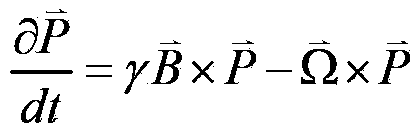Patents
Literature
1132results about "Rotary gyroscopes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
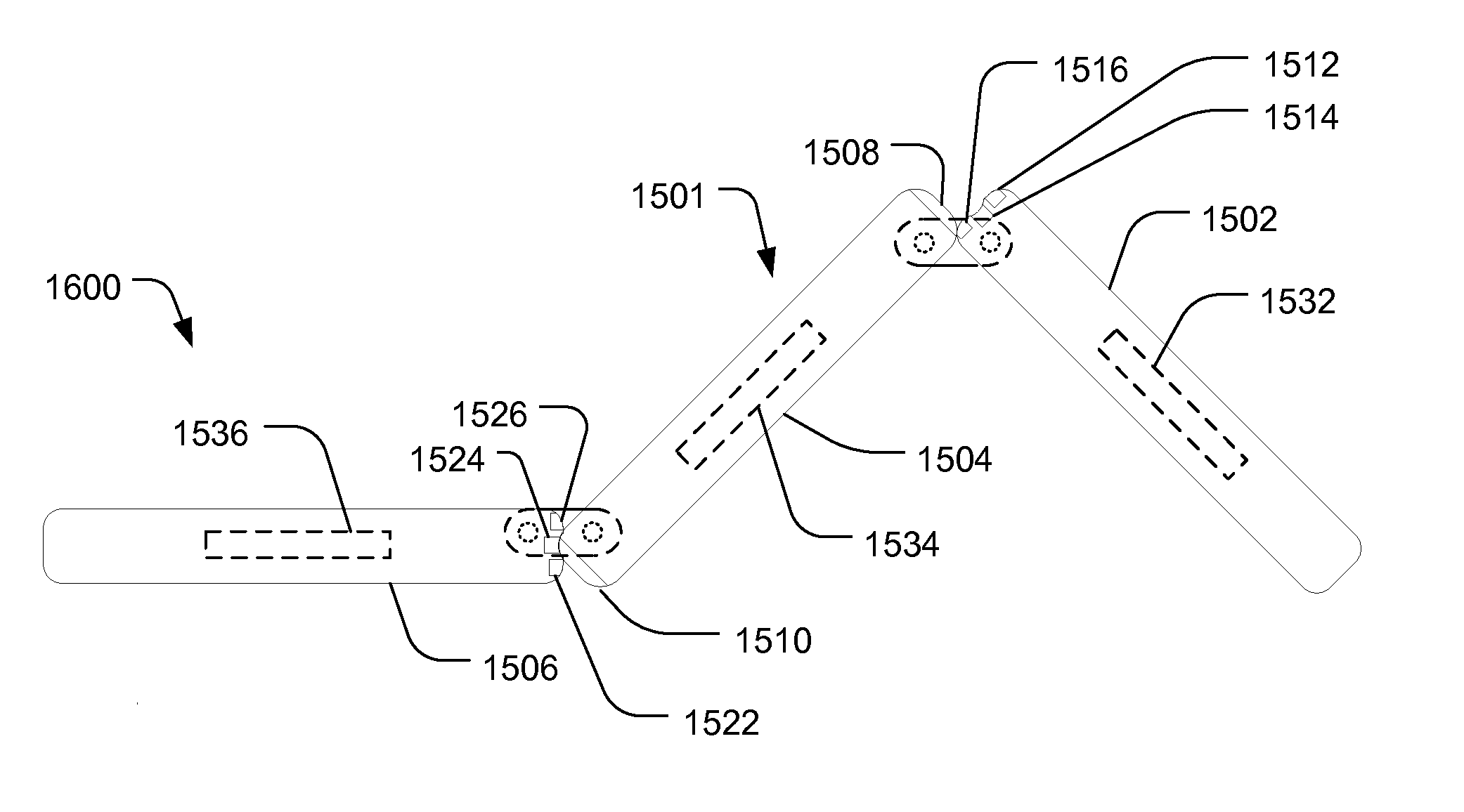
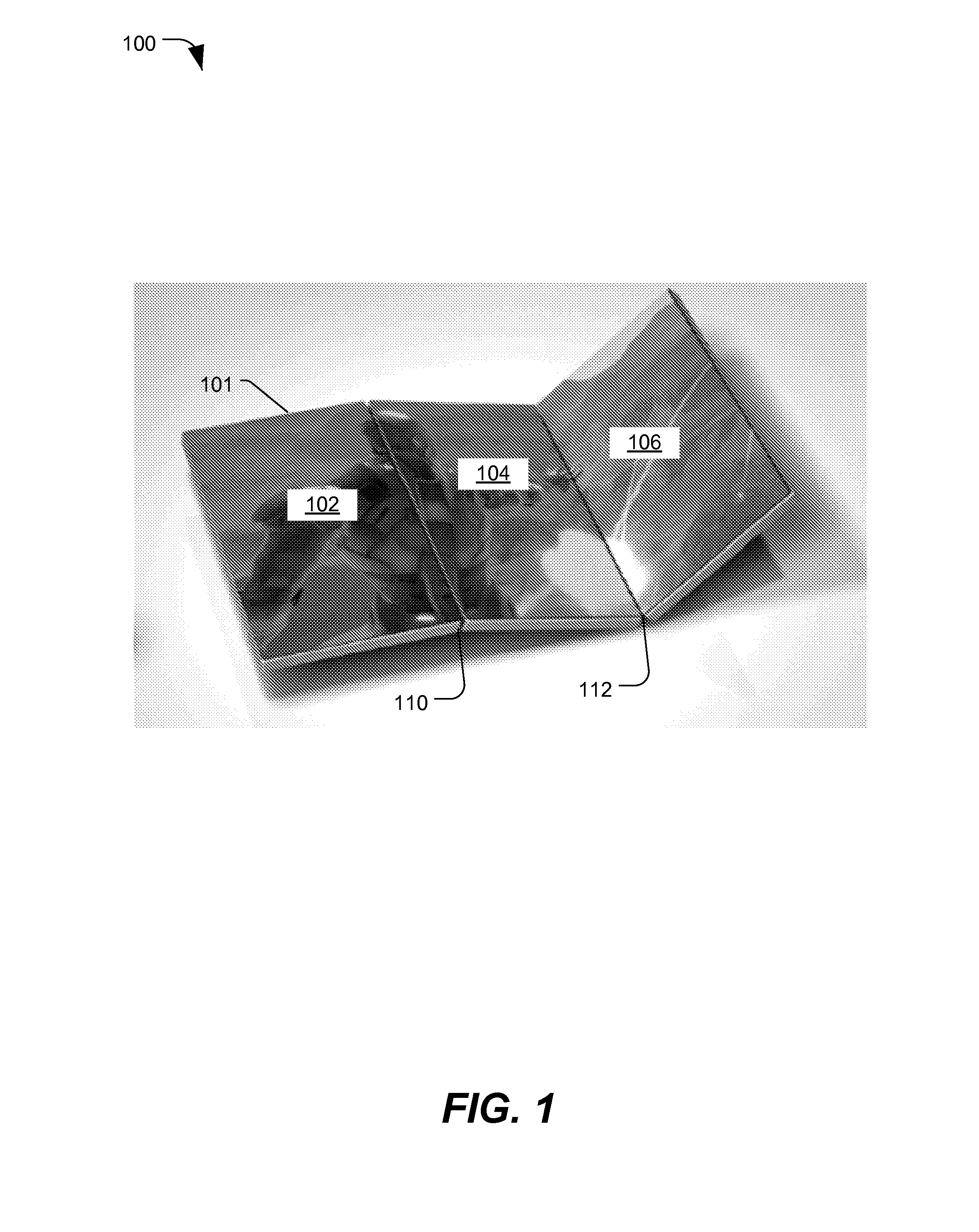
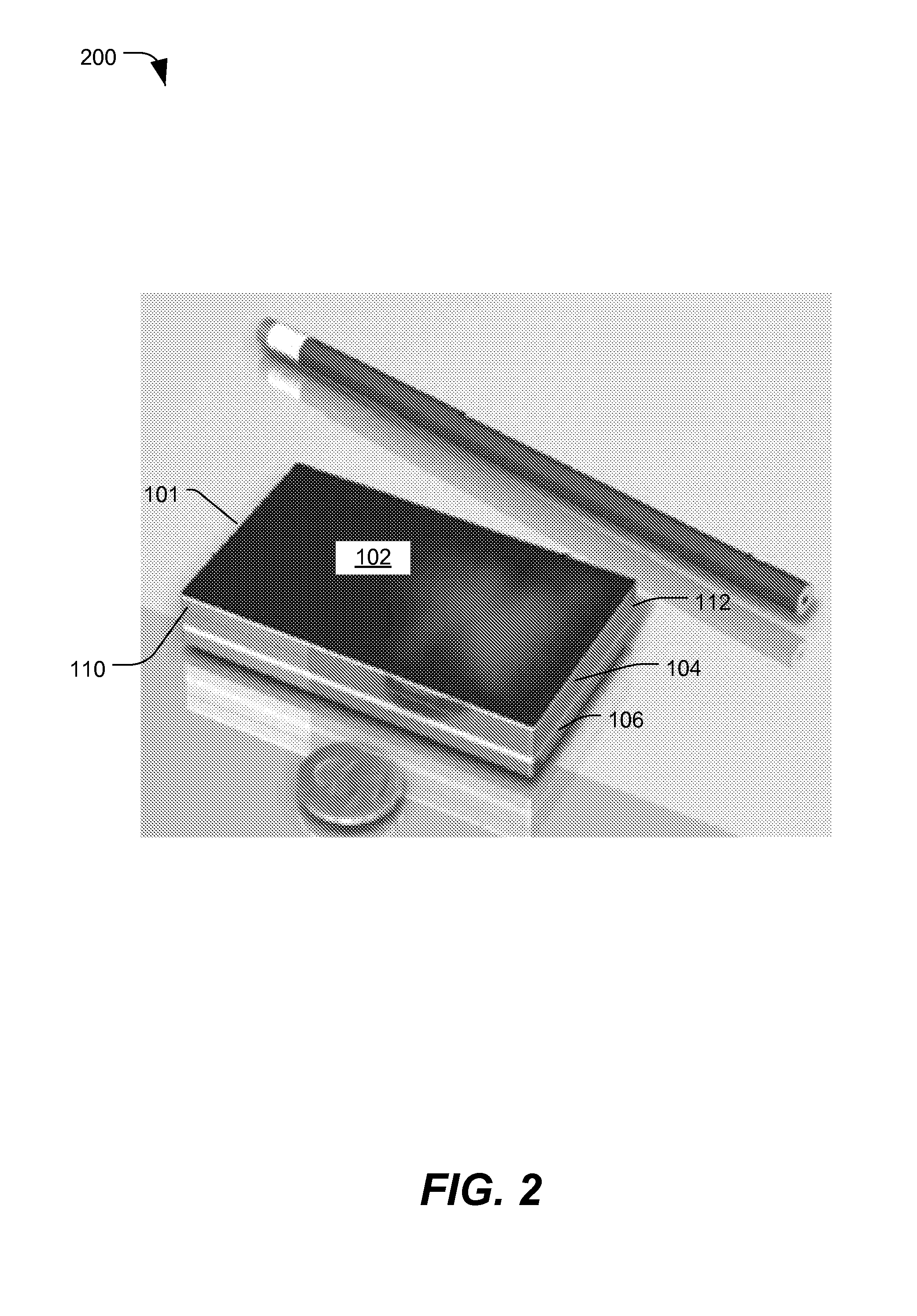
Multi-panel electronic device
ActiveUS20100064536A1Extended large displaySmall sizeDevices with multiple display unitsDevices with sensorArtificial intelligenceAcceleration Unit
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Systems and methods for powering a gimbal mounted device
Gimbal power systems and methods are operable to provide power to a device attached to the gimbal. An exemplary embodiment is configured to rotate a rotational member of the gimbal system about an axis, wherein a stator of a rotary power transformer affixed to the rotational member rotates about the axis, and wherein an end of an electrical connection coupled to a power connector of a rotor winding of the rotary power transformer remains substantially stationary as the stator of the rotary power transformer rotates about the axis.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Orientation detector for use with a hand-held surgical or dental tool
Provided is a device for monitoring the orientation of a hand-held surgical or dental tool. The device includes one or more orientation sensors that generate signals indicative of an orientation of the device. A processor calculates from the signals a current orientation of the device, where the current orientation is specified by a unit vector defined by a first angle formed between the unit vector and a predetermined first fixed axis and a second angle formed by the unit vector and a second predetermined axis. The processor compares a current orientation of the device with a predetermined reference orientation of the device stored in the memory and provides an indication of the deviation between a current orientation of the device and the reference orientation.
Owner:CREATIVE TEAM INSTR
Self-calibrated azimuth and attitude accuracy enhancing method and system (SAAAEMS)
ActiveUS20090089001A1Digital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAccelerometerGyroscope
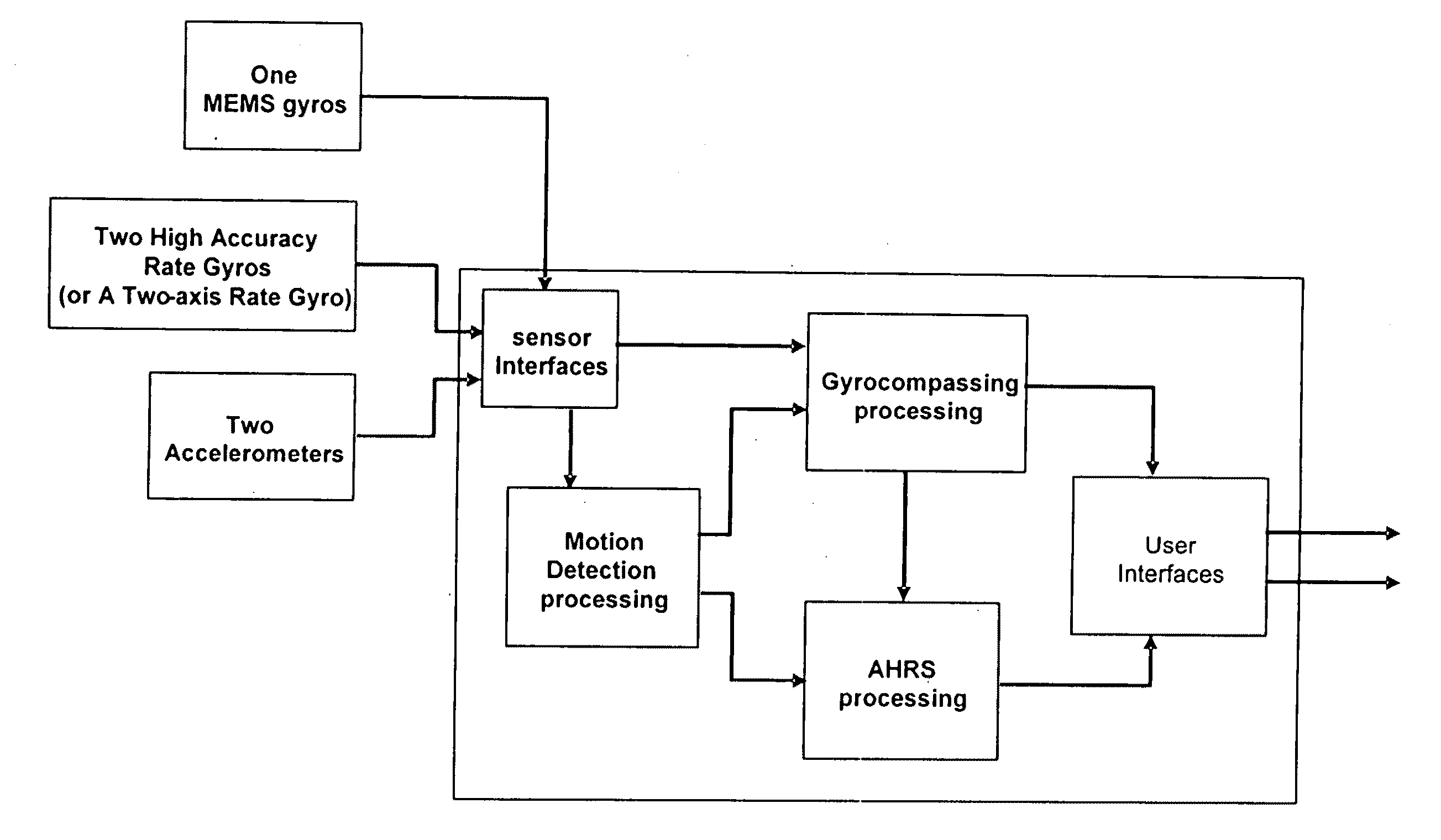
A method and system for Self-calibrated Azimuth and Attitude Accuracy Enhancing are disclosed, wherein SAAAEMS approach is based on fully auto-calibration self-contained INS principles, not depending on magnetometers for azimuth / heading determination, and thus the system outputs and performance are not affected by the environmental magnetic fields. In order to reduce the system size and cost, this new innovative methods and algorithms are used for SAAAEMS system configuration and integration. Compared to a conventional INS for gyrocompassing, AGNC's approach uses a smaller number of high accuracy sensors: SAAAEMS uses only one 2-axis high accuracy gyro (for example, one DTG) instead of 3-axis; the third axis gyro is a MEMS gyro. It uses only 2 high accuracy accelerometers instead of 3, since the two accelerometers are used only for gyrocompassing not for navigation. These two changes to the conventional INS system configuration remarkably reduce the whole system size and cost. SAAAEMS, uses dynamic gyrocompassing processing for isolation of Base motion disturbance / interference and vibration. SAAAEMS provides a method and system for using automatic methods for system calibration.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
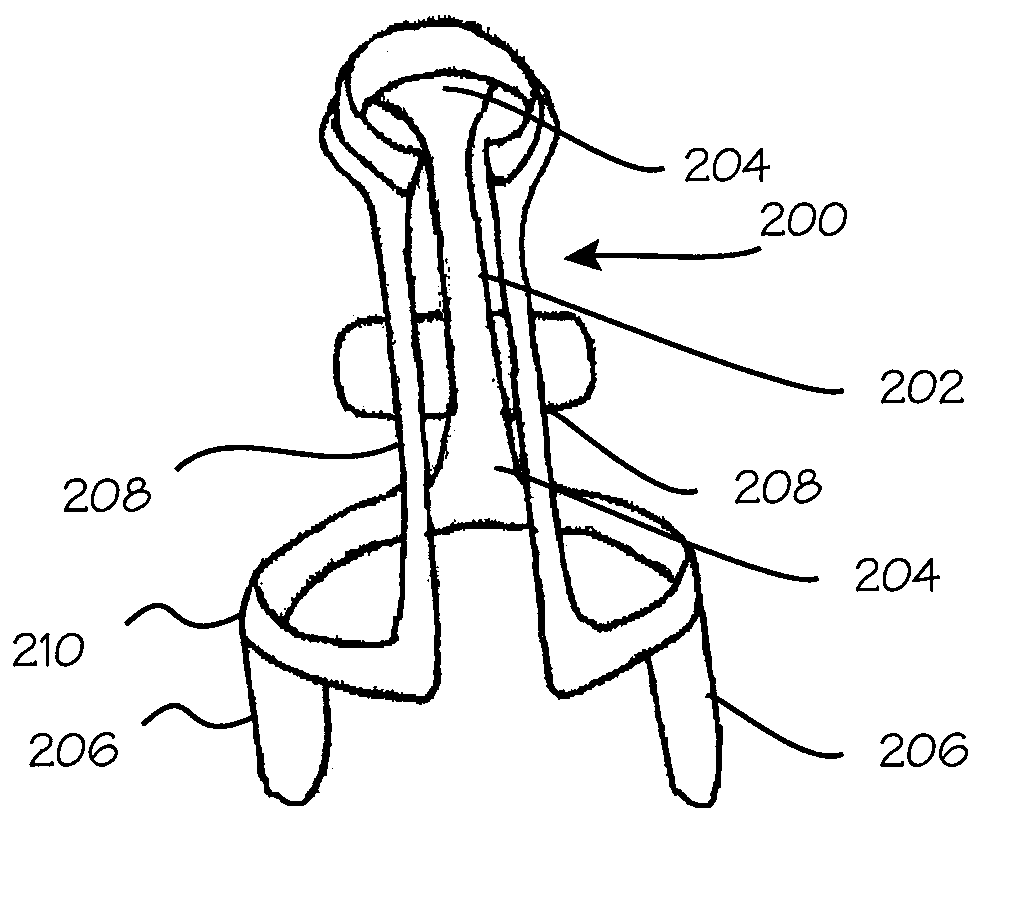
Method and Apparatus for Body Impact Protection
ActiveUS20090254003A1Maximum precisionPrevent unwanted of pressureAcceleration measurement using interia forcesPerson identificationCushioningOrgan damage
This invention relates to active protective garments which are inconspicuously worn by an individual and which activate upon certain conditions being met. Activation causes inflation of regions of the active protective garment to provide padding and impact cushioning for the wearer.The invention is an active protective garment such as pair of shorts or pants, a jacket, a vest, underwear, and the like. The garments comprise multiple layers of material that constrain pockets or regions that are inflatable by a source of compressed gas or foam. The garments also comprise sensors to detect ballistic parameters such as acceleration, distance, relative acceleration, and rotation. The sensor information is used to determine whether activation is required. Detection and activation are accomplished in a very short time period in order to offer maximal protection for the individual wearing the garment. The system comprises a computer or logic controller that monitors the sensor data in real time and coordinates the information from all sensors. The system calculates velocity, distance, and rotational velocity. A rule-based system is used to detect a complex fall in progress and discriminate said fall in progress from the events of every day life. The pockets or inflatable regions of the garment protect the individual against falls and other impacts that may cause bone fracture or organ damage.
Owner:ACTIVE PROTECTIVE TECH
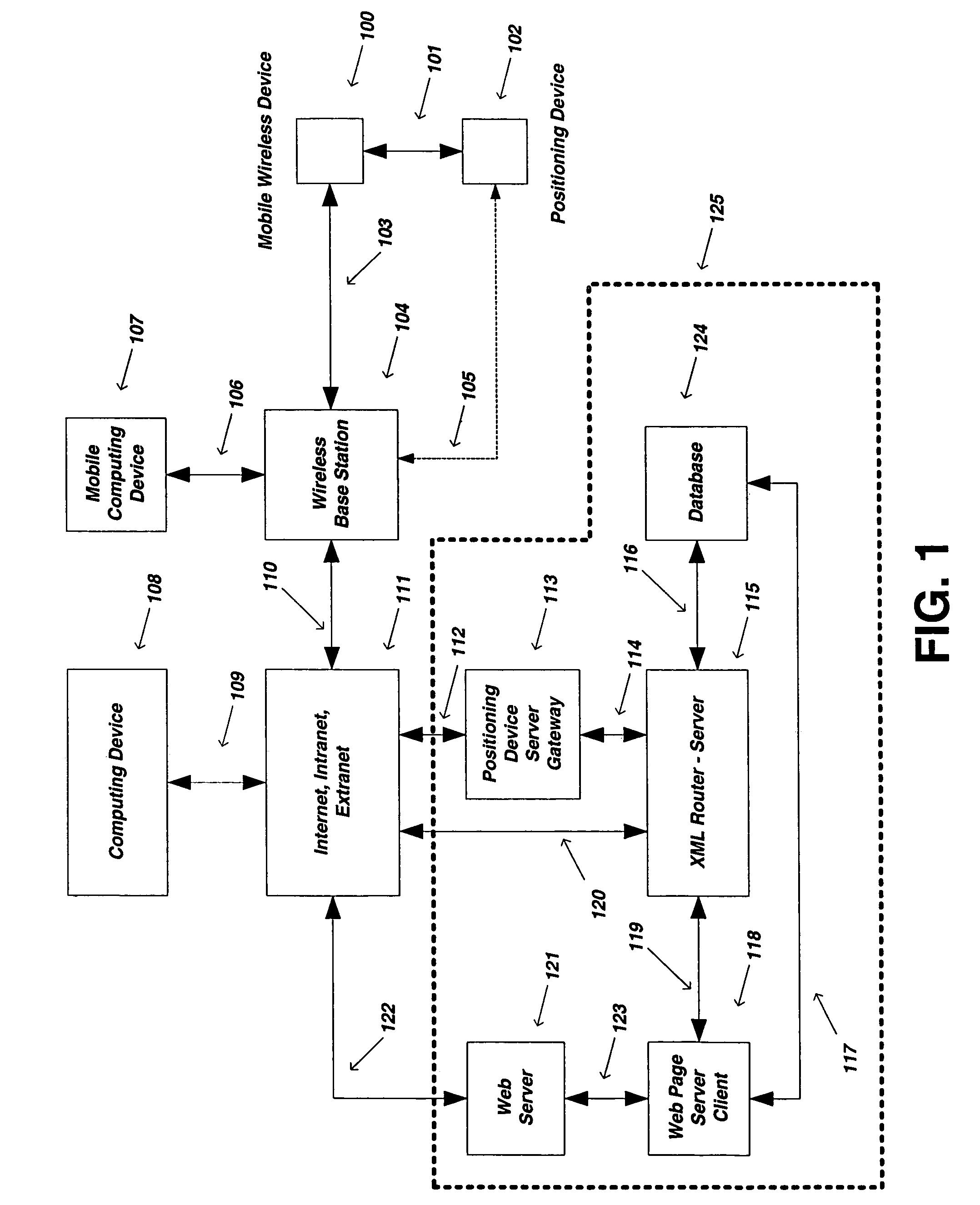
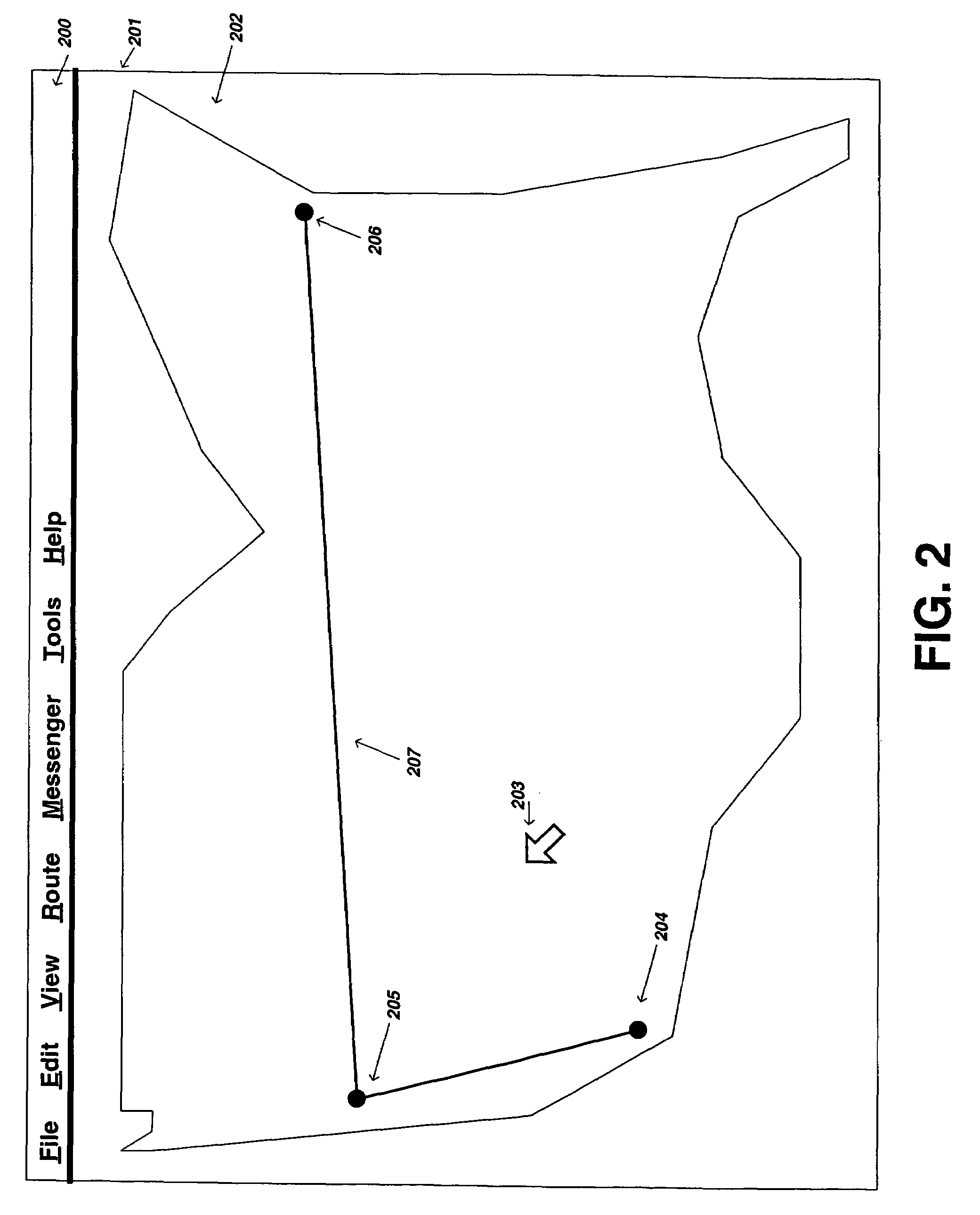
Method and system for dynamic estimation and predictive route generation
InactiveUS7565155B2Instruments for road network navigationData processing applicationsGraphicsAdaptive routing
The preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to methods and systems for dynamic route estimation and prediction using discrete sampled location updates from various mobile devices for the purpose of providing a graphical representation of a mobile device's route along a known network path of map data. The embodiments also provide supplemental route metrics, such as traveled distance, elapsed time, etc., and the capability to assign destination points for the purpose of providing the ability to modify location update points in an application, such as a route planner, and / or to store the dynamically generated route based on various preferences for later retrieval.
Owner:BLUESTONE VENTURES
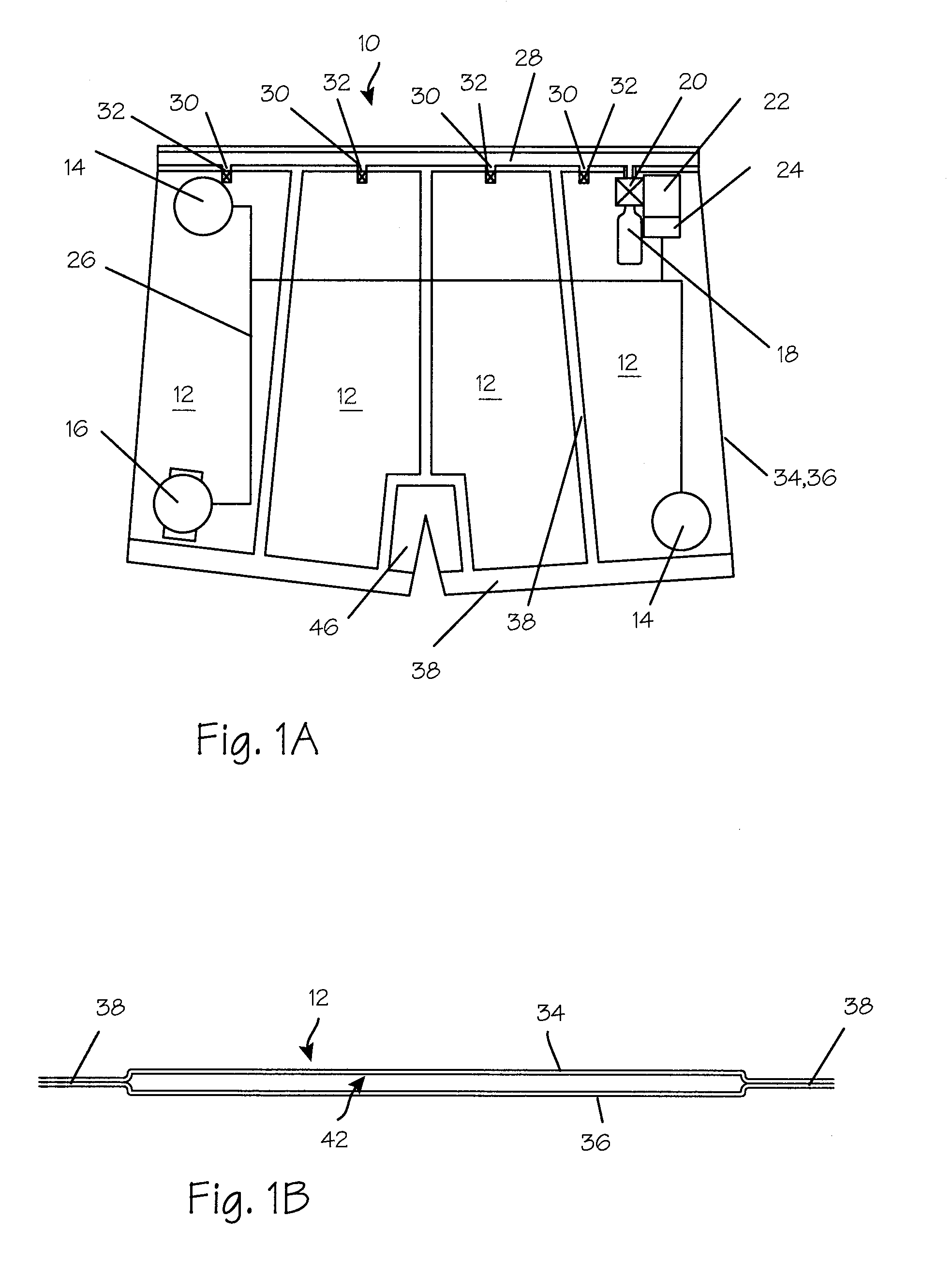
Compact navigation system and method
InactiveUS20050022402A1Compact and accurate navigationMore compact and accurate navigation systemSurveyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeTriaxial accelerometer
A compact navigation system for a rover is provided. The navigation system includes a housing configured to be transported by the rover; a gimbal system having two or more gimbals that includes at least an outer gimbal connected to the housing and an inner gimbal nested in and connected to the outer gimbal; a solid state three-axis gyro assembly mounted on the inner gimbal; a solid state three-axis accelerometer assembly mounted on the inner gimbal; a gyro logic circuit responsive to the three-axis gyro assembly for producing an inertial angular rate about each gyro input axis; an accelerometer logic circuit responsive to the three-axis accelerometer assembly for producing a non-gravitational acceleration along each accelerometer input axis; and a processor responsive to the gyro logic circuits and the accelerometer logic circuits for determining the attitude and the position of the housing to provide for long term accuracy of the attitude and the position for navigation of the rover.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
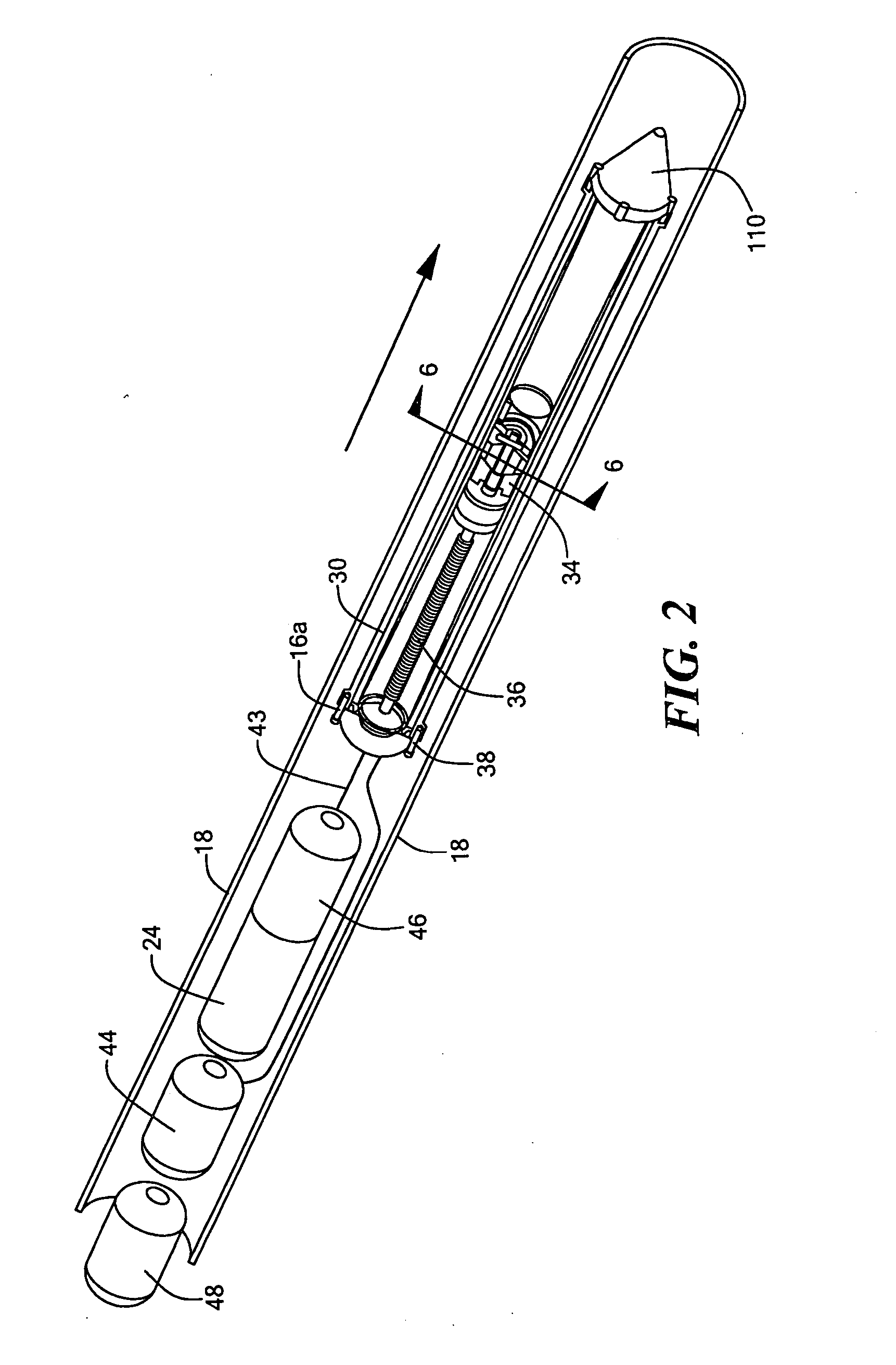
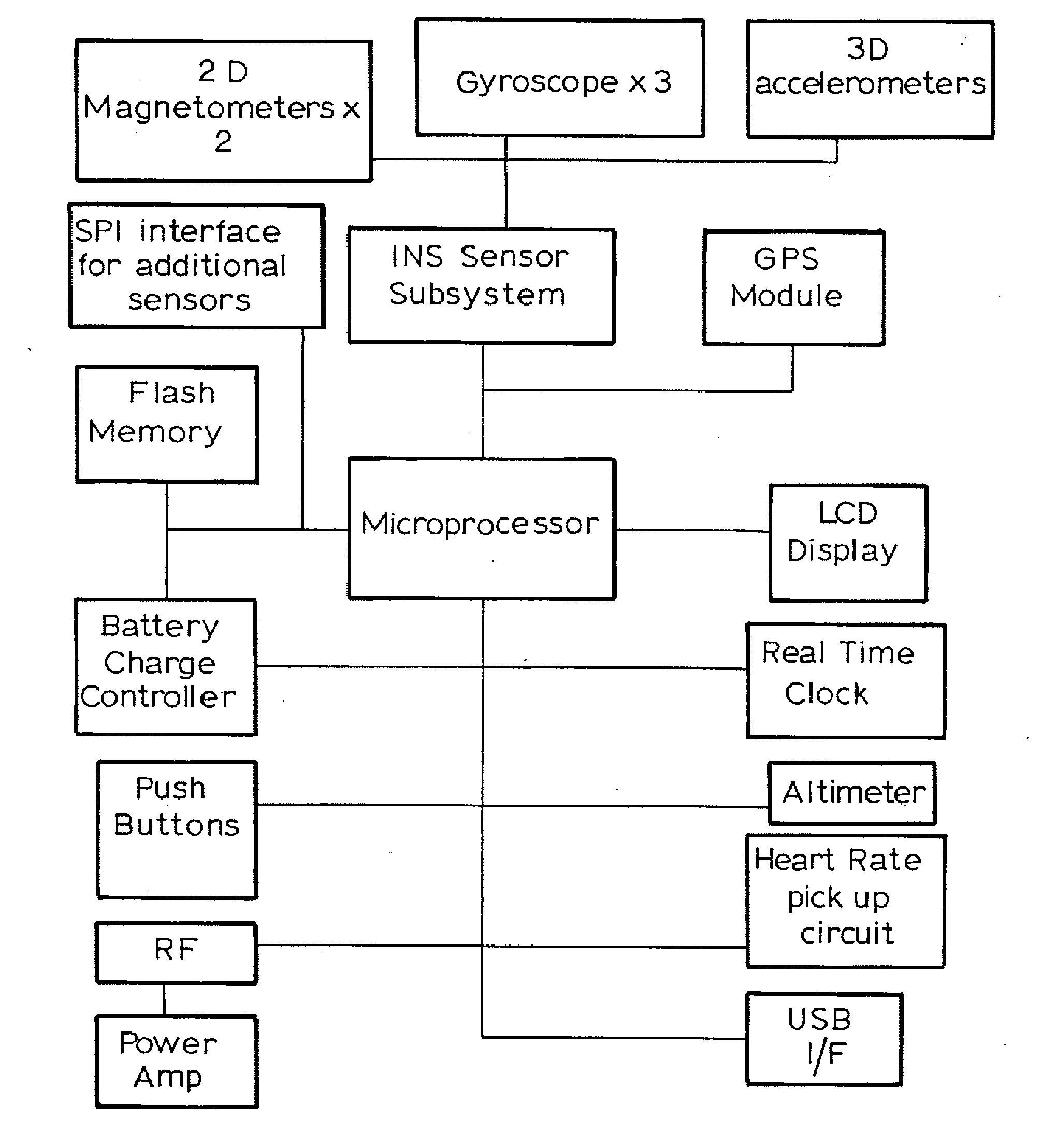
Sports Sensor
ActiveUS20080284650A1Show efficiencyShow powerGymnastic exercisingPosition fixationGyroscopeAccelerometer
A data logger for a monitoring sports which includes an accelerometer, a gyro sensor to sense angular displacement, a GPS unit to sense position and velocity, a magnetometer to sense direction of movement, a heart rate monitor, and a controller programmed to manipulate the data and provide a display of the heart rate, speed, and other sport parameters. The data can be stored or transmitted to a remote computer for use by the coach. The device is useful in football codes, athletics, swimming, snow sports and cycling.
Owner:CATAPULT GRP INT
Sports sensor
ActiveUS8036826B2Accurate outputSimple mathematicsGymnastic exercisingPosition fixationGyroscopeAccelerometer
A data logger for a monitoring sports which includes an accelerometer, a gyro sensor to sense angular displacement, a GPS unit to sense position and velocity, a magnetometer to sense direction of movement, a heart rate monitor, and a controller programmed to manipulate the data and provide a display of the heart rate, speed, and other sport parameters. The data can be stored or transmitted to a remote computer for use by the coach. The device is useful in football codes, athletics, swimming, snow sports and cycling.
Owner:CATAPULT GRP INT
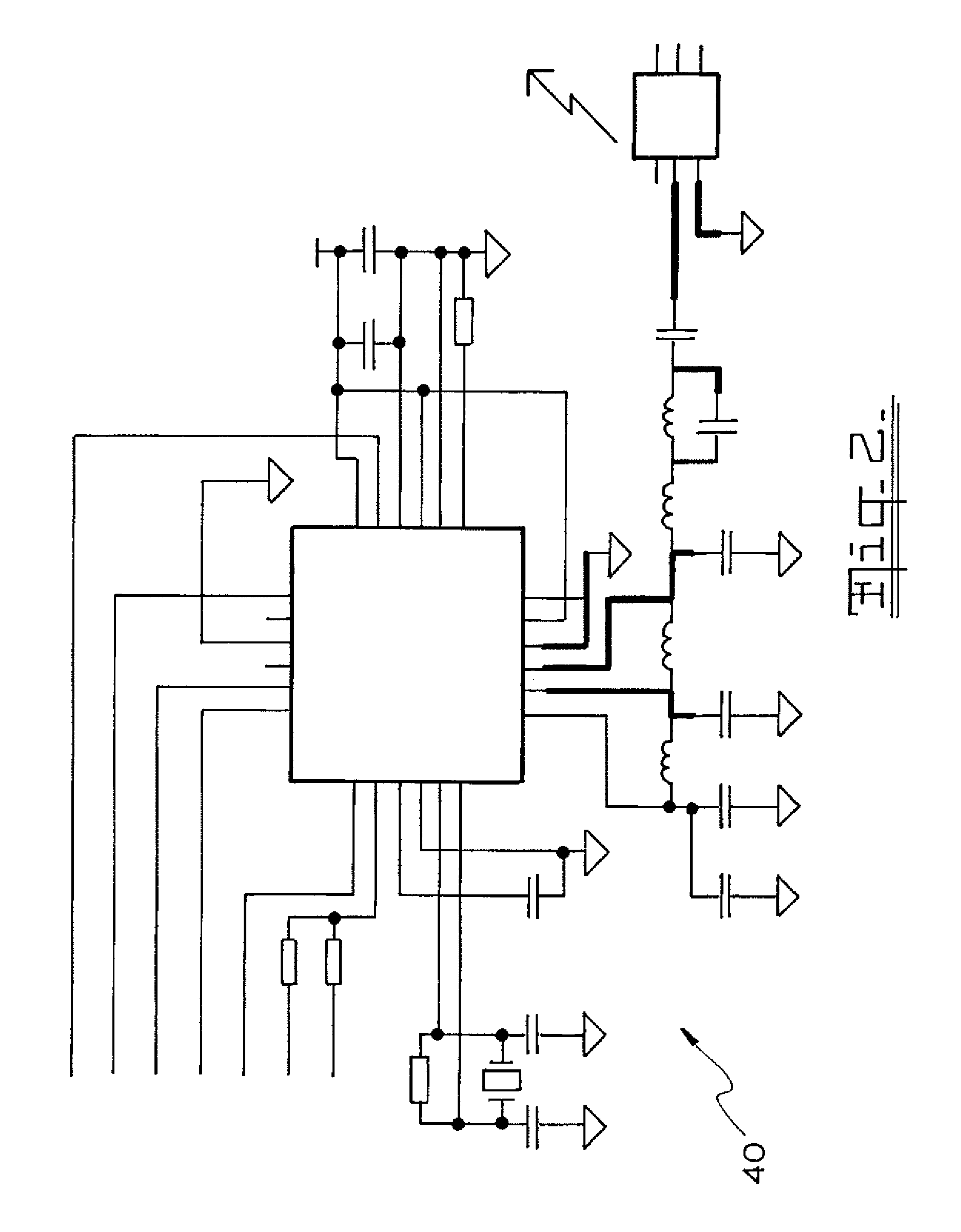
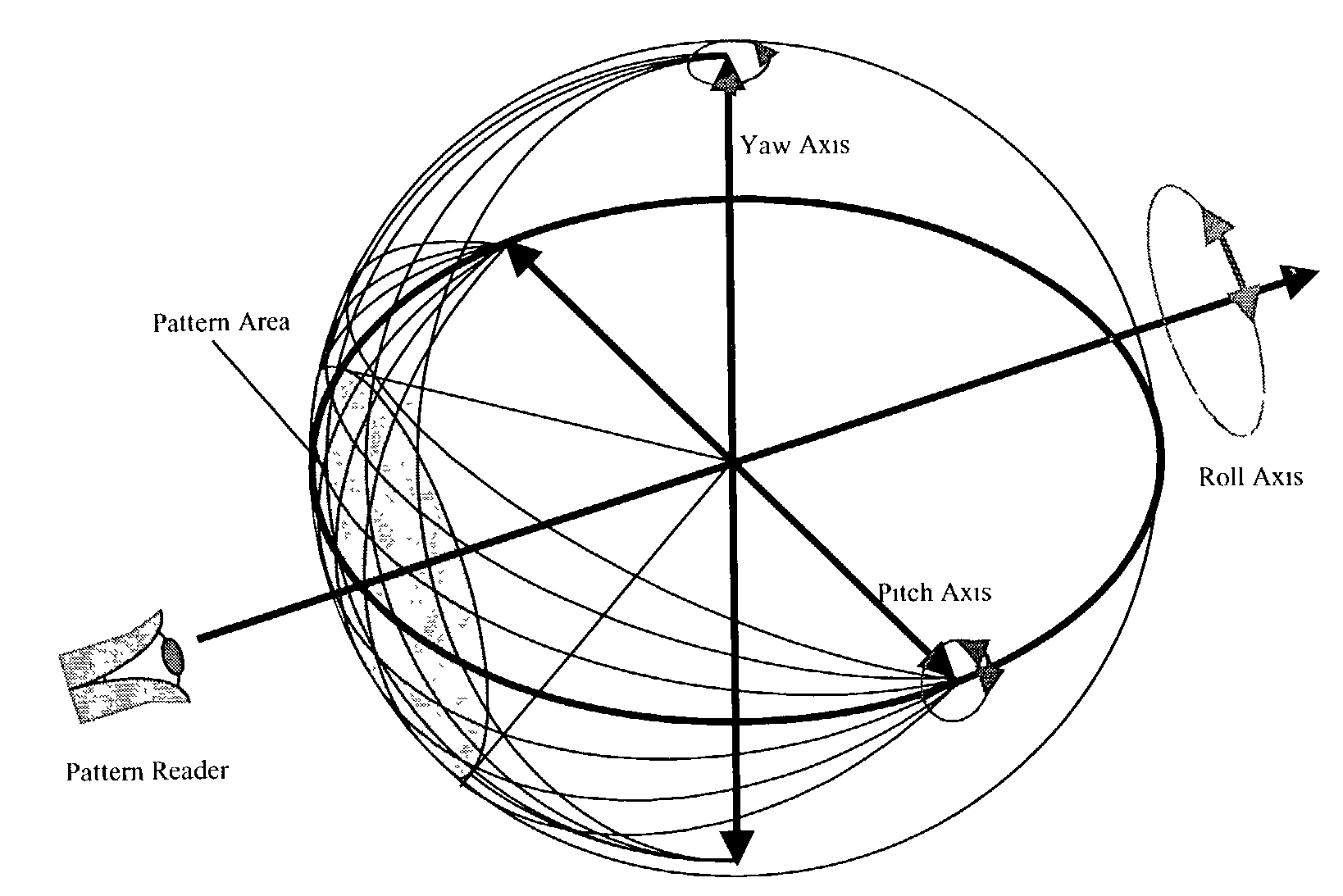
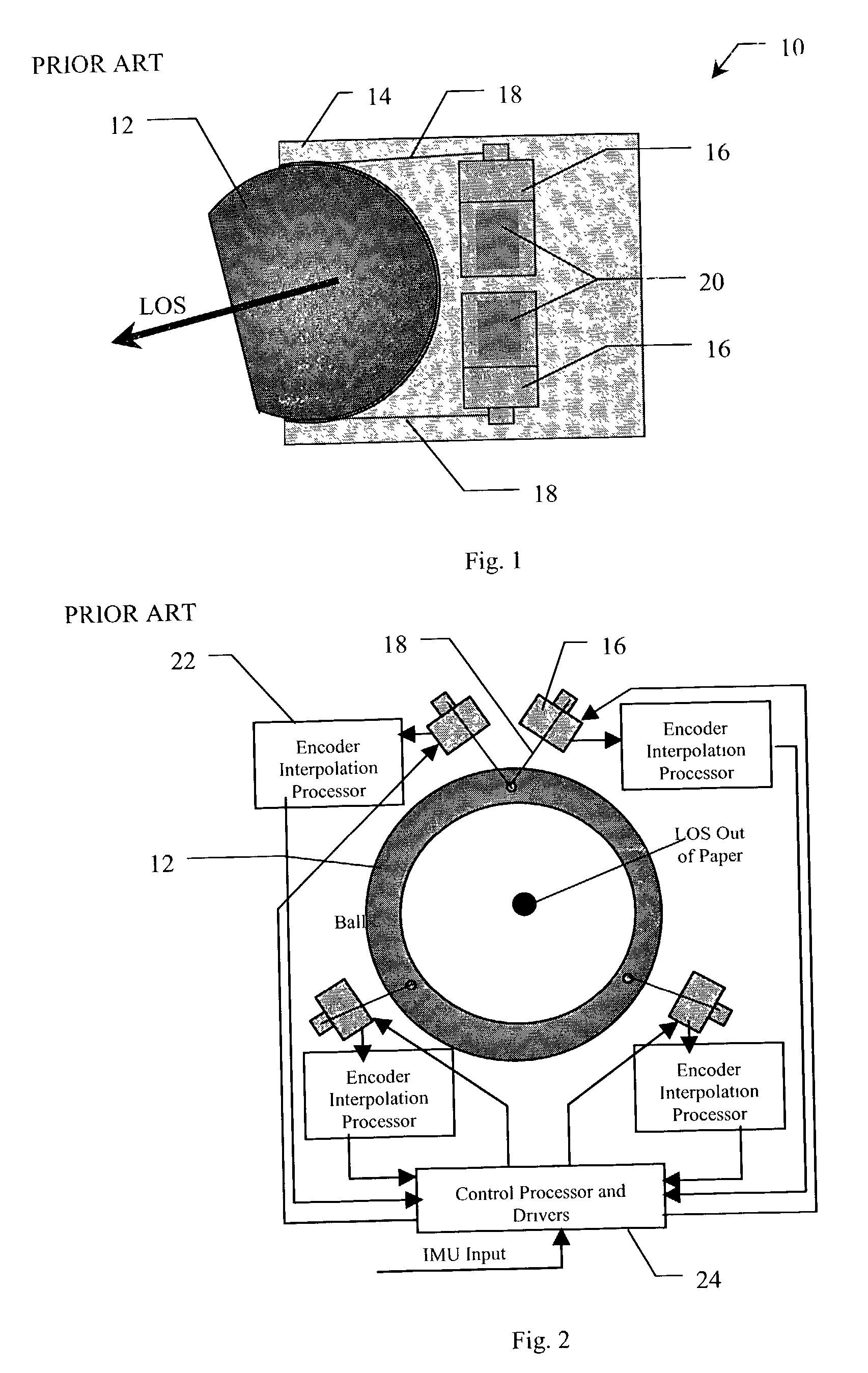
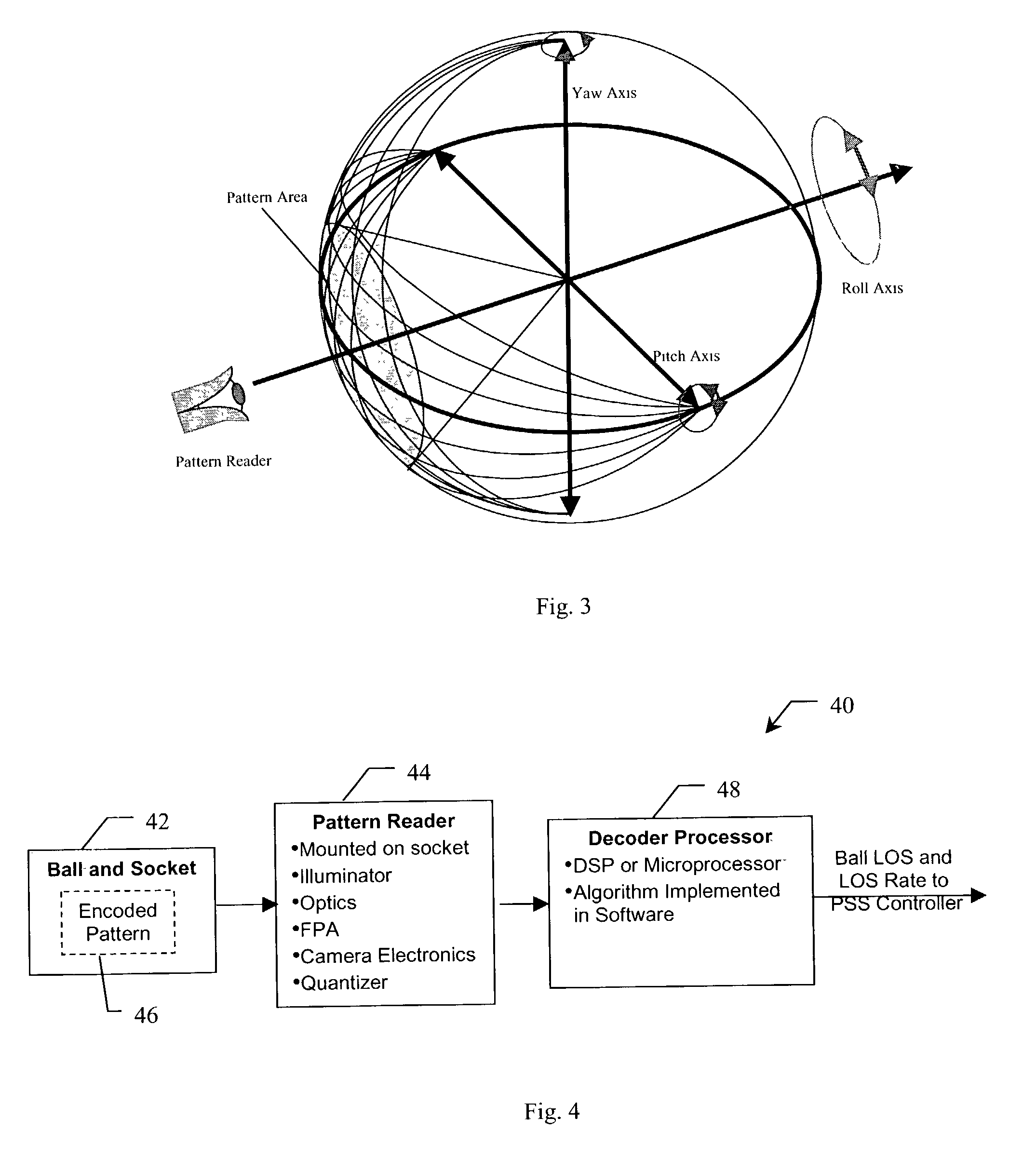
Three axes line-of-sight transducer
A system and method for measuring orientation of an object. In the illustrative embodiment, the object is a ball (42) in a ball and socket type pointing and stabilization system. The novel system (40) includes an encoded pattern (46) applied to a portion of the surface of the ball (42), a pattern reader (44) which reads the pattern (46) off the ball (42) and outputs data representative of the pattern (46), and a processor (48) which decodes the data into orientation information. In the preferred embodiment, the pattern reader (44) is an electro-optical sensor, and the encoded pattern (46) includes a grid of dots (52) arranged in a first predetermined number of dot code cycles (58) wherein each dot code cycle (58) includes a second predetermined number of dots. The processor (48) includes an algorithm (100) which computes pitch, yaw, and roll angles from the pattern reader data.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
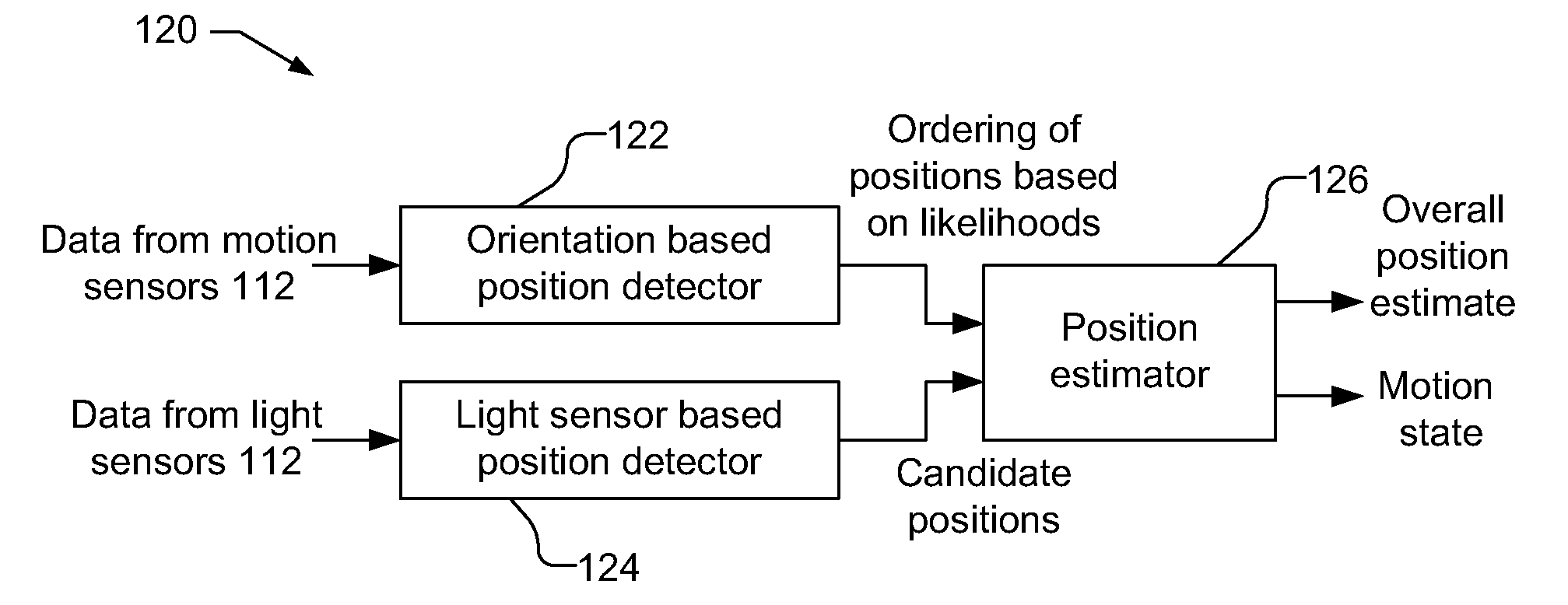
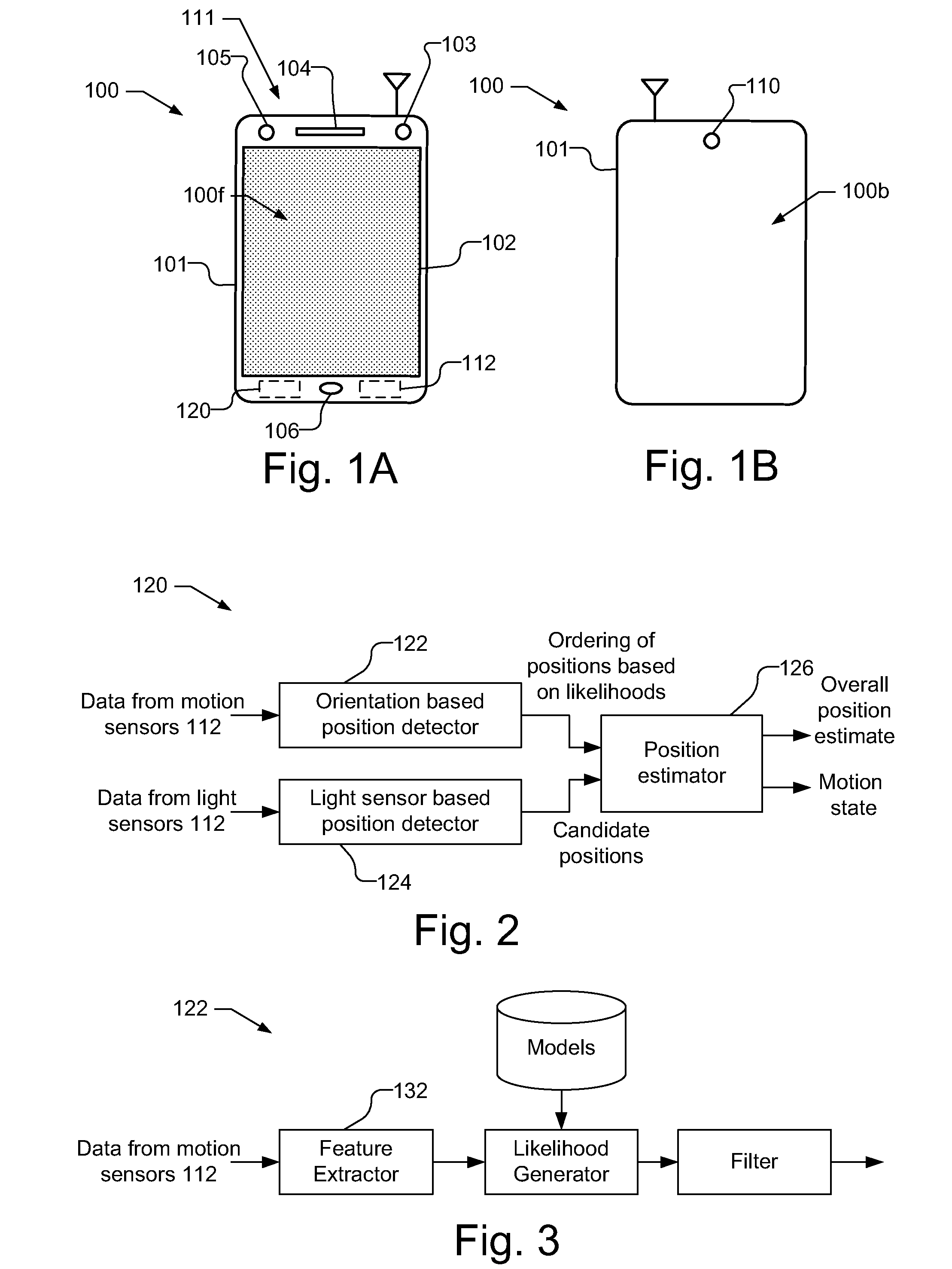
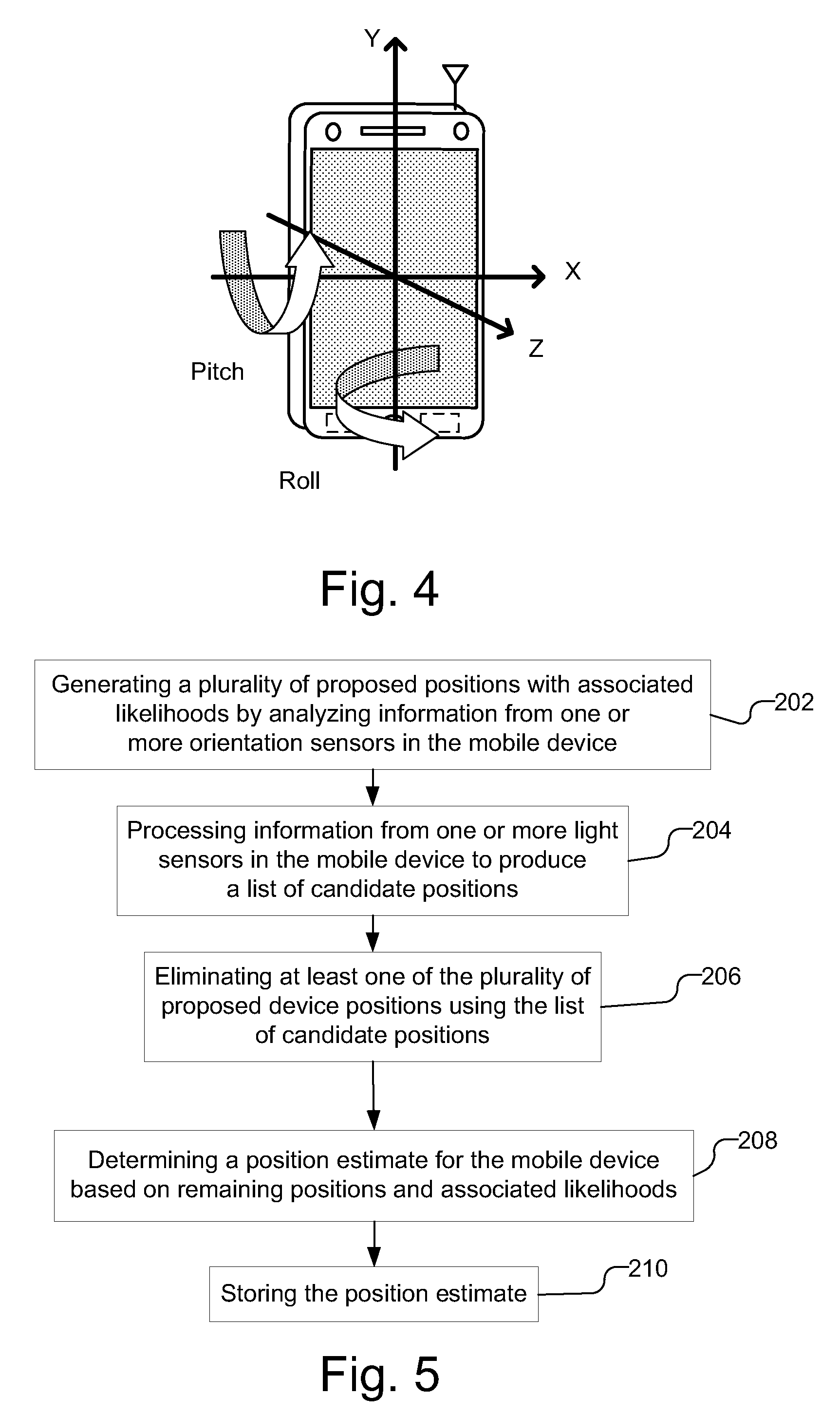
Device position estimates from motion and ambient light classifiers
ActiveUS20120265482A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsProximity sensorAccelerometer
A position estimate for a mobile device is generated using data from motion sensors, such as accelerometers, magnetometers, and / or gyroscopes, and data from light sensors, such as an ambient light sensor, proximity sensor and / or camera intensity sensor. A plurality of proposed positions with associated likelihoods is generated by analyzing information from the motion sensors and a list of candidate positions is produced based on information from the light sensors. At least one of the plurality of proposed positions is eliminated using the list of candidate positions and a position estimate for the mobile device is determined based on the remaining proposed positions and associated likelihoods. The proposed positions may be generated by extracting features from the information from the motion sensors and using models to generate likelihoods for the proposed positions. The likelihoods may be filtered over time. Additionally, a confidence metric may be generated for the estimated position.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
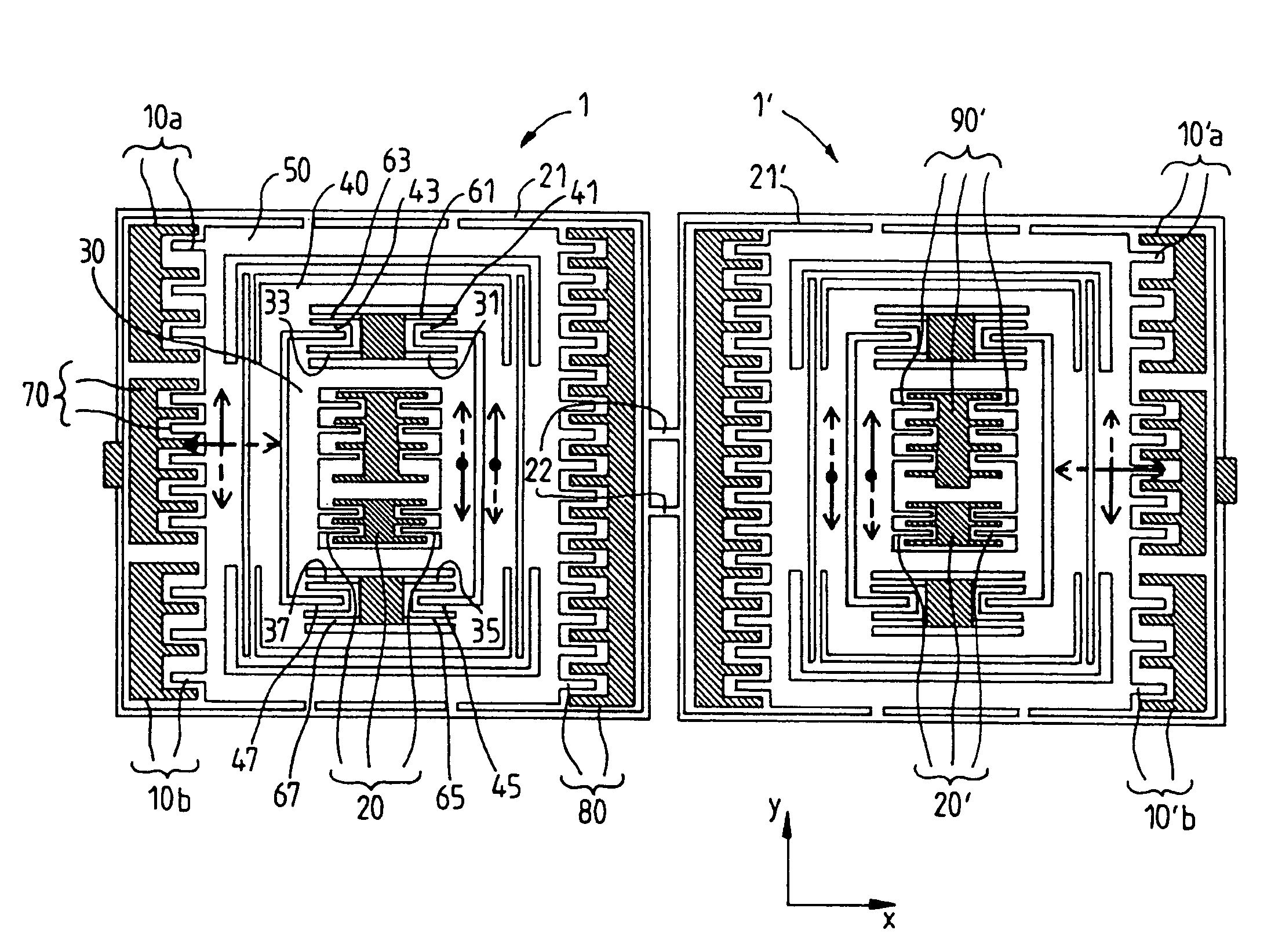
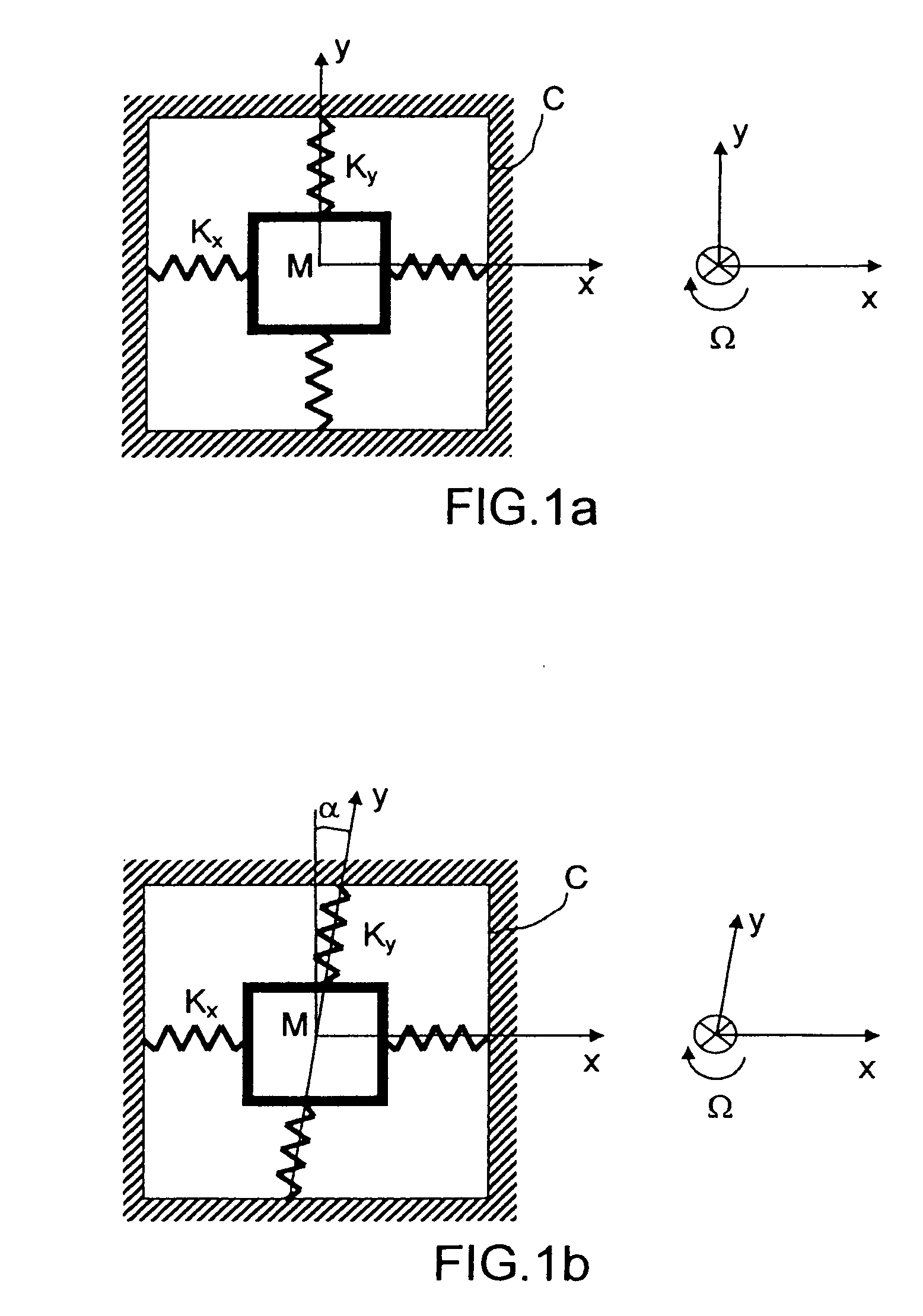
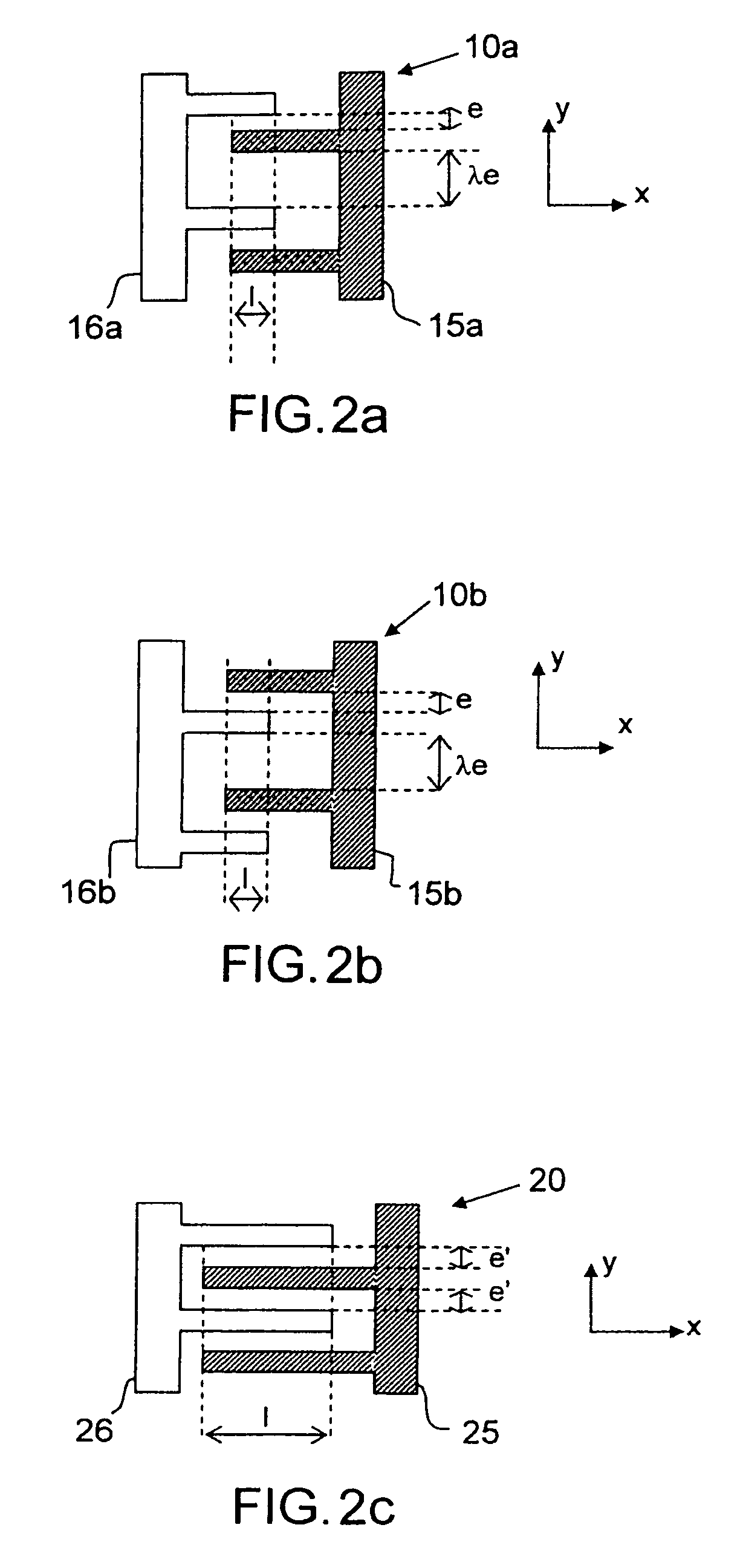
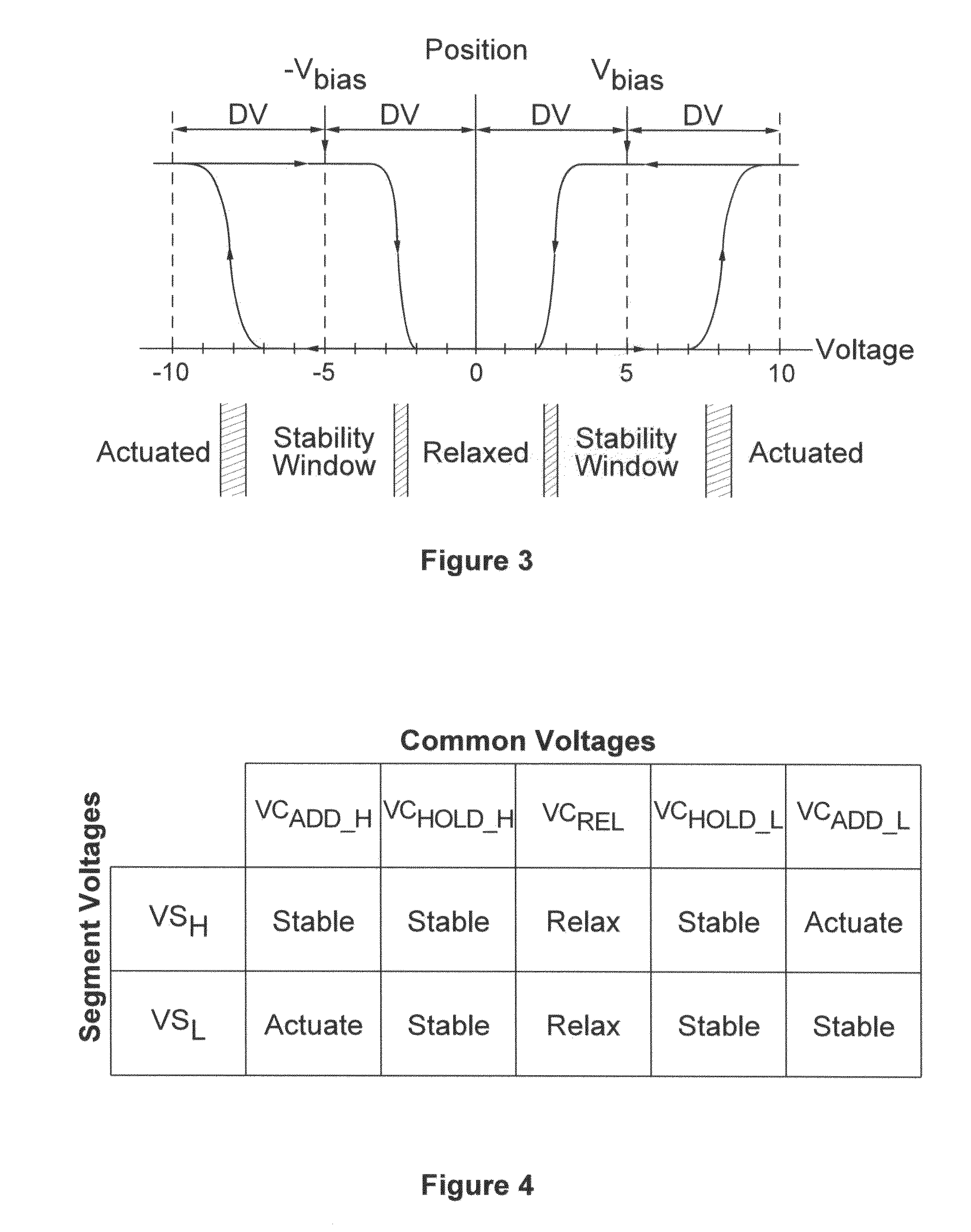
Vibratory Gyroscope Balanced by an Electrostatic Device
ActiveUS20080282833A1Mechanical apparatusSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAdjustable stiffnessDc voltage
The invention relates to a gyroscope with a vibrating structure, produced by micromachining in a thin wafer, which comprises a movable inertial assembly (1) comprising at least one movable mass (50) able to vibrate in the plane of the wafer along a drive axis x and along a sense axis y roughly perpendicular to the x-axis, an interdigital sensor comb (90) and an interdigital drive comb (70). It furthermore comprises at least one additional interdigital comb (10a), called the quadrature-error compensation comb, connected to the mass (50) and which has two asymmetric air gaps e and λe, λ being a positive real number, for subjecting the mass to an adjustable electrostatic stiffness due to coupling between the x-axis and the y-axis by applying a variable DC voltage V to this comb, the adjustable stiffness allowing compensation for the quadrature error of the gyroscope.
Owner:THALES SA
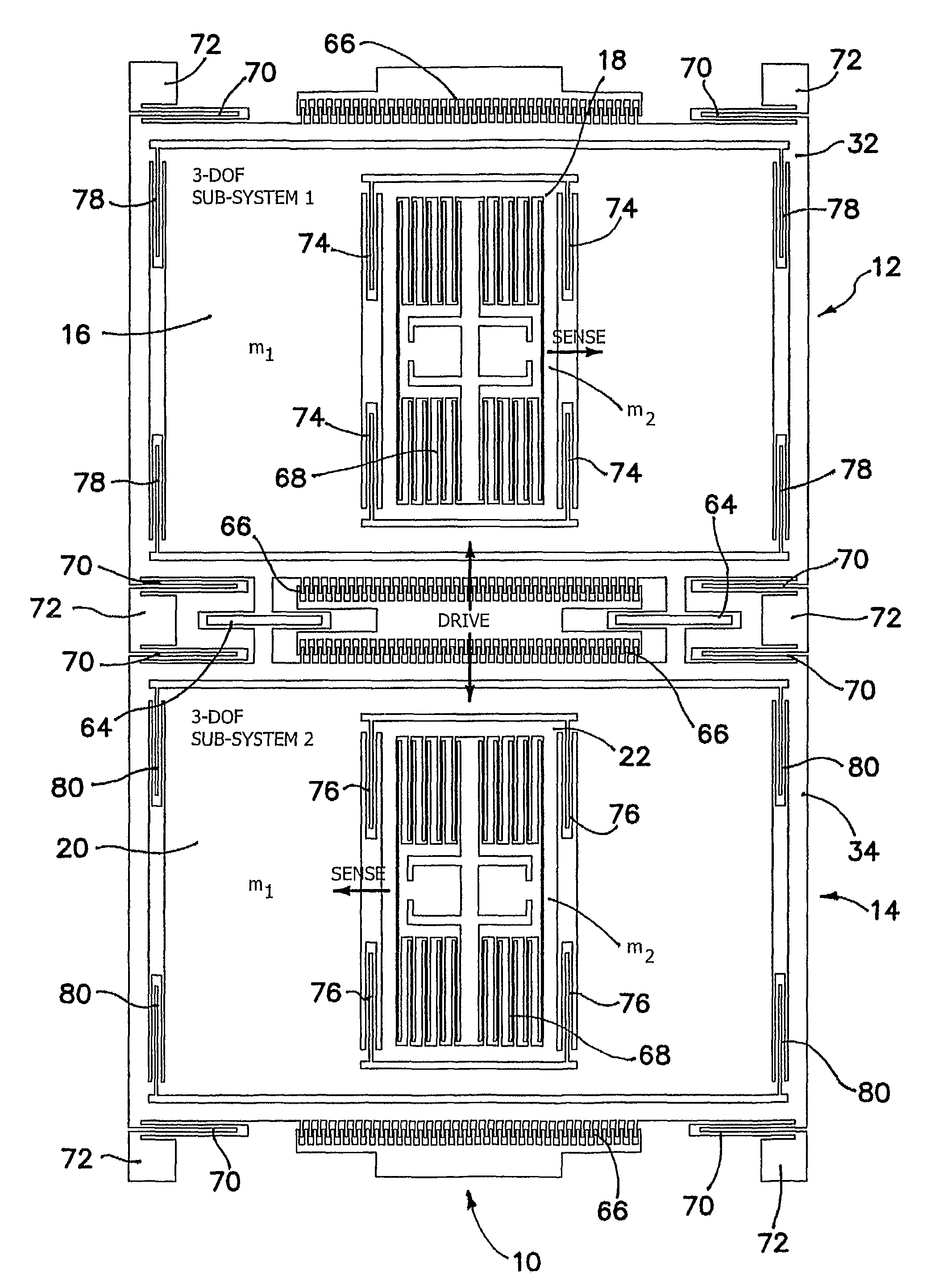
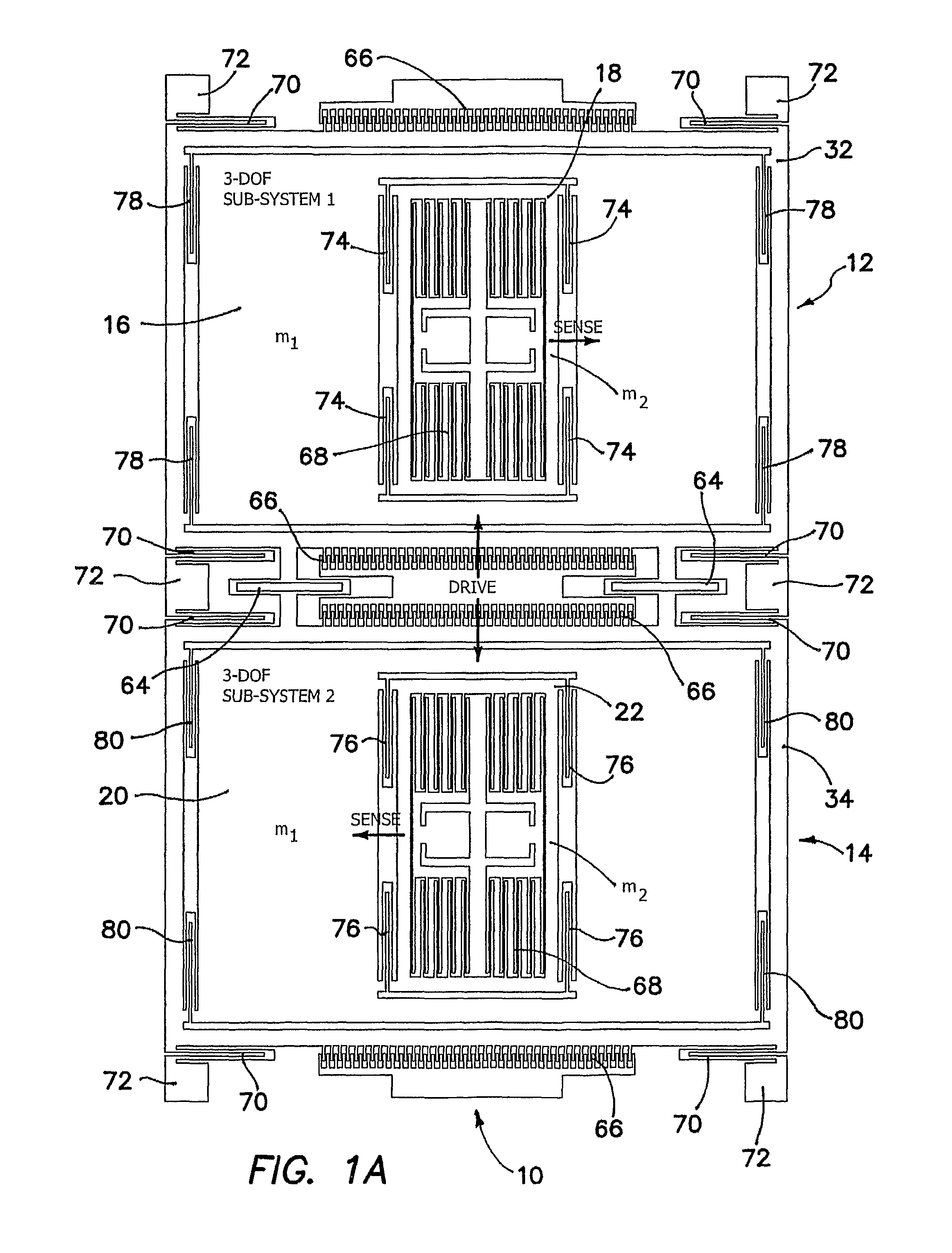
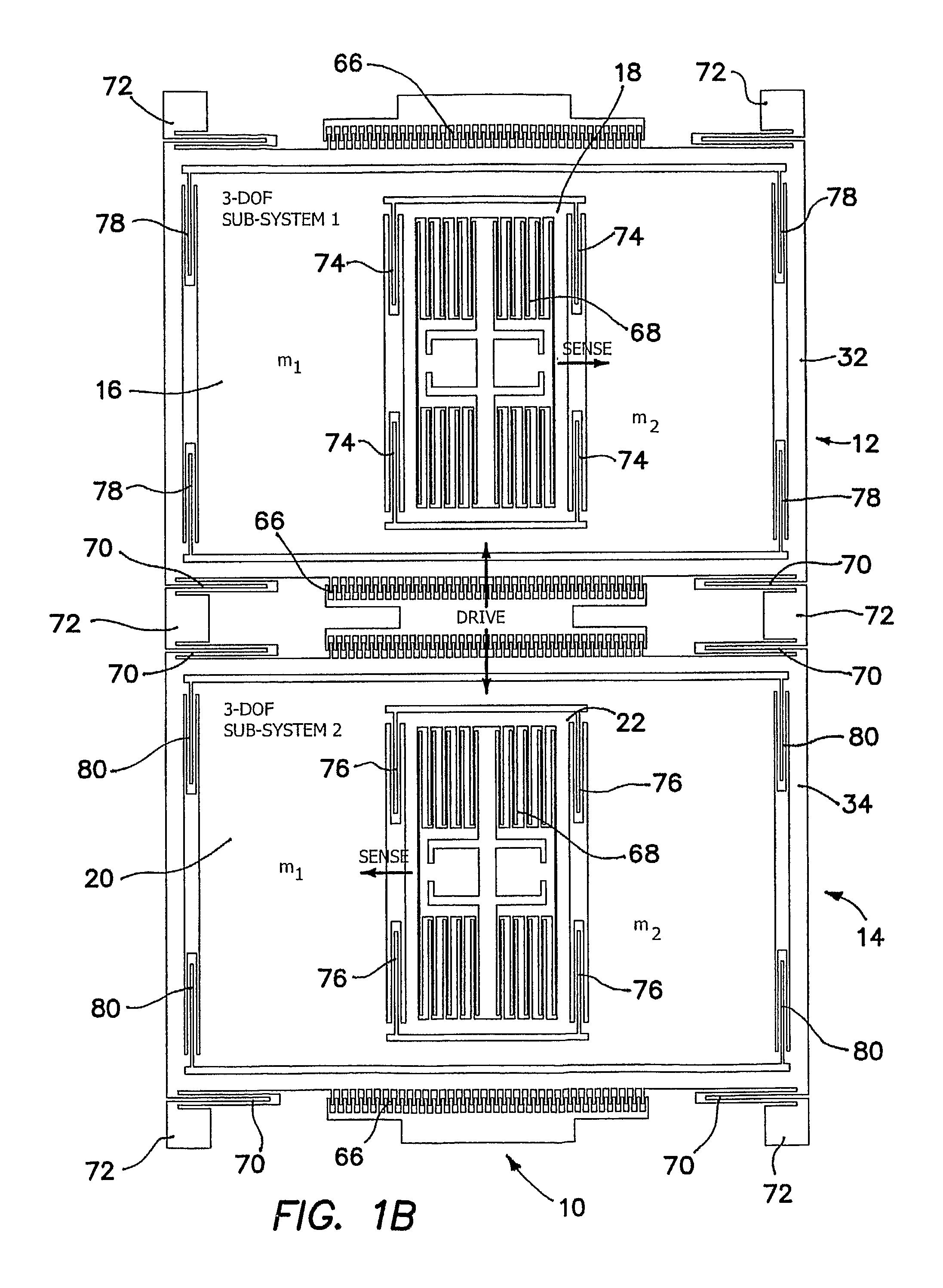
Robust six degree-of-freedom micromachined gyroscope with anti-phase drive scheme and method of operation of the same
ActiveUS8113050B2Effectively and substantially rejectEfficiently rejectedMechanical apparatusAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTuning forkGyroscope
A method of operating an anti-phase six degree-of-freedom tuning fork gyroscope system comprises the steps of driving a first three degree-of-freedom gyroscope subsystem, and driving a second three degree-of freedom gyroscope subsystem in an anti-phase mode with the first gyroscope subsystem at an anti-phase resonant frequency. Acceleration or an angular rate of motion is sensed by the first and second three degree-of-freedom gyroscope subsystems operating in a flat frequency response range where the anti-phase resonant frequency is designed. Response gain and phase are stable and environmental and fabrication perturbations are avoided by such operation. A anti-phase six degree-of-freedom tuning fork gyroscope system which operates as described is also characterized.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
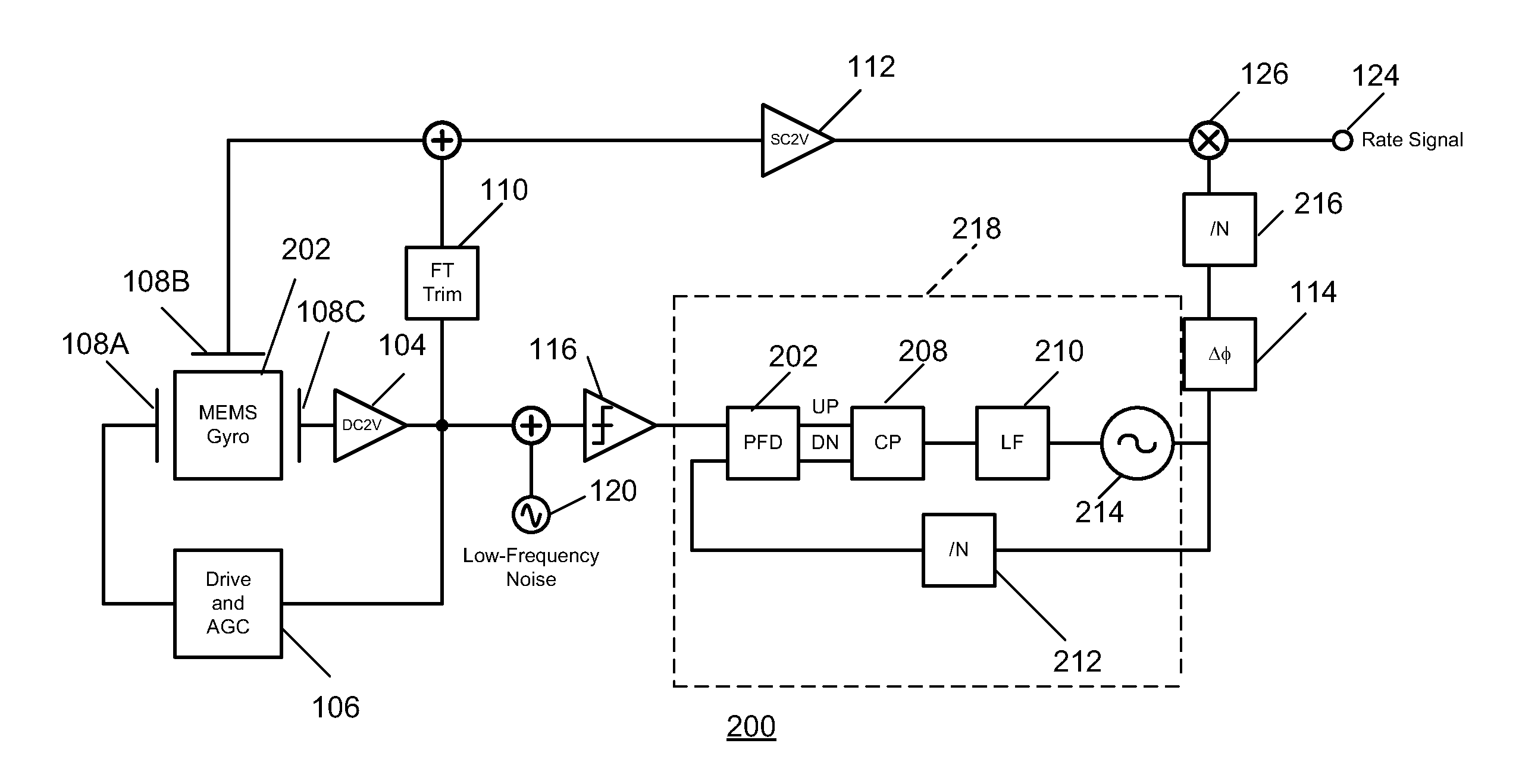
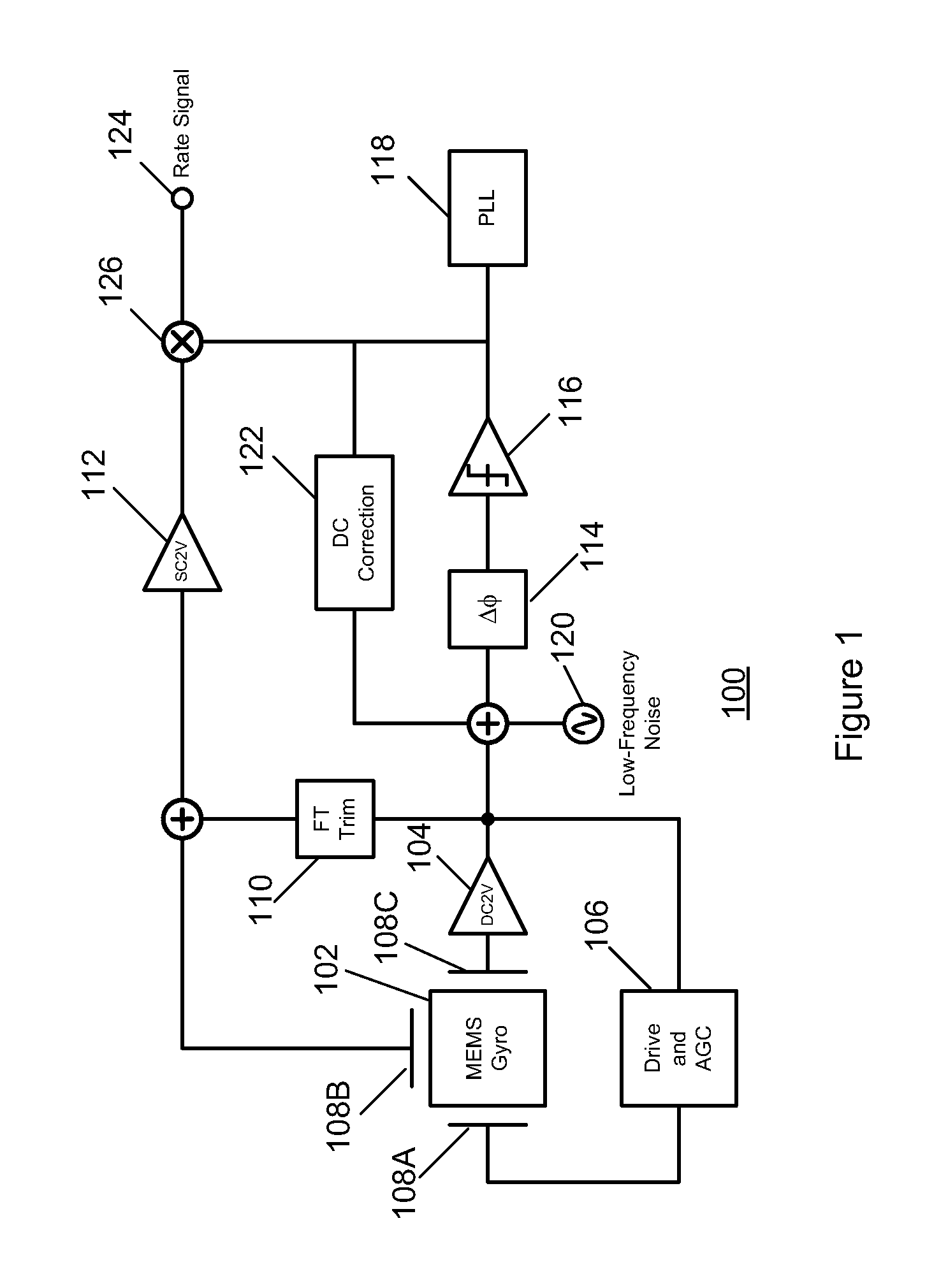
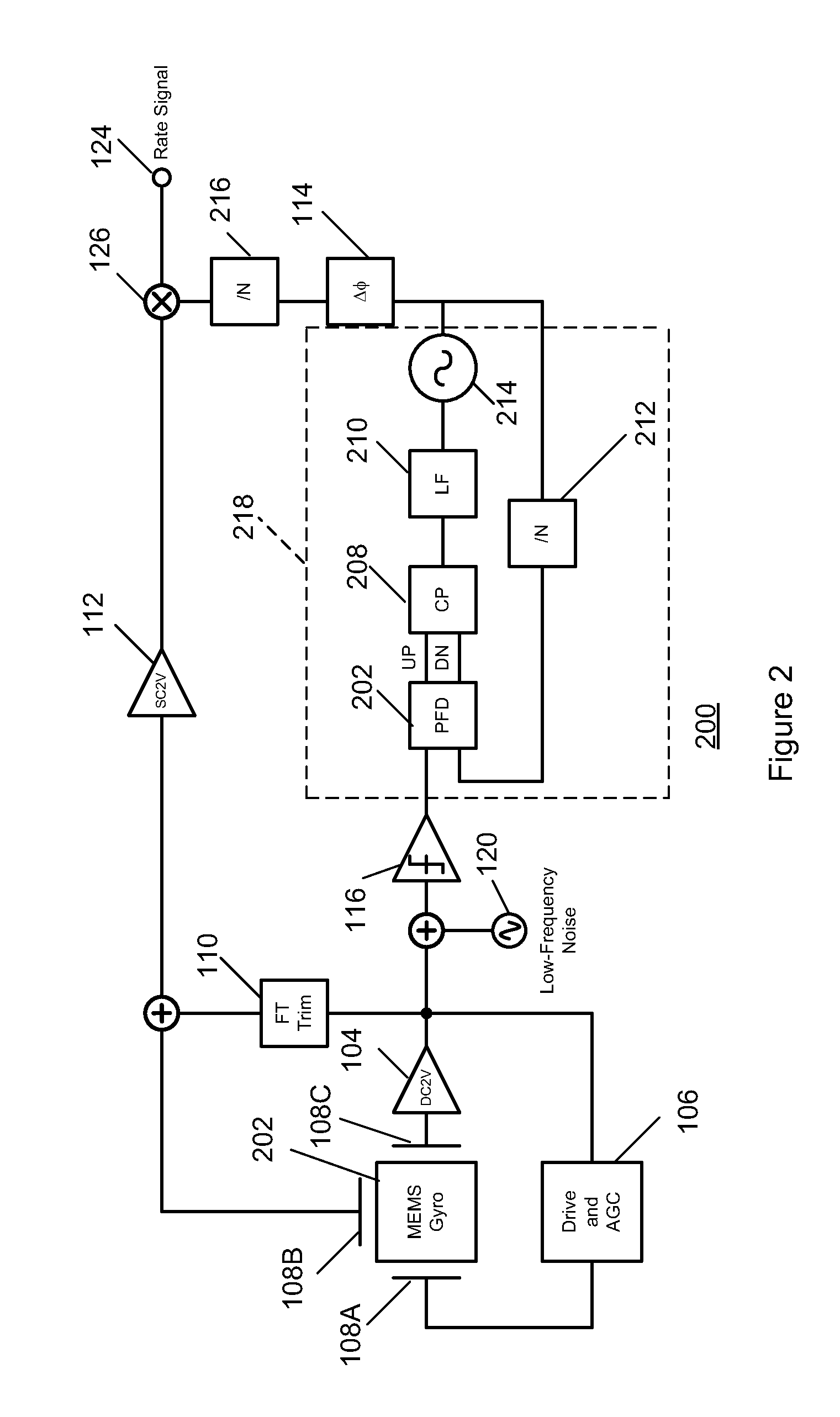
Gyroscope with phase and duty-cycle locked loop
ActiveUS20130099836A1Improve Noise PerformanceImprove bias stabilityMechanical apparatusPulse automatic controlGyroscopeSmall footprint
A system and method in accordance with the present invention provides a gyroscope incorporating an improved PLL technique. The improved PLL auto-corrects its own reference low-frequency noise, thereby eliminating this source of noise, improving the noise performance of the gyroscope and allowing a compact implementation. The net result is a gyroscope with improved bias stability that can meet noise requirements with a smaller footprint.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Micromachined piezoelectric x-axis gyroscope
InactiveUS20110265564A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSolid-state devicesElectricityGyroscope
This disclosure provides systems, methods and apparatus, including computer programs encoded on computer storage media, for making and using gyroscopes. Such gyroscopes may include a sense frame, a proof mass disposed outside the sense frame, a pair of anchors and a plurality of drive beams. The plurality of drive beams may be disposed on opposing sides of the sense frame and between the pair of anchors. The drive beams may connect the sense frame to the proof mass. The drive beams may be configured to cause torsional oscillations of the proof mass substantially in a first plane of the drive beams. The sense frame may be substantially decoupled from the drive motions of the proof mass. Such devices may be included in a mobile device, such as a mobile display device.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Compact navigation system and method
InactiveUS6918186B2More compact and accurate navigation systemCompact and accurate navigationSurveyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeTriaxial accelerometer
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Sensor device
ActiveUS7814791B2Avoid excess performanceAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeZ-Coordinate
The present invention is related to sensor arrangements and particularly to sensor arrangements for symmetric response in a x-, y- and z-coordinate system. The arrangement comprises four gyroscopes with one axis arranged into different directions of sensitivity.
Owner:IMEGO
Multi-panel electronic device
ActiveUS9009984B2Extended large displaySmall sizeDevices with multiple display unitsDevices with sensorSoftware engineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
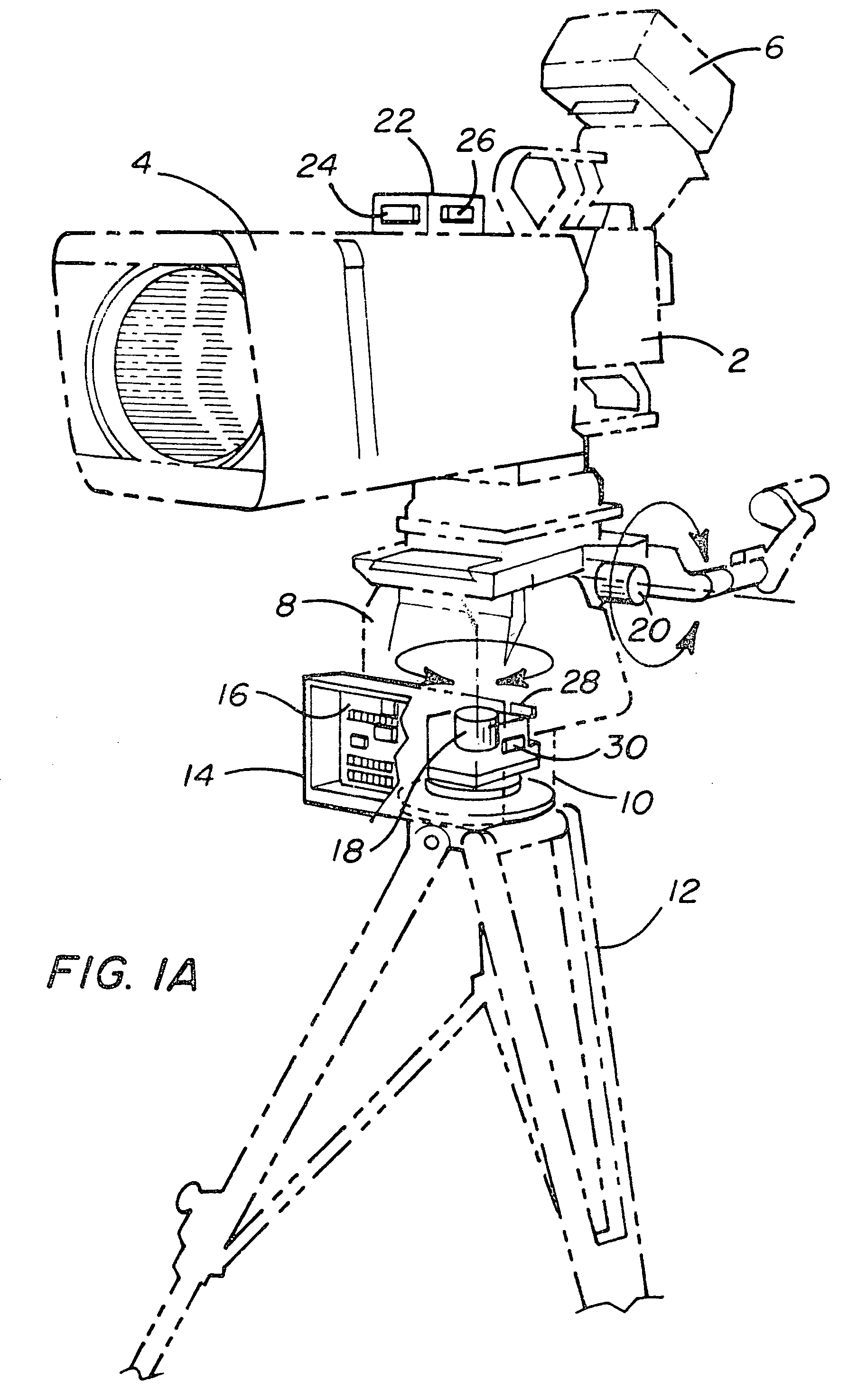
Measuring camera attitude
A system is disclosed for using camera attitude sensors with a camera. A camera assembly includes a tripod base, a tripod head interface mounted on the tripod base, a tripod head mounted on the tripod head interface and a camera mounted on the tripod head. The tripod head enables the camera to pan and tilt. The system also includes a first optical encoder for detecting the amount that the camera has been panned and a second optical encoder for detecting the amount that the camera has been tilted. Two inclinometers are mounted on the tripod head interface to measure attitude of the tripod head. Two gyroscopes (“gyros”) are mounted on the camera assembly. Data from the encoders, gyros and inclinometers are packaged and sent to graphics production equipment to be used for enhancing video captured by the camera.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
Attitude control system for small satellites
Various embodiments of the present invention include an attitude control system for use with small satellites. According to various embodiments, the system allows rapid retargeting (e.g., high slew rates) and full three-axis attitude control of small satellites using a compact actuation system. In certain embodiments, the compact actuation system includes a plurality of single-gimbaled control moment gyroscopes (SGCMG) arranged in a pyramidal configuration that are disposed within a small satellite.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
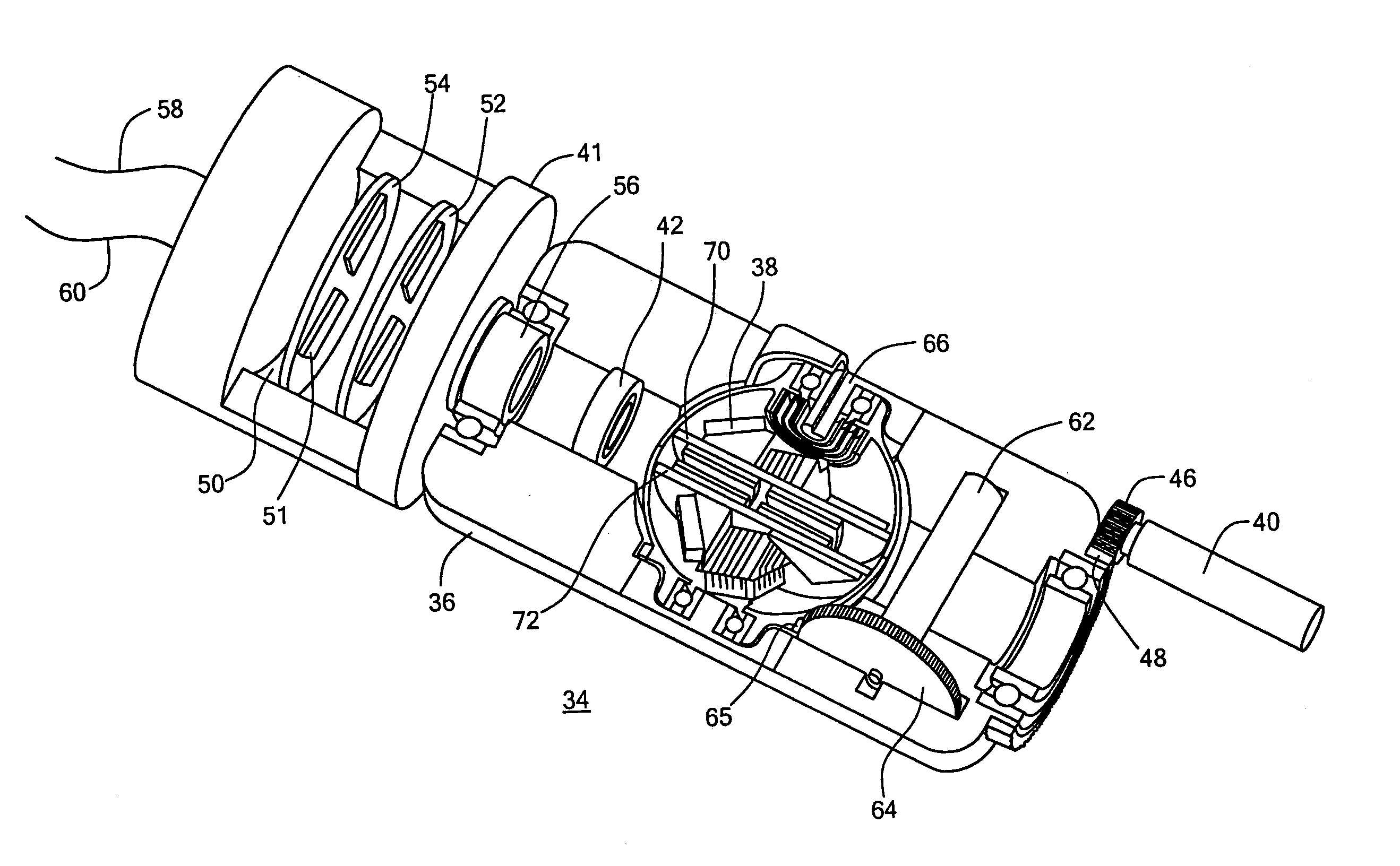
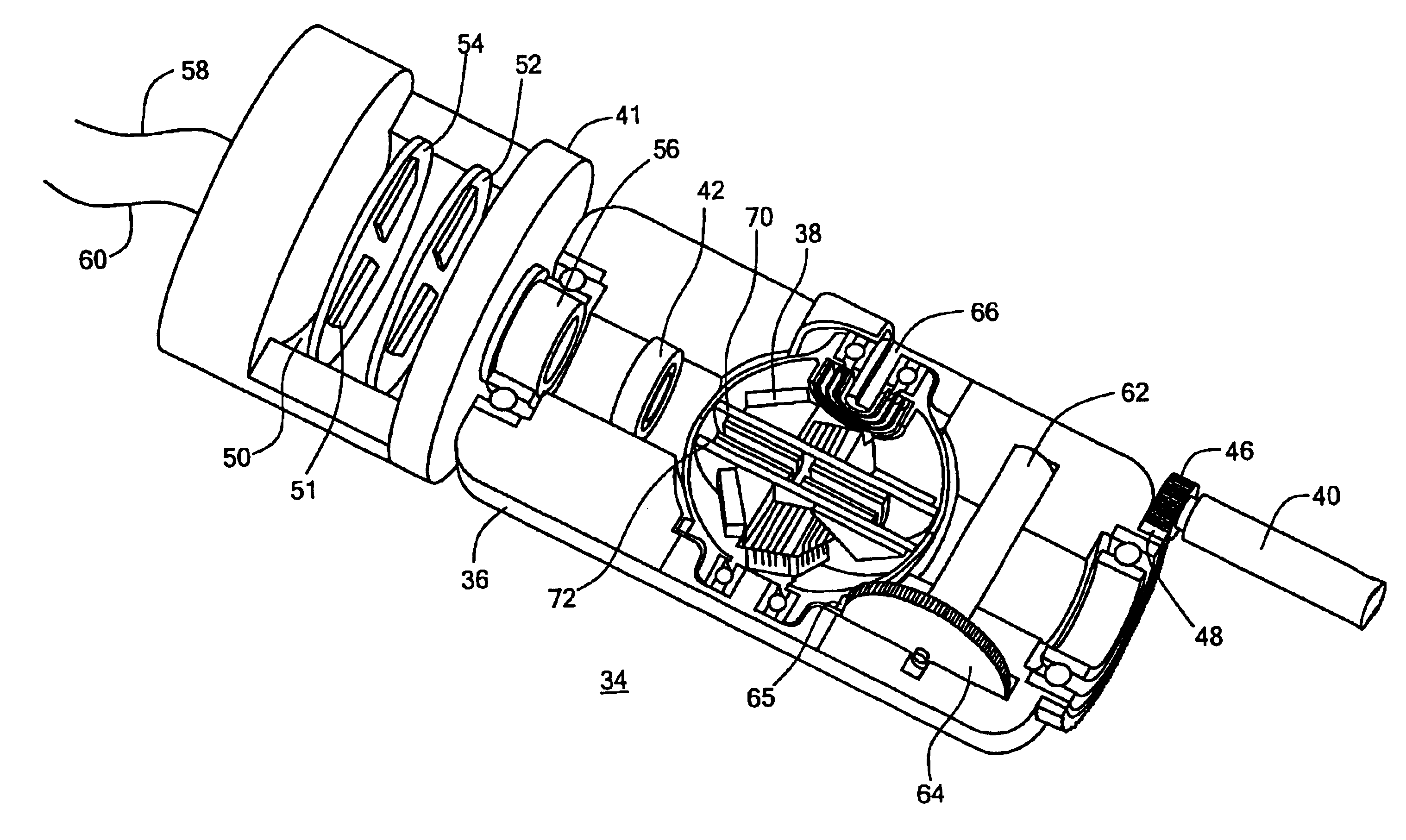
Integrated inertial measurement system and methods of constructing the same
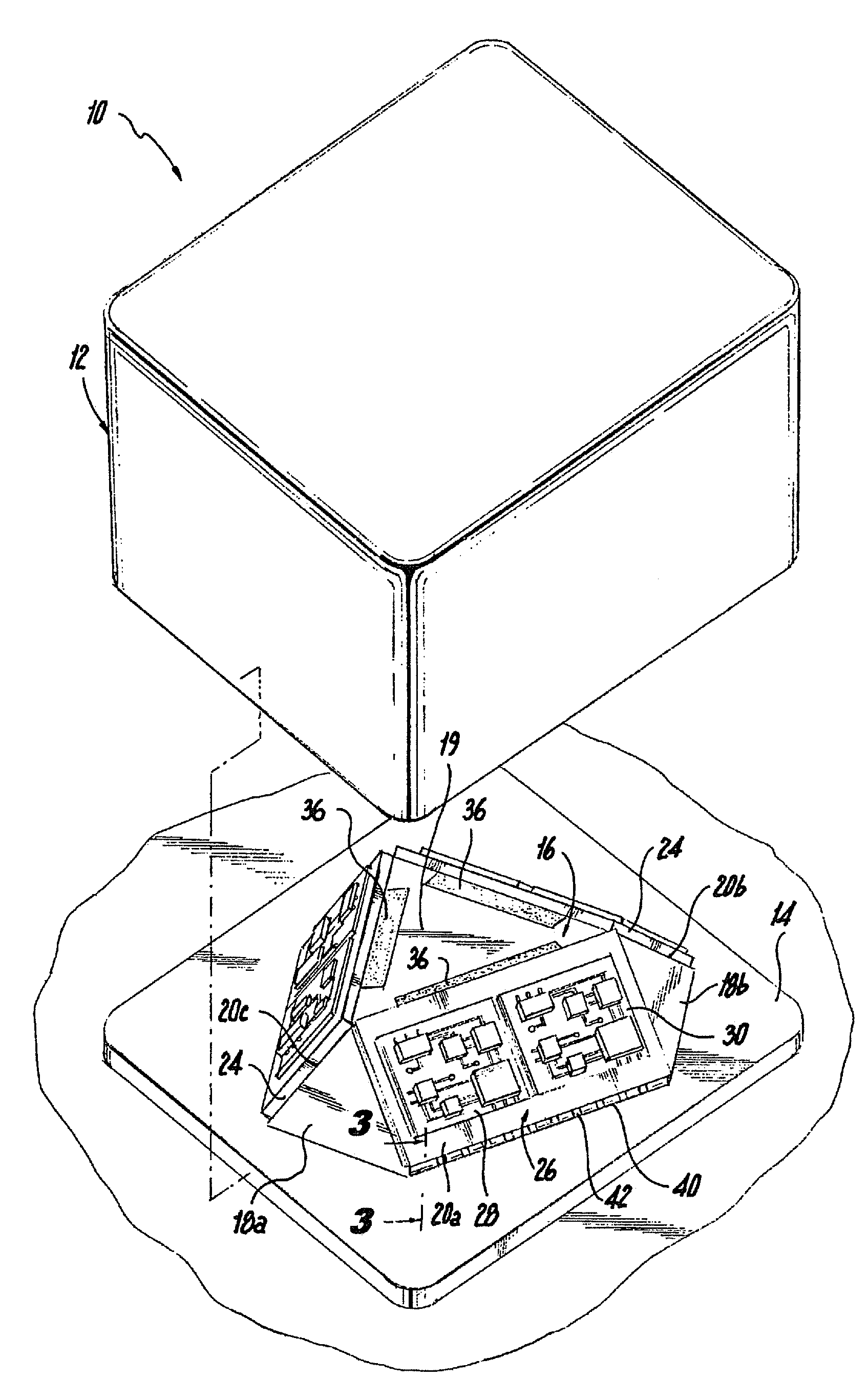
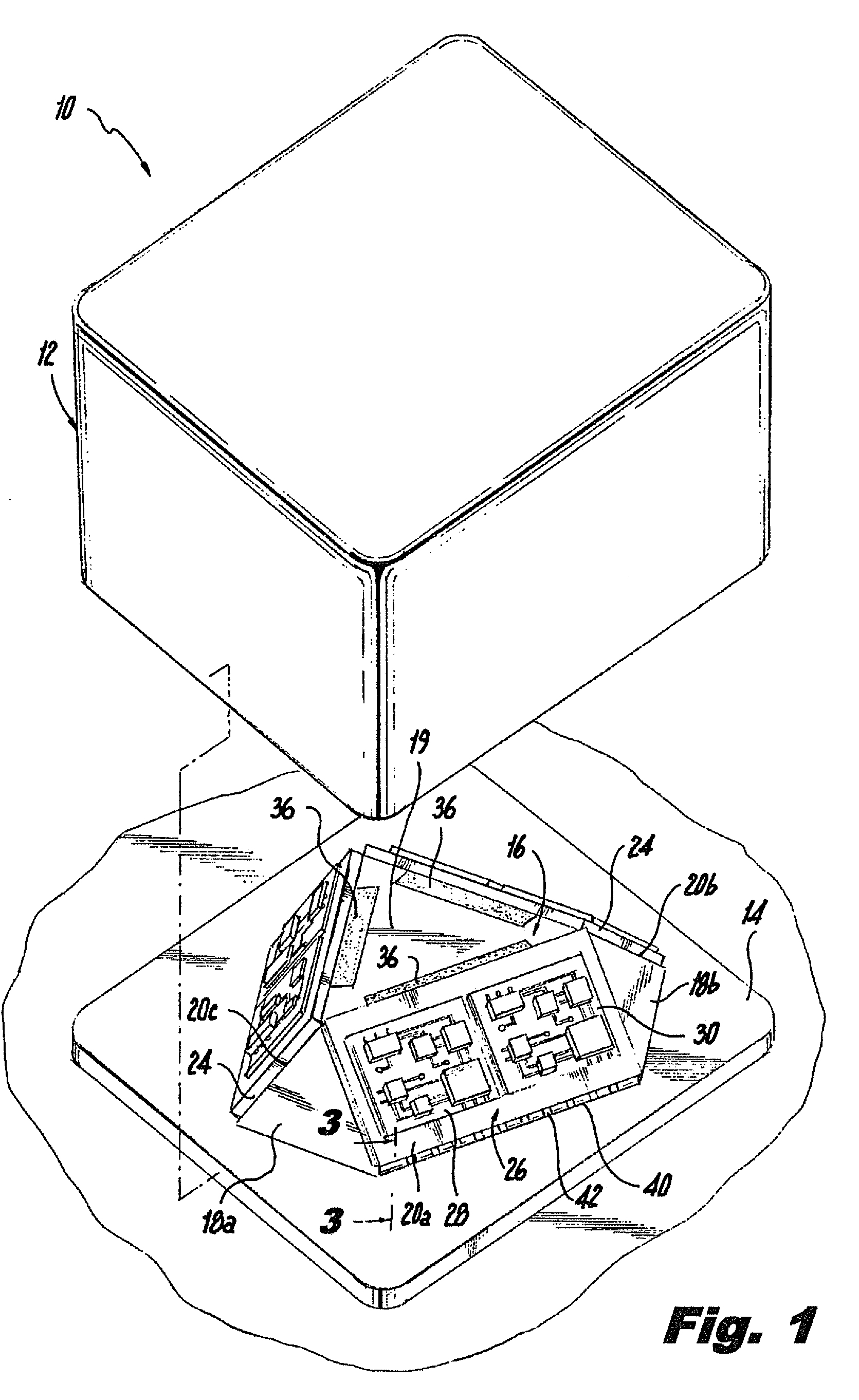
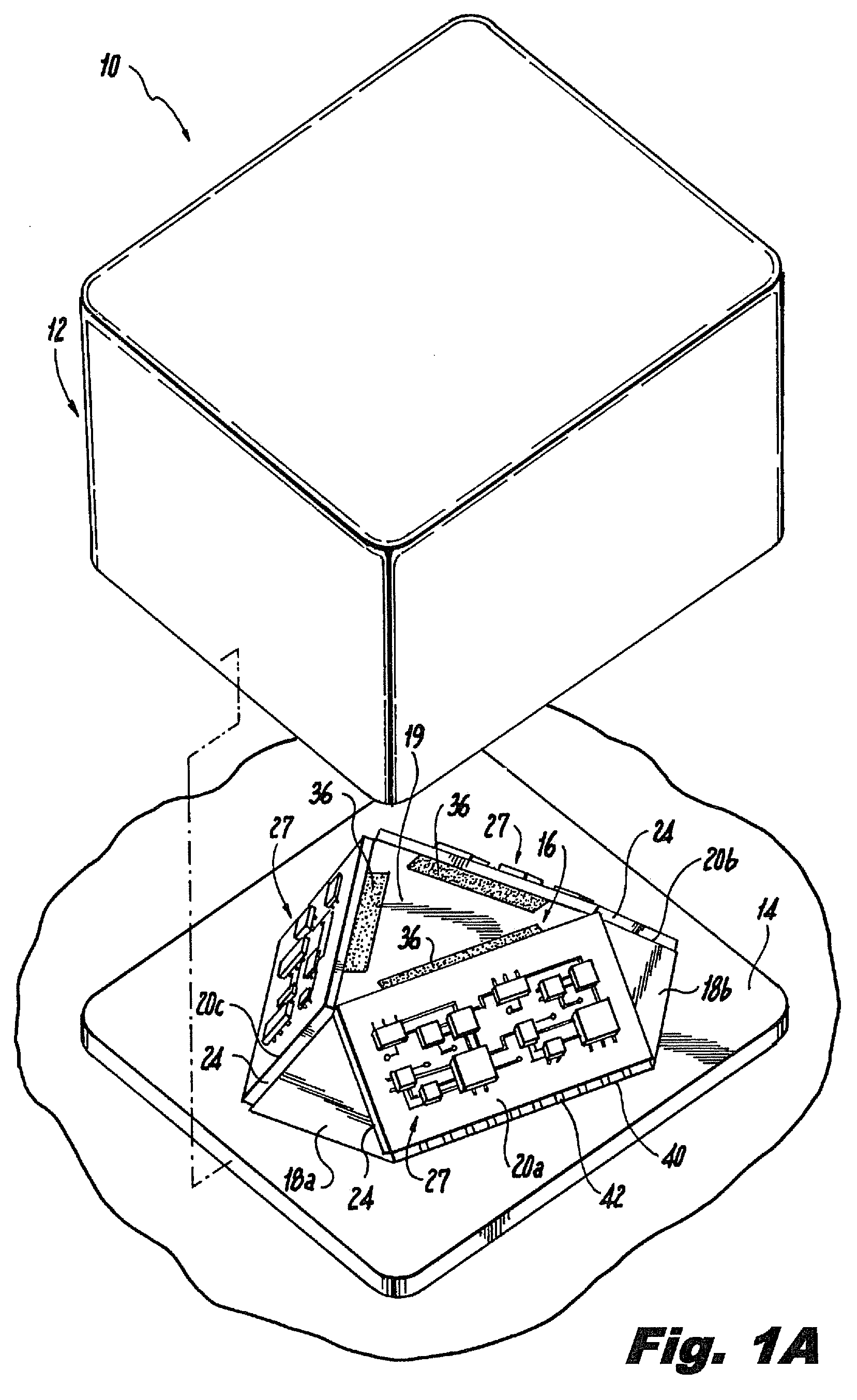
InactiveUS20090308157A1Easy to fixAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSoldering apparatusGyroscopeAccelerometer
An inertial measurement system having a triangular cupola shaped base structure with three mutually orthogonal sides and a bottom surface surrounding a hollow core. The bottom surface includes an aperture providing access to the hollow core. An inertial module is mounted on each of the sides and includes a gyroscopic rotational rate sensor and a linear accelerometer connected to a circuit board. The inertial measurement system also includes a motherboard and a plurality of metallization elements. The metallization elements extend from the bottom surface to the sides of the base structure and conductively connect the inertial module to the motherboard. The inertial measurement system may also include a non-conductive adhesive underfill positioned between the inertial module and the base structure.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
Apparatus and method for monitoring the stability of a construction machine
InactiveUS20090125196A1Mechanical apparatusAnalogue computers for trafficGyroscopeMechanical stability
Systems and methods for monitoring the stability of a construction machine are provided. A gyroscope is configured to detect an angle of inclination of the construction machine relative to a vertical axis and generate an inclination signal representative thereof. A processor in operable communication with the gyroscope is configured to receive the inclination angle and generate a warning signal when the angle of inclination exceeds a predetermined threshold. An alarm device in operable communication with the processor is configured to generate an alarm to indicate to a user of the construction machine when the angle of inclination has exceeded the predetermined threshold.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
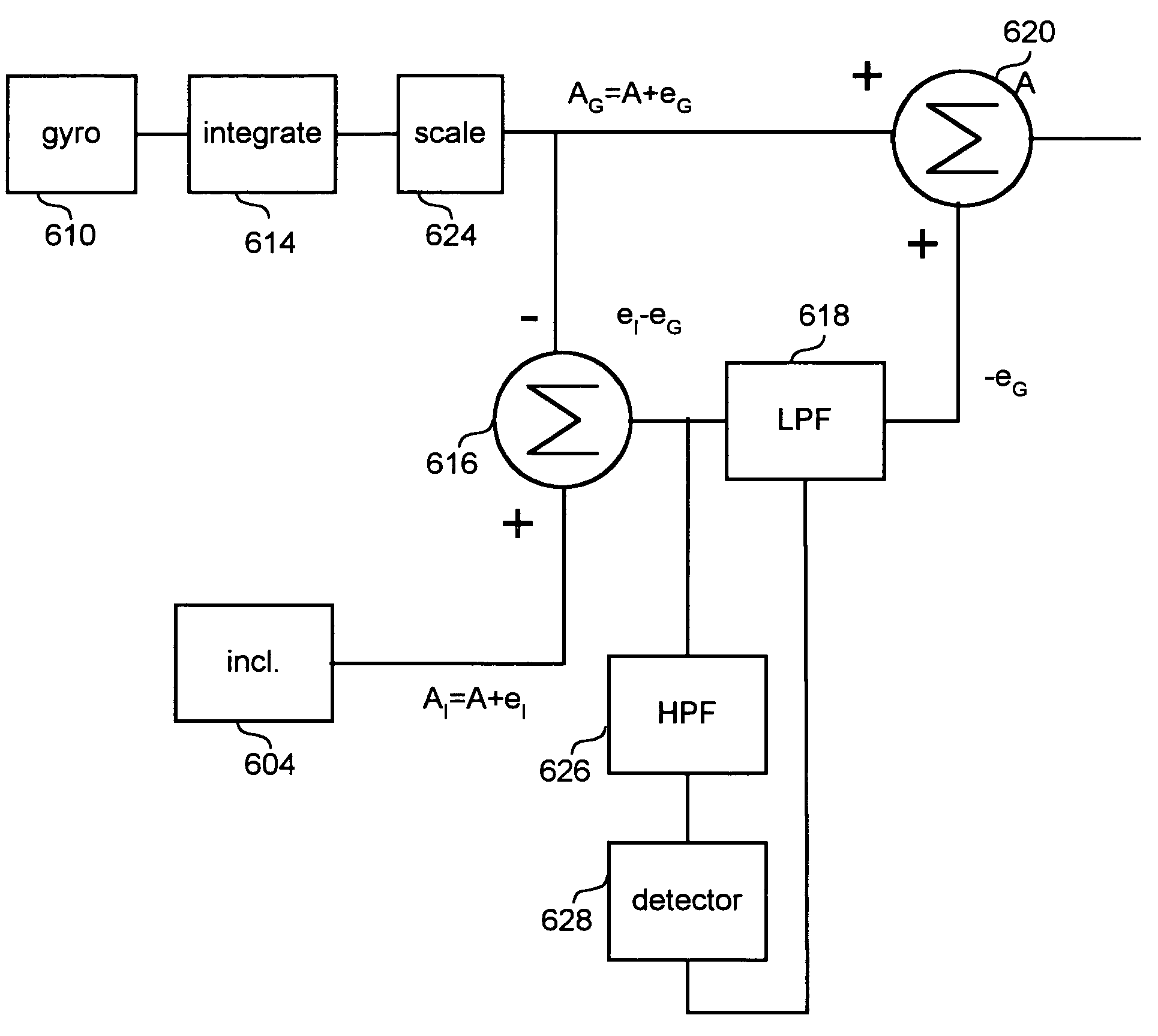
Inertial measurement system and method with bias cancellation
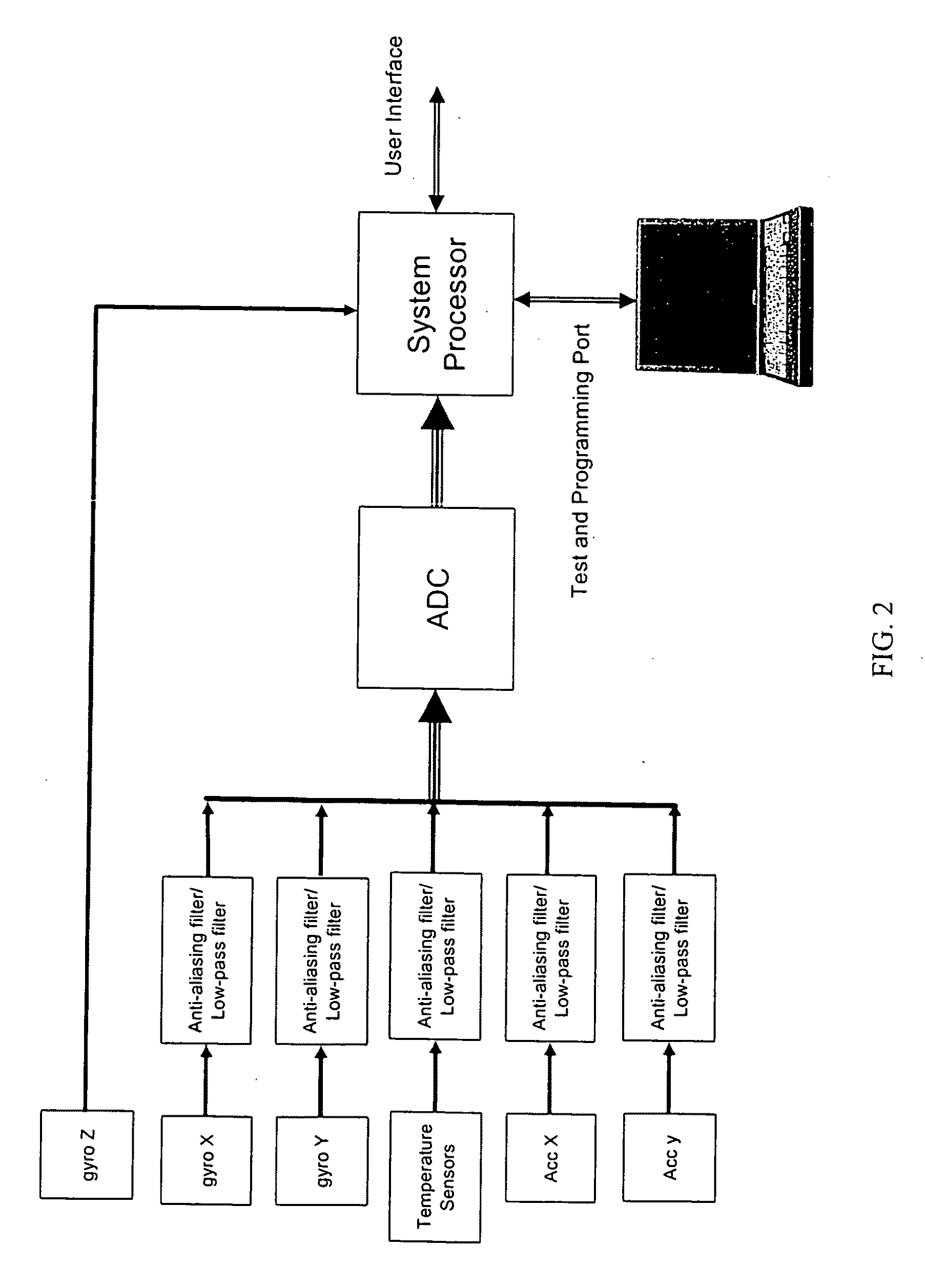
ActiveUS20070240486A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEngineeringSignal-to-noise ratio
System having one or more inertial sensors in which one or more of the sensor input axes are modulated in orientation about an axis substantially perpendicular to the input, or sensitive, axis of the sensor and, in some embodiments, by also enhancing the accuracy of such a system to provide improved signal to noise ratio and reduced sensitivity to errors in alignment of the sensor axes to the dither axes.
Owner:EMCORE INC
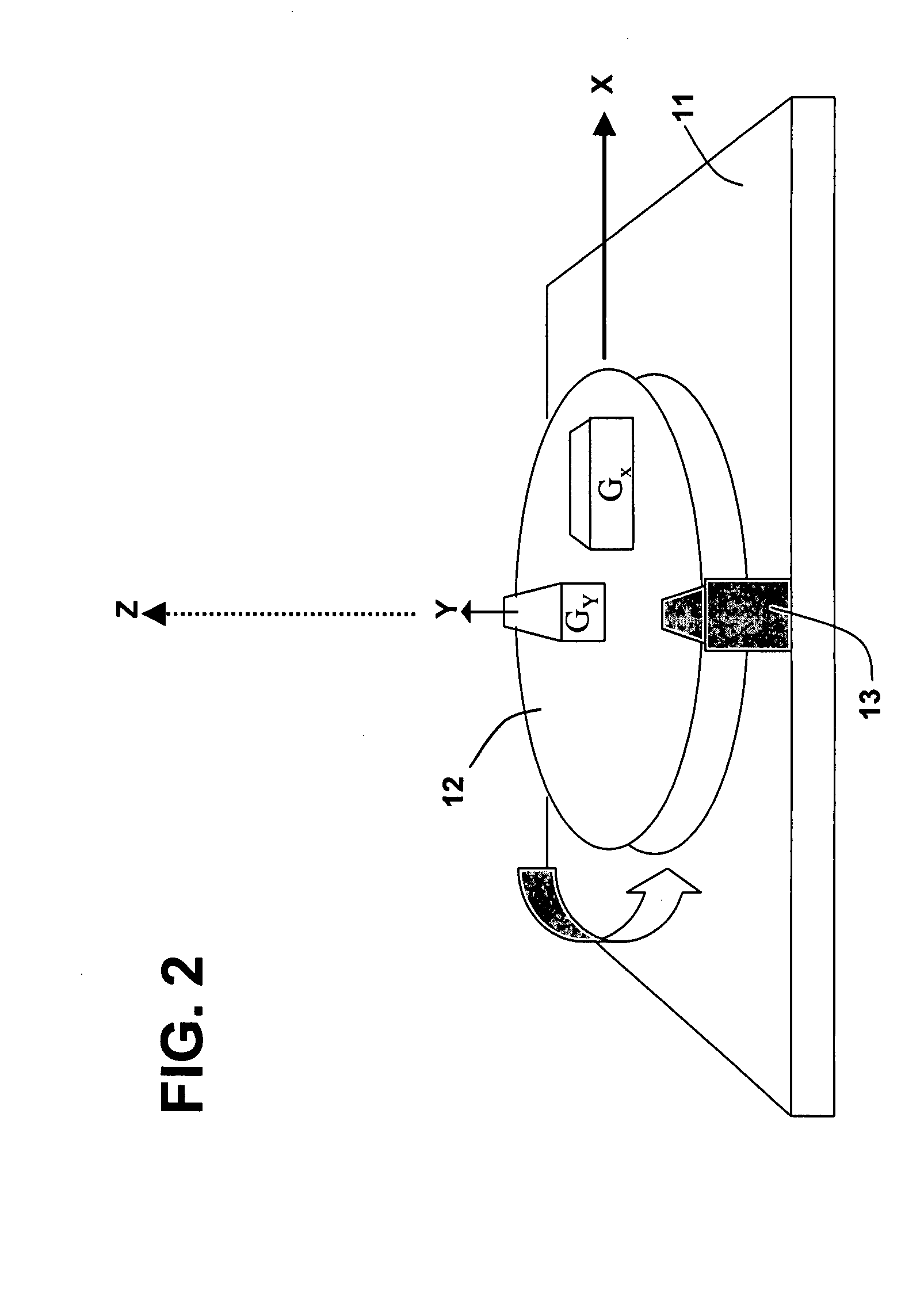
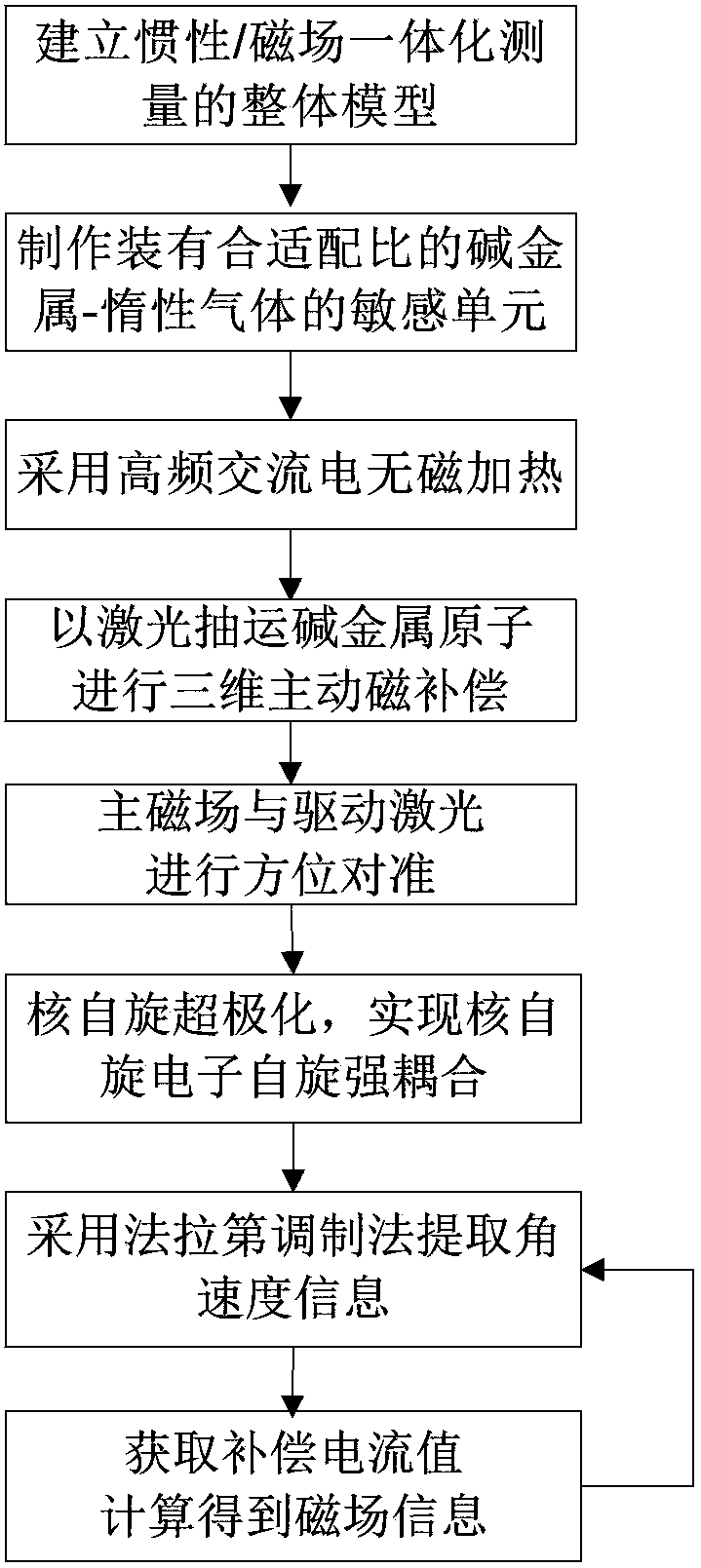
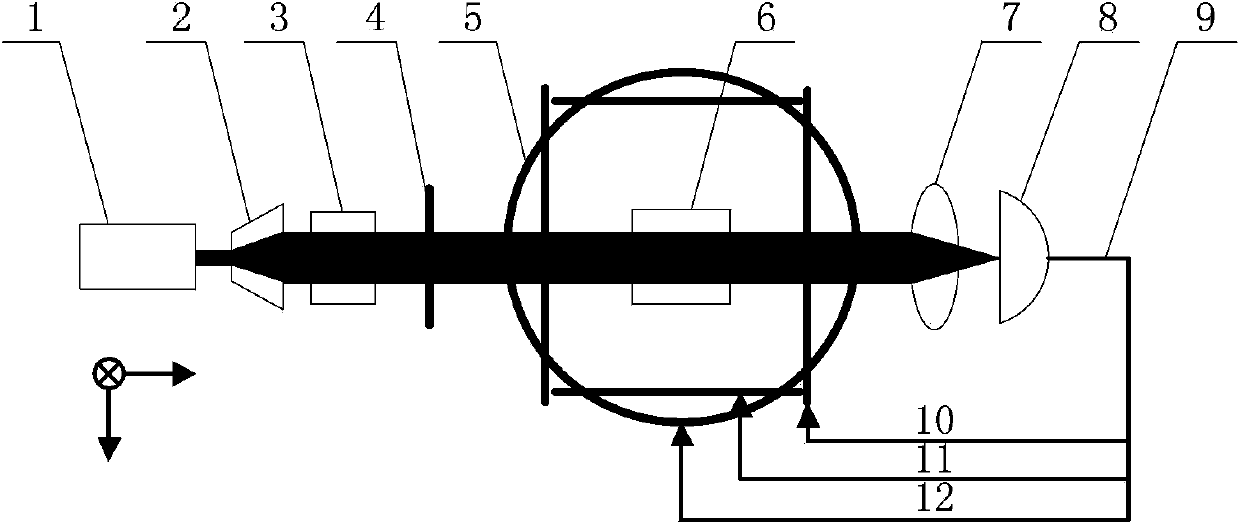
Inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on SERF (spin-exchange-relaxation-free) atomic spin effect
ActiveCN103438877AHigh measurement accuracyStrong autonomyRotary gyroscopesMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsSpin effectClosed loop
The invention provides an inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on an SERF (spin-exchange-relaxation-free) atomic spin effect. The inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on the SERF atomic spin effect comprises the following steps: firstly establishing an overall model for the inertia and magnetic field integration measurement; secondly, manufacturing a measurement sensing unit, and carrying out high-frequency alternating current non-magnetic electric heating; starting a driving laser (z-axis) for carrying out optical pumping on the sensing unit; and emitting a detection laser (x-axis) in a direction vertical to the z-axis; thirdly, carrying out driving magnetic compensation through a three-dimensional magnetic compensation coil so as to counteract a magnetic field of the outside world; fourthly, carrying out azimuth alignment on a main magnetic field and the driving laser and hyperpolarization nucleon self-spin so as to realize the nuclear spin-electron spin strong coupling; fifthly, extracting the information of the atomic spin precession movement in the detection laser by adopting a closed-loop faraday modulation detection method, and obtaining inertia angular speed information; and finally, obtaining the current value of a compensation signal of the magnetic field, and calculating to obtain the information of the current magnetic field. The inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on the SERF atomic spin effect has the characteristics of high measurement accuracy and strong autonomy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
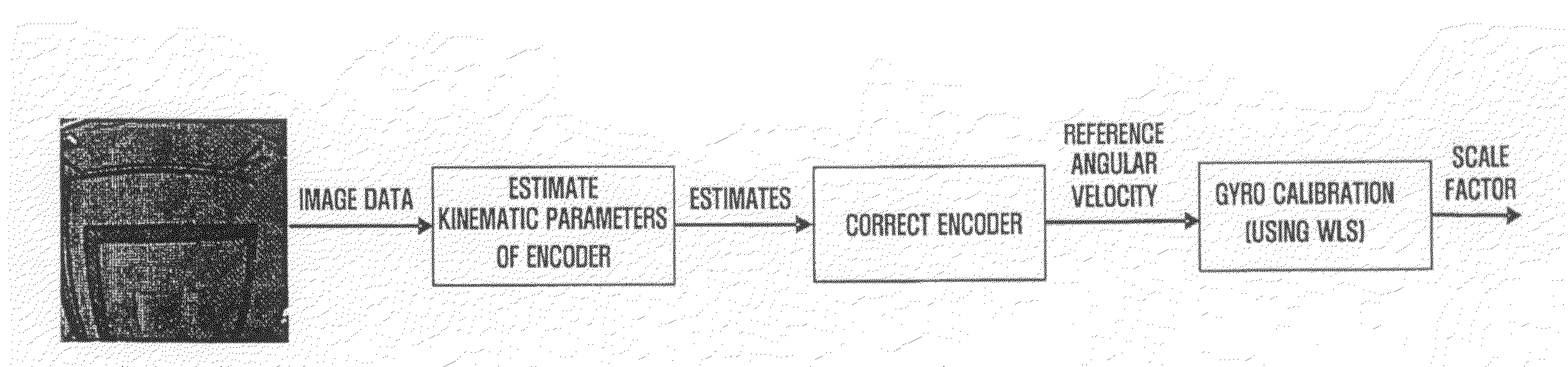
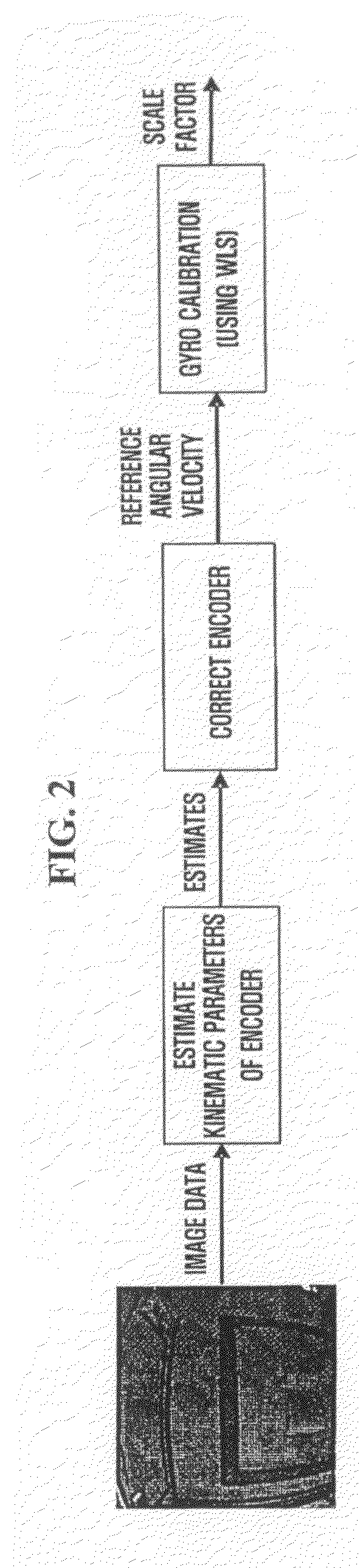
System, method and medium calibrating gyrosensors of mobile robots
ActiveUS20080249732A1Improve accuracyLow costProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlSimulationAngular velocity
Provided are a system, method and medium calibrating a gyrosensor of a mobile robot. The system includes a camera to obtain image data of a fixed environment, a rotation angle calculation unit to calculate a plurality of angular velocities of a mobile robot based on an analysis of the image data, a gyrosensor to output a plurality of pieces of raw data according to rotation inertia of the mobile robot and a scale factor calculation unit to calculate a scale factor that indicates the relationship between the pieces of raw data and the angular velocities.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
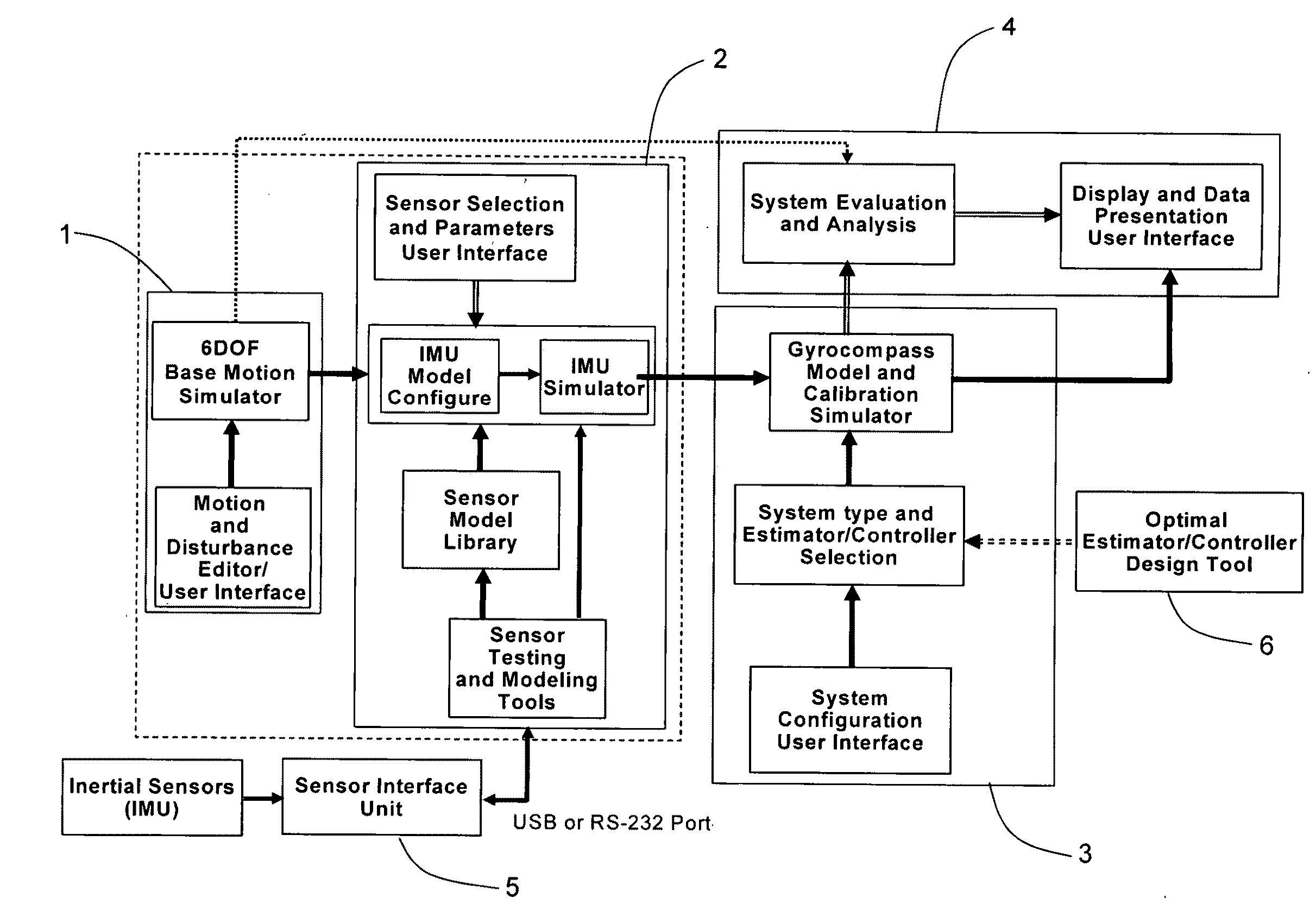
Gyrocompass modeling and simulation system (GMSS) and method thereof
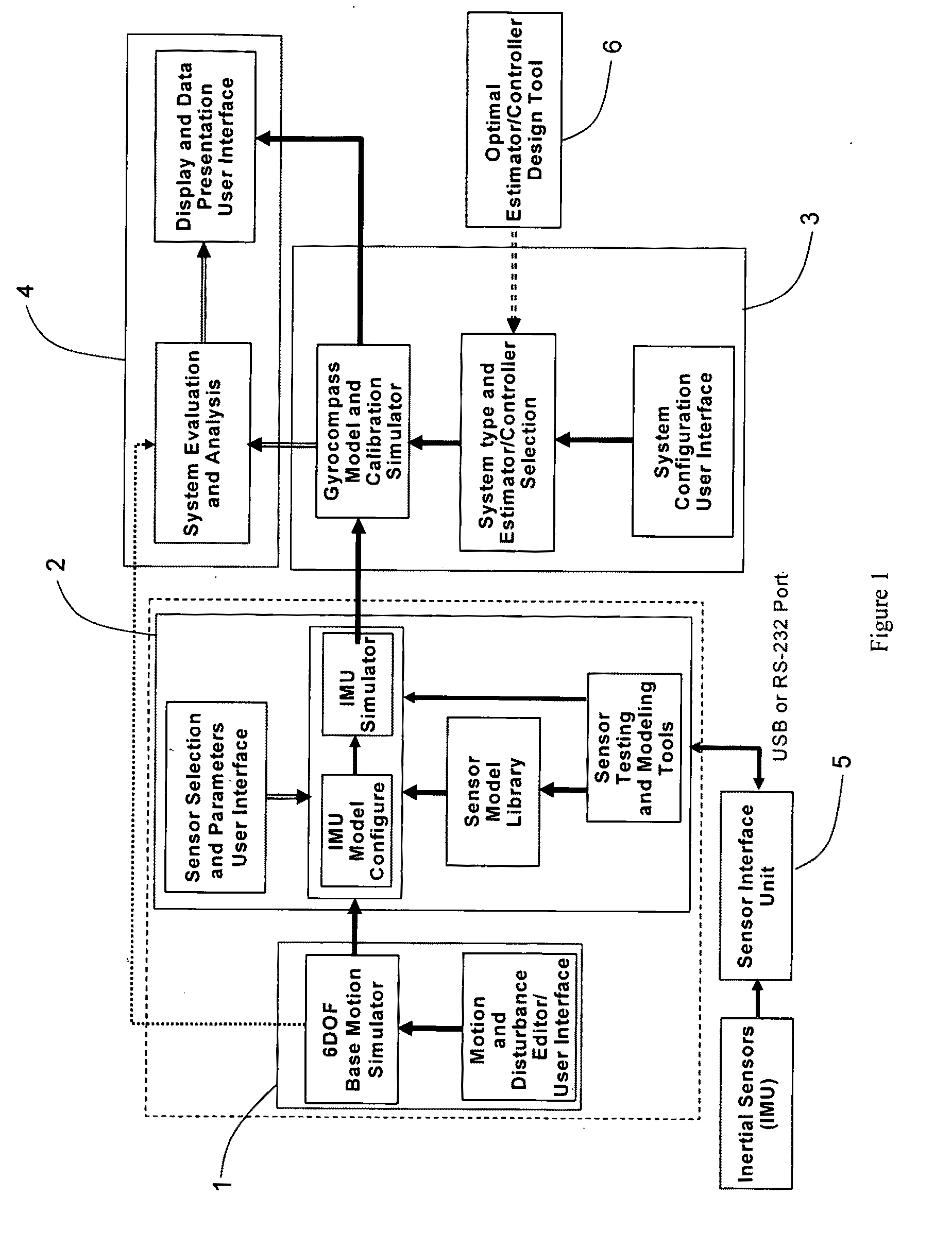
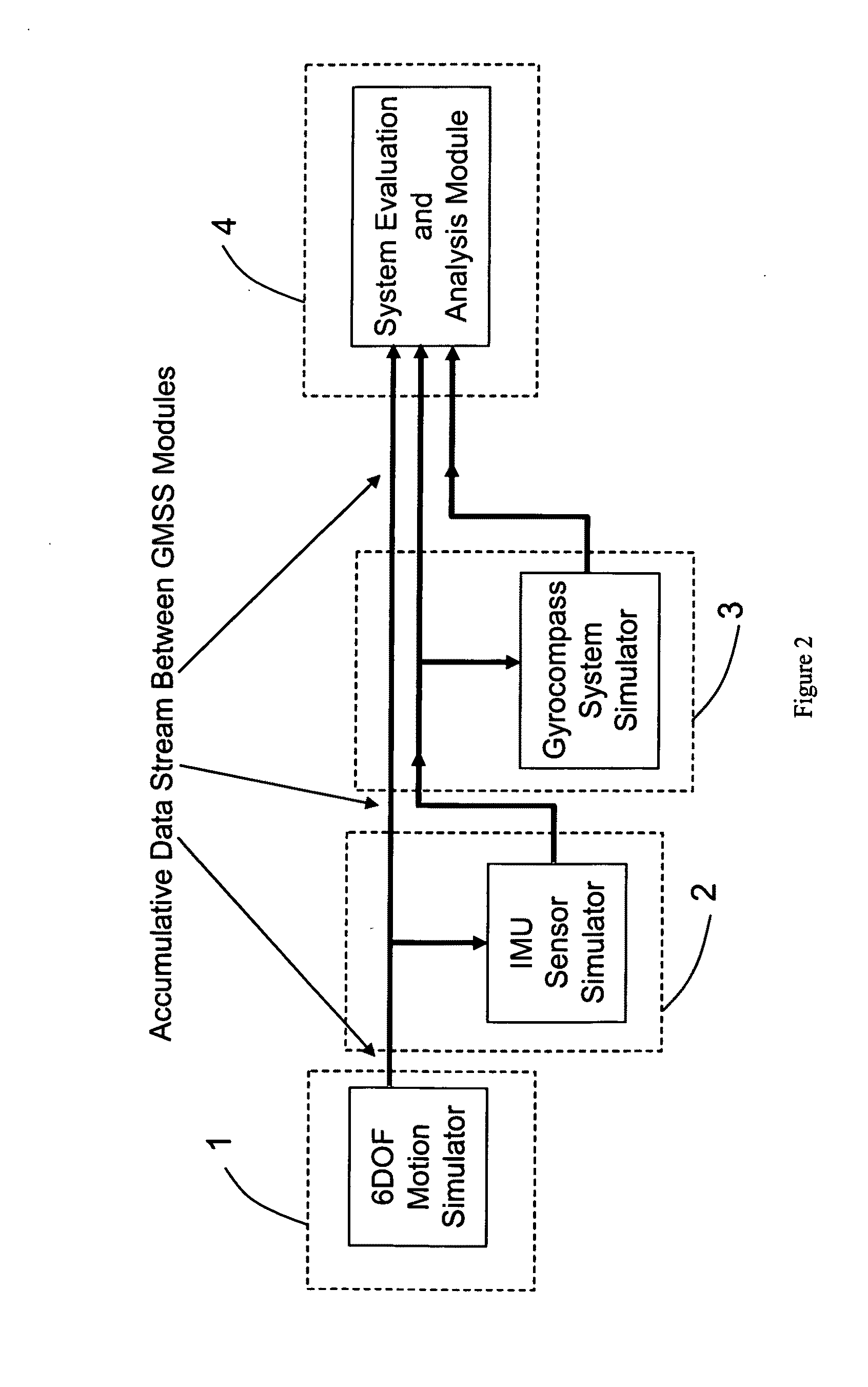
ActiveUS20110093250A1Flexible for programming and testingAvoid spendingGeometric CADRotary gyroscopesStatistical analysisSoftware system
A Modeling, Design, Analysis, Simulation, and Evaluation (MDASE) aspects of gyrocompassing in relation to Far-Target Location (FTL) systems include a Gyrocompass Modeling and Simulation System (GMSS). The GMSS is a modularized software system which has four major components: the 6DOF Motion Simulator, the IMU Sensor Simulator, the Gyrocompass System and Calibration Process Simulator, the Gyrocompass System Evaluation and Analysis Module. Each module has one or two graphic user interfaces (GUIs) as user interfaces for simulation components selection and parameter setting. The modular architecture of GMSS makes it very flexible for programming and testing. And, the component-based software development technology greatly eases system extension and maintenance. The simulators can be used as either an off-line tool or as a real-time simulation tool. The realization of the GMSS can be based on any computer platforms, for it is written in high level language and tools and is portable. The stochastic signal analysis and sensor testing and modeling tools comprise a suite of generic statistical analysis software, including Allan Variance and PSD analysis tools, which are available to every GMSS module and greatly enhanced the system functionality.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
Digital angular velocity detection device
InactiveUS7328616B2Simple structureImprove accuracyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesMaterial analysis by optical meansCapacitanceAngular velocity
A digital angular velocity detection device, including a stat or formed on a substrate. A rotor operable to rotate in response to an external force is provided. The rotor has a plurality of electrodes formed at regular intervals on a curve at a predetermined radius away from a center of the rotor. A detector having detection electrodes facing the plurality of electrodes is provided. The detection electrodes are operable to detect a rotation frequency of the rotor based on a number of electrostatic capacitance variations generated between the plurality of electrodes and the detection electrodes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for azimuth measurements using gyro sensors
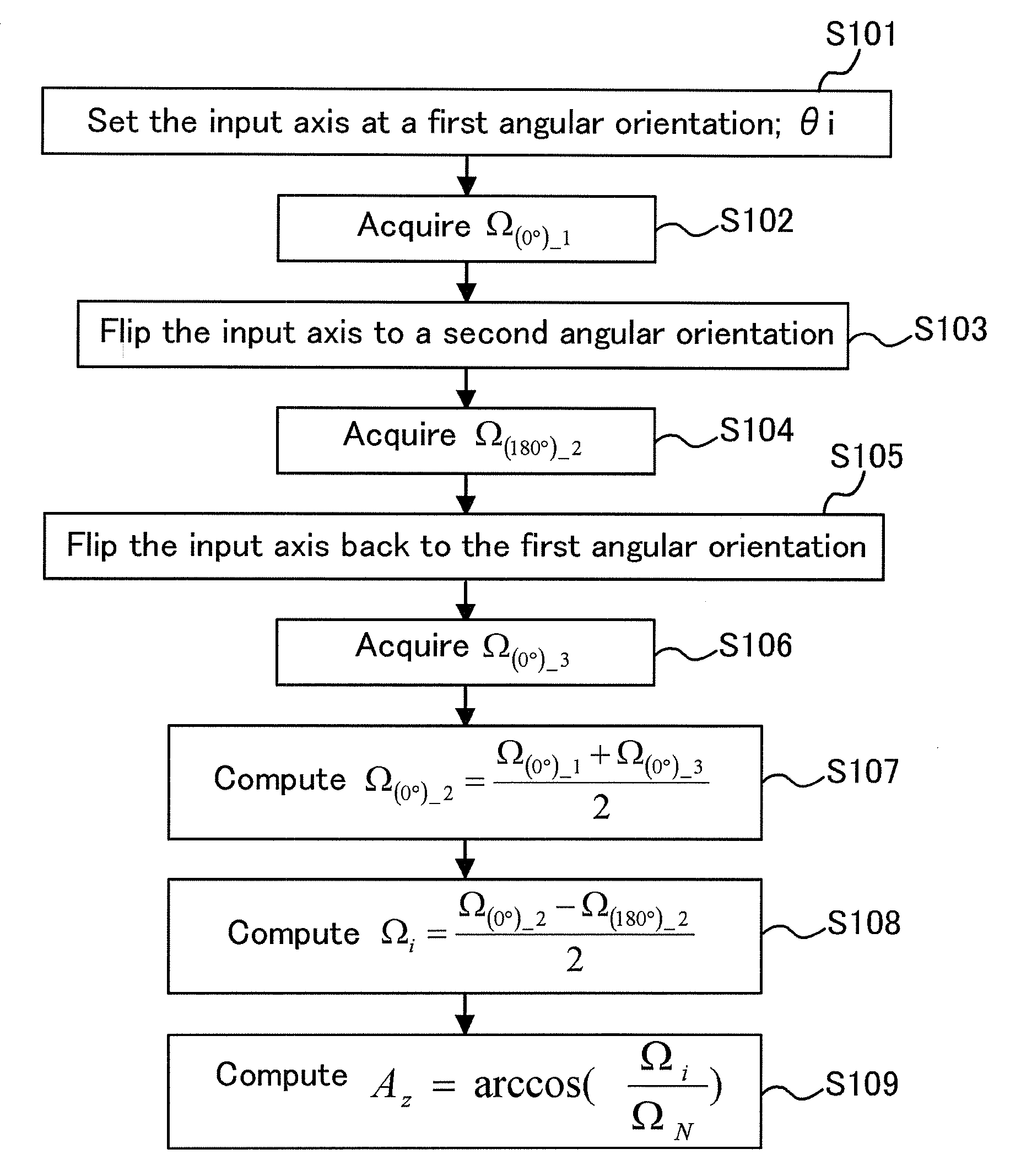
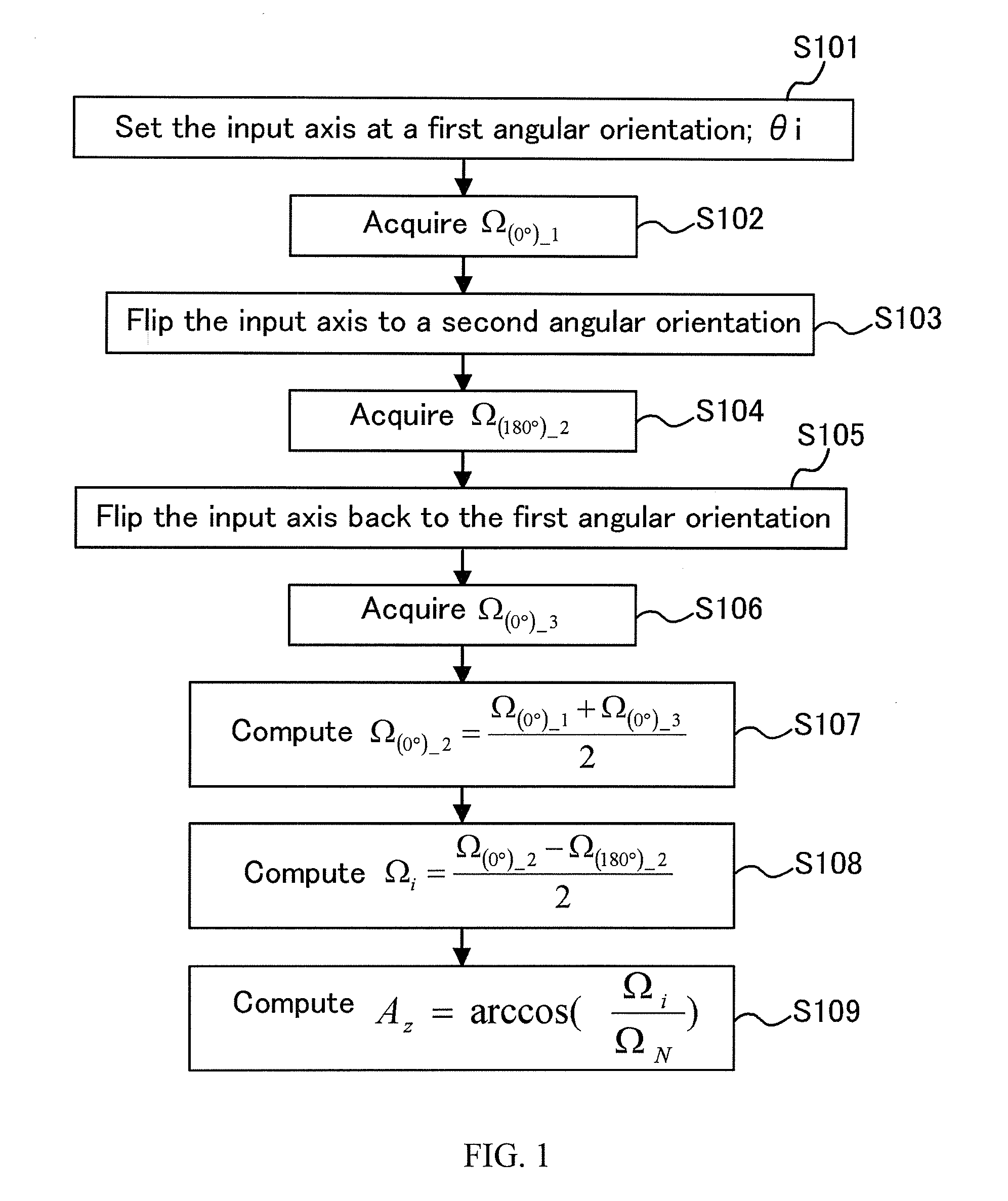
ActiveUS20090287451A1SurveyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGyroscopeAngular orientation
A method and system for azimuth measurements using one or more gyro sensors is disclosed. The method includes acquiring a first data from each of the gyro sensors with an input axis aligned to a first angular orientation and acquiring a second data from each of the gyro sensors with the input axis flipped to a second angular orientation opposite to the first angular orientation. An earth rate component at the first angular orientations is determined based on a difference between the first data and the second data to cancel out bias of each of the gyro sensors. The method may include acquiring a third data of the gyro sensor with the input axis aligned to the same angular orientation as the first angular orientation. An average of the first data and the third data may be used instead of the first data for determining the earth rate component.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Multi-position strapping north-seeking system direction effect calibration method
InactiveCN101187568AImprove measurement accuracyEliminate measurement errorsRotary gyroscopesObservational errorGyroscope
The invention belongs to a calibration method of an error which is measured by a multi-position strapdown north seeking device, in particular to a calibration method of orientation effect of a multi-position strapdown north seeking device. A true north prism, two theodolites and a mechanical dividing rotating platform are used as auxiliary testing tools, the multi-position strapdown north seeking device is fixed on the mechanical dividing rotating platform, and is divided according to one circle equipartition point, an angle of a benchmark prism of a strapdown north seeking system and the true north direction is defined through rotating an equipartition angle value at one time by the mechanical rotating platform and through the true north prism system in an initial rotating position of the north seeking system, and then the angle is compared with a north-oriented value which is measured by the strapdown north seeking system, the error is calculated, and an azimuthal effect of a gyroscope which is simulated according to the characteristic of the error is marked. The invention effectively eliminates measuring error which is caused by the azimuthal effect, thereby improves the measuring accuracy of the multi-position strapdown north seeking system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magneto meter using lorentz force for integrated systems
ActiveUS8402666B1Easy to useHigh device yieldSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsRotary gyroscopesCMOSLorentz factor
Embodiments of the present invention can provide an integrated electronic compass and circuit system having a semiconductor substrate and one or more CMOS integrated circuits formed on one or more portions of the semiconductor substrate. The system can have an electronic compass device operably coupled to the one or more CMOS integrated circuits. The system can also have a plurality of electronic compass devices configured in a parallel arrangement in a hub and spoke configuration.
Owner:MOVELLA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com