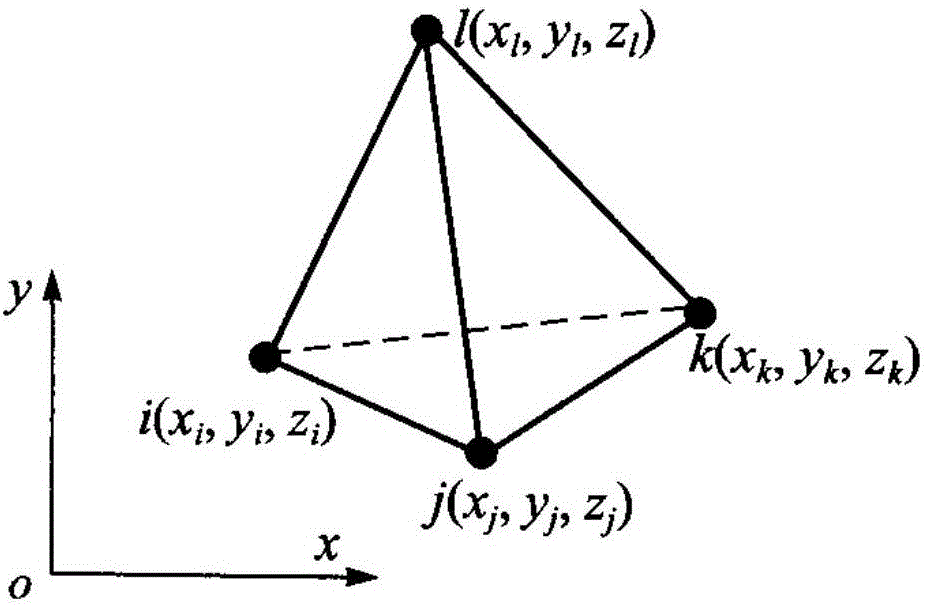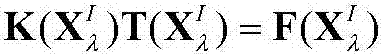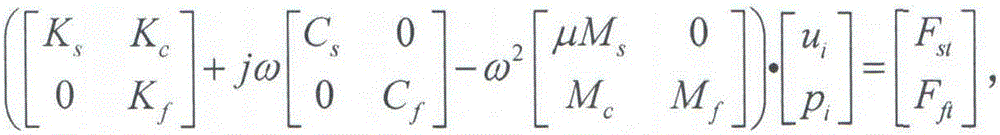Patents
Literature
77 results about "Finite element equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
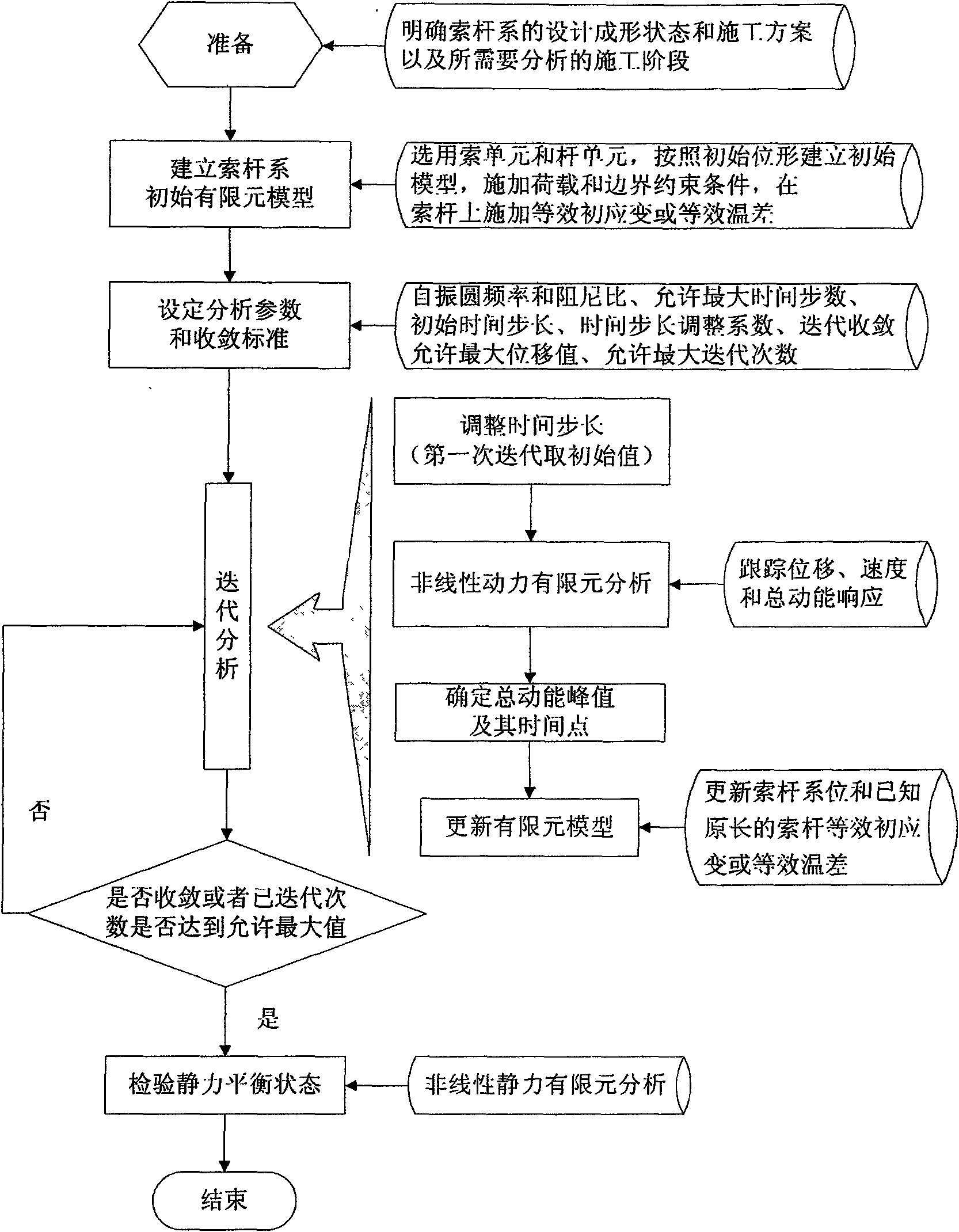
Non-linear dynamic finite element method for determining cable-strut system static balancing state
ActiveCN101582095ASolve the form-finding problemHolisticSpecial data processing applicationsViscous dampingDynamic balance
The invention relates to a non-linear dynamic finite element method for determining cable-strut system static balancing state. In the construction processes of traction mounting and stretch-draw forming, a cable-strut system as a mechanism has super large displacement, mechanism displacement and guy cable looseness, and a conventional linear dynamic finite element method cannot obtain the static balancing state in the construction stage. The non-linear dynamic finite element method adopts form-finding analysis to establish a non-linear dynamic finite element equation by introducing inertia force and viscous damping force so as to change a static problem which is difficult to solve into a dynamic problem which is easy to solve, and gradually converge the dynamic balancing state of the cable-strut system into a static balancing state through iteration updating of the configuration of the cable-strut system. The cable-strut system is in a static unbalancing state before analysis, is in the dynamic balancing state in the analysis, and reaches the static balancing state after the convergence, namely the cable-strut system discontinuously moves (non-continuous movement) from the initial static unbalancing state to the stable static balancing state.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
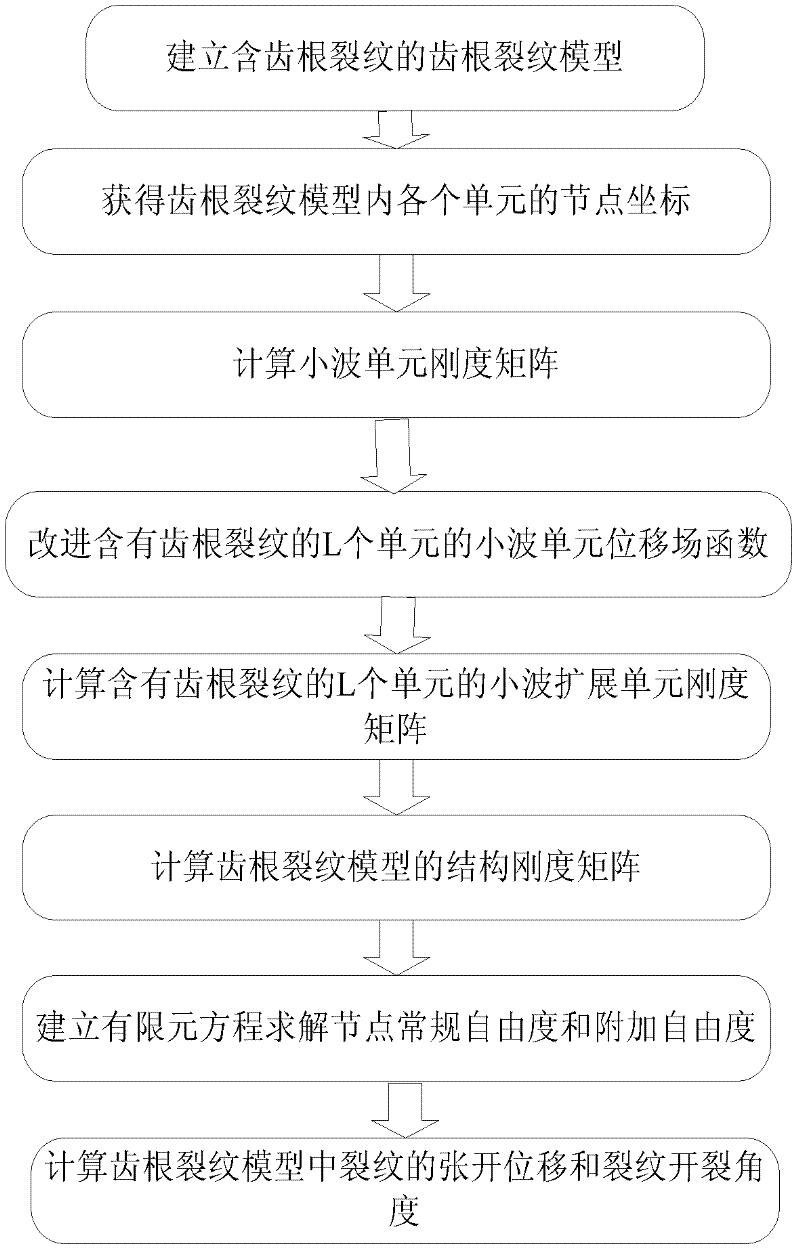
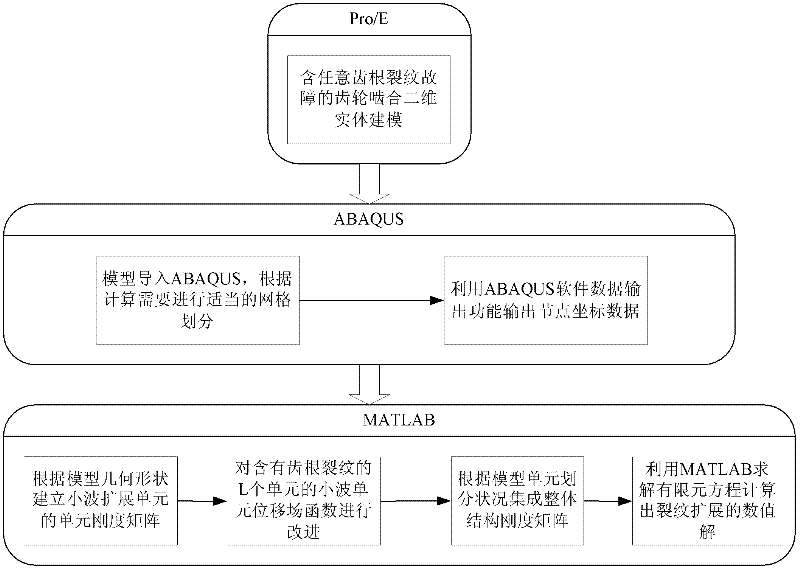
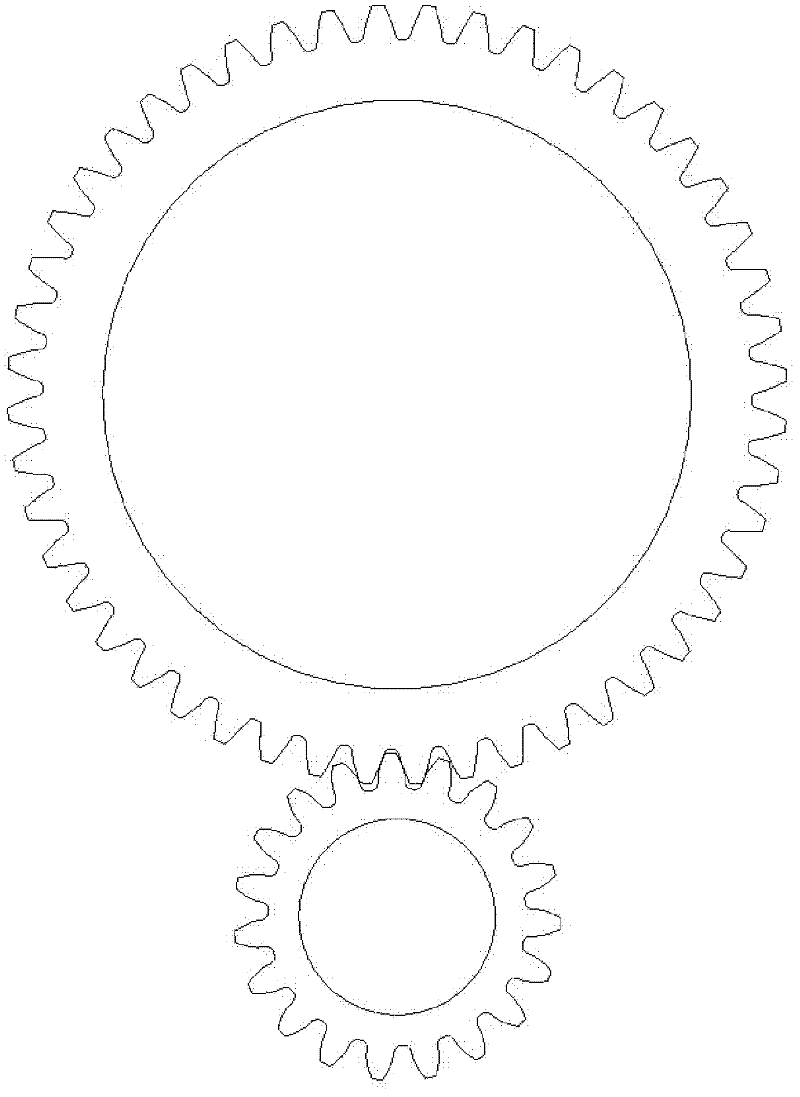
Gear crack propagation simulated wavelet extension finite element simulation analysis method
InactiveCN102332046AConvenient researchAvoid difficultiesSpecial data processing applicationsFinite element equationComputer-aided
The invention relates to a finite element analysis method for crack propagation, in particular to a numerical value analysis method using wavelet extension as a new finite analysis unit. The method comprises the following steps that: based on a computer-aided drawing software, a gear meshing model containing any crack failure is built; the module is imported into a finite element analysis software ABAQUS, and geometric data of a finite element mesh is obtained by combination of ABAQUS meshing and data output functions; according to the obtained data, a mathematics-assisted calculation software is applied to a program to calculate the element stiffness matrix of a wavelet extension unit, and then according to the mesh of the analyzed structure, the overall stiffness matrix of an integratedstructure is arranged; and after boundary constraint conditions and loads are introduced, a finite element equation is solved to obtain the numerical value solution of crack propagation. In the invention, the growth conditions of cracks can be tracked, and the difficulty brought by highly concentrated stress is also solved; and the method has higher computational accuracy and higher computationalefficiency, and facilitates the study of fault diagnosis of mechanical equipment.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Multi-Layer Finite Element Method for Modeling of Package Power and Ground Planes
ActiveUS20100217576A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringPolygon mesh
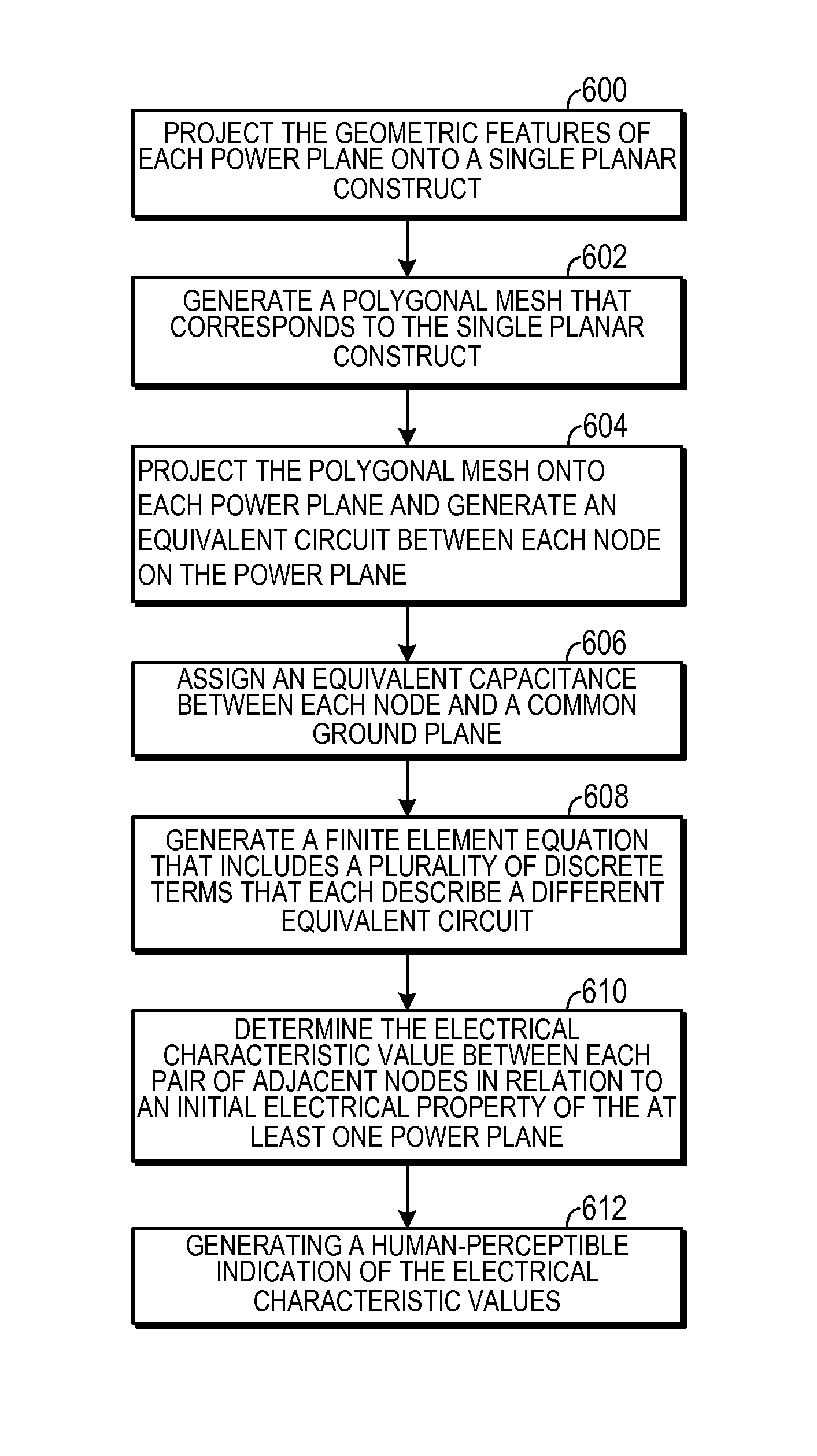
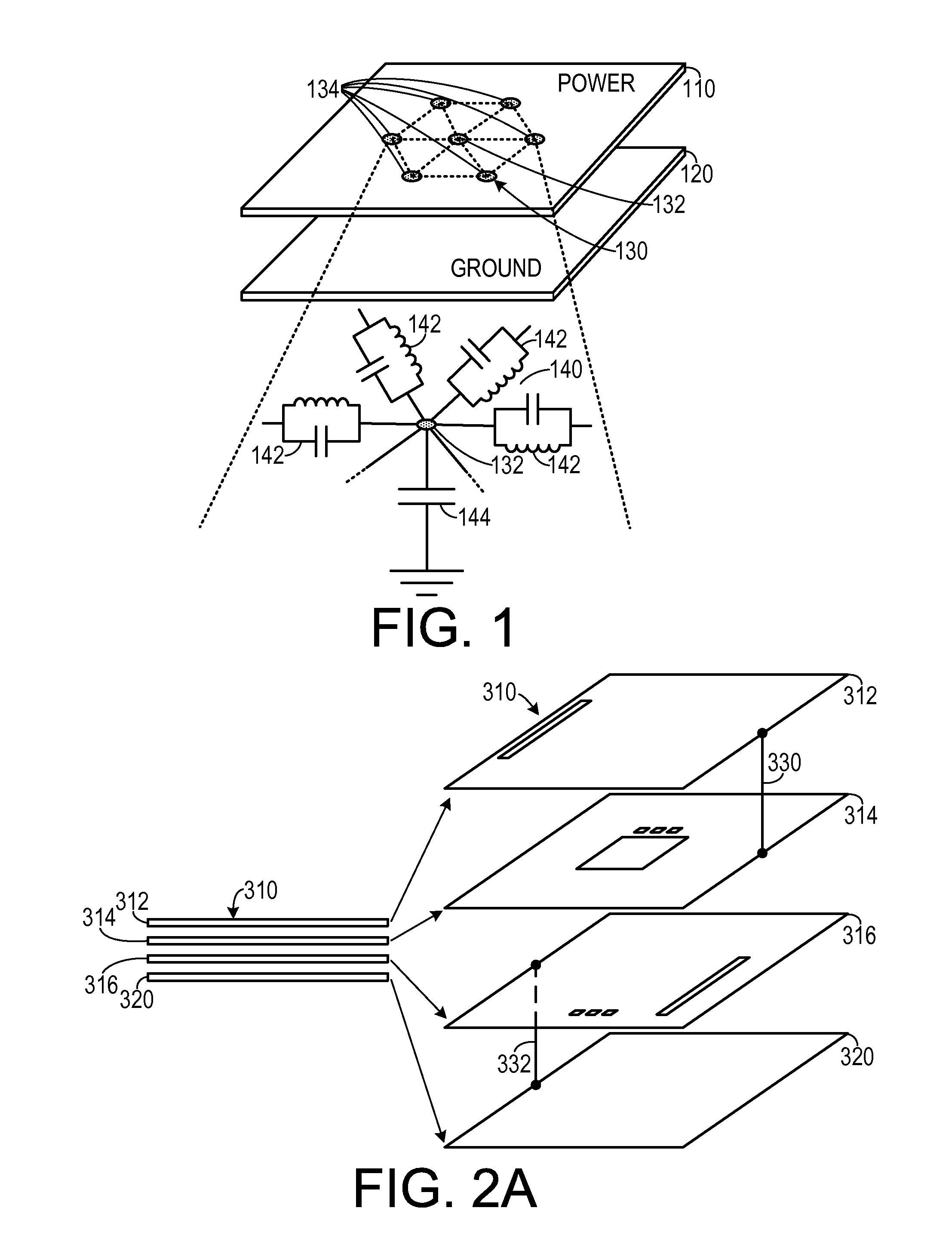
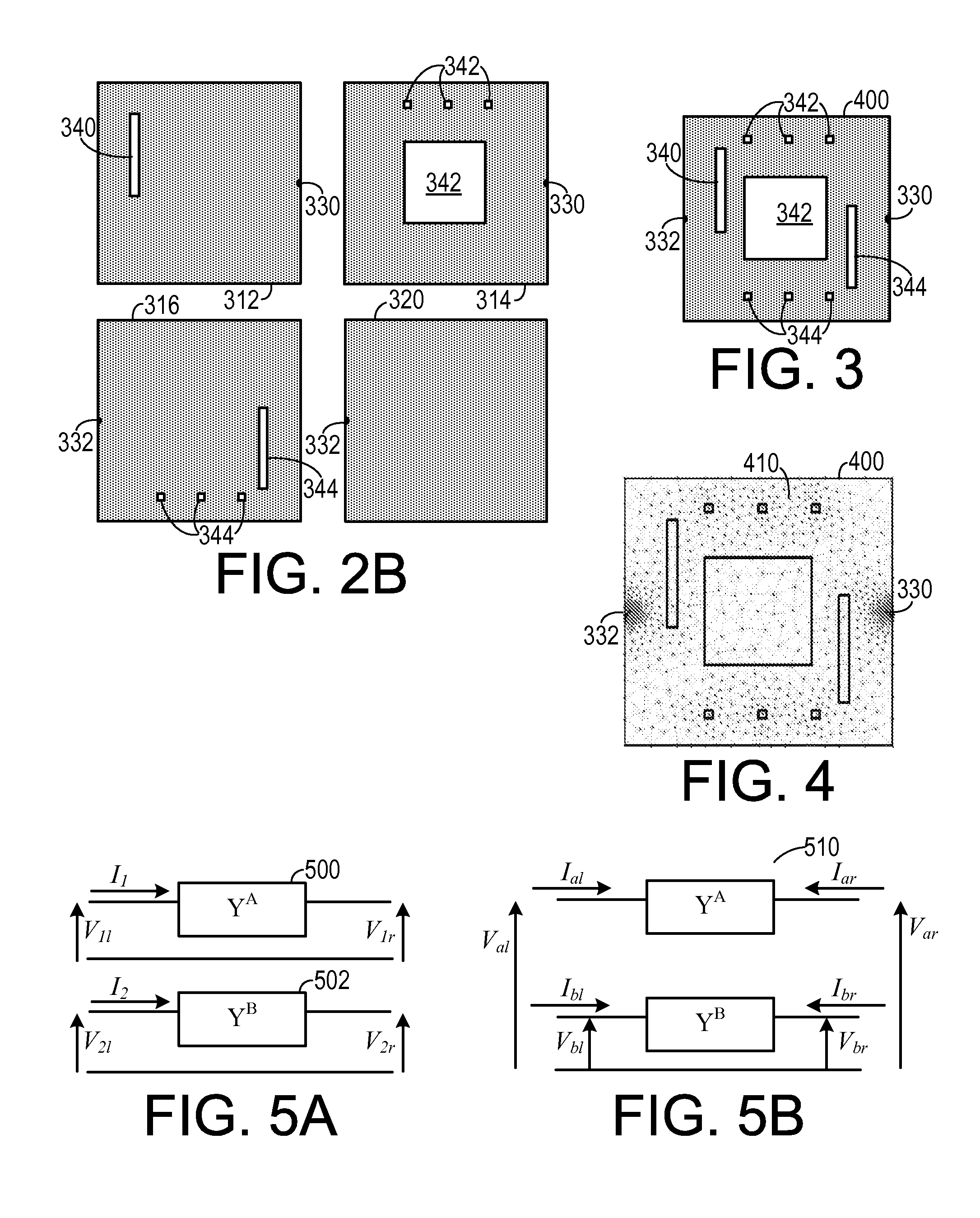
In a method for simulating electrical characteristics of a plurality of power planes, each power plane includes a plurality of geometric features. The geometric features of each power plane are projected onto a single planar construct. A polygonal mesh, including a plurality of pairs of interconnected nodes, that corresponds to the single planar construct is generated. The polygonal mesh is projected onto at least one power plane an equivalent circuit between each adjacent node of the plurality of interconnected nodes is projected onto the power plane. An equivalent capacitance is assigned between each node and a common ground planer. A finite element equation that includes a plurality of discrete terms is generated. The equation is solved, thereby determining the electrical characteristic value between each pair of adjacent nodes.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
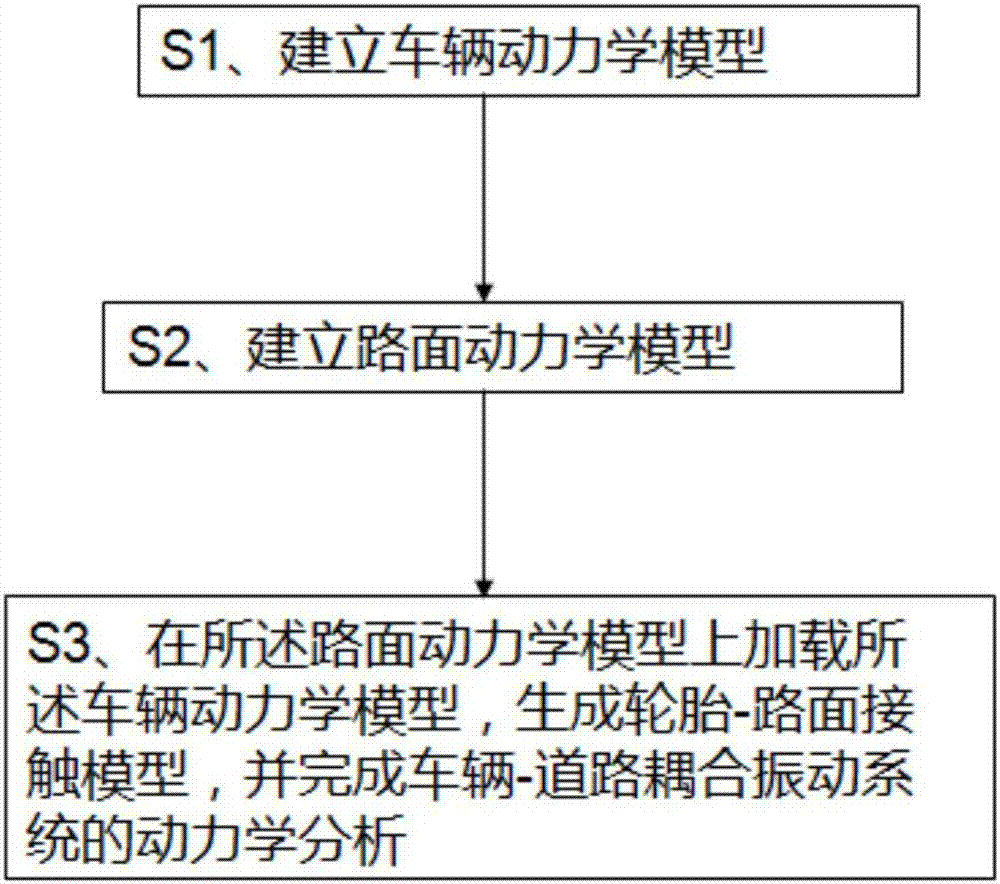
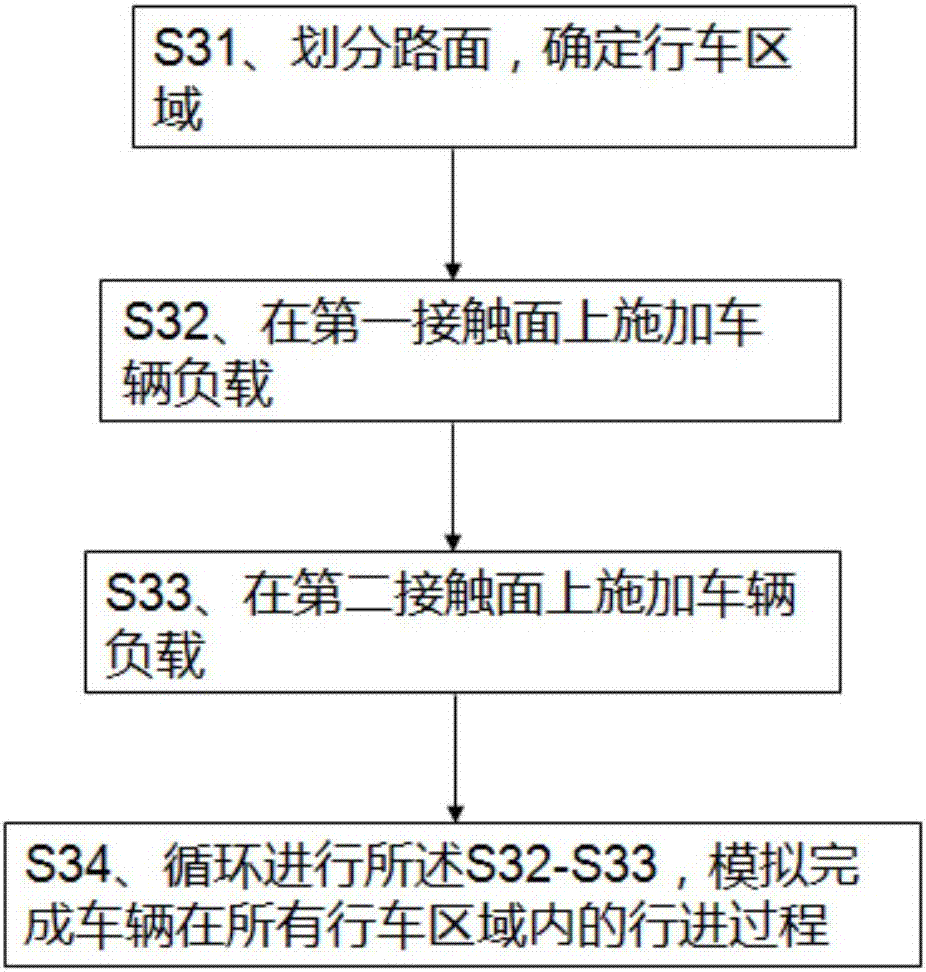
Joint simulation method for vehicle-road coupled vibration system
InactiveCN106897518AImprove accuracyEasy to operateGeometric CADSustainable transportationVehicle dynamicsDynamic models
The invention relates to a joint simulation method for a vehicle-road coupled vibration system. The method comprises the following steps of S1, building a vehicle dynamics model according to a dynamics equation; S2, building a pavement dynamics model according to a structural mechanics finite element equation; and S3, loading the vehicle dynamics model in the pavement dynamics model to generate a tire-pavement contact model, and finishing dynamics analysis of the vehicle-road coupled vibration system. According to the method, joint modeling of the vehicle-road coupled vibration system is realized by adopting efficient engineering software Matlab and Ansys; and by taking Matlab as control software and performing secondary development on Ansys, joint simulation of Matlab and Ansys is realized, and dynamics analysis of the vehicle-road coupled vibration system under complex road and vehicle conditions is finished.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
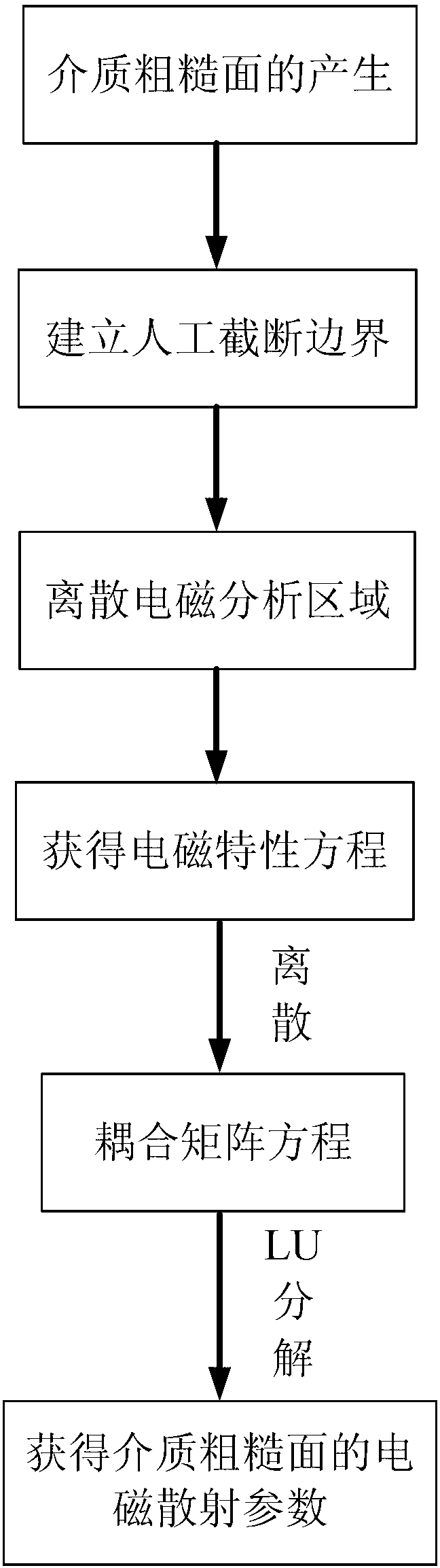
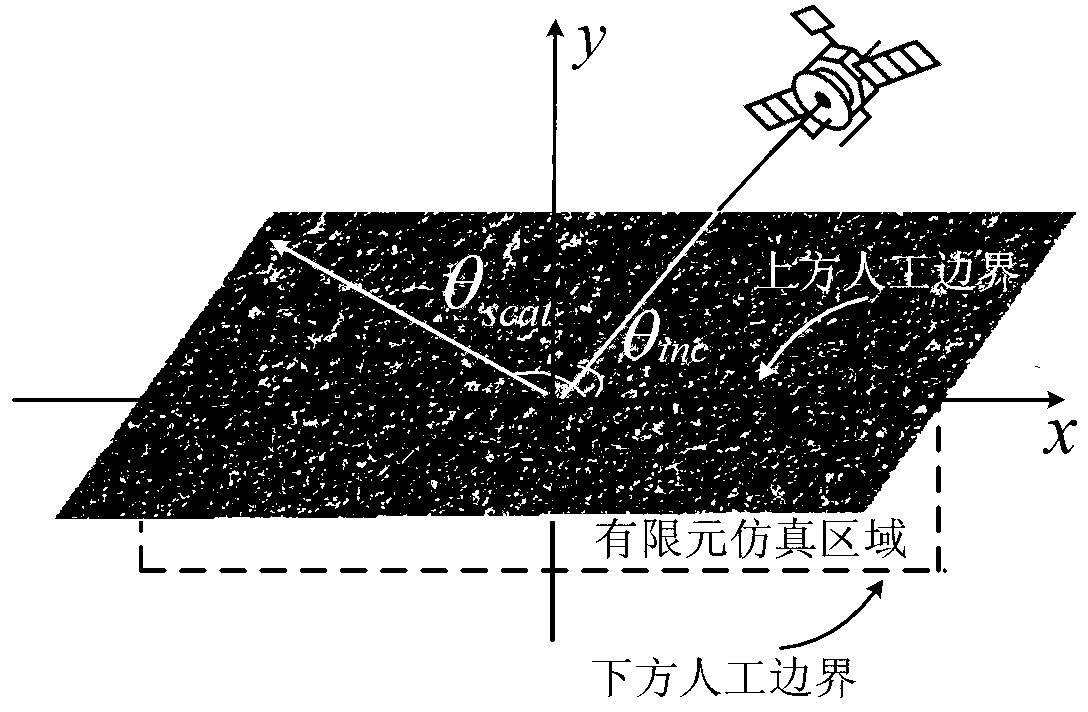
Medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on integral boundary
InactiveCN103279600AImprove accuracyAvoid incomplete absorptionSpecial data processing applicationsRough surfaceFunctional methods
The invention discloses a medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on integral boundary. The medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on the integral boundary mainly solves the problem that similarity of inhomogeneous media and approximate absorbing boundary are difficult to solve by integral equation class methods. The medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on the integral boundary comprises the achieving steps of using a monte carlo method for obtaining a medium rough surface, carrying out truncation processing and scattering on the medium rough surface through an artificial boundary, acquiring a finite element equation of a simulation area according to a functional method inside the simulation area, using an integral equation method for obtaining integral boundary conditions outside the simulation area, forming an electromagnetic coupled equation through continuous conditions, and finally obtaining radar scattering parameters of the medium rough surface by solving an electromagnetic coupled matrix equation. Compared with the prior art, the medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on the integral boundary can be more easily used for simulating inhomogeneous medium electromagnetic problems than the integral equation class methods, can improve electromagnetic simulation precision compared with the approximate absorbing boundary, and can be used for acquiring the electromagnetic scattering parameters of medium rough surface unbounded area problems.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Marine controlled source electromagnetic method finite element forward method of anisotropic media
InactiveCN106980736AAvoid the effects of singularityEasy constructionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsScalar potentialMaxwell's equations
The present invention is a marine controlled source electromagnetic method finite element forward method of anisotropic media. The method comprises: firstly, setting a reference electrical conductivity, wherein three non-zero diagonal elements of the reference electrical conductivity are electrical conductivities in the direction of three main axes: x, y, z; next, setting three Euler rotation angles, and after three times of Euler rotation, obtaining an electrical conductivity tensor model in any direction; then starting from Maxwell equations, obtaining a finite element equation that is satisfied by magnetic vector potential and scalar potential under Coulomb regulations on a condition that the electrical conductivity presents anisotropy; then, performing discrete segmentation on a research region by using a non-structural grid, so that a complicated geoelectric model can be constructed; combining an incomplete LU discomposition pre-condition factor with an IDR(s) algorithm, so as to realize efficient and precise solution of a large sparse linear equation; and finally, deriving vector potential and scalar potential of a secondary field by using weighted moving least squares solution, to obtain each component of an electromagnetic field. The method provided by the present invention has excellent universality and can be promoted for electromagnetic method numerical value simulation with complicated electrical conductivity distribution and high precision.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Three-dimensional frequency domain controllable source numerical simulation method
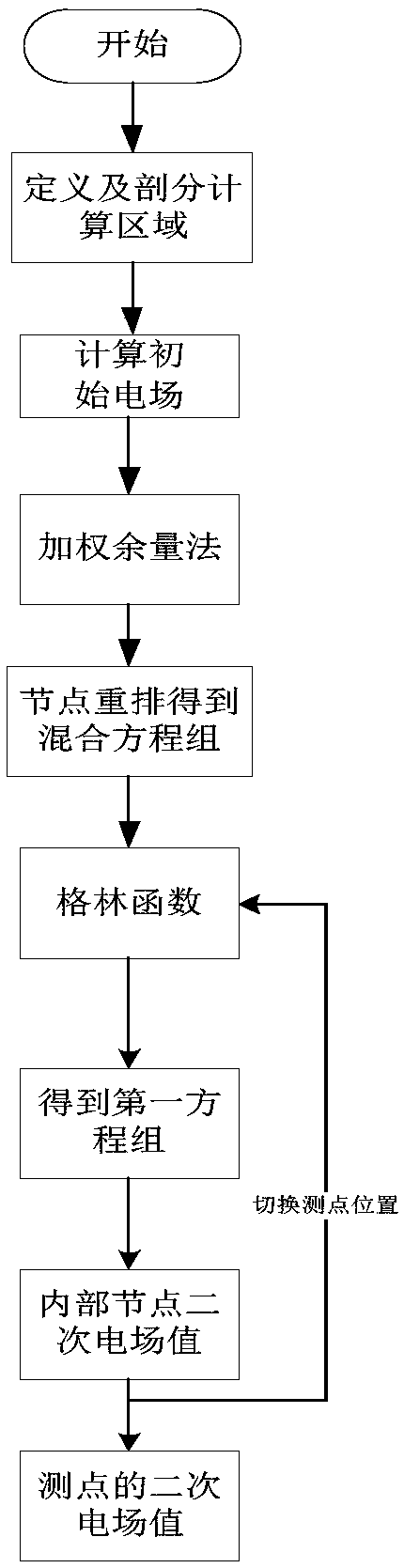
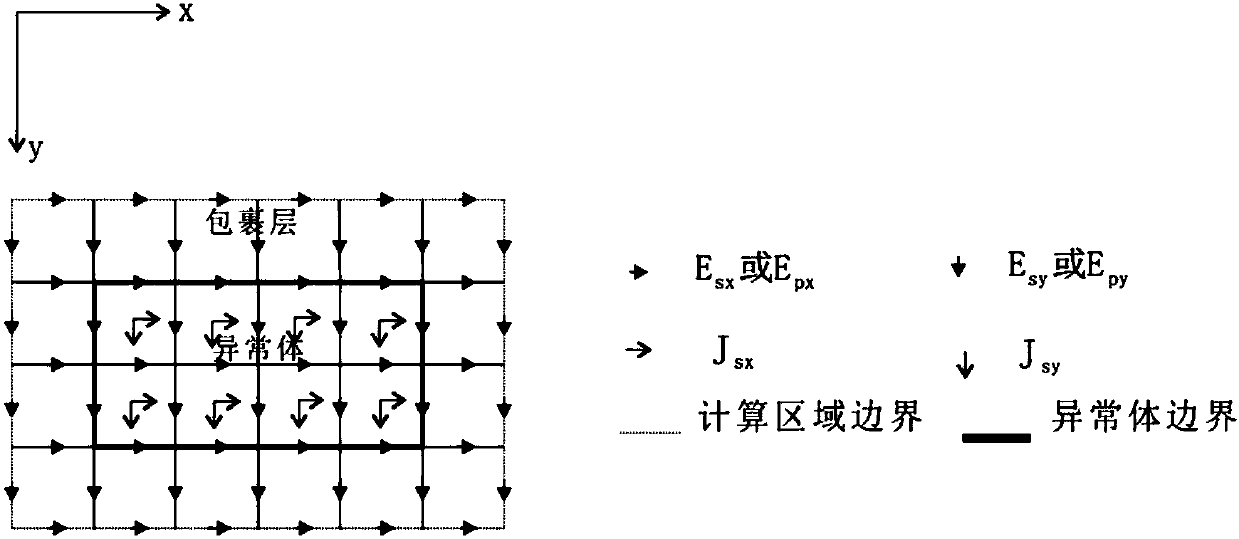
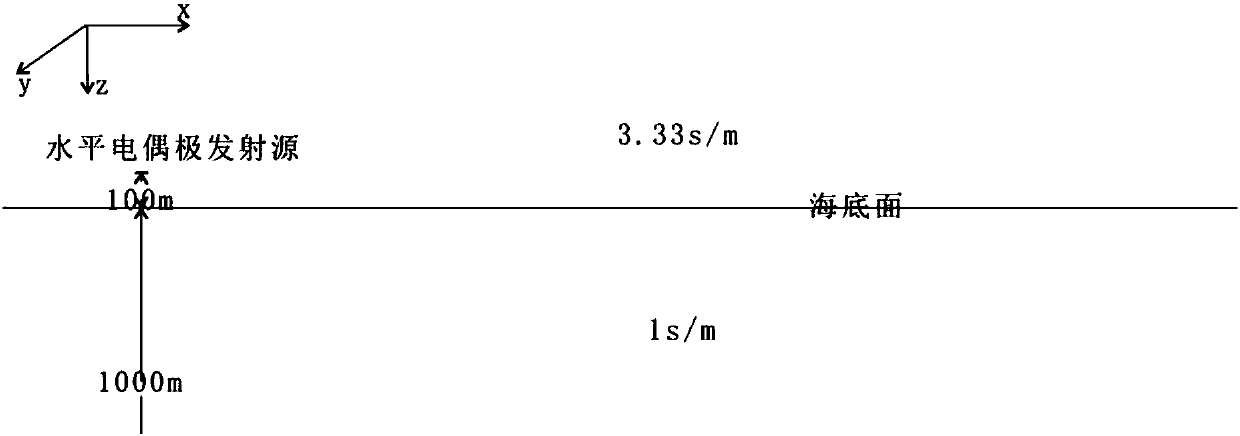
ActiveCN108509693ASmall scaleThe number of unknowns to be solved is smallDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMixed finite element methodFinite element equation
The invention provides a three-dimensional frequency domain controllable source numerical simulation method. The method comprises the steps of S100: defining a calculation region in a resistivity anomaly body and an adjacent wrapping layer, and dividing the calculation region into multiple regular unit bodies; S200: calculating an initial electric field under an artificial source excitation condition, and by adopting a weighted residual method, establishing a finite element equation set of edge midpoints of the unit bodies in the calculation region; S300: defining an observation point as a boundary node by using a Green function, and enabling a secondary electric field of an internal node to express a secondary electric field of the boundary node; S400: substituting a Green function expression into a mixed equation set to obtain a first equation set only about the secondary electric field of the internal node; and S500: solving the first equation set to obtain secondary electric fieldvalues of nodes comprised in the unit bodies. According to the method, a vector finite element method and a volume integral equation method are applied; the calculation region is reduced; the calculation amount is reduced; the calculation precision is improved; formed equations are sparse in coefficient matrix and good in condition number; and a calculation result is accurate.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Random finite element analysis based infrared-decoy-projectile pneumatic feature modeling method
InactiveCN106485035ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAerodynamic dragElement analysis
The invention discloses a random finite element analysis based infrared-decoy-projectile pneumatic feature modeling method. The pneumatic feature modeling method includes the steps of analysis and simplification of infrared-decoy-projectile working field, finite element subdivision of the decoy projectile working field, determination of unit interpolation based function, analysis of finite units, establishment of overall-random finite element equation, establishment and simulation of decoy projectile motion equation and the like. A temperature flow field distribution and random air-resistance movement feature model of a decoy projectile is provided on the basis of a finite analysis method by analyzing working mechanism and operating status of the decoy projectile; basis is provided for design of the infrared decoy projectile and research on an infrared guidance algorithm, and important guiding significance is achieved for establishment of an infrared visual simulation system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel anti-impact light interlayer structure
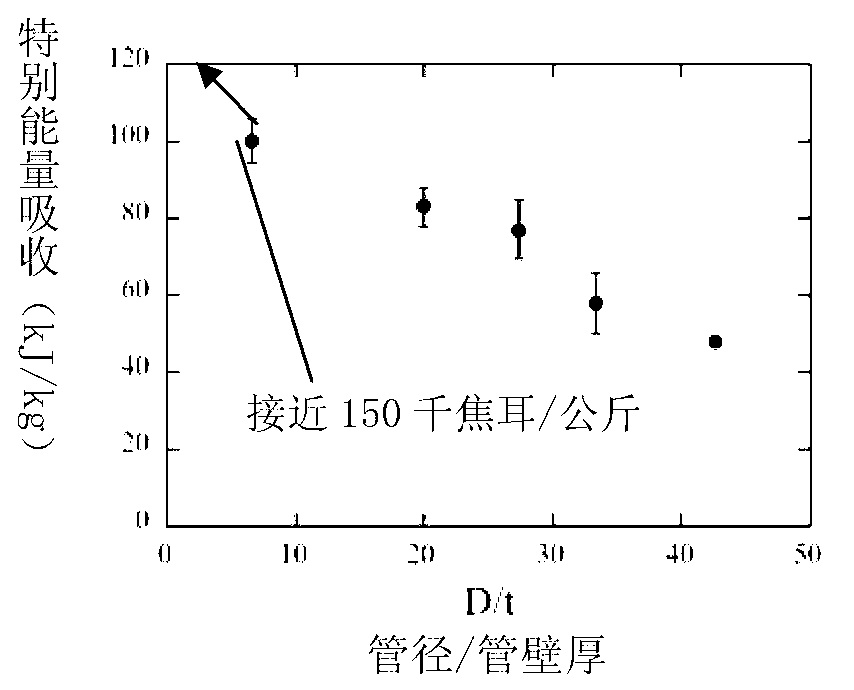
InactiveCN103009685AOptimum energy absorption-to-weight ratioReduce weightLayered productsFiberEnergy absorption
The invention discloses a novel anti-impact light interlayer structure. The structure comprises panels on both sides and a sandwich material between the two panels, wherein the panels and the sandwich material are bonded through resin layers; a plurality of composite tubes are arranged in the sandwich material; the shape, the caliber, the wall thickness of the composite tubes are set according to the simulation of a three-dimensional non-linear finite element equation; carbon fiber tubes are simulated to be anisotropic materials and are damaged under the control of a damage standard; the sandwich foam is simulated to be crushable hardened plastic foam; the panels made of composite materials are simulated in the same manner of the carbon fiber tubes; a minimum quantity of lightest materials are selected according to rules; and the interlayer structure achieves an optimal energy absorption-weight ratio through the structure optimization.
Owner:SHENZHEN FIBER SUPER NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
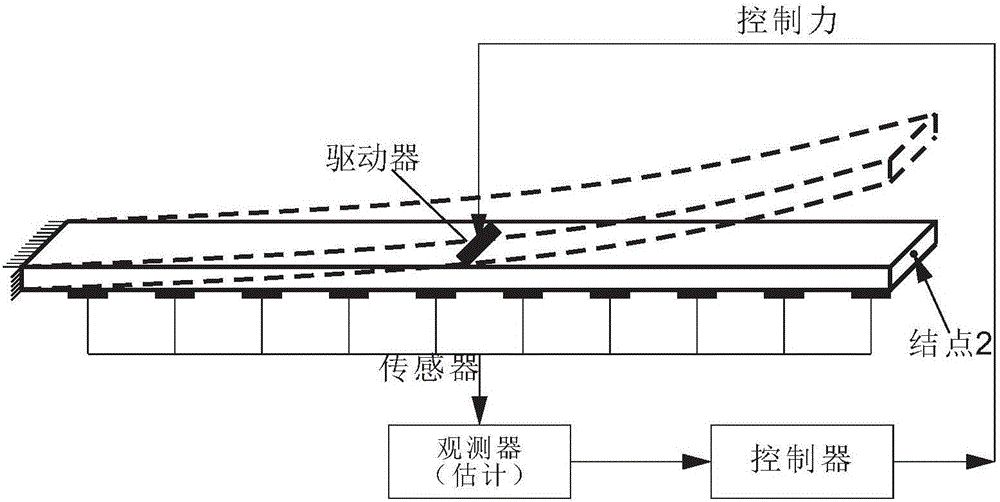
Nonprobability reliability optimization based design method of vibration optimal control system
ActiveCN105676903AMeet control requirementsMeet reliability design requirementsMechanical oscillations controlClosed loopState space
The invention relates to a nonprobability reliability optimization based design method of a vibration optimal control system. According to the method, a finite element equation of structural vibration is converted into a state space form via variable substitution, and a state space control equation of structural vibration is established; a nonprobability reliability analysis theory of an active control system of structural vibration is provided; and based on the provided nonprobability reliability analysis theory, reliability optimization is carried out on a controller obtained via an optimal control theory, and a closed-loop controller satisfying the reliability index is obtained. The uncertainly of a closed-loop control system is overcome in the aspect of reliability, and the problems that optimal control cannot satisfy the reliability requirement and robust control is too conservative can be effectively solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Three-dimensional mechanical modal simulation method based on hierarchical basis function
ActiveCN106354954AQuick buildDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorEigenvalues and eigenvectors
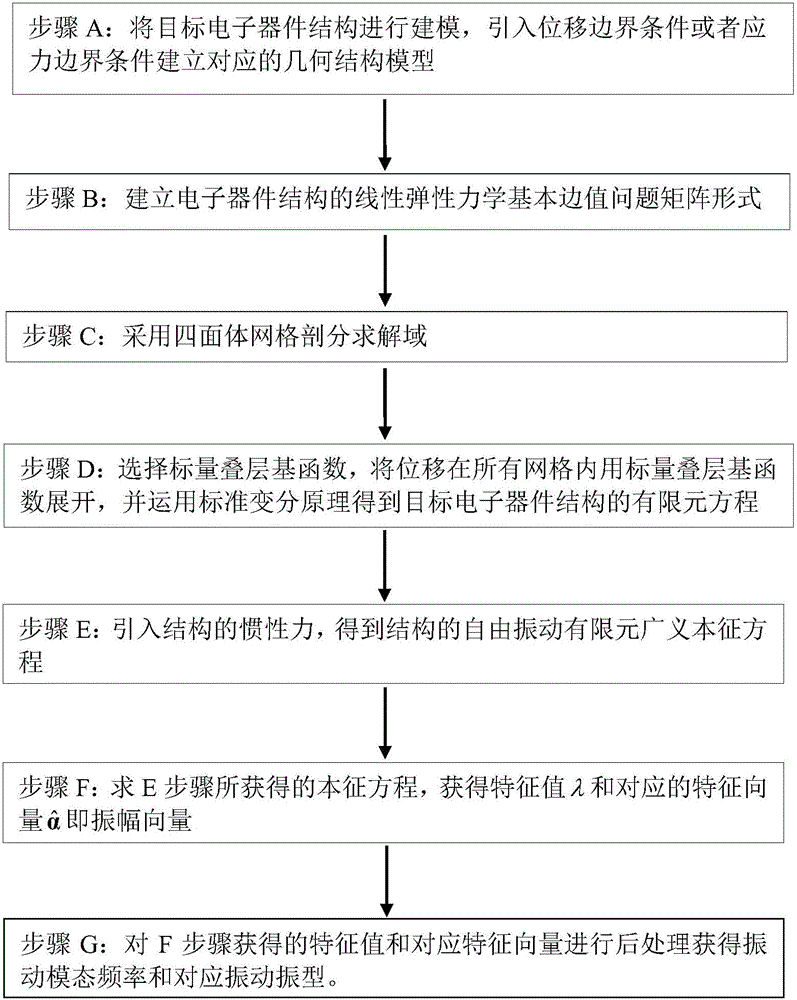
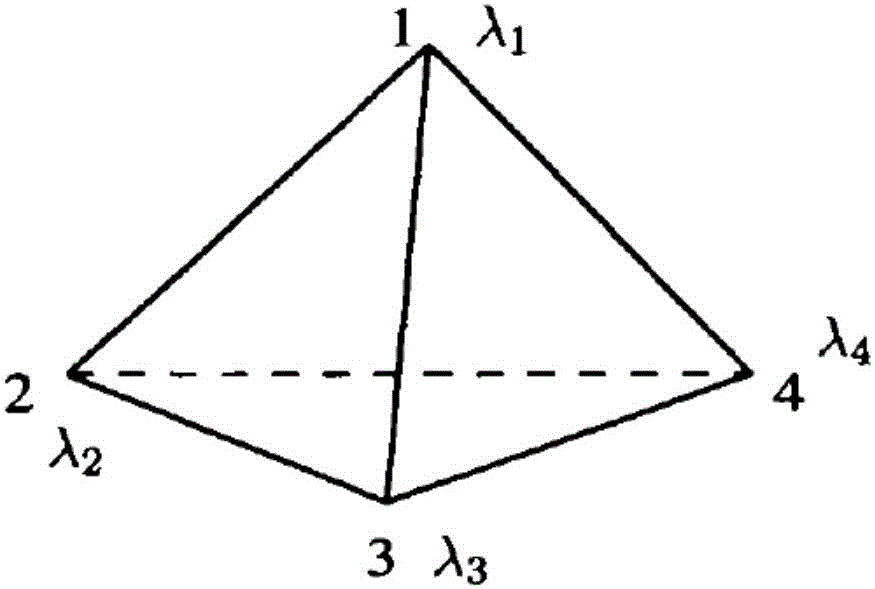
The invention belongs to the technical field of three-dimensional mechanical vibration analysis numerical solution and relates to a three-dimensional mechanical modal simulation method based on a hierarchical basis function. Firstly, modeling is conducted on a target electronic device, displacement or stress boundary conditions are introduced for building a corresponding geometric structure model, and a tetrahedral mesh generation solution domain is adopted; secondly, by selecting the scalar hierarchical basis function, displacement is expanded in all meshes through the scalar hierarchical basis function, and a finite element equation of the target electronic device structure is obtained by means of the canonical variational principle; finally, the equation is solved to obtain a feature value and a feature vector, and vibration modal frequency and vibration mode are obtained through post-processing. Thus, the high-order basis function is quickly constructed, and high-precision numerical calculation results are obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
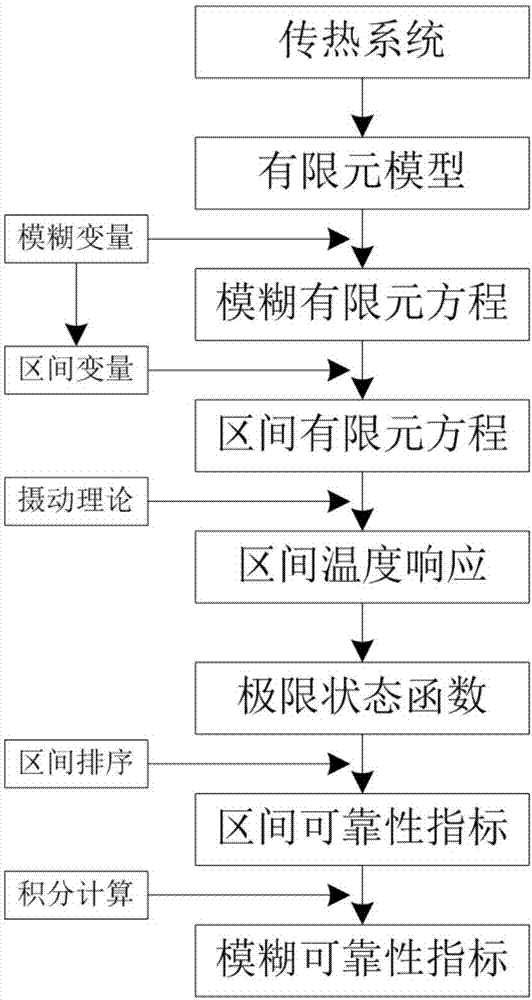
Reliability analysis method for heat transfer system containing fuzzy parameters
ActiveCN106897520ATake full advantage of interval computing technologyThe calculation result is accurateGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationTemperature responseElement modeling
The invention discloses a reliability analysis method for a heat transfer system containing fuzzy parameters. The method comprises the following steps that: carrying out the finite element modeling of a heat transfer system; utilizing a fuzzy variable to represent uncertain input parameters, and establishing the fuzzy finite element equation of the heat transfer system; selecting a cut set level, and converting the fuzzy variable into an interval variable so as to obtain one group of interval finite element equations; utilizing a perturbation theory to solve the interval finite element equations to obtain the upper and lower bounds of interval temperature response; according to the temperature response, establishing an ultimate state function which represents system reliability, and calculating the upper and lower bounds of the ultimate state function; utilizing an interval sorting method to process the ultimate state function to obtain an interval reliability index under each cut set level; and carrying out integral computation on the interval reliability index under the cut set level, and finally, obtaining the fuzzy reliability index of the heat transfer system. On a premise that calculation efficiency is guaranteed, by use of the method, the fuzzy reliability calculation accuracy of the heat transfer system can be effectively improved, which can not be realized by general commercial software.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
First-order perturbation expansion progressive homogenization method for statistical prediction of elastic constitutive matrix of random distributed composite materials
InactiveCN108153962APrediction Method of Reliable Material Structure Equivalent Elasticity MatrixAvoid repeating the tedious trial calculation processDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsVirtual workScale effects
The invention discloses a first-order perturbation expansion progressive homogenization method for statistical prediction of an elastic constitutive matrix of random distributed composite materials. The method comprises the steps that (1), according to an actual material domain, the source and range of random variables are determined, and a probability model is established; (2), the random variables are introduced by a material elastic constitutive flexibility matrix based on a first-order perturbation hypothesis, and a stiffness matrix is obtained by inversion; (3), a microscopic representative unit subdomain is intercepted in a macroscopic material structure system, and a functional scale effect relationship on a microscopic representative volume unit is hypothesized based on a progressive homogenization method to derive a virtual work principle equation and establish the equivalence relation between a macro elastic matrix and a finite element equation of a representative volume unitmaterial domain; (4), the equivalence relation between probability and statistical characteristics of the macroscopic elastic matrix and the finite element equation of the representative volume unitmaterial domain is solved; (5), probability and statistical characteristics of elastic engineering constanTS are derived from the macroscopic elastic matrix.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Displacement solving method capable of improving stability and convergence of iterative method
ActiveCN106126823AEasy to updateReduce the number of iterationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsUnit modelConjugate gradient method
The invention discloses a displacement solving method capable of improving the stability and the convergence of the iterative method. The displacement solving method is characterized in that during finite element mesh division, singular unit models exist, and a non-diagonal dominant stiffness matrix is as a basis in a unit stiffness matrix; non-singular nodes in non-singular units and singular units are processed through the conventional iterative method; abnormal nodes in the singular units are improved in unit, such as the volume is used as a penalty function to perform pretreatment on the basis of a precondition conjugate gradient method. The method can correct non-diagonal dominant finite element equation sets, can reduce the frequency of iterations, is fast in convergence speed, and is stable in effect; the method firstly multiplies unit stiffness and displacement and then performs superposition, and this way, calculation of combined total stiffness which is large can be avoided; through a data structure of unit stiffness, the data is conveniently updated, and parallel computing is facilitated.
Owner:INST OF IND TECH GUANGZHOU & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Complex frequency domain calculation method for a converter transformer alternating current and direct current composite electric field
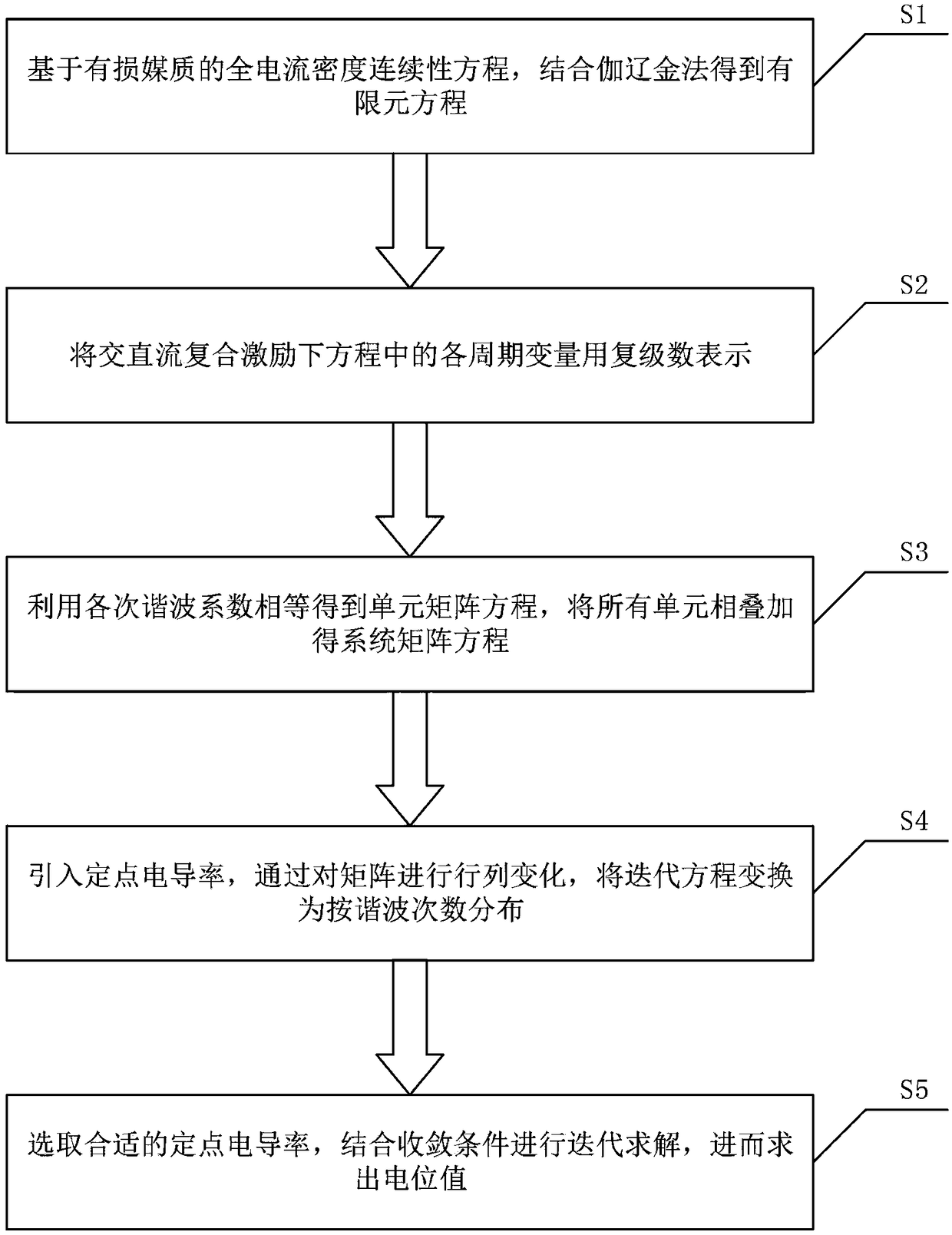
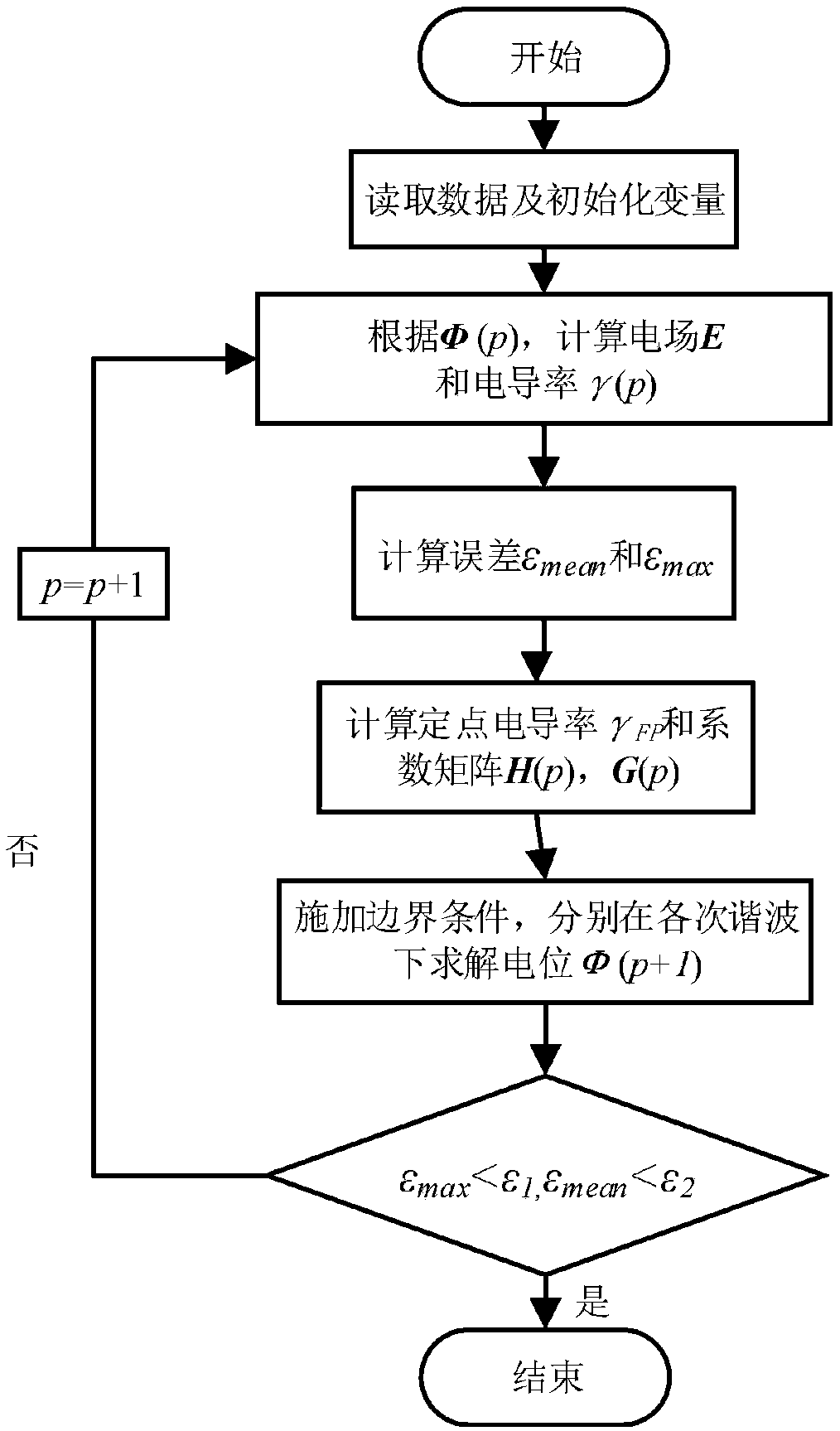
ActiveCN109492268AReduce repeat formationReduce storage memoryDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTransformerSystem matrix
The invention relates to a complex frequency domain calculation method for a converter transformer alternating current and direct current composite electric field, which comprises the following steps:obtaining a finite element equation by combining a Galerkin method based on a full current density continuity equation of a lossy medium; expressing each periodic variable in the equation under the AC / DC composite excitation by using a complex stage number; obtaining a unit matrix equation by using the equal harmonic coefficients, and superposing all the units to obtain a system matrix equation;introducing fixed-point conductivity, and converting an iterative equation into distribution according to harmonic frequency by performing row and column change on the matrix; and selecting fixed point conductivity, carrying out iterative solution according to a set convergence criterion, and carrying out convergence to obtain a potential value. According to the method, the finite element stiffness matrix of each iteration is decomposed according to the harmonic frequency by adopting a fixed-point method, so that the memory consumption of a harmonic balance algorithm is reduced, and the calculation cost for analyzing a nonlinear alternating-current and direct-current composite electric field can be effectively reduced.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
System and method for pre-estimating noise of single-phase oil-immersed transformer
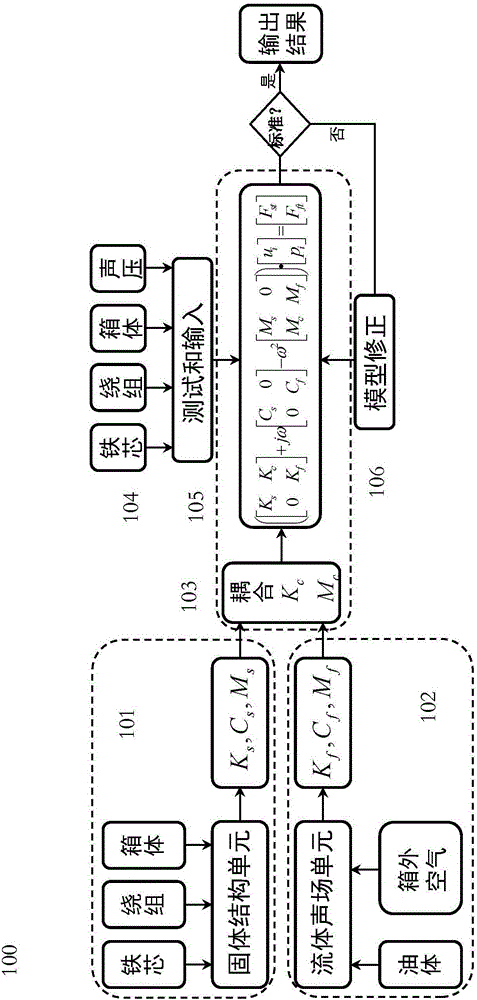
ActiveCN106153176AEstimated Radiated NoiseAccurately estimate radiated noiseSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing electrical meansFluid couplingAccelerometer
The invention discloses a noise pre-estimating system for pre-estimating noise of a single-phase oil-immersed transformer. The system includes a transformer component finite element unit for determining a solid unit stiffness matrix KS, a damping matrix CS and a mass matrix MS relevant to a solid; a fluid acoustic finite element unit which establishes a fluid acoustic finite element equation according to air parameters out of a box and a transformer internal fluid field; a solid and fluid coupling unit which establishes a solid and fluid coupling dynamic equation; a test unit which includes an optical fiber accelerometer, an acquisition instrument and a sound meter; an electromagnetic excitation analog input unit to which excitation vectors of a plurality of harmonic components of a solid structure are applied; and a data correction unit which takes the solid and fluid coupling dynamic equation as a pre-estimating model, and uses an acoustic model and a difference to calculate the coupling dynamic equation so as to obtain a sound pressure of a sensitive point.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Quick fuzzy sound pressure solving method based on high-order perturbation theory
InactiveCN105760585AReduce uncertaintyGuaranteed calculation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsElement modelElement modeling
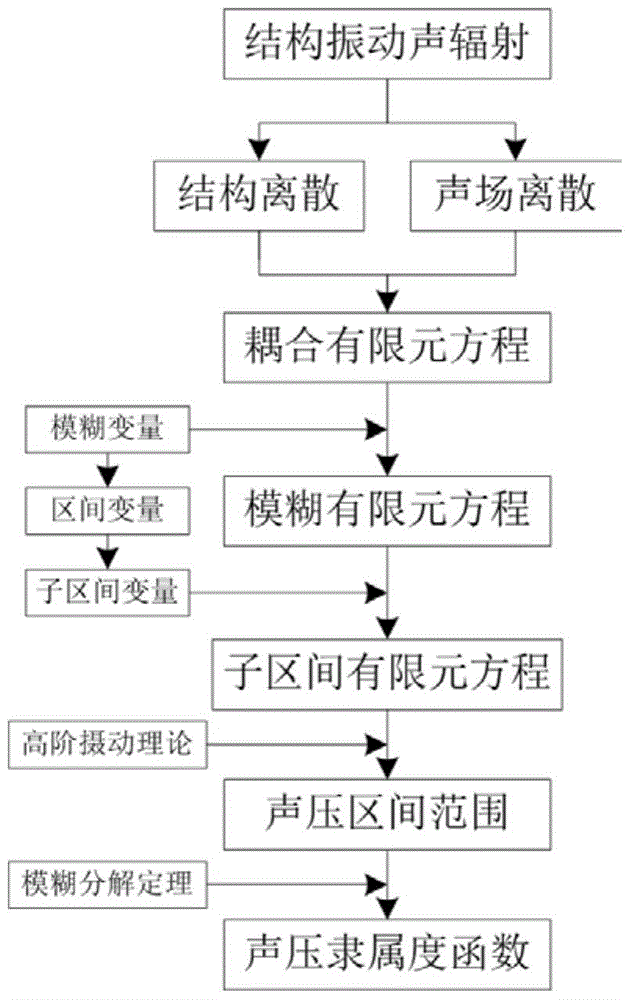
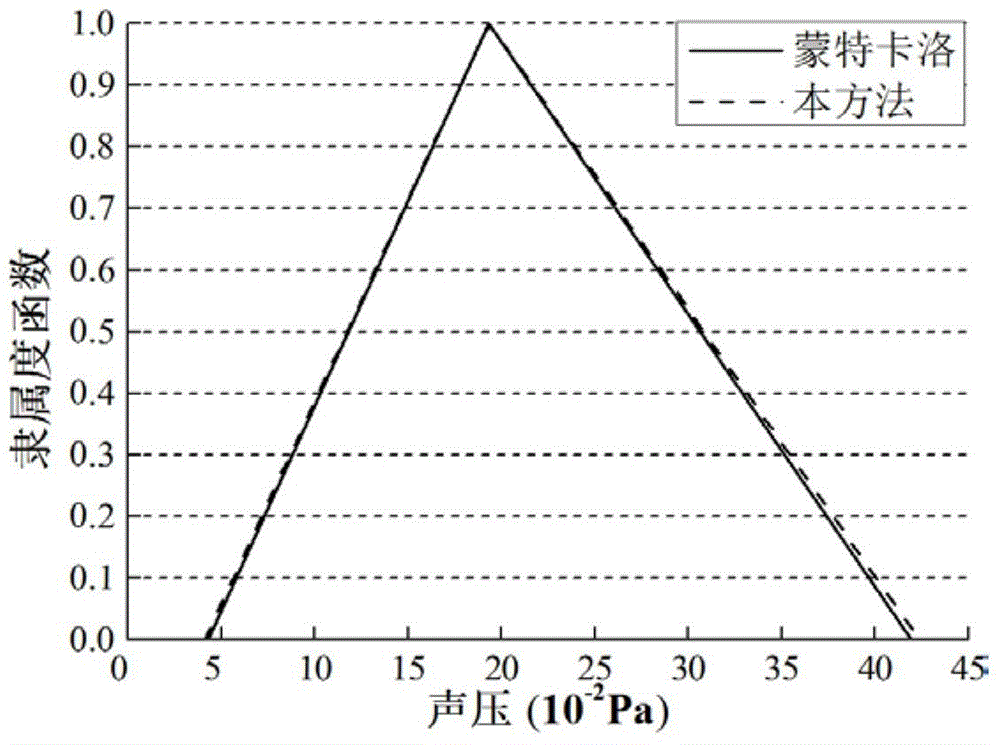
The invention discloses a quick fuzzy sound pressure solving method based on a high-order perturbation theory. The method comprises the following steps that finite element modeling on a structural vibration sound radiation problem is performed; a fuzzy finite element equation of the sound radiation problem is built by considering fuzzy uncertain variables of the model; a cut set level is selected, and the fuzzy variables are converted into interval variables through cut set calculation; the interval variables with the uncertainty exceeding 5% are decomposed into multiple subintervals through a subinterval decomposing technique, and then a set of subinterval finite element equations are obtained; all the subinterval finite element equations are solved on the basis of the high-order perturbation theory, and an interval change range of the sound pressure is obtained; all the sound pressure intervals at the cut set level are recombined to obtain a subordinating degree function of the fuzzy sound pressure. According to the method, the structural vibration sound radiation problem containing the fuzzy uncertain variables can be systematically solved, the calculating precision of a perturbation method is further improved while the calculating efficiency is guaranteed, and the advantages cannot be achieved by common commercial software.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
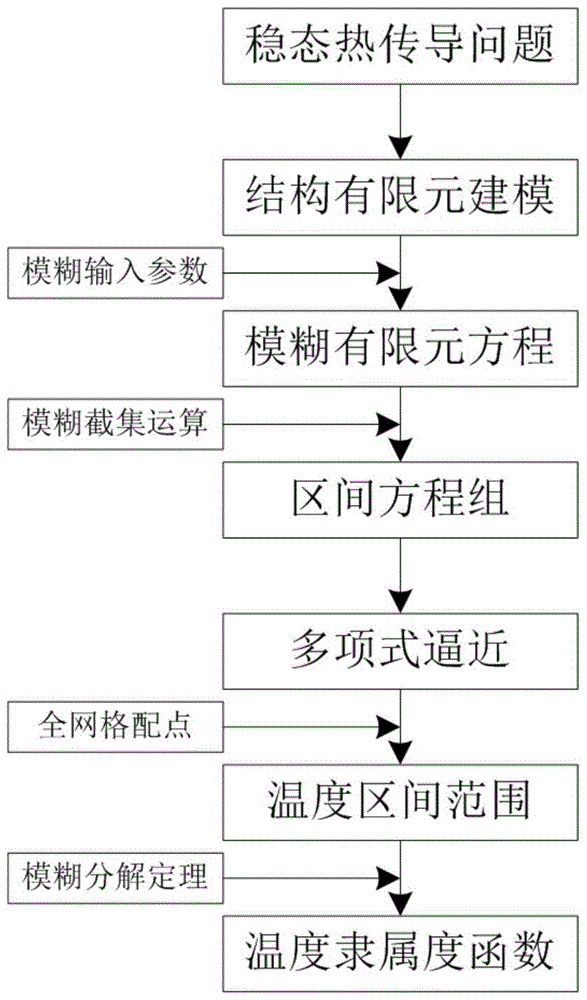
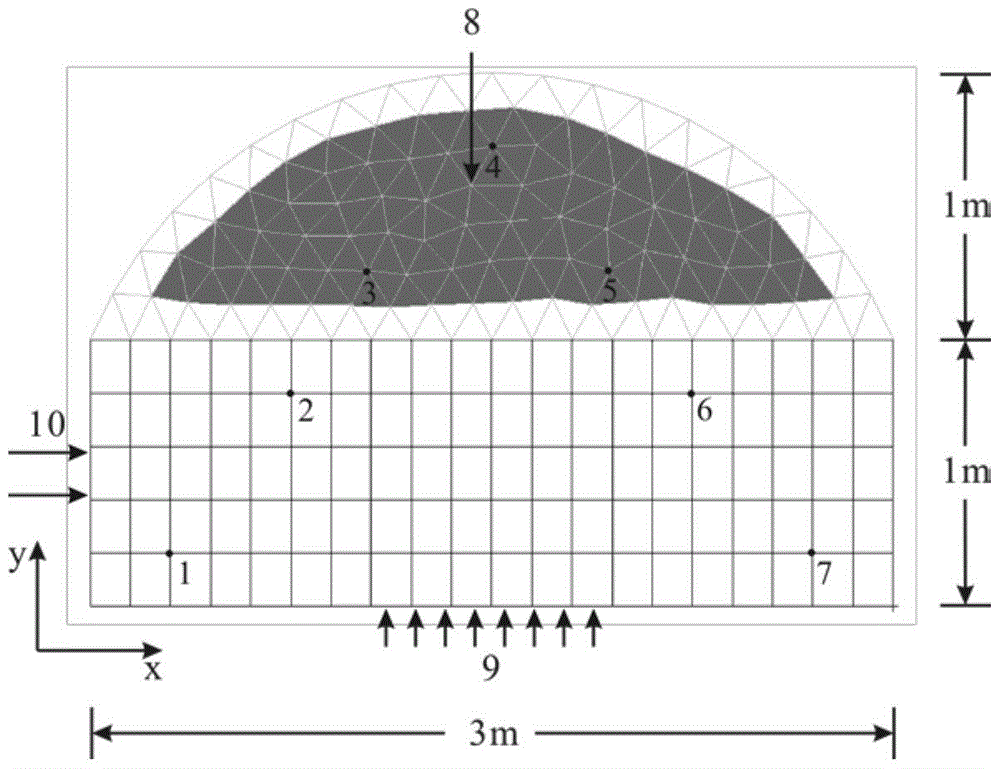
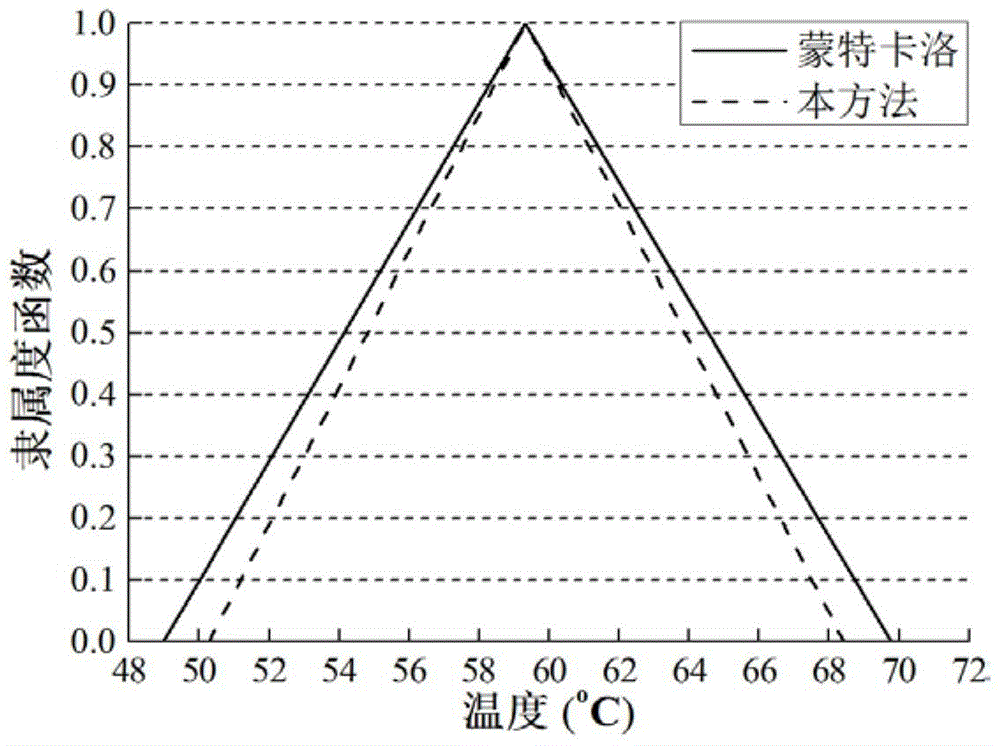
Method for numerical solution of fuzzy steady state heat conduction problem based on full grid point collocation theory
InactiveCN105677995AImprove approximation accuracyQuickly identify extreme pointsDesign optimisation/simulationFuzzy logic based systemsTemperature responseCommercial software
The invention discloses a method for numerical solution of a fuzzy steady state heat conduction problem based on a full grid point collocation theory. The method comprises the first step of carrying out finite element modeling of a steady state heat conduction structure; the second step of utilizing fuzzy variables to represent uncertain input parameters and then obtaining a fuzzy finite element equation of the heat conduction problem; the third step of utilizing cut set operation to rewrite the fuzzy finite element equation to be a group of interval finite element equations; the fourth step of performing approximate representation on temperature response functions in the interval finite element equations based on a polynomial theory; the fifth step of quickly solving the interval variation range of a temperature response approximate functions according to the full grid point collocation theory; the sixth step of utilizing a fuzzy resolution theory to recombine temperature response intervals under all cut set levels, and finally obtaining a membership function of the fuzzy temperature response. According to the method, the prediction of structure heat conduction temperature field containing fuzzy uncertain parameters can be achieved systematically, and the calculation accuracy can be effectively improved on the premise of guaranteeing that the calculation efficiency meets the engineering requirements, which cannot be achieved through common commercial software.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
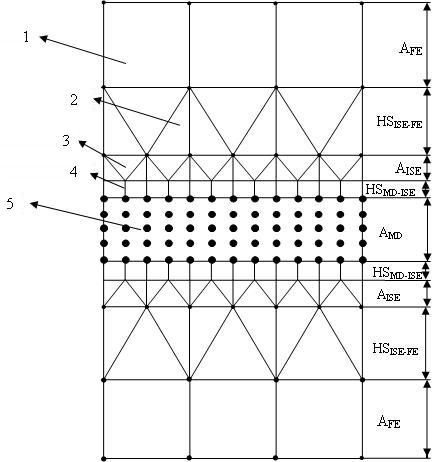
Scale-span design method for interface structure of micro/nano/photoelectronic device
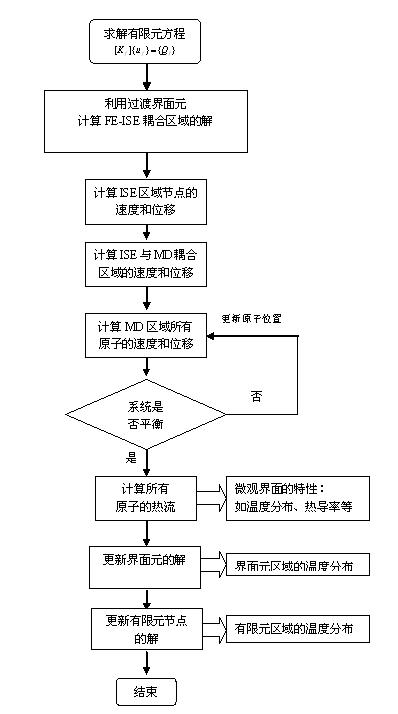
InactiveCN102222142ASolving Design ChallengesRealize macro/micro/nano simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCouplingComputer science
The invention discloses a scale-span design method for an interface structure of a micro / nano / photoelectronic device, which comprises the following steps of: designing a coupling area of a finite element and an interface element, and an interface element coupling area of molecular dynamics; constructing a finite element, interface element and molecular dynamics coupled model; solving a finite element equation in the finite element area by using a finite element method, and converting the finite element equation to a boundary of the interface element area to solve the interface element area; assigning atoms in the finite element coupling area of the molecular dynamics and converting the solution of the finite element area into a boundary condition of the atoms in the molecular dynamics area; initiating molecular dynamics solving in the molecular dynamics area, and solving new positions of atoms by using a non-equilibrium molecular dynamics model; and finally determining system balance of the molecular dynamics area. By the method, the energy coupled transfer is realized systematically, the macro / micro / nano simulation of interface characteristics of the micro / nano / photoelectronic device is realized, and the method has the characteristics of precision, scientific property and high efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
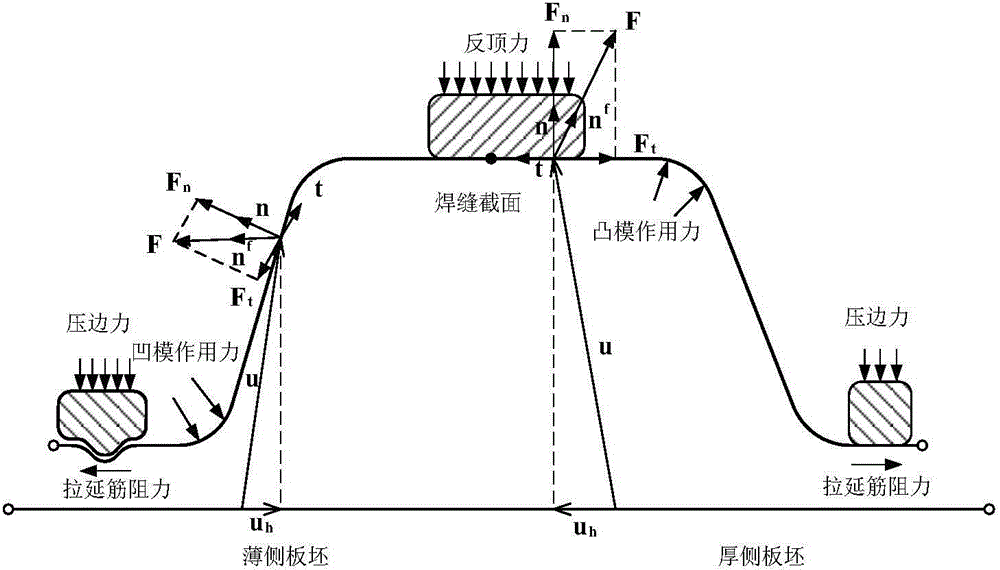
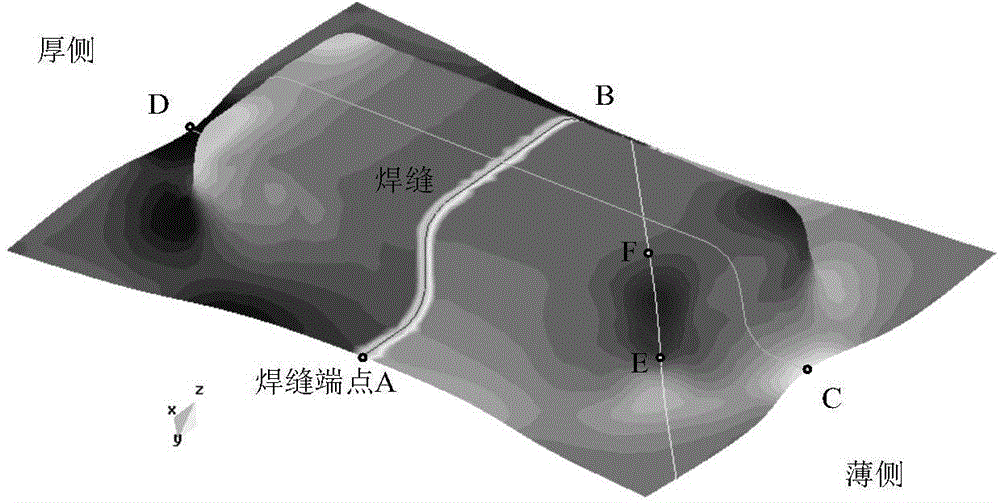
Method for rapidly predicting welding seam movement in deep-drawing forming process of laser tailor-welded blank
ActiveCN104942113AQuickly predict movementReduce performance degradationNonlinear systems of equationsBack calculation
The invention discloses a method for rapidly predicting welding seam movement in a deep-drawing forming process of a laser tailor-welded blank. The method comprises steps as follows: 1), a workpiece is dispersed to form triangle elements, formed part grids are obtained, and a virtual work equation is established for final configuration of a plate material; 2), a finite element equation of a one-step simulation method is established; 3), an iterative equation is established by adopting a Newton-Laplace method with convergence factors; 4), the iterative equation is solved; a non-linear equation set is obtained, and a second iterative equation is established by adopting the Newton-Laplace method with convergence factors; the second iterative equation is solved to obtain an initial displacement field; the process is transferred to the step 3), and tailor-welded blank grids obtained through back calculation can be output after Newton-Laplace iterative convergence; 5), two space curves 11 and 12 are obtained by connecting nodes of the elements in welding seams of the formed part grids and the tailor-welded blank grids obtained through back calculation; 6), the two space curves 11 and 12 are projected to the X-Y plane respectively so as to obtain two plane curves 1'1 and 1'2; the welding seam offset is calculated.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
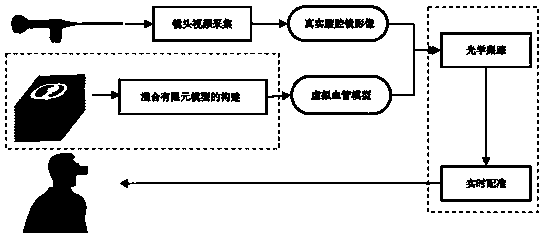
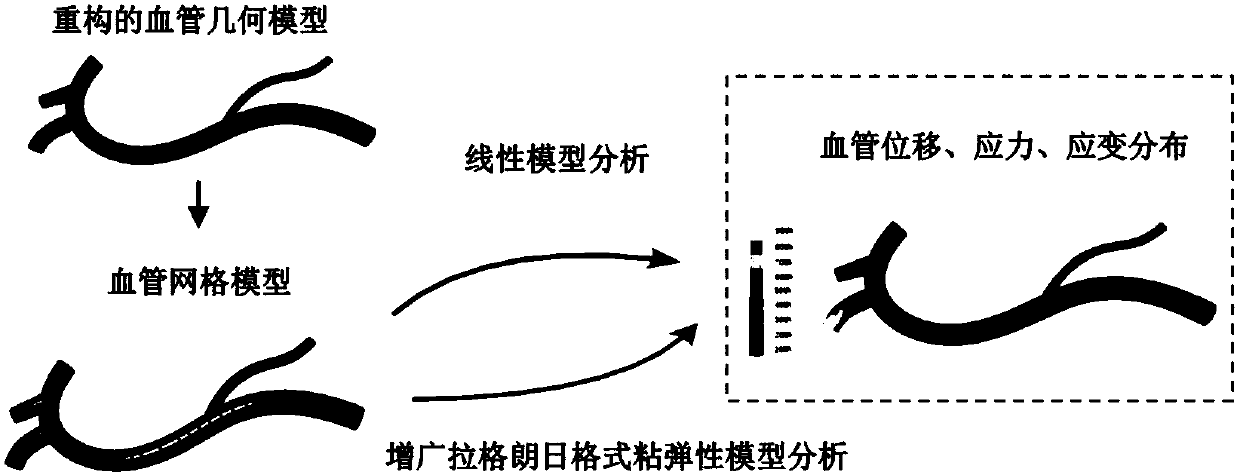
Method for constructing hybrid finite element deformation model for gastric cancer endoscopic surgery real-time navigation system
InactiveCN107704661AReduced Complications of InjuryOvercoming deformation matching problemsSurgical navigation systemsDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelData acquisition
The invention relates to a method for constructing a hybrid finite element deformation model for a gastric cancer endoscopic surgery real-time navigation system. The method comprises the following steps of: data acquisition: acquiring a CT image of a pre-operation abdomen enhancement stage film; construction of an original three-dimensional model; construction of the hybrid finite element deformation model: simulating a deformation process by adoption of a finite element model in an incremental form, and establishing a finite element equation; under a small deformation condition, carrying outanalysis by adoption of a finite element organization deformation simulation algorithm; under a large deformation condition; carrying out analysis by adoption of a semi-definite programming augmentation Lagrange viscoelastic model; and registering the hybrid finite element deformation model in an intra-operation laparoscopic image of a gastric cancer endoscopic surgery by utilizing optical tracking equipment, and providing blood vessel information that cannot be displayed by common laparoscopic surgeries in real time. The method is capable of effectively overcoming the matching difficulty of deformation tissues, improving the accuracy of navigation, accurately guiding the surgery process and improving the success rate of the surgeries, and is beneficial for the application and popularization of laparoscopic gastrointestinal surgeries.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
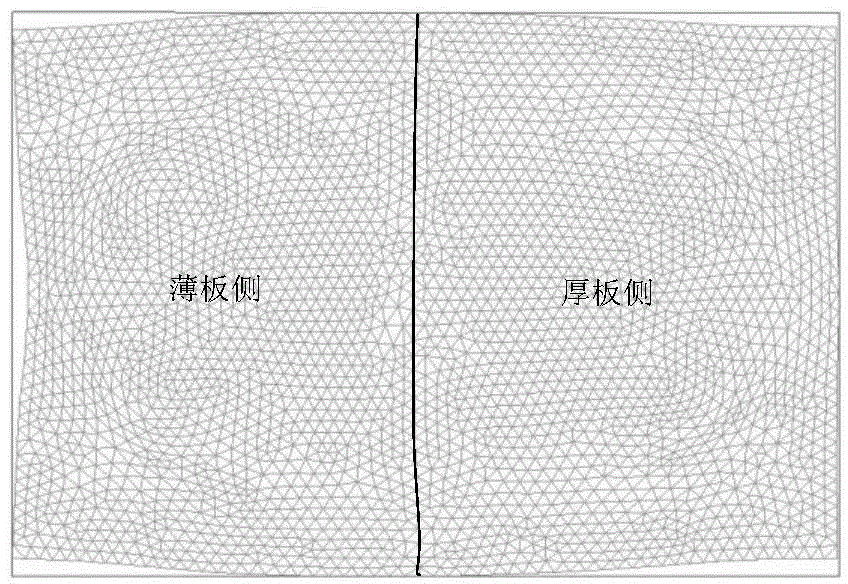
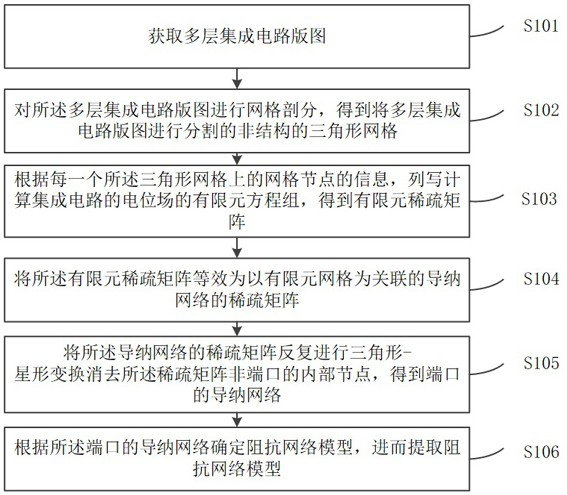
Integrated circuit impedance network model extraction method and system
ActiveCN112257372AFast extraction timeSolve the blockageGeometric CADCAD network environmentIntegrated circuit layoutNetwork model
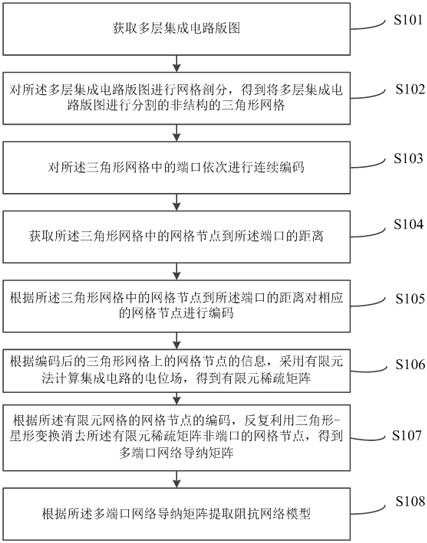
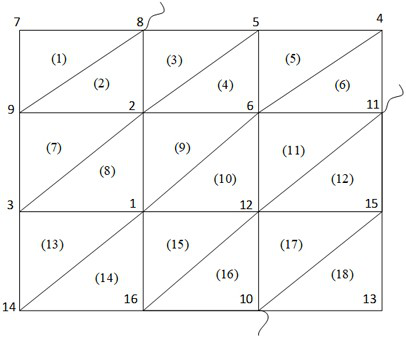
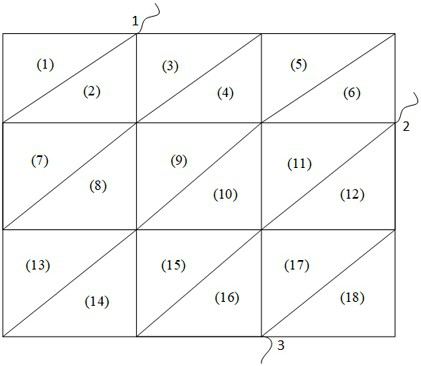
The invention relates to an integrated circuit impedance network model extraction method and system. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a multilayer integrated circuit layout; performing mesh generation on the multilayer integrated circuit layout to obtain a non-structural triangular mesh for segmenting the multilayer integrated circuit layout; listing a finite element equation set for calculating the potential field of the integrated circuit according to the information of the grid nodes on each triangular grid to obtain a finite element sparse matrix; enabling the finite element sparse matrix to be equivalent to a sparse matrix of an admittance network taking a finite element grid as association; repeatedly performing star triangle transformation on the sparse matrix ofthe admittance network to eliminate internal nodes of a non-port of the sparse matrix to obtain an admittance network of the port; and determining an impedance network model according to the admittance network of the port, and further extracting the impedance network model. The method improves the extraction speed of the impedance network model of the multi-layer super-large-scale integrated circuit.
Owner:北京智芯仿真科技有限公司
Wing structure stochastic-feature value analysis method based on probability density evolution
ActiveCN108763611AFit closelyShorten the design cycleGeometric CADSustainable transportationRandom methodStandard form
The invention discloses a wing structure stochastic-feature value analysis method based on probability density evolution, and belongs to the field of structure design. Uncertainty factors existing ina large complex structure are fully considered, and a stochastic method is utilized to quantitatively characterize uncertain parameters under a condition that sample information is sufficient. A finite-element equation of structure free-vibration is established, feature value analysis is transformed into a generalized feature value problem through modal coordinates, and feature value sensitivity is derived. A feature value probability density evolution equation is established on the basis thereof, and the feature value sensitivity is introduced into the equation to obtain a feature value probability density evolution equation based on sensitivity analysis. The feature value probability density evolution equation is reduced to a standard form through introducing new variables, and a finite-difference method and a total-variation-difference reduction format are employed to obtain a feature value probability density function by solving. Numerical results show that the feature value probability density function obtained by the method of the invention is in better agreement with a Monte Carlo method, and calculation time can be greatly reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Grid node encoding method and system based on integrated circuit impedance network extraction
ActiveCN112290955AHigh precisionError correction/detection using convolutional codesError correction/detection using single space codingEngineeringIntegrated circuit layout
The invention relates to a grid node encoding method and system based on integrated circuit impedance network extraction. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out mesh generation on a multi-layer integrated circuit layout to obtain triangular meshes; sequentially carrying out continuous encoding on ports in the triangular grid; obtaining a distance from a grid node to a port in the triangular grid; encoding the corresponding grid nodes according to the distances from the grid nodes in the triangular grid to the ports; listing and writing a finite element equation set for calculating the potential field of the integrated circuit according to the information of the grid nodes on the coded triangular grid to obtain a finite element sparse matrix; according to the codes of the grid nodes of the finite element grid, eliminating the non-port grid nodes of the finite element sparse matrix by repeatedly utilizing triangular star transformation to obtain a multi-port network admittance matrix; and extracting an impedance network model according to the multi-port network admittance matrix. The sequential elimination method provided by the invention improves the extraction accuracy of the impedance network model of the multi-layer super-large-scale integrated circuit.
Owner:北京智芯仿真科技有限公司
Boundary treatment method of coupling direct-current resistivity element-free method with finite element method
ActiveCN108108579AImprove computing efficiencyHigh simulationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsBoundary knot methodMixed finite element method
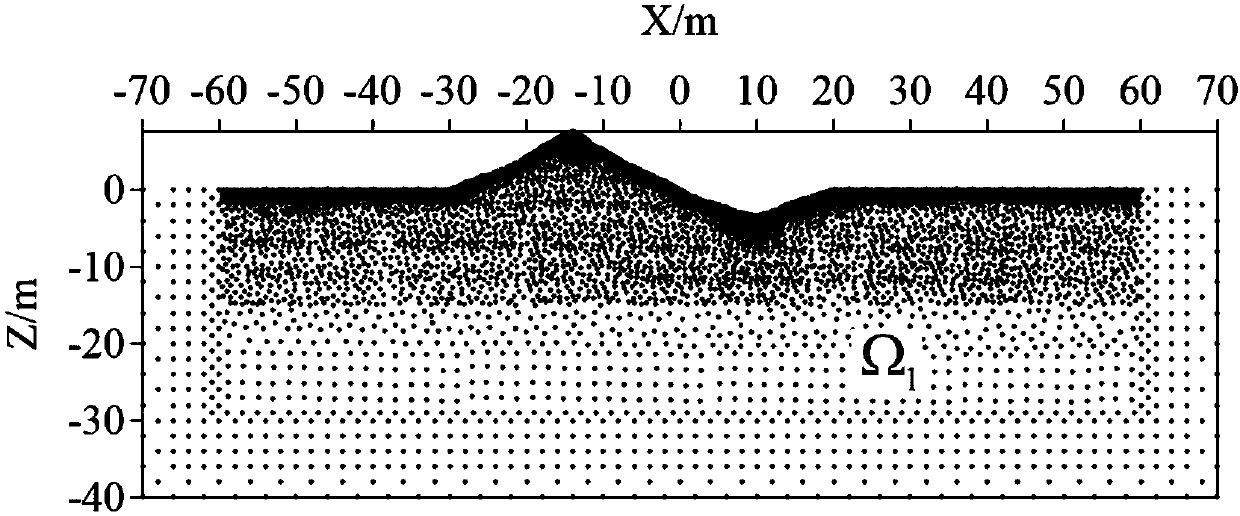
The invention provides a boundary treatment method of coupling a direct-current resistivity element-free method with a finite element method. The boundary treatment method includes the steps of building a small-range element-free method area omega 1 to a two-dimension geoelectric model, calculating by the element-free method for the area, covering the element-free method area omega 1 with regularly distributed rectangular or parallelogram background grid to obtain an element-free method equation set of the area; subdividing the periphery of the element-free method area omega 1 by finite element method grid which is capable of rapid expansion, building a large-enough finite element method area omega 2 which meets requirements of first class of boundary conditions, calculating by the finiteelement method to obtain a finite element equation set of the area; combing the equation sets of the two areas and solving to obtain parameter of the apparent resistivity of an observation point. Themodels can be discrete on the basis of arbitrary node distribution by the method, the boundary treatment method has high adaptability to any complex geoelectric models, and calculation efficiency of forward modeling in the conventional direct-current resistivity element-free method is improved since boundary treatment is carried out by means of the finite element method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Electromagnetic simulation method based on compression type finite element tearing butt joint method
InactiveCN112784459AImprove solution efficiencyReduce memory consumptionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStructural engineeringTerm memory
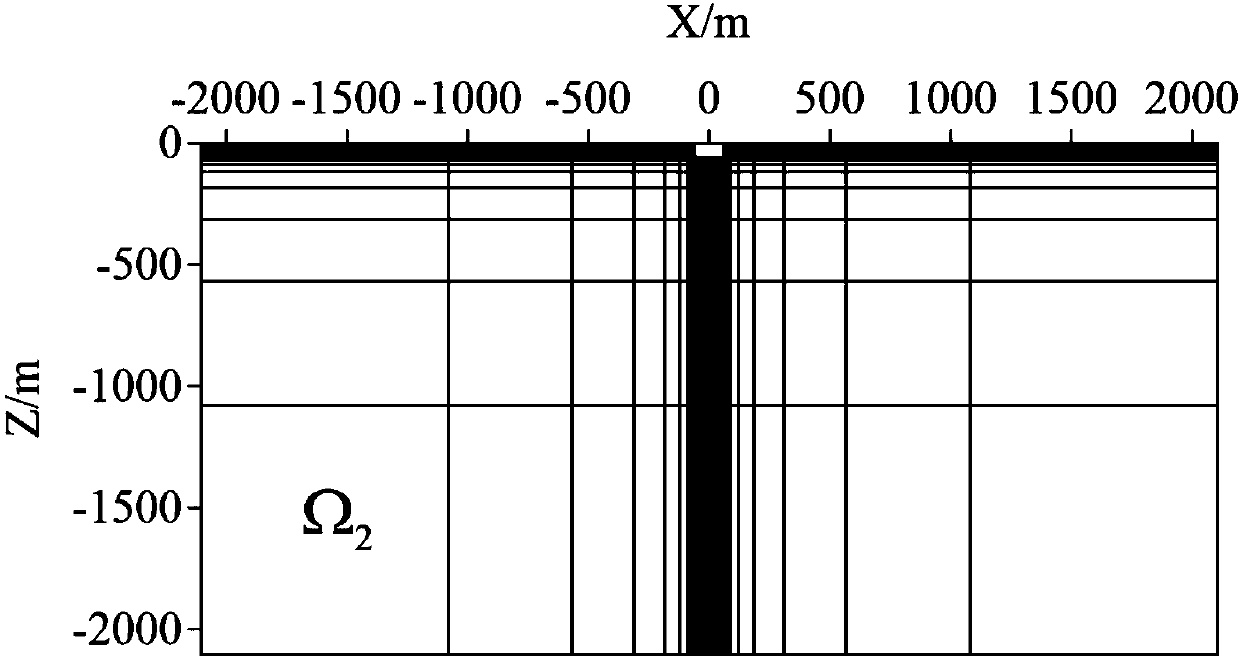
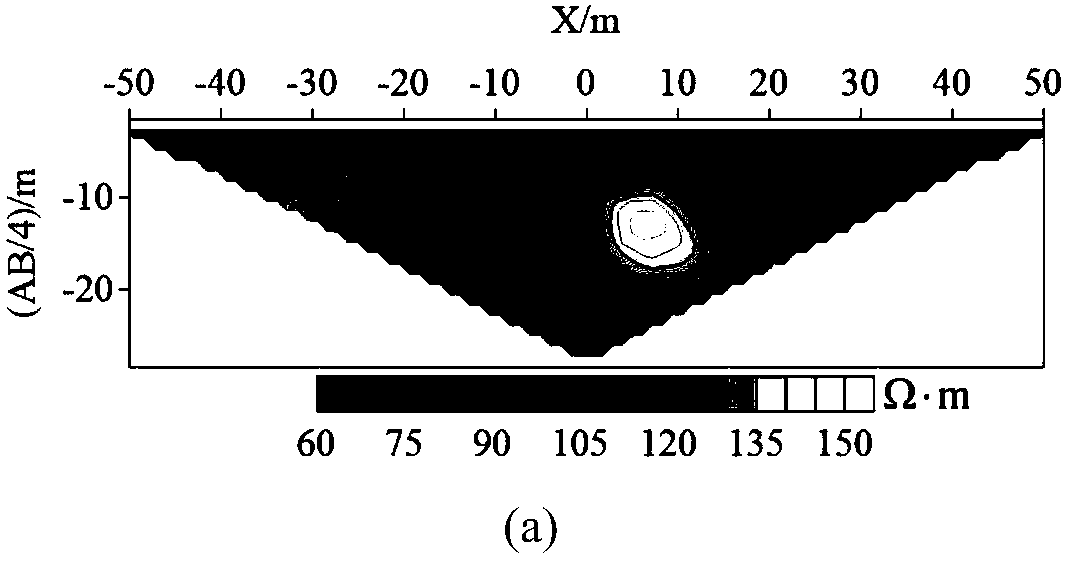
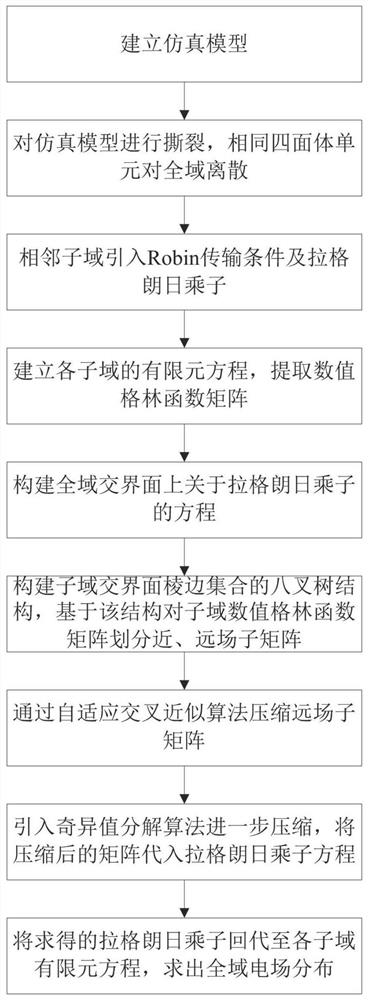
The invention discloses an electromagnetic simulation method based on a compression type finite element tearing butt joint method, which comprises the following steps: firstly, tearing a simulation model into a series of non-overlapping sub-domains; then, introducing a transmission condition into a sub-domain interface, building a sub-domain finite element equation and a global interface Lagrange multiplier equation, and compressing a numerical green function matrix involved in the sub-domain finite element equation and the global interface Lagrange multiplier equation in sequence through an adaptive crossover approximation algorithm and a singular value compression algorithm; and finally solving a Lagrangian multiplier and substituting the Lagrangian multiplier back into the sub-domain finite element equation to obtain global electric field distribution. Compared with a traditional finite element tearing butt joint method, the invention has higher solving efficiency and lower memory consumption. For a finite periodic structure, the compression process only needs to be carried out on several representative sub-domains, so that the invention has more obvious advantages compared with a traditional finite element tearing docking method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
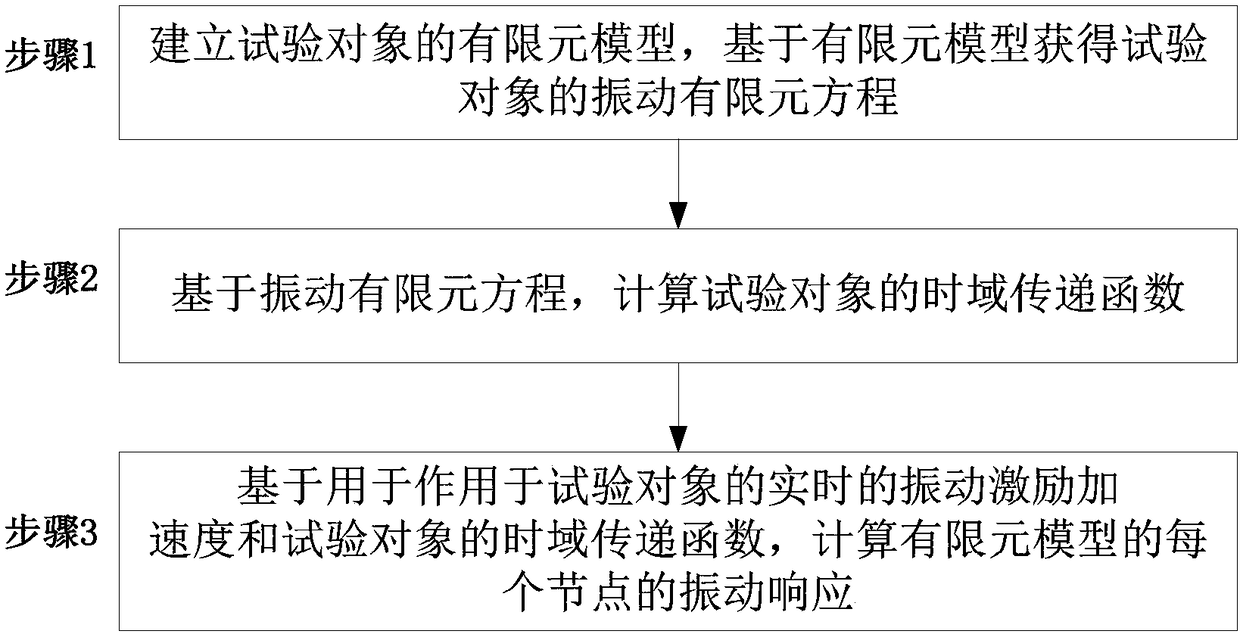
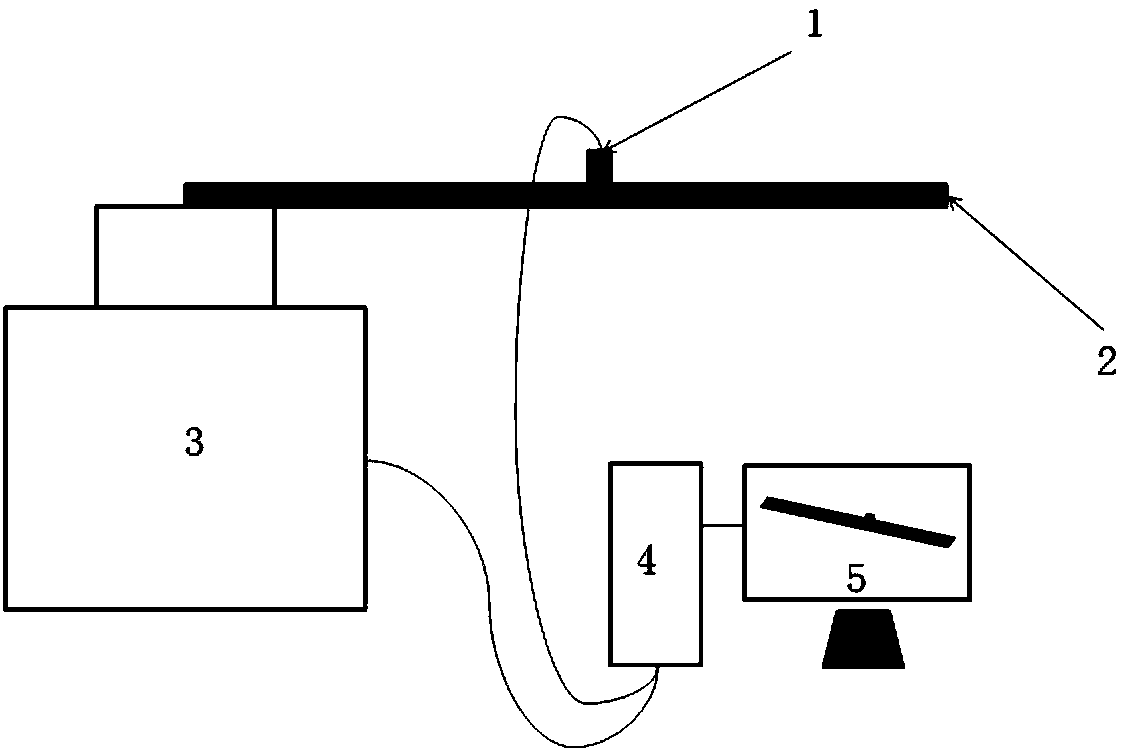
Environmental vibration testing method and system
ActiveCN108573084ACalculate vibration response in real timeCalculation speedDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainElement model
Provided are an environmental vibration testing method and system. The method comprises the steps that a finite element model of a tested object is established, and a vibrating finite element equationof the tested object is obtained based on the finite element model; based on the vibrating finite element equation, a time domain transfer function of the tested object is calculated; based on the real-time vibrational excitation acceleration acting the tested object and the time domain transfer function of the tested object, vibration response of each node of the finite element model is calculated. By adopting the environmental vibration testing method and the system, the global vibration response of the tested object can be accurately calculated based on the real-time vibrational excitationacceleration.
Owner:蒙上阳 +1
Establishment method of one-dimensional beam unit model of curved steel-concrete combined box beam
ActiveCN110309605AImprove accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationTangential displacementVirtual work
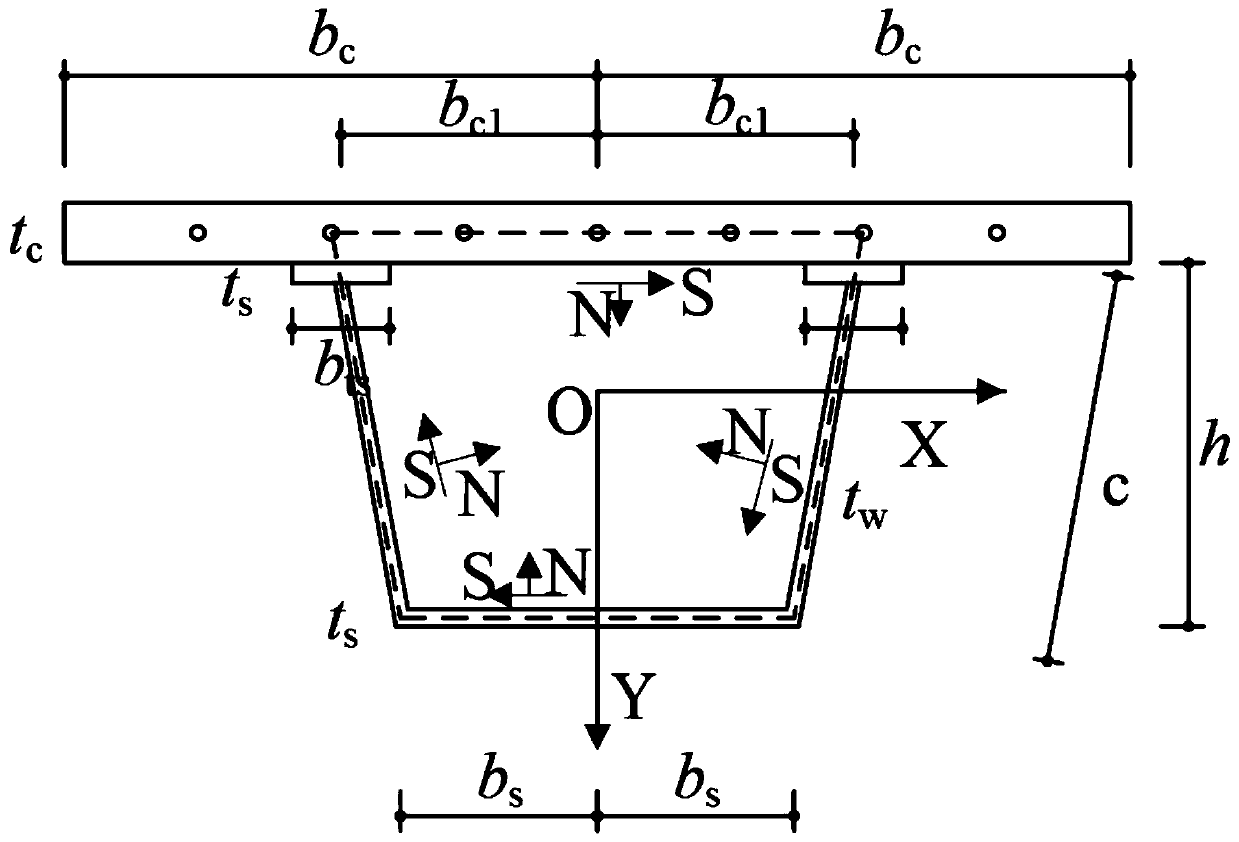
The invention discloses an establishment method of a one-dimensional beam unit model of a curved steel-concrete combined box beam. The method comprises the following steps: S1, selecting a coordinatesystem oxyz of a box beam; S2, based on the coordinate system, according to a torsion warping displacement function, calculating the displacement mode and the strain component of the combined box girder, wherein the displacement mode comprises longitudinal displacement, tangential displacement and normal phase displacement; S3, calculating to obtain a balance equation of the composite beam througha virtual work principle; and S4, establishing a finite element equation of the curve composite beam through the balance equation. The model is established by adopting the method, so that the subsequent calculation accuracy is higher, and the defect that the complex mechanical effects such as constraint torsion, distortion and interface bidirectional slippage of the curve composite beam are generally difficult to comprehensively consider in the existing research is overcome.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
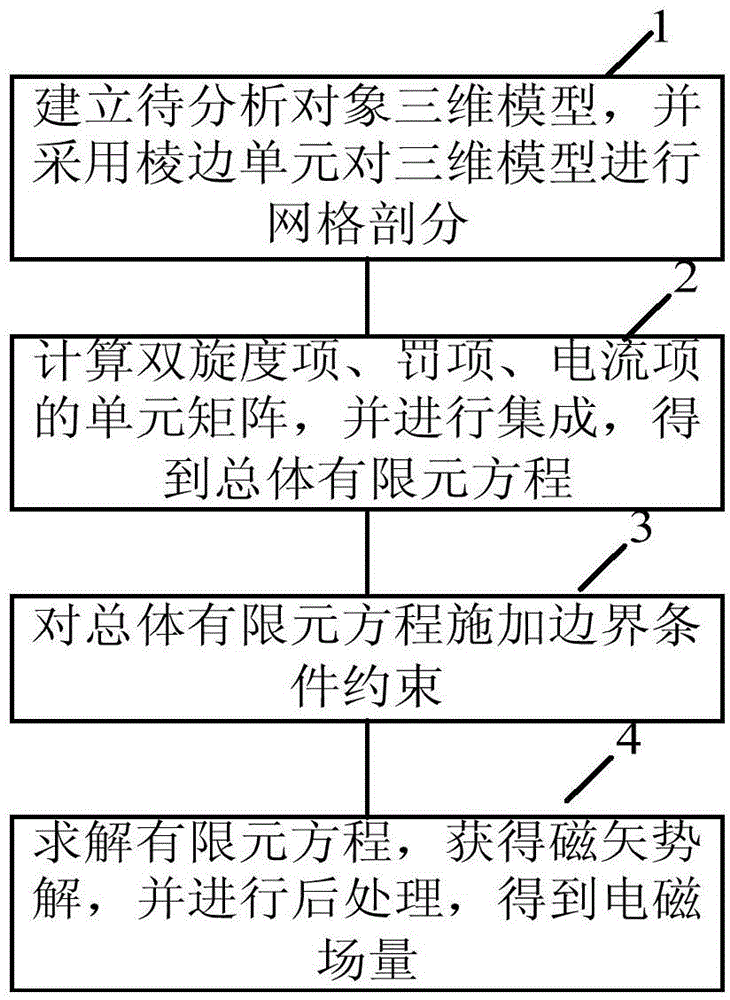
Method for applying standards in electromagnetic field edge element method
ActiveCN104091023ASolve the uniqueness problem of magnetic vector potentialPrevent buildupSpecial data processing applicationsVector potentialElectromagnetic field
The invention discloses a method for applying standards in an electromagnetic field edge element method. The method includes the steps that a three-dimensional model of an object to be analyzed is established, and the three-dimensional model is subjected to mesh generation; element matrixes corresponding to a magnetic vector potential double-rotation item,a coulomb standard item and an electric current density item of edge elements obtained through mesh generation are calculated, and integration is performed so that an overall finite element equation can be formed; corresponding boundary conditions are applied to the overall finite element equation; the overall finite element equation to which the corresponding boundary conditions are applied is solved, a unique magnetic vector potential basic solution is obtained, post-processing is performed on the obtained magnetic vector potential basic solution, and a corresponding electromagnetic field quantity solution is obtained. According to the method, on the premise that accuracy is guaranteed, the magnetic vector potential uniqueness problem in the edge element method is effectively solved; the establishment problem of a complex generating tree in a traditional method is avoided; meanwhile, the efficiency of the method is higher than that of a coulomb standard applying method adopted in the edge elements through a Lagrange multiplier method.
Owner:INTESIM DALIAN
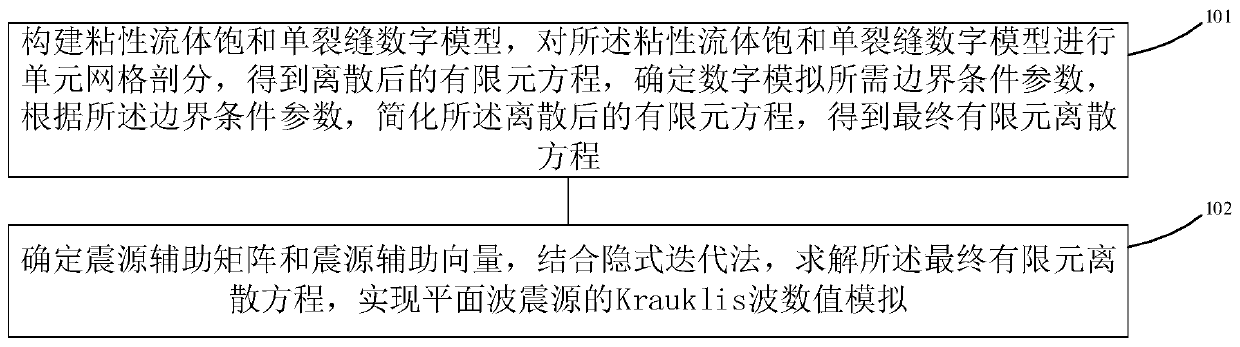
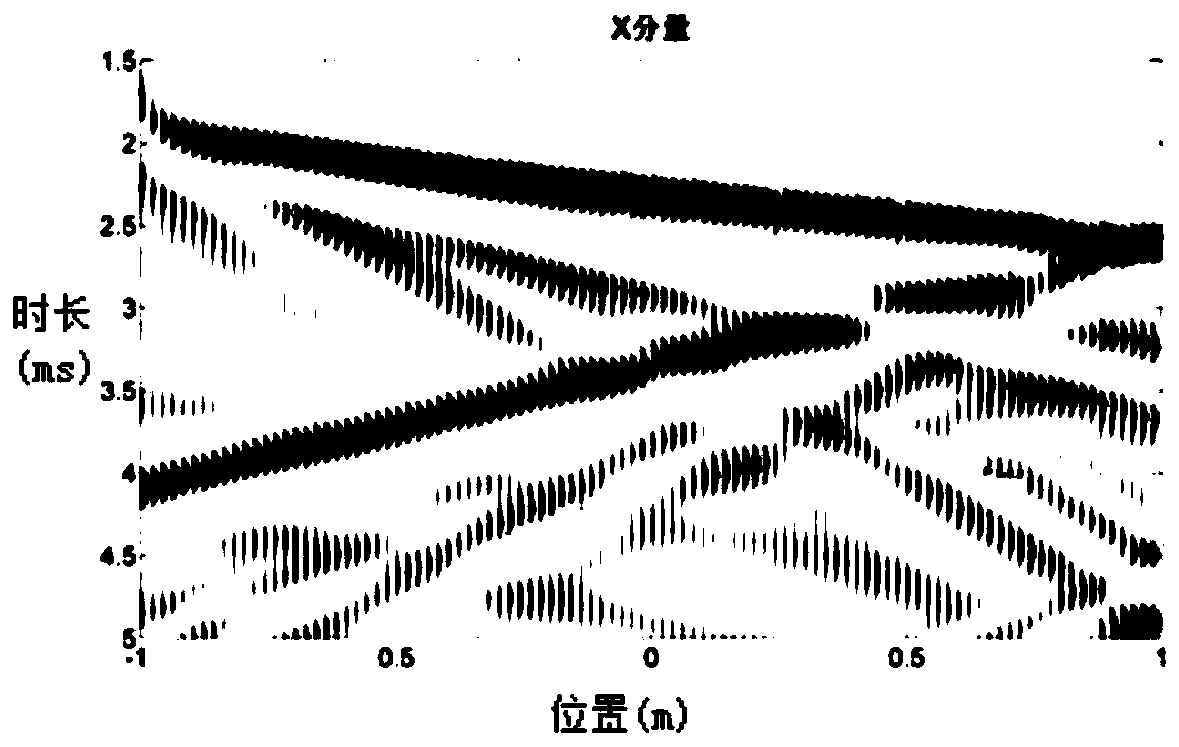
Krauklis wave numerical simulation method and equipment based on plane wave seismic source
ActiveCN110688785ARealize simulationDesign optimisation/simulationClassical mechanicsStructural engineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a Krauklis wave numerical simulation method and equipment based on a plane wave seismic source. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a viscous fluid saturated single-fracture digital model, performing unit mesh generation on the viscous fluid saturated single-fracture digital model to obtain a discrete finite element equation, determiningboundary condition parameters required by digital simulation, and simplifying the discrete finite element equation according to the boundary condition parameters to obtain a final finite element discrete equation; and determining a seismic source auxiliary matrix and a seismic source auxiliary vector, and solving the final finite element discrete equation in combination with an implicit iterationmethod to realize Krauklis wave numerical simulation of the plane wave seismic source. According to the Krauklis wave numerical simulation method and equipment based on the plane wave seismic source provided by the embodiment of the invention, Krauklis wave numerical simulation of the plane wave seismic source can be realized.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com