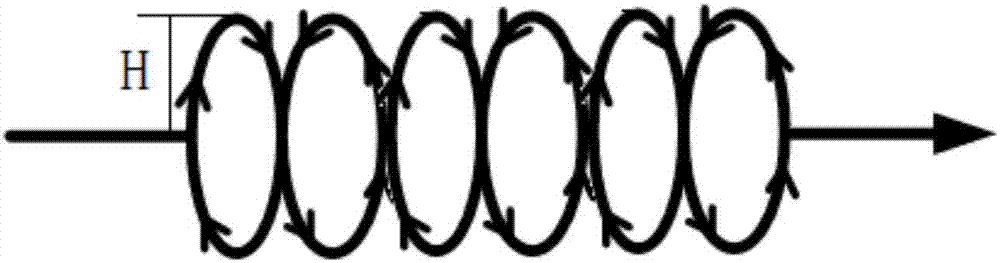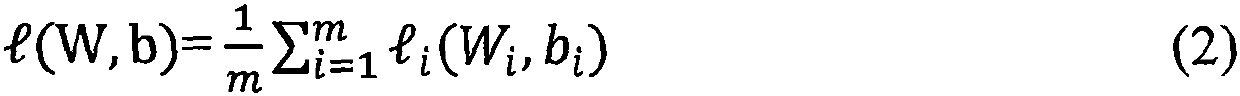Patents
Literature
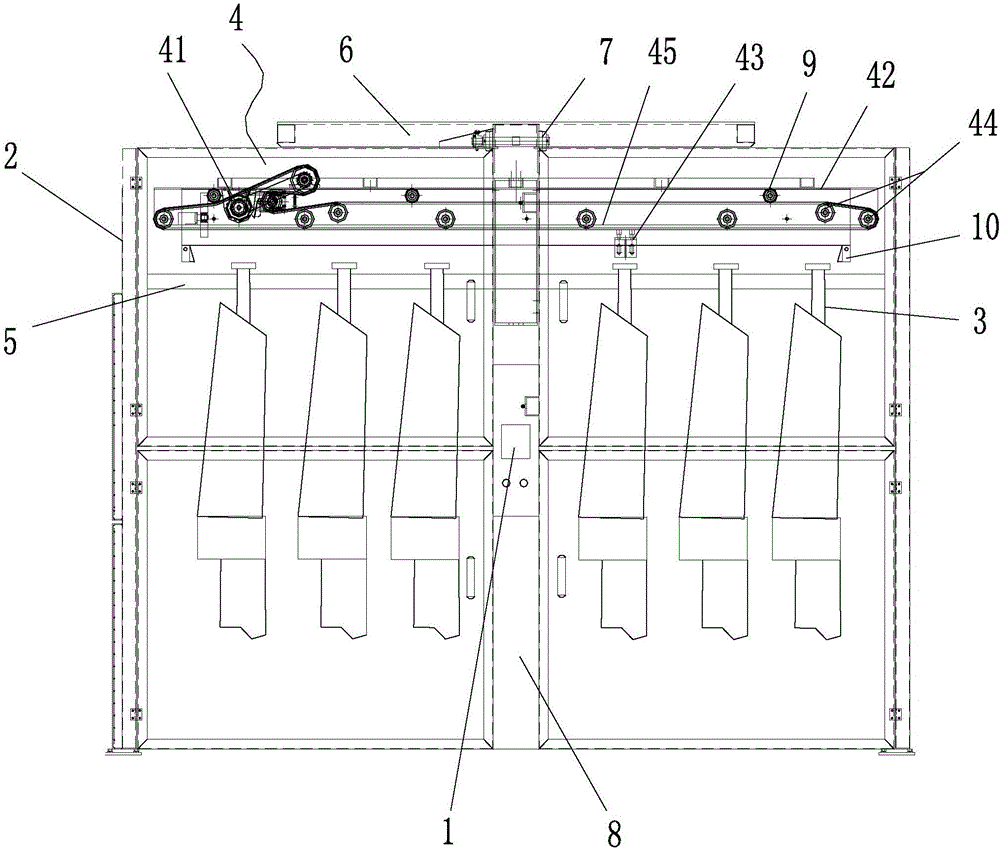
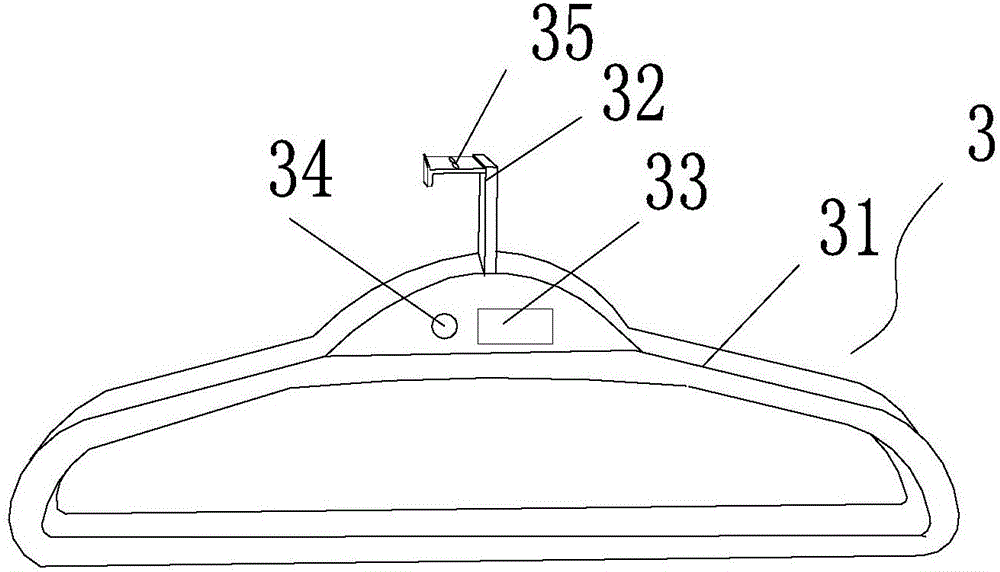
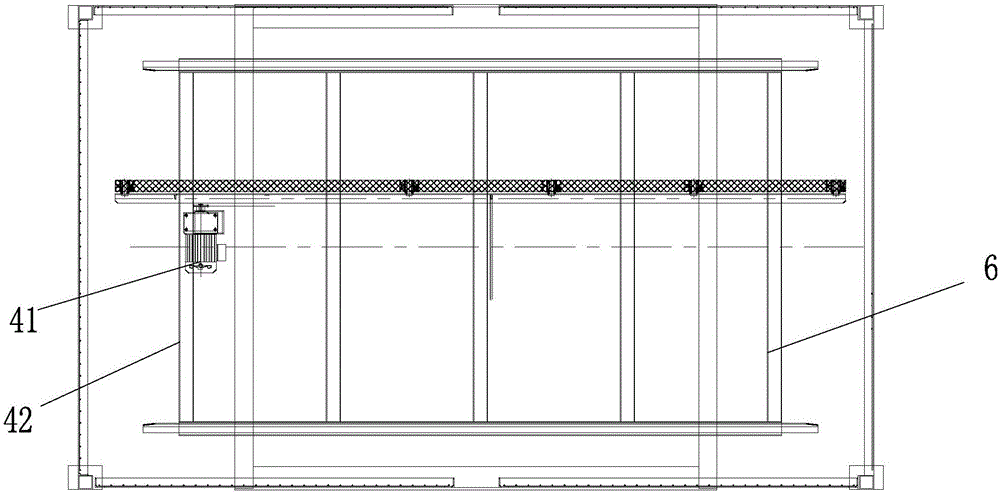
411 results about "Arabic numerals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arabic numerals are the ten digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9. The term often implies a decimal number written using these digits, which is the most common system for the symbolic representation of numbers in the world today, and is also called Hindu–Arabic numerals. However the term can mean the digits themselves, such as in the statement "octal numbers are written using Arabic numerals."
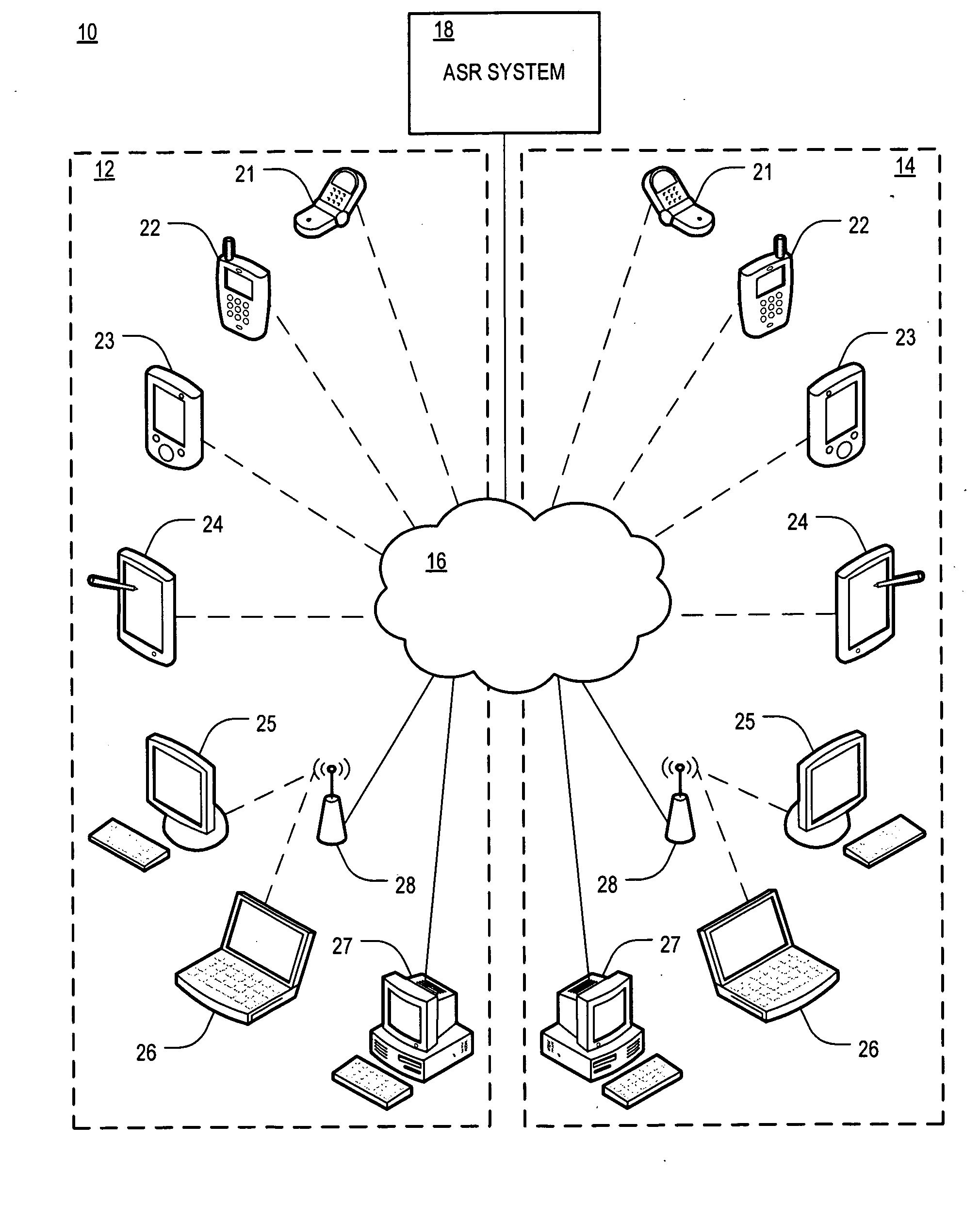
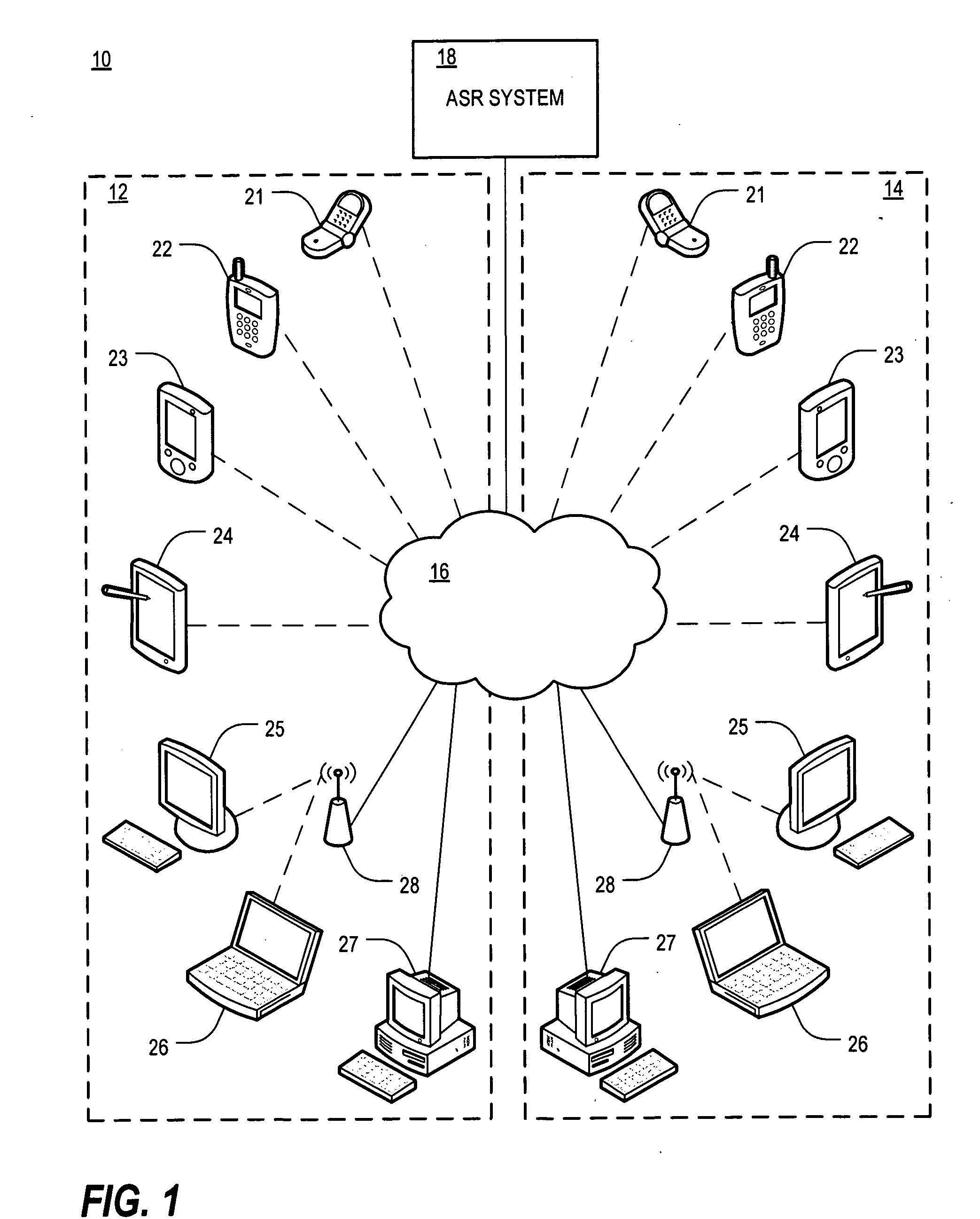
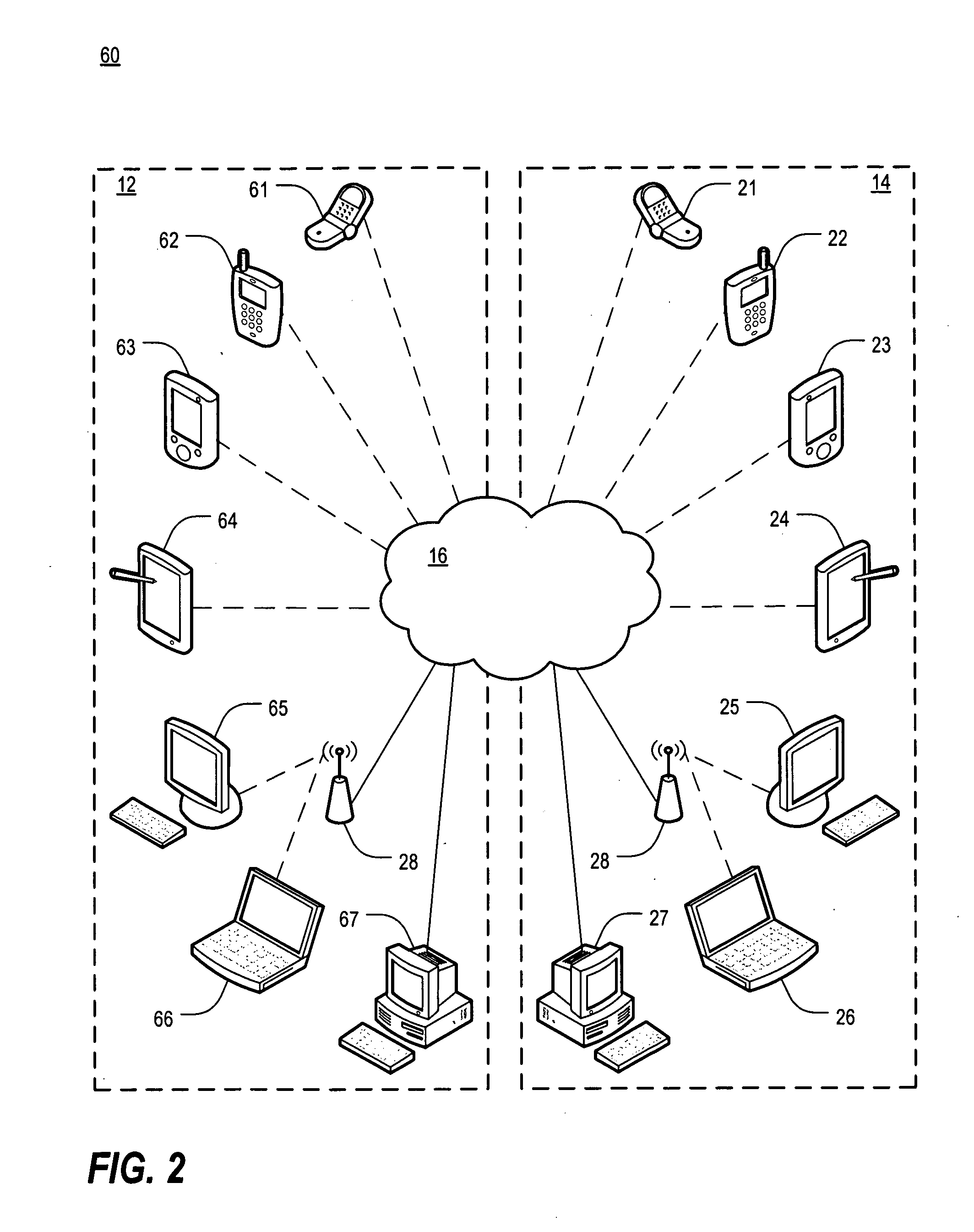
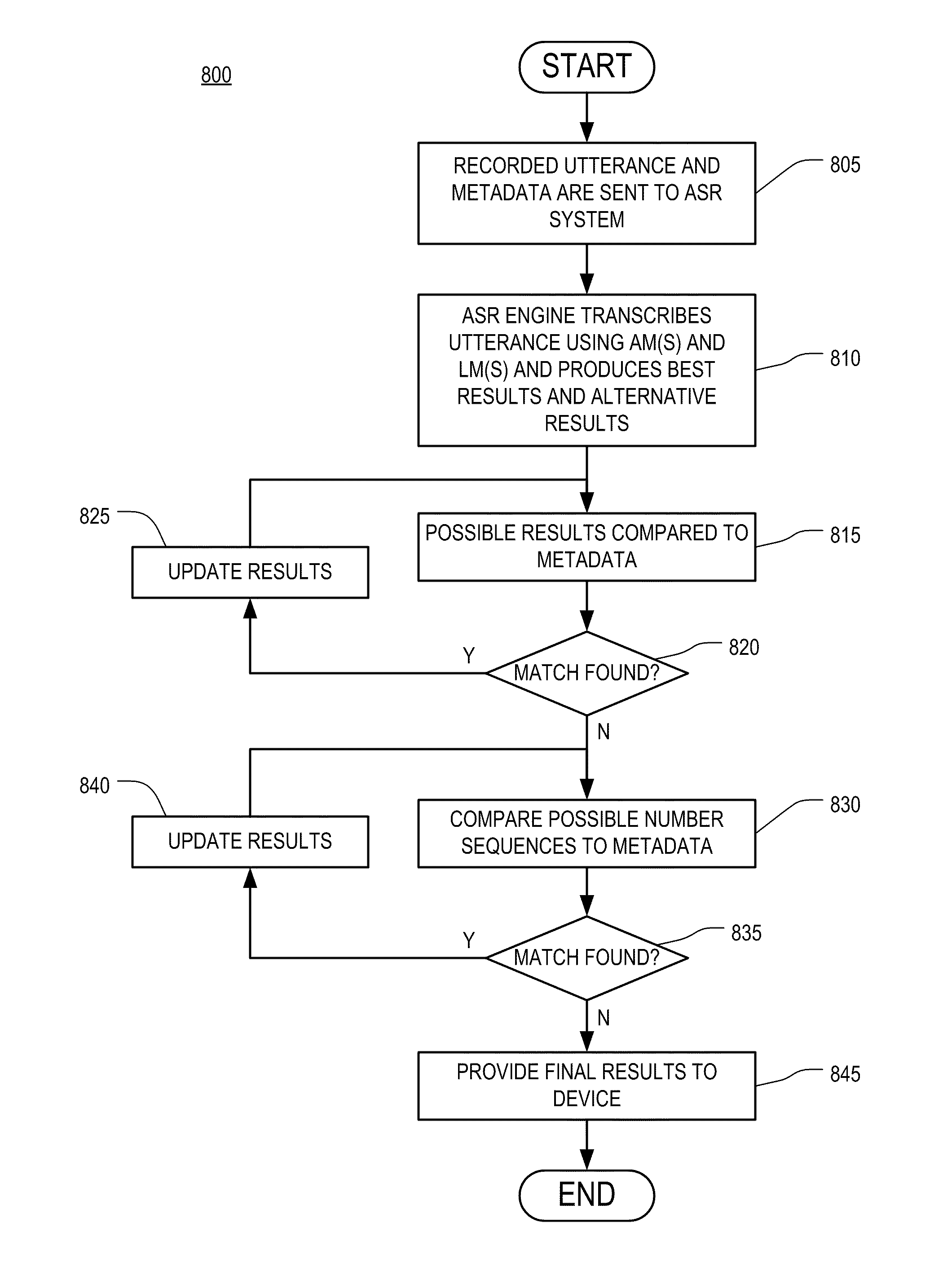
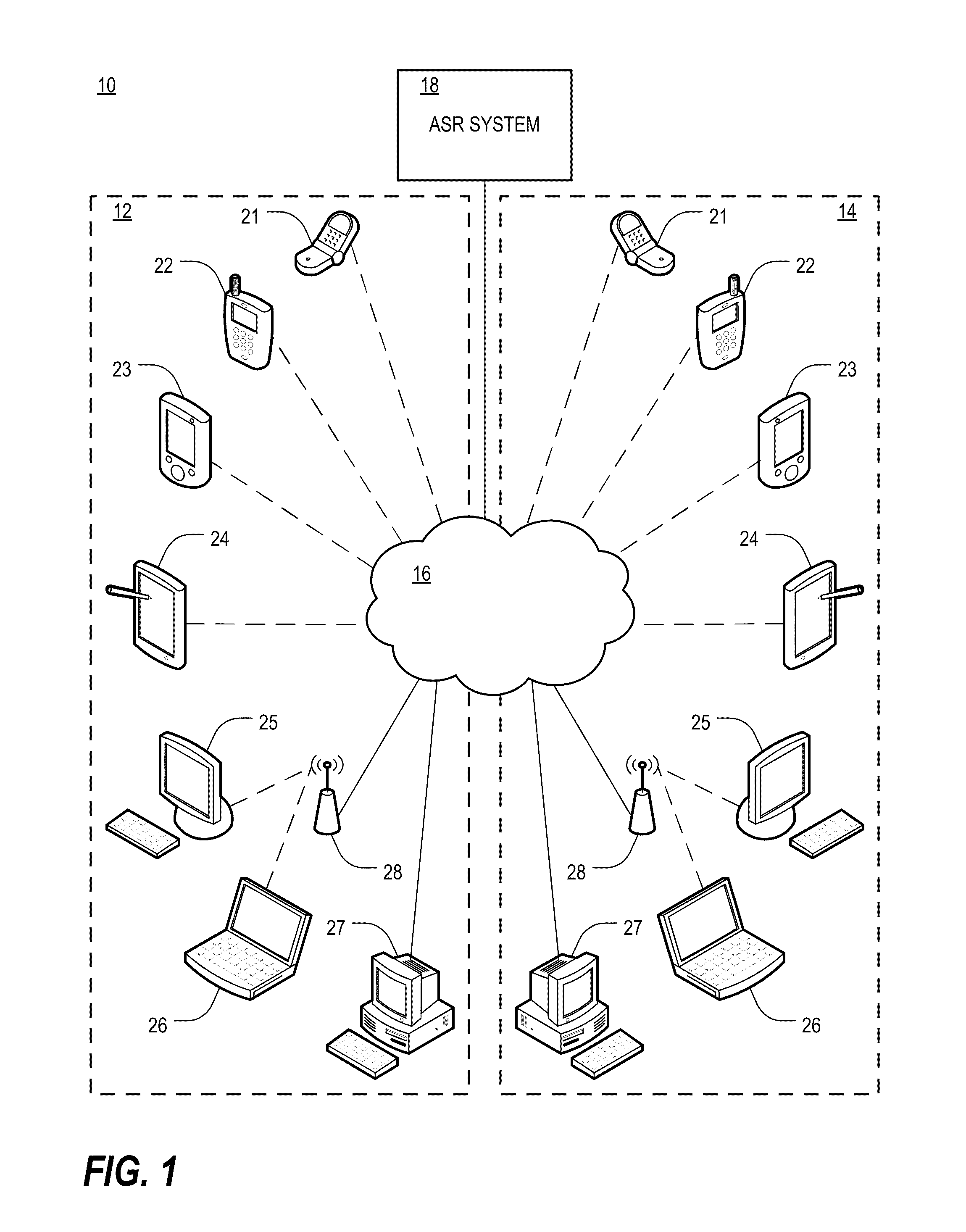
Use of metadata to post process speech recognition output
ActiveUS20090248415A1Easy to convertImprove accuracyMultiple digital computer combinationsSpeech recognitionArabic numeralsAddress book
A method of utilizing metadata stored in a computer-readable medium to assist in the conversion of an audio stream to a text stream. The method compares personally identifiable data, such as a user's electronic address book and / or Caller / Recipient ID information (in the case of processing voice mail to text), to the n-best results generated by a speech recognition engine for each word that is output by the engine. A goal of this comparison is to correct a possible misrecognition of a spoken proper noun such as a name or company with its proper textual form or a spoken phone number to correctly formatted phone number with Arabic numerals to improve the overall accuracy of the output of the voice recognition system.
Owner:YAP +1
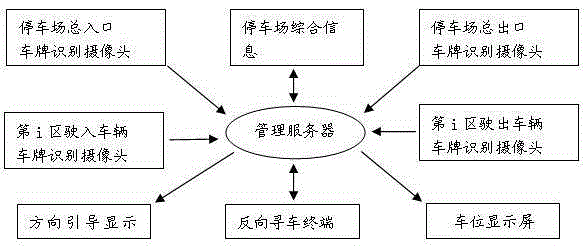
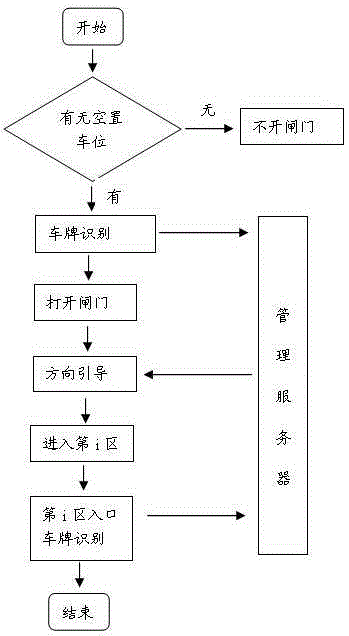
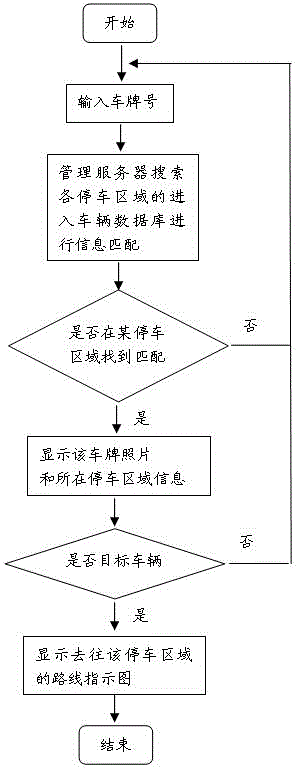
Intelligent parking lot management method
InactiveCN105206104AQuick searchReduce construction costsIndication of parksing free spacesParking areaLicense number
The invention discloses an intelligent parking lot management method, and belongs to the technical field of parking lot management. The intelligent parking lot management method is characterized by comprising the following steps: dividing the physical space of a parking lot into a plurality of parking areas, and sequentially performing serial numbering on all the parking areas with Arabic numerals, and arranging a parking spot display screen; driving cars to enter the parking areas by drivers according to the green ray prompt of the parking spot display screen and a direction guide display screen, inputting license numbers on a reverse car searching terminal, performing information matching by a management server, feeding pictures of cars and the information of the parking areas where the cars are placed back to the reverse car searching terminal after the matching is completed, and generating the indicating diagrams of the routes from departure points to the packing areas. According to the invention, the systematic framework is greatly simplified, the system construction cost is reduced, the system stability is improved, the rapid parking and reverse car searching are realized, and the method has the characteristics of being high in reverse car searching accuracy, and rapid and convenient in parking.
Owner:LESHAN NORMAL UNIV
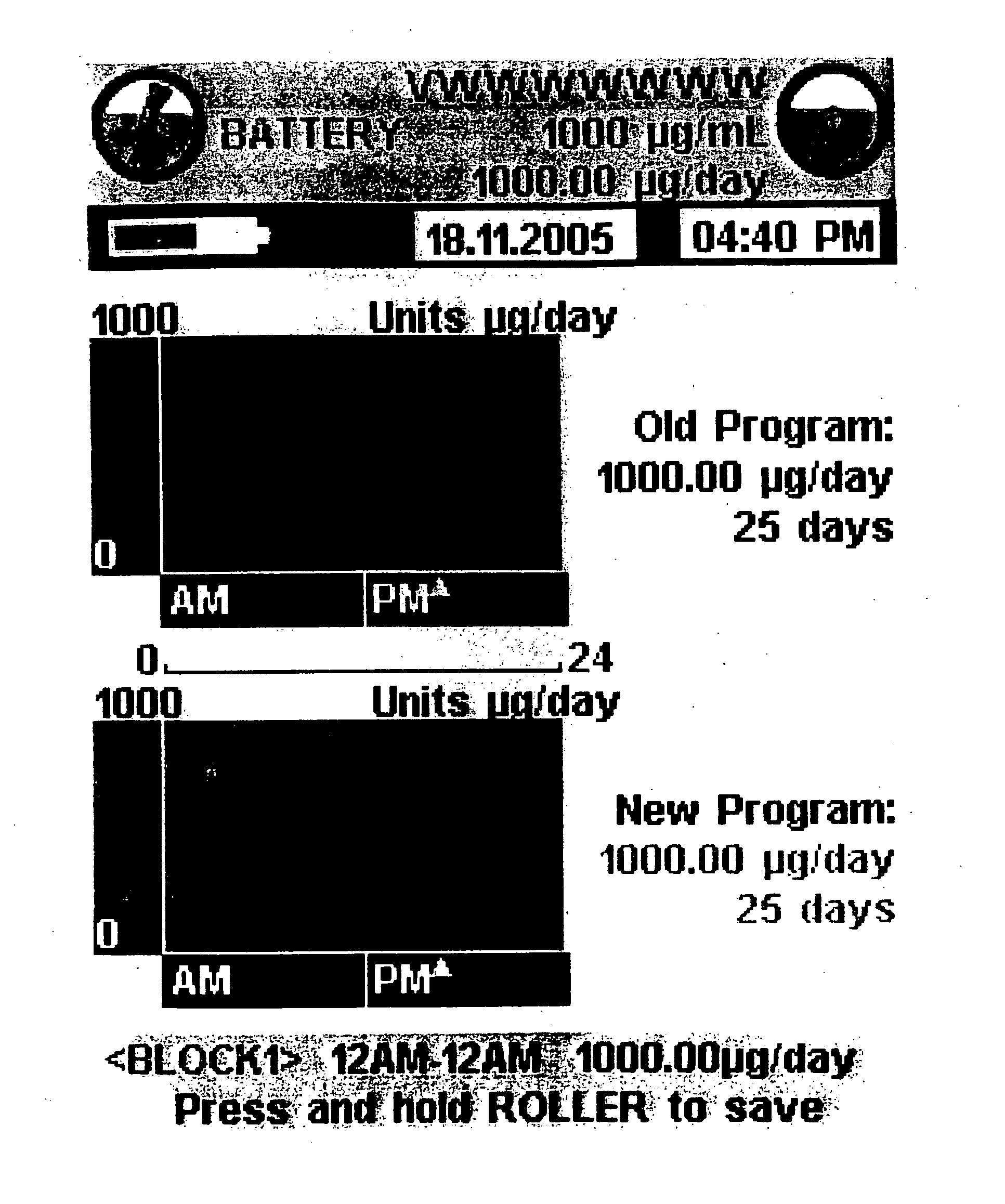
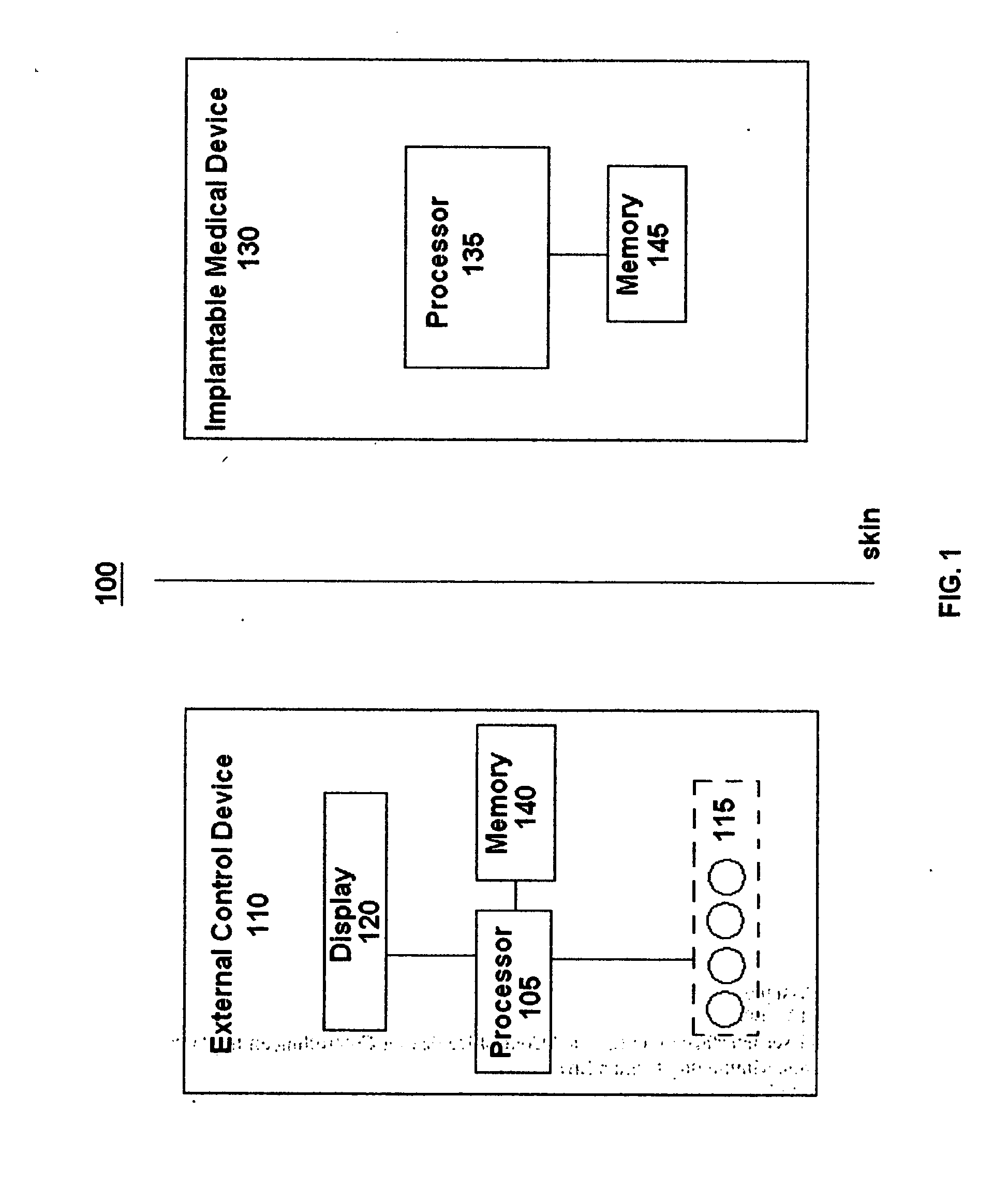
Graphical user interface of an external control device for controlling an implantable medical device while minimizing human error
InactiveUS20070245258A1Reduces and minimizes potentialAccurate operationElectrotherapyLocal control/monitoringGraphicsArabic numerals
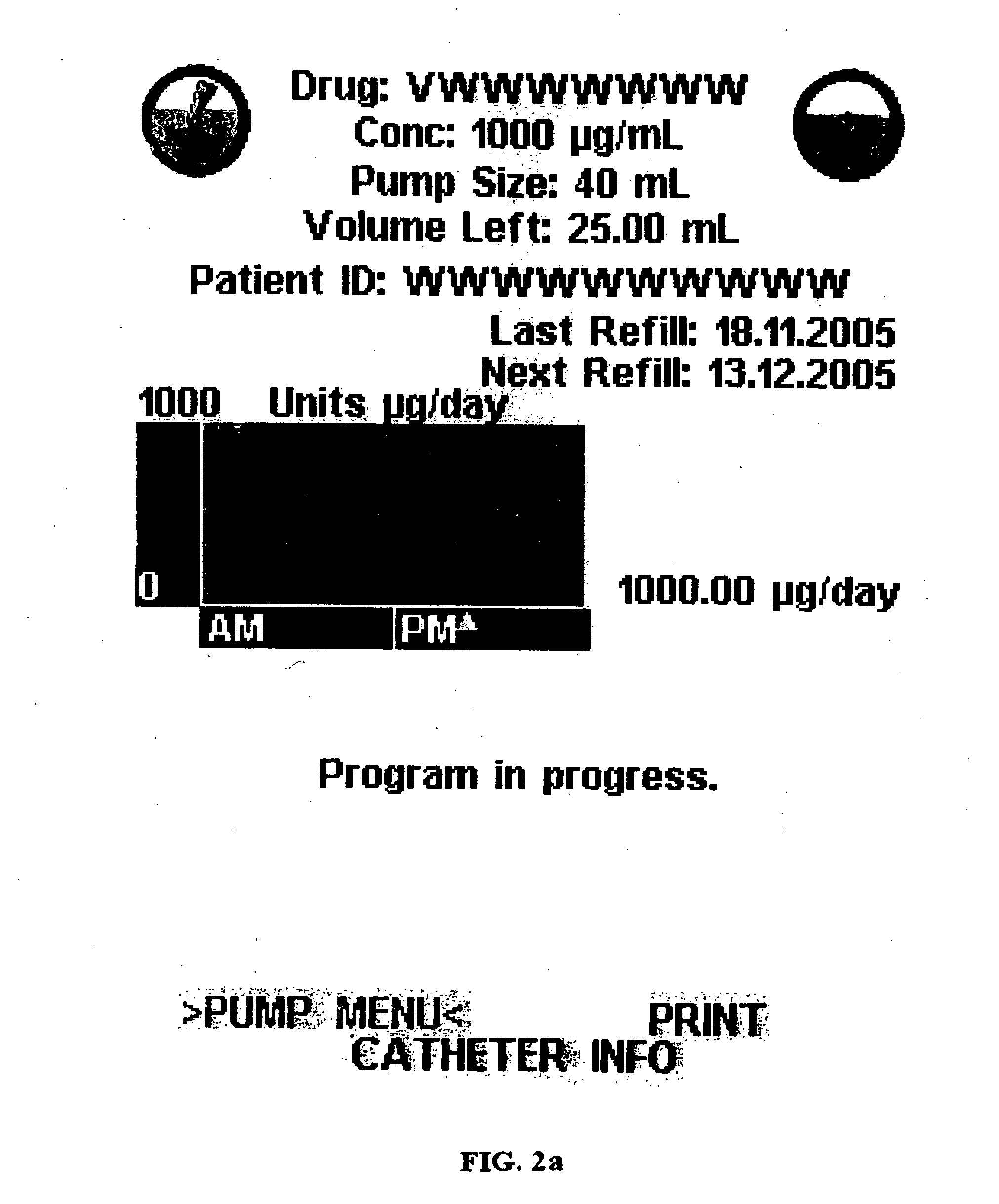
A graphical user interface of an external control device for controlling operation of an implantable medical device while minimizing the occurrence of human error. The graphical user interface displays the operating parameter of the implantable medical device simultaneously as an Arabic numeral and a graphical representation. When a parameter value is adjusted, the current and adjusted values are simultaneously displayed as both an Arabic numeral and graphical representation. Other means are described for increasing the probability of detection of an error during entry of an operating parameter value prior to implementation. Execution of the graphical user interface is subject to interruption. When function of the graphical user interface programming is restored operation resumes from that which it left off prior to interruption.
Owner:CODMAN NEURO SCI
Bidirectional domain names
InactiveUS20030110021A1Natural language data processingExecution for user interfacesDomain nameArabic numerals
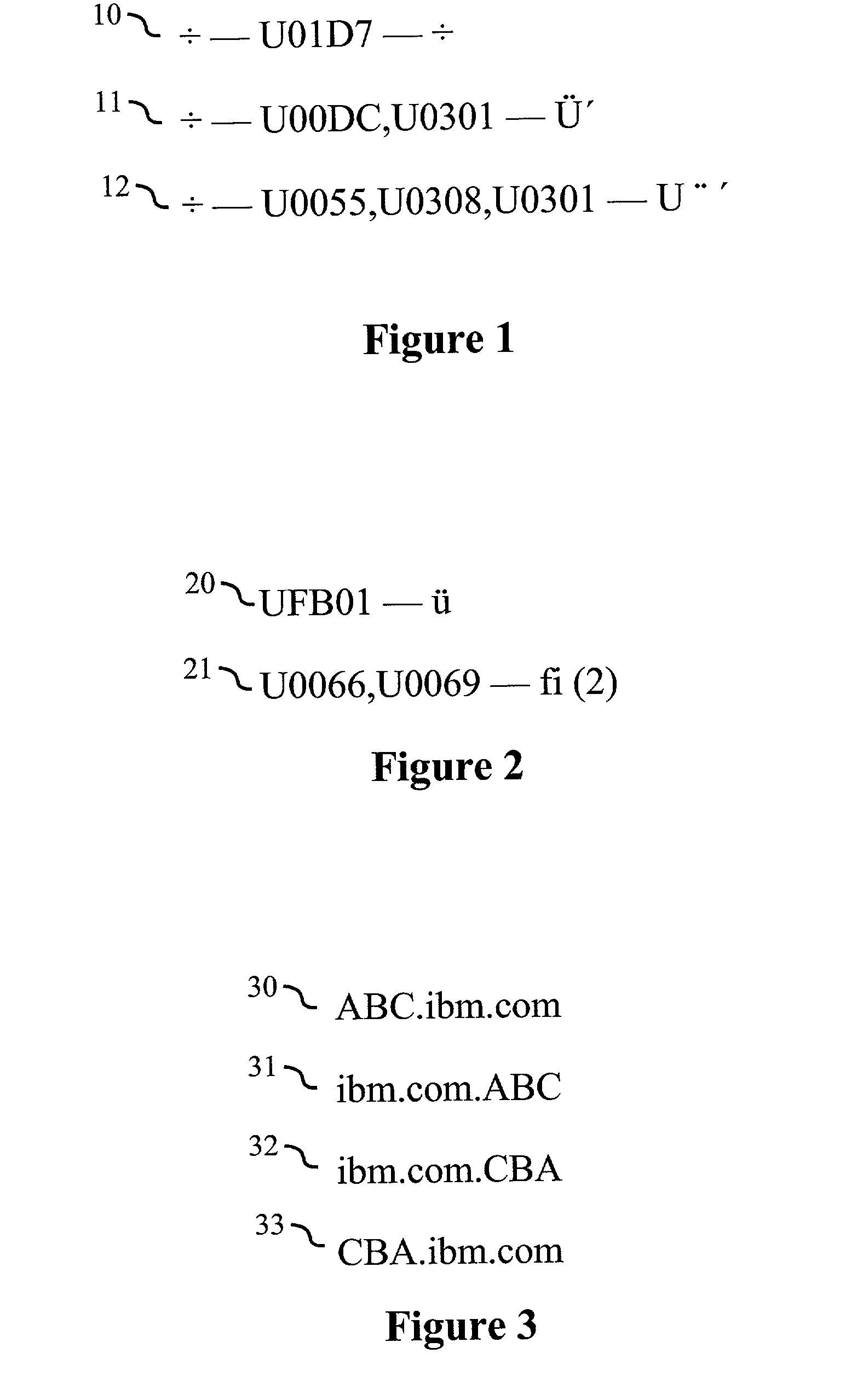
A two-phase system and method for determining a display order of characters in a multilingual domain name. First, inferencing resolves the direction of indeterminate characters, such as the fall stop or "dot", hyphen-minus, Arabic numeral, and European numeral, during which each character is assigned a strong direction left or right. Second, reordering takes the fully resolved characters and generates a display ordering for them. The inferencing phase is accomplished in several passes including assigning Arabic and Hebrew letters right-to-left direction, and assigning left-to-right direction to full stops and other alphabetic characters. Next, directions of digits are resolved by assigning all Arabic numerals a right-to-left direction; and assigning all European numerals left-to-right direction, unless the European numeral is surrounded by right-to-left characters. A final set of passes resolves the directions of hyphen-minus characters by assigning all hyphen-minus characters left-to-right, unless the hyphen-minus is surrounded by characters whose direction is right-to-left.
Owner:IBM CORP
Word art potted landscape and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103358801AWide range of materialsSeedling comprehensiveSpecial ornamental structuresHorticulture methodsArabic numeralsChinese characters
The invention provides a word art potted landscape cultivation technique which comprises comprehensive word art, including a foreign language word art, a Chinese character word art and an Arabic numeral word art; a word art potted landscape is easily available from trees, shrubs, vines and perennial trailing herbaceous plants, and also can be obtained by a plurality of seedling growing methods including seed propagation, cutting propagation, mound layering, ring-cutting reproduction, root stump propagation and the like; the technology combines a potted landscape cultivation technique and a typeface calligraphic art and utilizes nursery stock growth characteristics; by adopting a technical method that the growing nursery stock is reversely bound along a typeface character die rail and the turning position is subjected to twisting or stem-cutting and bud-retaining, a novel word art potted landscape can be obtained by methods including cutting off the stems, grafting, pruning and modeling, and artificially decorating and the like.
Owner:林慧
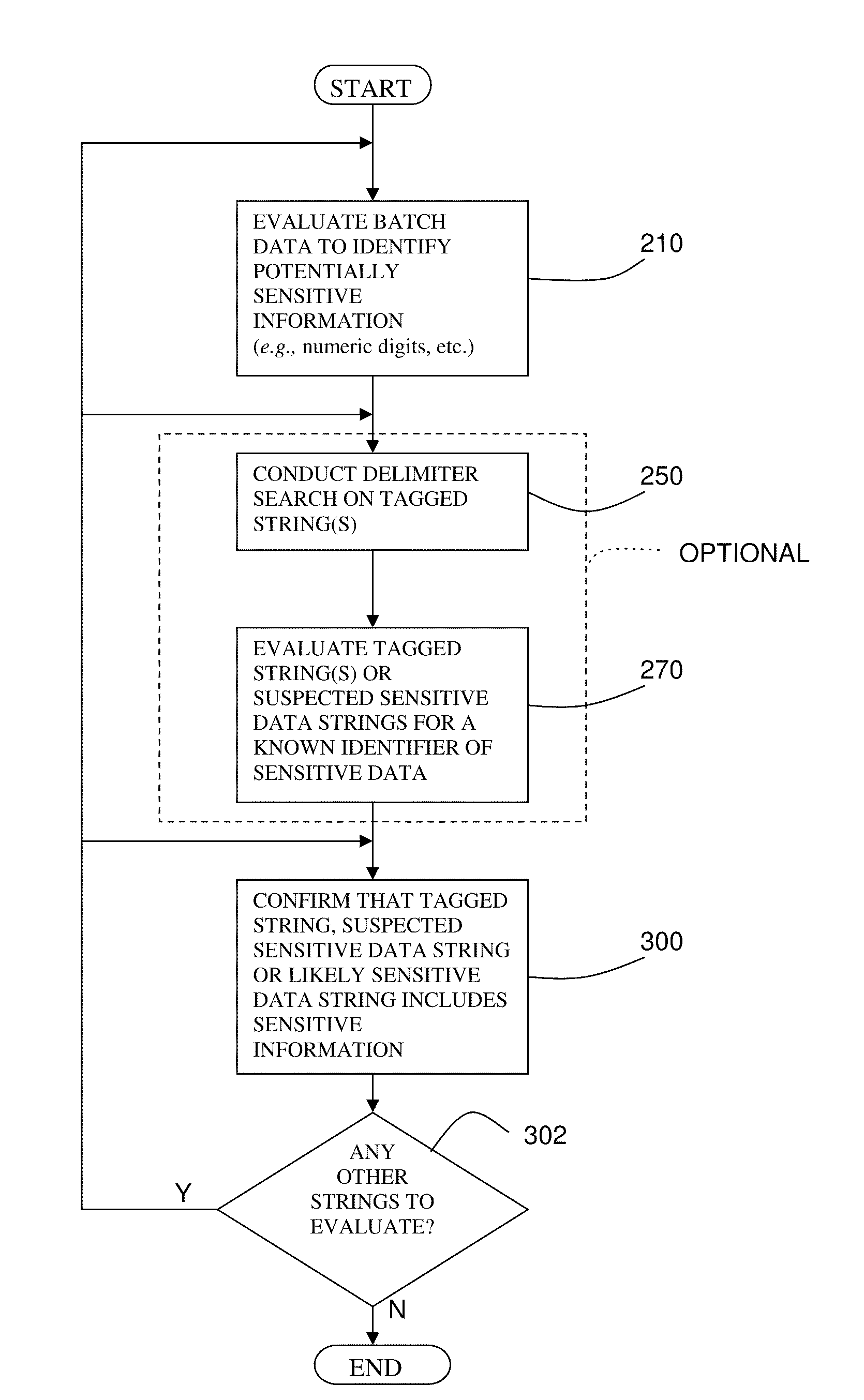
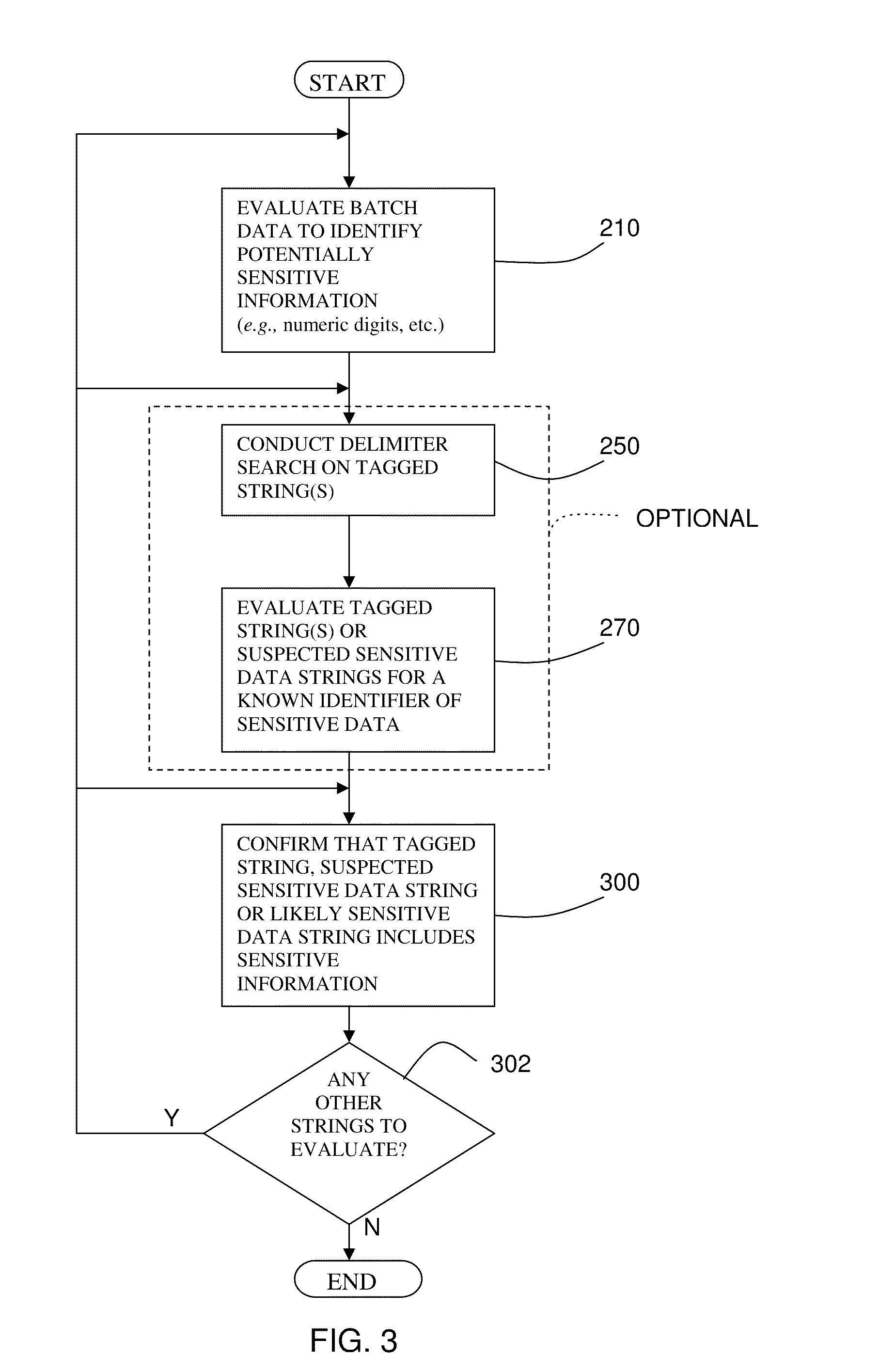
Systems and methods employing intermittent scanning techniques to identify sensitive information in data
ActiveUS20120023117A1Less intensiveConfidenceDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPaymentAnalysis data
Owner:SECURITYMETRICS
Rotation type automatic fire extinguisher for big data centre
The invention belongs to the technical field of big data, and particularly relates to a rotation type automatic fire extinguisher for a big data centre. The rotation type automatic fire extinguisher for the big data centre achieves the technical aims that automatic fire extinguishing can be carried out when a fire hazard occurs, manpower operation on a fire scene is not needed, and safety of fire extinguishing persons can be guaranteed. In order to achieve the above technical aims, the rotation type automatic fire extinguisher for the big data centre comprises a plate shaped like the Arabic numeral seven, installation plates, a bearing pedestal, a rotating shaft, a gear, a first electric push rod, a rack, a box, a dry powder fire extinguishing barrel, a dry powder spray pipe, a dry powder spraying nozzle and the like; and the installation plates are welded to the upper end and the lower end of the left side of the plate shaped like the Arabic numeral seven, and first through holes are formed in the installation plates. By means of the rotation type automatic fire extinguisher for the big data centre, the automatic fire extinguishing can be carried out when the fire hazard occurs, the fire extinguishing scope is enlarged, the fire extinguishing efficiency can be improved, and fire hazard losses are reduced.
Owner:严海良
Rapid dust reduction device for building construction
The invention relates to a dust-reducing device for building construction, in particular to a fast dust-reducing device for building construction. The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide a rapid dust reduction equipment for building construction that can wet the ground and further reduce dust in places with a lot of dust, without affecting the health of workers and polluting the environment. In order to solve the above technical problems, the present invention provides such a rapid dust reduction equipment for building construction, including a bottom plate, etc.; the left and right sides of the bottom of the bottom plate are connected by bolts to install wheels, the wheels are arranged symmetrically, and the left side of the bottom plate is connected by bolts. The connection method is installed with a push handle, and the push handle is inclined, and the left side of the top of the bottom plate is installed with a 7-type plate through bolt connection. The invention achieves the effects of being able to wet the ground, and further reducing dust in places with a large amount of dust, thereby not affecting the health of workers, and not polluting the environment.
Owner:惠安普科优利网络科技有限公司
Laser welding technological method for saddle-shaped aluminum alloy structure
InactiveCN107511584AAvoid crackingAvoid stomatal defectsWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesArabic numeralsSaddle shape
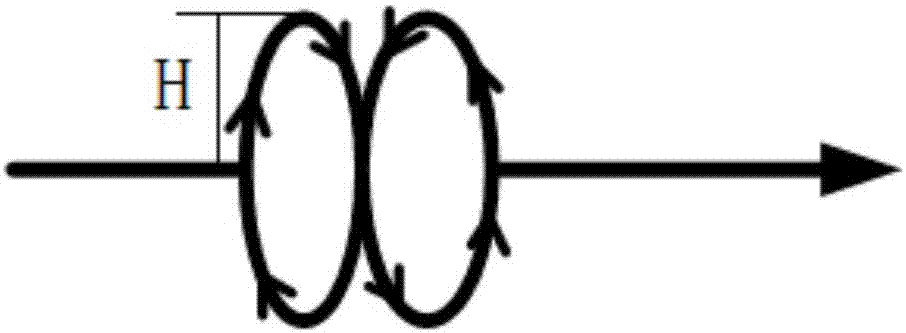
The invention discloses a laser welding technological method for a saddle-shaped aluminum alloy structure, and belongs to the technical field of welding. The method comprises the steps that a swing laser beam capable of achieving continuous outputting and uniform-speed movement is adopted for welding. In the welding process, the swing laser beam moves forwards along a shaft parallel to the welding direction. In the forward moving process, the swing laser beam swings with the shaft as a symmetrical shaft so as to from a movement path, and the movement path is composed of multiple paths shaped like a horizontal Arabic numeral 'eight'. By means of the method, laser welding joint internal cracks and air hole defects of the saddle-shaped aluminum alloy structure can be effectively avoided, a welding joint formed through welding is smooth in transition, and the welding joint comprehensive mechanical property is excellent.
Owner:BEIJING HANGXING MACHINERY MFG CO LTD
Manned submersible ultra short baseline positioning system on-sea calibration test method
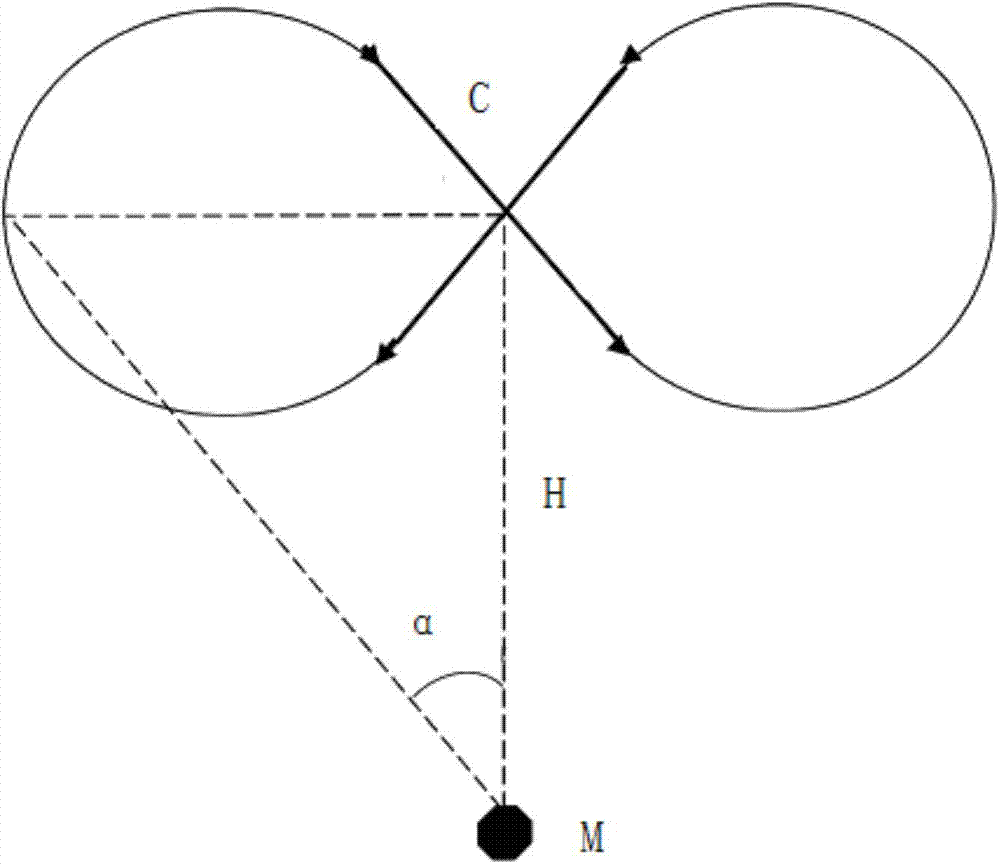
The invention relates to the technical field of ocean detection, in particular to a manned submersible ultra short baseline positioning system on-sea calibration test method. The manned submersible ultra short baseline positioning system on-sea calibration test method is used in the actual operation process. A mother ship is sailed to a sea area with the specific sea depth, and an instrument is started to record noise of the mother ship; then the steps including sound velocity section measurement, underwater subsurface buoy assembling and putting, transducer array installation error correction and the like are executed, and calibration parameters are reset to be initial values after an ultra short baseline positioning system is debugged to normally work; the mother ship sails in a track shaped like an Arabic numeral eight with a subsea beacon as a center, the diameter is 0.7 time of the depth, and it is required that the ship speed is smaller than 3 Kn in the sailing process; the subsea beacon is recovered. By means of the manned submersible ultra short baseline positioning system on-sea calibration test method, errors of the ultra short baseline system and all possibly-occurring conditions can be clearly recorded and analyzed, forceful guarantees are provided for sailing of a manned submersible, and hardware guarantees are provided for deep-sea detection.
Owner:NAT DEEP SEA CENT
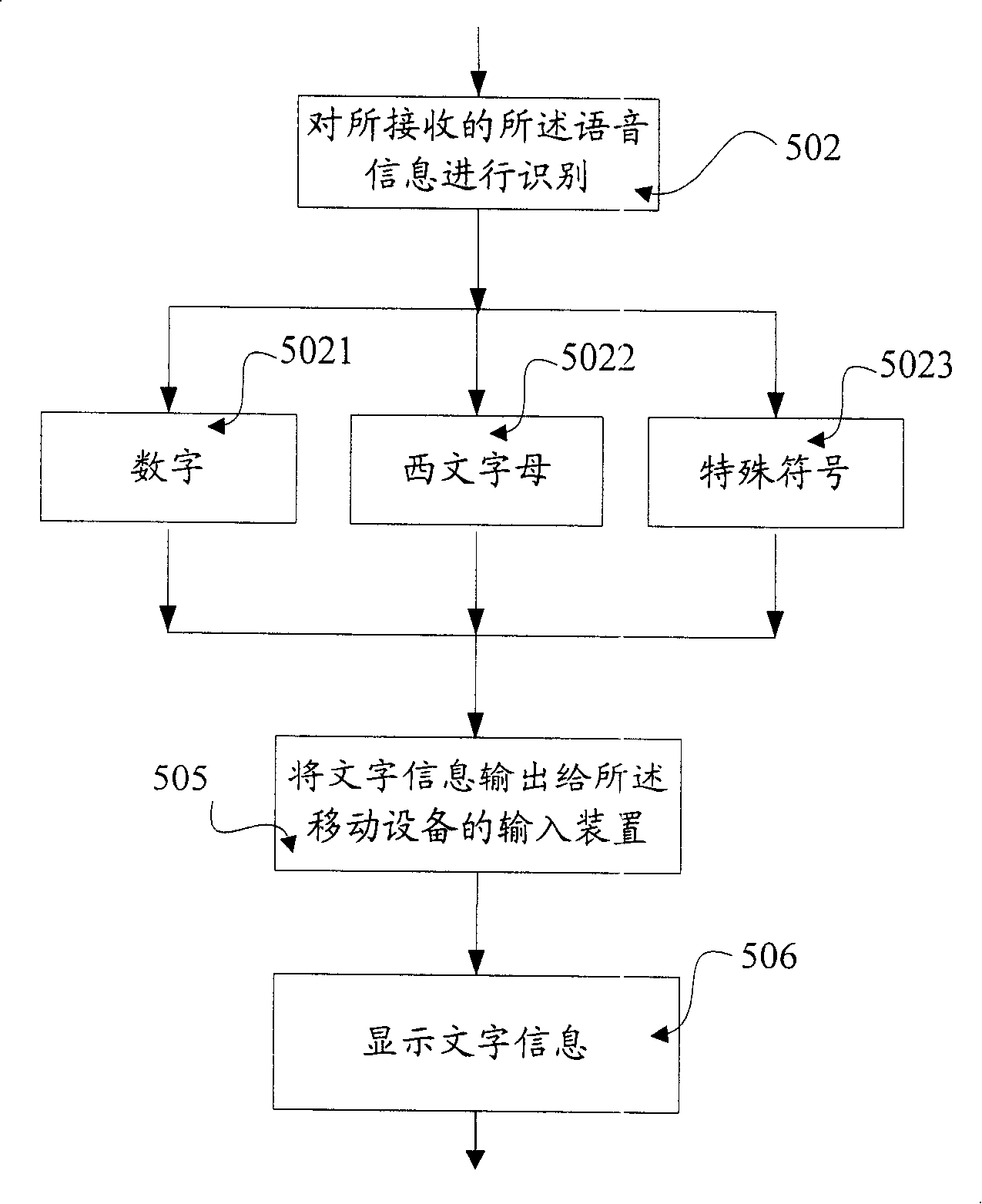
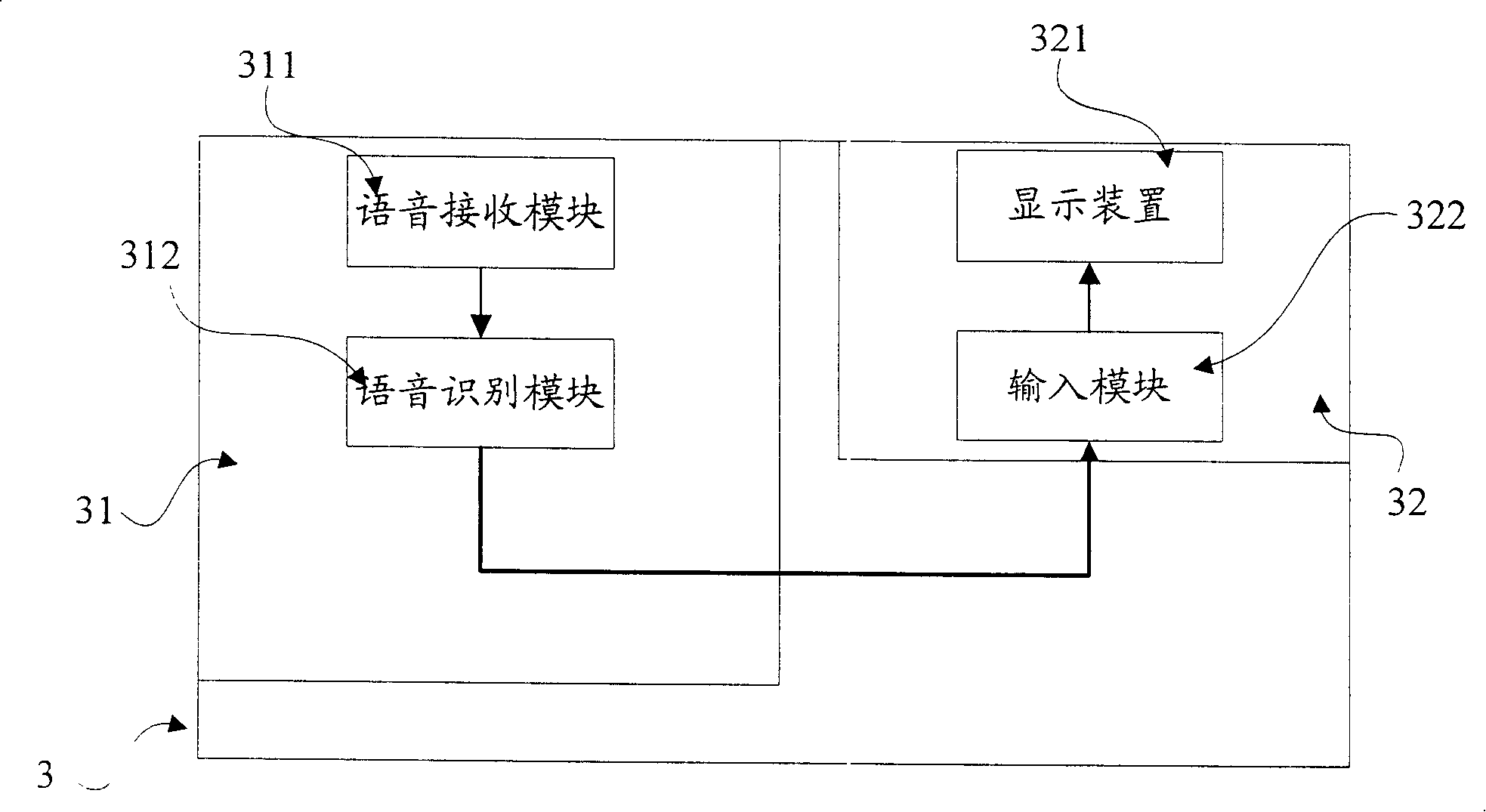
A method and device for controlling text input in mobile device
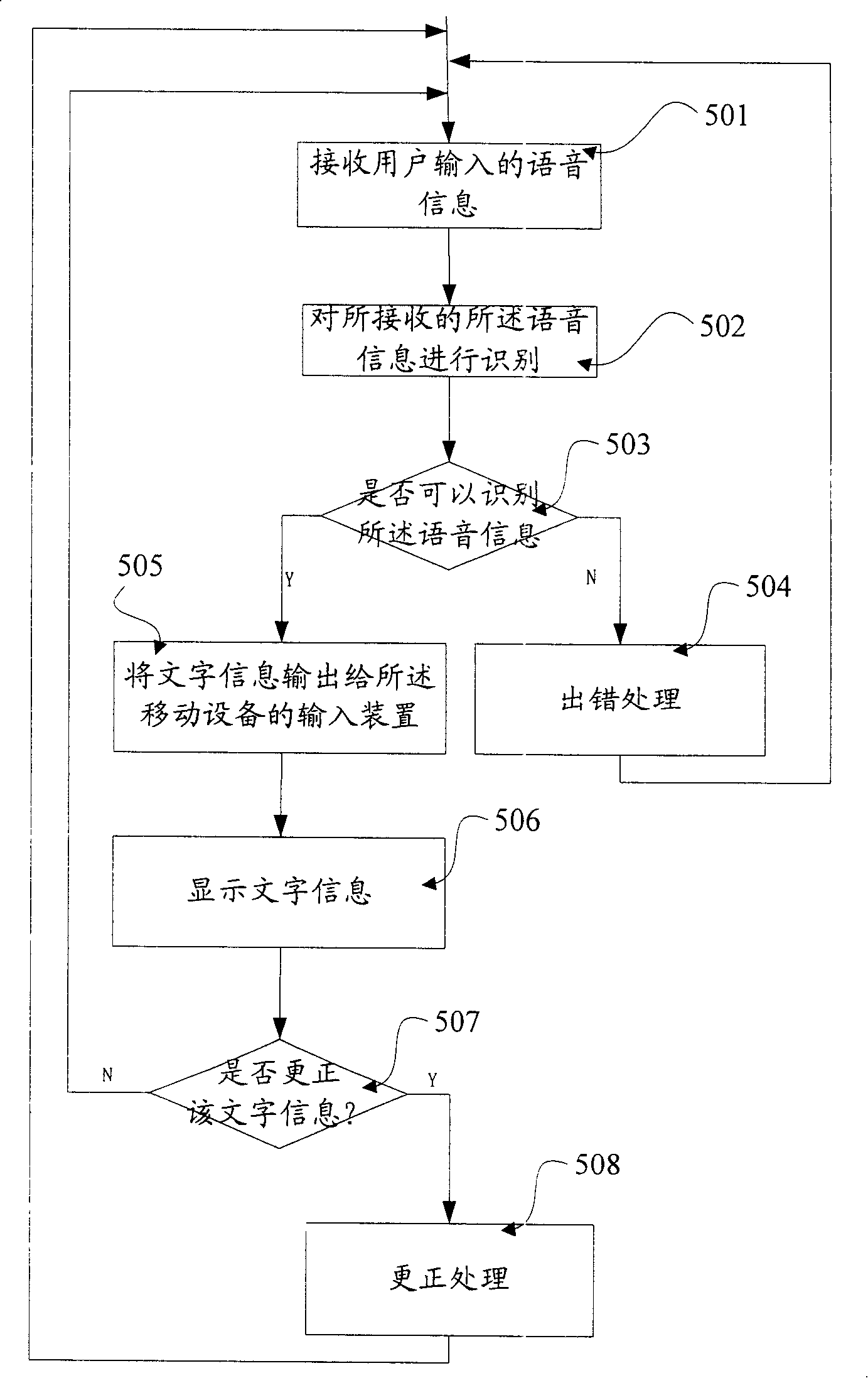
InactiveCN101170757AReduce capacityEasy inputSubscriber signalling identity devicesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsArabic numeralsChinese characters
The invention provides a method for controlling the text input in mobile equipment, which comprises a step of receiving voice information, a step of identifying the received voice information, and a step of displaying the text information corresponding to the voice information, wherein the text information is one or more types selected from western letter, Arabic number and special symbol. By repeating the steps, the process of inputting English word and the relevant Chinese pinyin is completed. The invention also provides a device for controlling the text input in mobile equipment, which comprises a voice reception module, a voice recognition module and a voice database. Additionally, the invention provides mobile equipment using the device, which may be mobile phone, personal digital assistant, pad computer, and so on. The invention can efficiently reduce the capacity of voice database and reduce the complexity of training process of voice recognition, and can be conveniently applied to various mobile equipment with good practicability.
Owner:YINGHUADA (SHANGHAI) ELECTRONIC CO LTD
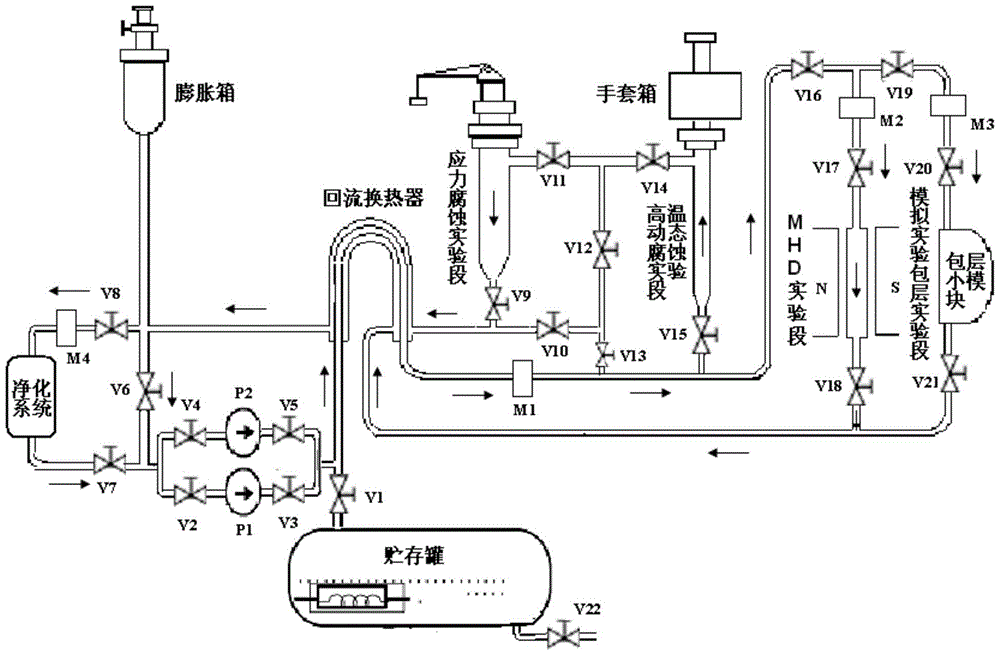
Liquid metal medium forced convection experimental loop
InactiveCN104457854AReduce potential harmAccurately obtain temperature distributionMeasurement devicesArabic numeralsLiquid metal
The invention discloses a liquid metal medium forced convection experimental loop. The liquid metal medium forced convection experimental loop comprises a hot area, a cold area and a support system, wherein a pipeline of the hot area and a pipeline of the cold area form the shape of the Arabic numeral eight, and the hot area and the cold area intersect at a reflux heat exchanger. Various experimental sections are arranged in the hot area according to needs and comprise the high-temperature dynamic corrosion experimental section, the stress corrosion experimental section, the MHD experimental section and the simulation experiment blanket experimental section. A liquid metal medium purification system, a power pump, an expansion box and a storage tank are arranged in the cold area. The support system comprises a gas system and a temperature control system, wherein the gas system is used for conducting vacuumizing and argon filling on the experimental loop, and the temperature control system is used for conducting heating and temperature monitoring on the pipelines. The experimental loop can be used for carrying out experiment researches on critical technical problems of blankets according to experimental purposes under the experimental environment where fusion reactor working conditions are created outside reactors.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
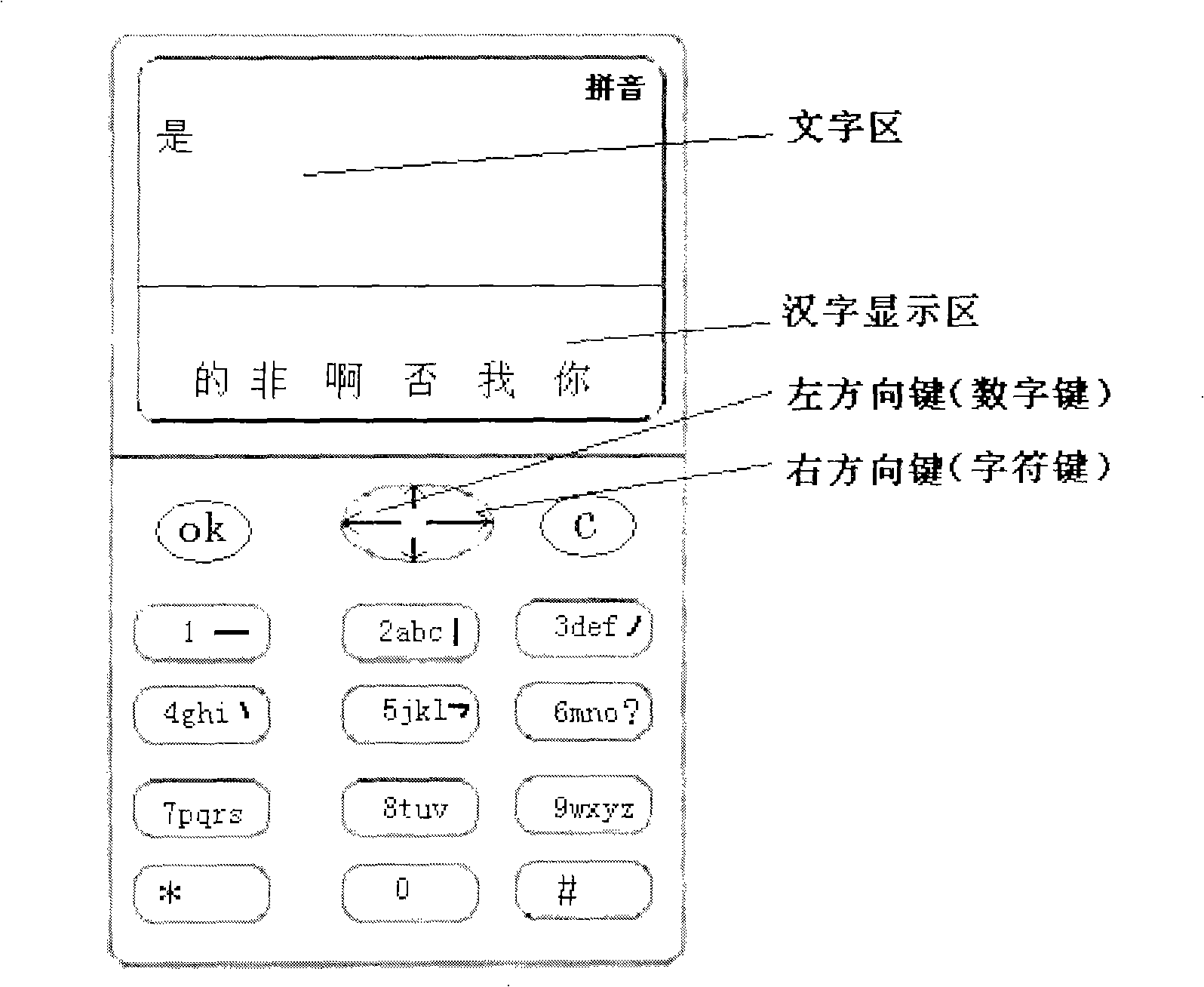
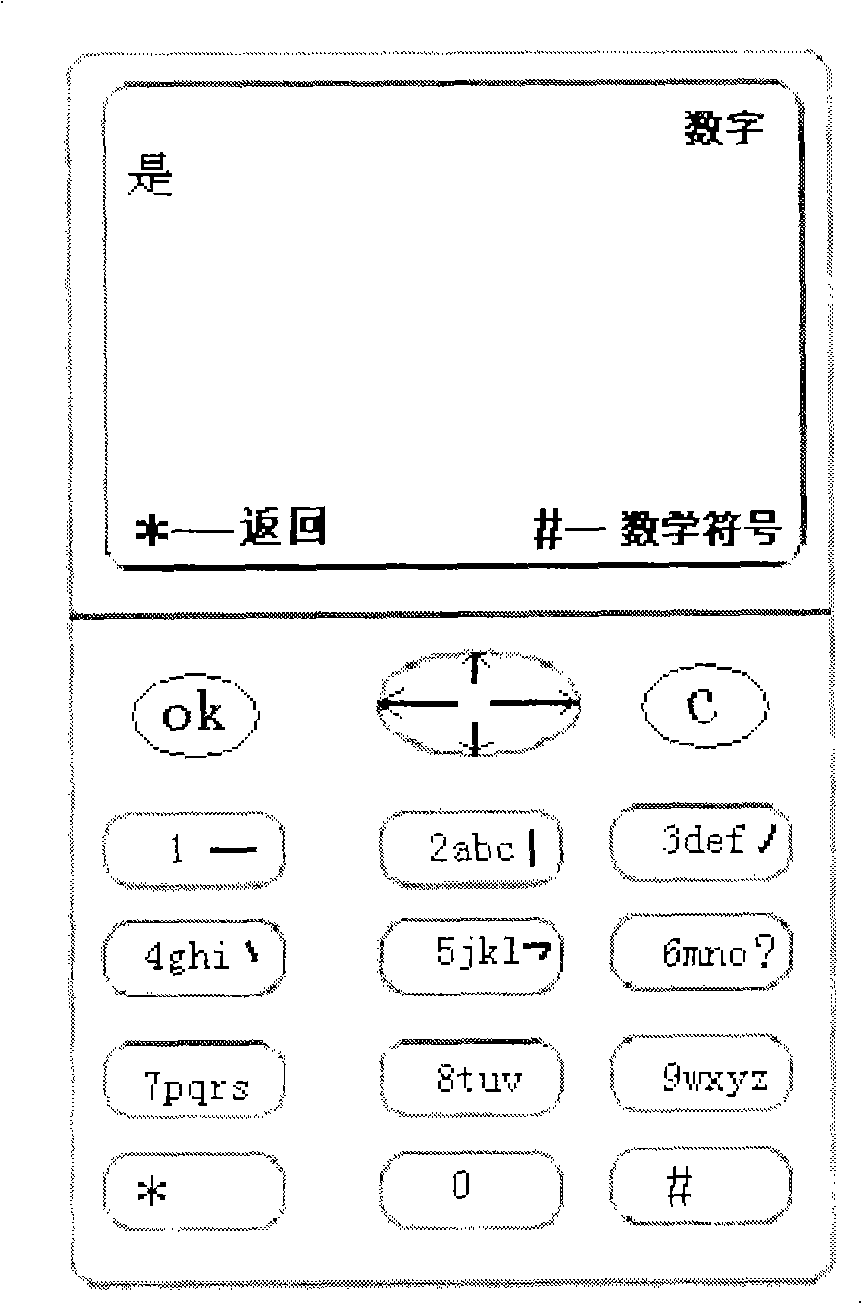
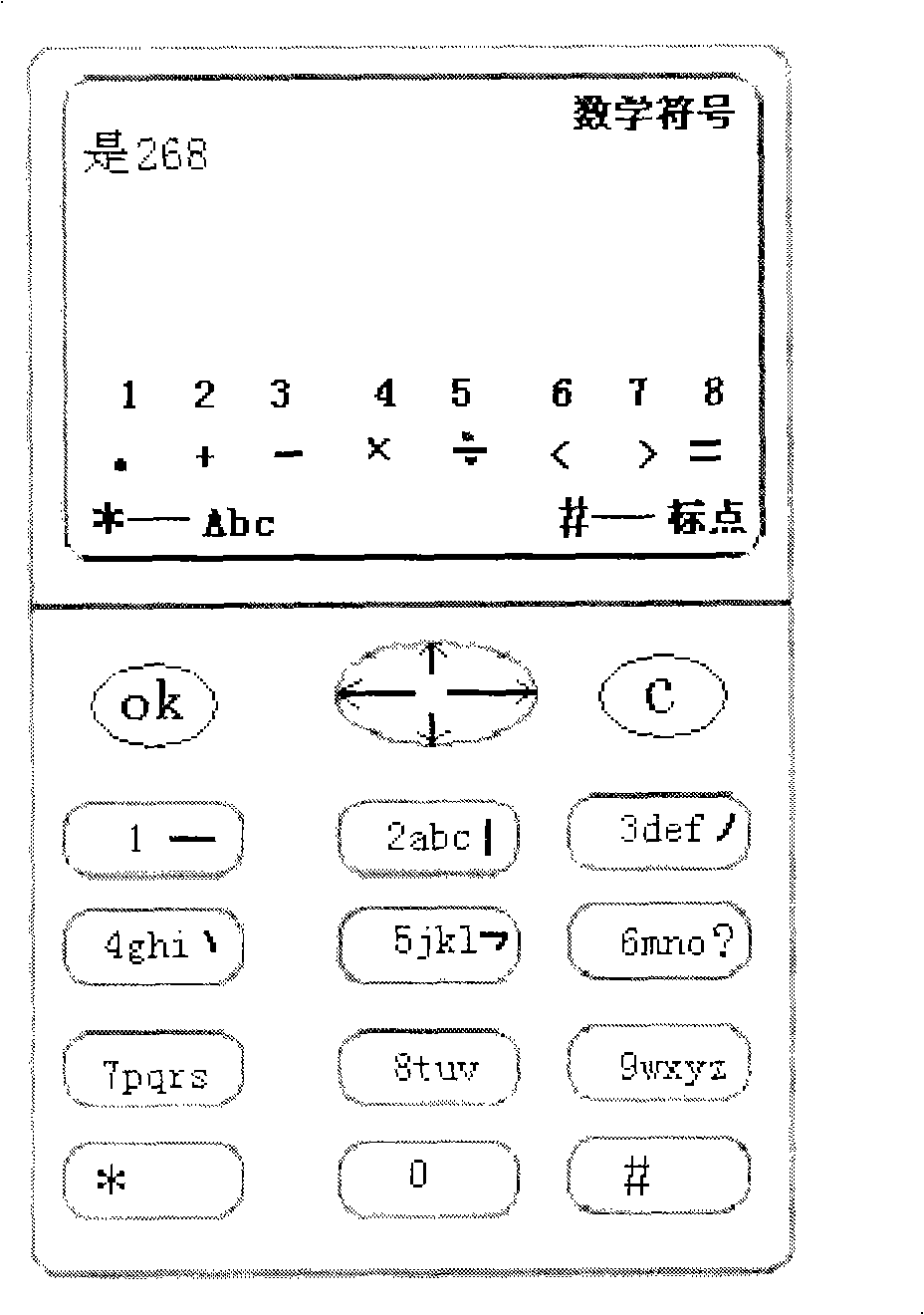
Digit, letter and punctuation and input mode direct switching method
InactiveCN101286096AHigh speedImprove efficiencyTelephone sets with user guidance/featuresTelephone set constructionsChinese charactersArabic numerals
The invention discloses a method for directly switching digit, letter, punctuation and input type. Under a Chinese character input state, unused keystrokes are used as function shift keys; when the function shift key is clicked, the program enters the input state corresponding to the shift key; furthermore, the keystrokes not used by the input state are defined as other function shift keys; the function shift key corresponding to the keystroke is marked on corresponding keystroke or screen for prompt. The method of the invention provides the user with the shift between different characters and all functions such as the returning of Chinese character, Arabic numerals, letter, foreign language, punctuation and input state, etc. when the digit keyboard is used for carrying out the inputting of texts and other characters.
Owner:孙强国
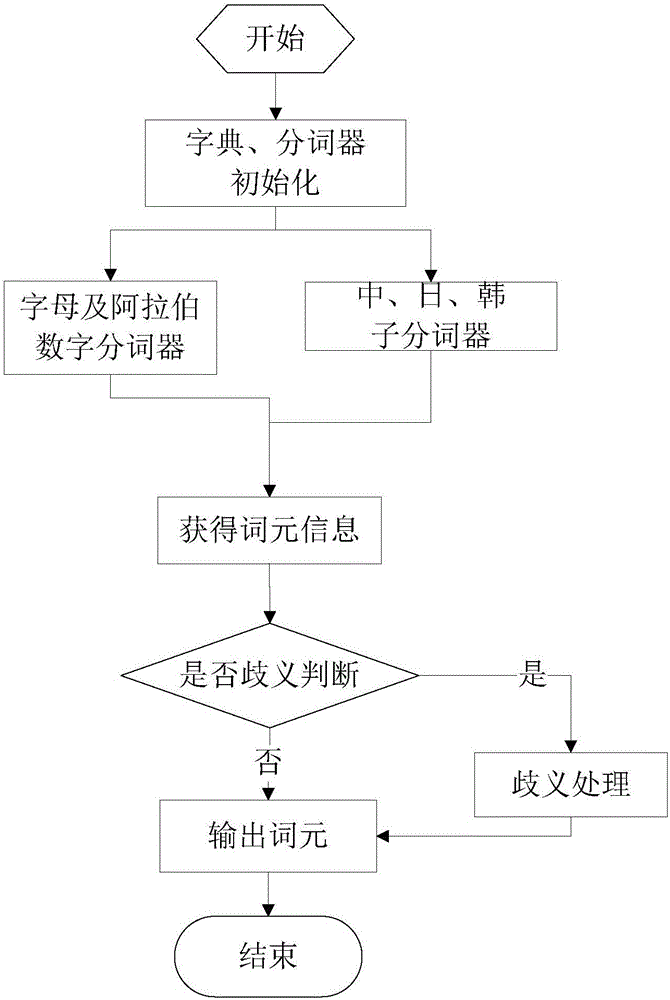
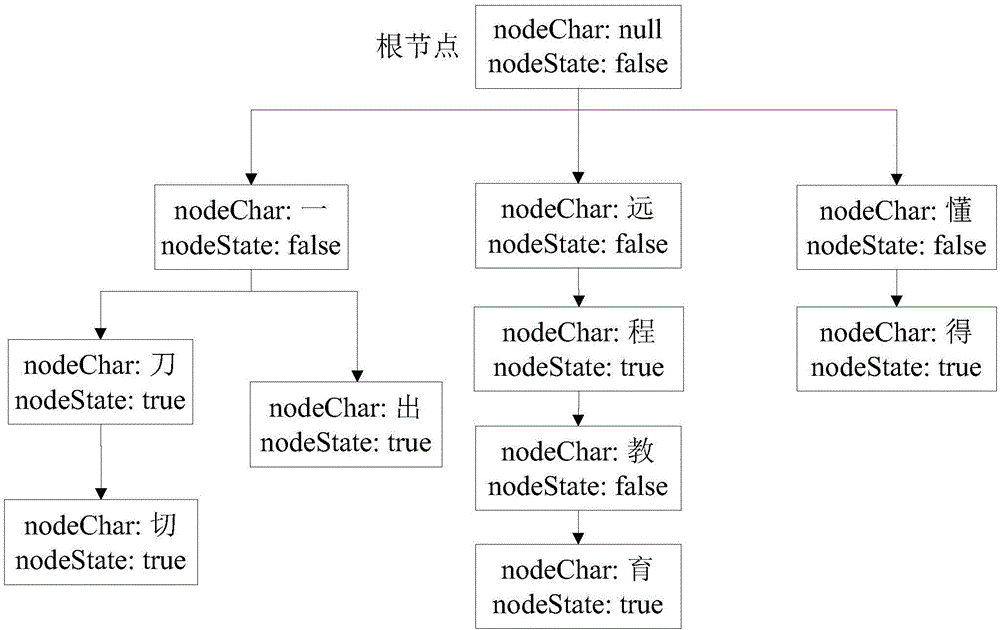
Multilingual word segmentation method based on dictionaries and grammar analysis
InactiveCN106528536ASolve the problem of garbled charactersSave storage spaceNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsArabic numeralsAutomatic summarization
The invention discloses a multilingual word segmentation method based on dictionaries and grammar analysis. Efficient and accurate word segmentation of mixed texts of Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Cantonese and the like can be realized, flexible lexicon expansion of words for different time periods and different professionals can be realized, lexicon information is updated effectively, and efficient and accurate multilingual language text word segmentation is realized; a word segmentation sub-device of Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Cantonese and other language families, a Chinese quantum word segmentation device and a western language word segmentation device are embedded to realize the accurate word segmentation of each language text; a text segment to be performed with word segmentation is segmented by a built-in language segment coded identification mechanism, each segmented text segment corresponds to a language family, and the word segmentation is carried out by using a corresponding word segmentation sub-device; the word segmentation of western inflectional languages and the smart mode word segmentation of the Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Cantonese can be realized by grammar analysis, and texts containing Arabic numeral information can be processed; and meanwhile, the word segmentation of texts with a plurality of mixed languages can also be realized by the multilingual word segmentation method provided by the invention, thereby getting rid of the limitation that a word segmentation tool can only realize the word segmentation of single language and some individual languages and ensuring the security, accuracy, efficiency, flexibility and universality of word segmentation of texts. The multilingual word segmentation method provided by the invention has a wide application prospect in the text word segmentation fields such as enhancement of mass data text classification, text information extraction, autoabstract, etc.
Owner:BEIJING SCISTOR TECH +1
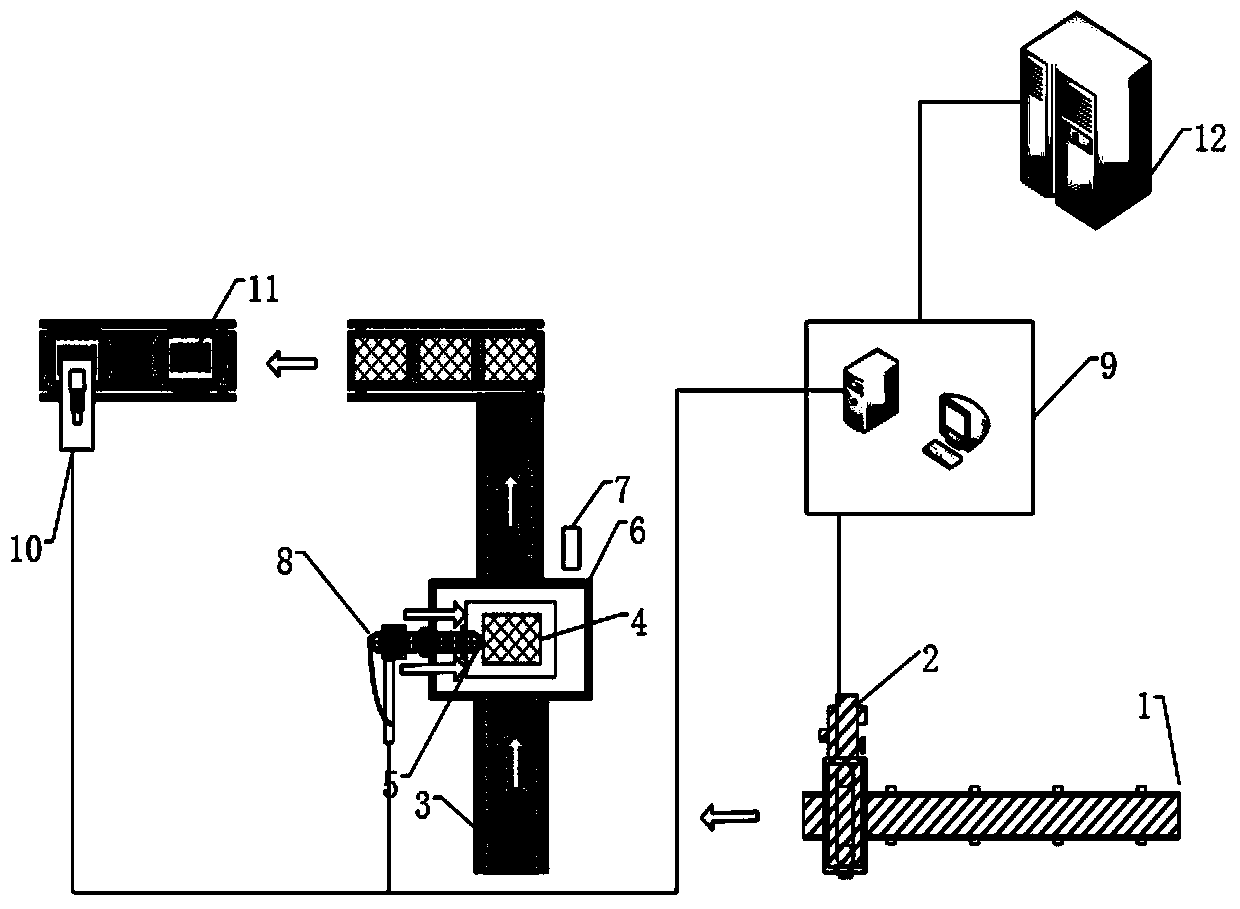
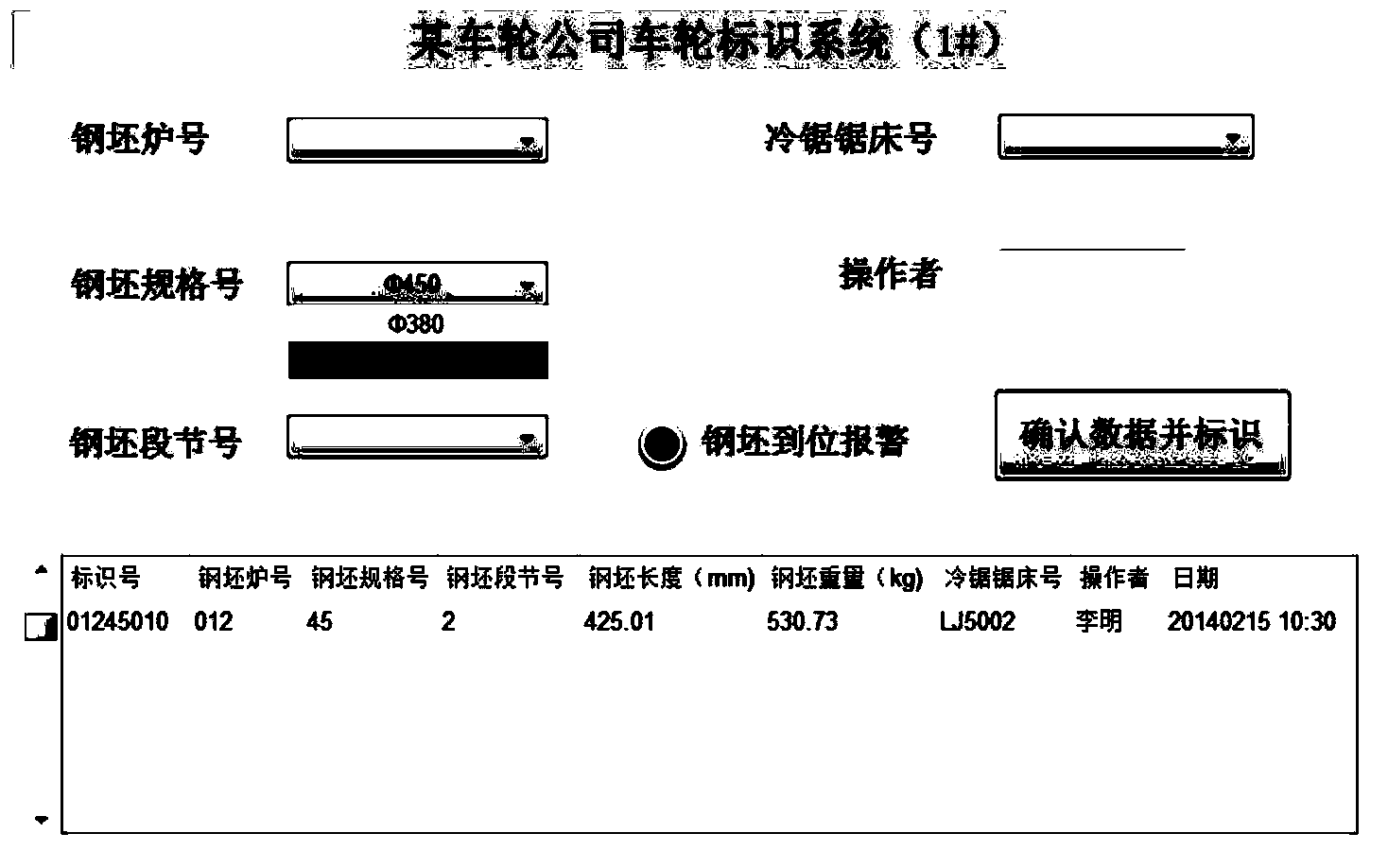
Identifying system and method for billets on blanking production line of train wheels
InactiveCN103870934AMeet the requirements of mandatory regulations on traceabilityRealize full trackingCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesProduction lineInformatization
The invention discloses an identifying system and method for billets on a blanking production line of train wheels, and belongs to the technical field of manufacturing industry informatization. The identifying system is composed of a code spraying identifying subsystem, a scanning recognition subsystem and others, after bar stocks are cut off through a cold sawing machine to obtain the train wheel billets through blanking, the end face of each billet is sprayed with a unique identifying code through a code spraying machine, each code is composed of eight Arabic numerals and a corresponding bar code, the corresponding billet heat number, the specification, the section number, the length, the weight, the number of the cold sawing machine, the name of an operator and other basic documents are stored in a data base, when the billets reach the underneath of an image scanner, the identifying codes are read by the image scanner and compared with an upper computer, the qualified billets meeting production plan batch numbers enter a heating furnace in sequence, and the unqualified billets are rejected. The identifying system builds basic data for follow-on production of the wheels, product tracking and identifying code attachment, wherein the identifying codes correspond to the product parameters uniquely.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
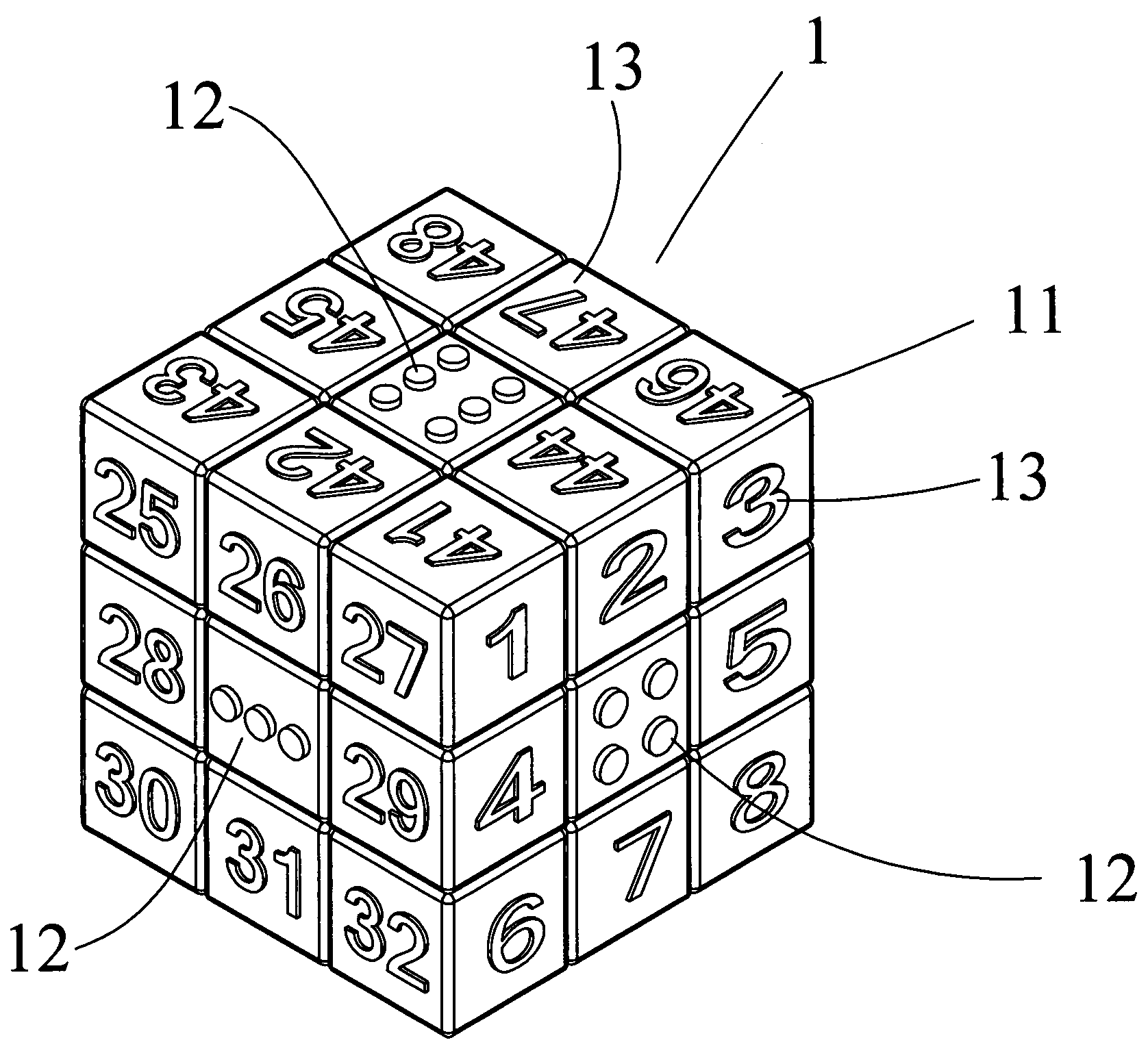
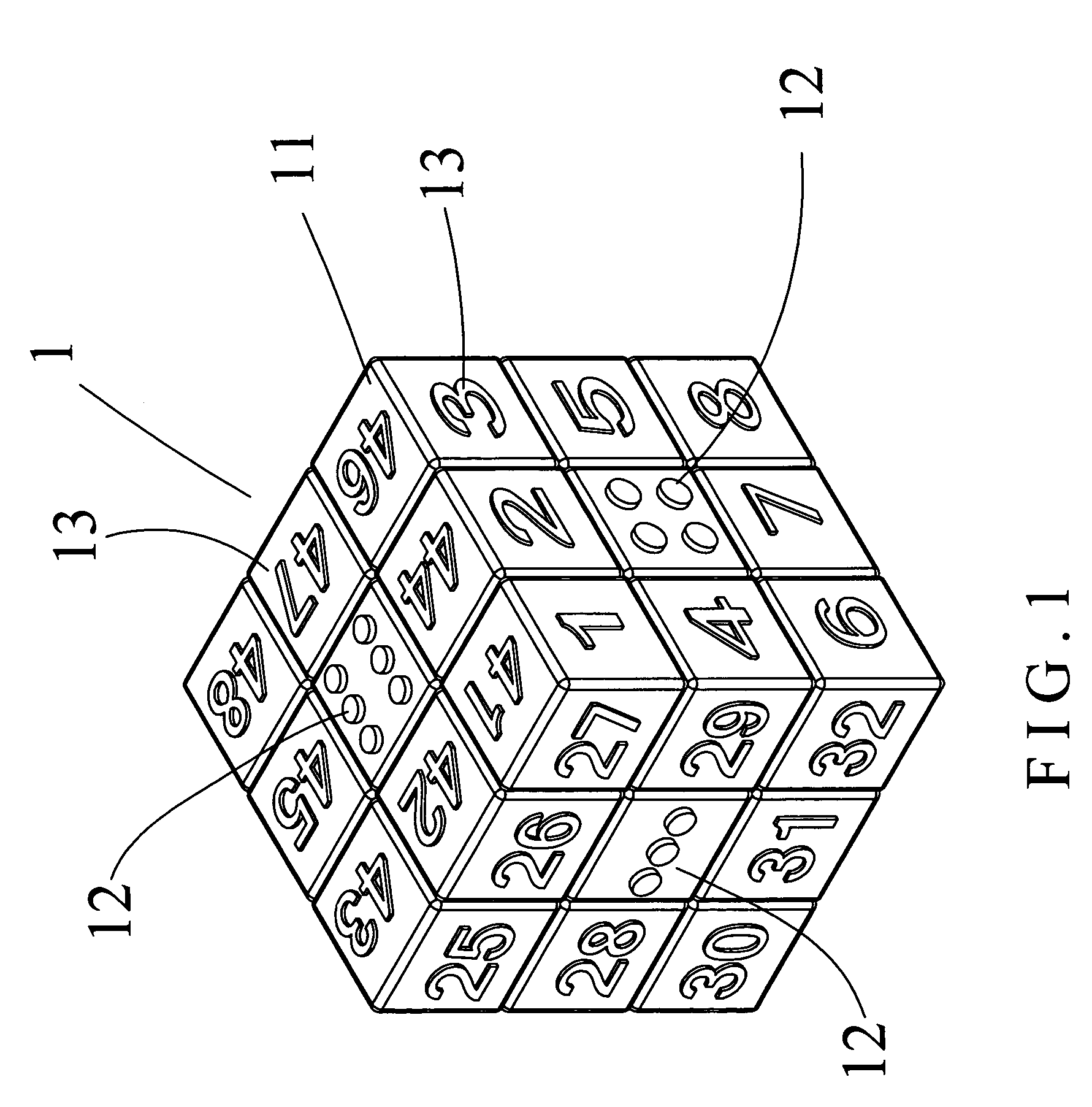
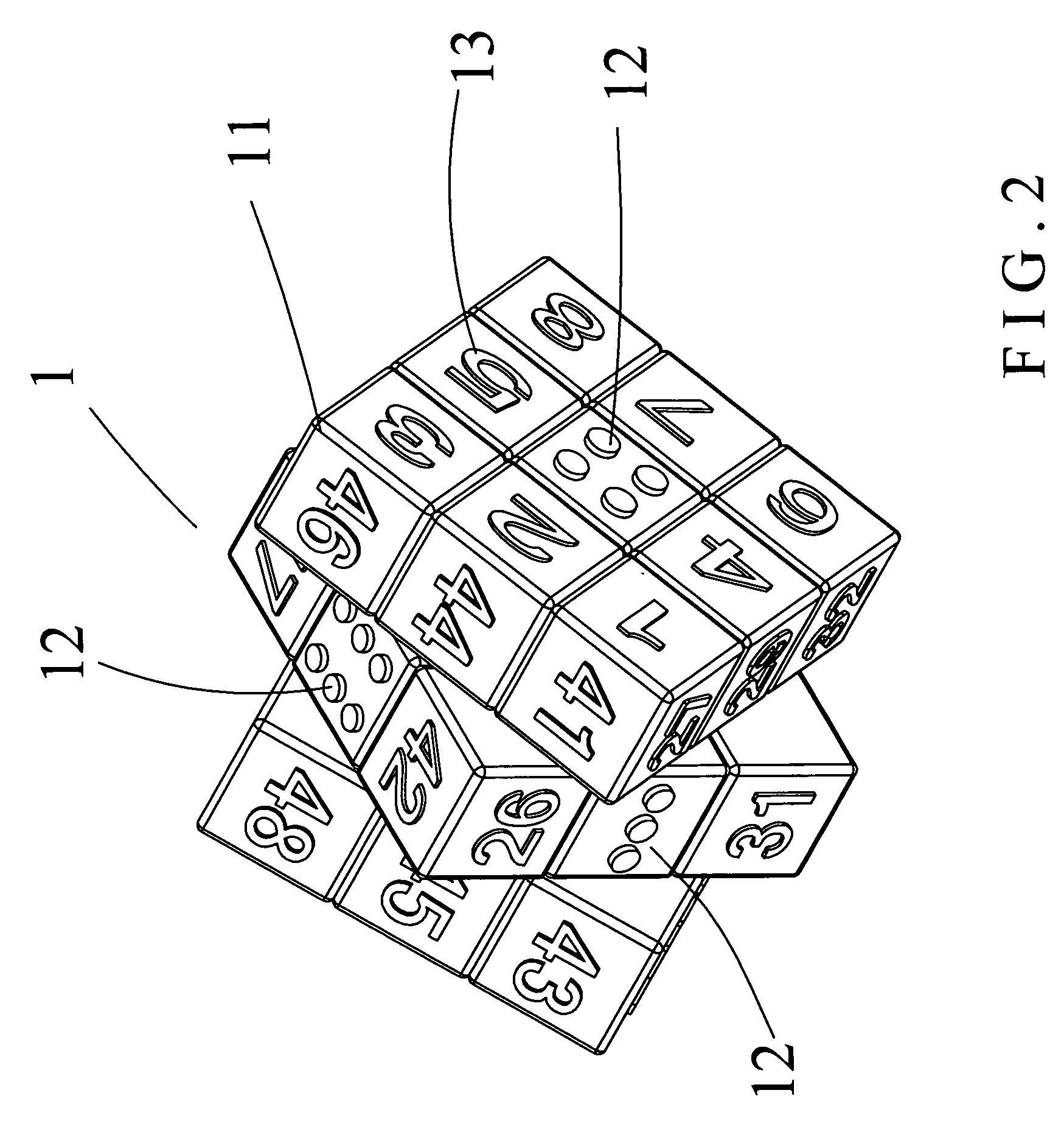
Magic cube
A magic cube includes a larger cubic block formed by a plurality of smaller cubic blocks. The larger cubic block has six larger faces each having nine smaller faces, wherein a central one of the nine smaller faces is indicated by a circular pointed marking ranged from 1 (one) to 6 (six) point, and the other ones of the nine smaller faces is indicated by an Arabic numeral ranged from 1 (one) to 48 (forty-eight). Thus, all of the Arabic numerals are arranged in an irregular manner, and all of the circular pointed markings are located at the central position of each of the six relatively larger faces.
Owner:WANG CHING TE
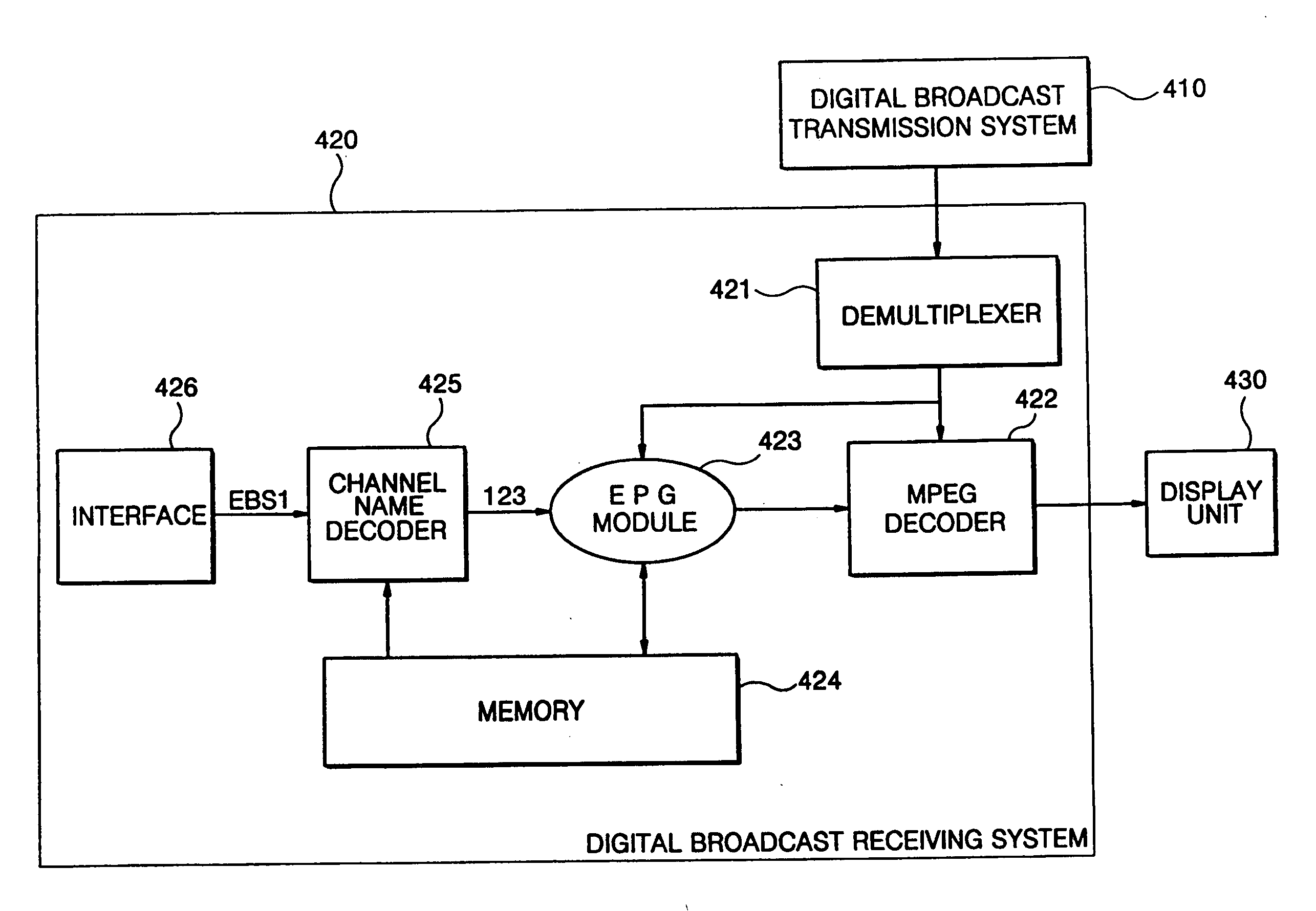
Apparatus and method for switching channels in a digital broadcasting system
InactiveUS20070016923A1Television system detailsGHz frequency transmissionBroadcast channelsArabic numerals
An apparatus and a method for switching channels in a digital broadcasting system. The apparatus and method of the invention can convert an abridged channel name comprised of alphabetic letters, or a combination of alphabetic letters and Arabic numbers, inputted by a user, into a corresponding channel number and switches into a digital broadcasting channel at a tuner according to the channel number so that a user can easily switch broadcast channels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Digital road sign, digital door plate address and electronic road guide system and applications thereof
InactiveCN101556164AInstruments for road network navigationData processing applicationsArabic numeralsShort Message Service
The invention relates to a digital road sign, a digital door plate address and an electronic road guide system and applications thereof. An orderly and regular digitized ground road sign system is constructed according to the design rules of regional location code, highway marking code of city and countryside, street marking code of city and countryside and digital door plate and address code, and the design and arrangement of digital road sign scutcheon and digital door plate scutcheon; in the premise of no change of the original road names, a group of Arabic numeral road signs which is known by almost everyone are added, thus leading a person to be capable of arriving at the destination smoothly without inquiring others or getting help from any road guide equipment as long as the person knows the digital road sign and the digital door plate address of the destination, no matter which country the person is from and which place the person is in; by utilizing the guide function of electronic information-based road of the system, people can also obtain more convenient road guide service by ways of telephones, short message services, websites, electronic digital road sign and the like; and the system use instruction manual enclosed with advertisements and the map enclosed with digital road sign code can be made.
Owner:丁佑年 +1
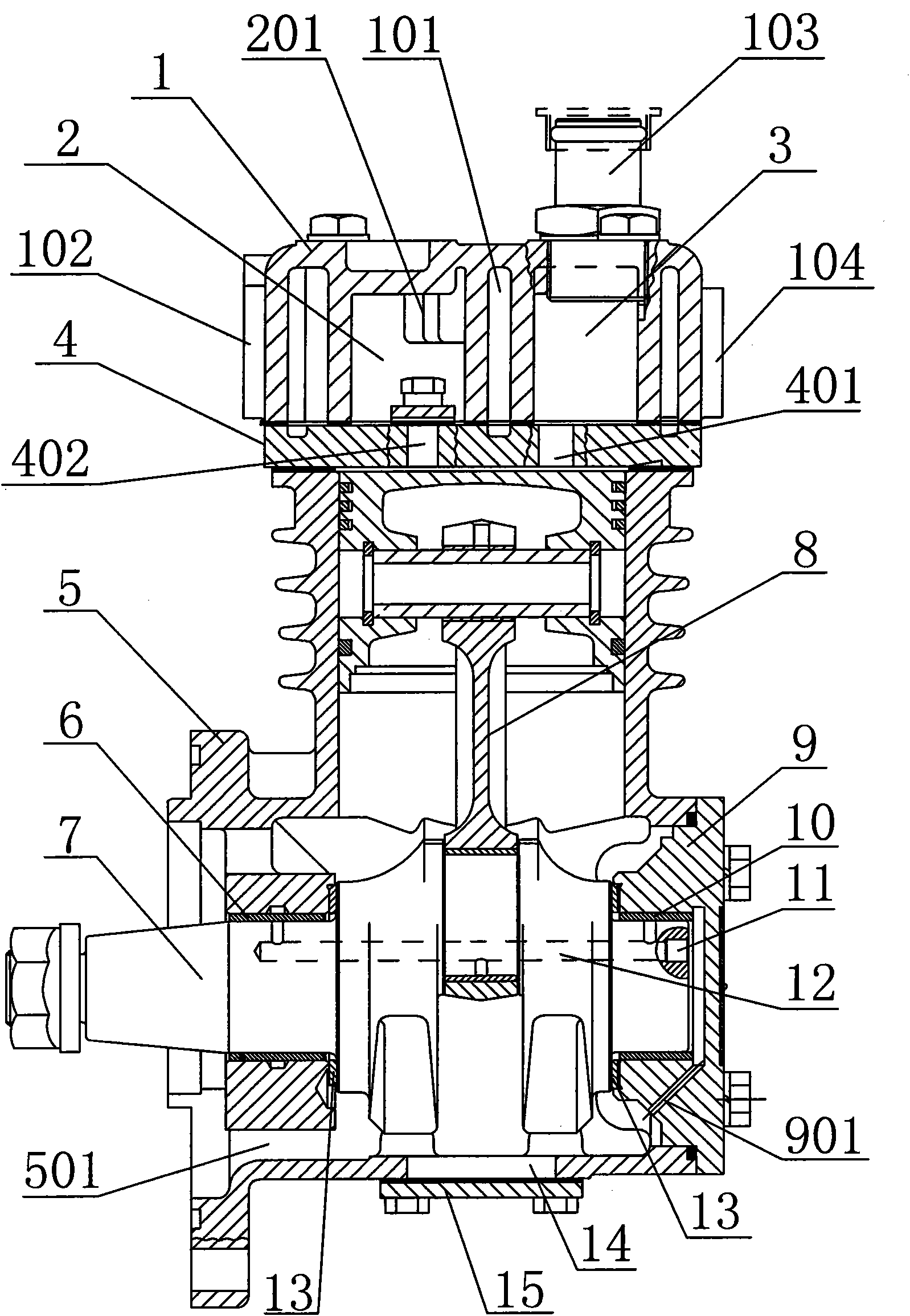
Energy-saving automobile water-cooling air compressor
InactiveCN101832252AImprove sealingLow failure ratePositive displacement pump componentsPositive-displacement liquid enginesFailure rateArabic numerals
The invention relates to an energy-saving automobile water-cooling air compressor which is designed to solve the technical problem that the crank shaft oil supply structure and the venting and cooling effects of the existing similar air compressor are poor. The air compressor of the invention comprises a cylinder cover, a valve plate and a crank shaft box body, and has the design key points that the loop-type water cavity of the cylinder cover is matched with the loop-type groove of the valve plate to form a loop-type water-cooling path which is in the shape of the Arabic numeral eight, and a venting cavity is internally provided with a cooling radiating fin connected with the water-cooling path. The crank shaft is provided with a straightaway-type oil hole eccentrically along the axial direction, the straightaway-type oil hole is provided with at least three radial through holes, and at least one through hole is communicated with an oil inlet hole on the crank shaft box body; and a front bearing hole in the crank shaft box body is provided with a front sliding bearing, and a blank cap hole is connected with a blank cap which is provided with a rear bearing pedestal and an oil return path. The invention further lowers venting temperature, reduces the oil discharge amount of the air compressor along air, adopts the eccentric straightaway-type oil hole, has unimpeded oil path, low failure rate and stable operation and is suitable for serving as the structure improvement of similar air compressors.
Owner:FENGHUA TIANFENG AUTOMOBILE AIR COMPRESSOR
Use of metadata to post process speech recognition output
ActiveUS8676577B2Easy to convertImprove accuracySpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisAddress bookArabic numerals
Owner:YAP +1
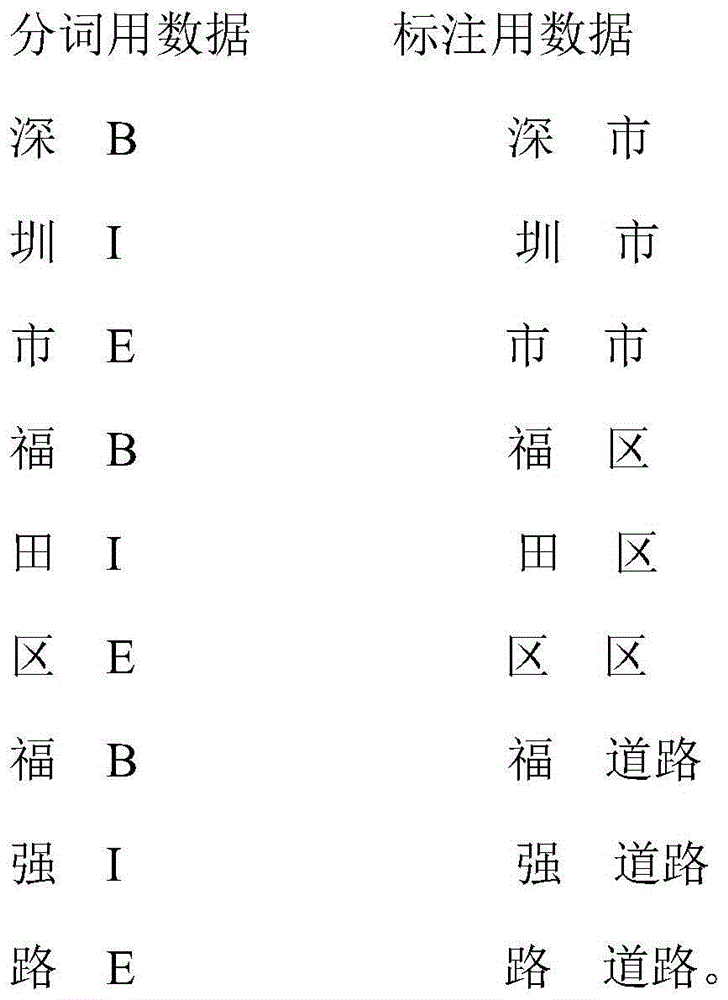
Chinese address word segmentation and annotation method
ActiveCN104933023AImprove accuracyNatural language analysisSpecial data processing applicationsArabic numeralsEnglish characters
The present invention relates to a Chinese address word segmentation and annotation method. The method comprises: step 11, selecting address data by means of manual word segmentation and annotation as training data; step 12, substituting specified a single Arabic numerical character or English character for a present single Arabic numerical character or English character and a plurality of continuous Arabic numerical characters or English characters; step 13, converting the training data into a data format desired by the CRF++ tool; step 14, defining a feature profile; step 15, respectively establishing a word segmentation model and an annotation model by using the CRF++ tool; step 16, substituting the specified single Arabic numerical character or English character for the single Arabic numerical character or English character and the plurality of Arabic numerical characters or English characters present in the address; step 17, performing word segmentation and annotation by using the CRF++ tool; and step 18, recovering the Arabic numerical character or English character before the substitution. The Chinese address word segmentation and annotation method according to the present invention achieves high accuracy.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Efficient cutting device for foam plastic board
InactiveCN106393223ASmooth cutBeautiful incisionMetal working apparatusArabic numeralsBolt connection
Owner:WUXI TONGXIN PLASTIC PROD
Optical character recognition method for deep learning model based on convolutional neural network
InactiveCN108681735AImprove robustnessImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsText recognitionData set
The invention discloses an optical character recognition method for a deep learning model based on a convolutional neural network. The method includes the following steps: collecting data sets of common Chinese characters of different fonts, 10 Arabic numerals and 26 English letters and converting the data sets into picture formats; slightly twisting and rotating the pictures to enhance the robustness of the model, and generating a model training database; establishing the deep learning model of optical character recognition; inputting the training sets into the model, continuously optimizinga target function and learning a multi-classifier by using the convolutional neural network model through the method of supervised learning; and for a novel test sample, carrying out feature extraction on the novel test sample based on the model obtained in the previous step and obtaining a final classification result by using the model classifier. The invention provides the novel model and methodfor deep learning based on the convolutional neural network in optical character recognition. The method can be applied to general pattern classification tasks, especially text recognition. The optical character recognition model based on deep learning can significantly improve the identification correct rate of character identification.
Owner:中科博宏(北京)科技有限公司
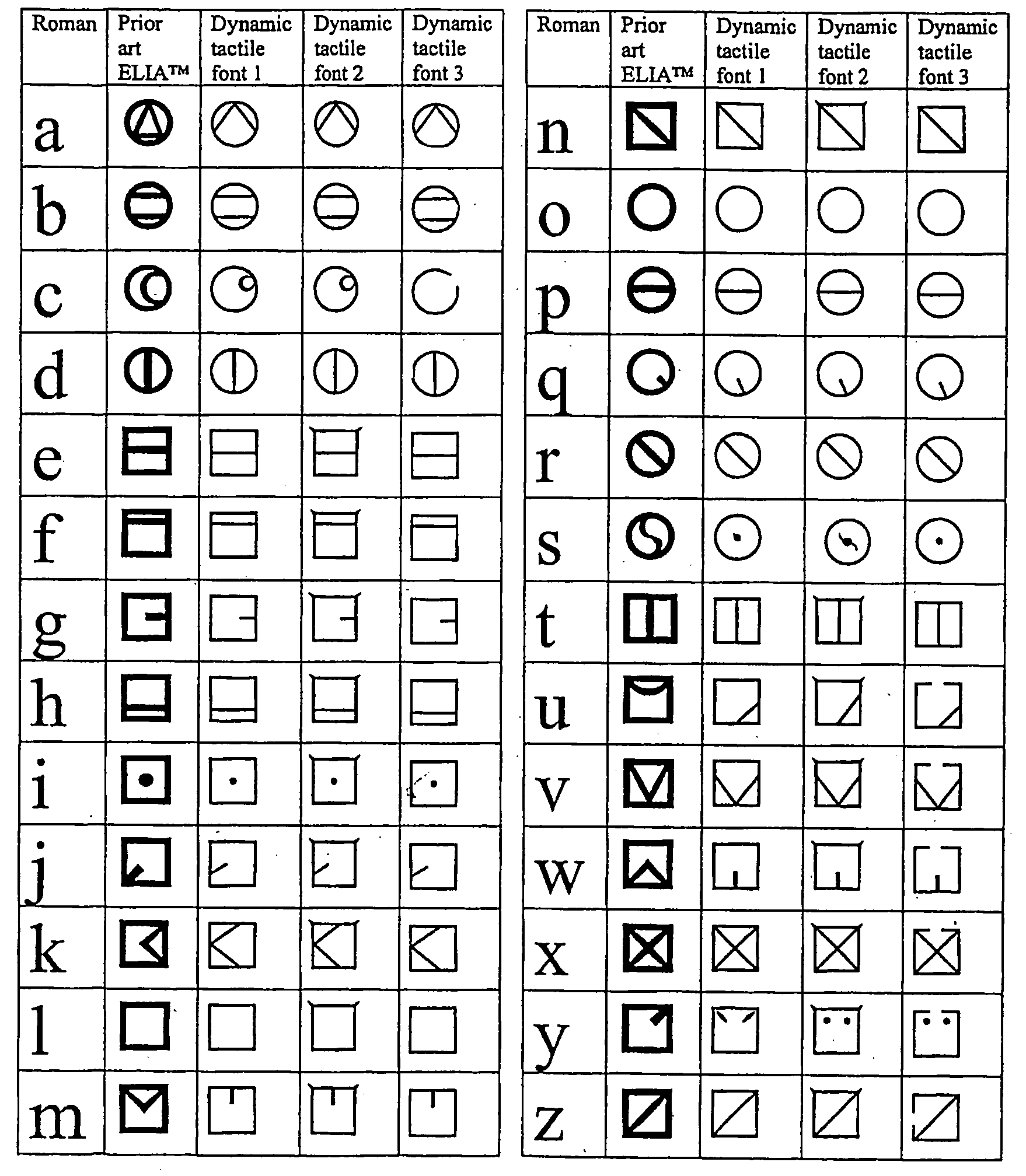
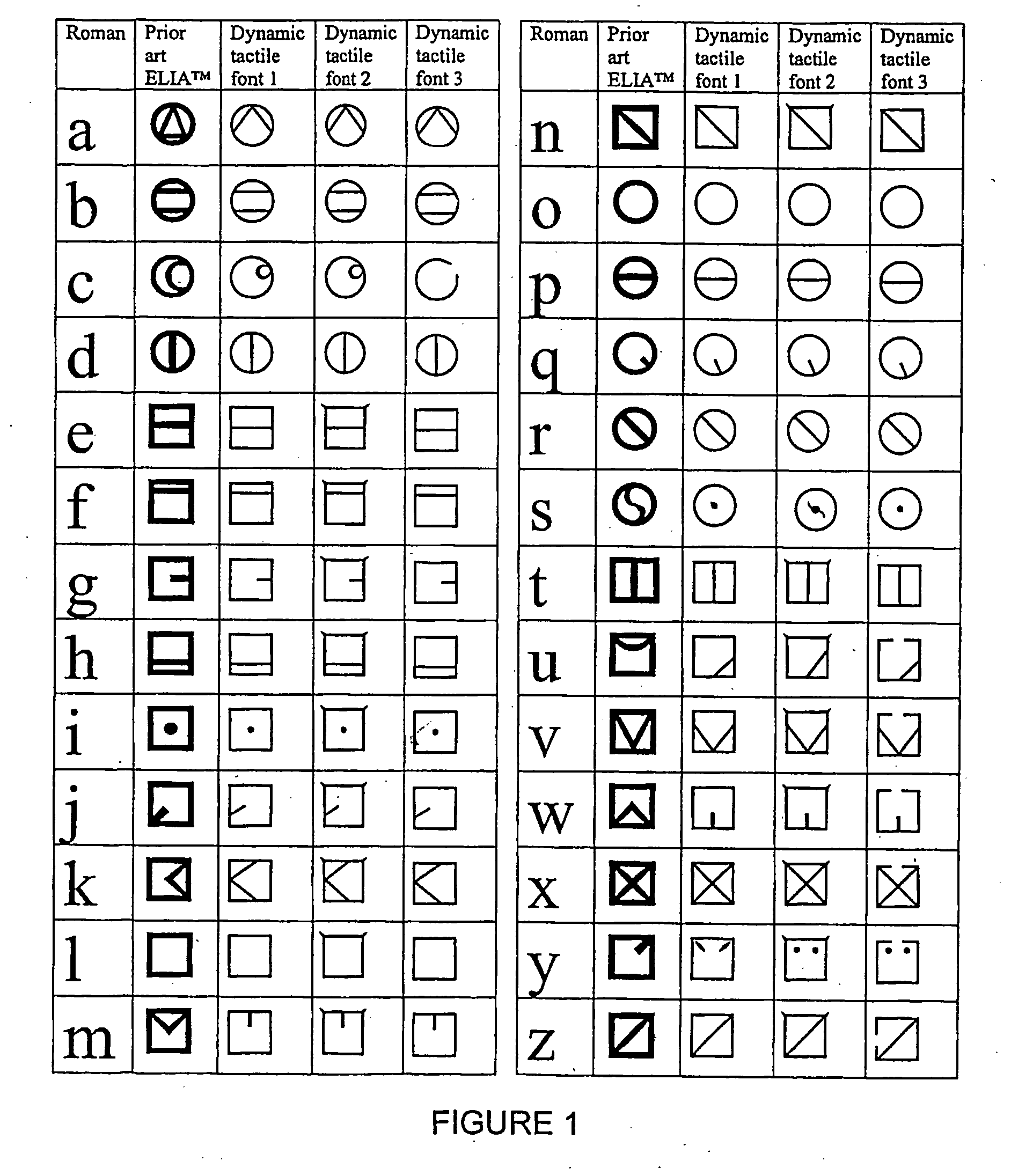
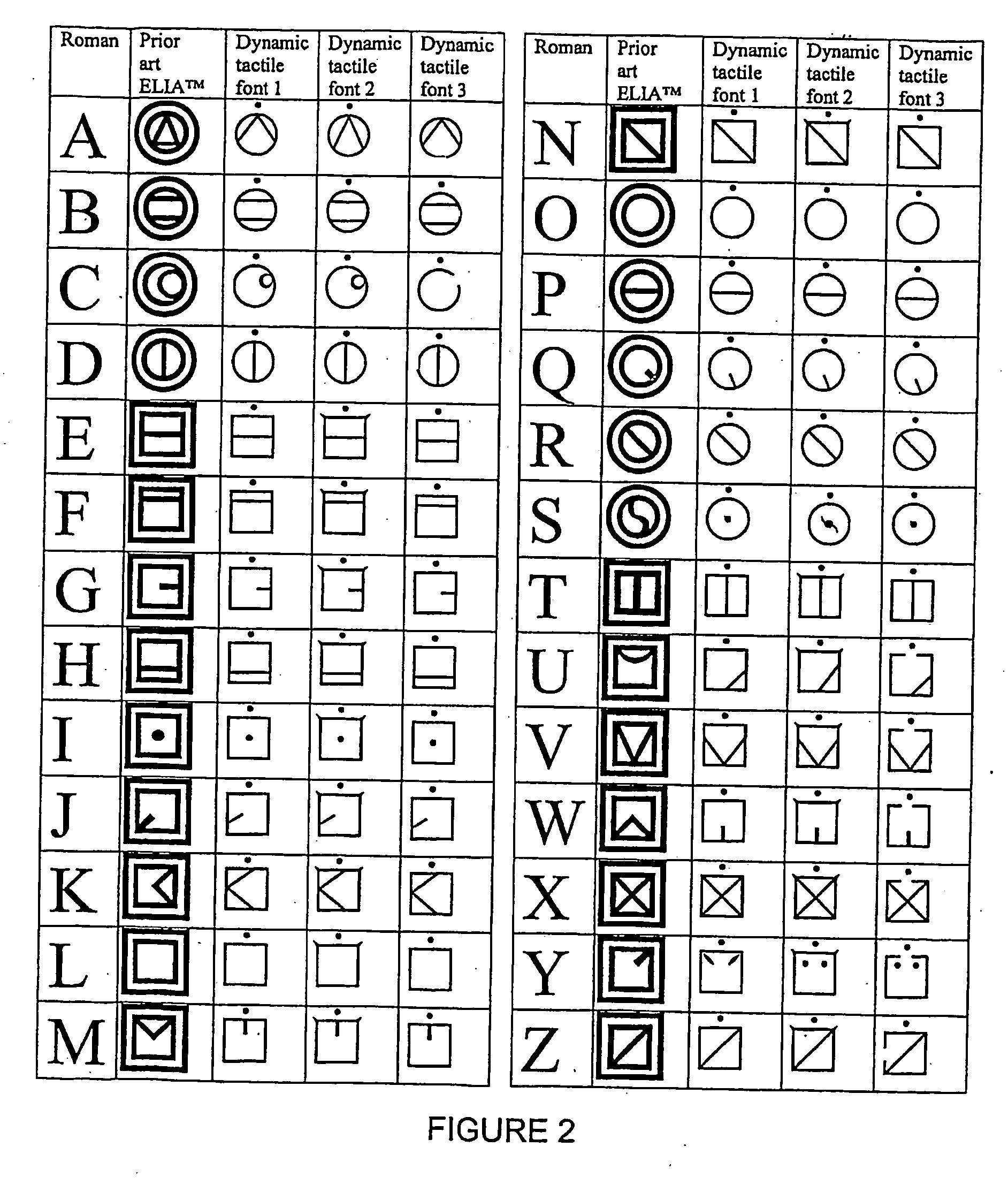
Dynamic tactile and low vision fonts
A dynamic tactile code in which embossed alphabetic symbols represent the letters of the conventional Roman alphabet and embossed numeric symbols represent the conventional Arabic numerals. The alphabetic symbols are divided into four regions, the alphabetic symbols in the first and third regions being denoted by a circular frame, and the alphabetic symbols in the second and fourth regions being surrounded by a square frame. At least some of the alphabetic symbols embody at least a physical association of their corresponding letter of the Roman alphabet. Uppercase symbols differentiate from the lowercase symbols by the placement of a dot centrally located above the lowercase symbol frame. The numeric symbols are denoted by a diamond-shaped frame. Certain essential attributes of the font remain constant while other attributes change as the font's size is changed. In particular, (1) inter-symbol spacing changes by a non-constant ratio; (2) line width changes by a non-constant ratio; (3) symbol element ratios changes by a non-constant ratio; (4) symbol element location changes by non-constant ratios; (5) symbol shape changes from font size to font size; (6) symbol elements can be present at some sizes and not present at other sizes or the element sizes can vary in different, non-constant proportions to each other; and (7) at one size, the symbol elements remain fixed or vary based on their location on a visual display, and symbols displayed in the middle of the display look different than when they are displayed at the side of the display.
Owner:CHEPAITIS ANDREW
Wardrobe provided with intelligent identification device
InactiveCN106360999AEasy to placeLight structureApparel holdersWardrobesArabic numeralsComputer module
The invention relates to the technical field of smart home, and in particular relates to a wardrobe provided with an intelligent identification device. The wardrobe comprises a central processing unit module, a display screen module, a wardrobe body, intelligent clothes hangers, a clothing searching mechanism and a hang rod, wherein the hang rod is transversely arranged in the wardrobe body, each intelligent clothes hanger comprises a hanger body and a hang hook, a bar code, a two-dimensional bar code reader or a photographing camera is arranged on the front of each hanger body, and an Arabic numeral recognition area is arranged on the upper part of each hang hook; the clothing searching mechanism comprises a stepping motor, a support frame, a miniature CCD camera and a plurality of belt pulleys, the plurality of belt pulleys are sequentially arranged along the horizontal direction of the support frame, a silent belt sequentially bypasses the belt pulleys, an output wheel of the stepping motor is connected with the silent belt, and the miniature CCD camera is mounted on the lower part of the silent belt. The device is designed by improving the existing wardrobe, meanwhile, the integral structure of the wardrobe is not damaged, therefore, the wardrobe can be applied to common families, the cost can be reduced, and the device only occupies a little space of the wardrobe.
Owner:汇森家具(龙南)有限公司
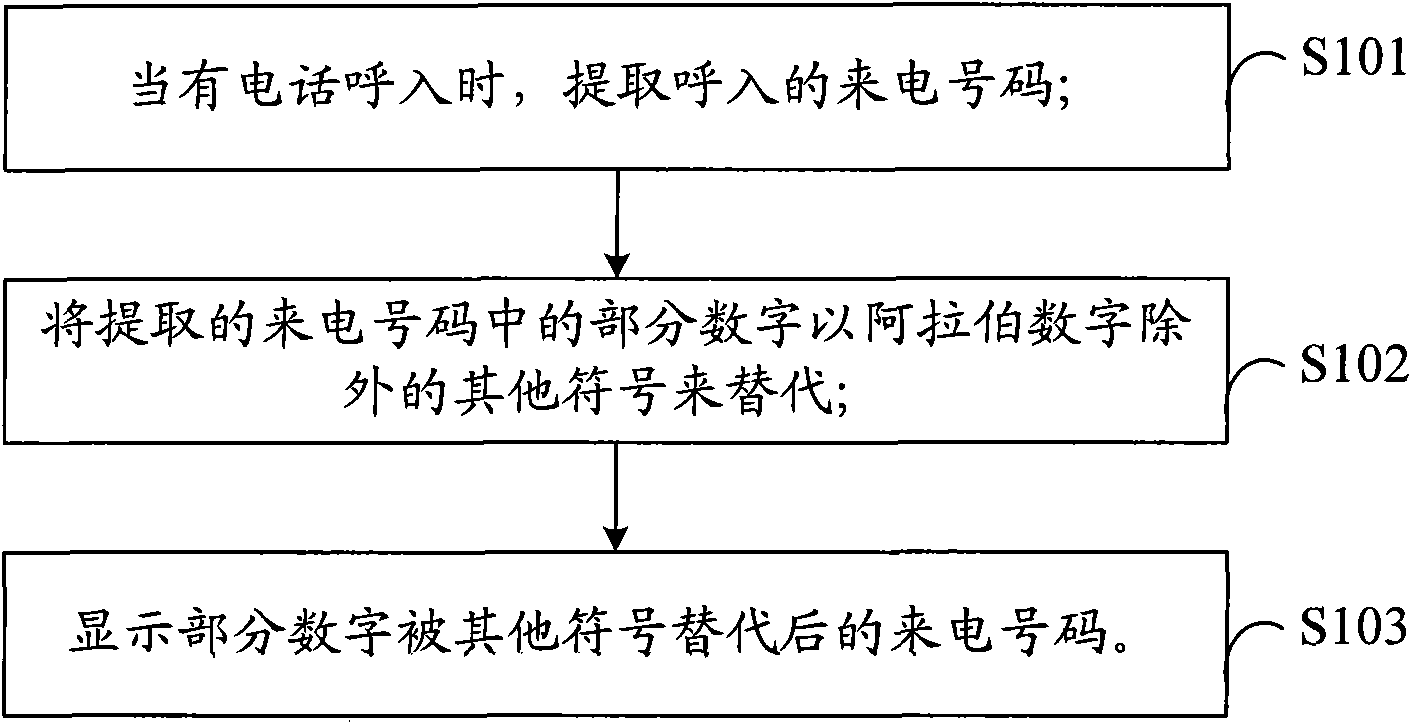
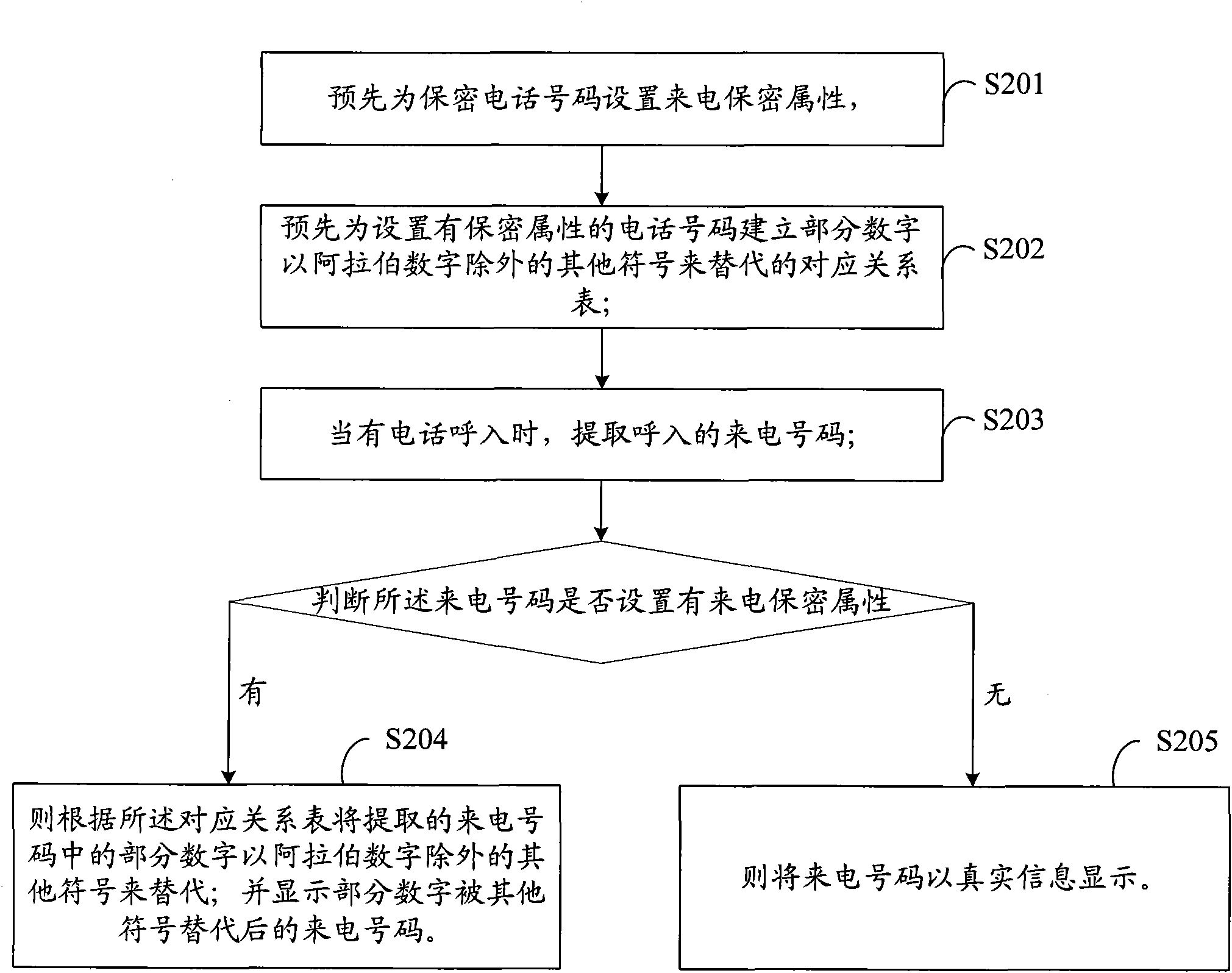
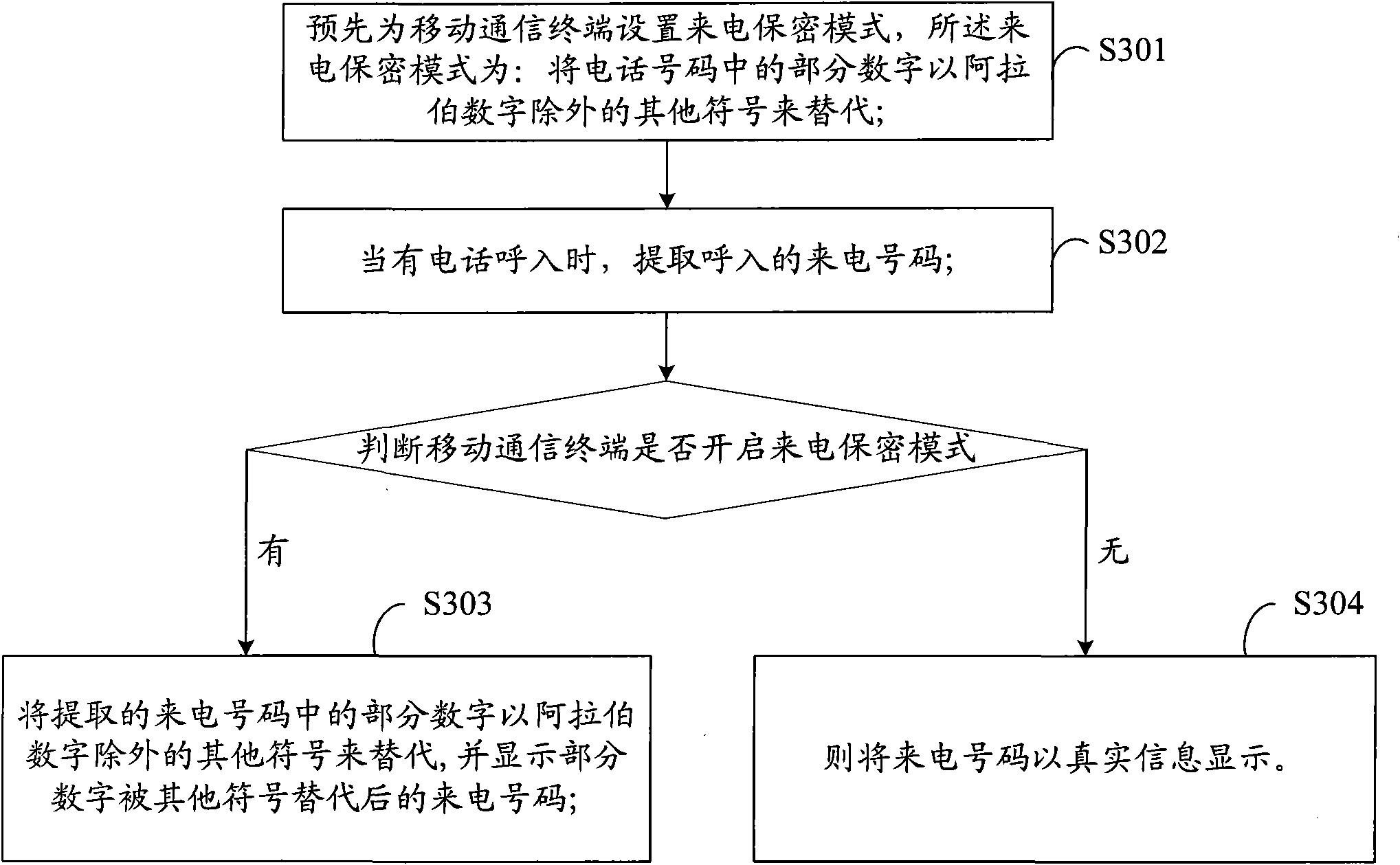
Incoming call confidentiality method, system and mobile communication terminal
InactiveCN101778148ASolve the problem of low confidentiality and easy leakageCalling susbscriber number recording/indicationWireless communicationArabic numeralsConfidentiality
The invention provides an incoming call confidentiality method, a system and a mobile communication terminal, which are applicable to the filed of the mobile communication terminal. The method comprises the following steps: extracting incoming call numbers when a call incomes; replacing parts of numbers in the extracted incoming call numbers with other signs except Arabic numbers; and displaying the incoming call numbers with parts of numbers replaced by other signs. The system comprises a number extracting module, a replacing module and a display module, wherein the number extracting module is used for extracting the incoming call numbers when the call incomes, the replacing module is used for replacing parts of numbers in the incoming call numbers with other signs except Arabic numbers, and the display module is used for displaying the incoming call numbers with parts of numbers replaced by other signs. The invention solves the problems of low incoming call number confidentiality and easy tattling caused by direct display of the incoming all numbers on an incoming call interface in the prior art.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Automatic partitioning method for optimizing image initial partitioning boundary
InactiveCN101231745AOptimizing Segmentation BoundariesOvercoming image noiseImage enhancementAutomatic segmentationArabic numerals
The invention relates to an image processing technology, in particular to an automatic optimization method of initially segmented boundary based on neighbor function criterion. The method comprises the following steps: initially segmented boundary points are detected, and are marked with Arabic numerals according to an initially segmented area; neighbor function values within a neighborhood are calculated for each boundary point; membership function values of the current boundary point are calculated according to the neighbor function values; the boundary points are reclassified according to the membership function values to get an optimized segmented boundary; the steps above are repeated to ensure the segmented boundaries of the entire image to be optimized. The method provided by the invention imitates some functions of human eyes during image processing, and can optimize inaccurately segmented boundaries automatically. In addition, the invention eliminates the influence of image noise, local bulk effect, overlapping intensity and non-uniformity of intensity, and well complements prior segmentation algorithm. The invention has important application values in the fields of medical image segmentation, remote sensing image segmentation, target identification and so on.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Abacus for Math and English
InactiveUS20080096169A1Effective learning methodGood computing powerEducational modelsTeaching apparatusPattern recognitionArabic numerals
Owner:KIM YE EUN
Method of switching input method editor
InactiveUS20100245251A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsArabic numeralsOn-screen display
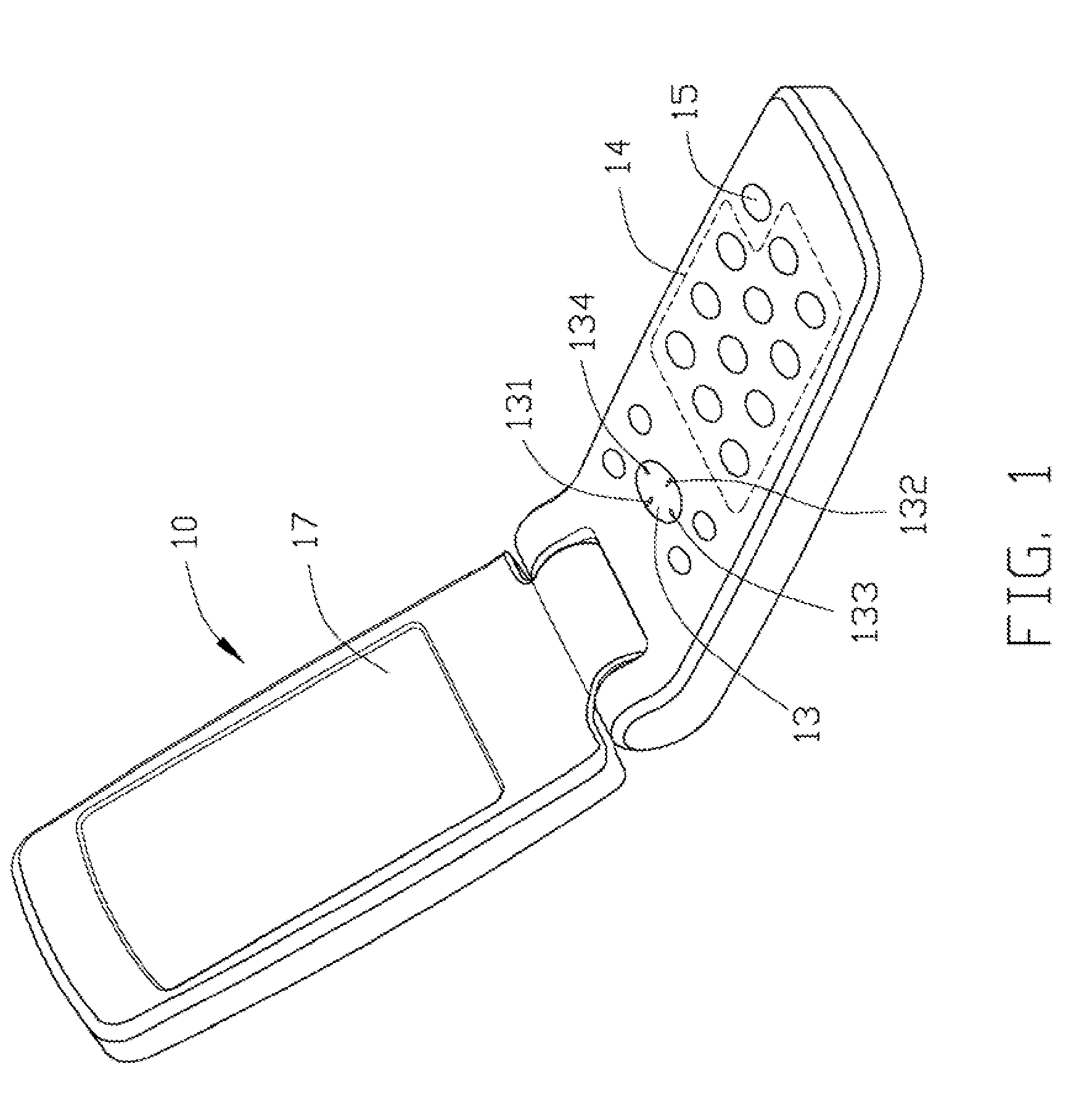
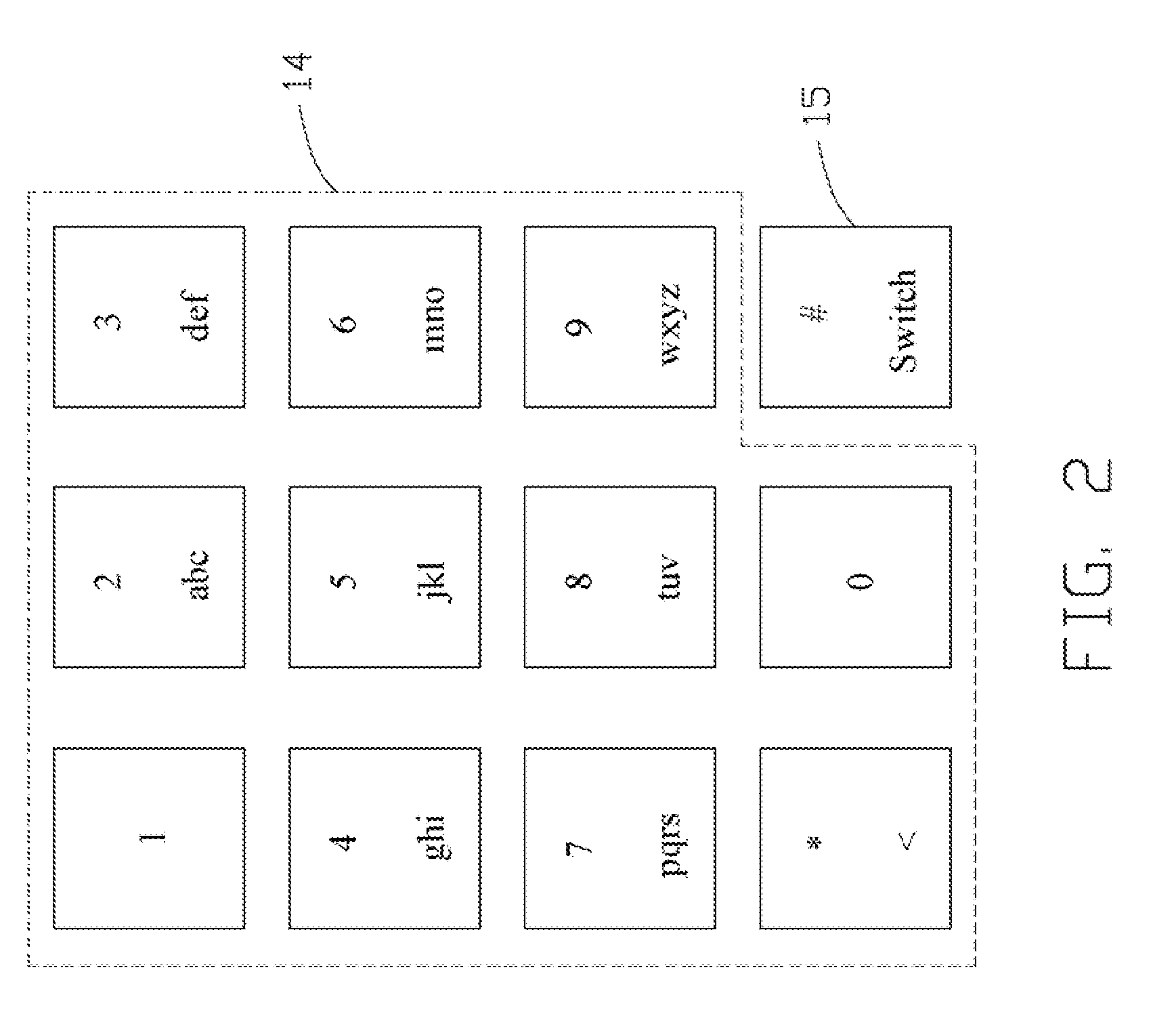
A method is used to switch input method editors (IMEs) in a mobile phone. The mobile phone includes a switch key, a screen, and a group of information input keys. The method includes the following steps. The switch key is firstly pressed to switch to an Arabic numeral IME. An information input key is pressed to input information., Corresponding Arabic numeral is shown on the screen for being inputted. If the Arabic numeral is not accepted within a pre-set time, the screen shows a plurality of letters corresponding to the pressed key of the group of information input keys. One key is pressed to switch to an English letter IME, and a letter is chosen from the plurality of letters to input.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Keyboard and electronic equipment for eliminating language difference
InactiveCN101673144AEliminate language differencesRealize editingAlphabetical characters enteringTelephone set constructionsBasic languageArabic numerals
The invention provides an electronic equipment keyboard for eliminating language difference by using transfer from a physical keyboard to a virtual keyboard, and electronic equipment with the keyboard. The electronic equipment keyboard is provided with a display part and a key part, wherein the display part displays a specific language part; and the key part comprises a plurality of keys, whereinat least one key can perform operation corresponding to the specific language part. The plurality of keys have self marks, and each mark comprises a number part, a basic language part and other control key parts. The number part is an Arabic number part; and the basic language part is a Latin letter part. The display part also displays a number part of the display part corresponding to the numberparts of the plurality of keys so as to play a role in indicating input. The specific language part comprises native language letters and / or native language strokes of an electronic equipment user. The electronic equipment is a mobile phone or a PDA.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com