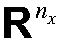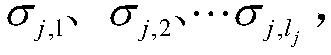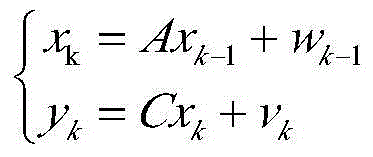Patents
Literature
68 results about "Time-invariant system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
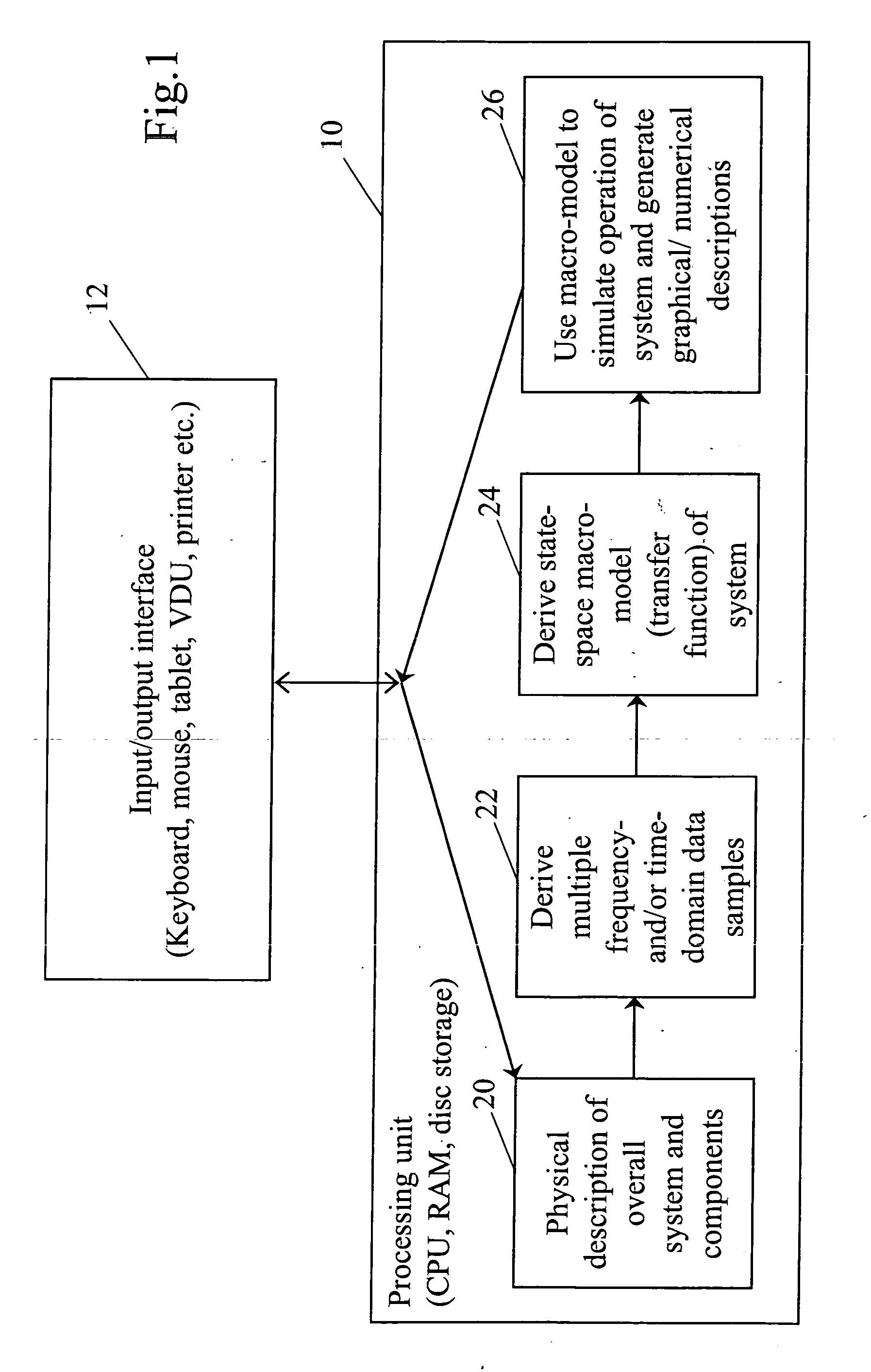
A time-invariant (TIV) system has a time-dependent system function that is not a direct function of time. Such systems are regarded as a class of systems in the field of system analysis. The time-dependent system function is a function of the time-dependent input function. If this function depends only indirectly on the time-domain (via the input function, for example), then that is a system that would be considered time-invariant.
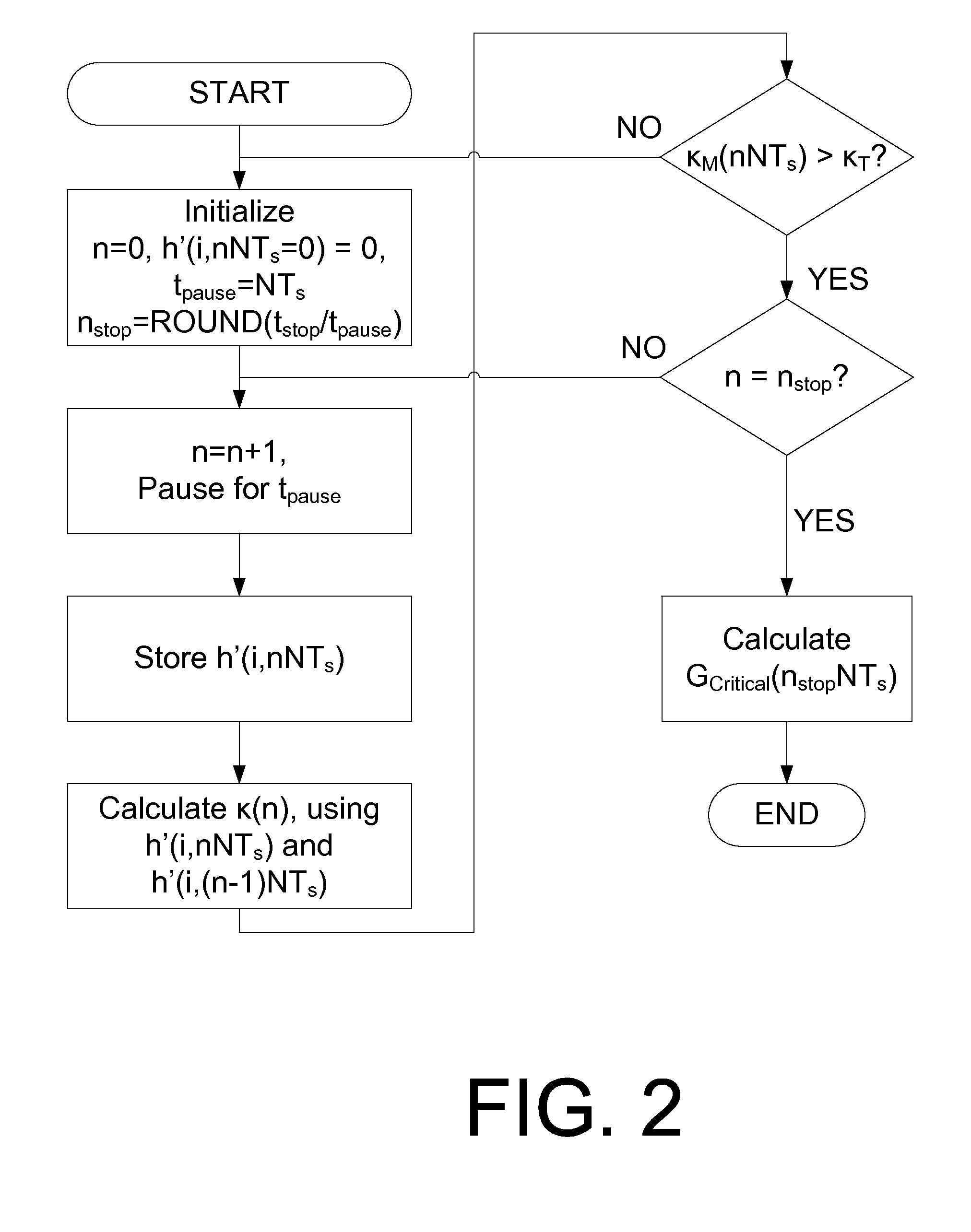
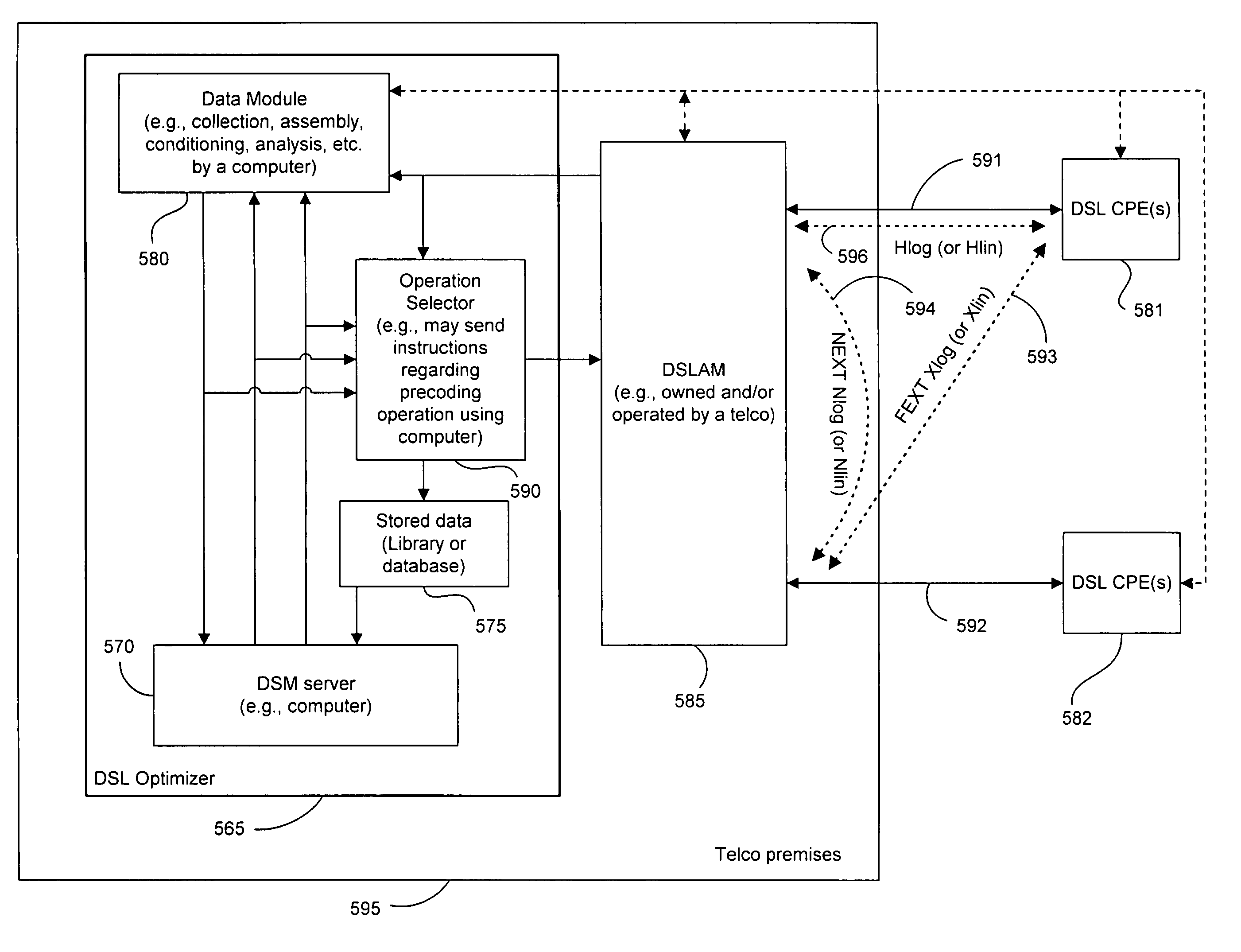
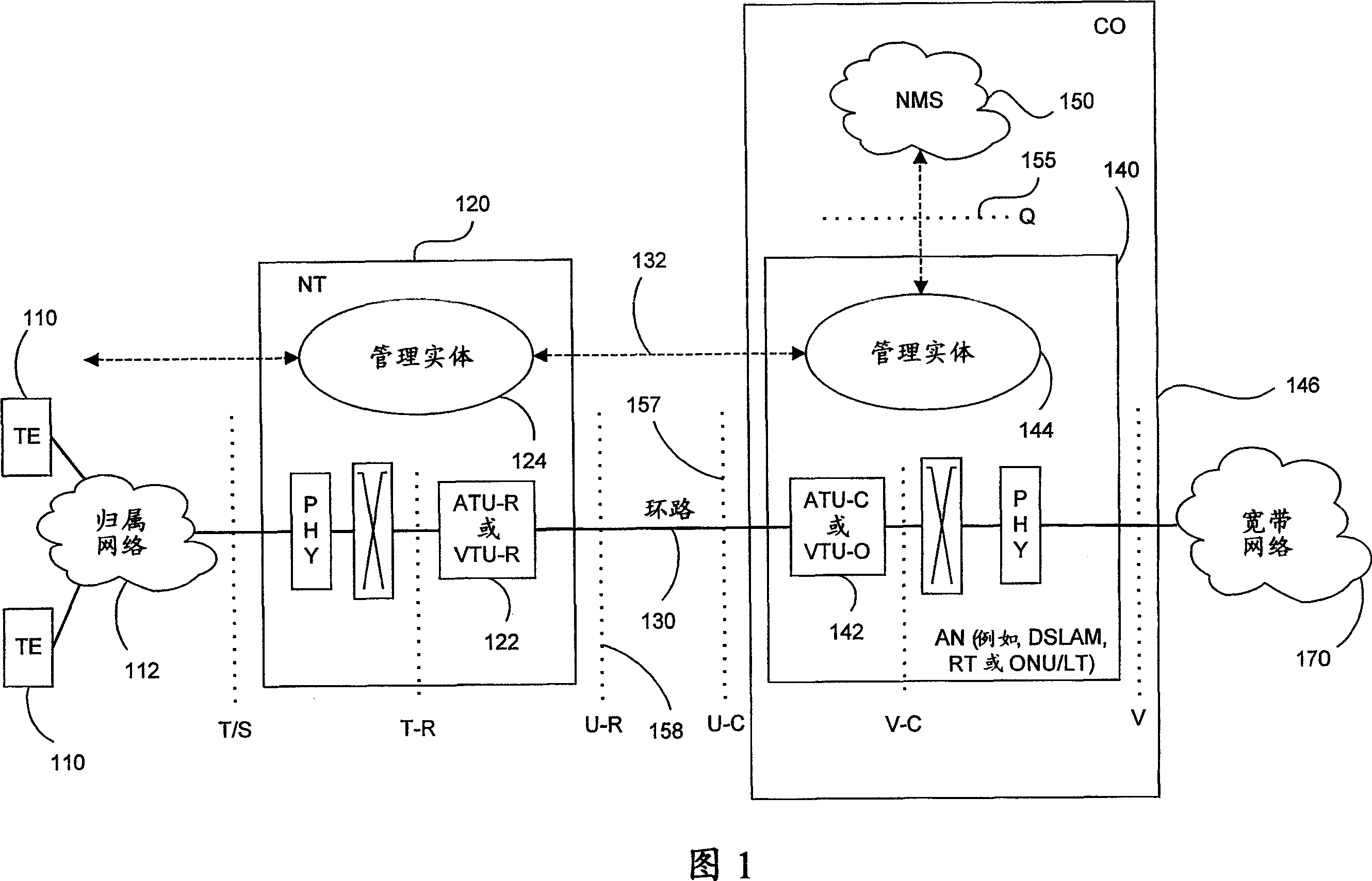
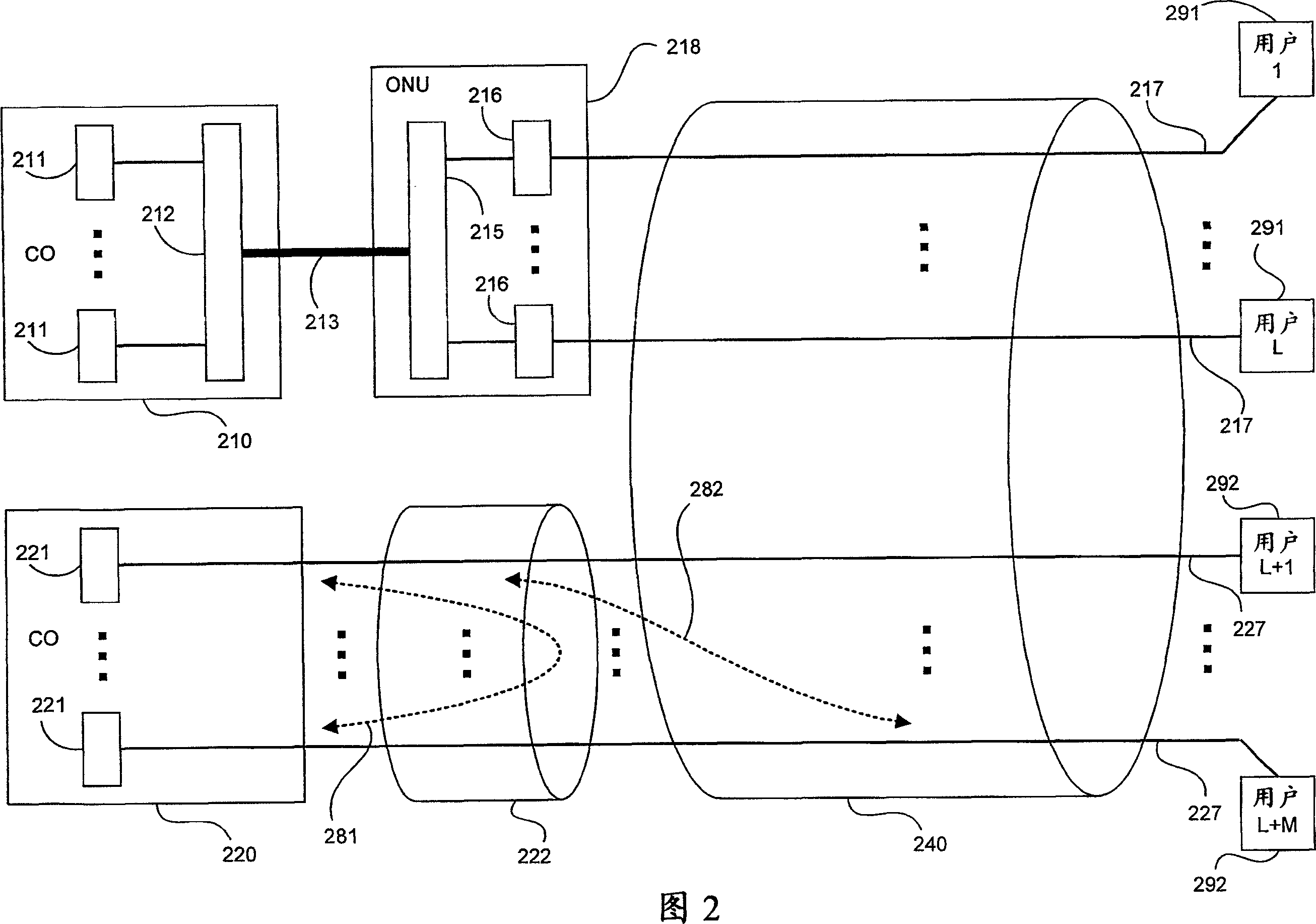
FEXT determination system
ActiveUS20050259725A1Error preventionTelephonic communicationSignal transfer functionTime-invariant system
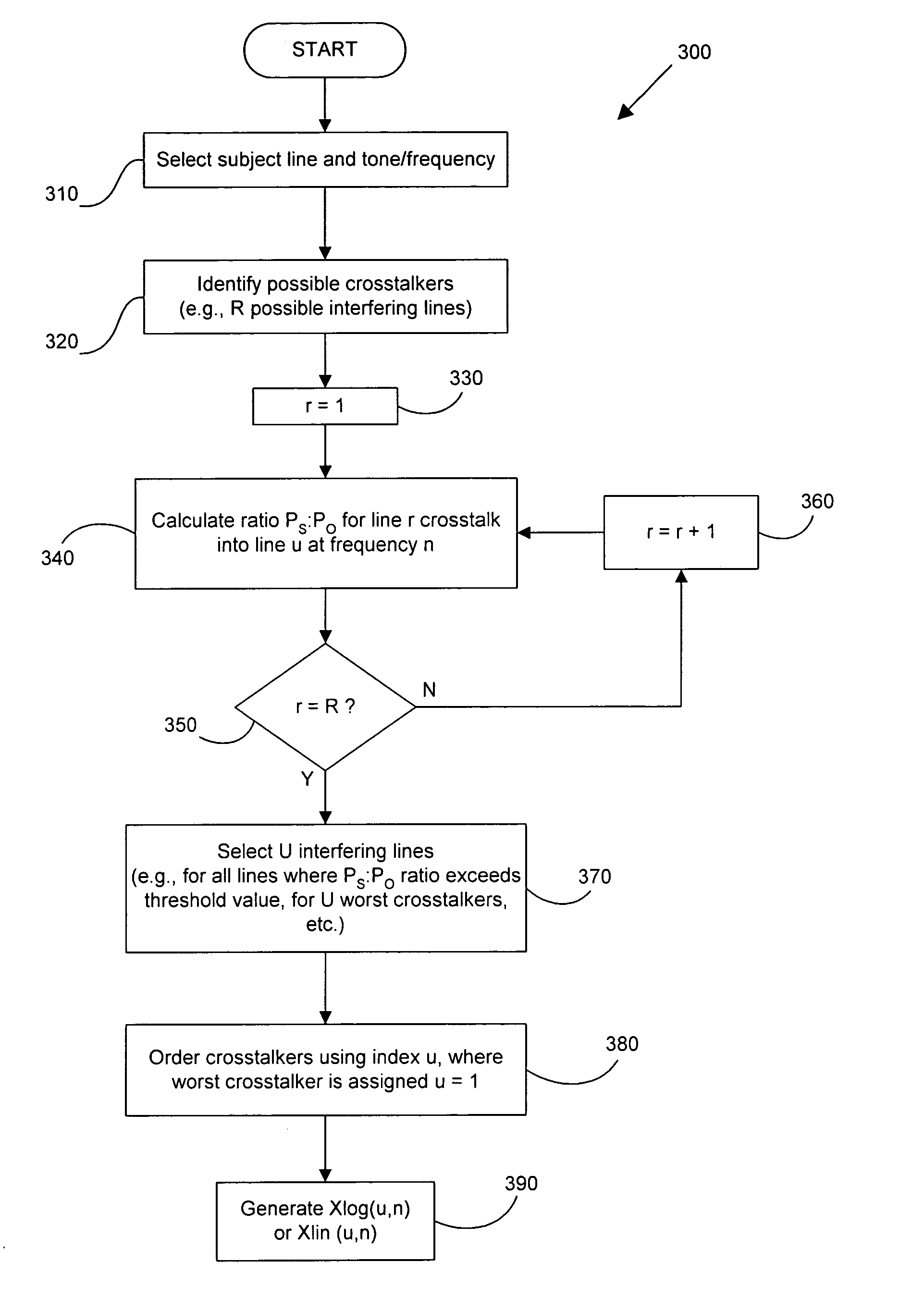
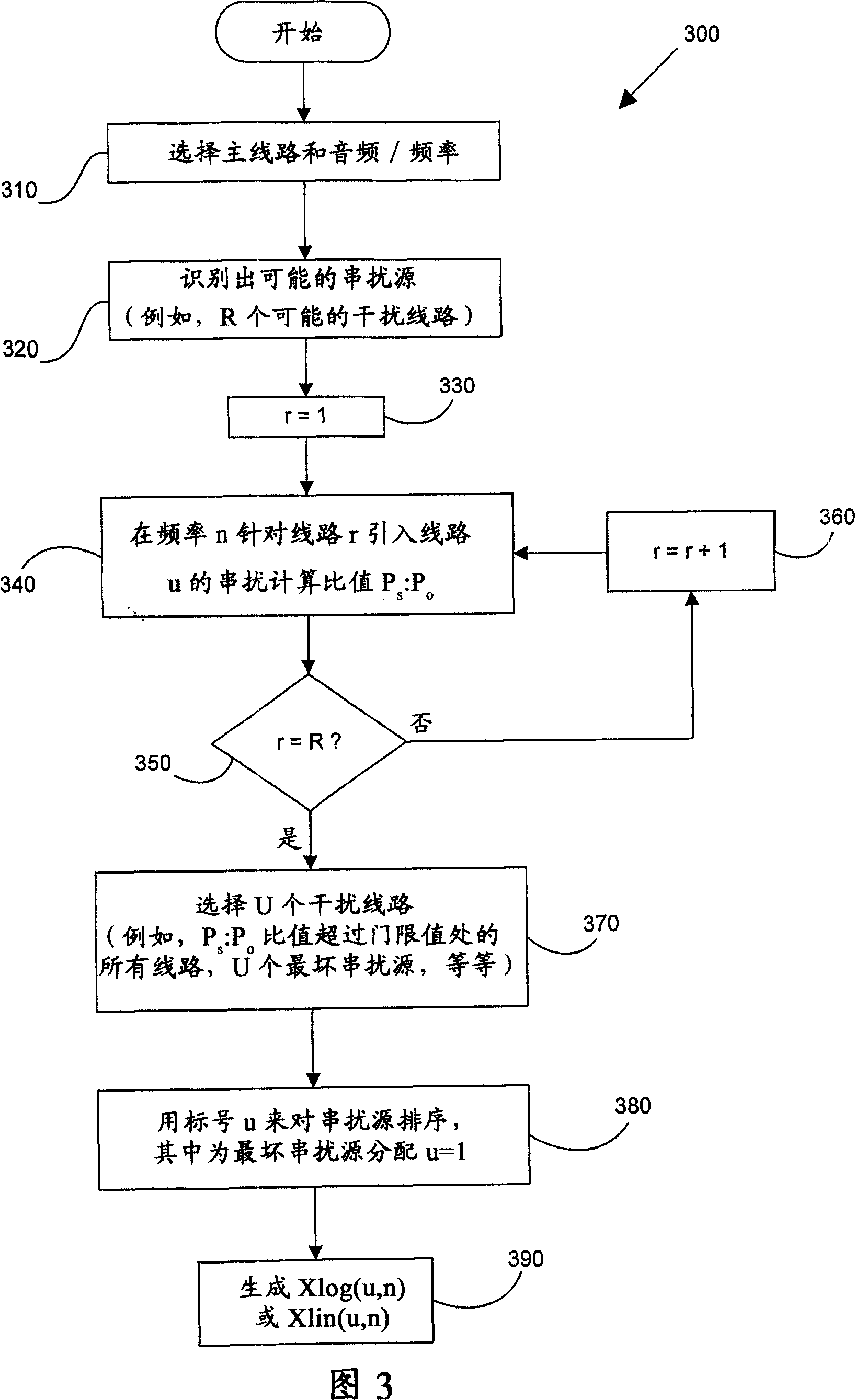
Operational data is utilized to determine the FEXT interference induced by one line into the other DSL line. FEXT interference can be calculated using the NEXT interference measured between the two lines at the upstream ends of the loops and the downstream channel transfer function of one of the loops. Because the NEXT and transfer function constitute a linear time-invariant system, as does the FEXT interference between the lines, the NEXT interference and line transfer function can be multiplied (if in linear format) or added (if in logarithmic format) to approximate the FEXT interference between the lines. The collection of data, calculations and other functions performed in these techniques may be performed by a system controller, such as a DSL optimizer. An Xlog(u,n) quantity is a decibel-magnitude representation of the insertion-loss equivalent of FEXT transfer functions and is defined as the ratio of (1) a line u's source power into a matched load of 100 Ohms when no binder is present to (2) the power at the output of the subject line when line u is excited with the same source and the binder is present. Xlin(u,n) is the linear equivalent of Xlog(u,n). The Xlog(u,n) and Xlin(u,n) quantities may be represented in specific formats that assist in their use in DSL and other systems. When defined as a line's insertion loss, Xlin (or equivalently Xlog) does not include the effect of any transmit filter.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
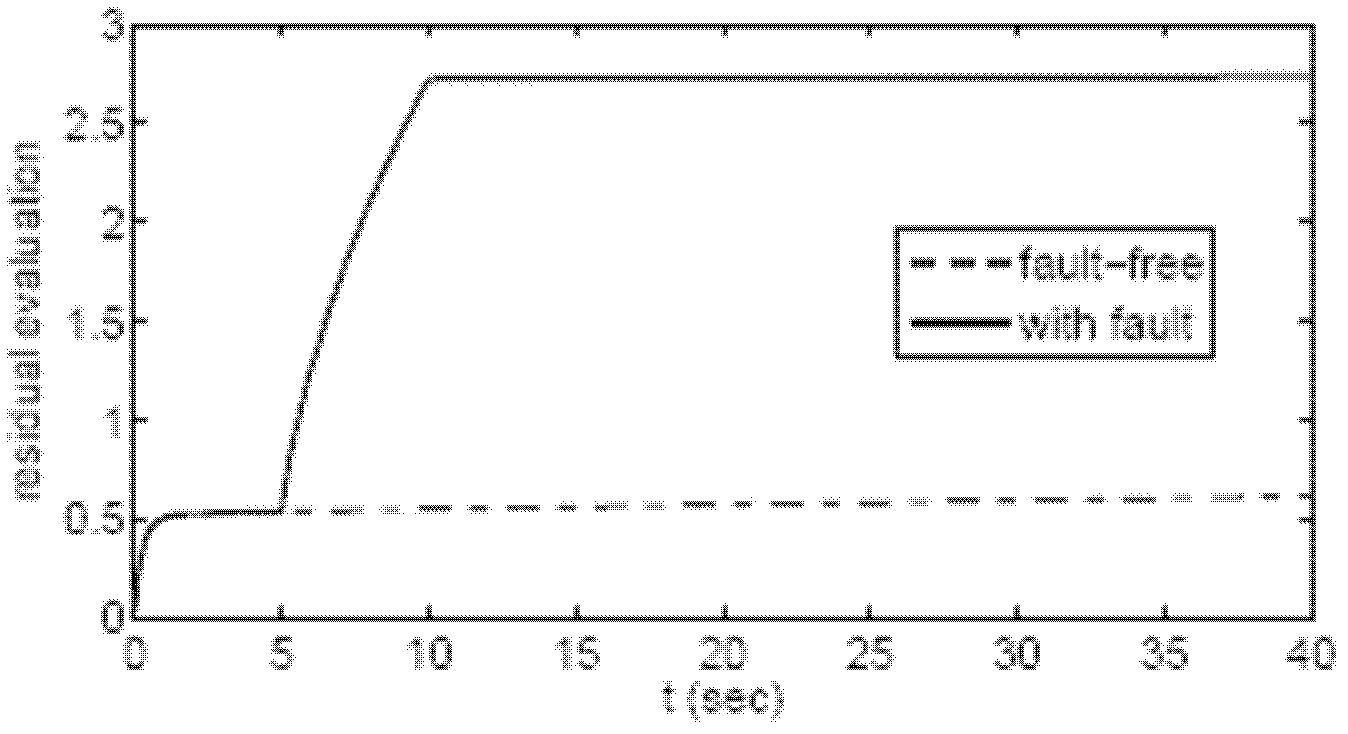
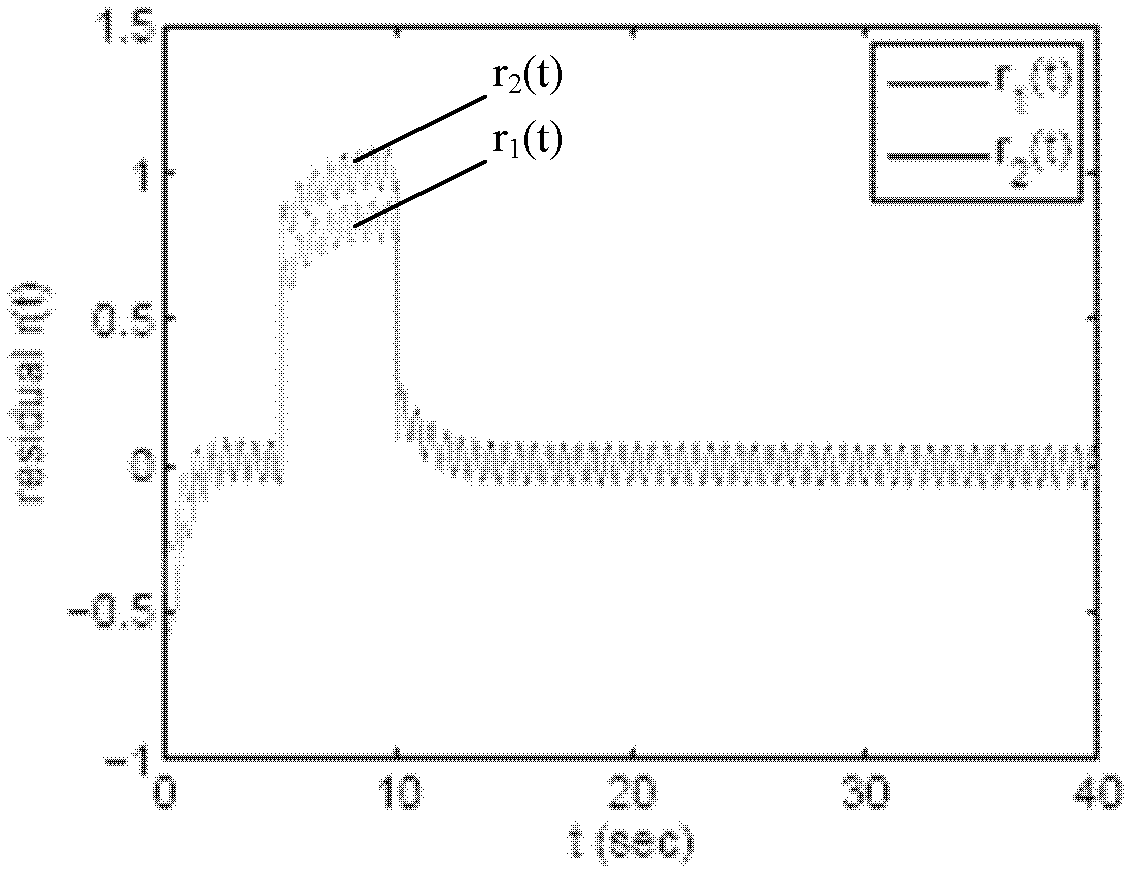
Design method of robustness fault detection filter of linear uncertain system
InactiveCN102436179ATest not conservativeExcellent RFDFTesting/monitoring control systemsAdaptive controlRobustificationUltrasound attenuation
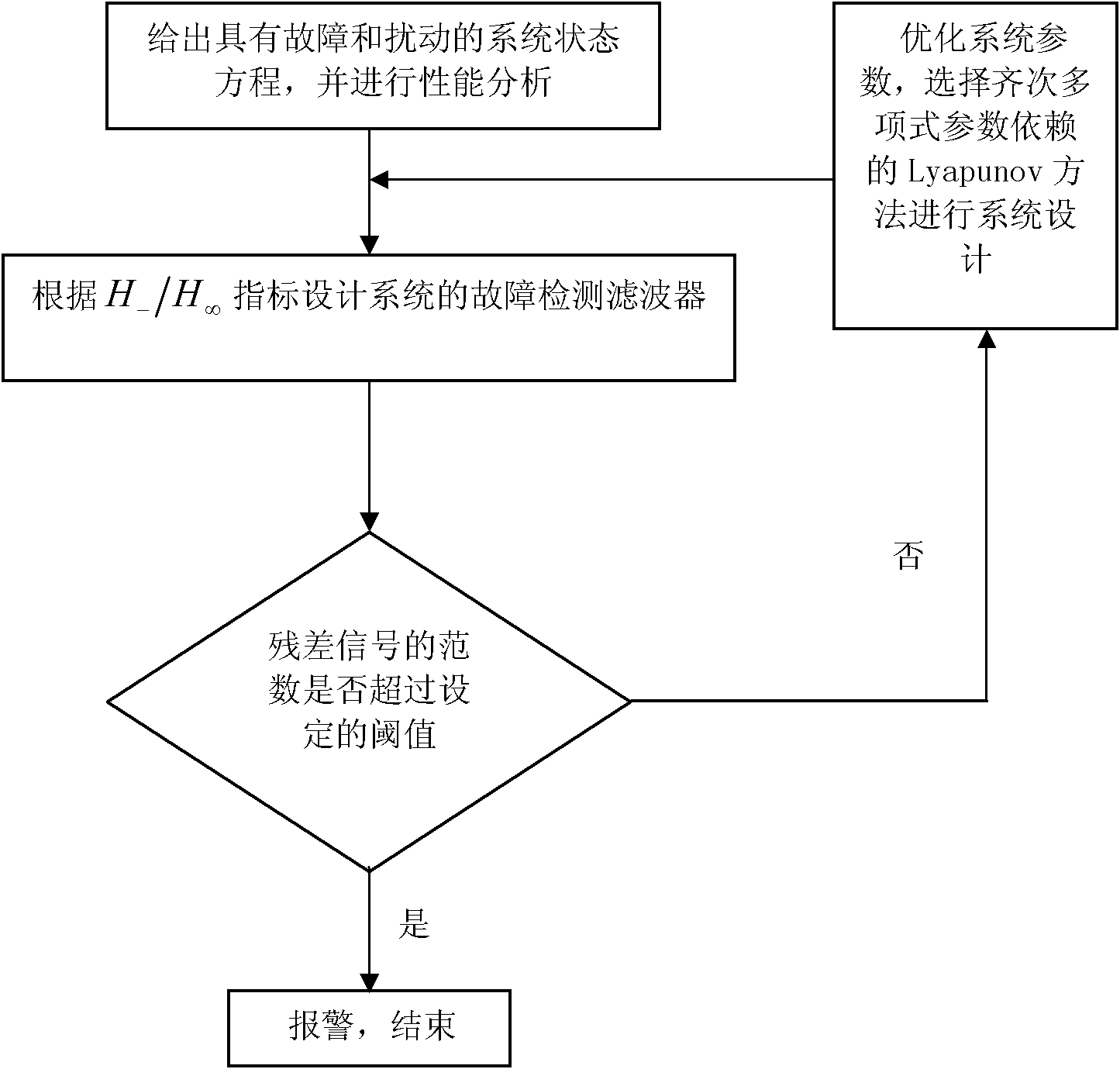
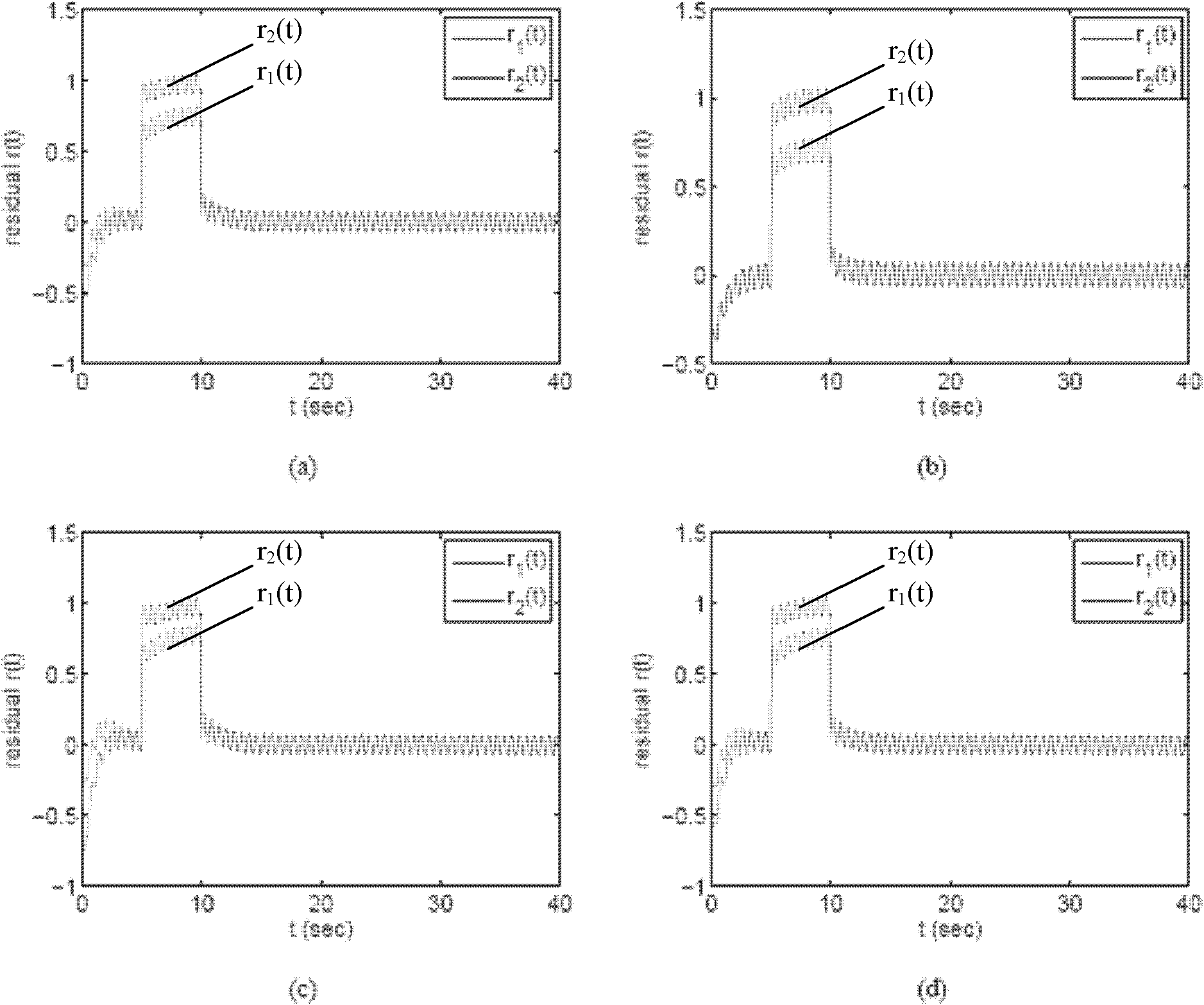
The invention belongs to the control field and provides a design method of a robustness fault detection filter of a linear uncertain system. A Lyapunov function method on which a homogeneous polynomial parameter depend is introduced into robustness fault detection of a linear time invariant system with convex polyhedron nondeterminacy. Firstly, existence of an HPPDL function used for designing an RFDF can be verified through feasibility of a linear matrix inequality; secondly, maximal fault sensitivity is obtained through solving a generalized eigenvalue problem, and an optimal RFDF is obtained. With increase of polynomial time, quantity of the linear matrix inequality and a free variable are increased, and conservation of verification is reduced substantially. The design method comprises two phases: (1) designing an optimal RFDF for a residual error generator with certain interference attenuation and largest fault sensitivity; (2) carrying out threshold design for a residual error generated by estimation. Compared with a previous analogy method, the design method in the invention has generality.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Method for monitoring the influence of ambient noise on stochastic gradient algorithms during identification of linear time-invariant systems
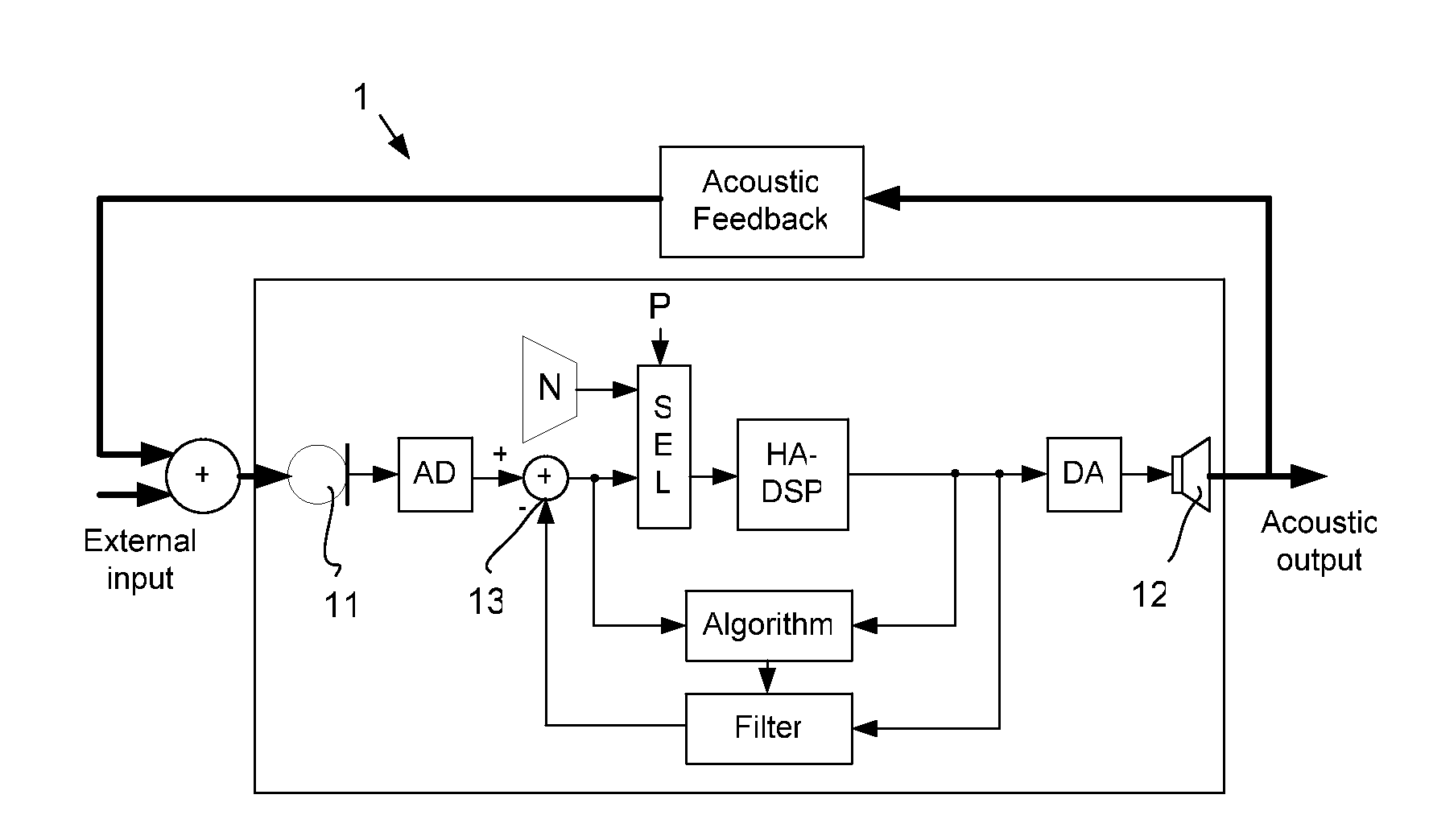
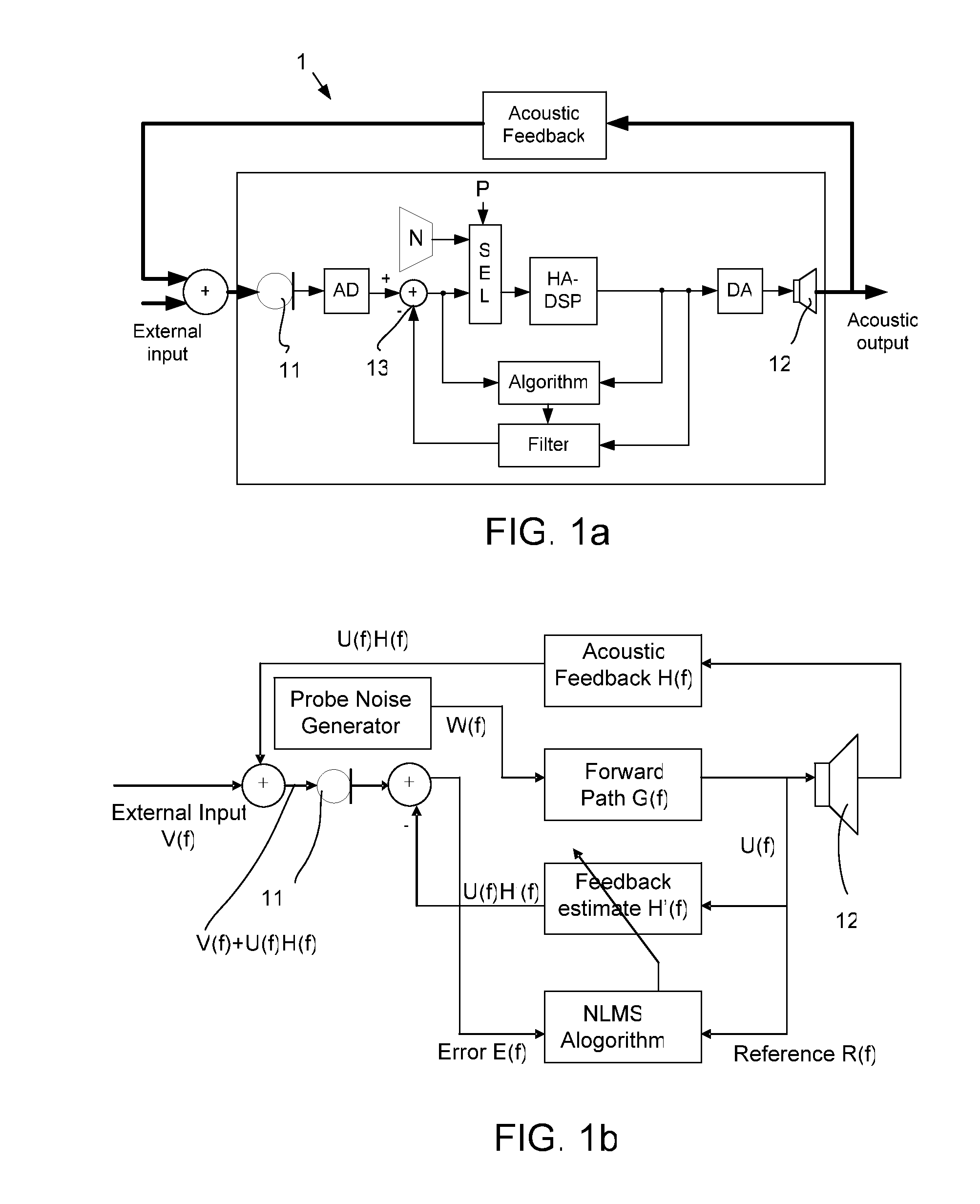
A hearing aid system and a method of estimating ambient noise in a listening device includes an input transducer and an output transducer, an electrical forward path between the input transducer and the output transducer providing a forward gain, an electrical feedback path comprising an adaptive filter for estimating the acoustic feedback gain from the output transducer to the input transducer. A method determines the quality of a critical gain measurement for a listening device. The method comprises a) monitoring the energy of the first-difference of the filter coefficients of the adaptive filter over time and b) applying a predefined threshold criterion to the change in energy content from one time instance to another to determine an acceptable impact of the ambient noise. This technique may e.g. be used for the fitting of hearing instruments where background noise is variable.
Owner:OTICON
FEXT determination system
ActiveUS7593458B2Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionSignal transfer functionEngineering
Operational data is utilized to determine the FEXT interference induced by one line into the other DSL line. FEXT interference can be calculated using the NEXT interference measured between the two lines at the upstream ends of the loops and the downstream channel transfer function of one of the loops. Because the NEXT and transfer function constitute a linear time-invariant system, as does the FEXT interference between the lines, the NEXT interference and line transfer function can be multiplied (if in linear format) or added (if in logarithmic format) to approximate the FEXT interference between the lines. The collection of data, calculations and other functions performed in these techniques may be performed by a system controller, such as a DSL optimizer. An Xlog(u,n) quantity is a decibel-magnitude representation of the insertion-loss equivalent of FEXT transfer functions and is defined as the ratio of (1) a line u's source power into a matched load of 100 Ohms when no binder is present to (2) the power at the output of the subject line when line u is excited with the same source and the binder is present. Xlin(u,n) is the linear equivalent of Xlog(u,n). The Xlog(u,n) and Xlin(u,n) quantities may be represented in specific formats that assist in their use in DSL and other systems. When defined as a line's insertion loss, Xlin (or equivalently Xlog) does not include the effect of any transmit filter.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
Method for constructing reduced-order models of systems
InactiveUS6188974B1Computing operations for integral formationAnalogue computers for electric apparatusTime delaysAlgorithm
A method comprising a computational procedure for obtaining reduced-order models of partial element equivalent circuit (PEEC) models of very large scale integrated (VLSI) interconnects. The methodology is not limited to PEEC applications, and can be used for generating reduced-order models of other systems which can be modeled with linear, time-invariant systems of ordinary differential equations with time delays.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fault detectable degree analytical method for unmanned aerial vehicle flight control system
ActiveCN106200629AProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringSingular value decompositionFault detection algorithm
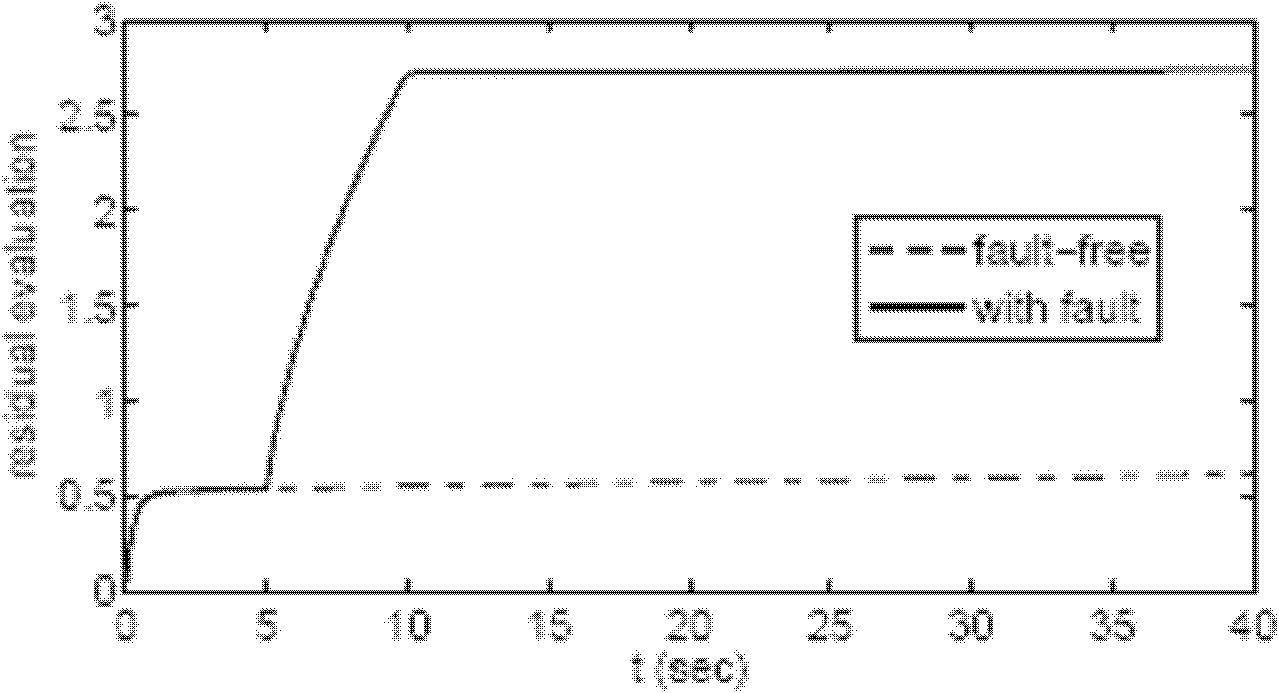
The invention relates to a fault detectable degree analytical method for an unmanned aerial vehicle flight control system. Unmanned aerial vehicle fault detection algorithm design and sensor configuration need to quantitatively analyze the difficulty level of fault detection. An unmanned aerial vehicle flight control system model is established according to an unmanned aerial vehicle closed loop nonlinearity flight control system and fault types; the flight process is segmented according to different flight states of an unmanned aerial vehicle, and small perturbation linearized models are established at all periods; faults and derivatives of the faults serve as extension states, and a dimension expansion piecewise linear time-invariant system model is established; a state observable degree index based on singular value decomposition serves as a quantitative evaluation index of fault detectable degree, according to the quantitative evaluation index, the difference of detectable degrees of the faults of the unmanned aerial vehicle in different flight states is quantitatively analyzed from the fault estimation view, and a reference basis is provided for the fault detection algorithm design and unmanned aerial vehicle sensor configuration.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Linear time-varying structure modal shape identification method
InactiveCN108416141ASolve practical engineering technical problemsBroad application prospectsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTime correlationStructural dynamics
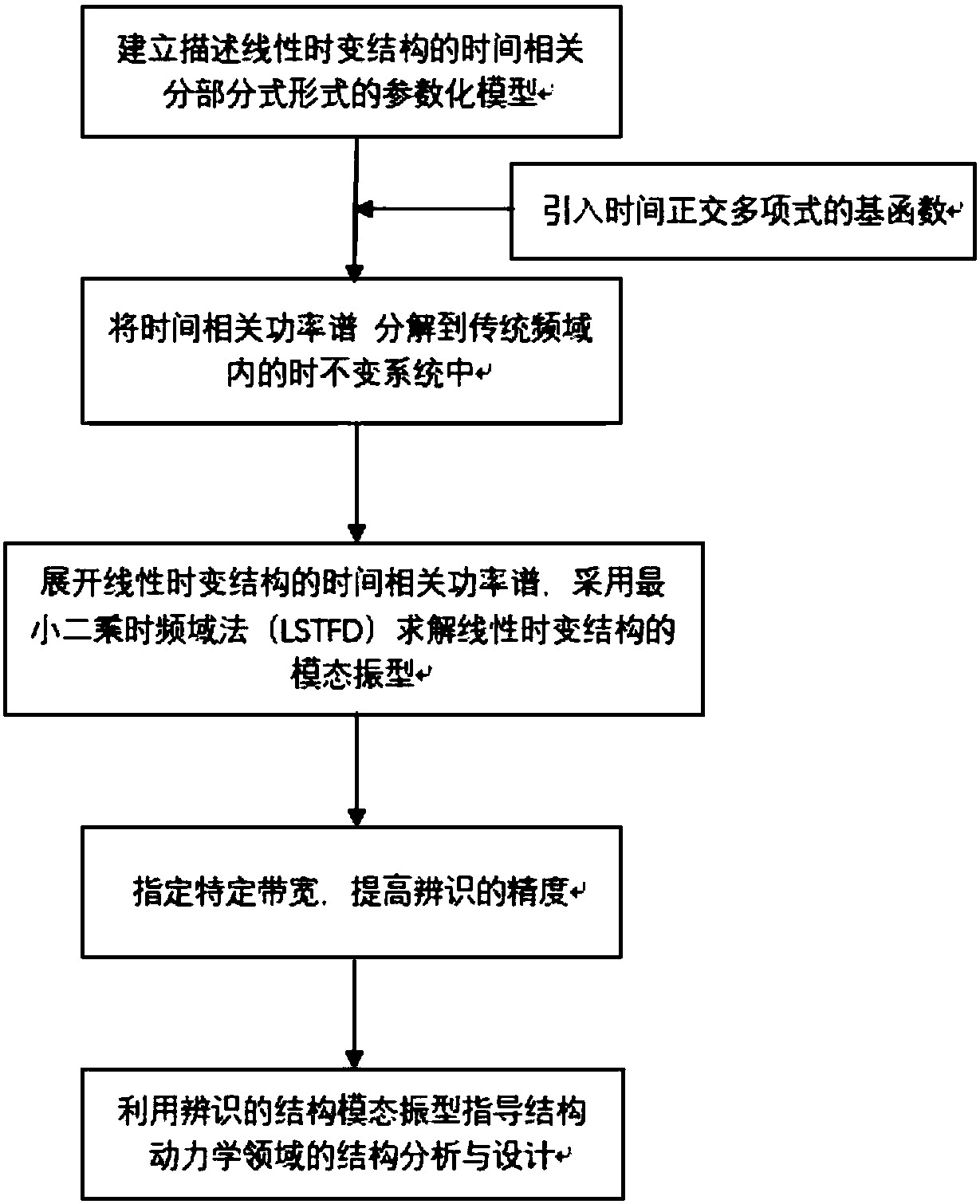
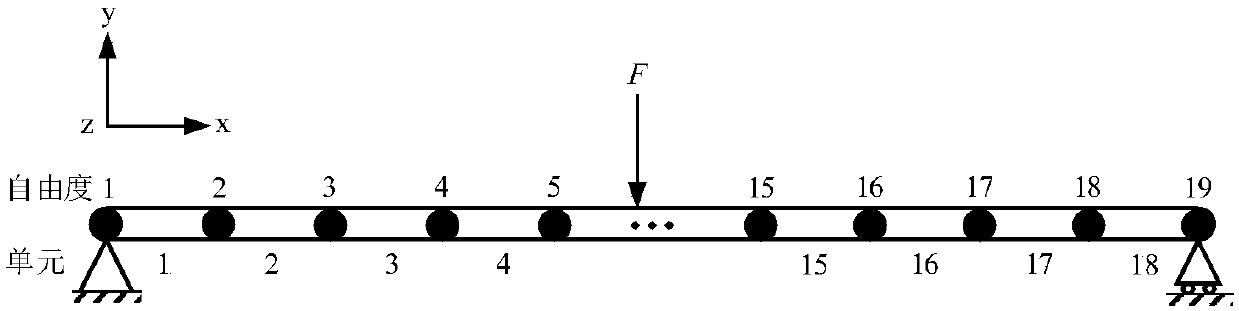
The invention discloses a linear time-varying structure modal shape identification method, and belongs to the technical field of structural dynamics. On the condition that the linear time-varying structure model frequency and model damping are known, a parameterized model describing a time correlation time division form of a linear time-varying structure is built; a time orthogonal polynomial basefunction is introduced, the parameterized model is unfolded on the basis of the base function, and a time correlation power spectrum defined in the description is decomposed in a time-invariant system in the traditional frequency domain; the linear time-varying structure-based time correlation power spectrum is unfolded, and a parameter estimation method is adopted for solving the linear time-varying structure modal shape. The technical purpose of providing the method for integrally estimating the linear time-varying structure modal shape in the whole time within the time-frequency domain isachieved; in addition, the integrity of the model shape on a time shaft is improved, the identification effect is improved by assigning a bandwidth mode, multiple experiments can be conducted, a random error is reduced by taking the average value, and the identification capacity of the low-order model shape is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
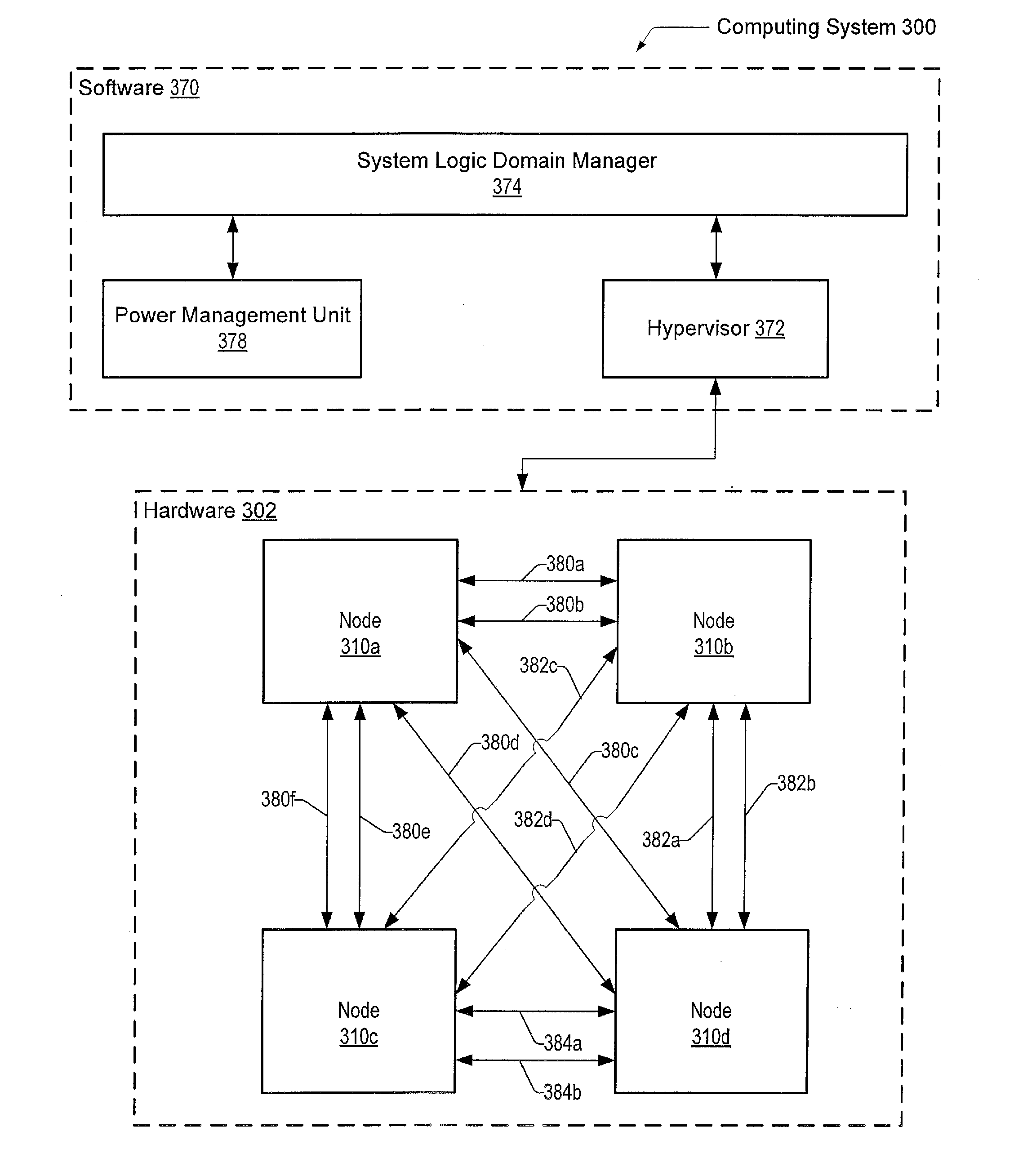
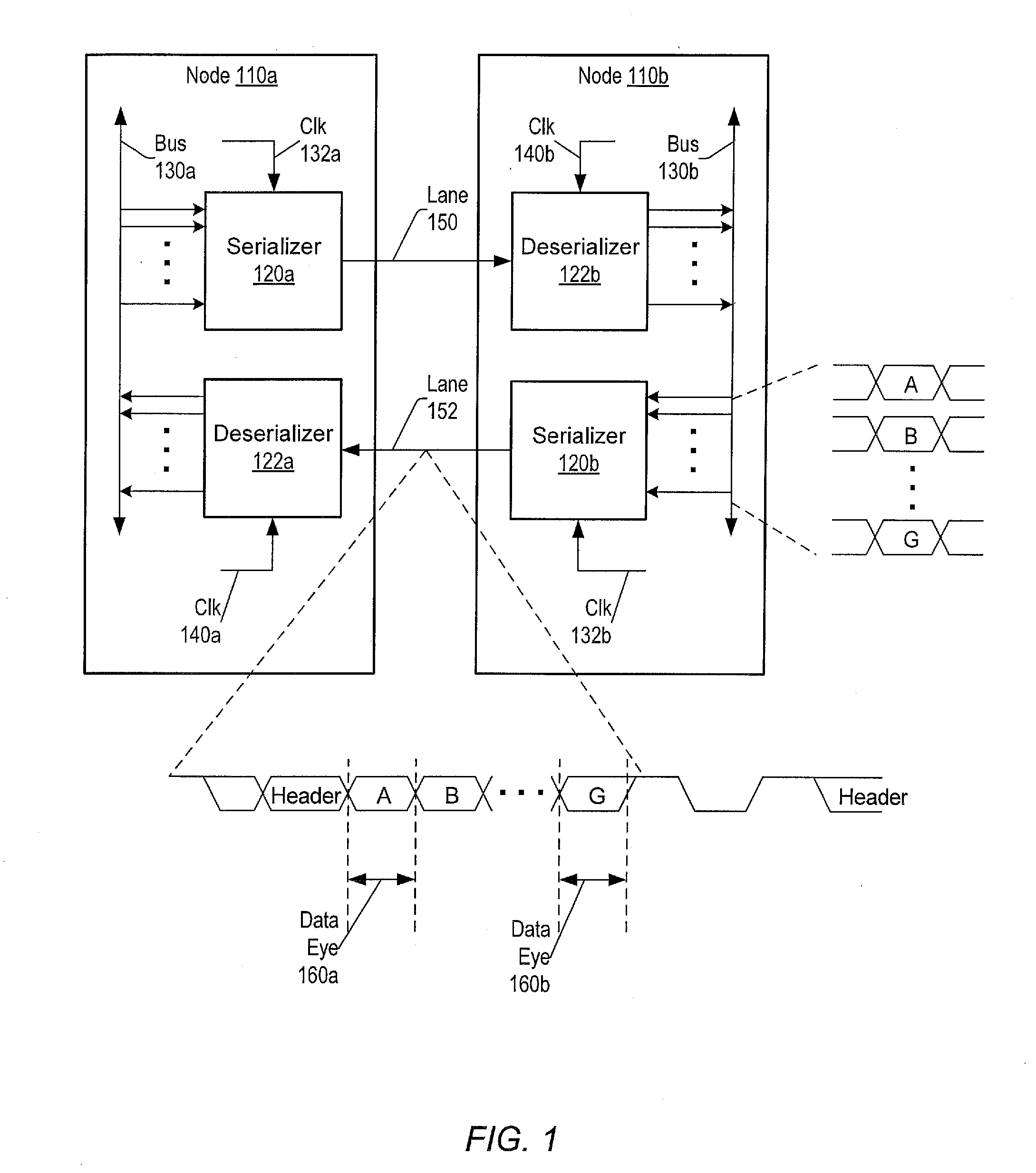
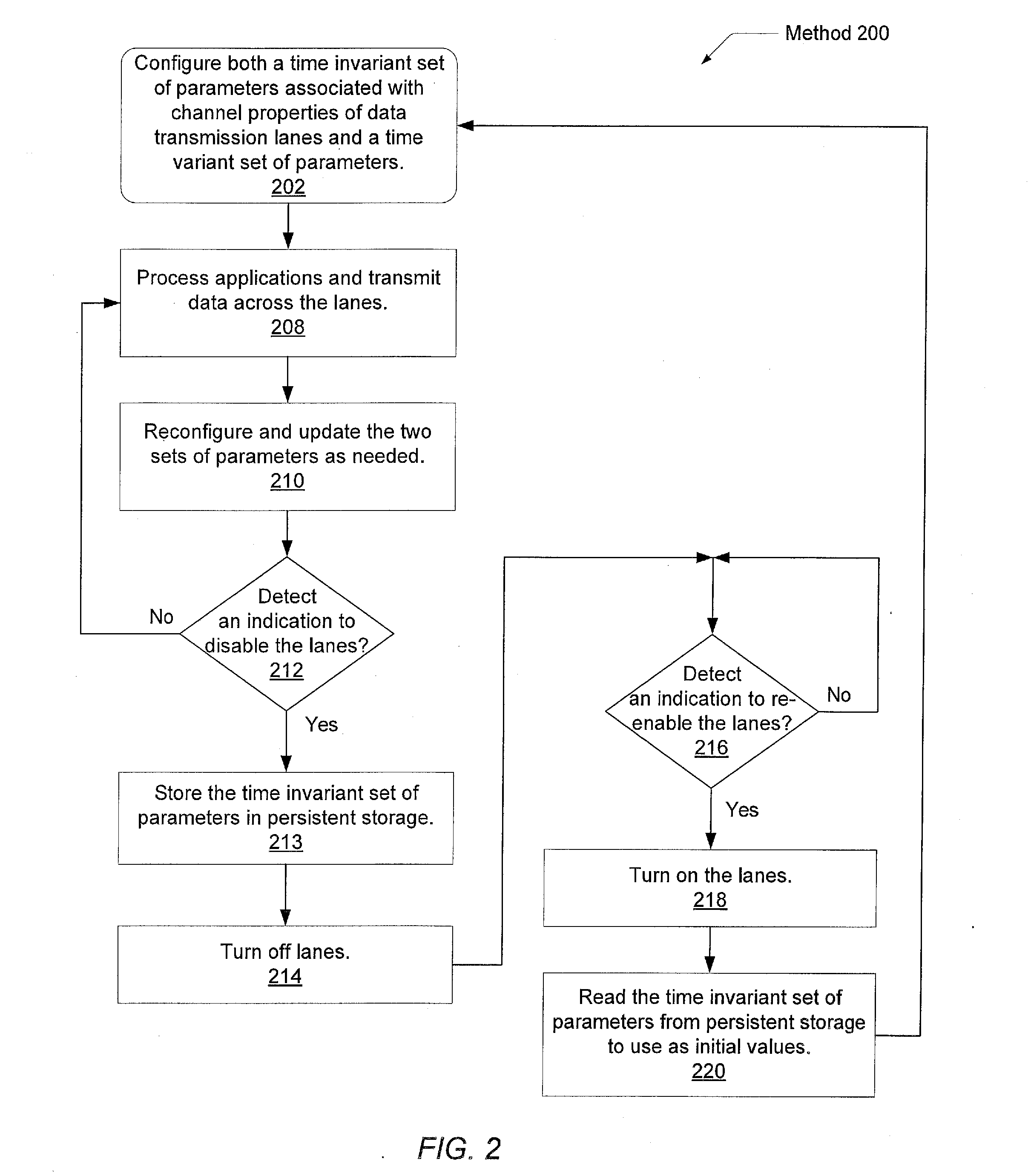
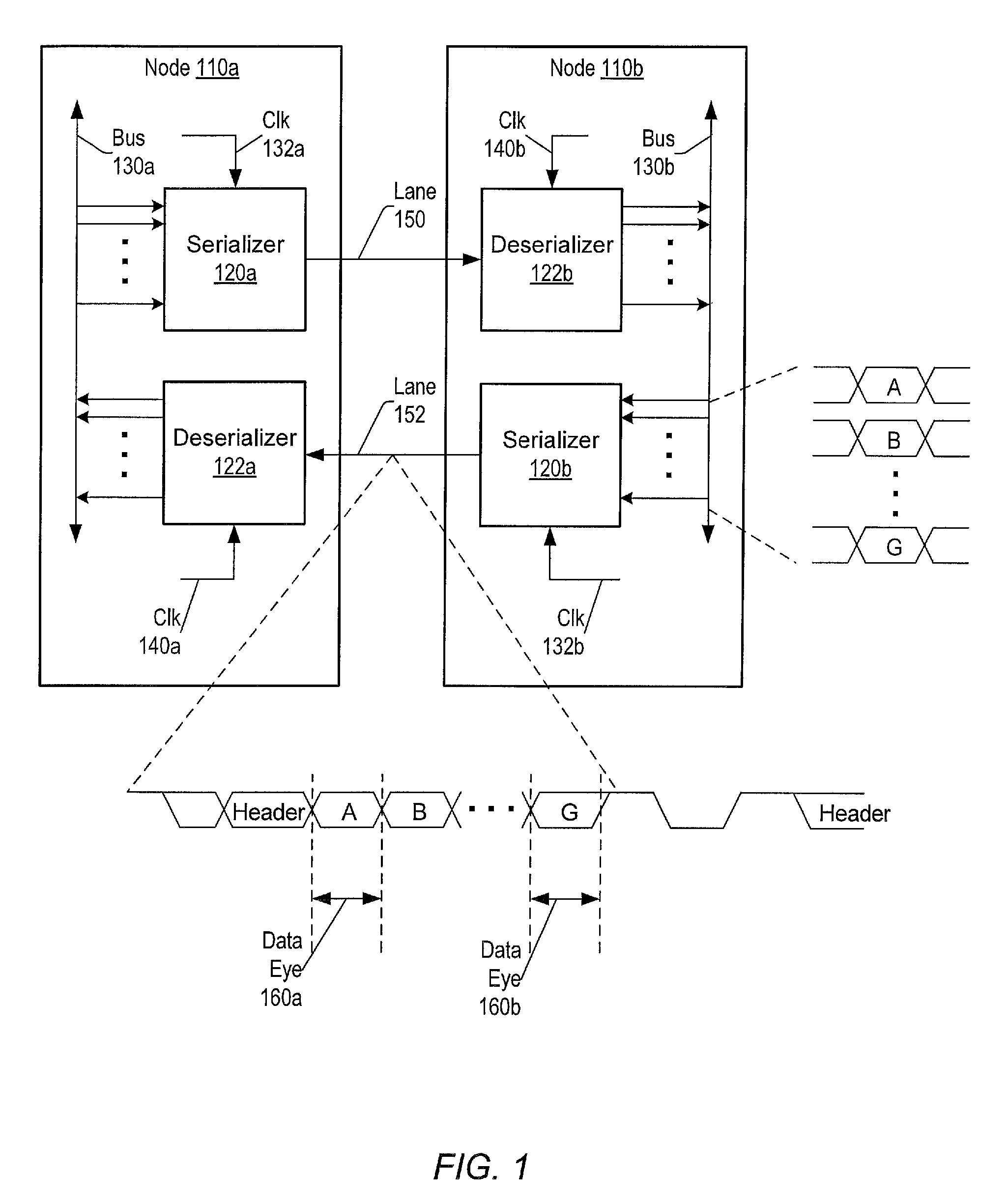
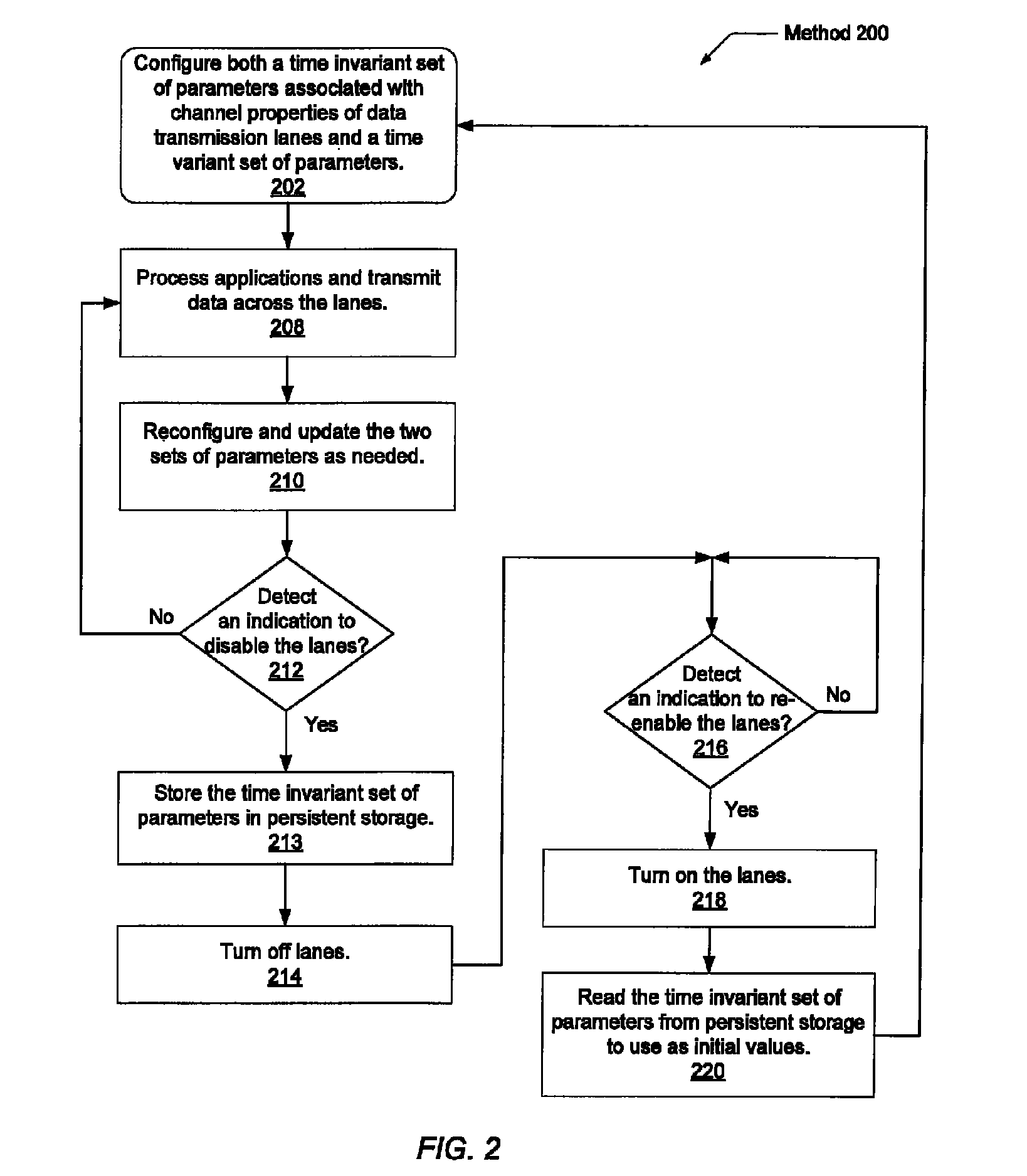
Serdes fast retrain method upon exiting power saving mode
ActiveUS20140215245A1Reduce power consumptionShorten the timeHybrid transportPower supply for data processingTime-invariant systemData transmission
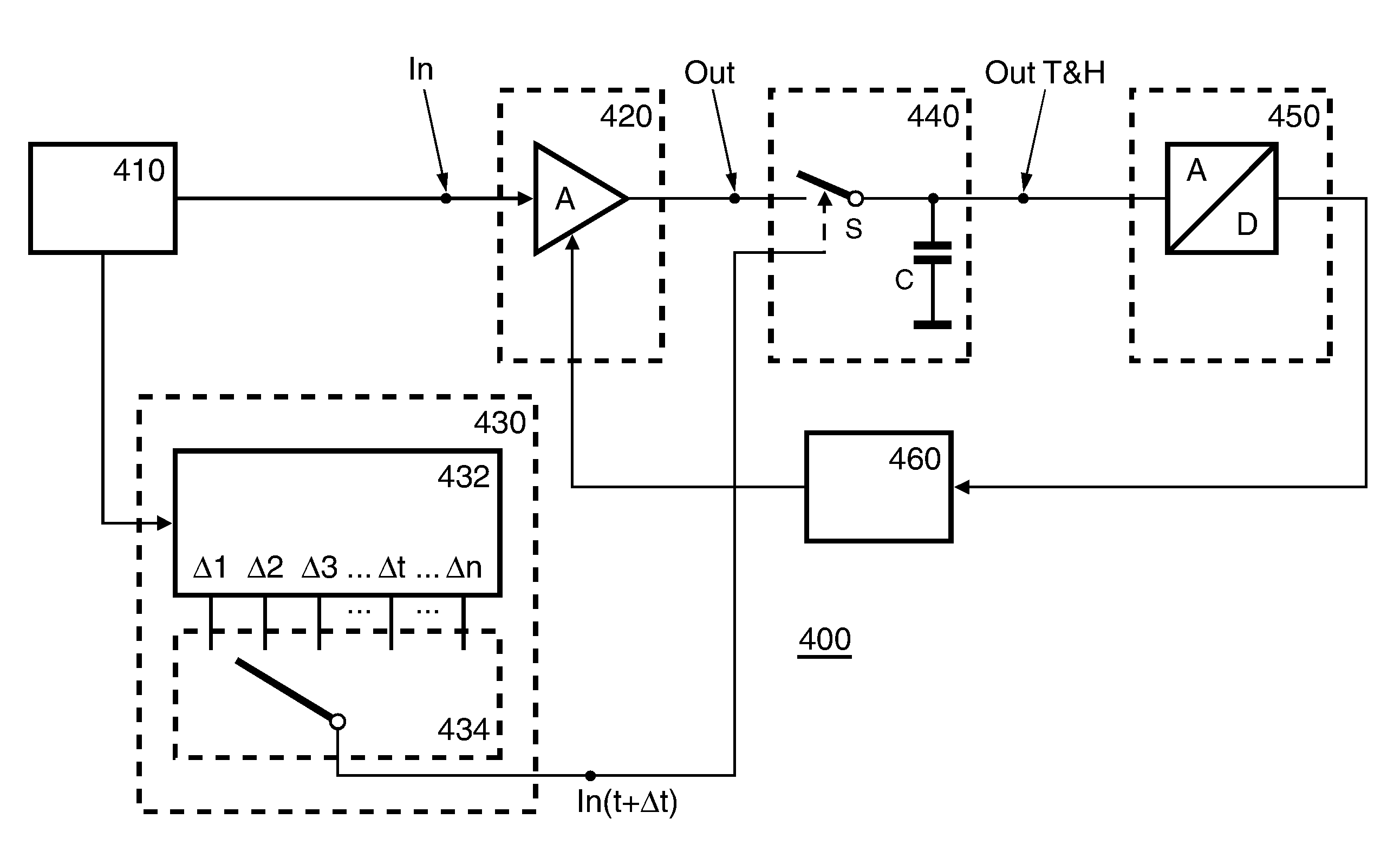
Systems and methods for reducing power consumption of systems using serialized data transmission. In a multi-node system, the reiterative steps for the setup of the lanes within links between the nodes produces both a time invariant set of parameters associated with the channel properties of the lanes and a time variant set of parameters associated with receiver clock alignment. The time invariant set is stored in persistent storage. Links may be turned on and turned off. When a link is turned on again, the stored time invariant set may be used as initial values to reconfigure both the time invariant and the time variant sets, thereby greatly reducing the delay to begin using the link again. The reduced delay may significantly speed up the wakening process for the links, thereby encouraging the use of low-power techniques that include tuning off lanes.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
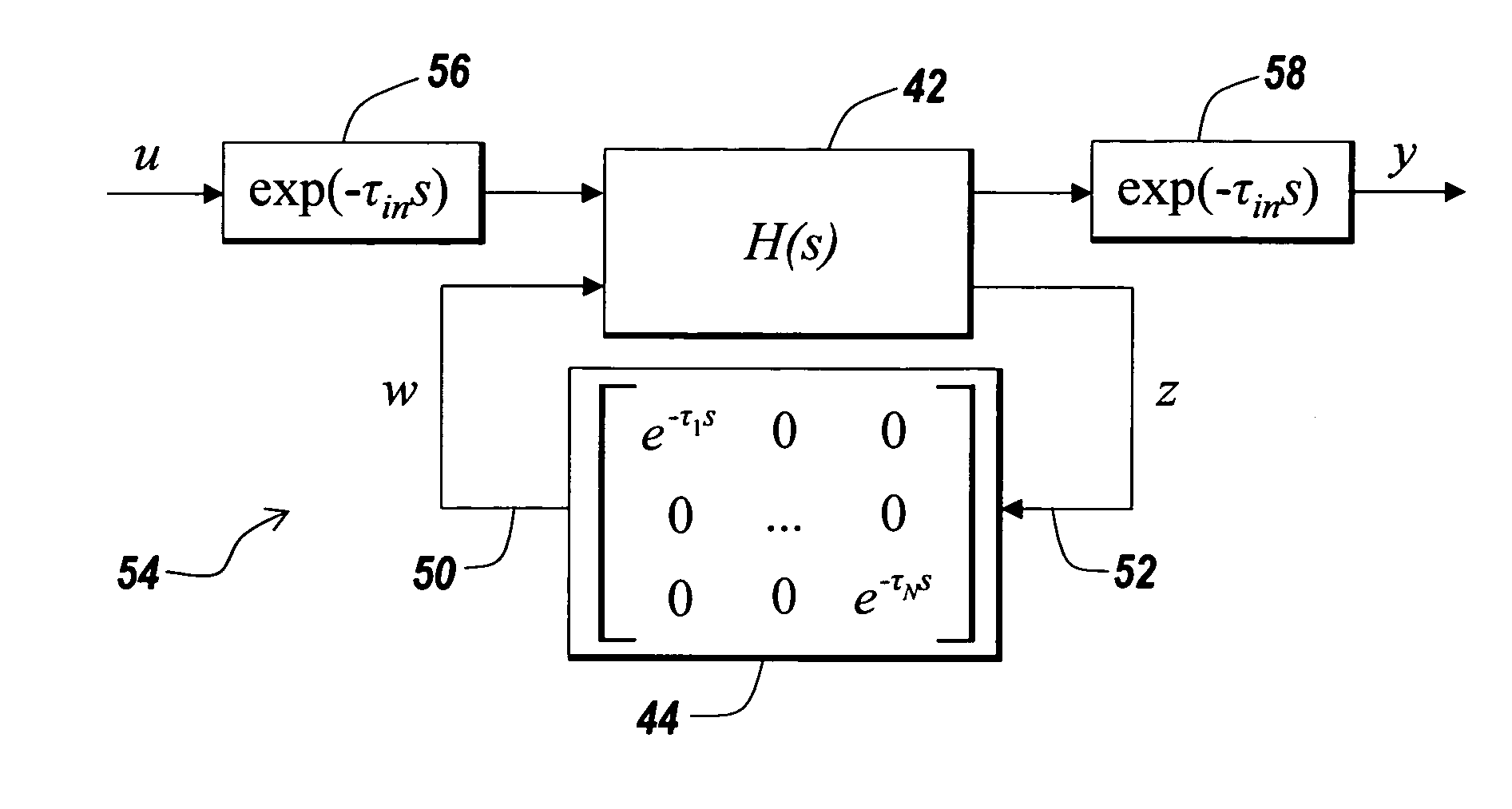
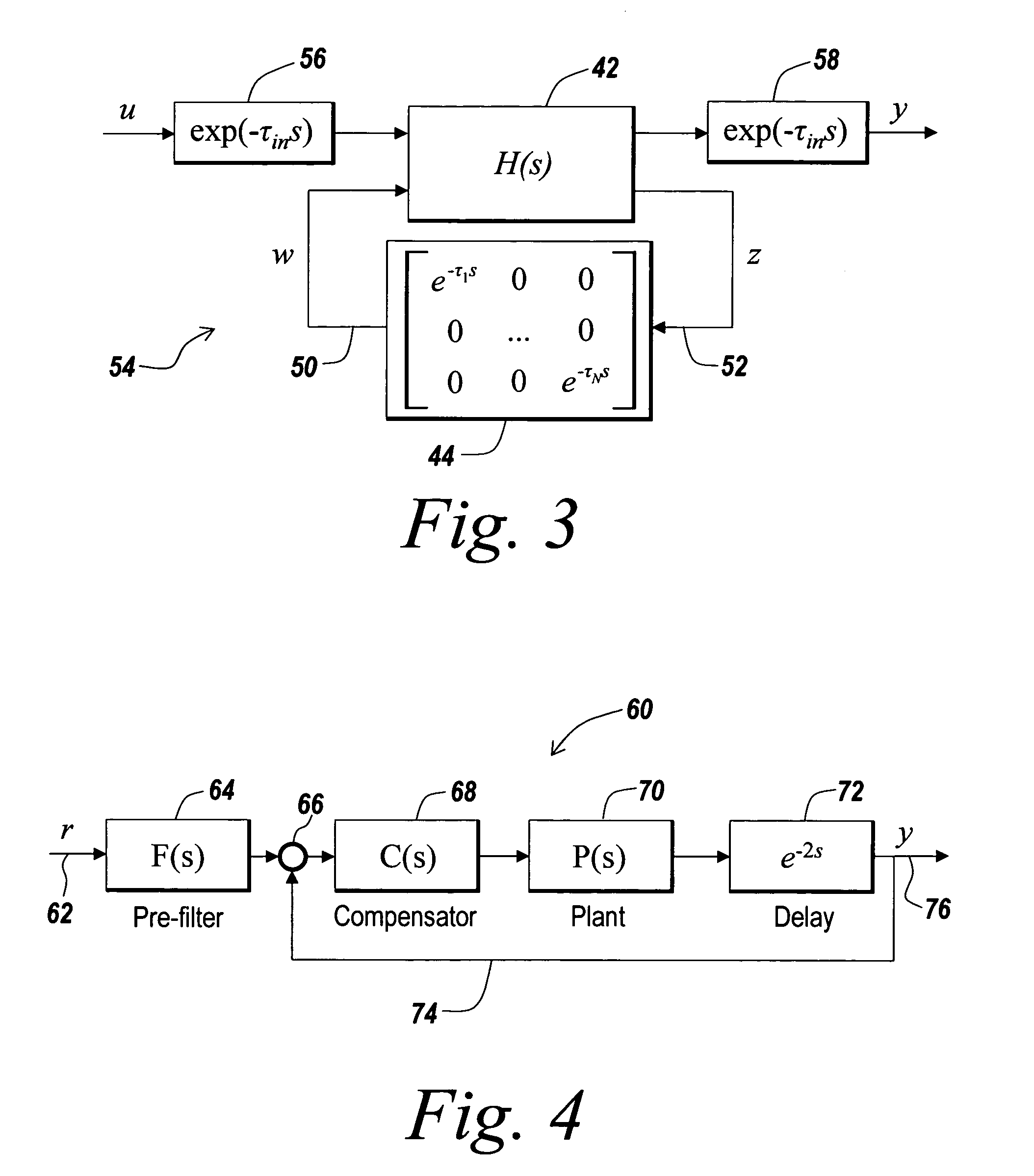
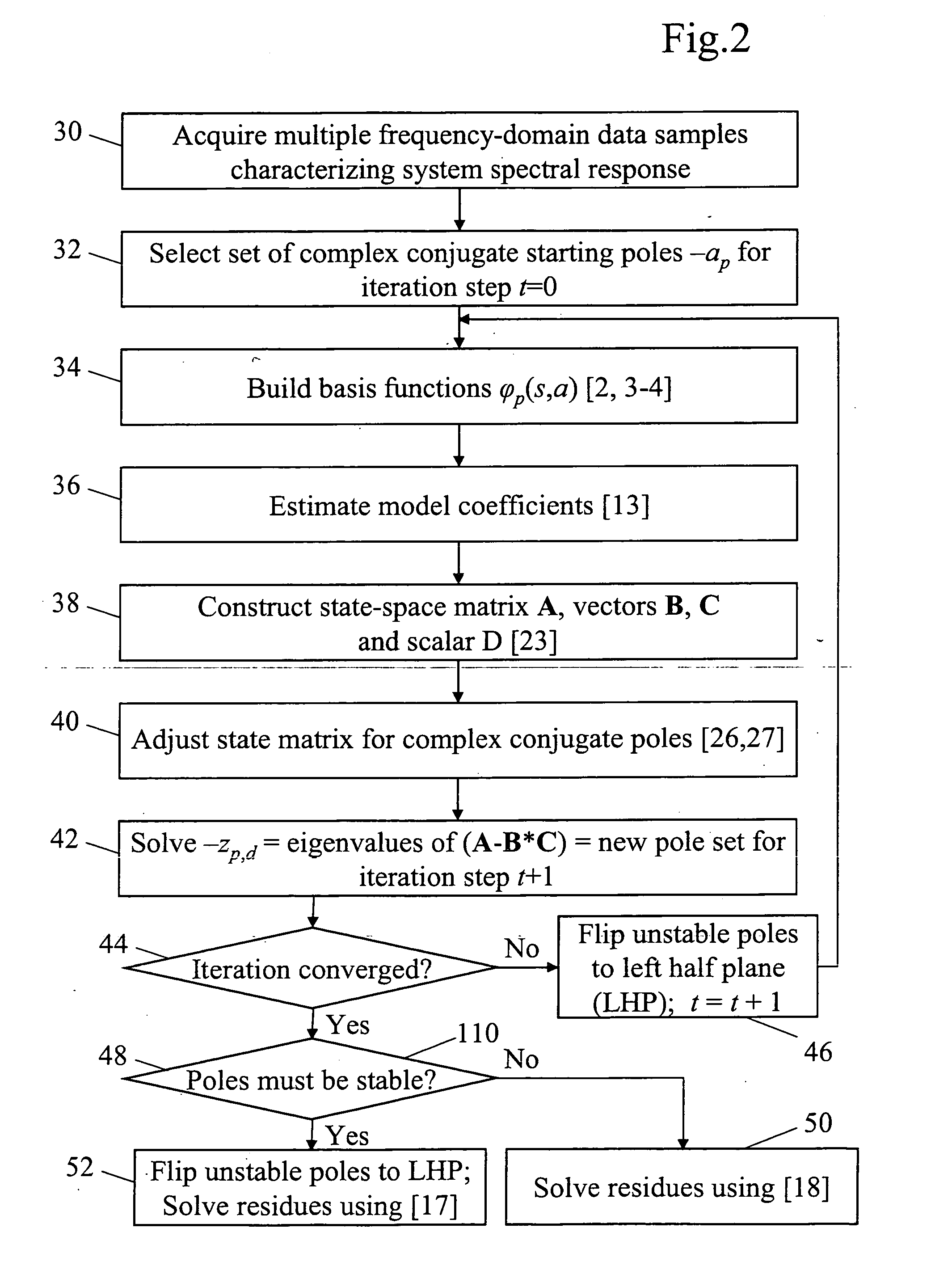
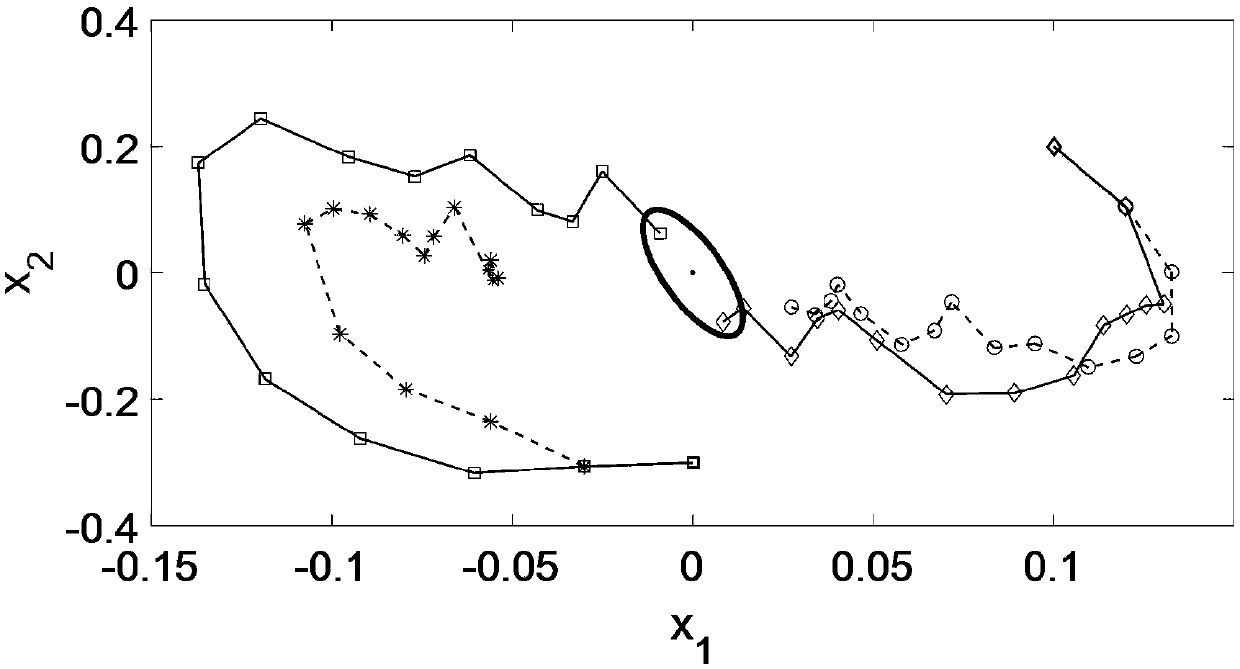
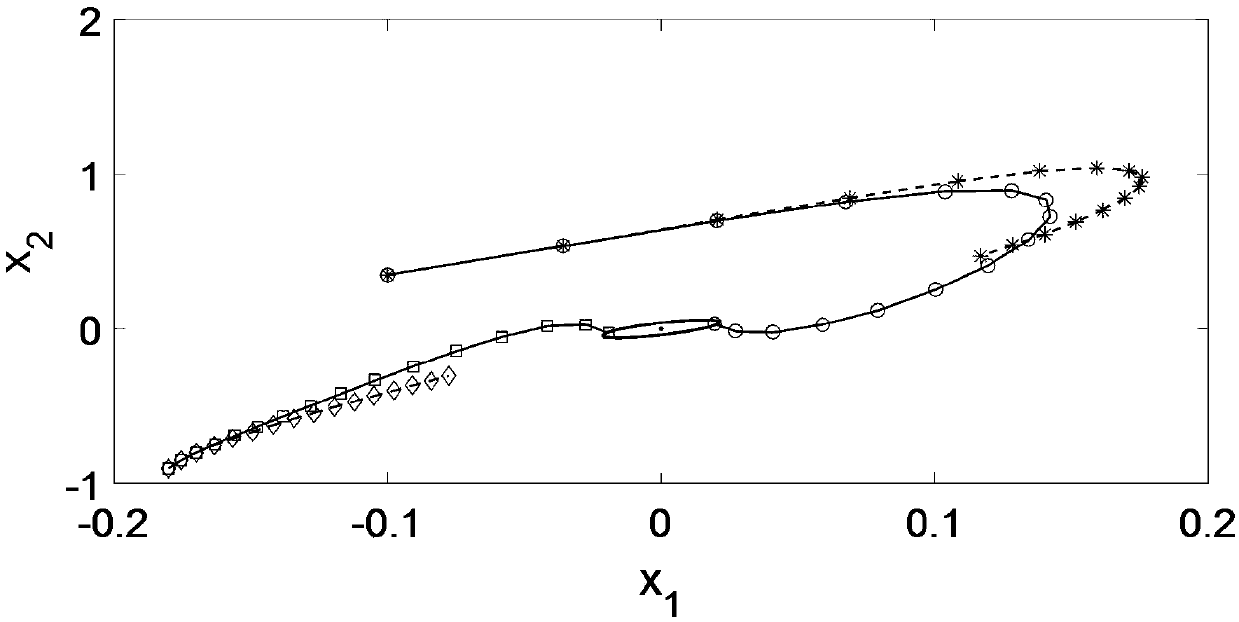
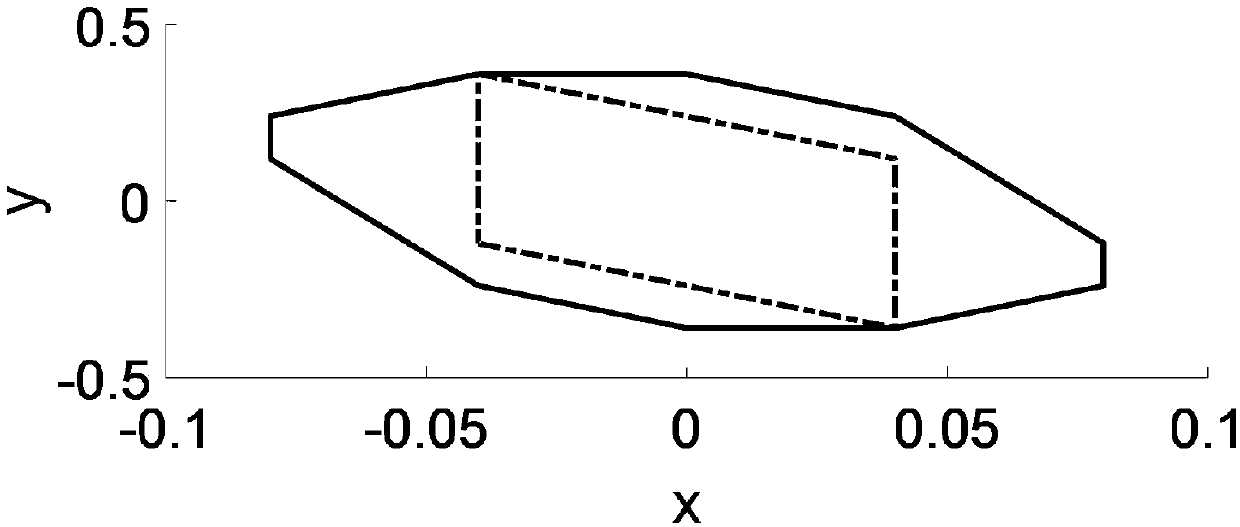
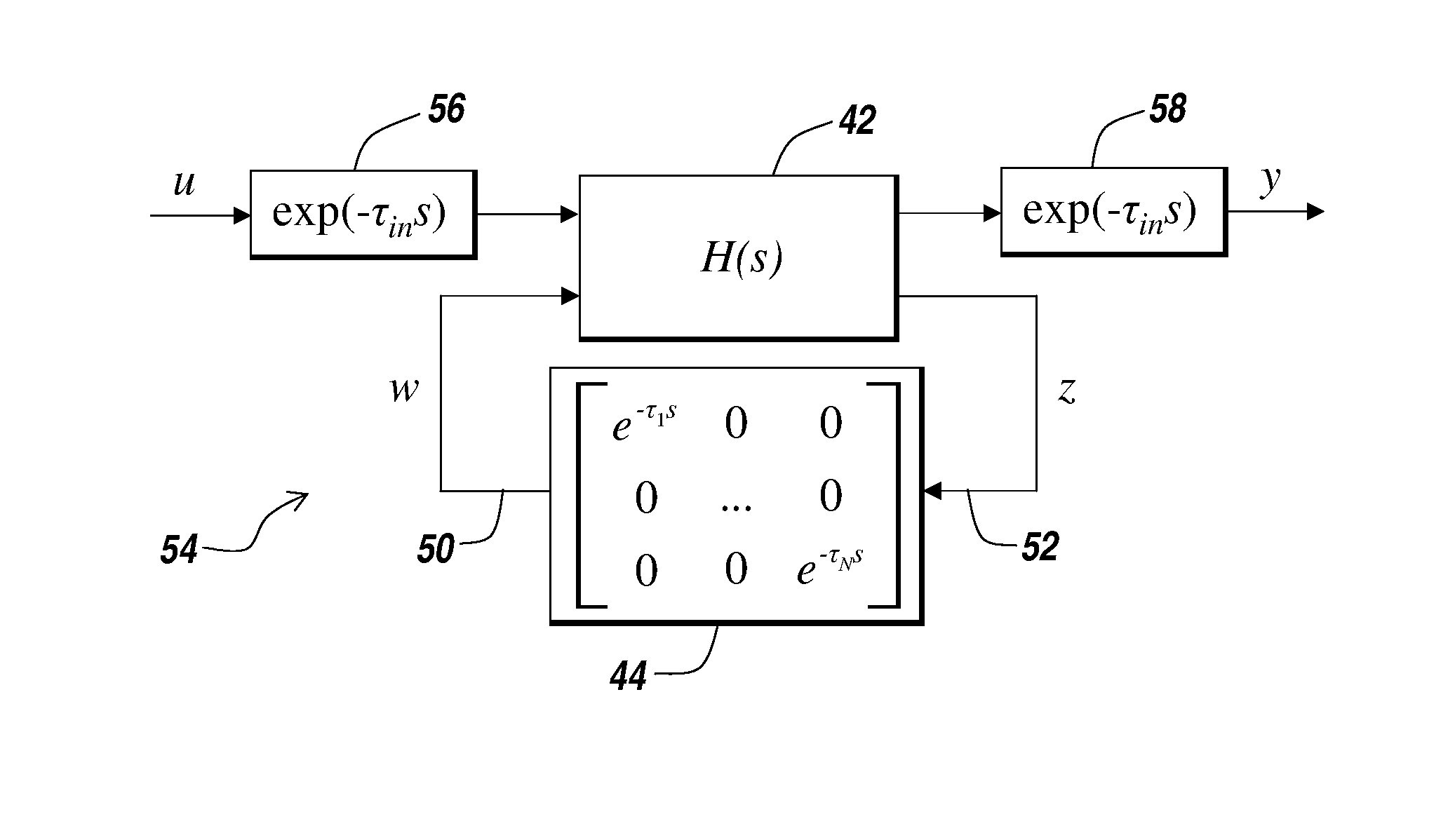
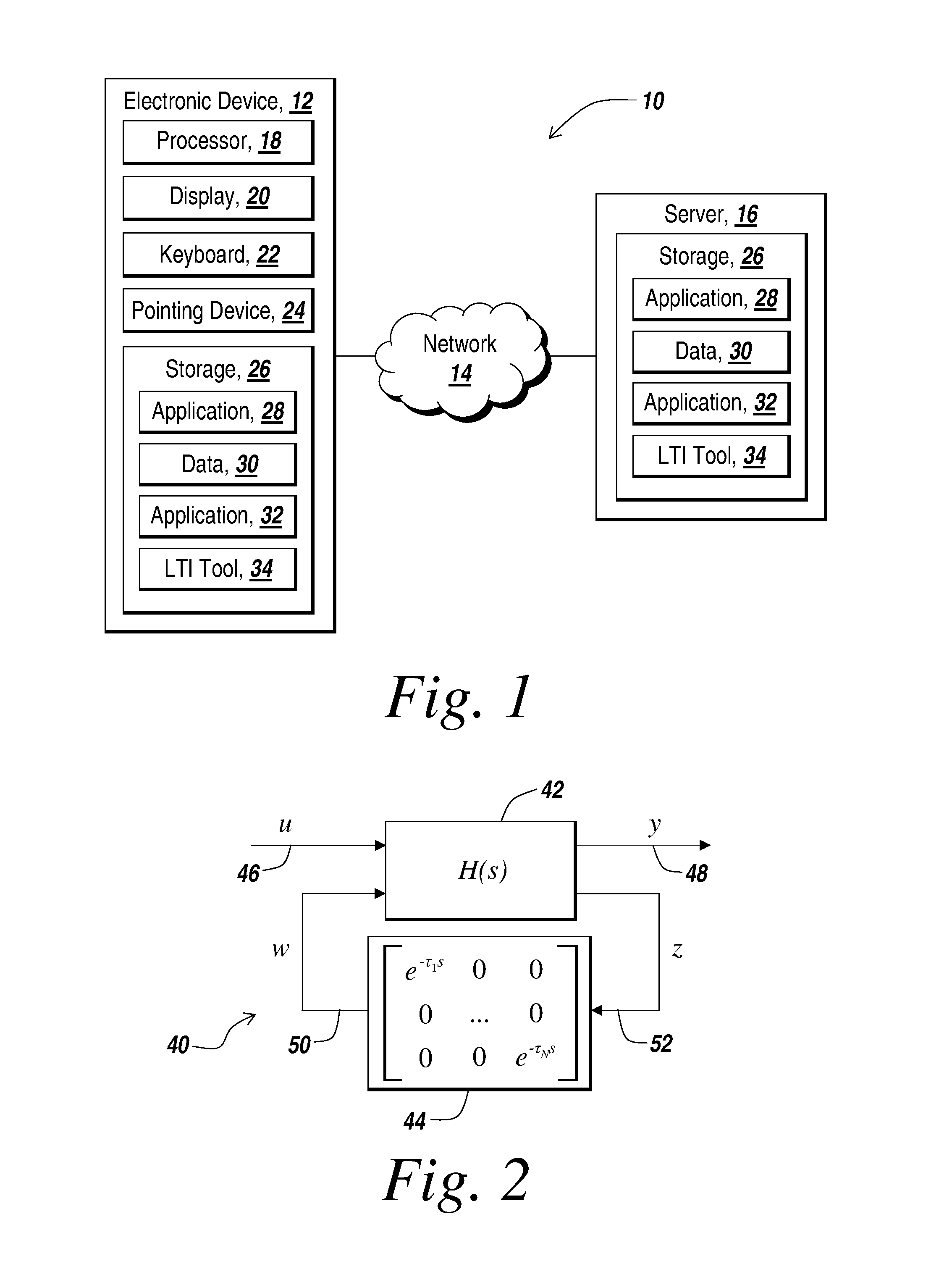
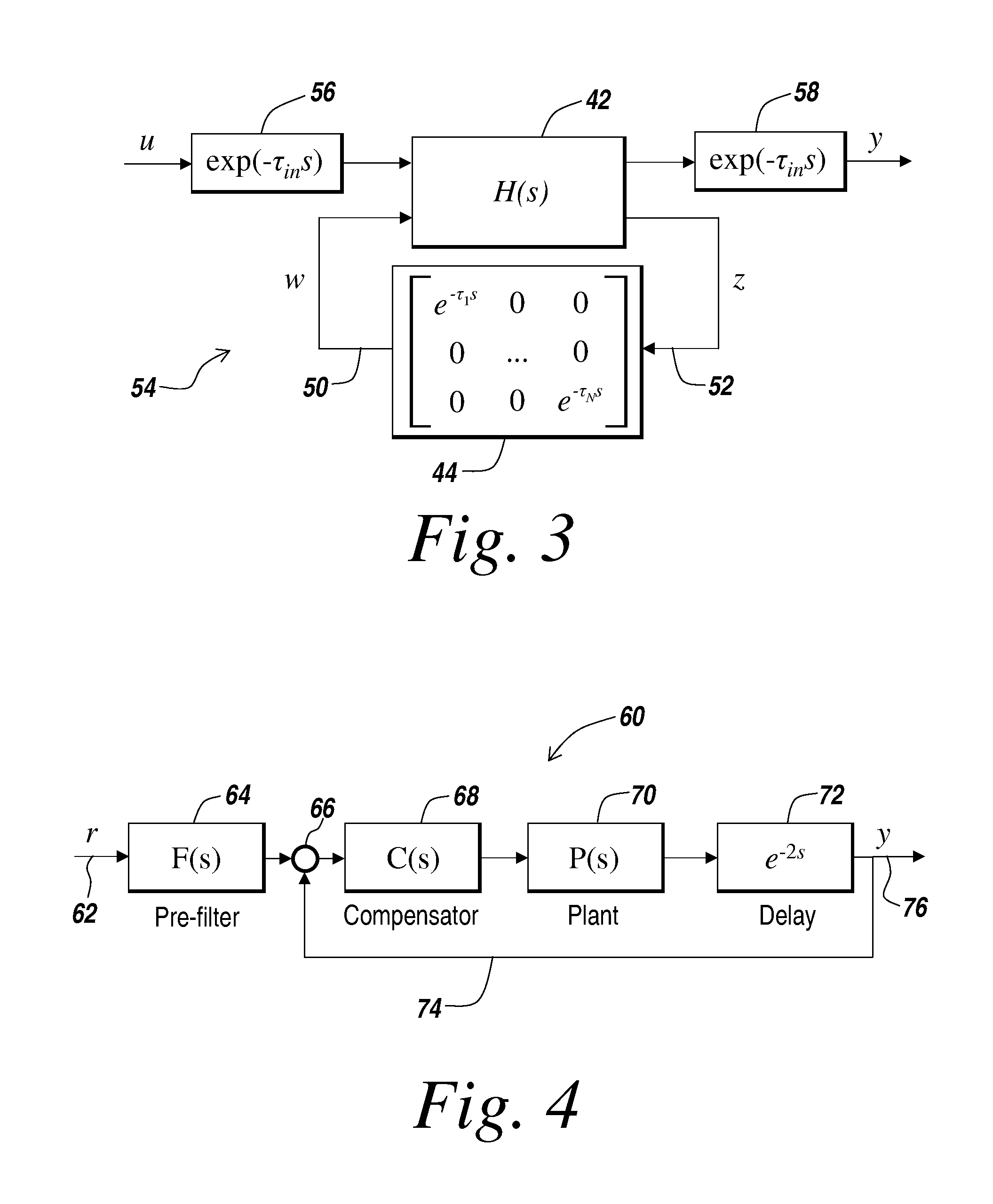
Method for modeling and analyzing linear time invariant systems with time delays
ActiveUS7647213B1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationTime delaysEngineering
A method and apparatus are provided to model, analyze, and build linear time invariant systems with delays. The method and apparatus model a linear time invariant system as a linear fractional transformation of matrices of a delay free linear time invariant model with a bank of pure delays. The method and apparatus of the present invention can further accommodate input delays and output delays associated with the linear time invariant system with delays.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Broadband transfer function synthesis using orthonormal rational bases
ActiveUS20070250559A1OptimizationEasy to convertComputation using non-denominational number representationAerodynamics improvementAlgorithmBroadband
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Generation method for self-adaptive sliding mode controller of uncertainty plane inverted pendulum system
InactiveCN105573124AImprove robustnessImprove performanceAdaptive controlHandoff controlControl system
The invention provides a generation method for a self-adaptive sliding mode controller of an uncertainty plane inverted pendulum system. The generation method comprises the steps that step 1, the sliding mode control law is generated for a linear time-invariant system with uncertainty items; and step 2, fuzzy system h<^> approximation switching control epsilonsgn(s) is adopted for the uncertainty items. The beneficial effects of the generation method are listed as follows: the self-adaptive fuzzy sliding mode controller is designed for the inverted pendulum system with the uncertainty items, the uncertainty inverted pendulum system is theoretically proved to be stable, and the designed control system is verified to be great in rapidity and robustness through simulation experiment.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
FEXT determination system
Operational data is utilized to determine the FEXT interference induced by one line into the other DSL line. FEXT interference can be calculated using the NEXT interference measured between the two lines at the upstream ends of the loops and the downstream channel transfer function of one of the loops. Because the NEXT and transfer function constitute a linear time-invariant system, as does the FEXT interference between the lines, the NEXT interference and line transfer function can be multiplied (if in linear format) or added (if in logarithmic format) to approximate the FEXT interference between the lines. The collection of data, calculations and other functions performed in these techniques may be performed by a system controller, such as a DSL optimizer. An Xlog(u,n) quantity is a decibel-magnitude representation of the insertionloss equivalent of FEXT transfer functions and is defined as the ratio of (1) a line u's source power into a matched load of 100 Ohms when no binder is present to (2) the power at the output of the subject line when line u is excited with the same source and the binder is present. Xlin(u, n) is the linear equivalent of Xlog(u, n). The Xlog(u, n) and Xlin(u,n) quantities may be represented in specific formats that assist in their use in DSL and other systems. When defined as a line's insertion loss, Xlin (or equivalently Xlog) does not include the effect of any transmit filter.
Owner:ADAPTIVE SPECTRUM & SIGNAL
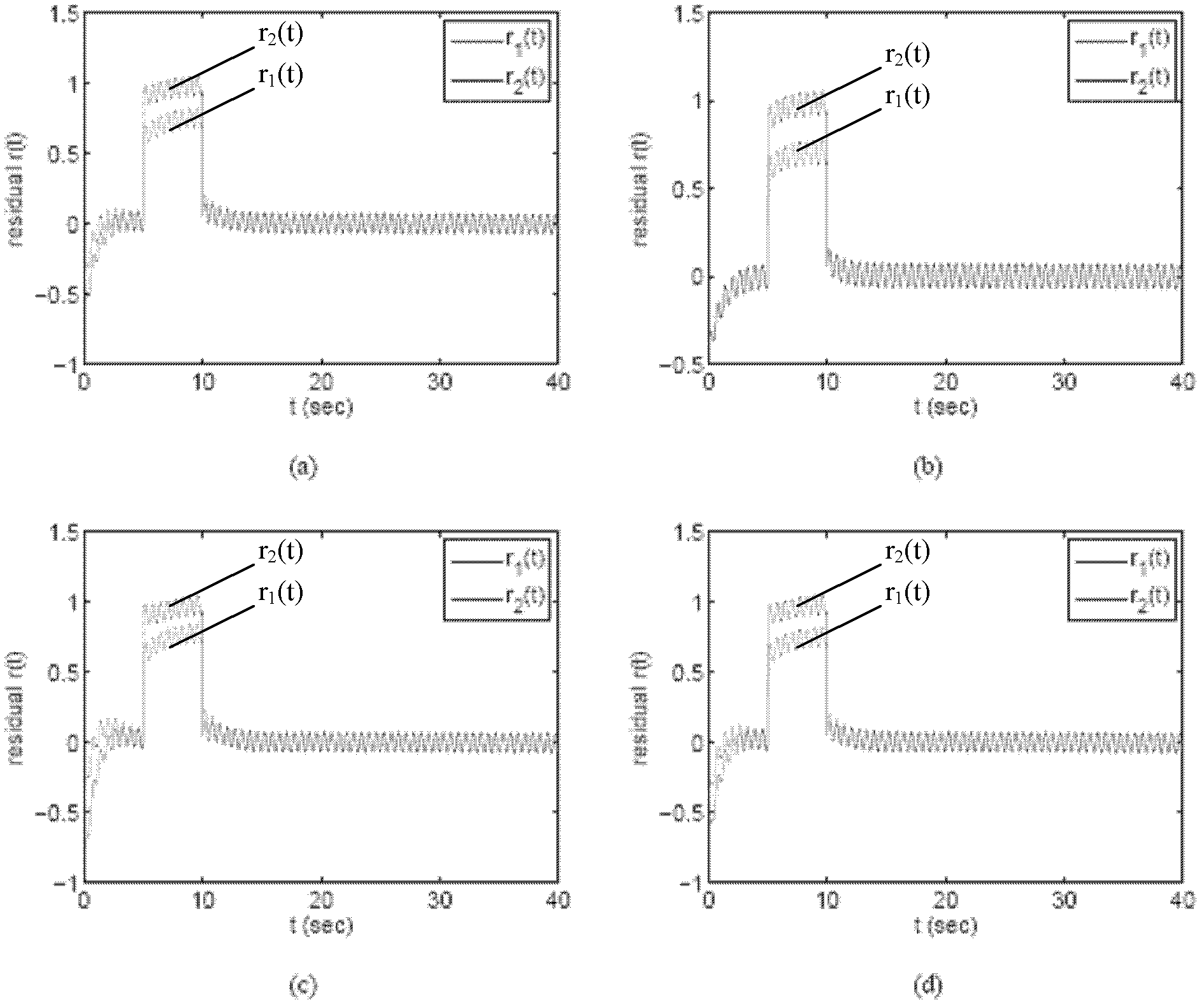
Design method for robust fault detection filter (RFDF)
InactiveCN102436180AReduce conservatismImprove fault detection rateTesting/monitoring control systemsAdaptive controlUltrasound attenuationRobust analysis
The invention belongs to the field of control, and provides a design method for a robust fault detection filter (RFDF) on the basis of a parameter-dependent Liapunov function method. A PDLF method is introduced into robust fault detection of a linear time-constant system with convex polyhedron non-determinacy. During processing of the RFDF design, the problem is distinguishing faults and other interference, which is remarkably different from robust analysis and control. An H_ / H infinite normal form is adopted, which comprises two phases: (1) an optimal RFDF design method of a residual error generator with certain interference attenuation and maximum fault sensitivity, and (2) a method for designing a threshold value for a residual error generated by estimation.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
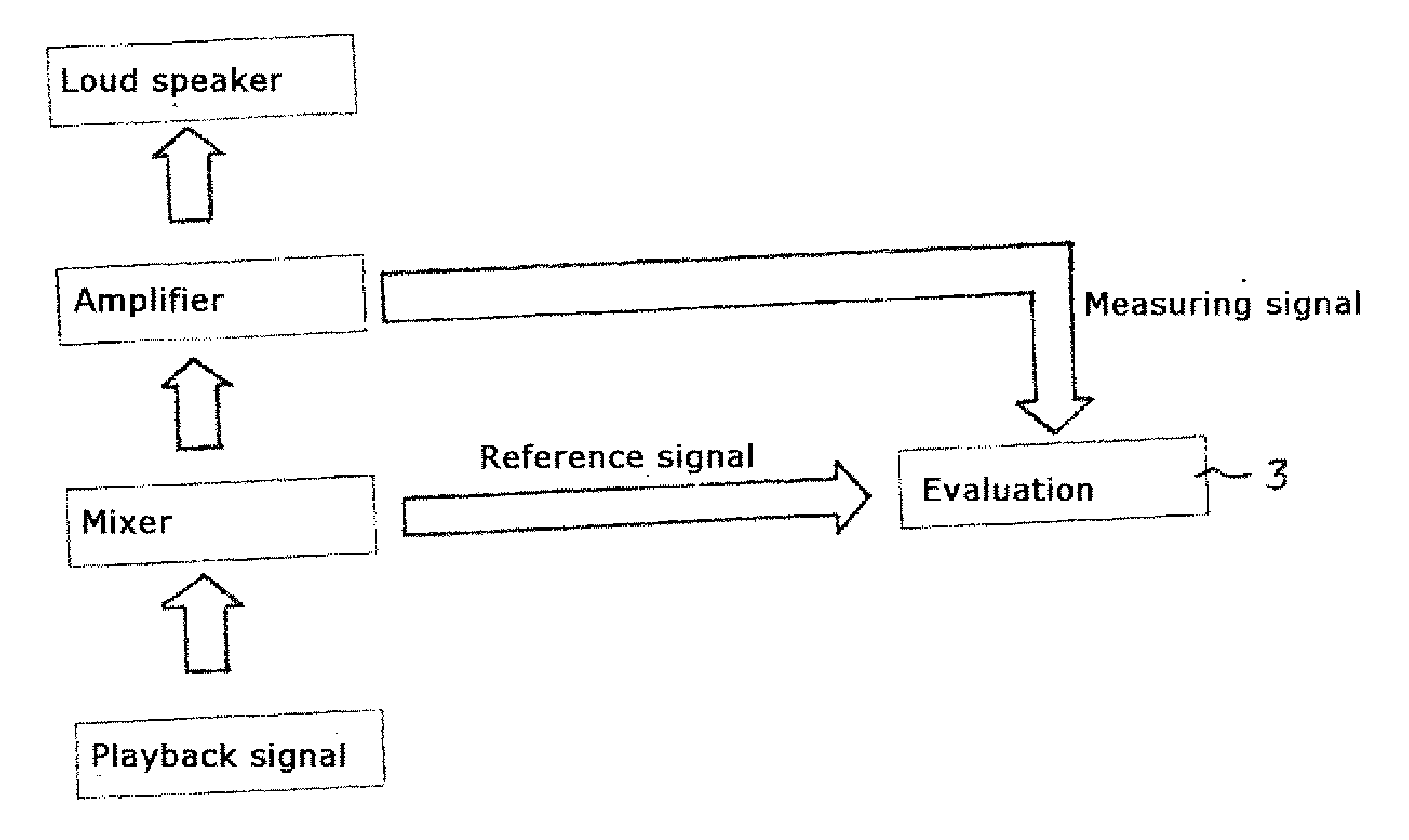
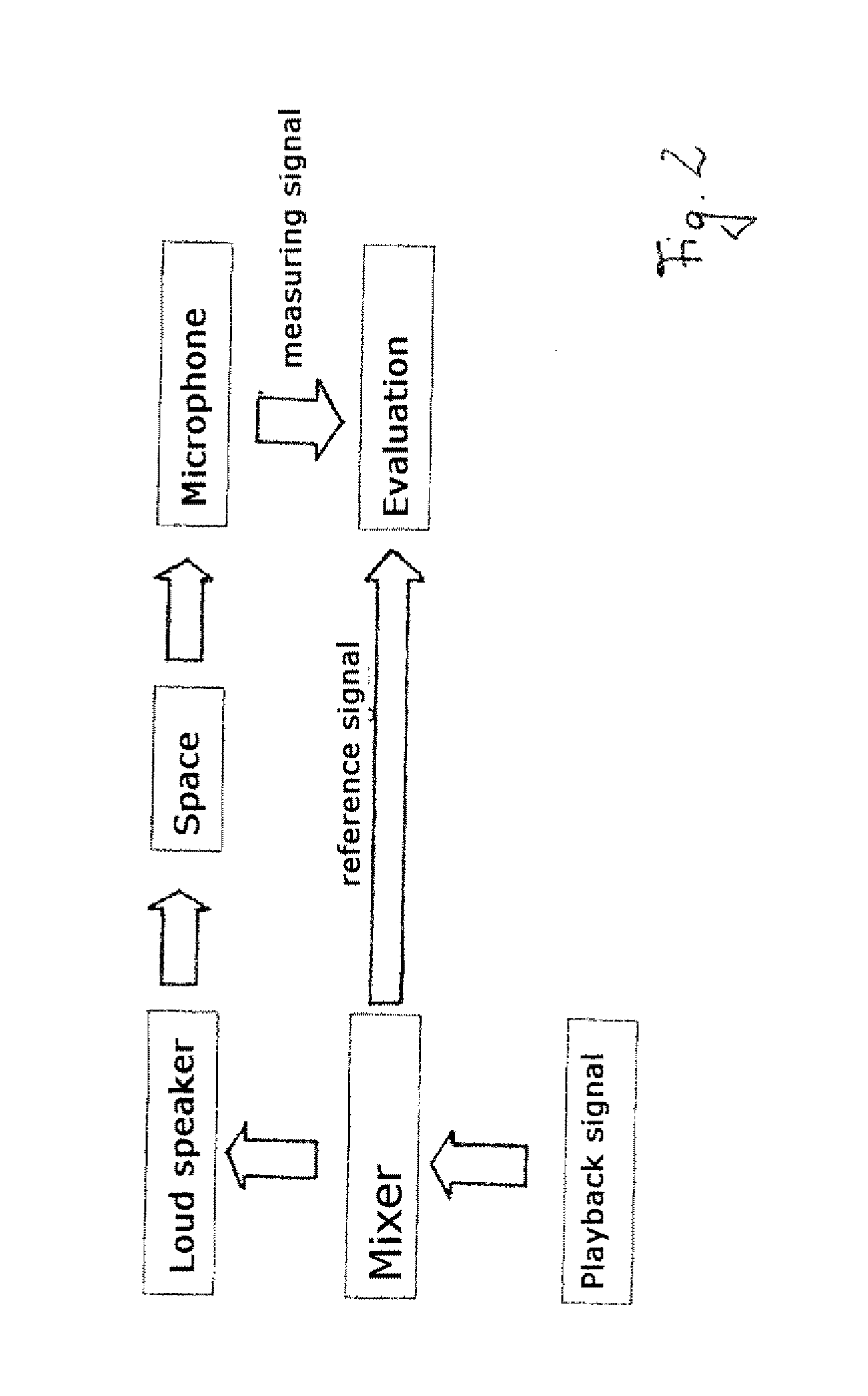
Method for Determining an Averaged Frequency-Dependent Transmission Function for a Disturbed Linear Time-Invariant System, Evaluation Device and Computer Program Product
InactiveUS20120143553A1Minimize measurement uncertaintyEasy to useElectrical measurementsTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesTime-invariant systemDeconvolution
The invention relates to a process for determining an averaged frequency-dependent transfer function for a perturbed linear time-invariant system by means of an evaluation device, wherein the process comprises providing frequency-dependent reference signals derived from excitations input in a linear time-invariant system, providing frequency-dependent measuring signals for the linear time-invariant system associated with the frequency-dependent reference signals, and determining an averaged frequency-dependent transfer function for the linear time-invariant system, in that, using signal deconvolution of mutually associated measuring and reference signals, frequency-dependent transfer functions are determined and the frequency-dependent transfer functions are averaged, and wherein during determination of the averaged frequency-dependent transfer function at least a part of the determined frequency-dependent transfer functions is included in the averaging corresponding to a respectively associated frequency-dependent weighting. Furthermore the invention comprises an evaluation device for determining an averaged frequency-dependent transfer function for a perturbed linear time-invariant system and a computer program product.
Owner:SDA SOFTWARE DESIGN AHNERT
Micro-positioning platform based on piezoelectric ceramic driving and modeling and control method thereof
PendingCN111142404AFew unknown parametersReduce the difficulty of selectionSimulator controlDynamic modelsControl manner
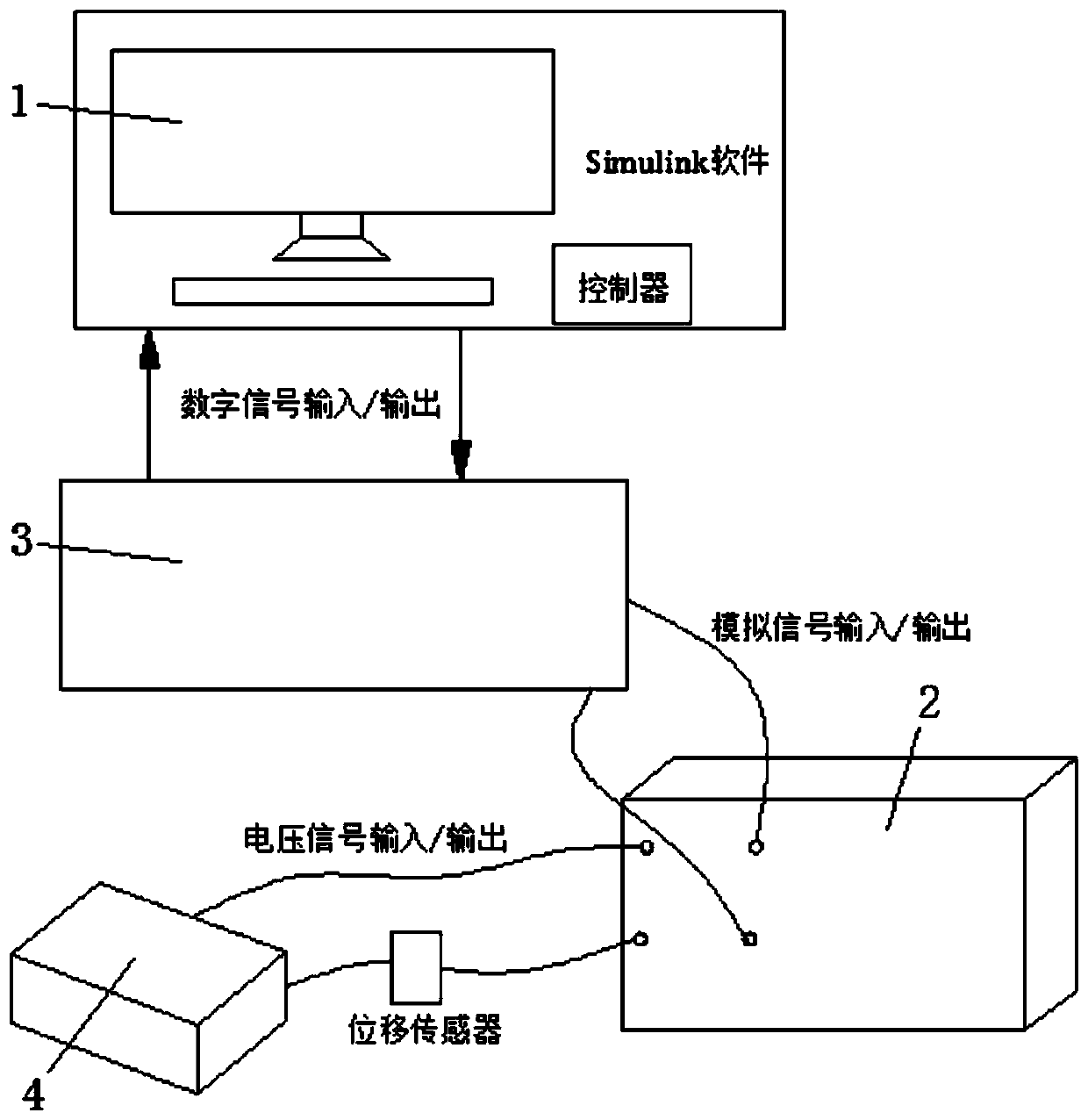
The invention belongs to the technical field of micro-positioning platforms. The invention discloses a micro-positioning platform based on piezoelectric ceramic driving and a modeling and control method thereof. The micro-positioning platform comprises a hardware part and a software part, the software part comprises Simulink software loaded in an industrial personal computer, and communication connection between the industrial personal computer and a data collection card is realized based on the software part to form closed-loop deviation control; the modeling method adopts a Hammerstein modelas a modeling basis, and comprises a static nonlinear part and a linear dynamic part: constructing a static nonlinear function based on a Boc-Wen model, and identifying unknown parameters of the model by adopting a particle swarm algorithm; a linear dynamic model is constructed, the model is equivalent to a linear second-order time-invariant system, and a Matlab recognition toolbox is adopted inthe model to obtain parameters; according to the control method, a composite control mode of feedforward control and feedback control is adopted; in conclusion, the high-precision positioning device has a high-precision positioning effect.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
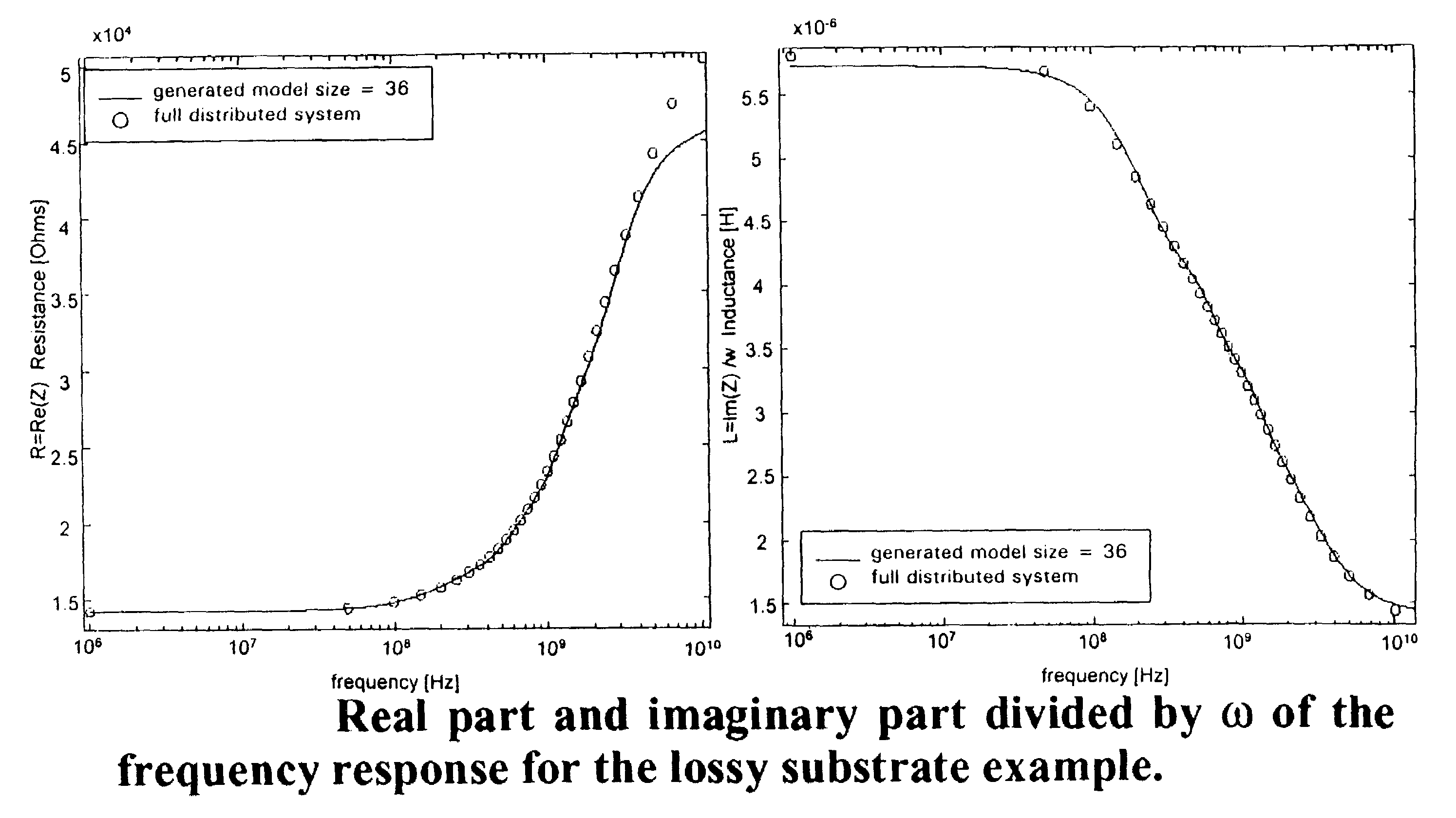
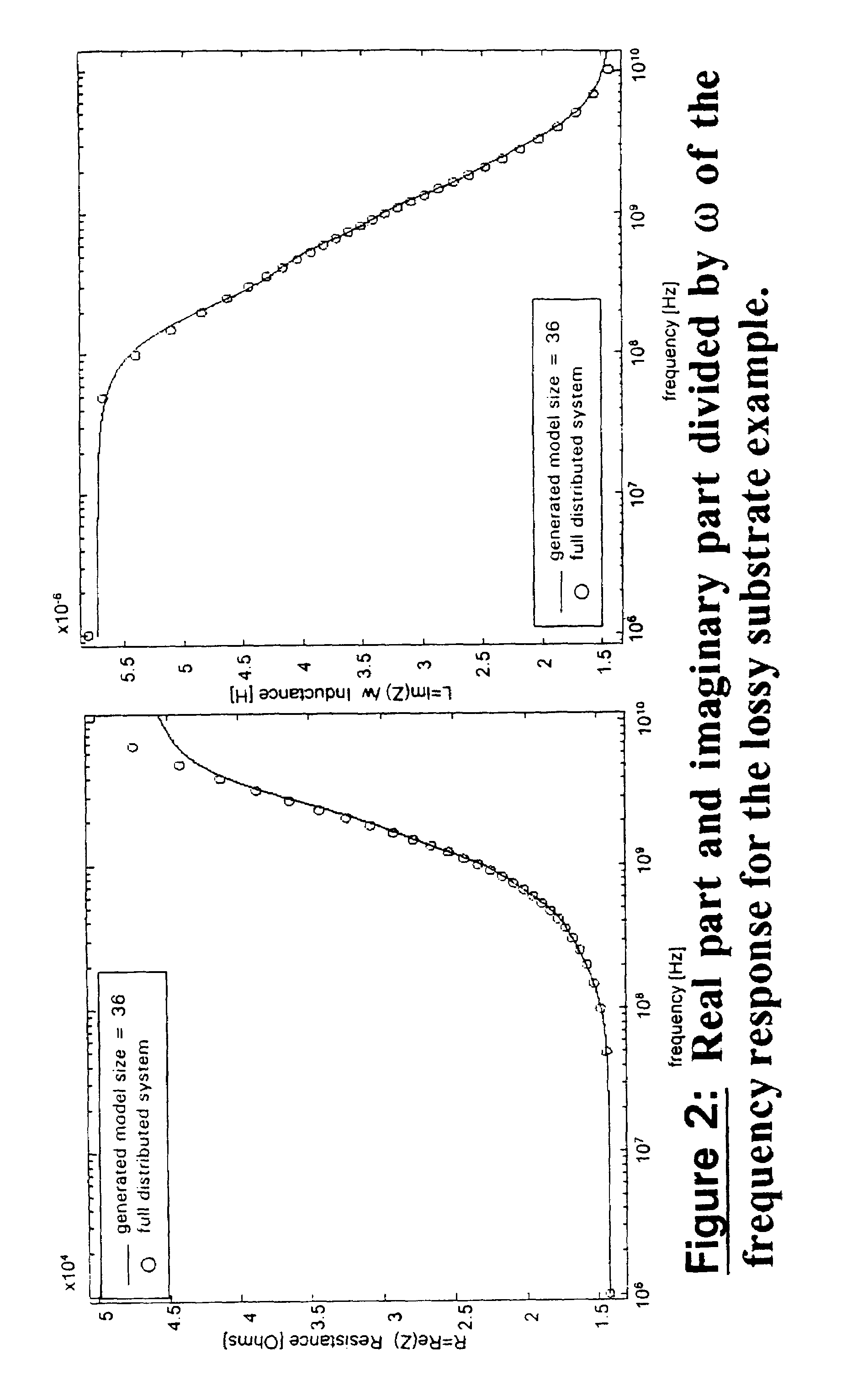
Method and system for modeling distributed time invariant systems
InactiveUS7487078B1Conveniently implementedAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designSystem matrixState space
A reduced order model of a distributed time invariant system is produced by projecting system matrices onto smaller matrices, interpolating the matrices and placing into a state-space system. The system matrices are an internal representation of the distributed time invariant system which comprises a description of the system to be modeled, mainly, for example, its inputs and outputs. The method is applied to distributed systems and guarantees accuracy in complicated systems and produces well-behaved models appropriate for use in simulators and simulations.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
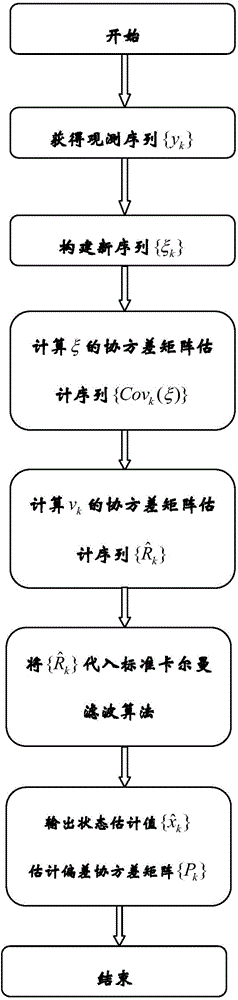
Kalman filtering method for recursive estimation under condition that observation noise covariance matrix is unknown
The invention provides a Kalman filtering method for recursive estimation under the condition that an observation noise covariance matrix of a discrete time time-invariant system is unknown, wherein the method solves the problem of system state filtering estimation under the condition that the observation noise covariance matrix of the discrete time time-invariant system is completely unknown. The method includes the steps that (1) a new statistic sequence is built by means of an observation sequence; (2) a recursion formula of the covariance matrix of the new statistic sequence is calculated; (3) an estimation sequence (f(R)k)of the observation noise covariance matrix is calculated; (4) an estimation sequence of the covariance matrix is calculated, and then real-time estimation of the observation noise covariance matrix is calculated through an algebraic relation; (5) an estimation sequence substitution true value of the observation noise covariance matrix is put into a standard Kalman filtering method, and real-time state estimation of the system and a covariance matrix of state estimation deviation are calculated.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Sound field measuring method and sound field measuring device
ActiveUS20090193895A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioPromote generationVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFrequency spectrumTime-invariant system
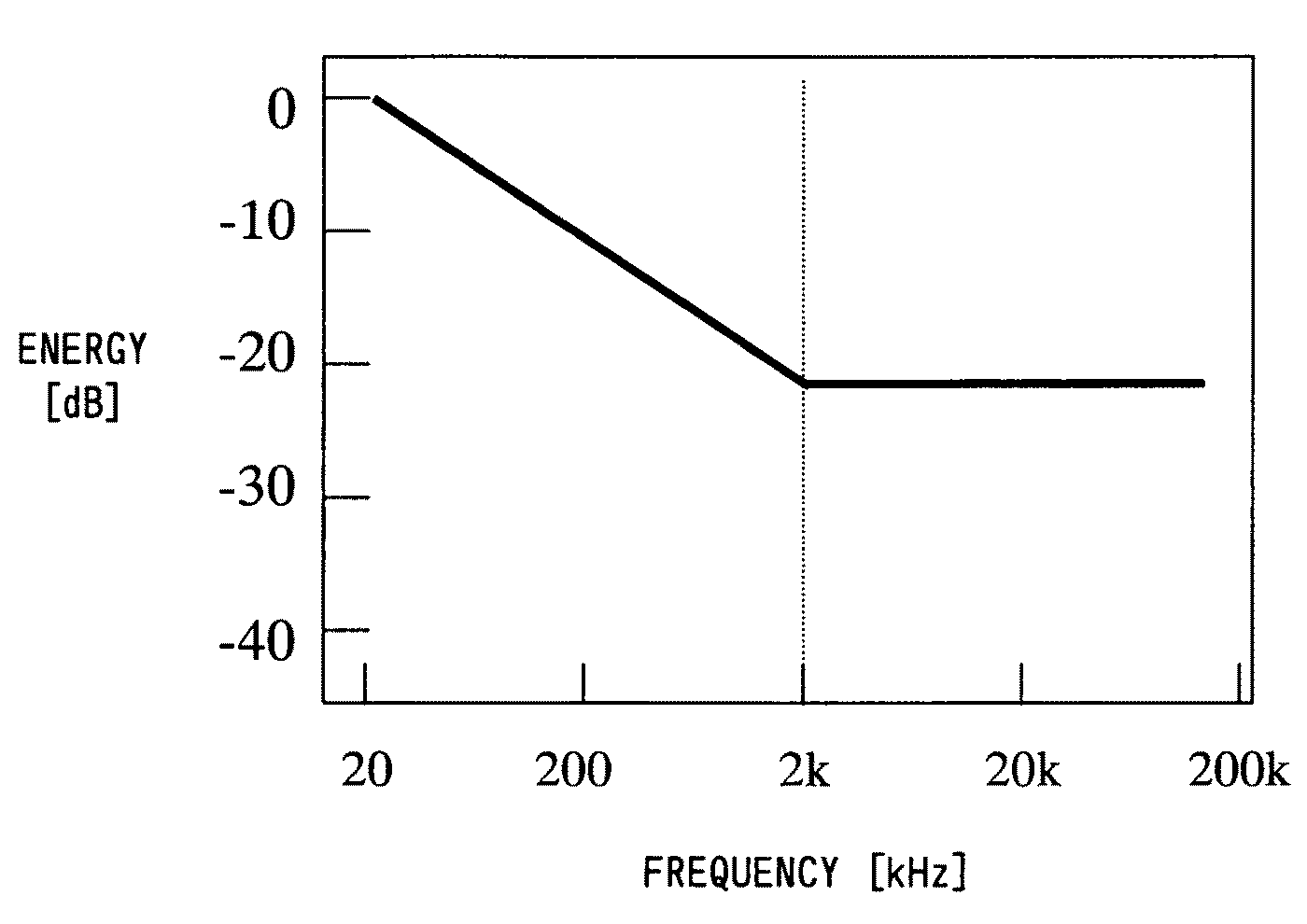
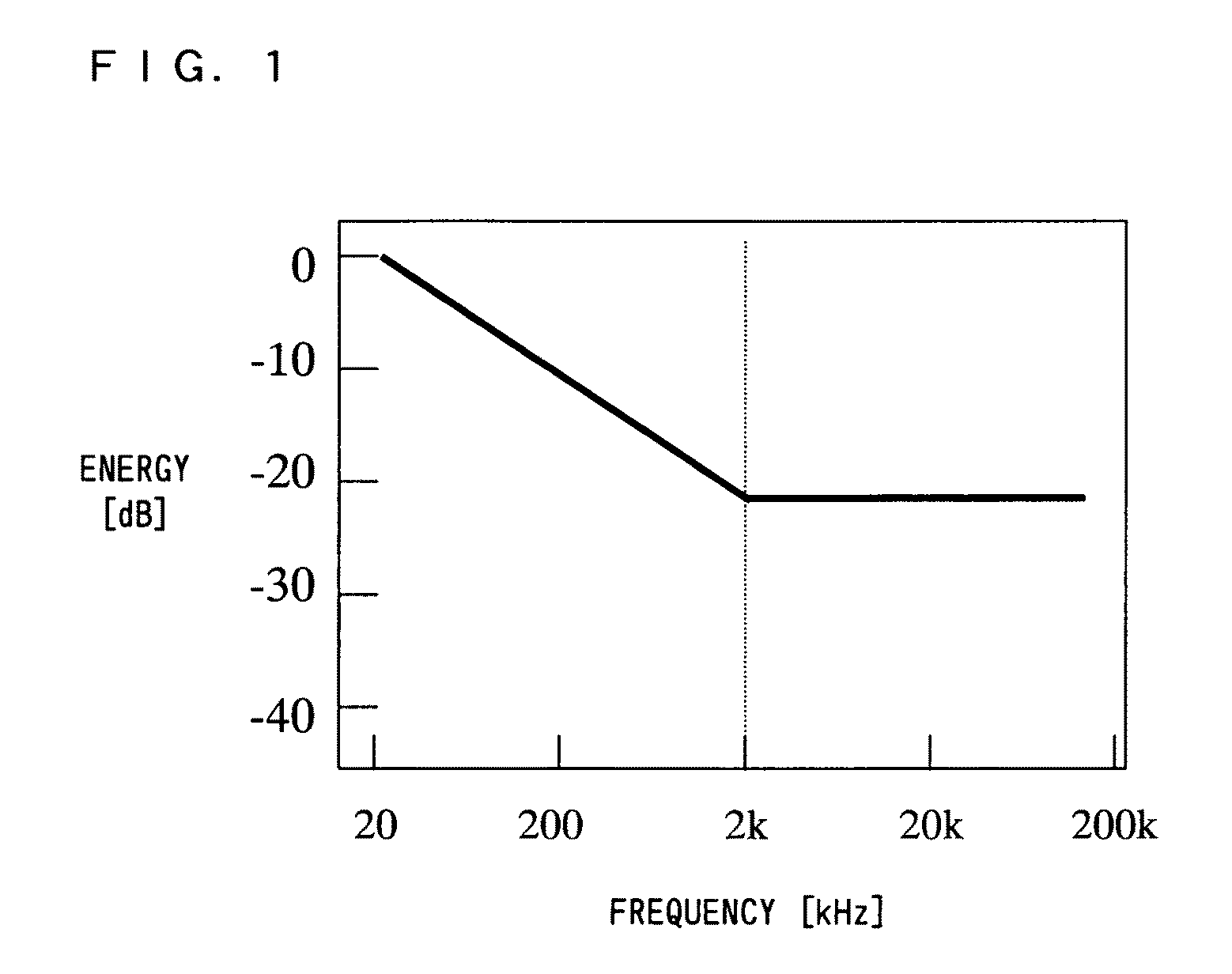
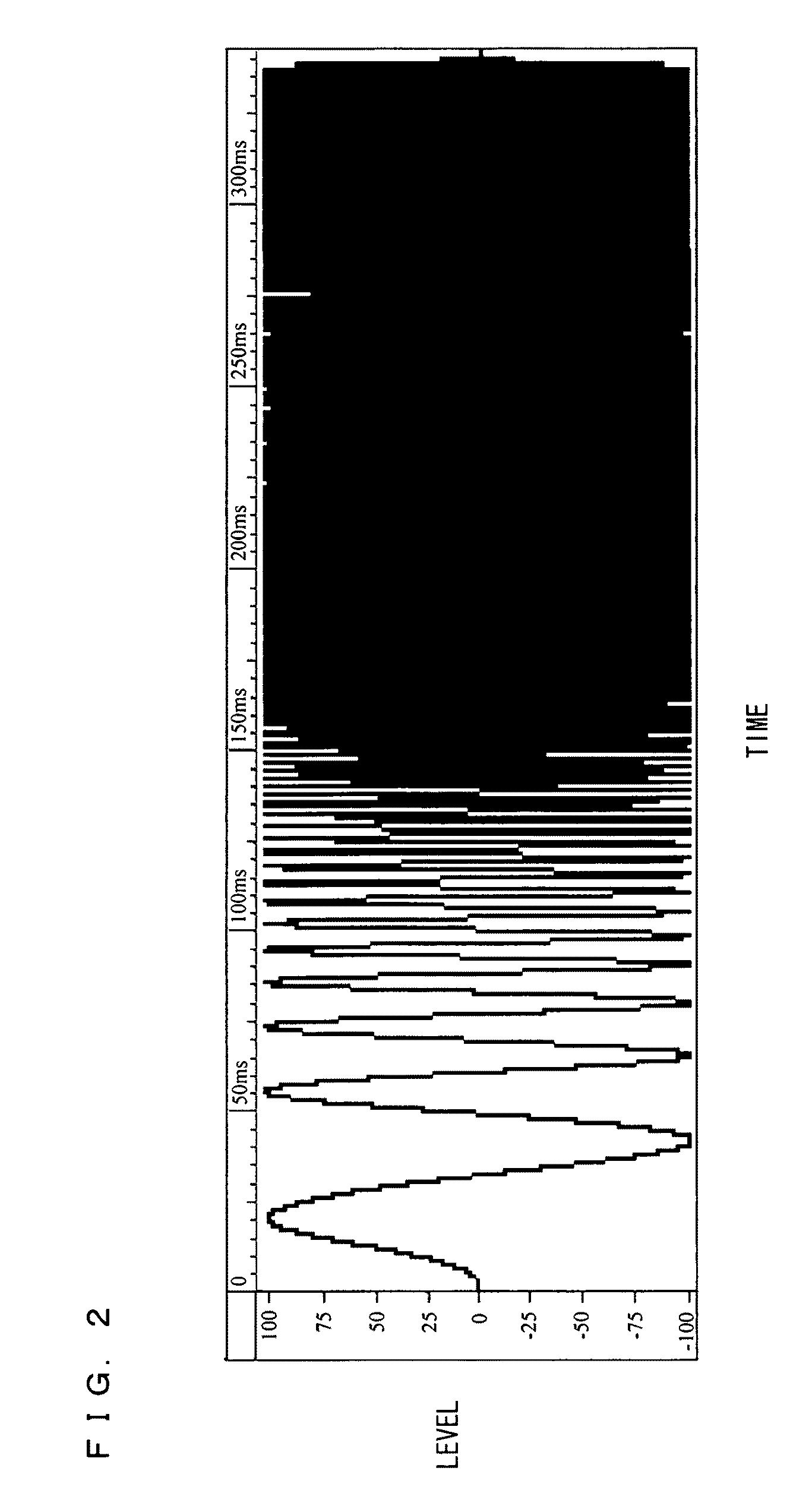
A sound field measuring device according to the present invention uses a measurement signal which has at least one change point and whose frequency spectrum has a shape corresponding to a shape of a frequency spectrum of a background noise. This enables a sound field measurement, which is for measuring an impulse response or transfer function of a sound field space which is a linear time-invariant system to be measured, to be performed with a high S / N ratio over a wide frequency band.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Calibration of linear time-invariant system's step response
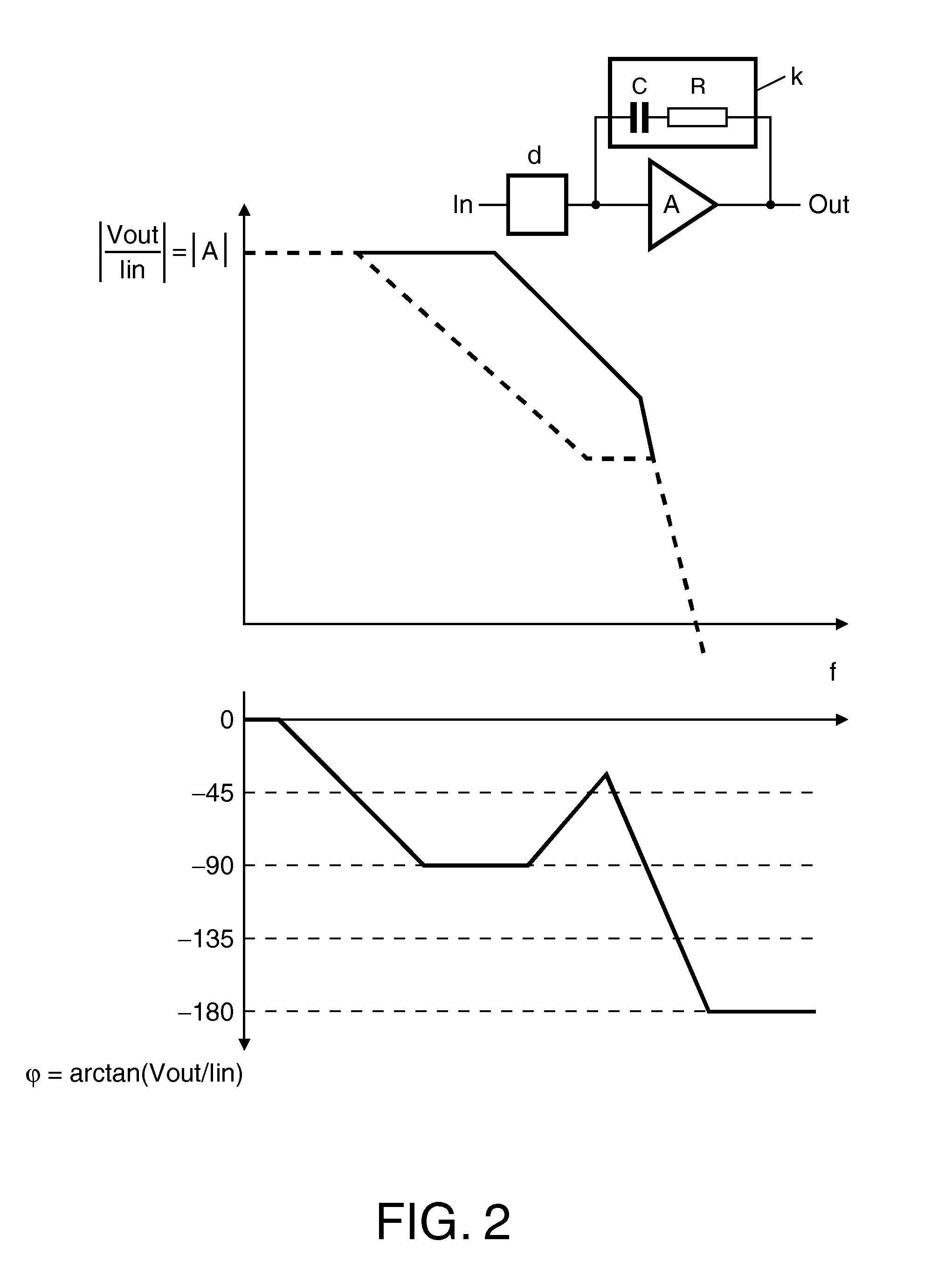
ActiveUS20110043267A1CalibrationMore phase marginNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPulse automatic controlEngineeringTime-invariant system
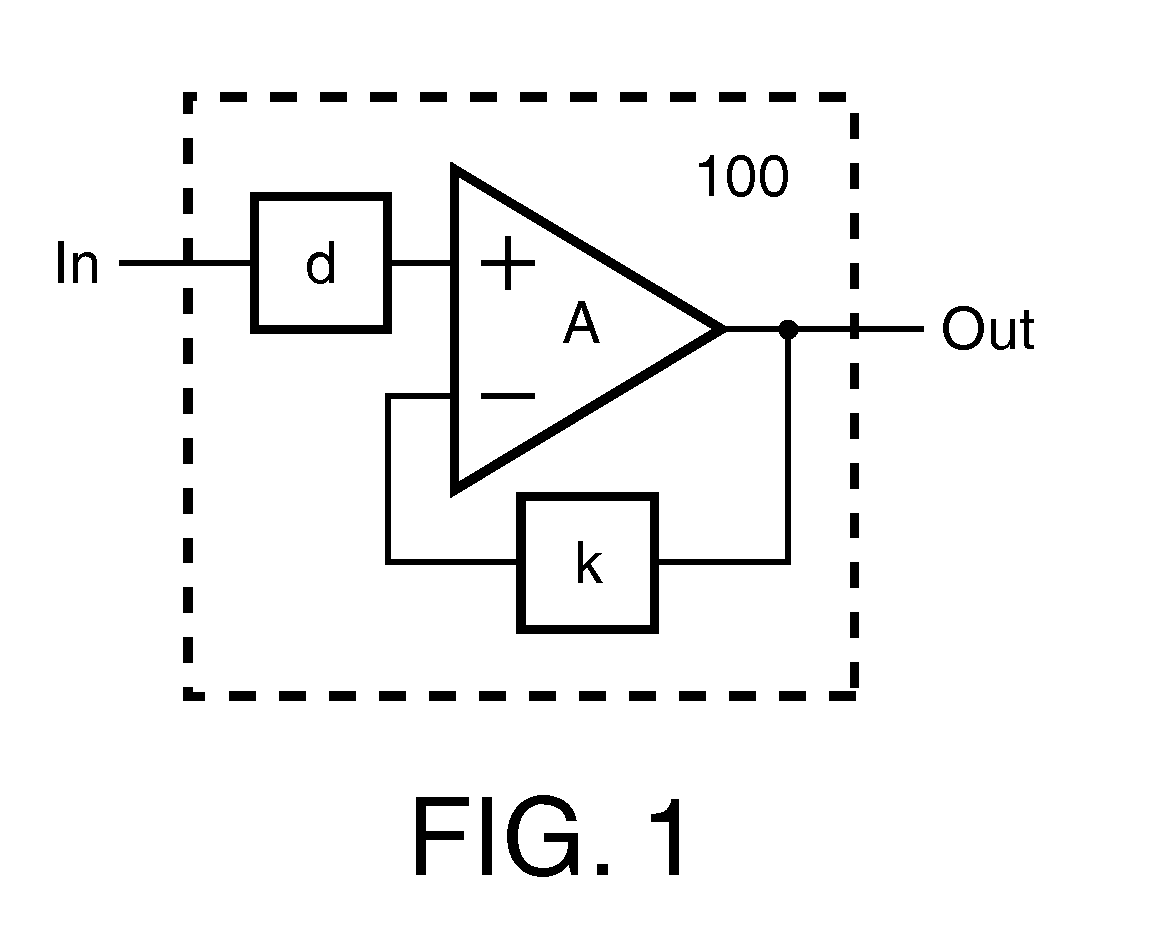
The invention concerns in general measurement of the transfer function of linear time invariant systems, more particular the calibration of such systems based on a measured transfer function. According to a first aspect the present invention an arrangement for measuring the transfer function of a linear time-invariant system is disclosed. According to a second aspect of the present invention the arrangement is implemented into a linear time-invariant circuitry having a transfer function representing the amplitude and phase characteristic of the circuitry, where by means of the arrangement for measuring the transfer function the transfer function can be optimized in accordance with certain criteria on-the-fly, i.e. in or before operation of the circuit. Finally, an effective and simple method for measuring of the transfer function of a linear time-invariant system together with the use or application of the method is shown.
Owner:NXP BV
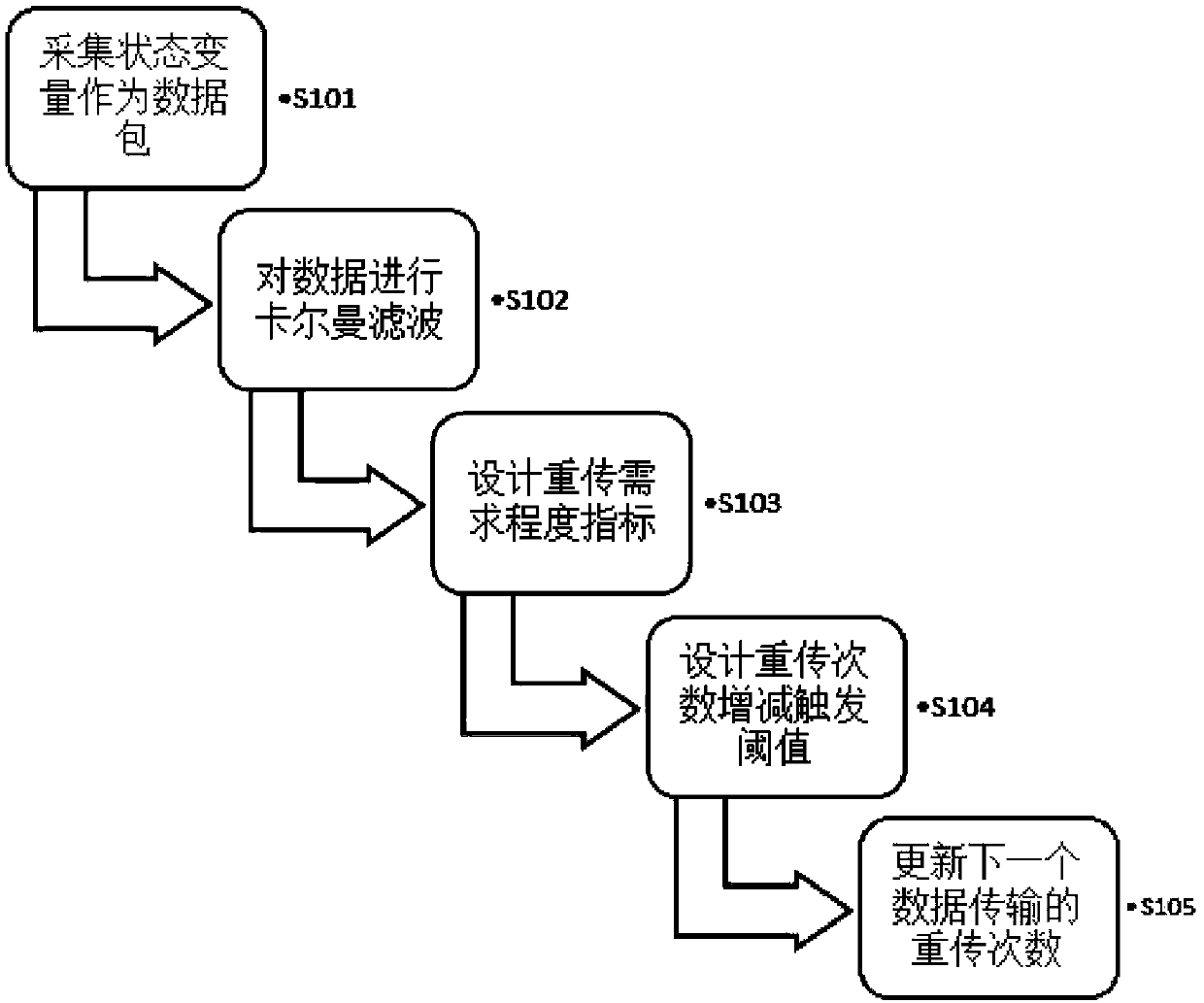
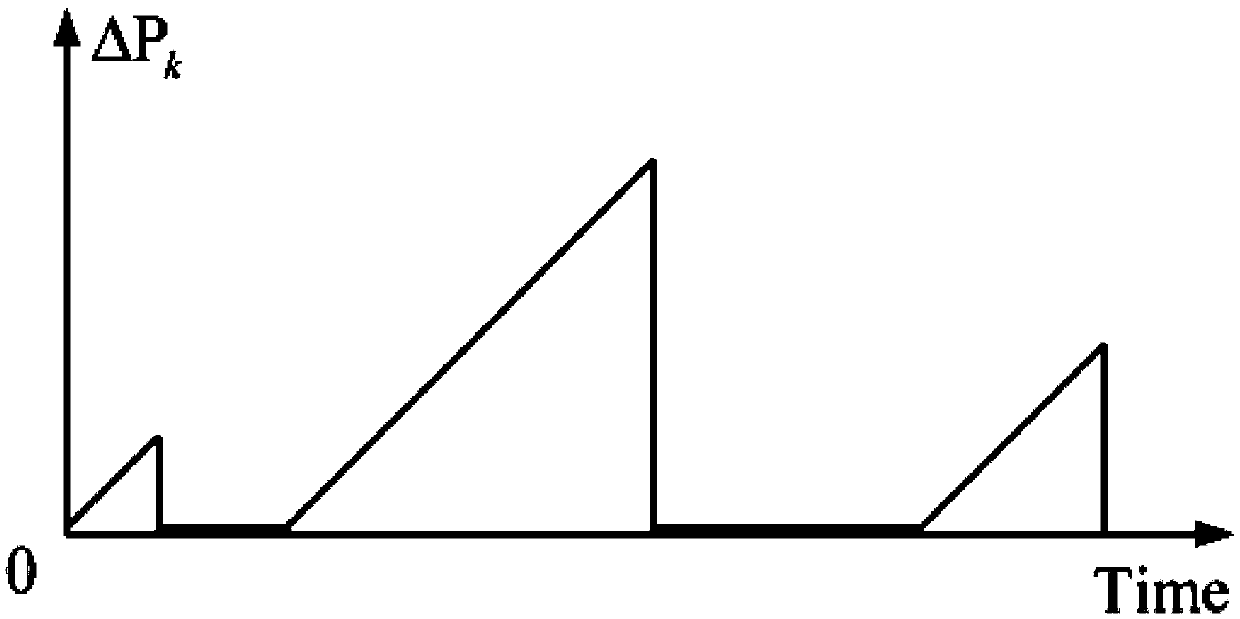
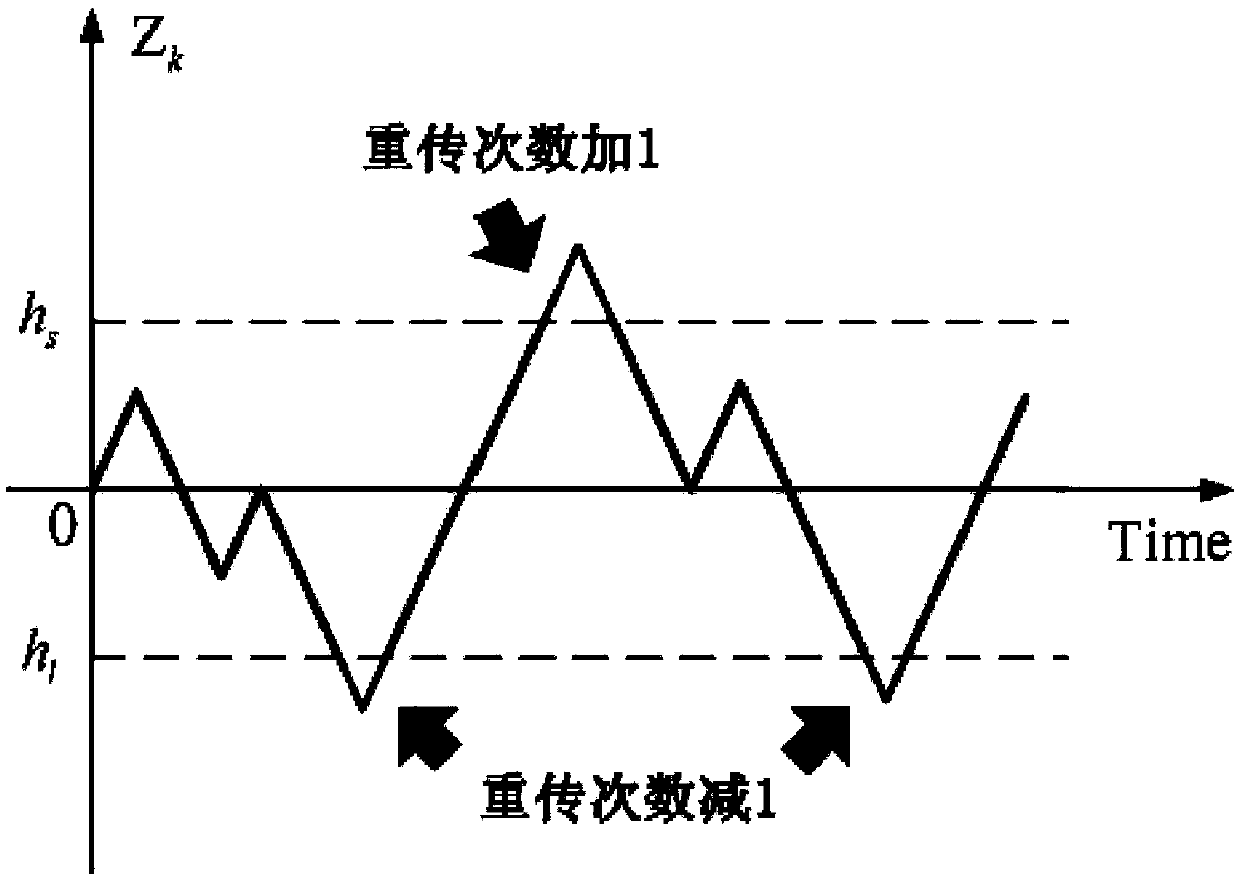
Retransmission times dynamic adjustment method based on real-time packet loss information triggering
InactiveCN108768591AReduce complexityEasy to use and flexibleError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission format adaptationPacket lossTransfer procedure
The invention provides a retransmission times dynamic adjustment method based on real-time packet loss information triggering. The method comprises the steps of collecting a system state of a discretelinear time invariant system, carrying out Kalman filtering on the system state and then transmitting the system state to a remote estimator; on the basis of the feature that a remote state estimation error covariance is converged or sharply enlarged according to whether a data packet arrives or is lost, designing a retransmission demand degree index, and automatically selecting a change functionof the index, thereby adjusting increase and decrease amplitude of the index; designing retransmission times increase and decrease triggering thresholds for the discontinuously changing demand degreeindex; and in a transmission process, when the demand degree index reaches the increase and decrease triggering thresholds, increasing and decreasing the retransmission times, and updating the transmission times for next-time data transmission. According to the algorithm provided by the invention, under the same energy consumption, compared with a retransmission times equal distribution algorithm, the retransmission times dynamic adjustment algorithm has the advantage that the remote estimation performance can be optimized well.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Second-order IIR digital notch filter and parameter quantization method
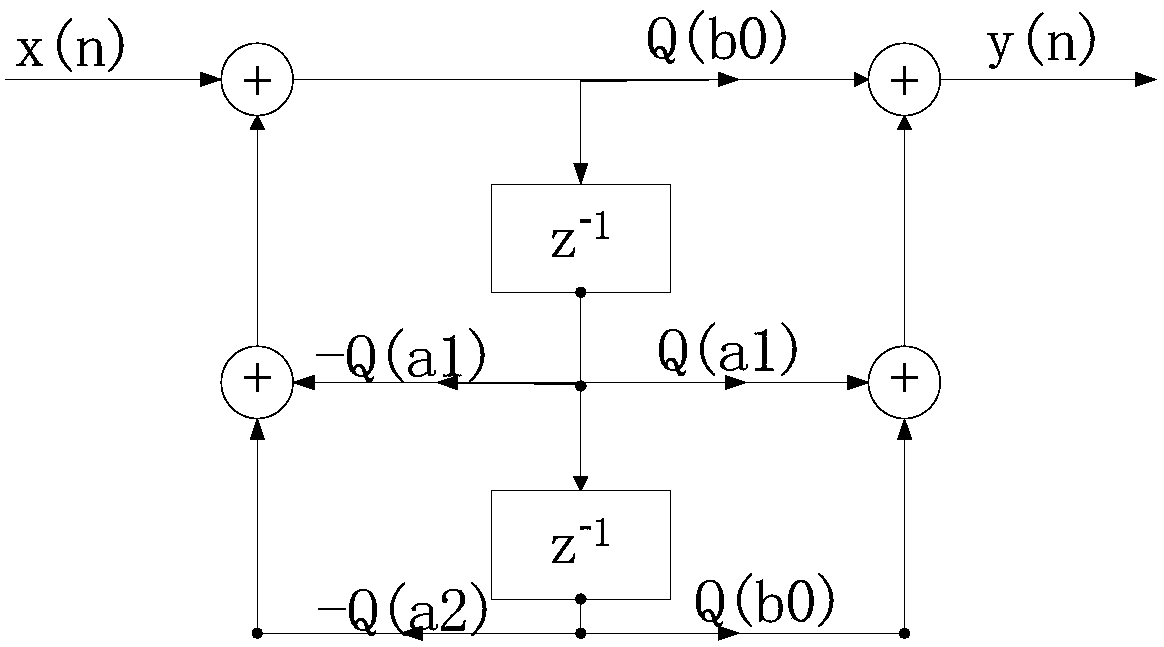
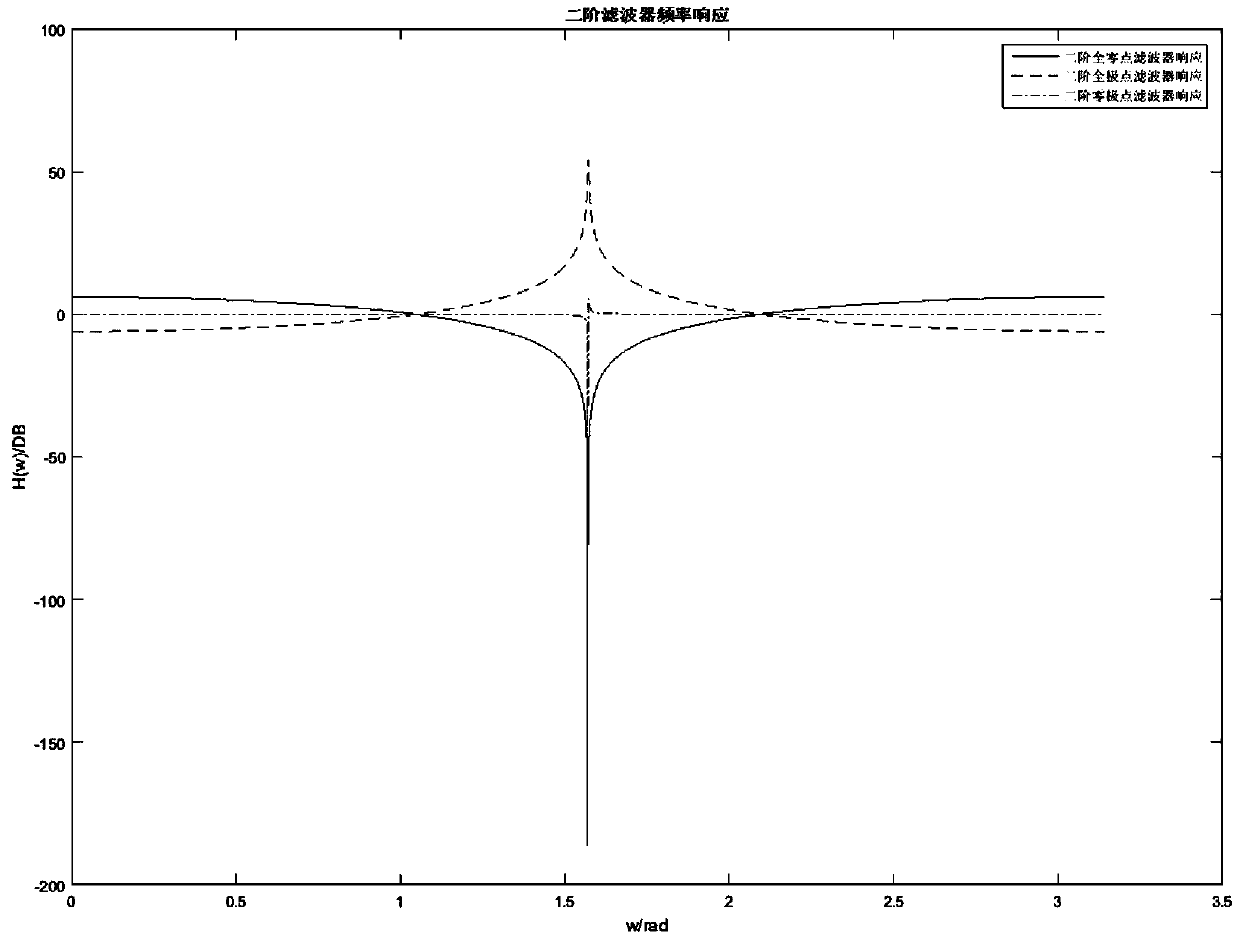
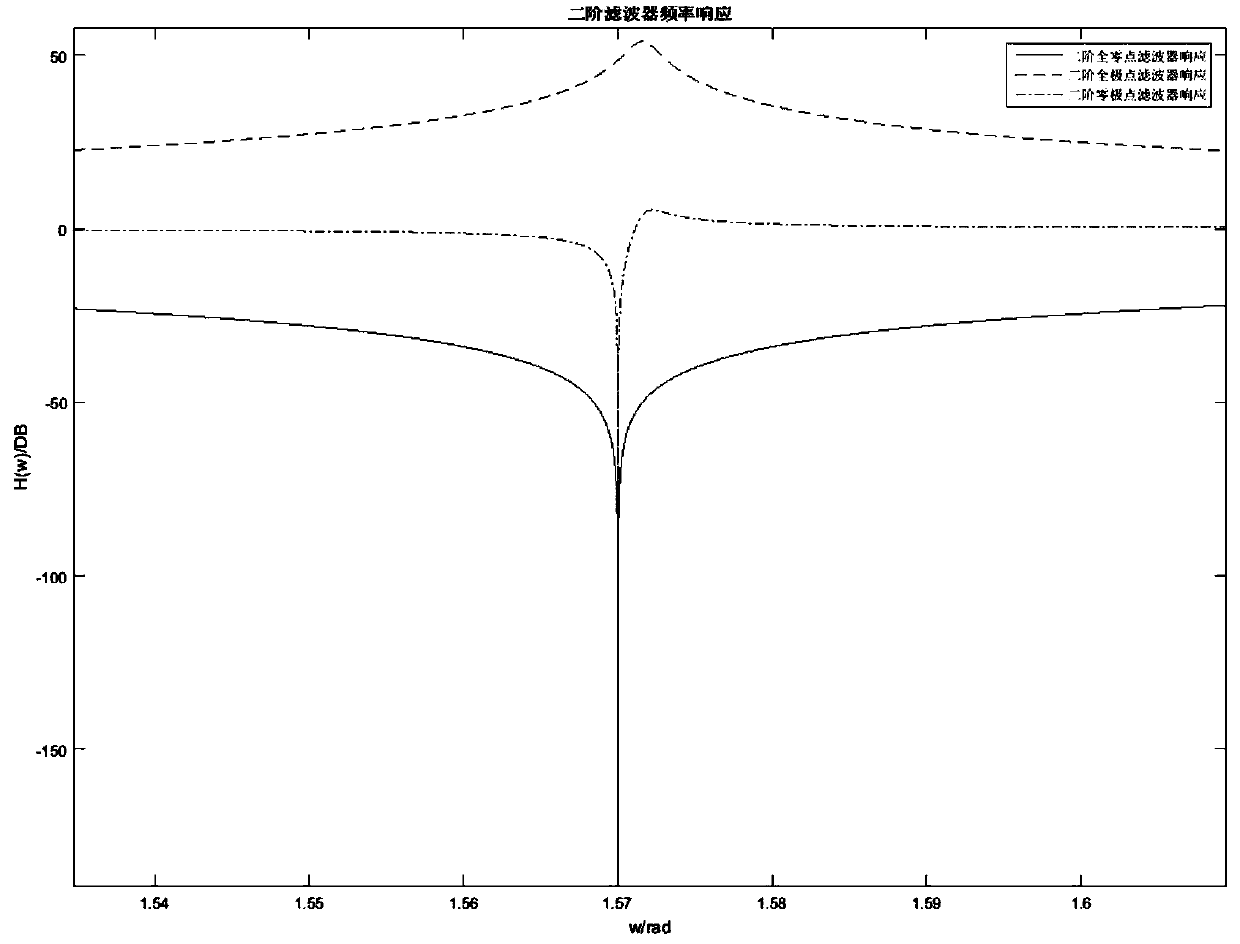
ActiveCN108566179AFilter performance is flatAvoid filteringAdaptive networkDigital technique networkIir filteringResource consumption
A second-order IIR digital notch filter and a parameter quantization method proposed by the invention may realize the suppression of the full-band narrow-band interference by parameter configuration,reduce the zero-pole polar angle deviation, and realize the perfect zero-pole matching of the full-band notch filter and the flatness of pass-band filtering performance by less resource consumption. The transfer function of the second-order IIR digital notch filter is FORMULA referred as follows, wherein b0, b1, b2, a1, and a2 are quantization parameters of a second-order IIR filter difference equation of a causally stable LTI linear time invariant system, and r and w0 are polar diameter and polar angle of the pole of the second-order IIR notch filter difference equation for the causally stable LTI linear time invariant system.
Owner:北京北方联星科技有限公司
Kalman filtering method based on recursion covariance matrix estimation
The invention discloses a Kalman filtering method based on recursion covariance matrix estimation, and belongs to the field of self-adaptive filtering. The method mainly aims at a discrete time linear time invariant system model. In the method, in case that a system noise covariance matrix is completely unknown, a new statistical sequence can be constructed from an observation sequence of a system, by use of a recursion calculating covariance matrix estimation method designed on the basis of the law of large numbers, the covariance matrix estimation sequence of the newly constructed sequence can be calculated in real time, through the correlation between the covariance matrix constructing the sequence and the covariance matrix of process noise, an estimation sequence of a process noise covariance matrix can be calculated, and then the real-time estimation value of the covariance matrix of process noise is used to replace a covariance matrix of real process noise so as to be subjected to a Kalman filtering method for calculating a covariance matrix of real-time estimation and estimation deviations of system states through recursion. The method provided by the invention is suitable for standard Kalman filtering.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
An electric motor arrangement and method of controlling thereof
ActiveCN102780442AEffective controlVector control systemsDc motor stoppersBrake torqueStator current vector
An electric motor arrangement comprises an electric motor and a controller. The electric motor includes: a stator having a plurality of coil windings, and a rotor having a plurality of permanent magnets. The controller is arranged to control current flow through the plurality of coil windings to generate a braking torque on the rotor. The current is defined by a stator current vector represented in a two co-ordinate time invariant system having a rotating quadrature and direct axis by a quadrature current component and a direct current component, wherein the controller is arranged to vary the quadrature current component and the direct current component so that the input electrical power of the electric motor is greater than or equal to zero.
Owner:PROTEAN ELECTRIC LIMITED
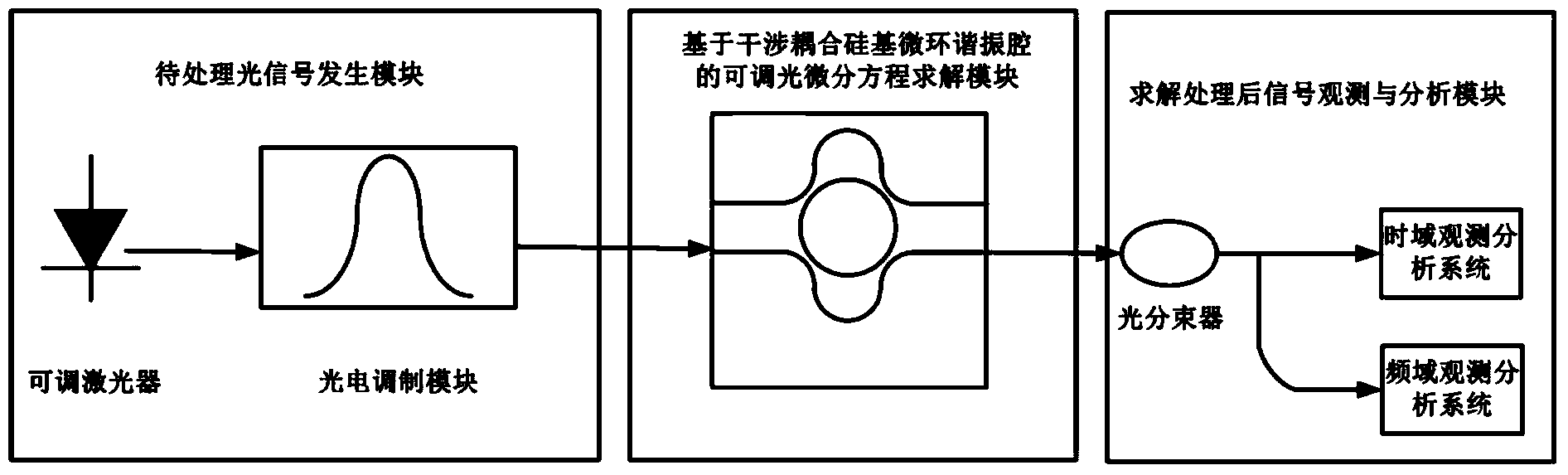
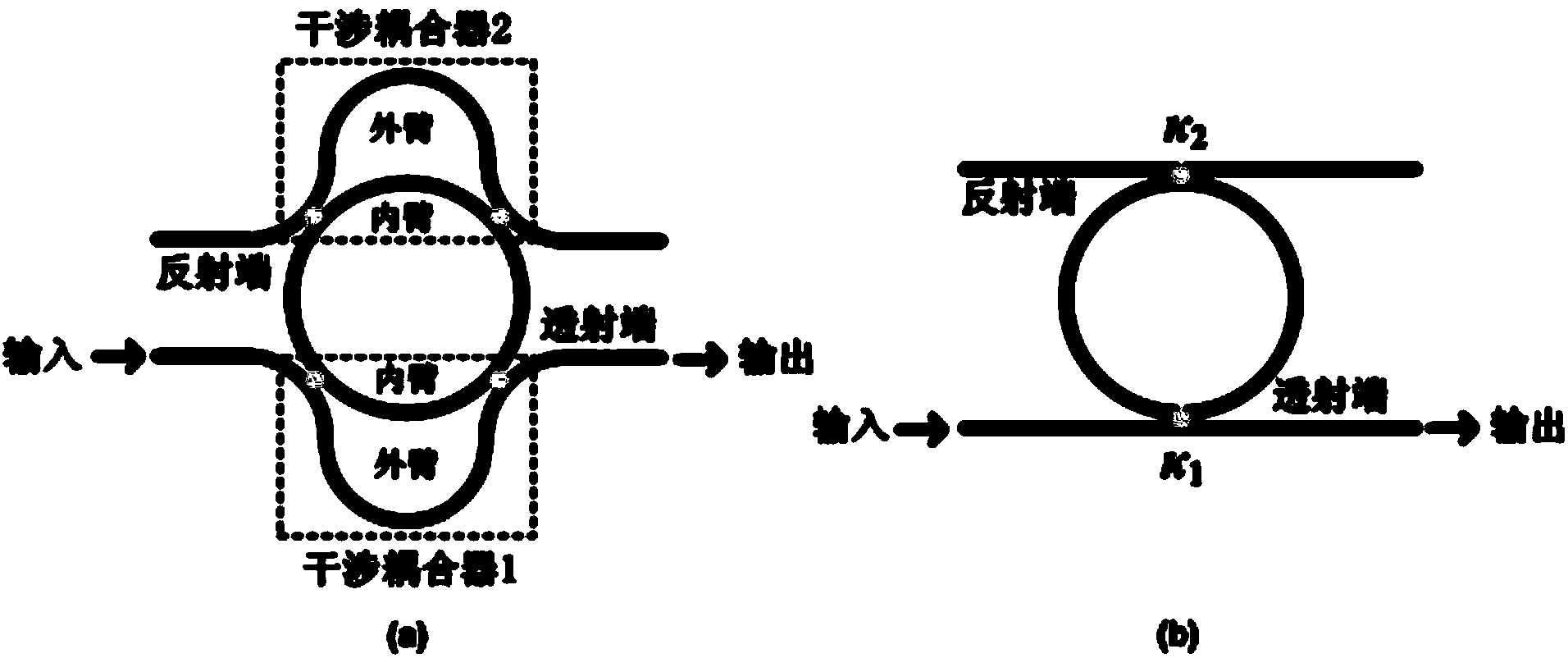
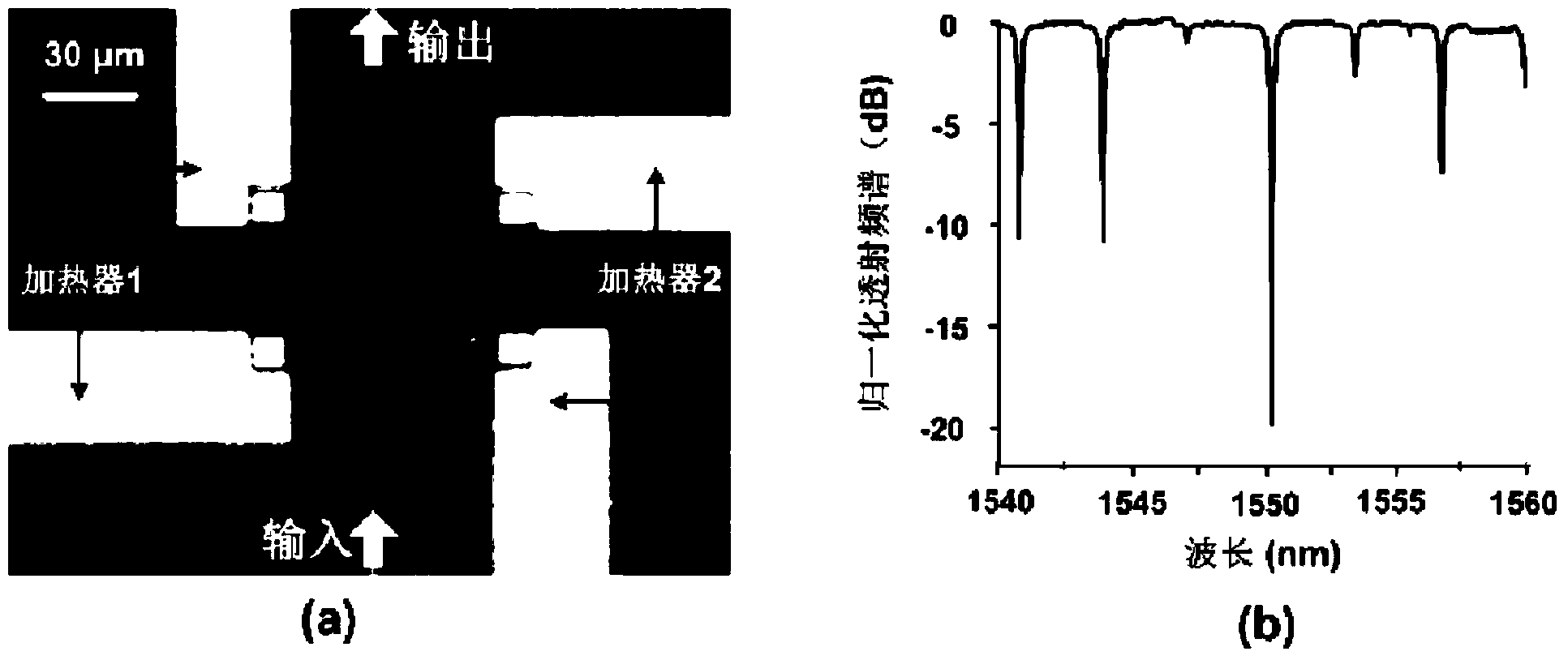
Dimmable differential equation solver based on interference couplers and silica-based micro-ring resonant cavity
InactiveCN104375354AUniversalThe coefficient can be adjustedNon-linear opticsWaveguideConstant coefficients
Provided is a dimmable differential equation solver based on interference couplers and a silica-based micro-ring resonant cavity in the field of multi-light-path multiplexing systems. A to-be-processed-signal generating module generates a light signal to be processed, and the light signal to be processed is input from the input end of a dimmable differential equation solving module; an output signal obtained by solving the dimmable differential equation solving module is output from the output end to a signal observation and analysis module to be displayed and observed. The dimmable differential equation solving module comprises the silica-based micro-ring resonant cavity, and micro-rings of the silica-based micro-ring resonant cavity are coupled with direct waveguides at a transmission end and a reflection end to form two interference couplers. The equivalent coupling strength between the micro-rings and the direct waveguides by changing outer arm phase shifts of the two interference couplers, and therefore dynamic adjustment on coefficients of constant-coefficient differential equations to be solved can be achieved. The dimmable differential equation solver is applied to simulation and analysis of linear time invariant systems and provides a solution for solving linear constant-coefficient differential equations of general types.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
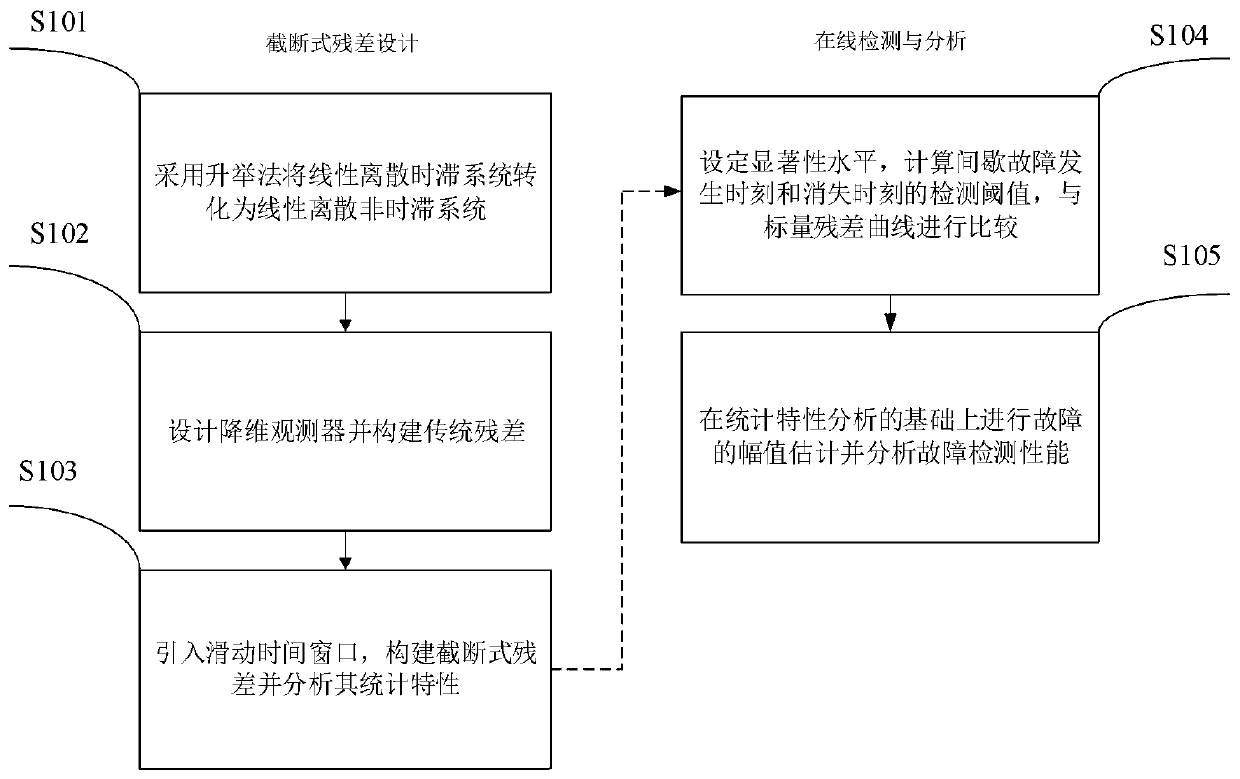
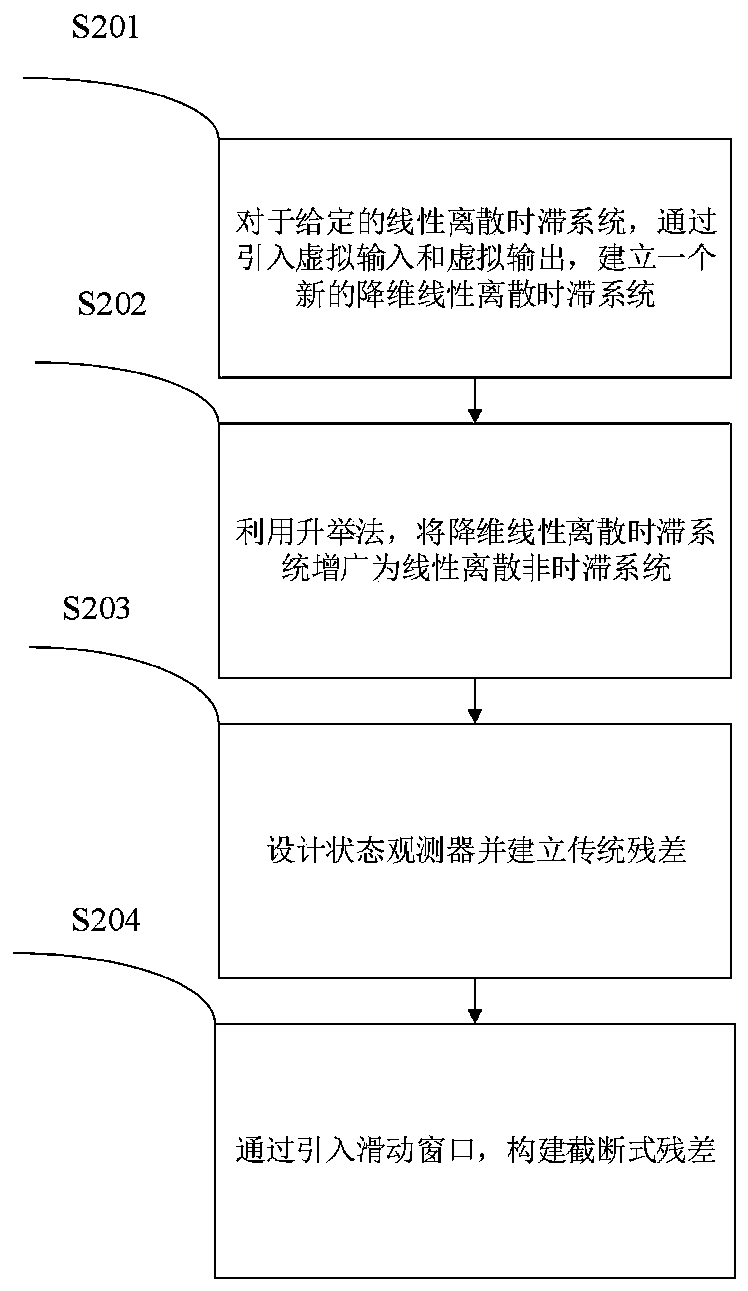
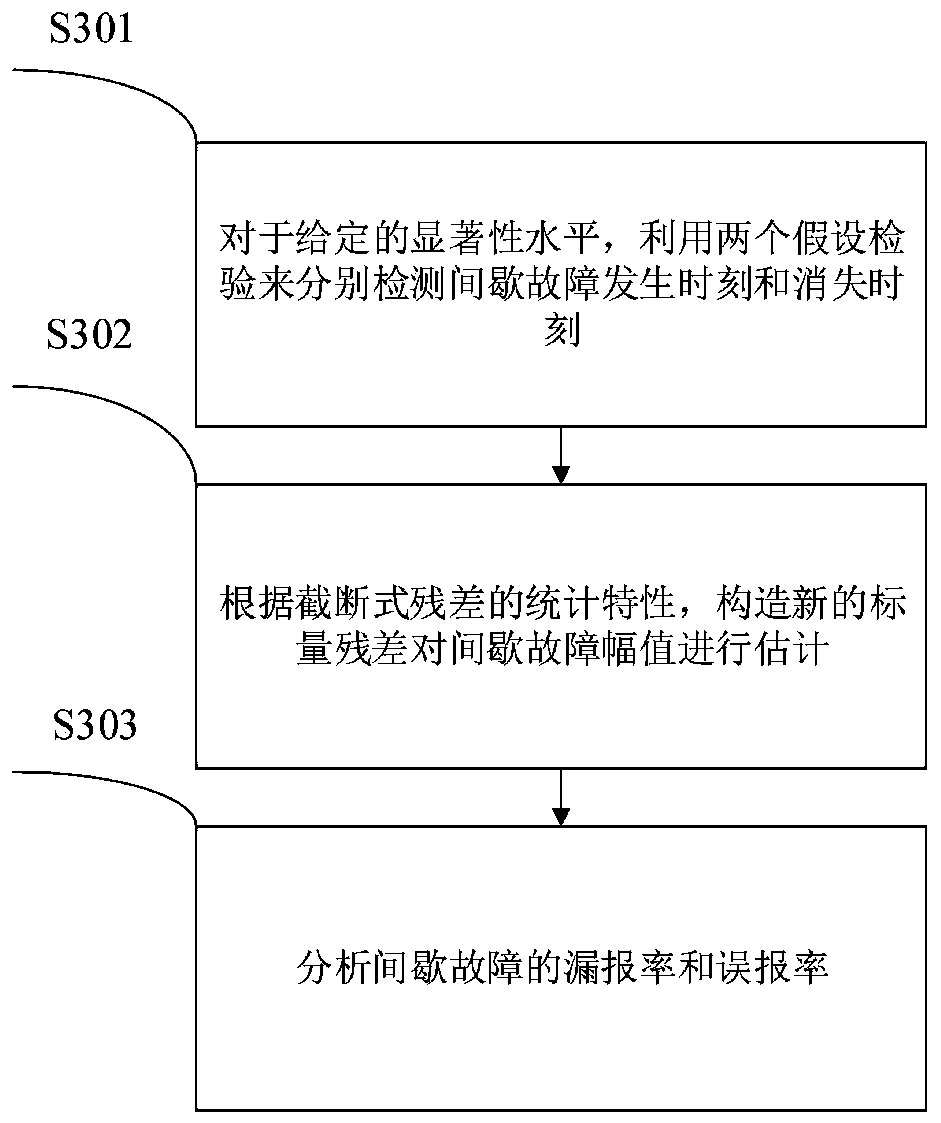
Intermittent fault detection method of linear discrete time-delay system
ActiveCN110058124AGuaranteed uptimeEfficient detectionFault locationSliding time windowVanishing moments
The invention relates to an intermittent fault detection method of a linear discrete time-delay system. The intermittent fault detection method comprises the steps that virtual input and virtual output are introduced according to the characteristics of the linear discrete time-delay system, a linear dimensionless discrete time-delay system is constructed, and the linear dimensionless discrete time-delay system is transformed into a linear dimensionless discrete time-invariant system by using a lifting method; on the basis of designing a state observer, truncated residual is constructed by introducing a sliding time window, and the statistical characteristics of the truncated residual are analyzed; and two hypothesis tests are used for setting detection thresholds of the intermittent faultoccurrence moment and vanishing moment respectively, amplitude of an intermittent fault is estimated, and the detectability problem of the intermittent fault is analyzed. The intermittent fault detection method of the linear discrete time-delay system is based on the lifting method and the designed state observer, the new truncated residual is designed by introducing the sliding window, the intermittent fault detection process can be quantitatively described, intermittent fault detection can be timely and effectively detected, the fault detection rate is increased, and the fault false alarm rate and missing report rate are decreased.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
Cabin structure vibration response reproduction method
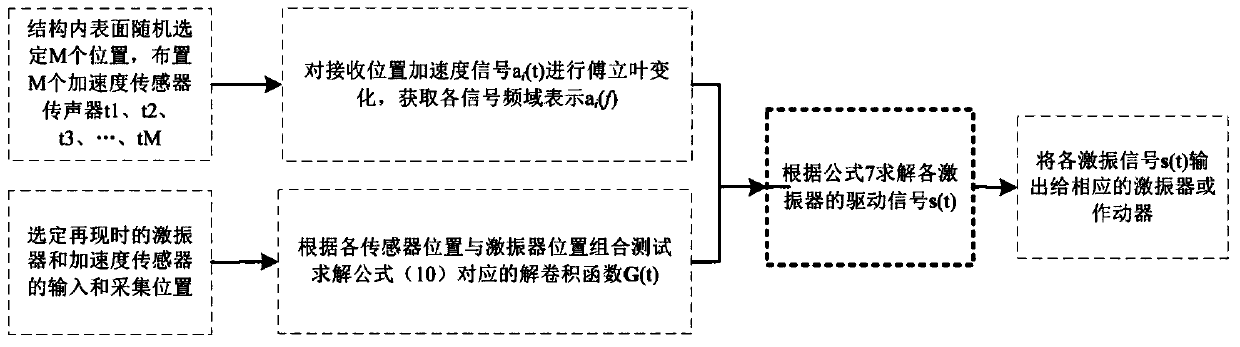
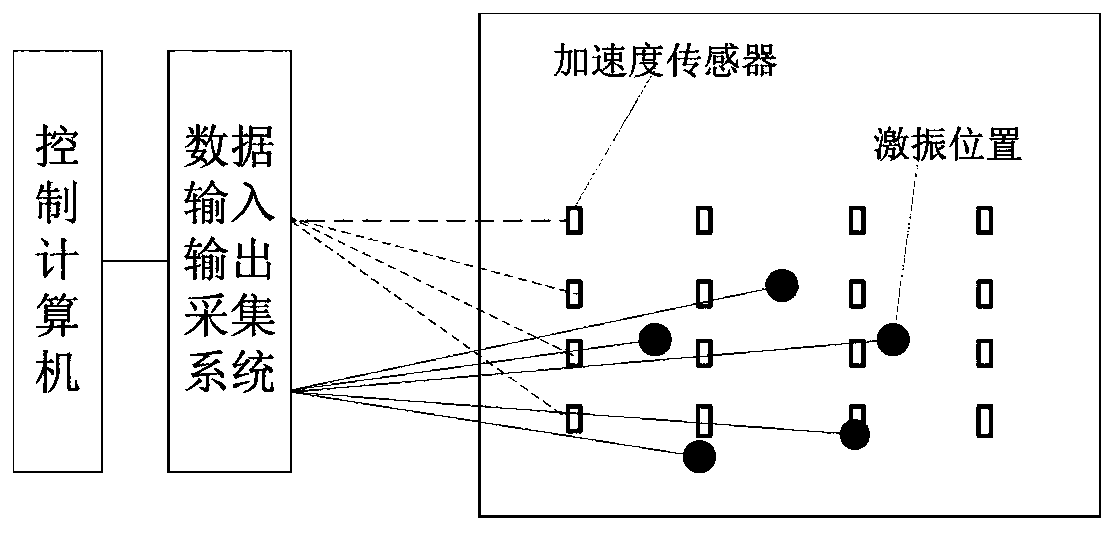
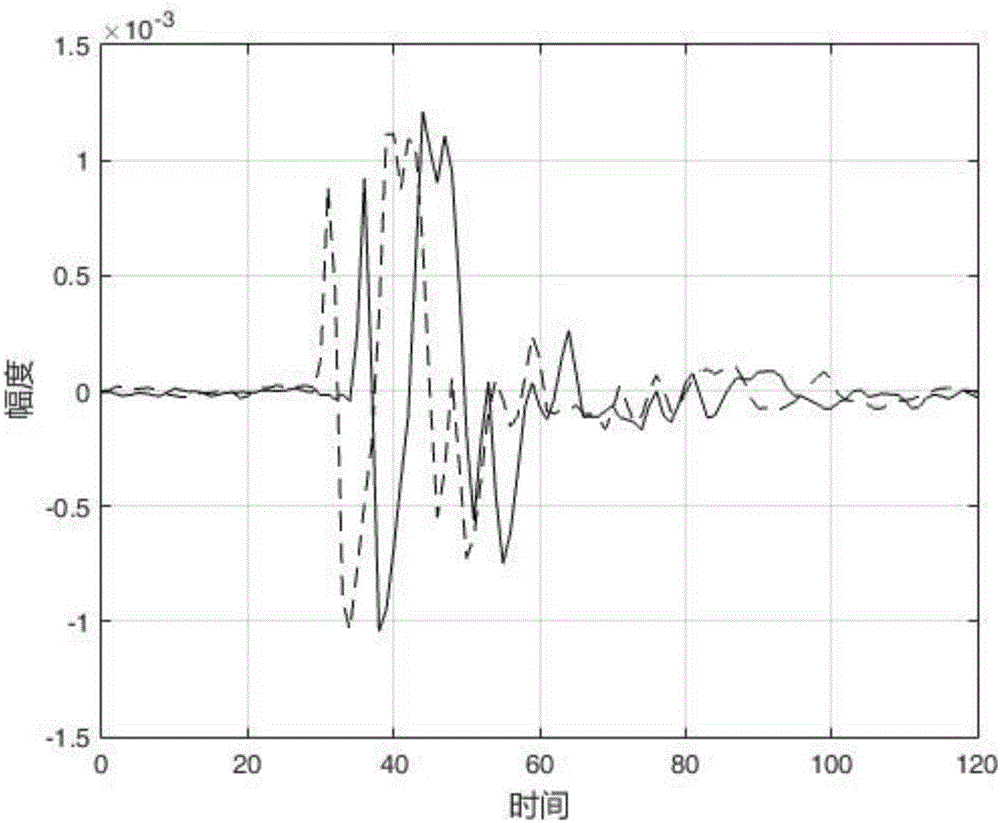
PendingCN110598238ASuitable for useSimple methodSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementComplex mathematical operationsEngineeringActuator
The invention discloses a cabin structure vibration response reproduction method, and belongs to the technical field of cabin structure vibration and noise reduction. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, assuming that the impact response between a measured vibration exciter or actuator and each receiving position is a linear time-invariant system, based on the hypothetical, measuring the impulse responses of the plurality of vibration exciters and the receiving positions by using a linear sweep method; after the impulse response is obtained, taking the collected data of the multiple vibration sensors installed on the surface of the structural wall as the input, and through a deconvolution model matched with the acceleration, solving the driving signals of all the vibrationexciters during vibration reproduction. According to the method, the plurality of excitation devices are arranged outside the structure to equivalently reproduce the structural vibration condition ofa sound field of the original cabin so as to better reproduce the original sound field. According to the theory of vibration and sound radiation, in a low-frequency range, the method can accurately reproduce the vibration distribution of the sound field of the original cabin.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
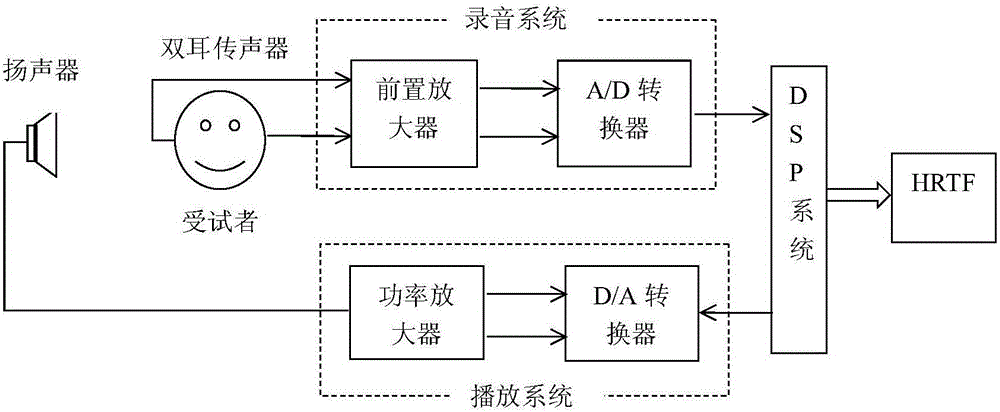
Asynchronous HRTF (Head Related Transfer Function) measurement method based on phase compensation
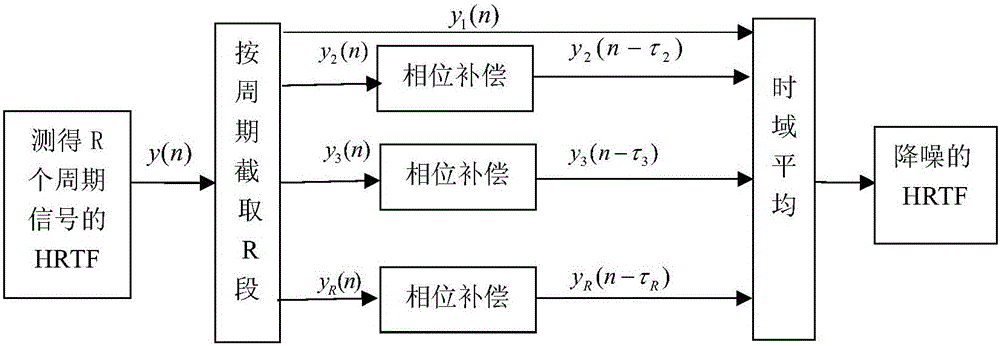
ActiveCN105910702AReduce the noise floorImprove signal-to-noise ratioSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioBackground noise
The invention discloses an asynchronous HRTF (Head Related Transfer Function) measurement method based on phase compensation. The method comprises the steps: 1), measuring transfer functions of a linear time invariant system for many times; 2), carrying out the phase compensation of transfer functions measured in different play periods, and compensating for the time difference among different play periods; 3), carrying out the averaging of the transfer functions in a time domain after phase compensation, and obtaining an HFTF. The method carries out the phase compensation of the HRTFs of different measurement periods because of time difference generated by asynchronous measurement, and reduces the background noise in an HRTF measurement environment, thereby obtaining a high signal to noise ratio HRTF measurement result.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Serdes fast retrain method upon exiting power saving mode
ActiveUS9052900B2Reduce power consumptionShorten the timeHybrid transportPower supply for data processingTime-invariant systemData transmission
Systems and methods for reducing power consumption of systems using serialized data transmission. In a multi-node system, the reiterative steps for the setup of the lanes within links between the nodes produces both a time invariant set of parameters associated with the channel properties of the lanes and a time variant set of parameters associated with receiver clock alignment. The time invariant set is stored in persistent storage. Links may be turned on and turned off. When a link is turned on again, the stored time invariant set may be used as initial values to reconfigure both the time invariant and the time variant sets, thereby greatly reducing the delay to begin using the link again. The reduced delay may significantly speed up the wakening process for the links, thereby encouraging the use of low-power techniques that include tuning off lanes.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Model prediction control method based on decreasing prediction step size
ActiveCN109613830AShorten the timeImprove performanceAdaptive controlAlgorithmModel predictive control
The invention discloses a model prediction control method based on a decreasing prediction step size. The model prediction control method based on the decreasing prediction step size is characterizedby comprising the steps that linear time invariant system model with a disturbing term is established, an H infinity type cost function is adopted, an affine state feedback control law with priori state memory is introduced, a decreasing step size model prediction control algorithm is proposed, and argumentation is conducted on feasibility and specified arrival time. The model prediction control method has the beneficial effects that based on variable step size prediction control, the arrival time is treated as an inflexible rule, decreasing step size model prediction control is proposed, it is guaranteed that system states can enter a terminal set in specified time, and meanwhile the time that the system enters the terminal set is reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for modeling and analyzing linear time invariant systems with time delays
ActiveUS8712753B1Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationTime delaysEngineering
A method and apparatus are provided to model, analyze, and build linear time invariant systems with delays. The method and apparatus model a linear time invariant system as a linear fractional transformation of matrices of a delay free linear time invariant model with a bank of pure delays. The method and apparatus of the present invention can further accommodate input delays and output delays associated with the linear time invariant system with delays.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com