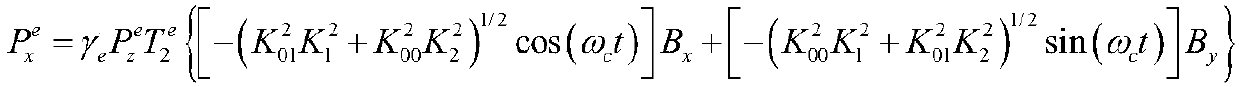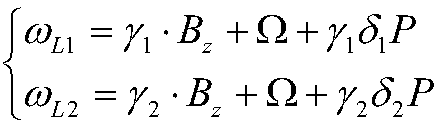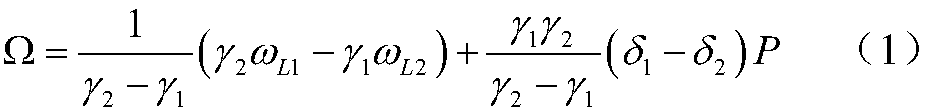Patents
Literature
61results about How to "Improve bias stability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
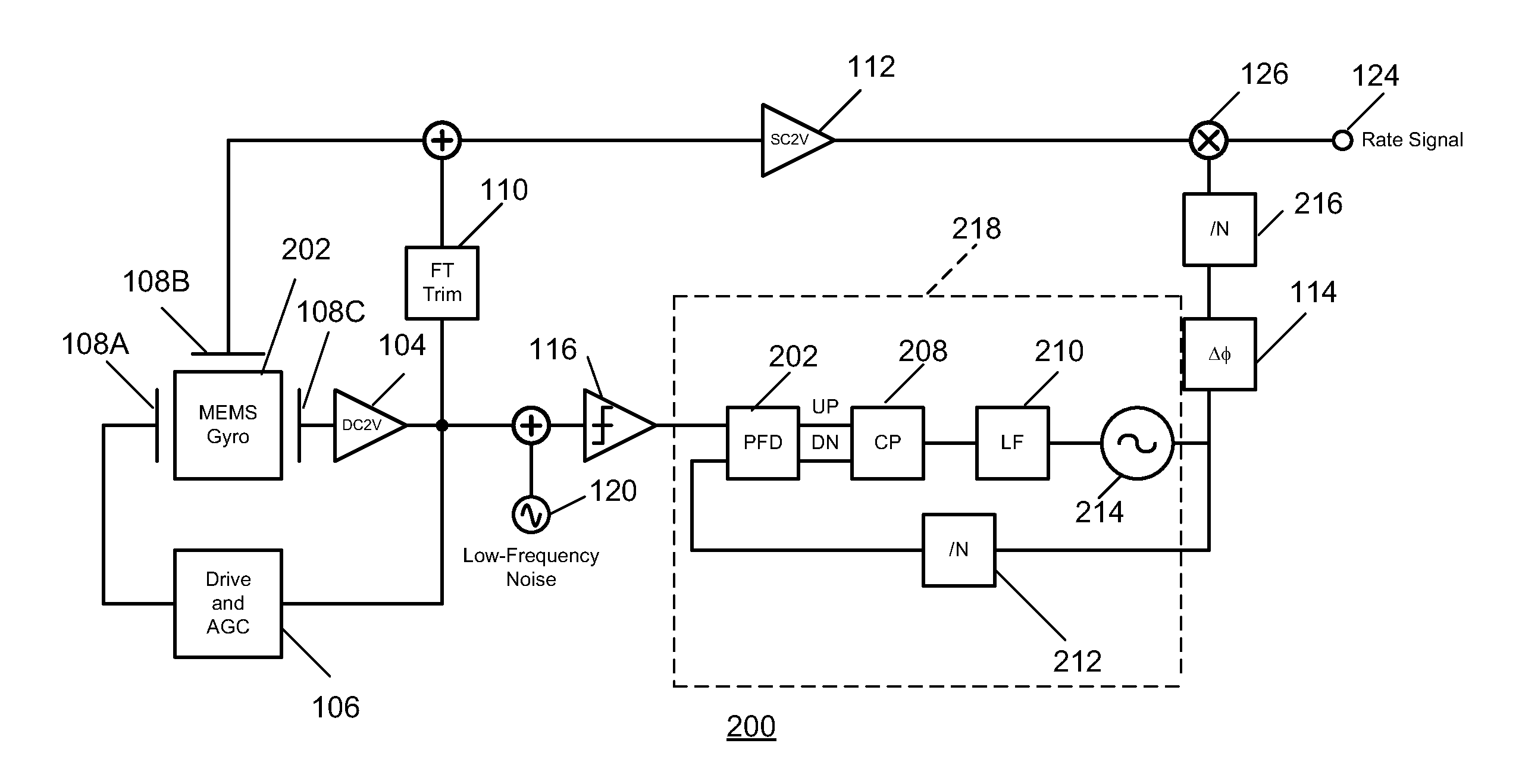
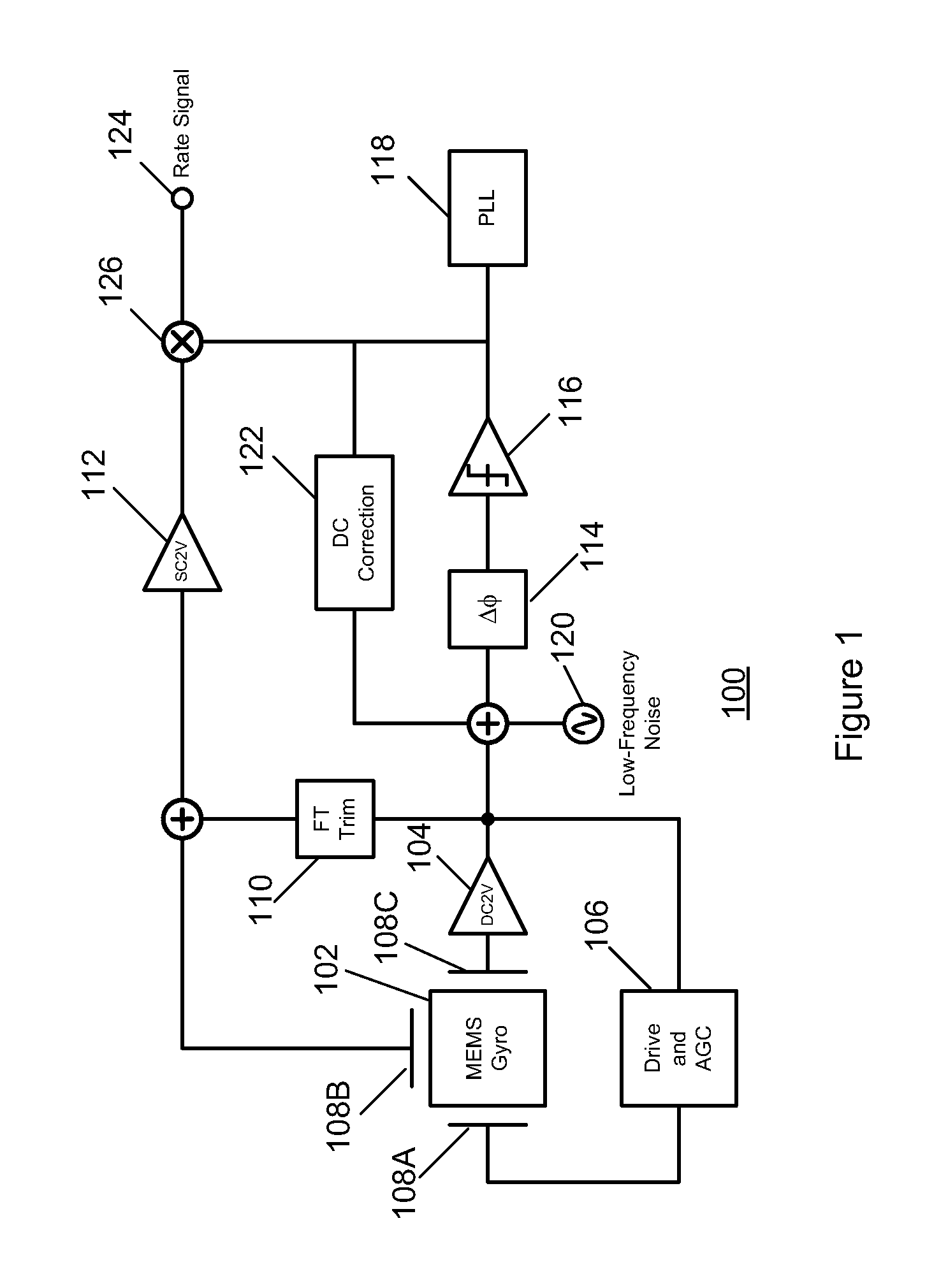
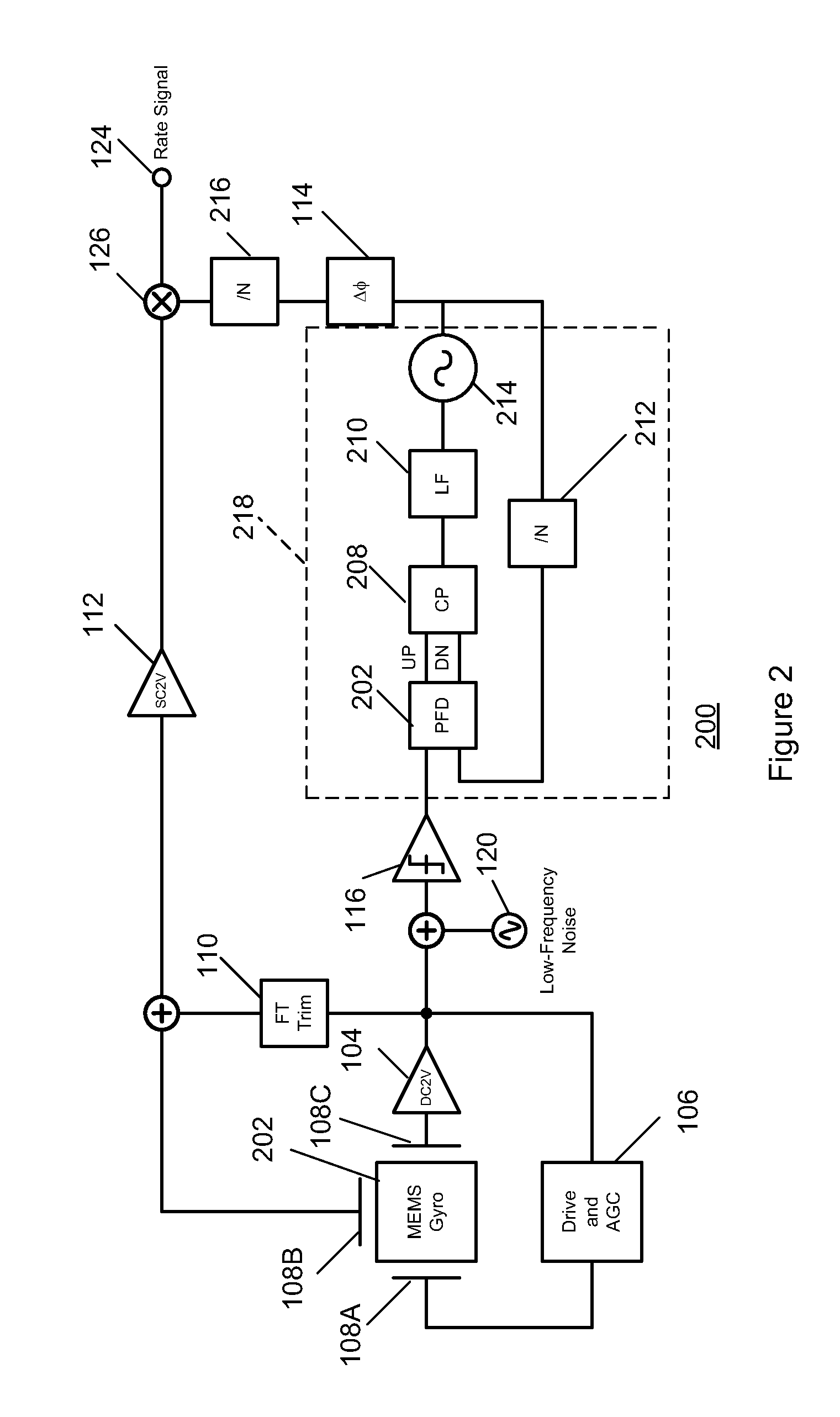
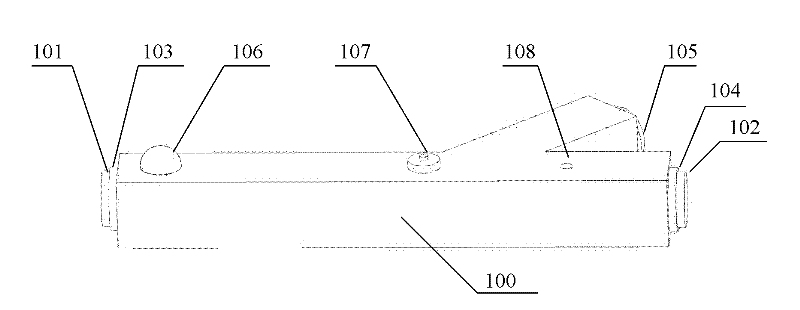
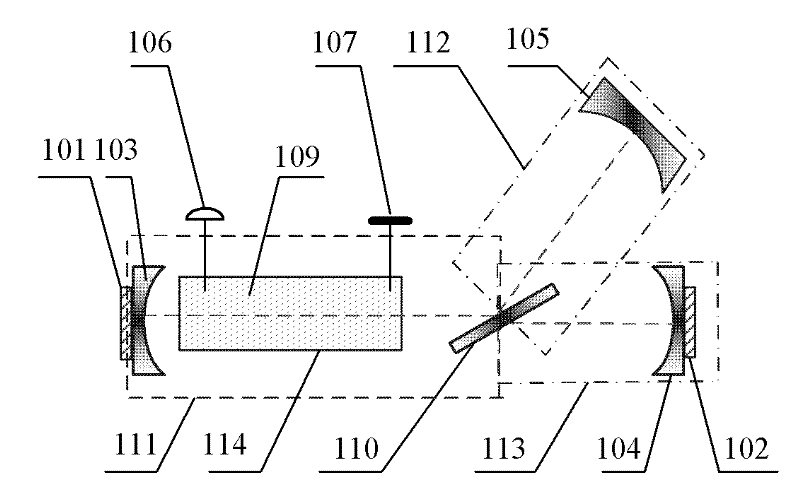
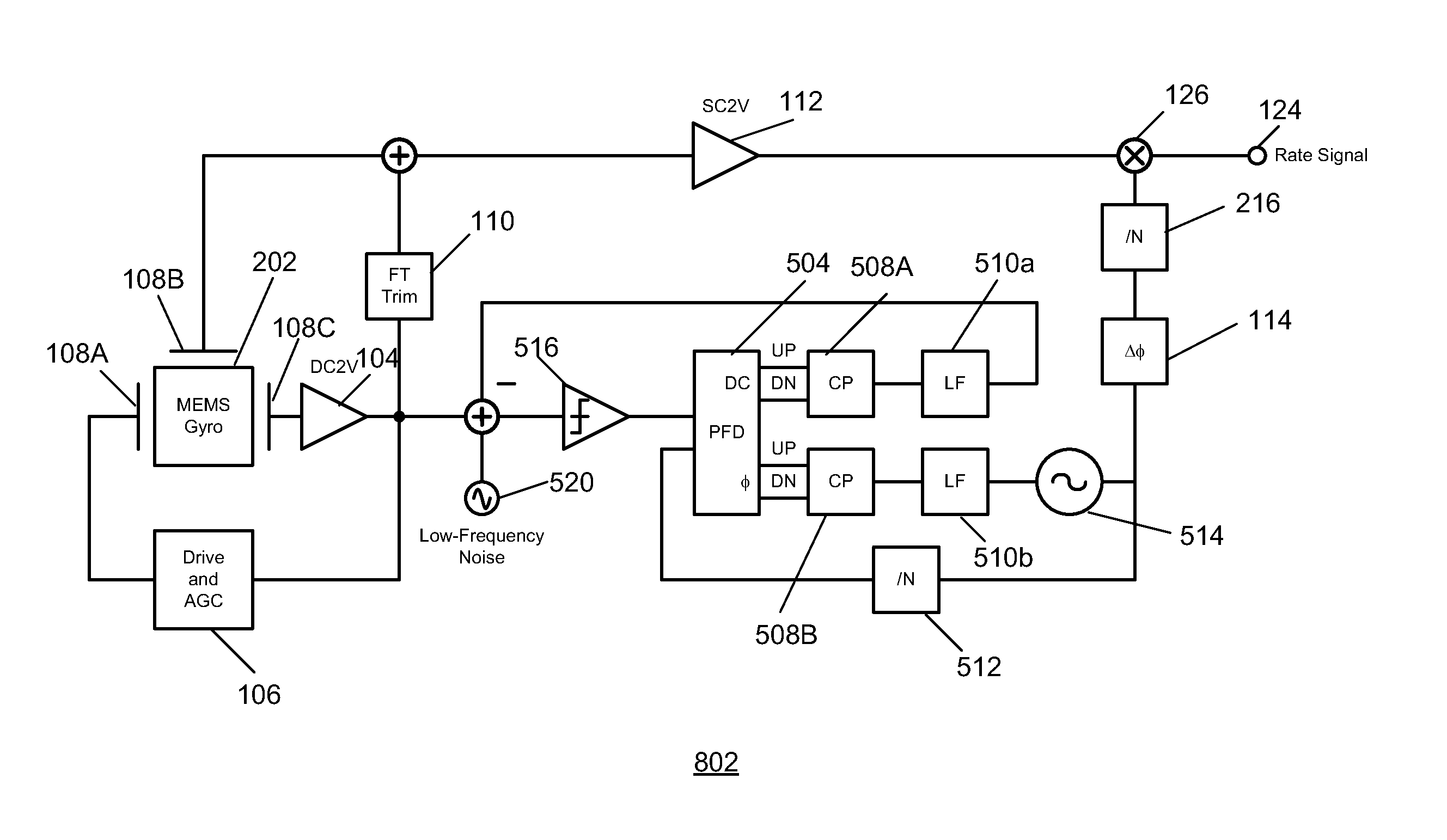
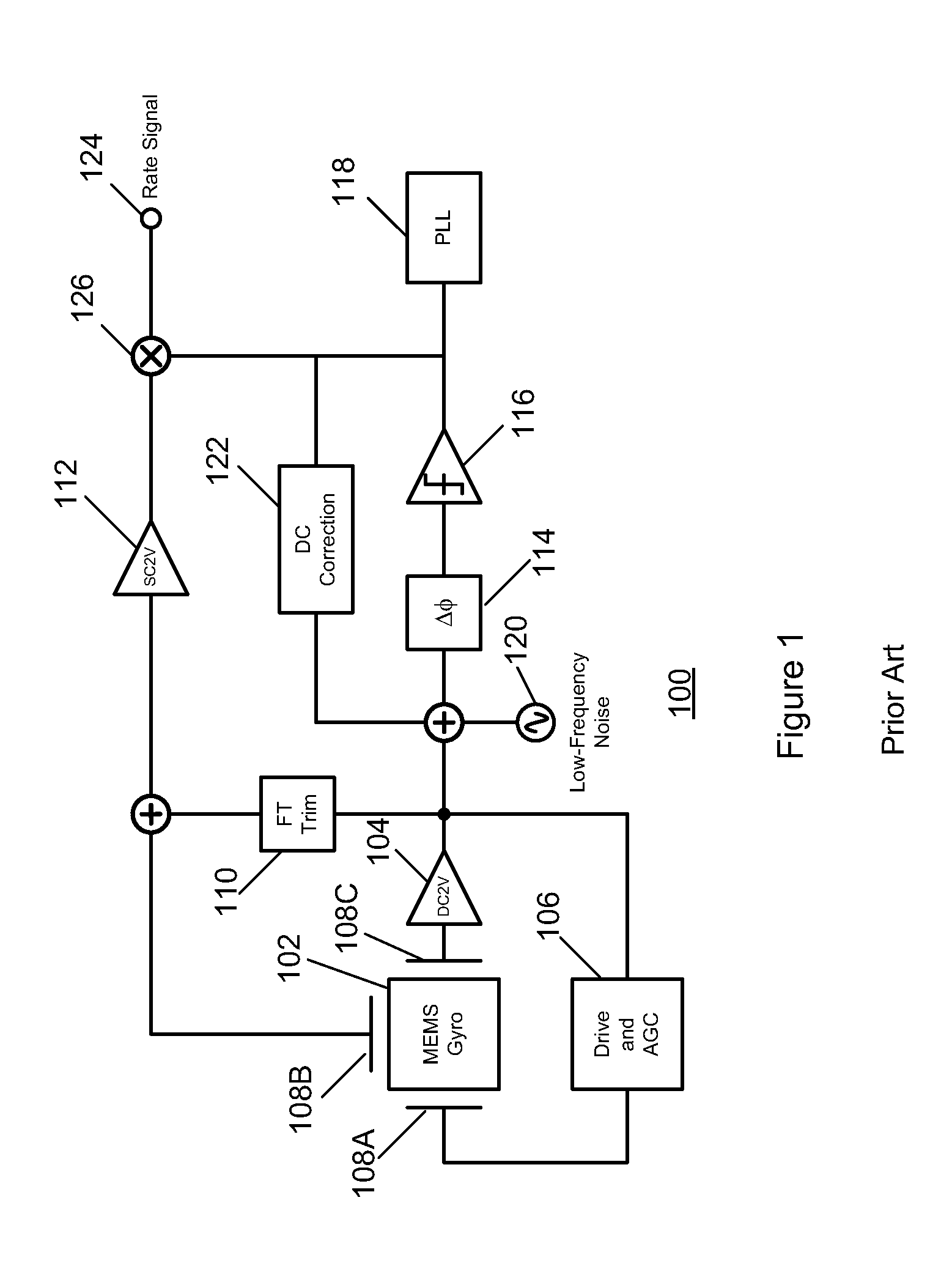
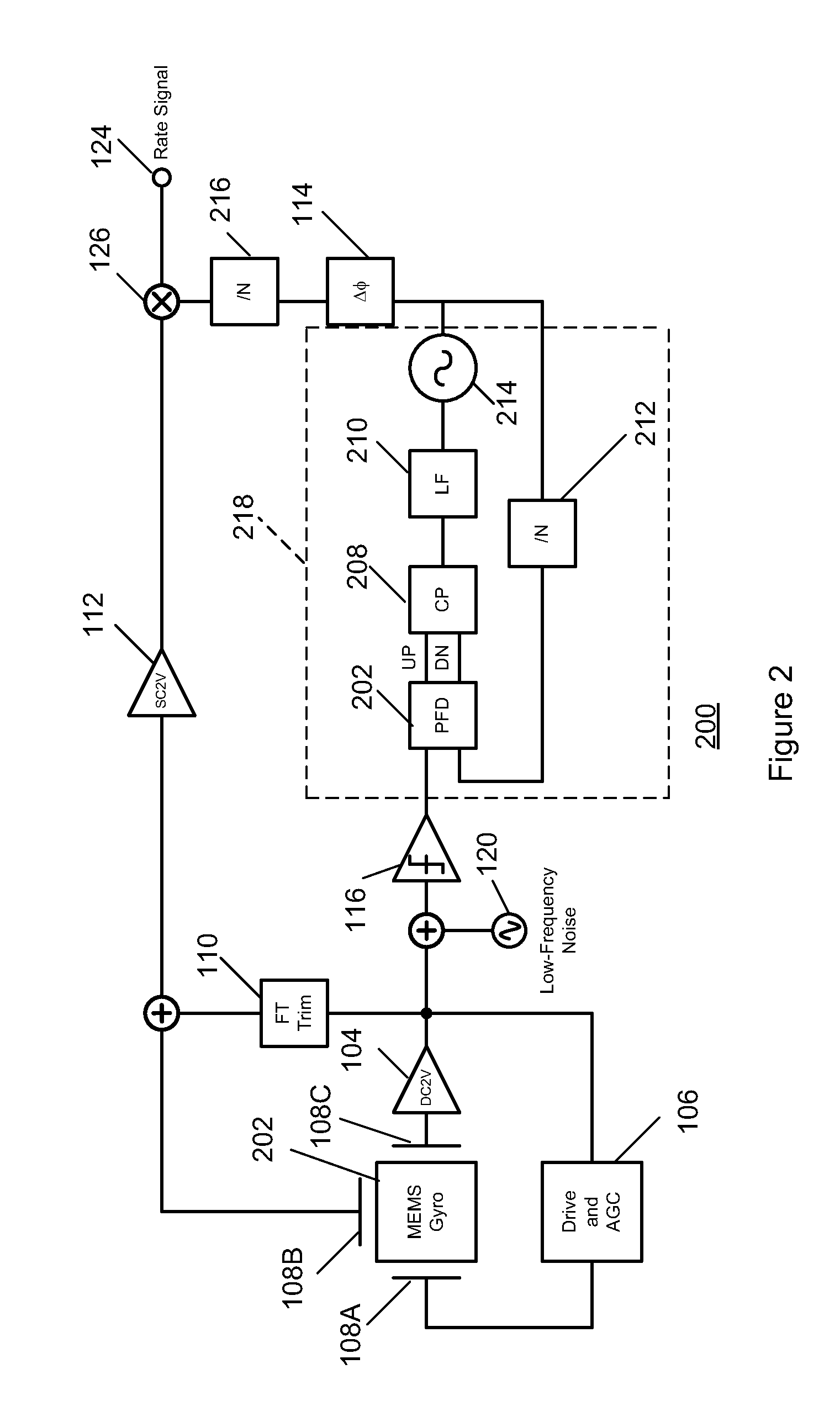
Gyroscope with phase and duty-cycle locked loop
ActiveUS20130099836A1Improve Noise PerformanceImprove bias stabilityMechanical apparatusPulse automatic controlGyroscopeSmall footprint
A system and method in accordance with the present invention provides a gyroscope incorporating an improved PLL technique. The improved PLL auto-corrects its own reference low-frequency noise, thereby eliminating this source of noise, improving the noise performance of the gyroscope and allowing a compact implementation. The net result is a gyroscope with improved bias stability that can meet noise requirements with a smaller footprint.
Owner:INVENSENSE
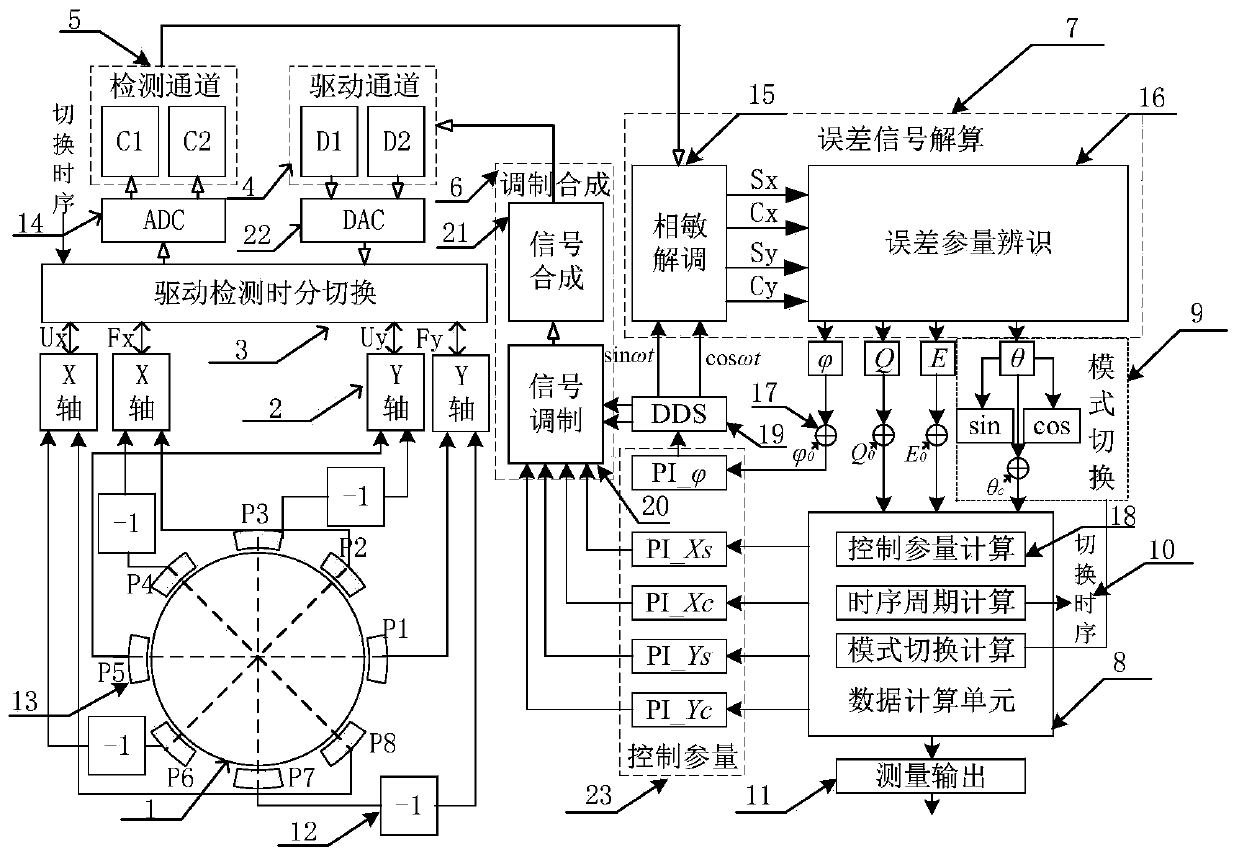
Hemispherical resonant gyro fully differential control system and method based on time division multiplexing
ActiveCN110865580AImprove performanceEquilibrium inconsistencyProgramme controlComputer controlControl systemSoftware engineering
The invention relates to a hemispherical resonant gyro fully differential control system and control method based on time division multiplexing. The control system comprises an electrode driving detection time division switching module, a sensing signal amplitude-phase demodulation module, an error parameter identification module, a working mode switching module, a control parameter calculation module, a time sequence period calculation module, a mode switching calculation module, a driving signal modulation synthesis module and a measurement output module. The sensing signal amplitude-phase demodulation module and the error parameter identification module form an error signal resolving module. The control parameter calculation module, the time sequence period calculation module and the mode switching calculation module form a data calculation unit. By means of time-sharing switching and two-rotation sensing mode difference of driving detection electrodes, gyro output error terms can be counteracted and inhibited, and the control precision of each control loop and stability of the performance of a hemispherical resonant gyro can be guaranteed.
Owner:TIANJIN NAVIGATION INSTR RES INST
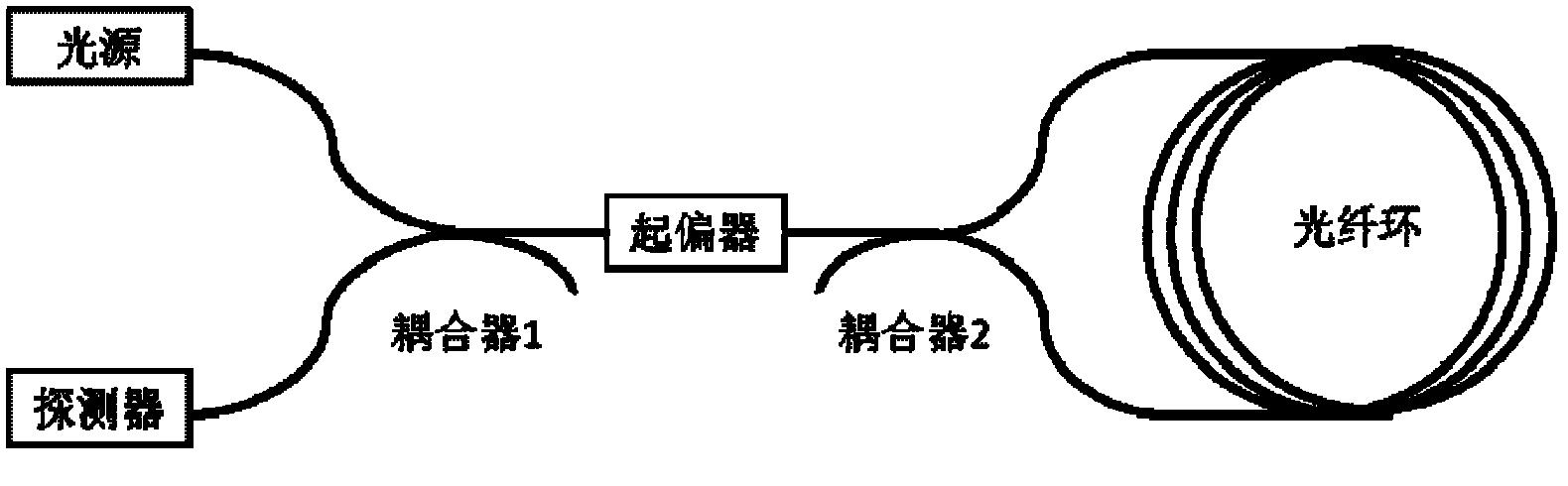
Polarization-maintaining photonic crystal fiber gyroscope and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105444750AImprove bias stabilityReduce polarization errorSagnac effect gyrometersFiber couplerGyroscope
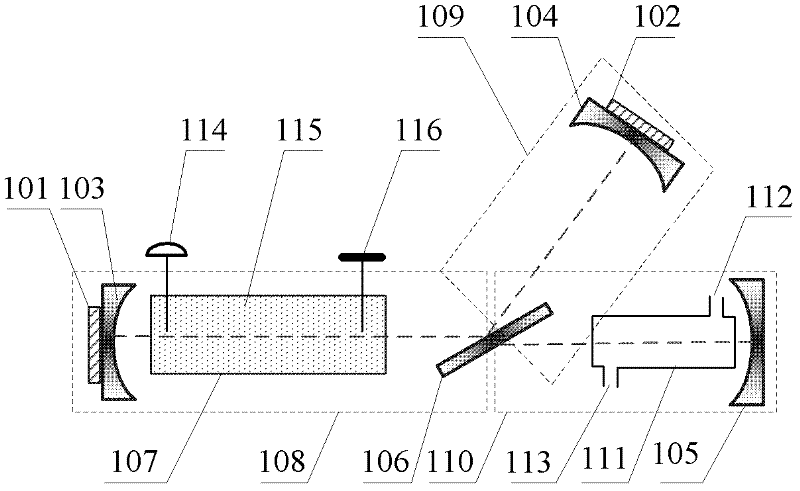
The invention discloses a polarization-maintaining photonic crystal fiber gyroscope light path. The polarization-maintaining photonic crystal fiber gyroscope light path comprises a polarization-maintaining fiber coupler, a broad band optical source, a Y waveguide, a polarization-maintaining photonic crystal fiber ring spliced with a Y waveguide output tail fiber and a detector and is characterized in that the polarization-maintaining fiber coupler acts on a polarization-maintaining fiber fast axis, a Y waveguide tail fiber is a stress birefringence polarization-maintaining fiber, 0-degree axis alignment splicing is performed between the fiber fast axis and the Y waveguide TE mode, the polarization-maintaining pohotonic crystal fiber ring is obtained by winding double macropore type polarization-maintaining photonic crystal fibers, 90-degree axis alignment splicing is performed between the axial direction of double macropore type polarization-maintaining photonic crystal fibers and the axial direction of the stress birefringence polarization-maintaining fiber, and useful signals in the gyroscope light path are all transmitted in the fast axis. The photonic crystal fiber gyroscope light path has the advantages of low temperature sensitiveness, radiation resistance and the like of a common photonic crystal fiber gyroscope, further effectively inhibits polarization errors of the gyroscope and facilitates improvement of zero-bias stability of the fiber gyroscope.
Owner:HUBEI SANJIANG AEROSPACE HONGFENG CONTROL
Three-optical-path signal compensation system in optical MEMS accelerometer and method thereof
ActiveCN105182000AImprove bias stabilityHigh precisionAcceleration measurementAccelerometerBeam splitter
The invention discloses a three-optical-path signal compensation system in an optical MEMS accelerometer and a method thereof. The three-optical-path signal compensation system comprises a three-optical-path compensation optical path and a signal processing system, wherein the three-optical-path compensation optical path comprises an optical isolator, a miniature beam splitter prism, a plane mirror, an adjustable attenuator and an photoelectric detector; and the compensation signal processing system comprises three analog-to-digital (AD) conversion modules, a subtracter, a divider, a data storage, summation and average module and multiplier, and the modules are realized through a programmable digital signal processor. The three-optical-path signal compensation system is relatively simple in structure, and can effectively reduce influences imposed on output signals by power fluctuation of a light source and ambient light. Compared with a scheme of adopting a laser with extremely high power stability, the cost of the optical MEMS accelerometer can be effectively reduced. In addition, the system and the method disclosed by the invention can be effectively applied to the optical MEMS accelerometer, disturbance of the output signals is reduced, and finally the zero-bias stability and the precision of accelerometer measurement are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
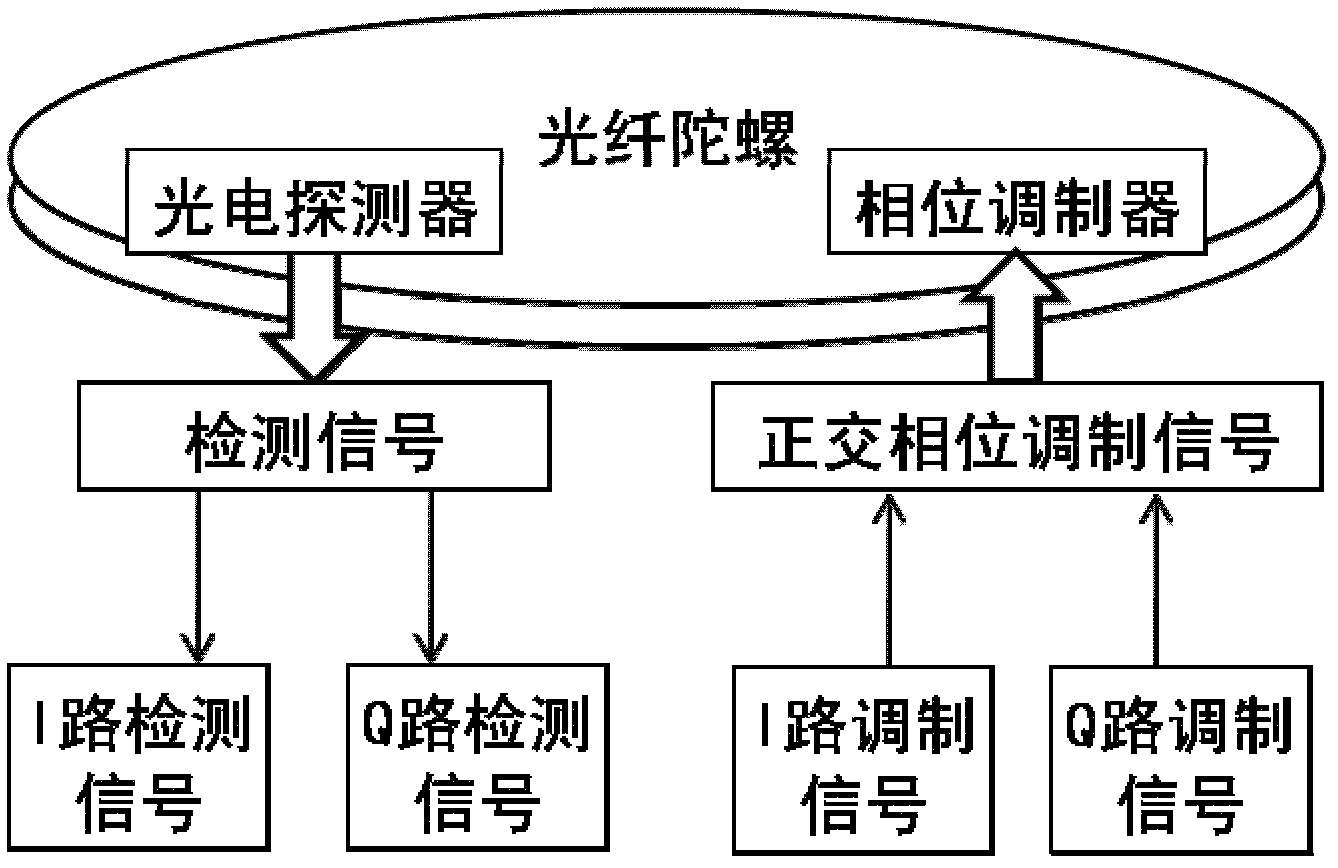
Digital domain balanced detecting method and device for optical fiber gyroscope
InactiveCN102607547AImprove bias stabilityEliminate common mode noise componentsSagnac effect gyrometersAngular velocityFibre optic gyroscope
The invention provides a digital domain balanced detecting method for an optical fiber gyroscope, which comprises the following steps of: applying a phase modulation signal to a phase modulator, wherein the phase modulation signal is obtained after a sinusoidal signal and a cosine signal which have the same modulation frequency are linearly combined; using the applied sinusoidal signal as an I-path reference signal and carrying out derivation on the I-path reference signal to obtain a Q-path reference signal; respectively carrying out coherent processing on a signal output by the optical fiber gyroscope and the I-path reference signal and the Q-path reference signal so as to obtain an I-path detection signal and a Q-path detection signal; respectively demodulating the I-path and Q-path detection signals to obtain an I-path angular velocity measured value and a Q-path angular velocity measured value; and according to a preset linear formula, combining the I-path and Q-path angular velocity measured values to obtain a measured value of an angular velocity to be measured, wherein the preset linear formula is predetermined according to the linear combination of the applied sinusoidal signal and cosine signal. Due to the utilization of the method, the bias stability of the optical fiber gyroscope can be improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Active magnetic suspension accelerometer
ActiveCN107727884AExtended stabilization timeHigh precisionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesImage resolutionTurn angle
The invention relates to an active magnetic suspension accelerometer with high alignment, high stability and high resolution; the active magnetic suspension accelerometer comprises a short circuit turn angle sensor, a permanent magnetism torquer, a liquid float plus jewel bearing and active magnetic suspension centering, and double-end bellows volume compensation; when an inertia acceleration applies on a floater, a vertical pendulum deflects, the angle sensor senses the deflection angle, a force feedback loop forms a control current, the control current is applied to a permanent magnetism torquer control coil, thus restoring the vertical pendulum back to the zero bit; control current size symbols are matched with inertia acceleration sizes and directions. Said measures can improve the accelerometer precision; the precision of the accelerometer working under the gate state can improve by almost an order of magnitude when compared with a liquid floating integration pendulum accelerometer. The accelerometer with the active magnetic suspension technology is firstly applied in our nation, thus greatly improving the accelerometer stability and dynamic adaptability; the accelerometer canbe applied to an inertia space navigation system.
Owner:TIANJIN NAVIGATION INSTR RES INST
Method and device for measuring refractive index of transparent medium based on Y-shaped-cavity orthogonal polarization laser
InactiveCN102507450ASignal readout device is simplePortable signal readout devicePolarisation-affecting propertiesRefractive indexLinearity
The invention relates to a method and a device for measuring refractive index of transparent medium based on a Y-shaped-cavity orthogonal polarization laser. The device is composed of a Y-shaped-cavity orthogonal polarization laser, a sample cell, a working point selecting and controlling unit and a signal collecting and processing unit. After the transparent medium is pumped in or pumped out the sample cell, the refractive index of the P sub-segment of the Y-shaped-cavity orthogonal polarization laser can change, therefore the optical length difference of an S sub-cavity and a P sub-cavity changes, the beat frequency difference of S polarized light and P polarized light in the Y-shaped-cavity orthogonal polarization laser also changes, and the change value of the beat frequency difference is proportional to the refractive index of the transparent medium. The device has the characteristics of high resolution ratio, high degree of linearity, direct digital output, simple structure, convenience for operation, fastness and the like. The device can also be used for monitoring the refractive index of the transparent medium in real time.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
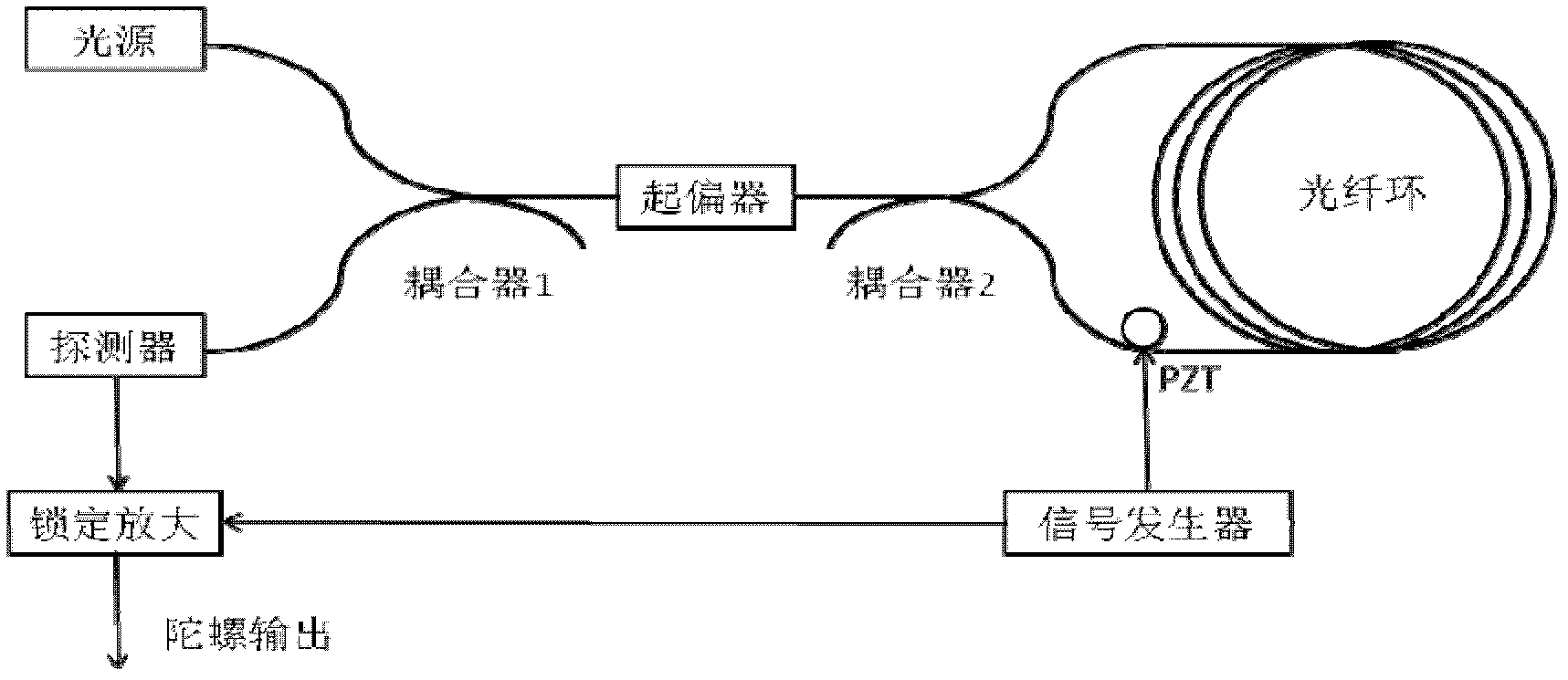
Novel detection method of optical fiber gyroscope
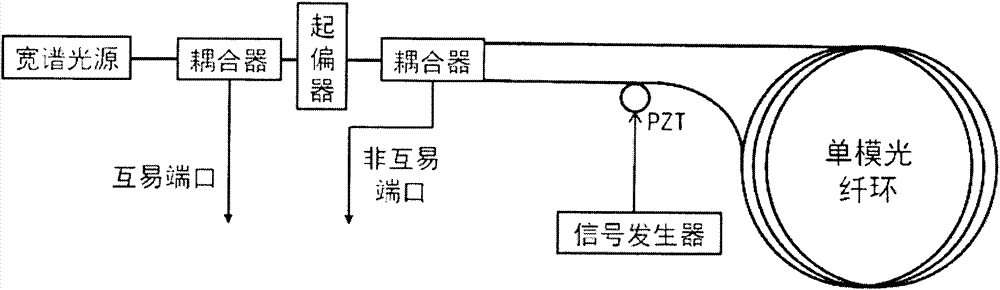
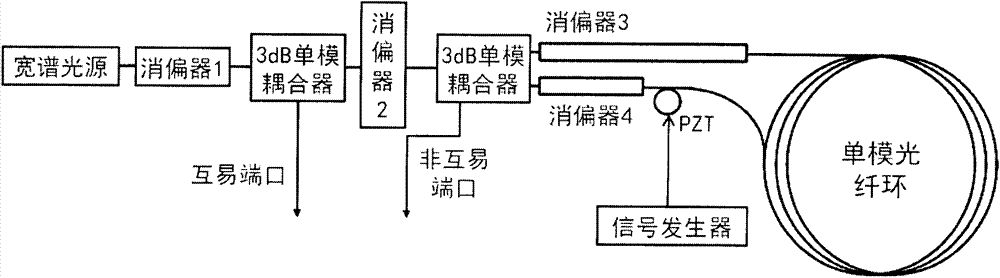
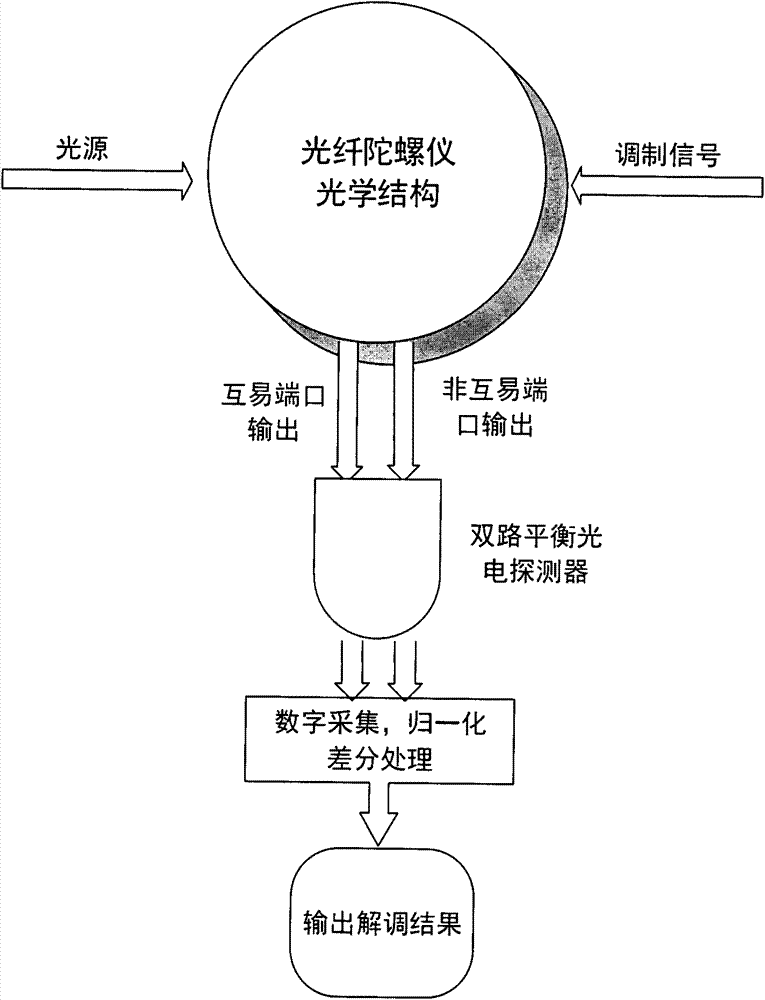
InactiveCN104729493AReduce random walkImprove bias stabilitySagnac effect gyrometersFiberDifferential signaling
The present invention provides a novel detection method of an optical fiber gyroscope, wherein the detection ports are a reciprocal port (I port) and a nonreciprocal port (II port) of an interferometric depolarization fiber optic gyroscope, and the signal processing adopts the differential signal processing manner. The method comprises that: the optical structure of the interferometric depolarization fiber optic gyroscope for testing requires that lyot depolarizers are respectively added between the light source and the light source coupler, the light source coupler and the optical fiber ring coupler, and the optical fiber ring coupler and the optical fiber ring, the phase modulation adopts the sine signal having optical fiber gyroscope eigenfrequency, the amplitude of the sine signal is correspondingly adjusted so as to make the modulation depth value be stabilized to near 1.841, a dual-channel photoelectrically balanced detector is utilized to concurrently detect the reciprocal port (I port) and the nonreciprocal port (II port) of the interferometric depolarization fiber optic gyroscope, the two electrical signals being subjected to photoelectric conversion are subjected to normalization and then are subjected to a differential treatment, and the differential result is utilized to demodulate the gyroscope signal. With the method of the present invention, the random walk of the optical fiber gyroscope can be effectively reduced, and the zero-bias stability of the optical fiber gyroscope can be improved.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Micro-machined gyrometric sensor for differential measurement of the movement of vibrating masses
ActiveUS7707886B2High sensitivityImprove linearityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopeDifferential measurement
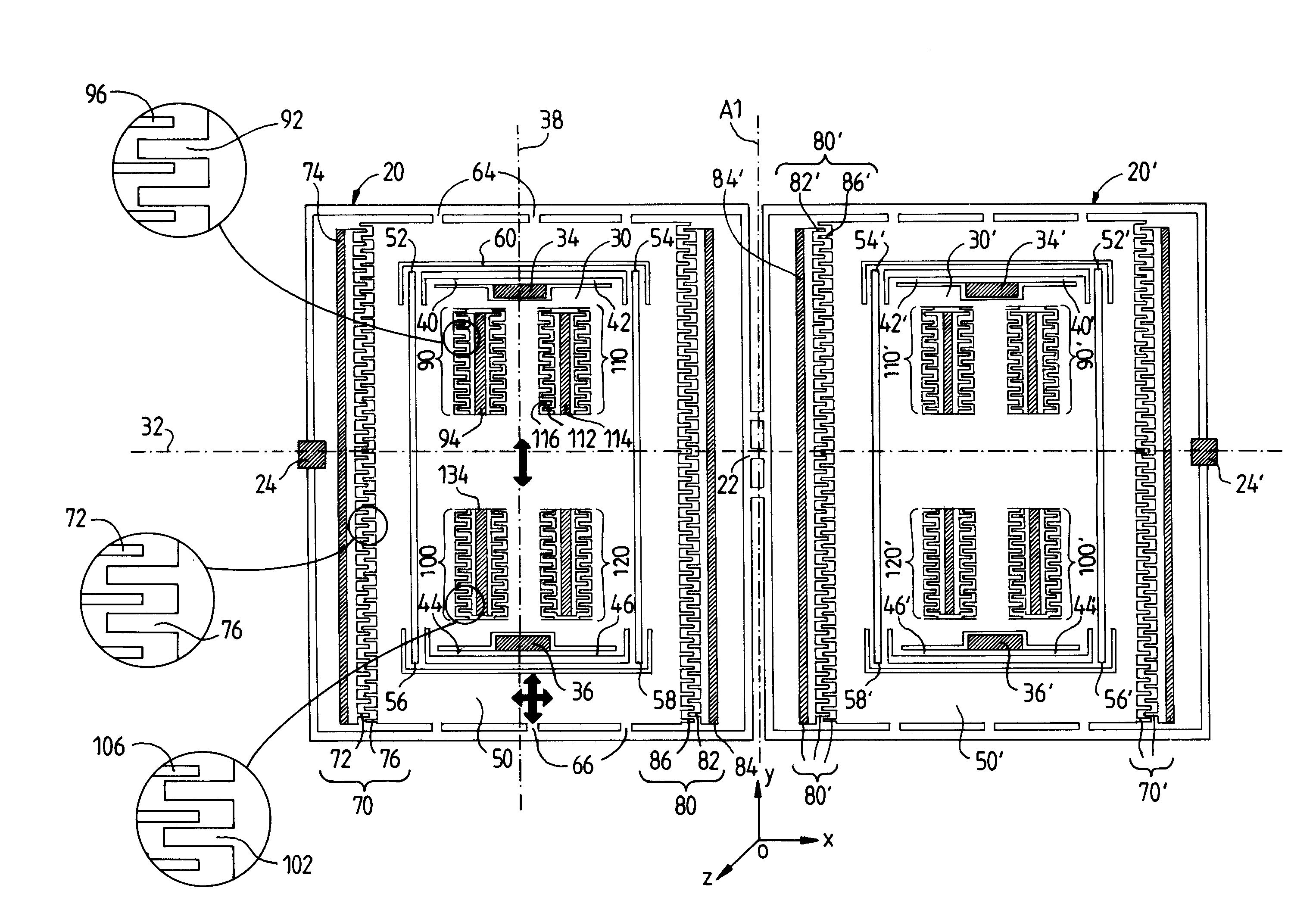
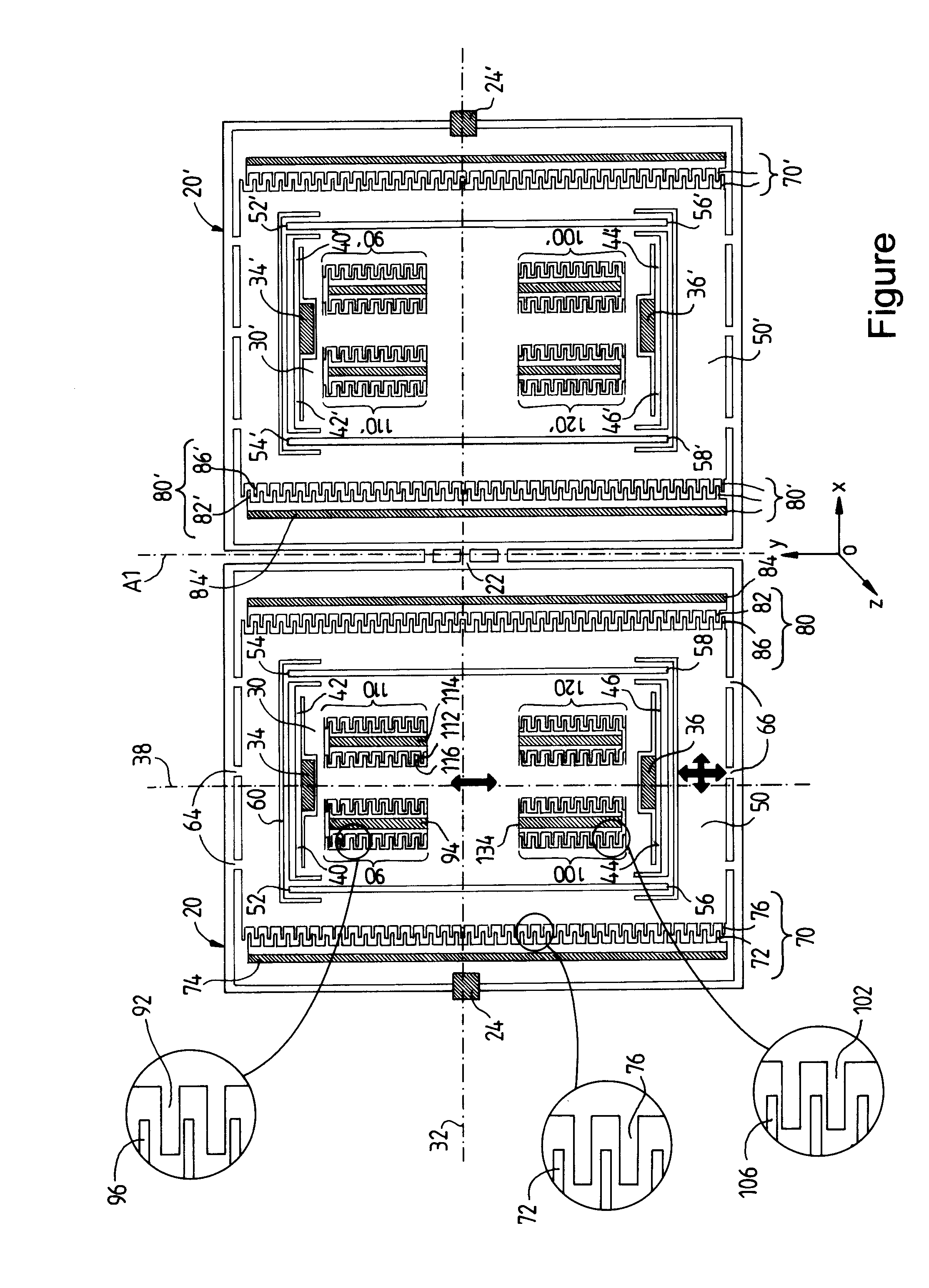
The invention relates to a microgyroscope, that is to say an inertial micromechanical sensor dedicated to the measurement of angular velocities, which is produced by micromachining techniques, and has a novel arrangement of the modules for measuring the movement of the vibrating masses. The gyroscope comprises two symmetrical moving assemblies (30, 50; 30′, 50′) that are coupled by a coupling structure (20, 20′, 22). Each of the two assemblies comprises a moving mass (30) surrounded by a moving intermediate frame (50). The frame (50) is connected to the coupling structure (20, 20′, 22) and can vibrate in two degrees of freedom in orthogonal directions Ox and Oy of the plane of the wafer. The mass (30) is connected, on one side, to the frame and, on the other side, to fixed anchoring regions (34, 36) via linking means (40-46; 52-58) that allow the vibration movement in the Oy direction to be transmitted to the mass without permitting any movement of the mass in the Ox direction. An excitation structure (70) is associated with the frame in order to excite its vibration along Ox. A movement detection structure (90) is associated with the mass (30) in order to detect its vibration along Oy.
Owner:THALES SA
Coil of optical fiber current sensor and optical fiber current sensor
ActiveCN102539873AReduce volumeReduce weightCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationCurrent sensorElectrical current
The invention relates to a coil of an optical fiber current sensor and the optical fiber current sensor. The coil comprises a first current sensing light path which is wound on a current to be measured and a second current sensing light path which is wound on the current to be measured and is opposite to the first current sensing light path in winding direction. The invention provides the coil of the optical fiber current sensor and the optical fiber current sensor, which are high in sensitivity and precision, are insensitive to vibration as the Sagnac effect can be eliminated, and are insensitive to a temperature as double-light-path sensing is adopted.
Owner:XIAN SINO HUAXIN MEASUREMENT & CONTROL
Avalanche photo diode detector systems
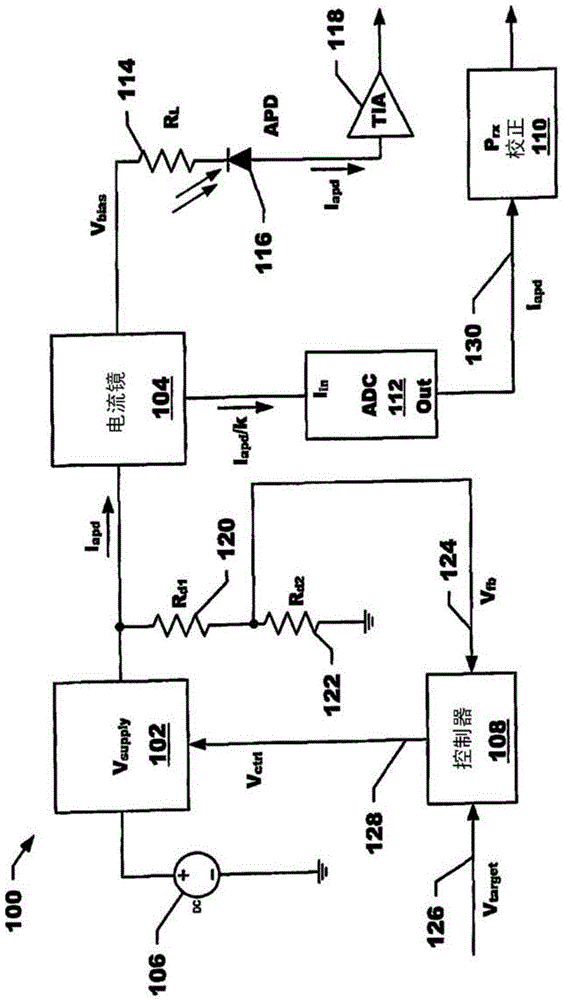
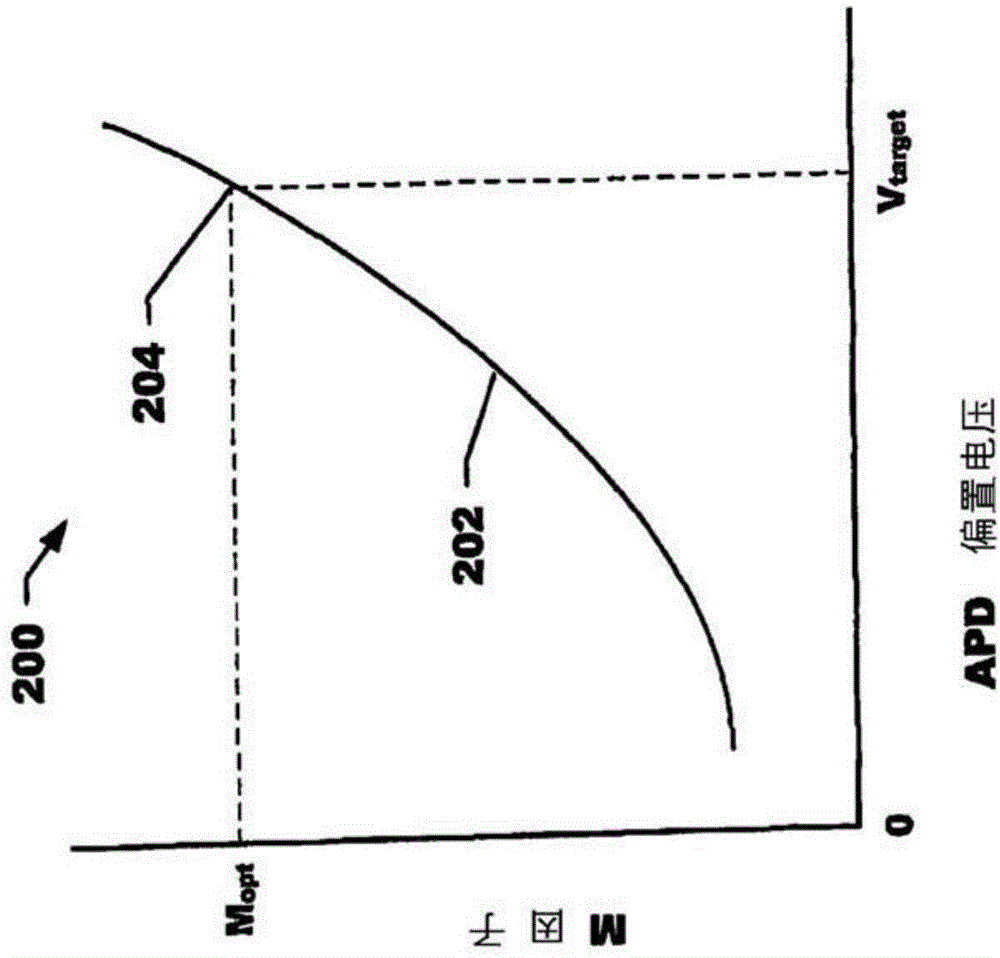
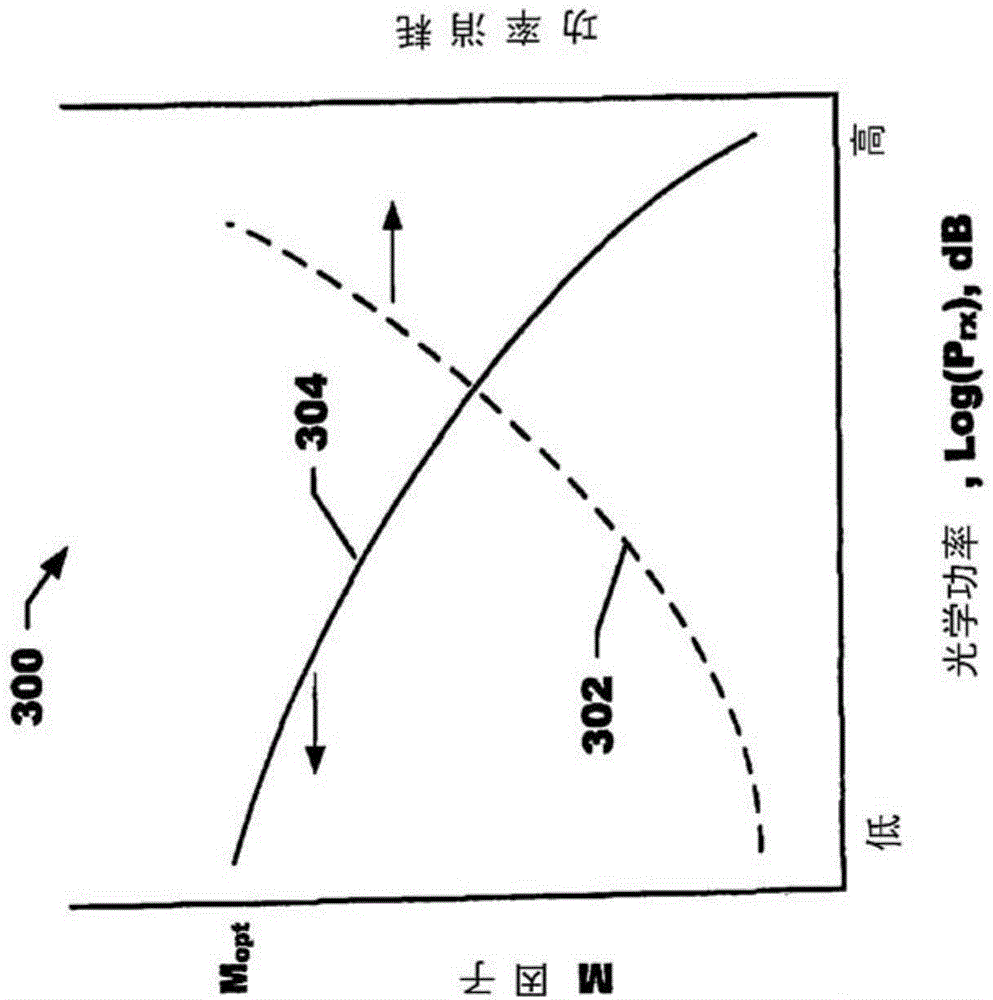
ActiveCN104049193AReduce power consumptionIncreased power consumptionGain controlPhotometry electrical circuitsPower flowOptical power
An avalanche photo diode detector including an avalanche photo diode, an adjustable voltage source, a current mirror coupled to the voltage source output of the adjustable voltage source and having a current measurement output, and a processor coupled to the adjustable voltage source and the current mirror. The processor implements a process of obtaining a signal current measurement from the current mirror, computing an estimate of an input optical power level from the signal current measurement and adjusting the output of the adjustable voltage source based upon on the estimate of the input optical power level.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Organic thin-film transistor and manufacturing method thereof
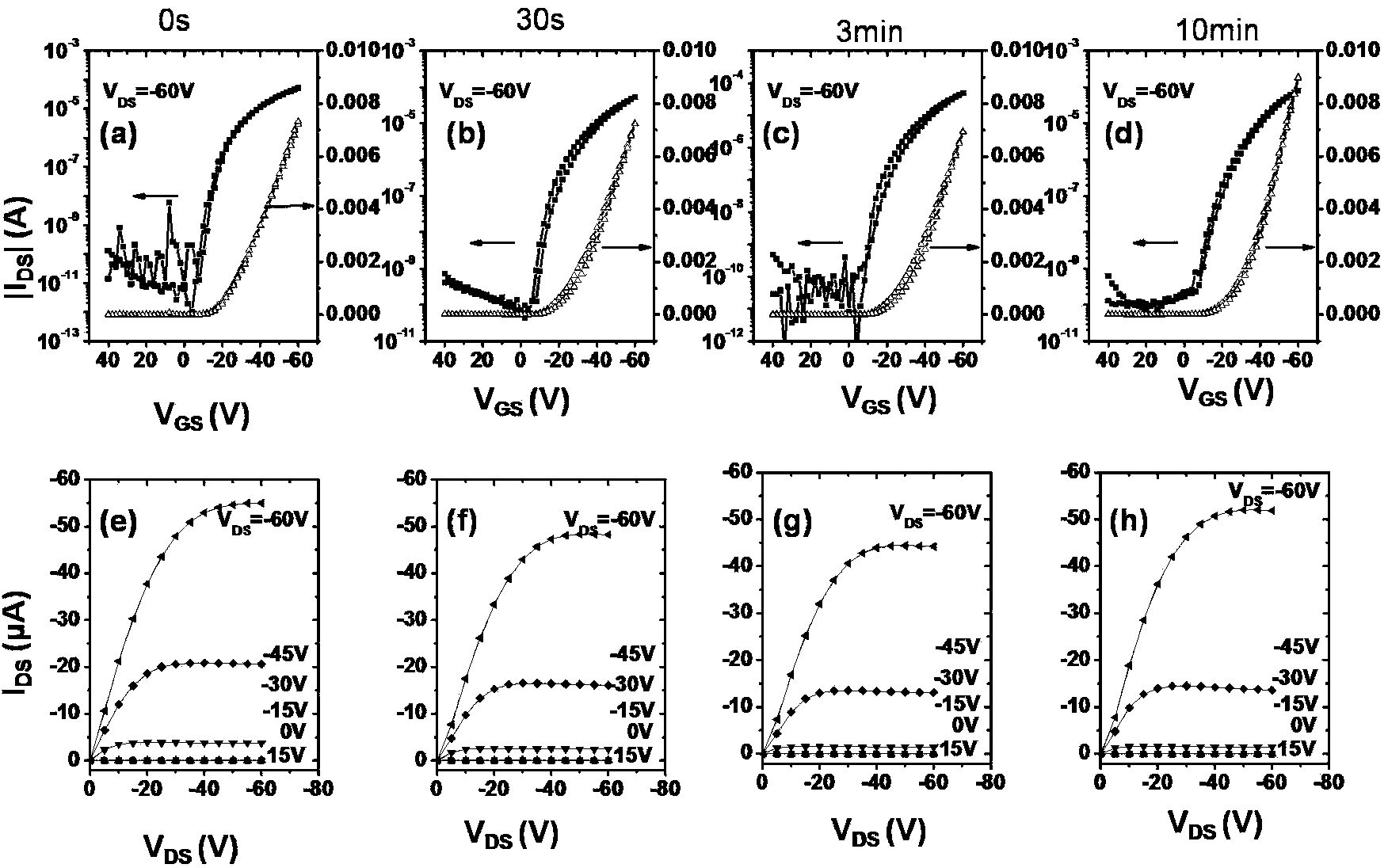
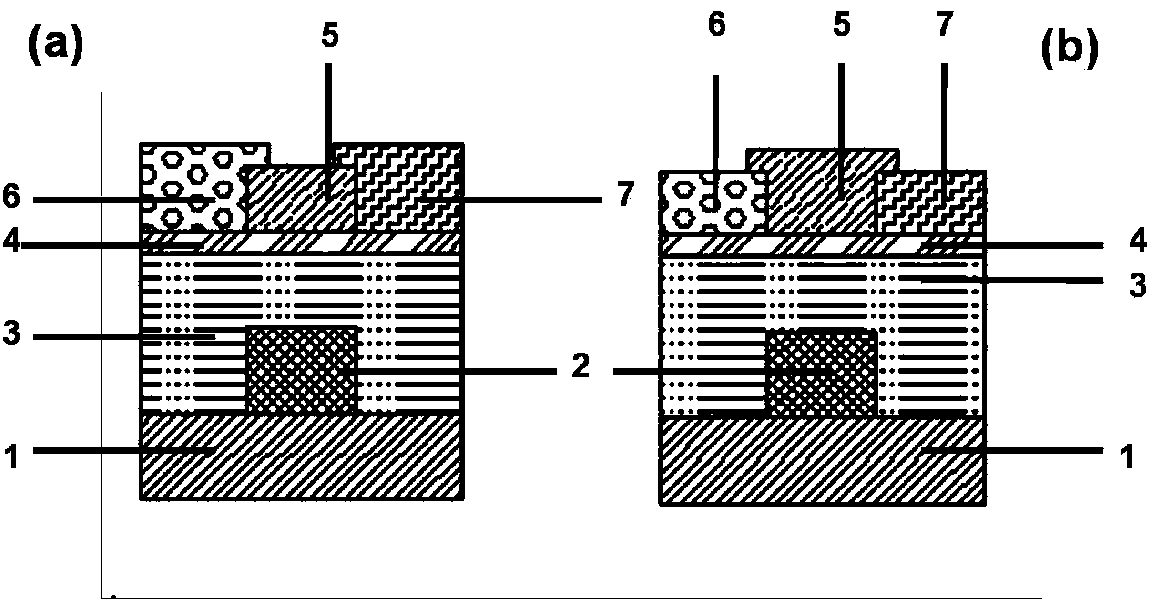
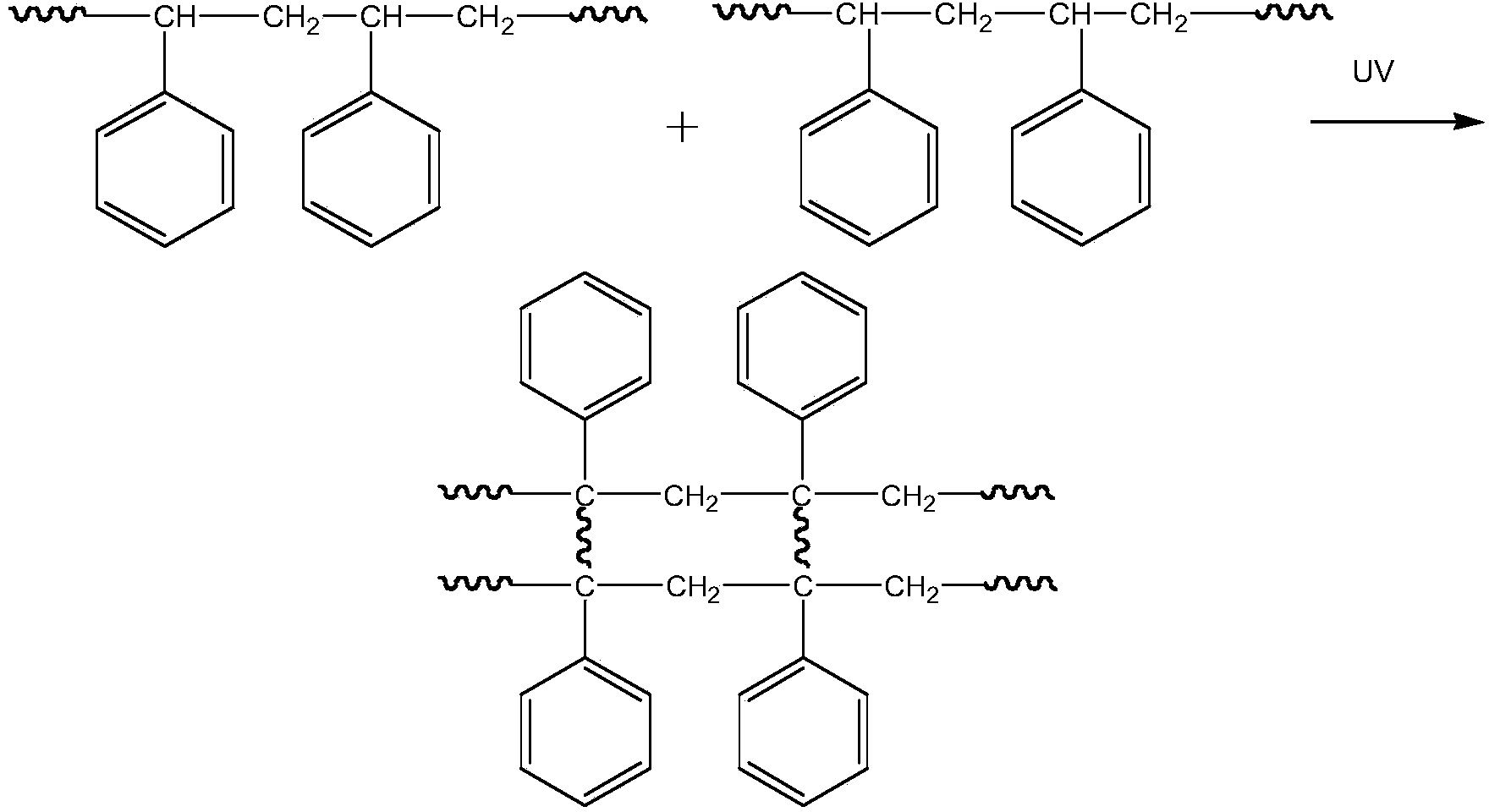
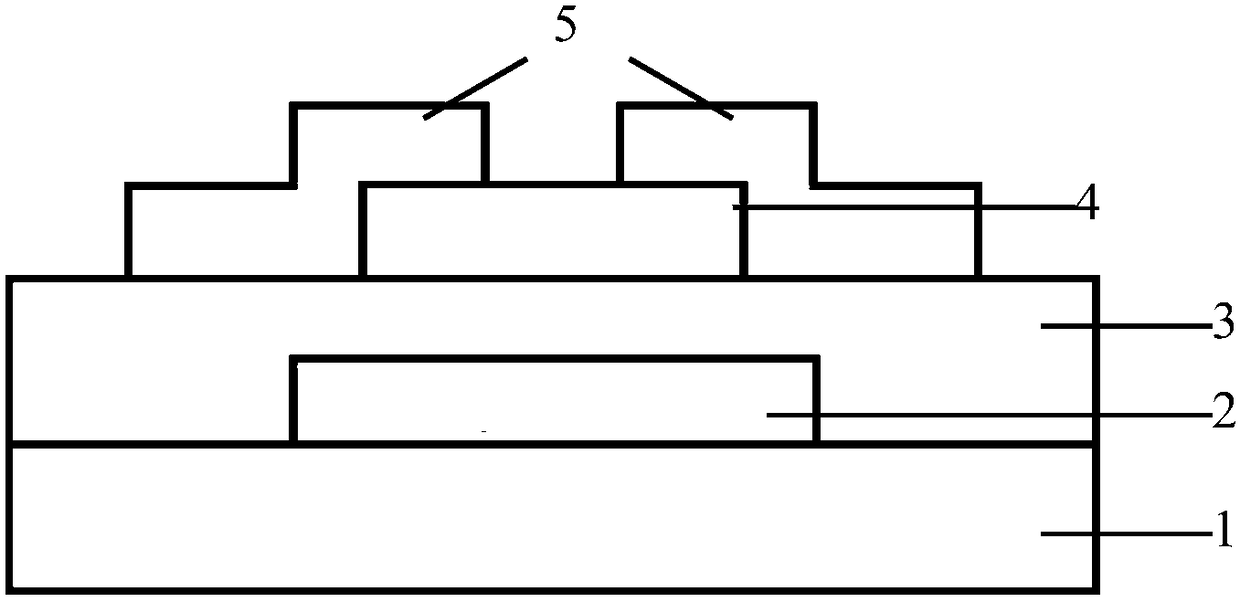
InactiveCN103730574AImprove mobilityImprove bias stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHysteresisInsulation layer
The invention discloses an organic thin-film transistor and a manufacturing method of the organic thin-film transistor. The organic thin-film transistor is characterized in that an insulation layer covers a substrate provided with a grid electrode; a surface decorative layer covers the insulation layer; after the surface decorative layer is illuminated by ultraviolet light, cross-linking reaction is conducted; an organic semiconductor layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode are arranged on the surface decorative layer after the cross-linking reaction is finished, wherein the organic semiconductor layer, the source electrode and the drain electrode are in ohmic contact with the organic semiconductor layer; the source electrode and the drain electrode are communicated through the organic semiconductor layer. According to the organic thin-film transistor, the surface decorative layer is illuminated by the ultraviolet light, so that the cross-linking reaction is conducted on macromolecular polymer; the macromolecular polymer interface decorative layer is additionally arranged between the semiconductor layer and the grid insulation layer, so that a carrier trap of a hydroxide radical group on the grid insulation layer is avoided, the good device performance is obtained, and the hysteresis effect is greatly reduced.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving bias voltage stability of TFT (Thin Film Transistor) with oxide insulating layer prepared by solution method
InactiveCN108346703AReduce defectsGood bias stabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVoltage stabilityMaterials science
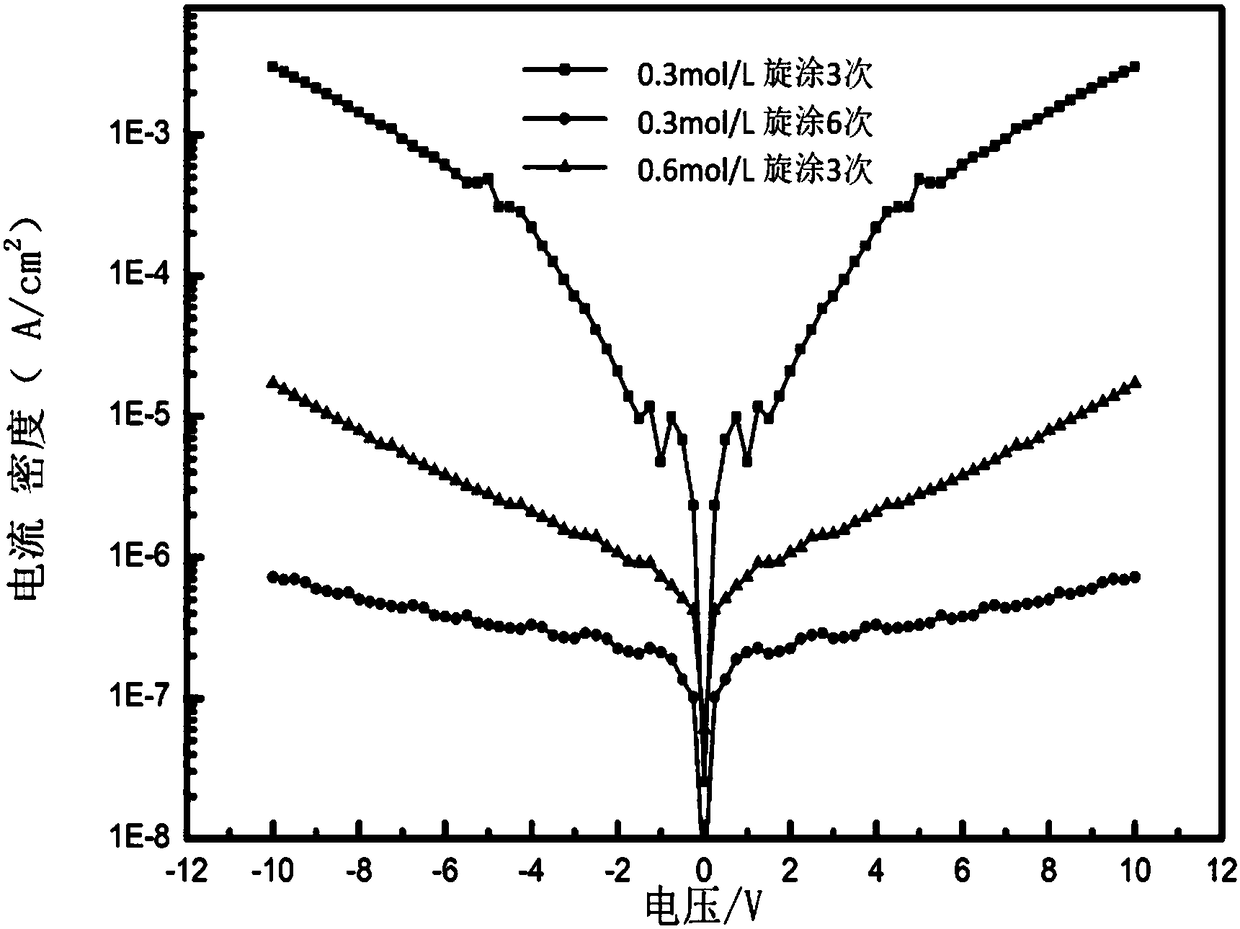
The invention belongs to the thin film transistor technical field and discloses a method for improving the bias voltage stability of a TFT (Thin Film Transistor) with an oxide insulating layer prepared by a solution method. According to the method of the invention, the insulating layer of the thin film transistor is prepared by means of spin-coating; a low-concentration metal oxide insulating layer precursor solution is subjected to spin-coating a plurality of times; annealing treatment is performed after spin coating is completed every time, so that a metal oxide insulating layer thin film isobtained; and the thin film is adopted as the insulating layer of the thin film transistor; and the concentration of the metal oxide insulating layer precursor solution ranges from 0 to 0.3 mol / L andis not 0. With the method of the present invention adopted, defects inside the insulating layer in the thin film transistor can be reduced, and the voltage bias stability of the thin film transistorcan be improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
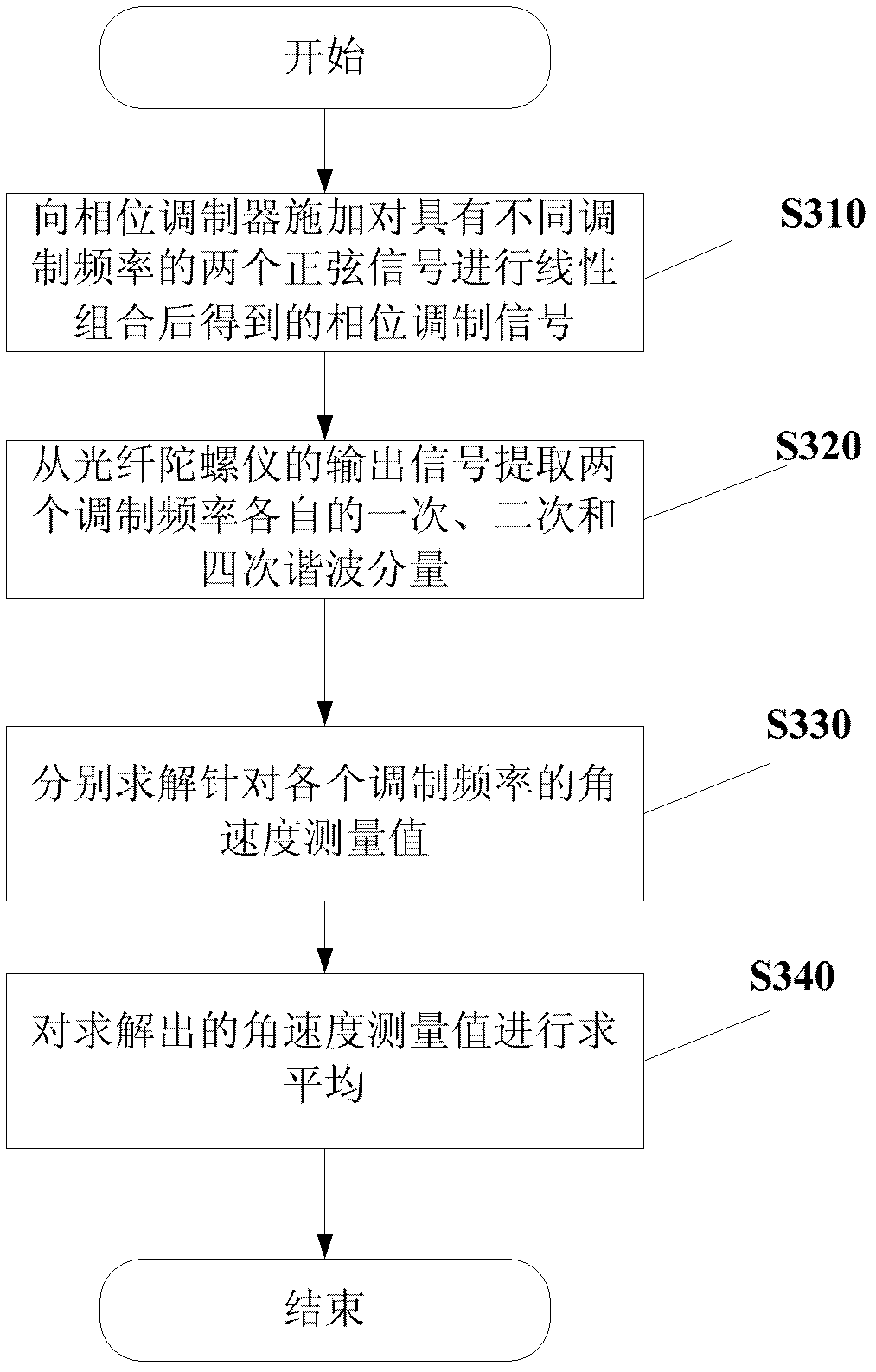
Method and device for measuring angular speed of optical fiber gyroscope based on double-frequency modulating signals
InactiveCN102607589AImprove bias stabilityImprove partial stabilitySagnac effect gyrometersFourth harmonicSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides a method for measuring angular speed of an interference optical fiber gyroscope by utilizing double-frequency modulating signals. The method comprises the following steps of: applying a phase modulating signal obtained by carrying out linear combination on two sinusoidal signals with different modulating frequencies omega 1 and omega 2 to a phase modulator; extracting respective first harmonic components, second harmonic components and fourth harmonic components of the two modulating frequencies from output signals of the optical fiber gyroscope; substituting the light intensity amplitudes of the extracted harmonic components into a preset revised solving equation to respectively solve angular speed measurement values aiming at the two modulating frequencies; and averaging the two obtained angular speed measurement values to obtain an angular speed measurement value to be measured. By utilizing the method, the bias stability of the optical fiber gyroscope can be improved, noise of rate random walks can be reduced, and the signal to noise ratio of detection signals can be improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
In-situ measurement method based on electron paramagnetic resonance-magnetic resonance imaging three-dimensional magnetic field
ActiveCN111060853AImprove bias stabilityHigh sensitivityStray field compensationGyroscopeNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses an in-situ measurement method based on an electron paramagnetic resonance-magnetic resonance imaging three-dimensional magnetic field. The in-situ measurement method comprisesthe following steps: step 1, performing heating; step 2, performing polarization; step 3, performing electron paramagnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging; and step 4, performing three-dimensional magnetic field in-situ measurement. The method has the following beneficial effects: the measurement sensitivity and precision of the residual magnetic field measurement after passive magnetic shielding in the magnetic resonance imaging gyroscope are improved; a sensitive source of the measured magnetic field and a sensitive source for measuring angular motion are located in the same atomicair chamber and are real magnetic fields with nuclear spin feeling, the active magnetic compensation precision is improved and thus the zero-bias stability of the gyroscope is further improved; meanwhile, an atom magnetometer constructed based on the method can work in a geomagnetic field environment, high sensitivity and precision are realized, and the in-situ measurement method can be applied tothe fields of magnetic anomaly detection, geomagnetic navigation, deep space detection and the like.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
Dual-core spin magnetic frequency shift suppression method
ActiveCN109883410ASuppressing Error DriftImprove bias stabilityTurn-sensitive devicesPolarizerElimination method
The invention belongs to an error elimination method, particularly relates to a dual-core spin magnetic frequency shift suppression method. The dual-core spin magnetic frequency shift suppression method comprises the steps that firstly, heating is conducted, specifically, an atomic chamber is heated to at least 120 DEG C in a non-magetic heating assembly, secondly, polarization is conducted, thirdly, resonance is conducted, fourth, inspecting is conducted, specifically, inspected laser enters the atomic chamber through polarizer, and resonant frequency is inspected; fifth, an electron spin polarization direction is overturned; and sixth, calculating is conducted. The dual-core spin magnetic frequency shift suppression method has the beneficial effects that on the basis of active magnetic compensation of an atomic magnetometer, dual-core spin magnetic frequency shift error drifting is compressed, and thus zero-bias stability of a gyroscope is improved.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
Y-shaped cavity orthogonal polarization laser-based force and mass measurement method and device
InactiveCN102507054ASignal readout method is simpleDoes not change the geometric lengthForce measurement by measuring optical property variationWeighing apparatusOperating pointRefractive index
The invention relates to a Y-shaped cavity orthogonal polarization laser-based force and mass measurement method and device. The device consists of a Y-shaped cavity orthogonal polarization laser, a gas diaphragm capsule, a force-applying unit, an operating point selection and control unit and a signal acquisition and processing unit. A force to be measured or the self-gravity of an object to be measured is transferred to an ultra-thin diaphragm of the gas diaphragm capsule through the force-applying unit, the ultra-thin diaphragm is subjected to elastic deformation, the volume of sensing gas in the gas diaphragm capsule is caused to be changed, the refractive index of sensing gas in a P subsection of the Y-shaped cavity orthogonal polarization laser communicated with the gas diaphragm capsule correspondingly changes, thus, the optical length difference between a resonant cavity of S polarized light and a resonant cavity of P polarized light is caused to be changed, the beat frequency difference between the S polarized light and the P polarized light is finally caused to be changed, and the change value of the beat frequency difference is directly proportional to the size of the inputted force. The Y-shaped cavity orthogonal polarization laser-based force and mass measurement method and device have the characteristics of high resolution, large dynamic range, high linearity, direct digital output and the like, and the device can be used as a micro / nano force and micro / nano mass measurement standard transferring instrument through optimizing structural parameters.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Gyroscope with phase and duty-cycle locked loop
ActiveUS8884710B2Improve Noise PerformanceImprove bias stabilityMechanical apparatusPulse automatic controlGyroscopeSmall footprint
A system and method in accordance with the present invention provides a gyroscope incorporating an improved PLL technique. The improved PLL auto-corrects its own reference low-frequency noise, thereby eliminating this source of noise, improving the noise performance of the gyroscope and allowing a compact implementation. The net result is a gyroscope with improved bias stability that can meet noise requirements with a smaller footprint.
Owner:INVENSENSE
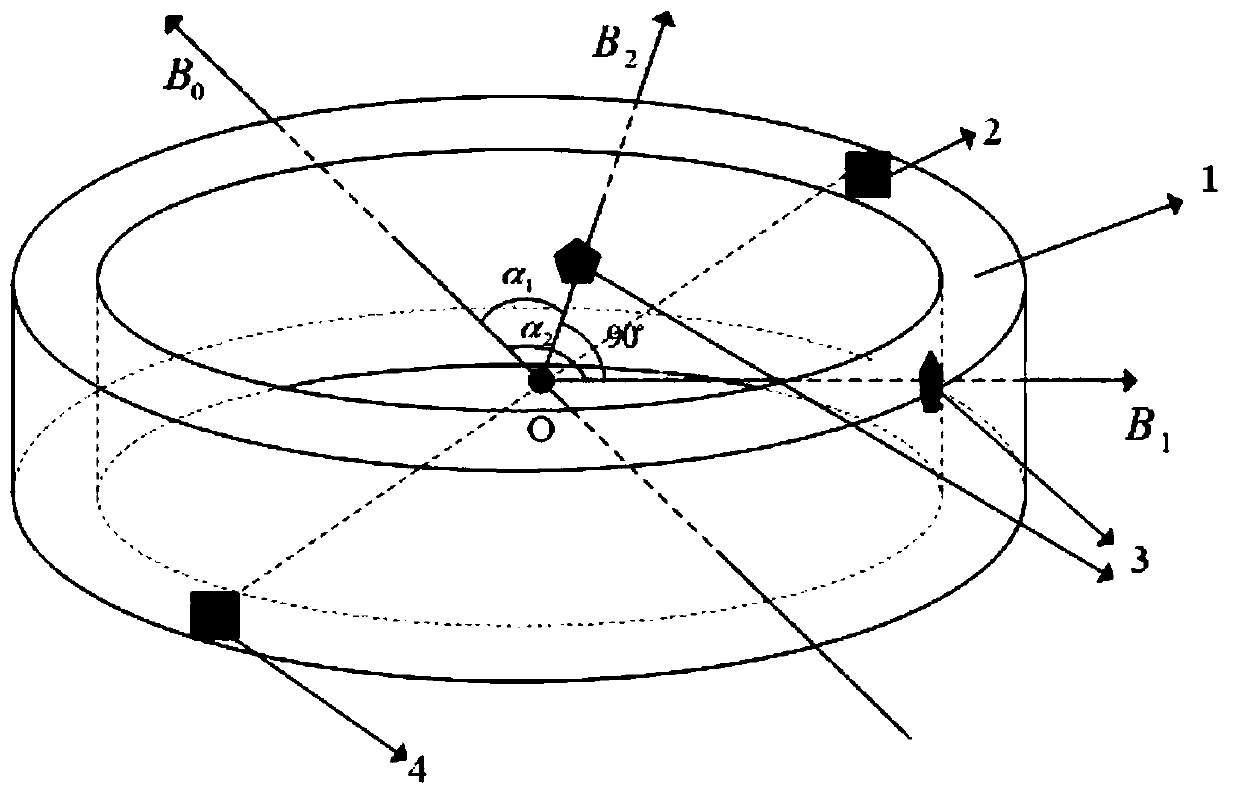
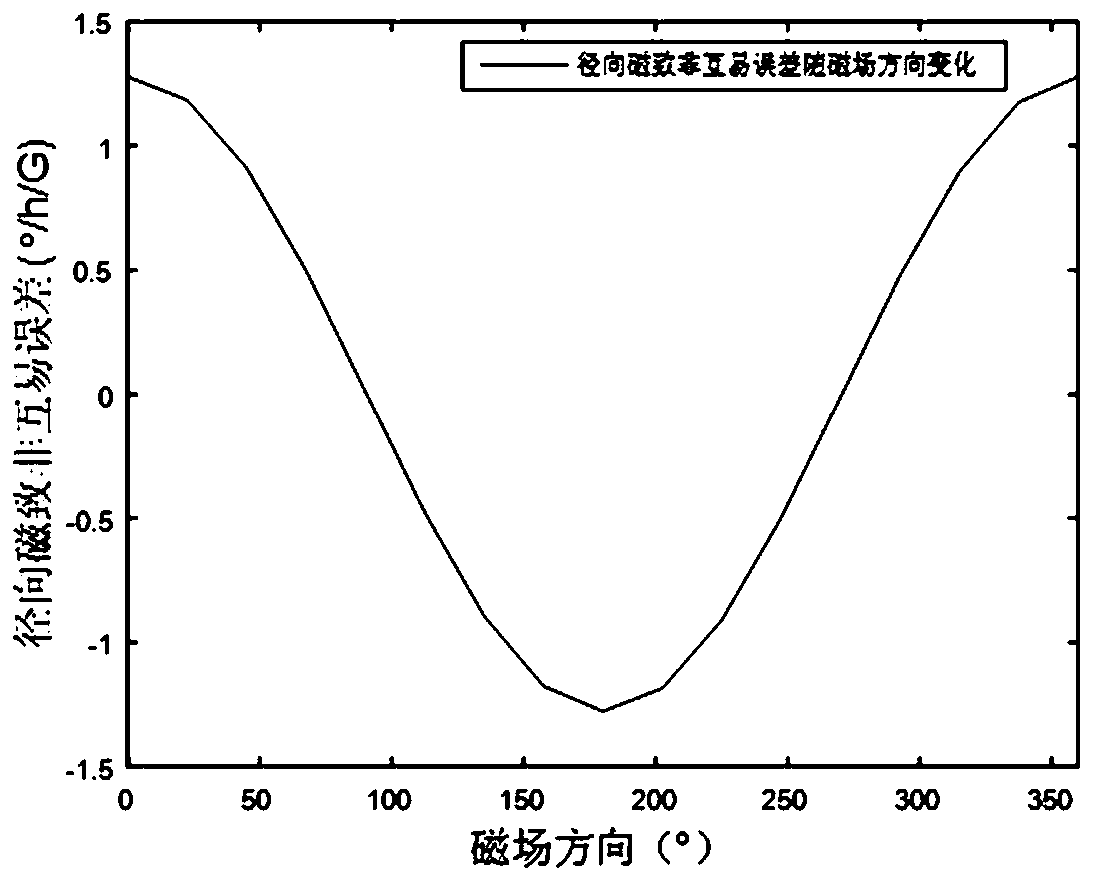
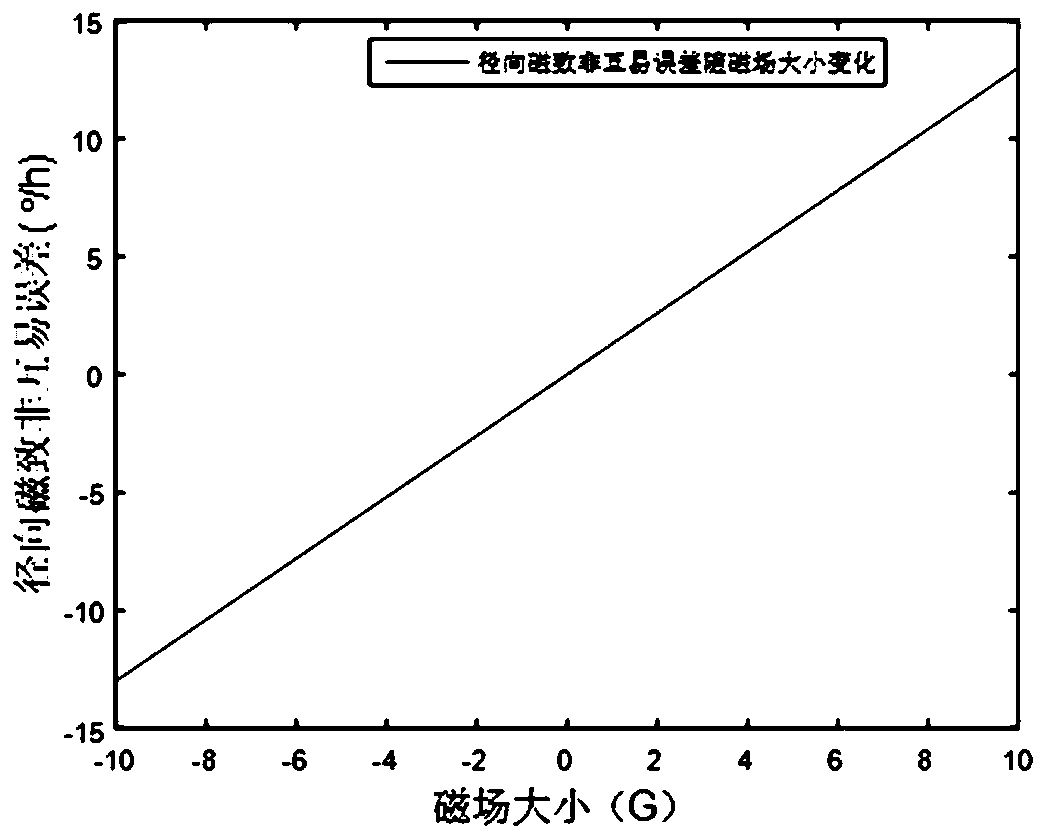
Two-dimensional compensation method of optical fiber gyroscope magnetic temperature cross-linking coupling error
The invention discloses a two-dimensional compensation method of an optical fiber gyroscope magnetic temperature cross-linking coupling error. The method comprises the following steps of A, attachingat least one temperature sensor to each of upper and lower surfaces of an optical fiber ring of an optical fiber gyroscope; B, attaching two magnetic field sensors to a side surface of the optical fiber ring of the optical fiber gyroscope, wherein magnetic sensitive shafts of the two magnetic field sensors are orthogonal to the side surface of the optical fiber ring and pass through a central axisof the optical fiber ring; C, through an experiment, acquiring an error model of a relationship among the optical fiber gyroscope magnetic temperature cross-linking coupling error, magnetic field distribution and temperature distribution, wherein the error model Y=B T (the Y is the optical fiber gyroscope magnetic temperature cross-linking coupling error, the B is the magnetic field distribution,and the T is the temperature distribution); and D, using the error model to compensate the optical fiber gyroscope magnetic temperature cross-linking coupling error in a two-dimensional mode. In theinvention, the optical fiber gyroscope magnetic temperature cross-linking coupling error is compensated through detecting a radial magnetic field and a temperature of an environment where the opticalfiber gyroscope is located in real time, a non-reciprocal error generated by the optical fiber gyroscope under a combined action of a magnetic field and a temperature field is effectively reduced, andenvironmental adaptability and application precision of the optical fiber gyroscope are finally increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and device for realizing square wave quadrature demodulation of closed-loop resonant optical gyroscope
ActiveCN112697124ASuppression of demodulation curve fluctuationsAvoid demodulated signal fluctuationsSagnac effect gyrometersResonant cavityOptical gyroscope
The invention discloses a method and a device for realizing square wave quadrature demodulation of a closed-loop resonant optical gyroscope, and belongs to the technical field of optical sensing and signal detection. A photoelectric detector is used for detecting light output by an optical resonant cavity, then orthogonal demodulation is conducted on signals output by the photoelectric detector through a square wave orthogonal demodulation module, and orthogonal demodulation signals are obtained; wherein the square wave quadrature demodulation module comprises two channels, and in the first channel, a signal output by the photoelectric detector obtains a first demodulation signal according to a first channel reference signal; in the second channel, the signal output by the photoelectric detector obtains a second demodulation signal according to a second channel reference signal; and obtaining a finally output square wave quadrature demodulation signal according to the difference between the first demodulation signal and the second demodulation signal. According to the invention, the problem that the performance of the closed-loop resonant optical gyro system is reduced due to the phase fluctuation of the square wave signal can be effectively inhibited, and the precision of the optical gyro is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
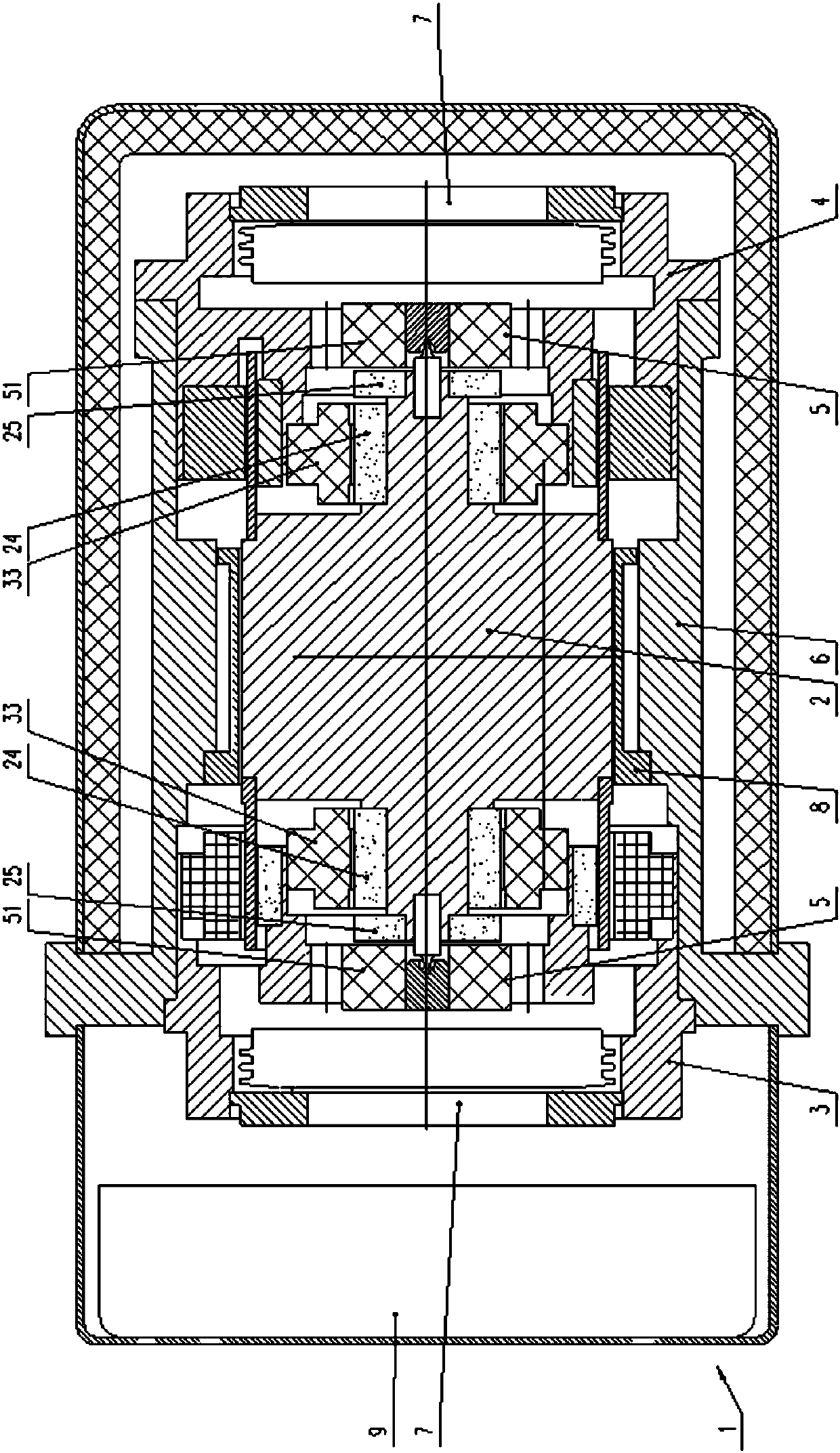
Novel MEMS (micro electro mechanical system) centrifugal-type gyroscope
InactiveCN102305626BEliminate quadrature coupling errorsReduce consumptionRotary gyroscopesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesCapacitanceGyroscope
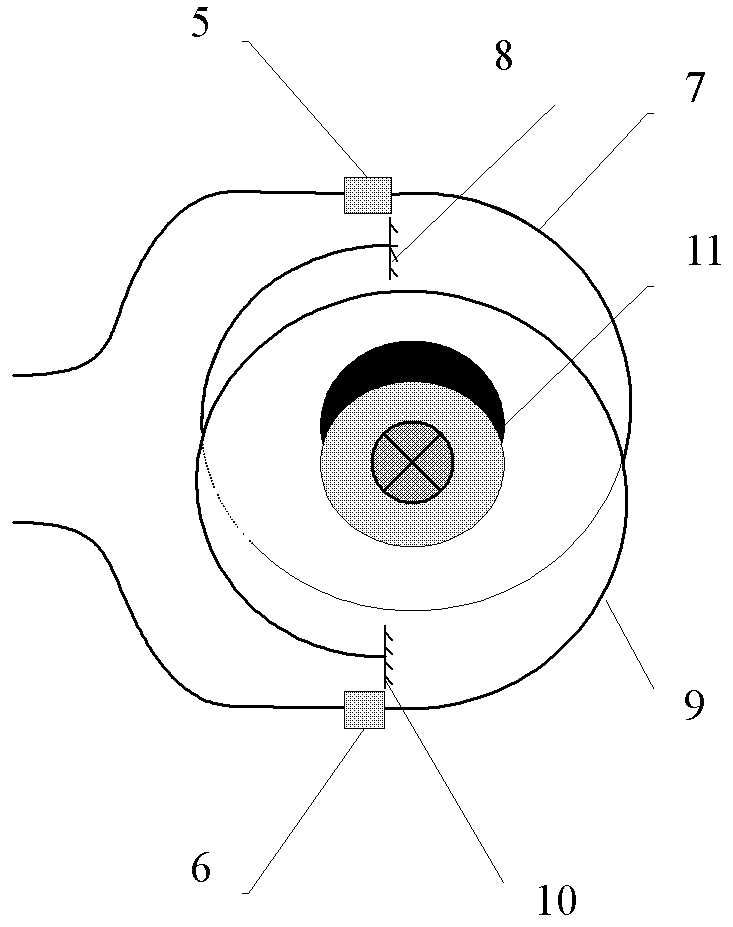
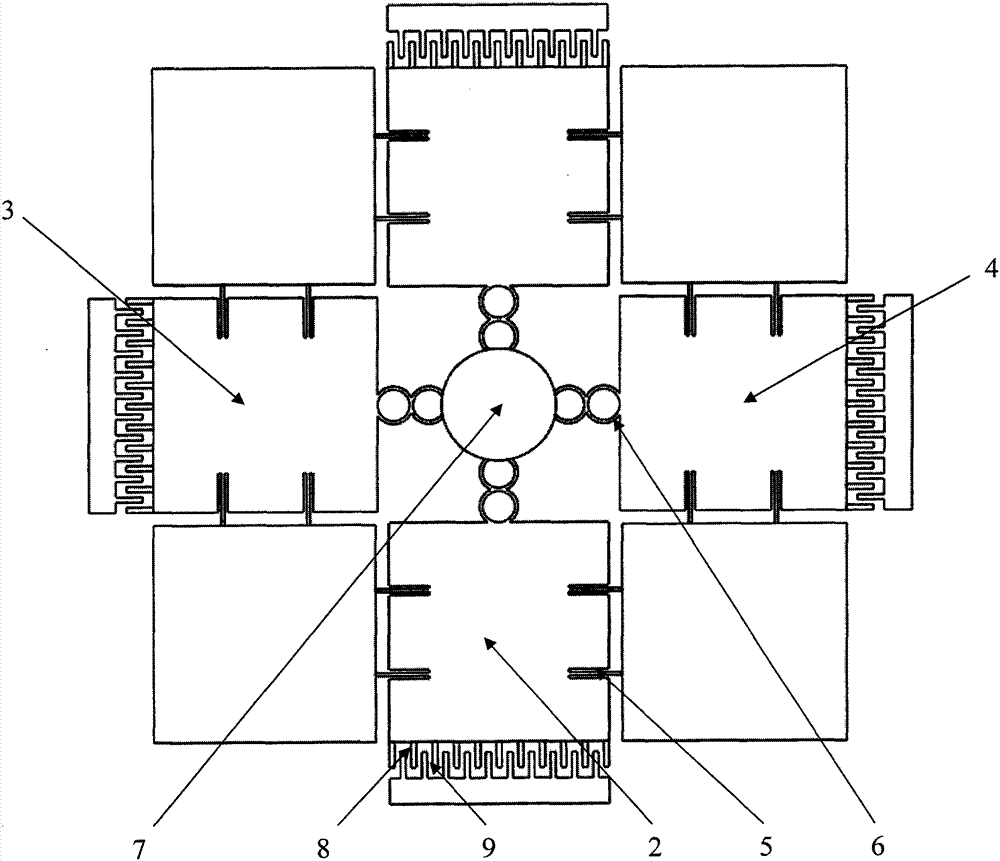
The invention discloses a novel MEMS (micro electro mechanical system) centrifugal-type gyroscope technology, belonging to the field of inertia measurement. Four mass blocks of a gyroscope are distributed annularly and uniformly at the periphery of a central anchor point 7, and each mass block and the central anchor point 7 are connected through an elastic beam 6; the adjacent mass blocks are connected through two parallel arc decoupling beams 7; and a group of movable comb teeth 8 are distributed on each mass block 4, and form comb tooth capacitance with corresponding fixed comb teeth 9. When the angularity speed is input in the environment, the MEMS centrifugal-type gyroscope is subjected to displacement because of centrifugal force, and the angularity speed which is input in the environment can be reckoned through the detection of the displacement. Compared with the other MEMS gyroscopes, the gyroscope is not required to be driven, the detection of the angularity speed can be realized by utilizing the inertial motion of the gyroscope, thus the energy consumption is reduced; driving does not exist, the Brown noise can be reduced greatly, and the zero deflection stability is improved greatly; and simultaneously the cross coupling error of the MEMS oscillating-type gyroscope can be eliminated, and the precision is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Micro gyroscope excitation and protection device and method
ActiveCN111272161AImprove detection resolutionImprove stabilityTurn-sensitive devicesElectric variable regulationGyroscopeHarmonic
The invention belongs to the technical field of gyroscopes, and particularly discloses a micro gyroscope excitation and protection device and method. The micro gyroscope excitation and protection device is used for detecting and analyzing the resonant frequency of the gyroscope in real time and adjusting the passband frequency of the passband adjustable buffer on line, so that low-frequency and high-frequency noises can be effectively prevented from entering the gyroscope, and the detection resolution ratio and the dynamic response range of the gyroscope are improved. Besides, high-frequency harmonics superposed in the tuning signal are processed, so that the modal matching performance of the gyroscope is improved, and the zero-bias stability of the gyroscope is further improved. Finally,measures such as isolation and passband adjustability are adopted, input ripples, backflow noise and direct-current bias components are inhibited from entering the gyroscope, irreversible damage to the mechanical structure of the gyroscope is prevented, potential safety threats are effectively avoided, the service life of the gyroscope is prolonged, and the gyroscope is suitable for the application field of long-time operation.
Owner:尚同电子科技(淄博)有限公司
Step-by-step temperature compensation method for fiber-optic gyroscope
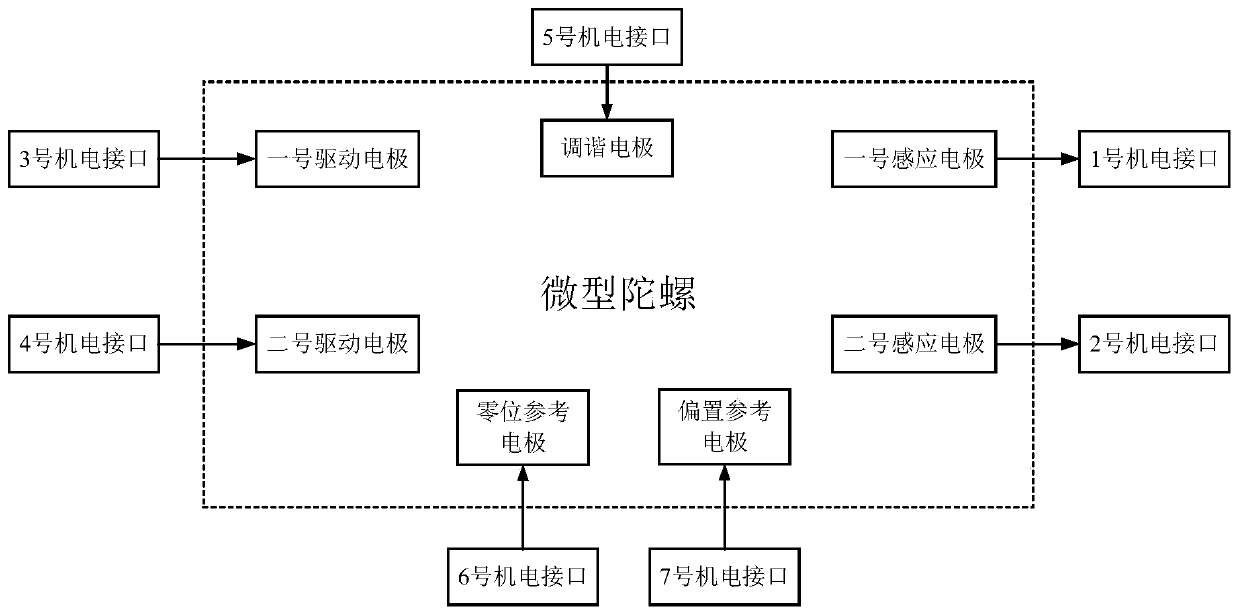
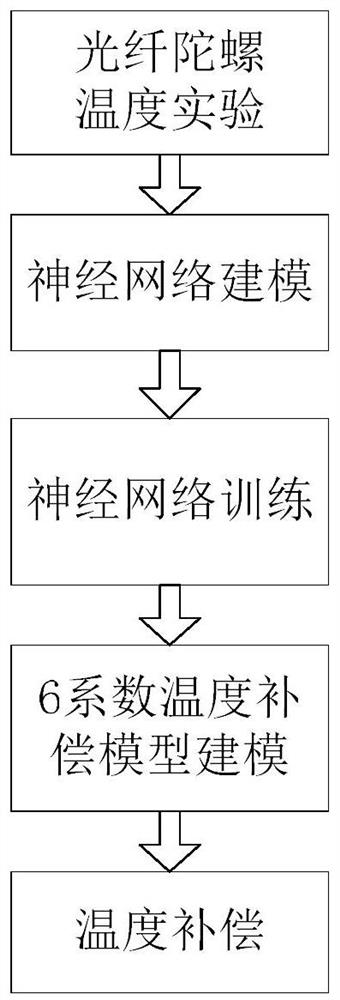
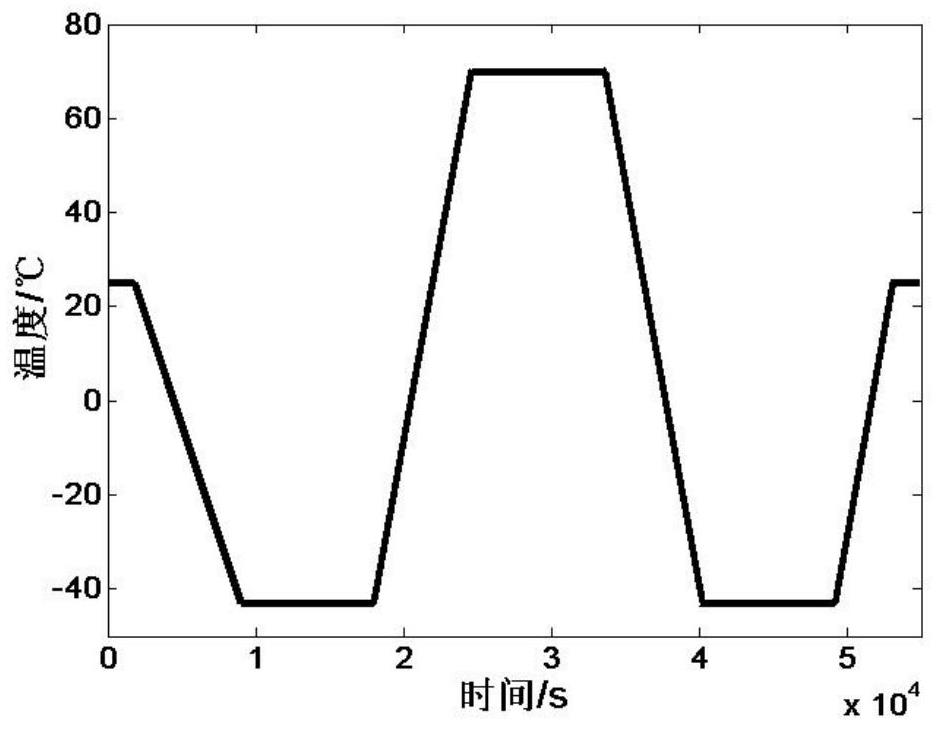
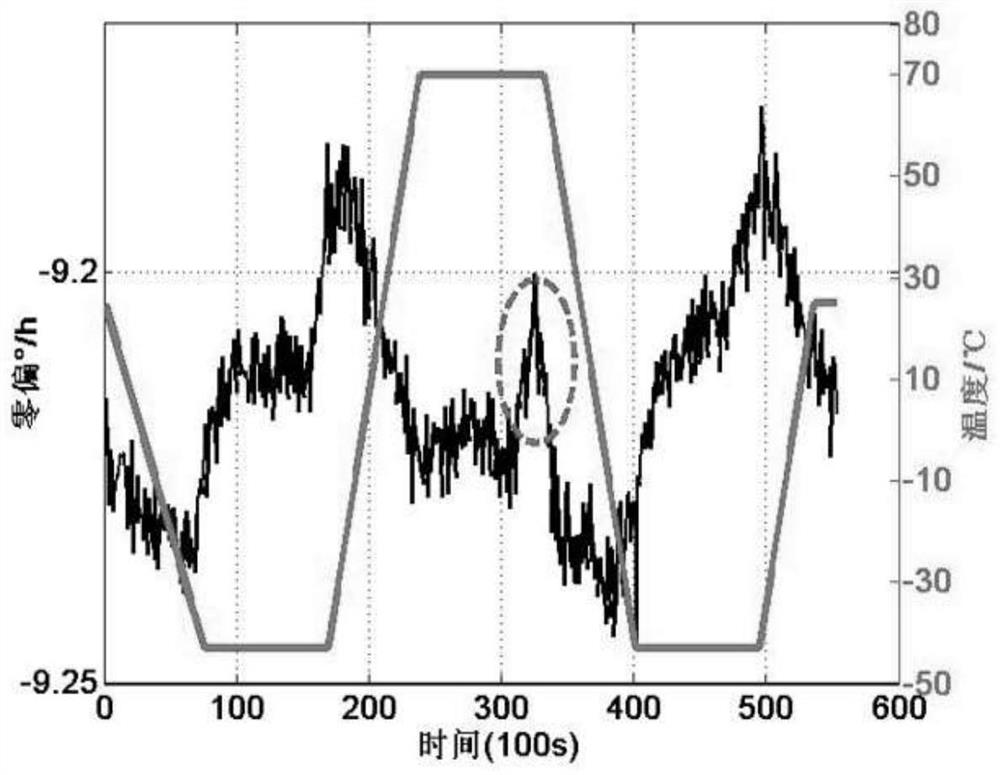
ActiveCN114046802AImprove bias stabilityImprove yieldSagnac effect gyrometersNeural architecturesHidden layerGyroscope
The invention relates to a step-by-step temperature compensation method for a fiber-optic gyroscope, which comprises the following steps of: 1, carrying out temperature test on the fiber-optic gyroscope in a set temperature range, simultaneously collecting the output angular velocity and the temperature value of the gyroscope, and constructing a test temperature curve; 2, establishing a neural network model based on a multi-layer perceptron, wherein the model adopts a three-layer structure and comprises an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer; 3, training the established neural network model; 4, establishing a polynomial model, wherein the polynomial model adopts a 6-coefficient temperature compensation model; and 5, obtaining a temperature drift compensation value of the fiber-optic gyroscope by utilizing the model in the step 4, and subtracting the temperature drift compensation value of the fiber-optic gyroscope from real-time output data of the fiber-optic gyroscope to finish temperature compensation of the fiber-optic gyroscope. The temperature environment adaptability of the fiber-optic gyroscope is improved by combining the characteristics of high nonlinear fitting precision of the neural network and easy realization of the polynomial model.
Owner:TIANJIN NAVIGATION INSTR RES INST
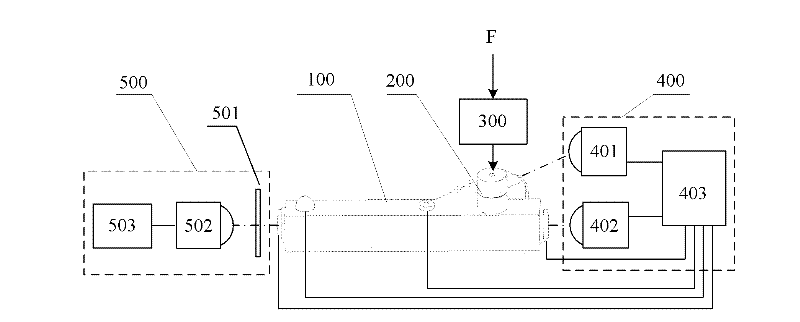
An Adaptive Closed-loop Measurement System of Resonant Accelerometer
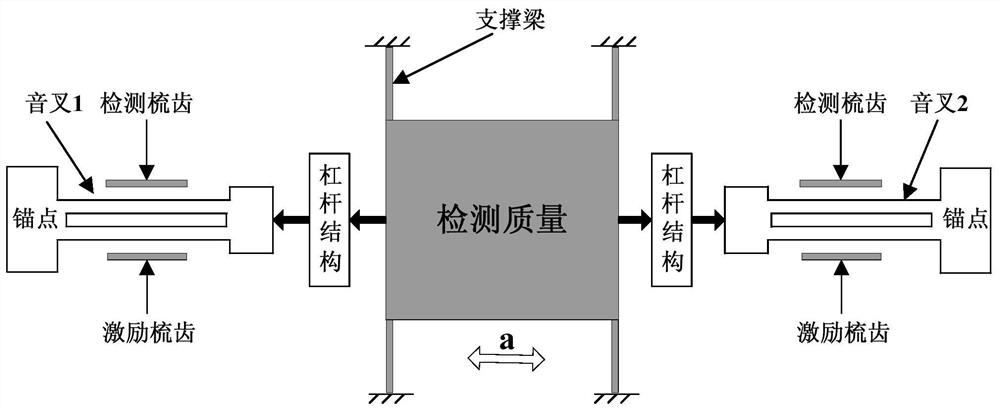
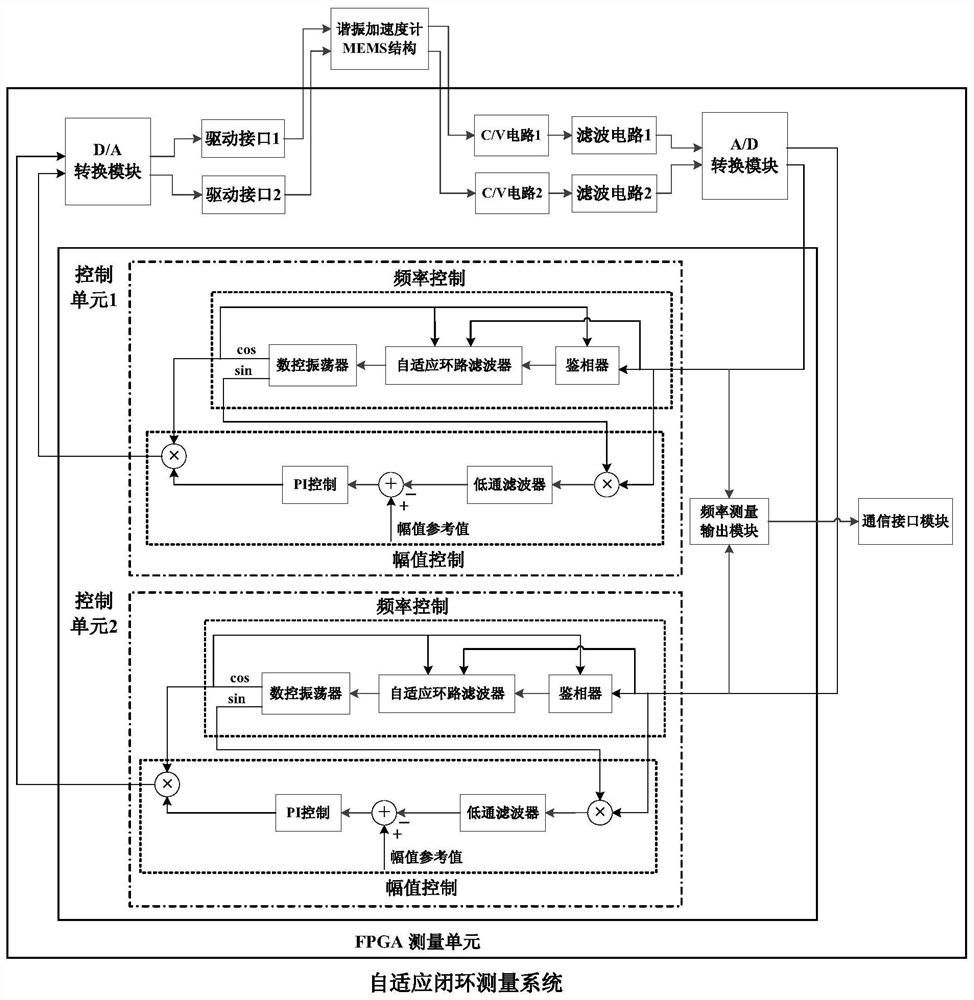
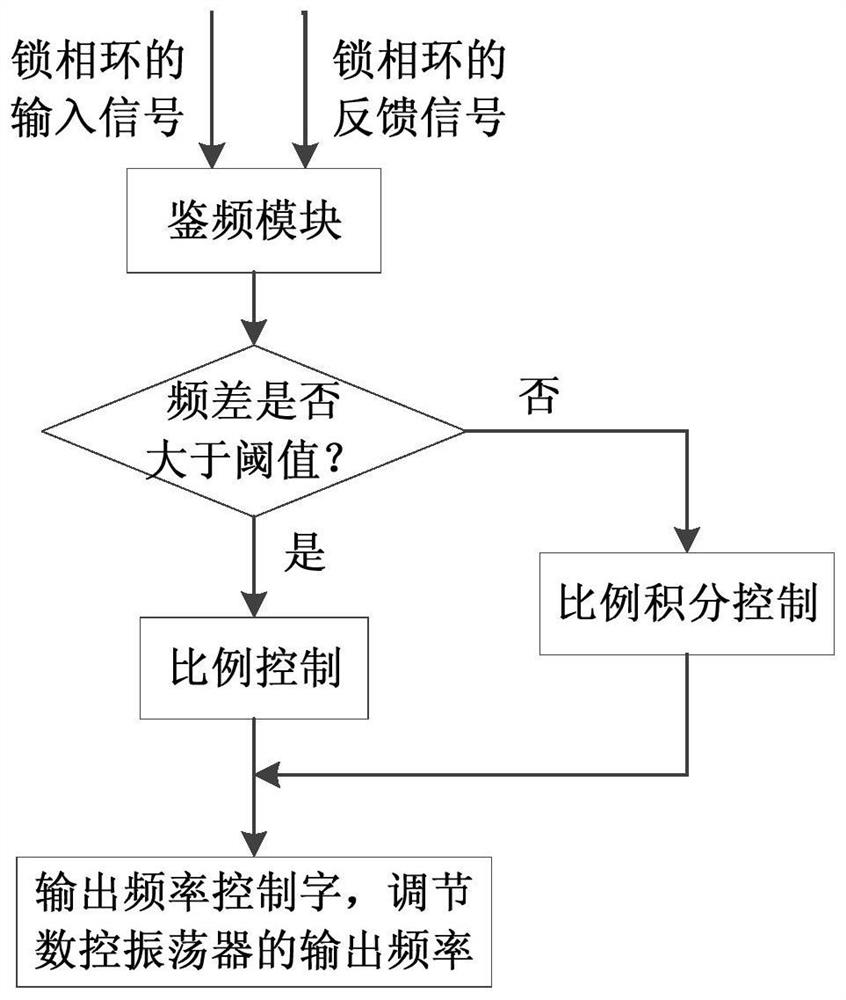
ActiveCN108519498BIncrease rangeImprove bias stabilityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAccelerometerControl cell
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device, array substrate and display apparatus
ActiveCN106992116AImprove mobilityReduce defectsTransistorSolid-state devicesOxide semiconductorDecomposition
The invention provides a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, an array substrate and a display apparatus. The method of manufacturing the semiconductor device comprises the following steps of depositing a first oxide semiconductor layer on a substrate and spraying an H2O2 solution on the first oxide semiconductor layer; using ultraviolet light to irradiate the H2O2 solution so as to promote H2O2 decomposition; and drying the H2O2 solution existing on the first oxide semiconductor layer and continuously depositing a second oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
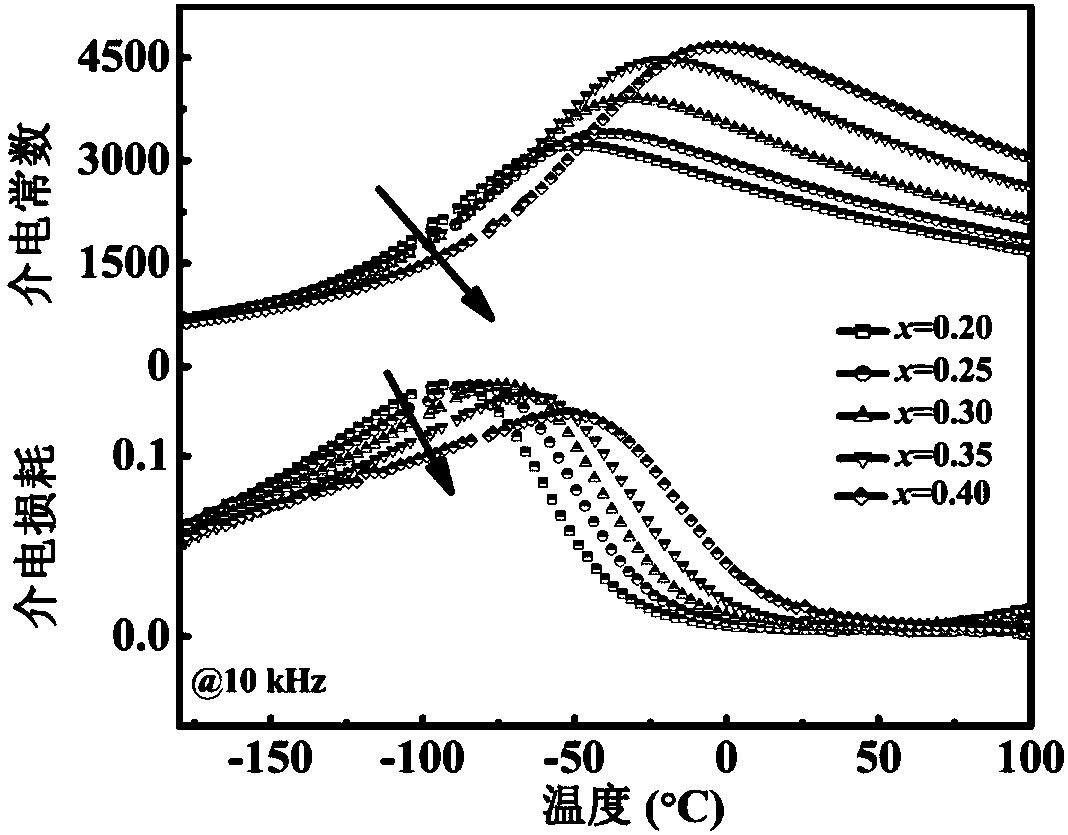
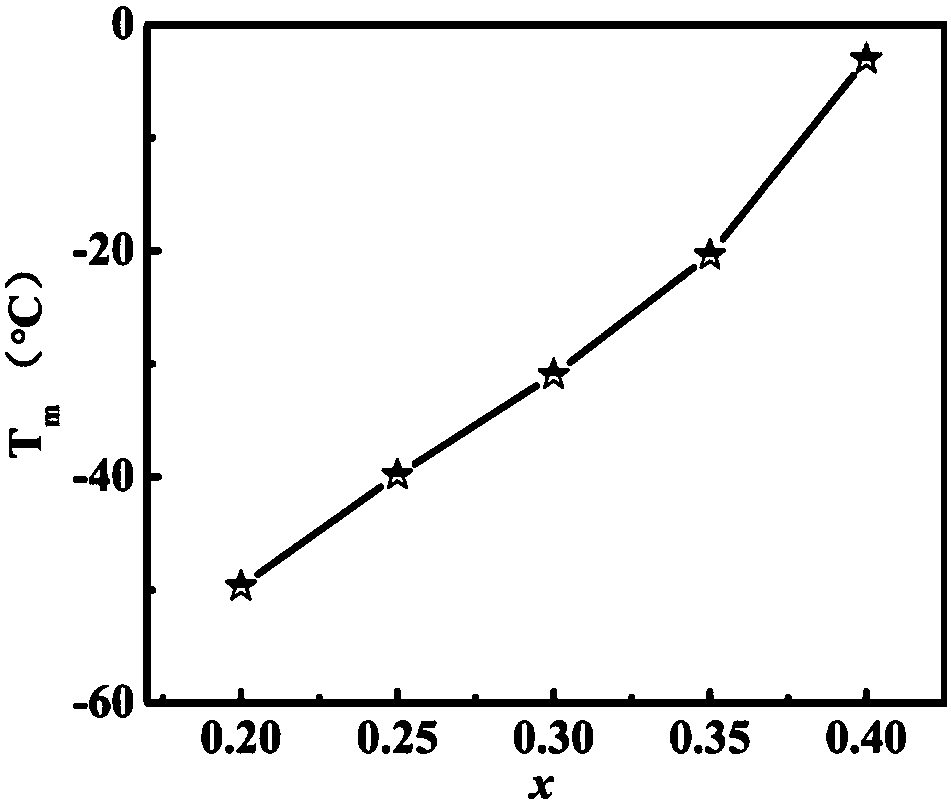
ST-NBT-BT ceramic material with high energy storage density and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an ST-NBT-BT ceramic material with high energy storage density and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, weighing raw materials with corresponding masses respectively according to a molar ratio to synthesize ST powder, NBT powder and BT powder, mixing the ST powder, the NBT powder and the BT powder, performing ball milling, drying and briquetting to form fully-graded materials, and then screening the fully-graded materials sequentially to form sieved materials; secondly, pressing the sieved materials into samples, and sintering the prepared samples to obtain sintered samples; and finally, grinding and cleaning the sintered samples, uniformly coating front and back surfaces of the polished and cleaned sintered samples with silver electrode slurry, and sintering the samples coated with silver electrodes to obtain the ST-NBT-BT ceramic material with high energy storage density. The ST-NBT-BT ceramic material high energy storage density, obtained by the method provided by the invention, not only has high energy storage density, but also has a simple preparation process and a low material cost and is environment-friendly.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application method of composite film in axisymmetric shell harmonic oscillator
PendingCN114783655AHigh precisionImprove bias stabilityConductive layers on insulating-supportsCarbon compoundsComposite filmMetal nanowires
The invention discloses an application method of a composite film in an axisymmetric shell harmonic oscillator. The axisymmetric shell harmonic oscillator comprises a cylindrical shell harmonic oscillator and a hemispherical shell harmonic oscillator. The inner surface of the cylindrical shell harmonic oscillator and the lower lip edge part of the resonant ring are plated with first metal nanowires and graphene film electrodes; and second metal nanowires and graphene film electrodes are plated on the inner surface of the hemispherical shell harmonic oscillator and the lower lip edge part of the hemispherical shell. The method has the advantages that the thickness is smaller (the thickness of a single layer is smaller than 10 nm), the conductivity is high, the Q value of the harmonic oscillator coated with the film is remarkably improved under the condition that the conductivity of the film is not affected, and higher gyro precision can be obtained.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
MEMS gyroscope
PendingCN112683256AReduce displacementImprove bias stabilitySpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesPhysicsDetection performance
The invention provides an MEMS gyroscope which comprises an annular structure, a first coupling structure connected to the annular structure, mass blocks connected to the first coupling structure, anchor points connected with the mass blocks, second coupling structures connected between the adjacent mass blocks and transduction assemblies connected to the annular structure and the mass blocks. The MEMS gyroscope comprises 4N mass blocks arranged around the center of the annular structure at equal angles, N is an integer larger than or equal to 2, each mass block comprises a main body connected with the first coupling structure and provided with a containing groove and an elastic structure connected to the main body and located in the containing groove, and the anchor points are arranged in the containing grooves and connected with the elastic structures. According to the scheme, the area utilization rate of the chip region can be improved, the sensitivity is increased, the bias stability is improved, the detection performance is improved, and the mechanical noise is reduced.
Owner:AAC TECH NANJING
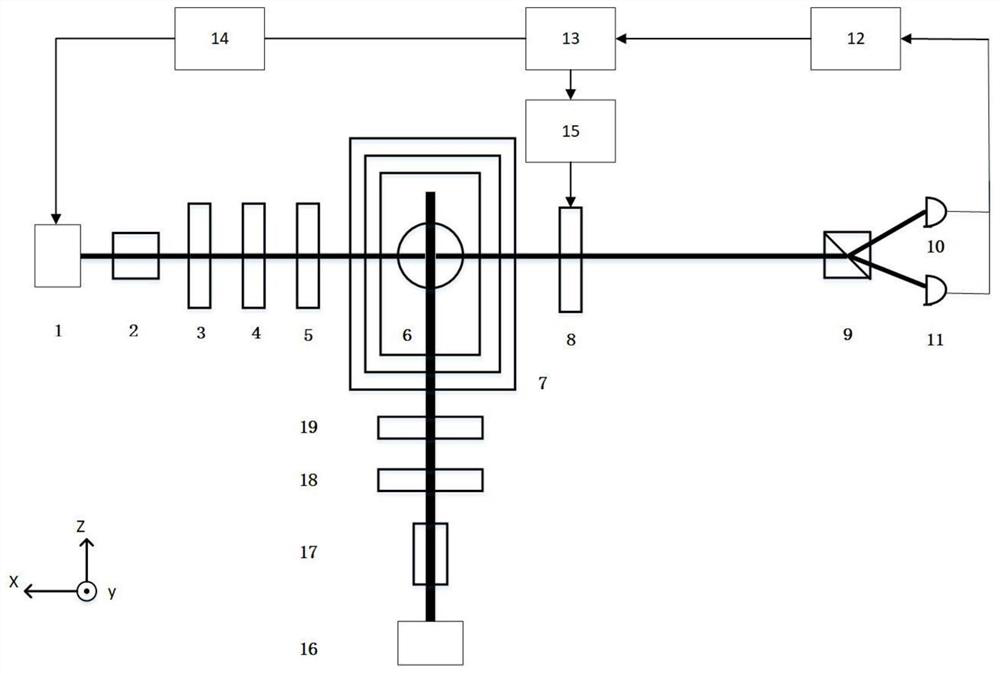
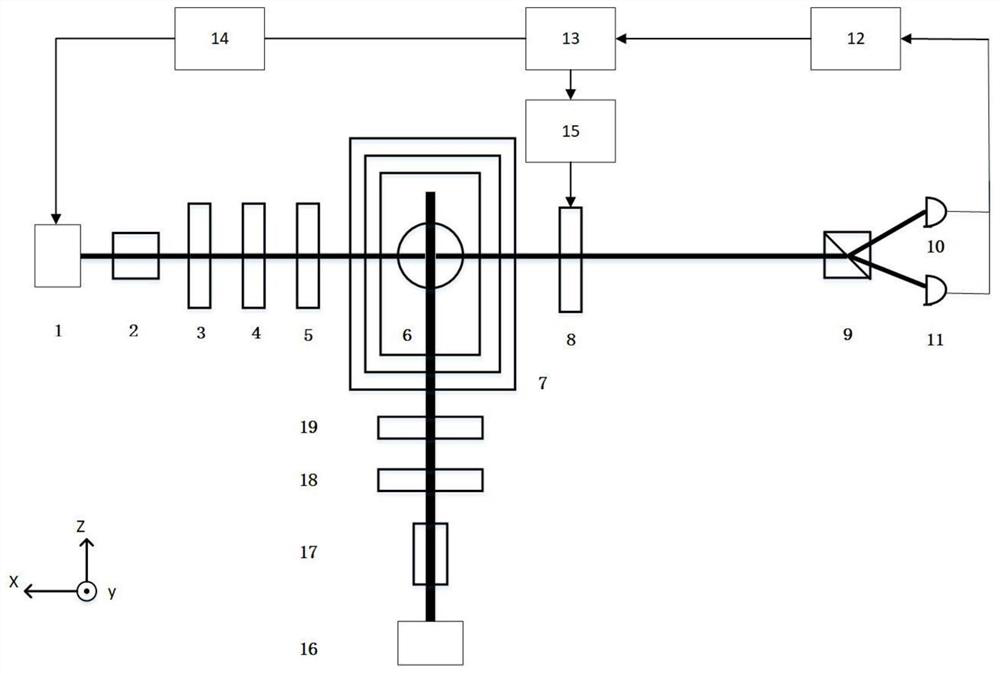
Fiber-optic gyroscope temperature control structure and method for using same
ActiveCN110986909AInterference that reduces measurement accuracyImprove bias stabilityTemperatue controlSagnac effect gyrometersPhysicsThermal insulation
The invention provides a fiber-optic gyroscope temperature control structure and a method for using the same. The structure includes: first, second and third thermal insulation layers, first and second temperature control layers, a first heat insulation layer, a first temperature control layer, a second heat insulation layer, a second temperature control layer and a third heat insulation layer, all of which are sequentially arranged. The first heat insulation layer is arranged on the outer side of a fiber-optic gyroscope sensitive gauge outfit structure; the first heat insulation layer is usedfor carrying out heat insulation on the fiber-optic gyroscope sensitive gauge outfit structure; the first temperature control layer is used for maintaining the working temperature of the first temperature control layer within a first set temperature range; the second heat insulation layer is used for conducting heat insulation on the first temperature control layer, the second temperature controllayer is used for maintaining the working temperature of the second temperature control layer within a second set temperature range, and the third heat insulation layer is used for conducting heat insulation on the second temperature control layer to reduce the influence of external temperature disturbance on the temperature of the second temperature control layer. By applying the technical scheme of the invention, the technical problem that the temperature compensation method in the prior art is difficult to meet the precision requirement of the high-precision optical fiber gyroscope meter is solved.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
Method for inhibiting residual rotation light angle of atomic spin gyroscope
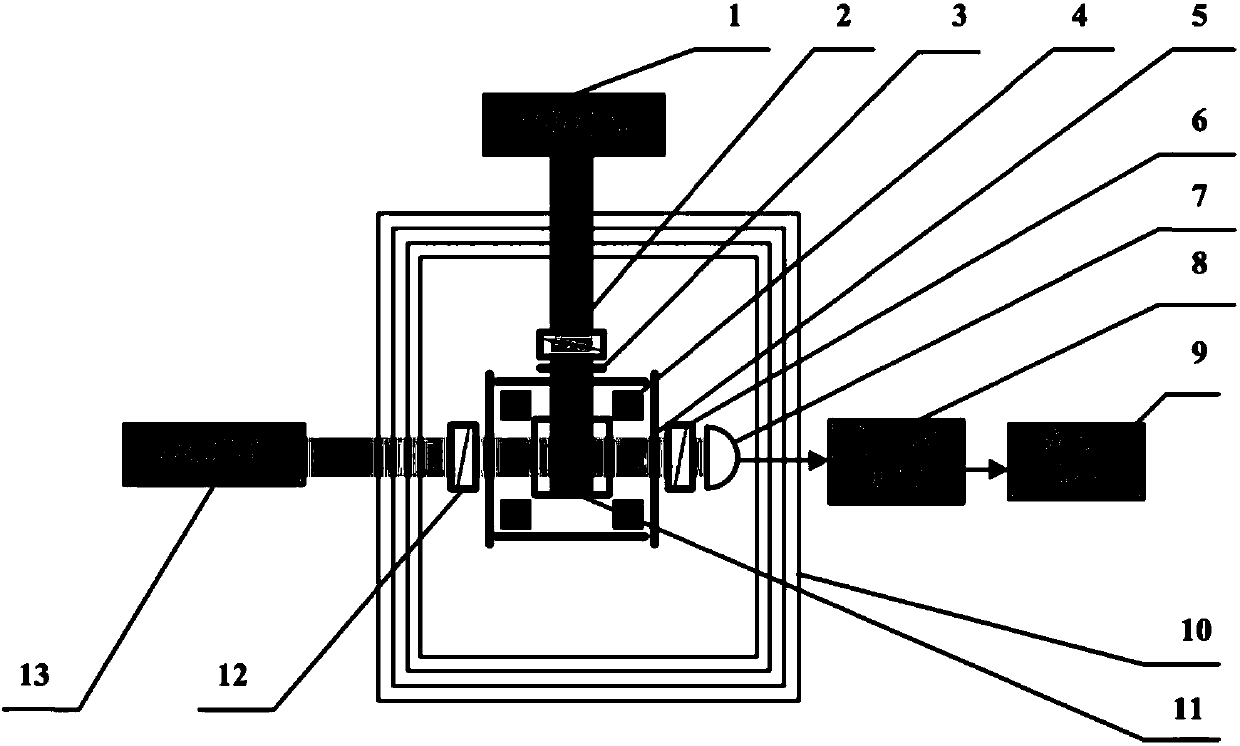
PendingCN113959425AImprove bias stabilityImprove performanceTurn-sensitive devicesData processingParticle physics
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting a residual rotation optical angle of an atomic spin gyroscope, which comprises the following steps of: emitting detection laser from a detection laser, sequentially passing through an optical isolator ISO, a polarizer, a 1 / 2 wave plate and a polarization analyzer to become linearly polarized light, entering an alkali metal gas chamber, and emitting the linearly polarized light carrying angular rate information out of the gas chamber through a small hole in a magnetic shielding layer, dividing emergent detection light into two independent beams of detection light through a liquid crystal phase delayer and a Wollaston prism, receiving the two independent beams of detection light by two photoelectric detectors, transmitting thetwo independent beams of detection light to a data processing unit through a lock-in amplifier, and enabling the data processing unit to control a detection laser through a laser tube temperature controller; using the liquid crystal controller to controll the liquid crystal phase delayer to suppress the residual rotation angle, so that the signal bias of the gyroscope is reduced, the zero-bias stability of the gyroscope is improved, and the comprehensive performance of the gyroscope is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com