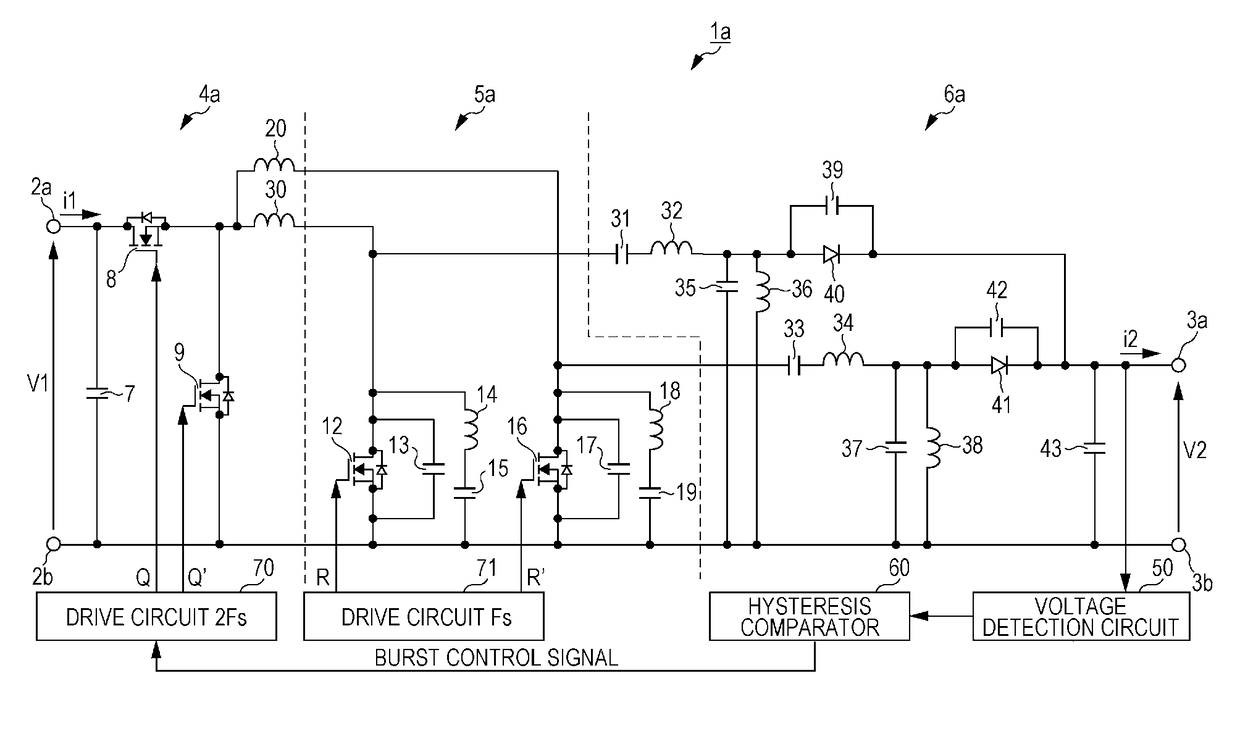
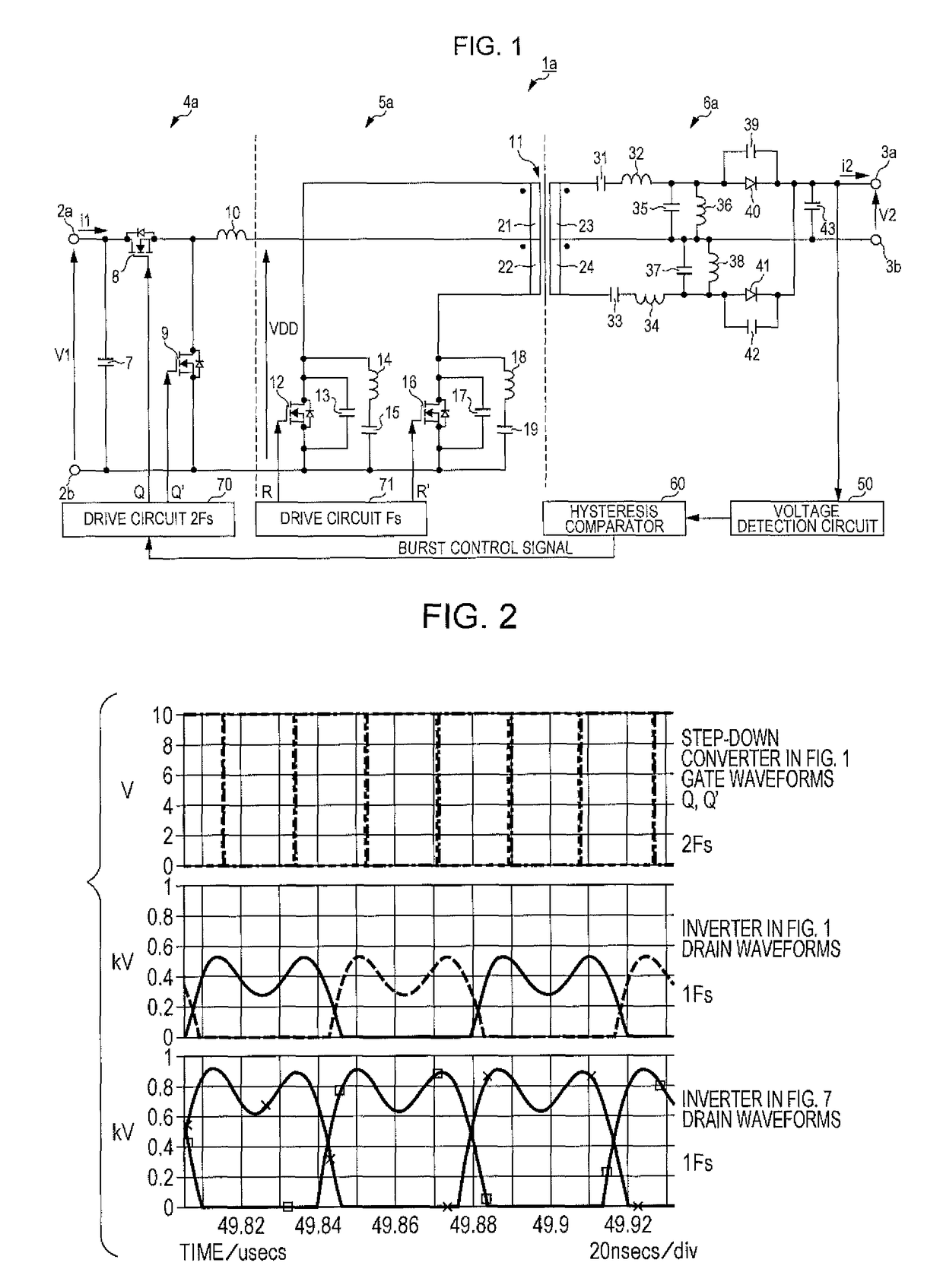
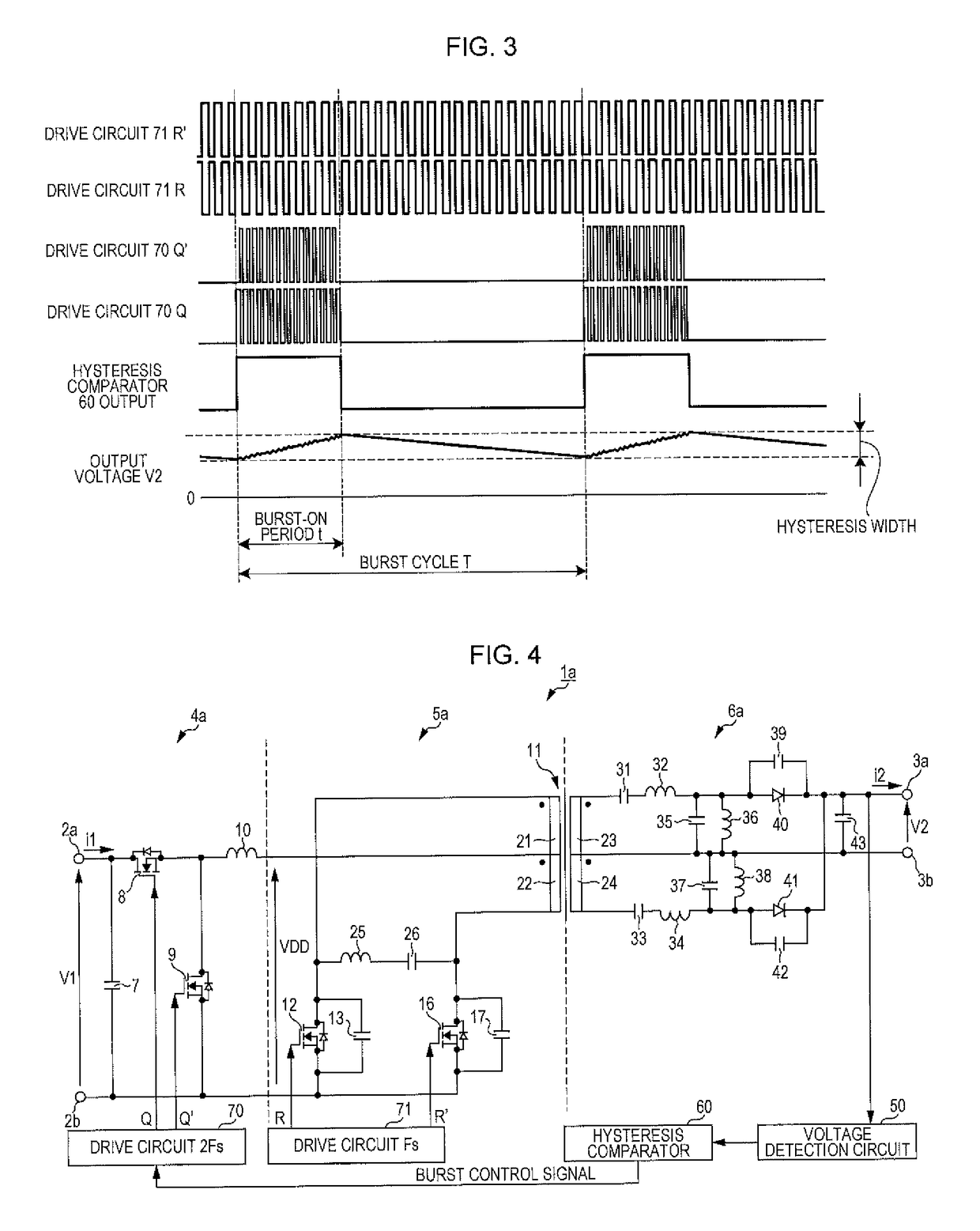
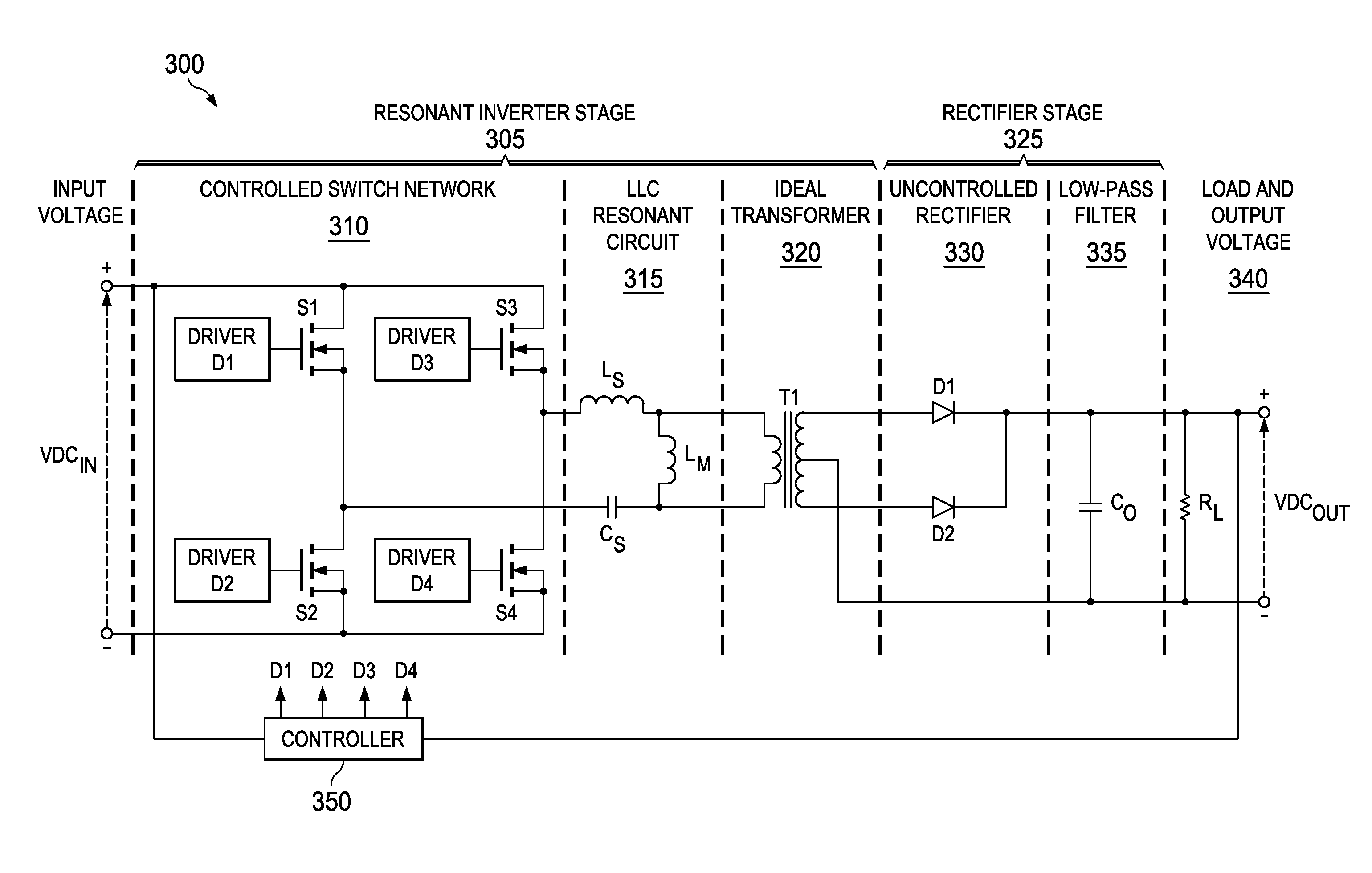
Patents
Literature
222 results about "Resonant inverter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
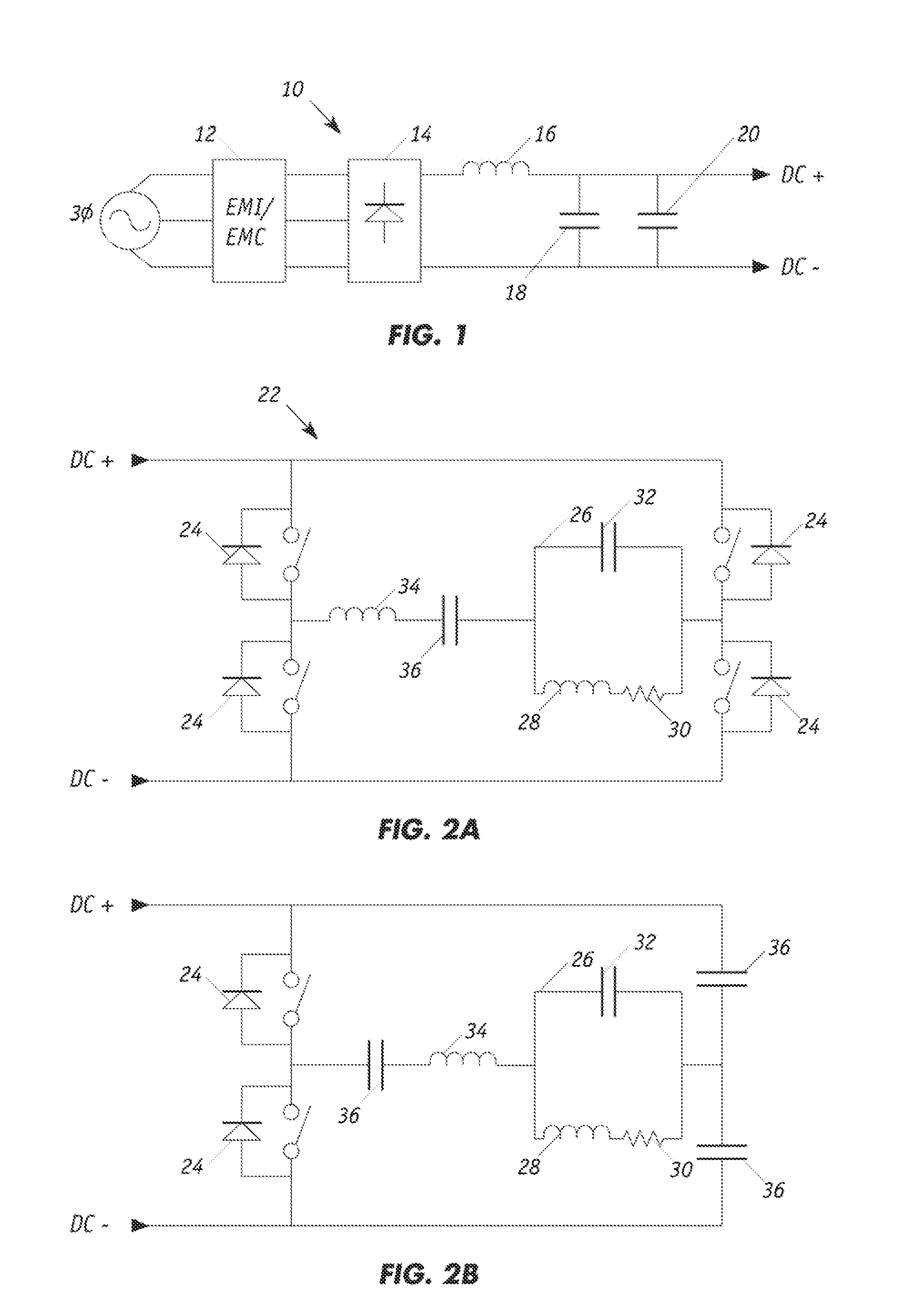
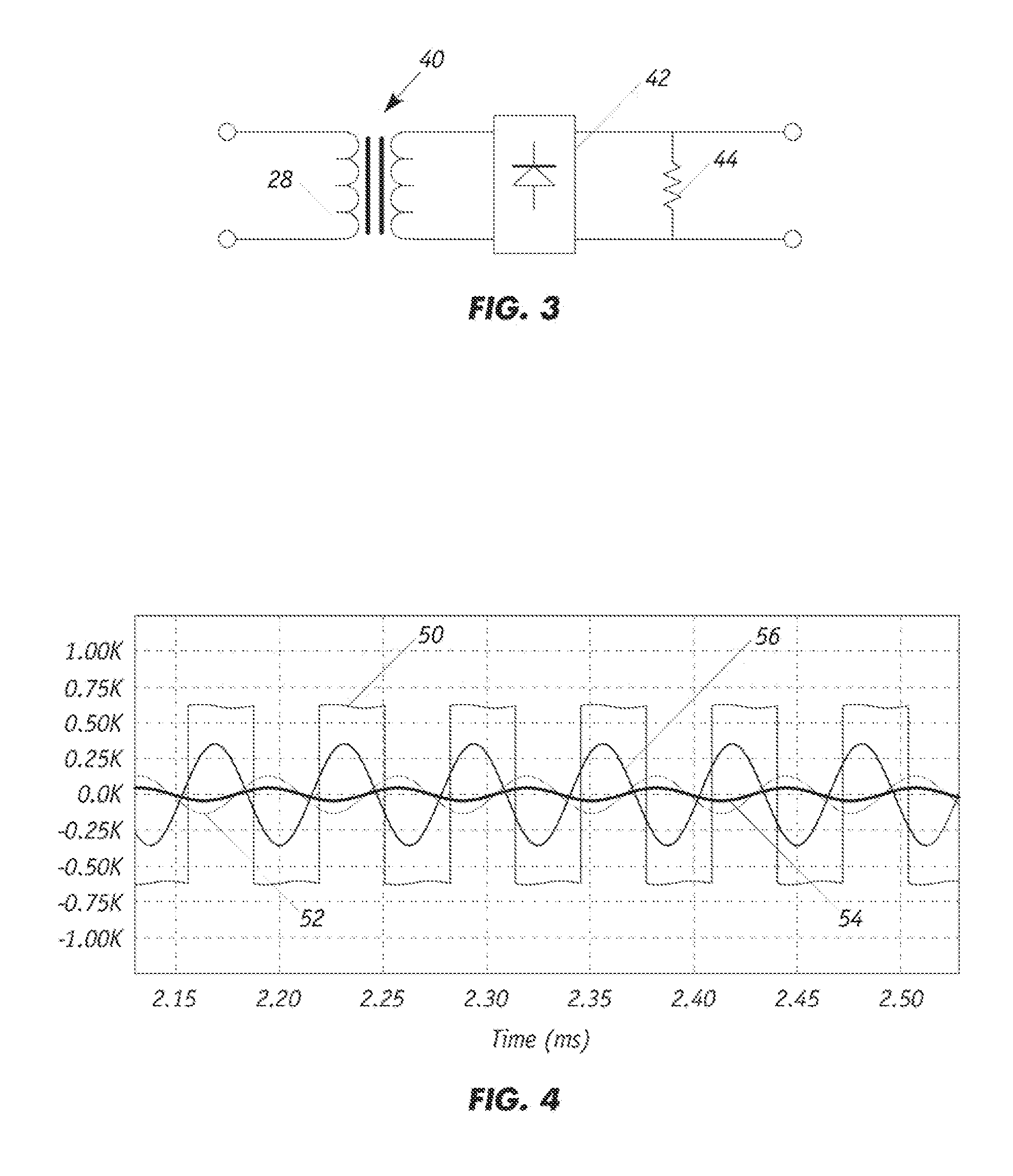
Resonant inverters are electrical inverters based on resonant current oscillation. In series resonant inverters the resonating components and switching device are placed in series with the load to form an underdamped circuit. The current through the switching devices fall to zero due to the natural characteristics of the circuit. If the switching element is a thyristor, it is said to be self-commutated.
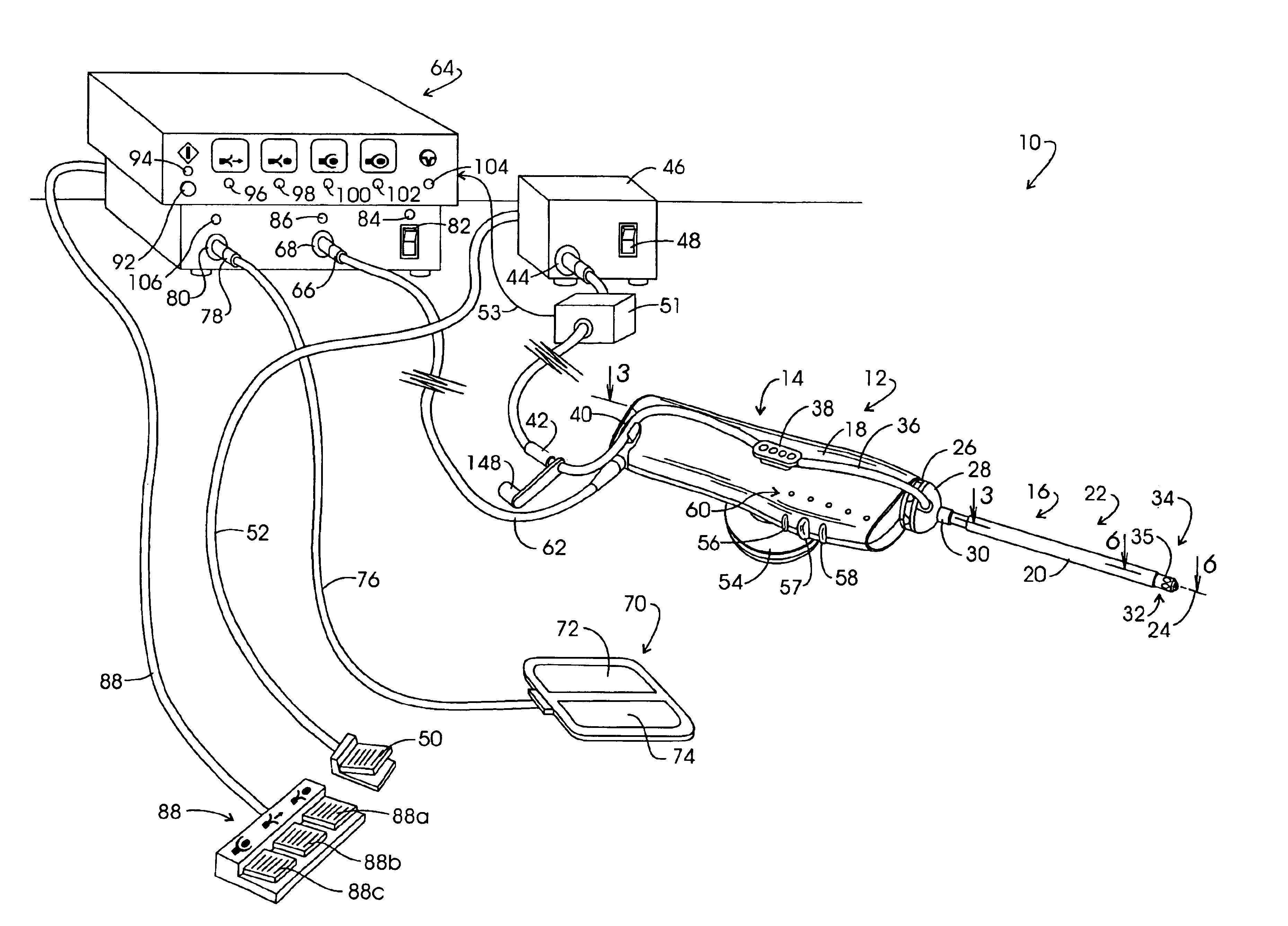
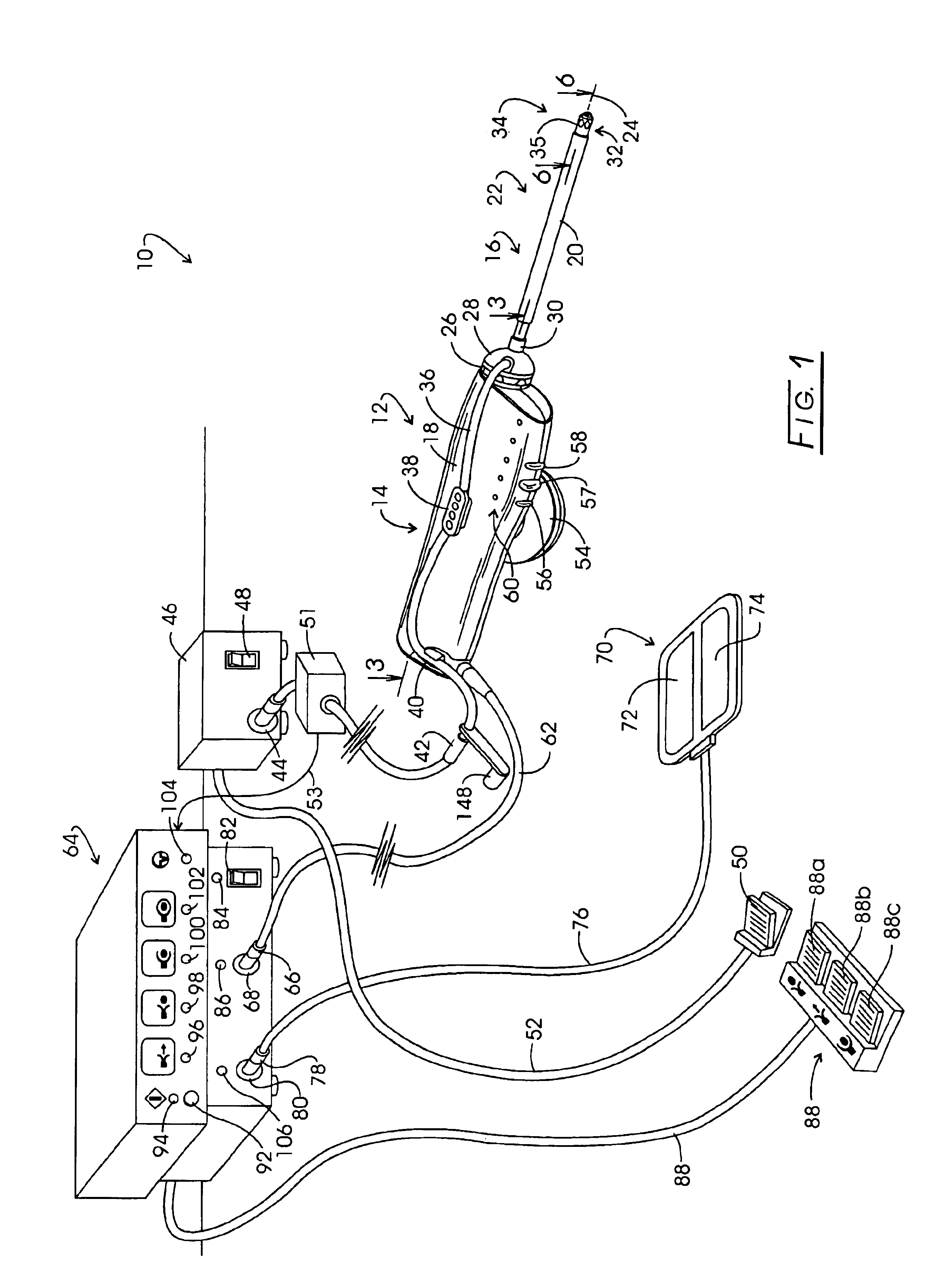
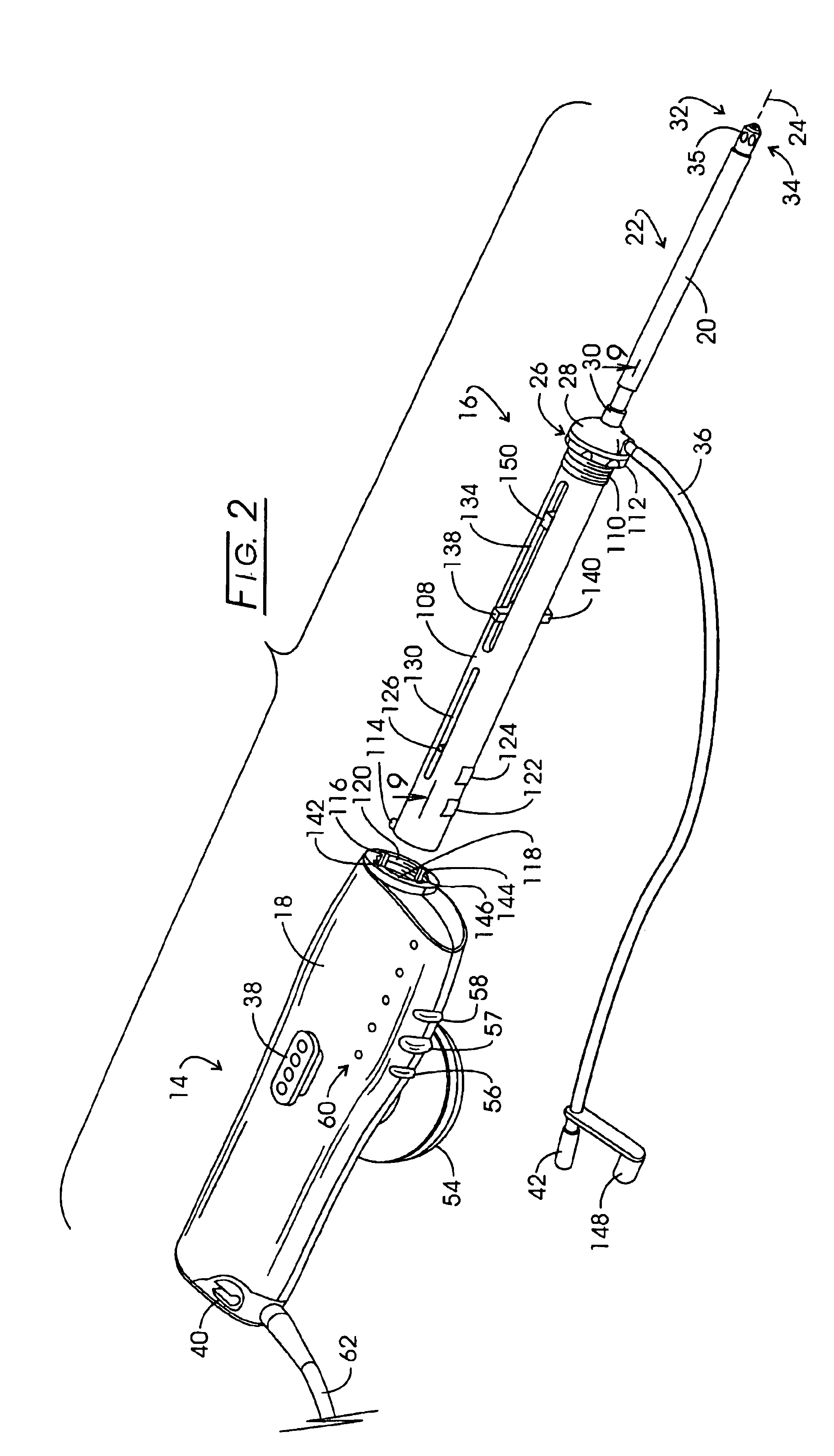
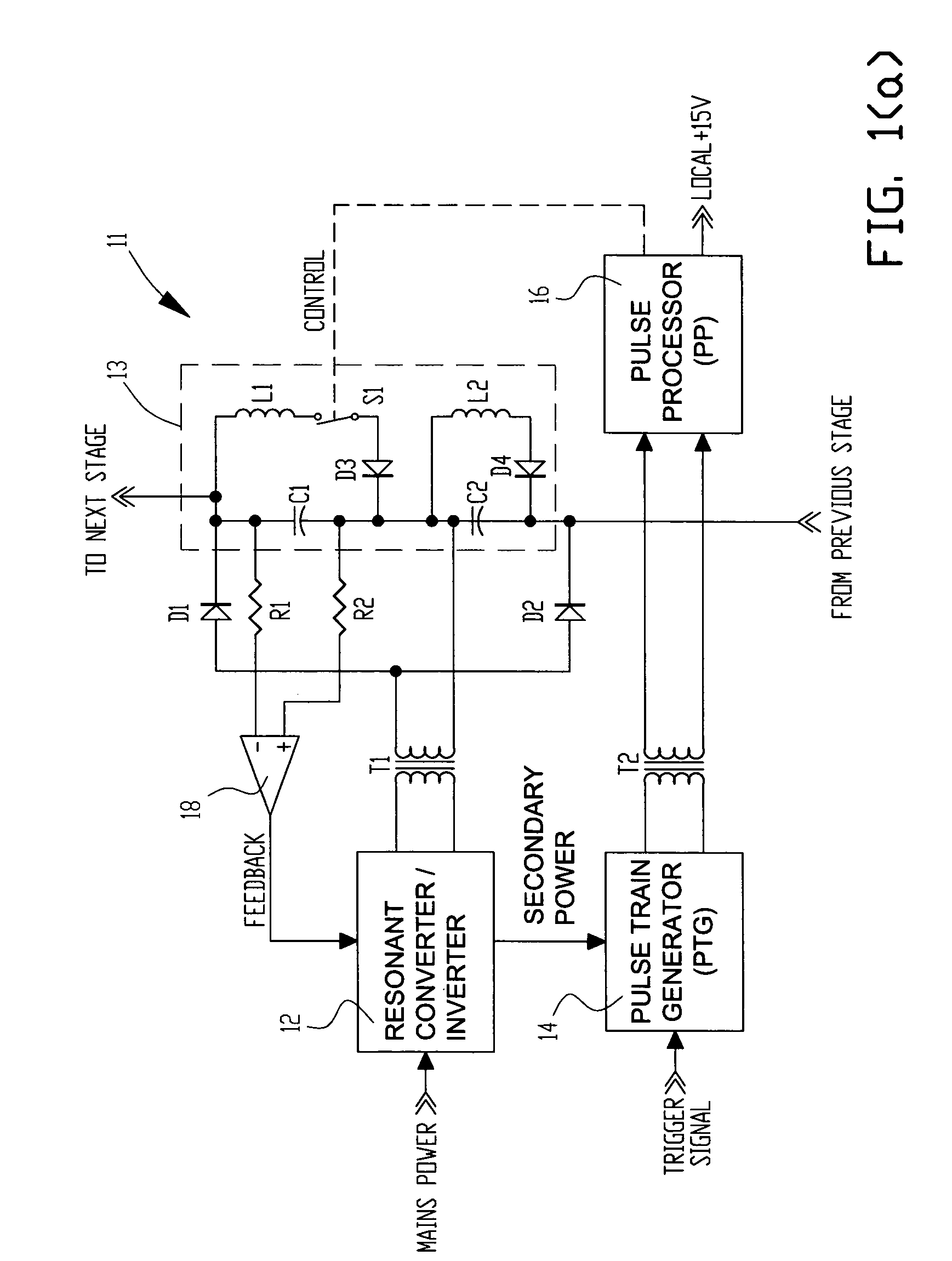
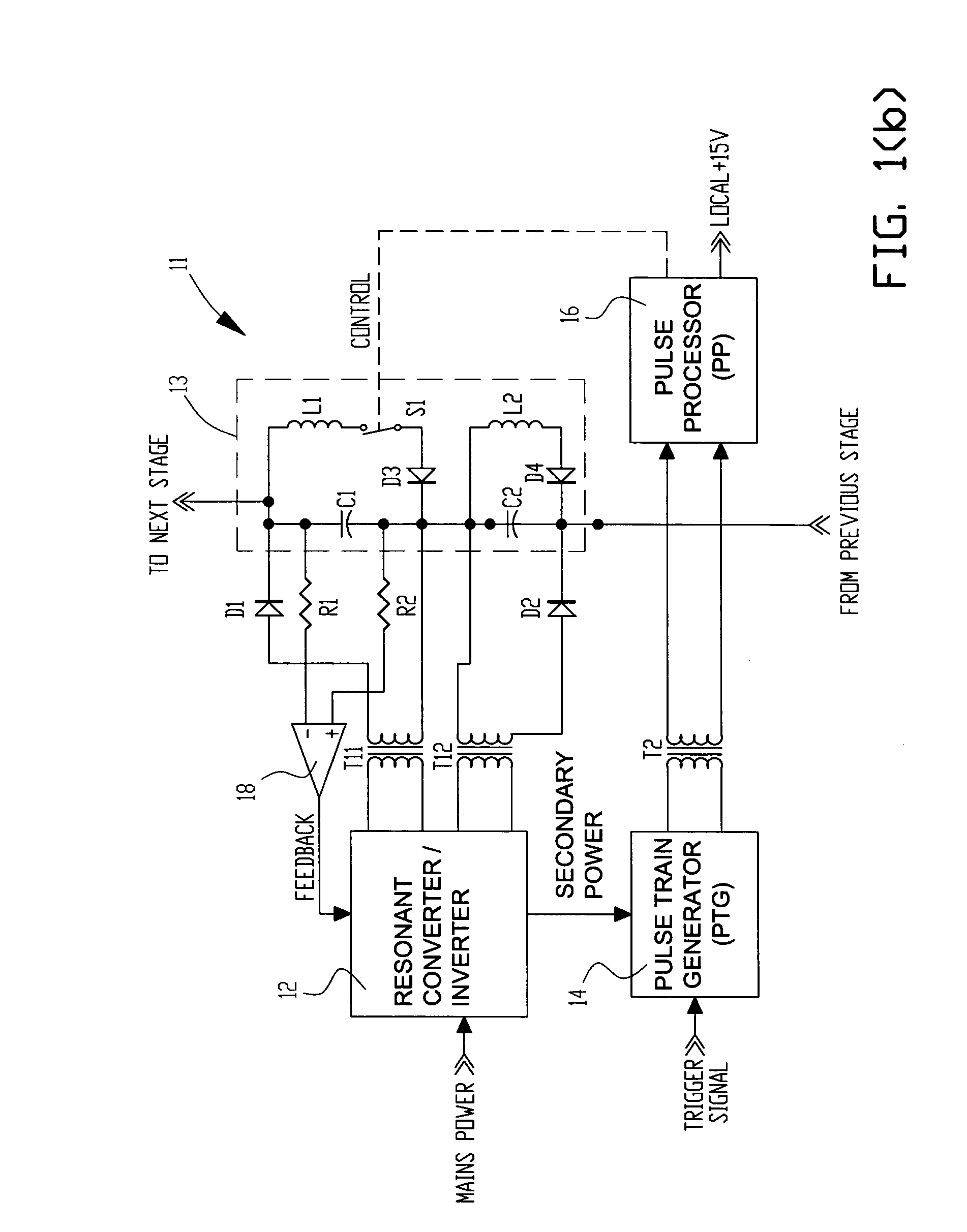
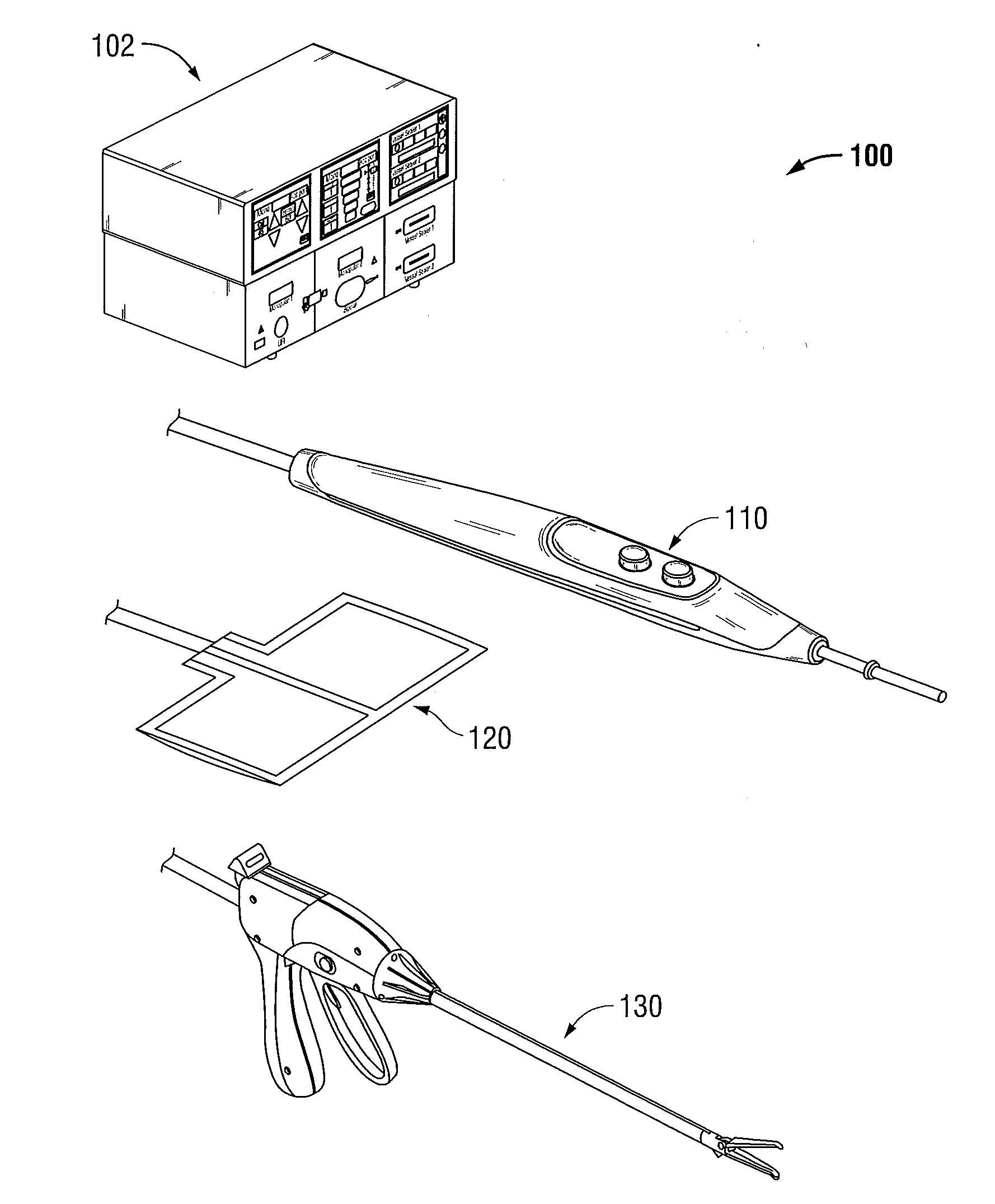
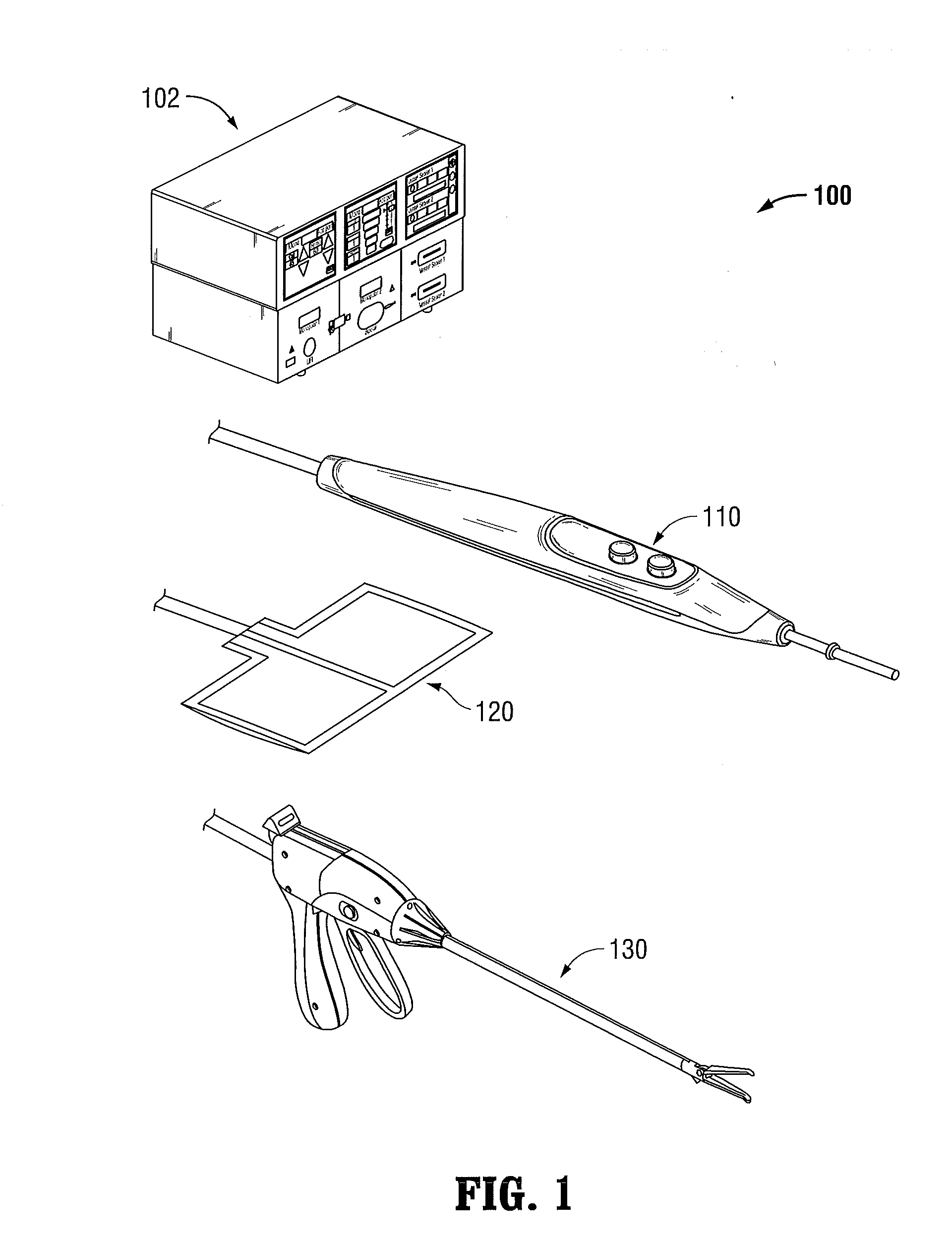
Electrosurgical generator
InactiveUS6923804B2Improving impedanceIncrease resistanceSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesResonant inverterConstant power
An electrosurgical generator which provides a constant power output particularly suited for cutting arc formation at an active electrode which exhibits a dynamic active surface area of varying geometry. Essentially constant power-based control is achieved through the utilization of a d.c. link voltage the level of which functions to establish the amplitude of the output of an RF resonant inverter. A dual loop feedback control is described wherein output power based control signals are slowly introduced at low gain, while link voltage based controls are comparatively rapidly applied. Enhanced development of a controlling d.c. link voltage is achieved through the utilization of an input network incorporating a power factor correction stage.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
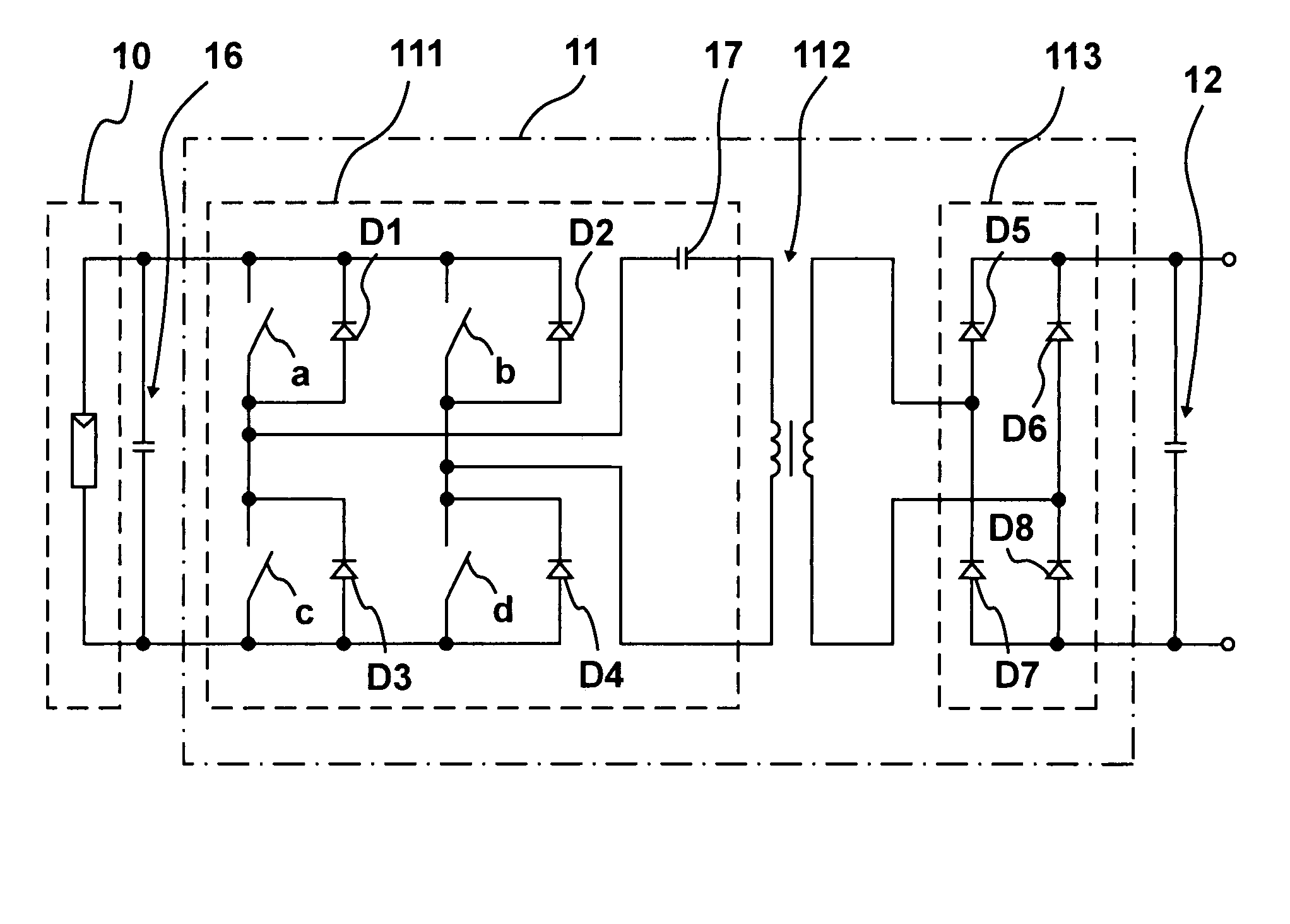
Device for feeding electrical energy from an anergy source
InactiveUS20080192510A1Reduce ripple current loadIncrease internal resistanceDc network circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionResonant inverterGalvanic isolation
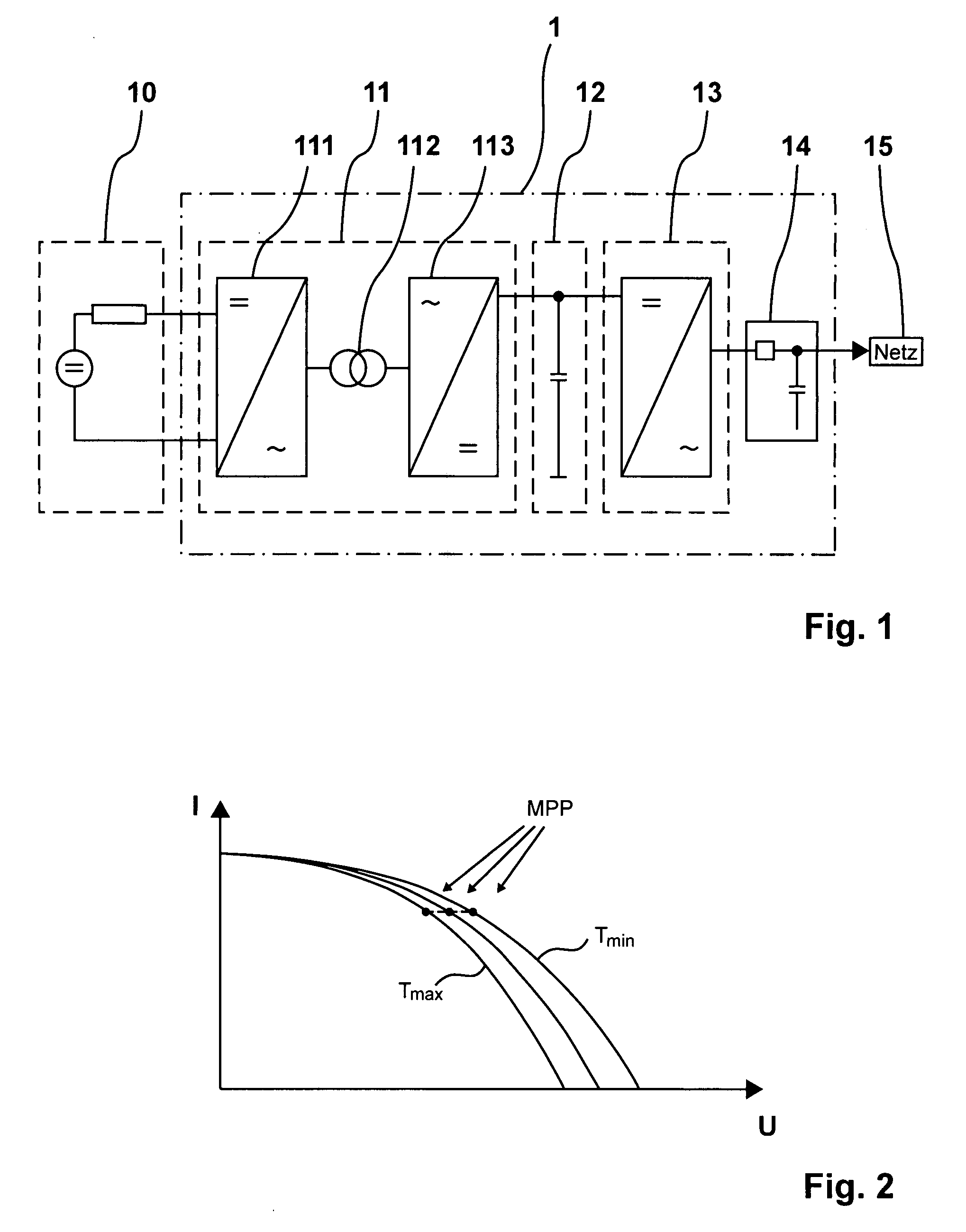
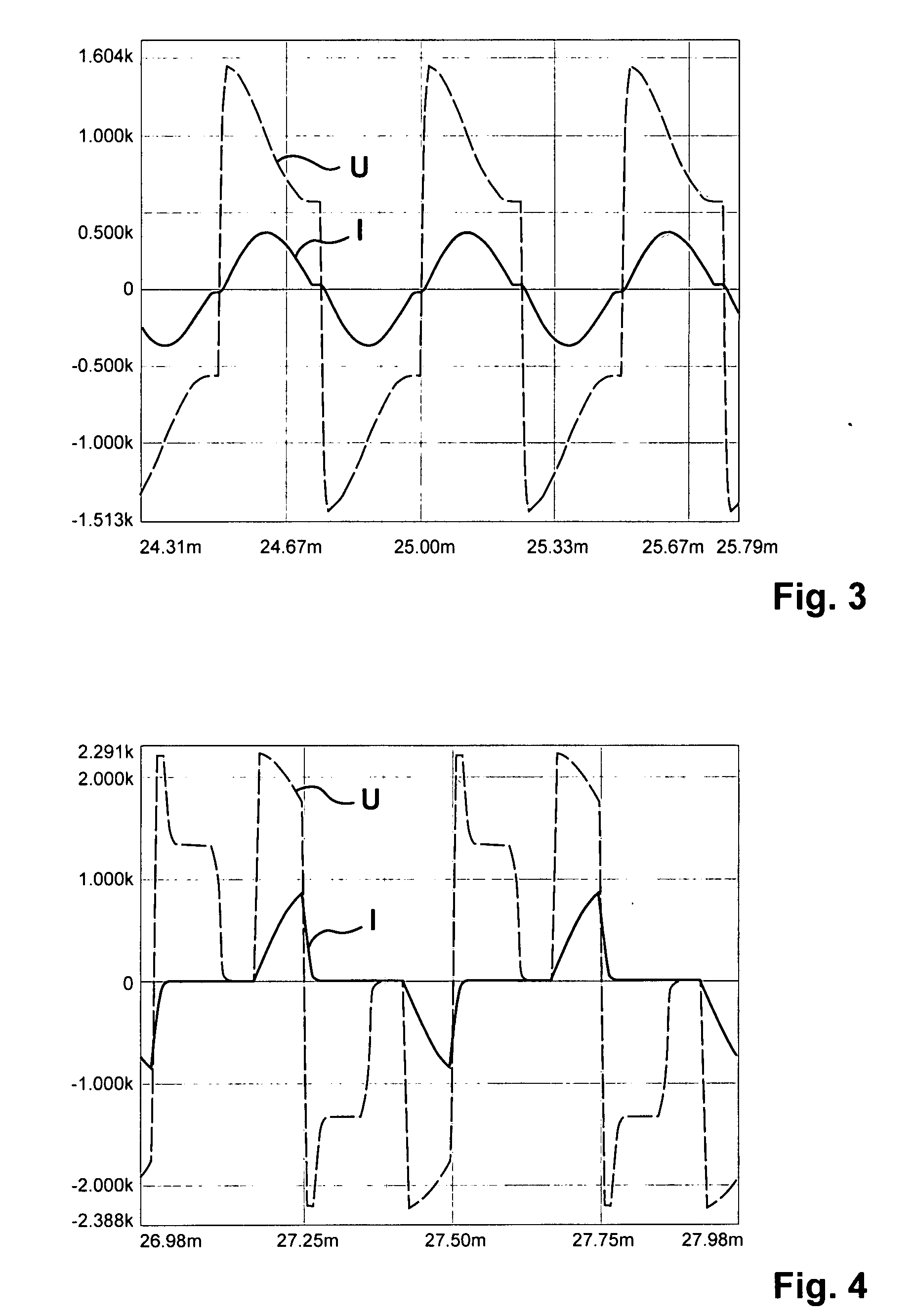
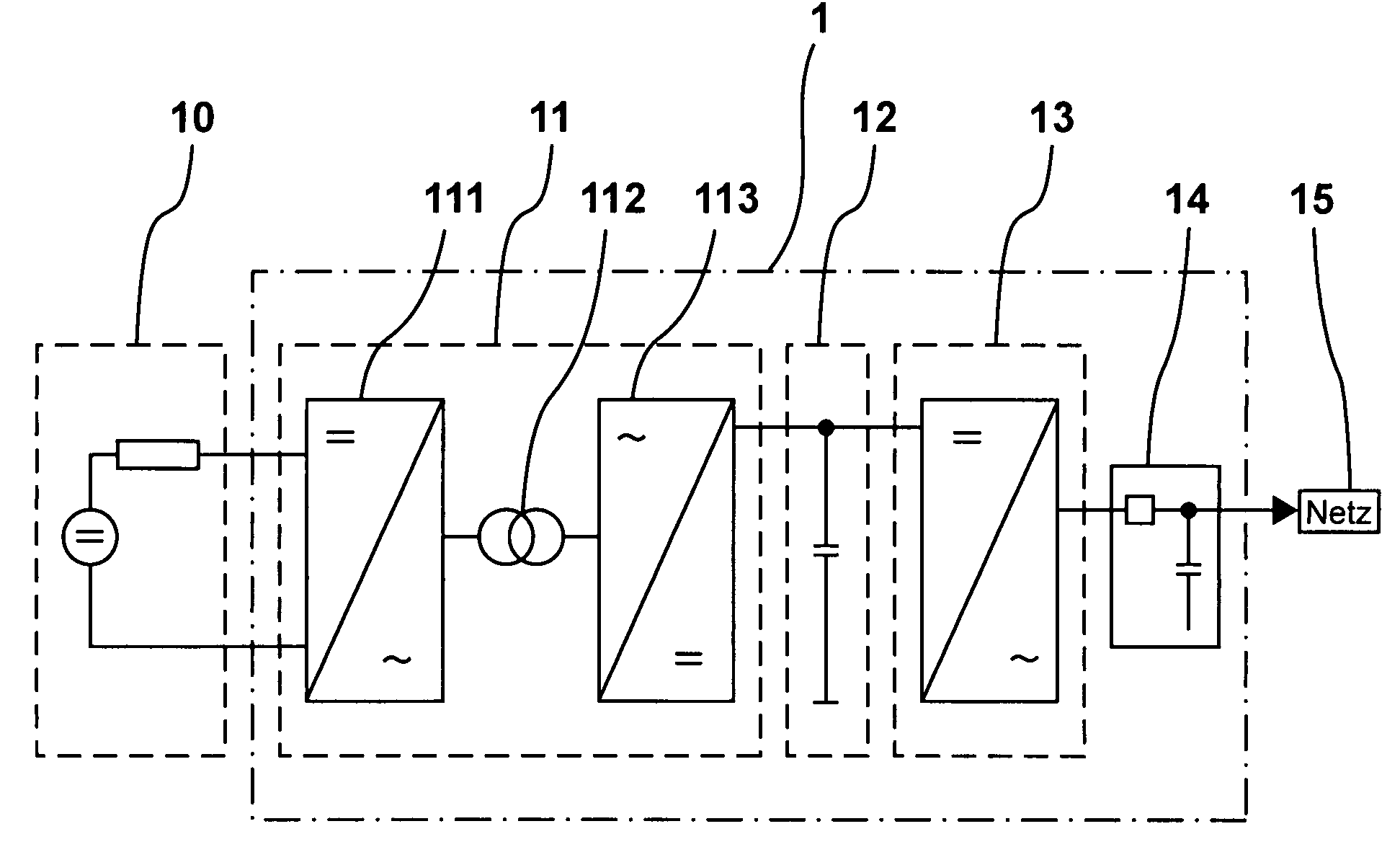
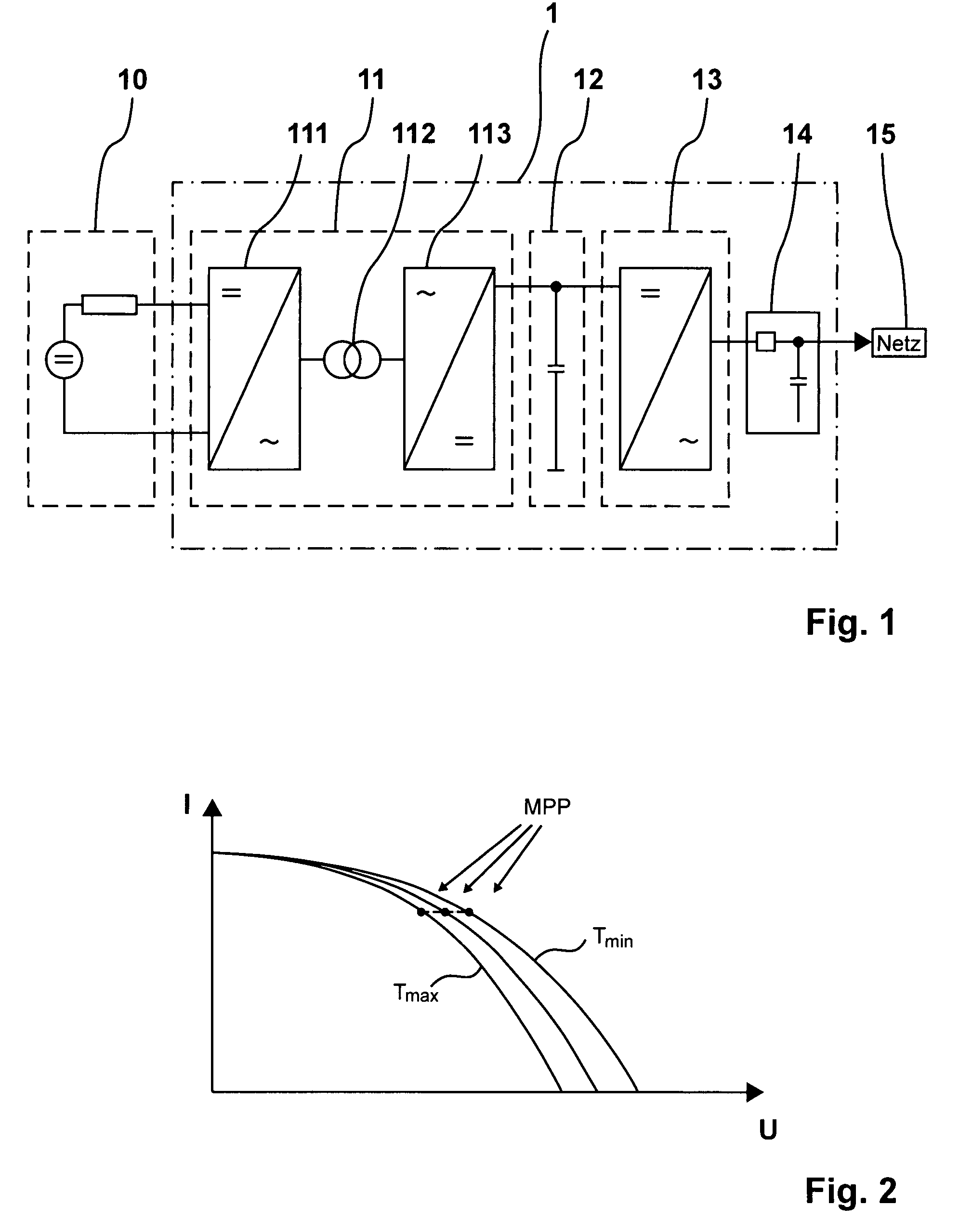
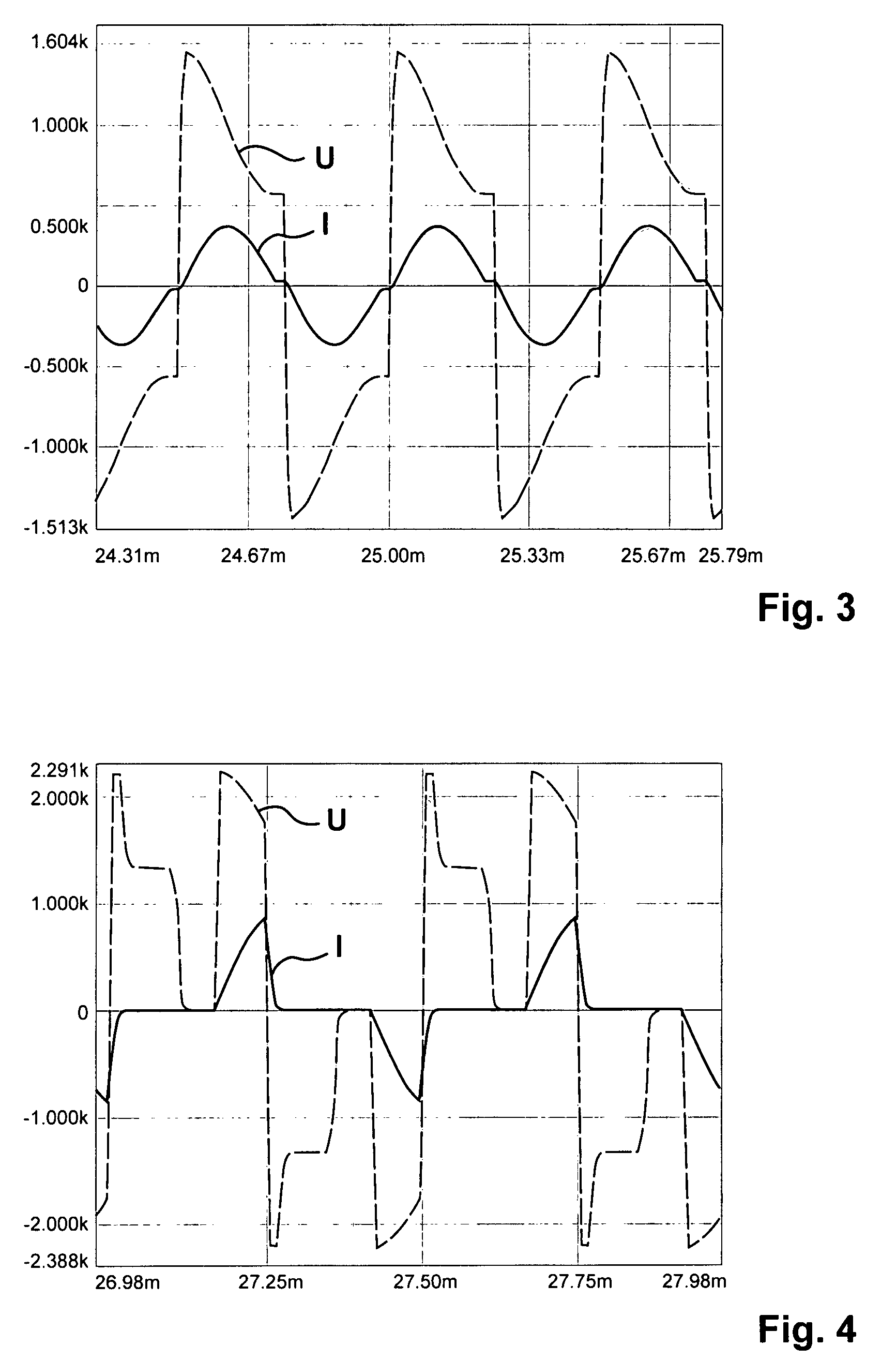
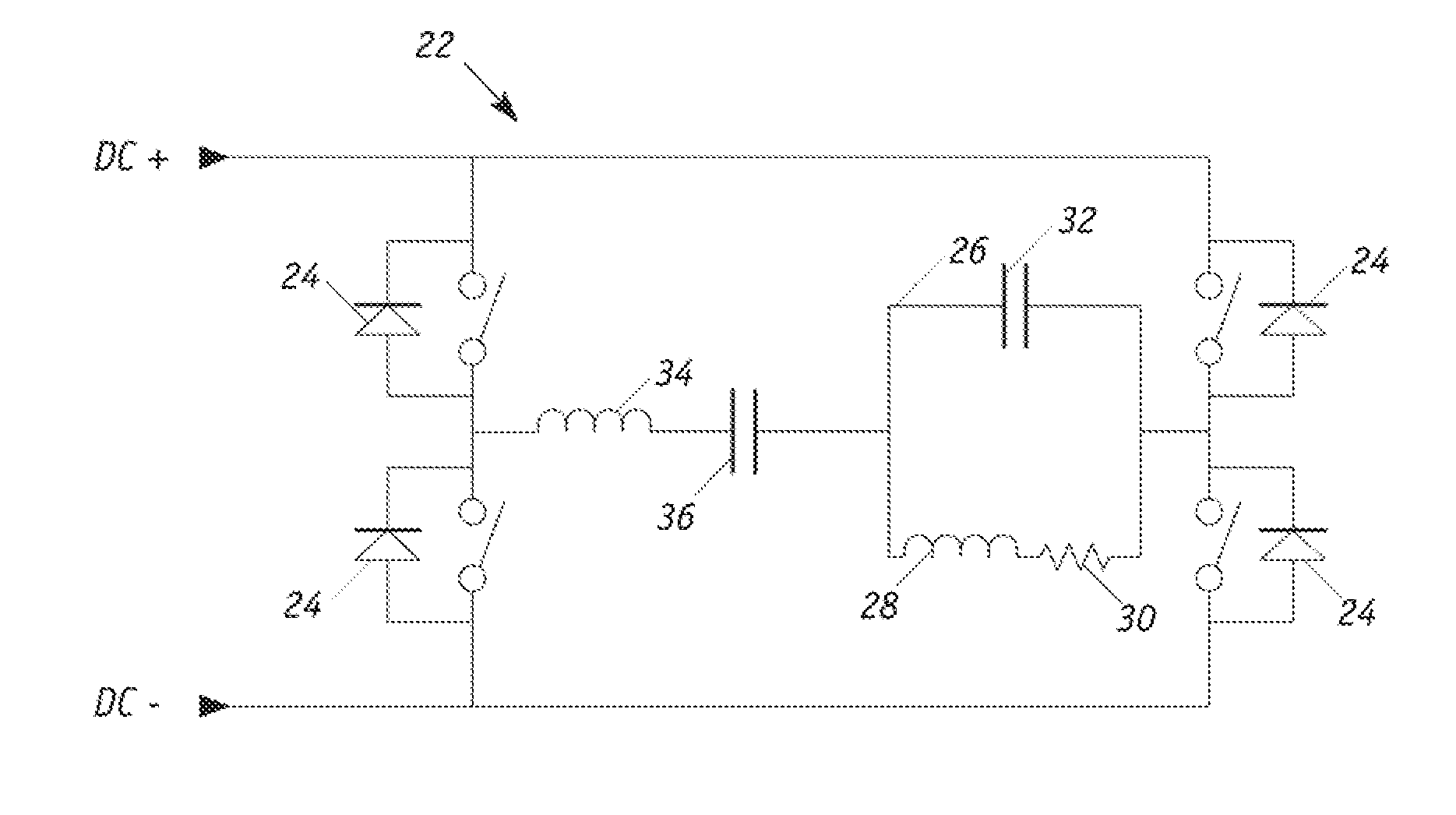
A device (1) for feeding electrical energy from an energy source with variable source voltage into an electric power supply network (15), said device (1) including a transformer (112) for galvanic isolation, a resonant inverter (11) with semi-conductor switches (a-d; A, B), one or several resonant capacitors (17; 18, 19; 20, 21) and one rectifier (113), is: intended to provide high efficiency and have galvanic isolation. This is achieved in that the resonant inverter (11) is operated in the full resonant mode if the operating voltage is in an operation point (MPP) and in the hard-switching mode if the voltages exceed the operation point (MPP).
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
Frequency Controller Resonant Converter
ActiveUS20080211478A1Overcome disadvantagesEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionElectricityCapacitance
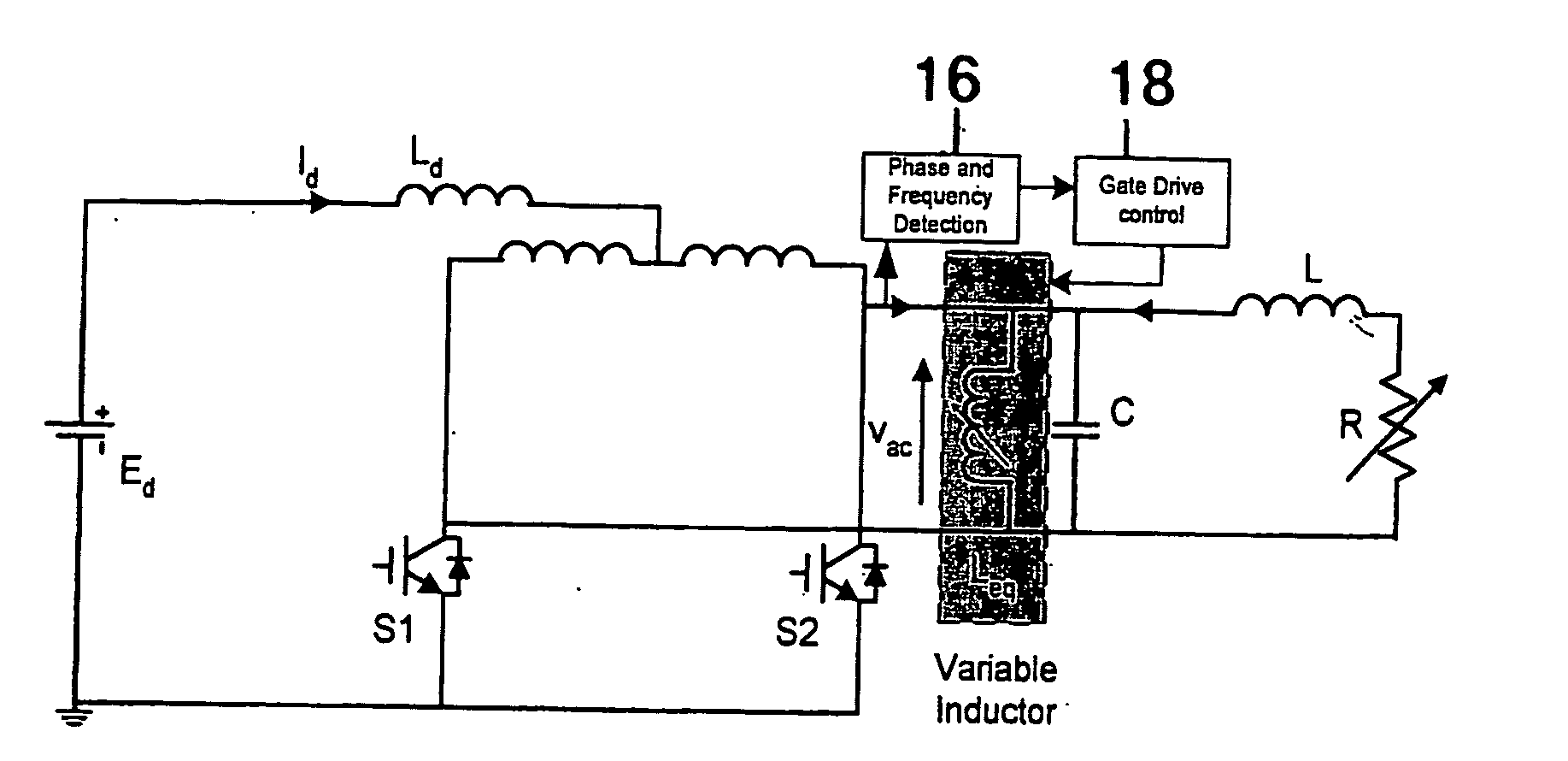
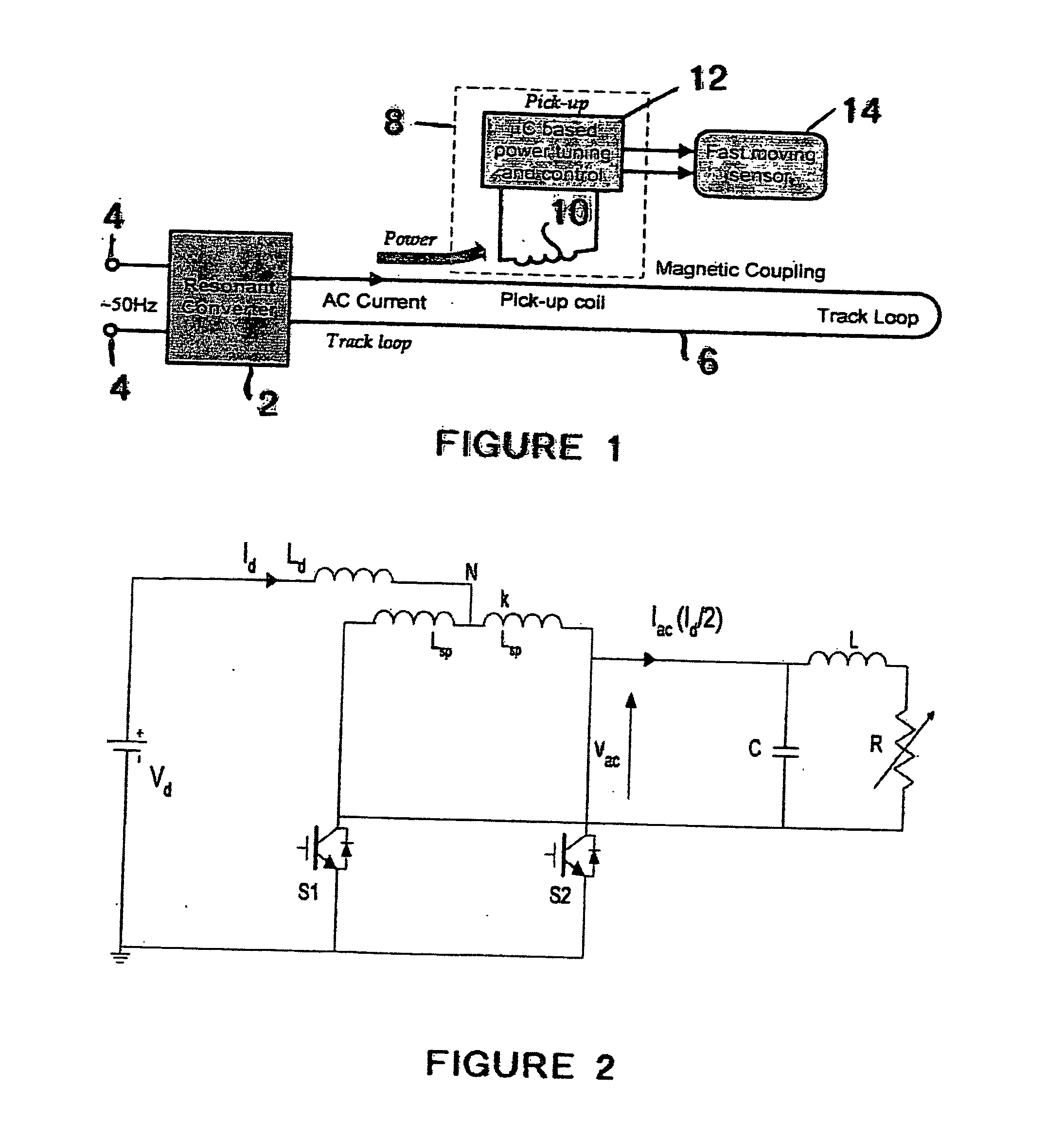
A resonant converter is provided which may be used for supplying power to the primary conductive path of an inductively coupled power transfer (ICPT) system. The converter includes a variable reactive element in the resonant circuit which may be controlled to vary the effective inductance or capacitance of the reactive element. The frequency of the converter is stabilised to a nominal value by sensing the frequency of the converter resonant circuit, comparing the sensed frequency with a nominal frequency and varying the effective inductance or capacitance of the variable reactive element to adjust the converter frequency toward the nominal frequency.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
Wide range power supply
ActiveUS20070008745A1Operation efficiency is highHigh operating requirementsEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcResonant inverterAnalog feedback
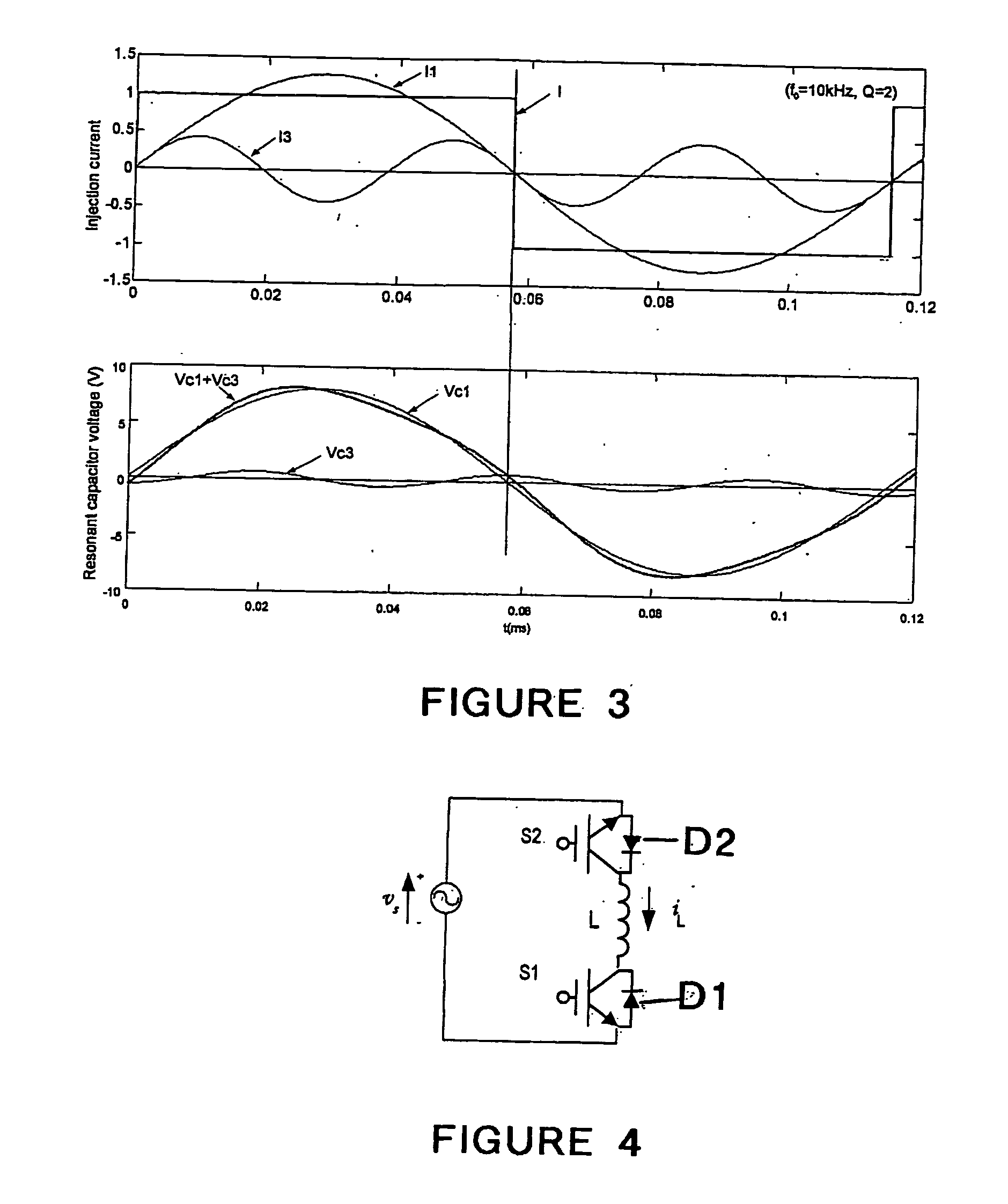
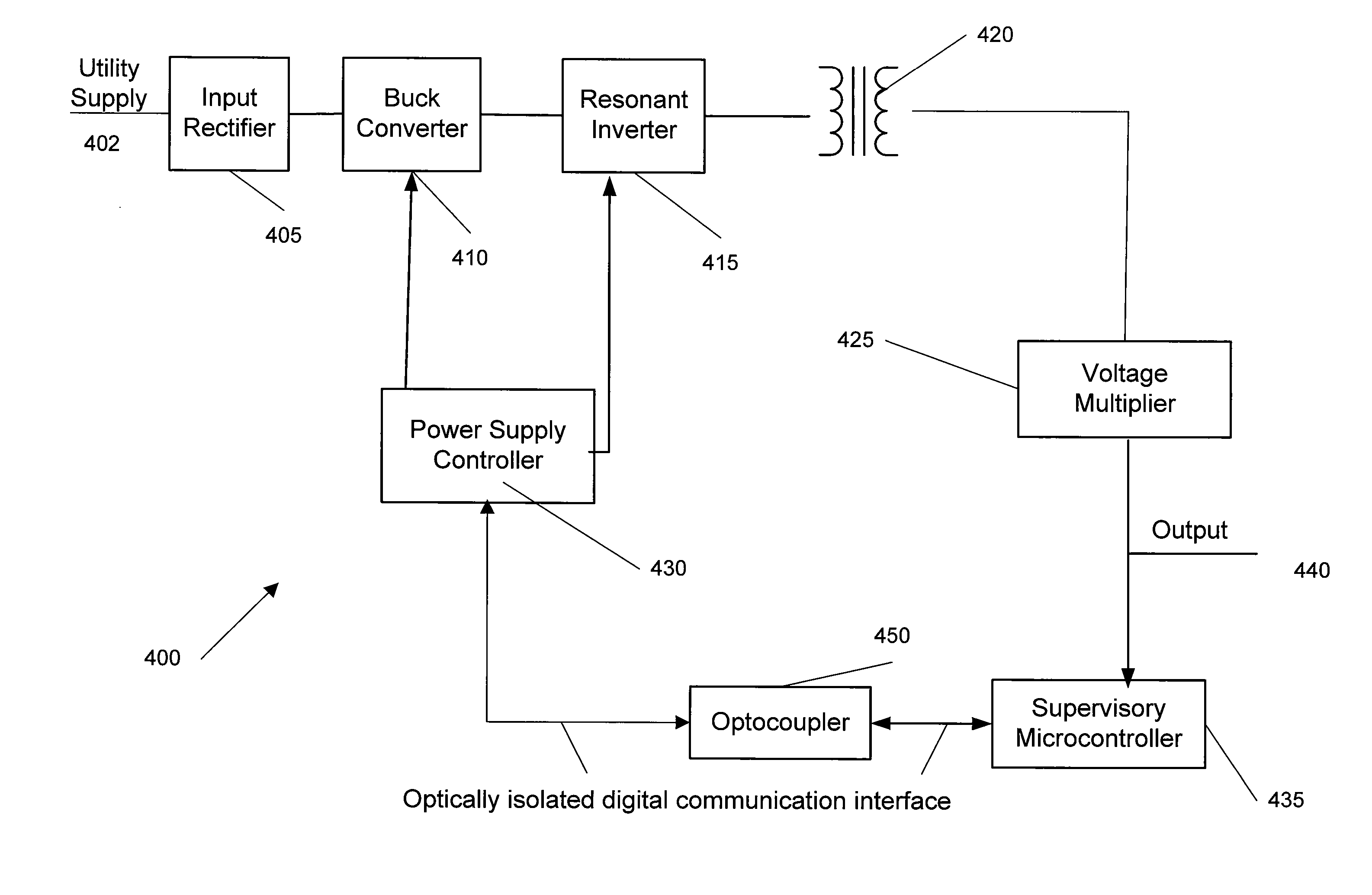
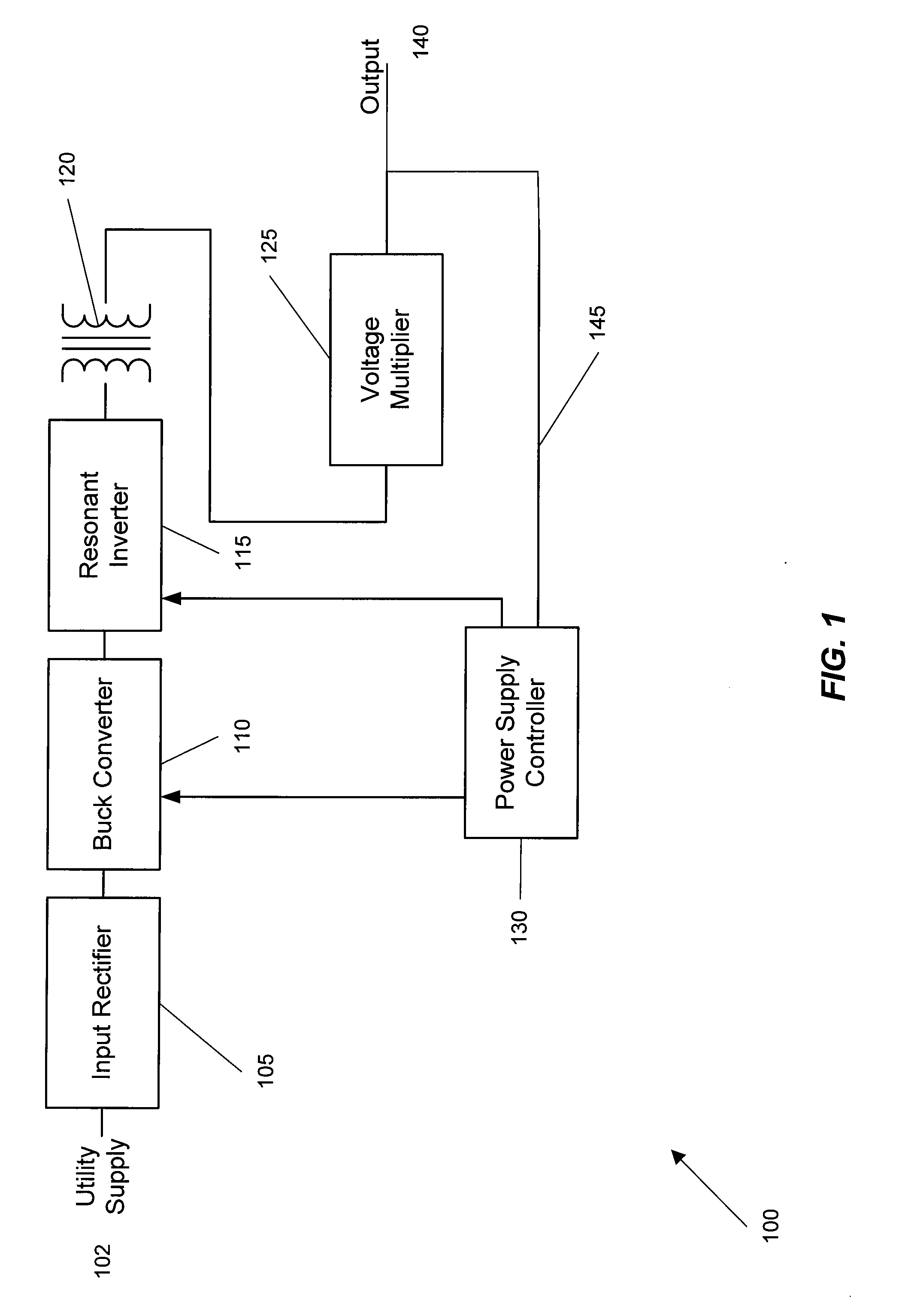
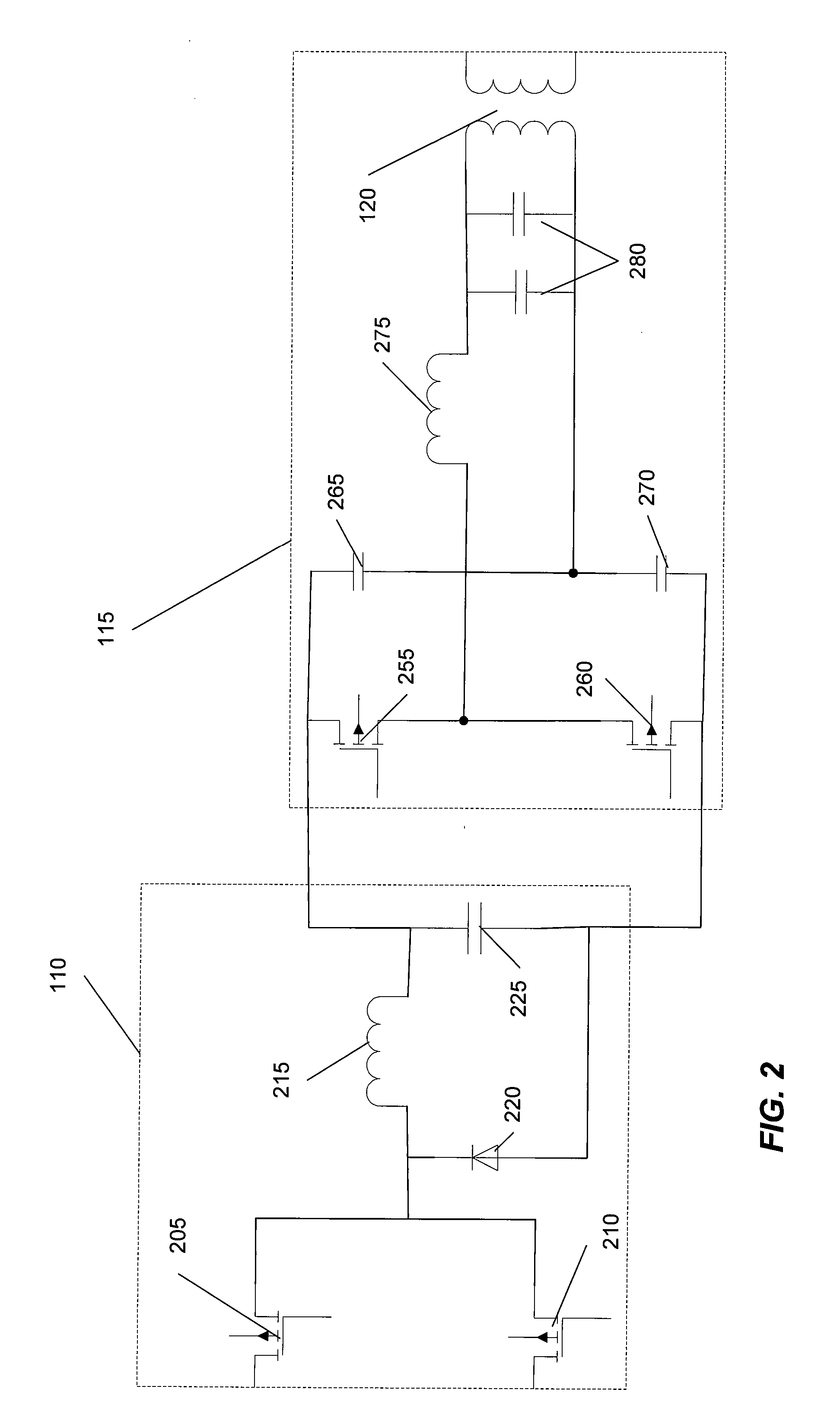
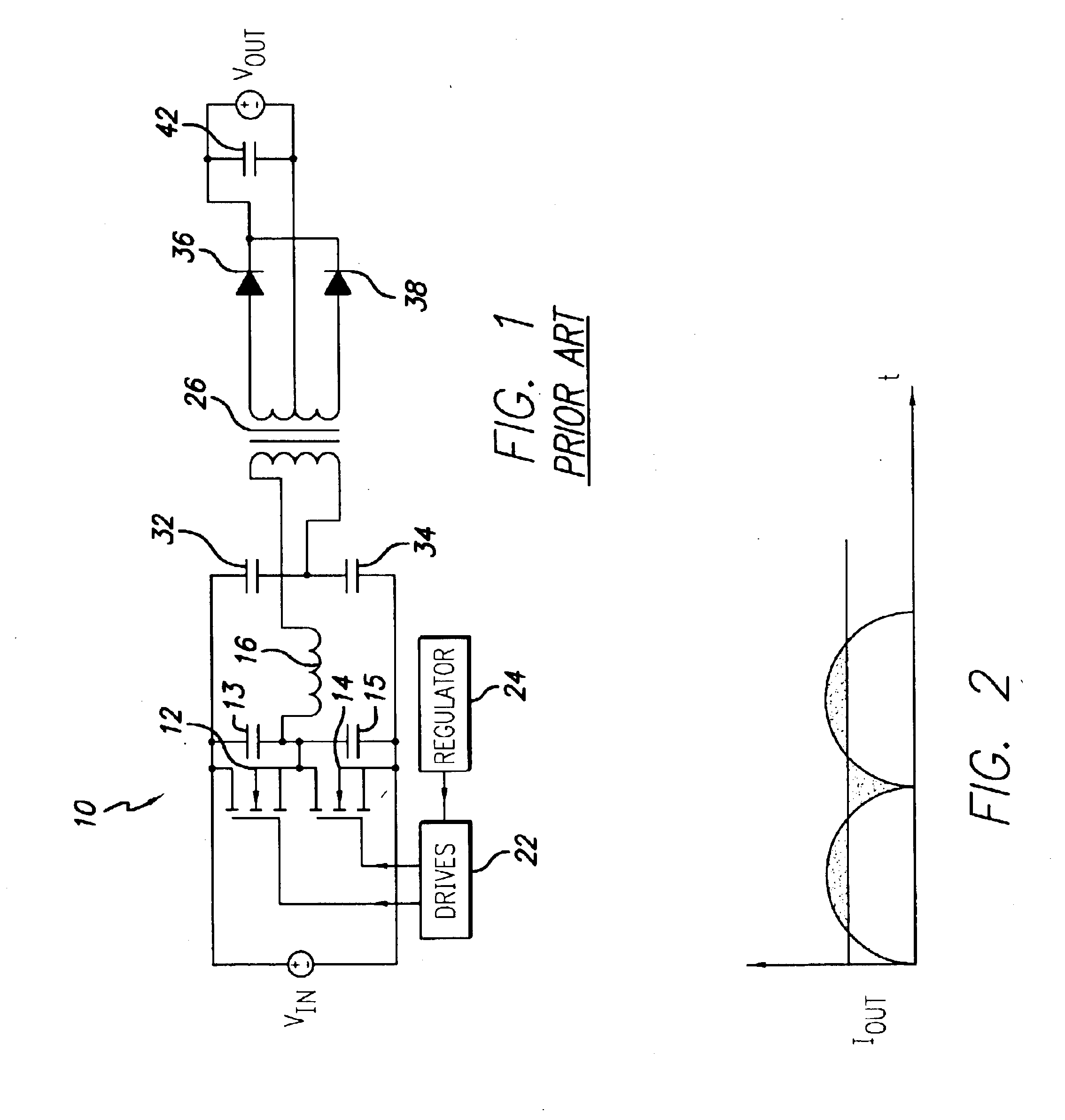
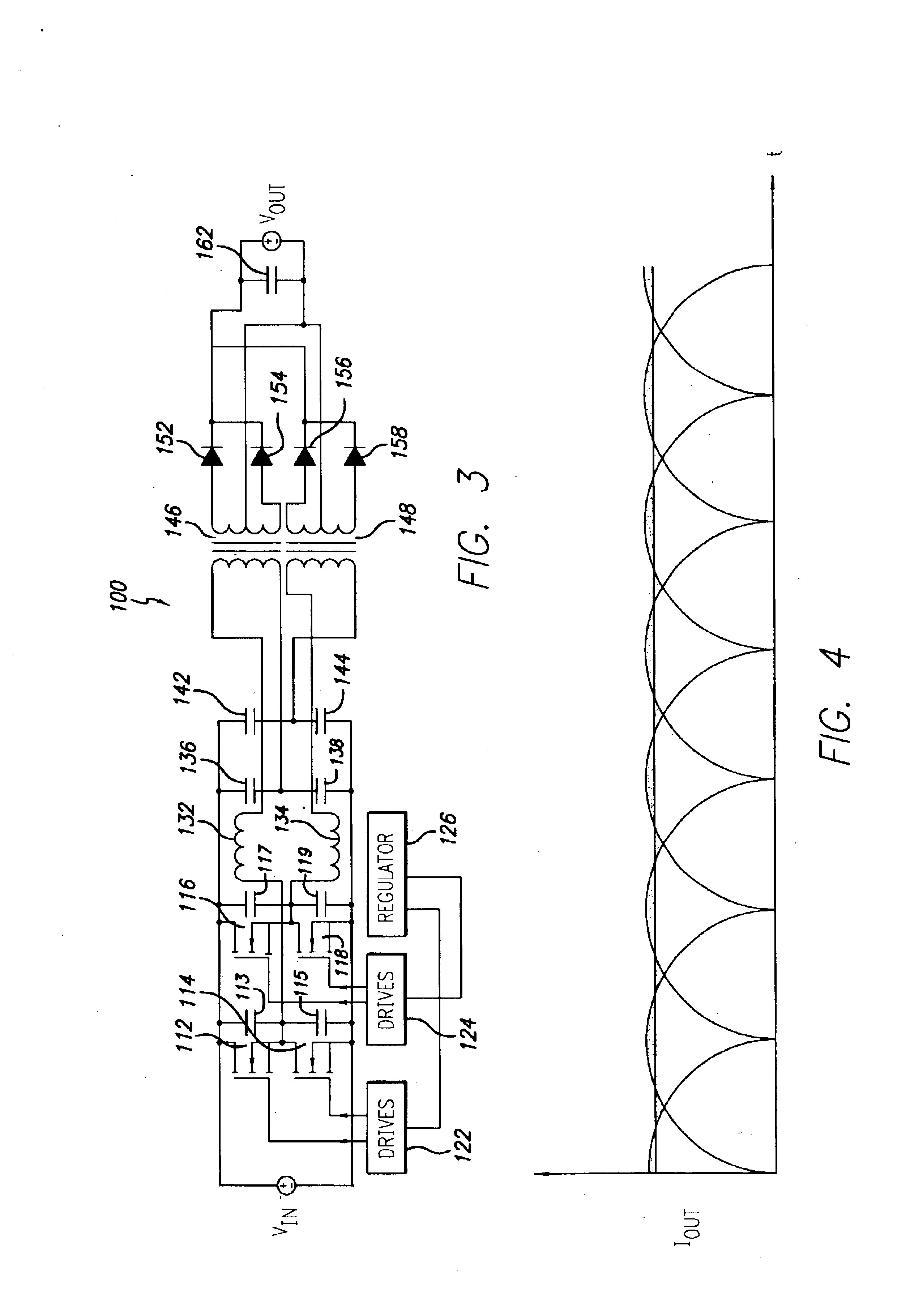
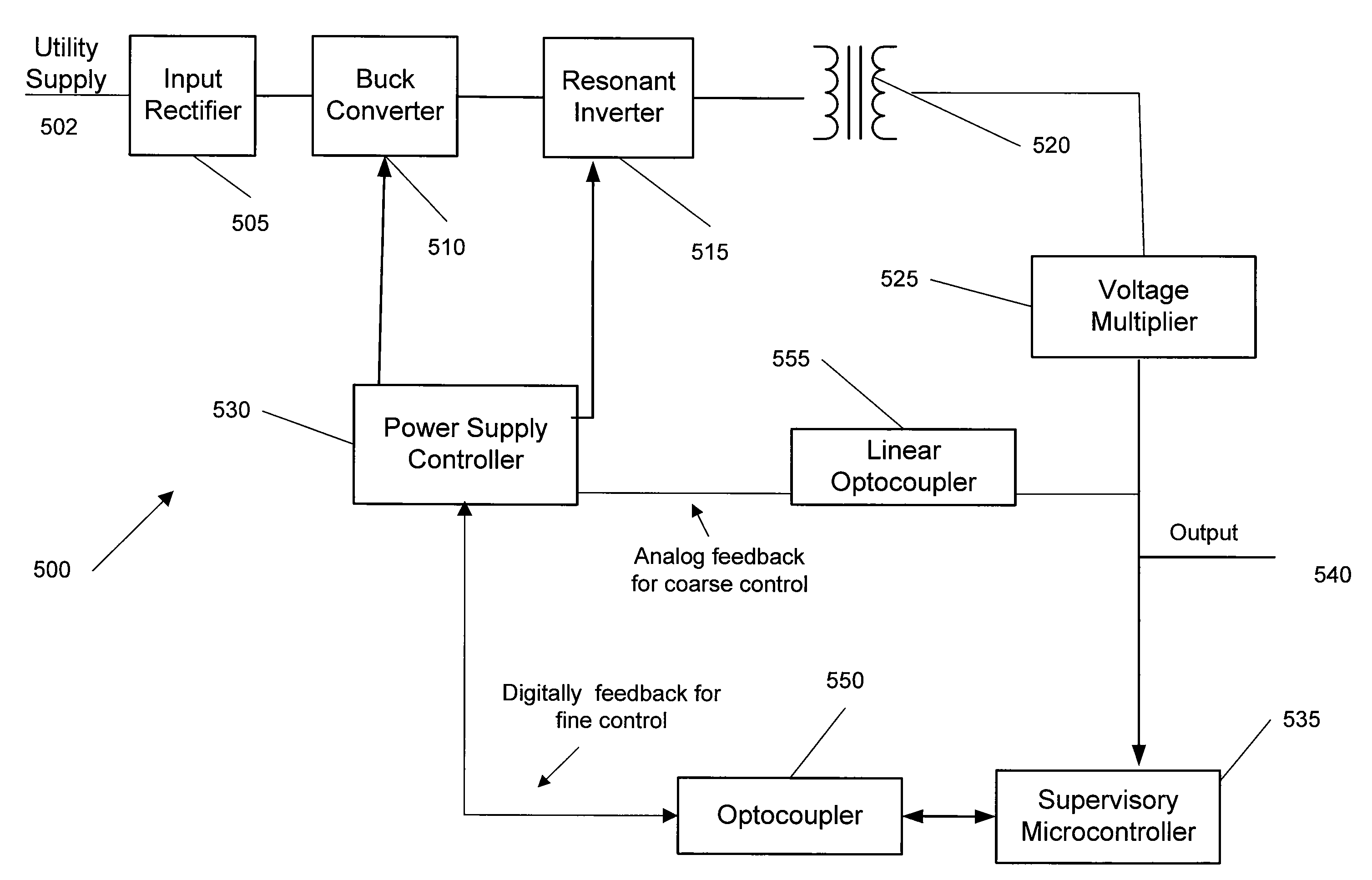
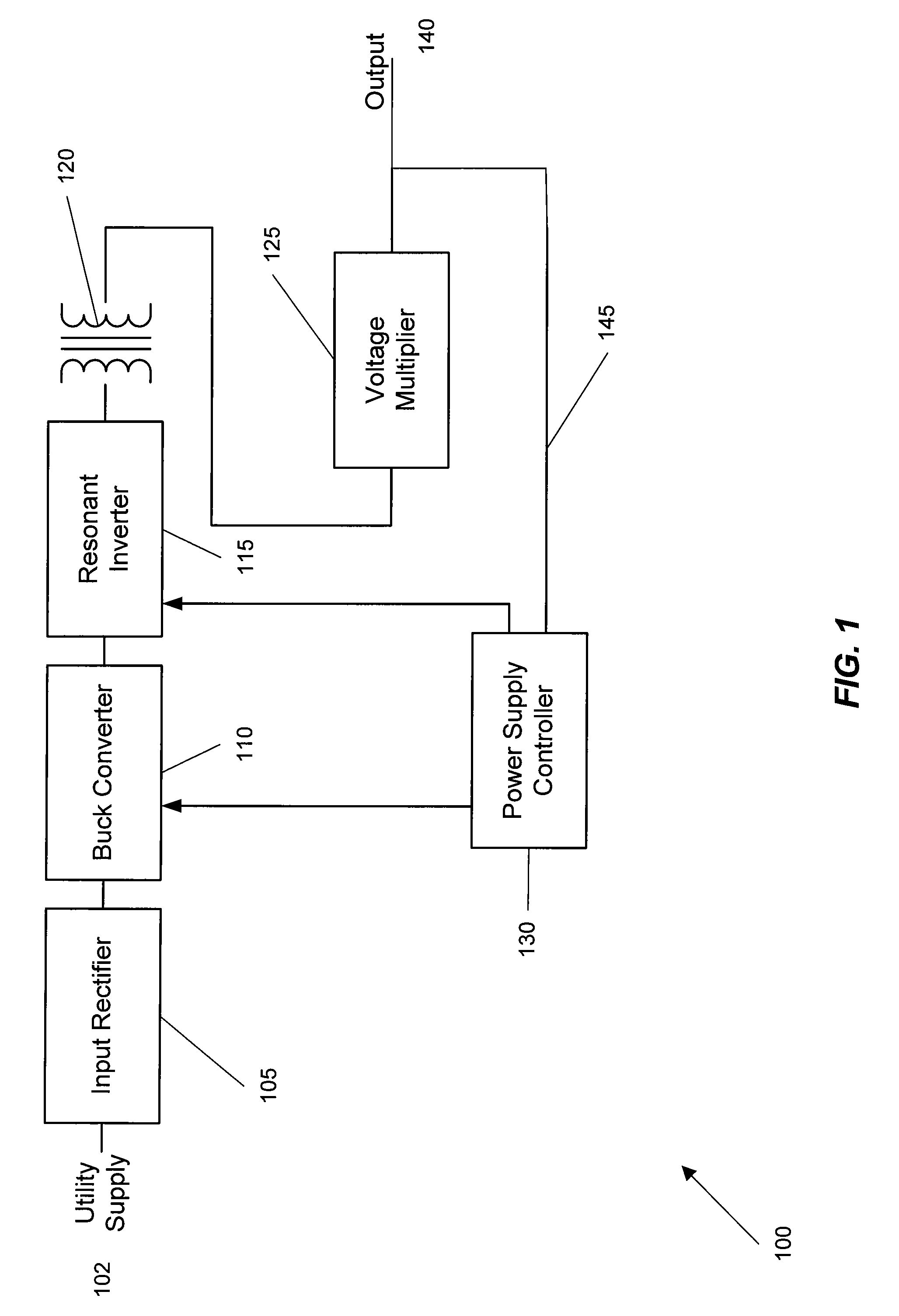
A wide range power supply capable of delivering 20V to 5000V is provided. The power supply of the present invention uses switch mode technology to achieve high overall operating efficiency and is capable of operating from no load to full load without loss of regulation. The power supply in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention operates directly from the utility supply (e.g., 110V / 220V and 50 Hz / 60 Hz). In one embodiment, the power supply's power conversion stage includes the following stages: an input rectifier; a buck converter; a quasi-resonant inverter; and a voltage multiplier. The above indicated stages are connected in series to achieve the large output voltage range. High precision is obtained from a use of a digital feedback loop, possibly in connection with an analog feedback loop.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
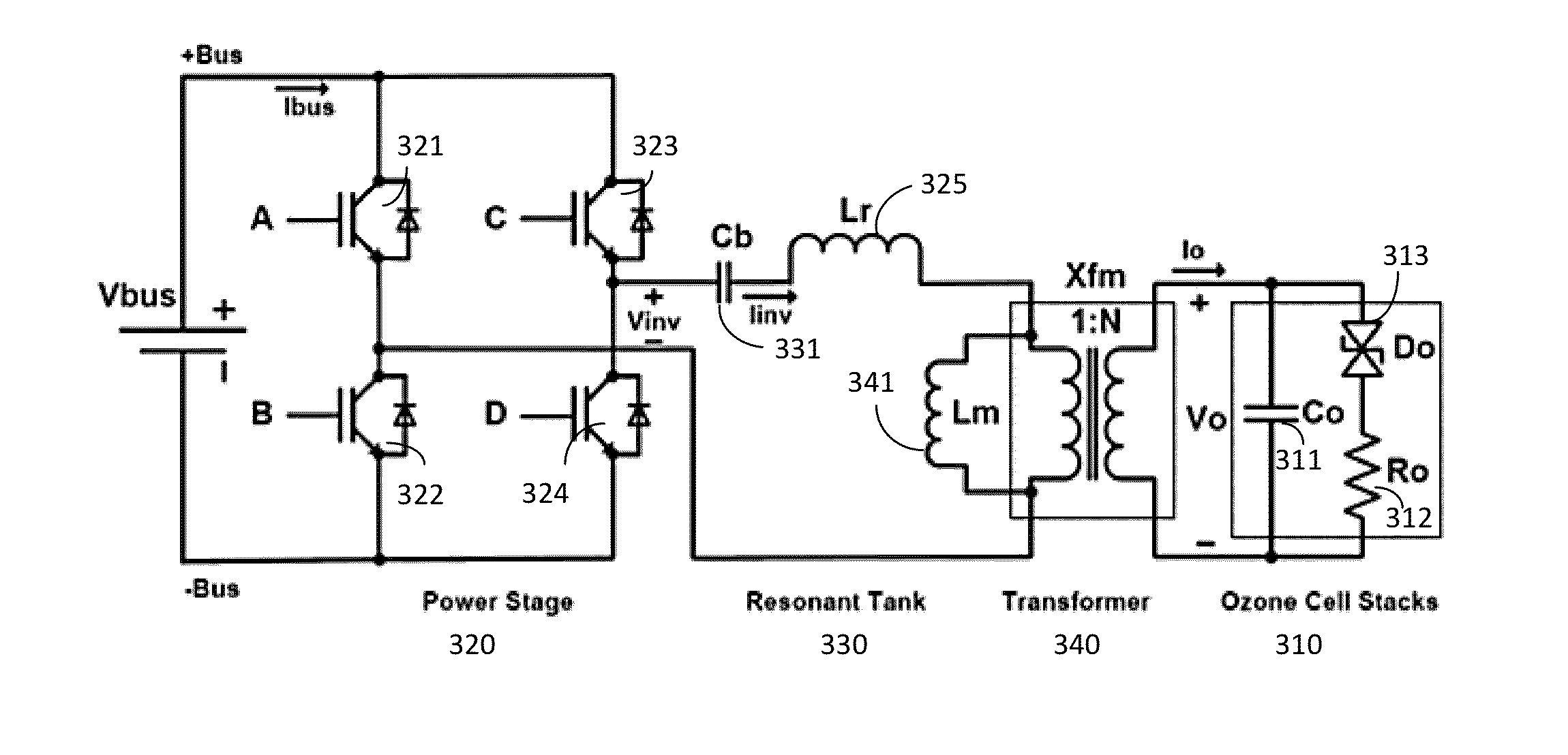
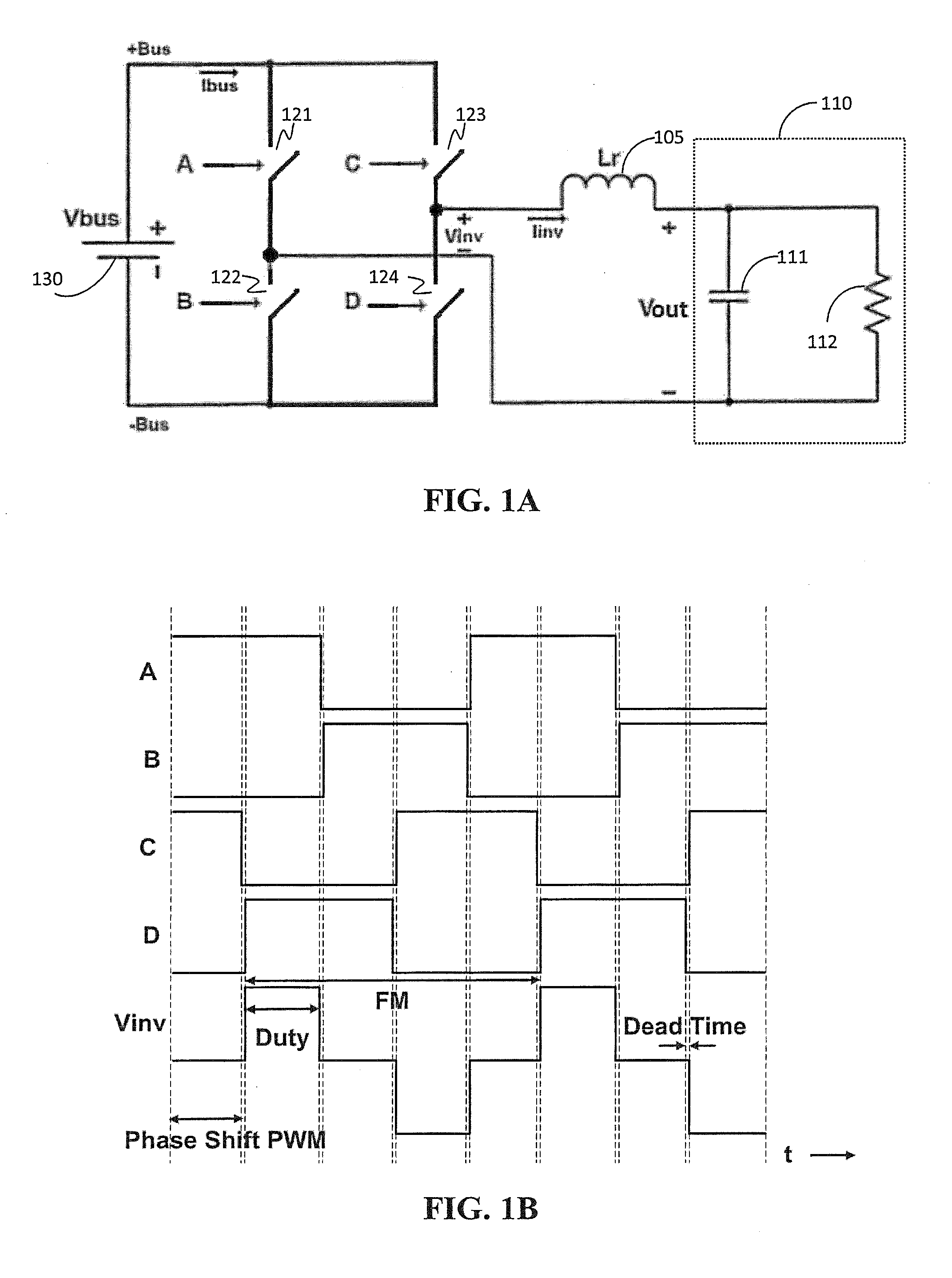
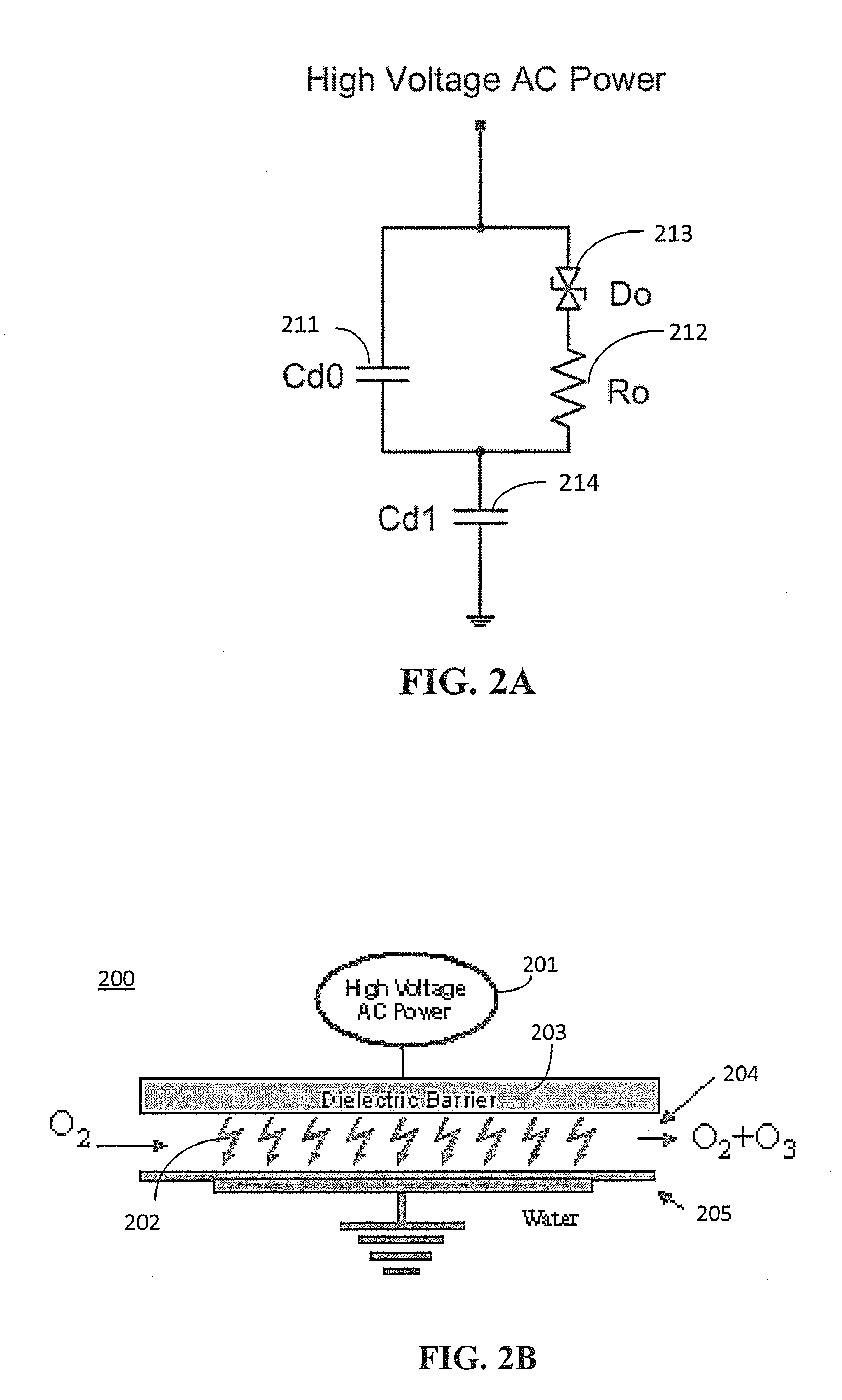
Versatile zero-voltage switch resonant inverter for industrial dielectric barrier discharge generator applications
ActiveUS20130257311A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove stabilityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesResonant inverterSoft switching
A power system for a dielectric barrier discharge system, such as used for generating ozone, can include a full bridge inverter stage and parallel resonant tank outputting a signal for powering a dielectric barrier discharge cell stack. The inverter stage is controlled using a combination of pulse width modulation (PWM) and frequency modulation (FM) to enable soft switching through all load conditions—from full load to light load. A current control loop error amplifier compensator can provide a duty cycle adjustment signal to a phase shift PWM controller chip that generates the switching signals for the inverter stage. A feedback signal is also used to adjust a clock frequency time constant of the PWM controller chip to provide the FM. In one embodiment, the feedback signal is an output of an inverting amplifier connected at an output of the current control loop error amplifier compensator.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
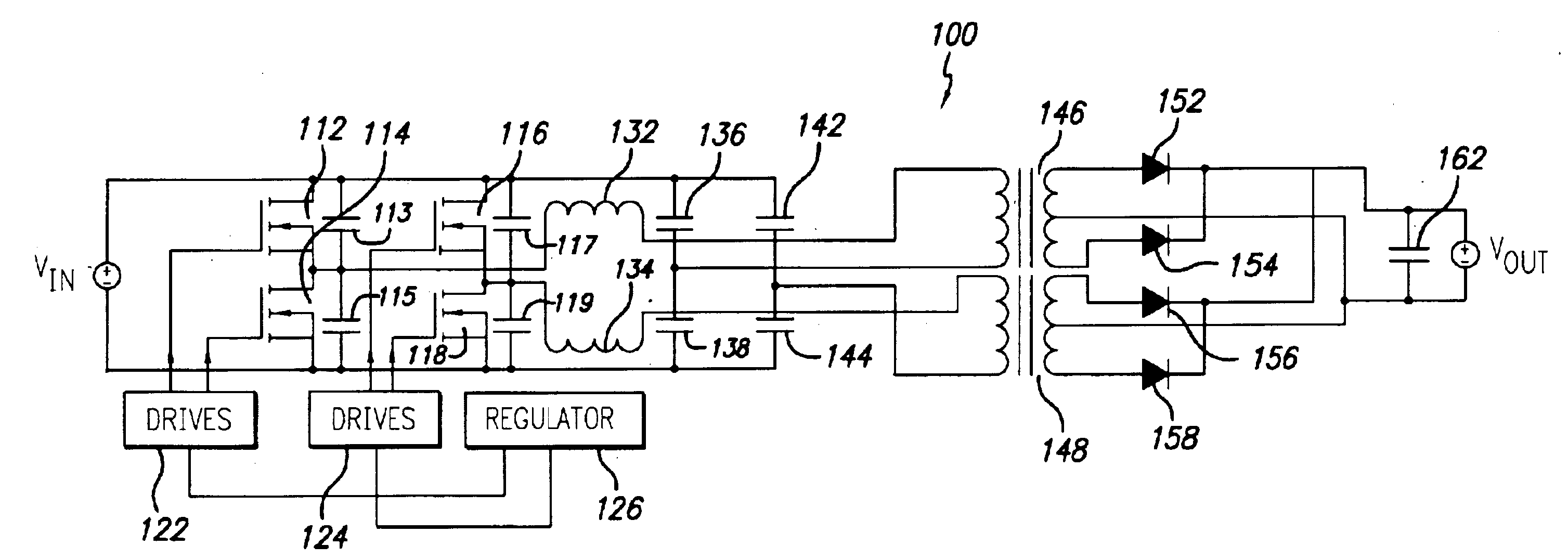
Phase-shifted resonant converter having reduced output ripple
ActiveUS6970366B2Prevent frequency shiftPreventing overvoltage conditionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEnergy industryResonant inverterPhase shifted
A power converter comprises a pair of resonant converter circuits coupled together in parallel and operated at respective switching frequencies that are out of phase. The power converter includes a first resonant converter circuit and a second resonant converter circuit operatively coupled together. The first resonant converter circuit includes at least one power switch adapted to convey power to a first resonant circuit and a first rectification stage adapted to rectify the conveyed power from the first resonant circuit. The second resonant converter circuit includes at least one power switch adapted to convey power to a second resonant circuit and a second rectification stage adapted to rectify the conveyed power from the second resonant circuit. A filter capacitor is coupled to the first and second rectification stages to provide DC output power therefrom. A regulator is operatively coupled to the first and second resonant converters to control switching frequency of the power switches, such that the switching frequency of the at least one power switch of the second resonant converter is shifted in phase with respect to the switching frequency of the at least one power switch of the second resonant converter. In a preferred embodiment, the switching frequency of the at least one power switch of the second resonant converter is shifted in phase by approximately 90° with respect to the switching frequency of the at least one power switch of the second resonant converter.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
Power supply with a digital feedback loop
ActiveUS7324354B2High operating requirementsLow costEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcResonant inverterDigital feedback
A wide range power supply capable of delivering 20V to 5000V is provided. The power supply of the present invention uses switch mode technology to achieve high overall operating efficiency and is capable of operating from no load to full load without loss of regulation. The power supply in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention operates directly from the utility supply (e.g., 110V / 220V and 50 Hz / 60 Hz). In one embodiment, the power supply's power conversion stage includes the following stages: an input rectifier; a buck converter; a quasi-resonant inverter; and a voltage multiplier. The above indicated stages are connected in series to achieve the large output voltage range. High precision is obtained from a use of a digital feedback loop, possibly in connection with an analog feedback loop.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Resonant Converter
ActiveUS20090196074A1Drive stabilityEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionResonant inverterSquare waveform
A resonant converter includes a square wave generator including a first switch and a second switch, and generating a first square wave corresponding to an input voltage by alternately turning on / off the first and second switches; a resonator including a first coil of a primary coil of a transformer, and generating a resonance waveform corresponding to the first square wave; and an output unit including a second coil of a secondary coil of the transformer, and outputting a voltage corresponding to a current generated in the second coil corresponding to the resonance waveform. The square wave generator includes a pulse frequency modulation controller for turning on / off the first and second switches, comparing a first voltage linearly increased while the second switch maintains the turn-on state and a second voltage corresponding to an integration value on the time of the current flowing to the second switch when the second switch is turned off, and changing on / off drive frequencies of the first and second switches according to a comparison result. Therefore, a resonant converter driven with safety is realized.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Symmetrical half-bridge LLC resonant bidirectional DC-DC converter
ActiveCN102201739AMitigate transient overvoltageMitigate transient overcurrentEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionResonant inverterDc dc converter
The invention discloses a symmetrical half-bridge LLC resonant bidirectional DC-DC converter, which belongs to the technical field of power electronic application. Topological structures on the two sides of the converter are symmetrical, and adopted components adopt a complex function design. When a switching network and a resonant network on one side of a high frequency transformer function, the switching network and the resonant network on the other side are automatically evolved into a rectifier-load network, and the networks on the two sides commonly form the whole LLC resonant converter to realize power conversion in a corresponding direction. Because the structures are completely symmetrical, reverse conversion can be possible; and in the reverse conversion, the topological structures can be automatically reconstructed to form a reverse LLC resonant converter to realize reverse power conversion. The symmetrical half-bridge LLC resonant bidirectional DC-DC converter achieves effective improvements in conversion efficiency, power density, dynamic performance and electromagnetic compatibility, reduces the electrical stress of components at work, has a reduced volume and a reduced weight, and realizes highly-efficient, isolated and bidirectional DC / DC power conversion.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Resonant converter with auxiliary resonant components and holdup time control circuitry
InactiveUS20130194831A1Improve efficiencyLow efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionResonant inverterCapacitance
A resonant power converter is provided with auxiliary circuit branches and control circuitry for switchably coupling the auxiliary branches to resonant circuit components during holdup times. Auxiliary branches are coupled in parallel with any one or more of a resonant inductor, a resonant capacitor, and a magnetizing inductive winding via respective switches. When a holdup time condition is detected in accordance with, for example, a drop in the mains line voltage, the switches are controlled to adjust the corresponding inductance or capacitance for the duration of the holdup time condition or otherwise for a predetermined duration. The power converter in normal operation is configured for high efficiency and in a holdup time operation is configured to produce sufficient holdup time.
Owner:BEL POWER SOLUTIONS INC
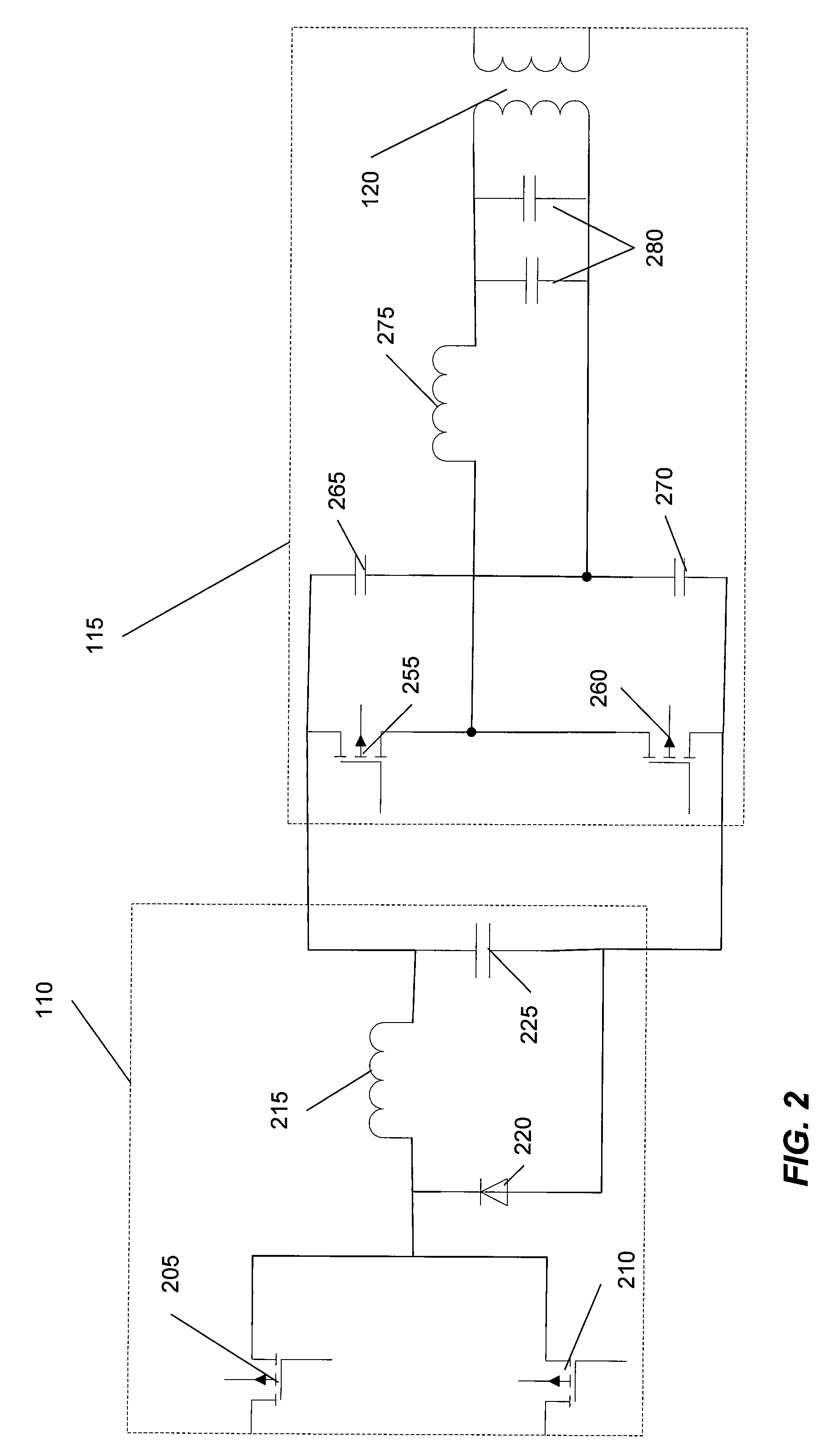
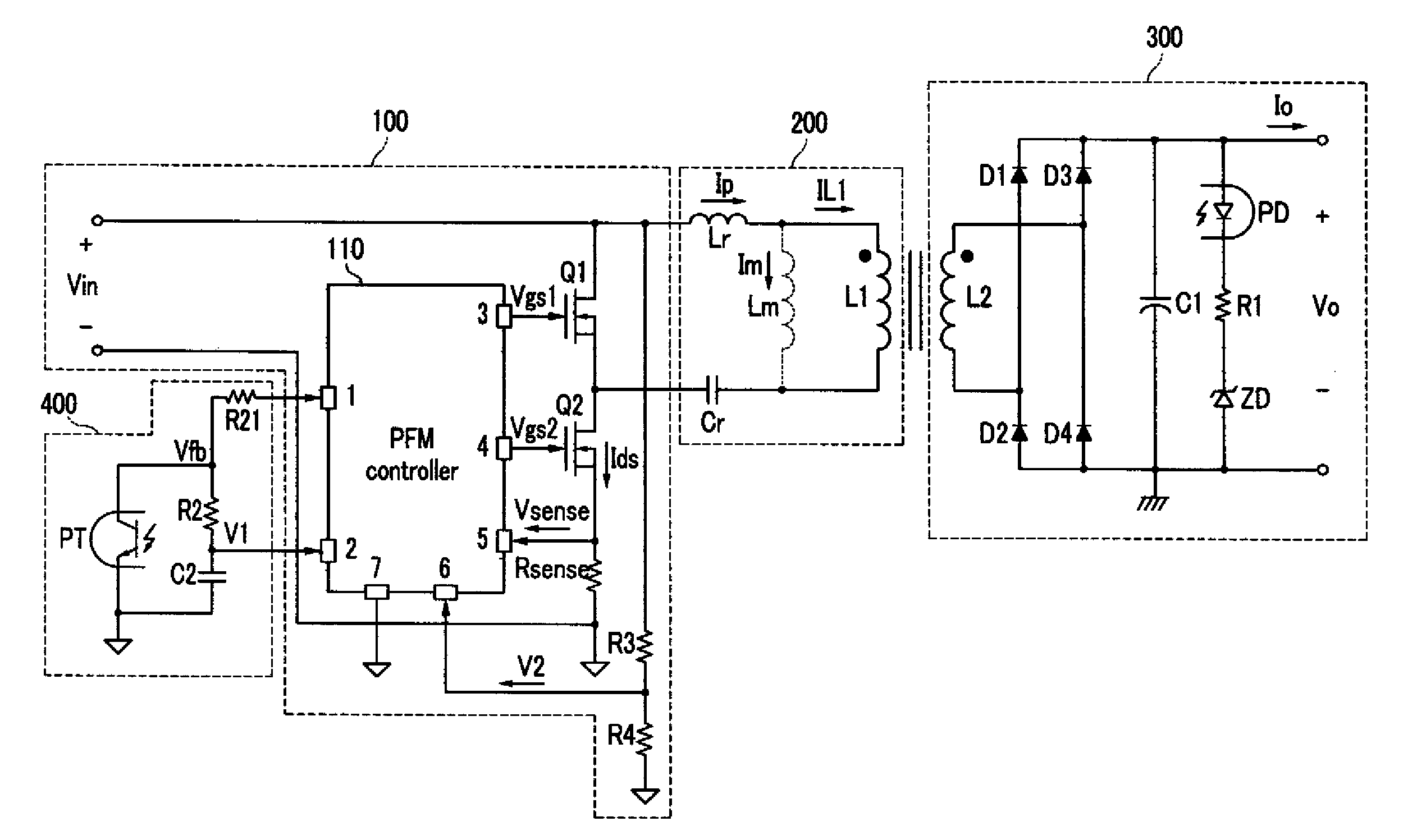
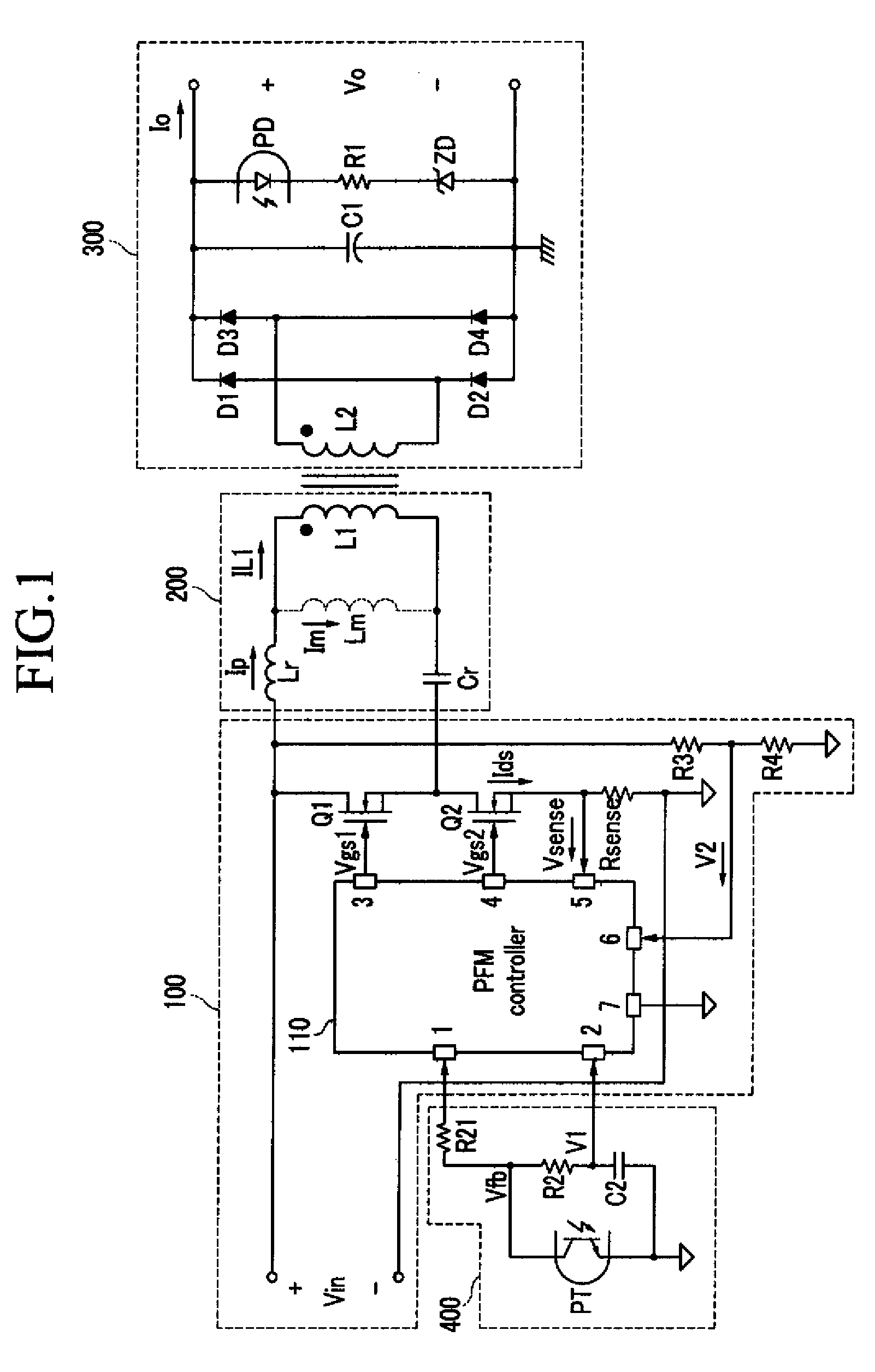
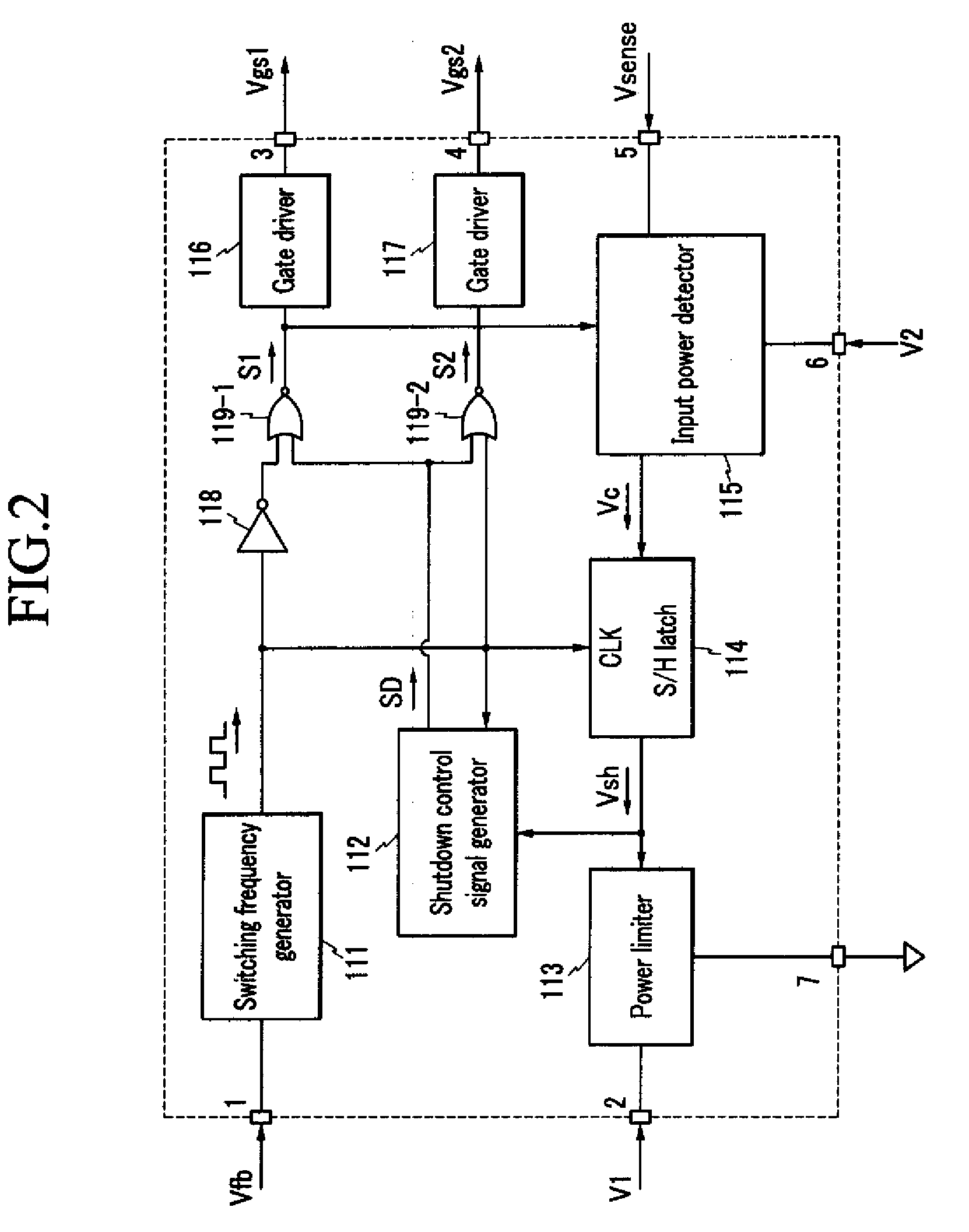
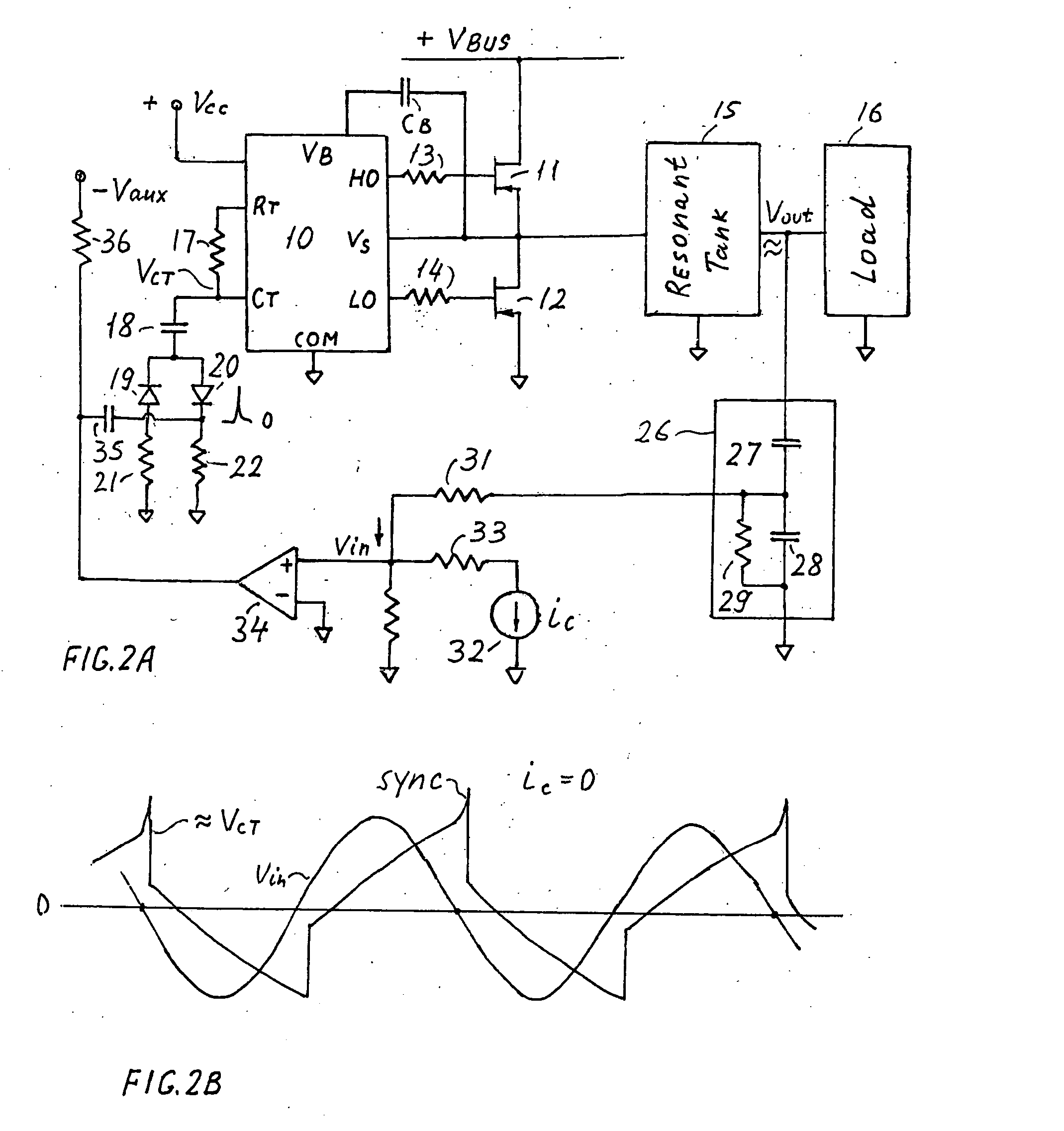
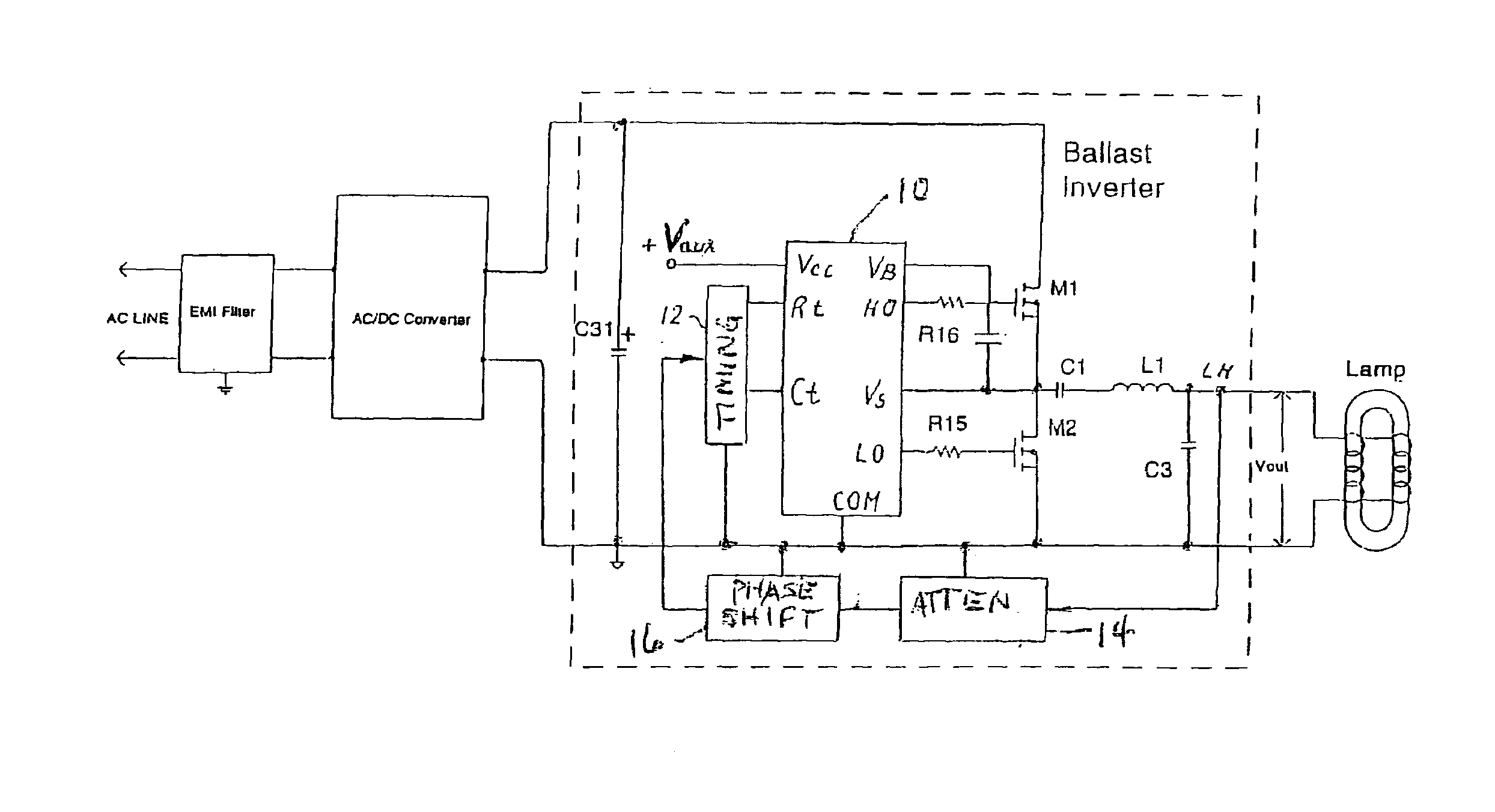
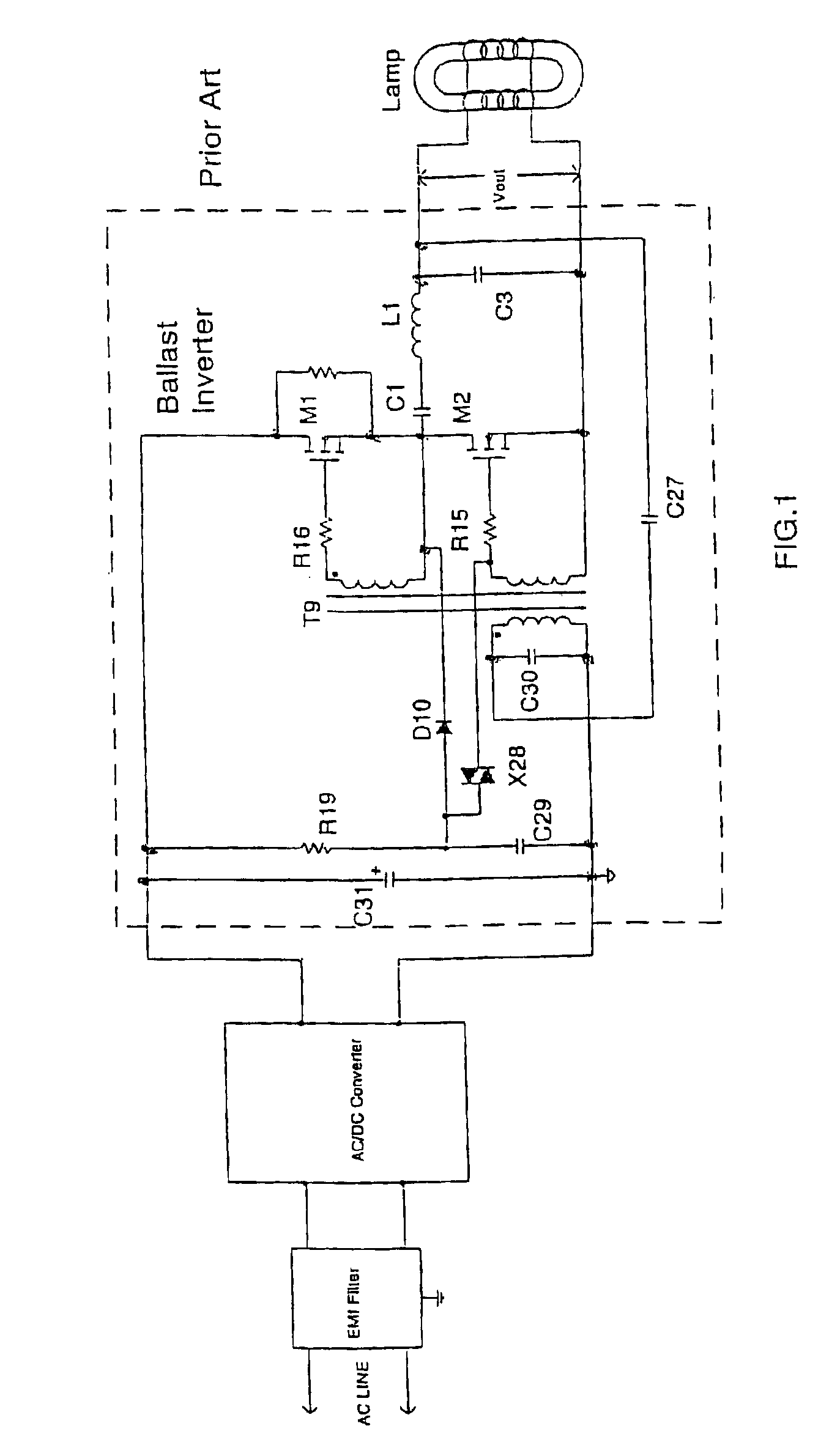
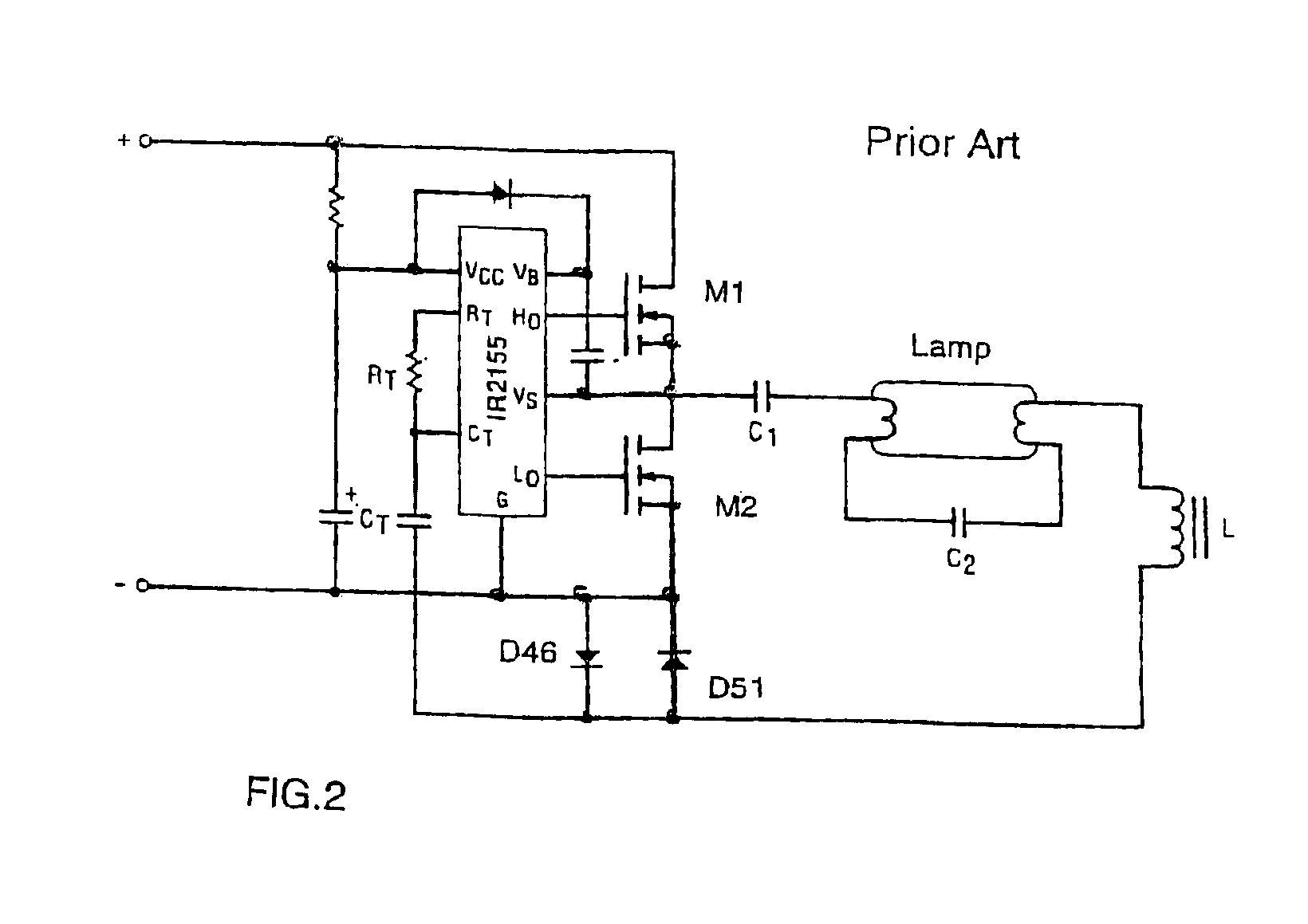
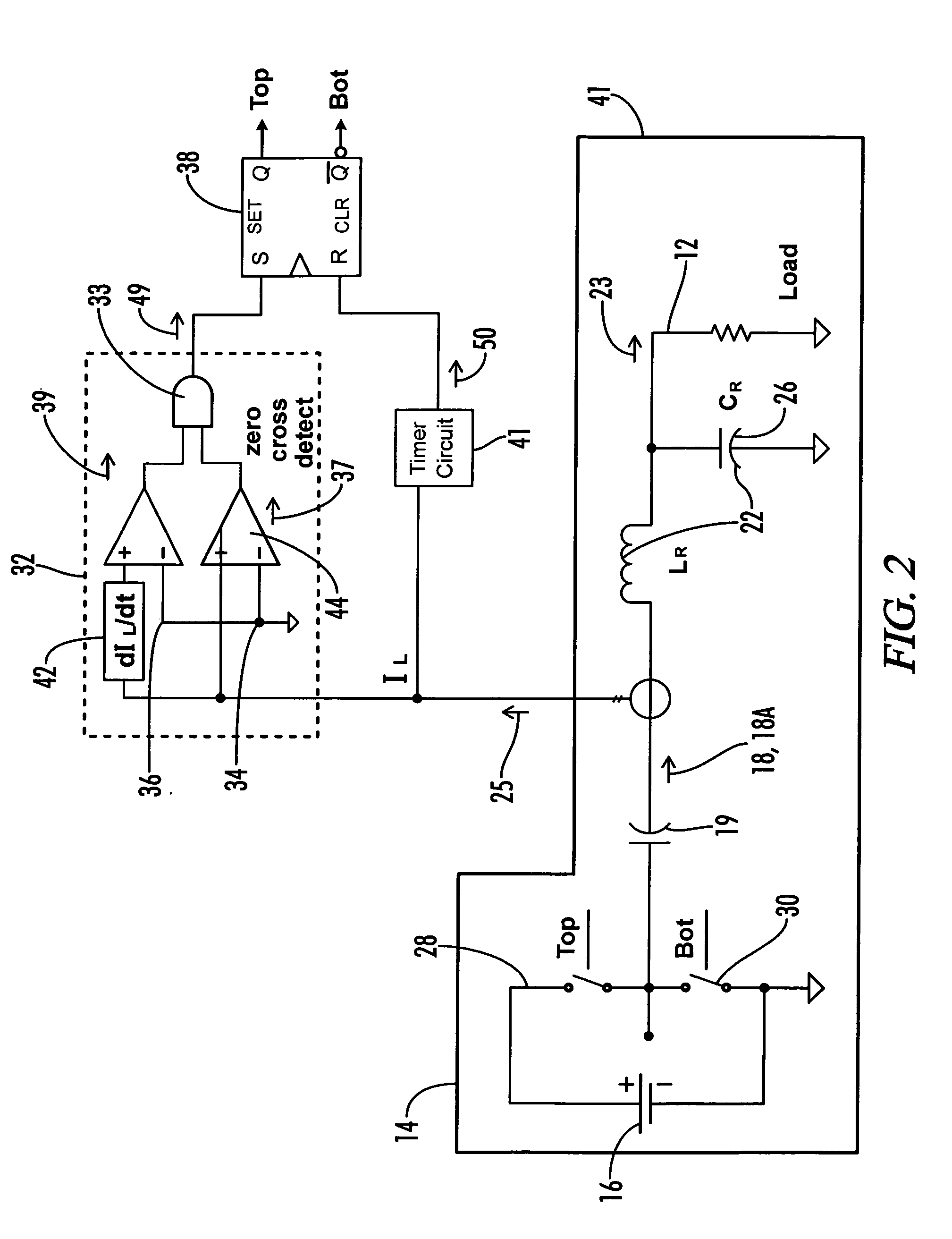
Resonant inverter including feed back circuit having phase compensator and controller
InactiveUS20060006816A1Wide range reliable synchronizationEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionGas-discharge lampResonant inverter
A resonant inverter with a self-oscillating driver IC for powering AC loads, such as gas discharge lamps or regulated DC / DC converters, includes a timing circuit that generates control strobe pulses that are injected into the timing circuit. The timing circuit is coupled to an inverter resonant tank through a feed back circuit providing phase lock for the resonant inverter. The feed back circuit connects the resonant tank circuit to a zero signal detector. The feed back circuit includes a phase compensator and a controller that has a source of a bias current connected to the zero signal detector.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
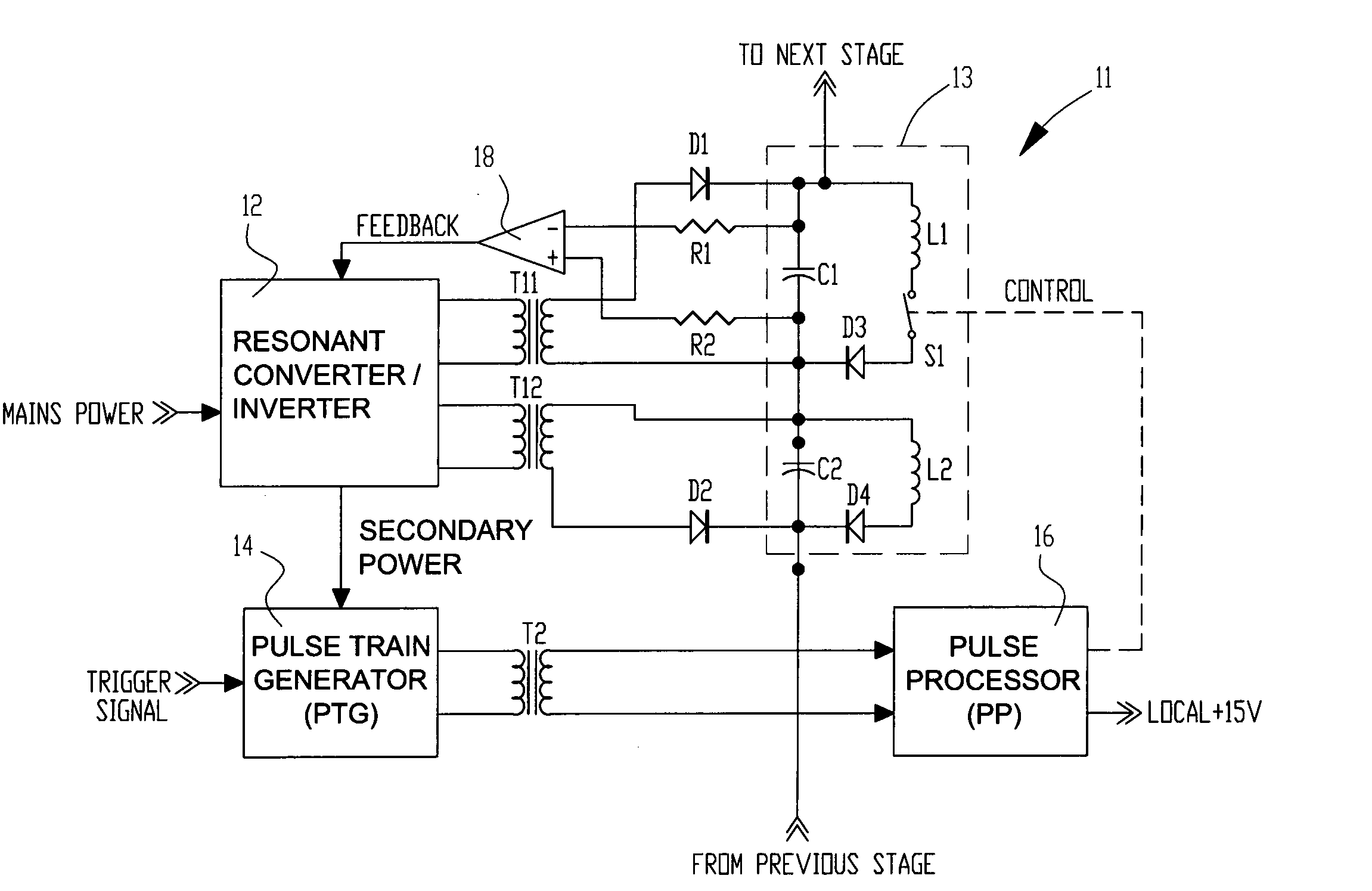
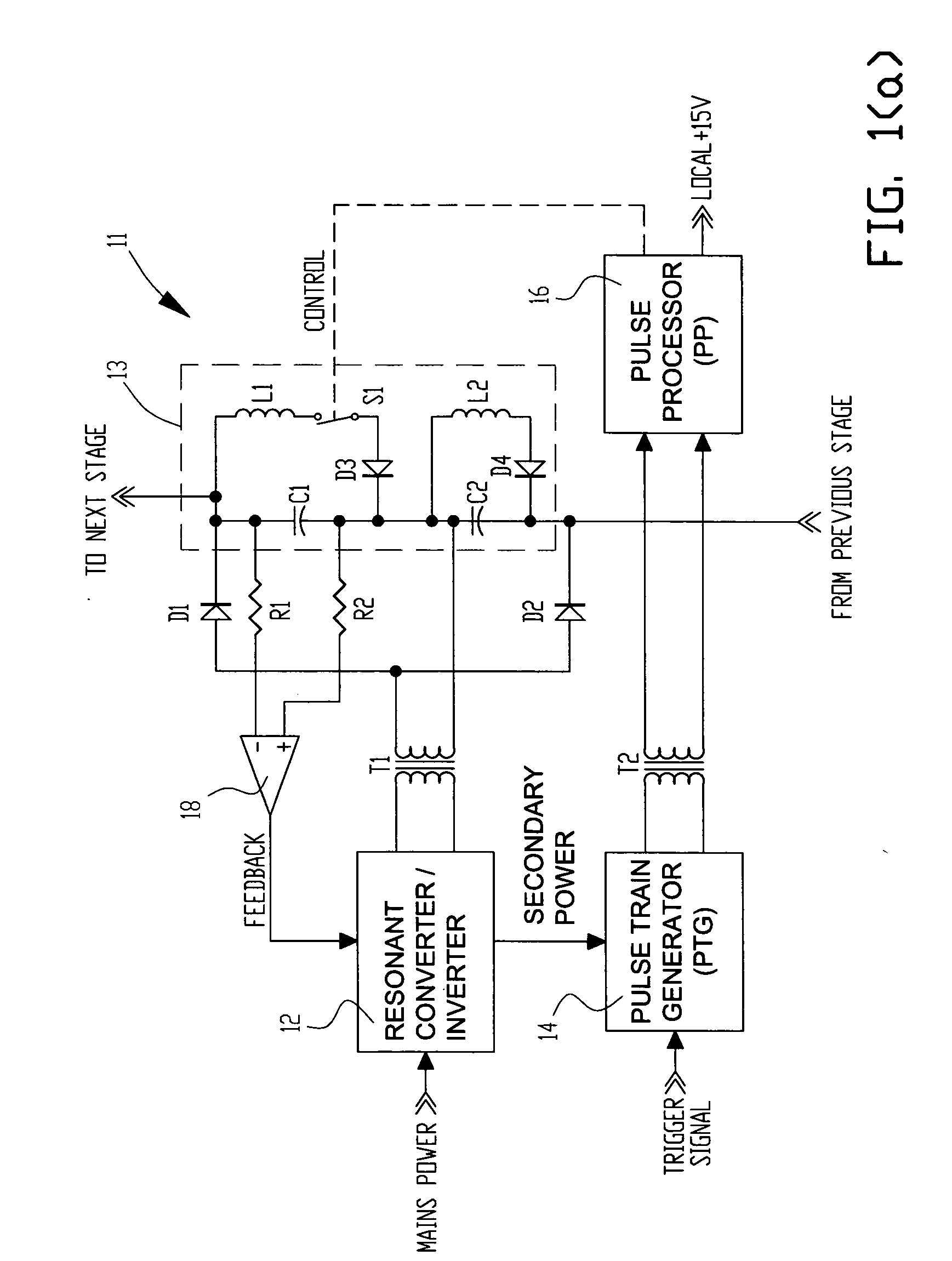
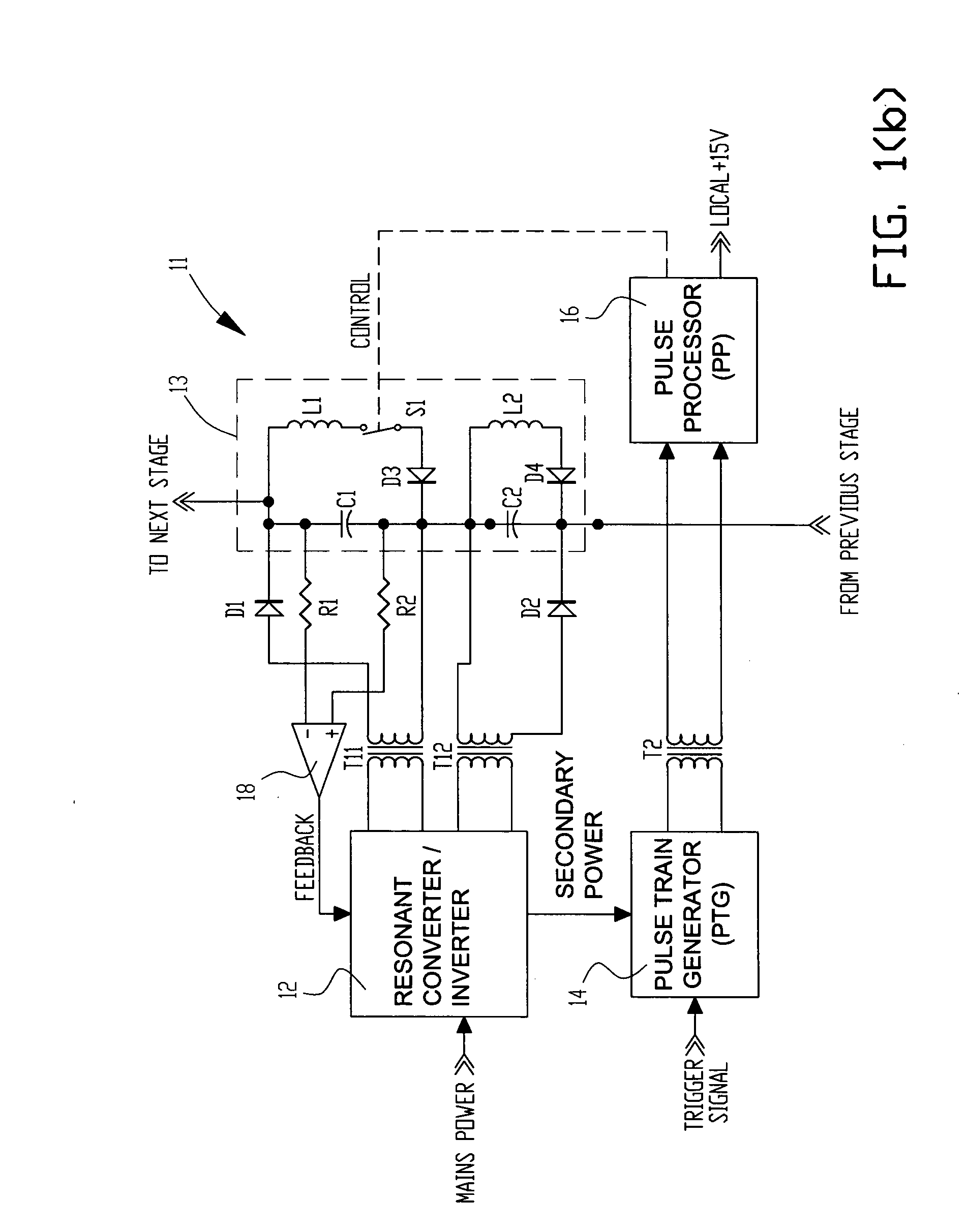
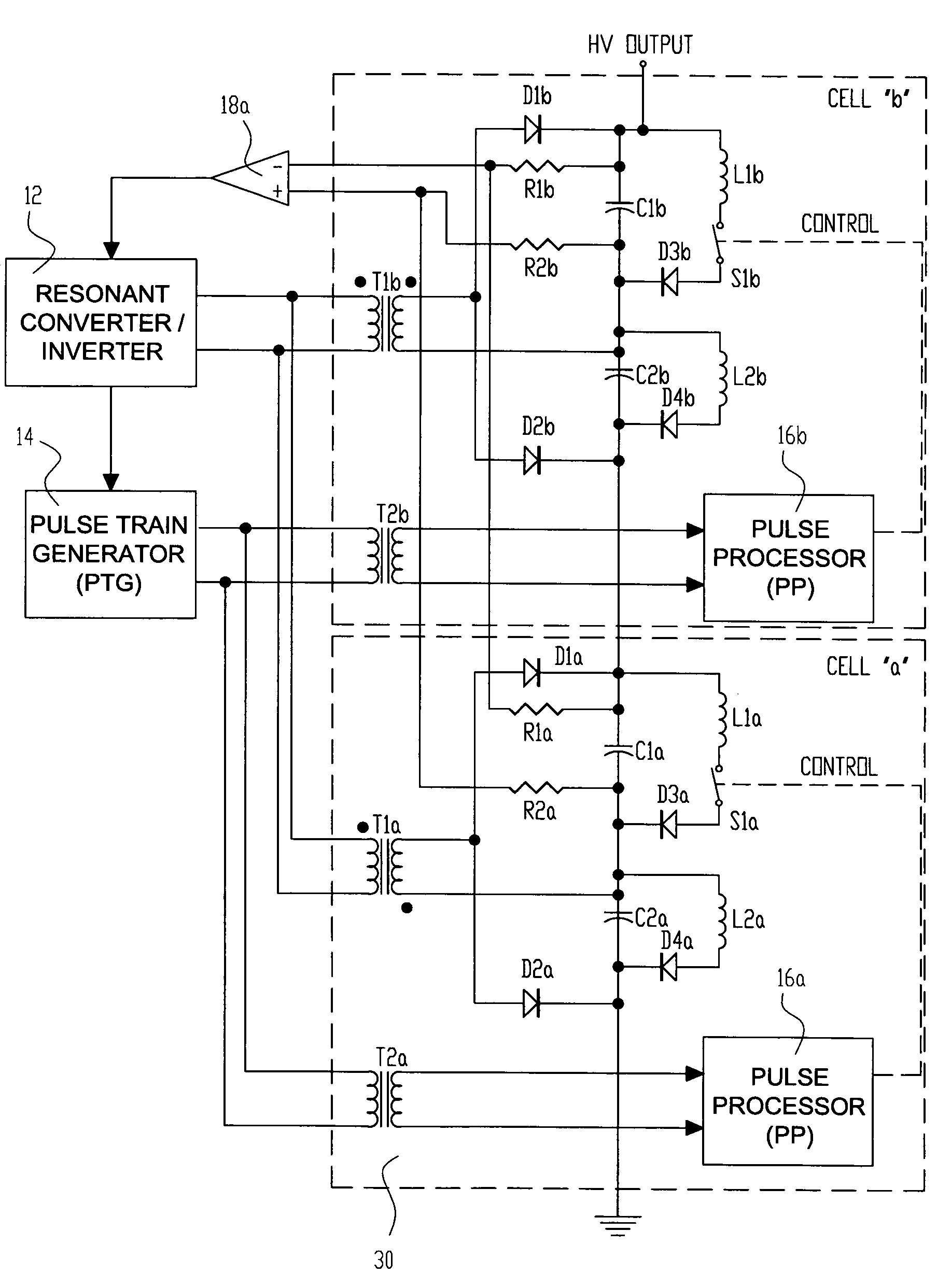
High voltage pulse generator
ActiveUS20060139977A1Efficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionResonant inverterTransformer
A high voltage pulse generator utilizes an even number of Marx cells using L-C inversion topology. Each Marx cell is associated with an individual inverter transformer having a primary winding connected to the output of an ac power supply such as a series resonant inverter. The secondary of each inverter transformer is half-wave rectified to charge the energy storage capacitors in each Marx cell. A distributed voltage sensing scheme can be provided for accurate feedback to the inverter's controller. An inductive element can be used to achieve a magnetic diode effect in the L-C inversion circuit to reduce component stress and improve efficiency. A transformer-coupled floating gate drive circuit is used to provide local power conditioning and trigger timing for discharge of the energy storage capacitors.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Resonant converter and switching power supply device
ActiveUS9948198B2Low working voltageReduce voltageEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionResonant inverterResonant converter
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Llc converter with dynamic gain transformation for wide input and output range
ActiveUS20140036545A1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionResonant inverterFull bridge
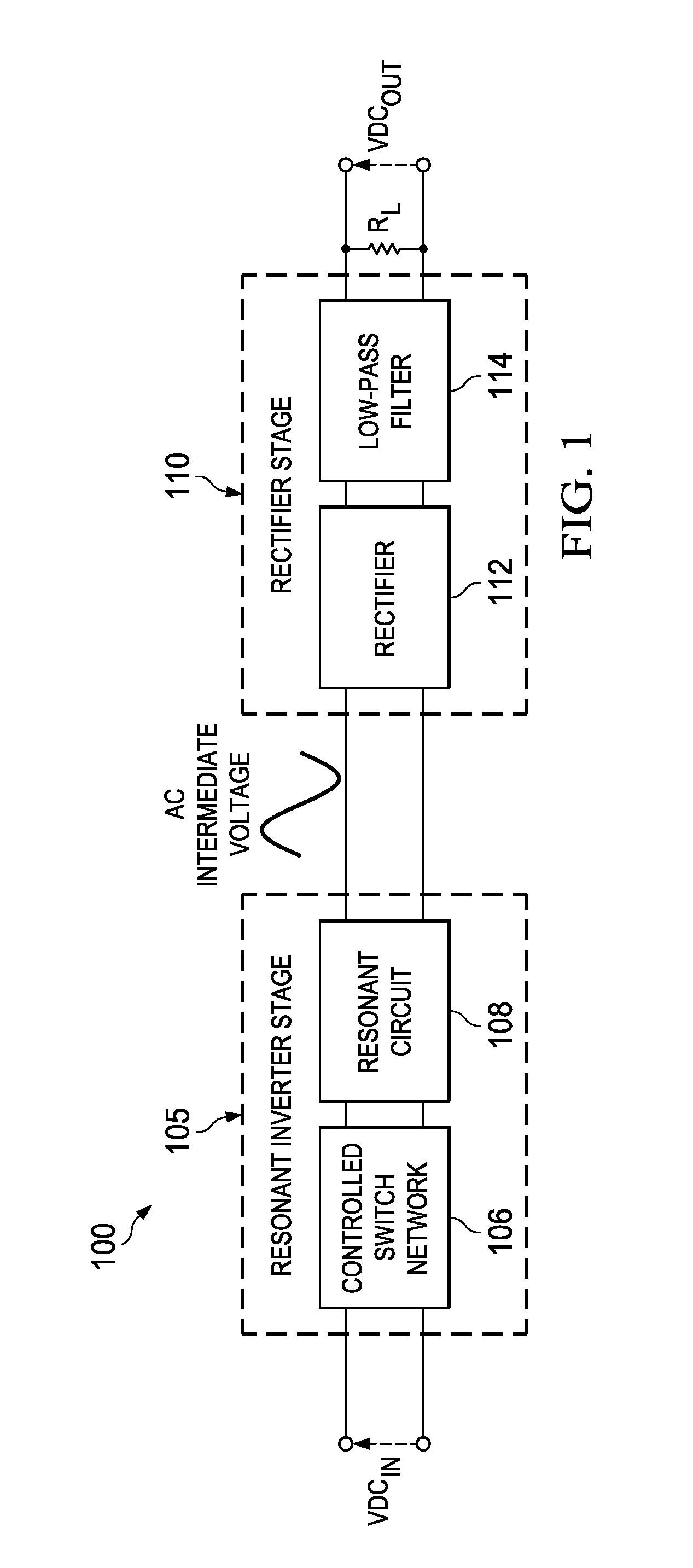
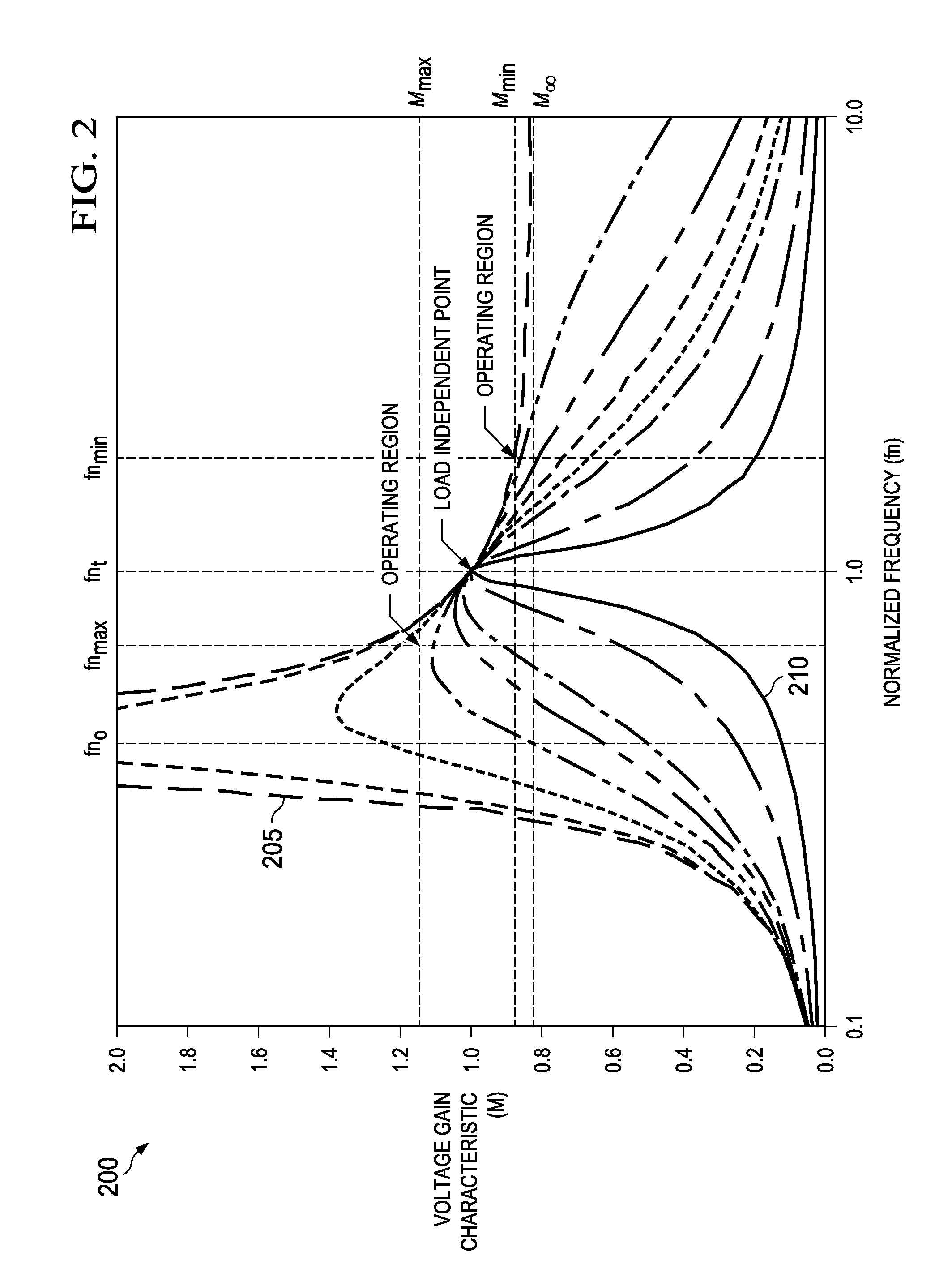
A resonant power converter system includes an output load and a rectifier stage that provides a DC output voltage to the output load from an AC intermediate voltage. The resonant power converter system also includes a resonant inverter stage that provides the AC intermediate voltage from a DC input voltage, wherein an inverter gain is controlled by switching between full-bridge and half-bridge topologies based on an external variable of the resonant power converter system. The resonant power converter system further includes a controller that controls the resonant power converter system. Additionally, a method of operating a power converter includes rectifying an AC intermediate voltage to provide a DC output voltage and providing the AC intermediate voltage by inverting a DC input voltage, wherein an inversion gain of the AC intermediate voltage is controlled by switching between full-bridge and half-bridge inversion topologies based on an external variable.
Owner:ACLEAP POWER INC
System and method for regulating resonant inverters
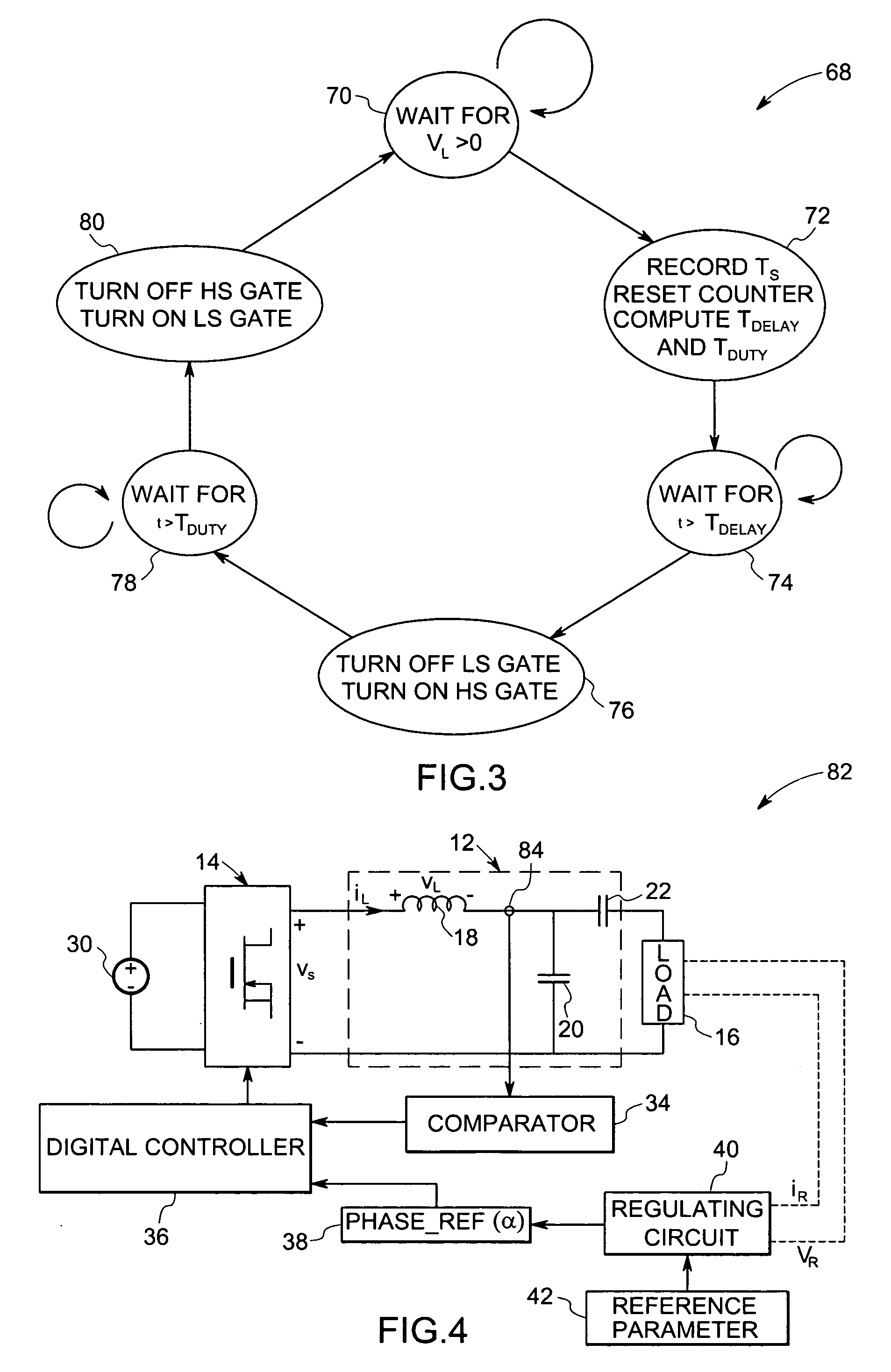
InactiveUS20050265058A1Rapid design cycleEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcResonant inverterControl system
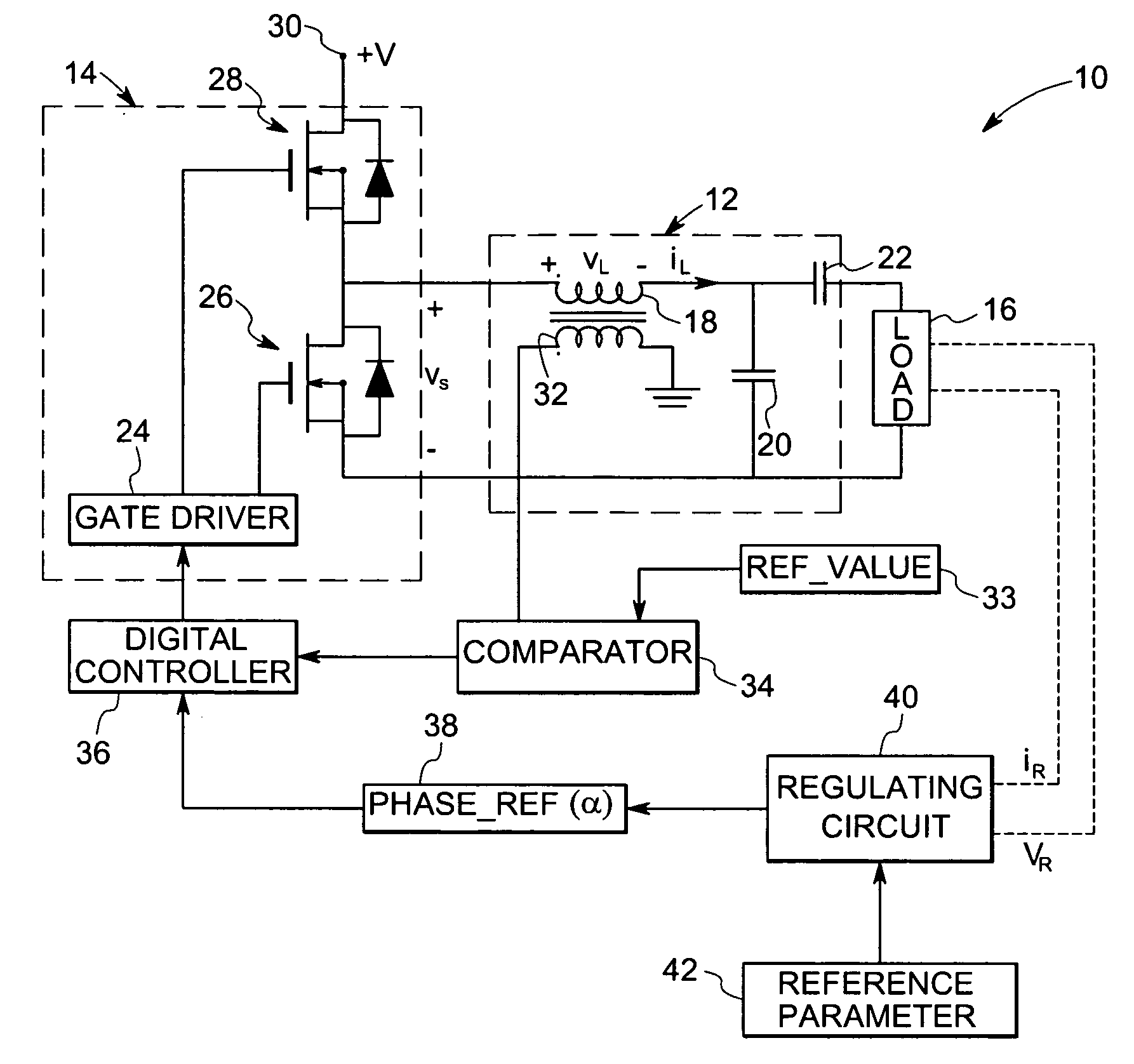
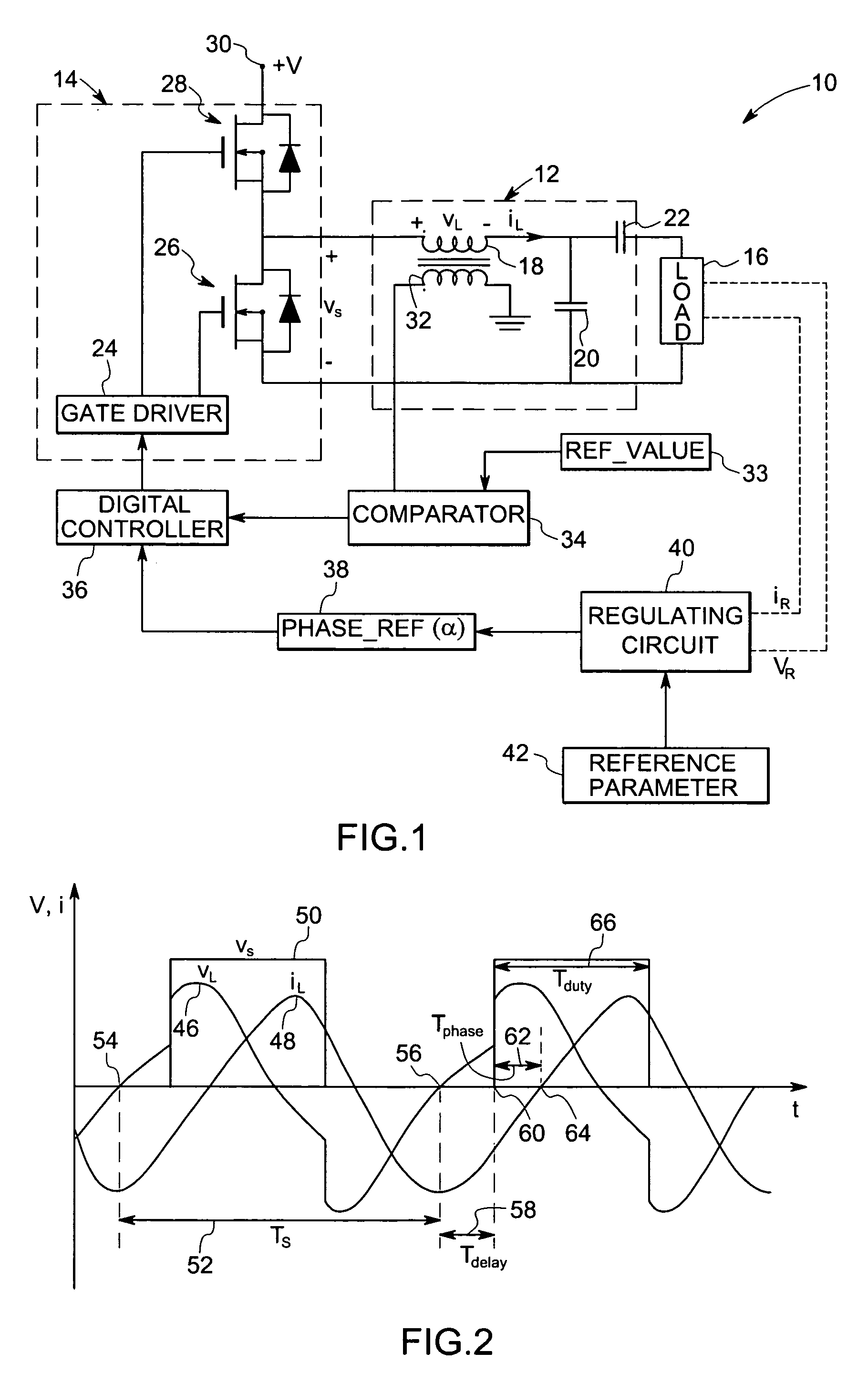
A technique is provided for direct digital phase control of resonant inverters based on sensing of one or more parameters of the resonant inverter. The resonant inverter control system includes a switching circuit for applying power signals to the resonant inverter and a sensor for sensing one or more parameters of the resonant inverter. The one or more parameters are representative of a phase angle. The resonant inverter control system also includes a comparator for comparing the one or more parameters to a reference value and a digital controller for determining timing of the one or more parameters and for regulating operation of the switching circuit based upon the timing of the one or more parameters.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
LLC resonant transformation device
InactiveCN101471606AImprove efficiencyImprove reliabilityEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionResonant inverterControl signal
The invention discloses an LLC resonant converter comprising a primary side bridge circuit, an LLC resonant network, a primary side controller, a power supply conversion circuit, a synchronous rectifier circuit, a secondary side controller and a current detection circuit. The current detection circuit is connected in a loop of the synchronous rectifier circuit in series, a detection signal output terminal thereof is connected with an input terminal of the secondary side controller, and a control signal output terminal of the secondary side controller is connected with the synchronous rectifier circuit; and the secondary side controller controls the switching-on / off of the synchronous rectifier circuit through the zero-crossing detection of the output current of the power supply conversion circuit, thereby enabling the synchronous rectifier circuit to be switched on when the current is greater than zero and be switched off in the remaining time. The LLC resonant converter can avoid the coupling delay when a switch tube of the primary side bridge circuit and the switch tube of the synchronous rectifier circuit are conducted, thereby improving the efficiency and the reliability of the converter.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
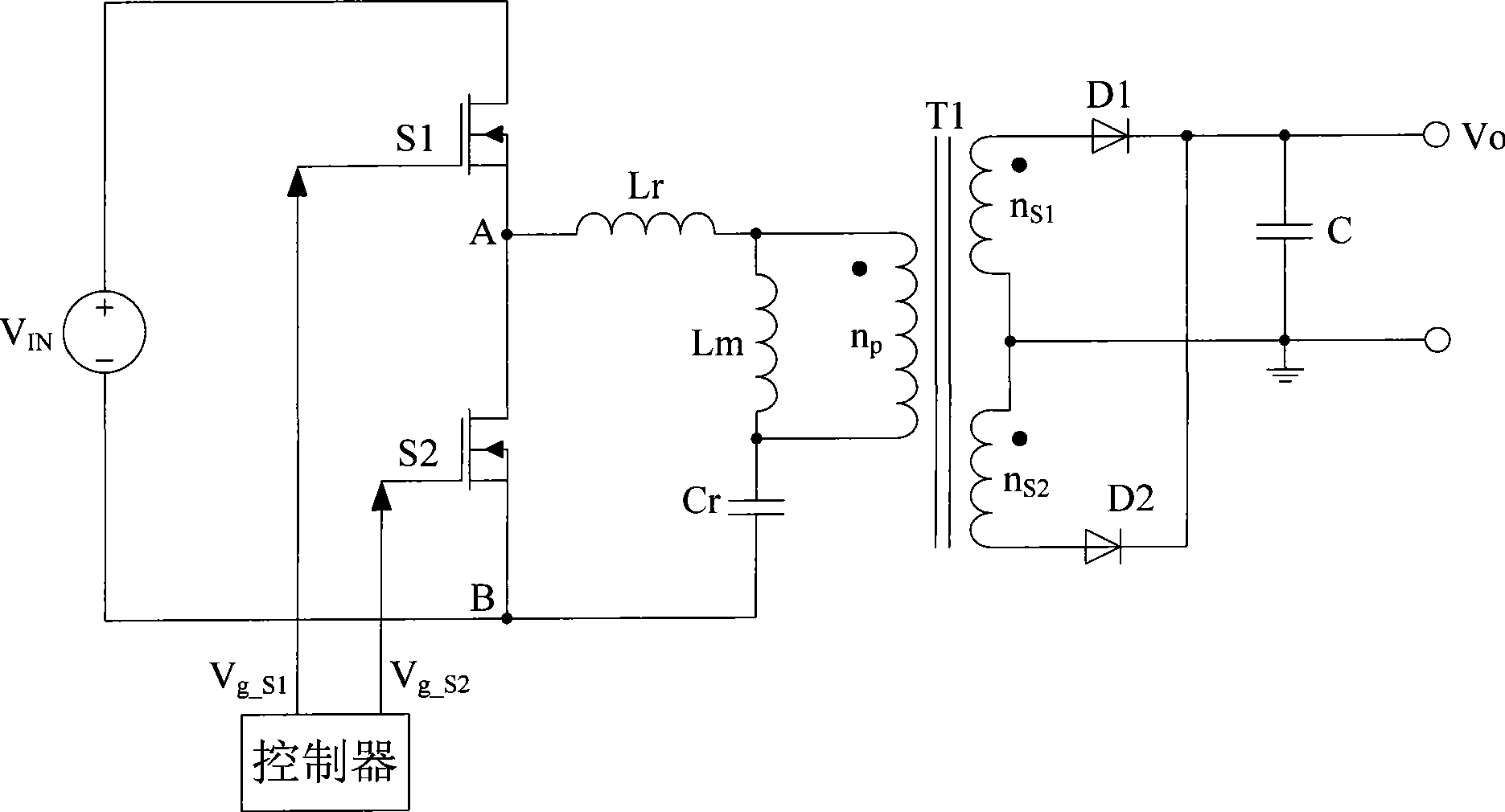
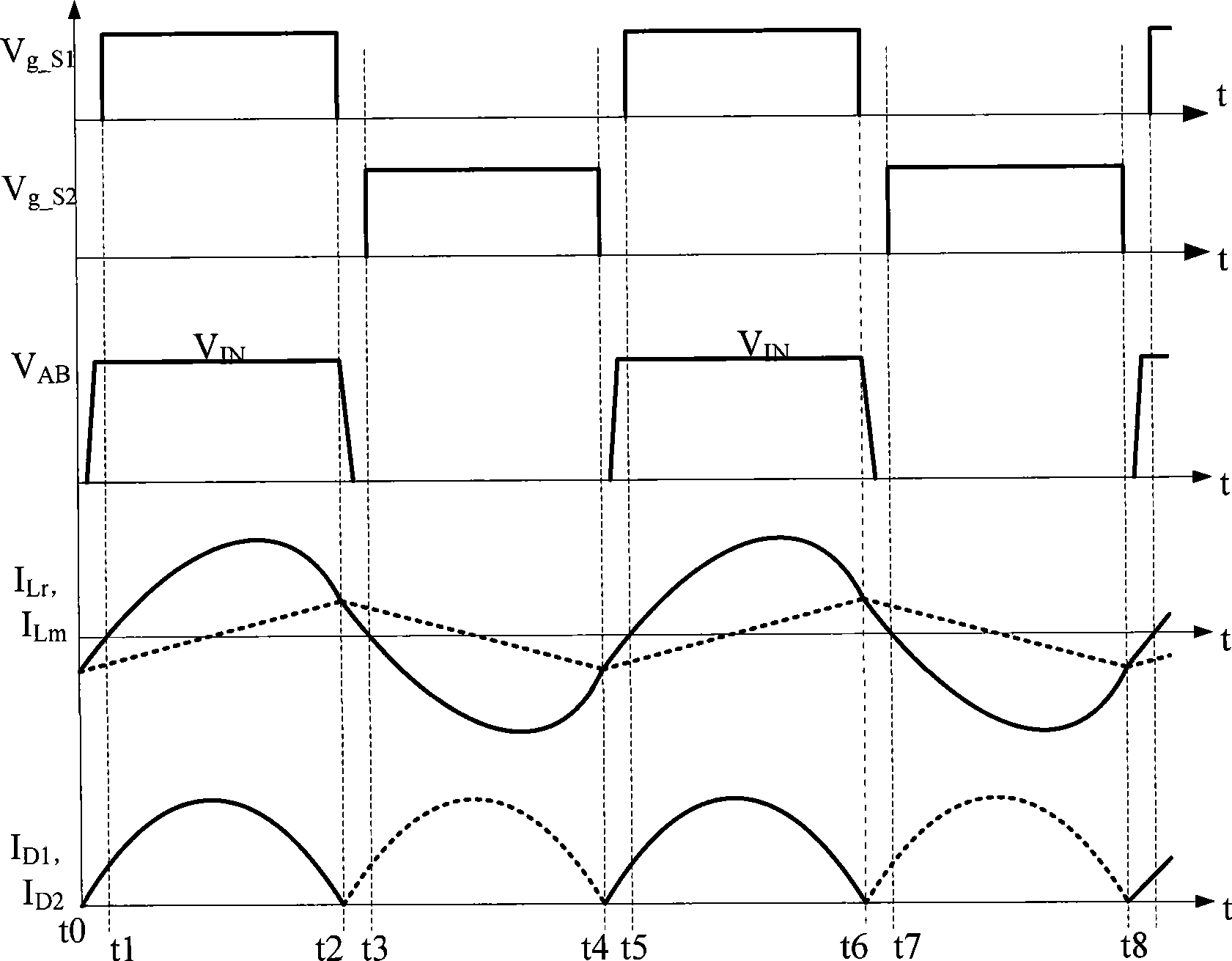
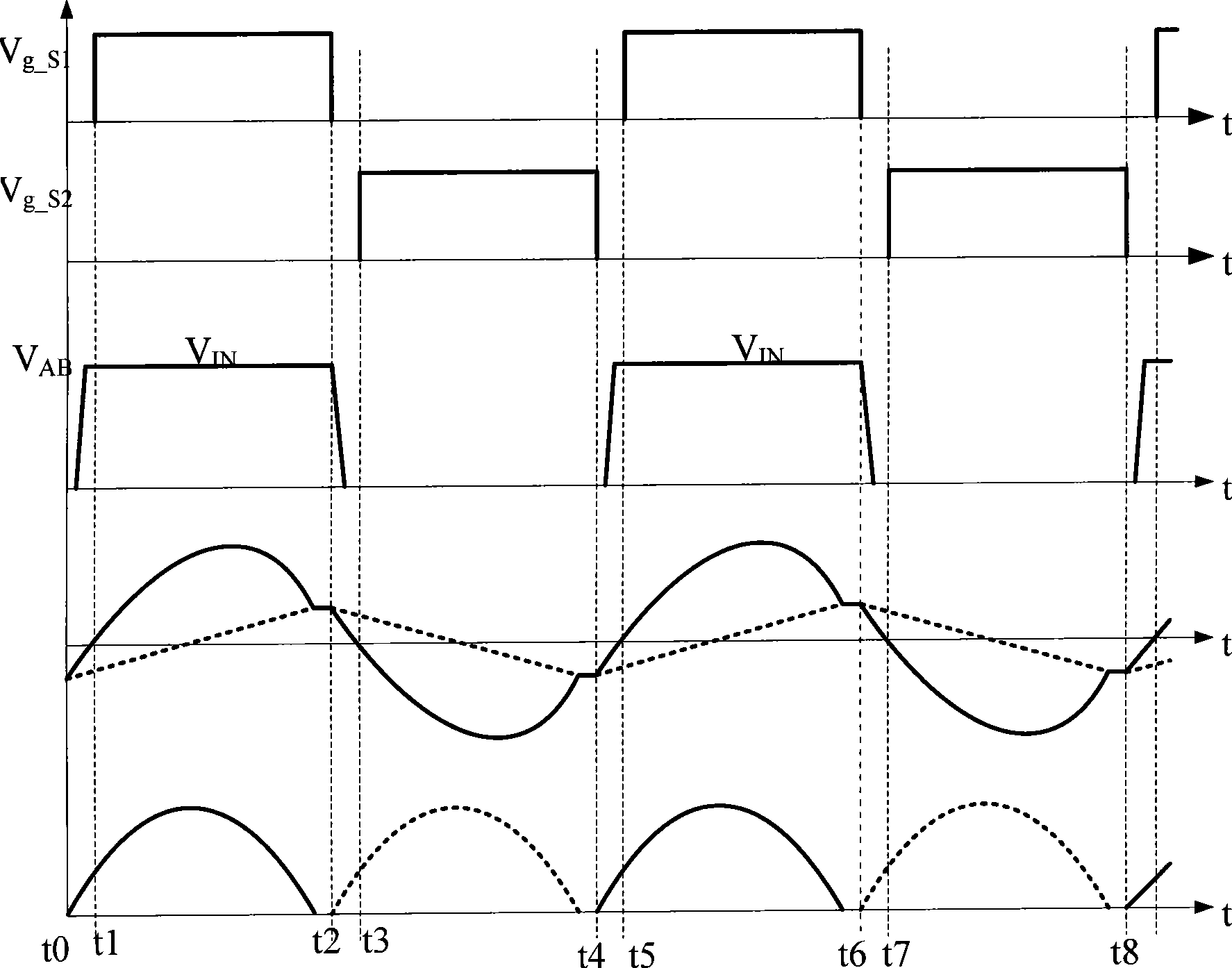
Series resonance inverter and implementation method thereof
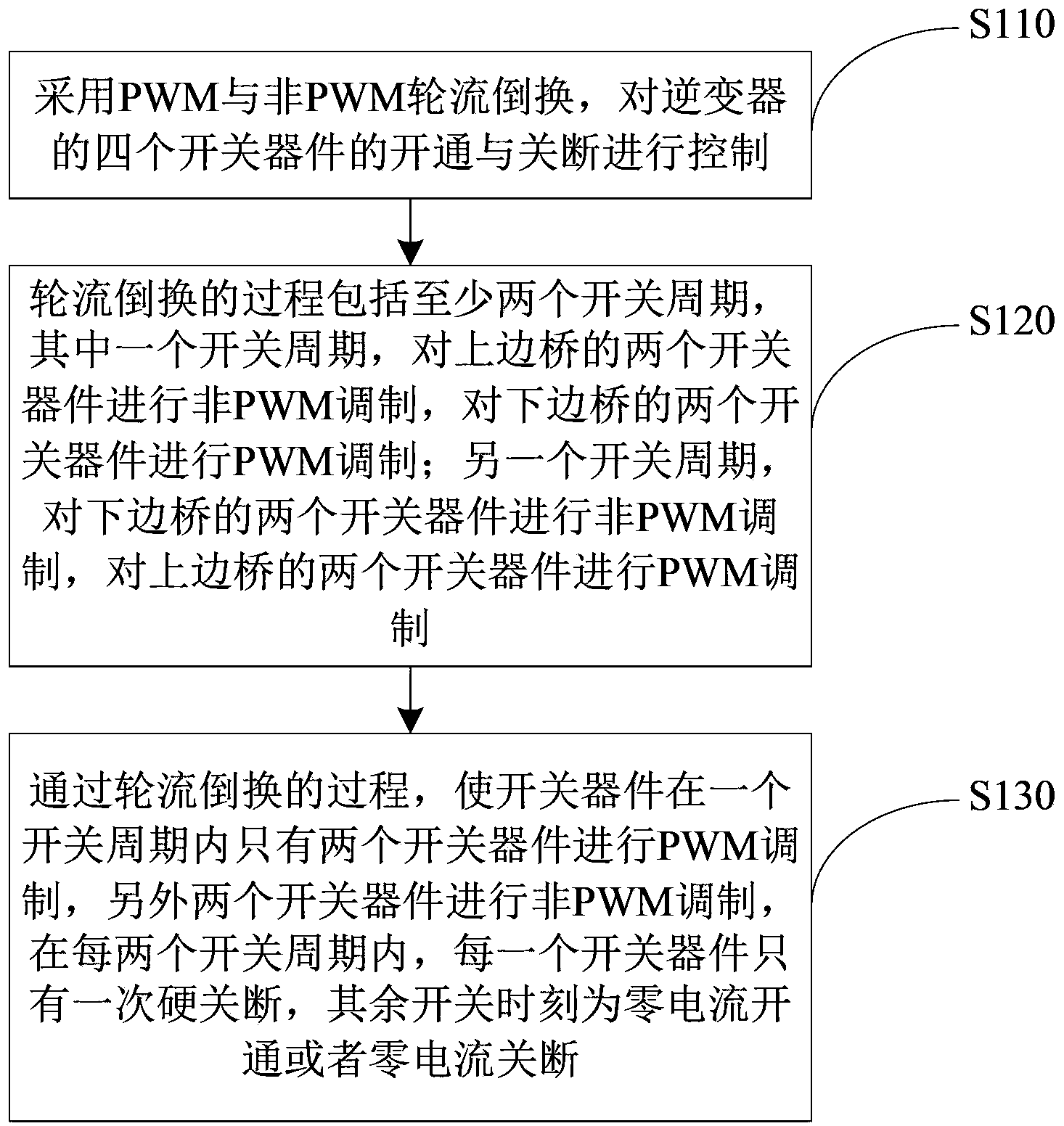
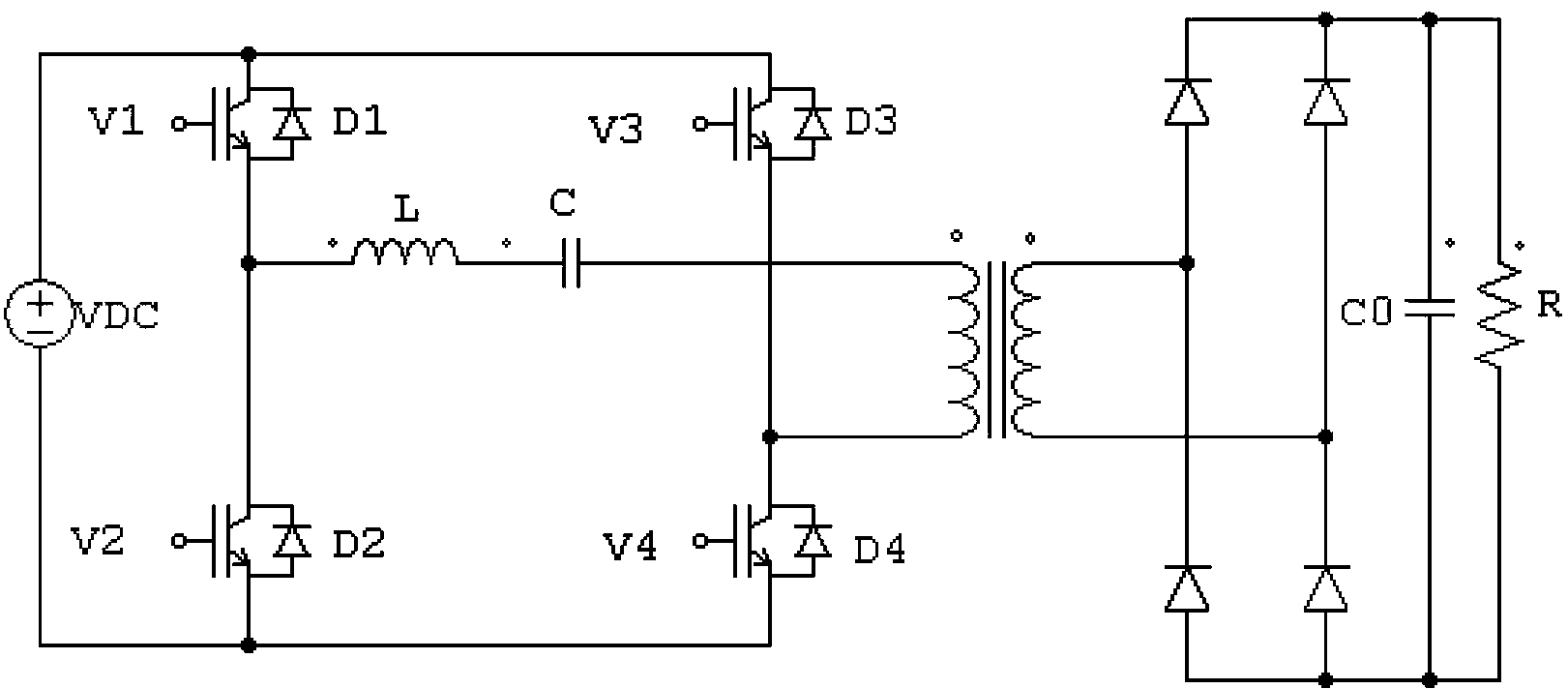
The invention provides a series resonance inverter and an implementation method of the series resonance inverter. The implementation method of the series resonance inverter comprises the steps that control over starting and stopping of four switching devices of the series resonance inverter is carried out through alternate switching between PWM modulation and non-PWM modulation, wherein the starting frequency and the stopping frequency of the switching devices are adjusted according to resonance current. The process of alternate switching comprises at least two switching periods, wherein in one of the switching periods, two paths of driving signals are used for driving two switching devices of an upper edge bridge to carry out non-PWM modulation so that the two switching devices can work with a preset duty ratio, the other two paths of driving signals are used for driving two switching devices of a lower edge bridge to carry out PWM modulation; in the other switching period, the two paths of driving signals are used for driving the two switching devices of the lower edge bridge to carry out non-PWM modulation so that the two switching devices can work with the preset duty ratio, and the other two paths of driving signals are used for driving the two switching devices of the upper edge bridge to carry out PWM modulation. The series resonance inverter and the implementation method of the series resonance inverter can be beneficial to achieving loss balance of the switching devices and the design of heat dissipation structures of the switching devices.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
Device for feeding electrical energy from an energy source
InactiveUS7672149B2Improve efficiencyLow costDc network circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionResonant inverterEngineering
A device (1) for feeding electrical energy from an energy source with variable source voltage into an electric power supply network (15), said device (1) including a transformer (112) for galvanic isolation, a resonant inverter (11) with semi-conductor switches (a-d; A, B), one or several resonant capacitors (17; 18, 19; 20, 21) and one rectifier (113), is intended to provide high efficiency and have galvanic isolation. This is achieved in that the resonant inverter (11) is operated in the full resonant mode if the operating voltage is in an operation point (MPP) and in the hard-switching mode if the voltages exceed the operation point (MPP).
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
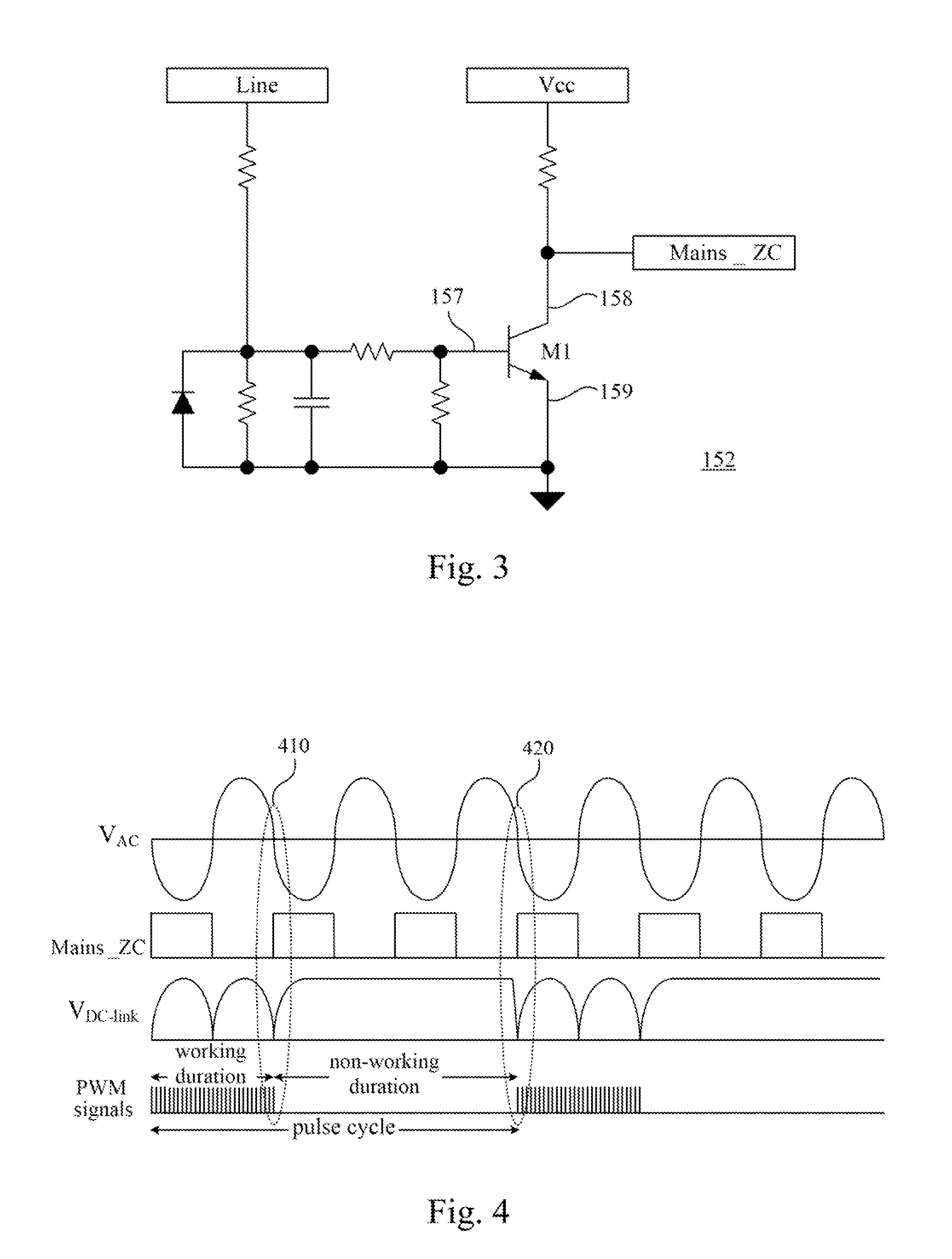
System and method for controlling quasi-resonant inverter and electric heating device employing the same
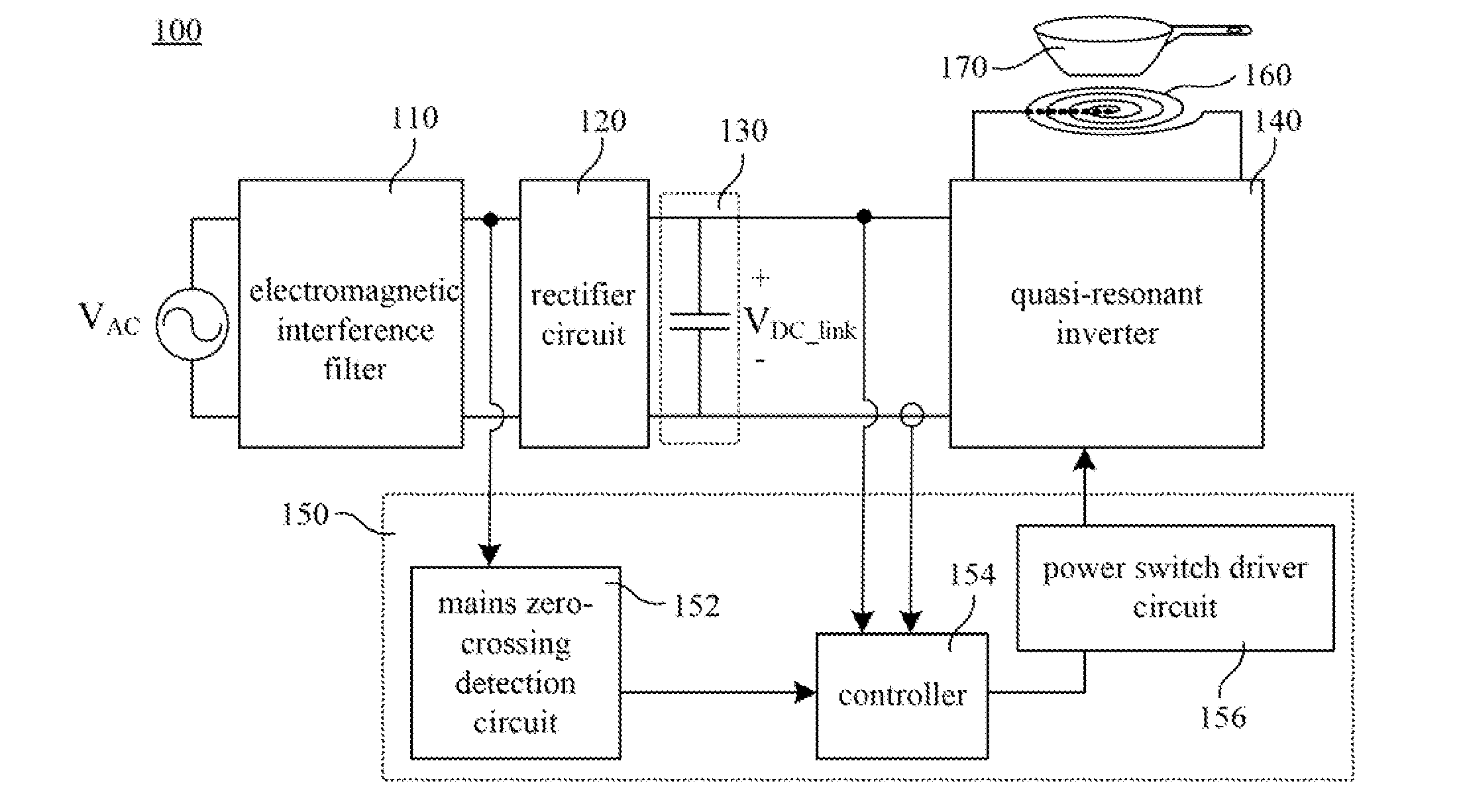
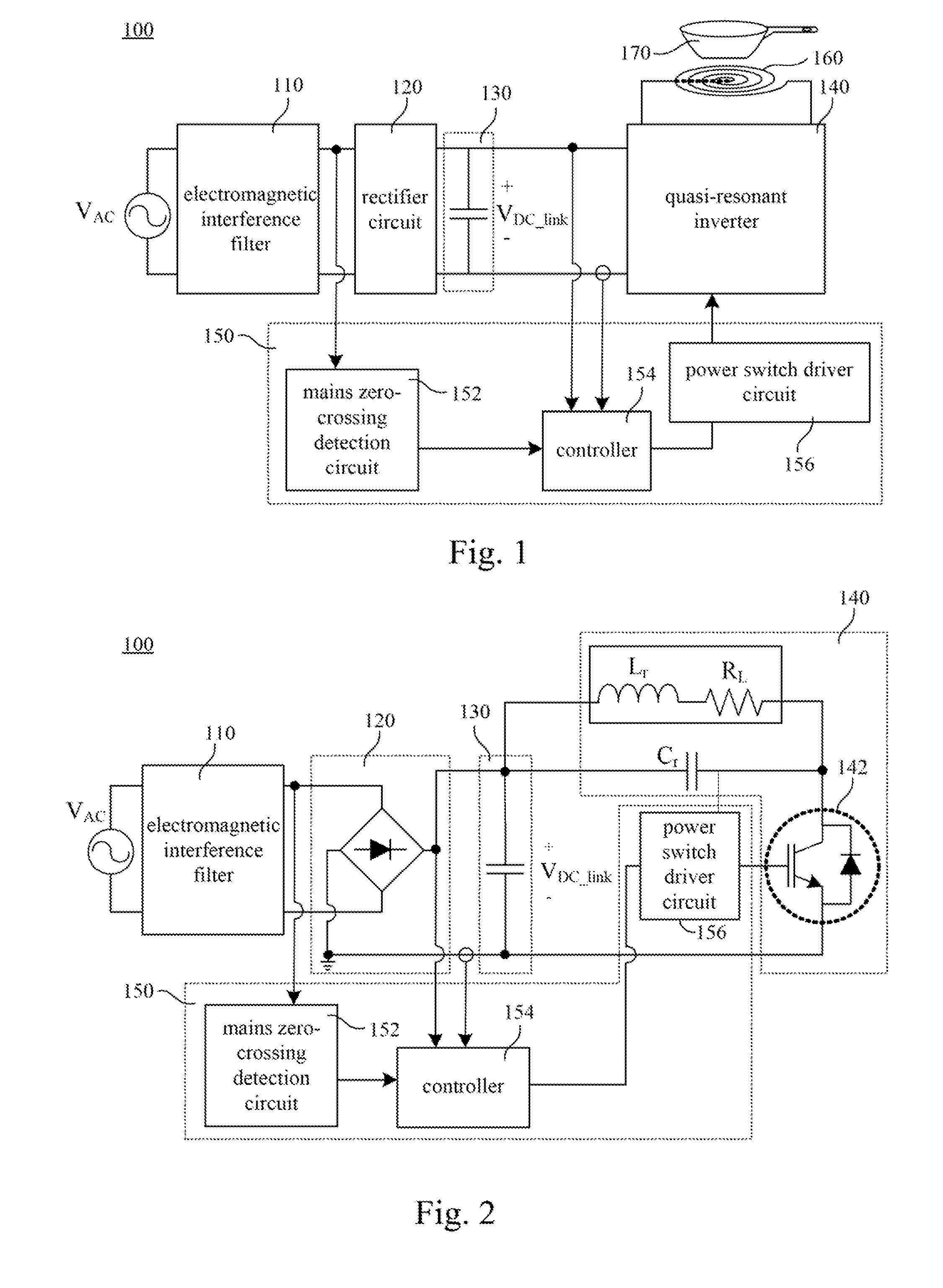
InactiveUS20120187107A1Improve the problemAvoid significant variation of temperatureEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionResonant inverterElectricity
A quasi-resonant inverter control system includes a mains zero-crossing detection circuit and a controller. The mains zero-crossing detection circuit is operable to detect a plurality of zero-crossing points of an input alternating-current voltage and output a zero-crossing detection signal based on the zero-crossing points. The controller is operable to control a plurality of burst mode period and receives the zero-crossing detection signal. Each of the burst mode periods includes a working duration and a non-working duration. Each of the working durations includes a start point and an end point. The controller is operable to determine the start points and the end points of the working durations based on the zero-crossing detection signal and outputs a control signal based on the start points and the end points of the working durations. An electric heating device and a method for controlling the quasi-resonant inverter are also disclosed herein.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
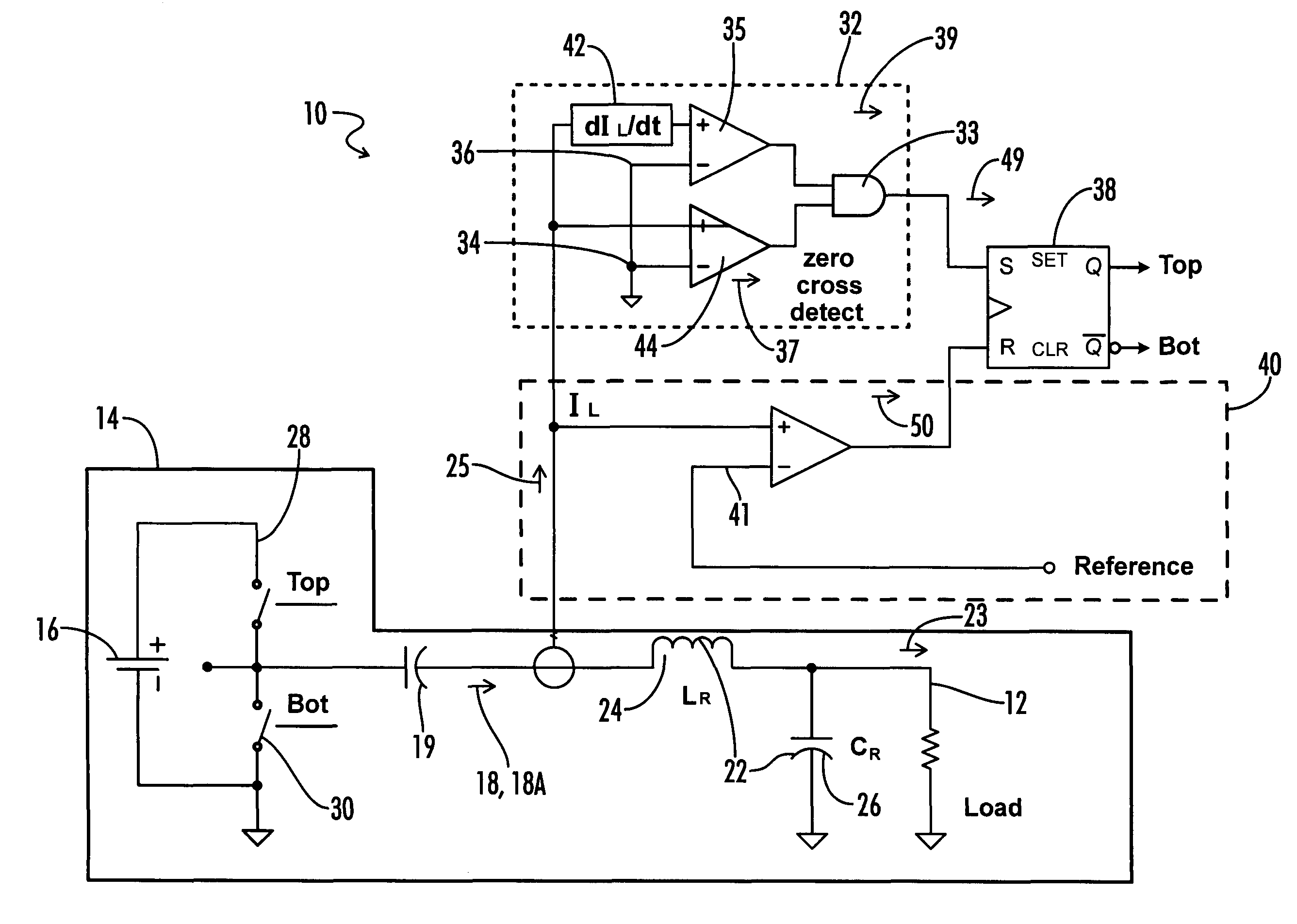
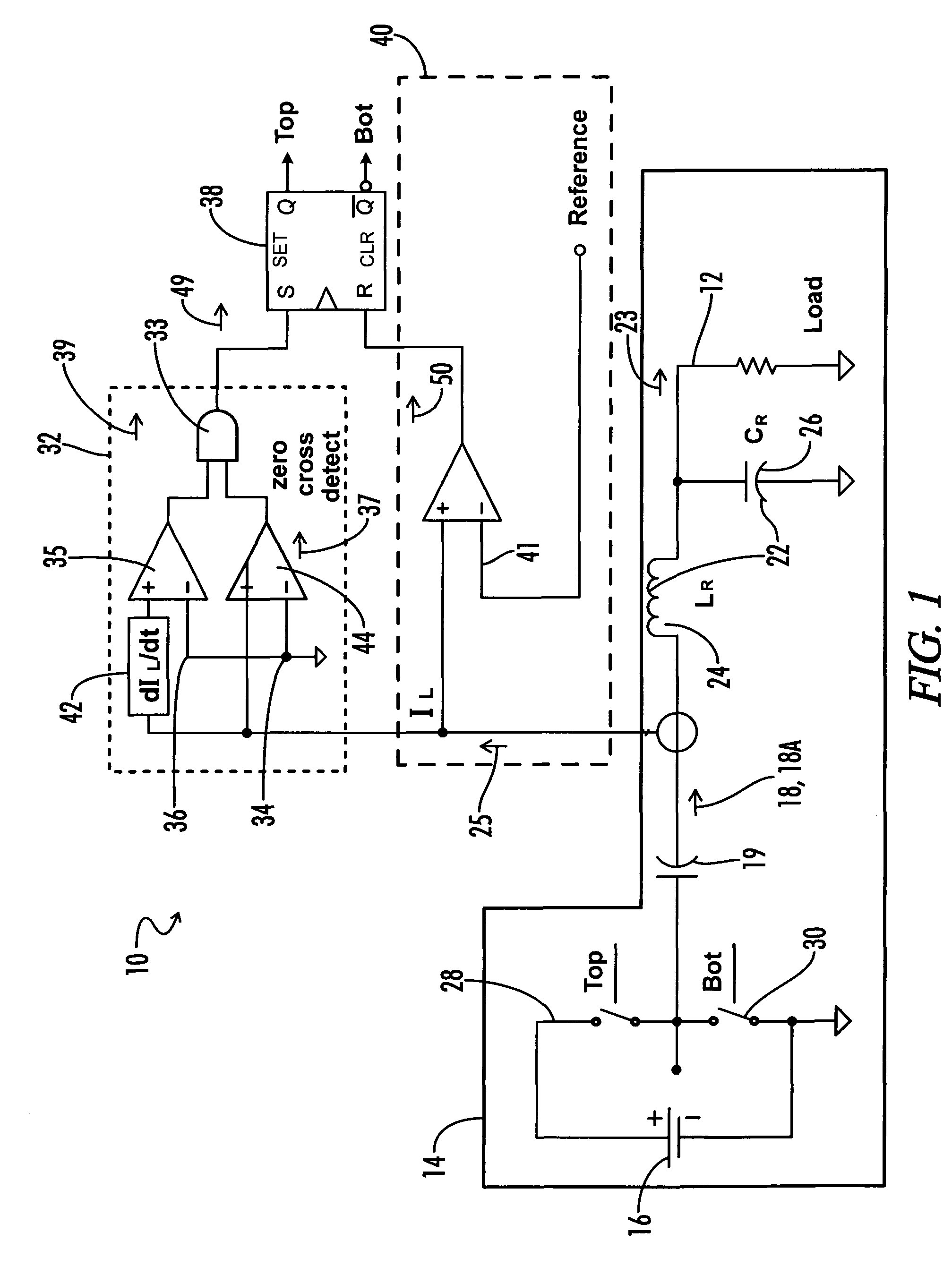
Feedback circuit and method of operating ballast resonant inverter
InactiveUS6906473B2Conducive to stable operationElectric light circuit arrangementGas discharge lamp usagePower inverterGas-discharge lamp
A ballast resonant inverter with a self-oscillating driver IC powers and dims a gas discharge lamp. A feedback circuit automatically adjusts IC oscillator frequency for safe and stable inverter operation above the resonant frequency following changes in the resonant load. The feedback signal is derived from resonant inverter output voltage, by attenuating, programmed phase shifting and injecting the resulting signal in a timing circuit of the IC. The feedback circuit includes an active inverter circuit or passive RC phase boosting networks coupled in series. Phase control of the feedback signal by variable RC networks is used in transient modes of ballast-lamp operations.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
High voltage pulse generator
ActiveUS7209373B2Efficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionResonant inverterHigh pressure
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
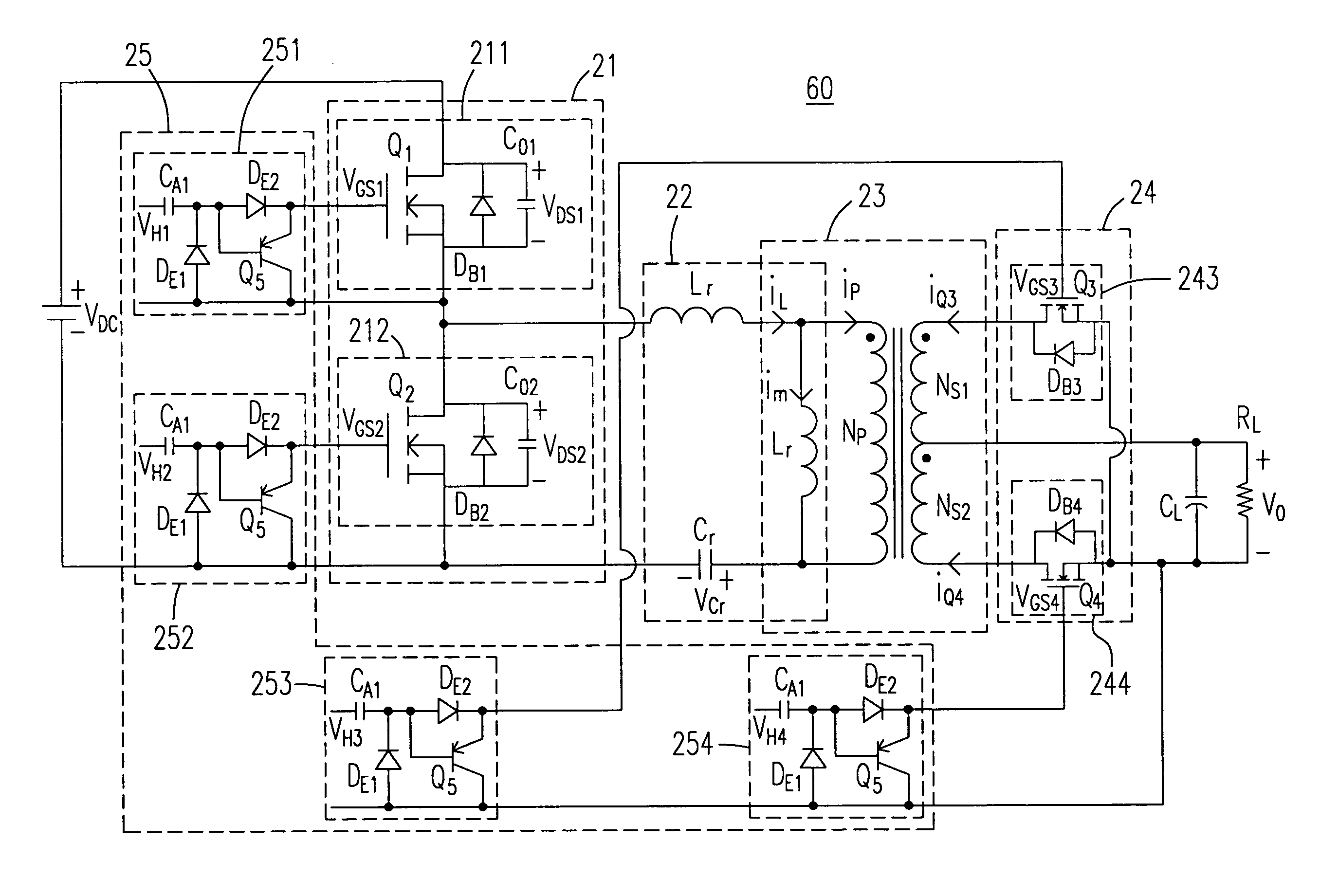
Resonant converter with synchronous rectification drive circuit
InactiveUS7706156B2Improve efficiencyShorten the overall cycleEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionResonant inverterFull wave
The present invention provides a resonant converter with a synchronous rectification drive circuit. The resonant converter with the synchronous rectification drive circuit includes a switch circuit, a resonant circuit, a transformer, a full-wave-rectifier circuit and a synchronous rectification drive circuit, wherein the switch circuit at least includes a half-bridge circuit, the resonant circuit is coupled to the switch circuit and has a resonant frequency, the transformer has a primary side coupled to the resonant circuit, the full-wave-rectifier circuit is coupled to a secondary side of the transformer and includes two switches, the synchronous rectification drive circuit includes four voltage-clamped drive circuits having output terminals coupled to the switch circuit and the corresponding switch of the full-wave-rectifier circuit, and each voltage-clamped drive circuit includes a transmission / discharge circuit for reducing the turn-off period of the coupled switch during turning off the coupled switch.
Owner:TUNGNAN INST TECH
Resonant DC converter
InactiveUS20140112026A1High voltage conversionSoft switchingEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionResonant inverterCapacitance
A resonant DC converter, combines a voltage type auto charge pump circuit with a full-bridge or half-bridge resonant DC conversion circuit at a primary side of a transformer, combines a double-voltage rectifier circuit at a secondary side of the transformer, and grants the circuit of the invention with characteristics of variable circuit architecture by means of the design of circuit parameters and the action of the LC resonant circuit. Integration of switching elements of the converter circuit and the use of characteristics of automatically changing the circuit architecture contribute to reduce the switching losses and increase the circuit conversion efficiency. Low output voltage ripple enables the circuit of the invention to avoid using large-capacitance electrolytic capacitors and be able to extend the service life of the transformer. The operation of the circuit of the invention at boost or buck mode can be controlled by adjusting the circuit parameters.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for universal metallurgical simulation and analysis
InactiveUS20050151306A1High degree of accuracyHigh precisionPreparing sample for investigationBlast furnace detailsResonant inverterControl system
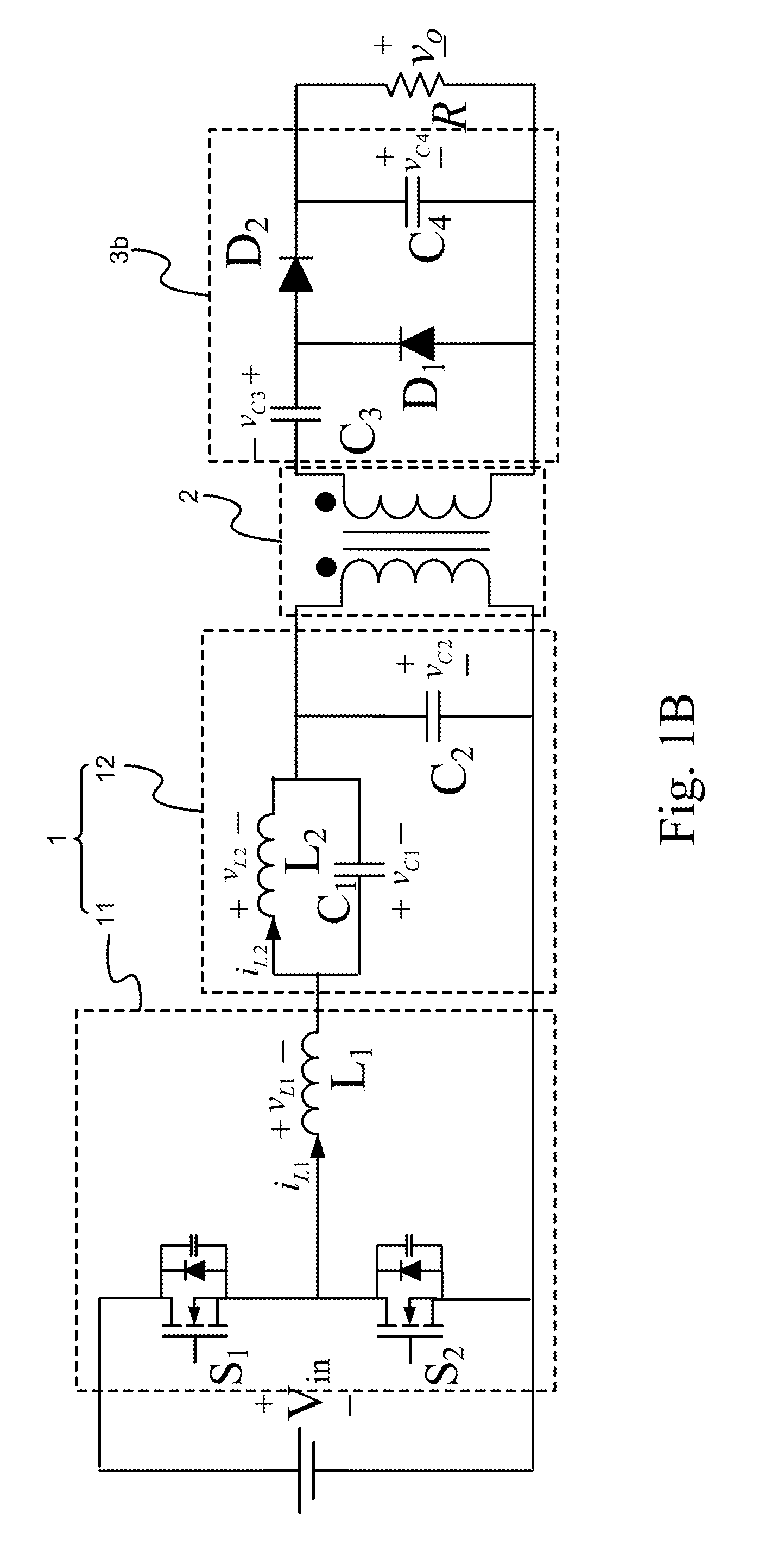
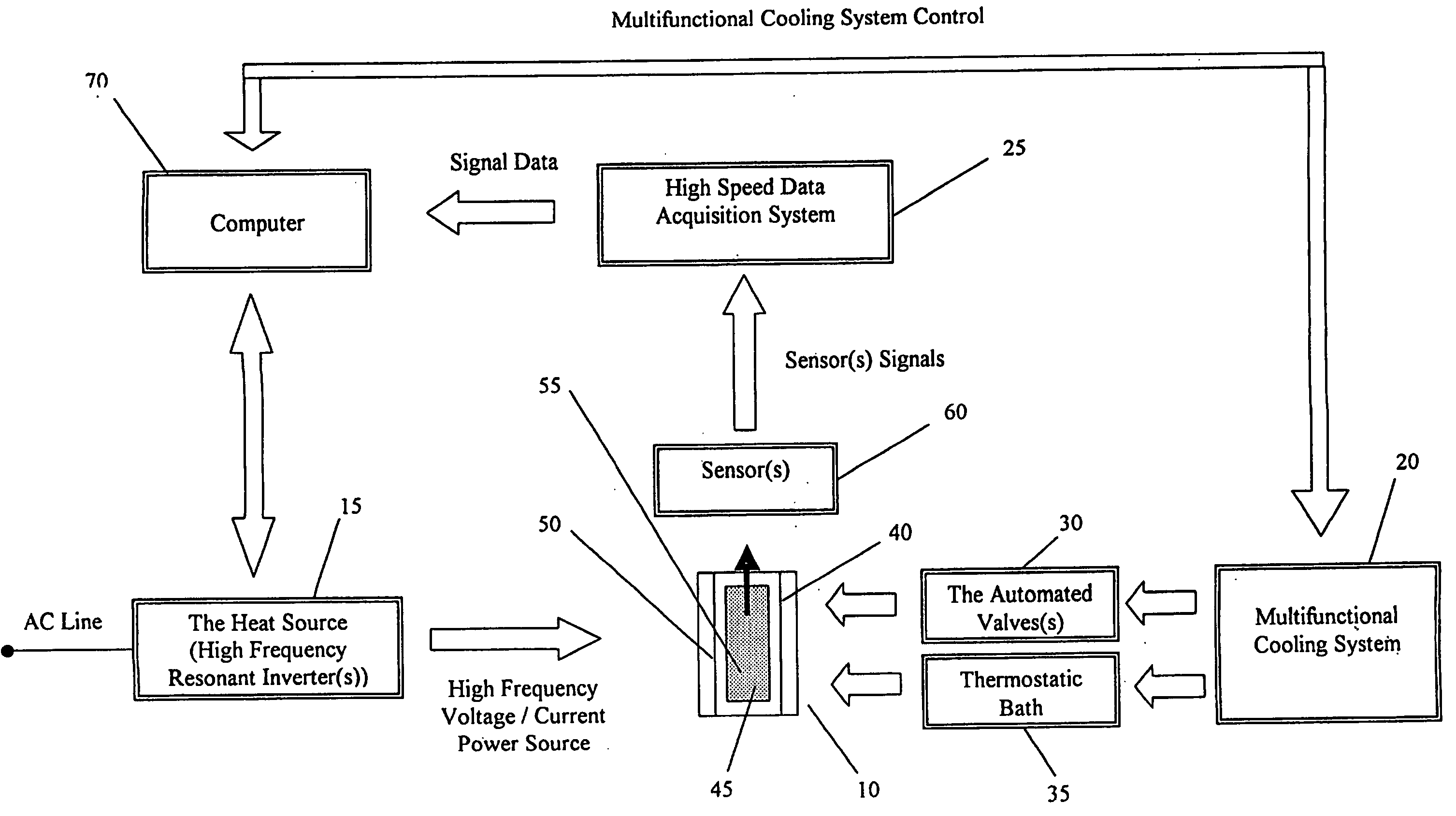
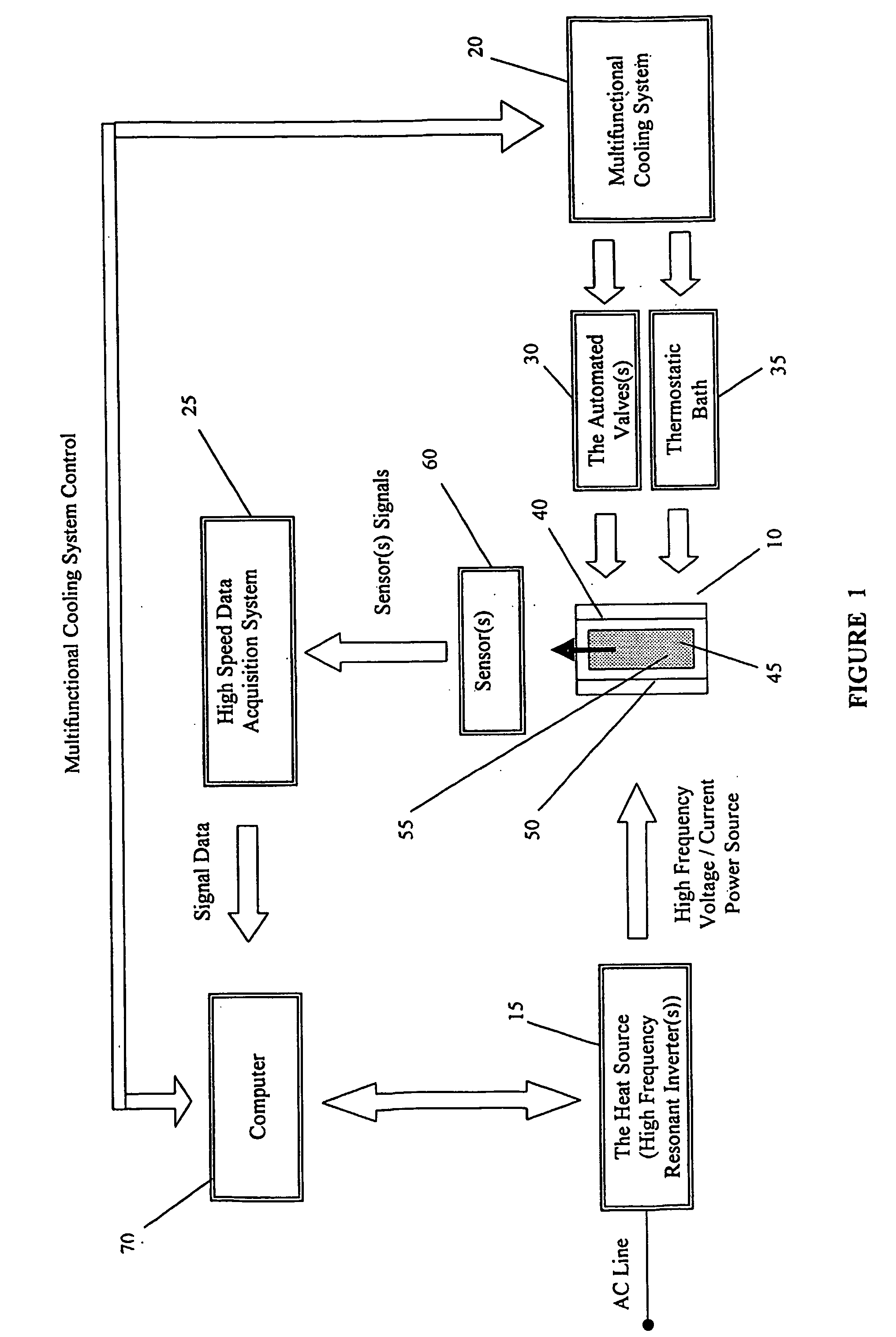
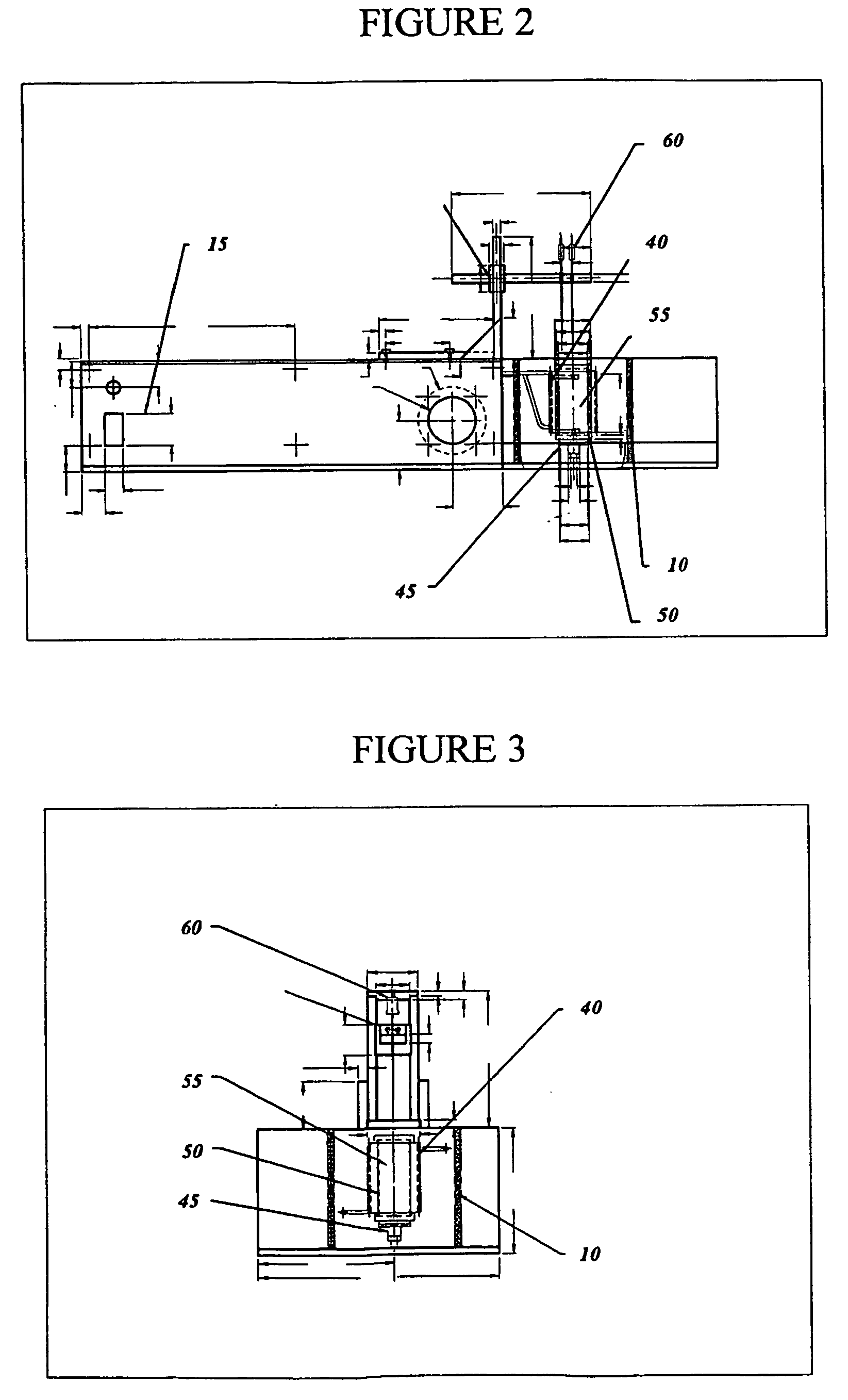
A method and apparatus (5) for simulating and analyzing industrial thermal processes, including industrial heat-treatment, processes, melting, solidification, quenching and the like, used in the manufacture of metals, alloys and metal matrix composite components. The apparatus (5) includes an optional environmental chamber (10) used for situations where testing room conditions are too hot or too cold and would thus interfere with operation of the apparatus (5) without such chamber (10). The apparatus (5) includes a multifunctional excitation coil (40) that serves the function of the omitted environmental chamber (10). The apparatus (5) also includes one or more high frequency resonant inverters (15) and a cooling means (20). The apparatus (5) integrates melting and thermal processing capabilities with a thermal analyzer and a control system. The apparatus (5) allows for the rapid design and optimization of industrial thermal processes used in the manufacture of metallurgical engineering material with superior structural and metallurgical chactacterics, suitable for advanced component service performance.
Owner:SOKOLOWSKI JERZY H +3
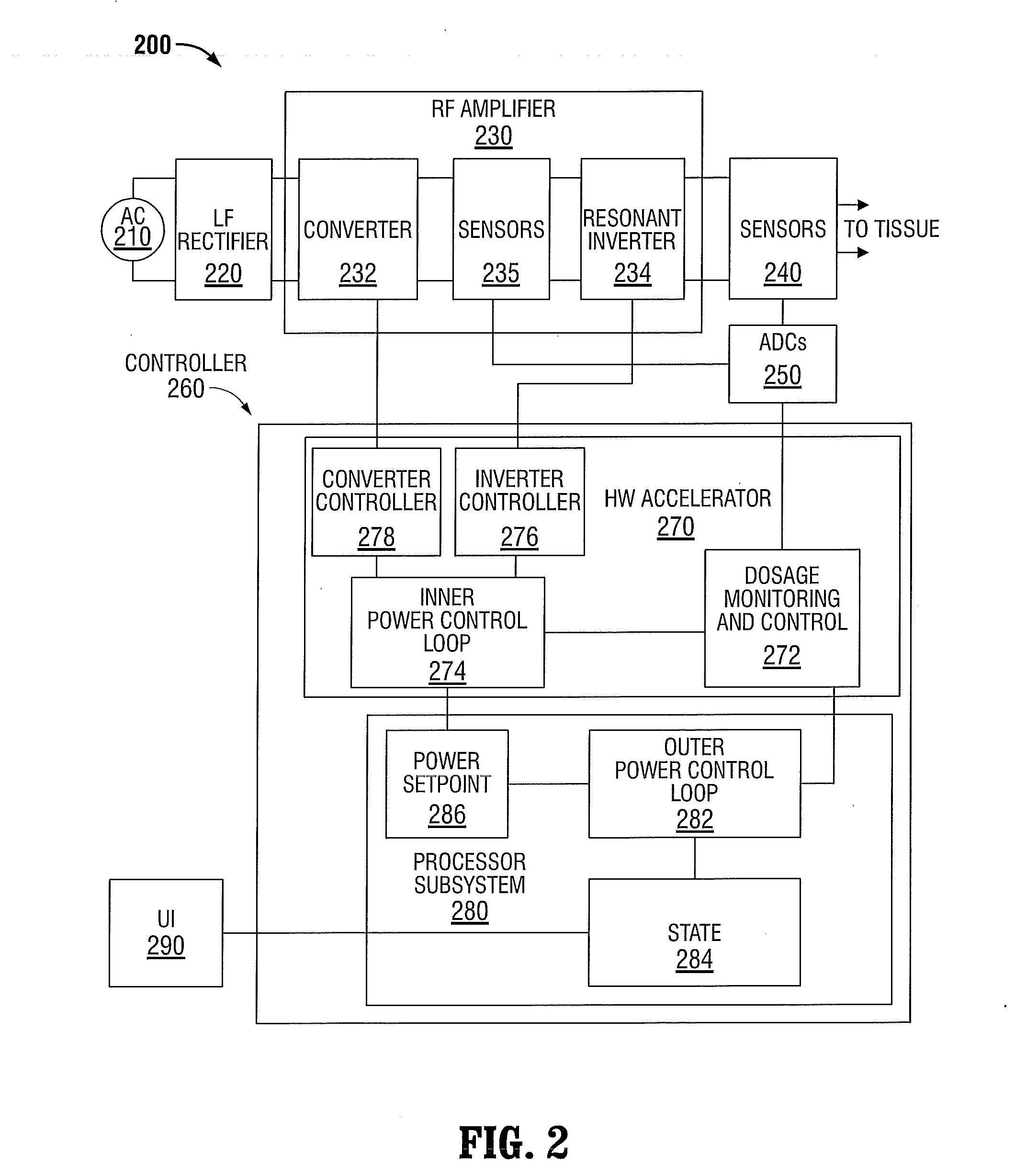
Systems and methods for generating electrosurgical energy using a multistage power converter
ActiveUS20150032096A1Good dynamic responseReduce heat spreadAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionResonant inverterElectricity
The electrosurgical systems and methods according to the present disclosure use a multi-stage power converter for generating electrosurgical energy. The electrosurgical systems include an electrosurgical generator having a power converter coupled to an electrical energy source and configured to generate electrosurgical energy. The power converter includes a boost converter configured to convert a first direct current from the electrical energy source to a second direct current, and a phase-shifted pulse width modulation (PS-PWM) resonant inverter configured to invert the second direct current to an alternating current. The electrosurgical generator also includes a plurality of sensors configured to sense a voltage and a current of the generated electrosurgical energy and a controller coupled to the power converter and the plurality of sensors. The controller includes a signal processor configured to determine tissue impedance based on the sensed voltage and current, and an output controller configured to select one of a plurality of output characteristics based on the determined tissue impedance, and to generate control signals to control the boost converter and the PS-PWM resonant inverter, according to the selected output characteristic.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
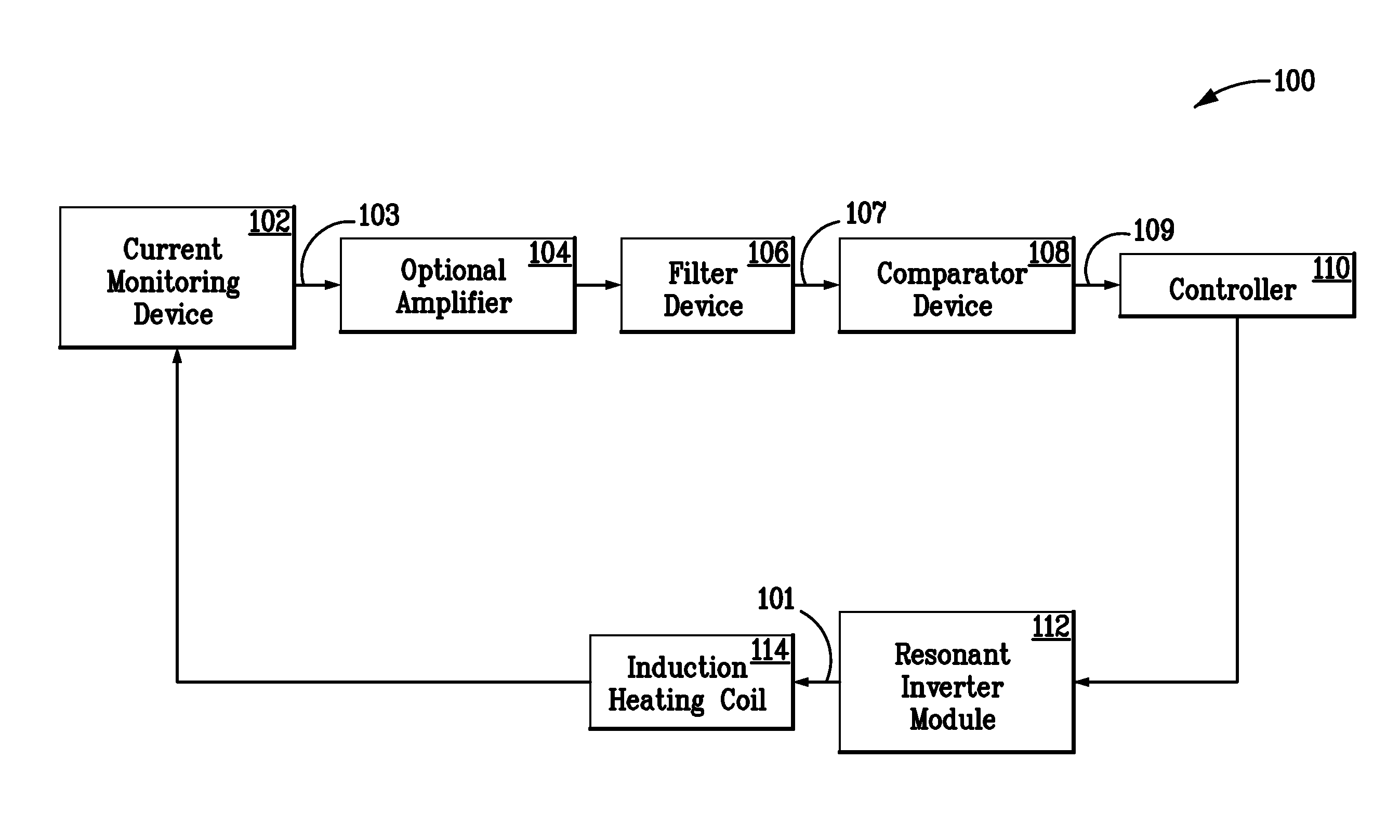
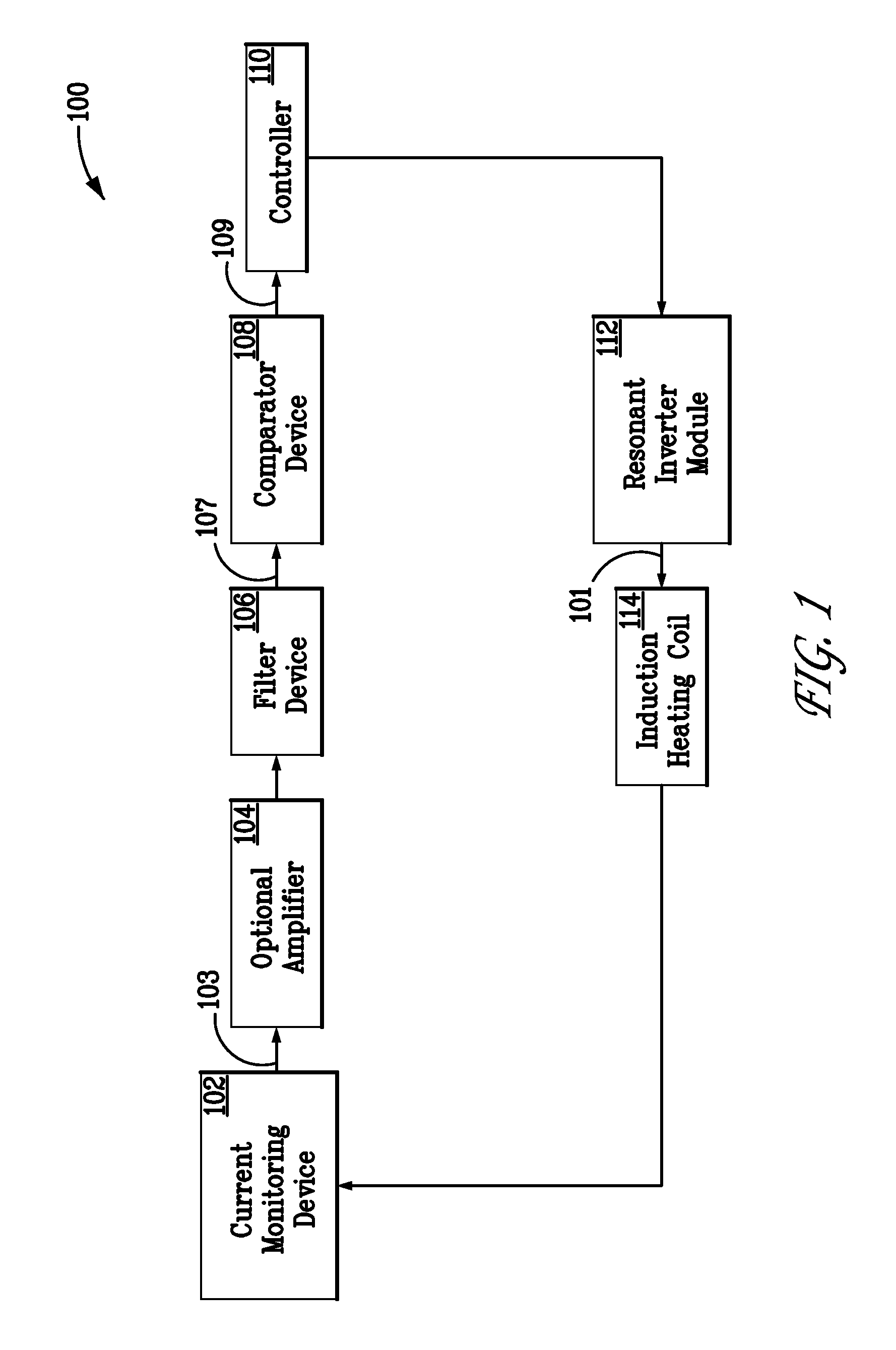
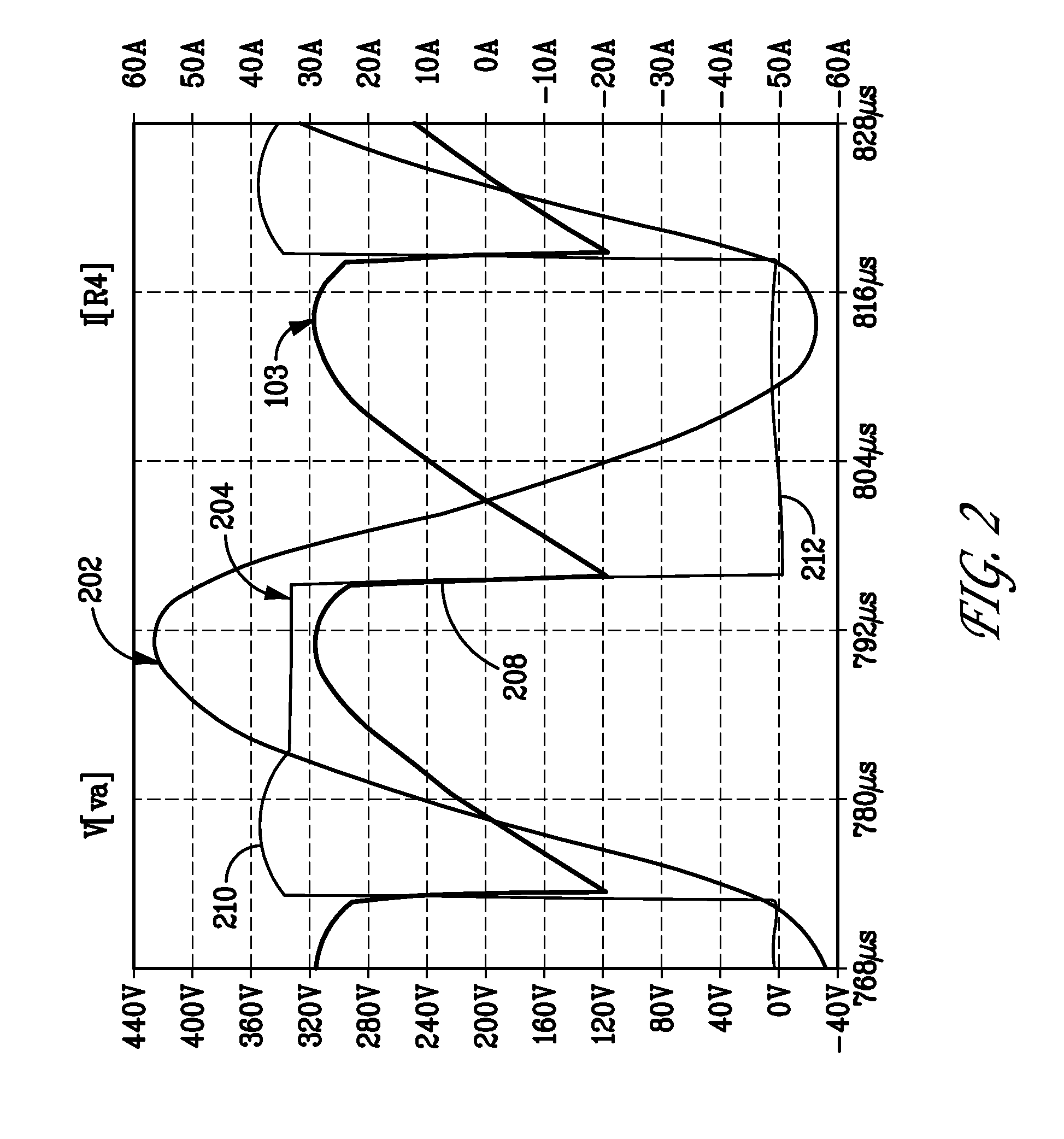
Resonant frequency detection for induction resonant inverter
An induction heating system includes an induction heating coil operable to inductively heat a load with a magnetic field, a detector for detecting a current feedback signal corresponding to a current flowing through the induction heating coil, and a controller for detecting a switching transient in the current feedback signal and determining a resonant frequency of the system based on a characteristic of the switching transient.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
Method of operating a resonant inverter using zero current switching and arbitrary frequency pulse width modulation
InactiveUS7800928B1Increase output impedanceExtended maintenance periodConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionResonant inverterGas-discharge lamp
A method of controlling a series-resonant, half-bridge inverter includes turning off the bottom switch and turning on the top switch the inverter when the current through the resonant inductor crosses the zero axis while the current is increasing, thereby insuring zero voltage switching of the inverter switches and increases the overall switching period so that the actual inverter frequency is closer to the resonant frequency of the series-resonant circuit. Using an on-time control circuit, the method further includes controlling the current delivered to the load (such as a gas discharge lamp) by varying the on-time of the top inverter switch.
Owner:UNIVERSAL LIGHTING TECHNOLOGIES
Current-mode resonant inverter circuit
InactiveUS20060193152A1Convenient lightingHigh convertion efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcResonant inverterElectrical polarity
A high conversion efficiency inverter circuit by providing the current-mode resonant type efficient in using a power source. A current-mode resonant inverter circuit comprises a step-up transformer; the secondary winding side of the step-up transformer is composed of a resonant circuit between leakage inductance of the step-up transformer secondary winding and a capacitive component present in the secondary side circuit; one end of the step-up transformer primary winding is connected to the power source side; the other end of the primary winding is connected to a switched snubber circuit through the primary winding of a current transformer; the switched-snubber circuit comprises a pair of transistors different from each other in polarity; bases or gate of the pair of transistors, connected to each other, are connected to the secondary winding of the current transformer; either collector of the pair of transistors is connected to the primary winding of the current transformer; the other collector of the transistor is connected to the current transformer primary winding through a capacitor.
Owner:CHEN HONG FEI +1
Control system for a resonant inverter with a self-oscillating driver
ActiveUS7095183B2Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionResonant inverterPower inverter
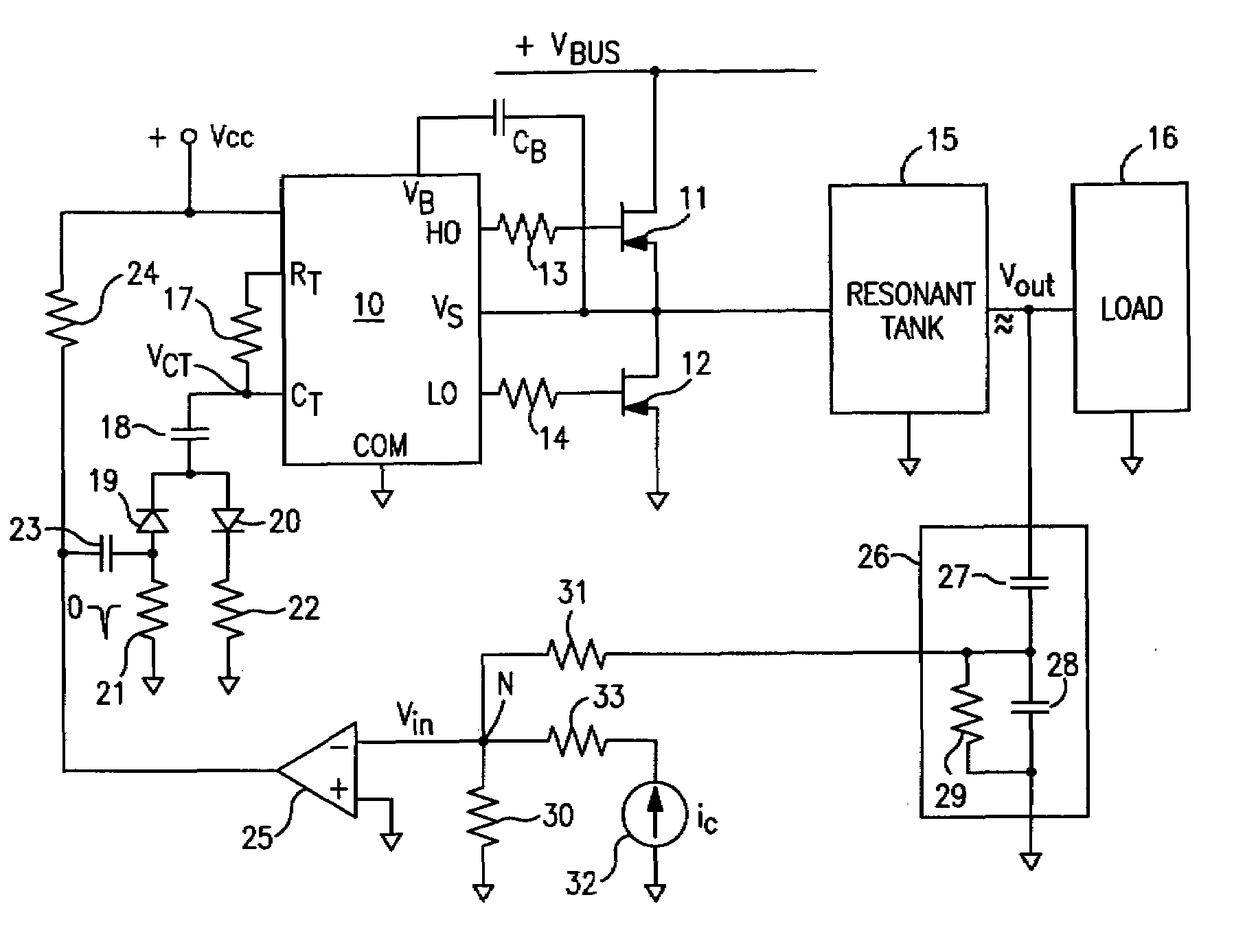
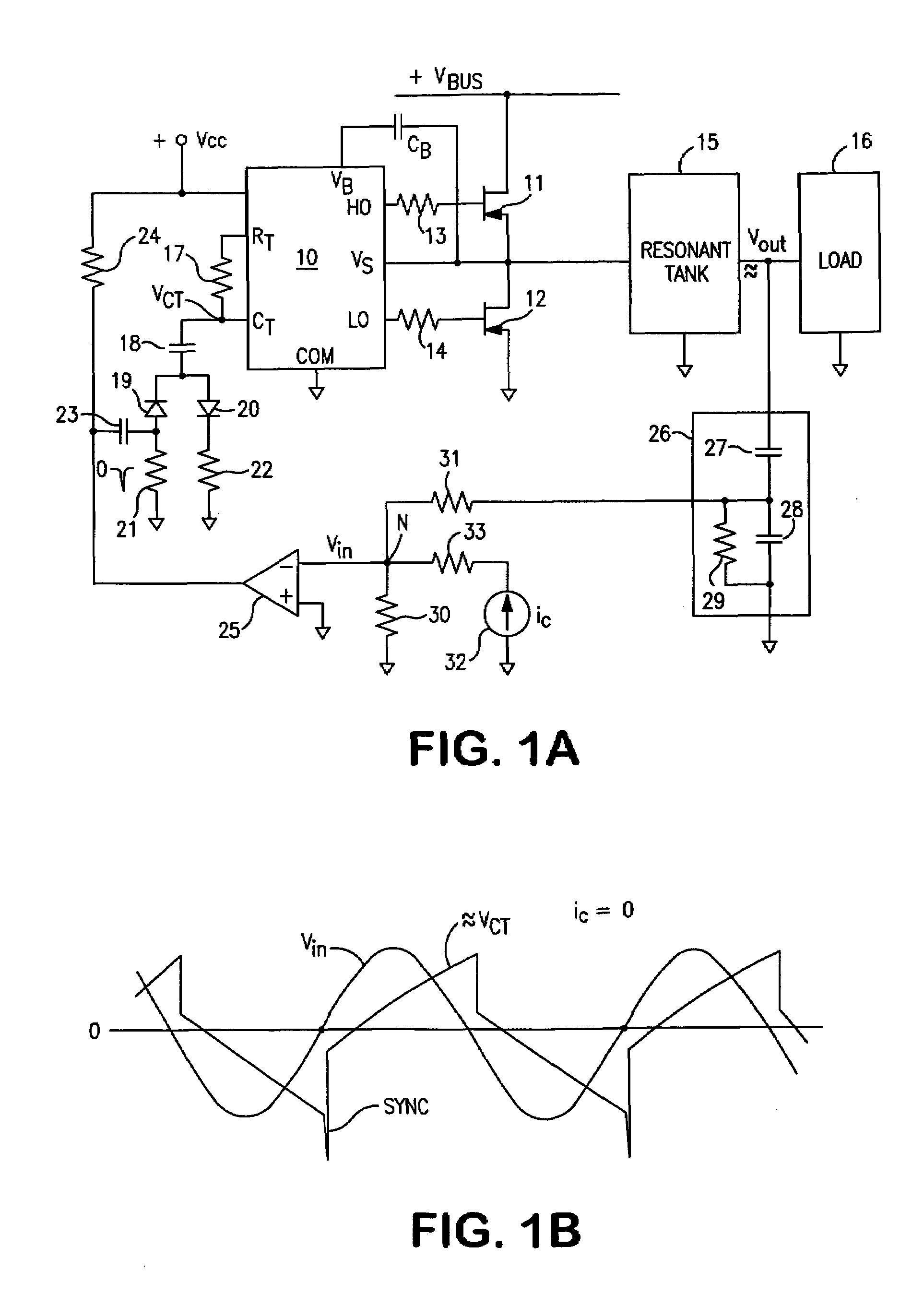
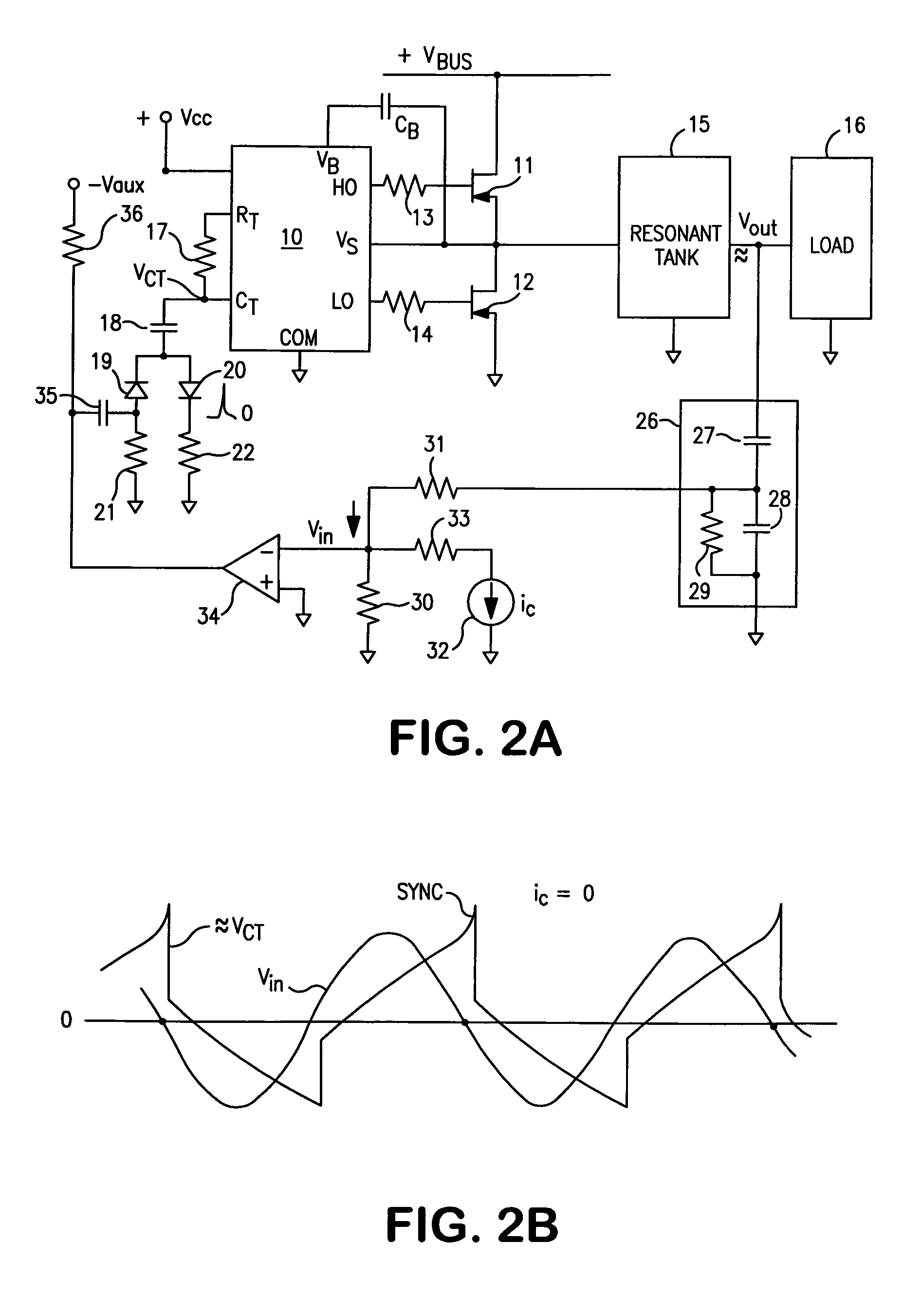
A controller for a resonant inverter with a self-oscillating driver IC for powering AC loads, such as gas discharge lamps or regulated DC / DC converters, includes a timing circuit that generates control strobe pulses that are injected into the timing circuit. The timing circuit is coupled to an inverter resonant tank through a feed back circuit providing phase lock for the resonant inverter. The feed back circuit includes a passive phase shifting circuit for 360° closed loop phase shift. Phase controlled strobe pulses automatically adjust IC oscillator frequency for safe and stable inverter operation above resonant frequency. By injecting a small AC or DC control signal into the timing circuit, sync strobe pulse phase angle can be advanced or delayed and thus frequency and power of the phase lock system can be controlled.
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
Series-Parallel Resonant Inverters
InactiveUS20110139771A1High input voltage operationHigh operating requirementsEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionResonant inverterVoltage reference
A series-parallel resonant inverter inductively couples a switchable DC power source, which has a positive reference voltage node, a negative voltage reference node and a common reference node to a load. The load comprises a parallel resonator that is inductively coupled to the work piece and a series resonator. The series and parallel resonators each preferably has impedance, where the series circuit's impedance is greater than the impedance of the parallel circuit. The series resonator could include a high impedance inductor and a DC blocking capacitor in series with each other.
Owner:HONEYWELL ASCA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com