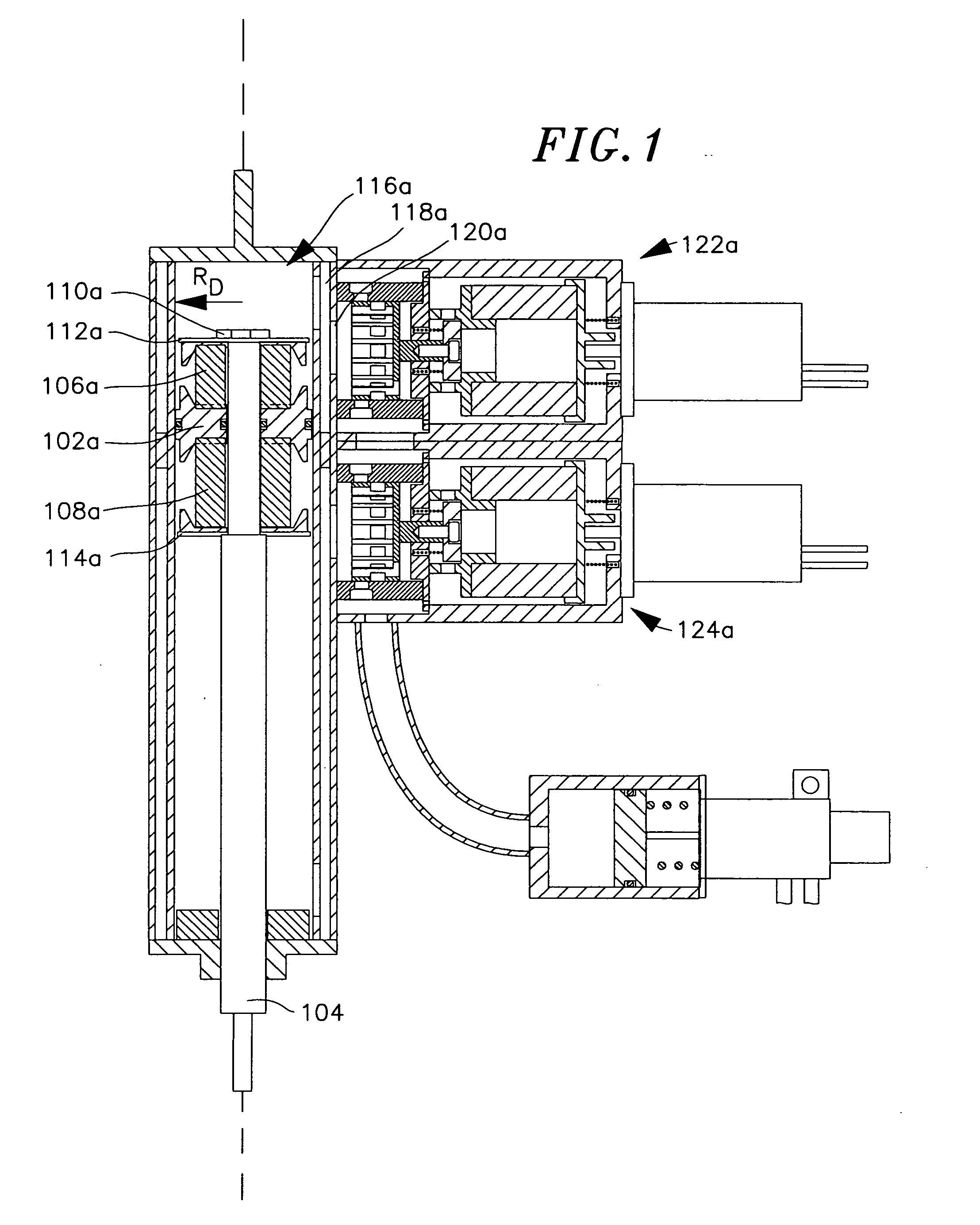
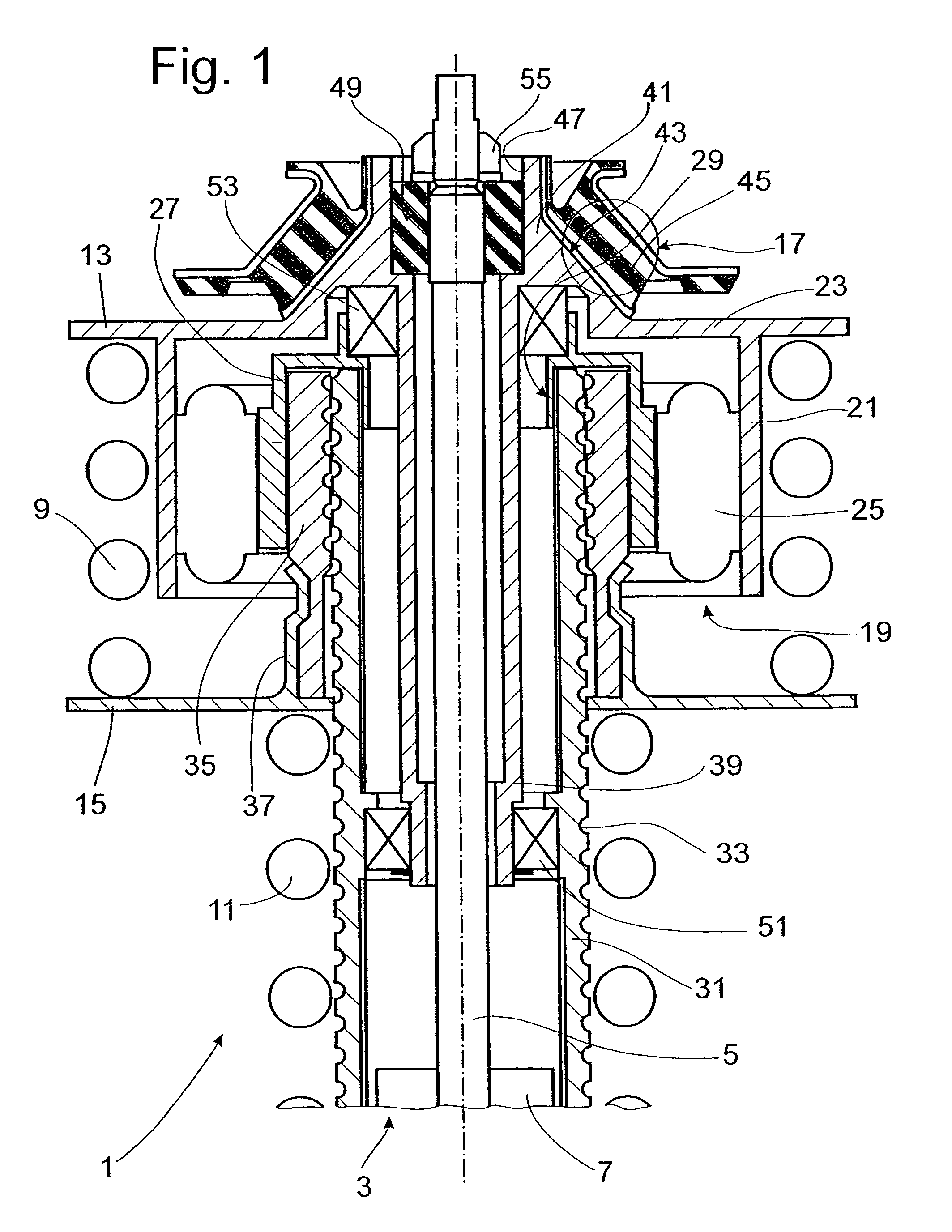
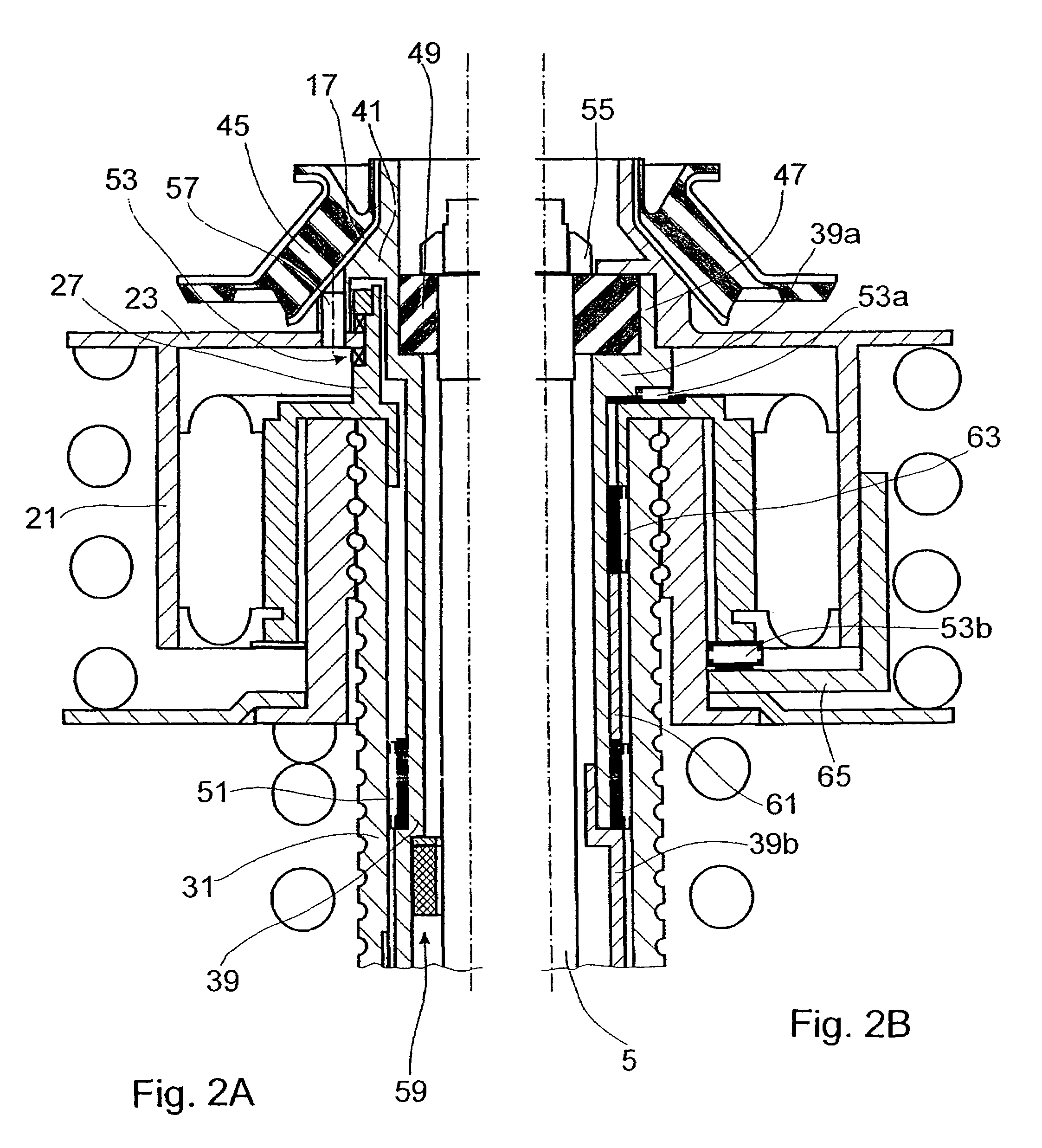
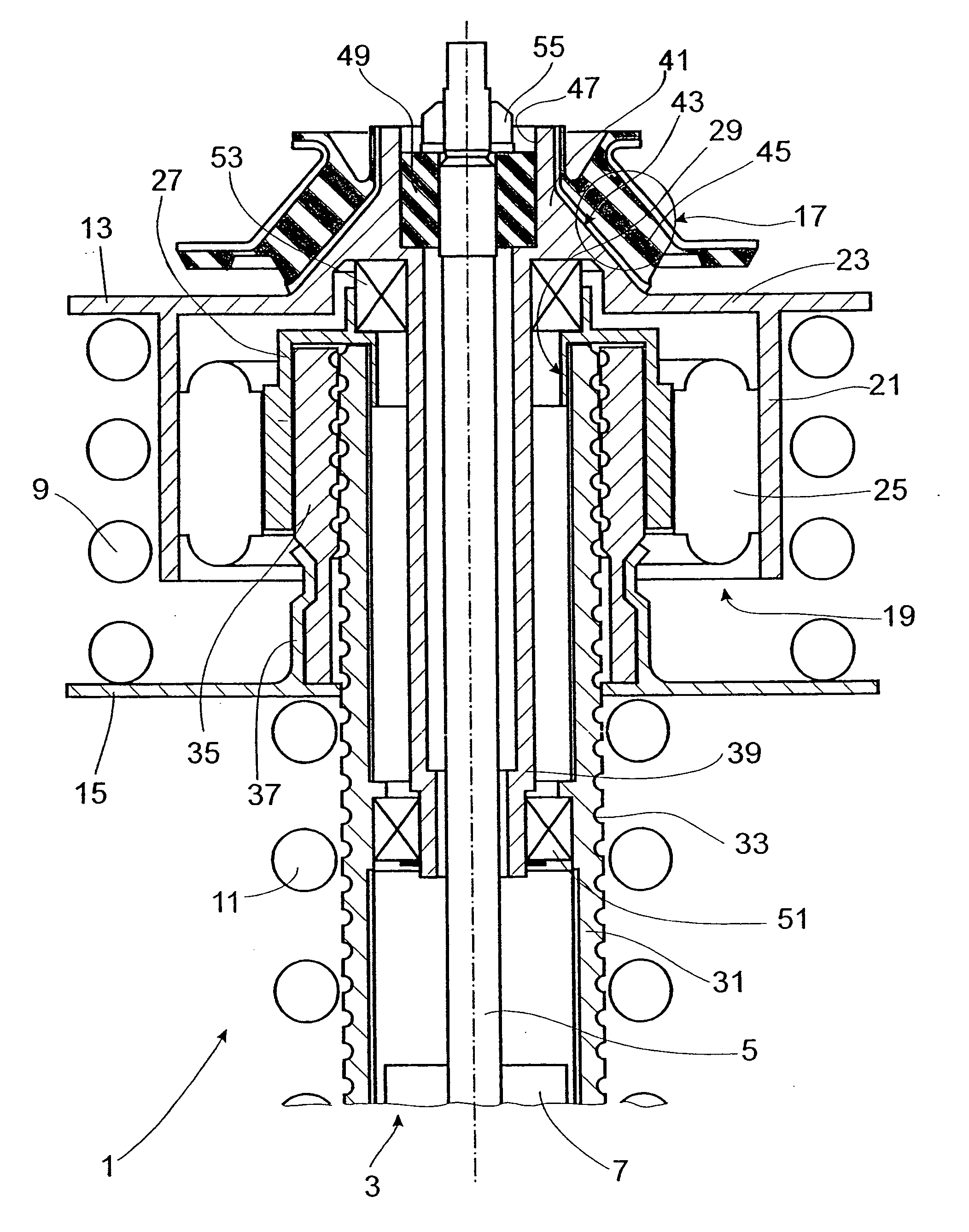
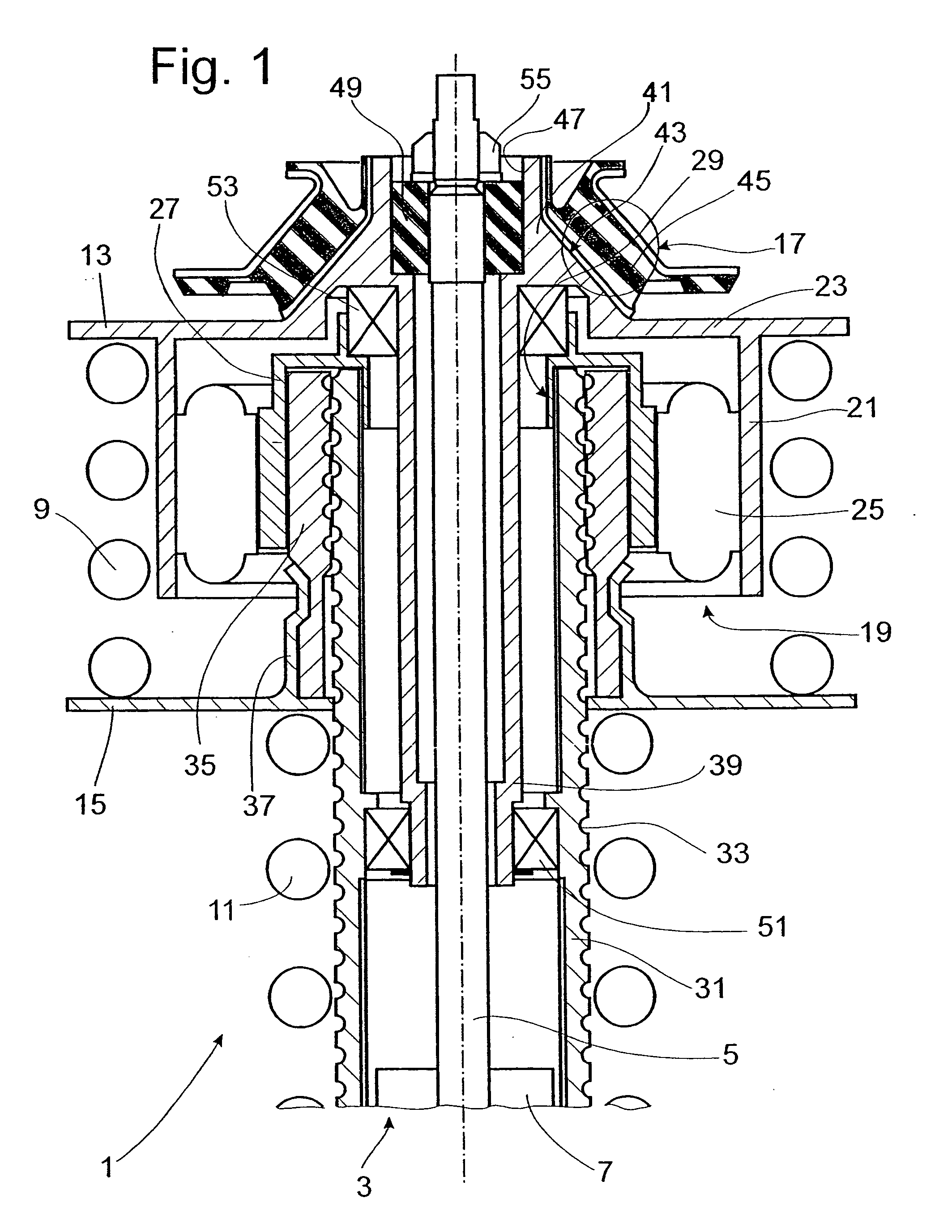
Damping force generation system and vehicle suspension system constructed by including the same
InactiveUS7722056B2High utilityMore roomSpringsVehicle cleaning apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceElectromagnetic absorbers
It is an object of the invention to improve the utility of an electromagnetic absorber system which is disposed in a suspension system of a vehicle and which generates a damping force by a generation force of a motor. The electromagnetic absorber system 18 is equipped with high-speed-motion responding means, thereby obviating an insufficiency of the damping force and a deterioration of the controllability in a high-speed stroke motion. More specifically, a hydraulic absorber 64 is provided in combination with the electromagnetic absorber system such that the hydraulic absorber 64 operates in the high-speed motion in which an electromotive force of the motor 68 exceeds a power source voltage Further, two motors having mutually different T-N characteristics are provided, and the two motors are selectively operated depending upon a stroke speed. Further, a variable resistor is interposed between the motor and the power source, and a resistance value of the variable resistor is increased in the high-speed motion to realize a decrease in a time constant of the motor, etc. Moreover, to cope with a large extent of unevenness of a road surface, an active stroke motion is performed by a drive force of the motor, thereby preventing the high-speed motion from being performed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
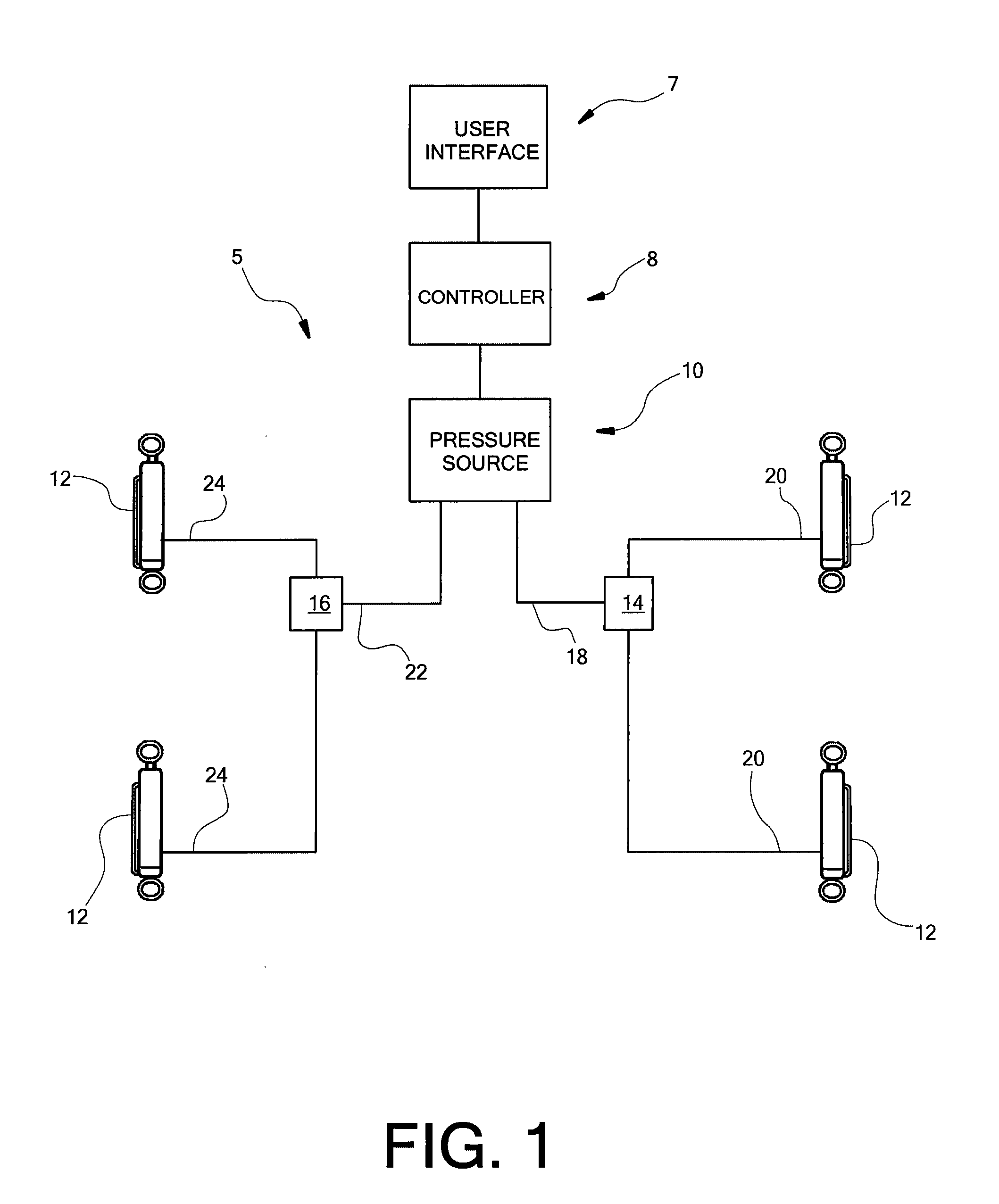
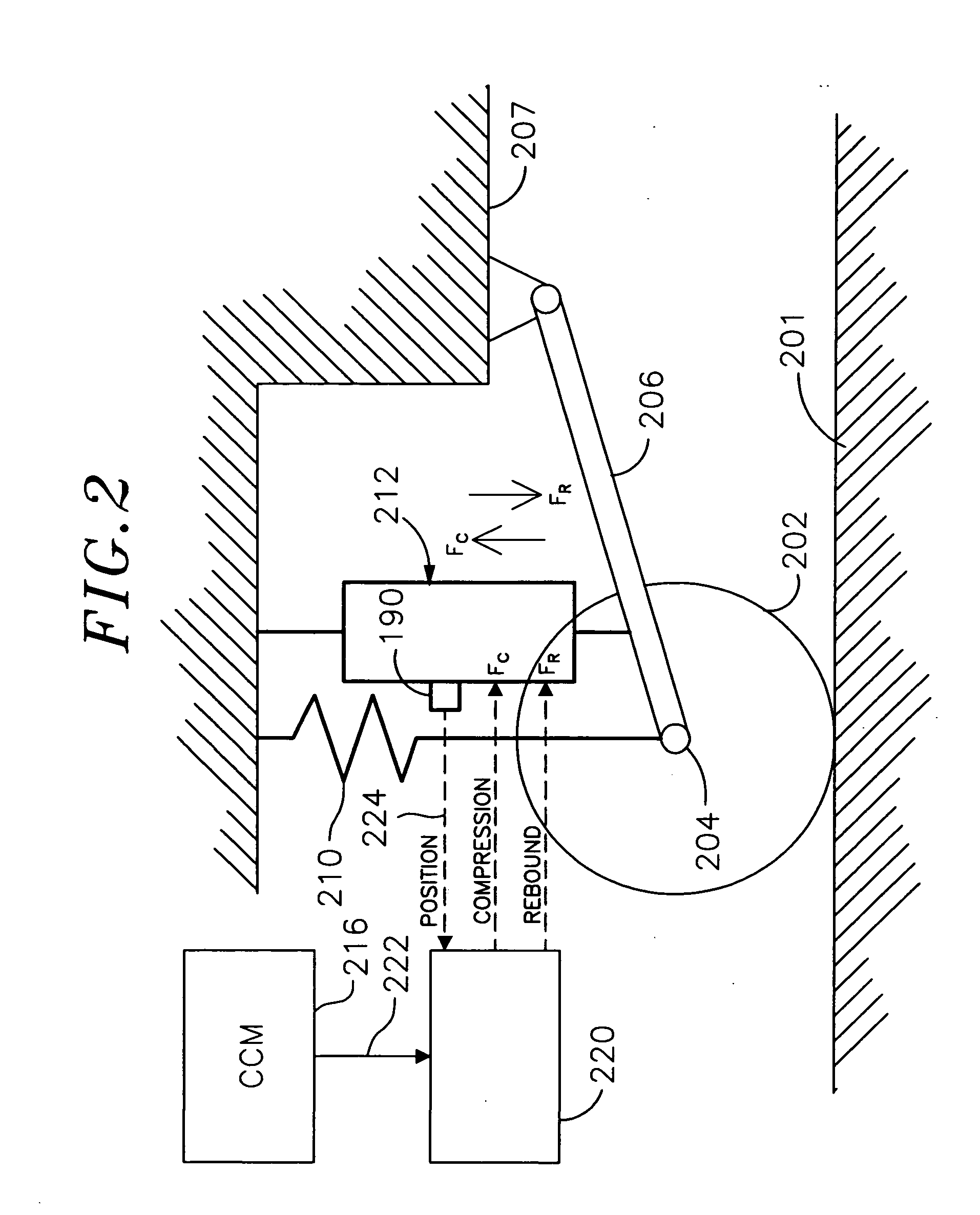
Enhanced computer optimized adaptive suspension system and method
InactiveUS20050098401A1Minimizing body motionIncrease fluid pressureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSpringsComputer optimizationControl signal
A system and method for controlling a damping system. The system has at least two dampers for damping between sprung and unsprung masses in the compression and rebound directions. Sensors generate signals based on position and other parameters of motion representative of the displacement between the sprung and unsprung masses. The process determines the appropriate compression and rebound forces to be applied at the wheels. A regulator responds to at least one of the independent compression and rebound control signals for adjusting, respectively, at least one of compression and rebound resisting forces of the dampers between the masses. Compliance for the dampers is emulated with software to produce the desired compliance forces. The distributed controller includes a processor that is responsive to signals representative of the position signals for forming the compression and rebound control signals for the regulator as a function of motion between the masses or a motion of a vehicle in which the dampers are located. The system has the capability of locking the suspension when parked.
Owner:GREAT NORTHERN TECH
Vehicle height adjustment suspension device
ActiveUS8262100B2Easily fitted to vehicleVehicle cleaning apparatusLoading/unloading vehicle arrangmentVehicle frameShock mount
A vehicle height adjustment suspension device provides for both automatic and selective raising and lowering of a supported portion of a vehicle frame relative a ground surface, while also providing shock absorption. The device includes a suspension assembly for absorbing shocks mounted on a rotatable threaded screw connected to a motor and extending into the suspension assembly. The assembly may be extended and retracted on the screw by rotating the screw in first and second directions to raise and lower the supported portion while the shock absorber assembly simultaneously provides shock absorption capability.
Owner:9092854 CANADA
Suspension tilting module for a wheeled vehicle and a wheeled vehicle equipped with said suspension tilting module
A tilting suspension system is provided for two wheels (2, 3) of a vehicle (200) disposed on a common axle with the module comprising a rigid frame (17) adapted to be firmly fixed to the chassis of the vehicle so as to be tilted together with the whole vehicle and a tilting arm (14) pivotally linked to the rigid frame. The tilting of the rigid frame is obtained as a result of the counter torque arising when activating hydraulic actuating means (101, 102) pivotally interposed between the tilting arm (14) and the rigid frame (17), with the tilting arm being pivotally connected to shock absorbers (18). The tilting module further comprises suspension arms (10, 11, 12, 13) pivotally connected to the rigid frame, with the suspension arms supporting, in cooperation with supporting uprights, the two wheels thus allowing both tilting and steering of the two wheels. The hydraulic actuating means (101, 102) are actuated by a hydraulic pump (112) driven by an electric motor (108).
Owner:FONDAZIONE TORINO WIRELESS
Dampers for mountain bikes
InactiveUS20110127706A1Adjustable levelIncrease dampingSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionControl theoryTimer
An apparatus of a damper (46) for a bicycle comprising a housing defining a chamber, and a piston, movable in the chamber along a first direction. The apparatus further comprises a controllable means to vary the resistance to movement of the piston in the chamber, a sensor (62), and a controller (58) including a timer. Said sensor measures at least one dynamic quantity and produces an output signal based thereon. Said output signal is received by the controller, and said controller controls said controllable means based on said dynamic quantity as a function of time to control the level of damping. The invention further provides means for manually adjusting the level of rebound damping.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD
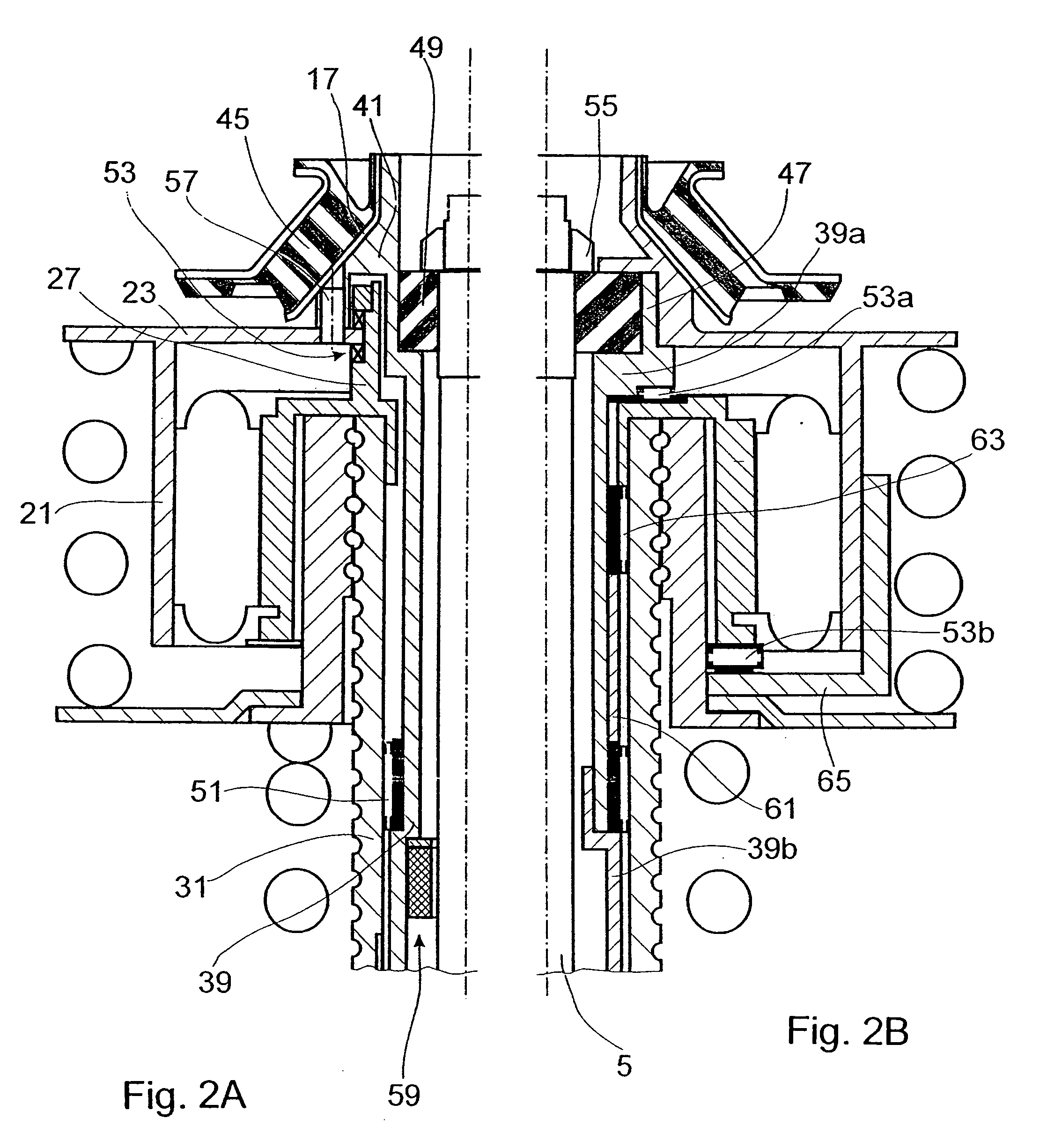
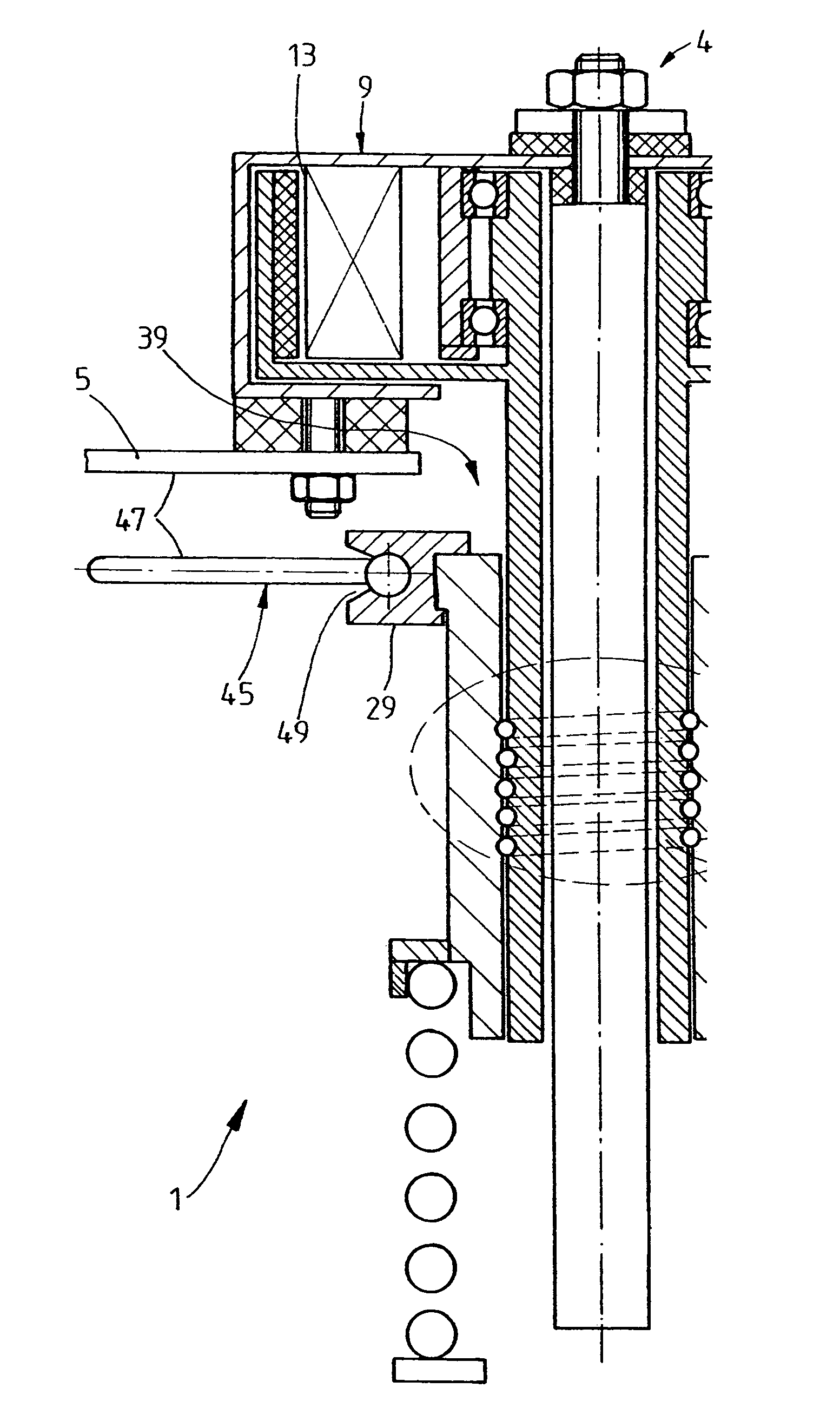
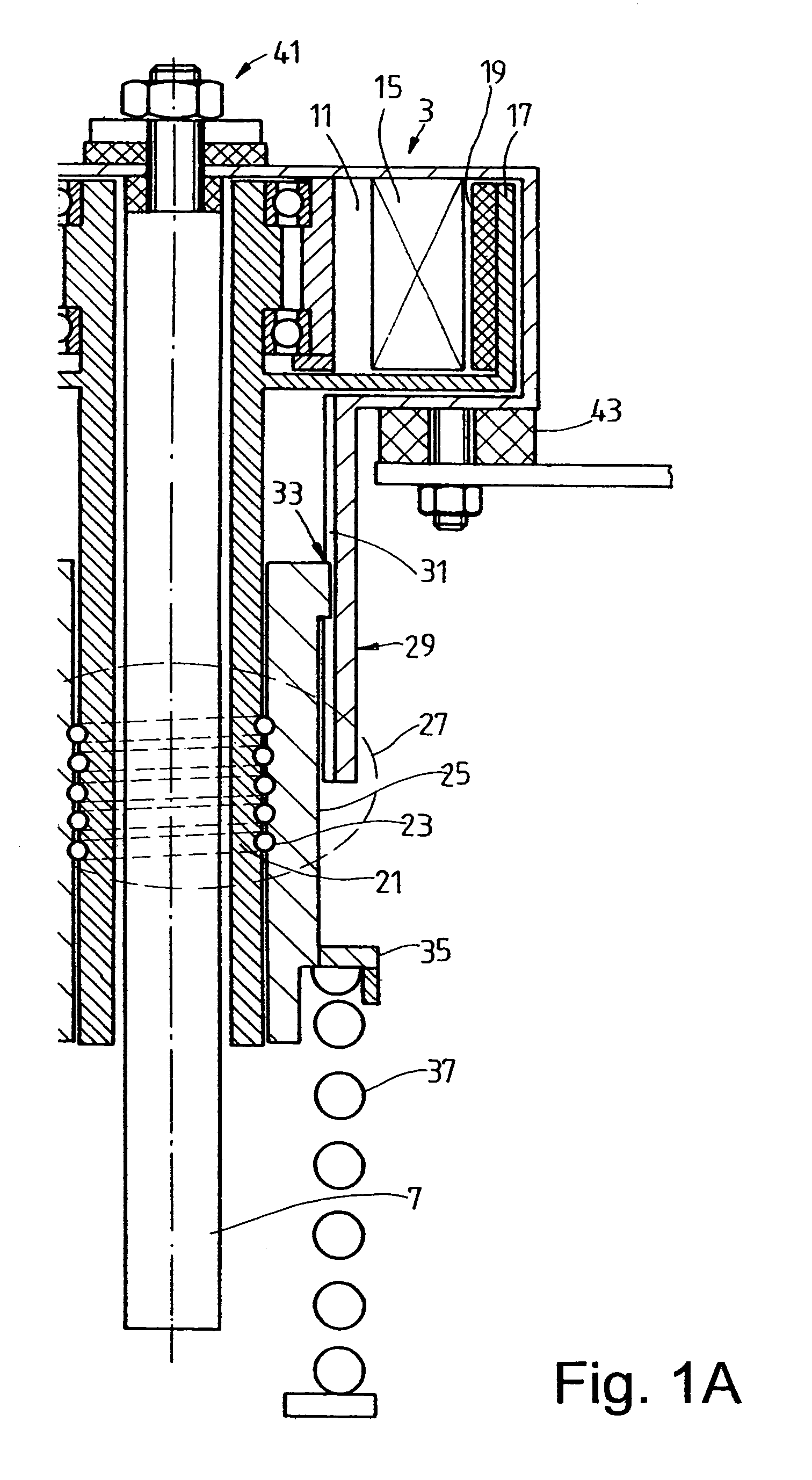
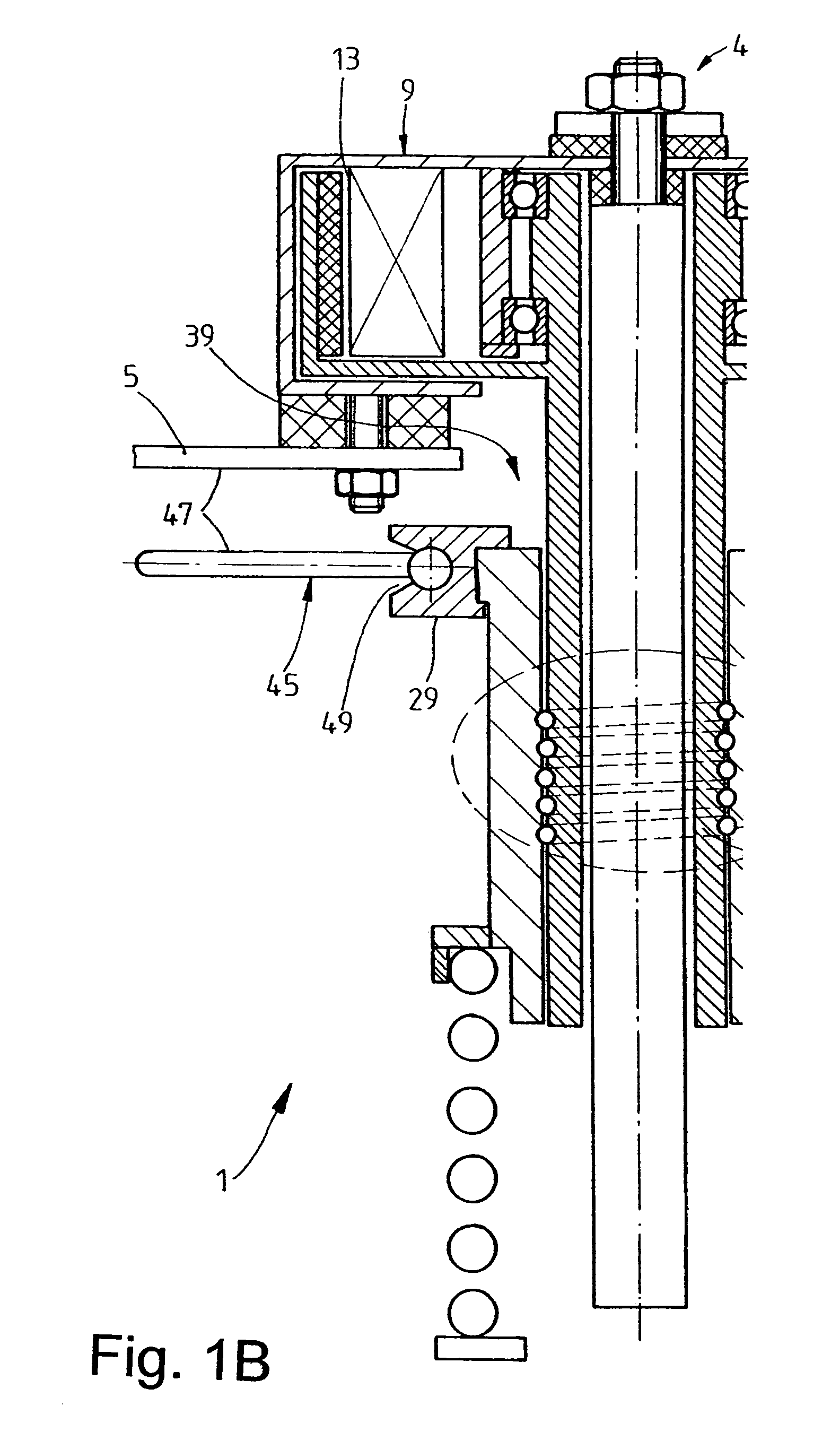
Spring carrier with adustable spring collar
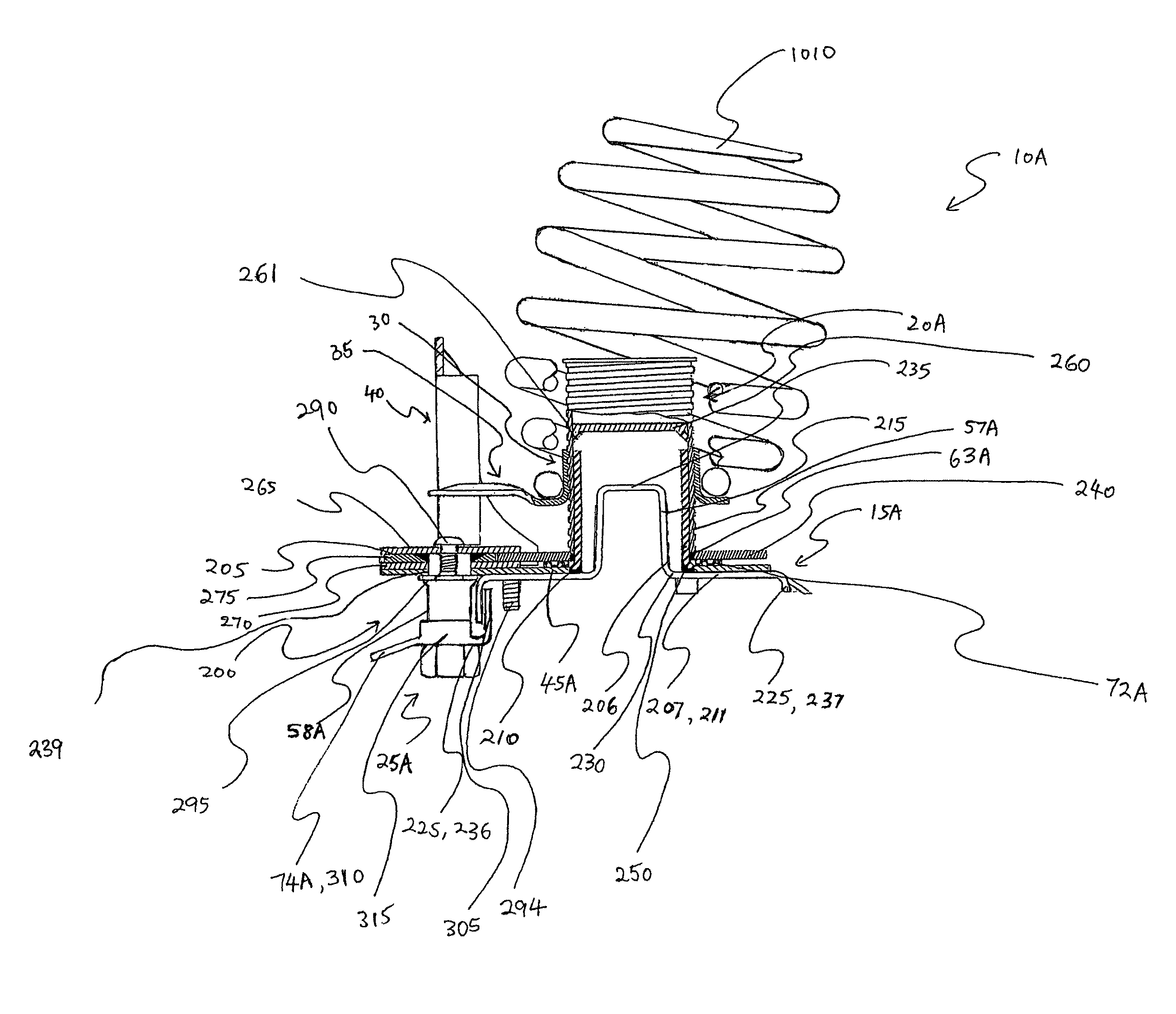
InactiveUS7469910B2Easy to assembleIncrease elasticityNon-rotating vibration suppressionResilient suspensionsActuatorControl theory
A spring carrier for mounting a spring strut to a vehicle body includes a vibration damper having a cylinder and a piston rod which is axially guided in the cylinder, first and second spring collars, and a spring located between the spring collars. An actuator includes a nut and a threaded spindle surrounding the piston rod, the actuator being driven to change the relative axial position of the spring collars. A guide tube extends coaxially between the piston rod and the threaded spindle, the guide tube being fixed to the vehicle body by a first resilient mount, the piston rod being fixed to the guide tube by a second resilient mount, whereby the piston rod can move relative to the first resilient mount.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Spring carrier with adjustable spring collar
InactiveUS20060163787A1Easy to assembleIncrease elasticitySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringActuator
A spring carrier for mounting a spring strut to a vehicle body includes a vibration damper having a cylinder and a piston rod which is axially guided in the cylinder, first and second spring collars, and a spring located between the spring collars. An actuator includes a nut and a threaded spindle surrounding the piston rod, the actuator being driven to change the relative axial position of the spring collars. A guide tube extends coaxially between the piston rod and the threaded spindle, the guide tube being fixed to the vehicle body by a first resilient mount, the piston rod being fixed to the guide tube by a second resilient mount, whereby the piston rod can move relative to the first resilient mount.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Spring support having a height-adjustable spring plate
InactiveUS7135794B2Reliable absorptionIncrease resistanceToothed gearingsResilient suspensionsEngineeringActuator
Owner:ZF SACHS AG
Apparatus for facilitating reduction of vibration in a work vehicle having an active CAB suspension system
InactiveUS6898501B2Reduce vibrationEar treatmentAnalogue computers for trafficEngineeringSignal processing
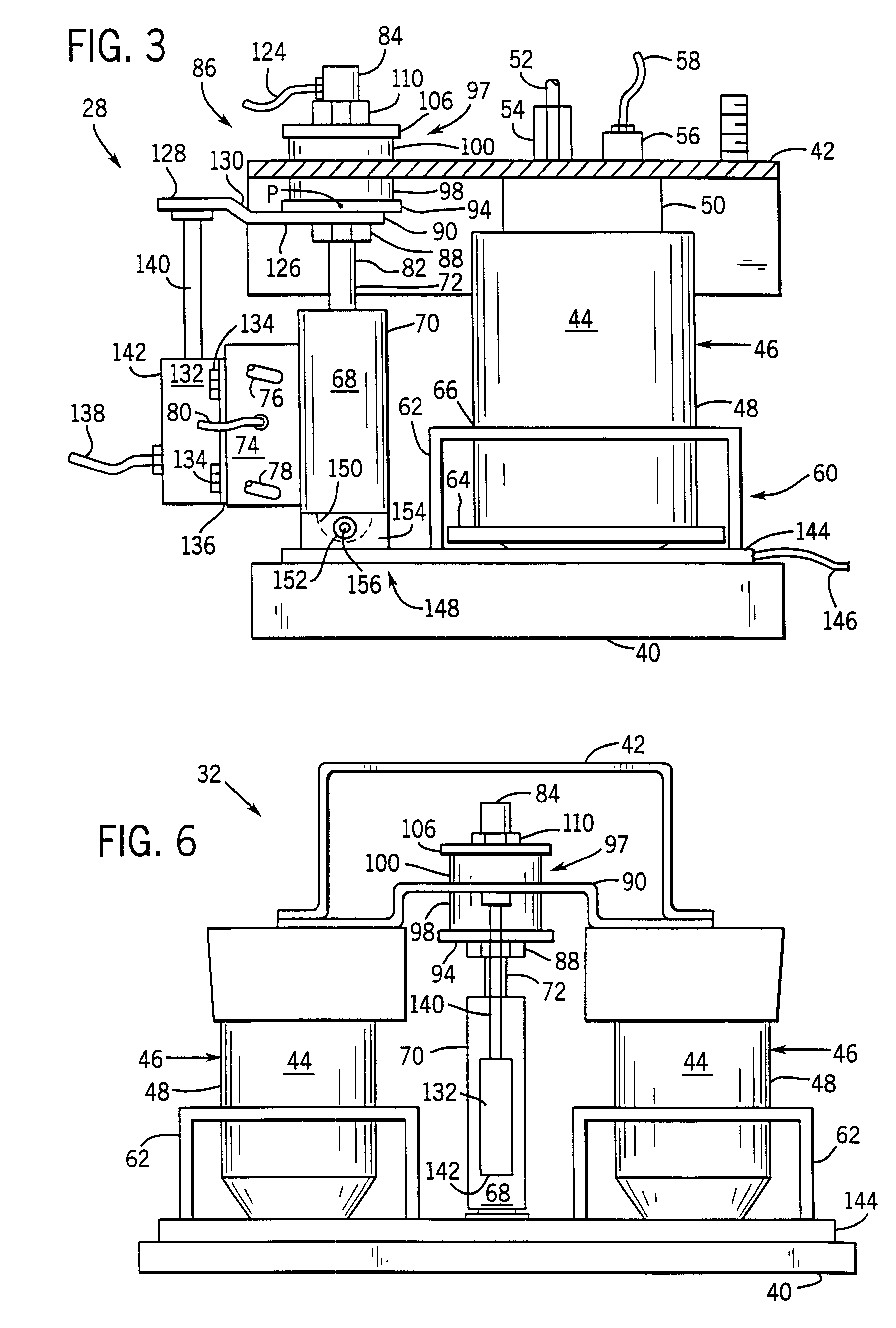
An apparatus and method for determining when a component of a work vehicle experiences vibration above a predetermined threshold, and responding to the vibration so that the vibration is reduced below the predetermined threshold. The apparatus, which is in a work vehicle that includes a chassis, an operator's cab and an active cab suspension system, includes a sensor that is configured to sense a quantity representative of the vibration experienced by the component of the work vehicle and to develop a first signal indicative of that quantity. The apparatus also includes a signal processor that is coupled to the sensor and is configured to develop, in response to the first signal, a second signal indicative of whether the vibration experienced by the component is above the predetermined threshold. The apparatus further includes a device that is coupled to the signal processor and, in response to the second signal, is either configured to provide an indication or configured to take an action to reduce the vibration below the predetermined threshold when the vibration is above the predetermined threshold.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC +1
Suspension height adjustment mechanism
InactiveUS8087676B2Easy to useEasy to adjustVehicle cleaning apparatusLoading/unloading vehicle arrangmentEngineeringScrew thread
This disclosure relates to a suspension height adjustment mechanism comprising a main body, a rotatable assembly being rotatably mounted to the main body and having a first threaded portion, a tool engagement portion for rotating the rotatable assembly, a spring support having a second threaded portion engaging the first threaded portion, an anti-rotation means on the spring support adapted to cooperate with a corresponding anti-rotation means on the main body to prevent rotation of the spring support with respect to the main body, such that, in use, rotation of the tool engagement portion causes the spring support to axially translate along the rotatable assembly, thus adjusting the height of the suspension. This disclosure also relates to a vehicle suspension system comprising the suspension height adjustment mechanism and to a vehicle comprising the vehicle suspension system.
Owner:MCINTIRE KEVIN JOSEPH
Air spring assembly and method
A piston assembly for an air spring includes an outer shell and a structural insert. The outer shell includes a side wall and an end wall at least partially defining a shell cavity having an open end. The structural insert is received in the shell cavity and includes a central portion and a plurality of support walls extending outwardly from the central portion toward the side wall of the outer shell. The central portion includes first and second opposing ends with the first end disposed toward the end wall of the outer shell and the second end disposed toward the open end of the outer shell. An air spring assembly includes such a piston assembly. A method of manufacturing an air spring assembly is also included.
Owner:FIRESTONE IND PROD COMPANY
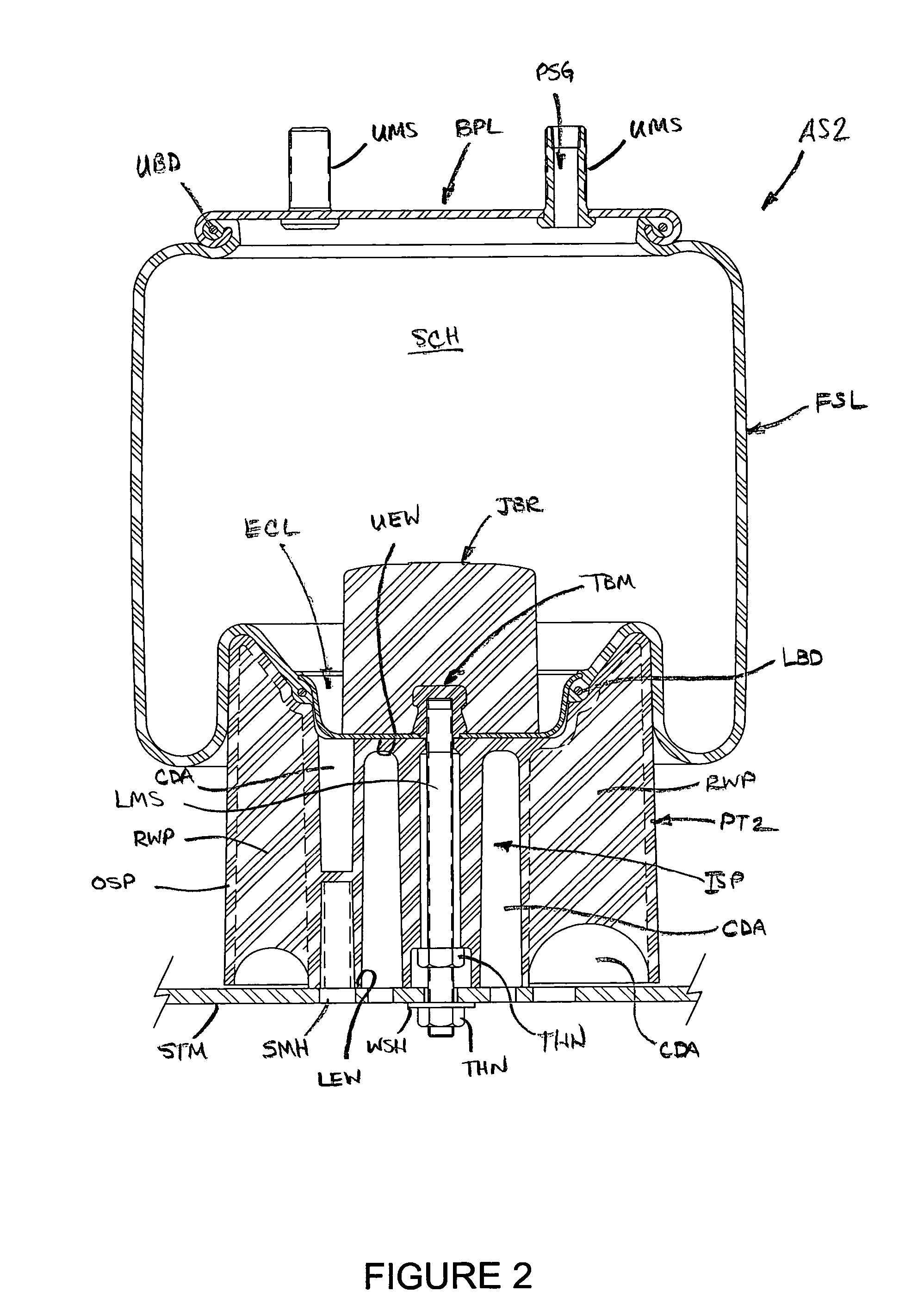
Wheelchair with damping mechanism
InactiveUS20060076748A1Reduce forward pitchIncrease damping forceWheelchairs/patient conveyanceRigid suspensionsWheelchairEngineering
A wheelchair has a damping system to reduce the forward pitch of the wheelchair upon sudden deceleration or upon descent of a sloped surface. The damping system includes a clamp that selectively grips a shaft.
Owner:SUNRISE MEDICAL HHC INC
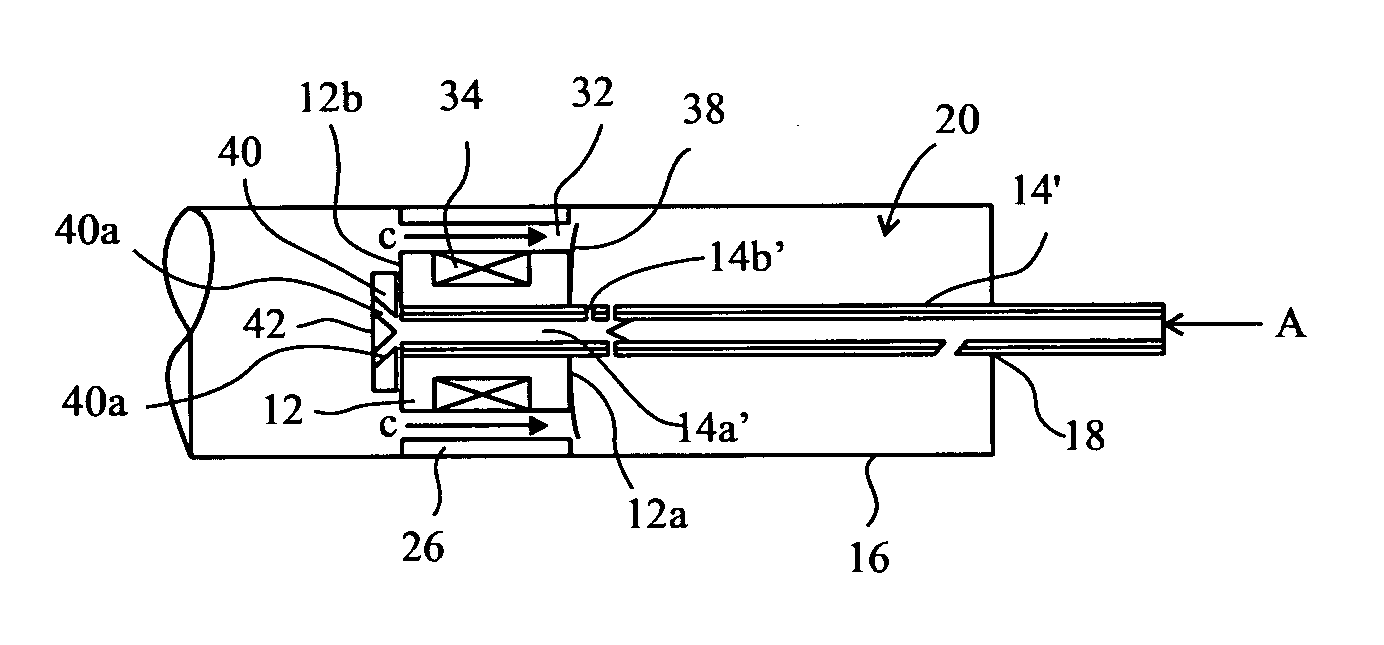
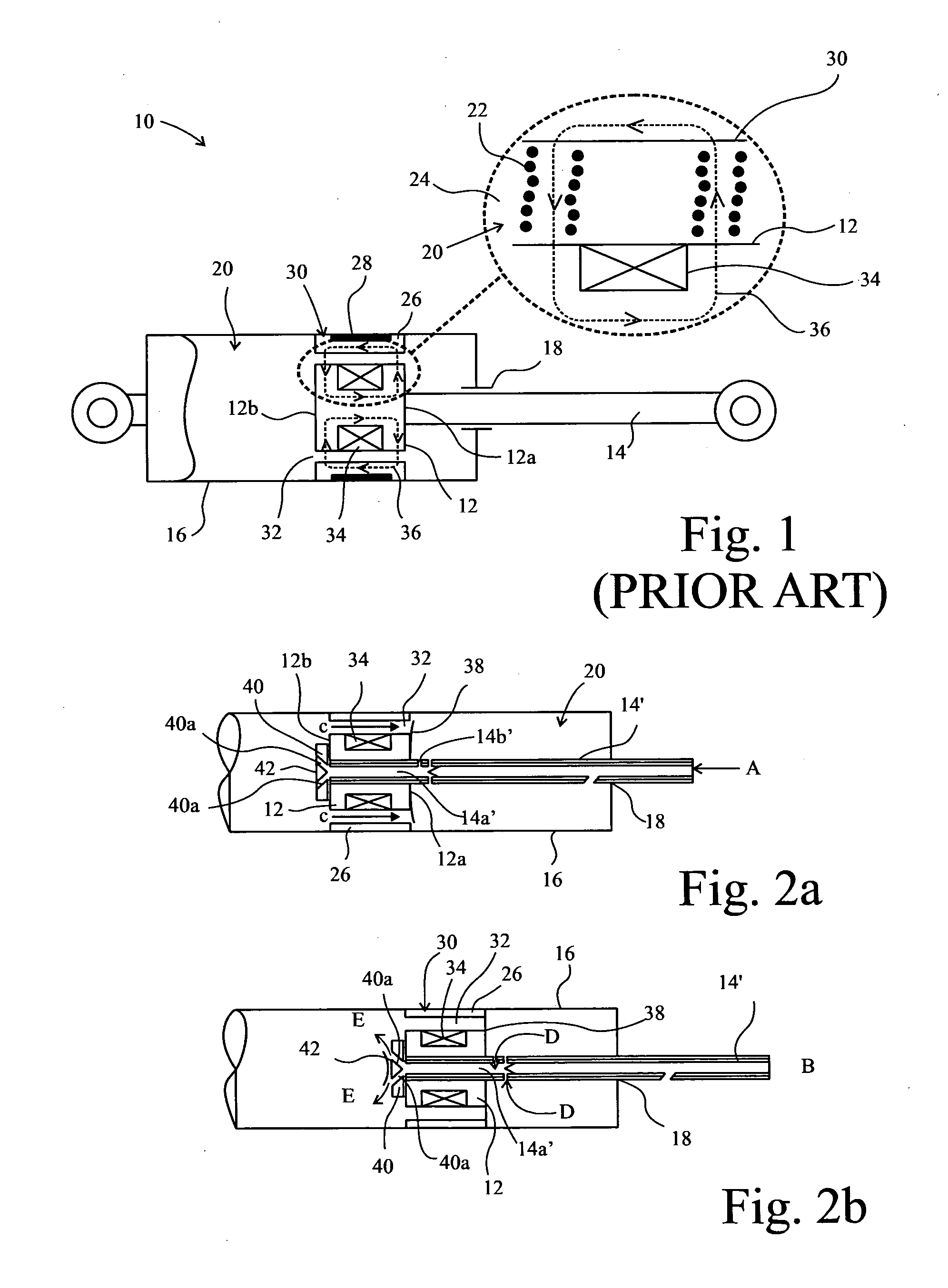
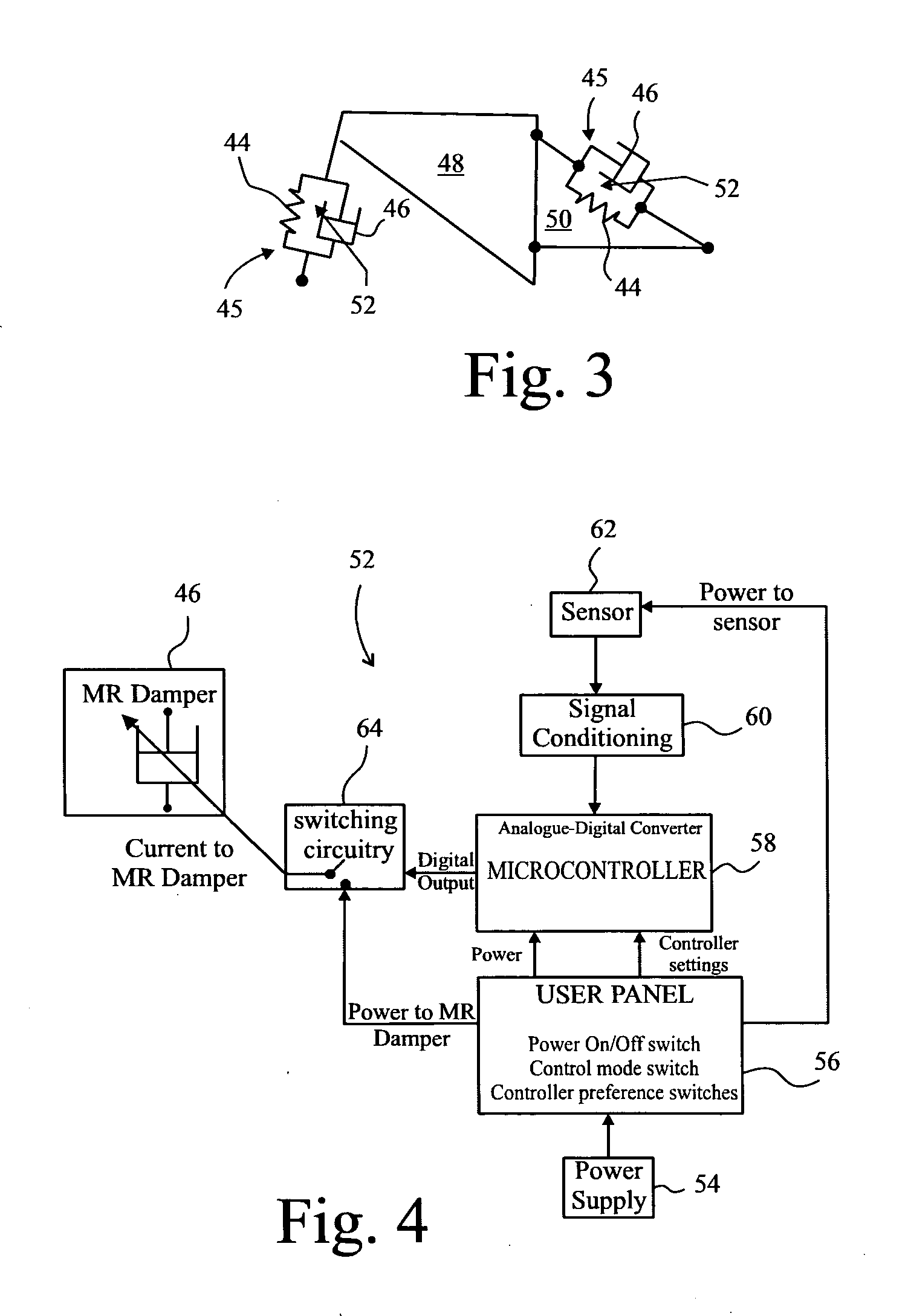
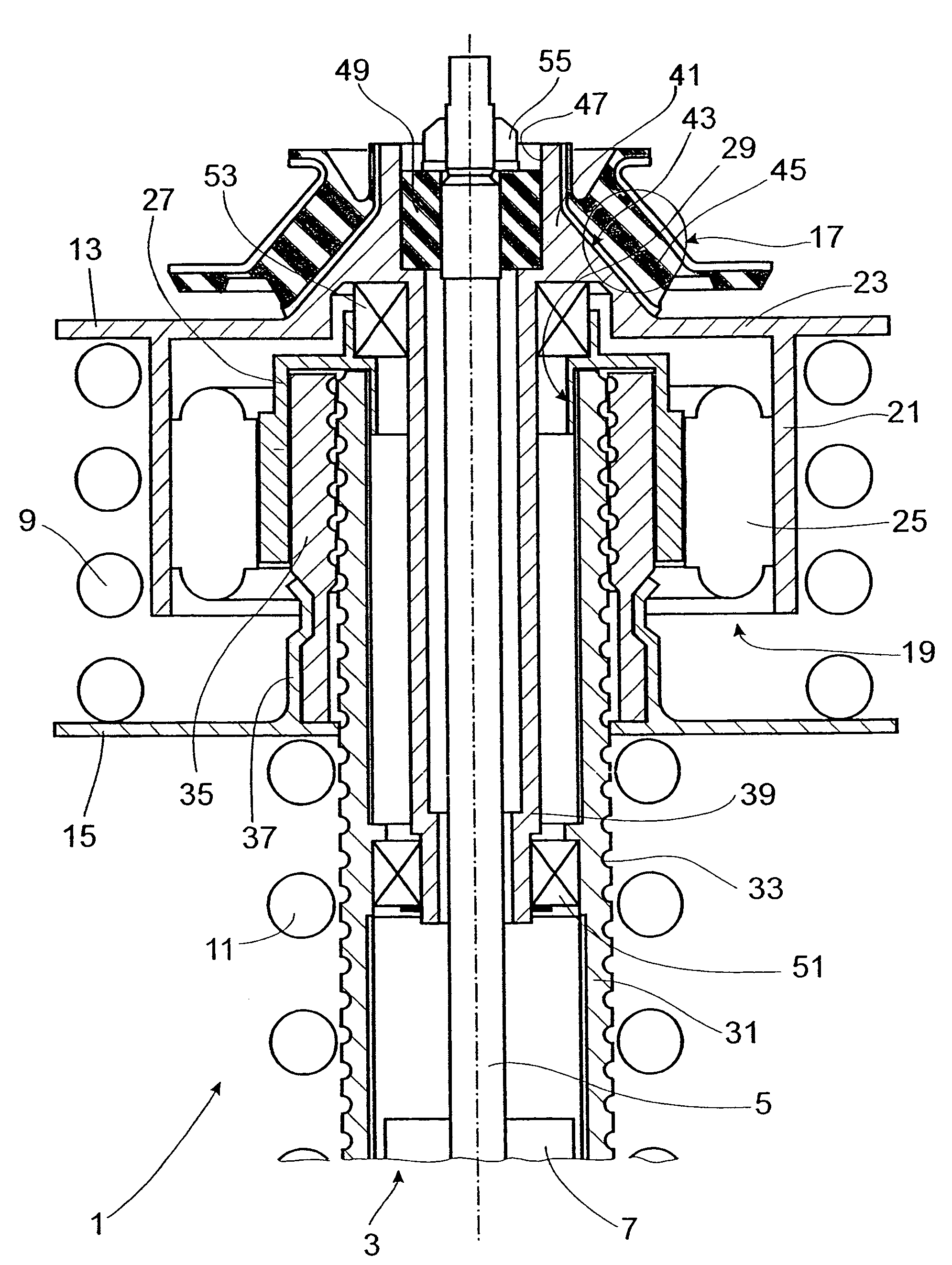
Magnetorheological fluid-controlled vehicle suspension damper
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
System and method for vehicle chassis control
ActiveUS20140312580A1Reduces or even eliminates tyre scrubReduce impactCyclesSteering deviceHydraulic cylinderHydraulic fluid
There is provided a vehicle comprising a chassis, two surface-engaging front wheels, at least one surface-engaging rear wheel and a propulsion unit for driving either the front wheels or the rear wheel or wheels. Each front wheel being connected to the chassis by means of a front wheel support assembly, wherein the front wheel support assembly comprises a hydraulic cylinder associated with each front wheel. Each hydraulic cylinder comprises a housing connected to one of the chassis and the front wheel support assembly, and a piston connected to the other of the front wheel support assembly and the chassis. The piston is moveable within the housing and arranged to divide the hydraulic cylinder into first and second chambers each having respective ports arranged to allow hydraulic fluid to enter and exit the respective chamber, the ports of the first chambers of each hydraulic cylinder being in fluid communication and the ports of the second chambers of each hydraulic cylinder being in fluid communication such that movement of hydraulic fluid from the first or second chamber of one hydraulic cylinder to the respective first or second chamber of the other hydraulic cylinder displaces the pistons of the hydraulic cylinders in opposing directions relative to the respective housings to enable the vehicle to tilt.
Owner:GALE DAVID ANDREW
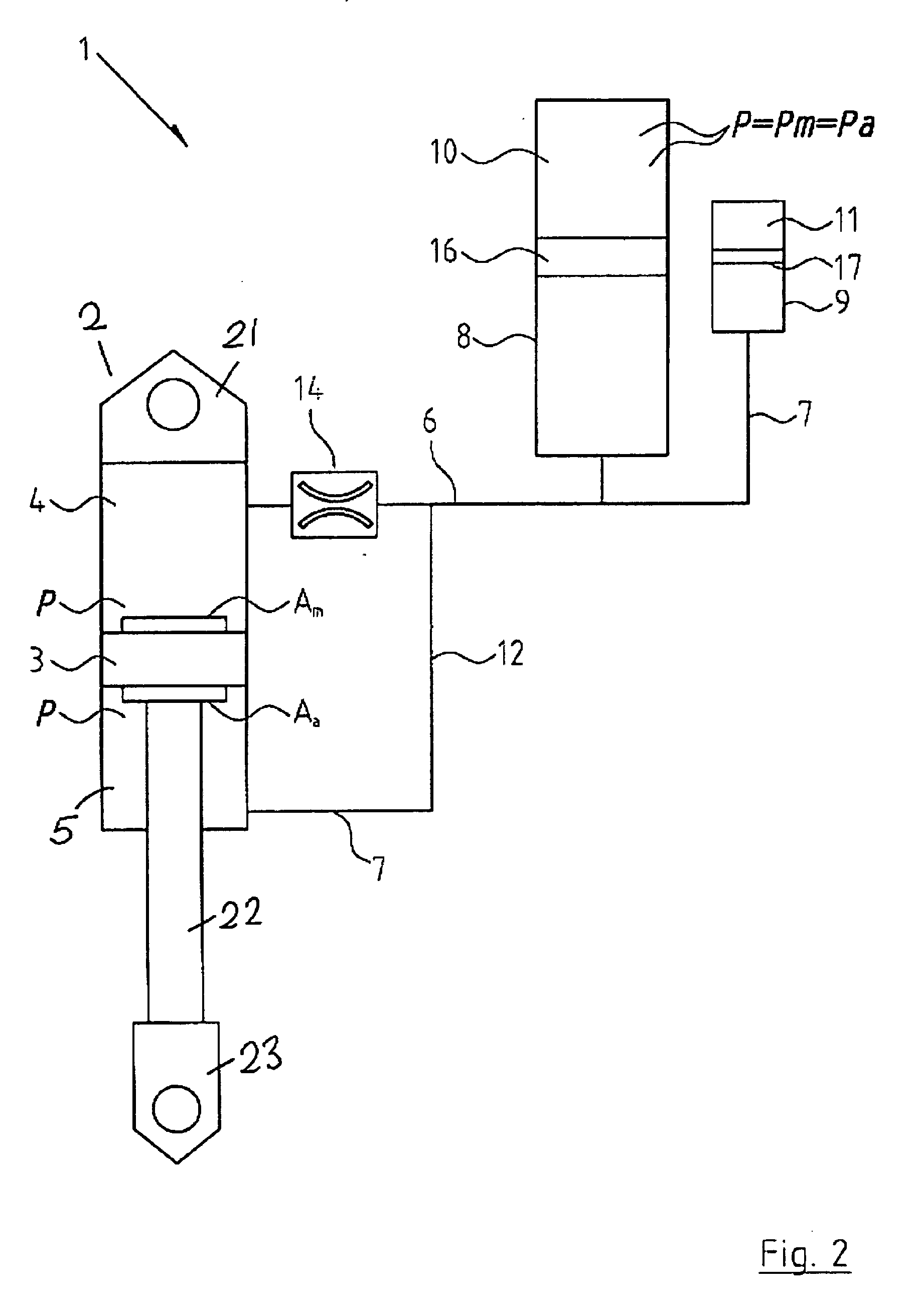
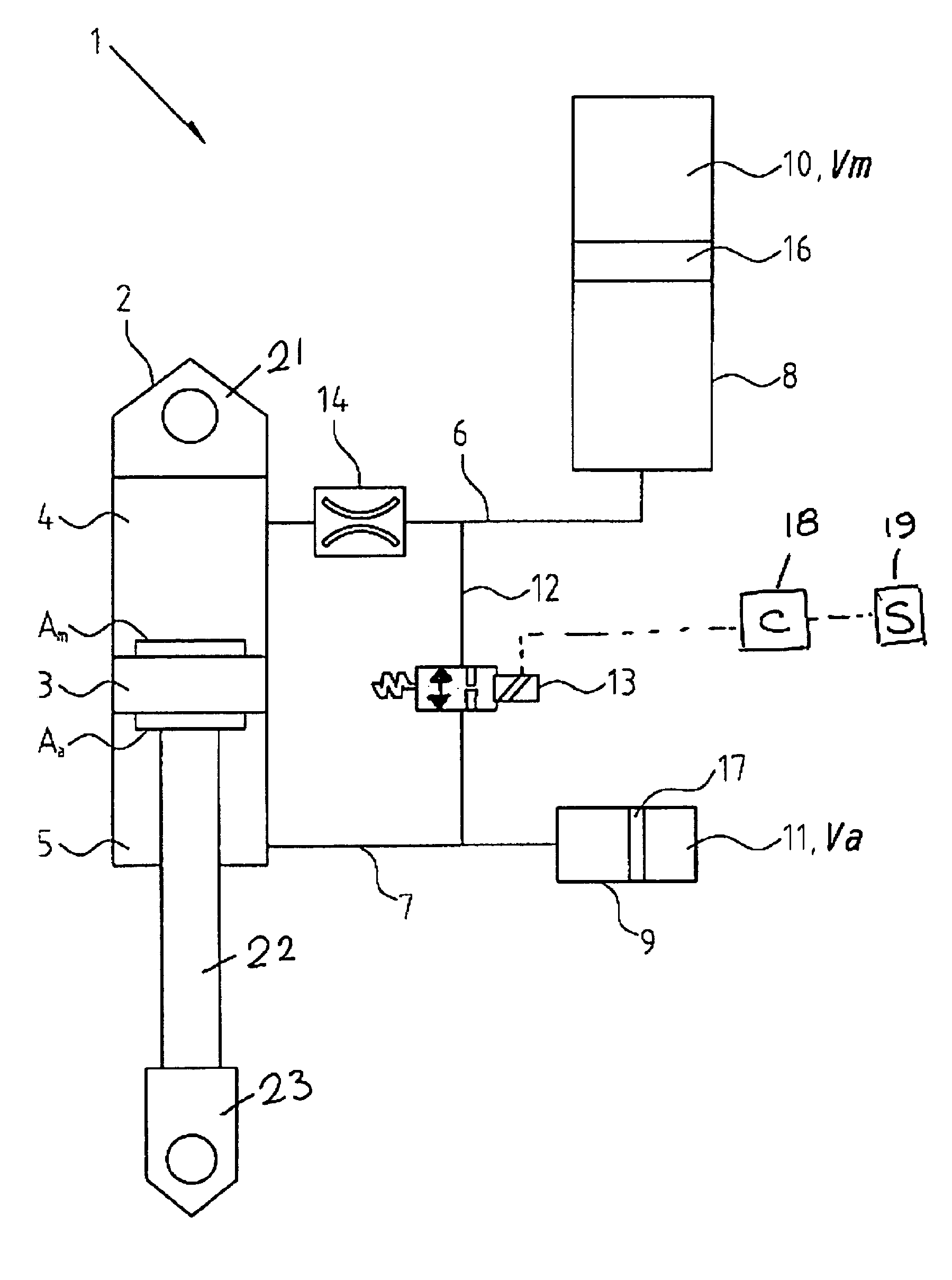
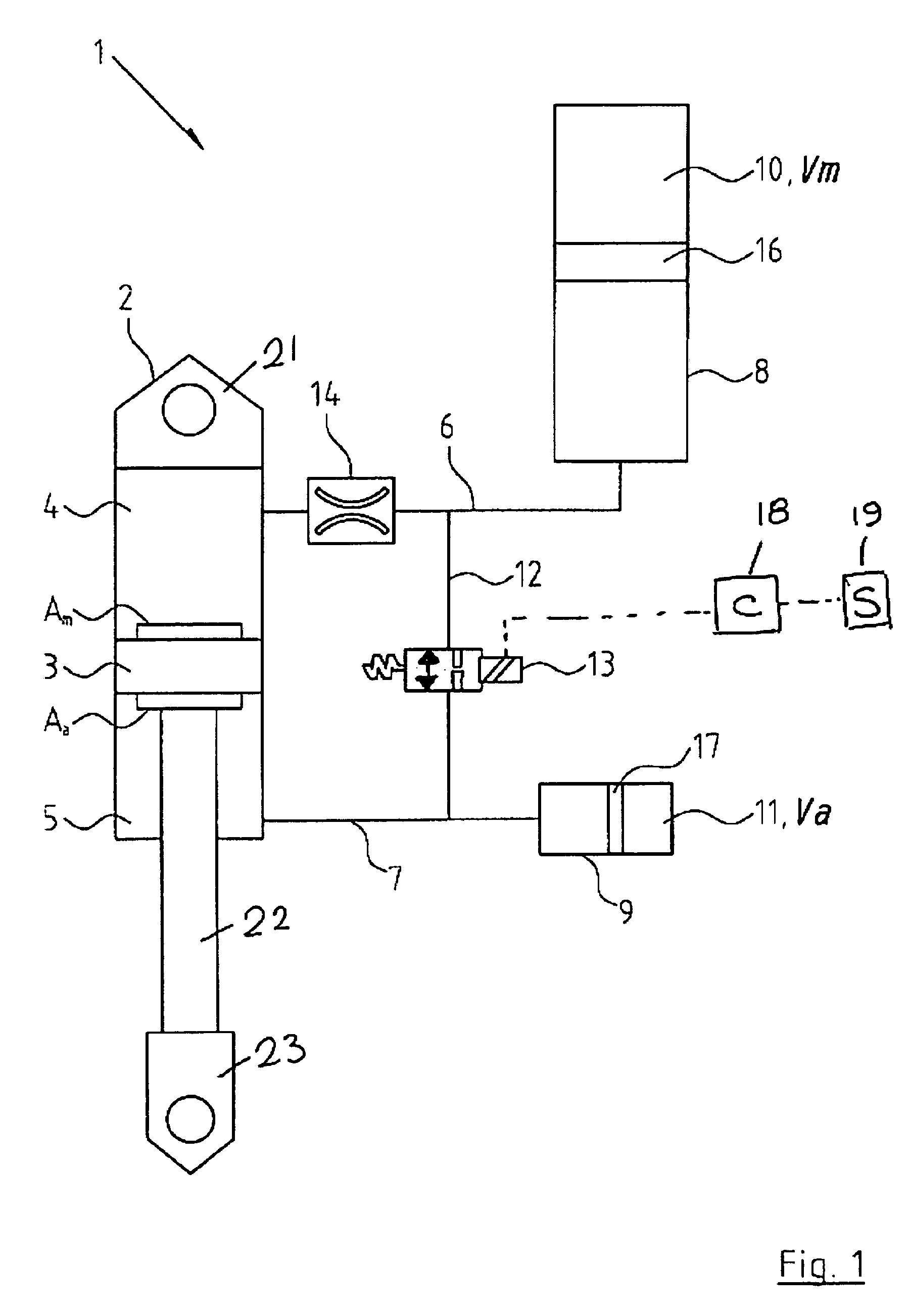
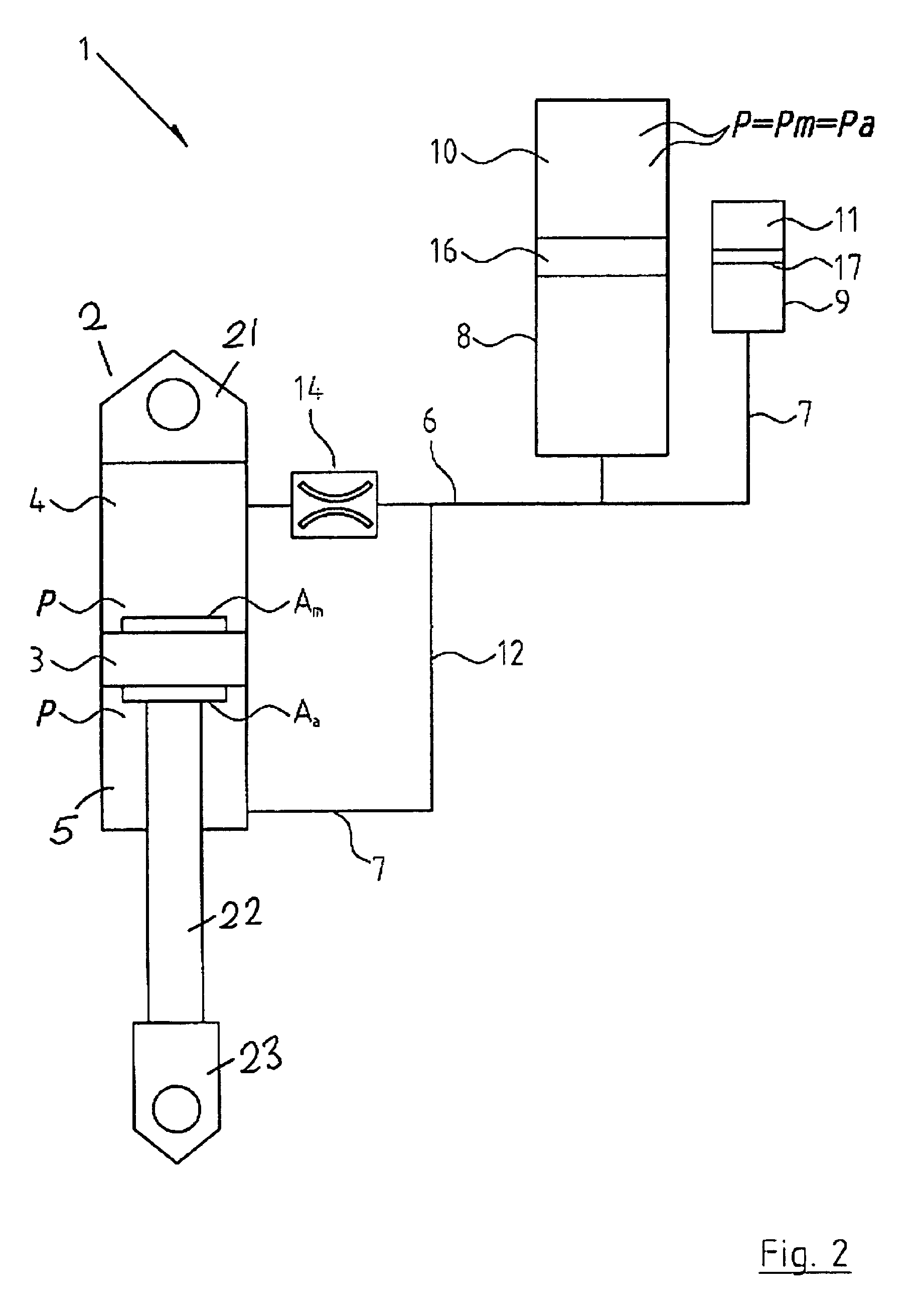
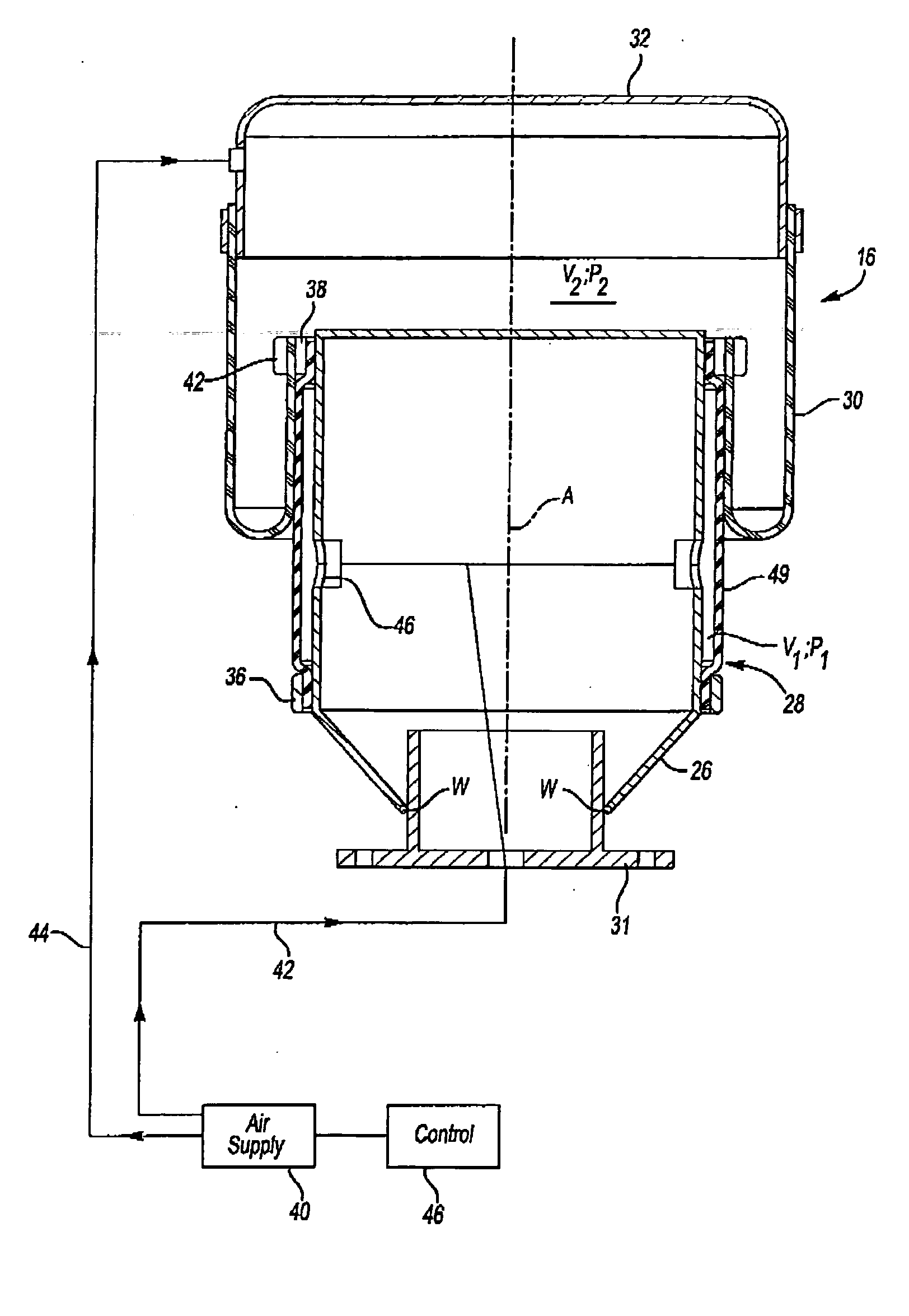
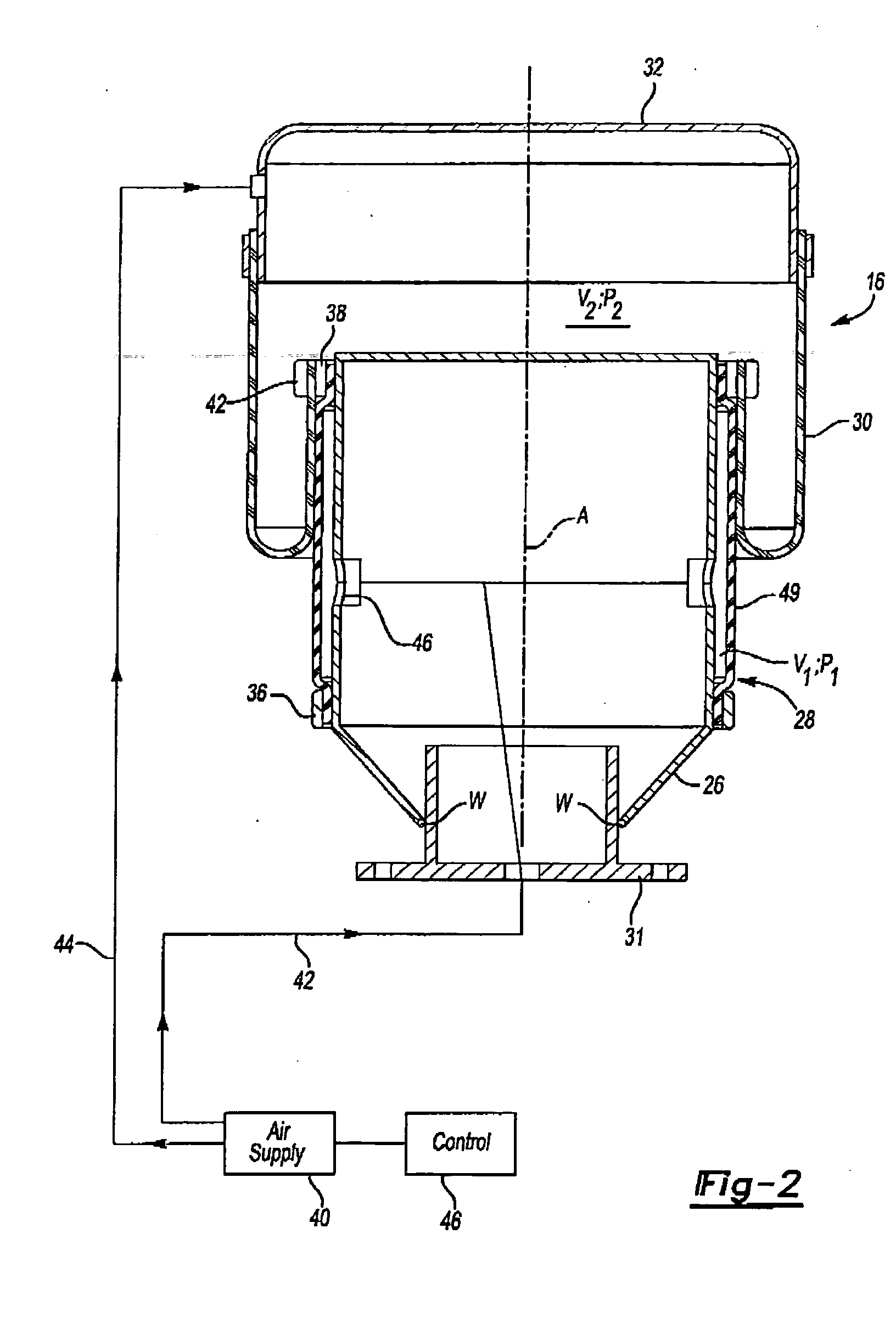
Vehicle suspension spring system
InactiveUS20070039790A1Displacement minimizationMinimising rollSpringsResilient suspensionsHydraulic cylinderIsolation valve
A vehicle suspension spring system for a vehicle wheel station includes a hydraulic cylinder or strut having a piston which divides the cylinder volume into a main oil volume and an annular oil volume. The main oil volume communicates via a first oil passage with a first accumulator having a main gas volume. The annular oil volume communicates via a second oil passage with a second accumulator having an auxiliary gas volume. The oil in each accumulator is separated from the gas by a separator piston or diaphragm. A third oil passage with an isolating valve interconnects said first and second oil passages. Operation of the isolating valve is regulated by a controller. At least one sensor for sensing a parameter associated with vehicle attitude is connected to the controller. The controller is operable for switching the isolating valve between open and closed positions for altering spring stiffness of the strut in response to said sensed vehicle attitude parameter when the vehicle is in motion.
Owner:TECH INVESTMENTS
Vehicle suspension spring system
InactiveUS7779974B2Eliminate the effects ofDisplacement minimizationSpringsResilient suspensionsHydraulic cylinderIsolation valve
A vehicle suspension spring system for a vehicle wheel station includes a hydraulic cylinder or strut having a piston which divides the cylinder volume into a main oil volume and an annular oil volume. The main oil volume communicates via a first oil passage with a first accumulator having a main gas volume. The annular oil volume communicates via a second oil passage with a second accumulator having an auxiliary gas volume. The oil in each accumulator is separated from the gas by a separator piston or diaphragm. A third oil passage with an isolating valve interconnects said first and second oil passages. Operation of the isolating valve is regulated by a controller. At least one sensor for sensing a parameter associated with vehicle attitude is connected to the controller. The controller is operable for switching the isolating valve between open and closed positions for altering spring stiffness of the strut in response to said sensed vehicle attitude parameter when the vehicle is in motion.
Owner:TECH INVESTMENTS
Methods and apparatus for controlling a fluid damper
A method and apparatus for a fluid damper comprising a first fluid-filled chamber, a second chamber filled with a fluid having variable flow characteristics and at least partially displaceable by the first fluid, and a gas chamber, the gas chamber compressible due to the displacement of the second chamber. In one embodiment, the fluid in the second chamber is a variable rheology fluid.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Dual airbag airspring
ActiveUS20050173851A1Rapid pressure changeRapid volume changeLiquid springsResilient suspensionsAir springEngineering
An air spring assembly includes a primary airbag mounted to a piston air bag such that the piston airbag provides a rolling surface for the primary airbag. A change in the piston airbag pressure changes the effective rate of the primary air spring. A relatively small change in the piston airbag volume provides a change in the spring rate of air spring assembly as the diameter of the rolloff surface is selectively modified.
Owner:ARVINMERITOR TECH
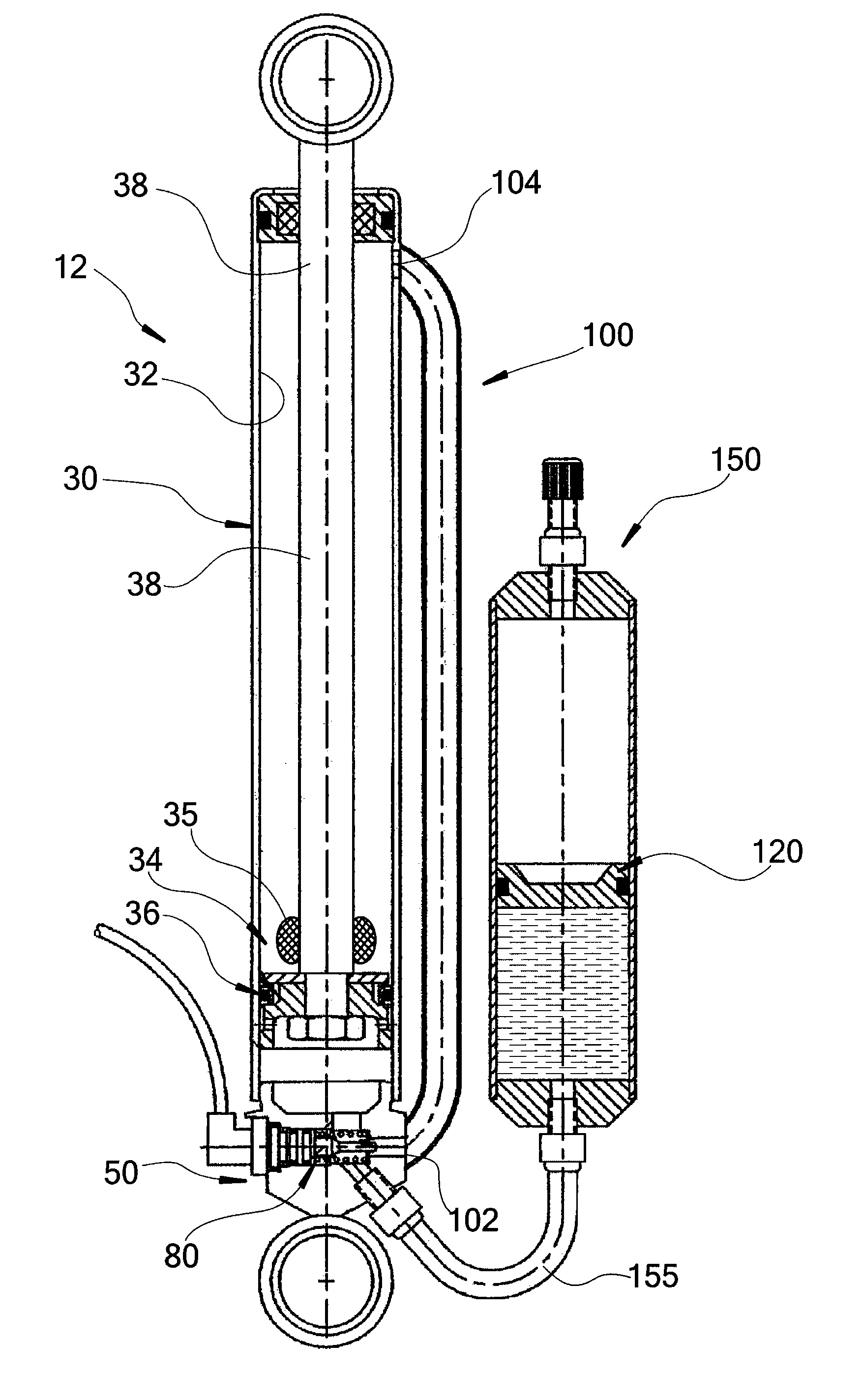
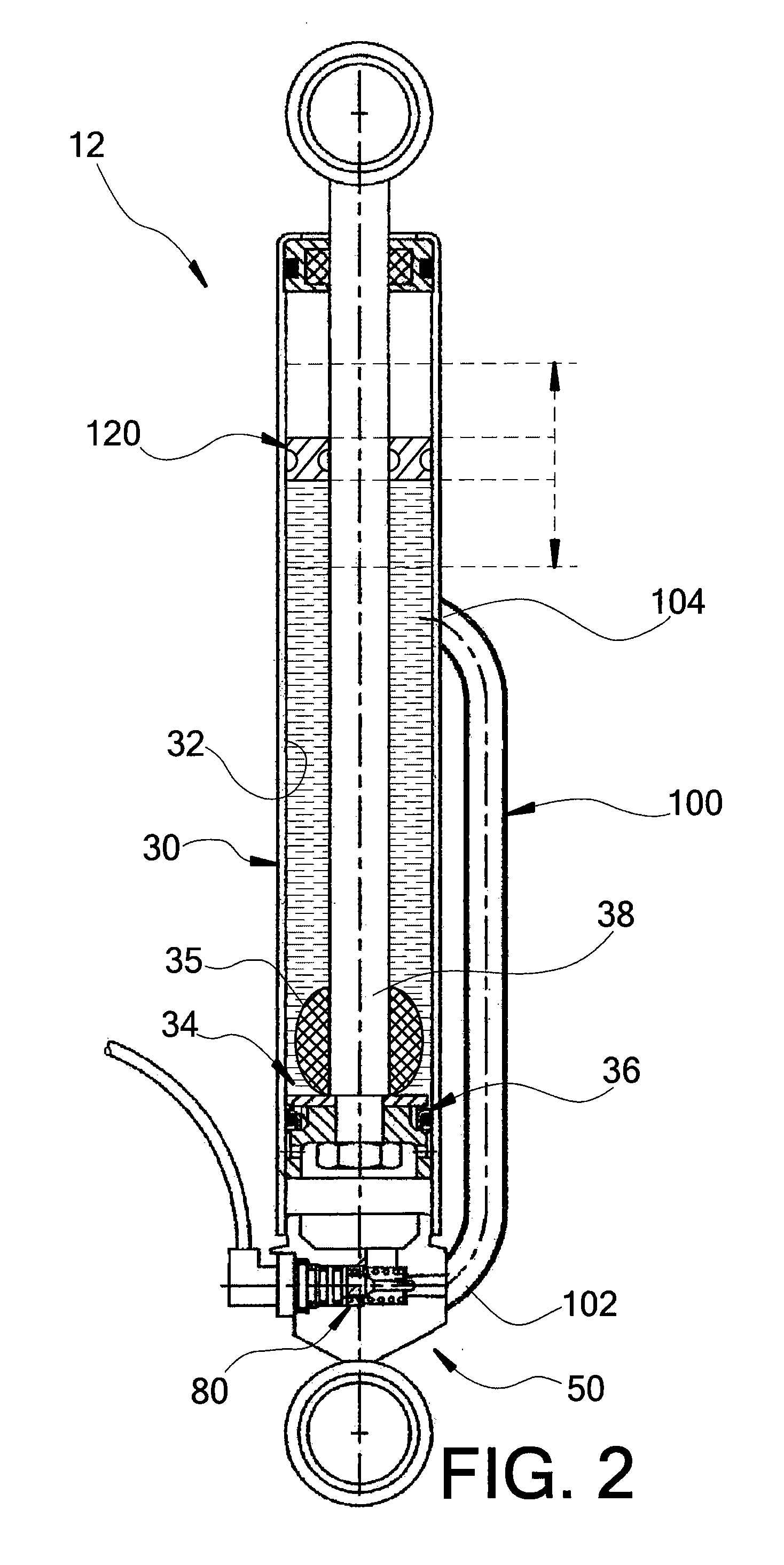
Methods and Apparatus for Suspension Adjustment
A shock absorber includes a gas spring cylinder containing a piston moveable between an extended position and a compressed position within the gas spring cylinder. A mechanical actuator is arranged whereby a bleed port is automatically closed when the gas spring is compressed to a predetermined position corresponding to a desired sag setting. In one embodiment, the position corresponds to a predetermined sag setting whereby the gas spring is partially compressed. In another embodiment, a proper sag setting is determined through the use of a processor and sensor that in one instance measure a position of shock absorber components to dictate a proper sag setting and in another instance calculate a pressure corresponding to a preferred sag setting.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com