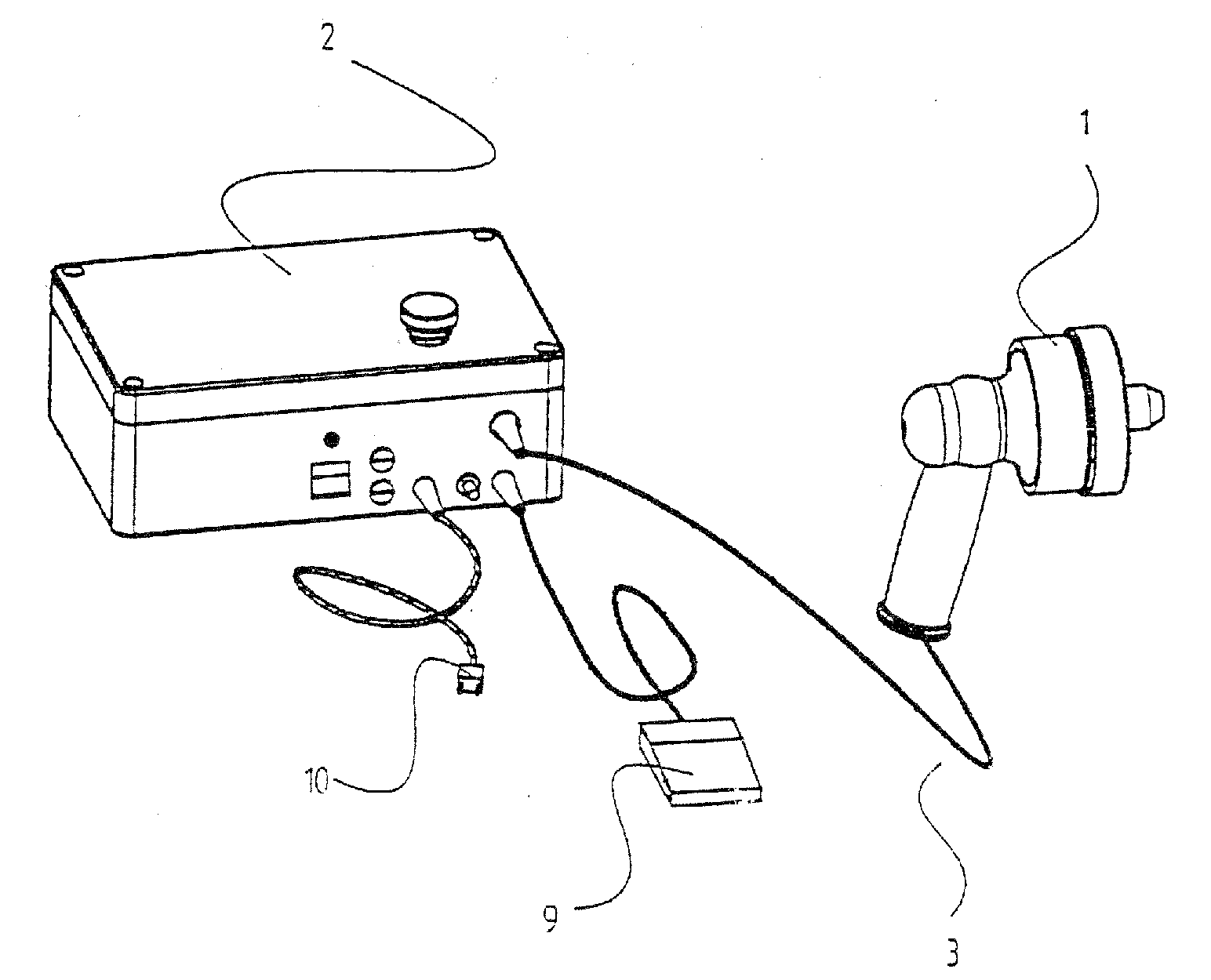
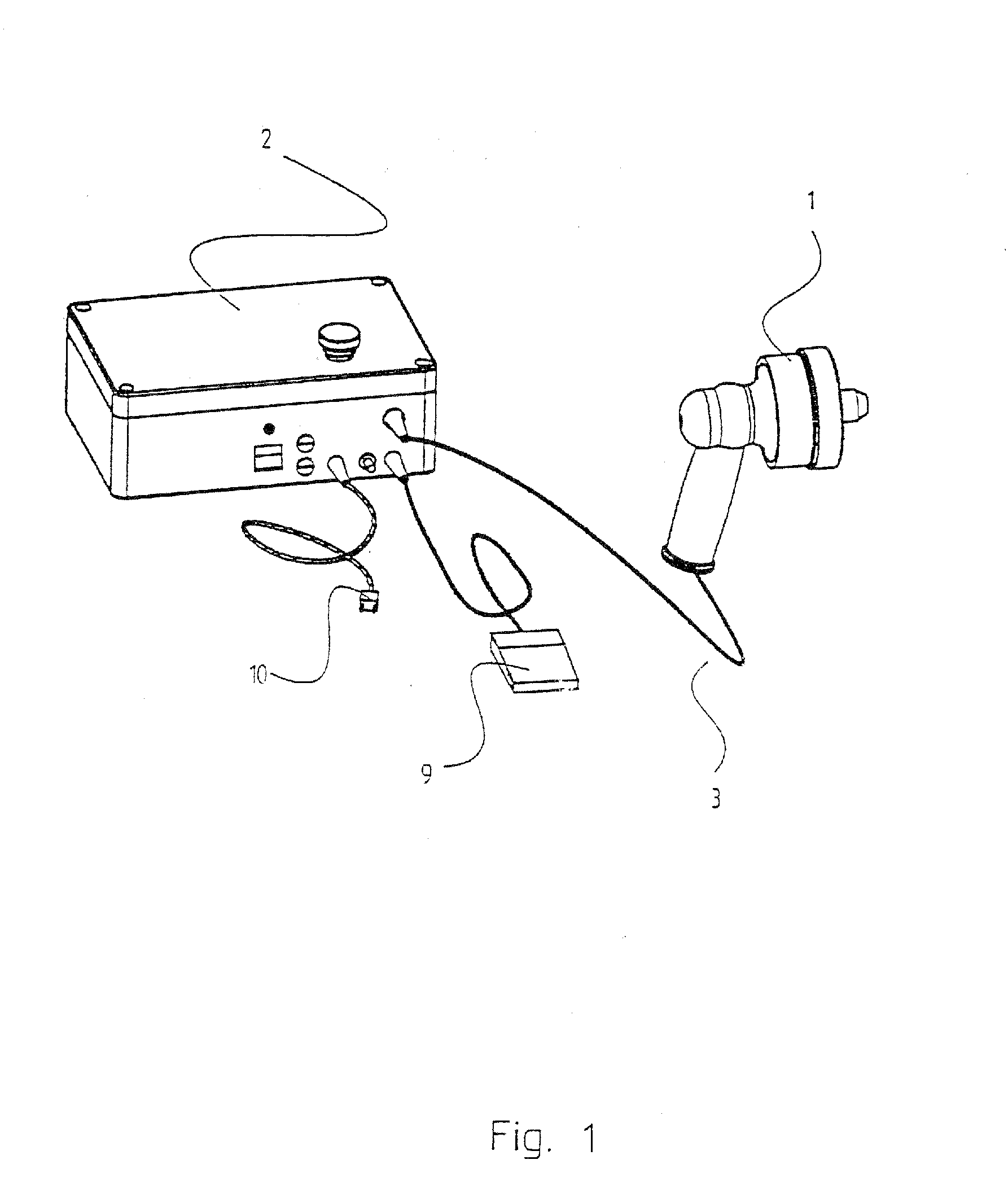
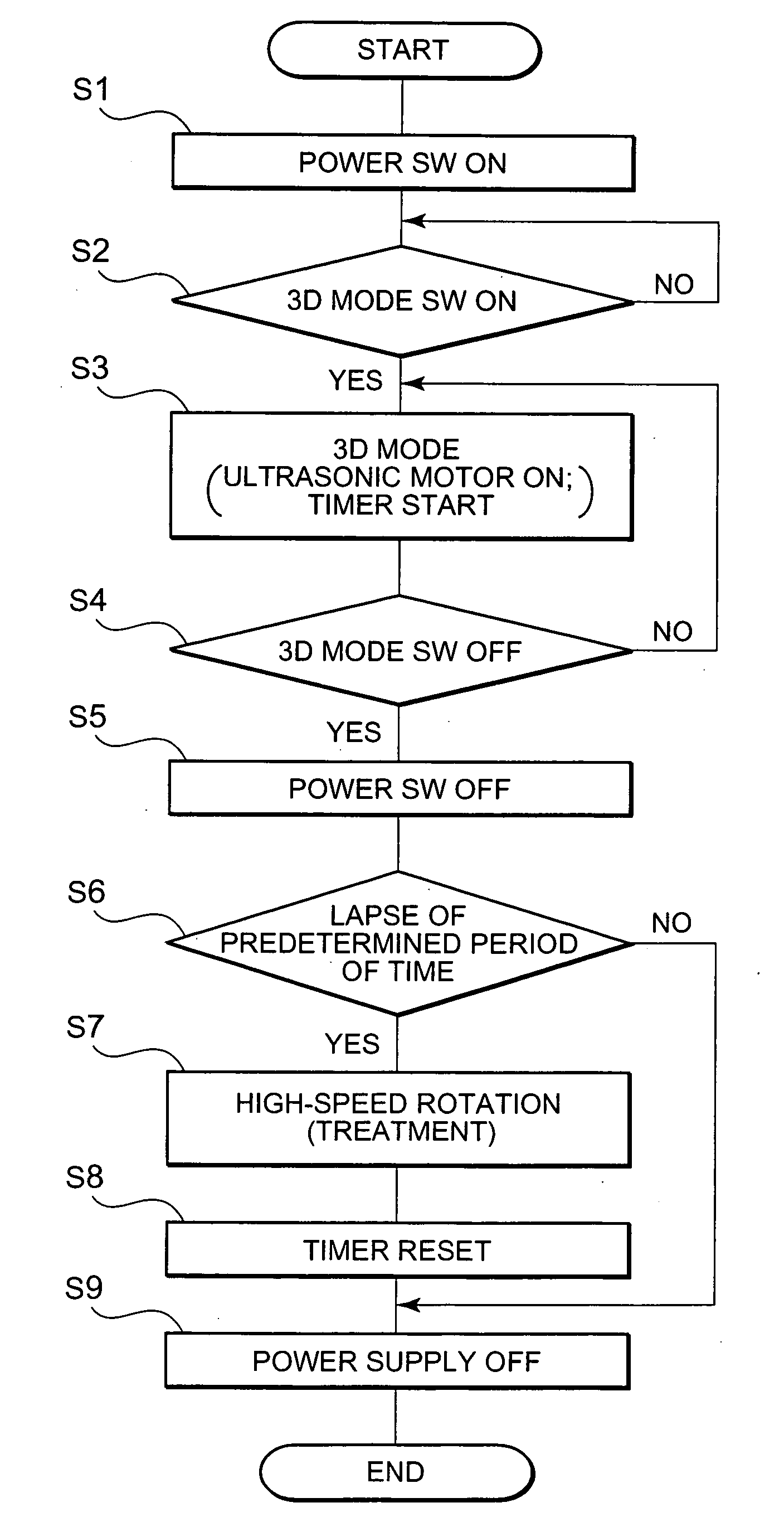
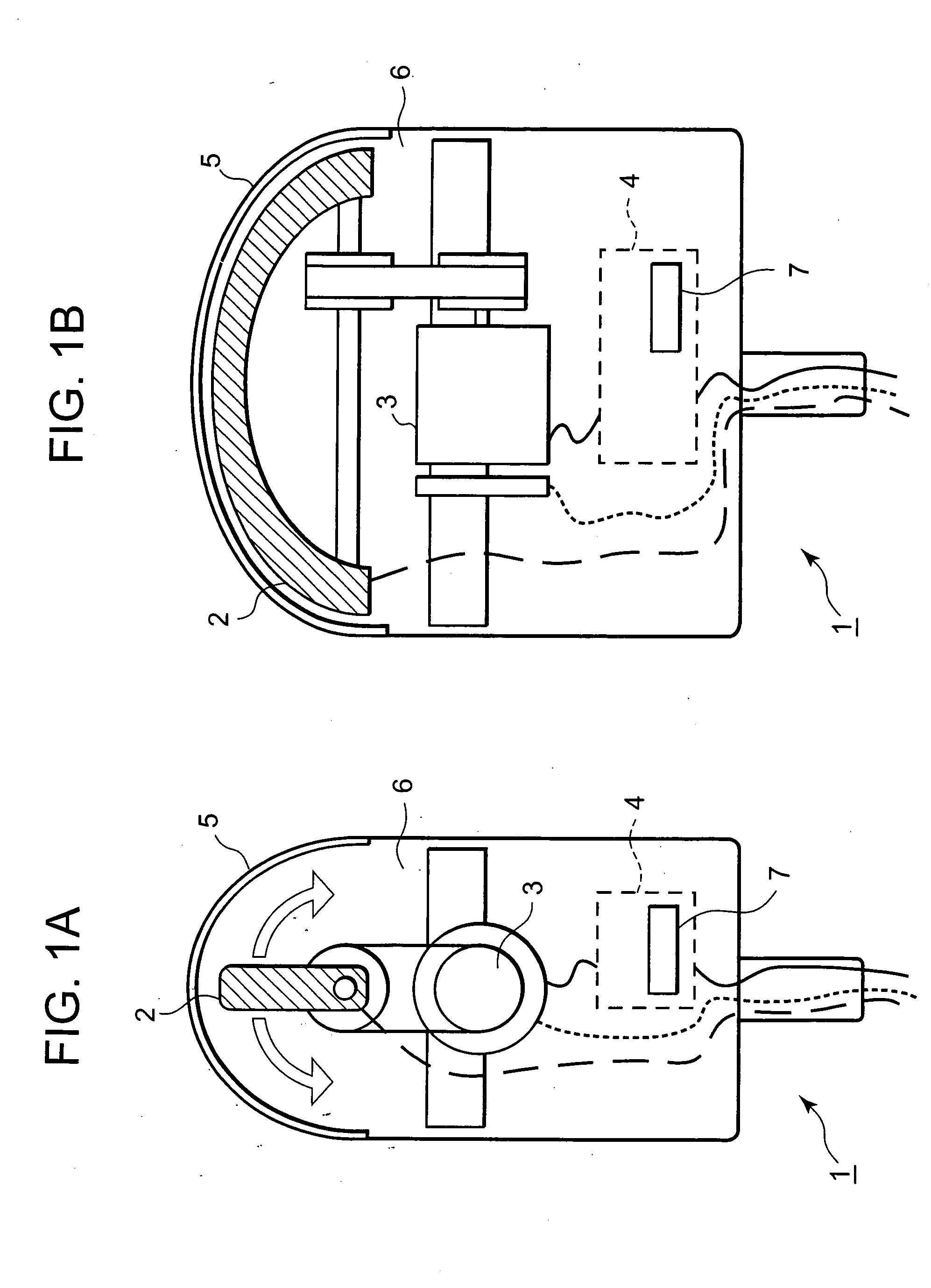
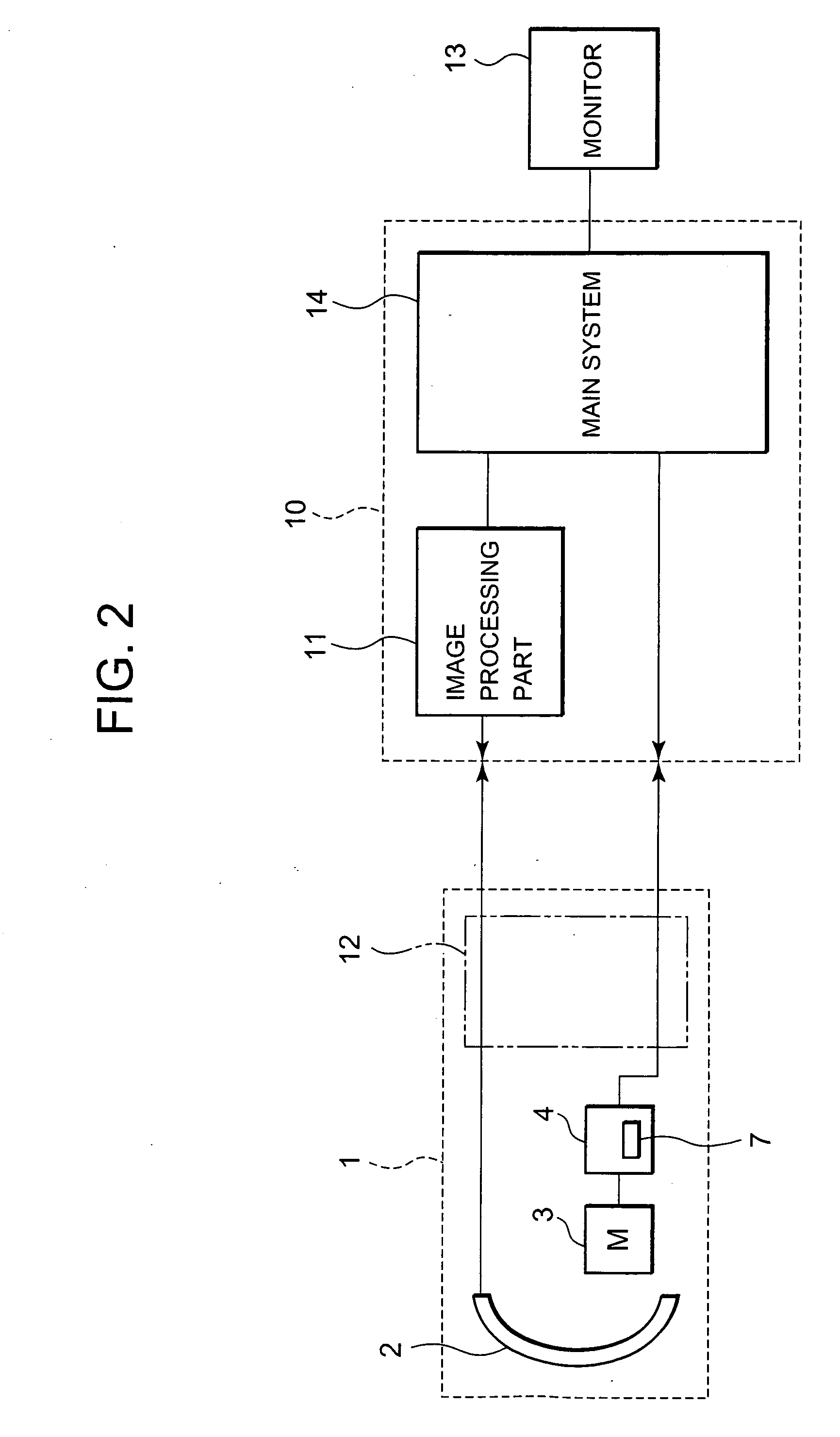
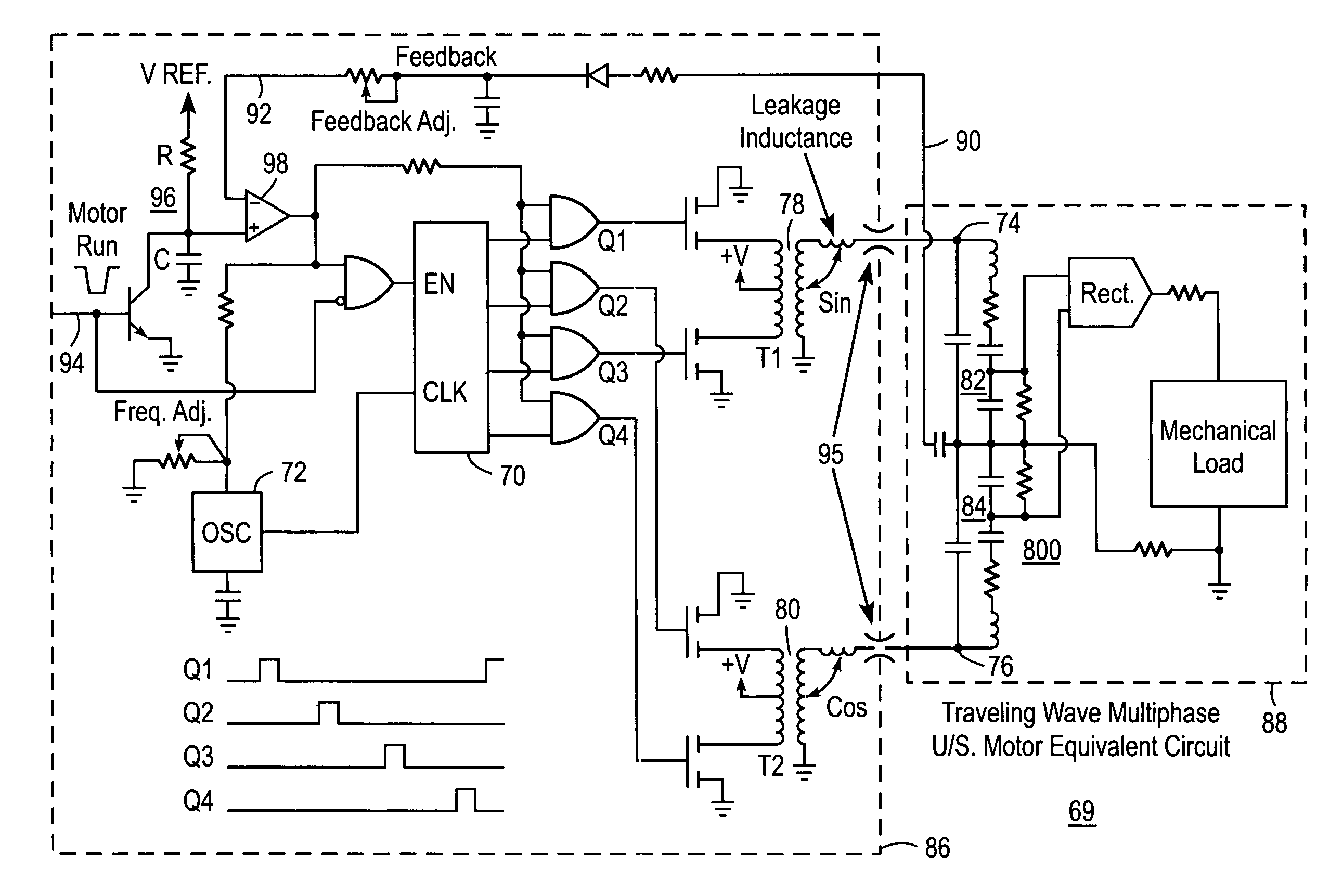
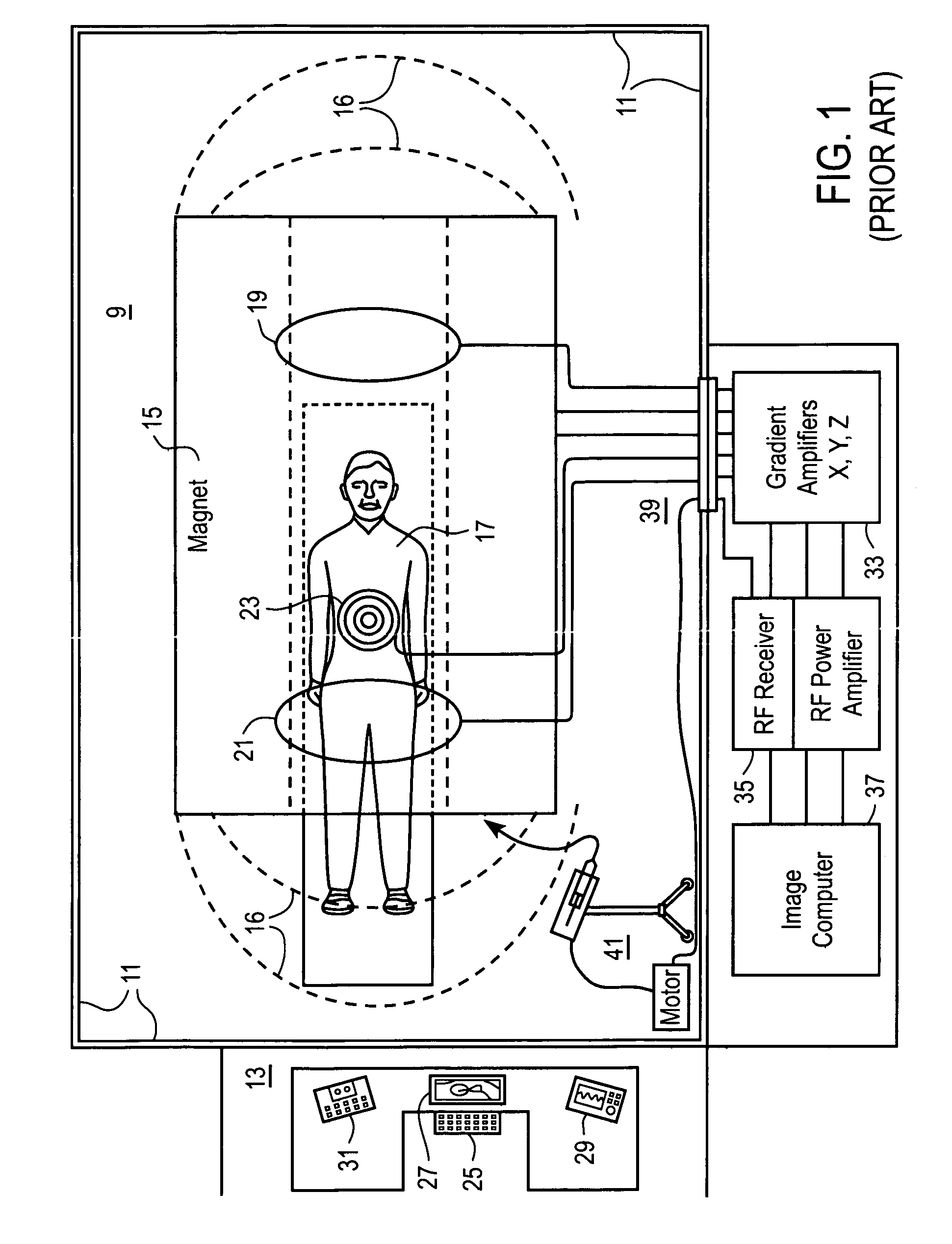
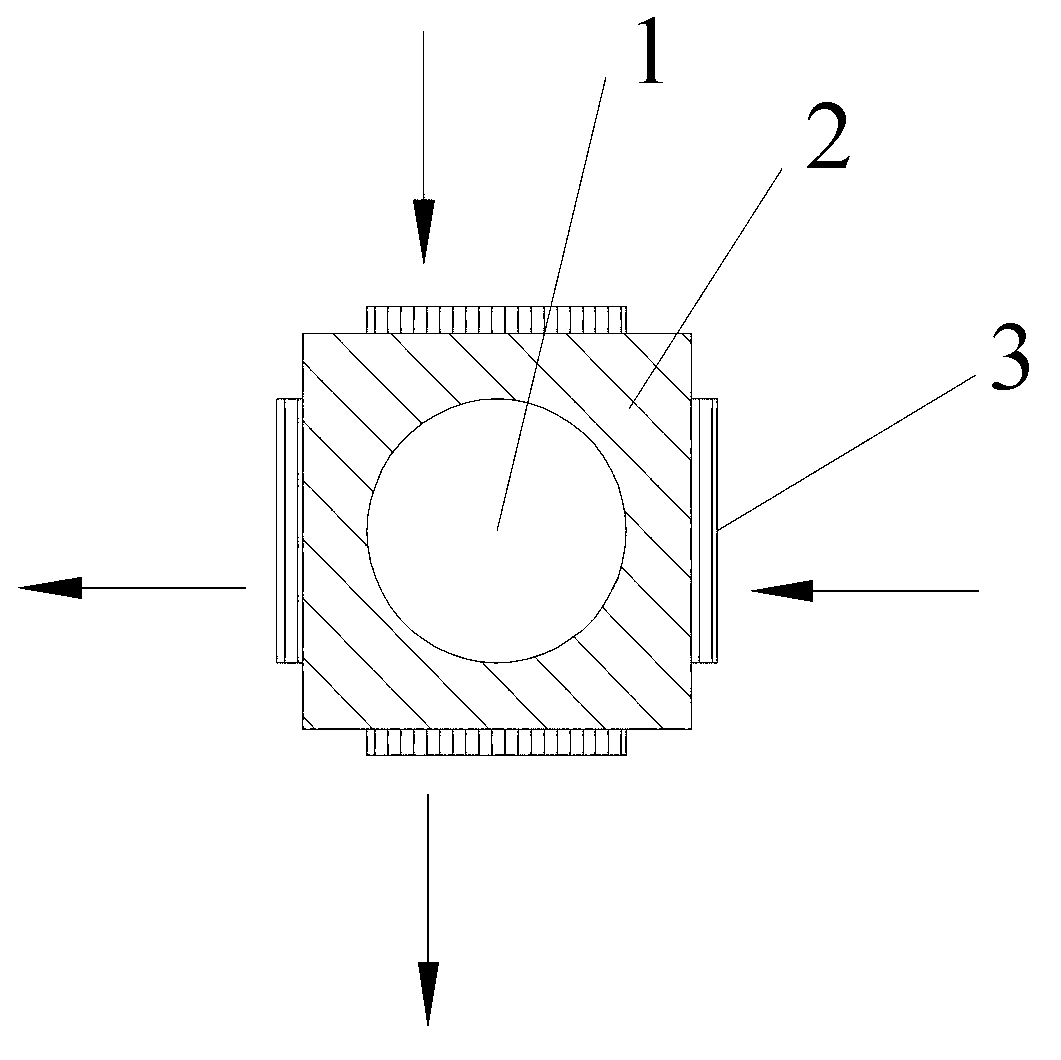
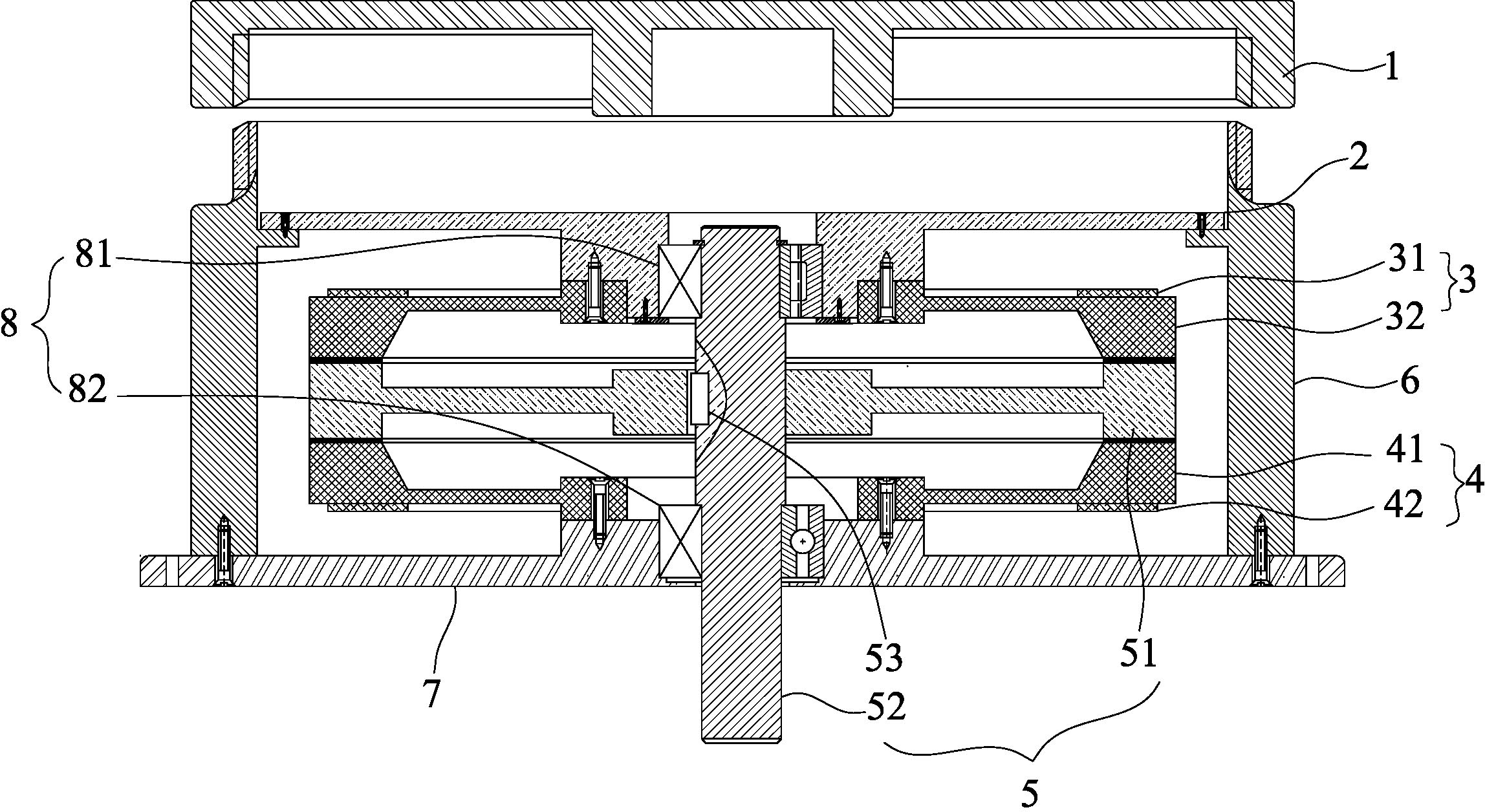
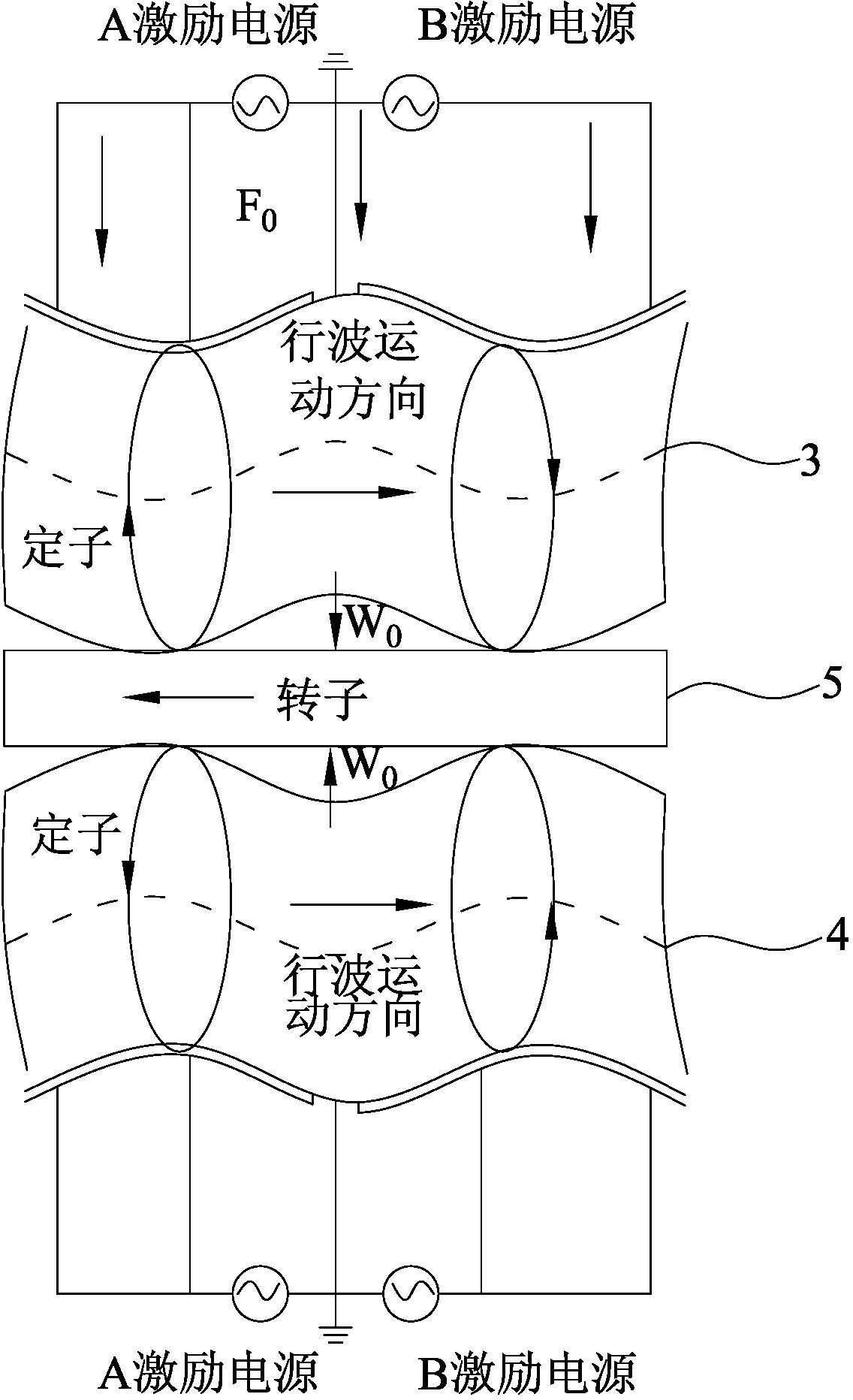
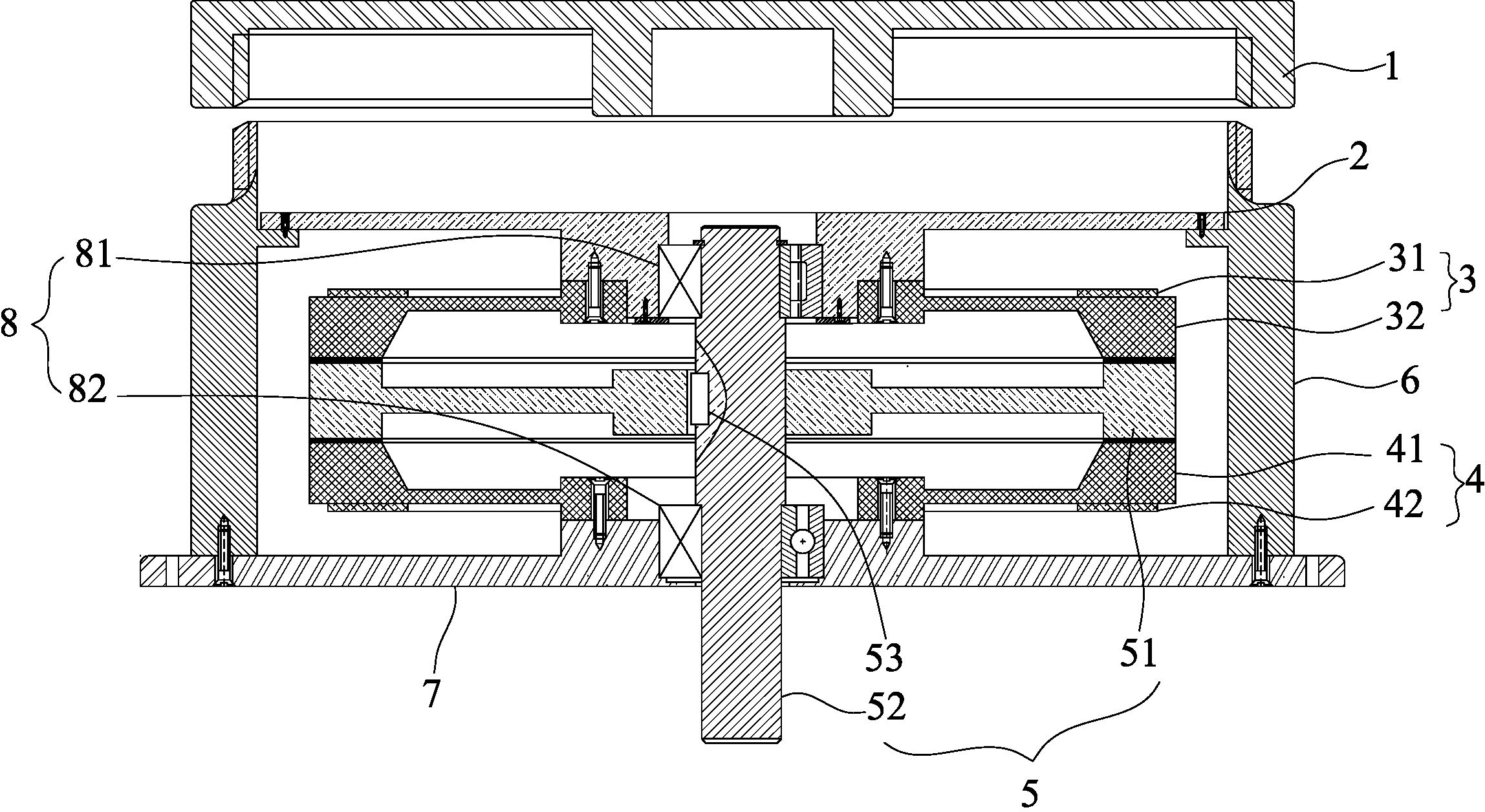
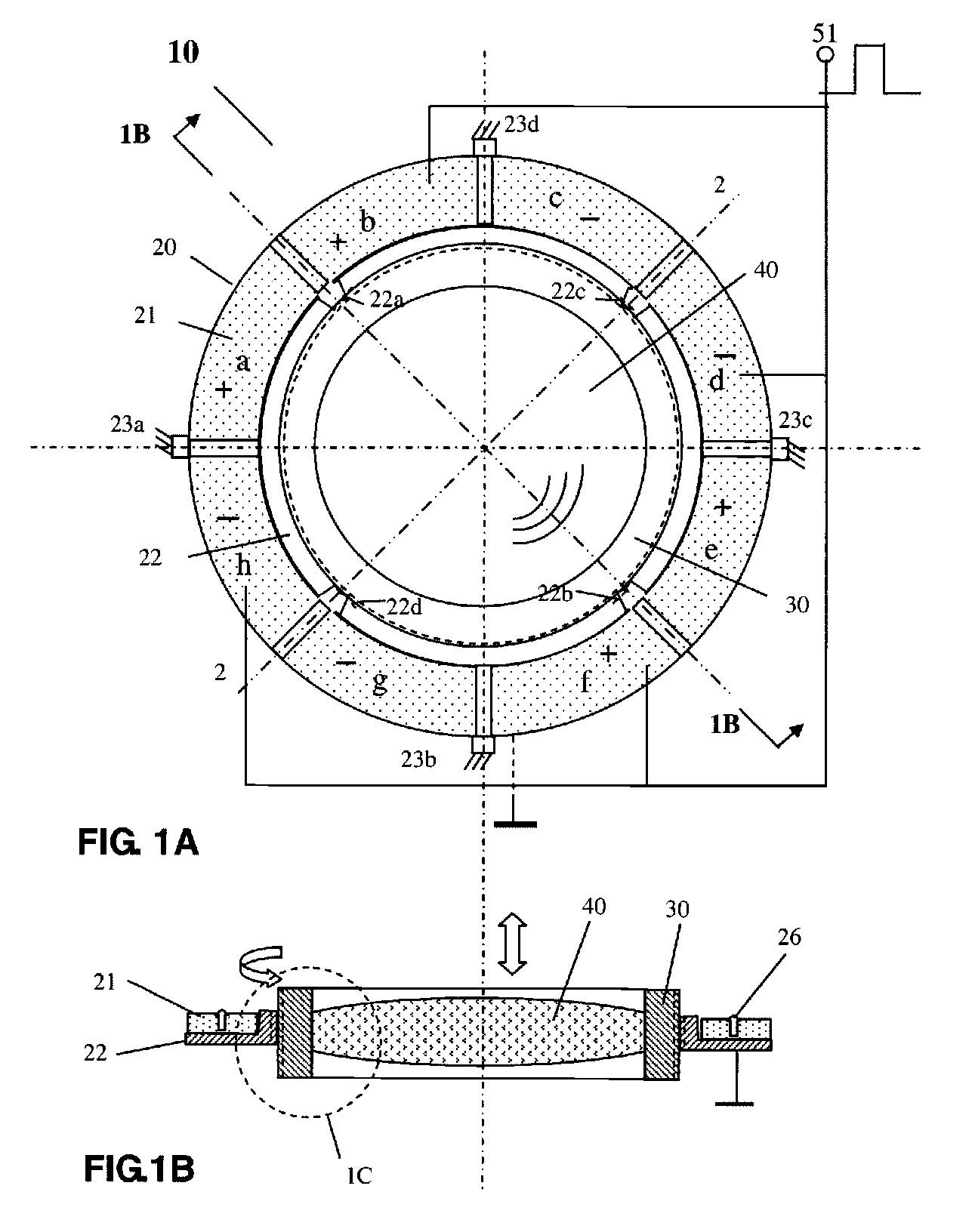
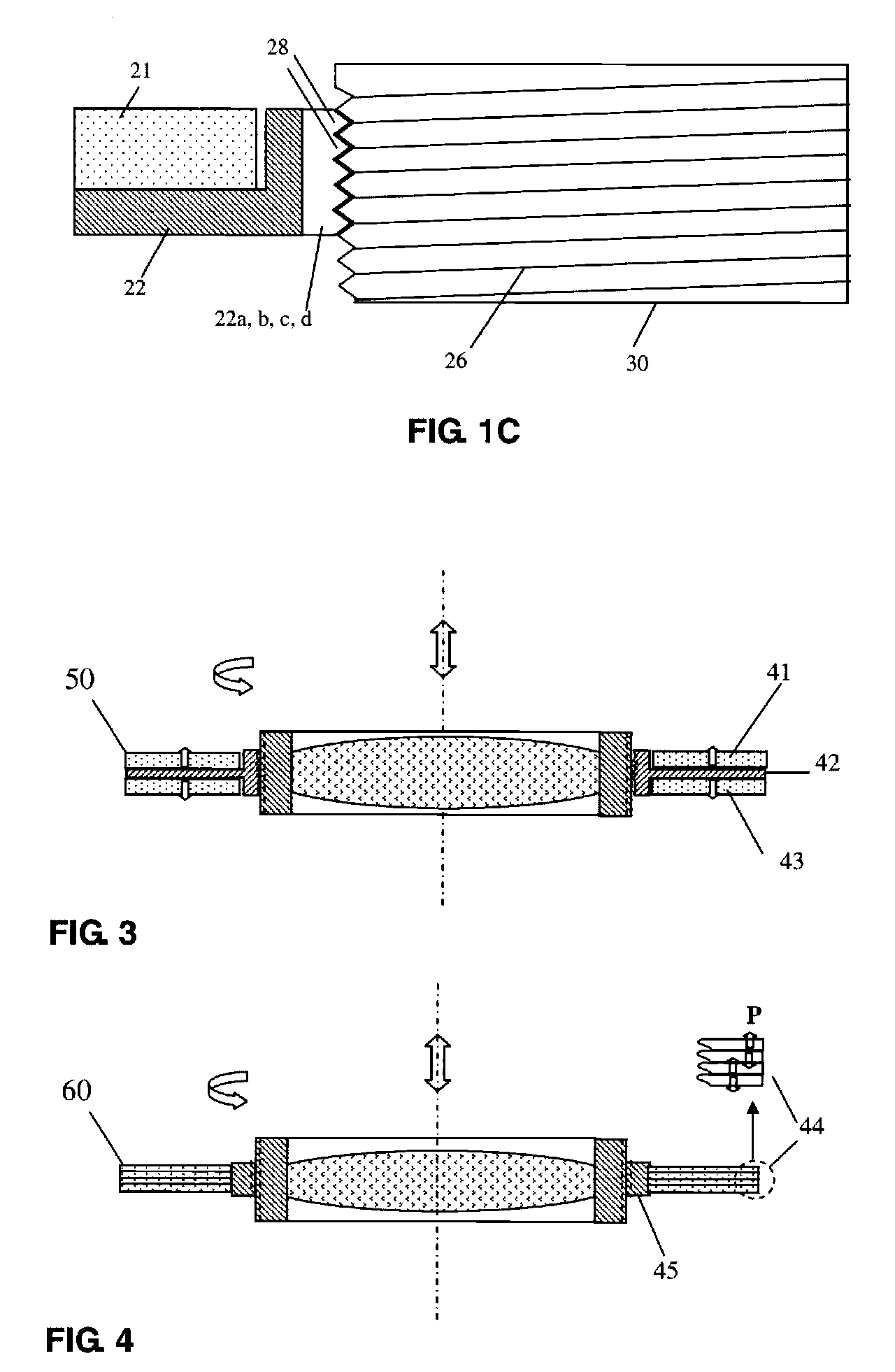
Patents
Literature
1566 results about "Ultrasonic motor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
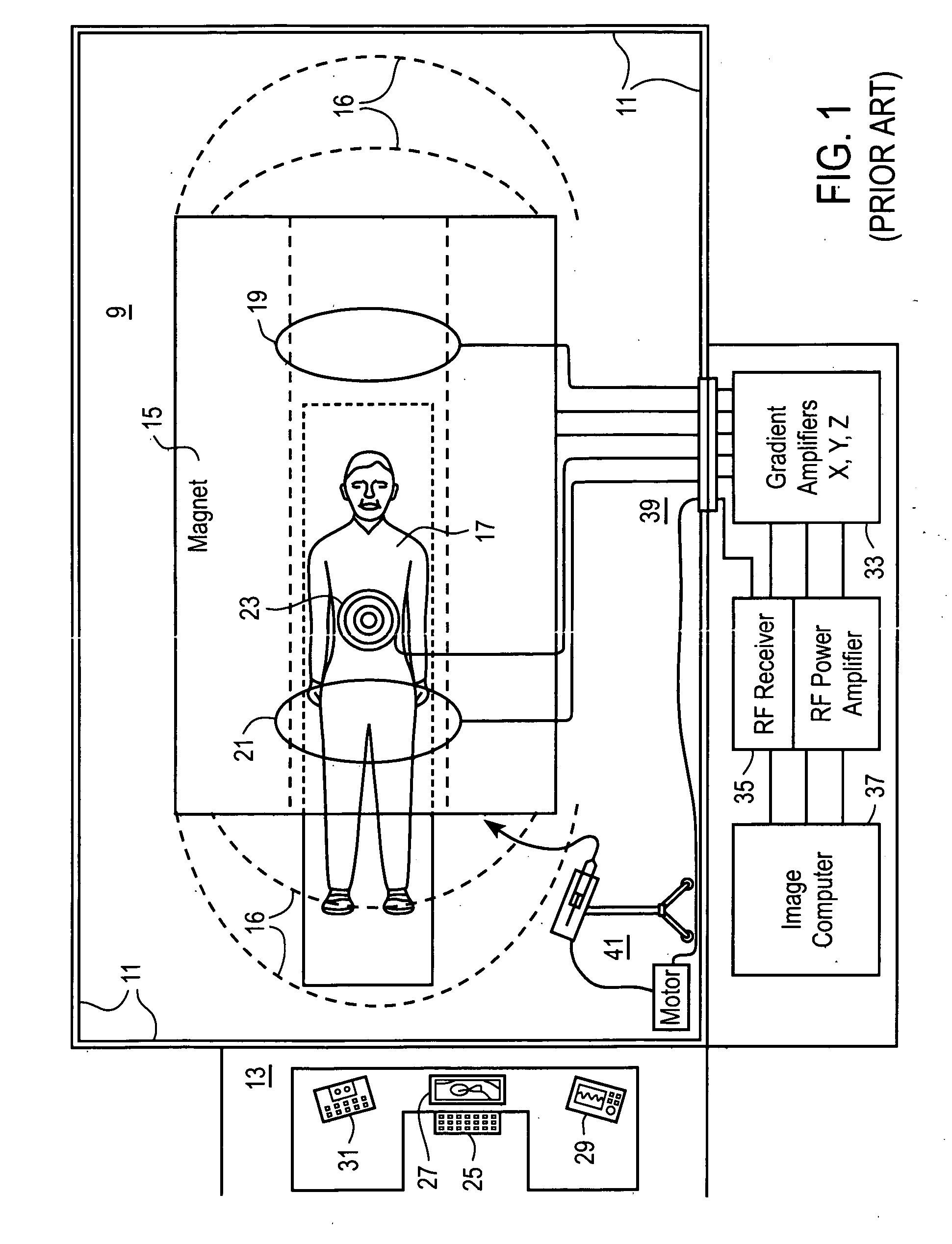
Minimally-Invasive Approach to Bone-Obstructed Soft Tissue
InactiveUS20080177268A1Improve shielding effectLow magnetic susceptibilitySurgeryMagnetic susceptibilityImaging quality
The subject invention pertains to a method and apparatus for placing a minimally-invasive access with respect to a patient's bone or other non-soft tissue. The subject invention can use a drilling machine incorporating an ultrasound motor. The subject drilling machine can be applied to sample, for example, bone biopsies under MRI control. In a specific embodiment, the subject ultrasound motor can be completely manufactured of non-magnetic materials, such as plastics, titanium, and titanium alloy, or ceramics and piezoceramics. The subject drilling apparatus can be placed into an MRI near field without influencing the image quality, and without the drilling apparatus itself being disturbed by the MRI magnet, gradient, or high-frequency field. The subject invention can incorporate good shielding with the subject drilling apparatus use of these materials, and can achieve minimal, if any, image distortions or so-called artifacts. Thus, the subject invention can involve the problem by use of non-magnetic materials of low magnetic susceptibility for the design of an actuation unit.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Ultrasonic motor driving device and ultrasonic diagnosis apparatus
InactiveUS20060250046A1Reduce stepsUnstable operationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyLow speedEngineering
A technology, wherein unstable operation of the ultrasonic motor is prevented, when the ultrasonic motor is driven at the lower speed out of at least two types of speeds, and life extension is attempted, is disclosed, and according to this invention, when the ultrasonic motor 3 is driven at a comparatively low-speed during normal driving, unstable operation due to driving at a comparatively low-speed can be prevented and life extension can be attempted by driving the ultrasonic motor at a comparatively high-speed every predetermined period of time.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
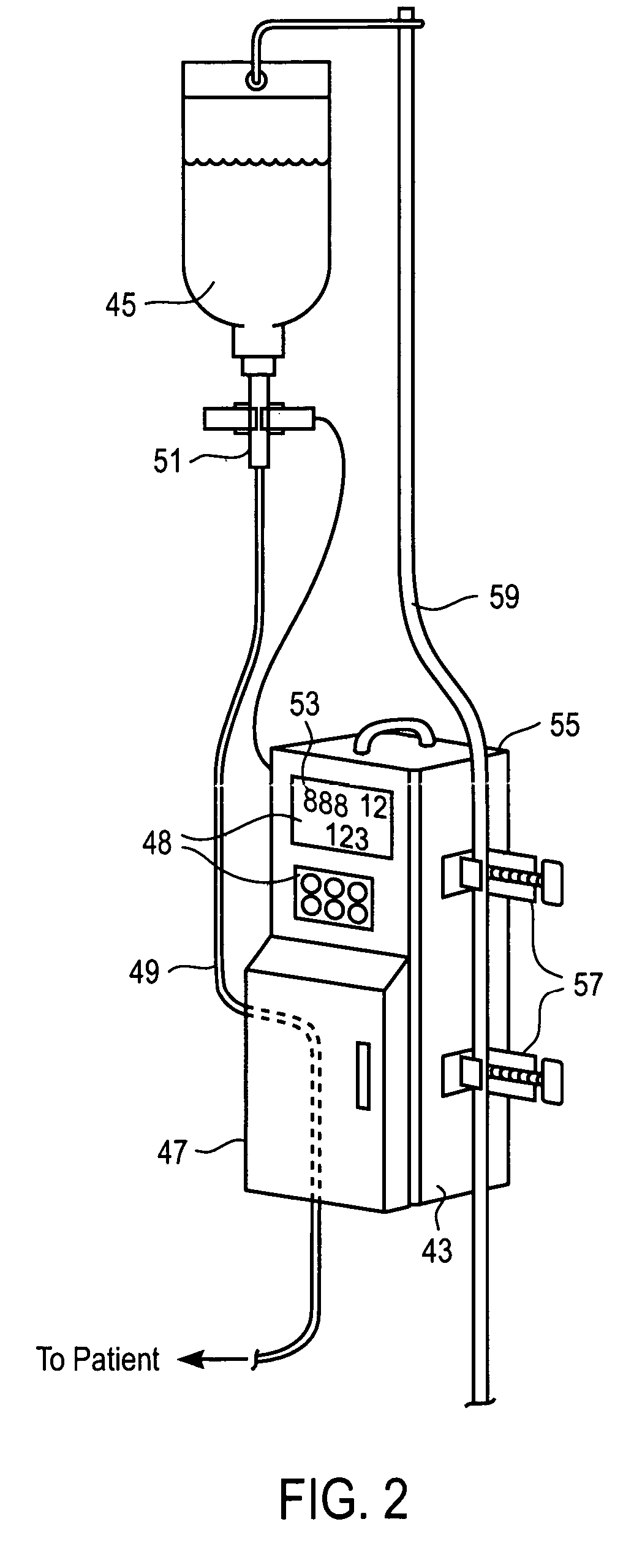
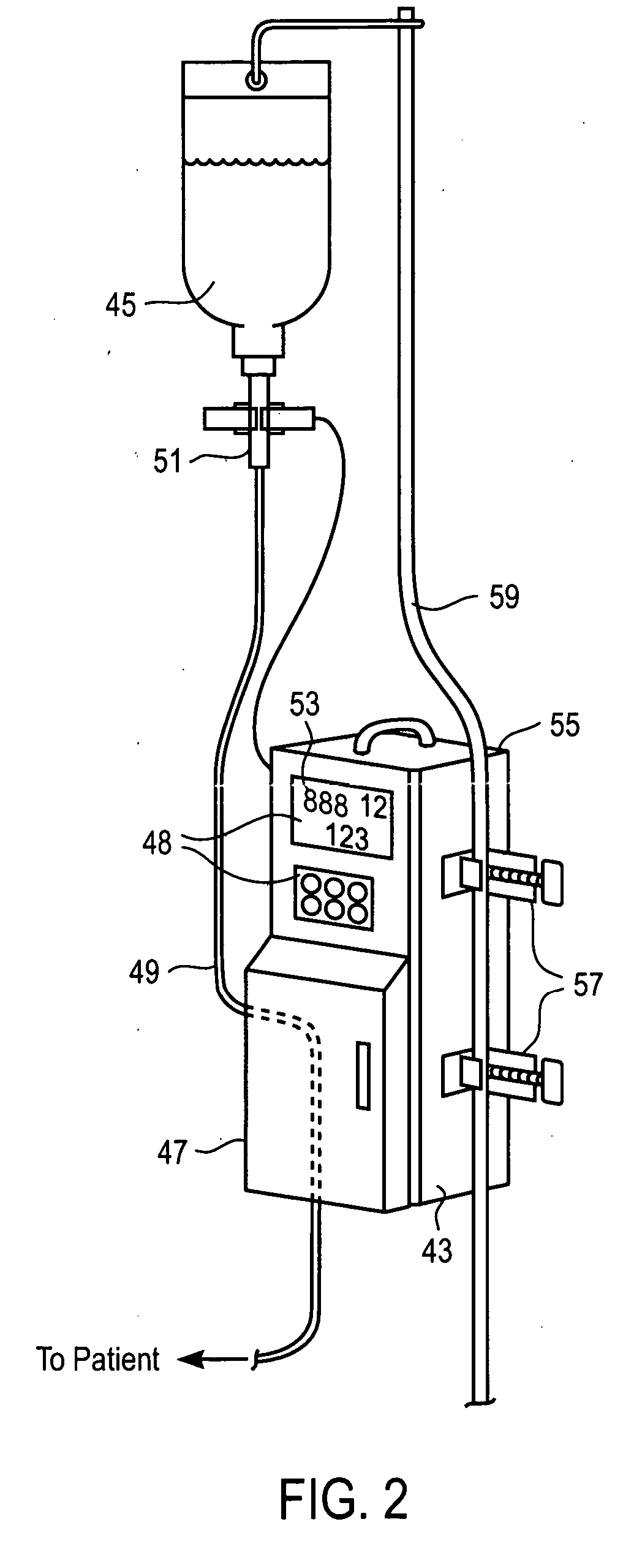
Liquid infusion apparatus
InactiveUS7553295B2Reduce materialEasy to controlDC motor speed/torque controlFlexible member pumpsPeristaltic pumpEngineering
Liquid infusion apparatus includes non-magnetic materials in a pumping structure and ultrasonic drive motor therefor, and in a controller that supplies drive signals to the motor to facilitate convenient operation in intense magnetic fields without distorting the magnetic fields and without radiating objectionable radio-frequency interference. A non-MRI-compatible liquid infusion apparatus is temporarily replaced with MRI-compatible, non-magnetic liquid infusion apparatus without disconnecting a patient from an installed intravenous infusion set to continue infusing liquid within the MRI environment. The pumping apparatus operates on a segment of a liquid conduit that is mounted in tension between a linear peristaltic pump and platen, with associated safety interlocks to assure proper operation of infusing liquid into a patient compatibly with conditions in an MRI environment. Drive circuitry generates low-harmonic signals for operating the ultrasonic motor at variable speeds to compensate for flow rate discontinuities through the peristaltic pumping cycles.
Owner:IRADIMED CORP
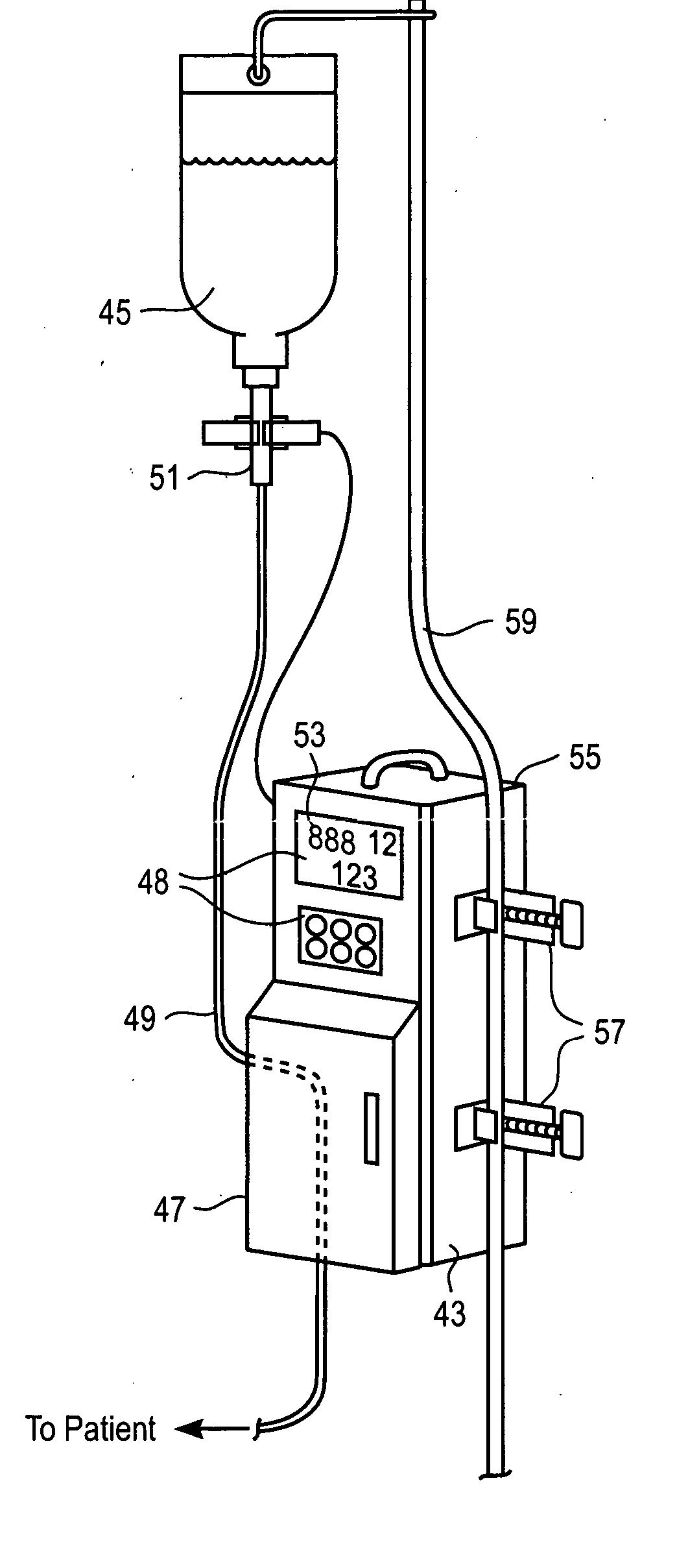
Liquid infusion apparatus
InactiveUS20060173412A1Reduction of magnetic materialEliminate the problemDC motor speed/torque controlFlexible member pumpsPeristaltic pumpEngineering
Liquid infusion apparatus includes non-magnetic materials in a pumping structure and ultrasonic drive motor therefor, and in a controller that supplies drive signals to the motor to facilitate convenient operation in intense magnetic fields without distorting the magnetic fields and without radiating objectionable radio-frequency interference. A non-MRI-compatible liquid infusion apparatus is temporarily replaced with MRI-compatible, non-magnetic liquid infusion apparatus without disconnecting a patient from an installed intravenous infusion set to continue infusing liquid within the MRI environment. The pumping apparatus operates on a segment of a liquid conduit that is mounted in tension between a linear peristaltic pump and platen, with associated safety interlocks to assure proper operation of infusing liquid into a patient compatibly with conditions in an MRI environment. Drive circuitry generates low-harmonic signals for operating the ultrasonic motor at variable speeds to compensate for flow rate discontinuities through the peristaltic pumping cycles.
Owner:IRADIMED CORP
Operating apparatus and an electric instrument
ActiveUS7224102B2Minimized in sizePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesEngineeringContact element
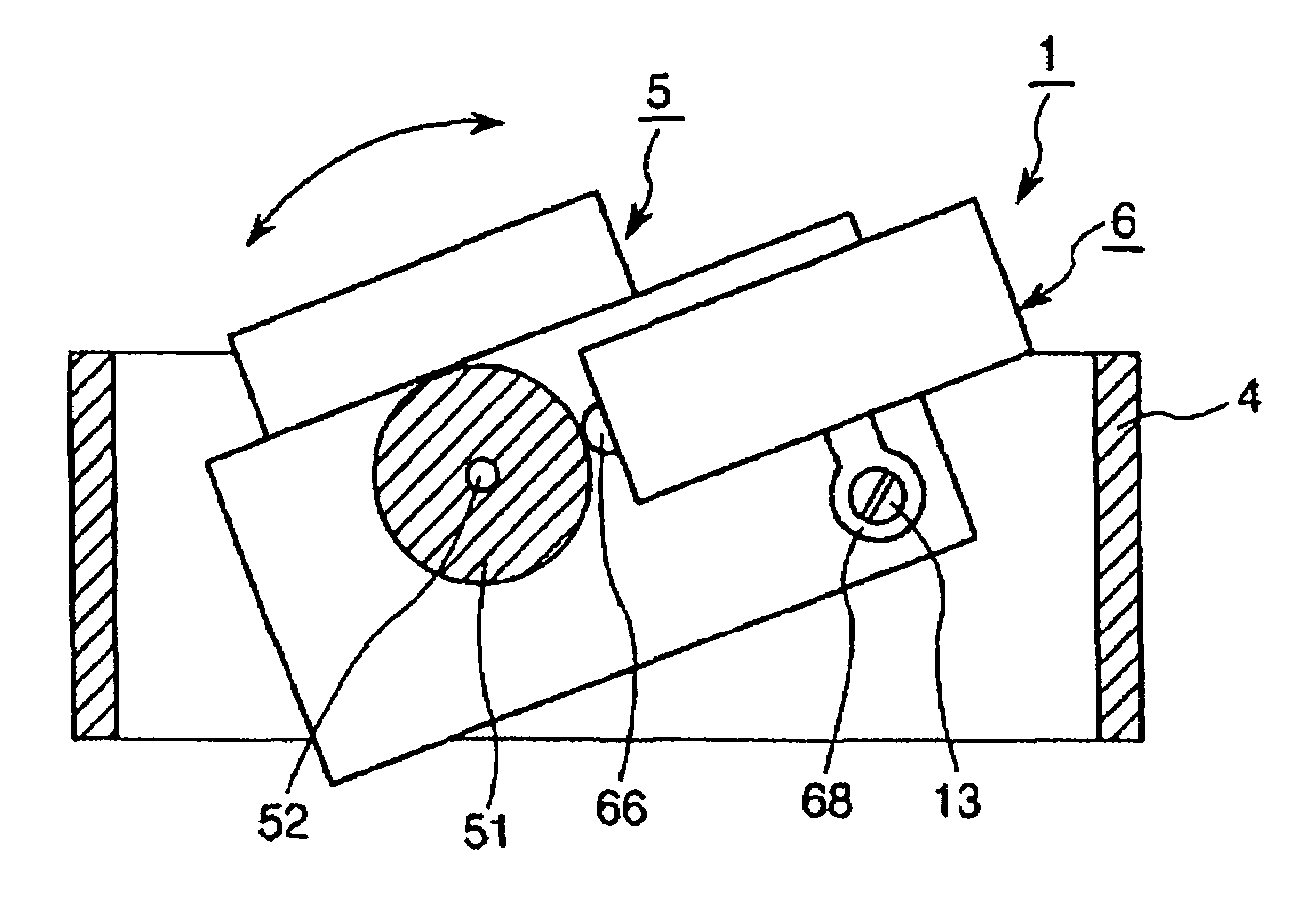
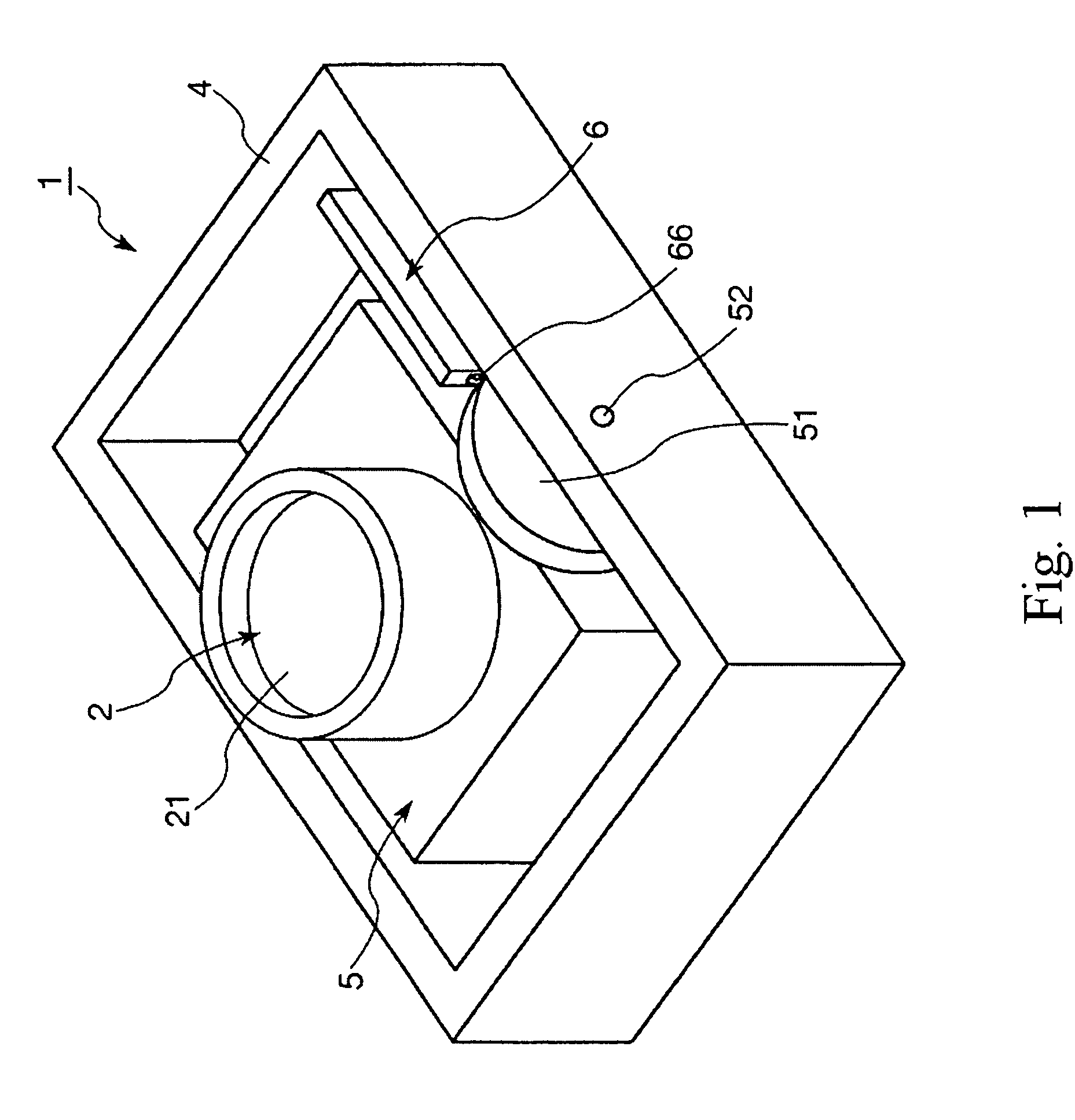
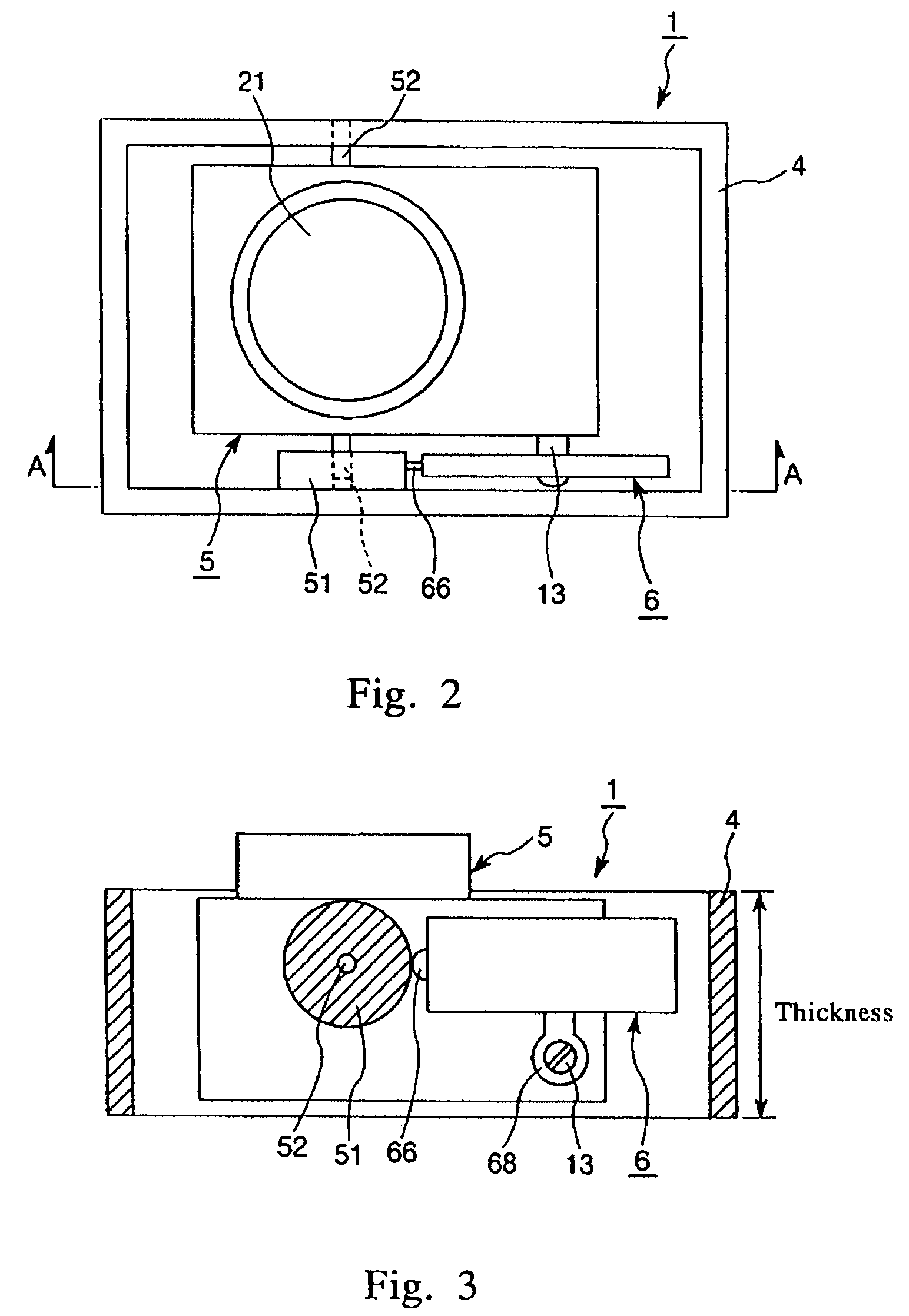
An operating apparatus 1 of the present invention has a driven element 5, a frame 4 having a contacted element 51 and rotatably supporting the driven element 5, and an ultrasonic motor. The ultrasonic motor includes a vibrating element 6. The vibrating element 6 includes a first piezoelectric element 62 that undergoes extension and contraction by application of an AC voltage, a reinforcing plate 63 having a contact portion 66 and an arm portion 68, and a second piezoelectric element 64 that undergoes extension and contraction by application of an AC voltage. The first piezoelectric element 62, the reinforcing plate 63, and the second piezoelectric element 64 are laminated in this order. The vibrating element 6 is fixedly mounted on the driven element 5 in a state where the contact portion 66 abuts on the contacted element 51. Further, the vibrating element 6 receives reaction force from the contacted element 51 when the vibrating element 6 vibrates so that the driven element 5 is rotated together with the vibrating element 6 by means of the reaction force.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
K shaped linear ultrasound motor based on continuous amplitude transforming rod principle
InactiveCN101404467AHigh speedHigh outputPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransformerOperating speed
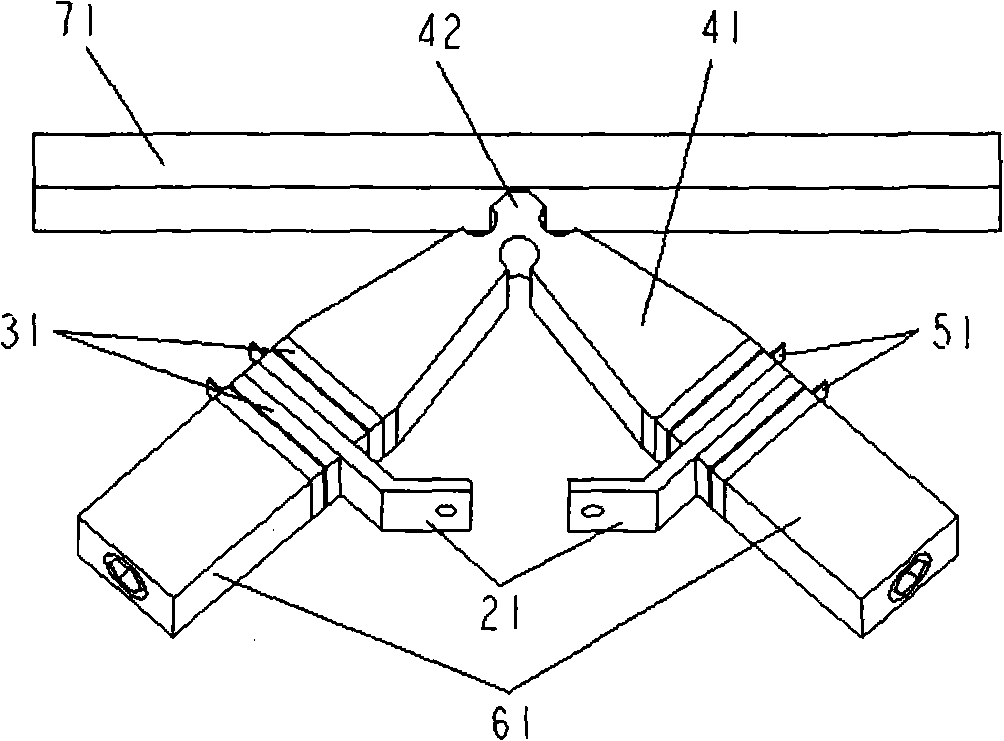
The invention discloses a K-shaped linear ultrasonic motor based on the theory of a continuous amplitude transformer, belonging to the field of ultrasonic motor. The motor comprises a stator and a rotor; wherein, the rotor is a linear guide way; the stator consists of two Langevin oscillators, center lines of which are crossed; each Langevin oscillator consists of a front end (41), a rear end (61), a piezoelectric ceramic chip (31) and corresponding electrode plates (51); the head parts of the two Langevin oscillators are connected into a whole to form a driving leg (42); the linear guide way and the two Langevin oscillators are arranged in the same plane and form a K-shaped structure. The invention is characterized in that the Langevin oscillators are in the rod structure; the section of the rod is a continuous section that is gradually reduced from the rear end (61) to the front end (41). The linear ultrasonic motor of the invention has the advantages of simple structure, high output power, fast operating speed and high output efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Piezoelectric element, and liquid jet head and ultrasonic motor using the piezoelectric element
InactiveUS20080067898A1Improve featuresInking apparatusPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLiquid jetUltrasonic motor
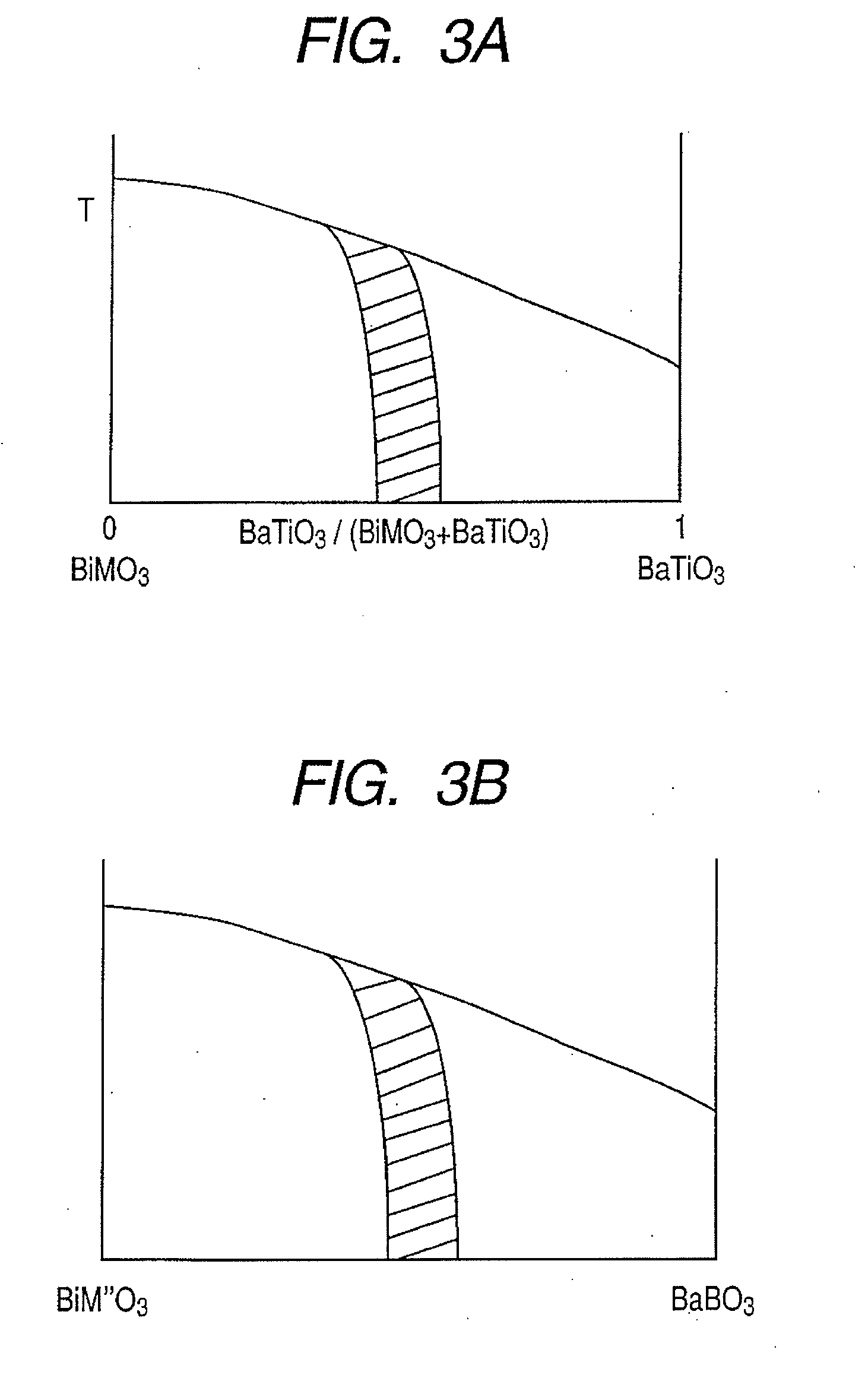
There is disclosed a piezoelectric element having, on a substrate, a piezoelectric body and a pair of electrodes which come in contact with the piezoelectric body, wherein the piezoelectric body consists of a perovskite type oxide represented by the following formula (1):(Bi,Ba)(M,Ti)O3 (1)in which M is an atom of one element selected from the group consisting of Mn, Cr, Cu, Sc, In, Ga, Yb, Al, Mg, Zn, Co, Zr, Sn, Nb, Ta, and W, or a combination of the atoms of the plurality of elements.
Owner:CANON KK
Ultrasound transducer
InactiveUS20100324418A1Move preciselyShort response timeInfrasonic diagnosticsTomographyUltrasonic sensorSonification
An ultrasound system having a transducer probe unit including at least one transducer for transmitting and receiving ultrasonic signals, wherein the transducer is moved with respect to the probe unit in a repetitive motion by an ultrasonic motor.
Owner:SIGNOSTICS LTD
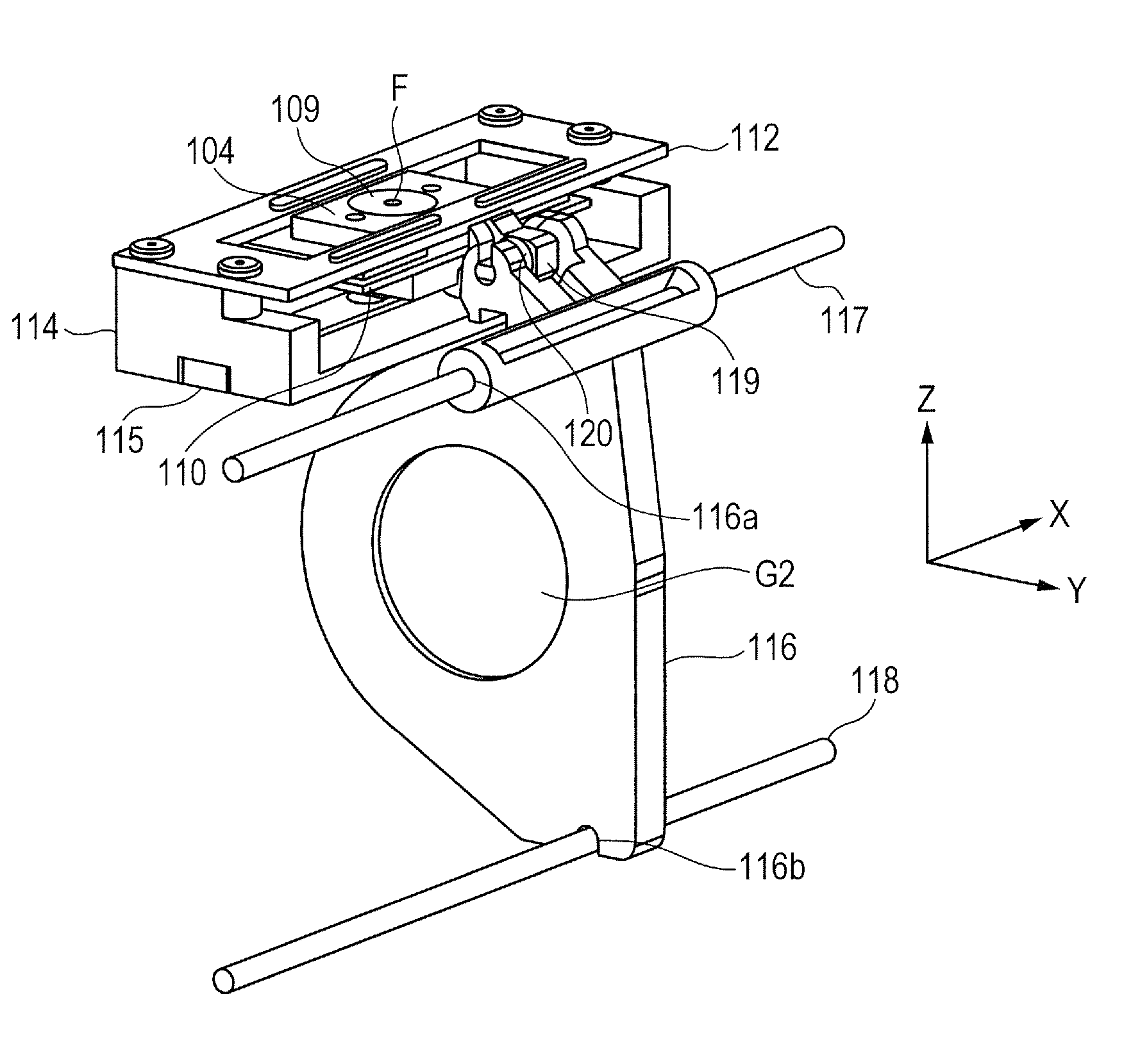
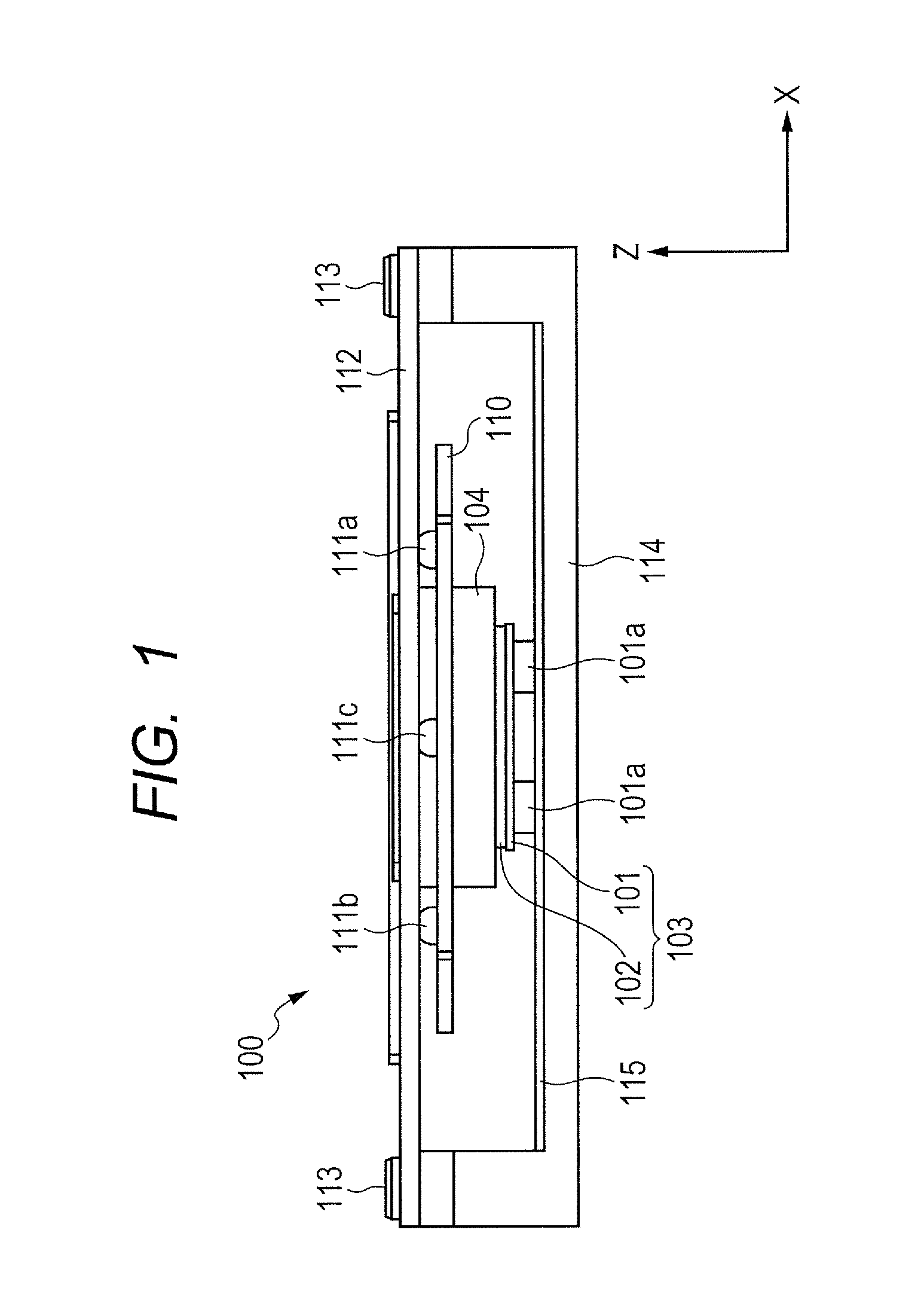
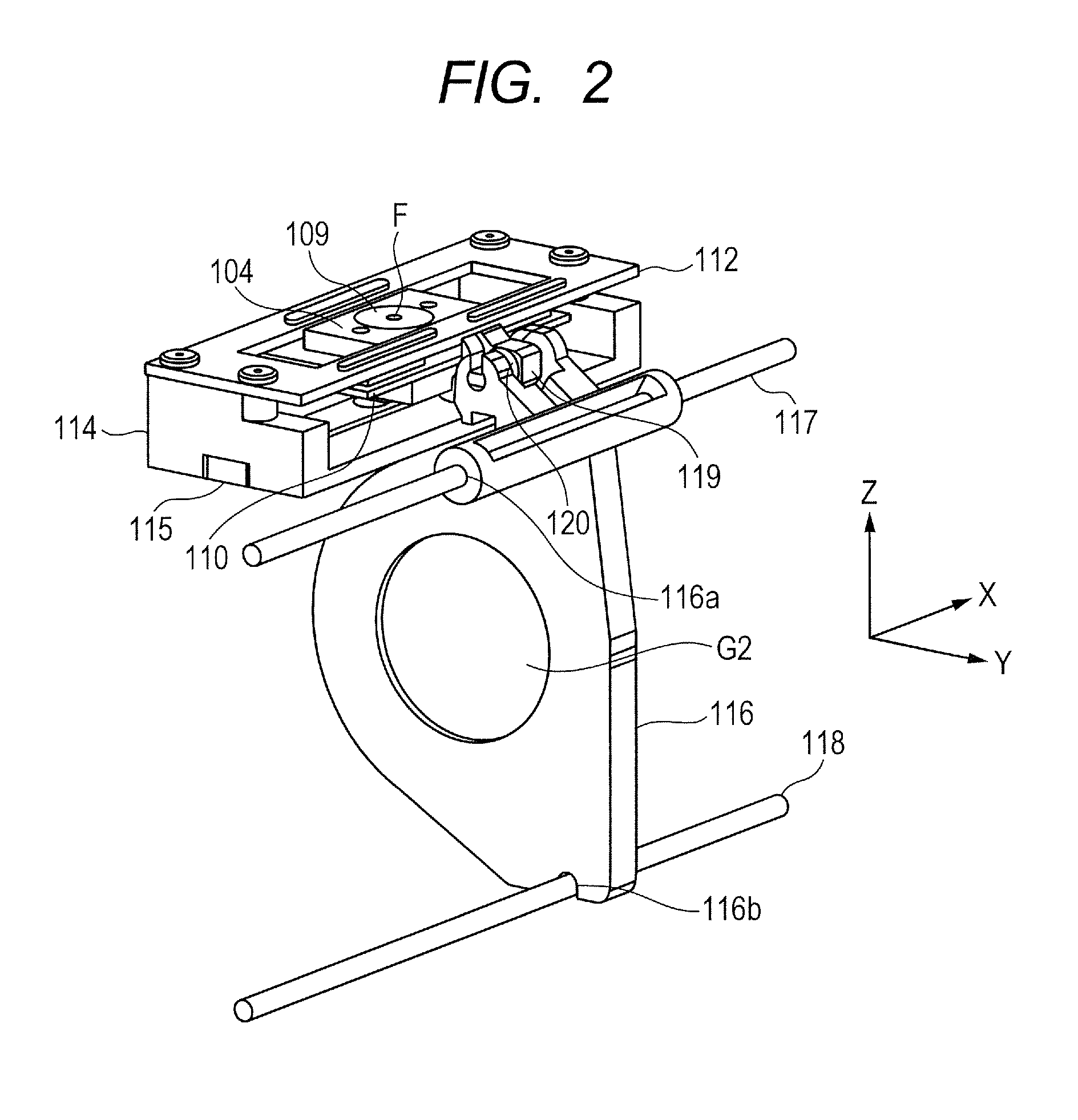
Linear ultrasonic motor and lens apparatus and image pickup apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20140293463A1Provide driving forcePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMountingsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A linear ultrasonic motor includes a vibrator having a piezoelectric element, a movable part applying a pressurization force to the vibrator and bringing the vibrator into pressurized contact with a base part, a cover part being fixed to the base part, a rolling part being rollably held between a movable guide part of the movable part and a cover guide part of the cover part, and a body to be driven having a transmission member that is pivotably supported and being able to move only in the movable direction. The transmission member includes a bias part that abuts on a transmission part of the movable part and applies a biasing force of biasing the movable part to the rolling part, to the transmission part. The rolling part is held by a resultant force of the pressurization force or a reaction force of the pressurization force, and the biasing force.
Owner:CANON KK
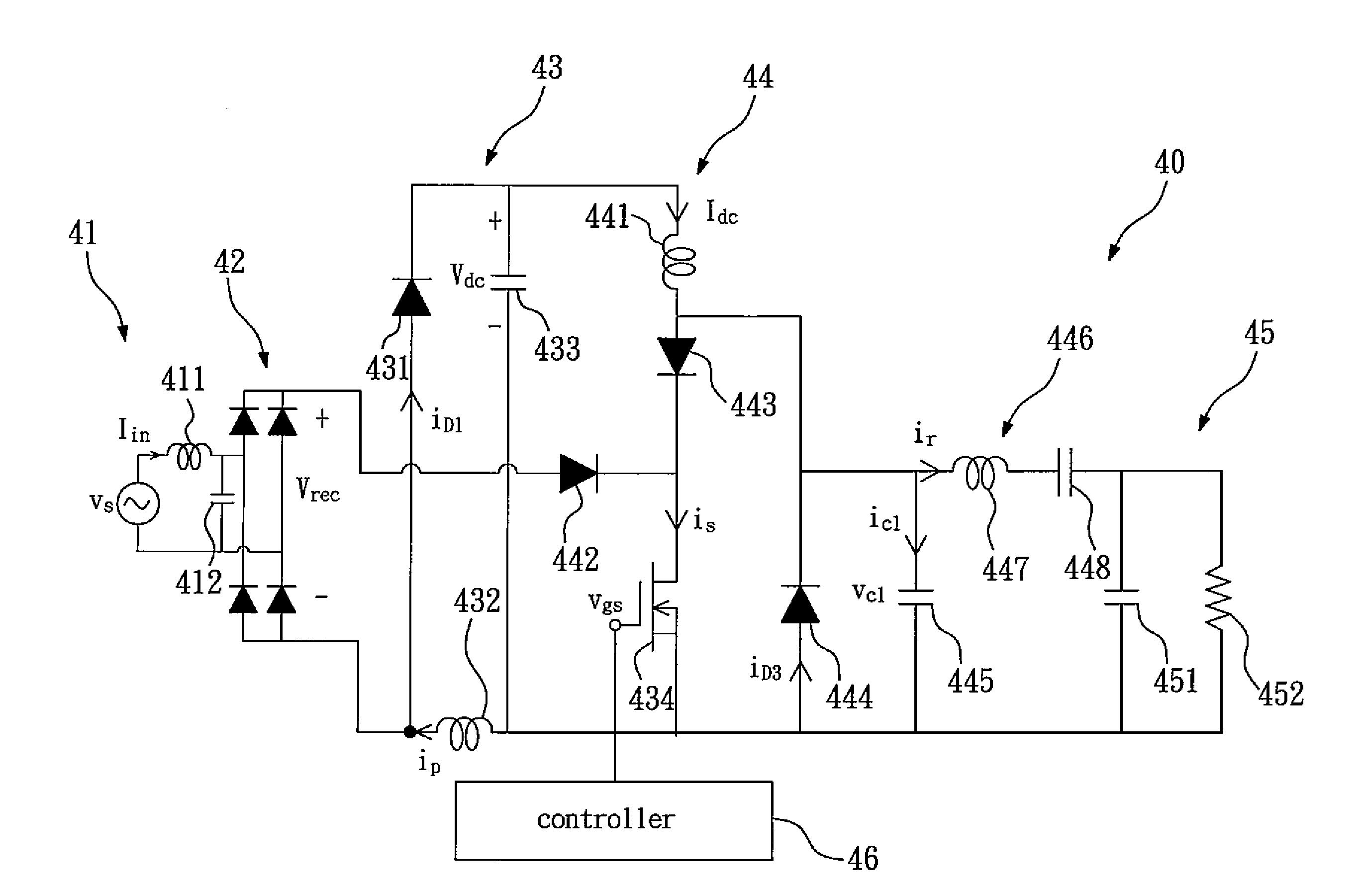
Single-stage zero-current switching driving circuit for ultrasonic motor
ActiveUS20110095711A1Improve power factorReduce switchingAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlUltrasonic motorCurrent switch
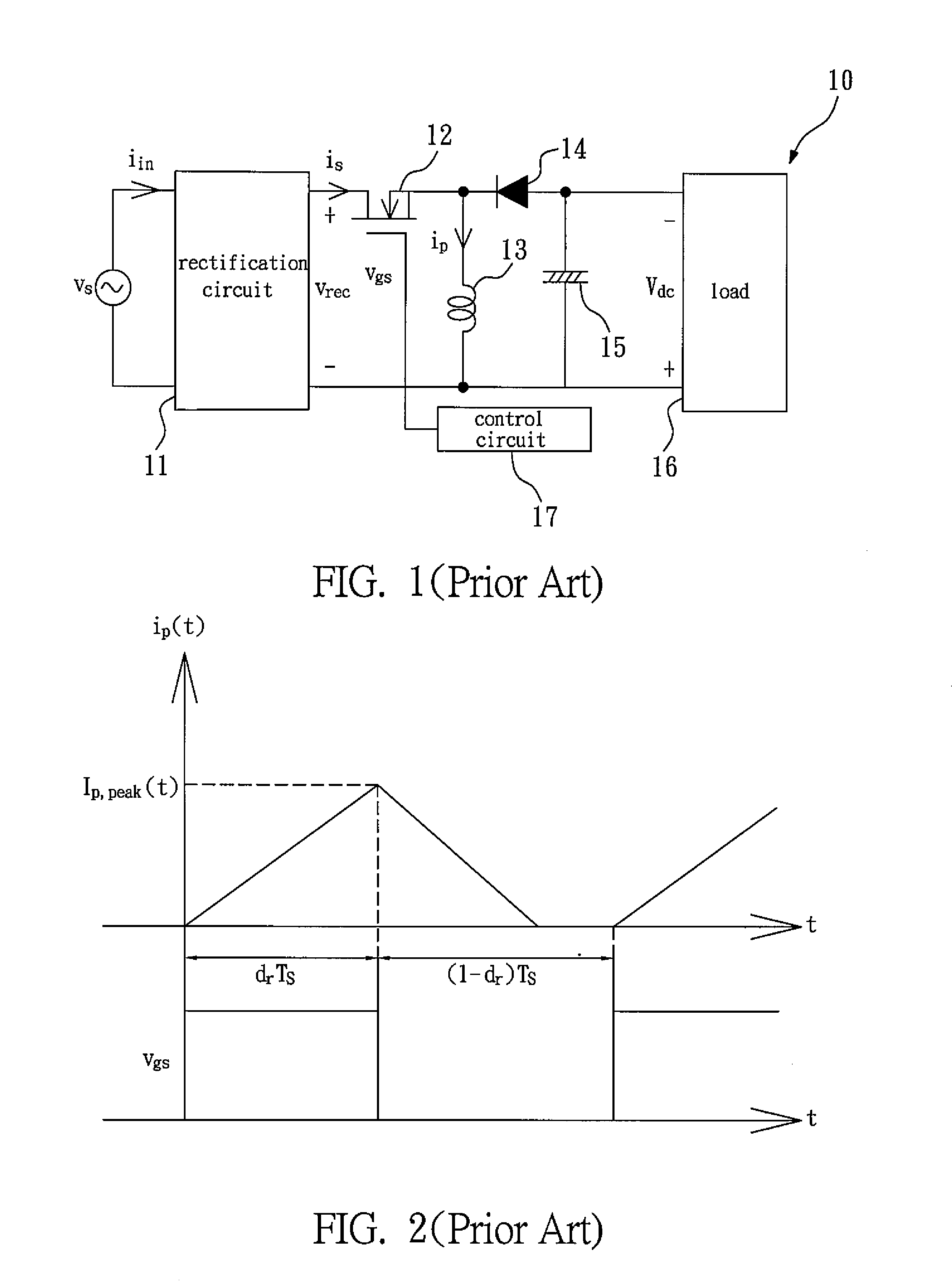
The present invention relates to a single-stage zero-current switching driving circuit for ultrasonic motor, which comprises: a buck-boost converter and a zero-current switching resonant inverter. The driving circuit according to the present invention integrates the buck-boost converter and the resonant inverter into a single-stage structure, so that the buck-boost converter and the resonant inverter share an active switch and a trigger signal, and therefore, the circuit is simplified and the loss caused by stage switching is reduced. Moreover, the buck-boost converter operates in a discontinuous-conduction mode (DCM), which allows the circuit to have high power factor, and enables the active switch to be capable of zero-current switching (ZCS), so that the loss caused by switching is largely reduced. In the driving circuit according to the present invention, there's no interaction of power between the buck-boost converter and the resonant inverter, so that the two circuits can be analyzed individually. Therefore, the driving circuit according to the present invention having simplified circuit, low loss caused by switching, and low manufacturing cost, can be a competitive product after being commercialized.
Owner:METAL INDS RES & DEV CENT
Temperature-resistant resin modified polyphenyl ester ternary alloy ultrasonic motor friction material
The invention discloses a ternary alloy hyperacoustic motor frictional material of the fire resistance resin modified polyphenyl ester, which solves the low friction coefficient problem, the low impact strength problem, the low abradability problem and the bad processability problem of the prior hyperacoustic motor. The invention is made by 5-25% politef, 5-20% fire resistant resin and the rest polyphenyl, which can also add one or a plurality of 10-35% fortifying fiber, 1-15% metal powder and 1-15% ceramic powder. The invention keeps all the advantages of the present polyphenyl ester plastic alloy hyperacoustic motor frictional material, which is provided with the high friction coefficient, the good abradability, the low noise, the high hardness and the high impact strength.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Triangle bended plate type piezoelectric straight line ultrasound electric motor
InactiveCN101119079ASimple structureLow costPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElastomerPiezoelectric actuators
The present invention relates to a triangular bent-plate piezoelectric linear ultrasonic motor, including a stator and a rotor. The rotor is a linear guide rail, the upper part of which is supported by two guide wheels with the spring support parallel arranged, while the lower part is supported by the stator. The stator consists of a hollow triangular elastic frame and a piezoelectric actuator adhering on the outside surface of the frame. The triangular top point of the hollow triangular elastic frame has a projection abutting with the bottom surface of the linear guide rail, while the midpoint of the bottom edge of the triangle has a clamp fastener connected with the seat. The motor of the invention has a relatively small lateral dimension, can be used for the bidirectional driving and controlling, and has the advantages of simple structure, use convenience and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Annular standing wave linear ultrasonic motor oscillator
InactiveCN1665119AReduce manufacturing costSimple structurePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElastomerUltrasonic motor
The invention discloses a vibrator of annular standing wave linear ultrasonic motor, solving the problems of different-order or ¿Ctype two-mode operation, complicated structure, uneasy design and high manufacturing cost; the invention is composed of metallic elastomer and piezoelectric ceramic piece, there are several vibrator teeth on the metallic elastomer and it is characterized in that: the said metallic elastomer is a square or long ring in shape, composed by the closing of straight beam segment and arc segment and works in internal-bending vibrating mode of two surfaces with the same order and frequency or the approximately same frequency; its advantages lie in: working by using the same order vibrating type and the same frequency, thus its driving circuit is simple and its manufacturing cost is lower; its structure is simple and easy to design; etc.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Vibrator of beam type linear ultrasonic motor using bending vibration modes
ActiveCN101626203AImprove mechanical output capabilityImprove performancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngineeringControl theory
A vibrator of a beam type linear ultrasonic motor using bending vibration modes belongs to the technical field of piezoelectric ultrasonic motors and is used for the piezoelectric ultrasonic motors. The vibrator solves the problem that the mechanical output capabilities of the ultrasonic motors are restricted because of low tensile strength and low electromechanical coupling efficiency of ceramic materials in the prior art. The vibrator comprises two driving pads, two end covers, two insulating sleeves, two pairs of piezoelectric ceramics with polarization directions being thickness directions, a flange, two thin-walled beams and mounting bases; wherein, studs extend out from the end faces of the flange along the axis of the flange; each stud is sleeved with a pair of piezoelectric ceramics; an end cover is screwed at the overhanging end of each stud; the tail end of each end cover is provided with a driving pad; each piezoelectric ceramic is composed of two symmetrical half piezoelectric ceramics which are combined after being split; the polarization directions of the two half piezoelectric ceramics are opposite; the splitting lines of the two pairs of piezoelectric ceramics at both sides of the flange are vertical to each other; the polarization directions of the piezoelectric ceramics in each pair are opposite.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Medical robot for use in a MRI
A medical robot for use inside a magnetic resonance imager includes a horizontal motion assembly, a vertical motion assembly and a controller. The horizontal motion assembly includes a motion joint, an ultrasonic motor operably connected to the motion joint and an encoder operably connected to the ultrasonic motor. The motor and encoder are positioned proximate to the joint of the horizontal motion assembly. The vertical motion assembly is operably connected to the horizontal motion assembly and it includes a motion joint, an ultrasonic motor operably connected to the motion joint and an encoder operably connected to the ultrasonic motor. The motor and encoder are positioned proximate to the joint of the vertical motion assembly. The controller is operably connected thereto and is adapted to be powered off when the magnetic resonance imager is being used to collect images. A medical instrument assembly is connectable to the medical robot.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK +1
Rotary input device and electronic equipment
InactiveCN101872257AFirmly graspImprove the sense of operationInput/output processes for data processingSwitching signalEngineering
Disclosed is a rotary input device, including: a rotary operation device; a rotation detecting section; a rotation driving section; a judging section to judge whether the detected rotation angle of the rotary operation device is a predetermined angle corresponding to a displayed selection item or not; a generating section to generate a switching signal when it is judged the rotation angle is the predetermined angle; and a rotation controlling section to control of a rotation drive to give the operator a force sense by a combination of at least any two of applying the rotary force in a normal rotation direction, applying the rotary force in a reverse rotation direction, and stopping applying the rotary force, when the judging section judges that the rotation angle of the rotary operation device is the predetermined angle.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Bending single-phase driven rotary ultrasonic motor
InactiveCN101030740AReduce manufacturing costLarge driving torquePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesBody shapeAxis of symmetry
The invention is concerned with the ultrasound electric machine of the electrical micro-machine, especially the bending rotation ultrasound electric machine that is single-phase drive. It consists of: the six-sliced piezoelectric ceramic slice, the stator, the rotor and the pinch device. Each piezoelectric ceramic slice devices into two parts that are reversed phase polarization by the diameter as the axis of symmetry, one part expands and the other part reduce after giving the same voltage. The piezoelectric ceramic slice rotates 60 degree from top to bottom withershins. All the piezoelectric ceramic slices drive by the single-phase voltage with same phase. The body shape of the machine is pyramid shape.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Column structure dual-wheel foot driving linear ultrasonic motor and electric exciting manner
InactiveCN101071996ALarge outputGuaranteed effective working cyclePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDrive wheelPre compression
The ultrasound motor is composed of subassemblies of stator, mover and bracket. The stator consists of stepped cylinder, eight pieces of piezoelectric ceramics (PC), pressing block, support and two driving wheels. Electrodes distributed along circumferencial direction evenly are plated on surface of PC. Mover includes slide block and slide bar. The slide bar is contacted to two drive feet of the stator; and the slide bar is fixed on the bracket. The mover is held between bracket and stator. Through supporting effect, springs and nuts on the bracket provide needed pre-compression between stator and mover. Through different fan-shaped electrodes, the drive signal acts on pieces of PC. Under inverse piezo effect, PCs vibrate to excite a natural vibration of stator so as to realize reciprocating rectilinear motion of slide block of mover. Realizing rectilinear motion in two directions of mover, the motor provides features of large output force and speed, and higher efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU FENGKE ULTRASONIC MOTORS TECH
Precise micro-dynamic parallel locating system and method for micro-nano operation environment
ActiveCN104317218AEliminate playEliminates rotational joint playProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorMicro nanoKinematics
The invention discloses a precise micro-dynamic parallel locating system and method for micro-nano operation environment. The precise micro-dynamic parallel locating system for the micro-nano operation environment comprises a mechanical body, a calibrating device and a control device which are connected in sequence; the mechanical body comprises a pedestal, more than three groups of the same ultrasonic motor drive branched chains and a movable platform; the calibrating device is used for calibrating the actual value of a kinematics parameter, feeding back the movement position of a joint and correcting the original point of the movable platform; the control device is used for processing each module signal, processing correspondingly and driving the mechanical body to move according to a scheduled track. The precise micro-dynamic parallel locating system and method avoid the disadvantages of a traditional electromagnetic motor and reduce the influences of such nonlinear factors as friction and elastic deformation of additional mechanisms and gaps between additional mechanisms, and the precise micro-dynamic parallel locating system is gapless, high in intensity, compact in structure, capable of eliminating assembly error and size error and suitable for the micro-nano operation environment; the precise micro-dynamic parallel locating system and method for the micro-nano operation environment can achieve sub-micron locating precision and millimeter travel and can also be used for macro-micro locating tables.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Screw-thread-driven rotary-linear ultrasonic motor using columnar stator high-order bending vibration mode
ActiveCN102843063AImprove performanceMeet miniaturizationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLinear motionMiniaturization
The invention discloses a screw-thread-driven rotary-linear ultrasonic motor using a columnar stator high-order bending vibration mode, which belongs to the technical field of ultrasonic motors and is used for solving the problem of small output torque during miniaturization of a screw-thread-driven rotary-linear ultrasonic motor using the columnar stator high-order bending vibration mode. The screw-thread-driven rotary-linear ultrasonic motor comprises a screw thread output shaft, a metal tube elastic sleeve and m groups of piezoelectric ceramic sheets, or comprises a screw thread output shaft, a piezoelectric ceramic tube, two metal caps and p groups of outer electrodes. Two mutually orthogonal high-order bending vibrations such as two-order or three-order bending vibration modes on a free stator space are excited, driving travelling waves are generated on the inner surface of a stator driving end consisting of the metal tube elastic sleeve and the m groups of piezoelectric ceramic sheets by laminating and coupling the vibrations, and a stator and the screw thread output shaft are driven through a screw thread pair, so that rotary-linear motion output of the output shaft is realized under the action of axial loading force. The screw-thread-driven rotary-linear ultrasonic motor is taken as a rotary-linear ultrasonic motor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Novel rotating travelling-wave ultrasonic motor
InactiveCN102437787AIncrease the maximum output torqueImprove efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectric machineFriction loss
The invention discloses a novel rotating travelling-wave ultrasonic motor. The ultrasonic motor comprises the following main parts: two stators, a rotor, a pedestal, a friction pad, a check ring, a bearing and the like. The two stators which are in a same shape are symmetrically arranged and compact on two end faces of the rotor. Working faces of the two stators can be parallelly contacted with a surface of the rotor so that a contact surface of the stators and the rotor bears stress evenly. In a current rotating travelling-wave ultrasonic motor based on a single stator structure, radial contact between the stator and the rotor is nonuniform, a contact scope is small, and radial sliding friction losses and other defect are existed in the stator and the rotor. By using the ultrasonic motor of the invention, the above defects can be overcome. A maximum output torque and an efficiency of the rotating travelling-wave ultrasonic motor can be increased and a service life of the rotating travelling-wave ultrasonic motor can be prolonged.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Ultrasonic motor
InactiveUS6252332B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsUltrasonic motorUltrasound
An ultrasonic motor includes a vibrator vibrating in conformity with a frequency voltage. A relative motion member effects relative vibration in conformity with the vibration of the vibrator. The vibrator is adapted to vibrate in a first vibration mode and a second vibration mode vibrating in a direction differing from the first vibration mode. The resonance frequency of the first vibration mode is higher than the resonance frequency of the second vibration mode.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Miniature Piezoelectric Motor and Method of Driving Elements Using Same
InactiveUS20080247059A1Reduce module sizeImprove efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMountingsElectricityLinear motion
The present invention provides a piezoelectric ultrasonic motors and a method of driving a motor with a standing wave. The motors include a thin ring / cylinder-type stator having one or two piezoelectric (ceramic or single crystal) rings / cylinders, coated with a segmented top / outer electrode and a bottom / inner electrode and poled in a thickness / radial direction, a metal ring / cylinder which is laminated with piezoelectric ring(s) / cylinder(s) having several inner threaded protrusions. The motor also includes a power source for supplying an alternating voltage to one group of electrodes of the piezoelectric stator to excite a standing wave vibration along one diameter direction of the stator ring / cylinder. The motor further includes a short cylinder rotor, which may have a lens inside for certain optical applications, or it may include other elements. The rotor is attached to the stator at the threaded surface of the protrusions and is driven to produce a circular motion, which may also be translated into a linear motion by the threaded surface through standing wave deformation at protrusions. Reverse motion of the rotor can be realized by applying the alternating voltage to another group of electrodes of the stator.
Owner:DONG SHUXIANG
Novel ferroelectric single-crystal lead ytterbium niobate-lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate
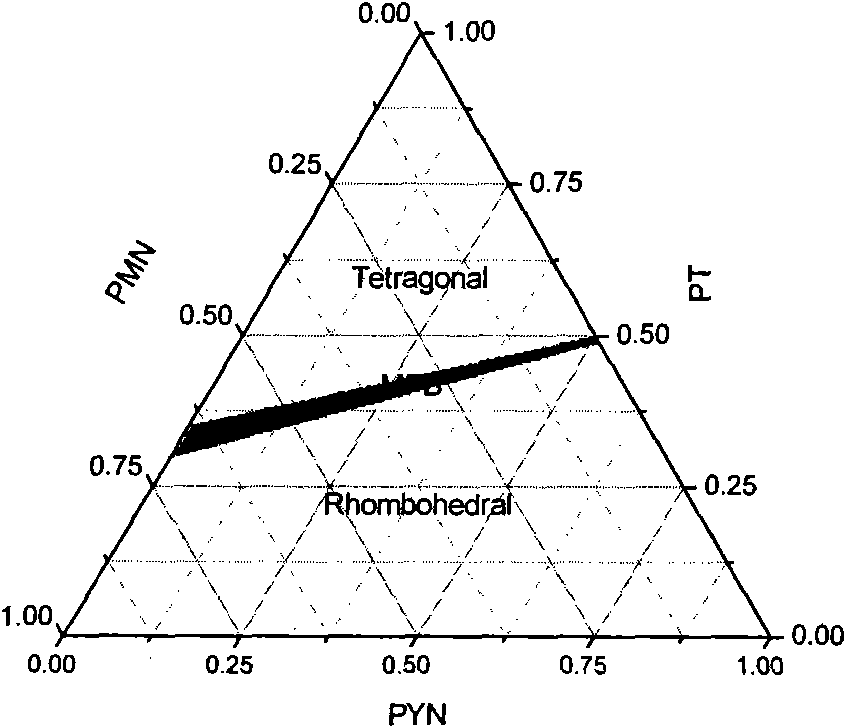
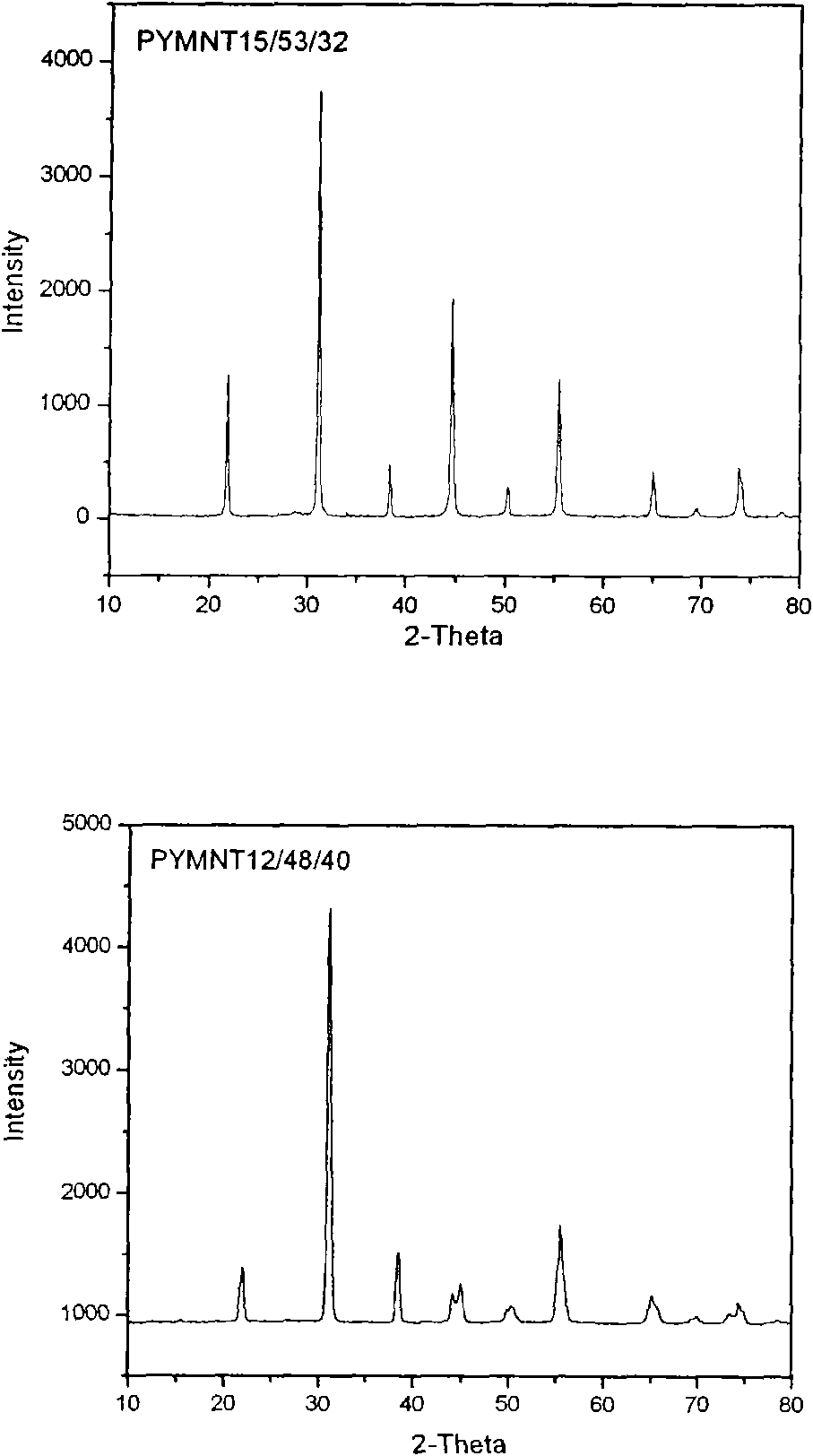
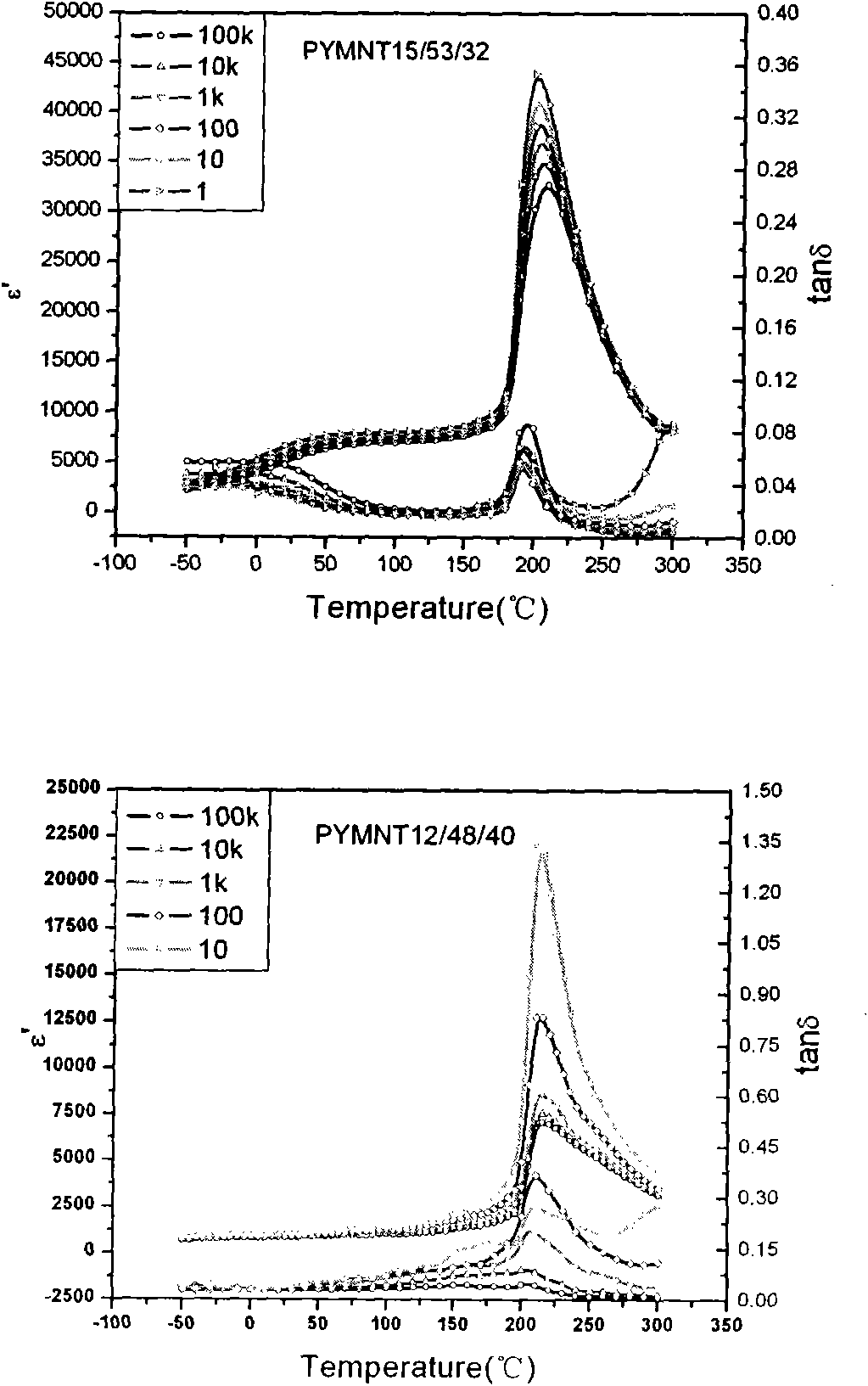
InactiveCN102051685APolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsCrystal rotationSingle crystal
The invention relates to the growth, the structures and the properties of novel ferroelectric single-crystal lead ytterbium niobate-lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate. The crystal belongs to a perovskite structure, has an MPB region and has a chemical formula of (1-x-y)Pb(Yb1 / 2Nb1 / 2)O3-xPb(Mg1 / 3Nb2 / 3)O3-yPbTiO3 which is short for PYMNT or PYN-PMN-PT. By adopting a top crystal-seeded method, the crystal with large size and high quality can grow under the conditions that the growth temperature of the crystal is 950-1100 DEG C, the crystal rotation speed is 5-30rpm, and the cooling speed is 0.2-5 DEG C / day, and the grown crystal exposes a 001 natural growth surface. Through X-ray powder diffraction, the system is confirmed as the perovskite structure; and through ferroelectric, dielectric and piezoelectric measurement, the ferroelectricity, the dielectric property and the piezoelectricity of the crystal are analyzed. The crystal has high Curie temperature and trigonal-tetragonal phase transition temperature, large piezoelectric constant and electromechanical coupling factor, high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss and better heat stability. The crystal can be widely applied to devices in the piezoelectric fields of ultrasonically medical imaging, sonar probes, actuators, ultrasonic motors, and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single-driving foot sandwiched transducer type longitudinal bending linear ultrasonic motor
InactiveCN101072000AIncrease amplitudeRealize linear motionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerEngineering
The disclosed variation pole is quadrangular body with rectangular section thinned gradually from two ends to central section. Drive feet are located at middle position of the pole. Piezoelectric ceramic piece in longitudinal vibration and piezoelectric ceramic piece in bending vibration are respectively installed on inner and outer sides of bolts on two flange bolts. Two end plates are installed on outer sides of bolts on two flange bolts. Through two flange bolts, two end plates, two groups of piezoelectric ceramic piece, and thin copper sheet are fastened and integrated to two larger ends of the pole. Advantages are: simple structure, smooth operation, large output thrust, and motion in high speed.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
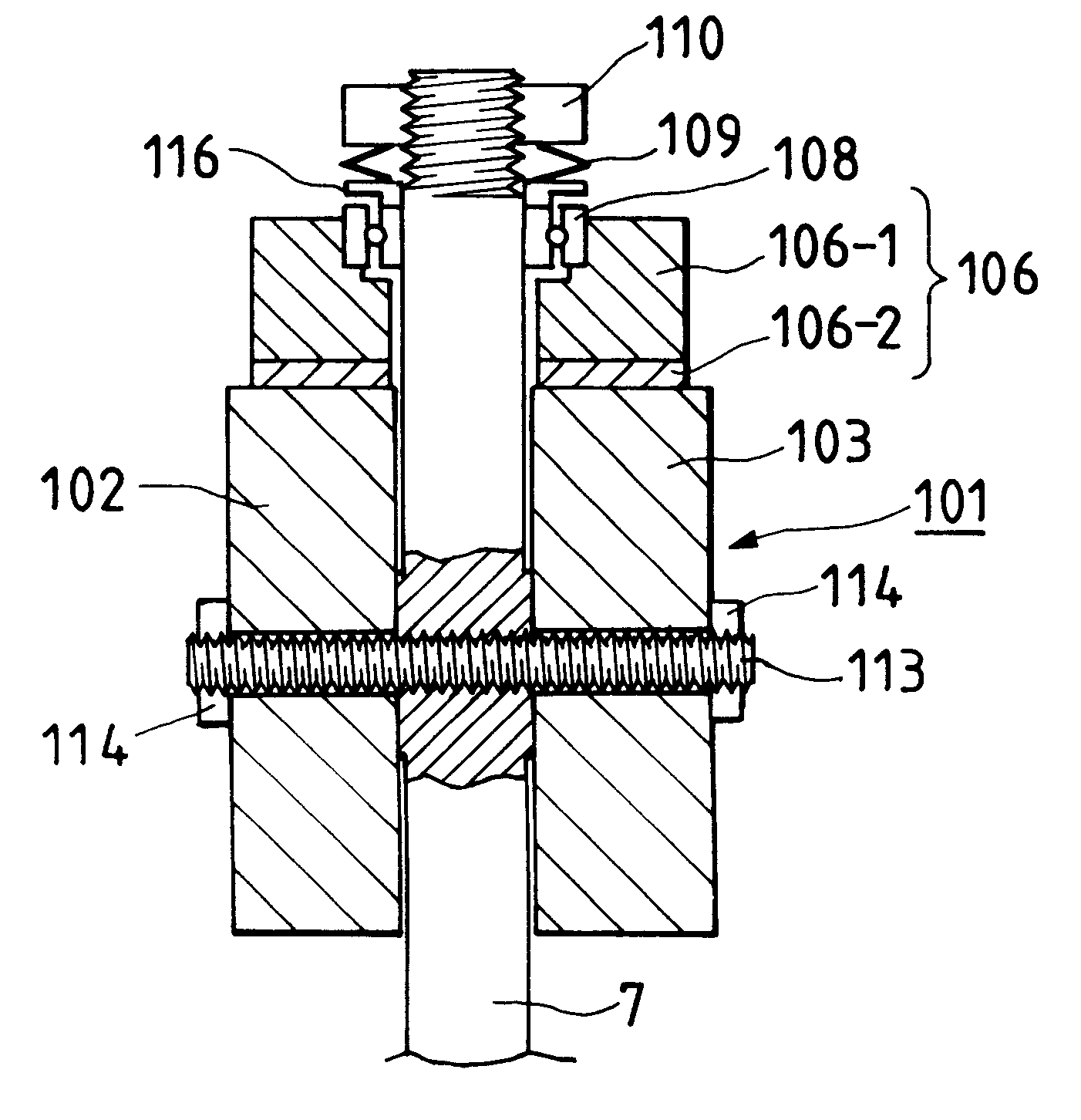
Ultrasonic motor and pressing mechanism of ultrasonic vibrator
InactiveUS20080174206A1Improve efficiencyImprove balancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesContact pressureEngineering
Contact pressures between a driven member and an ultrasonic vibrator are balanced, making the driving characteristics in the forward and reverse directions uniform, and the driven member is driven with high driving efficiency. The invention provides a pressing mechanism of an ultrasonic vibrator for pressing sliding members against a driven member, the sliding members being provided at two or more positions corresponding to antinodes of a standing wave vibration of the ultrasonic vibrator. The pressing mechanism includes a pressing member configured to make contact with the ultrasonic vibrator at two or more positions corresponding to nodes of the standing wave vibration of the ultrasonic vibrator; and pressing-force adjusting units configured to adjustably apply pressing forces, which press the sliding members against the driven member, to the pressing member at two or more separate positions in the direction of a gap between the two or more nodes of the standing wave.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Ultrasonic motor and electronic apparatus equipped with ultrasonic motor
InactiveUS7005776B1Reduce the burden onGreat magnitudePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsSelf excited oscillationUltrasonic motor
An ultrasonic motor comprises a piezoelectric vibrating member having a detecting polarized portion for detecting a drive signal having a drive frequency of the detecting polarized portion and a driving polarized portion for receiving the drive signal to oscillate the piezoelectric vibrating member in self-excited oscillation to produce a drive force. The detecting polarized portion is disposed at a portion of the piezoelectric vibrating member for undergoing maximum deformation in at least one vibration mode of oscillation of the piezoelectric vibrating member. An amplifying circuit amplifies the drive signal detected by the detecting polarized portion and inputs the amplified signal to the driving polarized portion to oscillate the piezoelectric vibrating member.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Hollow annular traveling wave ultrasonic motor
InactiveCN103095174ACompact structureTake advantage ofPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltrasonic motorUltrasound
The invention discloses a hollow annular traveling wave ultrasonic motor which comprises a base, an outer shell, a rotor, a stator and a piezoelectric ceramic piece, wherein the base, the outer shell, the rotor and the stator are all in a hollow annular structure, the stator is arranged on the outer side of the base, the piezoelectric ceramic piece is adhered to the bottom of the stator, the rotor is arranged on the stator, the bottom of the outer shell is connected with the bottom of the base, and the rotor rotates relative to the outer shell. According to the hollow annular traveling wave ultrasonic motor, a rotating shaft is not needed to output torque, the structure is simple and compact, and hollow parts can be fully utilized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Ultrasonic motor and ultrasonic vibrator
InactiveUS20090256445A1Improve seismic performanceEasy to operatePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesEngineeringShock resistance
An ultrasonic motor includes a driven object, a piezoelectric element for driving the driven object, a vibration plate including a notch having an inner peripheral surface of an arc-shaped form having a central angle larger than 180 degrees and being vibrated by the piezoelectric element, and a contact portion made of a material different from that of the vibration plate, having a portion overlapping the piezoelectric element in a plan view and being smaller in thickness than the piezoelectric element, attached to the notch of the vibration plate by press fitting or forced fitting and being in contact with the driven object. Thereby, the ultrasonic motor can have a high shock resistance and a high wear resistance, and can be driven with high efficiency.
Owner:SHARP KK
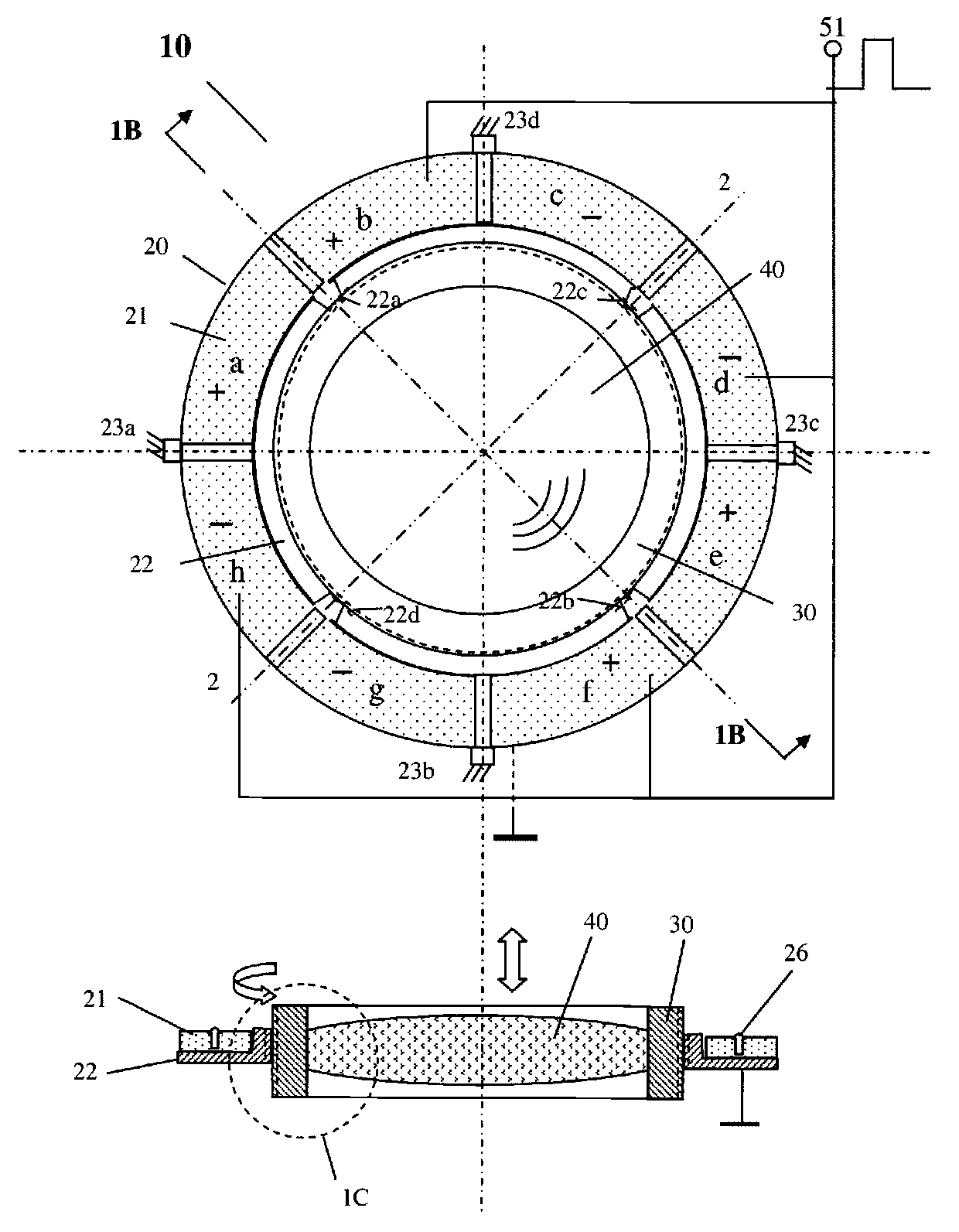
Magnetically suspended control moment gyro gimbal and locking control system
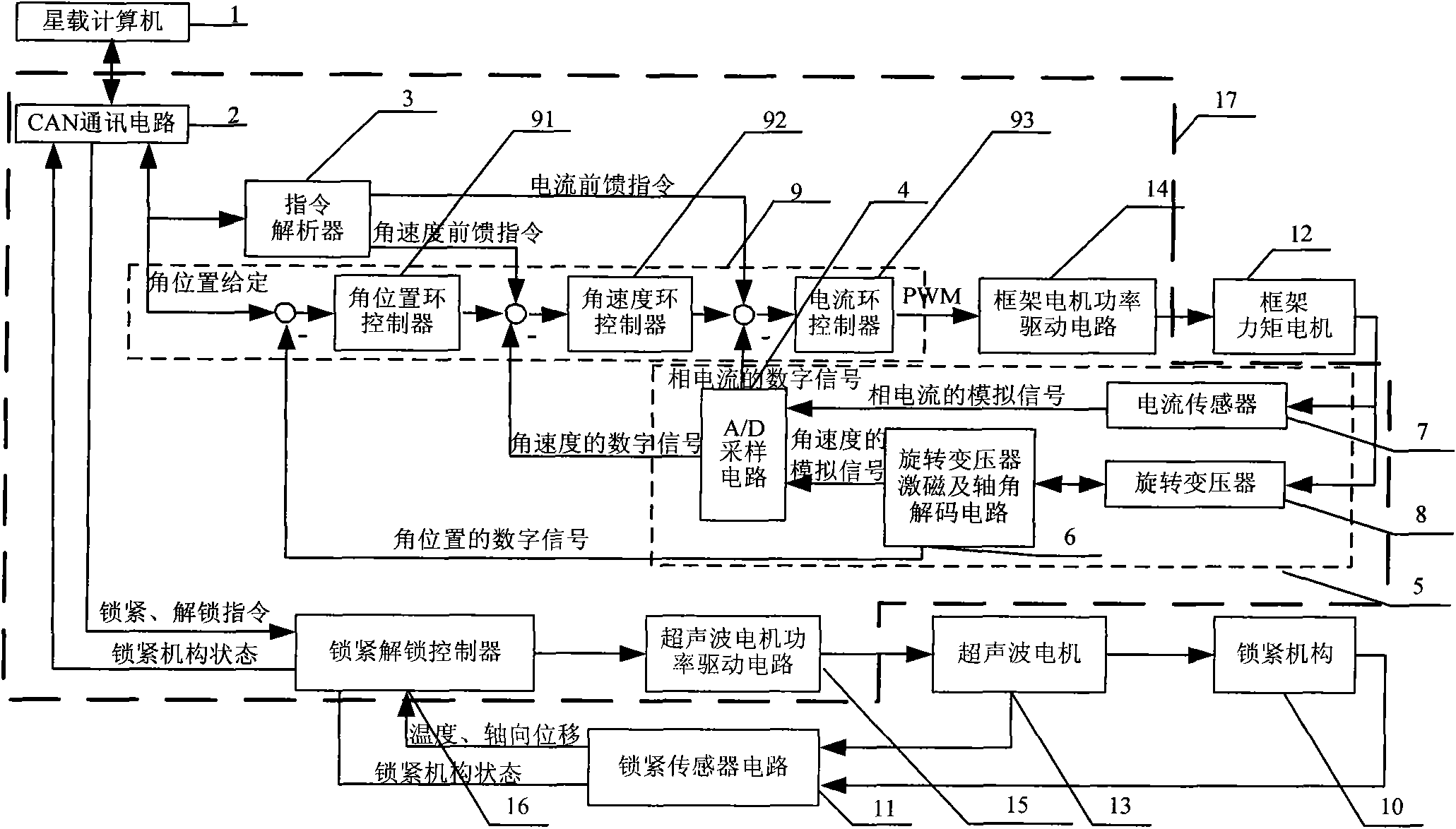
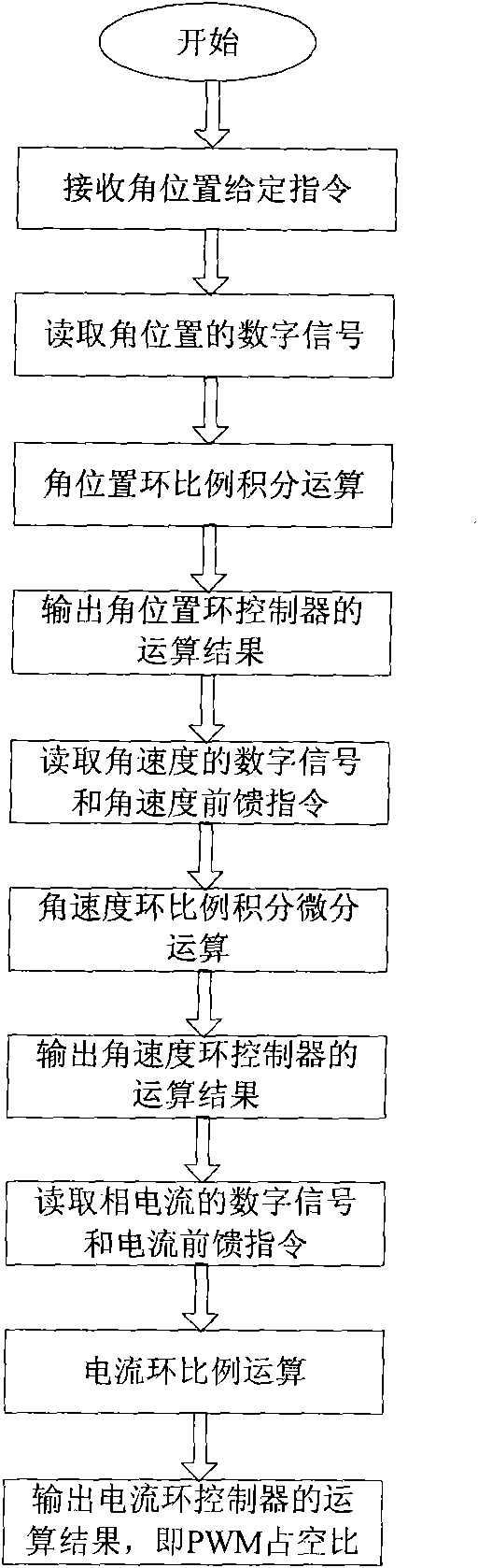
ActiveCN102009597AGuaranteed accuracyHigh speedMagnetic holding devicesElectric propulsionNumerical controlAxial displacement
The invention discloses a magnetically suspended control moment gyro gimbal and a locking control system. The magnetically suspended control moment gyro gimbal mainly comprises a gimbal moment motor, a locking mechanism, an ultrasonic motor, a locking sensor circuit and a digital signal processor (DSP) and field programmable gate array (FPGA) numerical control device, wherein the DSP and FPGA numerical control device comprises a controller area network (CAN) communication circuit, a command parser, a gimbal controller, a locking / unlocking controller, a gimbal motor power drive circuit, an ultrasonic motor power drive circuit and a gimbal motor sensor circuit; the gimbal controller performs the control of three closed loops and two feed forward according to an angle position, an angle speed, a current command value output by the CAN communication circuit and the command parser and a feedback value output by the gimbal motor sensor circuit to realize high precision and rapid response control of the gimbal moment motor; and the locking / unlocking controller selects the resonance frequency of the ultrasonic motor according to the temperature and an axial displacement value output by the locking sensor circuit and positively and negatively rotates the ultrasonic motor respectively according to locking and unlocking commands so as to lock or unlock the locking mechanism.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com