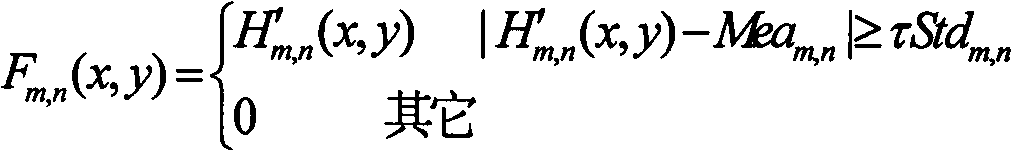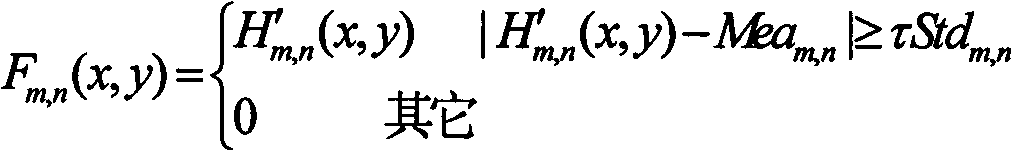Patents
Literature
121 results about "Density analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
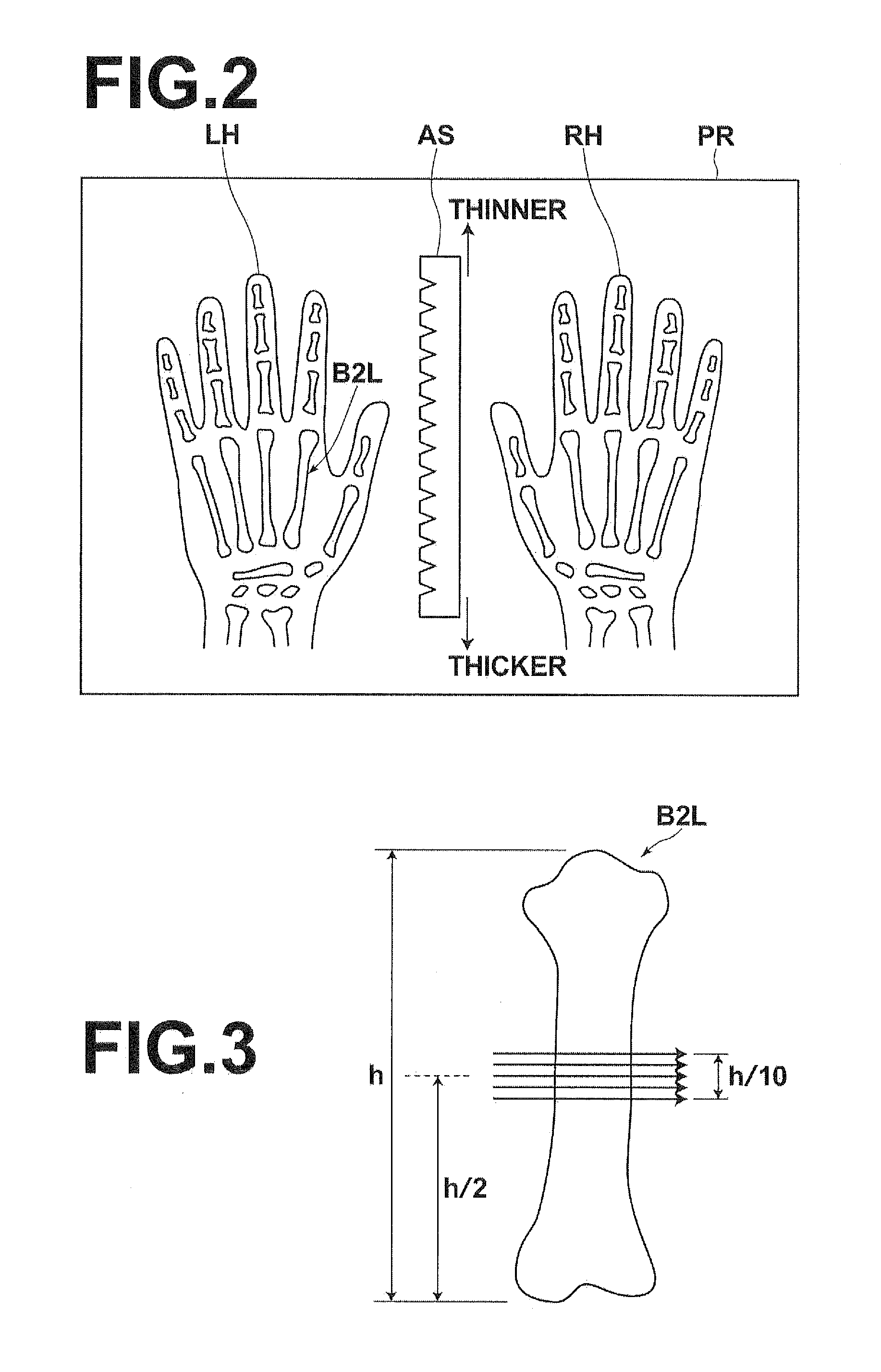
Density analysis takes known quantities of some phenomena and spreads it across the landscape based on the quantity that is measured at each location and the spatial relationship of the locations of the measured quantities.
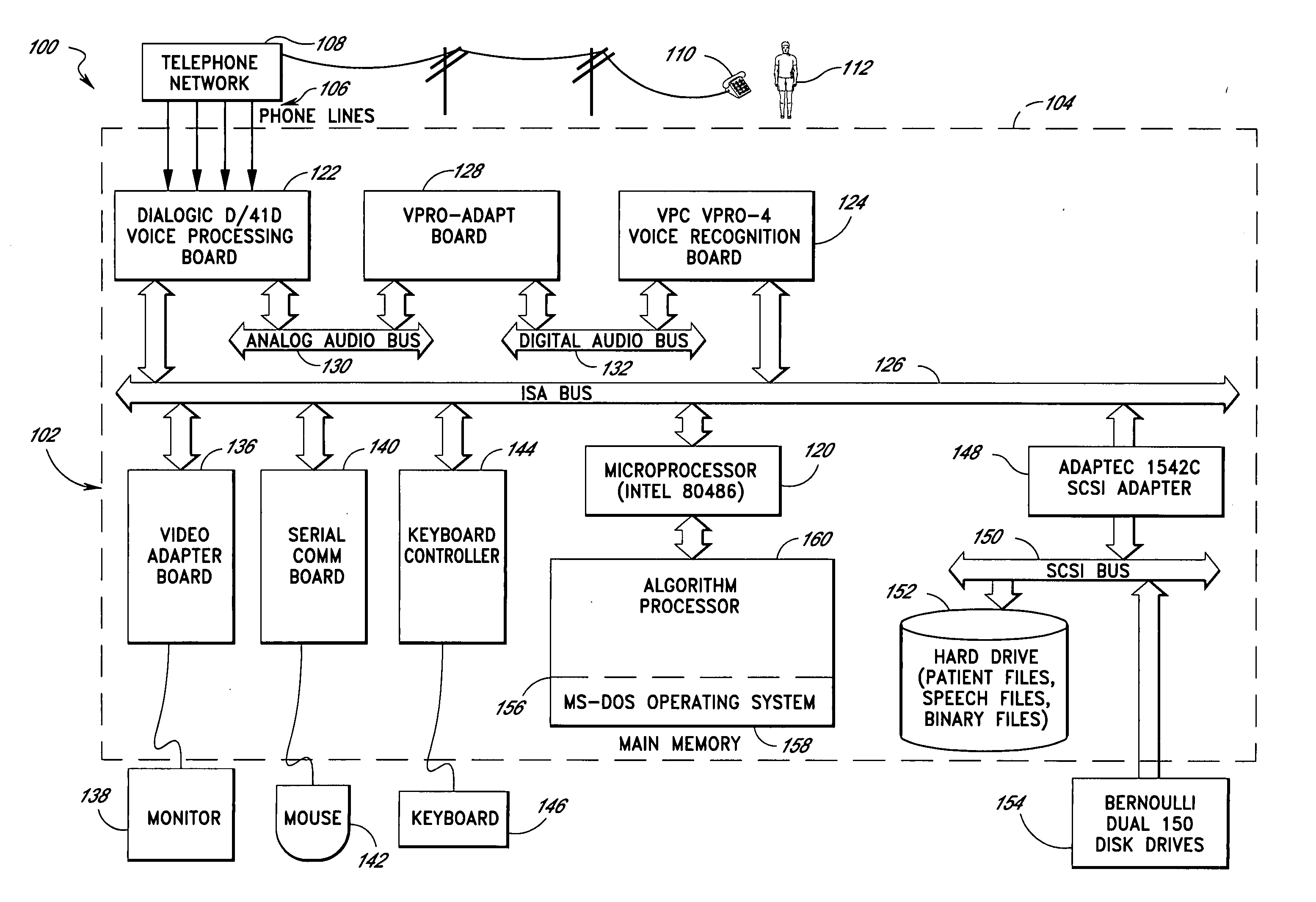
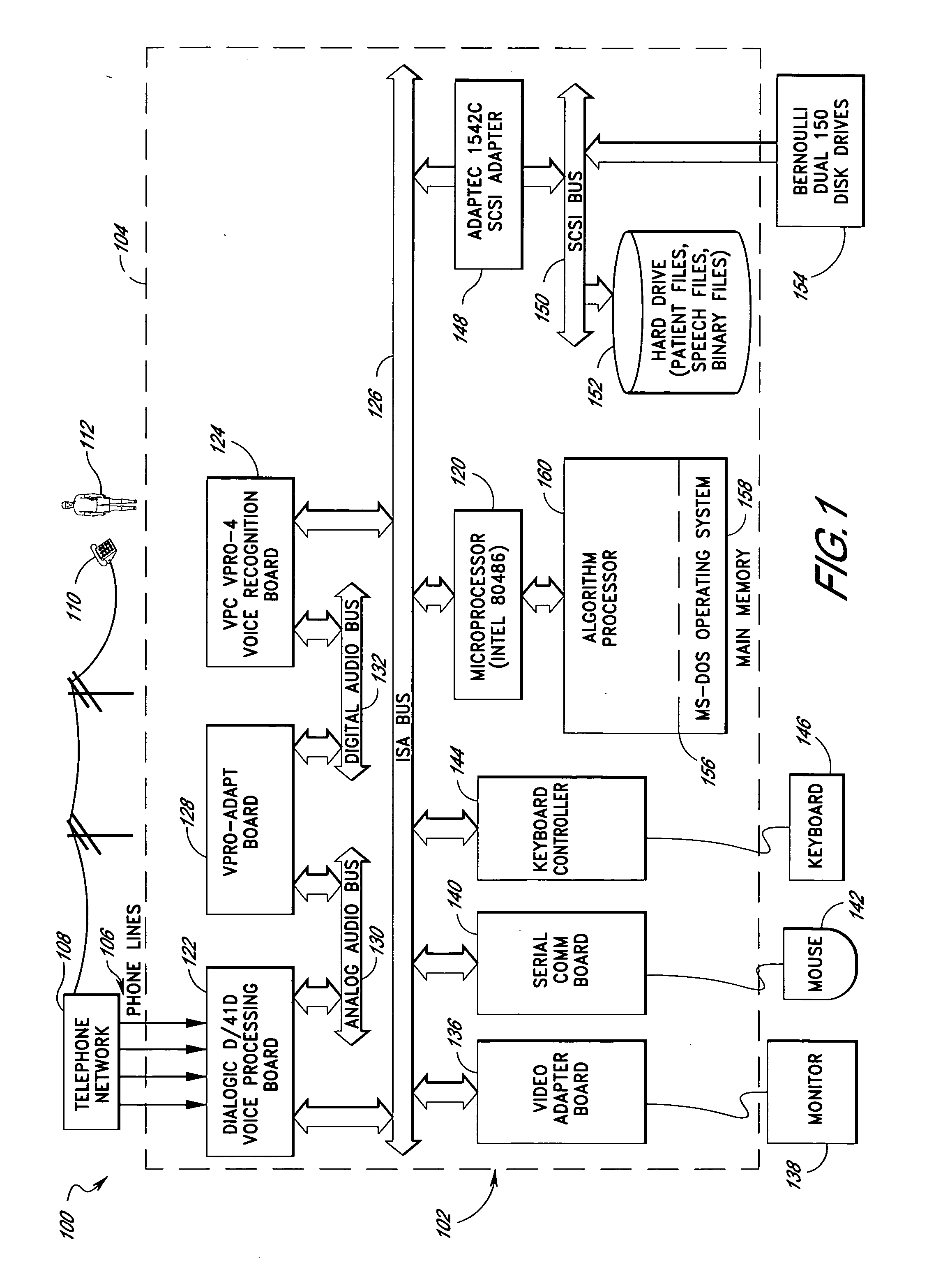
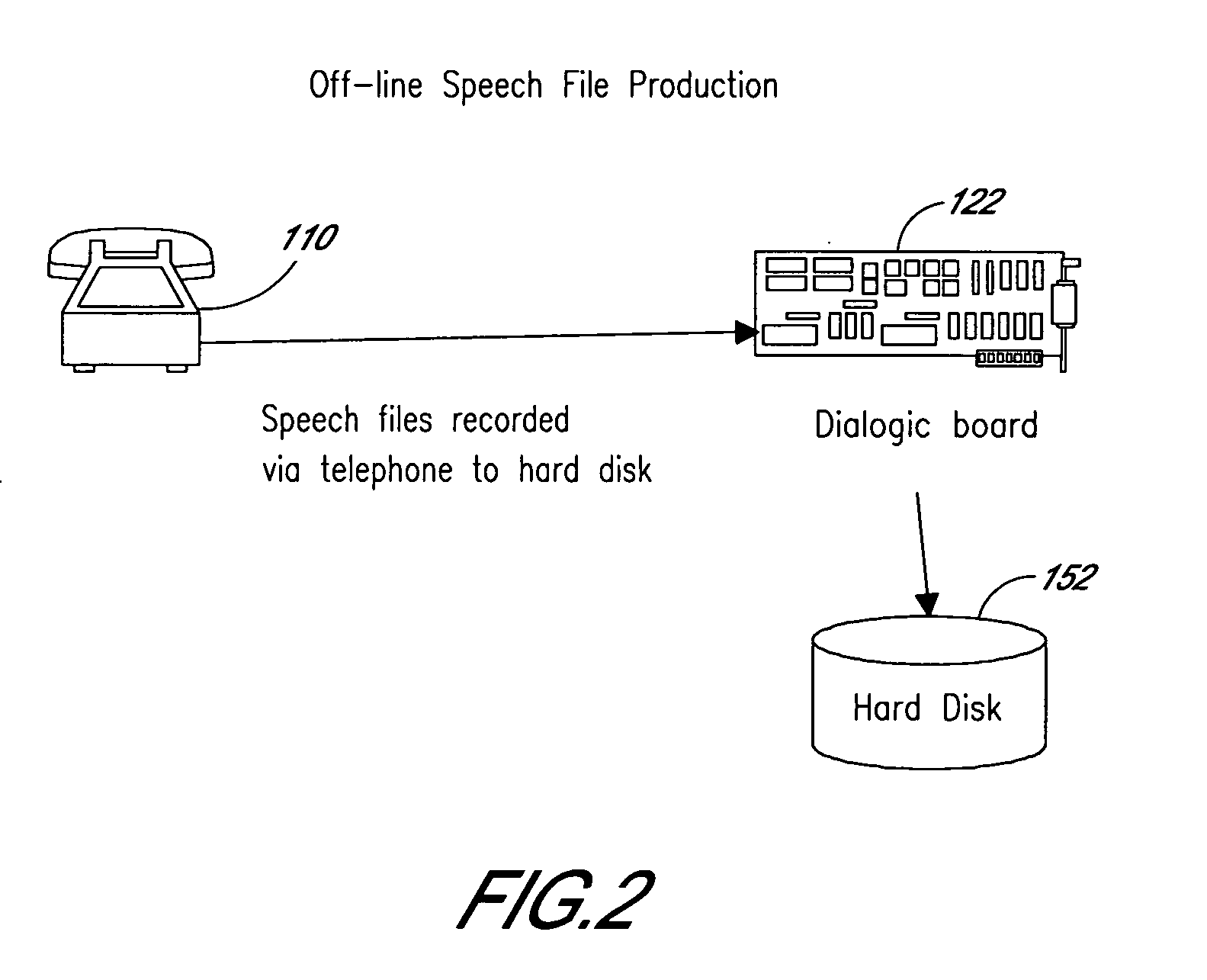
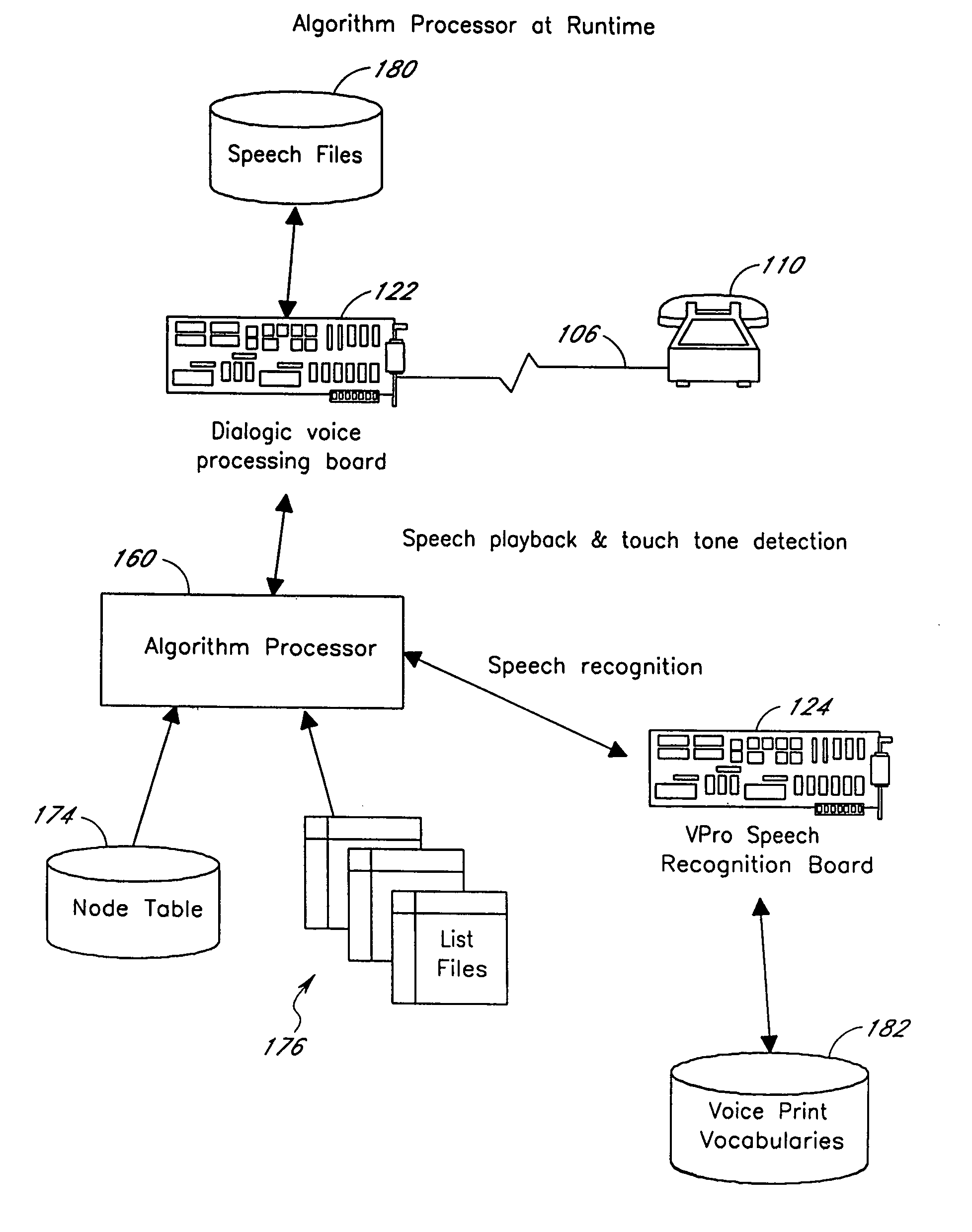
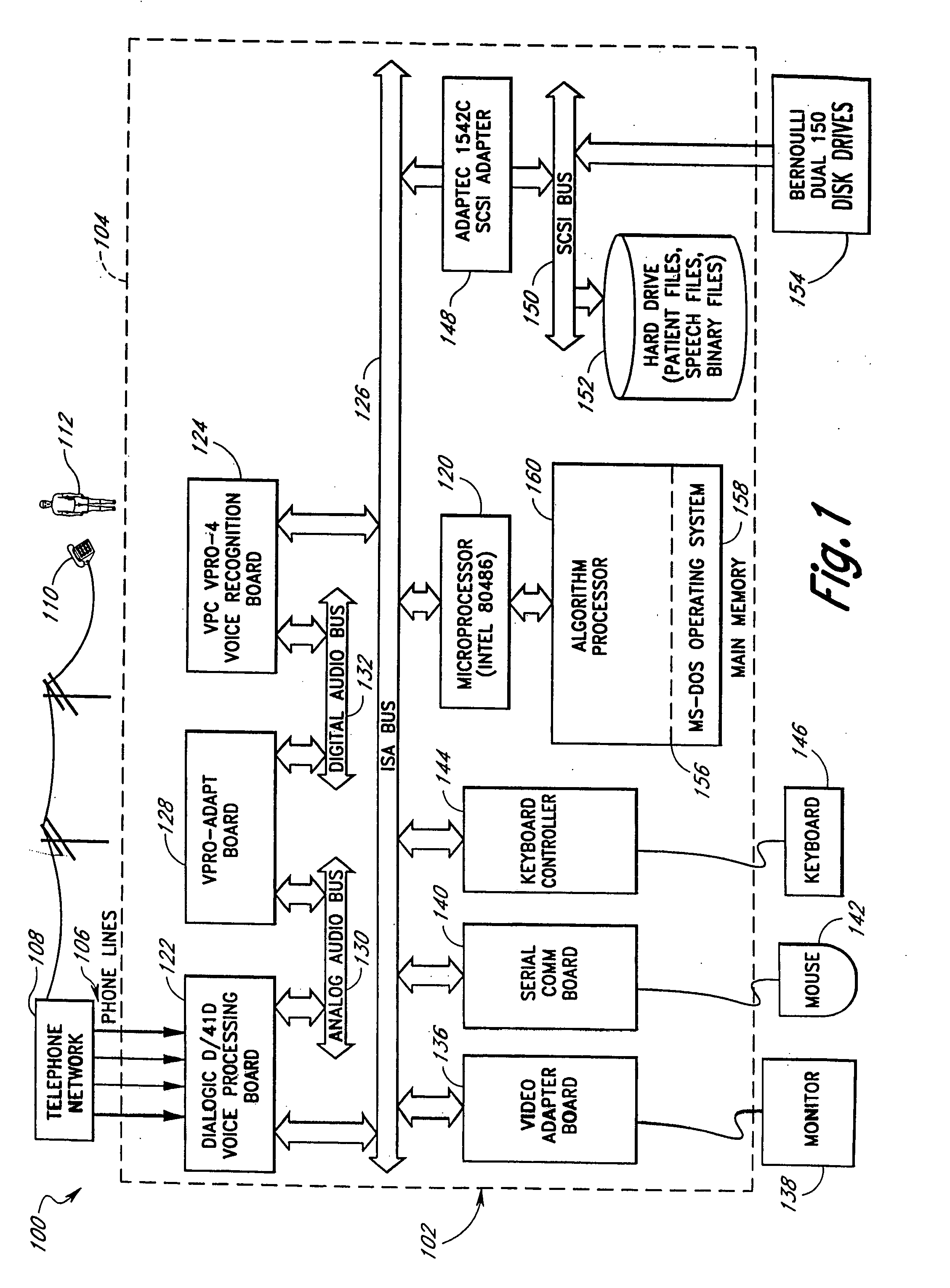
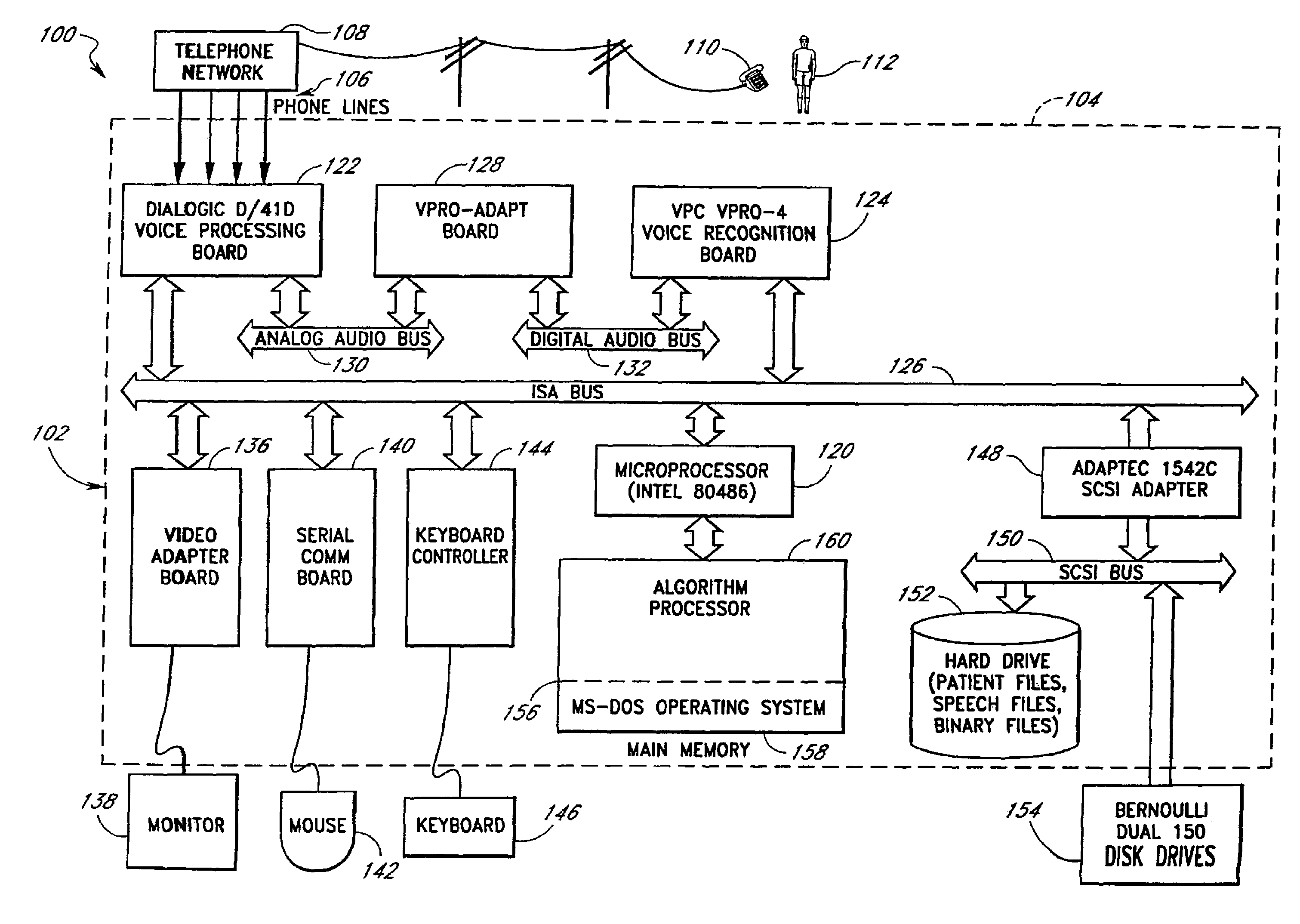
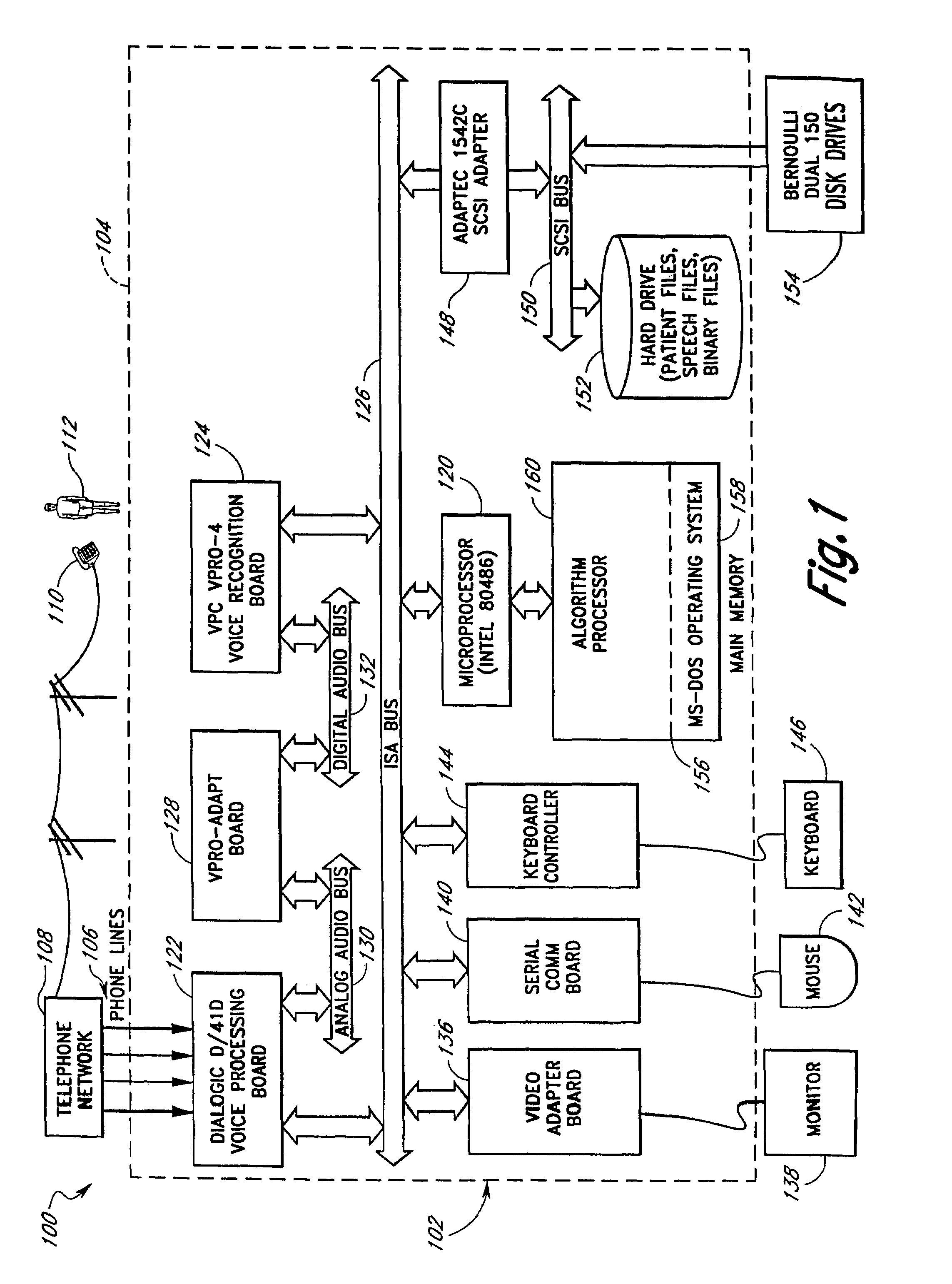
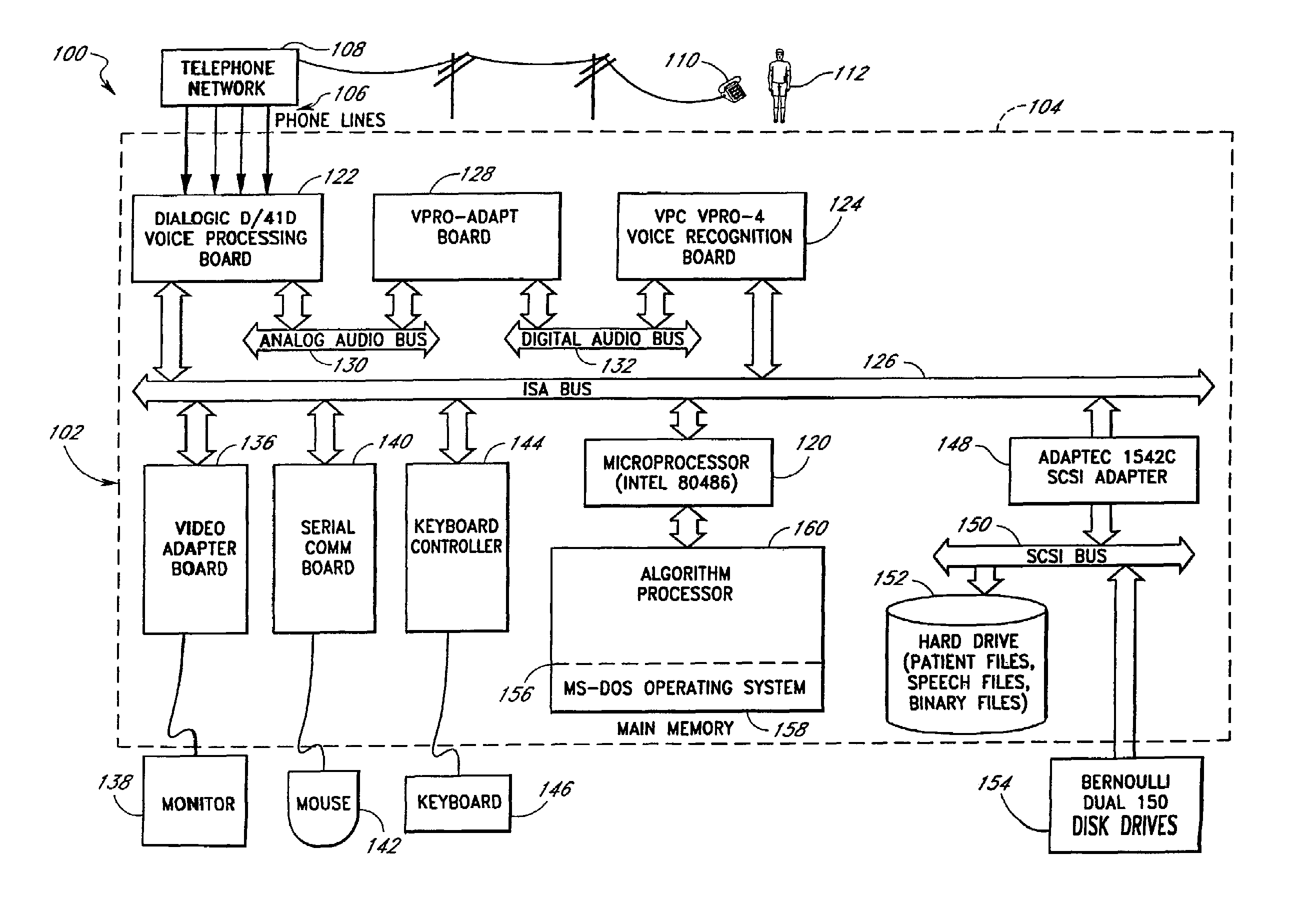
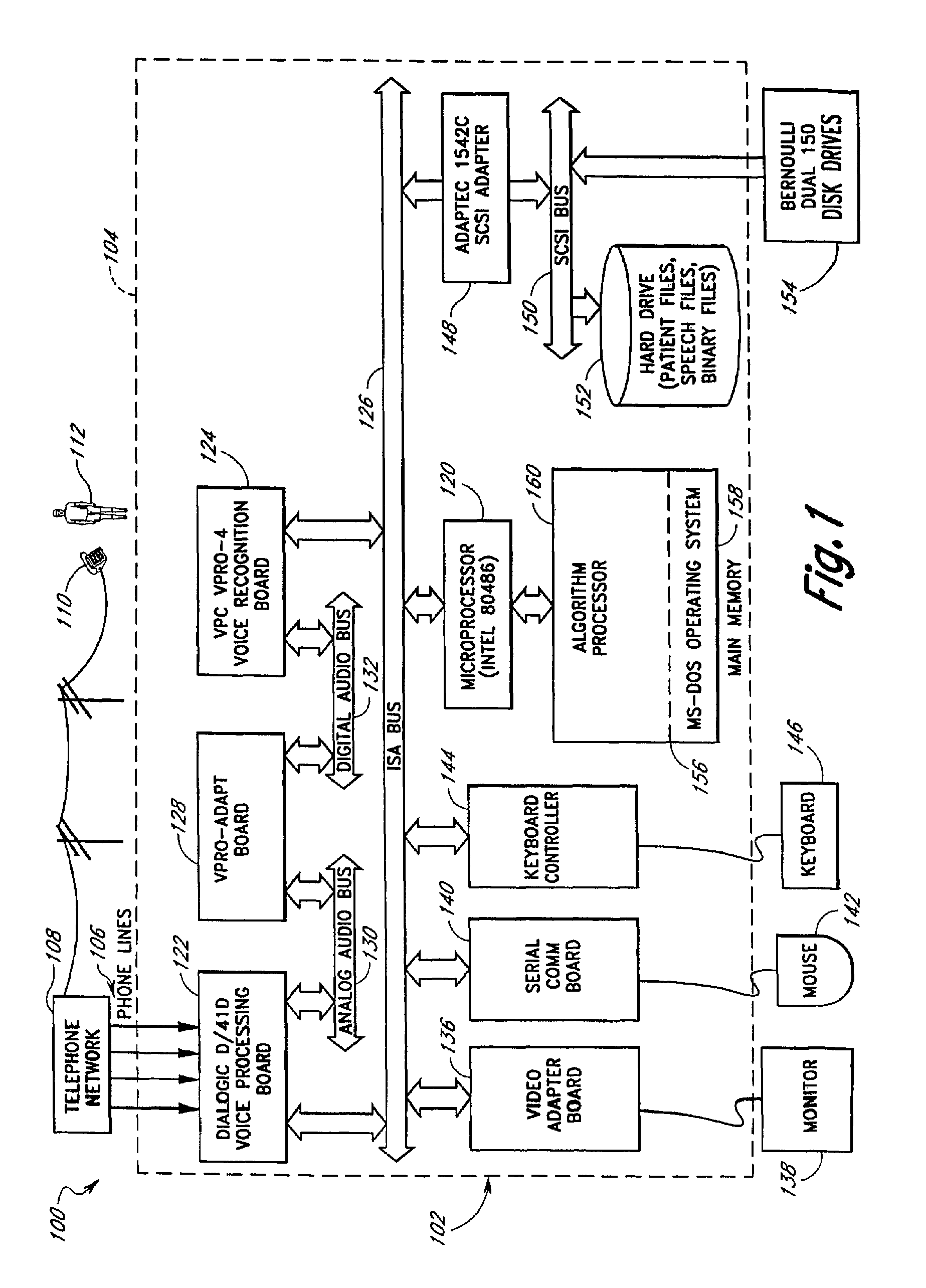
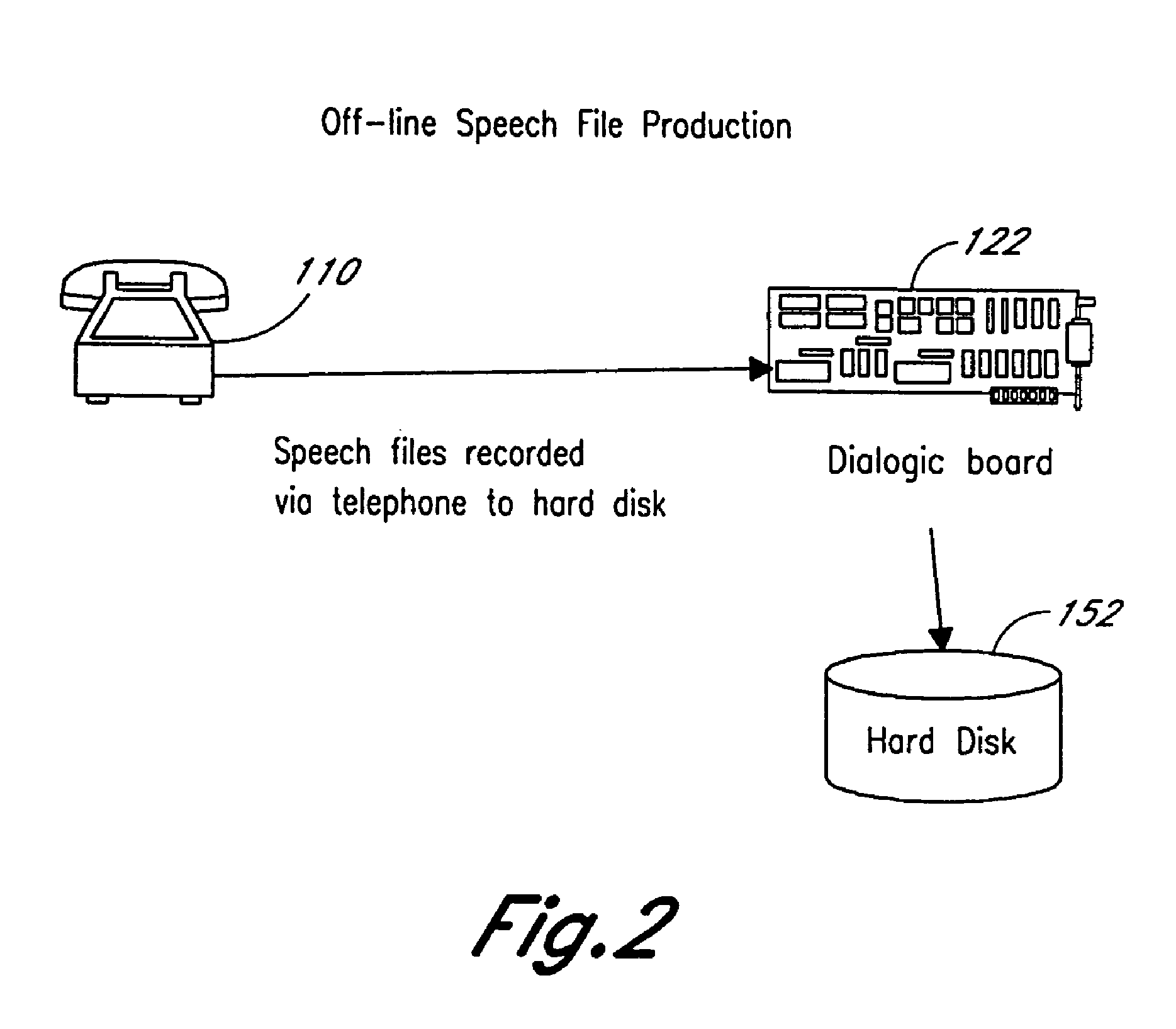
Computerized medical diagnostic and treatment advice system including network access
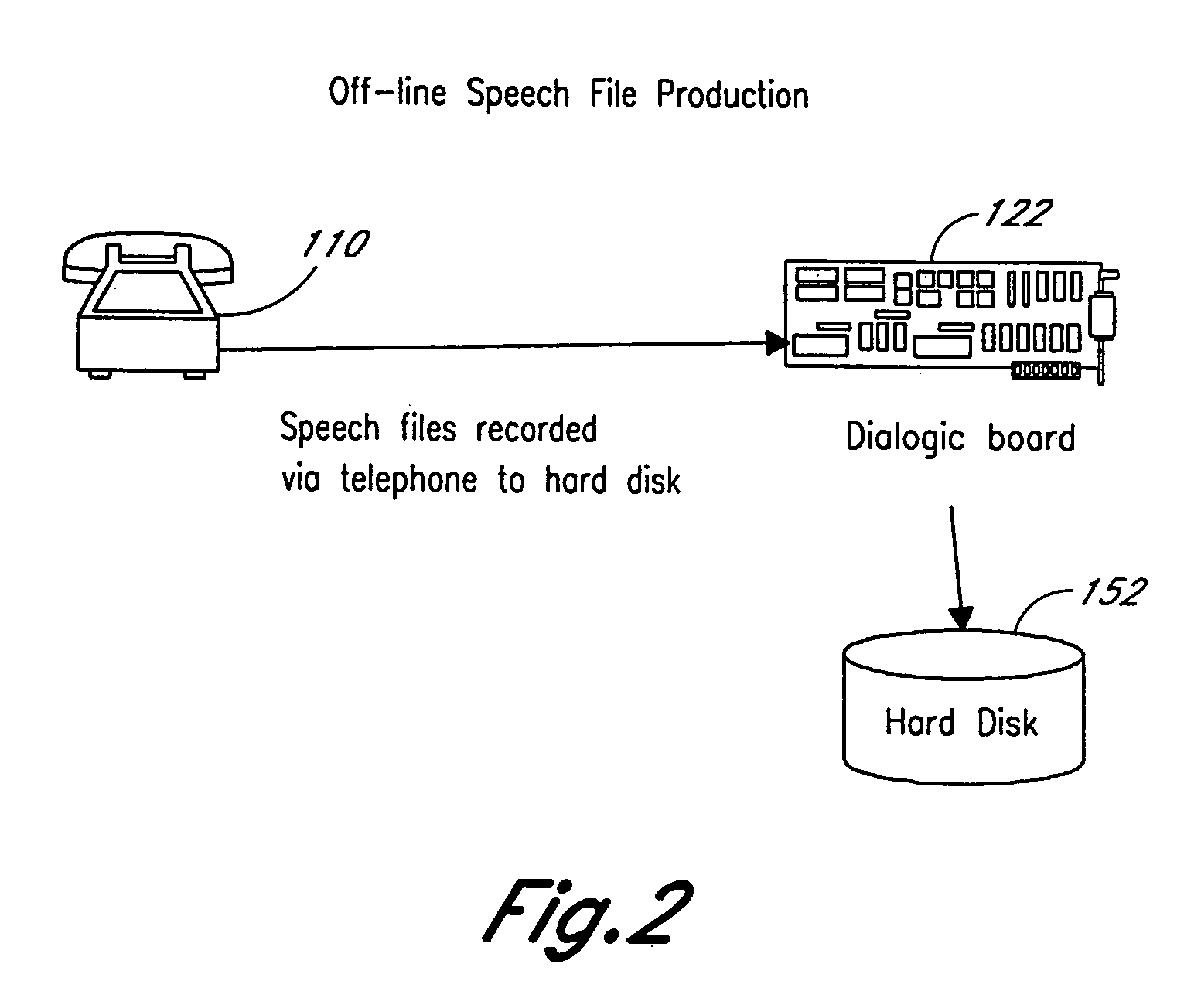
A system and method for providing computerized, knowledge-based medical diagnostic and treatment advice. The medical advice is provided to the general public over networks, such as a telephone network or a computer network. The invention also includes a stand-alone embodiment that may utilize occasional connectivity to a central computer by use of a network, such as the Internet. New authoring languages, interactive voice response and speech recognition are used to enable expert and general practitioner knowledge to be encoded for access by the public. “Meta” functions for time-density analysis of a number of factors regarding the number of medical complaints per unit of time are an integral part of the system. A re-enter feature monitors the user's changing condition over time. A symptom severity analysis helps to respond to the changing conditions. System sensitivity factors may be changed at a global level or other levels to adjust the system advice as necessary.
Owner:CLINICAL DECISION SUPPORT LLC
Computerized medical diagnostic and treatment advice system
InactiveUS20050154616A1Drug and medicationsSurgeryGeneral practionerInteractive Voice Response Technology
A system and method for providing computerized, knowledge-based medical diagnostic and treatment advice. The medical advice is provided to the general public over a telephone network. Two new authoring languages, interactive voice response and speech recognition are used to enable expert and general practitioner knowledge to be encoded for access by the public. “Meta” functions for time-density analysis of a number of factors regarding the number of medical complaints per unit of time are an integral part of the system. A semantic discrepancy evaluator routine along with a mental status examination are used to detect the consciousness level of a user of the system. A re-enter feature monitors the user's changing condition over time. A symptom severity analysis helps to respond to the changing conditions. System sensitivity factors may be changed at a global level or other levels to adjust the system advice as necessary.
Owner:CLINICAL DECISION SUPPORT LLC
System and method for analysis and transformation of layouts using situations
ActiveUS7418693B1Efficient executionCAD circuit designTotal factory controlDensity analysisIntegrated circuit layout
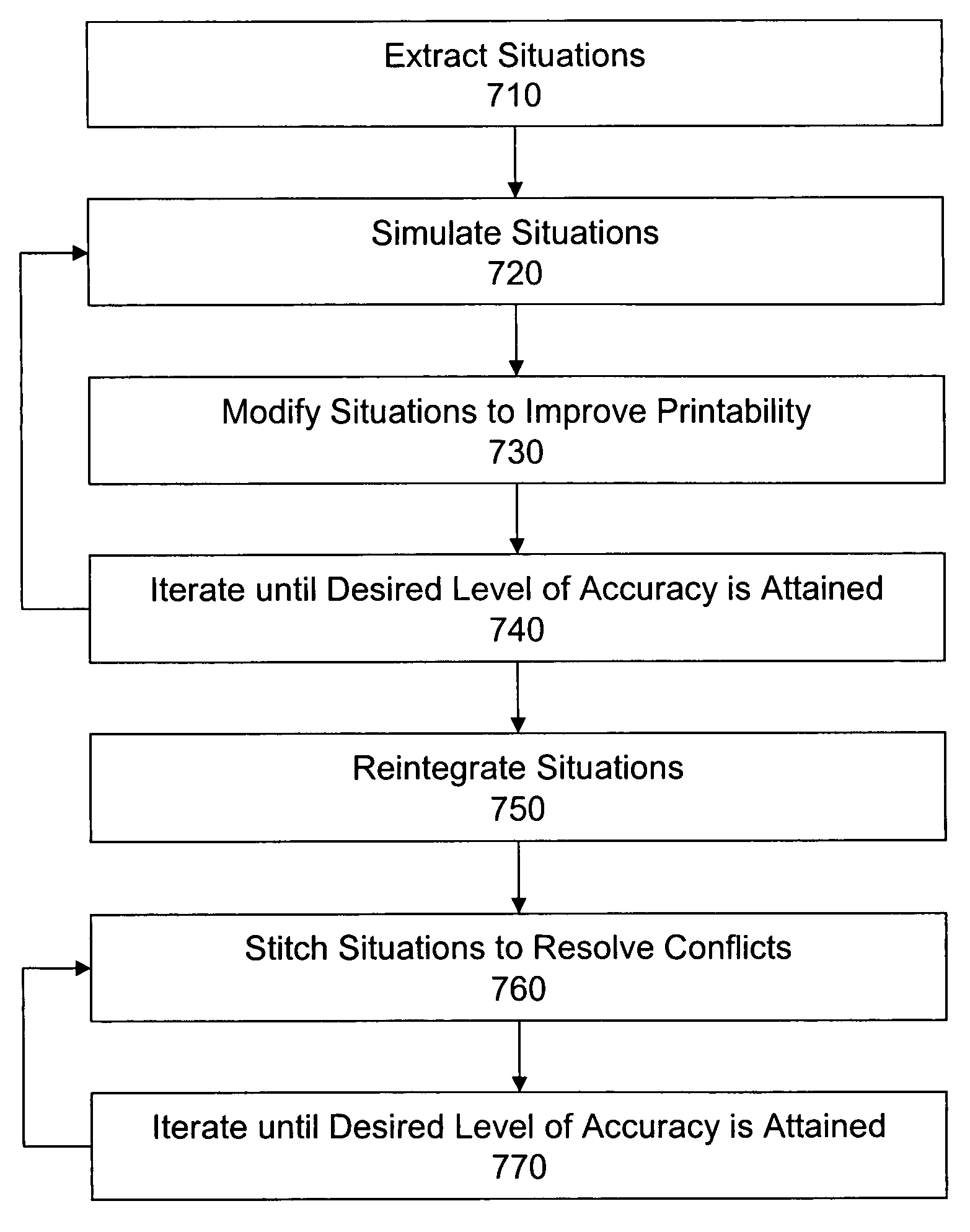
Systems, methodologies and technologies for the analysis and transformation of integrated circuit layouts using situations are disclosed. A method for transforming an integrated circuit (IC) layout includes recognizing shapes within the IC layout, identifying features for each of the shapes and extracting situations for the respective features. Extracted situations can be used to improve optical proximity correction (OPC) of the IC layout. This improved OPC includes extracting the situations, simulating the situations to determine a set of the situations identified for modification based on failing to satisfy a desired OPC tolerance level, modifying the set of situations to improve satisfaction of the desired OPC tolerance level, and reintegrating the modified set of situations into the IC layout. Extracted situations can also be used to improve aerial image simulation of the IC layout. This improved aerial image simulation includes extracting the situations, simulating a subset of the situations to determine aerial images of the subset, and tiling the subset of situations to form a larger aerial image. Extracted situations can further be used to improve density analysis of the IC layout. This improved density analysis includes extracting the situations for a window of the IC layout, removing overlap from the window based on the extracted situations, calculating a density for each of the situations, and calculating a density for the window based on the density for each of the situations.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Computerized medical diagnostic and treatment advice system
A system and method for providing computerized, knowledge-based medical diagnostic and treatment advice. The medical advice is provided to the general public over a telephone network. Two new authoring languages, interactive voice response and speech recognition are used to enable expert and general practitioner knowledge to be encoded for access by the public. “Meta” functions for time-density analysis of a number of factors regarding the number of medical complaints per unit of time are an integral part of the system. A semantic discrepancy evaluator routine along with a mental status examination are used to detect the consciousness level of a user of the system. A re-enter feature monitors the user's changing condition over time. A symptom severity analysis helps to respond to the changing conditions. System sensitivity factors may be changed at a global level or other levels to adjust the system advice as necessary.
Owner:CLINICAL DECISION SUPPORT LLC
Cloth defect detecting method based on machine vision
InactiveCN102706881AReduce the numberEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPattern recognitionMachine vision
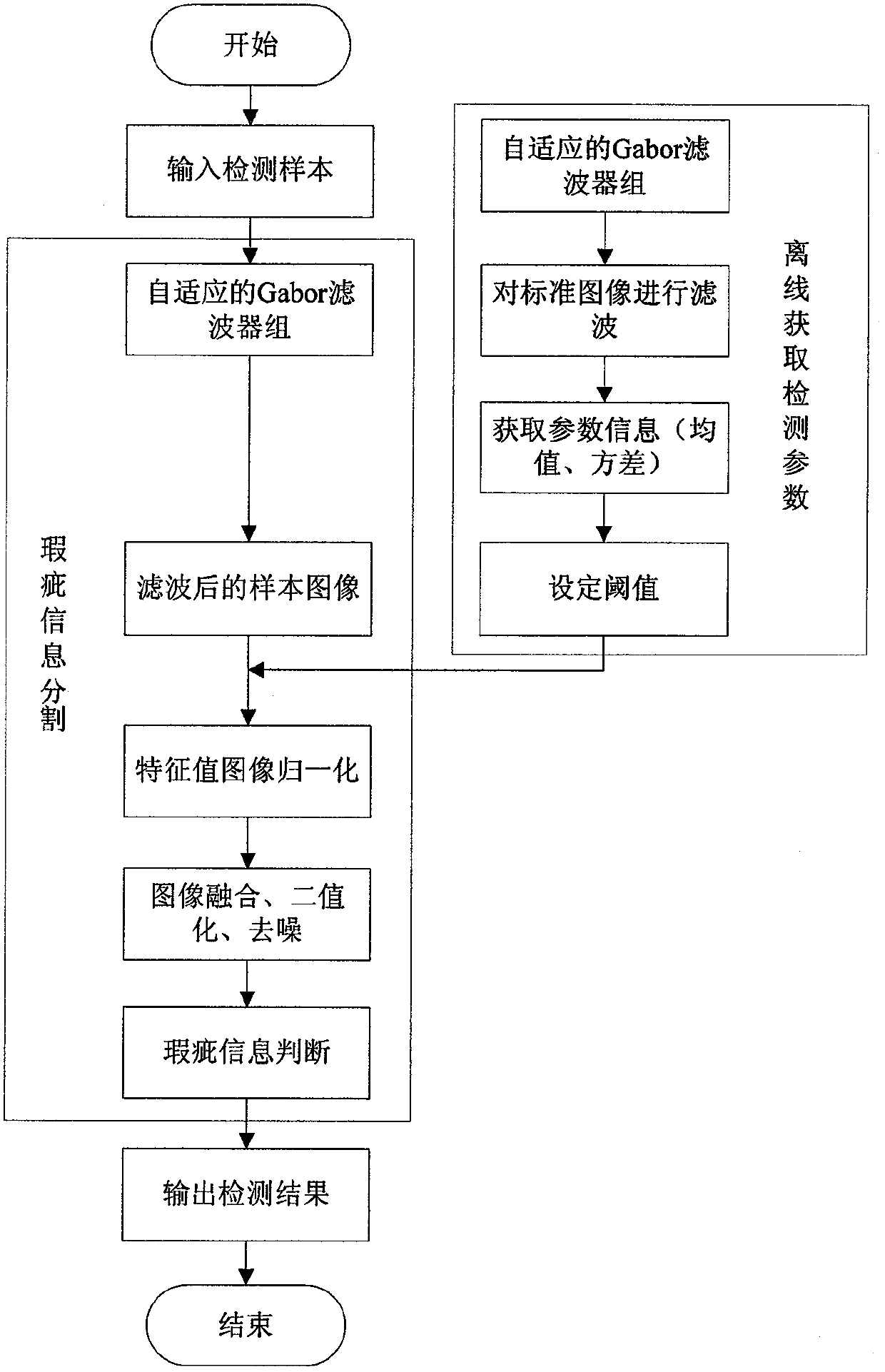
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing and pattern recognition, and relates to a cloth defect detecting method based on machine vision. The cloth defect detecting method includes performing power spectral density analysis for an image of a normal cloth texture and acquiring central frequency F and an azimuthal angle theta of the texture; constructing an SXL adaptive Gabor filter bank; filtering the image of the normal cloth texture to obtain a feature image group, and computing the mean value and the variance of each image of the feature image group; acquiring an image of to-be-detected cloth; filtering the image of the to-be-detected cloth to obtain a feature image group; performing threshold post-processing for the feature image group of the image of the to-be-detected cloth to obtain an absolute feature image group; carrying out normalization processing; fusing images and performing binarization processing for the images to obtain a detected binary image; and removing noise interference to obtain a final detection result. The S represents the number of the selected central frequency, and the L represents the number of the selected azimuthal angle. The cloth defect detecting method has the advantages of high universality and efficiency.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Dynamic population distribution density detecting method based on mobile phone positioning data
InactiveCN102609616ARealize detectionLocation information based serviceSpecial data processing applicationsArea coverageMobile communication network
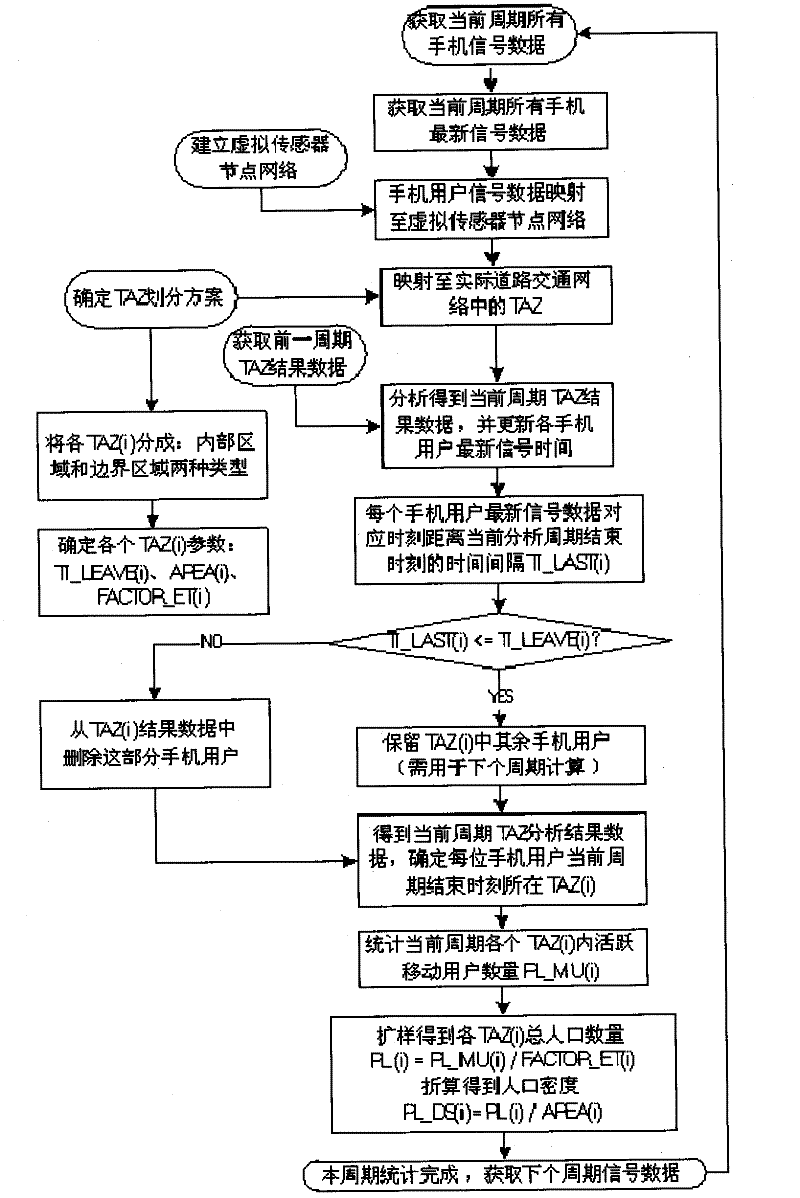
The invention provides a dynamic population distribution density detecting method based on mobile phone positioning data, which is characterized by including the steps: dividing an analysis area coverage, needing population distribution density analysis, of a target city into different subareas, subsequently, establishing a virtual sensor network, obtaining the mapping relation between each subarea and the virtual sensor network, and obtaining a sum of the population in each subarea according to mobile phone signals. The dynamic population distribution density detecting method based on the mobile phone positioning data has the advantage that dynamic population distribution density detection is realized by fully depending on existing mobile communication network resources, utilizing mass mobile phone signal data as input and employing a distinguishing mechanism based on traveling track continuous tracking and stay duration time in the area. The method can be used for automatically detecting population distribution density information at a high frequency.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEIHUI SOFTWARE
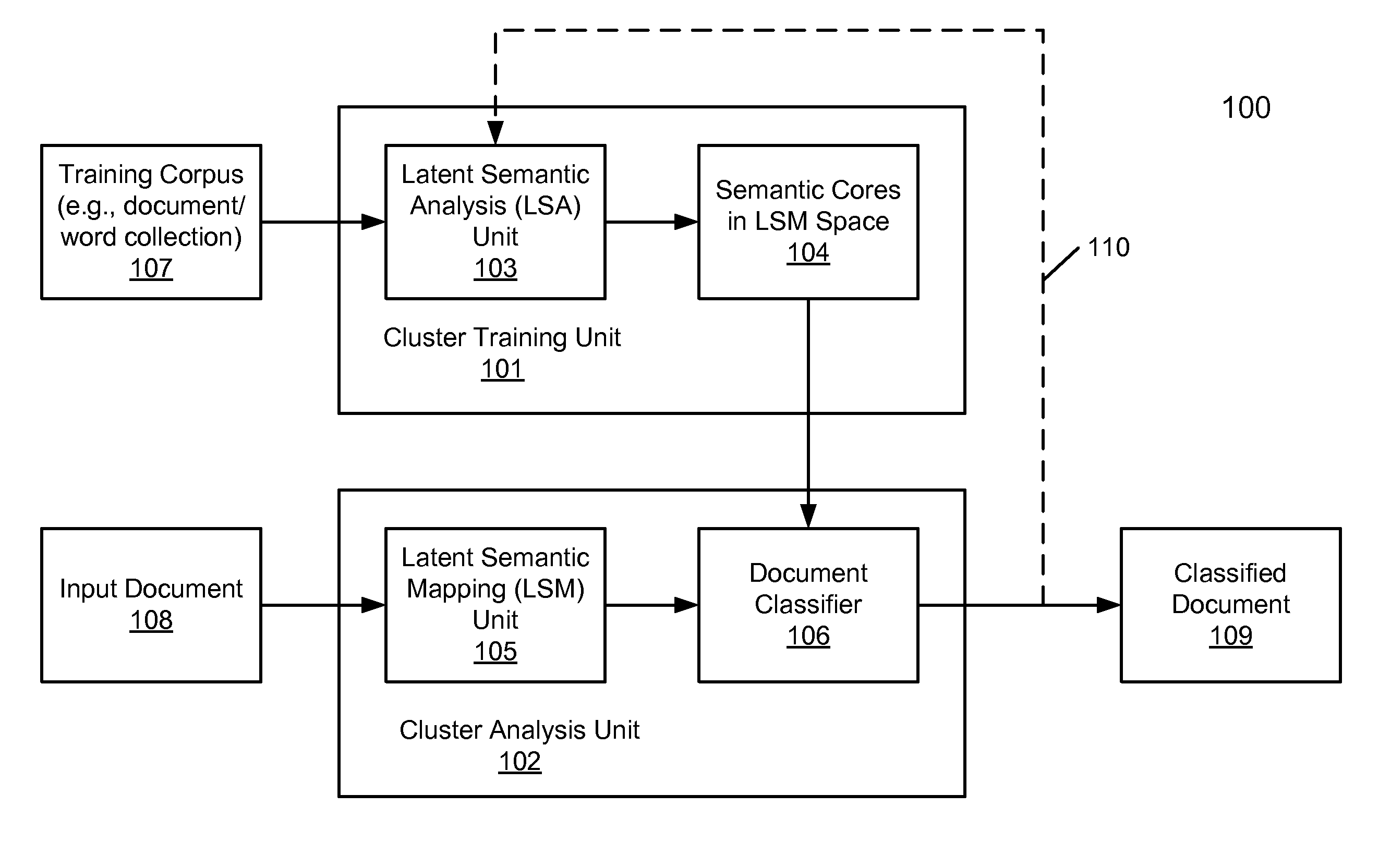
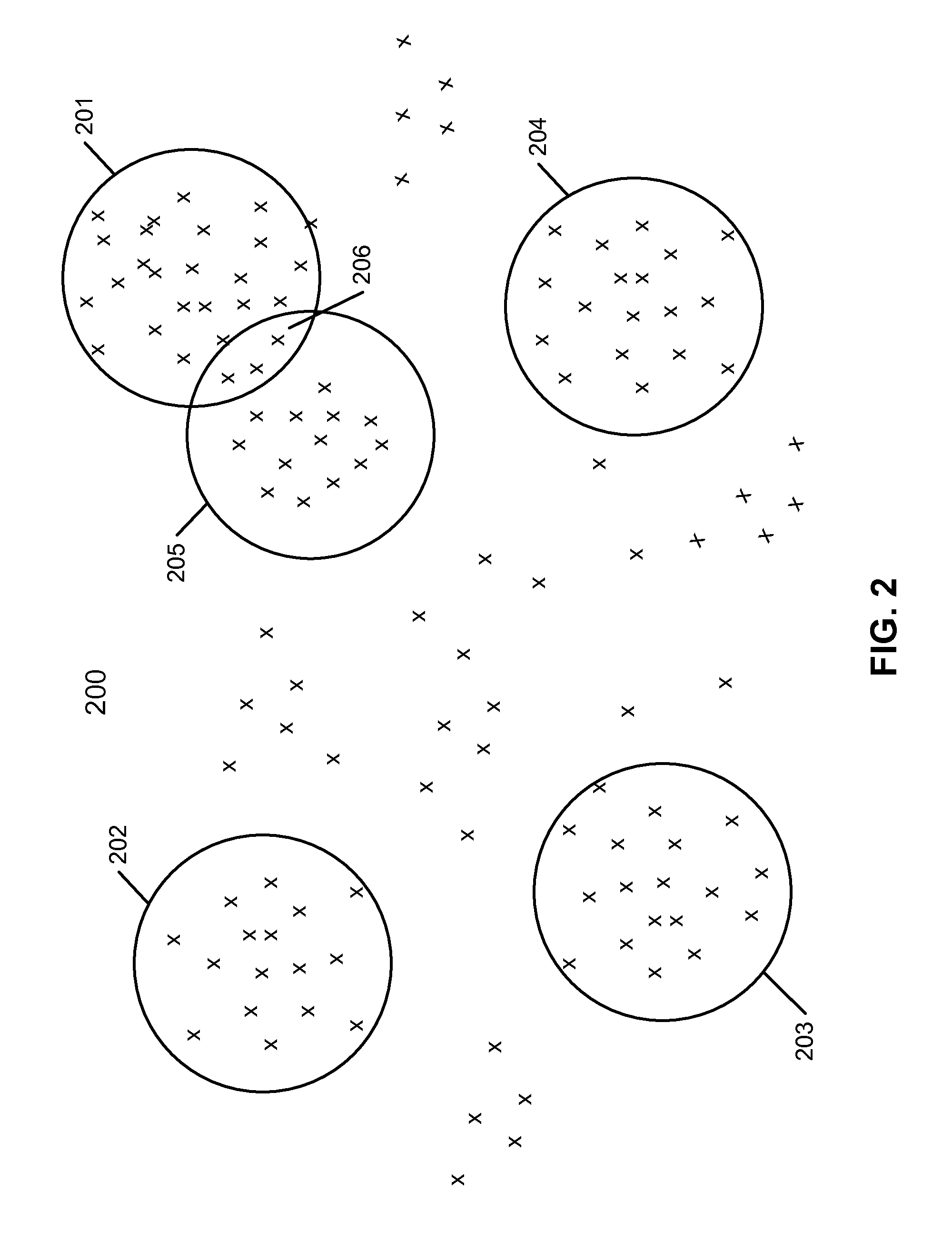
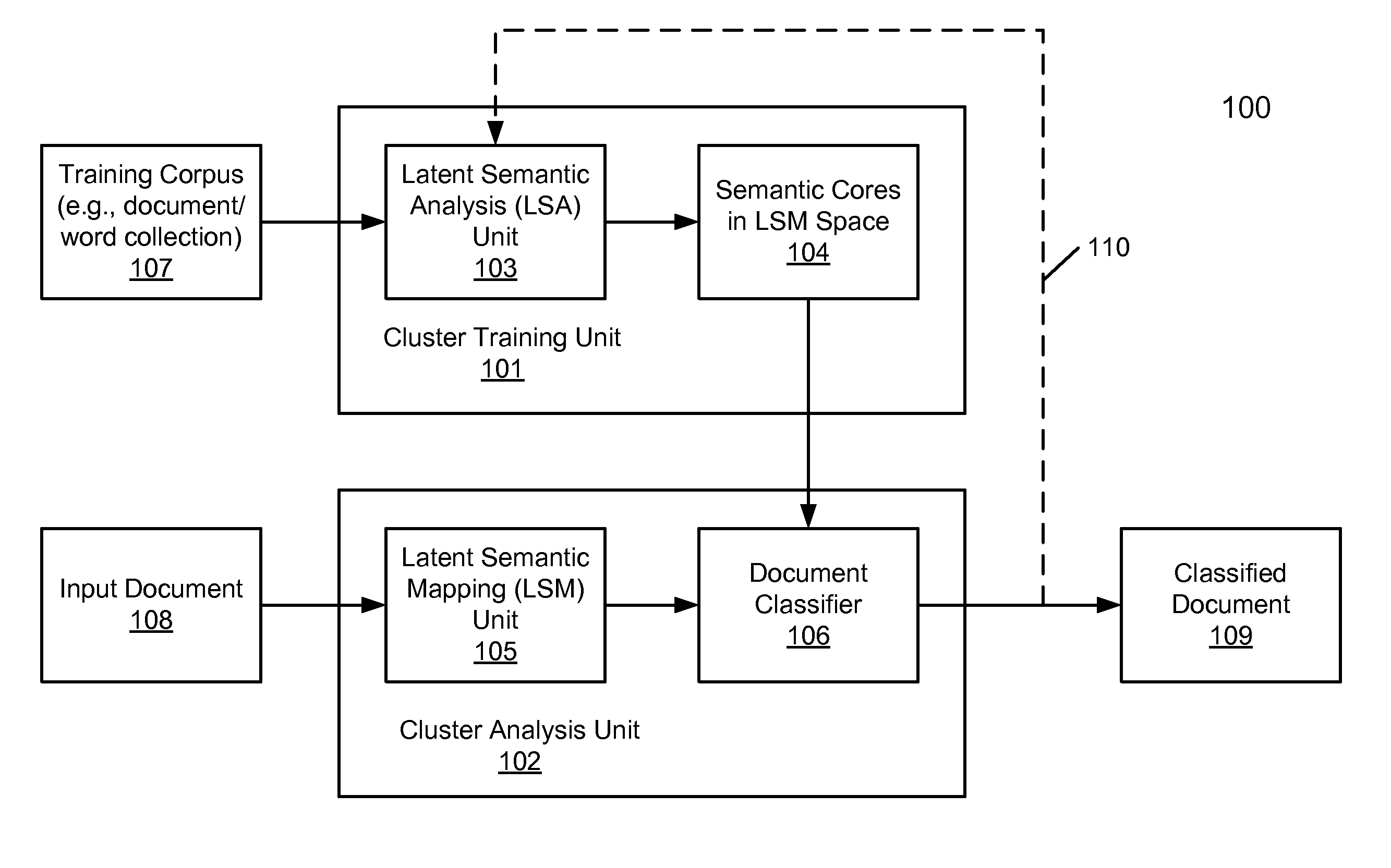
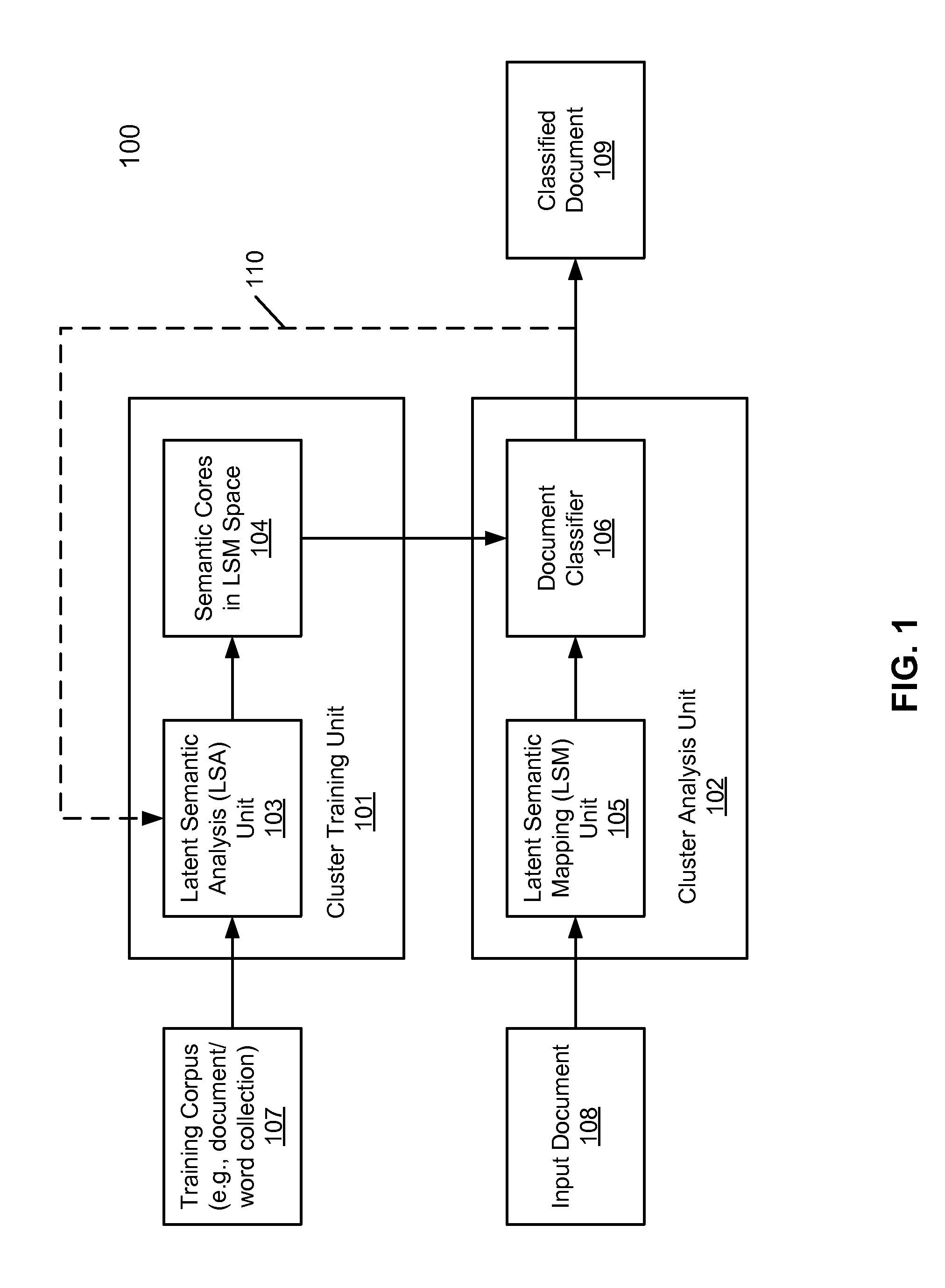
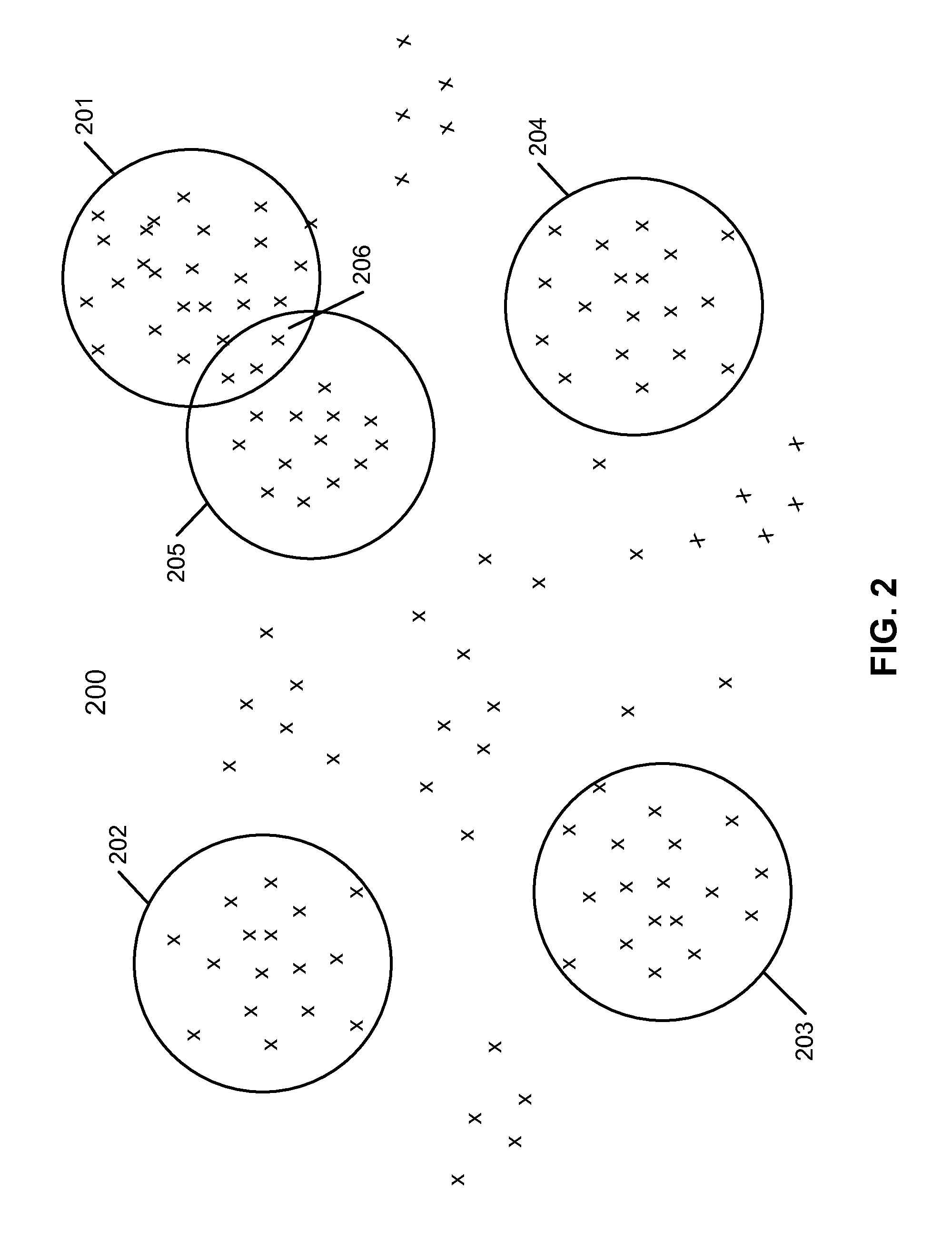
Unsupervised document clustering using latent semantic density analysis
ActiveUS20120011124A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsHypersphereDensity analysis
According to one embodiment, a latent semantic mapping (LSM) space is generated from a collection of a plurality of documents, where the LSM space includes a plurality of document vectors, each representing one of the documents in the collection. For each of the document vectors considered as a centroid document vector, a group of document vectors is identified in the LSM space that are within a predetermined hypersphere diameter from the centroid document vector. As a result, multiple groups of document vectors are formed. The predetermined hypersphere diameter represents a predetermined closeness measure among the document vectors in the LSM space. Thereafter, a group from the plurality of groups is designated as a cluster of document vectors, where the designated group contains a maximum number of document vectors among the plurality of groups.
Owner:APPLE INC
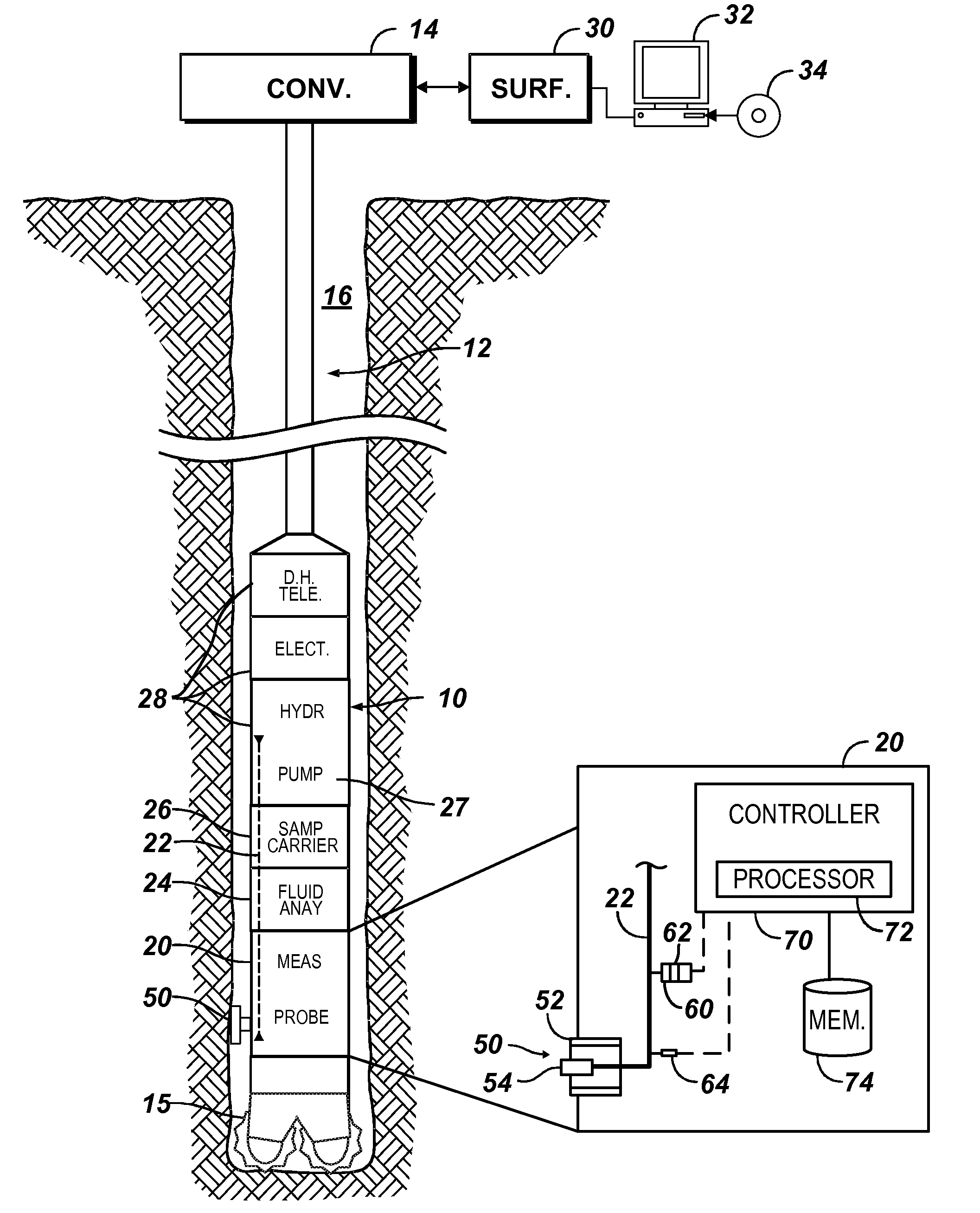
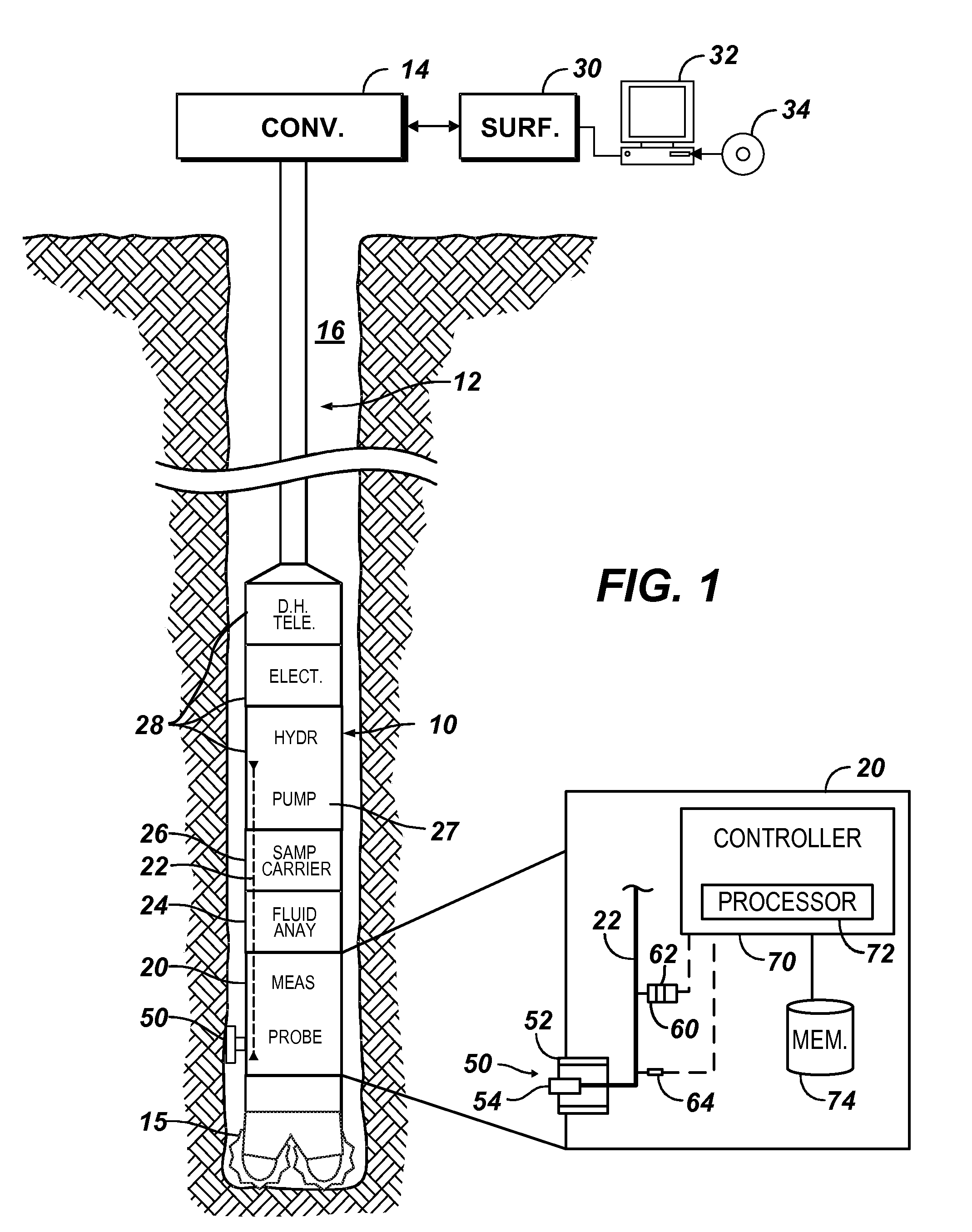
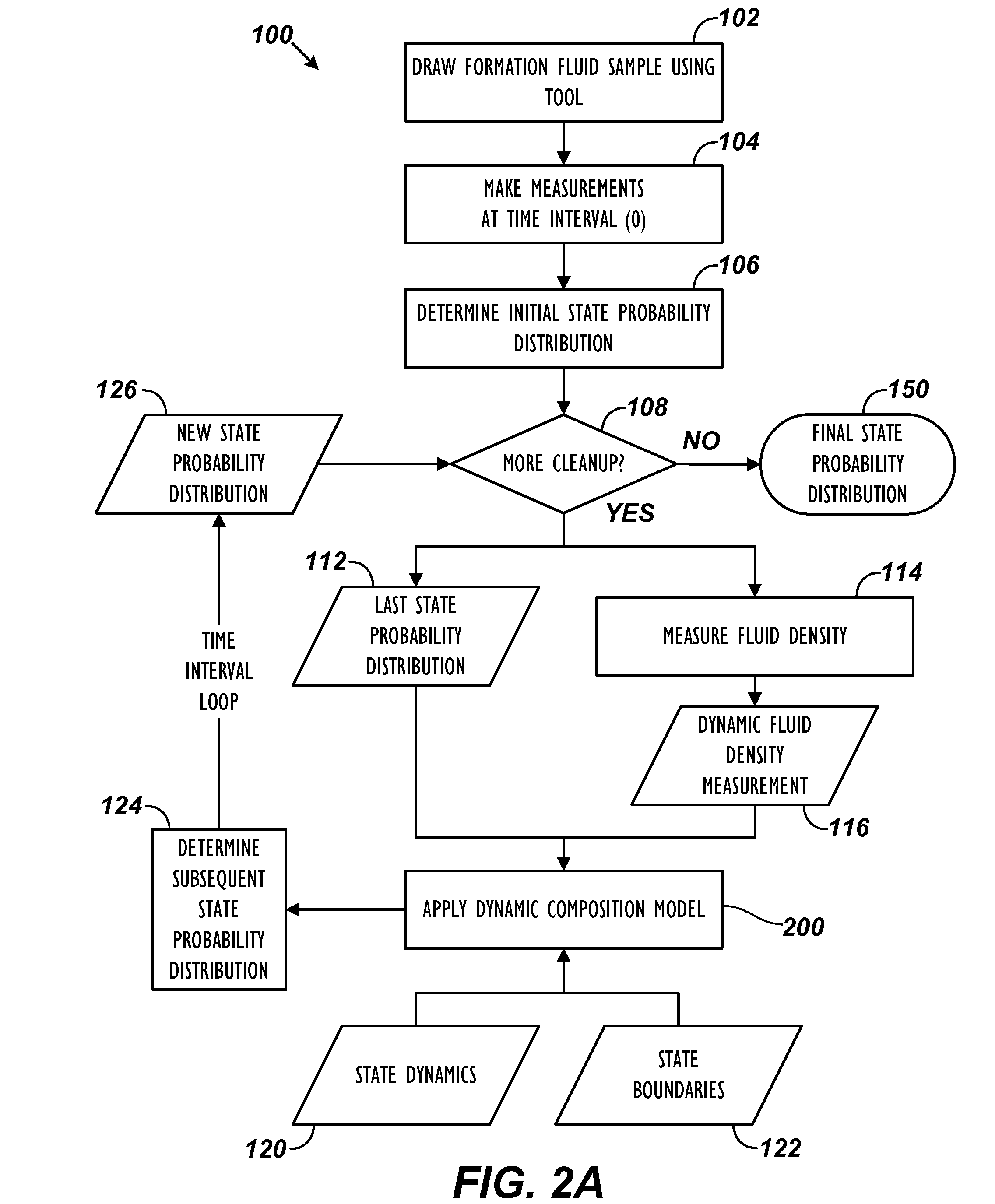
Real-Time Determination of Formation Fluid Properties Using Density Analysis
ActiveUS20140278113A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisDensity analysisFormation fluid
Analysis evaluates formation fluid with a downhole tool disposed in a borehole. A plurality of possible constituents is defined for the formation fluid, and constraints are defined for the possible constituents. The constraints can include boundary constraints and constraints on the system's dynamics. The formation fluid is obtained from the borehole with the downhole tool over a plurality of time intervals, and density of the obtained formation fluid is obtained at the time intervals. To evaluate the fluid composition, a state probability distribution of the possible constituents of the obtained formation fluid at the current time interval is computed recursively from that at the previous time interval and by assimilating the current measured density of the obtained formation fluid in addition to the defined boundary / dynamic constraints. The probabilistic characterization of the state of the possible constituents allows, in turn, the probabilistic inference of formation properties such as contamination level and GOR.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
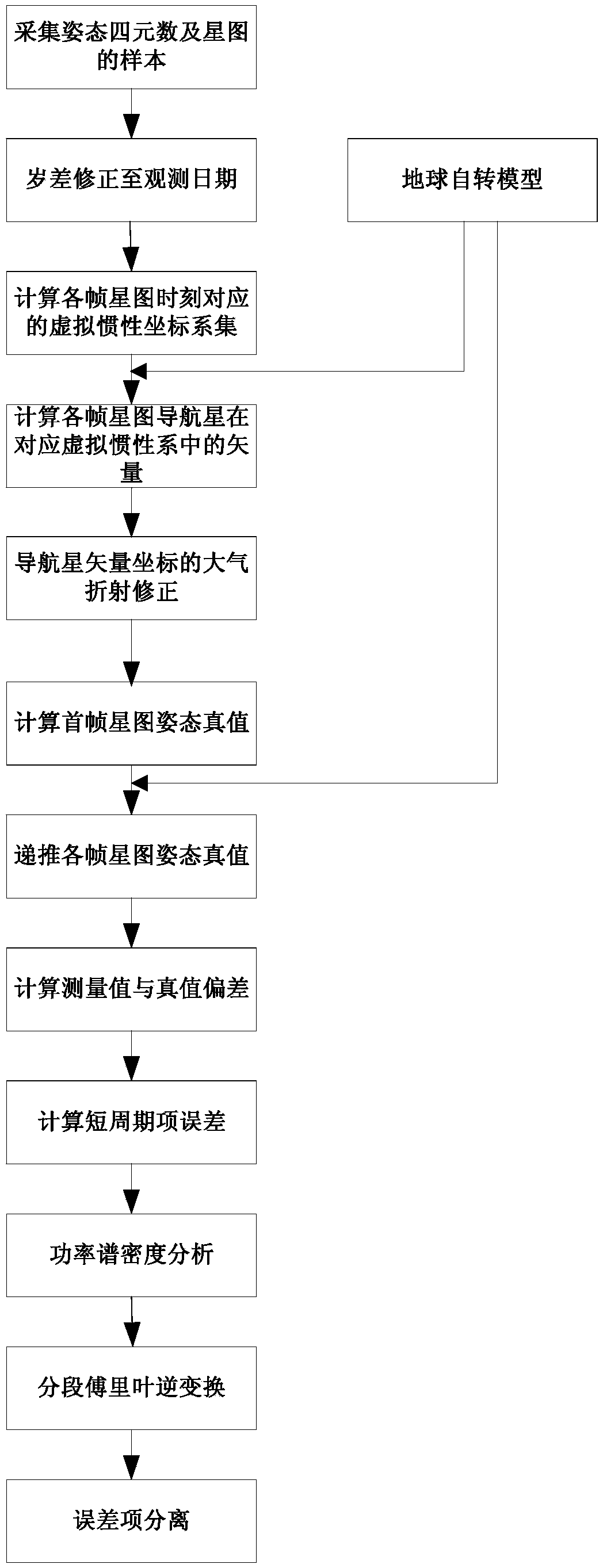
Outfield precision testing method for high-precision star sensor
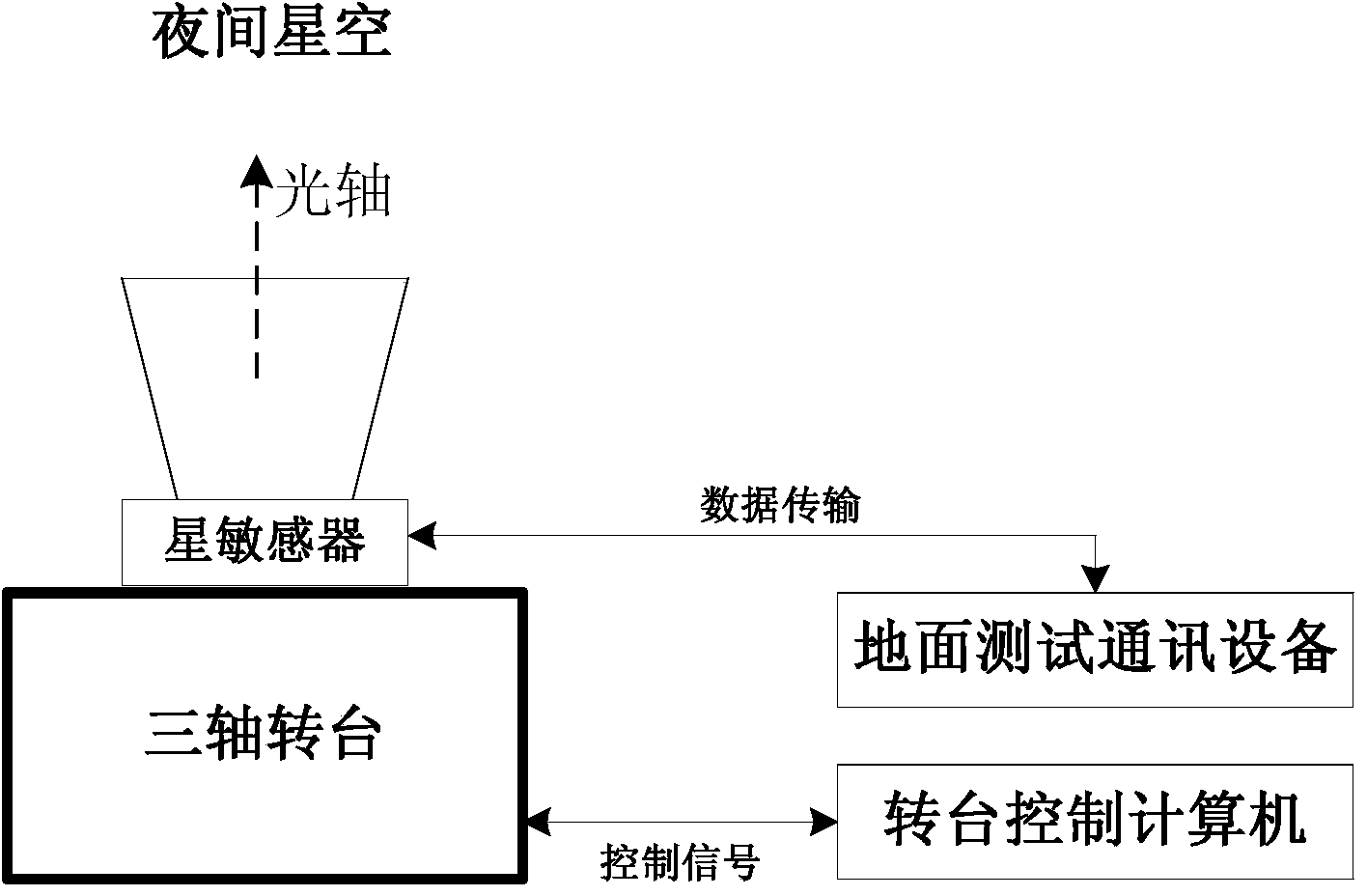
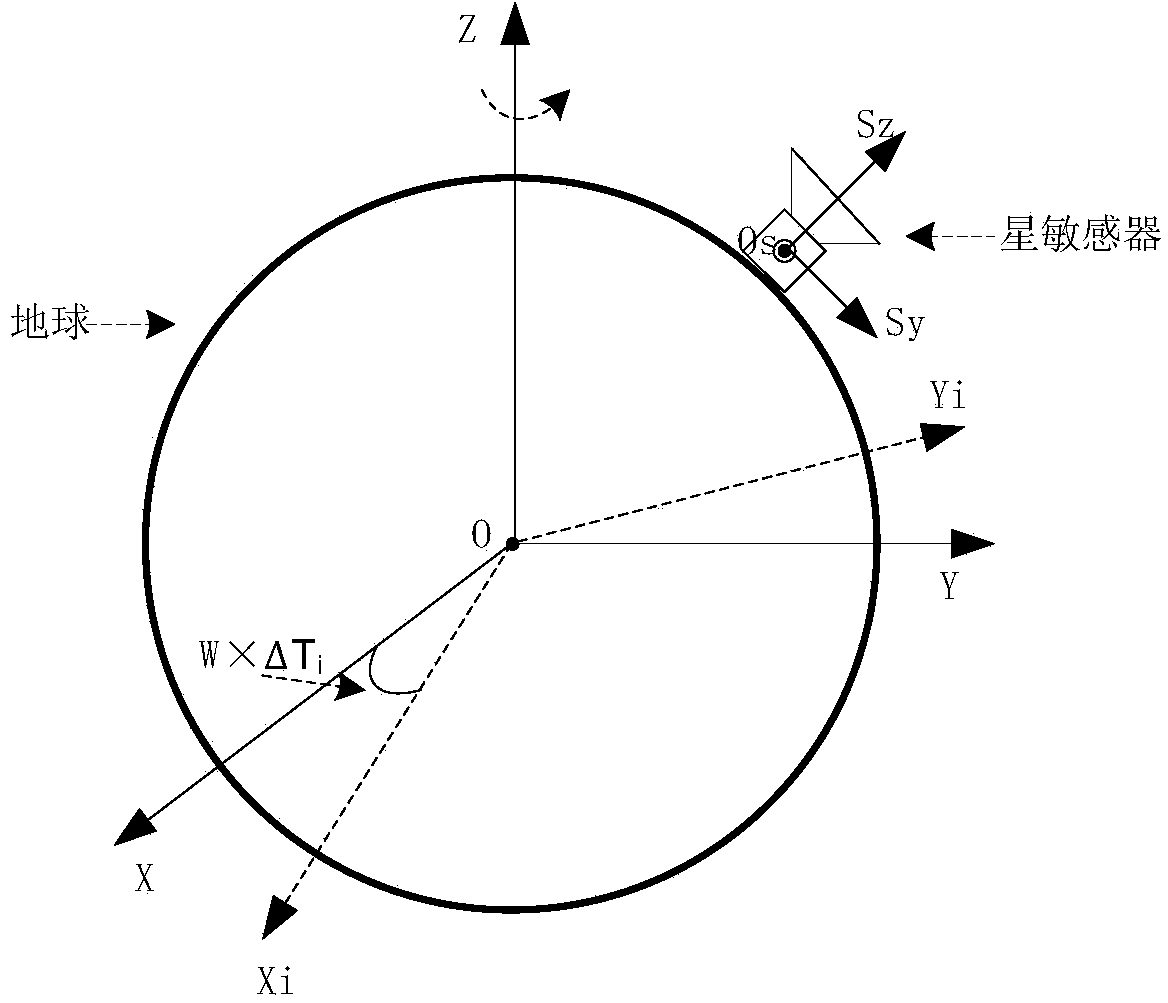
ActiveCN104280049AAchieving Frequency Domain StrippingAccurate calculationNavigation by astronomical meansStar patternObservational error
The invention discloses an outfield precision testing method for a high-precision star sensor. Accuracy in calculation of a star pattern posture of the star sensor and frequency domain stripping of short-period error terms of the posture are realized by utilizing a procession correction formula, an earth rotation model, an atmosphere correction model and a power spectral density formula, and the posture measuring error of the star sensor can be rapidly and effectively analyzed and evaluated. According to the method, the hardware resource is not occupied, the method is realized by utilizing software and does not need the ground intervention. According to the method, by combining the posture identification principle of the star sensor and adopting a data smoothing method, the posture truth value of each frame star pattern moment is calculated, so that a foundation is established for the subsequent analysis on the posture measuring error; by adopting the method for combining the time domain and the frequency domain, the short-period error term is decomposed into an airspace low-frequency error, a high-frequency error and a time-domain error by virtue of the power spectral density analysis, so that reasonable data support is provided for further evaluation of the precision indexes of the star sensor, and the index performance of the star sensor can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
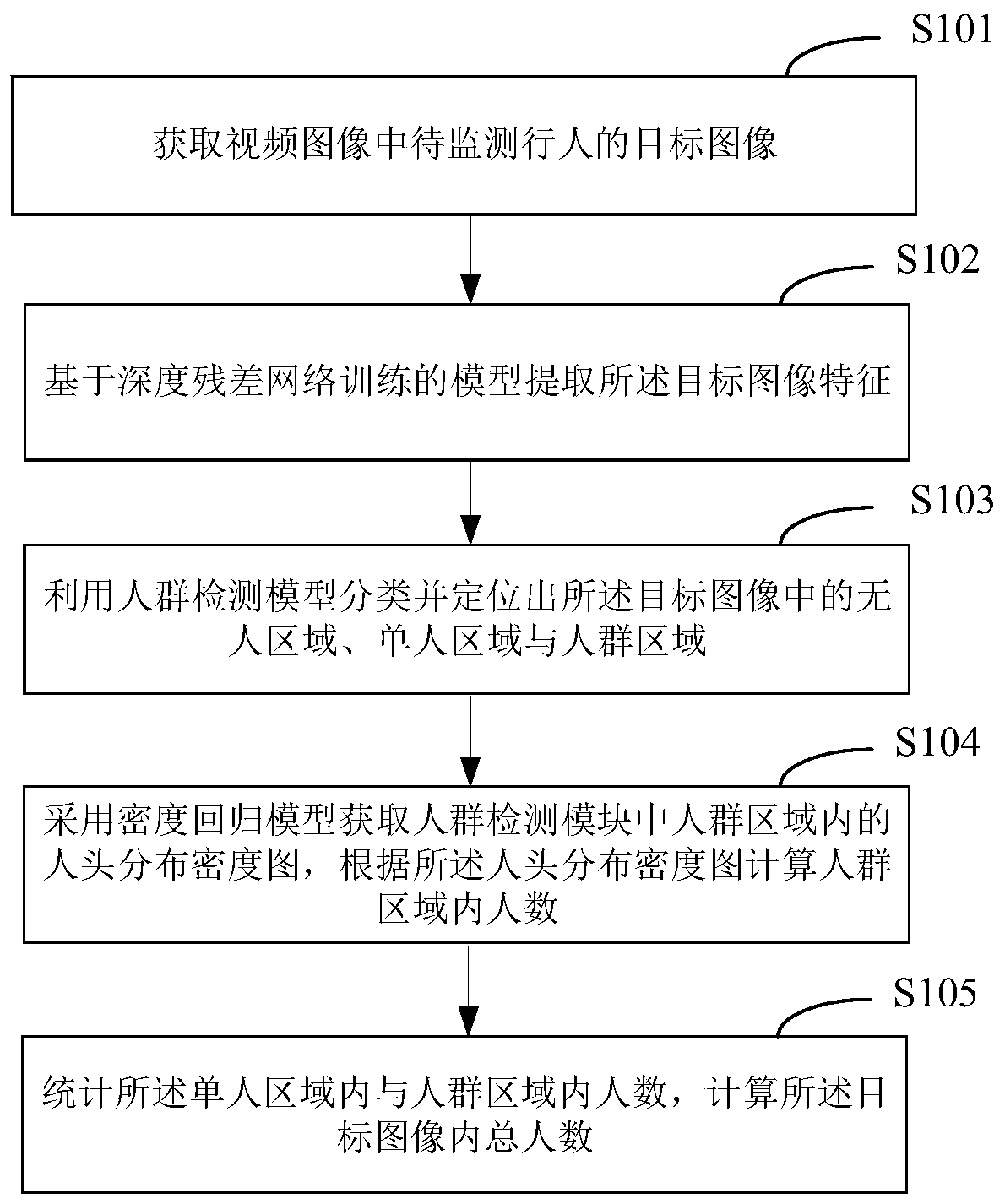
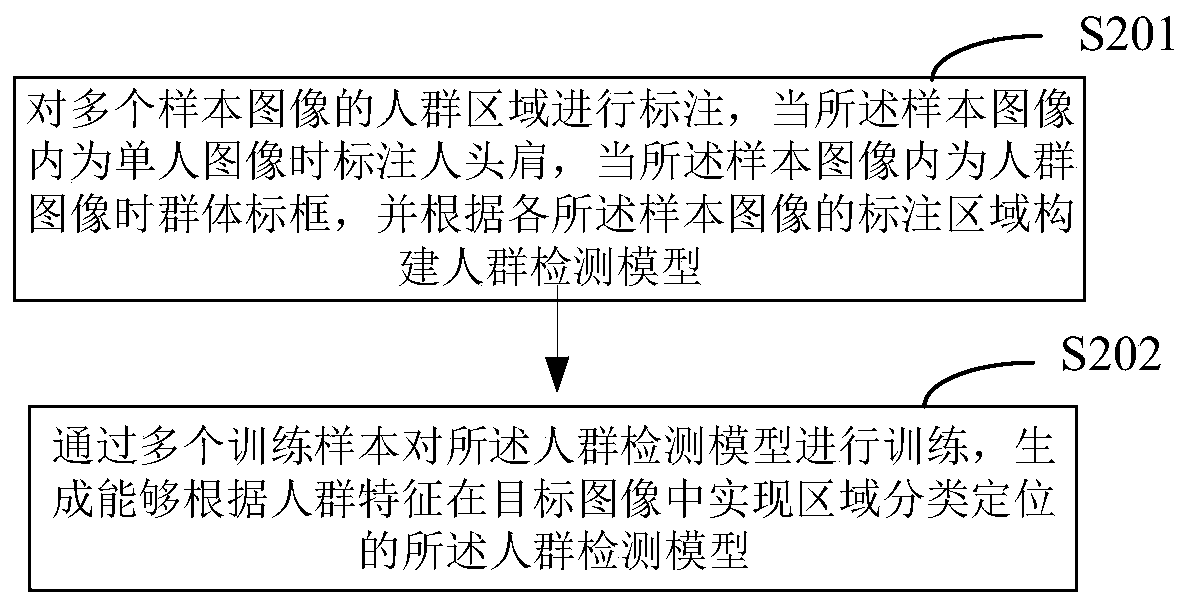
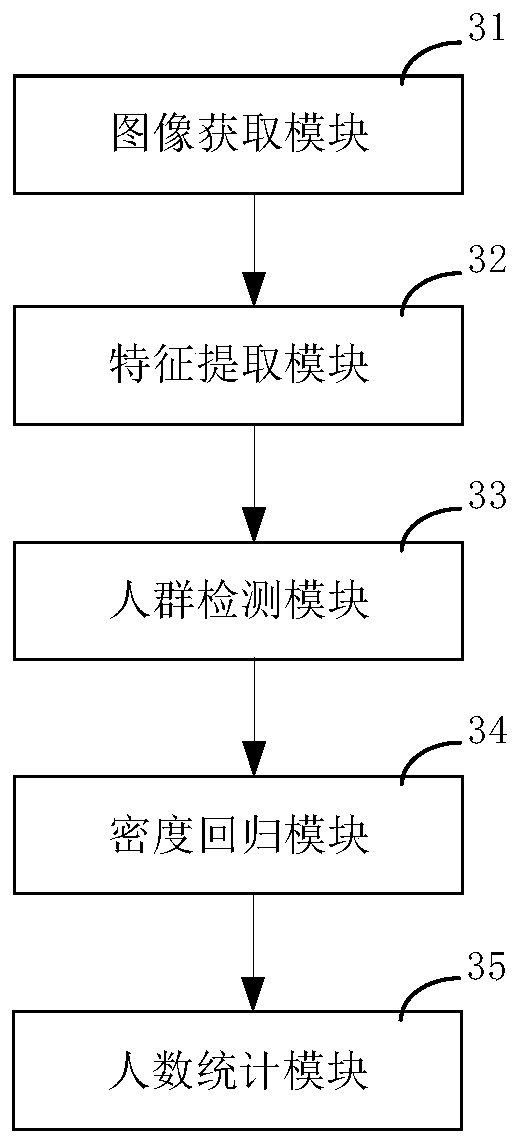
Pedestrian flow monitoring method and device, storage medium and equipment
ActiveCN109697435AStatistically accurateAccurate extractionCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsPattern recognition
The invention provides a visitor flow monitoring method and device, a storage medium and equipment, and is applicable to the technical field of image processing. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a target image of a to-be-monitored pedestrian in a video image; extracting graphic features by using a model trained based on a deep residual network; classifying and positioning an unmanned area, a single person area and a crowd area in the target image by utilizing a crowd detection model; adopting a density regression model to obtain a head distribution density map of the crowd detectionclassification as a crowd area, and calculating the number of people in the crowd area according to the head distribution density map; and counting the number of people in the single person area andthe number of people in the crowd area in the crowd detection classification, and calculating the total number of people in the target image. When people flow is monitored, the number of people in thevideo image is counted based on the deep residual network in combination with crowd detection and density analysis, the number of people in the image can be counted accurately and rapidly, and the method has good robustness.
Owner:CHONGQING ZHONGKE YUNCONG TECH CO LTD
Unsupervised document clustering using latent semantic density analysis
ActiveUS8713021B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsHypersphereDensity analysis
According to one embodiment, a latent semantic mapping (LSM) space is generated from a collection of a plurality of documents, where the LSM space includes a plurality of document vectors, each representing one of the documents in the collection. For each of the document vectors considered as a centroid document vector, a group of document vectors is identified in the LSM space that are within a predetermined hypersphere diameter from the centroid document vector. As a result, multiple groups of document vectors are formed. The predetermined hypersphere diameter represents a predetermined closeness measure among the document vectors in the LSM space. Thereafter, a group from the plurality of groups is designated as a cluster of document vectors, where the designated group contains a maximum number of document vectors among the plurality of groups.
Owner:APPLE INC
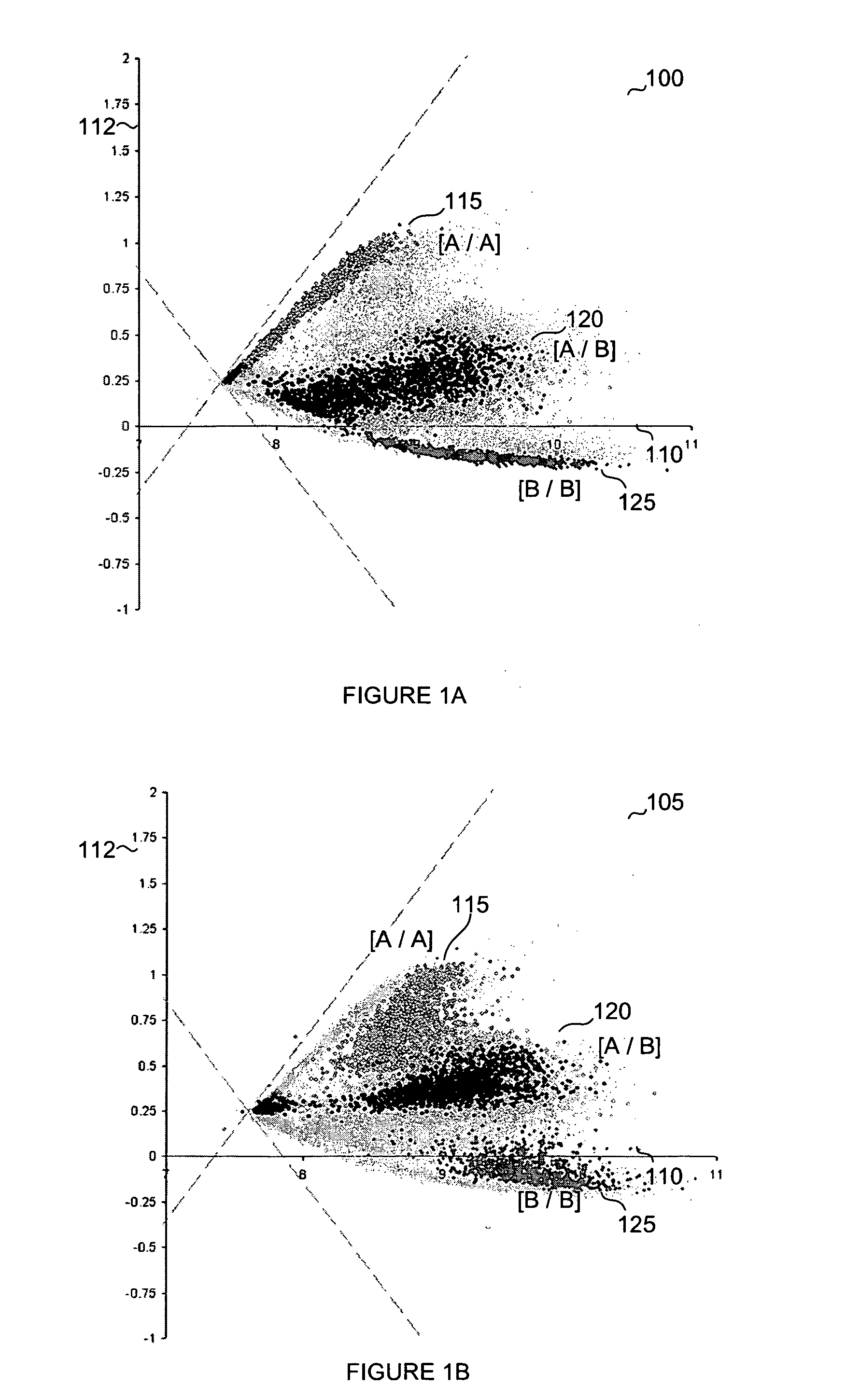
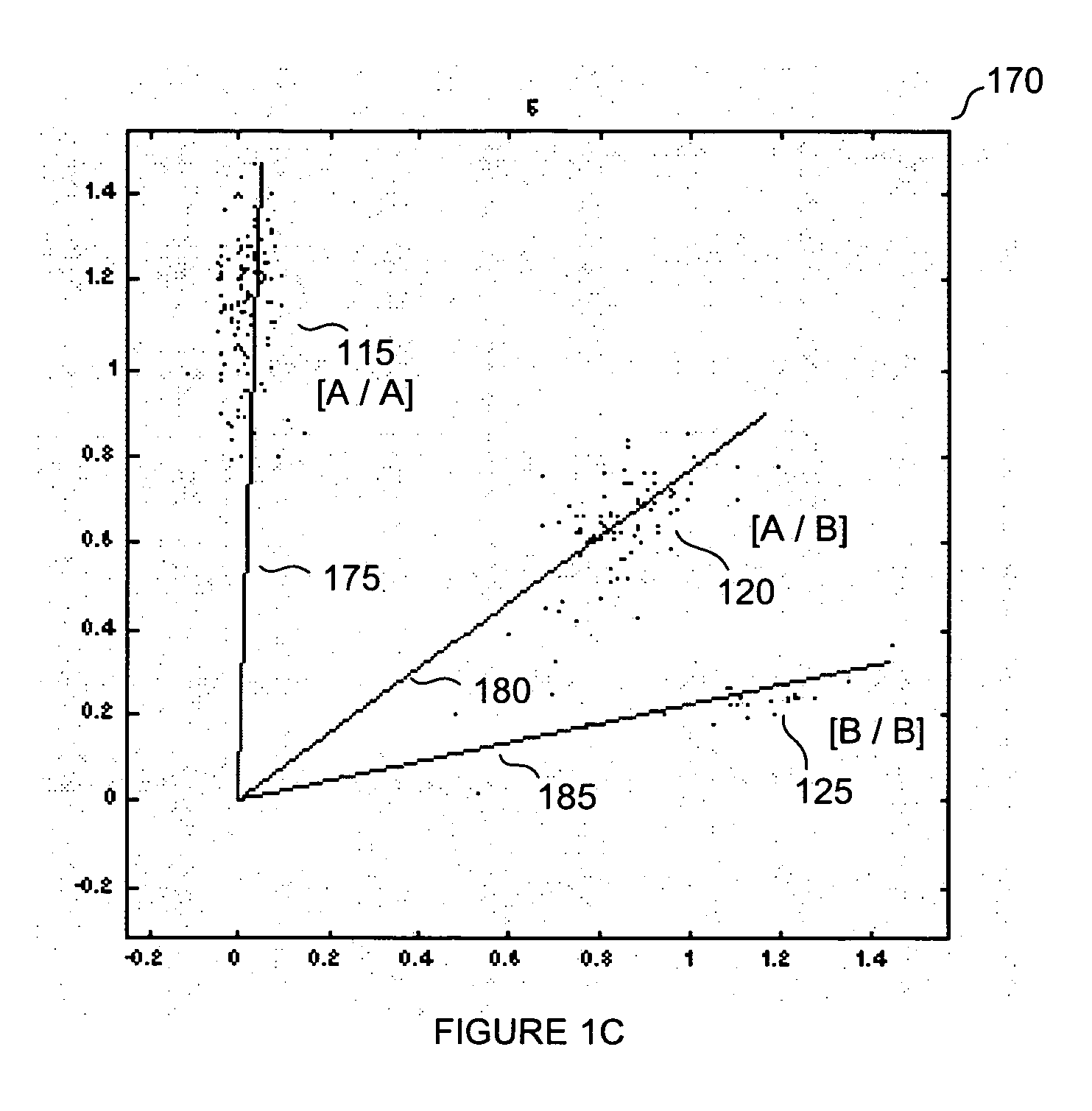
Normalization methods for genotyping analysis
InactiveUS20060178835A1Facilitate comparisonEasy to processBiostatisticsBiological testingData setHigh density
In arrays and other high density analysis platforms variabilities between data points and / or data sets may arise for a number of reasons. Disclosed are methods for addressing these variabilities and generating correction factors that may be used in conforming the data to expected or desired distributions. The methods may be adapted to operate with existing data analysis approaches and software applications to improve downstream analysis.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
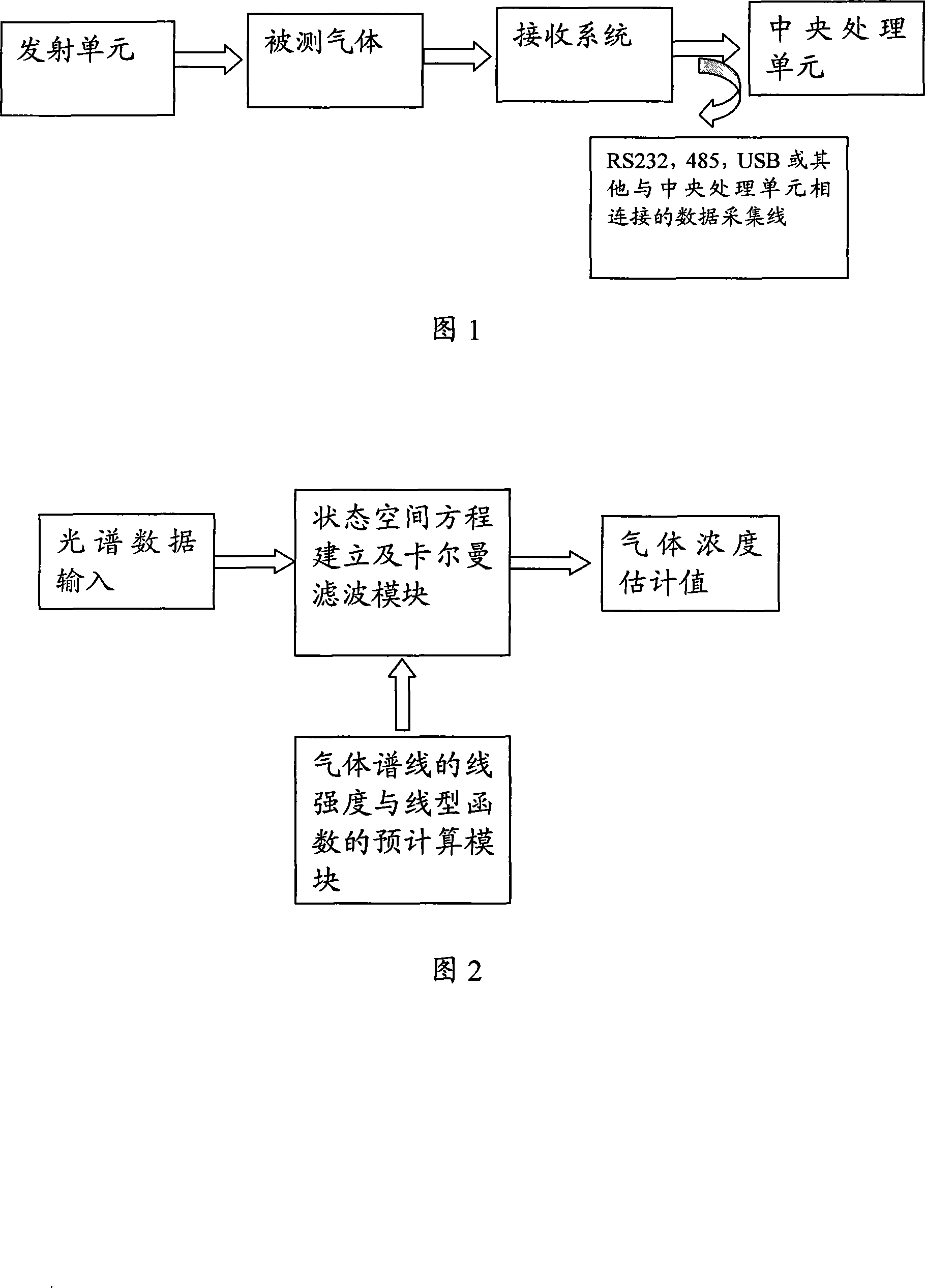
Gas concentration quantitative analyzer
InactiveCN101226147AHigh selectivityEasy to identifyTransmissivity measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsRefractive indexOpto electronic
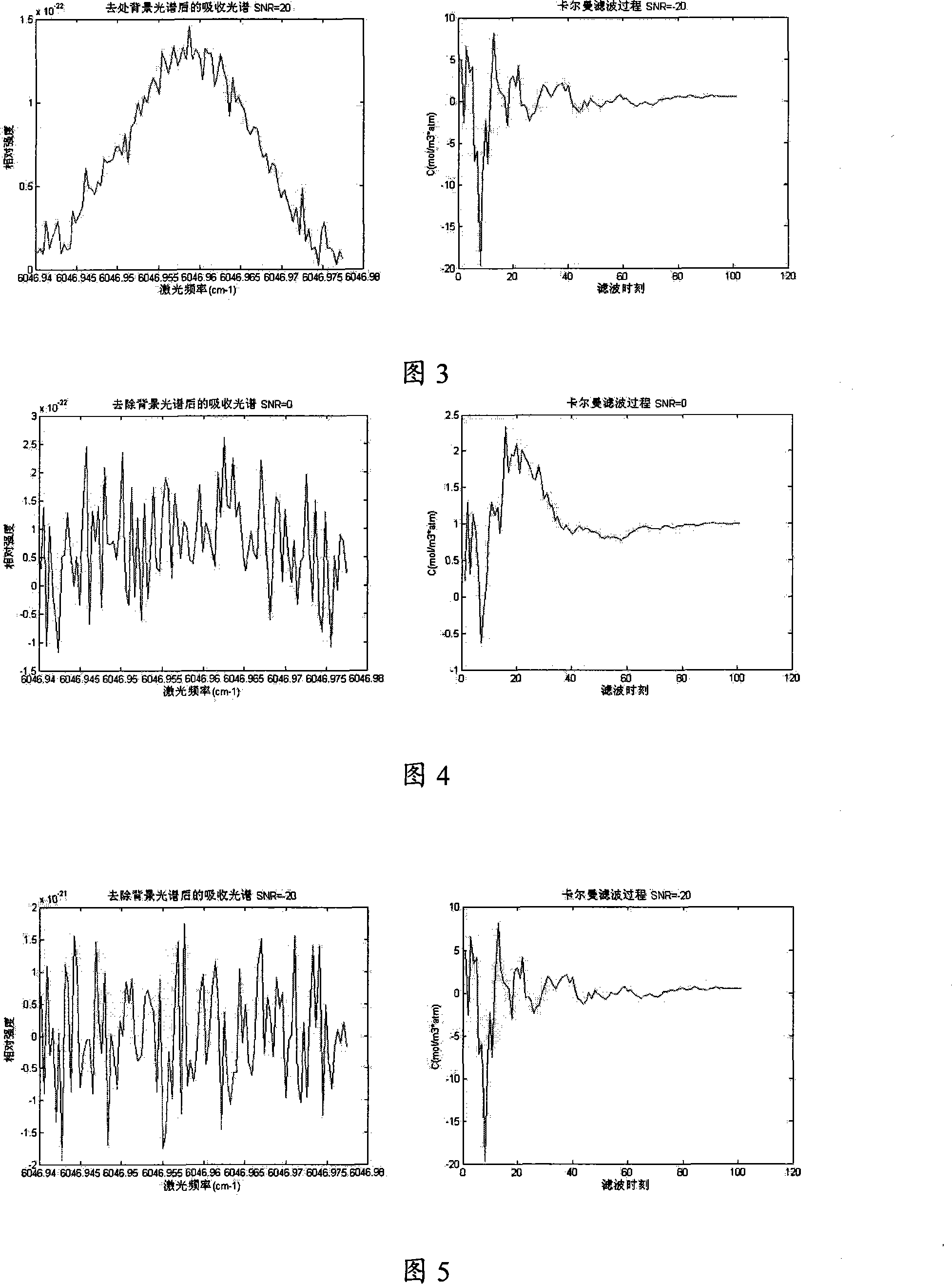
The invention discloses a gas density quantitative analyzer based on tunable diode laser absorption spectrum technique and state space theory, wherein the hardware portion is composed of an emitter, a receive system and a central processor or the like, the software portion uses Kalman filtering algorithm based on state space. The invention uses a laser beam with continuous frequency change generated by a tunable laser to scan the absorption peak of special gas, feeds the laser beam after the tested gas into a light-sensitive detector which obtains a refractive index relationship relative the laser beam of each frequency and gives strength spectrum data at relative wavelength to be sent to the central processor, uses the gas density analysis software in the central processor to model the spectrum data into a measurement equation and build a gas density state equation while sets density distribution stable along time, uses Kalman filtering algorithm to process and processes gas density robust inversion.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Apparatus and method for controlling power for v2x communication
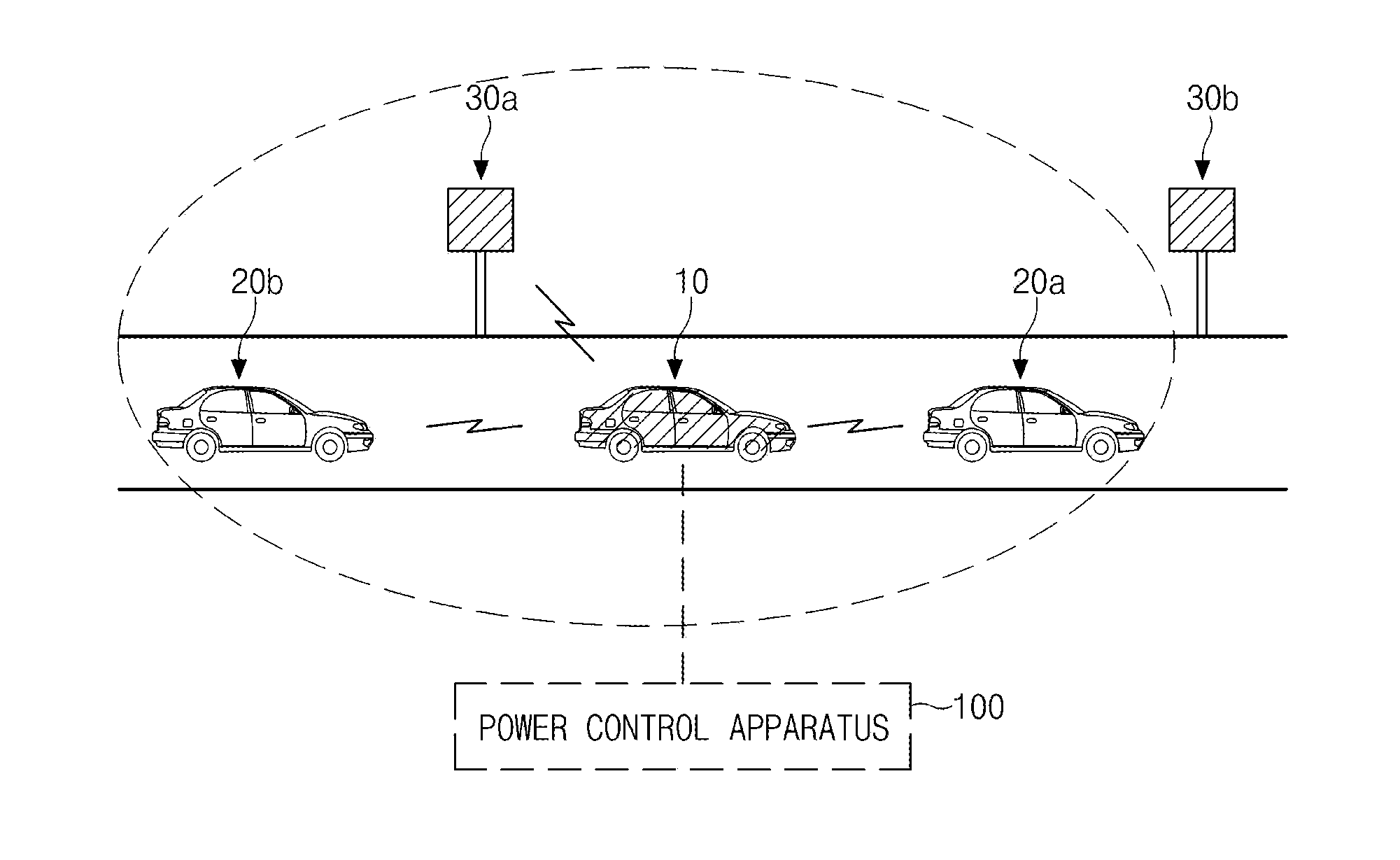
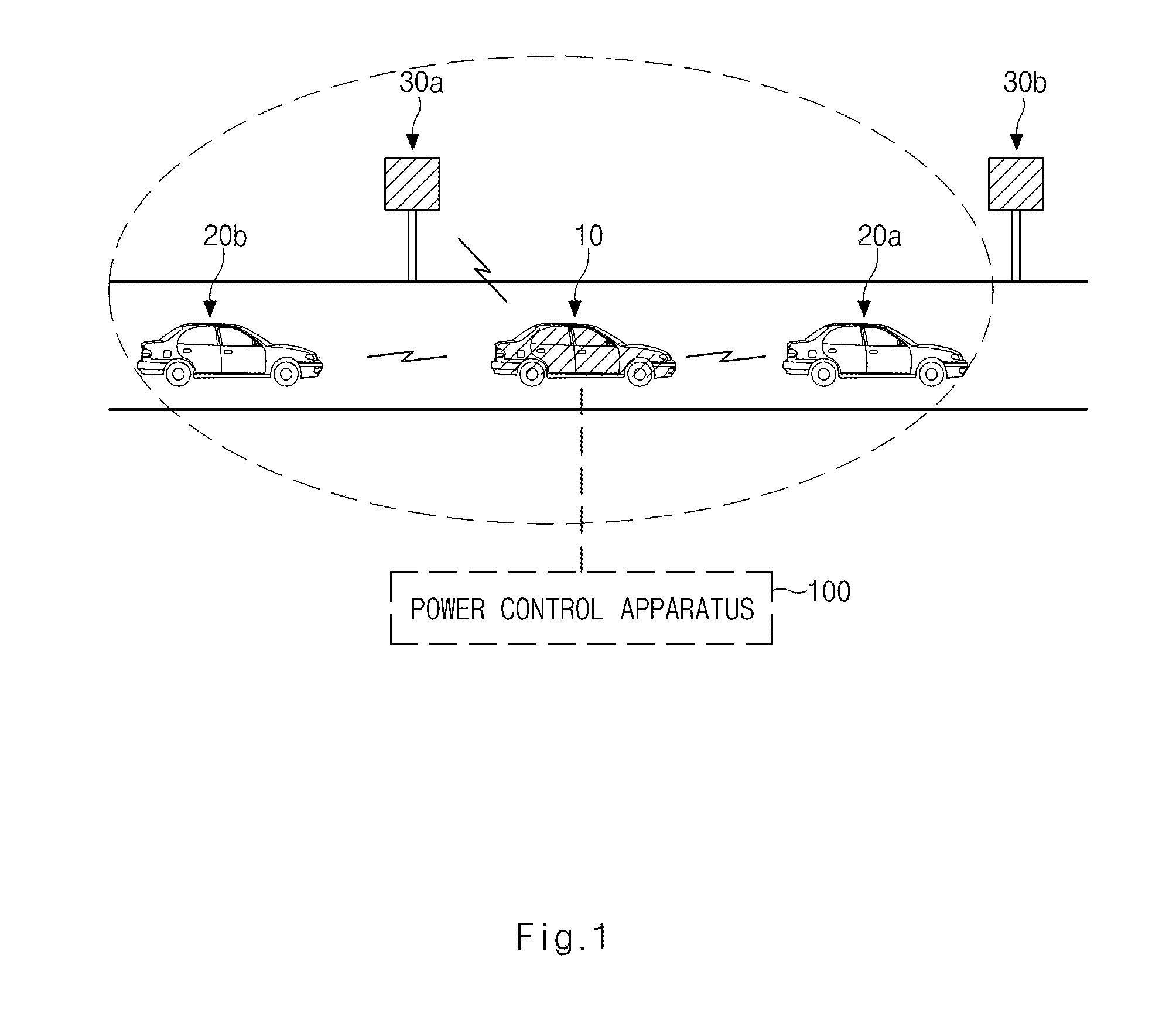
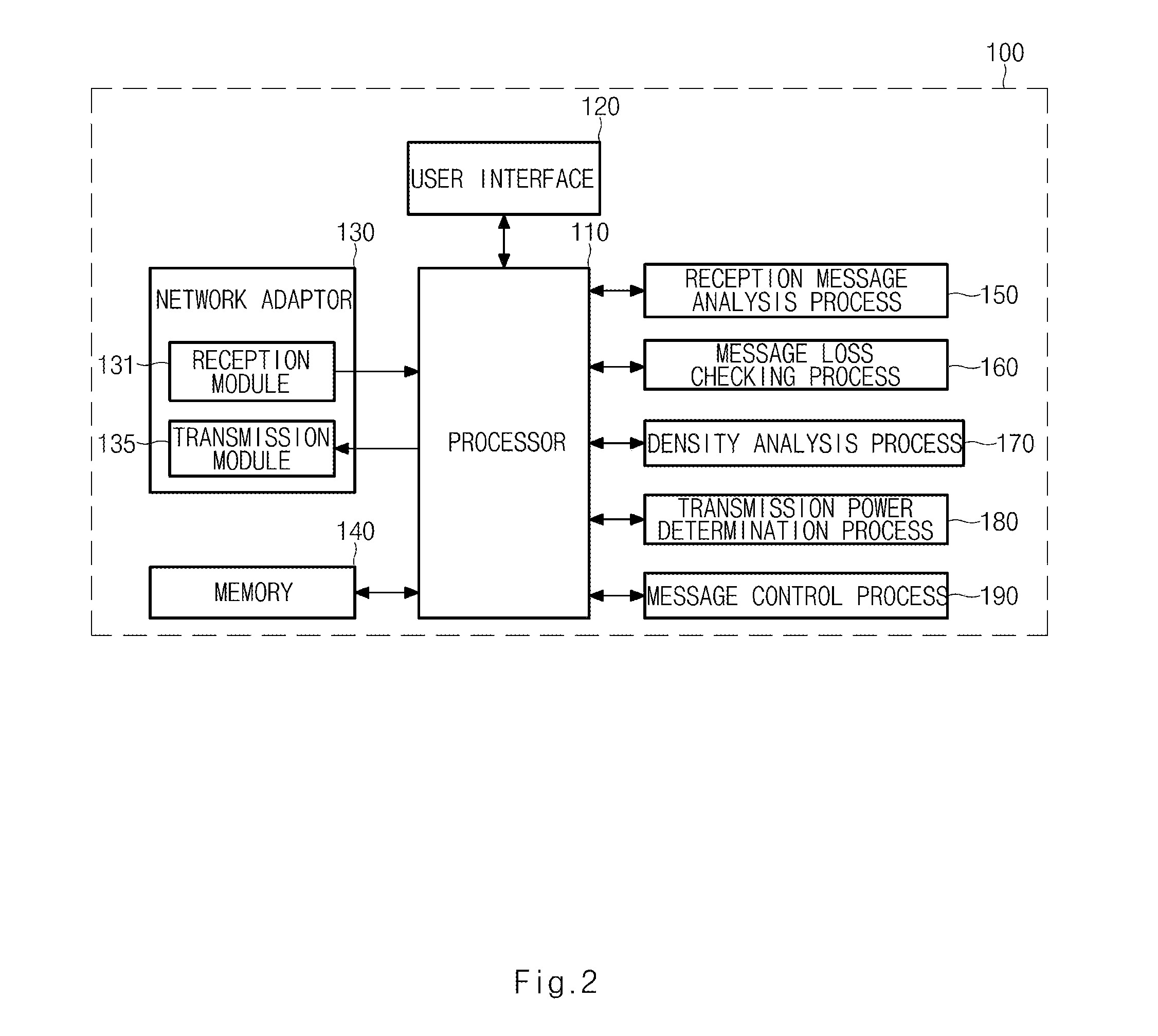
ActiveUS20130329651A1Improve communication performanceReduce power consumptionPower managementWireless commuication servicesControl powerDensity analysis
A technique for controlling power for V2X communication is provided. The apparatus includes a reception message analysis process configured to analyze headers of reception messages received from communication apparatuses of roadside apparatuses and surrounding vehicles located around a vehicle, a message loss checking process configured to check whether or not loss of the reception messages occurs by counting sequential numbers included in the headers of the reception messages, a density analysis process configured to analyze a density for each of communication apparatuses located in a communication radius of preset transmission power from the vehicle when the message loss checking process determines that the loss of the reception messages occurs, and a transmission power determination process configured to determine transmission power for V2X communication by deducting the preset transmission power in units of reference power according to the density when the density around the vehicle exceeds a reference value.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Instant, in-situ, nondestructive material differentiation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20140358447A1Improve abilitiesMaximize transmissivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalCell phenotypePrincipal component analysis
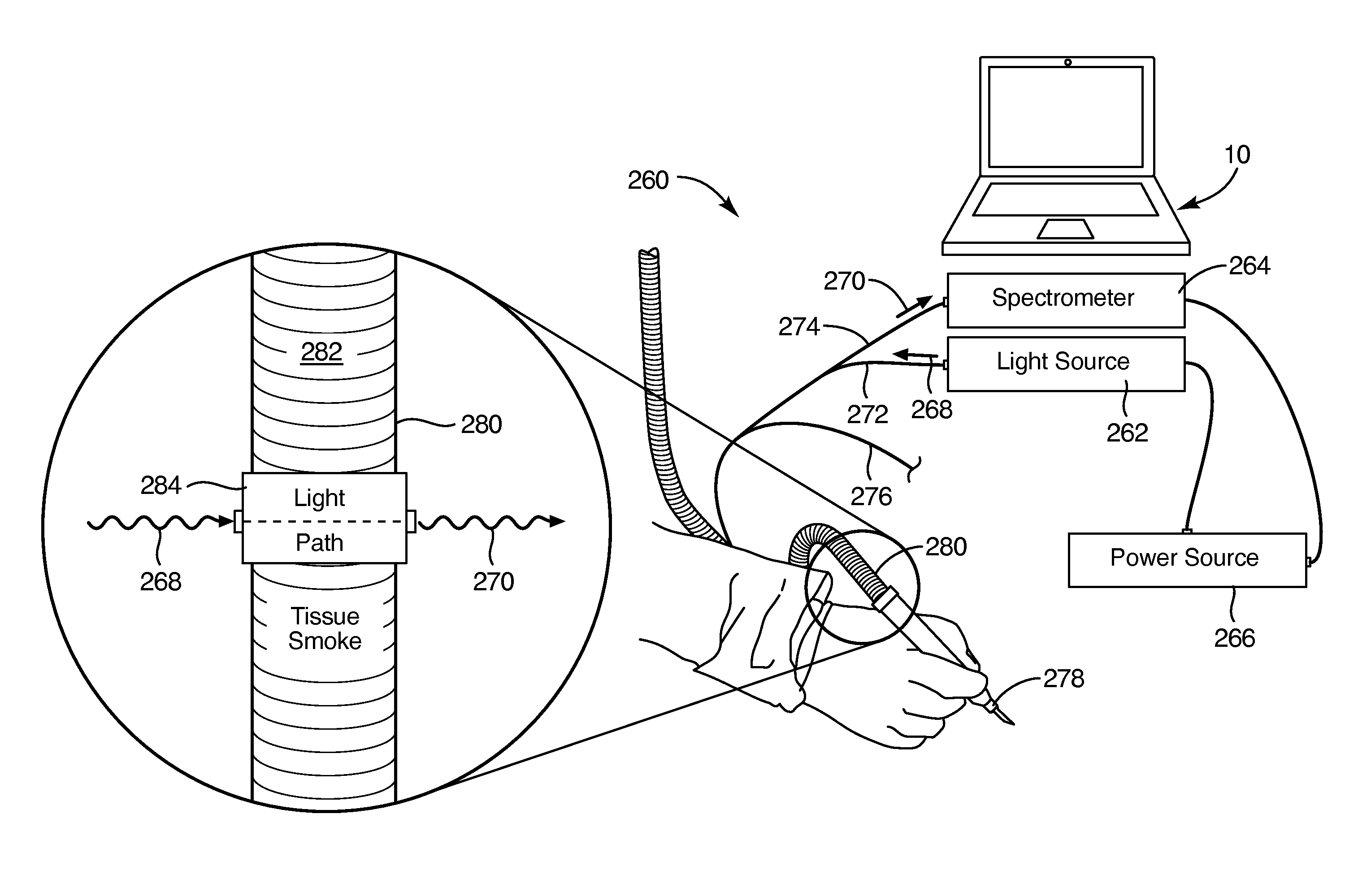
Specular, ultrasonic, piezoelectric, detection devices provide real-time, analytical, edge finding in tissues during tumor surgery. Piezoelectric probe sensors at high frequencies (e.g., 10 to 100 MHz) characterize microstructure of cells and tissues. Through-transmission or specular reflection enables nondestructive testing in real time. Peak density analysis in power spectra, second-order spectrum analysis measuring the slope of the Fourier transform of the power spectrum, artificial intelligence pattern recognition, and modeling interpret the results. Model-based data analysis may compare experimental data with a computer simulation. Such comparisons may be based upon pattern classifications, including principal component analysis (PCA). Combining the above detection devices and analytical methods provides speed, accuracy, simplicity, and nondestructive mechanisms that militate for reliable, real-time diagnosis of tumor margins, tissue pathology, cell phenotypes, and molecular subtypes.
Owner:UTAH VALLEY UNIVERSITY
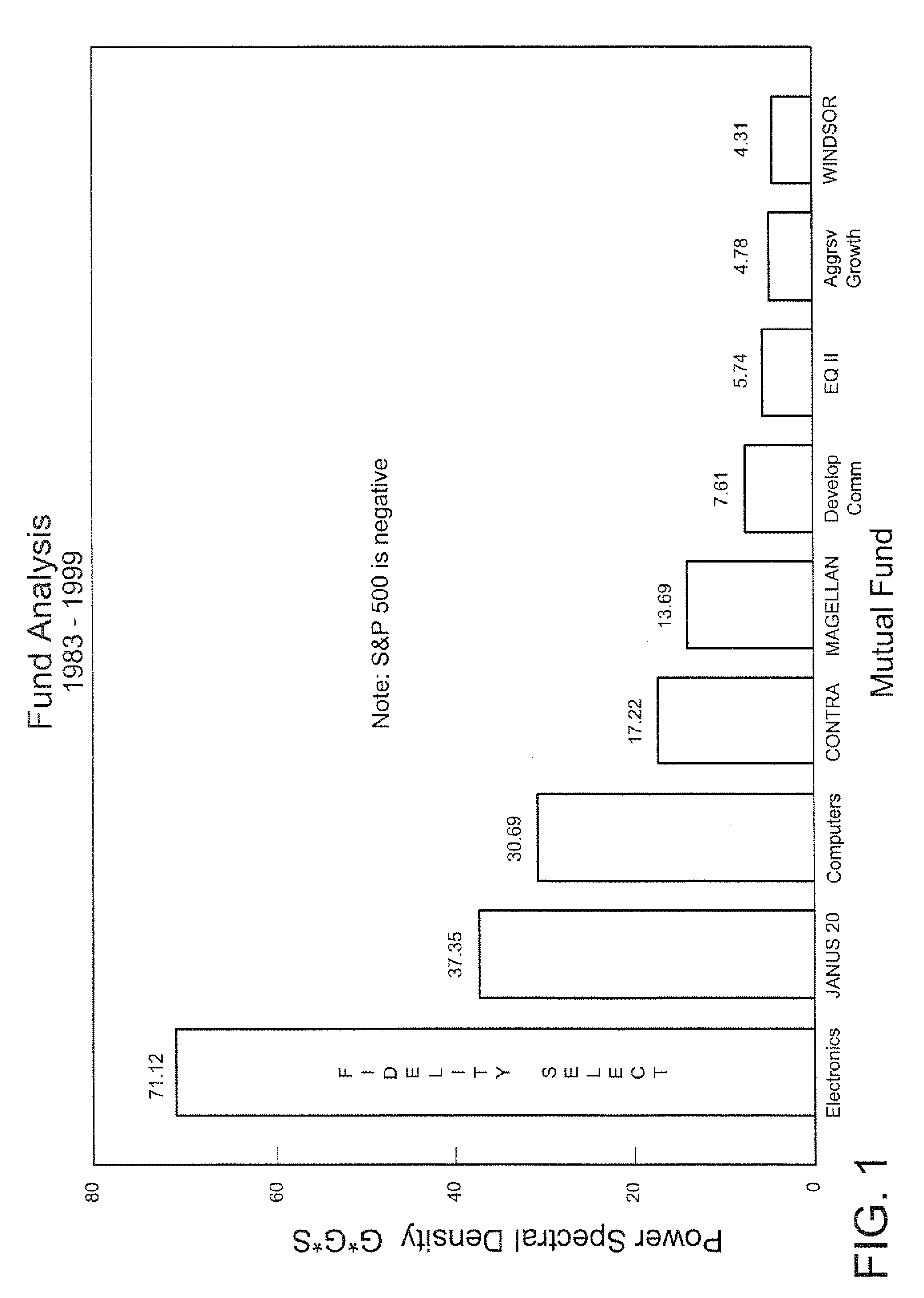
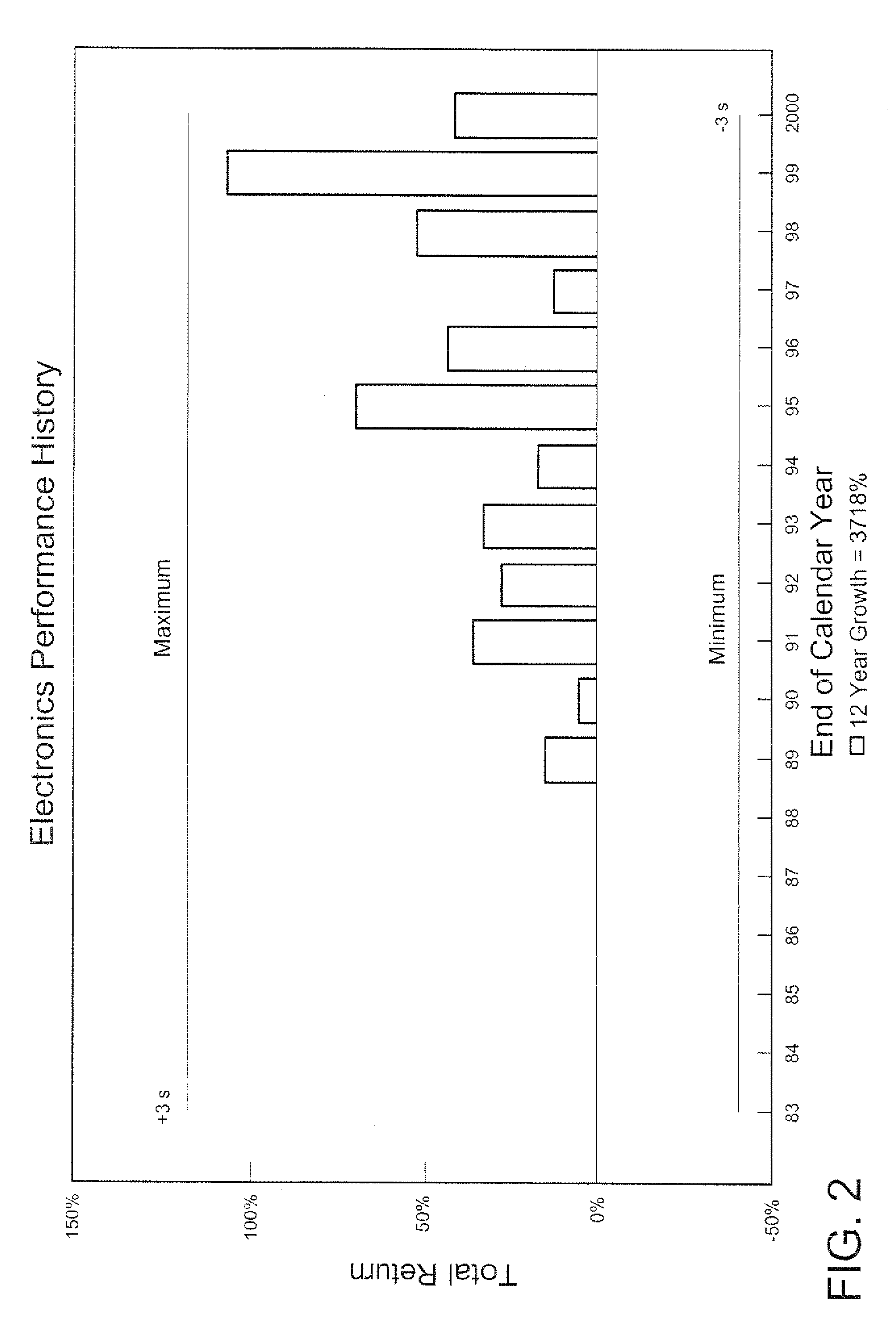
Mutual fund analysis method and system
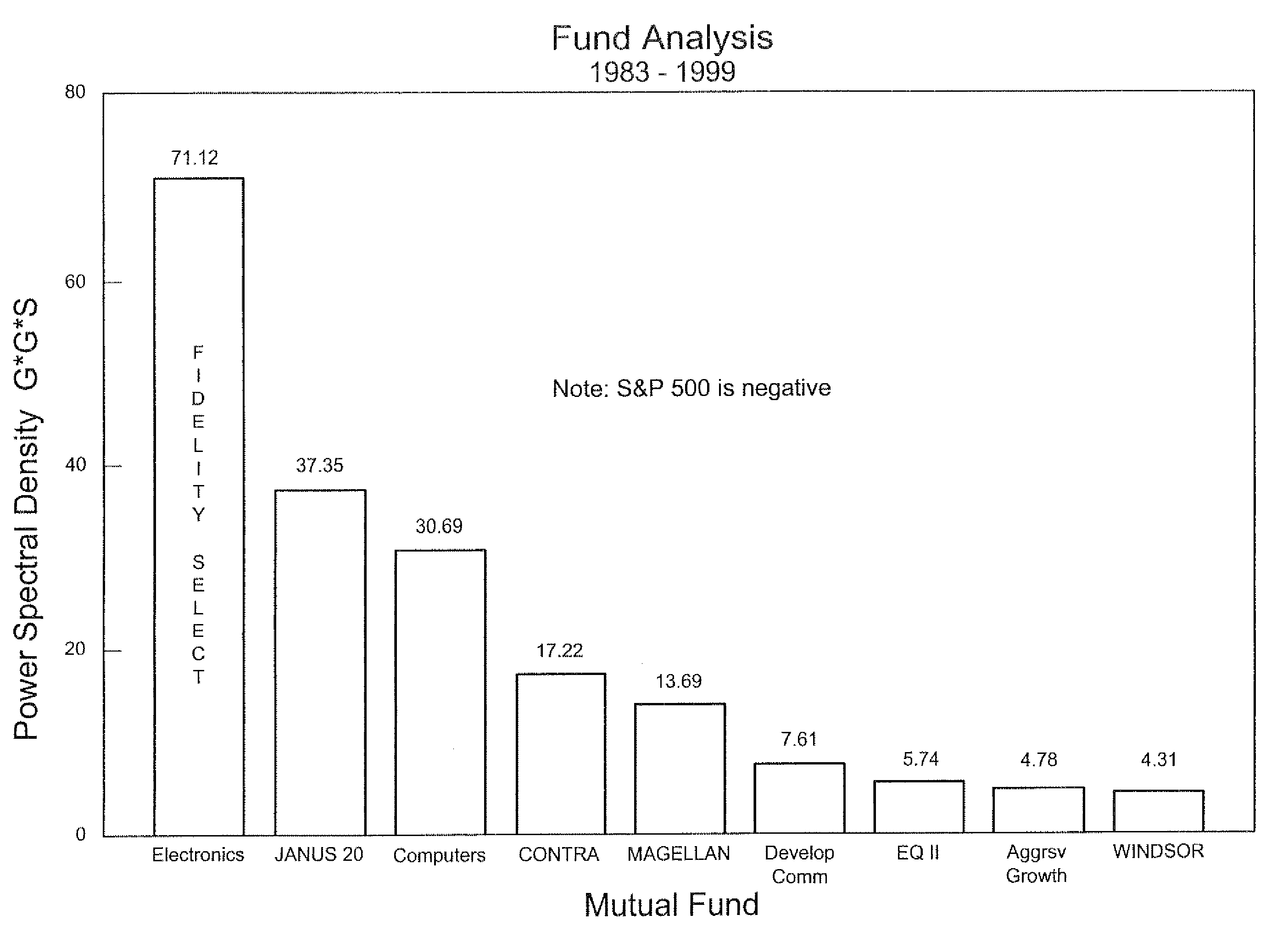
A method and system for comparing, ranking, selecting and tracking mutual funds provides a statistical analysis based on past history to facilitate the investment process. The comparing analysis incorporates a determination of power spectral density of each respective fund using a principal factor such as cumulative growth and stability. For tracking investments, upper and lower control limits are defined according to standard deviations of average total return over predetermined periods of time to improve chances of the investor achieving a profit as well as a near optimum performance. The power spectral density analysis provides a clear indication of comparative mutual fund performance.
Owner:GGS SYST
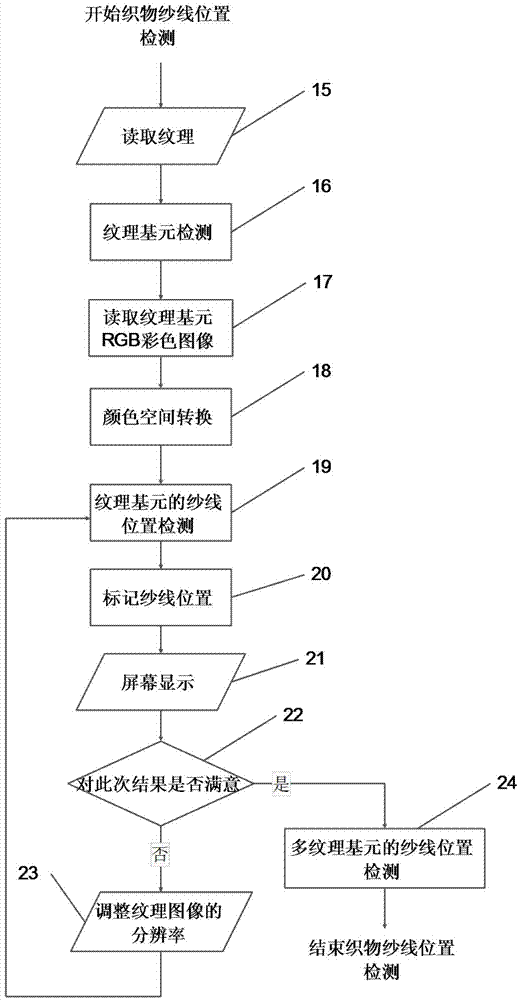
Image analysis method based on multi-scale and multi-zone woven fabric knitting tightness
InactiveCN104715477AOvercomes the inability to directly address yarn sloping areasReduce dependencyImage enhancementImage analysisYarnImaging analysis
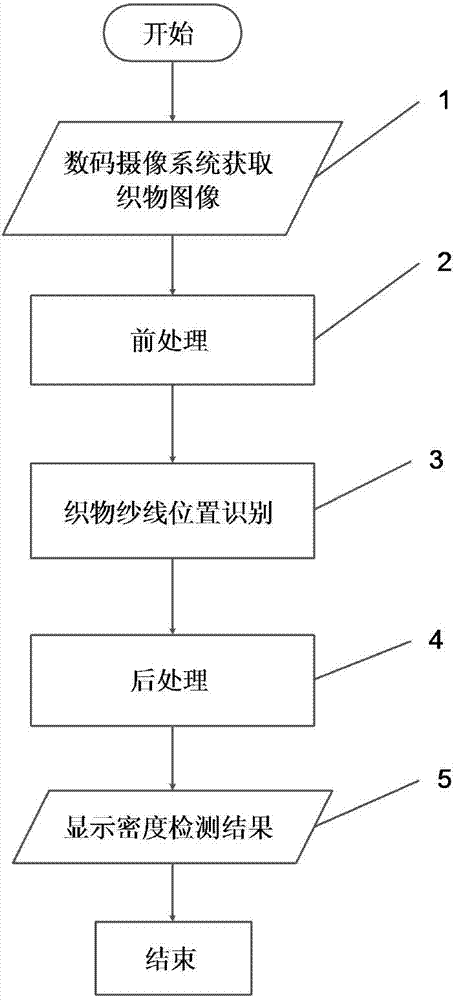
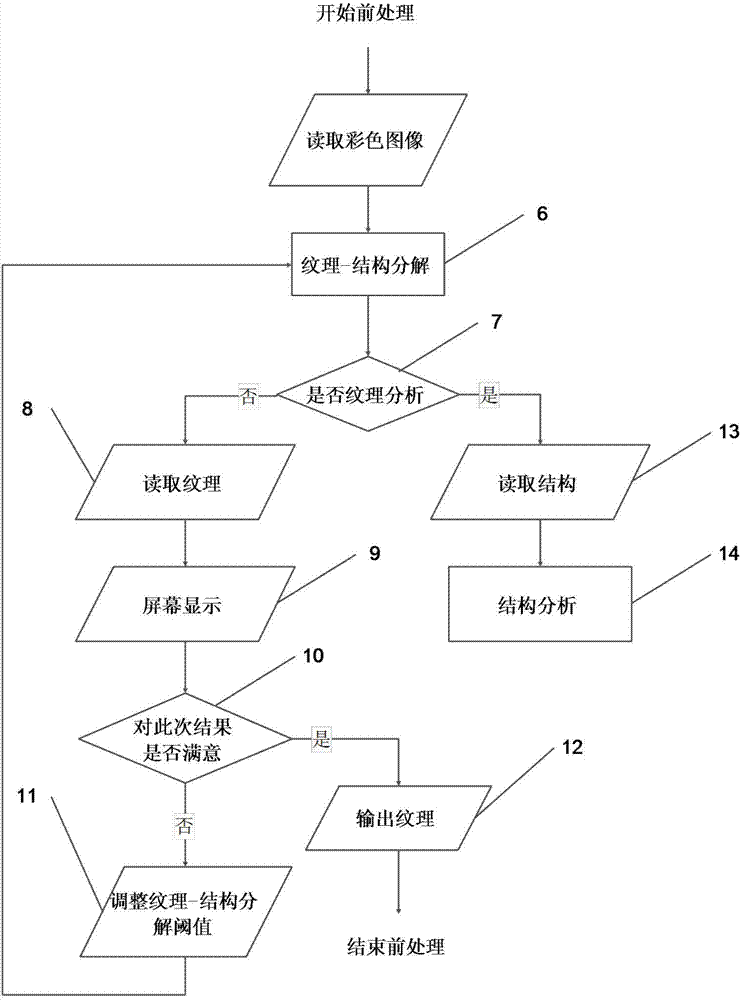
The invention discloses an image analysis method based on multi-scale and multi-zone woven fabric knitting tightness. The method comprises the steps that (1) a digital photography system obtains a fabric image; (2) pretreatment is carried out, wherein the woven fabric image is subjected to structure-grain analysis; (3) woven fabric yarn position detecting is carried out, wherein the fabric grain image output during pretreatment is read, grain elements in a large-scale image of the woven fabric are detected through a similar rule grain model; and (4) post-treatment is carried out, wherein the yarn position detecting results of grain elements extracted by multiple times are subjected to statistics in a two-dimension grid arraying direction, according to multi-zone grain element zone position information, yarn mean density is determined, a user processes a density detecting process of a certain batch, and according to the detecting results of similar rule grain, the accuracy of the mean density detecting results is judged. The efficiency and the accuracy of fabric knitting tightness are improved, and the method is close to a fabric density analysis method in practical production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG COLLEGE OF ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECHOLOGY
Traffic video comprehensive analysis cloud platform system
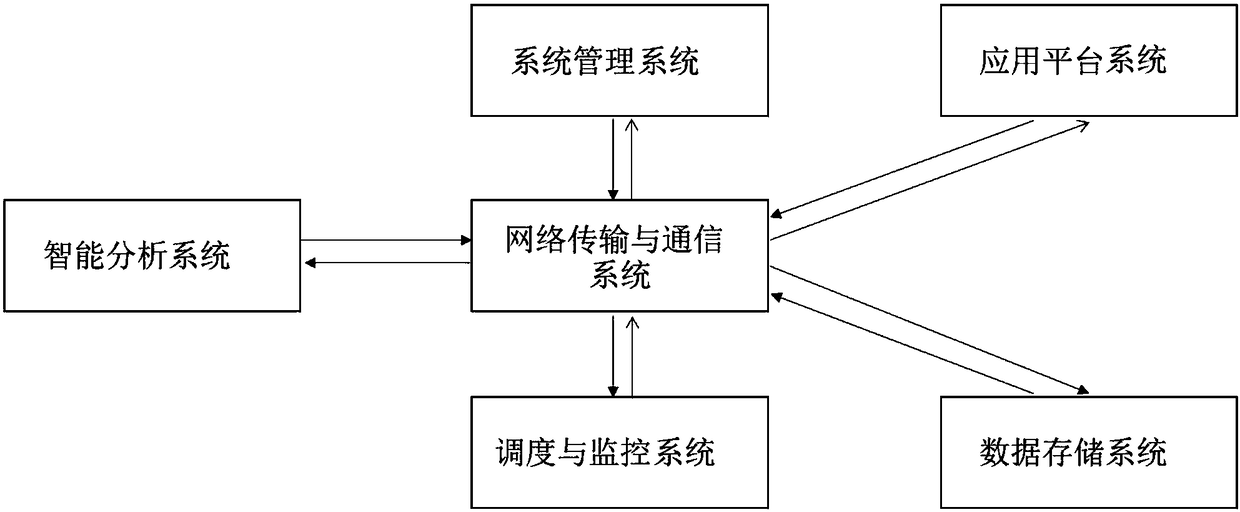
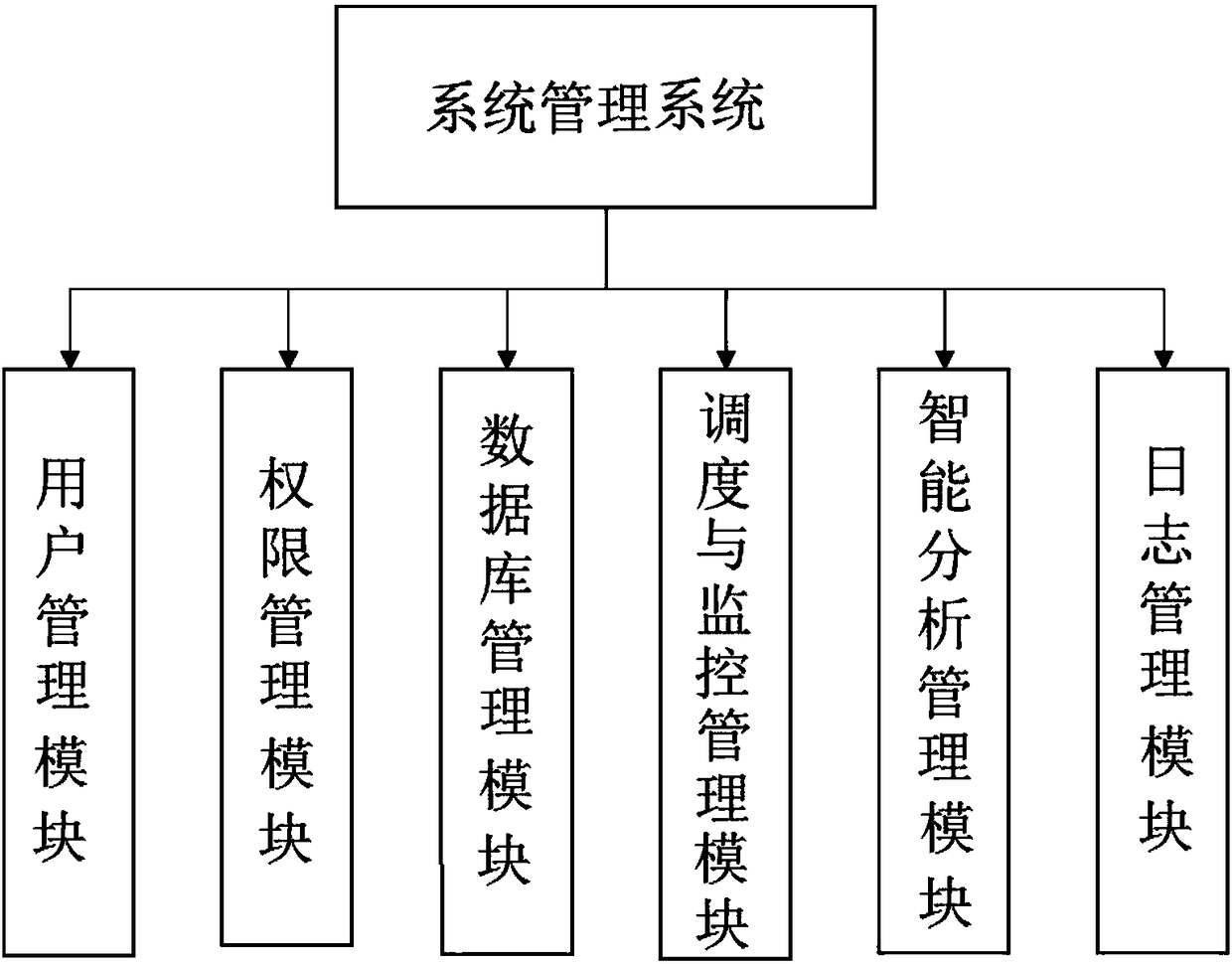
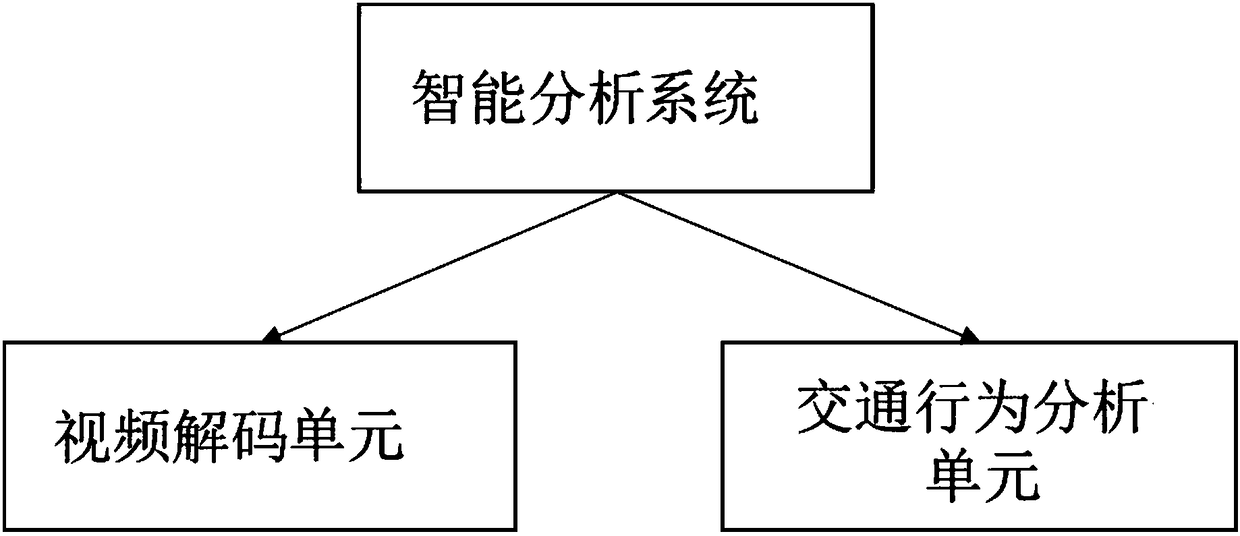
InactiveCN108734966ANo constructionNo maintenance issuesRoad vehicles traffic controlClosed circuit television systemsCommunications systemSystems management
The invention discloses a traffic video comprehensive analysis cloud platform system. The system comprises a host, a server, a monitoring device and a cloud platform system; the cloud platform systemis connected with the host, the server and the monitoring device; the cloud platform system comprises a system management system, a data storage system, an intelligent analysis system, a network transmission and communication system, a scheduling and monitoring system and an application platform system. According to the traffic video comprehensive analysis cloud platform system of the invention, existing video resources of existing traffic monitoring points, electronic polices, public security monitoring and the like can be fully utilized so as to realize automatic alarm, automatic analysis and snapping functions for traffic road conditions and motor vehicle rule violations; and on the basis of the application platform, vehicle density analysis, vehicle trajectory analysis, intersection rule violation statistics and the like can be performed on traffic road condition information and various rule violations, and therefore, sufficient basis and rich research data can be provided for traffic police in law enforcement and planning management.
Owner:杭州天象智能科技有限公司
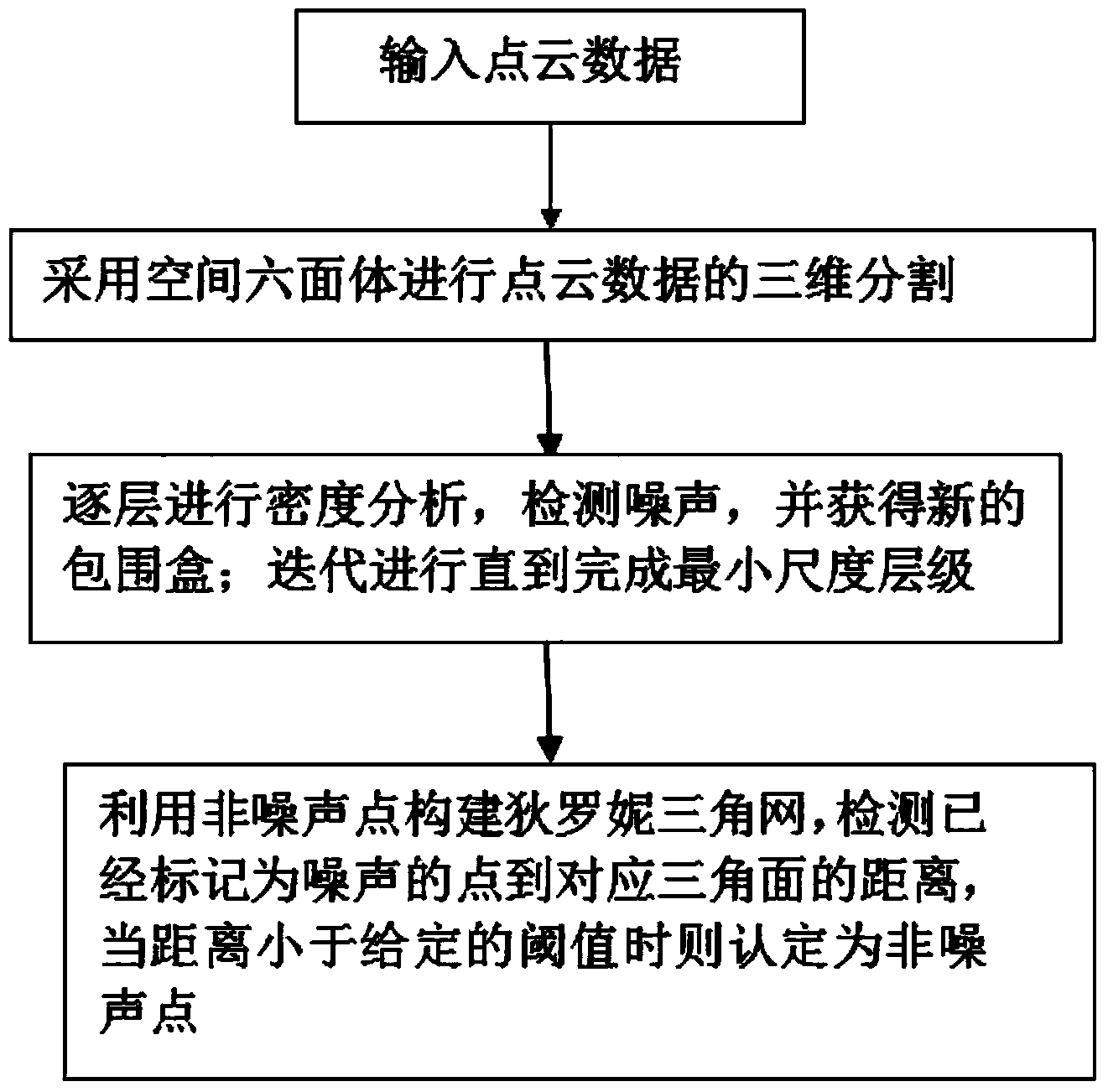
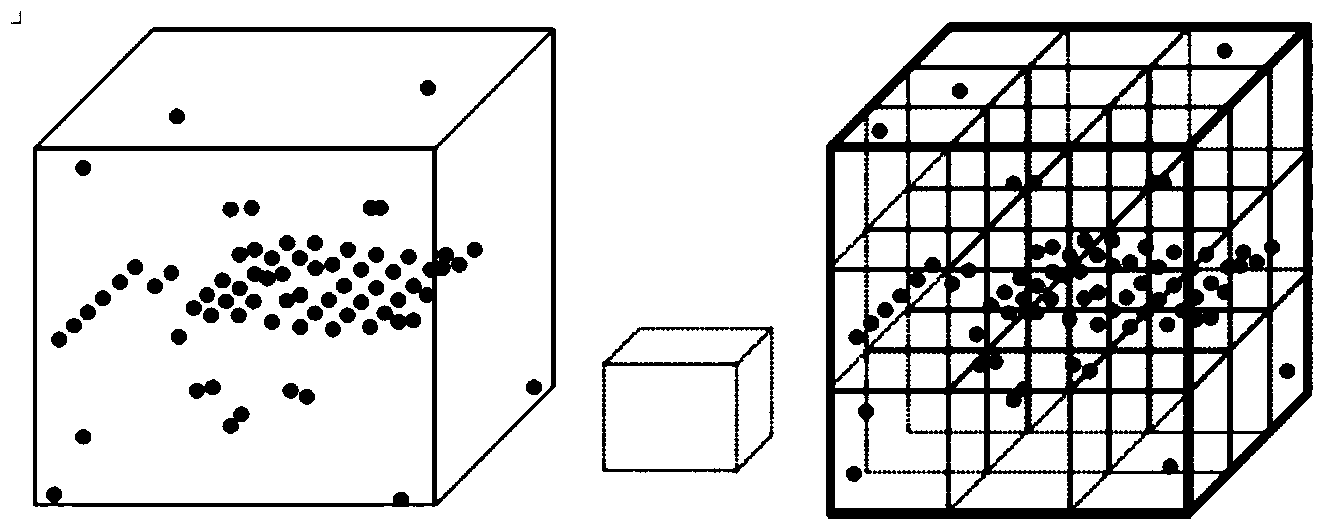
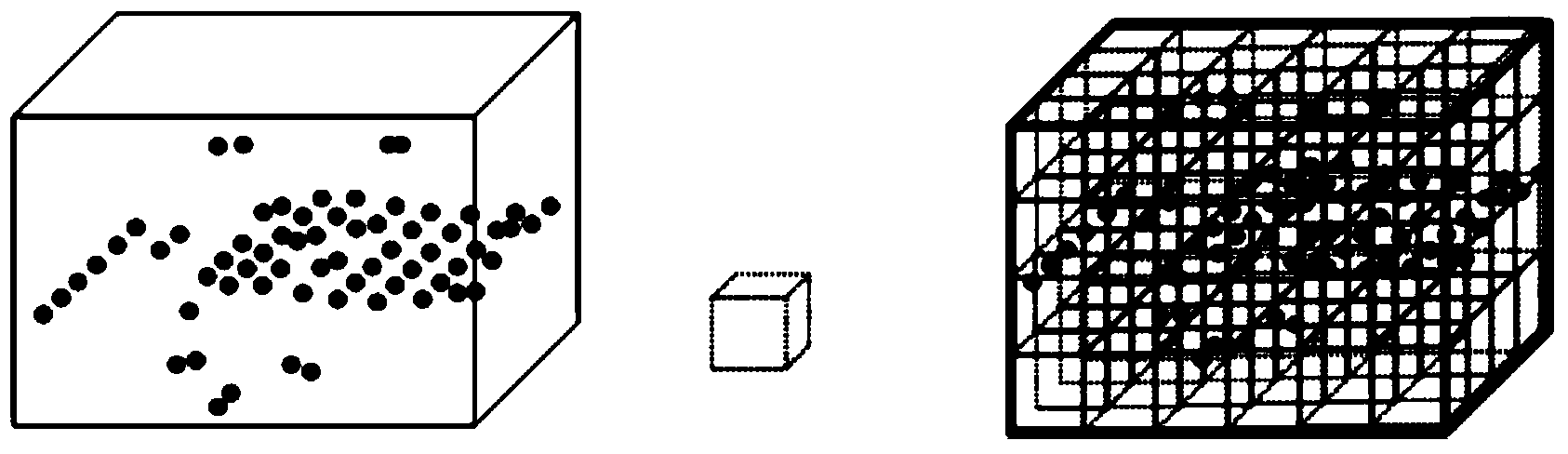
Multi-scale point cloud noise detection method based on density analysis
The invention provides a multi-scale point cloud noise detection method based on density analysis. The method mainly comprises the steps that firstly, a multi-scale density analysis algorithm is utilized for preliminarily judging points which possibly are noise; secondly, triangulation network constrains are utilized for classifying the points which are detected as noise in the last step by mistake to be non-noise points again. The multi-scale point cloud noise detection method based on density analysis can effectively detect out isolated noise and cluster noise contained in point cloud of laser radar and contained in point cloud obtained through image matching, and has the good application prospect in the fields of laser radar point cloud filter and image matching mistake-matching point detection, bundle adjustment noise detection and the like.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
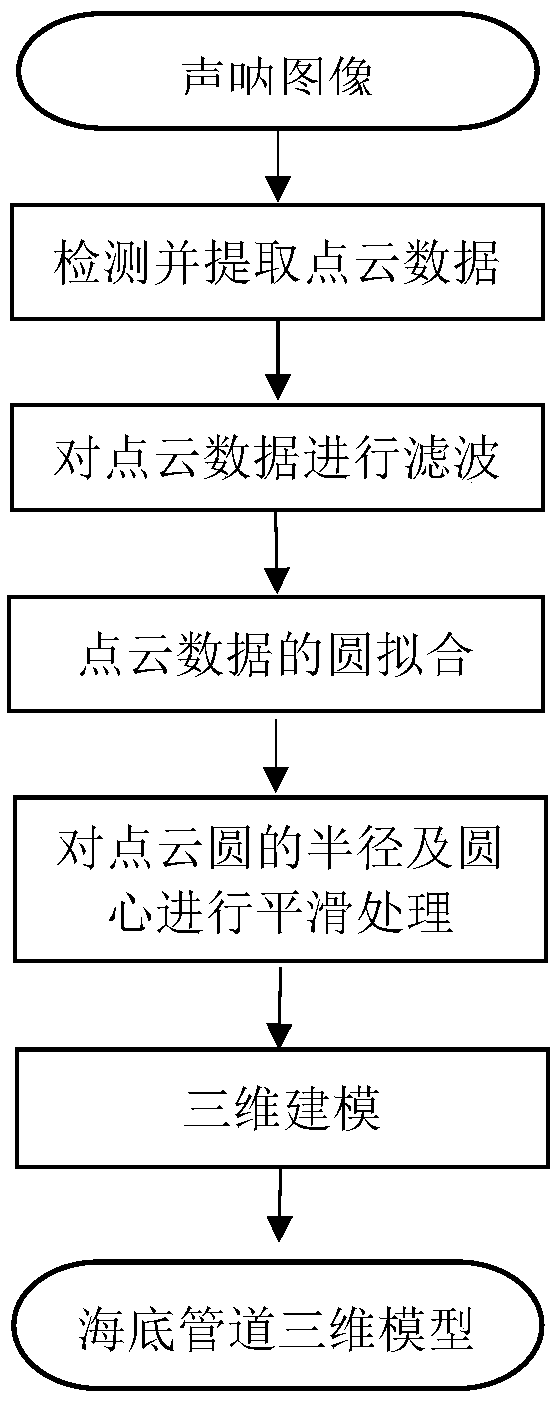
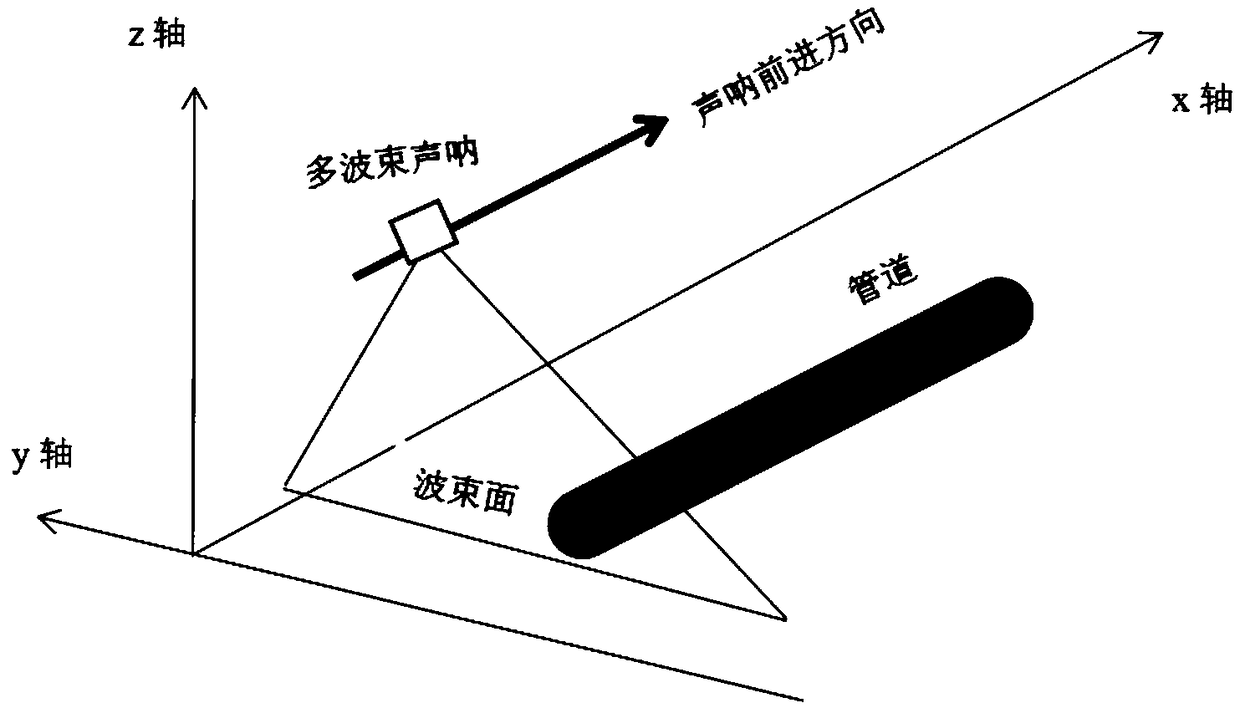
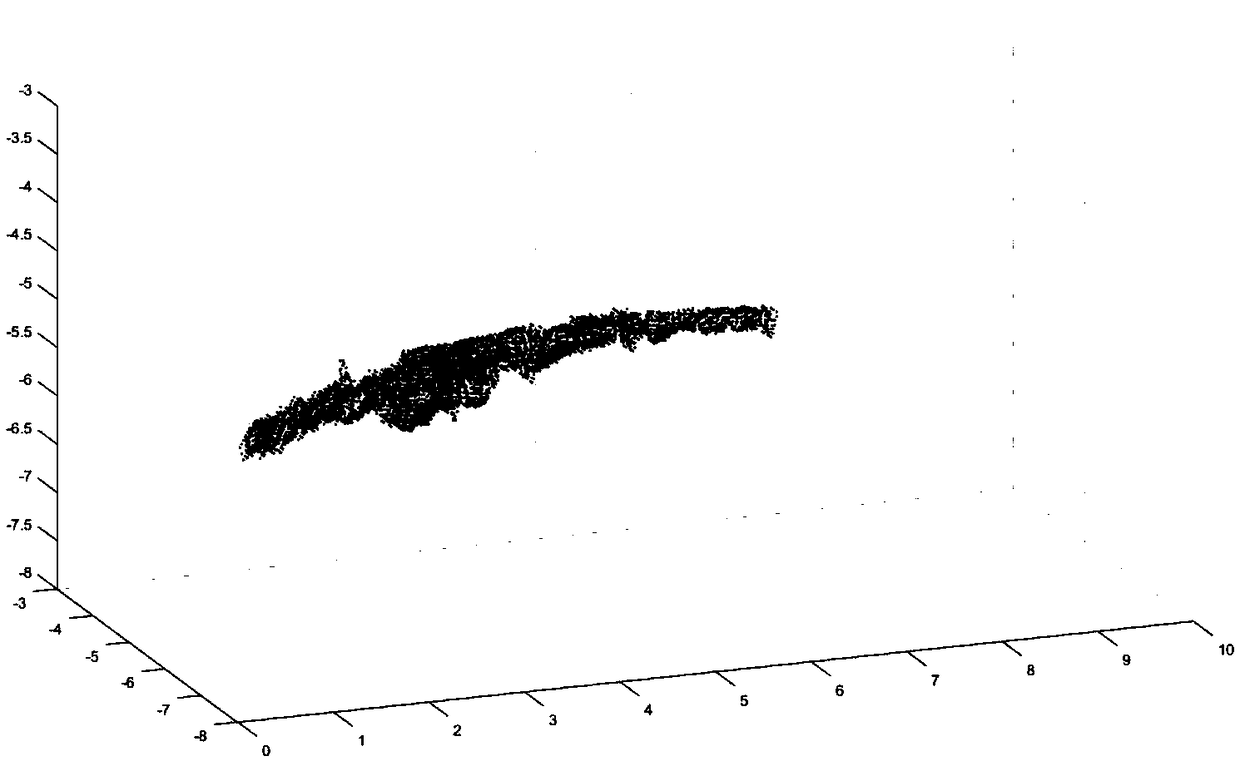
A subsea pipeline detection and three-dimensional reconstruction method based on multi-beam point cloud
ActiveCN109035224AFew point cloudsMulti-point cloud dataImage enhancementImage analysisOcean bottomPoint cloud
The invention relates to the field of multi-beam sonar underwater target detection and point cloud data modeling, in particular to a subsea pipeline detection and three-dimensional reconstruction method based on the multi-beam point cloud. According to the underwater sonar images obtained from multi-beam sounding sonar pipelines, the pixels are classified and extracted by threshold method to obtain three-dimensional point cloud data. Then, the denoising method based on density analysis is used to obtain the three-dimensional point cloud data of the pipeline after denoising. Then, the point cloud data of each section of the pipeline is fitted with a linear fitting method, and the radius of the fitted circle and the linearly varying center point of the circle are three-dimensionally reconstructed to obtain a three-dimensional picture of the pipeline; Compared with obtaining point cloud data through bathymetric points, the invention extracts point cloud data directly from sonar image, still can obtain more accurate point cloud model, and the calculation amount is small, which is suitable for detecting and three-dimensional reconstruction of various underwater pipelines.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
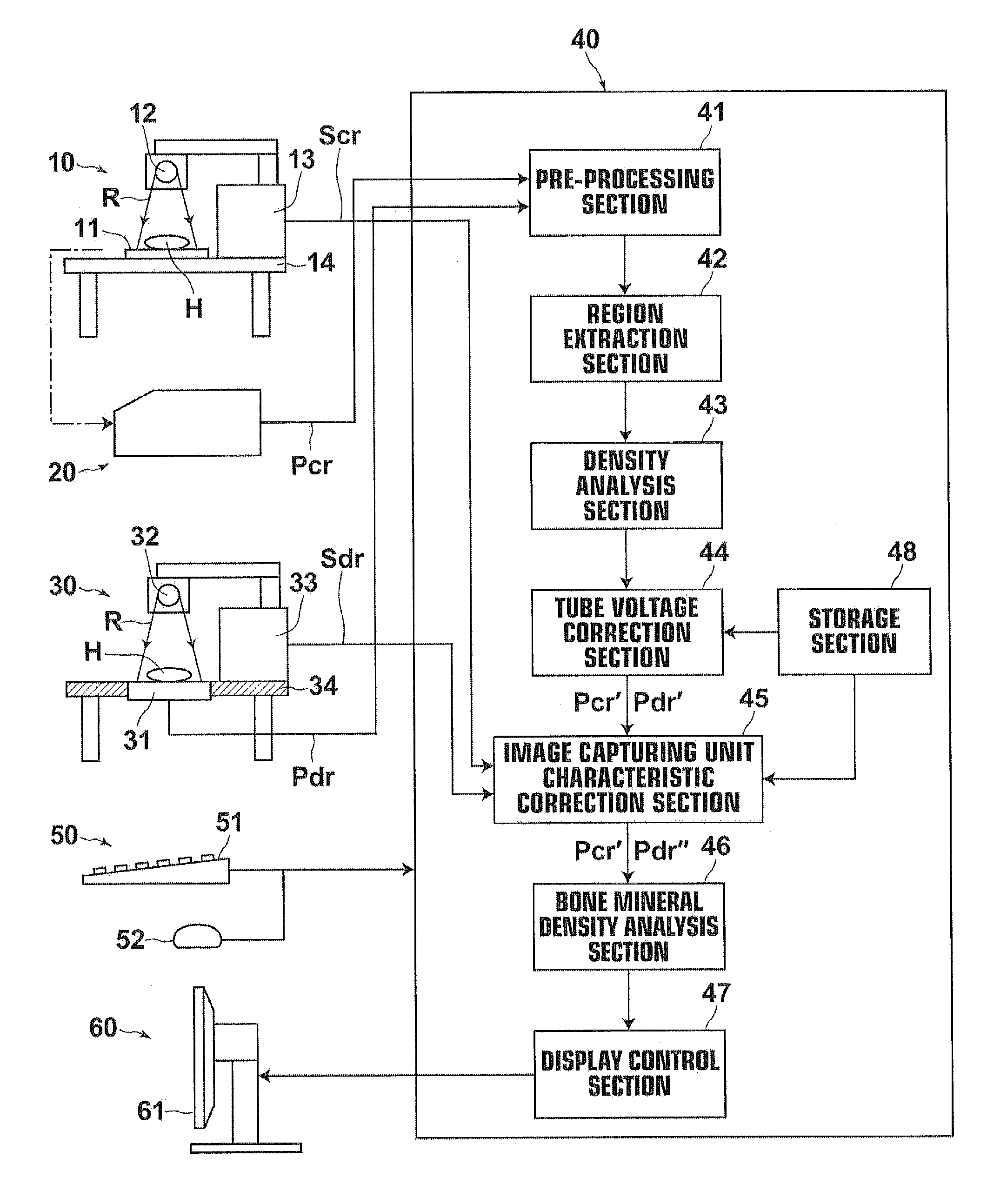
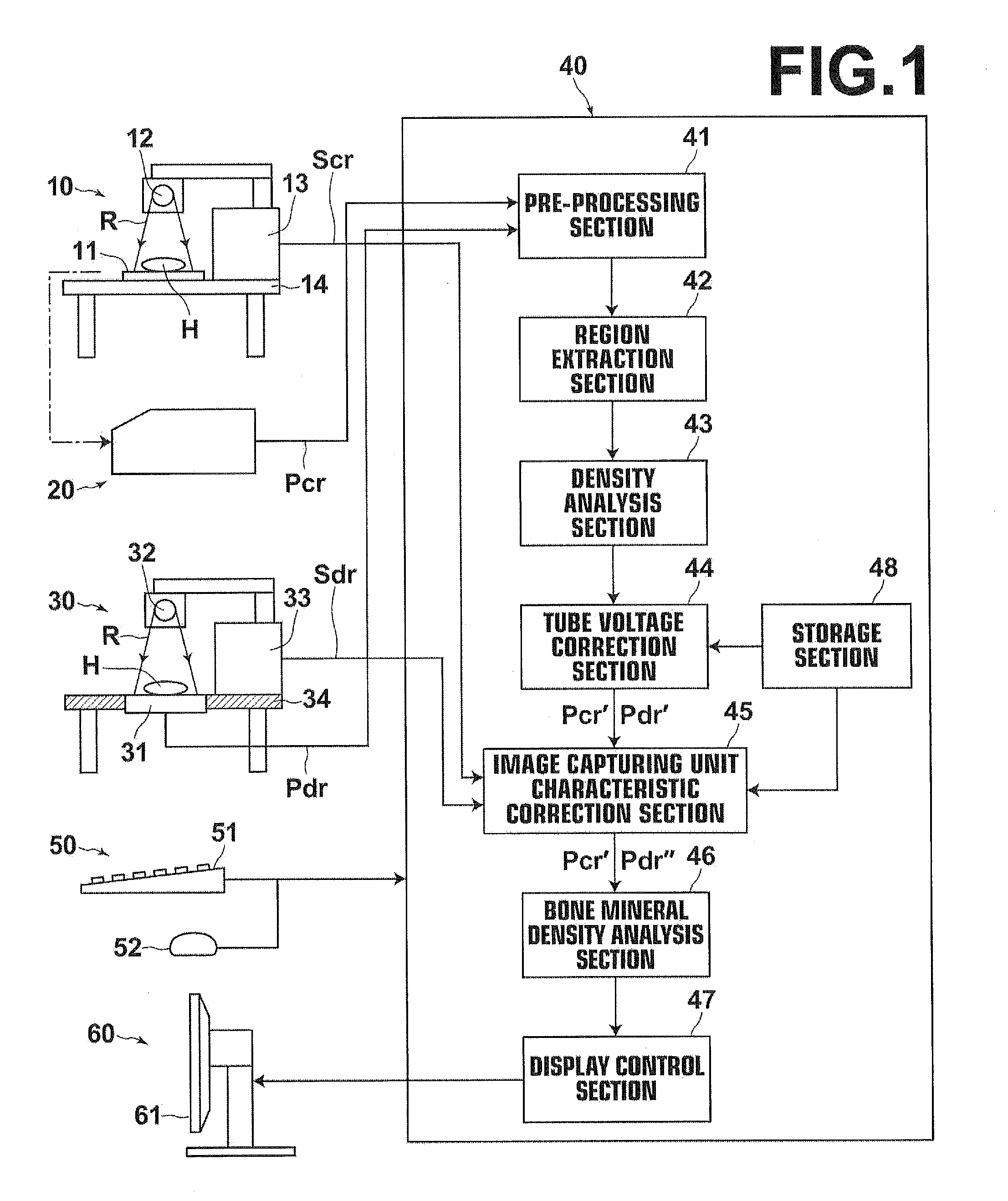
Bone mineral density analysis method, bone mineral density analysis apparatus, and recording medium
ActiveUS20130170614A1Health-index calculationUsing wave/particle radiation meansVolumetric Mass DensityBone mineral
From radiation images obtained by driving radiation tube with a plurality of tube voltages, including a normal tube voltage, a density gradient with respect to at least two sections of a reference substance having different radiation transmission characteristics is obtained for each of the plurality of tube voltages prior to obtaining a bone mineral density. If a radiation image captured for obtaining a bone mineral density is determined to have been captured under a tube voltage other than the normal tube voltage, an image signal representing the image and / or a bone mineral density analysis result is corrected so as to correspond to that which should have been obtained if the image had been captured under the normal tube voltage based on the relationship between the density gradient in the image and the density gradient in the radiation image captured under the normal tube voltage.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Computerized medical diagnostic and treatment advice system
InactiveUSRE43433E1Medical automated diagnosisSensorsInteractive Voice Response TechnologySymptom severity
A system and method for providing computerized, knowledge-based medical diagnostic and treatment advice. The medical advice is provided to the general public over a telephone network. Two new authoring languages, interactive voice response and speech recognition are used to enable expert and general practitioner knowledge to be encoded for access by the public. “Meta” functions for time-density analysis of a number of factors regarding the number of medical complaints per unit of time are an integral part of the system. A semantic discrepancy evaluator routine along with a mental status examination are used to detect the consciousness level of a user of the system. A re-enter feature monitors the user's changing condition over time. A symptom severity analysis helps to respond to the changing conditions. System sensitivity factors may be changed at a global level or other levels to adjust the system advice as necessary.
Owner:CLINICAL DECISION SUPPORT LLC
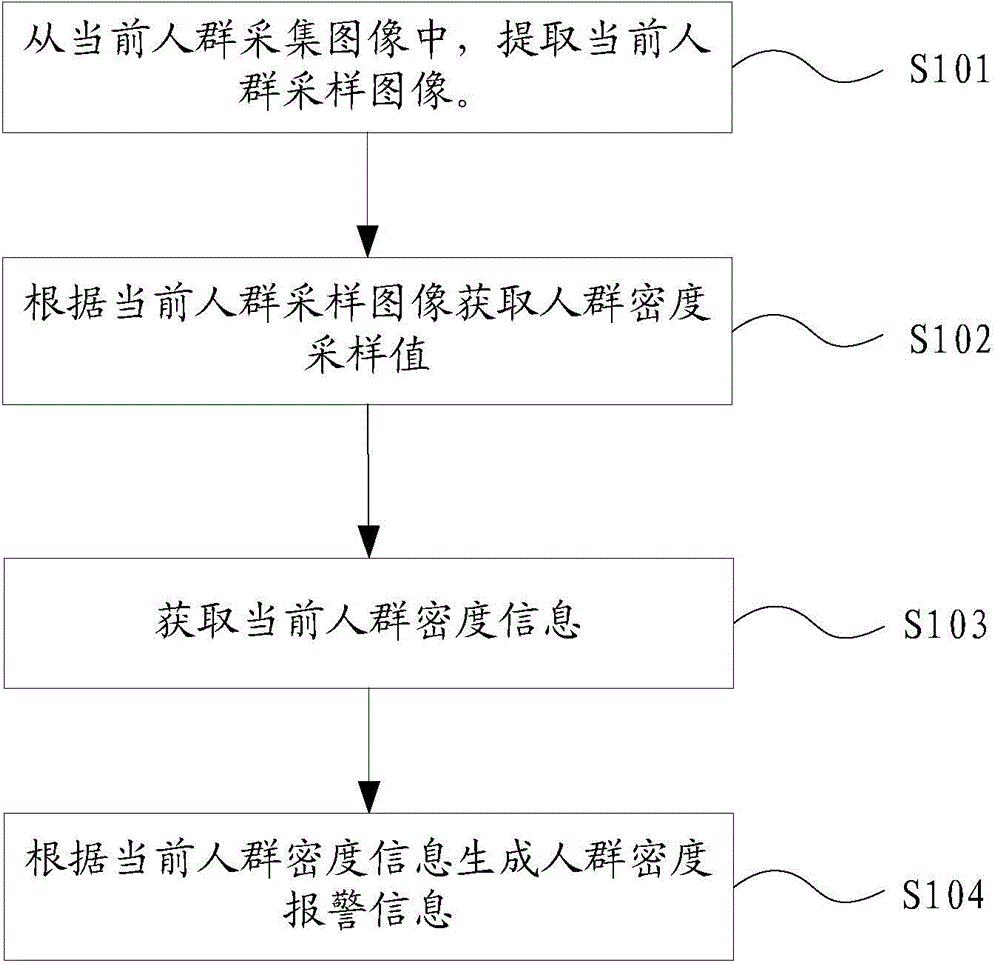
Crowd density information obtaining method
InactiveCN104463121ALow costImprove effectivenessBiometric pattern recognitionDensity analysisCrowds
The invention discloses a crowd density information obtaining method. The crowd density information obtaining method includes the steps of extracting a current crowd sampling image from current crowd collecting images; obtaining a crowd density sampling value according to the current crowd sampling image; conducting texture-based method density analysis or pixel-based method crowd density analysis to obtain current crowd density information according to judgment results of the crowd density sampling value and a set threshold value; generating crowd density alarm information according to the current crowd density information. The problem that the existing crowd density accuracy is low is accordingly solved. The condition that the density analysis accuracy is reduced due to the fact that an analysis method is improper is avoided. In this way, the crowd density collecting accuracy is improved, the crowd pre-storage cost is reduced, and the information effectiveness is improved.
Owner:NEW TECH APPL INST BEIJING CITY
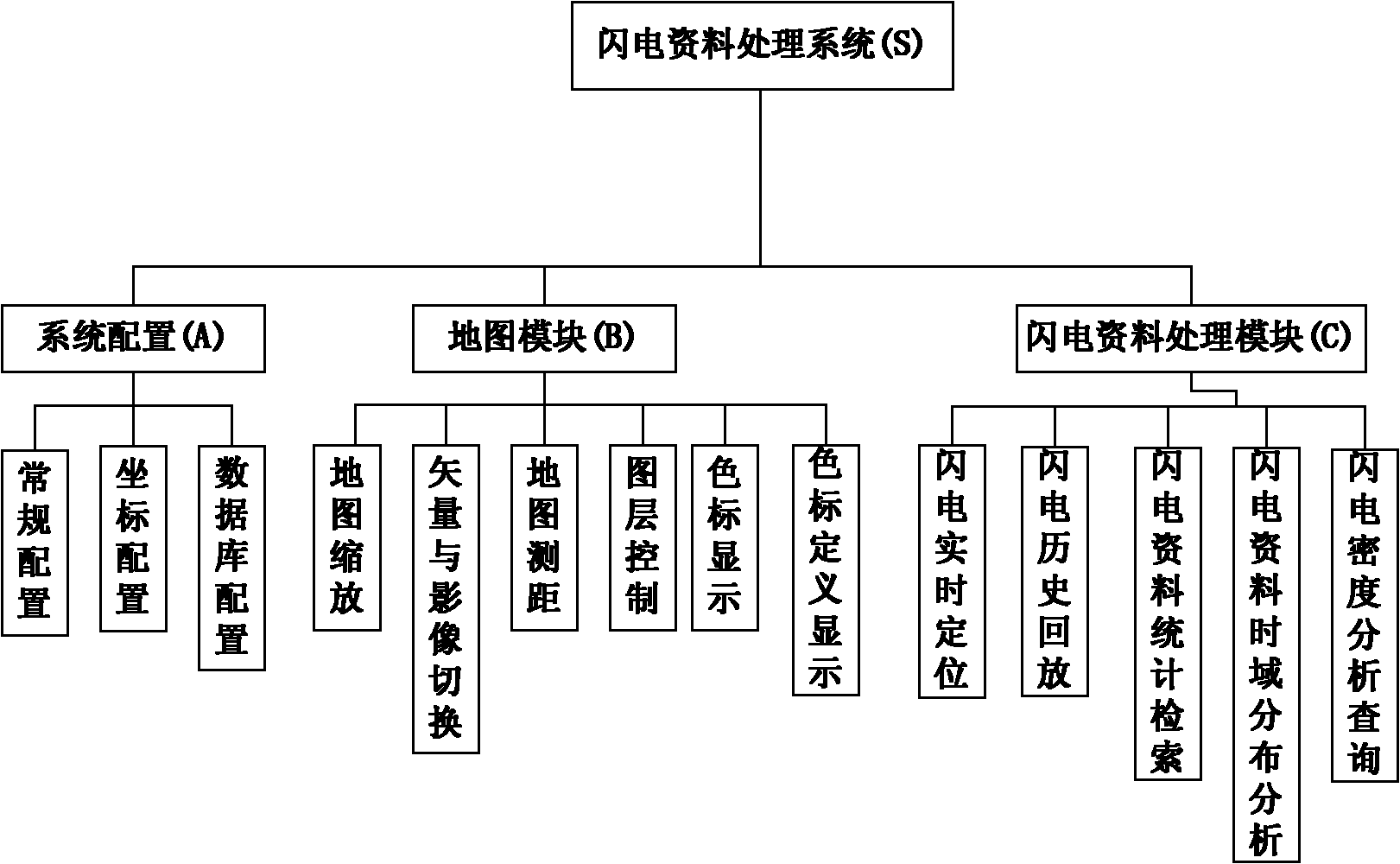
GIS (Geographic Information System) platform processing method for mass lightning data
InactiveCN102156739ARealize the fundamental goal of the serviceSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainDensity analysis
The invention discloses a GIS (Geographic Information System) platform processing method for mass lightning data, which comprises the following steps of: (1) establishing a lightning database to provide a basic data source for lightning analysis through inducing historical data and acquiring data in combination with a real-time lightning detection system, wherein lightning information is intuitively displayed by using a GIS platform for the convenience of predicting the development tendency of lightning; and (2) analyzing lightning data through an interactive method, and finally forming a weather product which can be issued, wherein the lightning data comprises the query and statistics of customized lightning information, lightning space density analysis and the like. As mass lightning data is processed on the GIS platform, the demand on lightning protection services is met. Real-time or delayed load, customized display as well as time domain and spatial analysis can be performed on a lot of lightning data, and therefore a technical support is provided for weather forecasters to observe and analyze lightning for the convenience of lightning prevention forecast in a better manner.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
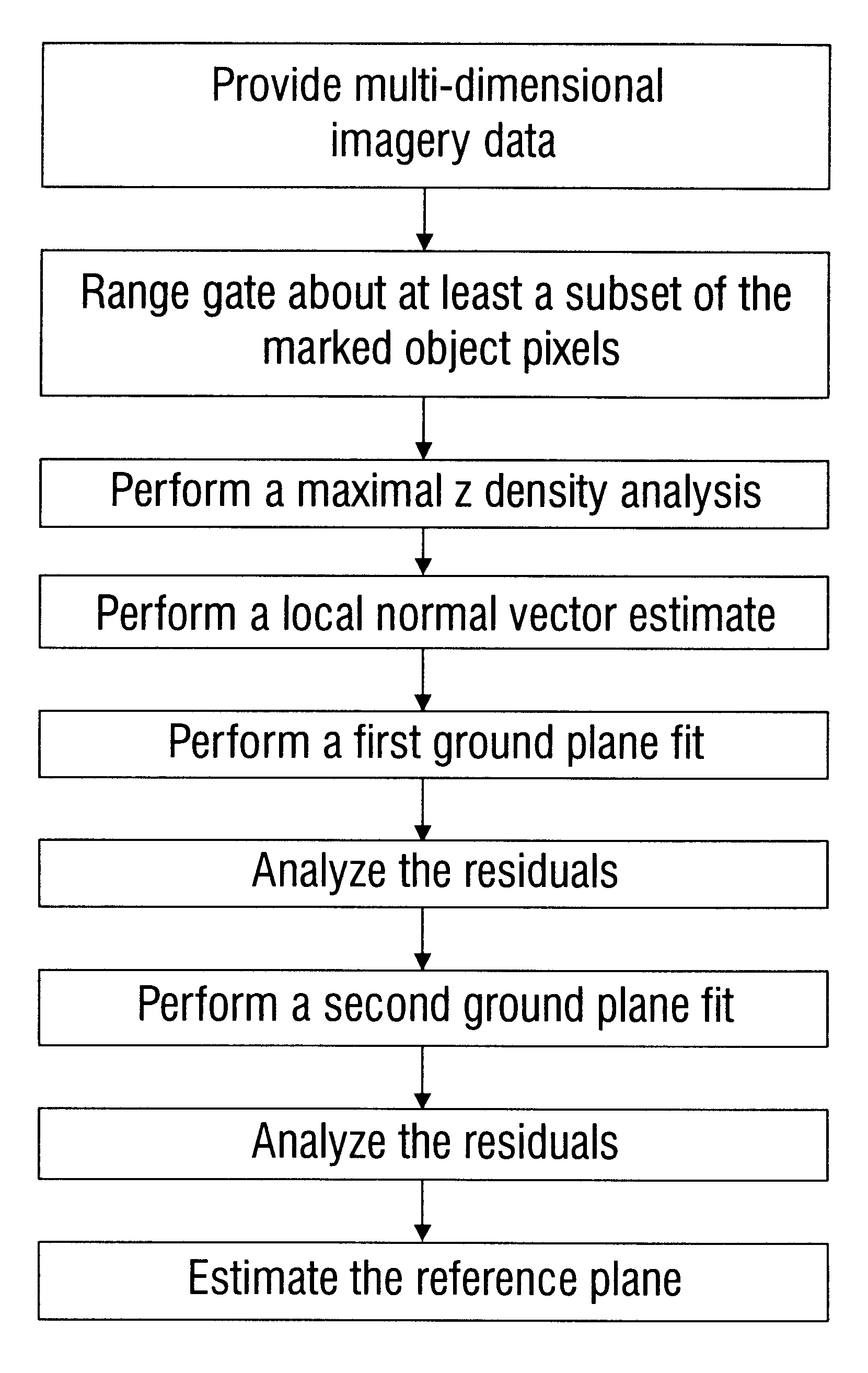
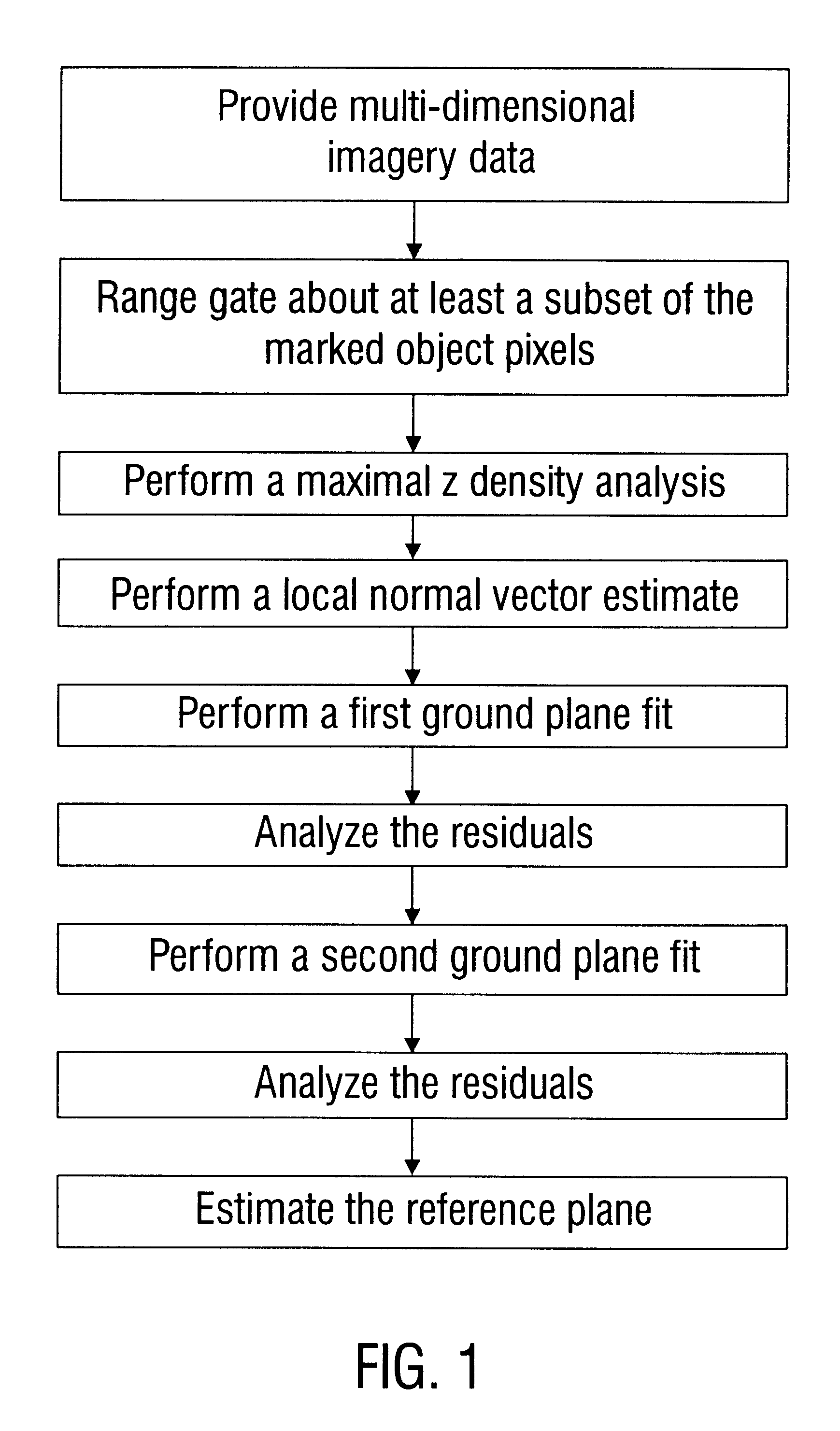
Method and software-implemented apparatus for ground plane estimation in multi-dimensional data
A method for determining the reference plane in multi-dimensional data is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method includes (a) providing multi-dimensional imagery data, referred to as set A, including an array of pixels having object pixels marked; (b) range gating about at least a subset of the marked object pixels, including marking pixels outside the range gate to form an unmarked pixel subset of set A, referred to as subset B; (c) performing maximal z density analysis on subset B, including marking pixels outside the maximum density to form an unmarked pixel subset of subset B, referred to as subset C; (d) performing a local normal vector estimate on subset C, including marking pixels having a normal vector exceeding specified threshold L from nominal to form an unmarked pixel subset of subset C, referred to as subset D; (e) performing a first ground plane fit on subset D, each pixel producing residual value X, cumulatively known as residual set X; (f) analyzing residual X, including performing a residual density analysis and marking pixels whose residual value X exceeds specified threshold M to form an unmarked pixel subset of subset D, referred to as subset E; (g) performing a second ground plane fit on subset E, each pixel producing residual value Y, cumulatively known as residual set Y; (h) analyzing residual set Y, including marking pixels whose residual value Y exceeds specified threshold N to form an unmarked pixel subset of subset E, referred to as subset F; and (i) estimating the reference plane for subset F.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Device for underground detecting sand production of oil well
The invention discloses a device for underground detecting sand production of an oil well, which comprises an underground part and an aboveground part. The device comprises a detector, a transmission line, an optical fiber grating demodulator, a computer, and the like. An optical fiber grating accelerator and an ultrasonic sensor are arranged at a measuring nipple. The detector is transmitted underground by a winch through a stranded wire, at the damaged part of a sleeve or at the place near the damaged part of a sieve tube, the sands contained in the fluid strike a rotary impeller arranged in the detector so as to generate vibration and sound, the optical fiber grating accelerator and the ultrasonic sensor detect the signal and transmit the signal to the optical fiber grating demodulator arranged on the ground through a cable, then the signal is amplified, filtered, subjected to analogue-digital conversion, and then is transmitted to the computer, the computer performs power spectral-density analysis by analysis software so as to identify the information such as sand production amount and sand production depth. The device is characterized by simple structure, low cost, convenience in operation, and wide temperature and pressure application range; a new method is provided for the detection of sand production places of the oil well. The device is applied to the technical field of sand production place measurement.
Owner:刘刚
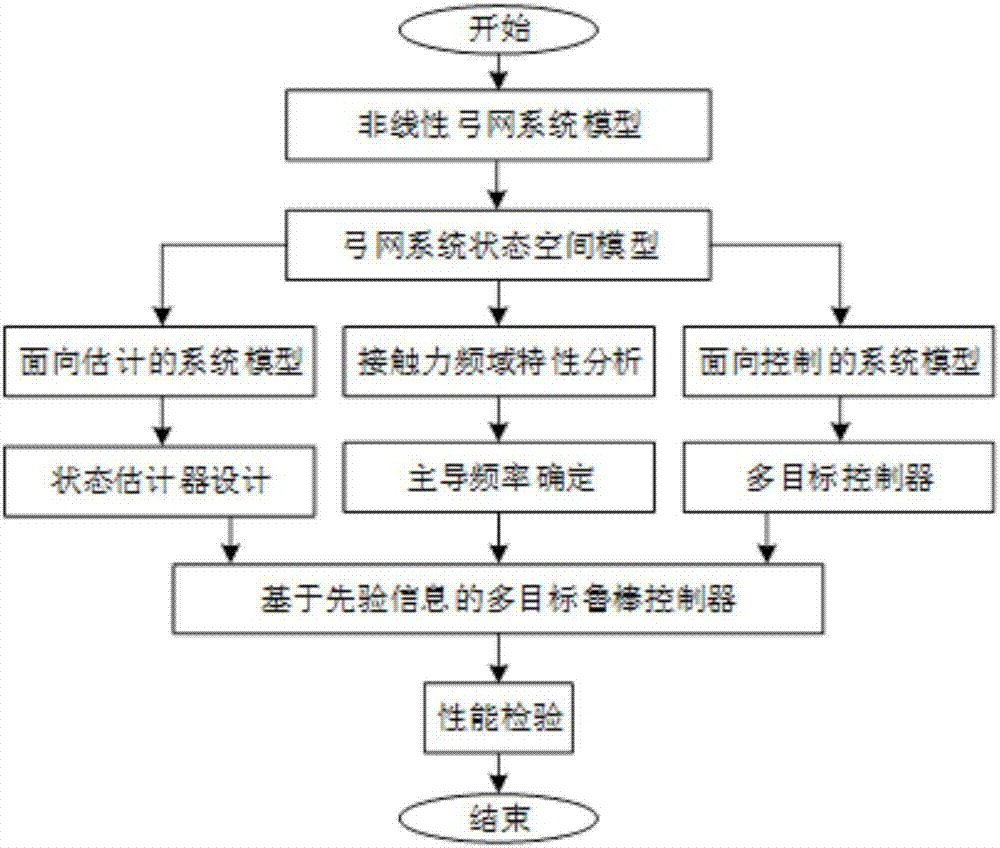
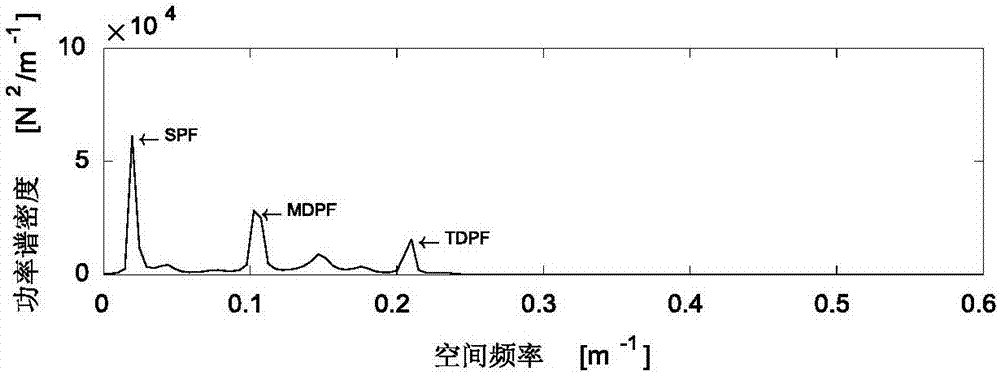
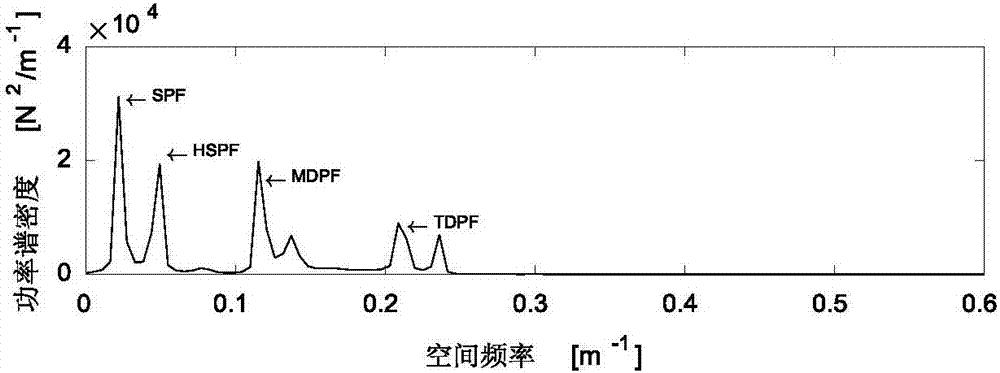
Design method for high-speed pantograph multi-target finite frequency domain controller
InactiveCN106855898AHigh precisionImprove controlDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNonlinear modelContact force
The invention discloses a design method for a high-speed pantograph multi-target finite frequency domain controller. The method comprises the following steps that a pantograph and overhead contact wire system nonlinear model and a state-space model are established; frequency domain characteristics of contact force fluctuation are analyzed by power spectral density, and therefore dominant frequency of the contact force is determined; a pantograph and overhead contact wire model for control is constructed, a control target is determined, then, the controller is designed, and a control gain matrix is calculated; a pantograph and overhead contact wire model for estimation is constructed, and noise statistics unknown or time-varying estimator design is considered. The controller takes advantages of the frequency domain characteristics of the contact force fluctuation and improves the control property, and the application of the estimator and the limitation for control force improve the practicality of a project.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
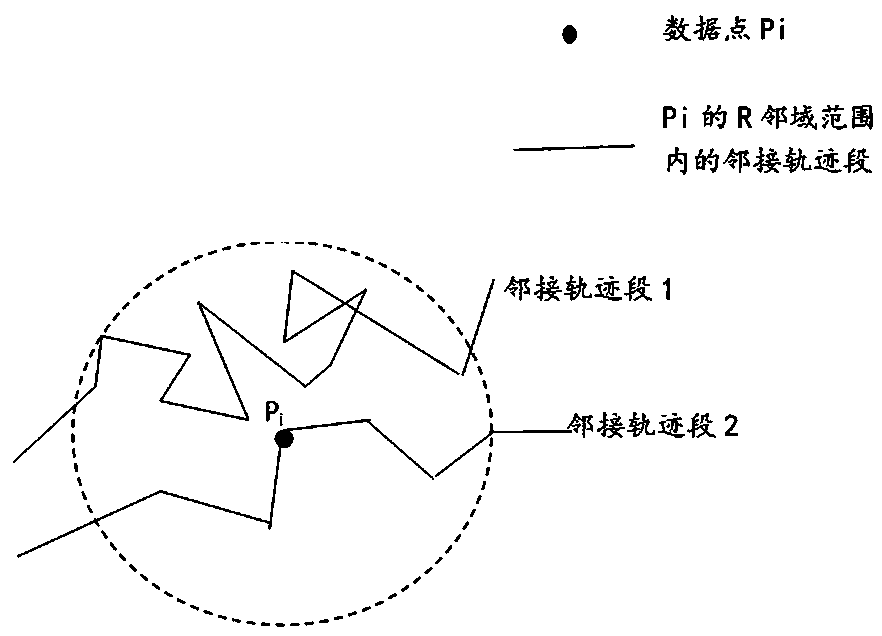
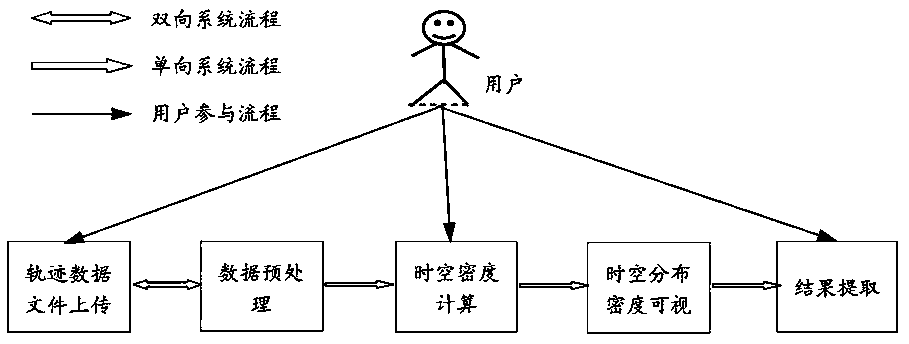
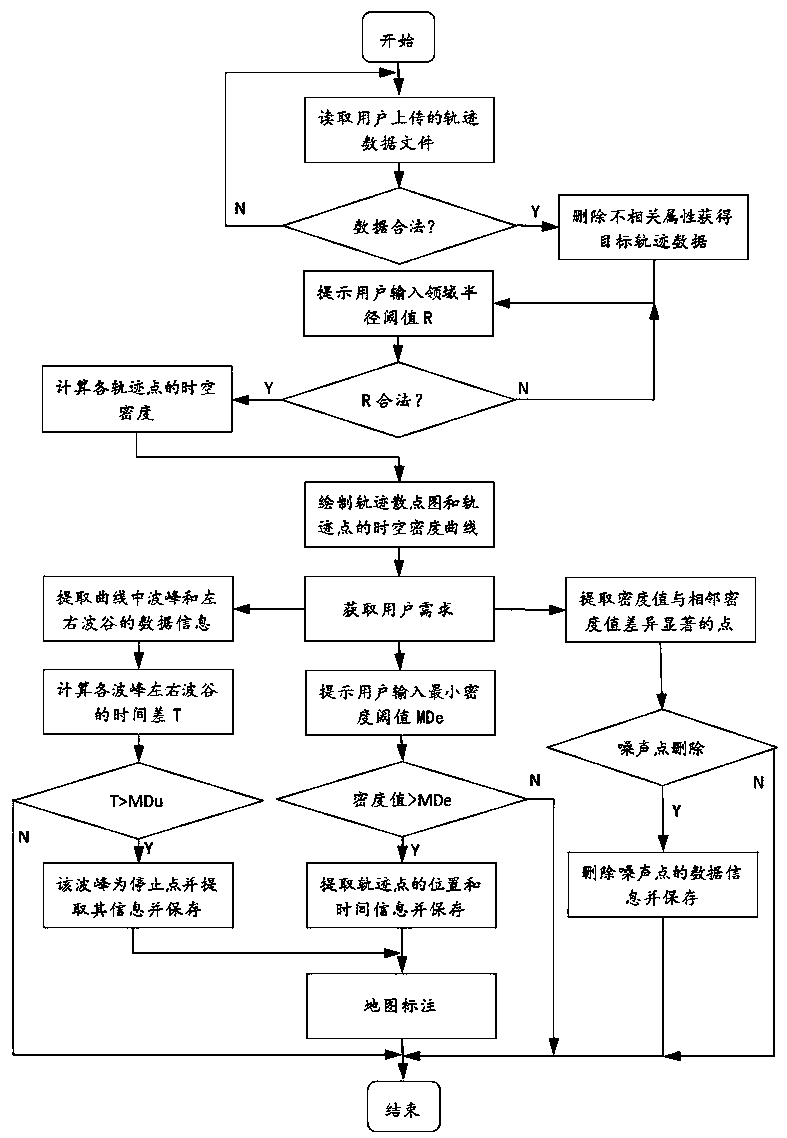
A trajectory data space-time density analysis system and an analysis method thereof
ActiveCN109684384AHigh precisionEasy to operateData miningSpecial data processing applicationsDensity curveTime information
The invention discloses a track data space-time density analysis system and an analysis method thereof. The technical scheme is as follows: the space-time density analysis module performs calculationby using target track data obtained by the track data preprocessing module to obtain space-time density values of track points, and the space-time distribution density visualization module draws the target track data and the space-time density values of the track points into a track scatter diagram and a space-time density curve respectively and presents the track scatter diagram and the space-time density curve to a user; And a result extraction module is used for extracting and storing a density analysis result which the user is interested in, and finally labeling at a corresponding positionon the map according to the latitude and longitude and the time information of the extraction result. The system and the method can serve wider application, the calculation process and result presentation are more visual, a user does not need to carry out excessive preprocessing on the data in advance, and the system is simpler to operate.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
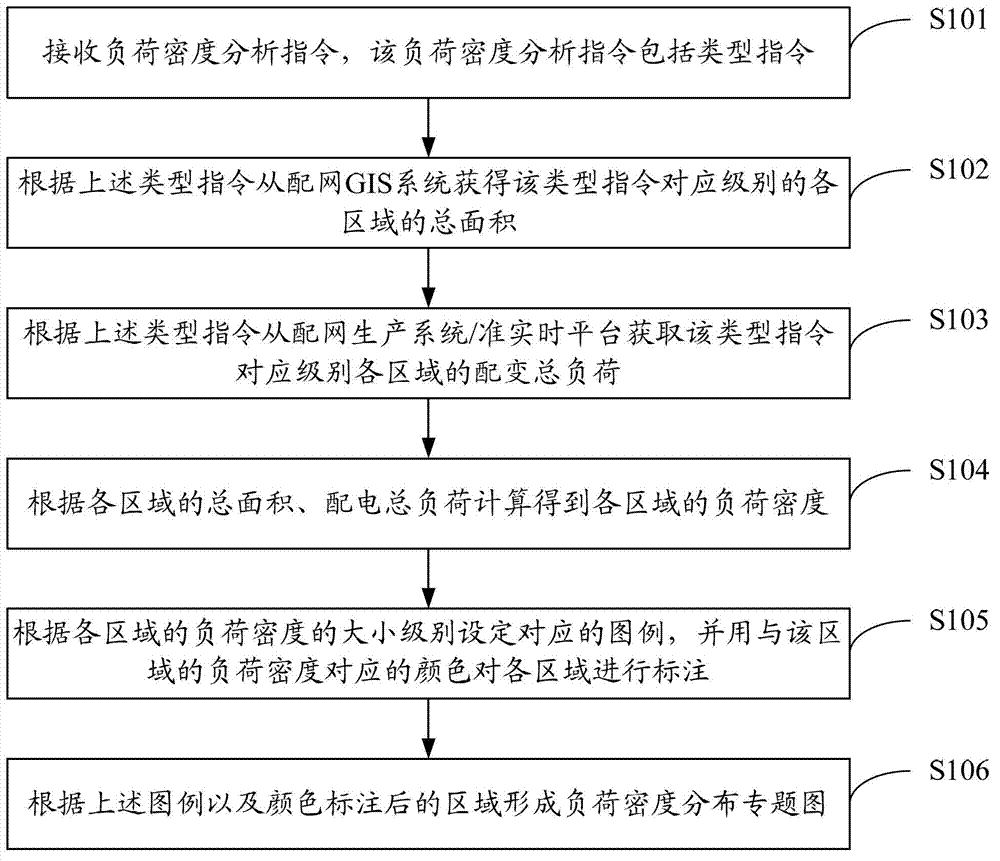
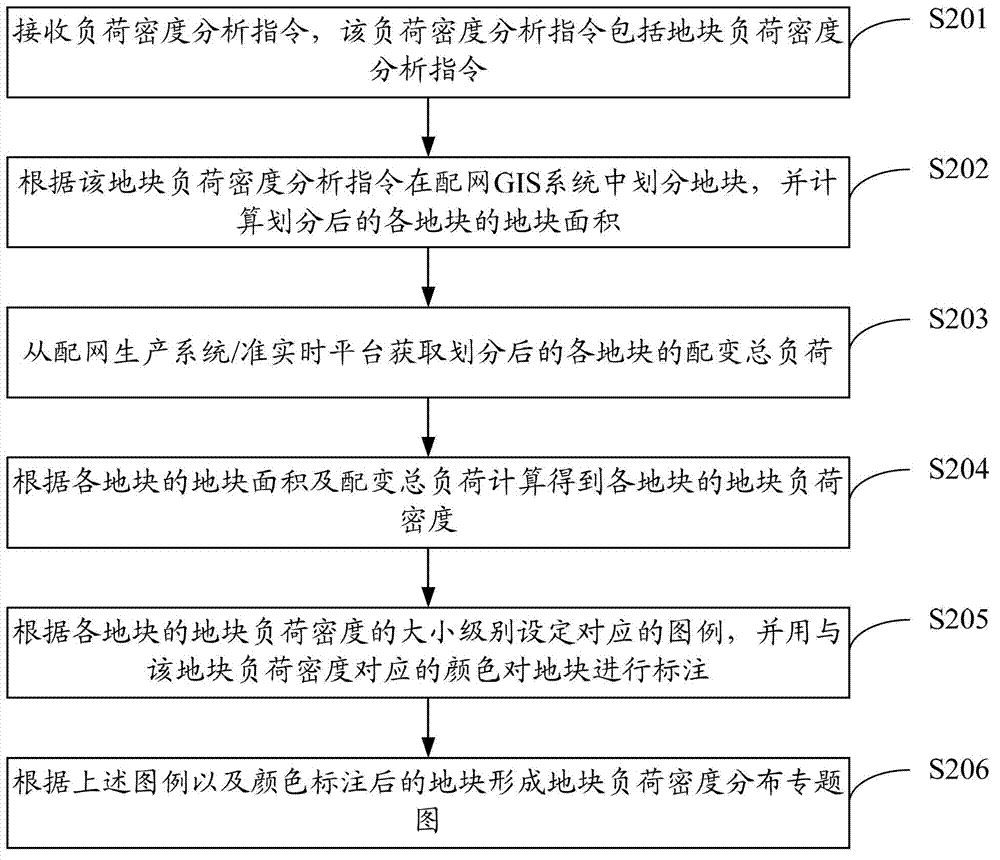
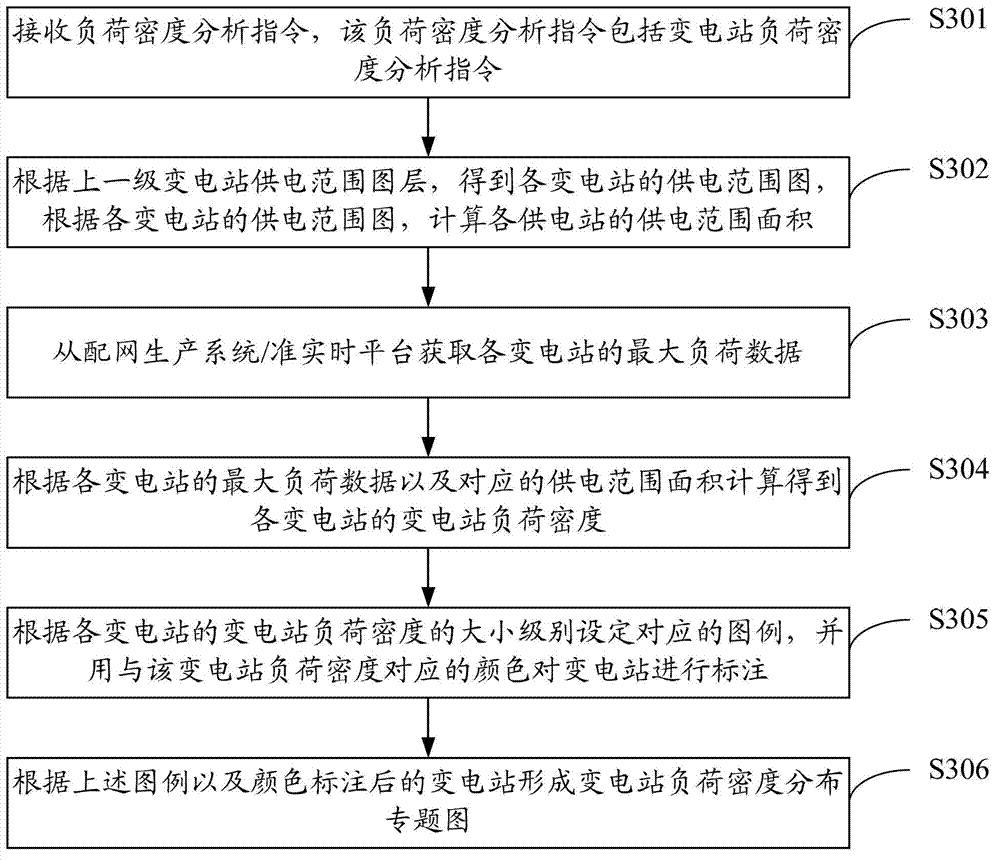
Method and system for analyzing power grid load density
ActiveCN102930481ARealize analysisGet real-time and convenientData processing applicationsDistribution transformerPower grid
The invention discloses a method and a system for analyzing the power grid load density. The method comprises the steps as follows: receiving a load density analyzing instruction comprising type instructions; obtaining the total area of the regions of the corresponding levels of the type instructions from a distribution network GIS (Geographic Information System) according to the type instructions; obtaining the total distribution transformer load of the regions of the corresponding levels of the type instructions from a distribution network production system / quasi real-time platform according to the type instructions; and calculating according to the total area and the total distribution transformer load of the regions to obtain the load densities of the regions. According to the scheme, the need for analyzing different load densities can be met, the load densities of various space ranges can be analyzed, and the analyzing efficiency is high.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD
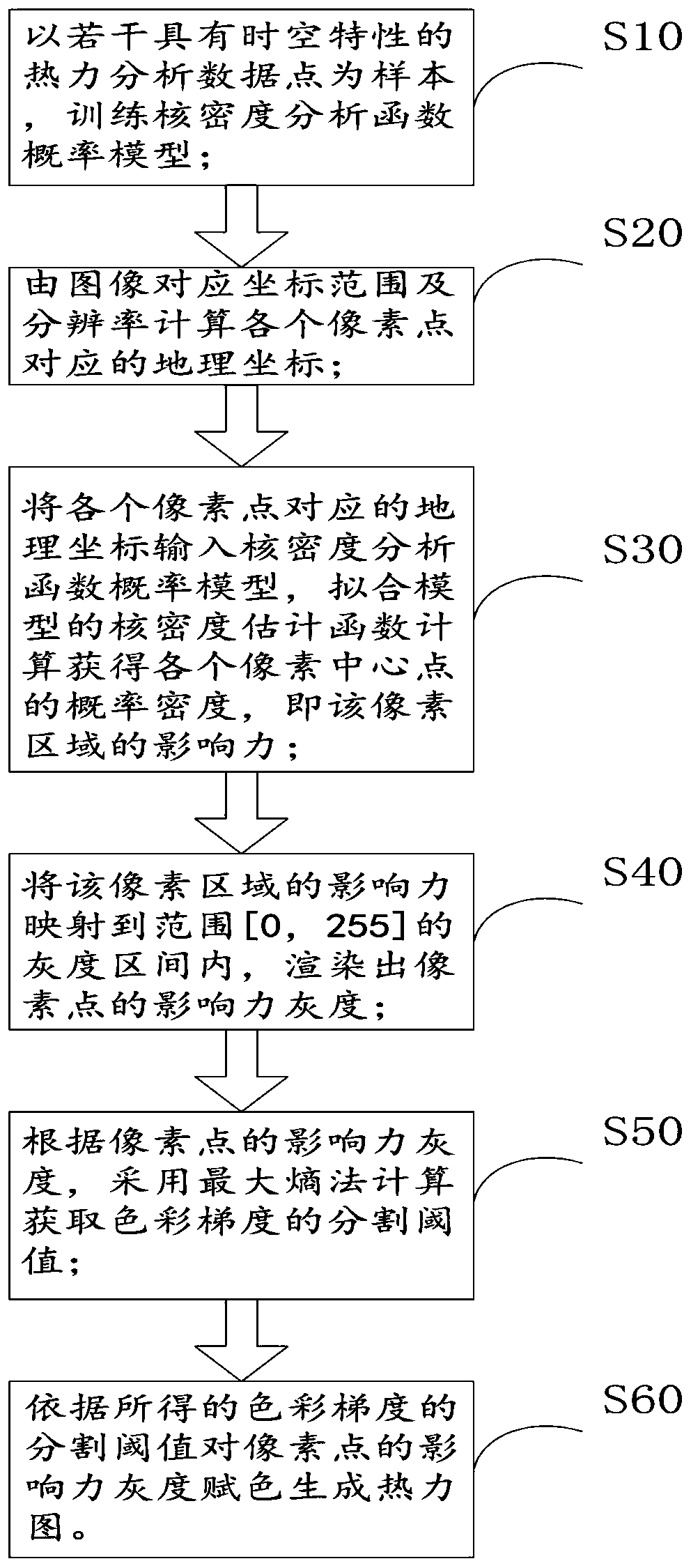
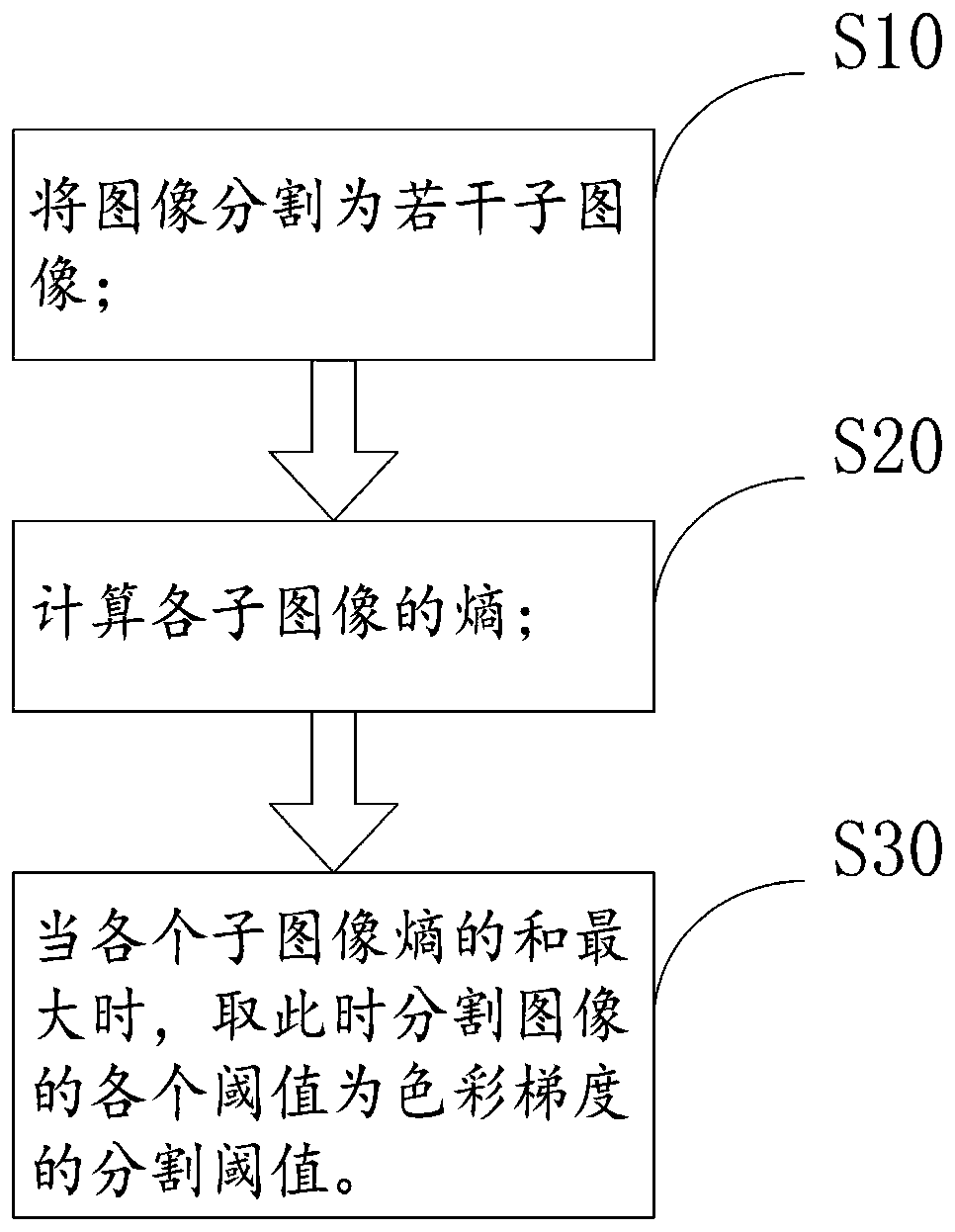
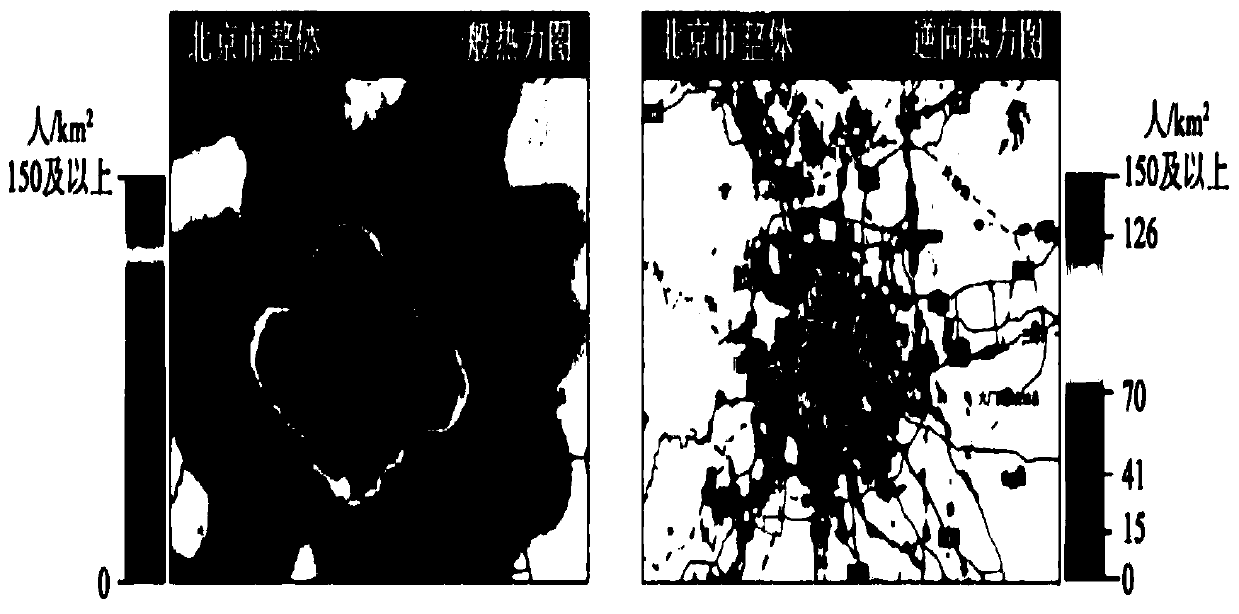
A method for reversely rendering and drawing a thermodynamic diagram
InactiveCN109712151ASmall granularityQuality assuranceImage analysisGeographical information databasesAnalysis dataSurrogate data
The invention discloses a method for reversely rendering and drawing a thermodynamic diagram, which comprises the following steps of: training a kernel density analysis function probability model by taking a plurality of thermodynamic analysis data points with space-time characteristics as samples; calculating a geographic coordinate corresponding to each pixel point according to the coordinate range corresponding to the image and the resolution; inputting the image into a kernel density analysis function probability model, and fitting a kernel density estimation function of the model to calculate and obtain the influence of a pixel region; mapping the influence of the pixel region into a gray scale interval of a range [0, 255], and rendering the influence gray scale of the pixel point; Obtaining a segmentation threshold value of the color gradient according to the influence gray level of the pixel point; and according to the obtained segmentation threshold value of the color gradient,color giving is carried out on the influence gray level of the pixel point to generate a thermodynamic diagram. According to the method, pixel points replace data points to serve as analysis elements, the calculation amount of geographic space analysis is greatly reduced, and the quality of thermodynamic diagram rendering can be guaranteed while the requirement for rendering of hundred million-level mass data thermodynamic diagrams is met.
Owner:航天精一(广东)信息科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com