Patents
Literature
245results about How to "Increase damping force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Isolator for alternator pulley
InactiveUS7207910B2Dampen rotational movementIncrease damping forceYielding couplingChain/belt transmissionSerpentine beltAlternator
A decoupler for an alternator pulley in a serpentine drive system has a resilient, helical spring member that couples the alternator pulley with a hub structure through a spring retaining member. A bushing is disposed between the spring retaining member and the hub structure to facilitate sliding engagement therebetween. An annular sleeve member is disposed between the spring member and the alternator pulley to facilitate sliding engagement therebetween. The spring member is connected at one end thereof to the hub structure and connected at an opposite end thereof to the spring retaining member. The resilient spring member transmits the driven rotational movements of the alternator pulley by the serpentine belt to the hub structure such that the alternator shaft is rotated in the same direction as the alternator pulley while being capable of instantaneous relative resilient movements in opposite directions with respect to the alternator pulley during the driven rotational movement.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
Wheelchair with damping mechanism
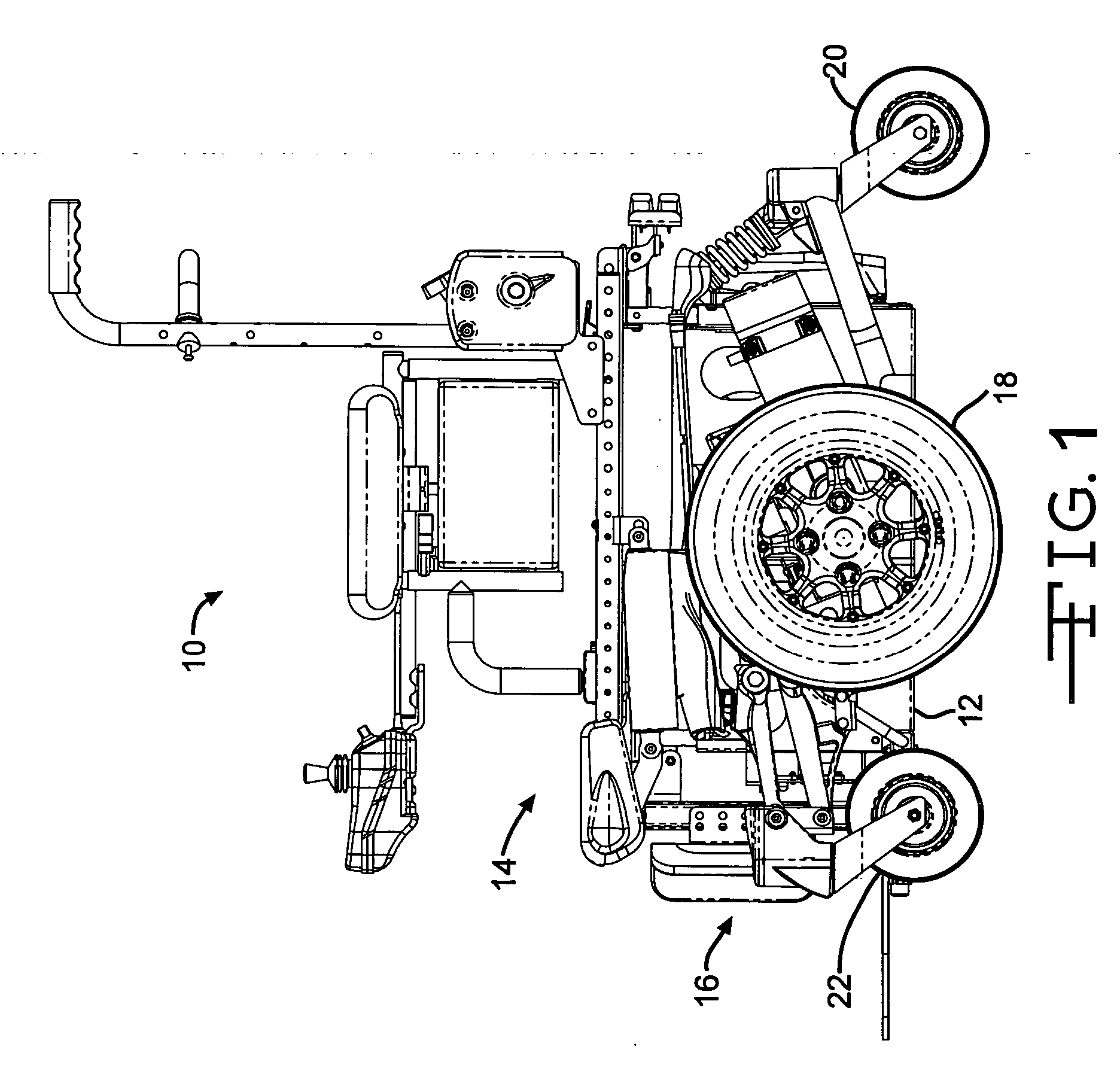
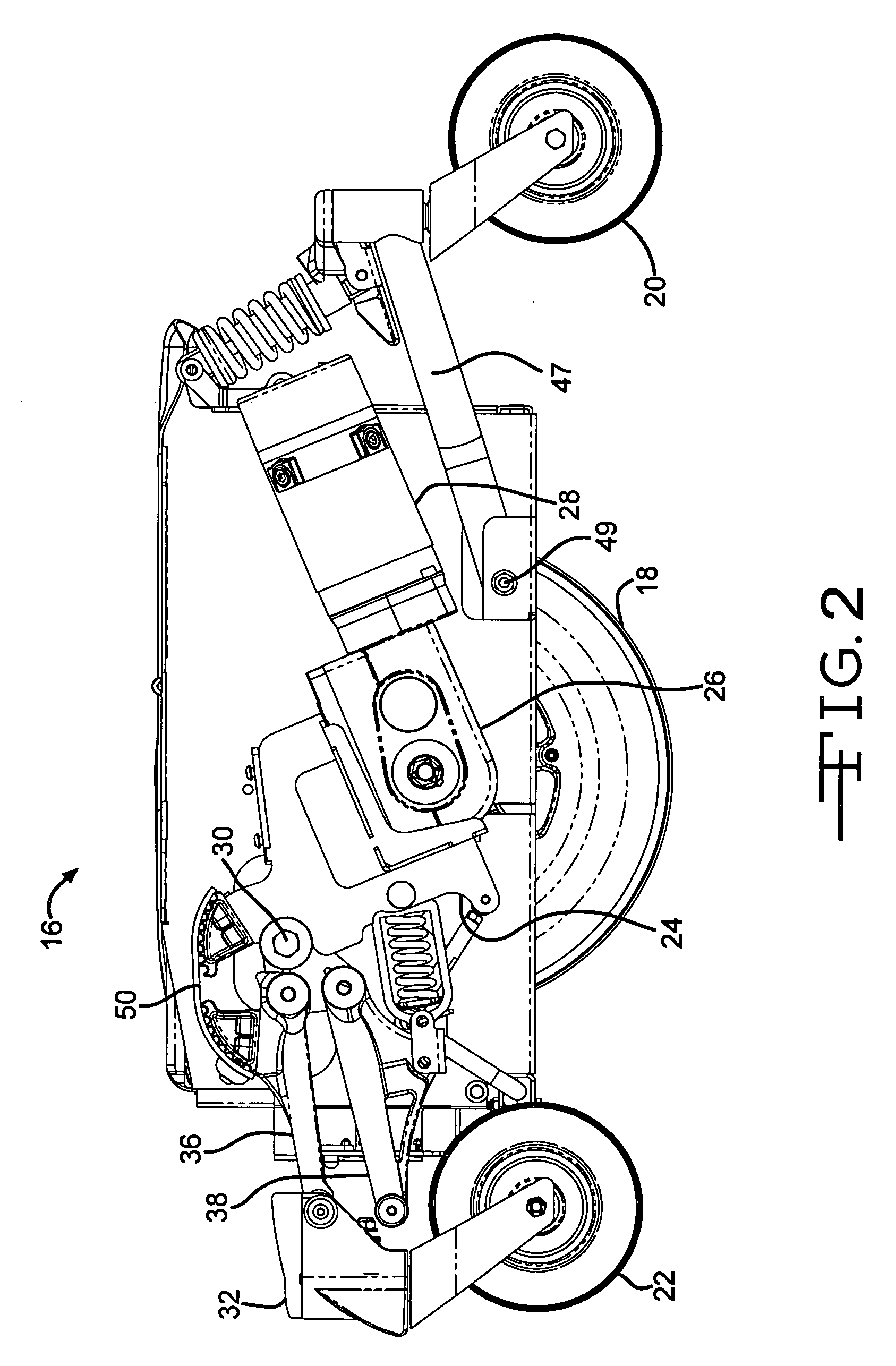
InactiveUS20060076748A1Reduce forward pitchIncrease damping forceWheelchairs/patient conveyanceRigid suspensionsWheelchairEngineering
A wheelchair has a damping system to reduce the forward pitch of the wheelchair upon sudden deceleration or upon descent of a sloped surface. The damping system includes a clamp that selectively grips a shaft.
Owner:SUNRISE MEDICAL HHC INC
Control device of variable damping force damper
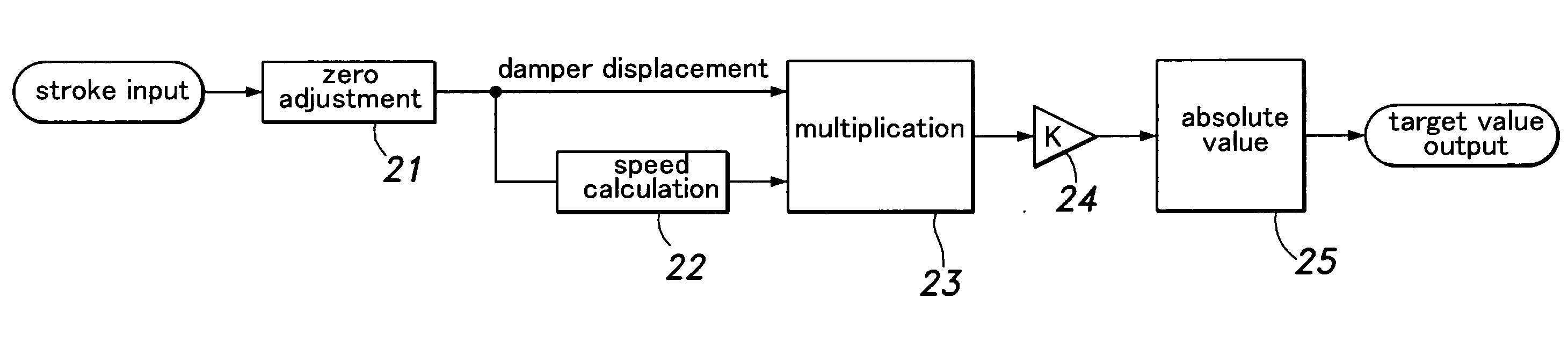
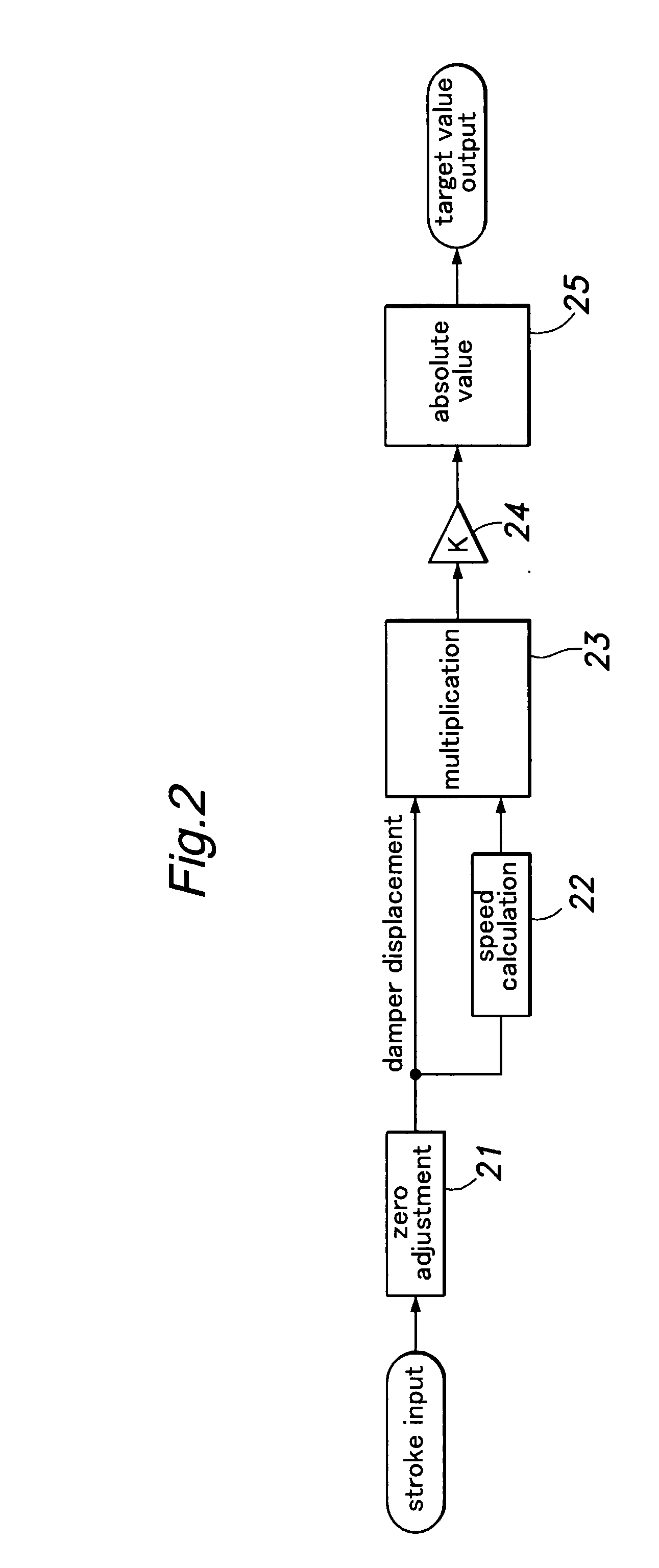
ActiveUS20080009992A1Optimizing damping characteristicHigh levelSpringsDigital data processing detailsRelative displacementRelative velocity
A control device of a variable damping force damper for controlling a damping force of a damper used in a vehicle suspension system comprises: relative displacement detection means for detecting a value corresponding to a relative displacement between a vehicle body and a wheel in a vertical direction; relative speed detection means for detecting a value corresponding to a relative speed between the vehicle body and the wheel in the vertical direction; multiplying means for multiplying the value corresponding to the relative displacement and the value corresponding to the relative speed; and means for setting a damping force control target value of the damper based on the output from the multiplying means.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Hydraulic shock absorber
ActiveUS8991571B2Increase damping forceIncrease changeSpringsShock absorbersEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Suspension system for a row crop planter unit
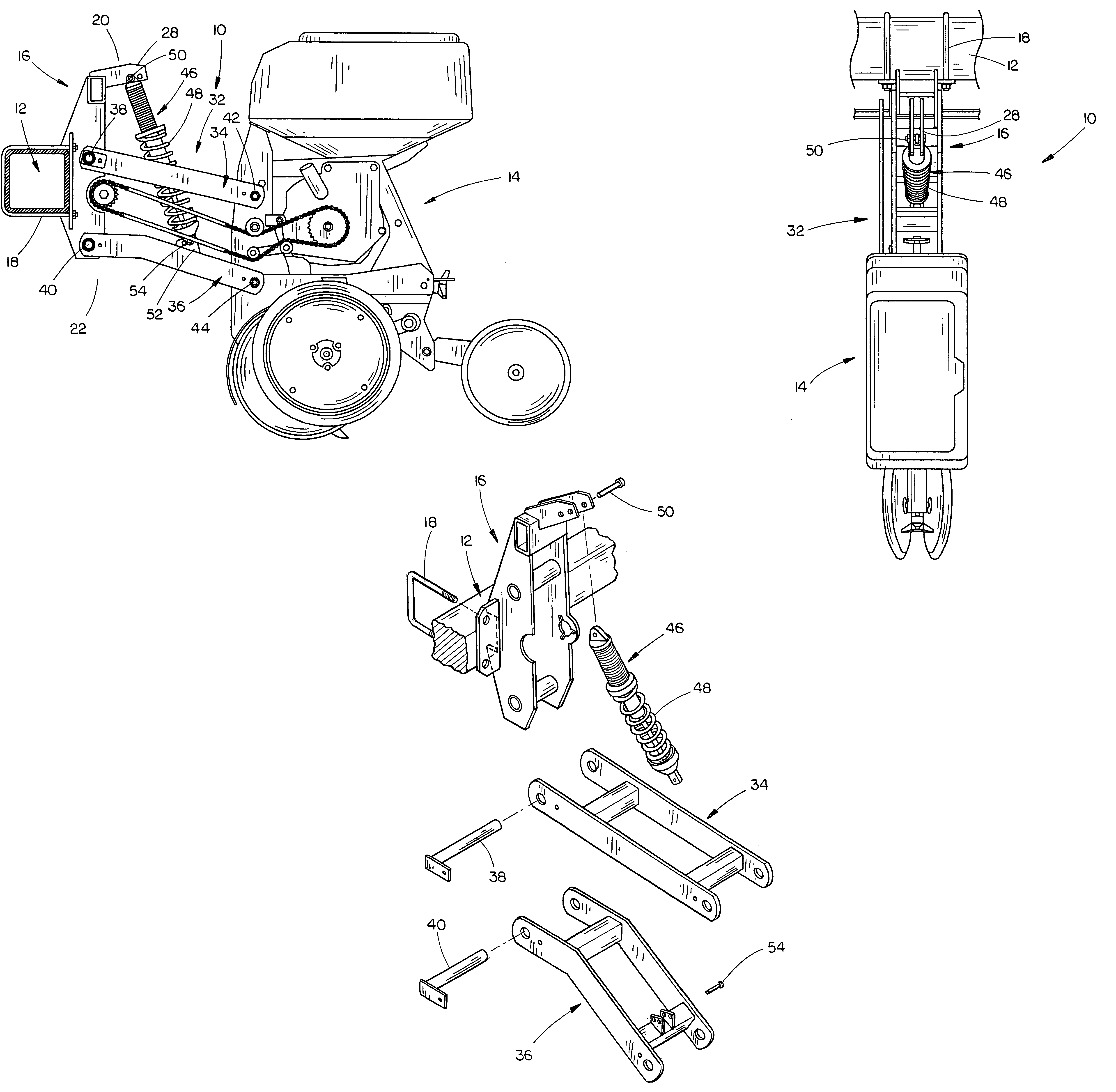
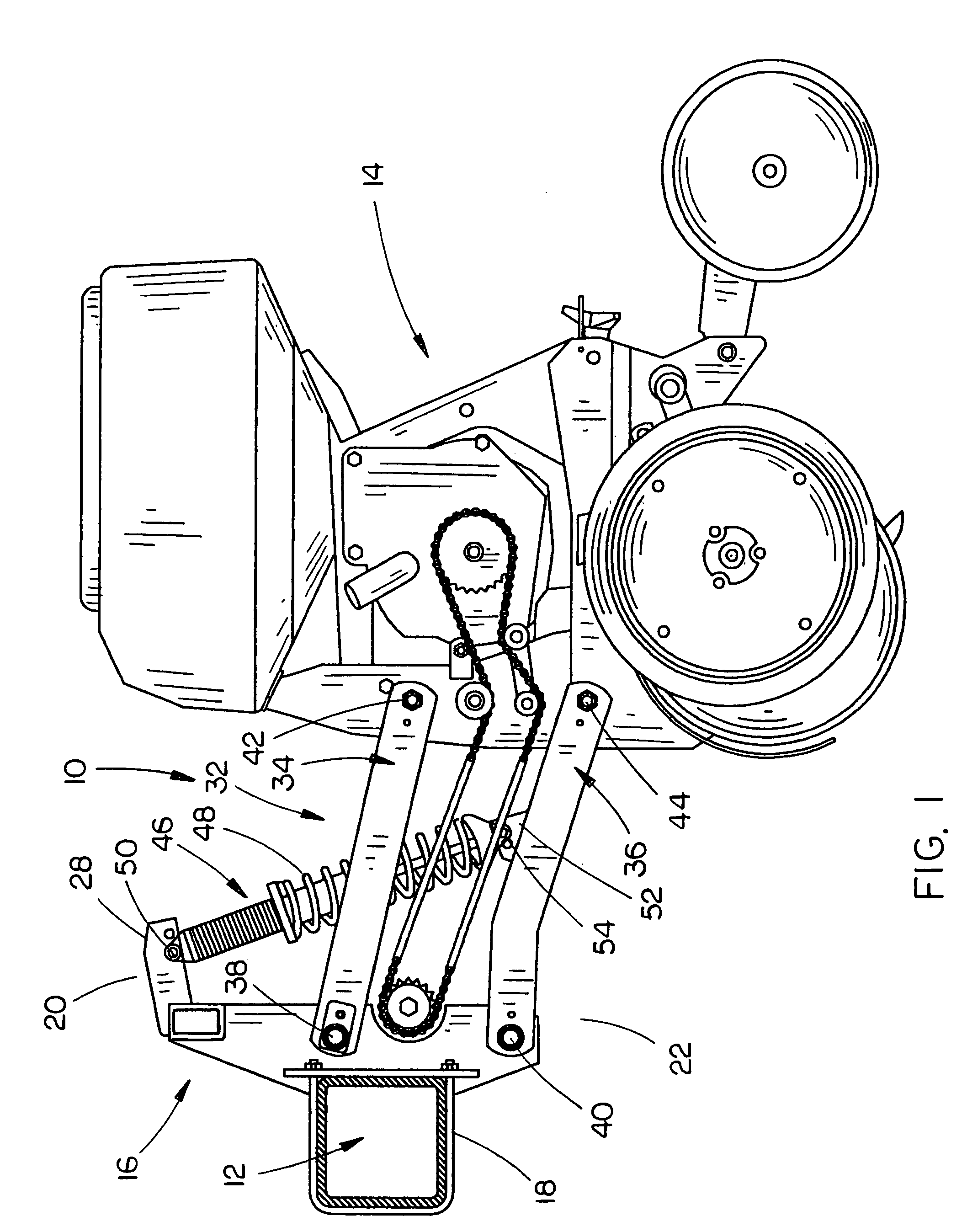
ActiveUS7401561B1Economical to manufactureDurable in usePlantingFurrow making/coveringEngineeringToolbar
A suspension system for a row crop planter unit which includes a shock absorber extending between the planter unit mounting bracket and the parallel arm linkage which vertically mounts the planter unit to a toolbar. The shock absorber permits the planter unit to move more quickly in the rebound cycle than in the compression cycle to reduce row unit bounce.
Owner:KURZ CLARE D
Shock absorbing device
ActiveUS20110056783A1Improvement in passenger comfortReduce gradientSpringsLiquid based dampersEngineeringPiston
A shock absorbing device includes a cylinder. A partition wall member is inserted into the cylinder to be free to slide and partitions an interior of the cylinder into two operating chambers. A passage connects the two operating chambers. A free piston is inserted into a pressure chamber to be free to slide and partitions the pressure chamber into one chamber that communicates with one operating chamber via a one side flow passage and another chamber that communicates with the other operating chamber via another side flow passage. A spring element generates a biasing force for suppressing displacement of the free piston relative to the pressure chamber. One or both of a bypass flow passage that connects the other chamber and the one operating chamber and a bypass flow passage that connects the one chamber and the other operating chamber is provided. A relief valve is provided in the bypass flow passage.
Owner:KYB CORP
Hydraulic shock absorber
A hydraulic shock absorber in which the flow of hydraulic fluid induced in each of extension and compression hydraulic fluid passages, by sliding movement of a piston, is controlled by a main disk valve to generate damping force. The valve opening pressure of the main disk valve is adjusted by the pressure in a back-pressure chamber. In a low piston speed region, the main disk valve closes a back-pressure chamber inlet passage. Therefore, the pressure in the backpressure chamber will not rise, and sufficiently small damping force is obtained. When the main disk valve opens, the backpressure chamber inlet passage opens simultaneously. Consequently, the pressure in the backpressure chamber rises, and the damping force increases.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
Hydraulic shock absorber
In the disclosed hydraulic shock absorber, the flow of hydraulic fluid induced in each of extension and compression hydraulic fluid passages by sliding movement of a piston is controlled by a main disk valve to generate damping force. The valve opening pressure of the main disk valve is adjusted by the pressure in a back-pressure chamber. In a low piston speed region, the main disk valve closes a back-pressure chamber inlet passage. Therefore, the pressure in the back-pressure chamber will not rise, and sufficiently small damping force is obtained. When the main disk valve opens, the back-pressure chamber inlet passage opens simultaneously. Consequently, the pressure in the back-pressure chamber rises, and the damping force increases.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
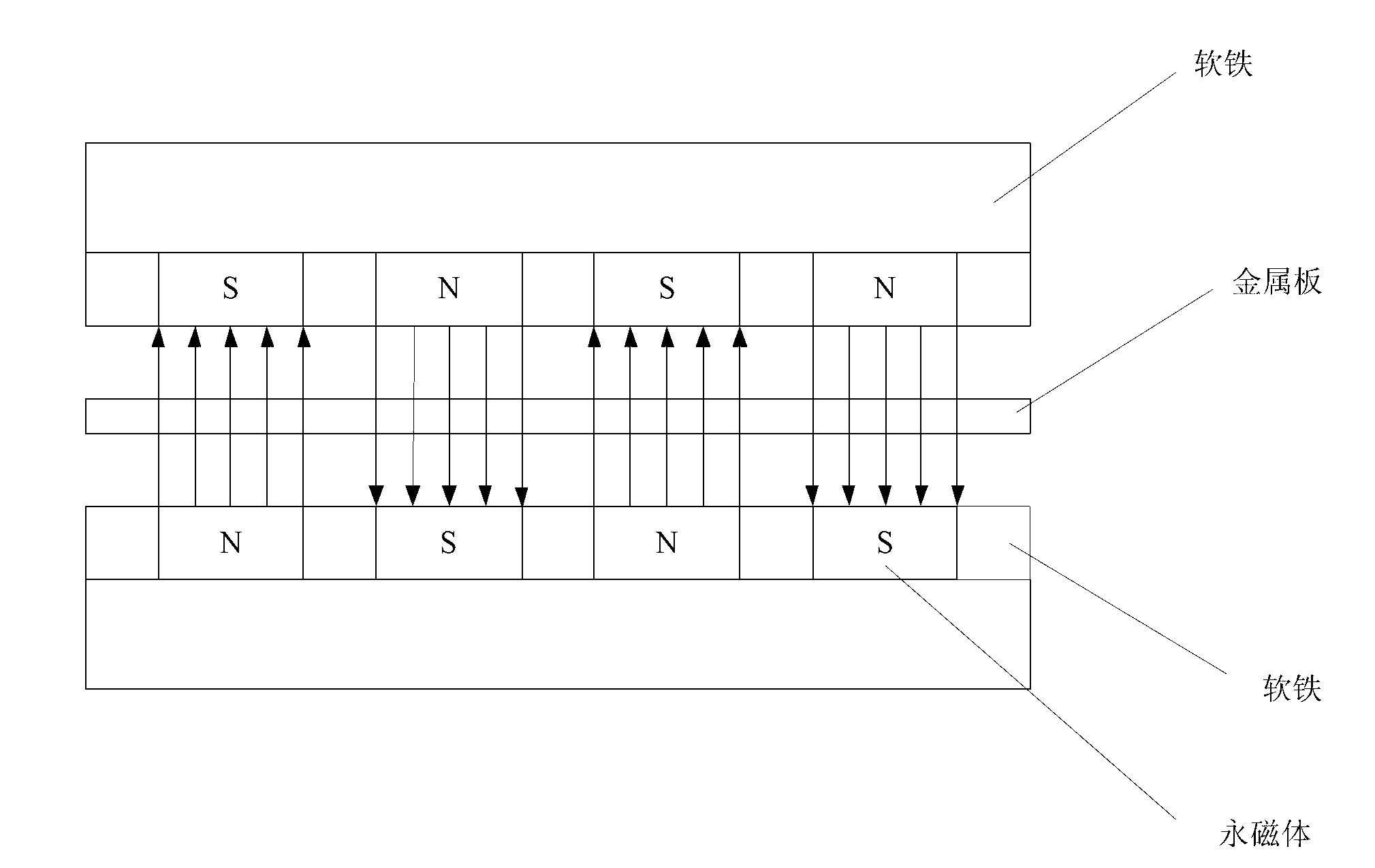
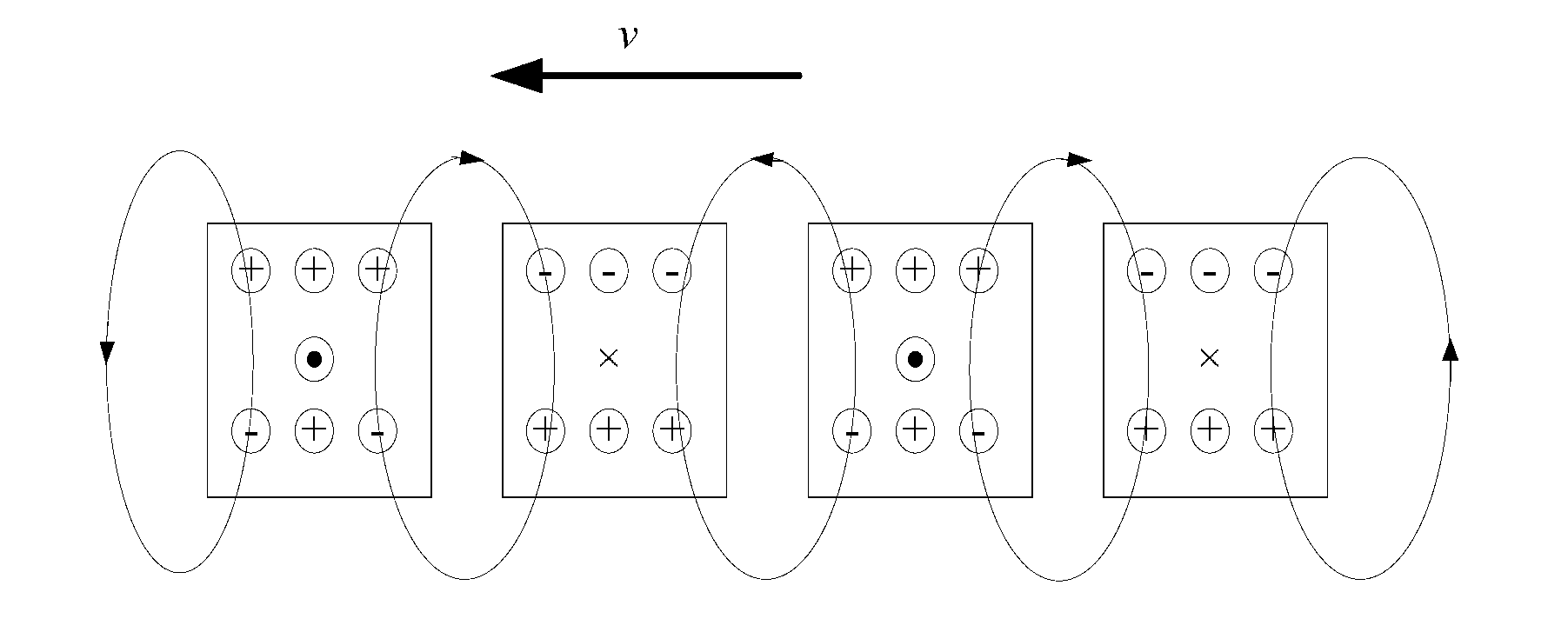
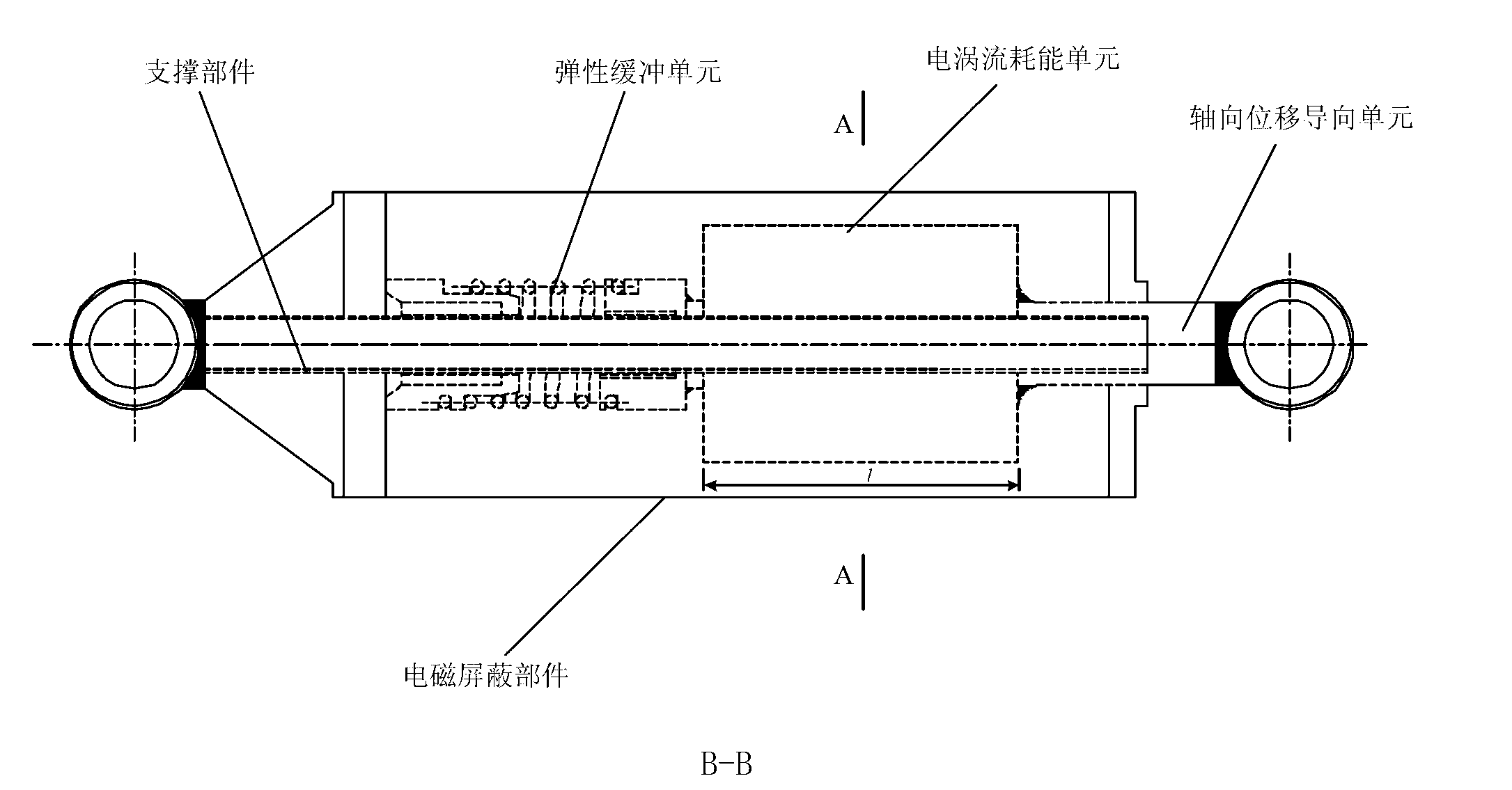
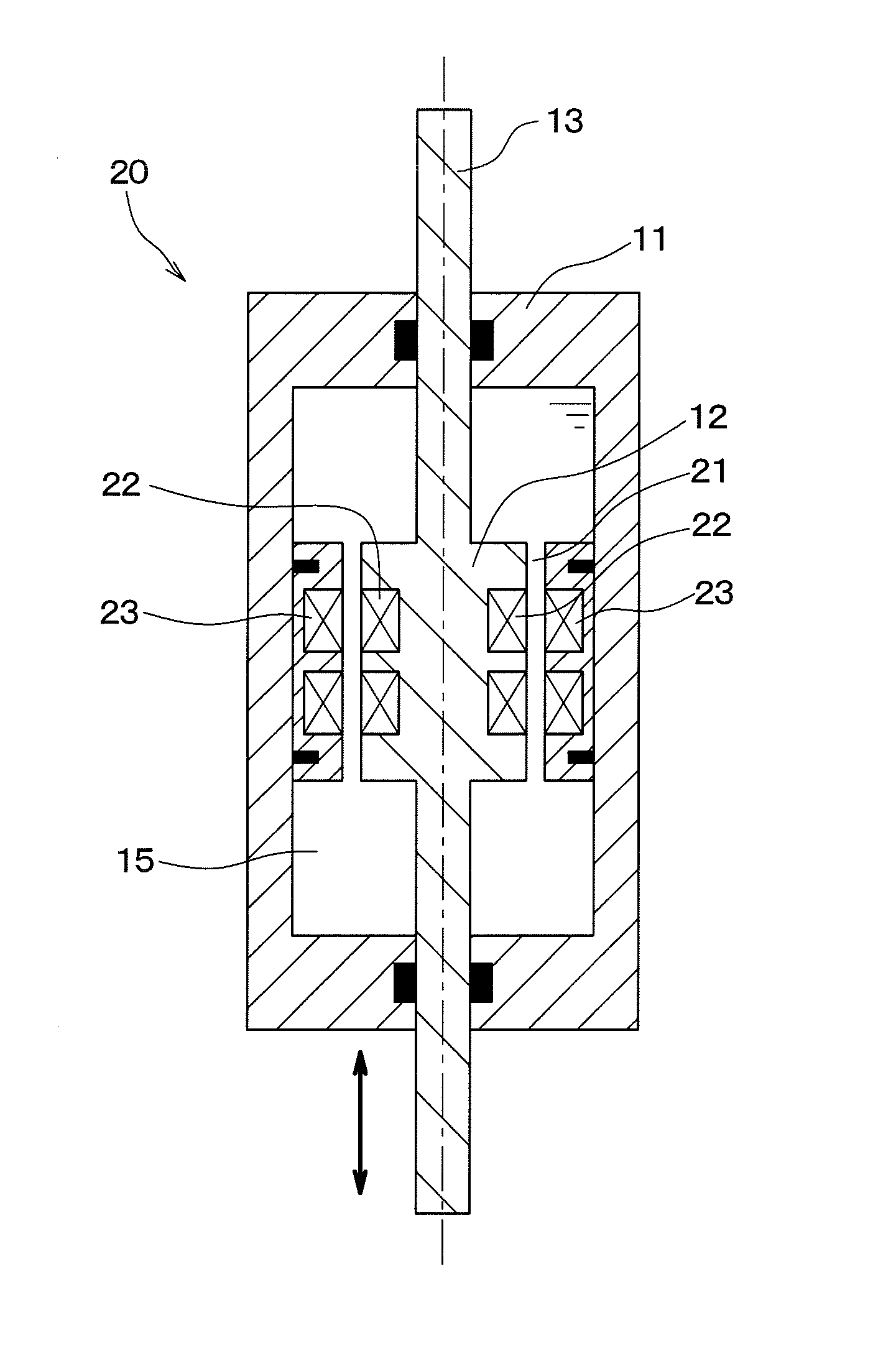
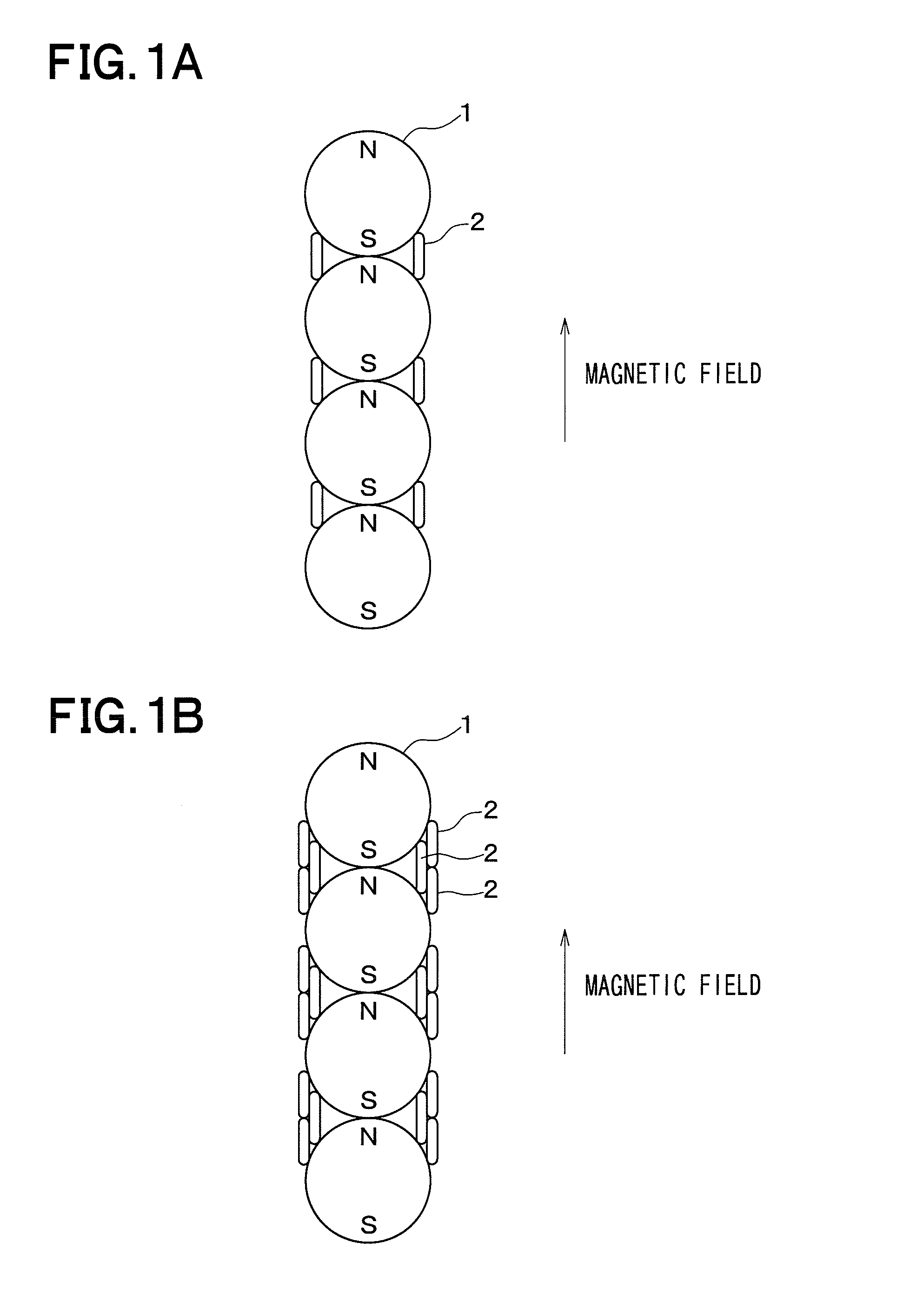
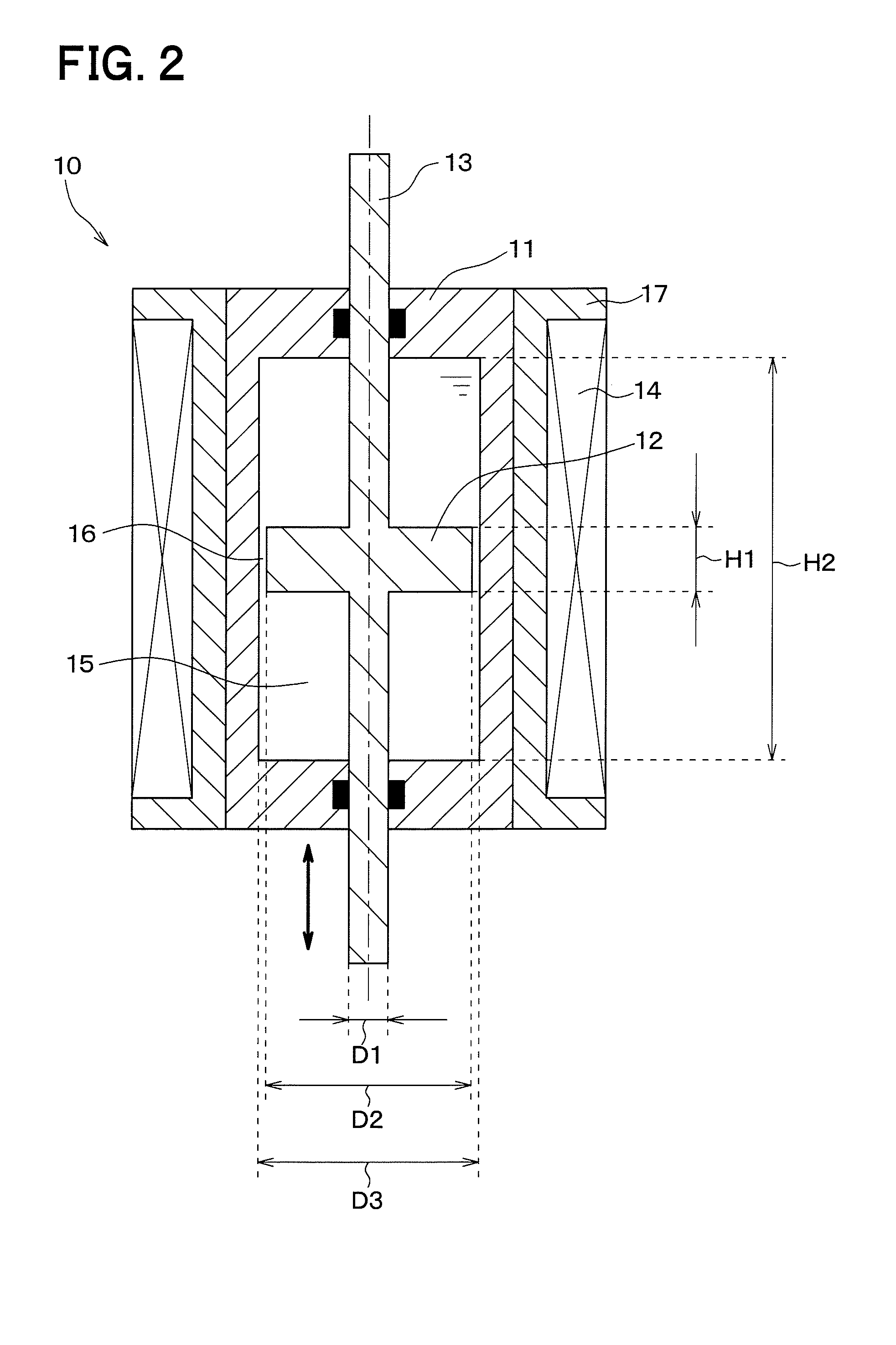
Array-type novel high-performance eddy current damper
InactiveCN102797786ACompact structureHigh damping force to damper mass ratioMagnetic springsShock absorbersElectricityEngineering
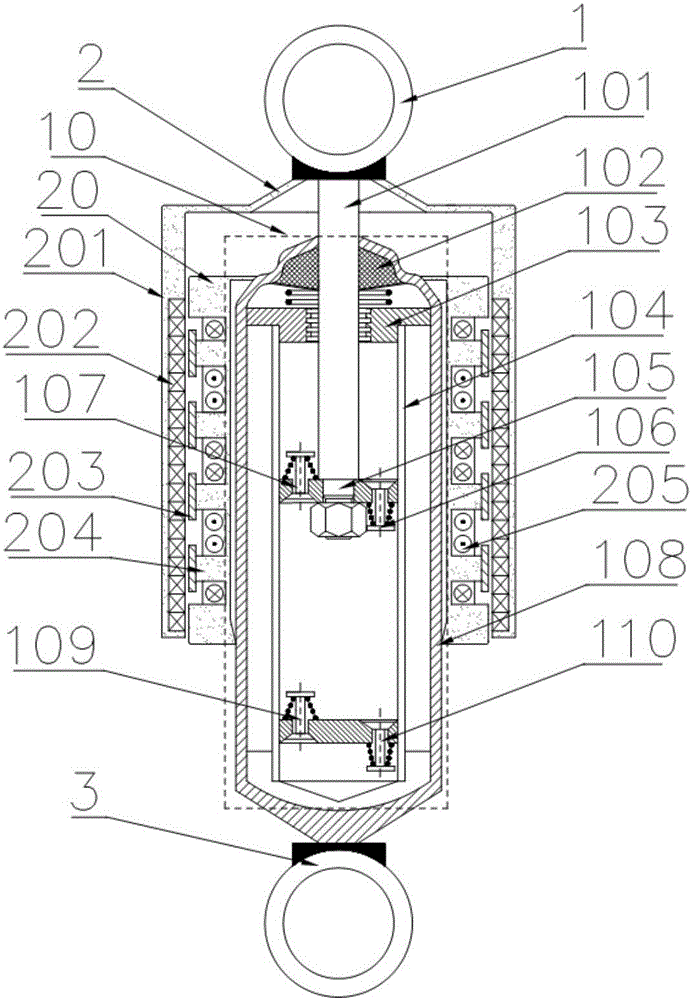
An array-type novel high-performance eddy current damper consists of an electrical eddy current energy consuming unit, an elastic buffer unit, an electromagnetic shielding component, an axial displacement guiding unit and a supporting component, wherein the elastic buffer unit, the electrical eddy current energy consuming unit and the axial displacement guiding unit are sequentially inlaid on the supporting component from the bottom up; the bottom of the electrical eddy current energy consuming unit serving as a core component of the damper is connected with the top of the elastic buffer unit; the top of the electrical eddy current energy consuming unit is connected with the bottom of the axial displacement guiding unit; a flexible spherical hinged support is arranged at the top end of the damper and is connected with the axial displacement guiding unit and an external load to output a damping force; and a flexible spherical hinged support is arranged at the bottom end of the damper and is used for fixing the damper. The array-type novel high-performance eddy current damper has the advantages of adjustable damping coefficient, high ratio of the damping force to the integral mass of the damper, compact structure, high reliability and the like; and in the technical field of structural vibration control, the array-type novel high-performance eddy current damper has relatively high practical value and wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Damping-adjustable magneto-rheological lag damper
ActiveCN104455178AAchieve regulationTake full advantage of mobilitySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionLagControl theory
The invention relates to a damping-adjustable magneto-rheological lag damper. The damping-adjustable magneto-rheological lag damper comprises a cylinder barrel, a piston rod, a piston component and a damping adjusting mechanism. Stub shafts are integrally produced at the outer edge of the left end of the cylinder barrel symmetrically and radially, and an end cover is mounted at the right end of the cylinder barrel hermetically and coaxially. The piston rod is penetratingly mounted in the cylinder barrel coaxially, and two ends of the piston rod are positioned outside the cylinder barrel. The piston component is mounted at the position, on the inner left side of the cylinder barrel, of the piston rod coaxially. The damping adjusting mechanism is slidably mounted at the position, corresponding to the piston component and positioned on the inner right side of the cylinder barrel, of the piston rod coaxially and rotates around an axial center by a certain angle prior to being fittingly mounted together with the piston component, and the left end, positioned outside the cylinder barrel, of the piston rod is in coaxial threaded connection with a rod-end joint bearing. The damping-adjustable magneto-rheological lag damper has the advantages of simple structure, low energy consumption, small size, rapidity in response, continuous forward and reverse adjustability in damping force within a wide range, good temperature stability, easiness in combination with a computer to achieve intelligent control and the like, thereby being quite promising in application prospect.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Damping valve assembly with a progressive damping force characteristic
InactiveUS20050115786A1No sacrifice of comfortIncrease damping forceSpringsMultiple way valvesEngineeringThrottle
Damping valve assembly includes a first damping valve, which, in a first operating range, opens as the flow velocity of the damping medium increases, where a second operating range with a progressive damping force characteristic is influenced by a throttle in conjunction with a control slide, which can be moved into a closed position. The control slide has a pressure-actuated surface, which, as a function of the flow velocity of the damping medium, acts in the closing direction on the control slide.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Three-cylinder type large-capacity magneto-rheological damper
InactiveCN101793302AMeet the needs of earthquake resistance and wind resistanceIncreased sensitivityNon-rotating vibration suppressionSolid based dampersVibration controlControl theory
The invention discloses a three-cylinder type large-capacity magneto-rheological damper for vibration control of a large civil engineering structure, which comprises a magneto-rheological damping cylinder (9), a puddle damping cylinder (5), an auxiliary cylinder (19), a magneto-rheological main piston (23), a puddle piston (6), a piston rod (17), a sealing baffle (20), a damping channel (16), a cylinder cover (3) and a spherical hinge joint (13), wherein magneto-rheological liquid (11) is filled in the magneto-rheological damping cylinder, and an annular excitation coil (8) capable of generating a magnetic field is arranged in the magneto-rheological damping cylinder; and the puddle damping cylinder is arranged adjacent to the magneto-rheological damping cylinder, and elastic puddle (7) is filled in the inner cavity of the puddle damping cylinder, thus the damper can generate large damping under the condition of large displacement, and the safety of the damper can be improved. By arranging a displacement splitting mechanism (18), the magneto-rheological damper has high rigidity and large damping in a low-frequency region and has low rigidity and small damping in a high-frequency region. Compared with the traditional magneto-rheological damper with the same size, the maximum capacity of the damper of the invention is improved by more than one time, and the vibration control of the large civil engineering structure is more effective.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
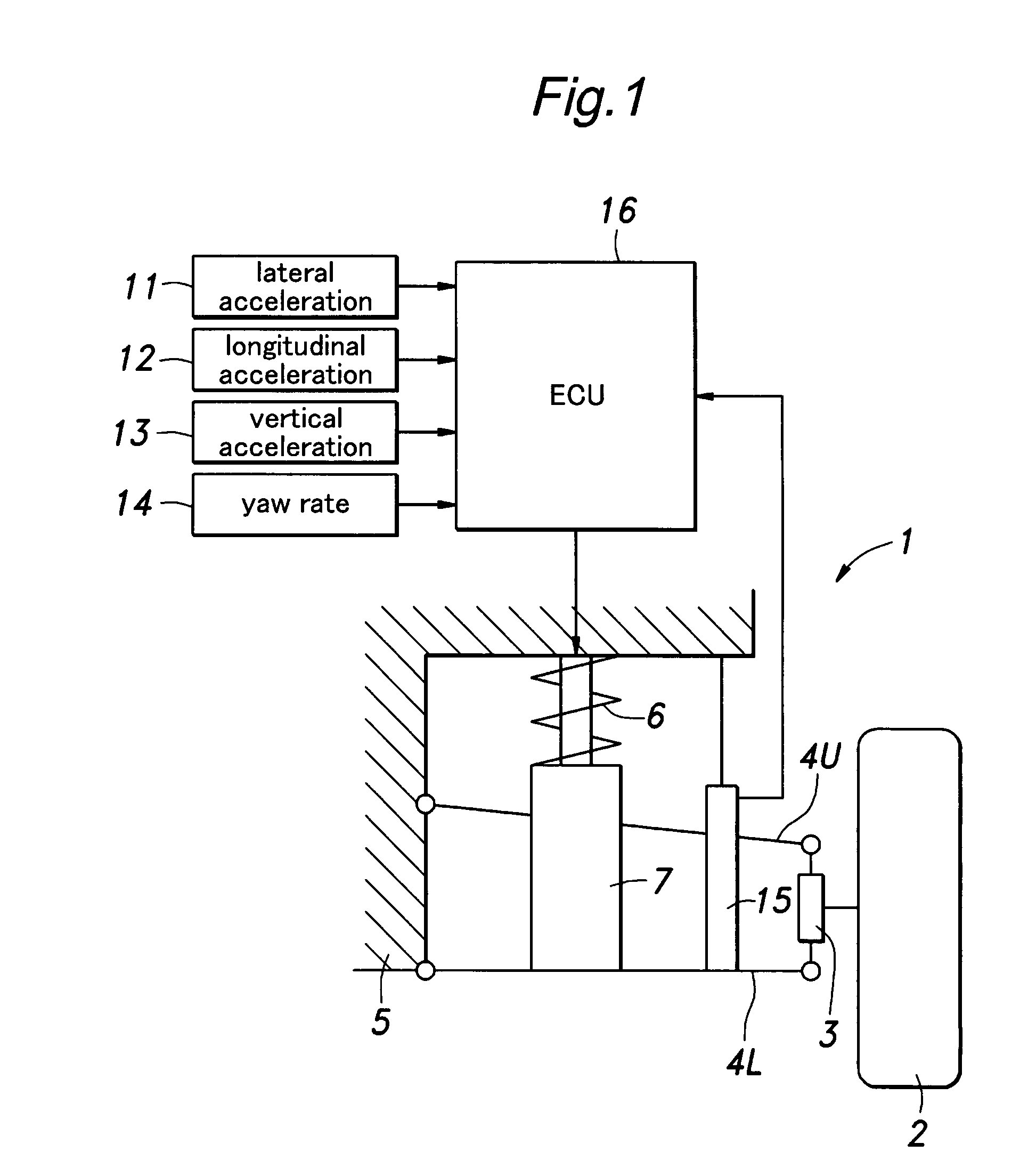
Damping force control apparatus
ActiveUS20120010780A1Comfortability can be improvedAvoid/suppress degradation of comfortabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesStep numberSnubber
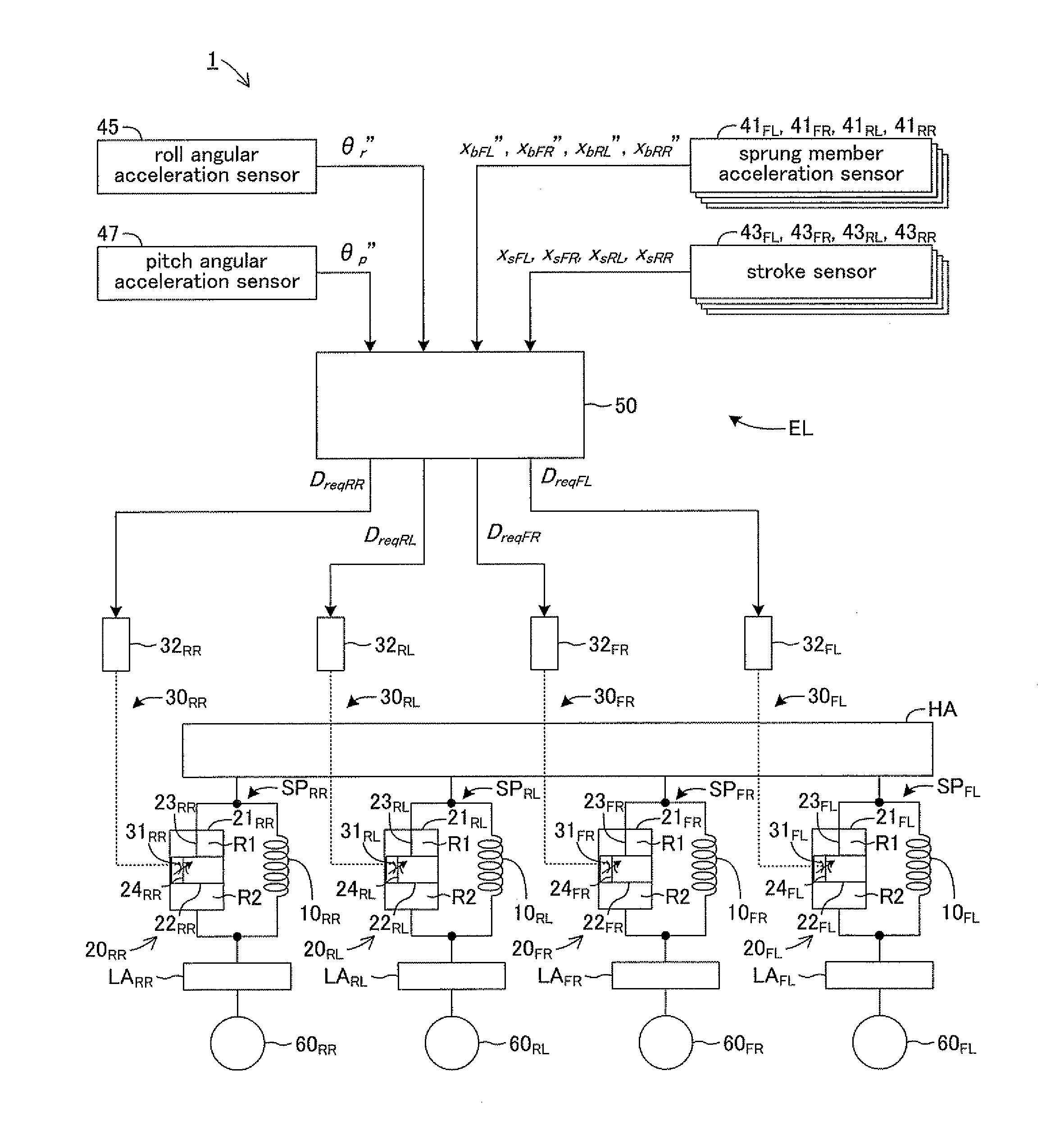
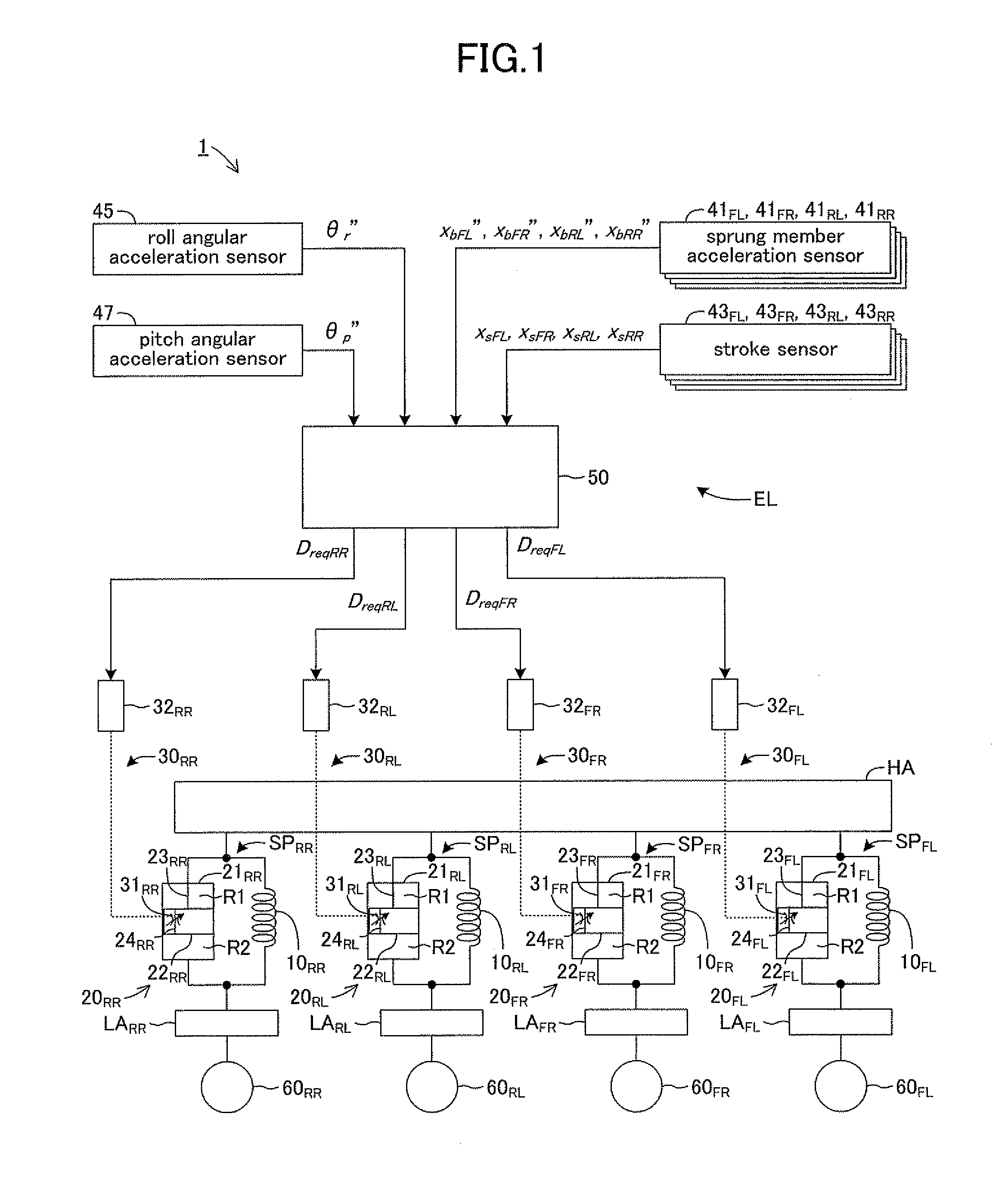
A control mode for a damping force characteristic is set to be a variable control when a product of the sum xb′ of sprung member speeds and a sprung-member-unsprung-member-relative-speed xs″ is positive. Accordingly, when the vibration in a middle / high frequency range is not being input to a suspension apparatus, an operation of a variable throttle mechanism is controlled so that a step number representing the damping force characteristic of a damper varies with a vibration state of a sprung member HA based on a Nonlinear H∞ control theory. When the product of xb′ and xs′ is negative, the control mode is set to be an operation prohibiting control. When the vibration in the middle / high frequency range is input to the suspension apparatus, operation of the variable throttle mechanism is prohibited, and suppresses an increase in the operation frequency or in the operation amount of the variable throttle mechanism.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Power transmission device for hybrid vehicle
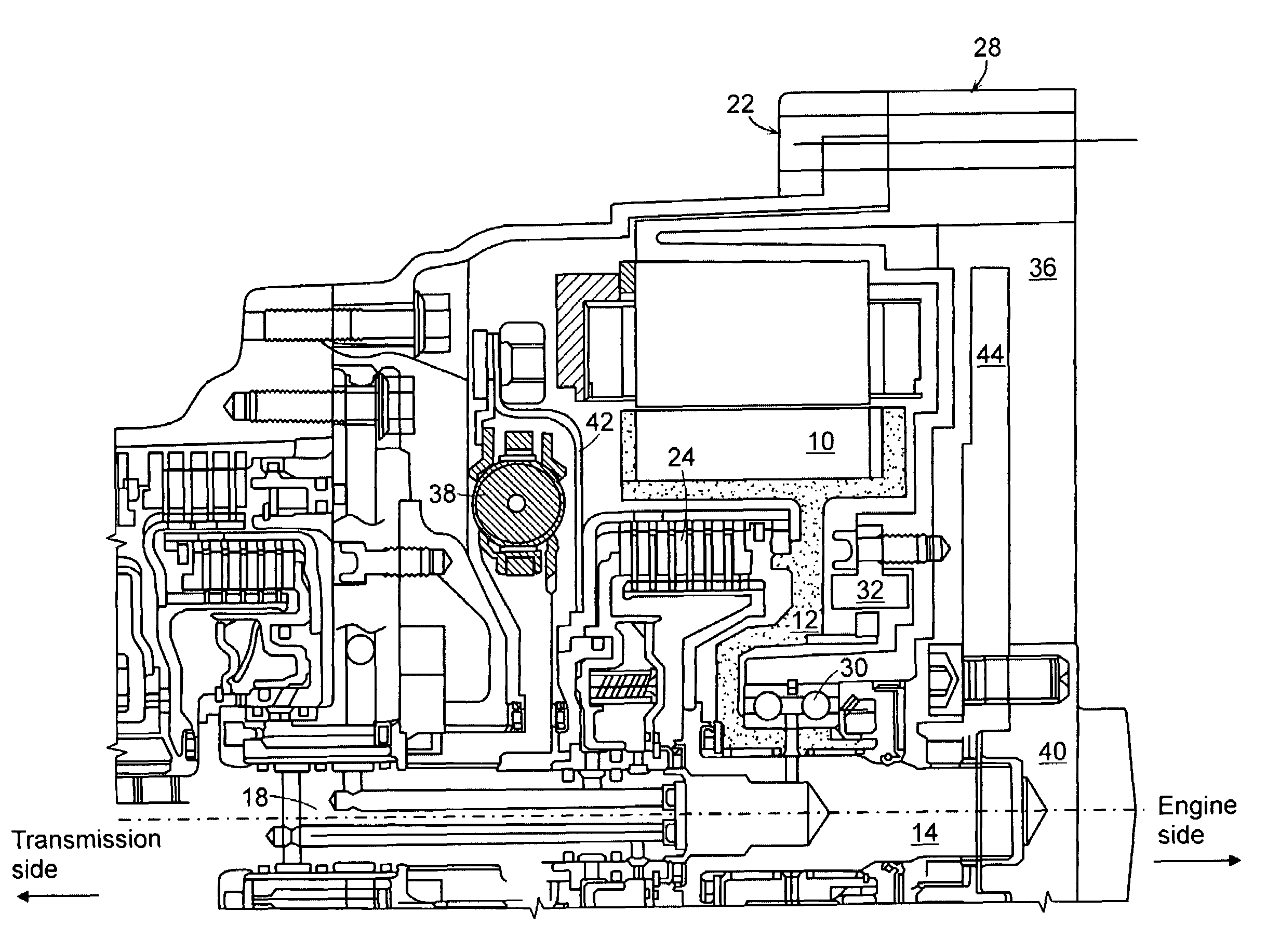
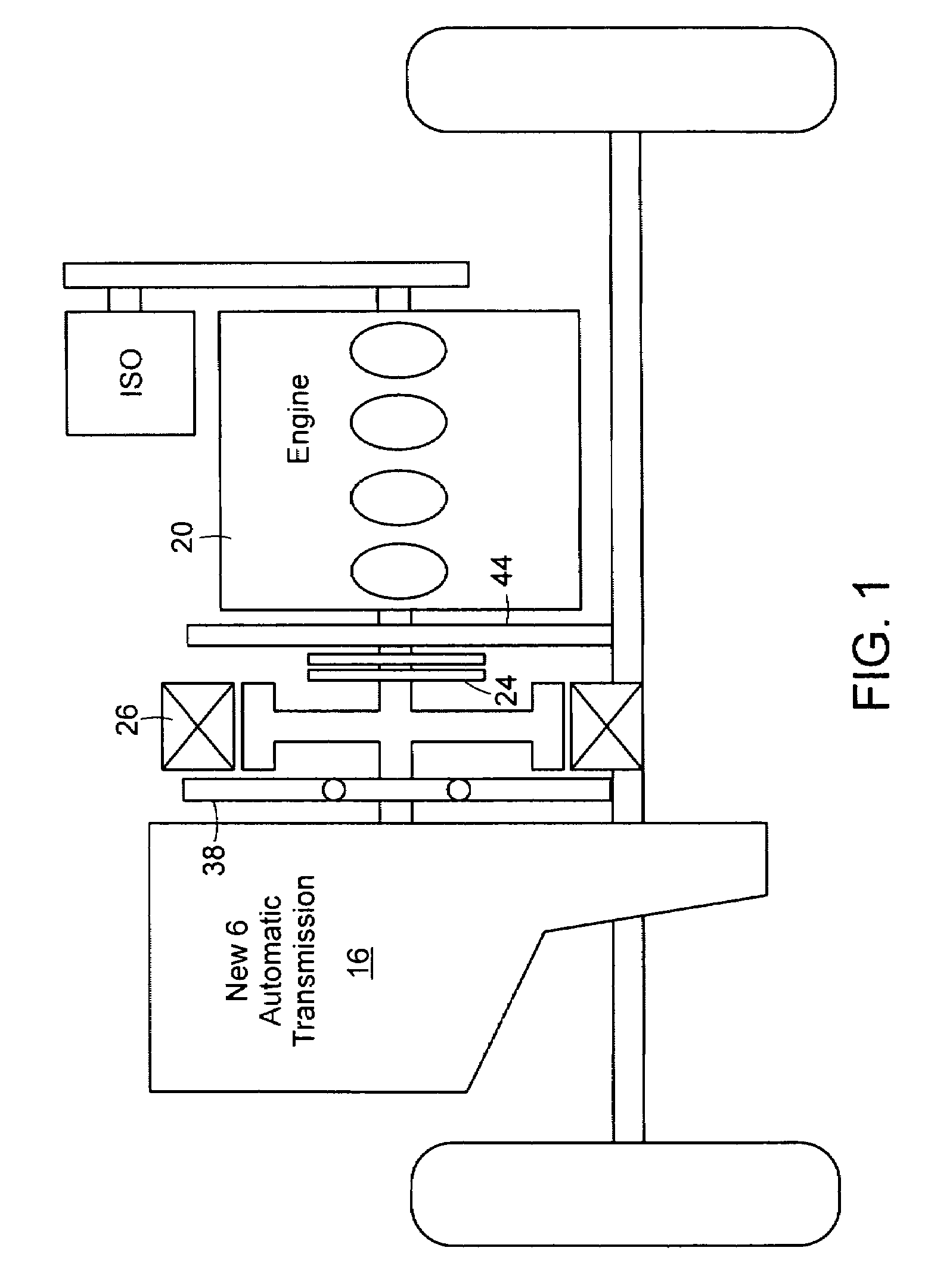
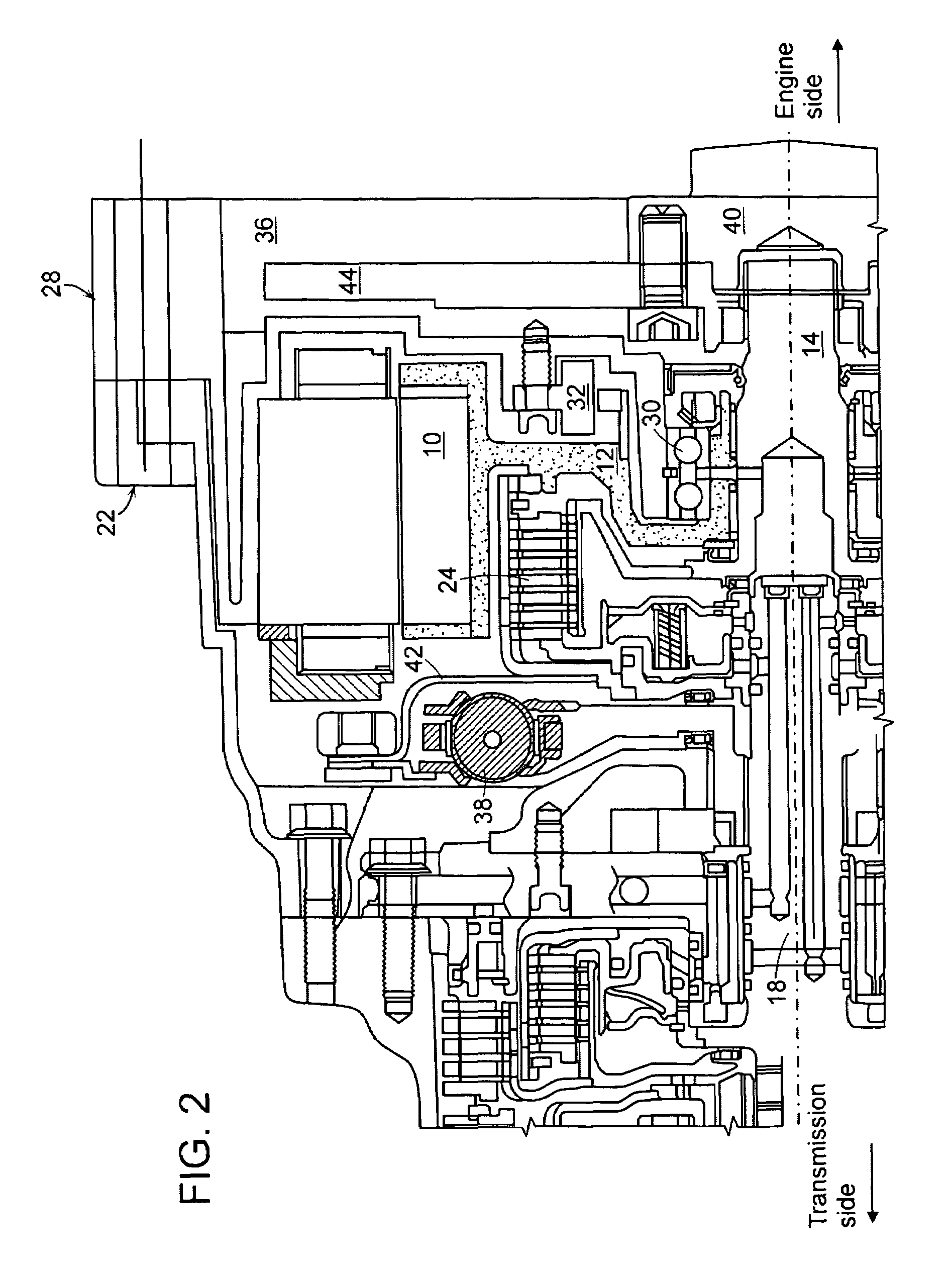
ActiveUS7578363B2Increase damping forceEfficient layoutAuxillary drivesElectric propulsion mountingAutomatic transmissionFlywheel
The present invention provides a layout of a power transmission device for a hybrid vehicle which provides a high damping force a high damping force against engine fluctuation at low RPM operation by an engineFor this, the preset invention provides a power transmission device for a hybrid vehicle, in which an automatic transmission having an input shaft, a motor, an engine clutch, a flywheel, and an engine having an output shaft connected to a crank shaft of the engine are directly connected to the same axis, the power transmission device including: a motor support shaft, the outer end of which is supported by a motor rotor and the inner end of which extends toward the boundary between the output shaft of the engine and the input shaft of the automatic transmission; a motor housing arranged so as to surround the outer circumference and the left side surface of the motor rotor; a torsion damper disposed between the left side end of the motor housing and the motor rotor; an engine clutch, disposed between the left side end of the motor housing and the left side surface of the inner end of the motor support shaft, for power transmission between the output shaft of the engine and the input shaft of the automatic transmission; a retainer connecting a housing of the engine clutch to the torsion damper; a motor cover housing arranged to cover the right side surface of the motor rotor and the right side surface of the inner end of the motor support shaft and including a concave portion on the right side surface thereof; and a flywheel positioned at the concave portion of the motor cover housing to be blocked from the motor rotor.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Semi-active energy regenerative suspension shock absorber based on mixed excitation and size determining method of shock absorber
ActiveCN106224425AAdjustable damping forceGood vibration isolationGeometric CADAuxillary drivesViscous dampingSemi active
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Damping device
ActiveUS20120234639A1Increase flow resistancePassage resistance of to increaseSpringsLiquid based dampersEngineeringRate dependent
A damping device comprises a piston that partitions an interior of a cylinder into first and second working chambers. A flow-rate-dependent damping force generating element connects the first and second working chambers. A first pressure chamber and a second pressure chamber divided by a free piston are formed integrally with the piston. A first connecting passage connects the first working chamber and the first pressure chamber, and a second connecting passage connects the second working chamber and the second pressure chamber. By providing a relief valve that allows fluid to flow from the first working chamber into the second working chamber, an increase in the generated damping force during a high speed operation of the piston can be suppressed, regardless of a vibration frequency of the piston.
Owner:KYB CORP
Suspension device
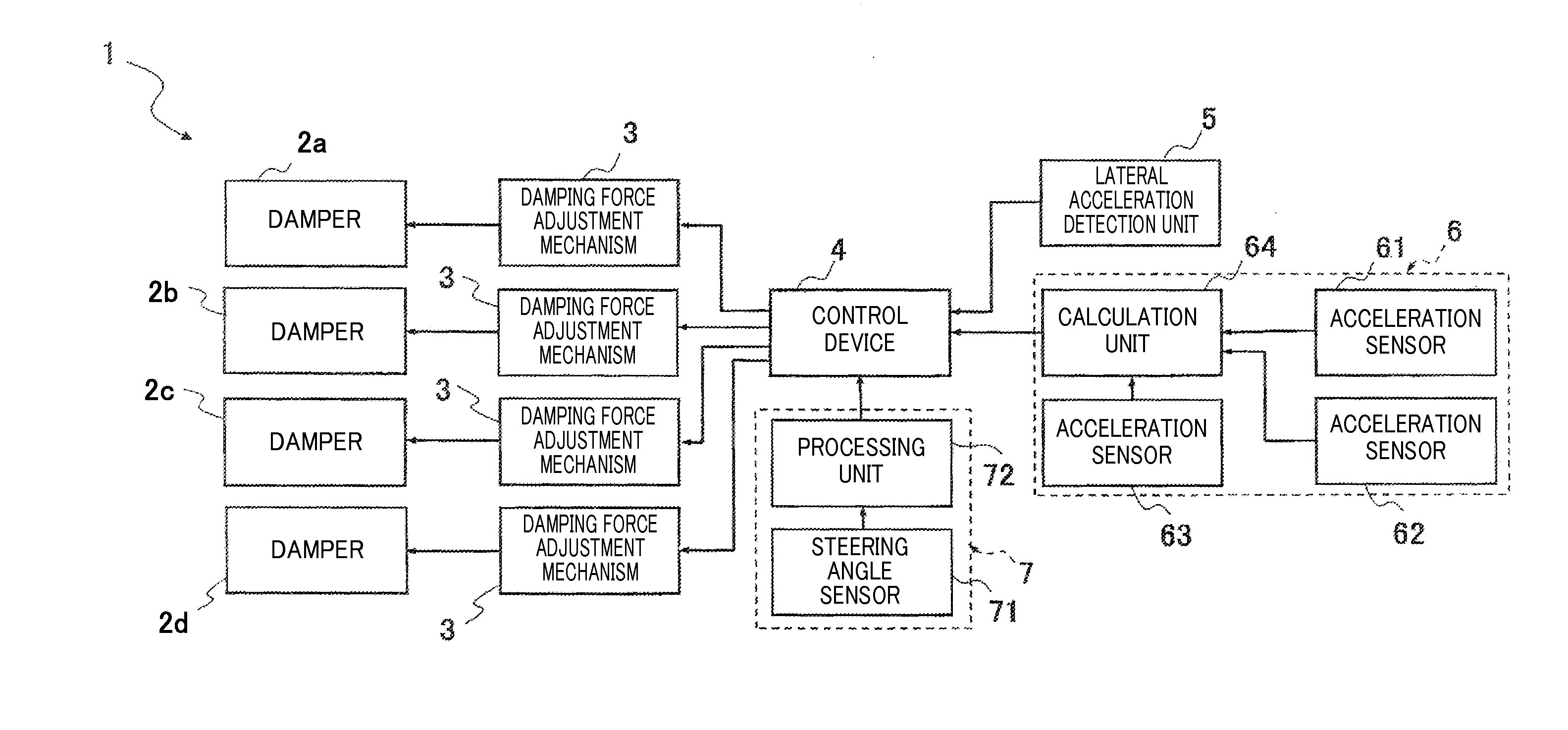
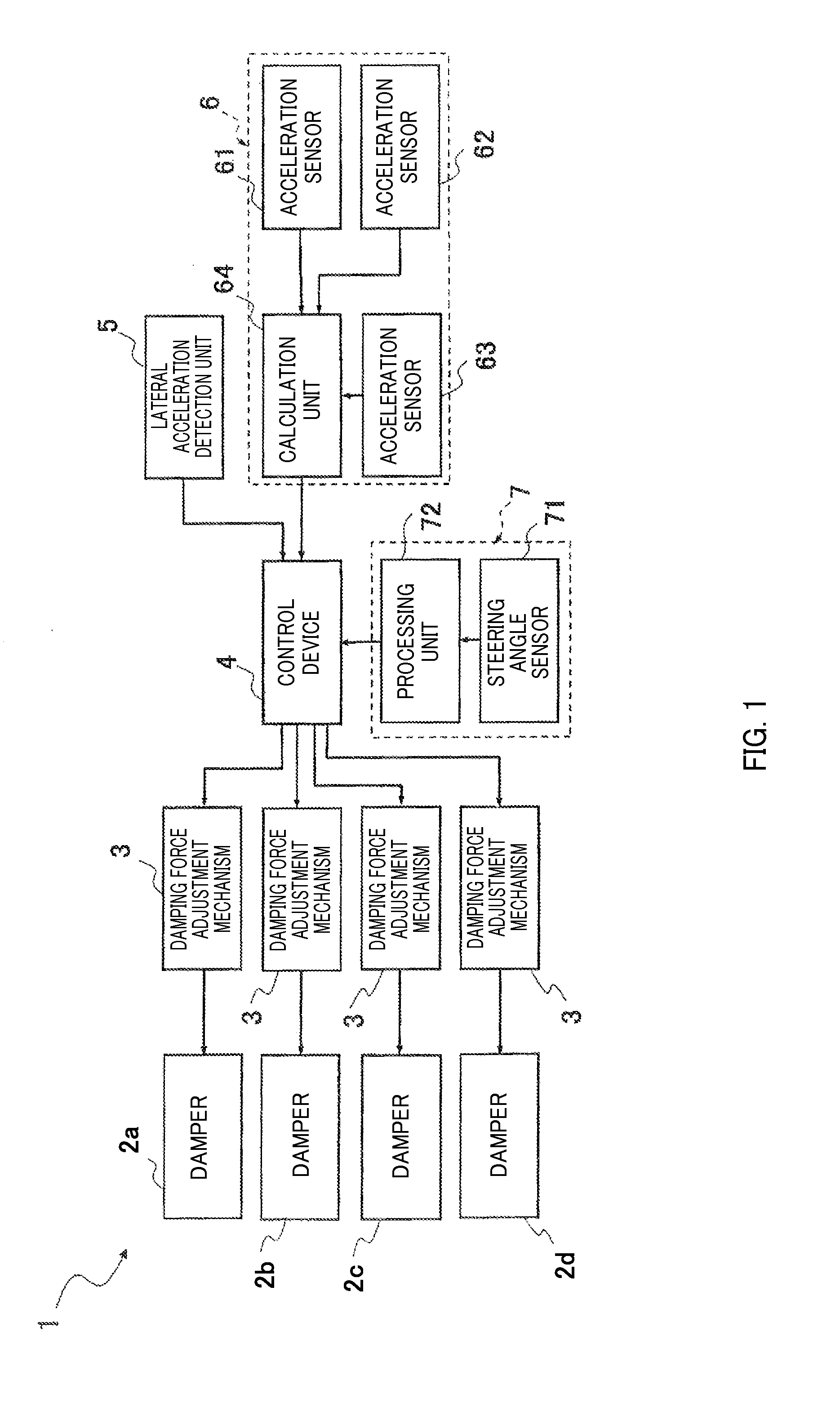
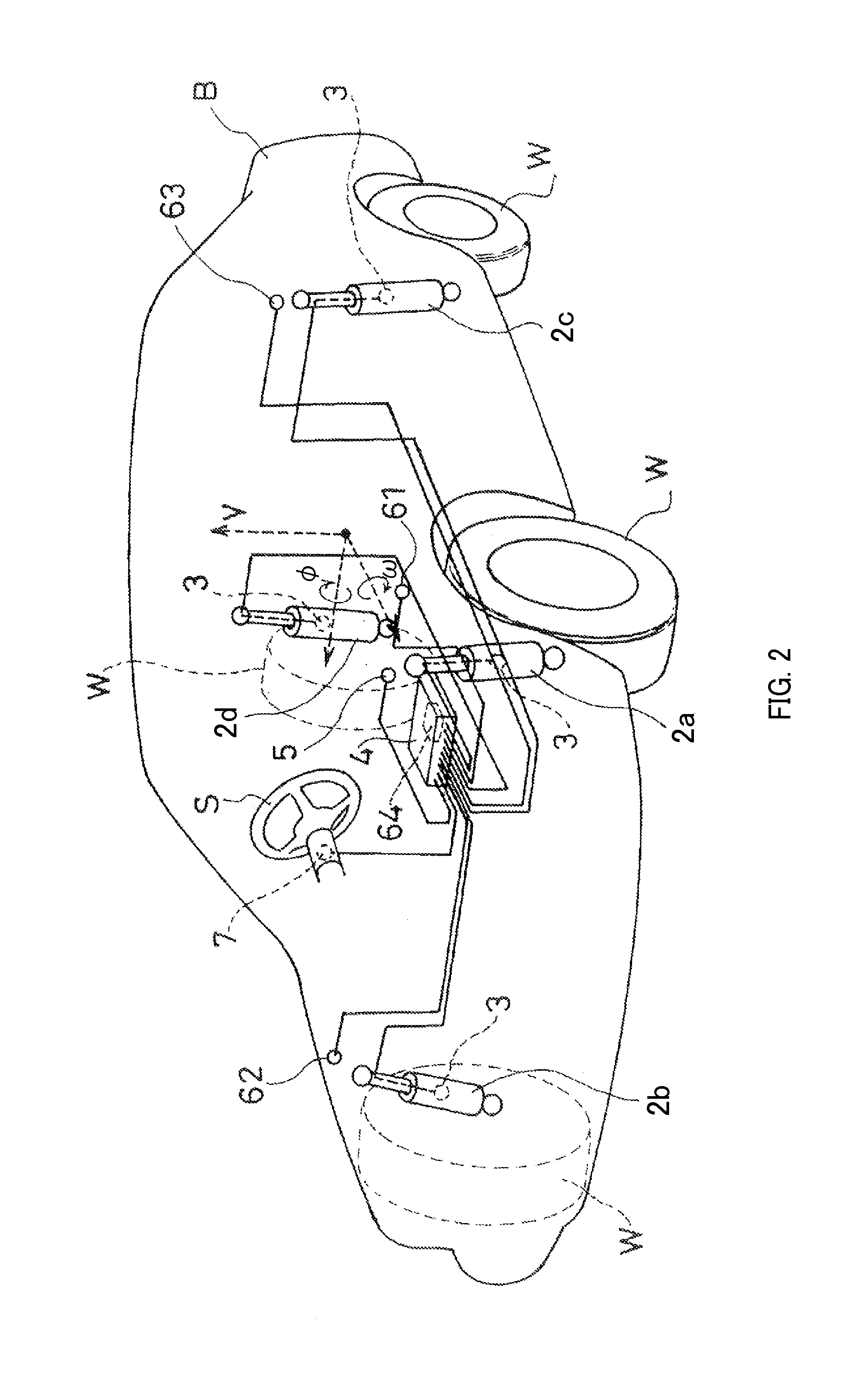
ActiveUS20130197755A1Force of damper increaseIncrease damping forceDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesSteering wheelIn vehicle
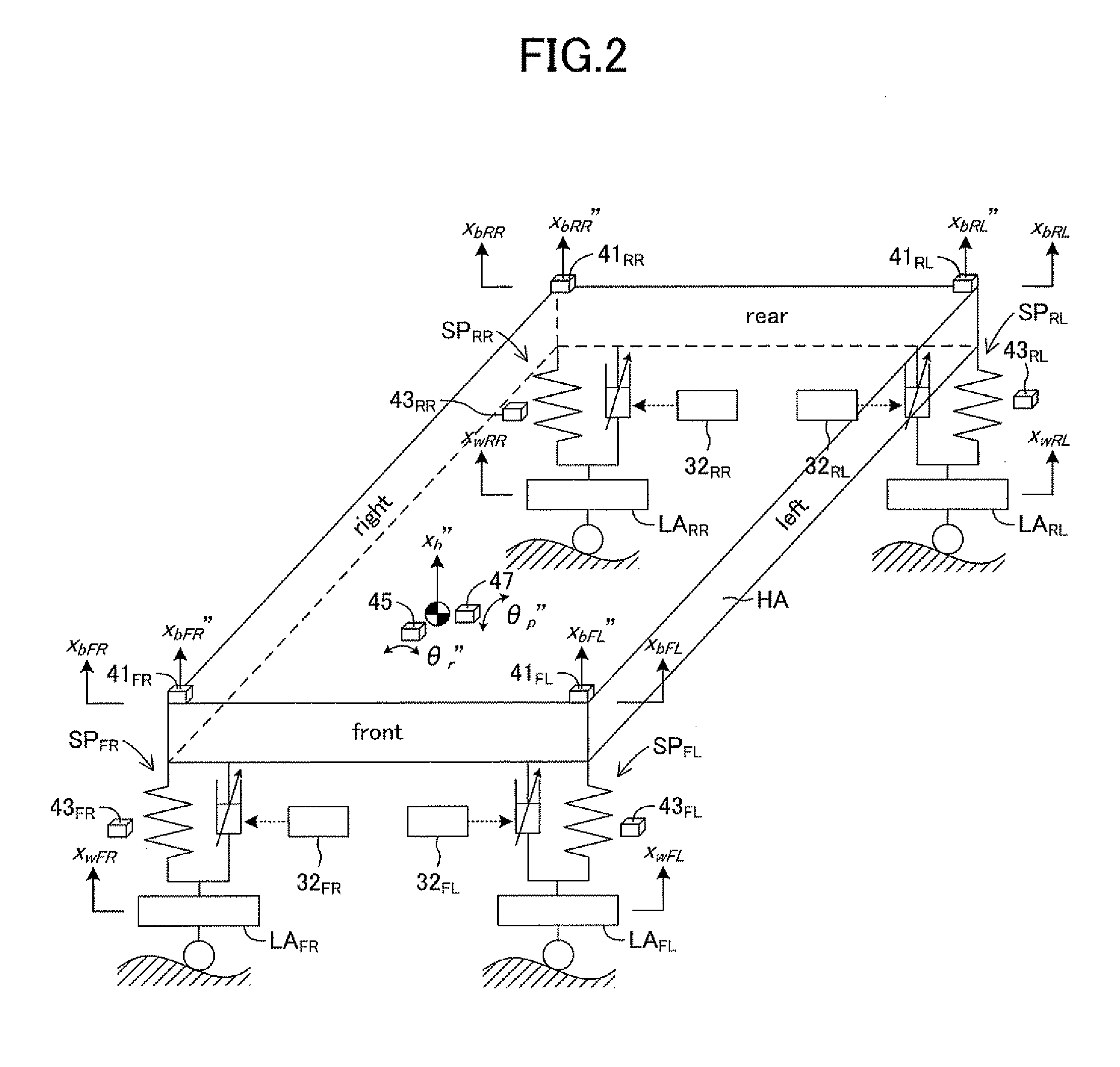
A suspension device includes damper interposed between vehicle body and wheel in vehicle and exerted damping force for suppressing vertical movements of vehicle body and wheel, damping force adjustment mechanism adjusts damping force, control device controls damping force adjustment mechanism, lateral acceleration detection unit detects an lateral acceleration acting on vehicle body, roll angular velocity detection unit detects roll angular velocity of vehicle body, and steering angular velocity detection unit detects steering angular velocity of steering wheel. The control device sets maximum damping force out of damping force calculated from steering angular velocity, damping force calculated from lateral acceleration and damping force calculated from roll angular velocity as steering initial stage additional damping force, calculates final damping force of damper using steering initial stage additional damping force and performs steering initial stage control of controlling damper when steering angular velocity exceeds predetermined dead band.
Owner:KYB CORP
Multistage extrusion-type magneto-rheological damper
ActiveCN103148157AIncrease the effective working areaExpand the working areaNon-rotating vibration suppressionSnubberVibration isolation
The invention relates to a magneto-rheological damper, in particular to a multistage extrusion-type magneto-rheological damper. The multistage extrusion-type magneto-rheological damper is suitable for the vibration isolation of an engine or other equipment. The damper comprises an upper end cover, an outer cylinder body, a piston rod, a sealing ring, a sealing bolt, a working cavity, a lower end cover and a piston head, and is characterized in that the damper also comprises a magnetic-isolation sleeve, a coil, an upper spacing spring, an auxiliary piston head, an inner cylinder body and a lower spacing spring, wherein the working cavity is divided into an inner working cavity and an outer working cavity by the inner cylinder body; the working cavity is filled with magneto-rheological liquid; the auxiliary piston head and the piston head connected to the piston rod respectively extrude the magneto-rheological liquid back and forth in the two working cavities to generate radial flowing so as to generate damping force; and the coil is arranged between the outer cylinder body and the magnetic-isolation sleeve to provide a magnetic field so as to regulate the magnitude of the damping force in real time. The output force of the multistage extrusion-type magneto-rheological damper is much more than that of a common magneto-rheological damper, and especially, the impact generated when the equipment is greatly and intensively vibrated under the severe environment can be avoided. The multistage extrusion-type magneto-rheological damper has the advantages of reasonability in design, simple construction, high efficiency, high response speed, high working reliability, good vibration damping effect and long service life.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Safety helmet with rotary impact buffering function
ActiveUS20180271198A1Effectively protect the heads of usersImprove buffering effectHelmetsHaberdasheryEngineering
A safety helmet with a rotary impact buffering function comprises a shell and an elastic liner arranged in the shell, wherein a gap is formed between the shell and the elastic liner, and a rotary impact buffering device enabling the shell to rotate relative to the elastic liner is arranged between the shell and the elastic liner. When the safety helmet is impacted by external force, the shell has the tendency to rotate relative to the elastic liner under the effect of component force applied to the shell in the tangential direction; however, through tangential deformation of the rotary impact buffering device, the shell can rotate relative to the elastic liner by a certain angle on the premise of keeping the elastic liner unmoved, and thus the impact to users from external force is greatly reduced.
Owner:KU CHENG HUEI
Suspension system for in-wheel motor vehicle
InactiveUS20140284122A1Avoid resonanceReduce vibrationSpringsElectric propulsion mountingResonanceEngineering
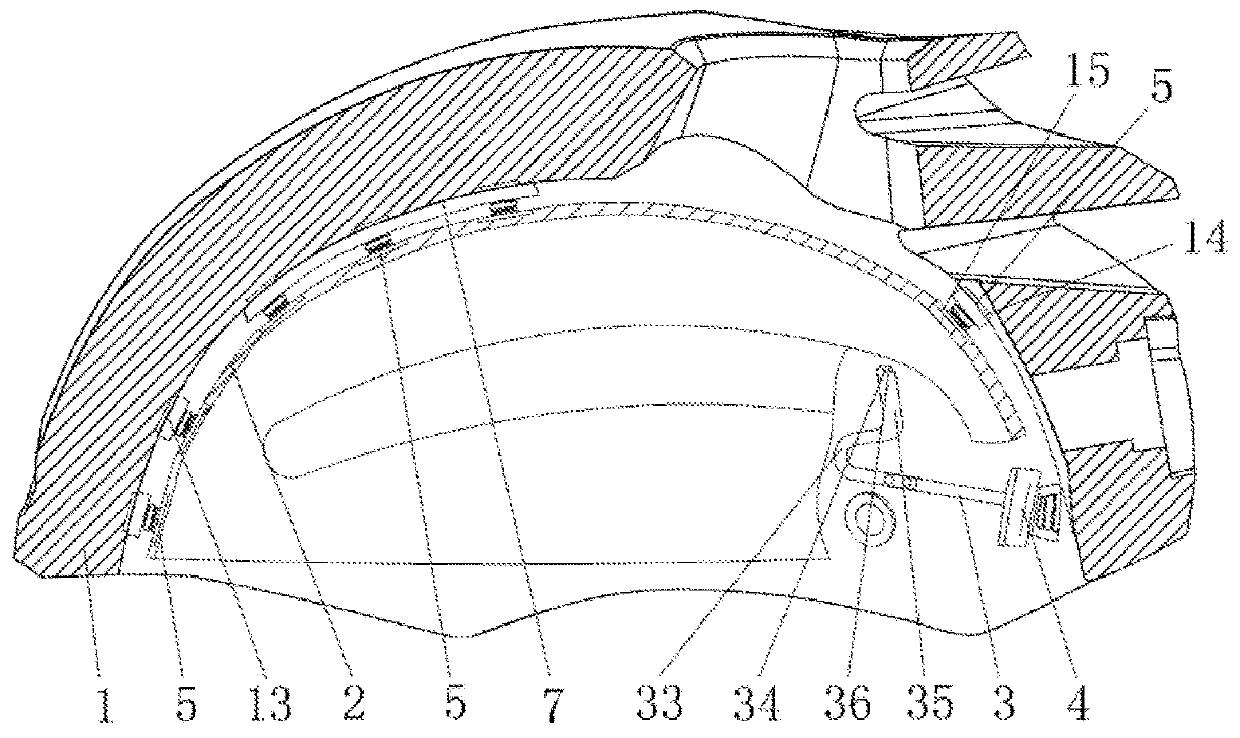
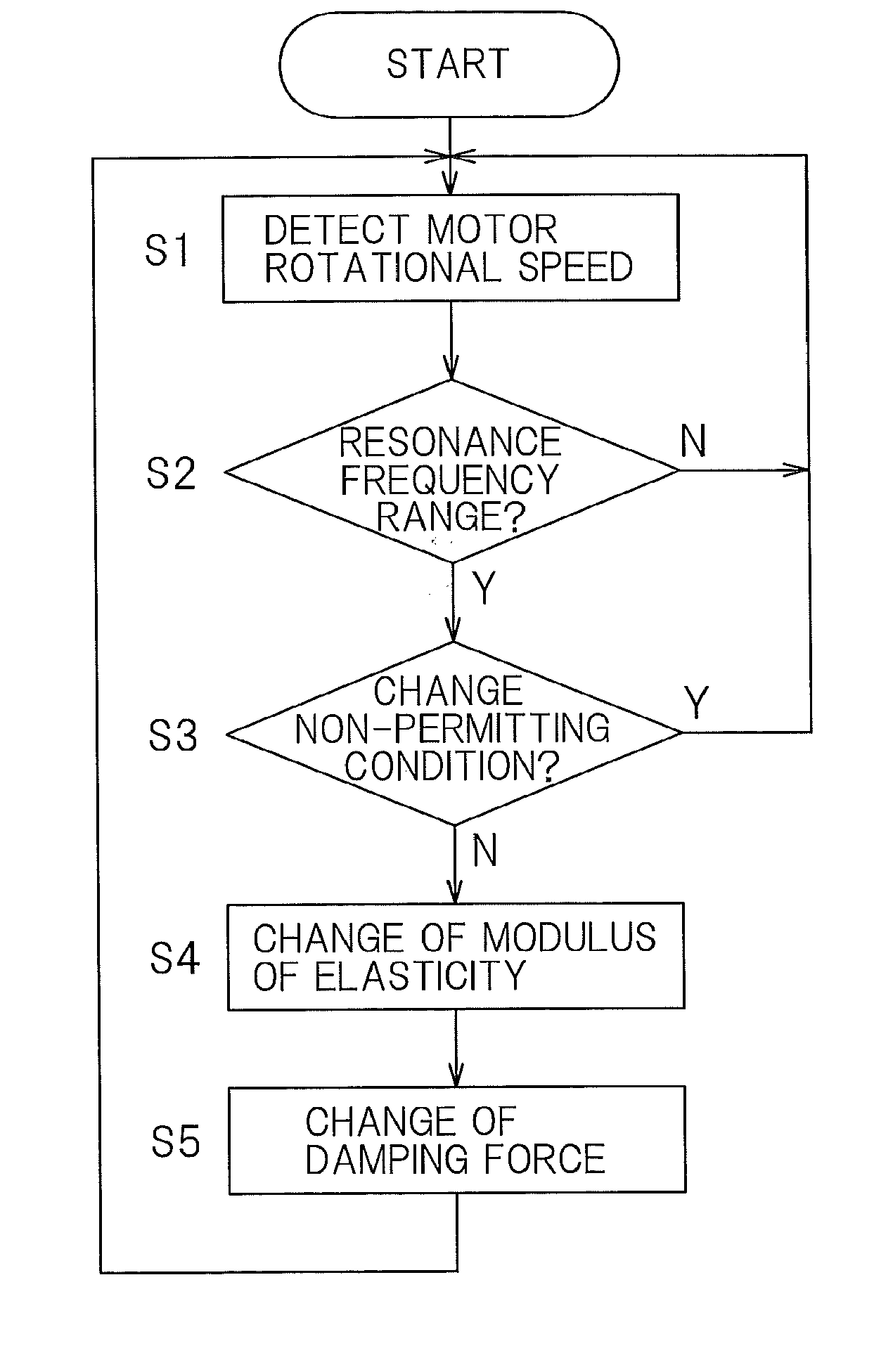
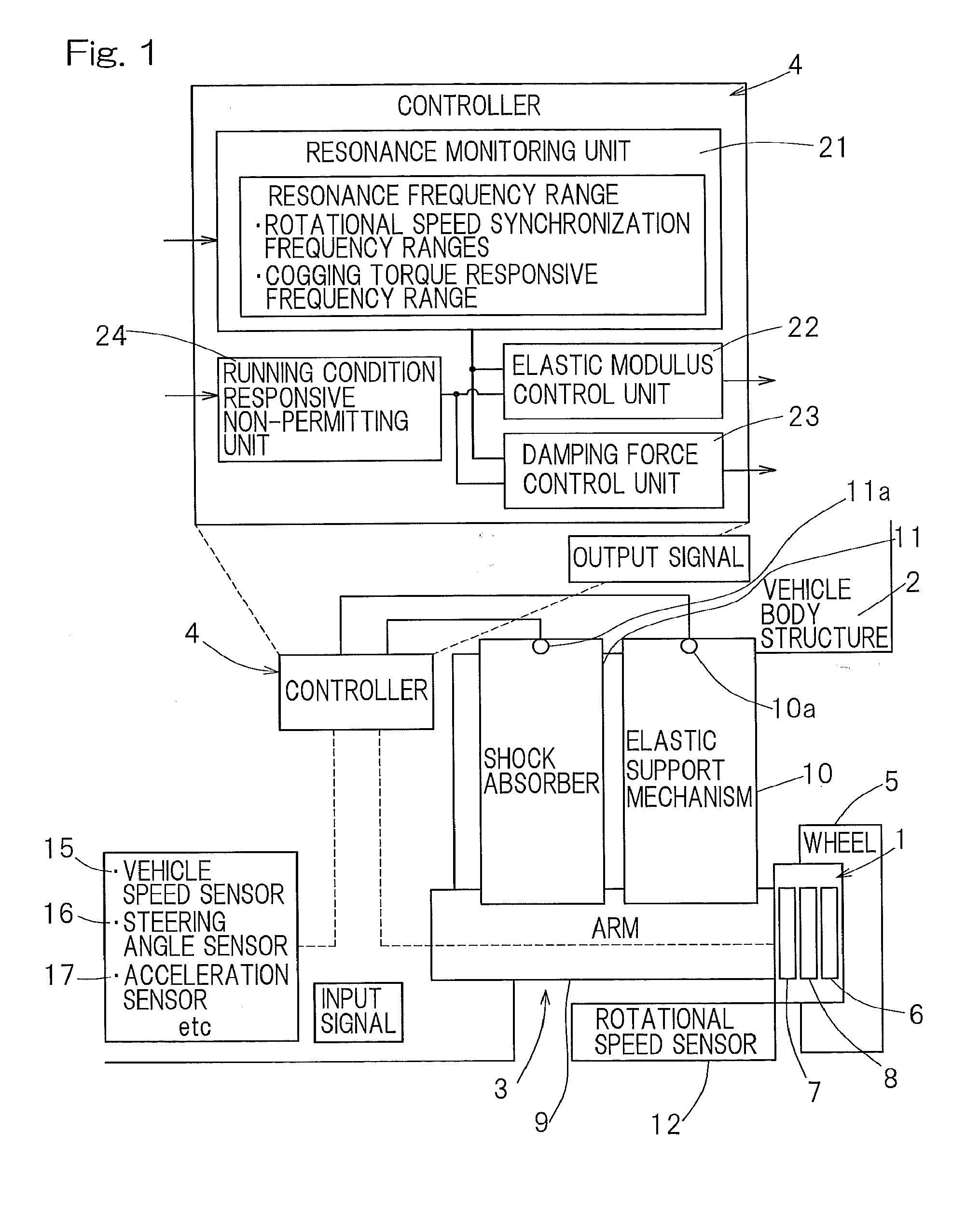
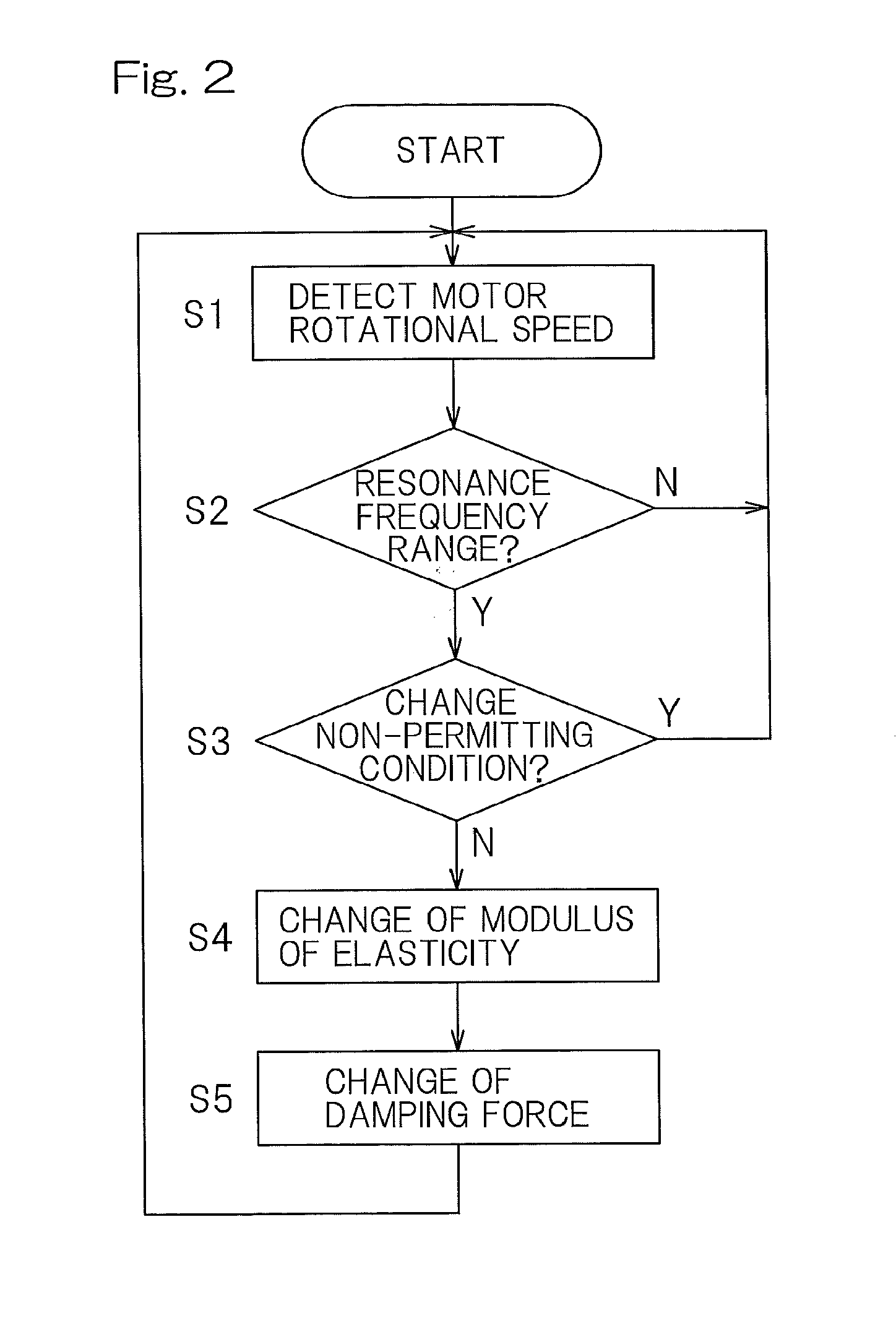
Included are an elastic support mechanism (10) and a shock absorber (11) in a suspension (3) interposed between an in-wheel motor device (1) and a vehicle body structure (2). The elastic support mechanism (10) can change a modulus of elasticity and the shock absorber (11) can change a damping force. The provision is made of a resonance monitoring unit (21) to monitor whether or not a rotational speed of a motor (7) falls within a predetermined resonance frequency range. When the rotational speed of the motor (7) is determined as falling within the resonance frequency range, an elastic modulus control unit (22) changes the modulus of elasticity, and a damping force control unit (23) changes the damping force of the shock absorber (11).
Owner:NTN CORP
Multistage composite type energy absorption and dissipation damping device, application and method
ActiveCN106907042AEffective Vibration ControlReduce loadDevices for damping mechanical oscillationsTowersEnergy absorptionMechanical energy
The invention discloses a multistage composite type energy absorption and dissipation damping device, an application and a method. According to the multistage composite type energy absorption and dissipation damping device, the defect that in the prior art, in complex load action, energy dissipation in multiple directions cannot be conducted is overcome, and multistage and polydirectional damping can be effectively realized. According to the scheme, the device comprises an outer box, a mass block and a liquid container, wherein permanent magnets are arranged on the top and at the bottom of the outer box correspondingly, and magnet poles of the two permanent magnets are opposite; the mass block is arranged inside the outer box, and the side face of the mass block is connected with the inner wall of the outer box through a first elastic damping assembly to realize the energy dissipation and damping effects of the mass block in the horizontal direction; the liquid container is arranged below the mass block, liquid with a set volume is contained in the liquid container, the liquid container is internally provided with a second elastic damping assembly, the bottom end of the second elastic damping assembly is connected with the inner bottom of the liquid container, and the top end of the second elastic damping assembly is fixed to the mass block; and meanwhile in the moving process of the mass block, magnetic induction lines generated by the two permanent magnets are cut to conduct dissipating in the mode that mechanical energy is transformed into electric energy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Steering damper apparatus, and method of using same
ActiveUS7377533B2Minimize steering damp apparatus-induced loadImprove mobilityWheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionSnubberControl theory
A steering damper is provided coaxially with a steering shaft, and a handlebar load is provided by causing a variable valve to generate damping force, using rotation of the steering shaft. The damping force is variably controlled in response to vehicle speed. The damping force is fixed to a minimum value C1 for vehicle speeds equal to or below first reference speed V1, fixed to a maximum value C2 for vehicle speeds equal to or above second reference speed V2, and variably controlled in response to vehicle speed and acceleration in an intermediate speed range. Fine maneuverability of a vehicle body is achieved by reducing a load on a handlebar at low vehicle speeds, and a stable movement of the vehicle body is maintained at high vehicle speed by increasing the load on the handlebar and thereby suppressing deflection of the handlebar.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
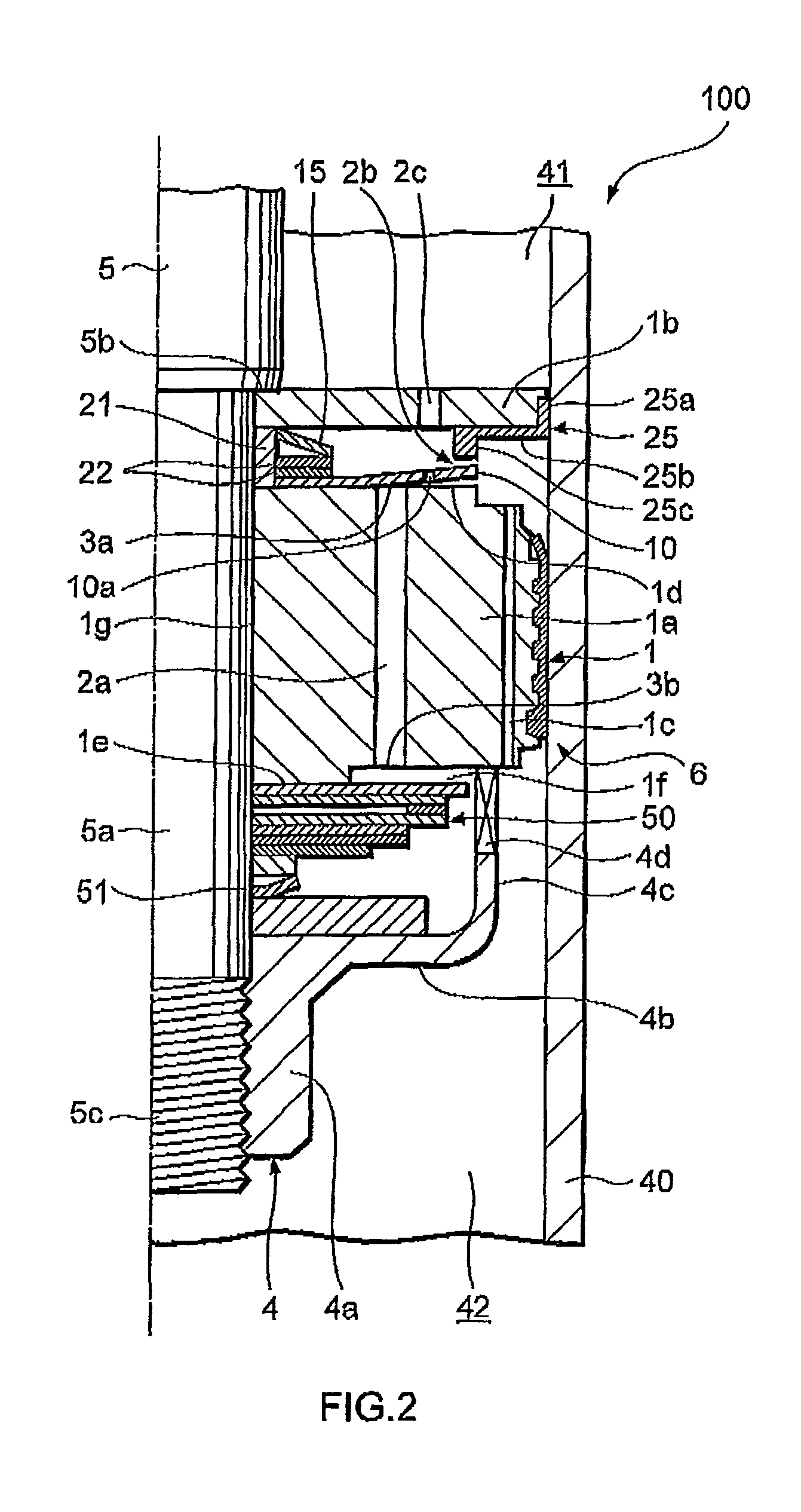
Shock absorber
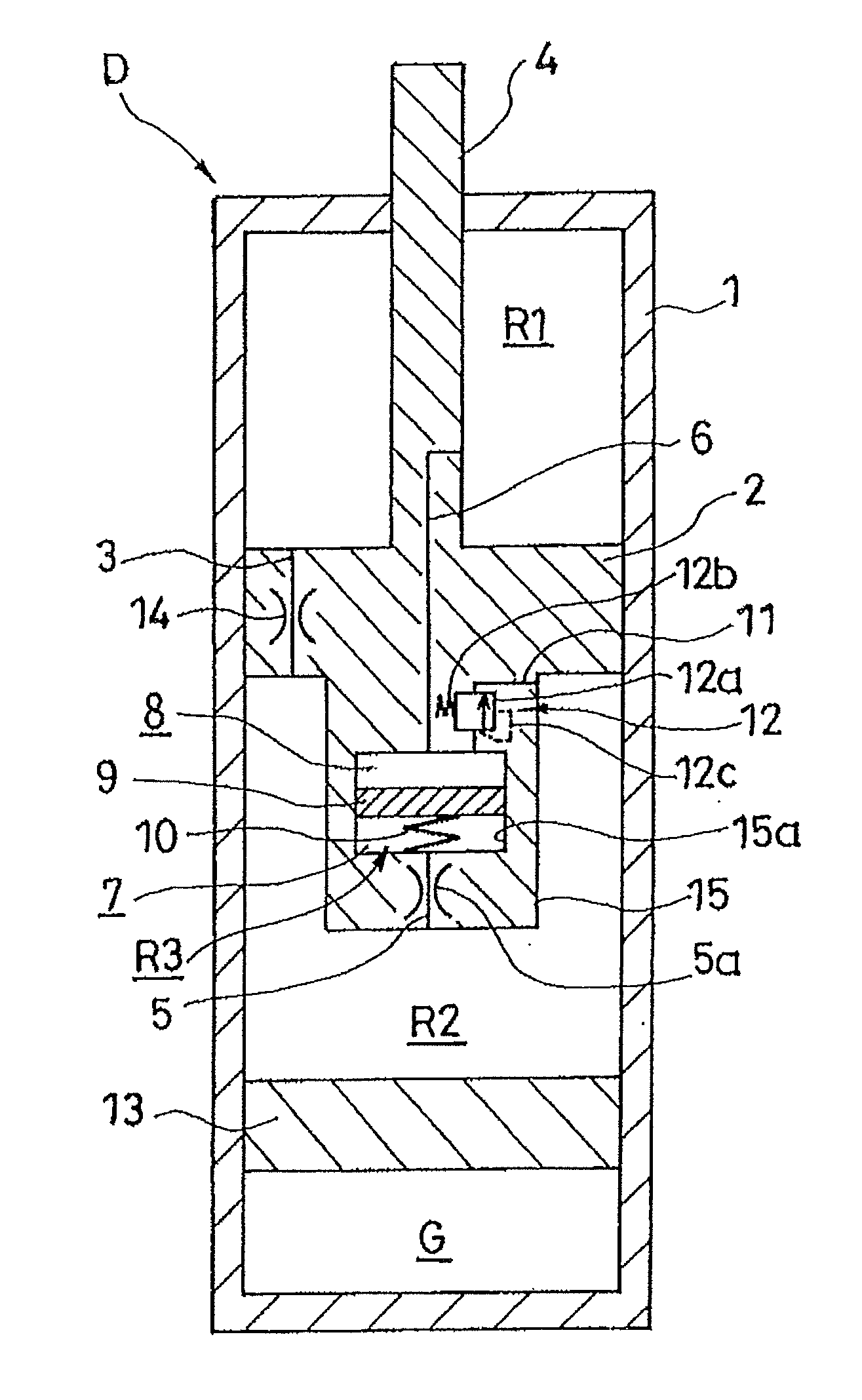
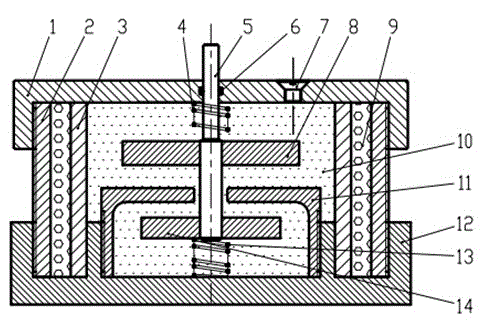
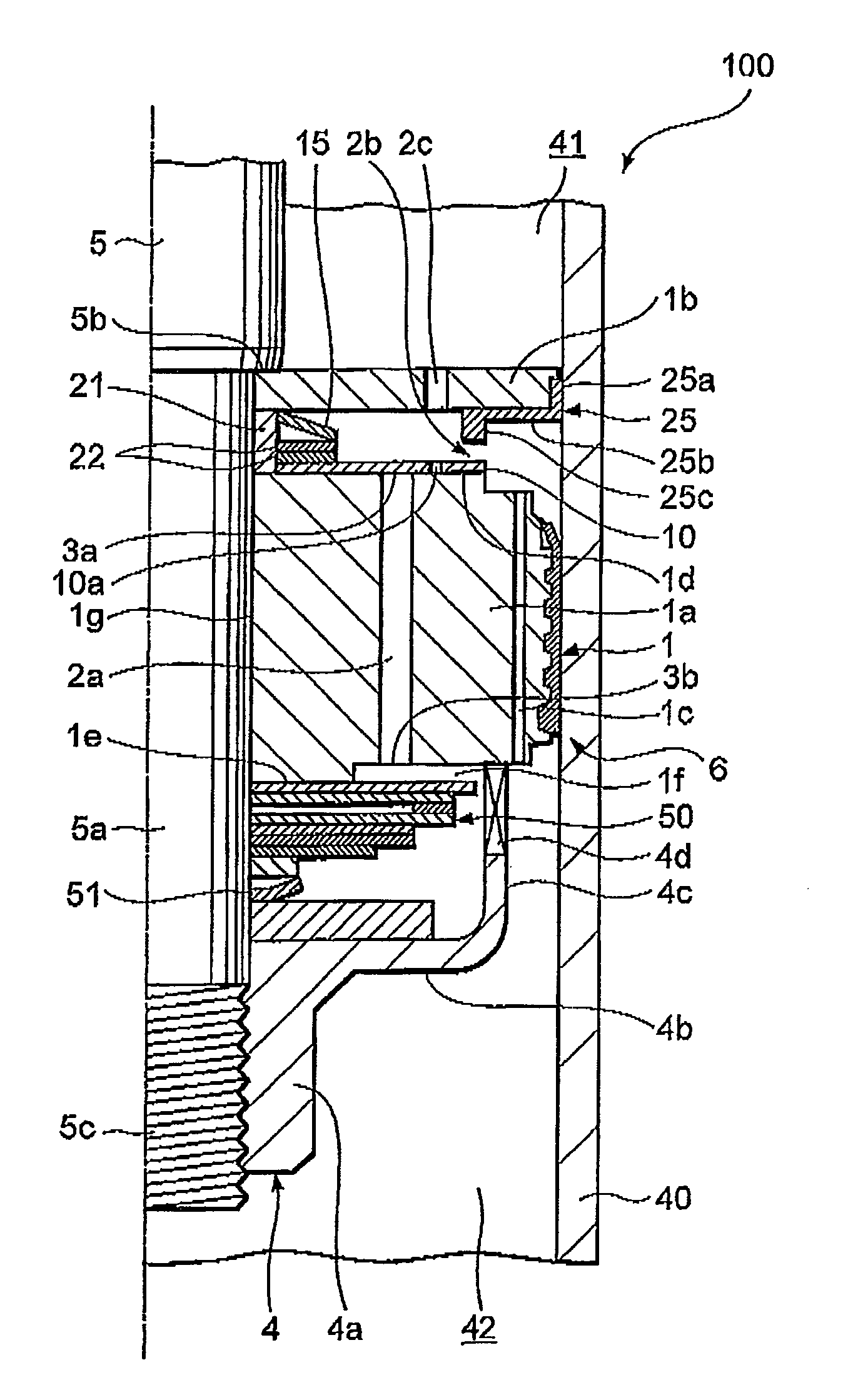
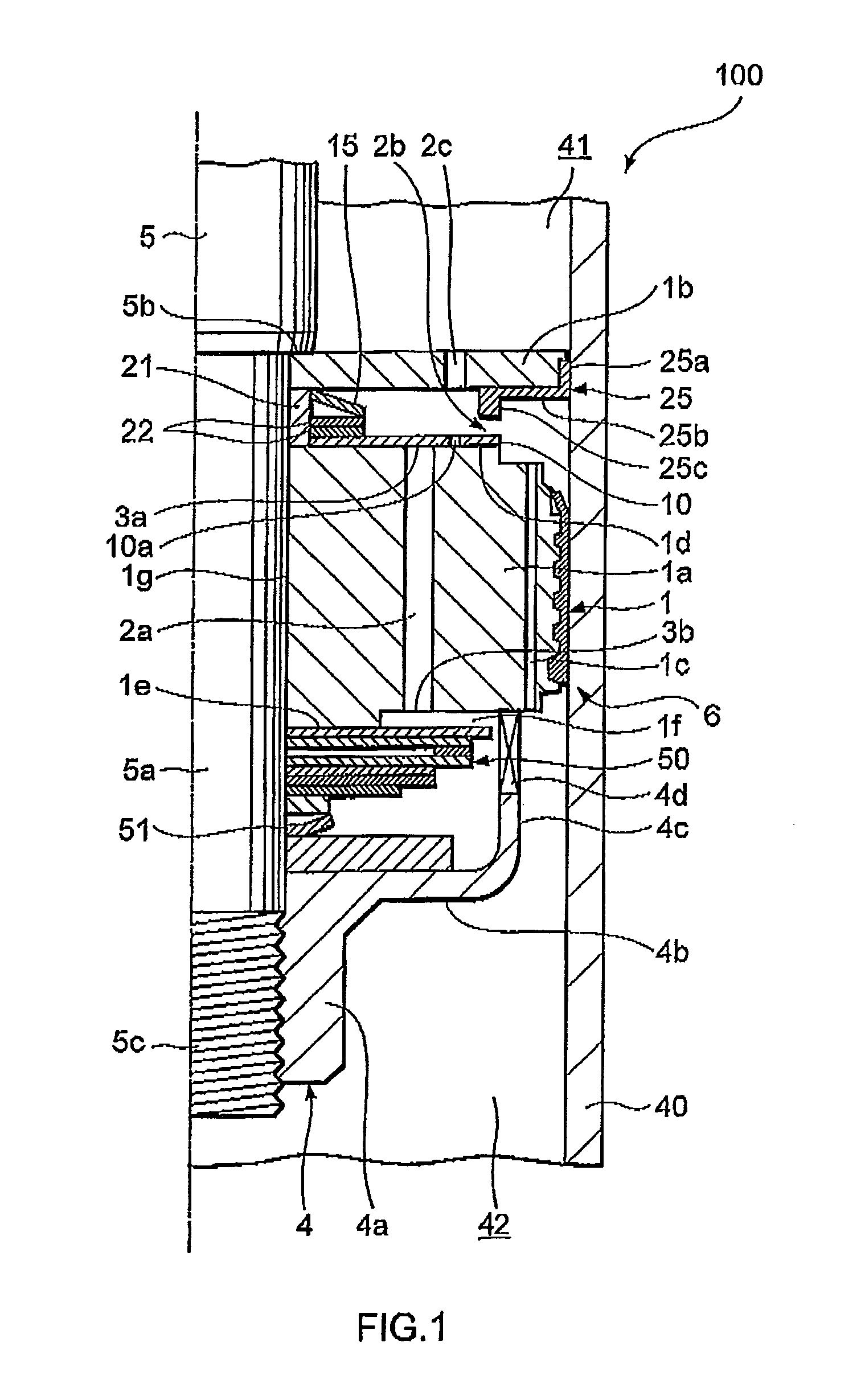
ActiveUS8042661B2Improve comfortImprovement in passenger comfortSpringsShock absorbersWorking fluidShock absorber
A shock absorber (100) for suppressing vibration in a vehicle includes a valve disk (1) that delimits the interior of a cylinder (40) in which a working fluid is sealed; a first passage (2a), a second passage (2b) and a third passage (2c), which are disposed in series so as to connect pressure chambers (41, 42) delimited by the valve disk (1); a valve body (10) that selectively opens the first passage (2a) and the second passage (2b); a biasing member (15) that biases the valve body (10) in a direction for closing the first passage (2a) against the pressure in one of the pressure chambers (42); and a bypass passage (10a) that connects the first passage (2a) to the third passage (2c) when the valve body (10), having displaced in accordance with the pressure in the one pressure chamber (42) so as to open the first passage (2a), displaces further so as to close the second passage (2b). The bypass passage (10a) is set to have a smaller flow passage area than a flow passage area when the first passage (2a) and the second passage (2b) are both open.
Owner:KYB CORP
Composite damping device for vibration and noise reduction of gear shafting
ActiveCN103982635AFlexible spaceCompact structureGear vibration/noise dampingVibration suppression adjustmentsEngineeringVibration transmission
The invention relates to a composite damping device for vibration and noise reduction of gear shafting, which belongs to the technical field of damping devices. The composite damping device acts on each gear shaft through an auxiliary bearing, a clamp and a vibration transmission frame with a flexible structure, vibration, which is generated by some factors in a process of transmission, of a gear pair is transferred to the auxiliary bearing, and the clamp and the vibration transmission frame so as to drive a piston soaked in high-viscosity damping liquid to do shearing motion in the damping liquid, generate a damping force large enough and absorb and dissipate vibration energy, thereby suppressing bending vibration of the shaft. On one hand, internal excitation of the whole gear is reduced, on the other hand, vibration which is transferred to a gearbox body is attenuated. By virtue of the composite damping device disclosed by the invention, the vibration of frequency components due to meshing impact in the gear shafting can be simultaneously reduced, and a vibration frequency band is wide. The composite damping device has the advantages of simple structure, easiness in removal and installation, flexibility of installation position, no worn parts, long service life and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Drawing device
InactiveUS20110203183A1Increased durabilityLarge damping forceBuilding braking devicesMan-operated mechanismEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
Provided is a drawing device that is capable of generating a damping force in accordance with the strength of a biasing force of an elastic member without increasing durability. The drawing device has a linear damper 24 of which a rod is extendable relative to a damper main body and a rotary damper 25 of which a rotation axis is rotatable relative to the damper main body. When a slider 14 of a drawing device main body 4 moves relative to a base 12 of the drawing device main body 4 in the longitudinal direction by the biasing force of the elastic member 15, first, the linear damper 24 starts to operate thereby generating the damping force, then, the linear damper 24 is switched with the rotary damper 25 and the rotary damper 25 starts to operate thereby generating the damping force.
Owner:SUGATSUNE IND CO LTD
Hinge
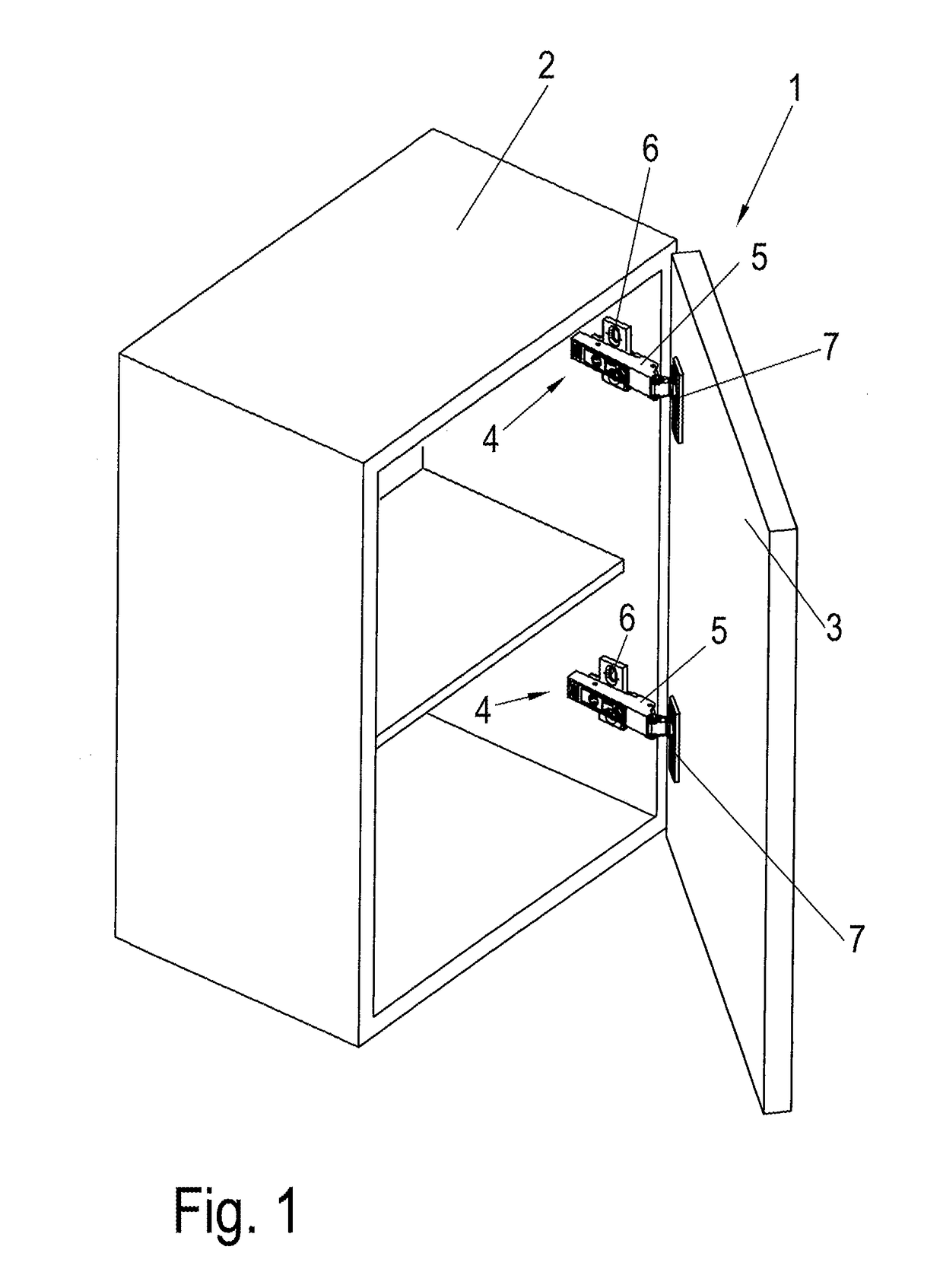
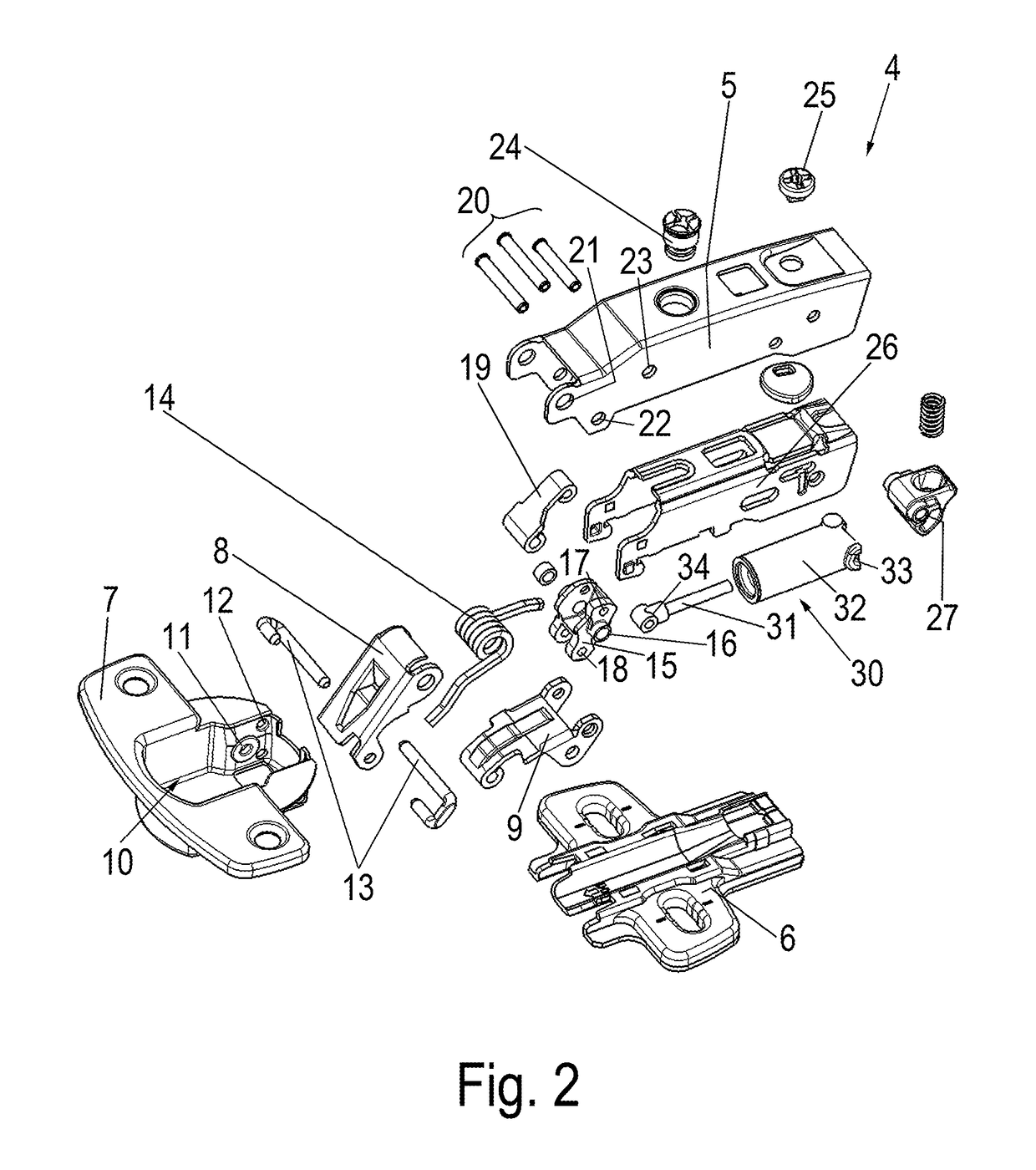
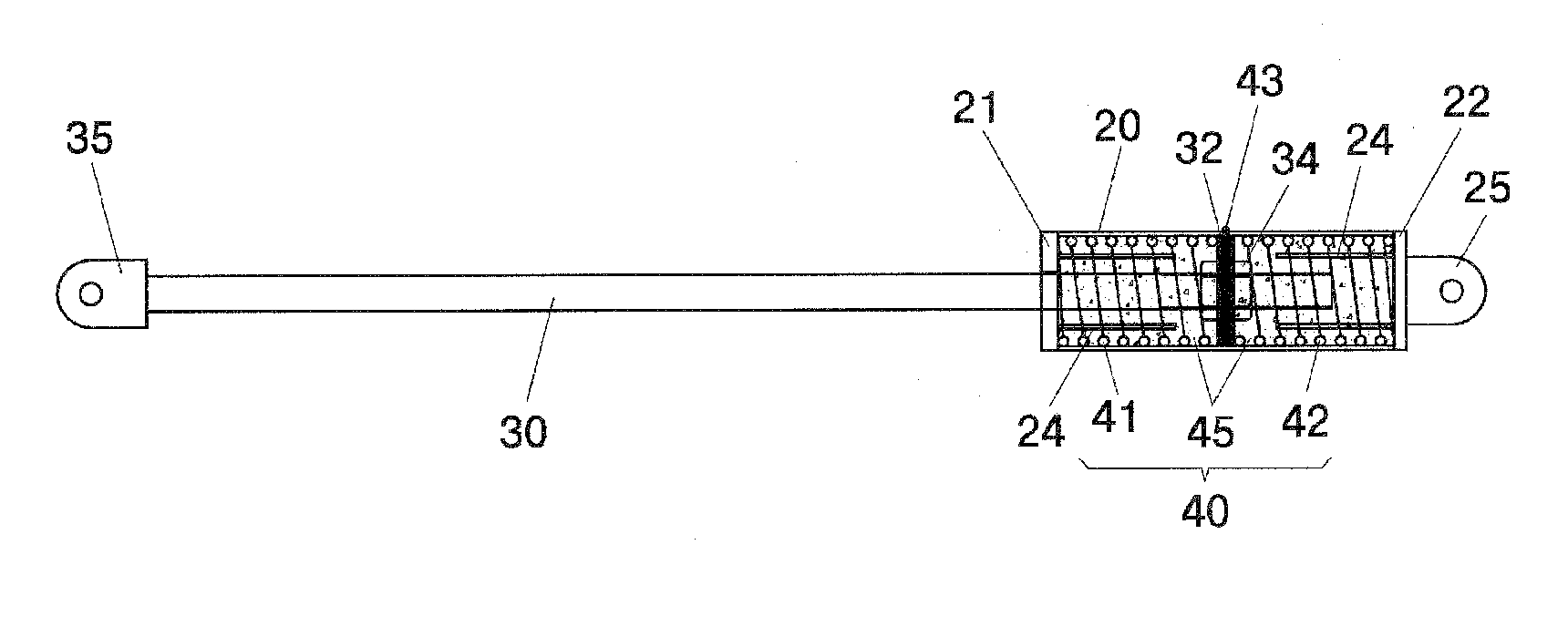
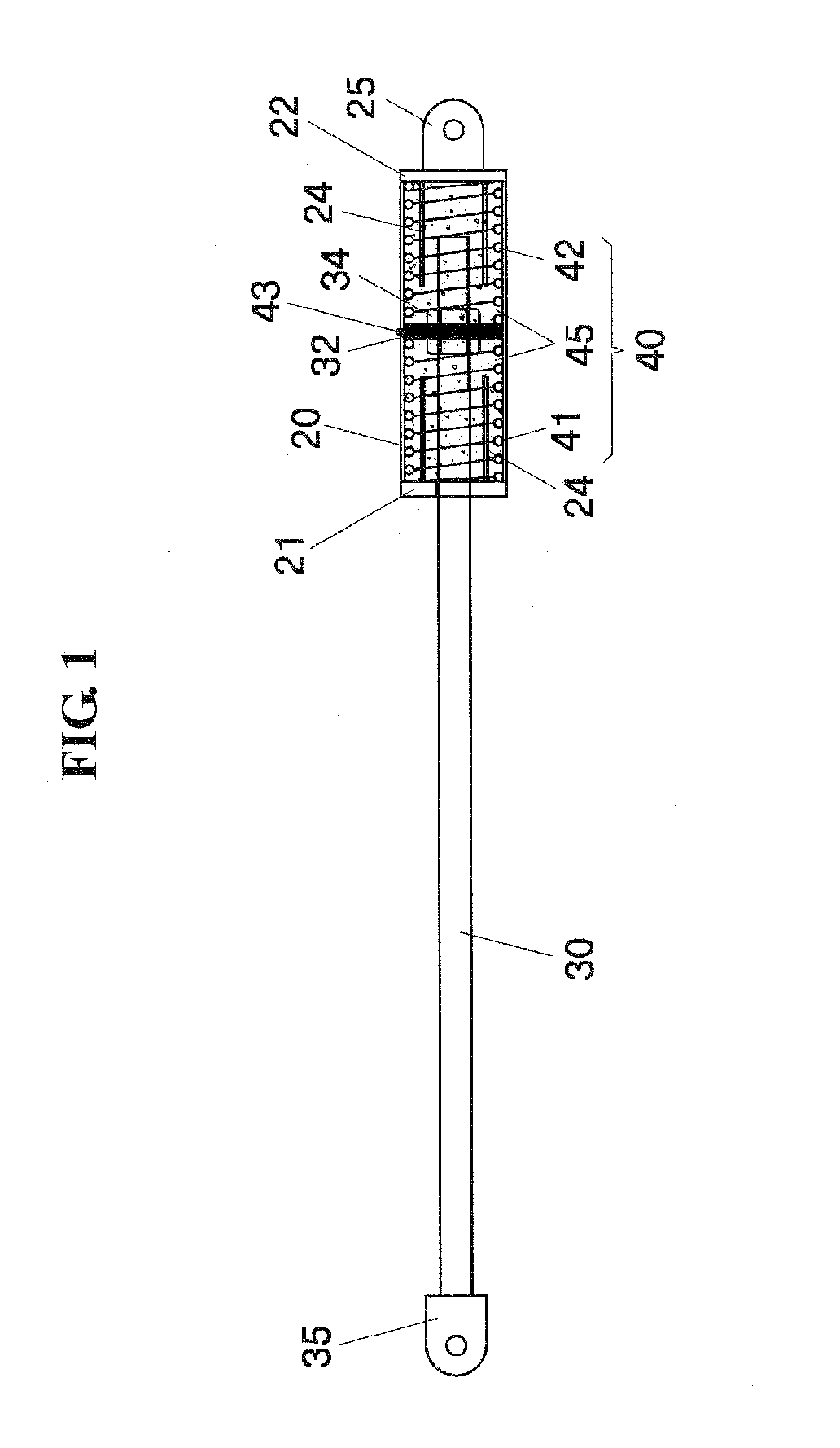
ActiveUS20170138106A1Great damp forceLow damping forceBuilding braking devicesHingesHinge angleEngineering
Owner:HETTICH ONI
Damping device for building seismic reinforcement
InactiveUS20140183802A1Improve performanceIncreased durabilityStands/trestlesProtective buildings/sheltersEngineeringLubricant
Provided is a damping device including a cylindrical body sealed with an inner cover and an outer cover at both ends, a support rod coupled to one end of the cylindrical body to perform an axial motion, the support rod including a moving plate having a damping orifice in the cylindrical body, the support rod including a nut configured to adjust a length of the support rod at an inner side end received in the cylindrical body, and a buffering device configured to store elastic energy in one of a first spring and a second spring based on a moving direction of the moving plate, the buffering device including the first spring inserted in the inner cover, the second spring inserted in the outer cover, and a lubricant in the cylindrical body.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +1
Multifunctional micro speaker
InactiveUS20110274308A1Control displacementIncrease damping forceTransducer detailsLoudspeakerEngineering
A multifunctional micro speaker including a frame; a diaphragm having an outer circumference portion fixed to the frame; a voice coil fixed to a lower surface of the diaphragm; a suspension fixed to the frame and having a predetermined elasticity; a yoke fixed to the suspension and including a receiving groove having a concave shape; a permanent magnet fixed to a bottom surface of the receiving groove; and a plate fixed to an upper surface of the permanent magnet, wherein a through hole is vertically formed through a central portion of a magnetic circuit including the yoke, the permanent magnet and the plate. The multifunctional micro speaker includes the through hole formed in a magnetic circuit, and thus, a vibration displacement of the magnetic circuit and a damping coefficient of the diaphragm may be controlled.
Owner:BSE CO LTD
Magnetic functional fluid, damper and clutch using magnetic functional fluid
InactiveUS20140339029A1Increase damping forceIncrease viscosity of fluidSpringsMagnetic paintsLong axisMaterials science
Magnetic functional fluid includes dispersion medium; and dispersed particles which are dispersed in the dispersion medium, wherein the dispersed particles includes: first ferromagnetic particles having an average particle diameter of 0.5 μm to 50 μm; and second ferromagnetic particles each having a needle-like shape, each having a smaller particle size than the first ferromagnetic particles, and each having a length ratio of a long axis to a short axis of 2 or more.
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
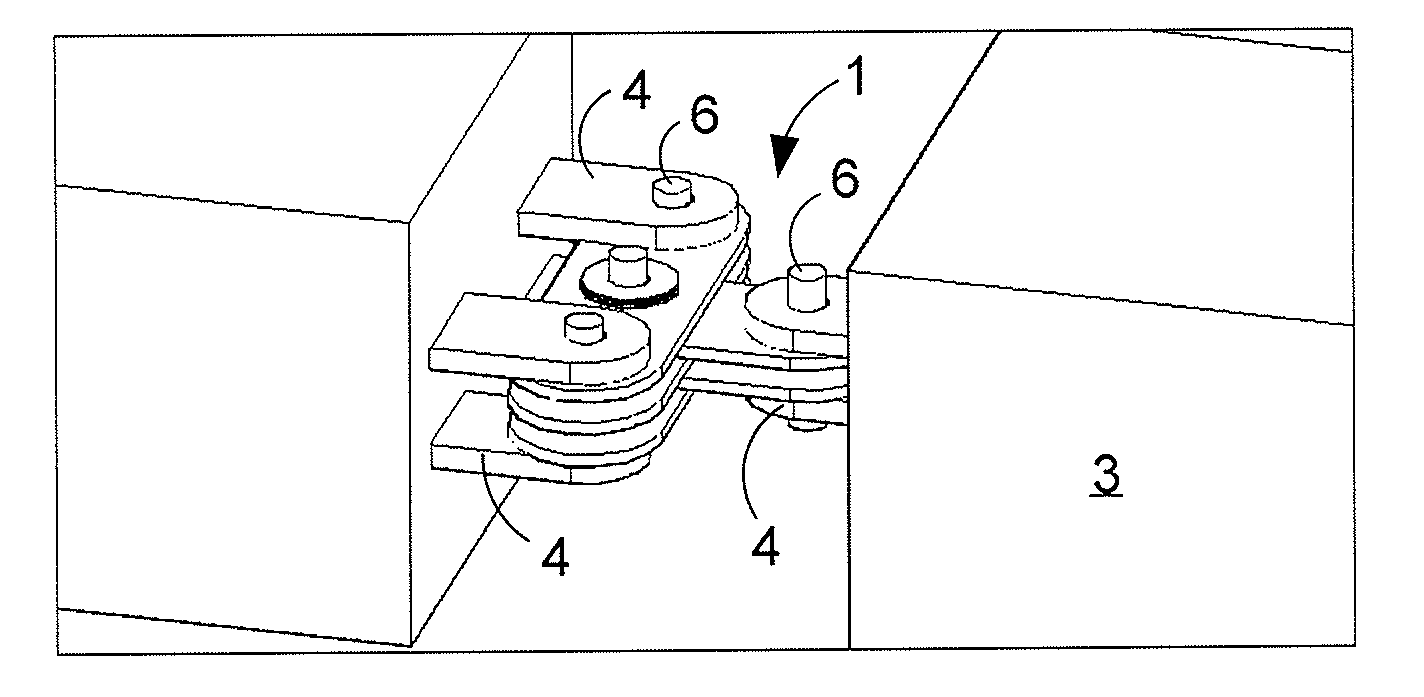
Passive damper
ActiveUS20140174002A1Prevent movementForce is smallVibration dampersNon-rotating vibration suppressionControl theoryRotational joint
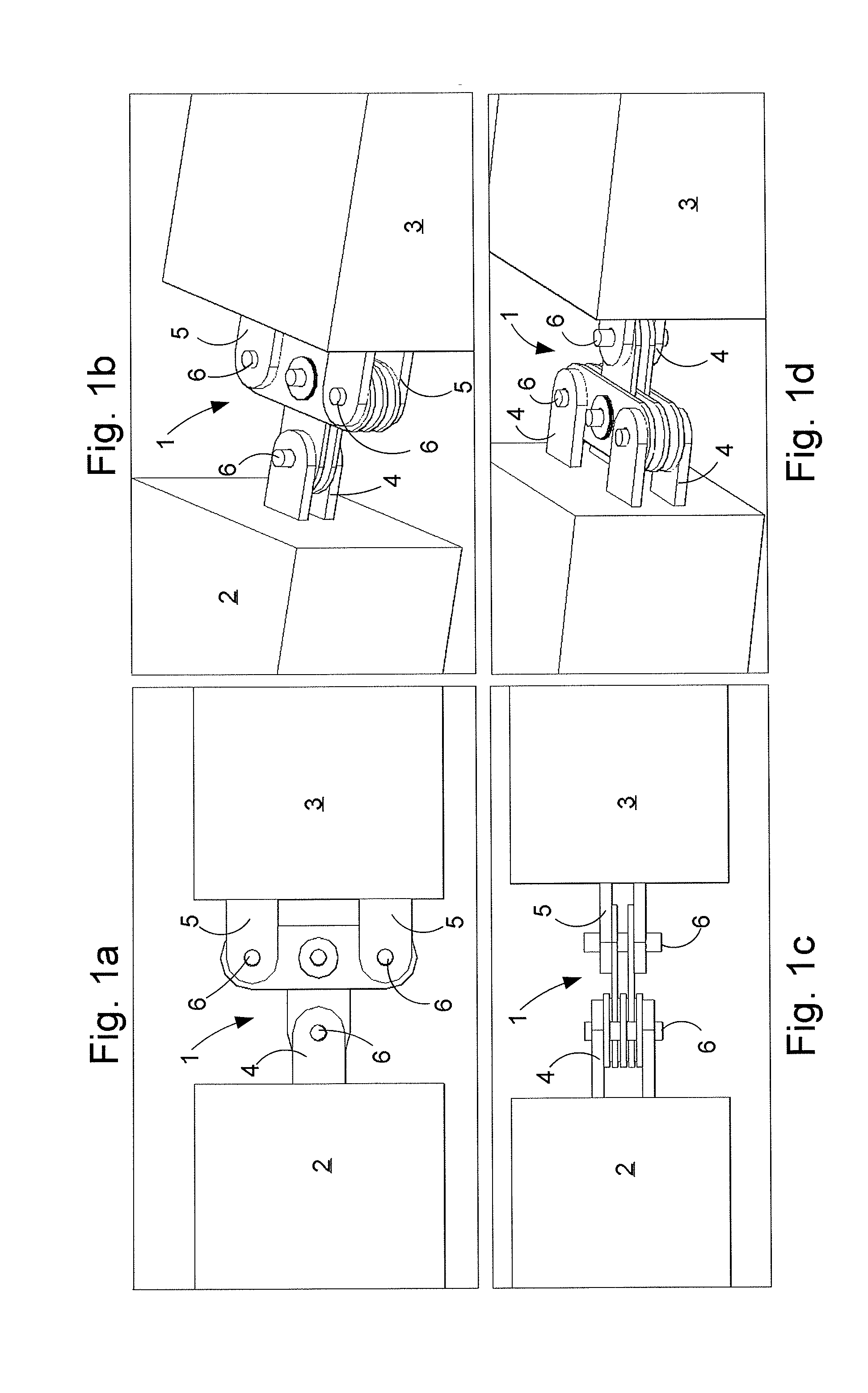
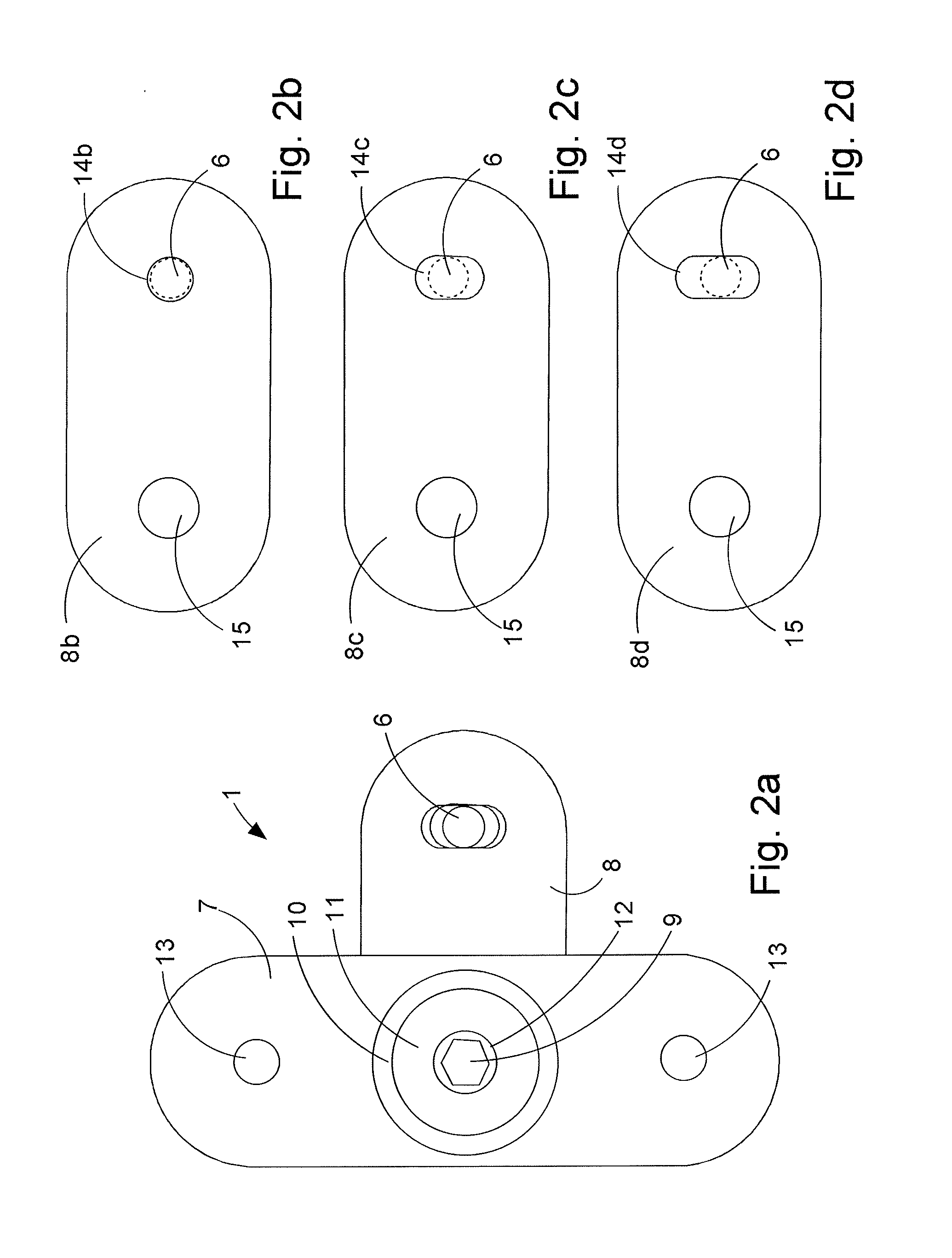
A passive damper (1) with a first set (7) of parallel disposed plates (7a) and a second set (8) of parallel disposed plates (8b,8c,8d), that overlap one another in an alternating fashion at a rotational joint with damping pads (15) between the plates (7a,8b,8c,8d). The rotational joint comprises a pin or bolt (9) inserted through apertures (15) in the plates (7a,8b,8c,8d) and there is a connection hole (14b) in each of the plates of the second set (8) of plates for receiving a connection pin (6) therein for connecting the second set of plates (8) to a members (2,3) of a structure. The connection holes (14c,14d) in a selection of the plates (8c,8d) of the second set (8) of plates is shaped and dimensioned to provide a predetermined amount of clearance with said connection pin (6) so that the connection pin (6) can move inside the connection holes (14c,14d) of the selection of plates (8c,8d) to a predetermined extent without the selection of plates (8c,8d) taking part in the damping action of the damper (1).
Owner:DAMPTECH AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com