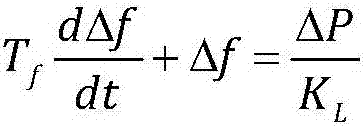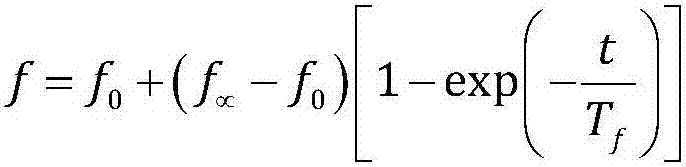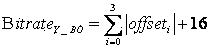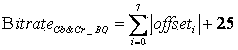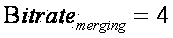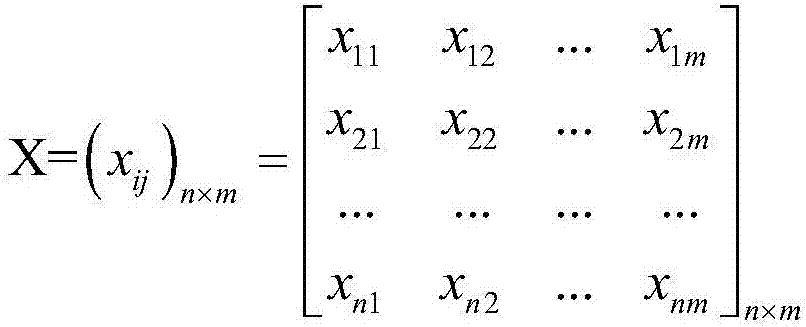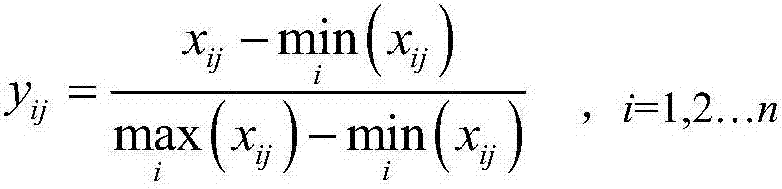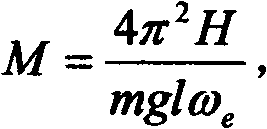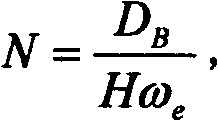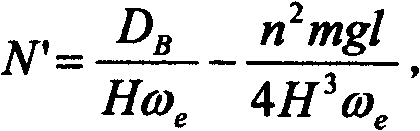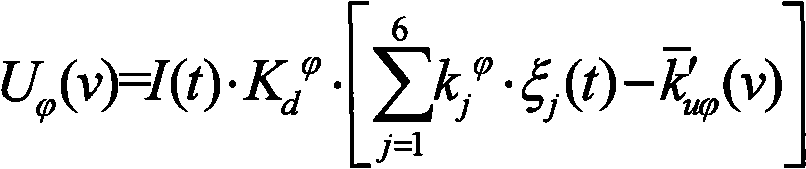Patents
Literature
113 results about "Constant coefficients" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, constant coefficients is a term applied to differential operators, and also some difference operators, to signify that they contain no functions of the independent variables, other than constant functions. In other words, it singles out special operators, within the larger class of operators having variable coefficients. Such constant coefficient operators have been found to be the easiest to handle, in several respects. They include for example the Laplacian of potential theory and other major examples of mathematical physics. In the case of ordinary differential equations, writing D = d/dx the general constant-coefficient differential operator is L = p, where p is any polynomial with complex number coefficients. The solution of equations Lf = g with a given function g(x) was given already in the eighteenth century, by Leonhard Euler. For partial differential equations, the constant-coefficient operators are characterised geometrically by their translation invariance, and algebraically as polynomials in the partial derivatives. According to the Ehrenpreis–Malgrange theorem, they all have fundamental solutions.
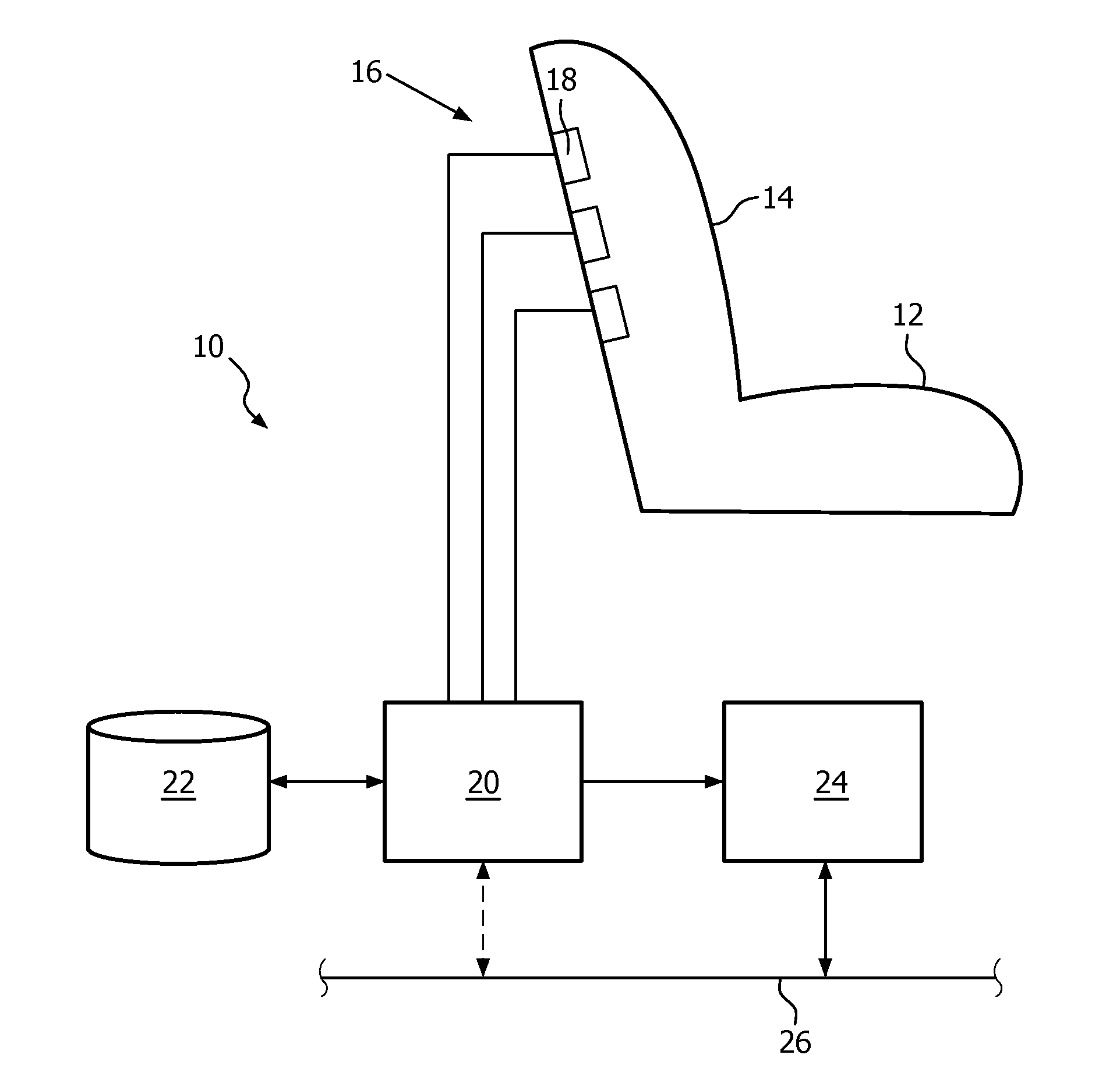
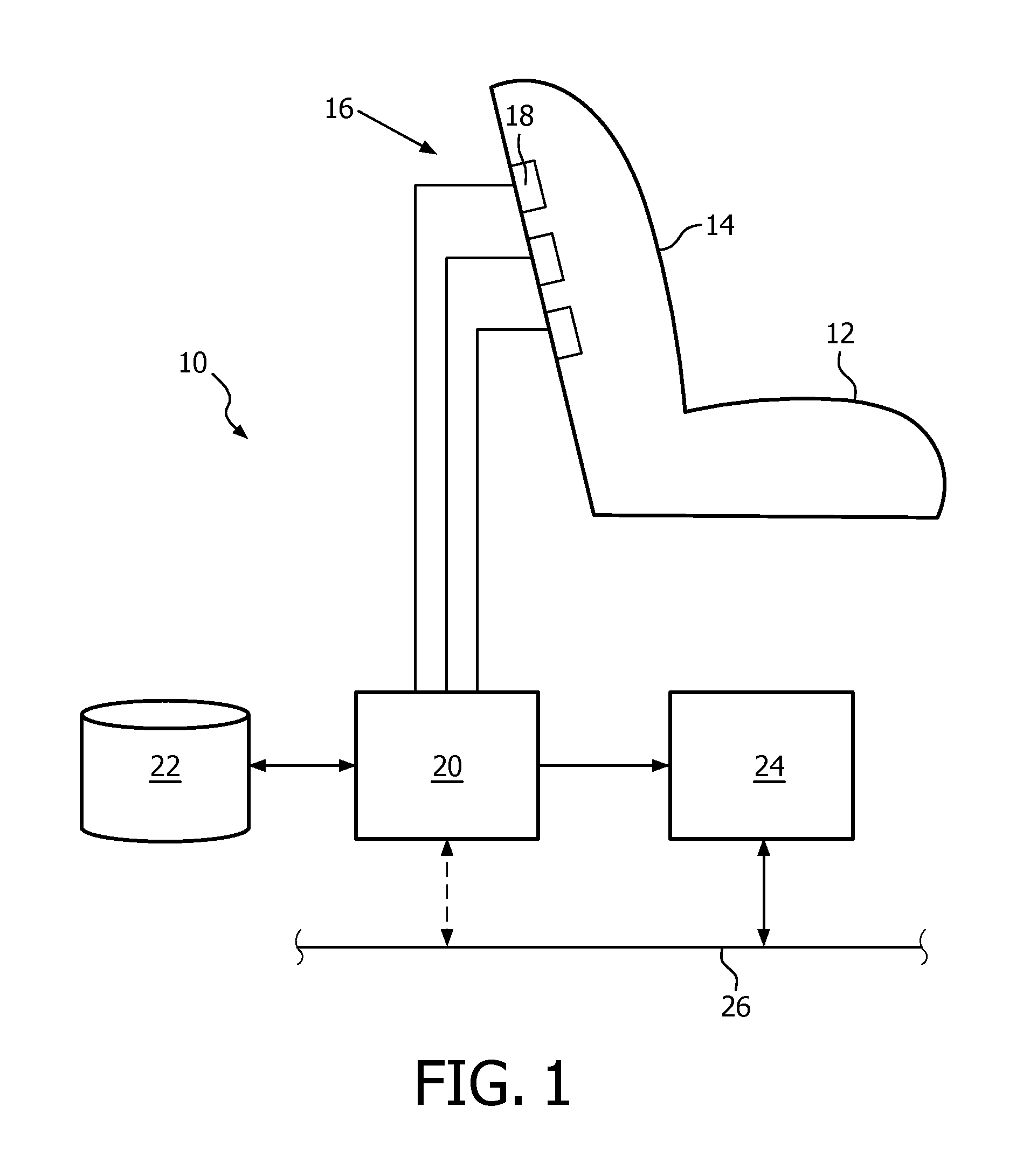
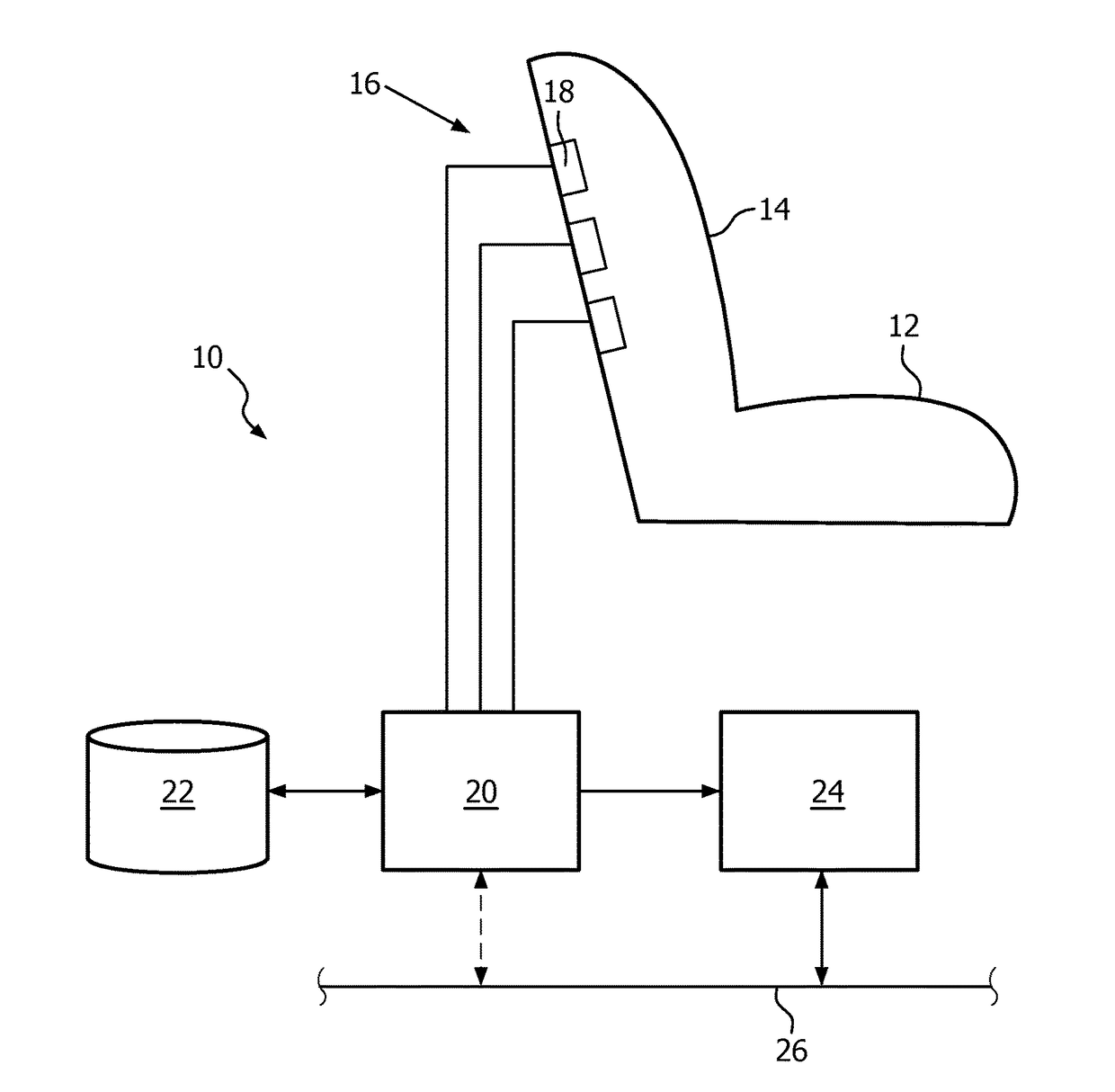
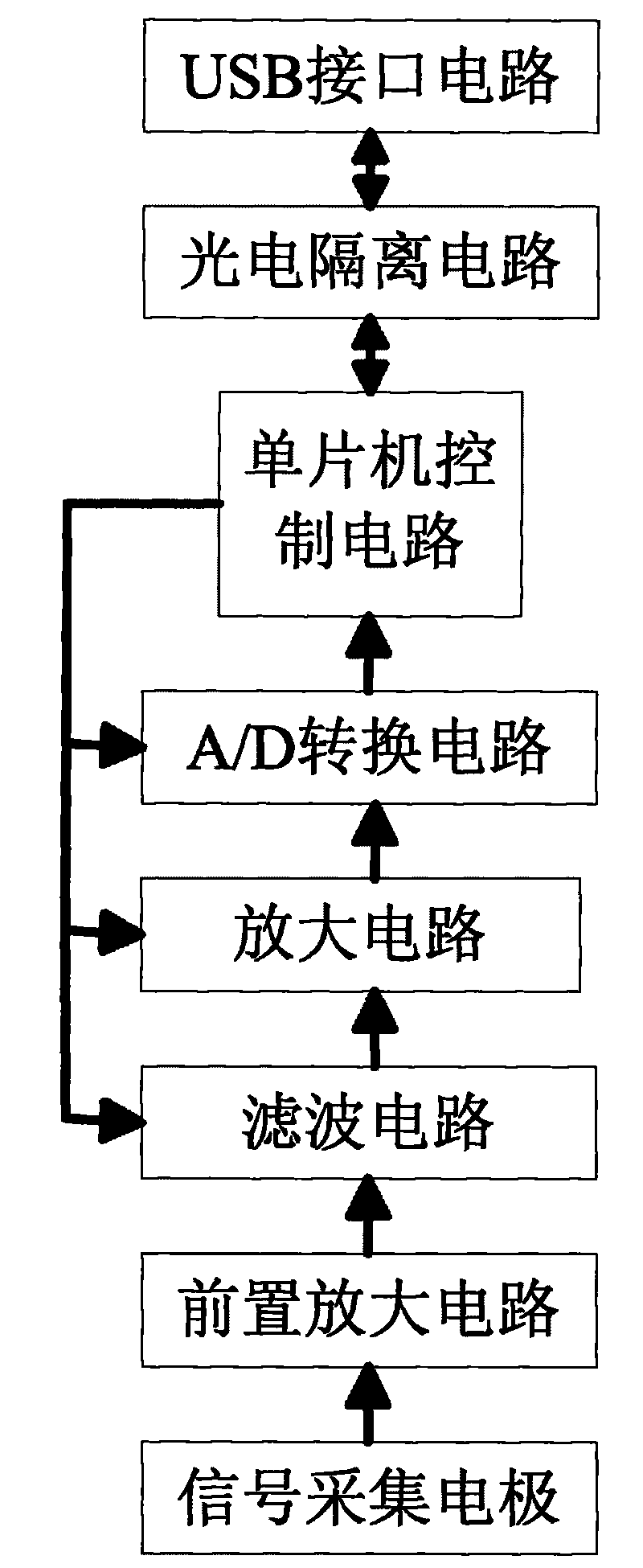
Method and apparatus for monitoring the respiration activity of a subject
ActiveUS20130172770A1Simplify the development processImprove reliabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionRespiratory organ evaluationInductive plethysmographyRadar
The invention relates to a method for monitoring the respiration activity of a subject, comprising the acquisition of a sensor signal of at least one Doppler-Radar sensor representing the respiration activity of a subject, the transformation of the sensor signal into a transformation signal being a series according to Formula (I) where ak is a set of predetermined constant coefficients specific for one individual subject, and processing the transformation signal S(t). The transformation signal can be analysed with basic signal processing techniques that are applied in the field of inductive plethysmography. The invention is further related to a corresponding monitoring system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
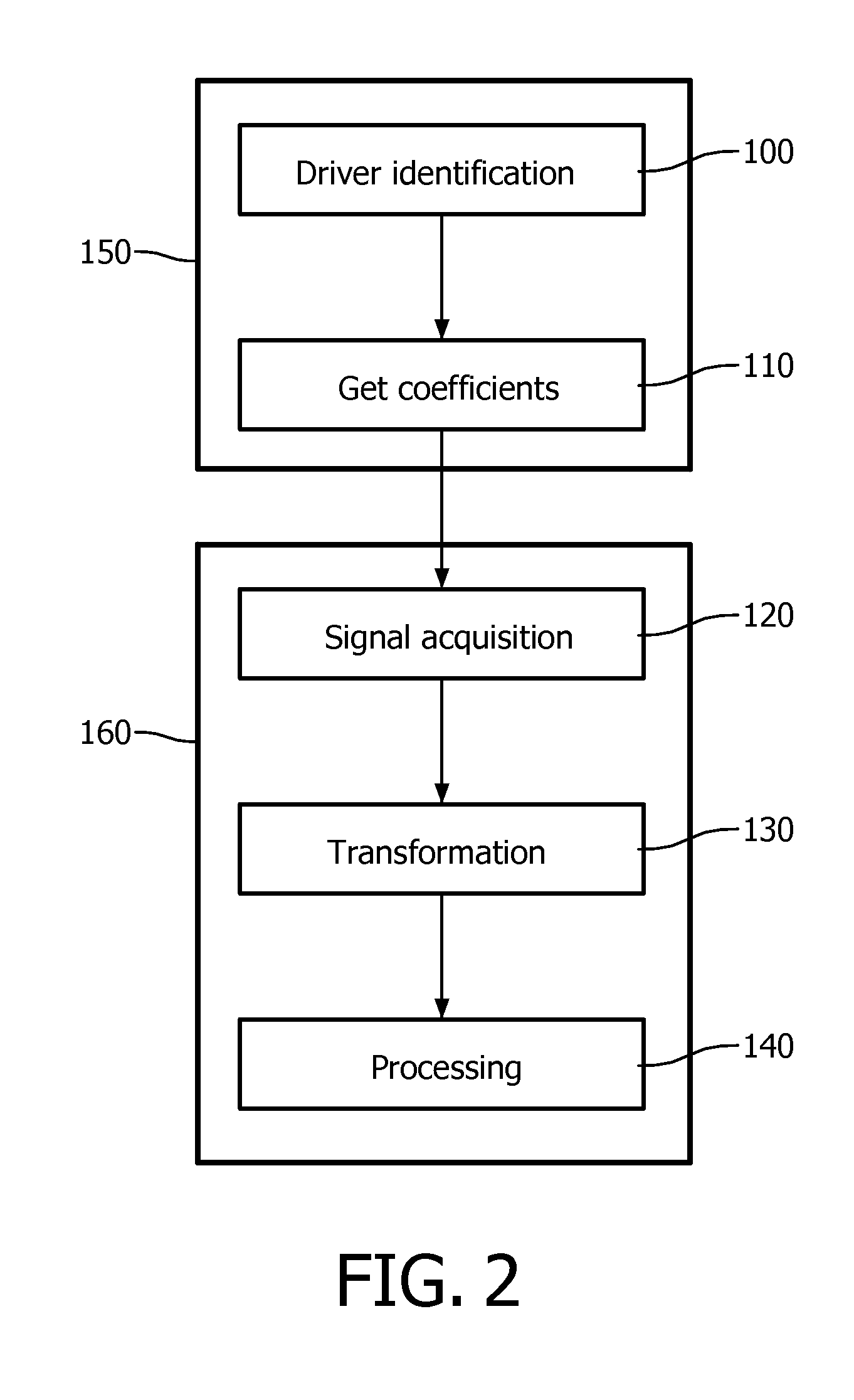
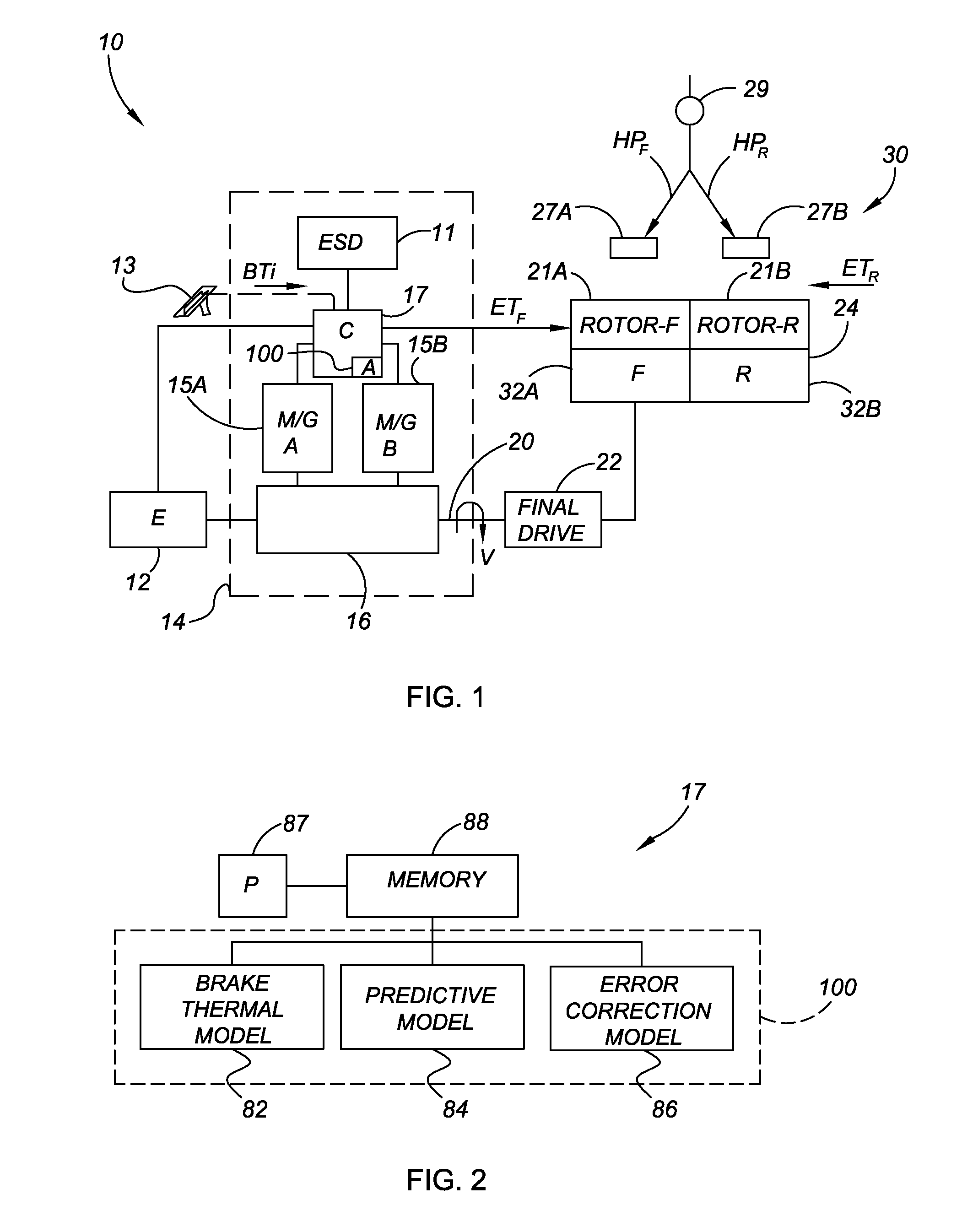
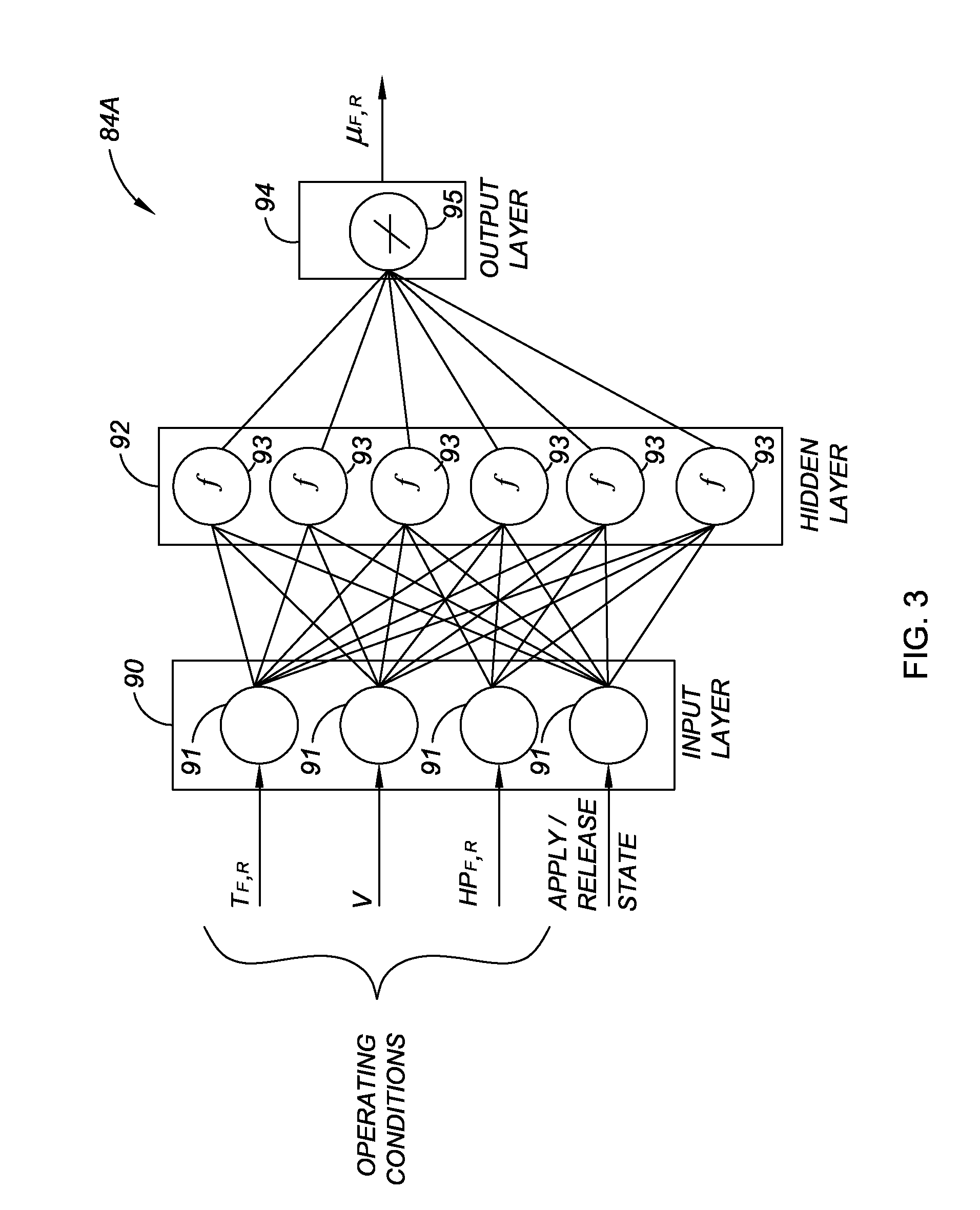
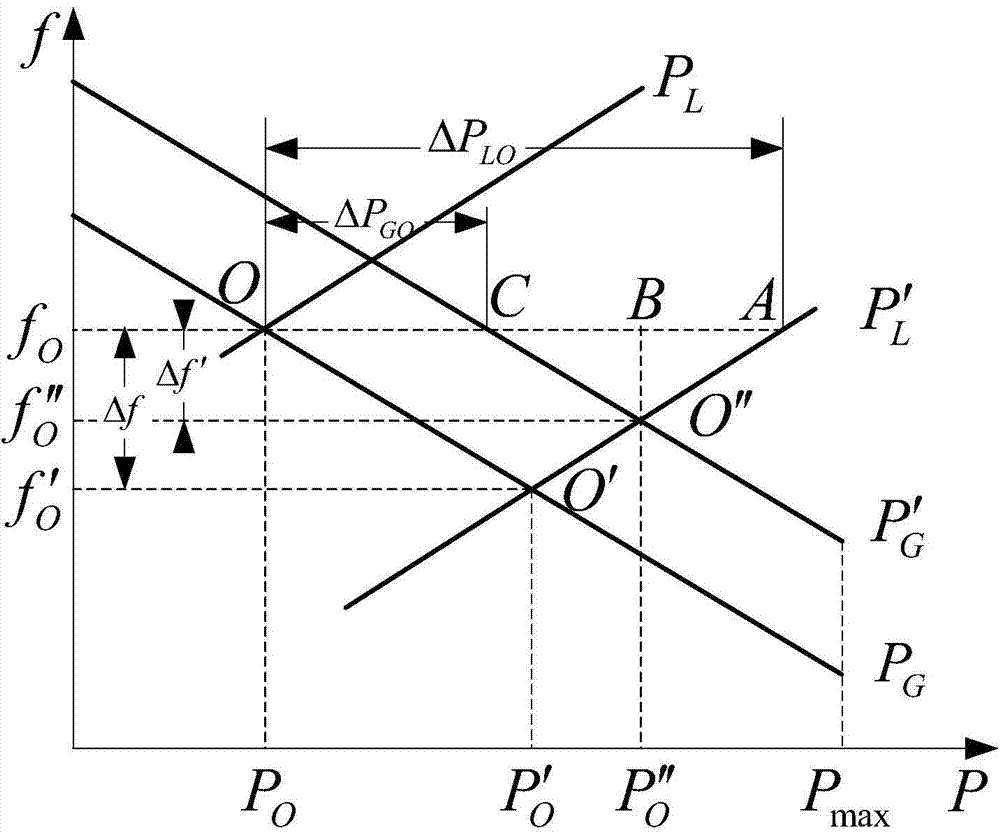
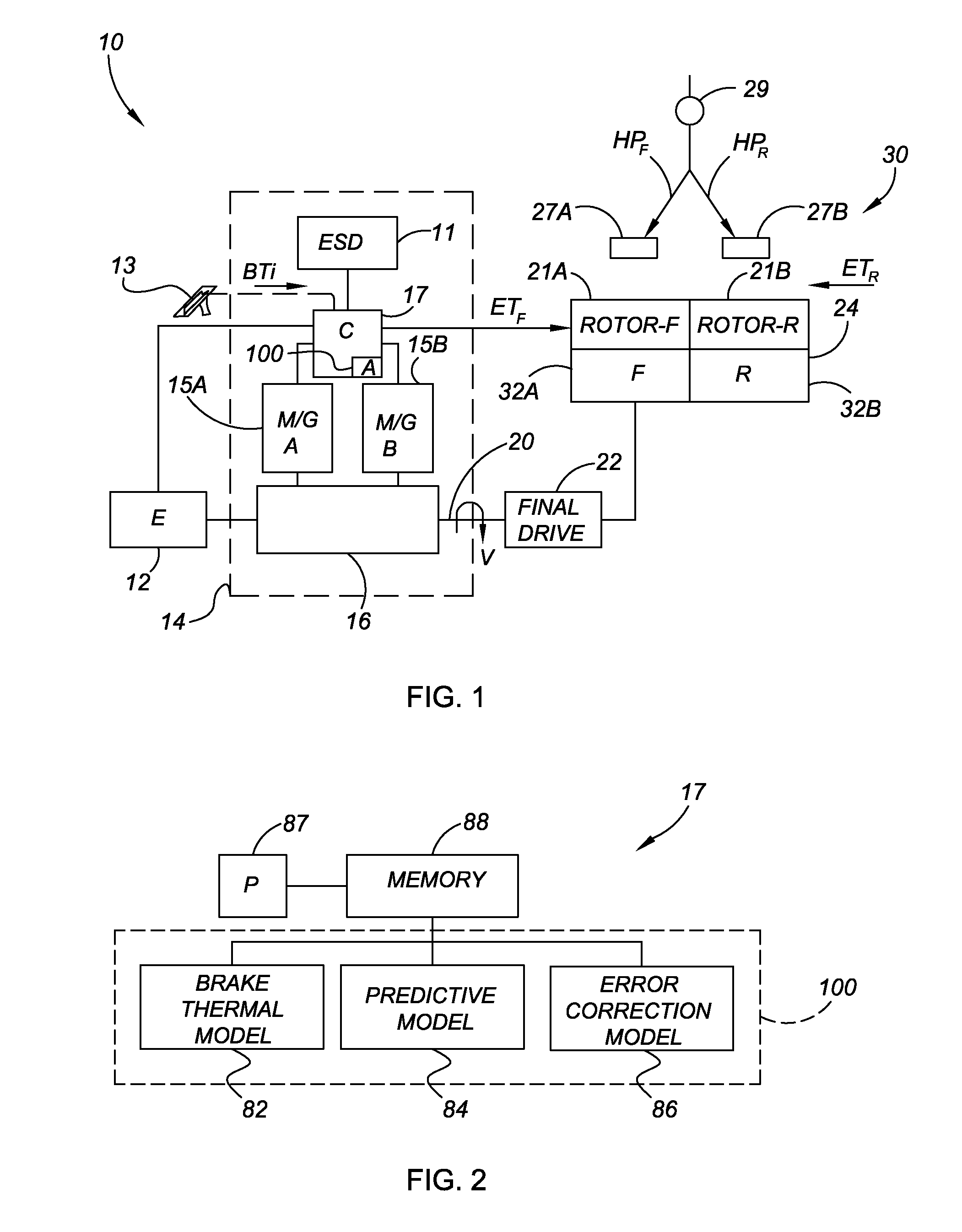
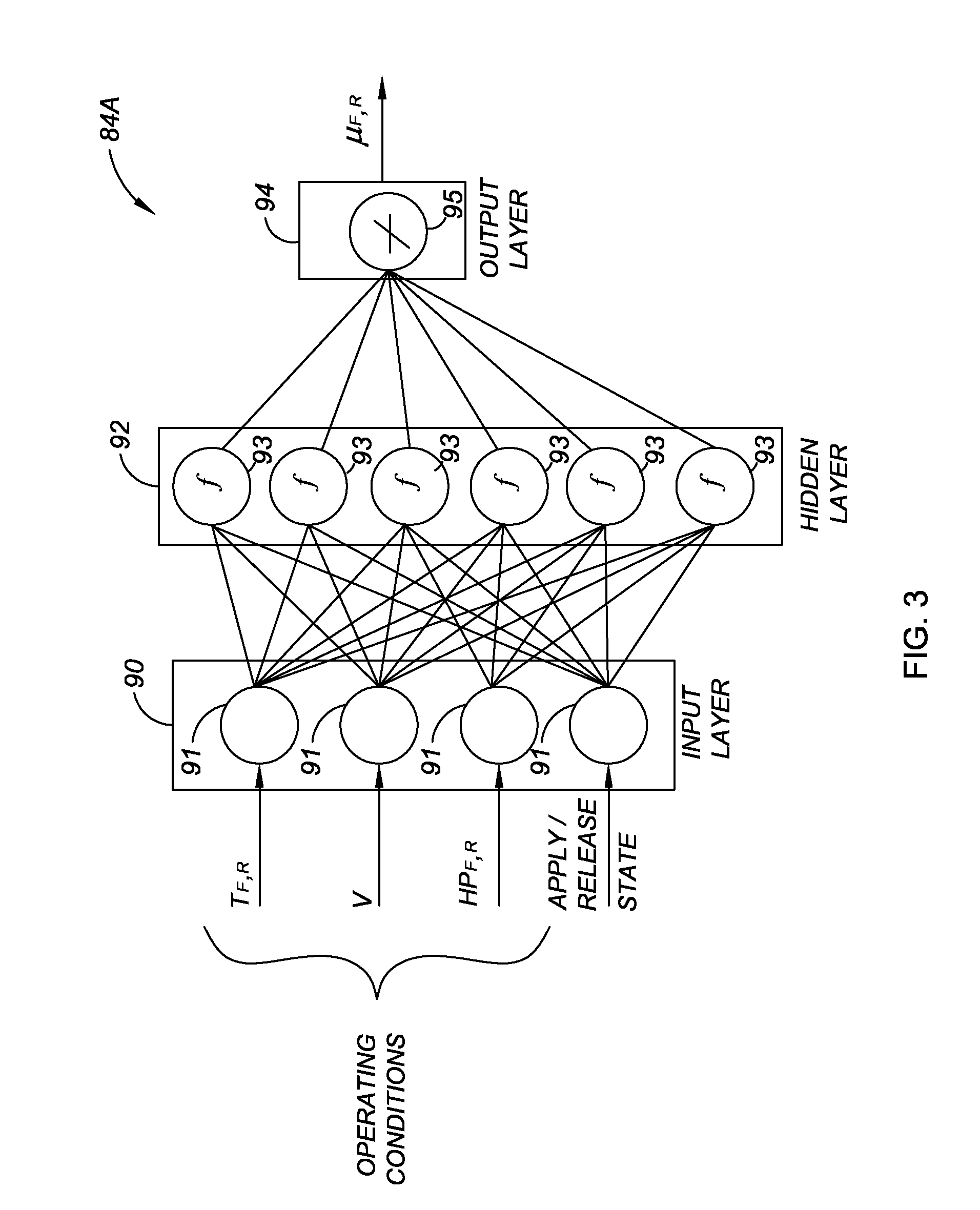
Method and apparatus for predicting braking system friction
InactiveUS20090187320A1Hybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficConstant coefficientsOperant conditioning
A brake system control method determines vehicle operating conditions, compares the conditions to an allowable range, and uses a neural network to predict an expected coefficient of friction when the conditions are within the range. When the conditions fall outside of the range, the method determines an amount of required braking force using a constant coefficient of friction, and calculates the required braking force using the expected coefficient of friction when the conditions are within the range. The vehicle operating conditions include a vehicle speed, brake pressure, modeled brake rotor temperature, and apply state. The expected coefficient is multiplied by a constant or a calculated correction factor. A vehicle has an engine, transmission, and braking system, with a controller and an algorithm for predicting a coefficient of friction for two brake rotors, calculating a hydraulic brake pressure, and for applying the braking system using the hydraulic brake pressure.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
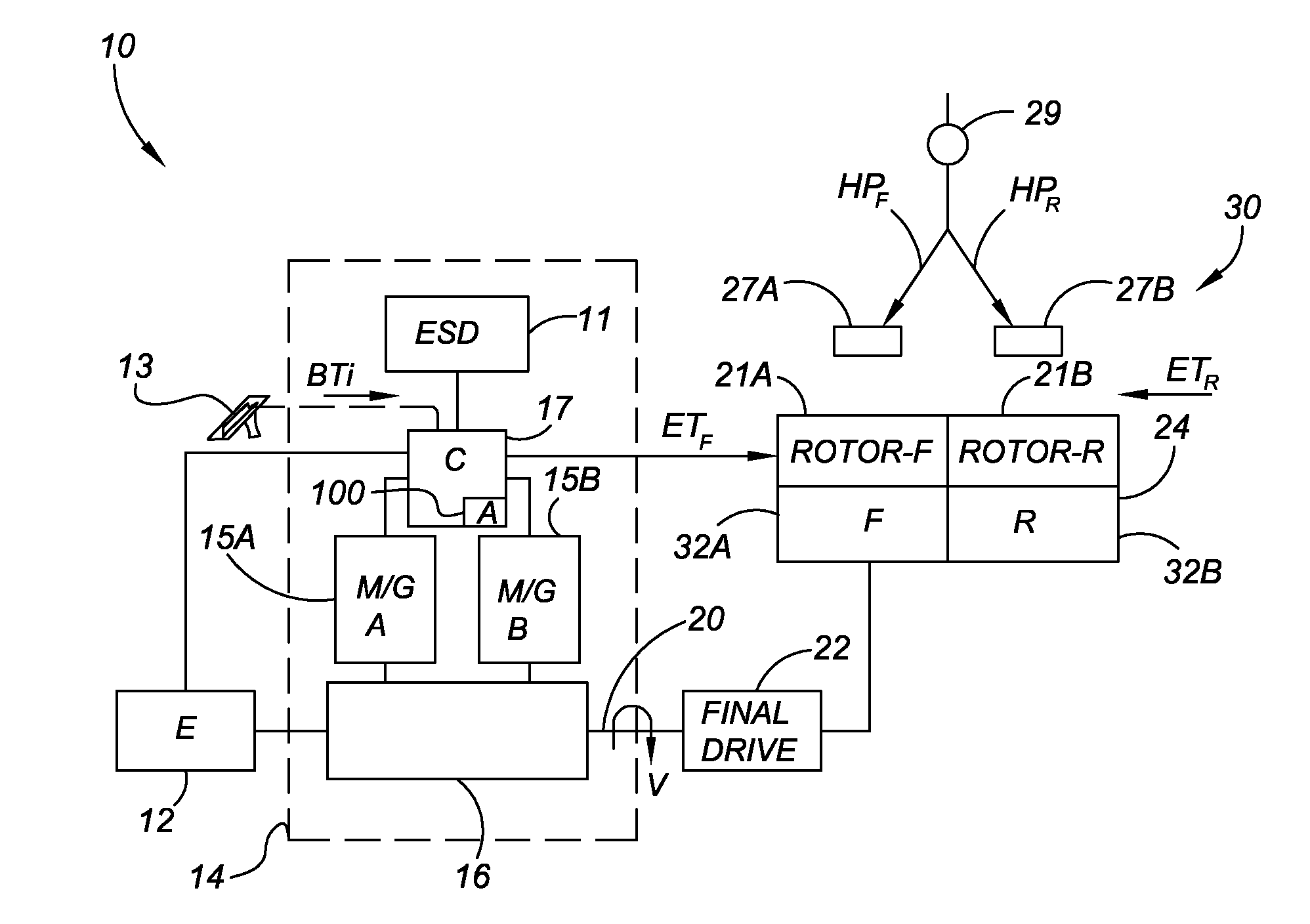
Inverter droop control method capable of achieving secondary frequency modulation and pressure regulation
InactiveCN103501021ARealize the second frequency modulation effectGuaranteed uptimeEfficient power electronics conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsLower limitPower inverter
The invention discloses an inverter droop control method capable of achieving secondary frequency modulation and pressure regulation and belongs to the technical field of distributed power supply inverter output control. According to the inverter droop control method capable of achieving secondary frequency modulation and pressure regulation, aiming at the defect that a traditional local inverter droop control method can not achieve secondary frequency modulation and pressure regulation, with the restriction of the purpose of meeting the upper limit, the lower limit and the specified working point of power output of an inverter, an S-shaped droop control curve is constructed based on a traditional droop control curve with the specified working point as a middle transition point; modeling is achieved by means of a cubic function or a piecewise function, traditional droop control constant coefficients are replaced with a quadratic function, so that power output can be adjusted dynamically along with load change; due to the fact that when a traditional electric generator operates under the control of a frequency modulator / pressure regulator, the movement track of the intersection point of the secondary frequency modulation and pressure regulation power output curve of the electric generator and a load characteristic curve is an S-shaped curve, the curve can be directly used for controlling the inverter, and then secondary frequency modulation and pressure regulation are achieved, and operation performance of the inverter is better than that when the inverter is under traditional droop control.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Image defogging method with optimal contrast ratio and minimal information loss
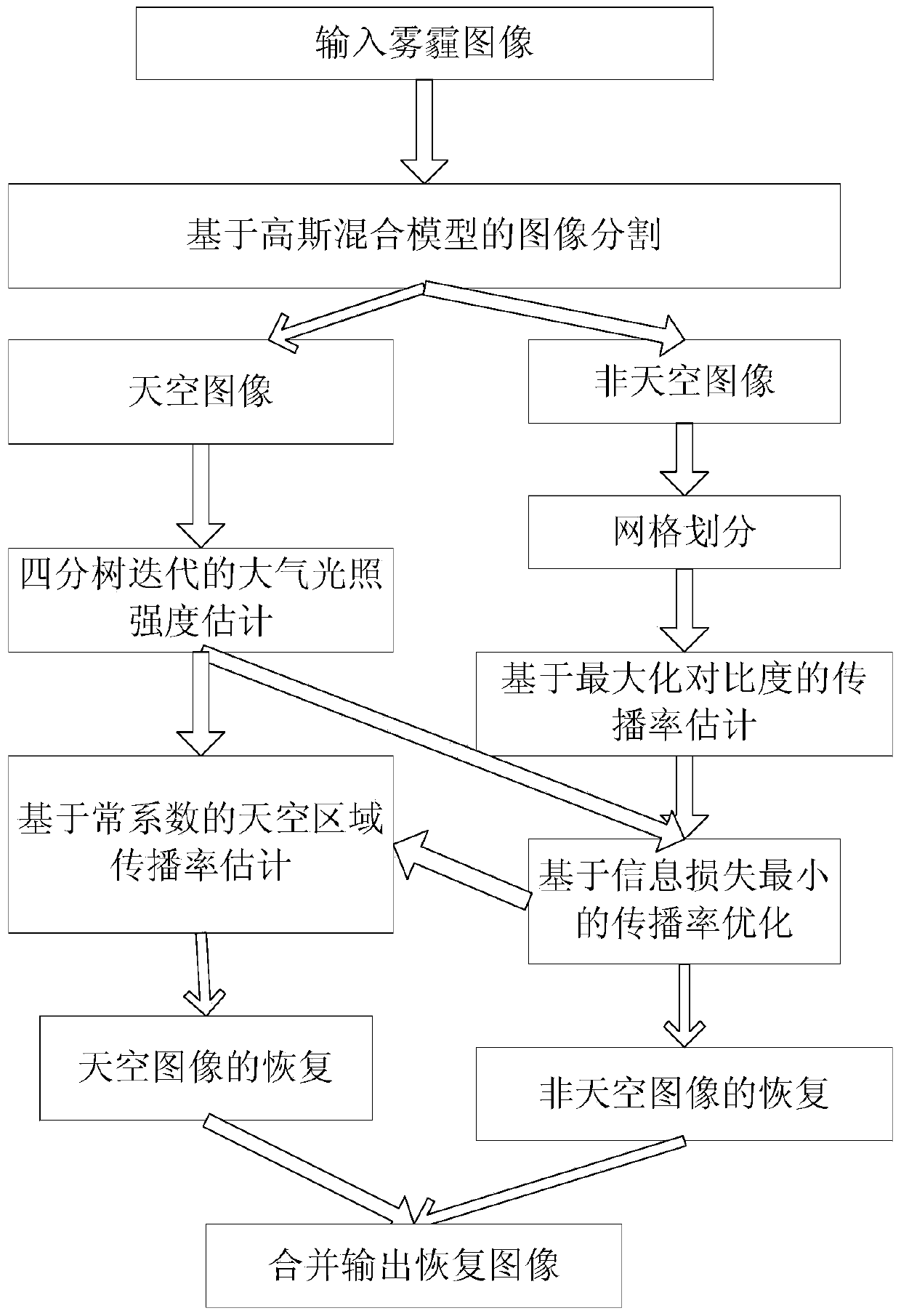
The invention relates to an image defogging method with optimal contrast ratio and minimal information loss. The image defogging method is characterized in that through the adoption of functions including the Gauss mixed model, the quadtree, the maximal contrast ratio and the minimal information loss, the image defogging method is realized. The image defogging method comprises the following steps: firstly, based on the Gauss mixed model and the expected value maximal algorithm, images are segmented into two categories, namely, a sky region and a non-sky region; secondly, the quadtree iteration method is adopted in the sky region of the images to estimate the atmospheric illumination intensity of an atmospheric scattering model; then, the grid partition method is adopted to partition the non-sky region of the images and the functions of the maximal contrast ratio and the minimal information loss are adopted to calculate the spreading rate of an atmospheric lighting model of each grid unit; based on the constant coefficient and the optimal spreading rate of the non-sky region, the spreading rate of the sky region is estimated; finally, the recovery images of the sky region and the non-sky region are merged and output.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
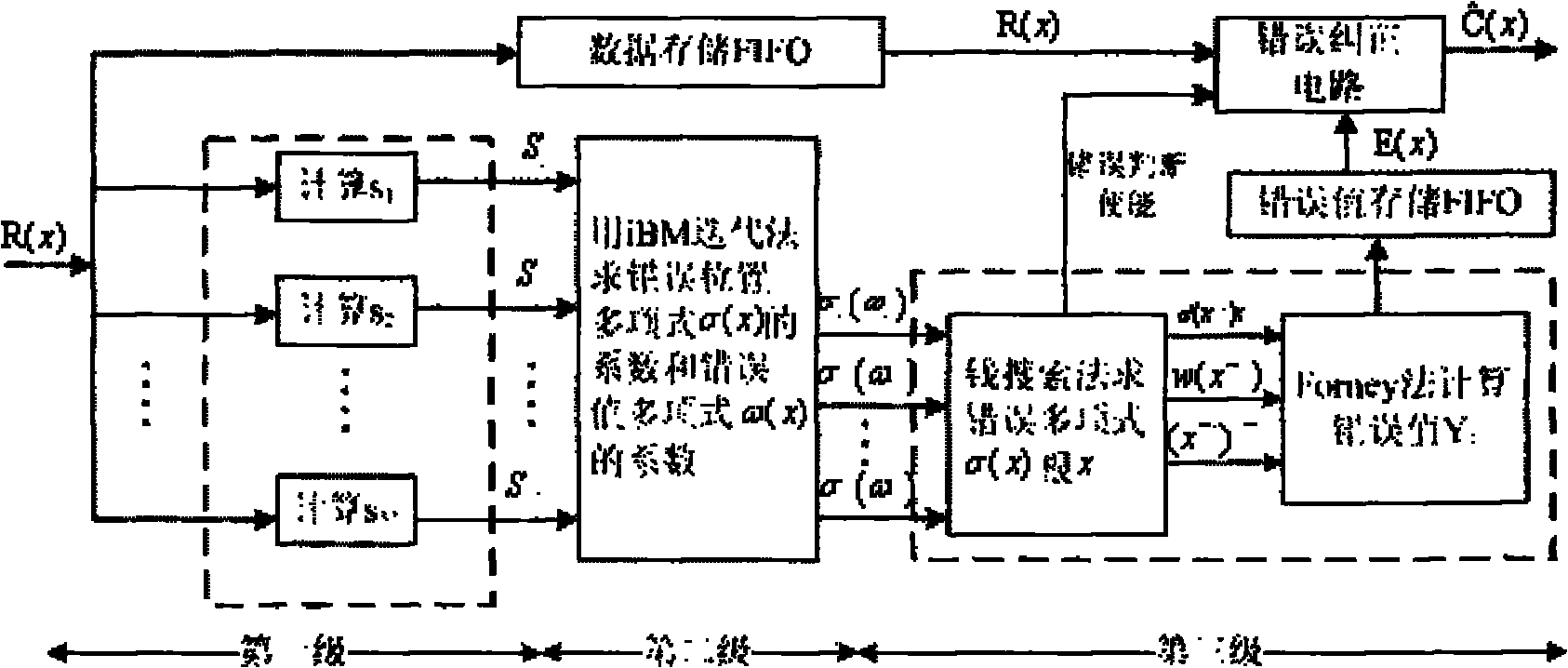
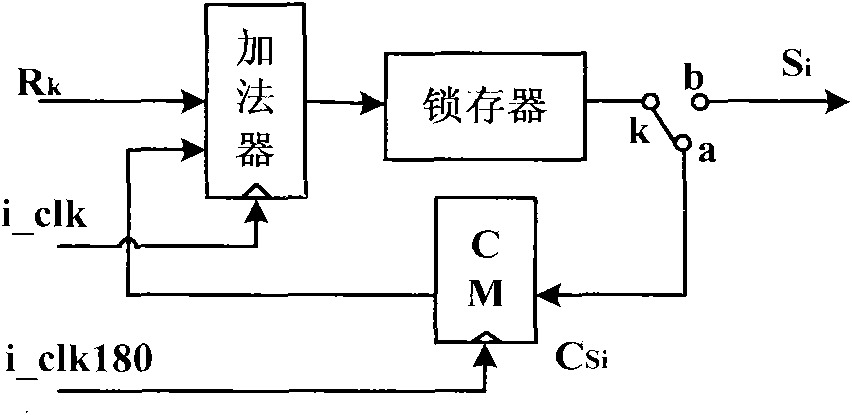
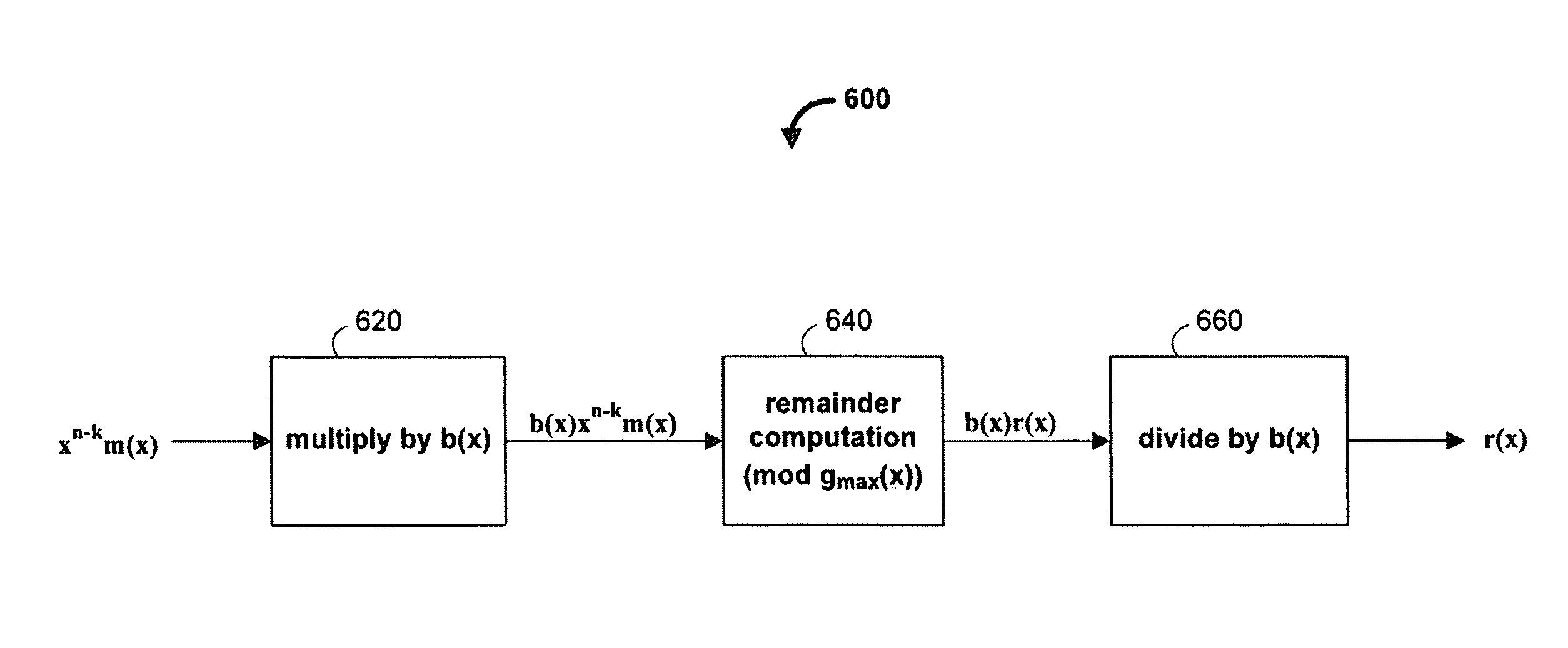
Implementation method of high-speed reed-solomon (RS) codec based on field programmable gate array (FPGA)
InactiveCN102122964AHigh data pass rateImprove efficiencyError preventionCyclic codesThree levelComputer architecture
The invention discloses an implementation method of a high-speed reed-solomon (RS) codec based on a field programmable gate array (FPGA), comprising FPGA implementation of a high-speed RS (244, 212) coder and FPGA implementation of a high-speed RS (244, 212) decoder. In the invention, the high-speed RS coder is a circuit based on polynomial division, and the high-speed RS decoder is based on three-level pipeline architecture, and dual-clock driving based on clock i_clk and reverse clock i_clk180 is adopted; In addition, based on a common Galois field (GF) multiplying unit, three basic computing units, including a constant coefficient GF multiply-add fused unit, a constant coefficient GF multiplying unit and a dual-clock period controlled GF multiplying unit are provided, thereby greatly improving the computing speed and reducing hardware complexity. The implementation method has the advantages of high supporting throughput rate and strong capacity of correcting burst errors and can be applied to many aspects.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
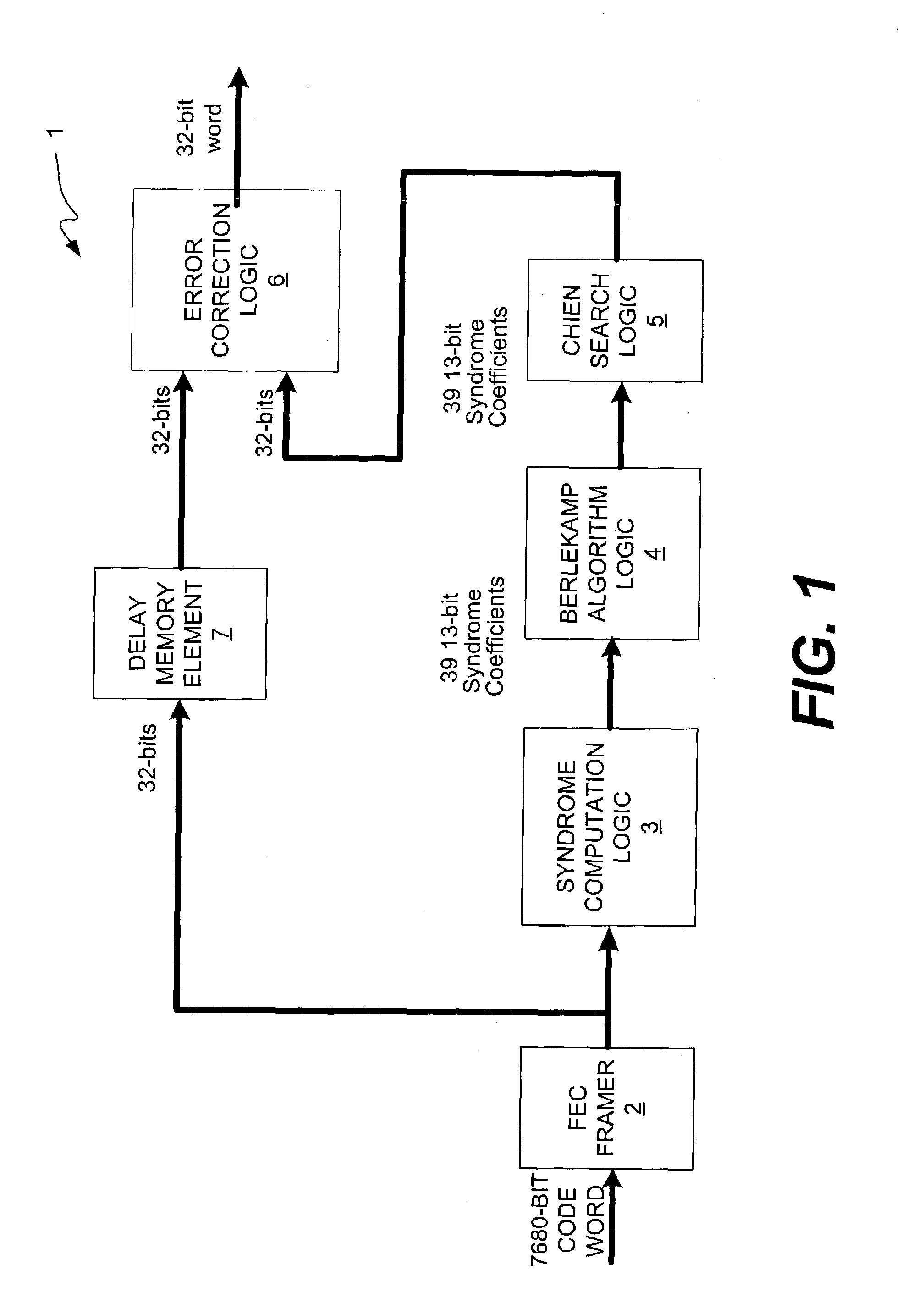
Method and apparatus for use in a decoder of a forward error correction (FEC) system for locating bit errors in a error locator polynomial
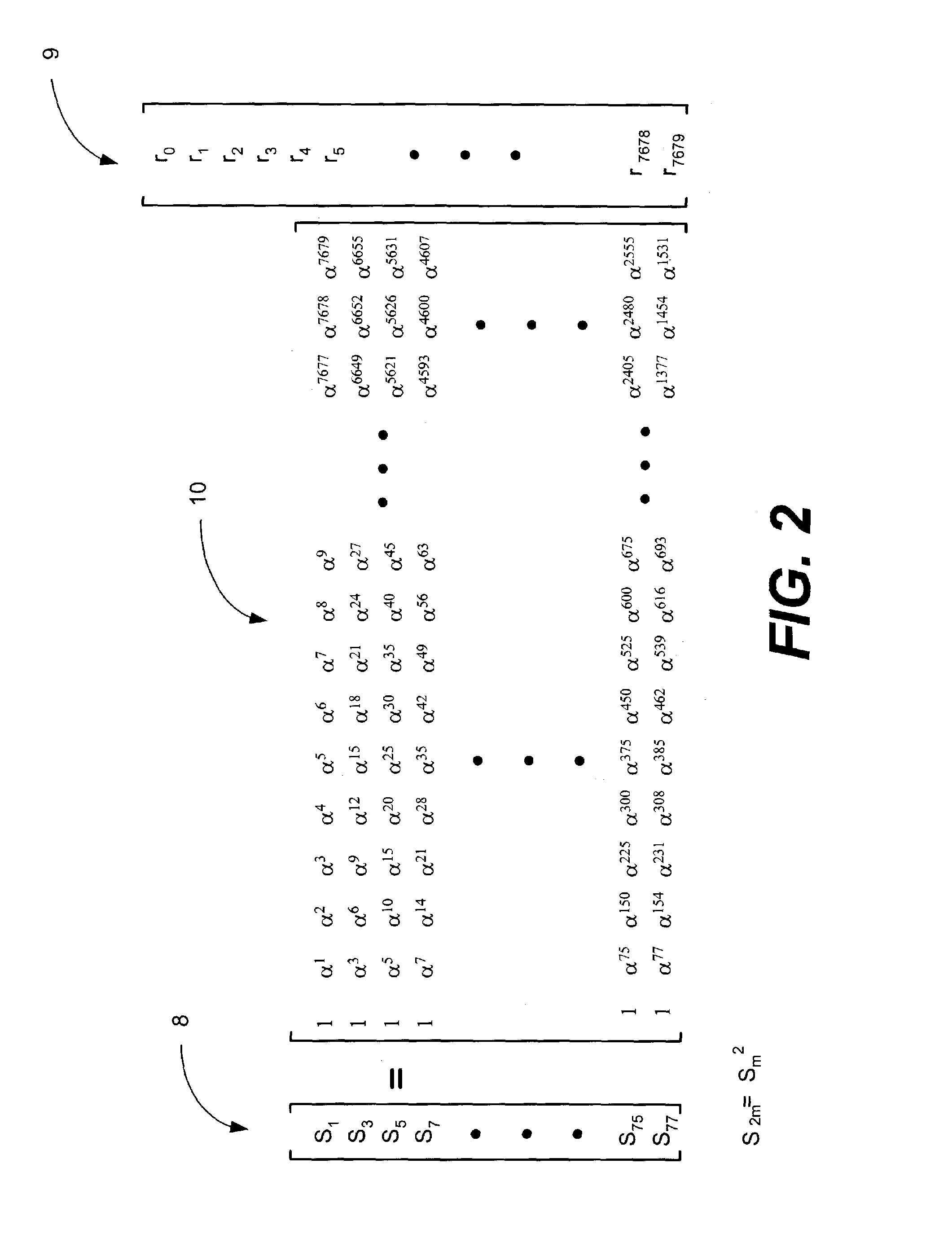
ActiveUS7058876B1Quickly and efficiently processingLimit amount of neededDigital data processing detailsCode conversionAlgorithmForward error correction
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for quickly and efficiently processing an error correction polynomial to locate bit errors using a Chien search algorithm. In accordance with the present invention, it has been determined that multiplying the Λ coefficients of the error locator polynomial by a scaling vector prior to performing the Chien search algorithm matrix operations, it possible to use constant coefficients in the matrix multiply logic. This enables a relatively small amount of logic to be used to perform the matrix multiplication operations of the Chien search algorithm. The Chien search algorithm logic of the present invention is configured to perform many matrix multiply operations in parallel, which enables the Chien search algorithm to be executed very quickly to locate the bit errors in the error locator polynomial. Such a large number of matrix multiply operations would normally require a very large number of gates. However, the constant coefficient matrix multiply logic configuration of the present invention that is made possible by the aforementioned scaling significantly limits the amount of logic needed to perform the matrix multiply operations. Therefore, the present invention enables very high-speed throughput with respect to error correction, and does so using a relatively small amount of logic. This renders the decoder of the present invention suitable for use in high data rate systems. Furthermore, the use of a relatively small amount of logic limits area and power consumption requirements.
Owner:CIENA
Least square fitting dynamic frequency measurement method
ActiveCN107271768AReal-time measurementEasy to monitorFrequency analysisComplex mathematical operationsFrequency measurementsContinuous signal
The invention discloses a least square fitting dynamic frequency measurement method. The method comprises steps that A / D conversion sampling of power grid continuous signals is carried out to form equal time interval discrete signals; an FIR digital filter is employed to extract relatively pure fundamental wave discrete signals, and a sampling matrix is formed; a binary function Taylor expansion is utilized, frequency deviation and frequency change deviation of the power grid signals are extracted, and a constant coefficient matrix is calculated in an offline mode; the least square method is utilized to solve an unknown parameter matrix containing frequency deviation and frequency change deviation; dynamic frequency of each sampling point in the data window is solved. The method is advantaged in that based on the multivariate Taylor series, a power grid signal measurement matrix equation is established, the least square method is utilized to solve an equation linearity fitting problem, on the condition that frequency tracking is realized, a frequency change rate can be further monitored, and high accuracy, good timeliness and strong interference immunity are realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
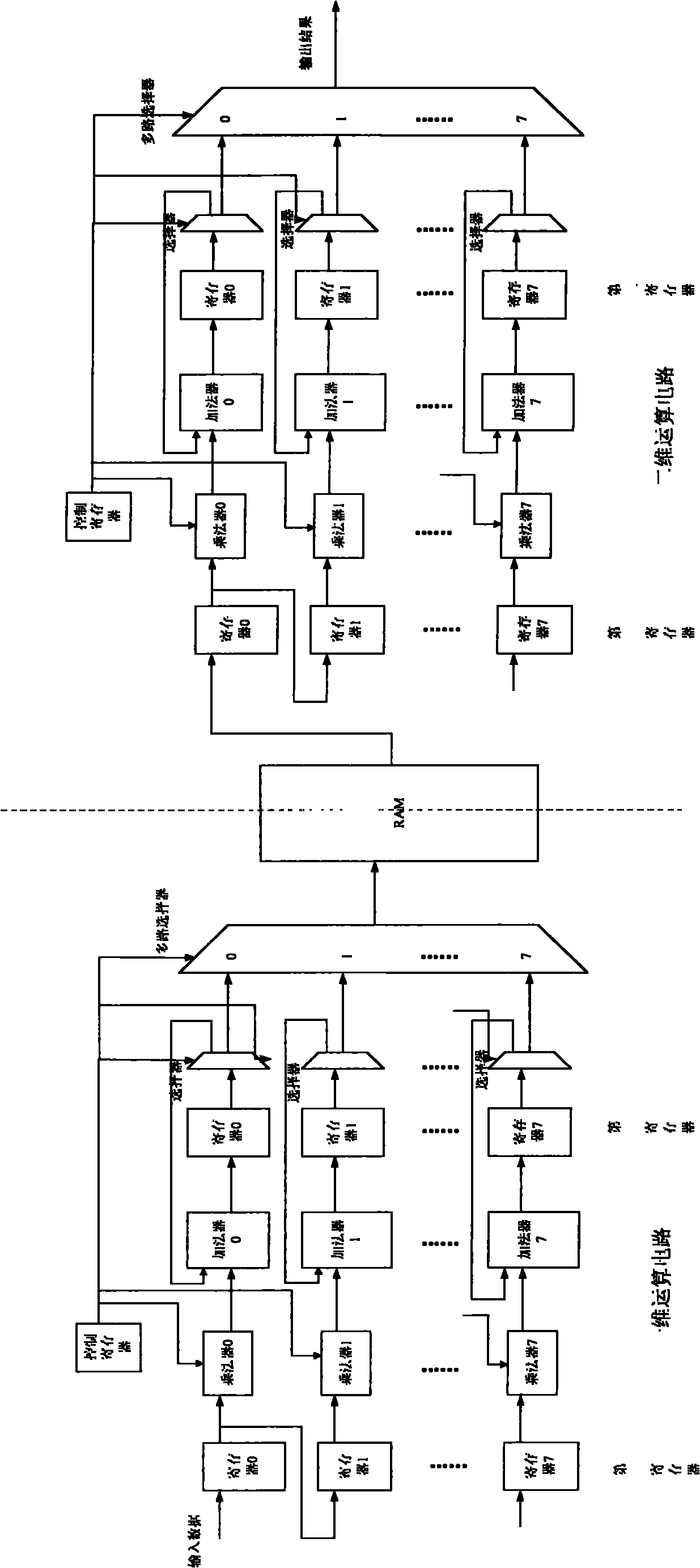
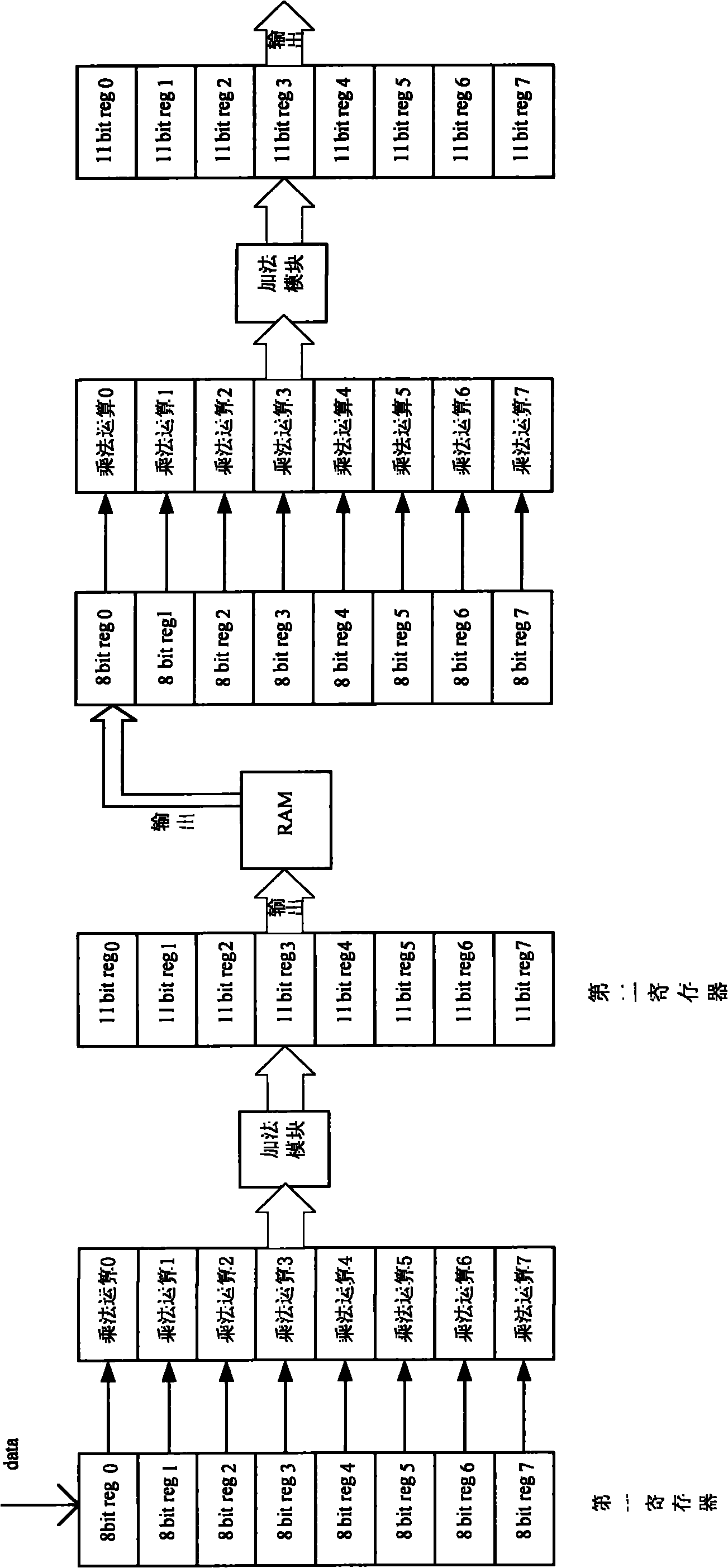
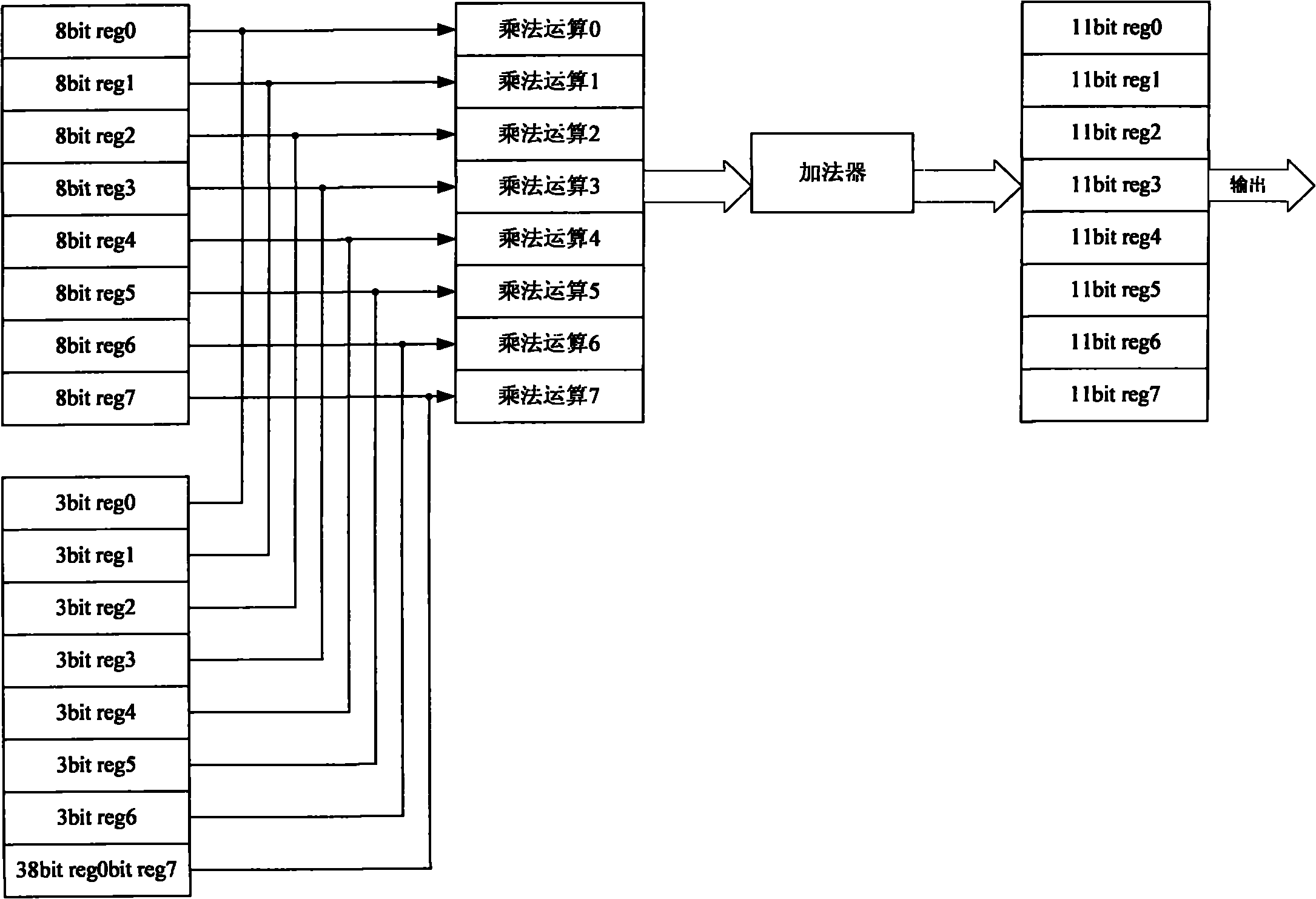
DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) realizing method and circuit
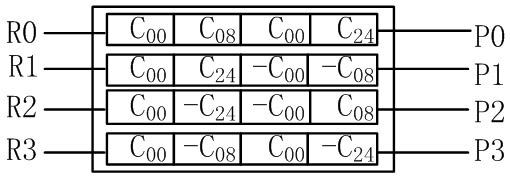
ActiveCN102065309AFast operationSave resourcesTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationInterference resistanceProcessor register
The invention discloses a DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) realizing method comprising the following steps of: 1. serially inputting data in an M*M image data block to M registers; 2. outputting the data to a multiplication module by the registers, multiplying the data with a constant coefficient matrix stored in the multiplication module and sending the result to an addition module; 3. summating the data by the addition module and outputting the result; 4. storing the data into a storage module row by row or column by column in an M*M matrix way to form an M*M data block to finish a one-dimensional DCT operation; and 5. inputting the data in the storage module into the other M registers row by row or column by column, and repeating the steps 2 and 3 to finish two-dimensional DCT operation. The invention also discloses a DCT realizing circuit comprising a one-dimensional operation circuit and a two-dimensional operation circuit which both adopt a serial operation way with rapid operation and without deserialization. The DCT realizing circuit has a stronger capacity of resisting disturbance and a function of interrupt recovery.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
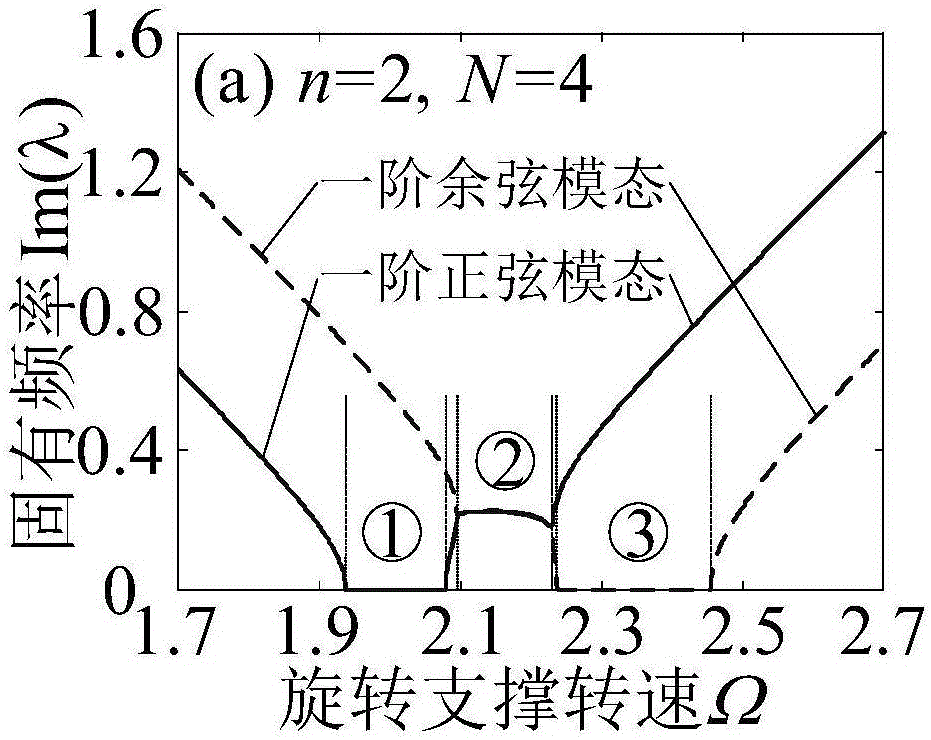
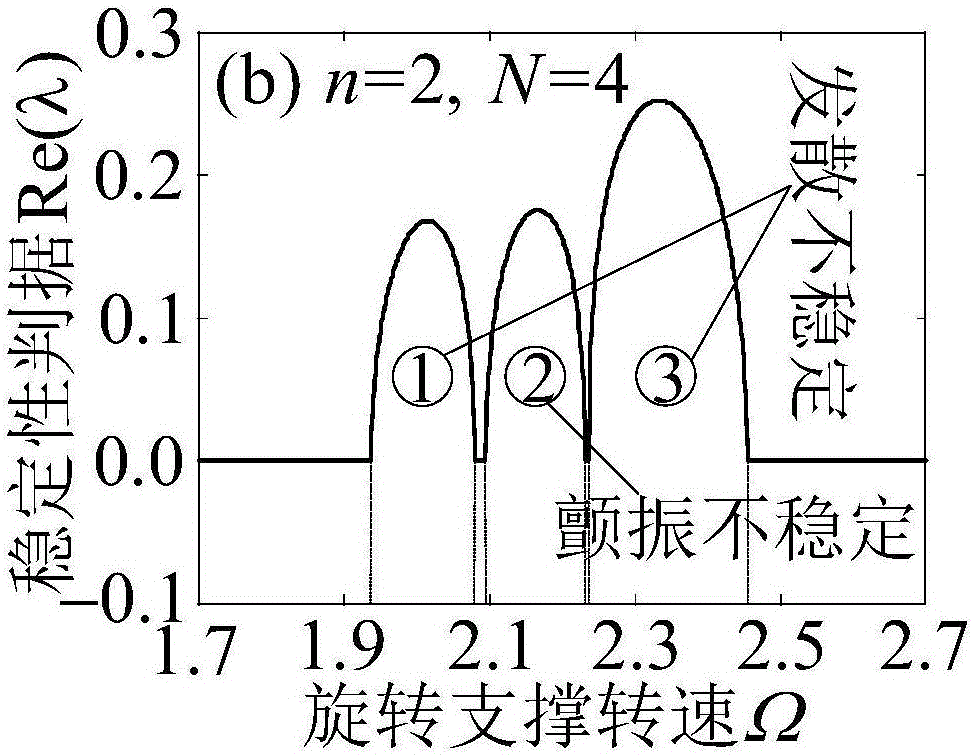
Parametric elastic vibration analysis method of rotating annular periodic structure
ActiveCN106547957AStable structural designOvercoming inefficienciesGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic modelsDynamic equation
A parametric elastic vibration analysis method of a rotating annular periodic structure comprises the steps of building a rigid-elastic coupling dynamic model of the rotating annular periodic structure according to a Hamilton principle under a global stationary coordinate system; introducing coordinate conversion, and converting the dynamic model to a support follow-up coordinate system so that a parametric item in an original equation is eliminated; performing discrete processing on a partial differential constant coefficient dynamic equation under the rotating support follow-up coordinate system by a Galerkin method to obtain an ordinary differential matrix equation; analyzing a characteristic value of the ordinary differential matrix equation by using a classical vibration theory; and respectively analyzing mode characteristic of the rotating annular periodic structure and a dynamic stability rule of parametric elastic vibration by employing an imaginary part and a real part of the characteristic value of the ordinary differential matrix equation. The parametric elastic vibration analysis method can be used for dynamic analysis of rotating machinery, calculation and solution of the mode characteristic of a system, and analysis on the dynamic stability and the dynamic response of the system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
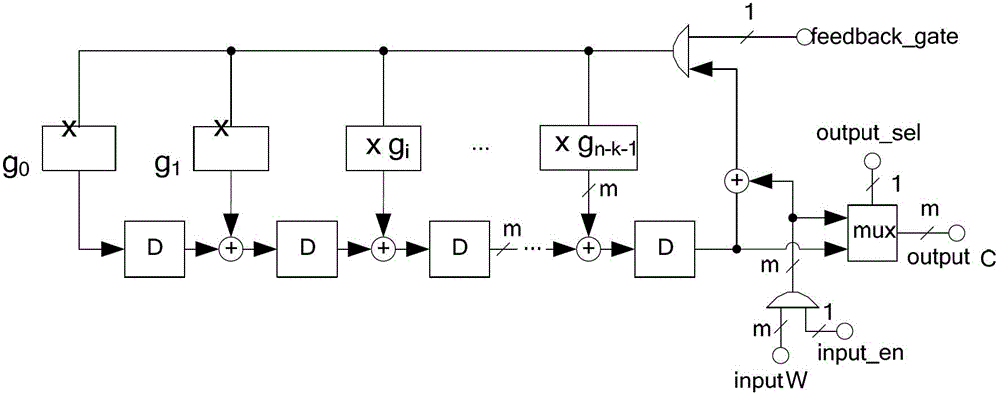
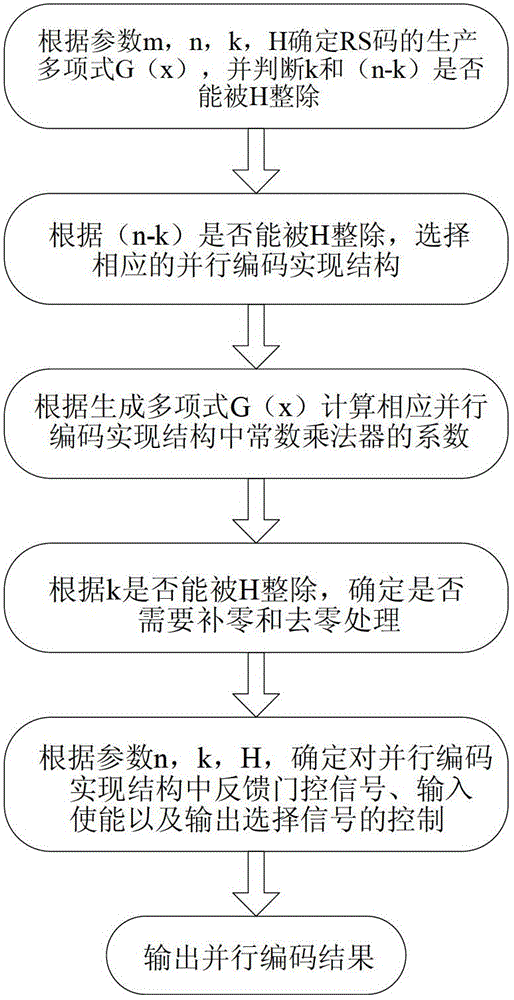
Parallel implementation method and device for reed-solomon (RS) code
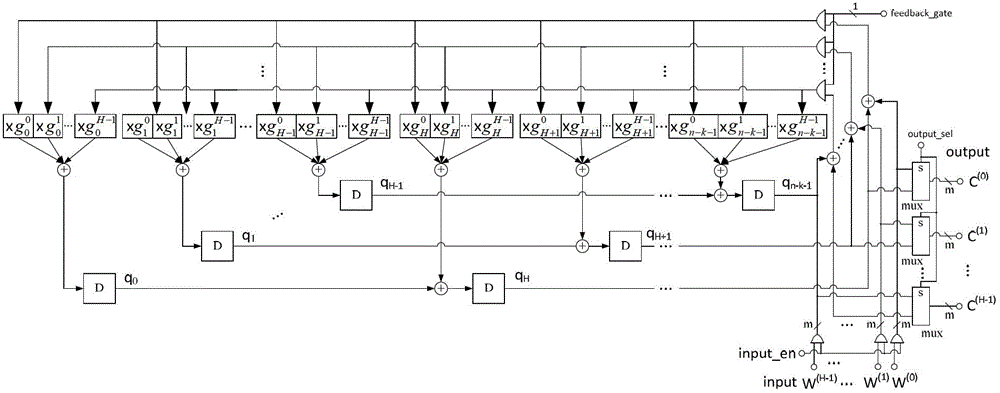
The invention discloses a parallel implementation method and a parallel implementation device for a reed-solomon (RS) code. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a generating polynomial G(x) of an RS code according to parameters m, n and k, judging whether k and (n-k) can be exactly divided by H; selecting a corresponding parallel code implementation structure according to the condition whether (n-k) can be exactly divided by H; calculating a coefficient of a constant coefficient multiplier in the parallel code implementation structure according to the generating polynomial G(x); determining whether zero-fill or zero-suppression processing is required according to the condition whether k can be exactly divided by H; determining control of feedback door control signal, and input enabling and output selection signals in the parallel code implementation structure according to the parameters n, k and H; and outputting a parallel coding result. The parallel implementation method and the parallel implementation device are suitable for the parallel implementation of an arbitrary RS code pattern on a Galois Field (GF)(2m) under arbitrary parallelism degree H (H is not greater than k).
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Universal method applied to kinds of video standards for multi-size two-dimensional integer cosine transform
InactiveCN102387367ALow costReduce operational complexityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
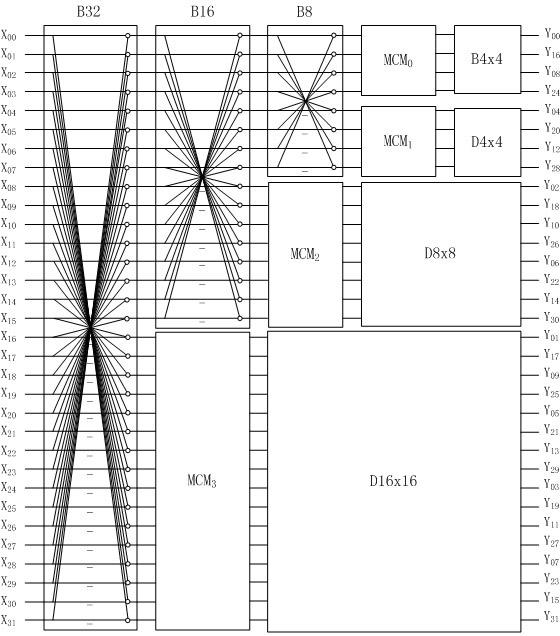
The invention belongs to the technical field of digital video signal coding, and particularly discloses a universal method applied to kinds of video standards for multi-size two-dimensional integer cosine transform. A plurality of different video coding standards can be supported by configuring a coefficient value of a constant coefficient multiplier, and simultaneously, the four transformation sizes of 4*4, 8*8, 16*16 and 32*32 are supported. By the method, two-dimensional discrete cosine transform is decomposed into twice one-dimensional discrete cosine transform; when the one-dimensional discrete cosine transform of four points is calculated, a computational load is reduced and computation speed is increased by adopting a conventional butterfly computation method; and an improved butterfly computation method is adopted for the one-dimensional discrete cosine transform of eight points, sixteen points and thirty-two points, so a relatively smaller one-dimensional discrete cosine transform unit can be multiplexed when the one-dimensional discrete cosine transform of a relatively larger size is computed, thereby greatly reducing the hardware resource overhead of the whole system.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
RS codec architecture that combines a compact encoder and serial BMA
A Reed-Solomon (RS) coding system is provided that can employ an RS code of varying correction power, and which can maintain a small area requirement. The Reed-Solomon coding system can include an RS encoder and an RS decoder. Both of these components can be implemented using primarily constant multipliers rather than more area-consuming general multipliers. For example, the programmable encoder can be realized by implementing polynomials with constant coefficients rather than variable coefficients, and a Berlekamp-Massey algorithm performed by the decoder can be realized using a serial implementation. To further reduce the area of the coding system, hardware sharing can be utilized between the RS encoder and the RS decoder.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for predicting braking system friction
InactiveUS7957875B2Digital data processing detailsWheel adhesionConstant coefficientsOperant conditioning
A brake system control method determines vehicle operating conditions, compares the conditions to an allowable range, and uses a neural network to predict an expected coefficient of friction when the conditions are within the range. When the conditions fall outside of the range, the method determines an amount of required braking force using a constant coefficient of friction, and calculates the required braking force using the expected coefficient of friction when the conditions are within the range. The vehicle operating conditions include a vehicle speed, brake pressure, modeled brake rotor temperature, and apply state. The expected coefficient is multiplied by a constant or a calculated correction factor. A vehicle has an engine, transmission, and braking system, with a controller and an algorithm for predicting a coefficient of friction for two brake rotors, calculating a hydraulic brake pressure, and for applying the braking system using the hydraulic brake pressure.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Bit rate estimation method of SAO mode decision applied to encoder of HEVC standard
ActiveCN103442229AIncrease working frequencyReduce overheadTelevision systemsDigital videoEstimation methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of high-definition digital video compression coding and decoding, and particularly relates to a bit rate estimation method of SAO mode decision applied to an encoder of the HEVC standard. A few statistical information is obtained according to a formula, then four offsets of a luminance component Y of a current block image in the SAO mode decision under 5 ED modes, namely 20 offsets, are obtained in total, and a chrominance component Cb and a chrominance component Cr which correspond to the Y respectively have 4 offsets under the EO modes. Distortion means distortion, lambda stands for a constant coefficient, Bitrate serves as a bit rate, and Cost is a cost value under a certain mode. According to the bit rate estimation method, bit rate estimation of the mode decision in an SAO module can be quickly carried out, hardware expenditure is reduced, meanwhile operating frequency of hardware can be obviously improved, and thus real-time coding of high-definition videos can be achieved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Design method for noise-absorption metal fibrous porous material, metal fibrous porous material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103031461AEfficient sound absorptionHigh porositySound producing devicesNoise controlPorosity
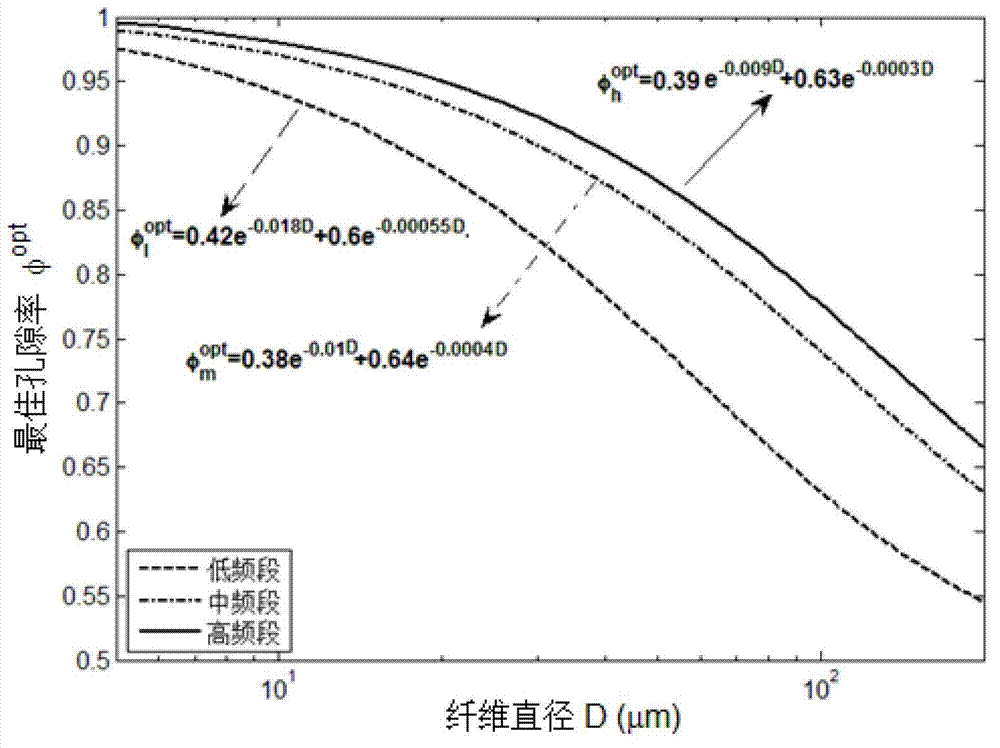
The invention provides a design method for a noise-absorption metal fibrous porous material, the metal fibrous porous material and a preparation method thereof. According to the design method, the porosity and the fiber diameter of the metal fibrous porous material meet the following relational expression: phi<opt>=x1e<x2D>+x3e<x4D>, wherein, phi<opt> is the optimal porosity, D is the fiber diameter, x1, x2, x3 and x4 are constant coefficients and are changed with change of the thickness and the noise frequency of the metal fibrous porous material and obtained by calculating a plurality of data points through an optimization method. Under the condition that the noise frequency band and the fiber diameter are determined, the optimal porosity of the metal fibrous porous material with high-efficiency noise absorption performance can be obtained by the design method. The metal fibrous porous material obtained by the design method can meet the noise absorption requirement of the specific frequency band and can be widely applied to noise control in rail traffic, aerospace, automobiles, machining operation and experimental places.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for monitoring the respiration activity of a subject
ActiveUS9883821B2Simplify the development processImprove reliabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionRespiratory organ evaluationInductive plethysmographyRadar
The invention relates to a method for monitoring the respiration activity of a subject, comprising the acquisition of a sensor signal of at least one Doppler-Radar sensor representing the respiration activity of a subject, the transformation of the sensor signal into a transformation signal being a series according to Formula (I) where ak is a set of predetermined constant coefficients specific for one individual subject, and processing the transformation signal S(t). The transformation signal can be analyzed with basic signal processing techniques that are applied in the field of inductive plethysmography. The invention is further related to a corresponding monitoring system.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
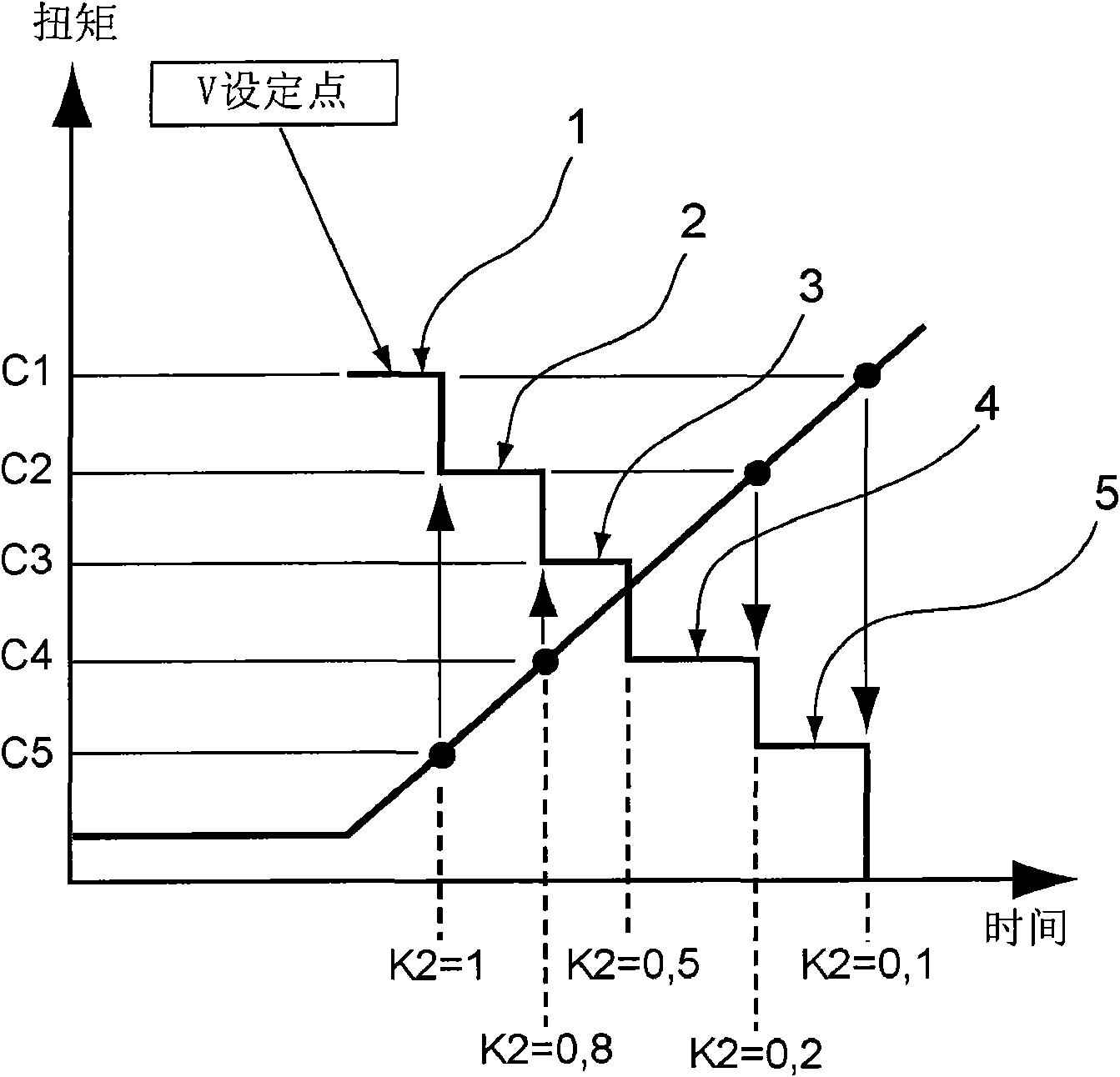
Method for automatically adjusting the screwing speed of a screwdriver in several successive steps and corresponding tool
InactiveCN101863004APrevent overshootRefinement parametersSpannersWrenchesLower limitComputer science
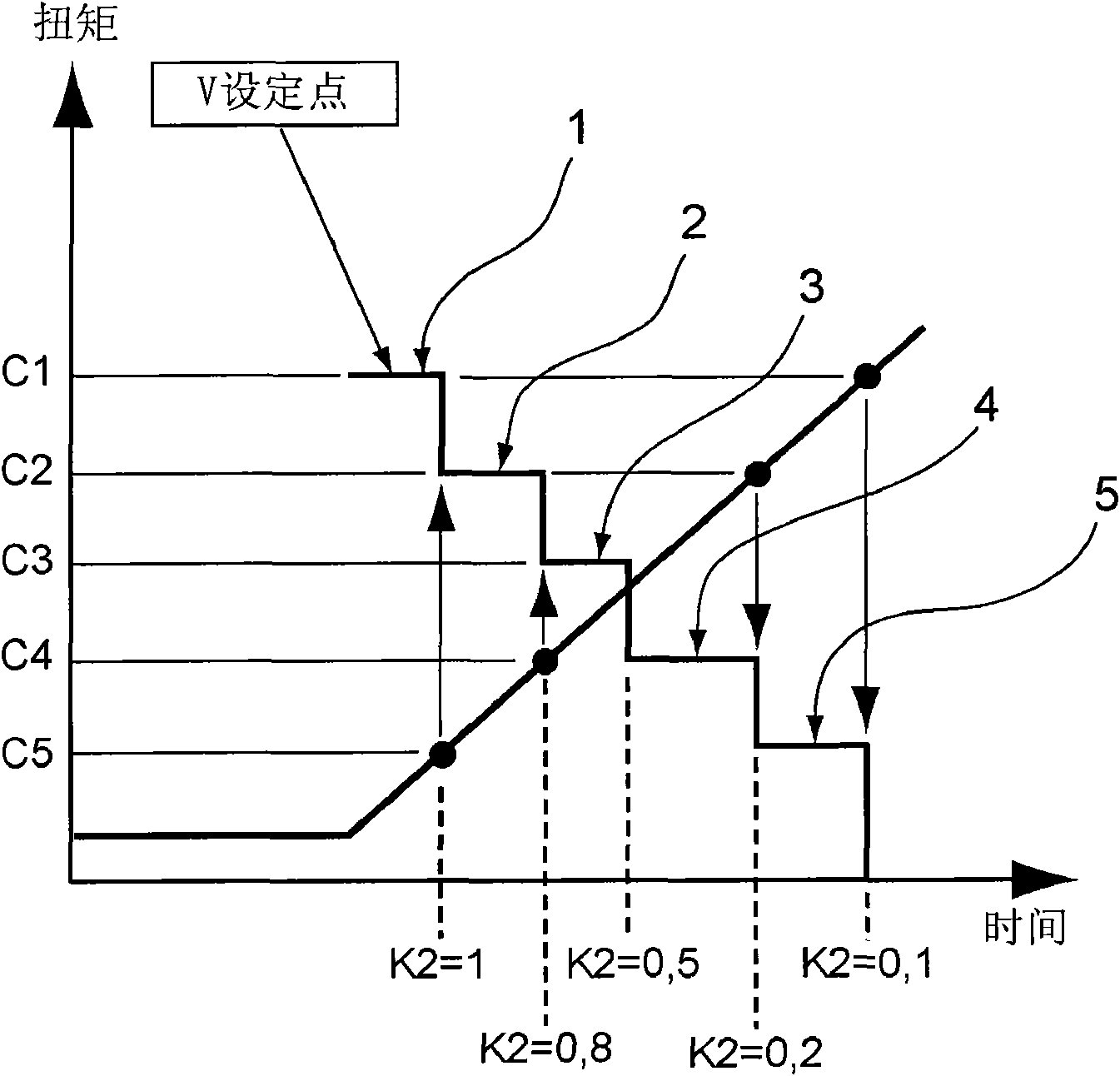
The present invention relates to a method for automatically adjusting the screwing speed of a screwdriver in several successive steps. The method is characterized by comprising executing at least two continuous grades, wherein a preset point speed Vc is kept constantly in the period of each grade and is adjusted from one grade to the next grade. Furthermore the preset point speed is calculated for satisfying an equation: Vc=VMax*K1*K2, wherein K1 is a constant coefficient of the variation range of torque that varies along with time. Furthermore K2 is a constant coefficient which aims at the percentage range of the final torque. Furthermore each grade is predefined by an upper limit and a lower limit that are represented by the percentage form of the final torque. Furthermore the variation from one grade to the next grade causes value variation of the coefficient K2.
Owner:ETAB GEORRENAULT
Information-entropy-based comprehensive evaluation method and system for battery pack inconsistency
ActiveCN107255787AWide adaptabilityImplement inconsistency evaluationElectrical testingNegationOriginal data
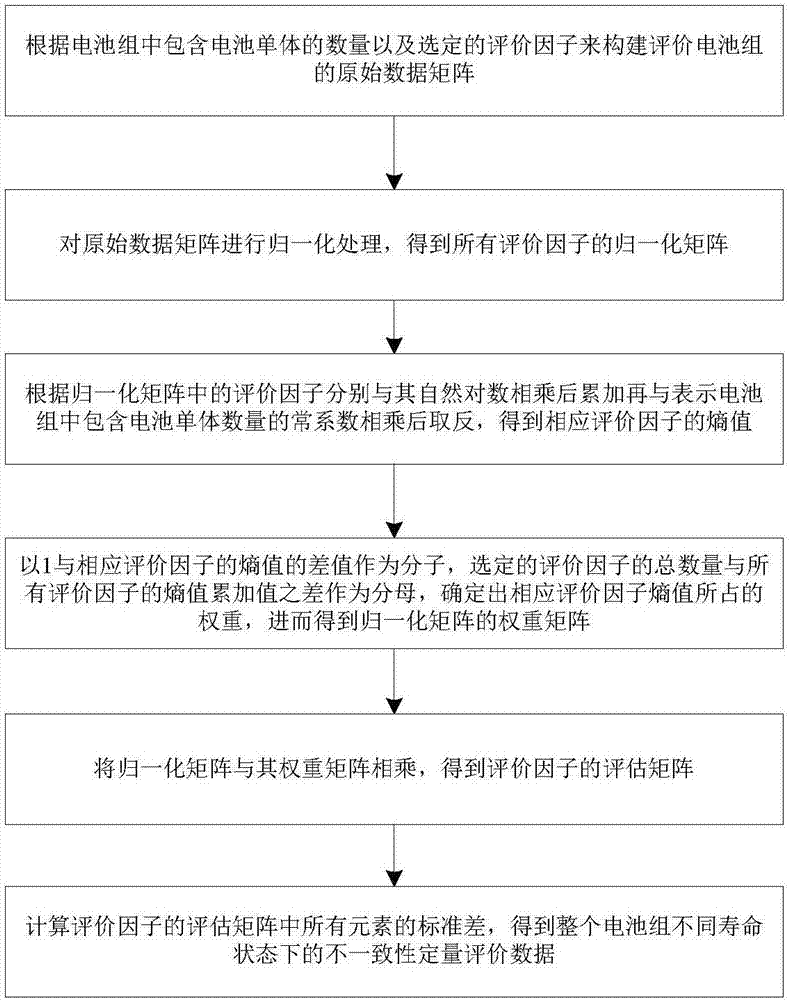
The invention discloses an information-entropy-based comprehensive evaluation method and system for battery pack inconsistency. The method comprises: constructing an original data matrix of an evaluated battery pack based on the number of single batteries included by the battery pack and selected evaluation factors; carrying out normalization on the original data matrix to obtain normalized matrixes of all evaluation factors; according to the evaluation factors in the normalized matrixes, carrying out multiplication with natural logarithms, carrying out accumulation, carrying out multiplication with a constant coefficient expressing the number of single batteries included by the battery pack and then carrying out negation processing to obtain entropies of the corresponding evaluation factors; determining weights of the entropies of the corresponding evaluation factors to obtain weight matrixes of the normalized matrixes; carrying out multiplication of the normalized matrixes and the weight matrixes to obtain an evaluation matrix of the evaluation factors; and calculating standard differences of all elements in the evaluation matrix of the evaluation factors to obtain inconsistency quantitative evaluation data of the battery pack.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Automatic latitude measuring and calculating and automatic precision compensating method of pendulum gyro north seeker
The invention relates to an automatic latitude measuring and calculating and automatic precision compensating method of a pendulum gyro north seeker. The method is characterized in that the geographic latitude is resolved by utilizing the pendulum period measured by an alidade of the pendulum gyro north seeker under a non-tracking state, and the directive coefficient is calculated, so that the precision compensation of deviation brought about by torsion zero deviating from true north is completed, and the method comprises the four steps of calibrating the relationship coefficient of the period and the latitude, starting a north seeking process, measuring the period under the non-tracking state, resolving the latitude by the non-tracking period, and correcting the torsion zero deviation automatically. Compared with the prior art, the automatic latitude measuring and calculating and automatic precision compensating method of the pendulum gyro north seeker has the advantages that in actual applications, the latitude is not required to be input before measurement, and the directive coefficient is also not required to be calibrated and calculated; through the constant coefficient relationship of the period and the latitude, which is calculated in advance in a calibrating site, the latitude at the site can be resolved only by measuring the non-tracking pendulum period of a measured site, and further a measurement result is corrected. The method can be widely applied to the fields of aviation, aerospace, geodetic measurement, guided missile aiming and the like.
Owner:PLA SECOND ARTILLERY ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY
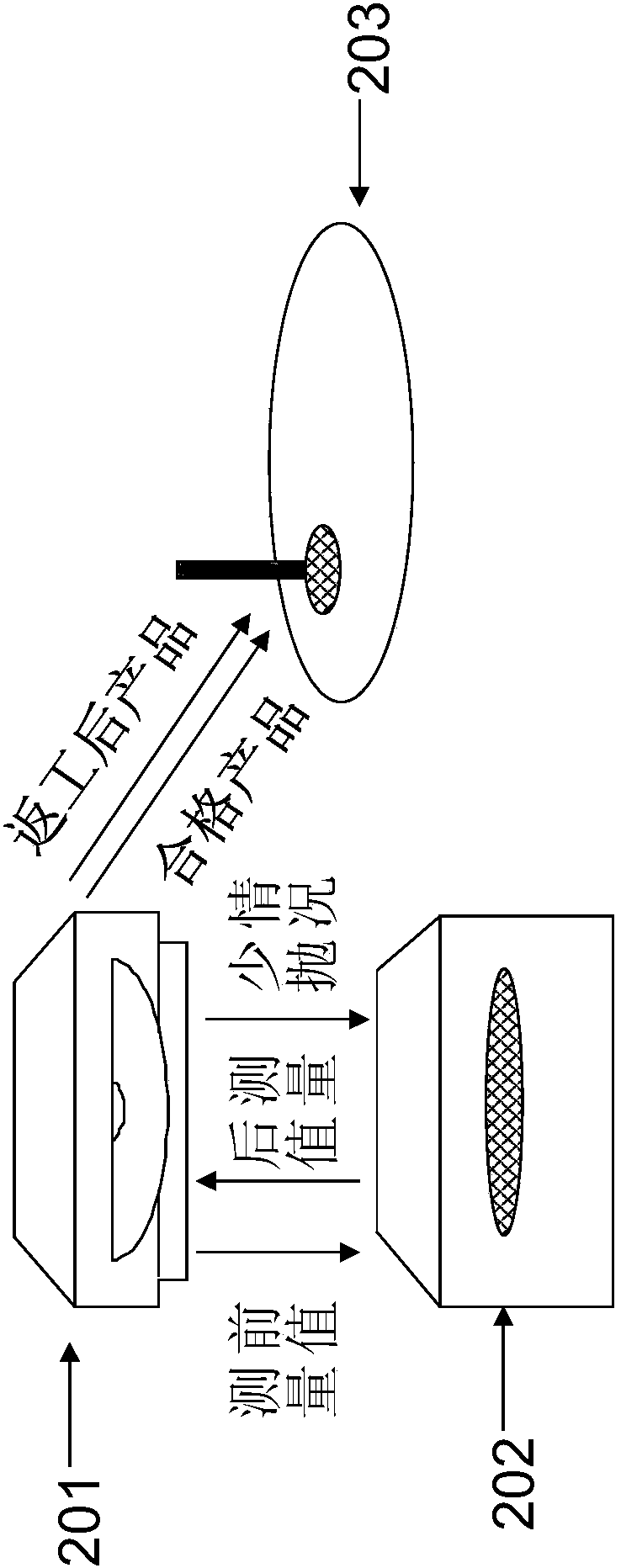
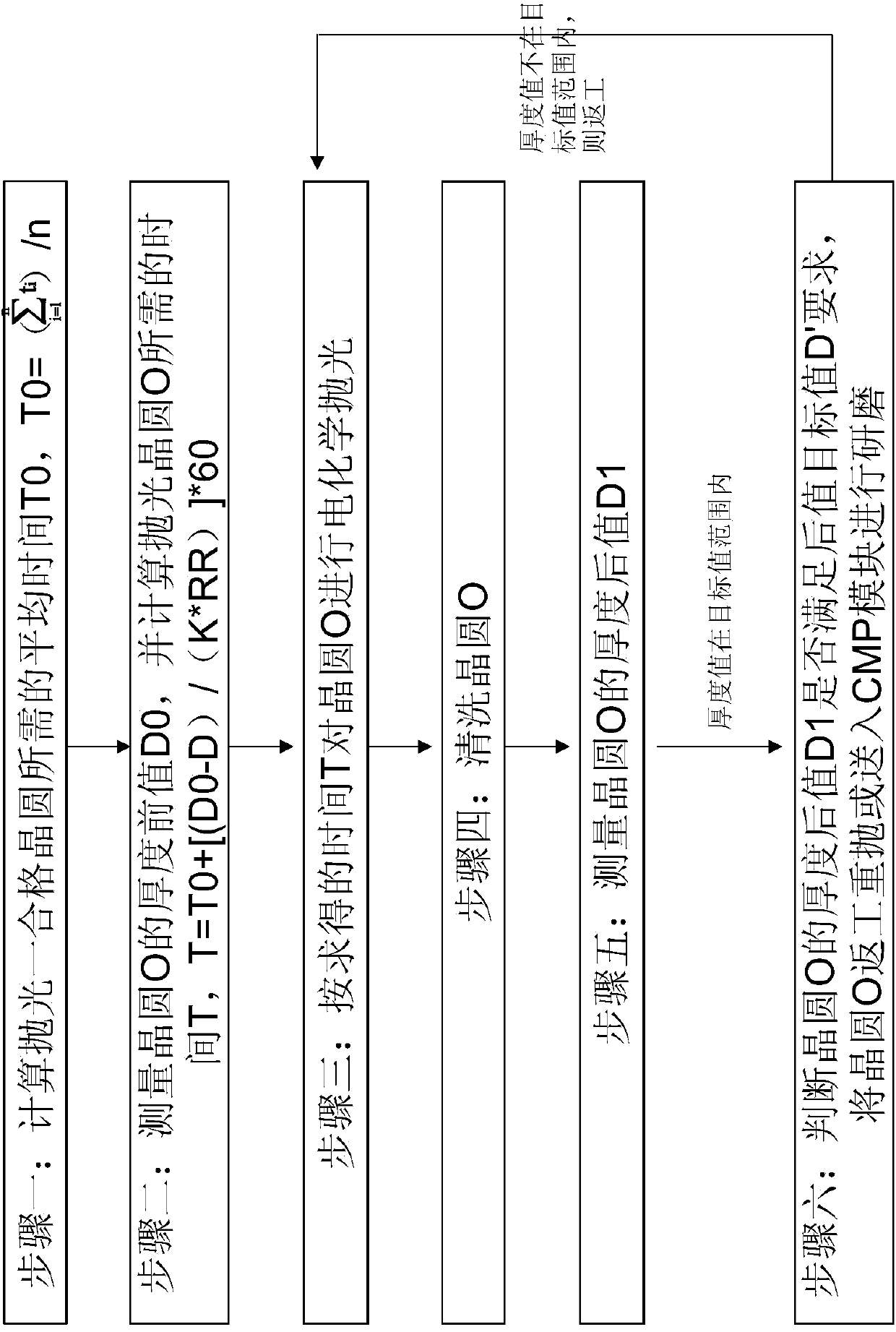
Method for electrochemical polishing of metal interconnection wafer structure
ActiveCN105448817AIncrease weightRaise the ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal interconnectEngineering
The present invention provides a method for electrochemical polishing of a metal interconnection wafer structure. The method provided by the invention comprises: the step 1, performing electrochemical polishing of one part of wafers in a wafer production, and obtaining an average time T0 being required to polish a qualified wafer; the step 2, measuring the thickness front value D0 of any one wafer O in the wafer production, and comparing the thickness front value D0 with a front value target value D; the step 3, performing electrochemical polishing of the wafer O; the step 4, cleaning the wafer O; the step 5, measuring the thickness back value D1 of the wafer O; the step 6, determining whether the thickness back value D1 of the wafer O meets the requirement of a back value target value D' or not, and reworking the wafer O or putting into a CMP module. The time T (which is required for polishing the wafer O)=T0+[(D0-D) / (K*RR)]*60, wherein RR is polishing rate and K is a constant coefficient; the RR slows down with increasing the batch number of polishing wafers, and the K is determined by the feature of the wafer production. The method for electrochemical polishing of a metal interconnection wafer structure is easy to implement and obvious in effect, and is able to greatly improve the yield rate of high polishing wafer productions.
Owner:ACM RES SHANGHAI
Transient response analytic calculation method for high-voltage direct current power transmission system
ActiveCN104820752AGuaranteed accuracyCalculation step size is smallSpecial data processing applicationsHigh-voltage direct currentEngineering
The invention provides a transient response analytic calculation method for a high-voltage direct current power transmission system. The method comprises the following steps that: A, a smoothing reactor, a direct current filter and a direct current power transmission circuit of the high-voltage direct current power transmission system are combined with a voltage current relationship to obtain a differential algebraic equation set of the high-voltage direct current power transmission system under different operation work conditions according to a circuit principle; according to the logic relationship of a control system, a differential equation of the control system is built, and a state equation (shown as the accompanying drawing) of the high-voltage direct current power transmission system is finally formed, wherein the differential algebraic equation set is a constant-coefficient nonhomogeneous linear differential equation set, x is the state quantity under the i-th operation work condition, Ai is a state matrix, Bi is an input matrix, the input u(t) is a rectifier-side and inverter-side three-phase voltage instantaneous expression, and Ci is a component after the addition of the control system; B, through the steady state response calculation on the high-voltage direct current power transmission system, the relationship x(t) of the state quantity of the high-voltage direct current power transmission system varying with time and initial values of each operation quantity of the control system are obtained; C, under the alternate current voltage change, the direct current transient response calculation is carried out; and D, the calculation is completed.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD
Simplified analysis method for inherent frequency and stability of rotational symmetric structure
ActiveCN106528959ASimplify the analytical analysis processEasy to studyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationDynamic equationPartial differential equation
The invention discloses a simplified analysis method for an inherent frequency and the stability of a rotational symmetric structure. The method comprises the steps of establishing a complete dynamic differential equation of a system, a dynamic differential equation adopting a no-extension hypothesis, and a dynamic differential equation adopting an extension hypothesis: establishing the complete dynamic differential equation of the system; establishing the dynamic differential equation adopting the no-extension hypothesis; establishing the dynamic differential equation adopting the extension hypothesis; introducing coordinate conversion for converting the three dynamic differential equations to a support follow-up coordinate system so as to obtain corresponding three constant coefficient partial differential dynamic equations; performing discrete processing on the three constant coefficient partial differential dynamic equations in the support follow-up coordinate system to obtain three constant differential matrix equations; obtaining an eigenvalue of the complete dynamic differential equation and eigenvalues of two simplified dynamic differential equations; and analyzing a parametrically excited vibration mode characteristic and a dynamic stability change law of the rotational symmetric structure according to the three eigenvalues. According to the method, a specific analysis expression of system eigenvalues can be obtained more clearly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
High-precision and low-power-consumption FFT (fast Fourier transform) processor
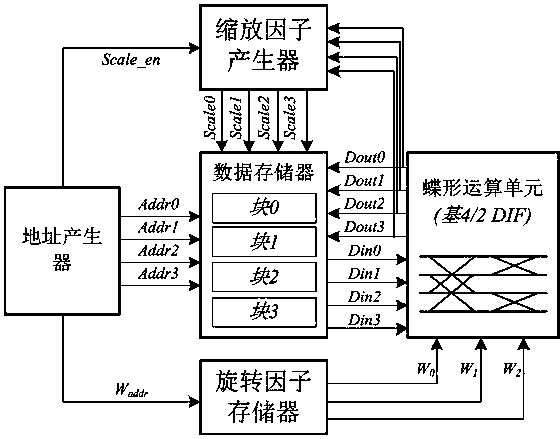
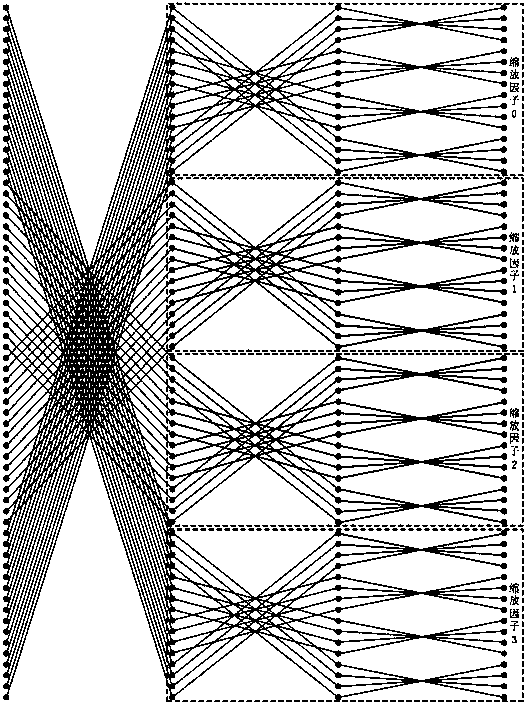
InactiveCN103412851AFlexible configurationReduce areaComplex mathematical operationsAddress generatorBlock floating-point
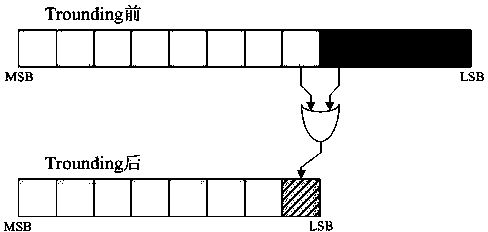
The invention belongs to the technical field of an integrated circuit design, and particularly relates to a high-precision and low-power-consumption FFT processor. The FFT processor adopts a storage device interaction based framework, and comprises a butterfly computation unit, an address generator, a data storage device, a twiddle factor storage device and a zoom factor generator. The high-precision and low-power-consumption FFT processor adopts an improved block floating point technology and or gate based Trounding technology, a data path is equipped with a constant coefficient multiplying unit array and a common plural multiplying unit, and which module is used for multiplying operation is selected according to a data sequence number based determination mechanism. The FFT process has small error and high entire conversion accuracy, and can effectively reduce the power consumption of the multiplying operation; and the FFT processor can be excellently applied to an embedded type low-power-consumption system.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Conversion method of control data of aircraft
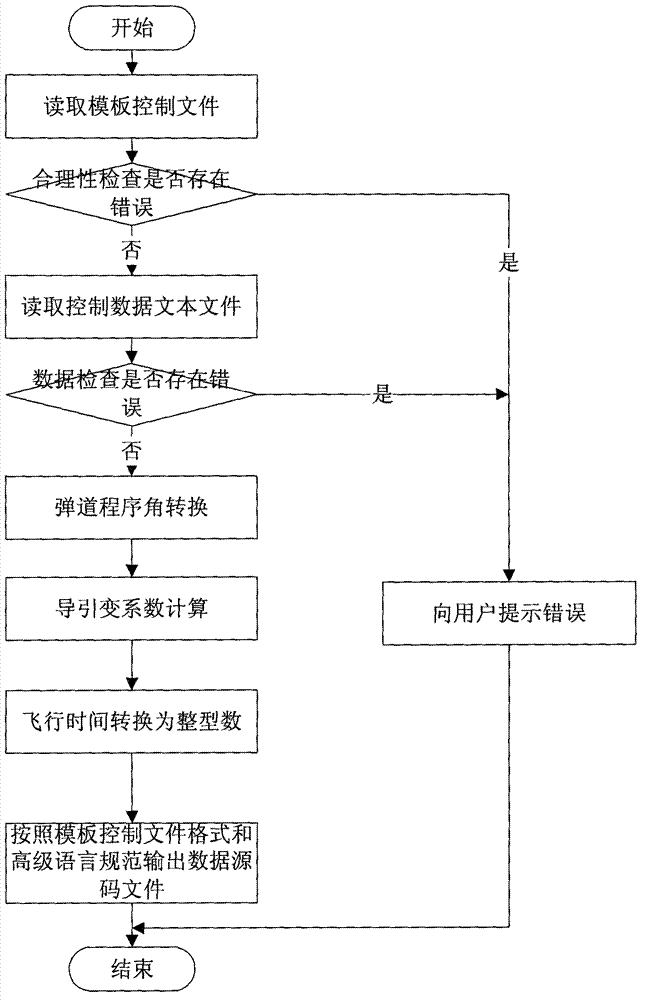
ActiveCN102930164AEnable autonomous analysisImplement extractionSpecial data processing applicationsSource code fileControl data
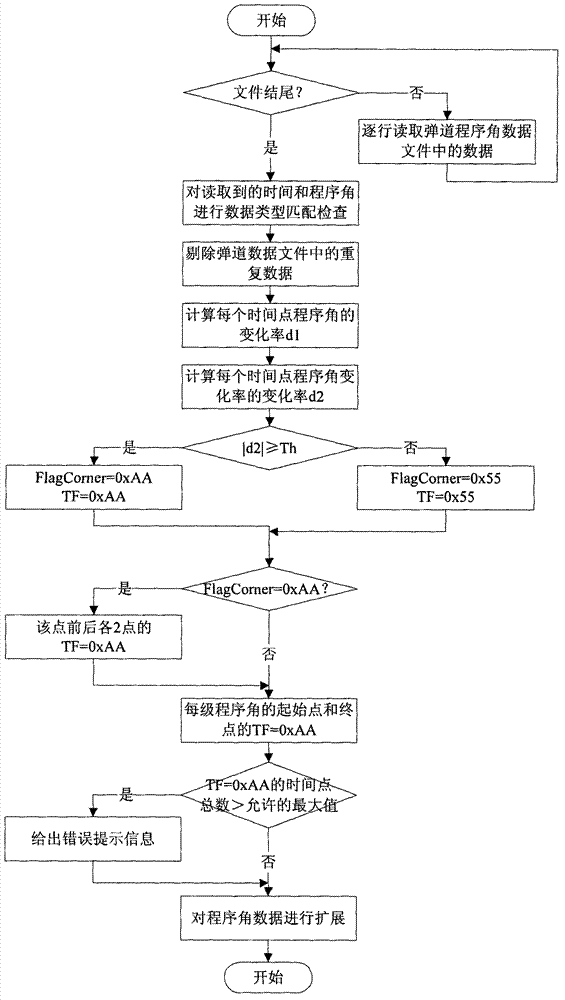
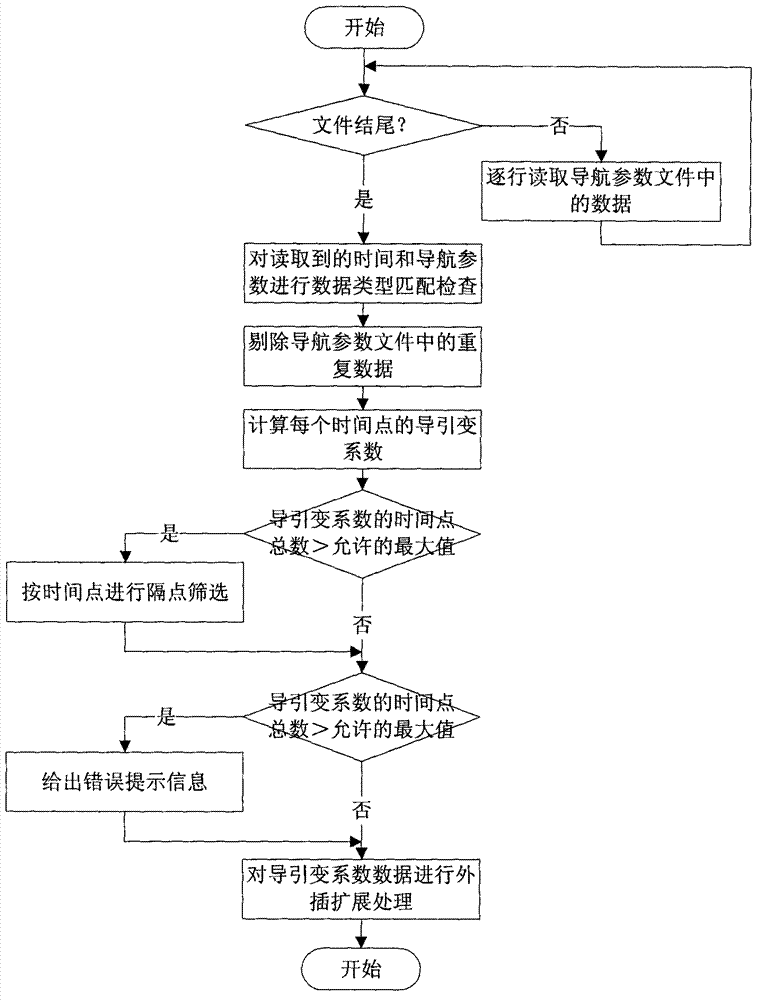
Disclosed is a conversion method of control data of an aircraft. According to the method, a template control file is used to acquire control parameters from a control data text file; a read trajectory program angle of each time point is subjected to analysis and extension to generate processed trajectory program angle data; according to a read navigation parameter and a guide constant coefficient of each time point, a trajectory guide variable coefficient corresponding to each time point is calculated, the trajectory guide variable coefficient corresponding to each time point is subjected to analysis and extension to generate a processed trajectory guide variable coefficient; and according to attributes of data read from the template control file, a data source code file which can be identified by high-level languages is generated. The conversion method is capable of achieving autonomous analysis and processing of the control data and rapidly and reliably converting the control data text file to the high-level language data source code file which can be identified by rocket flight control software.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST +1
Evoked potential recorder based on time characteristic indicators
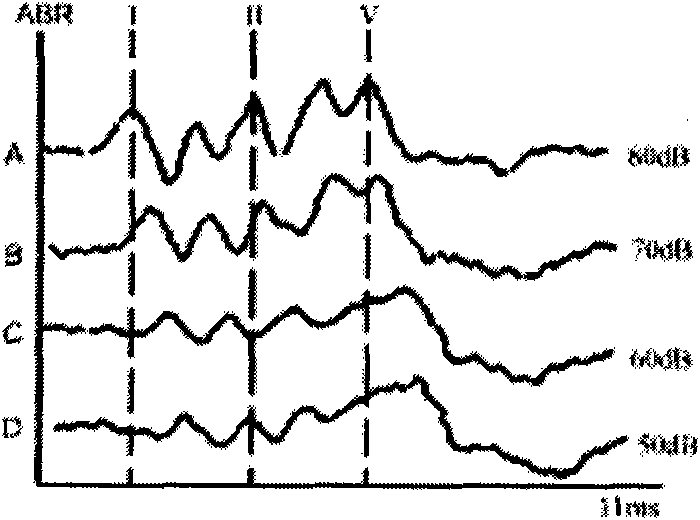
InactiveCN101716074AReduce workloadReduce inaccuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSynapseFunctional indices
The invention discloses an evoked potential recorder based on time characteristic indicators, which can carry out the computation and the function indicator measurement based on the following functional relation: L-Lmin=ae-bx or lg(L-Lmin)=-Bx+A, wherein L is response delay of a nervous system to a certain frequency simulating signal, x is logarithm of instantaneous strength of the simulating signal or constant coefficient of an increasing function; P(t) is the instantaneous strength; and Lmin, a and b, A(A=lga) and B(B=b / ln10), and K and T are constants relevant to the time response characteristics of the nervous system. Lmin is the shortest delay, T is a time conversion coefficient, K is a time (sound-electricity) conversion index, and the Lmin, the T and the K can respectively reflect various physiological functions and changes thereof of transfer characteristics of nerve fibers and synapses of hair cells, mechanical transfer characteristics of sound, sensibility of auditory center system nerve cells, sound-electricity conversion characteristics and the like.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Guidance control method for carrier rocket
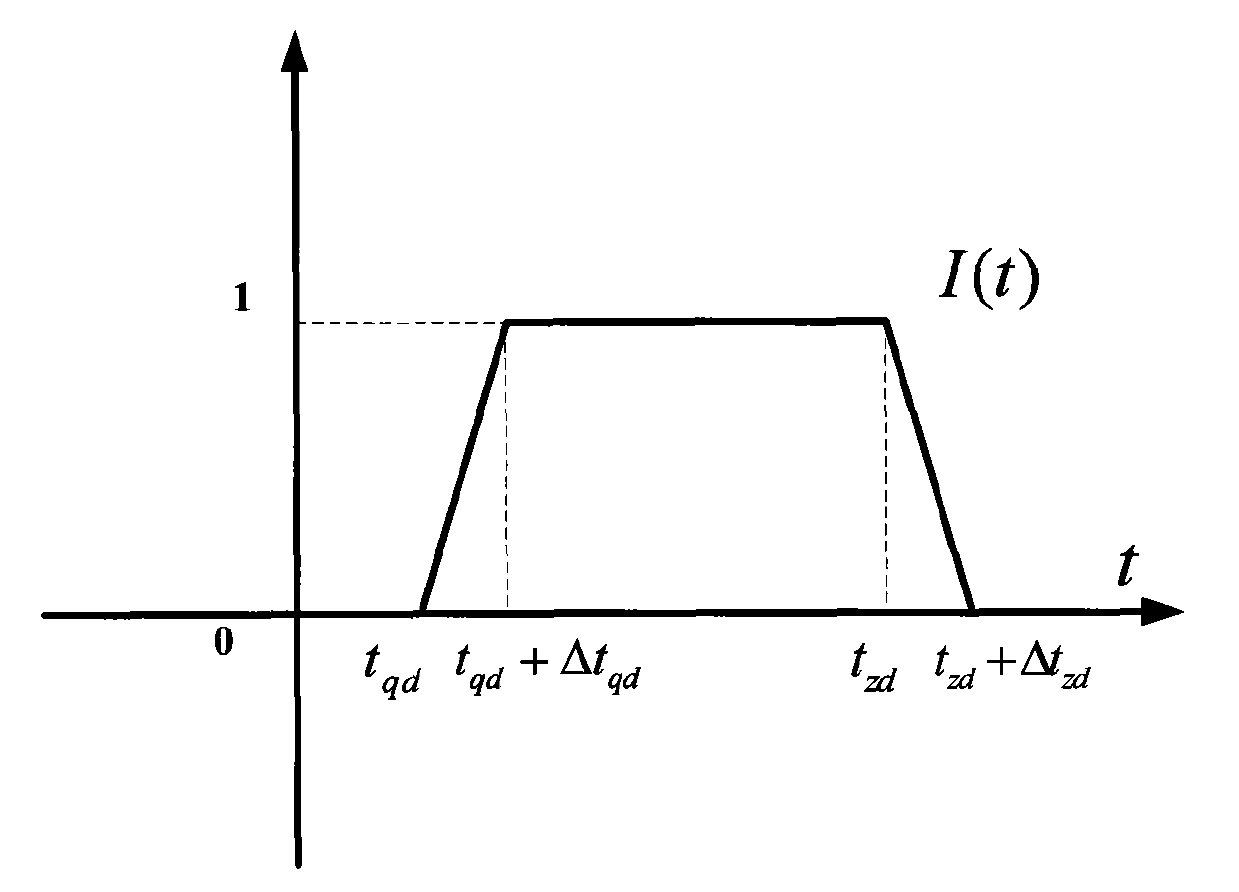
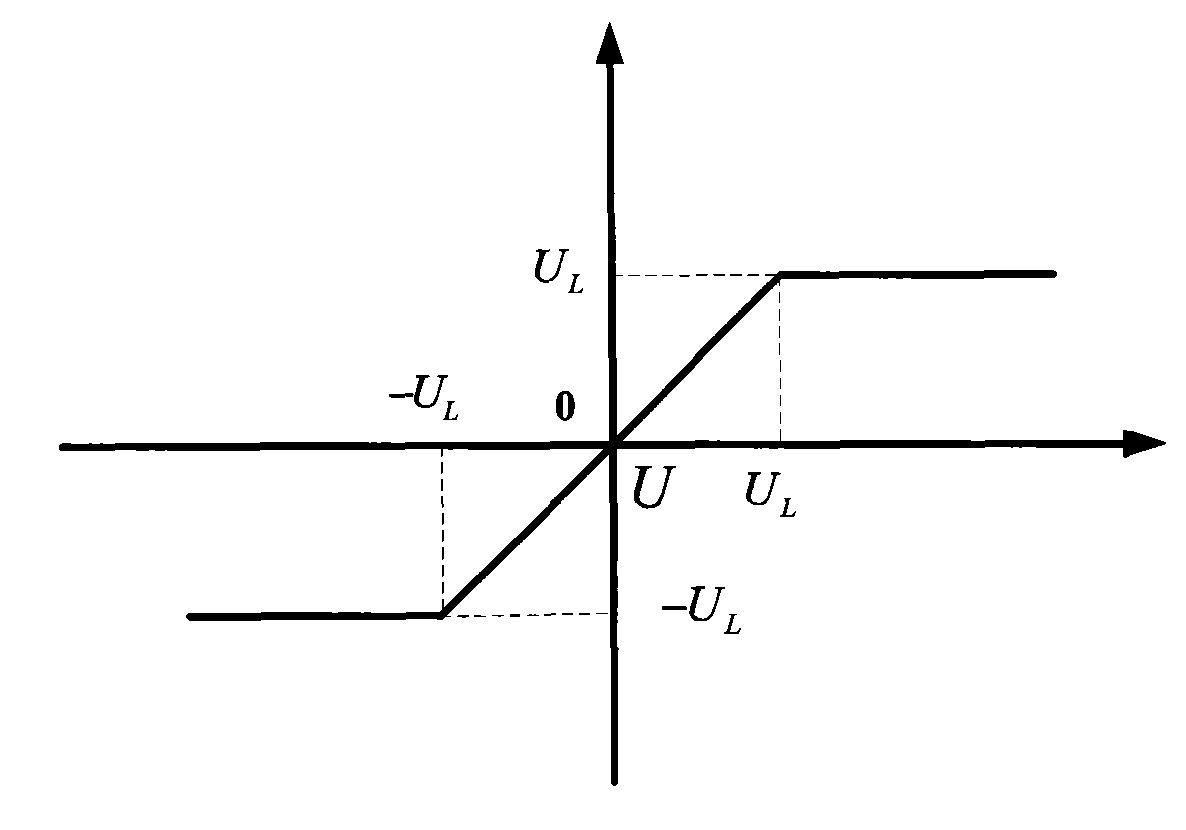
ActiveCN101672606AHigh precisionImprove effectivenessSelf-propelled projectilesTime deviationGuidance control
The invention relates to a guidance control method for a carrier rocket, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: binding standard values such as a standard speed module value v, guidance constant coefficients kuPhi(v) and kuPhi(v) corresponding to the standard speed module value v, and guidance amplification coefficients Kd<Phi> and Kd<Psi>, and the like; according to linear interpolation of two points, calculating the guidance constant coefficients k'uPhi(v) and k'uPsi'(v) of the current point; calculating the guidance weight function I(t) of the current point; further calculating the guidance quantity UPhi(v) and UPsi (v) of the current point, and carrying out amplitude limiting on Uphi(v) and UPsi (v) and then outputting to an attitude control system. By directly adopting rocket speed (or apparent velocity) for replacing the existing universal speed and taking flying time as independent variable, the guidance control method leads guidance calculation process not tobe influenced by each-class shutdown, separation and injection time deviation anymore and improves accuracy of guidance.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST
Thermal analysis modeling method for data extraction
InactiveCN102156775ASolve modelingSolve the problem of difficult mesh divisionSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationElement modeling
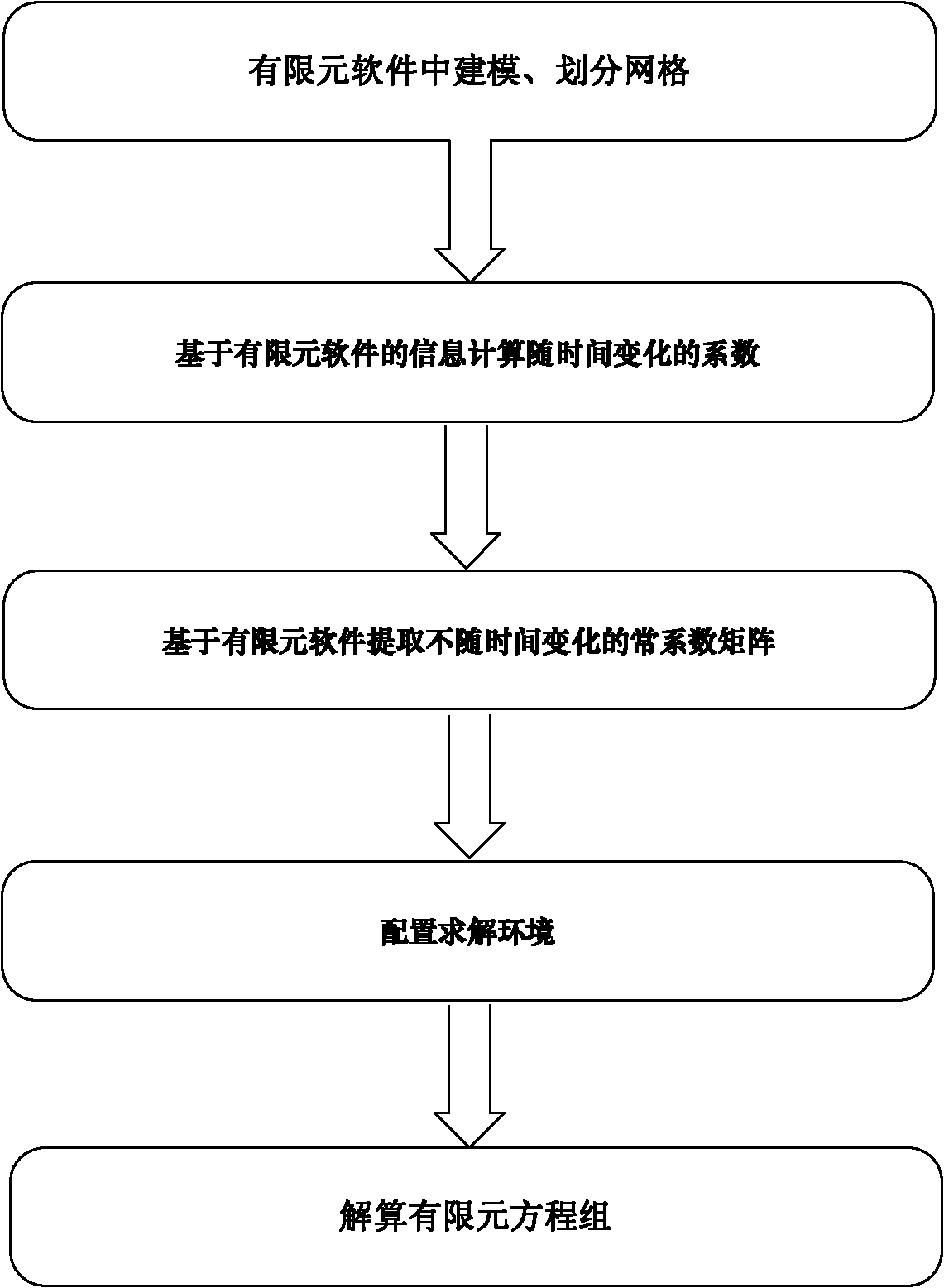
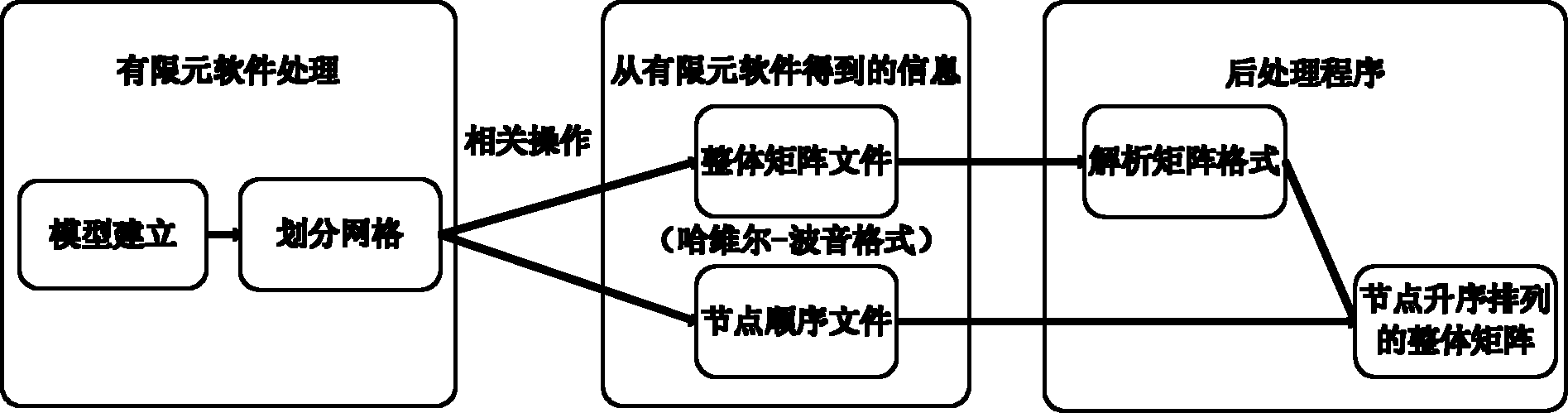
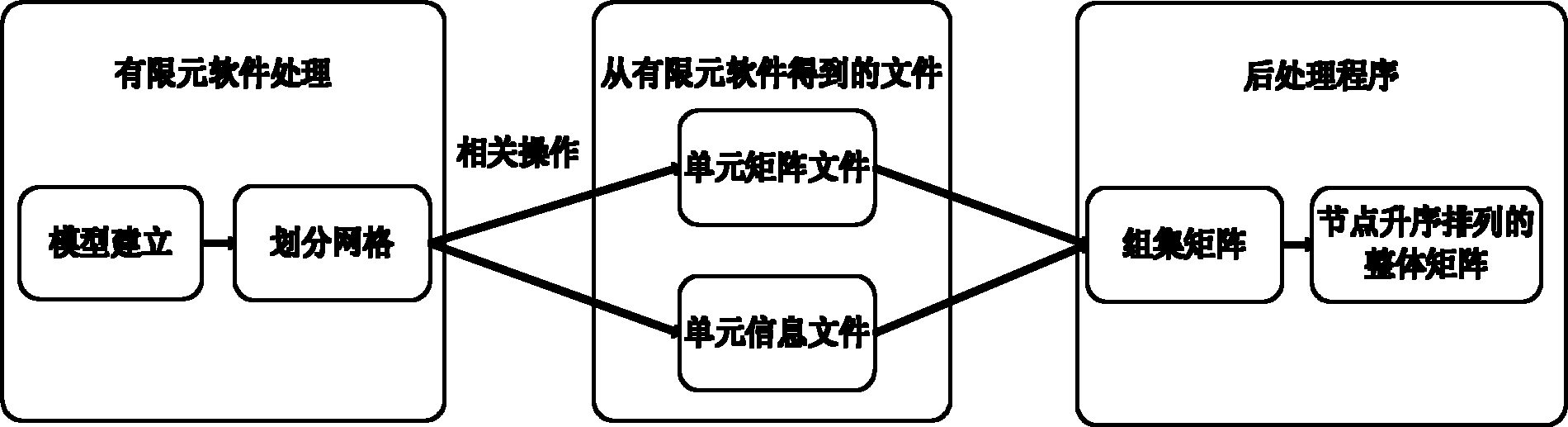
The invention provides a thermal analysis modeling method for data extraction, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, establishing a model in finite element software, and dividing grids; secondly, calculating coefficients changing with time changes on the basis of information of the finite element software; thirdly, extracting a constant coefficient matrix without changing with the timechanges on the basis of the finite element software; fourthly, configuring a solving environment; fifthly, setting initial conditions and boundary conditions; and sixthly, resolving the model. When the modeling method is adopted, the powerful modeling and grid-dividing functions of the finite element software can be utilized; the problem of difficulty in establishing a complex model and dividing the grids is solved; the workload of the finite element modeling can be reduced; and complex boundary conditions can be loaded conveniently and quickly.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for dynamically optimizing wash-out coefficient and fully performing overload capacity of movement platform
InactiveCN101488178AGive full play to the overload capacityAvoid brakingAnalogue computers for vehiclesDynamical optimizationWashout
The invention discloses a method for dynamically optimizing washout coefficient to bring the movement platform overload capacity into full play. A cost function is used for determining a washout module coefficient, and positions and gestures of six freedom degrees of the movement platform are generated after the implementation of real-time dynamic optimization. The variation of the overload, which is generated in the middle of the stroke of a mechanism is greater than the variation of the positions and gestures of the six freedom degrees, which is generated by a constant coefficient washout module, and in an attachment to the stroke end of the mechanism, the actually achieved positions and gestures of the six freedom degrees of the movement platform after the output of a previous command are taken into consideration so as to prevent the frequent brake in the neighborhood of the stroke end of the mechanism, so that the movement platform overload capacity is brought into full play and the aim of maximally developing the movement platform performance is achieved. The invention is used for improving the fidelity of dynamic simulation of a flight simulator and relates to the field of dynamic simulation of the six-freedom-degree movement system of the flight simulator.
Owner:PLA AIR FORCE AVIATION UNIVERSITY
Method of controlling rapid charging of an industrial storage cell having an alkaline electrolyte
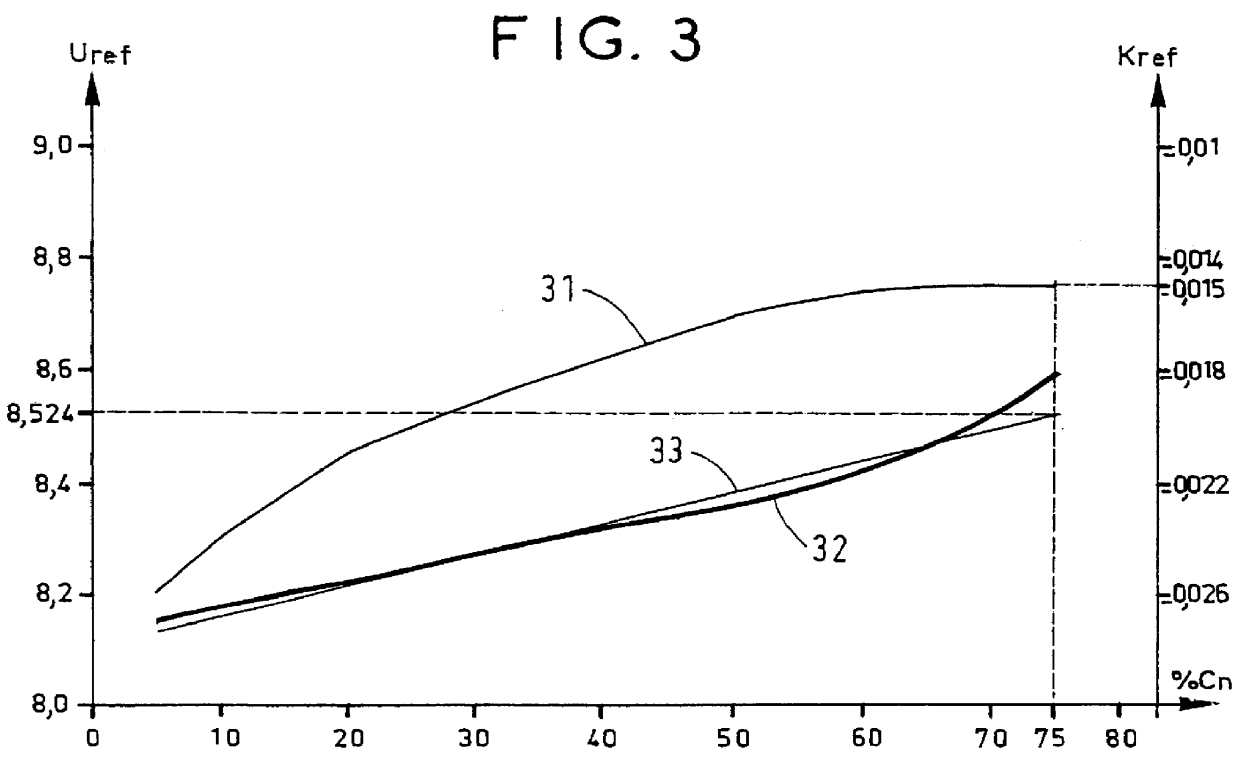
The present invention provides a method of controlling rapid charging of an alkaline-electrolyte industrial storage cell of the "maintenance-free" or "sealed" type, the cell possessing a nominal capacity Cn, a voltage U, and an internal temperature T, wherein charging is stopped at a percentage charge greater than 75% of Cn as follows: a voltage threshold Us is fixed which corresponds to the desired final percentage charge for said cell; the voltage U and the temperature T of said cell are measured; a corrected voltage Uc is calculated using the following formula:Uc=U-k(T-Tc)where voltages are expressed in volts, Tc is an arbitrarily-selected reference temperature, and k is a constant coefficient expressed in volts per temperature unit; and Uc is compared with said voltage threshold Us, and charging is stopped when Uc is not less than Us.
Owner:SAFT FINANCE S AR L
Feed source device and microwave antenna
The invention provides a feed source device and a microwave antenna, applicable to the field of antennae. The feed source device comprises a waveguide tube, a dielectric medium inserted at one end of the waveguide tube and an auxiliary reflecting surface nested on the internal surface of the dielectric medium. The feed source device also comprises a matching medium coating the periphery of the dielectric medium, and the dielectric constant and the thickness of the matching medium are respectively disclosed in the specifications, wherein epsilon r is the dielectric constant of the dielectric medium 20, a is a constant coefficient between 0.5 and 3.5, and lambda is the wavelength of electromagnetic waves in vacuum. Through the feed source device and the microwave antenna provided by the invention, the reflection of the external surface of the dielectric medium to the electromagnetic waves can be greatly reduced by means of the added matching medium, the deterioration of standing-wave ratio caused by waves reflected by the external surface of the dielectric medium is basically eliminated, and the limitation to the material selection of the dielectric medium is also lowered.
Owner:MOBILE ANTENNA TECH SHENZHEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com