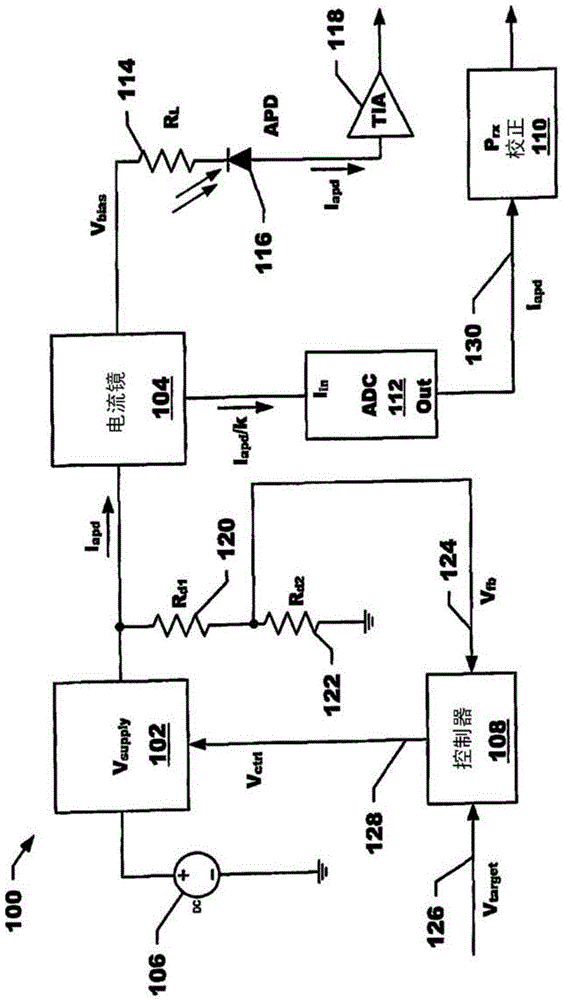
Avalanche photo diode detector systems
A diode detector, avalanche photoelectric technology, applied in the direction of using electric radiation detectors for photometry, electrical components, measurement circuits, etc., can solve the problem of increased bit error rate and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
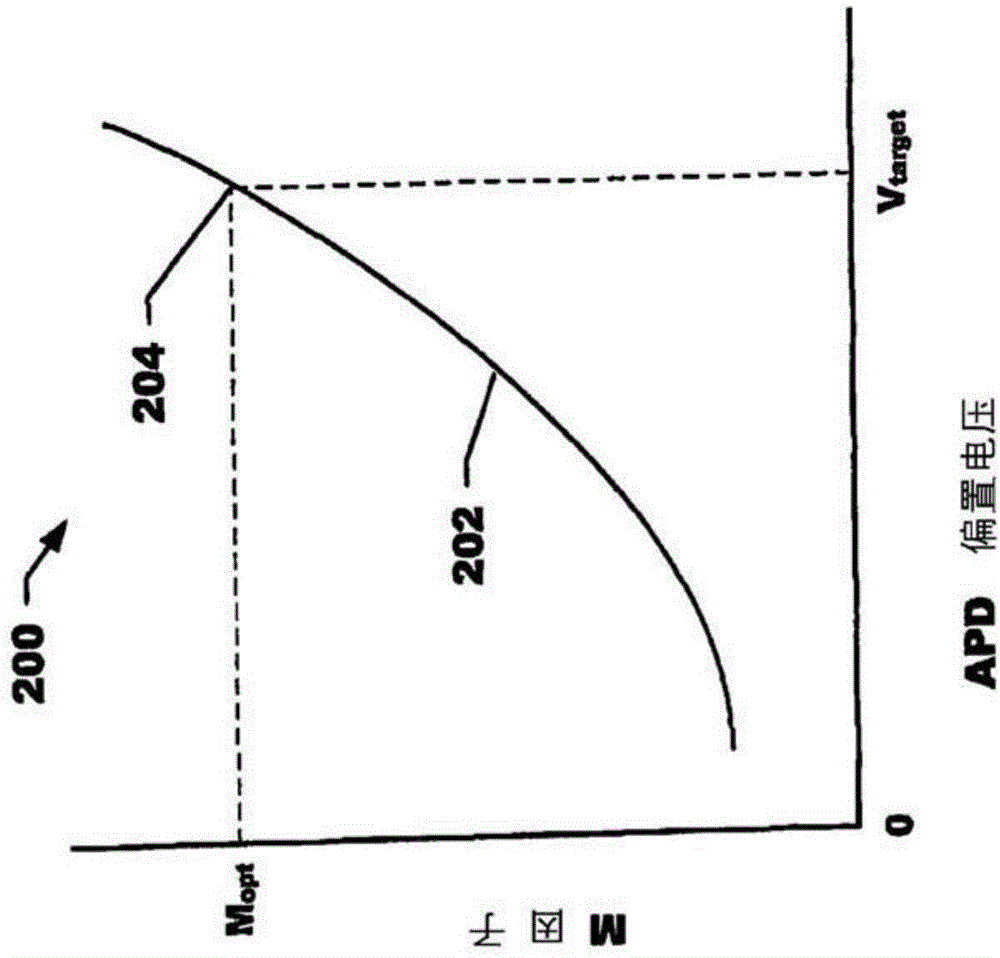
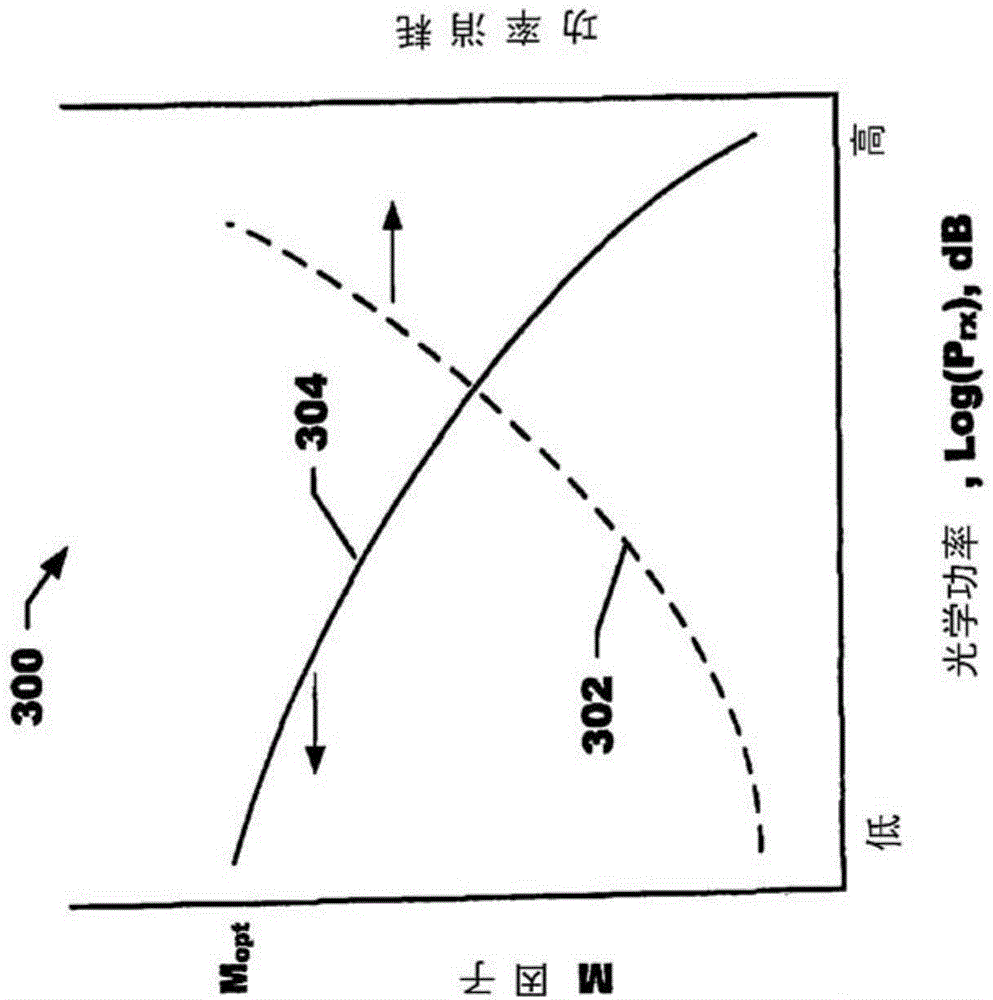
[0022] discussed with reference to prior art Figure 1-3 . Figure 4 is a graph 400 of the multiplication factor M as a function of APD bias voltage for an example control system embodiment. Plot 402 illustrates the variation of the M factor with applied bias voltage for the APD. A point 404 on the plot 402 is selected to yield the most desired working M factor M opt The high voltage (V H ) working point. This M factor is chosen for operation at the lowest suitable input optical power level and gives a sufficient output data signal level. For high input power levels at M min , plot 402 on corresponds to lower bias voltage V LAt point 406, under Work, select the second M factor. A lower M factor M was chosen for several considerations min . At high input optical power levels, the APD will generate large currents due to the higher illumination levels, and does not require a large M factor to generate sufficiently high output signal levels. In fact, operating the APD wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com