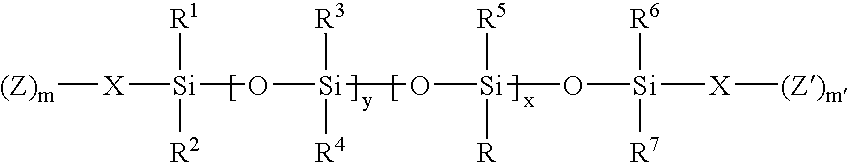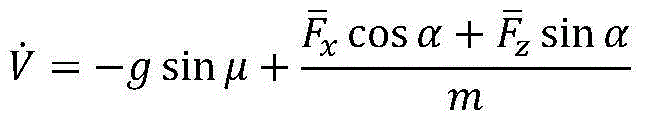Patents
Literature
304 results about "System matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
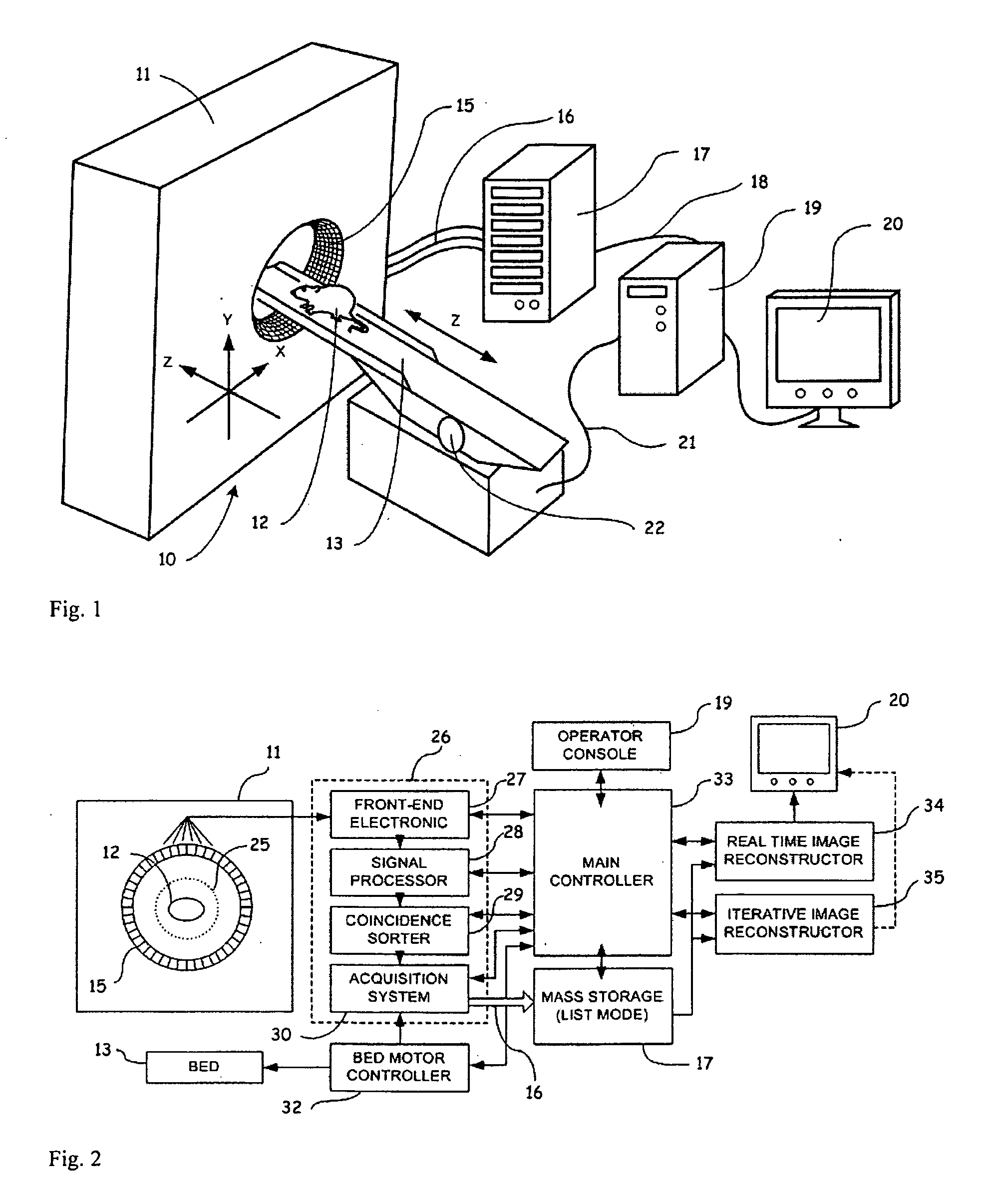
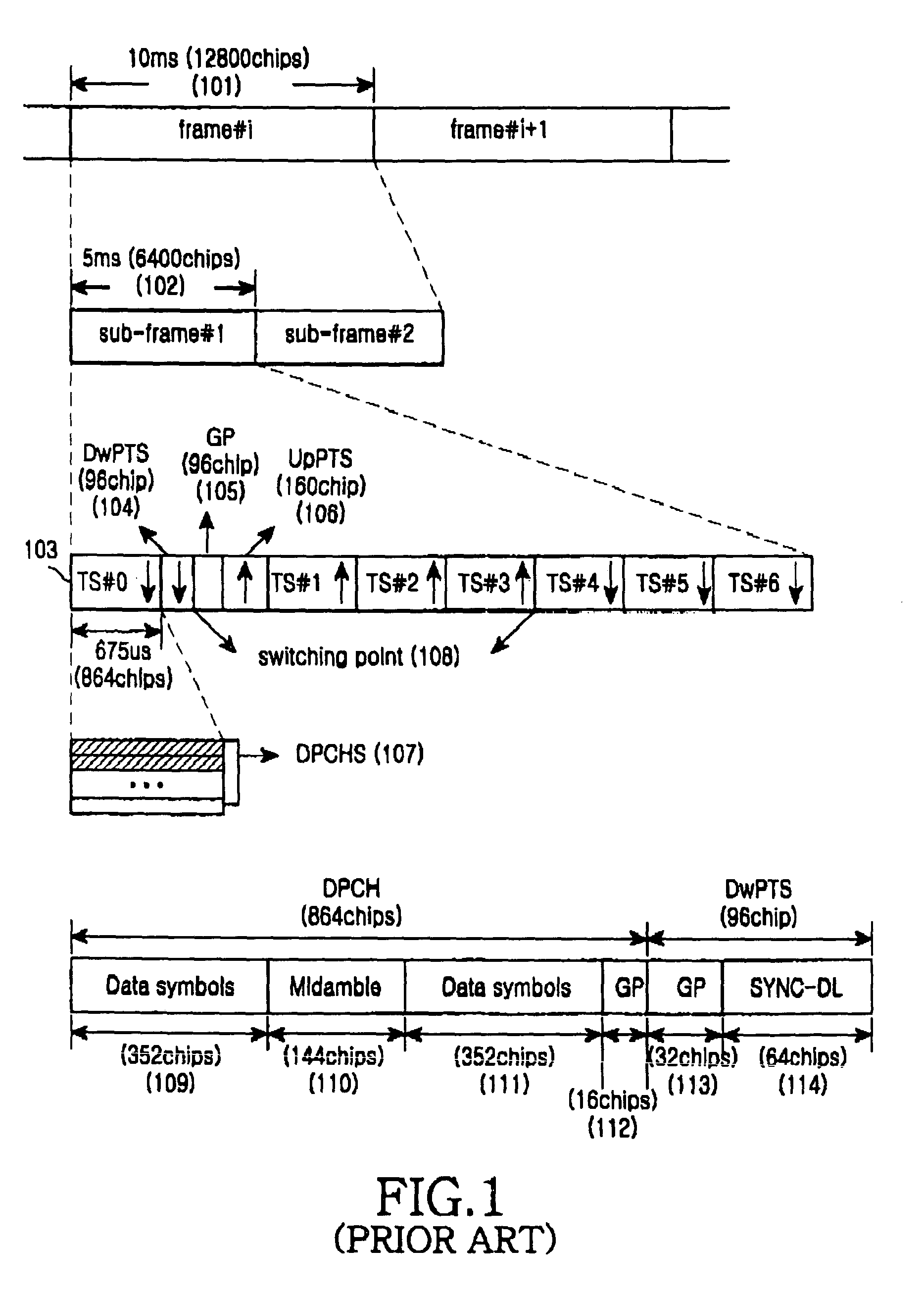
The matrix is built up by multiplying the refraction matrices and translation matrices. The positions of the principal planes, the front and back surface powers, and the equivalent focal length of Gullstrand's equation can be calculated from the system matrix. This is the form of the system matrix used by Meyer-Arendt.
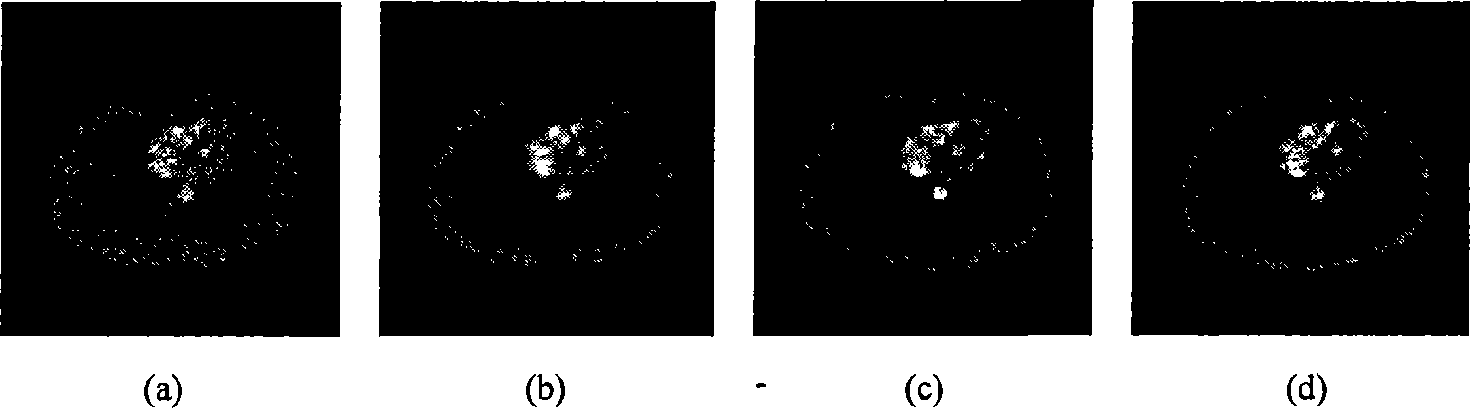
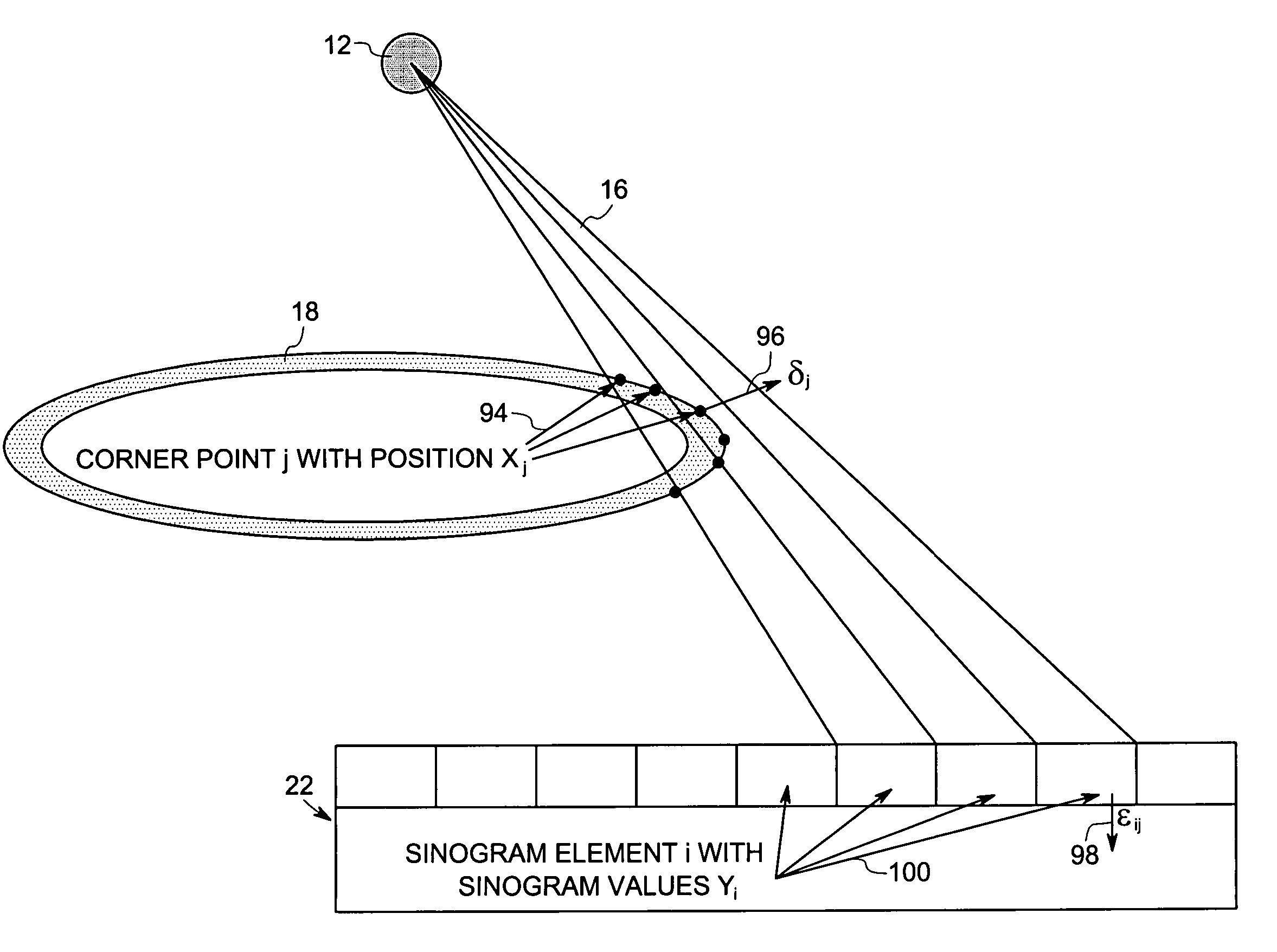
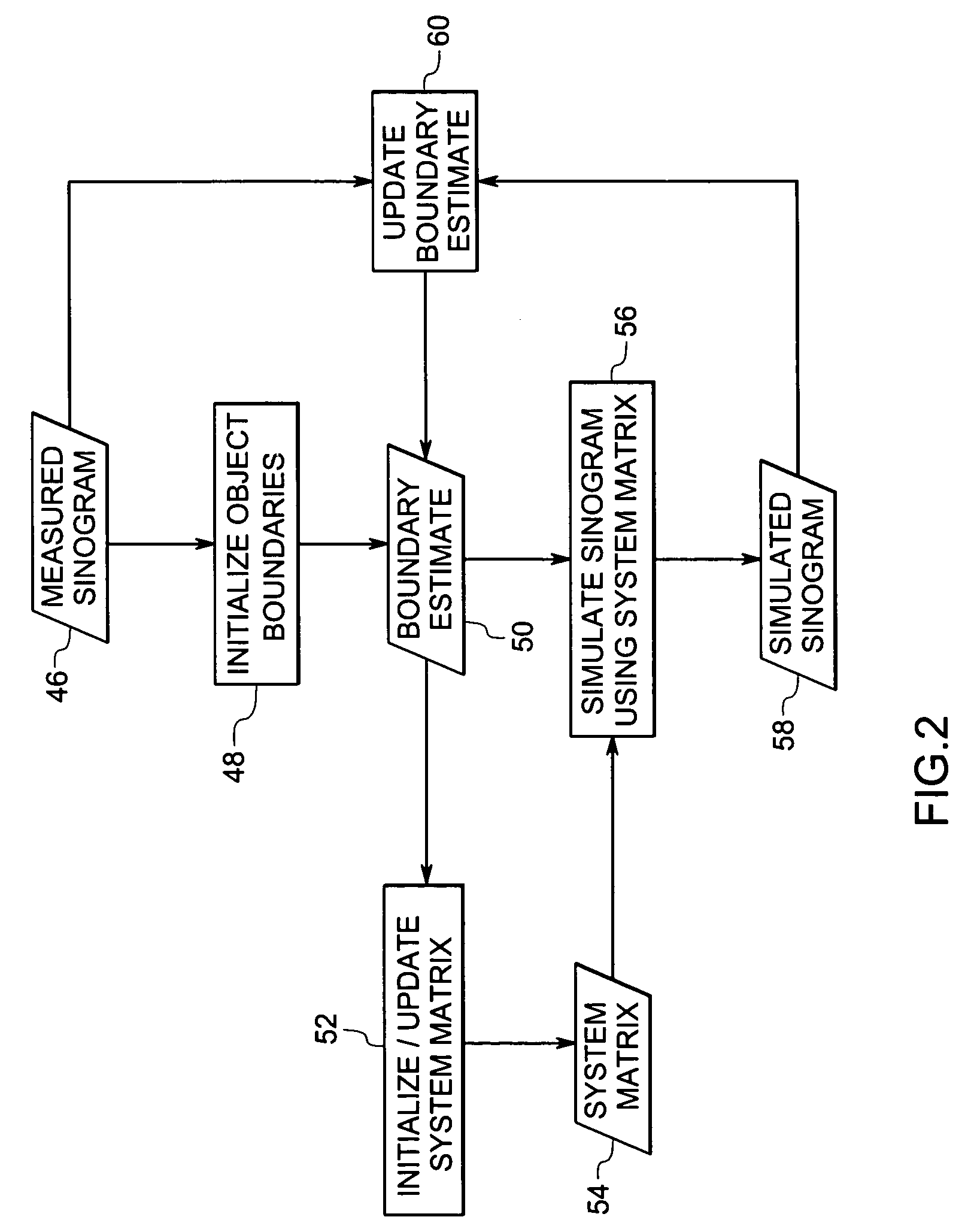
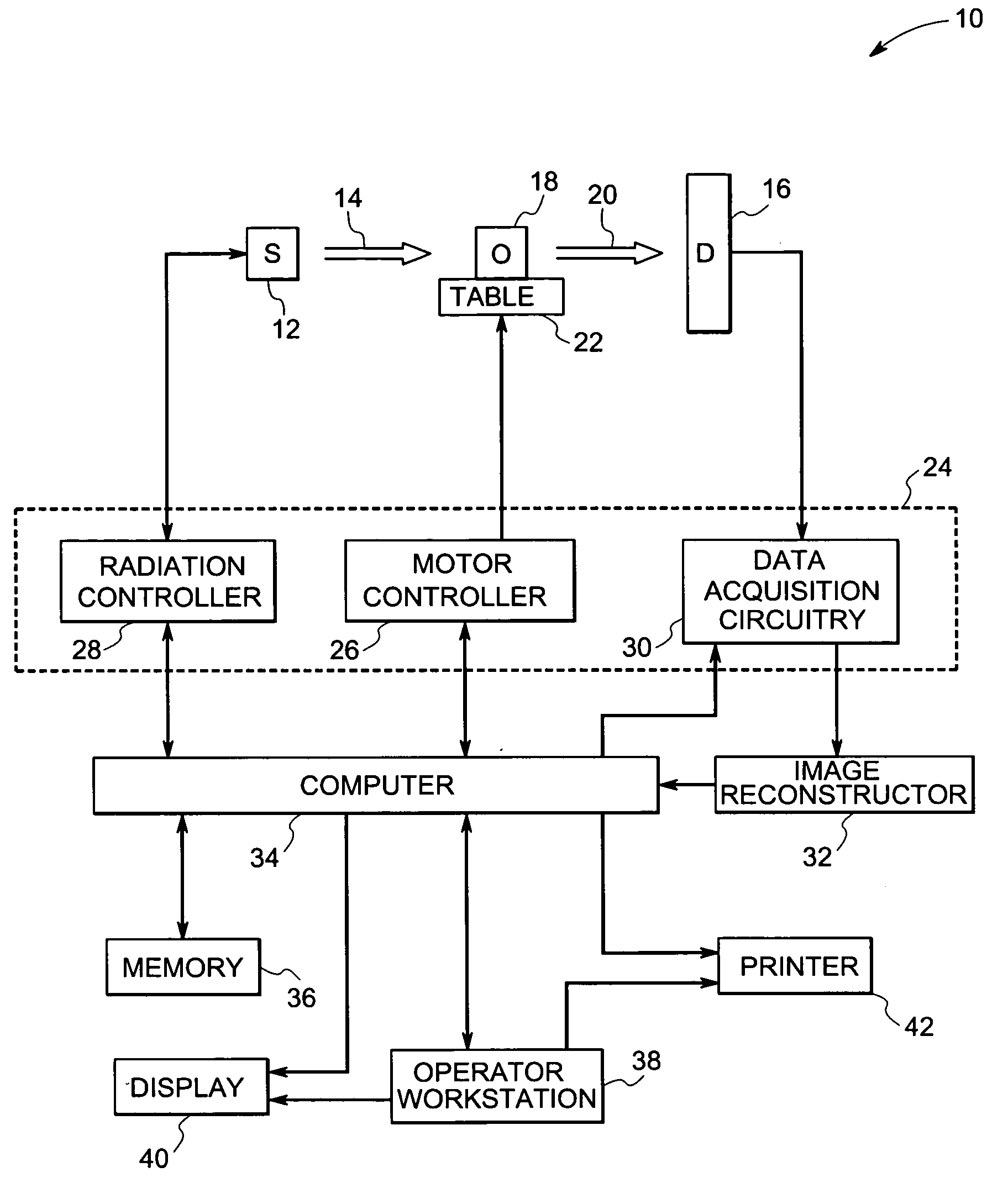
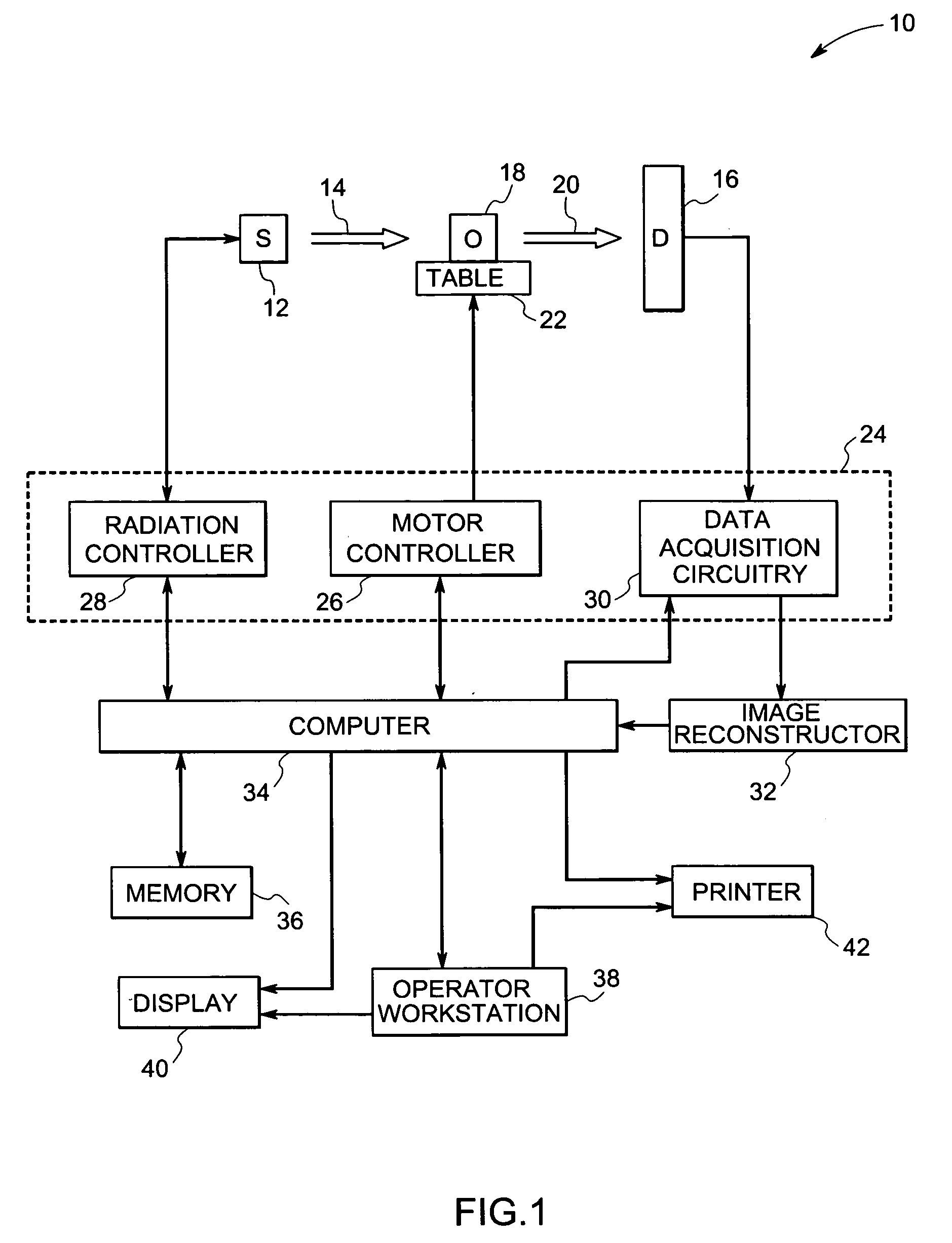
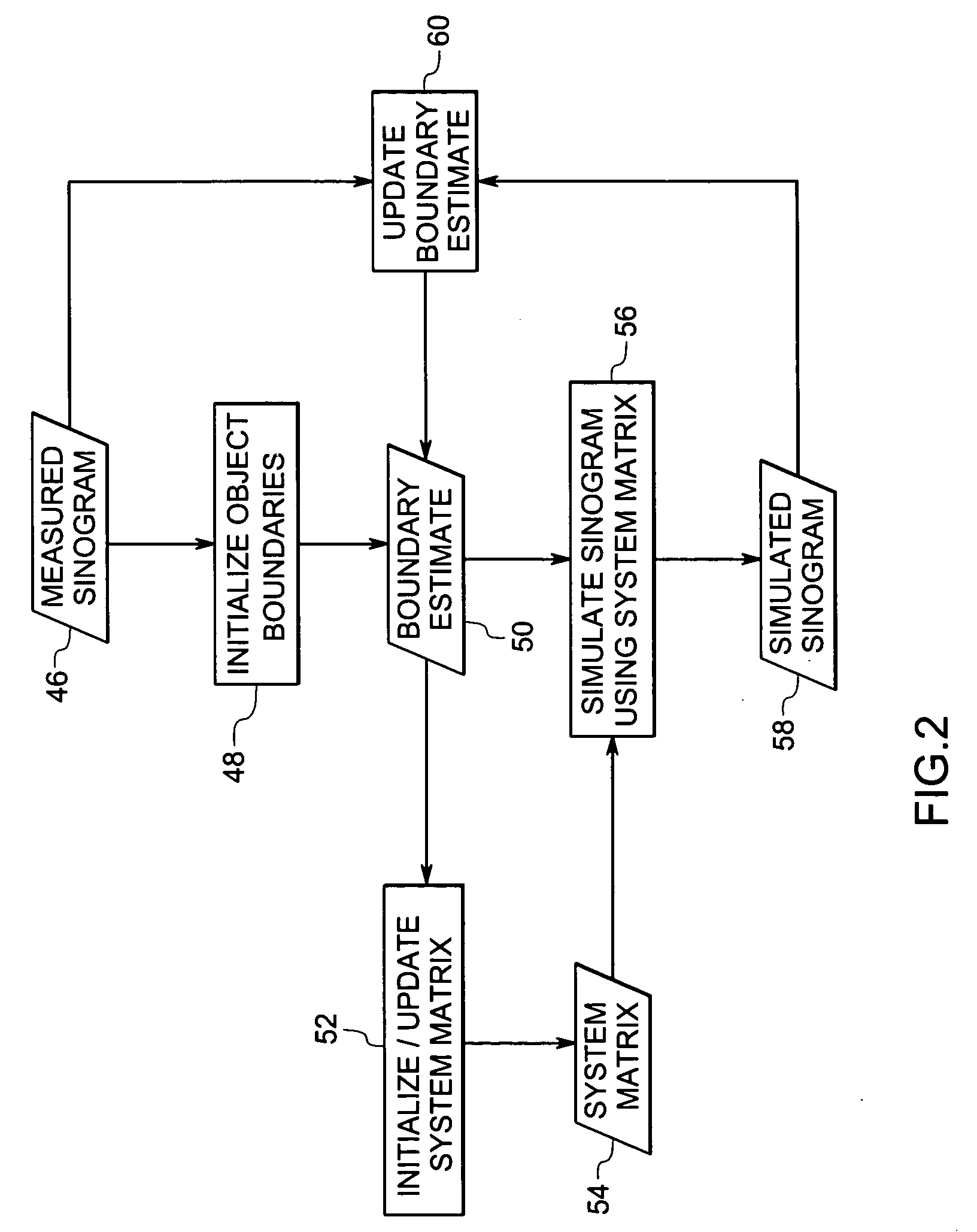
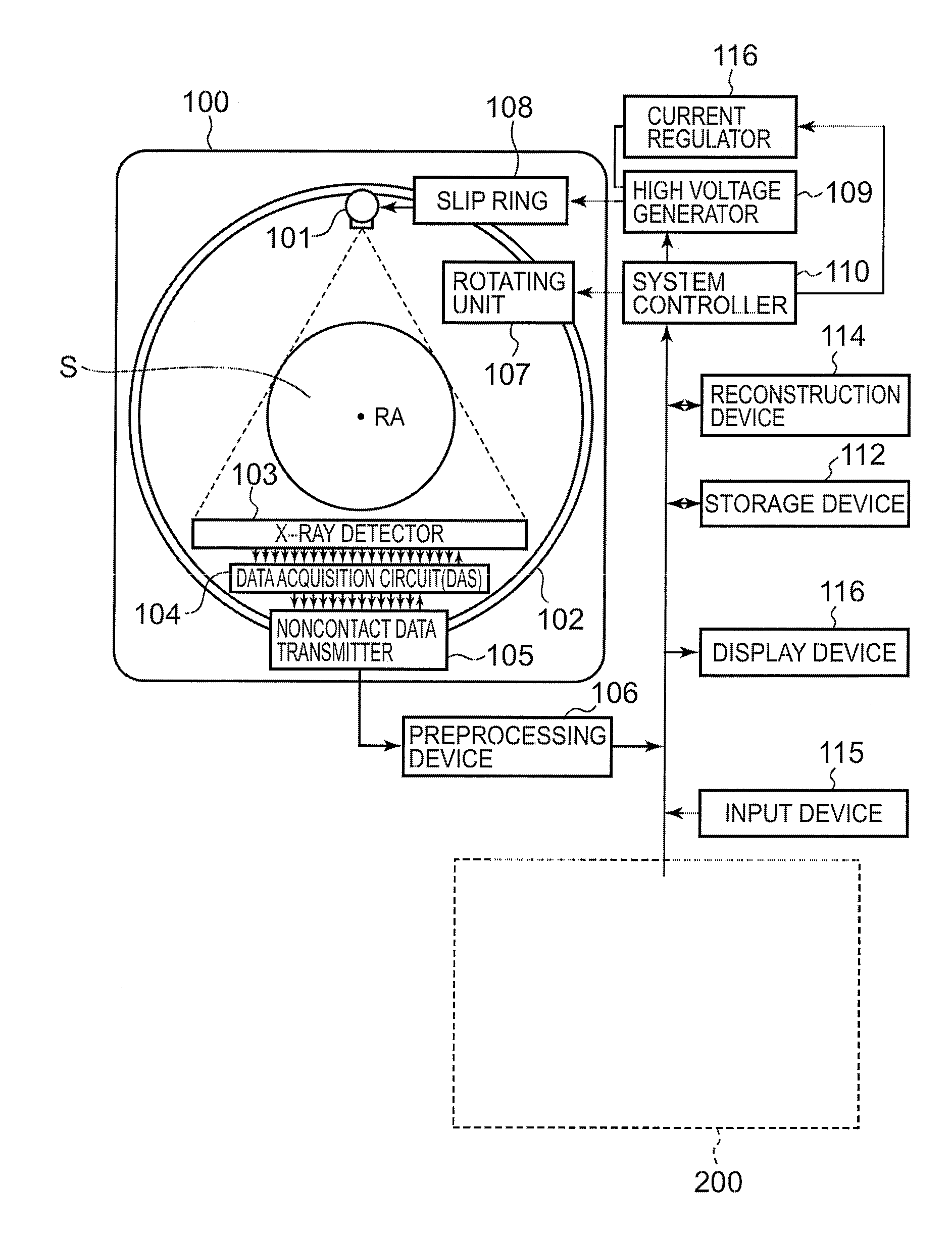
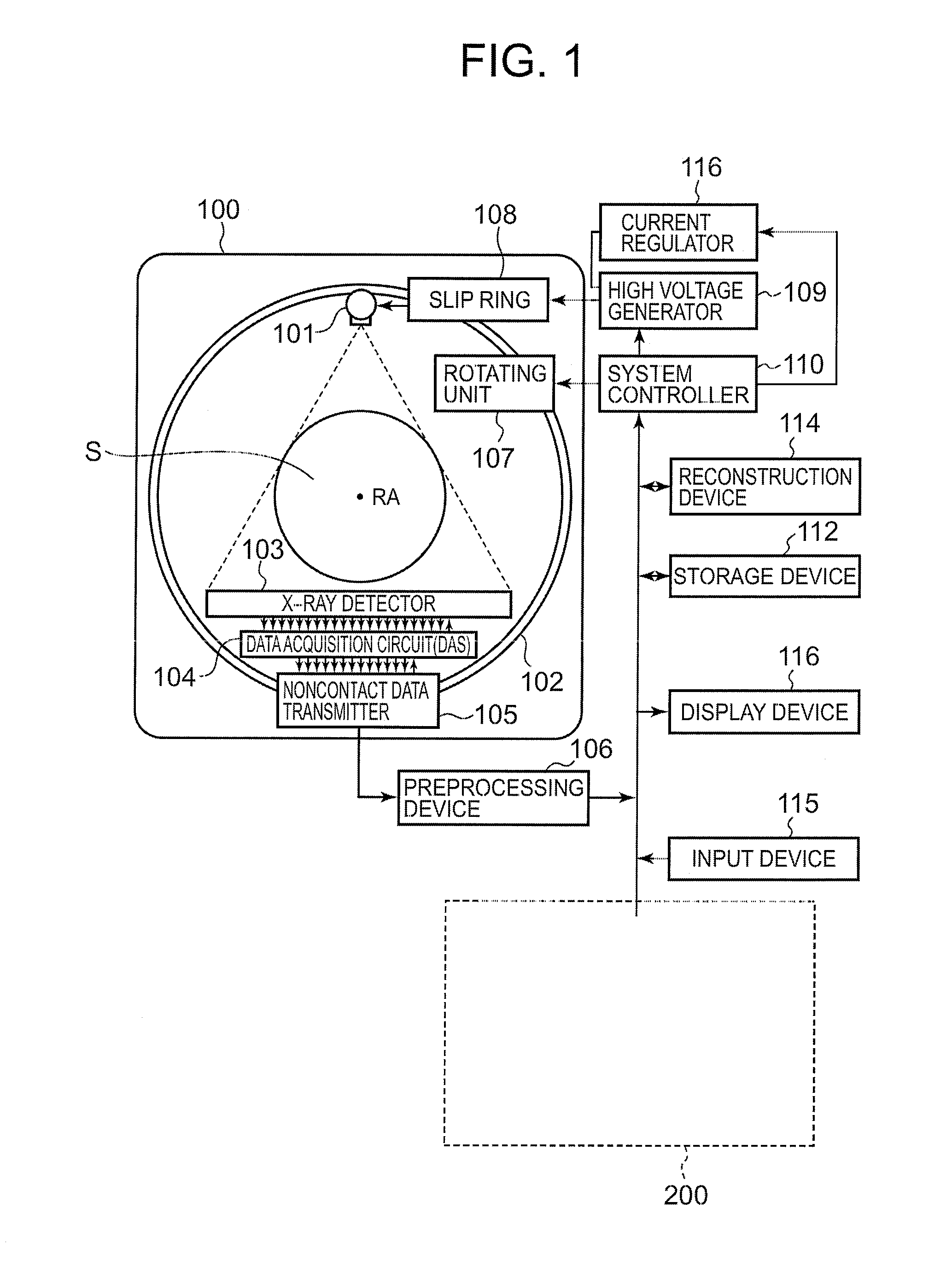
System and method for boundary estimation using CT metrology
InactiveUS7203267B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMetrologyAlgorithm
A technique is provided for CT reconstruction for use in CT metrology. The boundary based CT reconstruction method includes the steps of initializing a boundary of an object to obtain a boundary estimate, defining a forward model based on the boundary estimate, linearizing the forward model to obtain a system matrix and implementing an iterative image reconstruction process using the system matrix to update the boundary estimate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
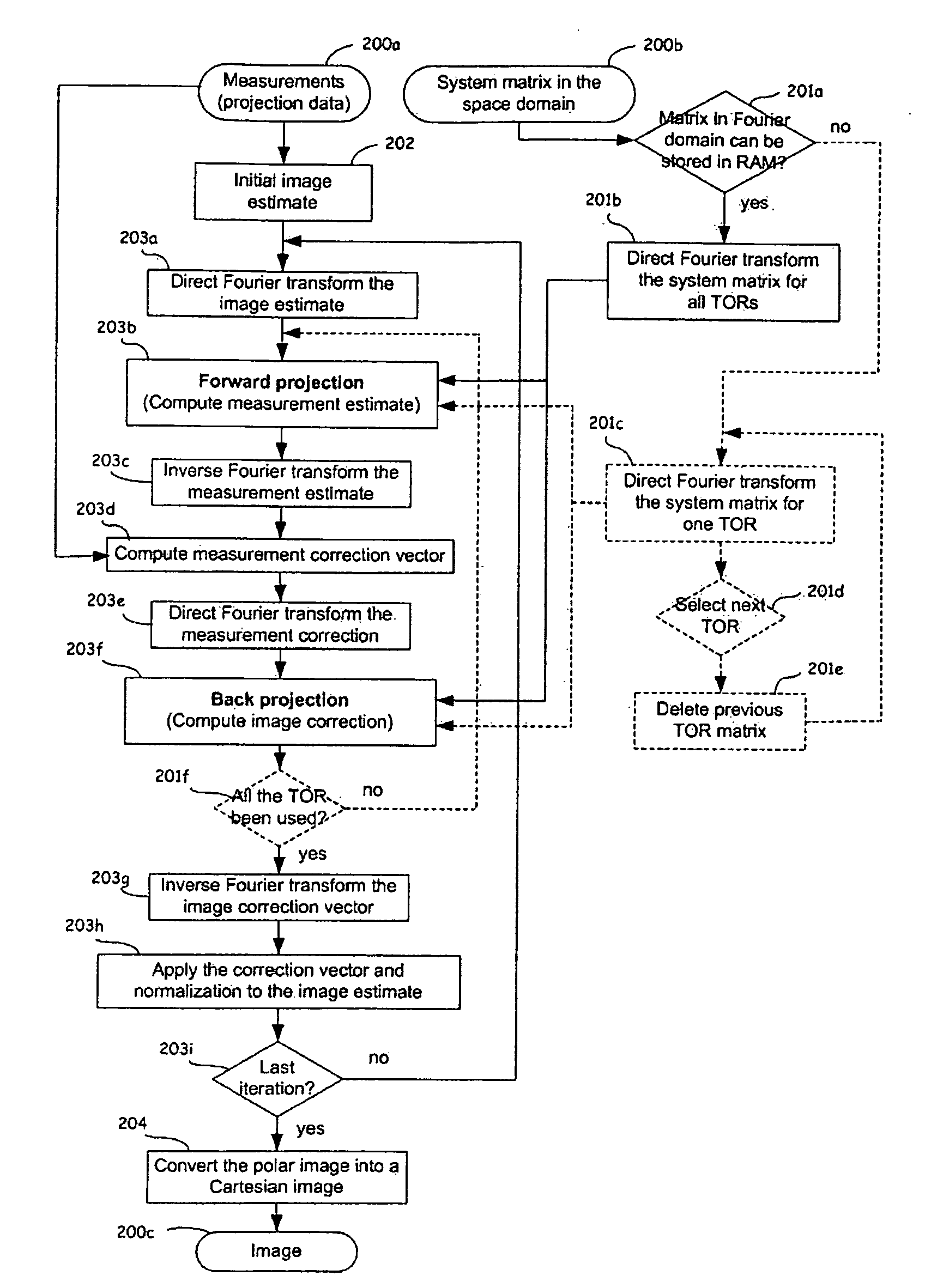
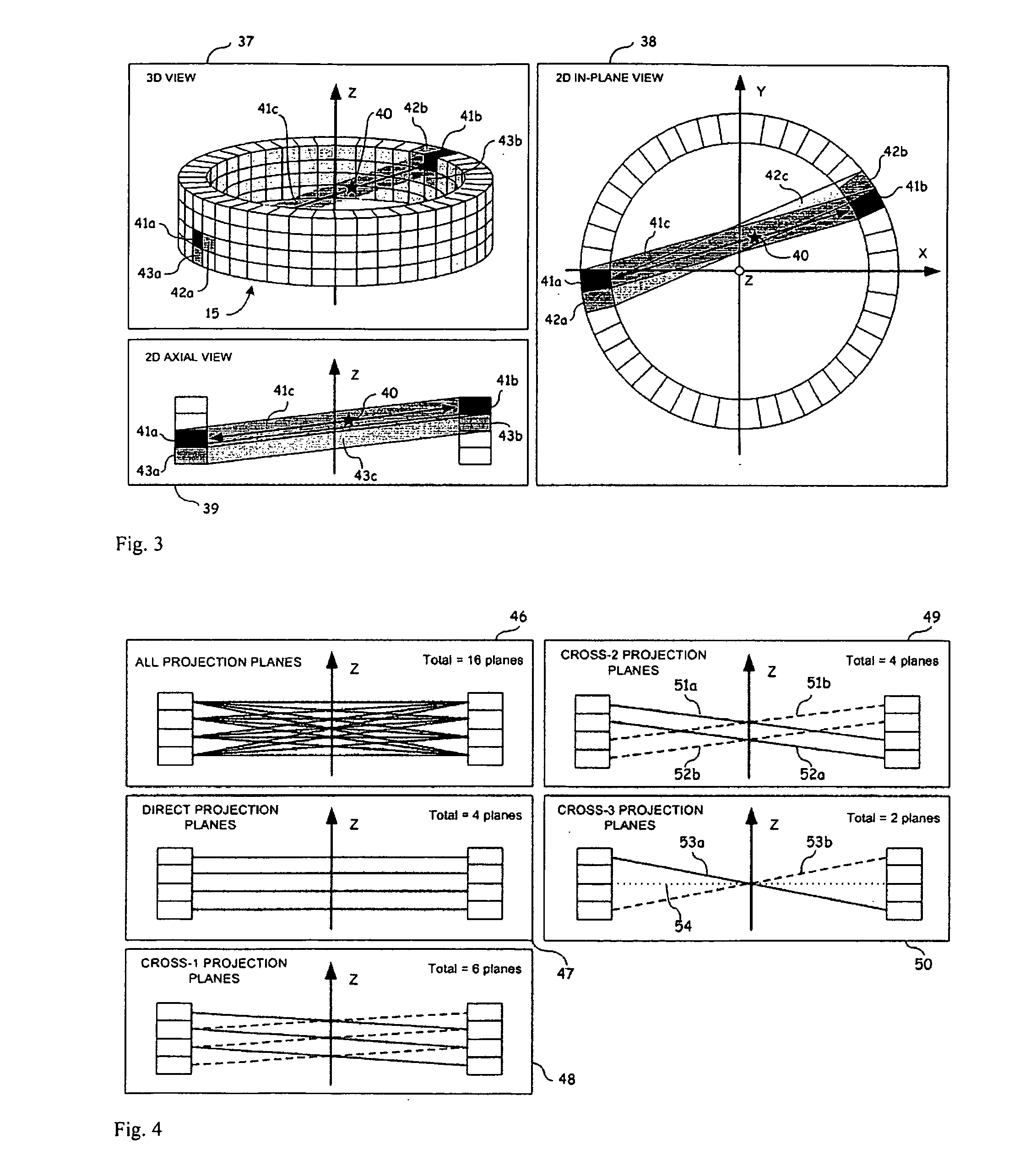
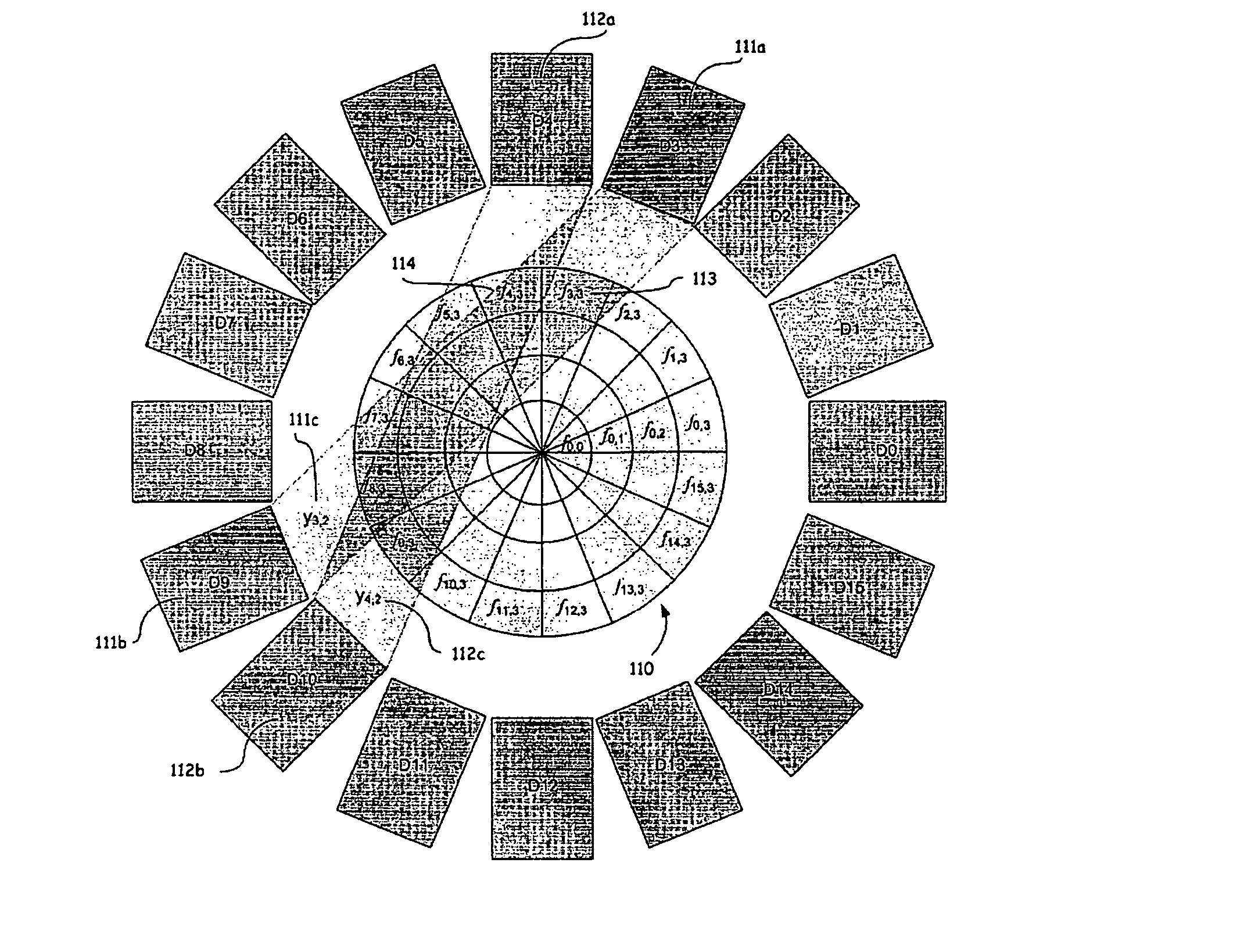
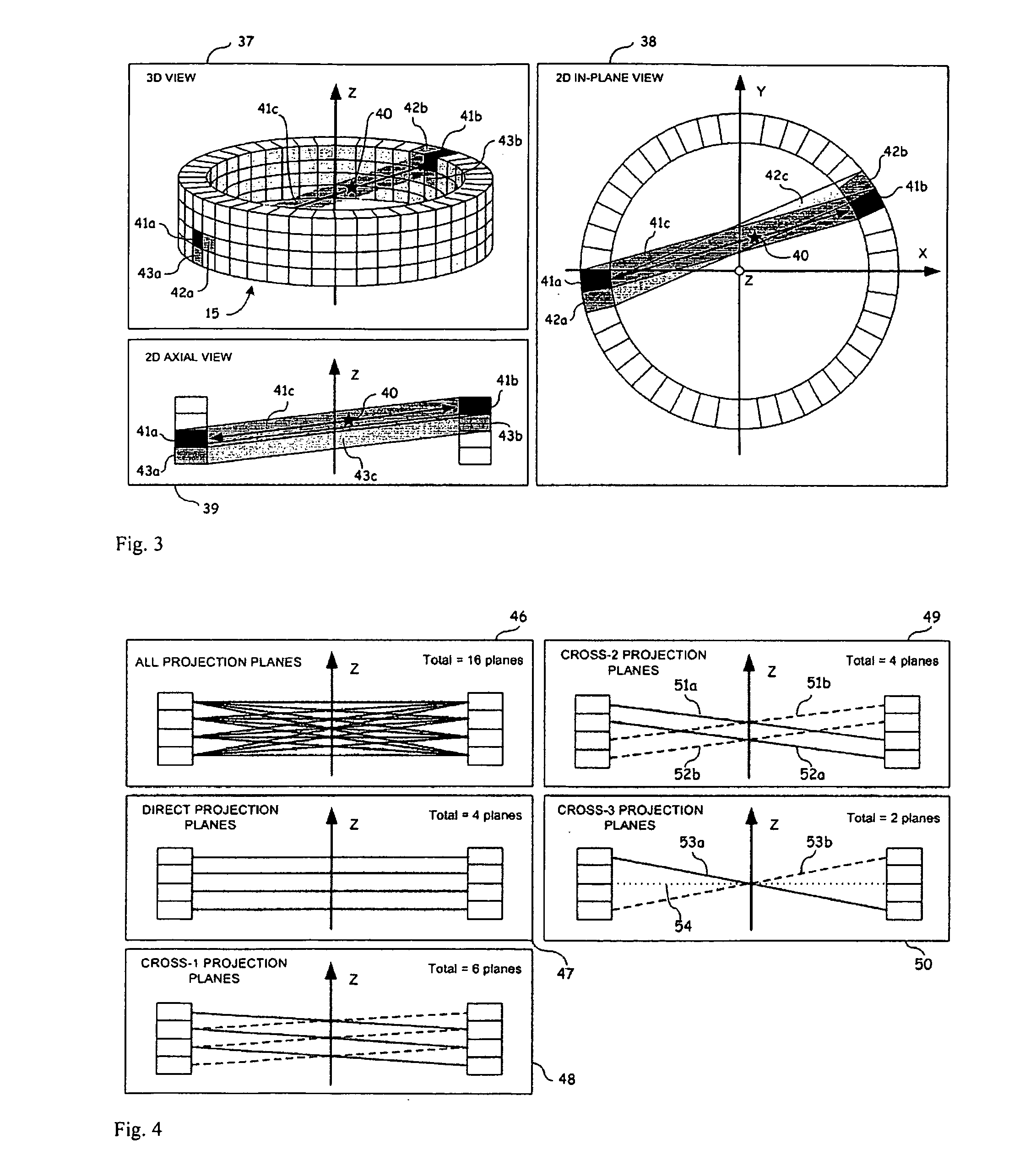
Image Reconstruction Methods Based on Block Circulant System Matrices
InactiveUS20090123048A1Minimized in sizeFast computerReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIn planeLines of response
An iterative image reconstruction method used with an imaging system that generates projection data, the method comprises: collecting the projection data; choosing a polar or cylindrical image definition comprising a polar or cylindrical grid representation and a number of basis functions positioned according to the polar or cylindrical grid so that the number of basis functions at different radius positions of the polar or cylindrical image grid is a factor of a number of in-plane symmetries between lines of response along which the projection data are measured by the imaging system; obtaining a system probability matrix that relates each of the projection data to each basis function of the polar or cylindrical image definition; restructuring the system probability matrix into a block circulant matrix and converting the system probability matrix in the Fourier domain; storing the projection data into a measurement data vector; providing an initial polar or cylindrical image estimate; for each iteration; recalculating the polar or cylindrical image estimate according to an iterative solver based on forward and back projection operations with the system probability matrix in the Fourier domain; and converting the polar or cylindrical image estimate into a Cartesian image representation to thereby obtain a reconstructed image.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
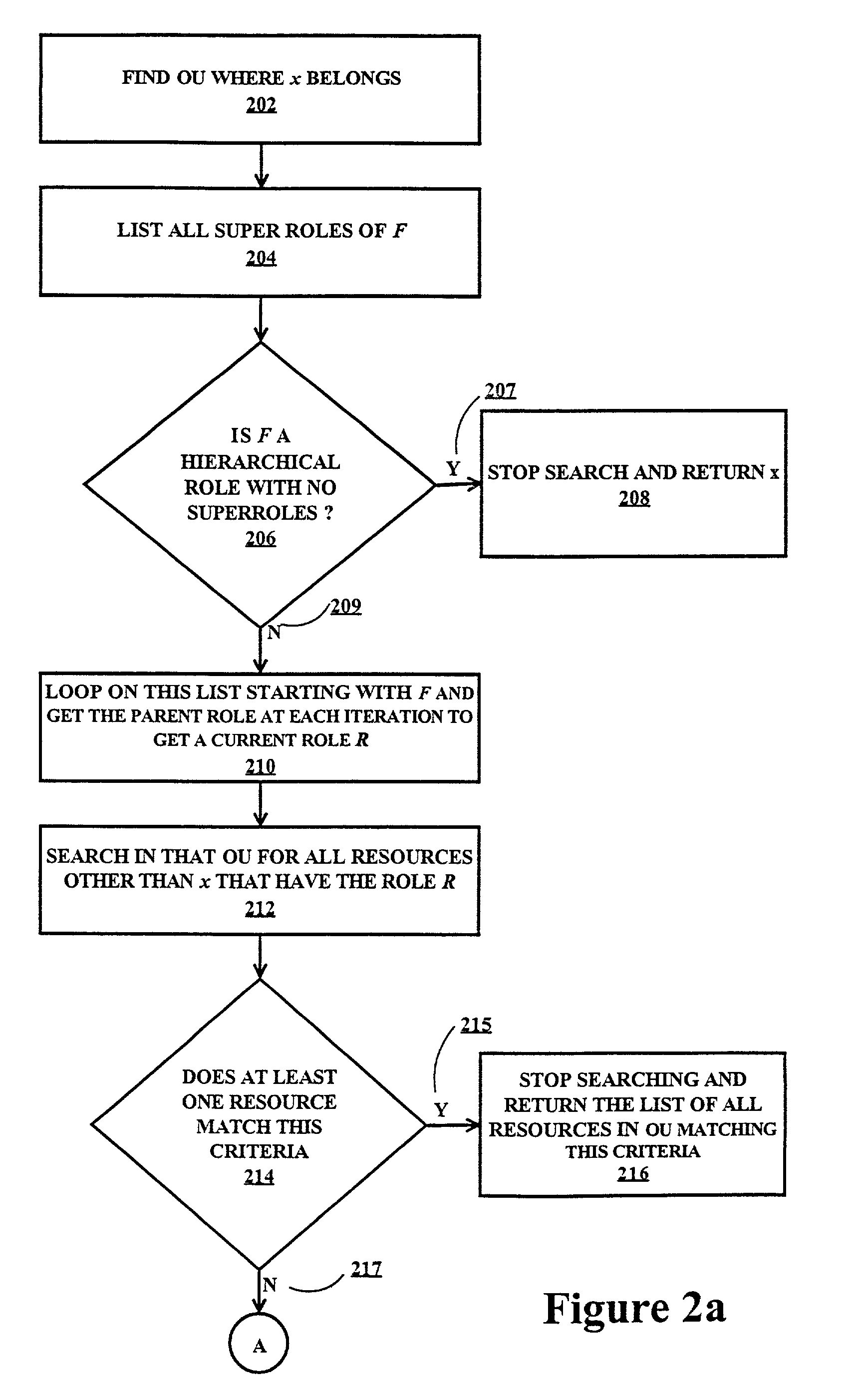
Workflow system matrix organization search engine
A rule-based search engine is used in conjunction with an automated network-based workflow system (which in turn is interfaced with an organizational database) to efficiently determine service routing requests from users / clients. The search engine employs search techniques adapted for use with multi-dimensional tree structures that define the matrix organizational model. Workflow services are preferably represented by roles that can be used to represent workflow actors in the workflow routing rules. These roles are preferably evaluated at run-time to best match recipients depending on the organization context from which the routing request is made.
Owner:GINEGAR LLC
Interference power measurement apparatus and method for space-time beam forming
InactiveUS20050276361A1Reduce implementation complexityEasy to useSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityMeasurement deviceChannel impulse response
A noise and interference power measurement apparatus for an antenna diversity system that services a plurality of users with an array antenna having a plurality of antenna elements. A channel estimator estimates a channel impulse response for a radio channel corresponding to a predetermined plurality of regularly spaced direction-of-arrival (DOA) values. A data estimator estimates the received data using a received signal and a system matrix. A quantizer quantizes the estimated data. An interference and noise calculator calculates noise vectors at the respective antenna elements by removing from the received signal an influence of the quantized data to which the system matrix is applied, calculates an estimated noise matrix at the plurality of antenna elements, calculates interference power by auto-correlating the estimated noise matrix, and calculates noise and interference power based on the interference power.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for boundary estimation using CT metrology
InactiveUS20060002504A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMetrologyAlgorithm
A technique is provided for CT reconstruction for use in CT metrology. The boundary based CT reconstruction method includes the steps of initializing a boundary of an object to obtain a boundary estimate, defining a forward model based on the boundary estimate, linearizing the forward model to obtain a system matrix and implementing an iterative image reconstruction process using the system matrix to update the boundary estimate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
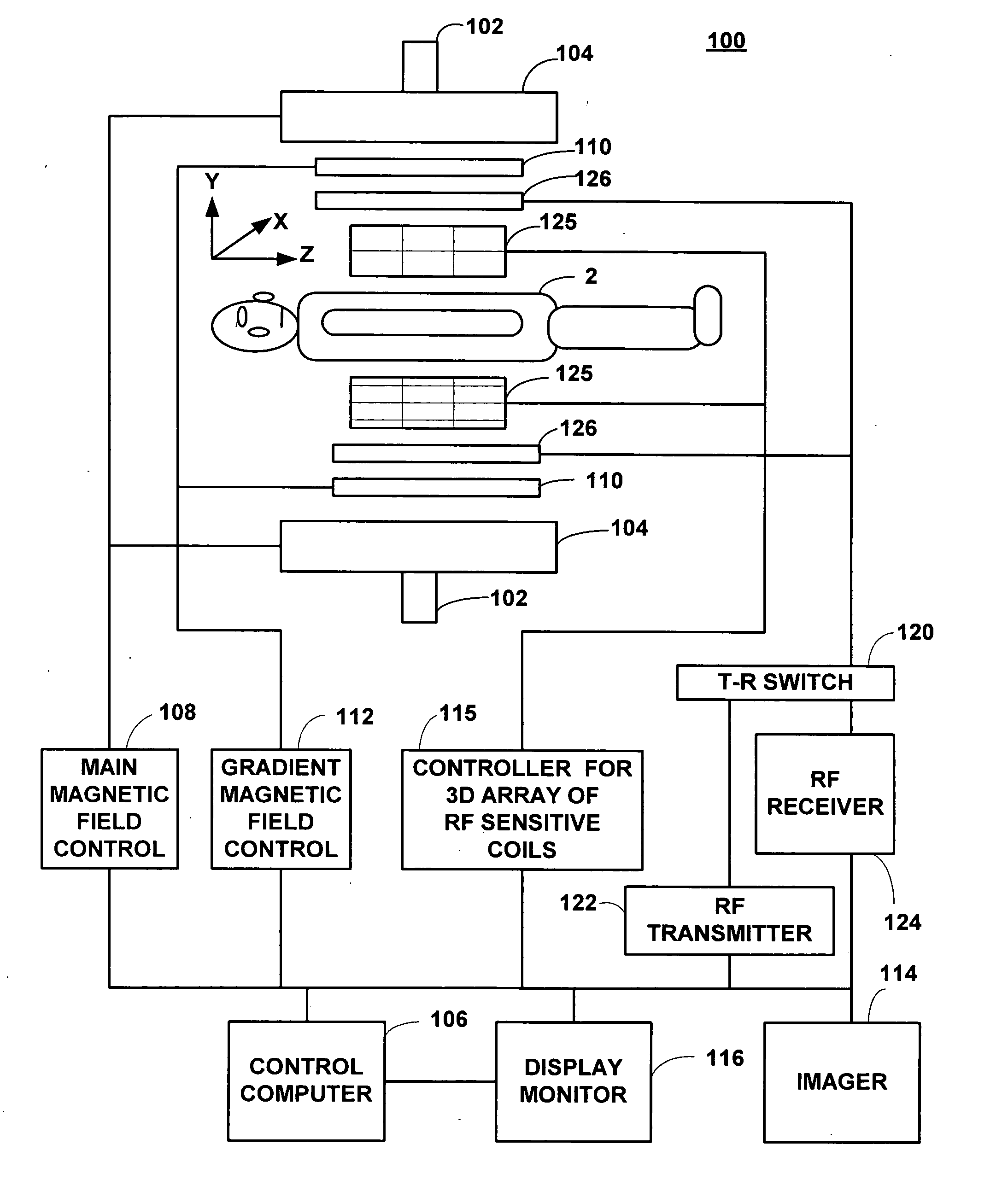
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20110115485A1Shorten the length of timeReduce usageMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
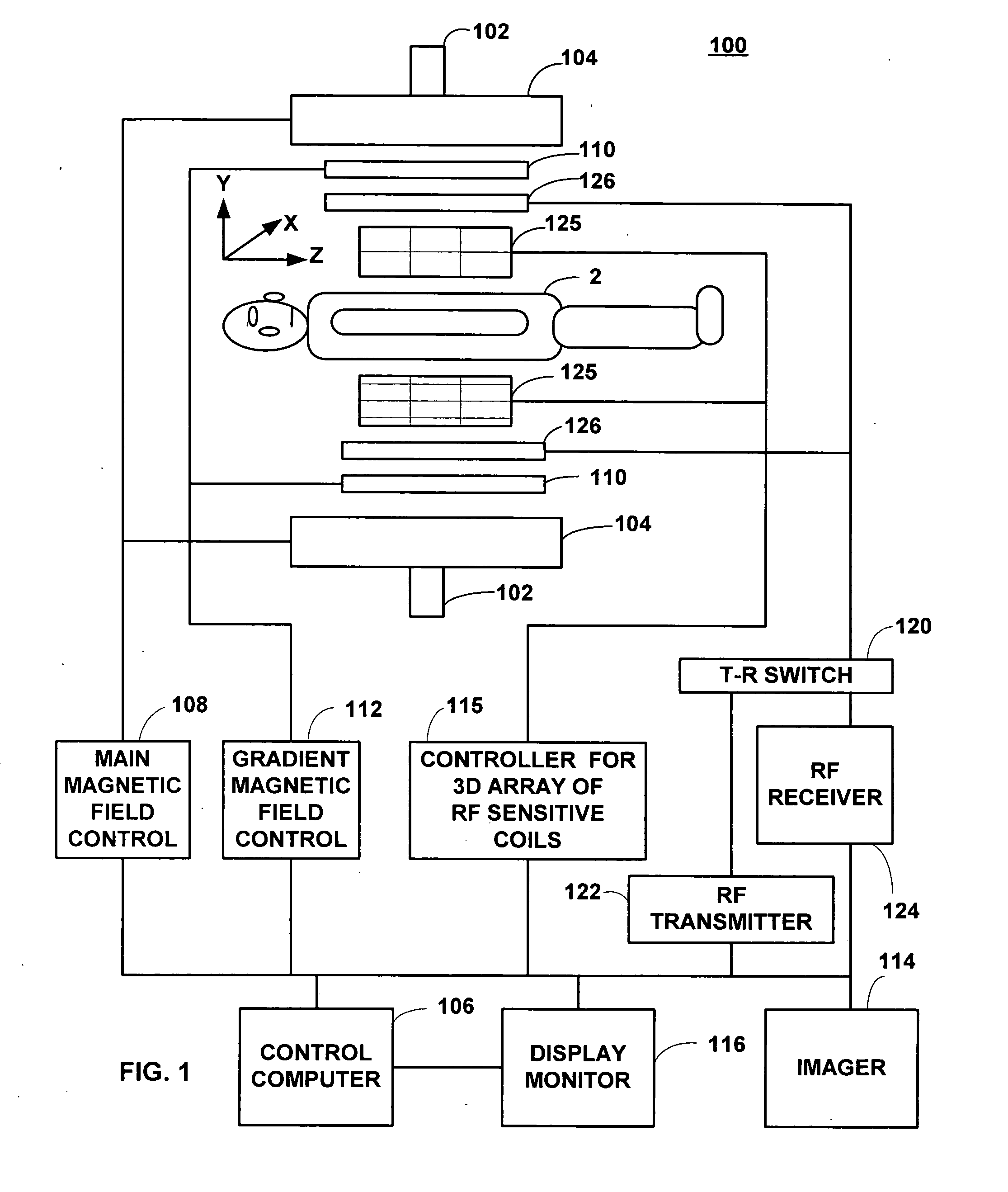
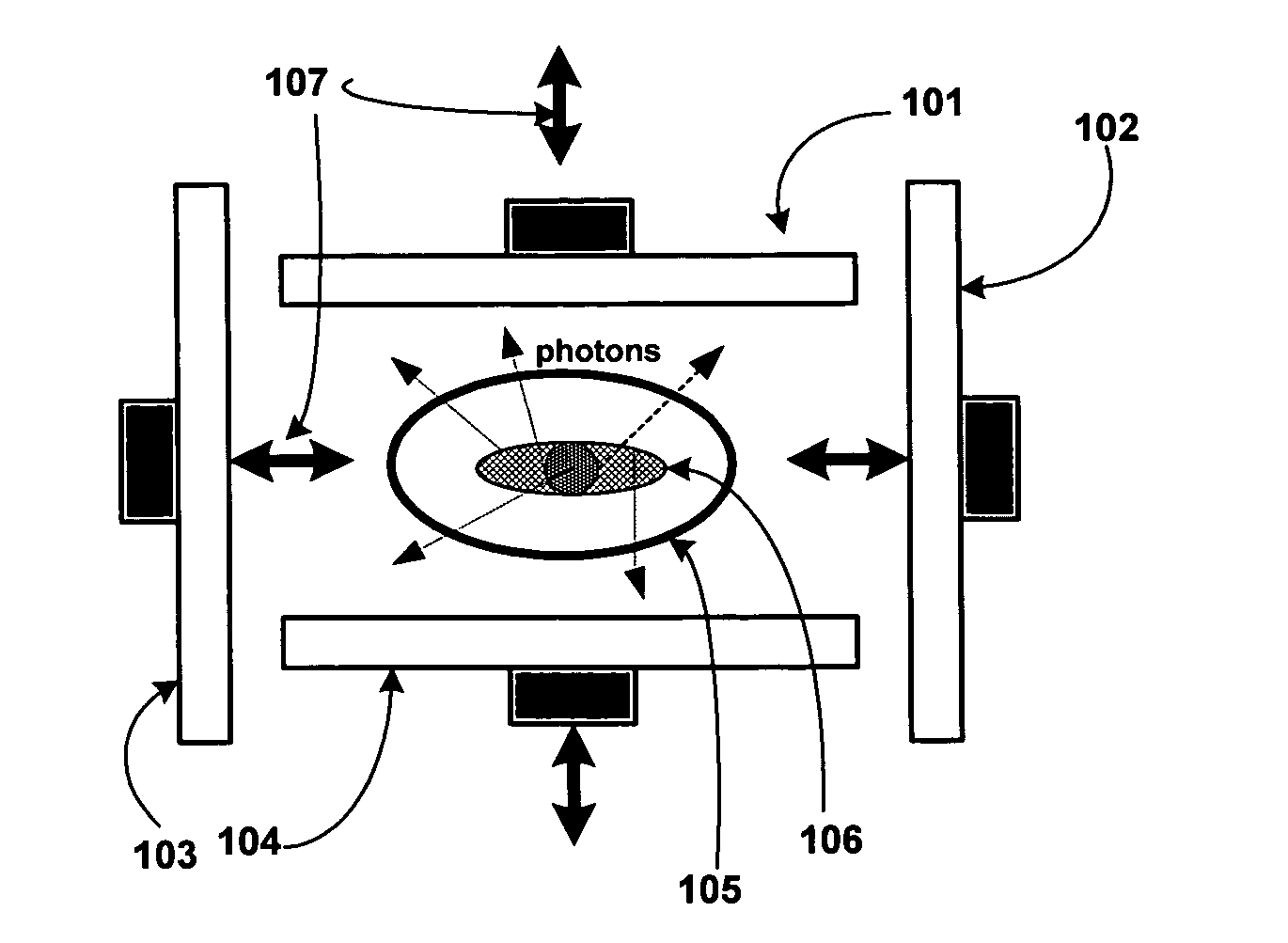
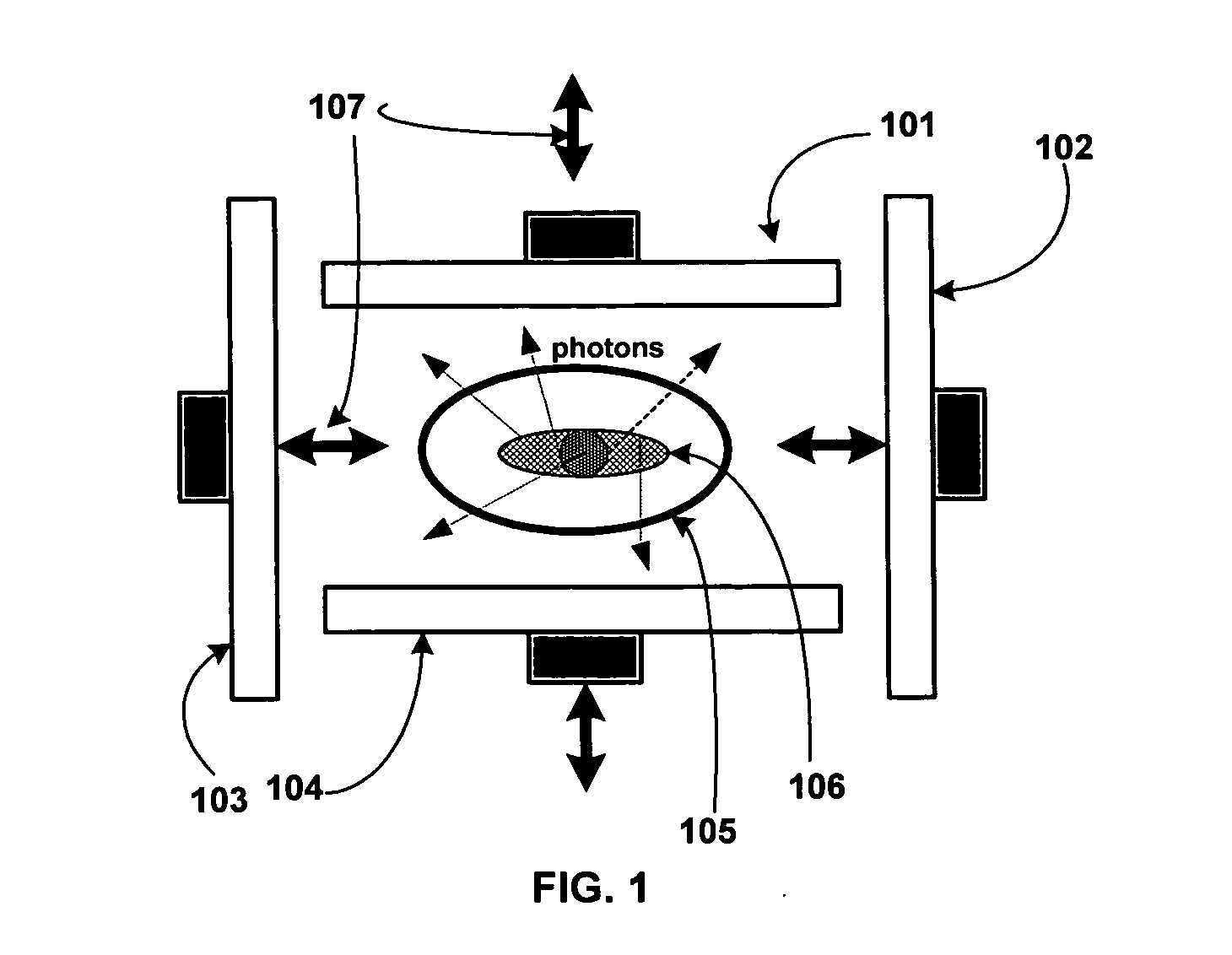
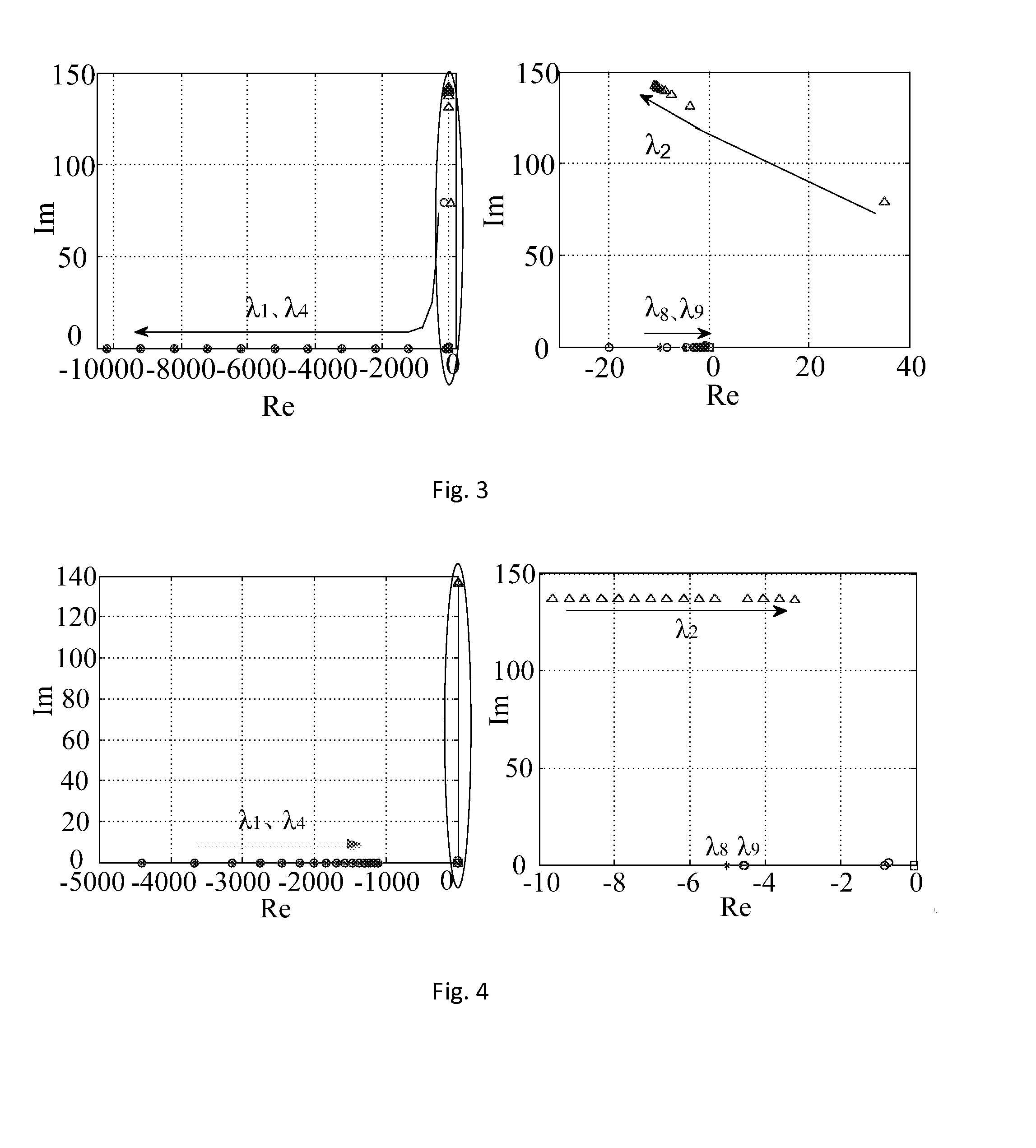
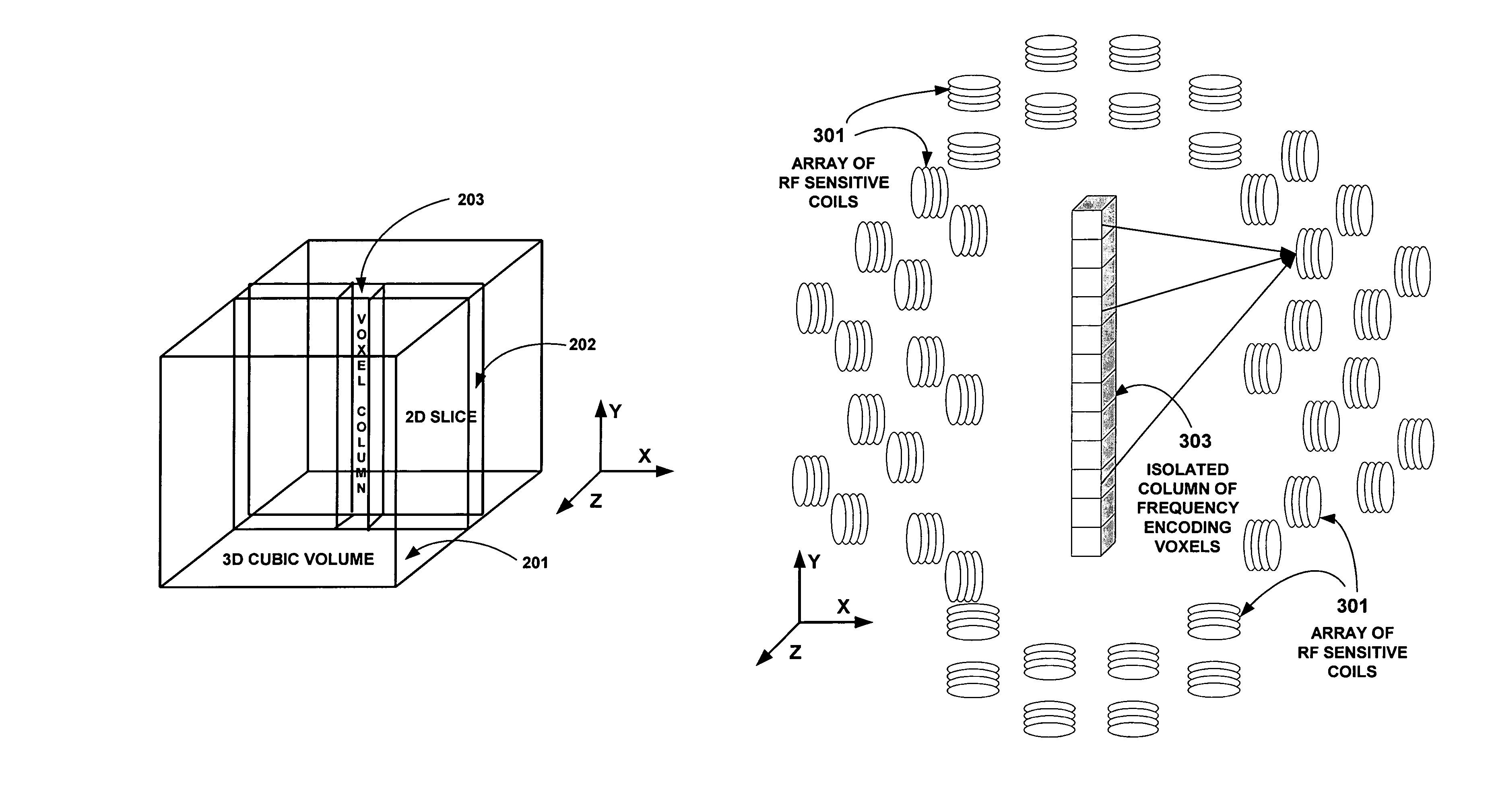
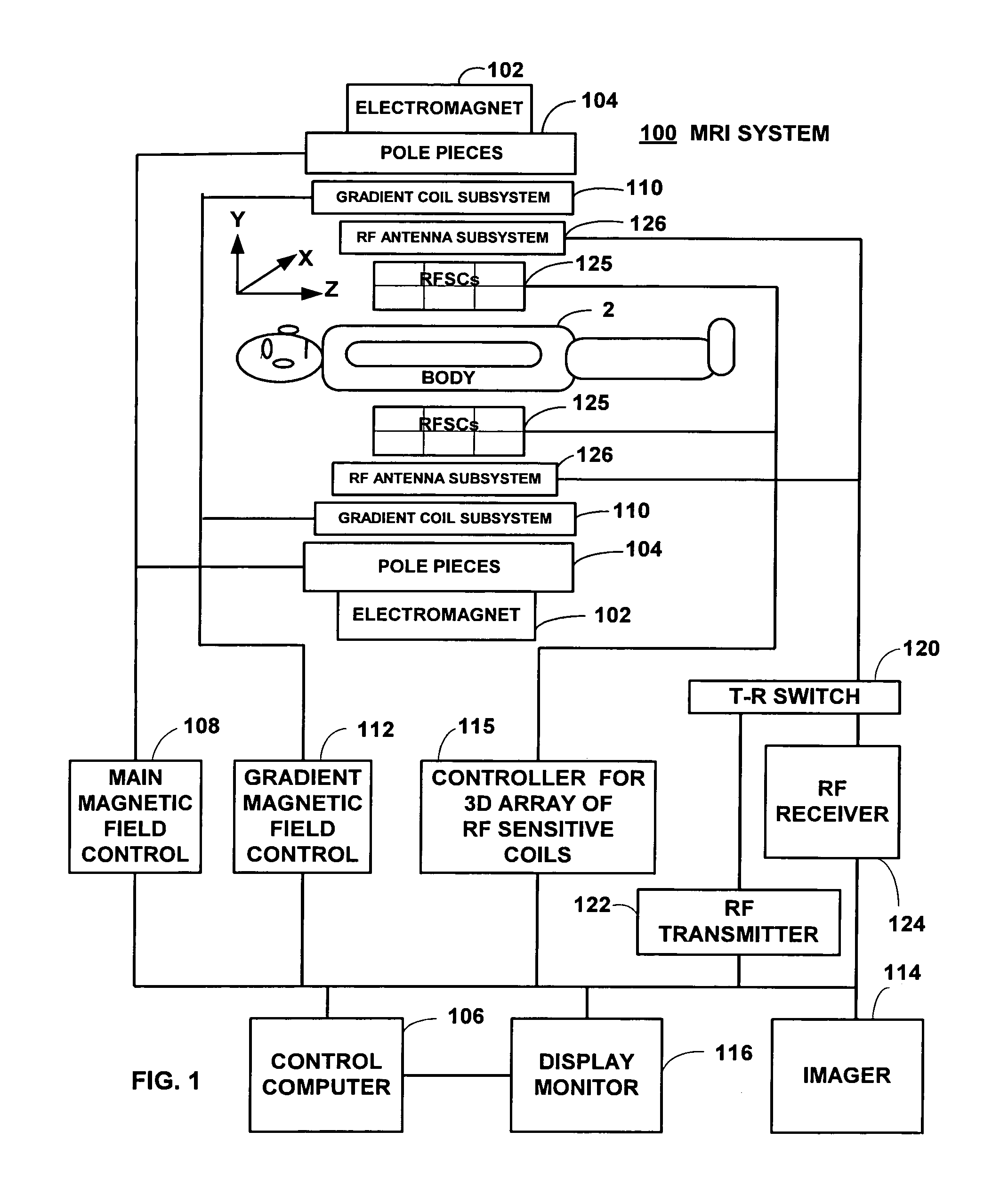
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
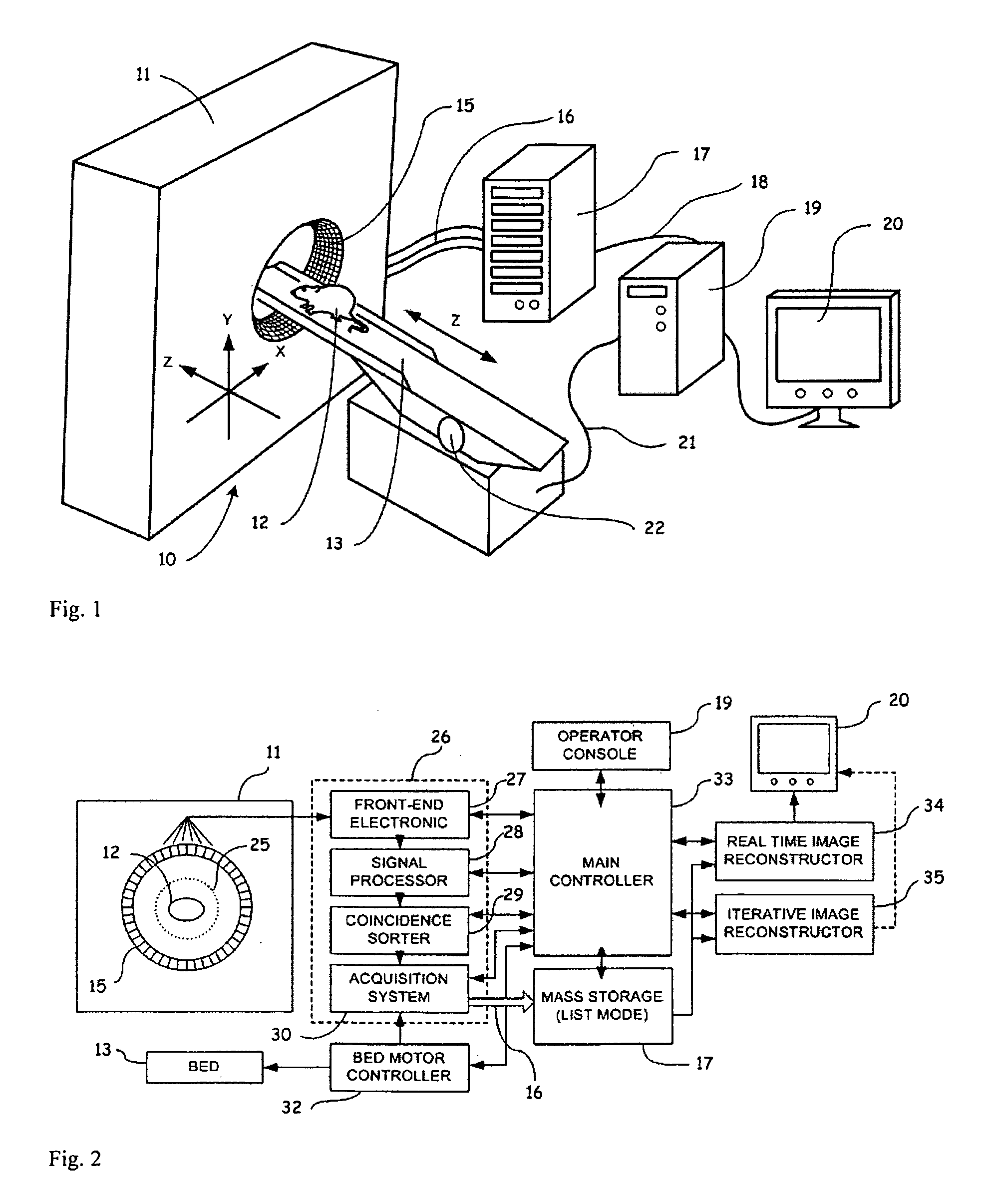
Method and apparatus for high-sensitivity Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography
ActiveUS20110073763A1Facilitates higher qualityAccurate clinical diagnosisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton emissionSystem matrix
A method and apparatus are disclosed for high-sensitivity Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT), and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). The apparatus includes a two-dimensional (2D) gamma detector array that, unlike a conventional SPECT machine, moves to different positions in a three-dimensional (3D) volume space near an emission source and records a data vector g which is a measure of gamma emission field. In particular, the 3D volume space in which emission data g is measured extends substantially along a radial direction r pointing away from the emission source, and unlike a conventional SPECT machine, each photon detector element in the 2D gamma detector array is provided with a very large collimator aperture. Data g is related to the 3D spatial density distribution f of the emission source, noise vector n, and a system matrix H of the SPECT / PET apparatus through the linear system of equations g=Hf+n. This equation is solved for f by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
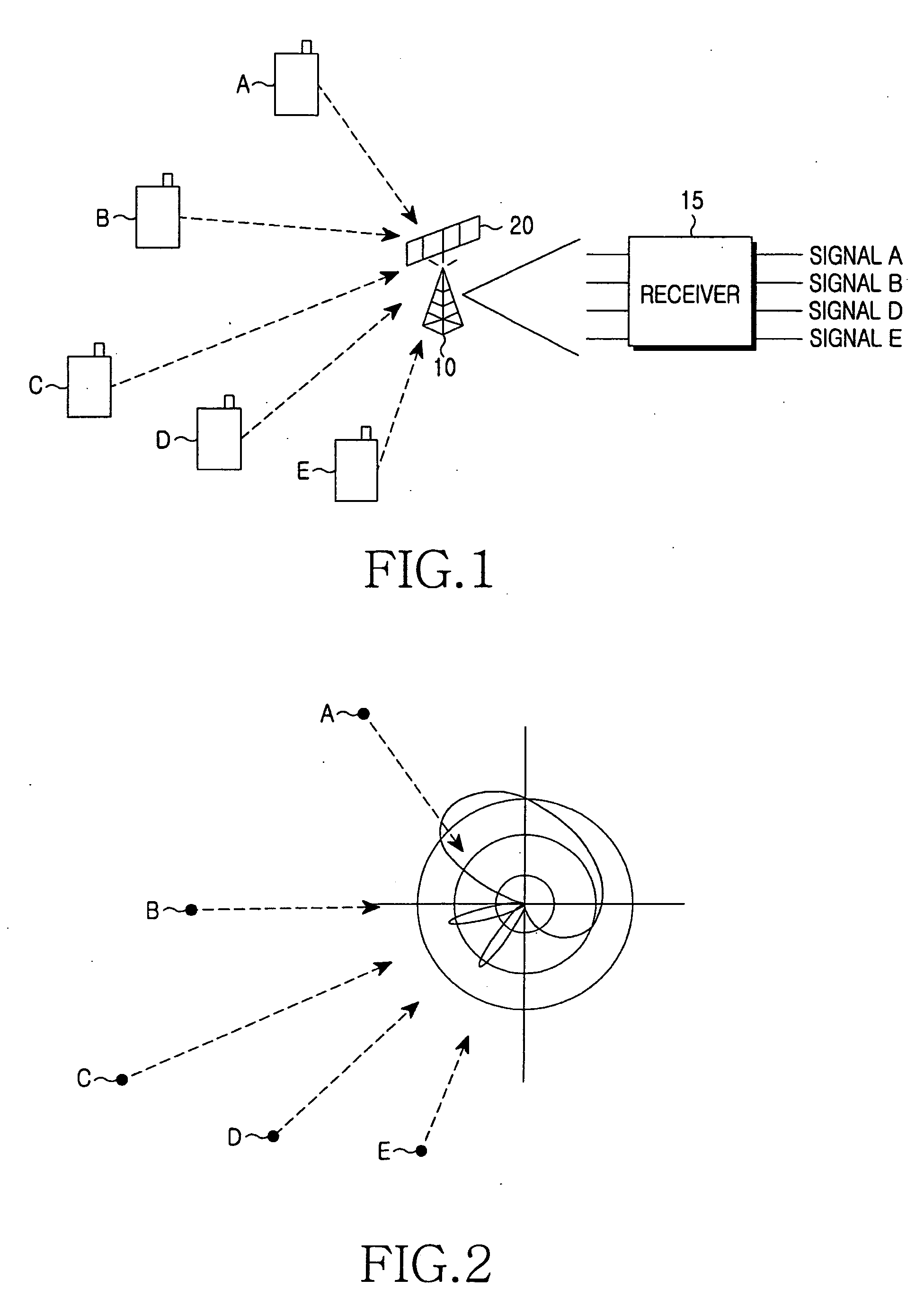
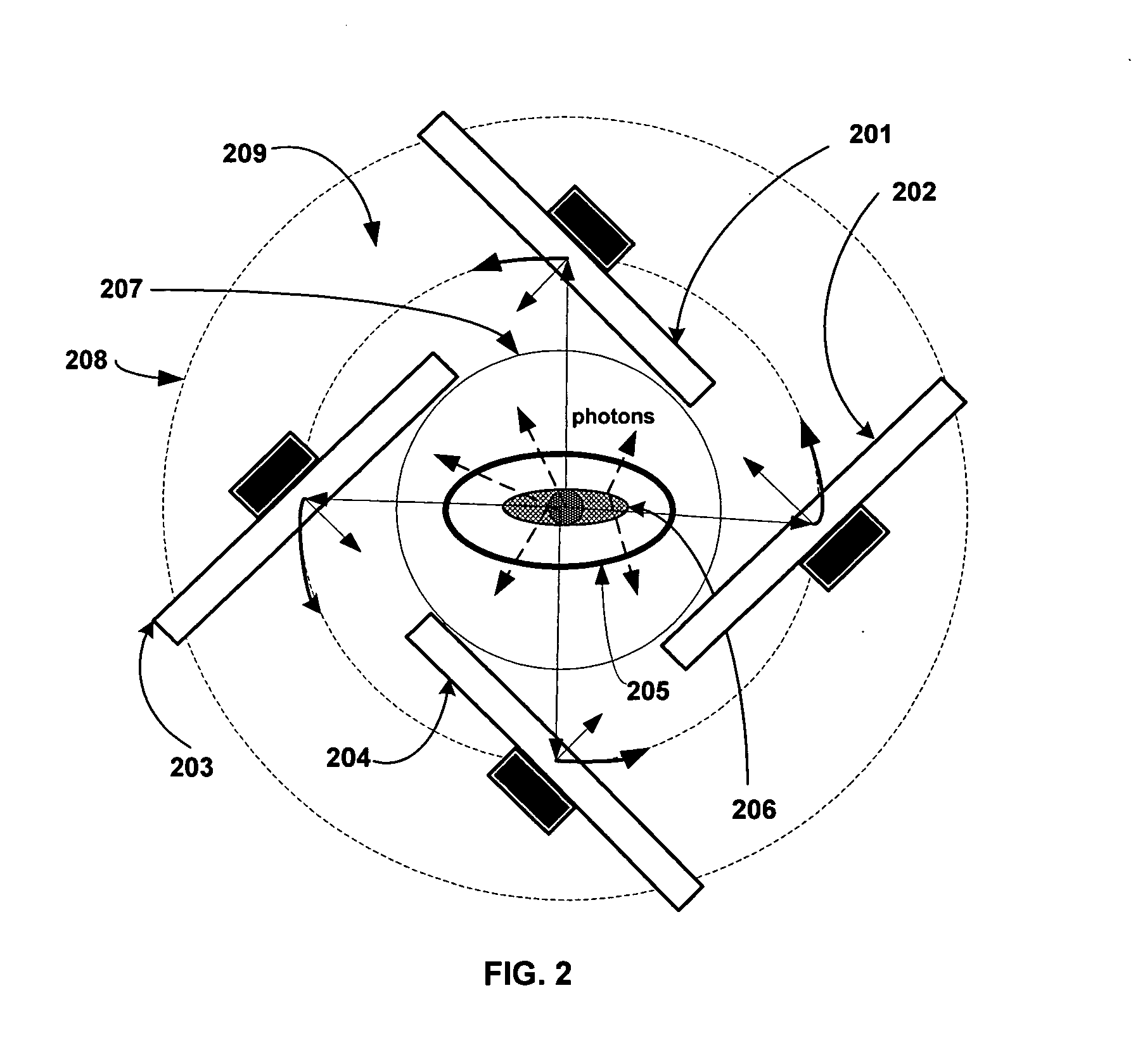
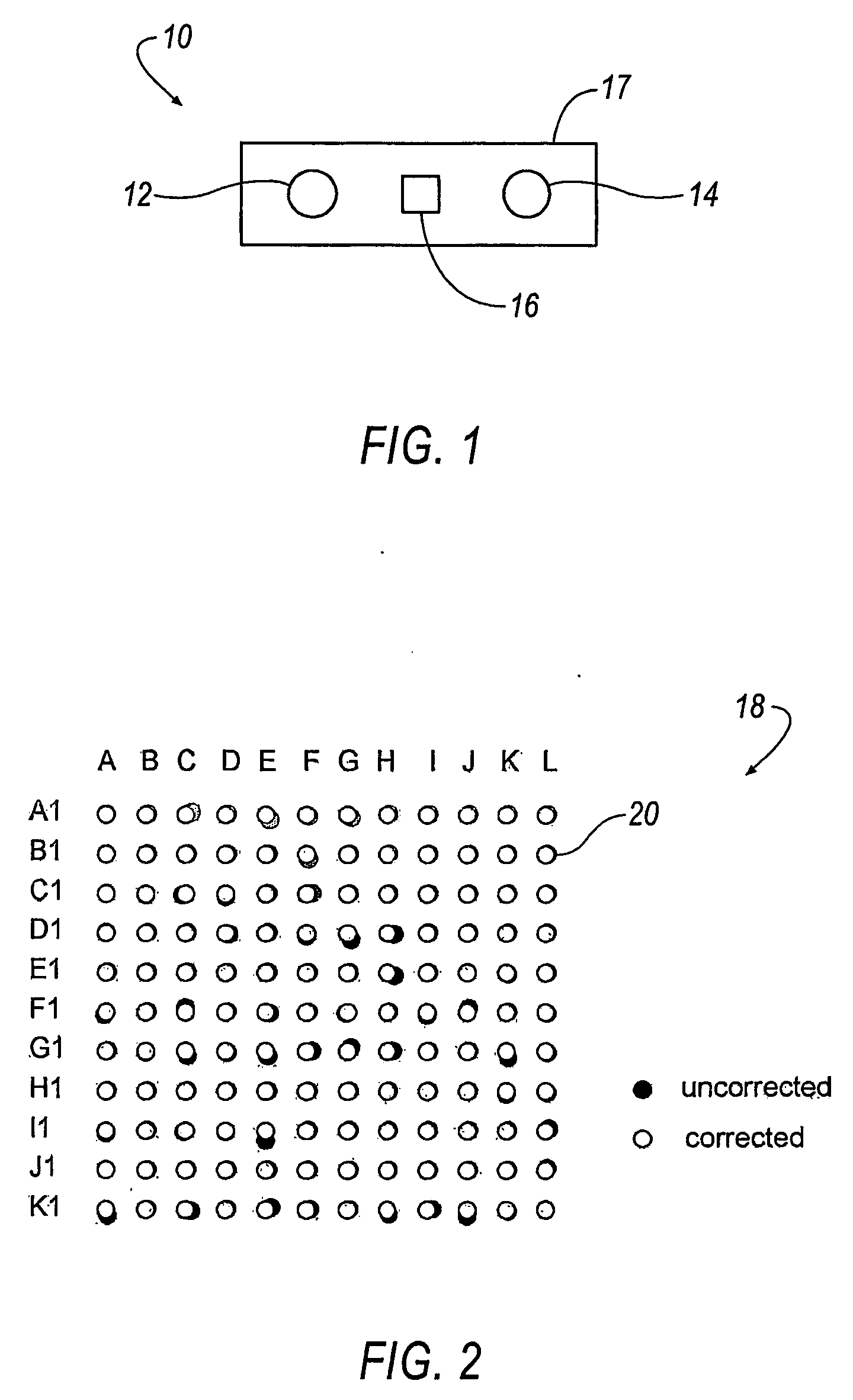
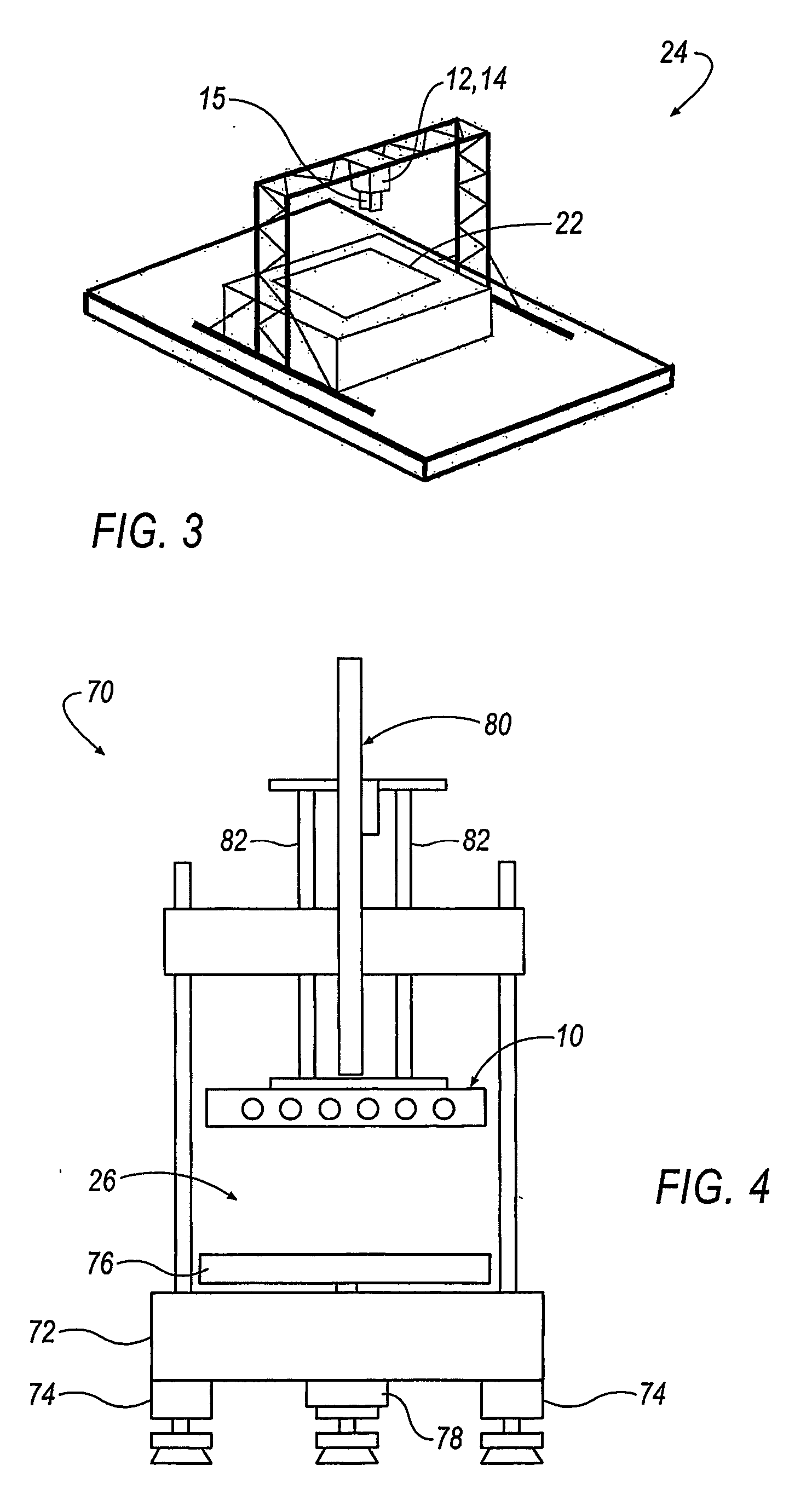
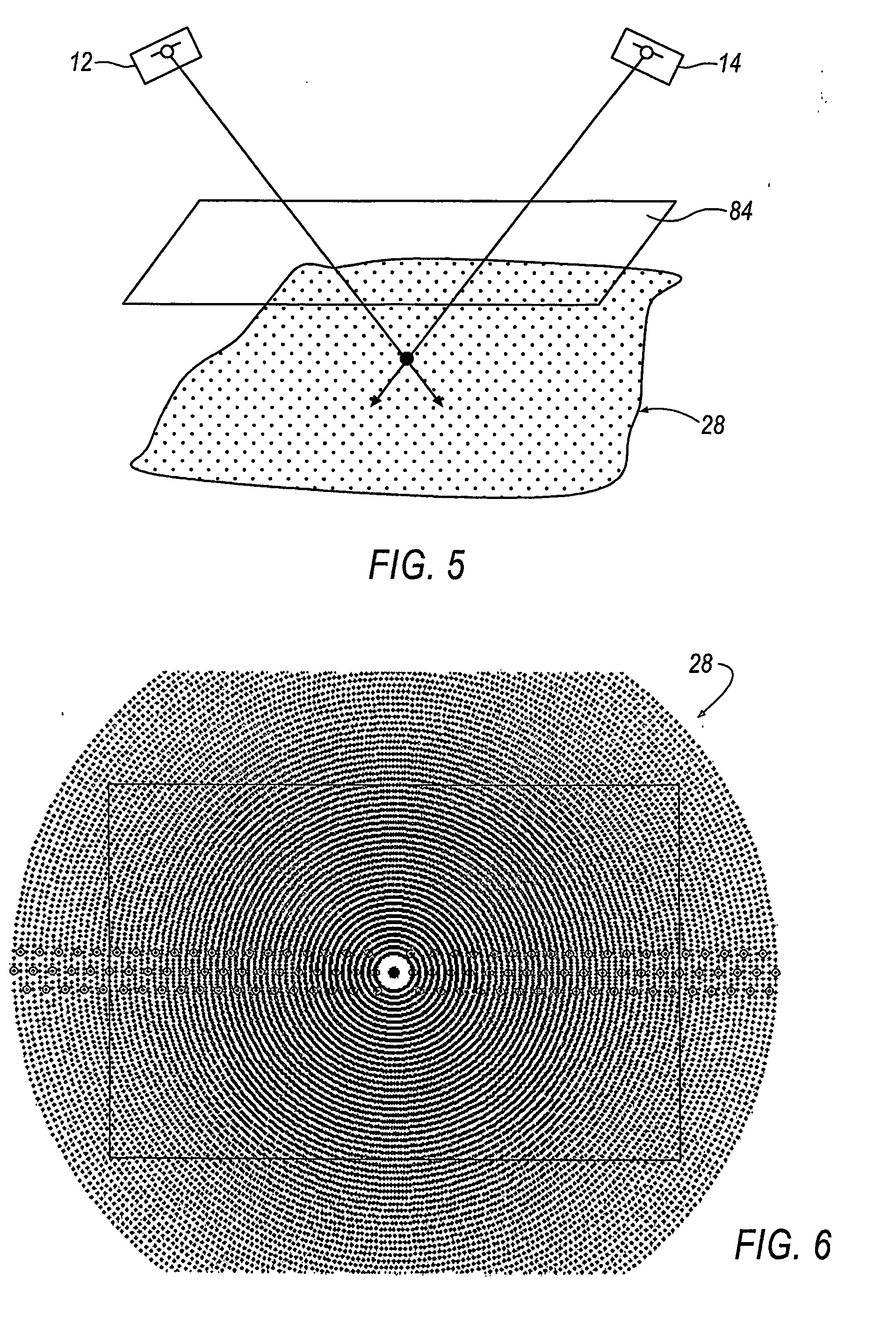
Scanning system with stereo camera set
A scanning system includes one or more stereo camera sets (10) for detecting qualitative and quantitative anomalies of an object (40). Each stereo camera set (10) includes two cameras (12, 14) and a projector (16). Each camera (12, 14) is calibrated to correct any distortion due to misalignment of the CCD matrix array (18) and deficiencies of the optical system. The projector (16) projects an absolute encoded pattern (32, 34, 36) onto the object (40) to be measured and is capable of varying the intensity of the emitted electromagnetic energy in the infrared, visible and ultraviolet spectrums. A plurality of camera sets (10) can be combined in a scanning system matrix (42, 44) capable of detecting anomalies of the object (40) in a three-dimensional room (26). The three-dimensional room (26) can be of any desirable size, depending on the number of stereo camera sets (10). The data from the cameras (12, 14) is pre-processed by gate arrays (62) before being transmitted via digital signal processors (66) to a computer interface (64) for display of the measurement. As a result, the amount of data transferred is streamlined, thereby reducing operating time and enabling the scanning system to very accurately detect anomalies of the object (40) in a very short period of time.
Owner:DIMENSIONAL TECH INT
Non-partial regularization prior reconstruction method for low-dosage X-ray captive test (CT) image
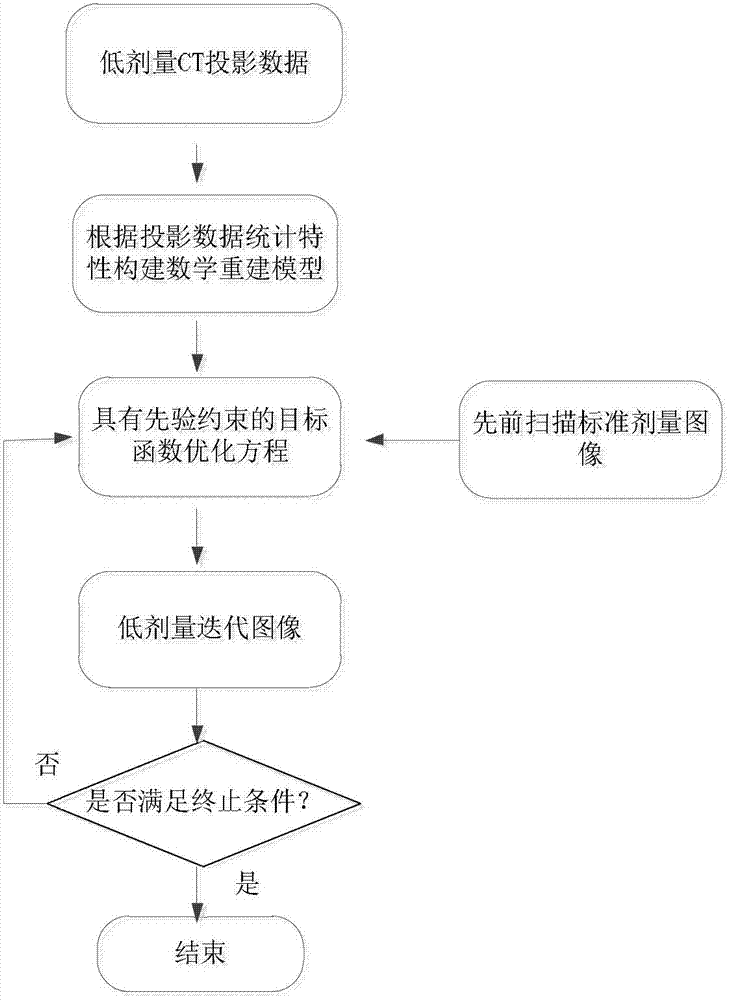
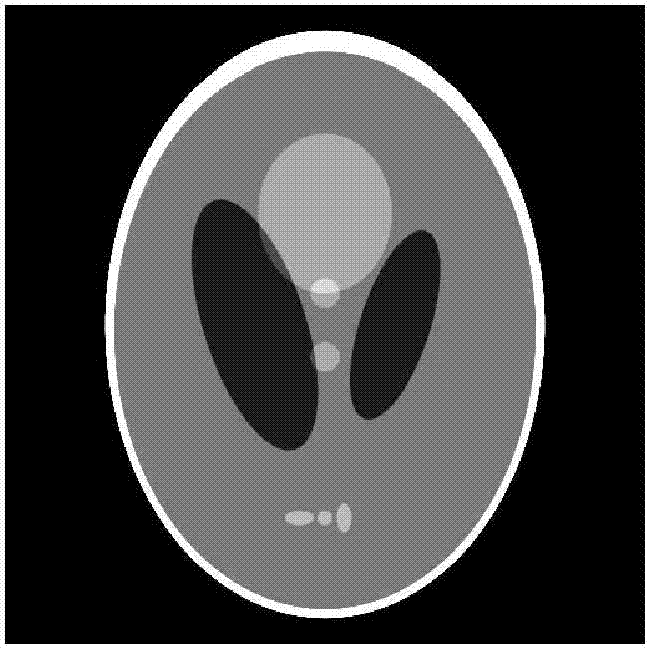
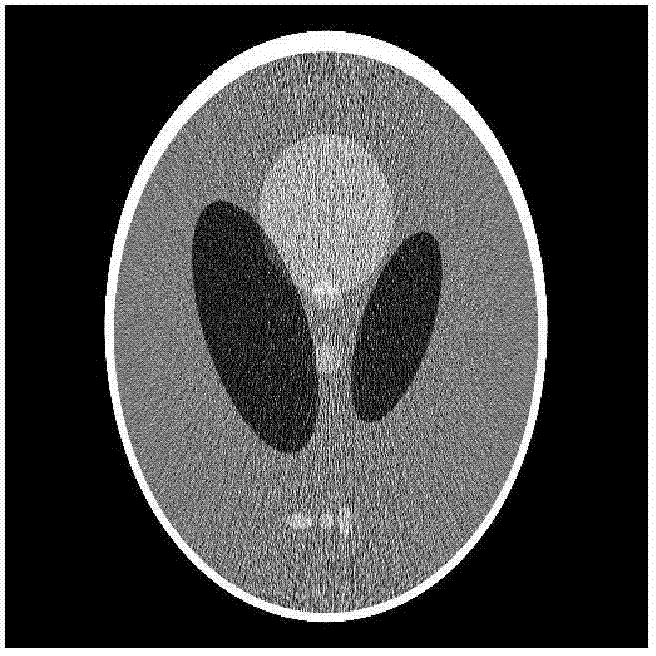
The invention discloses a non-partial regularization prior reconstruction method for a low-dosage X-ray captive test (CT) image. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring a previously scanned standard dosage image of a patient by X-ray CT imaging equipment; (2) acquiring CT projection data of the patient by the X-ray CT imaging equipment under a Low-mAs scanning protocol, and simultaneously acquiring a corresponding correction parameter and a system matrix; (3) constructing a math model for image reconstruction according to statistical distribution met by the projection data acquired in the step (2); (4) constructing a non-partial regularization prior guided by the previously scanned standard dosage image in the step (1), performing model transformation by adopting a maximum posterior estimation method, and constructing a target function for image reconstruction according to the math model obtained in the step (3); and (5) calculating the target function for CT image reconstruction, which is constructed in the step (4), by adopting an iteration algorithm to finish image reconstruction. By the method, the low-dosage CT image can be reconstructed under the Low-mAs scanning protocol.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Drug delivery systems
Matrix controlled diffusion drug delivery systems based on one or more silicone-containing monomers of the general formula:wherein x, y, m, m′, R, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, X, Z and Z′ are as defined herein are provided, wherein the matrix controlled diffusion drug delivery systems are sized and configured for back of the eye delivery.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
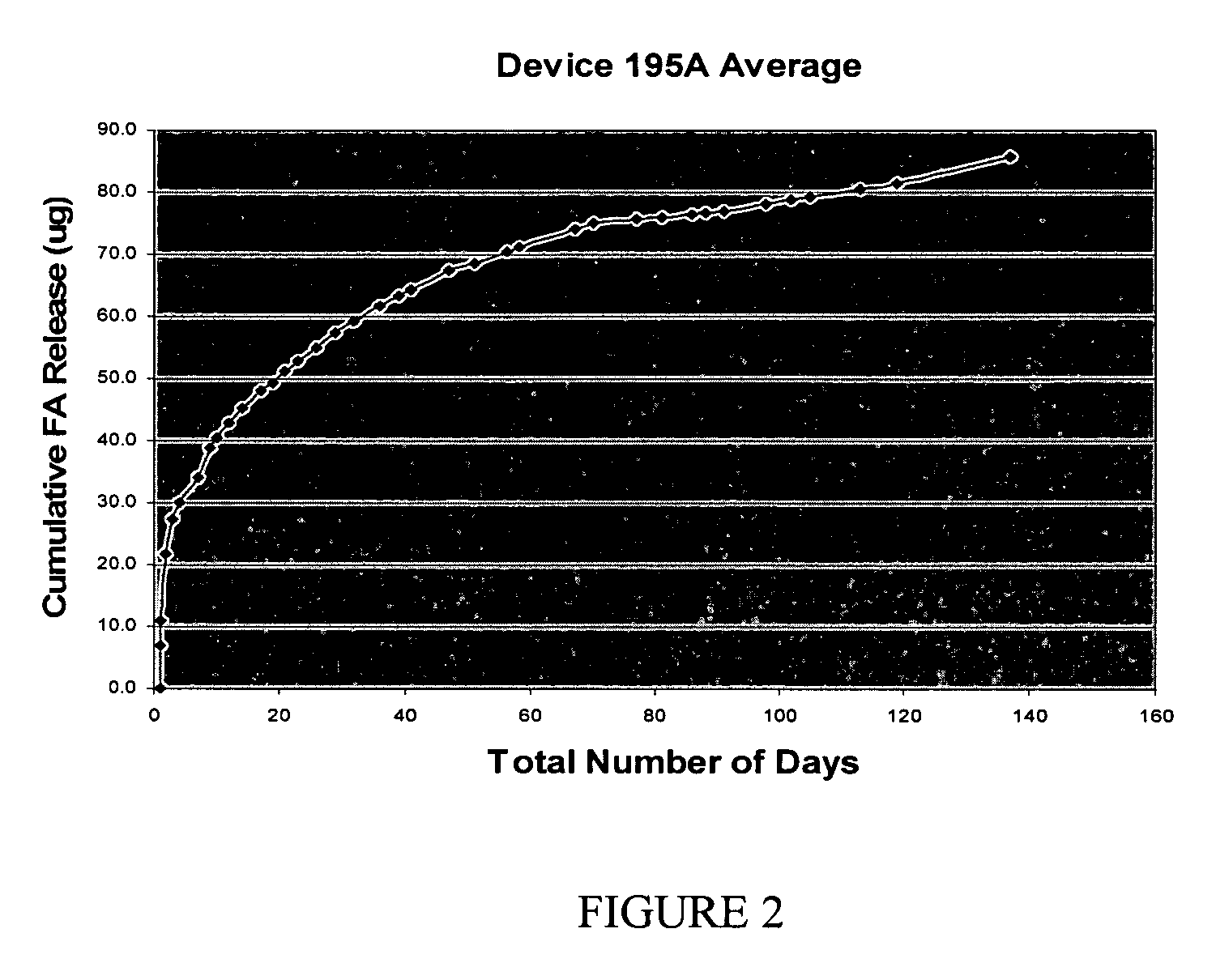
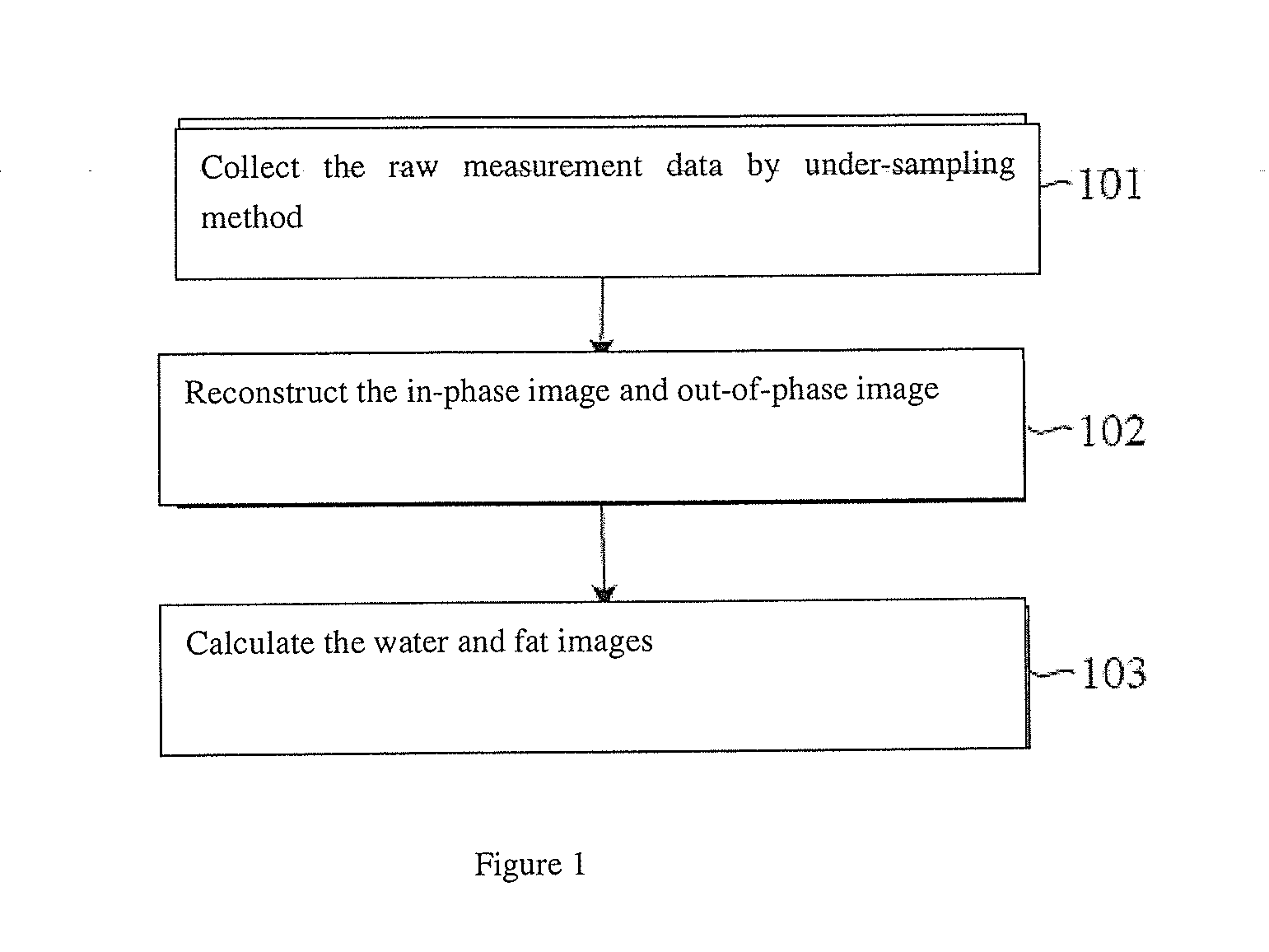
Magnetic resonance imaging water-fat separation method
ActiveUS20110267054A1Reduce MRI scan timeReduced imaging timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSystem matrixIterative method
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) water-fat separation method includes acquiring in-phase image raw measurement data and out-of-phase image raw measurement data with an MRI device, reconstructing an in-phase image and an out-of-phase image according to a system matrix and the raw measurement data using the penalty function regularized iterative reconstruction method, and calculating water and fat images according to the in-phase image and the out-of-phase image. The use of the penalty function regularized iterative method eliminates the need for k-space raw measurement data with a 100% sampling rate, thereby reducing the MRI scan time, shortening the entire imaging time, and improving the efficiency of the MRI device.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Apparatus and method for detecting space-time multi-user signal of base station having array antenna
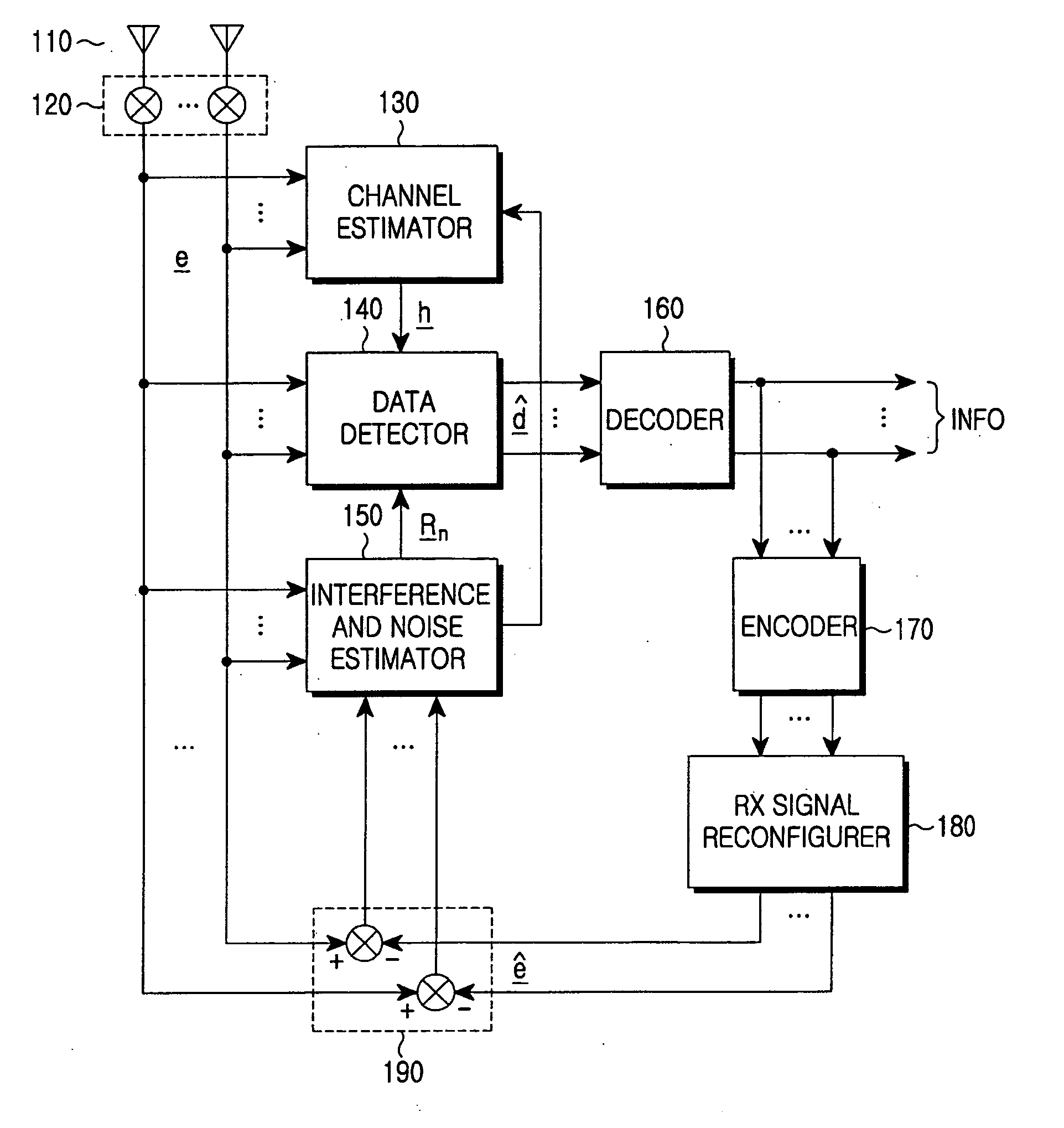
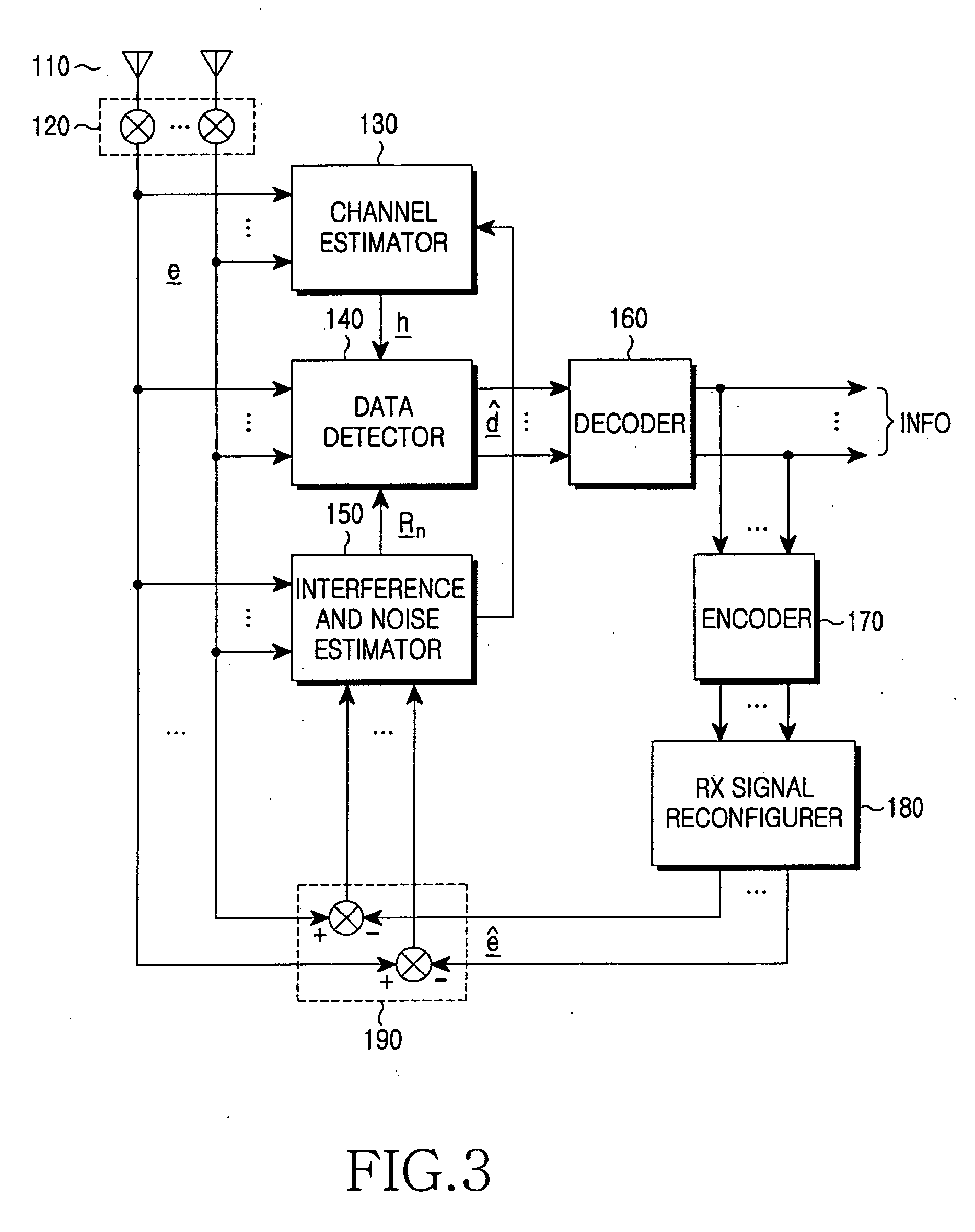
InactiveUS20060126753A1Eliminate distractionsDigital computer detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTemporal informationChannel impulse response
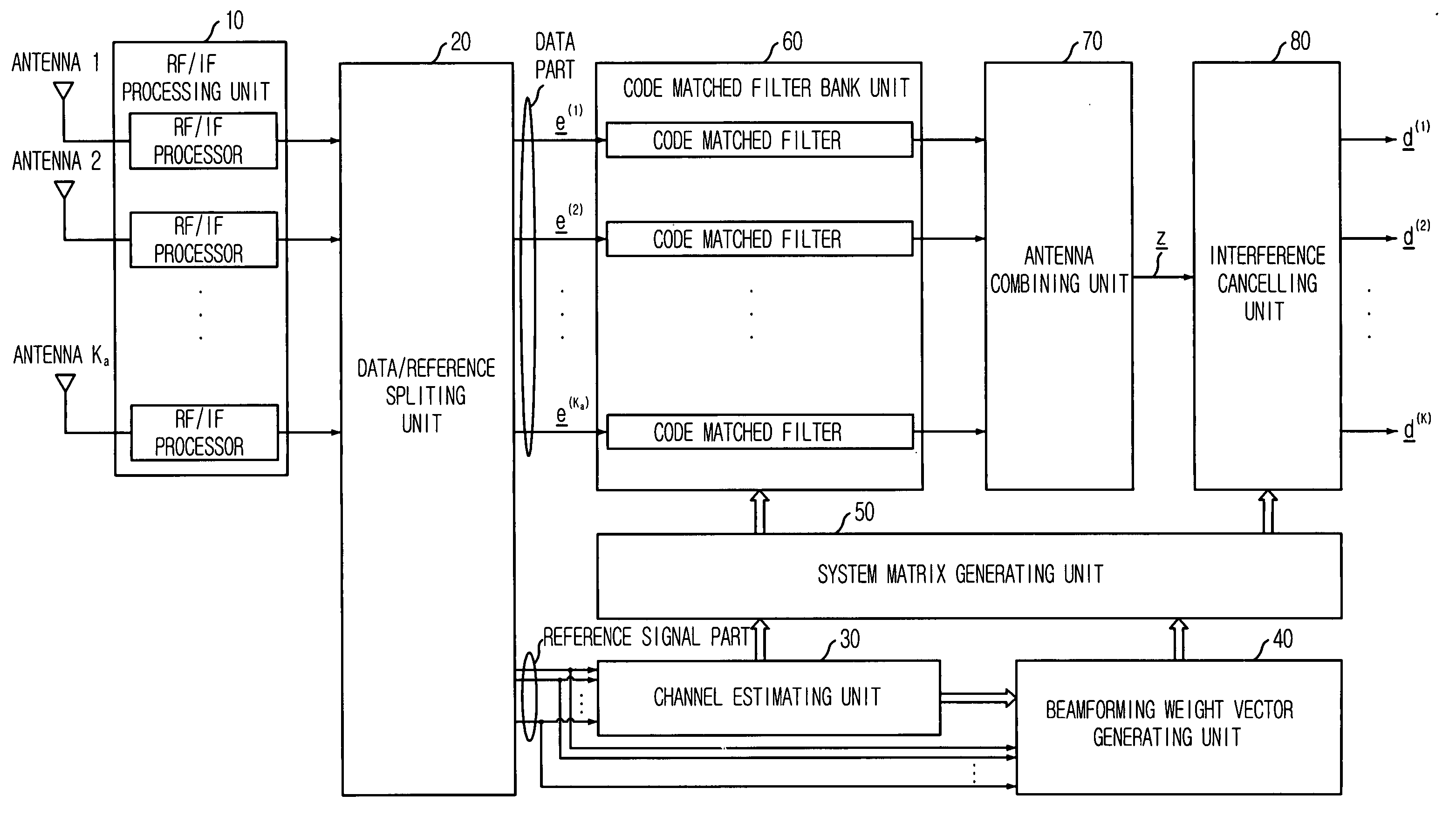
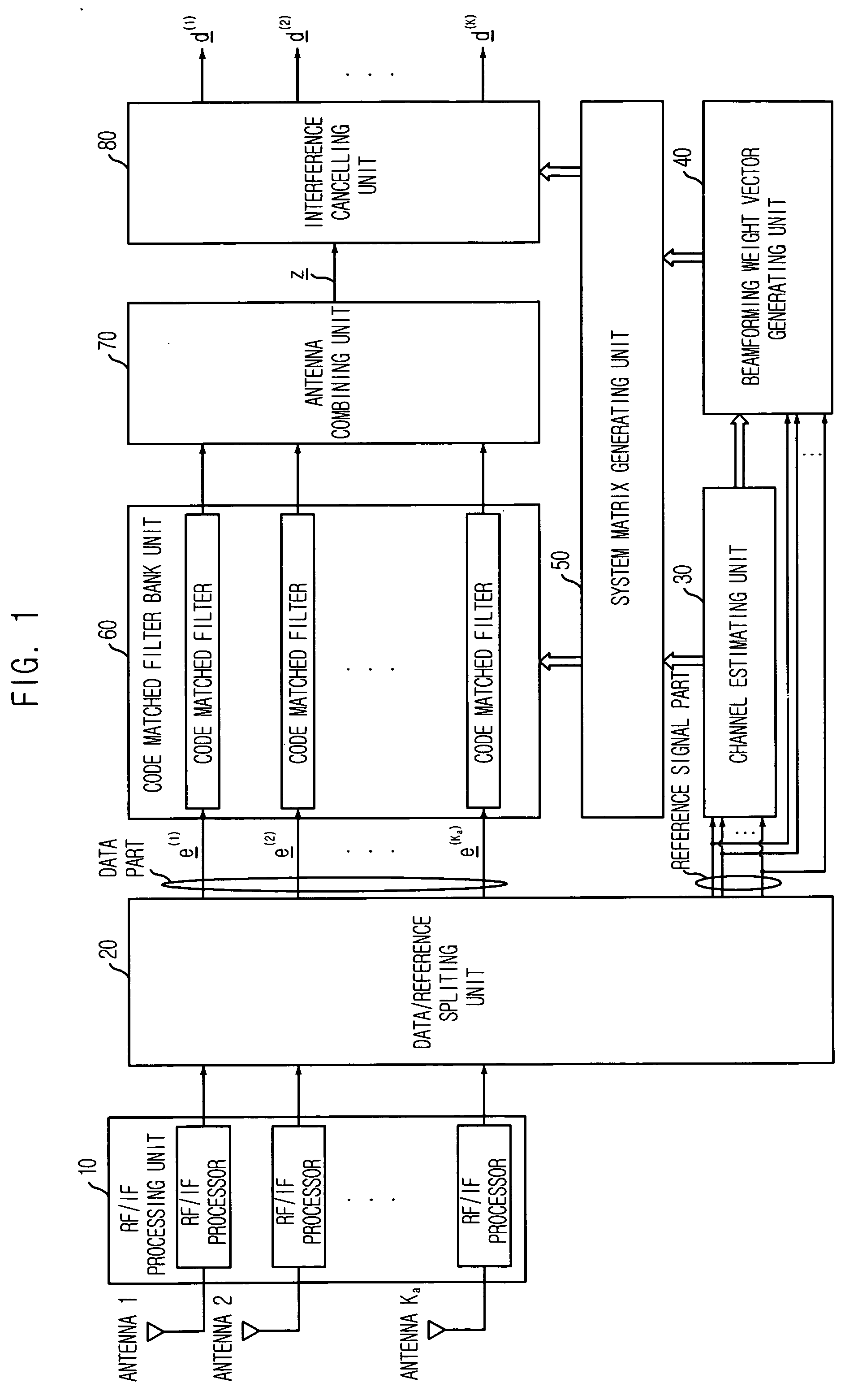
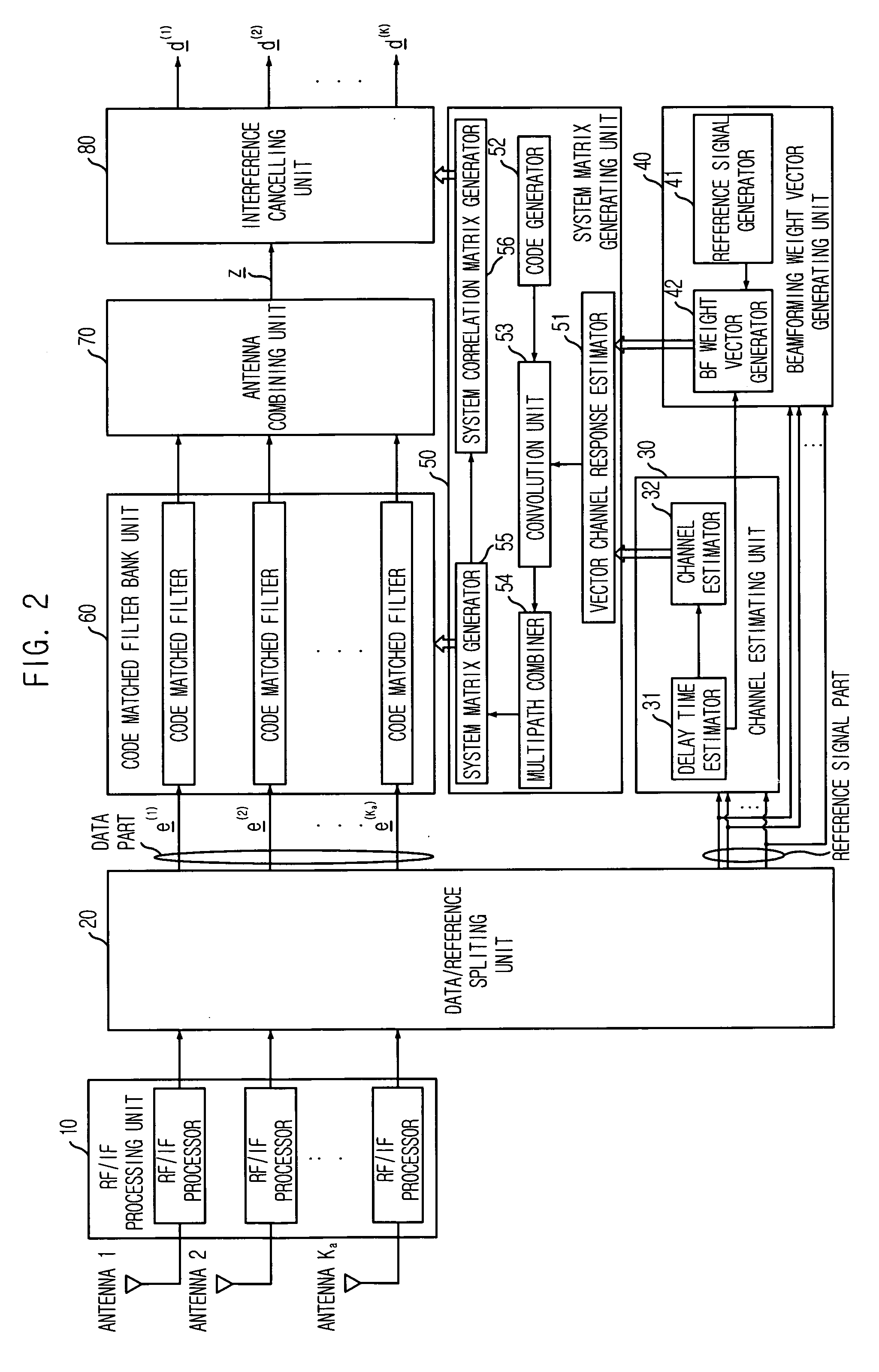
An apparatus and method for detecting a space-time multi-user signal are disclosed. The apparatus includes: an RF / IF processing unit for converting received signals through an array antenna into digital baseband signals; a splitting unit for dividing the digital baseband signals into data signals and reference signals; a estimating unit for estimating a delay time information and a channel impulse response; a vector generating unit for receiving the reference signals and the delay time information of to thereby generate a beamforming weight vector; a matrix generating unit for receiving the channel impulse response and the beamforming weight vector to there by generate a system matrix; a filtering unit for receiving the data signals and the system matrix to multiply the system matrix to data per each antenna; a antenna combining unit for combining signals outputted from the filtering unit; and an interference cancelling unit for cancelling an interference signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Power system transient stability simulating method based on implicit numerical integration
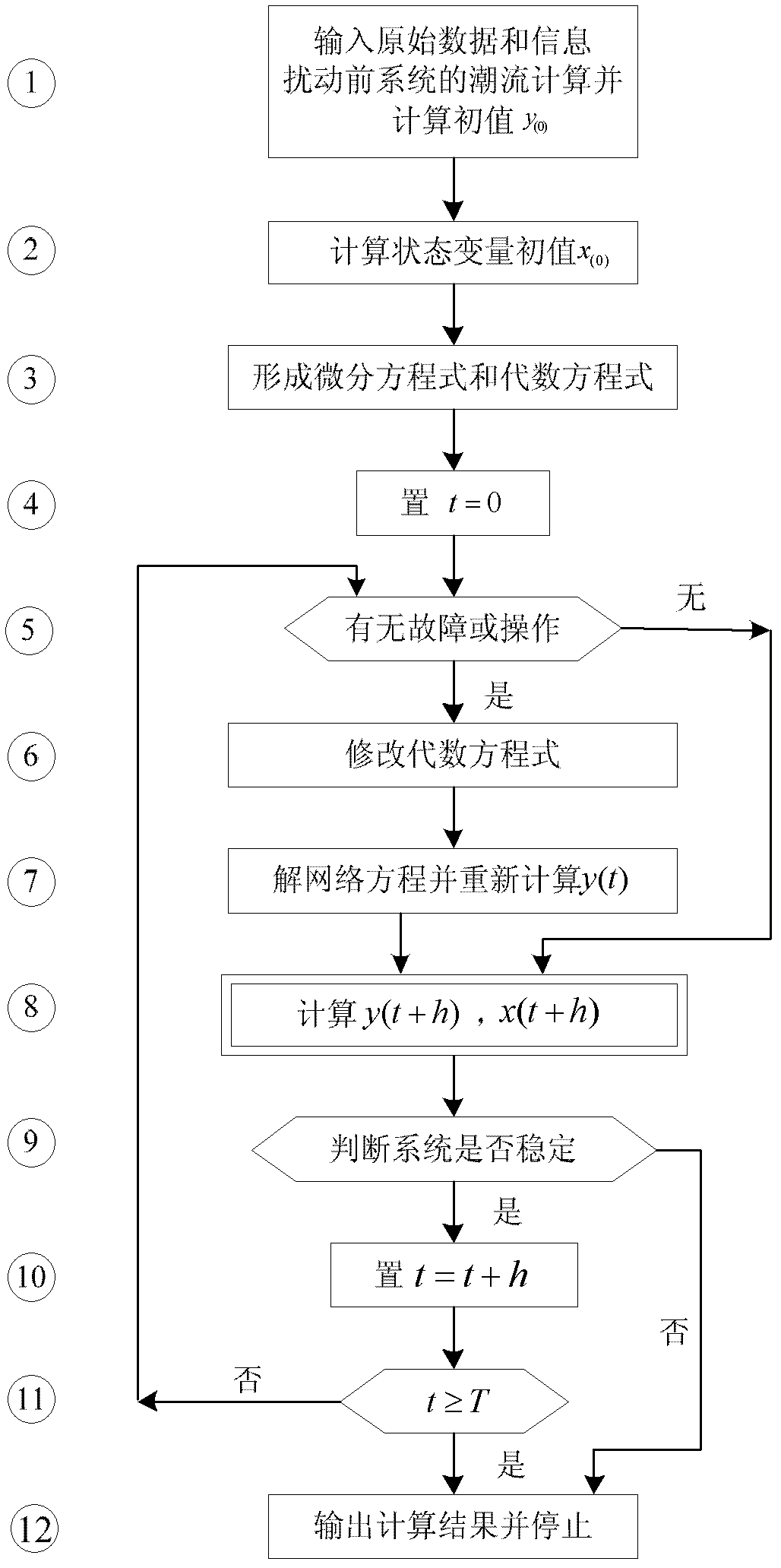
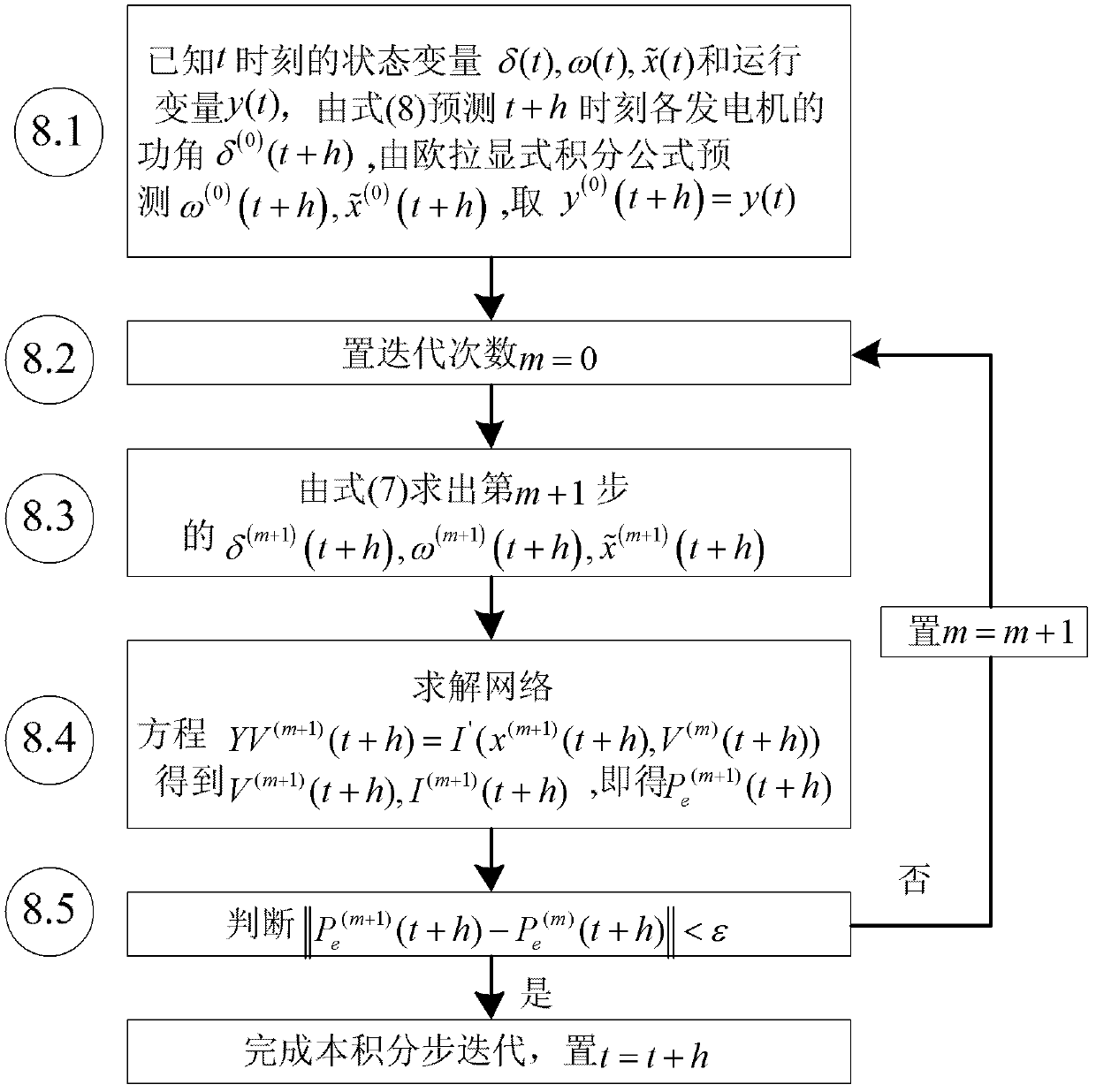
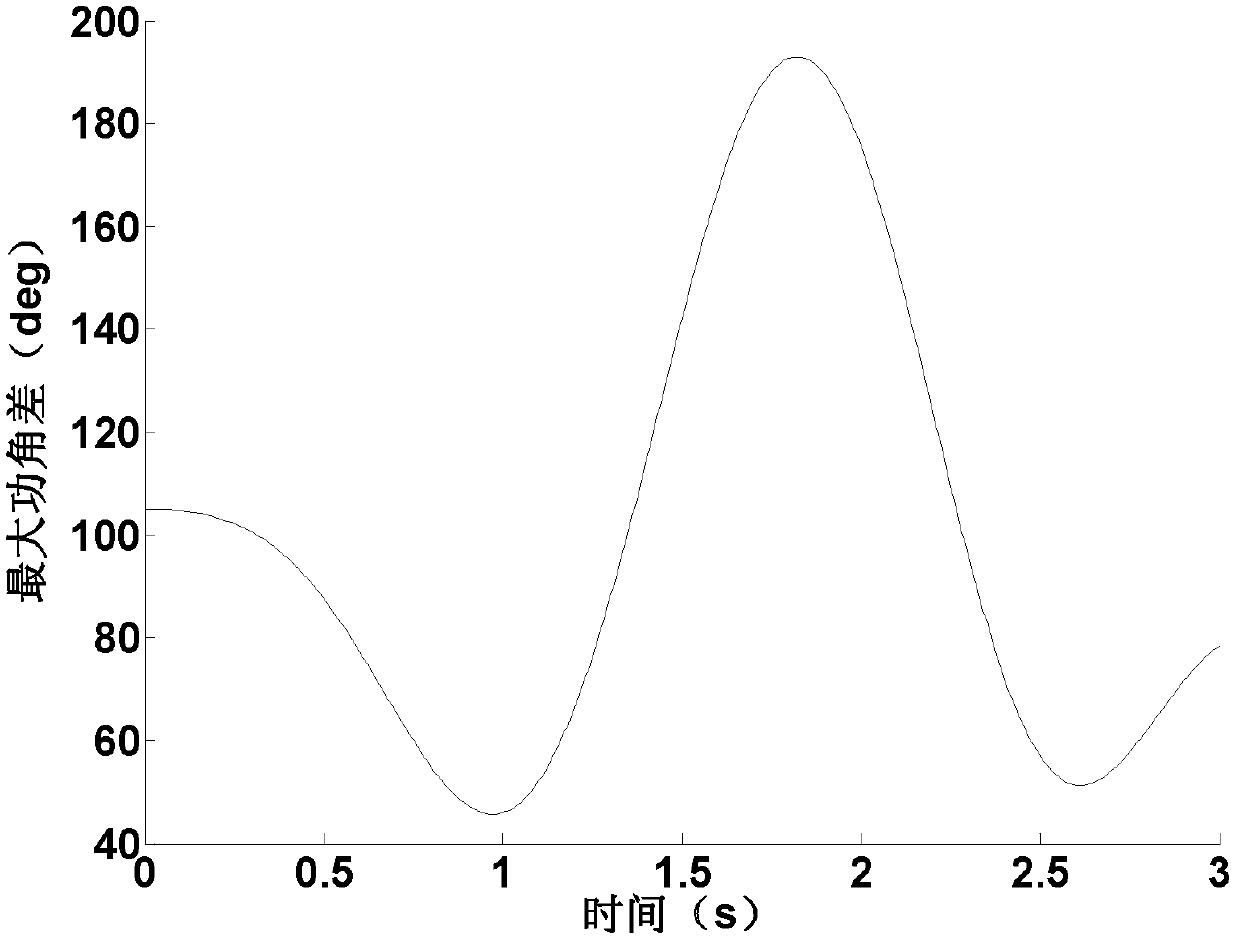
InactiveCN102609575ASmall amount of calculationReduced number of integration step iterationsSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemTruncation error (numerical integration)Transient state
The invention discloses a power system transient stability simulating method based on implicit numerical integration. Compared with an existing power system transient stability numerical simulation implicit trapezoidal integration method, the power system transient stability simulating method employs a power-angle integration formula with a smaller local truncation error, namely, enables a non-linear differential equation set for describing a power system transient process to be expressed as a linear portion and a non-linear portion. An accurate analysis expression of a state transition matrix is obtained by reasonably selecting a system matrix of the linear portion as a singular matrix, and a group of implicit integration formulas is obtained by leading linear integrable functions to be approximate to the non-linear portion of the differential equation set. The local truncation error of the power-angle implicit integration formulas of the generator refers to O (h5) which is larger than a local truncation error O (h3) of implicit trapezoidal integration, the calculated quantity of integration each time is equivalent to that of the implicit trapezoidal integration. By means of the high-precision implicit integration formulas, iteration times of each integration step under the same iteration precision condition are decreased, so that the simulated calculated quantity is remarkably decreased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
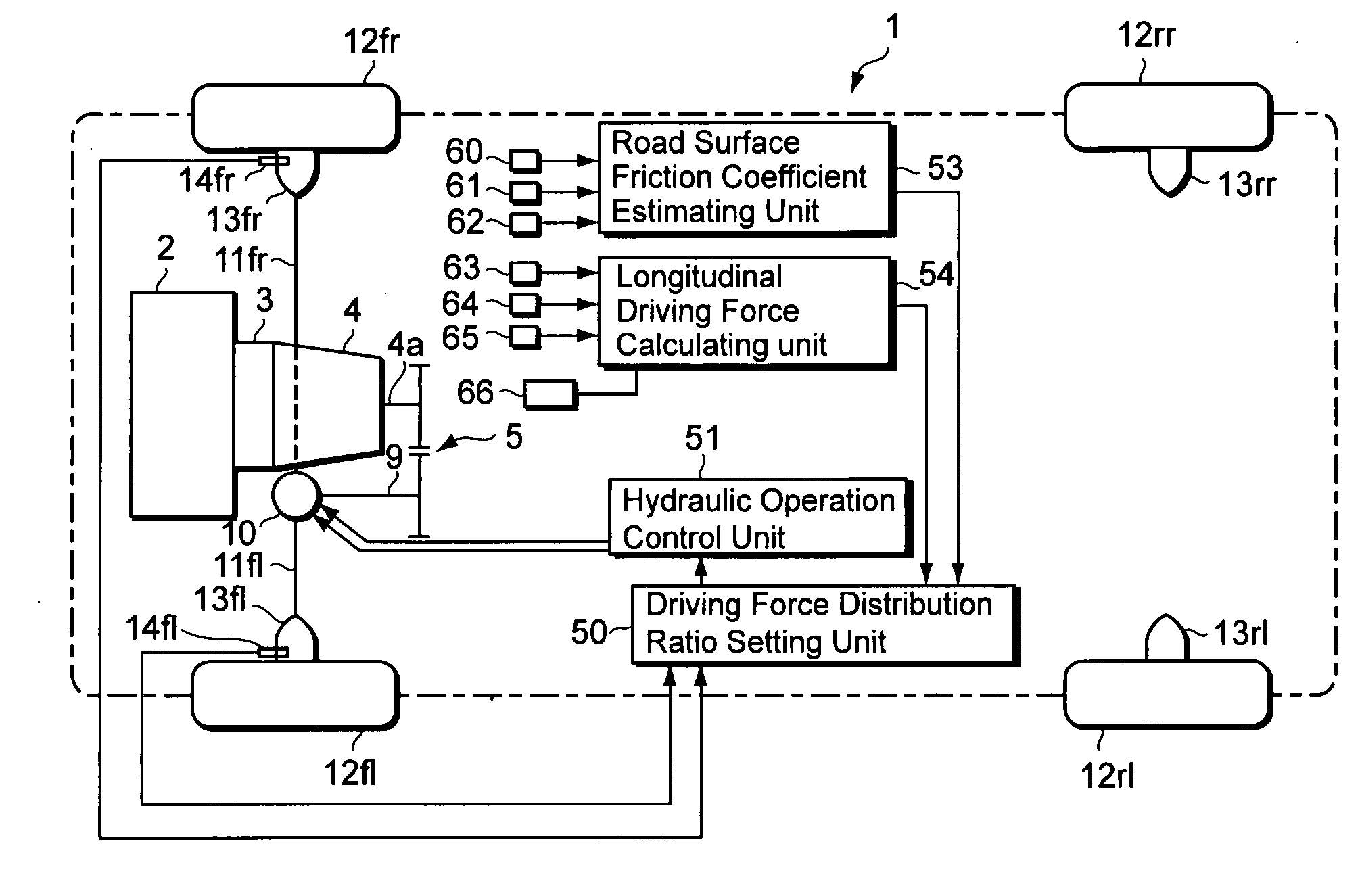
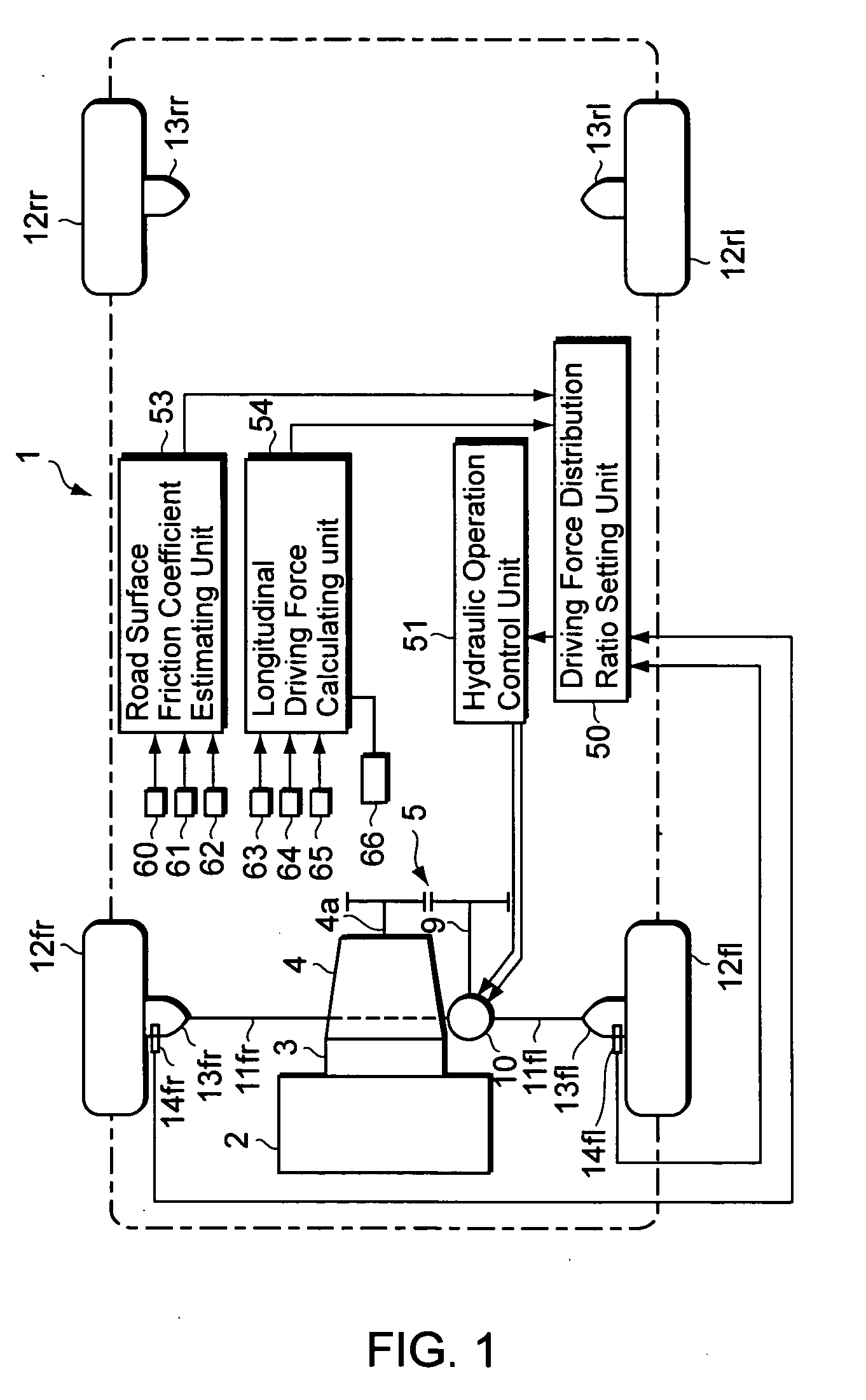
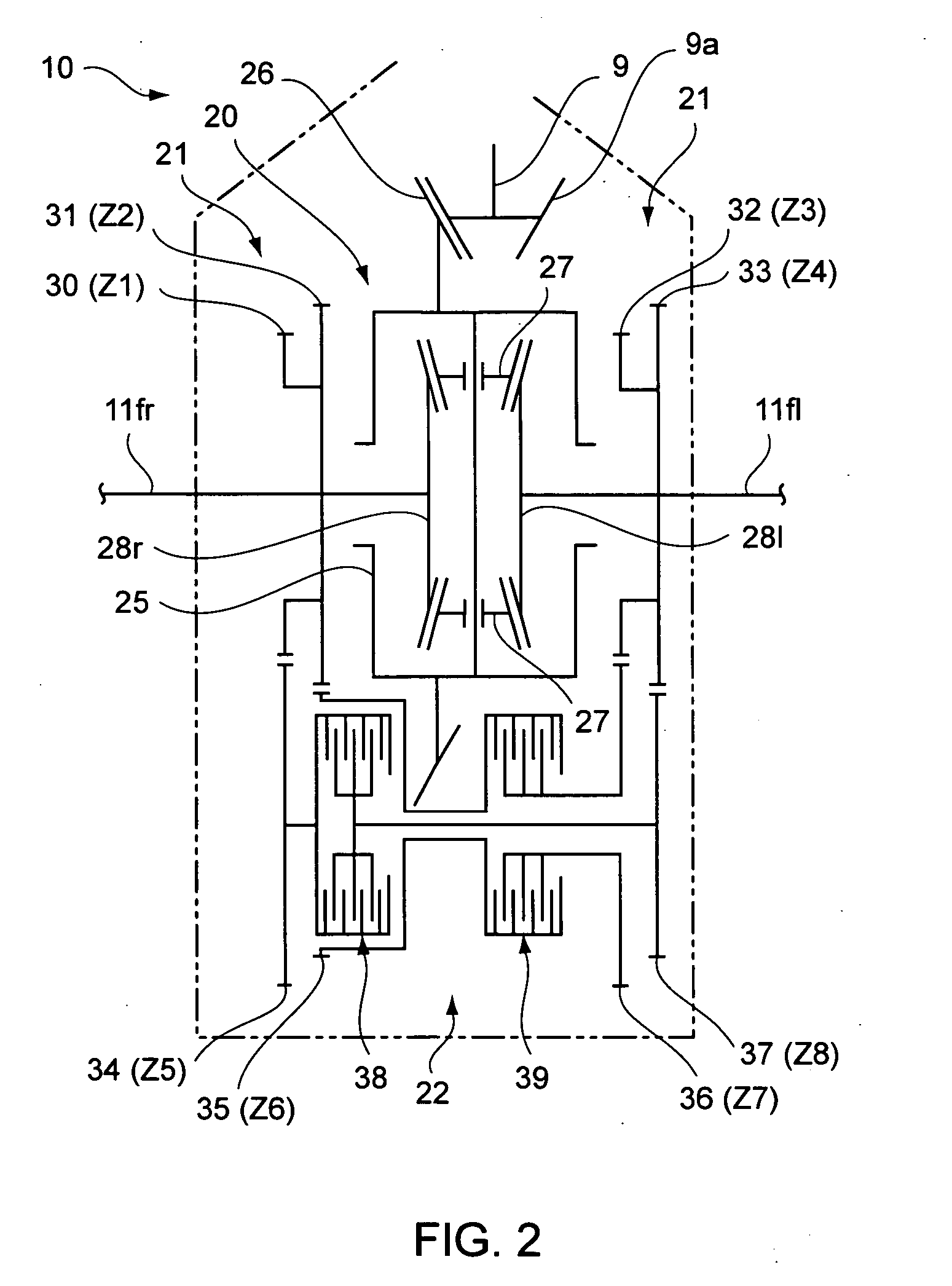
Vehicle motion control device and method
InactiveUS20060030974A1Improve stabilityImprove responseHand manipulated computer devicesAnalogue computers for trafficSystem matrixMotor control
The objective of the present invention is to provide a vehicle motion control device capable of controlling the driving force distribution to the wheels with superior stability and response while effectively utilizing the tire grip. Specifically, the present invention provides a vehicle motion control device for a vehicle, the vehicle having a plurality of wheels and a driving device for driving the wheels based on a driving force / load distribution ratio, having: a force detection unit for detecting forces that act on the wheels; a target distribution ratio calculating unit for obtaining nonlinear terms by use of a group of parameters including the forces detected by the force detection unit, and obtaining a target value of the driving force / load distribution ratio so as to minimize the nonlinear terms, the nonlinear terms being included in elements of a system matrix of equations of state that describe a state of motion of the vehicle; and a driving device control unit for controlling the driving device based on the target value of the driving force / load distribution ratio.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
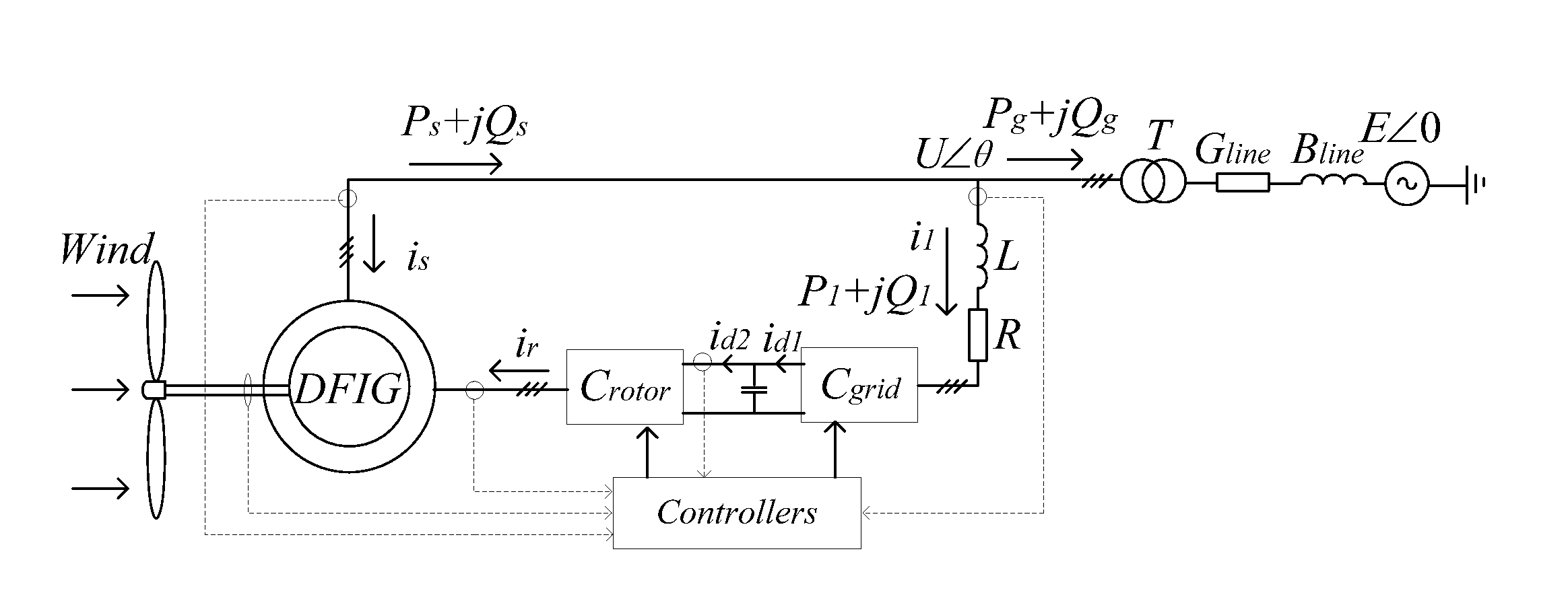
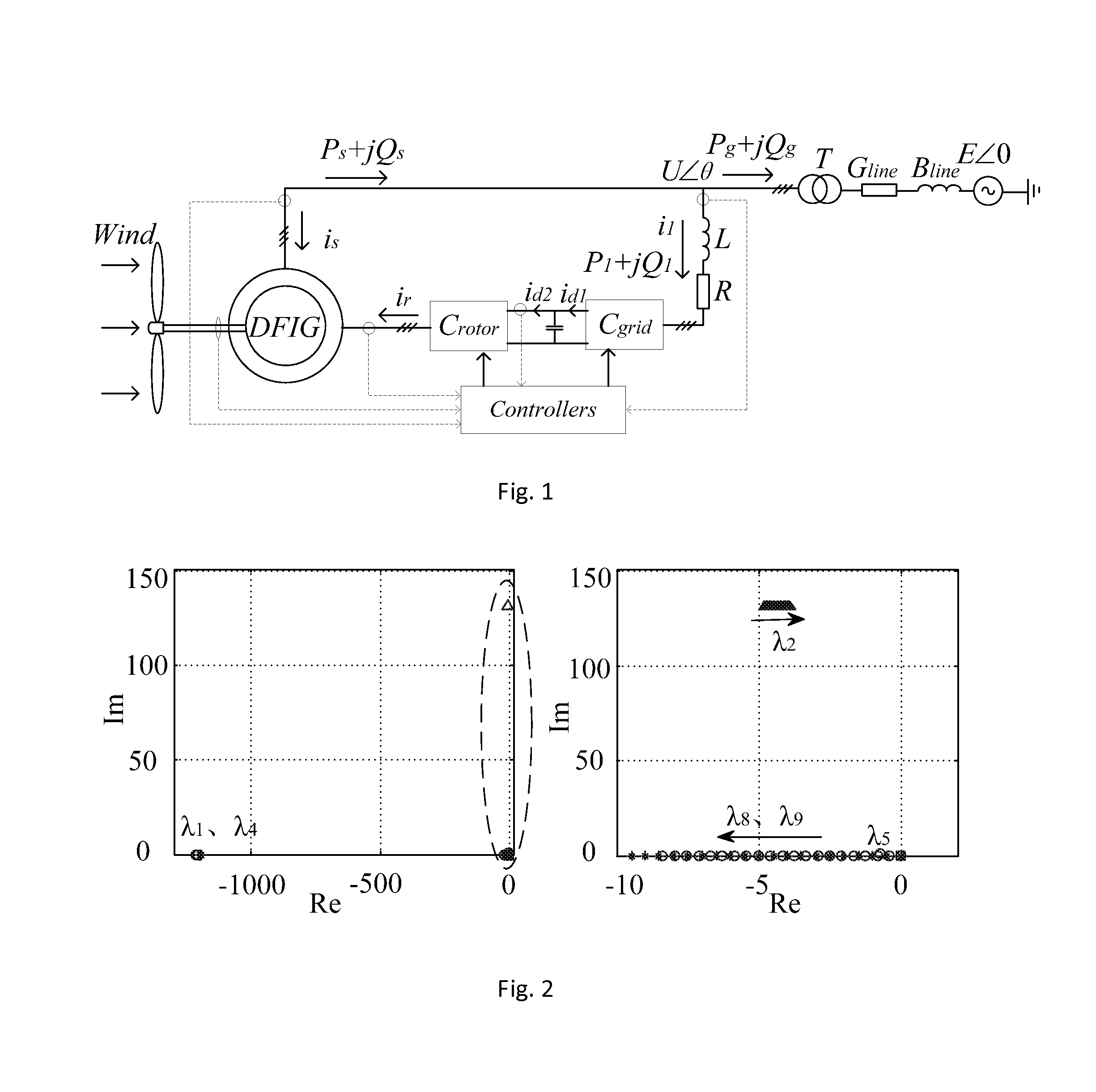
A method for improving small disturbance stability after double-fed unit gets access to the system
ActiveUS20150318697A1Improve dominant modal dampingReduce workloadMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlSystem matrixElectric power system
A method for improving system small disturbance stability after double-fed unit gets access to the system belongs to the field of electric power system operation and control technology. A sensitivity analysis is adopted to optimize parameter, through making sensitivity analysis on the non-ideal dominant mode happens to the system to find out several nonzero elements that are most sensitive to this mode in system matrix; elements of state matrix is adopted to replace the elements of system matrix to make analysis so as to find out the most relevant parameter set; setting parameters change in the interval to observe track for the change of eigenvalues of corresponding mode and then balancing and optimizing system parameters comprehensively according to the change of eigenvalues. Without adding other control means, the present invention can improve dominant modal damping caused by selecting improper controller parameters or system parameters after double-fed unit gets access to the system without increasing cost; as this method is also highly targeted, exhaustive efforts for all the adjustable parameters of the system can be avoided, which not only greatly decreases workload, but also improves computational efficiency, so that it is very instructive.
Owner:WIND POWER TECH CENT OF GANSU ELECTRIC POWER
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS8378682B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
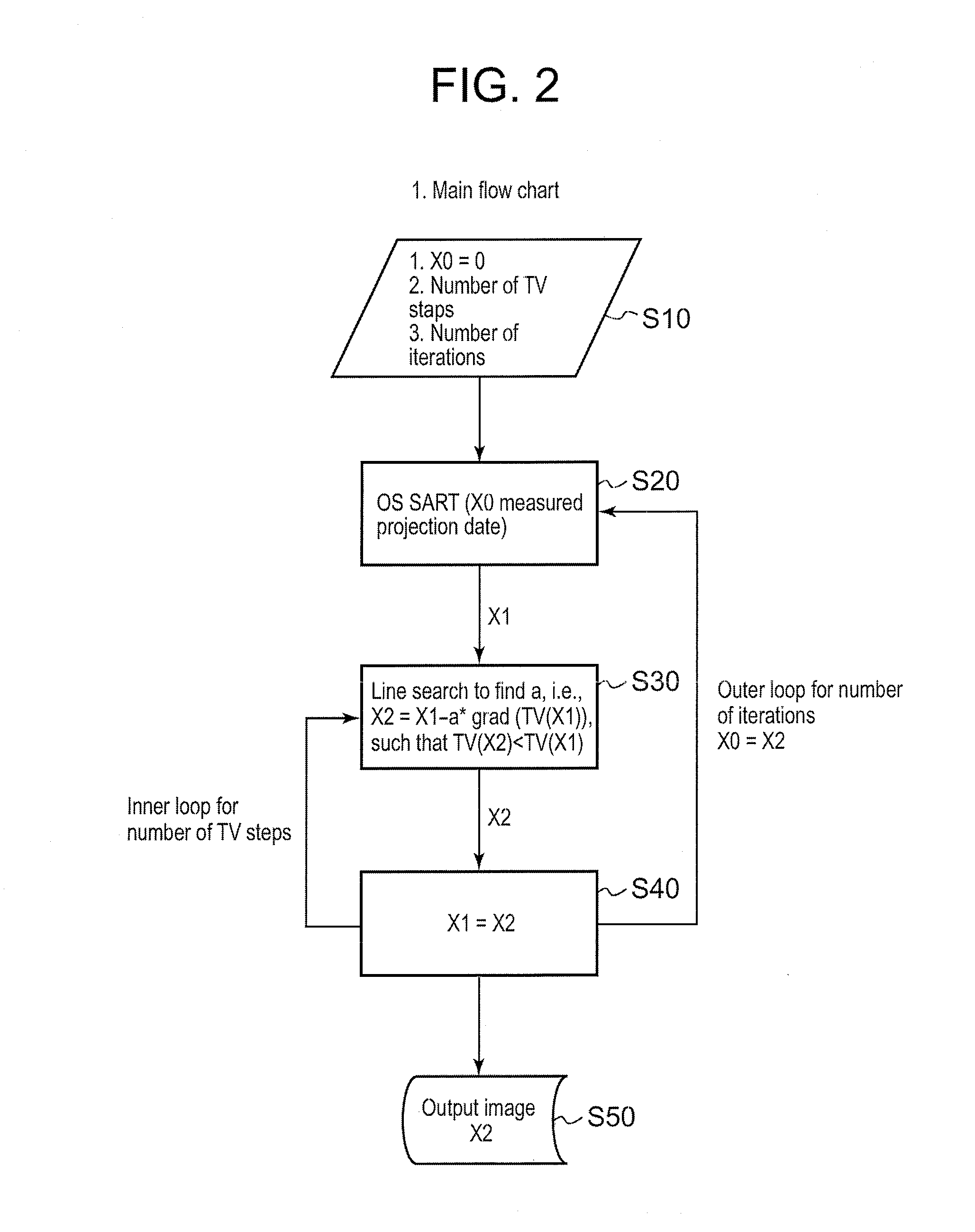
Novel implementation of total variation (TV) minimization iterative reconstruction algorithm suitable for parallel computation
InactiveUS20110164031A1Minimize changesReconstruction from projectionImage generationImaging qualityAlgorithm
The CT imaging system optimizes its image generation by frequently updating an image and adaptively minimizing the total variation in an iterative reconstruction algorithm using many or sparse views under both normal and interior reconstructions. The projection data is grouped into N subsets, and after each of the N subsets is processed by the ordered subsets simultaneous algebraic reconstruction technique (OSSART), the image volume is updated. During the OSSART, no coefficients is cached in the system matrix. This approach is intrinsically parallel and can be implemented with a GPU card. Due to the more frequent image update and the variable step value, an image quality has improved.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
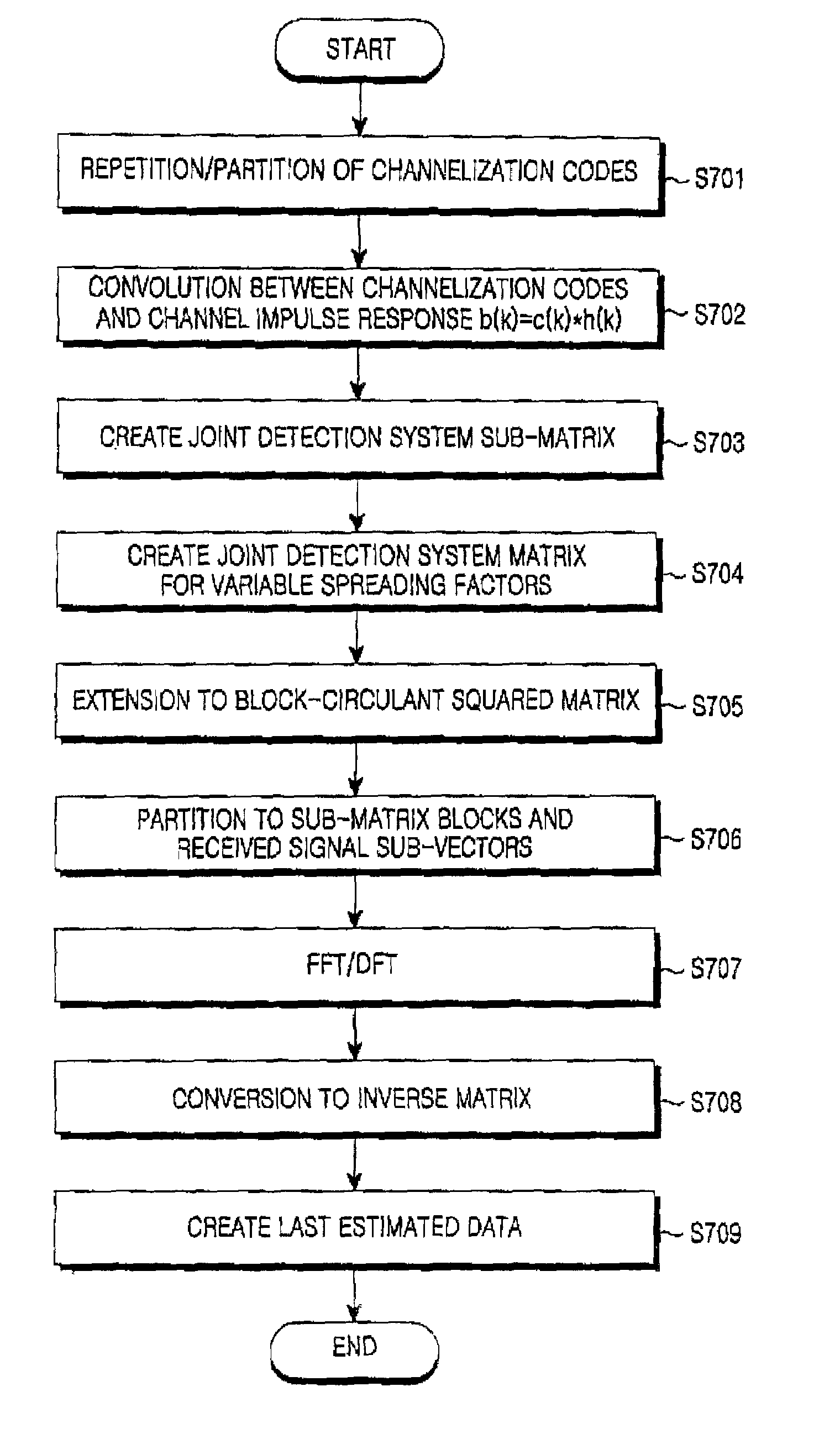
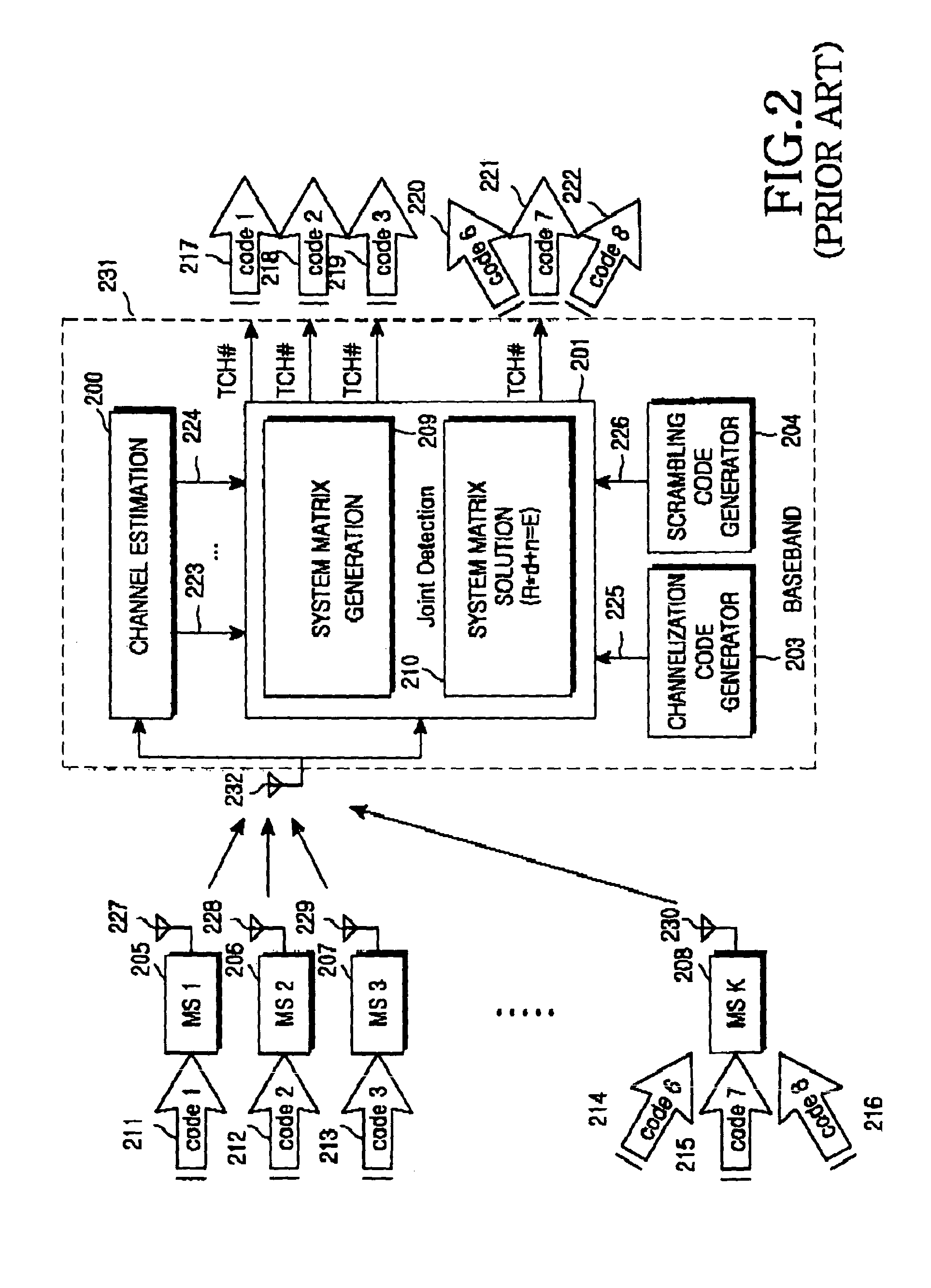
Apparatus and method for joint detection receiving irrespective of orthogonal code length in mobile communication system
A joint detection reception apparatus and method, which are utilized irrespective of a length of an orthogonal code in a TD-CDMA communication system. The joint detection reception method for creating a system matrix associated with a joint detection receiver in the same time slot includes the steps of a) repeating and partitioning individual channelization codes having variable lengths, and creating channelization code blocks having the same lengths, b) performing a convolution operation between the repeated and partitioned channelization code blocks and a channel impulse response, and acquiring combined impulse responses, c) grouping the combined impulse responses to construct sub-block matrices for a joint detection system, d) arranging the sub-block matrices for the joint detection system to be shifted by a predetermined column distance, and constructing a joint detection system matrix, and e) extending the joint detection system matrix to a squared-format matrix to create a block-circulant squared matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image reconstruction methods based on block circulant system matrices
InactiveUS7983465B2Minimized in sizeFast computerReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLines of responseIn plane
An iterative image reconstruction method used with an imaging system that generates projection data, the method comprises: collecting the projection data; choosing a polar or cylindrical image definition comprising a polar or cylindrical grid representation and a number of basis functions positioned according to the polar or cylindrical grid so that the number of basis functions at different radius positions of the polar or cylindrical image grid is a factor of a number of in-plane symmetries between lines of response along which the projection data are measured by the imaging system; obtaining a system probability matrix that relates each of the projection data to each basis function of the polar or cylindrical image definition; restructuring the system probability matrix into a block circulant matrix and converting the system probability matrix in the Fourier domain; storing the projection data into a measurement data vector; providing an initial polar or cylindrical image estimate; for each iteration; recalculating the polar or cylindrical image estimate according to an iterative solver based on forward and back projection operations with the system probability matrix in the Fourier domain; and converting the polar or cylindrical image estimate into a Cartesian image representation to thereby obtain a reconstructed image.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
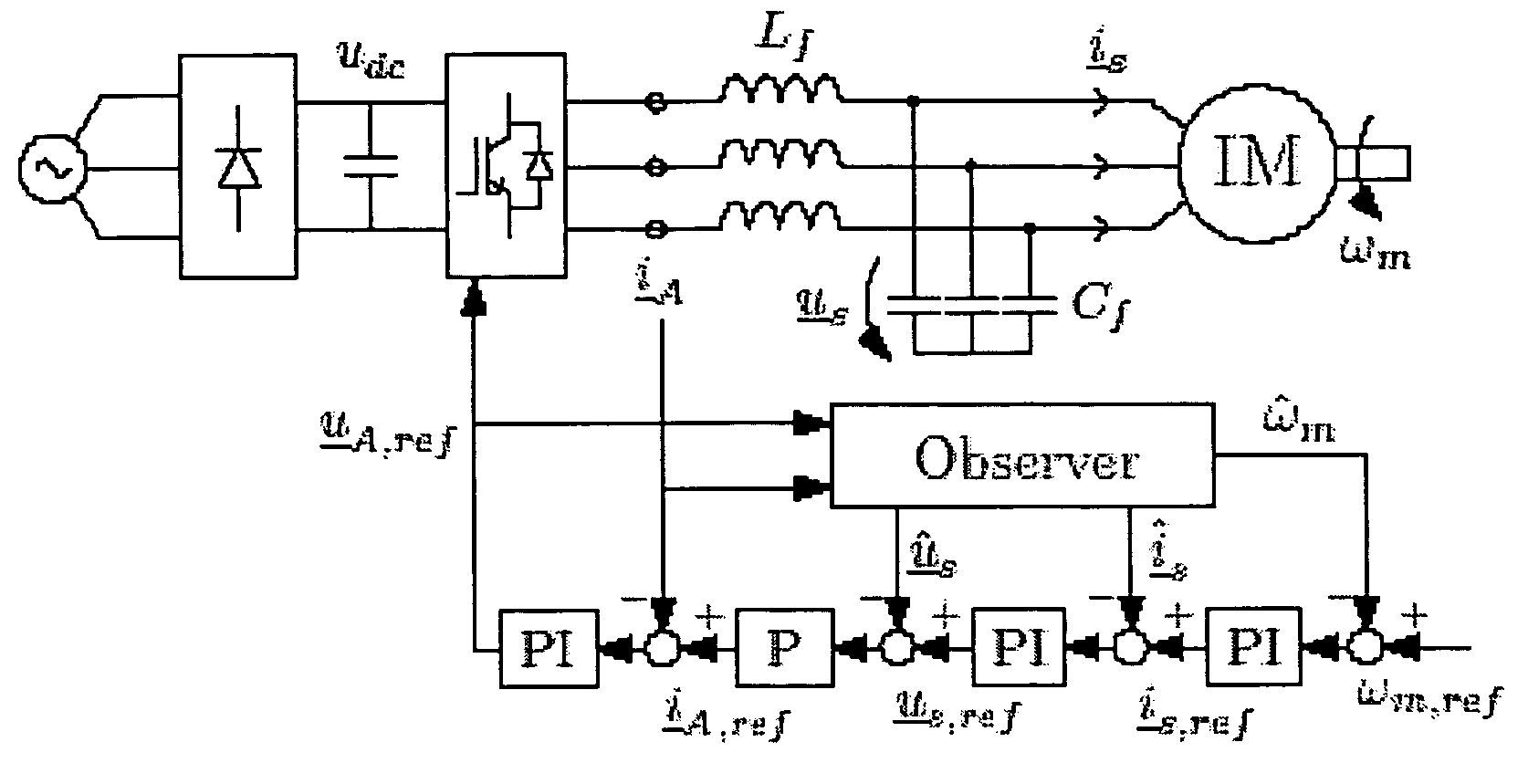
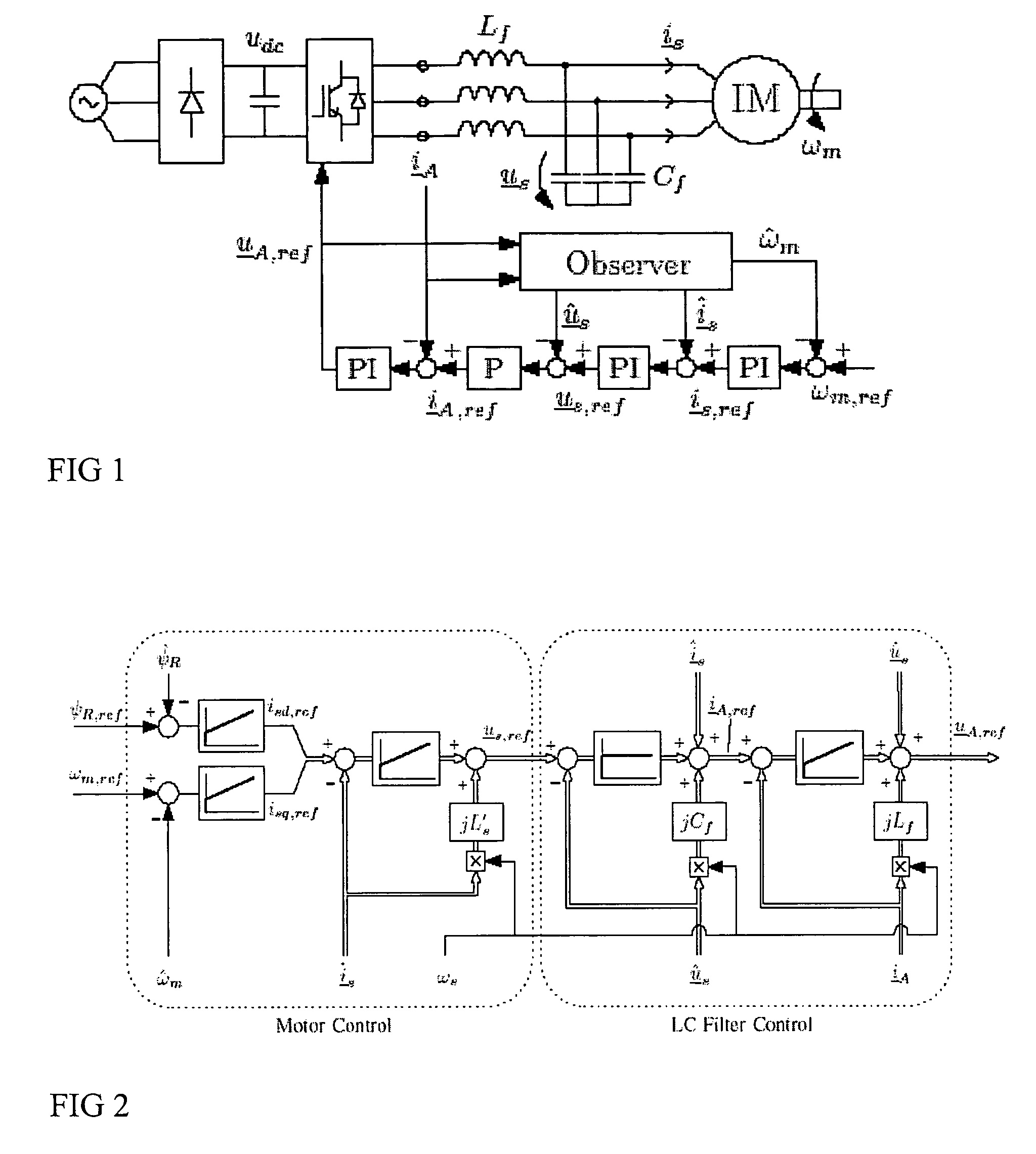
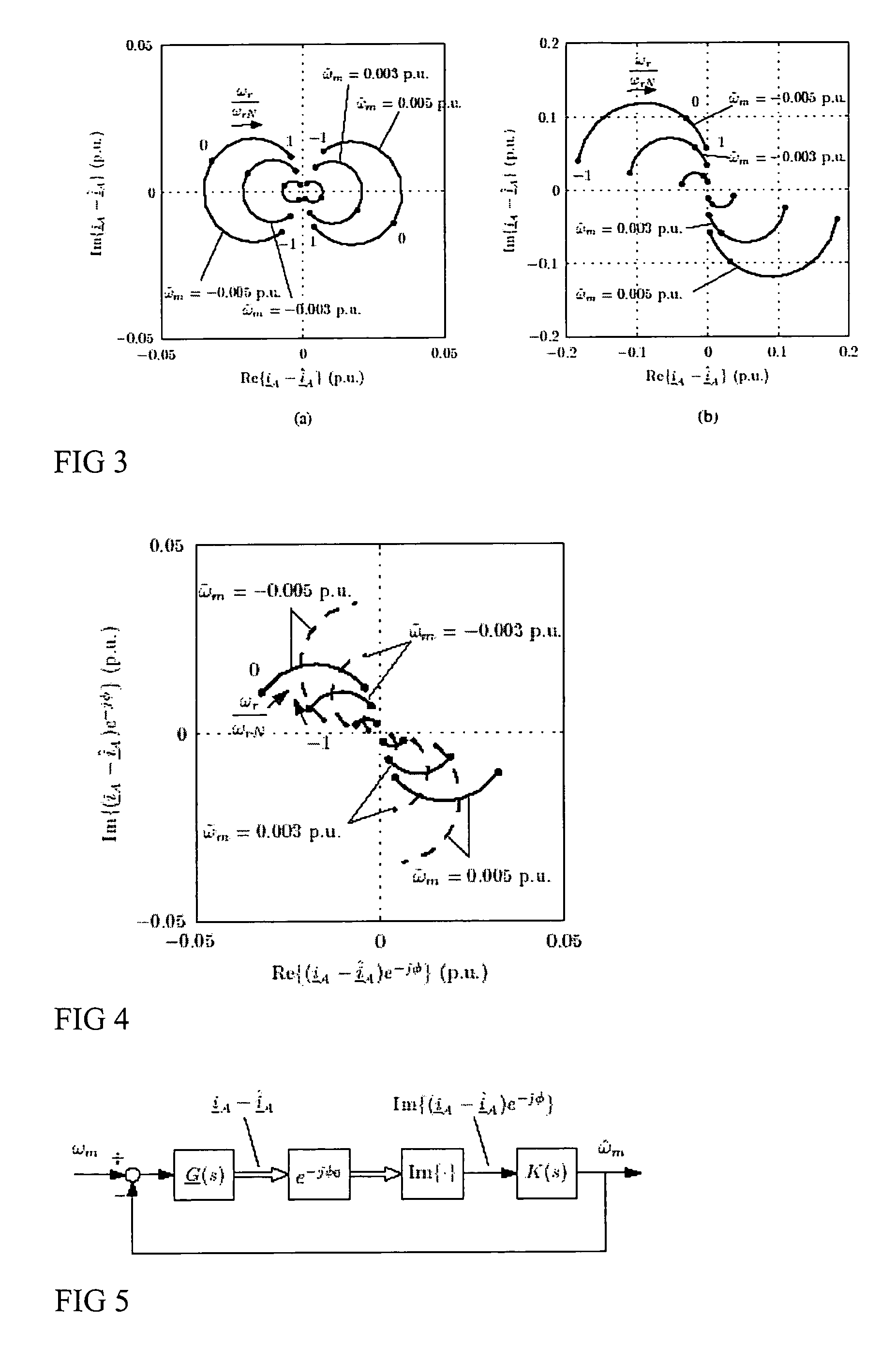
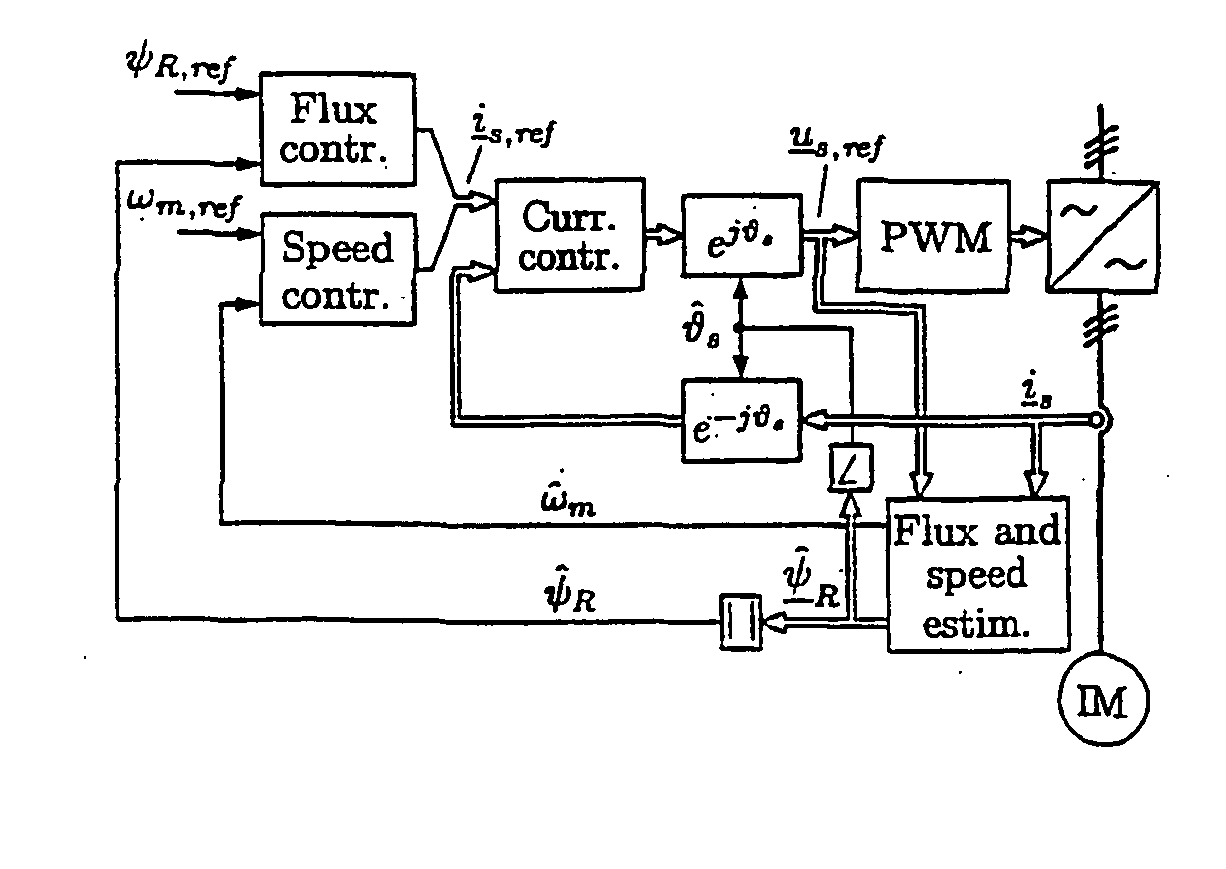
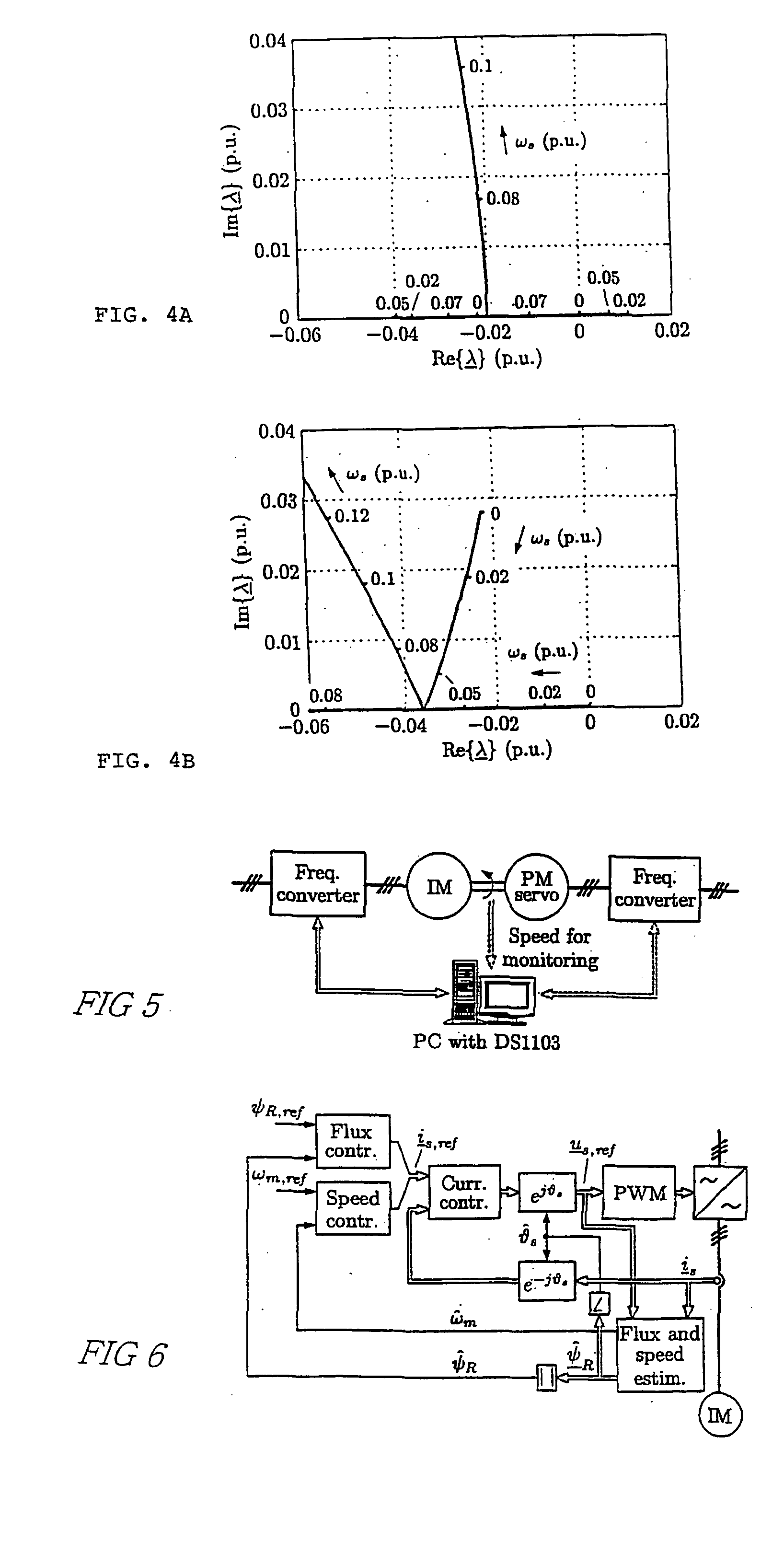
Speed sensorless control of an induction machine using a PWM inverter with output LC filter
InactiveUS7084604B2Single-phase induction motor startersVector control systemsVoltage vectorSystem matrix
Owner:ABB OY
Automatic construction method and device of text proofreading error word library
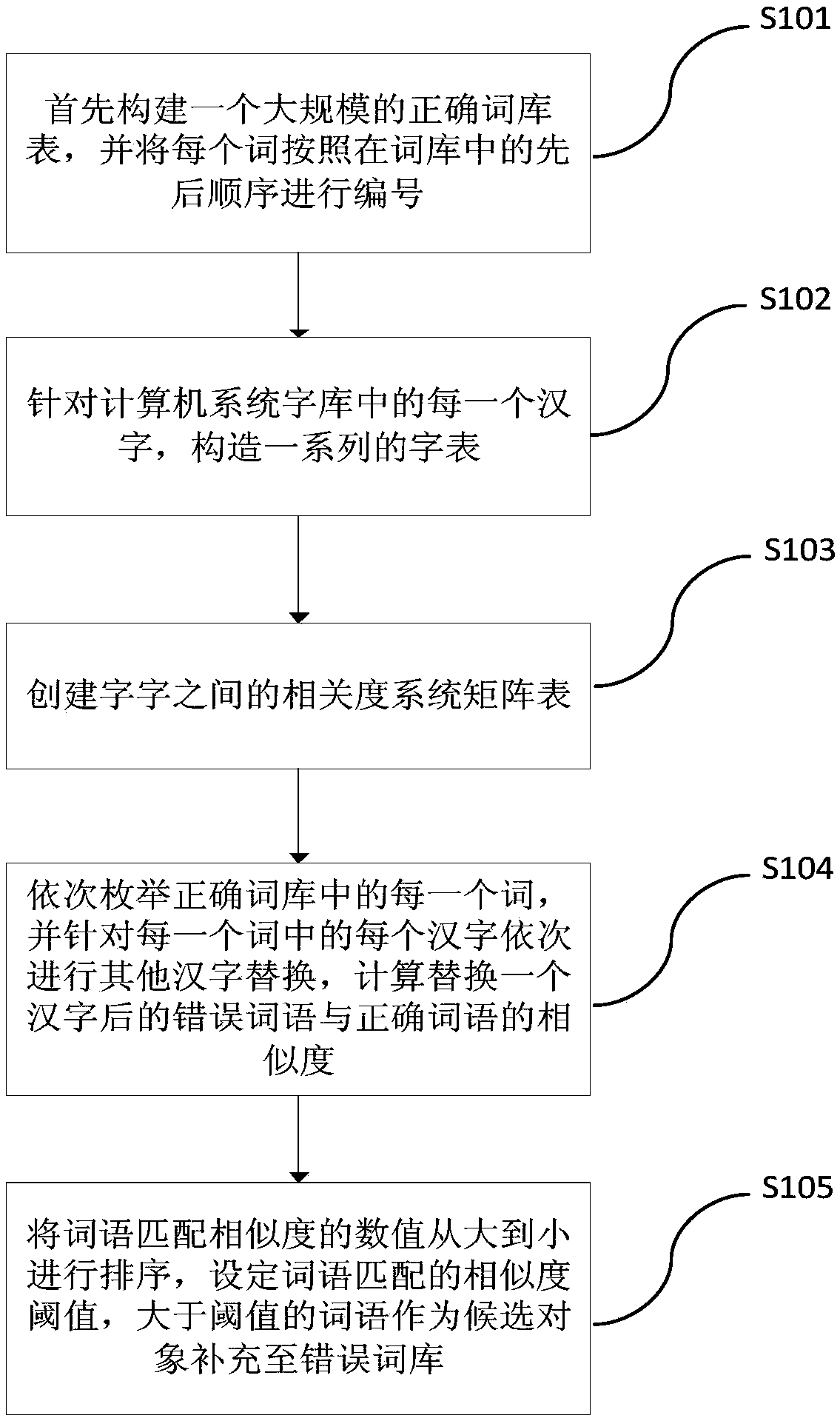
InactiveCN107665190AImprove matchCollection advantageCharacter and pattern recognitionNatural language data processingChinese charactersSystem matrix
The invention relates to an automatic construction method and device of a text proofreading error word library. The method comprises the steps of constructing a large-scale correct word library table,and numbering each word according to the order in the correct word library table; regarding each Chinese character in the word library of a computer system, constructing a series of word tables; creating a word relevancy system matrix table; sequentially enumerating each word in the correct word library table, sequentially replacing other Chinese characters for each Chinese character in each word, and calculating word matching similarities between correct words and error words after one Chinese character is replaced; ranking the values of the word matching similarities in a gradually decreasing mode, setting a similarity threshold value of word matching, and supplementing words with the similarity values larger than the threshold value to the error word library. The method can overcome the defects that in the prior art, error word table collection excessively relies on manual modes, the efficiency is low, the coverage surface is narrow, and the scale of the word library is limited; the accuracy of automatic text proofreading can be improved.
Owner:李晓妮
Specific fluorescent probe for recognizing fluorine ions and application of specific fluorescent probe
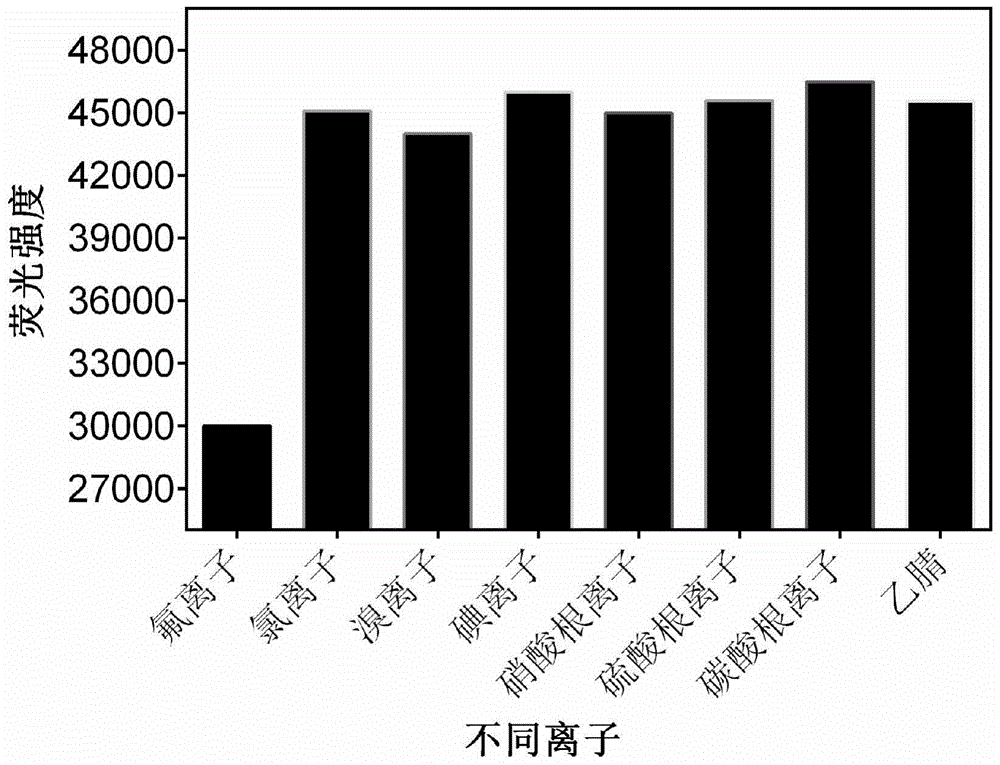
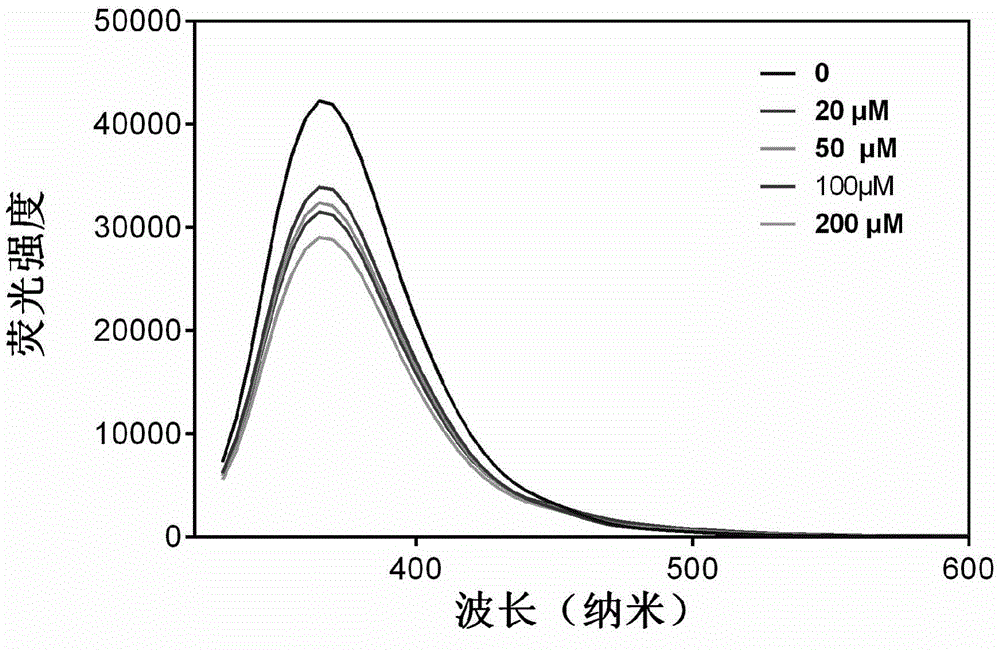
ActiveCN104449677AStrong specificityAchieve brokenGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceIon contentChemical synthesis
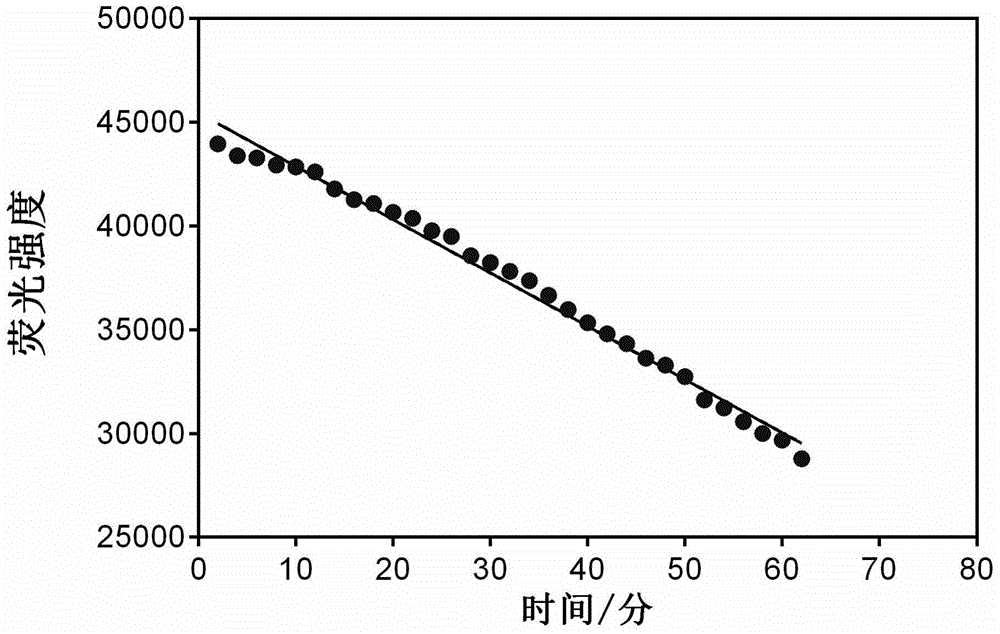
The invention discloses a specific fluorescent probe for recognizing fluorine ions and an application of the specific fluorescent probe, and belongs to the field of fine chemistry. The fluorescent probe is a 2-(2-hydroxycyclohexyl phenyl ketone) benzothiazole derivative. The 2-(2-hydroxycyclohexyl phenyl ketone) benzothiazole derivative and triethylamine are dissolved in tetrahydrofuran, acyl chloride is slowly dripped into the tetrahydrofuran in ice bath, and finally, purification is realized by silica gel chromatography to obtain the fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe and a corresponding fluorine ion content detection process cannot be interfered by a biological system matrix and impurities, and can be used for quantitatively measuring fluorine ion content in various biological systems. The fluorescent probe has high specificity, can specifically realize silicon-oxygen bond breakage under the action of fluorine ions, is cheap and available, high in sensitivity and suitable for detecting the fluorine ion content in cells and can be obtained by chemical synthesis, the synthesis process is simple and practicable, and the fluorine ions are quantitatively measured by drawing a standard curve.
Owner:苏州新启材料科技有限公司
Robust H-infinity-based variable-gain decoupling control method
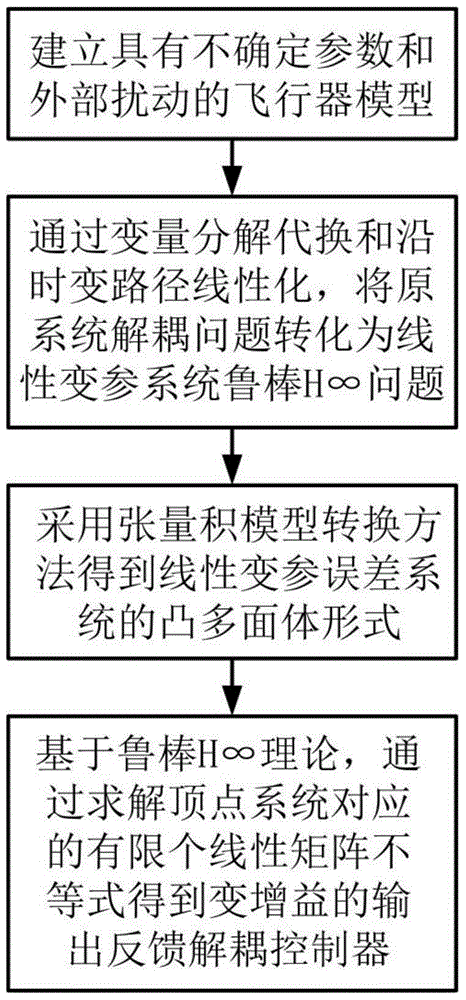
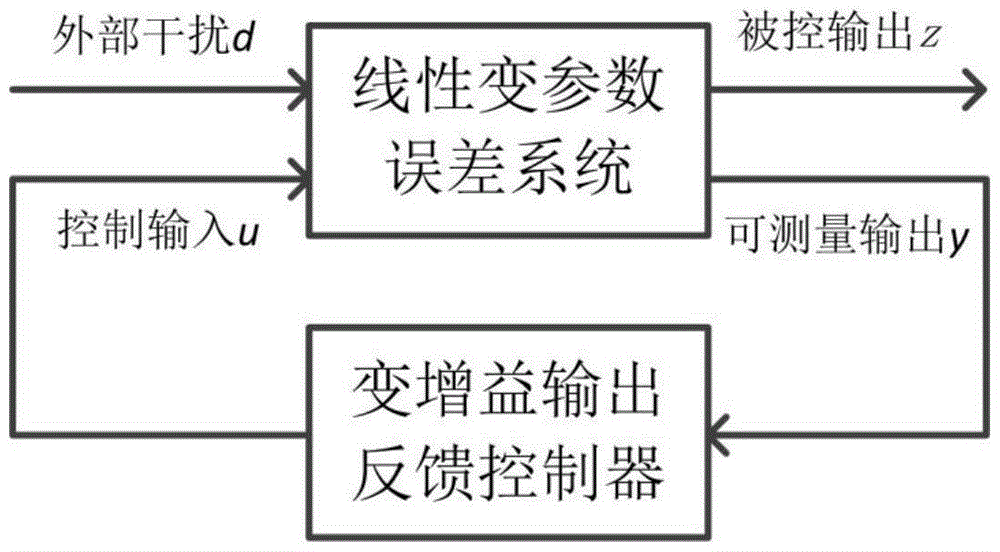
ActiveCN105182743AAchieving Steady State DecouplingAchieve approximate decouplingPosition/course control in three dimensionsAdaptive controlDecompositionSystem matrix
The invention discloses a robust H-infinity-based variable-gain decoupling control method. The objective of the invention is to solve the technical problem of little possibility to realize inter-channel decoupling control in wide-range flight of an aircraft. The method includes the following steps that: a longitudinal dynamics model of the aircraft is provided, wherein the model is characterized in nonlinearity, strong coupling, multi-variable performance and uncertainty; a decomposition problem of an original system is transformed to a robust H-infinity problem of an uncertain linear parameter-varying error system through variable decomposition and along-the-time path-varying linearization; the robust H-infinity problem of the uncertain linear parameter-varying error closed-loop system is transformed into a robust H-infinity problem of a corresponding certain system, and the convex polyhedron form of a system matrix can be obtained through adopting a tensor product model; and a limited number of linear matrix inequalities are solved based on the robust H-infinity theory, so that a variable-gain robust decoupling controller can be obtained. With the controller adopted, approximate decoupling of the system can be realized, and the approximate decoupling degree can be measured by the performance index gamma of H-infinity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Maximum posteriori optimizing image rebuilding method in PET imaging
InactiveCN101156780AImage data processing detailsRadiation diagnosticsMathematical modelSystem matrix
The invention discloses a maximal posteriori optimized image reconstruction method for leading in a general Gibbs experiment in the PET imaging. The method comprises the following procedures: (1) PET imaging equipment is utilized to collect detector data before imaging, and the corrective parameter value and the system matrix of various data in the imaging equipment are obtained simultaneously; (2) a mathematical statistic statistical model used for reconstructing an image is reconstructed according to a statistical feature that is met by the corrective data acquainted by the procedure (1) before imaging; (3) the general Gibbs experiment is led in aiming at the compute of a mathematical model in the procedure (2) , a maximal posteriori estimate method is adopted to perform the conversion of a reconstruction model, to obtain an optimized equation with a constrained objective function used for obtaining a PET reconstruction image; (4) a parabola is adopted to replace a coordinate descent algorithm, to perform the iterative computation treatment and to reconstruct the image based on the selection of a global parameter in the optimized equation through a result obtained by the procedure (3). The invention can greatly improve the quality of the PET reconstruction image.
Owner:陈武凡
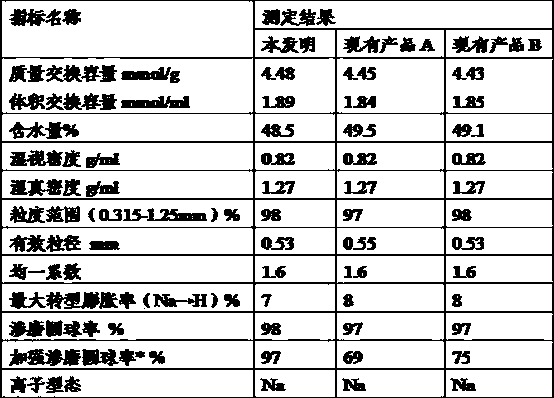
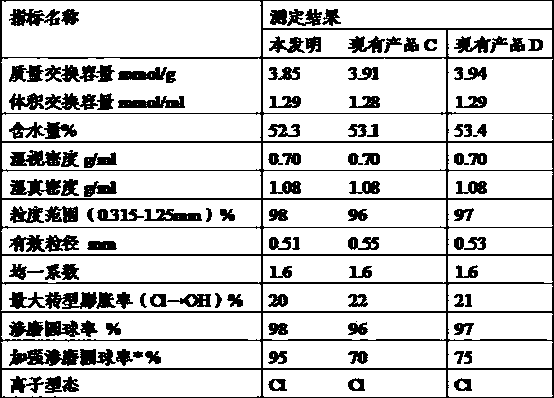
High-strength ion exchange resin with double-channel macroporous structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103387629AHigh strengthHigh mechanical strengthCation exchanger materialsAnion exchangersCross-linkPolymer science
The invention discloses a high-strength ion exchange resin with a double-channel macroporous structure and a preparation method thereof. The high-strength ion exchange resin is prepared by polymerization of a styrene system and / or acrylic acid system matrix, a cross-linking agent and an initiator to generate a condensate, which forms a skeleton with a porous sponginess structure containing uniformly distributed macropores and micropores, under effects of two different pore forming agents. The preparation method is as below: mixing the matrix, the cross-linking agent, a macropore forming agent and a micropore pore forming agent, and heating; then adding the initiator, and mixing uniformly; adding the mixture into hot water, then stirring and adjusting the stirring speed, and carrying out an insulation reaction in the hot water; heating to 95 DEG C, and insulating and reacting for 3 h; washing the polymer with cooling water, drying and screening out polymer microballoons with appropriate granularity; moving out the pore forming agents through a distillation or extraction mode; and carrying out acidic or alkali treatment to obtain the high-strength ion exchange resin with the double-channel macroporous structure. The resin has high mechanical strength.
Owner:JIANGSU SUQING WATER TREATMENT ENG GROUP
Cable structure monitoring method based on long gauge optical fiber grating sensors
ActiveCN106442541APromote rapid developmentRealize monitoringForce measurement by measuring optical property variationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationStructural monitoringGrating
The invention discloses a cable structure monitoring method based on long gauge optical fiber grating sensors. The method comprises the following steps that a healthy monitoring system on the cable structure is laid out by utilizing a cable clamp, wherein the healthy monitoring system is composed of a plurality of long gauge optical fiber grating sensors arranged on the cable structure, and a strain signals monitored by the healthy monitoring system is collected through a signal collection system; an exciting hammer is adopted to hammer the node position where the cable structure lays out the long gauge optical fiber grating sensors; the signal collection system collects an impact signal and a long gauge strain time history in a vibration test; a system array based on an identification algorithm of a subsystem is identified, and multi-layered parameters of the cable structure is further identified; identification on cable force is conducted by utilizing identified frequency, and damage of the cable structure is identified and located according to identified formation and flexibility. According to the cable structure monitoring method based on the optical fiber grating sensors, the optical fiber grating sensors are applied to health monitoring of an inhaul cable, and thus stable and reliable monitoring means and method are provided for long-term monitoring and performance evaluation of the cable structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Receiving device and method for TD-SCDMA system
InactiveCN101087283AImprove utilizationImprove performanceCode division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlChannel impulse responseTD-SCDMA
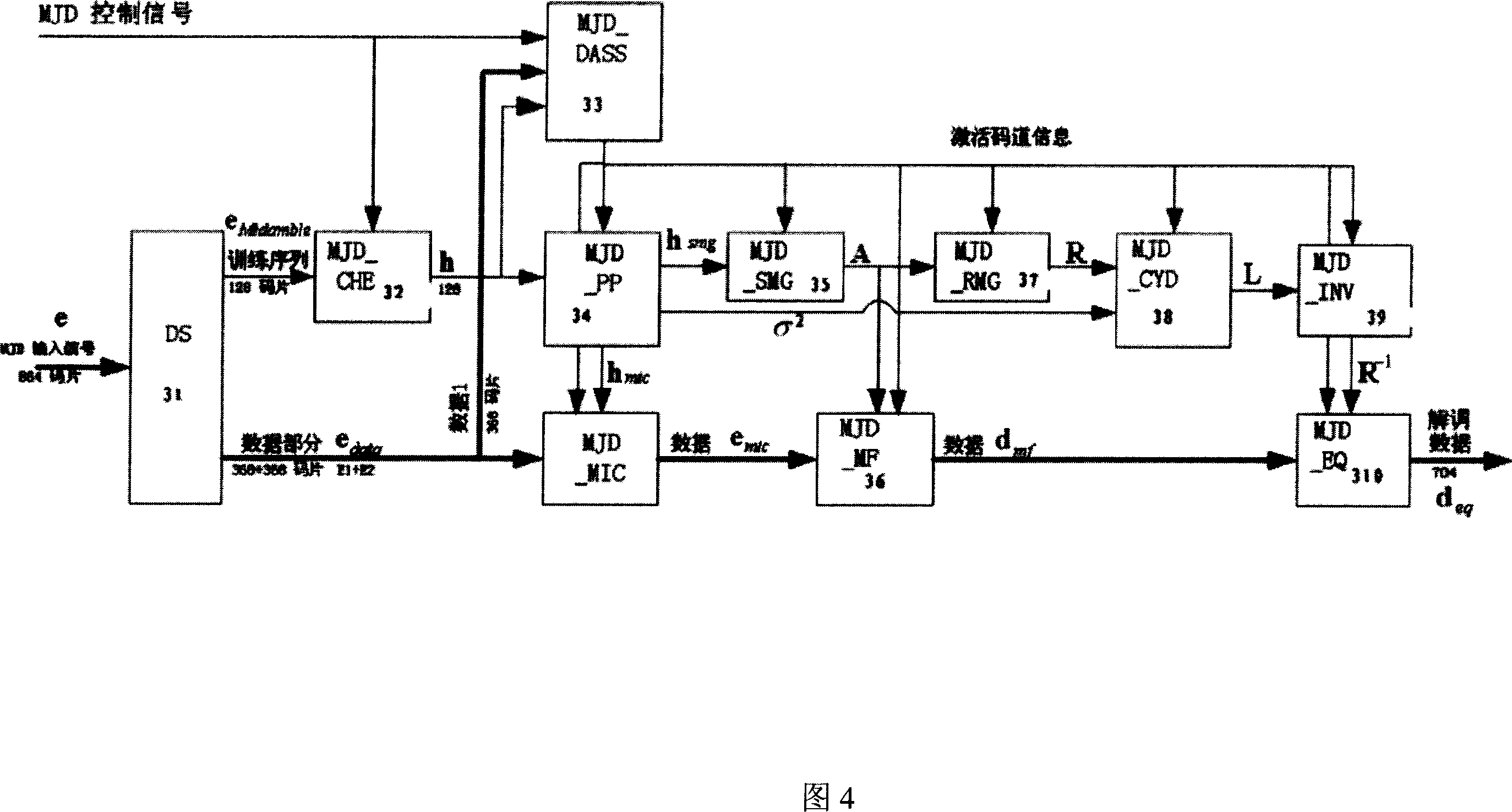
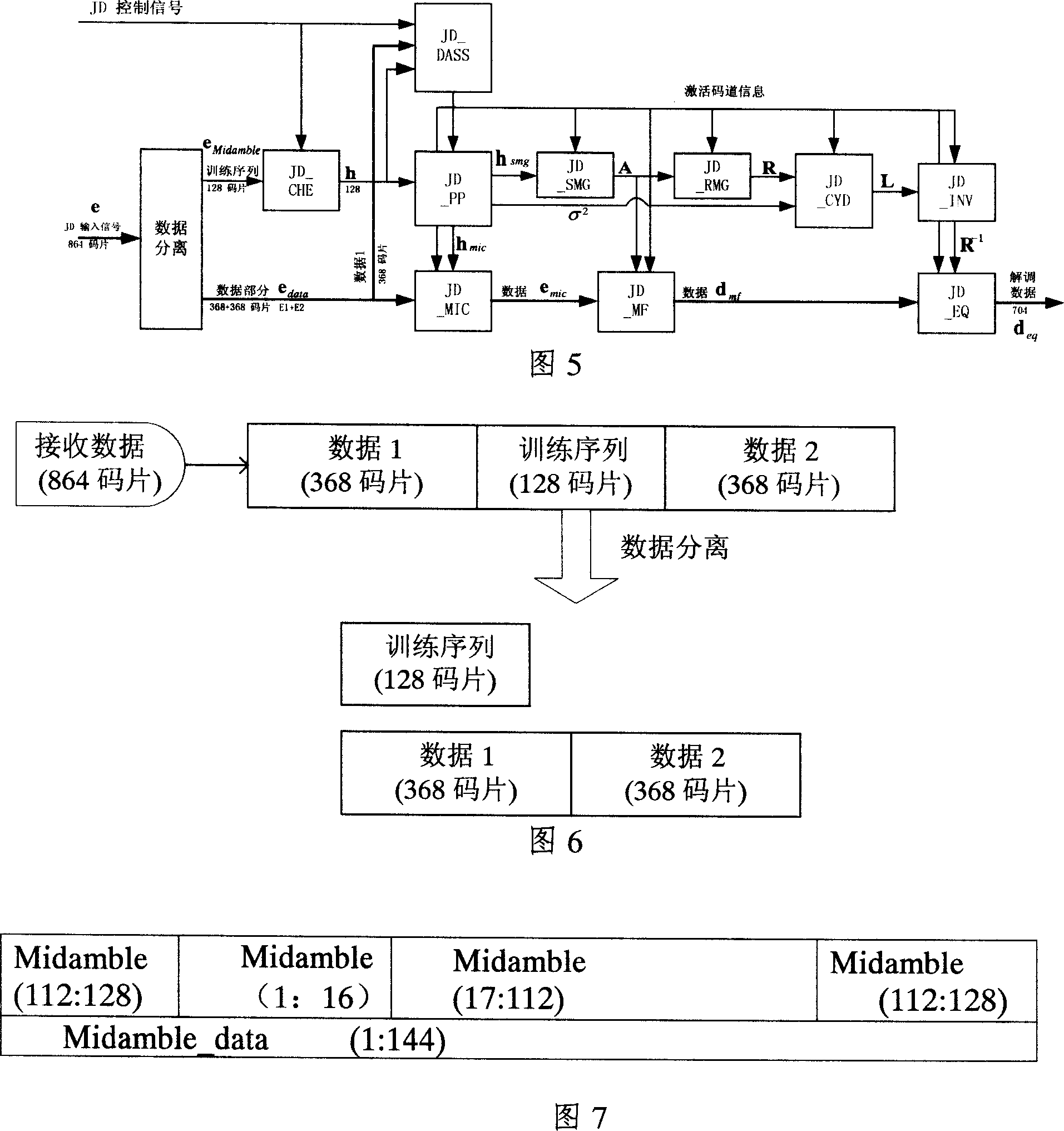
The invention discloses a receiving device and method in TD-SCDMA syste, the invention gives out a data demodulating device and method when TD-SCDMA is in the same frequency net to realize effective receiving of area under interference of the same frequency, so requirement of TD-SCDMA can be fulfilled. It includes: data separator which separates data received training sequence part and data part; channel evaluator which evaluates channel swash response based on training sequence of area and training sequence separated by data separator; multi-area code-track activating evaluator which evaluates activating code-track; multi-area channel activating response processor which eliminates noise and evaluates power of noise; multi-area system matrix generator, multi-area matching filter, multi-area relative matrix generator, Cholesky decomposer and a matrix inversion machine; multi-area equation resolver.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SEMICON BEIJING
The construction of mbr (minimum bandwidth regenerating) codes and a method to repair the storage nodes
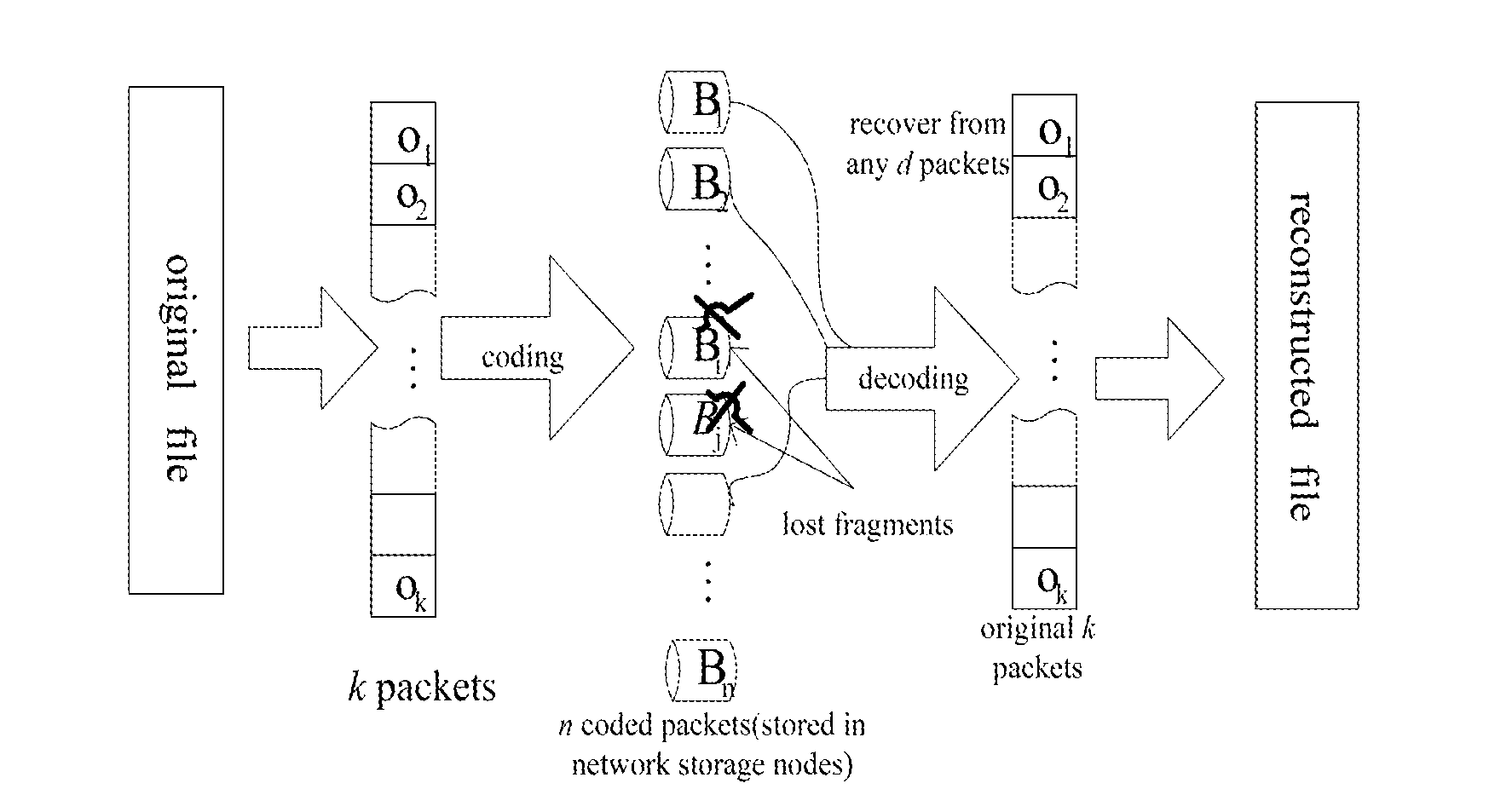
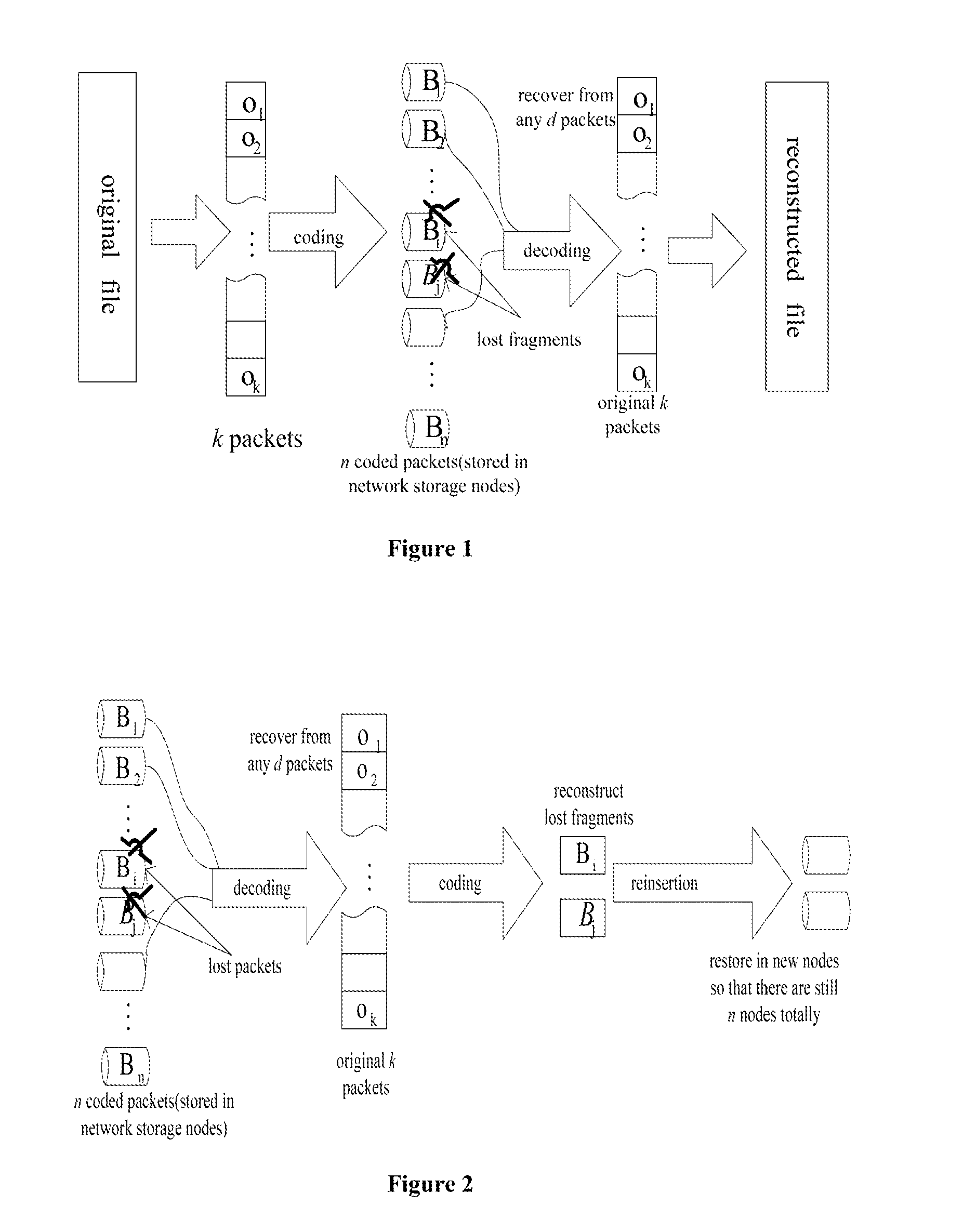
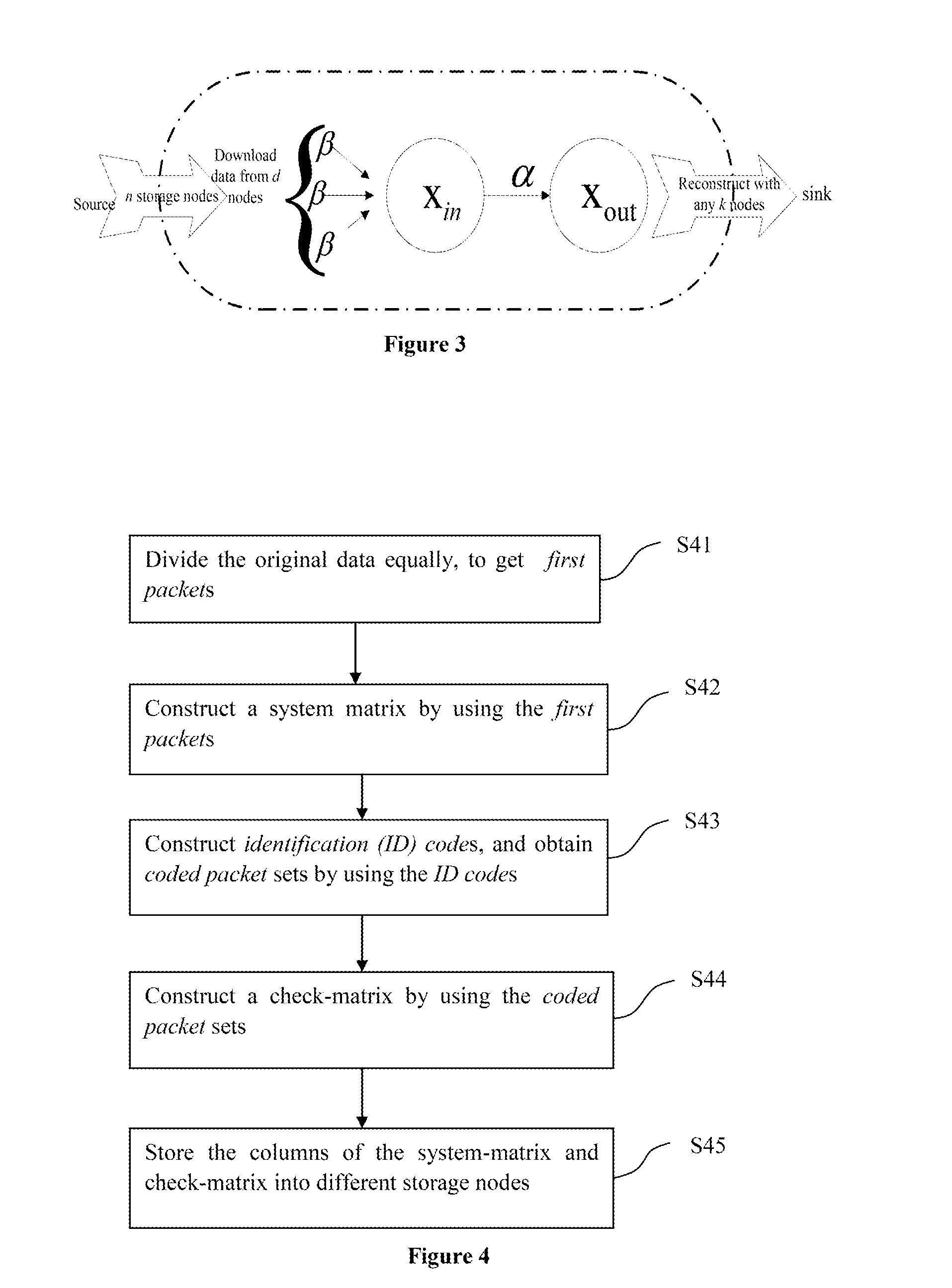
ActiveUS20160006463A1Easy to operateLittle overheadCode conversionCoding detailsAlgorithmNetwork packet
This invention gives a coding method of MBR (Minimum Bandwidth Regenerating) codes. The related method includes the following steps: equally divide the original file of size B into k(k+1) / 2 blocks, obtaining the first packets; construct a symmetrical k×k system matrix S with these first packets; generate k ID codes, wherein each ID code contains k elements; obtain the coded packet through operations between one column of the system matrix and the ID code; repeat the above steps with (n−k) different columns of the system matrix separately to get the (n−k) coded packets; construct the (n−k)×k check matrix P with the column number g which is the serial number of the ID codes in the coded packet set Pg; store the rows of the system matrix and coded matrix to n nodes, each node stores one row. The present invention also involves a method to repair the failed nodes of the above coding scheme.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +1
Method in connection with sensorless induction motors
ActiveUS20050001583A1Fast implementationFast reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlStator voltageSystem matrix
A method for the stabilization of full-order flux observers for speed-sensorless induction motors in the regenerative mode. The method comprises determining the current vector of the induction motor, determining the stator voltage vector of the induction motor, forming a full-order flux observer having a system matrix (A) and a gain matrix (L), the state-variable observer being augmented with a speed adaptation loop, and producing an estimated rotor flux linkage vector and an estimated stator current vector, determining an estimation error of the stator current vector, defining a correction angle, and forming a speed adapt-tion law based on the cross product of the estimation error of the stator current vector and the estimated rotor flux linkage vector, where the correction angle is used to turn the rotor flux linkage vector or the estimation error of the stator current vector in order to keep the observer stable.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Corner-Based Longitudinal Speed Estimation
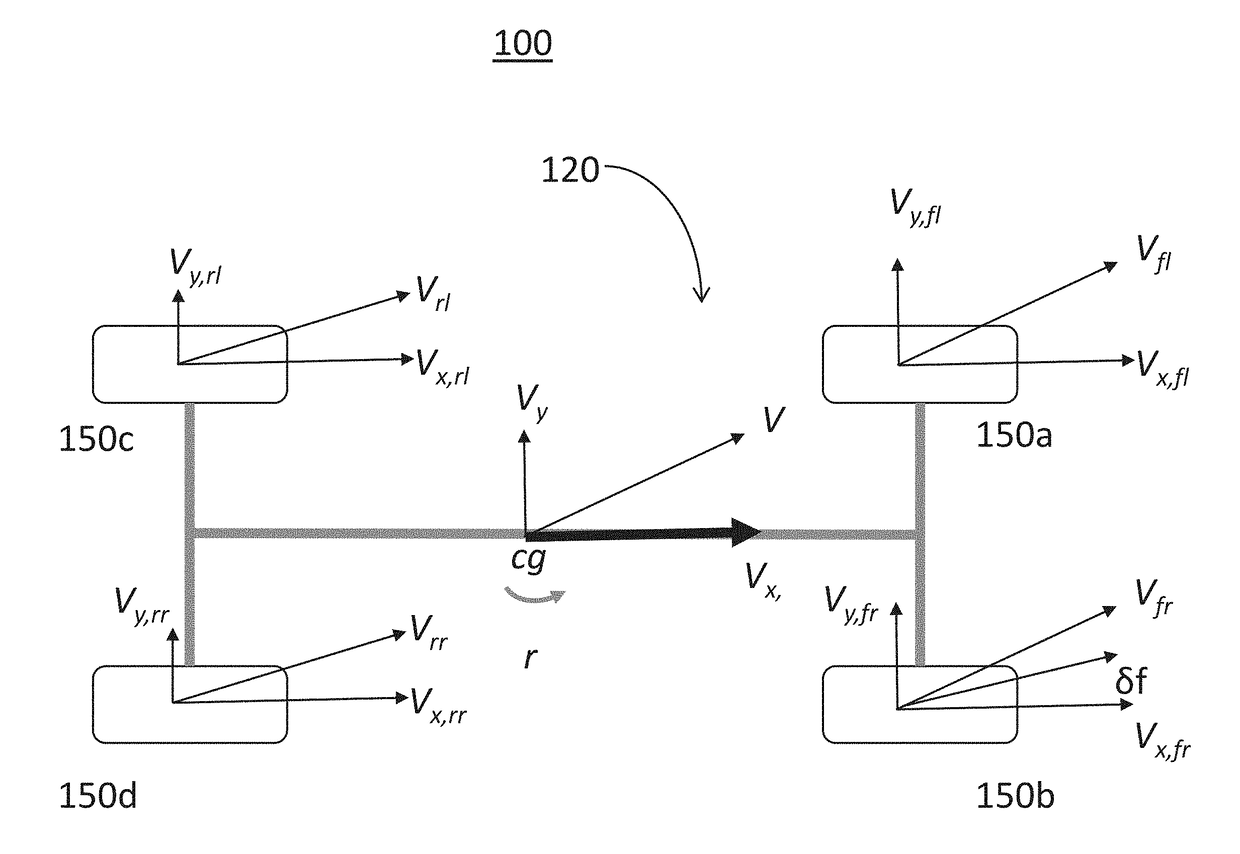
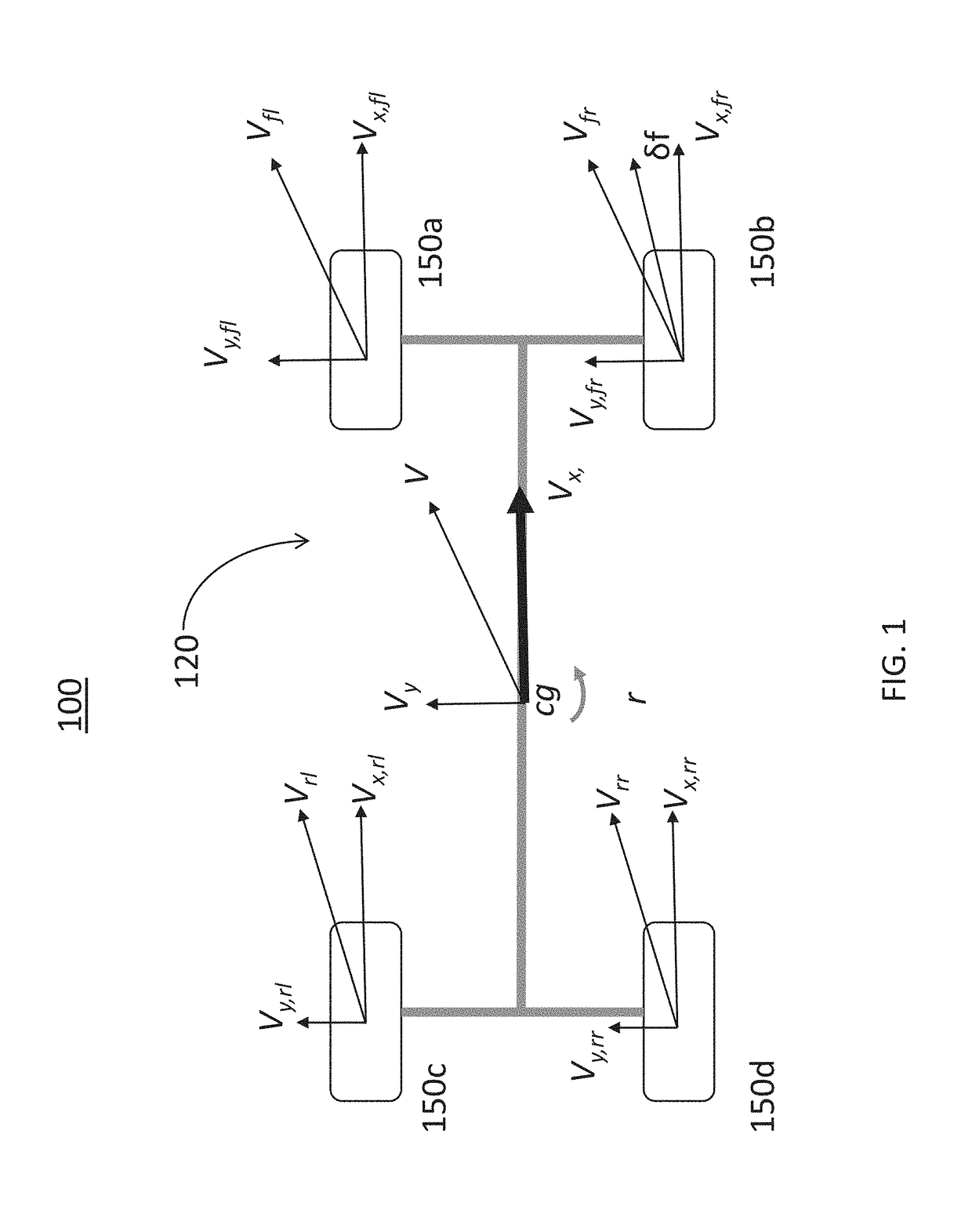
A system and method for computationally estimating a directional velocity of a vehicle in real time under different configurations and road conditions for use in vehicle antilock braking, adaptive cruise control, and traction and stability control by correcting measured accelerations with respect to the estimated road angles. A time window is used to provide reliable mapped acceleration for the transient regions and maneuvers on gravel surfaces with high fluctuations in the acceleration measurement. Longitudinal and lateral accelerations are mapped from the vehicle's CG into the tire coordinates using the vehicle's geometry, lateral velocity, yaw rate, and the steering wheel angle to generate system matrices of the combined kinematic-force estimation structure.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com