Method for calculating signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) RF coil
A magnetic resonance imaging, signal-to-noise ratio technology, applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable coil structure optimization, reduced computing efficiency, and increased subsections
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] The principle and specific implementation of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0058] Example (Torus Surface Coil):
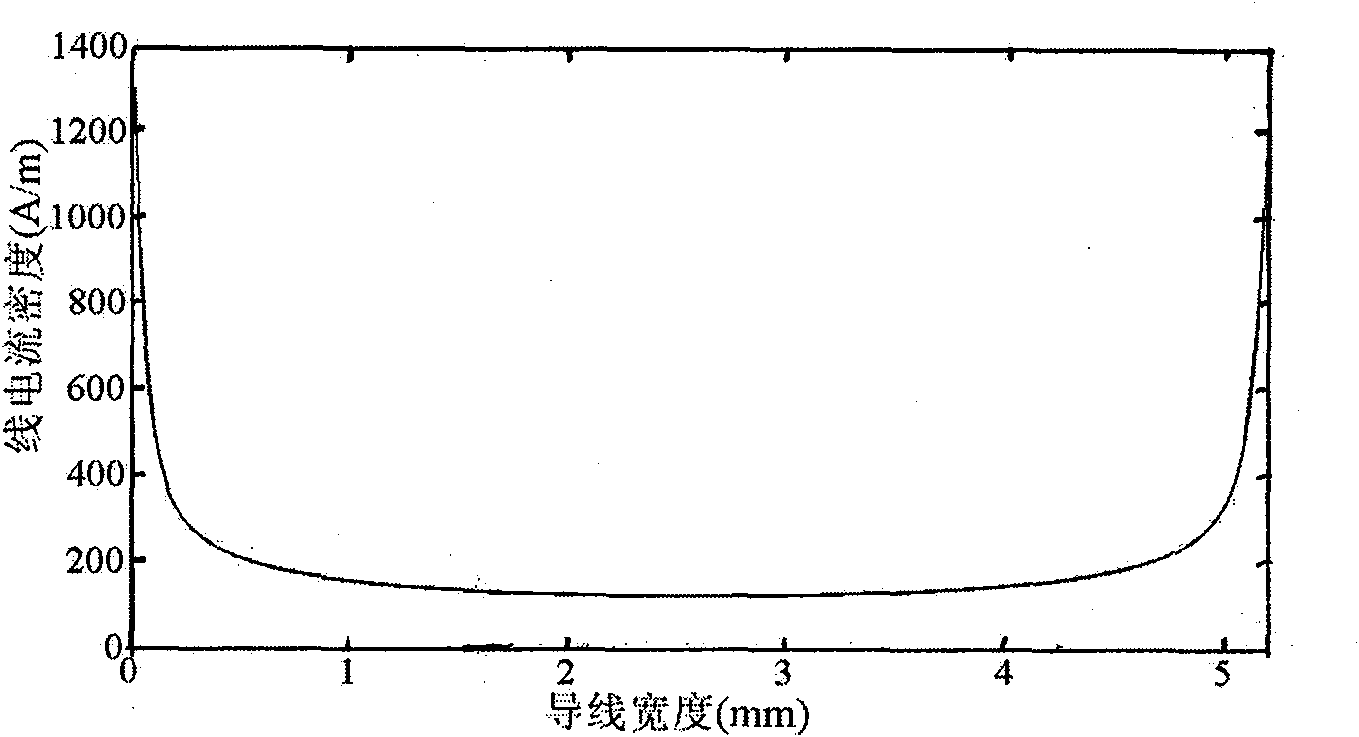
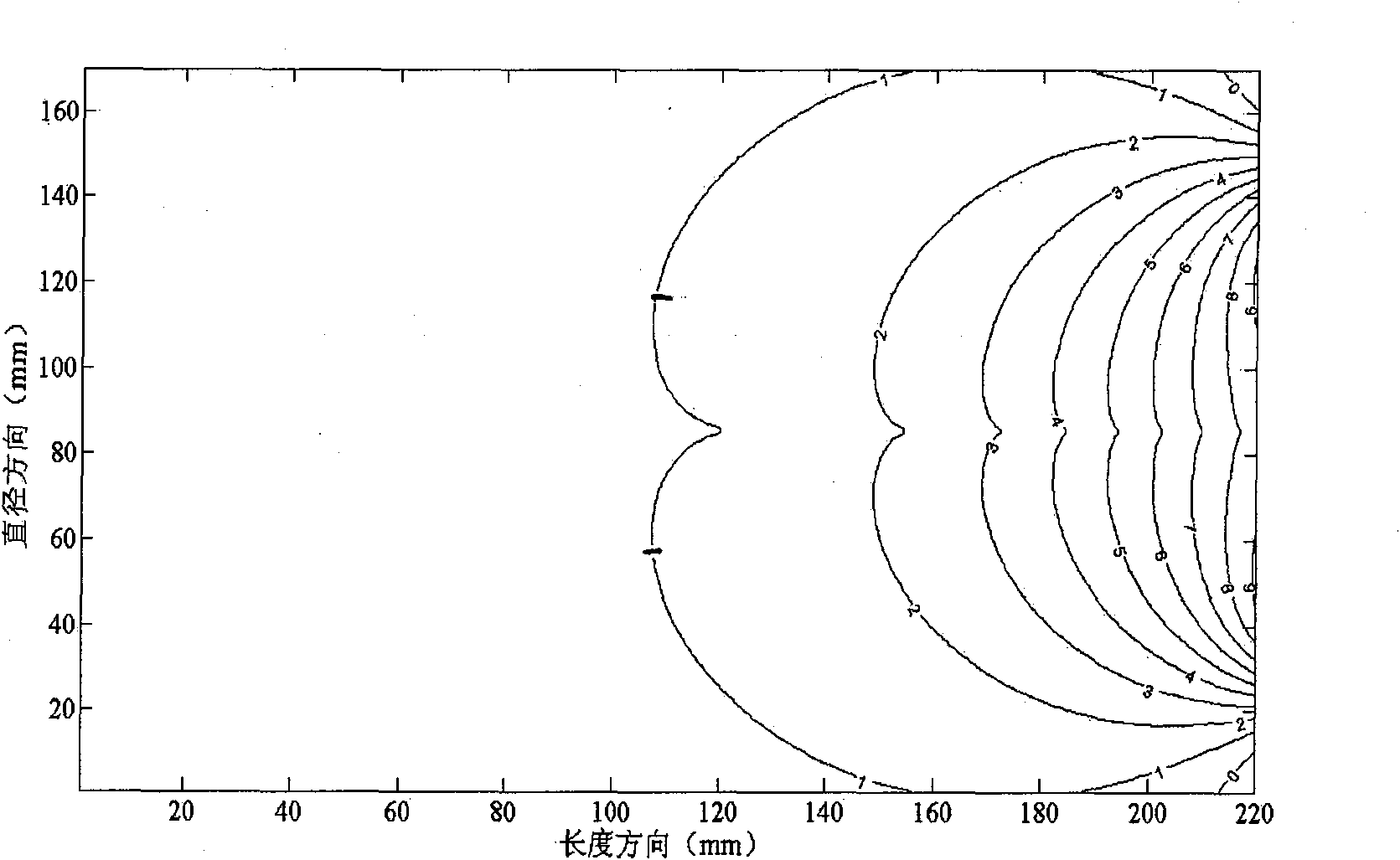
[0059] The coil is a circular coil with a radius of 62.1mm, and the cross-section of the conductor is a rectangle with a width of 5.2mm and a thickness of 0.2mm. Conductor material is copper strip, magnetic permeability is 4π×10 -7 H / m, the measured conductivity is 5.294×10 7 S / m. The load is a cylinder with a length of 22 cm and a diameter of 17 cm, with a conductivity of 0.8 S / m. The coil is 2 cm below the load. A current of radio frequency f=14.85MHz is passed through the coil. A. Calculate the equivalent resistance of the coil; B. Calculate the SNR of the coil.
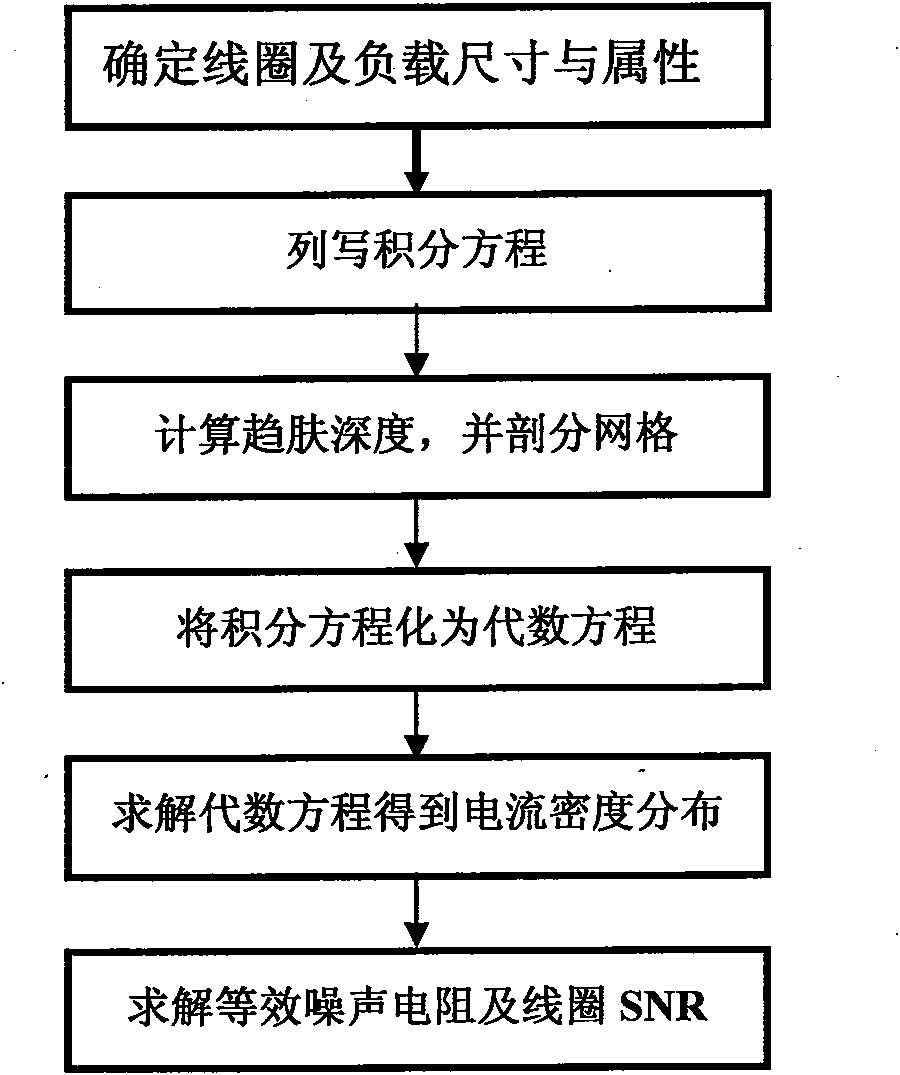
[0060] (1) Determine the size and material properties of the coil and load according to the actual situation.
[0061] (2) According to the quasi-steady-state assumption, the integral equation satisfied by the current densit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com