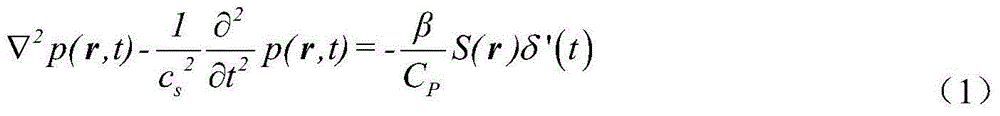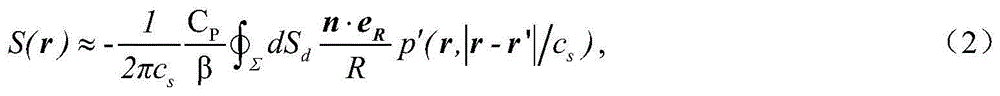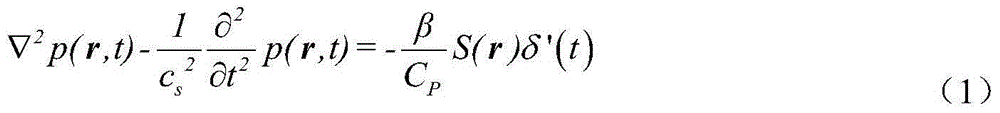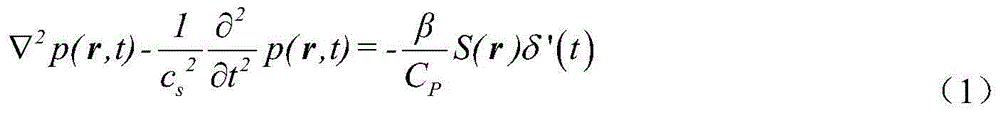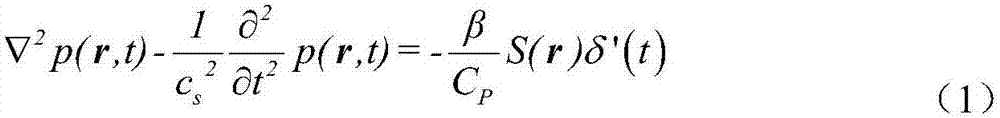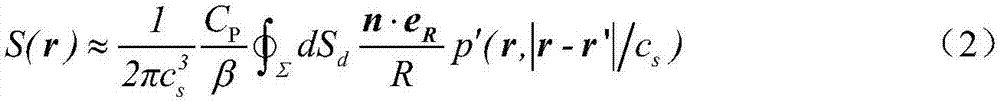Patents
Literature
70 results about "Vector potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
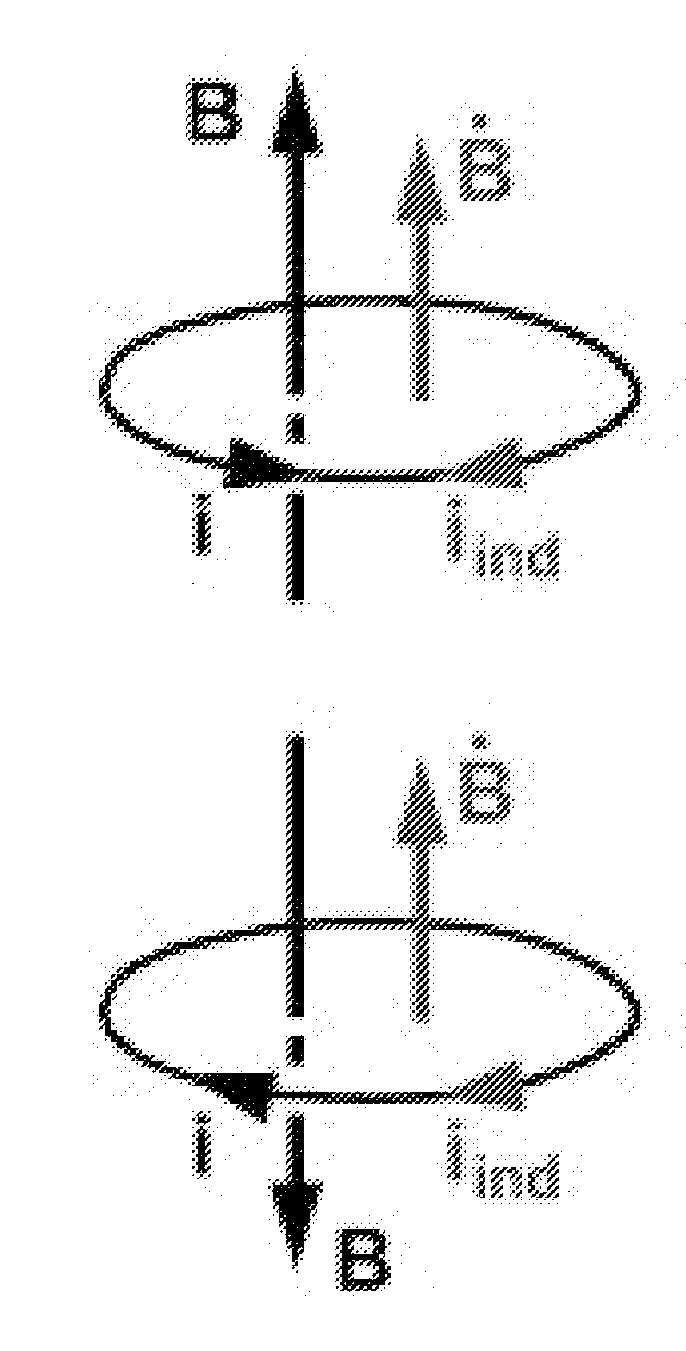
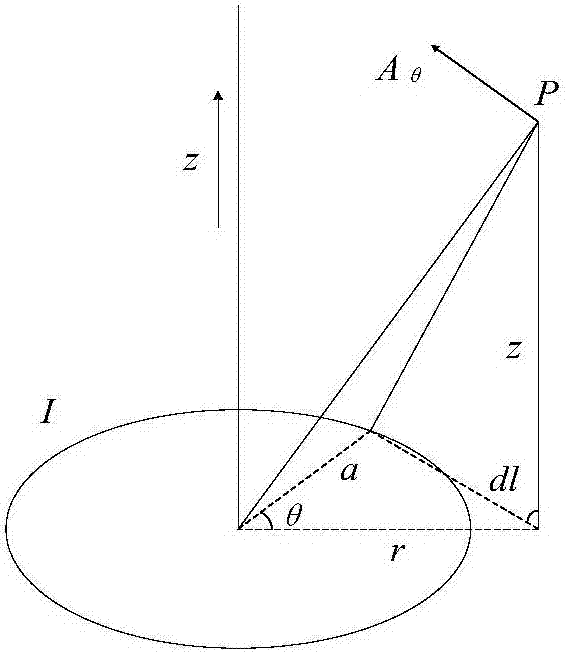
In vector calculus, a vector potential is a vector field whose curl is a given vector field. This is analogous to a scalar potential, which is a scalar field whose gradient is a given vector field. Formally, given a vector field v, a vector potential is a vector field A such that 𝐯=∇×𝐀.
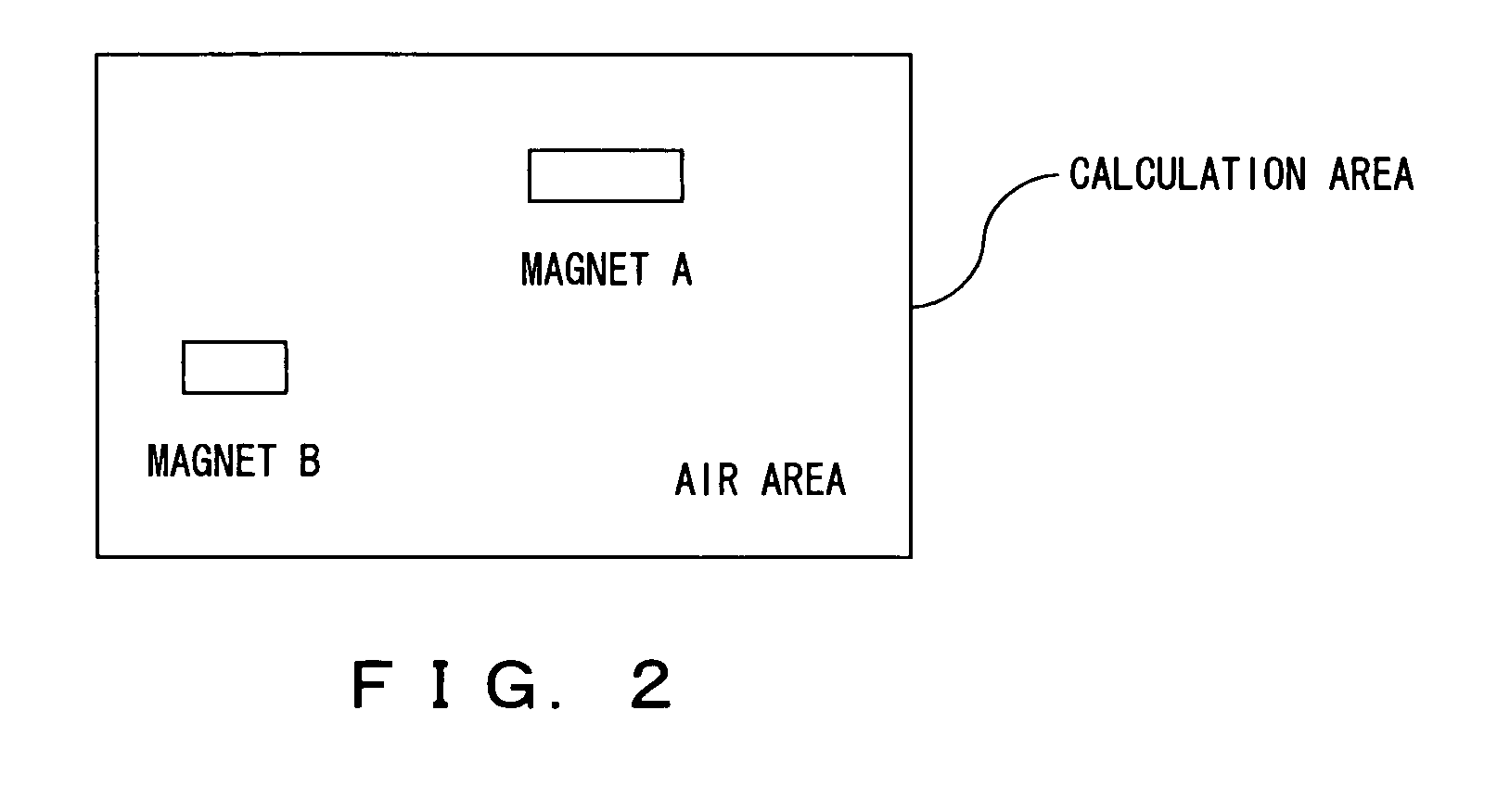
Method and apparatus for simulating physical fields
InactiveUS6665849B2Less storage spaceAvoid excessive intensityDetecting faulty computer hardwareAnalogue computers for chemical processesPhysical fieldEngineering
In order to design on-chip interconnect structures in a flexible way, a CAD approach is advocated in three dimensions, describing high frequency effects such as current redistribution due to the skin-effect or eddy currents and the occurrence of slow-wave modes. The electromagnetic environment is described by a scalar electric potential and a magnetic vector potential. These potentials are not uniquely defined, and in order to obtain a consistent discretization scheme, a gauge-transformation field is introduced. The displacement current is taken into account to describe current redistribution and a small-signal analysis solution scheme is proposed based upon existing techniques for static fields in semiconductors. In addition methods and apparatus for refining the mesh used for numerical analysis is described.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Method and apparatus for simulating physical fields
InactiveUS20020042698A1Simple structureLess storage spaceDetecting faulty computer hardwareAnalogue computers for chemical processesPhysical fieldEngineering
In order to design on-chip interconnect structures in a flexible way, a CAD approach is advocated in three dimensions, describing high frequency effects such as current redistribution due to the skin-effect or eddy currents and the occurrence of slow-wave modes. The electromagnetic environment is described by a scalar electric potential and a magnetic vector potential. These potentials are not uniquely defined, and in order to obtain a consistent discretization scheme, a gauge-transformation field is introduced. The displacement current is taken into account to describe current redistribution and a small-signal analysis solution scheme is proposed based upon existing techniques for static fields in semiconductors. In addition methods and apparatus for refining the mesh used for numerical analysis is described.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Analytical method based permanent magnet motor field analysis and torque calculation method
ActiveCN105005692AGuaranteed accuracyConvenient analytical solutionMagnetic circuitSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelSurface mounting
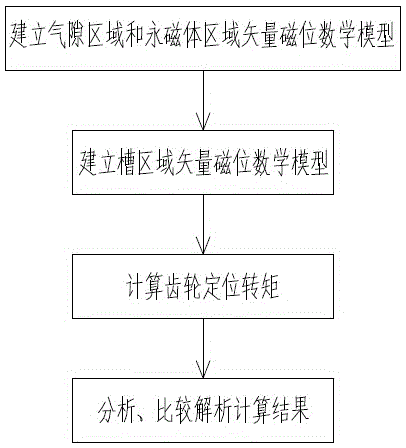
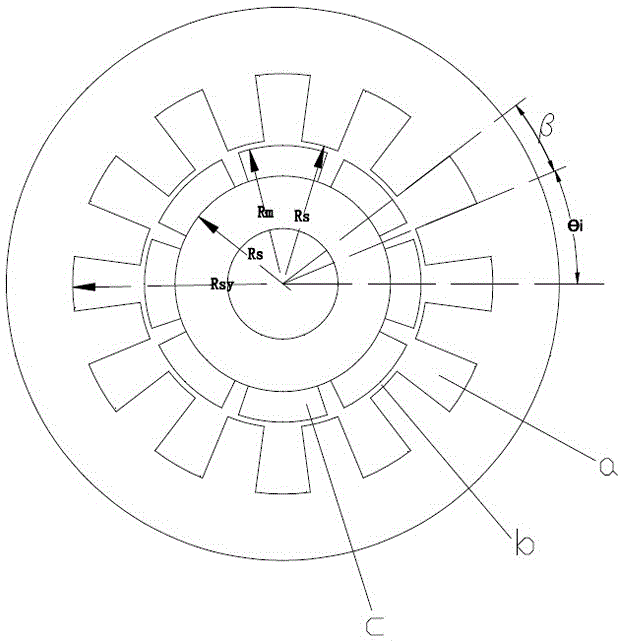
Provided is an analytical method based permanent magnet motor field analysis and torque calculation method. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1: establishing a magnetic vector potential mathematical model of a gap zone and a permanent magnet region; step 2: establishing a magnetic vector potential mathematical model of a slot area; step 3: calculating a cogging torque; and step 4: analyzing and comparing an analytical calculating result. The invention provides an analytical method based permanent magnet motor field analysis and torque calculation method. According to the structural features of a surface mounted radially magnetized permanent magnet motor model, the analytical model is divided into three sub-regions, namely a permanent magnet region, a gap zone and a slot area; a magnetic vector Laplace equation or a Poisson equation is established in each region; sub-region equations are connected through junction conditions, so as to obtain the analytical expression of a load air gap field and a slot field by using a direct analytical method.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
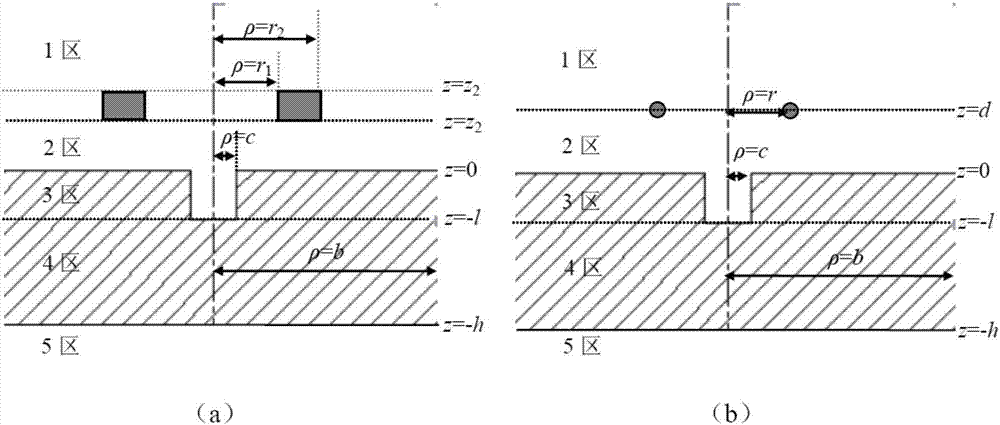
Electromagnetic flowmeter
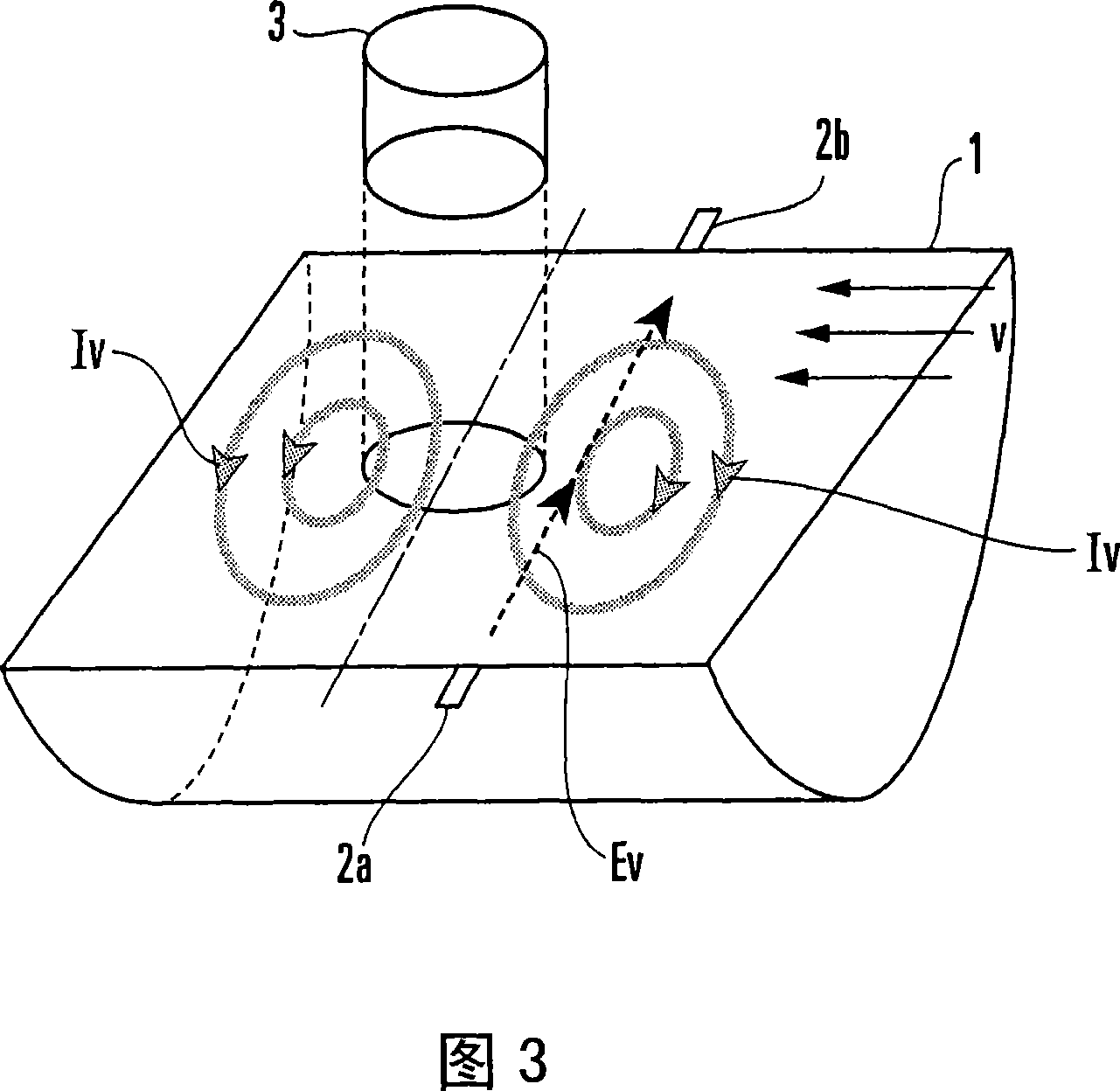
InactiveUS7369949B2Accurate measurementAccurate detectionIroning machinesHand ironVector potentialElectromotive force
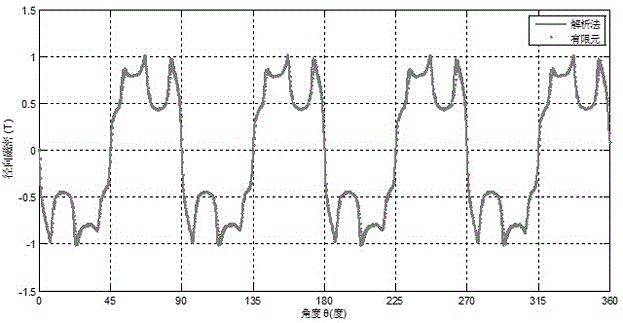
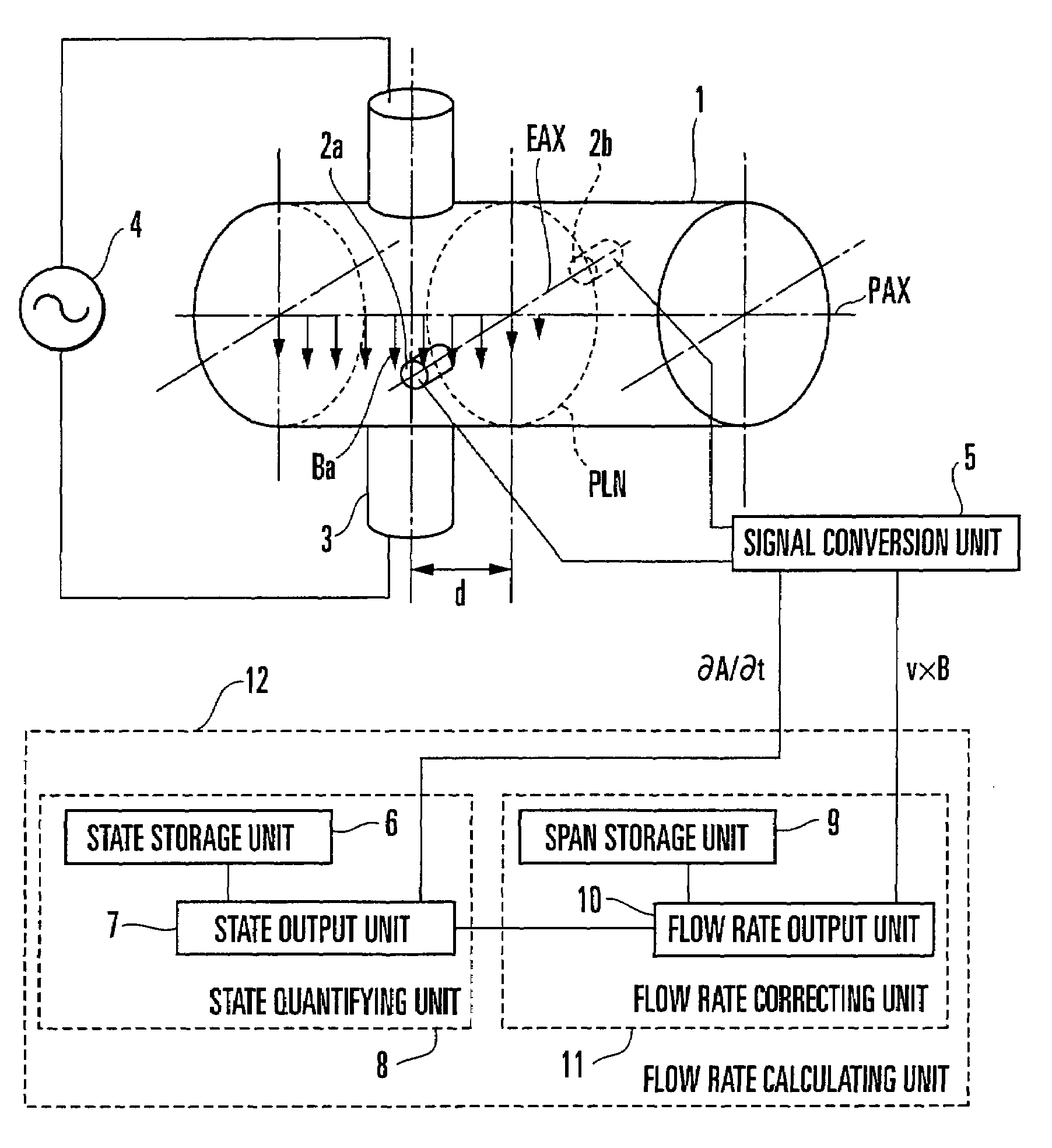
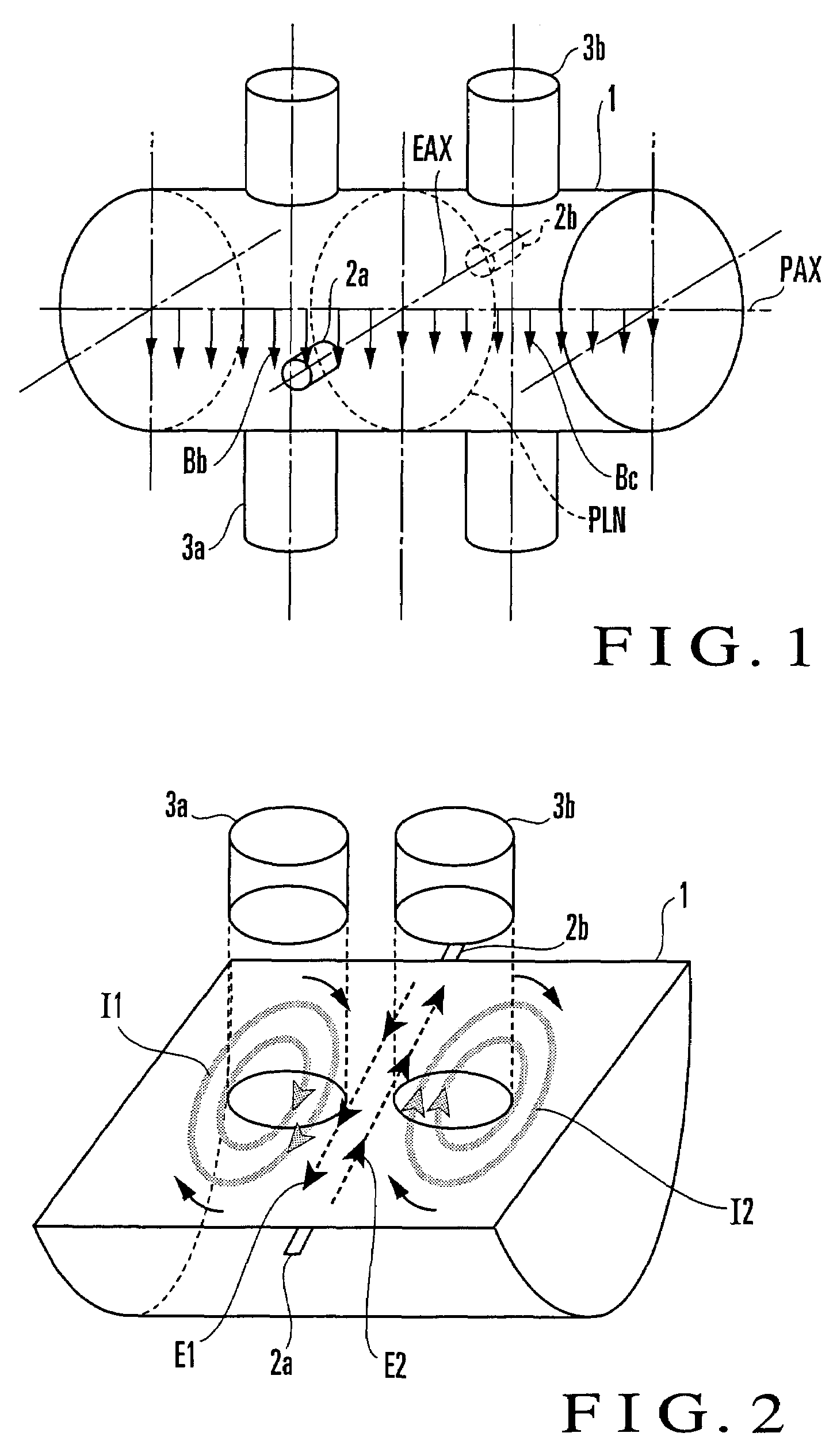
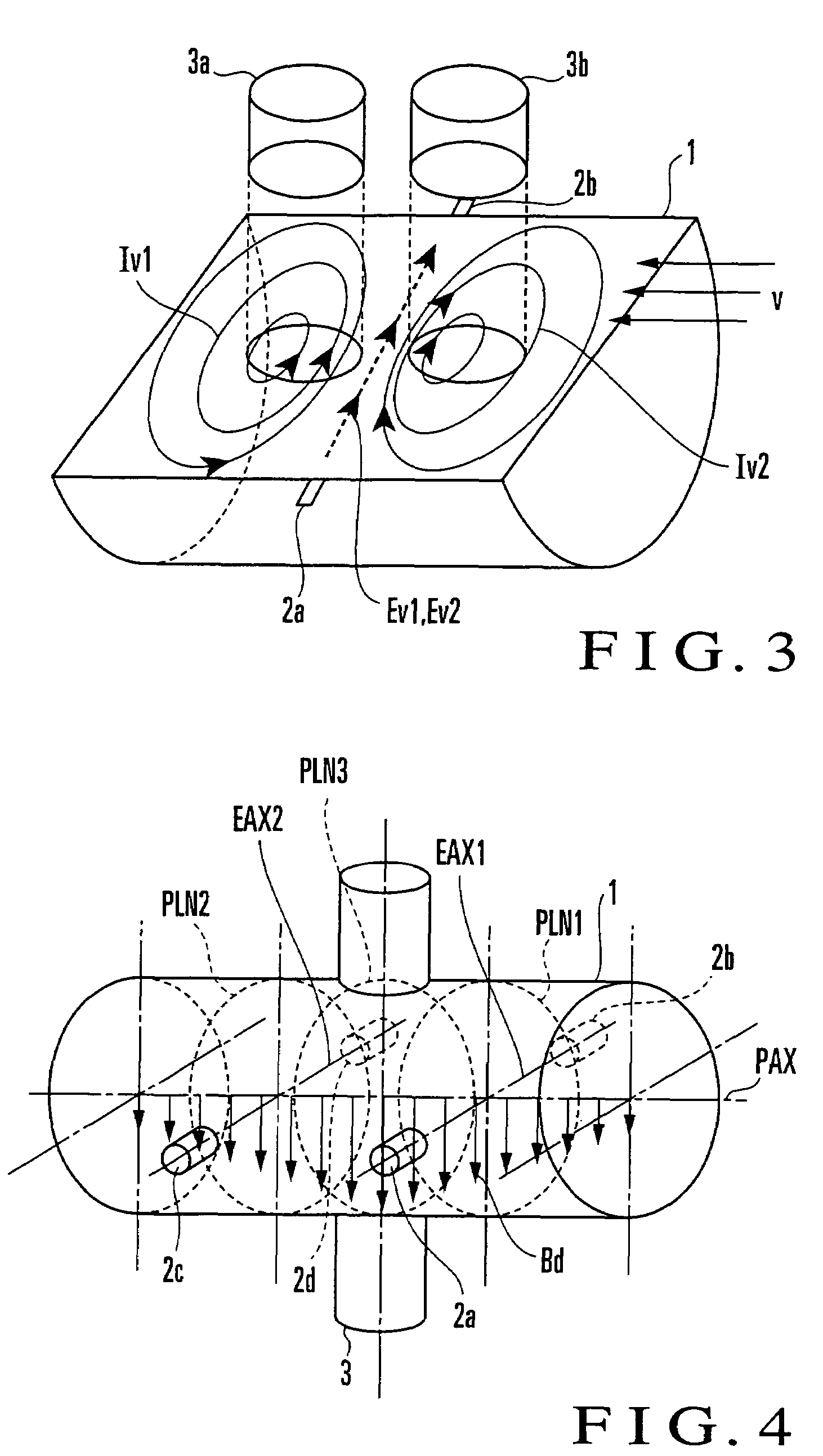
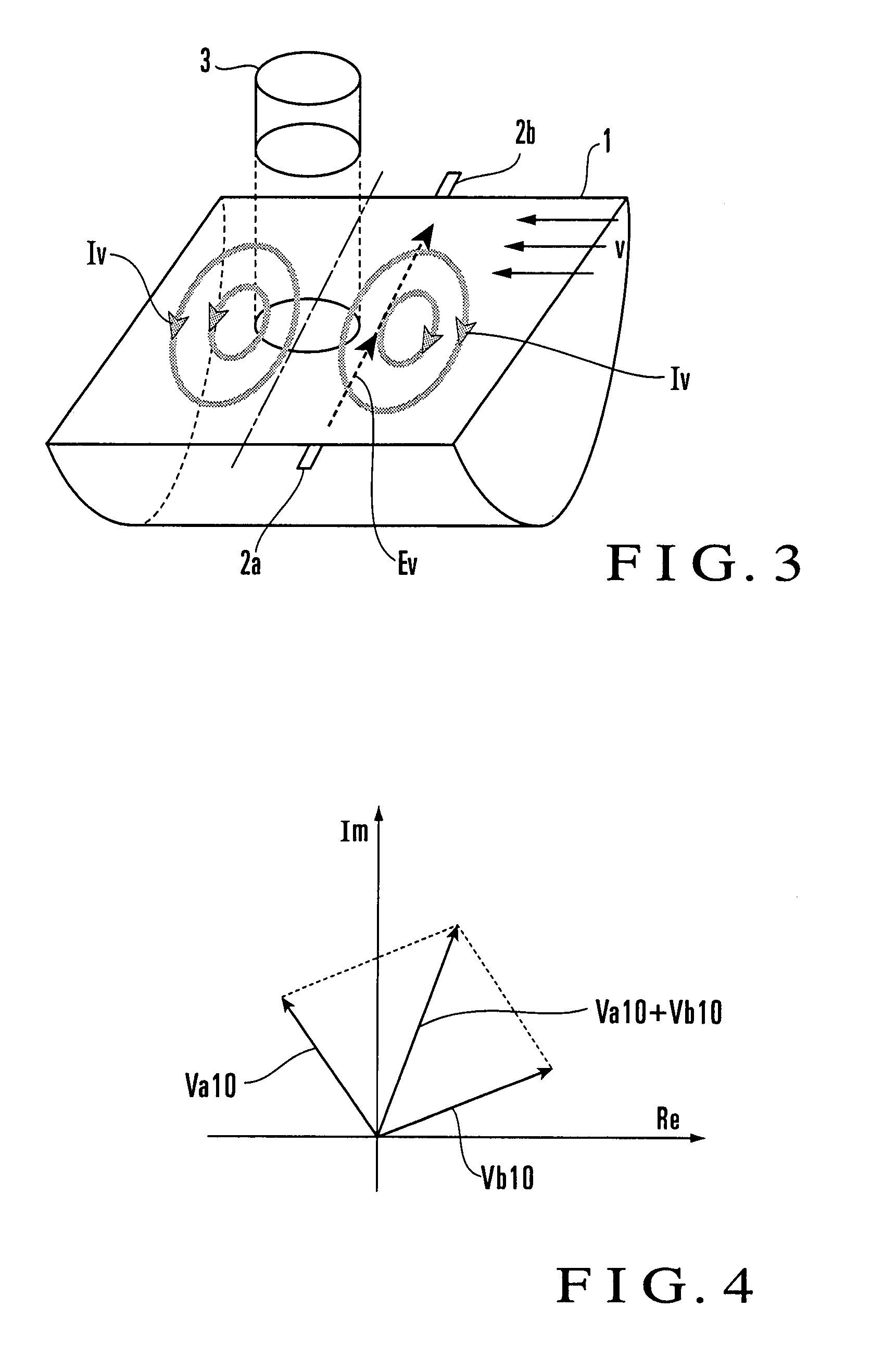
An electromagnetic flowmeter includes a measuring tube, an electrode, an exciting unit, a signal conversion unit, and a flow rate calculating unit. The signal conversion unit extracts a ∂A / ∂t component irrelevant to a flow velocity of the fluid and a v×B component originating from the flow velocity of the fluid from a resultant electromotive force of an electromotive force ∂A / ∂t, with A, t, v, and B respectively representing a vector potential, a time, a flow velocity, and a magnetic flux density. The flow rate calculating unit extracts a variation component dependent on a parameter from the ∂A / ∂t component, corrects a span which is a coefficient applied to a magnitude V of the flow velocity of the v×B component, and calculates the flow rate of the fluid from the v×B component whose span is corrected.
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
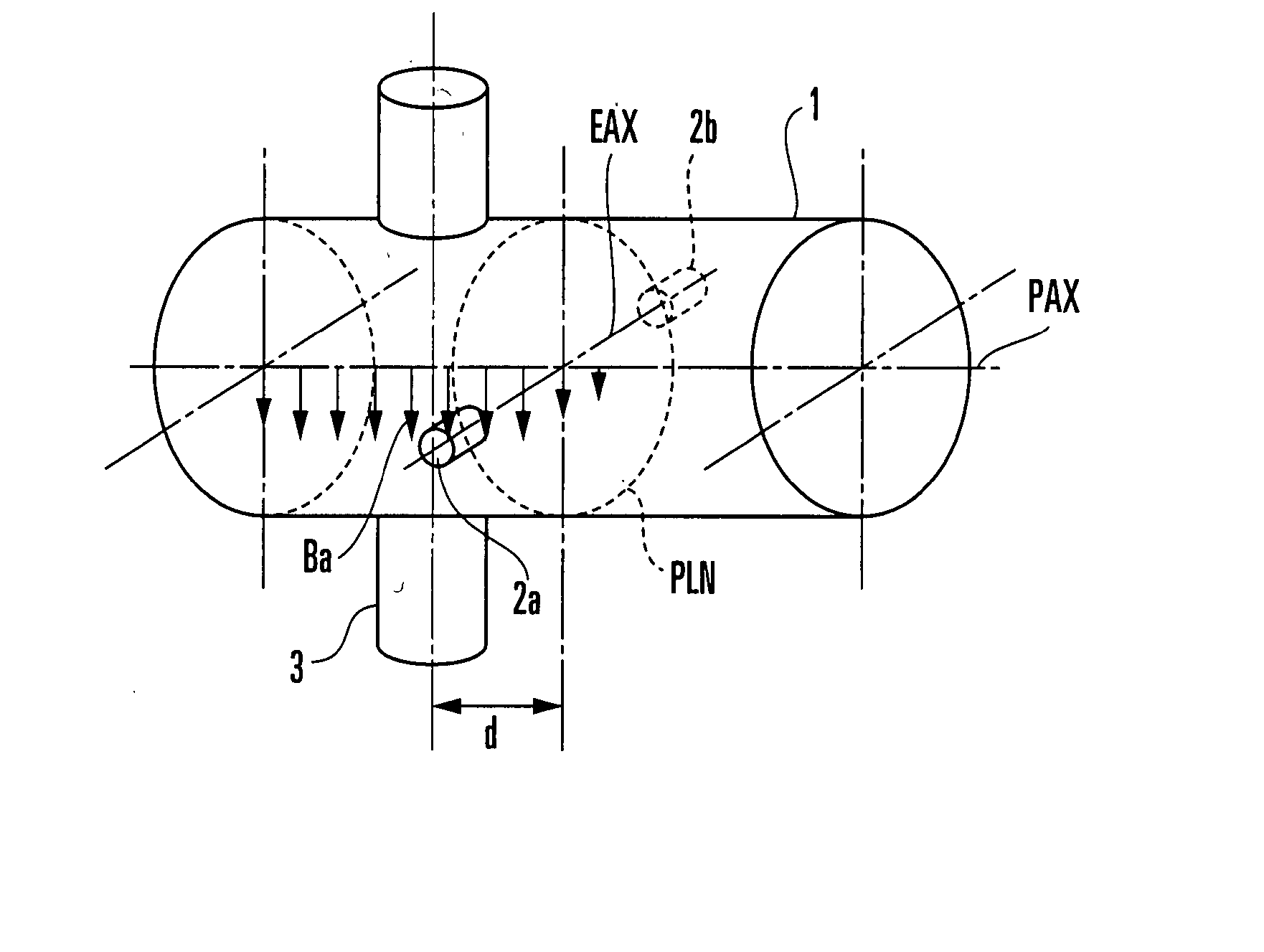
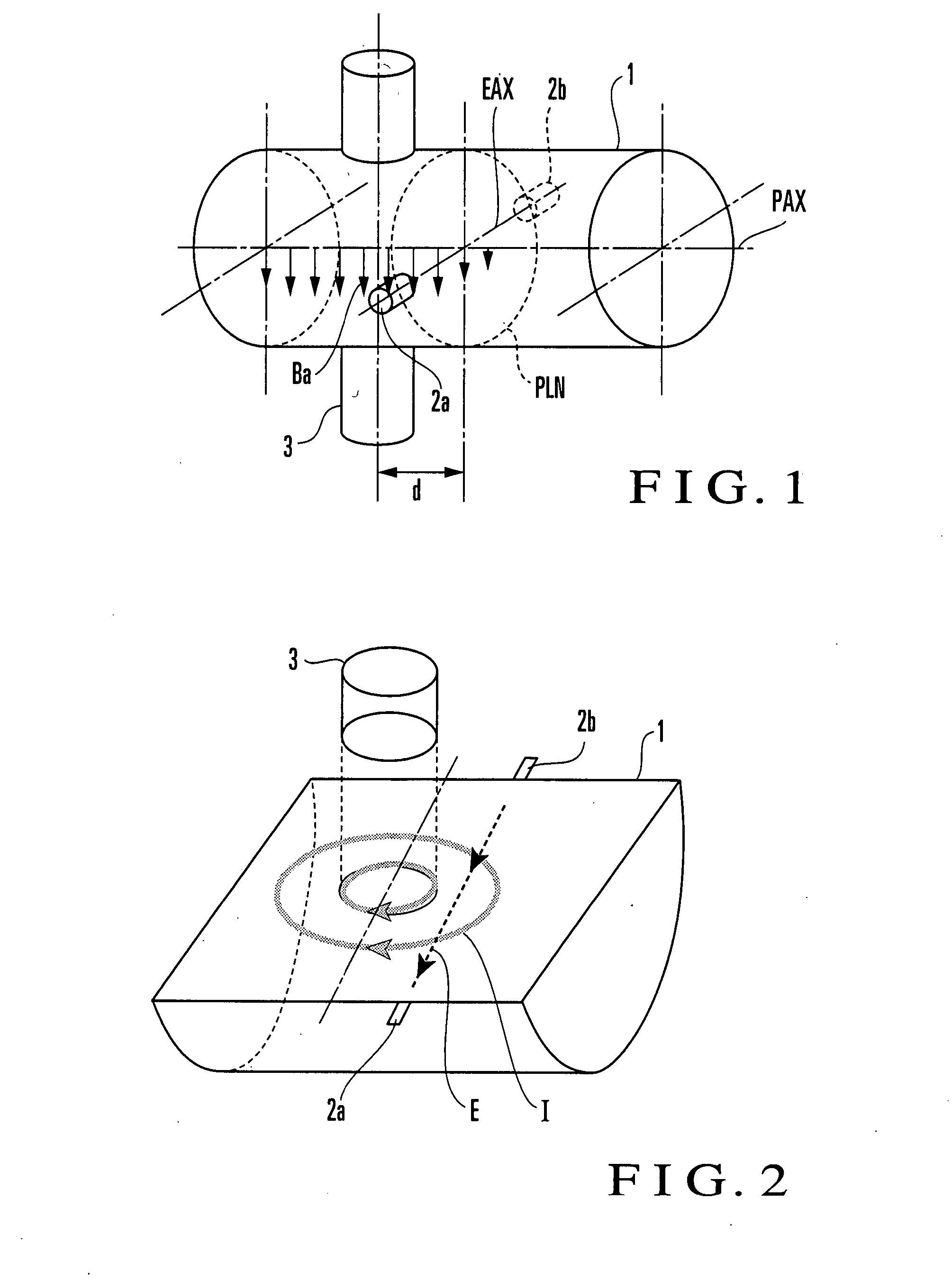
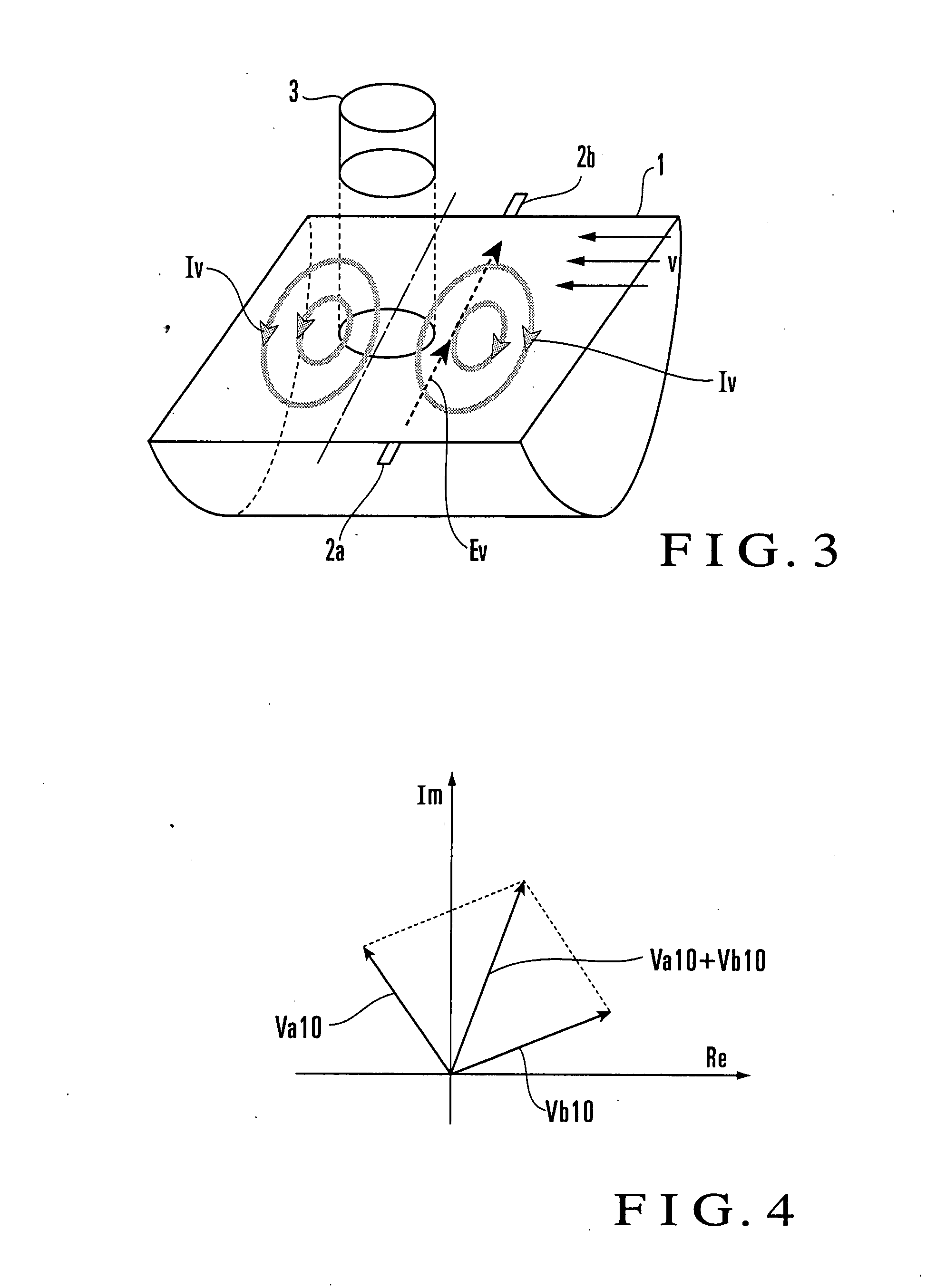
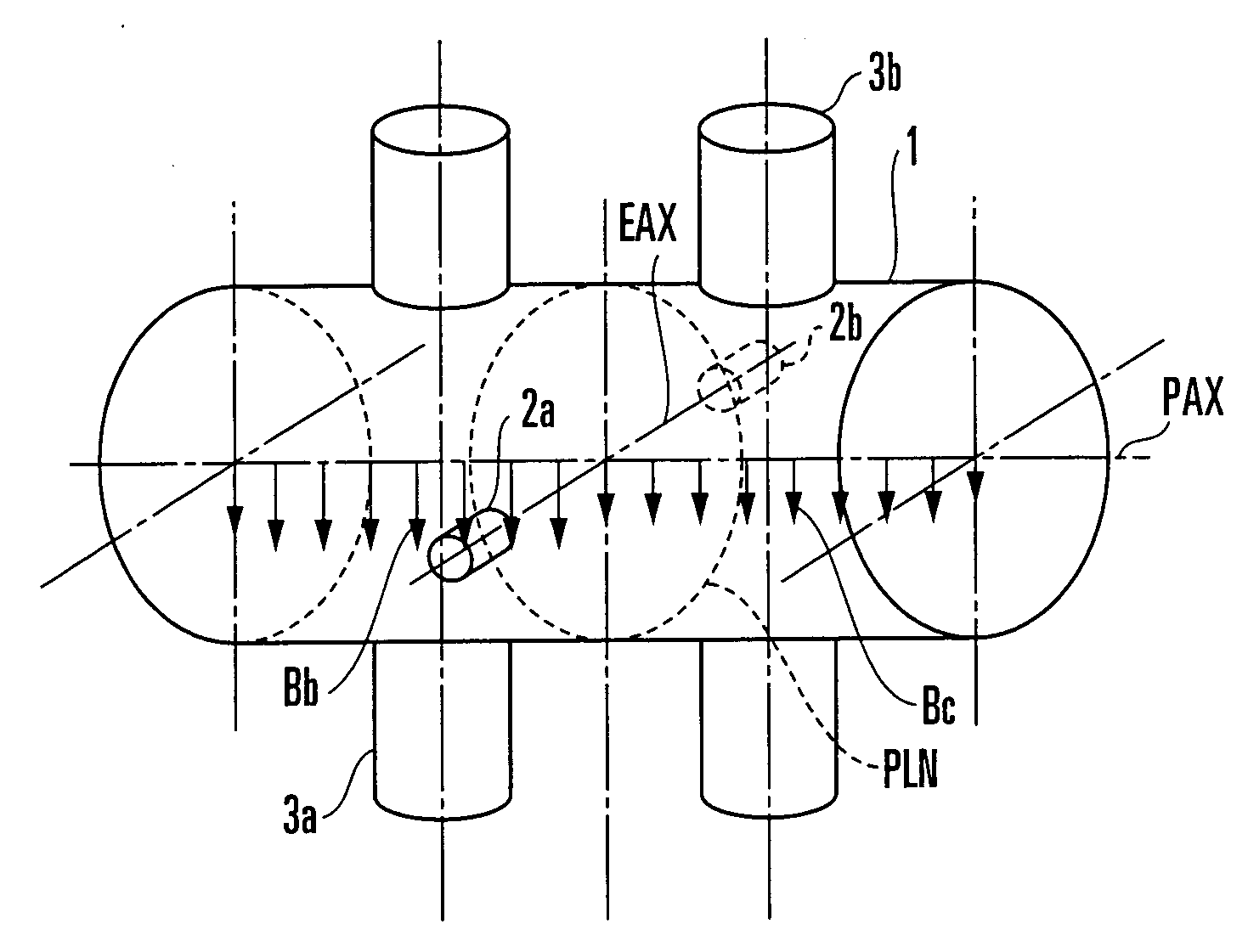
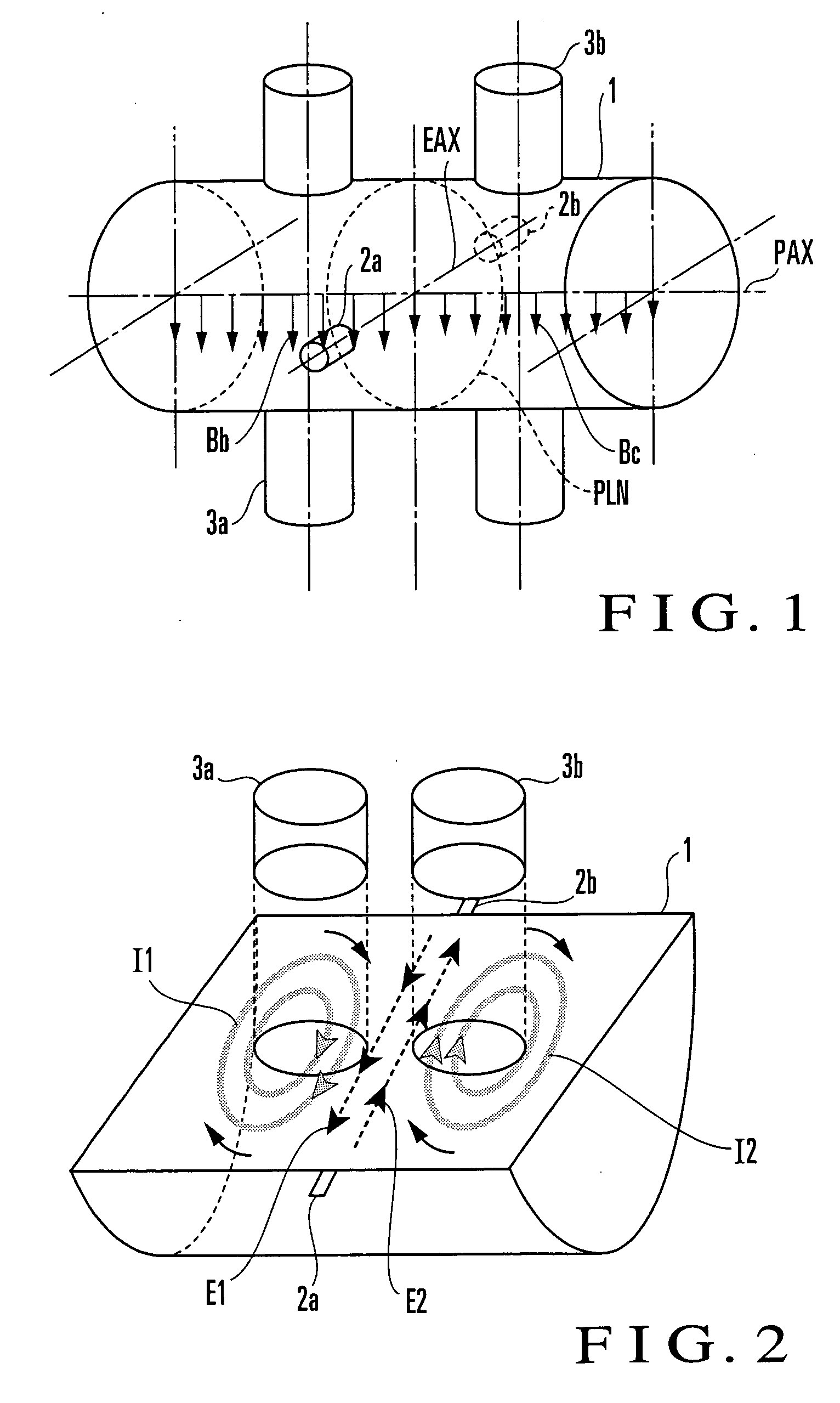
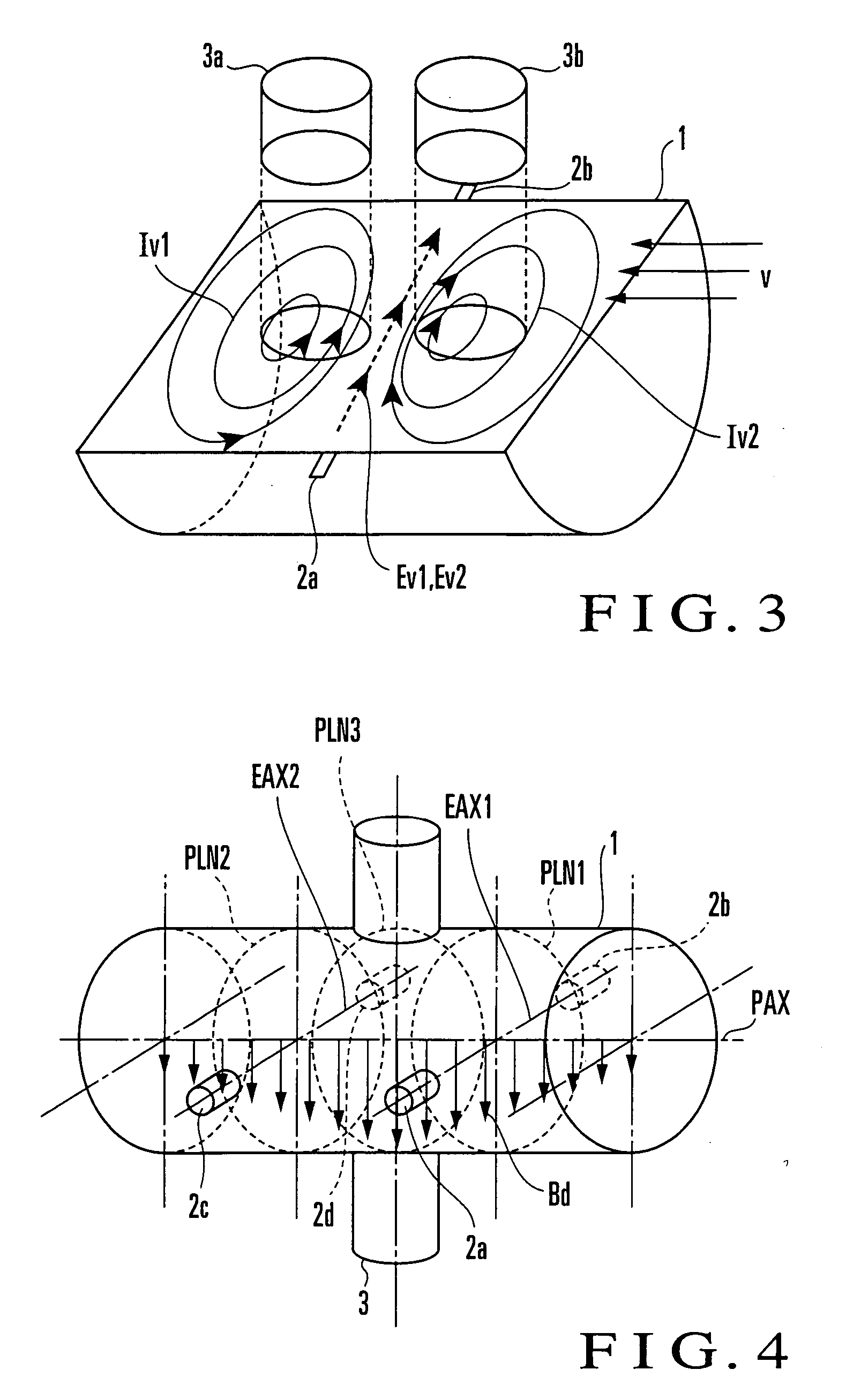
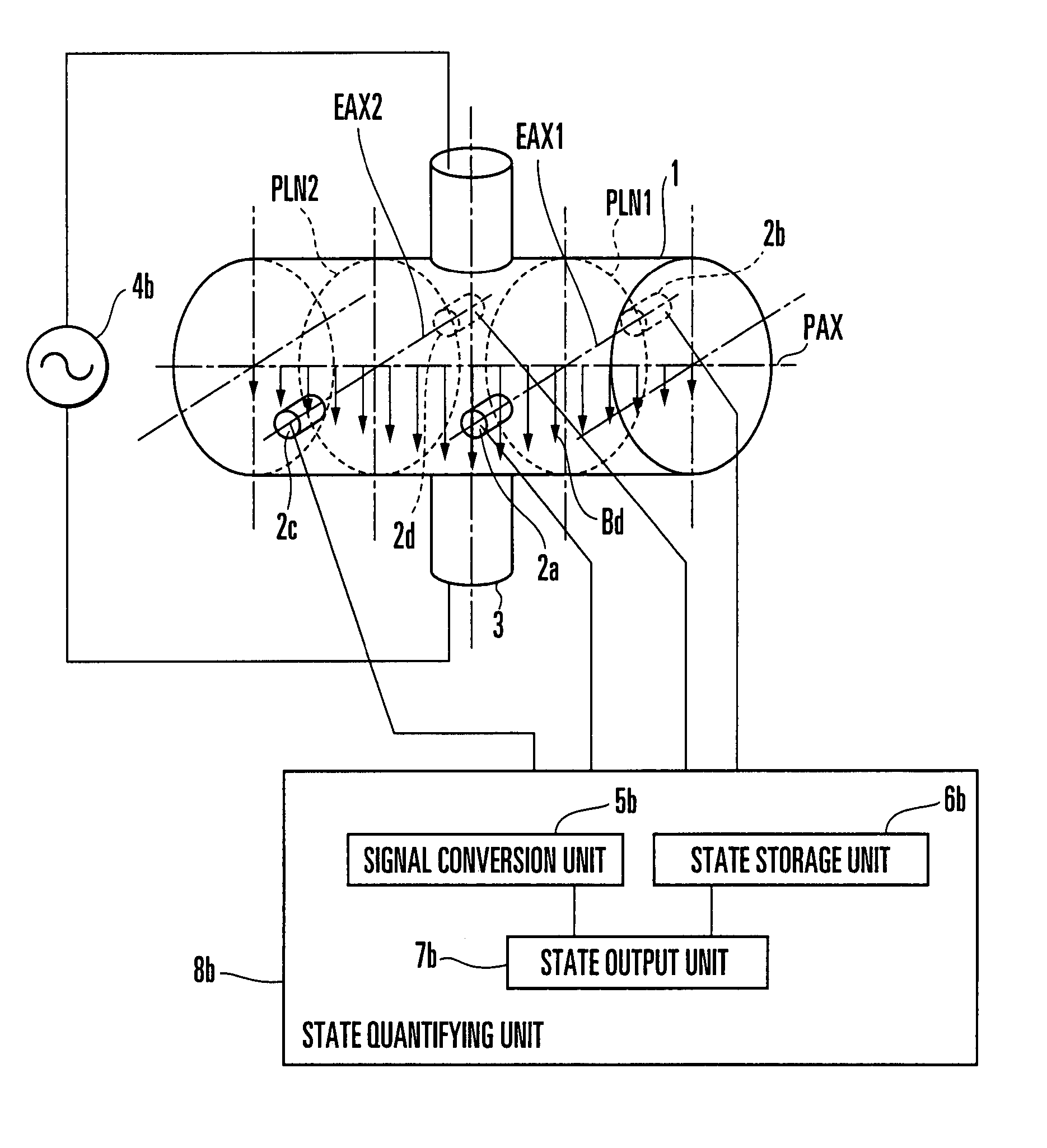
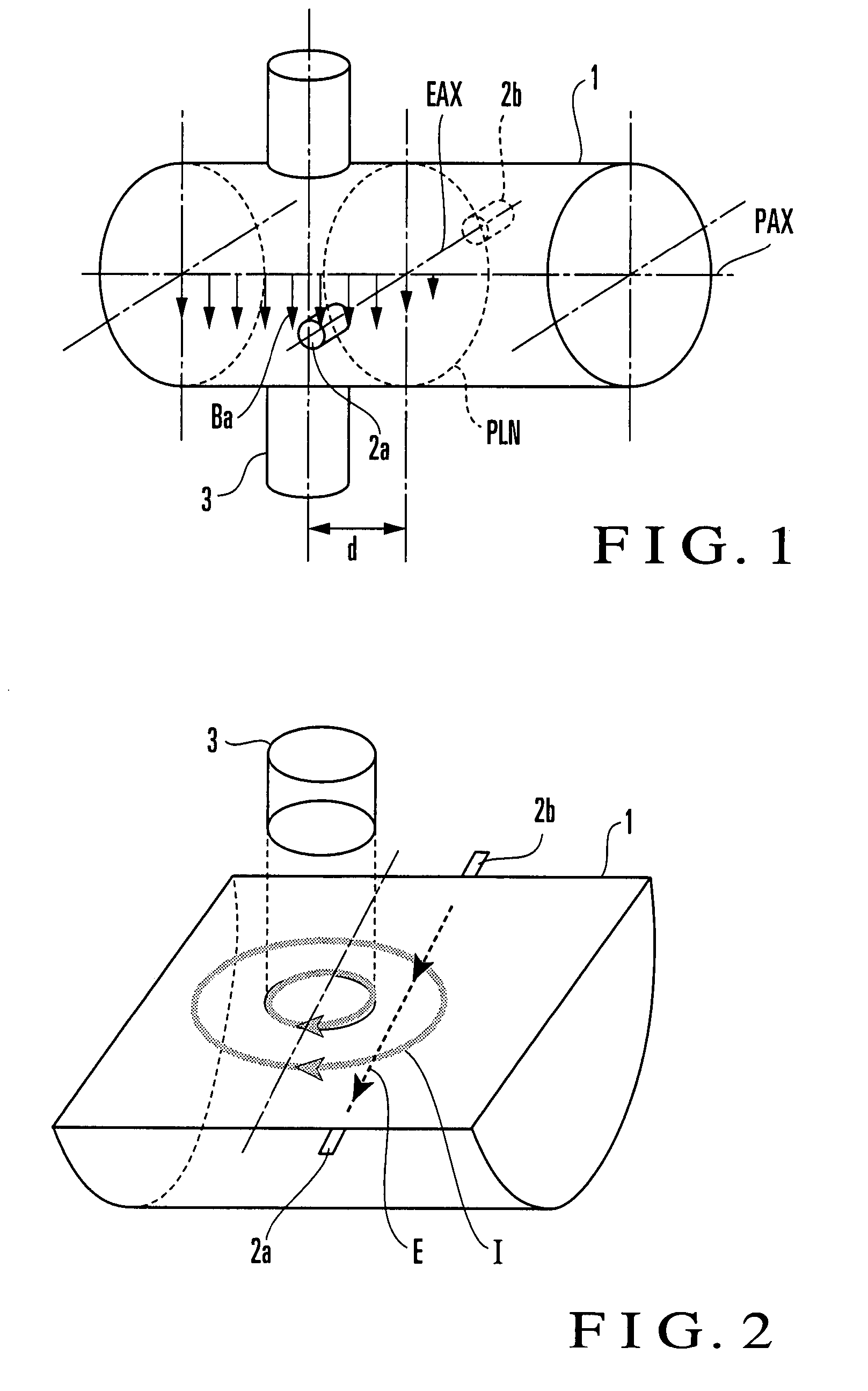
State Detection Device
In this invention, an exciting unit applies, to a fluid, a time-changing magnetic field asymmetrical to a plane (PLN). An electrode is placed on the plane in a measuring tube, and detects a resultant electromotive force of an electromotive force based on a ∂A / ∂t component (A: vector potential, t: time) irrelevant to a flow velocity of the fluid and an electromotive force based on a v×B component originating from the flow velocity of the fluid, the resultant electromotive force being generated by the magnetic field applied to the fluid and the flow of the fluid. A state quantifying unit extracts the ∂A / ∂t component from the resultant electromotive force detected by the electrode, extracts, from the ∂A / ∂t component, a variation factor dependent on a parameter to be detected, and quantifies the parameter on the basis of the variation factor. The parameter is at least one of a characteristic and state of the fluid and a state in the measuring tube. In this invention, the characteristic and state of the fluid and the state in the measuring tube can be detected regardless of the flow rate of the fluid by using the same hardware arrangement as that of an electromagnetic induction type flowmeter.
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
Marine controlled source electromagnetic method finite element forward method of anisotropic media
InactiveCN106980736AAvoid the effects of singularityEasy constructionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsScalar potentialMaxwell's equations
The present invention is a marine controlled source electromagnetic method finite element forward method of anisotropic media. The method comprises: firstly, setting a reference electrical conductivity, wherein three non-zero diagonal elements of the reference electrical conductivity are electrical conductivities in the direction of three main axes: x, y, z; next, setting three Euler rotation angles, and after three times of Euler rotation, obtaining an electrical conductivity tensor model in any direction; then starting from Maxwell equations, obtaining a finite element equation that is satisfied by magnetic vector potential and scalar potential under Coulomb regulations on a condition that the electrical conductivity presents anisotropy; then, performing discrete segmentation on a research region by using a non-structural grid, so that a complicated geoelectric model can be constructed; combining an incomplete LU discomposition pre-condition factor with an IDR(s) algorithm, so as to realize efficient and precise solution of a large sparse linear equation; and finally, deriving vector potential and scalar potential of a secondary field by using weighted moving least squares solution, to obtain each component of an electromagnetic field. The method provided by the present invention has excellent universality and can be promoted for electromagnetic method numerical value simulation with complicated electrical conductivity distribution and high precision.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Electromagnetic flowmeter
InactiveUS20070088511A1Accurate measurementAccurate detectionIroning machinesHand ironVector potentialElectromotive force
An electromagnetic flowmeter includes a measuring tube, an electrode, an exciting unit, a signal conversion unit, and a flow rate calculating unit. The signal conversion unit extracts a ∂A / ∂t component irrelevant to a flow velocity of the fluid and a v×B component originating from the flow velocity of the fluid from a resultant electromotive force of an electromotive force based on the ∂A / ∂t component and an electromotive force based on the v×B component, with A, t, v, and B respectively representing a vector potential, a time, a flow velocity, and a magnetic flux density. The flow rate calculating unit extracts a variation component dependent on a parameter from the ∂A / ∂t component extracted by the signal conversion unit, corrects a span which is a coefficient applied to a magnitude V of the flow velocity of the v×B component input from the signal conversion unit on the basis of the variation component, and calculates the flow rate of the fluid from the v×B component whose span is corrected, the parameter being at least one of a characteristic and state of the fluid and a state in the measuring tube which are independent of the flow rate of the fluid.
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
Educational tool
InactiveUS20100028840A1Easy to understandGenerate interestEducational modelsTeaching apparatusClassical mechanicsVector potential
A wave function of quantum mechanics is regarded as a vector potential having a component only in a θ-direction of polar coordinates (r, θ, φ). The result of applying a rotational vector operation to the vector potential is regarded as a magnetic field. The result of applying the rotational vector operation to the magnetic field is regarded as an electric field. A drawing on a plane or a three-dimensional model is configured to express both the magnetic and electric fields or one of the fields. The drawing or the model, as an educational tool, visualizes the figure of an atom, enables educands to have a close feeling toward sciences, and especially quantum mechanics, and enables them to have concrete images of various physical phenomena in the atom. The present invention, therefore, provides an educational tool that prevents educands from going away from sciences due to lack of an adequate educational tool of sciences and raises their interest in quantum mechanics inclined to be biased only toward mathematical research.
Owner:MATSUSHIMA HARUO
Magnetic field analytic calculating method for surface-mounted permanent magnet motor with tilted trough structure
ActiveCN104158458AThe calculation result is accurateElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsLinkage conceptNuclear magnetic resonance
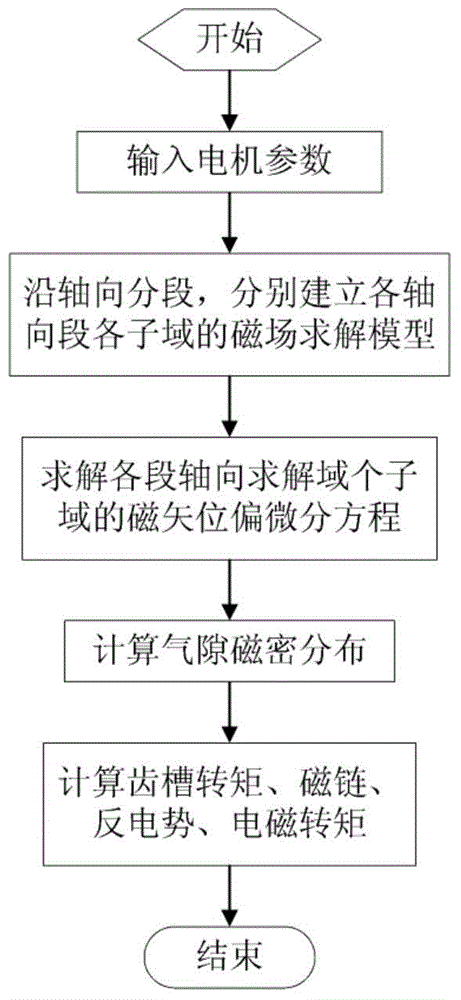
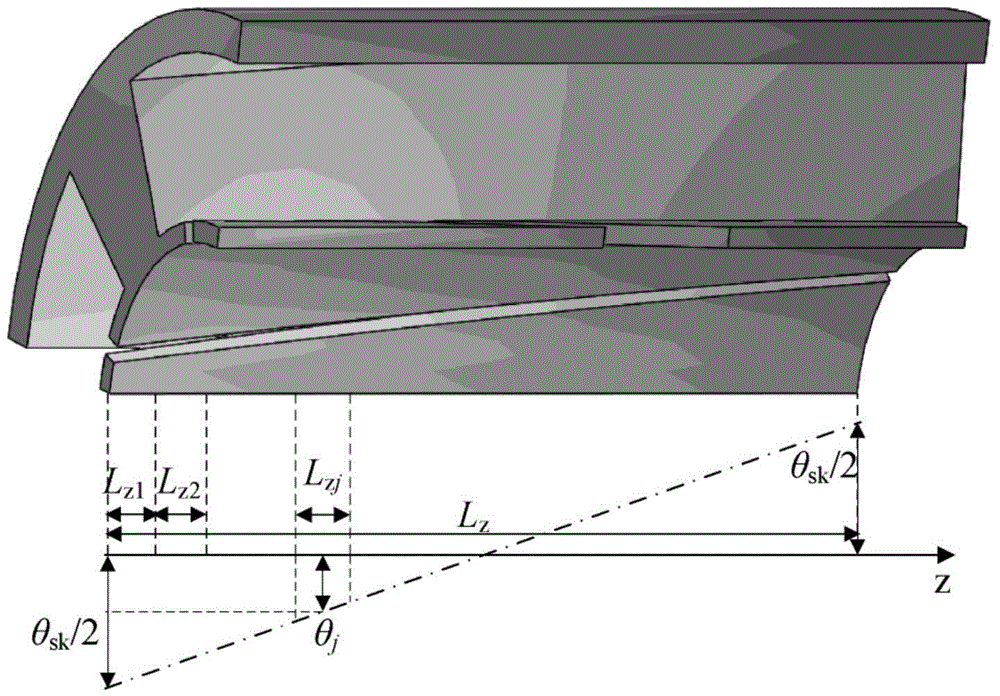
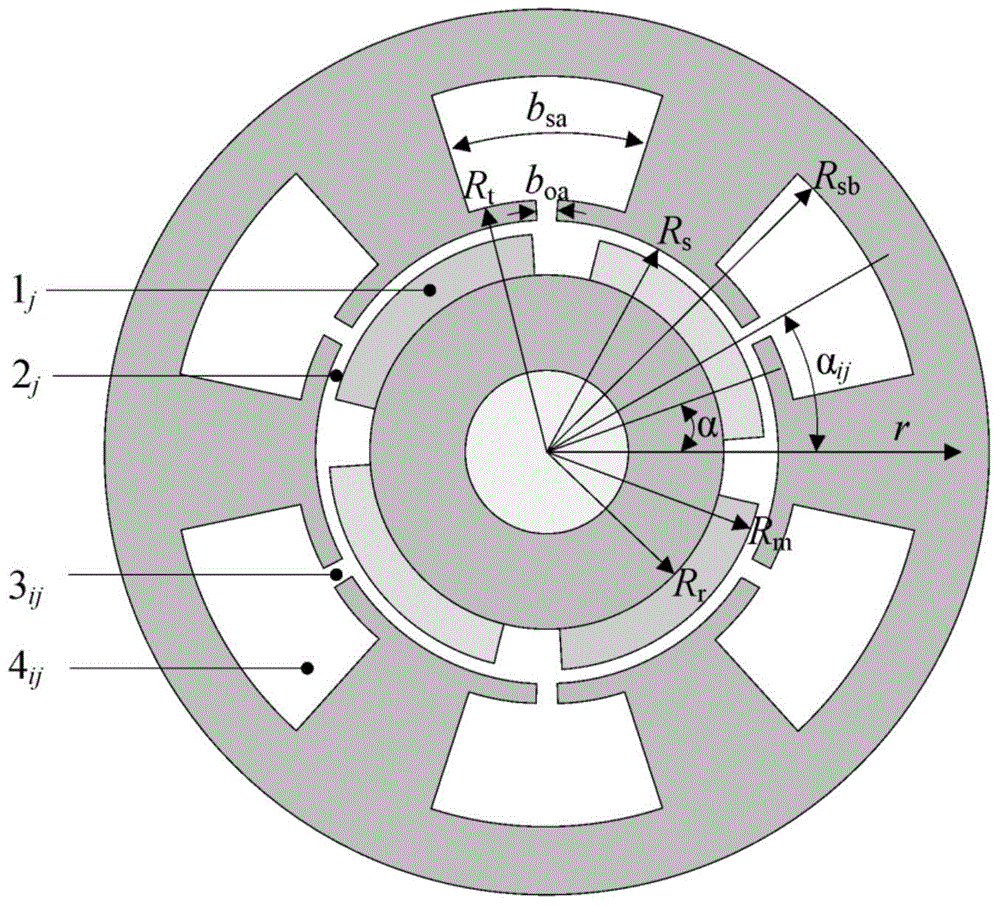
The invention discloses a magnetic field analytic calculating method for a surface-mounted permanent magnet motor with a tilted trough structure and relates to the field of permanent magnet motor magnetic field calculating technologies. The magnetic field analytic calculating method comprises the following steps: a motor is axially divided into Nz sections of magnetic field solution domains in three-dimensional space, each section of magnetic field solution domain is divided into four sub-domains, the magnetic vector potential partial differential equations of the sub-domains of each section are built respectively, the general solutions of the sub-domains of each section solution domain are worked out by adopting the separation quantity method, and the boundary conditions among the sub-domains of each solution domain are built to determine fourier coefficient values; the definite expressions of the magnetic vector potential partial differential equations of the sub-domains, namely, the magnetic vector potential functions of the sub-domains, are worked out; air gap magnetic flux density expressions are calculated based on the magnetic vector potential functions of the sub-domains, and the magnetic linkage, the cogging torque, the counter emf and the electromagnetic torque of the motor can be further calculated. According to the invention, the magnetic field calculation and performance analysis of the surface-mounted permanent magnet motor provided with a stator tilted trough can be conducted rapidly and accurately.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
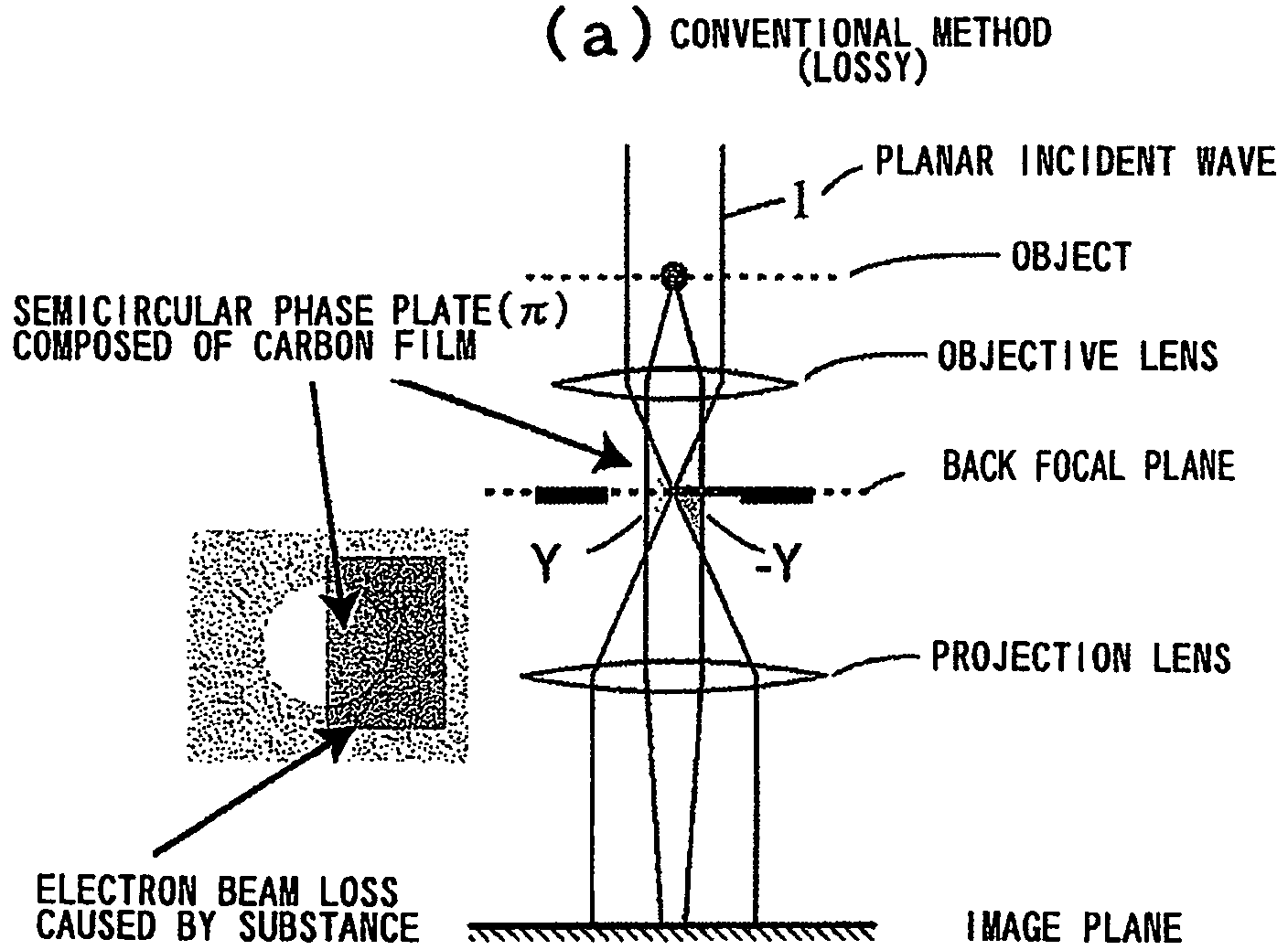
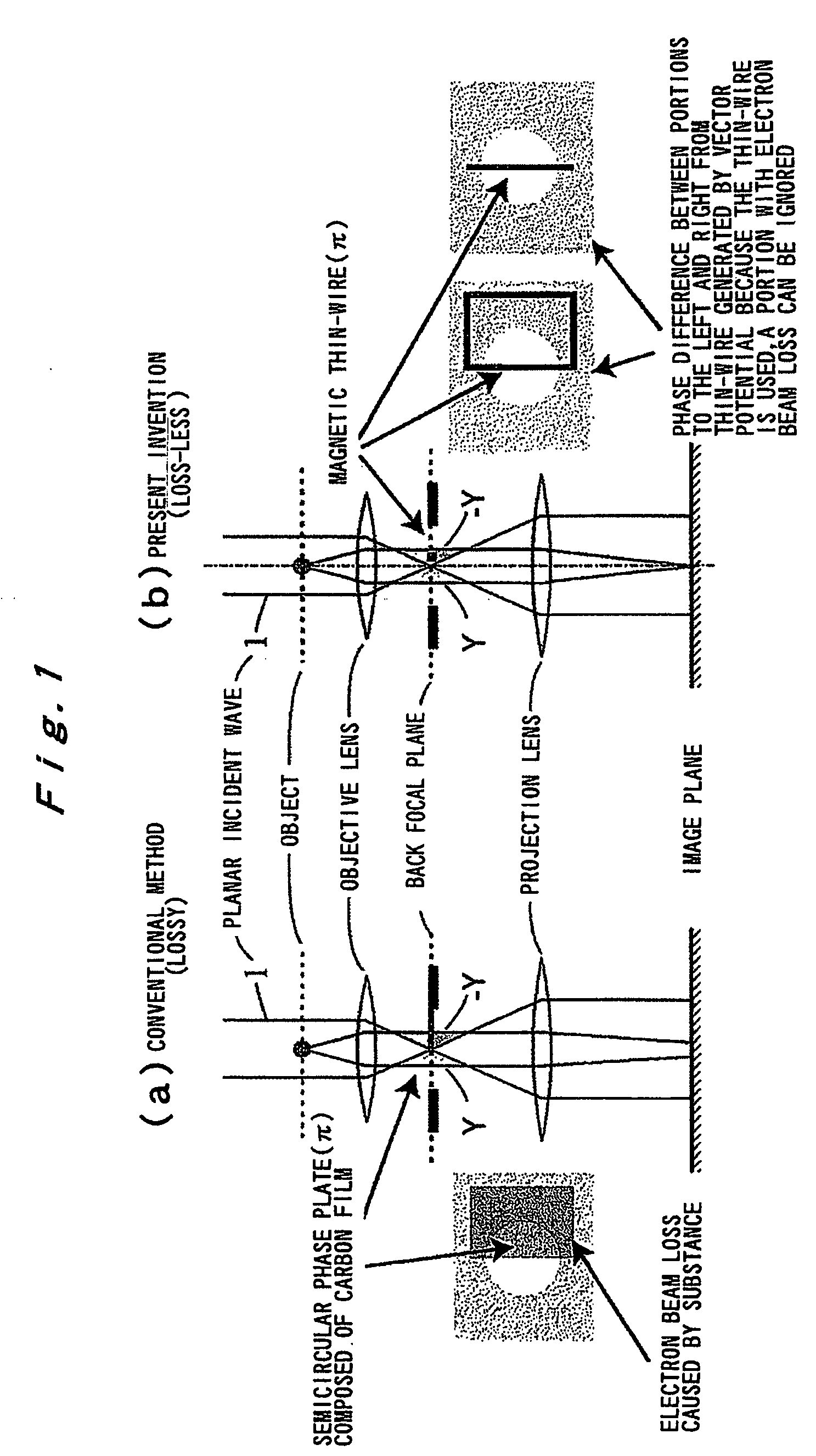
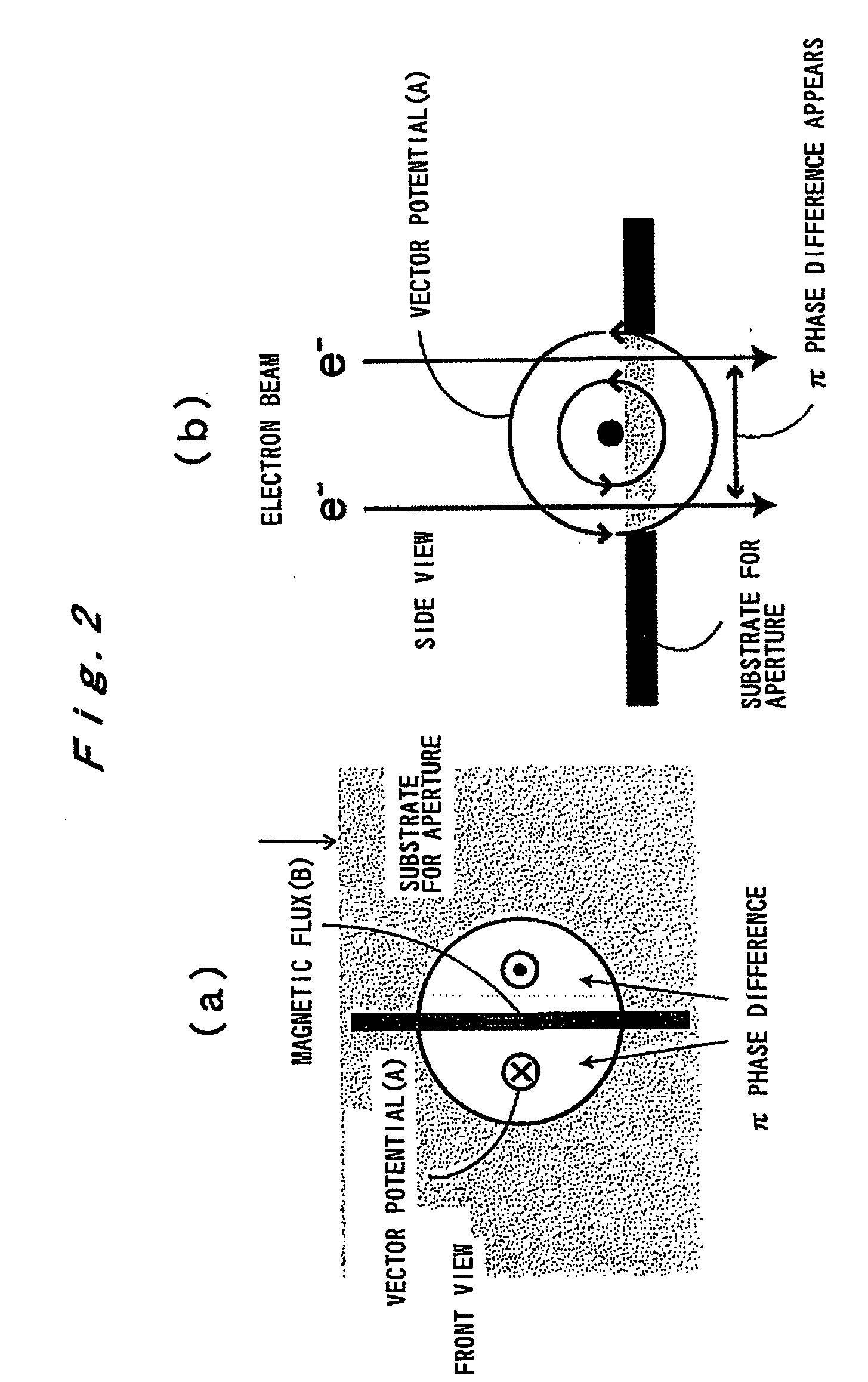
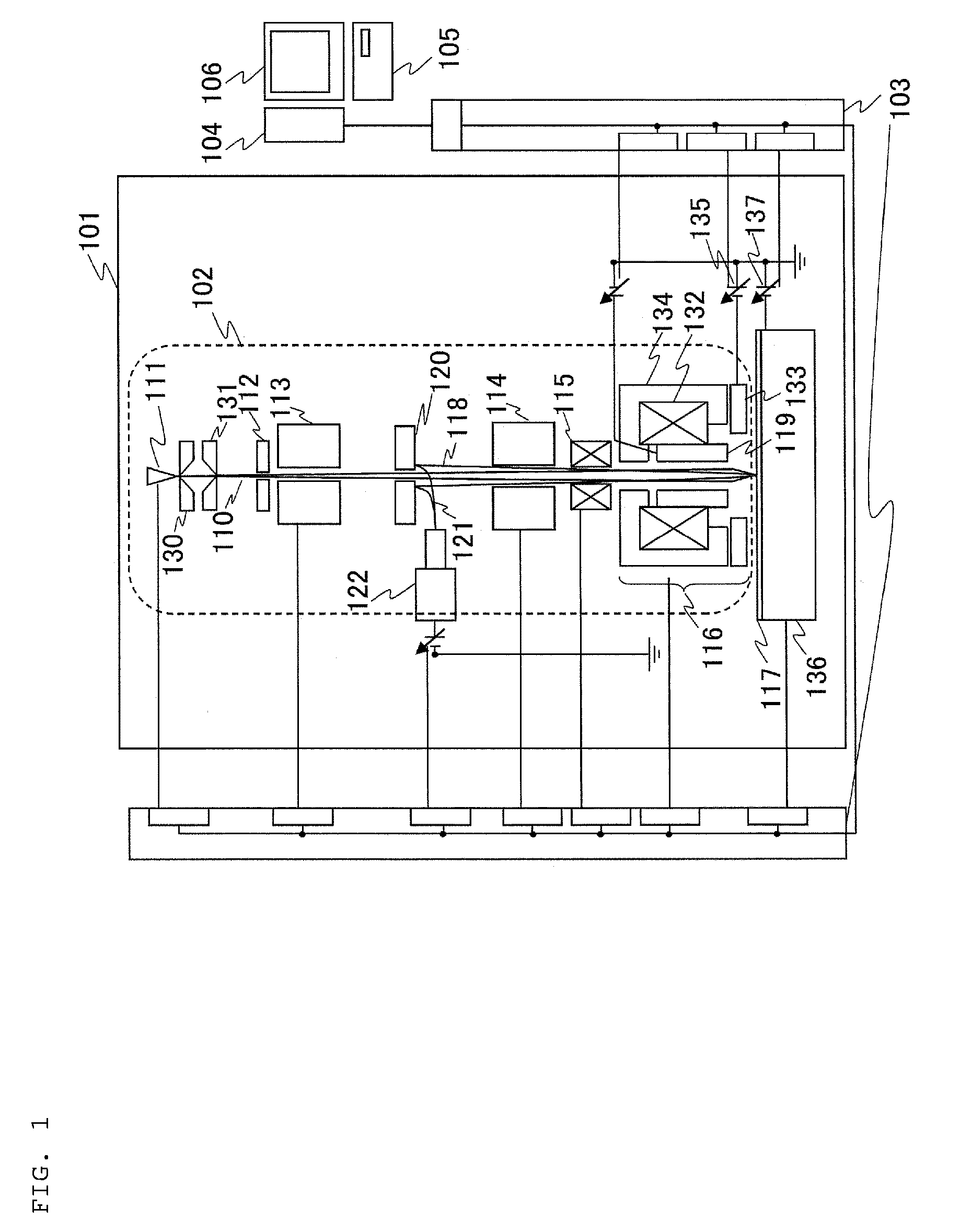
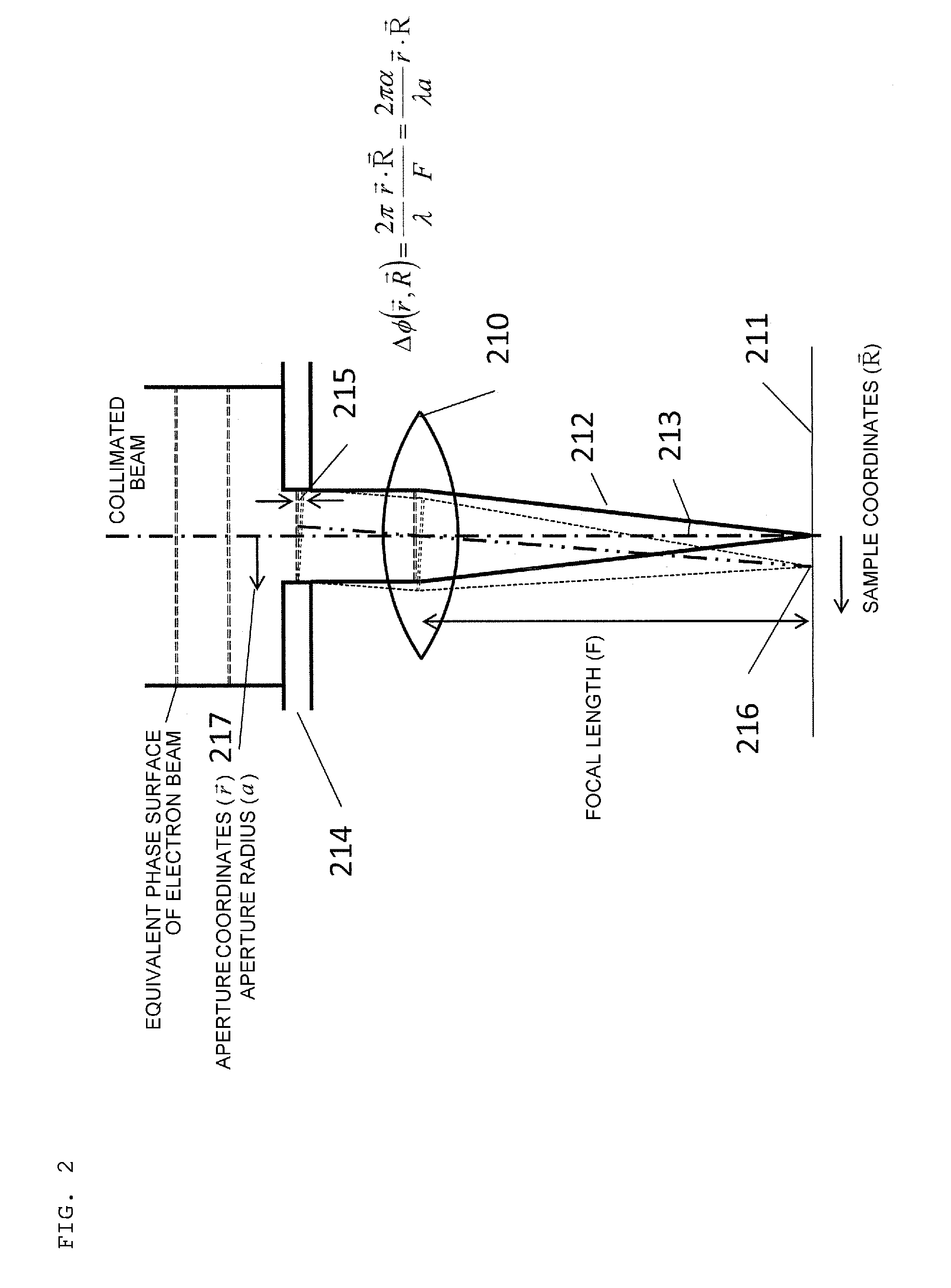
Phase Plate for Electron Microscope and Method for Manufacturing Same
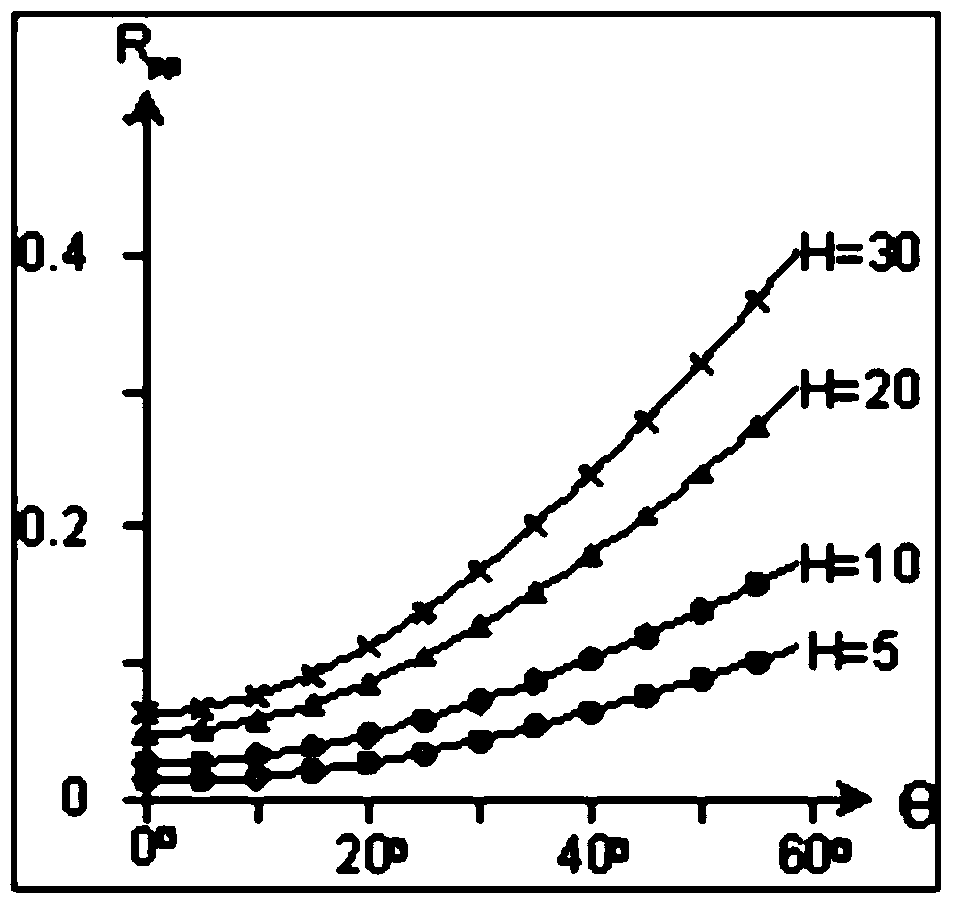
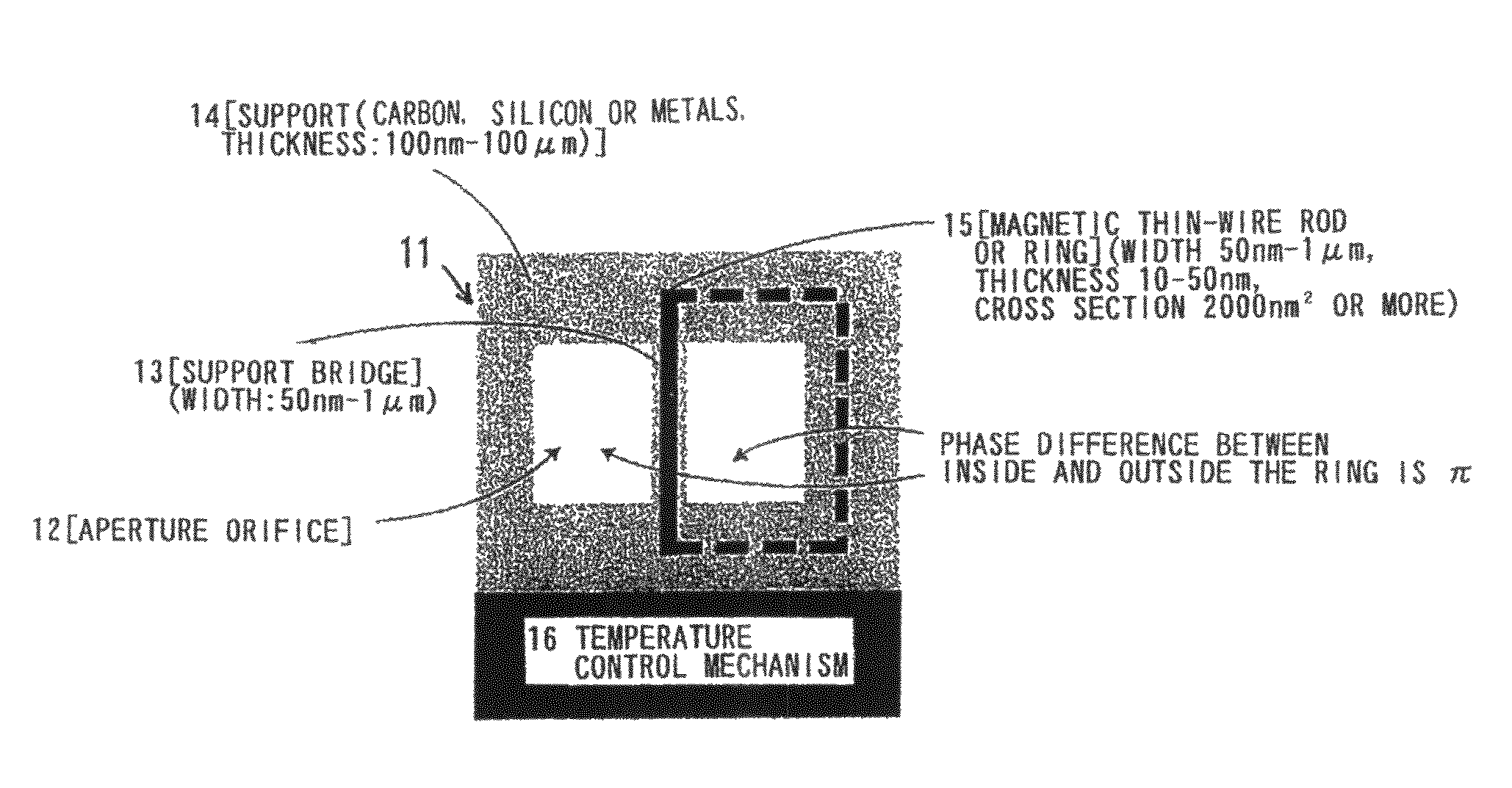
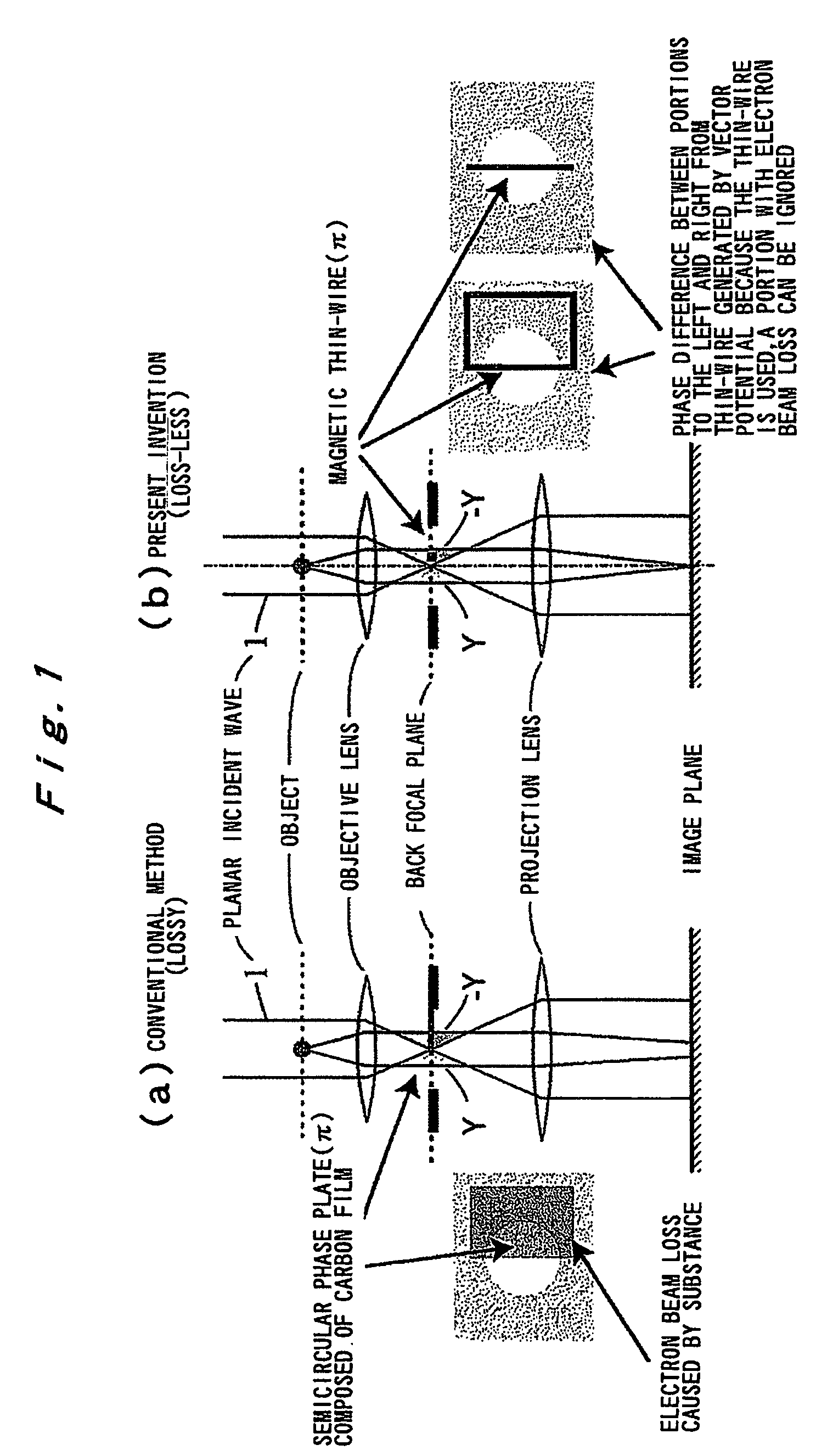
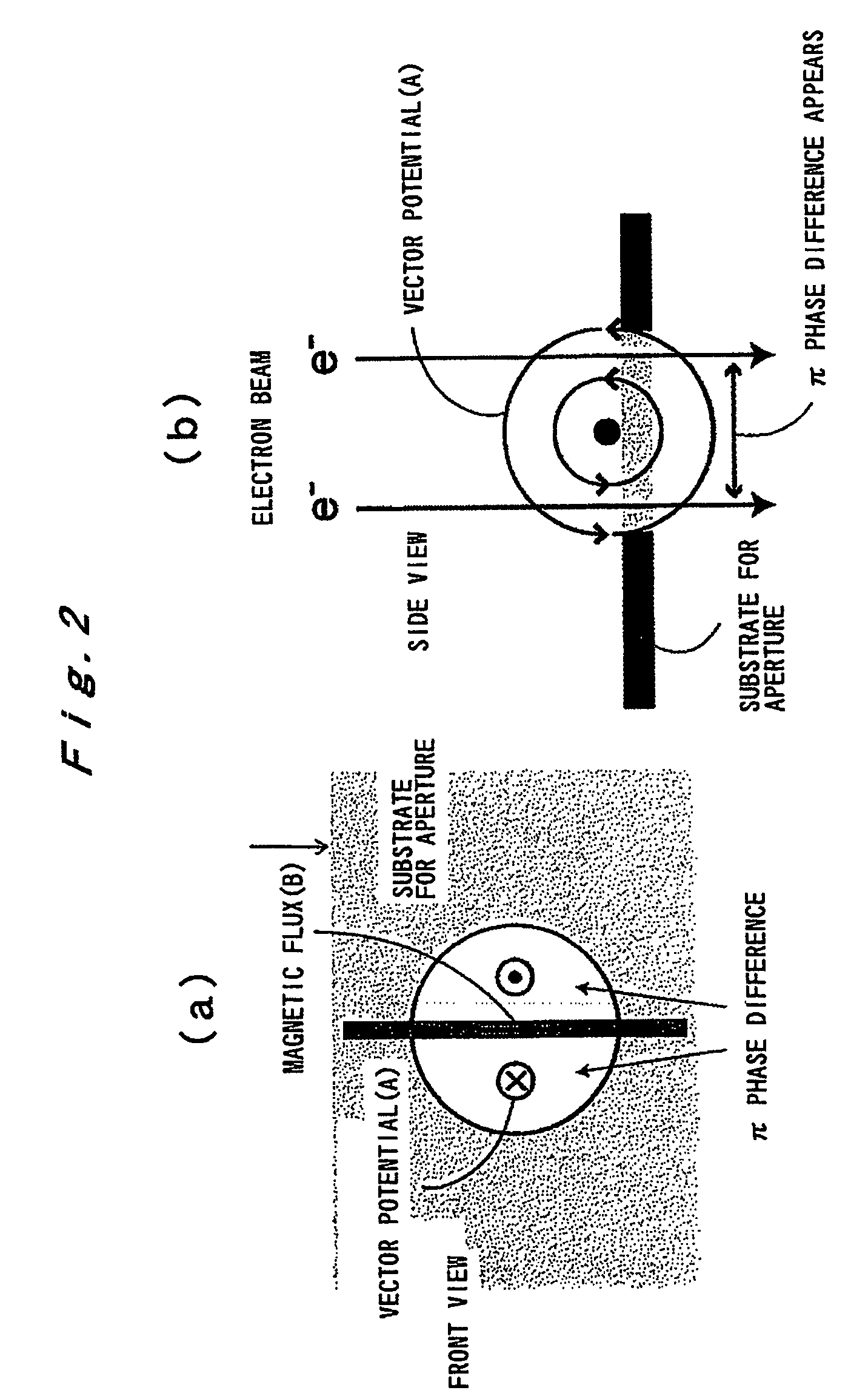
InactiveUS20090168142A1Avoid chargingPrevent electron beam lossMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesLow voltagePhase difference
A phase plate for an electron microscope in which a portion of a magnetic thin-wire ring or a magnetic thin-wire rod (15) spans an opening of a support member (14) having the opening, the magnetic thin-wire ring or magnetic thin-wire rod (15) generates a vector potential, and a phase difference is formed between electron beams that pass through left and right sides of a spanning portion of the magnetic thin-wire ring or the magnetic thin-wire rod (15). The phase plate prevents the electron beam loss more effectively, can be applied at an accelerating voltage within a wide rage from a low voltage to a high voltage, causes no difficulties in production, has good utility, and makes it possible to obtain a high-contrast image.
Owner:NAGAYAMA KUNIAKI
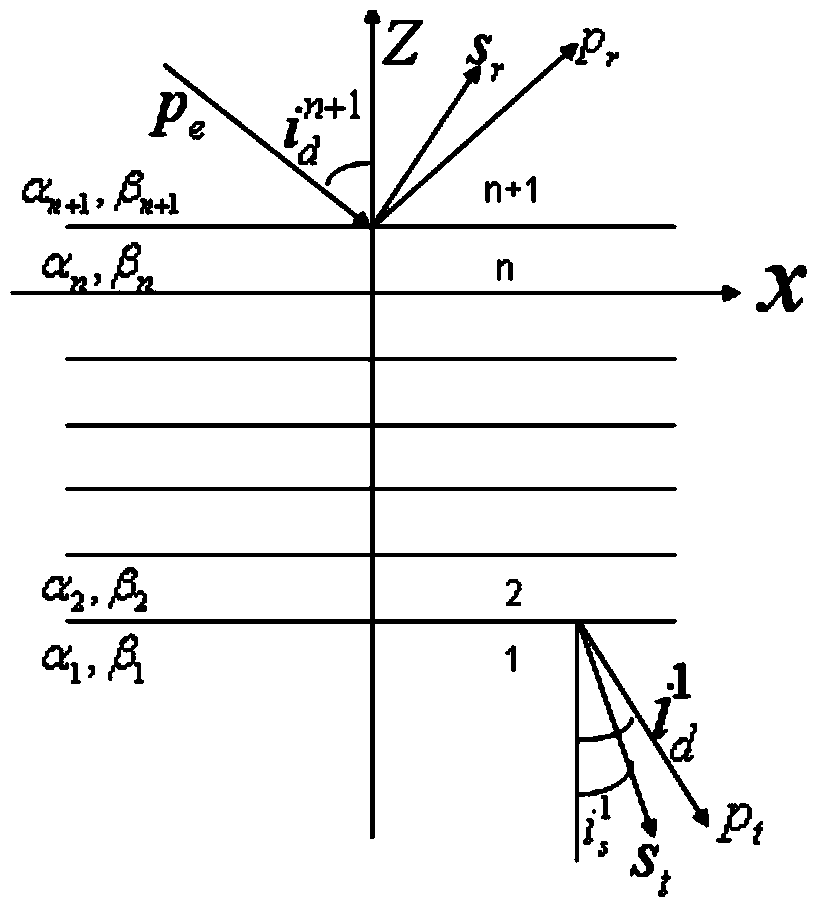
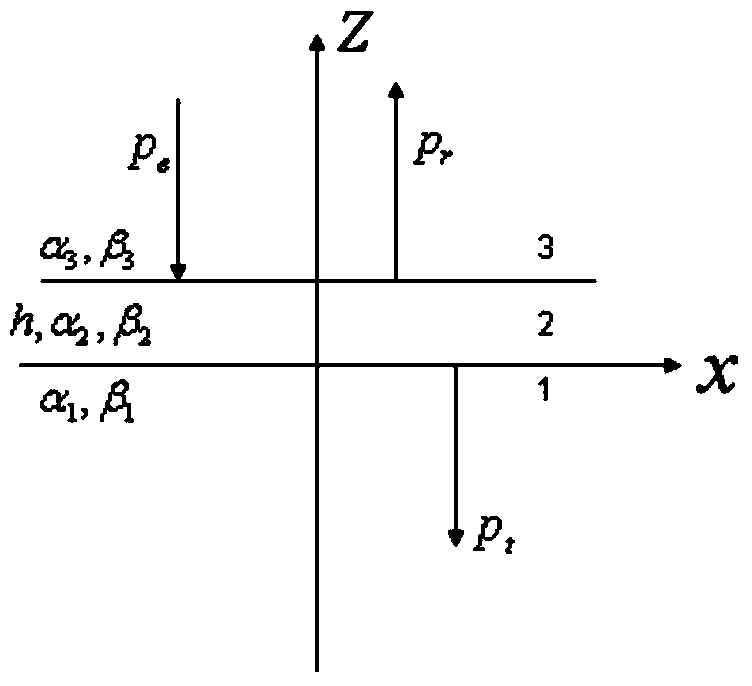
Method for calculating plane wave reflection coefficients in elastic multi-layered medium
The invention discloses a method for calculating plane wave reflection coefficients in an elastic multi-layered medium. The method comprises the following steps: (1) if plane harmonic waves enter into a target layer series from a medium n+1, generating reflected longitudinal waves and reflected transverse waves in the n+1 medium, generating transmitted longitudinal waves and transmitted transverse waves in a medium 1, and writing each medium layer in a scalar potential form and a vector potential form; (2) determining relation among the displacement, stress and bit shift; (3) loading the scalar potential and vector potential of the step (1) into the step (2) to obtain a displacement and stress relation expression between the (n+1)th layer and the first layer; and (4) obtaining a displacement and stress transfer matrix containing elasticity coefficients of each layer according to the displacement and stress relation expression, which is obtained in the steps (3), between the (n+1)th layer and the first layer, solving, and obtaining reflection and transmission coefficients. According to the method, the influence of multiple waves and transformed waves of the elastic layer series as well as thickness and frequency on the reflection coefficient is considered fully, so that the method is applicable to thin-layer AVO (Amplitude Variation with Offset) analytical simulation and is high in calculation efficiency.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Phase plate for electron microscope and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS7851757B2Avoid lostImprove overall utilizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesLow voltagePhase difference
A phase plate for an electron microscope in which a portion of a magnetic thin-wire ring or a magnetic thin-wire rod spans an opening of a support member having the opening, the magnetic thin-wire ring or magnetic thin-wire rod generates a vector potential, and a phase difference is formed between electron beams that pass through left and right sides of a spanning portion of the magnetic thin-wire ring or the magnetic thin-wire rod. The phase plate prevents the electron beam loss more effectively, can be applied at an accelerating voltage within a wide rage from a low voltage to a high voltage, causes no difficulties in production, has good utility, and makes it possible to obtain a high-contrast image.
Owner:NAGAYAMA KUNIAKI
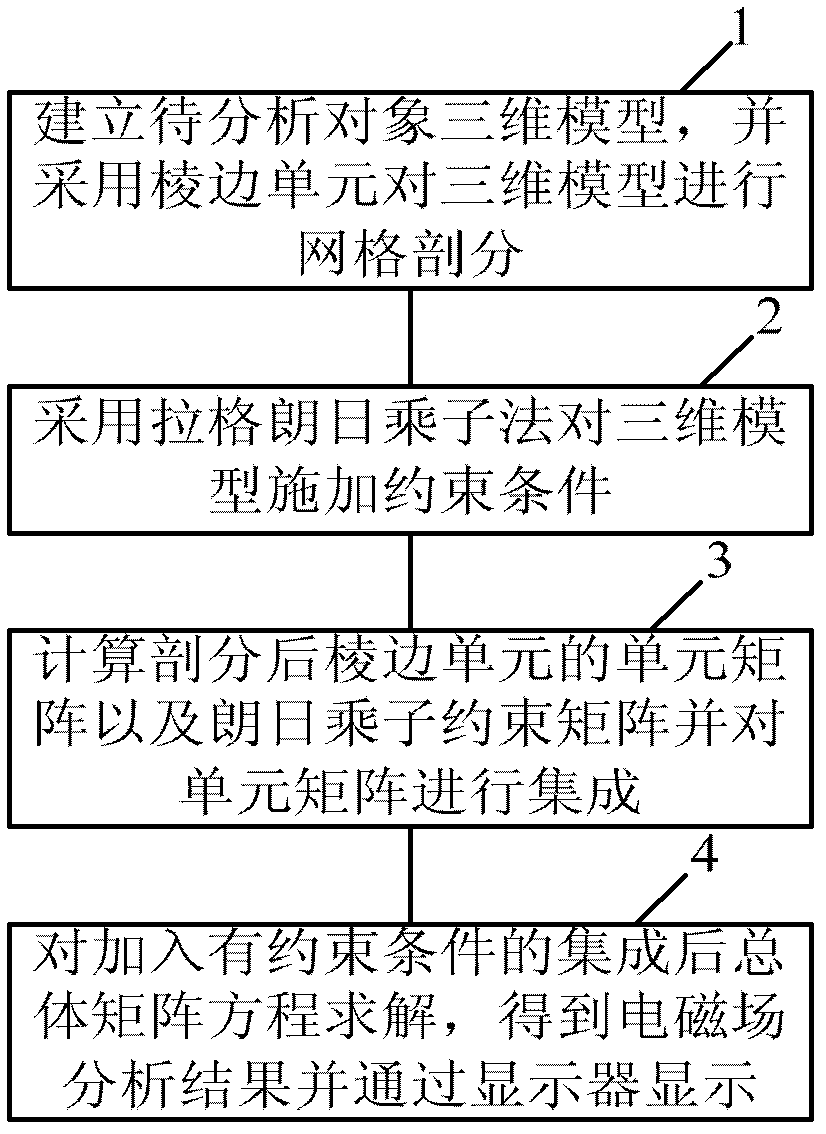
Electromagnetic field simulation analysis method
ActiveCN103186689AUniqueness guaranteedGuaranteed accuracySpecial data processing applicationsMulti fieldDisplay device
The invention discloses an electromagnetic field simulation analysis method which comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a three-dimensional model for an object to be analyzed, and performing mesh generation to the three-dimensional model by adopting a edge element; step 2, adopting the lagrangian multiplier method to apply constraint conditions to the three-dimensional model; step 3, calculating the element matrix of the edge element and the constraint matrix of the lagrangian multiplier method, and integrating the element matrix; and step 4, solving the integrated overall matrix equation with constraint conditions, obtaining analysis results of an electromagnetic field and displaying the analysis results through a display. According to the electromagnetic field simulation analysis method provided by the invention, a new constraint equation is introduced into the analysis field, a scalar multiplier space meeting the inf-sub condition is introduced, and the lagrangian multiplier method is adopted to realize constraints and ensure the uniqueness of the solution. The adaptability, reliability, and the accuracy of the solution of the electromagnetic field simulation analysis method are simultaneously ensured. The electromagnetic field simulation analysis method is applicable to a node vector potential unit and an edge vector potential unit, and is applicable to multi-field trans-boundary coupling problems.
Owner:INTESIM DALIAN
Computer simulation of electromagnetic fields
InactiveUS8886497B1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationVector potentialEngineering
A system and method for numerically computing electromagnetic fields that is based on extremizing the action integral. The scalar and vector potentials are parameterized. The electromagnetic fields that result from those scalar and vector potentials are derived, and then the parameters are varied to extremize the action integral. In an embodiment, a Lagrangian density is constructed from the electromagnetic fields and potentials. The variation of the action integral is computed as a series of equations in which each equation is the result of taking a derivative of the action integral with respect to a parameter of a Lagrangian density. Solving for the values of the parameters yields the electromagnetic fields.
Owner:VOLD TERJE GRAHAM
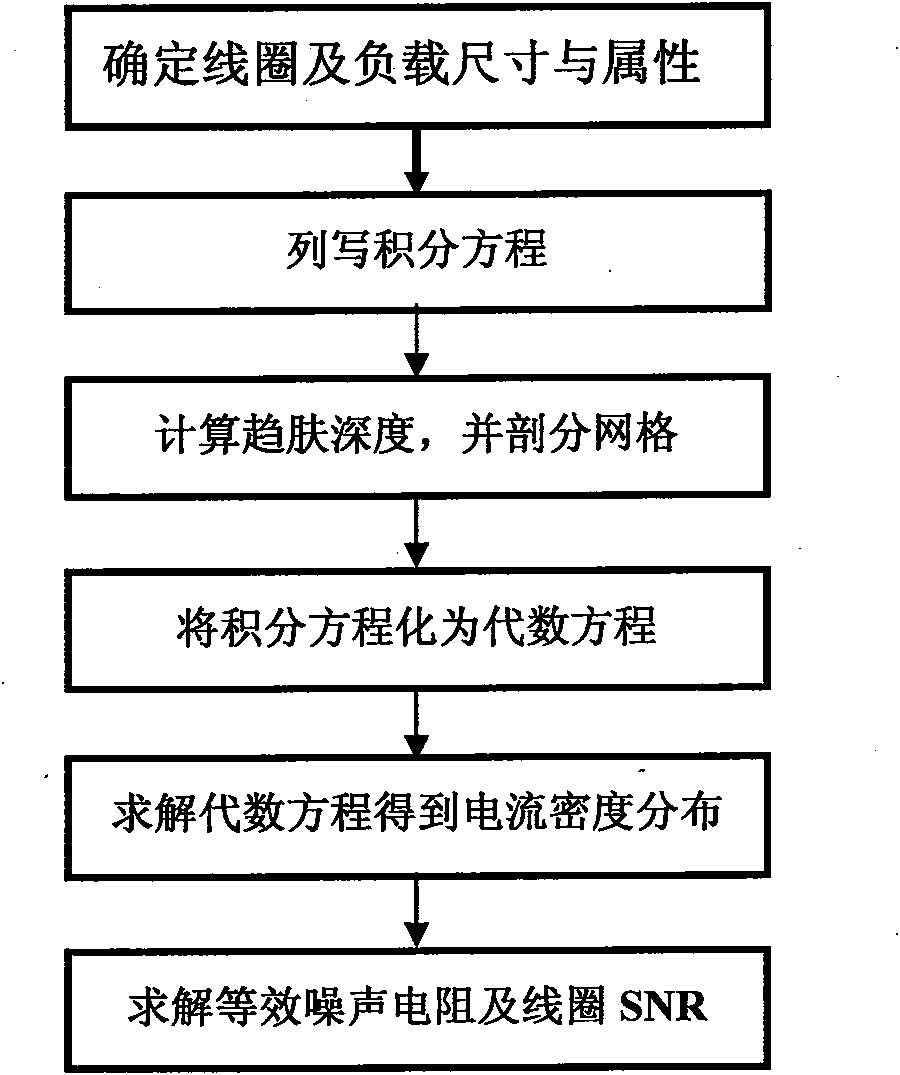
Method for calculating signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) RF coil
InactiveCN101794329AImprove accuracyAvoid computationSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical field strengthAlgebraic equation
The invention discloses a method for calculating a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) RF coil, belonging to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which is characterized by comprising the following steps: constructing an RF coil and a load size and material parameter model, listing integral equations satisfied by current densities, calculating skin depth and surface resistivity of a conductor and dissecting the conductor on the basis, converting the integral equations into algebraic equations, solving the algebraic equations to obtain current density distribution in the conductor, calculating magnetic flux density distribution in the load by using Biot-Savart integral, and adopting vector potential to obtain electric field strength distribution in the load, thus calculating self resistance, load eddy-current loss equivalent resistance and SNR of the RF coil. The invention improves the calculation efficiency of self resistance, load eddy-current loss and electric magnetic field space distribution of the conductor.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
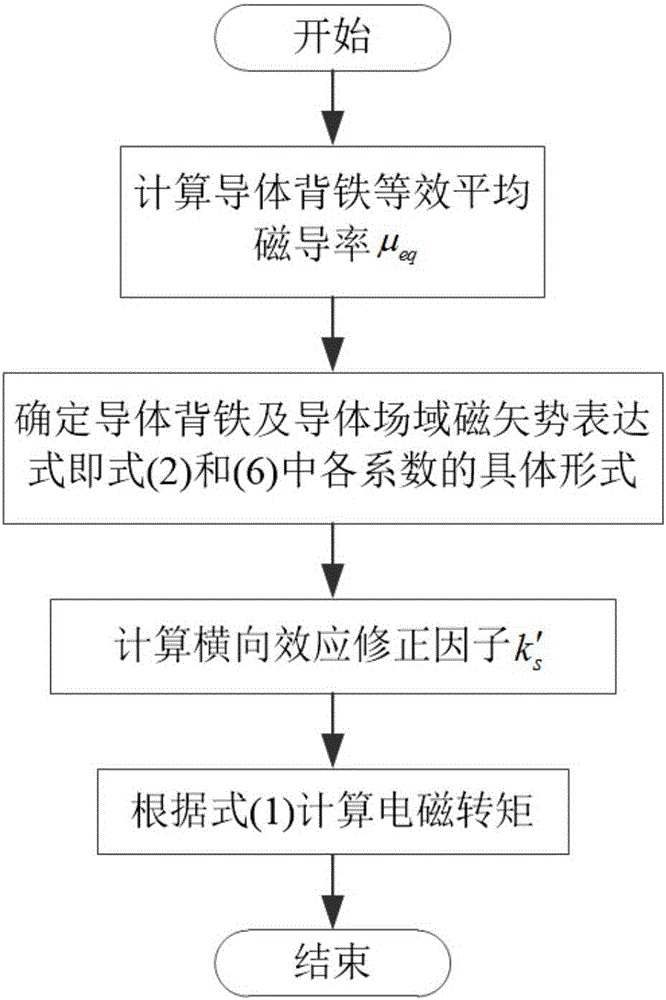
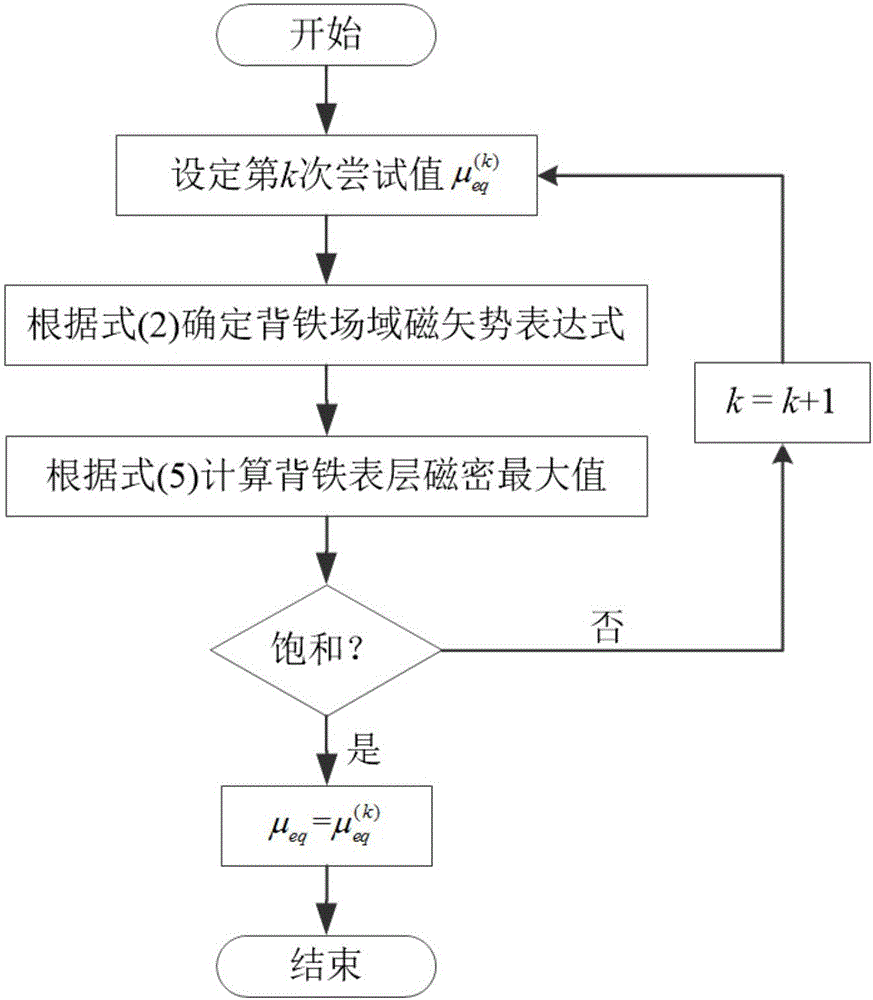
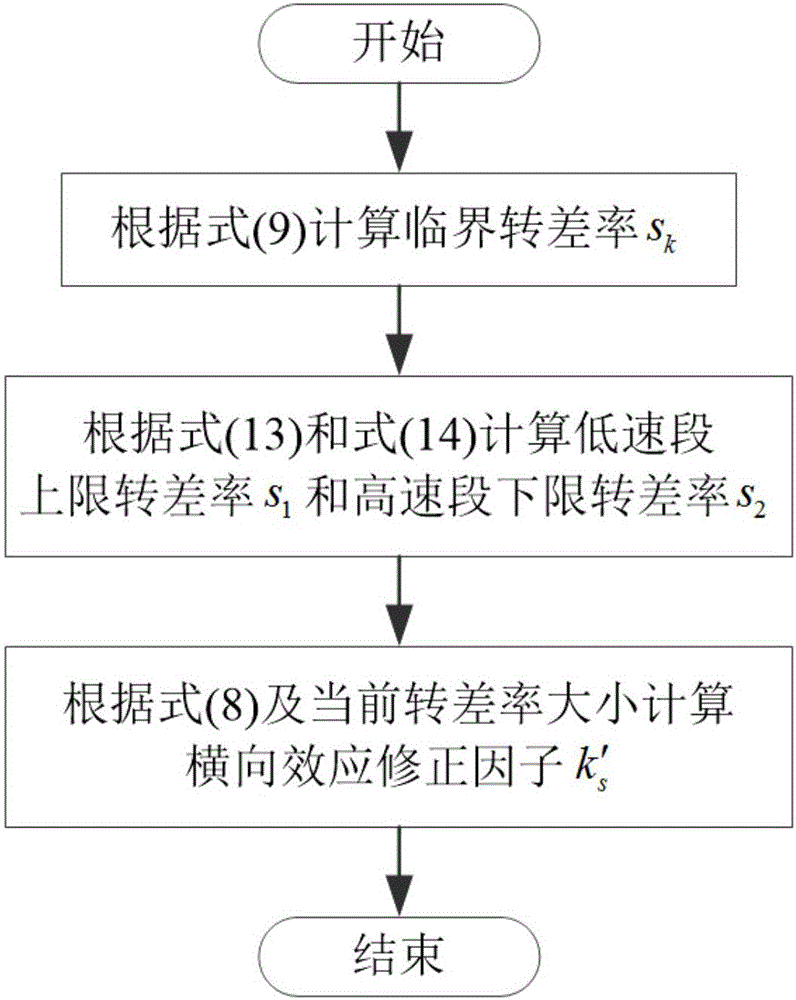
An axial magnetic flux permanent magnet eddy current coupler electromagnetic torque analysis algorithm
ActiveCN106021863ASmall differenceSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsElectrical conductorHarmonic
The invention provides an axial magnetic flux permanent magnet eddy current coupler electromagnetic torque analysis algorithm. The algorithm is characterized by firstly calculating the equivalent average magnetic conductivity [mu]eq of back iron of a conductor; determining the specific forms of various coefficients correlating with the number of times of harmonic n in field domain magnetic vector potential expressions of the conductor and the back iron thereof; then calculating an eddy current transverse effect correction factor k's; finally obtaining an electromagnetic torque value under the given air gap and slip ratio. The axial magnetic flux permanent magnet eddy current coupler electromagnetic torque analysis algorithm gives full consideration to the factor that the transverse effect correction factor changes with the speed (slip), the establish theoretical modeling is approximate to actual conditions, and permanent magnet eddy current coupler electromagnetic torques under various working conditions can be predicted accurately.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
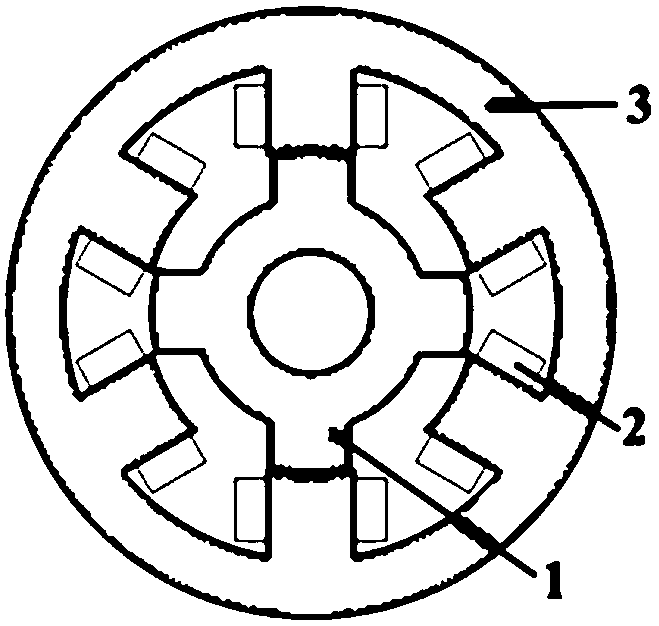
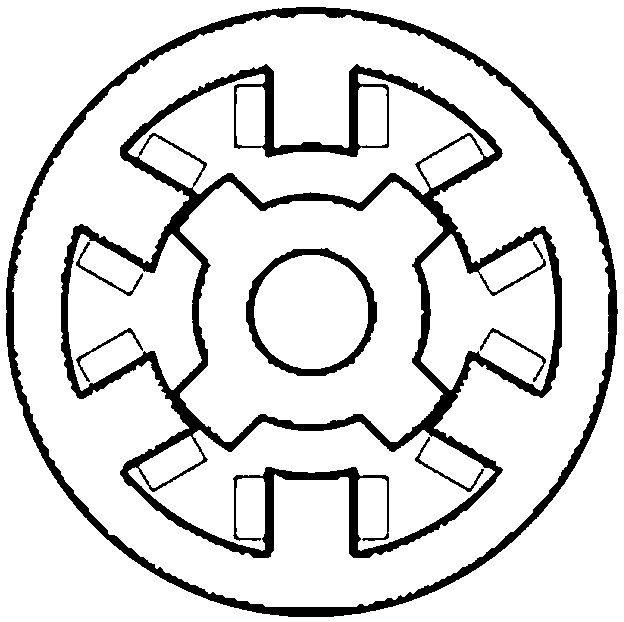
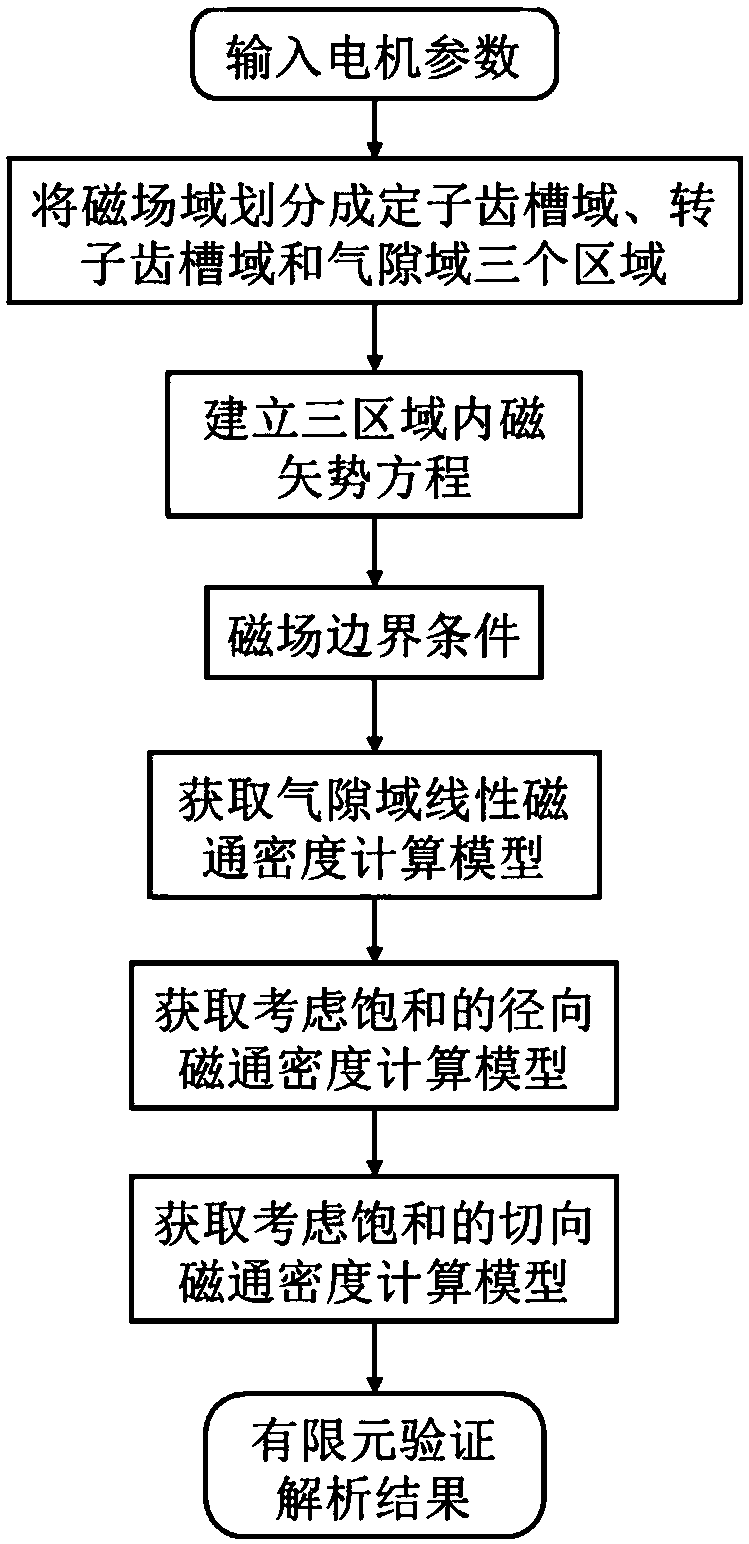
Switch reluctance machine magnetic field analysis calculation method capable of considering saturation
ActiveCN108875168AQuickly obtain analytical solutionsGet analytical solutionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDensity analysisVector potential
The invention relates to a switch reluctance machine magnetic field analysis calculation method capable of considering saturation. The method comprises the following steps that: 1) under a polar coordinate system, independently establishing the magnetic vector potential equations of a stator tooth socket domain, a rotor tooth socket domain and an air gap domain; 2) according to a magnetic field boundary condition and a relational expression between the magnetic vector potential and magnetic flux density, obtaining an air gap domain linear magnetic flux density parsing model; 3) under a Cartesian coordinate system, combining with the magnetic conductivity-magnetic flux density characteristic curve of a ferromagnetic material to obtain a radial magnetic flux density parsing model which considers the saturation; and 4) according to the saturation radial magnetic flux density, solving dynamic magnetic conductivity in a process, and further obtaining a tangential magnetic flux density analysis calculation model which considers the saturation. Compared with the prior art, the method is characterized in that the quick and accurate calculation of the switch reluctance machine air gap magnetic field is realized, and a theoretical basis is provided for designing a high-performance motor.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Resistivity reconstructing method utilizing linear doublecurl equation to proceed magneto thermo-acoustic imaging
ActiveCN104434099AInfrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringThermoacousticsVector potential
The invention discloses a resistivity reconstructing method by utilizing linear double curl equation to proceed magneto-thermo-acoustic imaging. The method includes the following steps: firstly, acquiring thermo-acoustic signals of conductive objects subjected to circular tomography; secondly, acquiring thermo-acoustic source distribution on an arbitrary fault surface of the conductive object by utilizing a time reversal algorithm according to an acoustic pressure wave equation of magneto-thermo-acoustics; thirdly, drawing forth a vector potential to assume an initial value of the resistivity of the conductive object through the current continuity theorem; fourthly, solving a vector potential spatial component with the initial value of the resistivity, and then substituting the solved spatial component of vector electric potential to the thermal-acoustic source distribution to acquire an updated conductivity distribution; fifthly, comparing the updated resistivity with a resistivity set with the initial value, checking whether a given relative error is met, if yes, confirming that the updated resistivity is the solved resistivity, if not, backing to the third step to perform iterating, and using the updated resistivity as an initial resistivity to further solve the updated resistivity, thereby acquiring the conductivity distribution of the conductive object.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
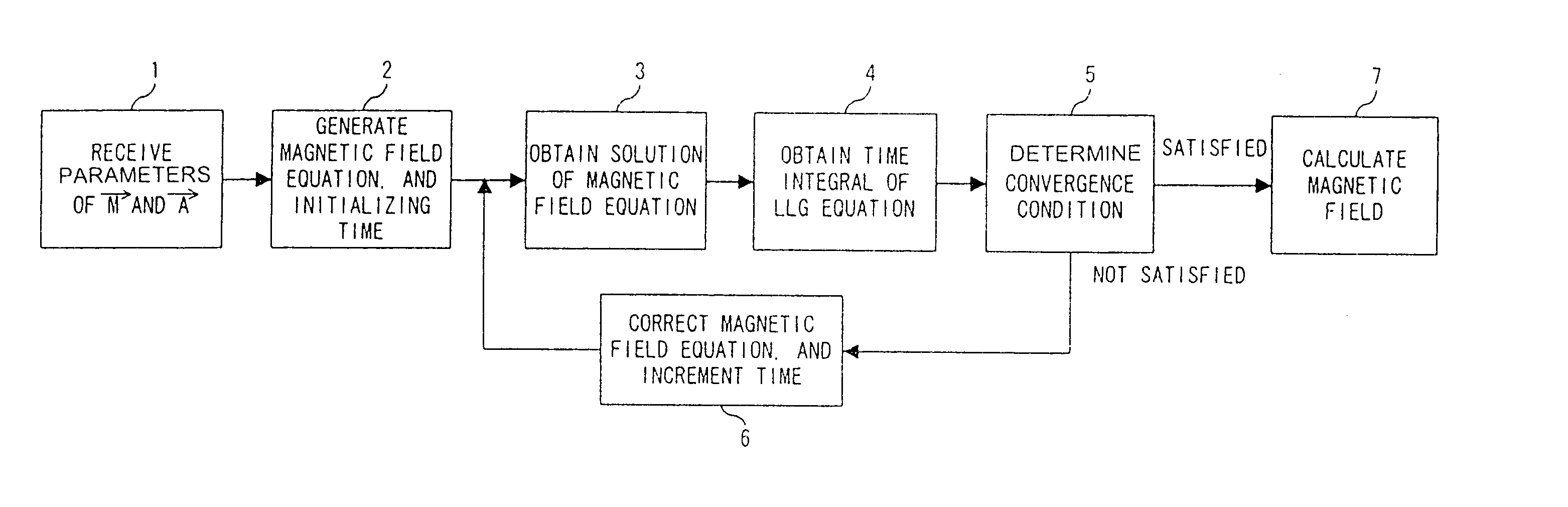
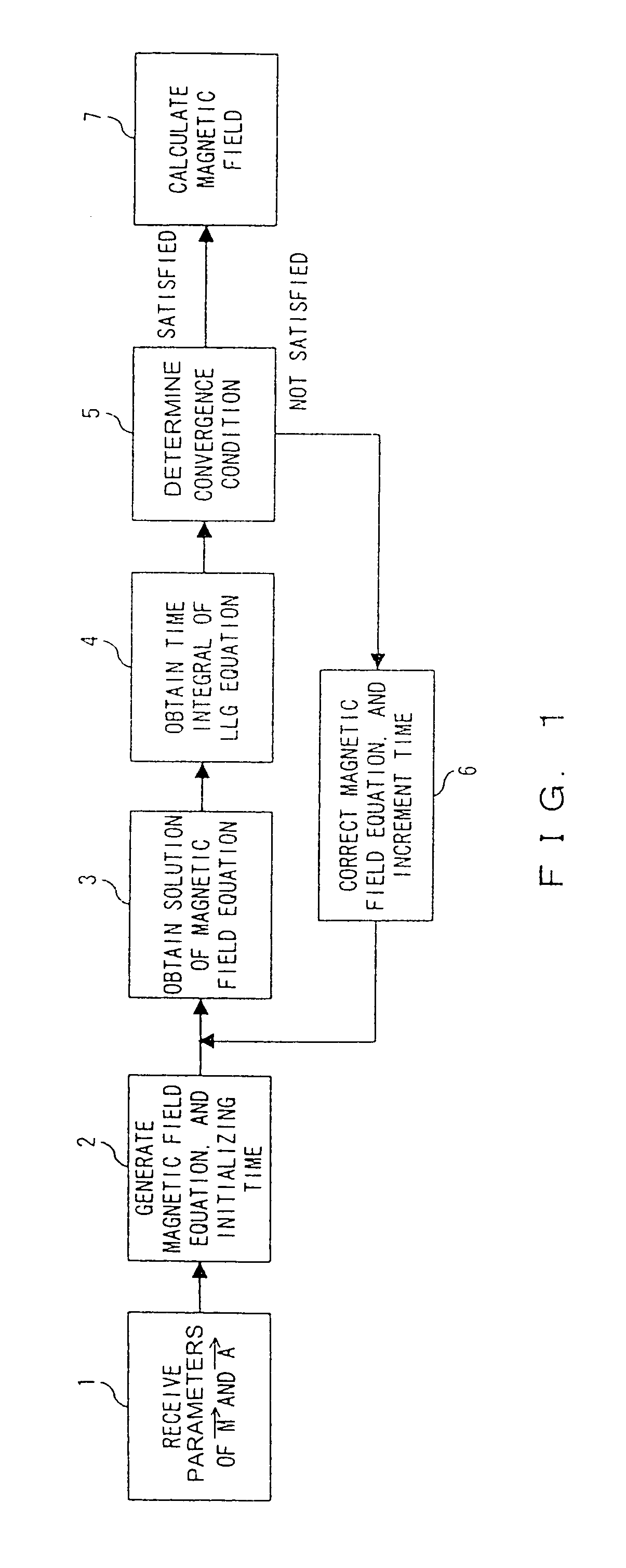
Micromagnetization analytical program and apparatus
InactiveUS7058527B2Improve analysis accuracyVehicle testingMagnetisation measurementsVector potentialDisplay device
The precision of a micromagnetization analysis is improved. Parameters of the micromagnetization assigned to the center of a divided microelement and the vector potential assigned to a side or a node of the element are received in procedure 1. A magnetic field equation which supplies an external magnetic field for micromagnetization is generated in procedure 2. A solution of the magnetic field equation is obtained in display 3. A time integral of a LLG equation is obtained using the solution in procedure 4. It is determined in procedure 5 whether or not the micromagnetization obtained in procedure 4 satisfies a convergence condition. When it is not satisfied, a magnetic field equation is corrected and a time is stepwise increased in procedure 6, and the procedures in and after procedure 3 are repeated.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Conductivity image reconstructing method for magneto-thermoacoustic coupled tomography
A conductivity image reconstructing method for magneto-thermoacoustic coupled tomography includes: acquiring a thermoacoustic source distribution of a conductive object by means of time inversion according to an electromagnetic ultrasonic signal received, and performing reconstruction according to the thermoacoustic source distribution to obtain a conductivity distribution of the conductive object. Specially, the method includes: acquiring a thermoacoustic source on a certain level by means of time inversion, acquiring a thermoacoustic source of the conductive object by means of interpolation, performing calculation by means of Biot-Savart's law according to excitation current to obtain a spatial component A1 of primary magnetic vector potential, subjecting the conductive object to spatial discretization, giving an initial value [Sigma]<0> of conductivity, according to the theorem of current continuity, solving a spatial component [Phi] <1> of scalar potential with the initial value [Sigma]<0> and the spatial component A1, substituting the spatial component [Phi]<1> of the scalar potential to a relation which the thermoacoustic source and conductivity meet so as to obtain updated conductivity [Sigma]<1>, replacing the initial value [Sigma]<0> with the updated conductivity [Sigma]<1>, repeating the process above, and stopping iteration until a relative error of the conductivity meets an equation: Sigma=||([Sigma]1-[Sigma]0) / [Sigma]0||2<=Sigma0.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
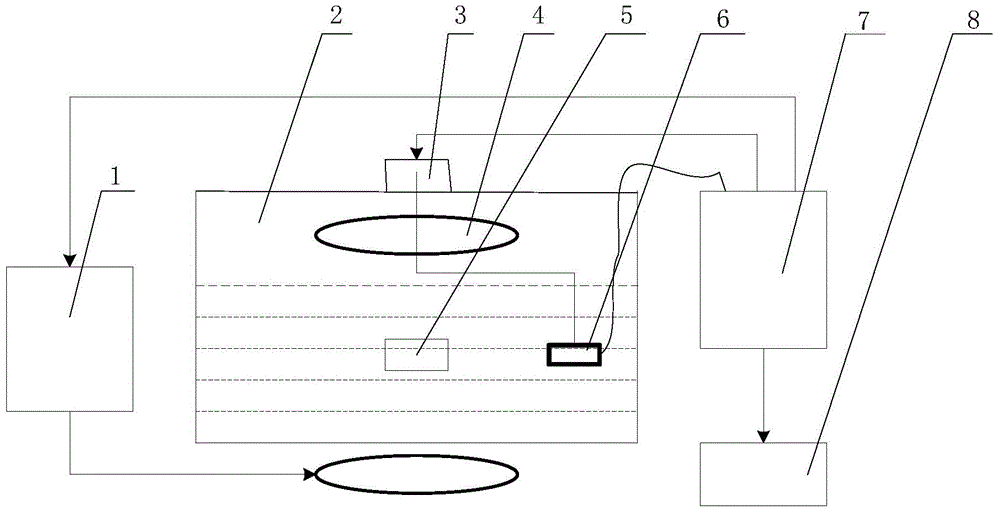
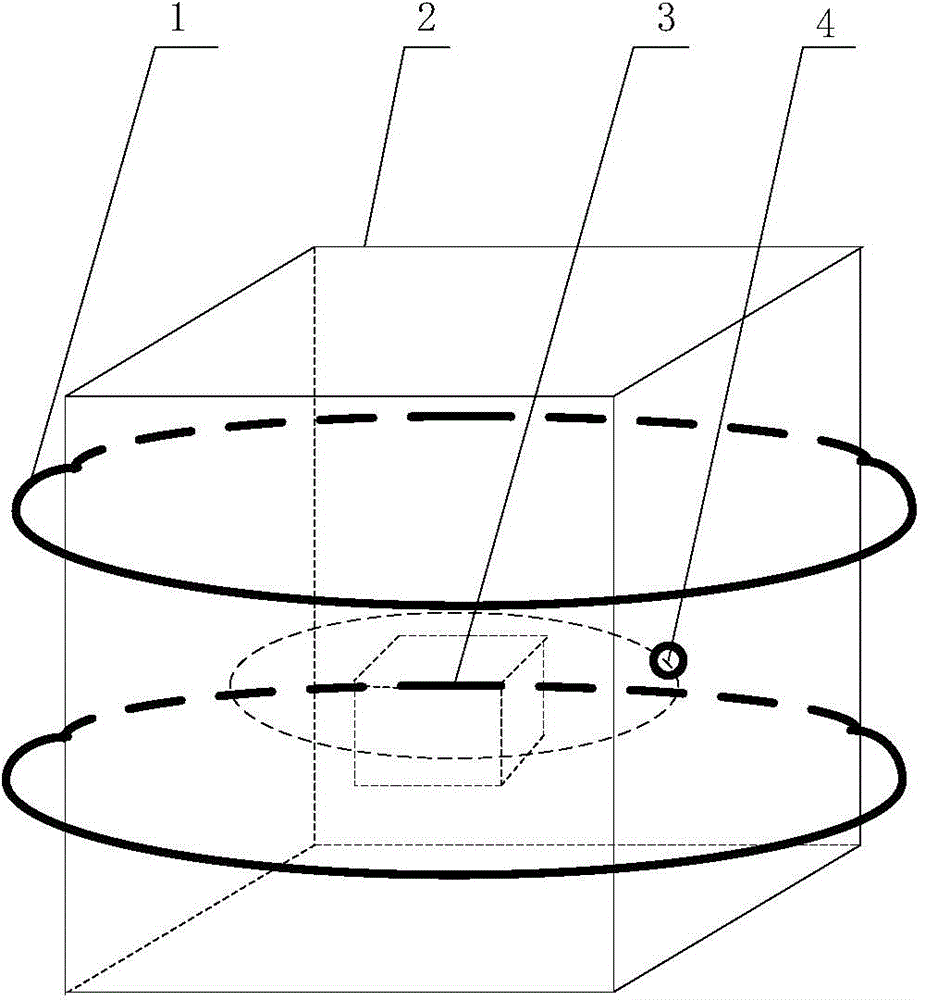
Resistivity reconstruction method for magneto-thermoacoustic tomography
A resistivity reconstruction method for magneto-thermoacoustic tomography includes the steps of 1, applying MHz current excitation to a conductive object (3) through an excitation coil (2), and allowing the conductive object (3) to generate joule heat under the action of induction current so as to generate a thermoacoustic signal; coupling the thermoacoustic signal to an ultrasonic transducer (4) through coupler; after the ultrasonic transducer (4) receives an ultrasonic signal, performing pre-amplification, filtration, secondary amplification and the like to the ultrasonic signal with an ultrasonic signal processing and acquiring subsystem, storing the ultrasonic signal, and acquiring a high-resolution magneto-thermoacoustic signal; 2, reconstructing a thermoacoustic source distribution through the acquired magneto-thermoacoustic signal; 3, reconstructing a vector potential spatial component; and 4, solving resistivity through the vector potential spatial component.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
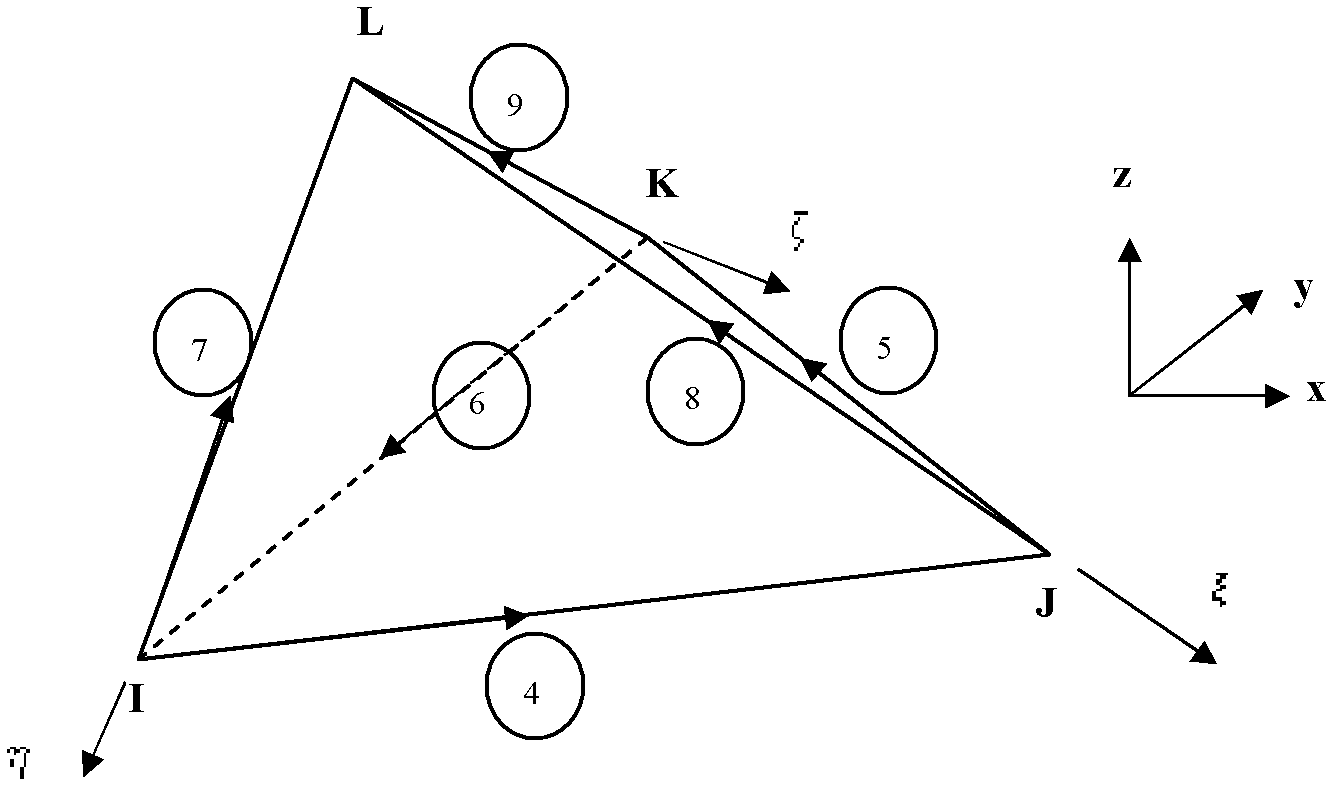
Coupling method for processing moving boundary problems in electromagnetic field based on edge element method
ActiveCN103699752AGood mannersAccurate and reliableSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringElectromagnetic field
The invention discloses a coupling method for processing moving boundary problems in an electromagnetic field based on an edge element method. The method includes: establishing a three-dimensional model, generating meshes of a moving region and a stationary region of the model, and forming a slip plane at a boundary of the two regions; establishing a basic equation for solving the electromagnetic field, adopting a Lagrangian multiplier method to apply standard conditions, calculating an edge element matrix of each region and integrating the edge element matrixes; when the meshes in the moving region move along the slip plane, adopting the Lagrangian multiplier method to couple degree of freedom of magnetic vector potential on the slip plane, generating a Lagrangian multiplier constraint matrix, and integrating the constraint matrix; on the slip plane, standardizing an introduced Lagrangian scalar multiplier, and coupling by adopting an MPC (multi-point constraint) method; applying boundary conditions to a finite element population equation obtained through the above steps and solving to obtain an electromagnetic field analysis result of a to-be-analyzed object. A finite element matrix obtained by the method is good in behavior, and computed results are accurate and reliable.
Owner:INTESIM DALIAN
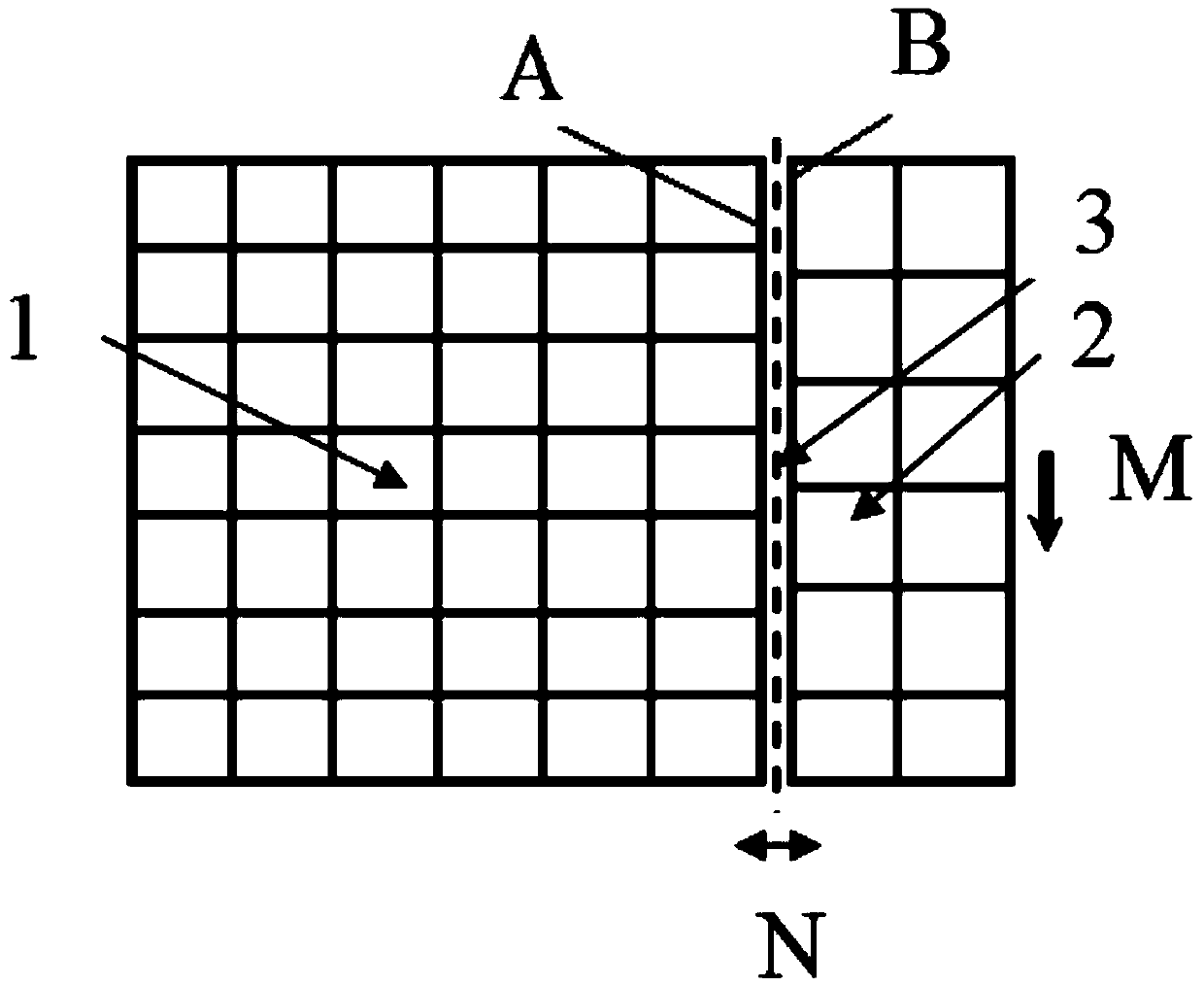
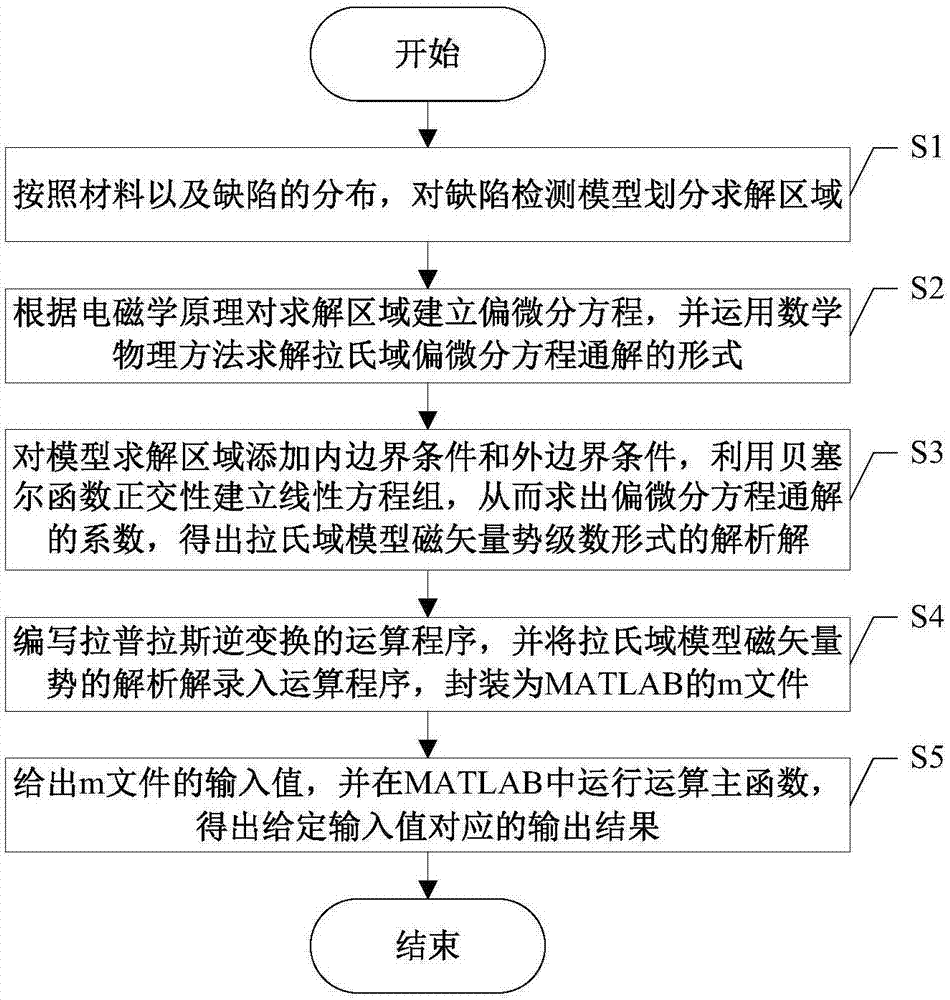
Semi-analytic calculation method for eddy nondestructive testing magnetic field containing column defect
ActiveCN107038302AImprove solution efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a semi-analytic calculation method for an eddy nondestructive testing magnetic field containing a column defect. According to the method, mathematical physics and electromagnetic field principles are utilized to obtain a precise analytic expression of magnetic vector potential under a Laplace domain, and numerical method inverse Laplace transformation is performed on a complex expression of a series form of the magnetic vector potential based on MATLAB to obtain a time-domain solution to an eddy nondestructive testing signal in a conductor containing the column defect. Through the method, the eddy nondestructive testing magnetic field of the conductor containing the column defect can be calculated accurately and efficiently, and a theoretical basis is provided for application of the eddy nondestructive testing technology in the defect quantitative recognition field.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
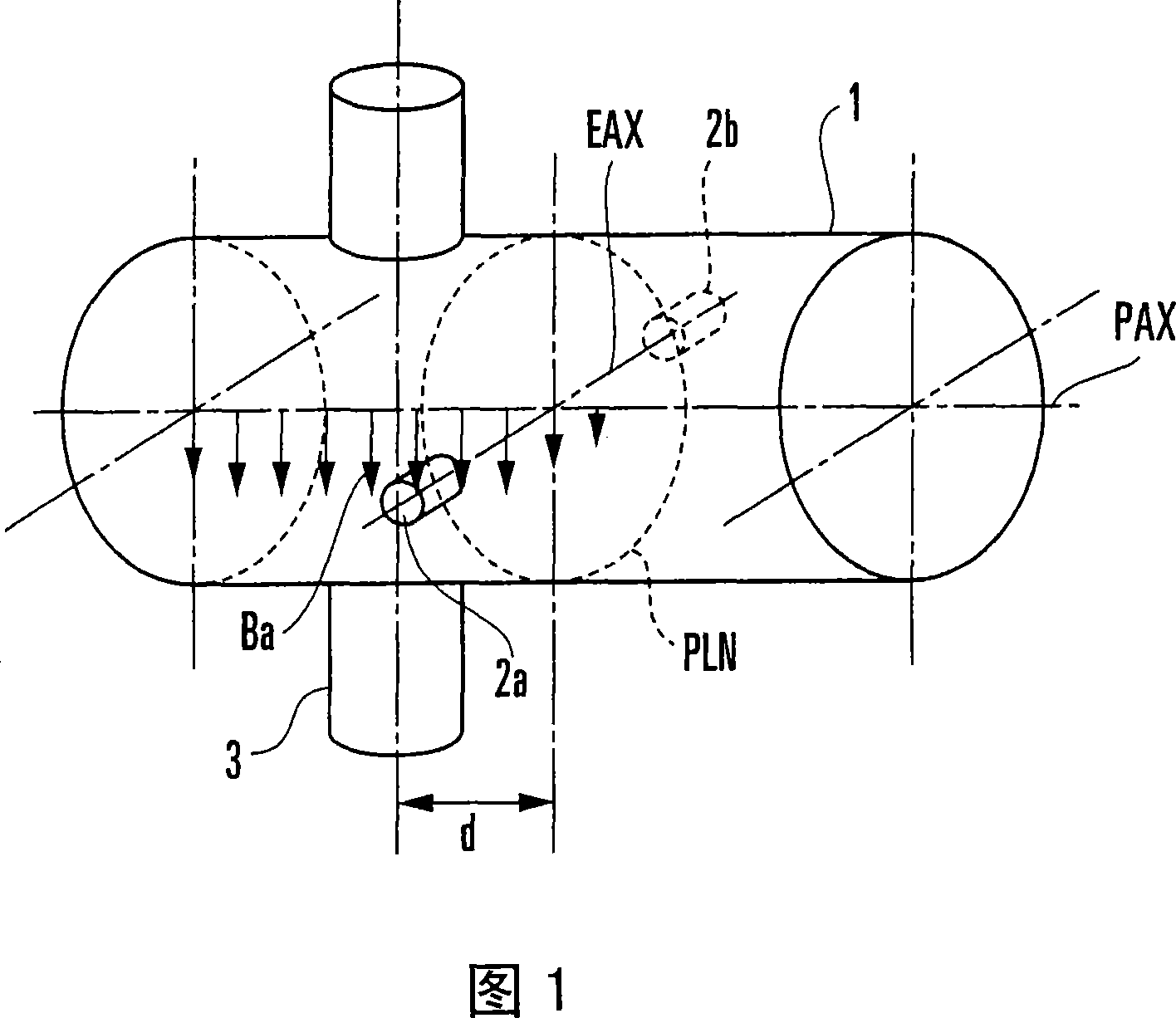
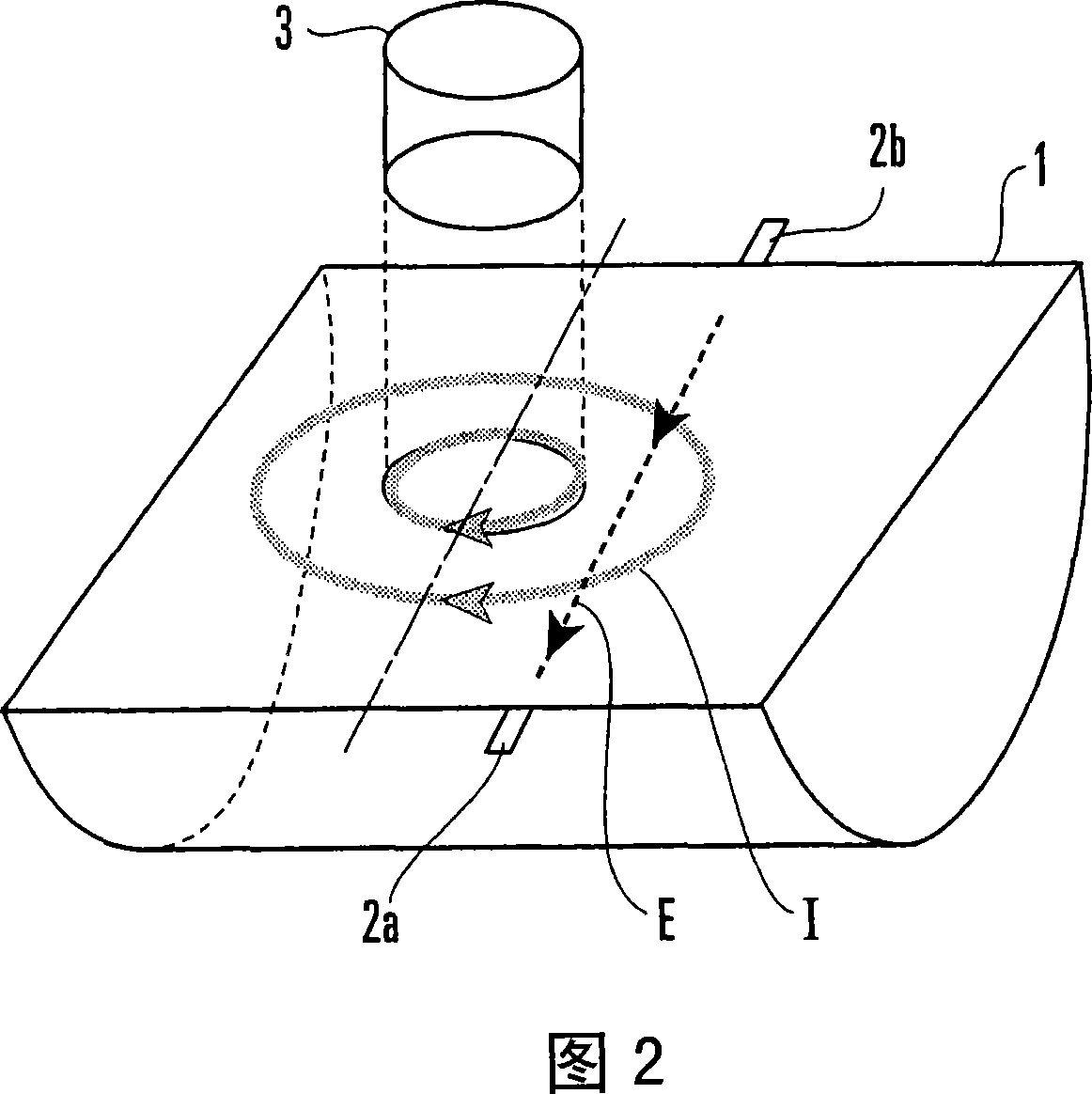
Status detection device
InactiveCN101061372AVolume/mass flow measurementLevel indicators by physical variable measurementVector potentialElectromotive force
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
Wireless power and communication systems using magnetic vector potential
InactiveUS20150249342A1Enhance skin effectReduce the amount requiredNear-field transmissionTransformersElectrical conductorVoltage pulse
Apparatuses and methods are provided for driving an input conductor with a signal comprising a series of voltage pulses. The pulses can beneficially invoke the skin effect to generate a time-varying magnetic vector potential that projects radially from a surface of the input conductor. The time-varying magnetic vector potential can provide an electric field for inducing output voltage pulses in an output circuit. The input conductor and output circuit can have various configurations. For example, the input conductor can extend along a plane, and the output circuit can at least partially reside in the plane and extend away from the input conductor in the plane. Such a geometry can reduce any back coupling between the two circuits, e.g., between electromagnetic fields caused by any current in the two circuits. Such a geometry would not normally allow for induction between the two circuits, which can reduce any Lenz effects.
Owner:DIVERGENT
Method of calculating inductance of reactor in inter-turn short circuit fault state
InactiveCN107153146AWeakening effect achievedImprove calculation accuracyResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingEngineeringRing current
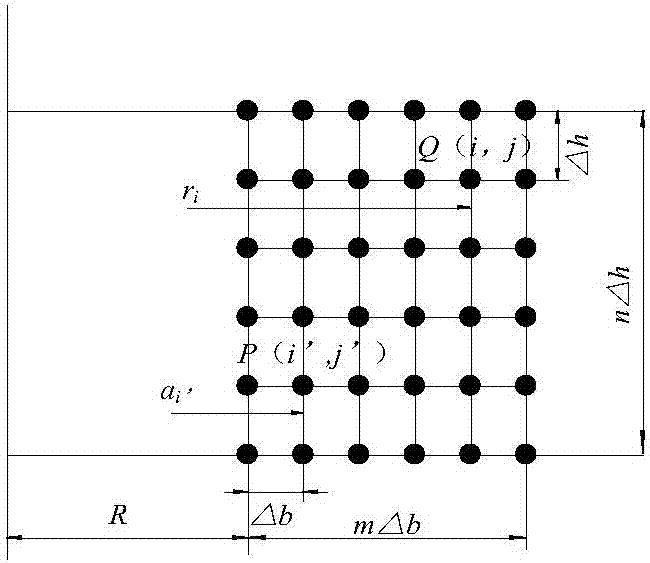
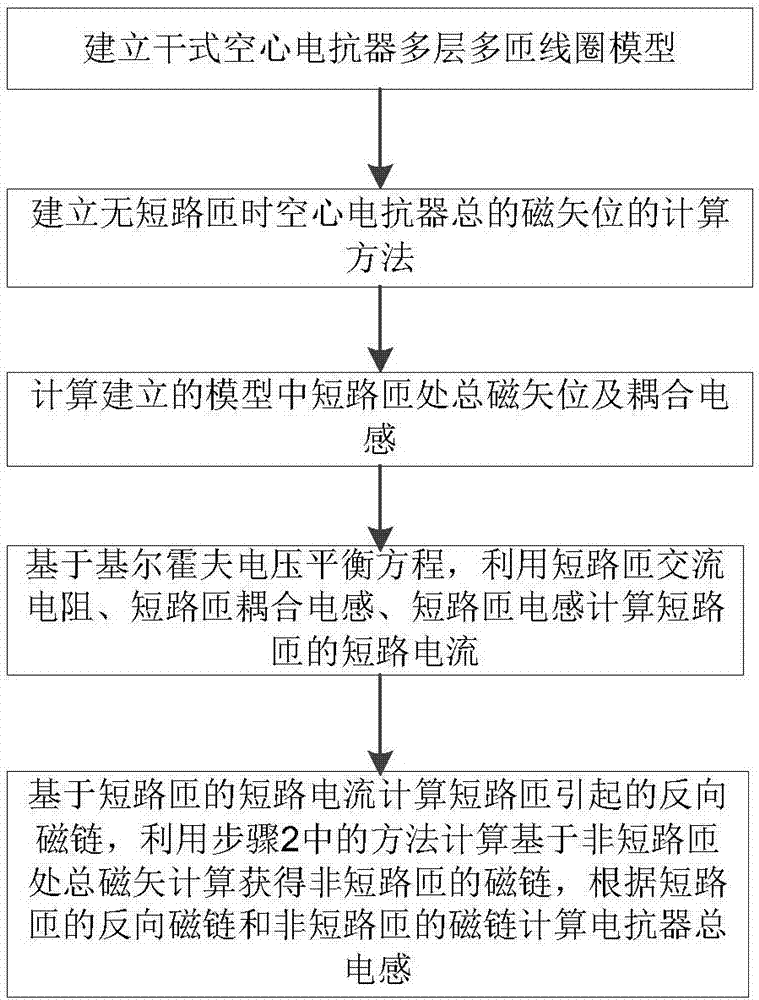
The invention discloses a method of calculating the inductance of a reactor in an inter-turn short circuit fault state, comprising the following steps: S1, building a multi-layer multi-turn coil model of a dry hollow reactor; S2, building a method of calculating the total magnetic vector potential of the hollow reactor under the condition of no short-circuit turn; S3, calculating the total magnetic vector potential and coupling inductance at a short-circuited turn in the built model; S4, based on the Kirchhoff voltage balance equation, calculating the short-circuit current of the short-circuited turn according to the AC resistance of the short-circuited turn, the coupling inductance of the short-circuited turn and the inductance of the short-circuited turn; and S5, calculating the reverse flux caused by the short-circuited turn based on the short-circuit current of the short-circuited turn, calculating the total magnetic vector potential at a non-short-circuited turn through the method in S2 to get the flux of the non-short-circuited turn, and calculating the total inductance of the reactor according to the reverse flux of the short-circuited turn and the flux of the non-short-circuited turn. The weakening effect of the ring current in the short-circuited turn on the inductance of the reactor is considered. The calculation accuracy of the total inductance of the dry hollow reactor in a fault state is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
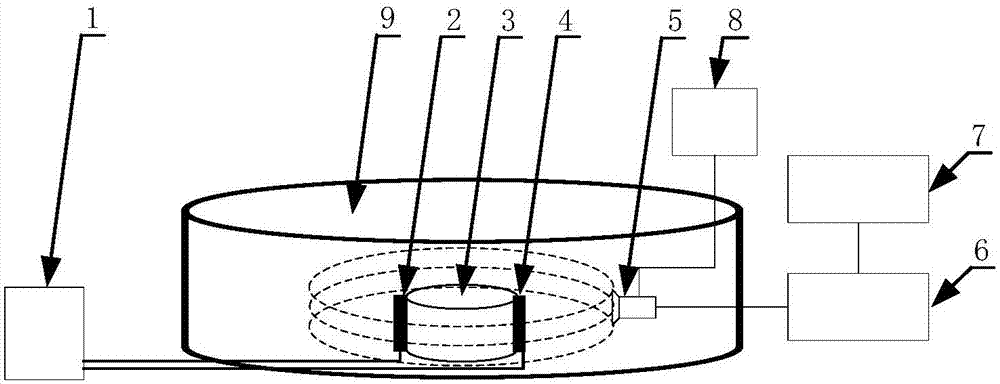
Current injection type thermoacoustic imaging electrical resistivity rebuilding method
ActiveCN106885842AMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic sensorFinite element solution
The invention relates to a current injection type thermoacoustic imaging electrical resistivity rebuilding method on the basis of current injection type thermoacoustic imaging principle. Pulse current is injected into an imaging objective object through an electrode; joule heat is generated in the imaging target body; heat expansion is caused; ultrasonic signals are generated; the ultrasonic signals are received by an ultrasonic transducer; the received ultrasonic signals are processed and collected; an electrical resistivity imaging rebuilding algorithm is used for obtaining the electrical resistivity image of the objective body. The method comprises the following concrete steps of 1, firstly obtaining the current injection type thermoacoustic signals; 2, rebuilding an objective body thermoacoustic source by using the obtained current injection type thermoacoustic signals; 3, rebuilding a vector potential by a nonlinear finite element solution method by using the thermoacoustic source; 4, rebuilding the specific resistance of the rebuilt current vector potential.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
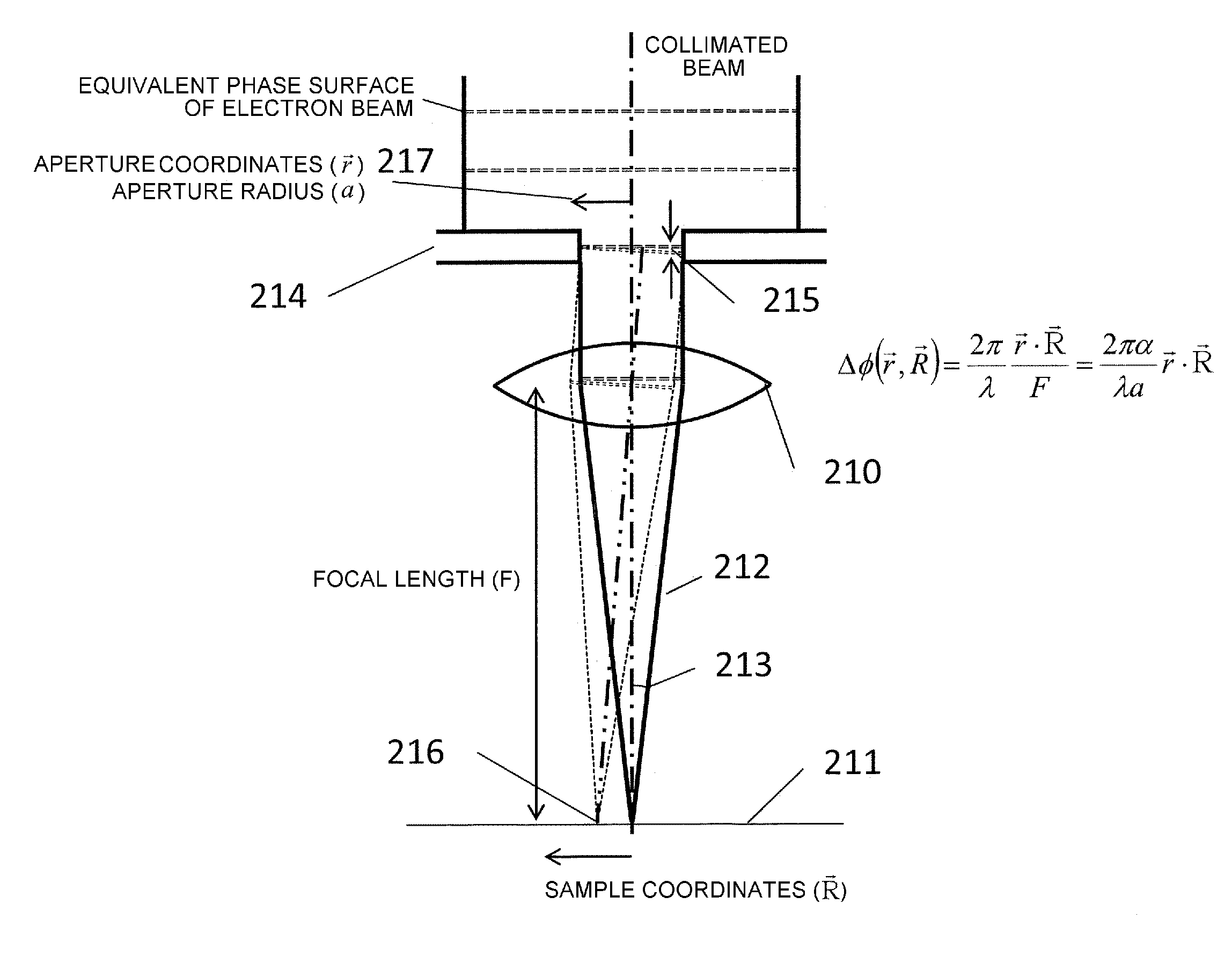
Device for correcting diffraction aberration of electron beam
InactiveUS9123501B2Aberration suppressionIncrease the differenceElectric discharge tubesPhase differenceAharonov–Bohm effect
A diffraction aberration corrector formed by the multipole of the solenoid coil ring and having a function of adjusting the degree of orthogonality or axial shift of the vector potential with respect to the beam axis. In order to cause a phase difference, the diffraction aberration corrector that induces a vector potential, which is perpendicular to the beam axis and has a symmetrical distribution within the orthogonal plane with respect to the beam axis, is provided near the objective aperture and the objective lens. A diffracted wave traveling in a state of being inclined from the beam axis passes through the ring of the magnetic flux. Since the phase difference within the beam diameter is increased by the Aharonov-Bohm effect due to the vector potential, the intensity of the electron beam on the sample is suppressed.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
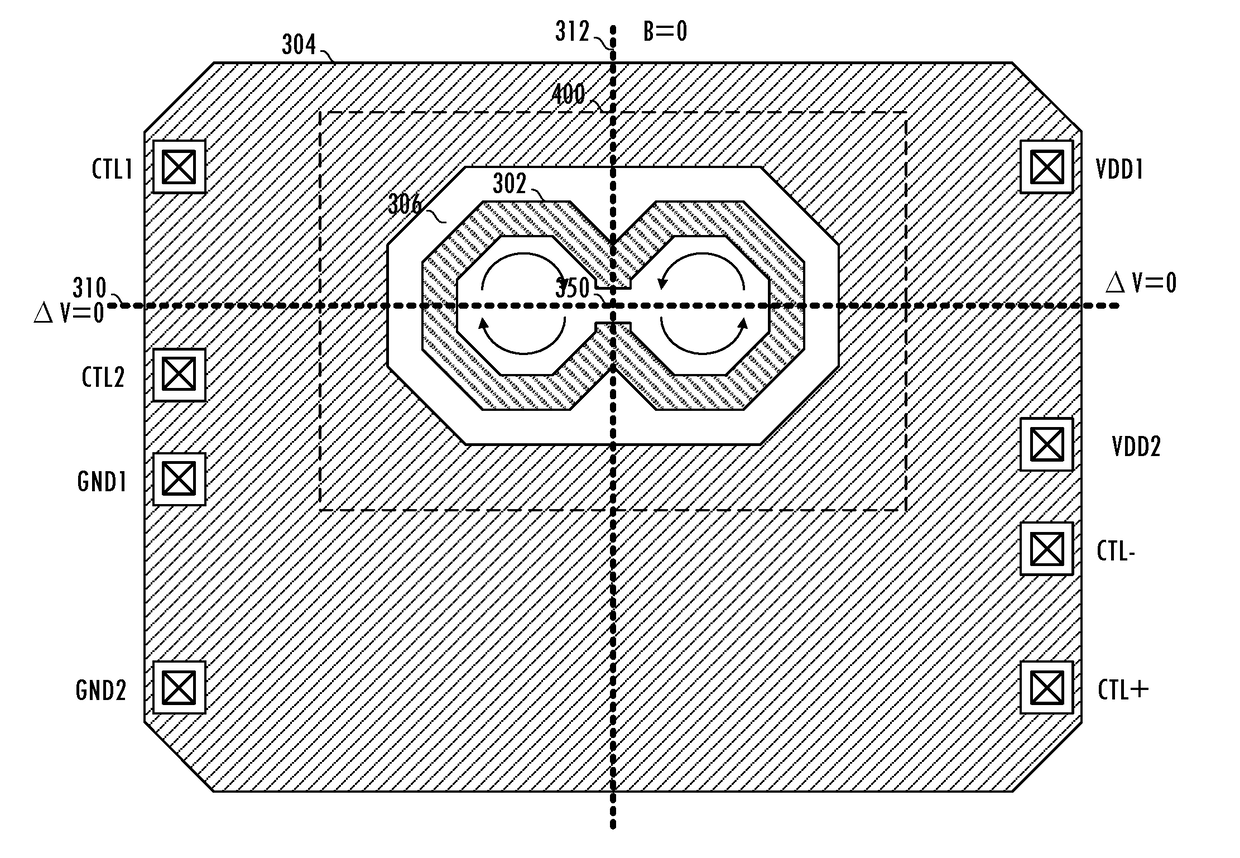
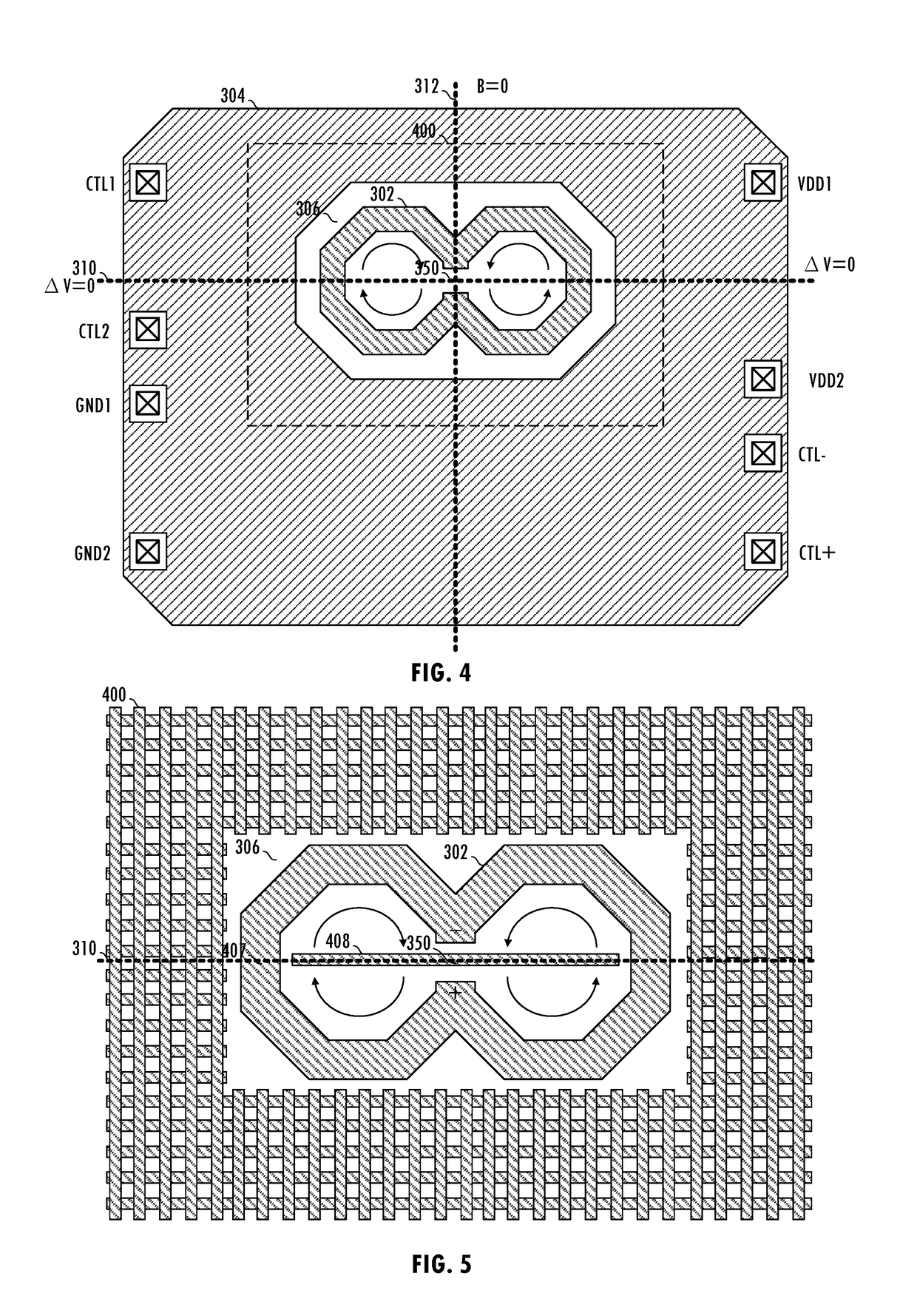
Physical design in magnetic environment
ActiveUS20180190424A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsCouplingVector potential
A technique for forming an integrated circuit including an inductor reduces magnetic coupling between the inductor and surrounding elements. The technique includes deliberate placement of circuit elements (e.g., terminals, pins, routing traces) in locations on the integrated circuit relative to a magnetic vector potential associated with the inductor and relative to a magnetic flux density field associated with the inductor to reduce or eliminate induced signals that degrade system performance.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
State detection device
An exciting unit, applies, to a fluid, a time-changing magnetic field asymmetrical to a plane (PLN). An electrode is placed on the plane in a measuring tube, and detects a resultant electromotive force of an electromotive force based on ∂A / ∂t component (A: vector potential, t: time) irrelevant to a flow velocity of the fluid and an electromotive force based on a v×B component originating from the flow velocity of the fluid. A state quantifying unit extracts the ∂A / ∂t component and a variation factor dependent on a parameter to be detected, and quantifies the parameter on the basis of the variation factor. The characteristic and state of the fluid and the state in the measuring tube can be detected regardless of the flow rate of the fluid by using the same hardware arrangement as that of an electromagnetic induction type flowmeter.
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com