Suspension system for in-wheel motor vehicle
a suspension system and motor vehicle technology, applied in the direction of shock absorbers, electric propulsion mountings, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of causing vehicle passengers to feel uncomfortable, vibration occurs, vibration is generally occurring, etc., to prevent vibration from becoming considerable, the effect of reducing vibration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
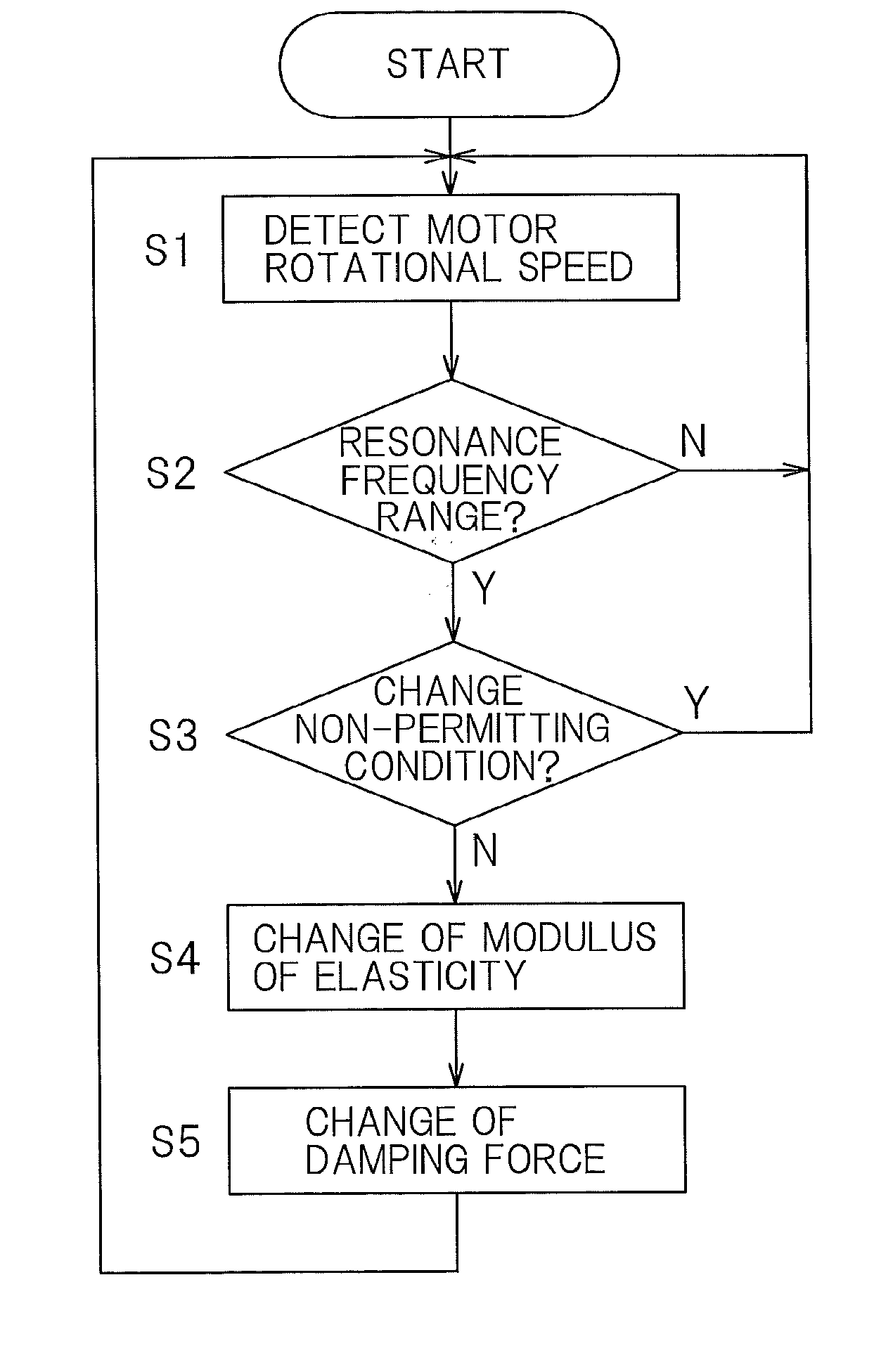
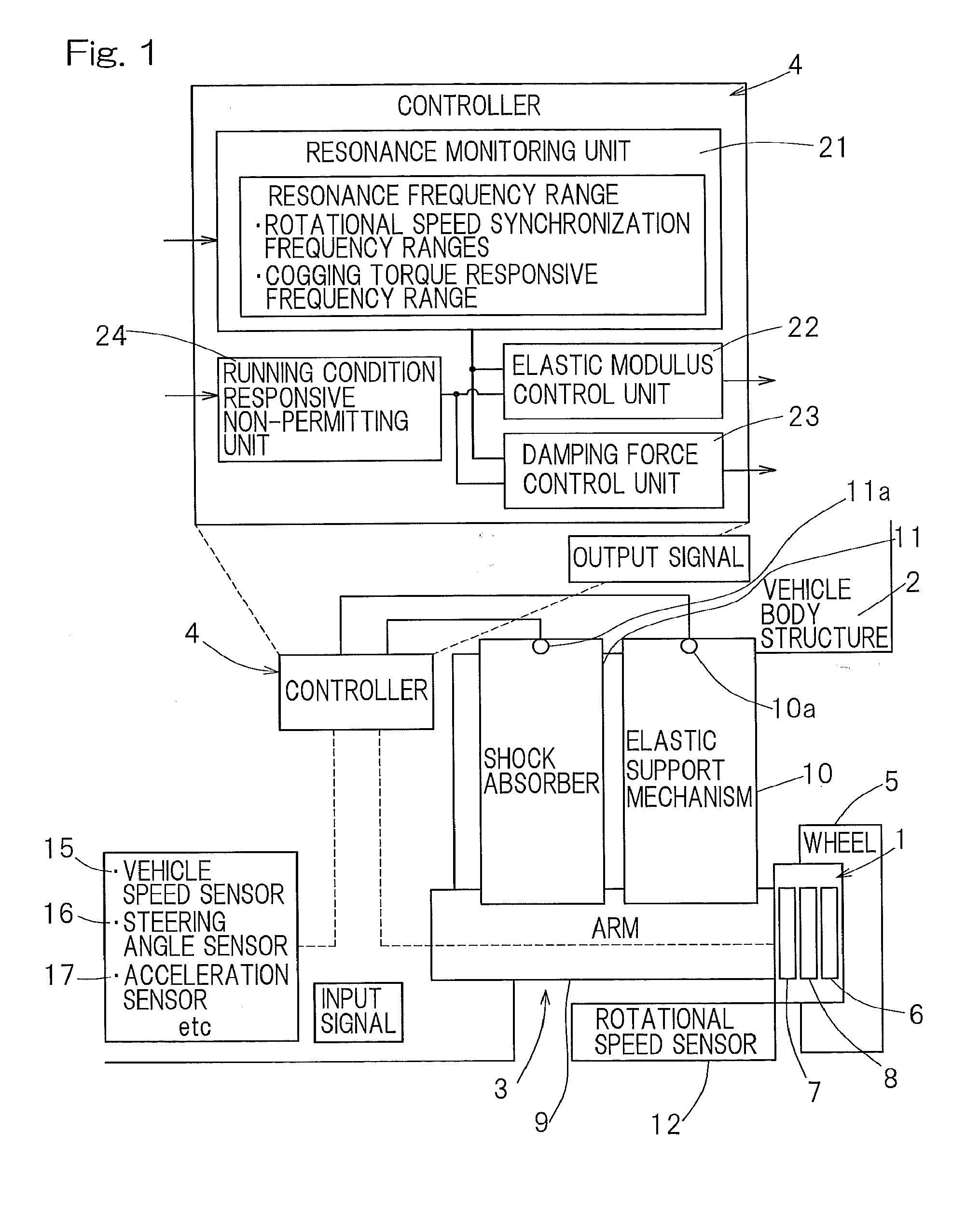
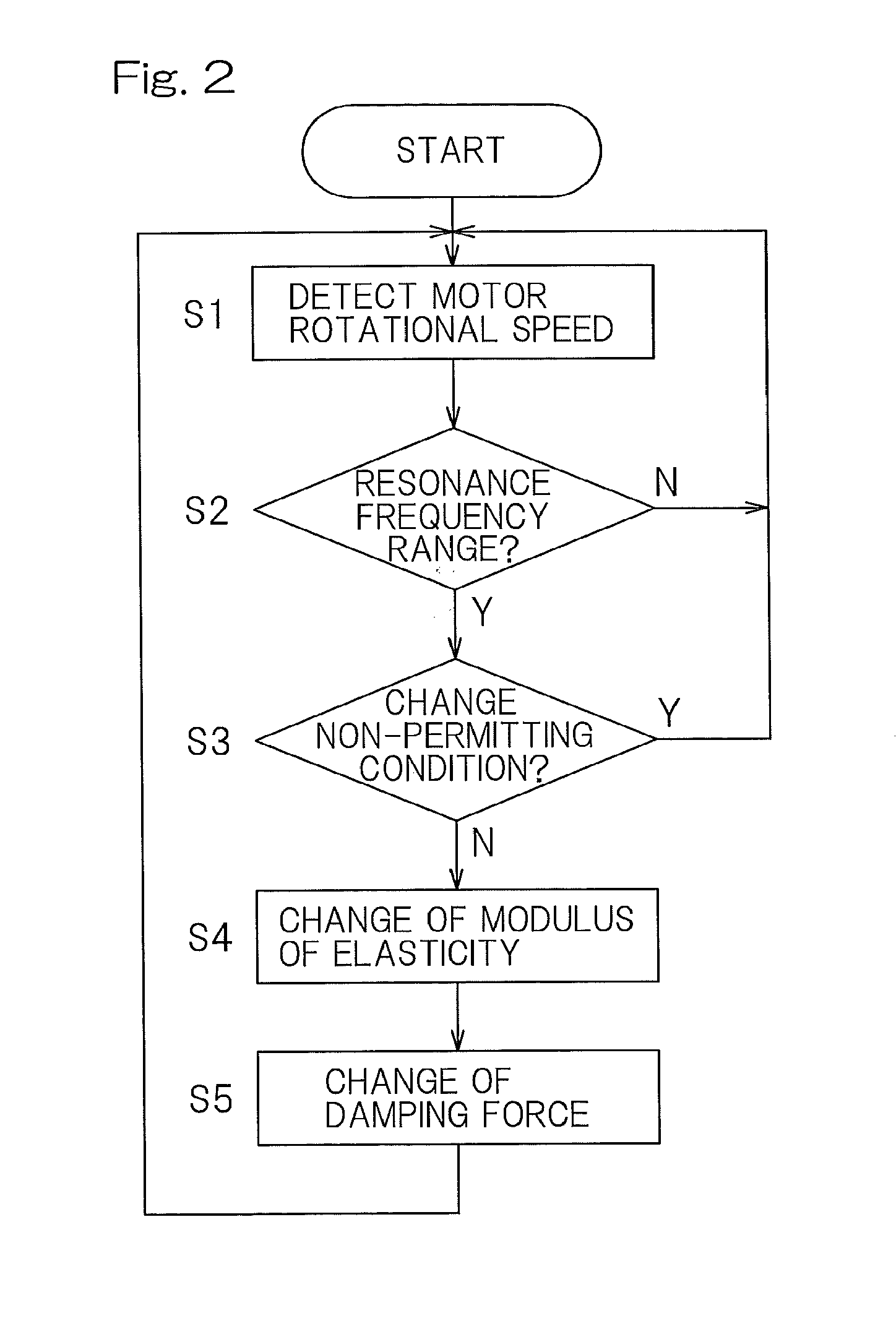
[0027]A preferred embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. A suspension system for an in-wheel motor mounted vehicle according to the present invention includes a suspension 3 interposed between an in-wheel motor device 1 and a vehicle body structure 2, and a controller 4 to control the modulus of elasticity and the damping force of the suspension 3.
[0028]The in-wheel motor device 1 includes, as shown in, for example, FIG. 3, a wheel support bearing assembly 6 to support a wheel 5, a motor 7, and a reduction gear 8 to transmit the rotation of the motor 7 to a rotatable side raceway of the wheel support bearing assembly 6. The wheel support bearing assembly 6 is of a type in which a plurality of rows of rolling elements 33 are interposed between an outer member 31, which will become a stationary side raceway, and an inner member 32, which will become the movable side raceway, and a rim for the wheel 5 is fitted to a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com