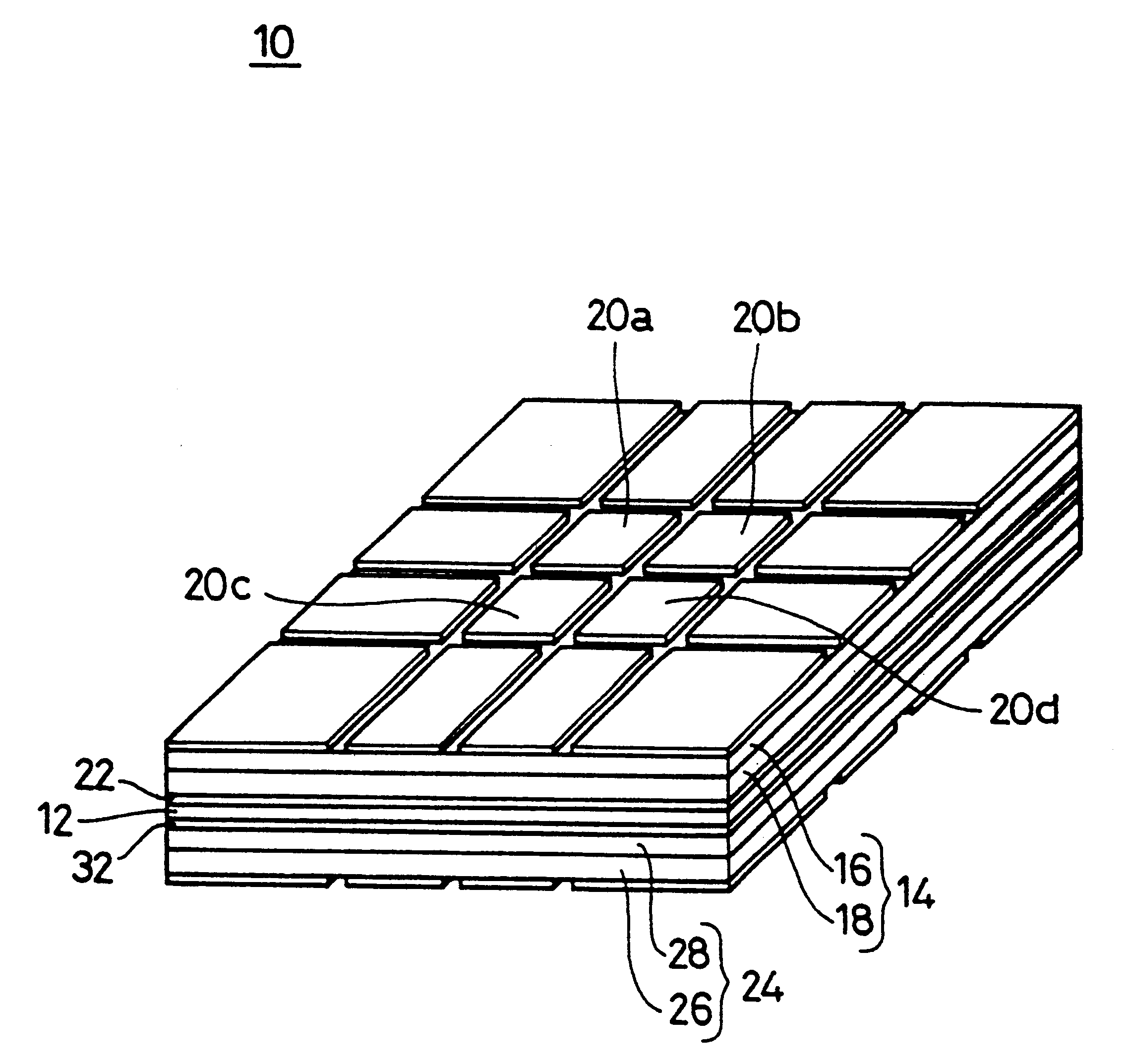
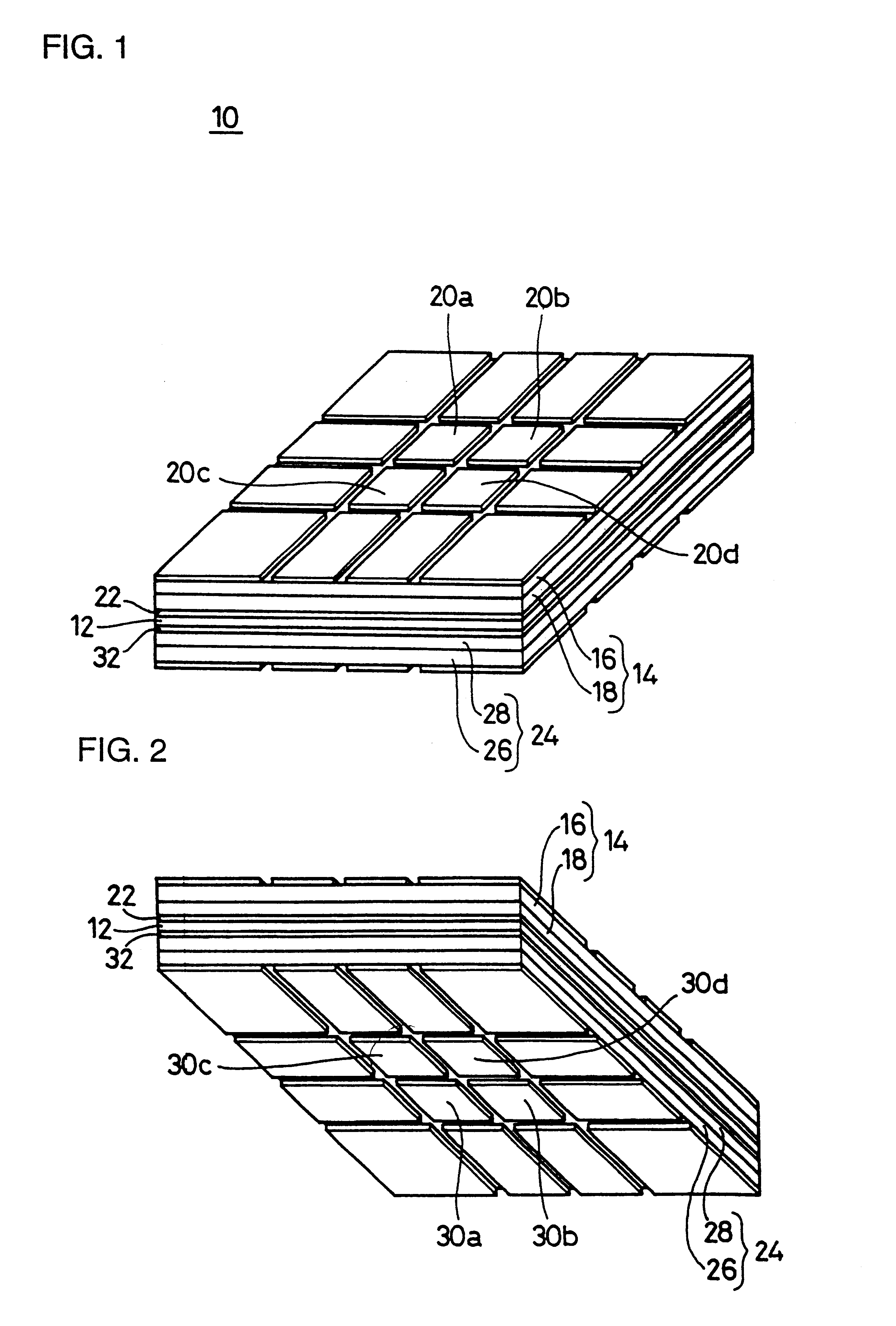
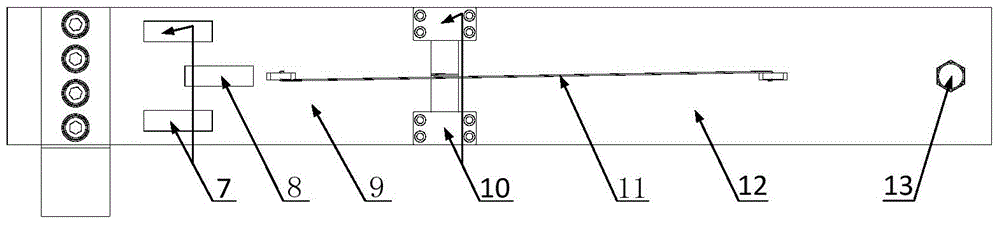
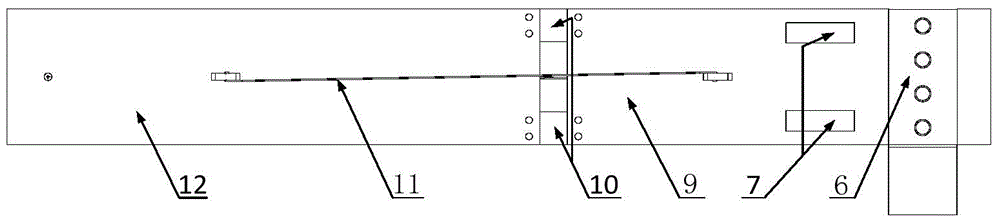
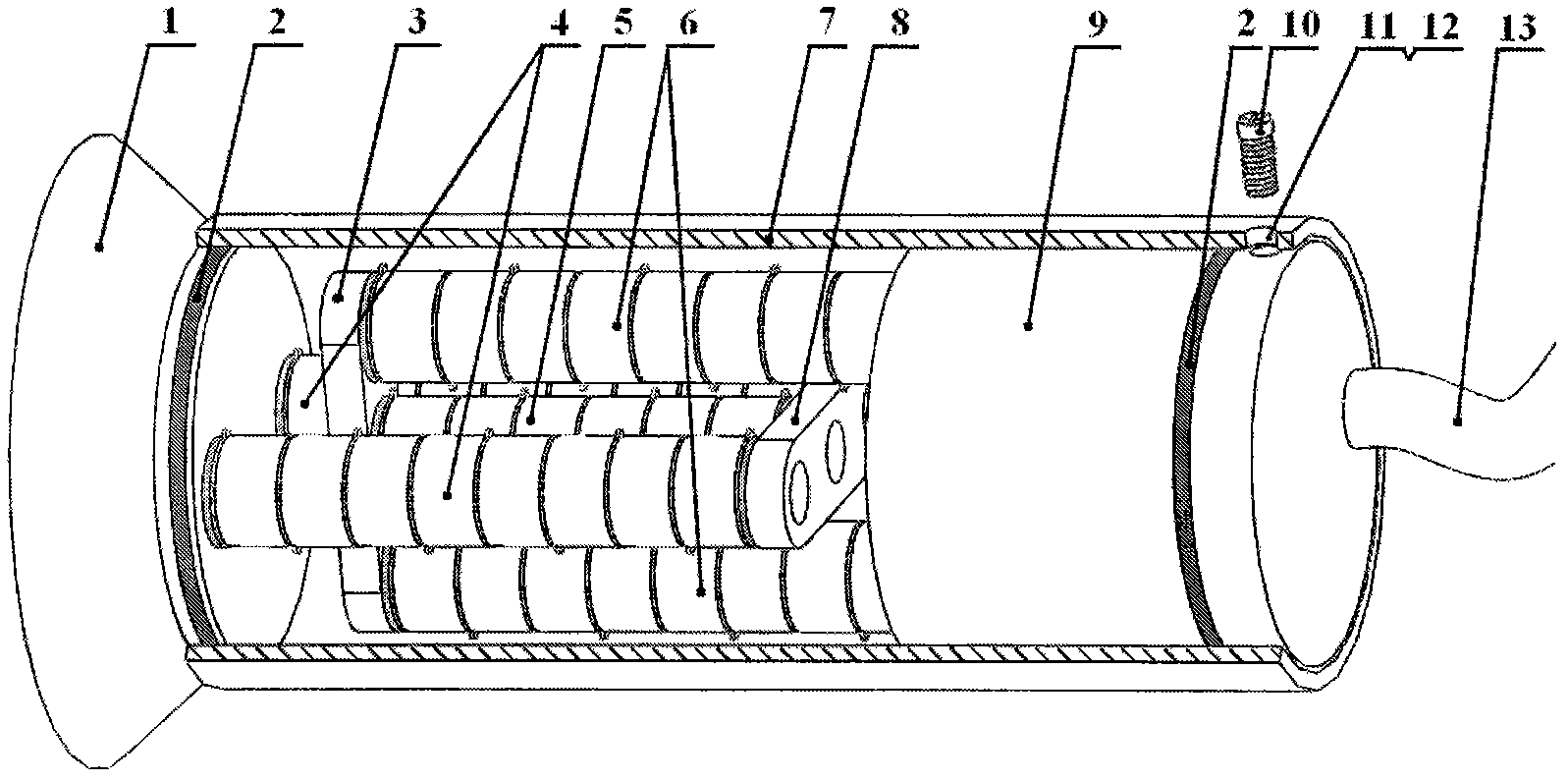
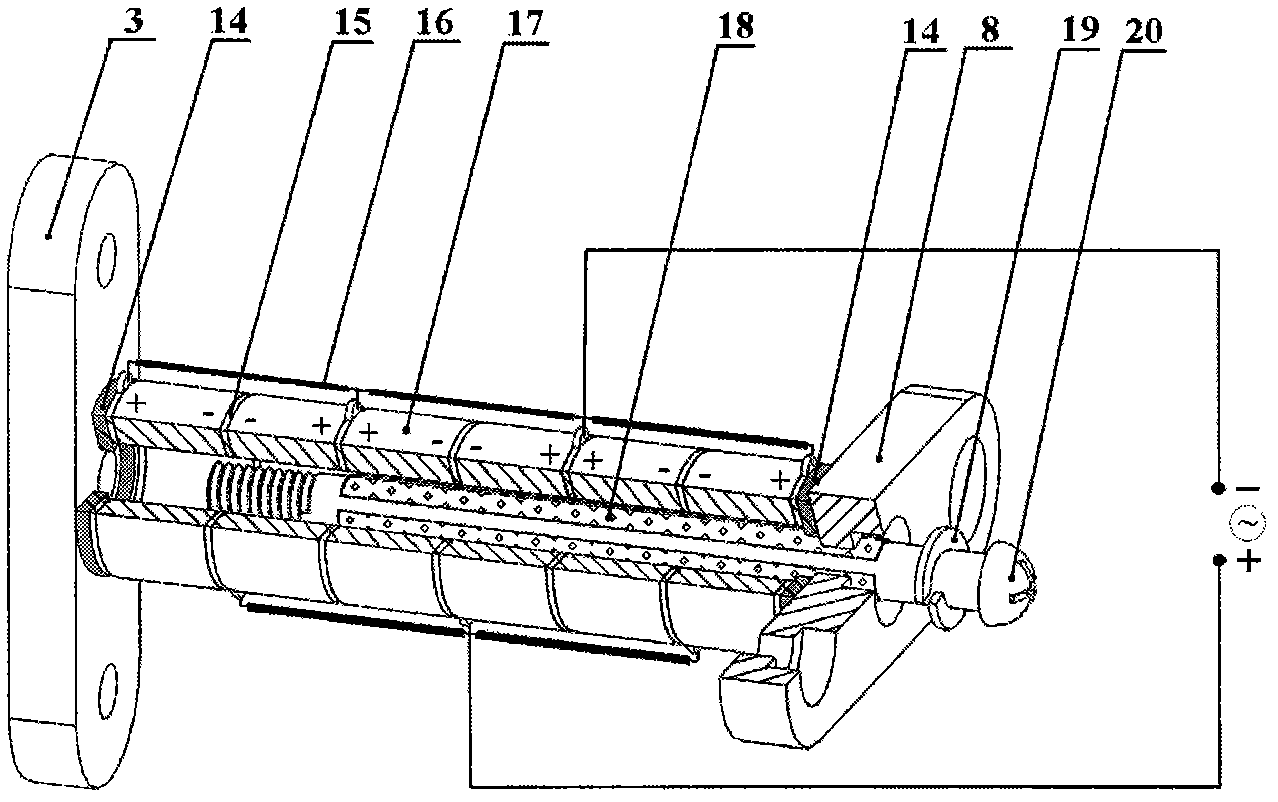
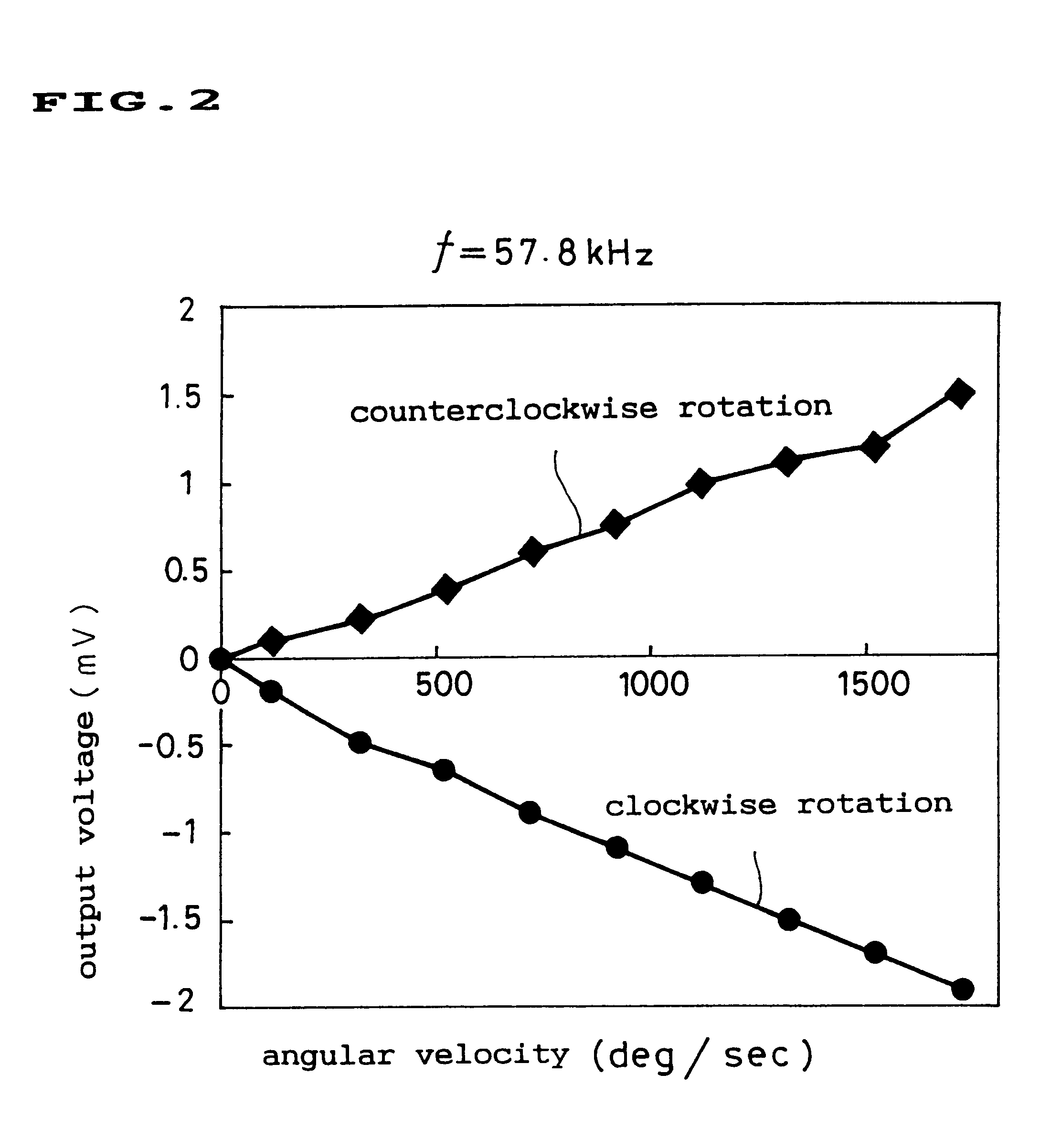
Patents
Literature
754 results about "Bending vibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
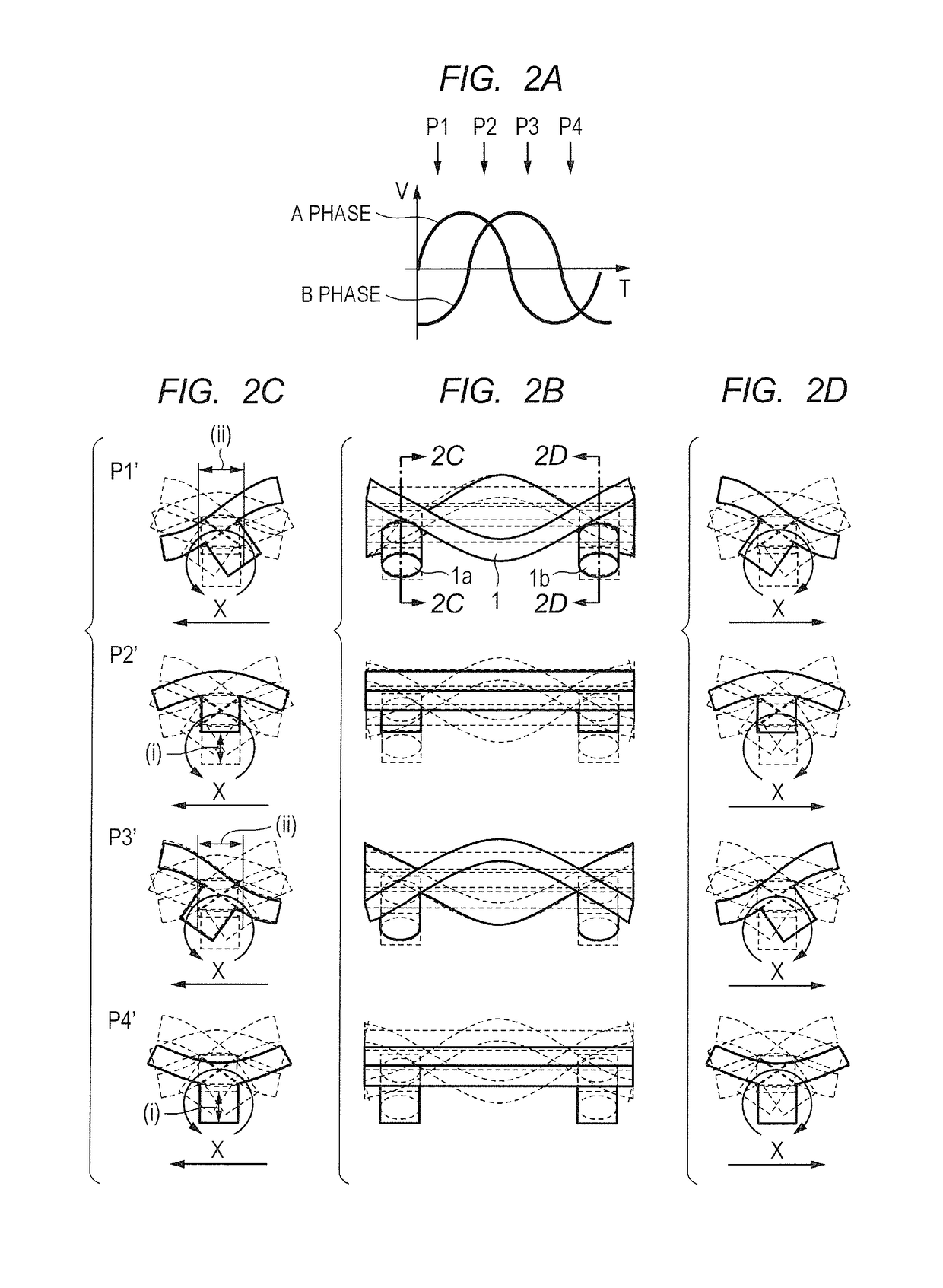
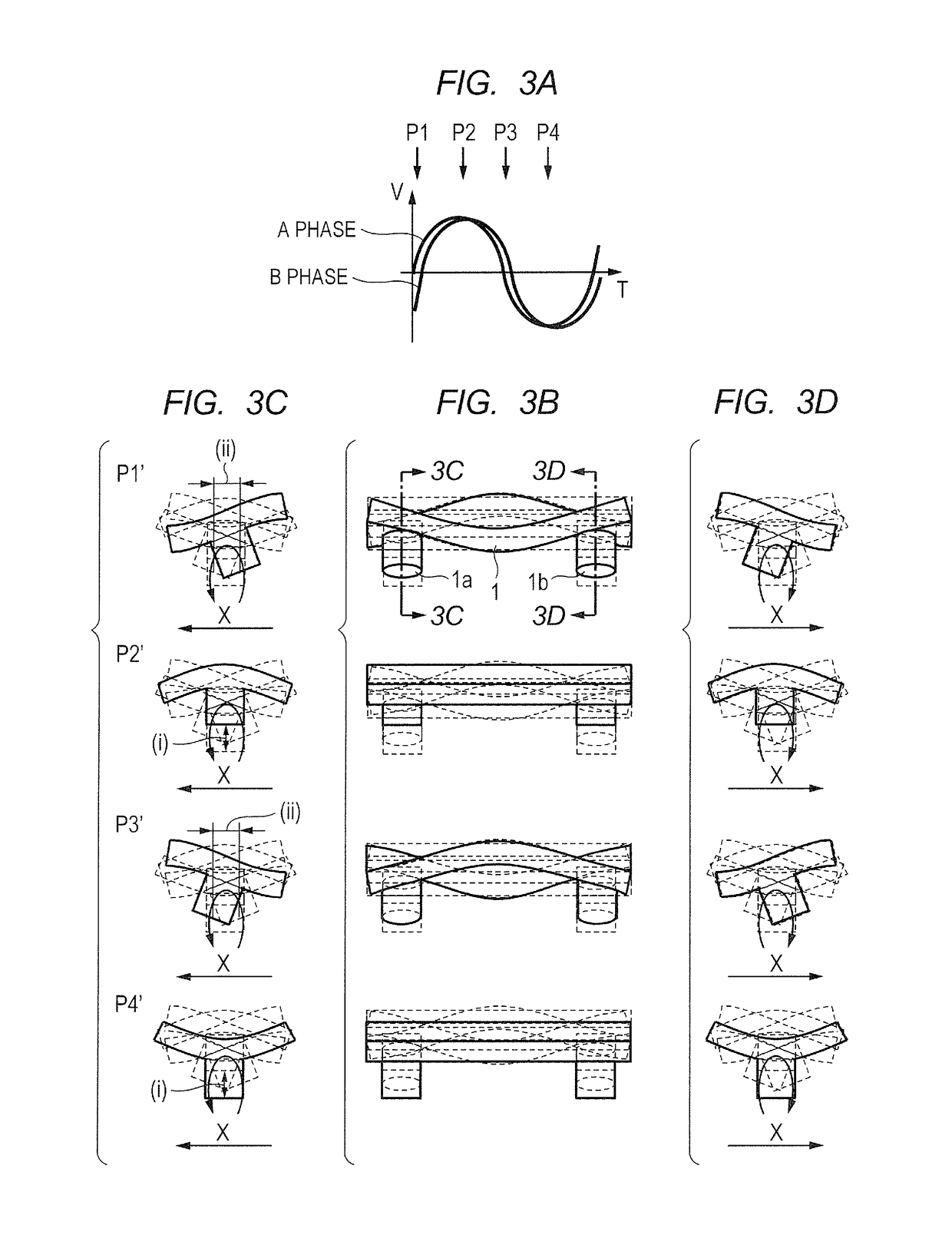
Bending Vibrations. Bending vibrations change the angle between two bonds. There are four types of bending vibration. Scissoring is the movement of two atoms toward and away from each other.
Fluid pump
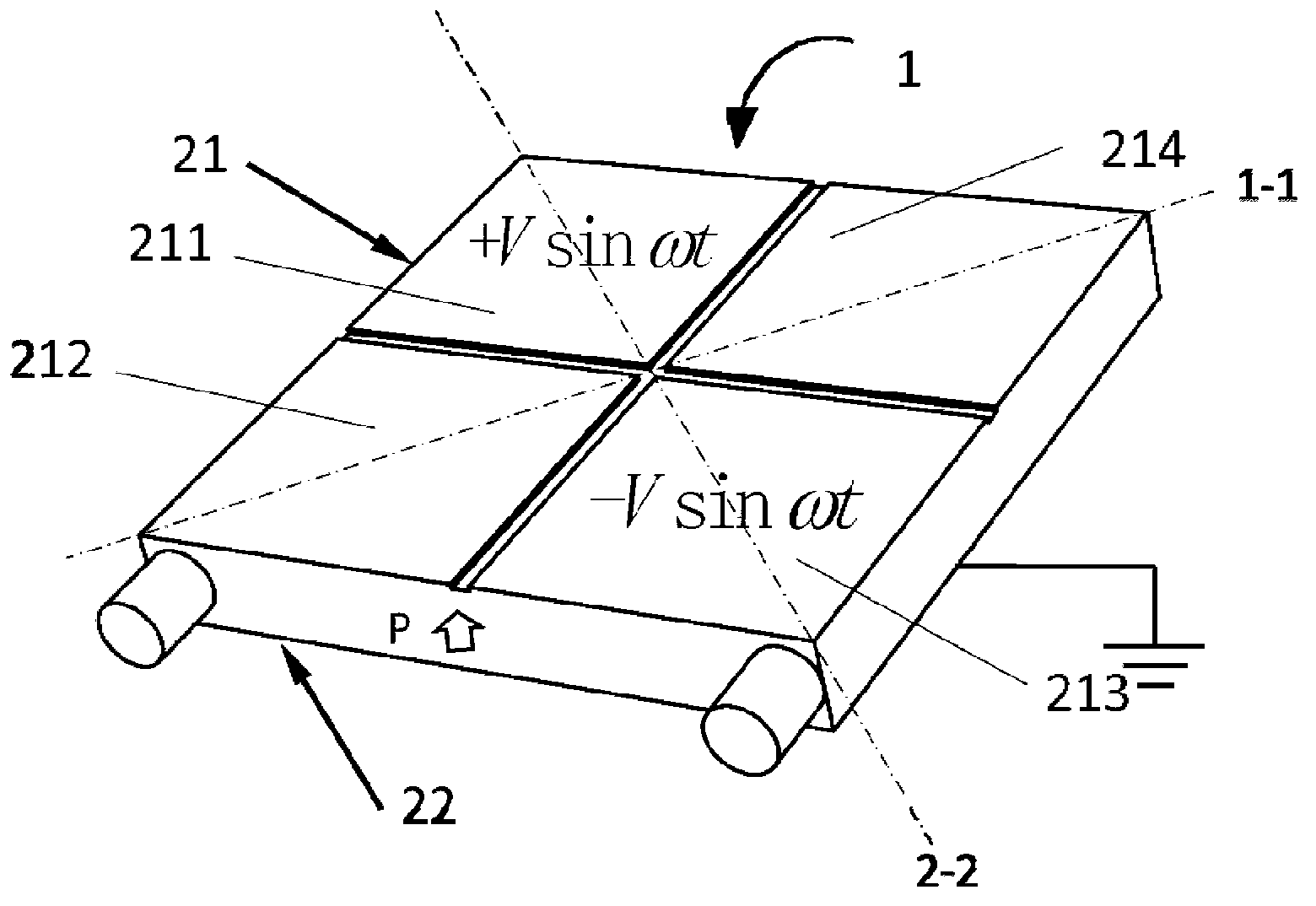
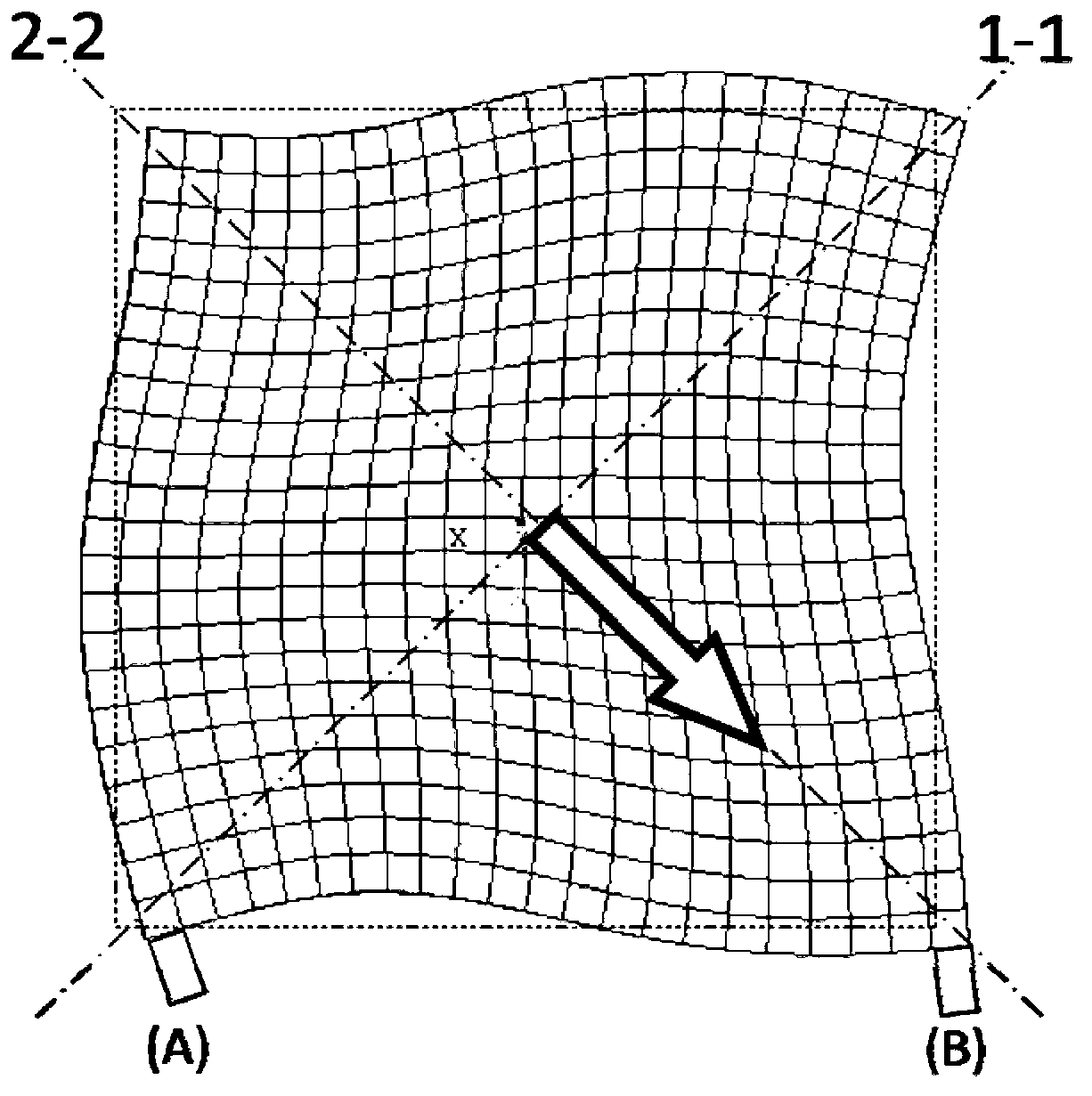
ActiveUS20120171062A1Improve abilitiesPumping capability can be improvedPositive displacement pump componentsWorking fluid for enginesSquare waveformActuator
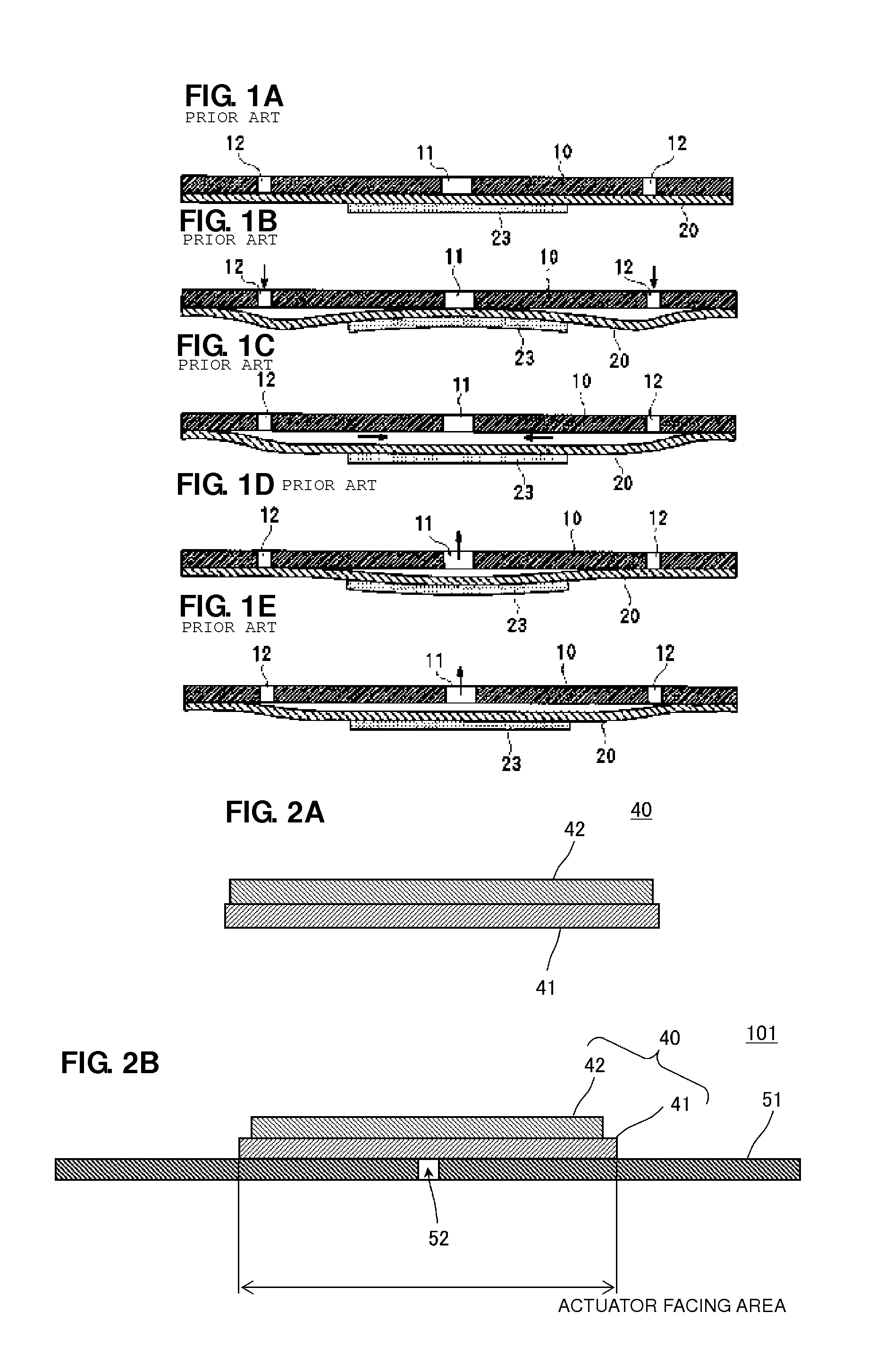
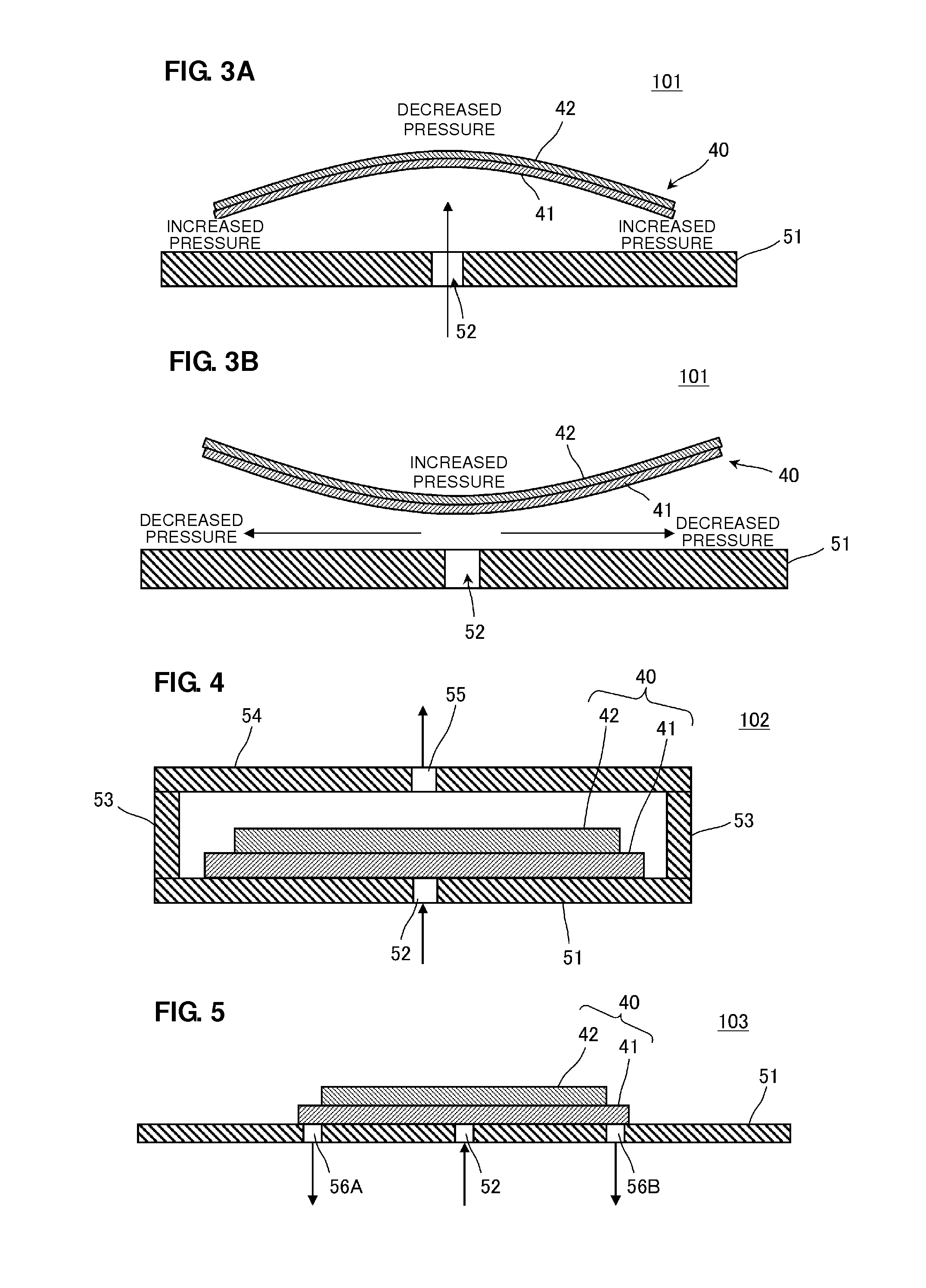
A small-sized, low-profile fluid pump having high pumping capabilities includes an actuator and a planar section including a metal plate. The actuator includes a disk-shaped piezoelectric element attached to a disk-shaped diaphragm. As a result of application of a square-wave or sine-wave drive voltage, the actuator performs a bending vibration from the central portion to the peripheral portion. The peripheral portion of the actuator is not restrained. The actuator performs a bending vibration in the state in which it is in proximity to the planar section while facing the planar section. A center vent is provided at or in an area adjacent to the center of an actuator facing area of the planar section that faces the actuator.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Prism longitudinal bend composite vibrator linear supersonic motor
InactiveCN101051798AThe resonance frequency is consistentImprove efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElastomerPrism
The linear ultrasound electrical motor (LUEM) includes drive oscillator, mover, chassis, and relevant locking gear for fastening them. The drive oscillator includes piezoelectric element and metal elastic body (MEB). The piezoelectric element includes piezoelectric ceramic piece (PCP) of bending vibration, and PCP of longitudinal vibration in use for generating rectilinear vibration. At least one dogtooth contacted to mover is setup on MEB. Slider of guiding bulge is setup on side of mover. The guiding bulge is corresponding to straight-line guidance groove setup on the chassis. The disclosed LUEM is longitudinal and bending composite driving LUEM with prism type oscillator. The drive oscillator is prism type longitudinal bending composite oscillator composed of connection terminals, longitudinal vibration rectangular PCP and front cover board fastened by double end bolts and nuts. The oscillator is as stator of LUEM to generate longitudinal and bending vibration.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Vibrator, vibratory gyroscope, and vibration adjusting method
InactiveUS6018212AGenerate efficientlyHigh sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesGyroscopeMechanical engineering
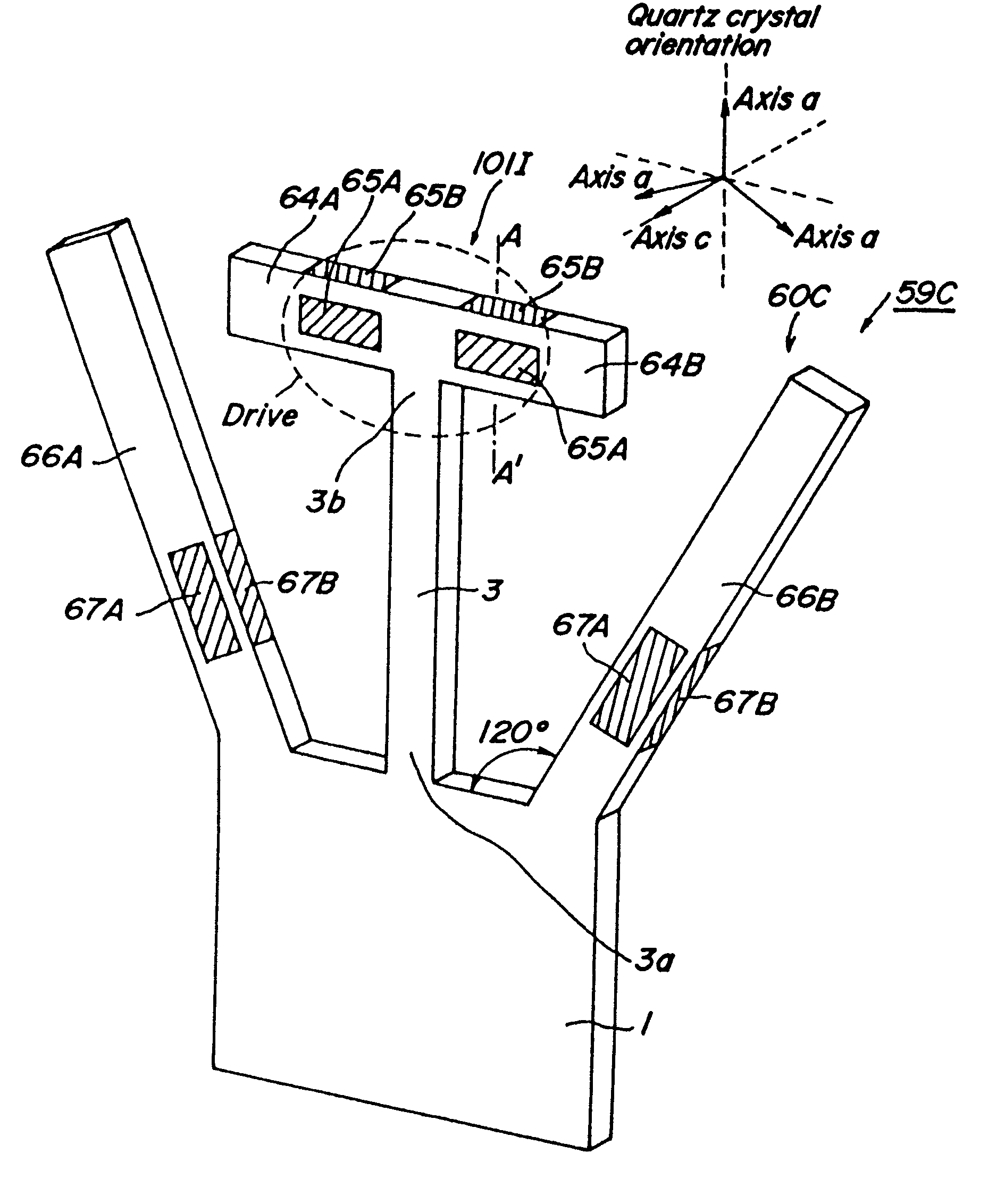
A vibrator of a vibratory gyroscope comprises a main arm having a base part and at least one bending-vibration piece extending from the base part in a direction crossing the longitudinal direction of the base part and a fixing part for fixing one end of the base part, and the base part and the bending-vibration piece are formed so as to extend substantially in a specified plane. Preferably, at the opposite side to one end of the base part, a projection projecting from the bending-vibration piece is provided, or at least a pair of resonant arms resonating with vibration of the base part, said pair of resonant arms projecting from the fixing part are provided. Thanks to this, it has been possible to detect a turning angular rate in a sufficiently high accuracy without providing a projection which has a certain weight and extends from the vibrator toward the axis of turning even in case of arranging the vibrator so that the vibration arm of the vibrator extends perpendicularly to the axis of turning.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Device and method for detecting pipeline closed cracks based on vibro-acoustic modulation technology
ActiveCN102226783AEfficient detectionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalFrequency spectrumAccelerometer
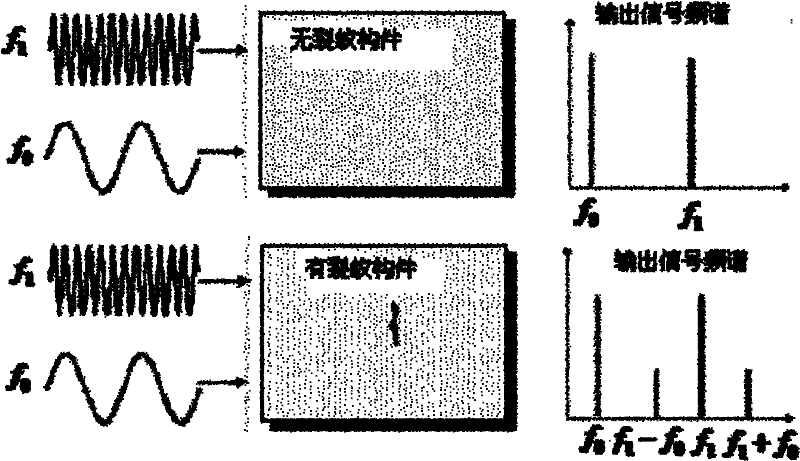
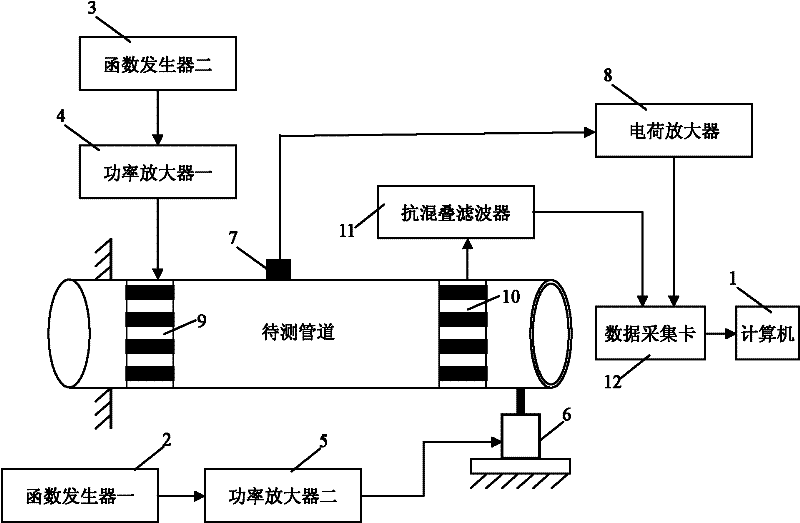
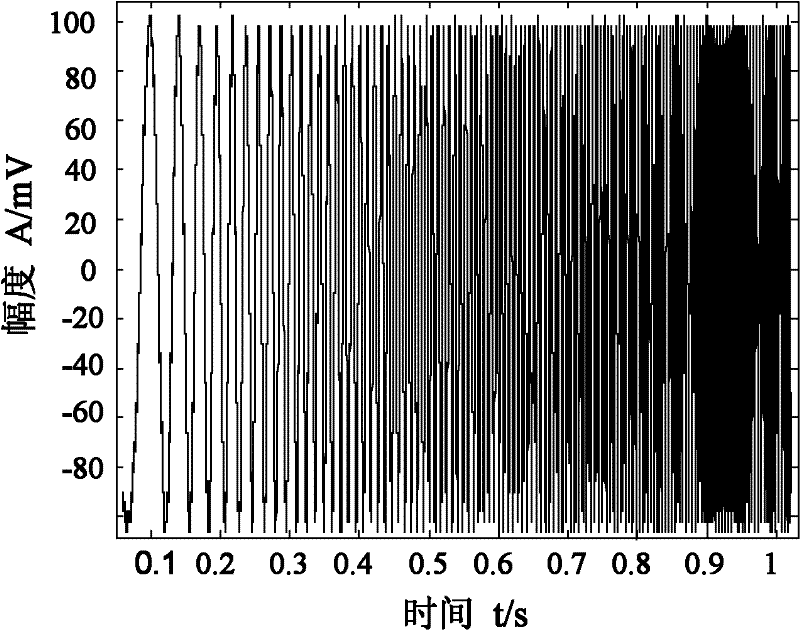
The invention relates to a device and a method for detecting pipeline closed cracks based on the vibro-acoustic modulation technology and belongs to the pipeline nondestructive testing field. The device provided by the invention comprises a computer, a first function generator, a second function generator, a first power amplifier, a second power amplifier, a vibration exciter, an accelerometer, acharge amplifier, a first thickness concertina-type piezoelectric ceramic sheet array and a second thickness concertina-type piezoelectric ceramic sheet array, an anti-aliasing filter and a data collection card. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: acquiring a pipeline first-order bending vibration inherent frequency by swept frequency excitation; taking the frequency as the one of low-frequency vibration in the vibro-acoustic modulation detection; simultaneously exciting low-frequency bending vibration and high-frequency supersonic waves into the pipeline, determining whether there exists closed cracks inside the pipeline by the existence of frequency components which equal high frequency supersonic wave frequency subtracts or adds low frequency bending vibration frequency in a received signal frequency spectrogram. The device provided by the invention is utilized to solve the problem that it is hard to detect closed cracks by traditional methods, and can be applied to detect closed cracks in industrial pipelines.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Vibrators and vibratory gyroscopes
ActiveUS7043986B2Crystal impedance can be loweredHigh detection sensitivityMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateAcceleration measurement using interia forcesGyroscopeEngineering
A vibrator for generating a signal for measuring a physical quantity using a vibrator is provided, including at least one bending vibration arm vibrating in bending mode along a specified plane and having a first end, an opposed second end, and first and second main faces that are substantially parallel with each other. A base portion is provided at the first provided at the first end of the bending vibration arm, a weight portion is provided at the second end of the bending vibration arm, and grooves are formed on the first and second main faces. The vibrator further includes driving means for exciting a driving vibration in the vibrator, and detecting means provided on one of the bending vibration arms for detecting an output signal based on detection vibrations induced in the vibrator responsive to the physical quantity to be measured.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Piezoelectric generator for collecting bending vibration energy
InactiveCN101262189AQuick responseLow costPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityPiezoelectric generator
The invention relates to a piezoelectric generator collecting energy of bending vibration and pertains to the technical field of piezoelectric generators. The piezoelectric generator of the invention is characterized by the adoption of a three-layer structure with two cantilevered piezoelectric ceramic layers and a metal layer, namely, the upper layer and the lower layer of the piezoelectric generator are piezoelectric ceramic layers (1, 2), the polarization direction of which are opposite; the piezoelectric ceramic layers are respectively stuck with a metal layer (3) in the middle by conductive adhesive layers (4, 5) and electrode surfaces (6, 7) of the piezoelectric ceramic layers (1, 2) are connected with a power circuit with functions of rectification and energy collection by conducting wires (8, 9); the metal layer (3) at a fixed end of a piezoelectric device stretches outside the piezoelectric ceramic layers (1, 2) and the piezoelectric device is fixed through the metal layer (3) at the fixed end. The piezoelectric generator of the invention has the advantages of fast responding, low cost, simple structure, no heat emission, and no consumption of any material during operation, etc., and the piezoelectric generator meets the requirement of saving energy and has obvious commercial and social values.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Bending mode conversion type ultrasound wave torsional vibration energy converter
InactiveCN101259465ALarge vibration amplitudeHigh output powerMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransformerTransducer
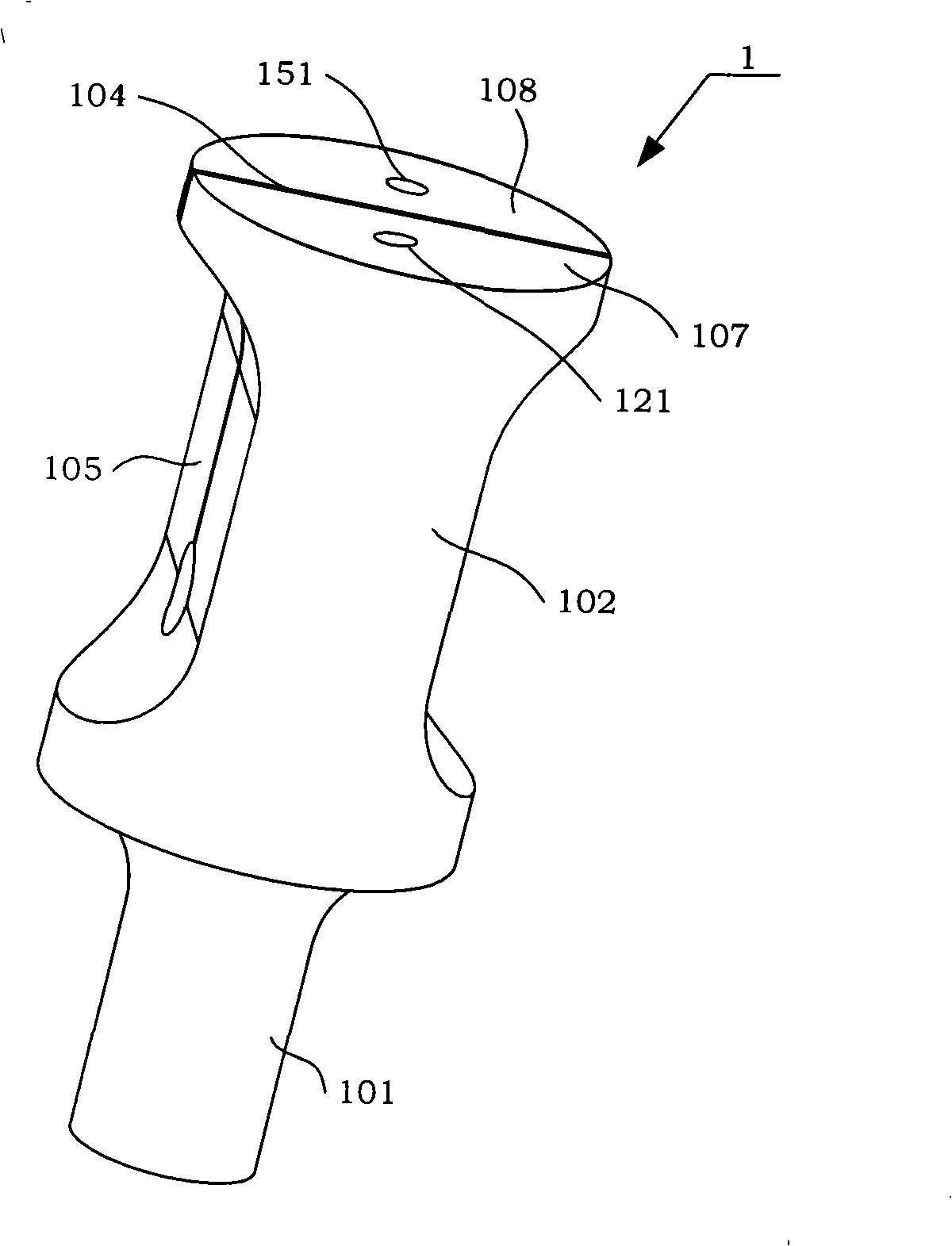
The invention discloses a bending-twisting conversion type ultrasonic torsion vibration transducer which comprises a bending-twisting vibrating body(1), a drive component (2) and a back cover (3) of the transducer; the drive component (2) is arranged between the bending-twisting vibrating body(1) and the back cover (3) of the transducer, and moreover, an A pretighting bolt (33) passes through the through hole of an A end cover (31), an A through hole (22) and an A pretighting screw hole (121) in turn through to arrange the A end cover (31) and an insulating block (21) on the A top surface (107) of the bending-twisting vibrating body(1); an B pretighting bolt (34) passes through the through hole of an B end cover (32), an B through hole (23) and an B pretighting screw hole (151) in turn to arrange the B end cover (32) and the insulating block (21) on the B top surface (108) of the bending-twisting vibrating body(1). A pair of bending vibrations with the same frequency swings and opposite vibrating directions generated by corresponding two groups of piezoelectric ceramics drive elements are amplified and transmitted to a converter by two bending arms; two bending vibrations are coupled and converted into a coupling torsion vibration (63) through a mode converter; a torsion vibration (64) is obtained and output after being amplified by an amplitude transformer (101), thus obtaining ultrasonic torsion vibration by a simpler mode.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Head suspension with flexure vibration clearance
ActiveUS7675713B2Increase flexibilitySuppressing color change and discolorationRecord information storageStructure of arm assemblyHard disc driveMechanical engineering
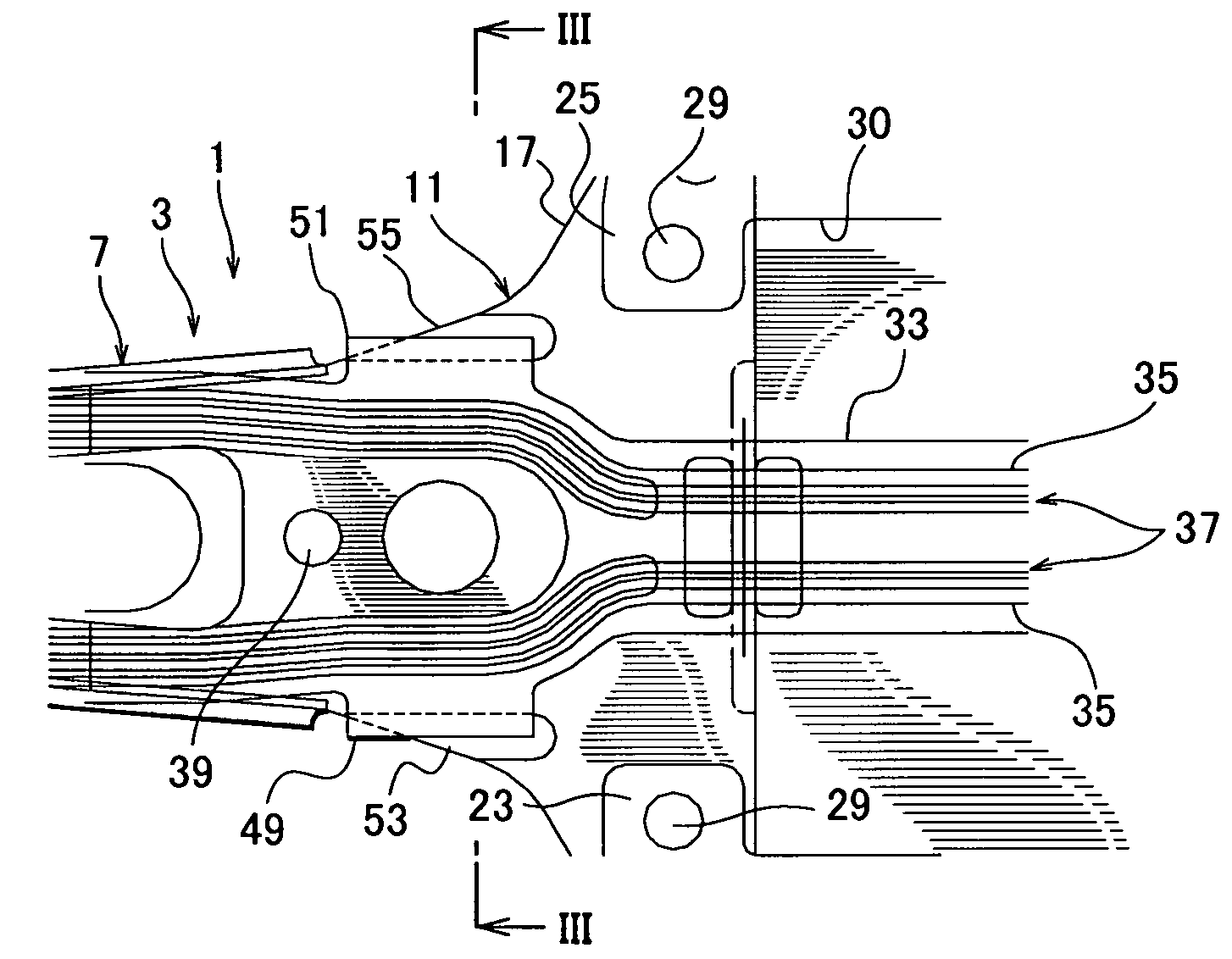
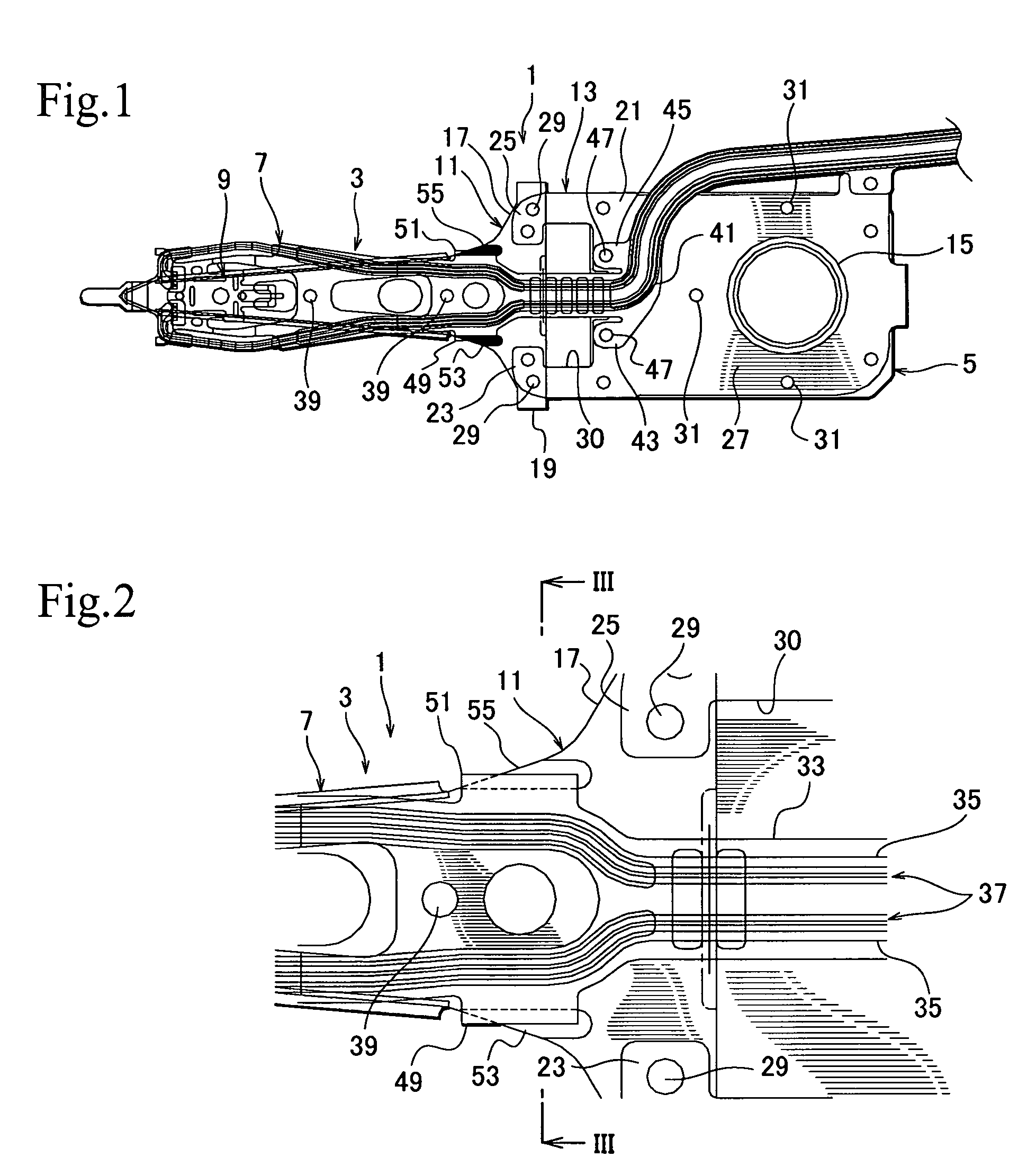
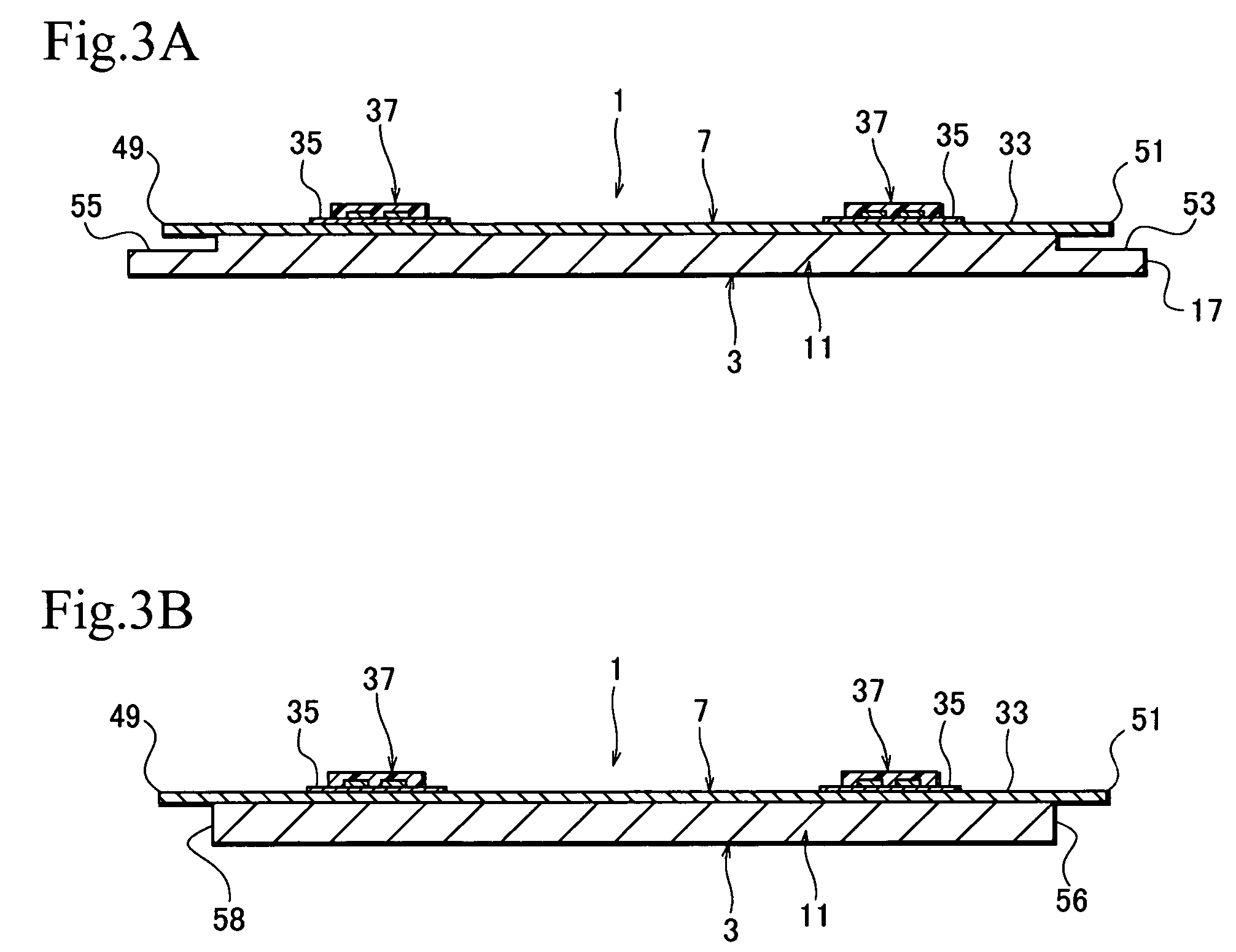
A head suspension for a hard disk drive has a base attached to a carriage of the hard disk drive and is turned around a spindle. A load beam includes a rigid part and a resilient part which applies load onto a head at a front end of the load beam to write and read data to and from a disk arranged in the hard disk drive. The rigid part is supported to the base through the resilient part. A flexure is attached to at least the rigid part of the load beam and has read / write wiring patterns connected to the head. A recessed portion or a through-hole portion is formed in at least one of the load beam and the base for avoiding vibration contact of the flexure.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Vibrator of beam type linear ultrasonic motor using bending vibration modes
ActiveCN101626203AImprove mechanical output capabilityImprove performancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngineeringControl theory
A vibrator of a beam type linear ultrasonic motor using bending vibration modes belongs to the technical field of piezoelectric ultrasonic motors and is used for the piezoelectric ultrasonic motors. The vibrator solves the problem that the mechanical output capabilities of the ultrasonic motors are restricted because of low tensile strength and low electromechanical coupling efficiency of ceramic materials in the prior art. The vibrator comprises two driving pads, two end covers, two insulating sleeves, two pairs of piezoelectric ceramics with polarization directions being thickness directions, a flange, two thin-walled beams and mounting bases; wherein, studs extend out from the end faces of the flange along the axis of the flange; each stud is sleeved with a pair of piezoelectric ceramics; an end cover is screwed at the overhanging end of each stud; the tail end of each end cover is provided with a driving pad; each piezoelectric ceramic is composed of two symmetrical half piezoelectric ceramics which are combined after being split; the polarization directions of the two half piezoelectric ceramics are opposite; the splitting lines of the two pairs of piezoelectric ceramics at both sides of the flange are vertical to each other; the polarization directions of the piezoelectric ceramics in each pair are opposite.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Vibration wave motor and driving apparatus using the vibration wave motor
InactiveUS10171008B2Downsizing of a driving apparatusSmall sizePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesWave motorTorsional vibration
A vibration wave motor includes a vibrating plate having a rectangular surface; a piezoelectric device bonded to the vibrating plate, and configured to vibrate at high frequency; and a projection provided on the vibrating plate or the piezoelectric device. In the vibration wave motor, a natural vibration mode, which has a resonant frequency equal to or adjacent to a resonant frequency of torsional vibration in a natural vibration mode under a state in which the vibrating plate, the piezoelectric device, and the projection are integrated, is a natural vibration mode of bending vibration in a direction parallel to or orthogonal to a torsion center axis of the torsional vibration in the natural vibration mode. The projection is provided at a position closer to an antinode than to a node, which are in the direction orthogonal to the torsion center axis of the torsional vibration in the natural vibration mode.
Owner:CANON KK
Vibrating gyroscope
InactiveUS6281618B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopeClassical mechanics
A vibrating gyroscope includes two planar vibrating plates arranged to oppose each other. The two vibrating plates vibrate under buckling vibration mode and a second-order bending vibration mode which is degenerated with or close to the buckling vibration mode. The vibrating gyroscope detects Coriolis force by detecting displacements in amplitude balance of the second-order bending vibration modes generated when an angular rotation velocity around an axis parallel to surfaces of the vibrating plates is applied.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Screw-thread-driven rotary-linear ultrasonic motor using columnar stator high-order bending vibration mode
ActiveCN102843063AImprove performanceMeet miniaturizationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLinear motionMiniaturization
The invention discloses a screw-thread-driven rotary-linear ultrasonic motor using a columnar stator high-order bending vibration mode, which belongs to the technical field of ultrasonic motors and is used for solving the problem of small output torque during miniaturization of a screw-thread-driven rotary-linear ultrasonic motor using the columnar stator high-order bending vibration mode. The screw-thread-driven rotary-linear ultrasonic motor comprises a screw thread output shaft, a metal tube elastic sleeve and m groups of piezoelectric ceramic sheets, or comprises a screw thread output shaft, a piezoelectric ceramic tube, two metal caps and p groups of outer electrodes. Two mutually orthogonal high-order bending vibrations such as two-order or three-order bending vibration modes on a free stator space are excited, driving travelling waves are generated on the inner surface of a stator driving end consisting of the metal tube elastic sleeve and the m groups of piezoelectric ceramic sheets by laminating and coupling the vibrations, and a stator and the screw thread output shaft are driven through a screw thread pair, so that rotary-linear motion output of the output shaft is realized under the action of axial loading force. The screw-thread-driven rotary-linear ultrasonic motor is taken as a rotary-linear ultrasonic motor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Actuator, and timepiece and notification device using the same
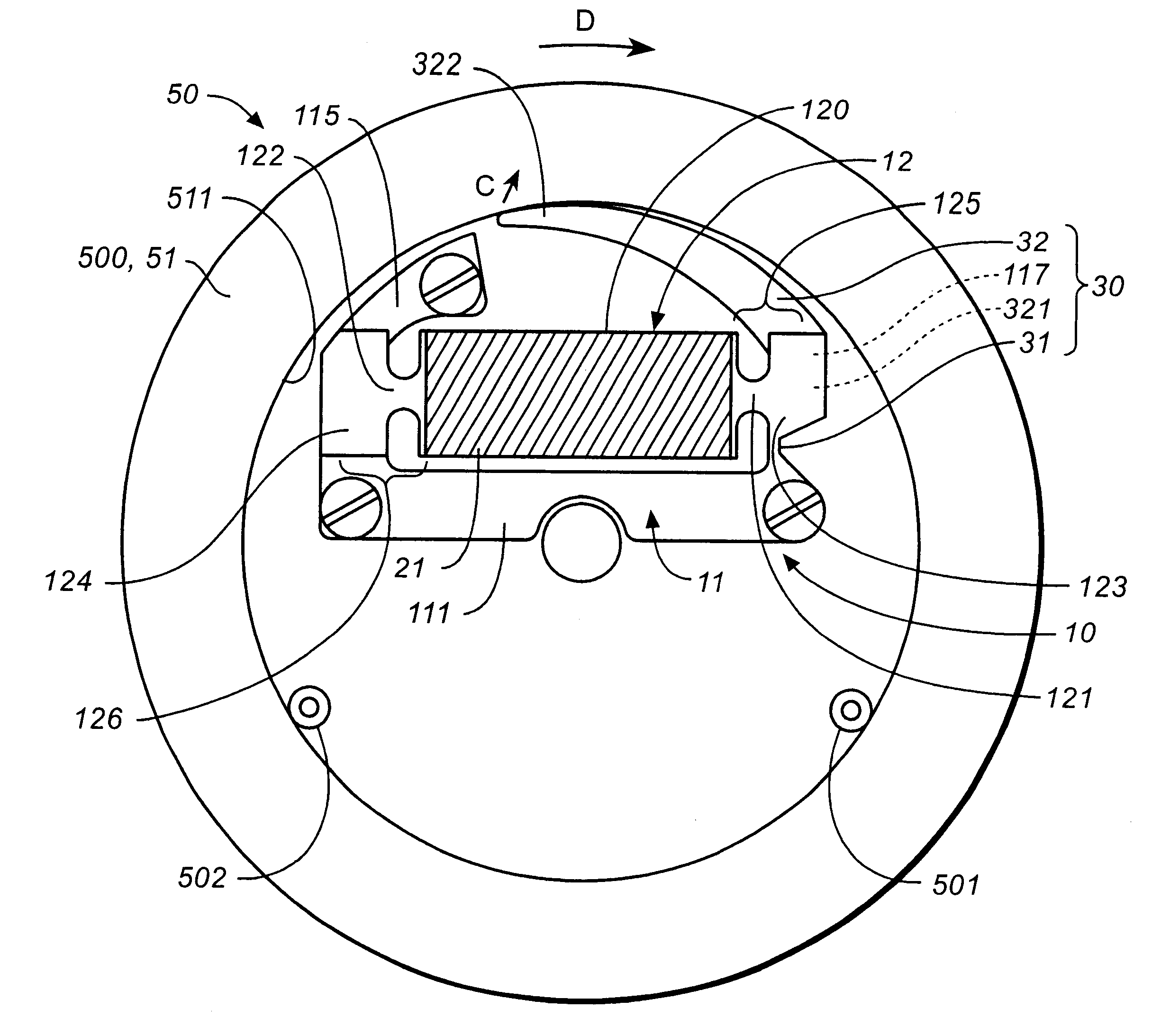
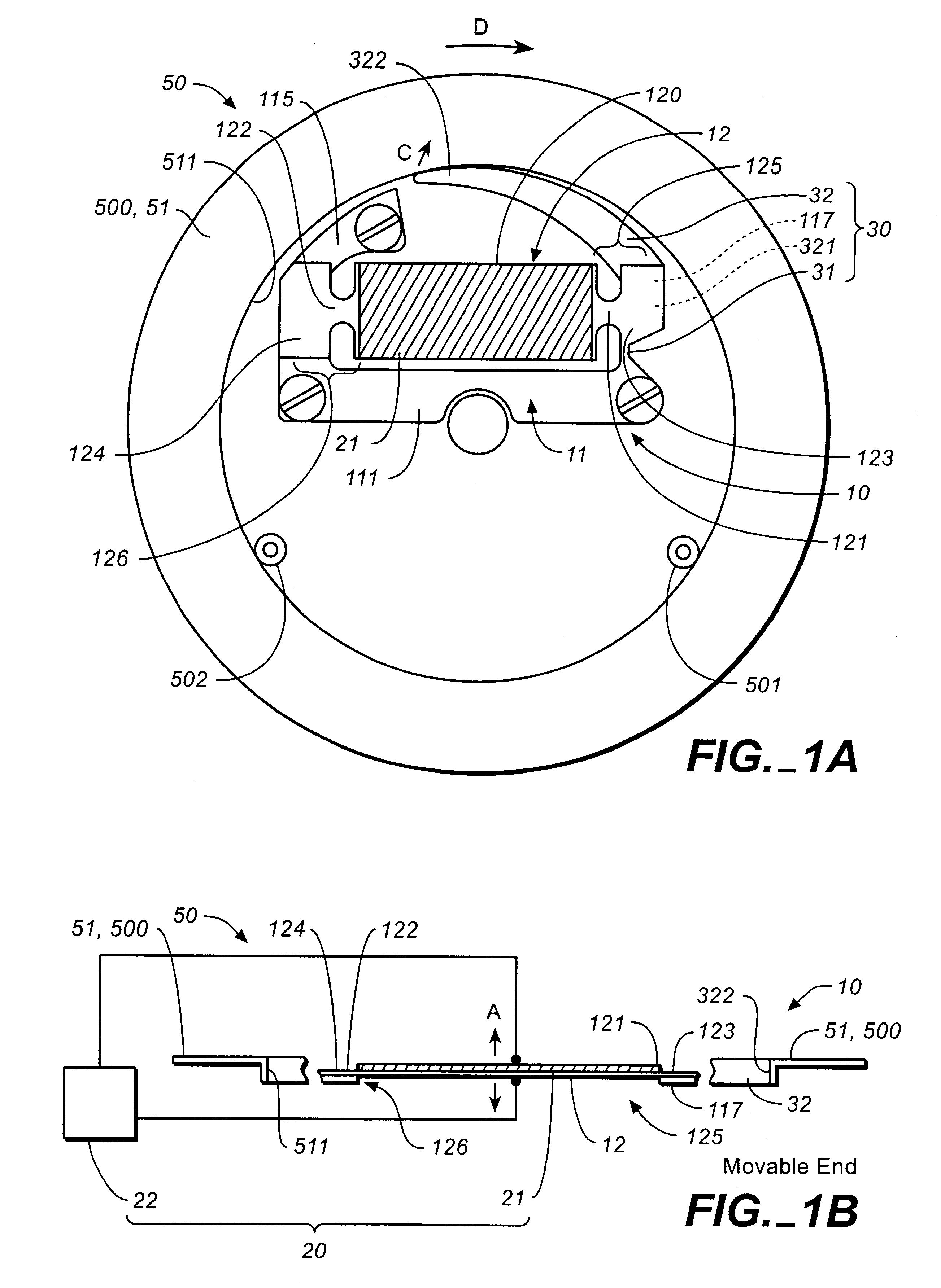
To provide an actuator which can achieve a reduction in size and weight of a device in which the actuator is mounted by amplifying and outputting displacement of a movable end of a vibrating plate as vibration in an in-plane direction, and to provide a timepiece and a notification device using the same, in an actuator (10), when a voltage is applied to a piezoelectric element (21) formed on a vibrating plate (12), the vibrating plate (12) generates bending vibrations in an out-of-plane direction, and one end portion (125) repeats displacement in an in-plane direction as a movable end. The displacement is transmitted to a lever (32) whose base end side (321) is connected to the end portion (125) of the vibrating plate (12) and an elastically deformable constricted portion (31), and a free end (322) of the lever (32) vibrates in the in-plane direction to drive a follower member (500).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Single-driving foot sandwiched transducer type longitudinal bending linear ultrasonic motor
InactiveCN101072000AIncrease amplitudeRealize linear motionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerEngineering
The disclosed variation pole is quadrangular body with rectangular section thinned gradually from two ends to central section. Drive feet are located at middle position of the pole. Piezoelectric ceramic piece in longitudinal vibration and piezoelectric ceramic piece in bending vibration are respectively installed on inner and outer sides of bolts on two flange bolts. Two end plates are installed on outer sides of bolts on two flange bolts. Through two flange bolts, two end plates, two groups of piezoelectric ceramic piece, and thin copper sheet are fastened and integrated to two larger ends of the pole. Advantages are: simple structure, smooth operation, large output thrust, and motion in high speed.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Flexible cantilever slab vibration detection device and method based on binocular vision
ActiveCN104729665ANo change in physical propertiesNo change in vibration characteristicsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansCcd cameraTorsional vibration
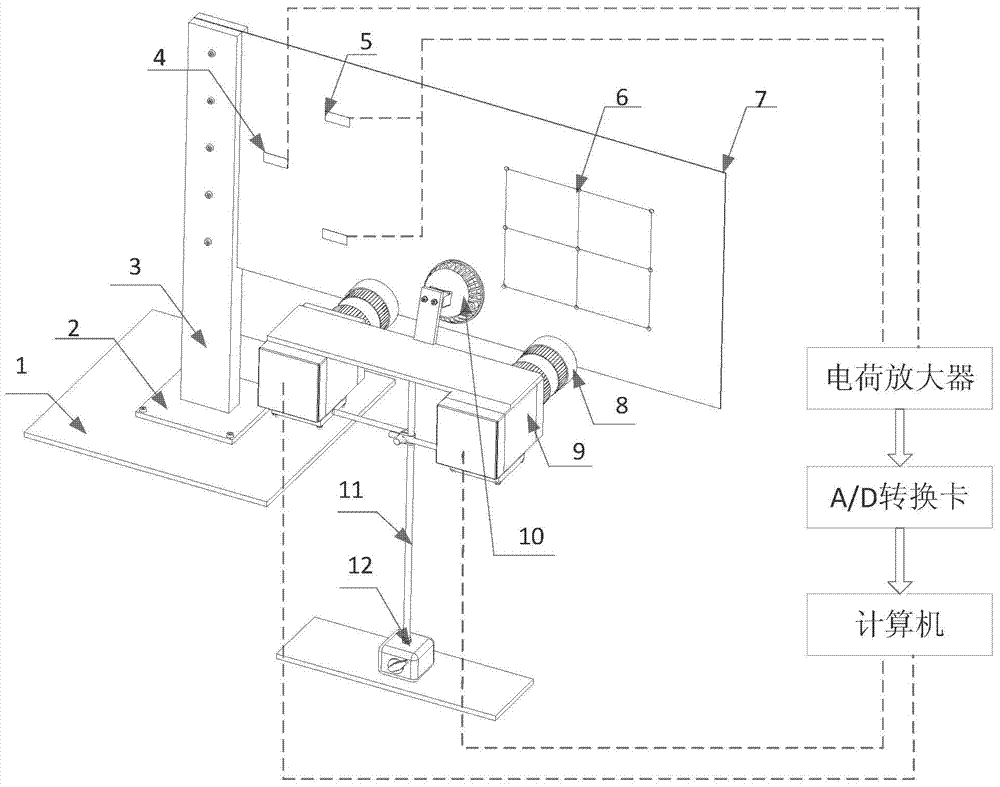
The invention discloses a flexible cantilever slab vibration detection device and method based on binocular vision. The detection device comprises a left CCD camera and a right CCD camera. One end of a flexible cantilever slab is the fixed end, and one end of the flexible cantilever slab is the free end. A first resistance strain gauge sensor and a second resistance strain gauge sensor are pasted on the flexible cantilever slab. Matts are drawn in the front of the flexible cantilever slab. The first resistance strain gauge sensor and the second resistance strain gauge sensor detect bending vibration and torsion information of the flexible cantilever slab. After being amplified through a charge amplifier, analog signals are converted into digital signals through an A / D conversion card, then the digital signals are input into a computer, the left CCD camera and the right CCD camera provided with lenses detect the vibration information of the matts in the front of the flexible cantilever slab and transmit the vibration information to the computer, double CCD camera sensors are utilized for solving three-dimensional coordinates of line intersection points of the matts on the cantilever slab according to the parallax principle, and therefore the vibration information of the points can be obtained. Accordingly, the bending and torsion vibration information of the cantilever slab can be obtained.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
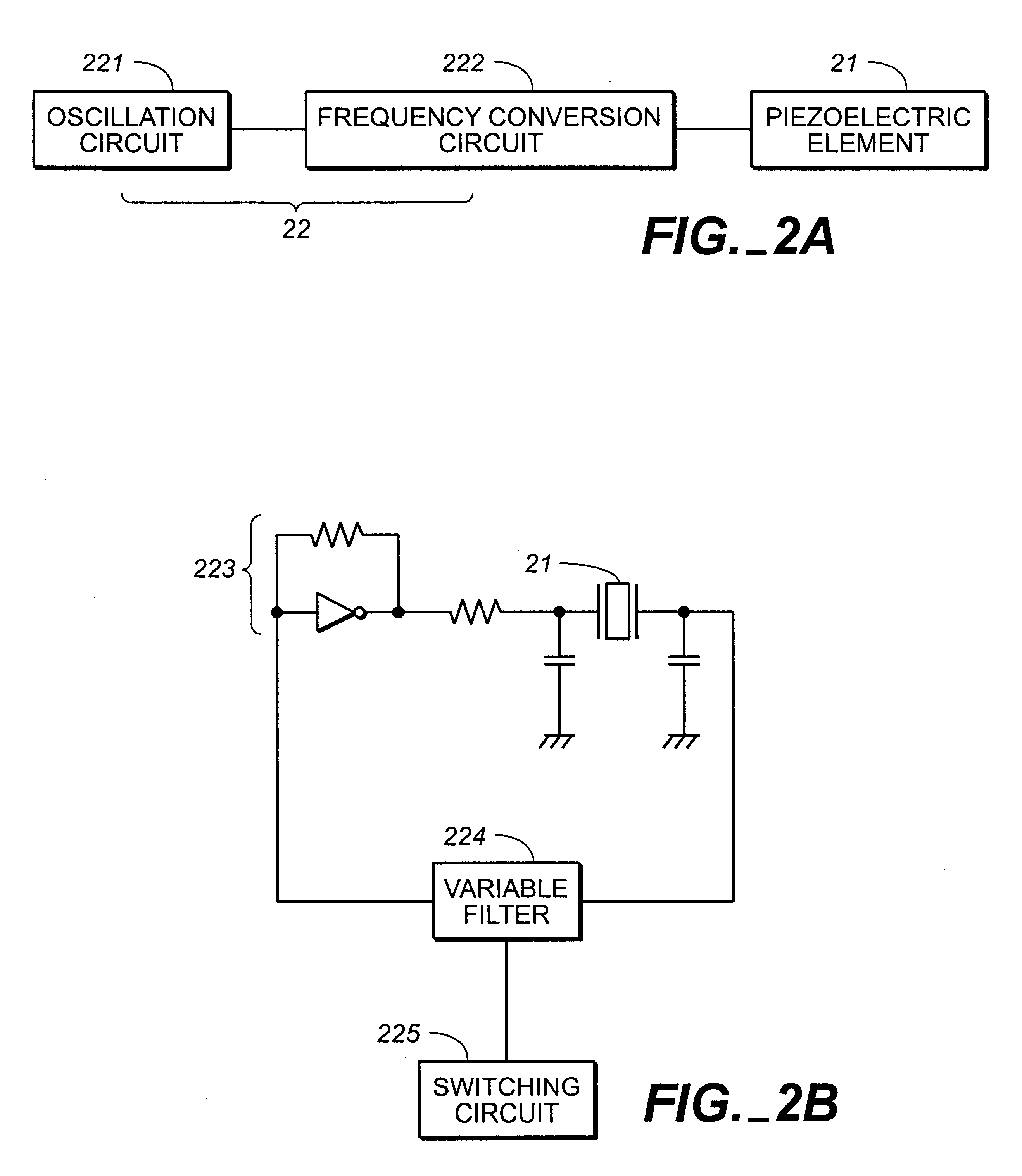
Piezoelectric vibrator, intrinsic frequency adjusting method of piezoelectric vibrator, piezoelectric actuator and electronic device
InactiveUS20070188050A1Easily and speedily adjustedImprove productivityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesPiezoelectric actuatorsEngineering
A piezoelectric vibrator includes: a flat plate piezoelectric element, the piezoelectric vibrator vibrating in a mixed mode of stretching vibration that generates a displacement in a first direction within a plane of the piezoelectric element and a bending vibration that generates a displacement in a second direction orthogonal to the first direction; a vibrating member provided with the piezoelectric element and vibrated by applying voltage on the piezoelectric element; a support member provided on the vibrating member to support the vibrating member in a vibratable manner the support member being provided on an outer edge of the vibrating member at a position adjacent to anti-node other than free end of the bending vibration, the support member including a first support section extending in a direction approximately orthogonal to the first direction and a second support section extending in a direction approximately orthogonal to the direction in which the first support section extends; and a fixing portion provided on the support member to be fixed on an object on which the piezoelectric vibrator is attached.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Piezoelectric power generator
ActiveUS20130320807A1Improve linearityAmplifies bending vibrationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesEngineeringPiezoelectric generator
A piezoelectric power generator including a resonator having a first weight member supported on a base member by a spring; a second weight member; and a generating device having a vibrating plate with a piezoelectric element attached to a surface thereof. Further, the vibrating plate has one end secured to the first weight member and the other end being a free end attached to the second weight member. The generating device is capable of bending and vibrating in an up-and-down direction, such that the first weight member can swing at a predetermined frequency about an axis perpendicular to a bending vibration plane of the generating device.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Vibration measurement and control device and method of rotary flexible hinge beam
InactiveCN104006110AGood for studying vibrationsAccurate Experimental PlatformNon-rotating vibration suppressionElectricityVibration measurement
The invention discloses a vibration measurement and control device and method of a rotary flexible hinge beam. The vibration measurement and control device comprises a flexible hinge beam body portion, a vibration signal detecting portion and a driving control portion. The flexible hinge beam is formed by connecting two beams through a hinge, and a prestretching shape memory alloy wire is arranged between the two beams, and is used for restraining low-frequency large-amplitude bending vibration of the connecting position. A piezoelectric ceramic piece sensor and a piezoelectric ceramic piece driver are pasted on to the front face and the rear face, close to a mechanical tightening device, of the flexible hinge beam respectively, and are used for detecting and restraining the bending vibration of the hinge beam. An acceleration sensor used for detecting vibration is arranged at the tail end of the hinge beam. The device is used for simulating vibration measurement and control over a space flexible joint and a flexible mechanical arm, the sensors and the composite control drivers are adopted, the corresponding control algorithm is operated, and active control over the bending vibration of the rotary hinge flexile beam is achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Bent piezoelectric-ceramic low-frequency underwater acoustic transducer
InactiveCN102136268ASimple structureIncreased vocal power capacitySound producing devicesElectricityTransducer
The invention discloses a bent piezoelectric-ceramic low-frequency underwater acoustic transducer comprising a front radiation head, a tail mass block, a front curved beam, a rear curved beam, a front piezoelectric crystal pile, a rear piezoelectric crystal pile, a middle opposite-phase piezoelectric crystal pile, a shell and an output cable, wherein the front curved beam, the rear curved beam, the front radiation head and the tail mass block are respectively stuck on two ends of the piezoelectric crystal piles in a certain mode, and thus the piezoelectric crystal piles are in a 'Z'-shaped bending structure of a zigzag rule shape. The shell is combined with a seal ring to realize underwater sealing. The output cable is characterized in that the leads of the piezoelectric crystal piles are connected to an outer driving source by the tail mass block. In the bent piezoelectric-ceramic low-frequency underwater acoustic transducer, the volume space of the transducer is fully utilized, and the sounding power volume of the transducer is increased; and the longitudinal stretching vibration mode of the piezoelectric crystal piles and the bending vibration mode of the curved beams are fully combined to realize the characteristics of low frequency, light weight and small volume of the underwater acoustic transducer to coexist. The bent piezoelectric-ceramic low-frequency underwater acoustic transducer has the advantages of simple structure, low construction cost and wide application, and is convenient to manufacture and convenient to disassemble.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Vibration gyroscope
InactiveUS6209393B1Reduce thicknessReduce widthAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsElectricityGyroscope
A piezoelectric unit is composed of a plurality of piezoelectric elements. In one embodiment, a first driving electrode is provided over the whole surface of the lower surface of the piezoelectric element. A second driving electrode is provided over the whole surface between the piezoelectric elements. The driving electrodes are connected to a driving signal source. Detection electrodes are provided on the upper surface of the piezoelectric element. At least one of the detection electrodes is connected to one of the output terminals and at least another of the detection electrodes is connected to the other of the output electrodes. One piezoelectric element is polarized upward and another piezoelectric element is polarized downward. A vertical 1st order vibration is driven in a longitudinal direction and a 2nd order bending vibration is detected by the detection electrodes, and a voltage proportional to a coriolis force (rotational angular velocity) is outputted. With this construction, a vibration gyroscope having a reduced thickness and width can be produced.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Multi-leg linear piezoelectric driver and workbench
ActiveCN101795088ASimple structureIncrease contact areaPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElliptic motionControl system
The invention belongs to a multi-leg linear piezoelectric driver and a workbench in the field of micro drivers. Diamond-shaped driving legs extending from a substrate of a piezoelectric driver form a comb-shaped structure, and square piezoelectric ceramic plates are bonded on the side surfaces of the driving legs, wherein the piezoelectric ceramic plates are polarized along the thickness direction of the piezoelectric ceramic plates, and the end faces of all the driving legs are on the same plane. Electrical signals are introduced to the electrode surfaces of the piezoelectric ceramic plates,the first-order stretching vibrations and the first-order or second-order bending vibrations of the driving legs can be simultaneously excited, and the coupling action of the two vibrations ensures that mass points on the bottom surfaces of the driving legs do elliptic motions and the elliptic vibrations of a plurality of leg bottoms of the driver are accumulated and superposed into a macroscopiclinear motion. The driver is arranged on a base of the workbench, and a grating bar and a grating head which are arranged on the base are used for providing a precise position of the workbench to realize the closed loop control of the workbench. Because the driver adopts a multi-leg driving mode, the driving force is increased in multiples; the contact areas of the piezoelectric ceramic plates with air are large so as to be beneficial to radiating heat; the assembly is convenient, and the cost is lower.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
Piezoelectric ceramic ultrasonic atomizing sheet
InactiveCN102553767AWiden the scope of atomization effectHigh bonding strengthLiquid spraying apparatusMetal sheetUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a piezoelectric ceramic ultrasonic atomizing sheet, comprising a piezoelectric ceramic sheet group and a metal sheet group, wherein the piezoelectric ceramic sheet group consists of at least two piezoelectric ceramic sheets, and the metal sheet group consists of at least one metal sheet. In the piezoelectric ceramic sheet group, through holes are arranged on the piezoelectric ceramic sheets; the piezoelectric ceramic sheets and the metal sheets are mutually crossed and overlapped; and the metal sheets cover the through holes entirely. The piezoelectric ceramic ultrasonic atomizing sheet disclosed by the invention is in a multilayer clamping structure, the metal sheets and the piezoelectric ceramic sheets have high bonding strength and are difficult to fall of, so that the metal sheets of one atomizing sheet are combined in various vibration modes, namely axial bending vibration and radial stretching vibration, is realized. Therefore, the vibration modes of the atomizing sheet with the structure are increased and the atomizing effect range of the atomizing sheet is widened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Piezoelectric electroacoustic transducer
InactiveUS6888947B2Prevent fluctuationsInhibition of variationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyTransducer detailsHeat resistanceTransducer
A piezoelectric electroacoustic transducer includes a substantially rectangular piezoelectric diaphragm having an internal electrode, a plurality of laminated piezoelectric ceramic layers having the internal electrode interposed between two of the piezoelectric ceramic layers, principal-surface electrodes disposed on top and bottom principal surfaces of the piezoelectric diaphragm, the piezoelectric diaphragm generating surface bending-vibrations in response to application of an alternating signal between the principal-surface electrodes and the internal electrode, a resin film that is larger than the piezoelectric diaphragm and having the piezoelectric diaphragm affixed onto substantially a central portion of a front surface thereof, and a housing having a support for supporting the outer periphery of the resin film. The resin film has heat resistance at least a reflow-soldering temperature and at least one undulated portion bending in the front and rear directions thereof and formed in the outer periphery thereof, and the perimeter of the resin film including the four corners thereof is fixed to the support of the housing by adhesion.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Multi travelling wave bending-rotation ultrasonic motor stator and ultrasonic motor using same
InactiveCN101026343ASimple processing technologyImprove stabilityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesExcitation signalEnergy conversion efficiency
The invention solves issues: poor working stability, low output rotation speed, small moment, and low efficiency of energy conversion caused by singlepoint contact between stator and rotor, existed in current ultrasonic electrical motor (UEM). The stator of bending revolving UEM in multiple traveling waves is composed of base body of stator, and 4n pieces of poles, and where n is natural number larger than or equal to 2. Being distributed on circle of base body of stator evenly, 4n pieces of poles are fixed on external surface of wave crest when base body of stator generates first order bending vibration. 4 pieces of poles are grouped, and there are total n groups. Actuating signals of traveling wave including sine wave, cosine wave, minus sine wave, and minus cosine wave near to or identical to natural frequency of stator are applied to 4 poles in a group. The disclosed UEM includes n contacts between stator and rotor so as to solve the said issues.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Piezoelectric actuator and piezoelectric motor
ActiveCN103259449ASimple structureEasy to manufacturePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityPiezoelectric actuators
The invention provides a piezoelectric actuator and a piezoelectric motor. The piezoelectric actuator comprises a piezoelectric body which is of a square platy structure and is polarized in the thickness direction. A first electrode layer is arranged on a main plane of a first end of the piezoelectric body in the thickness direction, a second electrode layer is arranged on a main plane of a second end of the piezoelectric body in the thickness direction, the first electrode layer comprises a plurality of electrode areas, and the second electrode layer comprises at least one electrode area. The piezoelectric actuator can work in a simple first-order bending vibration mode, generates reciprocating straight-line trajectory movement or elliptical orbit movement, is simple in structure and convenient to manufacture, and can solve problems which exist in a traditional piezoelectric actuator.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
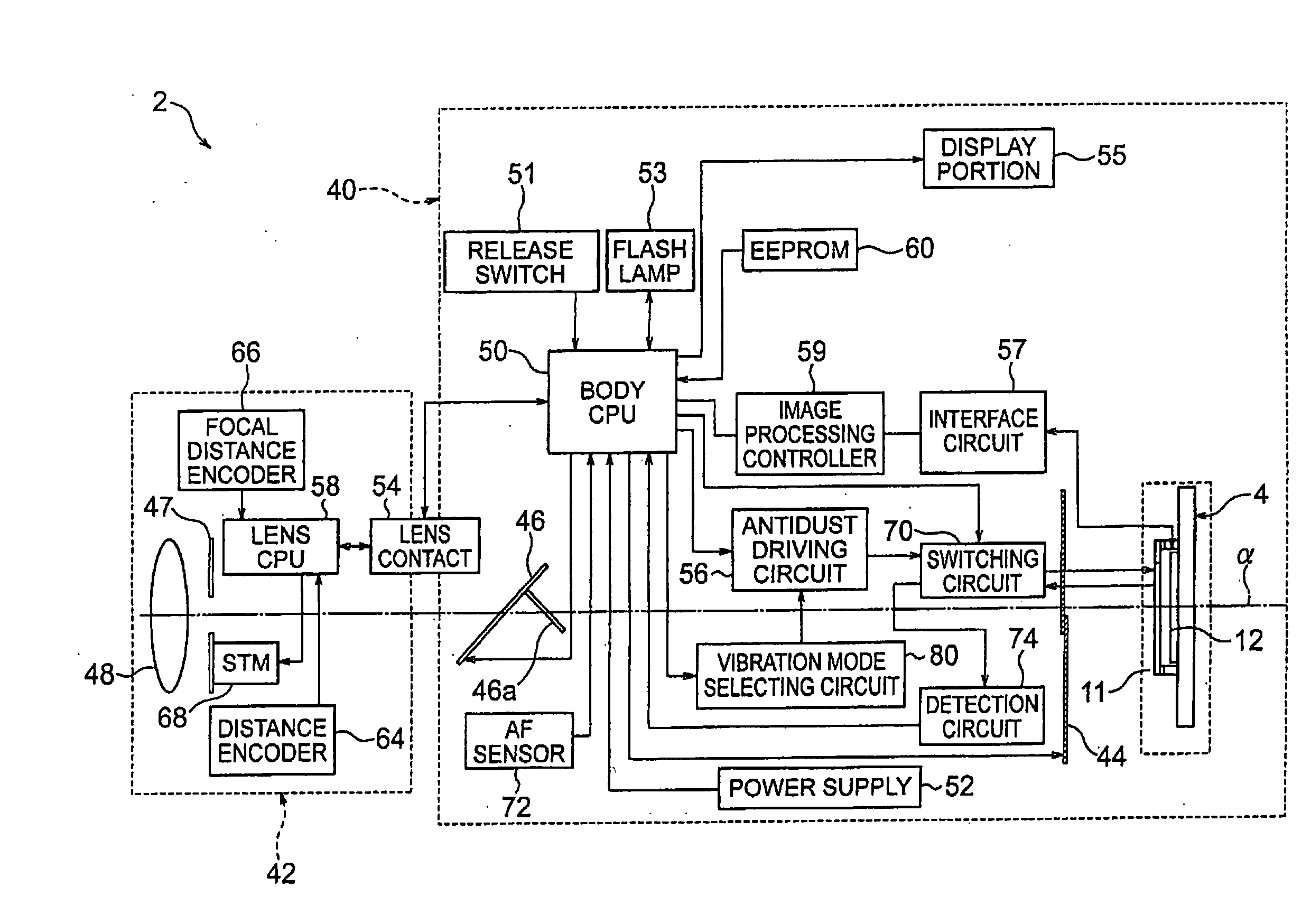
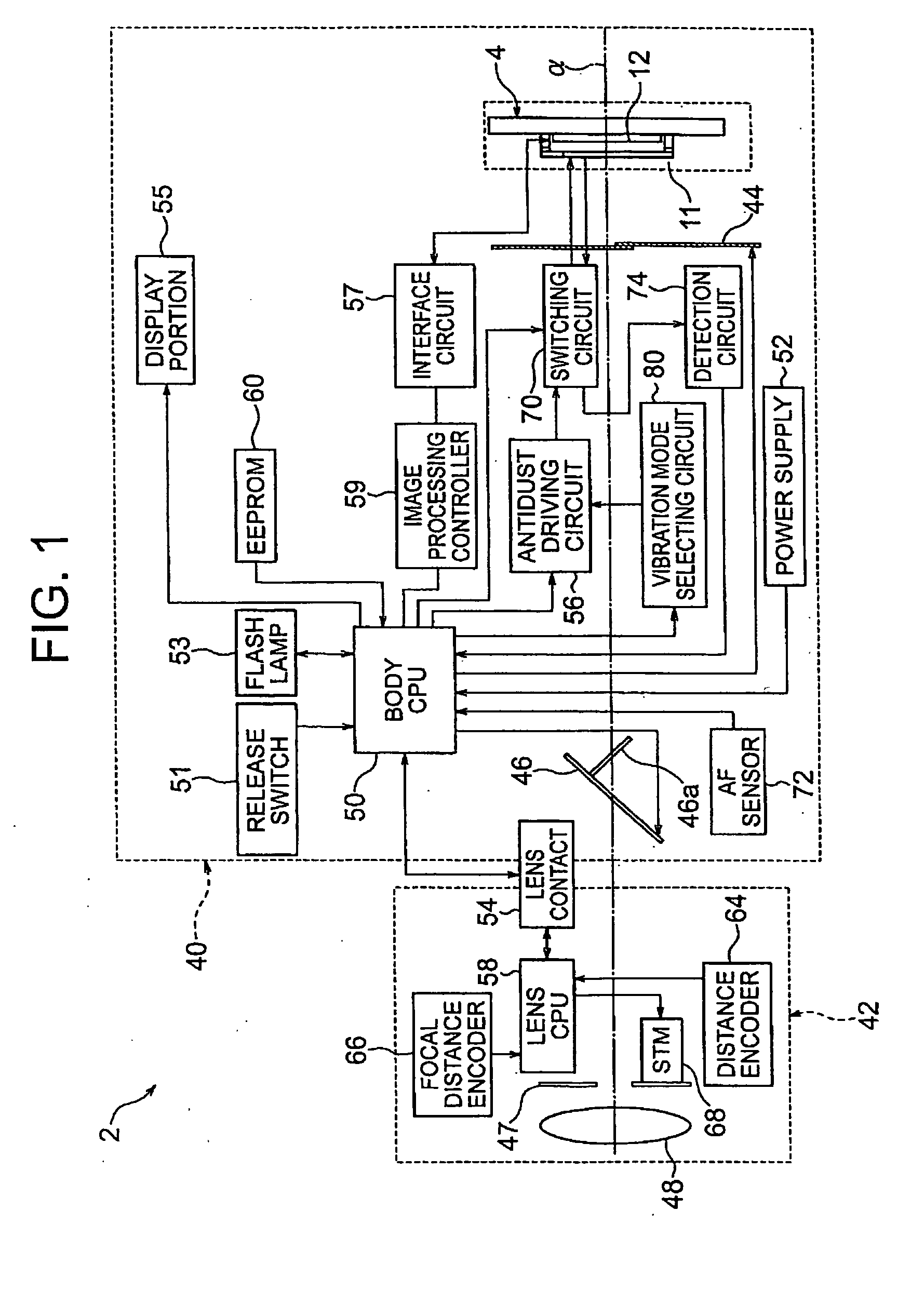
Vibration device, antidust device, camera, vibration device inspection method, method for manufacturing vibration device and vibration method
InactiveUS20090206698A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesOptical filtersEngineeringBending vibration
A vibration device comprising; a vibrator which generates bending vibration on a predetermined member, a controller which controls a driver to drive the vibrator, wherein; the vibrator comprises a plurality of driving electrodes electrically insulated respectively, the controller controls the driver to make phases of driving signals respectively output to the plurality of driving electrodes changeable relatively and adjust an order of the bending vibration.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Vibrator of beam type linear ultrasonic motor using bending vibration modes
ActiveCN101626203BImprove mechanical output capabilityImprove performancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectric machineryEngineering
A vibrator of a beam type linear ultrasonic motor using bending vibration modes belongs to the technical field of piezoelectric ultrasonic motors and is used for the piezoelectric ultrasonic motors. The vibrator solves the problem that the mechanical output capabilities of the ultrasonic motors are restricted because of low tensile strength and low electromechanical coupling efficiency of ceramicmaterials in the prior art. The vibrator comprises two driving pads, two end covers, two insulating sleeves, two pairs of piezoelectric ceramics with polarization directions being thickness directions, a flange, two thin-walled beams and mounting bases; wherein, studs extend out from the end faces of the flange along the axis of the flange; each stud is sleeved with a pair of piezoelectric ceramics; an end cover is screwed at the overhanging end of each stud; the tail end of each end cover is provided with a driving pad; each piezoelectric ceramic is composed of two symmetrical half piezoelectric ceramics which are combined after being split; the polarization directions of the two half piezoelectric ceramics are opposite; the splitting lines of the two pairs of piezoelectric ceramics at both sides of the flange are vertical to each other; the polarization directions of the piezoelectric ceramics in each pair are opposite.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Vibrator, vibratory gyroscope, and vibrator adjusting method
InactiveUS6346765B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopeEngineering
A vibrator of a vibratory gyroscope comprises a main arm having a base part and at least one bending-vibration piece extending from the base part in a direction crossing the longitudinal direction of the base part and a fixing part for fixing one end of the base part, and the base part and the bending-vibration piece are formed so as to extend substantially in a specified plane. Preferably, at the opposite side to one end of the base part, a projection projecting from the bending-vibration piece is provided, or at least a pair of resonant arms resonating with vibration of the base part, said pair of resonant arms projecting from the fixing part are provided. Thanks to this, it has been possible to detect a turning angular rate in a sufficiently high accuracy without providing a projection which has a certain weight and extends from the vibrator toward the axis of turning even in case of arranging the vibrator so that the vibration arm of the vibrator extends perpendicularly to the axis of turning.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Ultrasonic bending fatigue experimental device
InactiveCN101819114AGuaranteed resonance conditionsAvoid the influence of vibration wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMaterial strength using steady bending forcesAudio power amplifierResonance
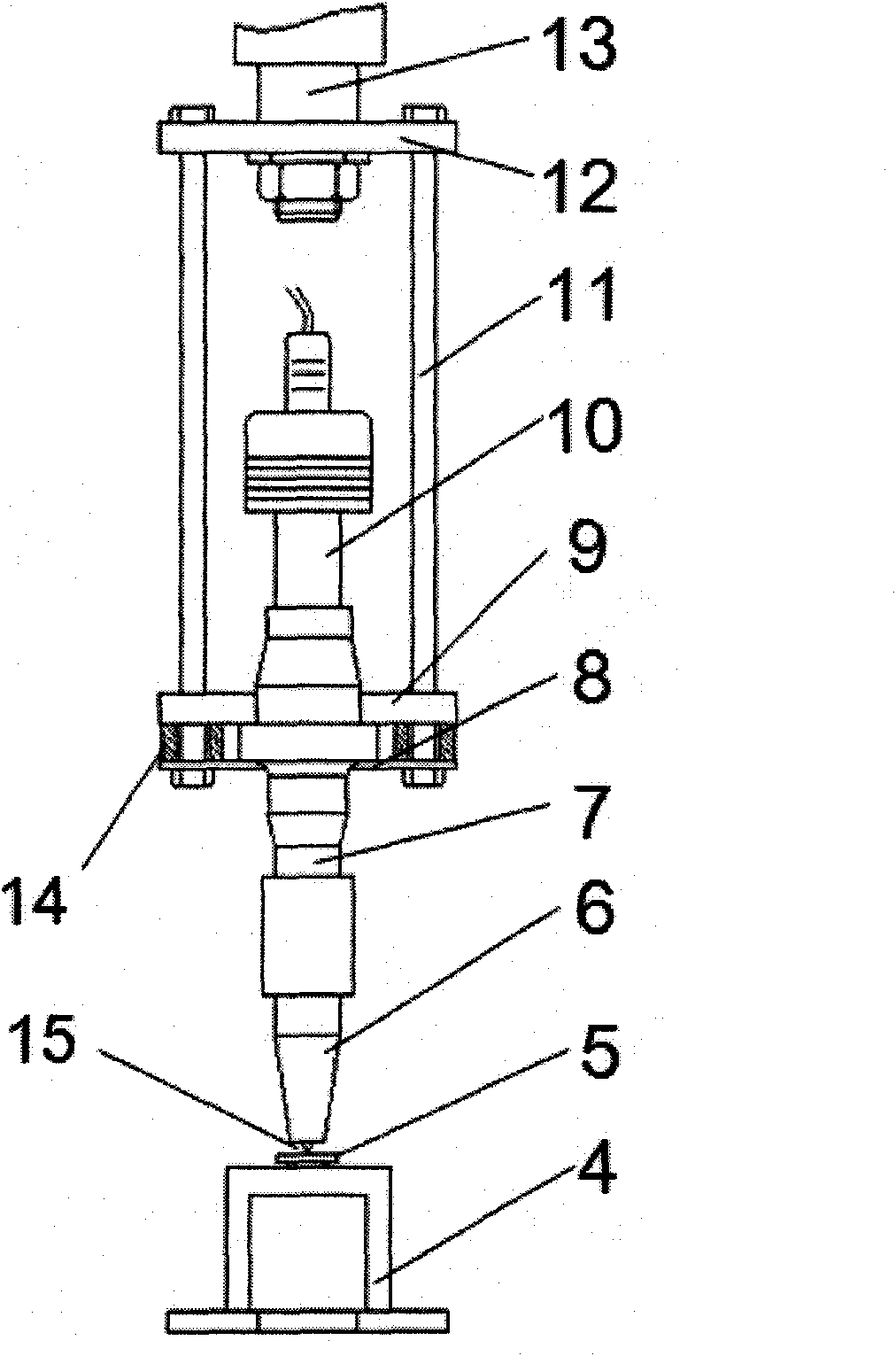
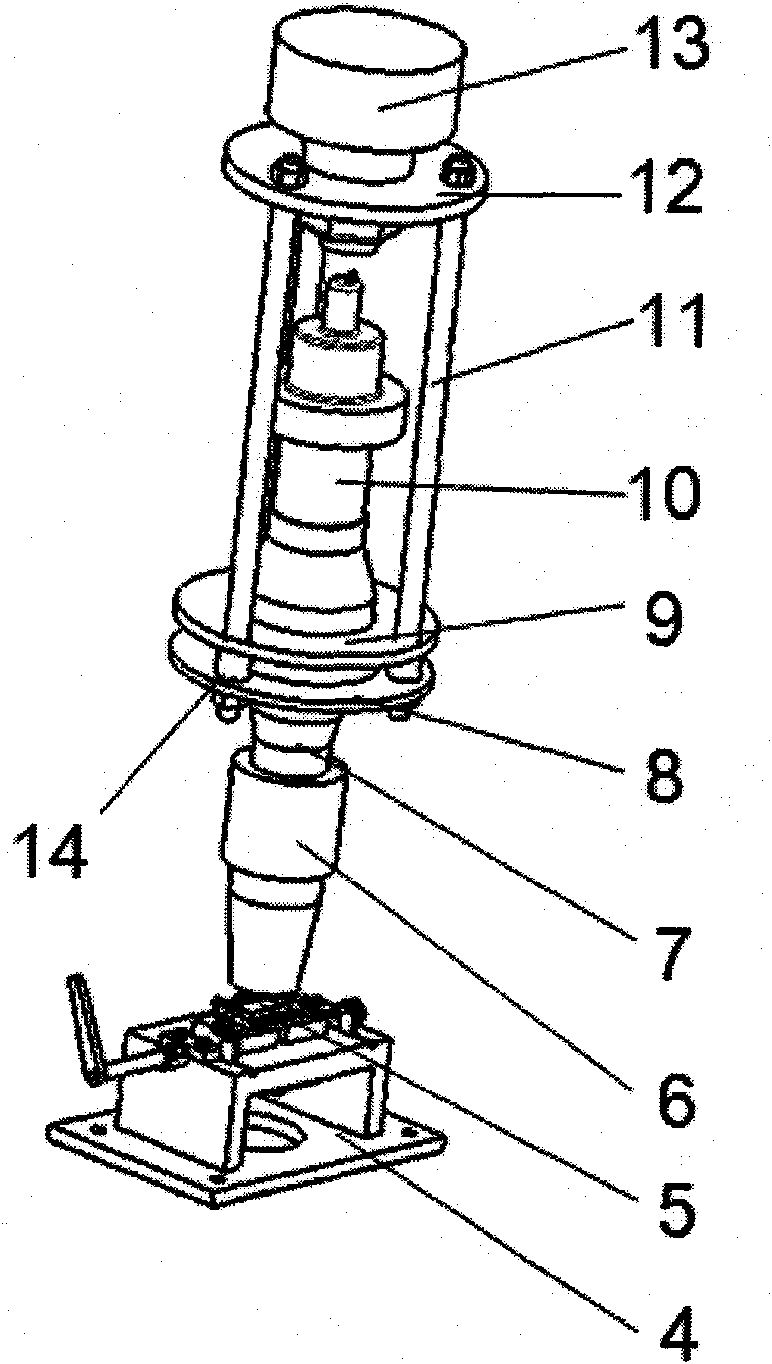
The invention relates to an ultrasonic bending fatigue experimental device, wherein a transducer is positioned in a force transmitter and connected with a connector. The transducer is positioned in the middle of the ultrasonic bending fatigue experimental device; a backing plate and an upper connecting plate as well as a lower connecting plate of the force transmitter are fixedly connected through force transmitting rods. One end of the connector penetrates through the lower connecting plate at the lower end of the force transmitter and is connected with a displacement amplifier, and the other end penetrates through the upper connecting plate and is connected with the transducer. A supporting device is positioned below the displacement amplifier; and a static load force applying device penetrates through the central hole of the backing plate and is fixedly connected with the backing plate. The transducer, the connector, the displacement amplifier and a pressure head form a longitudinal resonance system, and a longitudinal vibration load is transferred to a bending fatigue sample through the pressure head, so that bending vibration is generated by the bending fatigue sample. The position of the supporting point of the bending fatigue sample can be automatically regulated through a positioning guide screw to realize an ultrasonic bending fatigue experiment, the ultrasonic bending fatigue experiments of the samples with different loading loads and different geometrical sizes can be realized, and the ultrasonic bending fatigue experimental device is suitable for carrying out the bending fatigue experiment by utilizing an axial loading ultrasonic fatigue experiment machine.
Owner:NANTONG JINNIU MACHINERY MFR +1
Piezoelectric ceramic fibre containing metal core painted by electrode partly
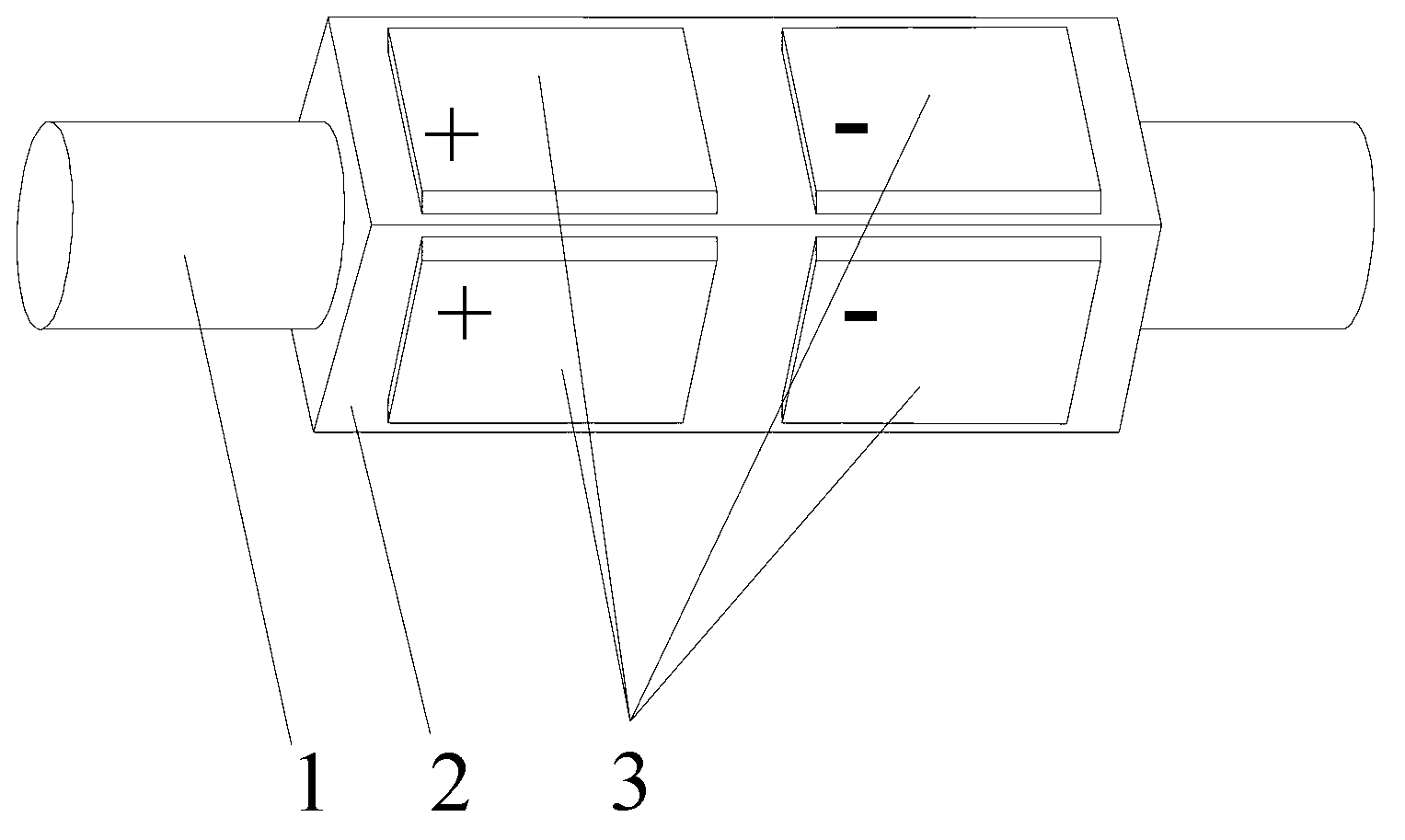
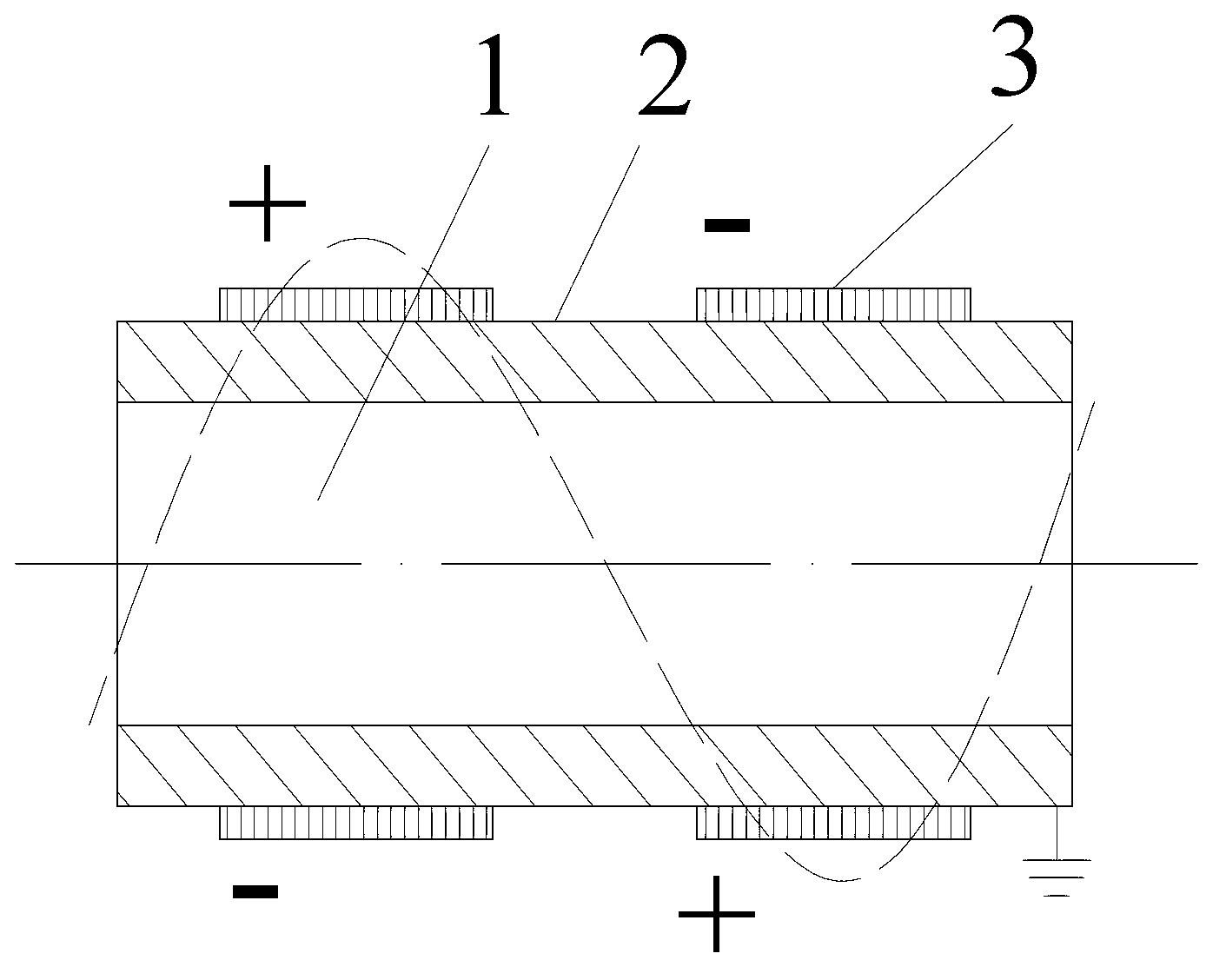
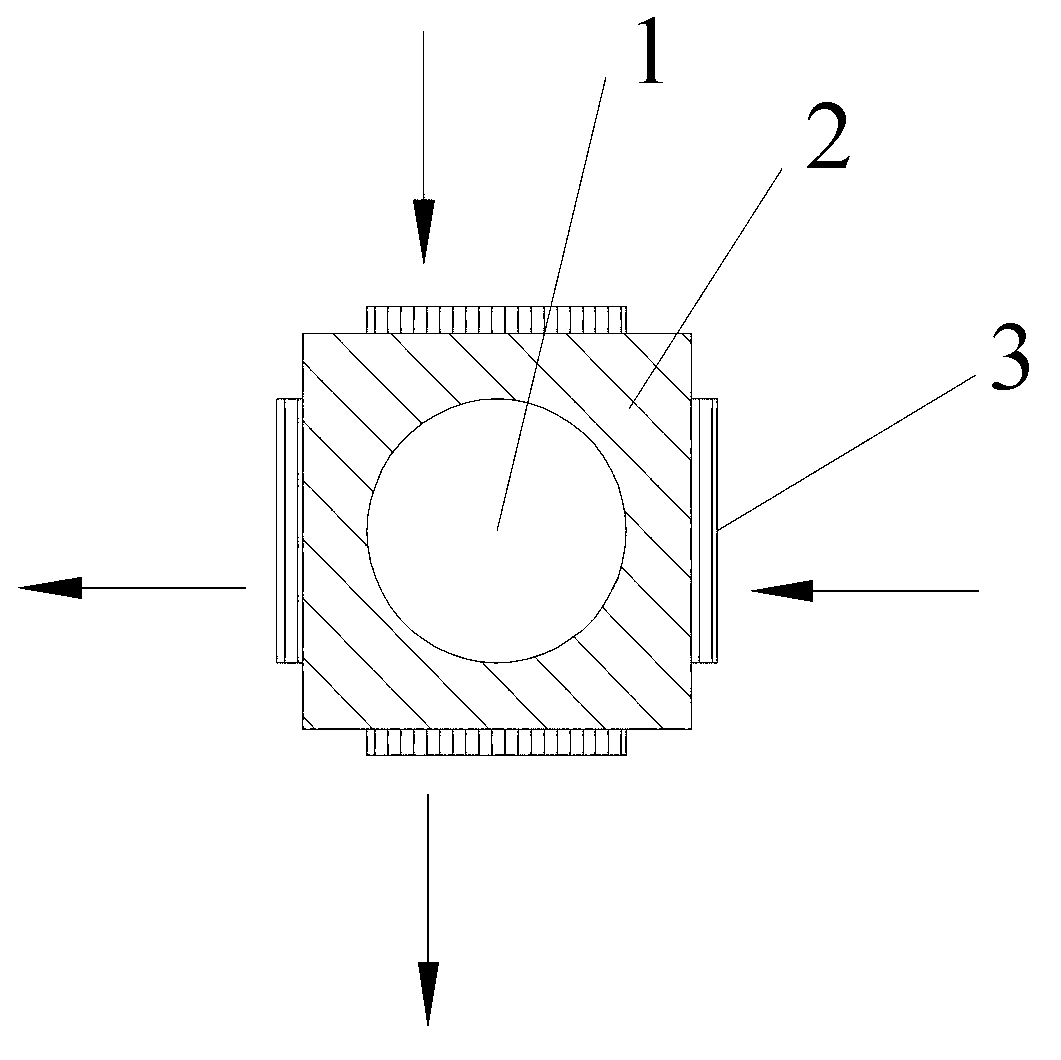
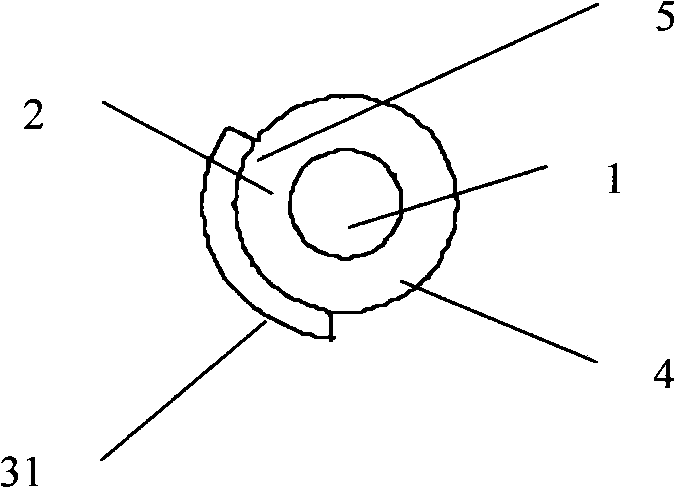
ActiveCN101304069AOvercome application flawsRealize the driving functionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesFiberVibration control
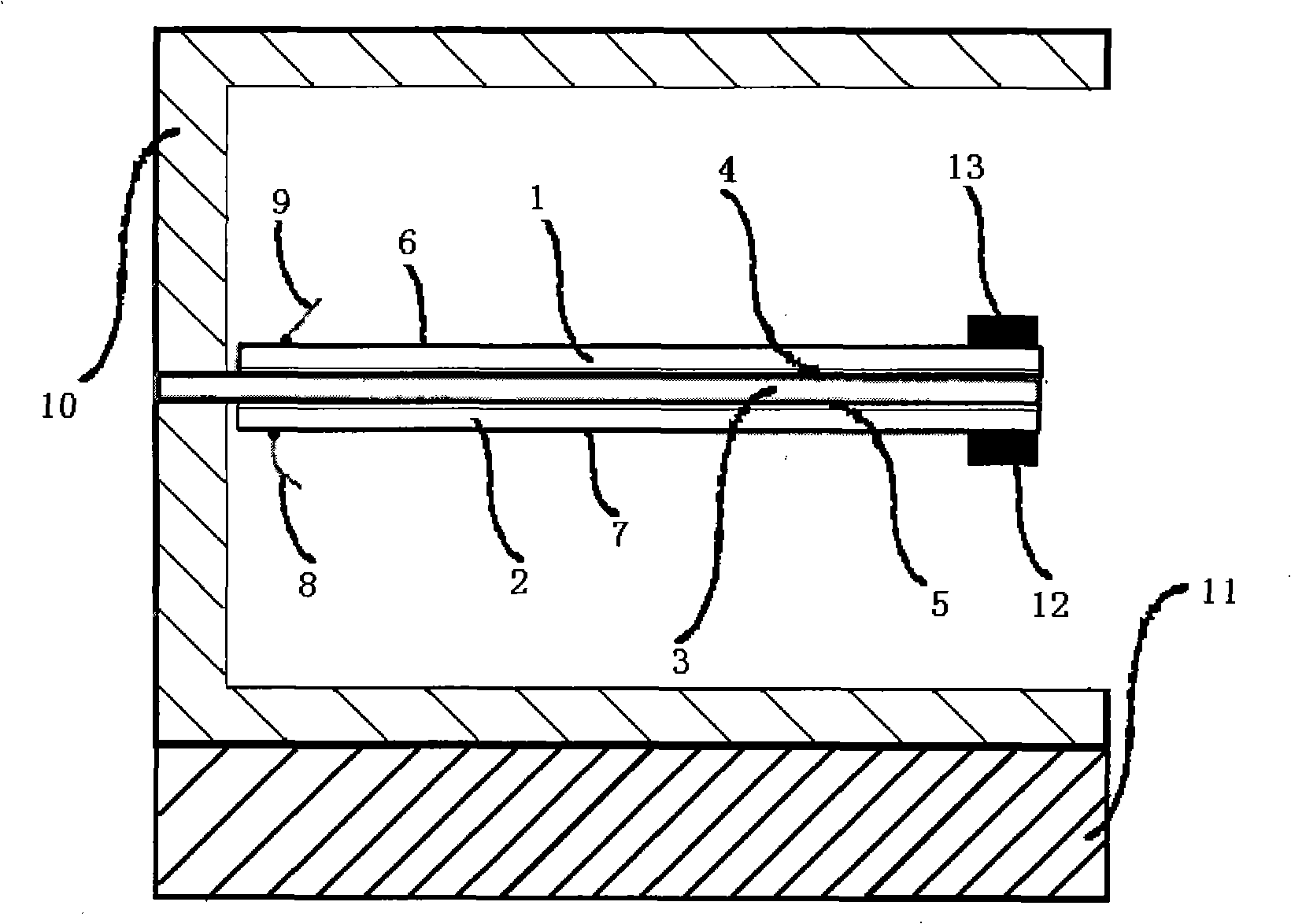
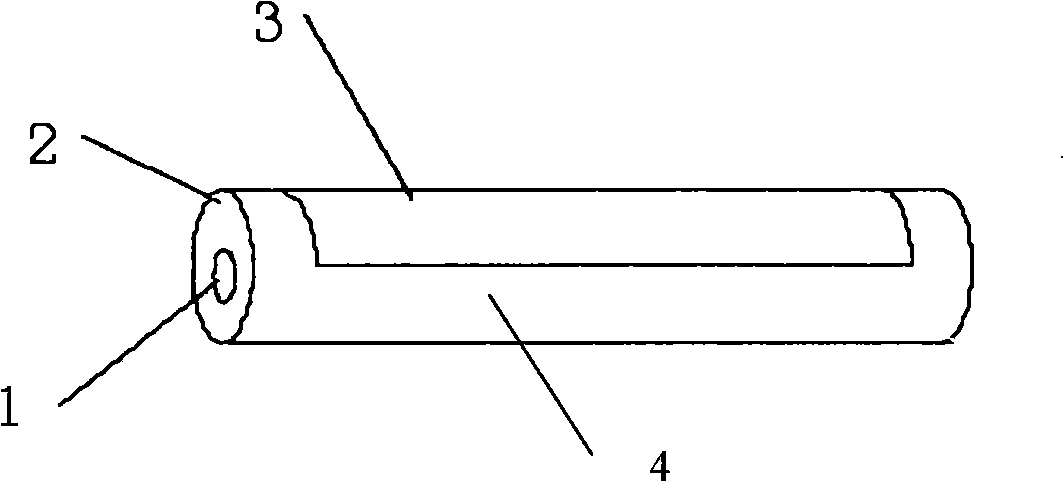
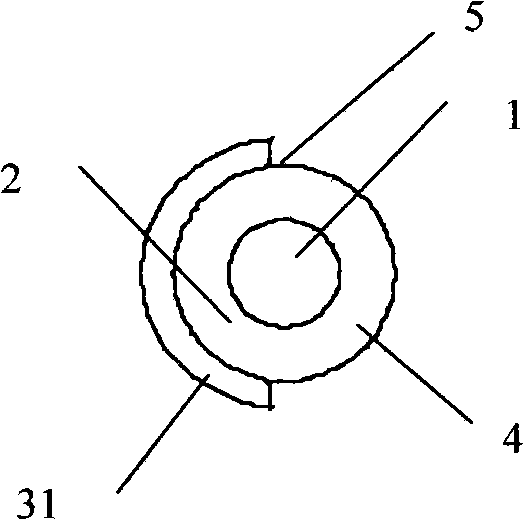
The invention relates to a piezoelectric fiber containing a metal core with part coated with an electrode, which comprises a metal core (1), a piezoelectric material (2) coating the metal core (1) and a coating electrode (3) coating the outer surface of the piezoelectric material (2). The surface of the piezoelectric material (2) comprises an electrode coated part (3) and a non electrode coated part (4); the electrode coated part (3) is a coated electrode (31) which partially covers the surface of the piezoelectric material (2) along the extending direction of the piezoelectric fiber containing a metal core. The piezoelectric fiber containing a metal core with part coated with electrode of the invention can realize the driving functions of driving components such as traditional piezoelectric bimorphs, can be used as micro-drivers and for energy recycling and vibration control, and especially can realize the function of bending vibration, thus overcoming the application disadvantages of the existing piezoelectric fibers.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com