Patents
Literature
509 results about "Flexible fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
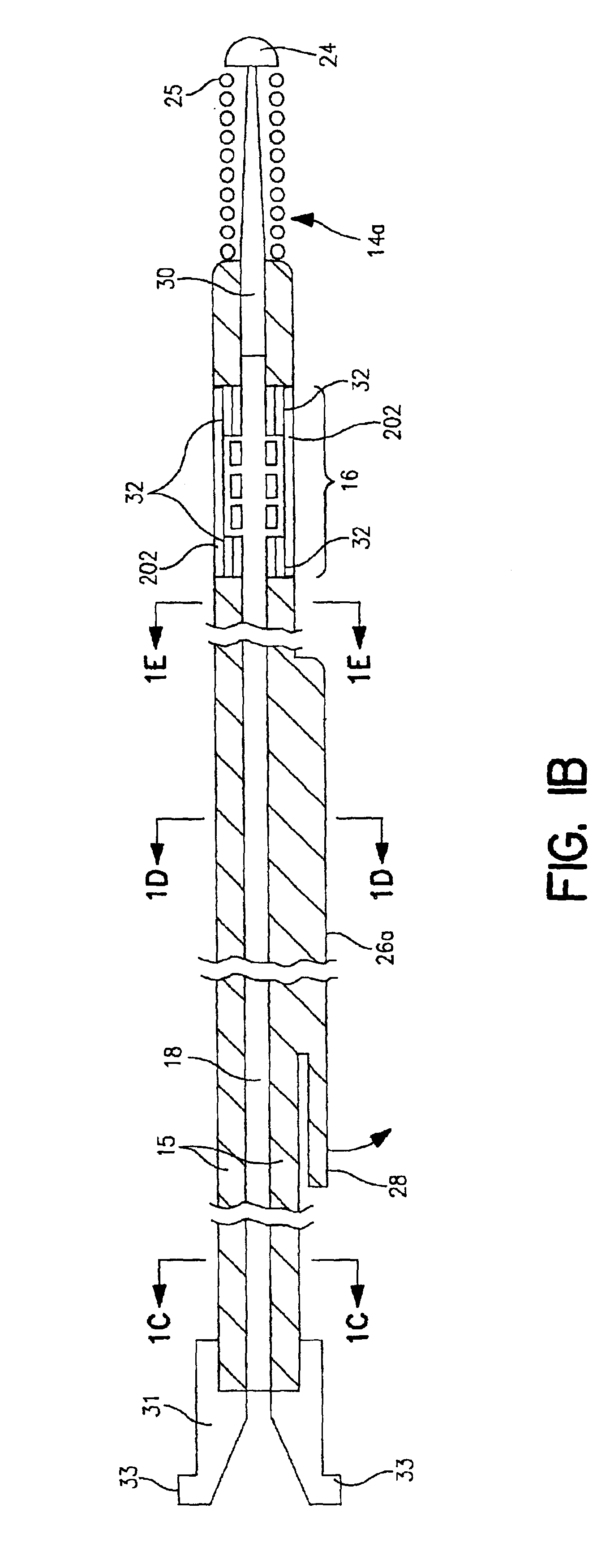
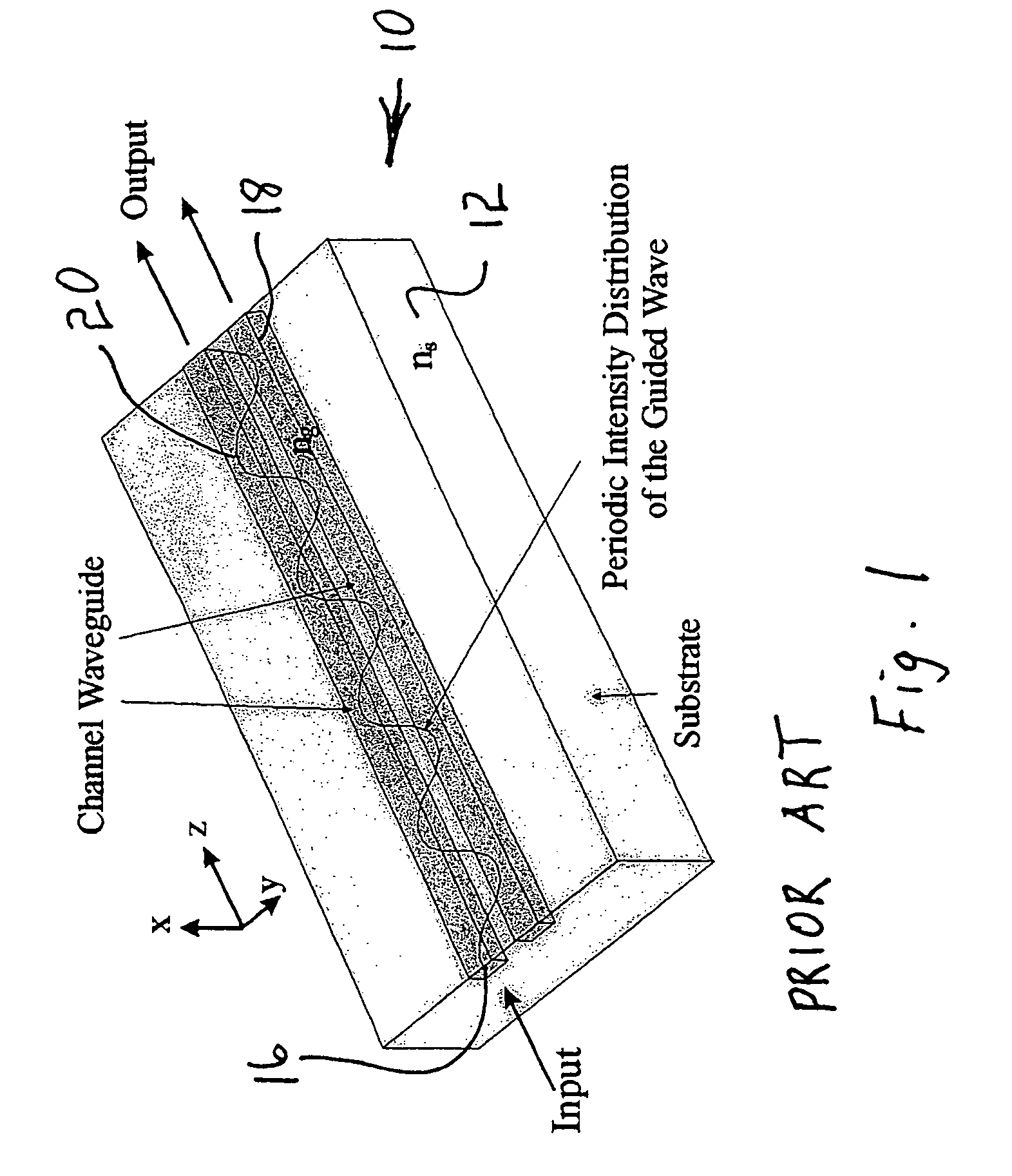
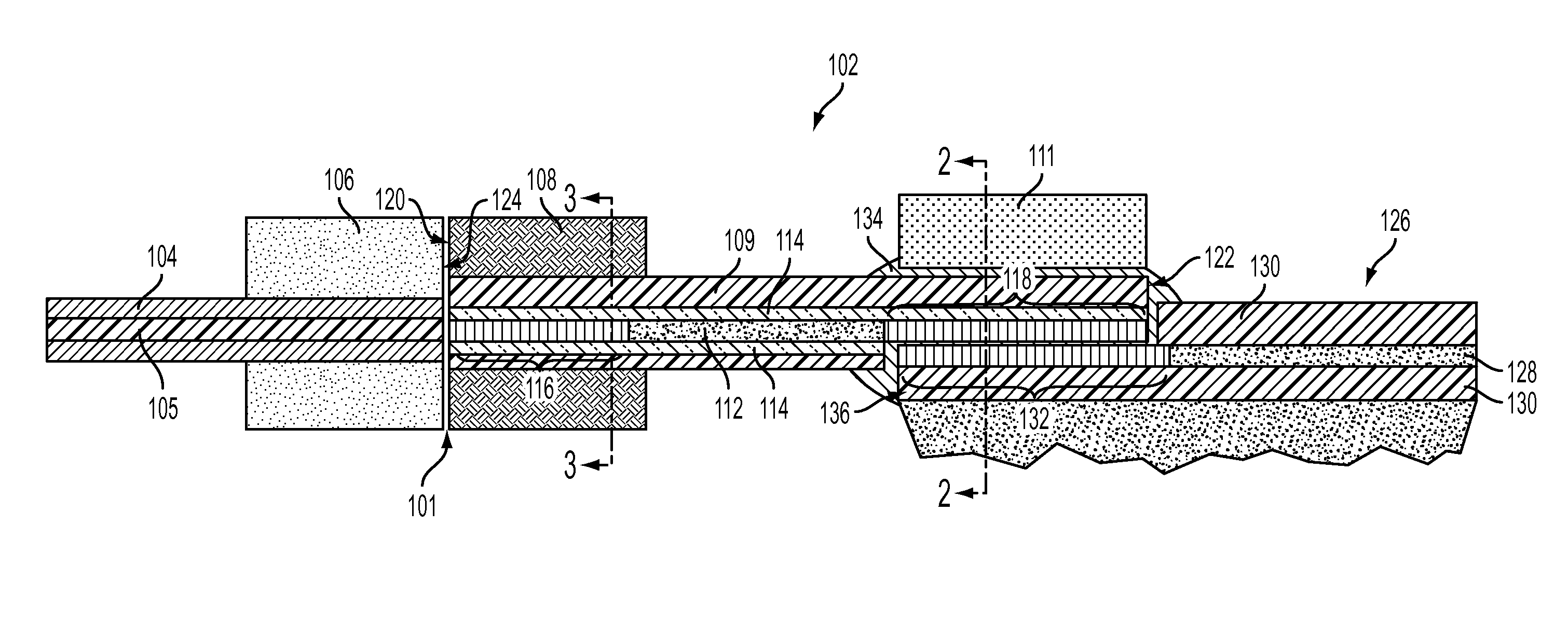
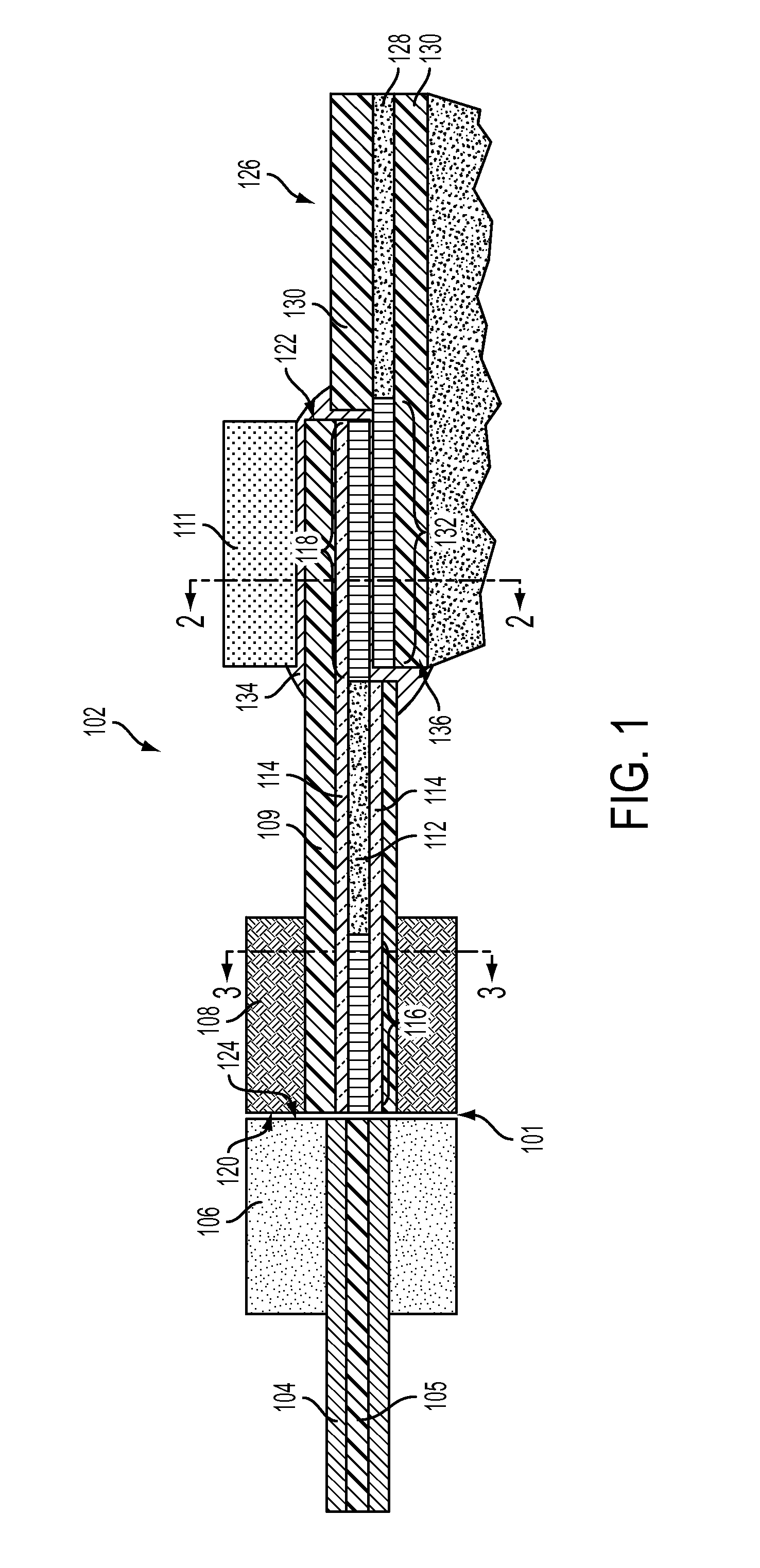
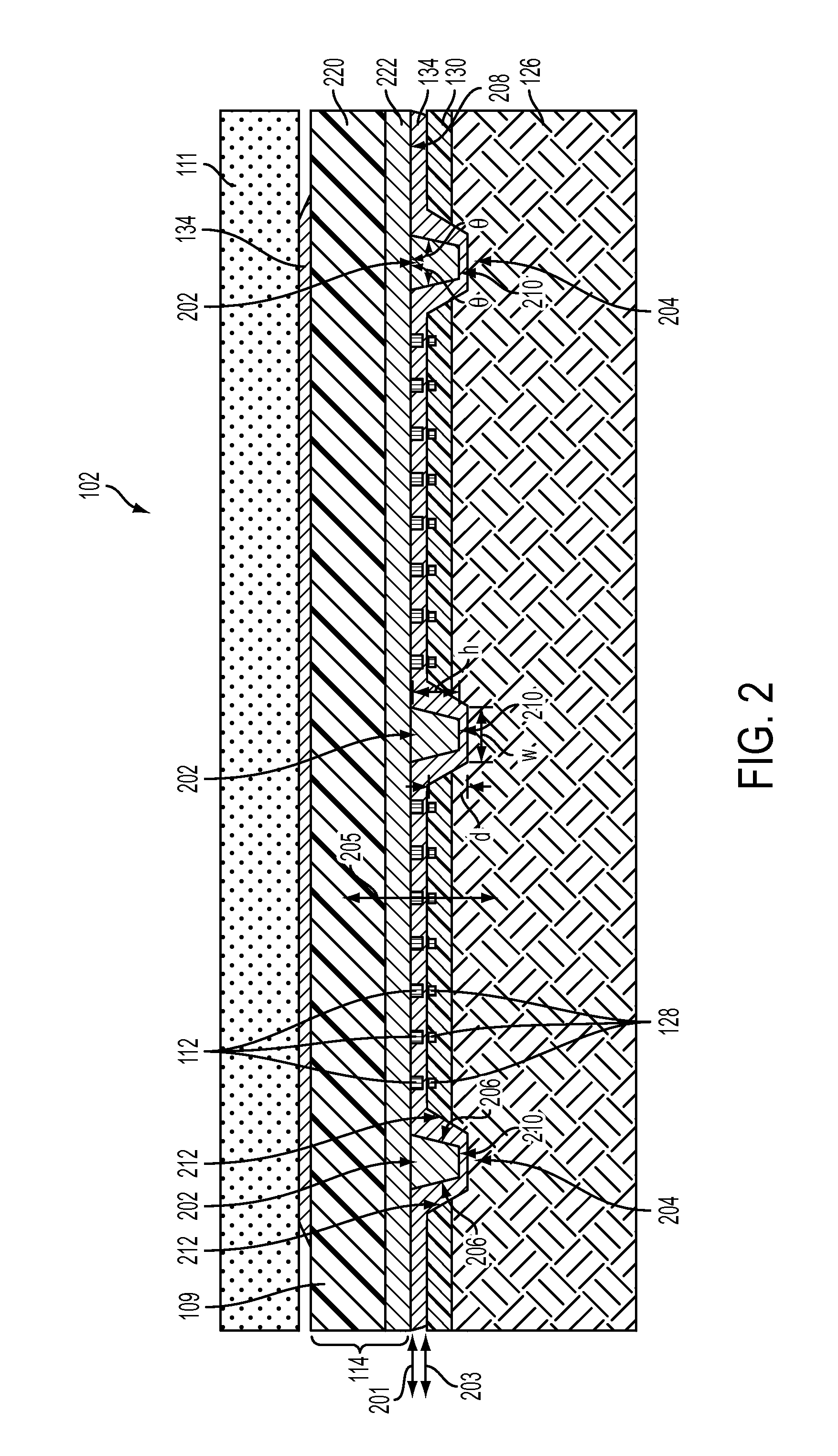
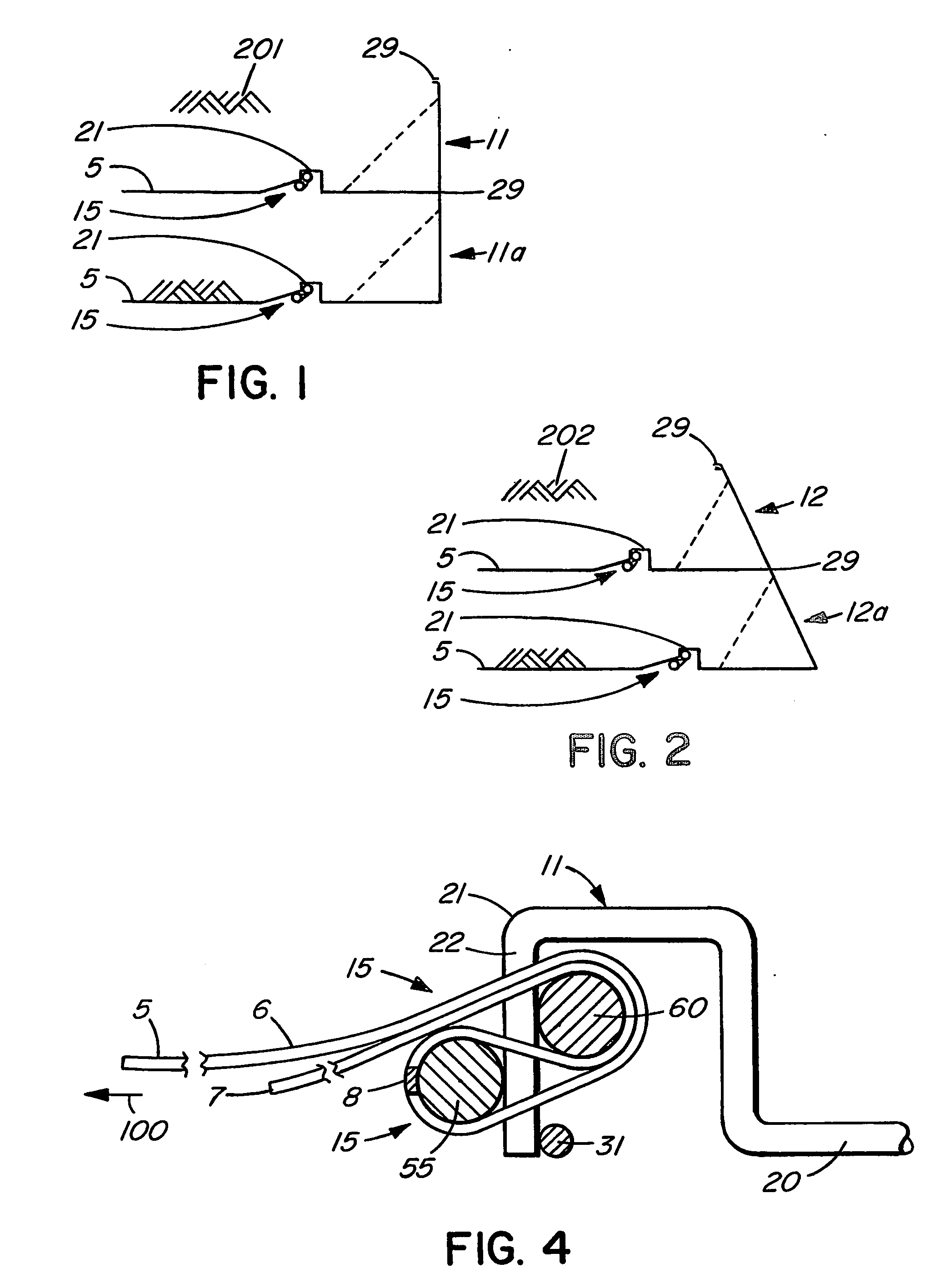
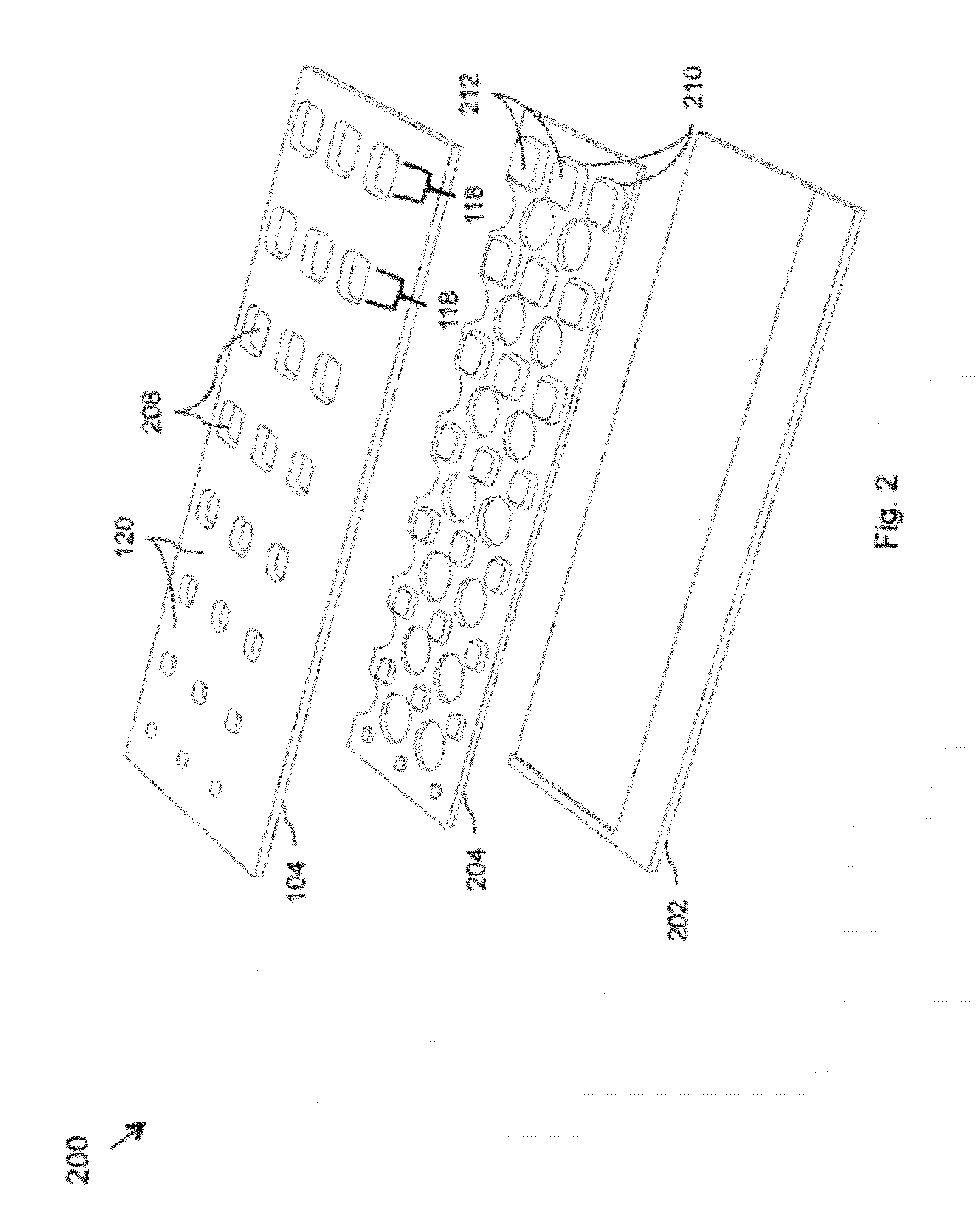
Scanning miniature optical probes with optical distortion correction and rotational control
InactiveUS20050201662A1Minimizing temperatureEliminate the effects ofSurgical instrument detailsCatheterViscous dampingOptical distortion
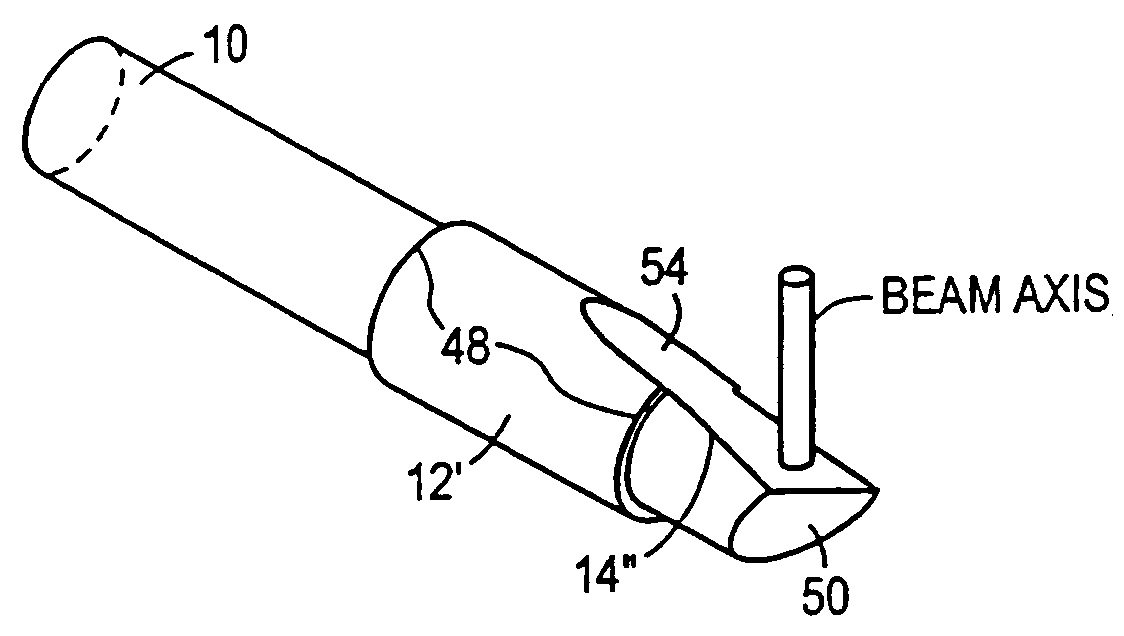
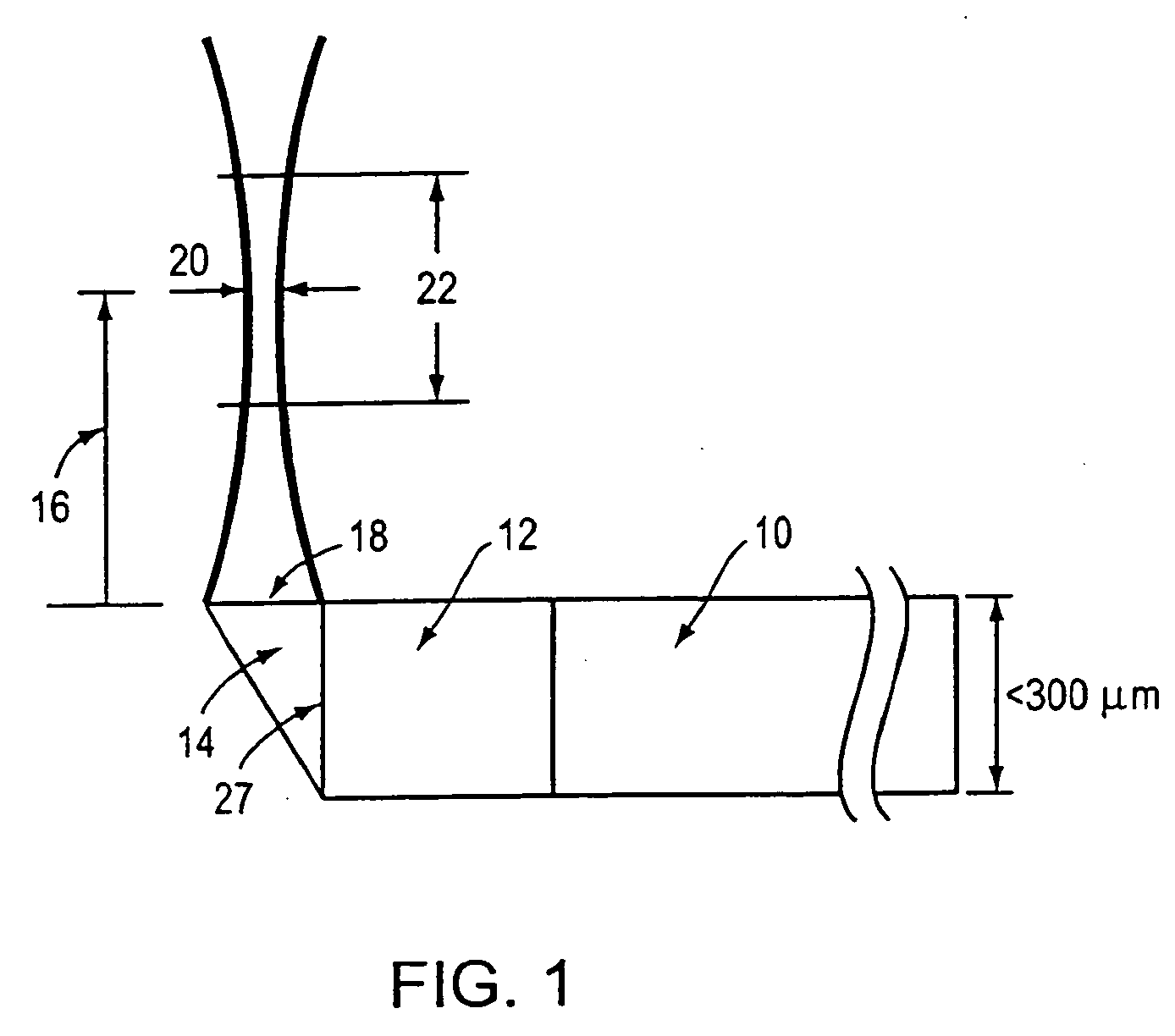
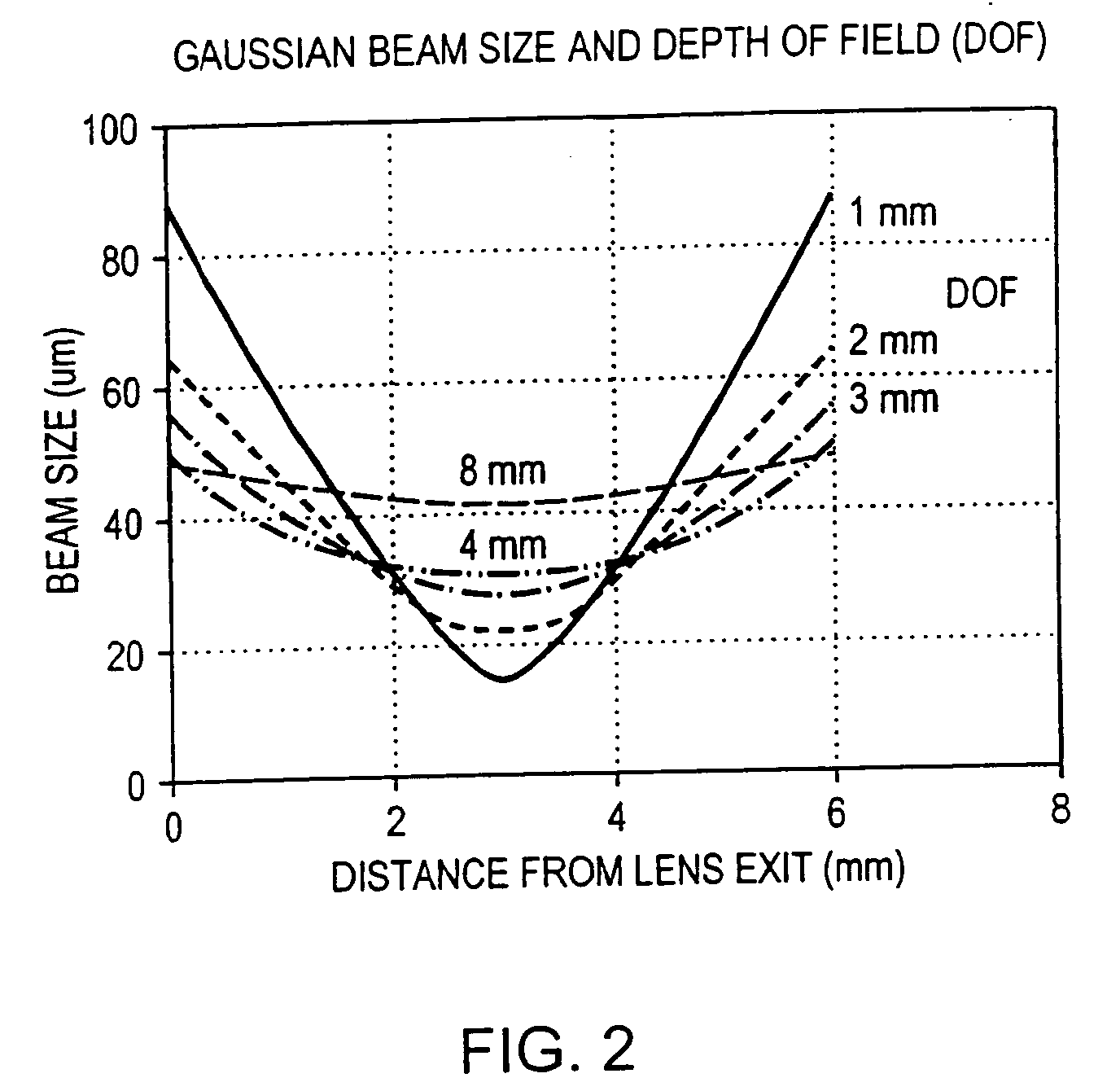
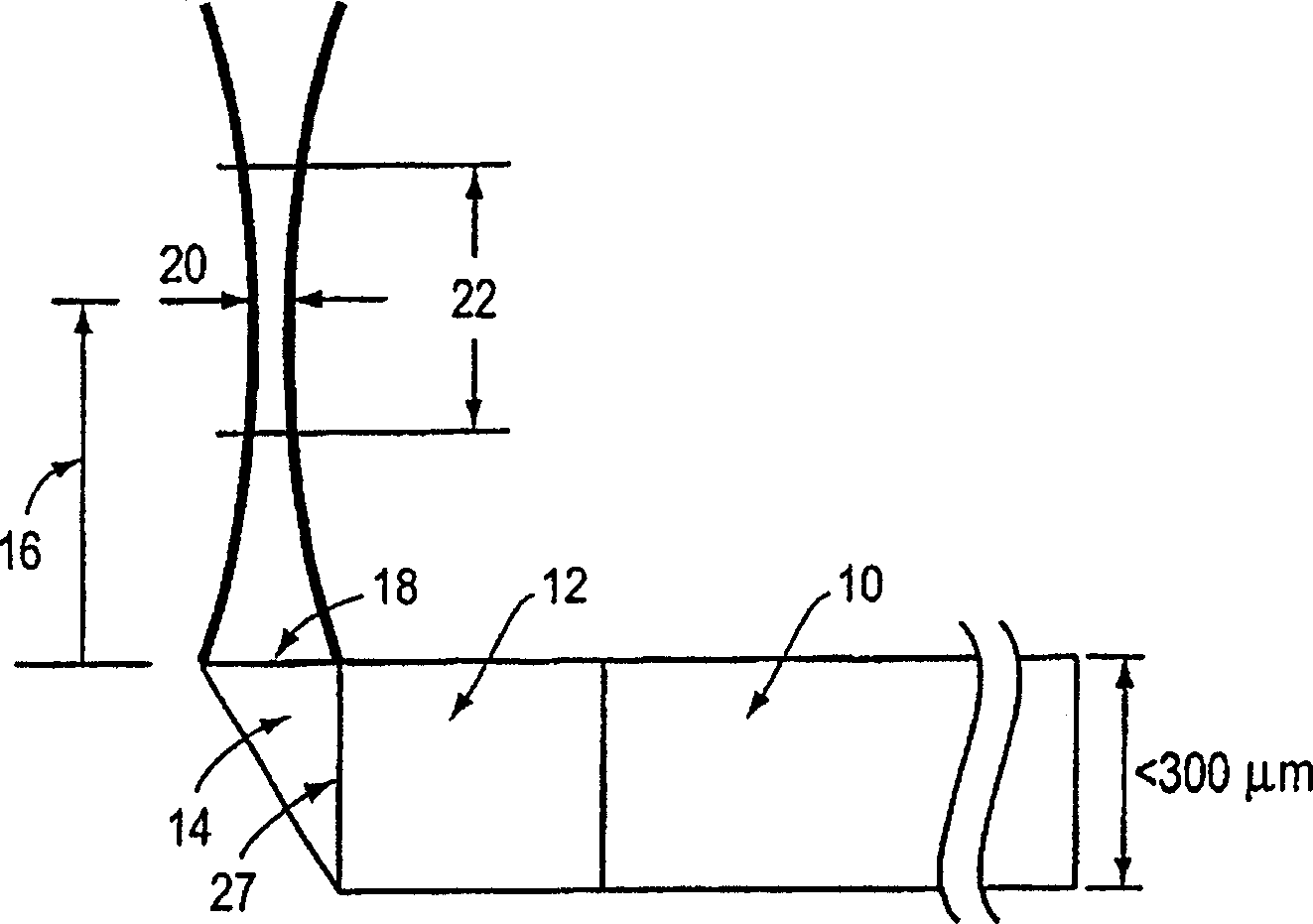
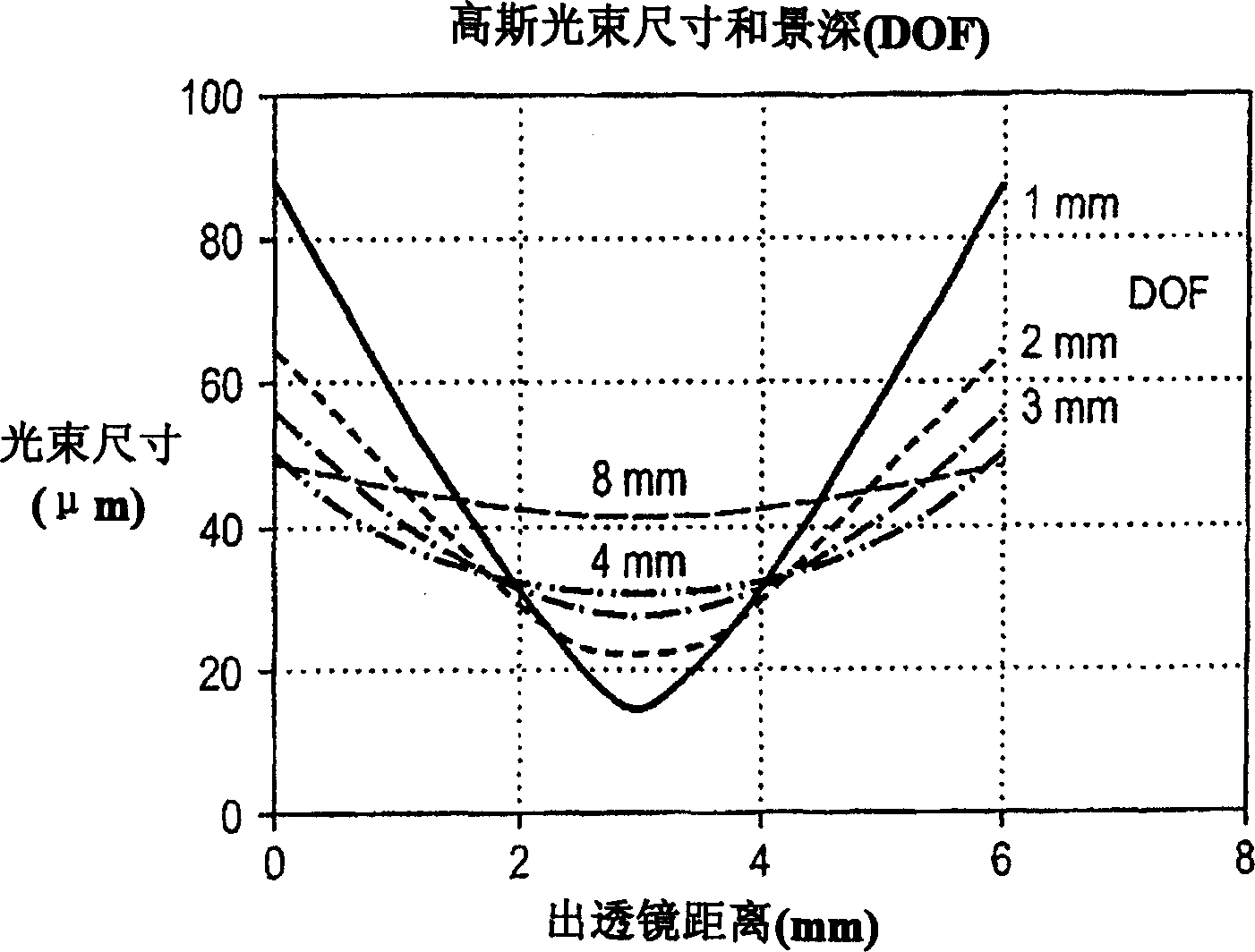
Optical probes having a diameter less than substantially 500 μm for use in scanning light from a long, highly flexible fiber to a sample. In one embodiment the probe includes a viscous damping fluid suitable to prevent non-uniform rotational distortion (NURD).
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Hydrogel implants for replacing hyaline cartilage, with charged surfaces and improved anchoring
InactiveUS20050287187A1High strengthIncreased durabilityFinger jointsWrist jointsKnee JointVolumetric Mass Density
Hydrogel devices for surgical implantation to replace damaged cartilage in a mammalian joint (such as a knee, hip, shoulder, etc.) are disclosed, with one or more of the following enhancements: (1) articulating surfaces that have been given negative surface charge densities that emulate natural cartilage and that interact with positively charged components of synovial fluid; (2) anchoring systems with affixed pegs that will lock into accommodating receptacles, which will be anchored into hard bone before the implant is inserted into a joint; (3) a three-dimensional reinforcing mesh made of strong but flexible fibers, embedded within at least a portion of the hydrogel.
Owner:MANSMANN KEVIN A
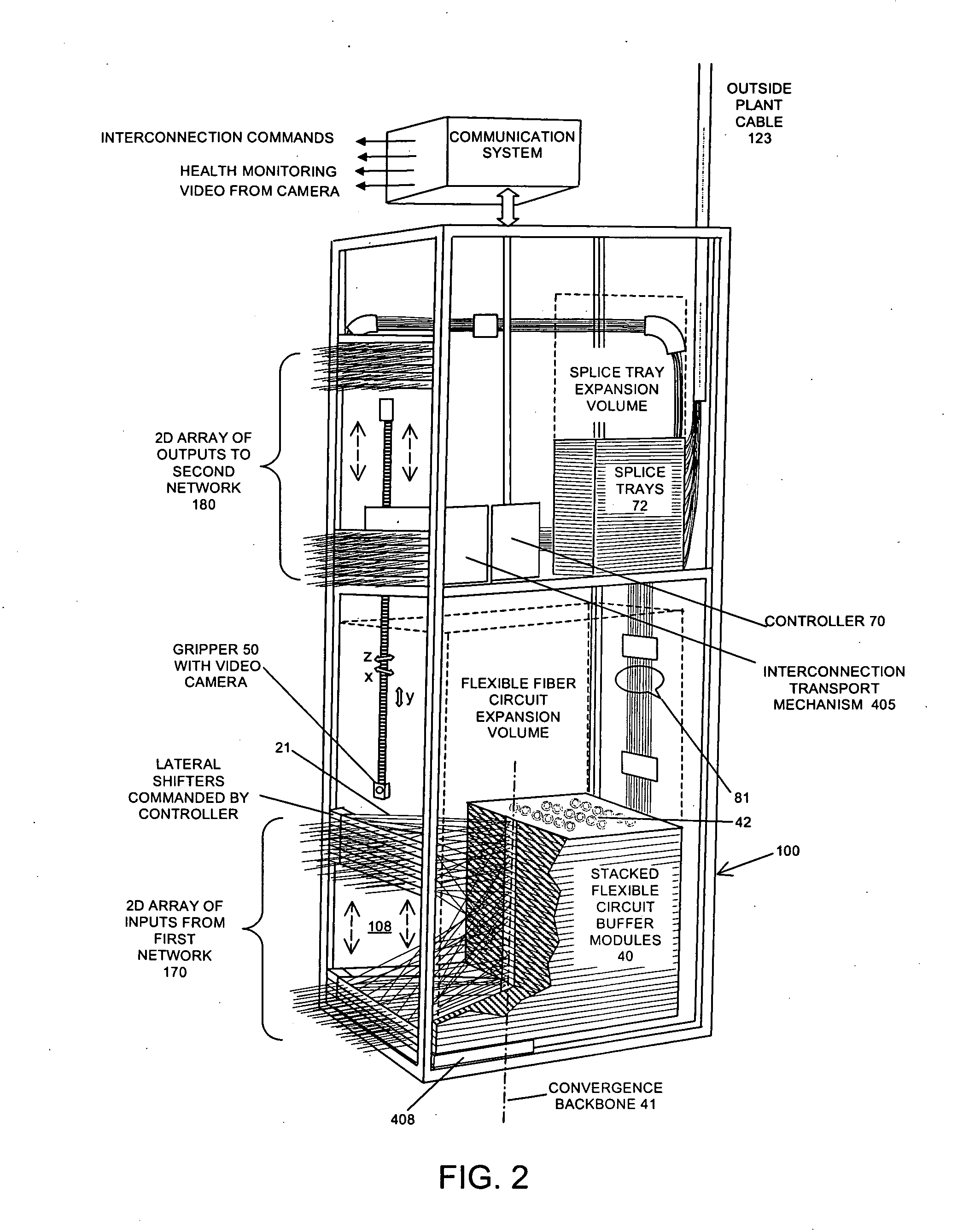
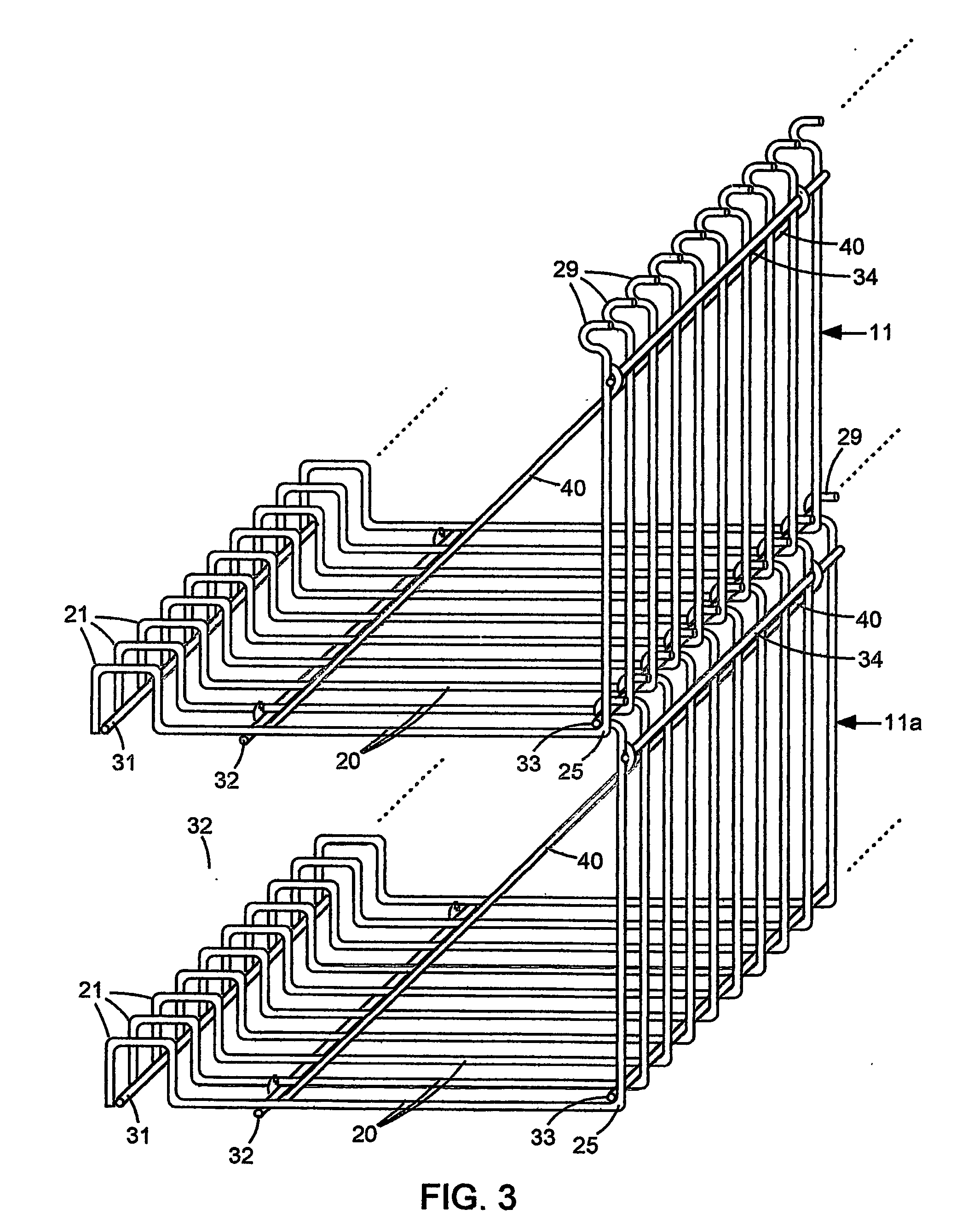
Scalable and modular automated fiber optic cross-connect systems
ActiveUS20100316334A1Improve reliabilitySmall sizeMultiplex system selection arrangementsProgramme controlComputer hardwareCross connection
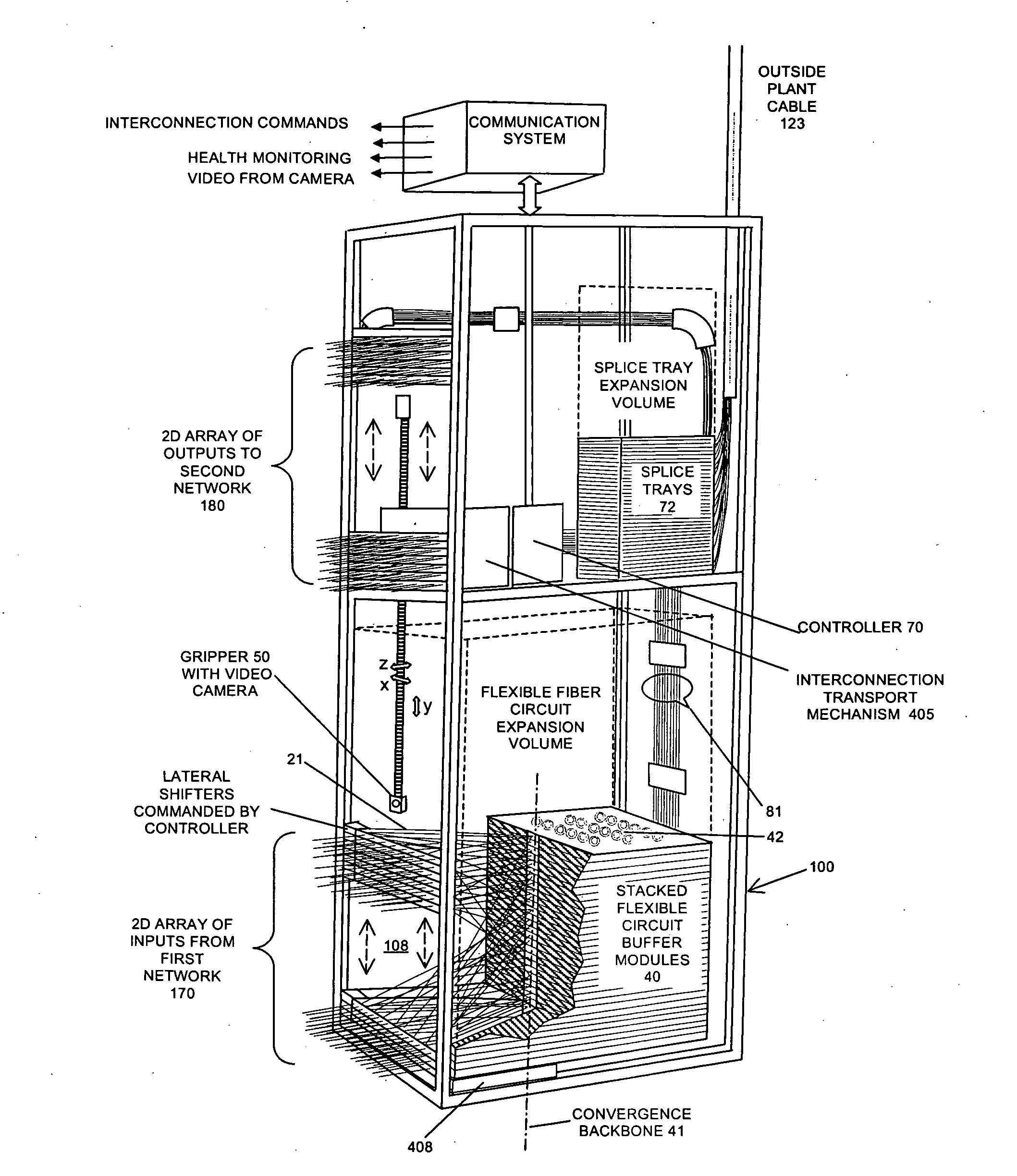
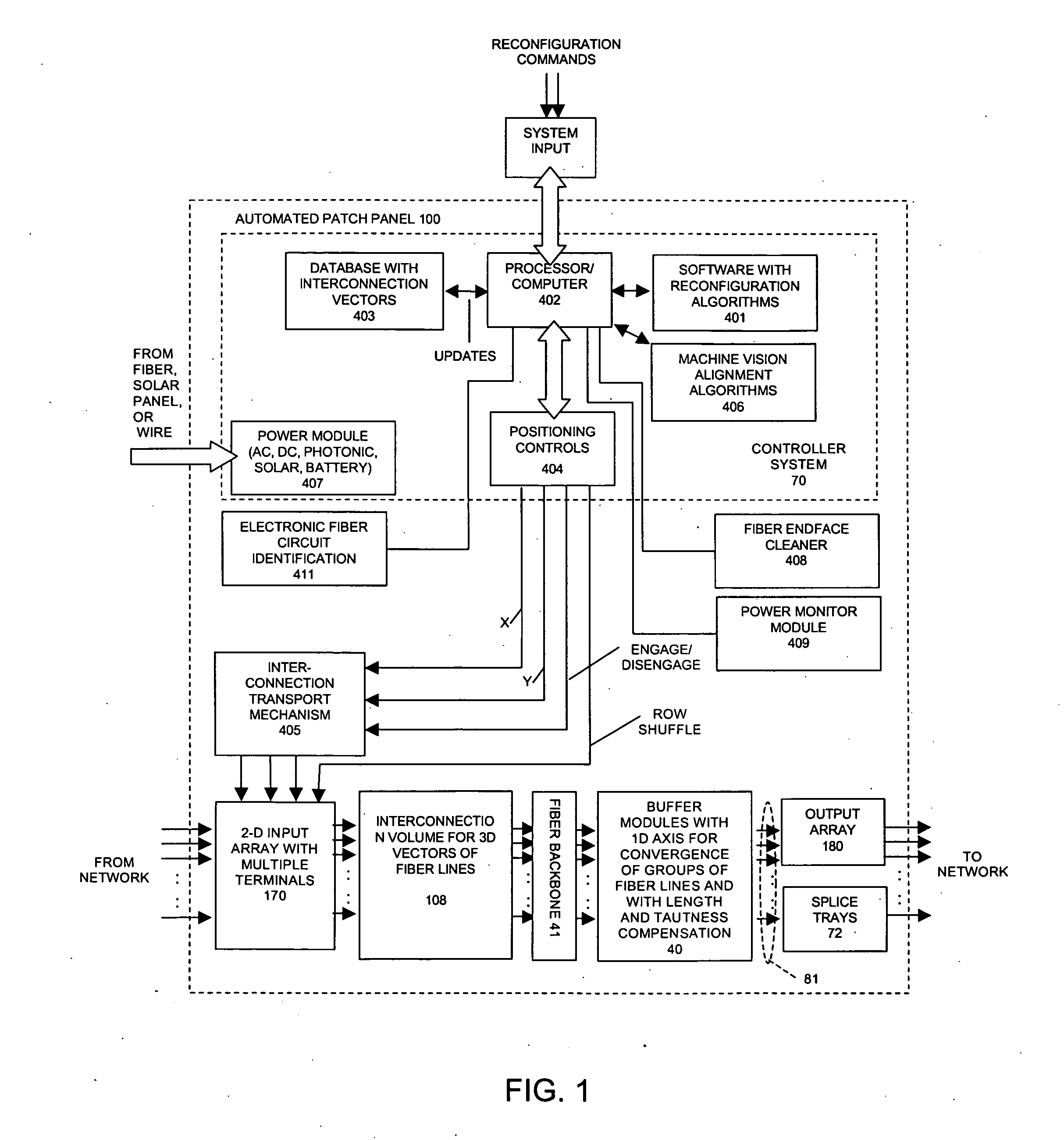
This invention discloses highly scalable and modular automated optical cross connect switch devices which exhibit low loss and scalability to high port counts. In particular, a device for the programmable interconnection of large numbers of optical fibers (100's-1000's) is provided, whereby a two-dimensional array of fiber optic connections is mapped in an ordered and rule-based fashion into a one-dimensional array with tensioned fiber optic circuit elements tracing substantially straight lines there between. Fiber optic elements are terminated in a stacked arrangement of flexible fiber optic circuit elements with a capacity to retain excess fiber lengths while maintaining an adequate bend radius. The combination of these elements partitions the switch volume into multiple independent, non-interfering zones, which retain their independence for arbitrary and unlimited numbers of reconfigurations. The separation into spaced-apart zones provides clearance for one or more robotic actuators to enter the free volume substantially adjacent to the two-dimensional array of connectors and mechanically reconfigure connectors without interrupting other circuits.
Owner:TELESCENT
Floorboard and method for manufacturing thereof
ActiveUS20080000188A1Reduce sound levelAttractive appearanceTongue/grooves making apparatusWallsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Floorboards with a surface of flexible fibers for laying a mechanically joined floating floor, and methods for manufacturing and profloorings containing such floorboards.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Water-absorbent article and method
An absorbent article including a flexible, fibrous support structure or framework in a fixed shape or configuration having particles of a superabsorbent material adhered thereto with temperature softened outer support surfaces, or with an adhesive to maintain sufficient spacing between adjacent superabsorbent particles such that liquid can more freely enter the absorbent article for contact with the superabsorbent particles.
Owner:BASF AG
Removable stent for body lumens
A removable stent for implantation into a lumen in a human body. The stent is made from a soft, flexible fiber having an outer surface. An outer bioabsorbable / degradable coating is applied to the outer surface of the filament causing it to become rigid. The coating softens in vivo through absorption and / or degradation such that the stent is readily passed or removed from the lumen as a softened filament after a pre-determined period of time through normal flow of body fluids passing through the lumen or by manual removal.
Owner:ETHICON INC
System and method for placing endocardial leads
InactiveUS6934589B2Desired locationTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesTunica intimaImplantation Site
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Casting product and method for forming the same
ActiveUS7037283B2Equally distributedPlaster of paris bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesFlexible fiberComposite material
A casting product for forming a hard structure about an object including a flexible fibrous substrate impregnated with a fluid-activated resin and a protective flexible casing surrounding the impregnated substrate. The casing includes a sealable passageway defined between the atmosphere and the interior of the casing, and is configured to permit injection of fluid, and removal of vapors and extant fluid with a vacuum from the casing.
Owner:KAUPTHING BANK
Low-density ablation thermal insulation type composite and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a low-density ablation thermal insulation type composite and a preparation method thereof. The composite adopts phenolic aerogel of the nanometer particle structure as a matrix and adopts a flexible fiber blanket or a fiber weaving body as a reinforcement body, and the composite is obtained through the steps of phenolic resin preparation, phenolic resin solution preparation, thermal treatment of the flexible fiber blanket or the fiber weaving body, steeping of the flexible fiber blanket or the fiber weaving body with the phenolic resin solution, a sol-gel reaction, aging, drying and curing of the composite and the like. Compared with the prior art, the composite is excellent in thermal protective performance, good in mechanical performance, high in designability, simple in preparation technology, low in cost and easy to process and mold, promotes later-period dimensional cutting, meets different thermal protective needs under the medium heat flow and medium and low heat flow environments, and can be applied to manned space flight and deep space detection aircrafts, outer thermal protective layers of various tactic and strategic weapons working for a short time, and inner ablation heat insulation and thermal protective layers of engines, disposable hypersonic vehicles and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Engineered fibers for well treatments
Mixtures of fibers and solid particles are effective for curing fluid losses and lost circulation in a subterranean well. Stiff fibers are more effective than flexible ones; however, mixtures of stiff and flexible fibers have a synergistic effect. The quantity and particle-size distribution of the solids are optimized according to the stiffness, dimensions and concentrations of fibers.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Engineered Molded Fiberboard Panels. Methods of Making the Panels, and Products Fabricated From the Panels
A honeycomb-shaped panel is formed from a plurality of generally sinusoidally shaped strips of molded fiberboard material each having spaced, oppositely directed flat peaks, the peaks of adjacent strips being secured together to form a plurality of hexagonally shaped cells extending perpendicular to the surfaces of the sheet. The strips may be cut from a single sheet of corrugated fiberboard sheet material and then secured together to form the honeycomb panel, or a plurality of such panels may be secured together face to face with their ribs aligned to form a stack, and selected cuts may be made through the secured, stacked panels to form a plurality of honeycomb panels of desired surface shape and height dimensions. The strips forming the cells are substantially rigid and resistant to collapse of the cells, and form a substantially rigid core when assembled between two flexible fiberboard skins, while the panel is bendable to adopt a desired panel curvature.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Engineered fibers for well treatments
Mixtures of fibers and solid particles are effective for curing fluid losses and lost circulation in a subterranean well. Stiff fibers are more effective than flexible ones; however, mixtures of stiff and flexible fibers have a synergistic effect. The quantity and particle-size distribution of the solids are optimized according to the stiffness, dimensions and concentrations of fibers.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
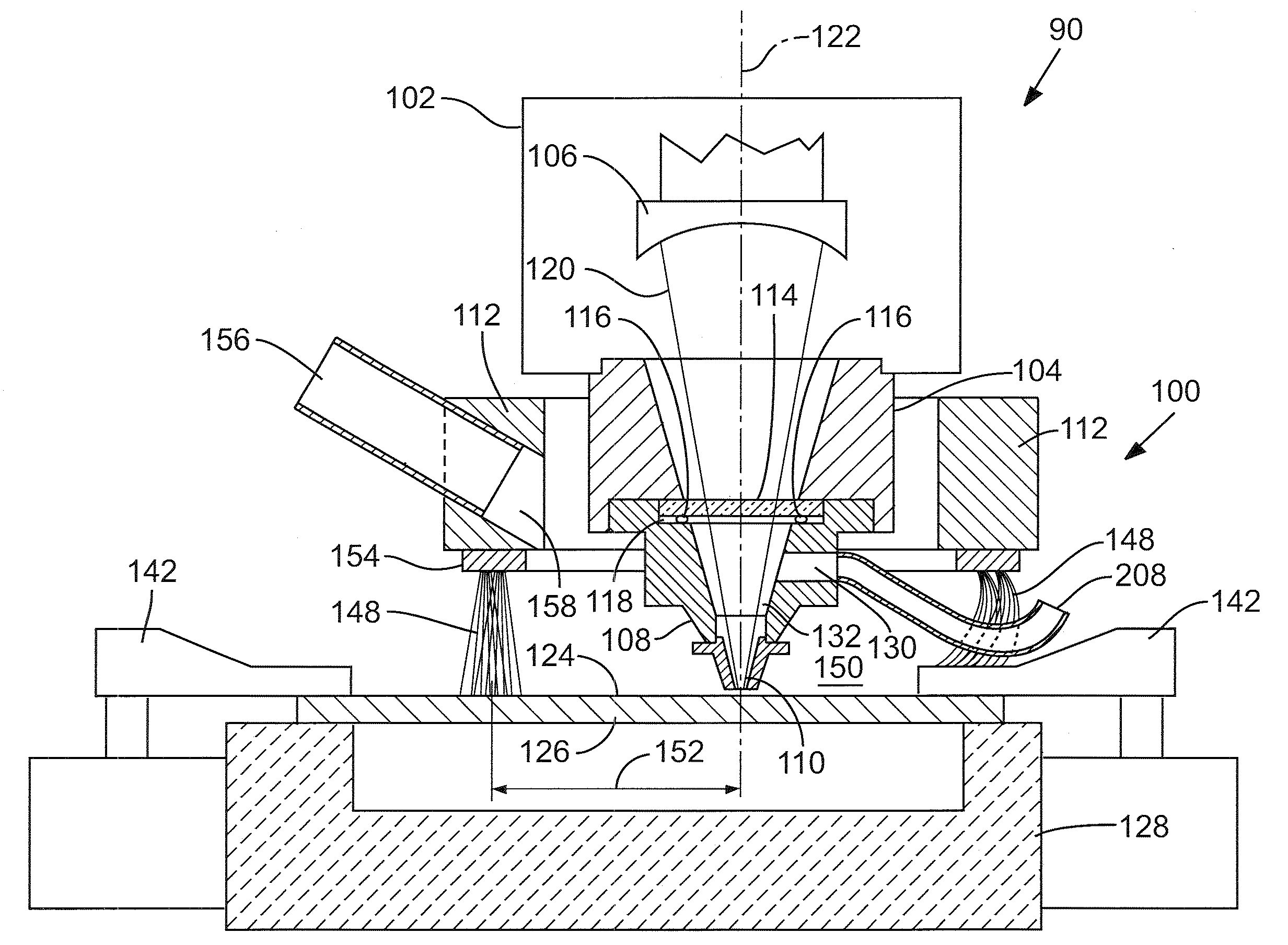
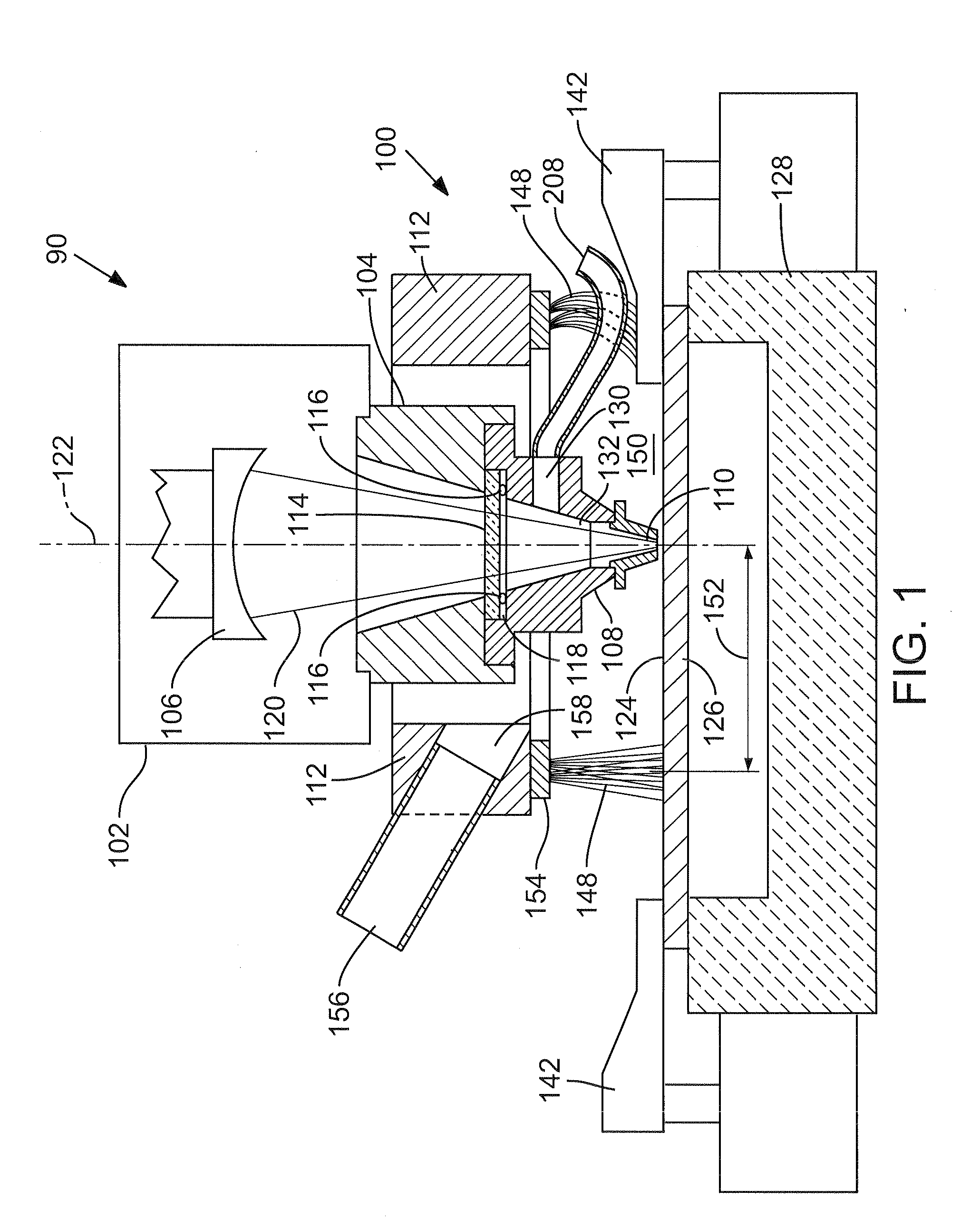
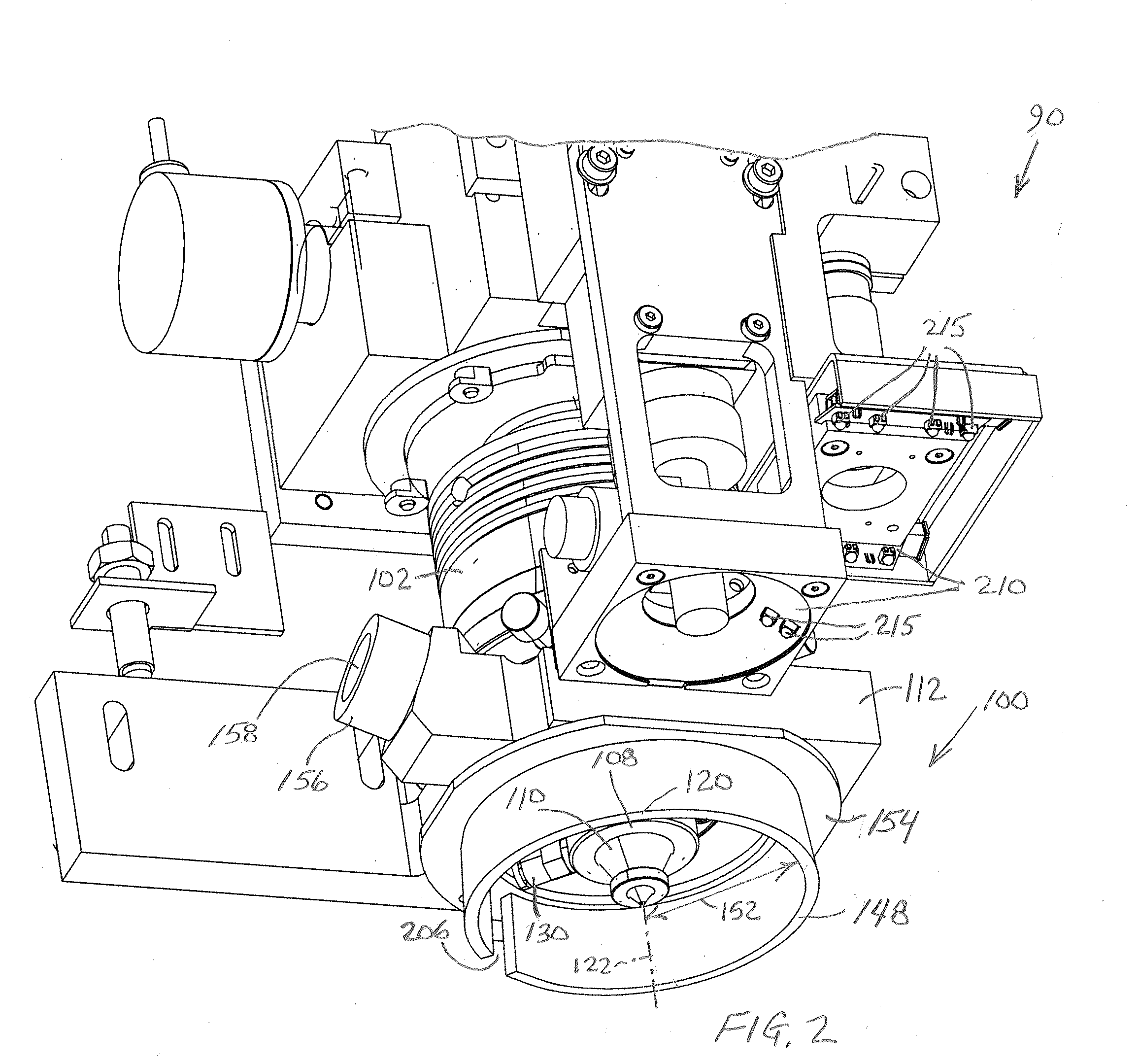
Debris capture and removal for laser micromachining
A method of capturing and removing metallic debris created on a target side of a target metal specimen undergoing laser micromachining entails providing a barrier that encompasses the immediate volume surrounding a laser cutting head output nozzle to contain the ejected debris and extracting the debris through a vacuum outlet. A preferred system implementing this approach to debris management includes a barrier in the form of a flexible fiber brush configured in the shape of a ring and positioned to trap ejected debris within a localized area surrounding a target area where the laser beam is incident on the target metal specimen. The ring brush is made of material that is robust to molten metals. An inert gas directed at a high flow rate along the target surface of the metal specimen carries ejected surface debris trapped in the ring brush toward a vacuum outlet.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
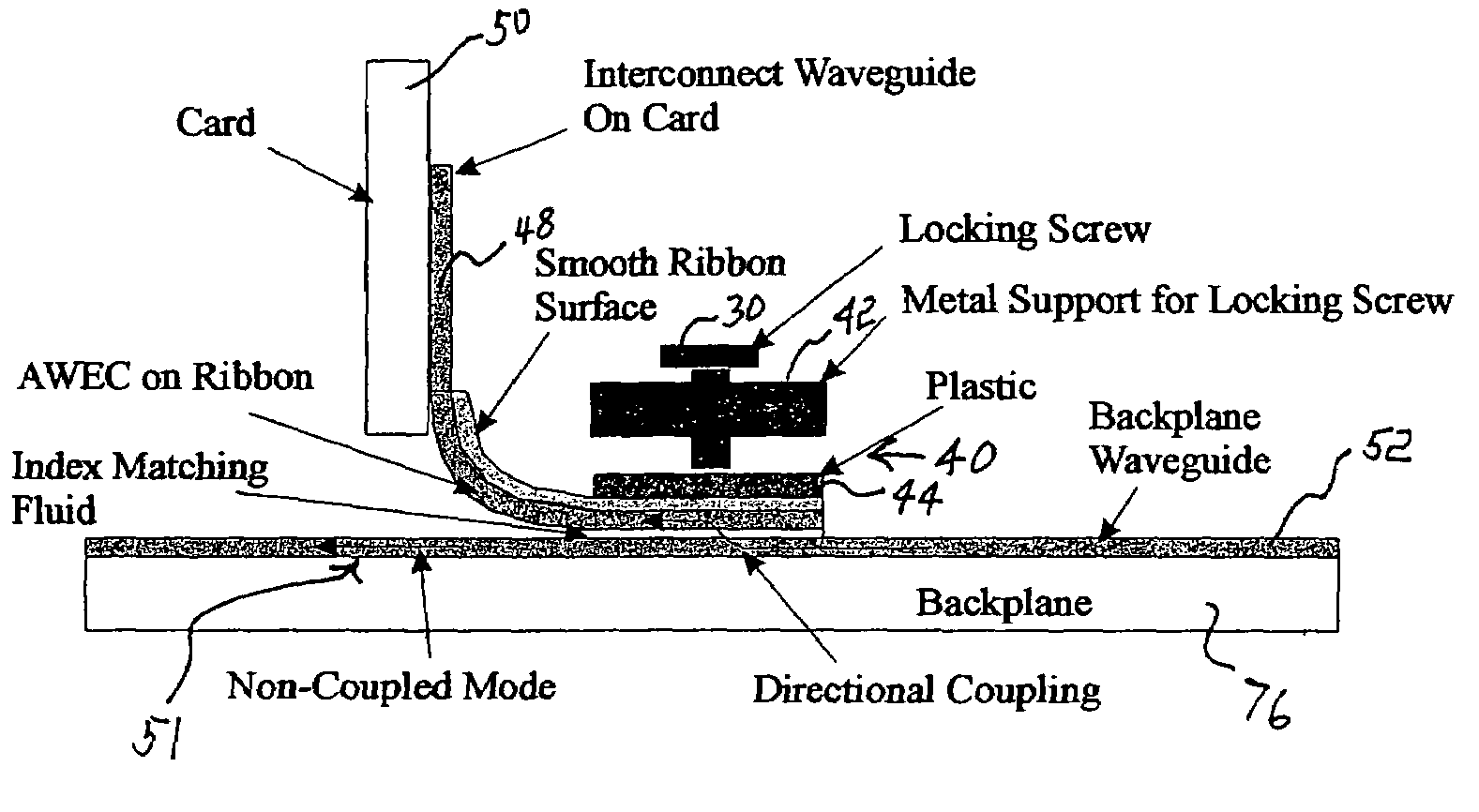
Optical waveguide evanescent ribbon coupler
InactiveUS7142748B1Low production costImprove reliabilityCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideFiber arrayRefractive index
An evanescent optically coupled electronic device including: a backplane wave guide or mother board including a set of parallel carriers that define a first plurality of parallel channels and include a first array of optical fibers having exposed cores in the first plurality of parallel channels; at least one electronic card or daughter board including a high speed optical waveguide bus; a flexible fiber ribbon or film including waveguides made up of individual optical fibers of locally increased refractive index joined by a web of suitable material forming the high speed optical waveguide bus and optically connecting the backplane waveguide and the at least one electronic card with no 90° angle turns; and a mechanism for retaining the first array of optical fibers having exposed cores in abutting and facing evanescent optical contact with the individual optical fibers in the flexible fiber or ribbon.
Owner:SEC OF THE ARMY
Flexible fiber reinforced composite rebar
InactiveUS20080141614A1Easy to bendCross sectionBuilding repairsLoad-supporting elementsFlexible fiberRebar
A flexible fiber reinforced composite rebar structure includes a plurality of continuous fibers embedded within a thermoplastic resin. The rebar structure has an elliptical cross sectional shape with an aspect ratio of about two to one and a twist with a twist pitch of about 30 cm. The thermoplastic resin matrix enables the rebar structure to be bent in the field by the application of heat to soften the structure and thereafter cooled to return to a rigid state.
Owner:KNOUFF BRIAN J +3
Flexible fiber to wafer interface
ActiveUS8534927B1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSingle mode waveguidesMechanical engineering
An interface device includes a flexible substrate portion, a flexible cladding portion arranged on the substrate portion, a flexible single-mode waveguide portion arranged on the cladding portion including a substantially optically transparent material, a first engagement feature operative to engage a portion of a wafer, and a connector portion engaging a first distal end of the flexible substrate portion, the connector portion operative to engage a portion of an optical fiber ferrule.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
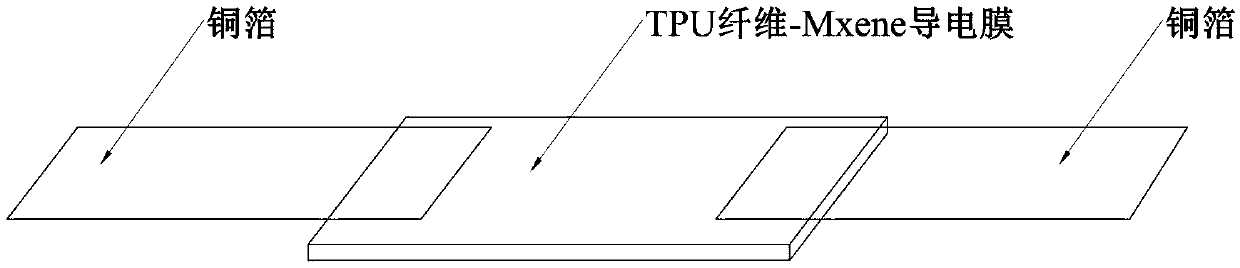
MXene-based flexible polyurethane fiber membrane strain sensor
ActiveCN109576905AHigh sensitivityExpand the scope ofPretreated surfacesElectro-spinningMicrometerEngineering
The invention relates to a MXene-based flexible polyurethane fiber membrane strain sensor. The sensor is prepared from a flexible substrate and a conductive layer; the flexible substrate is TPU flexible fiber film, the thickness of the fiber film is 100-300 micrometer; the conductive layer is an Mxene conductive layer wrapping the surface of the flexible substrate, the thickness of the conductivelayer is 20-50 micrometer; and the two ends of a thin film are connected with wires. Accordingly, the strain sensitivity of the sensor is improved, and the strain sensing range of the sensor is widened.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Composite material based on nanometer, preparation method of composite material and application in flexible energy storage device
InactiveCN102403050AImprove energy storage characteristicsImprove mechanical propertiesElectrolytic capacitorsElectrode carriers/collectorsHigh energyNetwork structure
The invention relates to the field of chemical energy storage devices such as super capacitors, batteries and the like, and particularly discloses a composite material based on nanometer, a preparation method of the composite material and application in a flexible energy storage device, which solve the problem that common energy storage devices are difficult to be bent and deform. Nanometer active materials are compounded with flexible fibers, high-energy-storage characteristics of the nanometer active materials and excellent flexibility of flexible fiber materials are integrated, the quality percentage of the nanometer active materials ranges from 0.1% to 40%, the rest components of the composite material are the flexible fibers, the flexible nanometer composite material in a three-dimensional communication network structure is formed, furthermore, the composite material can be used as an electrode active material and a current collector simultaneously so as to be assembled to form the bendable flexible energy storage device, higher specific capacity can be realized under a bending condition and is equivalent to that when the flexible energy storage device is not bent, and the composite material can be expected to be applied to the field of flexible devices in the future.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
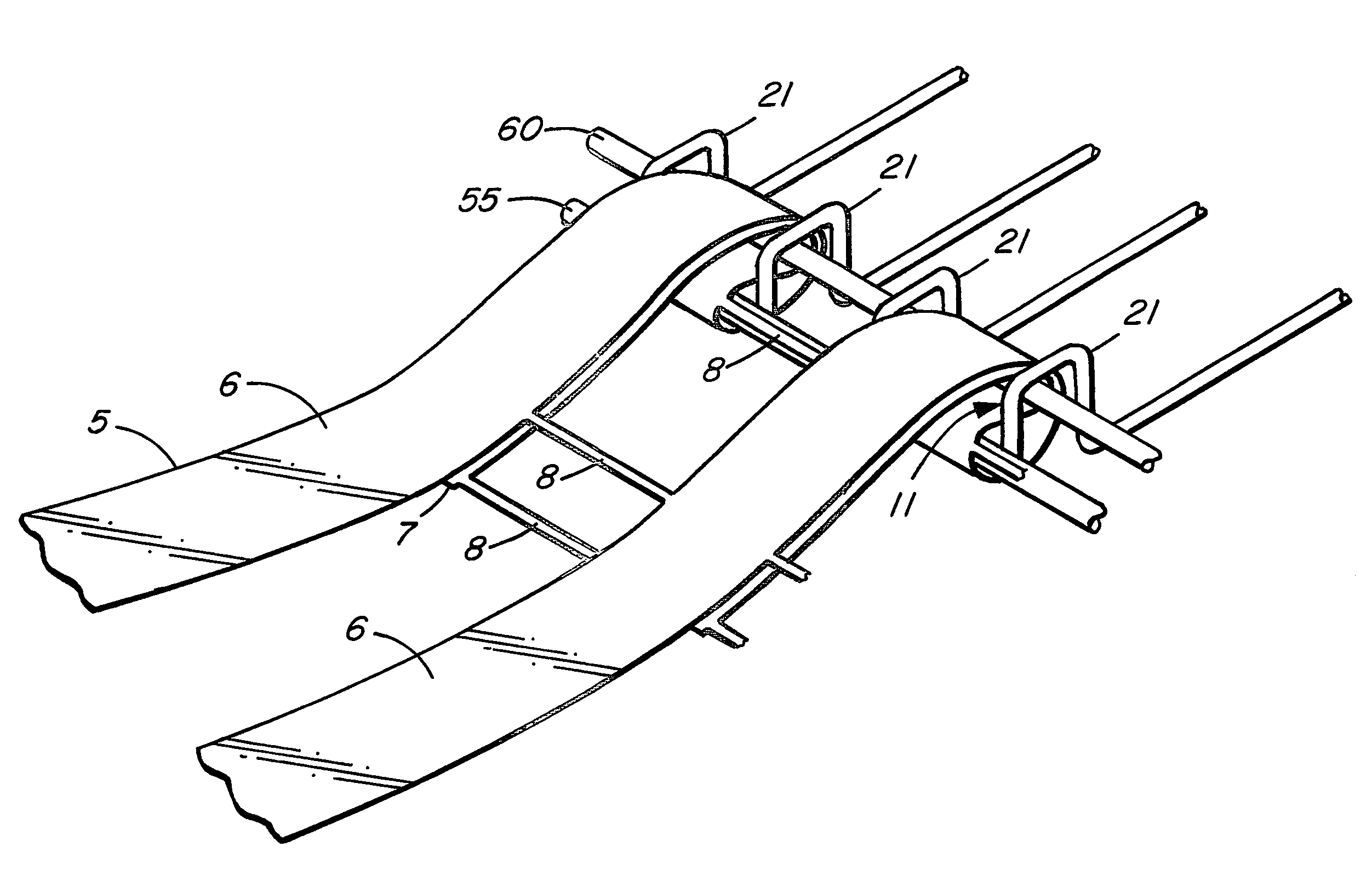
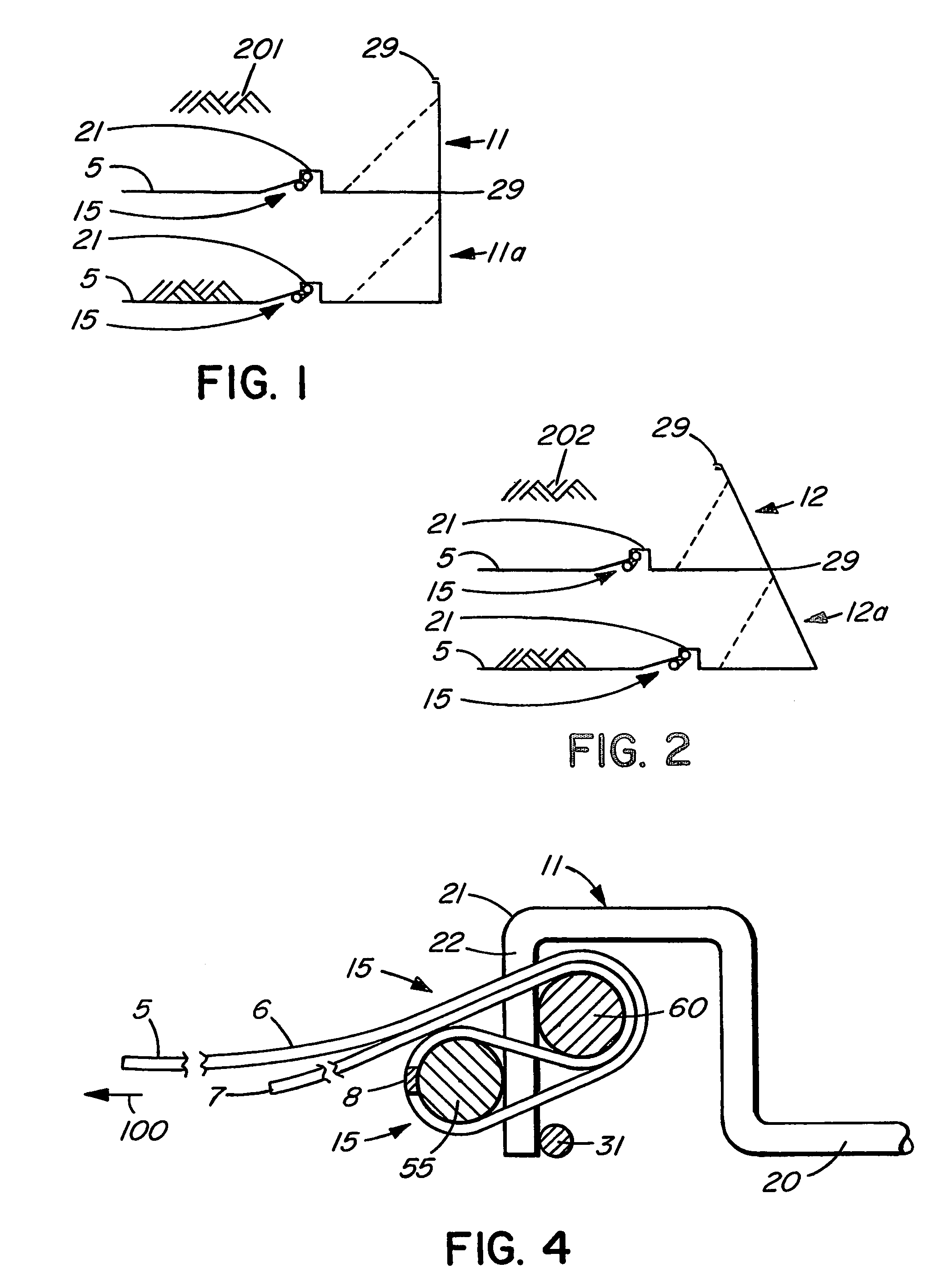
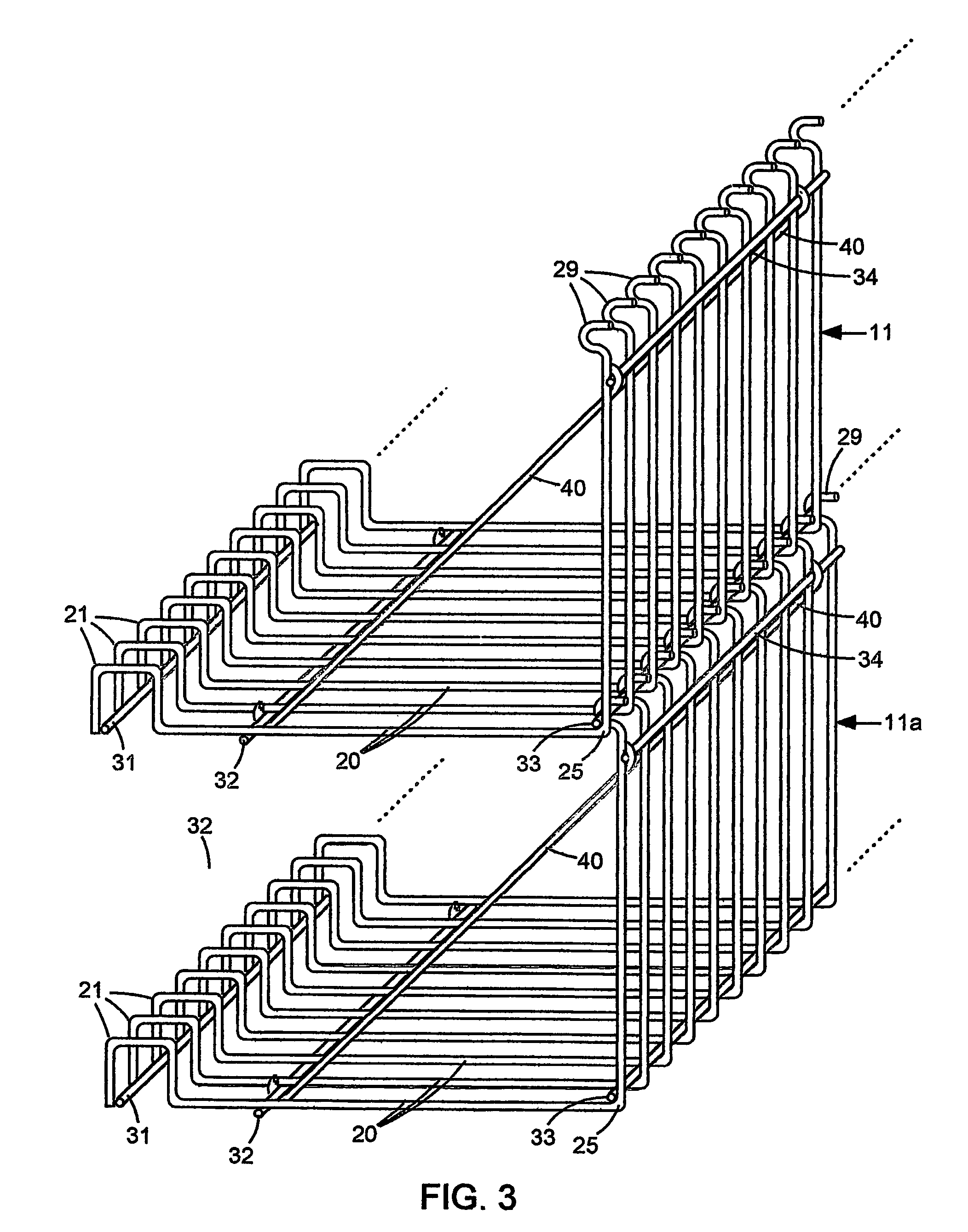
Apparatus and method for stabilizing an earthen embankment
InactiveUS20060239783A1Increase longitudinal tensionArtificial islandsExcavationsGeogridMechanical engineering
A structure for stabilizing an earthen embankment comprises an embankment support for restraining movement of at least a part of the embankment, a flexible fiber geogrid (5) extending longitudinally through the embankment from a first end portion secured to the support to a second end portion, and anchor means (55, 60, 11) for securing one of the end portions. The anchor means comprises a pair of anchor rods (55, 60) extending transversely in relation to the geogrid, and means (11) for limiting movement of the anchor rods. The end portion secured by the anchor means is wrapped back and forth around the anchor rods so as to tighten thereon when the geogrid is pulled in longitudinal tension away from the anchor means. A method of anchoring a flexible fiber geogrid to a support utilizing such anchor rods is also disclosed.
Owner:M D S K ENTERPRISES
Yoga mat with support and traction
The present disclosure provides a mat including a compressible first layer, openings formed through one or more first portions and columns disposed in / proximate to the openings. One or more second portions, or at least one column, or both may be configured to be depressed to provide support and traction. The present disclosure further provides a towel including an absorption layer and a compressible region of flexible fiber disposed on one or more first portions of a top surface of the absorption layer. The towel may further include one or more columns disposed either on one or more second portions or in / proximate to openings formed through the one or more second portions. The compressible region of flexible fiber may be configured to be depressed in a compressed configuration to provide support and traction. The mat or the towel may be further adapted to form a grip apparatus.
Owner:SEQUENCE
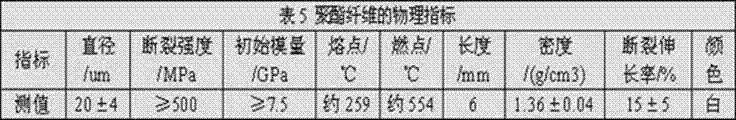
Crack self-healing bituminous concrete and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a crack self-healing bituminous concrete and a preparation method thereof. The bituminous concrete comprises coarse aggregate, fine aggregate, fillers, pitch, rigid fiber and flexible fiber, wherein the mixing amount of the rigid fiber is 0.50-2.5wt.% of the total amount of the coarse aggregate, the fine aggregate, the fillers and the pitch, and the mixing amount of the flexible fiber is 0.10-0.35wt.% of the total amount of the coarse aggregate, the fine aggregate, the fillers and the pitch. The preparation method of the concrete comprises the steps of weighing dried aggregates, placing the aggregates in a material containing disk, mixing the aggregates uniformly, preheating in a drying oven to the temperature of 180 DEG C, and heating the fillers separately to the temperature of 180 DEG C; preheating the pitch to the temperature ranging between 160 DEG C and 175 DEG C; drying the rigid fiber and the flexible fiber respectively for backup use according to the requirement; and firstly mixing the rigid fiber into the mixed aggregate with blending, then blending the aggregate and the liquid pitch, then blending with the fillers, then blending with the flexible fiber, and finally forming the bituminous concrete. According to the bituminous concrete and the preparation method, the low-temperature cracks of bituminous pavements are reduced to the minimum and can be healed spontaneously, early-stage cracking is avoided effectively, the service life of the bituminous pavements is prolonged, and the project implementation is convenient.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Apparatus and method for stabilizing an earthen embankment
A structure for stabilizing an earthen embankment comprises an embankment support for restraining movement of at least a part of the embankment, a flexible fiber geogrid (5) extending longitudinally through the embankment from a first end portion secured to the support to a second end portion, and anchor means (55, 60, 11) for securing one of the end portions. The anchor means comprises a pair of anchor rods (55, 60) extending transversely in relation to the geogrid, and means (11) for limiting movement of the anchor rods. The end portion secured by the anchor means is wrapped back and forth around the anchor rods so as to tighten thereon when the geogrid is pulled in longitudinal tension away from the anchor means. A method of anchoring a flexible fiber geogrid to a support utilizing such anchor rods is also disclosed.
Owner:M D S K ENTERPRISES
Flexible infrared delivery apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080308753A1Rapid coagulationMeet growth needsRadiation pyrometryEndoscopesProximateEndoscope
A flexible infrared delivery apparatus useful for endoscopic infrared coagulating of human or animal blood and tissue or for other uses employs a source of infrared radiation which is not a laser and an elongated flexible fiber optic member which transmits radiation from the source to a contact portion at a distal end of the member and to a material such as human or animal tissue proximate the contact portion. The elongated member has an outer diameter which enables it to be inserted into and through an accessory channel of an endoscope to view the human or animal tissue or material to be treated with infrared radiation. A connector on the proximal end of the member allows the elongated member to be quickly connected to and disconnected from the apparatus where the member is aligned for receiving infrared radiation from the source. The contact portion defines a size, direction and shape of a radiation delivery area from the member to the human or animal tissue or material proximate the contact portion.
Owner:PRECISION ENDOSCOPIC TECH LLC
Friction material
ActiveUS20060241207A1Improve heat resistanceHeat dissipation fastOther chemical processesFibre treatmentCarbon fibersMetallurgy
This friction material has a fibrous base material and preferably is a wet friction material for use in a fluid environment. The fibers have a small diameter and a high tensile modulus resulting in flexible fibers that performs well in a high temperature, high pressure fluid environment. The fibers have a diameter ranging from 1 to 20 micrometers and a tensile modulus greater than 70 Gpa. In the preferred embodiment, the small diameter fibers are small diameter carbon fibers or small diameter mineral fibers.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Scanning miniature optical probes with optical distortion correction and rotational control
Optical probes having a diameter less than substantially 500 mum for use in scanning light from a long, highly flexible fiber to a sample. In one embodiment the probe includes a viscous damping fluid suitable to prevent non-uniform rotational distortion (NURD).
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Flexible fiber to wafer interface
ActiveUS20130251304A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSingle mode waveguidesMechanical engineering
An interface device includes a flexible substrate portion, a flexible cladding portion arranged on the substrate portion, a flexible single-mode waveguide portion arranged on the cladding portion including a substantially optically transparent material, a first engagement feature operative to engage a portion of a wafer, and a connector portion engaging a first distal end of the flexible substrate portion, the connector portion operative to engage a portion of an optical fiber ferrule.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Compound leak preventive for oil-based drilling fluid
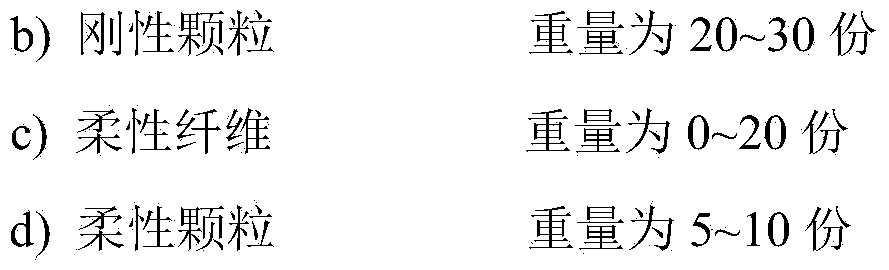
ActiveCN104388067ASolving Permeability Leakage ProblemsReduce thicknessDrilling compositionEmulsionMedicine
The invention relates to a compound leak preventive for an oil-based drilling fluid, and a preparation method of the compound leak preventive, and belongs to the technical field of a chemical drilling fluid treating agent for an oil field. The compound leak preventive for the oil-based drilling fluid comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: a) 40-50 parts of globular gel which is polymerized by an inverse emulsion, b) 20-30 parts of 5-18micron rigid material, c) 0-20 parts of a flexible fiber which is greater than 75-380 microns, and d) 5-10 parts of expanded graphite of 45-75micron flexible particles. The compound leak preventive for the oil-based drilling fluid is prepared from the components including the four substances in a manner of mixing evenly on general mixing equipment. The compound leak preventive for the oil-based drilling fluid disclosed by the invention is prepared from granular materials, fiber materials and expansive materials; the components have a deformation block function, and have good compatibility and mud cake improving properties with the oil-based drilling fluid; and the problem of permeability loss in the drilling process can be effectively solved.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Task lighting system
InactiveUS20050128769A1Improve impactResistant to breakageElectric lighting for hand-held usePoint-like light sourceEngineeringTask lighting
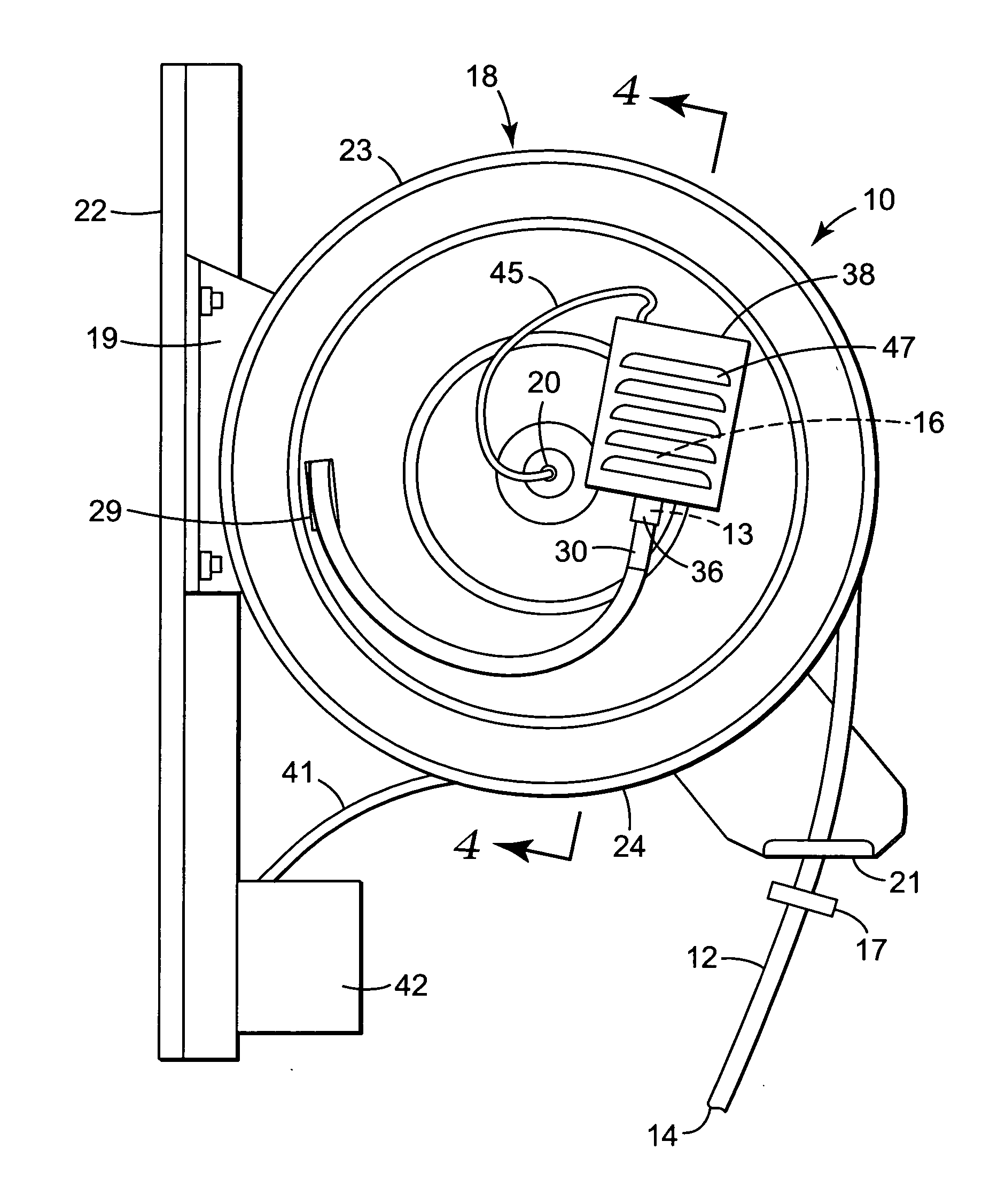
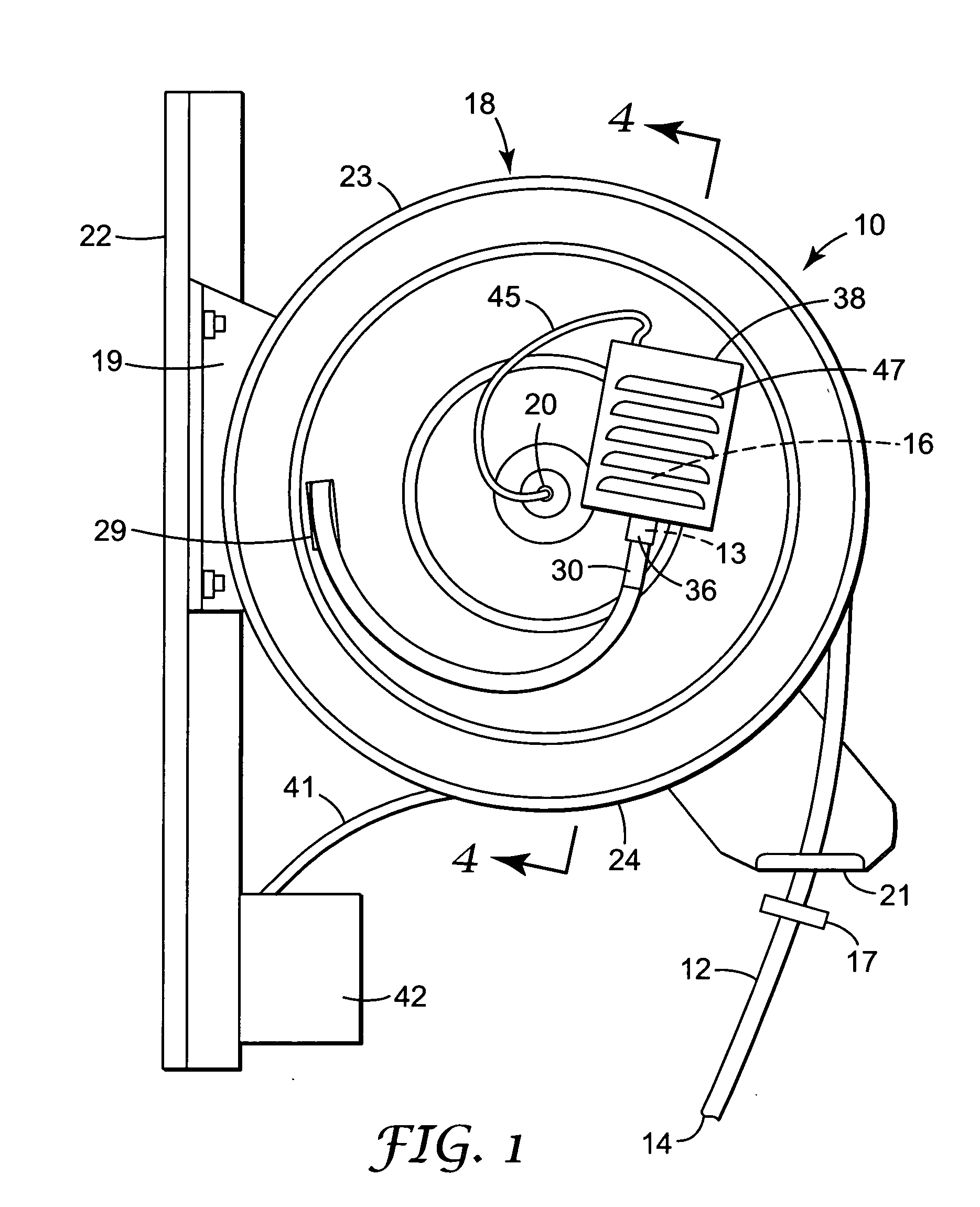
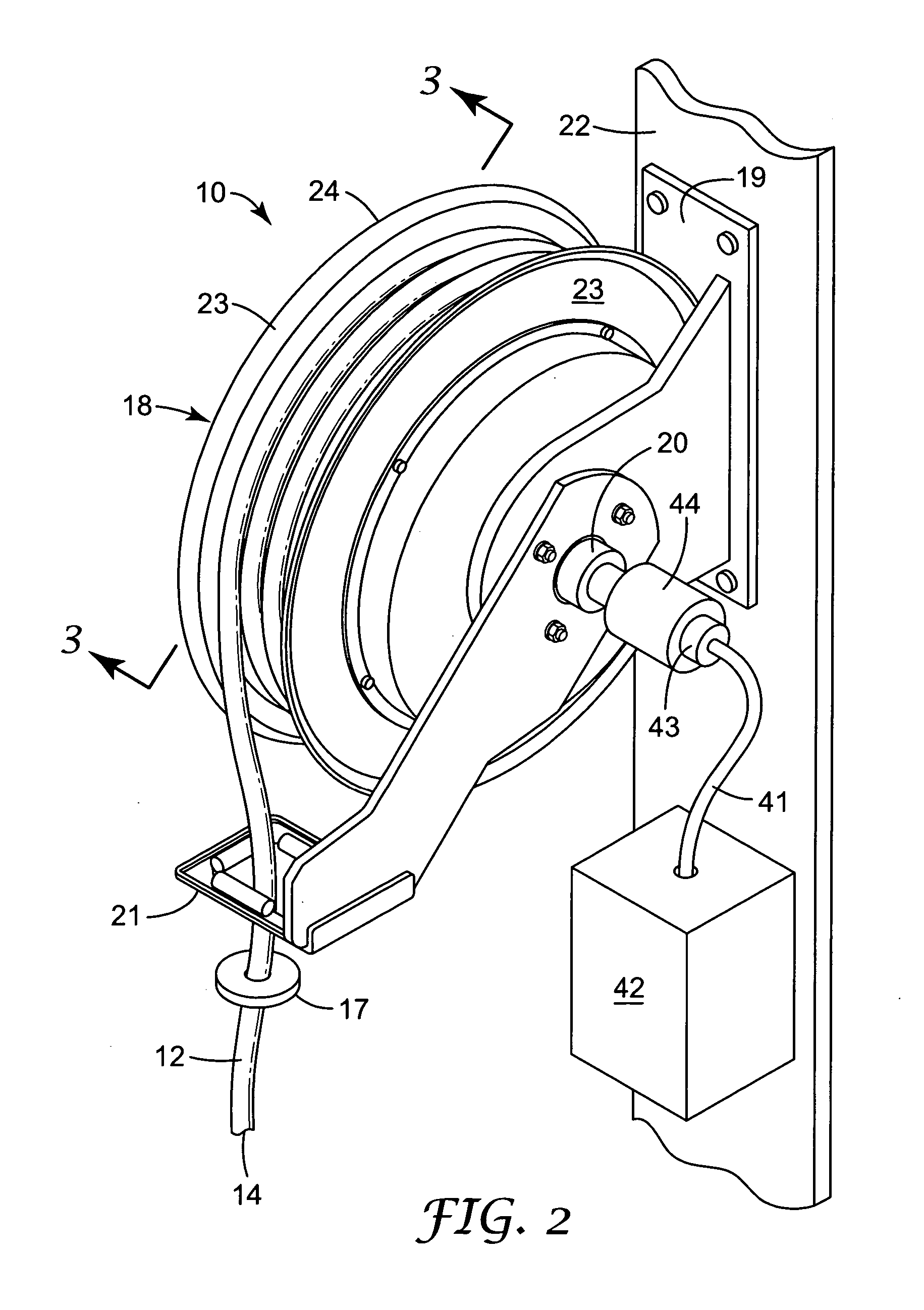
A task light assembly including a long flexible fiber optic element capable of transmitting light between light inlet and light outlet ends; a light source at the light inlet end of the fiber optic element; and a reel assembly for supporting the light source and the light inlet end of the fiber optic element and for allowing movement of the fiber optic element between a storage position with the light outlet end of the fiber optic element supported in a storage position, and an extended use position with the light outlet end of the fiber optic element at a work location remote from the storage position.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
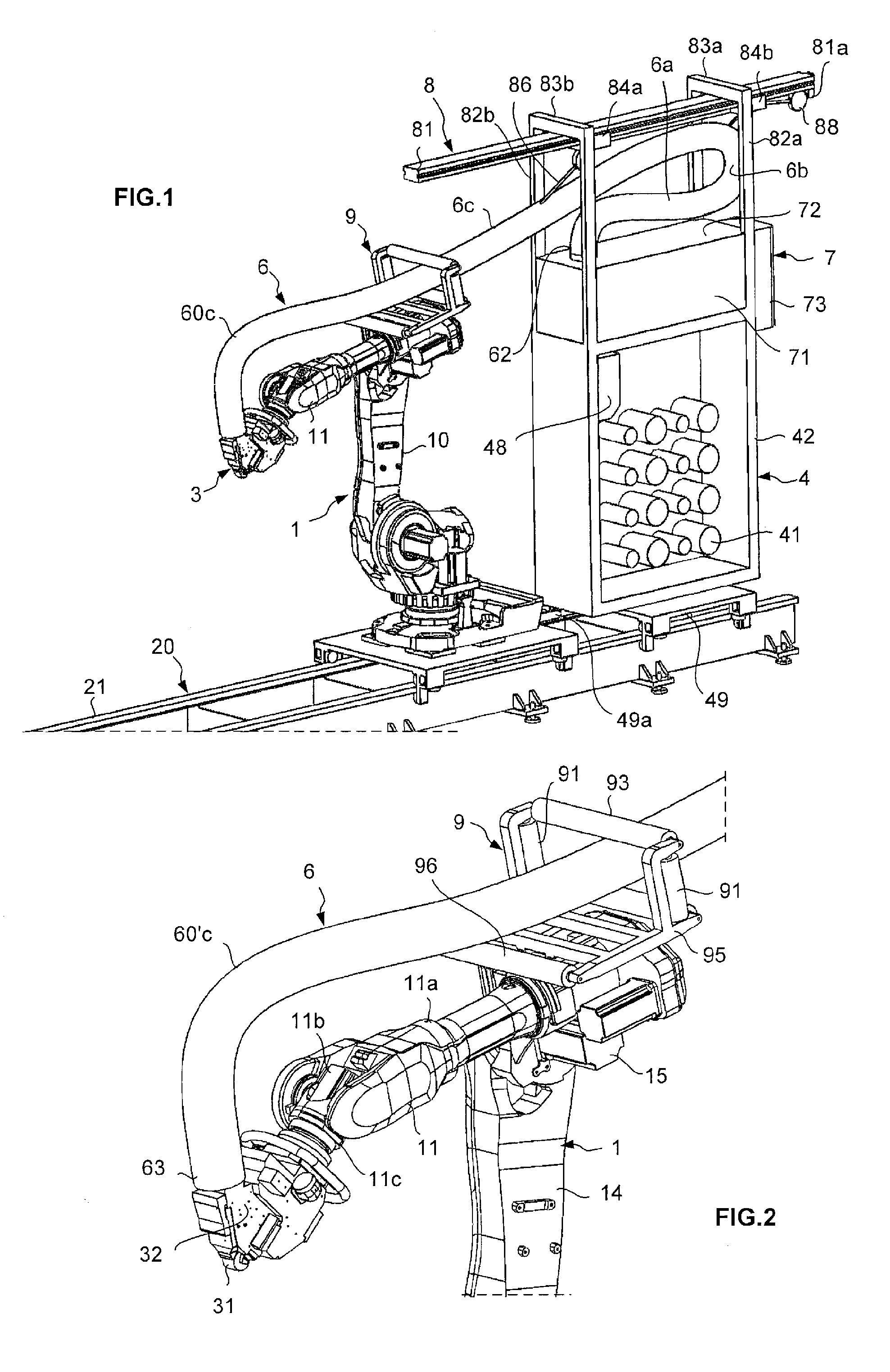
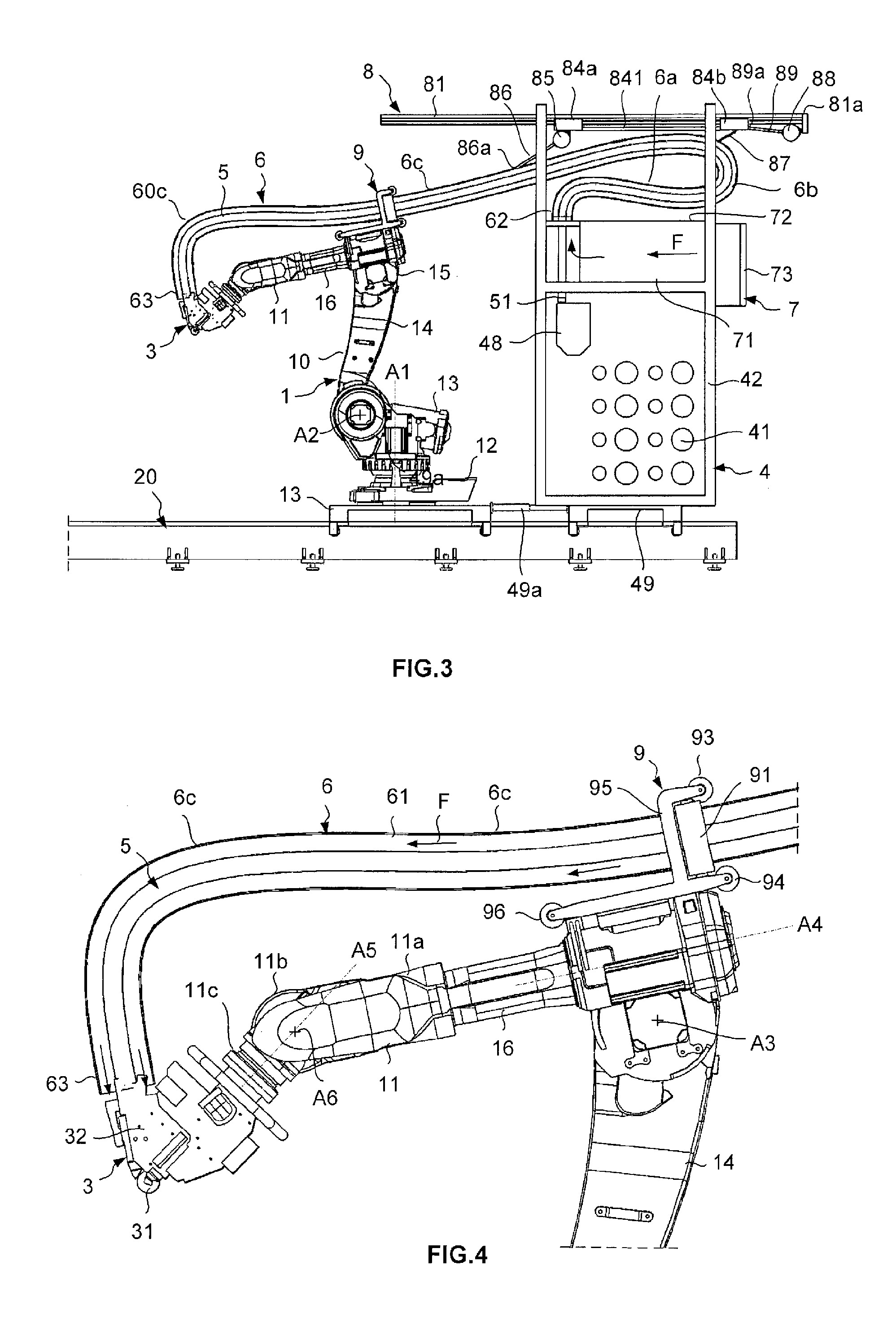
Fiber application machine provided with flexible fiber conveying tubes arranged within a cold sheath
ActiveUS20110272126A1Easy constructionReduce distanceAdhesivesTubular elementsEngineeringProduct gas
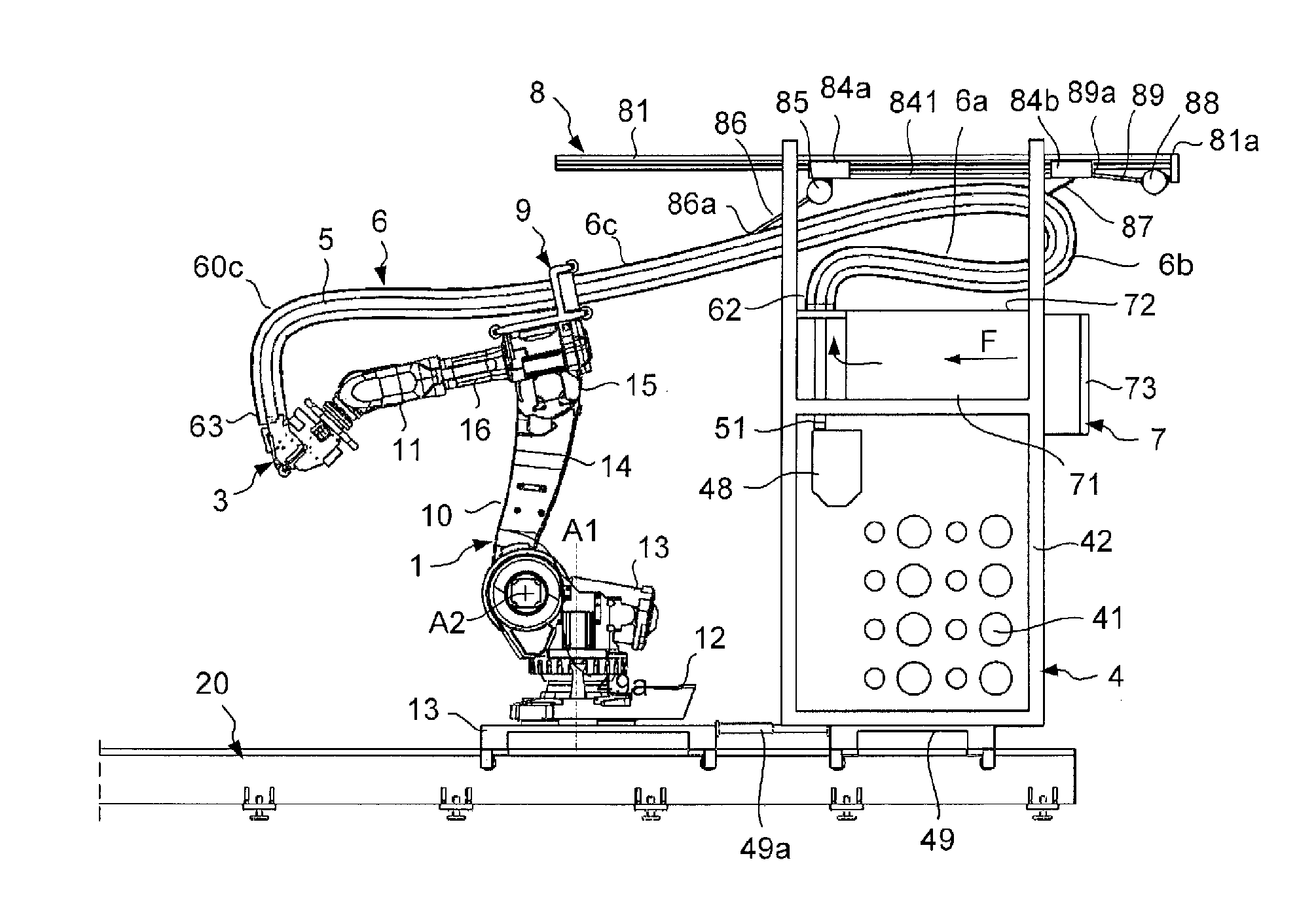
A fiber application machine for the production of composite material parts, comprising a system for displacing a fiber application head, a fiber storage, and a fiber conveyor for conveying the fibers from the fiber storage to the application head, the fiber conveyor being placed in the internal passage of at least one flexible tubular sheath, the machine further comprising a cooling system adapted to inject cold gas in the internal passage of the sheath.
Owner:CORIOLIS GRP
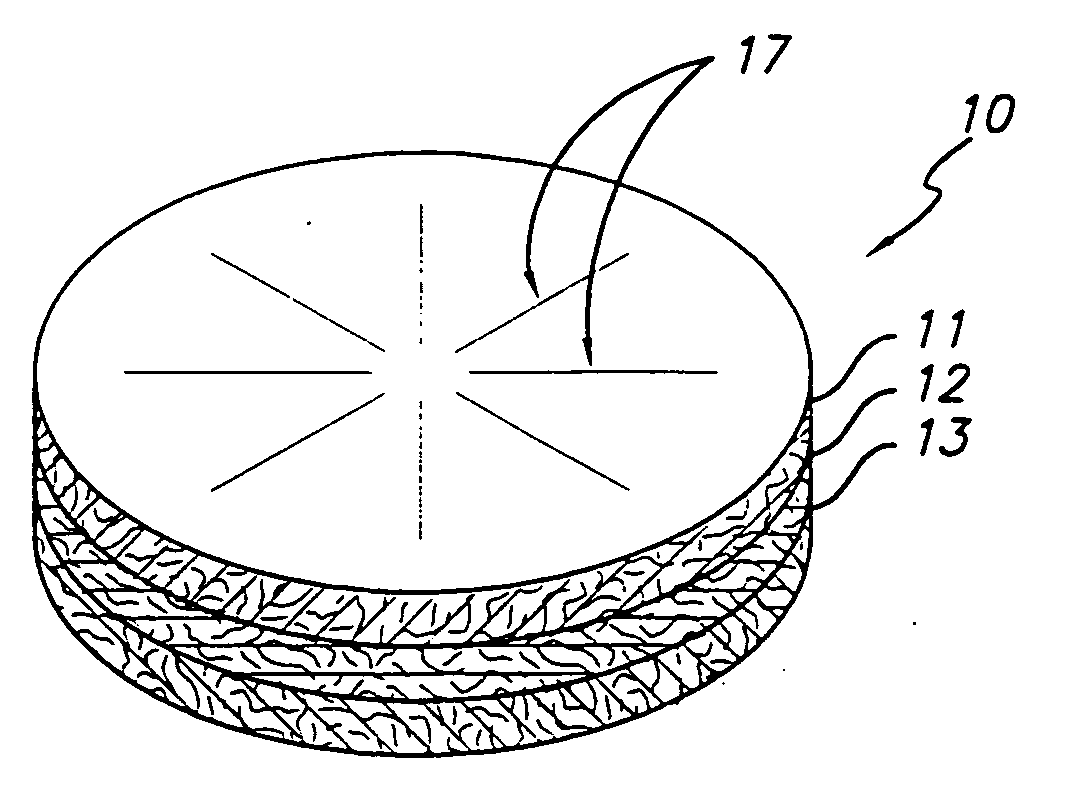
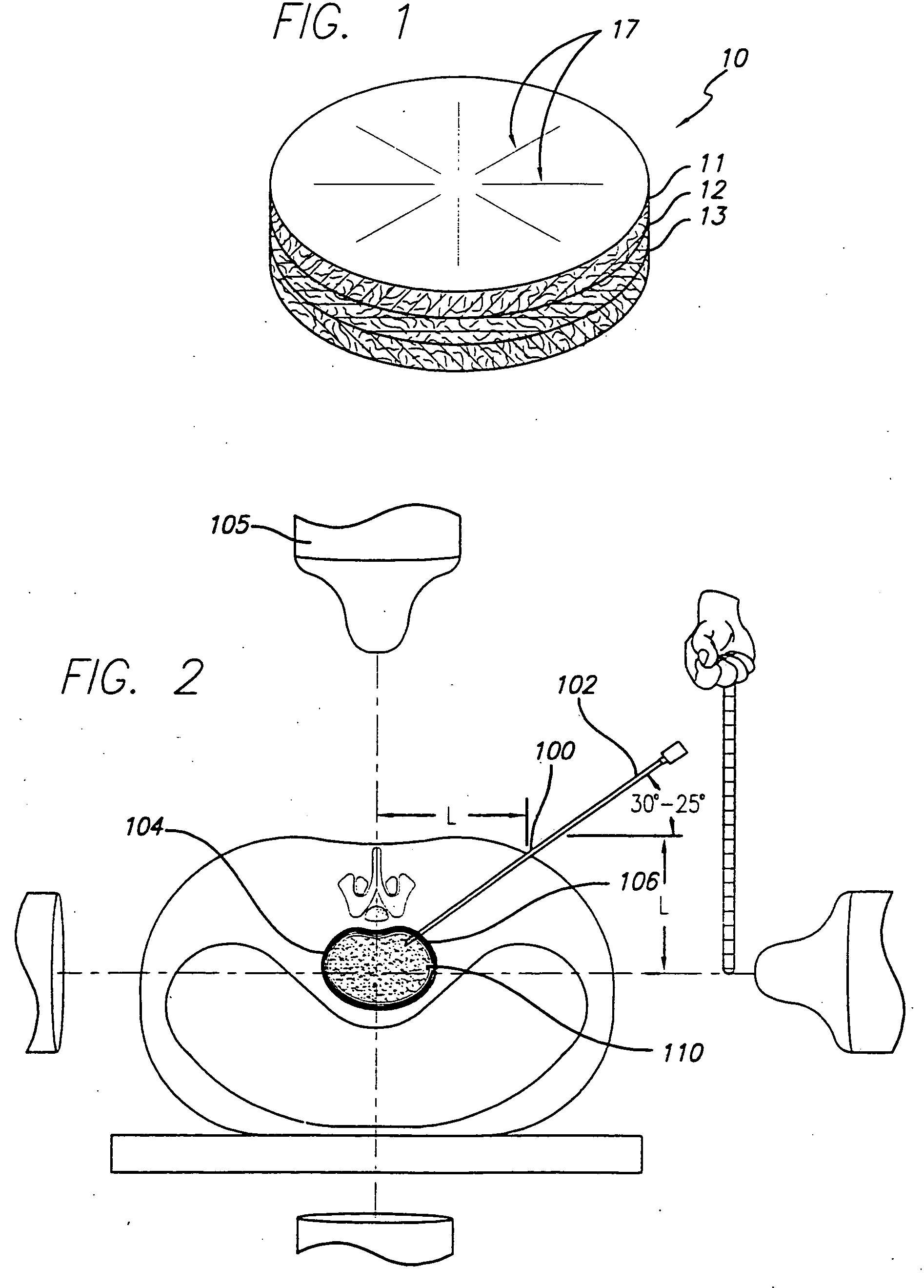
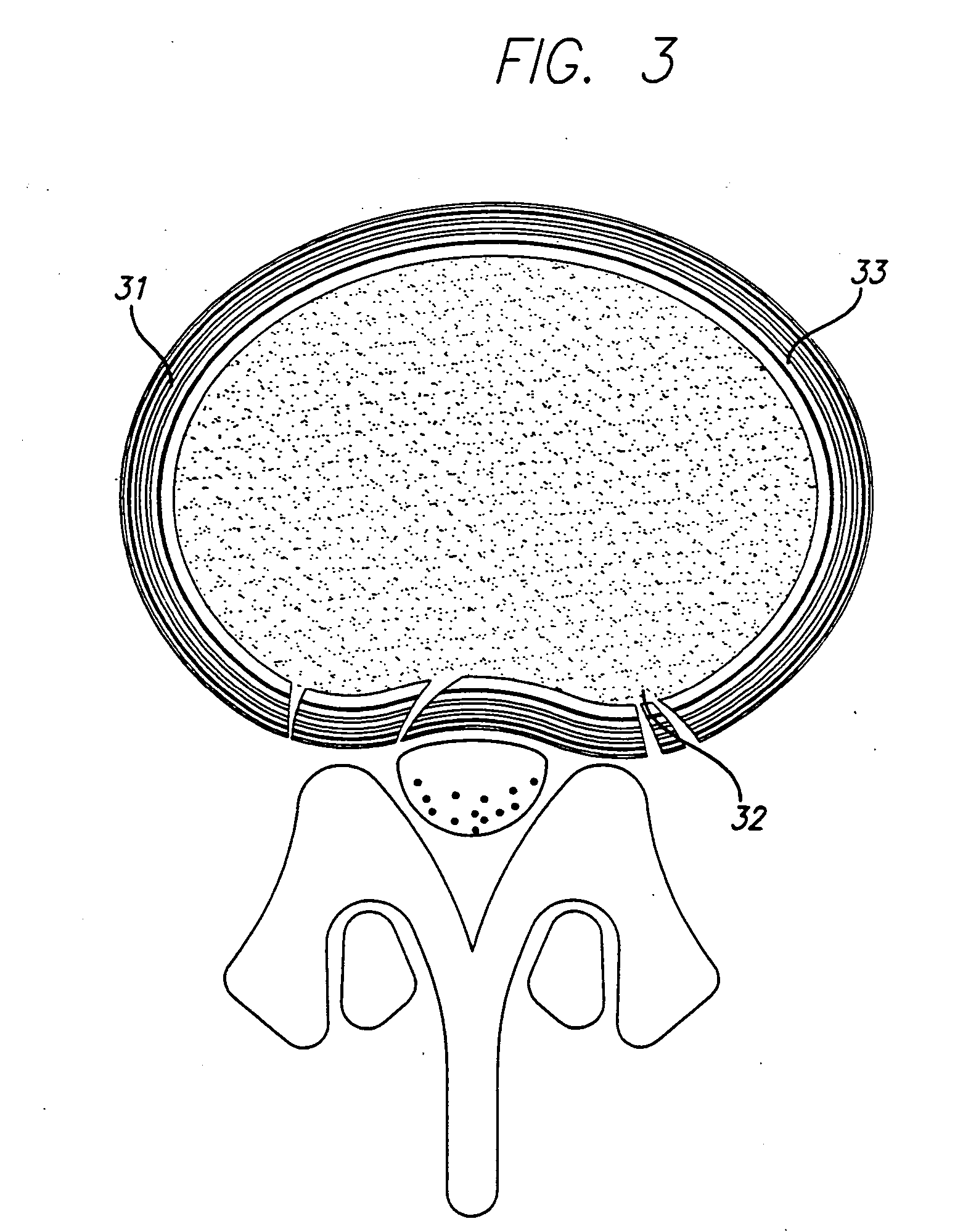
Patch material for intervertebral disc annulus defect repair
A patch for repairing defects in a intervertebral disc annulus, including a substantially thin layer of animal collagen arranged in a substantially circular shape, a fabric layer disposed beneath the layer of animal collagen and coupled to the layer of animal collagen by biological glue, a barrier layer of liquid resistant material disposed beneath the fabric layer, and coupled to the fabric layer by an adhesive, a plurality of flexible fibers disposed on a top surface of the patch and oriented in a radial direction and at least one suture disposed through the patch, the suture acting as a handle.
Owner:TSOU PAUL M
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com