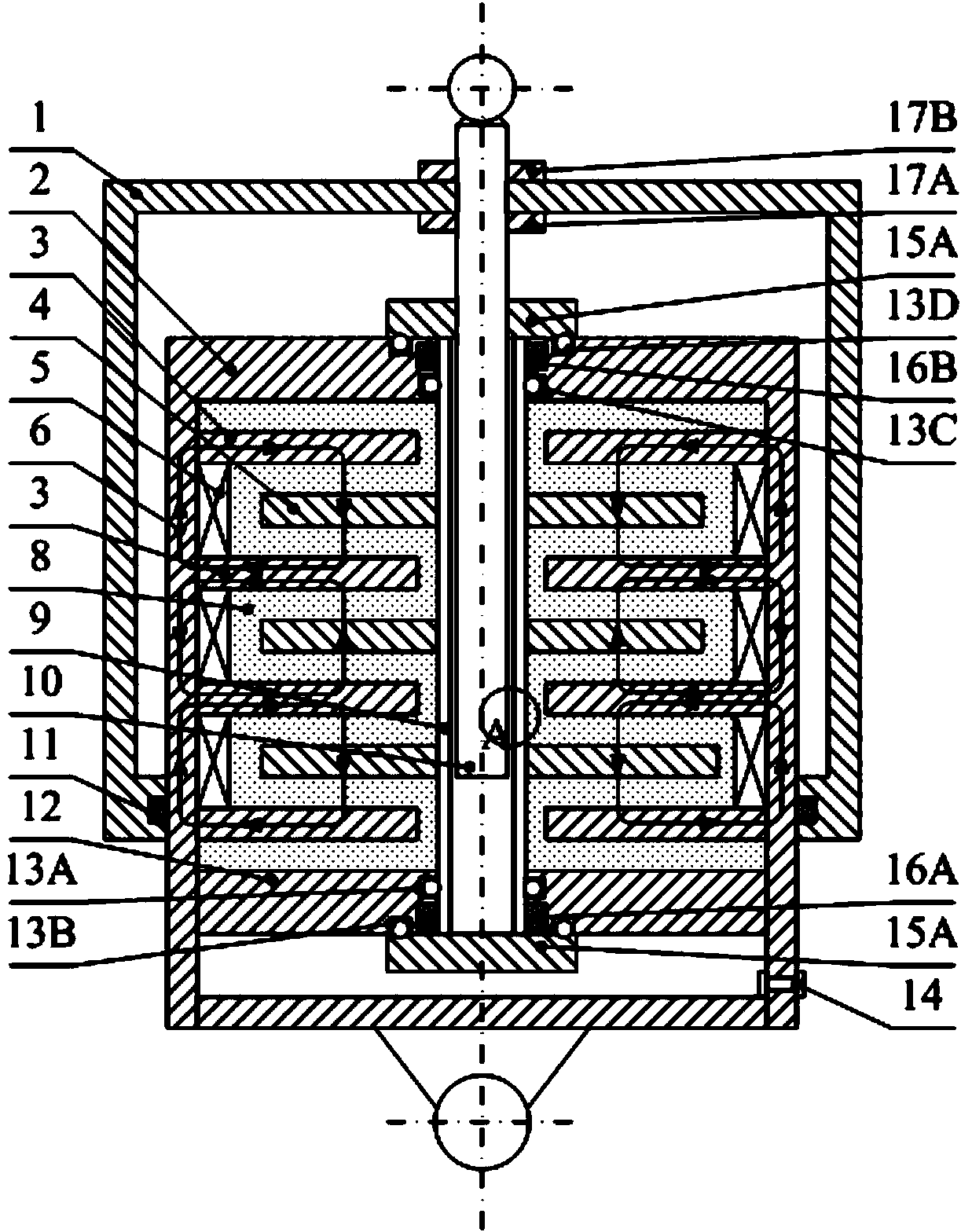
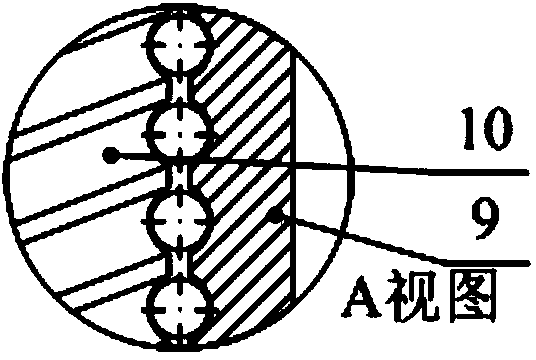
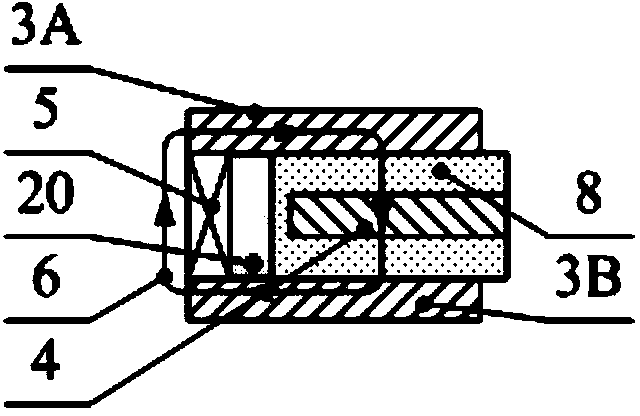
Patents
Literature
485 results about "Viscous damping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
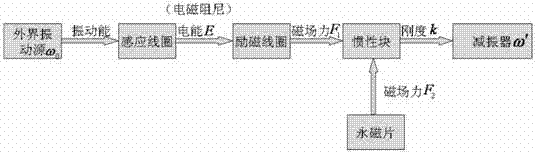
Viscous damping is a common form of damping which is formed in many engineering systems such as instruments adn shock absorbers. The viscous damping force is proportional to the first power of the velocity across the damper, and it always opposes the motion, so that the damping force is a linear continuous function of the velocity.
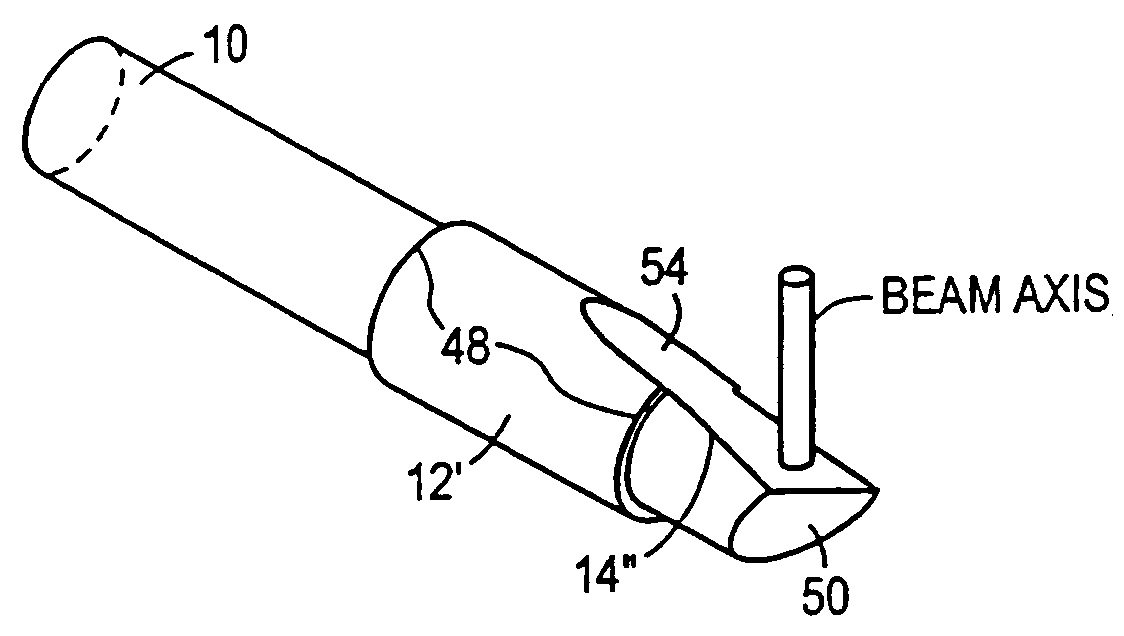
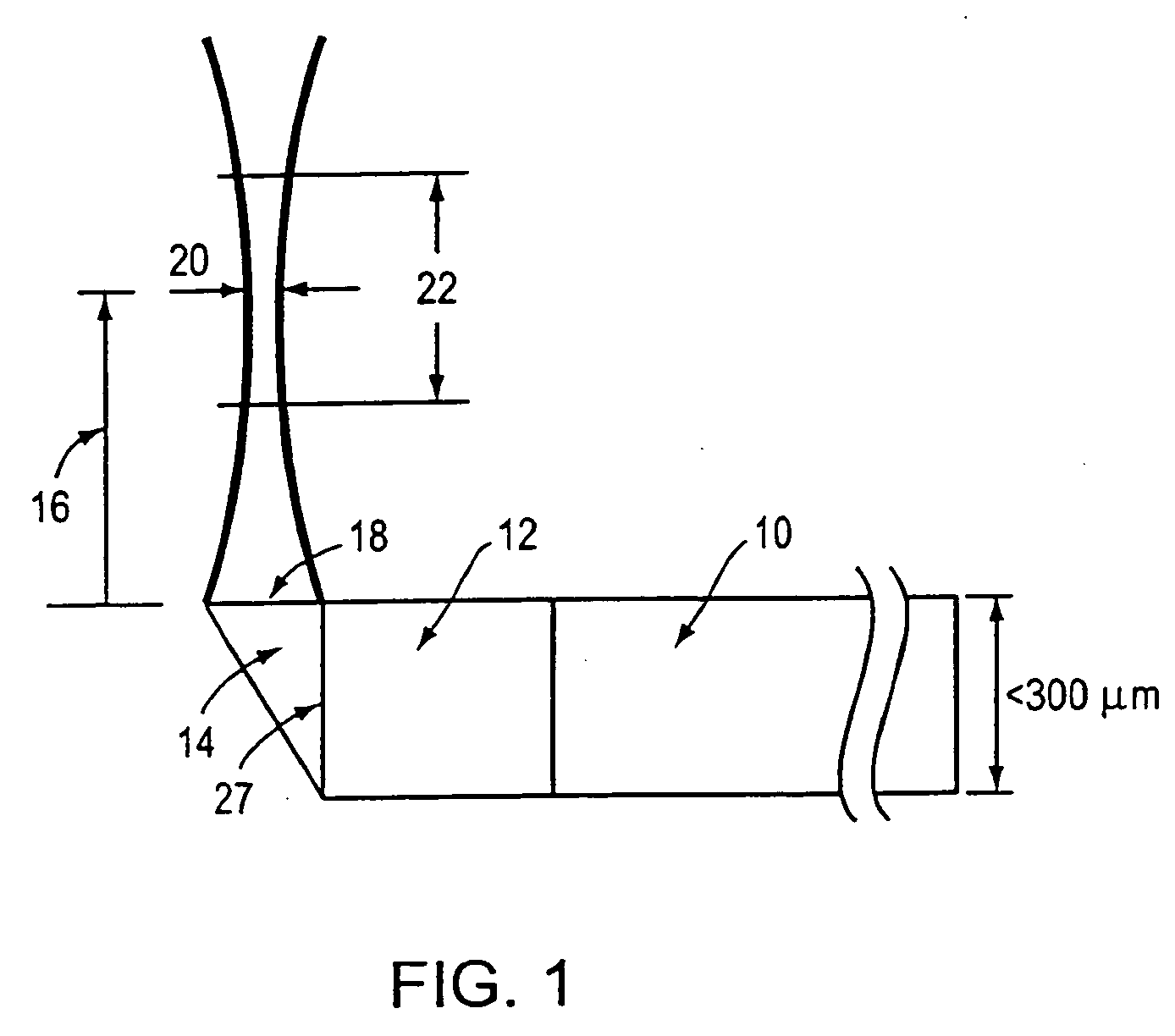
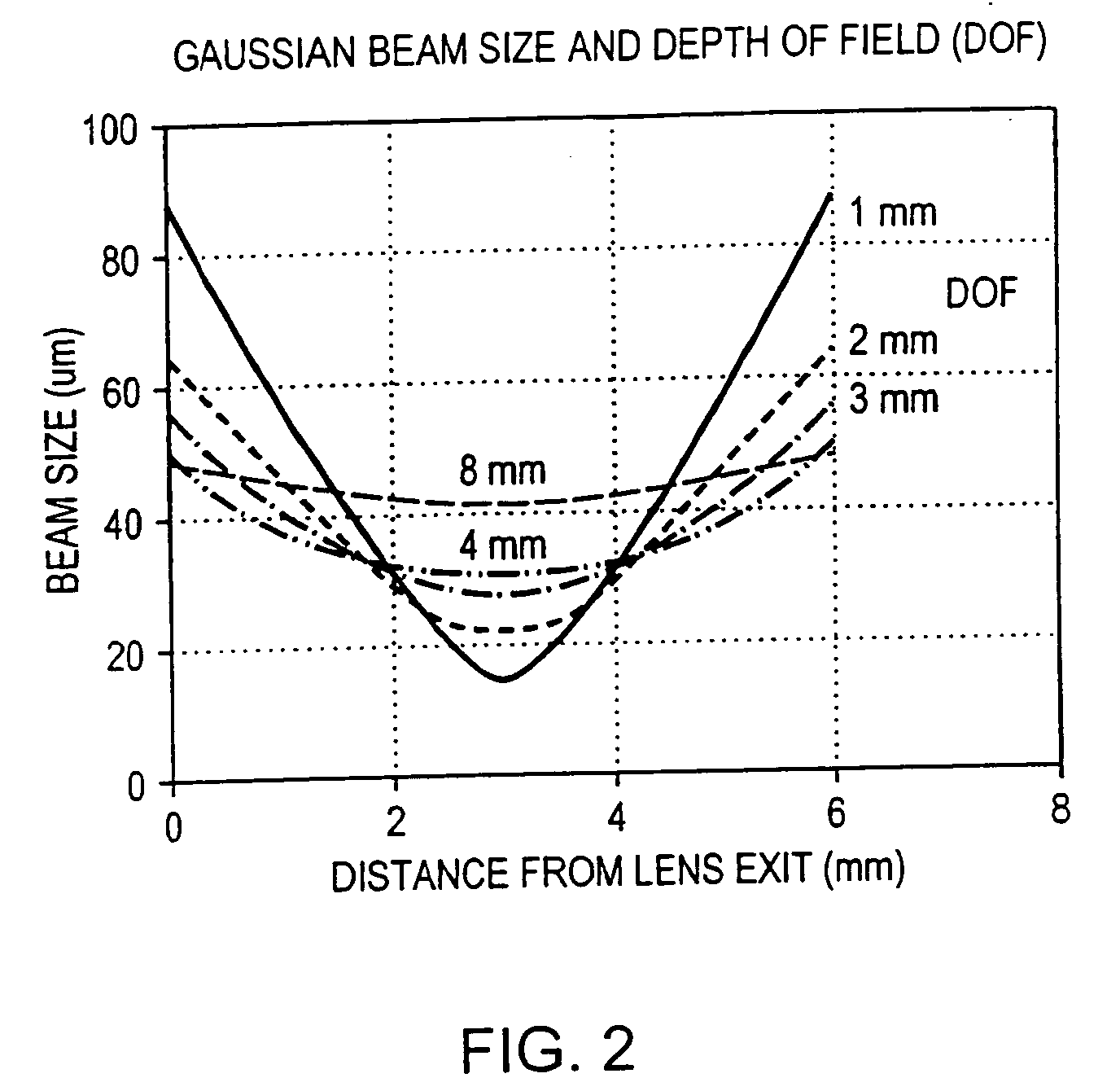
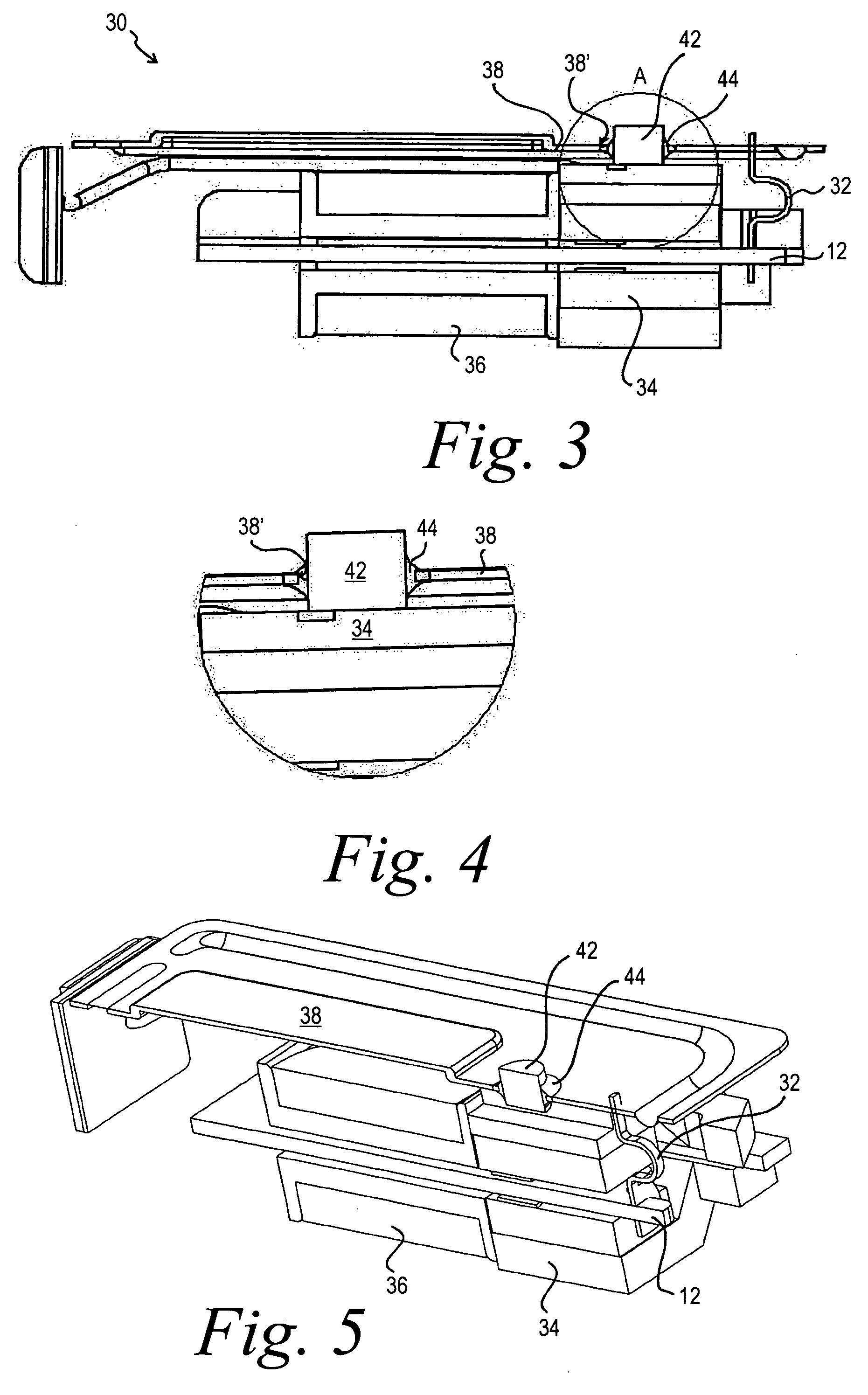
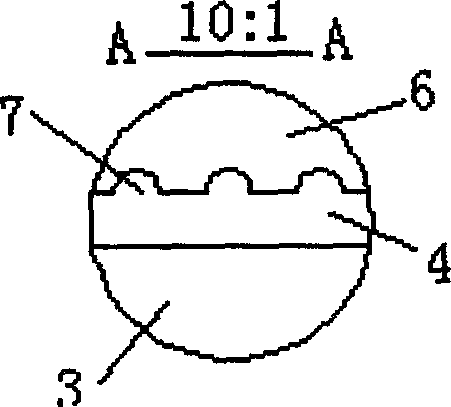
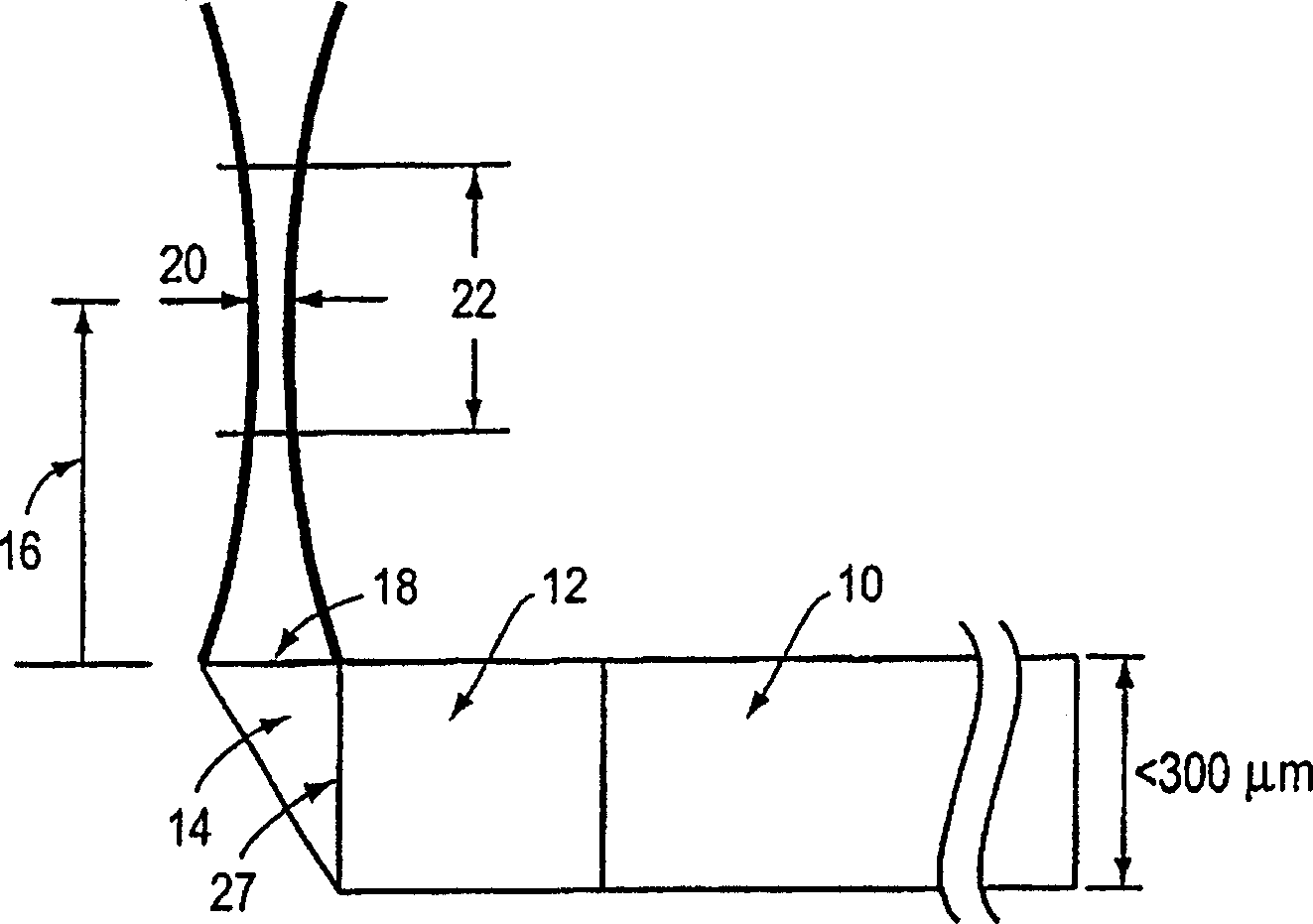
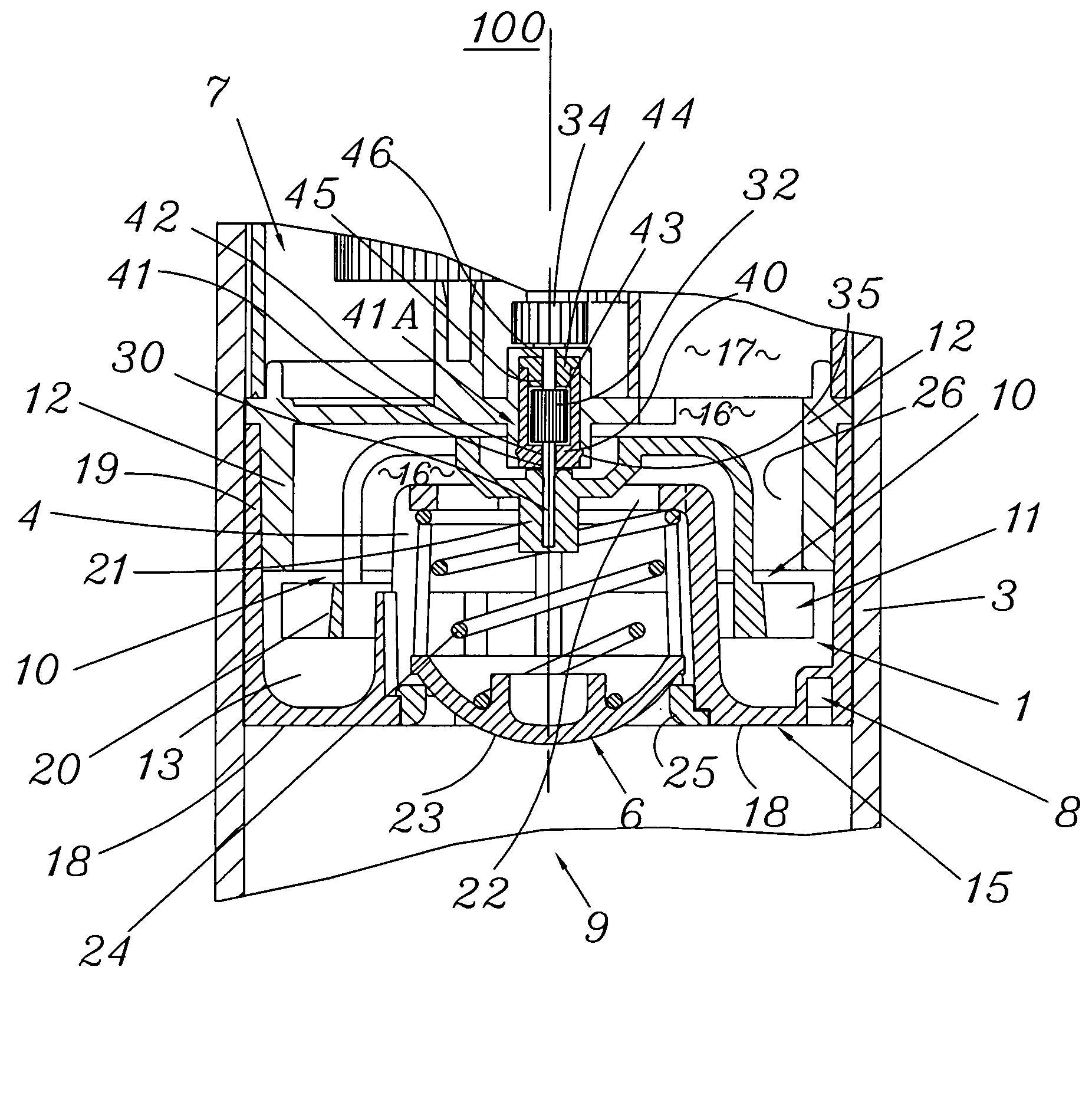
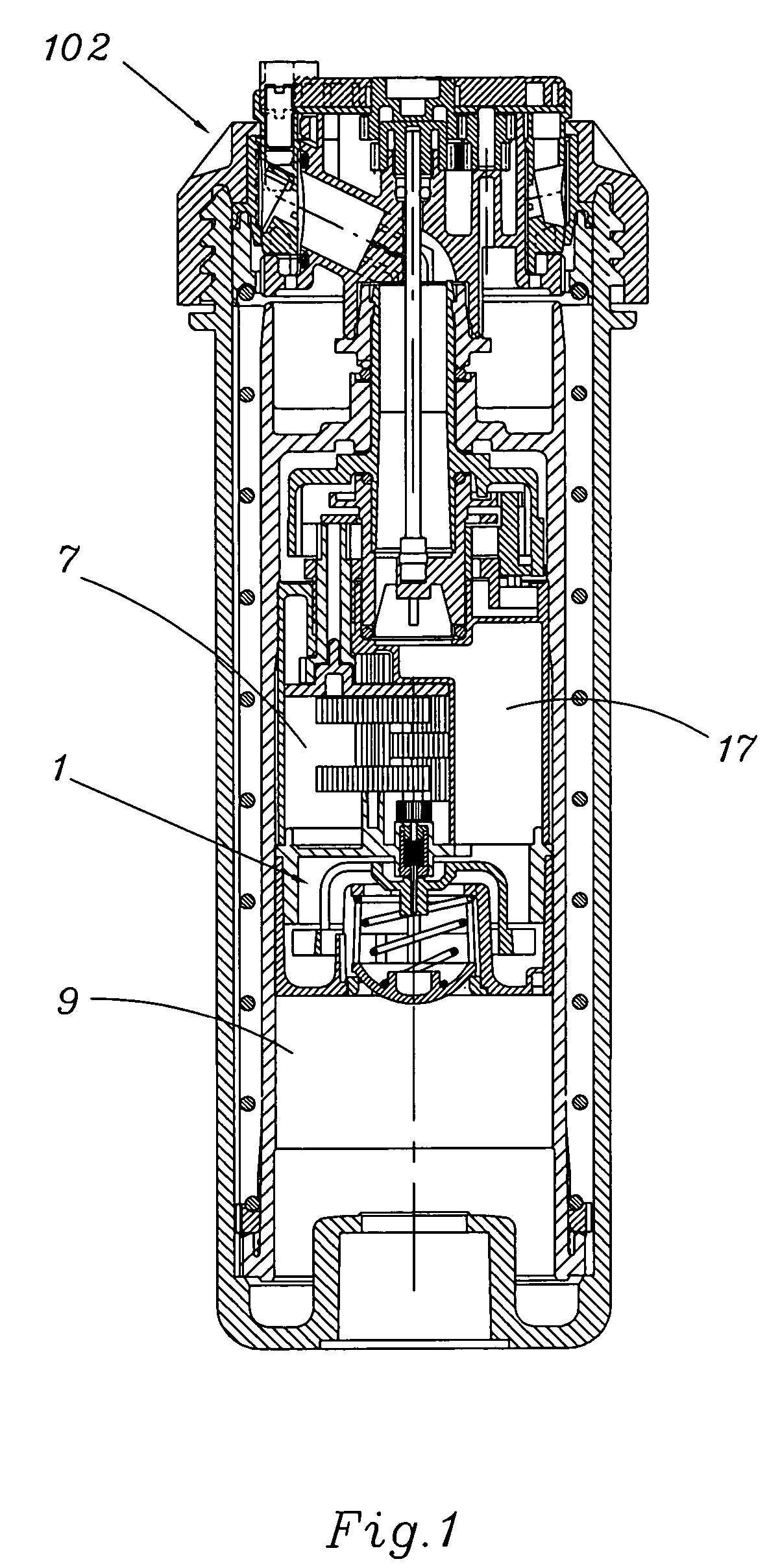
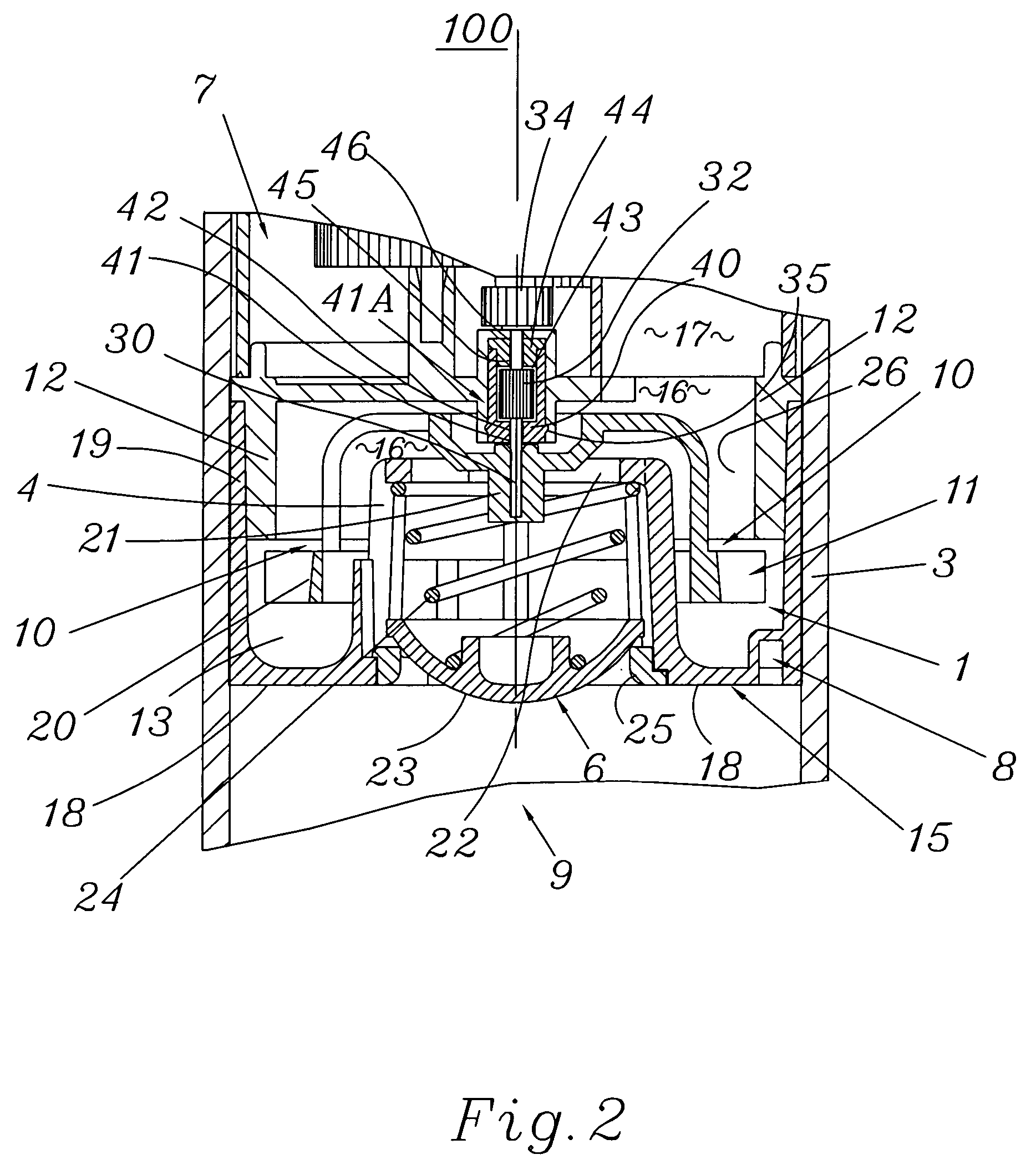
Scanning miniature optical probes with optical distortion correction and rotational control
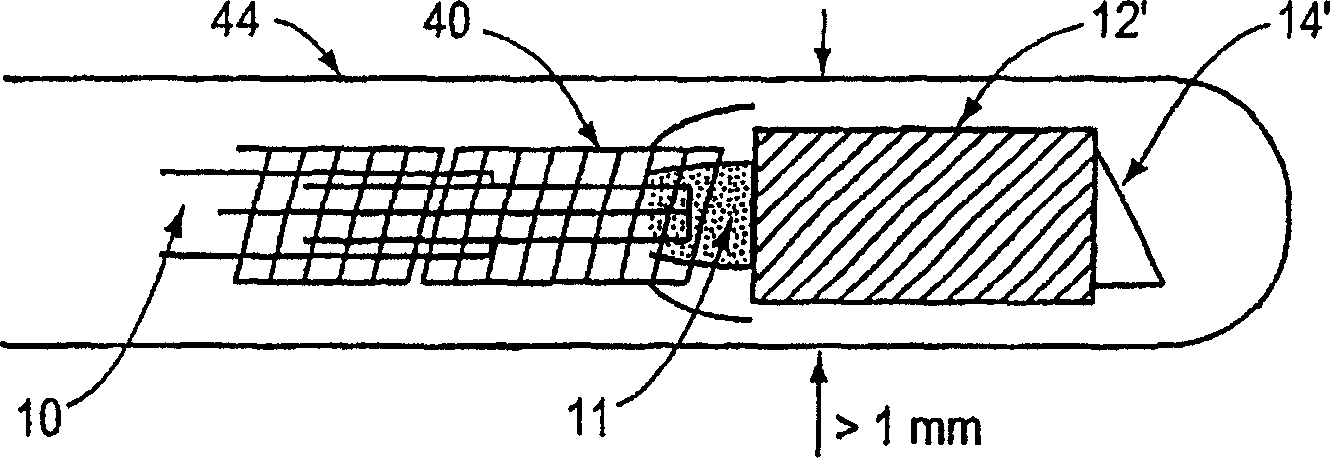
InactiveUS20050201662A1Minimizing temperatureEliminate the effects ofSurgical instrument detailsCatheterViscous dampingOptical distortion
Optical probes having a diameter less than substantially 500 μm for use in scanning light from a long, highly flexible fiber to a sample. In one embodiment the probe includes a viscous damping fluid suitable to prevent non-uniform rotational distortion (NURD).
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
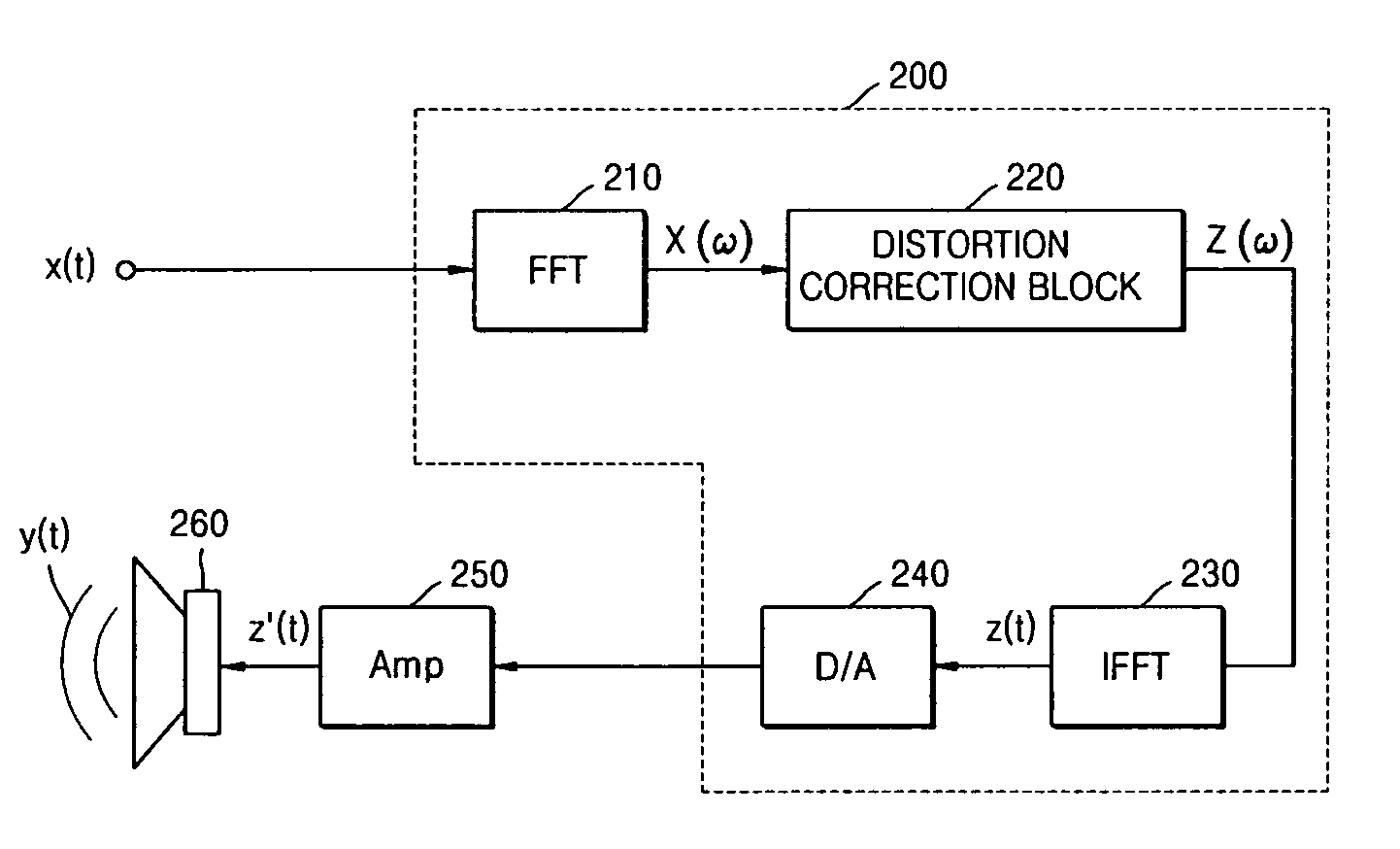
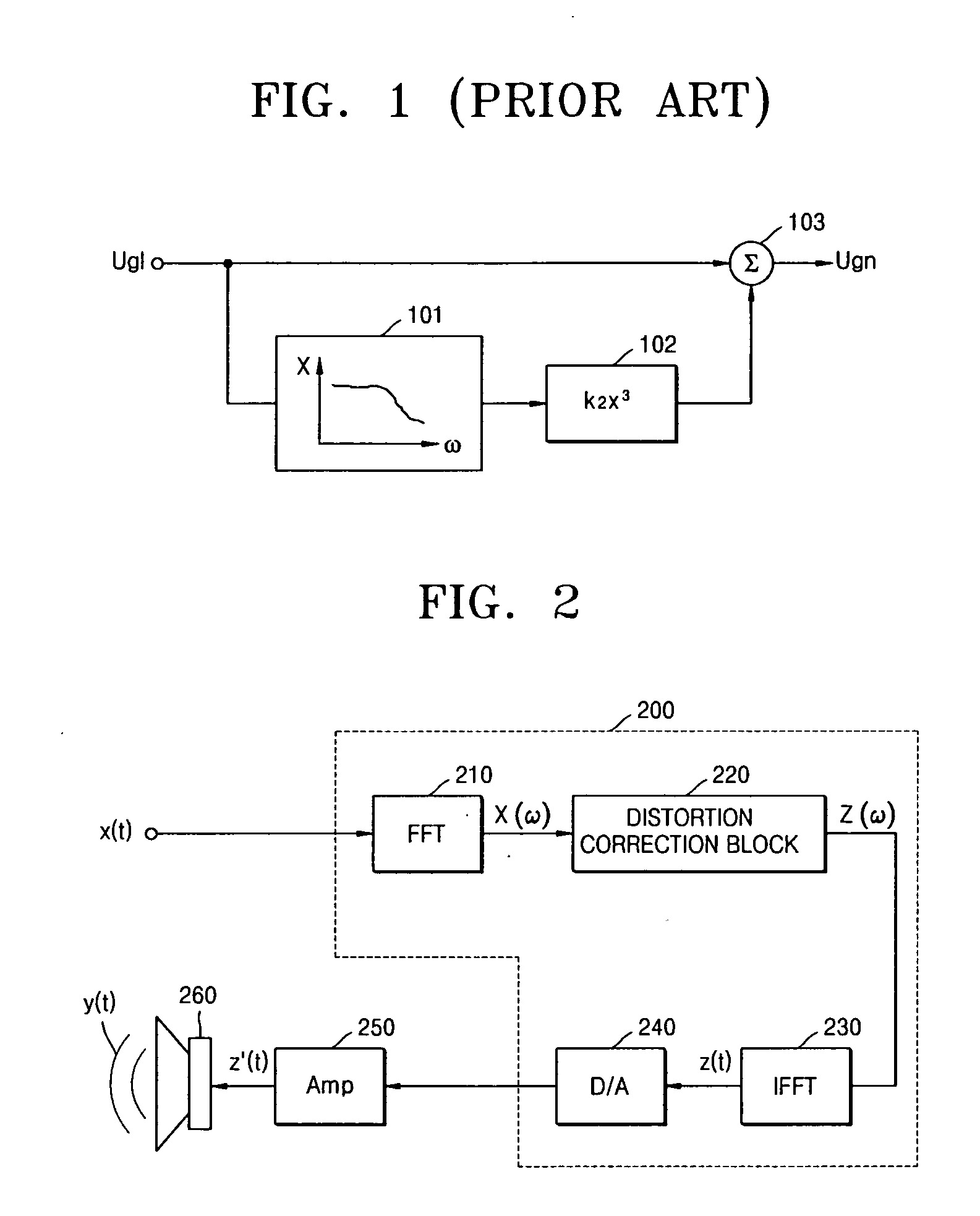
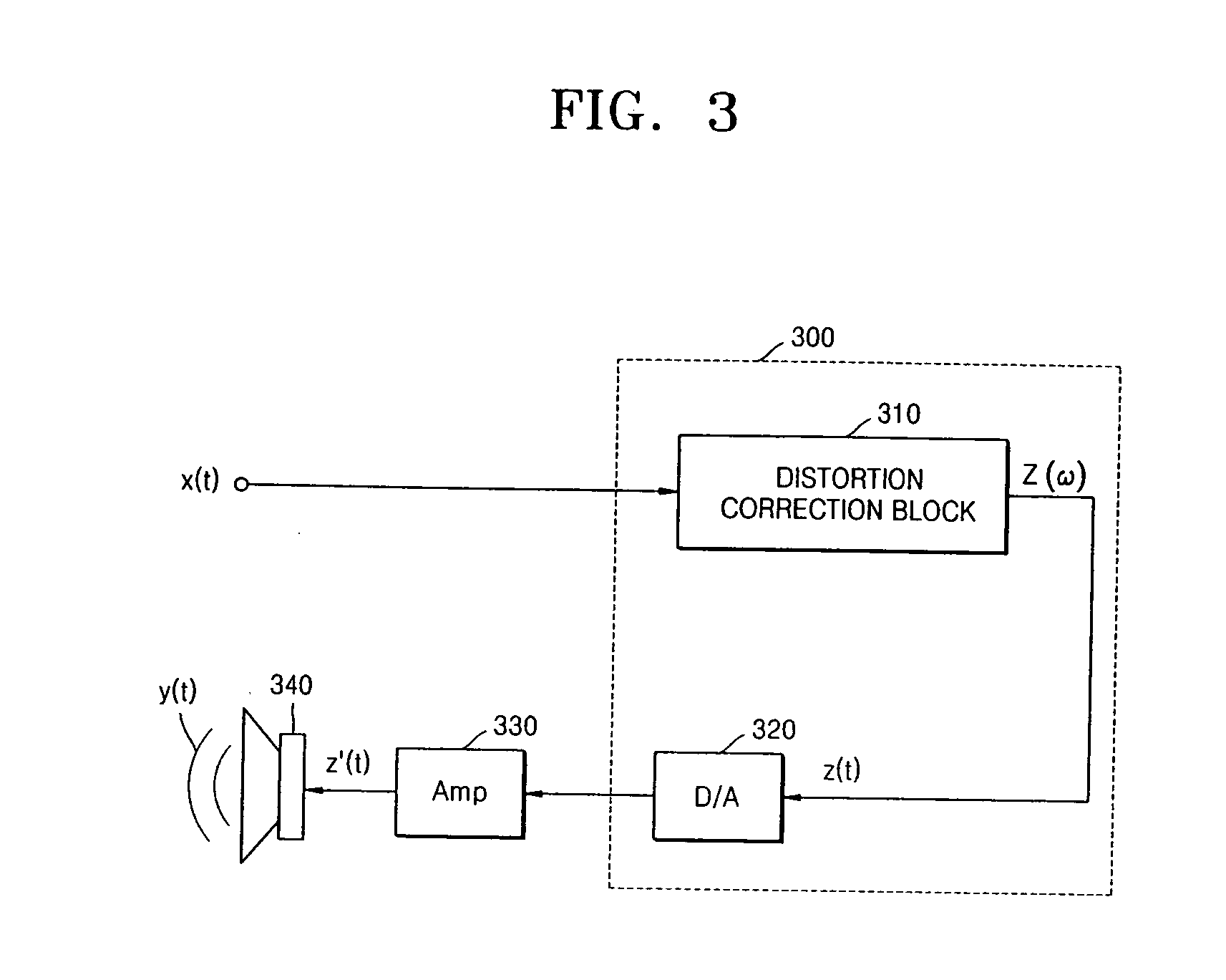
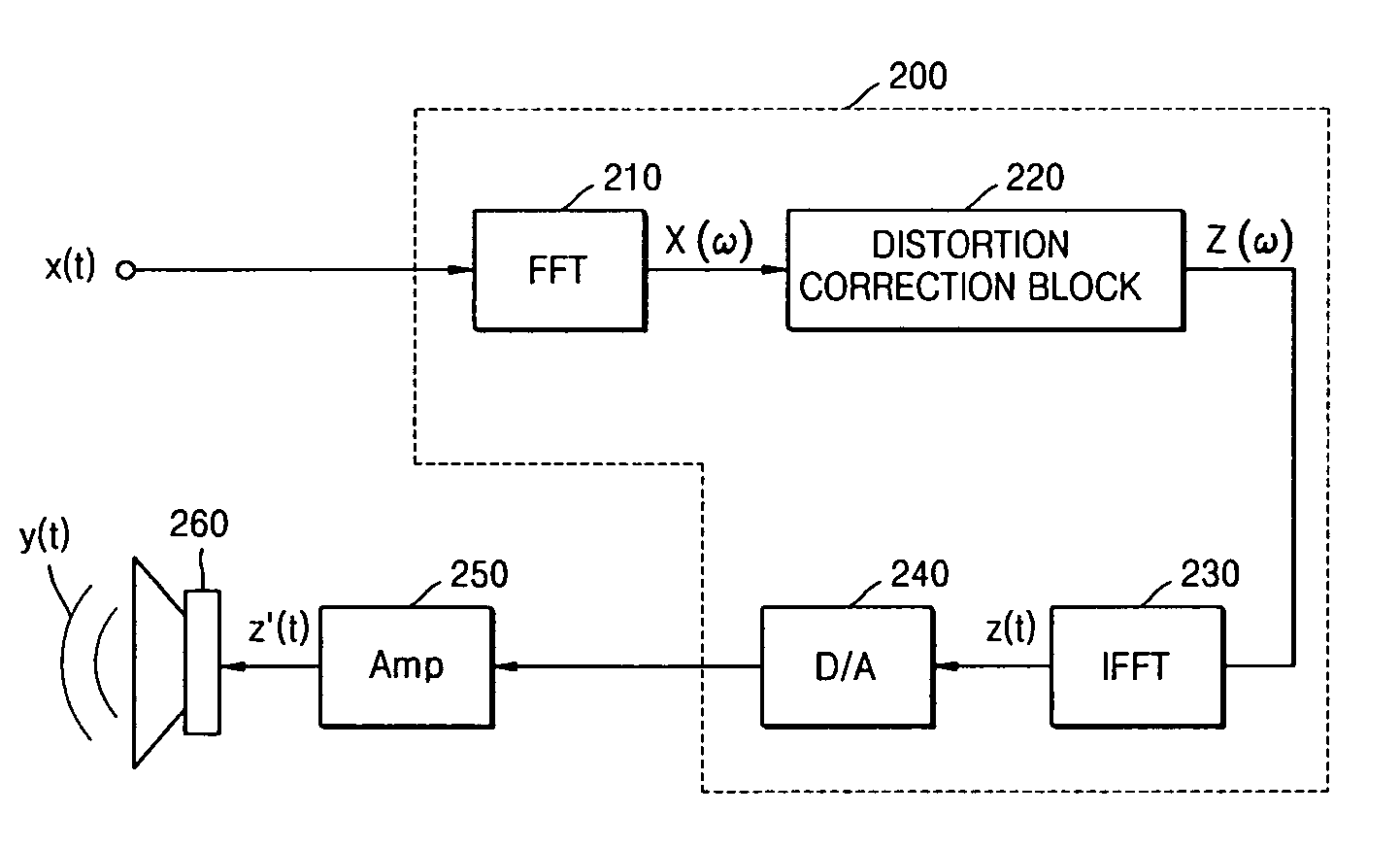
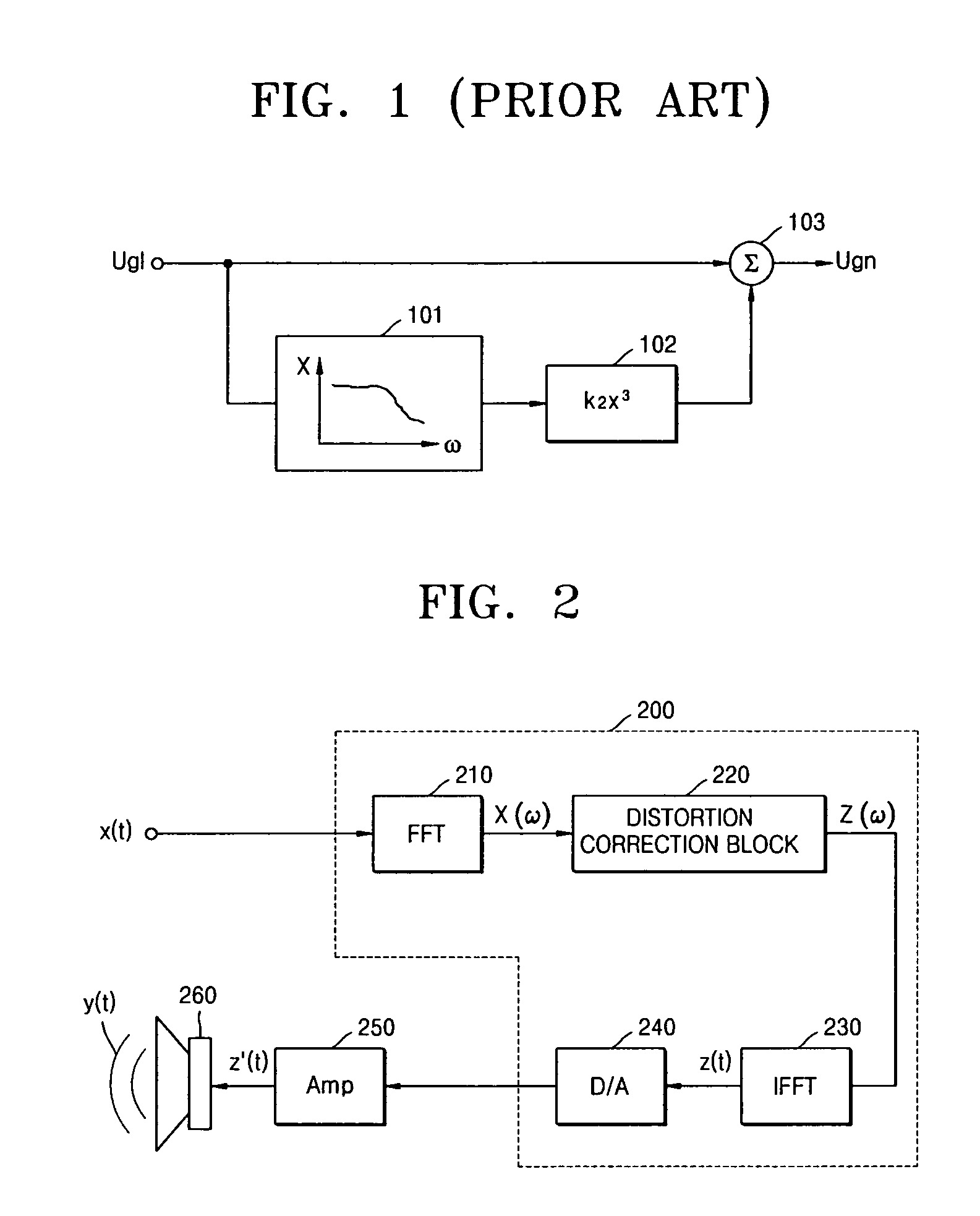
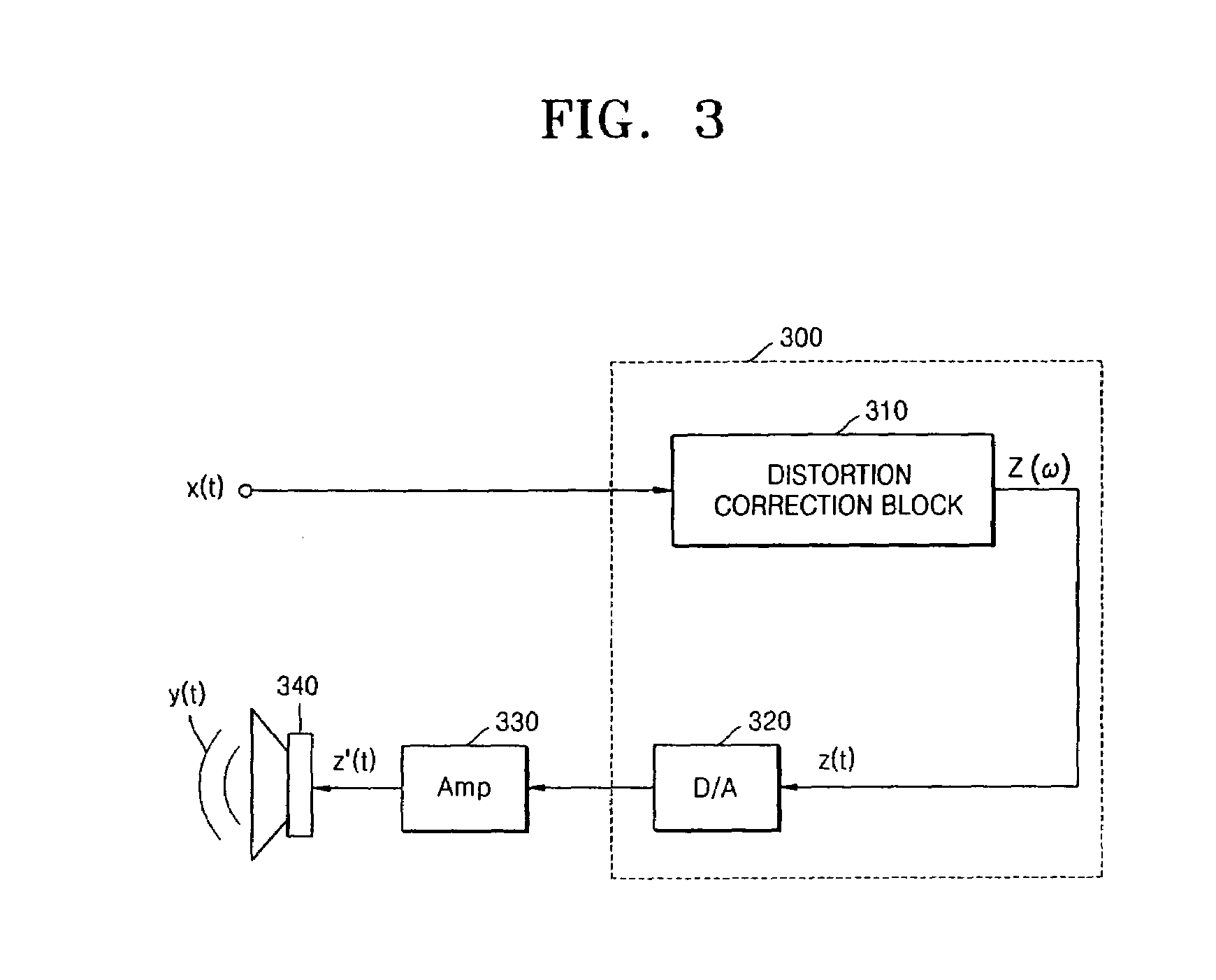
Method and apparatus for compensating for nonlinear distortion of speaker system
InactiveUS20050047606A1Improve output signal qualityEasy to implementTransducer circuit dampingFrequency response correctionTime domainViscous damping
A method and an apparatus for compensating for nonlinear distortion are provided to divide audio signals reproduced in a nonlinear speaker system into linear and nonlinear components in a time domain and a frequency domain, and then generate inversely-corrected signals by means of an inverse filtering scheme, so that it is possible to further consider a variety of nonlinear distortion characteristics such as viscous damping and structural damping which have not been reflected in the conventional lumped parameter method, and thus to obtain better sound quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transducers with improved viscous damping
A miniature receiver or transducer with improved viscous damping. The receiver may be a moving armature receiver using shearing forces for damping the deflection of the diaphragm. In this receiver, the damping element, which may be a liquid, extend in a direction of the deflection of the armature or diaphragm. Another embodiment relates to a transducer where the damping element engages the diaphragm.
Owner:SONION NEDERLAND
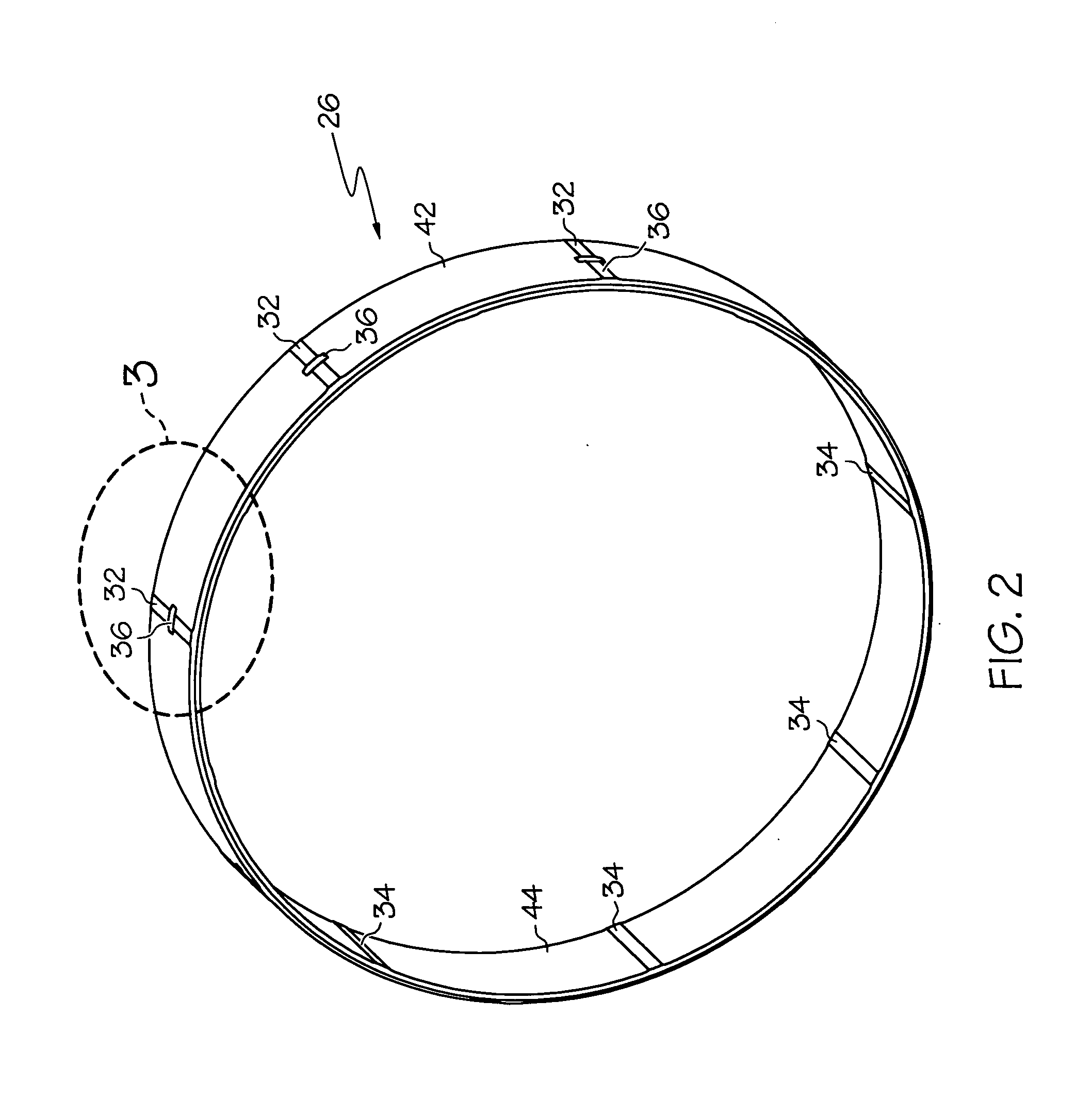
Compact resilient anisotropic support for bearing
InactiveUS20060204153A1Providing some stiffnessEngine manufactureShaftsViscous dampingElastic anisotropy
A support for a bearing comprises a resilient ring having unevenly spaced inner and outer bumpers. The unevenly spaced bumpers provide anisotropy to the rotor to preclude non-synchronous vibration. The inner bumpers can be ground to provide a vertical offset of the rotor centerline to accommodate the deflection due to the rotor weight. A tangential groove in the outer bumper allows oil passage during ring deflection so that oil can be squeezed out under dynamic load, providing additional viscous damping to the rotor.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
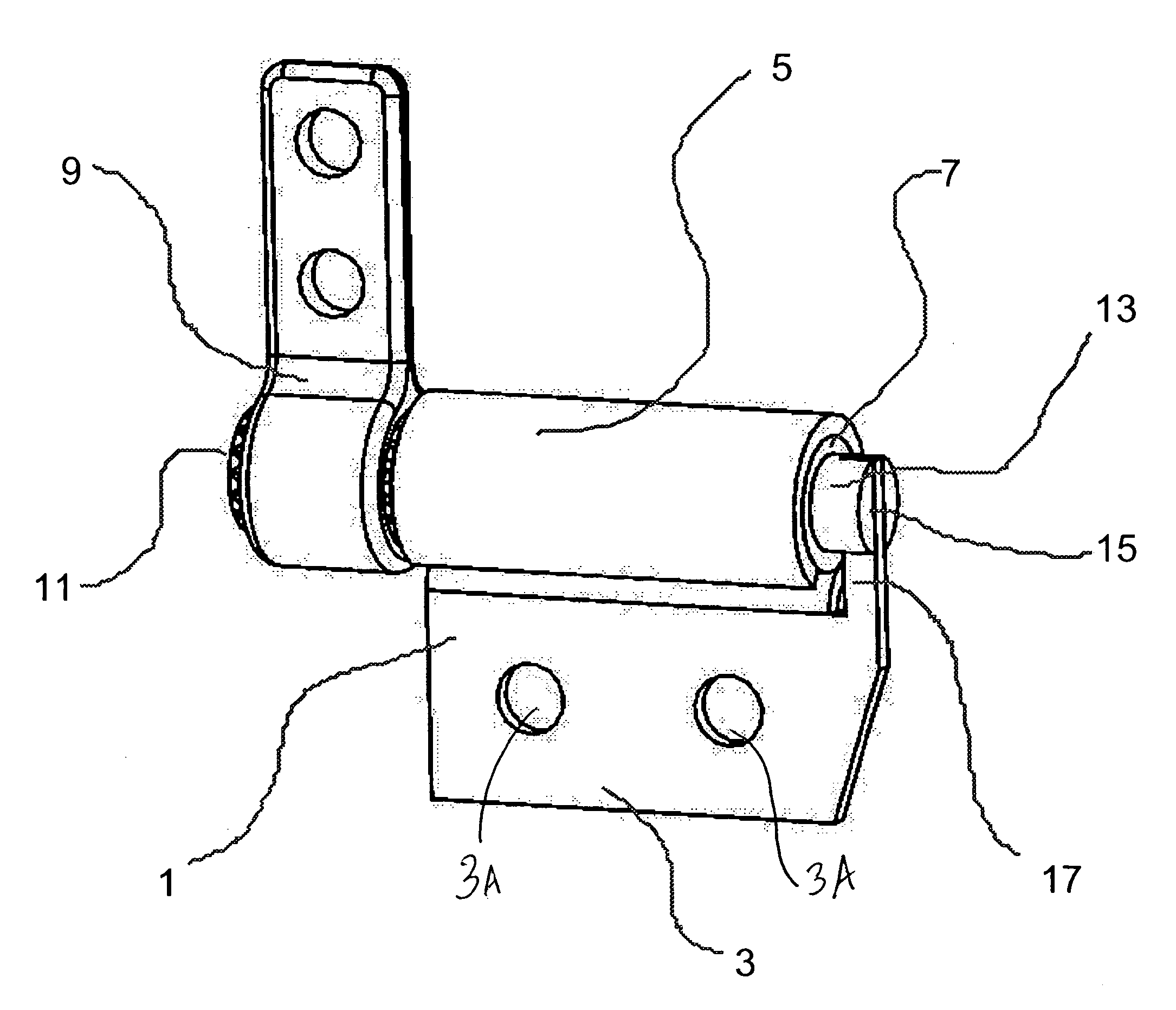
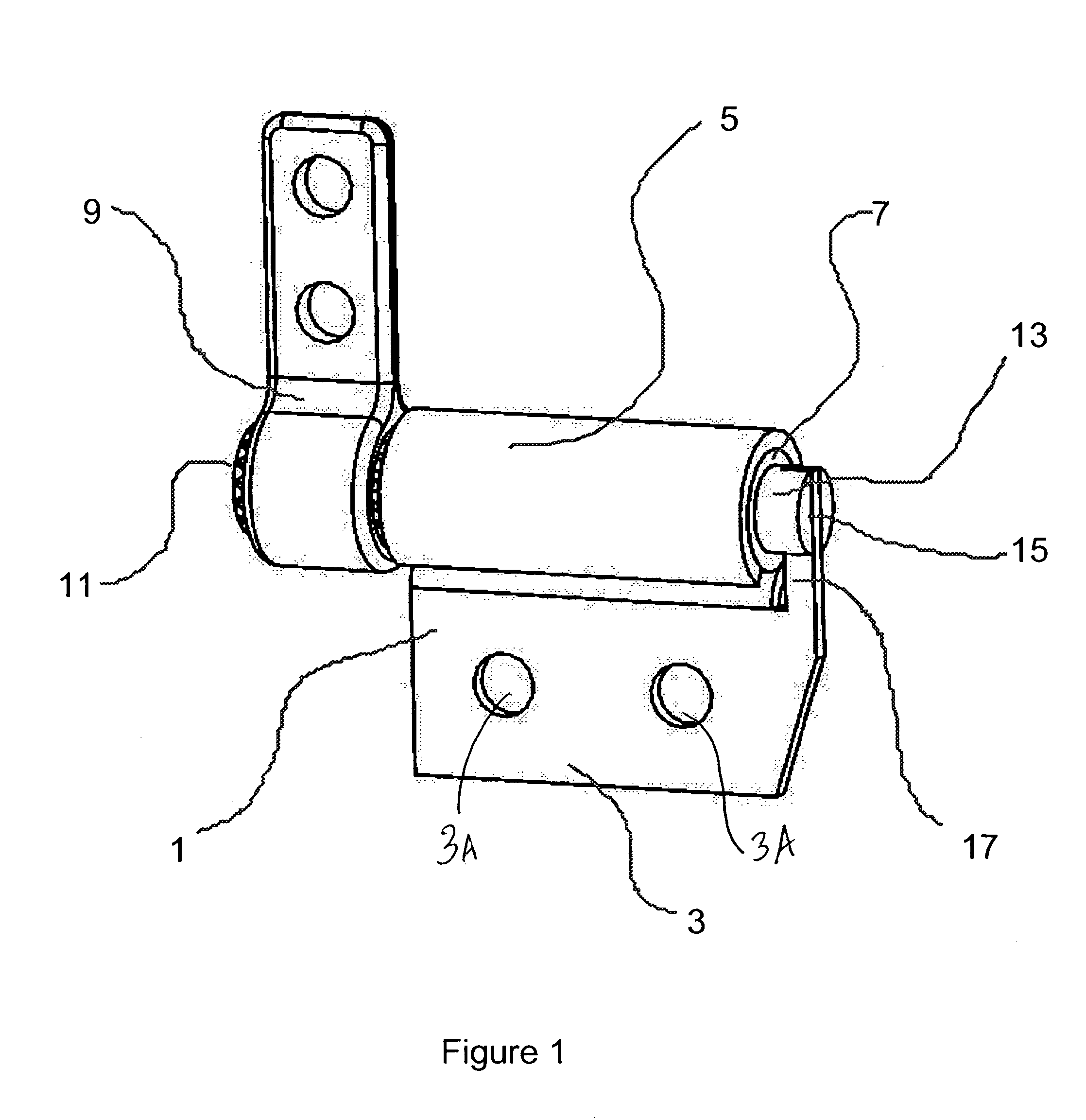
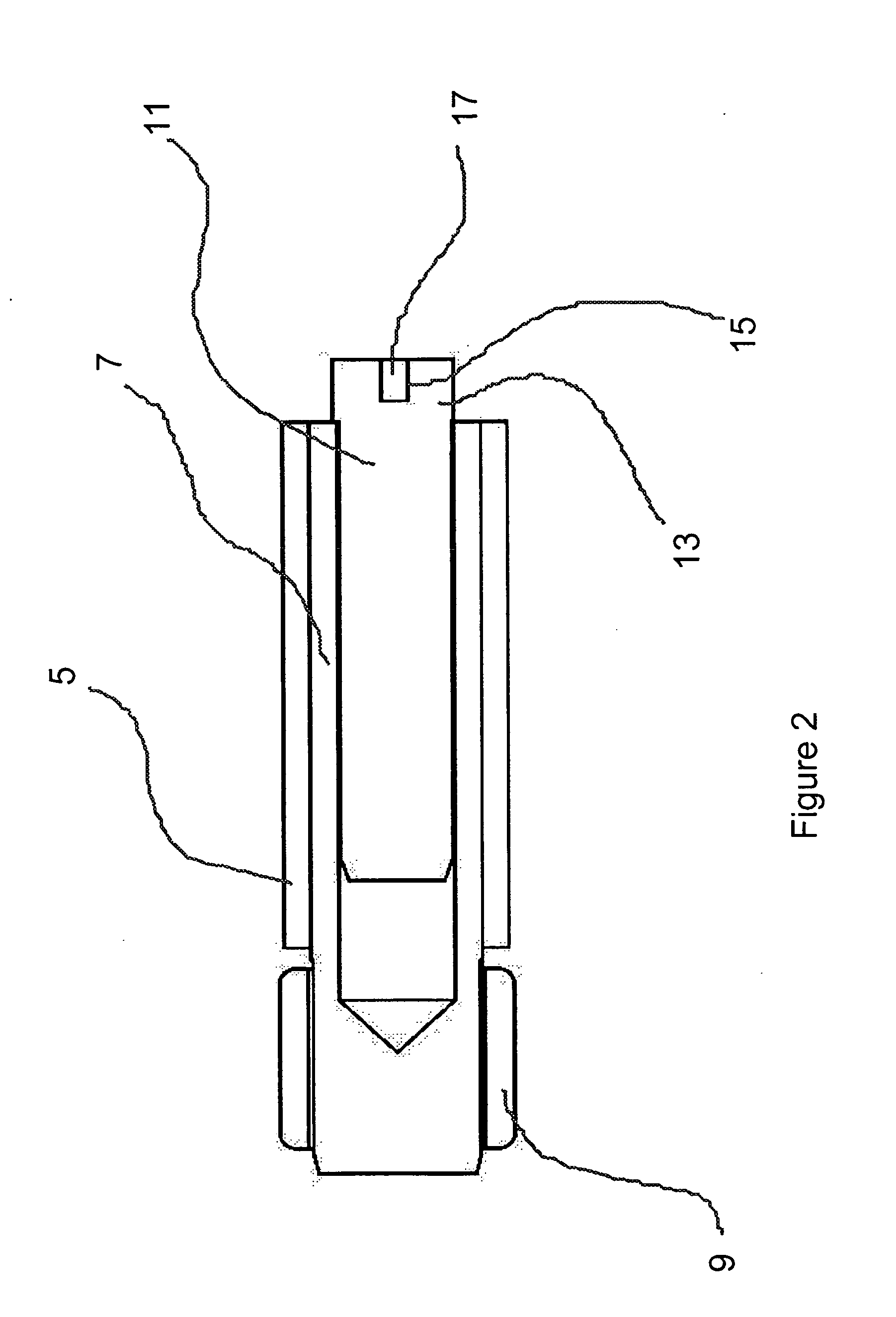
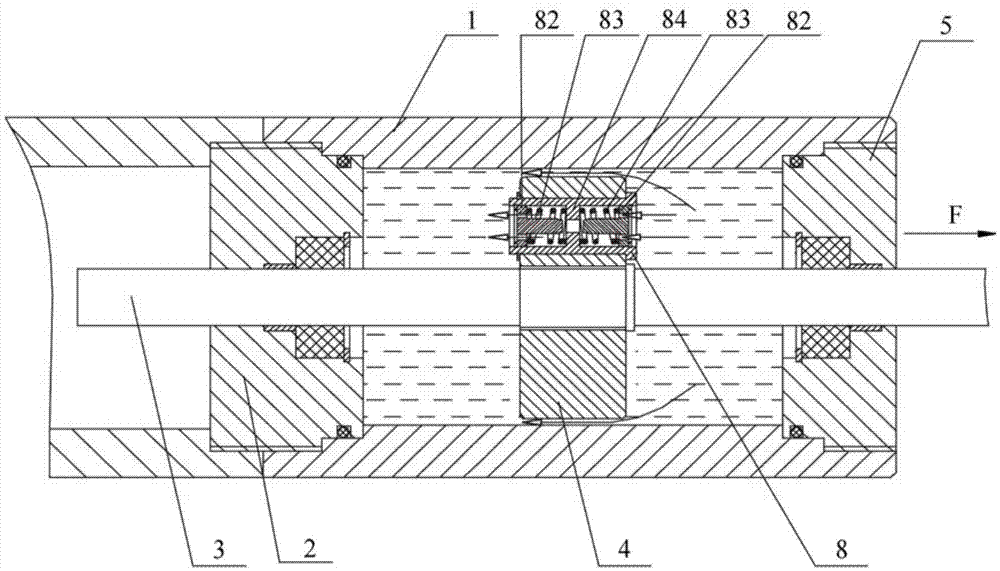
Friction hinge with viscous damping
InactiveUS20060272129A1Small sizeEasily and firmly attachedBuilding braking devicesWing fastenersViscous dampingFriction force
A hinge assembly rotationally connecting two components includes at least a shaft coupled to one of the components and a tubular member connected to the other component and a defining an annular space around said shaft. A viscous damping fluid is disposed in said space and provides a damping force resisting relative rotation between the two components. A second tubular member is also provided that is connected to the shaft and is arranged axially around the first tubular member. In this latter configuration, static and dynamic frictional forces are generated between the tubular members that resist rotation between the components as well.
Owner:TORQMASTER INC
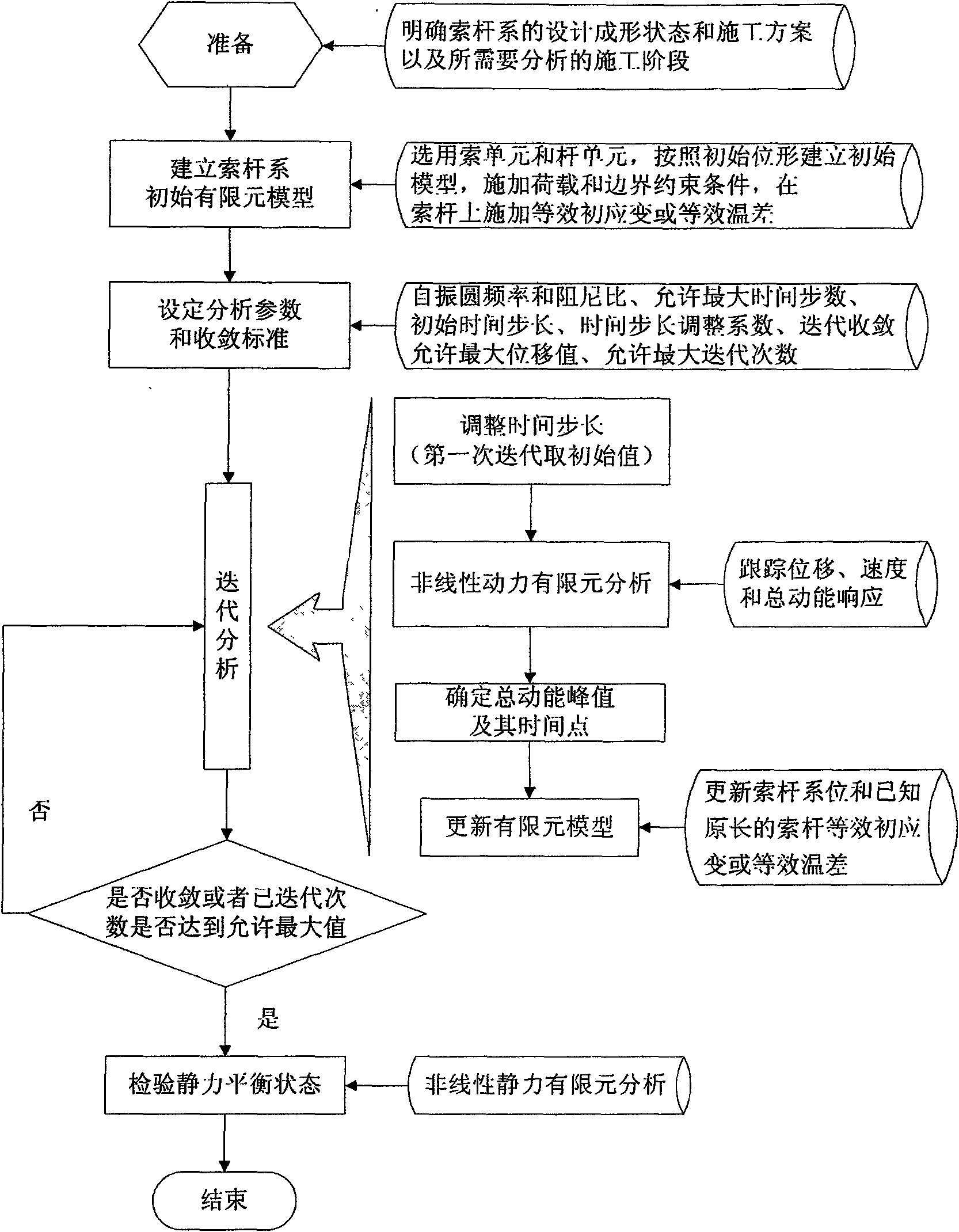
Non-linear dynamic finite element method for determining cable-strut system static balancing state
ActiveCN101582095ASolve the form-finding problemHolisticSpecial data processing applicationsViscous dampingDynamic balance
The invention relates to a non-linear dynamic finite element method for determining cable-strut system static balancing state. In the construction processes of traction mounting and stretch-draw forming, a cable-strut system as a mechanism has super large displacement, mechanism displacement and guy cable looseness, and a conventional linear dynamic finite element method cannot obtain the static balancing state in the construction stage. The non-linear dynamic finite element method adopts form-finding analysis to establish a non-linear dynamic finite element equation by introducing inertia force and viscous damping force so as to change a static problem which is difficult to solve into a dynamic problem which is easy to solve, and gradually converge the dynamic balancing state of the cable-strut system into a static balancing state through iteration updating of the configuration of the cable-strut system. The cable-strut system is in a static unbalancing state before analysis, is in the dynamic balancing state in the analysis, and reaches the static balancing state after the convergence, namely the cable-strut system discontinuously moves (non-continuous movement) from the initial static unbalancing state to the stable static balancing state.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Mining telescopic energy adsorption anti-impact viscous damping anchor rod and supporting method thereof
InactiveCN103573279AGuaranteed not to breakPlay a buffer roleAnchoring boltsHydraulic cylinderViscous damping
The invention discloses a mining telescopic energy adsorption anti-impact viscous damping anchor rod and a supporting method thereof. The mining telescopic energy adsorption anti-impact viscous damping anchor rod is formed by a pre-tightening nut, a tray, energy adsorption materials, an anchor rod body, a base plate and an avoidance buffering energy adsorbing device. The anchor rod body is composed of an anchor rod end and an anchor rod body, and the pre-tightening nut, the tray, the energy adsorbing materials and the base plate are arranged on the anchor rod end. The avoidance buttering energy adsorbing device is formed by arranging a lower sliding piston, a connecting rod piston and an upper sliding piston in a buffer hydraulic cylinder in sequence, wherein the lower sidling piston, the connecting rod piston and the upper sliding piston are respectively provided with 3-4 damping holes, the damping holes of adjacent pistons are not on the identical straight line, sealing rings are arranged on the circumferential face of the upper sliding piston and the circumferential face of the lower sliding piston, and the connecting rod of the connecting rod piston penetrates through the upper sliding piston and the upper face of the buffer hydraulic cylinder and then is connected with the anchor body together. The mining telescopic energy adsorption anti-impact viscous damping anchor rod can maintain constant resistance in the process of resisting rock burst, can retard impact loads, reduce the damage to the surrounding rock in the anchoring range of the anchor rod by the impact energy, and perform the function of further stabilization to the roof surrounding rock.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
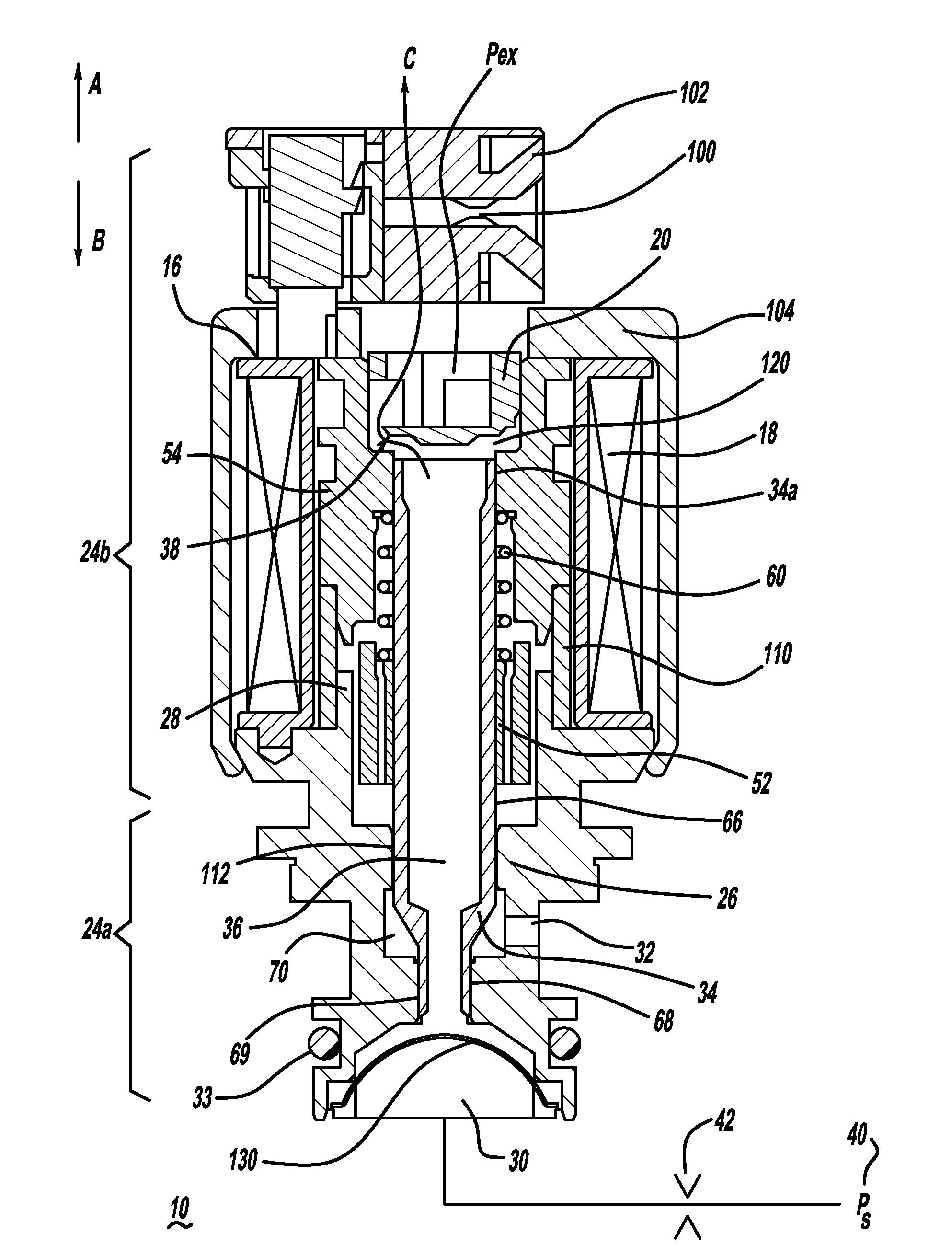
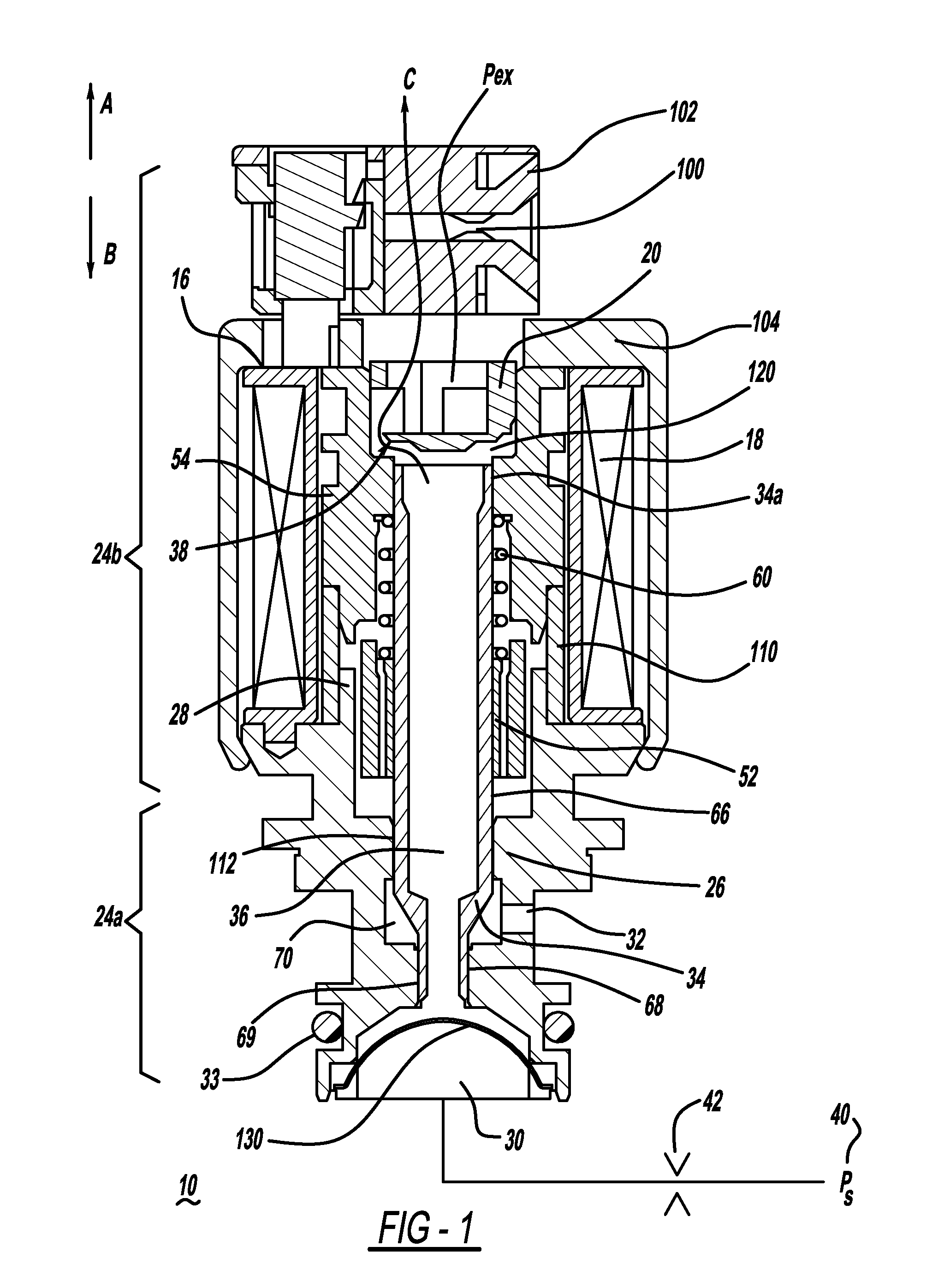
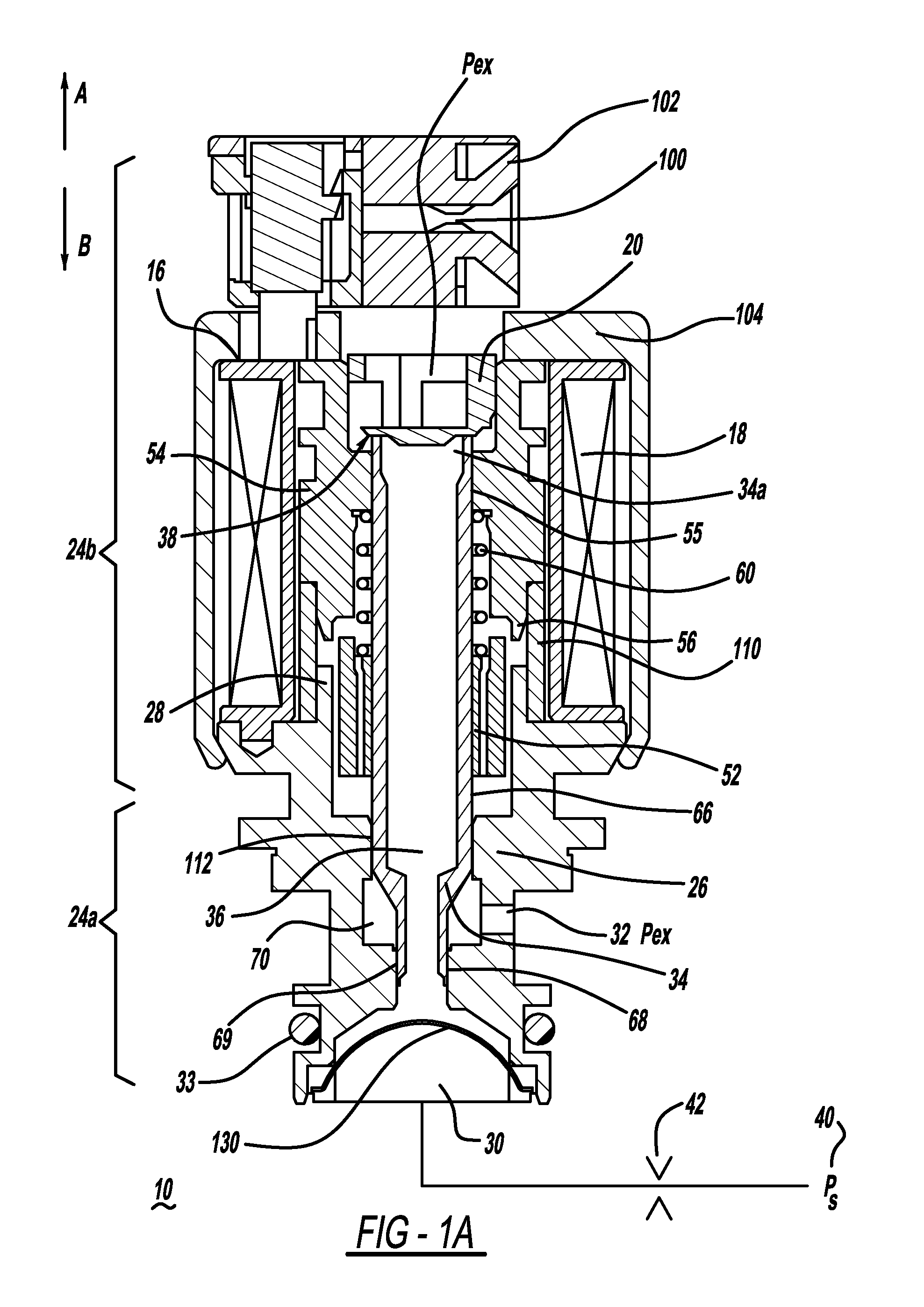
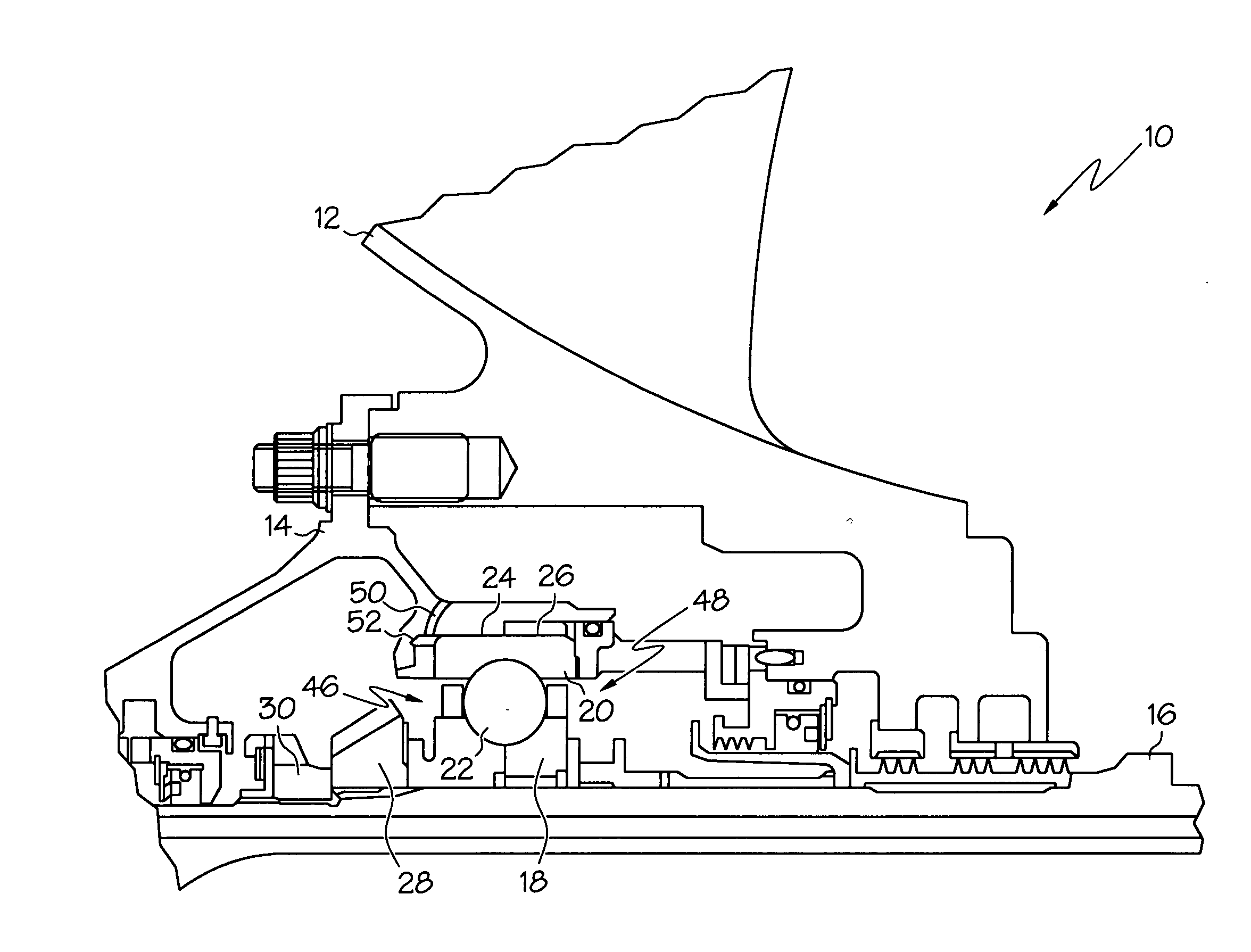
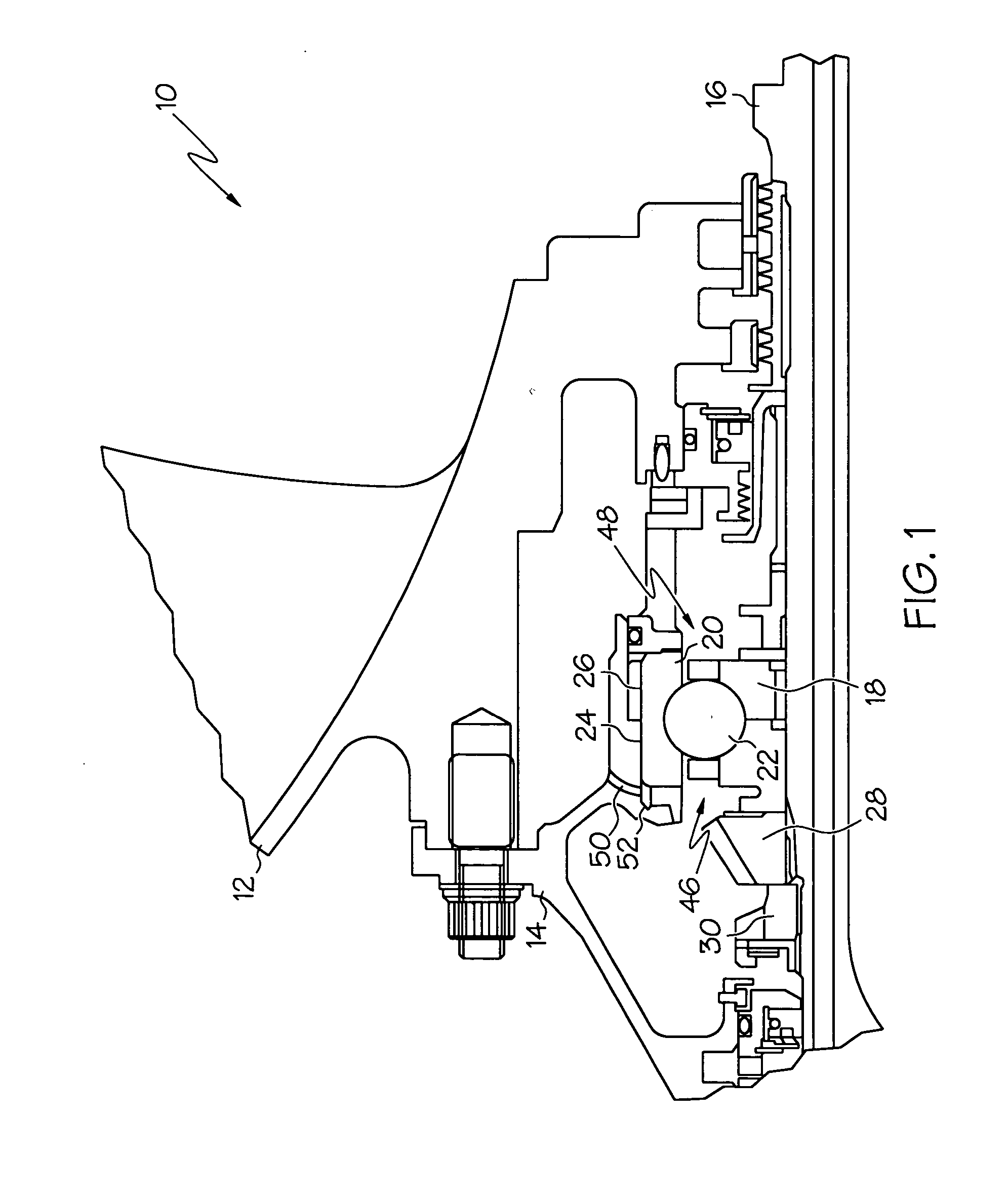
Open end variable bleed solenoid (VBS) valve with inherent viscous dampening
InactiveUS20110284783A1Increase in sizeSmall sizeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMagnetsViscous dampingSolenoid valve
A solenoid valve (10) includes a solenoid portion (24b) and a hydraulic portion (24a) having a valve housing (26) connectable to the solenoid portion (24b). A valve shaft (34) mounted in the housing (26) includes a first end positioned in the solenoid portion (24b) and a second end positioned in the hydraulic portion (24a). The valve shaft (34) includes a passage (36) disposed therethrough to allow fluid flow through the valve shaft (34). A valve (38) is located at the first end of the valve shaft (34). When the valve shaft (34) is moved in a first direction, the valve (38) moves toward a closed position, and when the valve shaft (34) is moved in a second direction, the valve (38) moves toward an open position.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Damper
ActiveCN1786510ASimple structureImprove performanceNon-rotating vibration suppressionLiquid based dampersViscous dampingEngineering
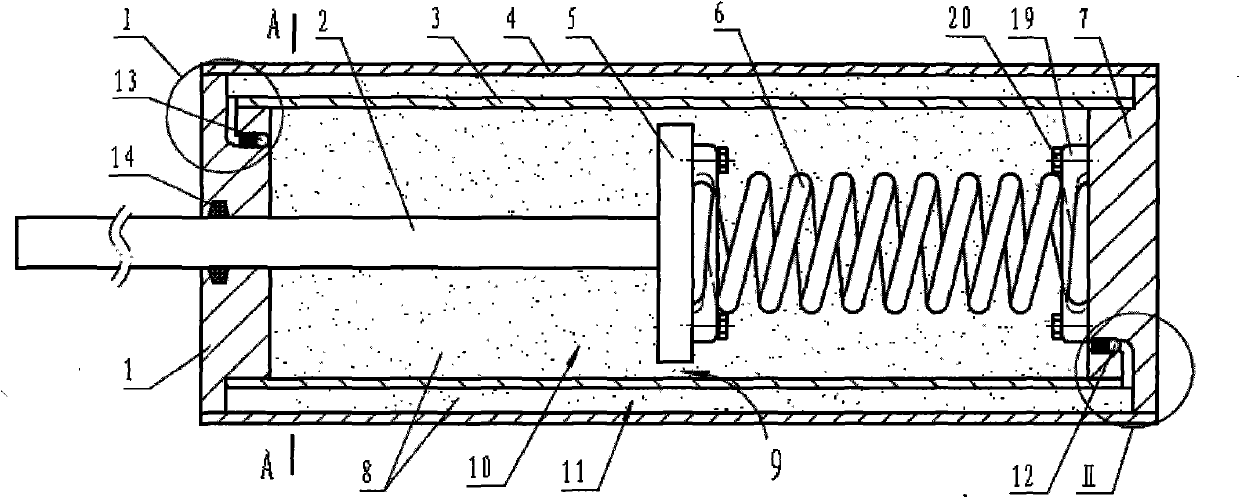
The invention relates to a vibration-absorbing dissipative damper, which comprises a cylinder body and a moving body. The moving body is partly located in the cylinder. At least one cavity extending along the shaft is disposed in the cylinder. Viscous damping liquid is filled in the cavity and formed damping cavity. The moving body is made up of moving vanes disposed in the damping cavity. A shearing cavity is formed via the moving vanes and the damping cavity wall.
Owner:尹学军 +1
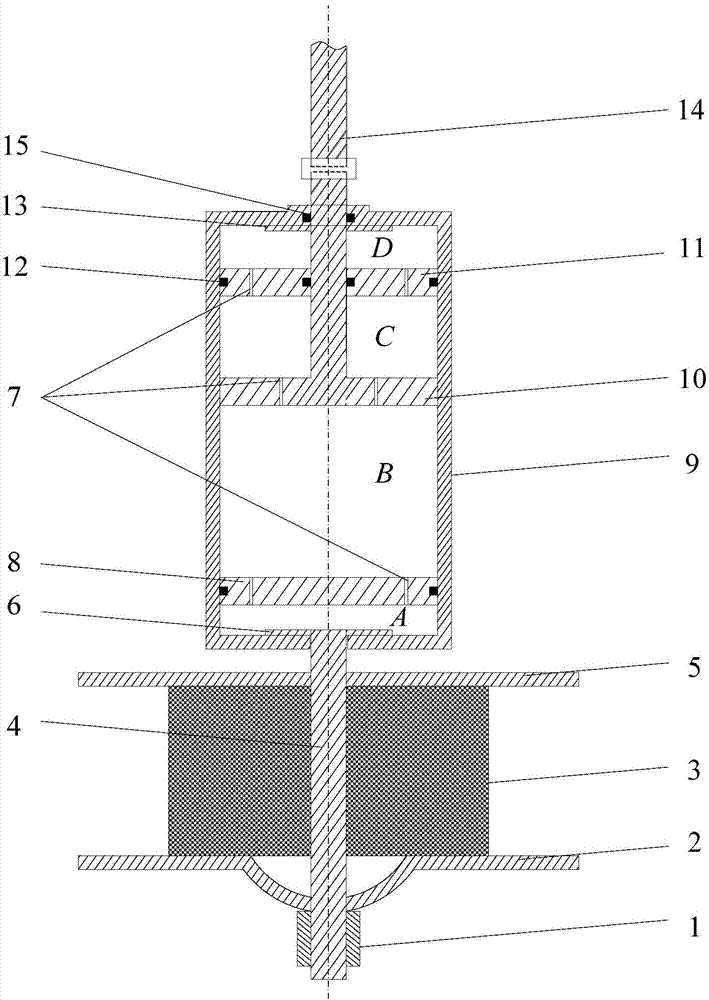
Viscous damping device with axial position limiter
ActiveCN101315112AIncrease the lengthPlay a limiting roleSpringsLiquid based dampersViscous dampingEngineering
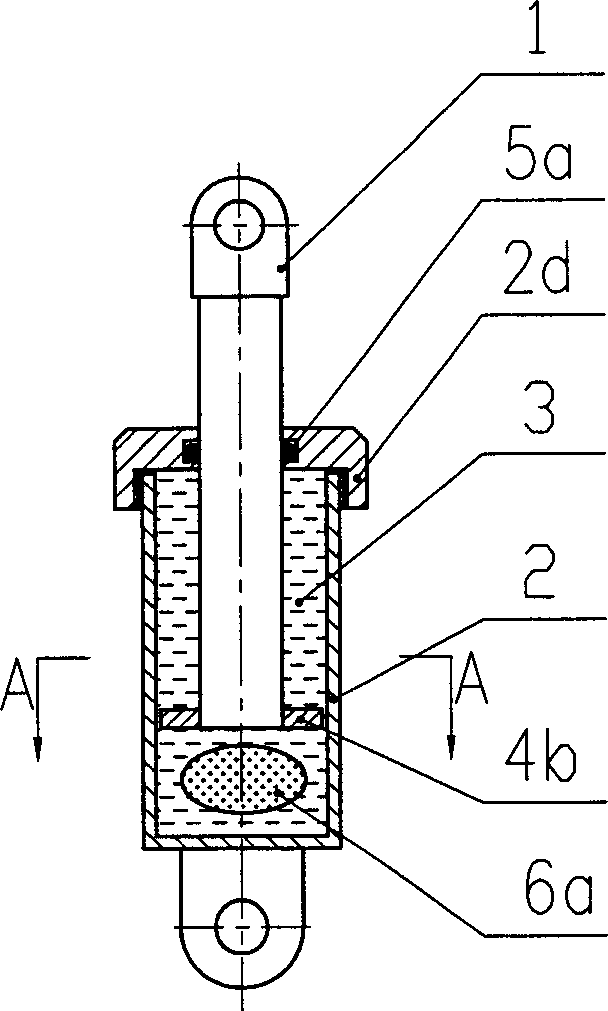
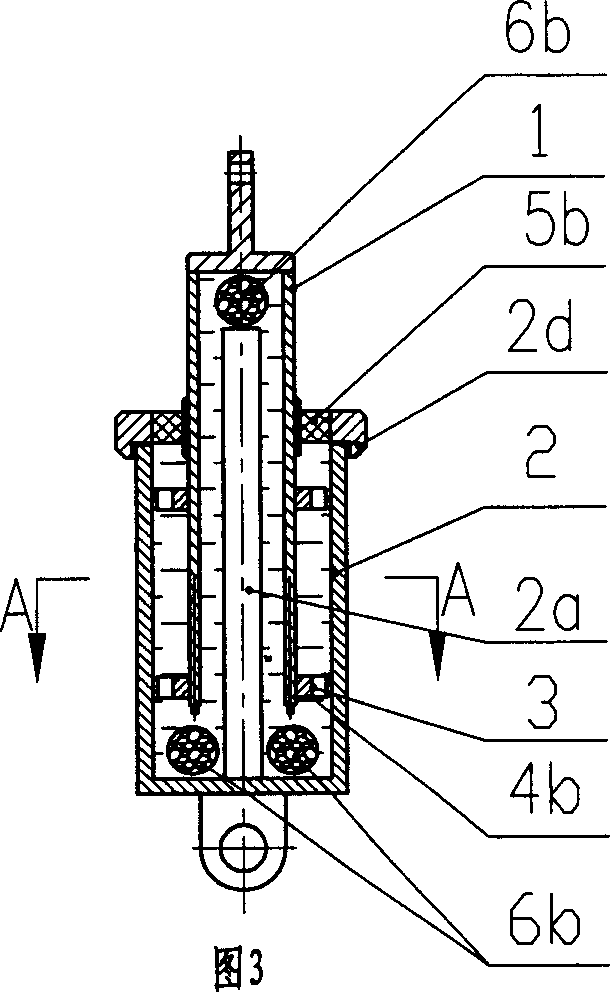
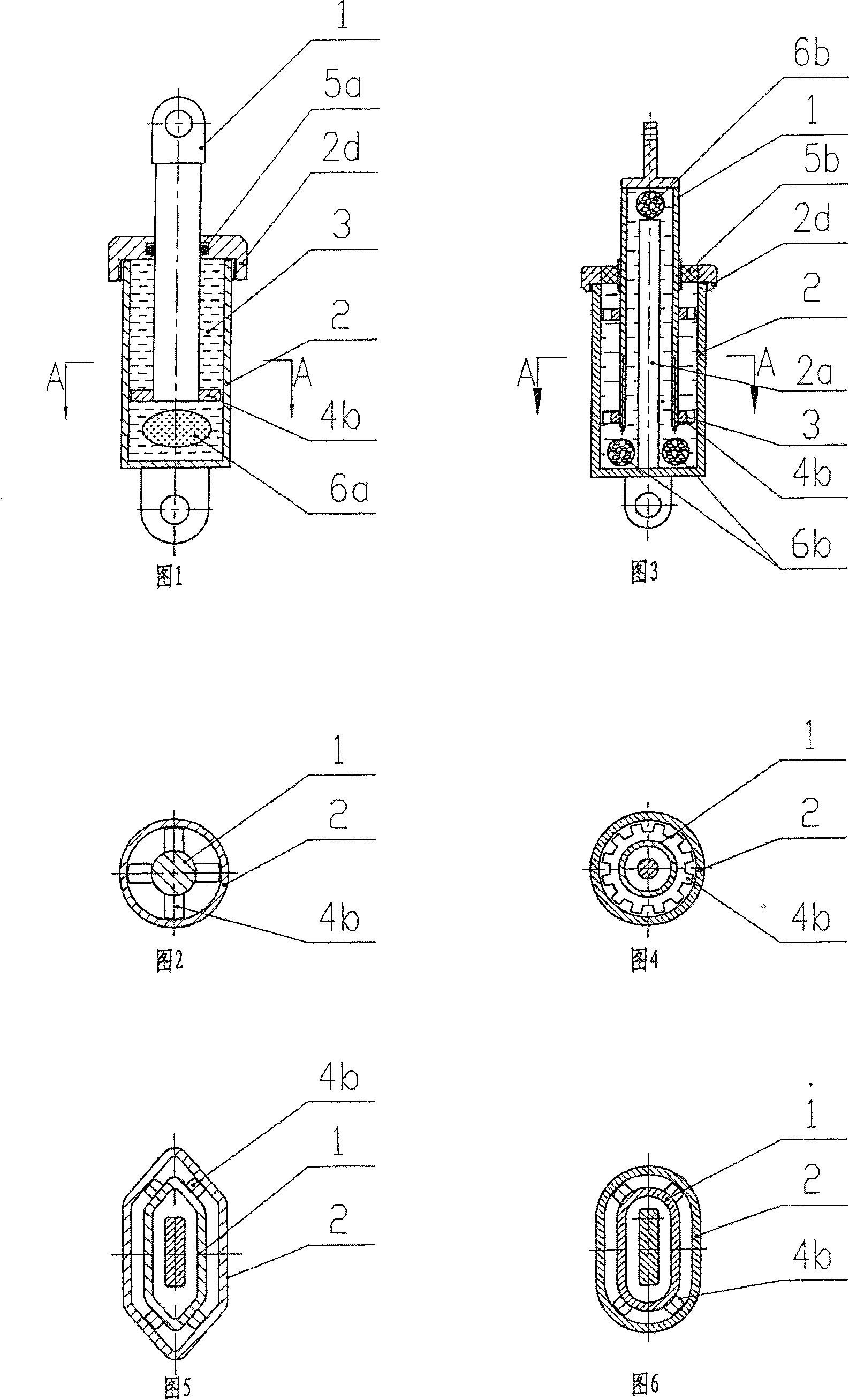
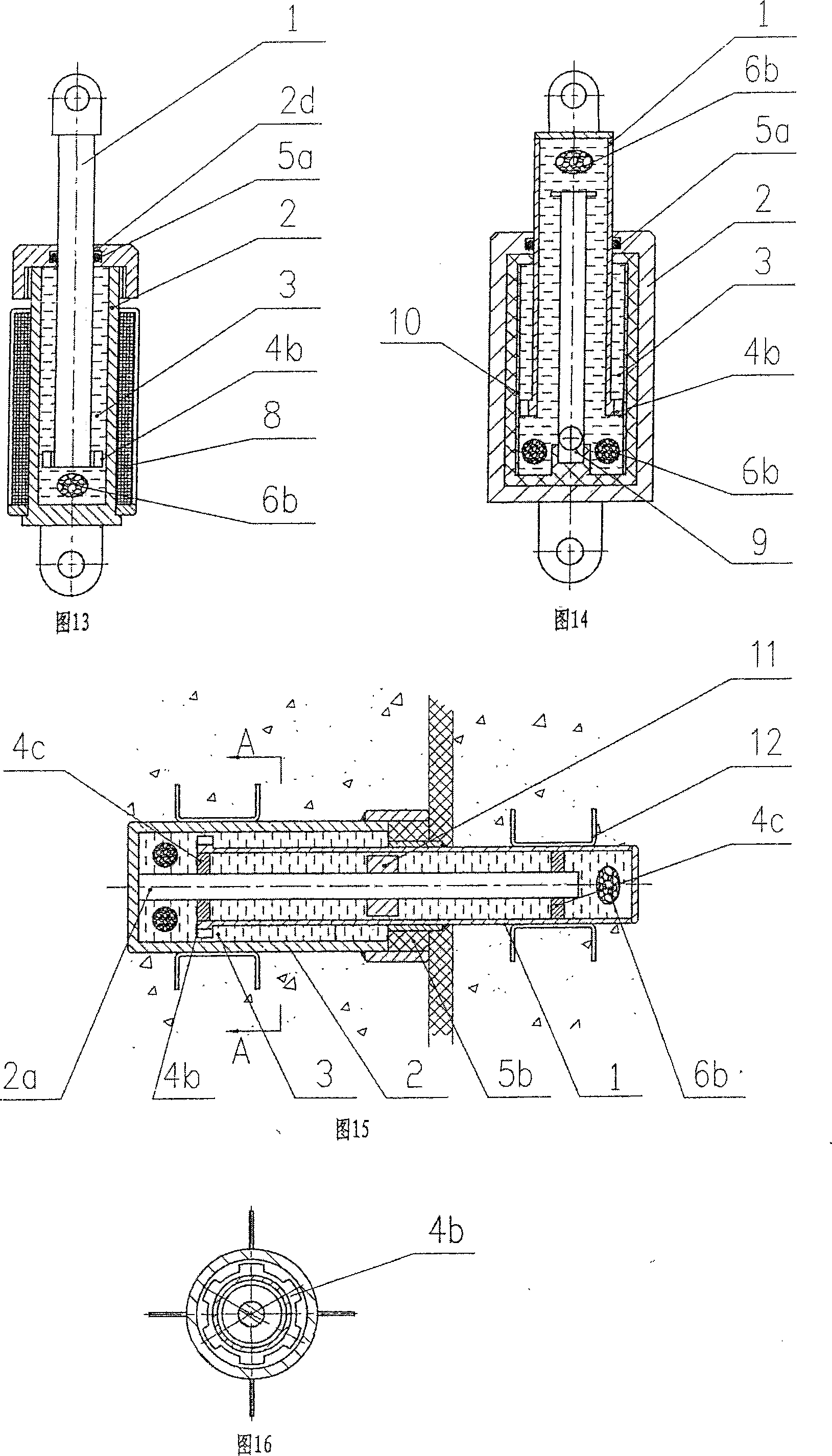
The invention relates to a viscous damper with an axial spacing device, which comprises a left spherical hinge seat, a piston rod, a piston, a damping cylinder body, a balancing bar, a right spherical hinge seat, damping medium, a combined disk spring, a spacing cylinder body, a pressure ring A, and a pressure ring B. The spacing cylinder body is arranged between the damping cylinder body and the right spherical hinge seat, internal threads are arranged at two ends of the spacing cylinder body, the left end of the spacing cylinder body is connected with the damping cylinder body via the pressure ring A, the right end of the spacing cylinder body is connected with the right spherical hinge seat via the pressure ring B, the length of the balancing bar is extended into the spacing cylinder body, a threaded small circular cylinder is arranged at the right end of the balancing bar, and the combined disk spring is installed on the small circular cylinder. Compared with the prior art, the inventive viscous damper can meet the technical requirements on dynamic energy dissipation for shock resistance, and meet the technical requirements on static load and excessive displacement limit.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF MATERIALS CO LTD
Offshore wind power spar buoyant foundation capable of towing
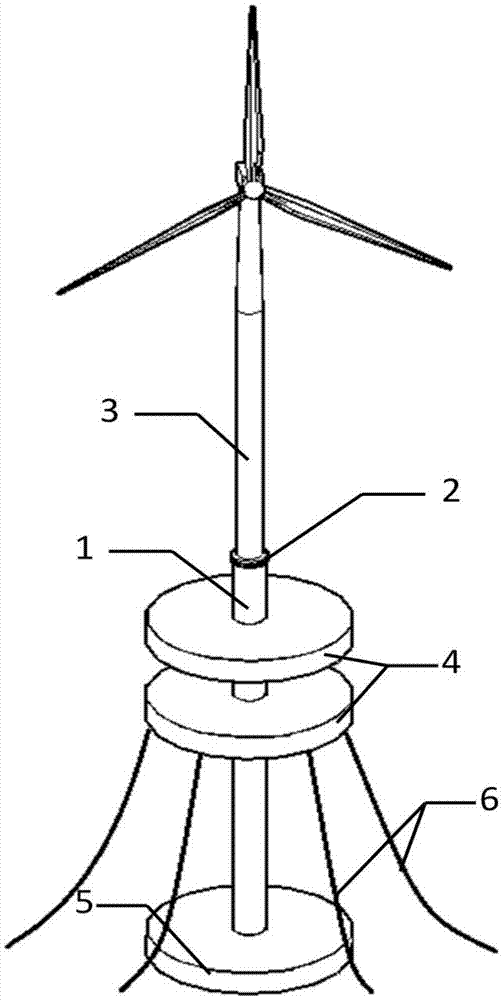
ActiveCN105438411AReduce resistanceSkip the dry mopping processFoundation engineeringFloating buildingsStress concentrationFatigue damage
The invention relates to an offshore wind power buoyant foundation form and in particular relates to an offshore wind power spar buoyant foundation capable of towing, which comprises a connecting column and is characterized in that the upper end of the connecting column is connected with a fan through a flange ring, a plurality of flat columnar closed air flotation boxes are arranged at the middle part of the connecting column, the closed air flotation boxes are not communicated with the connecting column, and the bottom of the connecting column is communicated with a loading cabin; a column body of the connecting column is provided with a detachable gear required for towing; and a mooring rope is arranged at the center of gravity of the buoyant foundation. Compared with the prior art, the offshore wind power spar buoyant foundation provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the construction is convenient, rolling towage can be realized, the resistance of a wave flow is reduced, the stress concentration and fatigue damage caused by the traditional spar foundation in a wet towing process are avoided, the construction difficulty and construction cost are greatly reduced, and the offshore wind power spar buoyant foundation can be recycled. The additional mass and viscous damping of heave motion are effectively improved by virtue of the flat air flotation boxes, the water surface profile area of a buoy is effectively increased by virtue of the flat air flotation boxes on the water surface, a relatively large restoring moment is provided, the structure stability is relatively good, the center of gravity is lower than the center of flotation, and the resistance to capsizing is good.
Owner:CEEC JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST
Spiral groove structured magneto-rheological damper
InactiveCN1865729AIncrease Coulomb forceAdjustable sizeSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionViscous dampingEngineering
The invention discloses a screw groove magnetic flow changeable damper, which comprises a cylinder, a piston inside the cylinder, a piston rod connected to the piston, an exciting coil mounted on said piston. Wherein, the outer side wall of piston and the inner wall of cylinder have throttle channel between them; the wall of piston has screw groove. The invention has the advantages that: via the micro and concentrated screw grooves, the coulomb force of yield flow can be improved without improving viscous damping force; the via the screw pattern, the peak of damping force can be adjusted; the invention can avoid local accumulation of magnetic flow changeable liquid, to avoid foam; and it can prevent the deposition of magnetic flow changeable flow.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Scanning miniature optical probes with optical distortion correction and rotational control
Optical probes having a diameter less than substantially 500 mum for use in scanning light from a long, highly flexible fiber to a sample. In one embodiment the probe includes a viscous damping fluid suitable to prevent non-uniform rotational distortion (NURD).
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
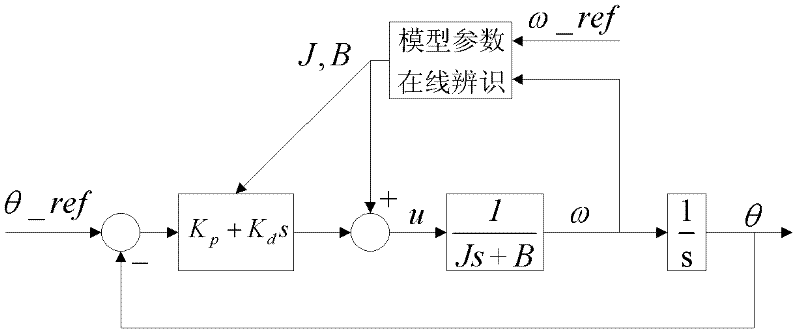
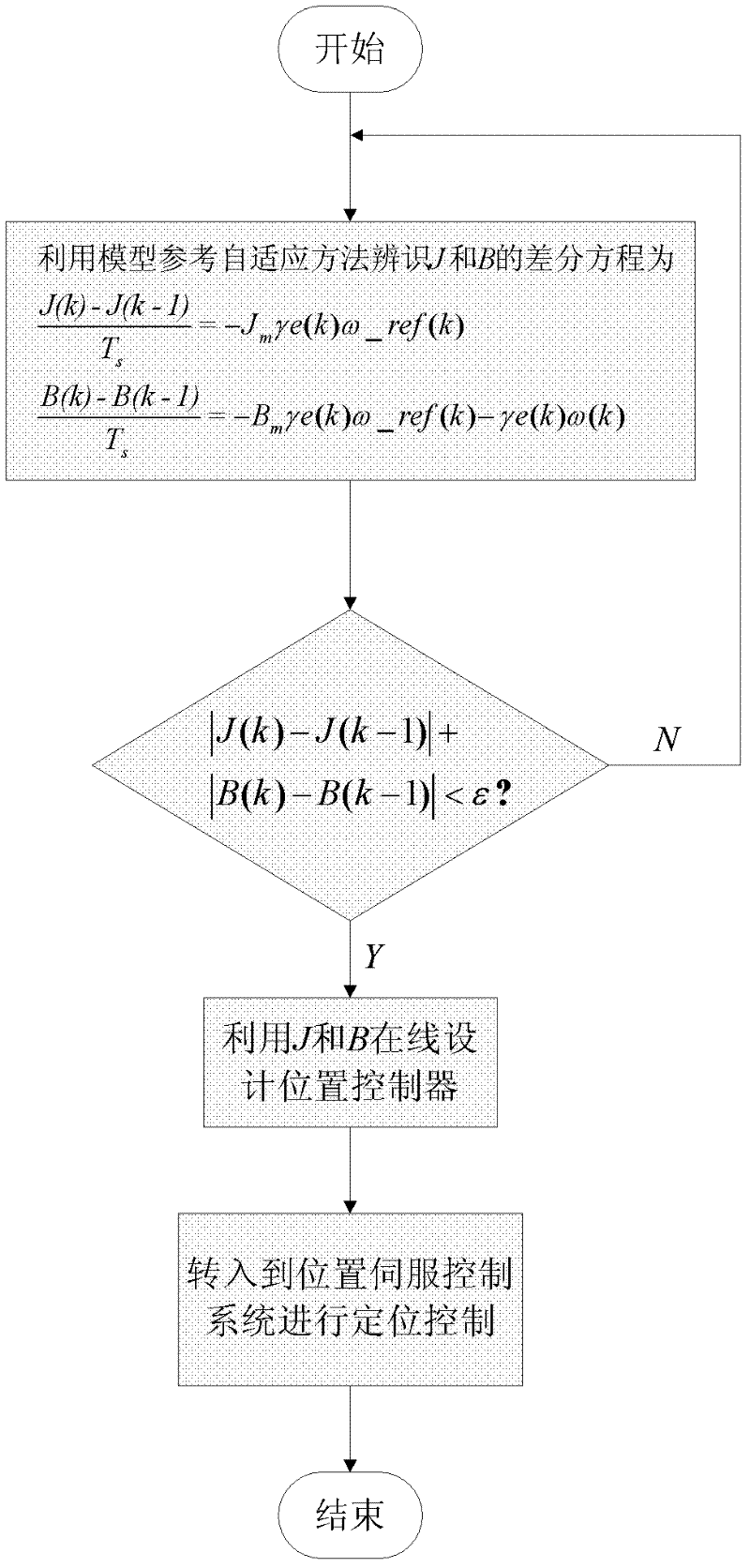
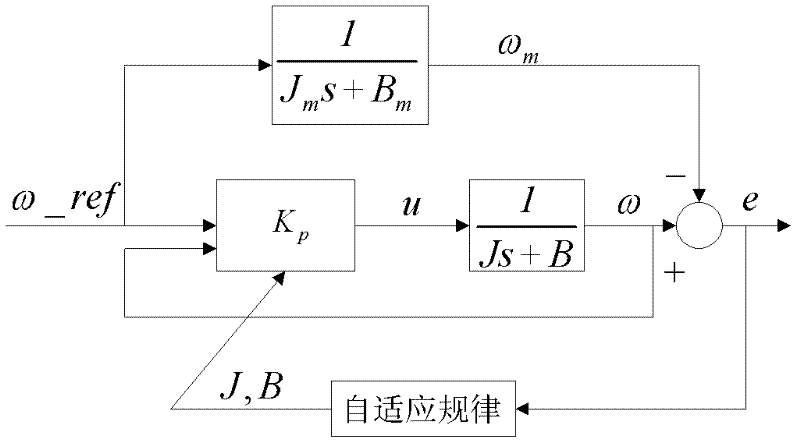
On-line identification and control method for parameter of alternating current position servo system model
The invention discloses an on-line identification and control method for a parameter of an alternating current position servo system model. According to the invention, a model reference adaptive identification algorithm based on a Lyapunov stability theory is utilized; and on-line identification is carried out on a rotary inertia J and a viscous damping coefficient B of a controlled object of an alternating current servo system; after convergence is carried out on an identification parameter, an on-line design on a position controller is carried out according to J and B values and the design is automatically switched to position control. According to the invention, an efficiency on an alternating current servo system design can be substantially improved.
Owner:常州固高智能装备技术研究院有限公司
Novel three-dimensional seismic isolation device
InactiveCN103774551AExtend the vertical cycleEnsure safetyBridge structural detailsVibration suppression adjustmentsViscous dampingStructural engineering
The invention provides a novel three-dimensional seismic isolation device which comprises a horizontal seismic isolation component, a transition steel structural platform and a vertical seismic isolation component. The horizontal seismic isolation component is fixedly connected with the vertical seismic isolation component by the transition steel structural platform; and the vertical seismic isolation component comprises an upper sleeve, a lower sleeve, a lower bottom plate, a belleville spring, a middle guide rod and viscous damping fluid. The novel three-dimensional seismic isolation device is simple and convenient to manufacture and is convenient to construct, install and maintain; horizontal damping and vertical damping are decoupled mutually and are not involved mutually. Due to adoption of the belleville steel plate spring, the novel three-dimensional seismic isolation device has low vertical stiffness when vertically moving, so that the vertical period of an upper structure is prolonged and the earthquake action is reduced; and meanwhile, a good viscous hole is formed by a gap between the belleville spring and the lower sleeve for the viscous damping fluid in the lower sleeve and a butterfly steel plate takes an effect of a piston in a viscous damper, so that the vertical earthquake action is further reduced by energy dissipation and safety of the upper structure is ensured.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
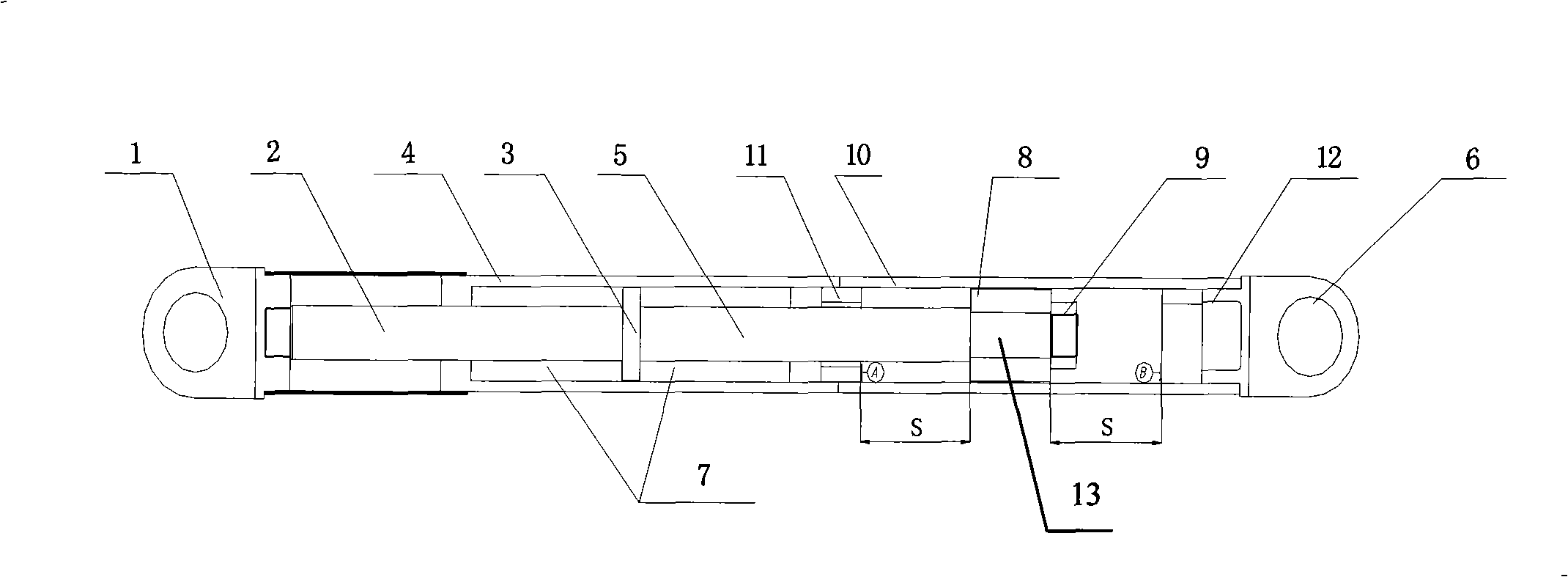
Viscous damping limiting method with limiting device and viscous damper
ActiveCN101942868AGood dynamic responseMeet the static limit requirementsShock proofingViscous dampingEngineering
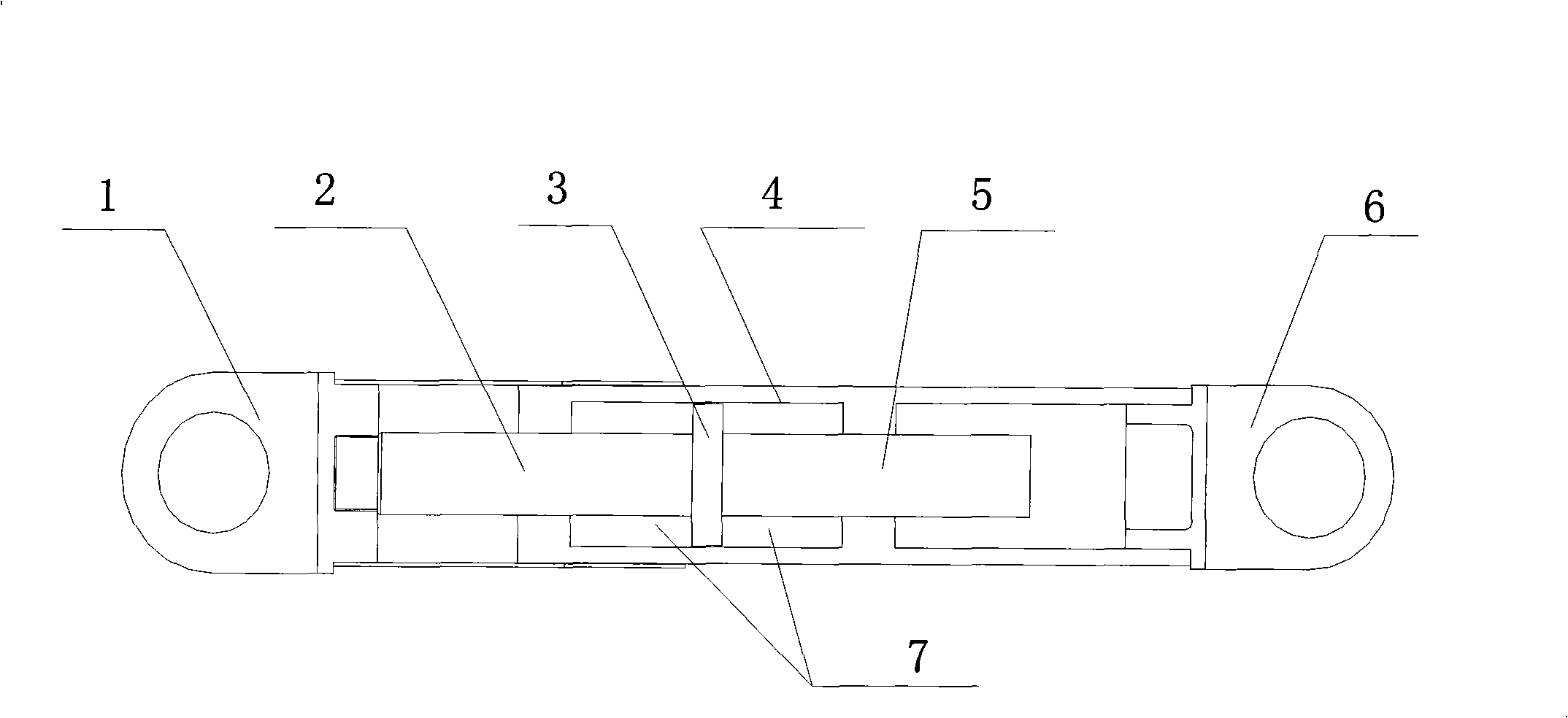
The invention discloses a viscous damping limiting method with a limiting device; the limiting device is arranged between a left ear ring and a right ear ring at one side of a conventional viscous damper; the viscous damper is limited through the limiting device when the static load deformation thereof exceeds the design stroke; the limiting device is in an elastic rubber block structure; and the elastic rubber block structure is connected with a piston rod at one end of the viscous damper, and performs the limiting function through the compression of the elastic rubber block when the static load deformation of the viscous damper exceeds the design stroke. The invention has the effects of improving the dynamic response to the structure and generating the limit resistance to the excessive displacement of the structure. Compared with the prior art, the invention has simple structure, and saves cost and installation space.
Owner:ZHUZHOU TIMES NEW MATERIALS TECH
Method for tuning and optimizing parameters of dynamic absorber based on machining process
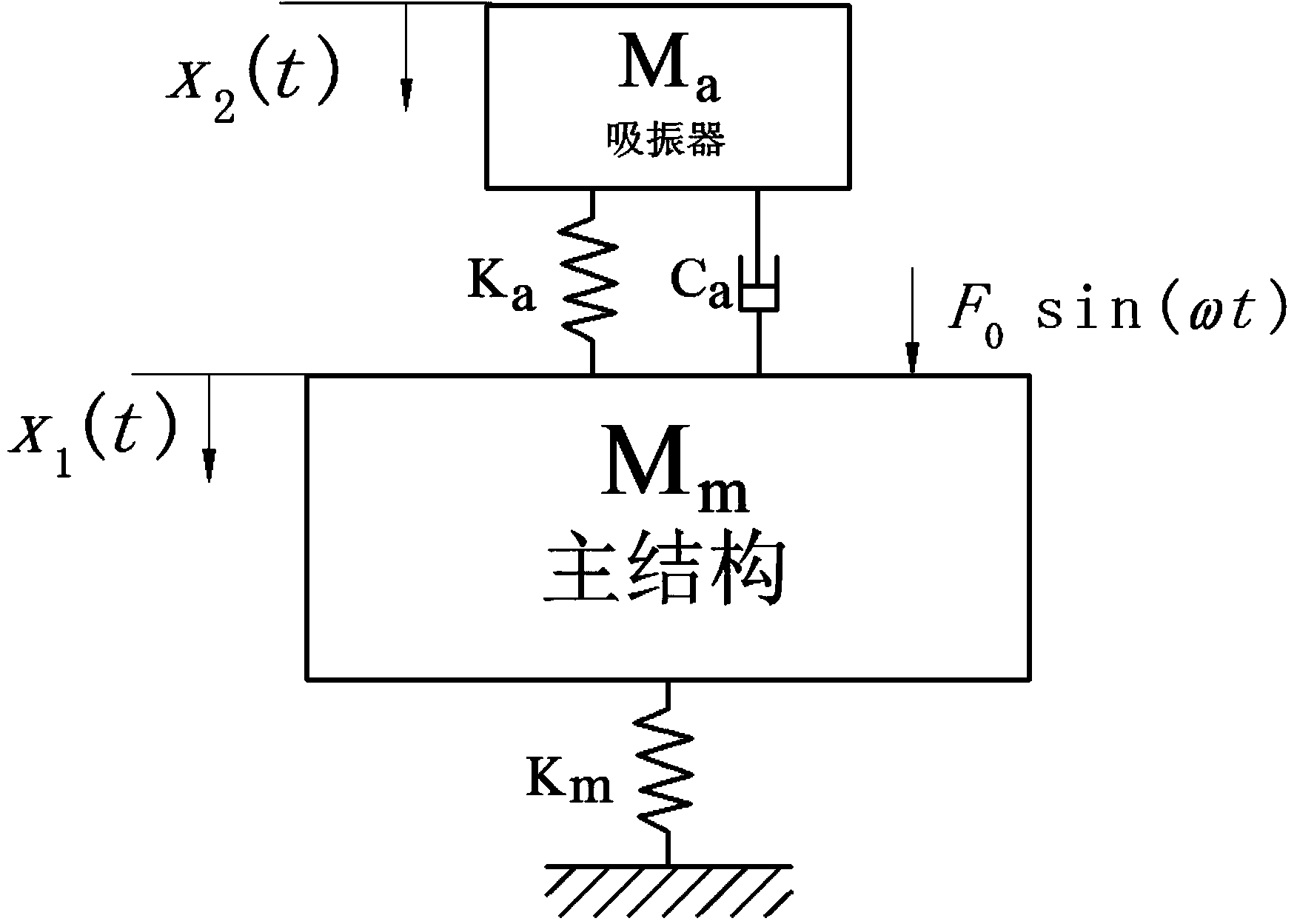
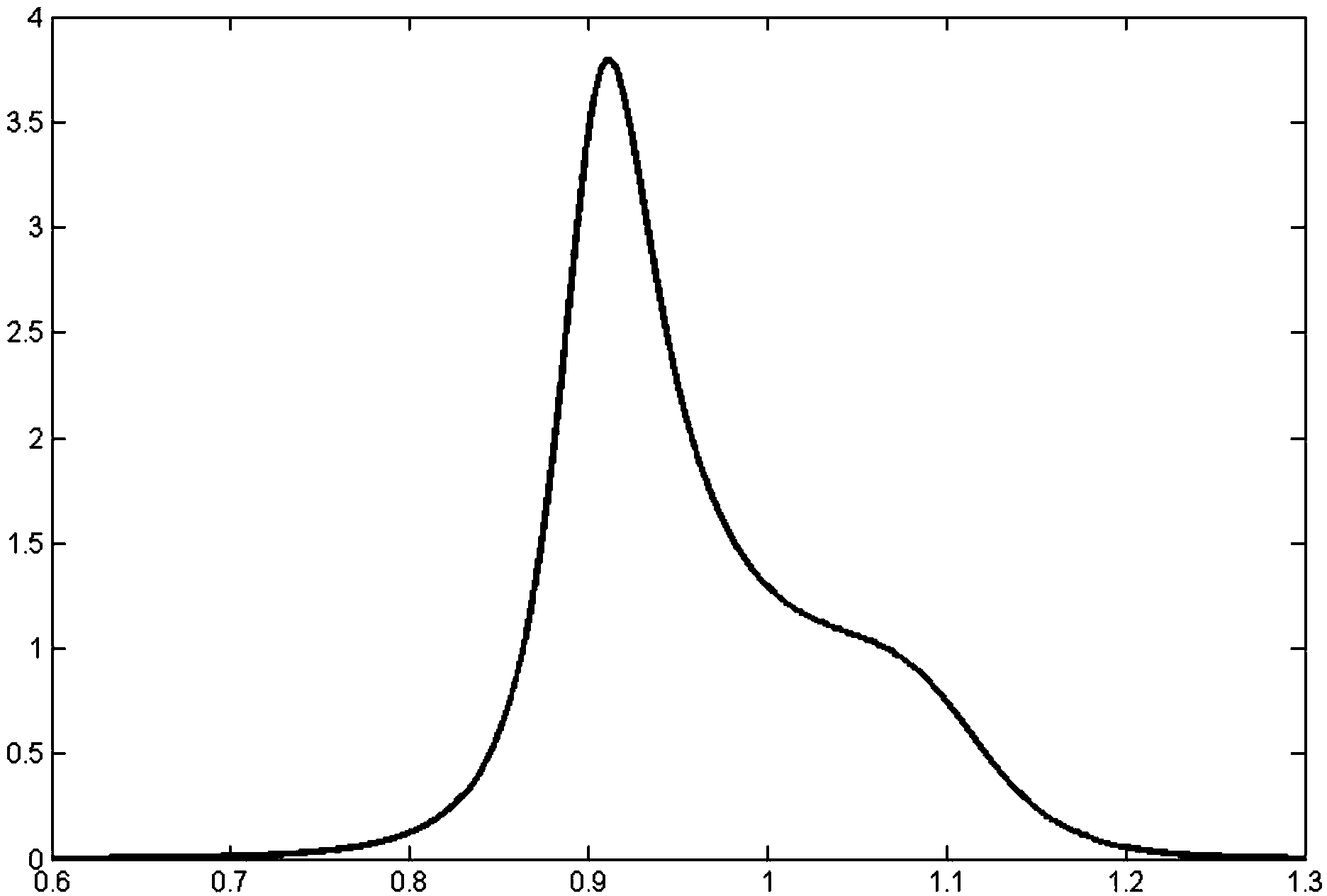
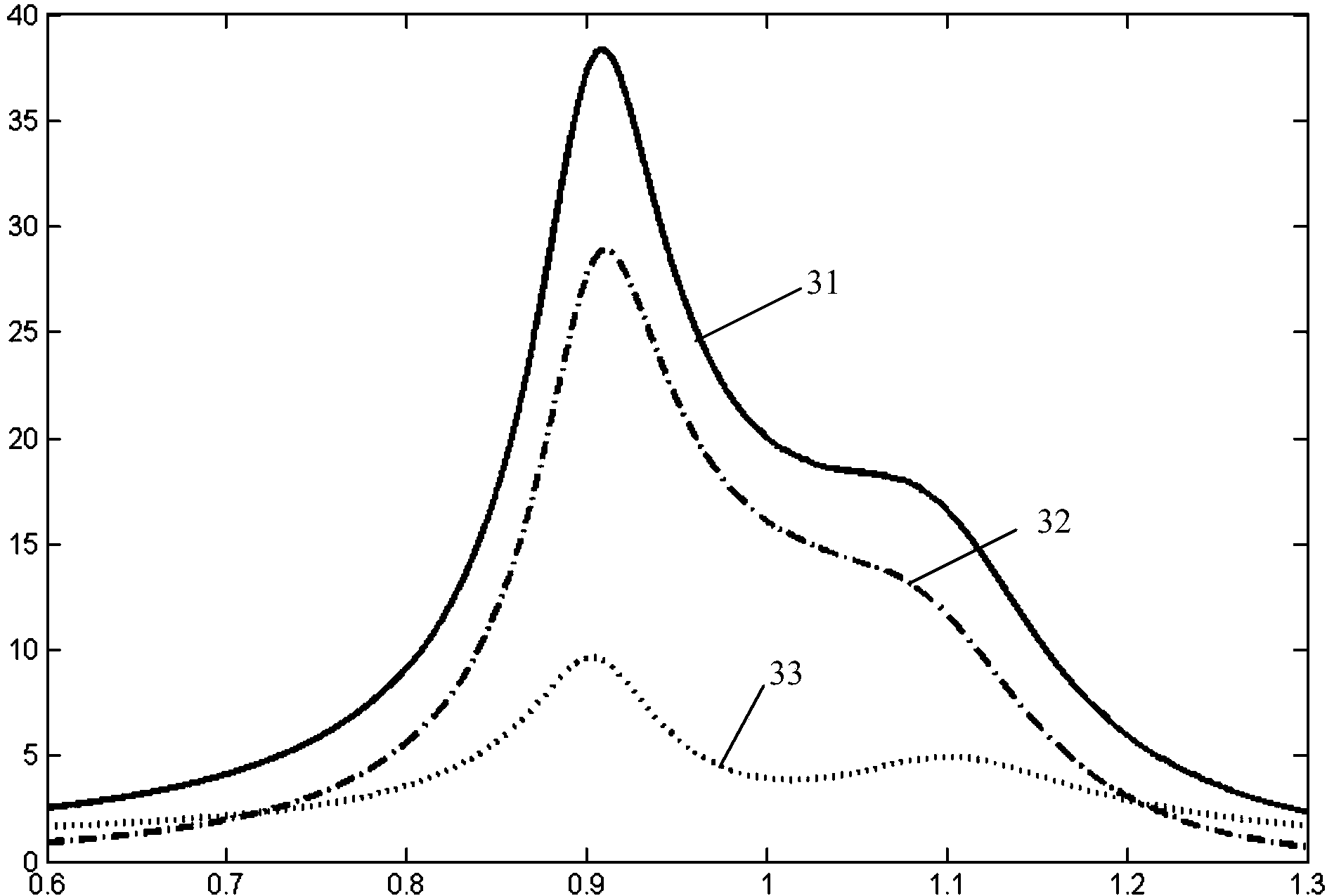
InactiveCN103455728AQuick responseClear thinkingSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelMass ratio
The invention discloses a method for tuning and optimizing parameters of a dynamic absorber based on a machining process, which comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a mathematical model of two degrees of freedom of a vibration system, and then solving the amplitude of the steady-state solution of a dynamics differential equation; taking the relative displacements of a main structure and the dynamic absorber in the viscous damping energy consumption formula; drawing an energy curve, and then making a statistics of the relation between a single factor vibration and the energy peak value; according to the statistics data, fitting the optimal frequency ratio and the optimal damping ratio corresponding to each mass ratio; according to the frequency range of an external disturbance signal, performing integration on the energy that the dynamic absorber can absorb; then, drawing an energy histogram and finding the maximum value so as to obtain the optimal mass ratio; finally, obtaining all optimal parameters of the dynamic absorber. With adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the vibration caused by external disturbance can be restrained, so that the response speed can be improved by about 50%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Speed limiting for rotary driven sprinkler
InactiveUS7232078B2Speed is limitedReduce speedWatering devicesMovable spraying apparatusViscous dampingLow speed
A speed limiting mechanisms for turbine-driven fluid distribution apparatus usable with compressible fluid such as compressed air and incompressible fluid such as water. Dynamic viscous damping of the turbine output power train is used to control the rotational speed of the turbine. This prevents overspeeding when the turbine is air driven, and also when the turbine is water driven, under abnormal conditions such as blockage of a bypass area designed to control the turbine speed by limiting flow to the turbine. The same mechanism can be used to impose a lower rotational speed in the turbine during normal operation in conjunction with a turbine optimized for lower speed operation to reduce the required gear reduction in the power train.
Owner:KAH JR CARL L
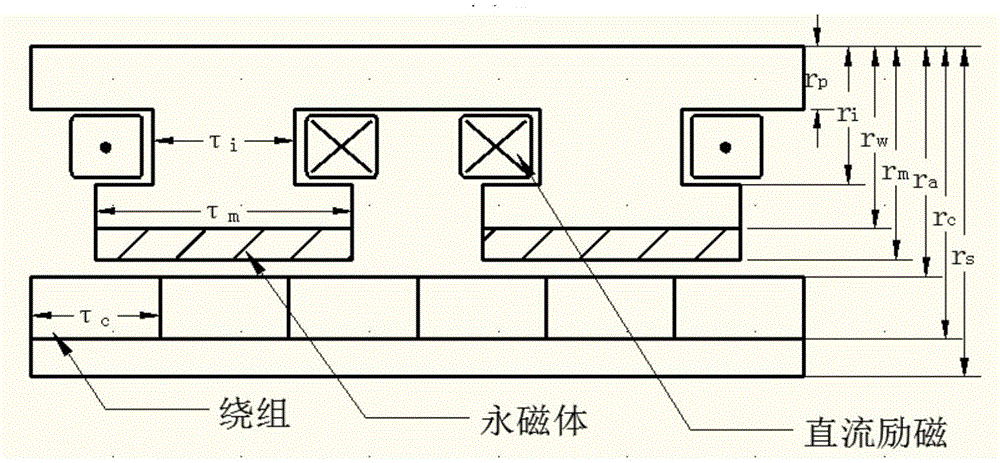
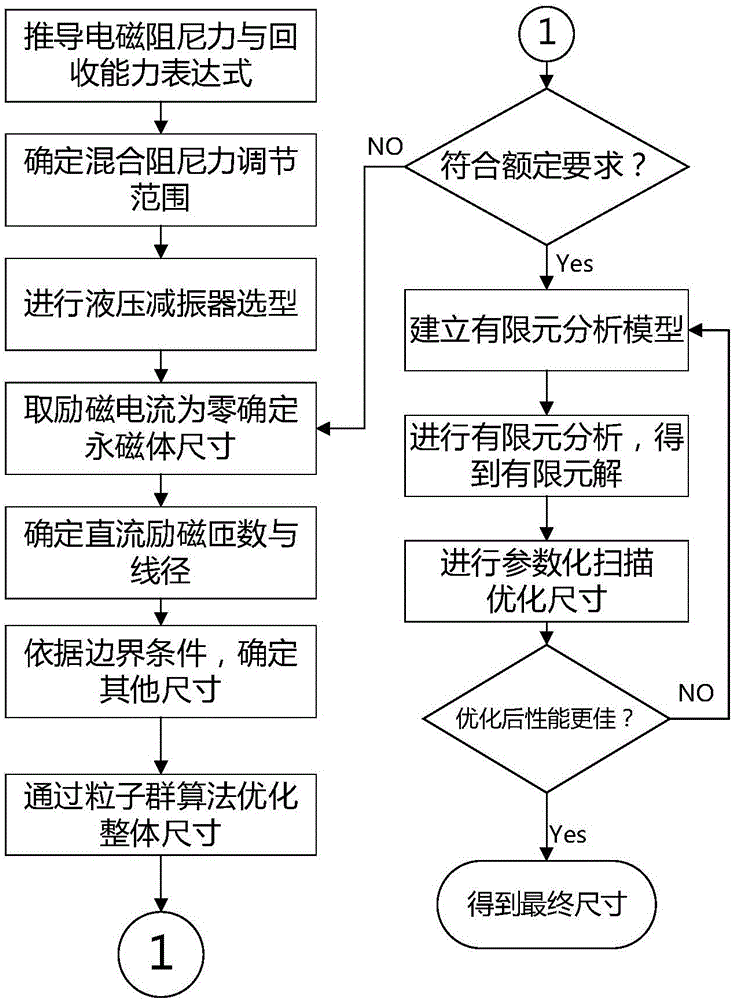
Semi-active energy regenerative suspension shock absorber based on mixed excitation and size determining method of shock absorber
ActiveCN106224425AAdjustable damping forceGood vibration isolationGeometric CADAuxillary drivesViscous dampingSemi active
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method and apparatus for compensating for nonlinear distortion of speaker system
InactiveUS7359519B2Improve output signal qualityEasy to implementTransducer circuit dampingFrequency response correctionViscous dampingNonlinear distortion
A method and an apparatus for compensating for nonlinear distortion are provided to divide audio signals reproduced in a nonlinear speaker system into linear and nonlinear components in a time domain and a frequency domain, and then generate inversely-corrected signals by means of an inverse filtering scheme, so that it is possible to further consider a variety of nonlinear distortion characteristics such as viscous damping and structural damping which have not been reflected in the conventional lumped parameter method, and thus to obtain better sound quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magneto-rheological damper
ActiveCN102913587AChange sizeChange viscositySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagneto rheological damperControl theory
A magneto-rheological damper comprises a cylinder barrel, a left end cap, a piston rod, a piston, a right end cap, a connecting barrel, a winding barrel, a coil, an external guide magnet and a cap nut. The magneto-rheological damper has the advantages that the coil slides on the cylinder barrel in the direction identical with motion direction of the piston rod, so that a magnetic core on the piston and the external guide magnet are always guaranteed to form a closed magnetic loop, flow guiding can be functioned by an axial central hole and a radial hole in the piston, and magneto-rheological fluid viscosity can be changed by changing the size of the holes during working of the damper, and further, high-viscosity damping force can be generated. The coil is arranged outside the cylinder barrel, convenient for winding, convenient to maintain and check and good in sealing performance. By directly inflating the damper, extra purchasing an energy storage device is omitted, and the magneto-rheological damper has high applicability. Since the magneto-rheological damper is good in damping property, the magneto-rheological damper can be mounted on mechanical structures required to be damped, such as suspension damping of automobiles, damping of undercarriages of planes, damping of seats and bridges.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
All-shearing type magneto-rheological damper
ActiveCN104179877AEffective control rangeIncreased controllable damping ratio rangeNon-rotating vibration suppressionViscous dampingVibration control
The invention discloses an all-shearing type magneto-rheological damper. The all-shearing type magneto-rheological damper is characterized by comprising an outer cylinder, an inner cylinder and a ball screw pair, wherein the inner cylinder is coaxially arranged with the outer cylinder, shearing discs are fixed by the ball screw pair, the inner wall of the inner cylinder is provided with electromagnetic coils and sharing ring sets corresponding to the shearing discs one by one, magneto-rheological liquid is filled in a cavity of the inner cylinder, at least one electromagnetic coil is arranged between adjacent shearing rings fixed on the inner wall of the inner cylinder, and the shearing discs, the shearing rings and the inner cylinder form a closed flux loop. On the premise of keeping same external size and energy consumption of a magneto-rheological damper, null-field viscous damping of the magneto-rheological damper is reduced, controllable damping ratio range is enlarged, and the all-shearing type magneto-rheological damper is added with potential for application to a high-speed impact / vibration control system. Besides, service efficiency of the magneto-rheological liquid in the magneto-rheological damper is improved, and cost of the magneto-rheological damper is effectively reduced.
Owner:ANQING HUITONG AUTOMOTIVE PARTS
Viscous damping wall
InactiveCN105019571AImprove plasticityEasy to processWallsShock proofingViscous dampingMechanical engineering
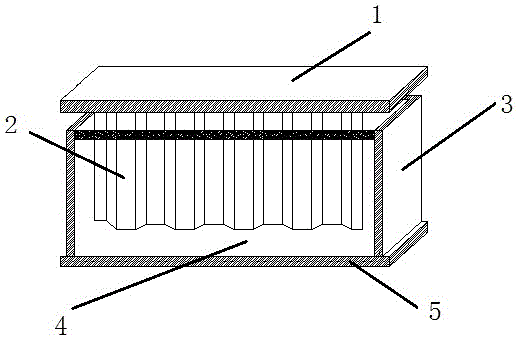
The invention relates to a viscous damping wall. The viscous damping wall comprises an upper connecting plate, inner steel plates, an outer steel box, a viscous damping material and a lower connecting plate, wherein the upper connecting plate is fixed to the bottom of an upper-layer floor beam; the inner steel plates are fixed to the central portion of the bottom surface of the upper connecting plate; the outer steel box is fixed to the lower connecting plate; the lower connecting plate is fixed to the top of a lower-layer floor beam; the outer steel box is filled with the viscous damping material; and the inner steel plates are arranged in the viscous damping material. The inner steel plates are designed into zigzag type soft steel plates, the parameter scopes of an ideal energy consumption test piece are respectively: a height b ranges from 380mm to 420mm, a width d ranges from 780mm to 820mm, a thickness t ranges from 4mm to 6mm, a half-wave amplitude H ranges from 25mm to 35mm, a wavelength lambda ranges from 190mm to 210mm, and a zigzag mode is a curved form or a trapezoidal form. According to the invention, conventional inner steel plates are designed into the zigzag type soft steel plates, and the soft steel plates, compared to conventional inner steel plates, are higher in plasticity, good in processing formability and weldability and is conveniently manufactured and connected.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
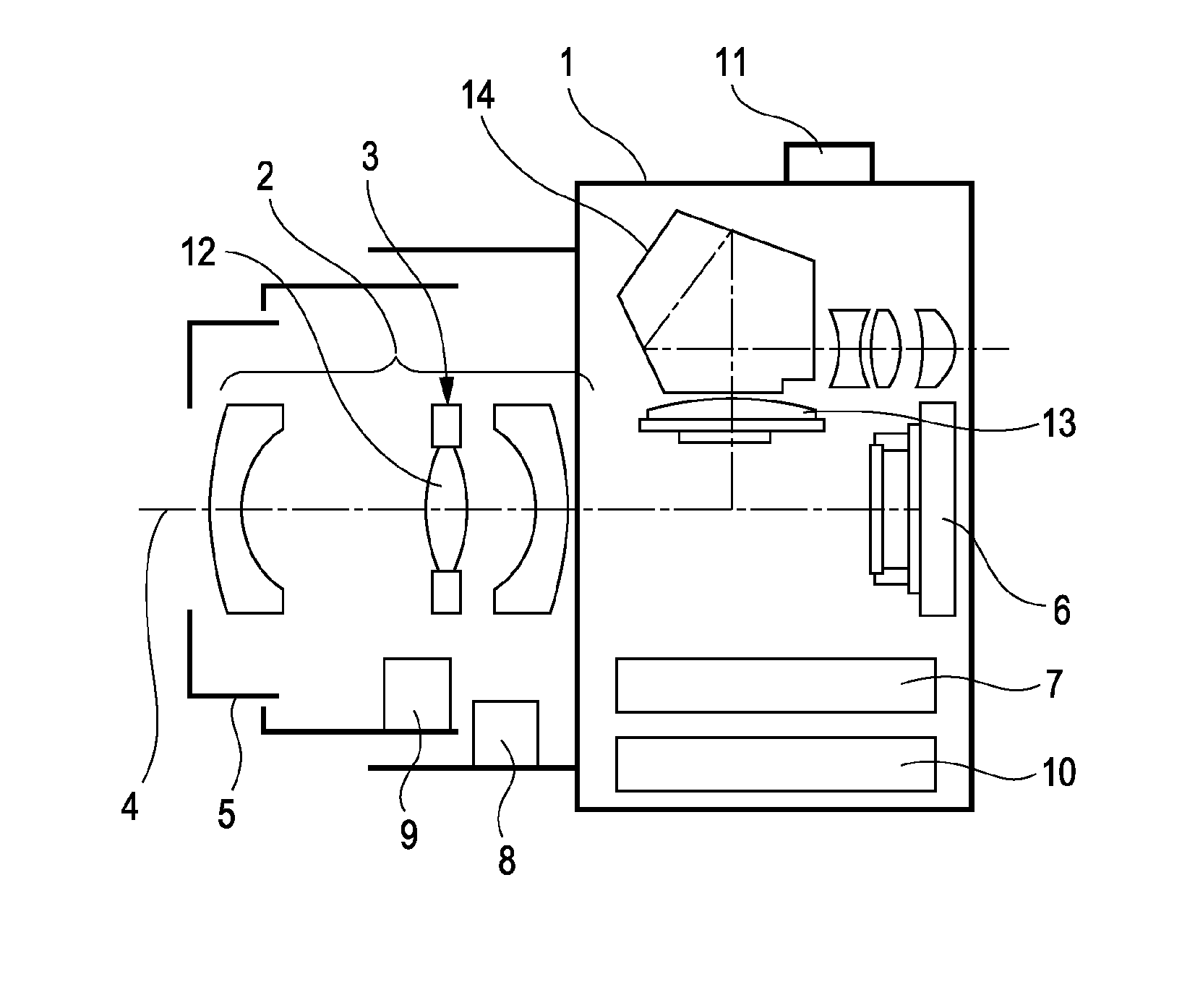
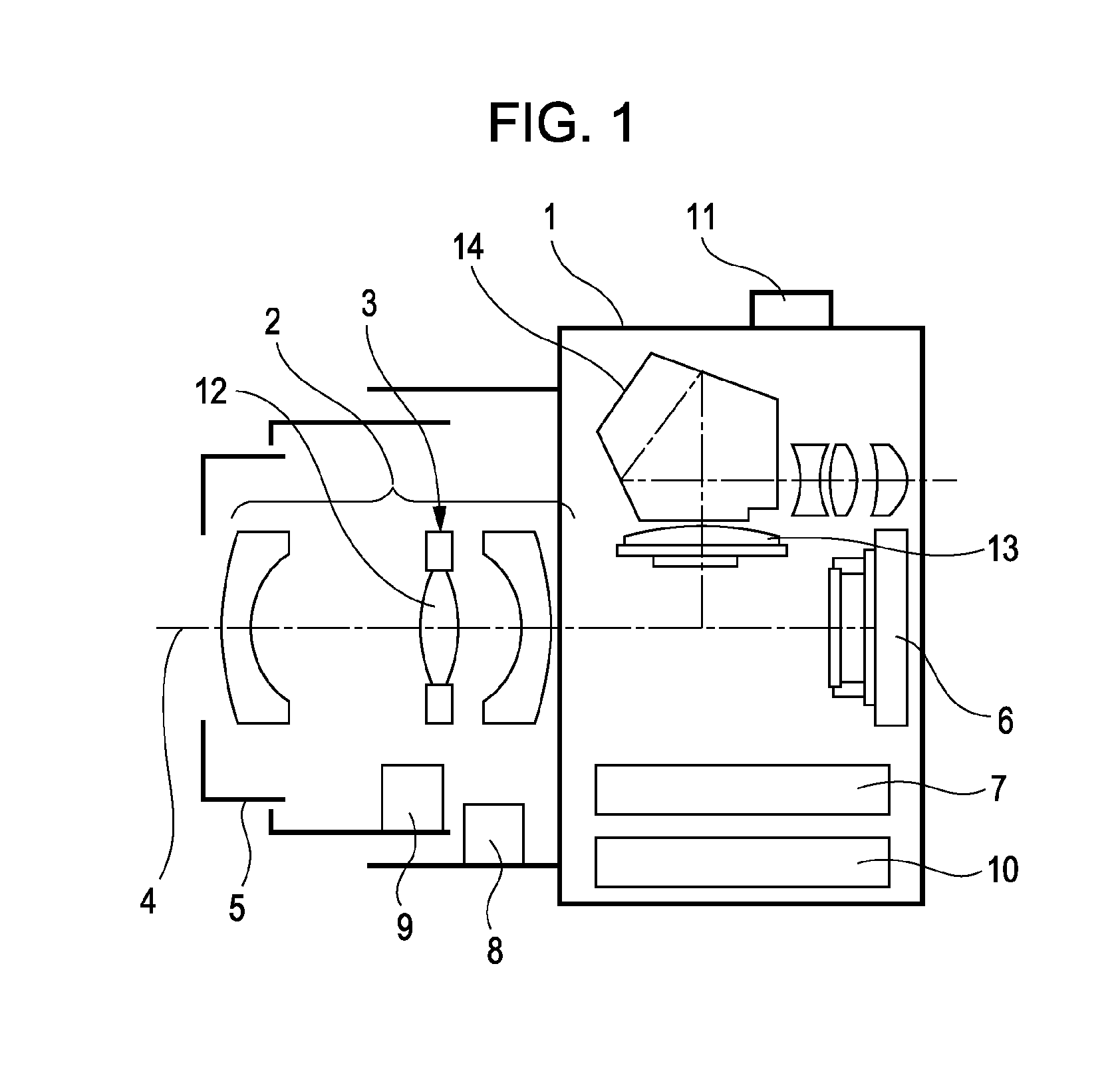
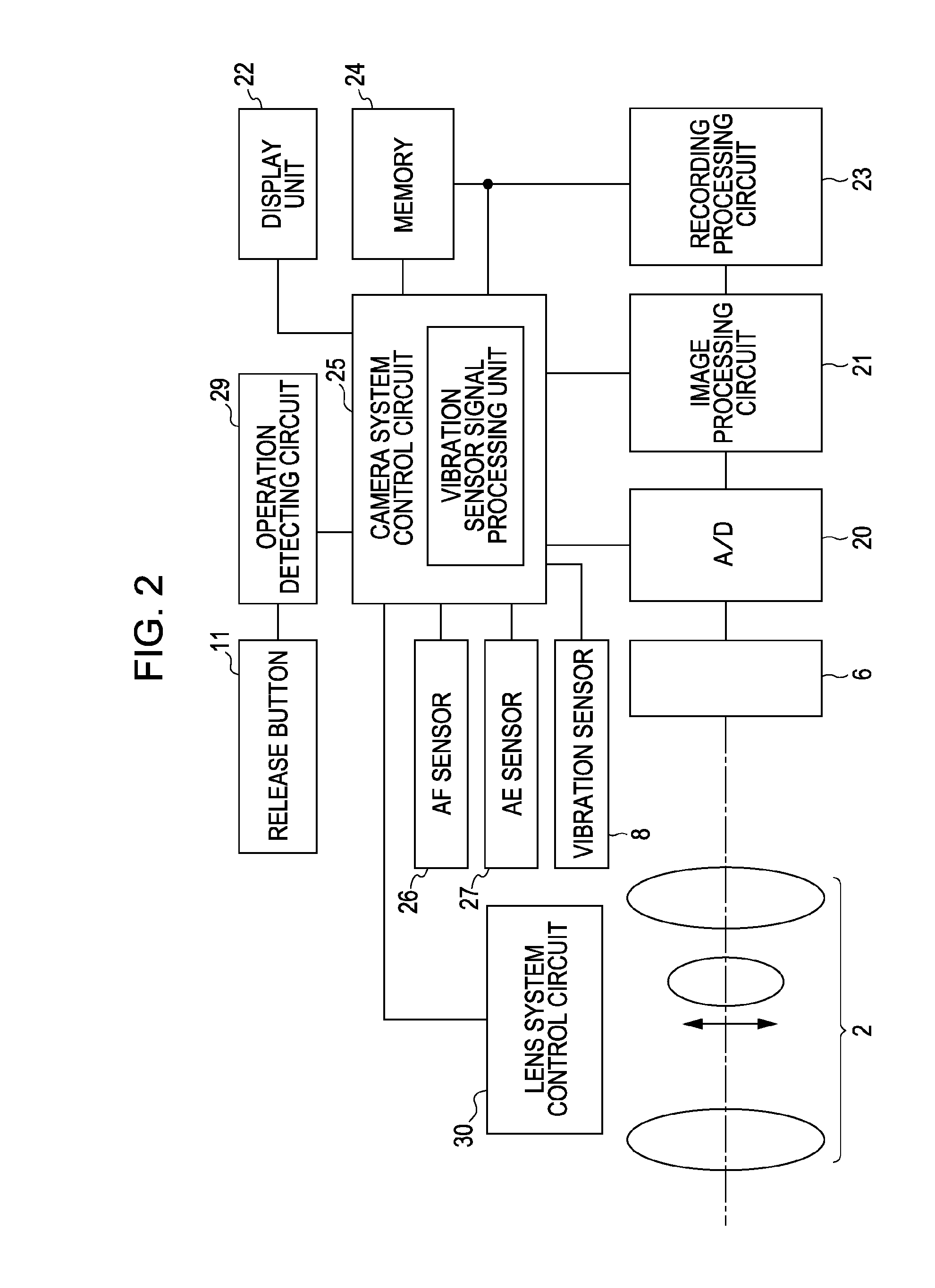
Lens driving device, image stabilizing unit, and image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS20100214426A1Simple structureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsViscous dampingOptical axis
A lens driving device having a simplified structure in which a holding member is moved relative to a stationary member with appropriate viscous damping is provided. The lens driving device includes the holding member configured to hold a compensation lens for image stabilization, the stationary member configured to support the holding member in a movable manner in a plane that is perpendicular to a light axis, a driving unit configured to change the position of the holding member relative to the stationary member, and a damping material disposed between the holding member and the stationary member. The damping material has a transition region in a frequency range between 0.3 Hz and 100 Hz.
Owner:CANON KK
Multistage articulated viscous damping wall
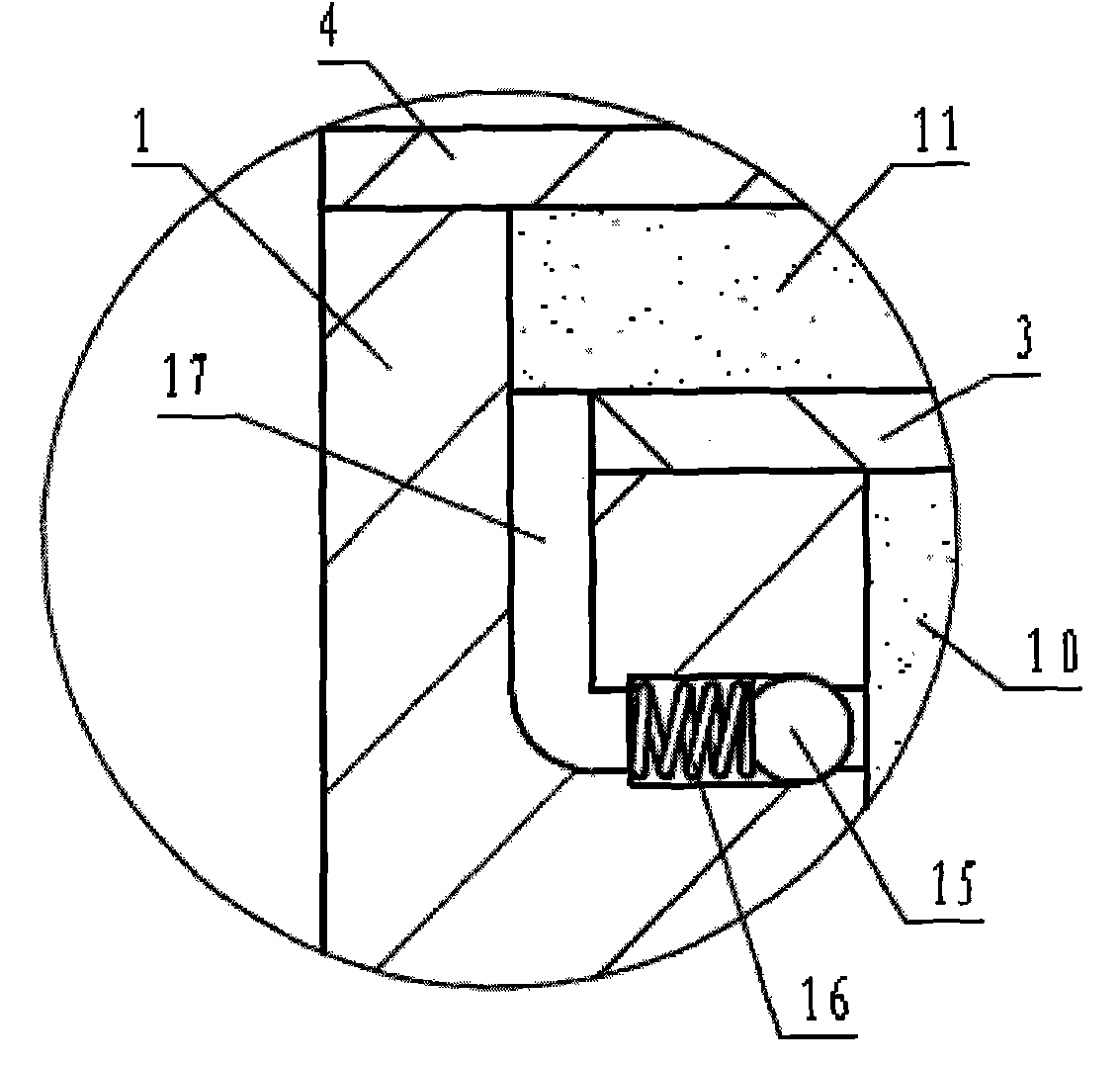
InactiveCN103835392AReduce bending deformationImprove energy consumptionWallsFire proofingViscous dampingMetallurgy
The invention discloses a multistage articulated viscous damping wall. The multistage articulated viscous damping wall comprises an inner steel plate and is characterized in that the inner steel plate is composed of an upper inner steel plate (15) and a lower inner steel plate (16), the upper inner steel plate (15) and the lower inner steel plate (16) are connected in a relative rotating mode, the inner steel plate is arranged in a box-structure steel box body (7) with the top end opened and the bottom and the side faces closed, the top end of the inner steel plate stretches out of the top end opening of the steel box body (7), the bottom end of the steel box body (7) is rigidly connected with a lower connecting plate (1), top stretch-out steel plates (13) perpendicularly stretching out for a certain distance are arranged on the peripheral edges of the top end opening of the steel box body (7), and a top sealing plate is arranged at the top end of the inner steel plate. The problem of deforming of the inner steel plate is reduced, and energy dissipating capacity of the damping wall is enhanced; when face external face is generated, rotating deformation of the inner steel plate will not be generated; the stability and the fire resistance of the damping wall are enhanced.
Owner:陈明中
Adaptive linear magnetic liquid damping vibration absorber
InactiveCN104500640AChange the stiffnessIncrease displacementSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionViscous dampingInertial mass
The invention relates to an adaptive linear magnetic liquid damping vibration absorber and belongs to the field of mechanical engineering vibration. A vibration pick-up system of the vibration absorber consists of an inertial mass block and a magnetic reed structure; the rigidity of a magnetic reed can respond to external vibration and can be automatically adjusted; the damping of the vibration absorber consists of electromagnetic damping and viscous damping. A cylindrical permanent magnet adsorbing magnetic fluid serves as the inertial mass block, is positioned in a circular tube, and is subjected to the action of repulsion of magnetic fields of a permanent magnetic sheet and an excitation coil at two ends of the circular tube; the magnetic repulsion resultant force provides restoring force for the inertial mass block, wherein the magnetic repulsion provided by the excitation coil is changeable, and is controlled by collection energy of an induction coil positioned on the outer wall of the circular tube from the external vibration, so the inherent frequency of the magnetic liquid vibration absorber adapts to the external vibration and constantly approaches to the frequency of the external vibration, and the vibration damping performance is improved.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Viscous damper
InactiveCN103671677AReduce damping forceReduce volumeSpringsLiquid based dampersViscous dampingCylinder block
The invention belongs to the technical field of damping (vibration reduction), and particularly relates to a viscous damper. The viscous damper comprises a cylinder body, a cylinder cover, a piston rod, a piston head, a guide sleeve and sealing and viscous damping fluid. The cylinder body and the cylinder cover form a damping cavity, the damping cavity is divided into a first damping chamber and a second damping chamber through the piston head, a two-way holding valve is arranged on the piston head, and the two ends of the two-way holding valve are connected with the first damping chamber and the second damping chamber respectively. According to the viscous damper, the two-way holding valve is arranged on the piston head, when the speed of the viscous damper is larger than the critical speed, due to the fact that force exerted on a valve core of the holding valve is larger than preloaded pressure of a spring, the holding valve is closed, and consequently the output damping force of the viscous damper can reach a rated value. In addition, the viscous damper is compact in structure and convenient to install, and a two-way locking function can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING JIUZHOUYIGUI SHOCK & VIBRATION ISOLATION
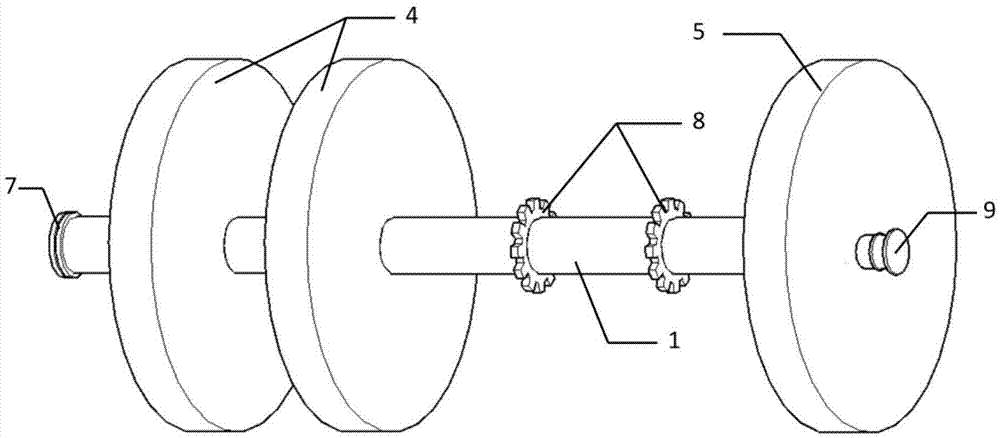
Compact compliant centering support for squeeze film damper
The present invention provides a centering feature to the bearing assembly of a turbomachine to provide optimum operating characteristics of the squeeze film damper. Unlike conventional bearing centering methods and apparatus, a compact compliant centering support for the squeeze film damper interfaces between a bearing outer race, and an outer support structure. The compact design is lightweight and inexpensive, can be retrofitted easily to an existing turbomachine, such as a turbine and compressor, for improved rotor dynamic performance. The compact compliant centering support damper may be comprised of a ring with bumpers spaced around the circumference at the inside and outside diameters to form spring elements between the bumpers. The centering support may lift the rotor inside the squeeze film cavity and may eliminate rotor weight effect on the damper performance. The centering support may be offset in the vertical direction to center the rotor under 1 g deflection to eliminate rub at the 6 o'clock location of a compressor or turbine shroud. Tangential grooves may be provided on the centering support outer bumpers to allow oil to squeeze out when the centering support is deflected to provide additional viscous damping. The outer bumper height may be controlled to limit maneuver deflection of the rotor.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Damper
InactiveCN101173703ASimple structureImprove performanceSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionViscous dampingEngineering
The invention relates to a damper, comprising a cylinder body and a moving body, wherein, part of the moving body is positioned in the cylinder body at least; at least one chamber extendable axially is arranged in the cylinder body; viscous damping liquid is filled in the chamber to form a damping chamber. The invention is characterized in that the moving body is formed with the moving vanes in the damping chamber, wherein, the vanes and the damping chamber form shearing chambers; the thickness of the shearing chamber is far less than the axial dimension of the shearing chamber; an elastic compensating body is arranged in the damping chamber or the compensating chamber communicated with the damping chamber. The invention has the advantages of mild damping, simple structure, low cost, stable performance, long service life, easy regeneration, and environmental protection.
Owner:尹学军 +1
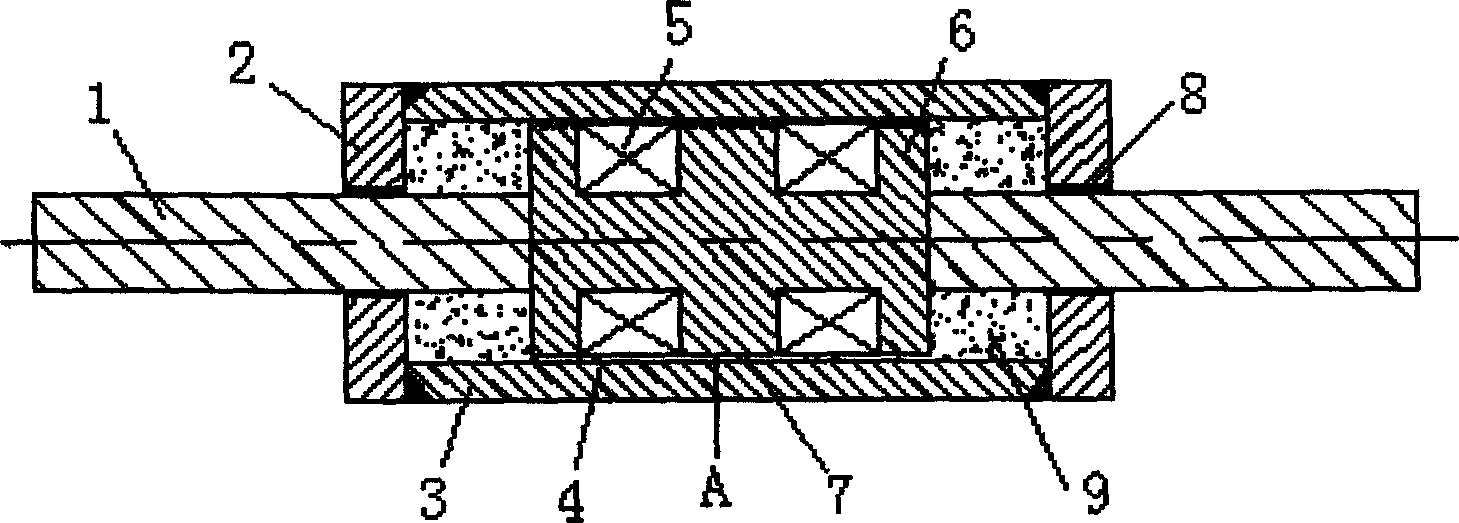
Composite damping single-piston rod viscous damper
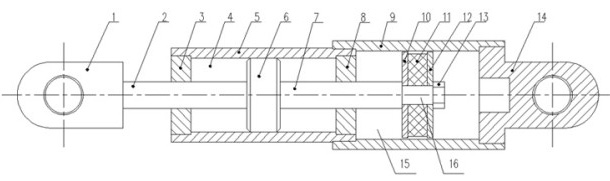
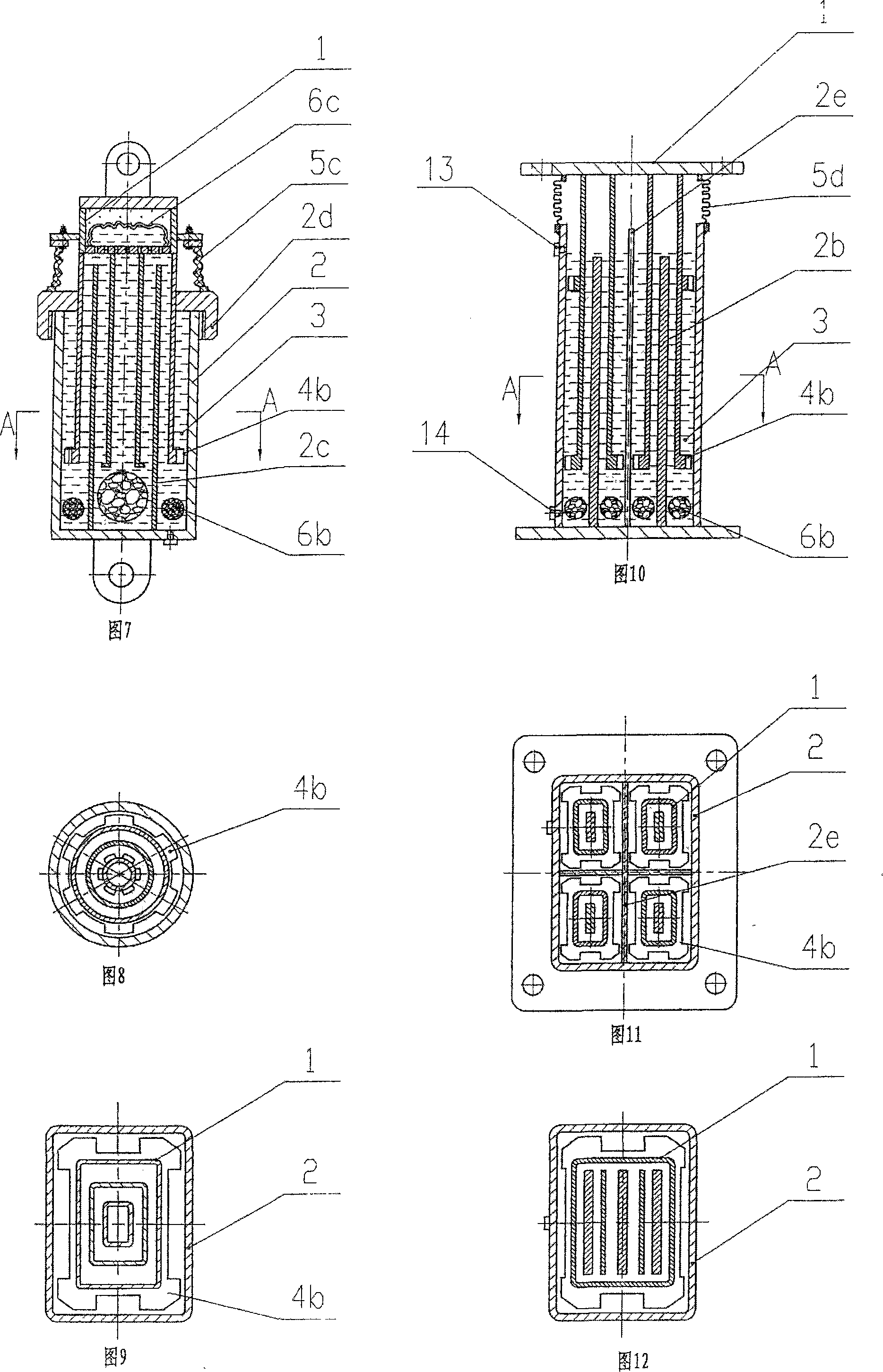
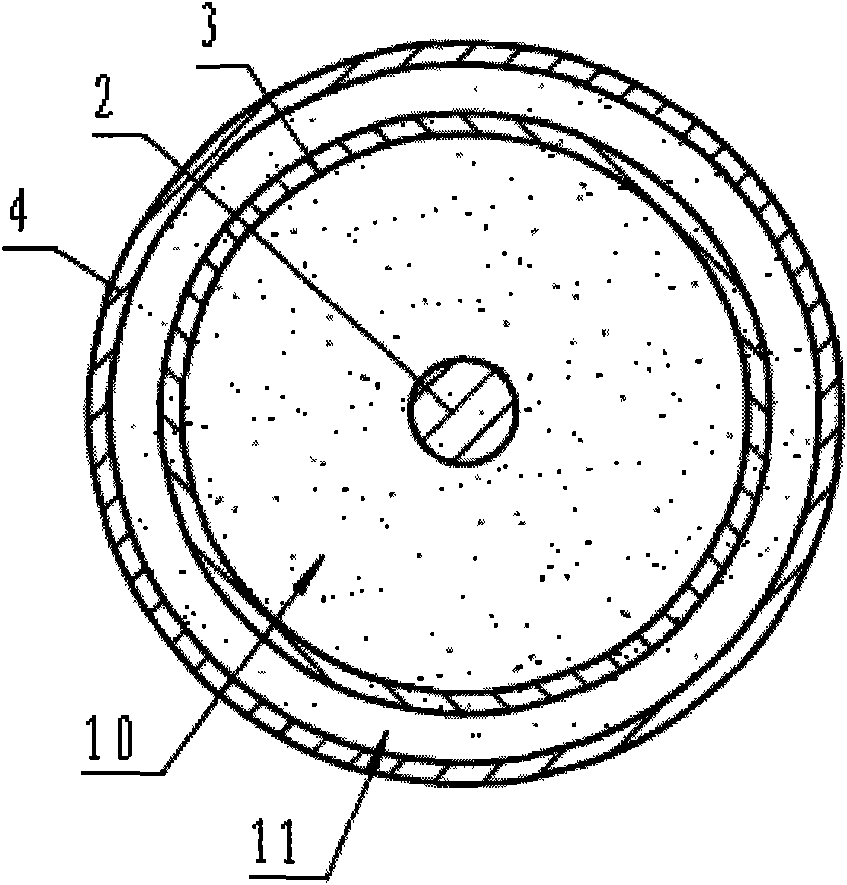
InactiveCN101994775AShorten design lengthSmall aspect ratioSpringsShock absorbersViscous dampingBuilding unit
The invention relates to a vibration-proof building unit, in particular to a composite damping single-piston rod viscous damper. The damper is a single-piston rod viscous damper and is characterized in that: a piston rod (2) of the single-piston rod viscous damper passes through a left end cover (1) through a working cylinder (10) on the left of a piston (5); a cylindrical spiral spring (60 is arranged in the working cylinder (10) on the right of the piston (5); one end of the spring is fixed on a right end cover (7), while the other end is fixed to the end face of the piston (5); an outer cylinder barrel (4) is sleeved outside an inner cylinder barrel (3) of the working cylinder (10); the left end cover (1) and the right end cover (7) are respectively arranged at two ends of the outer cylinder barrel (4), so that a gap between the inner cylinder barrel (3) and the outer cylinder barrel (4) forms a compensation cylinder (11); one one-way valve (13) is arranged in the body of the left end cover (1); and another one one-way valve (12) is arranged in the body of the right end cover (7). The viscous damper can simultaneously provide viscous damping and elastic damping in the whole moving process of the piston.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com