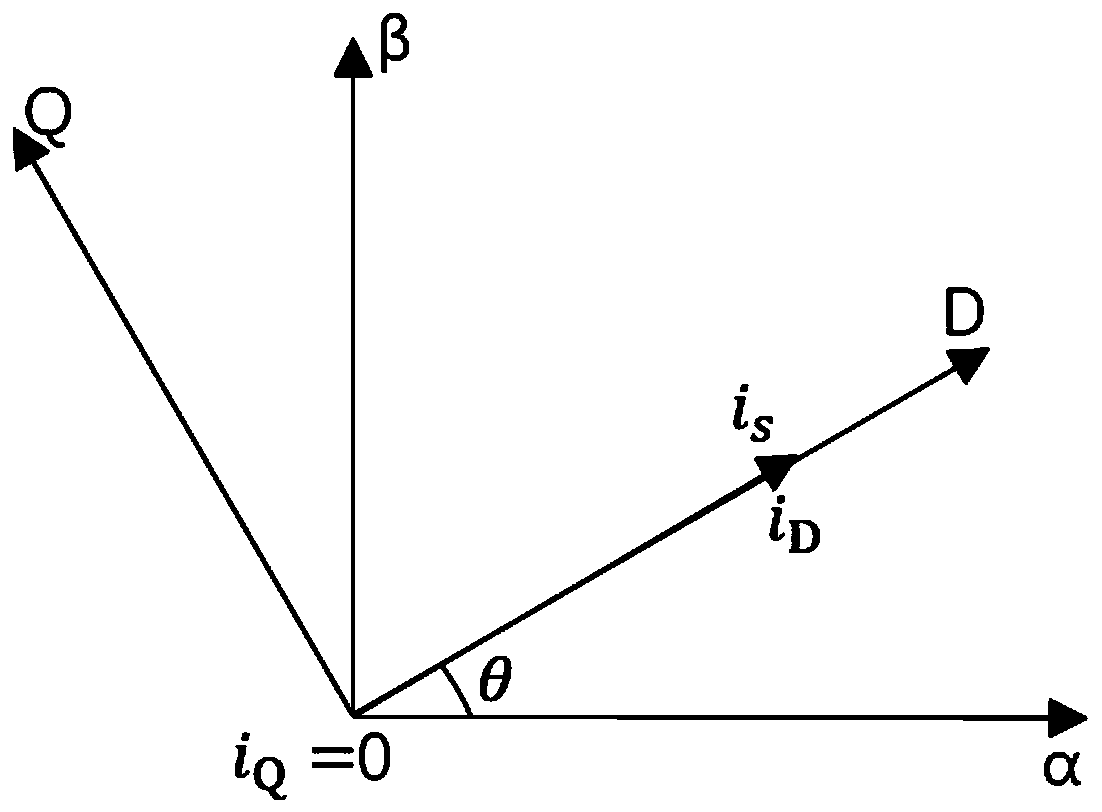
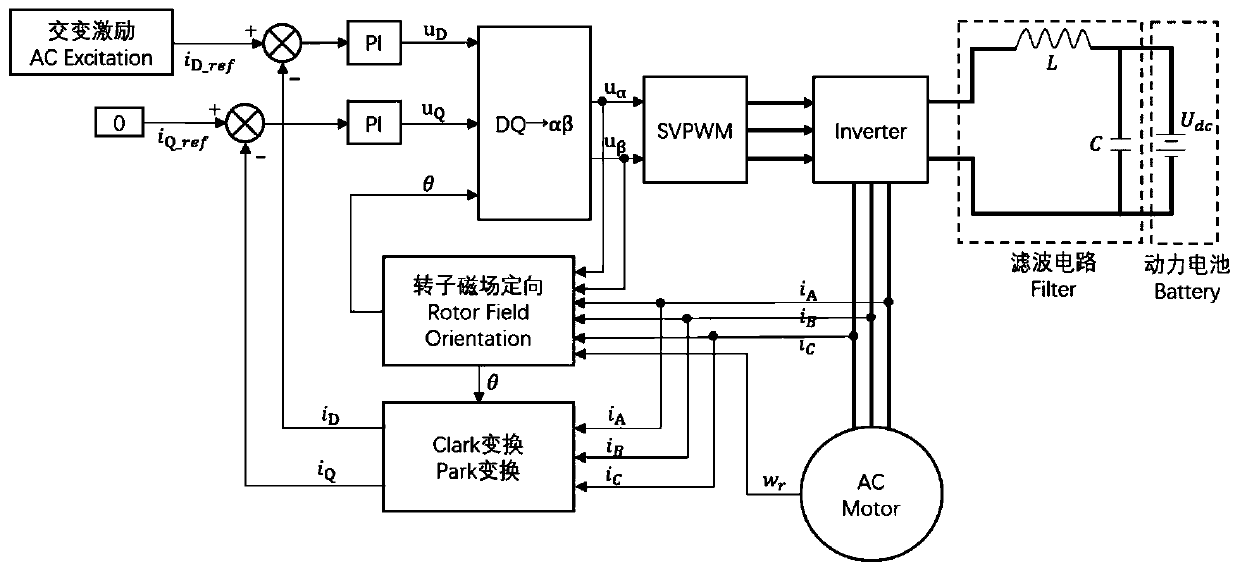
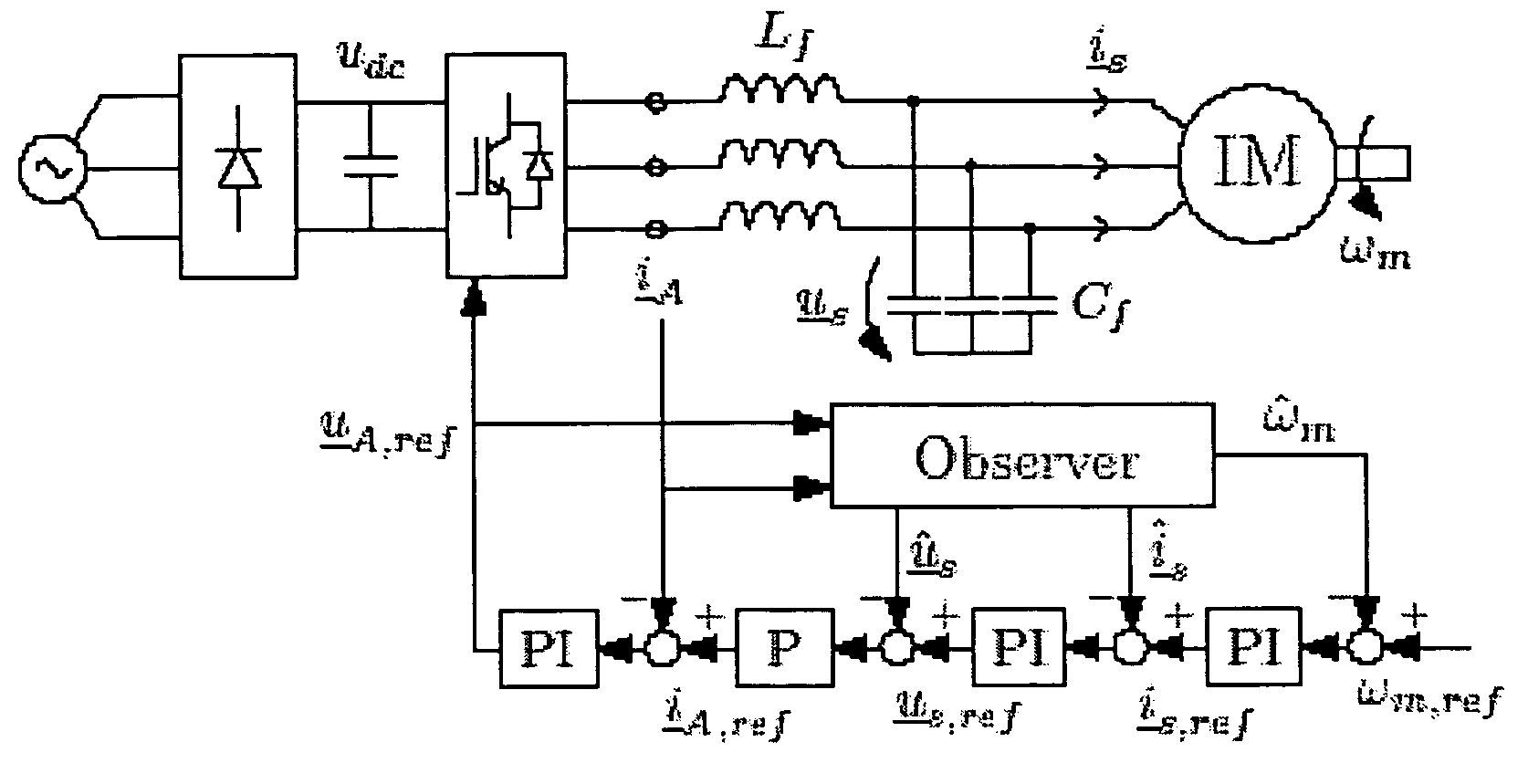
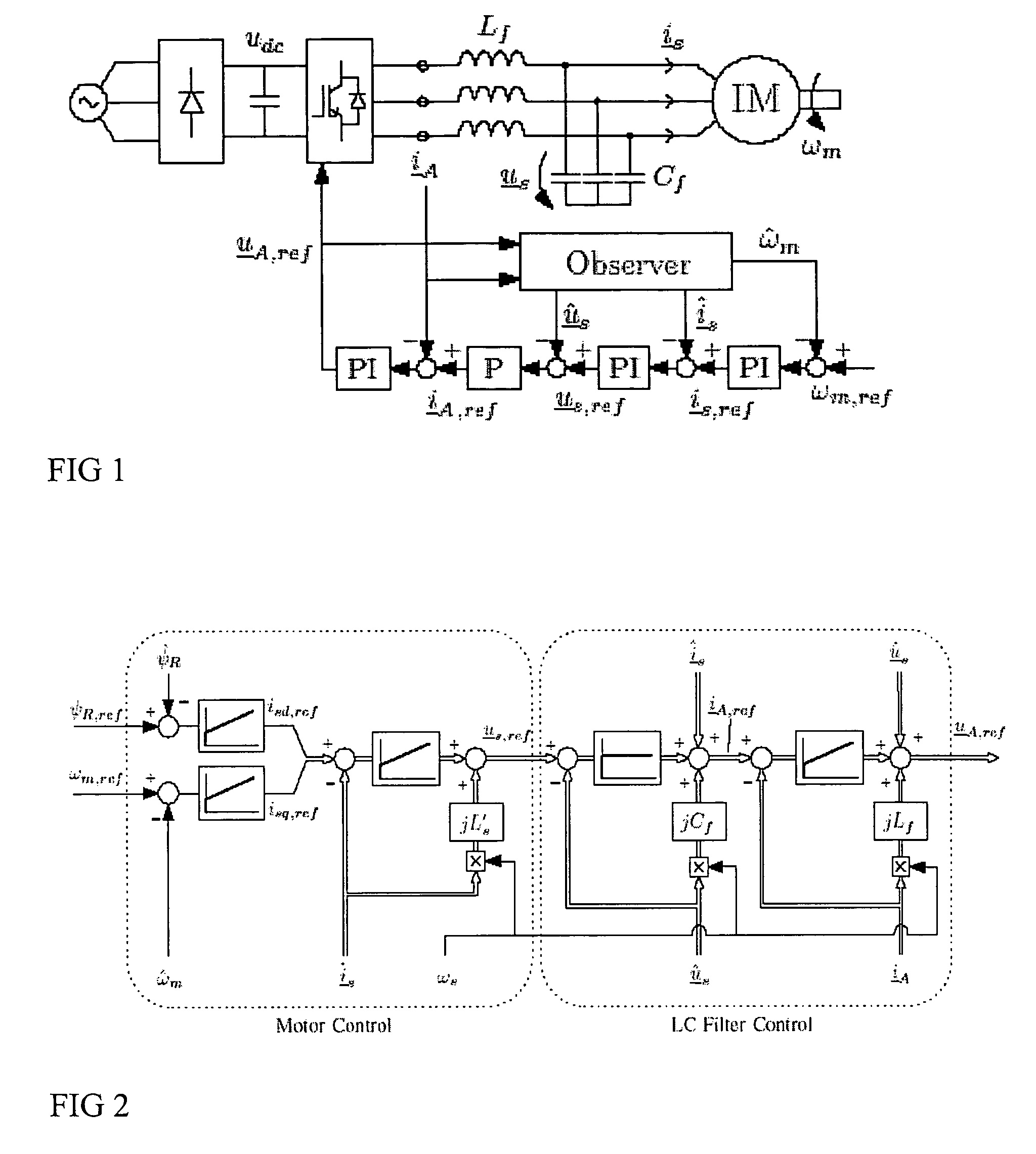
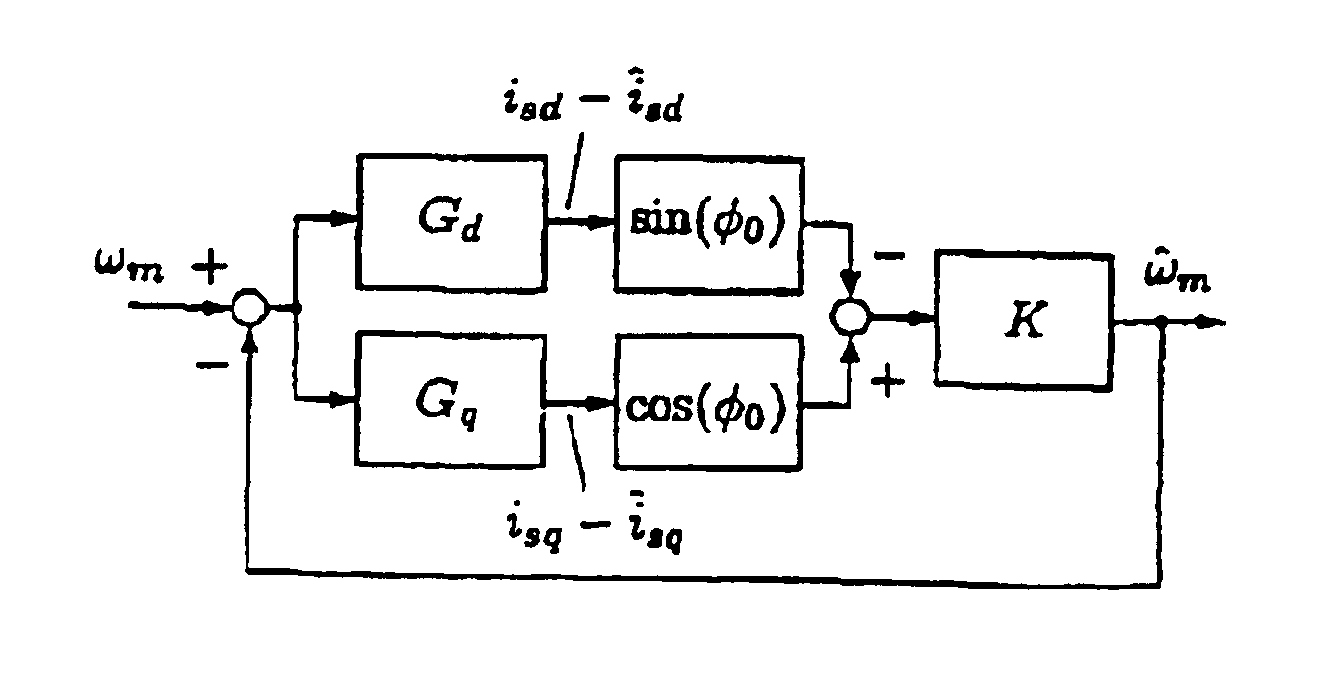
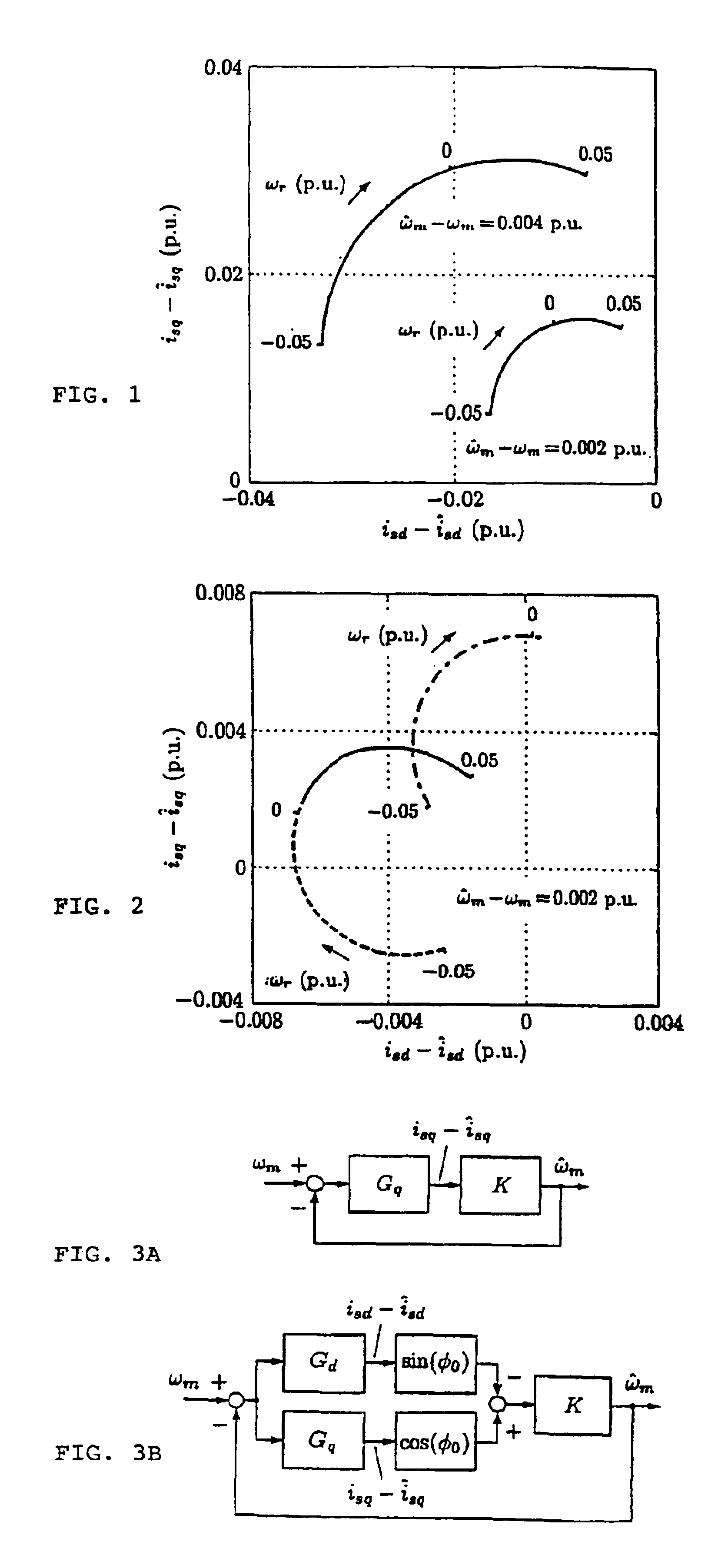
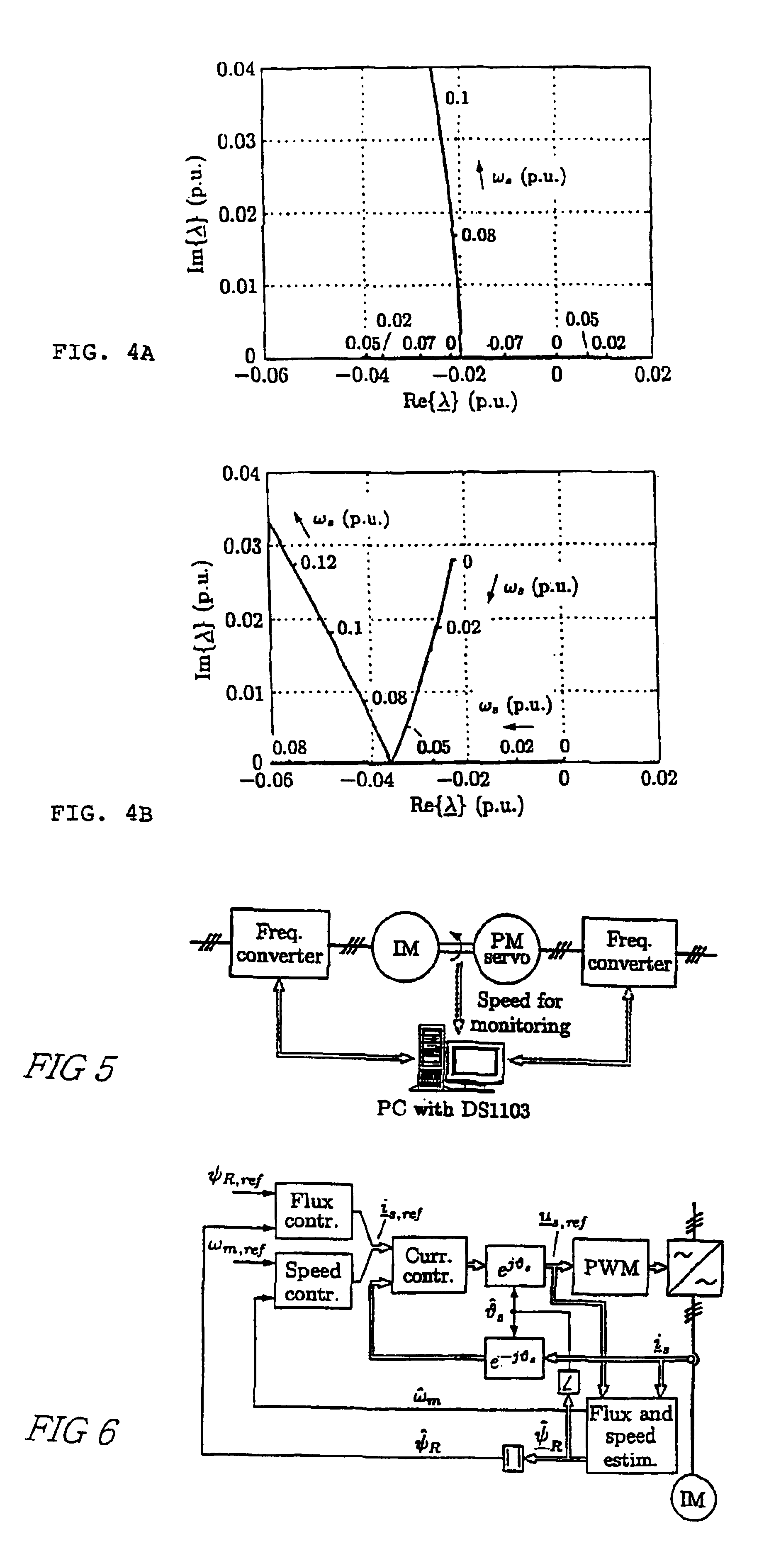
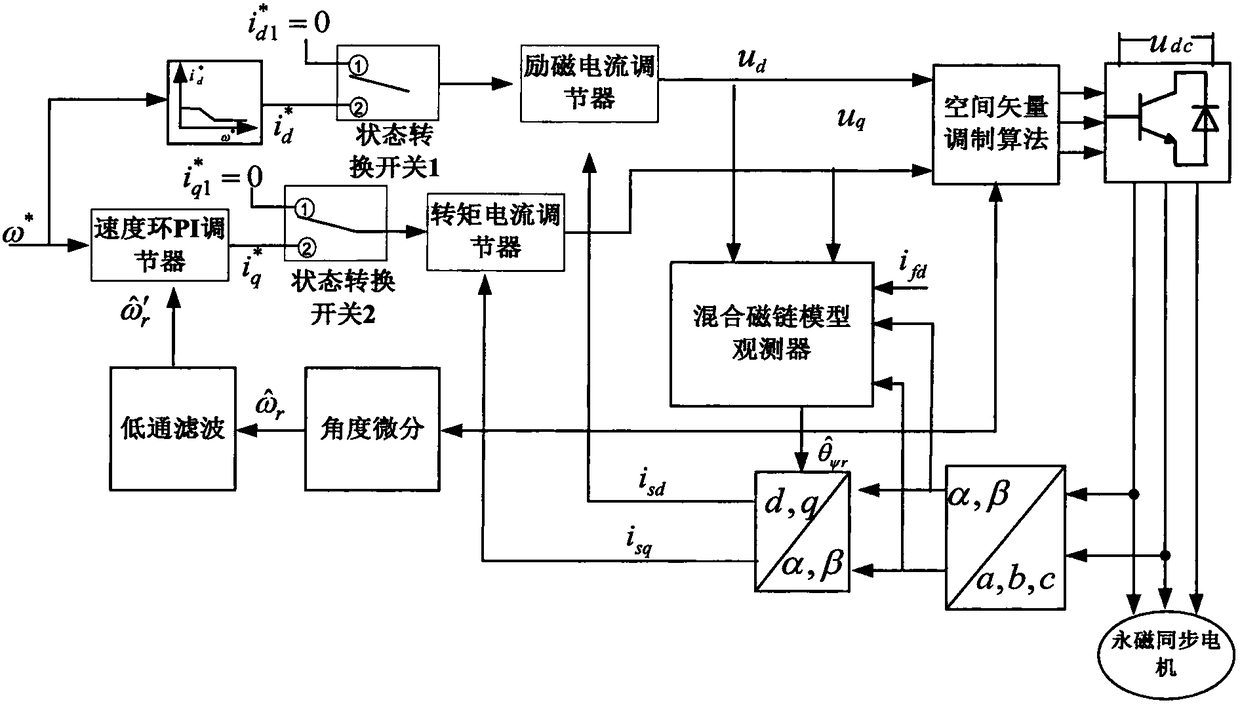
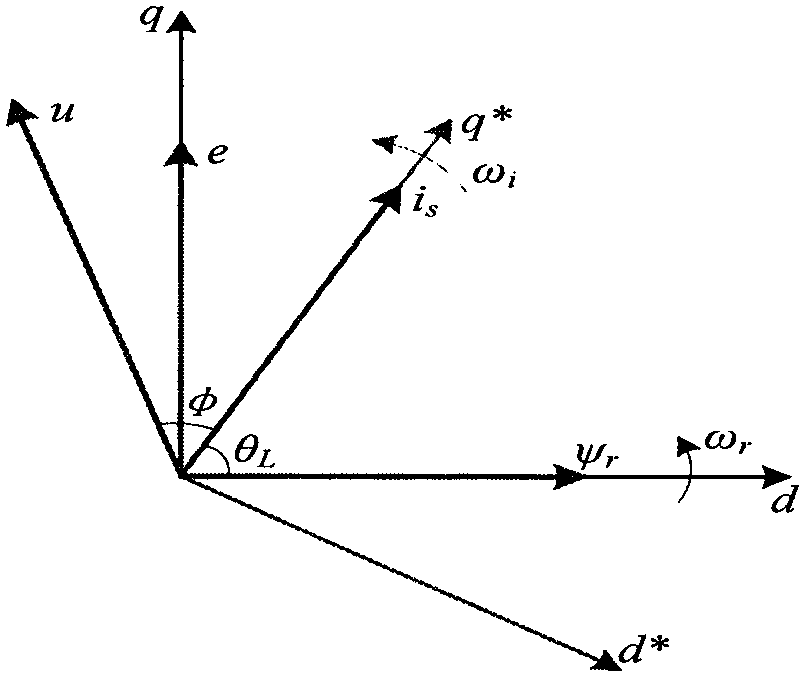
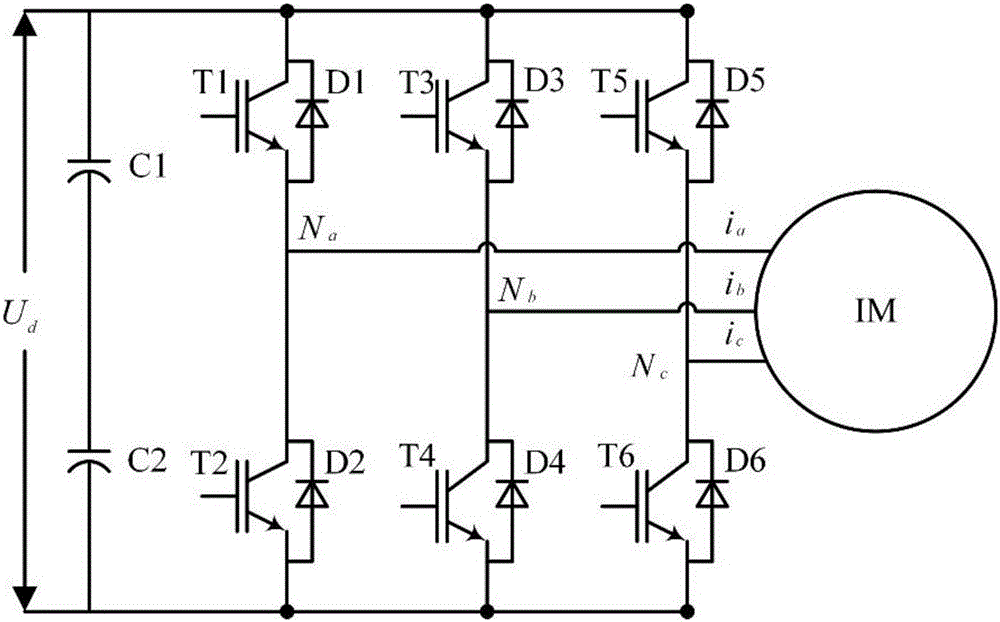
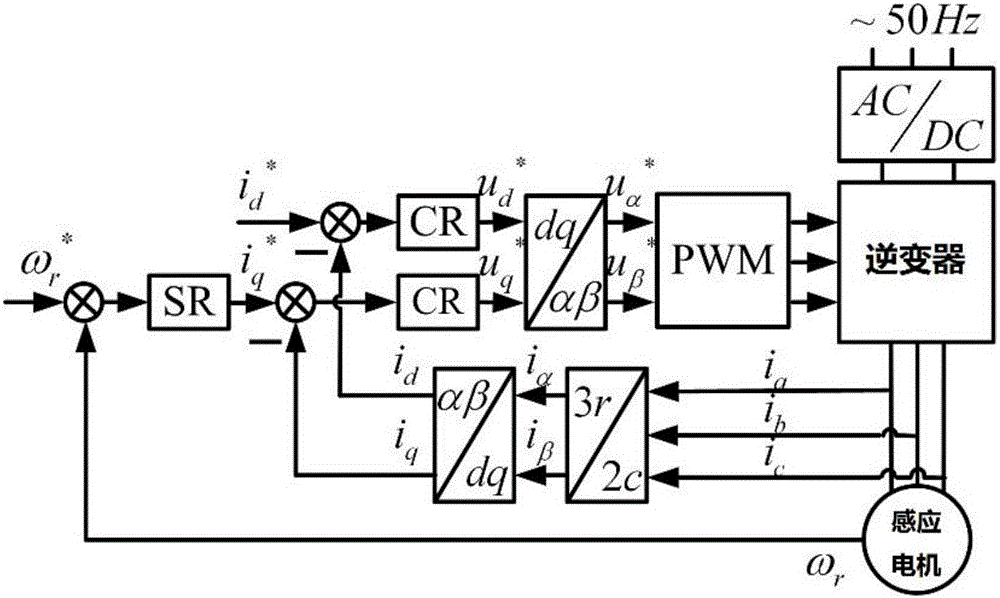
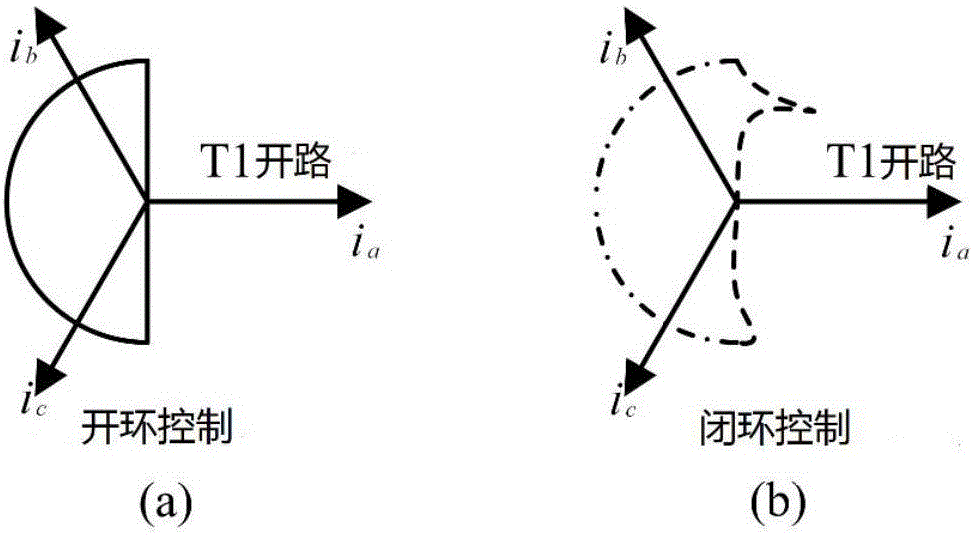
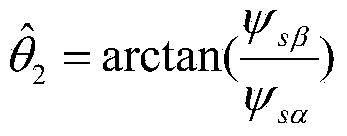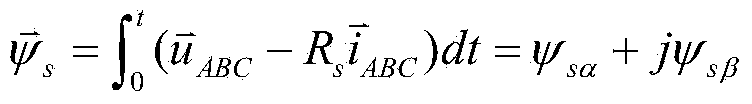Patents
Literature
82 results about "Stator current vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
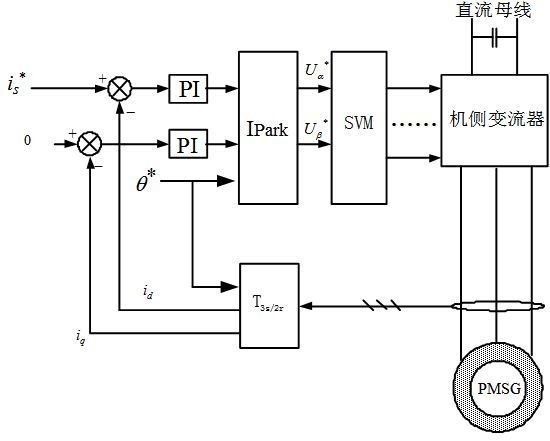
Composite vector control method for permanent magnet synchronous wind generator
ActiveCN101764567AConvenient and free switching controlReduce copper consumptionElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl mannerMathematical model
The invention relates to a composite vector control method for a permanent magnetic synchronous wind generator, comprising the following steps of: controlling the size and the direction of a stator current vector value according to a mathematical model of the permanent magnet synchronous wind generator by utilizing the vector control method, and establishing a composite vector control strategy of the permanent magnet synchronous wind generator based on stator current orientation. Through the stator current orientation, a maximum torque current ratio control mode is adopted between the cutting speed and the turning speed of the generator so as to improve the generated power of a system; and a weak magnetic control mode with maximum power output is adopted between the turning speed and the limiting speed, therefore, the system efficiency is improved, and the system stability is ensured.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
Power battery pre-heating method
The invention belongs to the technical field of power battery pre-heating, in particular to a power battery pre-heating method. The power battery pre-heating method comprises the following steps: controlling the stator current component in the rotor magnetic field direction in an automobile AC drive motor to change at a certain frequency so that the stator current vector and the rotor magnetic field direction are always the same or opposite; and exciting the DC side of the power battery to generate a high-frequency current, and charging and discharging the power battery at a high frequency. The invention combines the motor rotor magnetic field orientation technology and the stator current vector control method, so that the electric energy exchanged between the automobile AC drive motor andthe power battery is used as the reactive power, and then converted into the heat energy required for heating the power battery, thereby not causing additional energy loss except the loss of the transmission line, the motor coil and the inverter; no additional heating device or material is needed, and the pre-heating of the power battery is realized by using the drive system of the electric vehicle itself, and the method is simple to implement and the cost is low.
Owner:石不凡
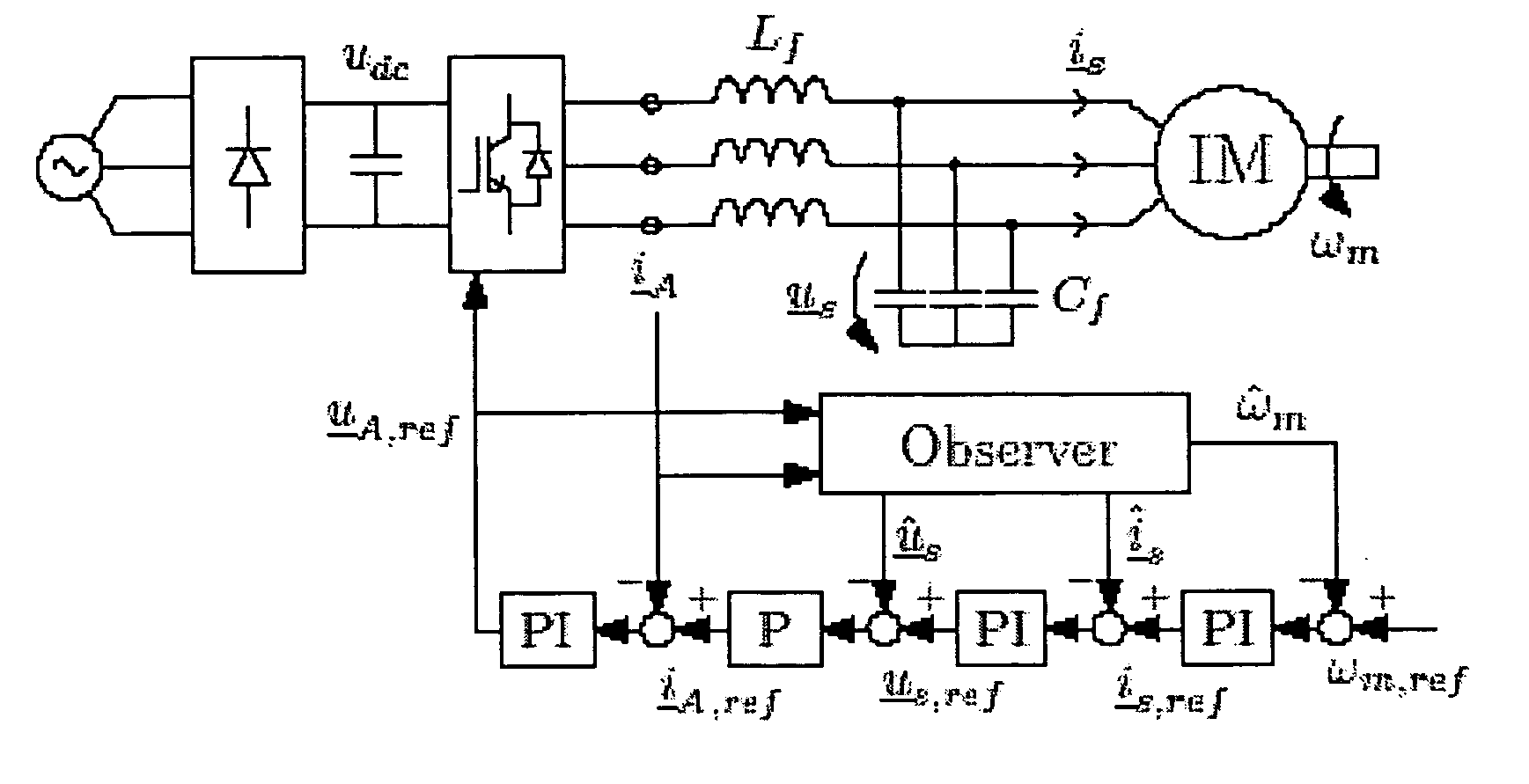
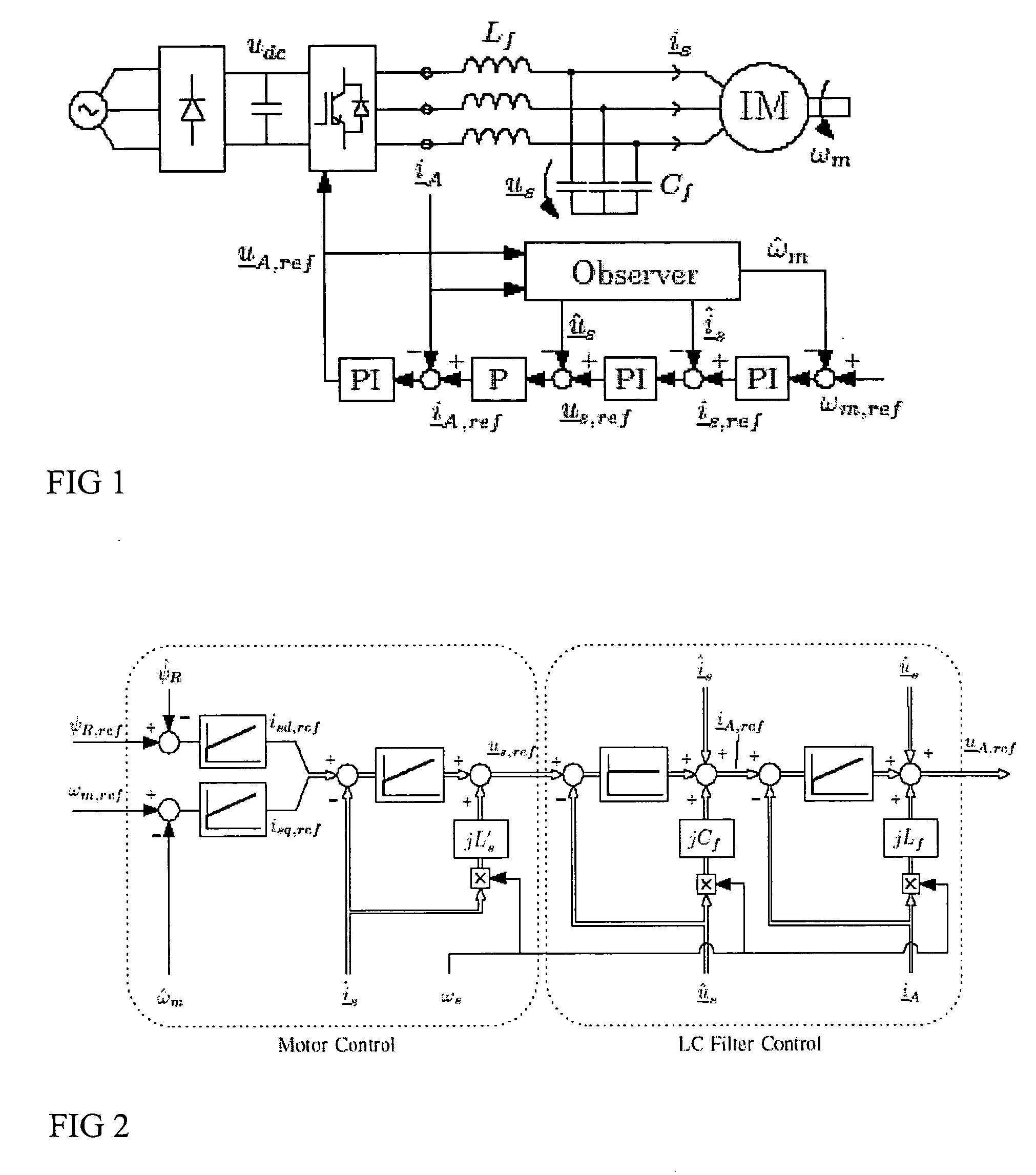
Speed sensorless control of an induction machine using a PWM inverter with output LC filter
InactiveUS7084604B2Single-phase induction motor startersVector control systemsVoltage vectorSystem matrix
Owner:ABB OY
Control method for directionally correcting rotor field of asynchronous motor
ActiveCN103326659AHigh orientation accuracyImproved Decoupling Control PerformanceElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsCurrent meterMotor speed
The invention discloses a control method for directionally correcting a rotor field of an asynchronous motor, and belongs to the field of motor speed regulation. The method is characterized by comprising the step of: forming a closed loop by dot products of stator flux linkage vectors and stator current vectors to directionally control and correct the magnetic field so as to realize complete uncoupling of torque and flux linkage. The method disclosed by the invention solves the problem of inaccurately directing the rotor filed caused by inaccurate parameters, so that the performance of vector control of the asynchronous motor is improved. A novel asynchronous motor decoupling control method is found, so that the control performance of the asynchronous motor is more approximate to that of a current motor.
Owner:黄山市开发投资集团有限公司
Method in connection with sensorless induction motors
ActiveUS20050001583A1Fast implementationFast reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlStator voltageSystem matrix
A method for the stabilization of full-order flux observers for speed-sensorless induction motors in the regenerative mode. The method comprises determining the current vector of the induction motor, determining the stator voltage vector of the induction motor, forming a full-order flux observer having a system matrix (A) and a gain matrix (L), the state-variable observer being augmented with a speed adaptation loop, and producing an estimated rotor flux linkage vector and an estimated stator current vector, determining an estimation error of the stator current vector, defining a correction angle, and forming a speed adapt-tion law based on the cross product of the estimation error of the stator current vector and the estimated rotor flux linkage vector, where the correction angle is used to turn the rotor flux linkage vector or the estimation error of the stator current vector in order to keep the observer stable.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
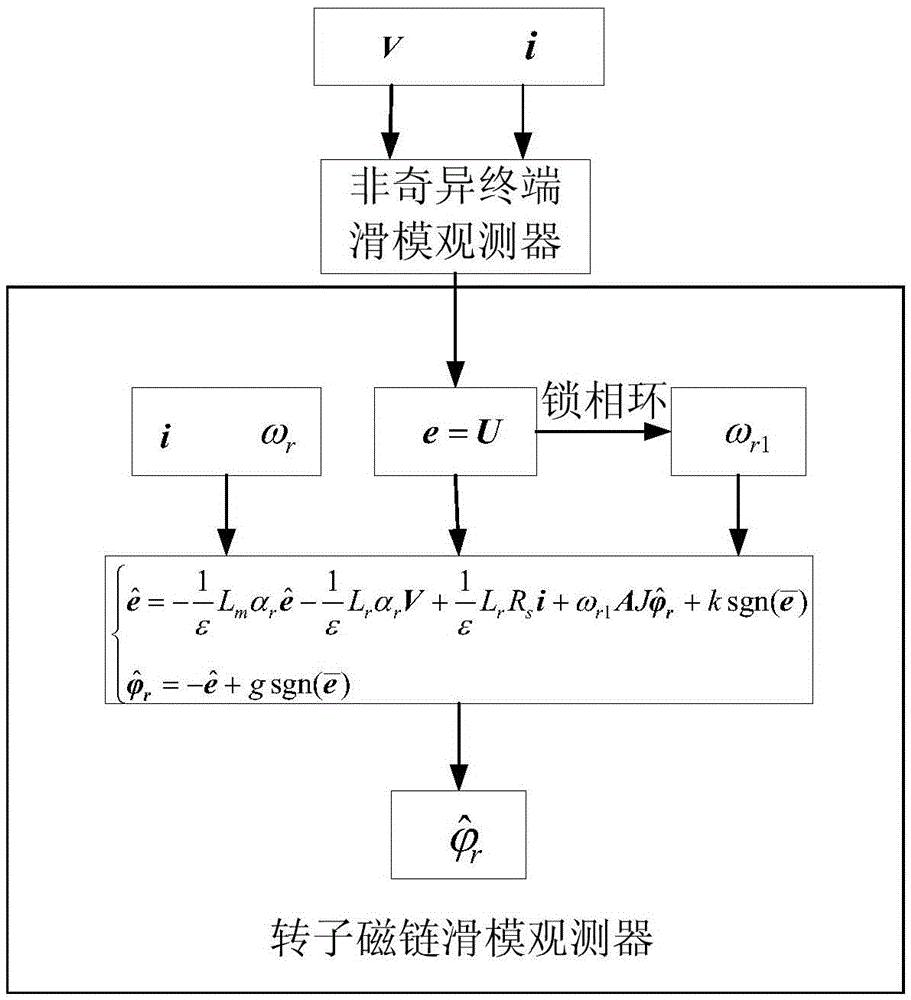
Sliding-mode observer based flux linkage observation method of asynchronous motor
ActiveCN105610369AWill not affect the accuracy of observationImprove robustnessElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator inductanceElectromotive force
The invention discloses a sliding-mode observer based flux linkage observation method of an asynchronous motor. The flux linkage observation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of acquiring a continuous counter electromotive force e by Omega<r> through a high-order current sliding-mode observer according to a stator voltage vector v, a stator current vector i and a rotor electric angular speed, which are obtained through acquisition and operation, of the motor under a two-phase static coordinate AlphaBeta; building a state space expression of the asynchronous motor according to a relation between the counter electromotive force and rotor flux linkage; and building a flux linkage sliding mode observer according to the space expression. By the flux linkage observation method, the integral problem in flux linkage observation is solved, and relatively high robustness is generated for parameters such as rotor resistance, excitation inductance, rotor inductance and stator inductance; and meanwhile, the observer is simple in design, and engineering implementation is easy.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Speed sensorless control of an induction machine using a pwm inverter with output lc filter
InactiveUS20060145650A1Single-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlVoltage vectorSystem matrix
A method of controlling of an induction machine using an inverter is disclosed with output LC filter. The method includes determining an inverter output current vector (iA), determining an inverter output voltage vector (uA), and forming a full-order observer having a system matrix (Â) and gain vector (K). The observer produces an estimated rotor flux linkage vector ({circumflex over (ψ)}R), an estimated stator current vector (îs), an estimated stator voltage vector (ûs) and an estimated inverter output current vector (îA). An estimation error (iA-îA) of the inverter output current vector is determined, and a speed adaptation law is formed based on the estimation error of the inverter output current vector for determining an estimate for electrical angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) of the induction machine. The induction machine is controlled based on the produced estimates and a measured inverter output current.
Owner:ABB OY
Method and system for controlling a doubly-fed induction machine
The present invention relates to a method and system for controlling a doubly-fed induction machine. In operation a rotor current vector is processed with a rotor position estimate vector. A scalar error quantity is the determined in dependence upon a stator current vector and the processed rotor current vector. The scalar error quantity is integrated and an estimate of the rotor angular frequency is determined in dependence upon the integrated scalar error quantity. To obtain a rotor position estimate, the estimate of the rotor angular frequency is integrated and a rotor position estimate vector is determined in dependence upon the rotor position estimate. The rotor position estimate vector is then provided for processing the rotor current vector. As output signals a signal indicative of the rotor position estimate vector and a signal indicative of the estimate of the rotor angular frequency are provided for controlling the doubly-fed induction machine.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Method in connection with sensorless induction motors
InactiveUS6940253B2Fast implementationFast reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlSystem matrixFlux linkage
A method for the stabilization of full-order flux observers for speed-sensorless induction motors in the regenerative mode. The method comprises determining the current vector of the induction motor, determining the stator voltage vector of the induction motor, forming a full-order flux observer having a system matrix (A) and a gain matrix (L), the state-variable observer being augmented with a speed adaptation loop, and producing an estimated rotor flux linkage vector and an estimated stator current vector, determining an estimation error of the stator current vector, defining a correction angle, and forming a speed adapt-tion law based on the cross product of the estimation error of the stator current vector and the estimated rotor flux linkage vector, where the correction angle is used to turn the rotor flux linkage vector or the estimation error of the stator current vector in order to keep the observer stable.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Rotating speed tracking method based on permanent magnet synchronous motor open loop vector
InactiveCN108155838ANo impactFast current responseElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMotor speedControl signal
The invention discloses a rotating speed tracking method based on a permanent magnet synchronous motor open loop vector. The method comprises the following steps of 1, using a mixing model flux linkage observer to estimate a current motor rotor flux linkage angle, then carrying out differential and estimating a current motor rotating speed; 2, carrying out coordinate conversion on a stator currentvector and acquiring an excitation current id and a torque current iq; 3, taking the id and zero as input, carrying out operation by an excitation current regulator and acquiring an excitation voltage ud; taking the iq and the zero as the input, through a torque current regulator, acquiring a torque voltage uq; 4, carrying out vector synthesis on the ud and the uq, carrying out space vector modulation wave calculation, and comparing with a triangular wave to generate a driving control signal so as to drive a permanent magnet synchronous motor; and 5, repeating the steps1, 2, 3 and 4 till thattwo current vectors are stabilized near the zero and maintain for a short time period, considering the rotating speed estimated at this moment to be a current motor rotation speed, taking the currentrotation speed as a start rotation speed and smoothly switching to synchronization motor speed control.
Owner:长沙市日业电气有限公司
Control method of initial position of rotor of vertical shaft permanent magnet wind-driven generator
ActiveCN102522943AConvenient Launch ControlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsWind drivenLoop control
The invention relates to a control method of an initial position of a rotor of a vertical shaft permanent magnet wind-driven generator. The method comprises the following steps that: under the circumstances of a zero speed and a speed within a 5% rated speed, stator current vector closed loop control is carried out and an oriented static stator linkage is established; because an included angle between a stator linkage and a rotor linkage generates an electromagnetic torque, the rotor linkage is forced to get closer to the stator linkage; and until a rotary set linkage is relatively static, the motor is stopped to make rotation and thus control on the rotor initial position is completed. According to the control method provided in the invention, on the basis of a traditional vector control framework, stator current closed-loop control is employed; only an original vector control is used to control a portion of the framework and there is no need to add any auxiliary hardware device. Under the circumstances that the system complexity is not substantially increased, the control method can be conveniently applied to starting control of a speed-free sensor of a permanent magnet wind-driven generator.
Owner:XJ ELECTRIC +1
Method and apparatus for estimating a rotation speed of an electric motor
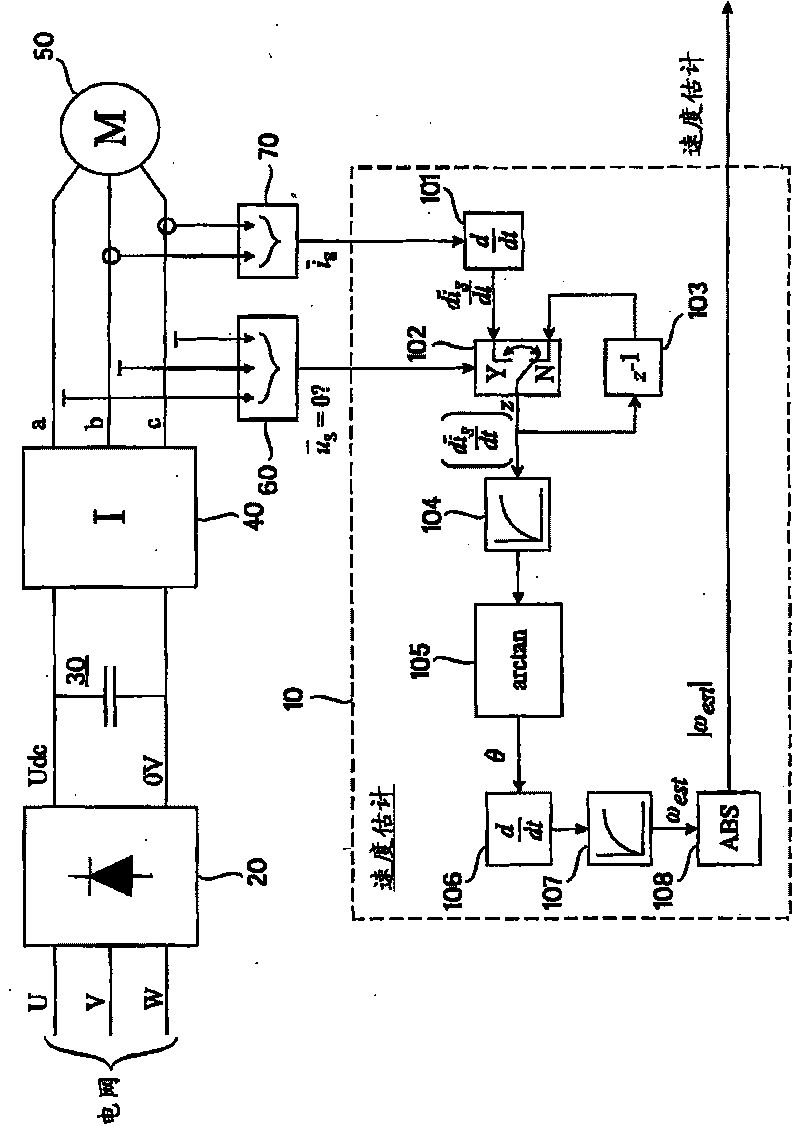
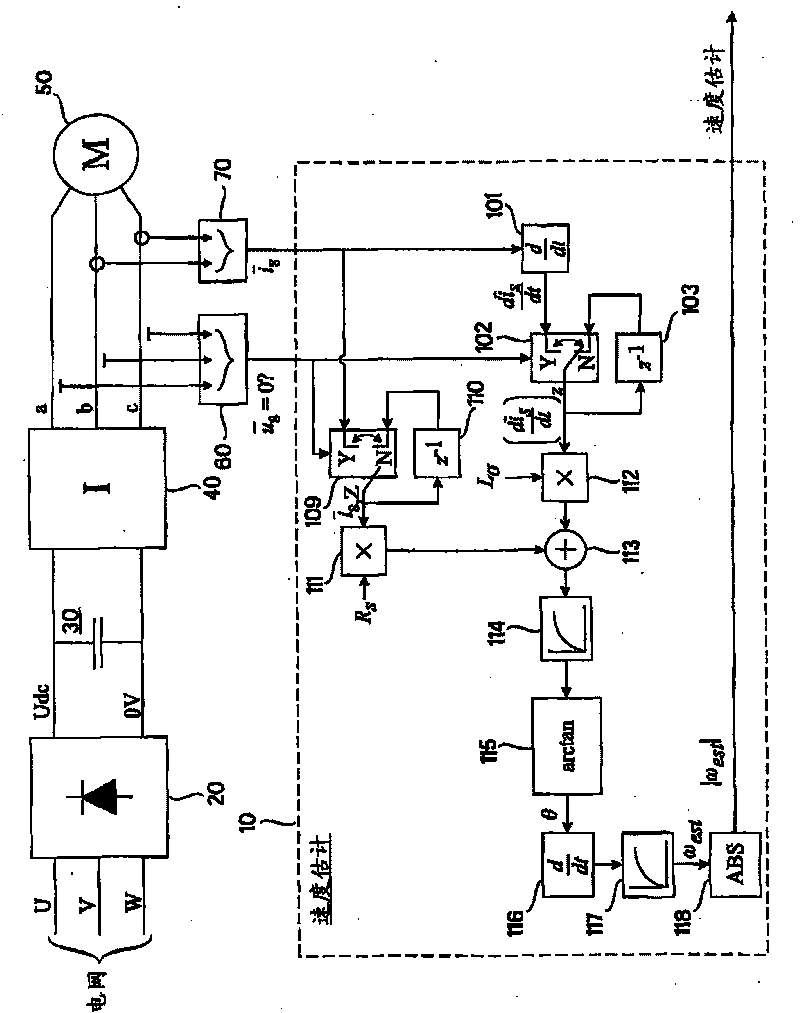
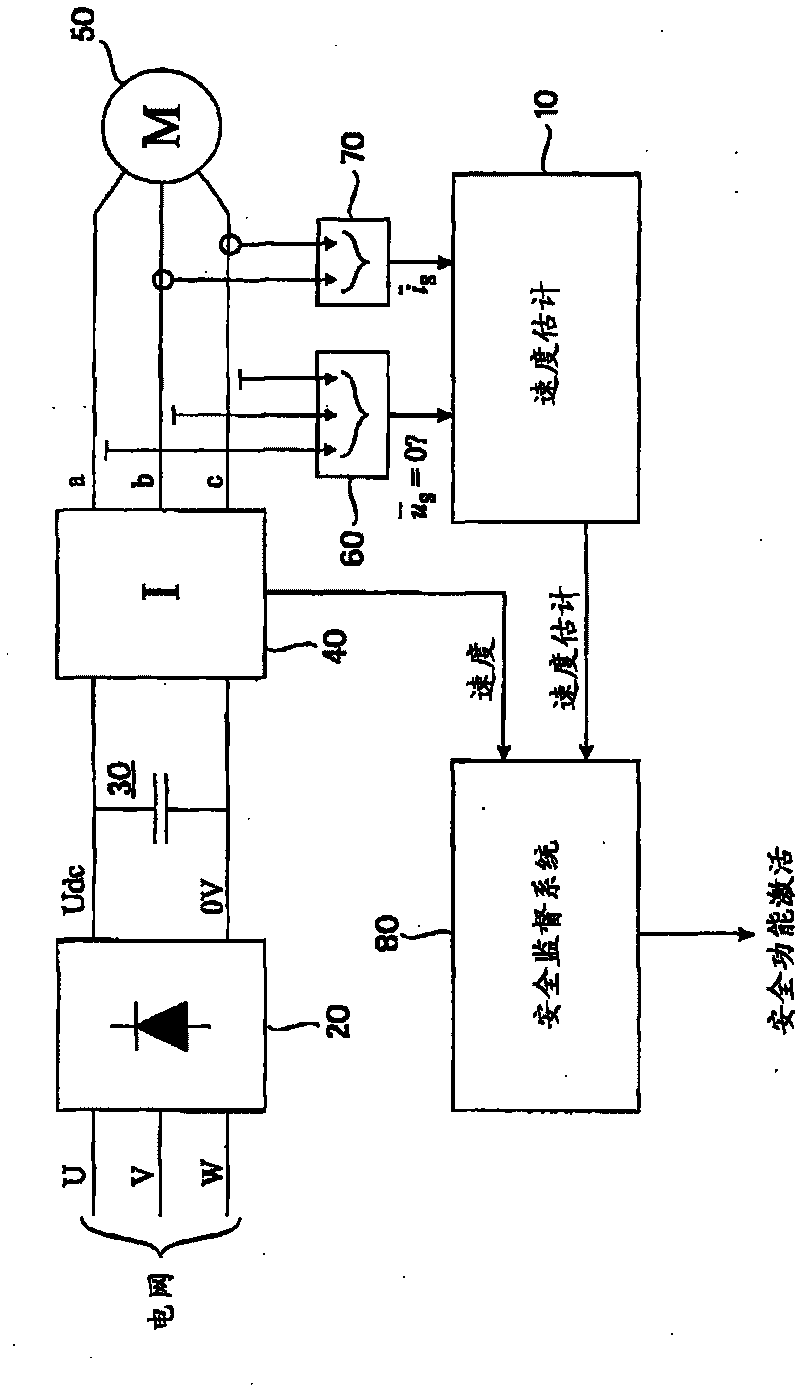
ActiveCN101750512AEstimated rotation speedDetermine the rotation speedElectronic commutation motor controlDevices using electric/magnetic meansStator current vectorEngineering
A method and apparatus for estimating a rotation speed of an electric motor supplied by an inverter, the apparatus comprising means (101, 102) for determining a time derivative of a stator current vector of the electric motor (50) during a zero vector state of the inverter (40); and means (104, 105, 106, 107) for determining an estimate of the rotation speed of the electric motor (50) on the basis of the determined time derivative of the stator current vector.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Dead zone compensating method under low frequency based on high voltage large power frequency converter
InactiveCN101834519AReduce or eliminate higher harmonic contentPrevent pulsating torqueAC motor controlPower conversion systemsFrequency changerPhase currents
The invention discloses a dead zone compensating method under a low frequency based on a high voltage large power frequency converter, which is characterized by mainly comprising the following steps: (a) starting the frequency converter, and collecting U and V two-phase current values iu and iv from stator current when the revolving speed of the frequency converter reaches a given frequency ranging from 1Hz to 60 Hz; (b) calculating the values of current components id and iq and an angle beta according to a 3S / 2R conversion formula; (c) calculating the value of a current vector angle theta according to the values of the current components id and iq, and judging the section in which current vector is located in a circle according to the vector angle theta; (d) judging positive and negative directions of each phase current by a CPU according to the section in which the stator current vector is is located; and (e) sending a compensated instruction waveform to each processing unit of the frequency converter by the CPU according to the positive and negative directions of each phase current obtained in step (d), and returning to step (a). The dead zone compensating method can reduce or eliminate higher harmonic content of the uncompensated output voltage, and effectively prevent a motor from generating impulse torque or severe system oscillation under some special frequency.
Owner:DONGFANG HITACHI CHENGDU ELECTRICAL CONTROL EQUIP CO LTD
Current control method and device without phase-locked loop of dual-fed induction power generator
ActiveCN107124126ASimplify the design processImprove adaptabilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageControl system design
The invention provides a current control method and device without a phase-locked loop of a dual-fed induction power generator. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a parameter of the dual-fed induction power generator, and performing coordinate conversion to obtain a stator voltage vector U<s Alpha Beta> and a stator current vector I<s Alpha Beta>; performing coordinate conversion on the stator voltage vector U<s Alpha Beta> and the stator current vector I<s Alpha Beta> to obtain a stator voltage vector U<s d q> and a stator current vector I<s d q>; calculating a d-axis instruction and a q-axis instruction of the stator current vector I<s d q> of the dual-fed induction power generator; calculating a rotor voltage instruction U<r d q> under a virtual synchronous rotation coordinate system; performing coordinate conversion on rotor voltage instruction U<r d q> to obtain a rotor voltage instruction U<r Alpha Beta> under a two-phase static Alpha-Beta coordinate system, and further generating a group of pulse width modulation (PWM) signals so as to control a rotor converter of the dual-fed induction power generator. With the technical scheme provided by the invention, the design and implementation process of a control system is simplified, and the adaptability to parameter change of the power generator of the control system is improved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Vector control method based on counter potential feedforward control
InactiveCN102025313AHigh control precisionAchieve continuous controlElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlStator voltageVoltage vector
The invention relates to a vector control method based on counter potential feedforward control, comprising the following steps: the V / F ratio of a motor is solved to obtain the needed counter potential amplitude of an asynchronous traction motor; exciting current and torque current are given; a counter potential phase angle is obtained by output frequency integral of an inverter; sampling is carried out to obtain the current of a three-phase stator of the motor, and the stator current vector amplitude and the phase angle are calculated; the offset voltage vector amplitude for stator impedance and the phase angle are solved; the stator current vector is decoupled into the torque current and the exciting current; the decoupled exciting current and the given exciting current form a PI(proportional-integral) regulator, and the output of the PI regulator is the counter potential amplitude regulated value; the decoupled torque current and the given torque current form a PI regulator, and the output of the PI regulator controls the slip of the motor directly; and the stator voltage amplitude output by the inverter is the sum of the regulated values of the counter potential amplitude of the motor, the offset voltage vector and the counter potential amplitude. In the invention, the control precision is high and the application range is wide.
Owner:XIANGTAN ELECTRIC MFG CORP LTD
Method and system for controlling a doubly-fed induction machine
The present invention relates to a method and system for controlling a doubly-fed induction machine. In operation a rotor current vector is processed with a rotor position estimate vector. A scalar error quantity is the determined in dependence upon a stator current vector and the processed rotor current vector. The scalar error quantity is integrated and an estimate of the rotor angular frequency is determined in dependence upon the integrated scalar error quantity. To obtain a rotor position estimate, the estimate of the rotor angular frequency is integrated and a rotor position estimate vector is determined in dependence upon the rotor position estimate. The rotor position estimate vector is then provided for processing the rotor current vector. As output signals a signal indicative of the rotor position estimate vector and a signal indicative of the estimate of the rotor angular frequency are provided for controlling the doubly-fed induction machine.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Asynchronous motor parameter online correction method based on rotor flux observer
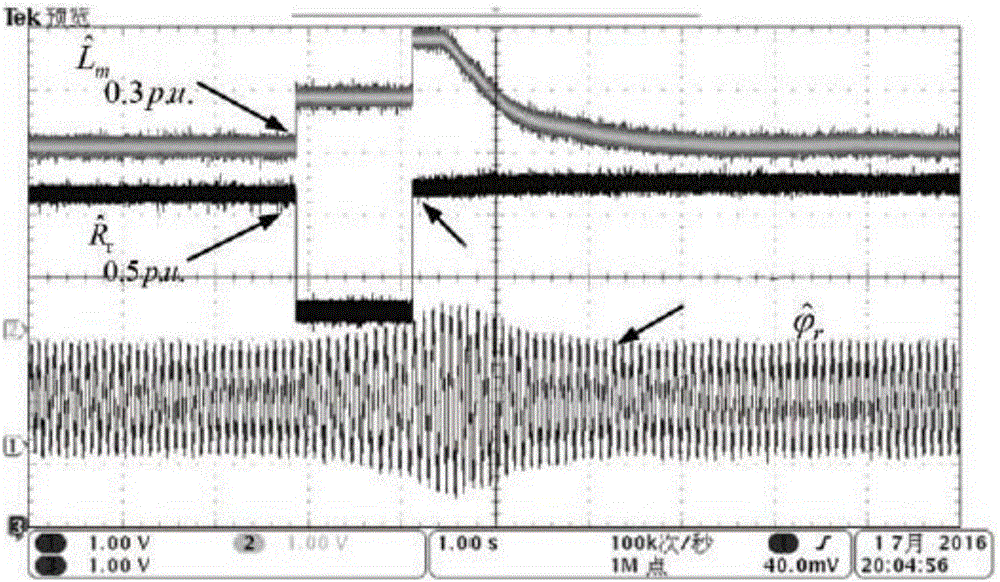
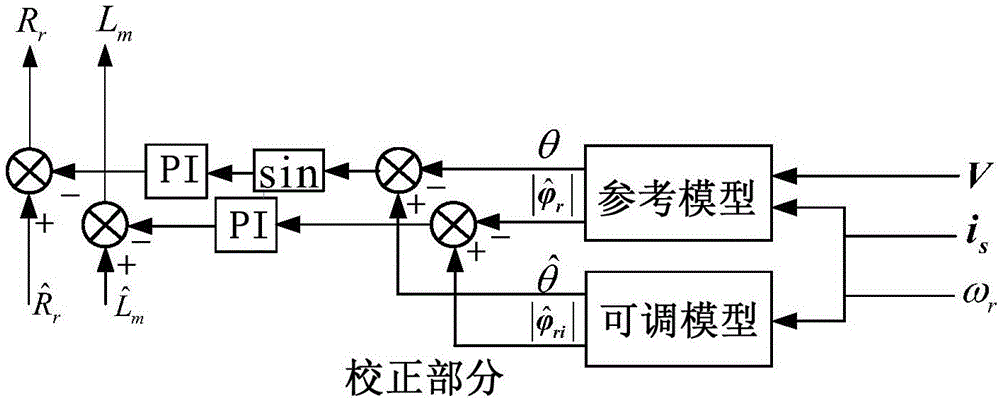
ActiveCN106452256ARealize online identificationAccurate rotor time constantElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase differenceAngular velocity
The invention discloses an asynchronous motor parameter online correction method based on a rotor flux observer. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: getting an accurate counter electromotive force e through a high-order current sliding-mode observer according to a motor stator voltage vector v, a stator current vector i and a rotor electrical angular velocity omega(r) under a two-phase static coordinate system (alpha-beta) obtained through acquisition and operation; setting up an asynchronous motor state space expression based on the relationship between the counter electromotive force and the rotor flux; constructing a rotor flux sliding-mode observer according to the space expression to observe a rotor flux vector phi(r); getting the calculated value phi<hat>(ri) of the rotor flux vector according to a current flux model; and further getting the phase difference sinusoidal quantity sin(delta theta) and the amplitude difference delta|phi(r)|; and using the phase difference sinusoidal quantity sin(delta theta) to correct a given rotor resistance R<hat>(r) in the system, and using the amplitude difference delta|phi(r)| to correct a given excitation inductance L<hat>(m) in the system. The integral problem caused by flux is overcome. Moreover, there is no transient flux problem, an accurate rotor time constant can be obtained, and online identification of excitation inductance is realized.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
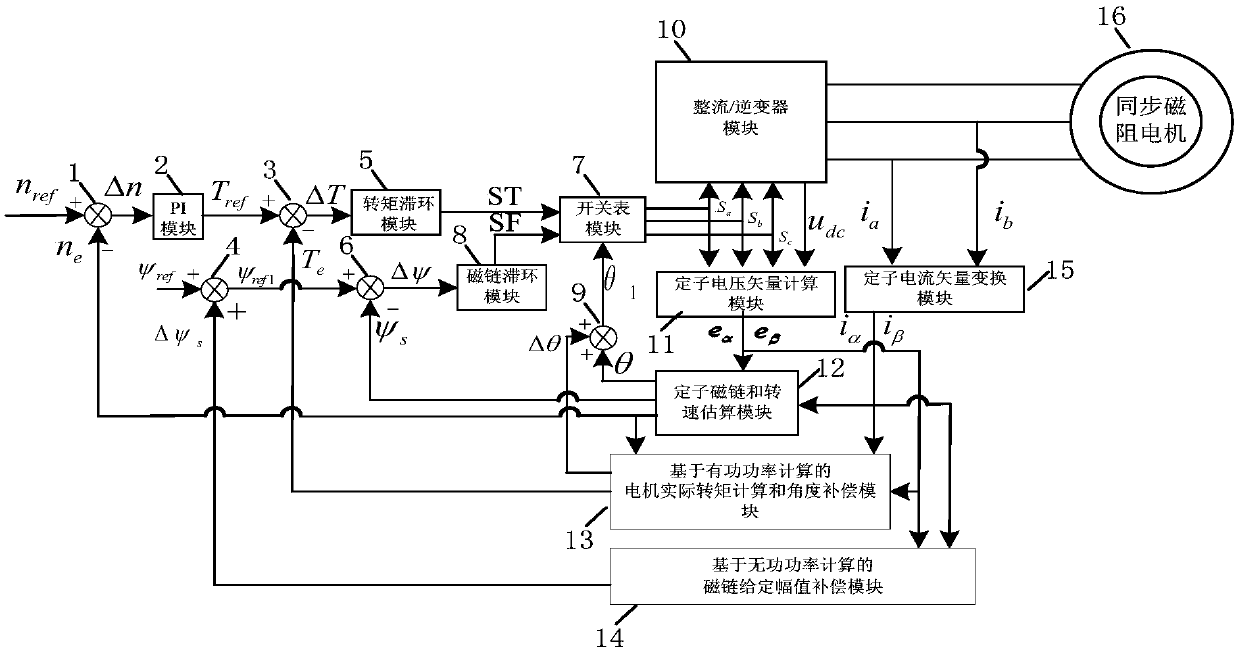
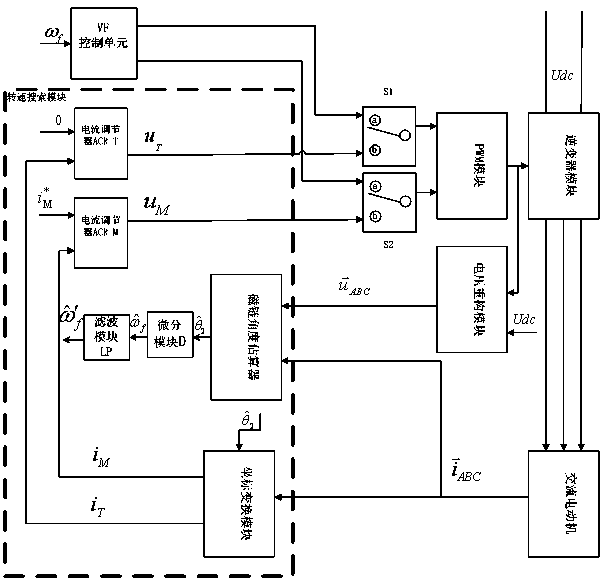
Synchronous reluctance motor sensorless direct torque control system based on power compensation
ActiveCN107863915AEasy to controlIncrease output capacityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlHysteresisSynchronous reluctance motor
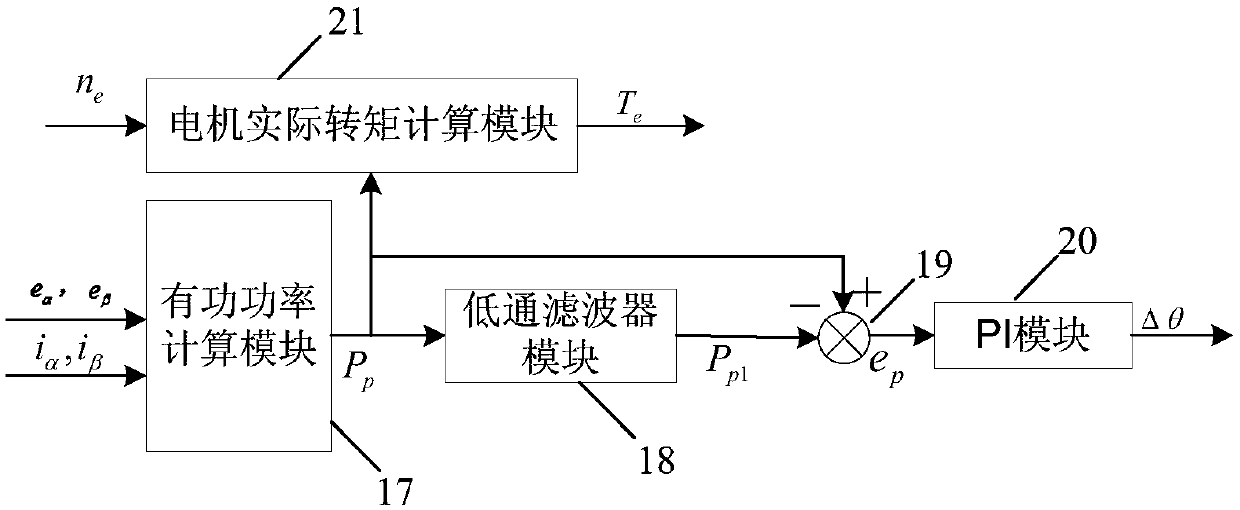
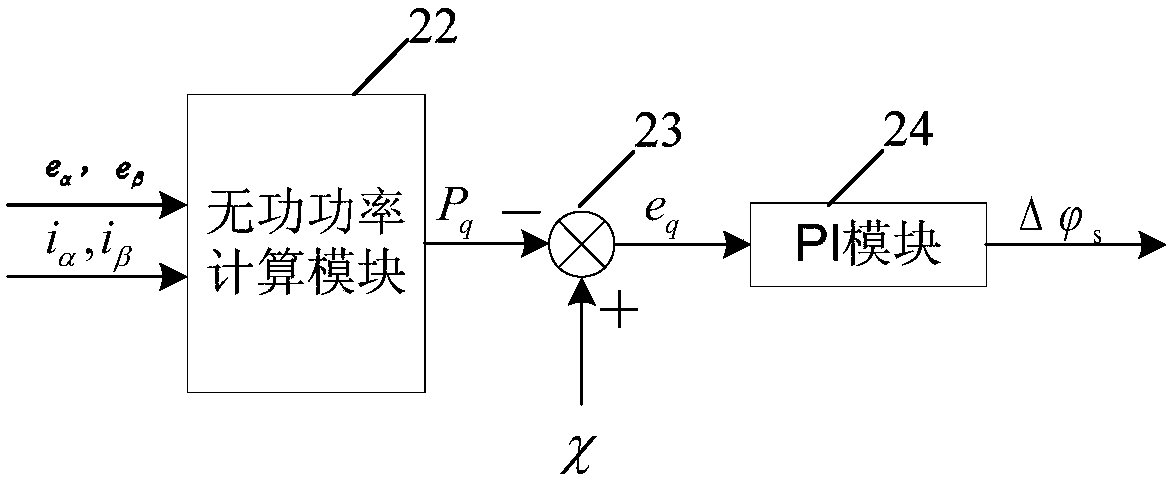
The invention provides a synchronous reluctance motor sensorless direct torque control system based on power compensation. The system comprises a first subtractor, a first PI module, a second subtractor, a first adder, a torque hysteresis module, a third subtractor, a switch table module, a switch table module, a magnetic linkage hysteresis module, a second adder, a rectifier / inverter module, a stator voltage vector calculation module, a stator magnetic linkage and rotating speed estimating module, an actual motor torque calculation and angle compensation module based on active power calculation, a magnetic linkage given amplitude compensation module based on reactive power calculation, a stator current vector transformation module and a synchronous reluctance motor. The power output capacity of the system is improved by the method that a reactive power calculation output value compensates flux linkage stator flux linkage and an active power calculation output value compensates statorflux linkage angles.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
AC motor revolving speed tracking method, speed control device and AC motor
ActiveCN103795319ASpeed search time is short and controllableA wide range of speeds can be estimatedElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPower flowControl signal
The invention discloses an AC motor revolving speed tracking method which is used to track a revolving speed when an AC motor restarts. The method includes the following steps: 1, a current flux linkage angle is estimated; 2, a stator current vector carries out coordinate conversion so as to obtain a first current value and a second current value which are respectively in line with and perpendicular to the flux linkage angle; 3, the first current value and a preset non-zero current values serve as input, and through calculation of a current regulator, a voltage is obtained (img file = 'dest_path_image002. TIF' wi = '24' he = '16' / ); the second current value and 0 serve as input, and through calculation of the current regulator, a voltage is obtained (img file = 'dest_path_image004. TIF' wi = '16' he = '16' / ); 4, voltages (img file ='891979dest_path_image002. TIF' wi = '24' he = '16' / ) and (img file ='996071dest_path_image004. TIF' wi ' = '16' he = '16' / ) carry out pulse width modulation to generate a driving control signal to drive the AC motor; and 5, steps from 1 to 4 are repeated, until the second current value is lower than a current threshold value and maintains for a period of a preset time, and differential calculation of a current flux angle is carried out to get the revolving speed when the AC motor restarts. The invention also discloses an AC motor speed control device and the AC motor. According to the invention, the advantages of being fast, accurate and low-cost are realized.
Owner:CHANGSHU SWITCHGEAR MFG CO LTD (FORMER CHANGSHU SWITCHGEAR PLANT)
PMSM torque ripple inhibition method in stator current vector orientation
ActiveCN108964527ASuppression of torque rippleTracking at full speedTorque ripple controlElectric motor controlBacksteppingMathematical model
The present invention provides a PMSM (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor) torque ripple inhibition method in stator current vector orientation. The control method comprises the steps of: establishinga dynamic mathematical model of a PMSM in the stator current vector orientation according to the actual operation parameters of the PMSM; and based on an electromagnetic torque equation in a PMSM magnetic co-energy model, establishing an optimal stator harmonic current constraint condition when the minimization of the torque ripple is ensured, and utilizing a backstepping control principle to establish a harmonic controller and a closed-loop I / f controller in the stator current vector orientation (for short, closed-loop I / f controller). In order to accurately obtain speed signals, the presentinvention designs a PMSM total-range speed identification method based on the least squares algorithm. The test result shows that the optimized motor torque ripple is effectively inhibited, parameters under the control can be rapidly converged and can achieve a stable value; and moreover, for low, middle and high rotation speeds, the PMSM torque ripple inhibition method in stator current vector orientation can perform accurate tracking and identification to achieve PMSM full-speed tracking.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Operation method for stepping constant torque control on permanent magnet brushless direct current motor
ActiveCN104506101AHighlight substantive featuresRealize constant torque step controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsDigital signal processingBrushless motors
The invention discloses an operation method for stepping constant torque control on a permanent magnet brushless direct current motor, and relates to a motor control technology. A DSP (digital signal processing) control module in a device used in the method calculates a current vector required by control according to a set cyclic number of beats bH, a number of advancing steps k, a given electromagnetic torque T* and an amplitude value of a current vector (is) corresponding to different space positions and converts the current vector required by control into a logic level pulse width modulation signal by a current control method so as to control on and off of a switching tube of a three-phase bridge type inversion circuit in a power circuit, so that stepping constant-torque control on the permanent magnet brushless direct current motor is realized. According to the method, a stator current vector synthesized by three-phase current is dispersed at an electric angle space position according to a certain cyclic number of beats so as to obtain a dispersed current vector for controlling operation of the motor; by increase of the cyclic number of beats, a smaller stepping angle can be obtained, and the position resolution is improved; therefore, the positioning precision of the permanent magnet brushless direct current motor can be improved under the condition of guaranteeing the loading capacity.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Permanent magnet synchronous motor control method based on virtual signal injection and gradient descent method
ActiveCN110336504AAchieve precise trackingRealize seamless switchingElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorStator current vector
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor control method based on a virtual signal injection and gradient descent method. In the real-time control process of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, a virtual signal is injected under a coordinate system, an angle reference value of a stator current vector is obtained by utilizing a virtual signal injection method and a gradient descent method, a reference value of a stator current vector axial component is obtained by adopting a torque compensation calculation method, a stator current vector reference value under a d-q coordinate system is further obtained by coordinate transformation, and a gradient value under the coexistence of the maximum current torque ratio control and weak magnetic control is corrected and controlled, so that seamless switching between the maximum current torque ratio control and the weak magnetic control is achieved. According to the invention, the gradient expression is corrected by introducingvoltage feedback, seamless switching between the maximum current torque ratio control and the weak magnetic control can be achieved, the rotating speed range is wide, complex signal processing is notrequired, and the dynamic response performance is good.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
An electric motor arrangement and method of controlling thereof
ActiveCN102780442AEffective controlVector control systemsDc motor stoppersBrake torqueStator current vector
An electric motor arrangement comprises an electric motor and a controller. The electric motor includes: a stator having a plurality of coil windings, and a rotor having a plurality of permanent magnets. The controller is arranged to control current flow through the plurality of coil windings to generate a braking torque on the rotor. The current is defined by a stator current vector represented in a two co-ordinate time invariant system having a rotating quadrature and direct axis by a quadrature current component and a direct current component, wherein the controller is arranged to vary the quadrature current component and the direct current component so that the input electrical power of the electric motor is greater than or equal to zero.
Owner:PROTEAN ELECTRIC LIMITED
Operation method for stepping dispersion control on permanent magnet brushless direct current motor
ActiveCN104506107AHighlight substantive featuresMany positioning pointsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsDigital signal processingBrushless motors
The invention discloses an operation method for stepping dispersion control on a permanent magnet brushless direct current motor, and relates to a motor control technology. A device used in the method comprises a DSP (digital signal processing) control module, a power circuit, the permanent magnet brushless direct current motor, an encoder position detection module and an input power module. For the common three-phase permanent magnet brushless direct current motor, a stator current vector synthesized by three-phase current is dispersed and subdivided, and a dispersion positioning position in a space is obtained according to a certain cyclic number of beats, so that positioning control on the motor can be realized by controlling the space position of a stator magnetic field, and the positioning precision of the motor is improved; furthermore, the stator current vector synthesized by the three-phase current is dispersed at an electric angle space position according to a certain cyclic number of beats so as to obtain a dispersed current vector for controlling operation of the motor; by increase of the cyclic number of beats, a smaller stepping angle can be obtained, and the position resolution is improved; therefore, the positioning precision of the permanent magnet brushless direct current motor can be improved under the condition of guaranteeing the loading capacity.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Simple on-line monitoring technology for magnetic performance attenuation of permanent-magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN107659235AReduce sizeEasy to operateElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlFrequency changerSynchronous motor
The invention discloses a simple on-line monitoring technology for magnetic performance attenuation of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor. A current of a motor stator winding is acquired by a current transformer arranged at an output end of a frequency converter, a core controller of the frequency converter is used for performing coordinate conversion by employing a vector control algorithm so that a motor stator current vector is decomposed to an excitation component Id and a torque component Iq, and the stator current can be all used for generating an electromagnetic torque by employing acontrol mode of Id equal to 0 according to an electromagnetic torque formula of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor. In the mode, the motor is controlled to gradually reach rated frequency by the frequency converter, at the moment, a counter potential induced by the motor stator can be equivalent to an output voltage of the frequency converter, the magnetic flux in a magnetic path is obtained according to a relation between the counter potential and a magnetic link, so that the magnetic performance attenuation condition of a permanent magnet of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor can bejudged; the core controller is used for transferring a voltage value obtained by calculation and the magnetic performance attenuation percent of the permanent magnet to an upper computer for displaying via series communication, and on-line monitoring is achieved; the technology is simple to operate and easy to implement and can be applicable to an industrial and automatic side with general requirement; and the permanent-magnet synchronous motor has the beneficial effects of simple structure and high practicability.
Owner:SHANDONG OURUIAN ELECTRIC
Applying a control unit to an asynchronous machine which is operated without a rotary encoder
ActiveCN101971482AAvoid current peaksReduce mechanical speedElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsFrequency changerVoltage vector
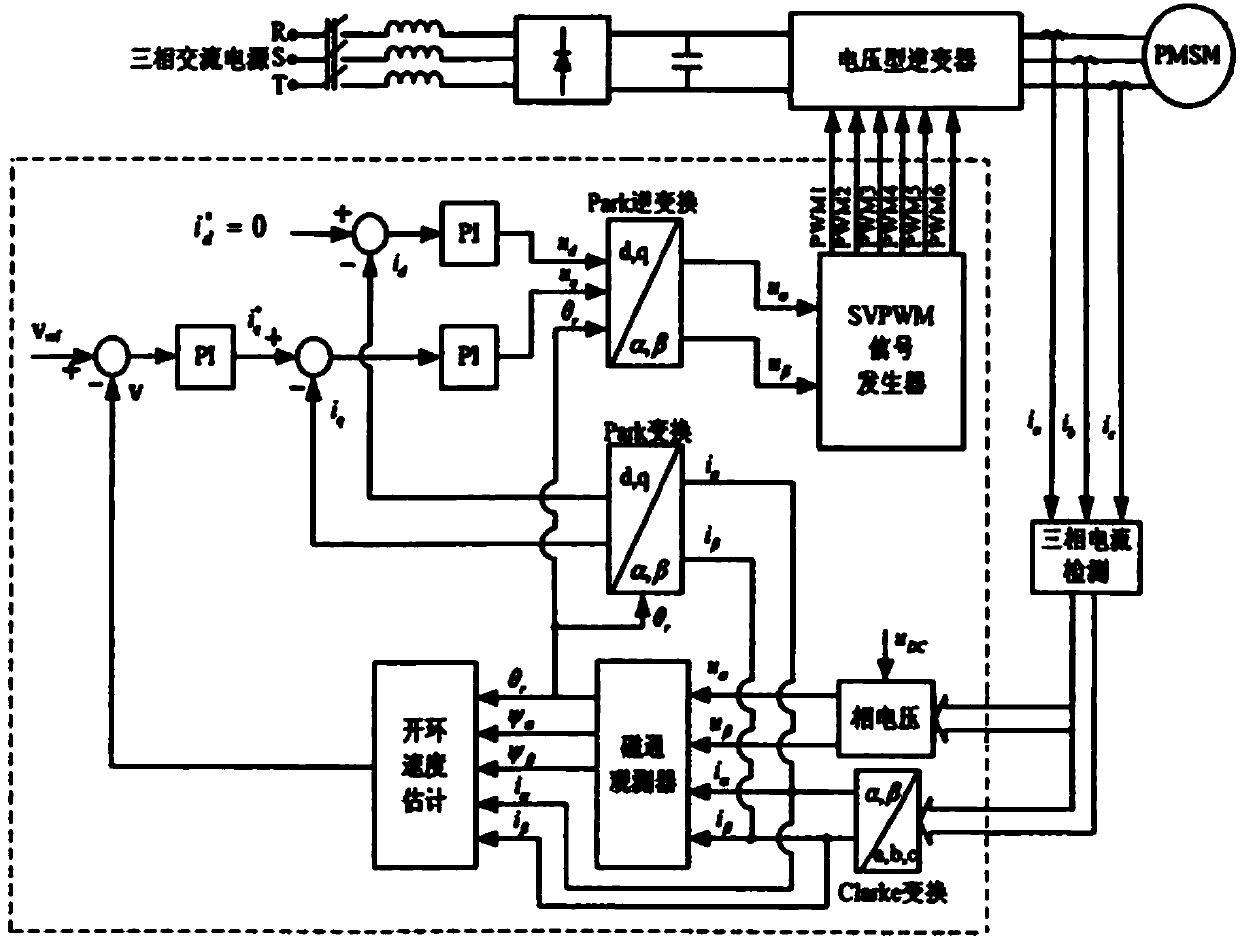
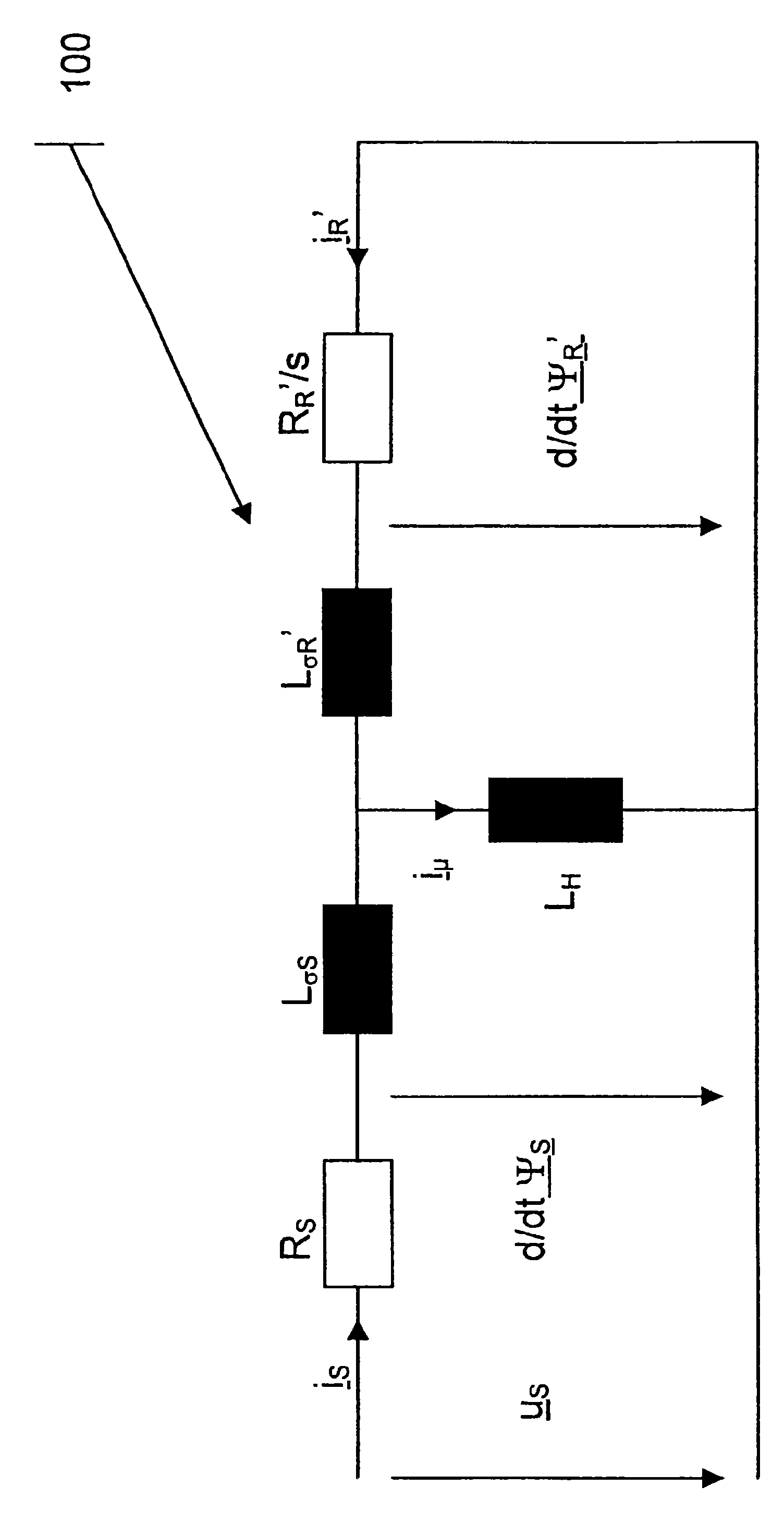
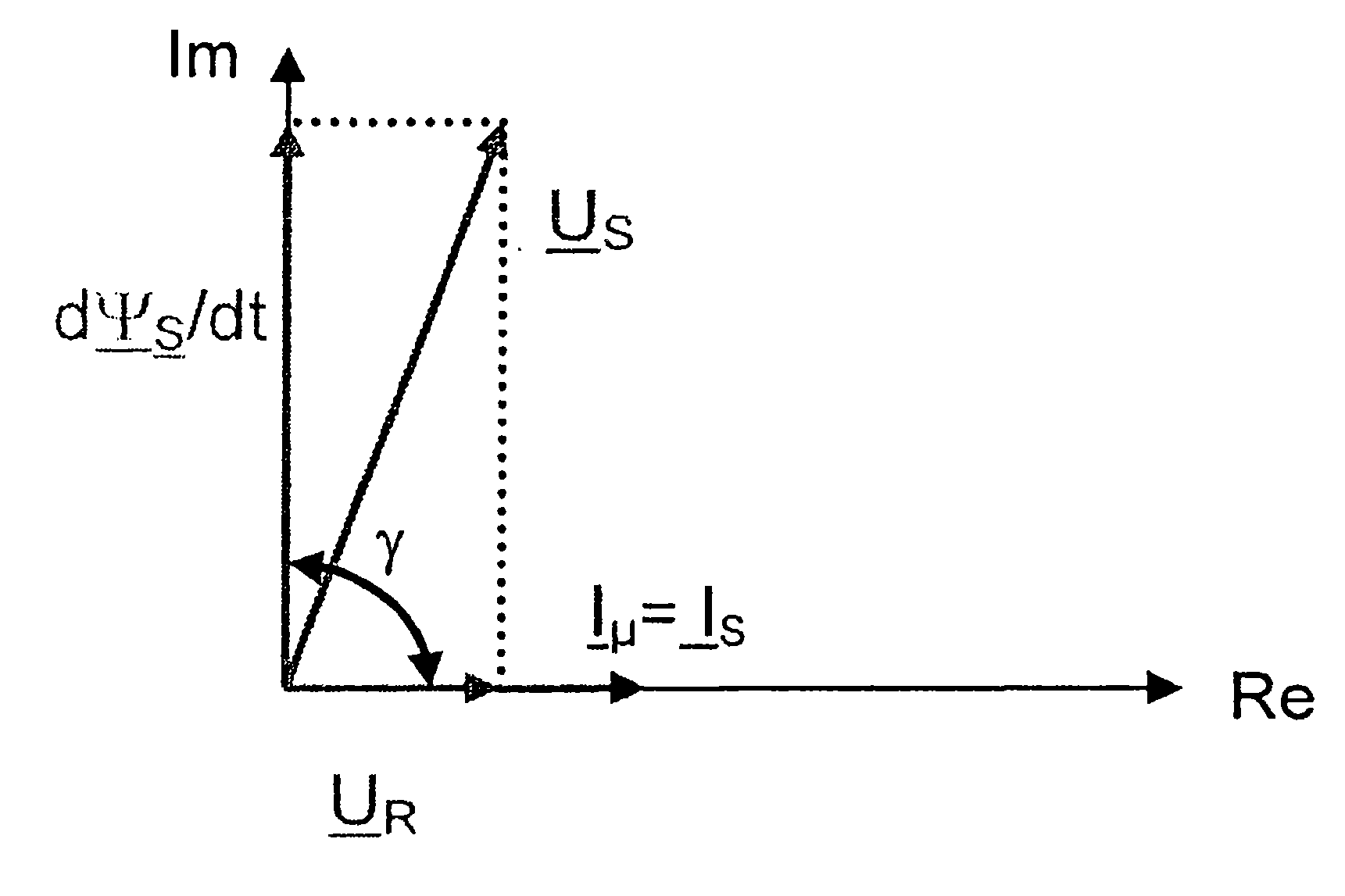
The problem of the invention is to achieve a connection or application of a converter to a rotating asynchronous machine, which is operated without an encoder, without a high current and without a torque surge. The mechanical system and the controlling system are not to be overloaded. The method is also to be capable of functioning independently of the residual magnetism. A method is proposed as a control unit, which employs an inverter or converter, in order to power the asynchronous machine (5), which rotates at a mechanical speed. The asynchronous machine is regulated by the control unit. A stator current vector (i s) is ascertained from measured currents of the stator windings of the asynchronous machine (5) and a rotating stator voltage vector (u s). A calculation of a stator flux change vector is performed from the stator current vector (i s), the stator voltage vector (u s), and a stator resistance (RS) according to a motor model (100). An angle difference (gamma) between the stator current vector (i S) and the stator change vector is calculated. This angle difference (gamma) is regulated to a target value of 90 DEG or -90 DEG , wherein an output signal of said controller corresponds to a rotating field frequency (omega) of the voltage vector of said stator which is to be applied. A regulation of an amplitude of the stator voltage vector is performed via a current controller (51), to which the difference of a current target value and a variable which corresponds to the amplitude of the stator current is provided at the input as the control difference (51a).
Owner:LENZE DRIVES
Reliable and smooth sensorless permanent magnet synchronous motor starting method
PendingCN111786607ACurrent controllablePrevent overcurrentVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlMotor speedSynchronous motor
The invention relates to the technical field of permanent magnet synchronous motor control, and discloses a reliable and smooth sensorless permanent magnet synchronous motor starting method. The method comprises the following steps: in a pre-positioning stage, controlling the angular velocity of a stator current vector to be unchanged, and increasing the amplitude to a set amplitude by a first setfunction, and then controlling the amplitude of the stator current vector to be unchanged and the instruction position angle to be increased by a second set function until the stator current vector is synchronous with the rotor position; in an I / F acceleration stage, enabling the stator current vector and the rotor flux linkage position to keep synchronous following through the torque-self-balancing characteristic until the lowest rotating speed of speed closed-loop operation is reached; in a closed-loop cut-in stage, keeping the rotating speed of the motor at the lowest rotating speed of speed closed-loop operation, gradually reducing the amplitude of the stator current vector, and when the included angle theta L is gradually attenuated to be less than the threshold theta LLmt, switchingthe closed-loop operation mode. The motor current is controllable before and after the system is started, the current pulsation is small when the system is switched into a closed loop, and the starting reliability and smoothness are improved.
Owner:青岛斑科变频技术有限公司
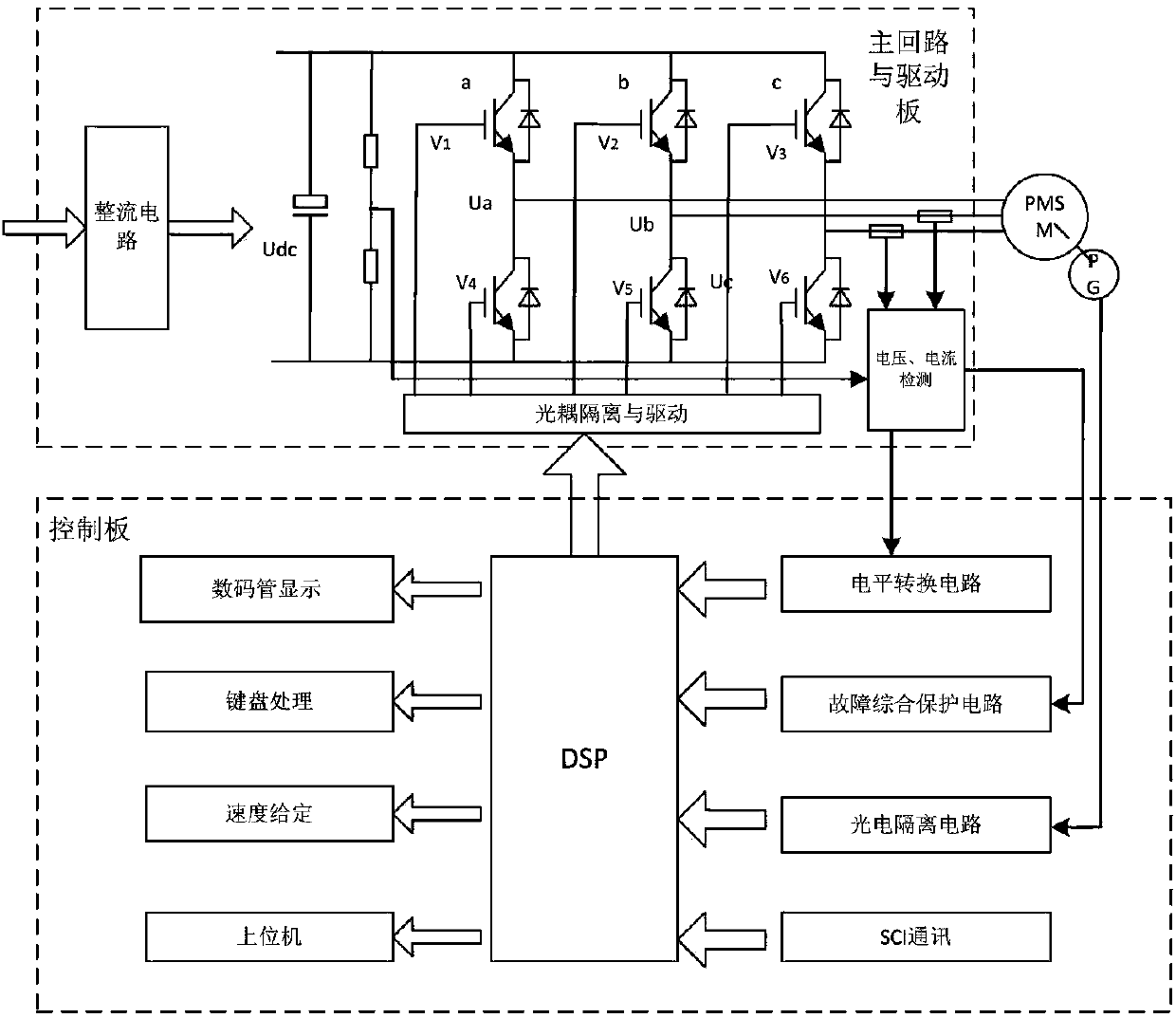
Vector control motor drive system inverter open-circuit fault diagnosis method
InactiveCN106019055ALow costImprove detection accuracyElectrical testingStator current vectorElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention discloses an inverter power tube open-circuit fault real-time detection method in a vector control motor drive system, and belongs to the technical field of online detection. The method comprises the following steps: judging whether a fault occurs according to a d shaft voltage value; and positioning the fault according to spatial position of the stator current vector locus entering an arc part, and circumference ratio of the arc part. The method is suitable for realizing open-circuit fault diagnosis of any single tube and any double tube of an inverter in the vector control motor drive system, and has the advantages of low cost, high detection precision, fast speed, high real-time performance, good robustness and high anti-interference capability.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
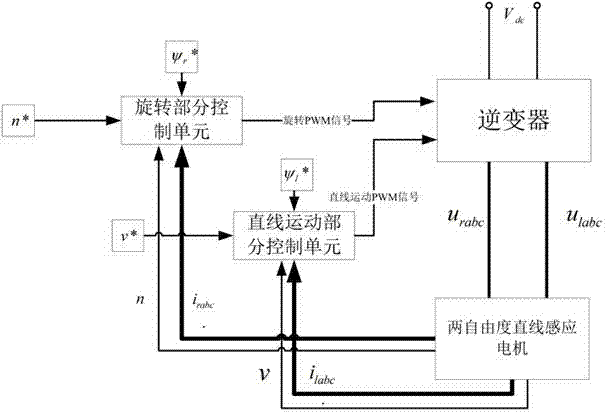
Two-degree-of-freedom linear induction motor control method
ActiveCN104716885APrecise rotational movementPrecise Vector ControlElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPower flowControl vector
The invention relates to the field of electromechanical control, in particular to a two-degree-of-freedom linear induction motor control method used for controlling a rotating arc-shaped linear induction motor and a straight-line arc-shaped linear induction motor. According to the method, a stator current is vectorially decomposed into a current component generating a magnetic field and a current component generating torque, and the current component generating the magnetic field and the current component generating the torque are controlled respectively. Through the two-degree-of-freedom linear induction motor control method, rotating movement part vector control and linear movement part vector control are combined, sot that a motor servo system is stable and high in precision.
Owner:横川机器人(深圳)有限公司
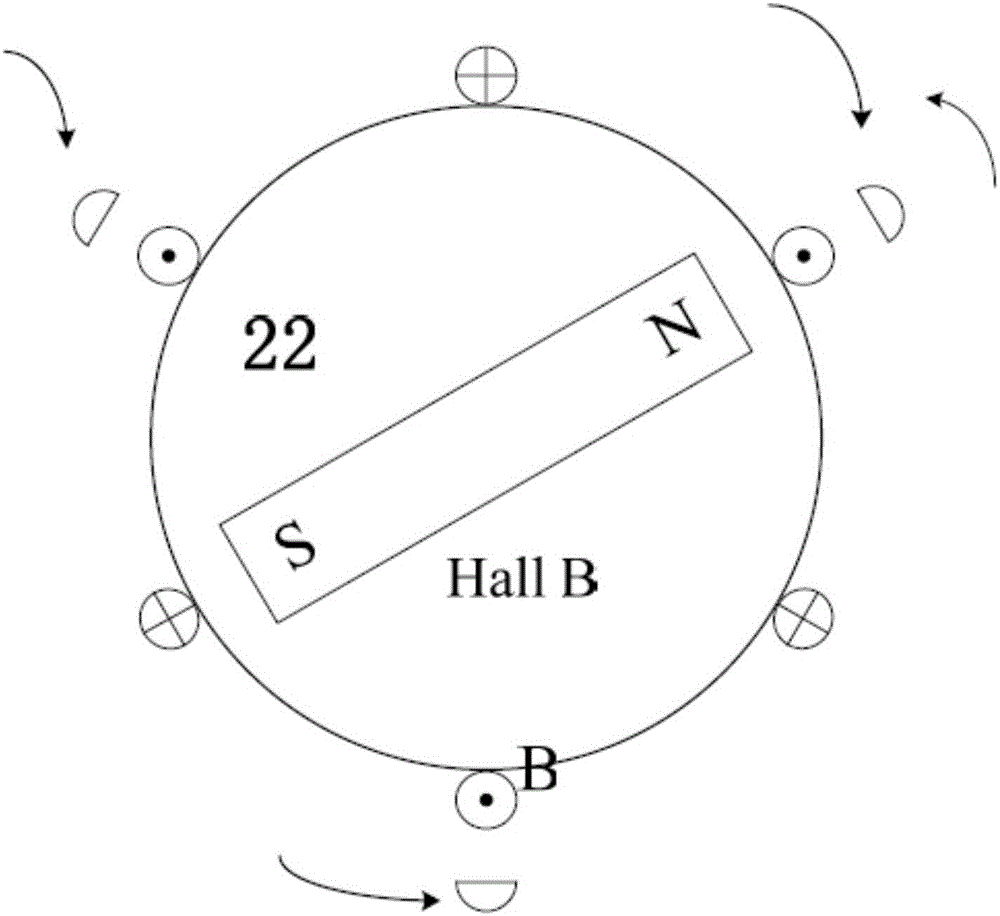
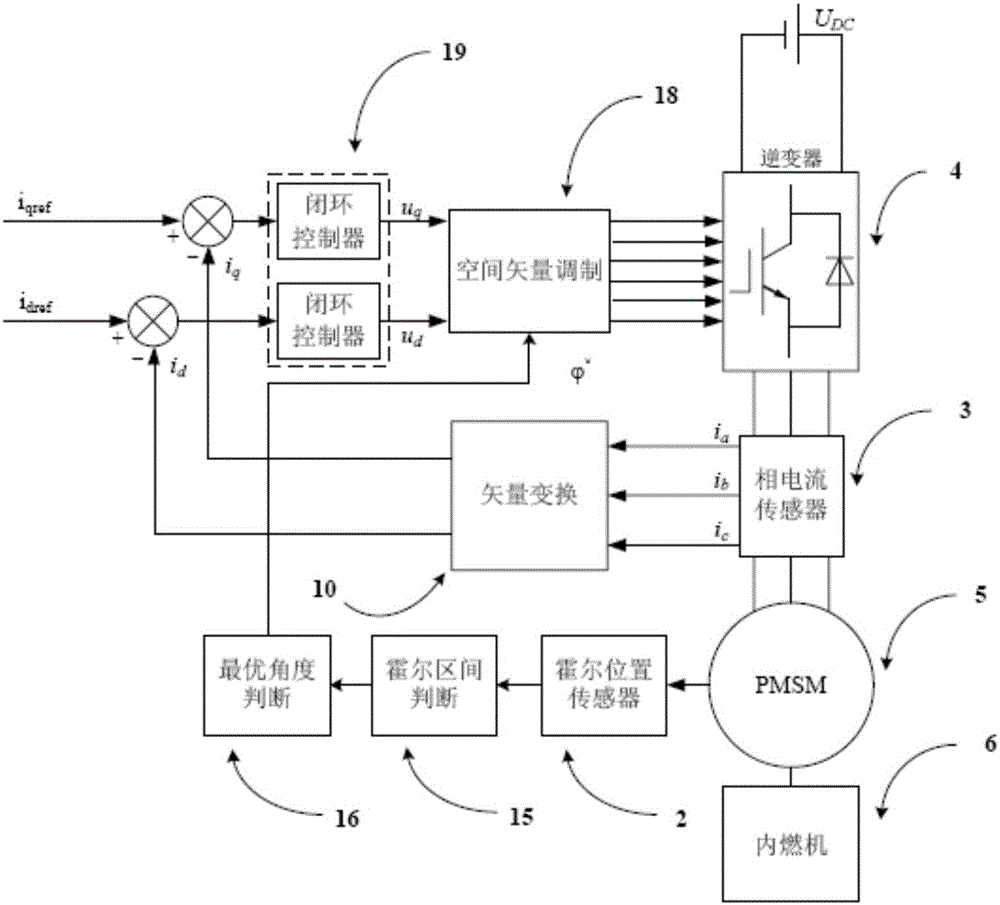
Permanent magnet synchronous motor starting method for mileage increasing system provided with hall position sensor
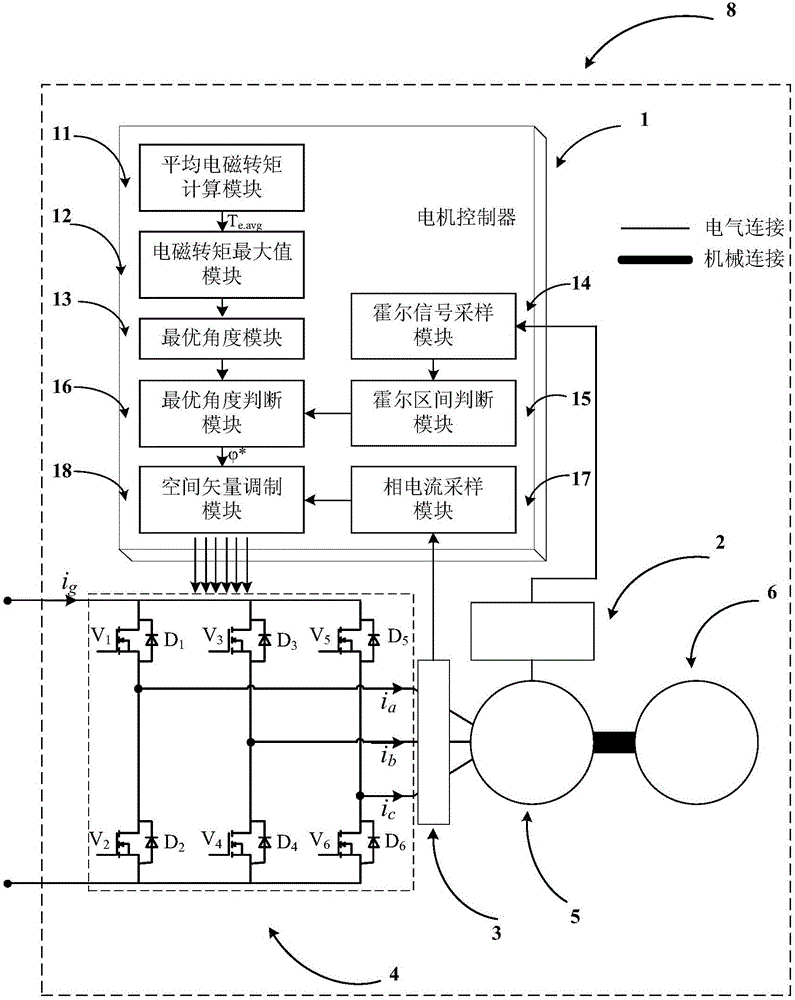
InactiveCN105897106AStart fastRealize the start functionElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPermanent magnet synchronous motorAngular degrees
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor starting method for a mileage increasing system provided with a hall position sensor, which belongs to the field of motor control. Due to three ways of digital signals outputted by a three-way switch hall sensor through filtering, six accurate rotor position signals can be determined, 360-DEG electric angle space is uniformly divided into six hall intervals, the maximum value of an average electromagnetic torque is solved through a trigonometric function extremum seeking method, a corresponding optimal angle phi<*> in each hall interval is acquired, the corresponding optimal angle phi<*> serves as an angle signal modulated by a space vector to be inputted, the output PWM signal modulated by the space vector controls a three-phase inverter bridge to generate a stator current vector IS, an electromagnetic torque is generated in a stator winding of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, the permanent magnet synchronous motor is dragged to start, an internal combustion engine is further dragged to start, the mileage increasing system permanent magnet synchronous motor starting function is realized, the maximum electromagnetic torque output is ensured, real-time estimation does not need to be carried out on a rotor position, the algorithm is simple and effective, and the space and the cost are saved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com