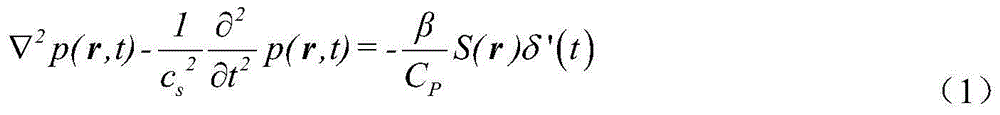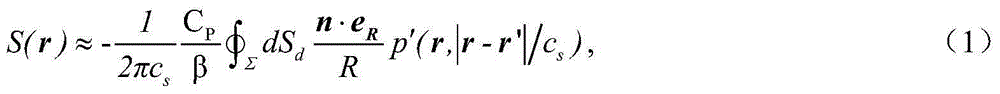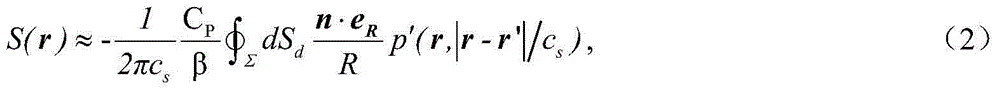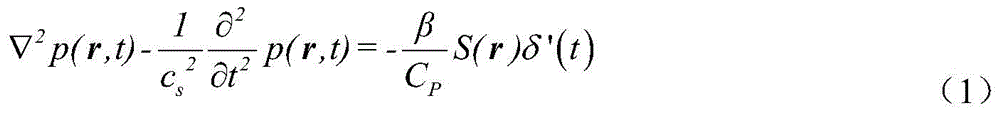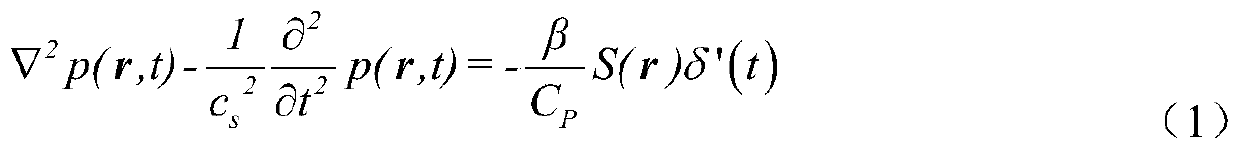Patents
Literature
37 results about "Scalar potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Scalar potential, simply stated, describes the situation where the difference in the potential energies of an object in two different positions depends only on the positions, not upon the path taken by the object in traveling from one position to the other. It is a scalar field in three-space: a directionless value (scalar) that depends only on its location. A familiar example is potential energy due to gravity.
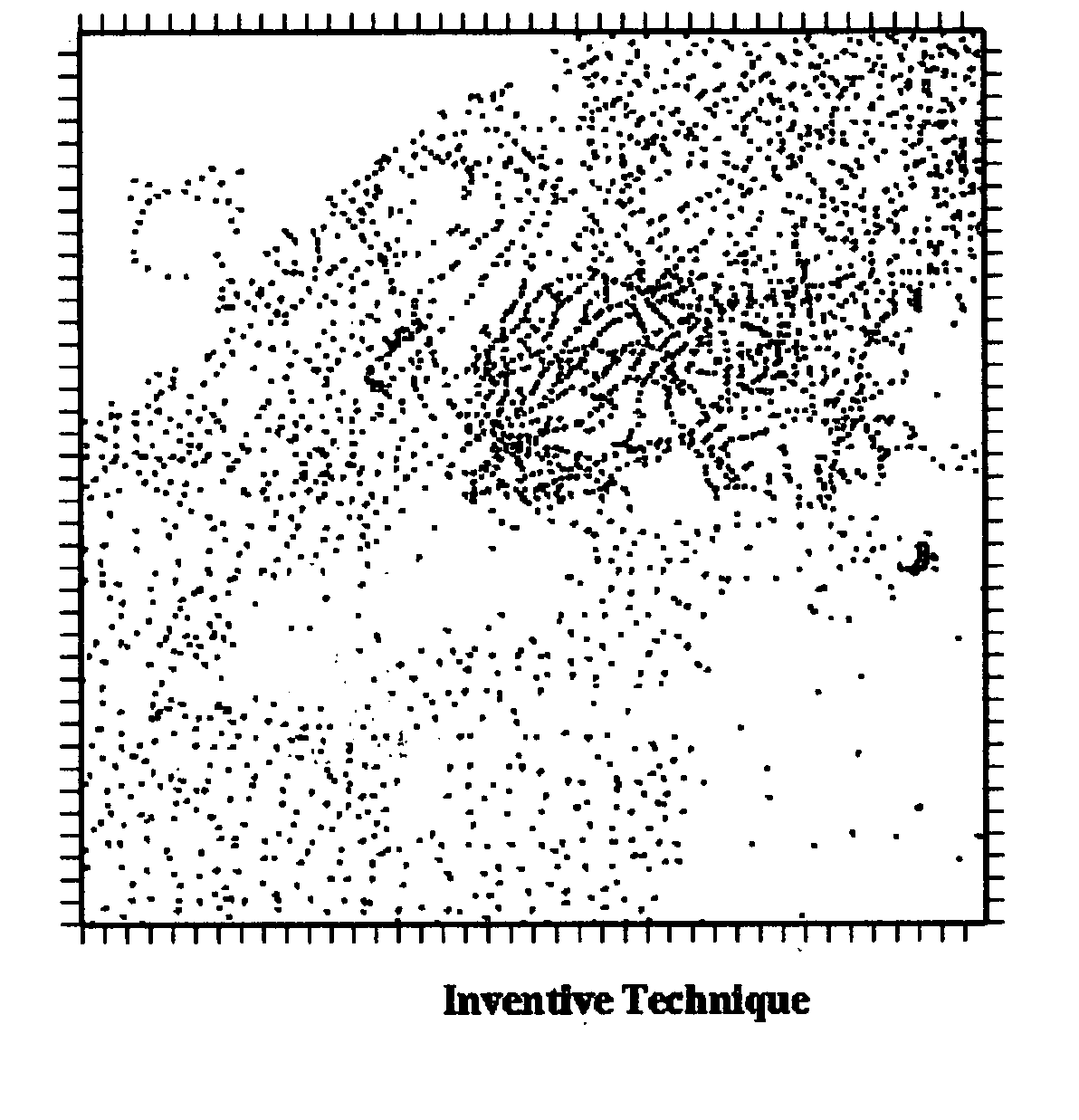
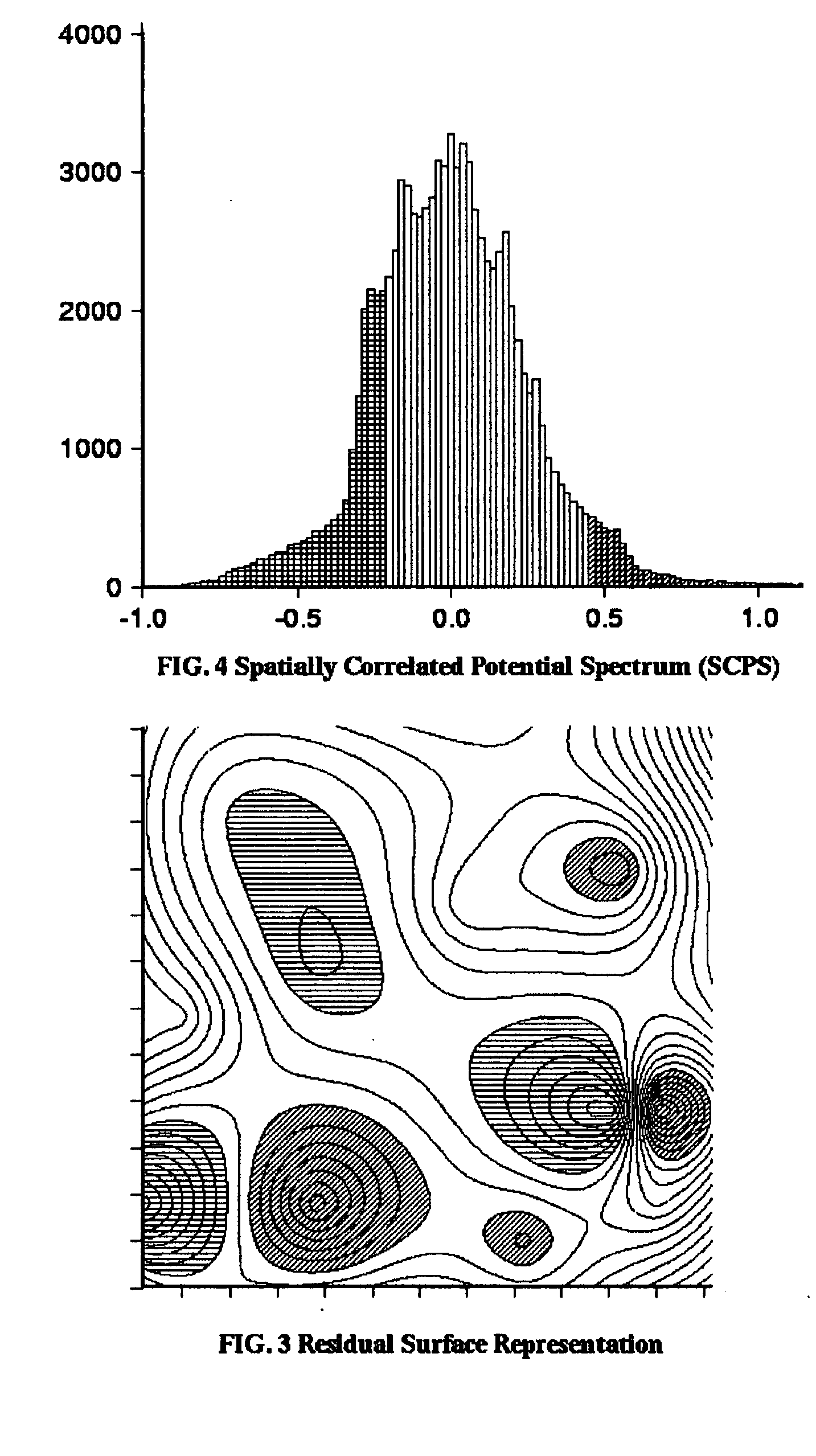
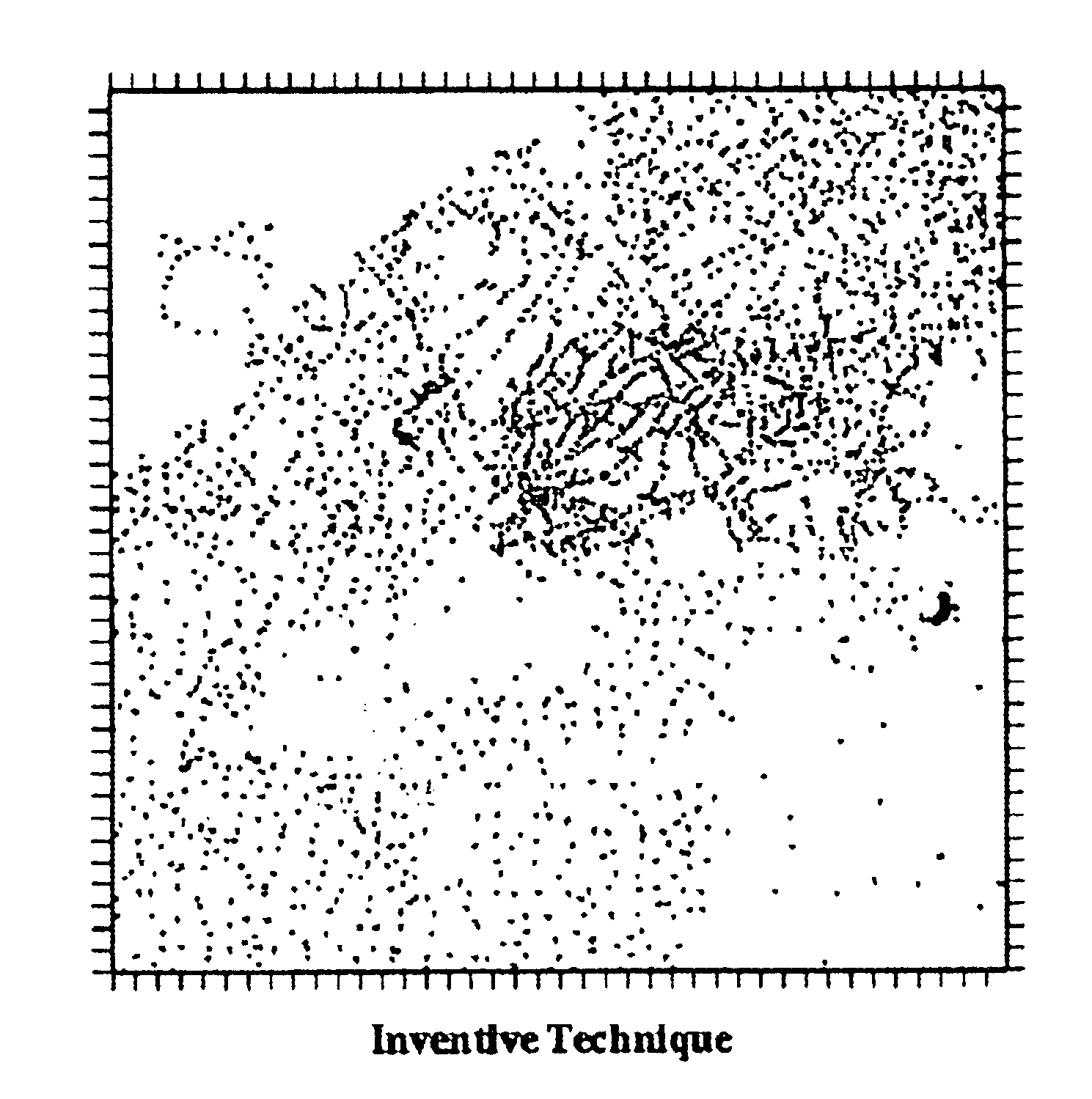
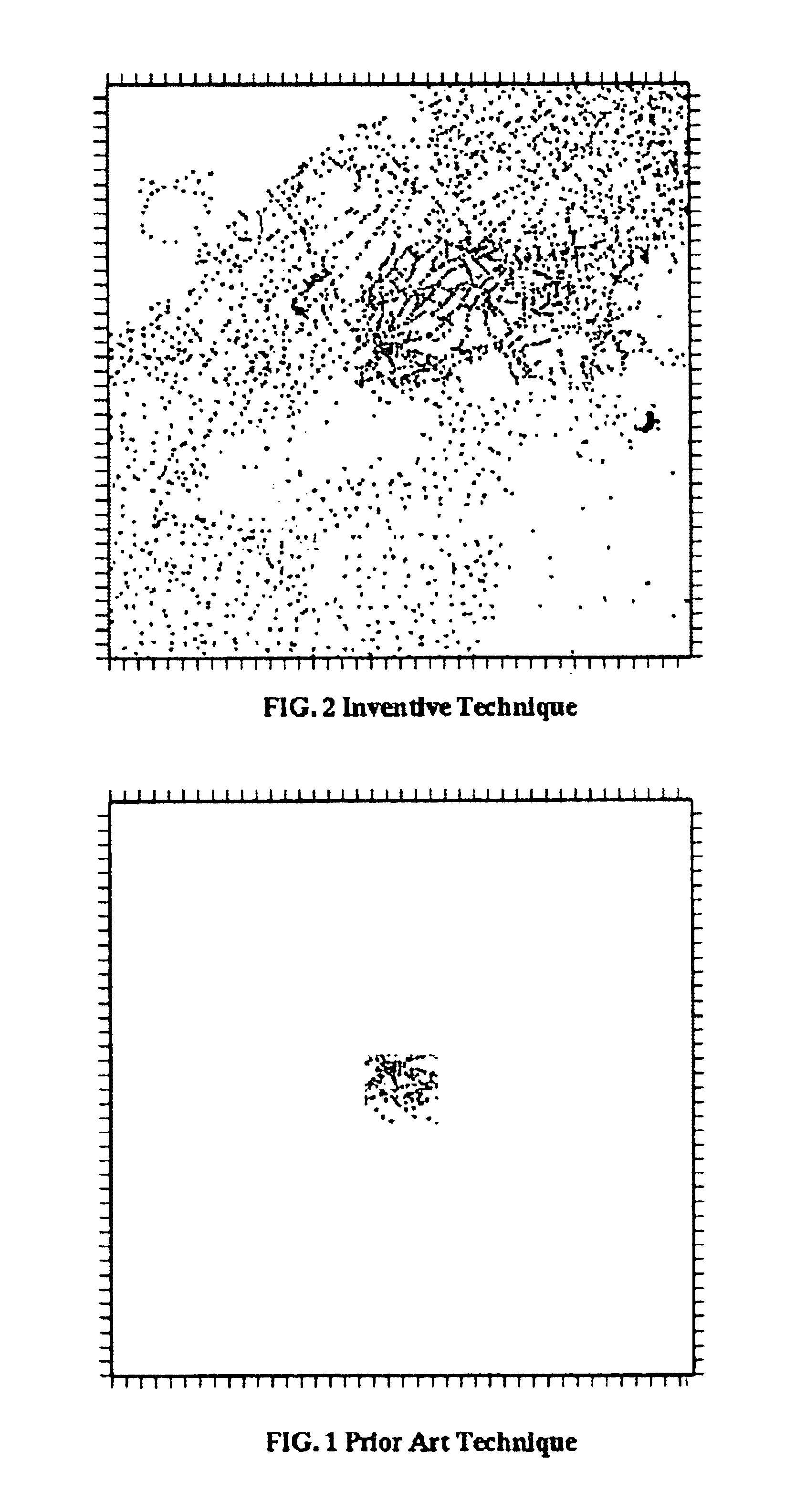
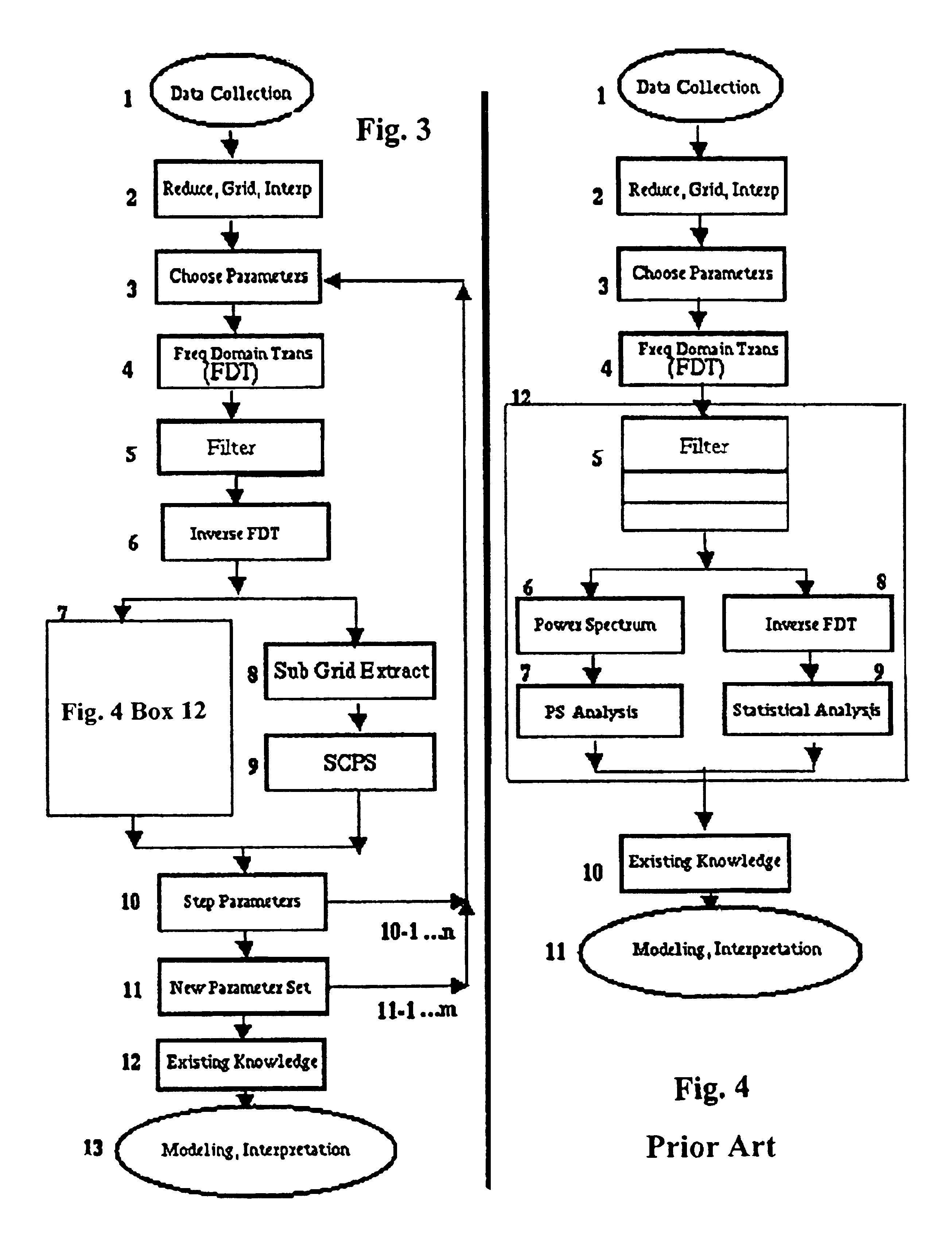
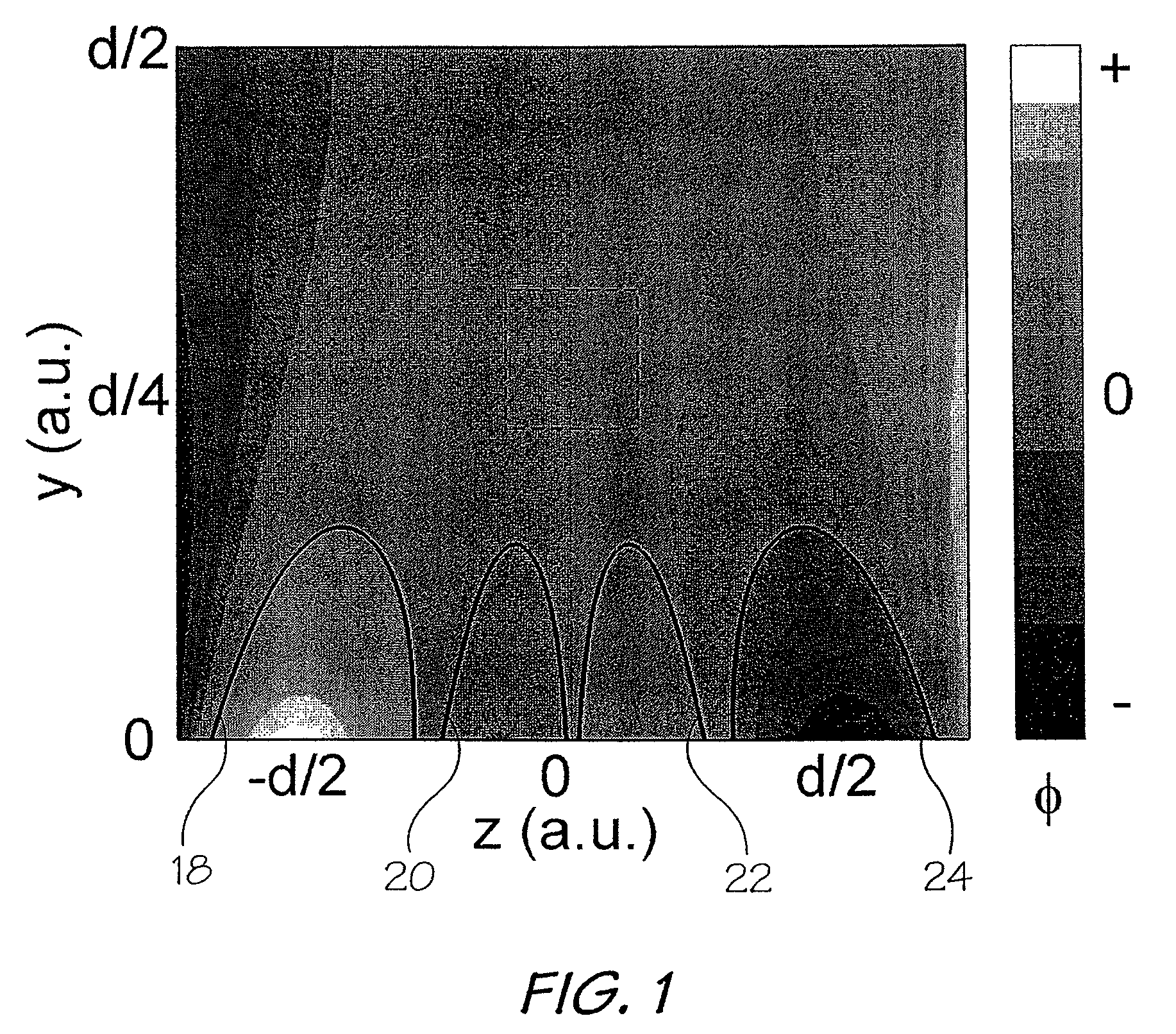
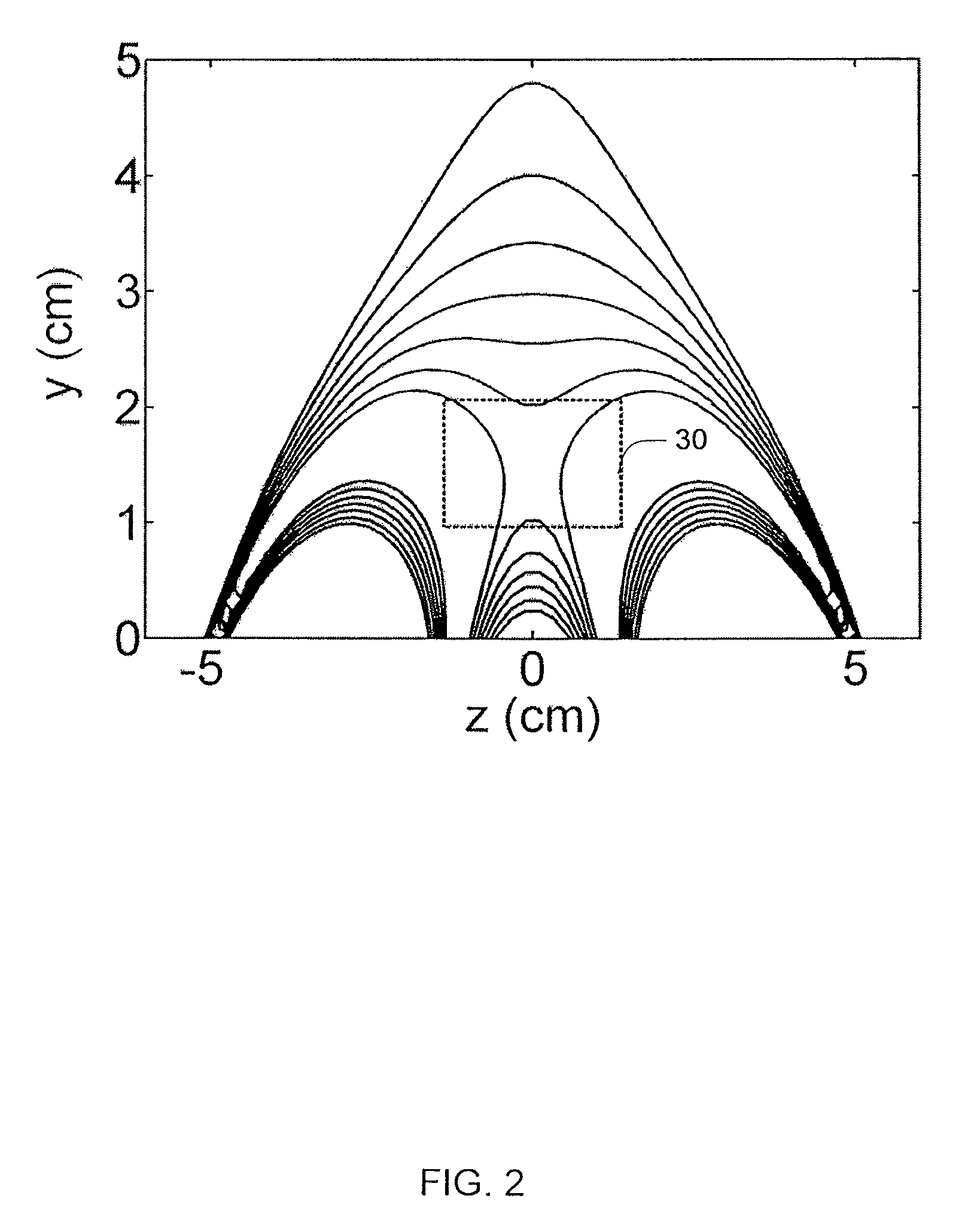
Method for enhancing depth and spatial resolution of one and two dimensional residual surfaces derived from scalar potential data
InactiveUS20040260471A1Special data processing applicationsElectric/magnetic detectionScalar potentialAlgorithm
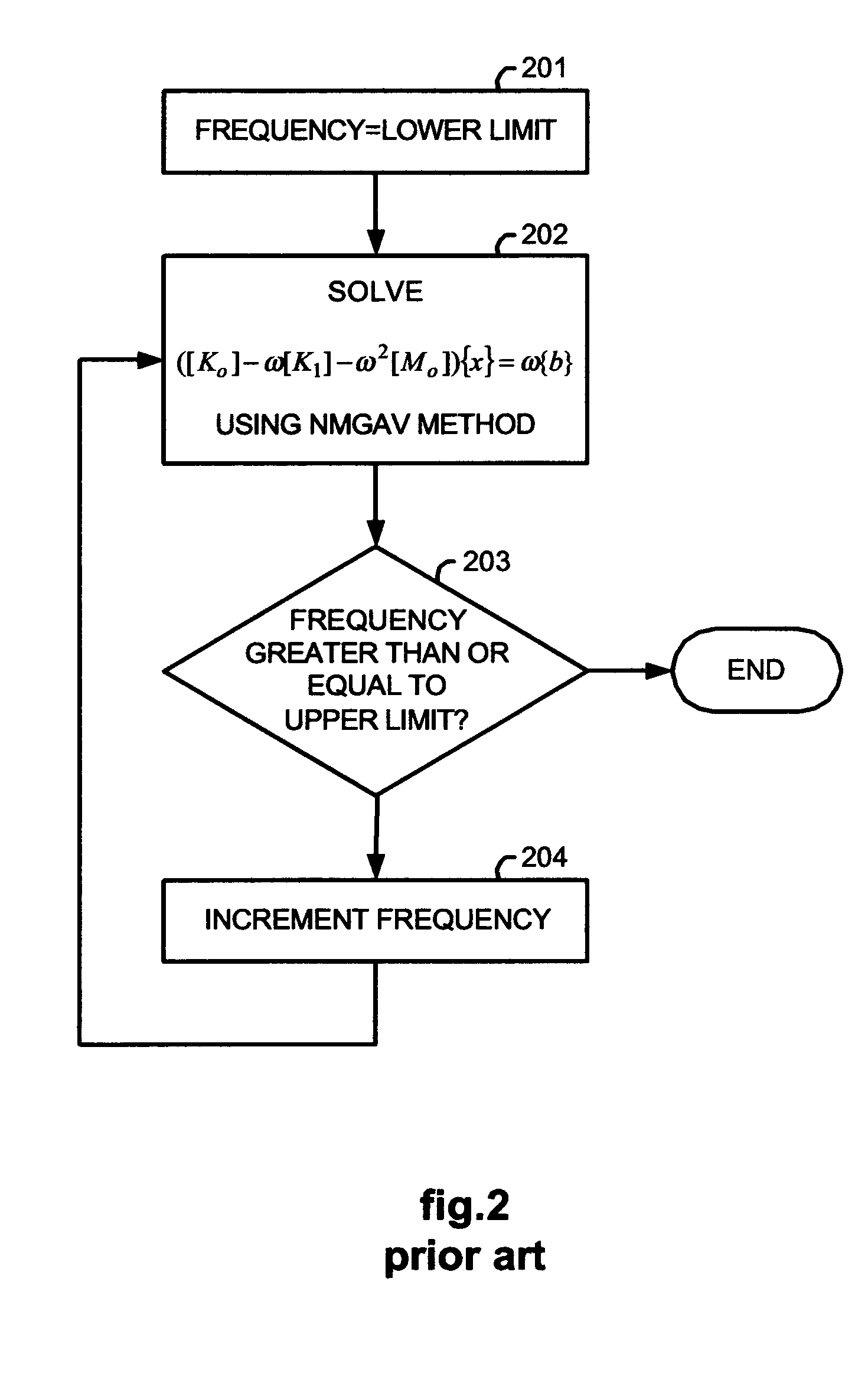
An improved method is disclosed for collecting or assembling scalar potential data measurements that are to be subsequently prepared as a surface representation for analysis via frequency domain transform filters. Measurements are made over a geographic reference region which extends in all cardinal directions from the center of some previously determined primary region. The reference dimensions must contain the primary region and must be plural multiples of the greatest depth to be considered in analyzing the contributions to the measurements. A combined or separate improved method for delineating or defining geospatial information contributing to a scalar potential surface is disclosed. This method is implemented using traditional statistical techniques to construct an histogram from the set of values comprising a surface representation. This histogram constitutes a Spatially Correlated Potential Spectrum for the surface. These combined and separate methods improve resolution of geological structures over depths and spatial extents under consideration.
Owner:MCDERMOTT ANDREW MARTIN
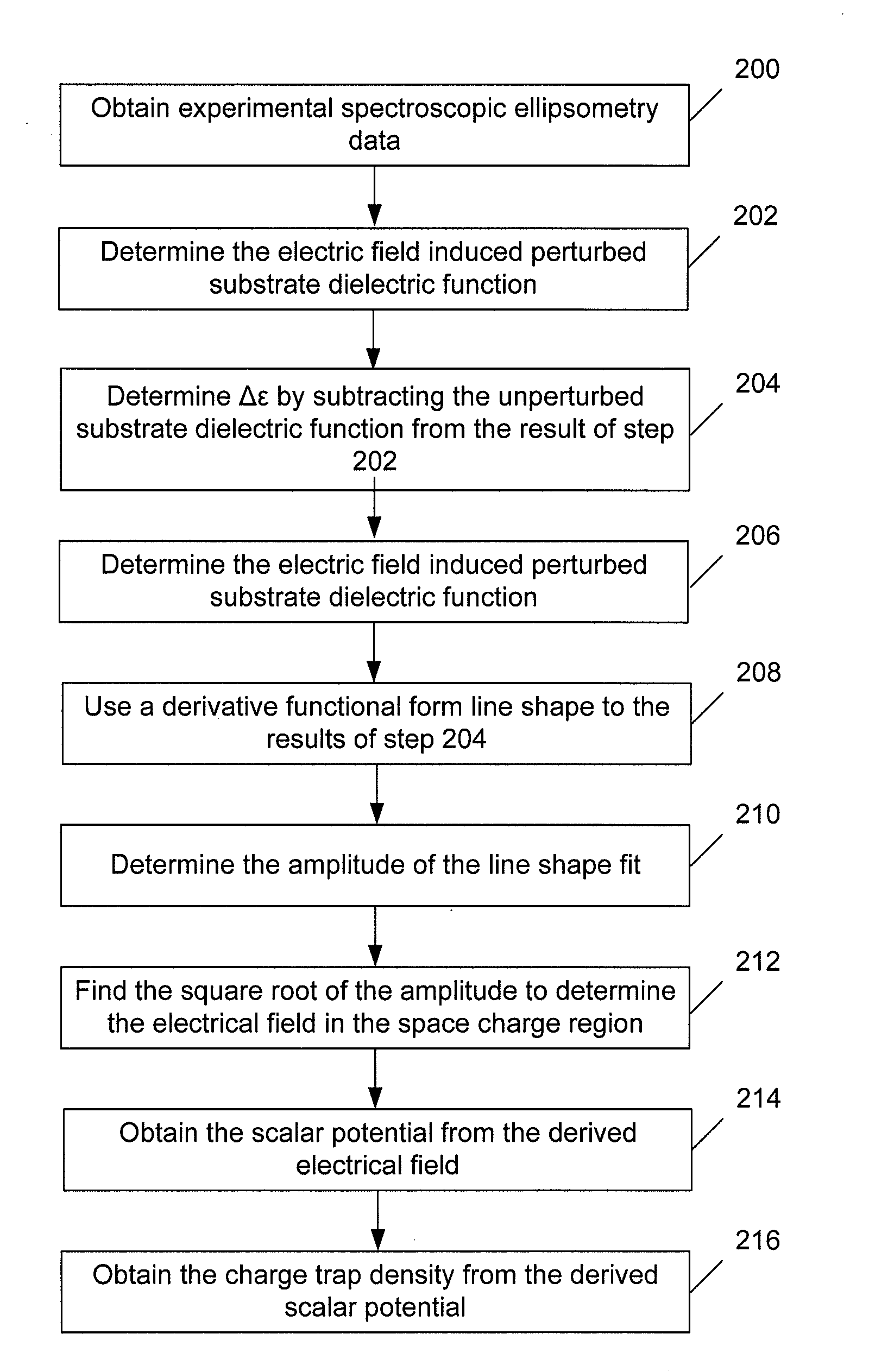
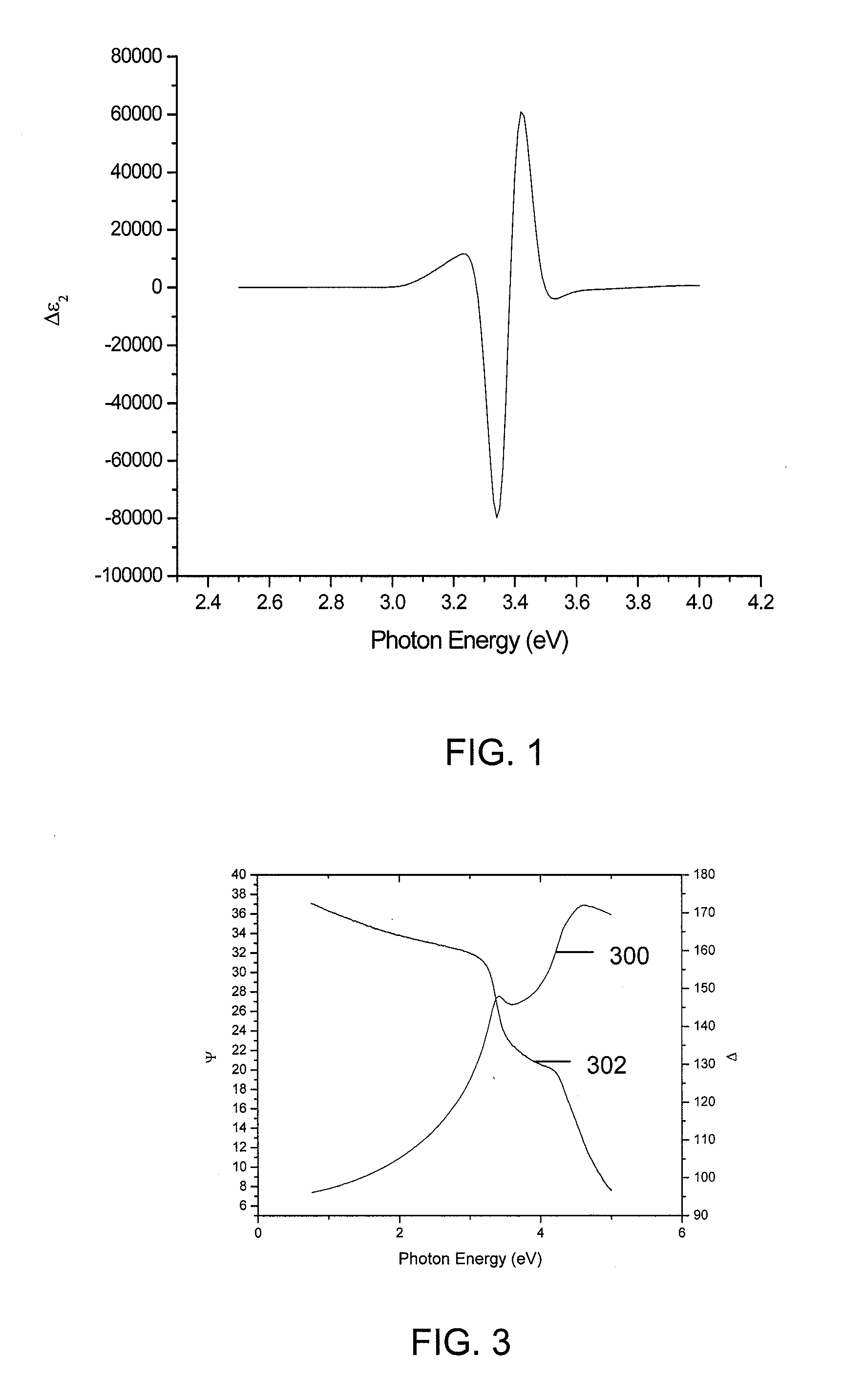
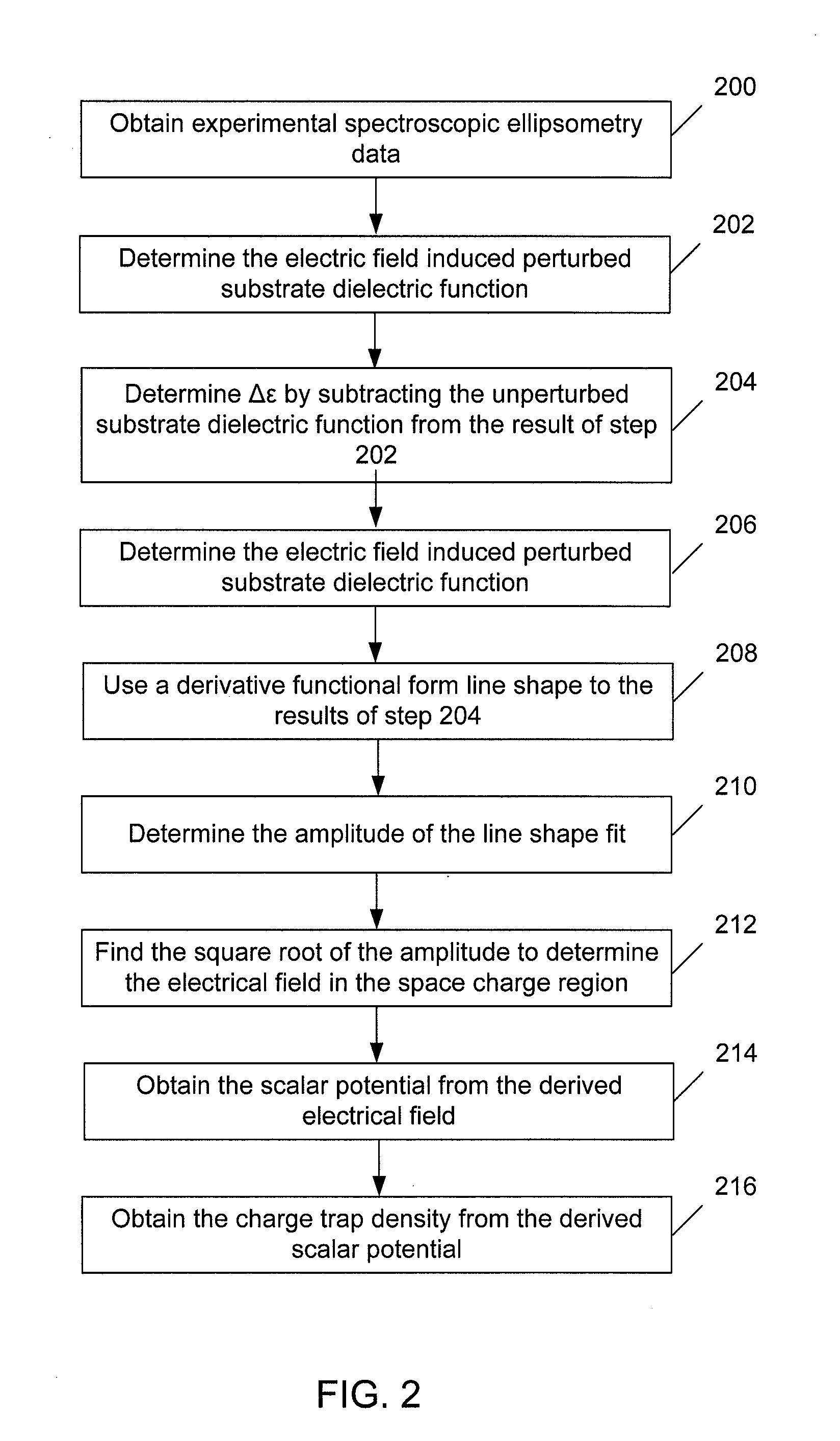
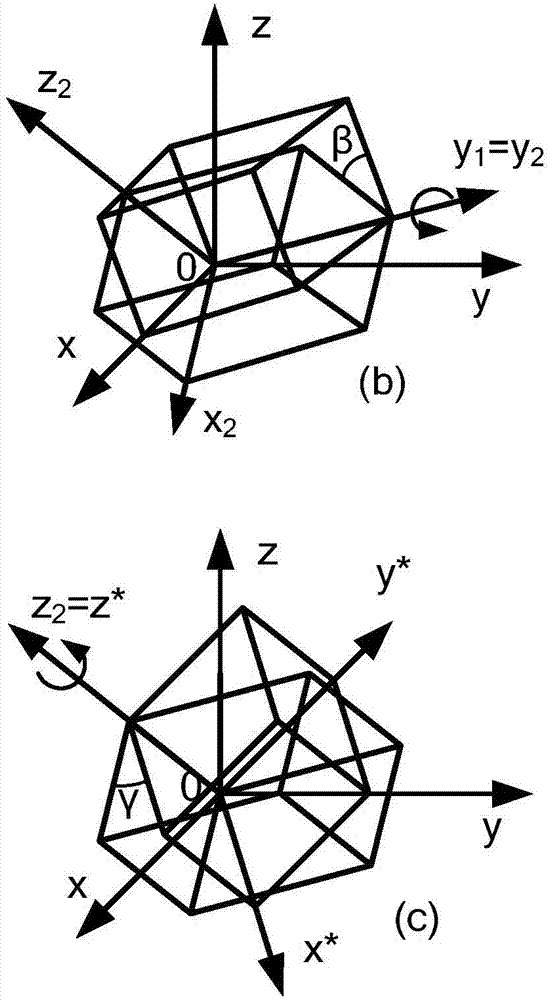
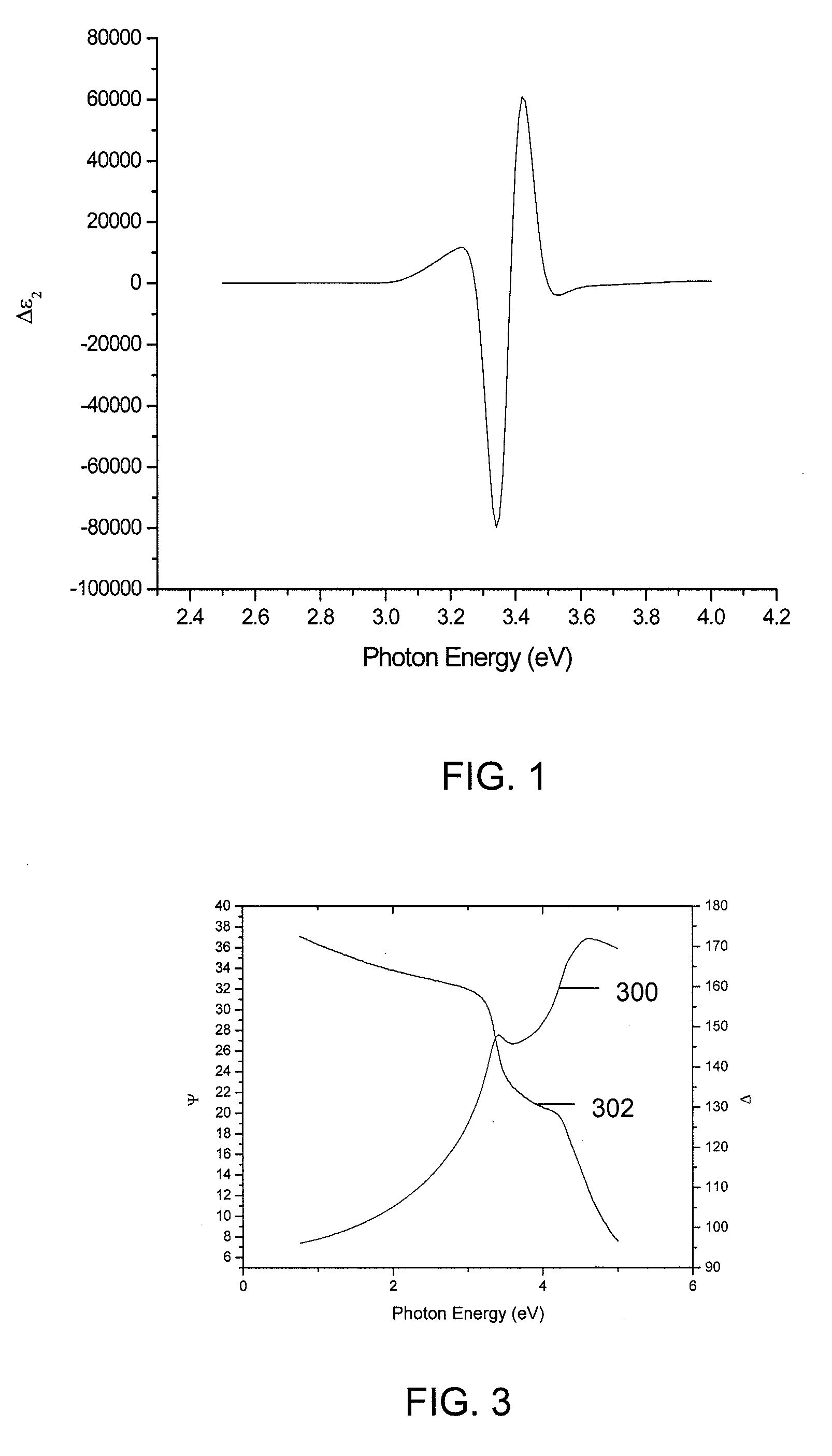
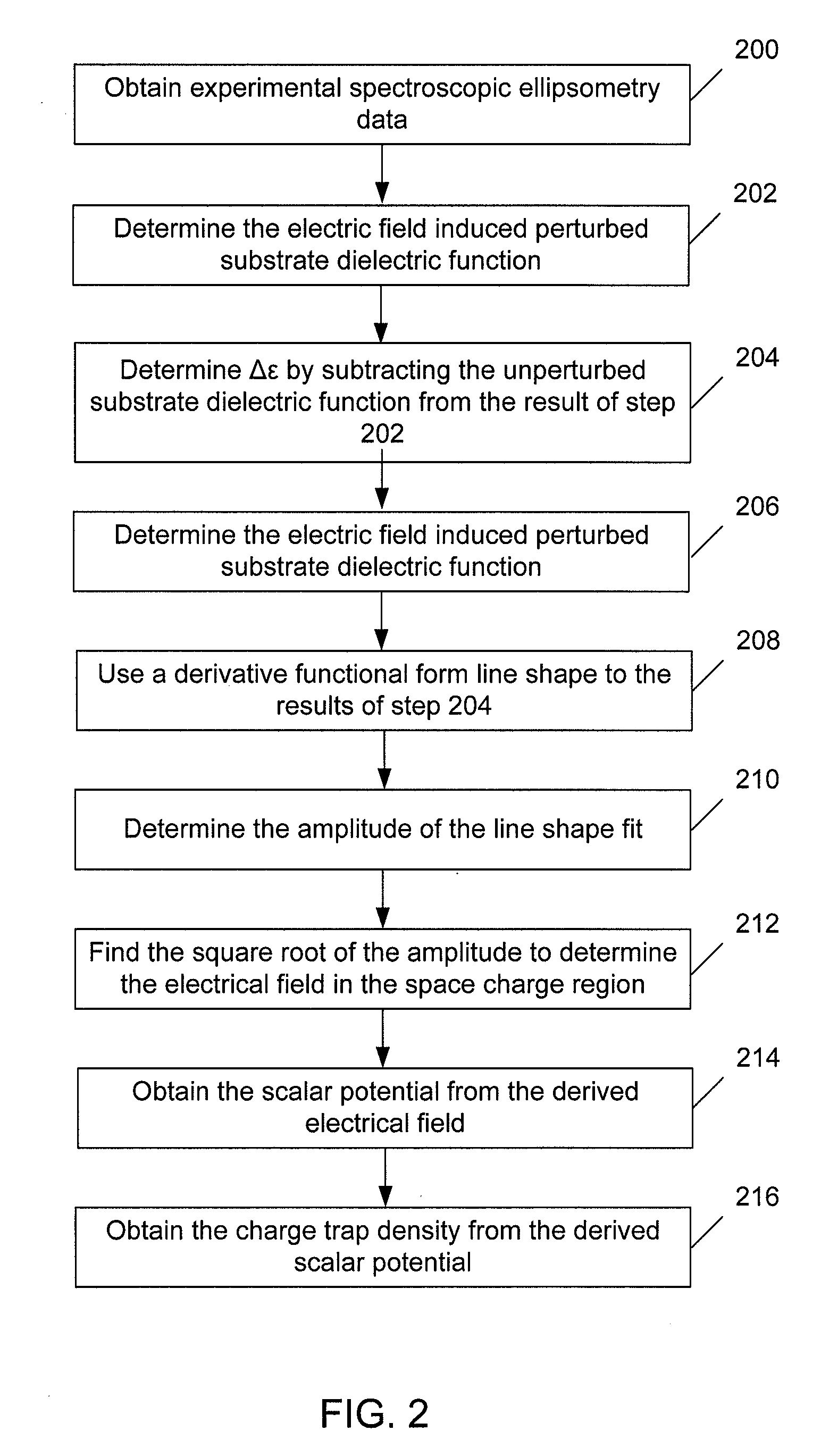
Methods and Systems for Determining Trapped Charge Density in Films
InactiveUS20070213954A1Improve accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesScalar potentialSemiconductor materials
Methods and systems for determining a charge trap density between a semiconductor material and a dielectric material are disclosed. In one respect, spectroscopic data of the semiconductor material may be determined and used to determine a change in dielectric function. A line shape fit of the change in the dielectric function may be applied using derivative function form. The amplitude of the line shape fit may be determined and used to determine an electric field of a space charge region of the semiconductor material. By applying Poisson's equations, the scalar potential due to the electric field in the space charge region may be determined. Subsequently, using the scalar potential the charge trap density may be determined.
Owner:SEMATECH
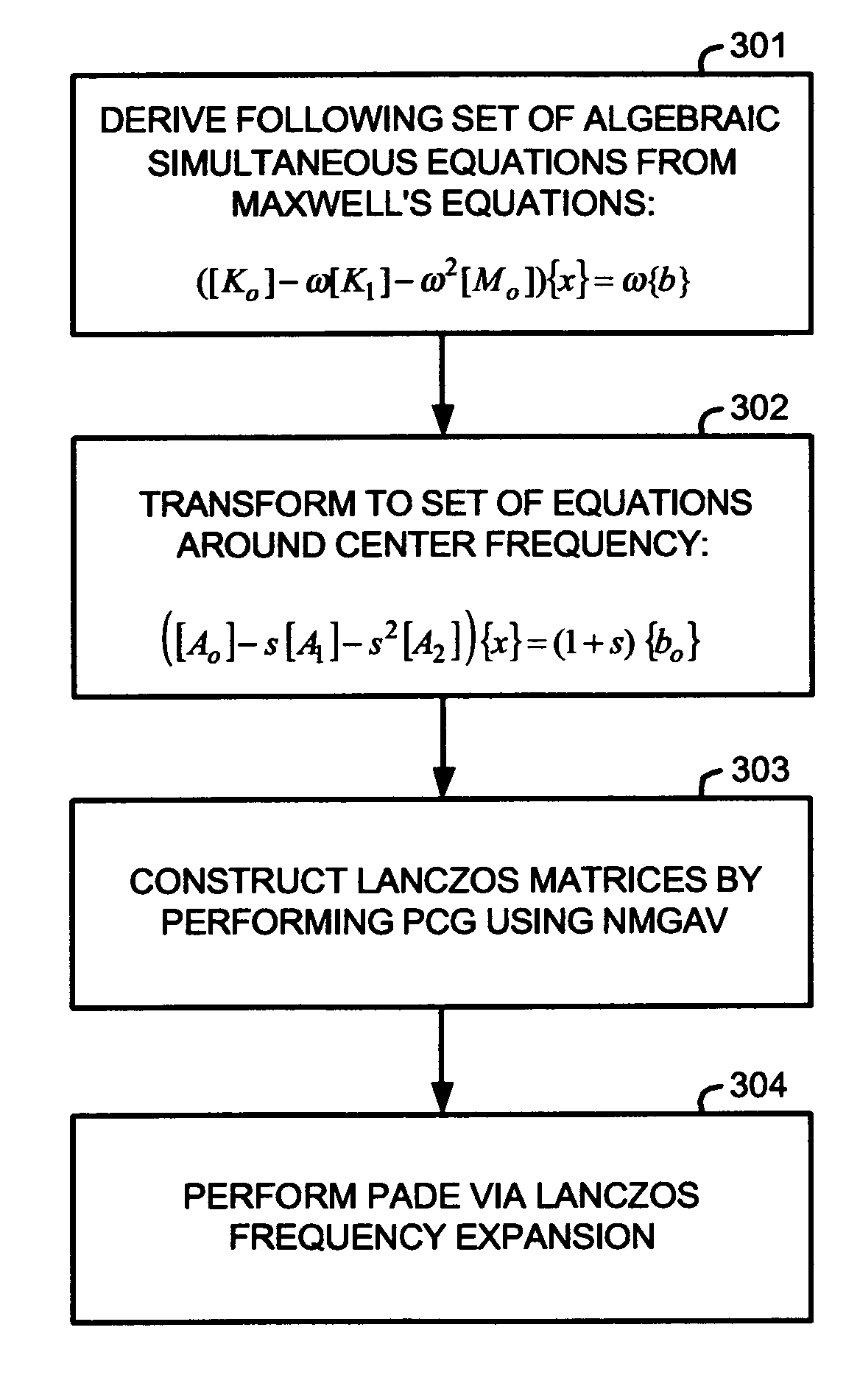
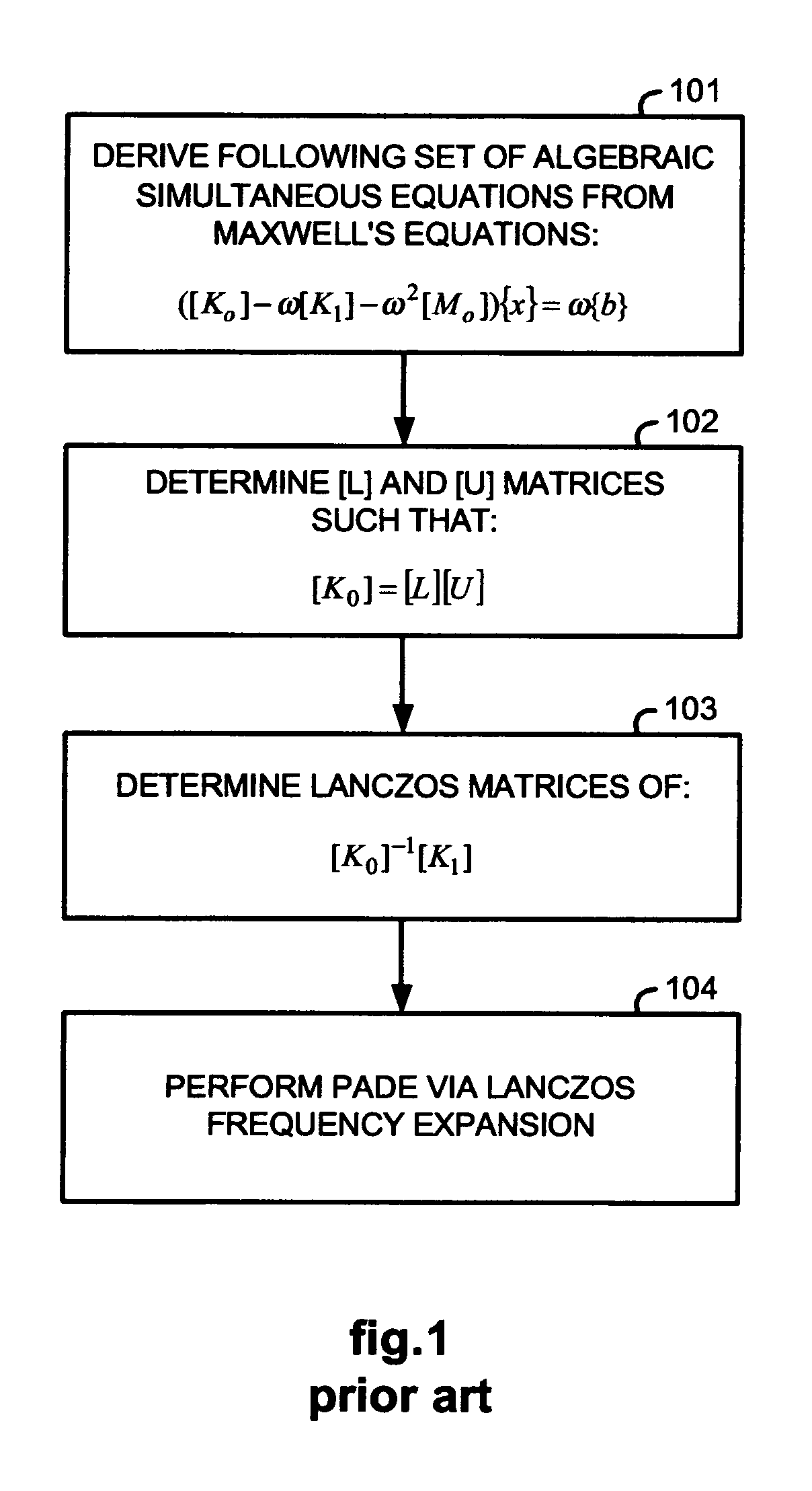
Method for determining electrical and magnetic field effects
InactiveUS20050197808A1Computation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsMatrix decompositionScalar potential
A method for determining electrical and magnetic field effects determines Lanczos matrices by performing a preconditioned conjugate gradient method using a nested multi-grid, vector and scalar potential preconditioner so that Pade via Lanczos frequency expansion may be used to determine the electrical and magnetic field effects over a frequency range without having to perform computationally slow and memory intensive matrix decomposition.
Owner:OPTIMAL CORP
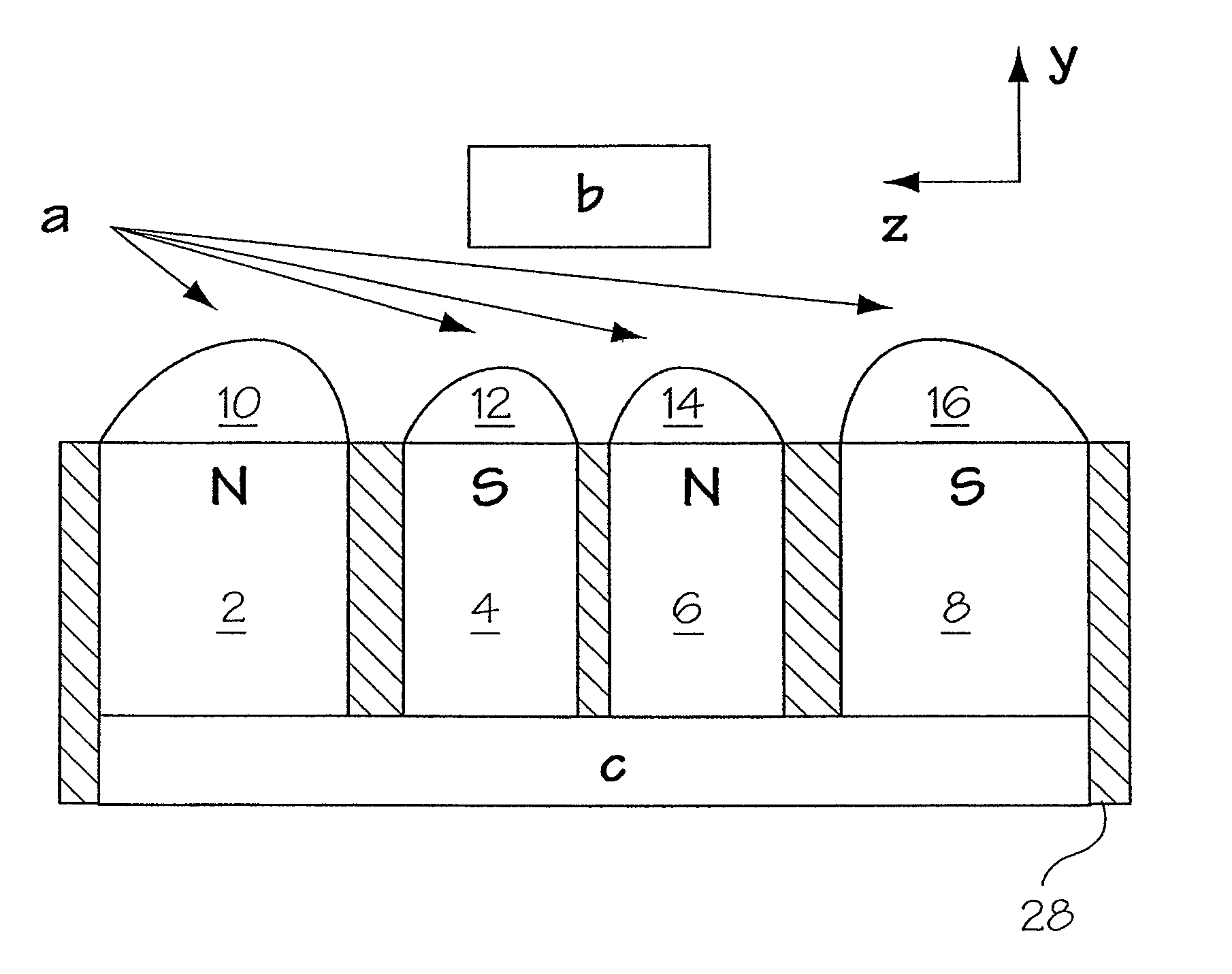
Sensor and magnetic field apparatus suitable for use in for unilateral nuclear magnetic resonance and method for making same
InactiveUS7319326B2Improve permeabilityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceScalar potential
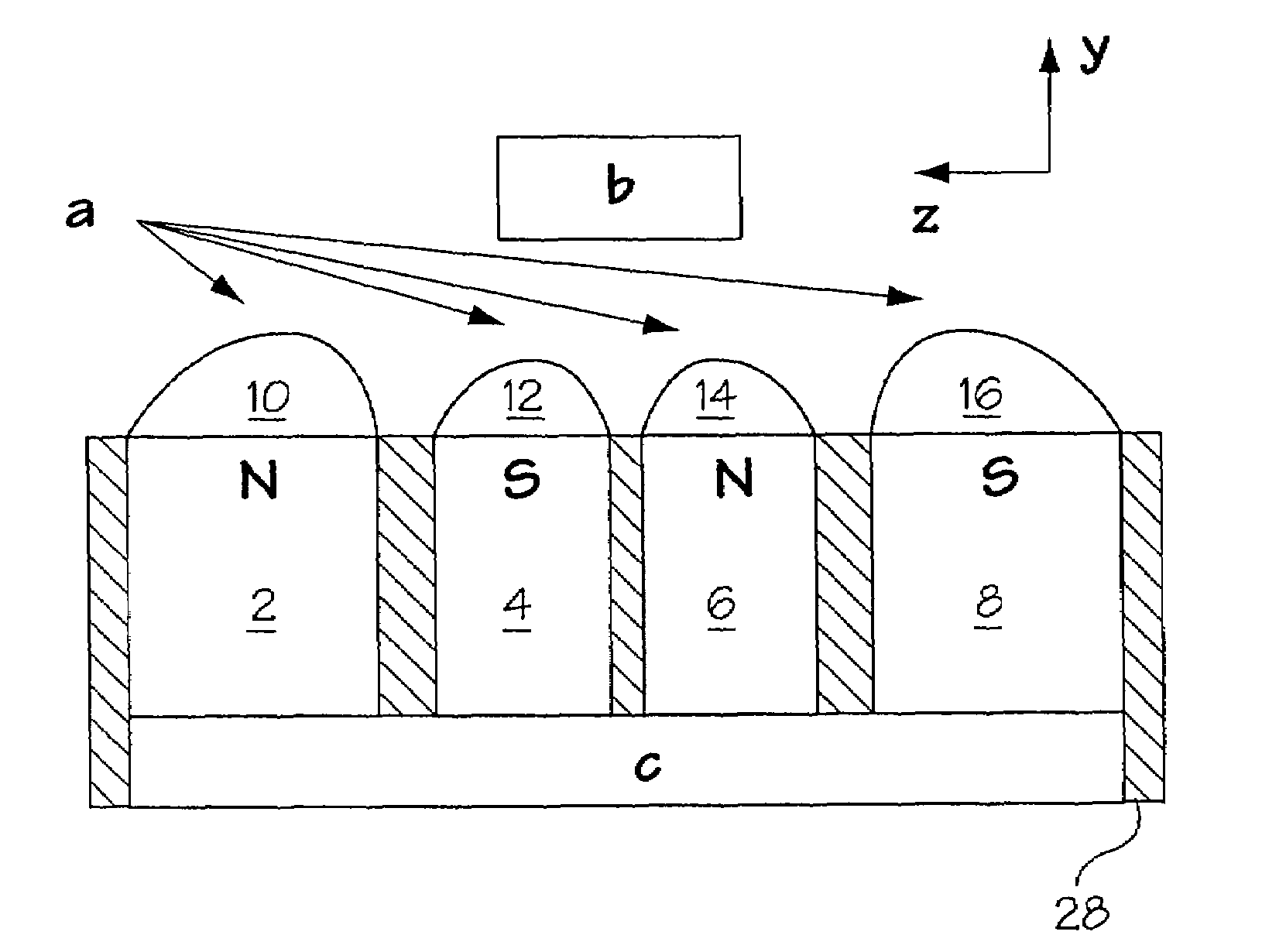
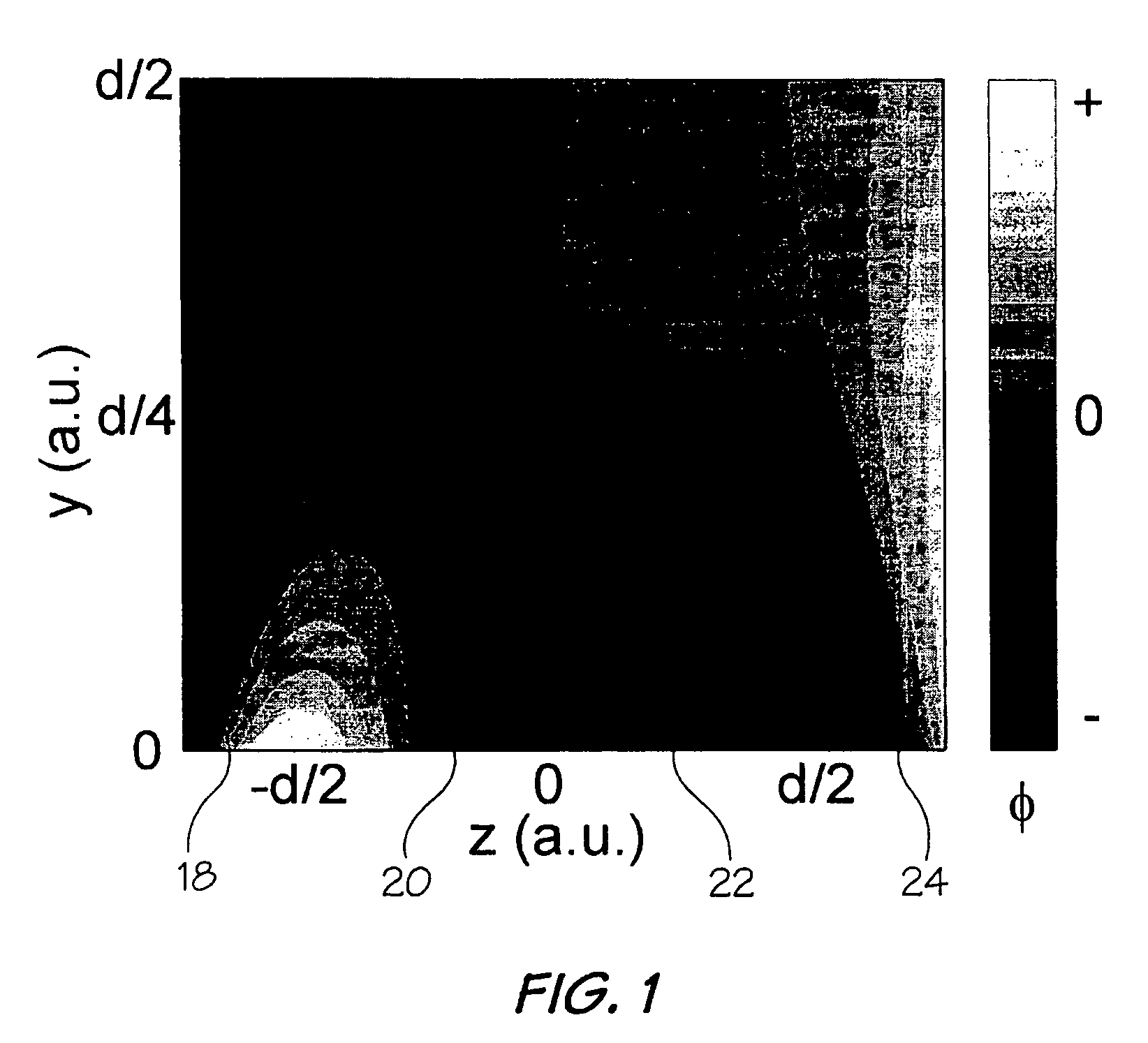
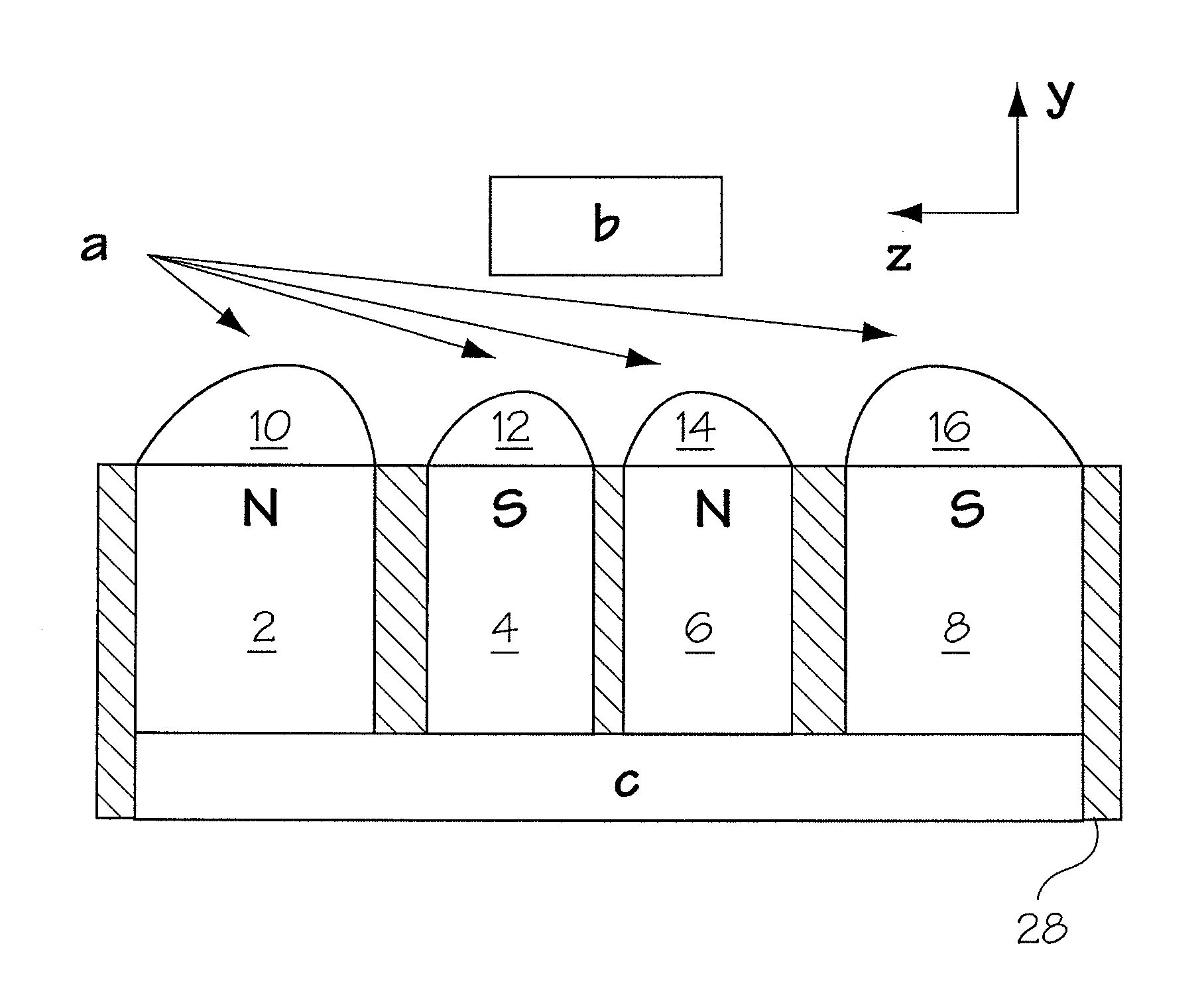
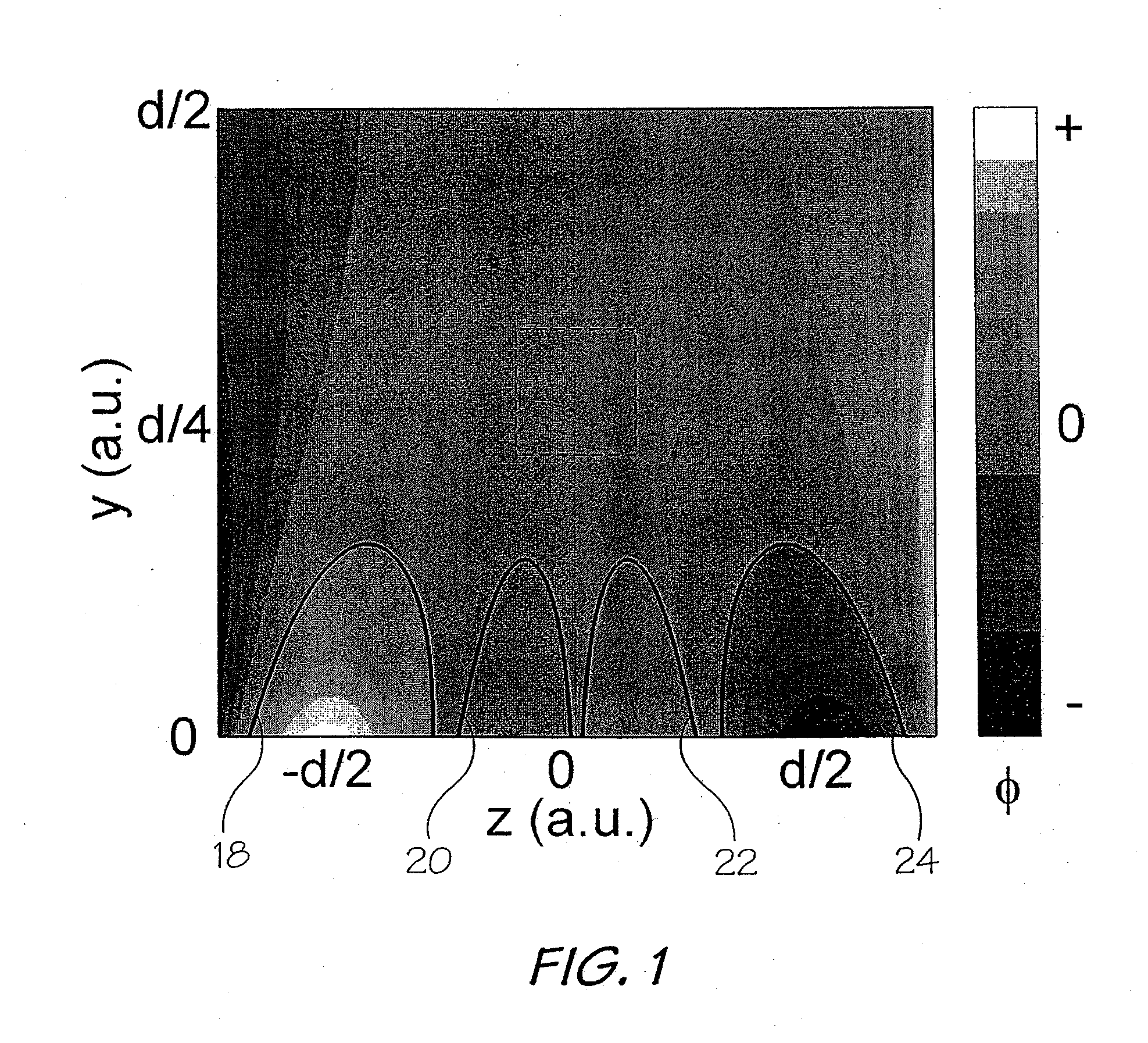
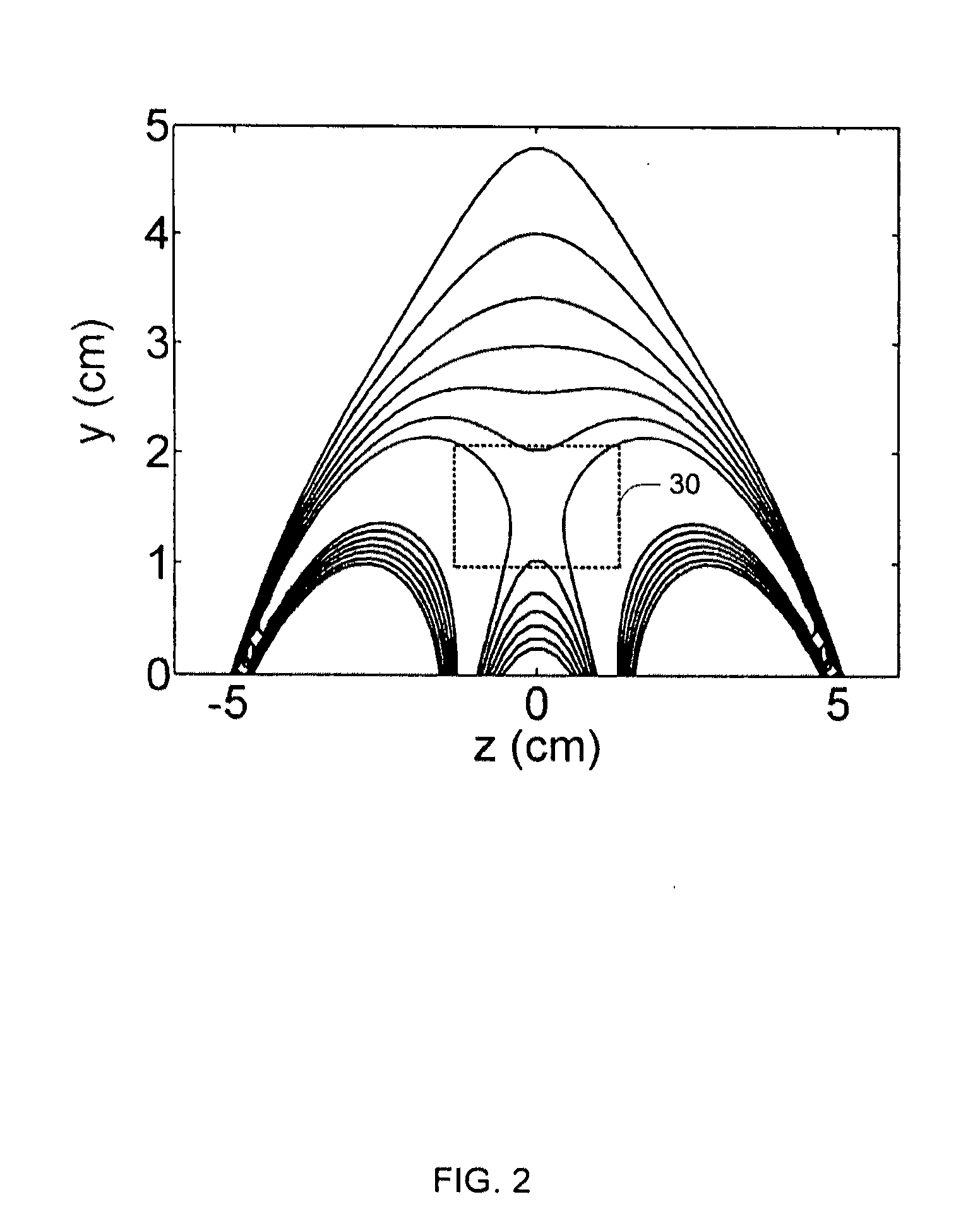
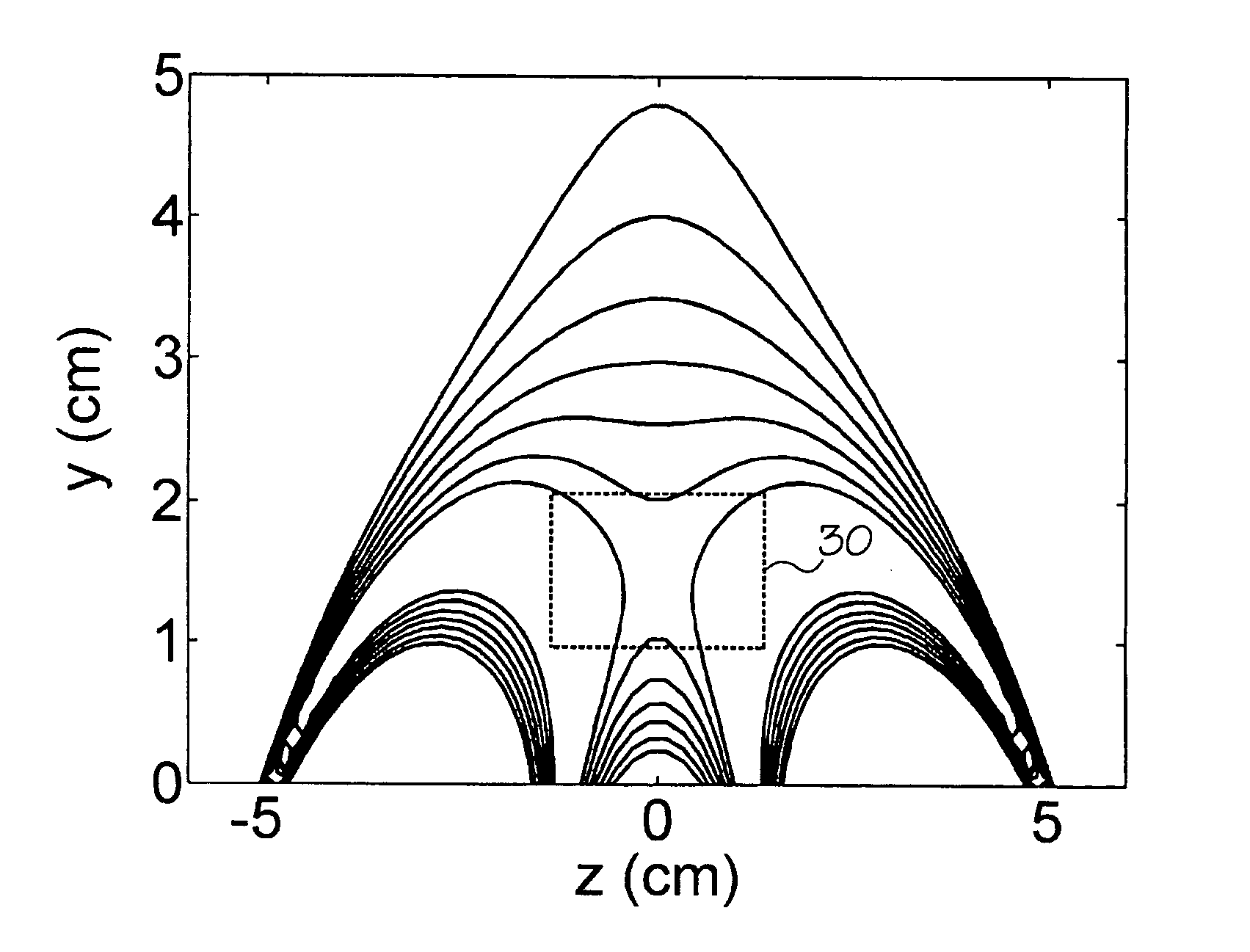
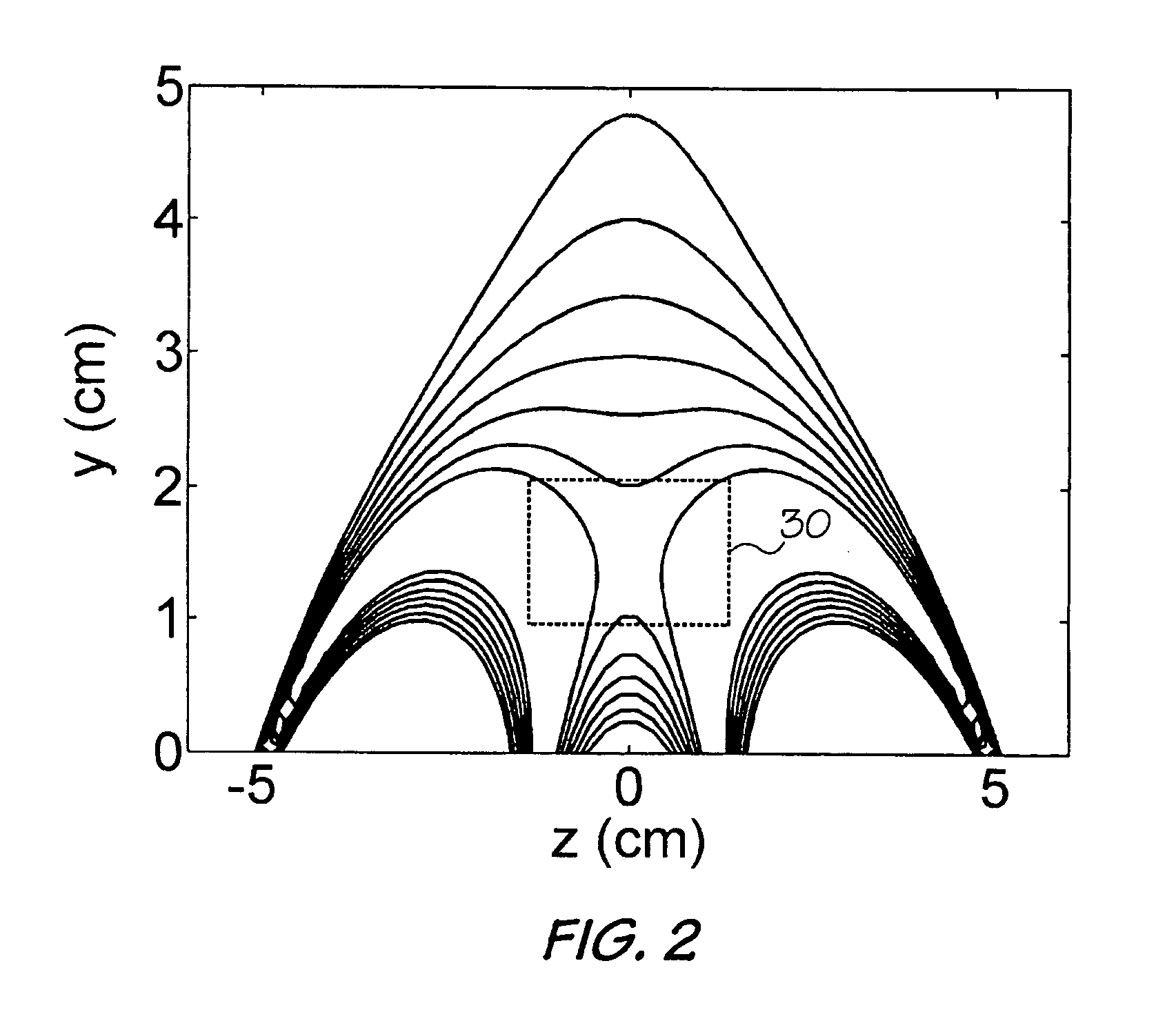
A unilateral NMR sensor comprising a ferromagnetic yoke; a permanent magnet arranged on the yoke; a pole piece on the magnet; the pole piece including an air-pole piece interface surface whose shape corresponds to an equipotential contour of magnetic scalar potential.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
Magnetic field generator suitable for unilateral nuclear magnetic resonance and method for making same
InactiveUS20120049849A1Suitable for measuringRemarkable effectMetal working apparatusElectric/magnetic detectionScalar potentialNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
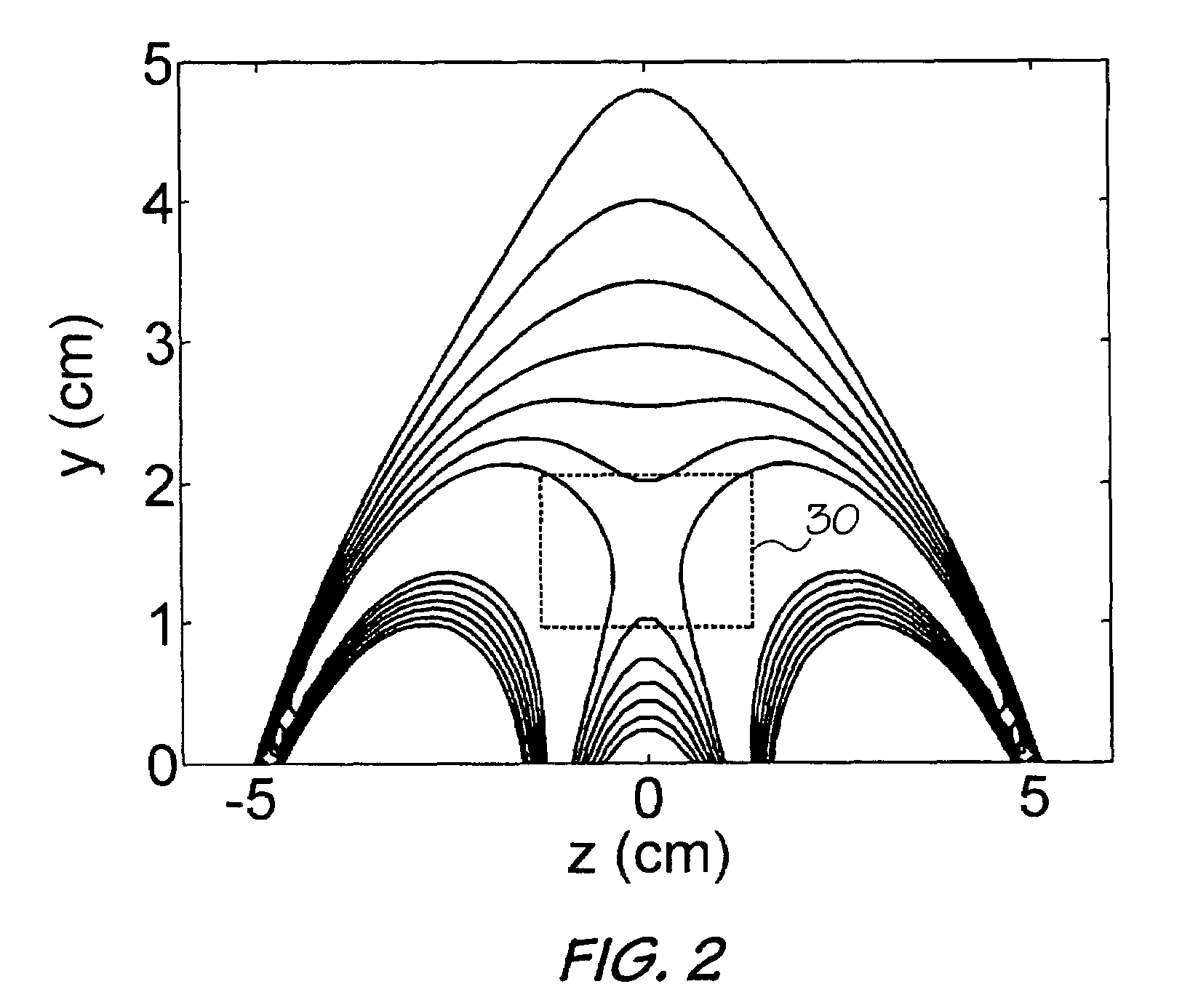
A unilateral NMR sensor comprising a ferromagnetic yoke; a permanent magnet arranged on the yoke; a pole piece on the magnet; the pole piece including an air-pole piece interface surface whose shape corresponds to an equipotential contour of magnetic scalar potential. An approach for designing single-sided magnets suitable for unilateral magnetic resonance (UMR) measurements is presented. The method uses metal pole pieces to shape the field from permanent magnets in a target region. The pole pieces are shaped according to solutions to Laplace's equation, and can be designed using a combination of analytical methods and numerical optimization. The design leads to analytical expressions for the pole piece shape and magnetic field. The method is developed in Cartesian, polar, and spherical coordinates, and the merits of each system are discussed. The effects of finite magnet size on the field quality are explored through simulation, and are found to have a substantial effect in many cases. A magnet is designed using our method to produce a static field with a constant gradient over a region 2 cm in diameter and 2 mm thick. This leads to a compact cylindrical magnet just over 11 cm in diameter, topped with a single metal pole piece. The design is validated through simulation. The simulated field is found to agree closely with that specified analytically through the design procedure.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
Marine controlled source electromagnetic method finite element forward method of anisotropic media
InactiveCN106980736AAvoid the effects of singularityEasy constructionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsScalar potentialMaxwell's equations
The present invention is a marine controlled source electromagnetic method finite element forward method of anisotropic media. The method comprises: firstly, setting a reference electrical conductivity, wherein three non-zero diagonal elements of the reference electrical conductivity are electrical conductivities in the direction of three main axes: x, y, z; next, setting three Euler rotation angles, and after three times of Euler rotation, obtaining an electrical conductivity tensor model in any direction; then starting from Maxwell equations, obtaining a finite element equation that is satisfied by magnetic vector potential and scalar potential under Coulomb regulations on a condition that the electrical conductivity presents anisotropy; then, performing discrete segmentation on a research region by using a non-structural grid, so that a complicated geoelectric model can be constructed; combining an incomplete LU discomposition pre-condition factor with an IDR(s) algorithm, so as to realize efficient and precise solution of a large sparse linear equation; and finally, deriving vector potential and scalar potential of a secondary field by using weighted moving least squares solution, to obtain each component of an electromagnetic field. The method provided by the present invention has excellent universality and can be promoted for electromagnetic method numerical value simulation with complicated electrical conductivity distribution and high precision.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Methods and systems for determining trapped charge density in films
InactiveUS7595204B2Improve accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesScalar potentialSemiconductor materials
Methods and systems for determining a charge trap density between a semiconductor material and a dielectric material are disclosed. In one respect, spectroscopic data of the semiconductor material may be determined and used to determine a change in dielectric function. A line shape fit of the change in the dielectric function may be applied using derivative function form. The amplitude of the line shape fit may be determined and used to determine an electric field of a space charge region of the semiconductor material. By applying Poisson's equations, the scalar potential due to the electric field in the space charge region may be determined. Subsequently, using the scalar potential the charge trap density may be determined.
Owner:SEMATECH
Method for calculating plane wave reflection coefficients in elastic multi-layered medium
The invention discloses a method for calculating plane wave reflection coefficients in an elastic multi-layered medium. The method comprises the following steps: (1) if plane harmonic waves enter into a target layer series from a medium n+1, generating reflected longitudinal waves and reflected transverse waves in the n+1 medium, generating transmitted longitudinal waves and transmitted transverse waves in a medium 1, and writing each medium layer in a scalar potential form and a vector potential form; (2) determining relation among the displacement, stress and bit shift; (3) loading the scalar potential and vector potential of the step (1) into the step (2) to obtain a displacement and stress relation expression between the (n+1)th layer and the first layer; and (4) obtaining a displacement and stress transfer matrix containing elasticity coefficients of each layer according to the displacement and stress relation expression, which is obtained in the steps (3), between the (n+1)th layer and the first layer, solving, and obtaining reflection and transmission coefficients. According to the method, the influence of multiple waves and transformed waves of the elastic layer series as well as thickness and frequency on the reflection coefficient is considered fully, so that the method is applicable to thin-layer AVO (Amplitude Variation with Offset) analytical simulation and is high in calculation efficiency.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Spacecraft formation cooperative control method for guaranteeing communication and avoiding collision
ActiveCN109765921AGuaranteed uptimeEfficient and reliable completionAttitude controlRobustificationAnti jamming
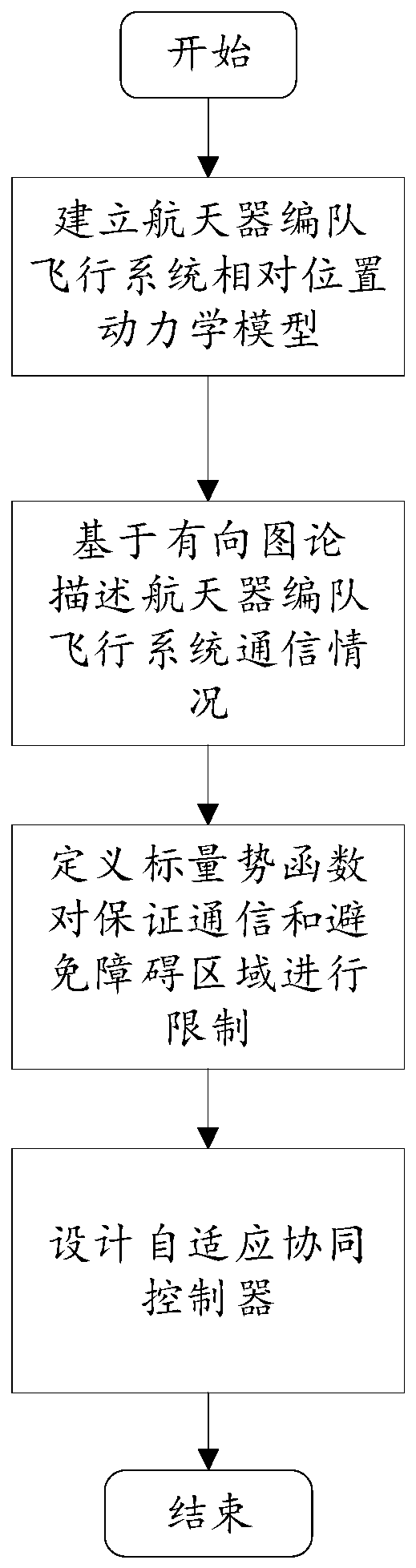
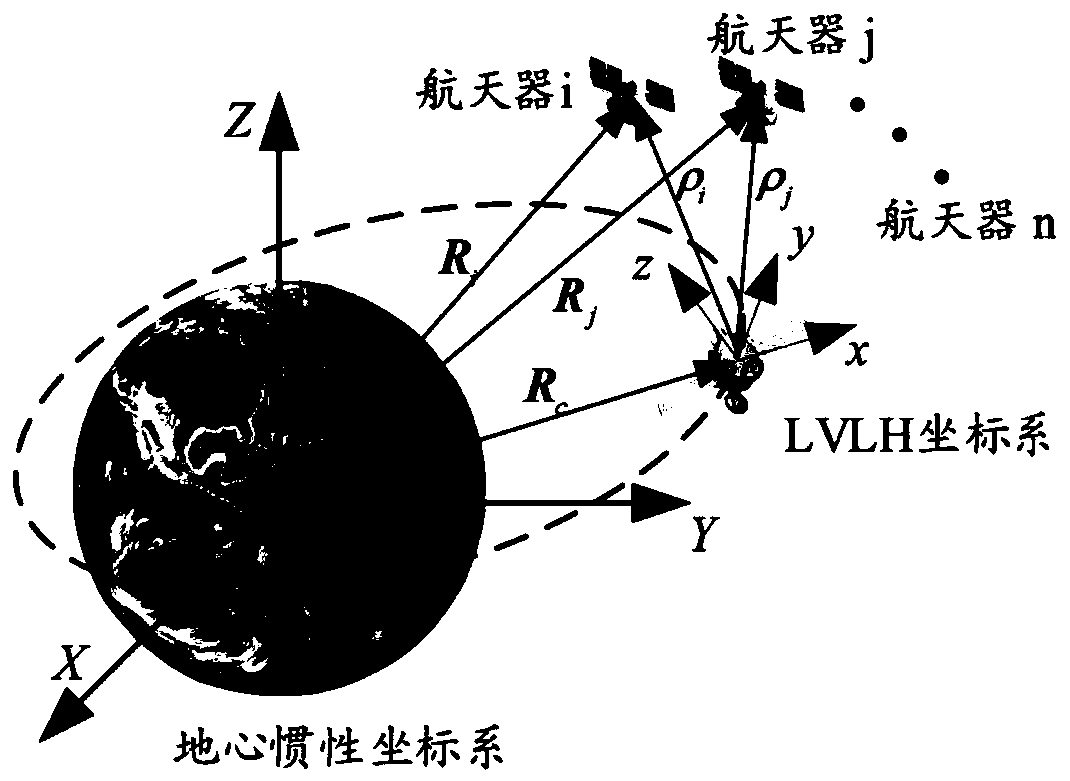
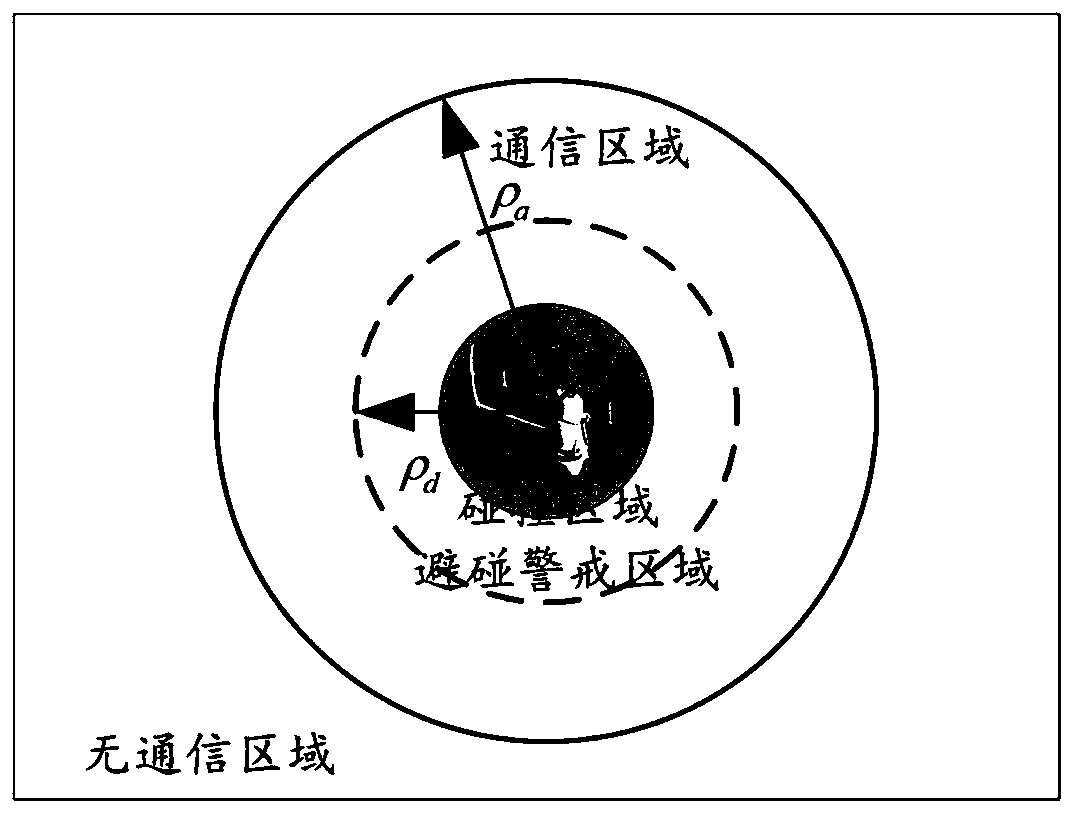
The invention discloses a spacecraft formation cooperative control method for guaranteeing communication and avoiding collision. The method comprises the following steps that: considering a situationthat external interference is in the presence to establish the relative position kinetic model of a spacecraft formation flight system; on the basis of a directed graph theory, describing the communication situation of the spacecraft formation flight system; defining a scalar potential function, and restricting a safe and reliable area capable of guaranteeing the effective communication and the collision avoidance of the spacecraft; and designing an adaptive cooperative controller to enable the final speed of the spacecraft formation to approach to be consistent. By use of the method, while the formation spacecraft realizes a consistent integral speed, the formation spacecraft is guaranteed to carry out effective communication and collision avoidance, and in addition, the method has the advantages of high anti-jamming capability, good robustness and the like, and is suitable for the cooperative control of the relative position of spacecraft formation flight.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Electric conductivity rebuilding method for magnetocaloric acoustical imaging
ActiveCN104473640AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Scalar potential
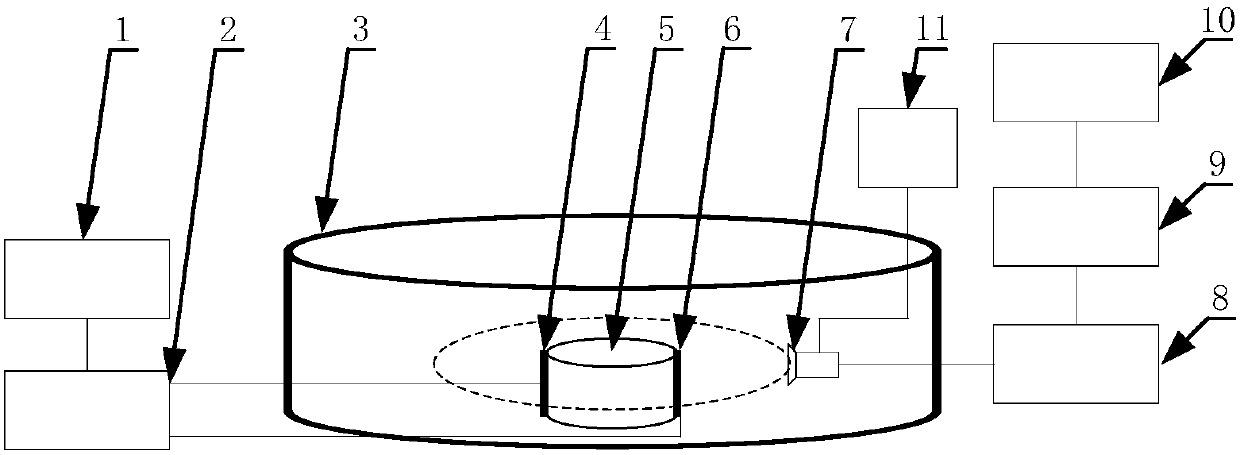
The invention relates to an electric conductivity rebuilding method for magnetocaloric acoustical imaging. The electric conductivity rebuilding method is based on a magnetocaloric acoustical imaging principle. An exciting coil is used for exerting MHz current excitation on a conducting object, joule heat is generated in the conducting object, and further, ultrasonic signals are generated. An ultrasonic transducer is used for receiving the ultrasonic signals, the received ultrasonic signals are processed and collected, and then, an electric conductivity image of the conducting object is obtained by adopting an electric conductivity image rebuilding algorithm. The electric conductivity rebuilding method comprises the concrete steps that 1, firstly, high-signal-to-noise-ratio magnetocaloric acoustical signals are obtained; 2, the obtained magnetocaloric acoustical signals are used for rebuilding to obtain thermal sound source distribution of the conducting object; 3, the thermal sound source distribution and a one-order magnetic vector space component are used, and a non-linear finite element solution method is adopted for rebuilding a scalar potential space component; 4, the rebuilt scalar potential space component is used for rebuilding the electric conductivity.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic thermal sound imaging resistivity rebuilding method based on optimization iterative algorithm
ActiveCN104473639AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSound imageScalar potential
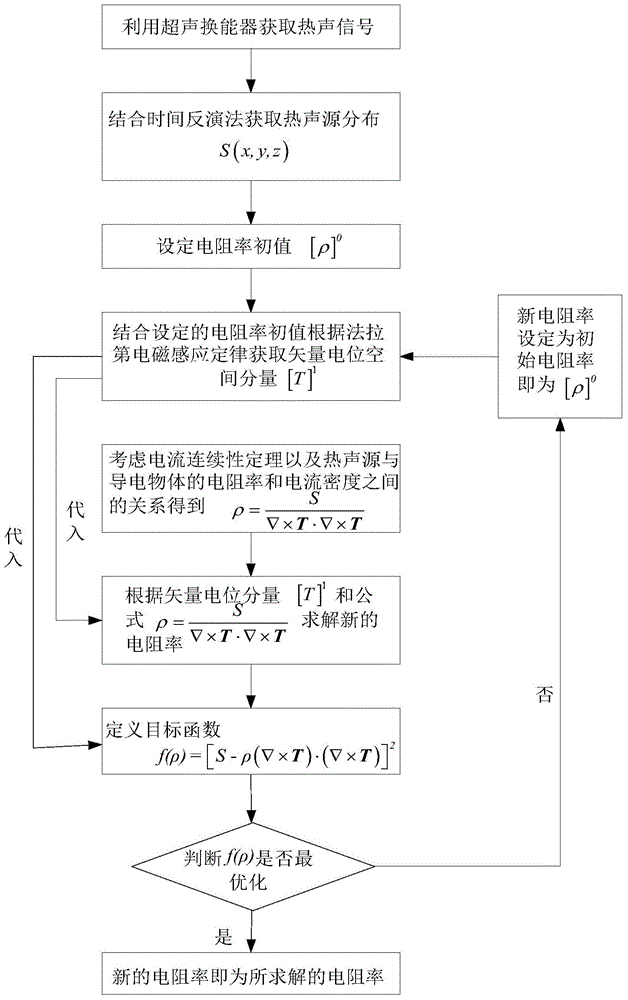
The invention provides a magnetic thermal sound imaging resistivity rebuilding method based on an optimization iterative algorithm. An exciting coil generates electromagnetic thermal sound signals on a conducting object, an ultrasonic transducer receives the electromagnetic thermal sound signals, the signals are processed through an ultrasonic signal processing and collecting sub system, and a control circuit controls the synchronization of a current excitation source, the ultrasonic transducer and the ultrasonic signal processing and collecting sub system. The ultrasonic transducer carries out fault circumference scanning on the electromagnetic thermal sound signals, electromagnetic ultrasonic signals on each fault circumference are obtained, and finally, the rebuilding of a resistivity image is realized through being combined with an image rebuilding algorithm. The resistivity image rebuilding method has the advantages that an objective function satisfying a thermal sound source, the resistivity, a primary magnetism loss position space component and a scalar potential space component is firstly defined, under the condition that the thermal sound source distribution is known, the scalar potential space component is solved according to the current continuity theorem, then, the scalar potential space component and the magnetism loss position space component are substituted into the objective function, and the resistivity distribution is rebuilt.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for reconstructing specific conductivity of thermoacoustic tomography based on current injection
ActiveCN107064302AAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResistance/reactance/impedenceSonificationUltrasonic sensor
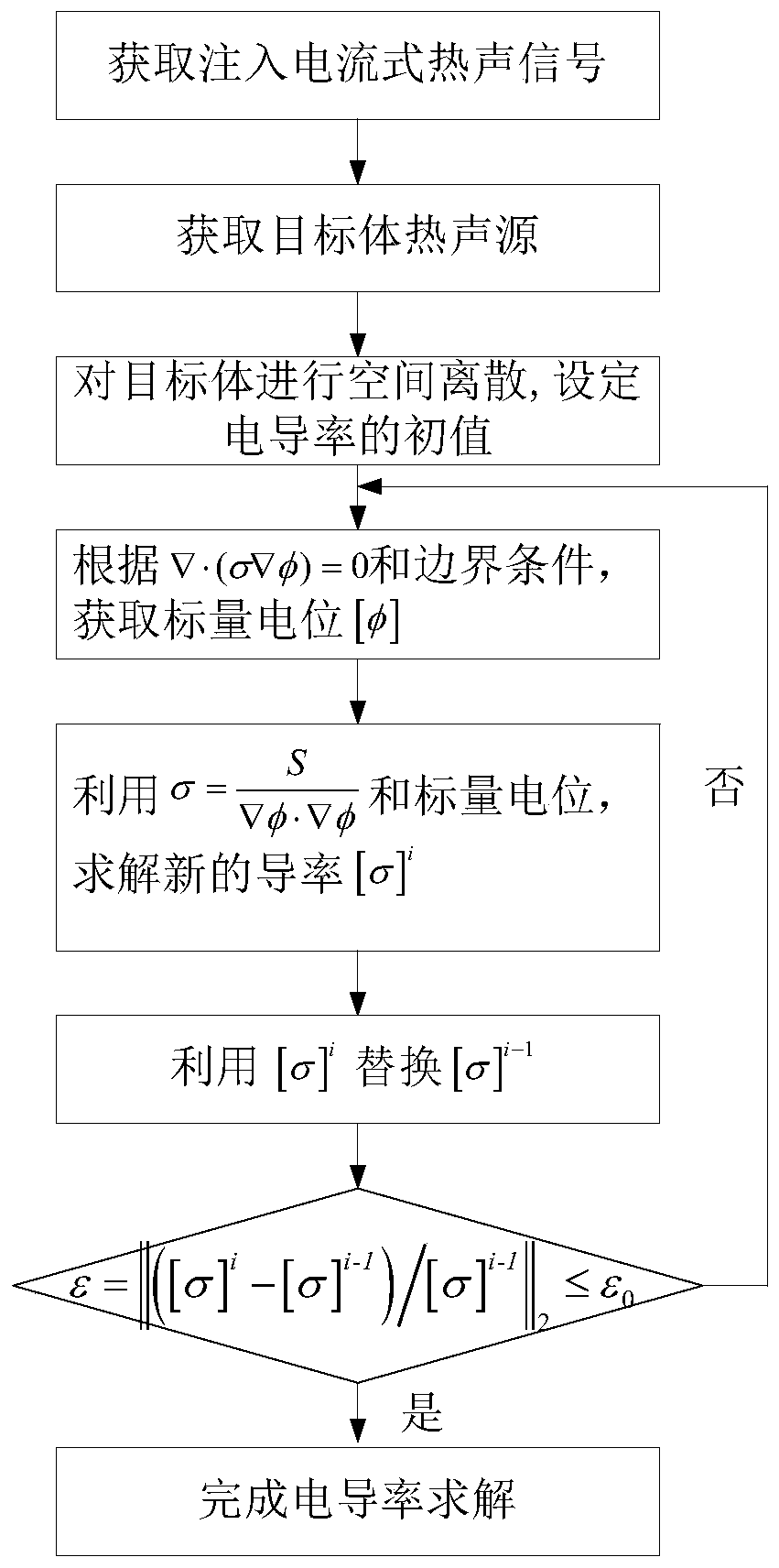
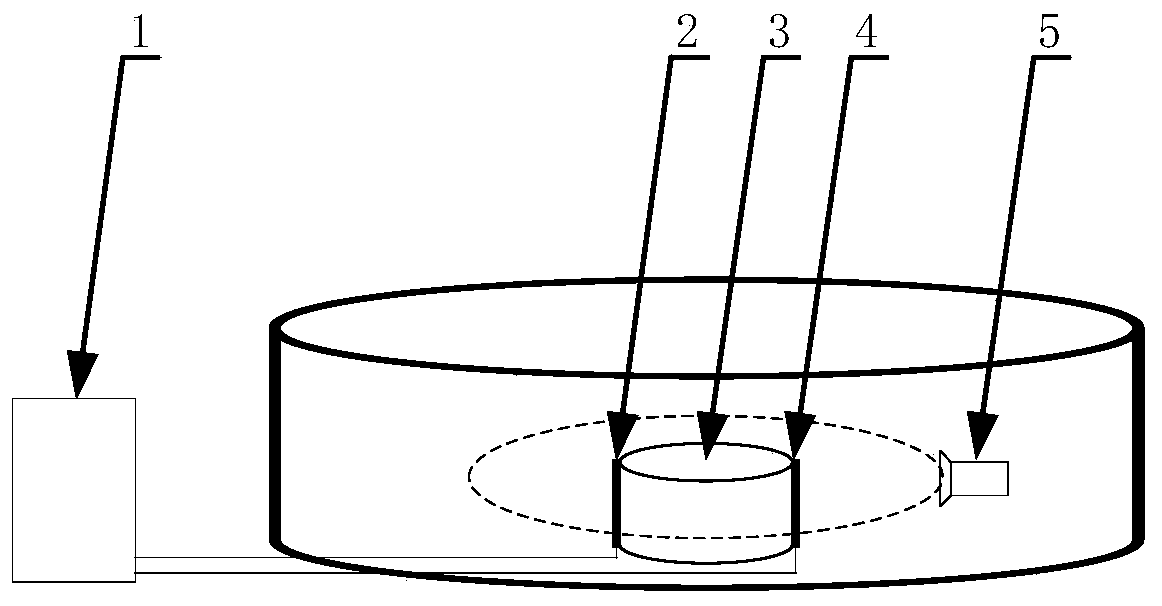
The invention provides a method for econstructing specific conductivity of thermoacoustic tomography based on the principle of current injection thermoacoustic tomography. A pulse current is injected into an imaging object via an electrode to generate joule heat in the imaging object, which then induces thermal expansion and generates an ultrasonic signal, the ultrasonic signal is received by an ultrasonic transducer and then processed and collected, and the specific conductivity images of the object is obtained by a specific conductivity image reconstruction algorithm. The specific steps are as follows: (1) obtaining a current injection type thermoacoustic signal; (2) reconstructing a thermoacoustic source of the object by using the obtained current injection type thermoacoustic signal; (3) reconstructing an electric scalar potential from the thermoacoustic source by a nonlinear finite element solution method; and (4) reconstructing specific conductivity by using the reconstructed electric scalar potential.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Conductivity image reconstructing method for magneto-thermoacoustic coupled tomography
A conductivity image reconstructing method for magneto-thermoacoustic coupled tomography includes: acquiring a thermoacoustic source distribution of a conductive object by means of time inversion according to an electromagnetic ultrasonic signal received, and performing reconstruction according to the thermoacoustic source distribution to obtain a conductivity distribution of the conductive object. Specially, the method includes: acquiring a thermoacoustic source on a certain level by means of time inversion, acquiring a thermoacoustic source of the conductive object by means of interpolation, performing calculation by means of Biot-Savart's law according to excitation current to obtain a spatial component A1 of primary magnetic vector potential, subjecting the conductive object to spatial discretization, giving an initial value [Sigma]<0> of conductivity, according to the theorem of current continuity, solving a spatial component [Phi] <1> of scalar potential with the initial value [Sigma]<0> and the spatial component A1, substituting the spatial component [Phi]<1> of the scalar potential to a relation which the thermoacoustic source and conductivity meet so as to obtain updated conductivity [Sigma]<1>, replacing the initial value [Sigma]<0> with the updated conductivity [Sigma]<1>, repeating the process above, and stopping iteration until a relative error of the conductivity meets an equation: Sigma=||([Sigma]1-[Sigma]0) / [Sigma]0||2<=Sigma0.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sensor for unilateral nuclear magnetic resonance and method for making same
InactiveUS20060066310A1Improve permeabilityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceScalar potential
A unilateral NMR sensor comprising a ferromagnetic yoke; a permanent magnet arranged on the yoke; a pole piece on the magnet; the pole piece including an air-pole piece interface surface whose shape corresponds to an equipotential contour of magnetic scalar potential
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
Model verification method for prediction model of underwater ship corrosion-related static magnetic field
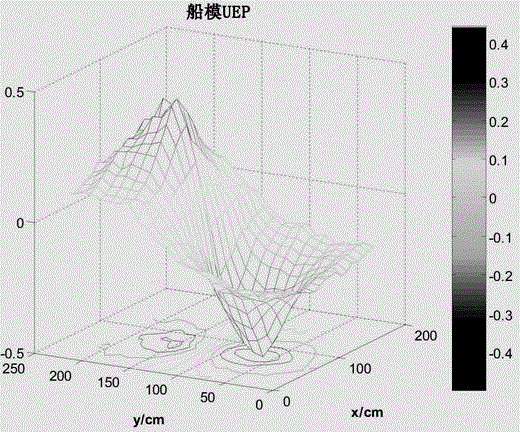
InactiveCN104569627AClever implementation of loadingImprove accuracyWeather/light/corrosion resistanceElectrostatic field measurementsPower flowScalar potential
The invention provides a model verification method for a prediction model of an underwater ship corrosion-related static magnetic field. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, simulating seawater and ocean environments in a lab, constructing a ship model and an impressed current cathodic protection system of the ship model according to a certain scale ratio, measuring electric scalar potential distribution below the ship model, and constructing the horizontal current line prediction model of the underwater ship corrosion-related static magnetic field; secondly, loading a horizontal current line in the same experimental environment to replace the ship model, repeatedly measuring electric scalar potential in the same position below the ship model, and synchronously measuring magnetic field distribution in water; thirdly, comparing the measured electric scalar potential of the current line with a measurement result of the ship model to prove the feasibility of field source equivalency; comparing the measured magnetic field with a prediction result of the prediction model to prove the correctness of a prediction process of the prediction model. According to the method, the feasibility of field source equivalency is proved by comparing the electric field distribution, and the correctness of the prediction process is proved by comparing the magnetic field distribution, so that a model verification problem of the prediction model of the underwater ship corrosion-related static magnetic field is solved.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
Magnetic thermoacoustic imaging conductivity reconstruction method based on linear Poisson's equation
The invention discloses a magnetic thermoacoustic imaging conductivity reconstruction method based on a linear Poisson's equation. An exciting coil generates an electromagnetic thermoacoustic signal on a conductive object; an ultrasonic transducer receives the electromagnetic thermoacoustic signal; an ultrasonic signal processing and acquiring subsystem acquires and processes the signal; and a control circuit controls the synchronization of a current excitation source, the ultrasonic transducer and the ultrasonic signal processing and acquiring subsystem. The method comprises the following steps: performing circular fault scanning on the electromagnetic thermoacoustic signal by virtue of the ultrasonic transducer, acquiring an electromagnetic ultrasonic signal on the circumference of each fault, and finally combining an image reconstruction algorithm to realize the conductivity image reconstruction. The conductivity image reconstruction method comprises the following steps: firstly defining an objective function meeting a thermoacoustic source, the conductivity, a primary magnetic dislocation spatial component and an electric scalar potential spatial component, giving the initial value of the conductivity, solving the electric scalar potential spatial component according to a current continuity theorem under the condition that the thermoacoustic source distribution is known, substituting the electric scalar potential spatial component and magnetic dislocation spatial component into the objective function, and reconstructing the conductivity distribution.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
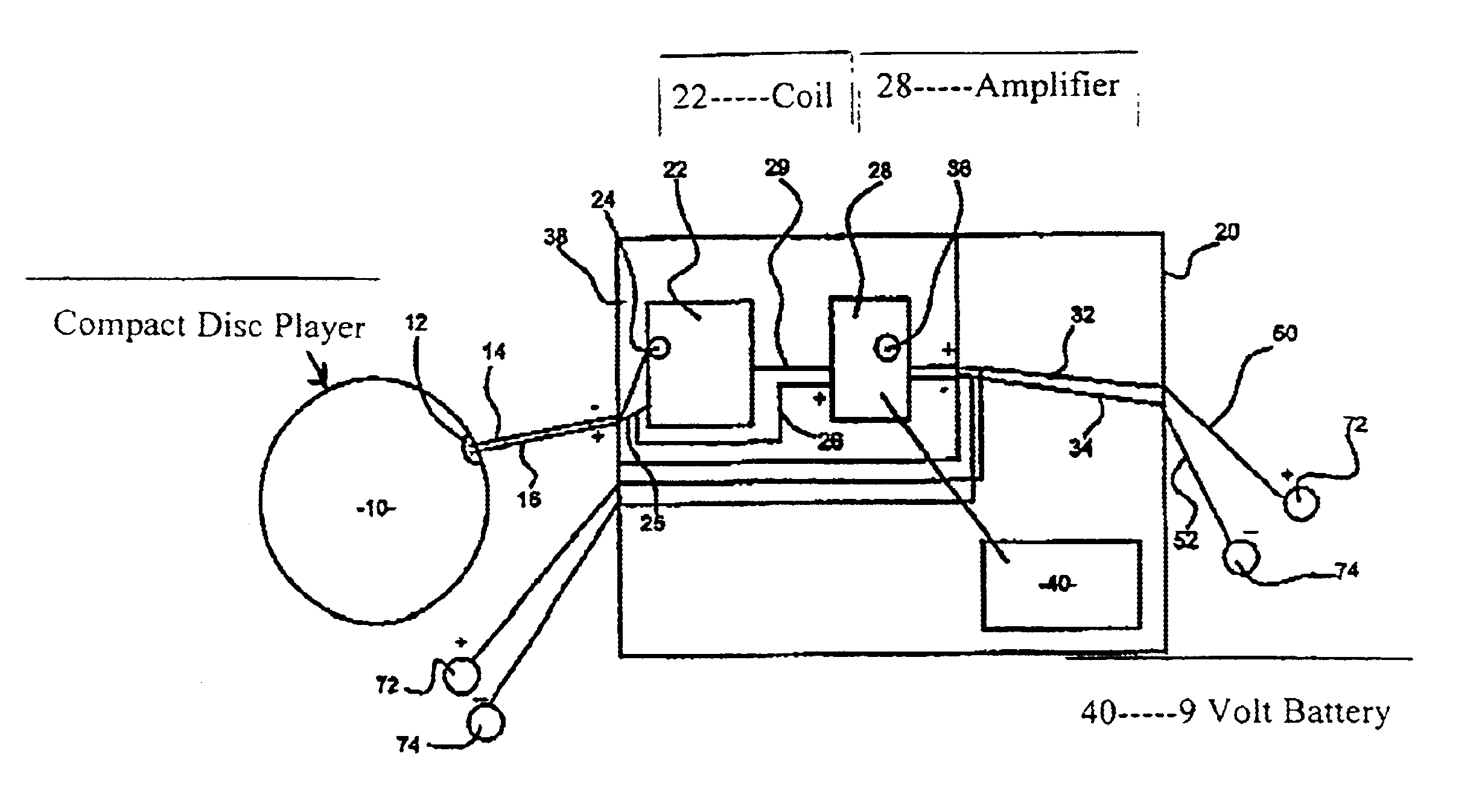
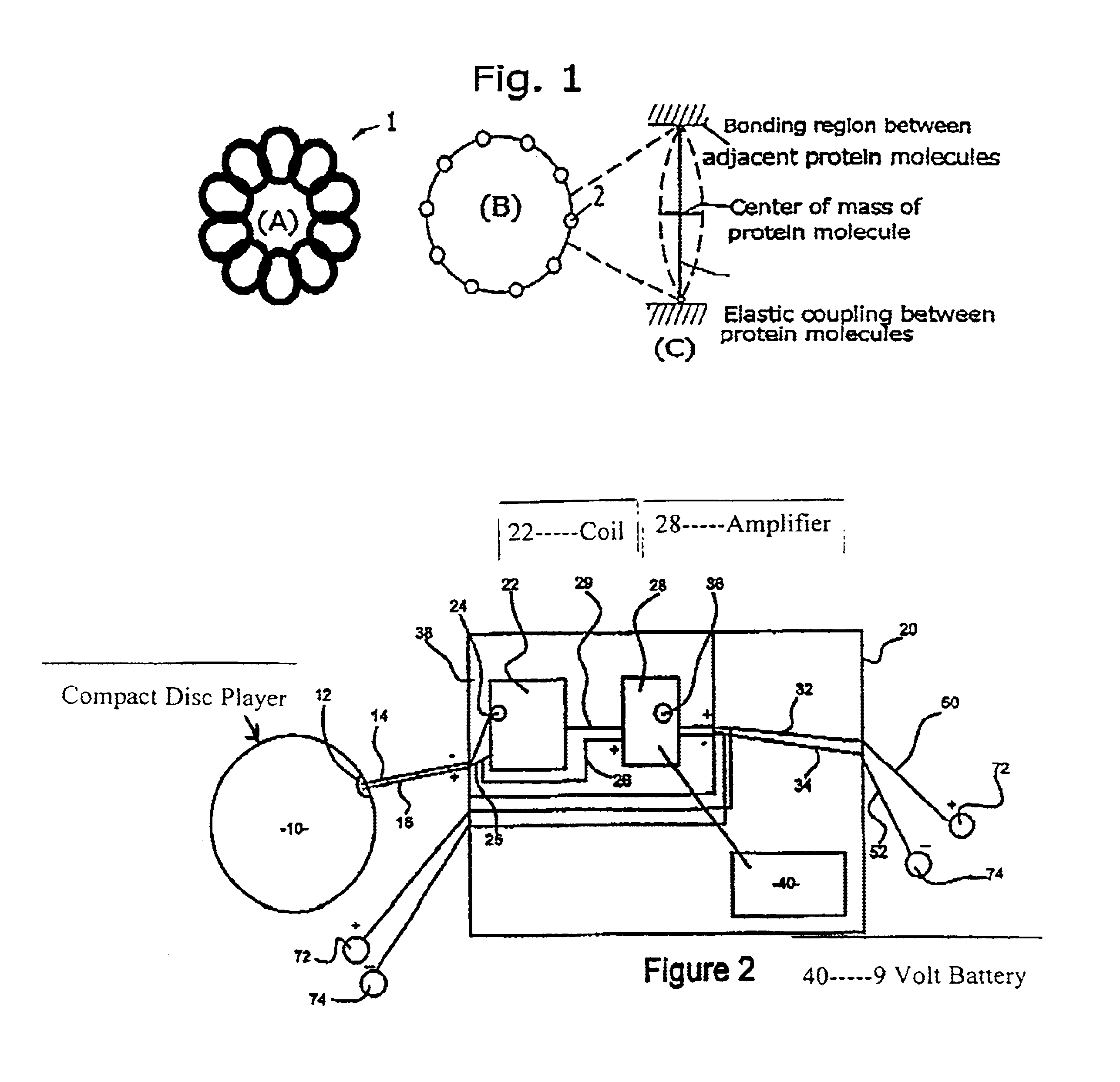
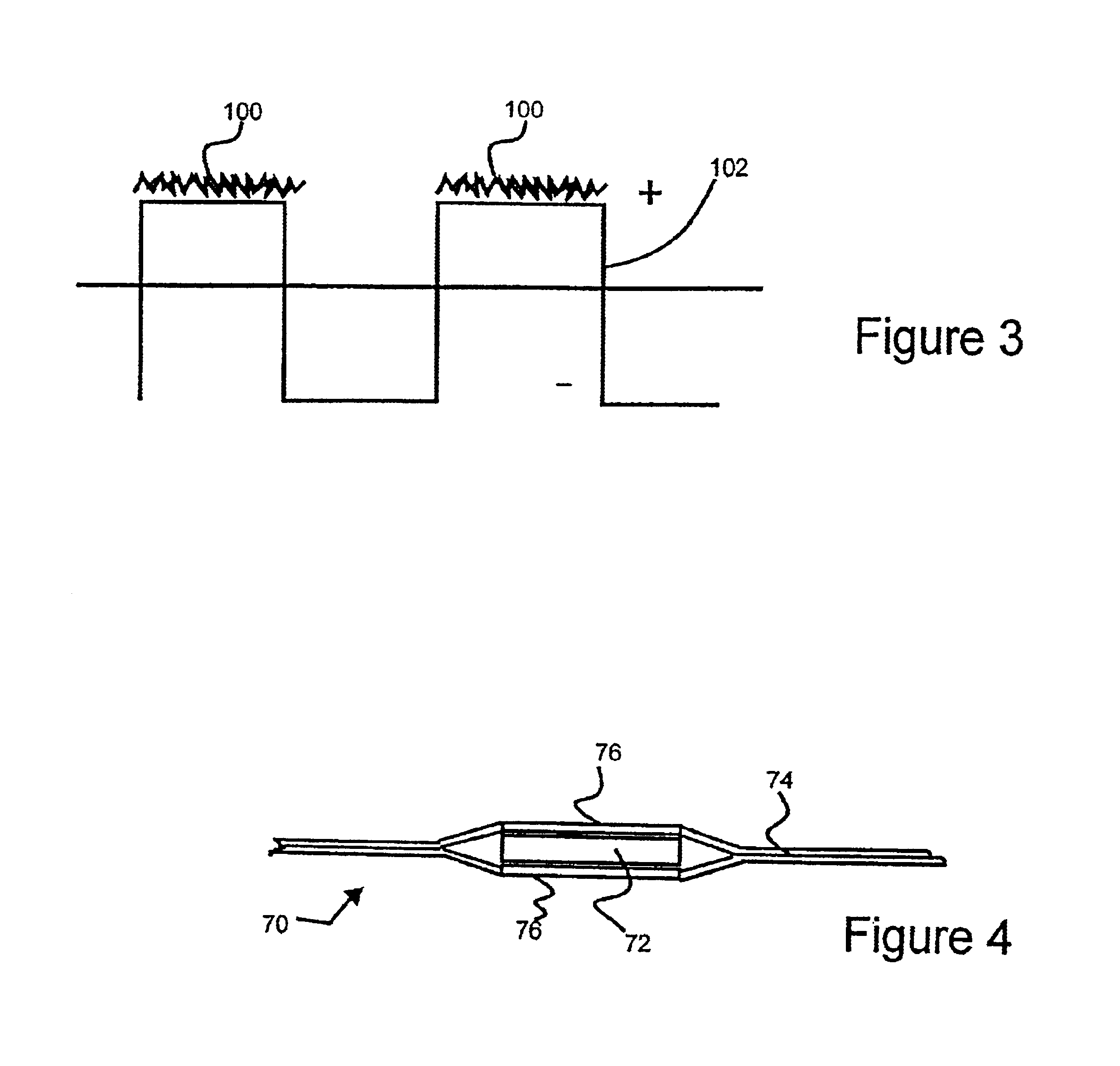
Apparatus for destroying pathogen molecules using frequencies
A frequency transfer system for the destruction of pathogens using a recorded medium and a transfer unit is disclosed. The recorded medium contains at least one square wave at a frequency known to affect specific pathogens. Additional mathematically congruent square waves can also be recorded on the medium for simultaneous transmission. The transfer unit contains a coil and an amplifier. The coil absorbs the magnetic flux from the electromagnetic square waves and outputs scalar square waves. The amplifier increases the voltage and reverses the wave polarities to place the greatest scalar potentials at the positive node of said output square wave. The scalar waves are transferred to the user's body through output leads and electrodes.
Owner:DEBROUSE JOSEPH W
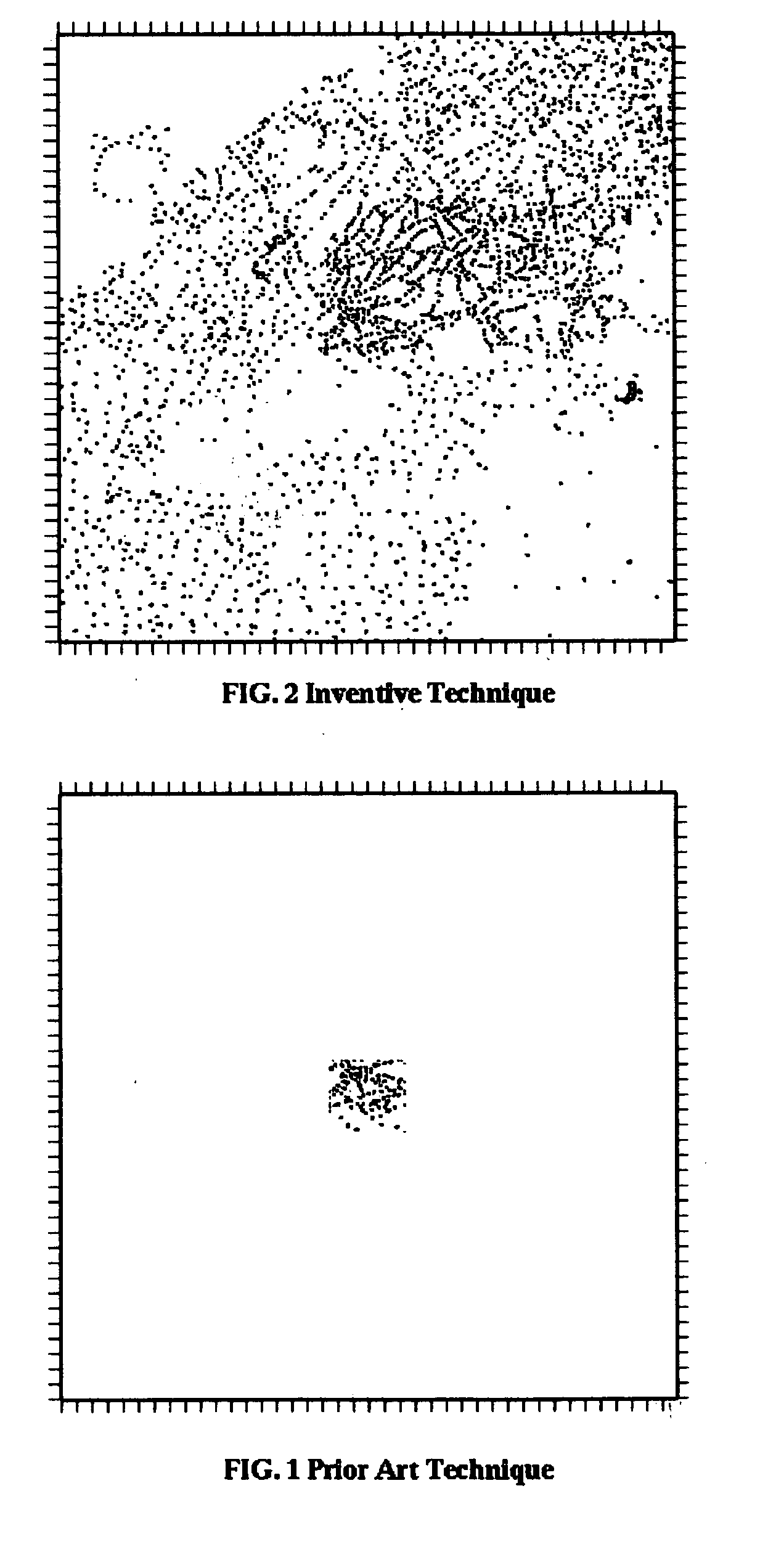
Method for enhancing depth and spatial resolution of one and two dimensional residual surfaces derived from scalar potential data
InactiveUS7043366B2Seismic signal processingElectric/magnetic detectionScalar potentialReference Region
An improved method is disclosed for collecting or assembling scalar potential data measurements that are to be subsequently prepared as a surface representation for analysis via frequency domain transform filters. Measurements are made over a geographic reference region which extends in all cardinal directions from the center of some previously determined primary region. The reference dimensions must contain the primary region and must be plural multiples of the greatest depth to be considered in analyzing the contributions to the measurements. A combined or separate improved method for delineating or defining geospatial information contributing to a scalar potential surface is disclosed. This method is implemented using traditional statistical techniques to construct an histogram from the set of values comprising a surface representation. This histogram constitutes a Spatially Correlated Potential Spectrum for the surface. These combined and separate methods improve resolution of geological structures over depths and spatial extents under consideration.
Owner:MCDERMOTT ANDREW MARTIN
Magnetic field generator suitable for unilateral nuclear magnetic resonance and method for making same
InactiveUS8237440B2Improve correspondenceEasy to controlMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionScalar potentialPole piece
A unilateral NMR sensor comprising a ferromagnetic yoke; a permanent magnet arranged on the yoke; a pole piece on the magnet; the pole piece including an air-pole piece interface surface whose shape corresponds to an equipotential contour of magnetic scalar potential. An approach for designing single-sided magnets suitable for unilateral magnetic resonance (UMR) measurements is presented. The method uses metal pole pieces to shape the field from permanent magnets in a target region. The pole pieces are shaped according to solutions to Laplace's equation, and can be designed using a combination of analytical methods and numerical optimization. The design leads to analytical expressions for the pole piece shape and magnetic field. The method is developed in Cartesian, polar, and spherical coordinates, and the merits of each system are discussed. The effects of finite magnet size on the field quality are explored through simulation, and are found to have a substantial effect in many cases. A magnet is designed using our method to produce a static field with a constant gradient over a region 2 cm in diameter and 2 mm thick. This leads to a compact cylindrical magnet just over 11 cm in diameter, topped with a single metal pole piece. The design is validated through simulation. The simulated field is found to agree closely with that specified analytically through the design procedure.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
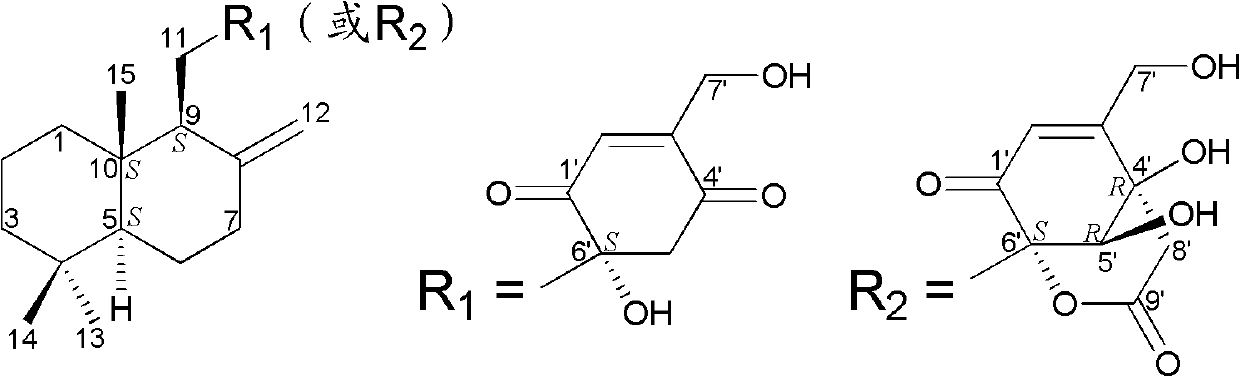
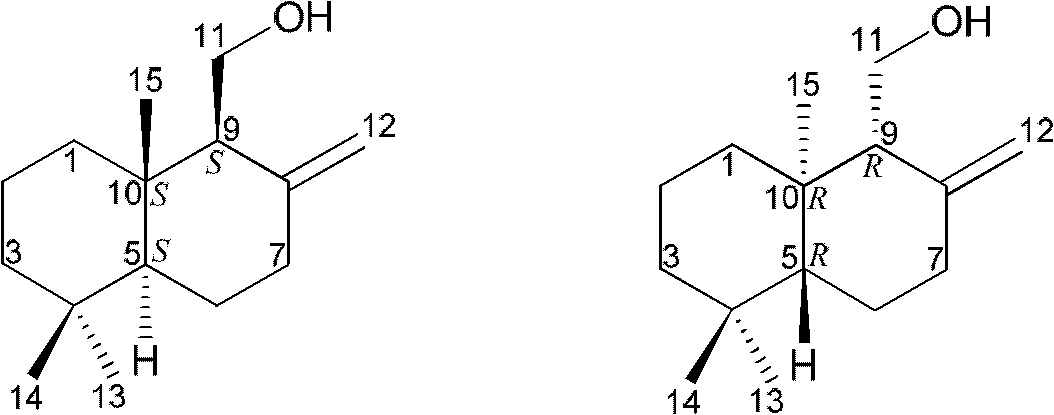
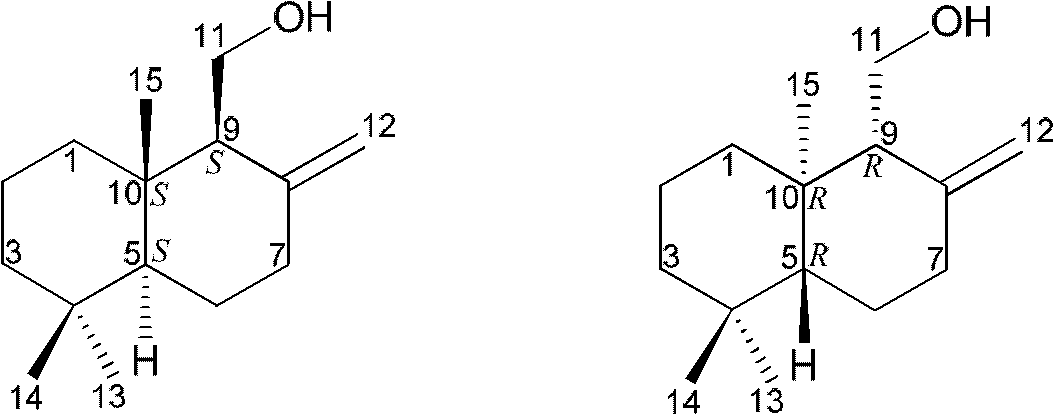
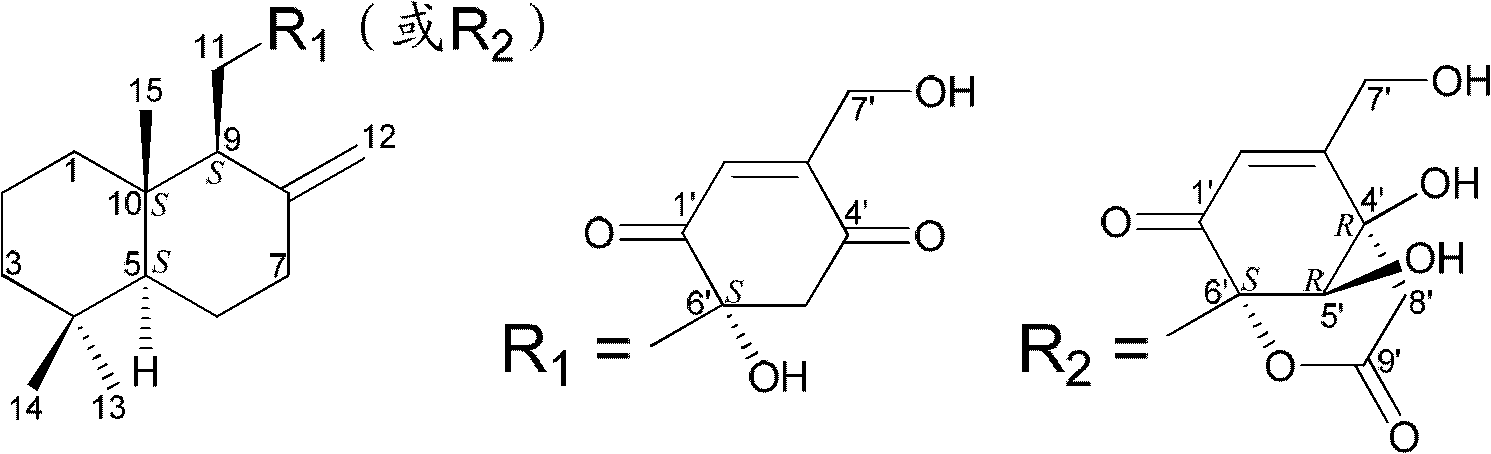
Drimane-type sesquialter terpene cyclohexenone derivative, preparation method thereof and application
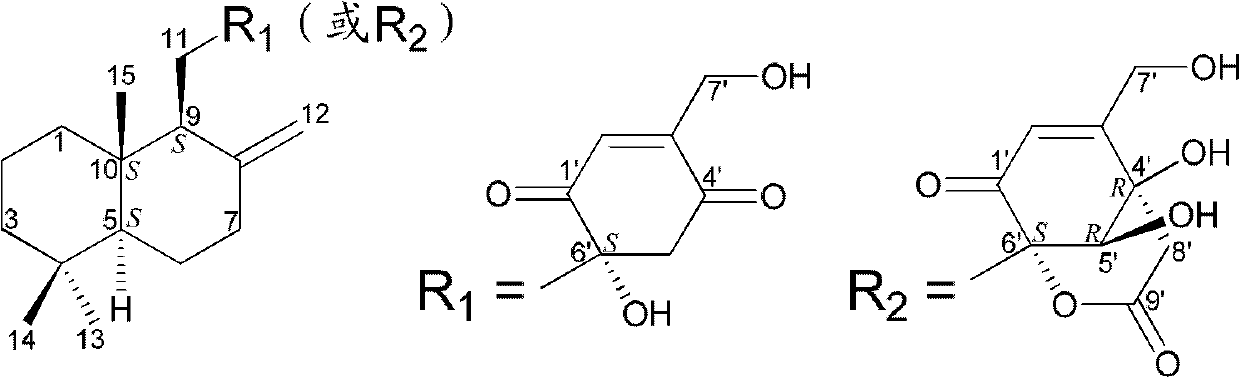
InactiveCN102618448AEfficient killingPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsFungiAbsolute configurationScalar potential
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemicals, and relates to drimane-type sesquialter terpene cyclohexenone derivative, a preparation method thereof and application. Particularly, the drimane-type sesquialter terpene cyclohexenone derivative relates to a compound in a formula I, wherein Arabic numerals in the formula I indicate scalar potentials, and an R and an S respectively represent absolute configurations of carbon atoms with the corresponding potentials. The invention further relates to the preparation method of the compound, a composition containing the compound and the anti-tumor application. The invention further relates to penicillium purpurogenum BD-1-6 capable of being used for preparing the compound. The compound in the formula I can effectively kill tumor cells or suppress proliferation of the tumor cells, has excellent anti-tumor activity and has the potential of being used as an anti-tumor medicine. Attached is the formula I.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
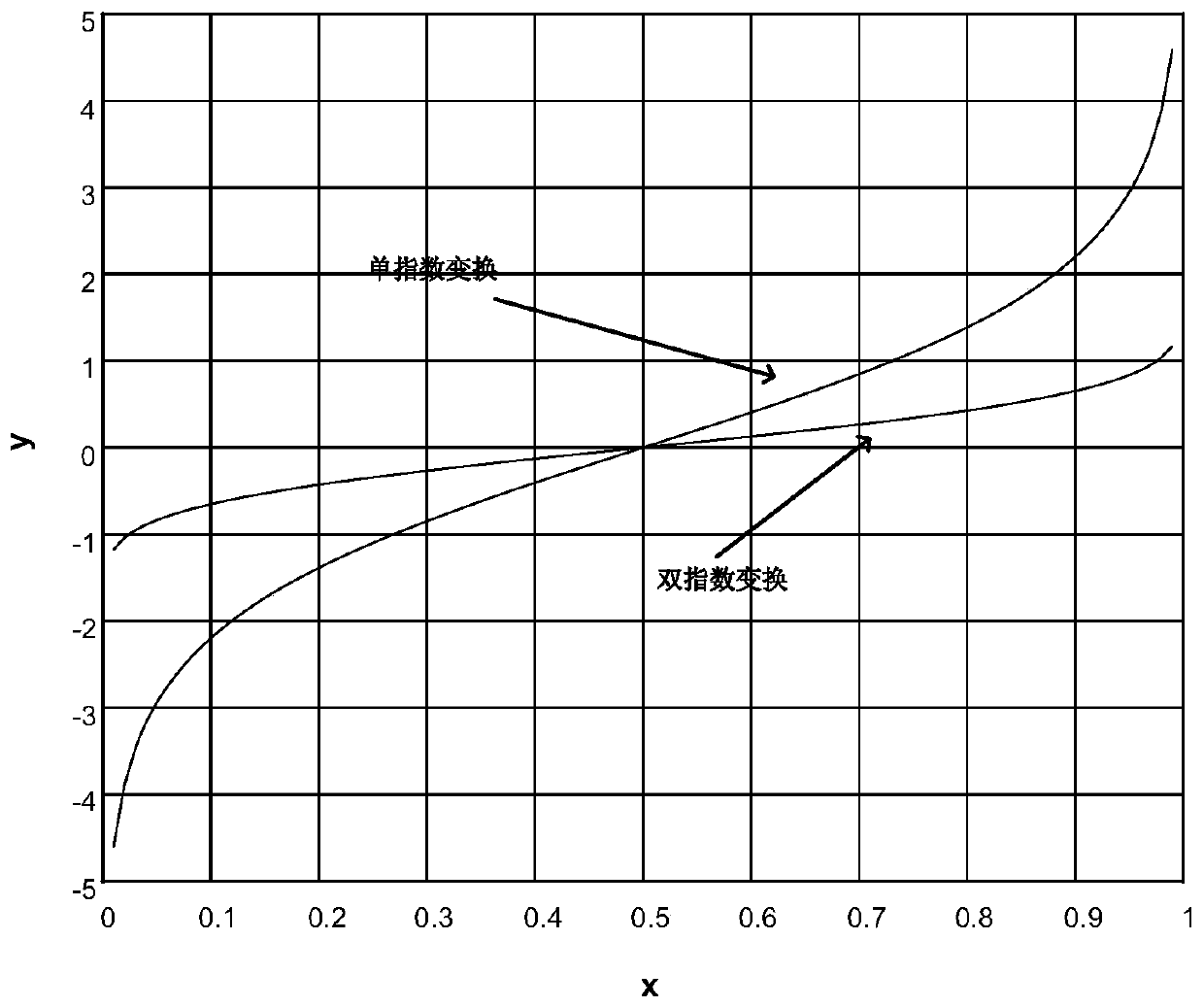
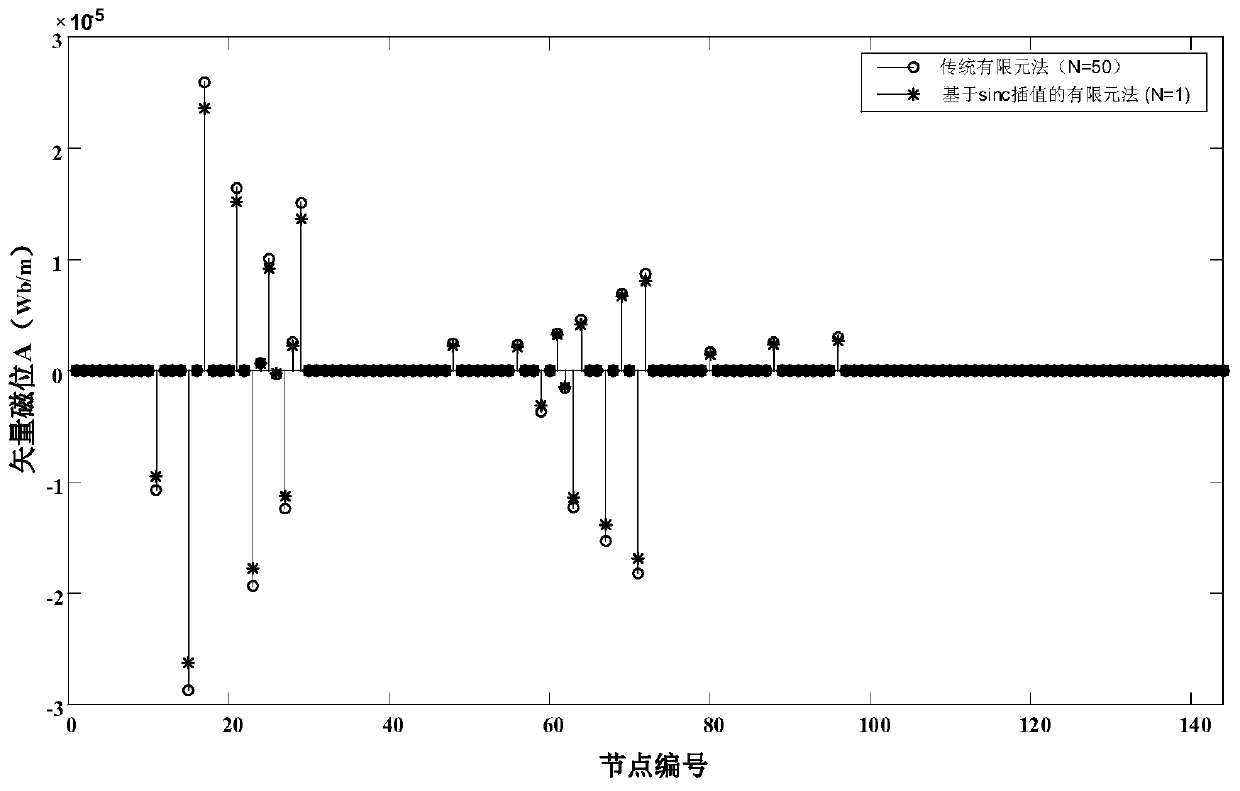
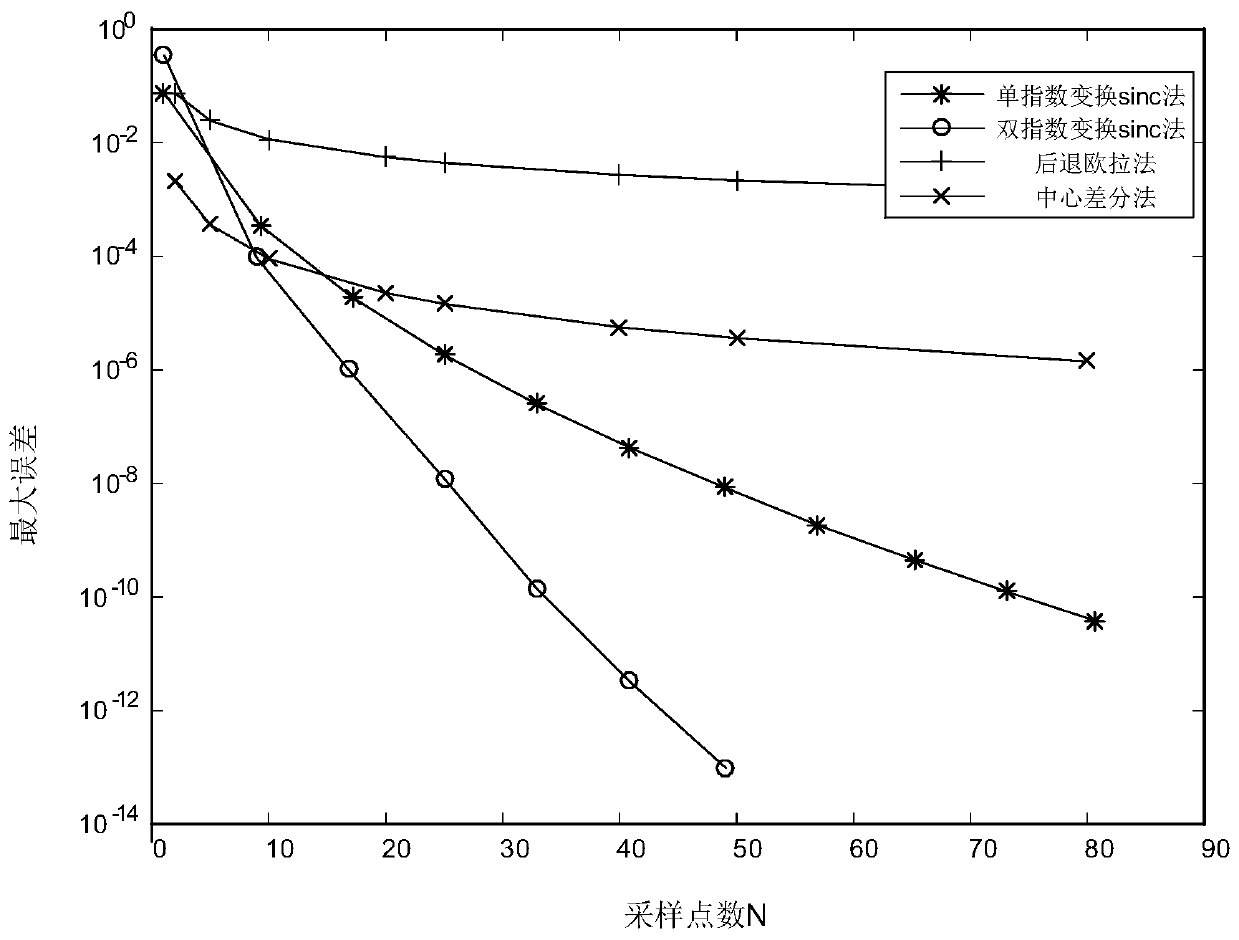
Transformer vortex field finite element solving method based on sinc function
ActiveCN108875218AFast convergenceHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationMulti-objective optimisationScalar potentialMathematical model
The invention discloses a transformer vortex field finite element solving method based on a sinc function. According to the method, first, a model is established for a transformer, and then meshing isperformed on the established model according to a finite element method; the finite element method is adopted to calculate a stiffness matrix and a damping matrix of the model according to unit nodeinformation obtained through meshing; and a magnetic vector potential and a scalar potential are selected to serve as an unknown function of a vortex field mathematical model, a discretization formatis exported through a Galerkin finite element method, a discretization equation set is established, solutions of the discretization equation set are solved through a sinc interpolation method, electric field distribution and magnetic field distribution in a transformer solving domain can be obtained according to the solutions of the equation set, and therefore vortex distribution and loss of the transformer can be calculated. The method is simple in design, easy to implement and easy to popularize, provides more precise analysis for vortex field and loss calculation of large and ultra-large power transformers, provides a basis for transformer design and manufacturing and improves the security and stability of transformer operation.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Communications system
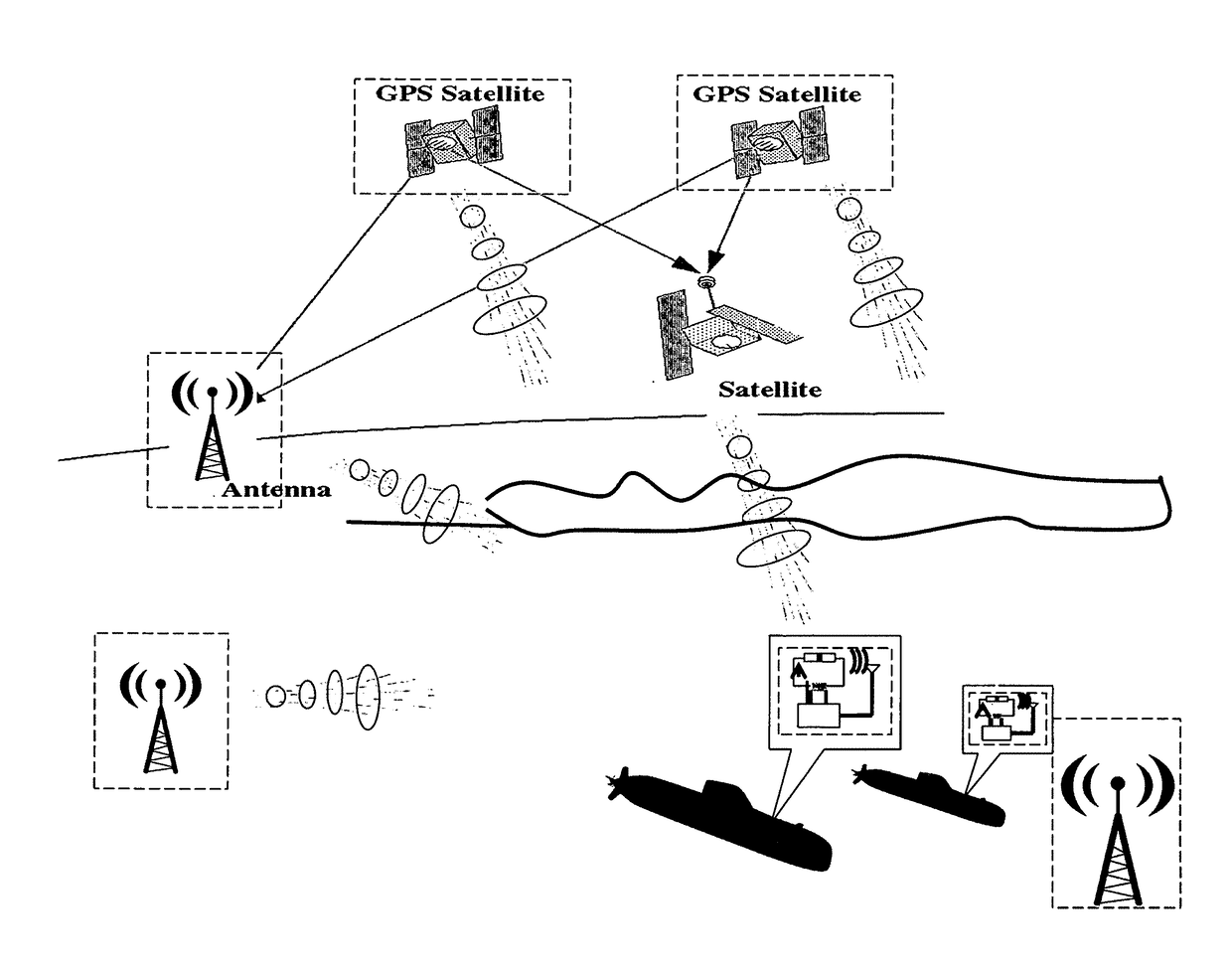
ActiveUS20180062765A1Rule out the possibilityBeacon systems using radio wavesAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesScalar potentialScreening effect
A communication system using vector and scalar potential is disclosed. The system uses field-free potentials signaling for many applications where the absence of shielding effects in sea water, plasma or other dense media due to the fact that the absence of (E,B) fields eliminates the possibility of induced charge and current response in the media being transited.
Owner:QUANTCOMM LLC
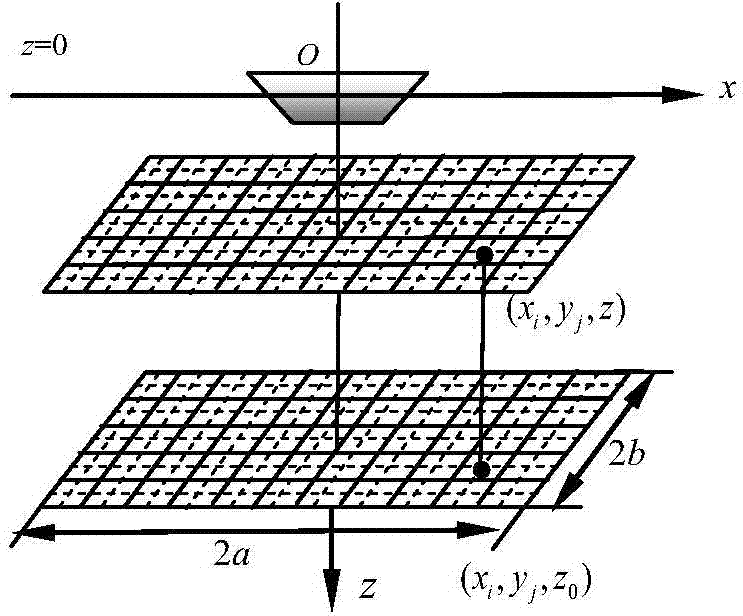
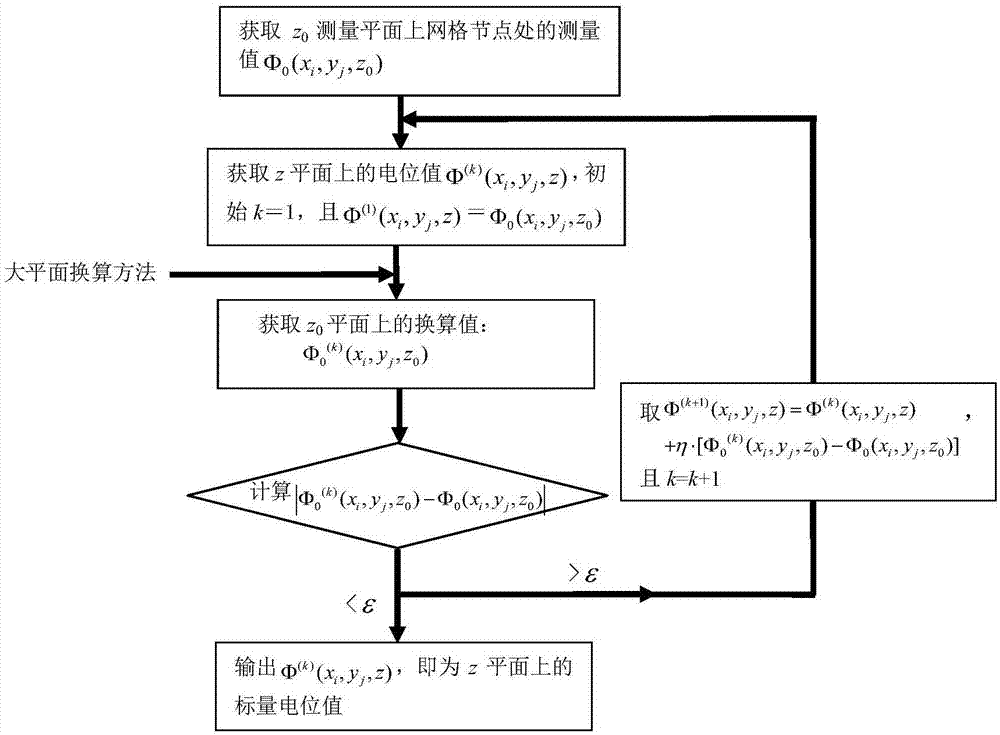
Large-plane iteration method for upward depth conversion of underwater static electric field of deep-sea ship
InactiveCN104764939AEasy programmingLarge conversion accuracyElectrostatic field measurementsScalar potentialUnderwater
The invention discloses a large-plane iteration method for upward depth conversion of an underwater static electric field of a deep-sea ship. The electric field distribution of a target plane is acquired by the iteration method according to the scalar potential distribution of a measurement plane. According to the invention, a method suitable for upward depth conversion of an underwater static electric field of a ship in a deep-sea environment is designed by combining a large-plane depth conversion method and the iteration idea. Upward depth conversion of an underwater static electric field of a ship in a deep-sea environment can be realized. Moreover, the algorithm is simple, the stability is high, the conversion accuracy is high, and the conversion range is large.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
A Conductivity Image Reconstruction Method Based on Magnetic-Thermal-Acoustic Coupling Imaging
ActiveCN104434094BConductivity reconstructionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSound sourcesScalar potential
A conductivity image reconstructing method for magneto-thermoacoustic coupled tomography includes: acquiring a thermoacoustic source distribution of a conductive object by means of time inversion according to an electromagnetic ultrasonic signal received, and performing reconstruction according to the thermoacoustic source distribution to obtain a conductivity distribution of the conductive object. Specially, the method includes: acquiring a thermoacoustic source on a certain level by means of time inversion, acquiring a thermoacoustic source of the conductive object by means of interpolation, performing calculation by means of Biot-Savart's law according to excitation current to obtain a spatial component A1 of primary magnetic vector potential, subjecting the conductive object to spatial discretization, giving an initial value [Sigma]<0> of conductivity, according to the theorem of current continuity, solving a spatial component [Phi] <1> of scalar potential with the initial value [Sigma]<0> and the spatial component A1, substituting the spatial component [Phi]<1> of the scalar potential to a relation which the thermoacoustic source and conductivity meet so as to obtain updated conductivity [Sigma]<1>, replacing the initial value [Sigma]<0> with the updated conductivity [Sigma]<1>, repeating the process above, and stopping iteration until a relative error of the conductivity meets an equation: Sigma=||([Sigma]1-[Sigma]0) / [Sigma]0||2<=Sigma0.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Communications system
ActiveUS10992035B1Beacon systems using radio wavesAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesCommunications systemScalar potential
A communication system using vector and scalar potential is disclosed. The system uses field-free potentials signaling for many applications where the absence of shielding effects in sea water, plasma or other dense media due to the fact that the absence of (E,B) fields eliminates the possibility of induced charge and current response in the media being transited.
Owner:QUANTCOMM LLC
A Conductivity Reconstruction Method for Magnetothermoacoustic Imaging
ActiveCN104473640BConductivity reconstructionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSonificationUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to an electric conductivity rebuilding method for magnetocaloric acoustical imaging. The electric conductivity rebuilding method is based on a magnetocaloric acoustical imaging principle. An exciting coil is used for exerting MHz current excitation on a conducting object, joule heat is generated in the conducting object, and further, ultrasonic signals are generated. An ultrasonic transducer is used for receiving the ultrasonic signals, the received ultrasonic signals are processed and collected, and then, an electric conductivity image of the conducting object is obtained by adopting an electric conductivity image rebuilding algorithm. The electric conductivity rebuilding method comprises the concrete steps that 1, firstly, high-signal-to-noise-ratio magnetocaloric acoustical signals are obtained; 2, the obtained magnetocaloric acoustical signals are used for rebuilding to obtain thermal sound source distribution of the conducting object; 3, the thermal sound source distribution and a one-order magnetic vector space component are used, and a non-linear finite element solution method is adopted for rebuilding a scalar potential space component; 4, the rebuilt scalar potential space component is used for rebuilding the electric conductivity.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Imaging reconstruction method based on injected current thermoacoustic conductivity
A drect iteration-based injection current type thermoacoustic conductivity image reconstruction method is disclosed and comprises the following steps: in a first step, injection current type thermoacoustic signals of an object body are obtained; in a second step, a time reversal method is used for obtaining a thermoacoustic source of the object body according to the thermoacoustic signals; in a third step, an initial value of conductivity is given, and an electric scalar potential is solved; in a fourth step, new conductivity is solved; in a fifth step, the conductivity is solved via iteration. The method comprises the following specific processes: the time reversal method is used for obtaining thermoacoustic source distribution on a certain fault plane, an interpolation method is used for obtaining an overall thermoacoustic source of the object body, the initial value [sigma]0 is given, the electric scalar potential [phi]1 is solved via the known [sigma]0 based on a current continuity theorem, the electric scalar potential [phi]1 is substituted into a relational expression for the thermoacoustic source and the conductivity, updated conductivity [sigma]1 is obtained, [sigma]0 is replaced with [sigma]1, and the above processes are repeated till relative error of the conductivity satisfies epsilon=||([sigma]i-[sigma]i-1) / [sigma]i-1||2<=epsilon0.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A finite element solution method for transformer eddy current field based on sinc function
ActiveCN108875218BFast convergenceHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationMulti-objective optimisationScalar potentialTransformer
The invention discloses a transformer vortex field finite element solving method based on a sinc function. According to the method, first, a model is established for a transformer, and then meshing isperformed on the established model according to a finite element method; the finite element method is adopted to calculate a stiffness matrix and a damping matrix of the model according to unit nodeinformation obtained through meshing; and a magnetic vector potential and a scalar potential are selected to serve as an unknown function of a vortex field mathematical model, a discretization formatis exported through a Galerkin finite element method, a discretization equation set is established, solutions of the discretization equation set are solved through a sinc interpolation method, electric field distribution and magnetic field distribution in a transformer solving domain can be obtained according to the solutions of the equation set, and therefore vortex distribution and loss of the transformer can be calculated. The method is simple in design, easy to implement and easy to popularize, provides more precise analysis for vortex field and loss calculation of large and ultra-large power transformers, provides a basis for transformer design and manufacturing and improves the security and stability of transformer operation.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
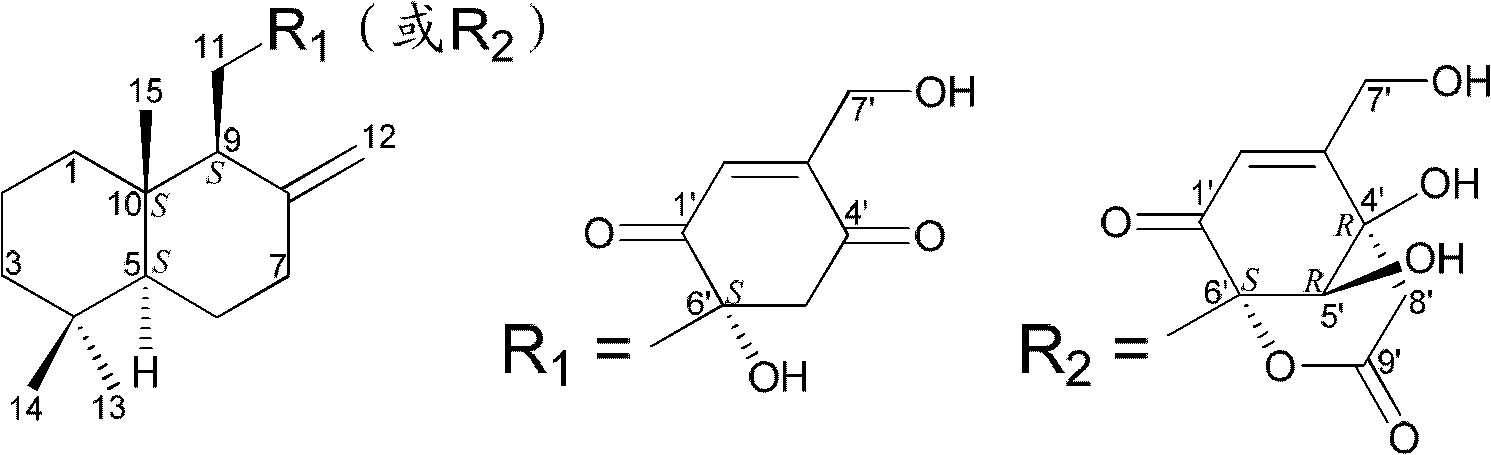
Drimane-type sesquialter terpene cyclohexenone derivative, preparation method thereof and application
InactiveCN102618448BEfficient killingPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsFungiAbsolute configurationCyclohexenone
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemicals, and relates to drimane-type sesquialter terpene cyclohexenone derivative, a preparation method thereof and application. Particularly, the drimane-type sesquialter terpene cyclohexenone derivative relates to a compound in a formula I, wherein Arabic numerals in the formula I indicate scalar potentials, and an R and an S respectively represent absolute configurations of carbon atoms with the corresponding potentials. The invention further relates to the preparation method of the compound, a composition containing the compound and the anti-tumor application. The invention further relates to penicillium purpurogenum BD-1-6 capable of being used for preparing the compound. The compound in the formula I can effectively kill tumor cells or suppress proliferation of the tumor cells, has excellent anti-tumor activity and has the potential of being used as an anti-tumor medicine. Attached is the formula I.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
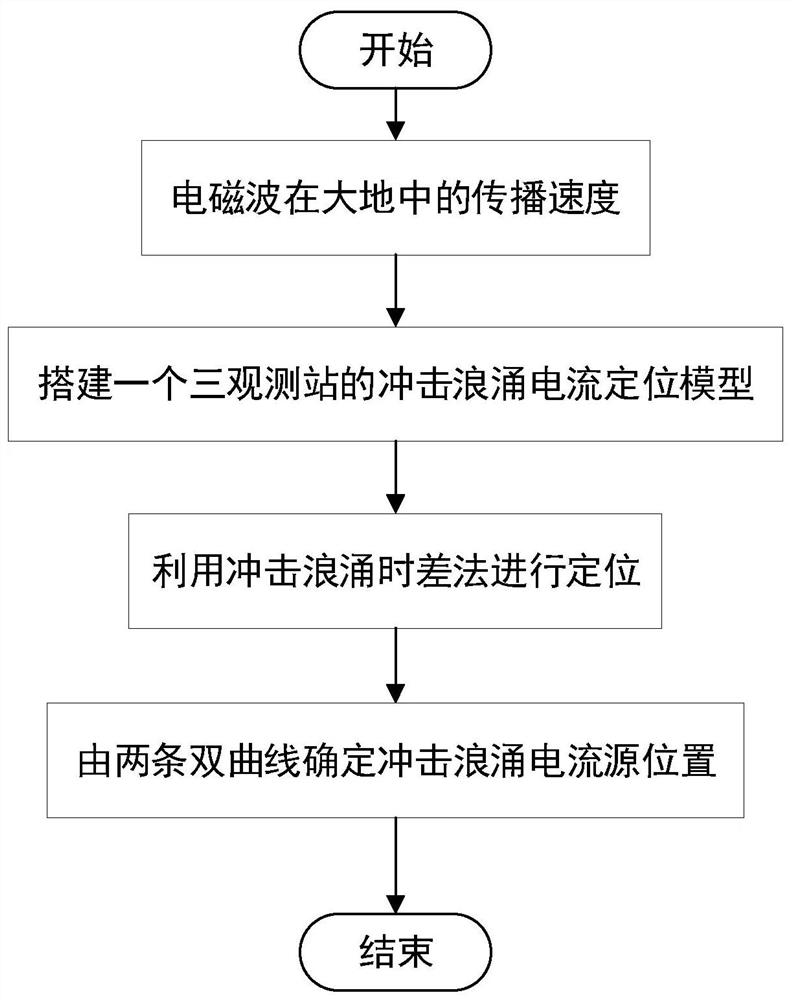
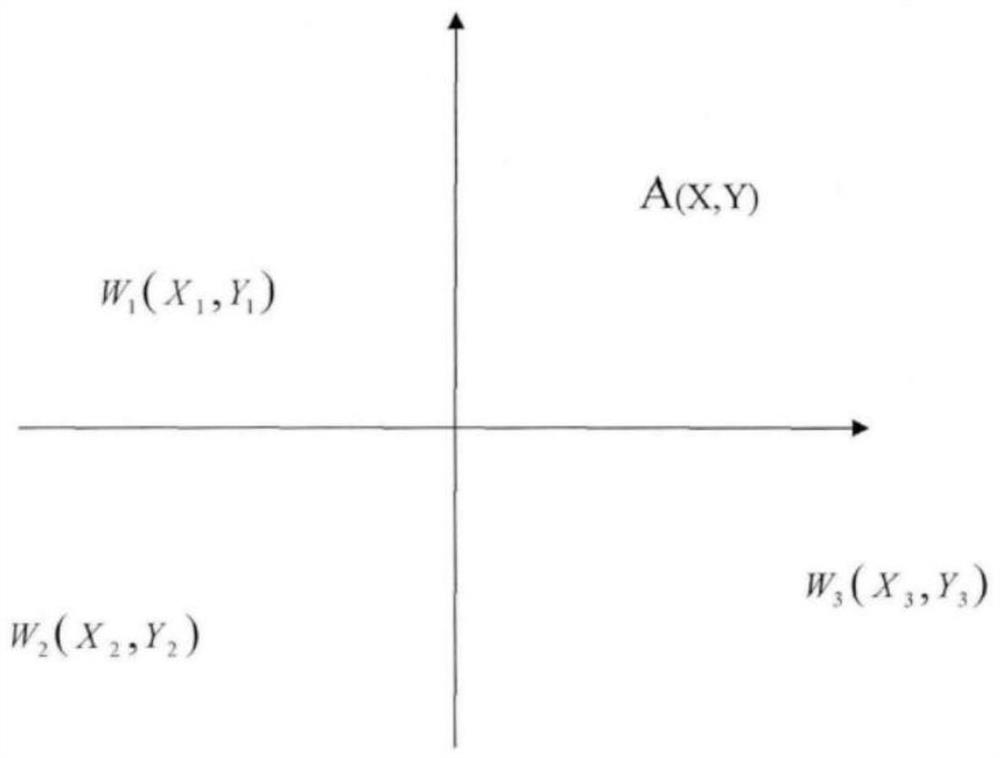
Impact surge current positioning method
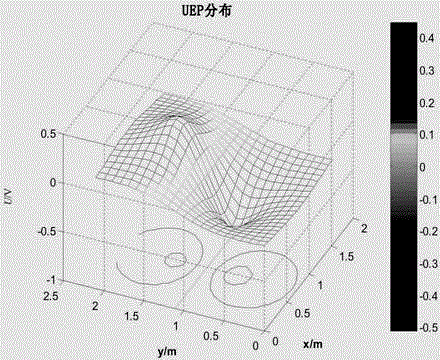
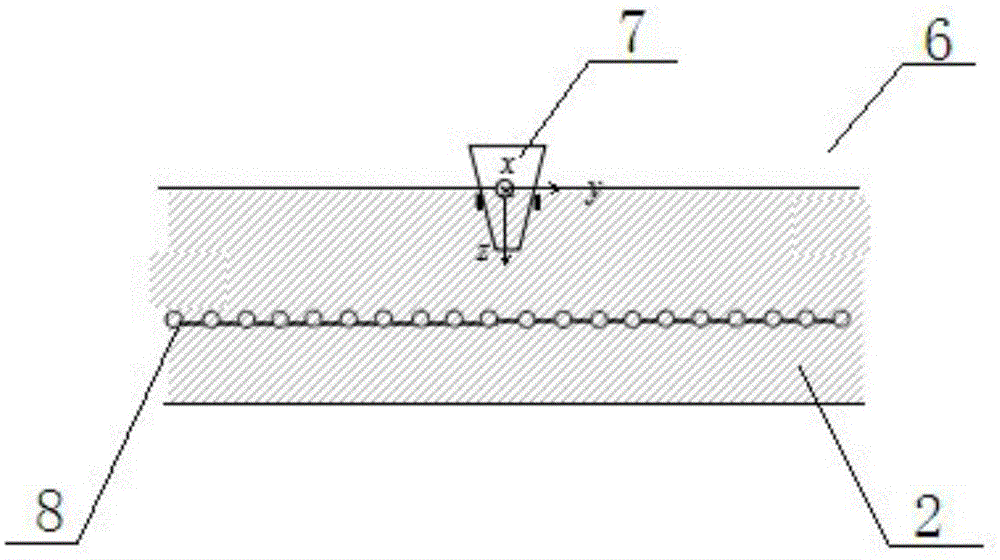
ActiveCN113030651APrecise positioningThe technical means are clearTransformers testingWater resource assessmentScalar potentialObservation point
The invention discloses an impact surge current positioning method, and the method comprises the steps: determining the propagation velocity V of an electromagnetic wave in the ground; establishing at least three earth surface potential observation points, analyzing the time domain waveform of the scalar potential of the earth surface potential observation points caused by the impact current, and obtaining the time difference from the time domain waveform; performing positioning based on animpact surge time difference method,wherein the time for the electromagnetic waves to reach the surface potential detection station is as follows: the distance difference between the electromagnetic waves generated at the position of the earth current and different surface potential observation points is a constant value; and determining two hyperbolic curves among every three earth surface potential observation points, wherein the intersection position of the two hyperbolic curves determines the position of an impact current inflow point, and the average value of the positions of the impact current inflow point is the final position of the impact current inflow point.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com