Patents
Literature
269results about "Error correction/detection using single space coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
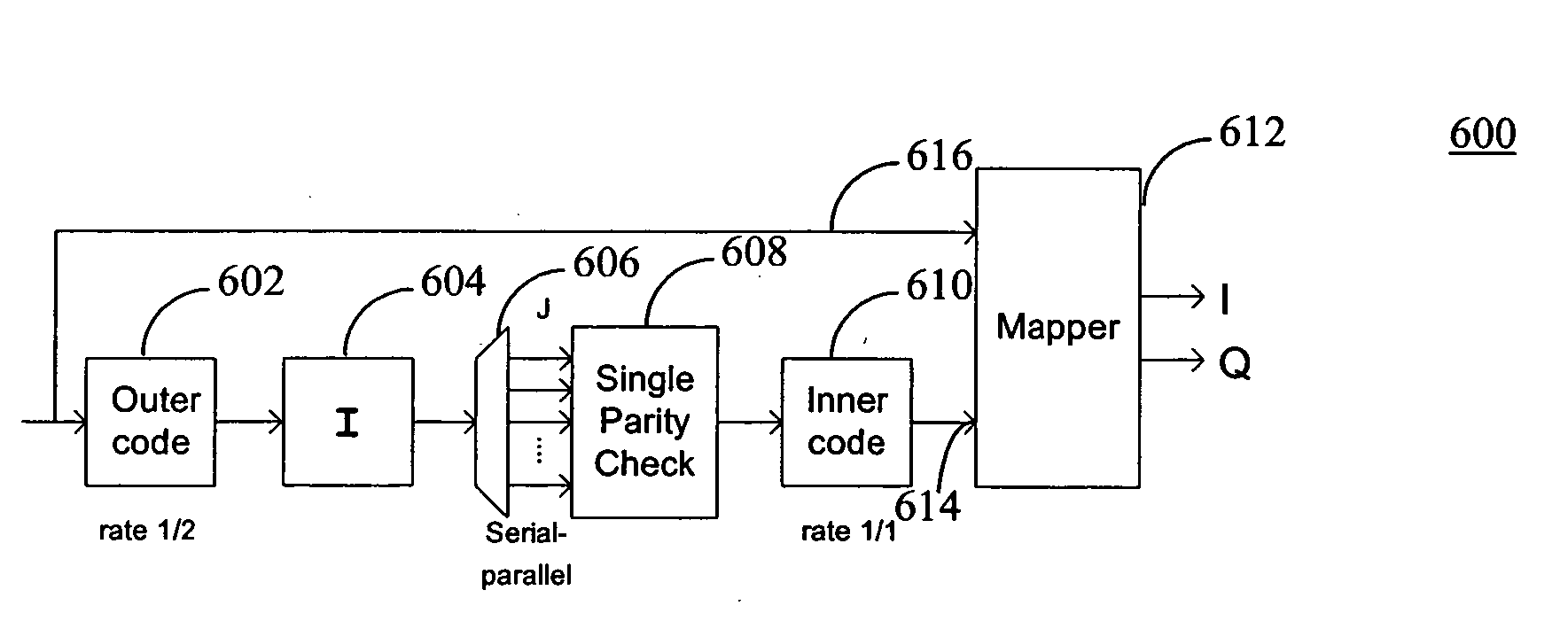
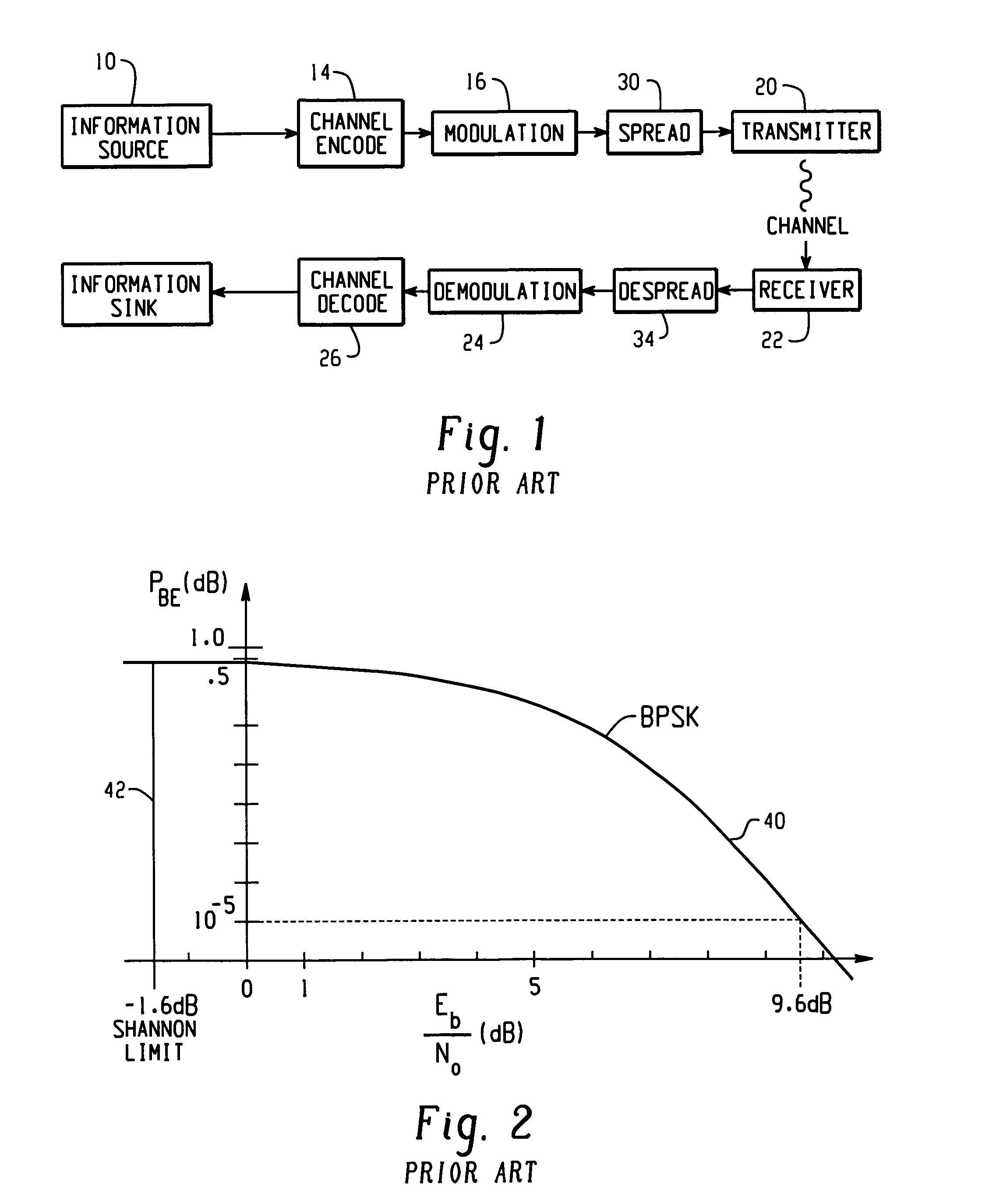
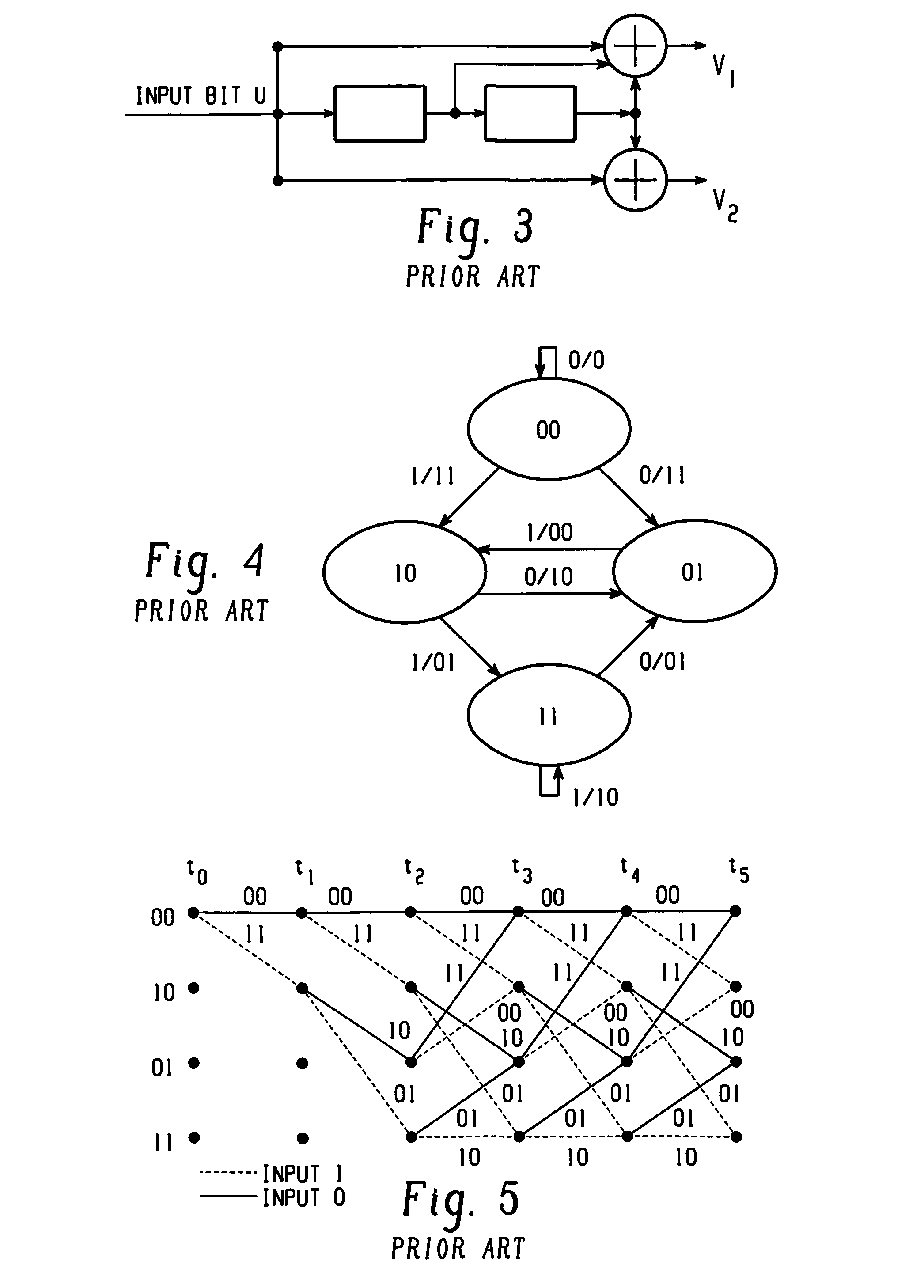
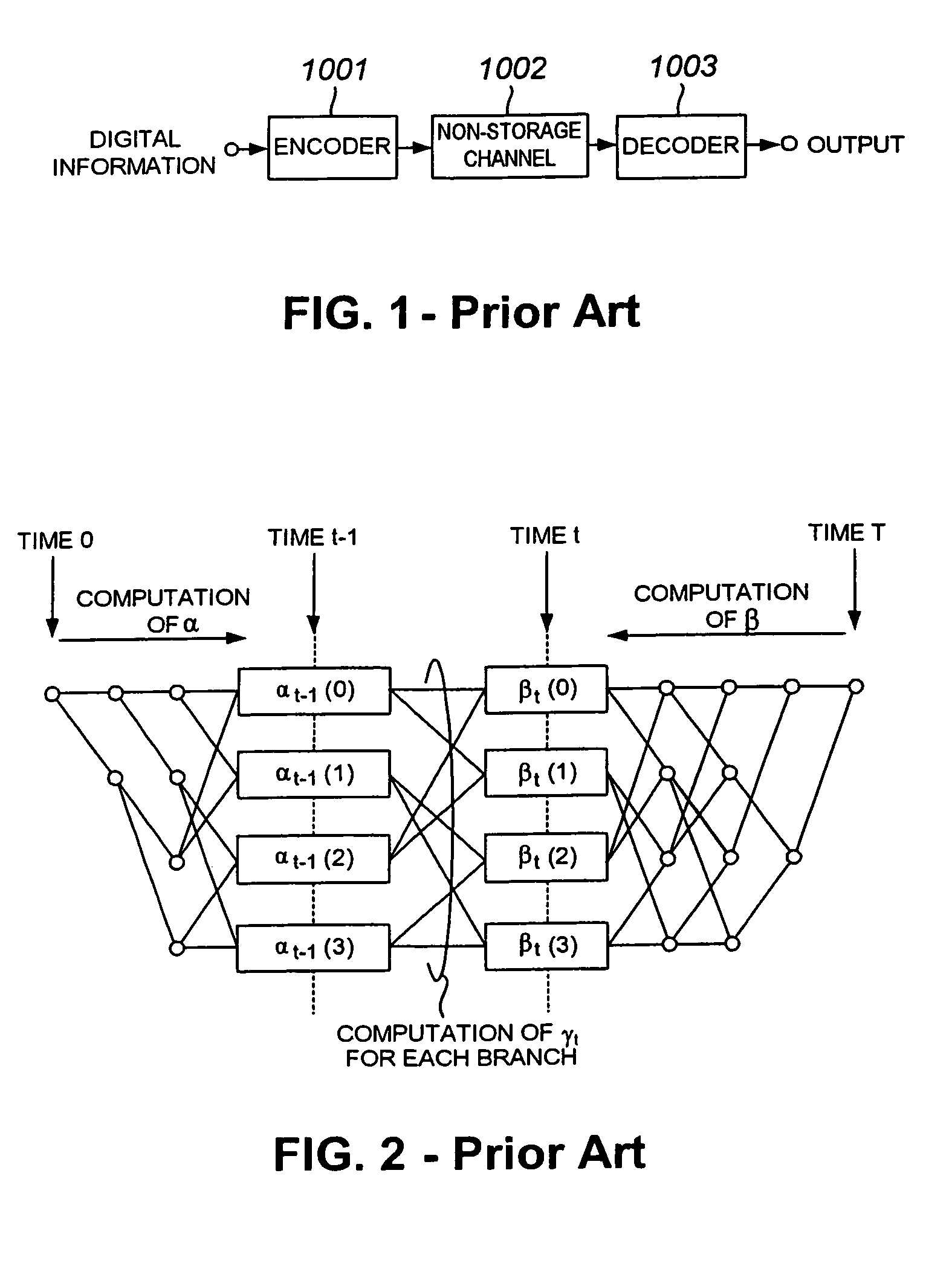
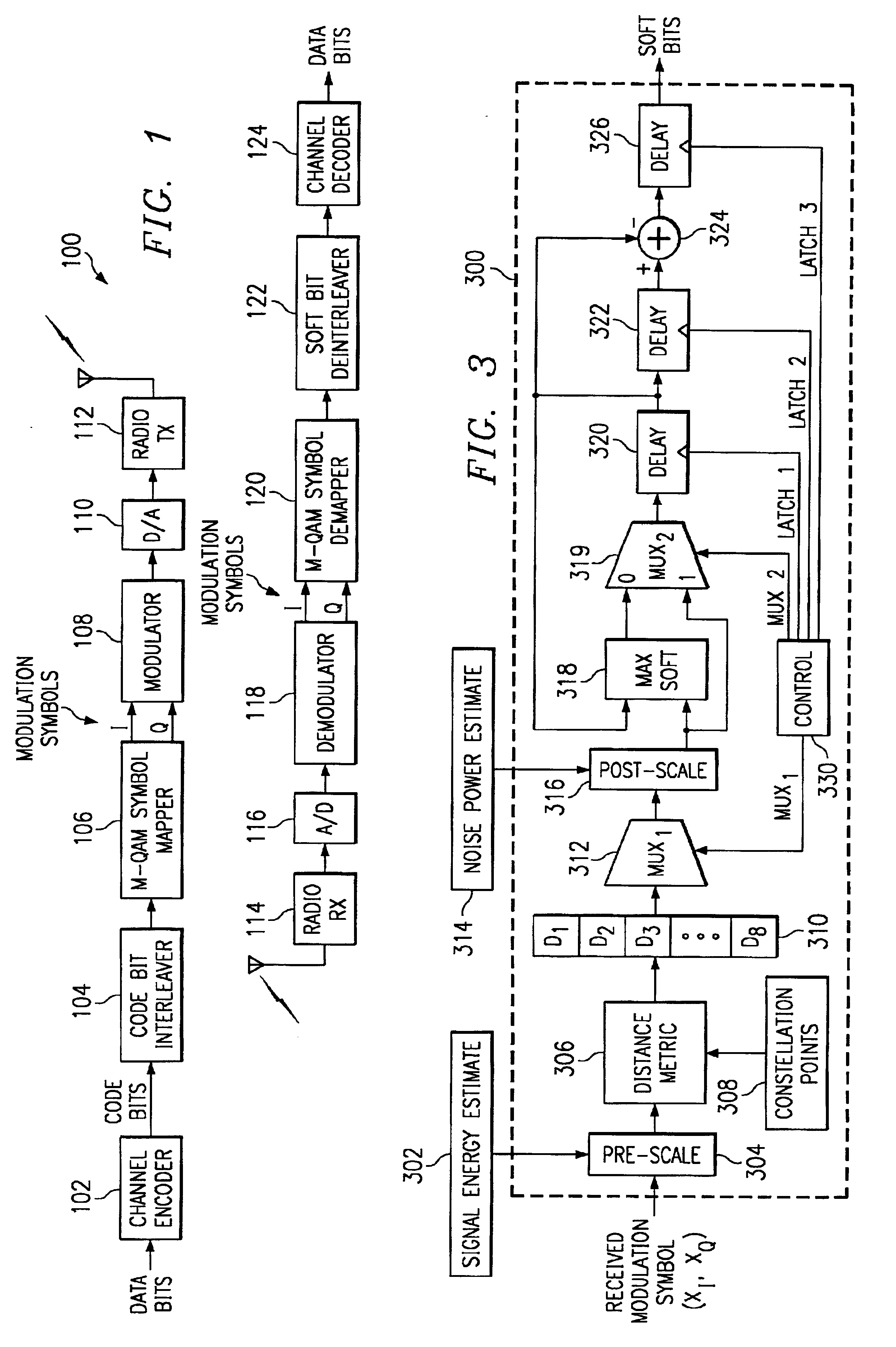
Method and apparatus for communications using turbo like codes
The present invention relates to methods, apparatuses, and systems for performing data encoding involving encoding data bits according to an outer convolutional code to produce outer encoded bits processing the outer encoded bits using an interleaver and a logical unit to produce intermediate bits, wherein the logical unit receives a first number of input bits and produces a second number of corresponding output bits, the second number being less than the first number, and wherein the logical unit takes each of the first number of input bits into account in producing the second number of output bits, encoding the intermediate bits according to an inner convolutional code to produce inner encoded bits, wherein the inner convolutional code is characterized by at least two states, and combining the data bits and the inner encoded bits to produce encoded outputs.
Owner:TRELLIS WARE TECH
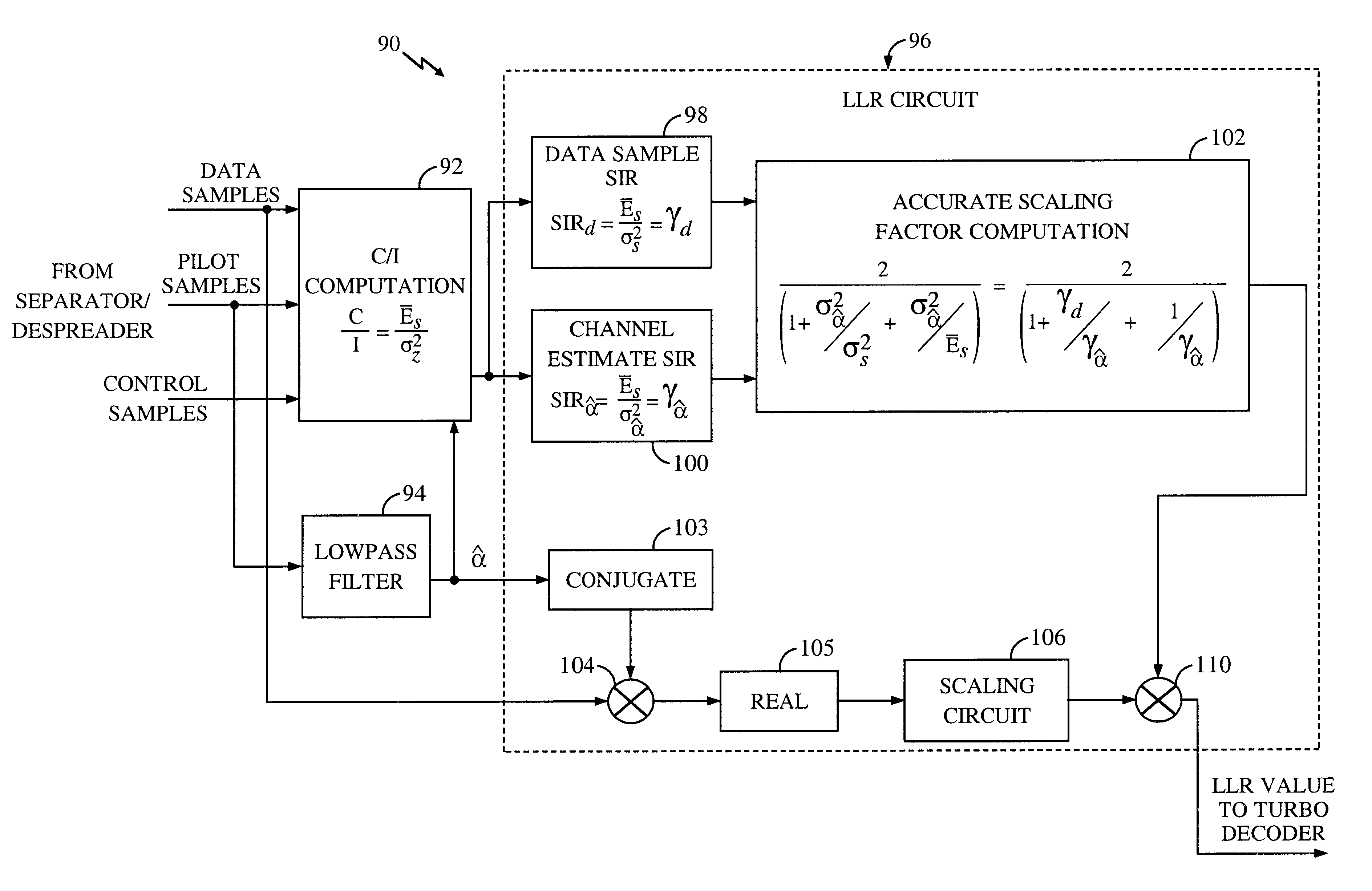
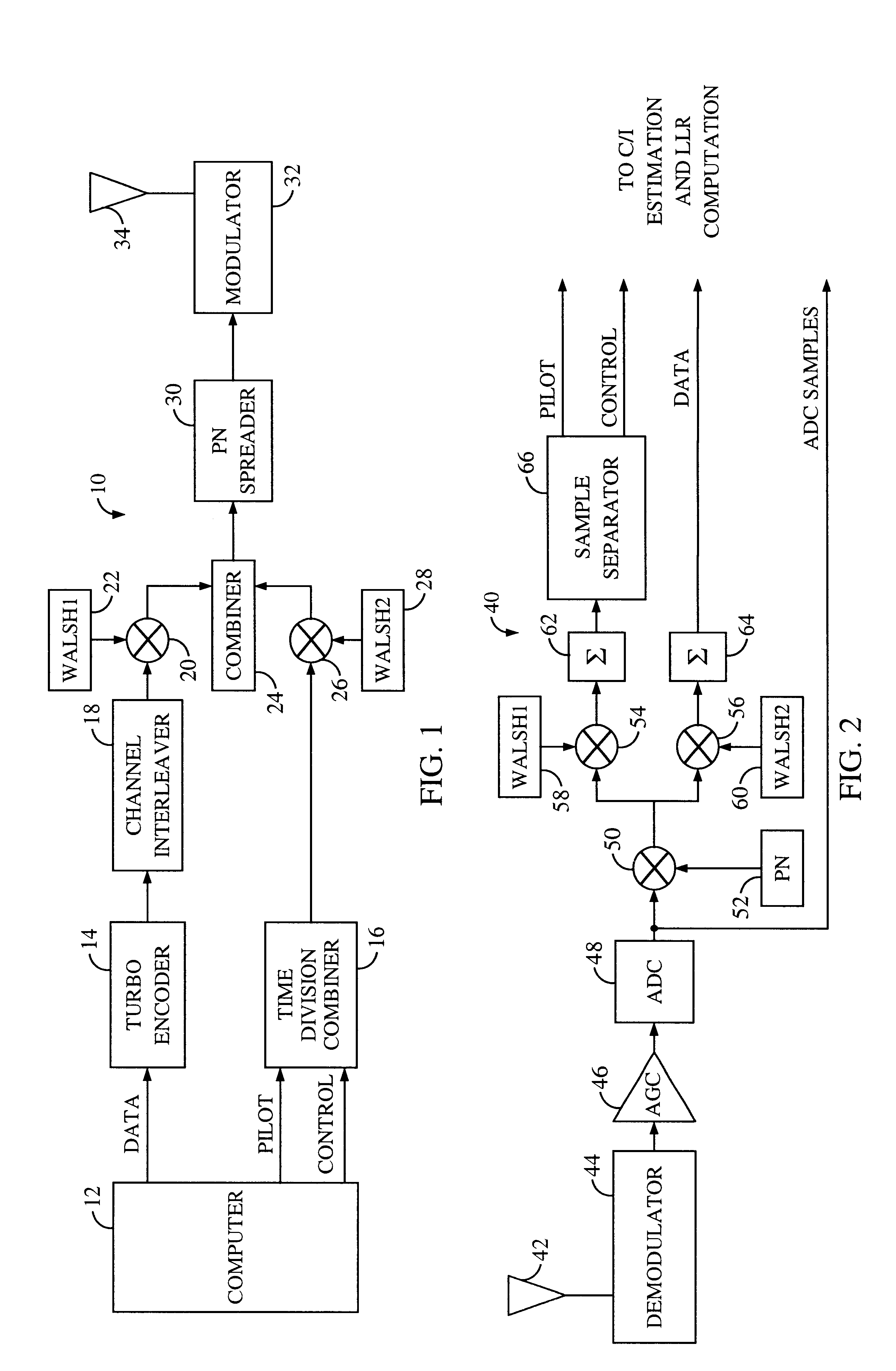
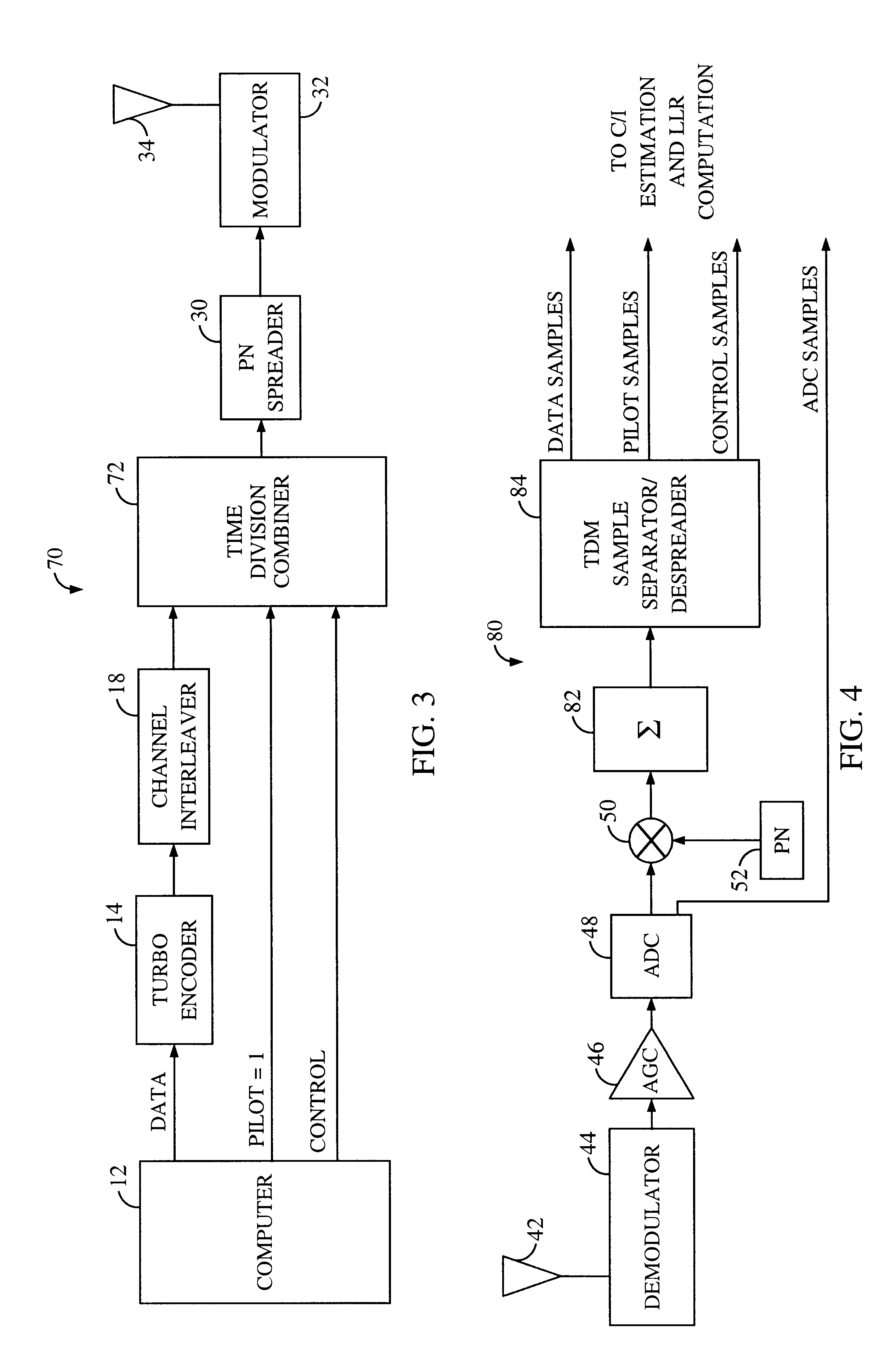
System and method for performing accurate demodulation of turbo-encoded signals via pilot assisted coherent demodulation
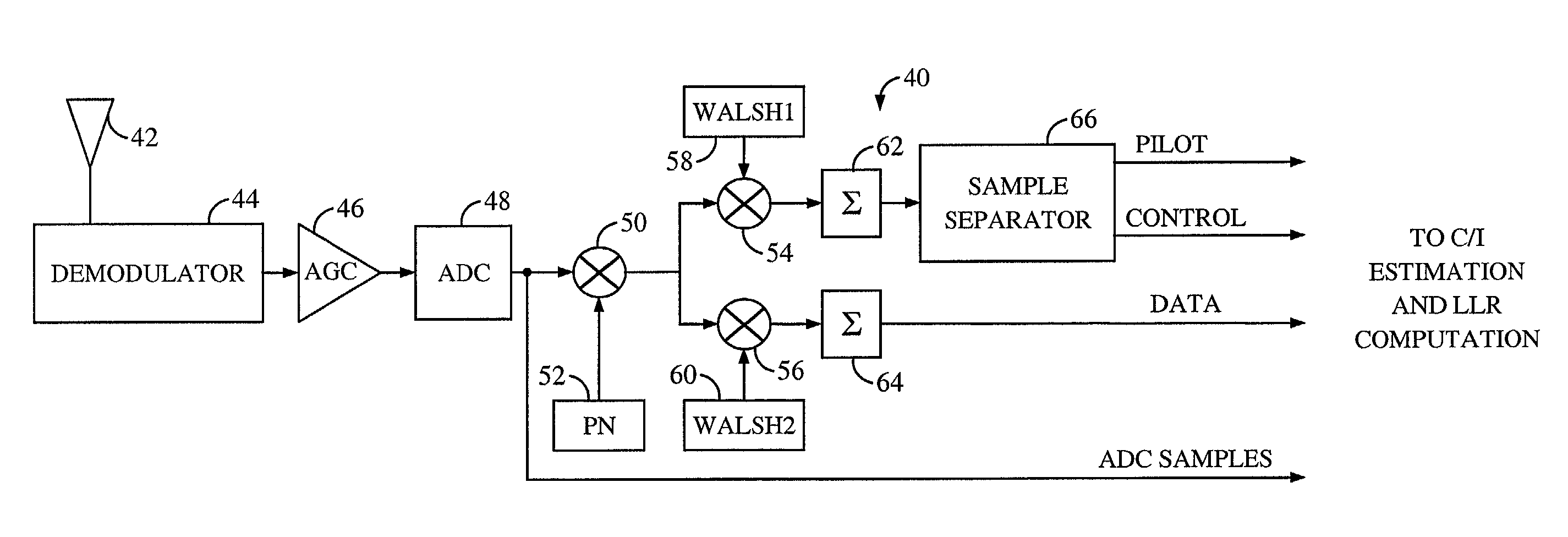
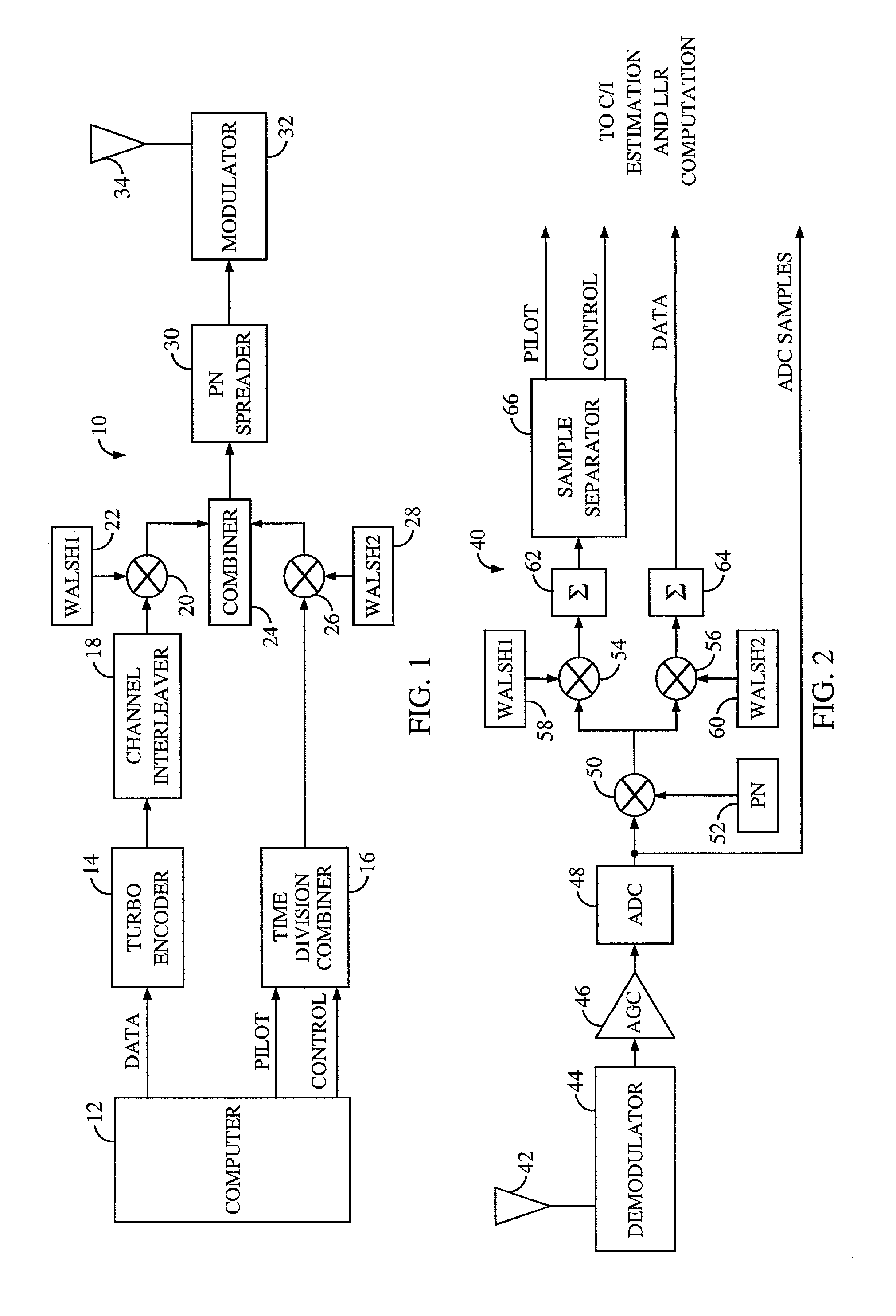
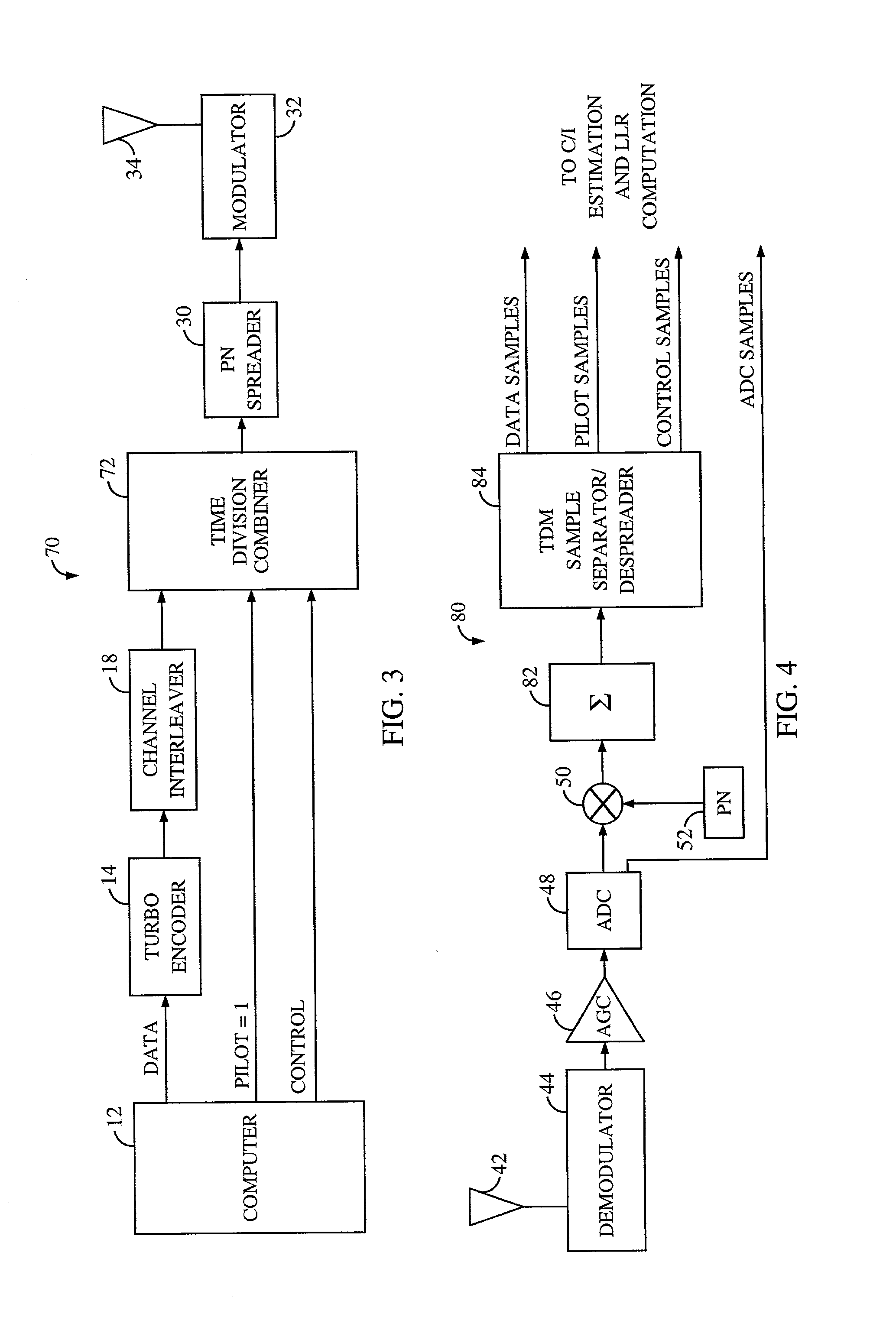
InactiveUS6377607B1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorError correction/detection using convolutional codesTransceiverInterference ratio
An efficient telecommunications receiver system for accurately decoding a received composite signal having a data signal component and a pilot signal component. The receiver system includes a first circuit for receiving the composite signal and extracting a pilot signal and a data signal from received composite signal. A second circuit calculates a log-likelihood ratio as a function of a channel estimate based on the pilot signal. A third circuit scales the log-likelihood ratio by a predetermined log-likelihood ratio scaling factor and provides an accurate log-likelihood value in response thereto. A fourth circuit decodes the received composite signal based on the accurate log-likelihood value and the data signal. In a specific embodiment, the pilot signal and the data signal comprise pilot samples and data samples, respectively. The third circuit includes a carrier signal-to-interference ratio circuit for computing a first signal-to-interference ratio and a second signal-to-interference ratio based partly on the pilot signal. The first signal-to-interference ratio is based on the data samples, and the second signal-to-interference ratio is based on the pilot samples. The first signal-to-noise ratio and the second signal-to-noise ratio provide input to a circuit for computing the predetermined log-likelihood ratio scaling factor that is included in the third circuit. In a more specific embodiment, the first circuit includes a despreader for despreading the received composite signal in accordance with a predetermined spreading function and providing a despread signal in response thereto. The spreading function is a pseudo noise sequence or a Walsh function. The first circuit further includes a decovering circuit that extracts the pilot signal and the data signal from the despread signal. In the illustrative embodiment, the accurate receiver system further includes a circuit for generating a rate and / or power control message and transmitting the rate and / or power control message to an external transceiver in communication with the efficient receiver system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Decoding system and method for digital communications
InactiveUS20020051498A1Reduction in uncorrectable errorReduction in packet lossData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesPacket lossDependability
A Viterbi decoding system interprets bits in received QAM constellations as many-valued parameters rather than binary valued parameters. It performs the Viterbi algorithm using these many-valued parameters to provide results superior to hard decision decoding. Rather than applying a hard 0-1 function to the QAM data, the system uses a non-stepped linear or curved transfer function to assign values to the bits. In another aspect, a system differentiates between data bits based on their estimated reliability, giving more emphasis to decoding reliable bits than unreliable bits using any of a variety of techniques. By differentiating between god and bad bits and de-emphasizing or ignoring unreliable bits, the system can provide a significant reduction in uncorrectable errors and packet loss.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Apparatus and method for trellis encoding data for transmission in digital data transmission systems
InactiveUS6937617B2Sufficient redundancyIncorrect determinationPulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionDigital dataPhase difference
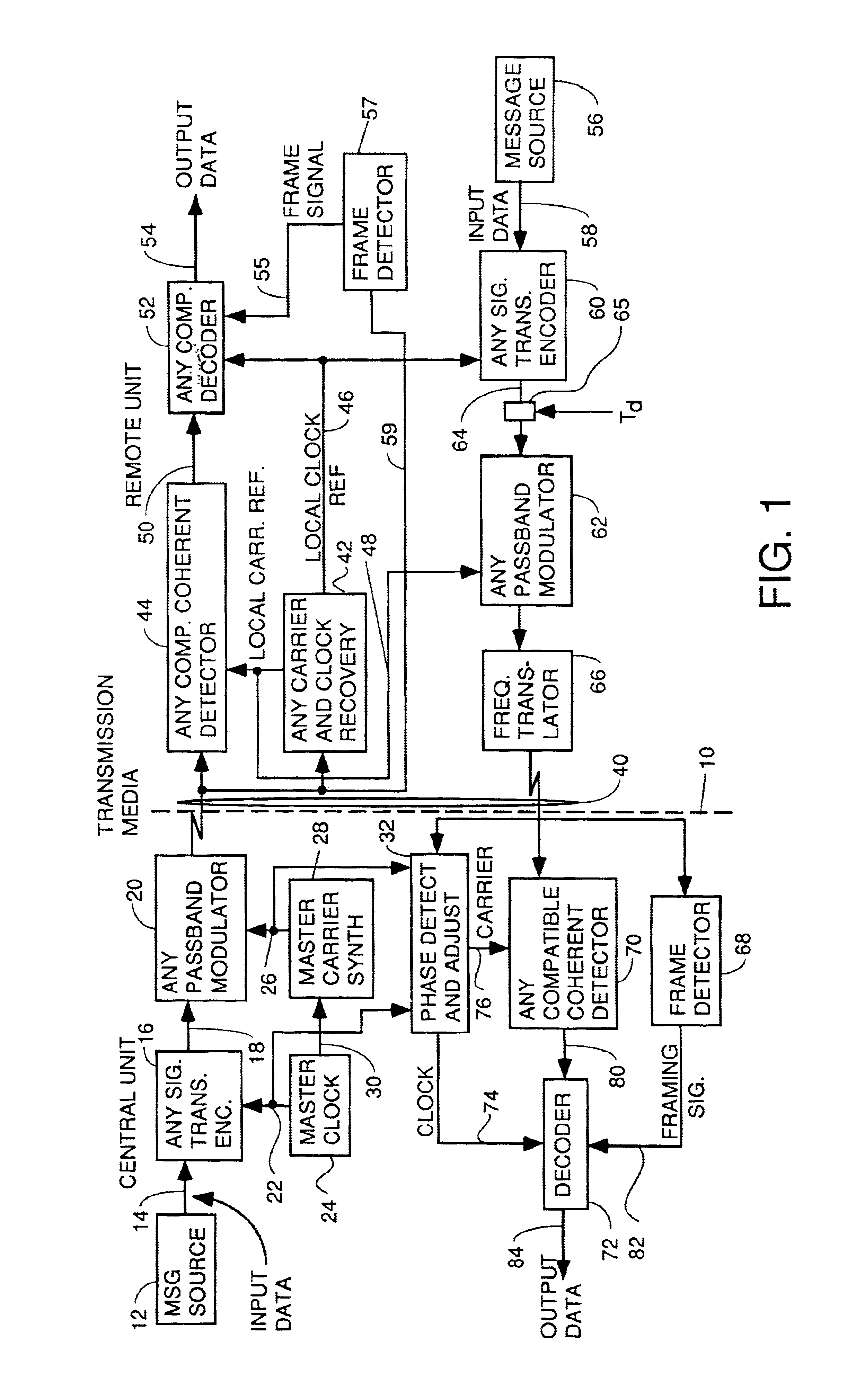
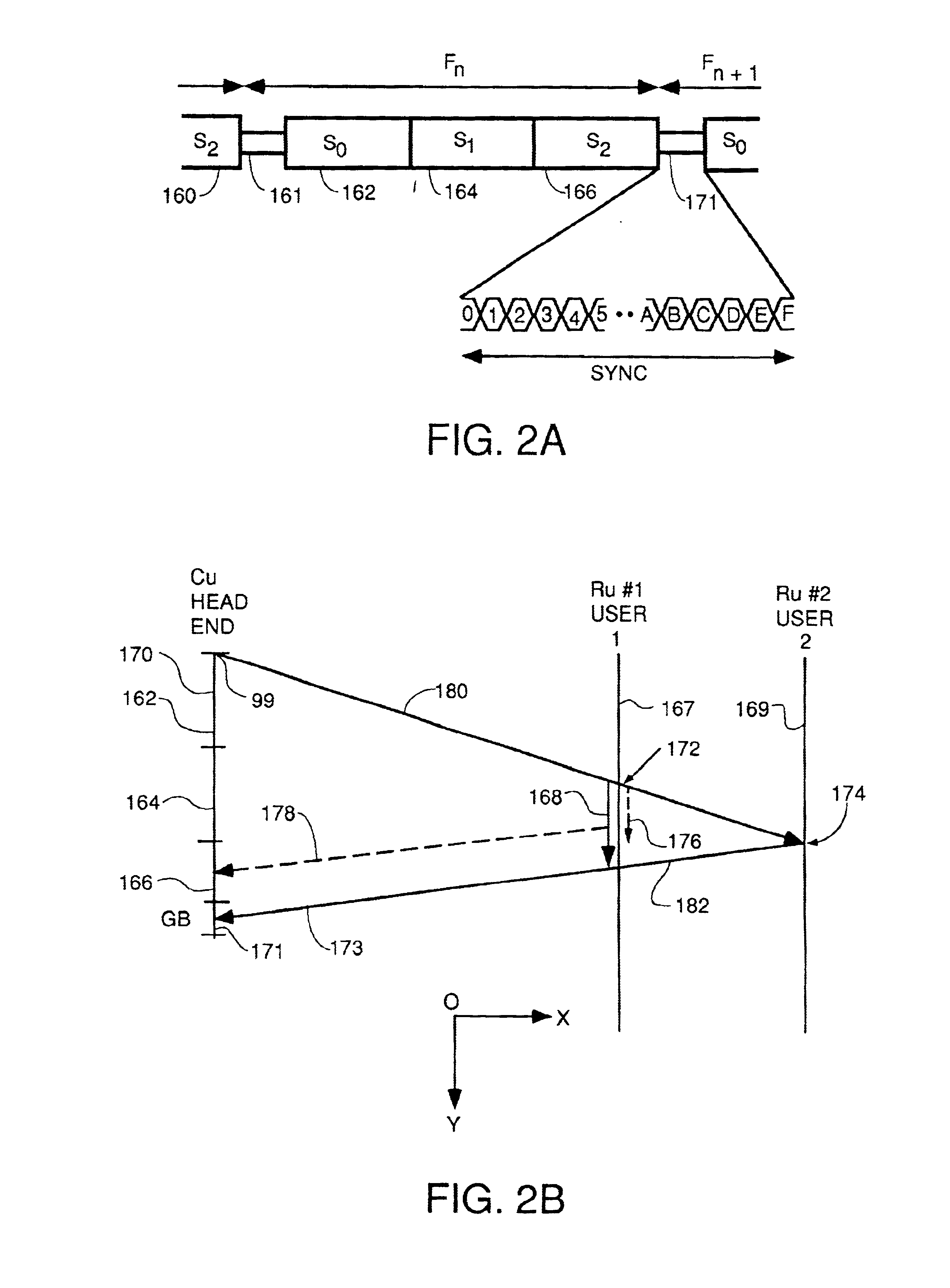
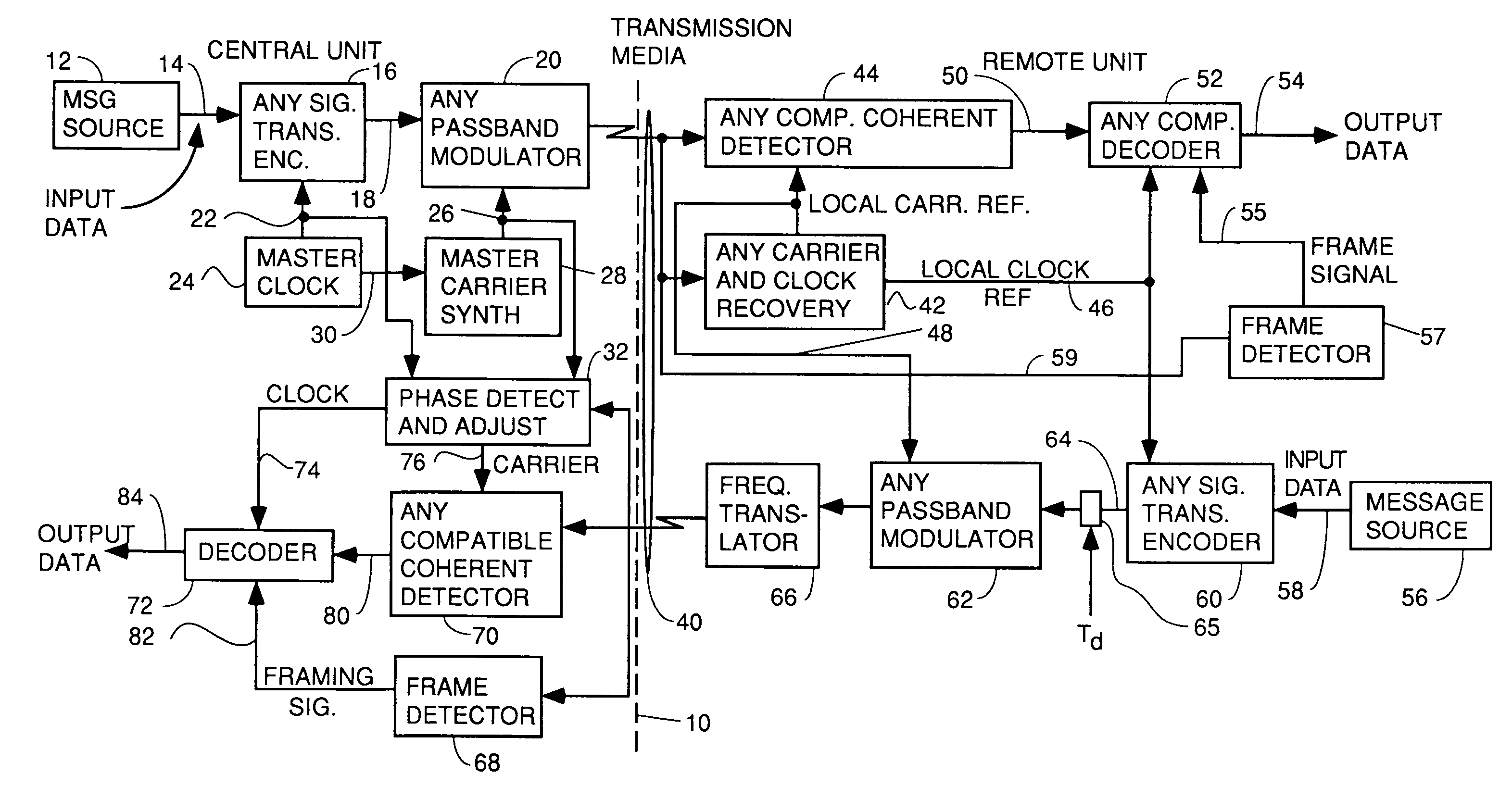
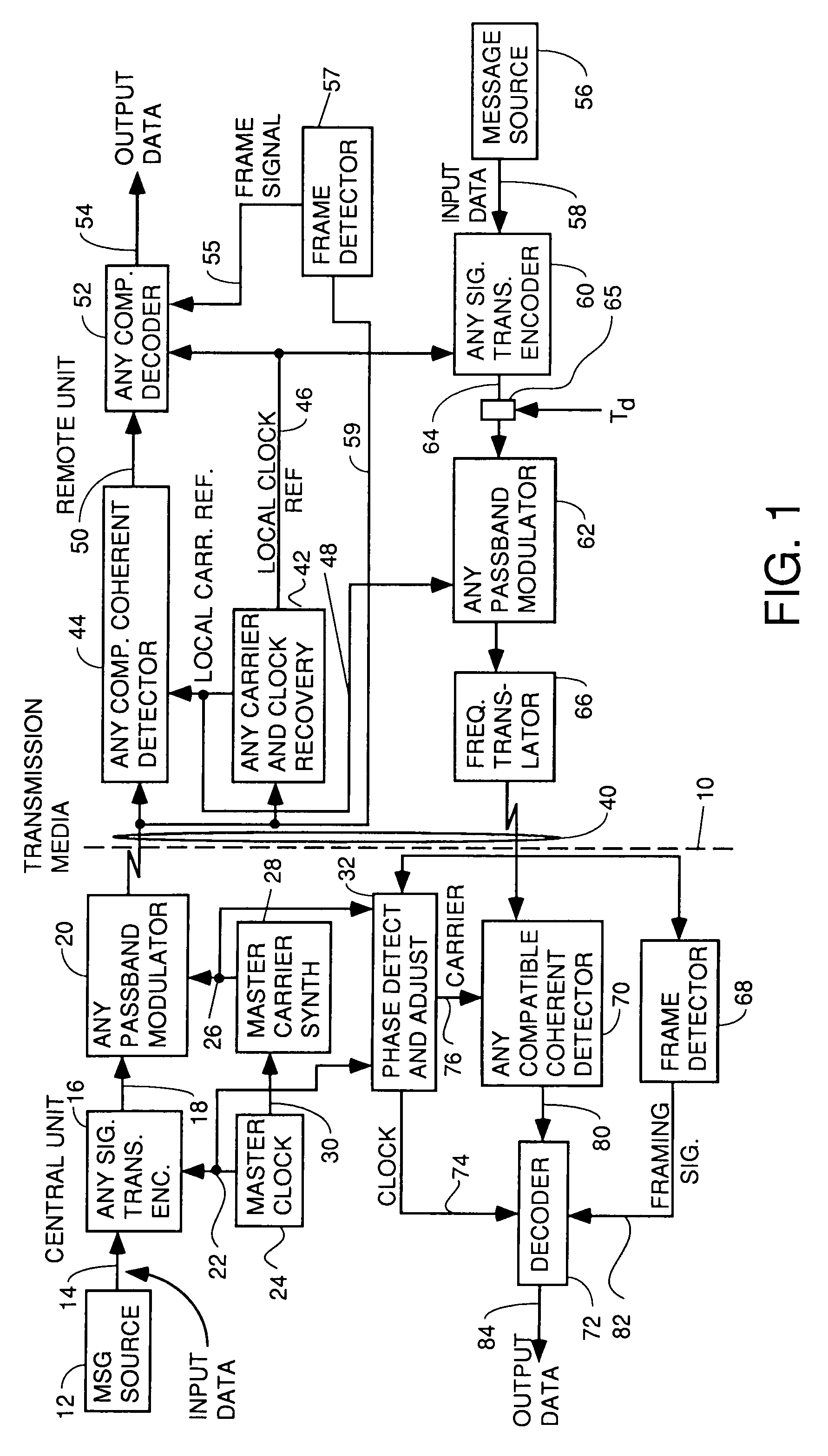
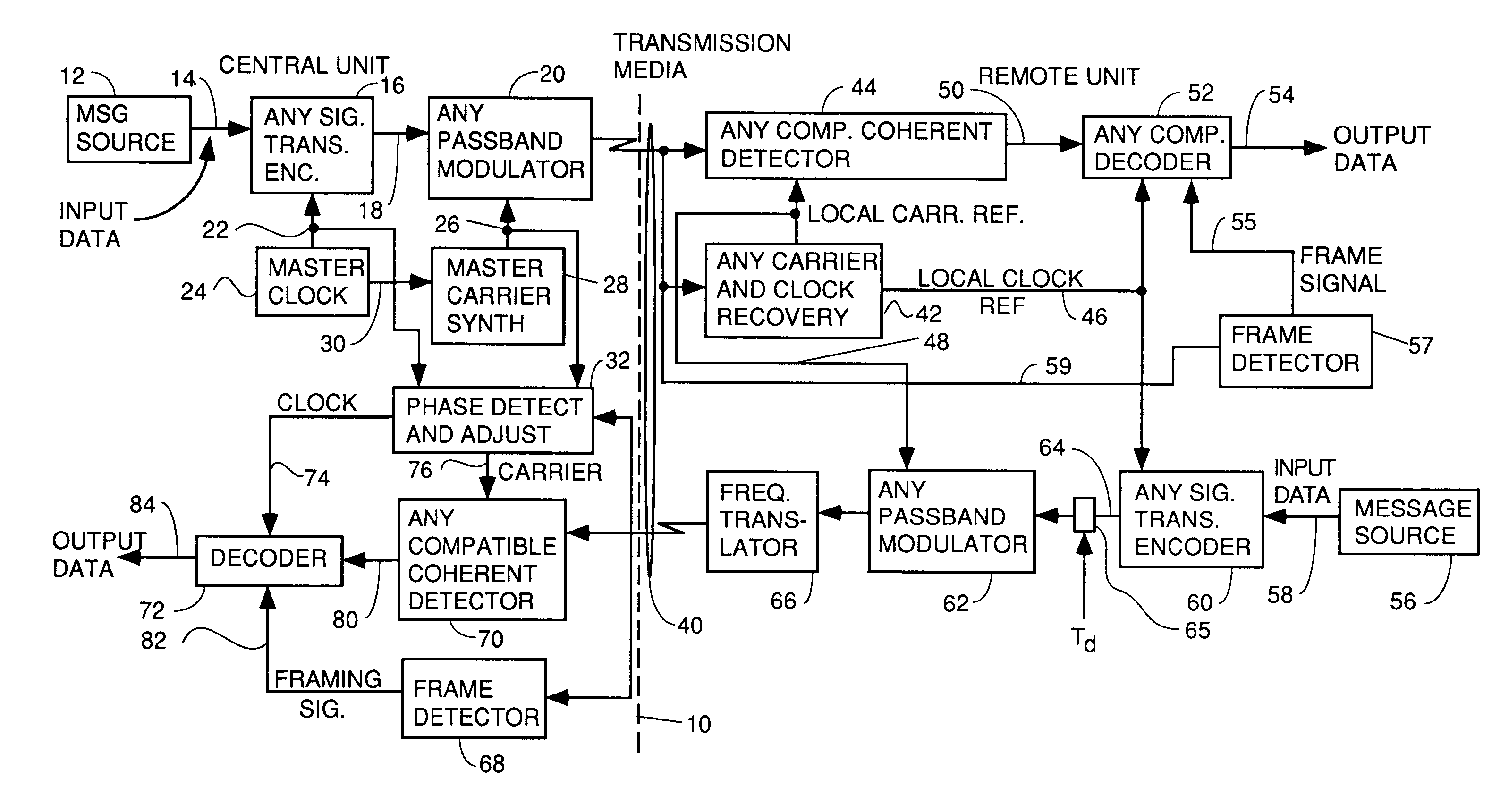
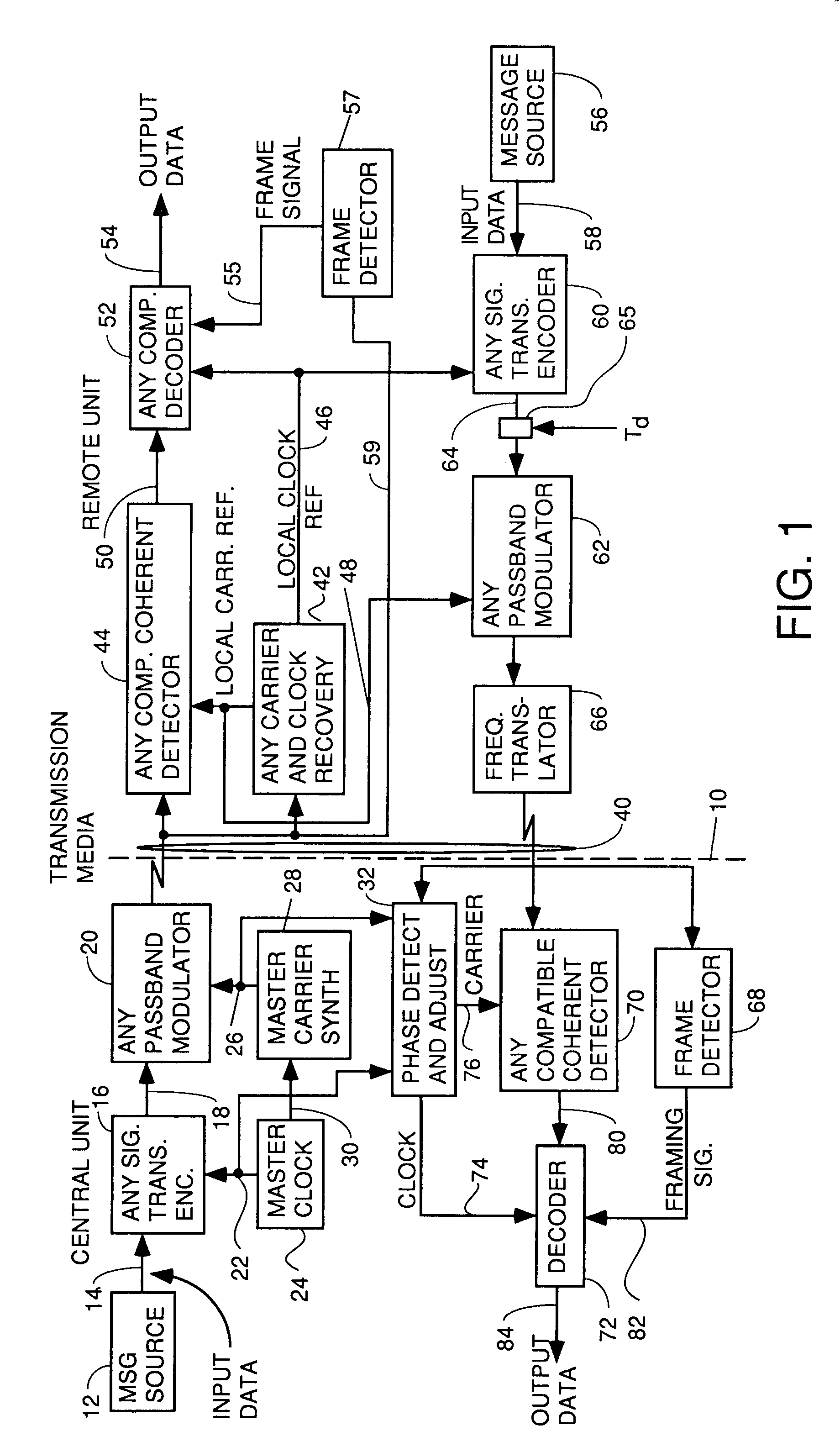
A system for bidirectional communication of digital data between a central unit and a remote unit wherein the need for tracking loops in the central unit has been eliminated. The central unit transmitter generates a master carrier and a master clock signal which are used to transmit downstream data to the remote units. The remote units recover the master carrier and master clock and synchronize local oscillators in each remote unit to these master carrier and master clock signals to generate reference carrier and clock signals for use by the remote unit receiver. These reference carrier and clock signals are also used by the remote unit transmitters to transmit upstream data to the central unit. The central unit receiver detects the phase difference between the reference carrier and clock signals from the remote units periodically and adjusts the phase of the master carrier and master clock signals for use by the central unit receiver to receive the upstream data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
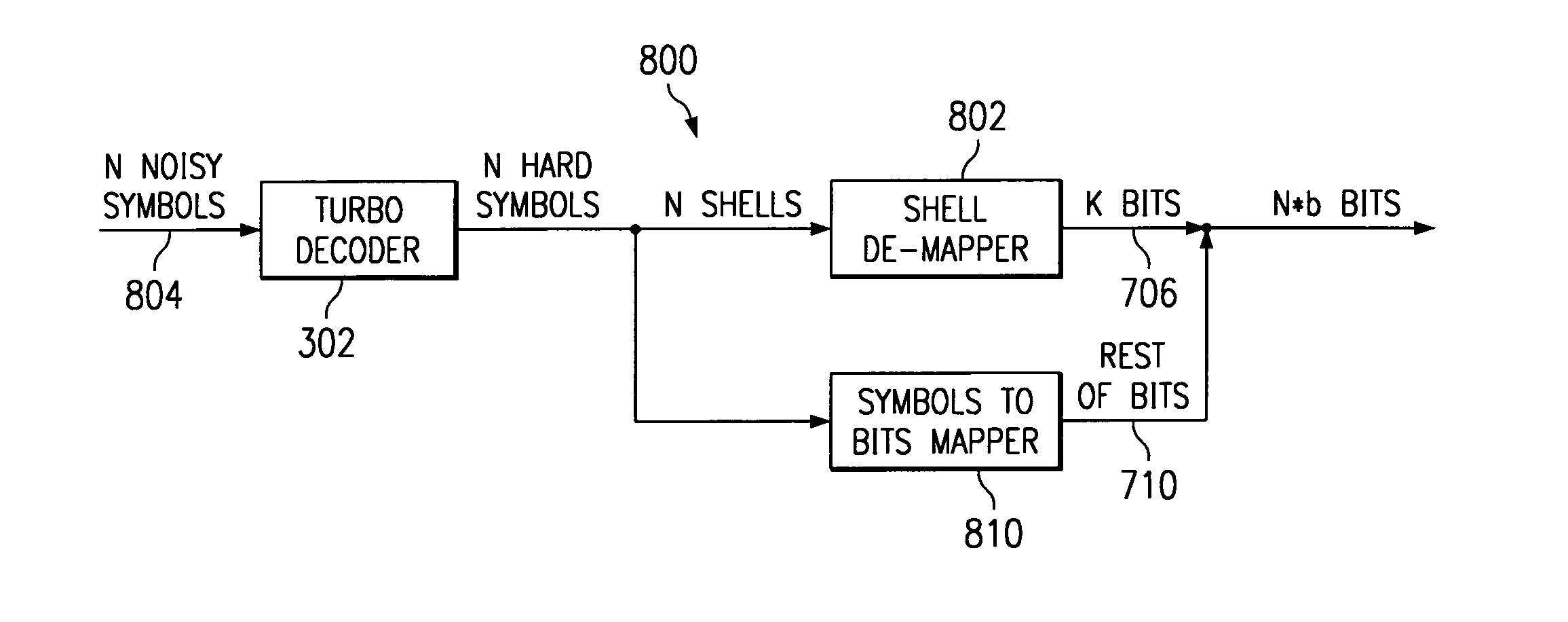
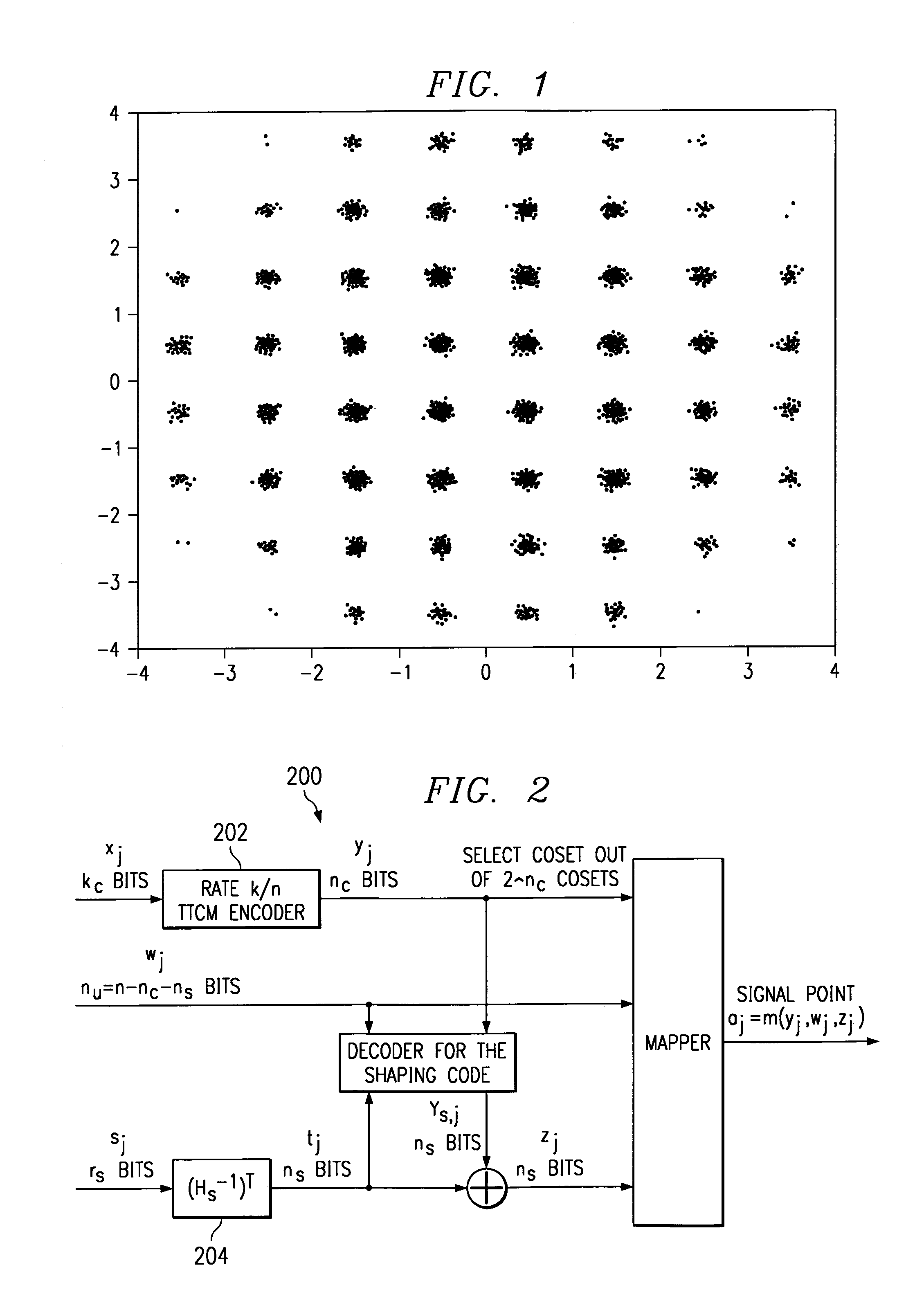
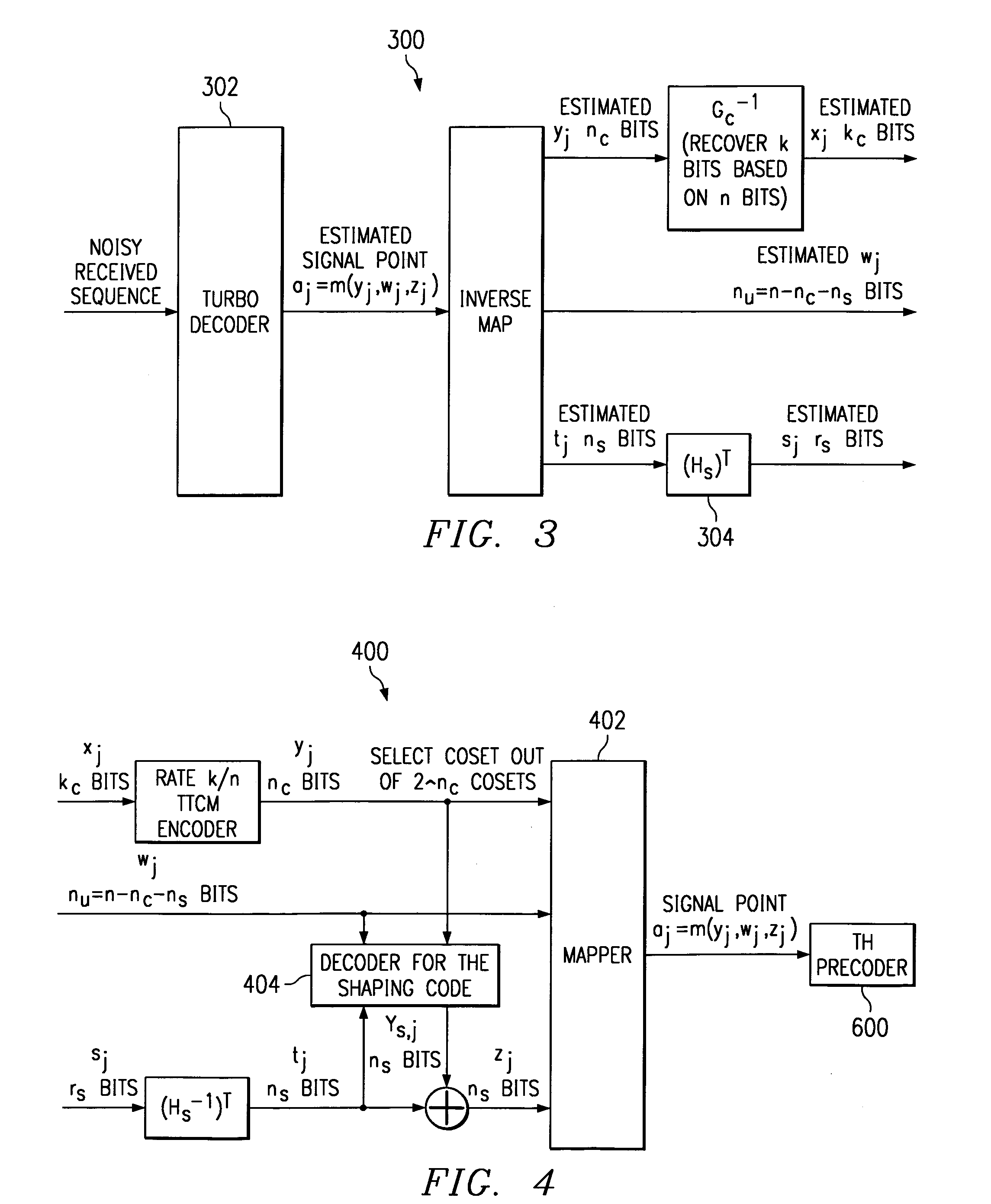
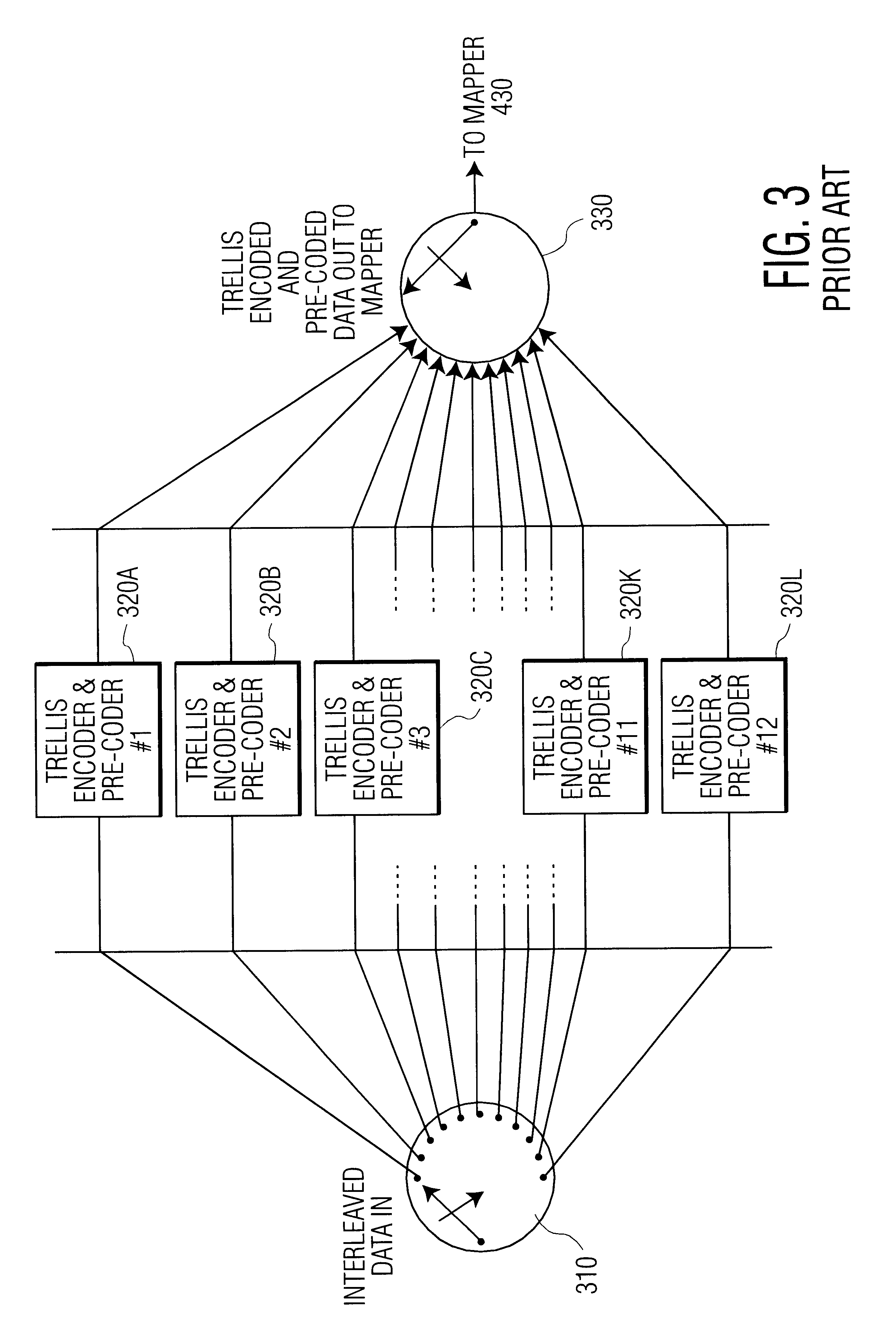
System and method of data communication using turbo trellis coded modulation combined with constellation shaping with or without precoding
InactiveUS7065147B2Improve performanceHigh coding gainsData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionPrecodingCommunications system
A technique that combines a turbo trellis coded modulation (TTCM) coding scheme with constellation shaping and precoding schemes to implement a binary coded communication system and method that can achieve high performance (high coding gains achieved in combination with shaping gain, and when necessary, also with high performance in ISI-channels via preceding).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
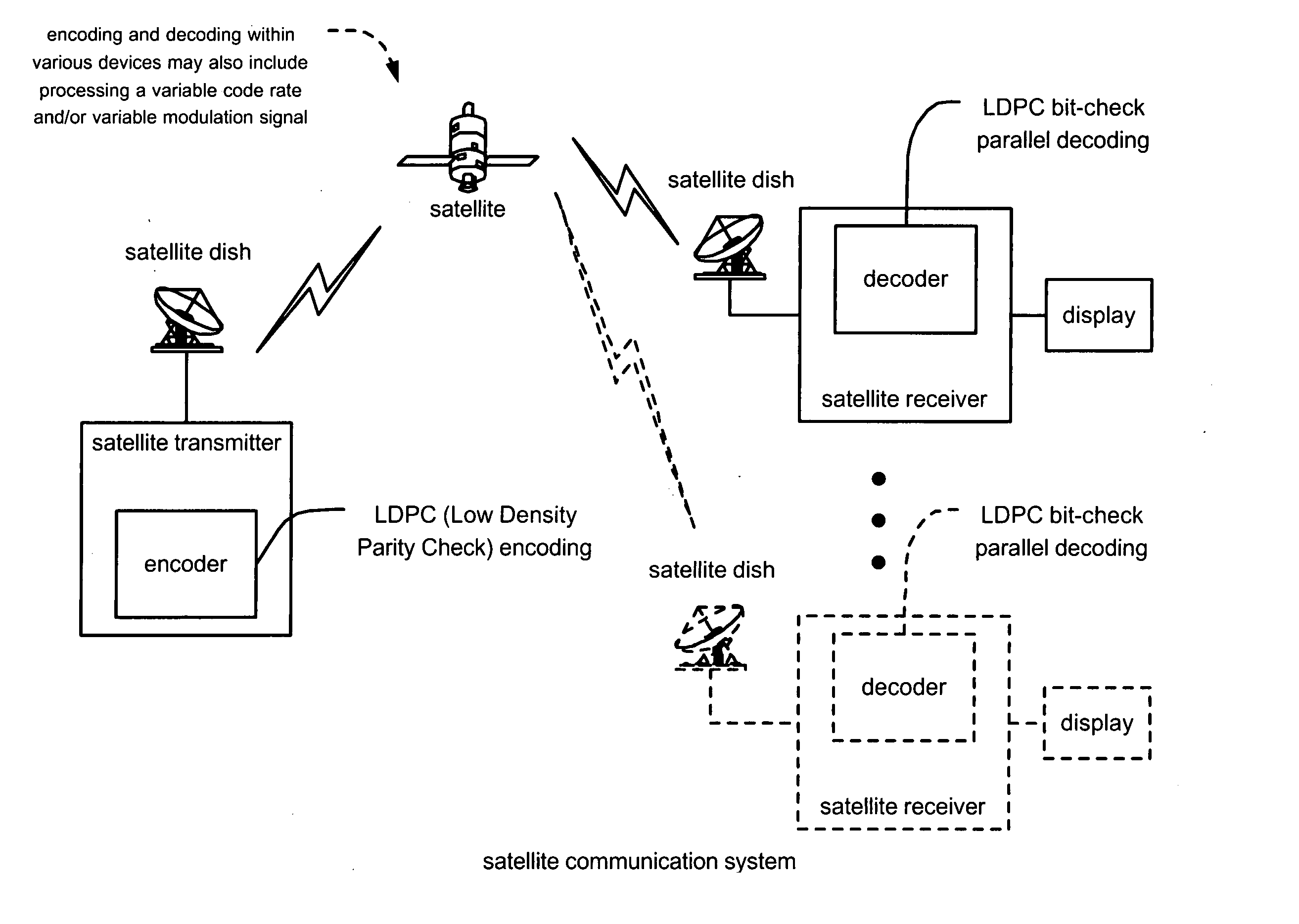
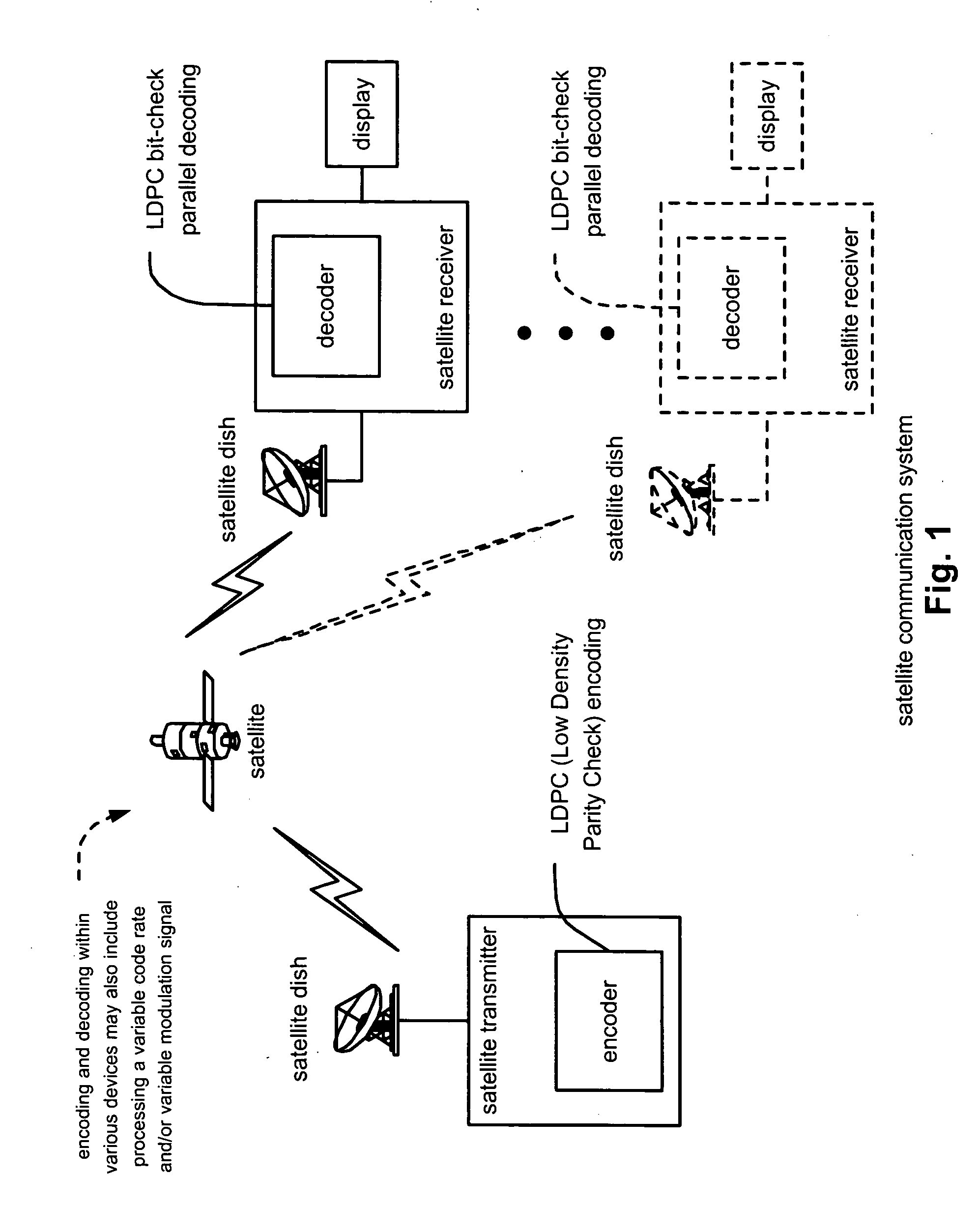
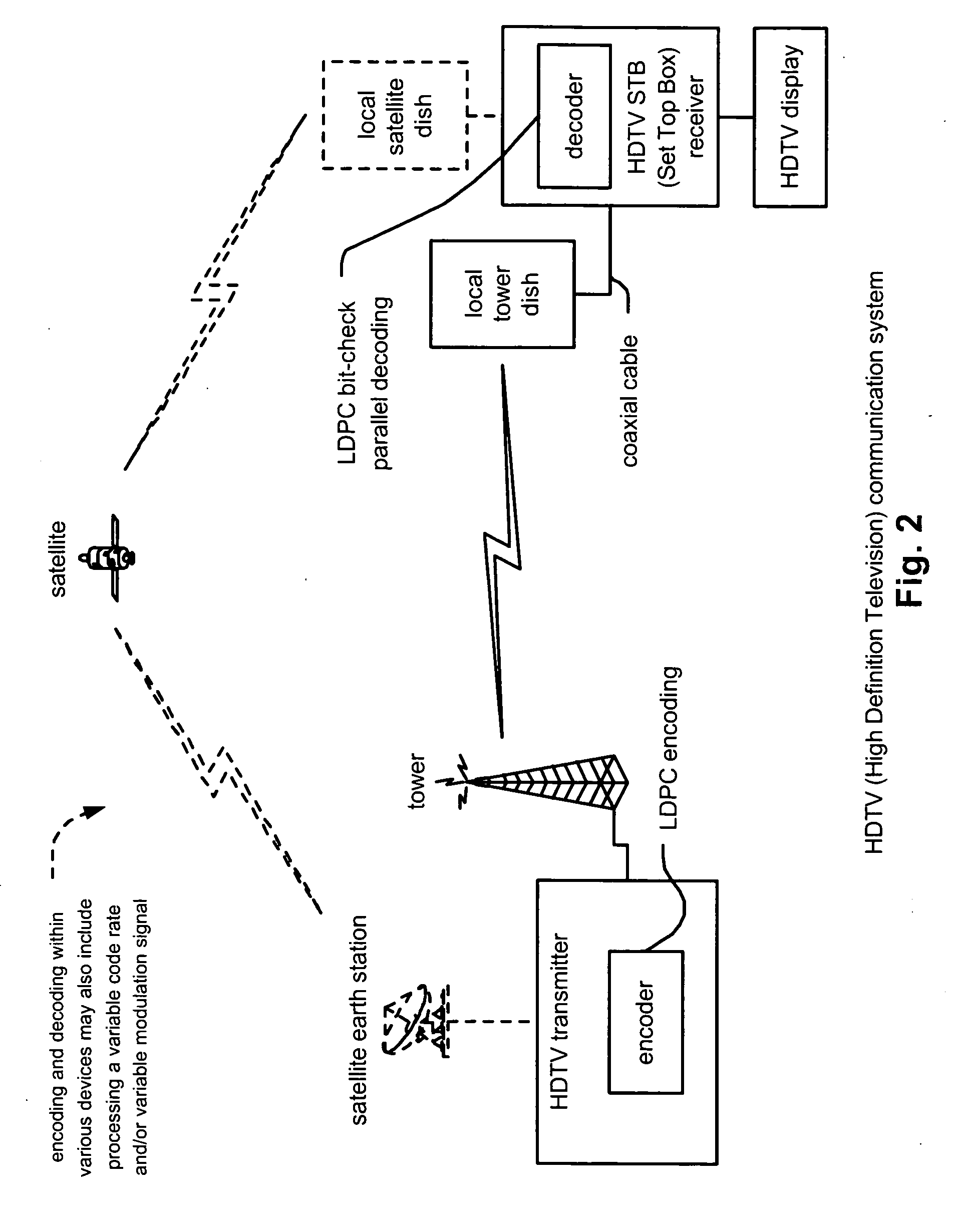
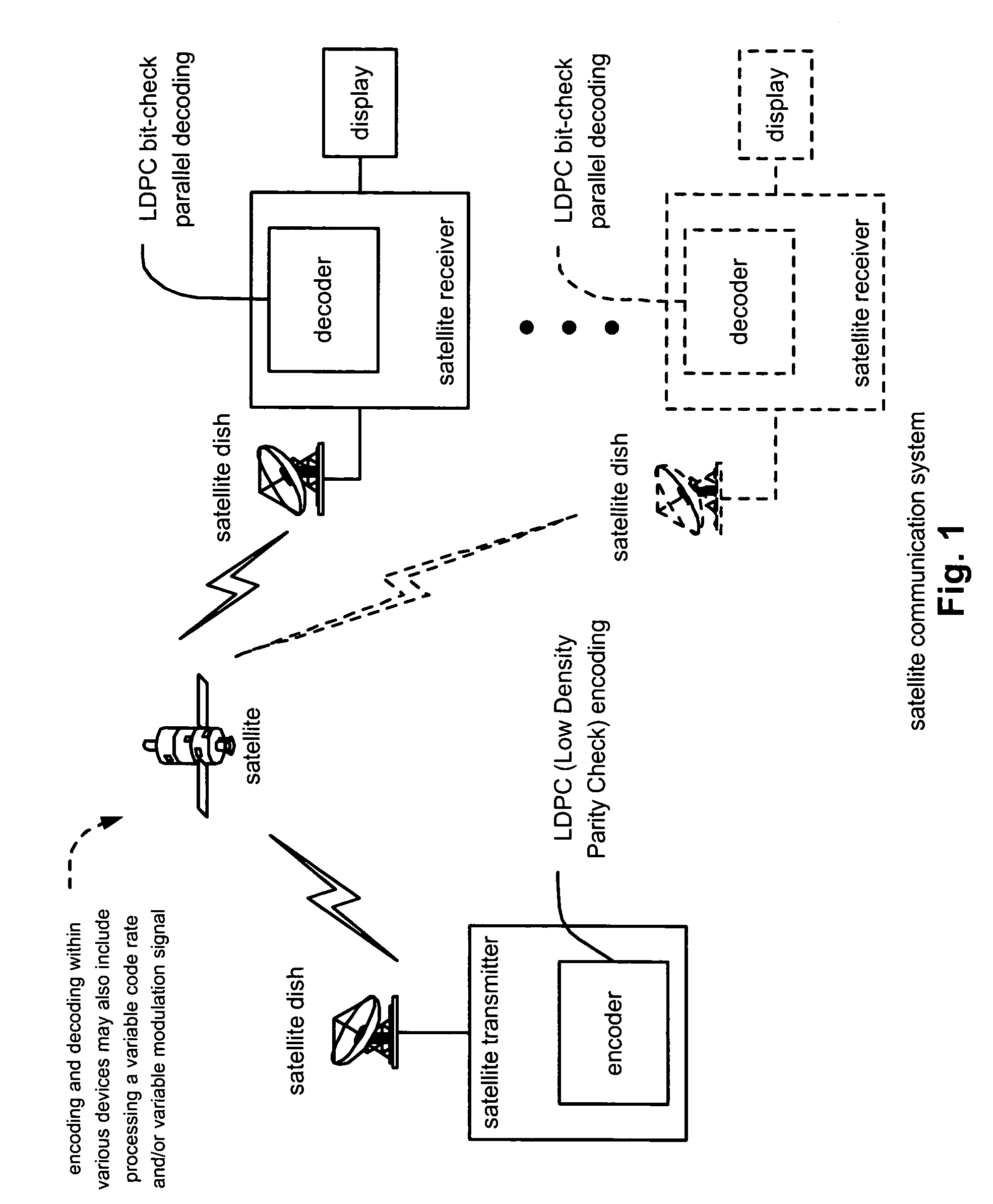
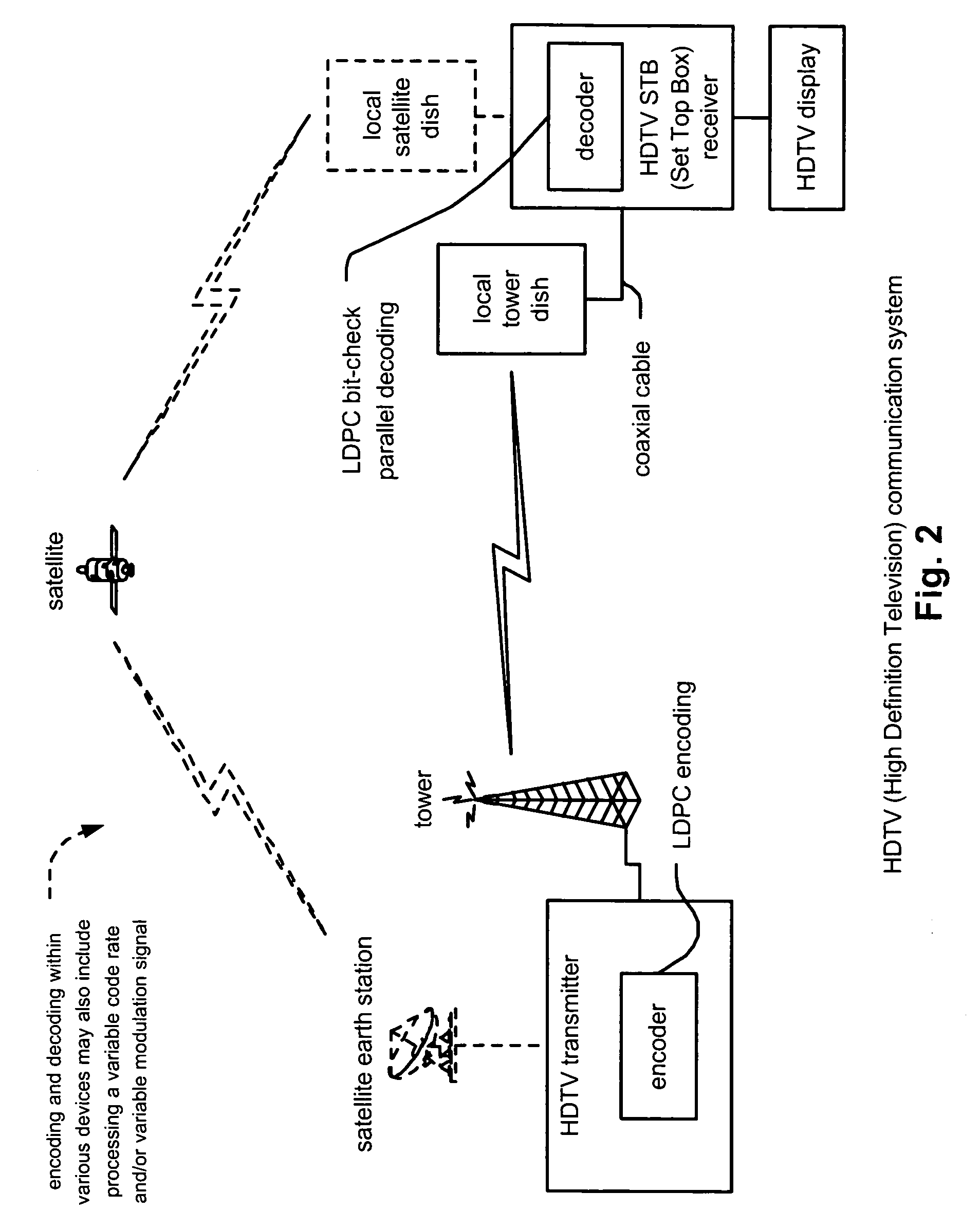
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) coded signal decoding using parallel and simultaneous bit node and check node processing
InactiveUS20050229090A1Error detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow densityComputer science
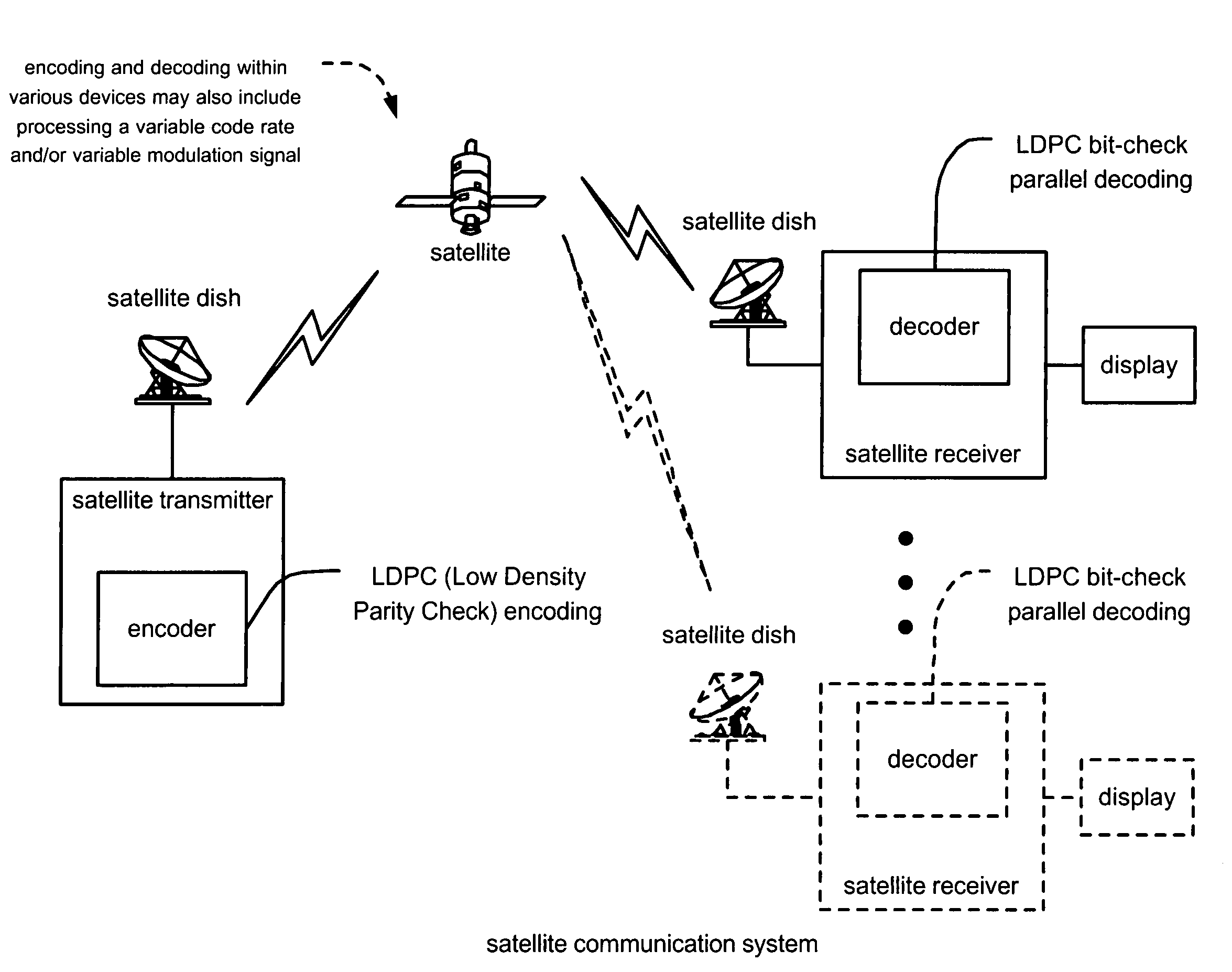
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) coded signal decoding using parallel and simultaneous bit node and check node processing. This novel approach to decoding of LDPC coded signals may be described as being LDPC bit-check parallel decoding. In some alternative embodiment, the approach to decoding LDPC coded signals may be modified to LDPC symbol-check parallel decoding or LDPC hybrid-check parallel decoding. A novel approach is presented by which the edge messages with respect to the bit nodes and the edge messages with respect to the check nodes may be updated simultaneously and in parallel to one another. Appropriately constructed executing orders direct the sequence of simultaneous operation of updating the edge messages at both nodes types (e.g., edge and check). For various types of LDPC coded signals, including parallel-block LDPC coded signals, this approach can perform decoding processing in almost half of the time as provided by previous decoding approaches.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Error detection/correction coding for hierarchical QAM transmission systems
InactiveUS7073116B1Data representation error detection/correctionModulated-carrier systemsComputer hardwareData stream
The power of the respective codes used by the first and second error detection / correction circuitry are such that the coded bit error rate of the first data stream is more closely matched to the coded bit error rate of the second data stream. A hierarchical QAM system allows the transmission of different sources by embedding the relative constellation points. The hierarchical QAM transmitter encodes the first data stream using a code having a first detection / correction power and encodes the second data stream using a code having a second detection / correction power.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Method and apparatus for communications using turbo like codes
The present invention relates to methods, apparatuses, and systems for performing data encoding involving encoding data bits according to an outer convolutional code to produce outer encoded bits processing the outer encoded bits using an interleaver and a logical unit to produce intermediate bits, wherein the logical unit receives a first number of input bits and produces a second number of corresponding output bits, the second number being less than the first number, and wherein the logical unit takes each of the first number of input bits into account in producing the second number of output bits, encoding the intermediate bits according to an inner convolutional code to produce inner encoded bits, wherein the inner convolutional code is characterized by at least two states, and combining the data bits and the inner encoded bits to produce encoded outputs.
Owner:TRELLIS WARE TECH
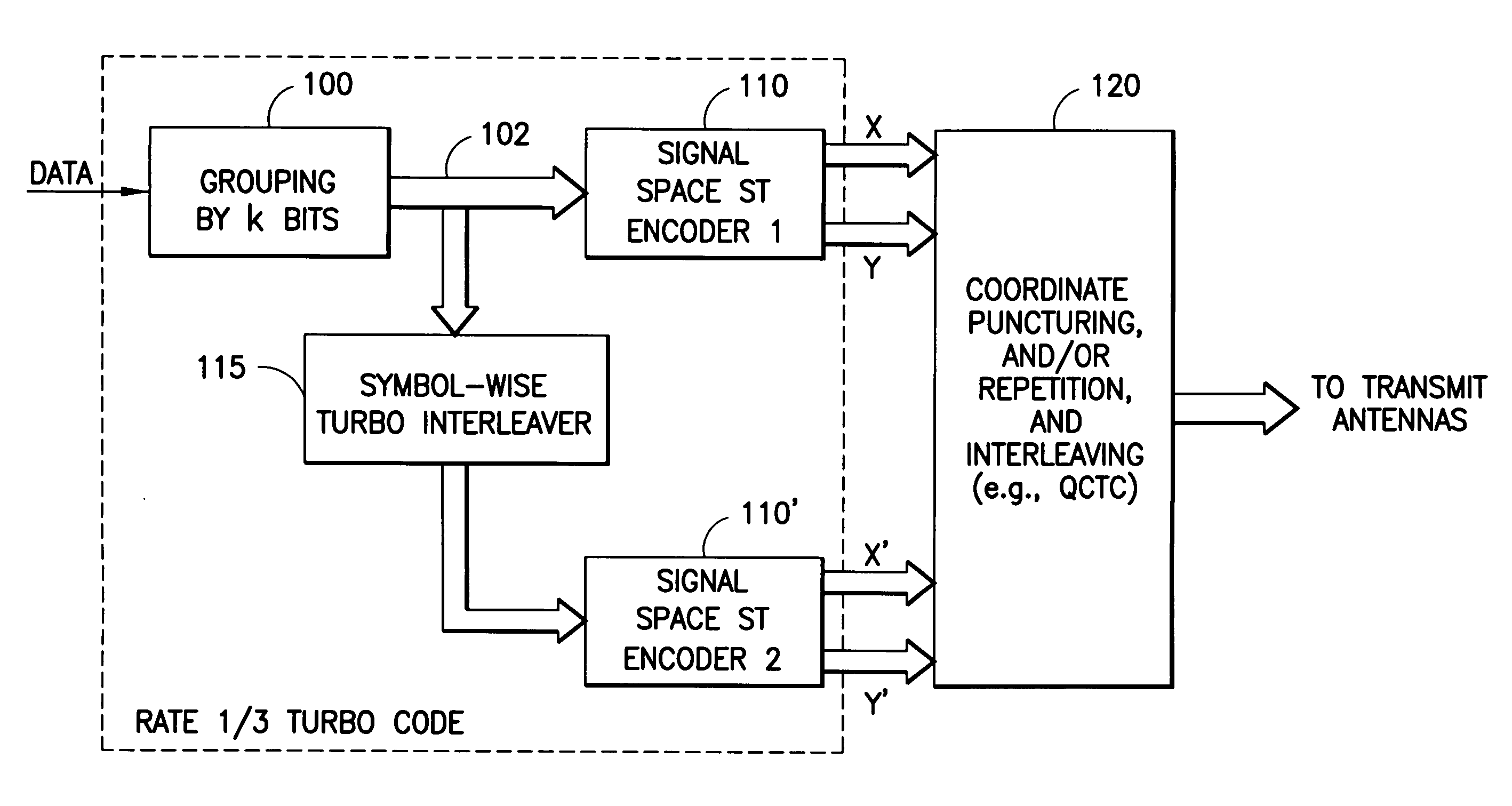
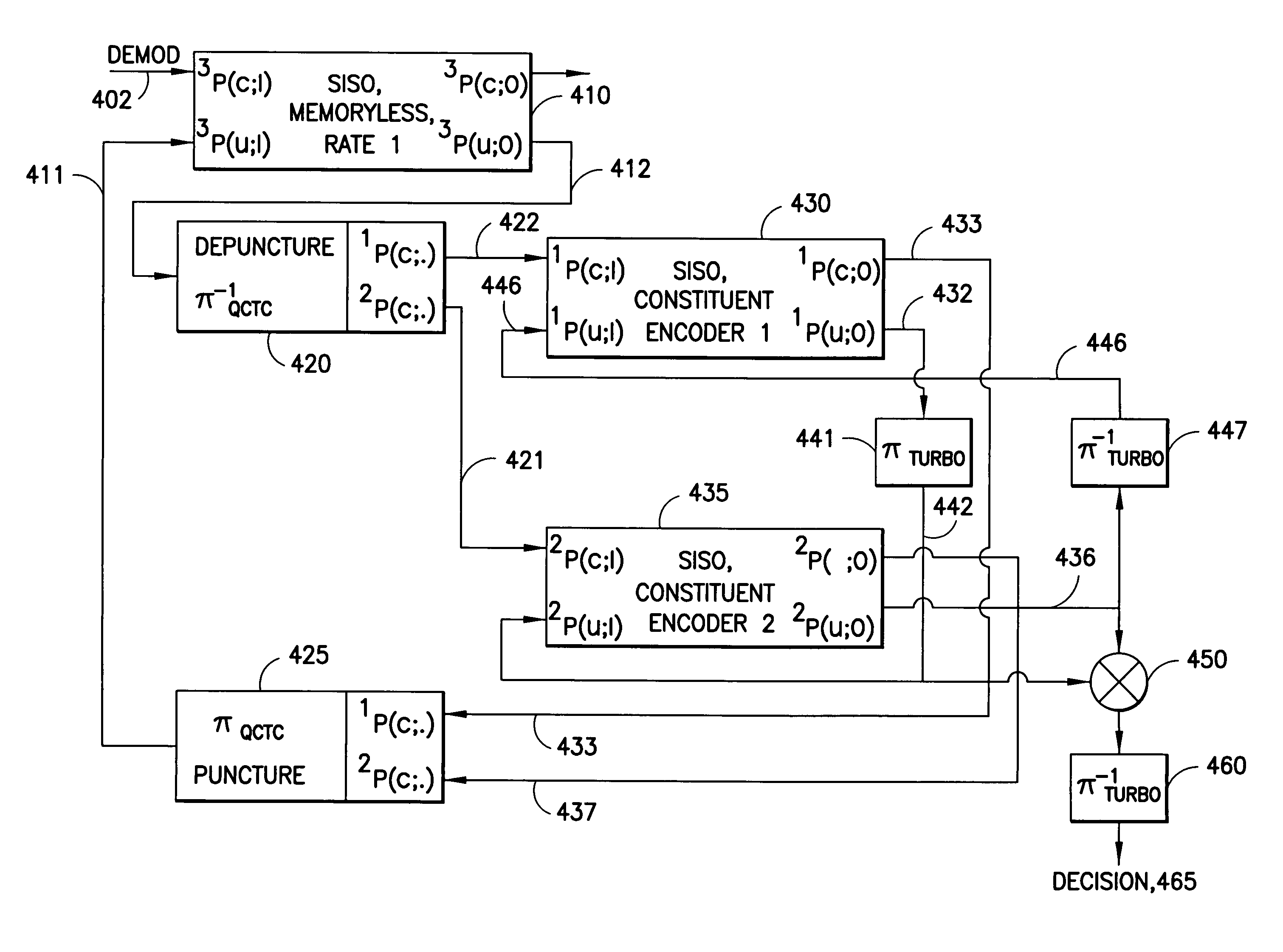
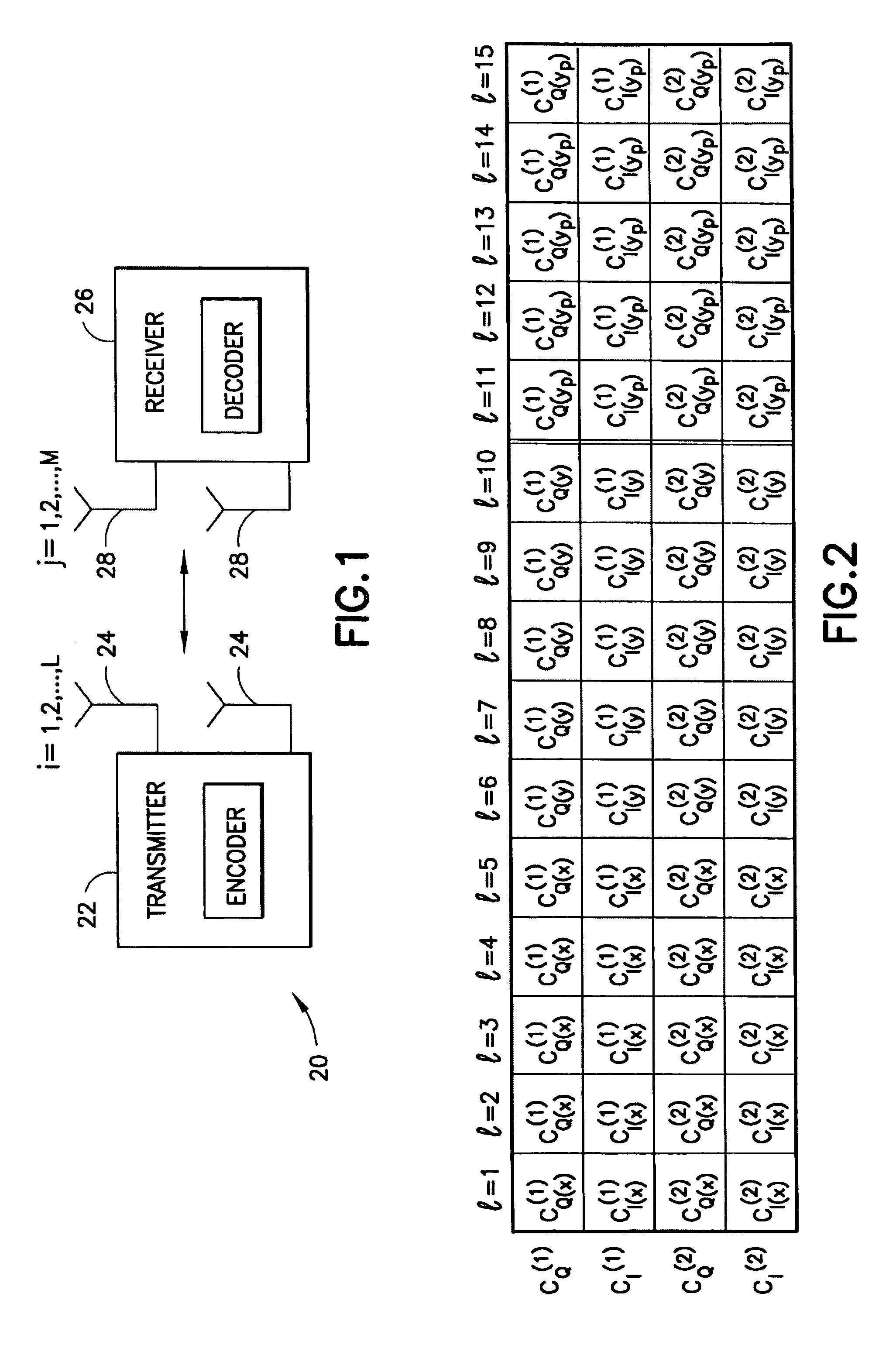
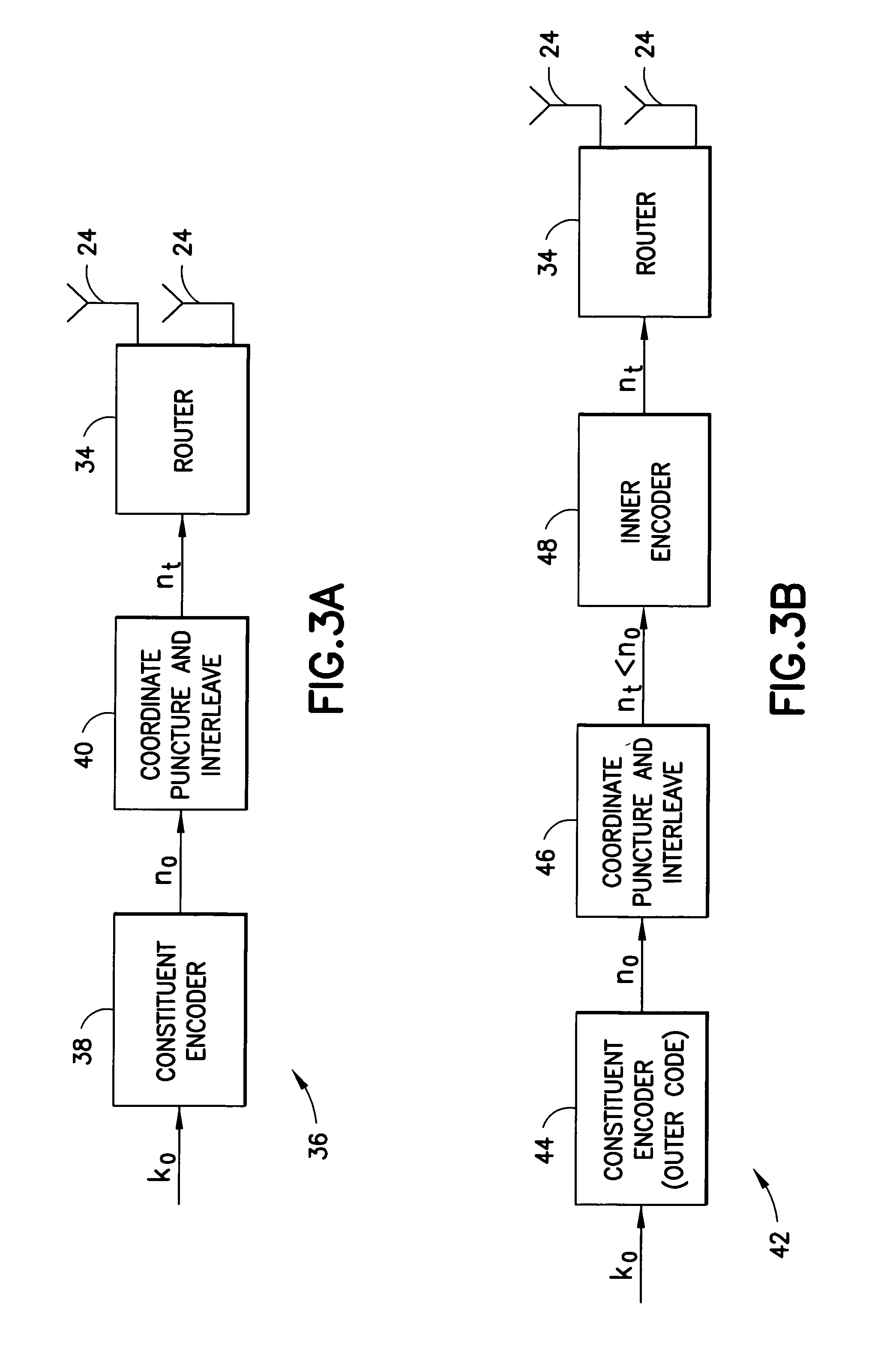
Apparatus using concatenations of signal-space codes for jointly encoding across multiple transmit antennas, and employing coordinate interleaving
InactiveUS20060159195A1Accommodate usageCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresHamming distanceComputer science
A system for transmitting data over a MIMO channel has a transmitter and a receiver. In the transmitter, the input data is encoded over at least two pipes by a concatenation of at least two constituent signal-space encoders. Each constituent encoder is used to generate, in response to the input data, a sequence of symbols from a channel alphabet having at least one dimension. Each symbol of the channel alphabet includes at least one complex symbol having real and imaginary coordinates. The transmitter interleaves the coordinates of the sequence of channel alphabet symbols, and transmits (from at least two transmit antennas) the interleaved coordinates. Preferably, each constituent encoder maximizes a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance between members of all valid pairs of symbol sequences, maximizes a minimum Euclidean distance between members of all valid pairs of different codewords, and obeys an equal eigenvalue criterion.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Apparatus and method of CTCM encoding and decoding for a digital communication system
InactiveUS7010052B2Improve energy efficiencyData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesCommunications systemMulti dimensional
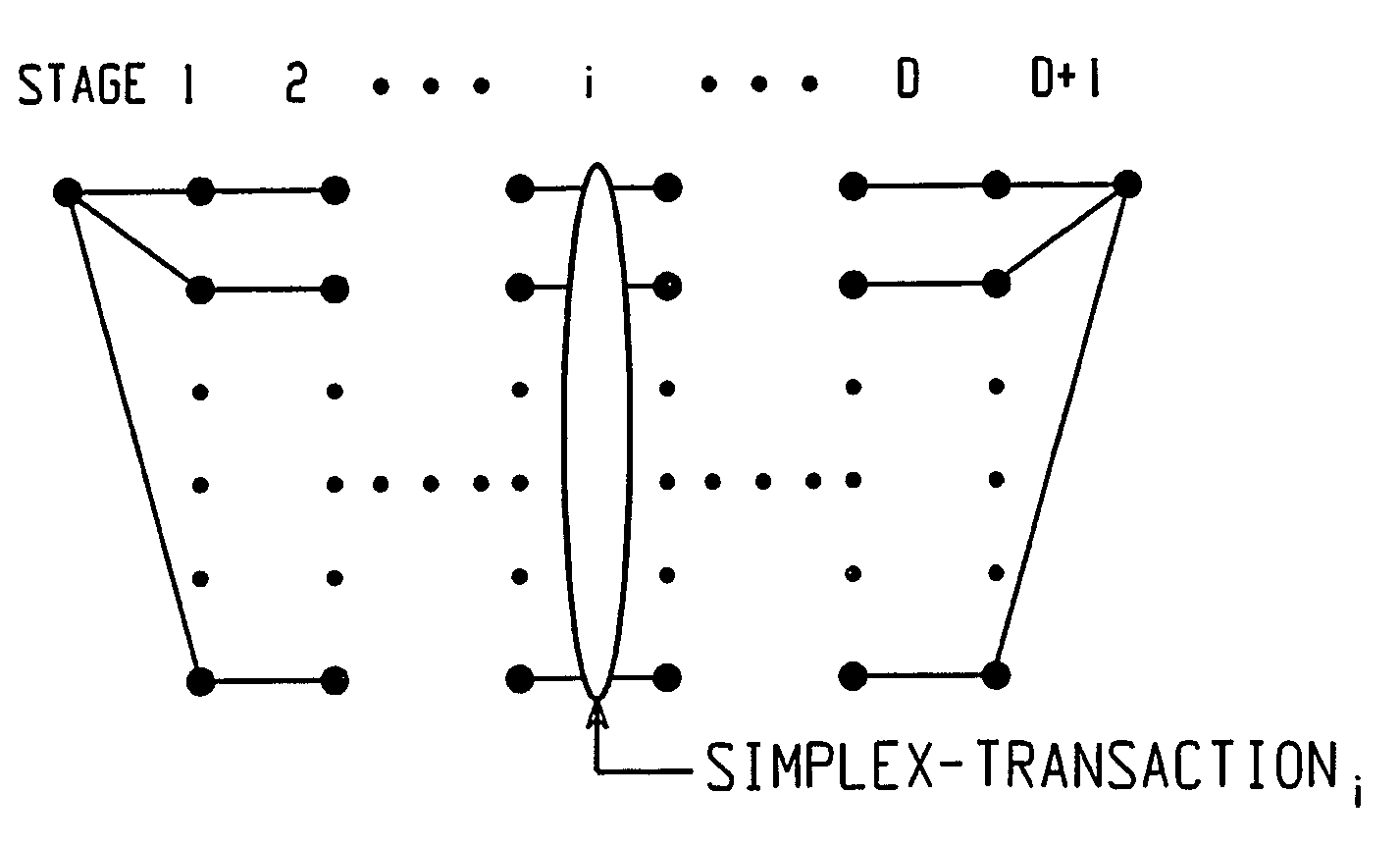
A method of building systematically a multi-dimensional (n, D, L) circular trellis coded modulation (CTCM) encoder with properties of optimal energy efficiency, strong tail biting and maximum minimum distance (dmin) of trellis paths is disclosed. In addition, a communication system for use in a power limited channel application is disclosed comprising a circular trellis coded modulation (CTCM) encoder with permuted state structure for encoding based on a circular trellis path associated with a sequence of digital information bits and a set of simplexes identified for the path from a multi-dimensional signal constellation; a transmitter coupled to said CTCM encoder for transmitting said sequence of channel symbols over said channel; a receiver for receiving a transmission from said transmitter including said sequence of channel symbols and any noise induced therein; and a CTCM decoder coupled to said receiver for decoding the received transmission without knowledge of the starting state of the circular trellis path of the CTCM encoder to recover the sequence of information bits. Apparatus and methods of encoding and decoding are also disclosed utilizing a combination of circular trellis-coded modulation with permuted state structure and simplex signal constellation techniques for use in the digital communication system.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
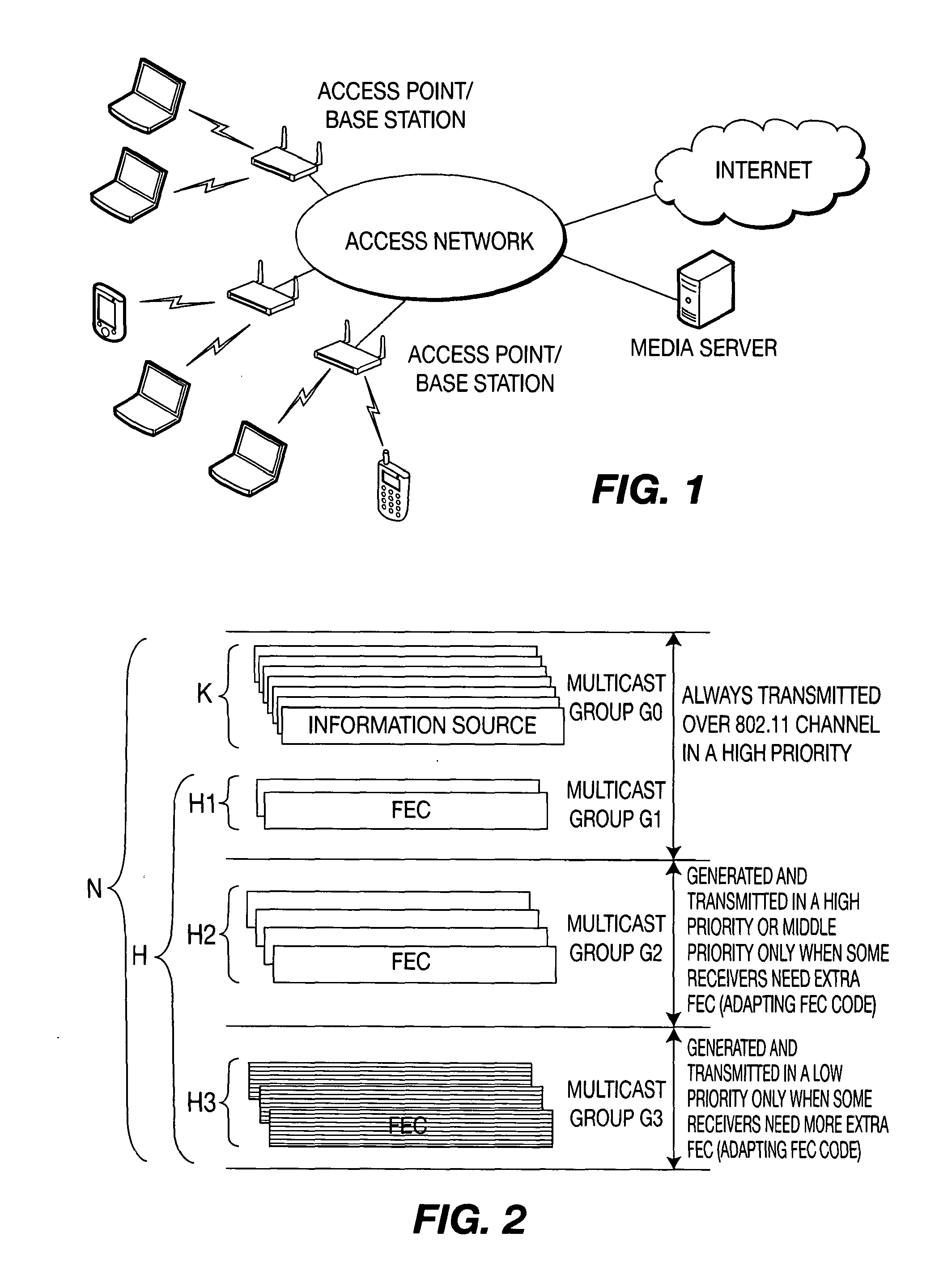
Method and system for adapting forward error correction in multicast over wireless networks
ActiveUS20120011413A1Efficient and reliable deliverySystem throughput is maximizedTransmission systemsUnequal/adaptive error protectionWireless mesh networkForward error correction
A method and apparatus are described including receiving channel condition feedback from a device over a wireless channel, determining response to the channel condition feedback if a forward error correction coding rate is sufficient for the device to recover lost data, adjusting the forward error correction coding rate responsive to the second determining act and generating forward error correction packets using the adjusted forward error correction coding rate from source data.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
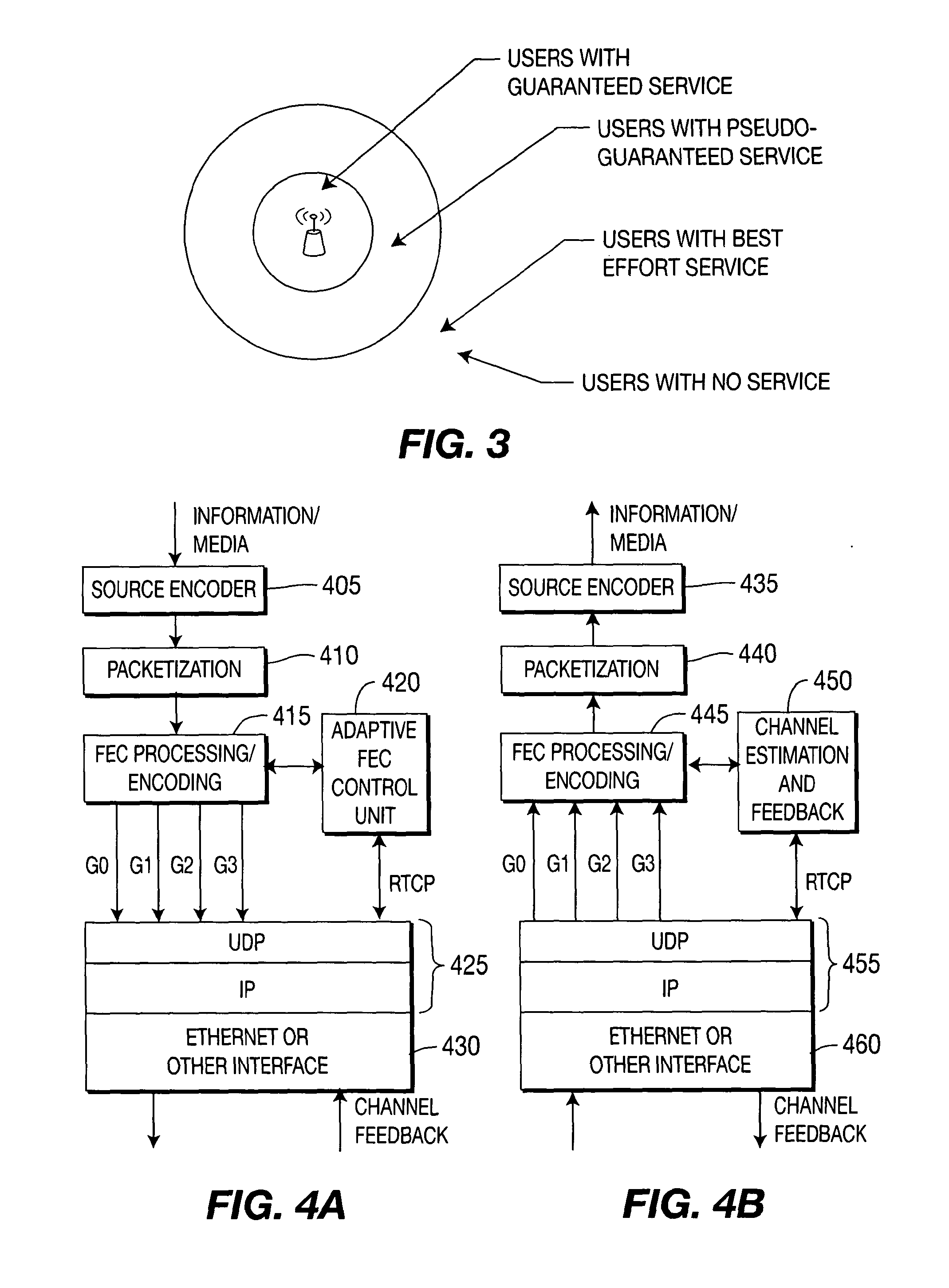
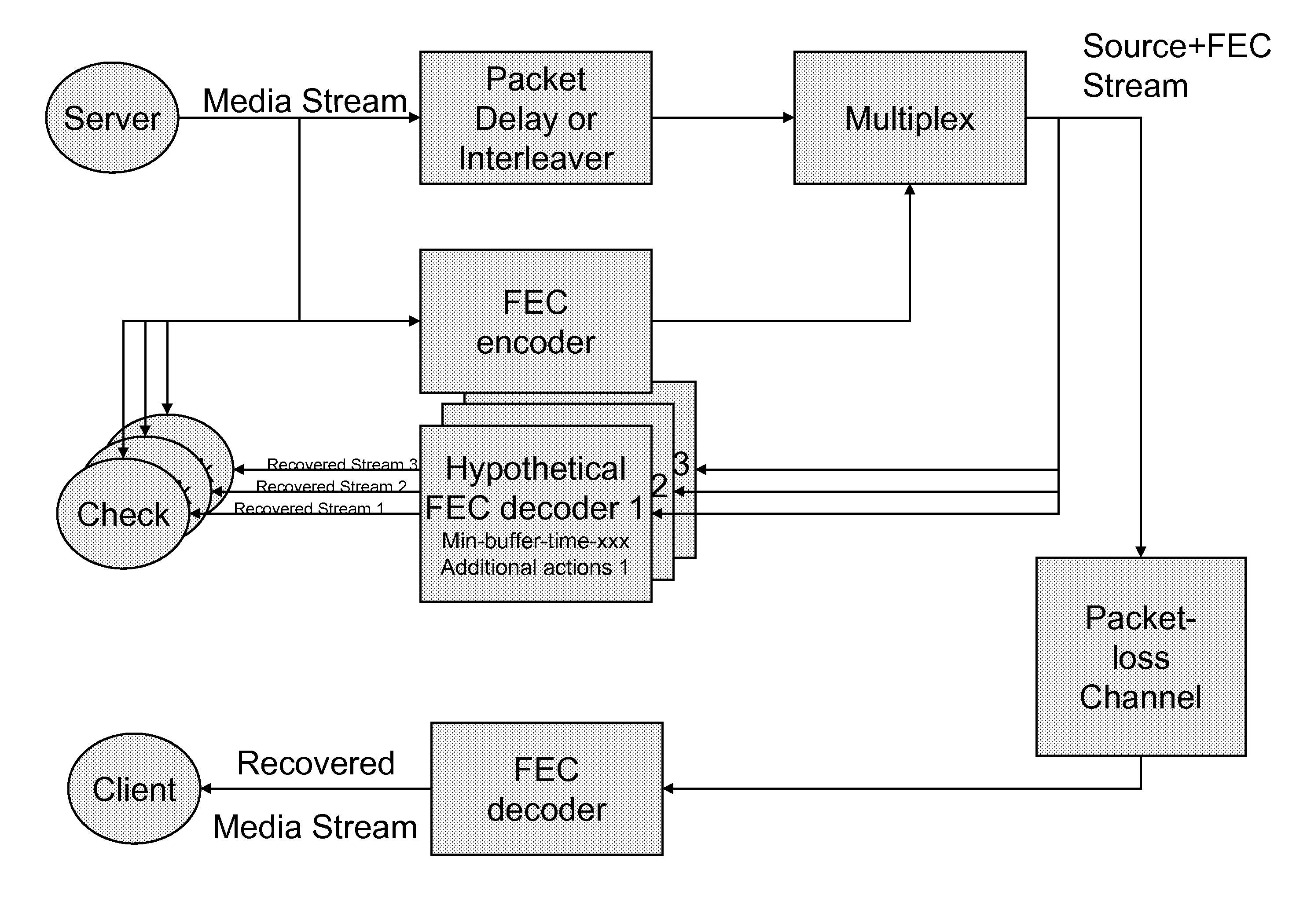
Hypothetical fec decoder and signalling for decoding control
A communication system wherein a transmitter transmits a media stream to a receiver encoded using FEC, comprising at least one hypothetical FEC decoder at the transmitter for decoding the media stream encoded at the transmitter. The transmitter determines what optimization signals to provide the receiver given the outputs of the at least one hypothetical FEC decoder and signals to the receiver those optimization signals. The optimization signals might include slowdown of media consumption signals, indications of variable buffering parameters and / or indications of FEC and source data ordering.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Apparatus and method for trellis encoding data for transmission in digital data transmission systems
InactiveUS7020165B2Improve throughputReduce error ratePulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionDigital dataPhase difference
A system for bidirectional communication of digital data between a central unit and a remote unit wherein the need for tracking loops in the central unit has been eliminated. The central unit transmitter generates a master carrier and a master clock signal which are used to transmit downstream data to the remote units. The remote units recover the master carrier and master clock and synchronize local oscillators in each remote unit to these master carrier and master clock signals to generate reference carrier and clock signals for use by the remote unit receiver. These reference carrier and clock signals are also used by the remote unit transmitters to transmit upstream data to the central unit. The central unit receiver detects the phase difference between the reference carrier and clock signals from the remote units periodically and adjusts the phase of the master carrier and master clock signals for use by the central unit receiver to receive the upstream data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) coded signal decoding using parallel and simultaneous bit node and check node processing
InactiveUS7281192B2Error detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow densityComputer science
LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) coded signal decoding using parallel and simultaneous bit node and check node processing. This novel approach to decoding of LDPC coded signals may be described as being LDPC bit-check parallel decoding. In some alternative embodiment, the approach to decoding LDPC coded signals may be modified to LDPC symbol-check parallel decoding or LDPC hybrid-check parallel decoding. A novel approach is presented by which the edge messages with respect to the bit nodes and the edge messages with respect to the check nodes may be updated simultaneously and in parallel to one another. Appropriately constructed executing orders direct the sequence of simultaneous operation of updating the edge messages at both nodes types (e.g., edge and check). For various types of LDPC coded signals, including parallel-block LDPC coded signals, this approach can perform decoding processing in almost half of the time as provided by previous decoding approaches.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and Method for Generating Codebooks with Small Projections per Complex Dimension and Utilization Thereof
ActiveUS20160049999A1Reduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityMultiplex code generationCommunications systemData stream
A method for data transmission by a device in a communication system includes modulating a first data stream using a codebook to produce a second data stream, wherein the codebook is in correspondence with a multi-dimensional modulation map that includes a number of distinct projections per complex dimension that is smaller than a number of modulation points of the multi-dimensional modulation map, and transmitting the second data stream over allocated resources in the communication system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
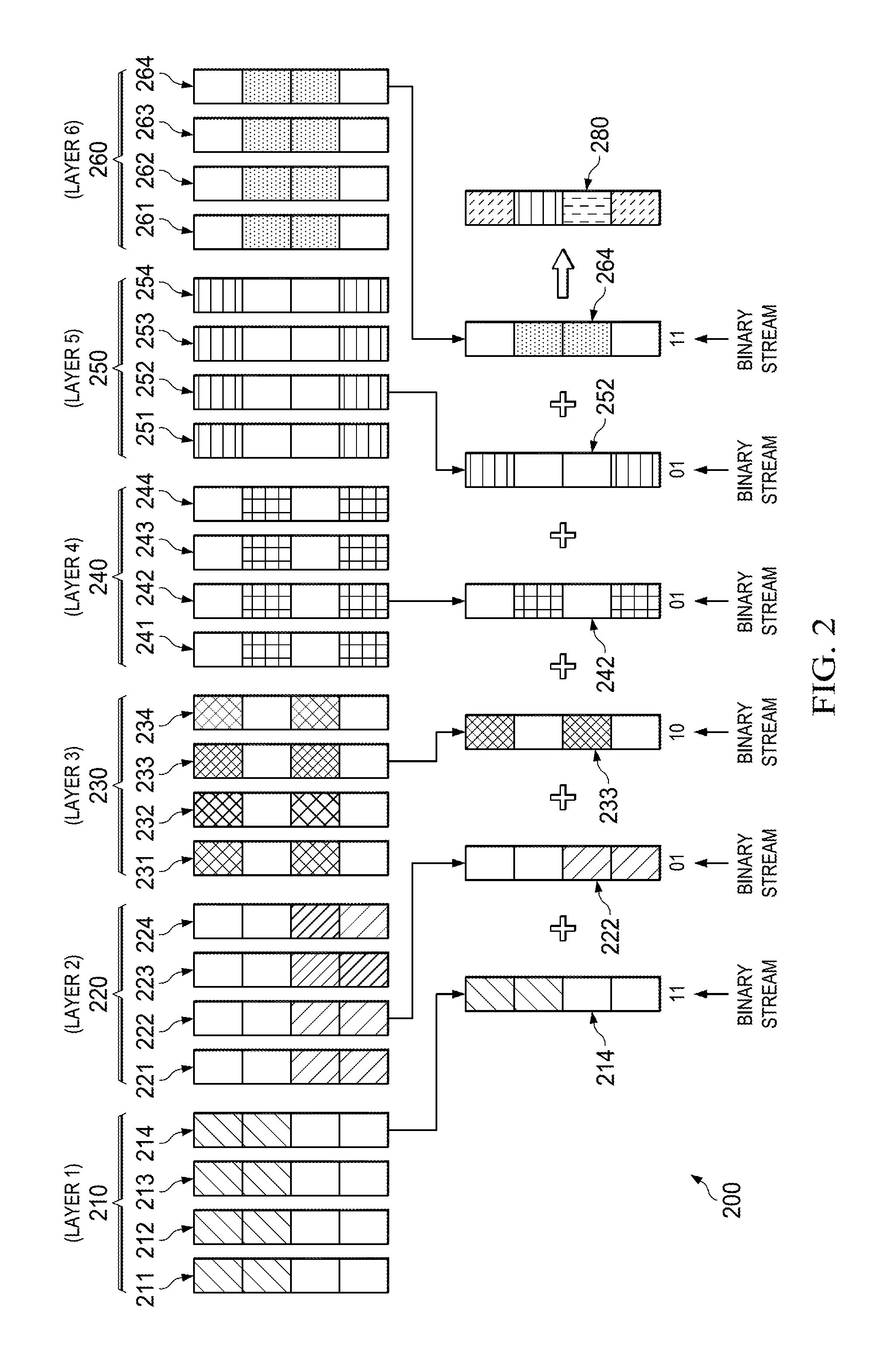
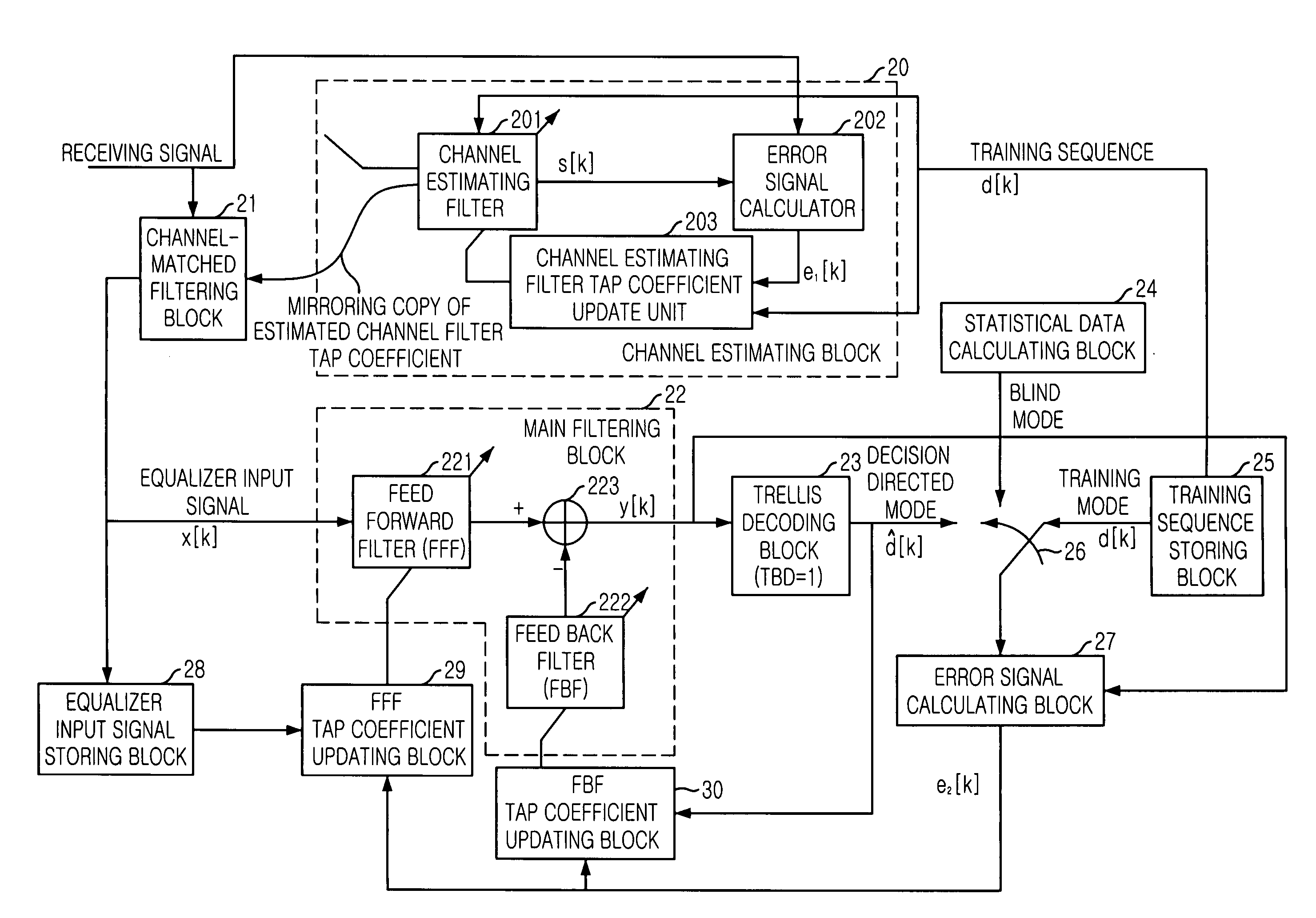
Generation of decision feedback equalizer data using trellis decoder traceback output in an ATSC HDTV receiver
InactiveUS6823489B2Error propagationReduce errorsTelevision system detailsData representation error detection/correctionAdaptive filterMultiplexer
For use in a receiver capable of decoding trellis encoded signals of the type comprising a trellis decoder and a decision feedback equalizer coupled to each path memory output of said trellis decoder, wherein said decision feedback equalizer is capable of obtaining symbol values from each path memory output of said trellis decoder for use as estimates in channel equalization, an apparatus and method is disclosed for reconstructing symbol values from trace back path information stored within said trellis decoder. The apparatus and method of the present invention reconstructs a symbol stream from the trellis decoder using data signal selection circuitry to obtain bit values that represent the reconstructed symbols. In one embodiment of the present invention, each of a plurality of multiplexers selects one of four symbol value inputs to send to a first adaptive filter tap cell in a set of twelve adaptive filter tap cells. The four symbol values represent (1) a symbol at trellis point "t", and (2) a symbol at trellis point "t-12", and (3) a symbol having the value "plus five", and (4) a symbol having the value "minus five."
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Apparatus using concatenations of signal-space codes for jointly encoding across multiple transmit antennas, and employing coordinate interleaving
InactiveUS8031793B2Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresSymbol of a differential operatorSpatial encoding
A system for transmitting data over a MIMO channel has a transmitter and a receiver. In the transmitter, the input data is encoded over at least two pipes by a concatenation of at least two constituent signal-space encoders. Each constituent encoder is used to generate, in response to the input data, a sequence of symbols from a channel alphabet having at least one dimension. Each symbol of the channel alphabet includes at least one complex symbol having real and imaginary coordinates. The transmitter interleaves the coordinates of the sequence of channel alphabet symbols, and transmits (from at least two transmit antennas) the interleaved coordinates. Preferably, each constituent encoder maximizes a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance between members of all valid pairs of symbol sequences, maximizes a minimum Euclidean distance between members of all valid pairs of different codewords, and obeys an equal eigenvalue criterion.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
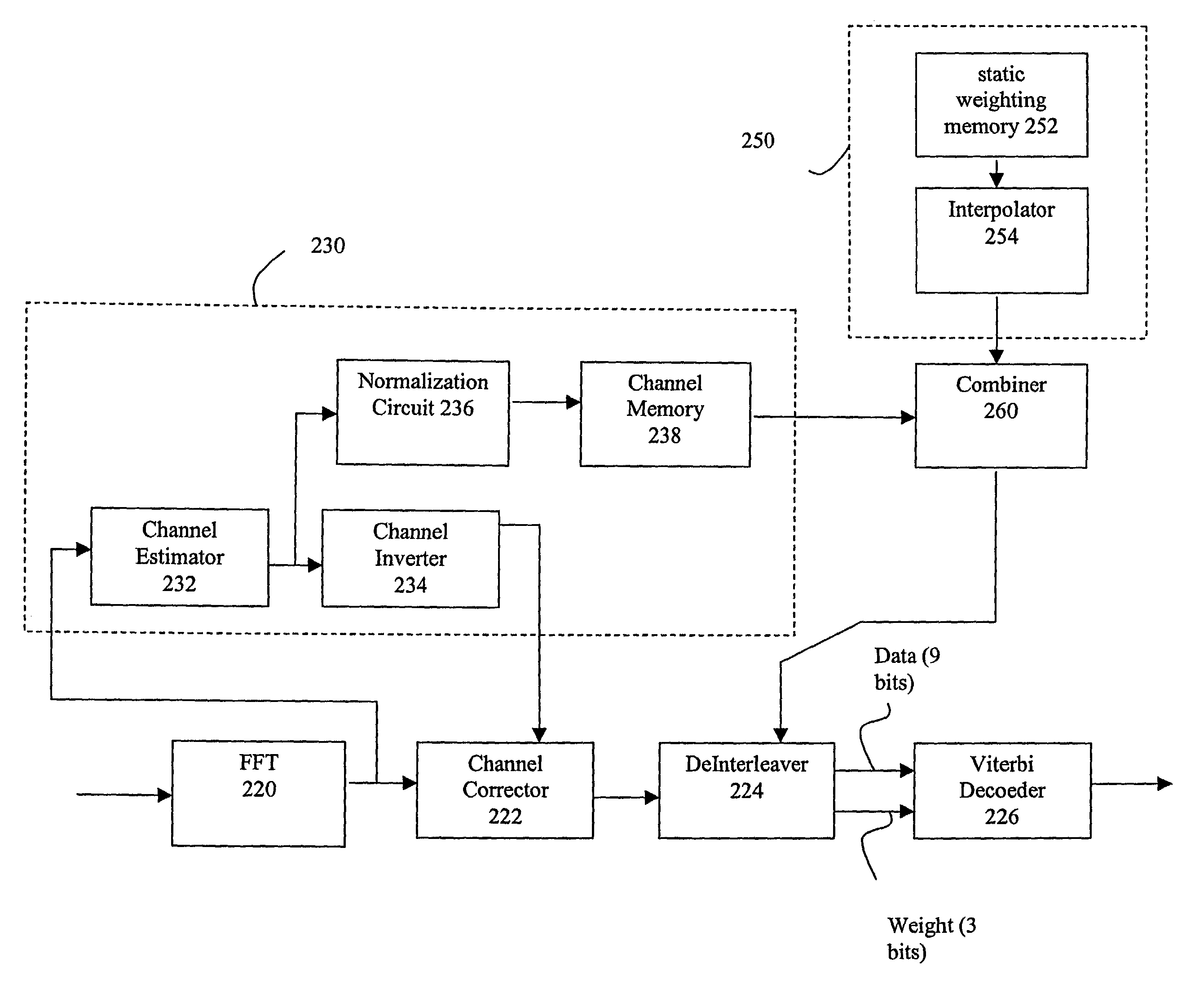
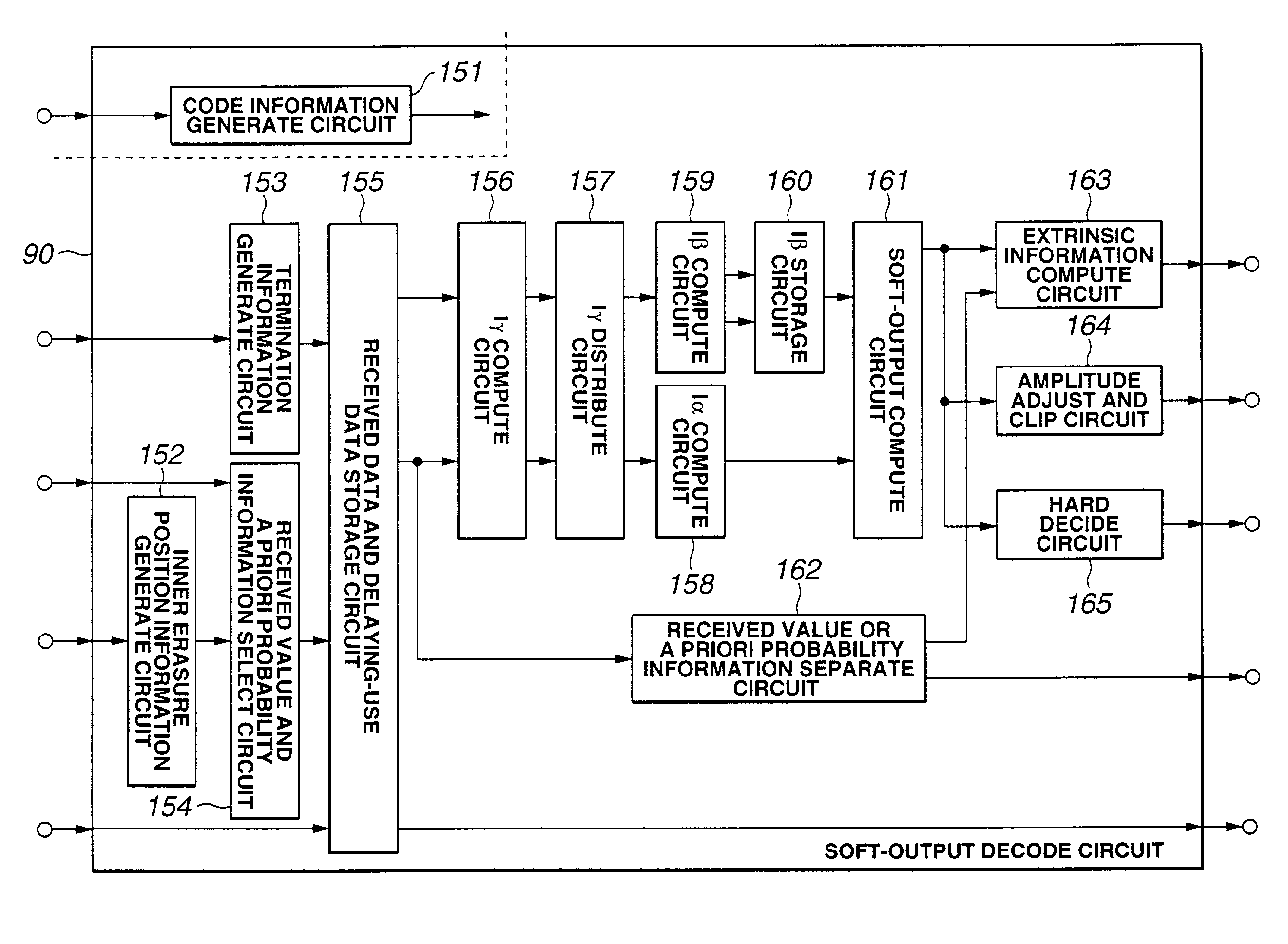
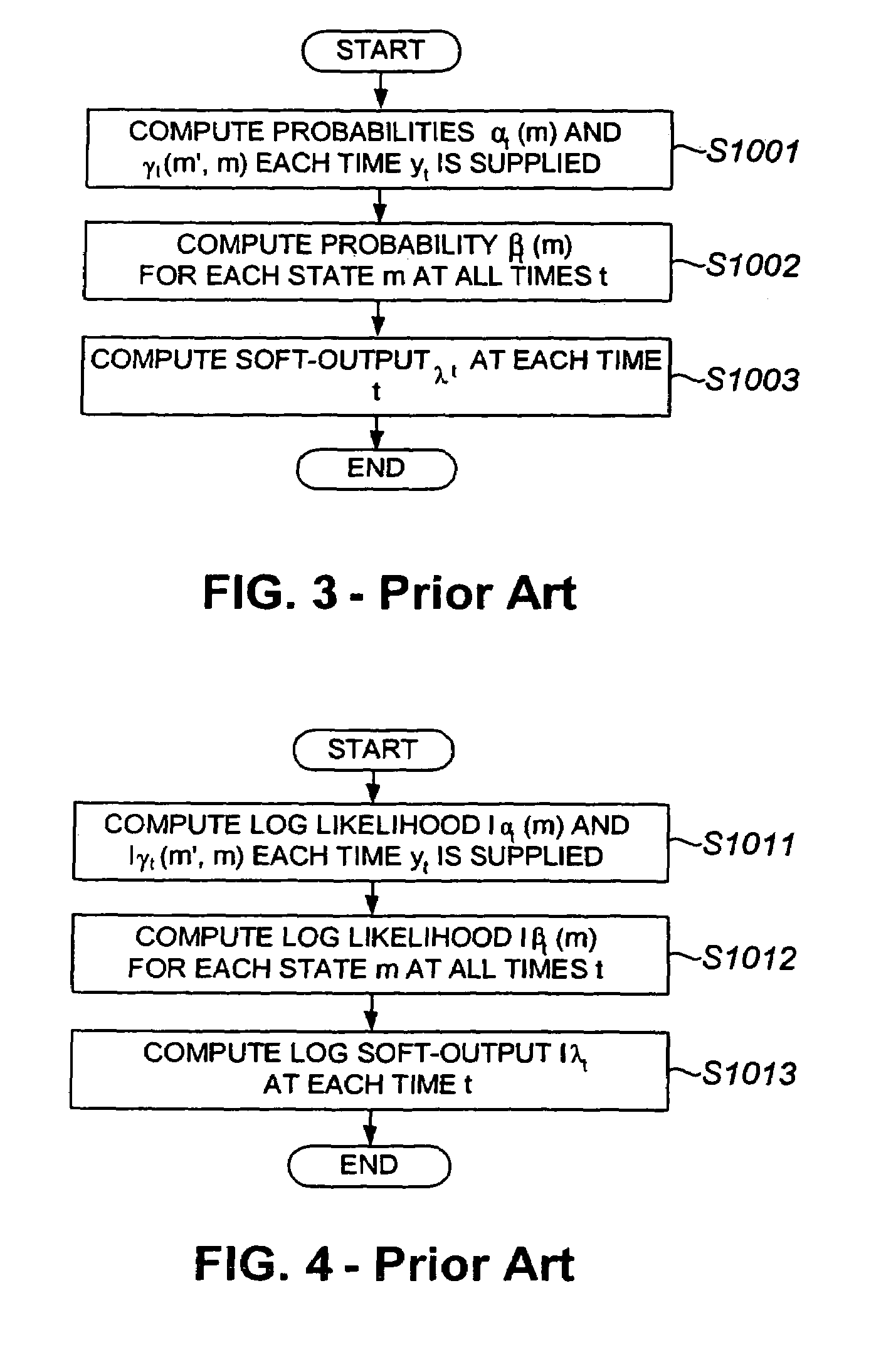
Soft-output decoding
InactiveUS7180968B2Method is suitableReduce operational burdenData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesA priori probabilityComputer science
To appropriately express an erasure position of a code by a small-scale, simple-structured circuit, a soft-output decoding circuit (90) in each element decoder includes a received value and a priori probability information selection circuit (154) to select an input to-be-decoded received value TSR and extrinsic information or interleaved data TEXT, whichever is necessary for soft-output decoding. Based on inner erasure position information IERS supplied from an inner erasure information generating circuit (152), the received value and a priori probability information selection circuit (154) replaces a position where no coded output exists due to puncture or the like with a symbol whose likelihood is “0”. That is, the received value and a priori probability information selection circuit (154) outputs information which assures a probability in which a bit corresponding to a position where there is no coded output is “0” or “1” to be “½”.
Owner:SONY CORP
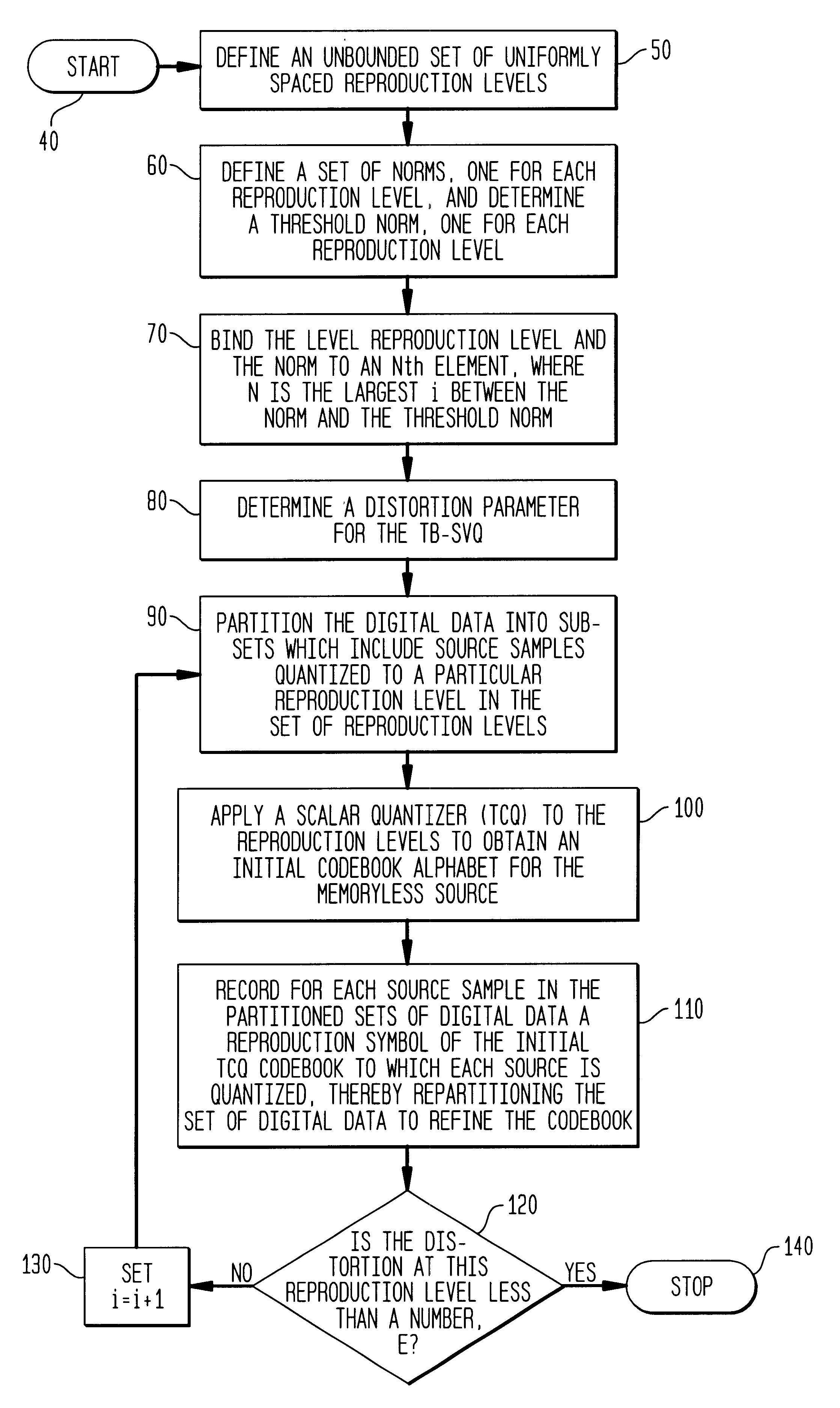
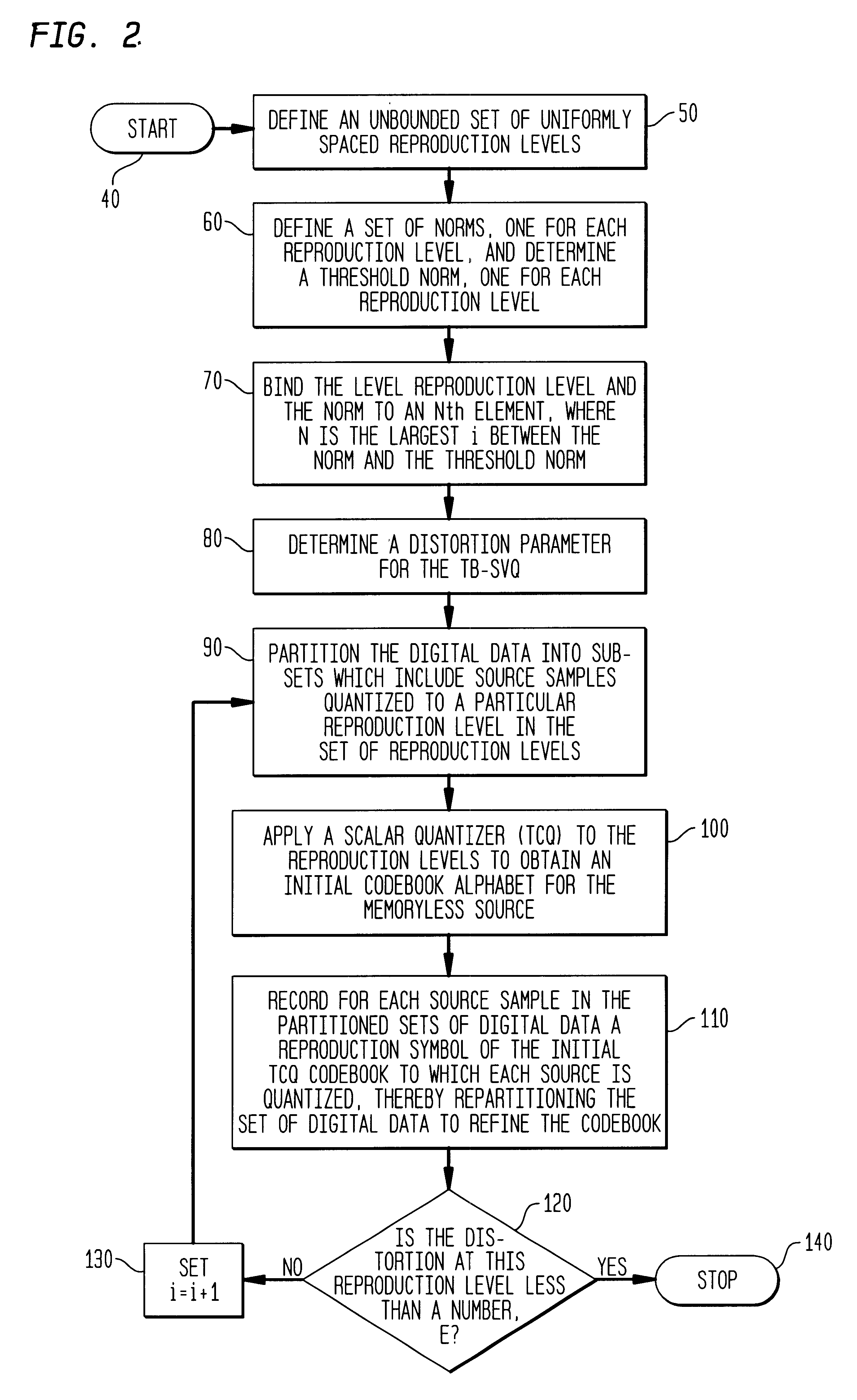
Successively refinable Trellis-Based Scalar Vector quantizers
Methods of designing successively refinable Trellis-Based Scalar-Vector quantizers (TB-SVQ) include a multi-stage process wherein a TB-SVQ is applied to a set of digital data to set up a codebook boundary and to obtain a non-uniform density gain for a constellation in which the data signals will be encoded. In at least one more stage, a Trellis coded quantizer (TCQ) is applied to the output codebook boundary of the first stage to obtain a granular or shaping gain of 1.53 dB. The inventive methods successively refine the TB-SVQ so that robust signal transmission is achieved. By applying a multi-stage process wherein a TB-SVQ is utilized in the first stage and a TCQ is utilized in the second and successive stages, the computational complexity and time for encoding the constellation are greatly reduced.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
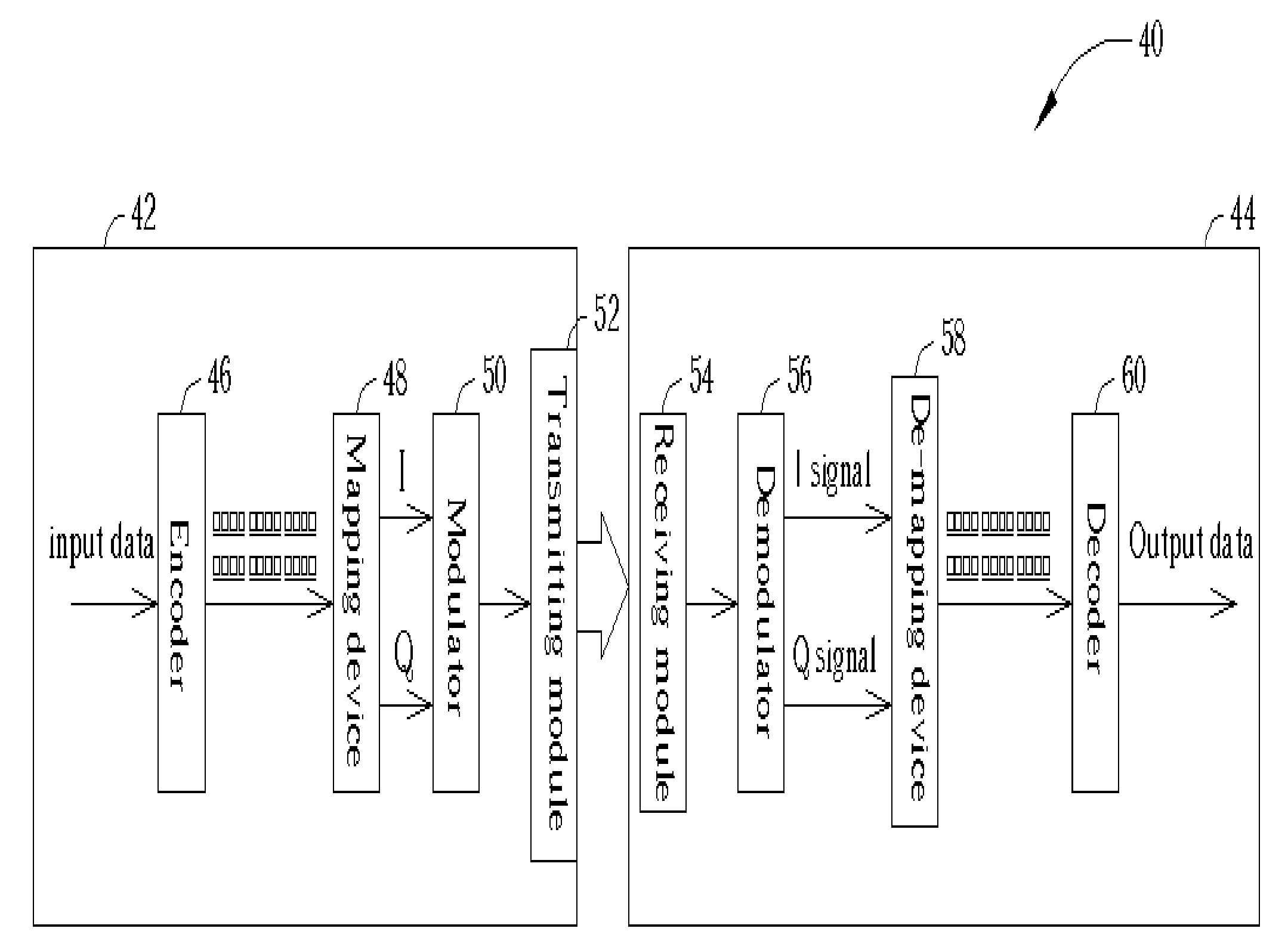
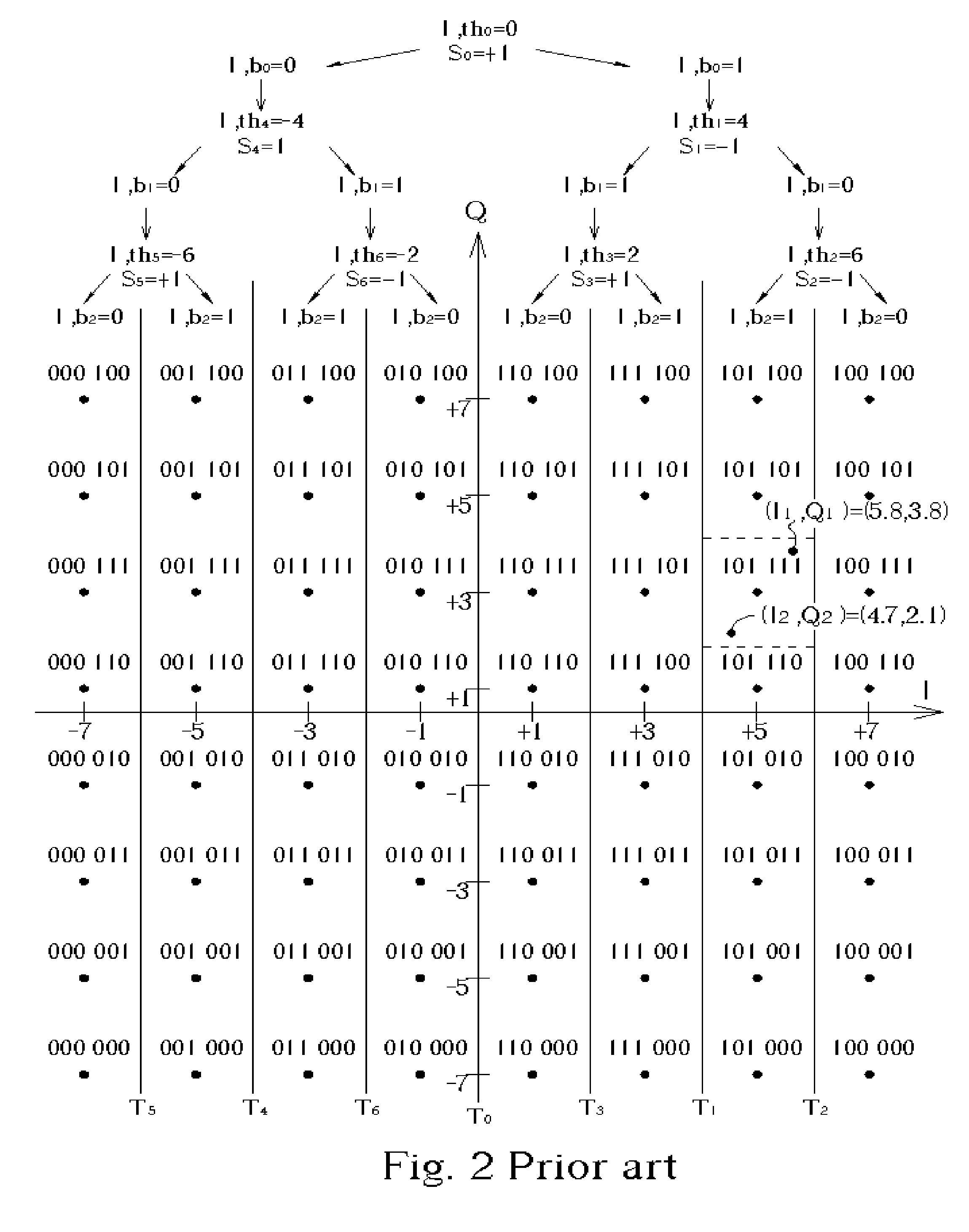
De-mapping method for wireless communications systems
InactiveUS20050111563A1Resolve insufficiencyFew stepsMulti-frequency code systemsMultiple carrier systemsCommunications systemComputer science
A de-mapping method for wireless communications systems transforms an I signal and a Q signal transformed from wireless signals received by a receiver in a wireless communications system into a plurality of sequentially ordered I and Q weighting values respectively. The first I and the first Q weighting values are set to be values of the I and Q signals respectively, and following I and Q weighting values are set to be products of bit signs corresponding to preceding respective I and Q weighting values and differences between the preceding I and Q weighting values and a threshold value corresponding to the preceding I and Q weighting values by determining signs of the preceding I and Q weighting values.
Owner:SYNCOMM TECH
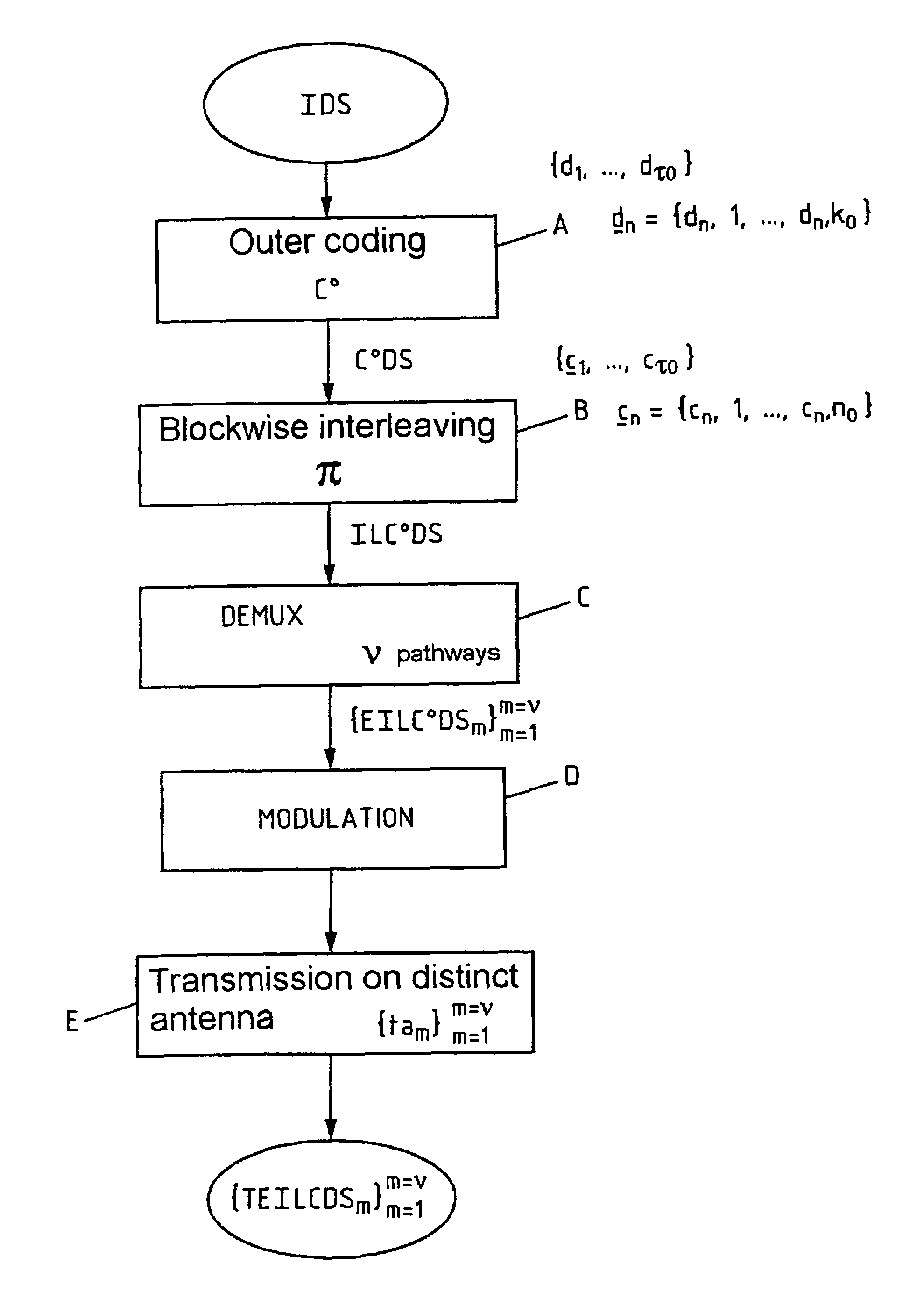
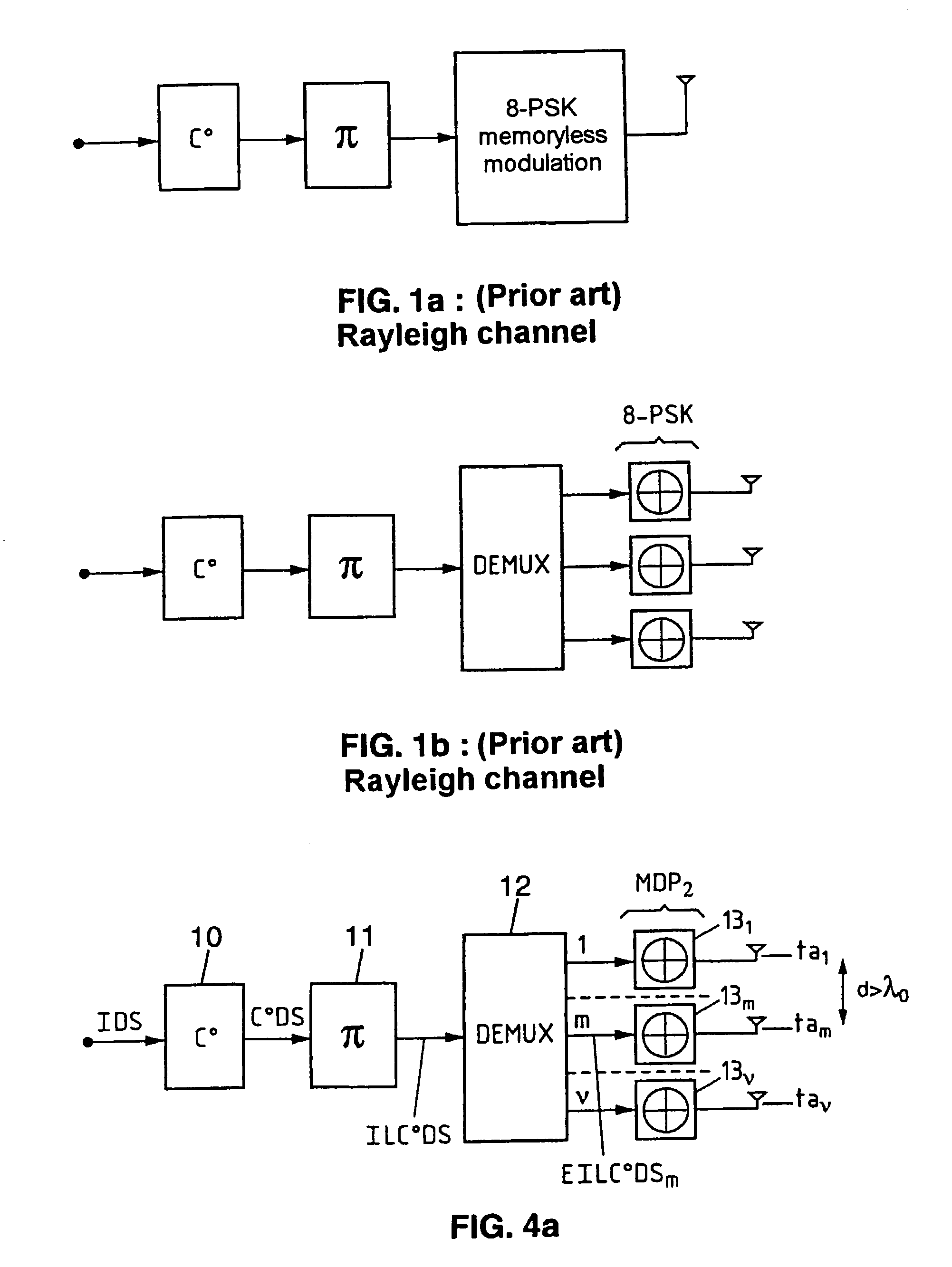
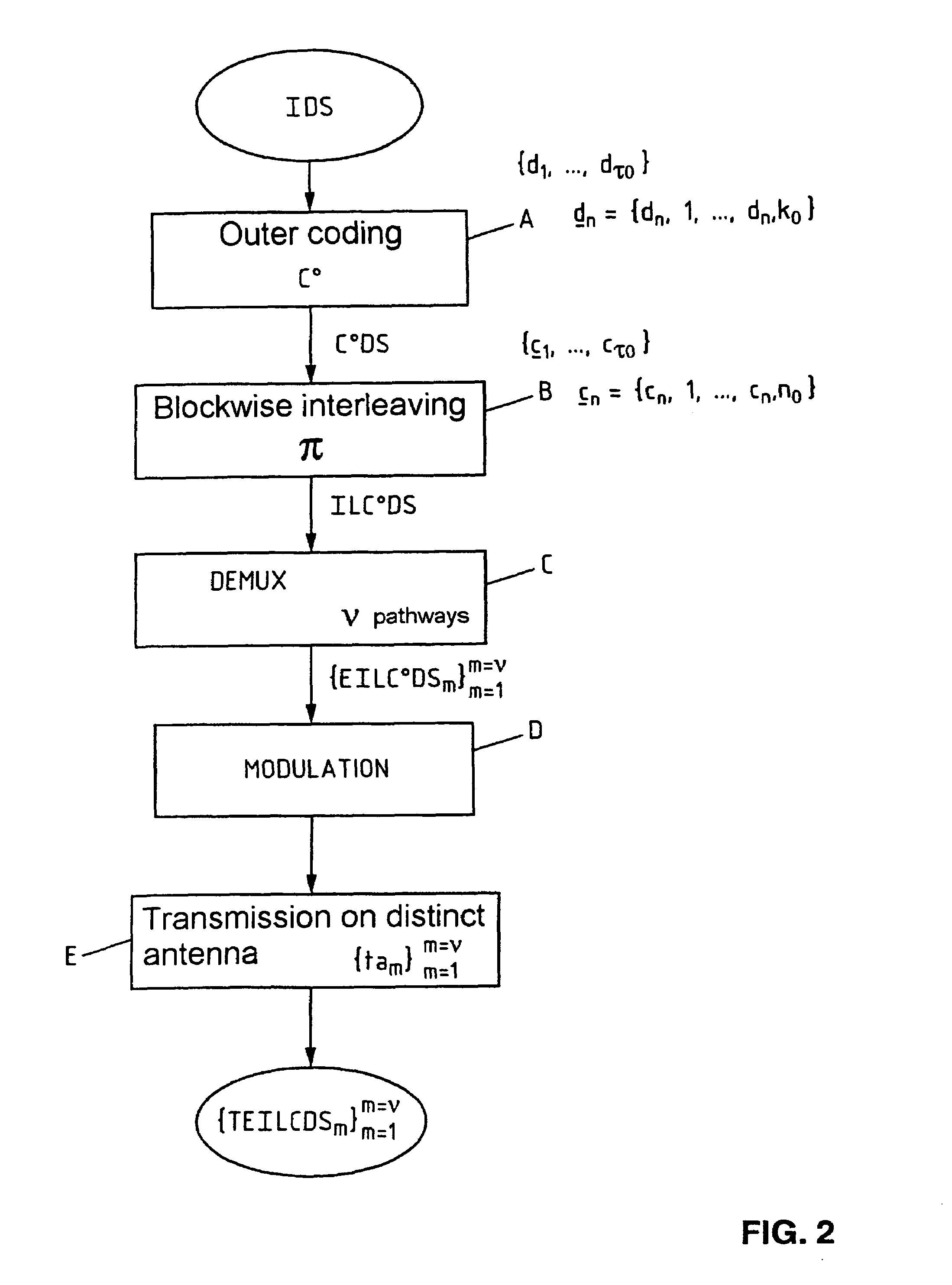
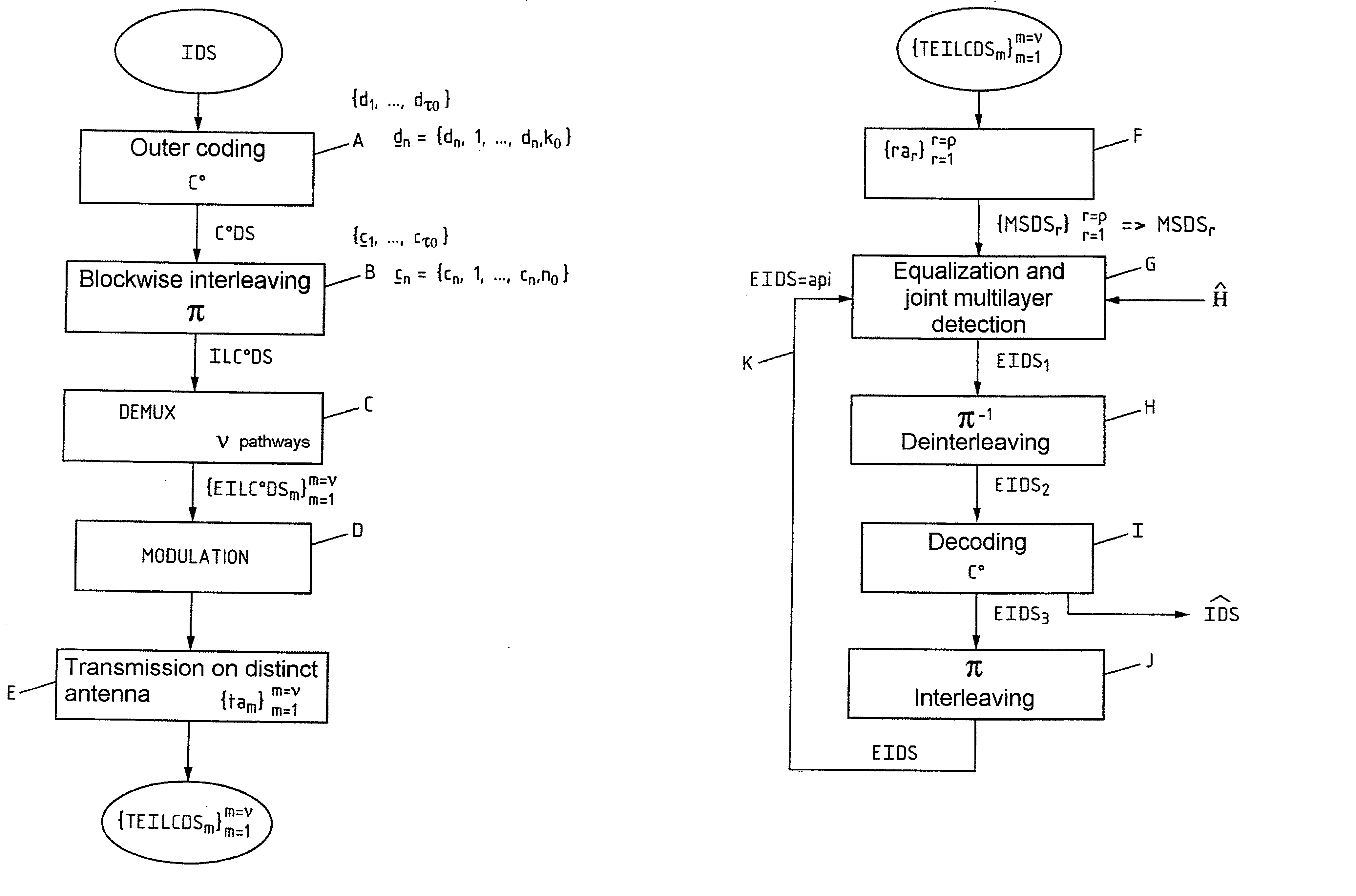
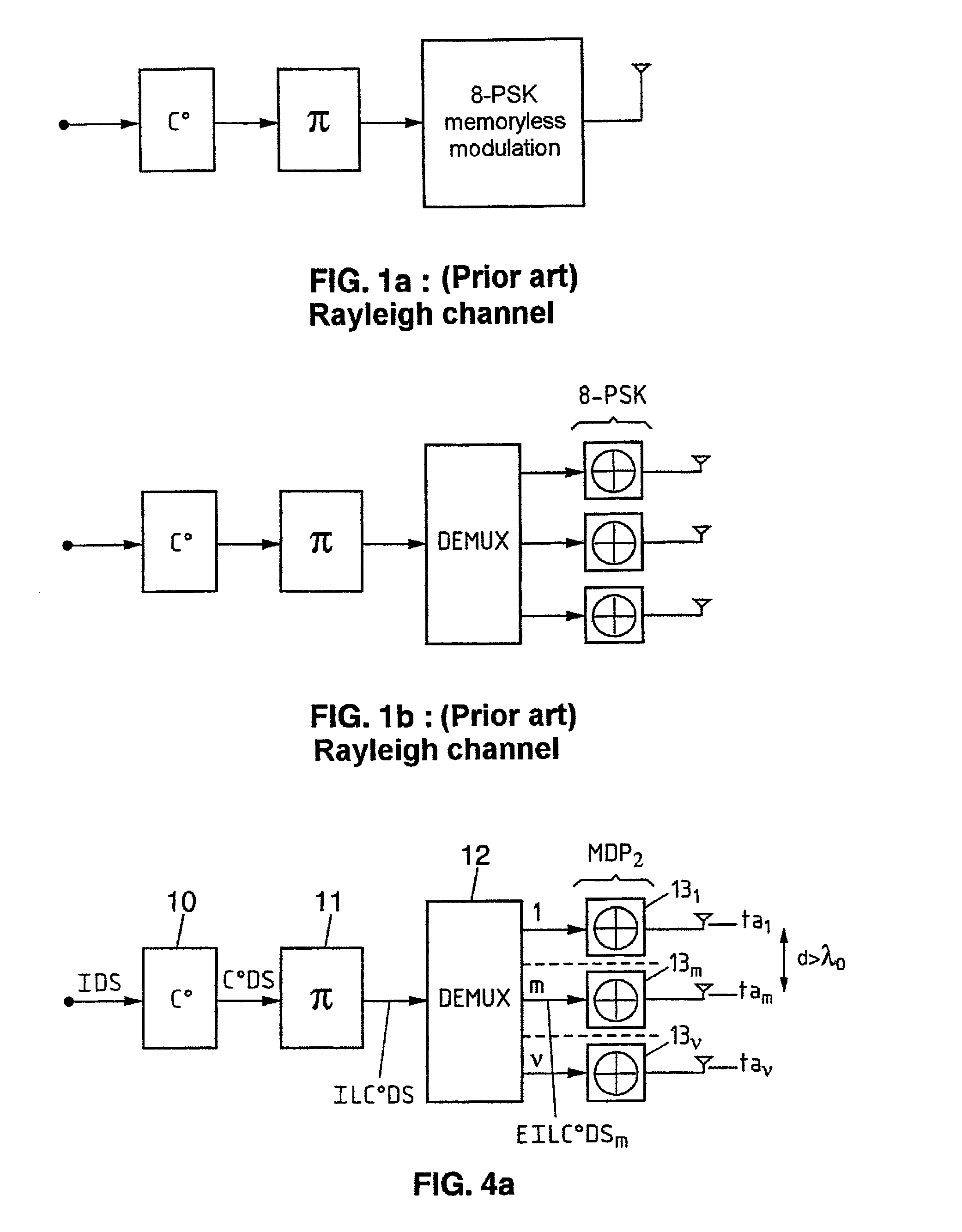
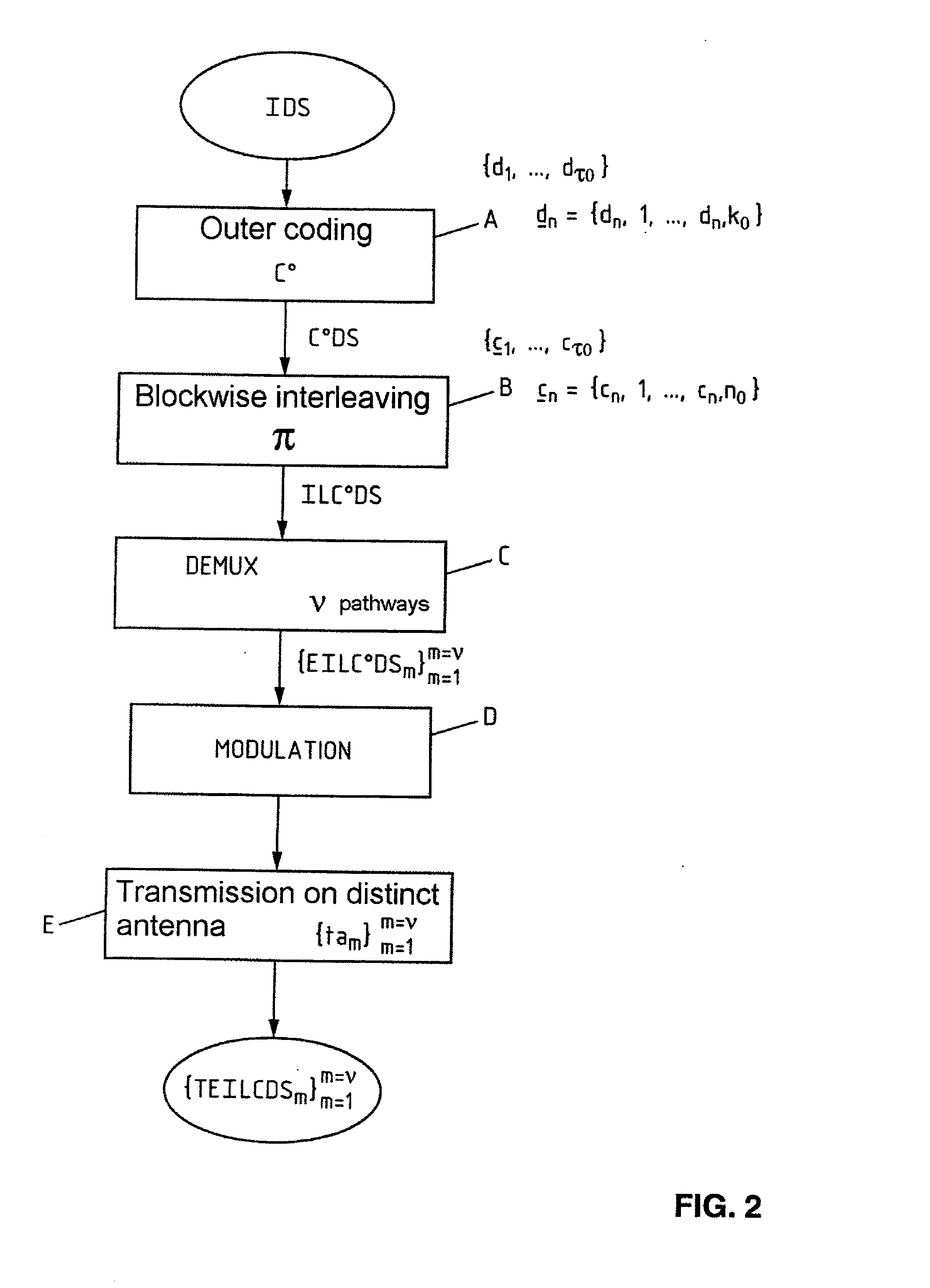
Method of coding/decoding a digital data stream coded with bitwise interleaving in multiple transmission and reception in the presence of intersymbol interference and corresponding system
InactiveUS7127009B2Improve spectral efficiencyEasy to implementOther decoding techniquesPolarisation/directional diversityDigital dataData stream
Method and system for coding / decoding a digital data stream coded with bitwise interleaving in multiple transmission and reception for a radio interface, in which the coding includes subjecting an initial digital data stream to an outer coding, an interleaving, a layer demultiplexing on multiple pathways, converting by modulation successive bits of each layer into Qm-ary symbol then transmitting each symbol by means of a transmission antenna of an array of antennas and the decoding includes receiving the digital data stream transmitted on multiple r reception antennas forming an array, subjecting the set of symbols received to an iterative process of equalization and joint multilayer detection, on the basis of an a priori information item, subjecting the first extrinsic information stream obtained to a deinterleaving, subjecting a second extrinsic information stream obtained to an outer decoding and a third extrinsic information stream obtained to an interleaving so as to generate the a priori information item and reinjecting the latter into the process.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
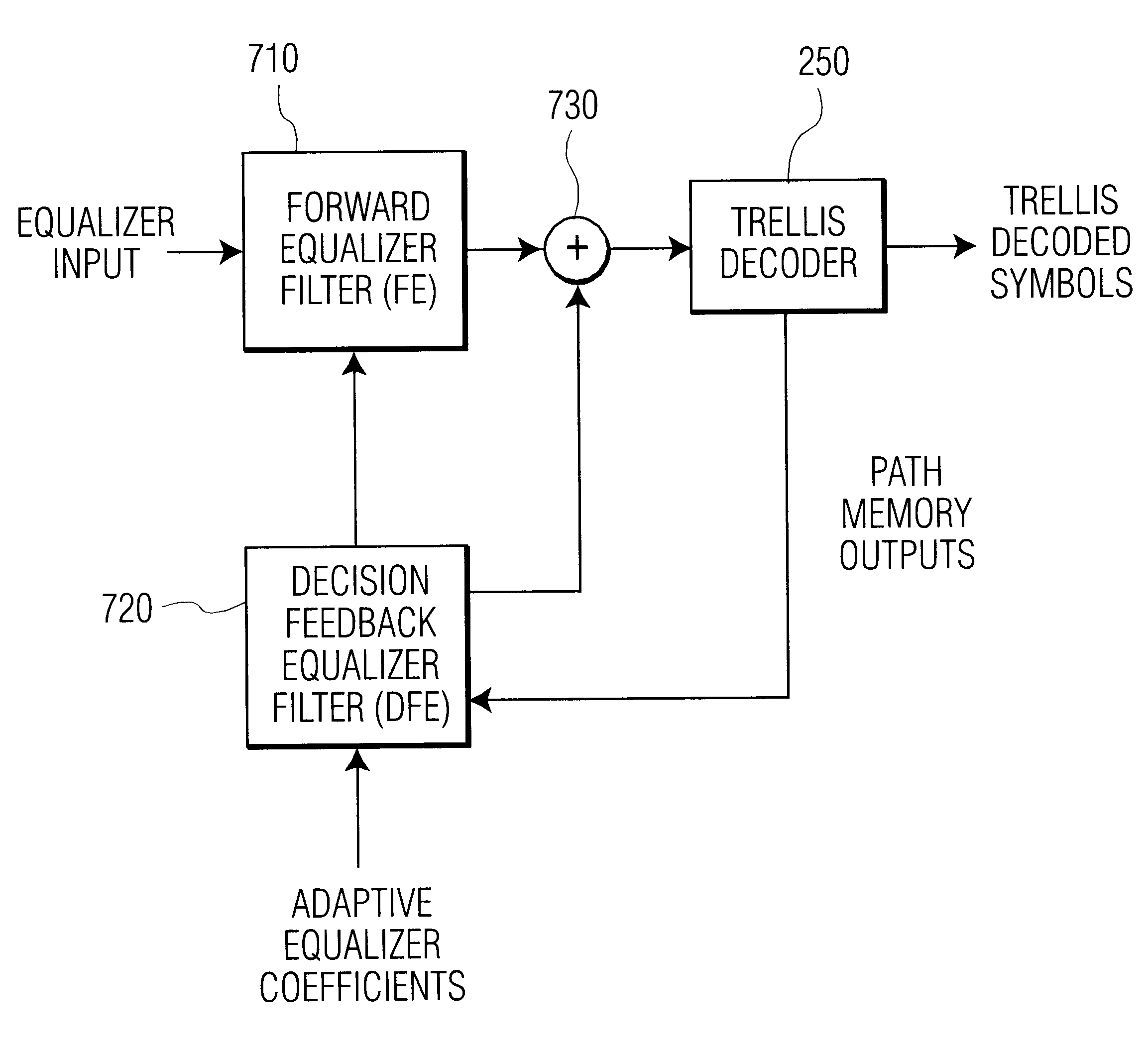
Apparatus and method of decision feedback equalization in terrestrial digital broadcasting receiver
InactiveUS20070104264A1Decreases decision errorReduce complexityTelevision system detailsCoupling device connectionsEqualizationArtificial intelligence
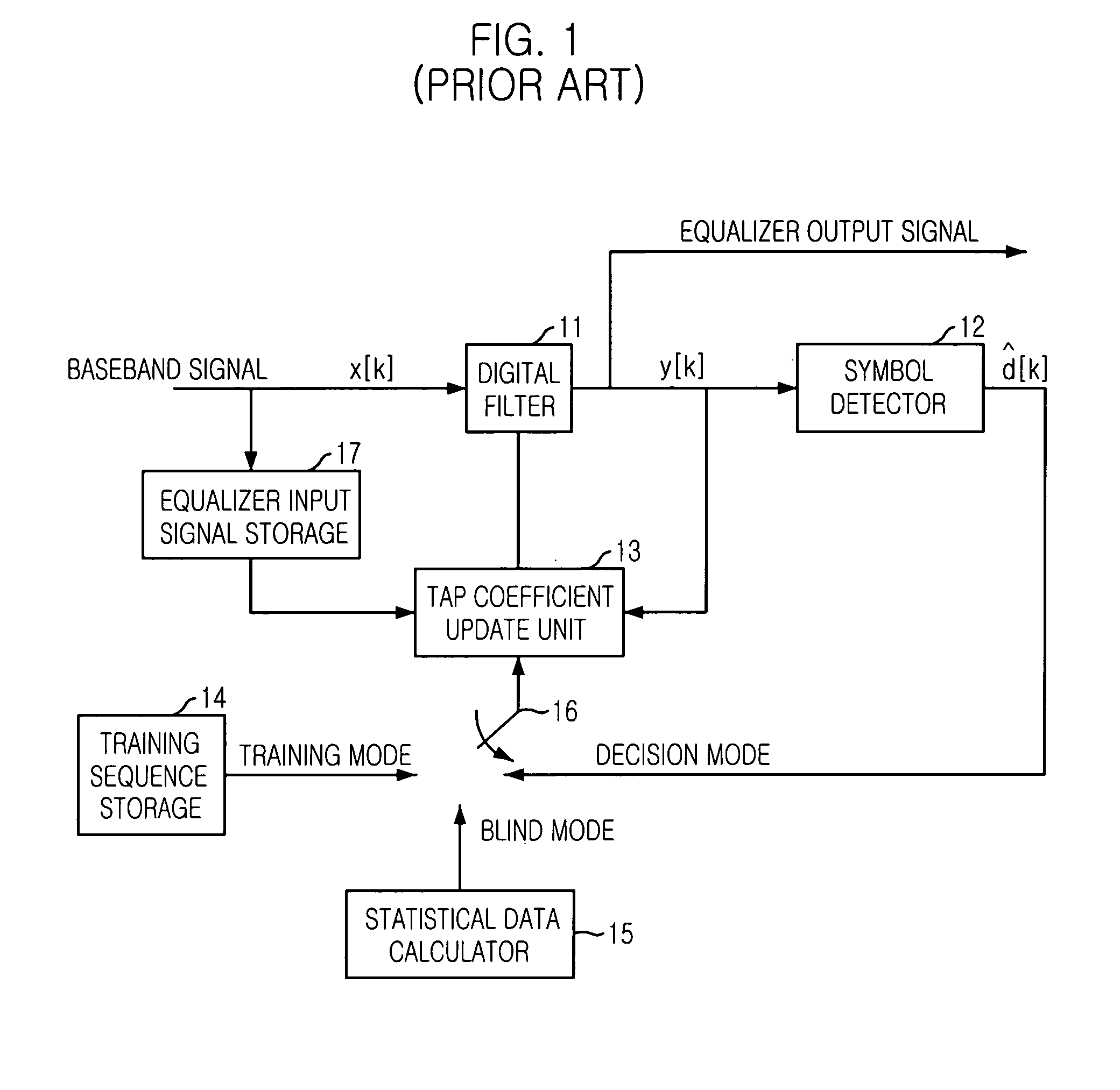
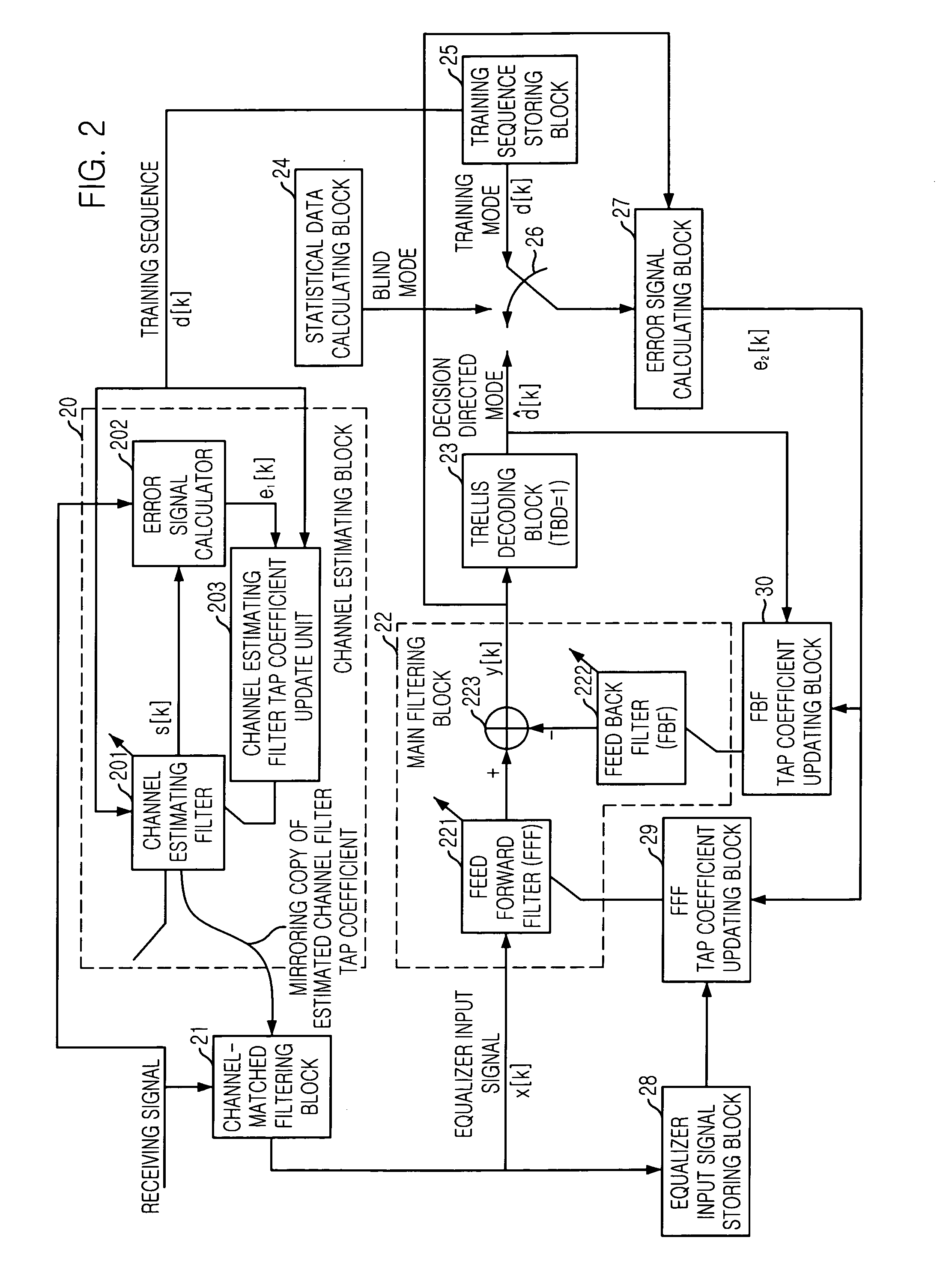
The present invention is related to a decision feedback equalizing apparatus and a method thereof. The object of the invention is to provide to an apparatus and a method of decision feedback equalization that make a channel property of an inferior receiving signal to mild by using a channel-matched filter and decreases decision errors of symbol detector output signals by using a trellis decoder with decreased complexity, whose trace back depth is 1 (TBD=1).
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
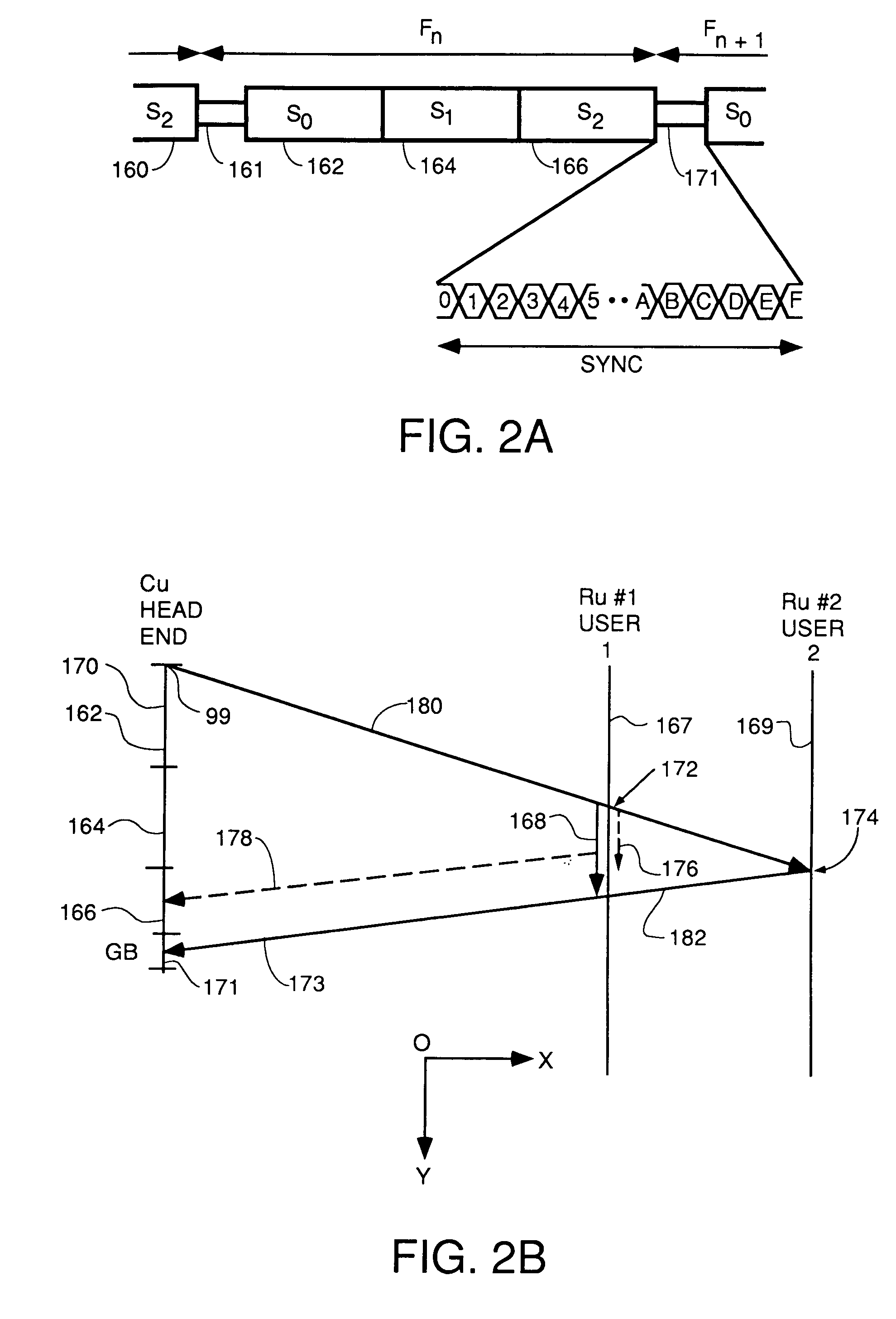
Apparatus and method for SCDMA digital data transmission using orthogonal codes and a head end modem with no tracking loops
InactiveUS7031344B2Improve throughputReduce error ratePulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionDigital dataModem device
A system for bidirectional communication of digital data between a central unit and a remote unit wherein the need for tracking loops in the central unit has been eliminated. The central unit transmitter generates a master carrier and a master clock signal which are used to transmit downstream data to the remote units. The remote units recover the master carrier and master clock and synchronize local oscillators in each remote unit to these master carrier and master clock signals to generate reference carrier and clock signals for use by the remote unit receiver. These reference carrier and clock signals are also used by the remote unit transmitters to transmit upstream data to the central unit. The central unit receiver detects the phase difference between the reference carrier and clock signals from the remote units periodically and adjusts the phase of the master carrier and master clock signals for use by the central unit receiver to receive the upstream data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
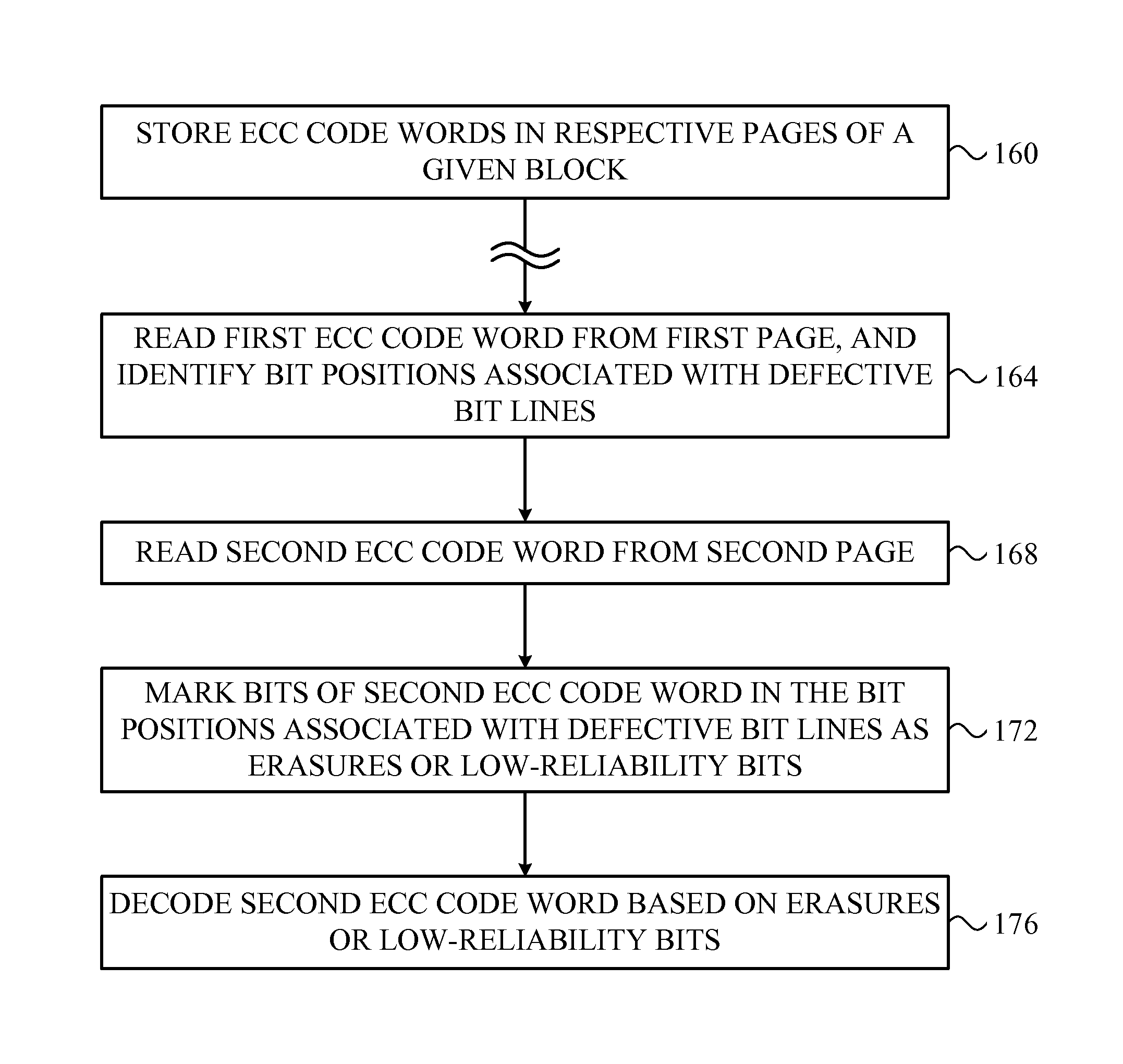
Automatic defect management in memory devices
ActiveUS20120159281A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionParallel computingStorage cell
Owner:APPLE INC
Automatic defect management in memory devices
ActiveUS8595573B2Error correction/detection using convolutional codesError detection/correctionParallel computingStorage cell
Owner:APPLE INC
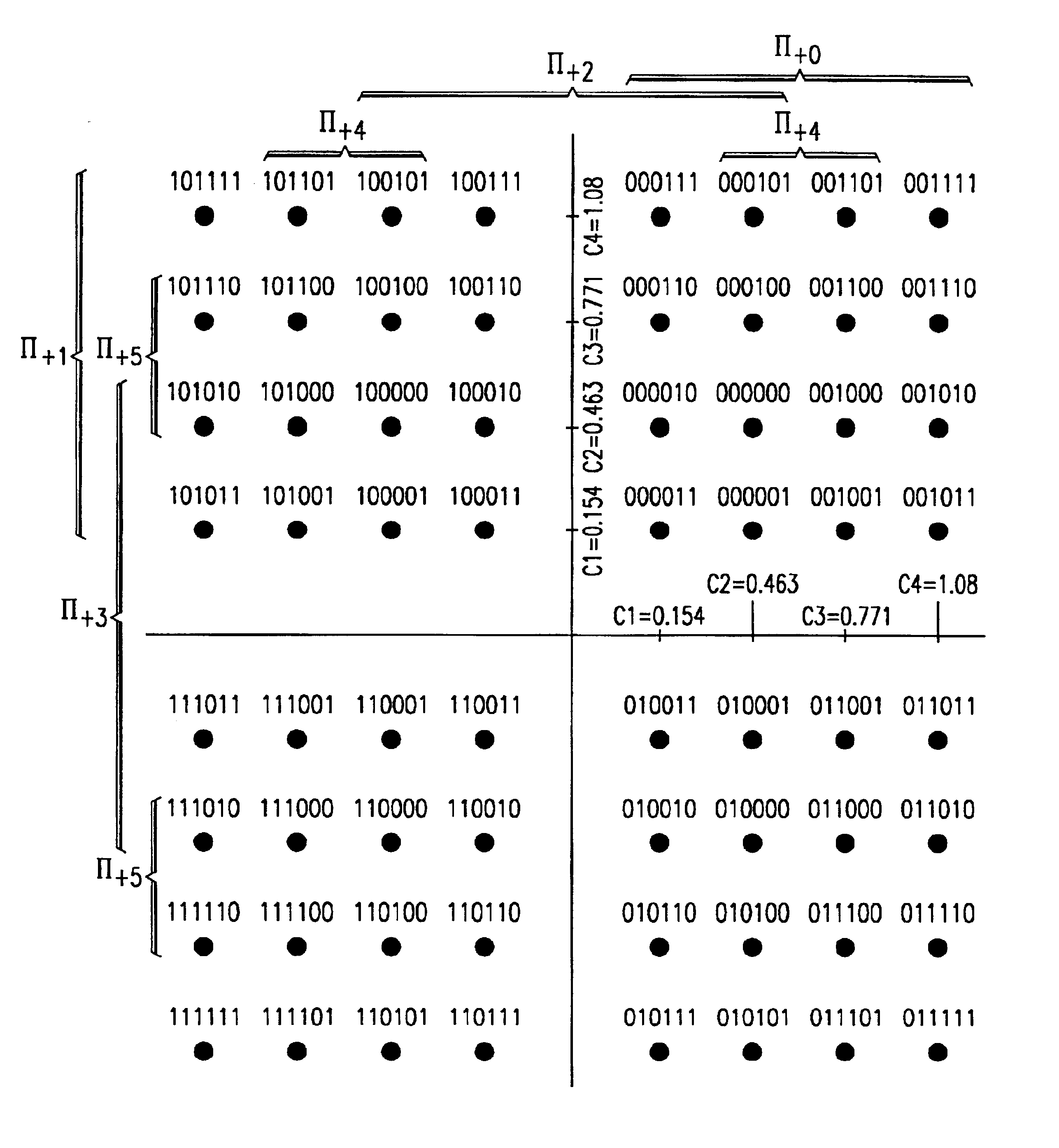
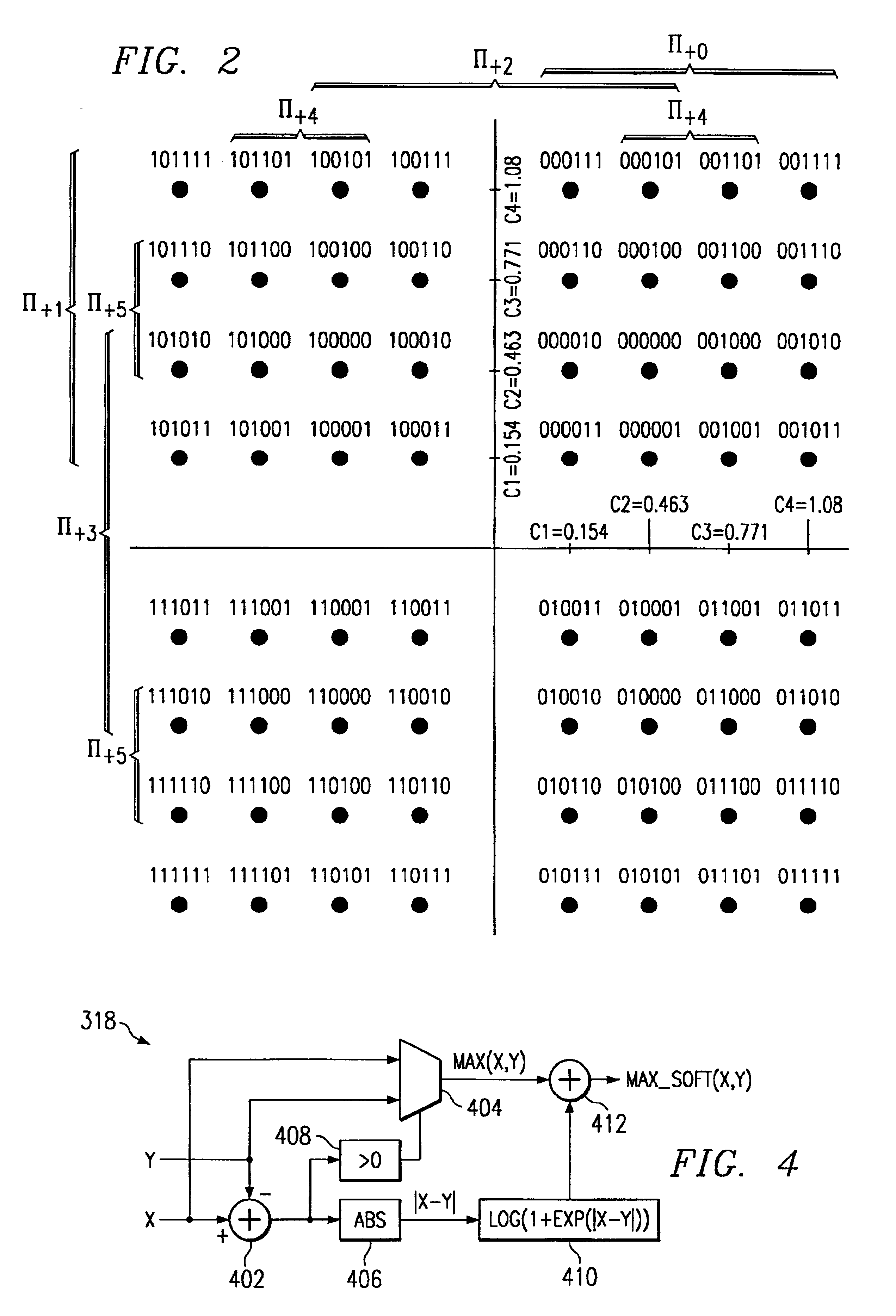
Method and apparatus for processing modulation symbols for soft input decoders
ActiveUS6907084B2Enhanced decoder performanceHigh computational complexityError prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionLog likelihoodComputer science
A method and apparatus for processing modulation symbols for soft input decoders using an efficient method of calculating an accurate log-likelihood ratio without relying on approximations is described. In contrast to other techniques that calculate distance metrics based on the individual constellation points, the method of the invention analyzes distances based on different groupings of points, where a given group (e.g., one of the II+k or II−k sets) is defined by the same bit (1 or 0) in the same bit position. A recursive scheme is preferably used where previous computations are saved and used for subsequent computations or iterations and the decoupled processing of real and imaginary components associated with the I and Q components.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of coding/decoding a digital data stream coded with bitwise interleaving in multiple transmission and reception in the presence of intersymbol interference and corresponding system
InactiveUS20020186800A1Improve spectral efficiencyEasy to implementPolarisation/directional diversityOther decoding techniquesDigital dataData stream
A method of and a system for coding / decoding a digital data stream coded with bitwise interleaving in multiple transmission and reception. The coding consists in subjecting (A) an initial digital data stream to an outer coding (C0), subjecting (B) the coded digital stream to an interleaving (pi), subjecting (C) the interleaved coded digital stream to a layer demultiplexing on nu pathways, converting (D) by modulation qm successive bits of each layer into Qm-ary symbol then transmitting (E) each symbol by means of a transmission antenna of an array of antennas {tam}m=1m=nu. The decoding consists in receiving (F) the digital data stream transmitted {TEILC0DSm}m=1m=nu on rho reception antennas {rar}r=1r=rho forming an array, subjecting (G) the set of symbols received to an iterative process of equalization and joint multilayer detection, on the basis of an a priori information item (EIDS=api), subjecting (H) the first extrinsic information stream (EIDS1) obtained to a deinterleaving (pi-1), subjecting (I) the second extrinsic information stream obtained (EIDS2) to an outer decoding (C0), subjecting (J) the third extrinsic information stream obtained (EIDS3) to an interleaving (pi) so as to generate the a priori information item (EIDS=api) and reinjecting (K) the latter into the process (G). Application to radio interfaces.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
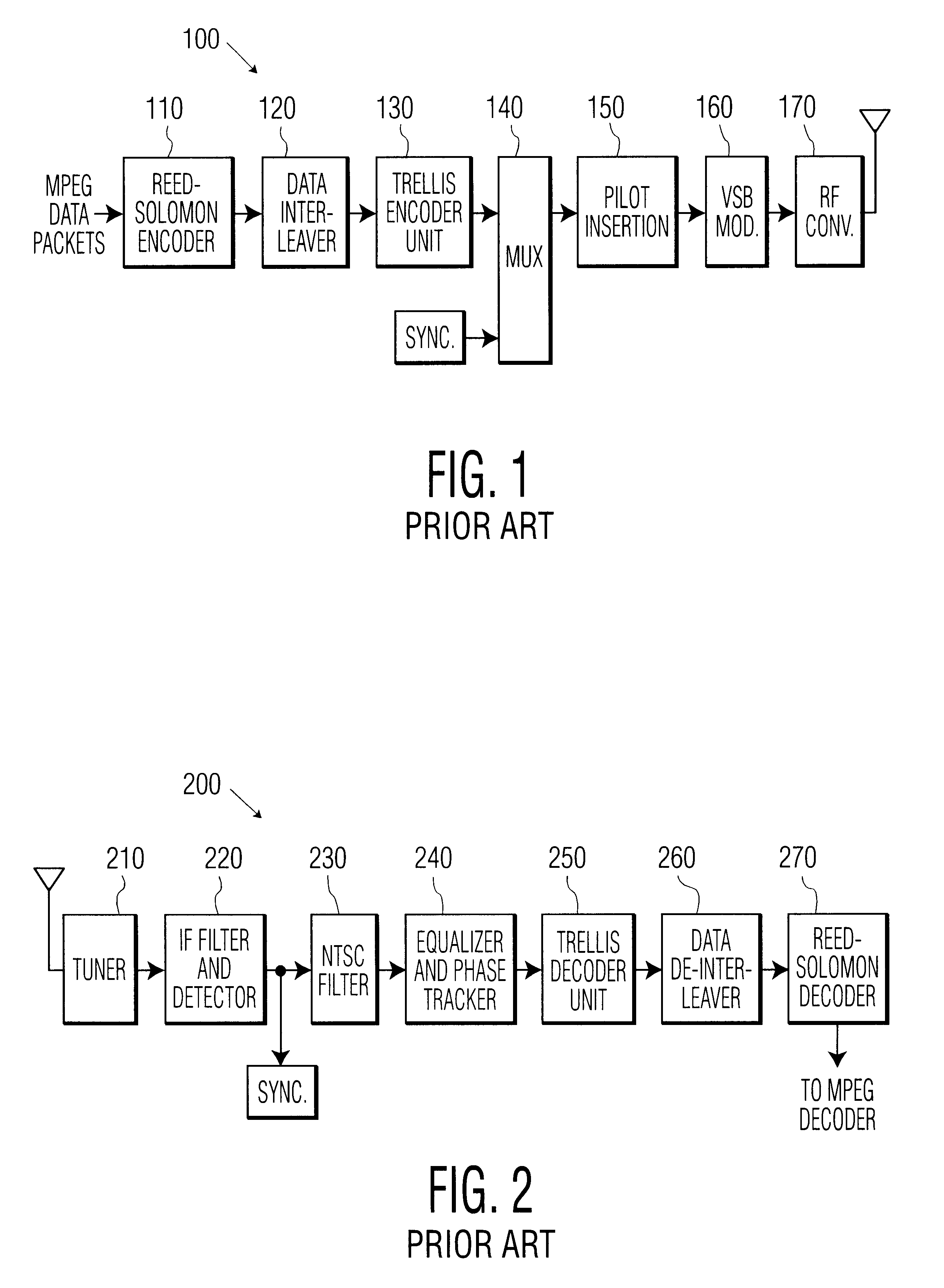
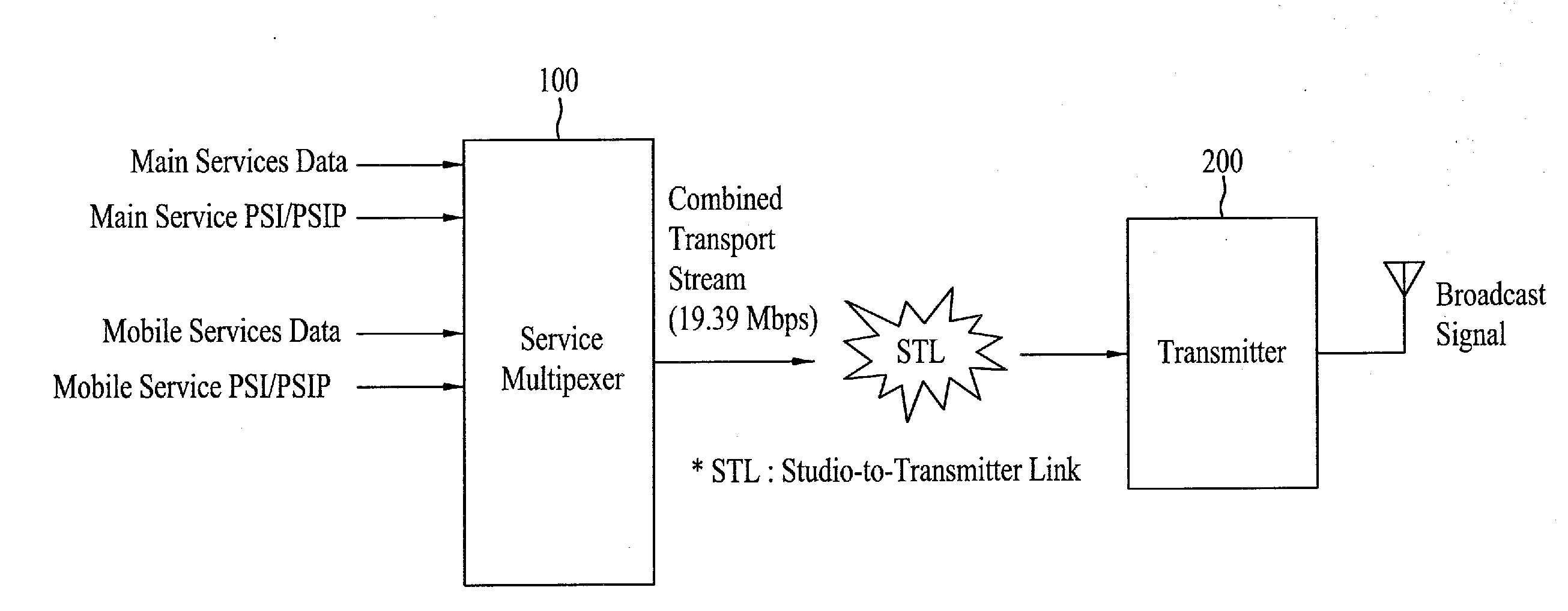
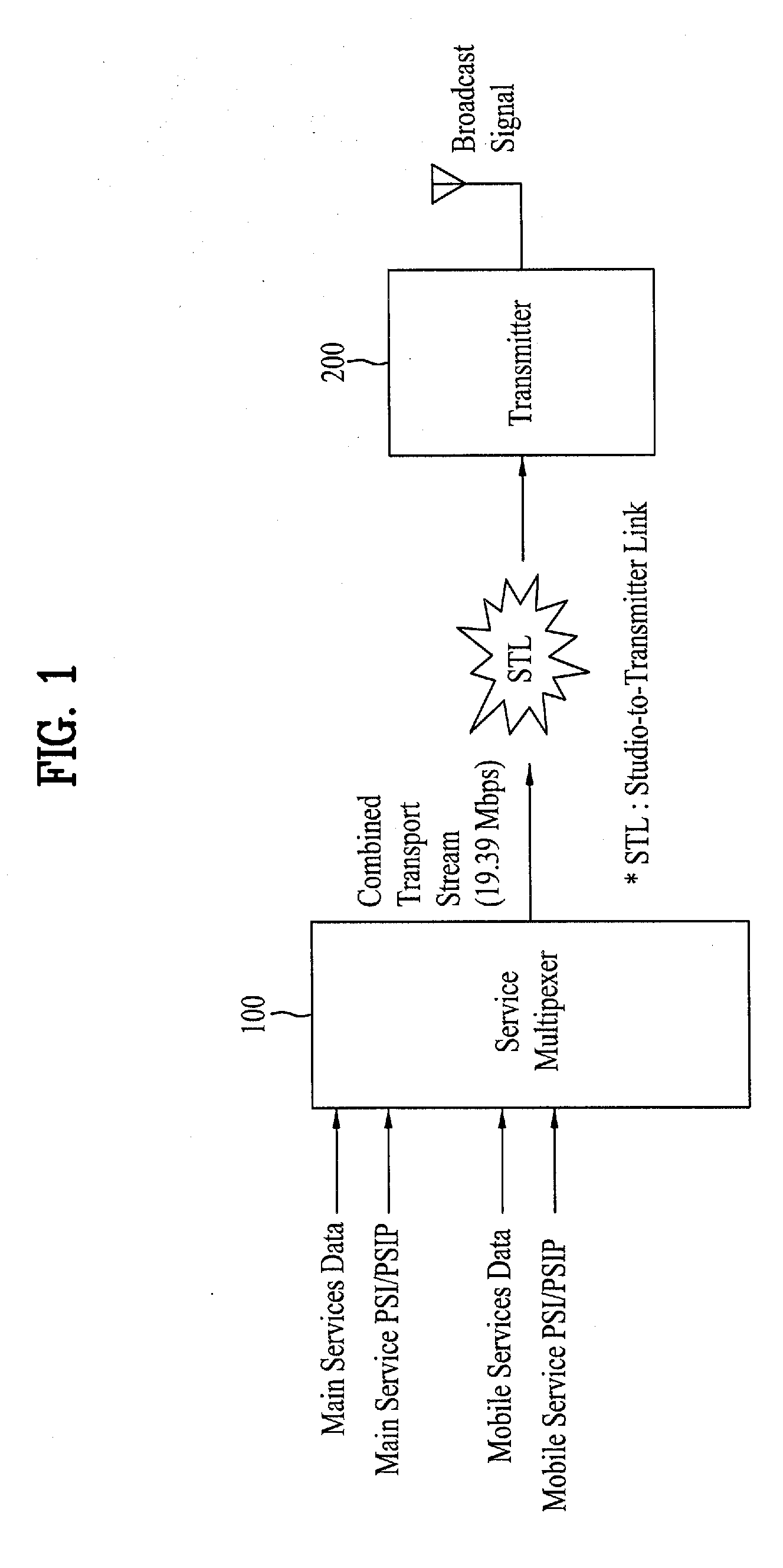
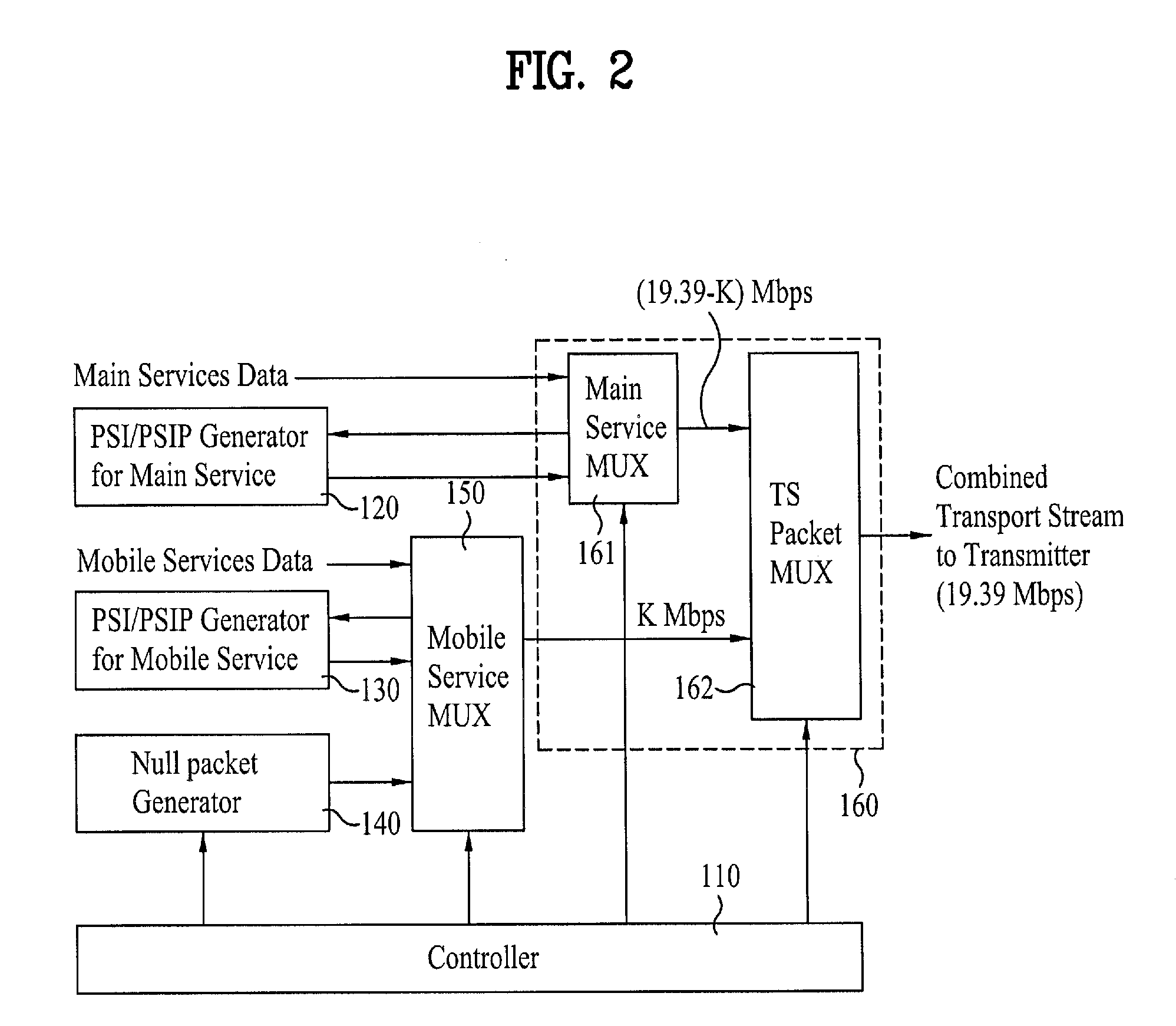
Digital broadcasting system and method of processing data
InactiveUS20090037792A1Improve reception performanceError preventionModulated-carrier systemsDigital broadcastingMobile service
A digital receiving system, and a method of processing data are disclosed. The digital receiving system includes a receiving unit, a known sequence detector, and a channel equalizer. The receiving unit receives a broadcast signal including mobile service data and main service data. The known sequence detector detects known data linearly inserted in a data group. The channel equalizer performs channel-equalizing on the received mobile service data using the detected known data.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
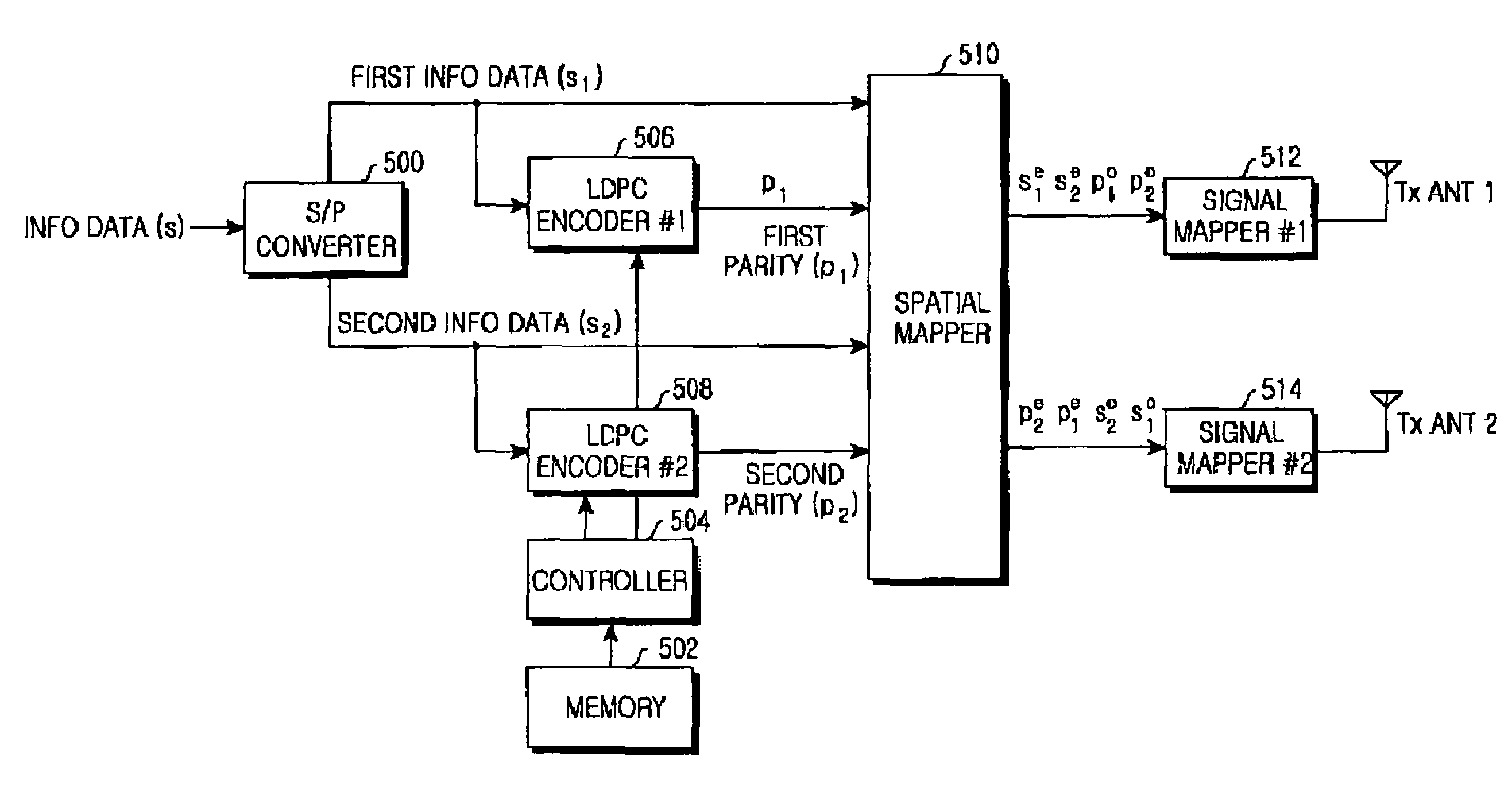
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding a space-time low density parity check code with full diversity gain
In a mobile communication system including a transmitter and a receiver, an LDPC code is generated by encoding received information data such that a fifth partial matrix obtained by combining a second partial matrix having even-numbered columns of a first partial matrix corresponding to the information data with a fourth partial matrix having odd-numbered columns of a third partial matrix corresponding to a parity, and an eighth partial matrix obtained by combining a sixth partial matrix having odd-numbered columns of the first partial matrix with a seventh partial matrix having even-numbered columns of the third partial matrix correspond to a ninth partial matrix obtained by exclusive-ORing the first partial matrix and the third partial matrix and a parity check matrix having a predetermined rank in a binary field. A space-time LDPC code is generated by spatial-mapping the LDPC code according to a predetermined spatial mapping scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for performing accurate demodulation of turbo-encoded signals via pilot assisted coherent demodulation
InactiveUS20020097785A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorInterference ratioData signal
An efficient telecommunications receiver system for accurately decoding a received composite signal having a data signal component and a pilot signal component includes a first circuit for receiving the composite signal and extracting a pilot signal and a data signal from received composite signal. A second circuit calculates a log-likelihood ratio as a function of a channel estimate based on the pilot signal. A third circuit scales the log-likelihood ratio by a predetermined log-likelihood ratio scaling factor and provides an accurate log-likelihood value in response thereto. A fourth circuit decodes the received composite signal based on the accurate log-likelihood value and the data signal. The third circuit includes a carrier signal-to-interference ratio circuit for computing a first signal-to-interference ratio and a second signal-to-interference ratio based partly on the pilot signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com