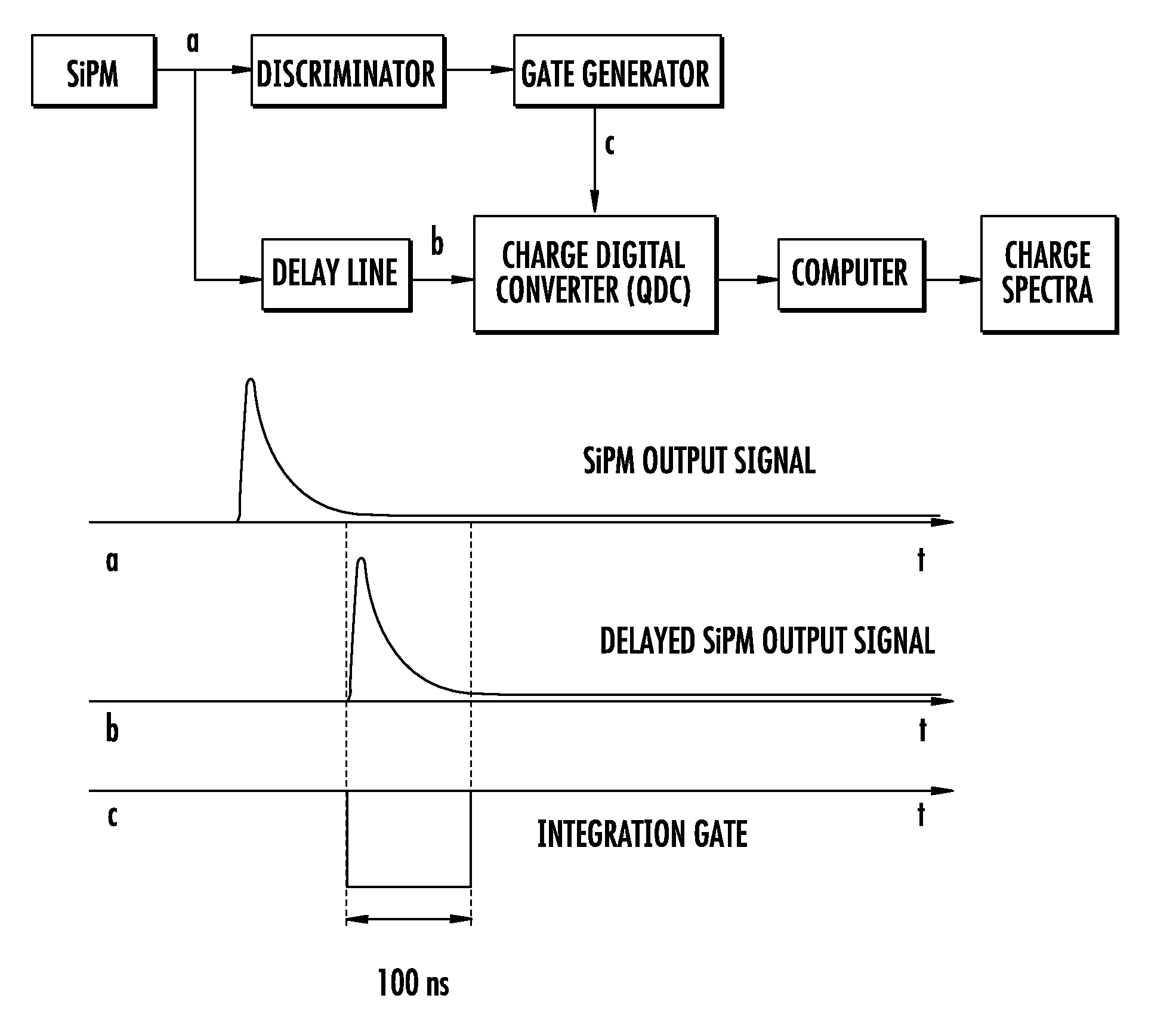
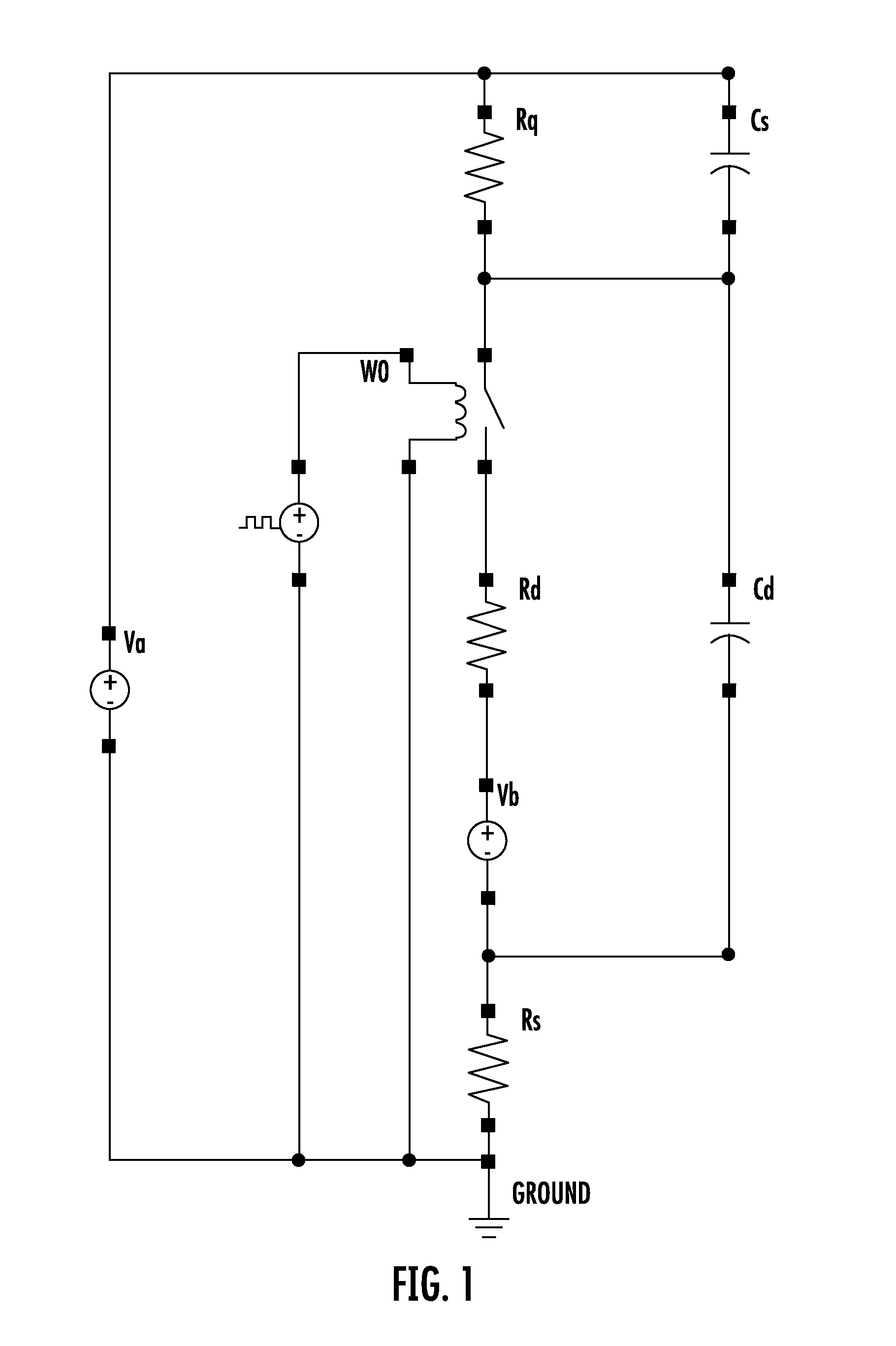
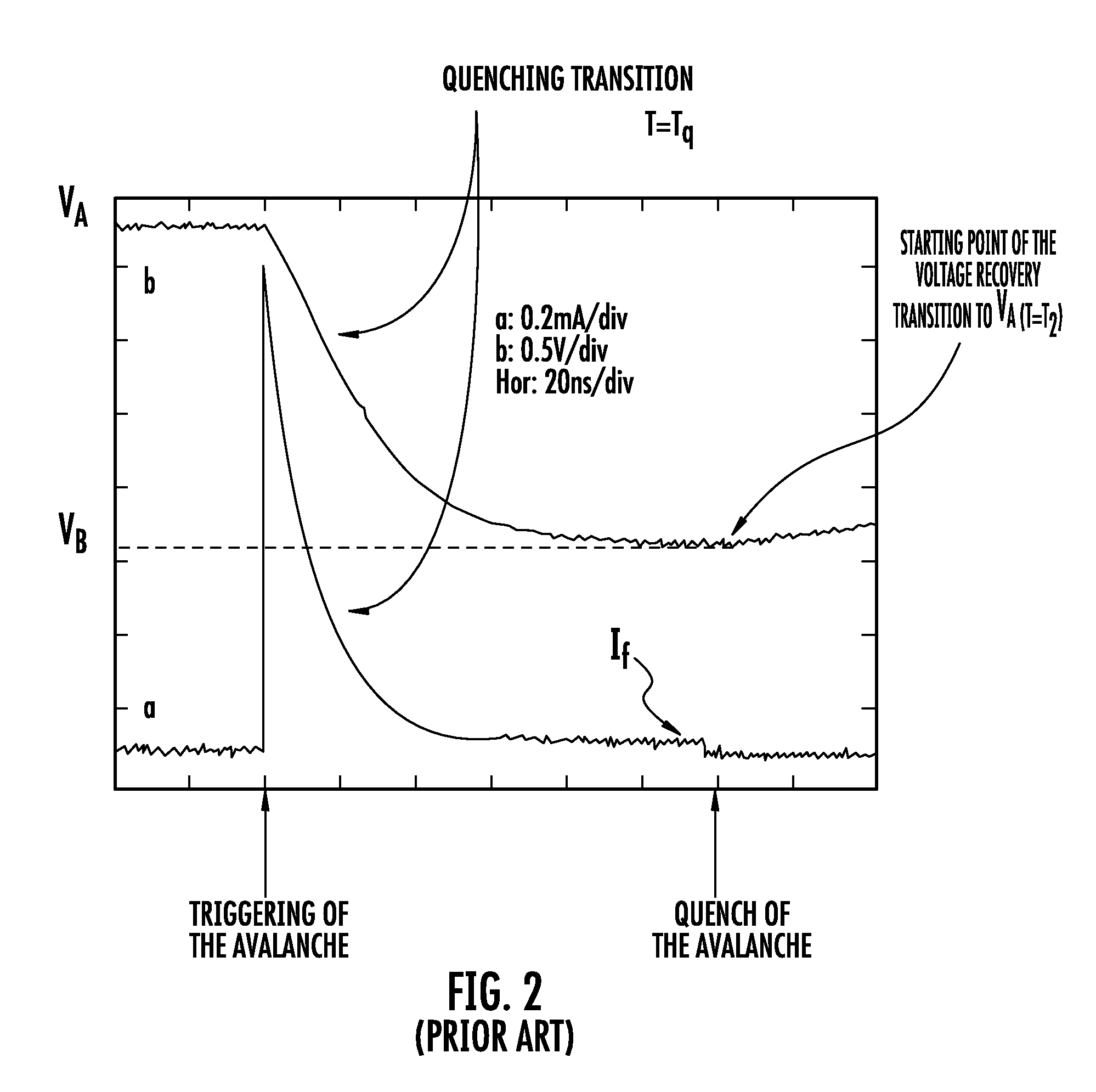
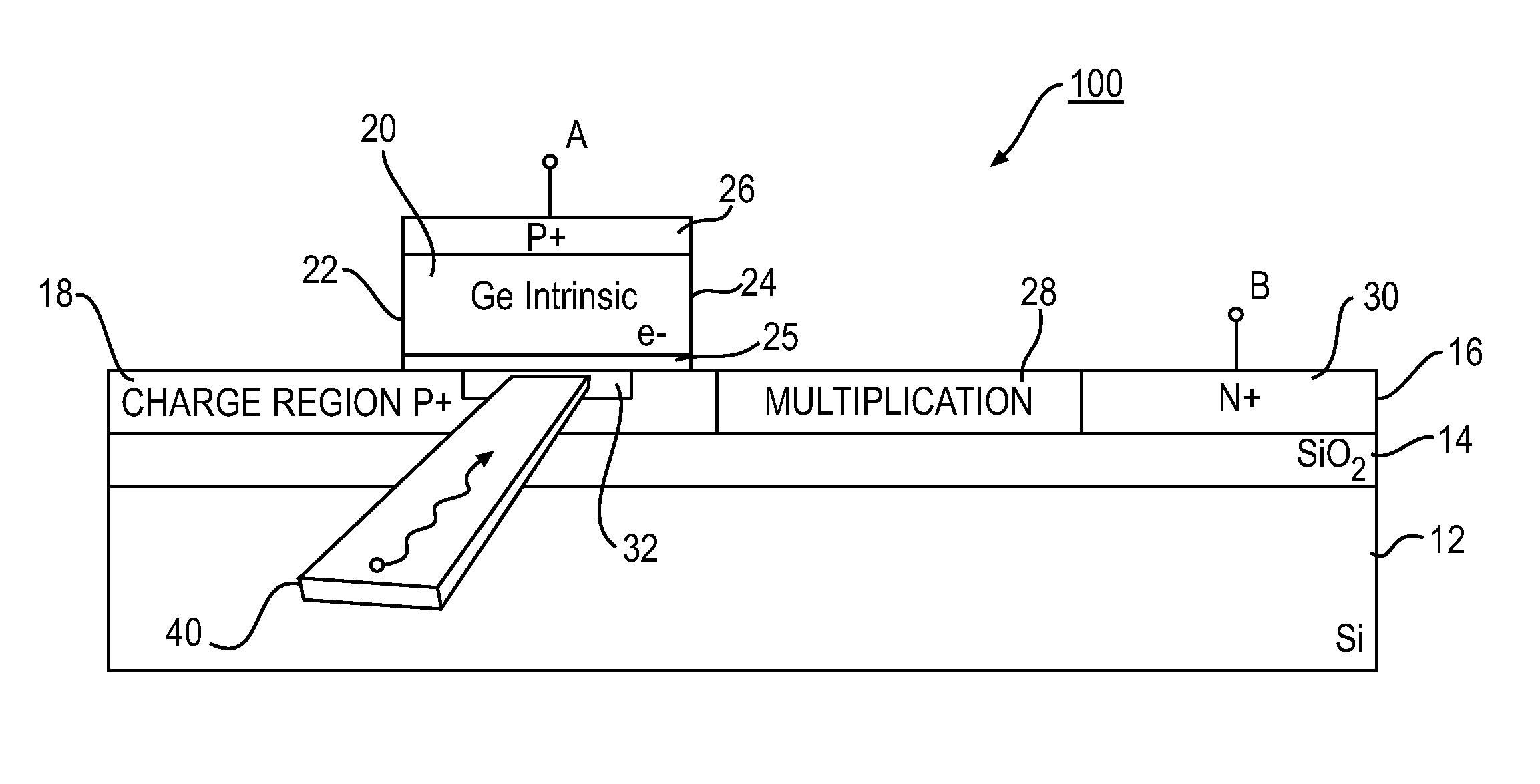
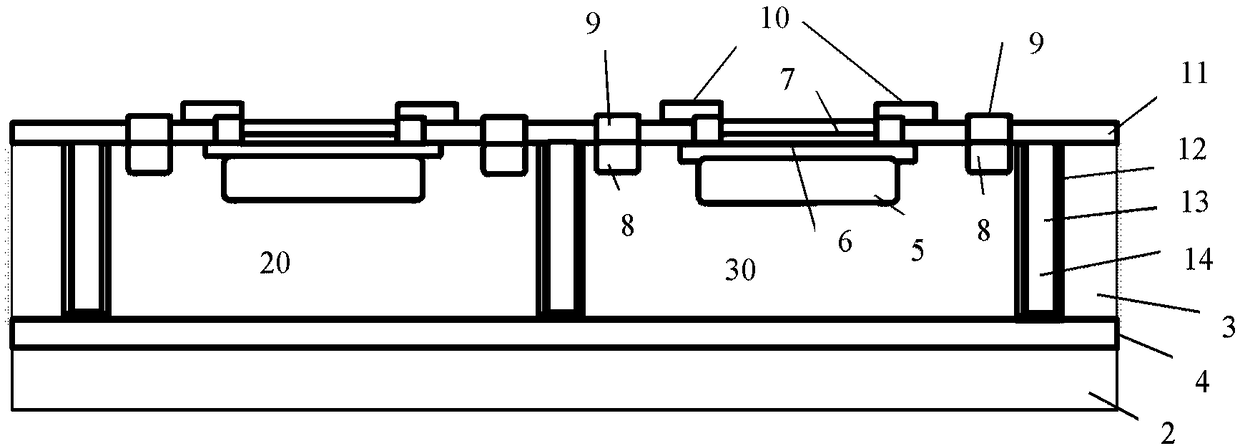
Patents
Literature
60 results about "APDS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Armour-piercing discarding sabot (APDS) is a type of kinetic energy projectile fired from a rifled-barrel gun to attack armoured targets. APDS rounds are sabot rounds, firing a spin-stabilized armor penetrating sub-projectile, and were commonly used in large calibre tank guns, up until the early 1980s, but have now been superseded by armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS) projectiles used in smooth-bore guns, firing a fin-stabilized armor penetrating sub-projectile. However, APDS rounds are still commonly used in small or medium calibre weapon systems. For a given calibre, this type of ammunition can effectively double the armour penetration of a gun, compared to those firing armour-piercing (AP), armour-piercing, capped (APC), or armour-piercing, capped, ballistic capped (APCBC) projectiles. The saboted light armour penetrator (SLAP) concept applies this technology to small arms calibres.
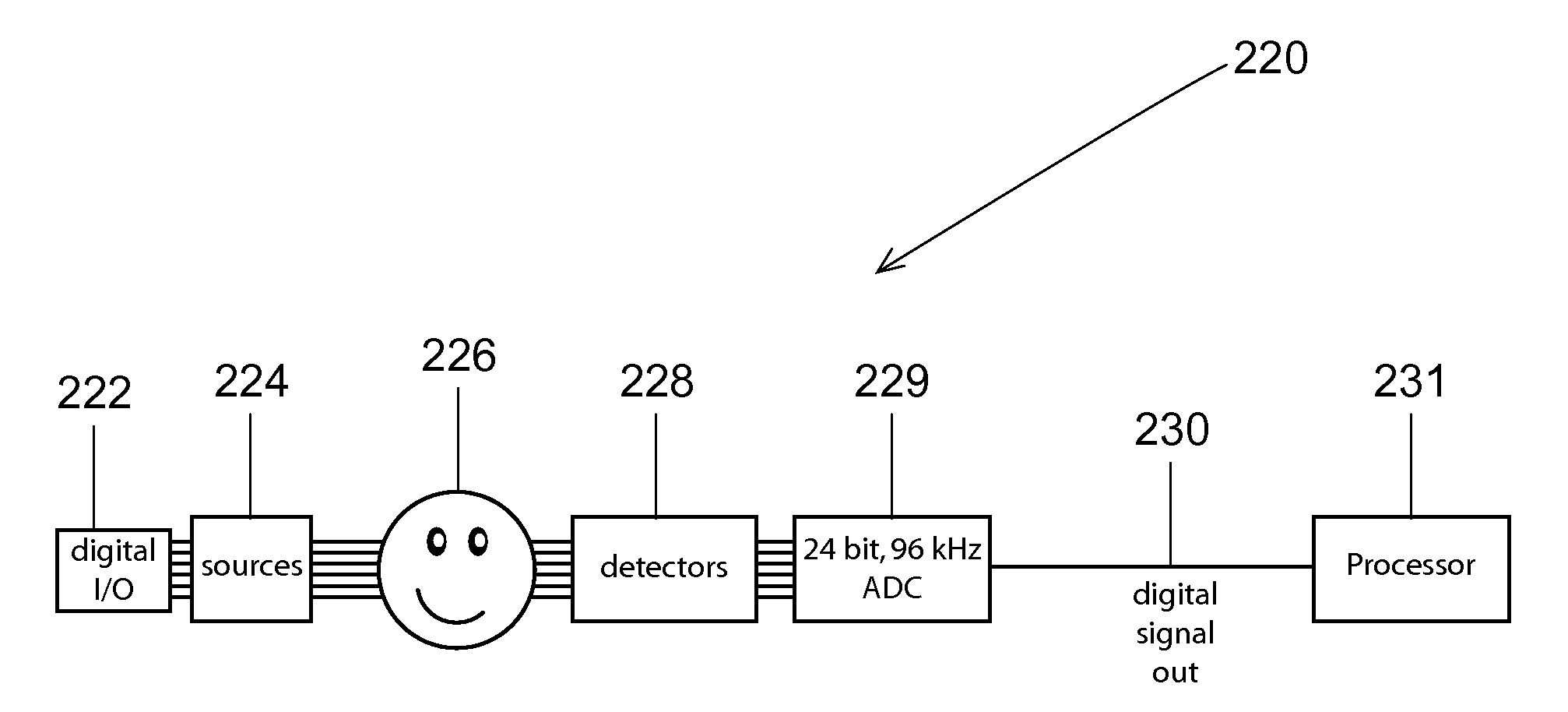
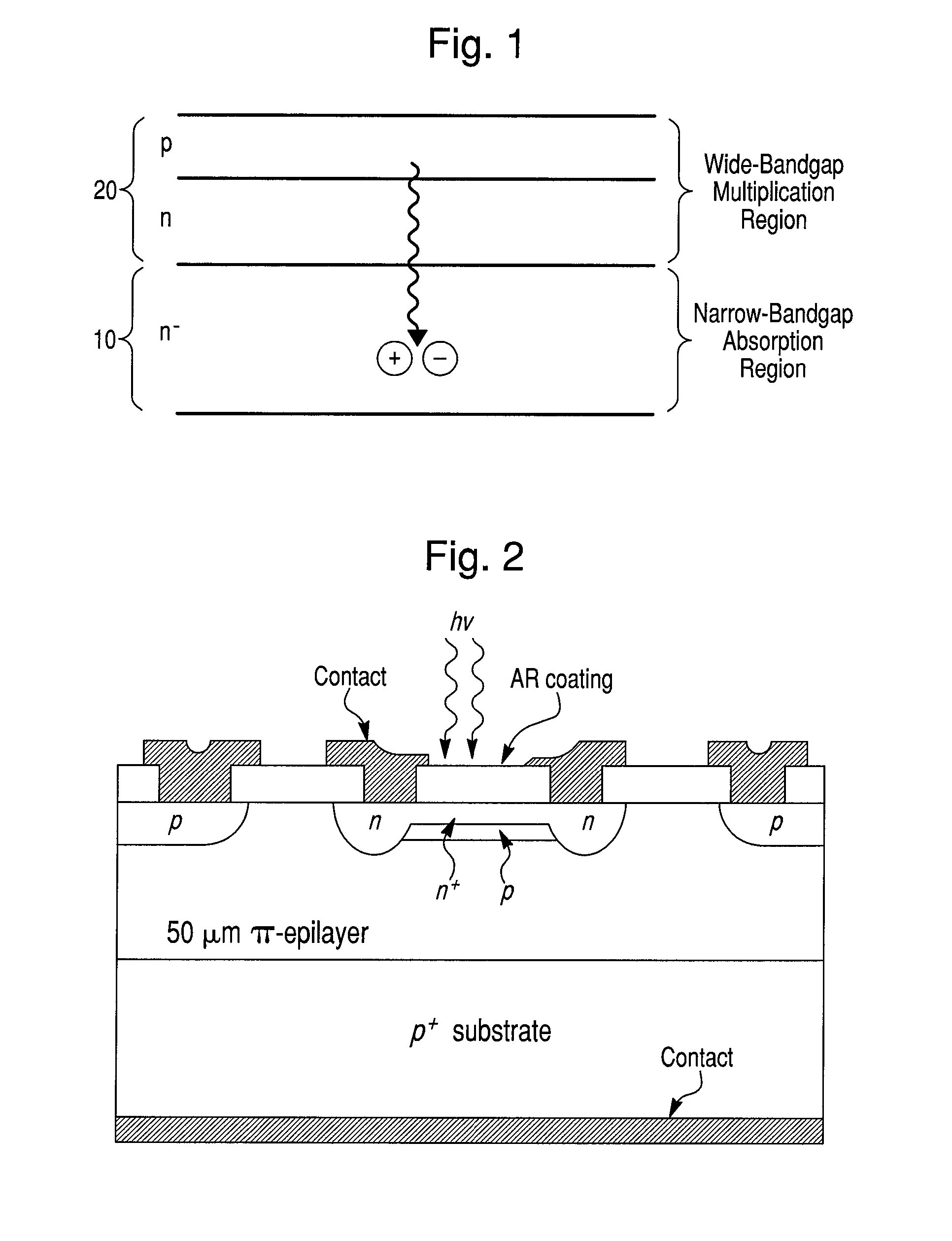
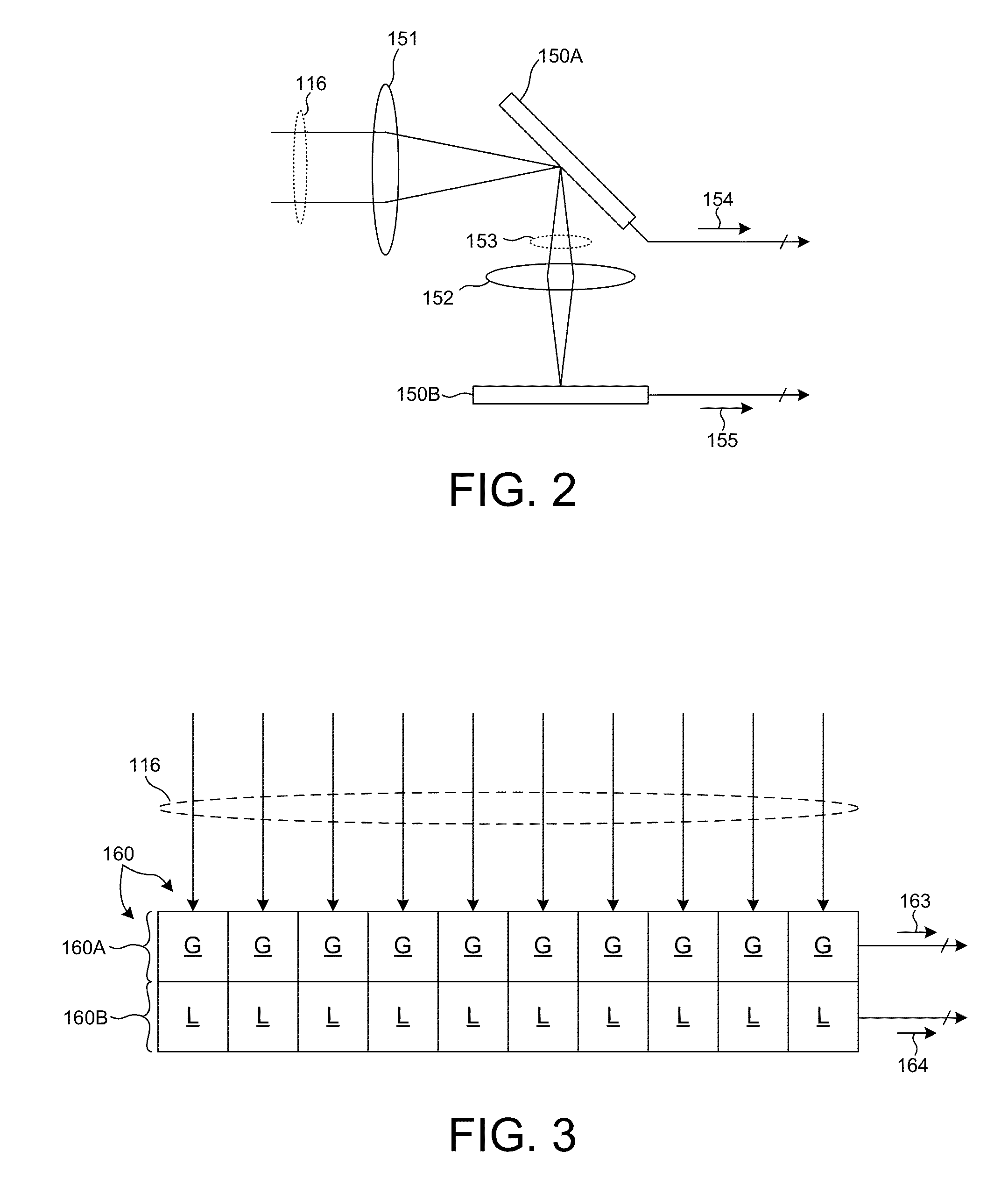
High performance imaging system for diffuse optical tomography and associated method of use
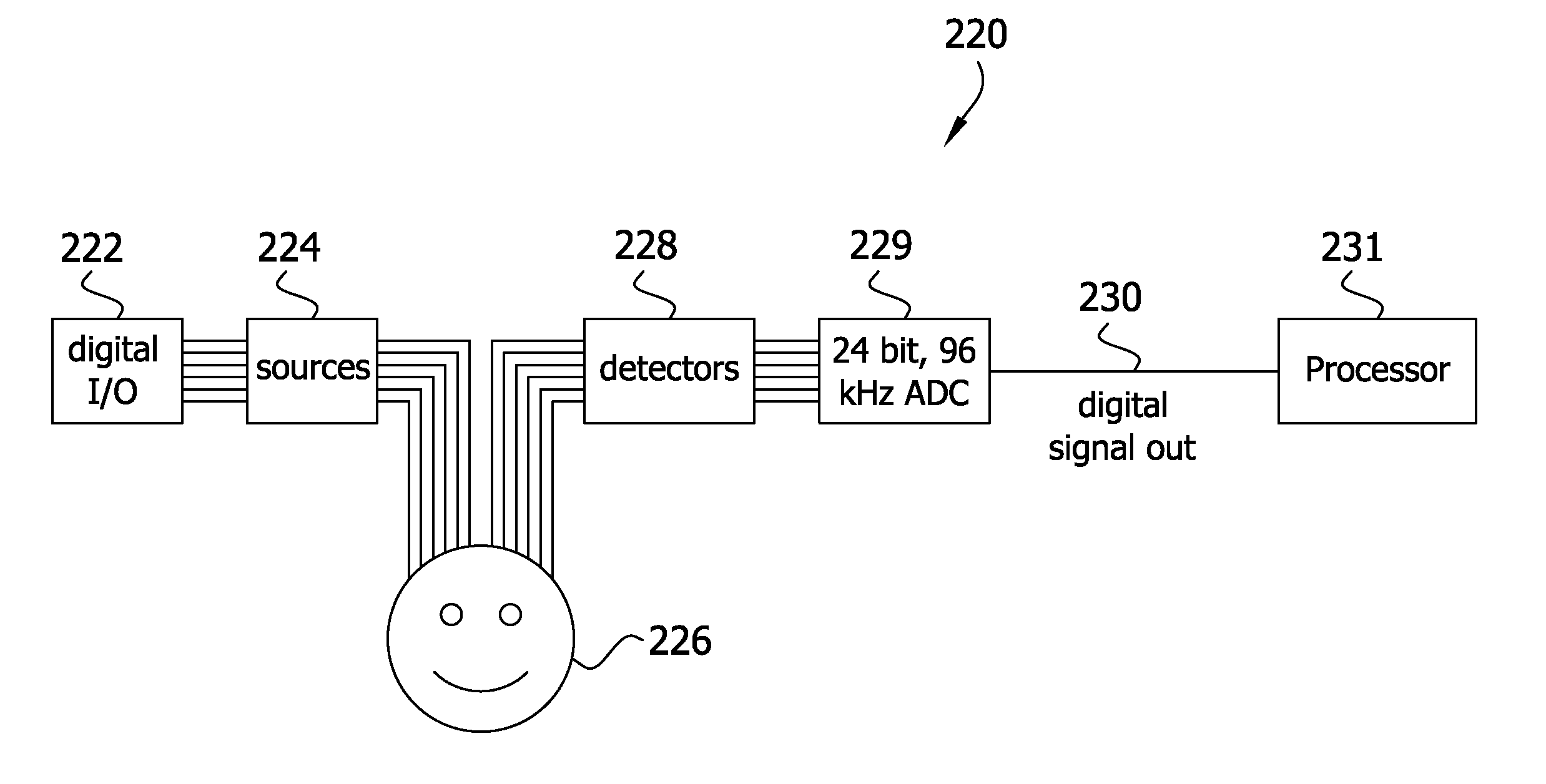
ActiveUS7983740B2High bandwidthImprove performanceDiagnostics using tomographySensorsOptical tomographyImaging quality
A high performance imaging system for diffuse optical tomography is disclosed. A dense grid utilizing sources, e.g., light emitting diodes (“LEDs”), that achieve high performance at high speed with a high dynamic range and low inter-channel crosstalk are complemented by a system of discrete, isolated receivers, e.g., avalanche photodiodes (“APDs”). The source channels have dedicated reconfigurable encoding control signals, and the detector channels have reconfigurable decoding, allowing maximum flexibility and optimal mixtures of frequency and time encoding and decoding. Each detector channel is analyzed by dedicated, isolated, high-bandwidth receiver circuitry so that no channel gain switching is necessary. The resulting improvements to DOT system performance, e.g., increased dynamic range and decreased crosstalk, enable higher density imaging arrays and provide significantly enhanced DOT image quality. A processor can be utilized to provide sophisticated three dimensional modeling as well as noise reduction.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
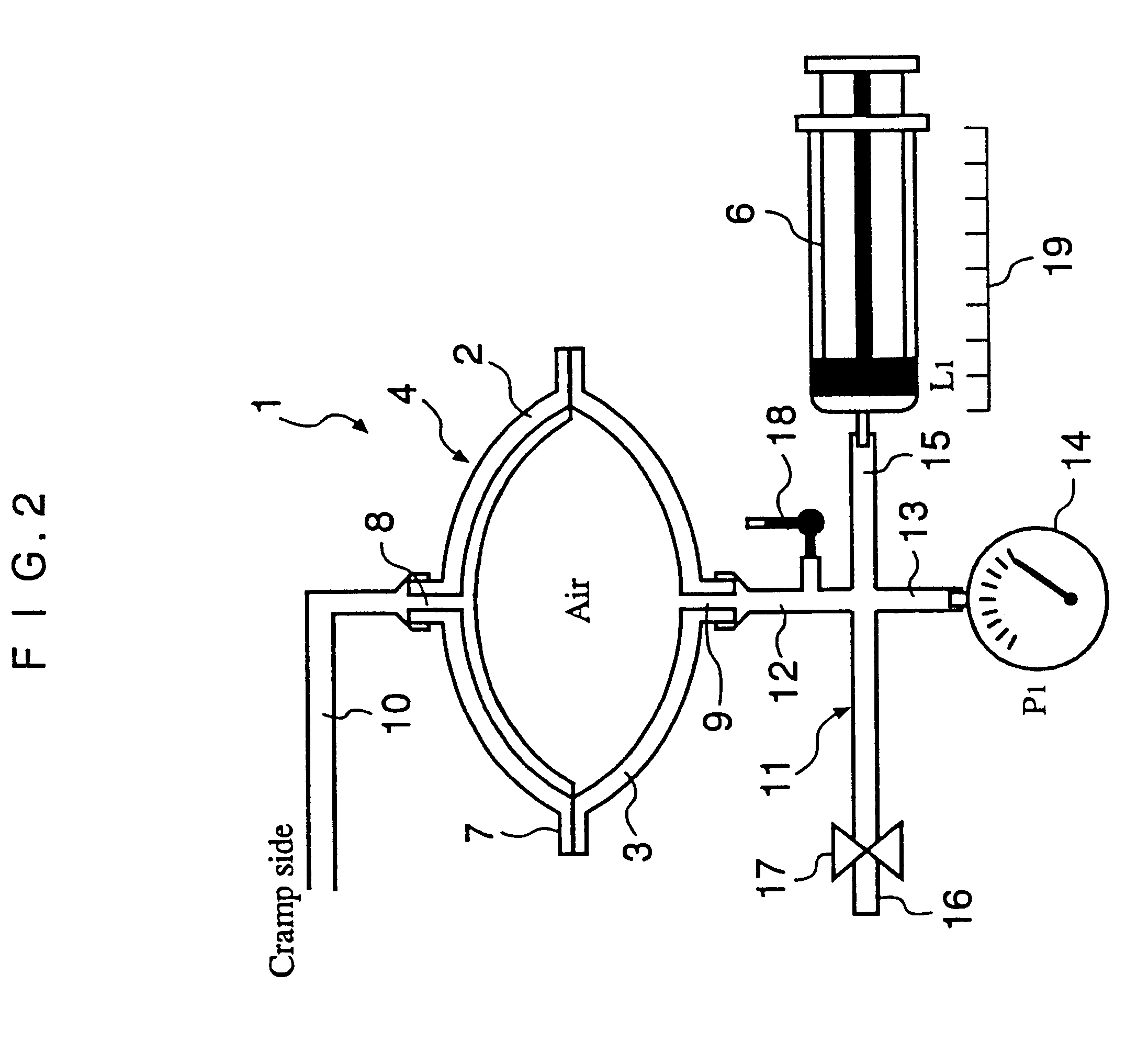
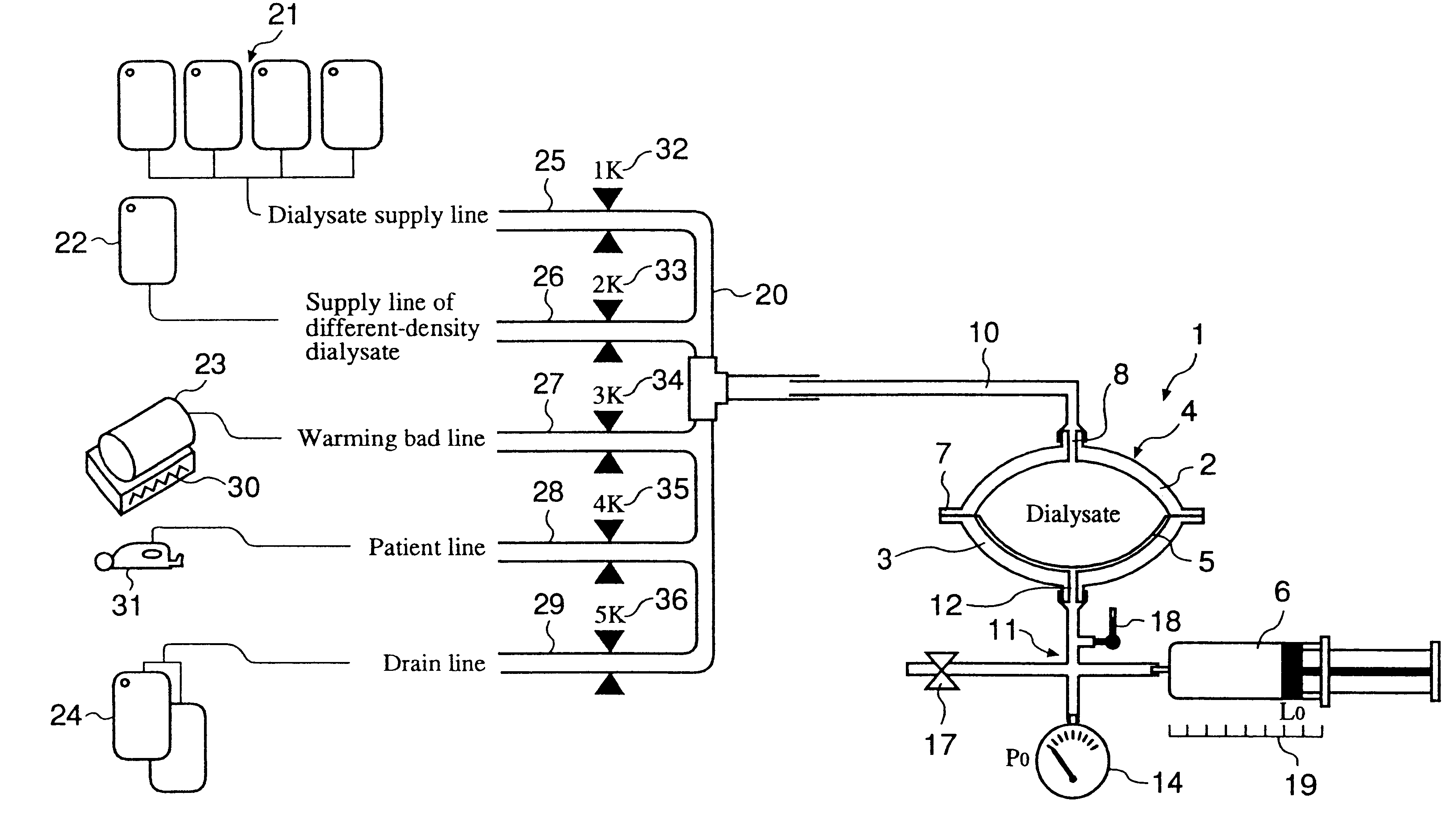
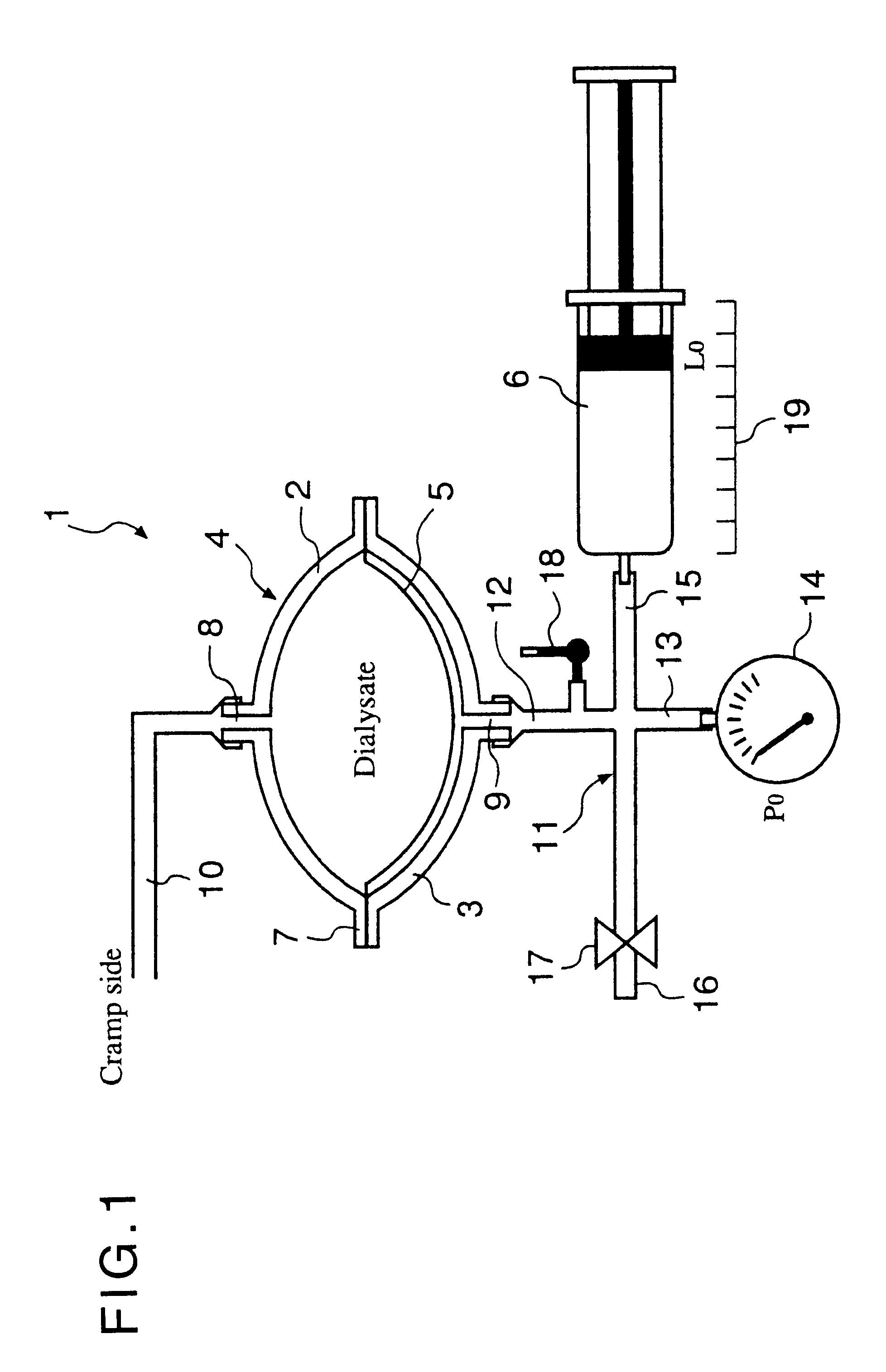
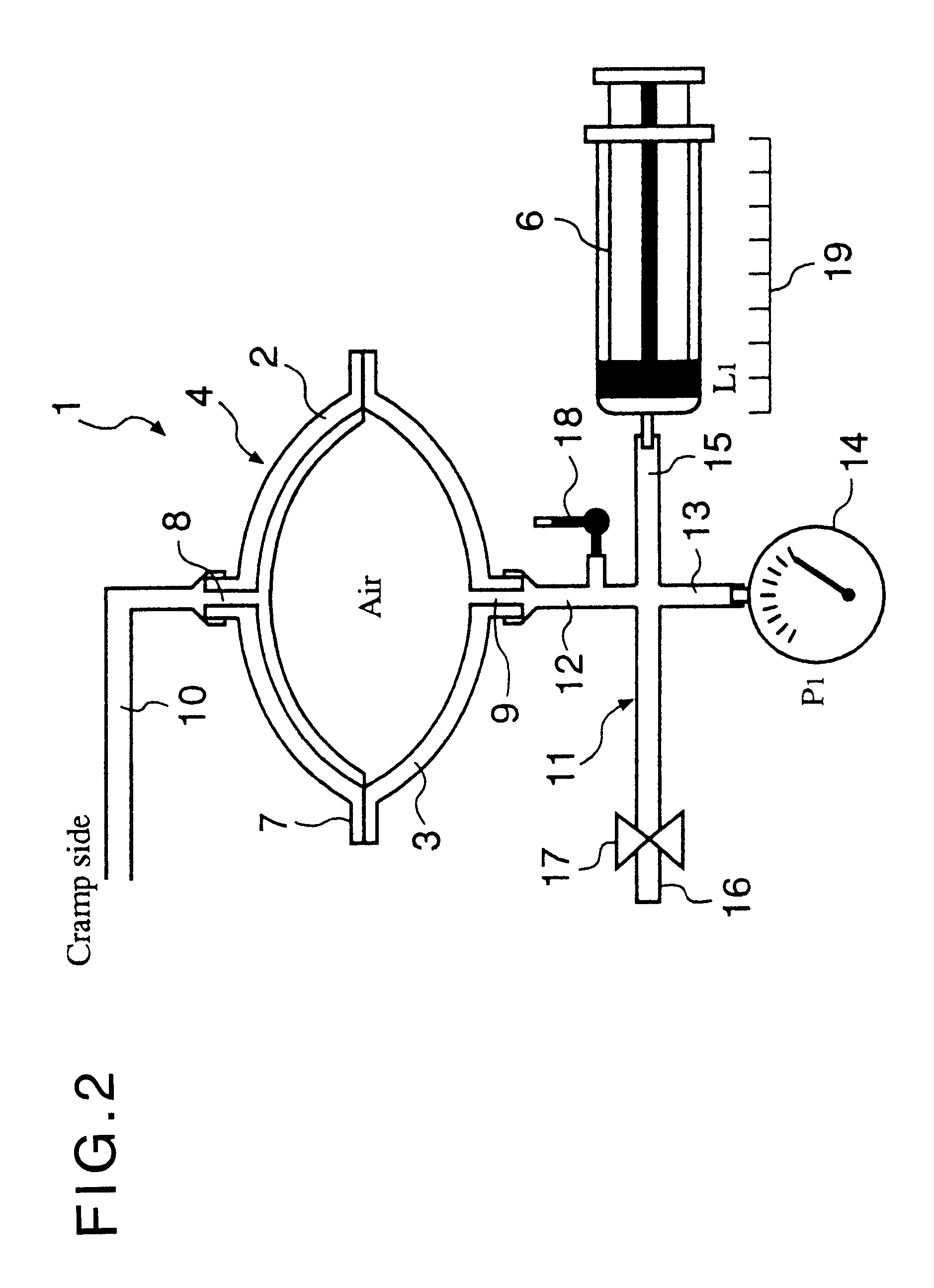
Automated solution injection-discharge system and automated peritoneal dialysis system
InactiveUS6491658B1Easy to controlOperational securityPeritoneal dialysisIntensive care medicineDialysis fluid
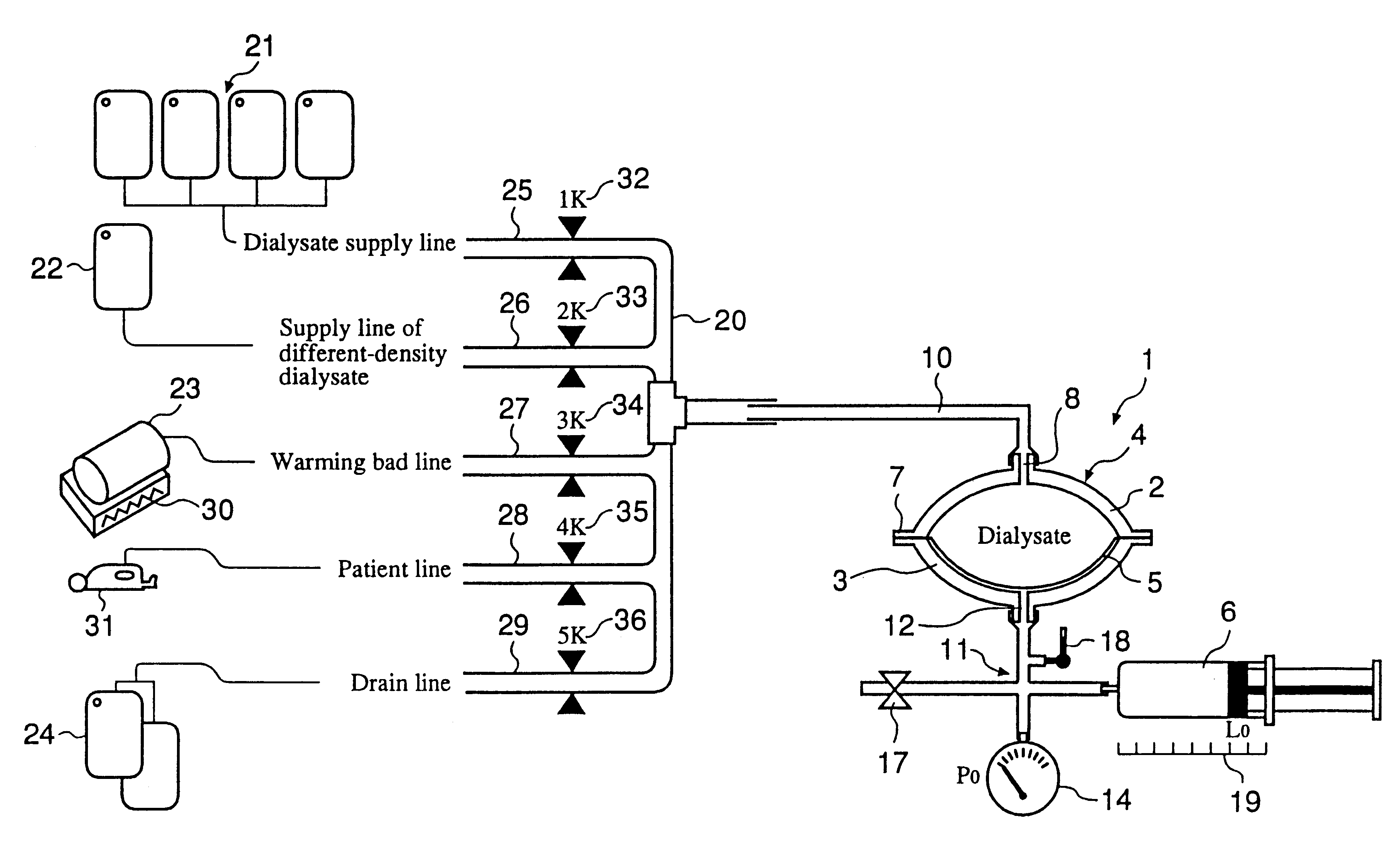
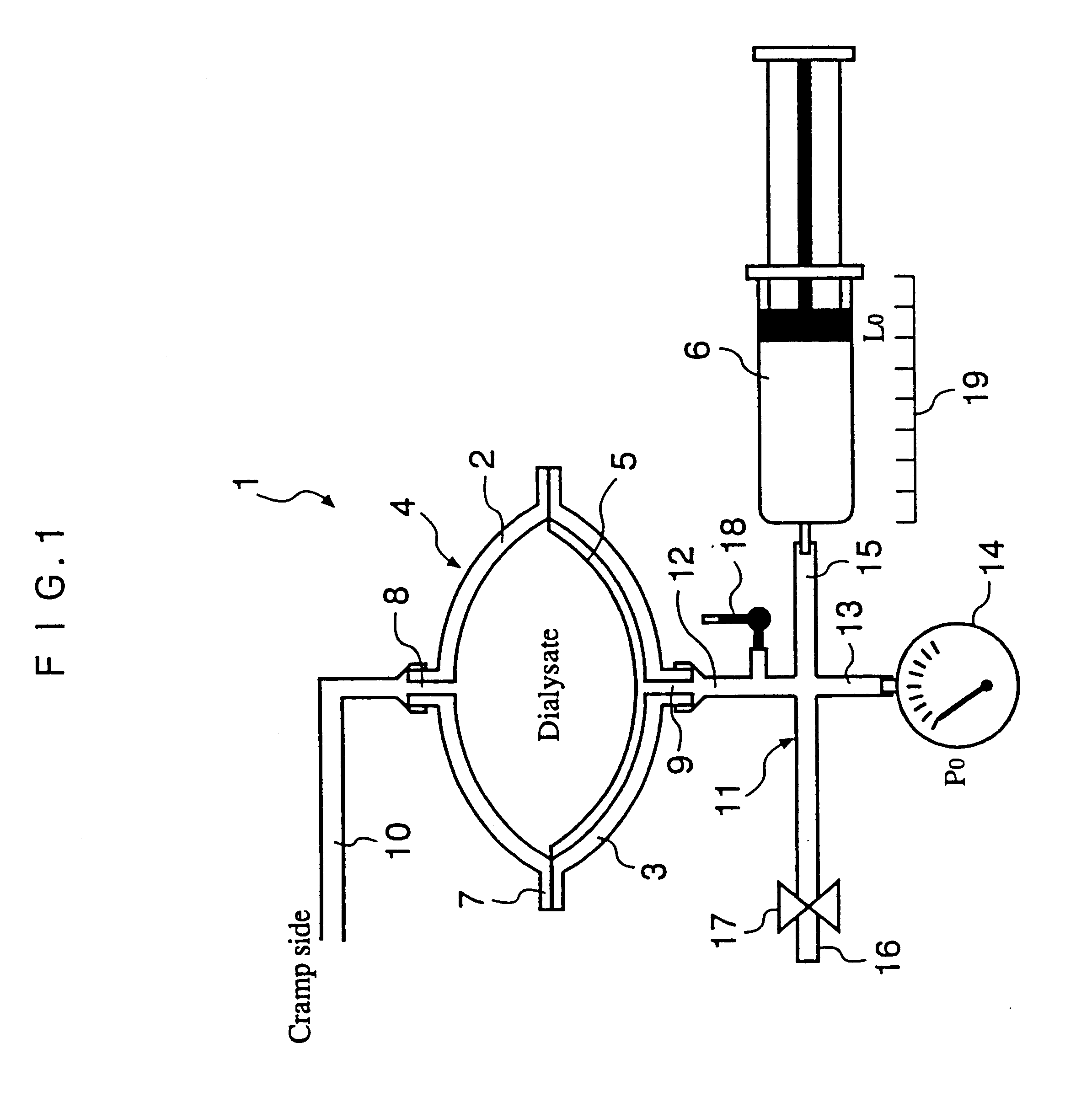
The automated solution injection-discharge system is used as an APDS system to supply and discharge a dialysate and a patient's drain. And an automated solution injection-discharge system provides free of contamination and operation mistakes, and can accurately control the injected dialysate volume and the discharged dwell solution volume even when a patient does not maintain a fixed posture while replacing the solution.
Owner:JMS CO LTD
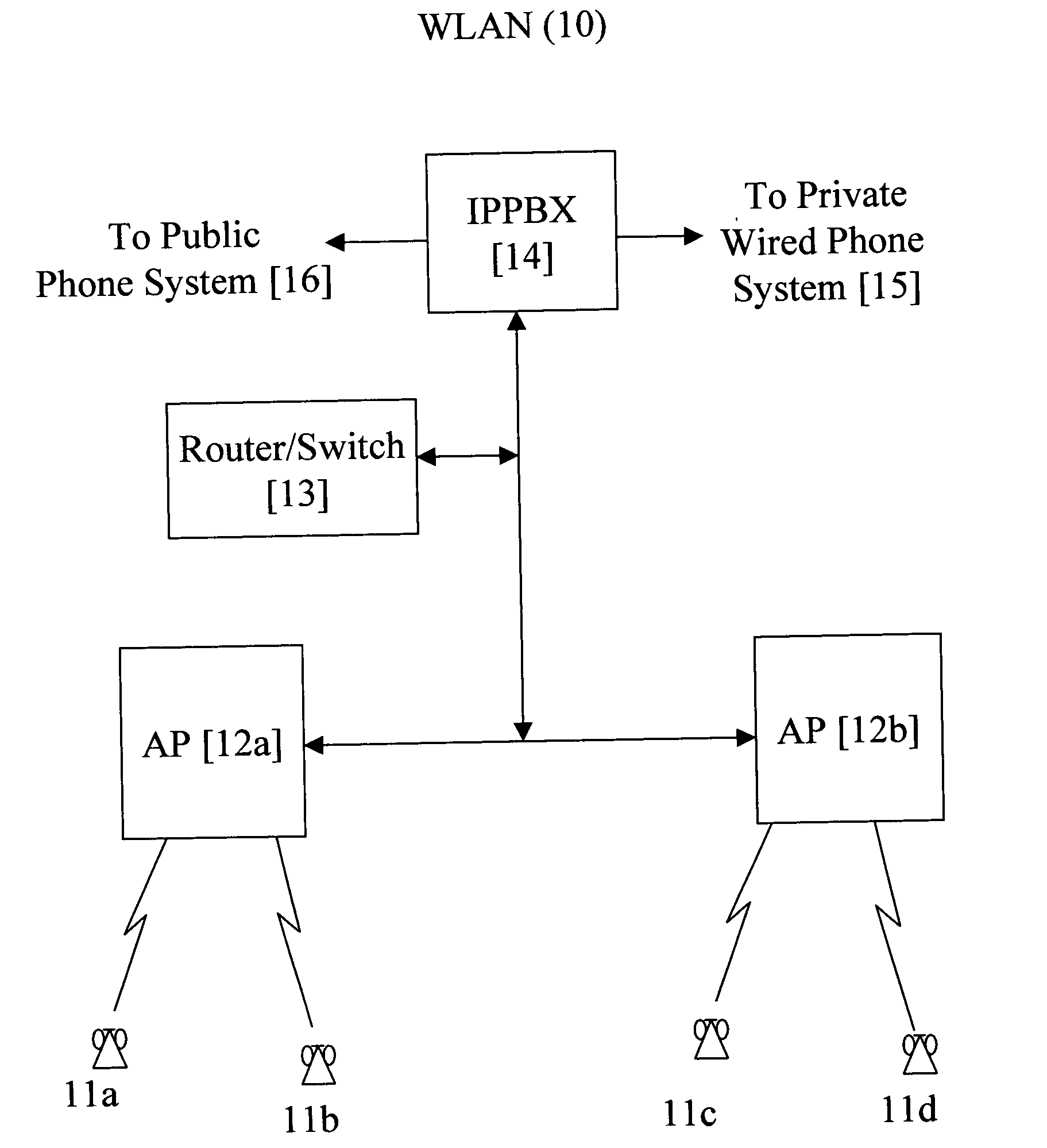
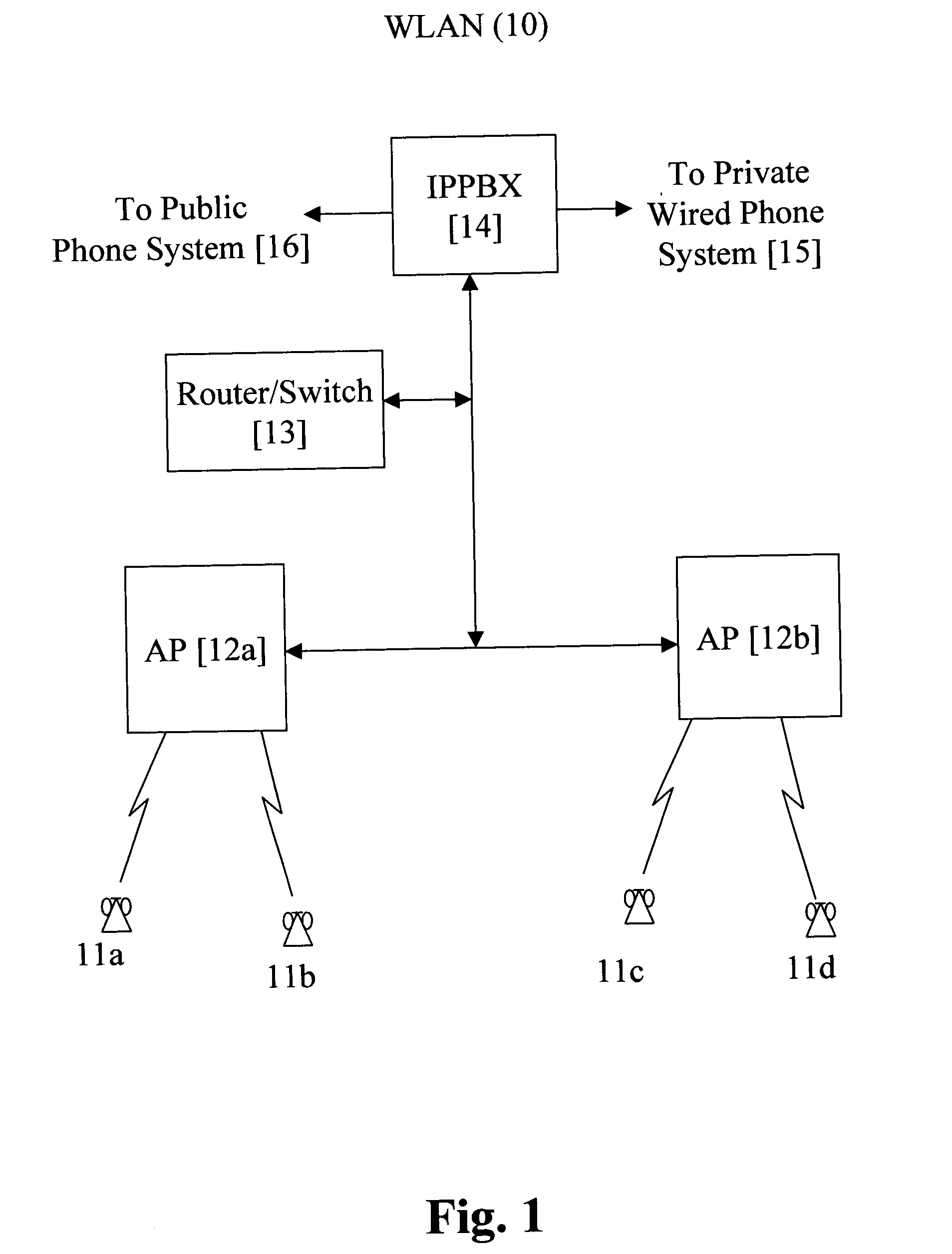
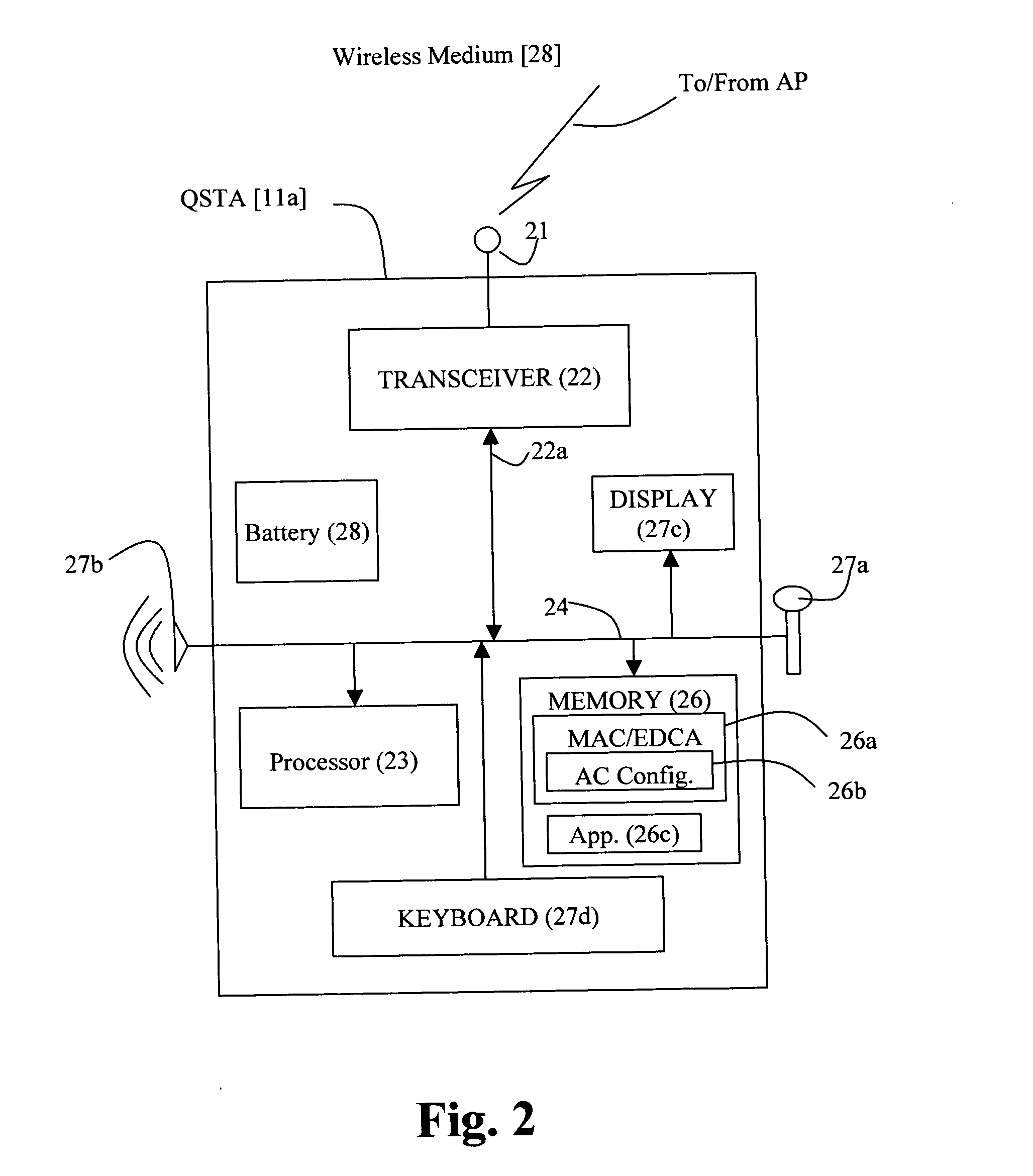
Method for actively synchronizing U-APSD service periods
InactiveUS20080101320A1Minimizes inter-service period timeNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsNetwork addressing
A wireless LAN environment includes at least one access point that supports a number of wireless communications devices which are configured to operate in the U-APSD mode. The transmission of packets by an access point to a wireless communications device operating in the U-APDS mode can be accomplished in an efficient manner by coordinating the unscheduled service periods of the wireless communication devices. The service periods are placed into a tightly packed list ordered according to a network address associated with each wireless communications device.
Owner:SPECTRALINK
Multi pixel photo detector array of geiger mode avalanche photodiodes
ActiveUS20120068050A1Possible to discriminateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A multi-pixel photodetector array may include a semiconductor substrate having a back side and a front side, Geiger mode avalanche photodiodes (GM-APDs) on the semiconductor substrate, each including an anode contact, and a common cathode for the GM-APDs and having a first connection lead on the backside of the semiconductor substrate. The multi-pixel photodetector array may include a second connection lead, and a common anode on the front side of the semiconductor substrate and configured to couple in common the anode contacts of the GM-APDs to the second connection lead. Each GM-APD may be configured to generate, when a photon impinges thereon, a current pulse of different shape for discrimination by an external circuit connected to the common cathode and the common anode.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Two-dimensional APDs and SPADs and related methods
ActiveUS9391225B1Great amplificationEasy to measureCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesImpact ionizationPhoton
Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) and single photon avalanche detectors (SPADs) are provided with a lateral multiplication region that provides improved amplification through increased impact ionization.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Automated solution injection-discharge system and automated peritoneal dialysis system (APDS)
InactiveUS6488647B1Easy to controlOperational securityPeritoneal dialysisIntensive care medicineDialysis fluid
The automated solution injection-discharge system is used as an APDS system to supply and discharge a dialysate and a patient's drain. And an automated solution injection-discharge system provides free of contamination and operation mistakes, and can accurately control the injected dialysate volume and the discharged dwell solution volume even when a patient does not maintain a fixed posture while replacing the solution.
Owner:MIURA HIROMU +1
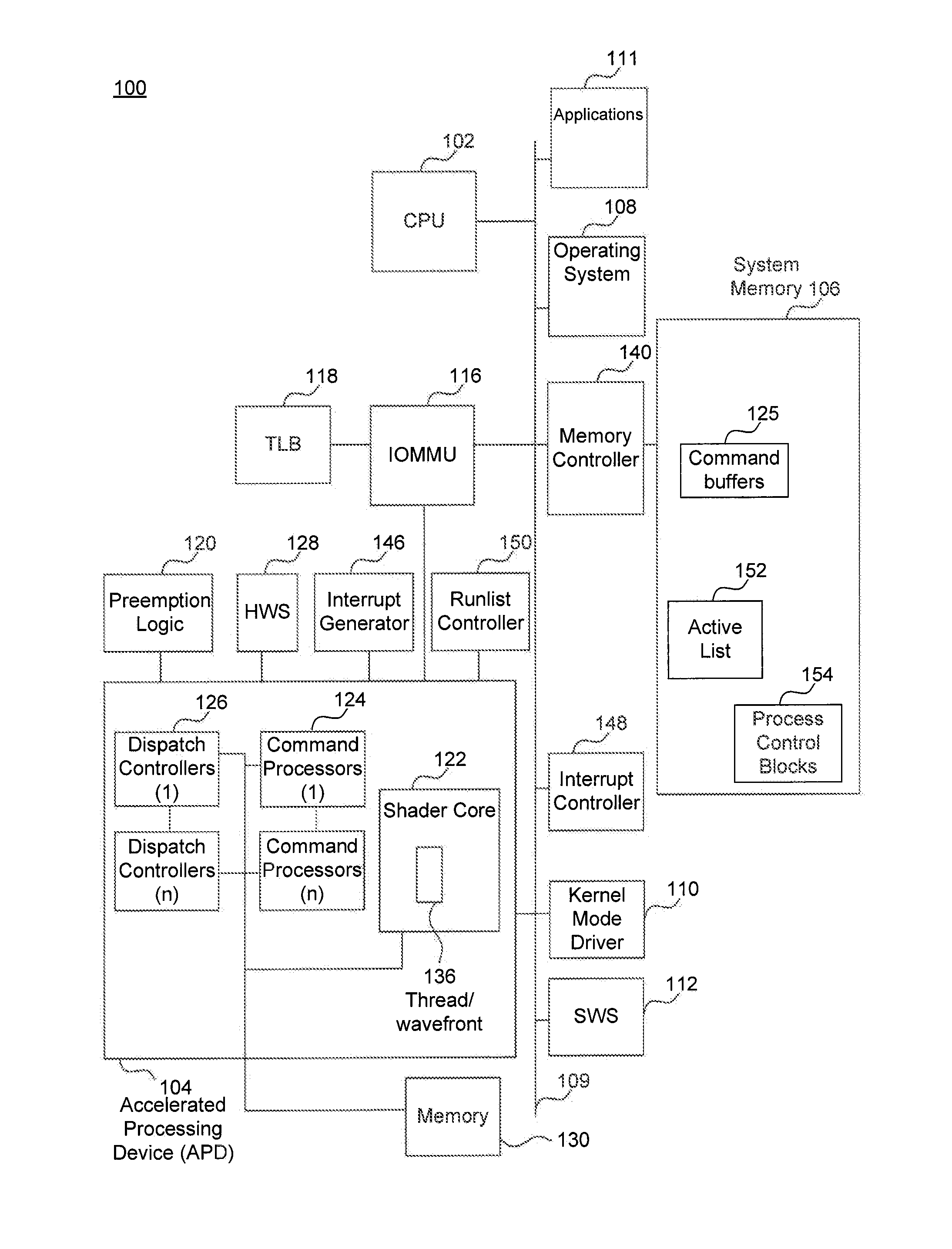
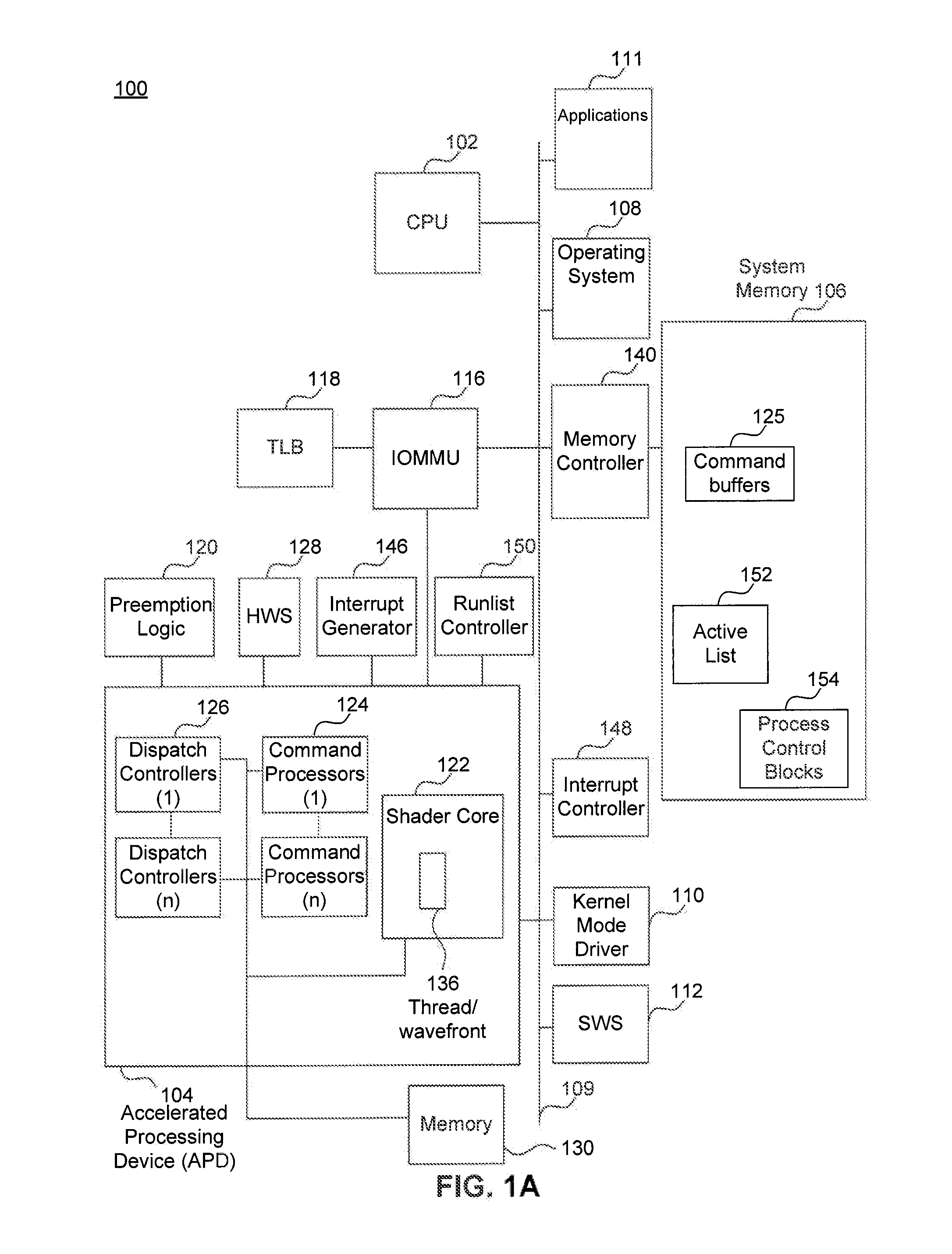
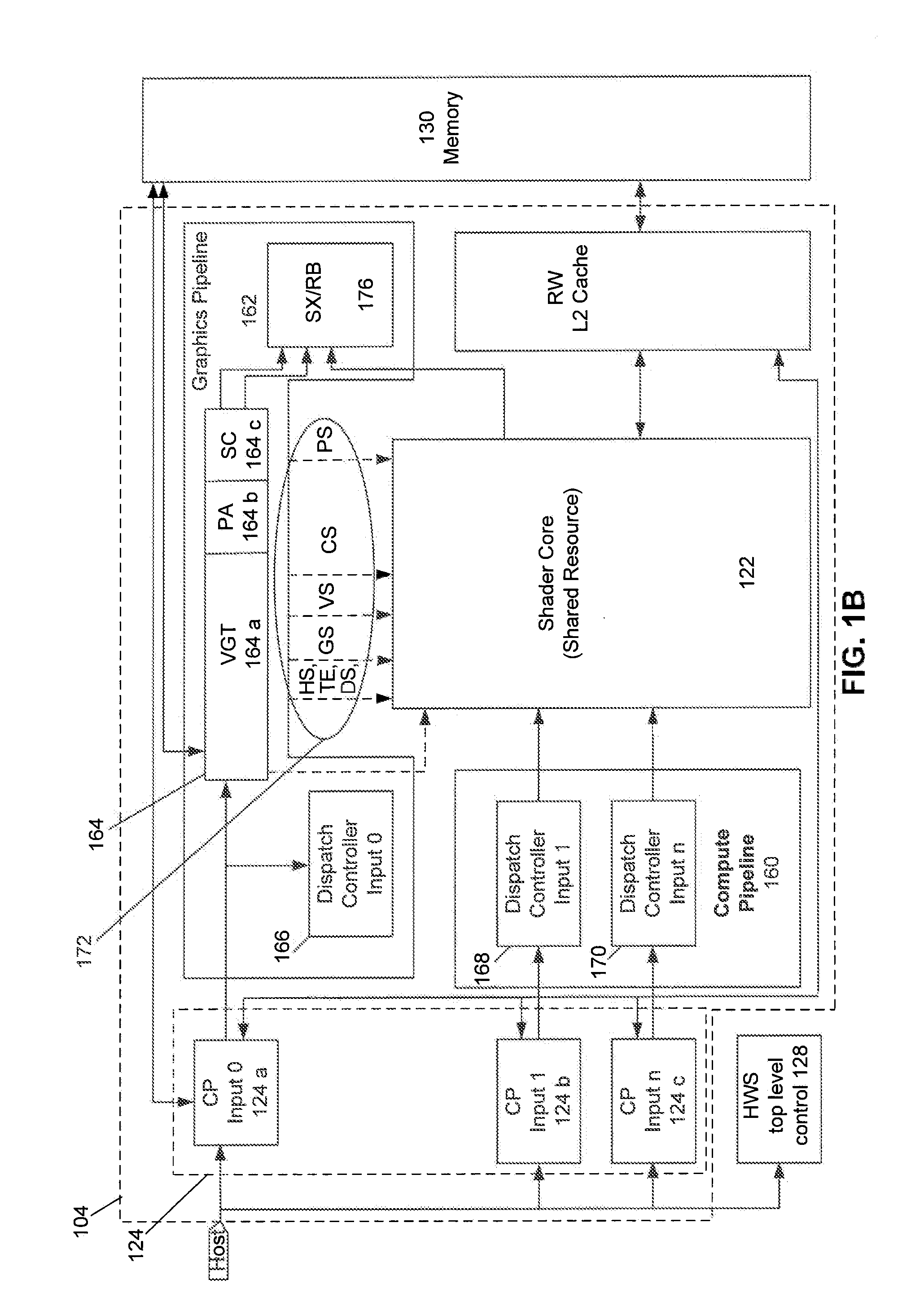
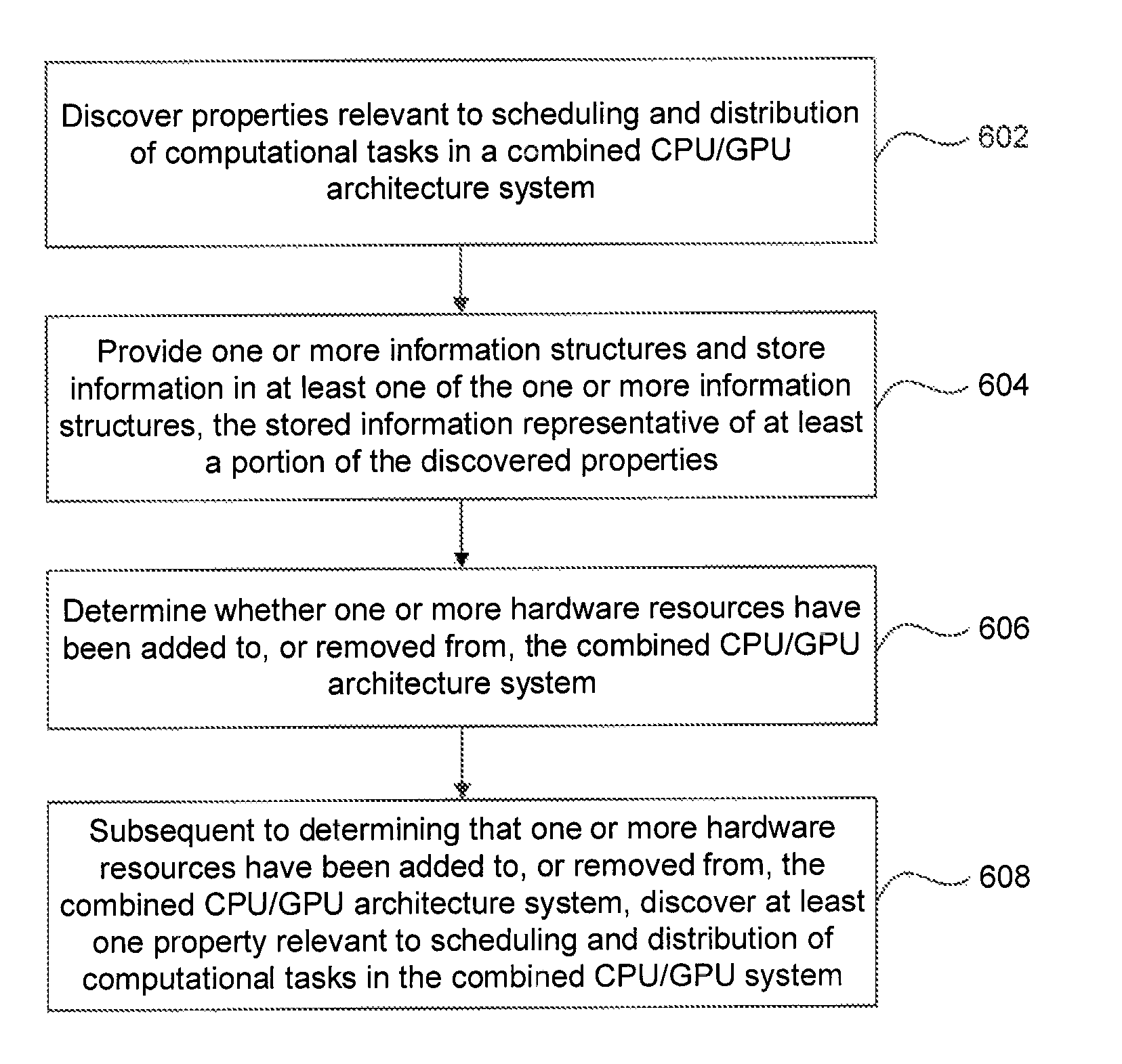
Device Discovery and Topology Reporting in a Combined CPU/GPU Architecture System
ActiveUS20120162234A1Efficient schedulingEffective distributionDigital computer detailsImage memory managementSystem topologyOperating system
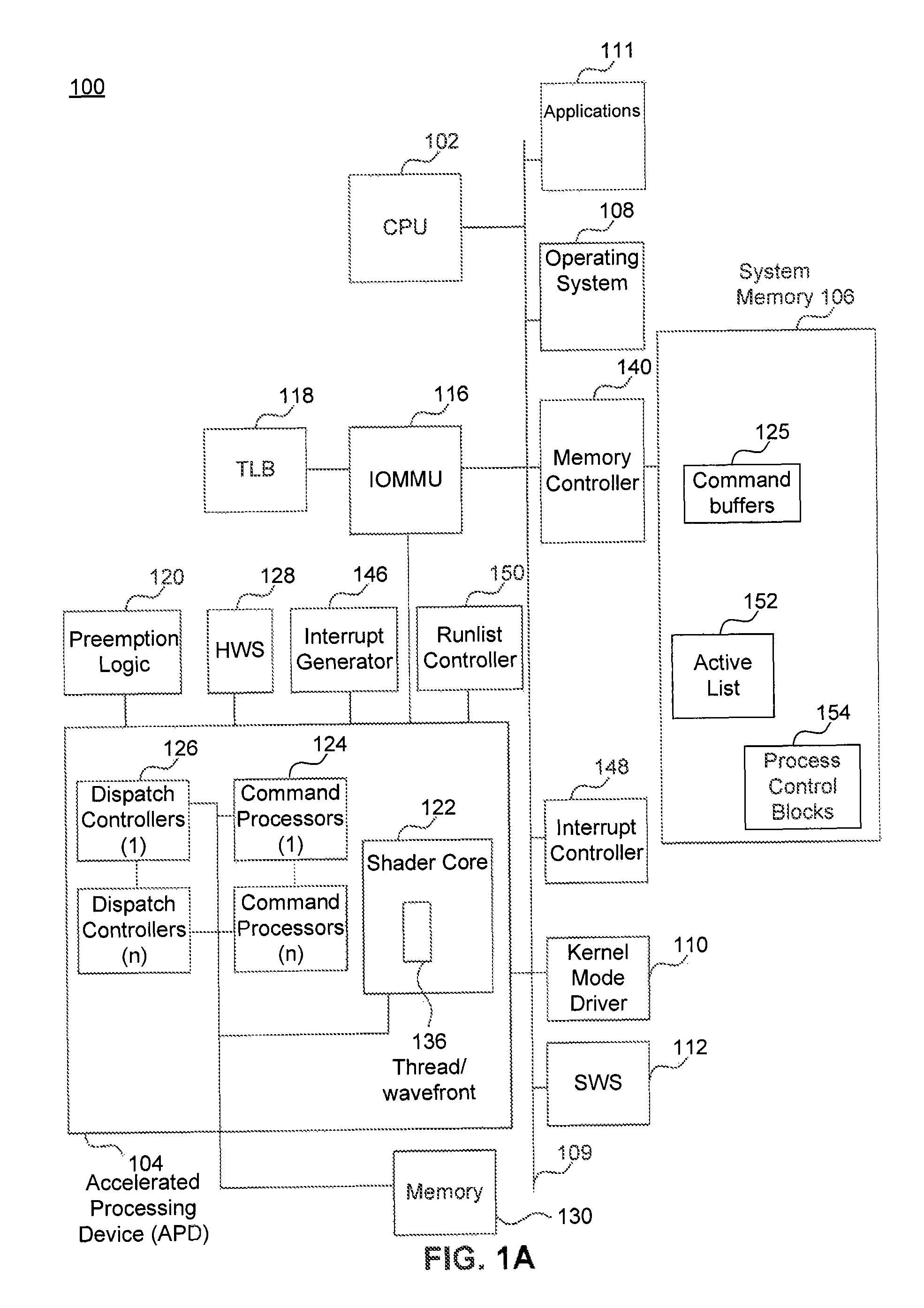
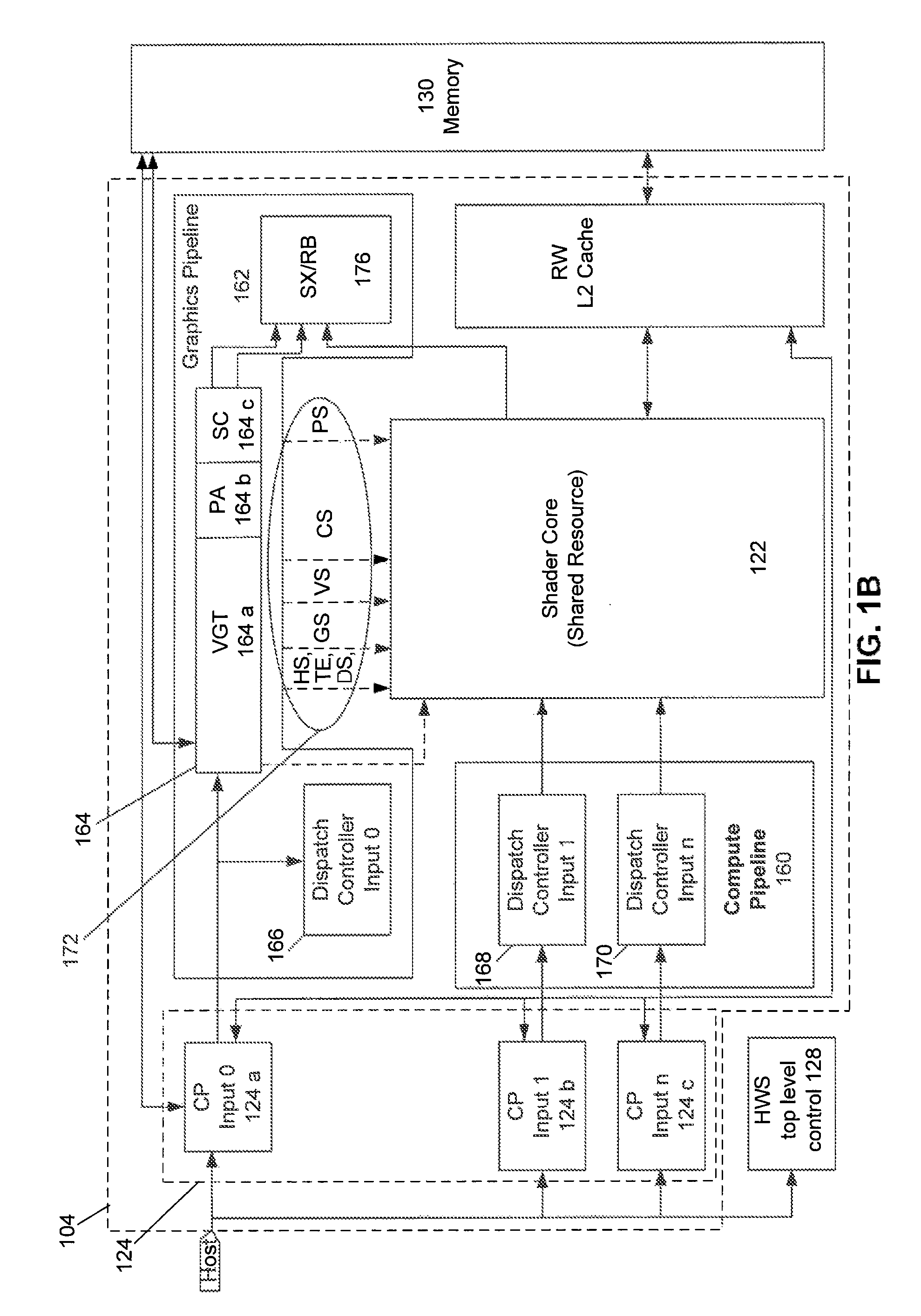
Methods and apparatus are provided, as an aspect of a combined CPU / APD architecture system, for discovering and reporting properties of devices and system topology that are relevant to efficiently scheduling and distributing computational tasks to the various computational resources of a combined CPU / APD architecture system. The combined CPU / APD architecture unifies CPUs and APDs in a flexible computing environment. In some embodiments, the combined CPU / APD architecture capabilities are implemented in a single integrated circuit, elements of which can include one or more CPU cores and one or more APD cores. The combined CPU / APD architecture creates a foundation upon which existing and new programming frameworks, languages, and tools can be constructed.
Owner:ATI TECH INC +1
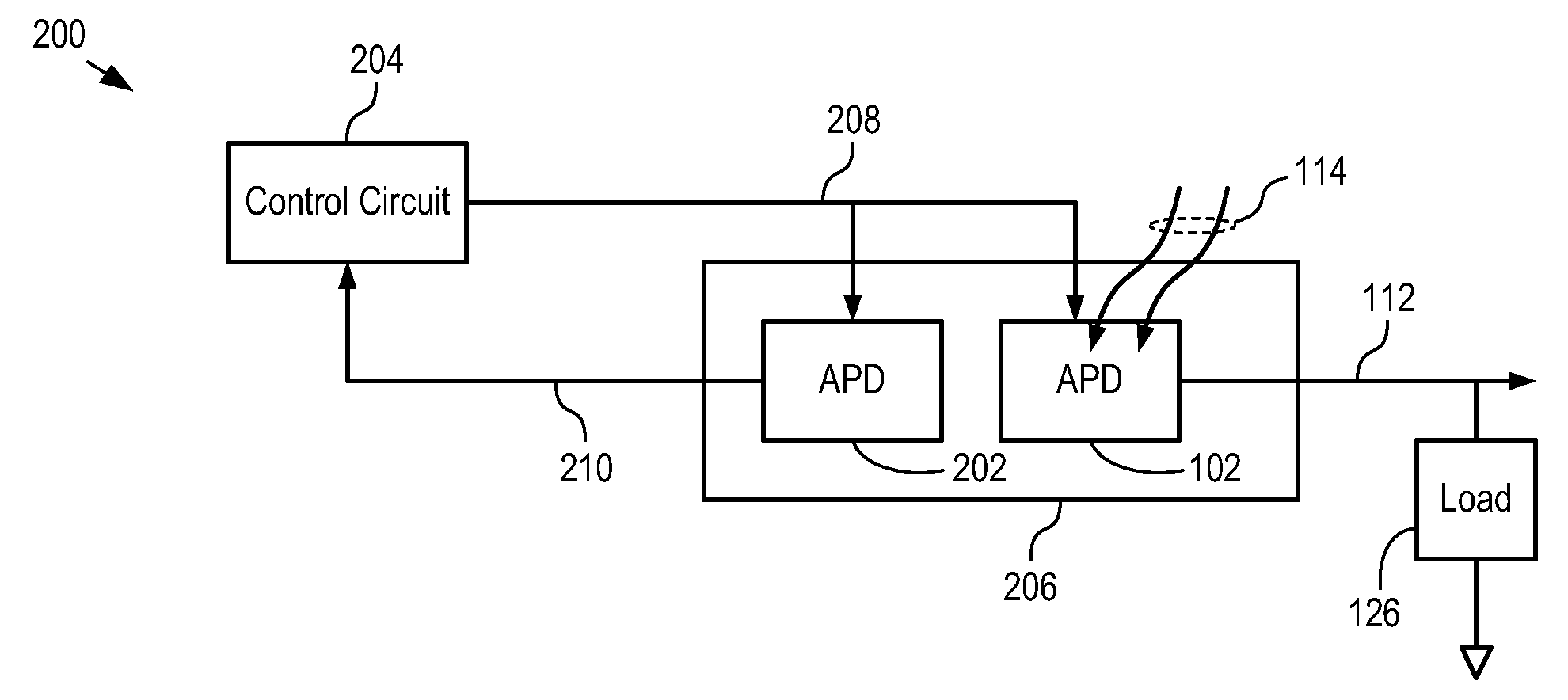
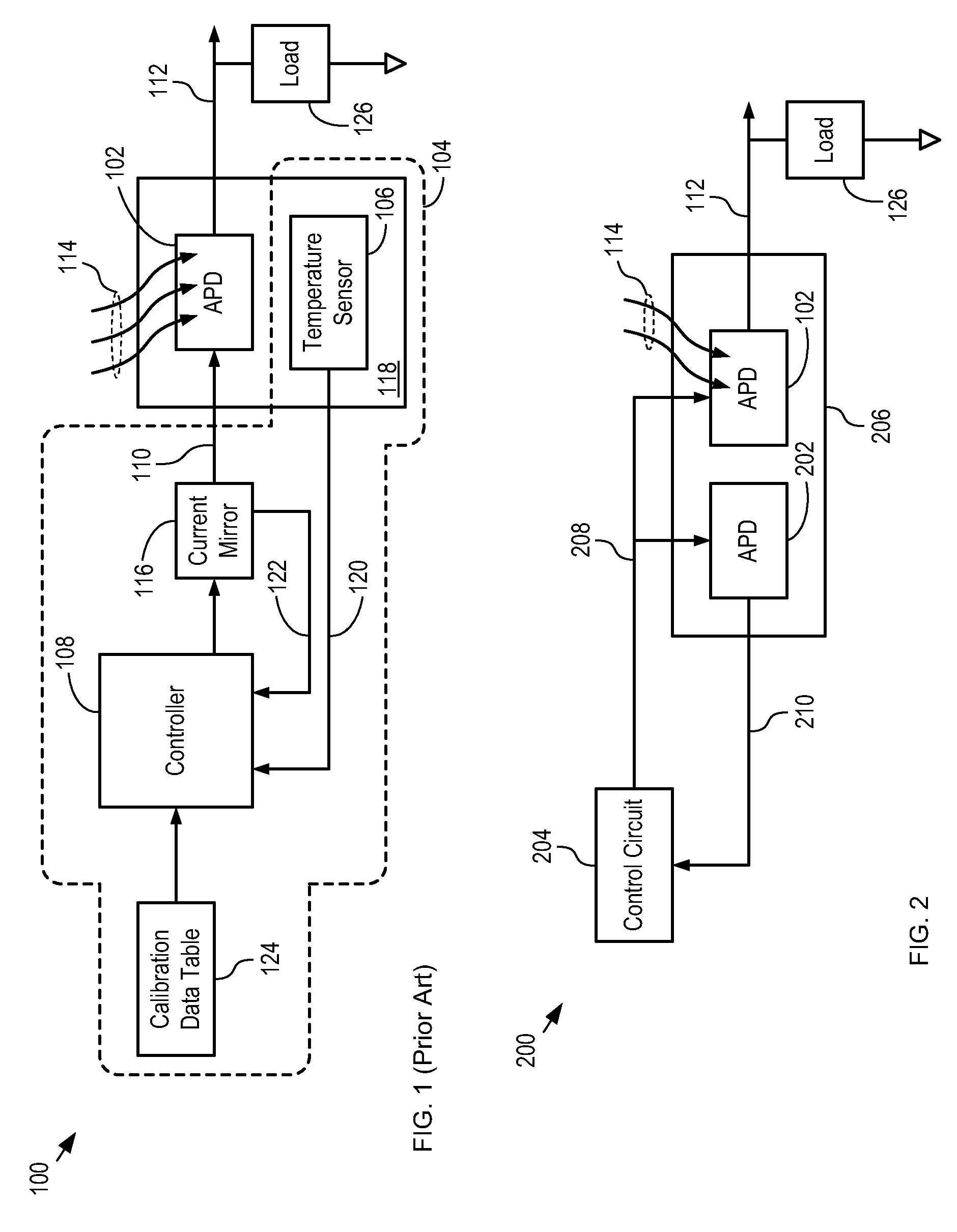
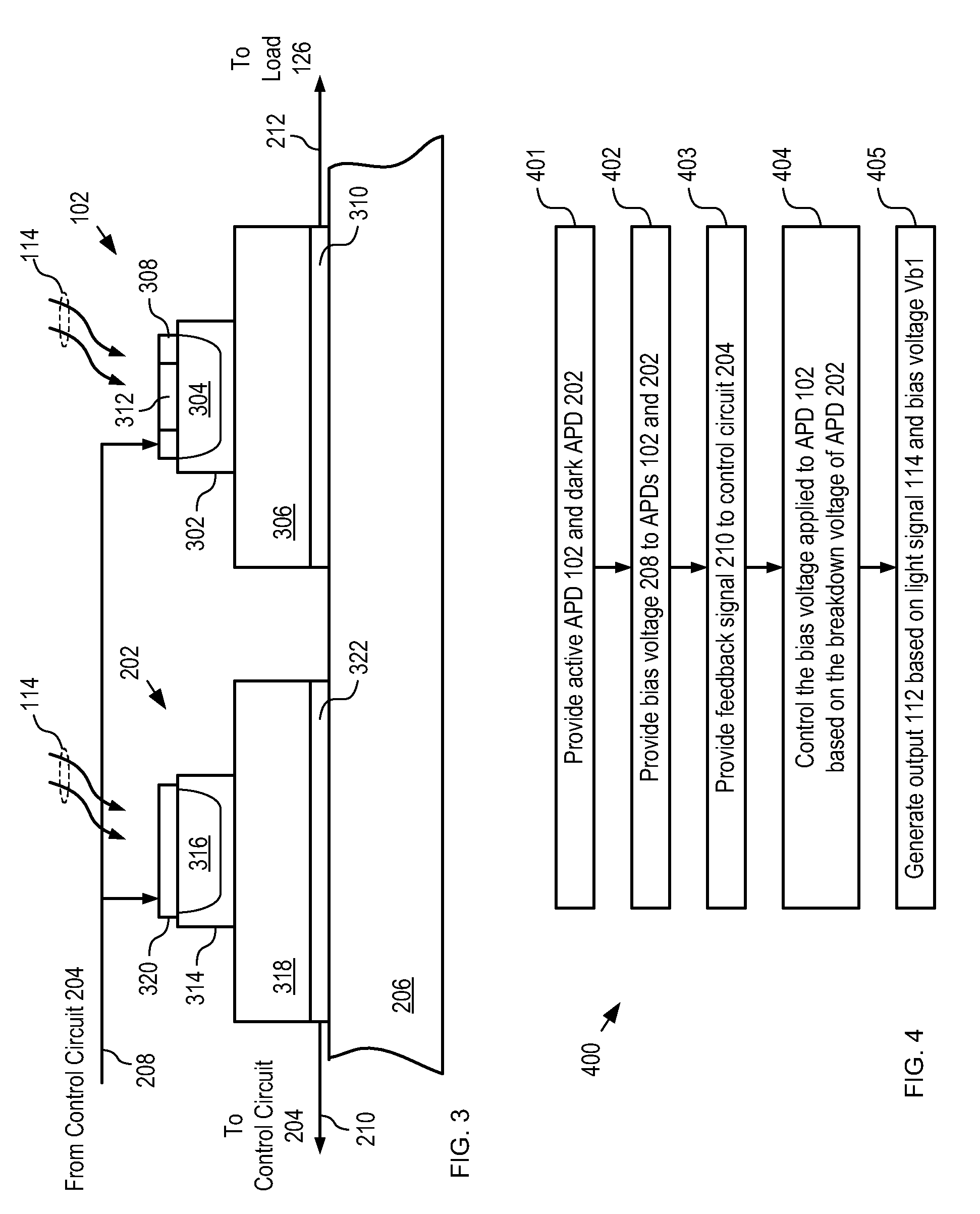
Optical Receiver Comprising Breakdown-Voltage Compensation
ActiveUS20100301194A1Accurate knowledgeHigh gainTransistorPhotometry using reference valueVoltage compensationOperating temperature
The present invention enables the detection of light using an APD that has high gain and / or a wide range of operating temperature. A first APD is biased with a voltage bias that is controlled based on the breakdown voltage of a second APD, which is thermally coupled with the first APD. Changes in the breakdown voltage of the second APD due to aging, temperature chances, and the like, are reflective of changes in the breakdown voltage of the first APD. As a result, the first APD can be operated with greater stability and reliability at high gain and over larger temperature excursions than APDs known in the prior art.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
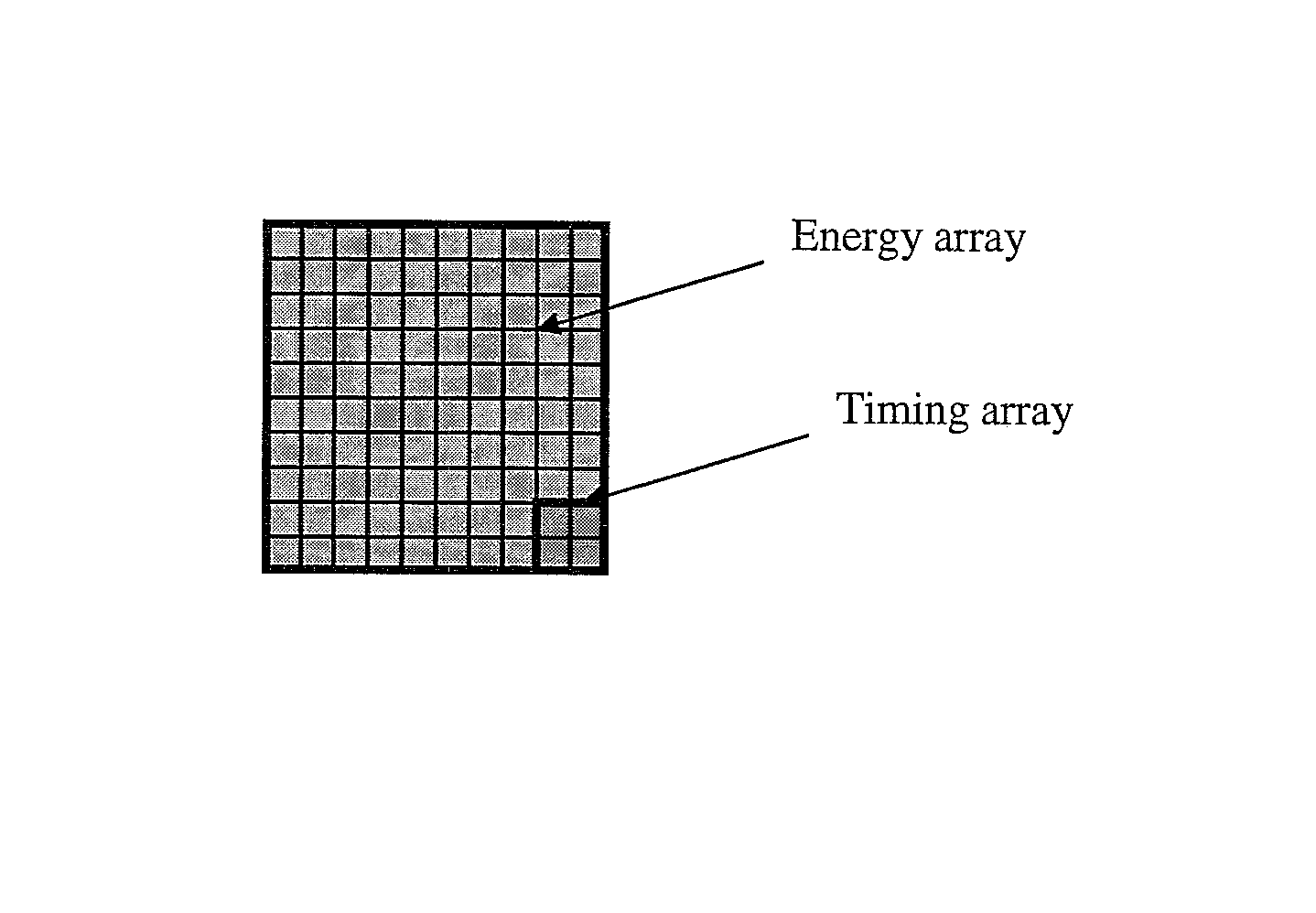
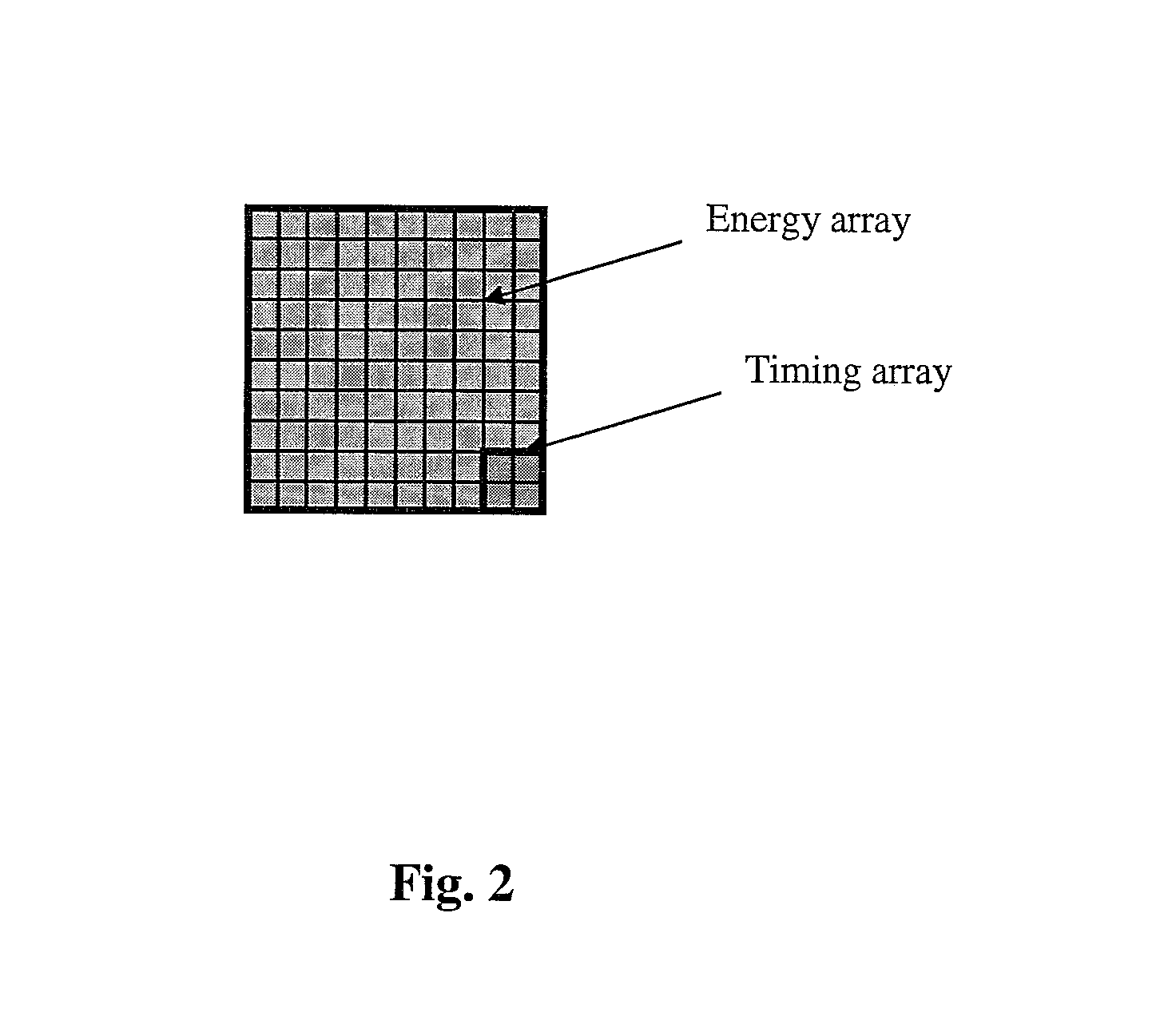
Dual channel SiPM for optimal energy and fast timing
ActiveUS7439509B1High gainReduce noiseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansLow noiseSilicon photomultiplier
Dual channel silicon photomultipliers (SiPMs) can replace PMTs and APDs for use in PET and other radiation detectors. The devices are compact, have high gain, high QE and low noise. Due to their timing performance, these devices can be used in time-of-flight PET applications. By dividing the device into two separate channels, one for timing resolution and one for energy resolution, both can be optimized simultaneously.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
High Performance Imaging System for Diffuse Optical Tomography and Associated Method of Use
ActiveUS20080154126A1Improve performanceReduce crosstalkMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostics using tomographyOptical tomographyImaging quality
A high performance imaging system for diffuse optical tomography is disclosed. A dense grid utilizing sources, e.g., light emitting diodes (“LEDs”), that achieve high performance at high speed with a high dynamic range and low inter-channel crosstalk are complemented by a system of discrete, isolated receivers, e.g., avalanche photodiodes (“APDs”). The source channels have dedicated reconfigurable encoding control signals, and the detector channels have reconfigurable decoding, allowing maximum flexibility and optimal mixtures of frequency and time encoding and decoding. Each detector channel is analyzed by dedicated, isolated, high-bandwidth receiver circuitry so that no channel gain switching is necessary. The resulting improvements to DOT system performance, e.g., increased dynamic range and decreased crosstalk, enable higher density imaging arrays and provide significantly enhanced DOT image quality. A processor can be utilized to provide sophisticated three dimensional modeling as well as noise reduction.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
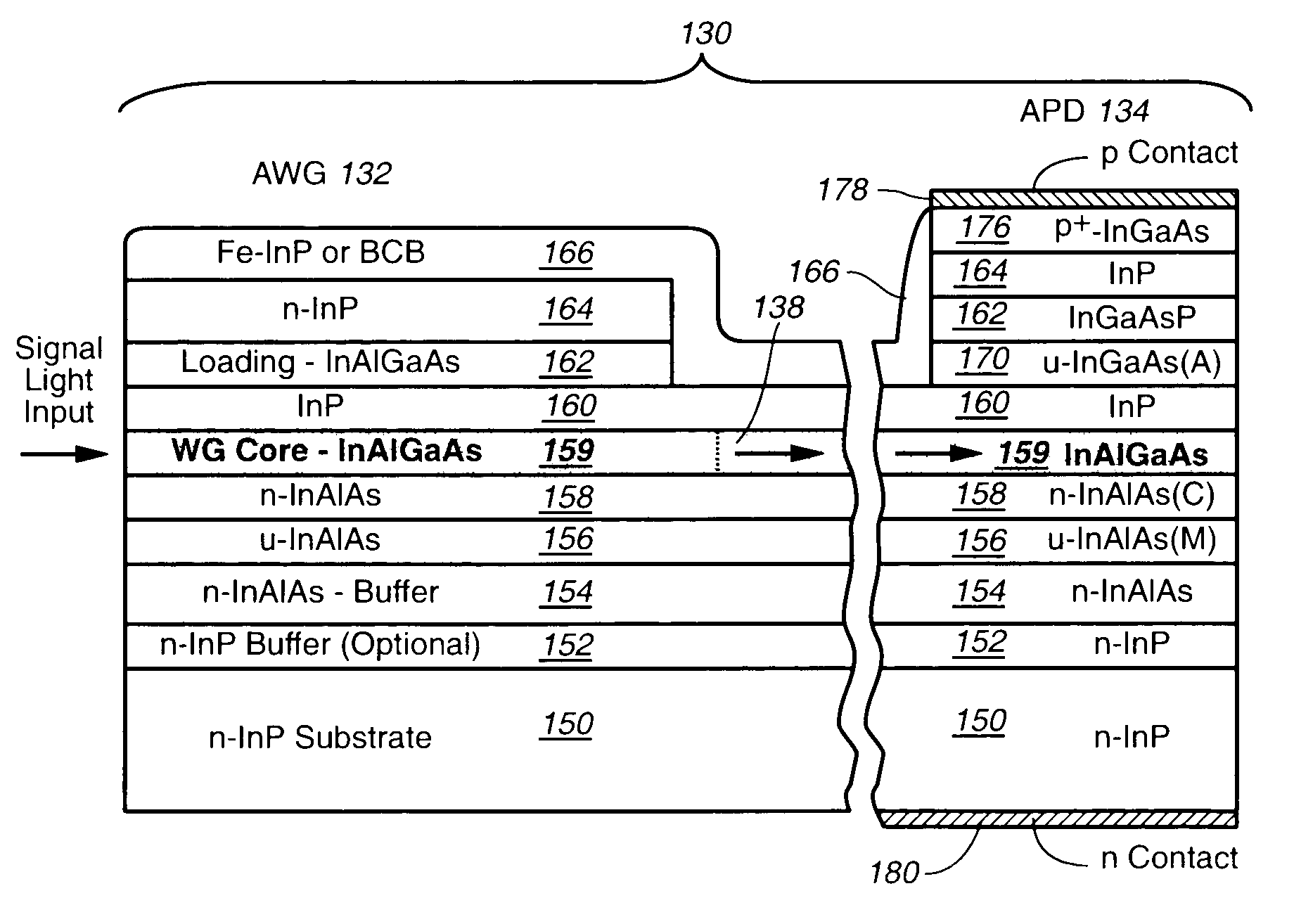
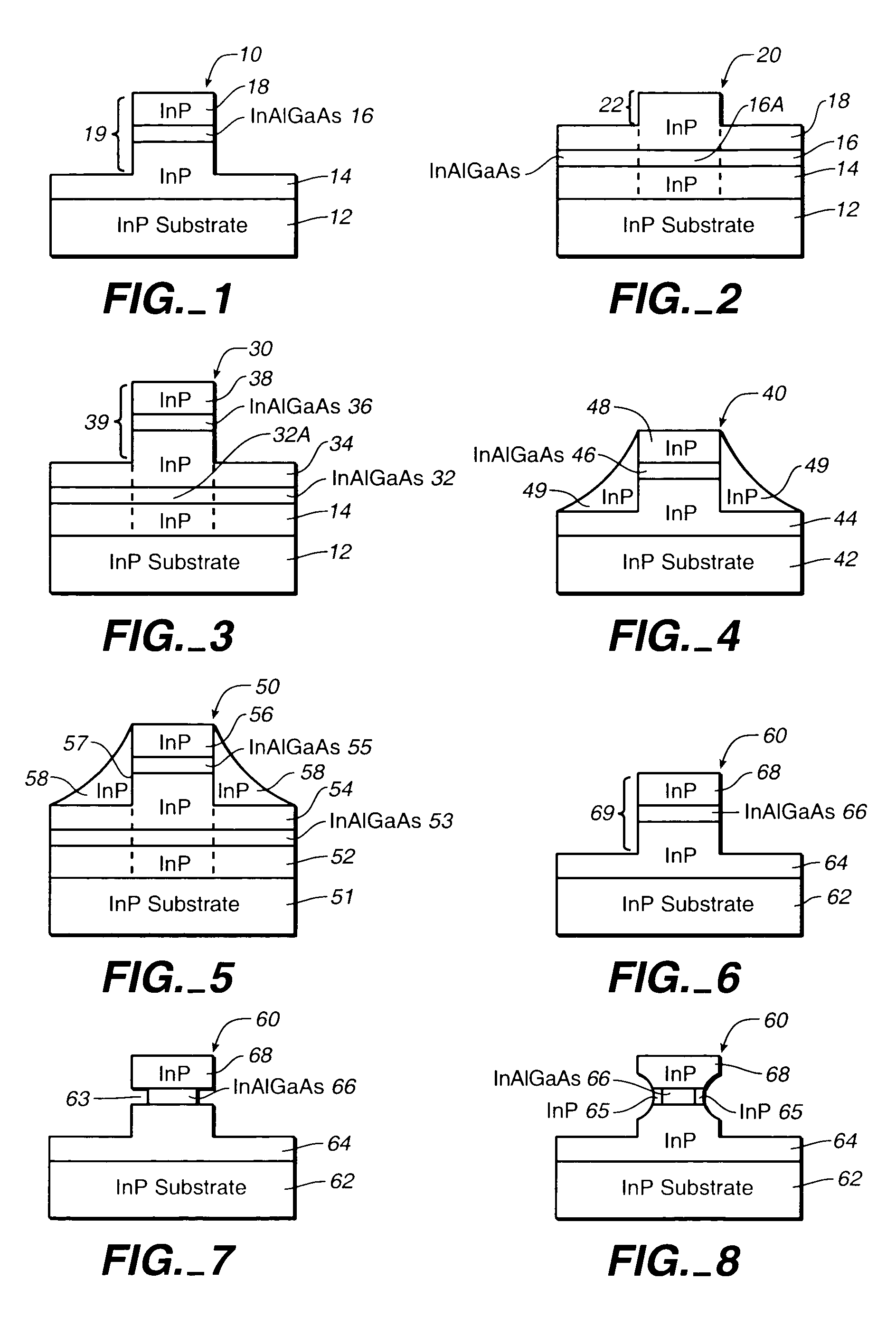
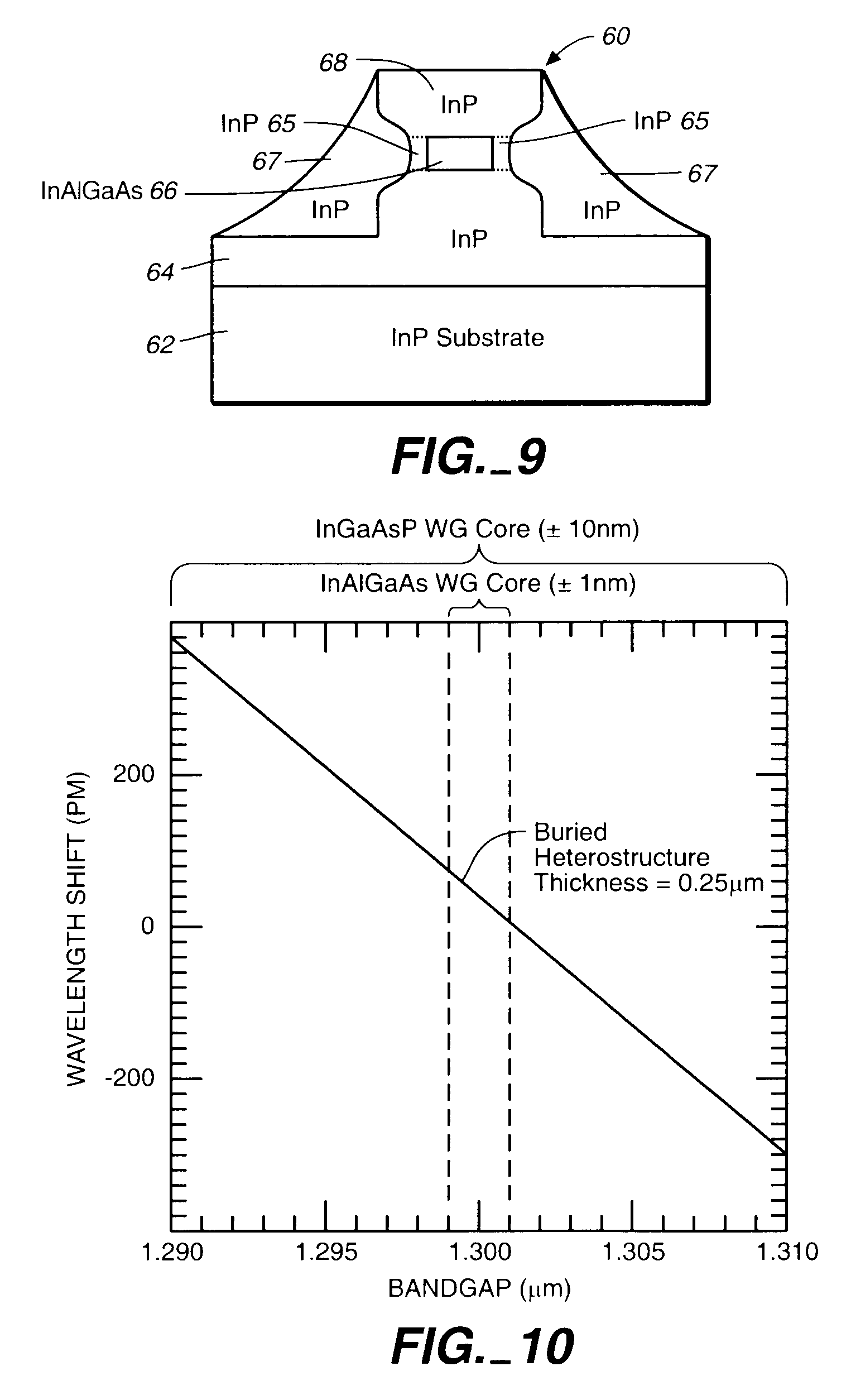
InP-based photonic integrated circuits with Al-containing waveguide cores and InP-based array waveguide gratings (AWGs) and avalanche photodiodes (APDs) and other optical components containing an InAlGaAs waveguide core
InactiveUS7072557B2Improve performanceHigh yieldSemiconductor lasersOptical waveguide light guidePhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The Group III–V quaternary, InAlGaAs is employed as a waveguide layer in optical components, such as In-P based array waveguide gratings (AWGs), avalanche photodiodes (APDs) or other optical components that contain a waveguide core in the InP regime. The deployment of InAlGaAs waveguides provides for high uniform photoluminescent (PL) emission wavelength across the wafer for InAlGaAs waveguides as compared to InGaAsP waveguides as now commonly employed in such optical devices or components. The use of an InAlGaAs waveguide core has particular utility when deployed in a photonic integrated circuit (PIC) such as an AWG with a plurality of outputs optically integrated with a plurality of photodetectors, such as APDs which are exemplified in this disclosure. In lieu of an InAlGaAs waveguide, combination layers of InGaAs / InAlAs, InGaAs / InAlGaAs or InAlAs / InAlGaAs may be employed or stacks of such layers to form the waveguides in the PIC chip.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
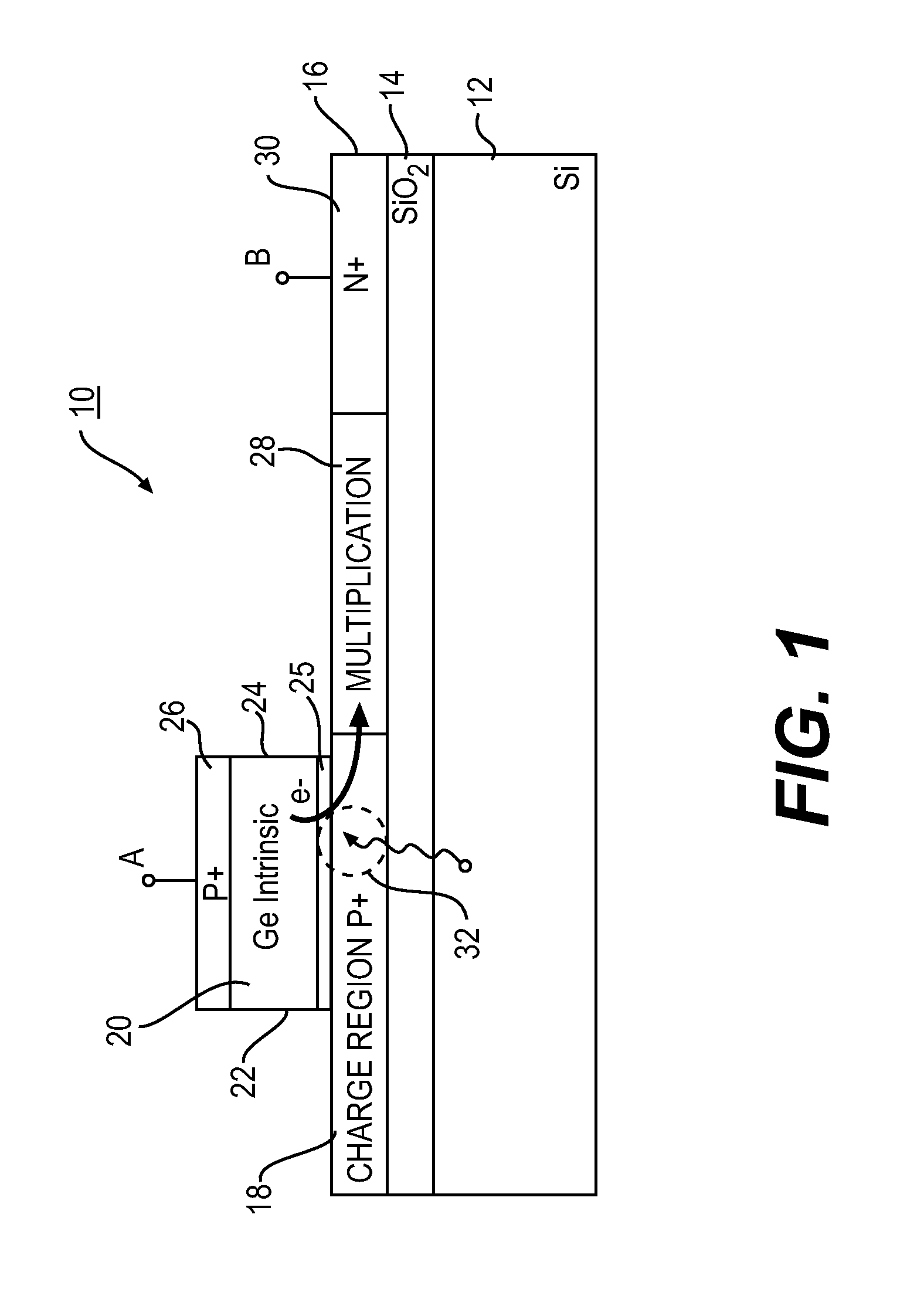
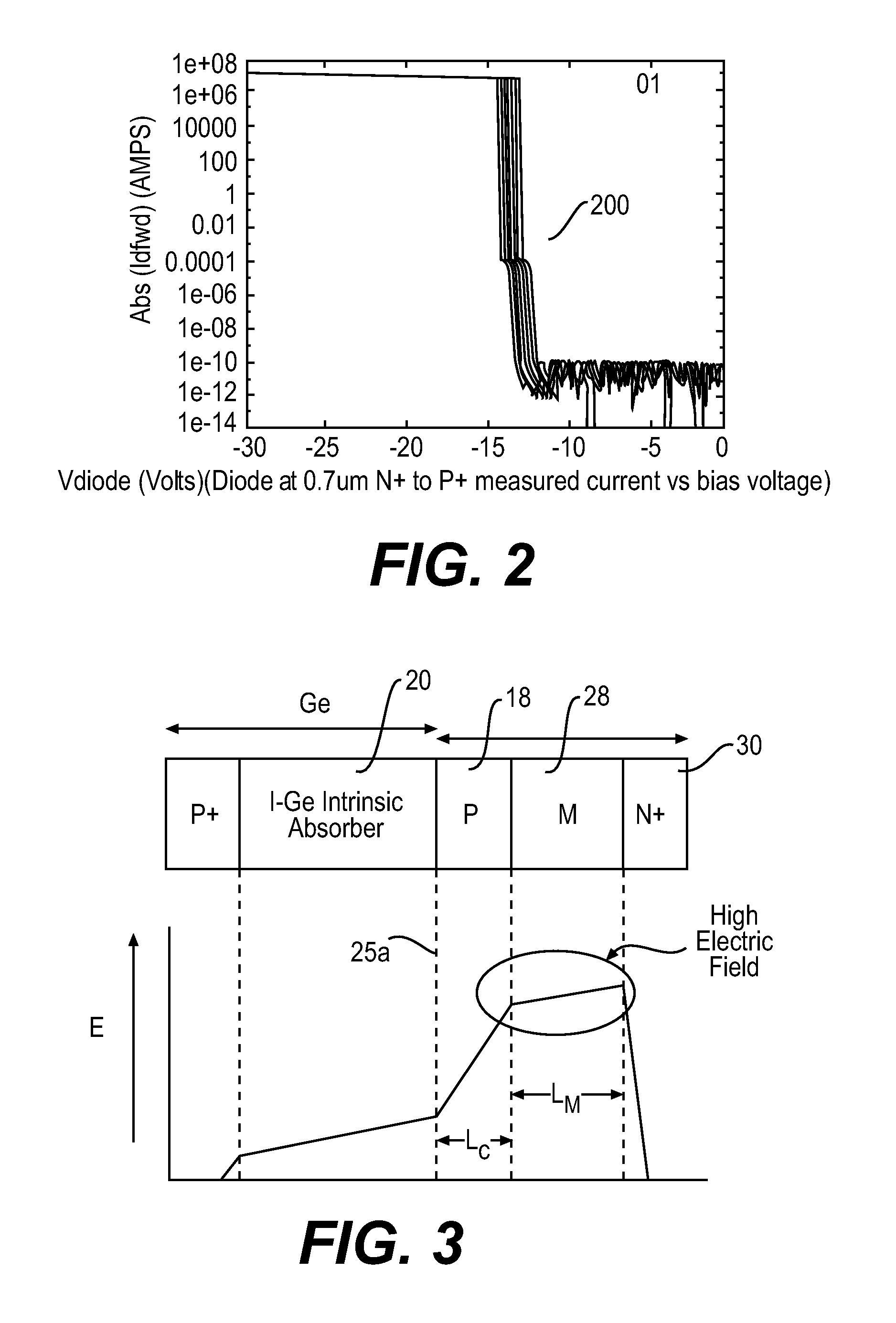
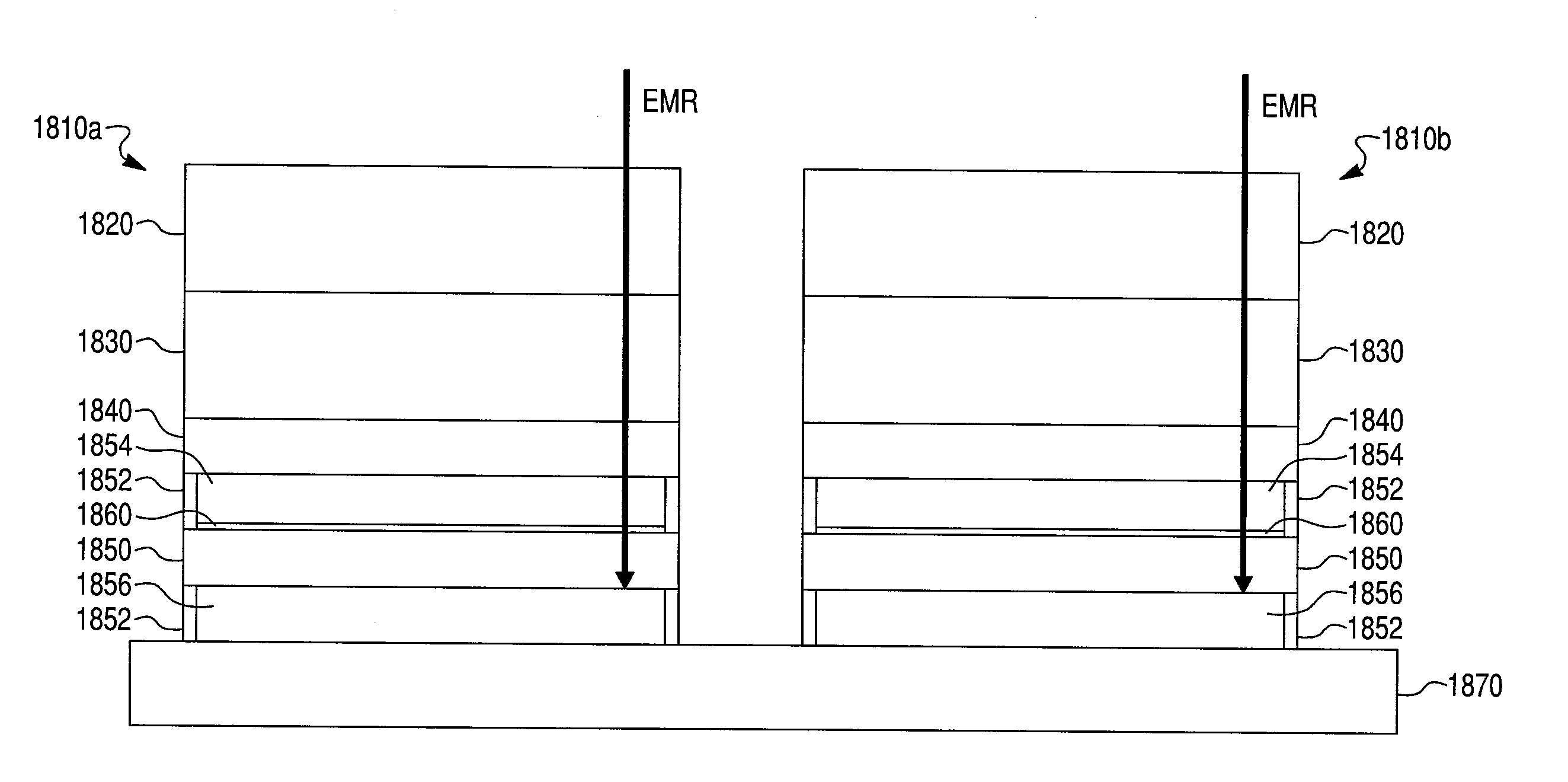
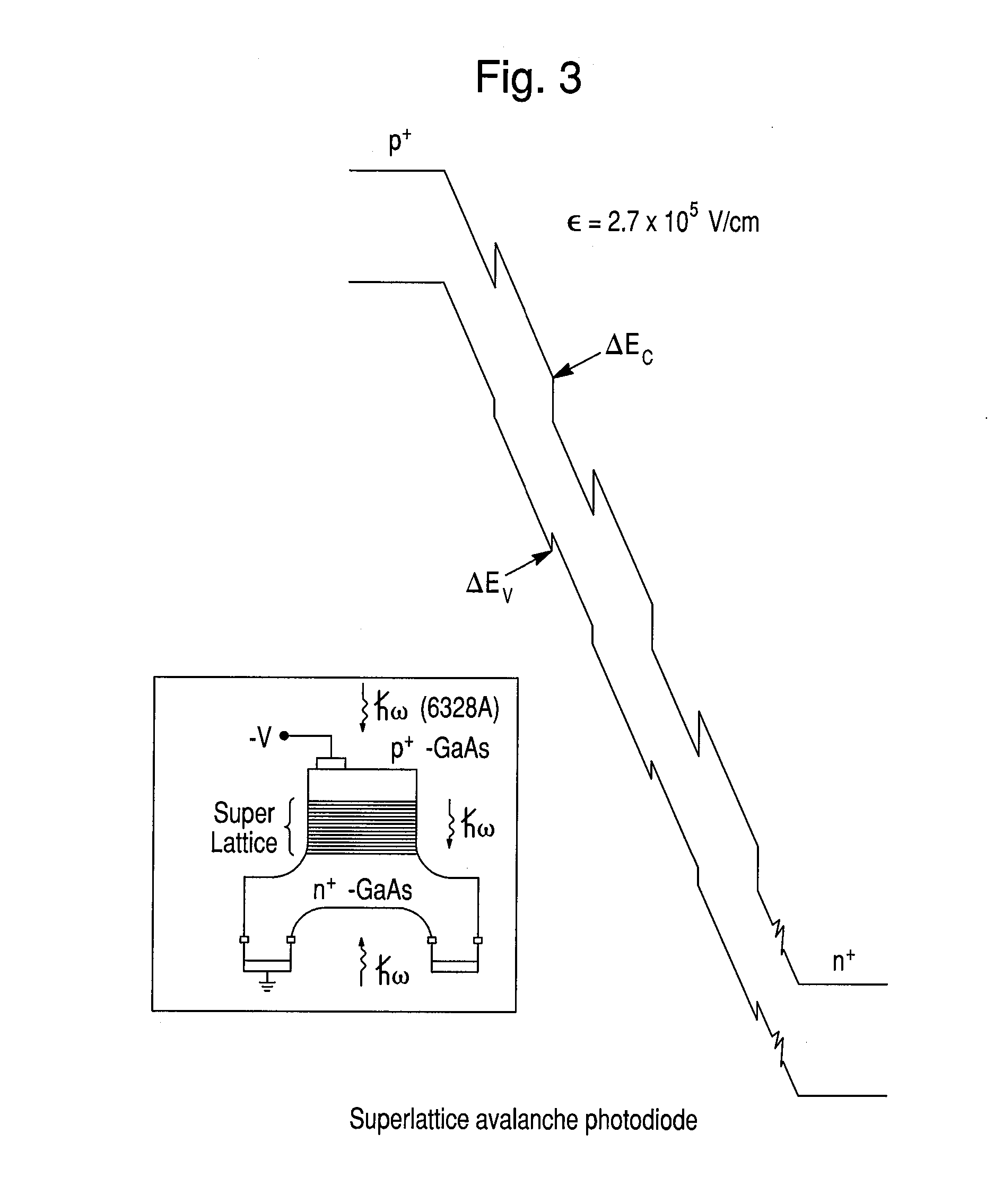
APDs using nano-plasmonic metamaterials
An avalanche photodiode (APD) electro-magnetic radiation (EMR) detector is described. The detector includes an EMR absorption region, a voltage biasing element, and a charge multiplication region. The EMR absorption region includes a substantially regular array of nano-particles embedded in a matrix material. The voltage biasing element is configured to apply a bias voltage to the matrix material such that electrical current is directly generated in the EMR absorption region based on a cooperative plasmon effect in the detector material when electro-magnetic radiation in a predetermined wavelength range is incident upon the detector material, where the dominant mechanism for decay in the cooperative plasmon effect is non-radiative. The charge multiplication region is arranged relative to the EMR absorption region to avalanche multiply the electrical current generated in the EMR absorption region.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
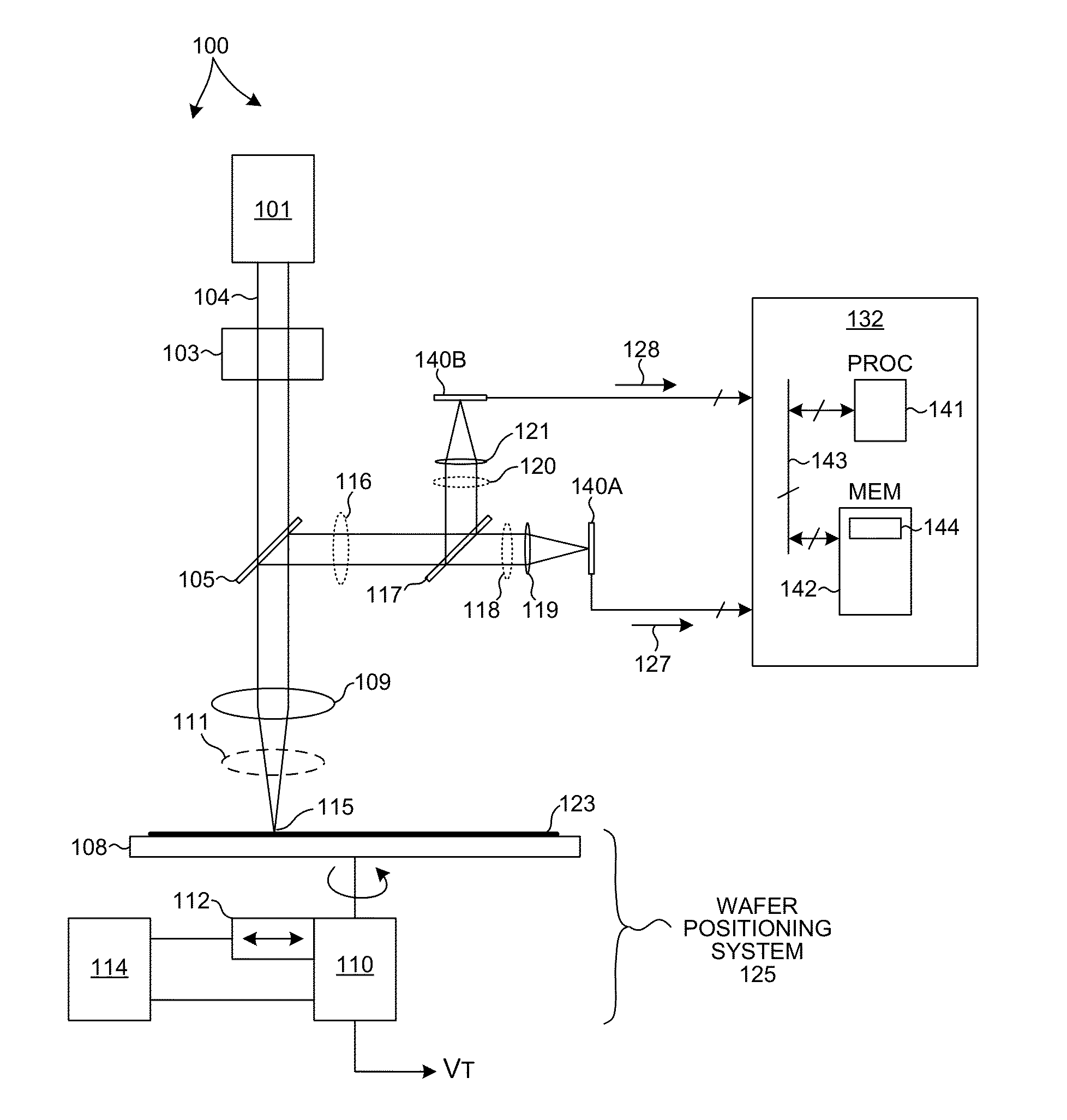
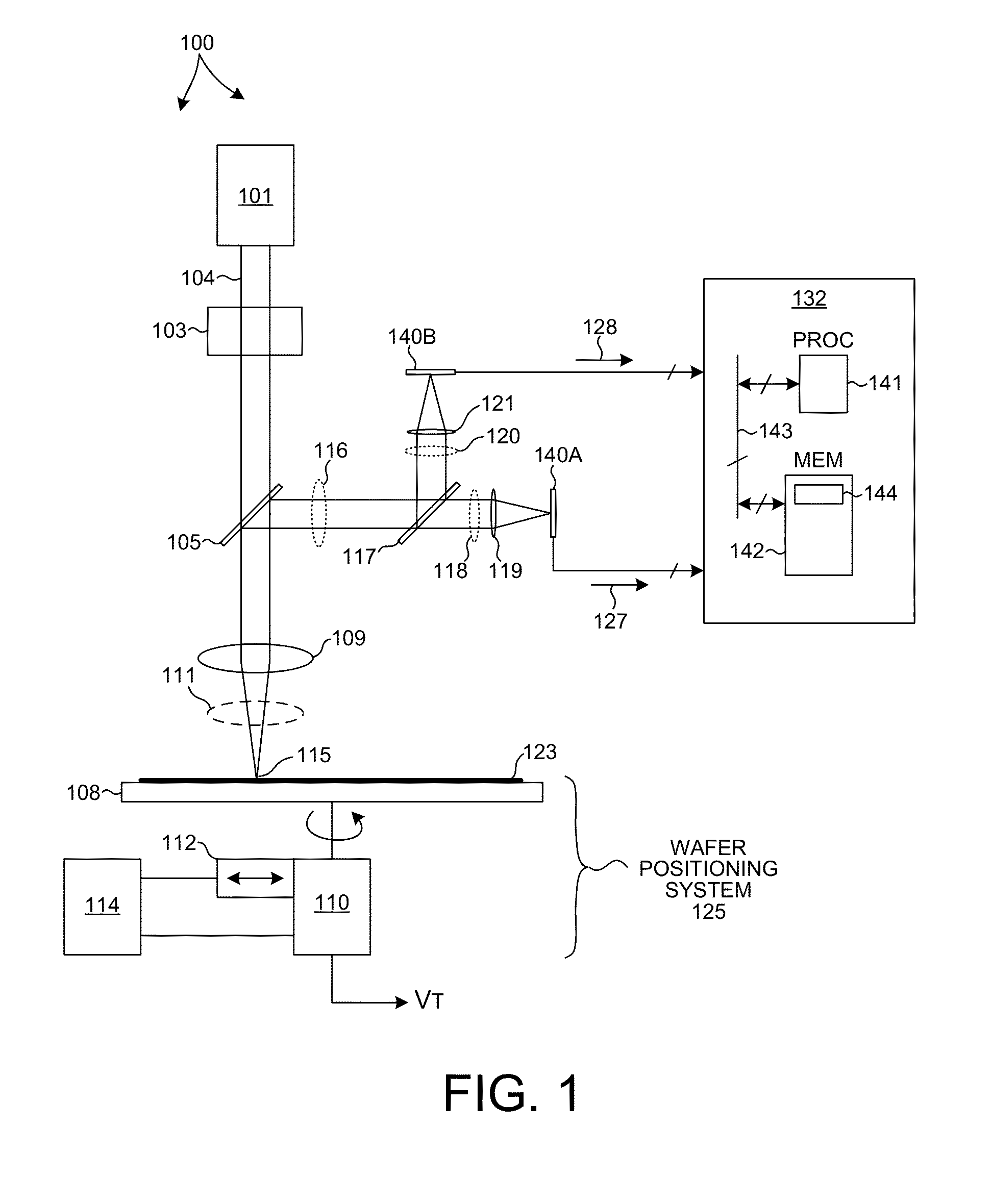
Sample Inspection System Detector
ActiveUS20140118730A1Improve dynamic rangeDifferent resolutionSolid-state devicesOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Methods and systems for enhancing the dynamic range of a high sensitivity inspection system are presented. The dynamic range of a high sensitivity inspection system is increased by directing a portion of the light collected from each pixel of the wafer inspection area toward an array of avalanche photodiodes (APDs) operating in Geiger mode and directing another portion of the light collected from each pixel of the wafer inspection area toward another array of photodetectors having a larger range. The array of APDs operating in Geiger mode is useful for inspection of surfaces that generate extremely low photon counts, while other photodetectors are useful for inspection of larger defects that generate larger numbers of scattered photons. In some embodiments, the detected optical field is split between two different detectors. In some other embodiments, a single detector includes both APDs operating in Geiger mode and other photodetectors having a larger range.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
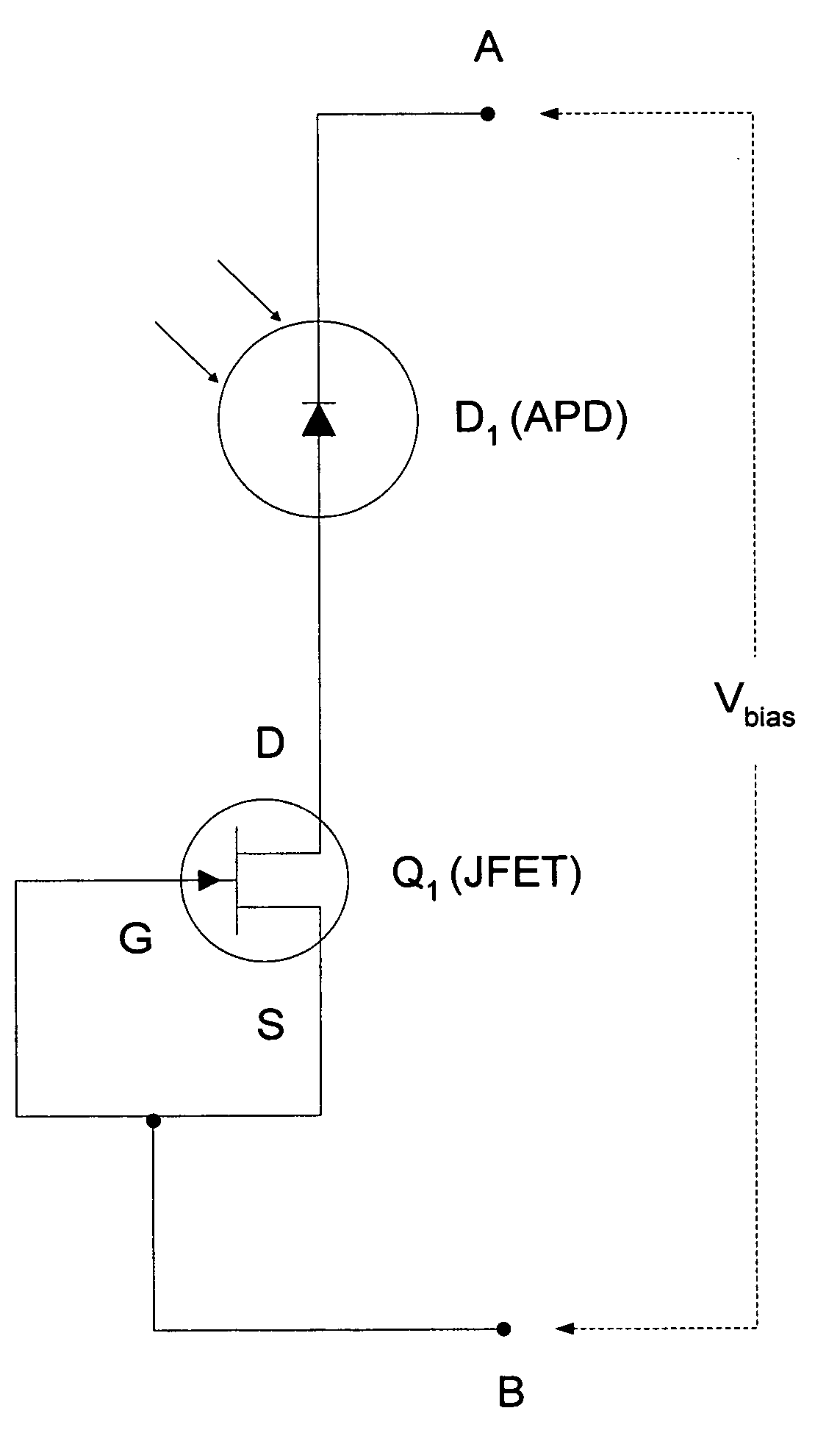
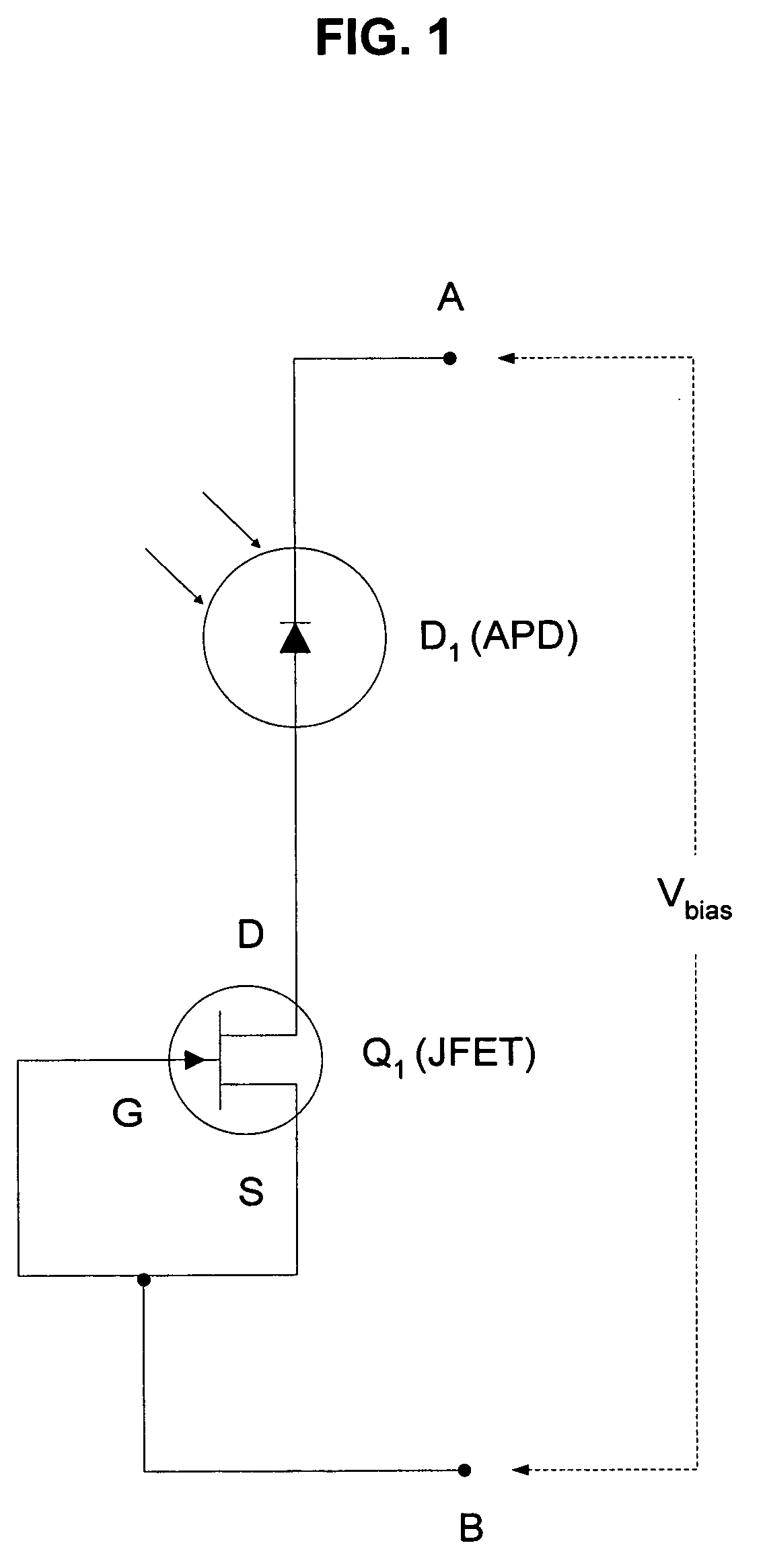
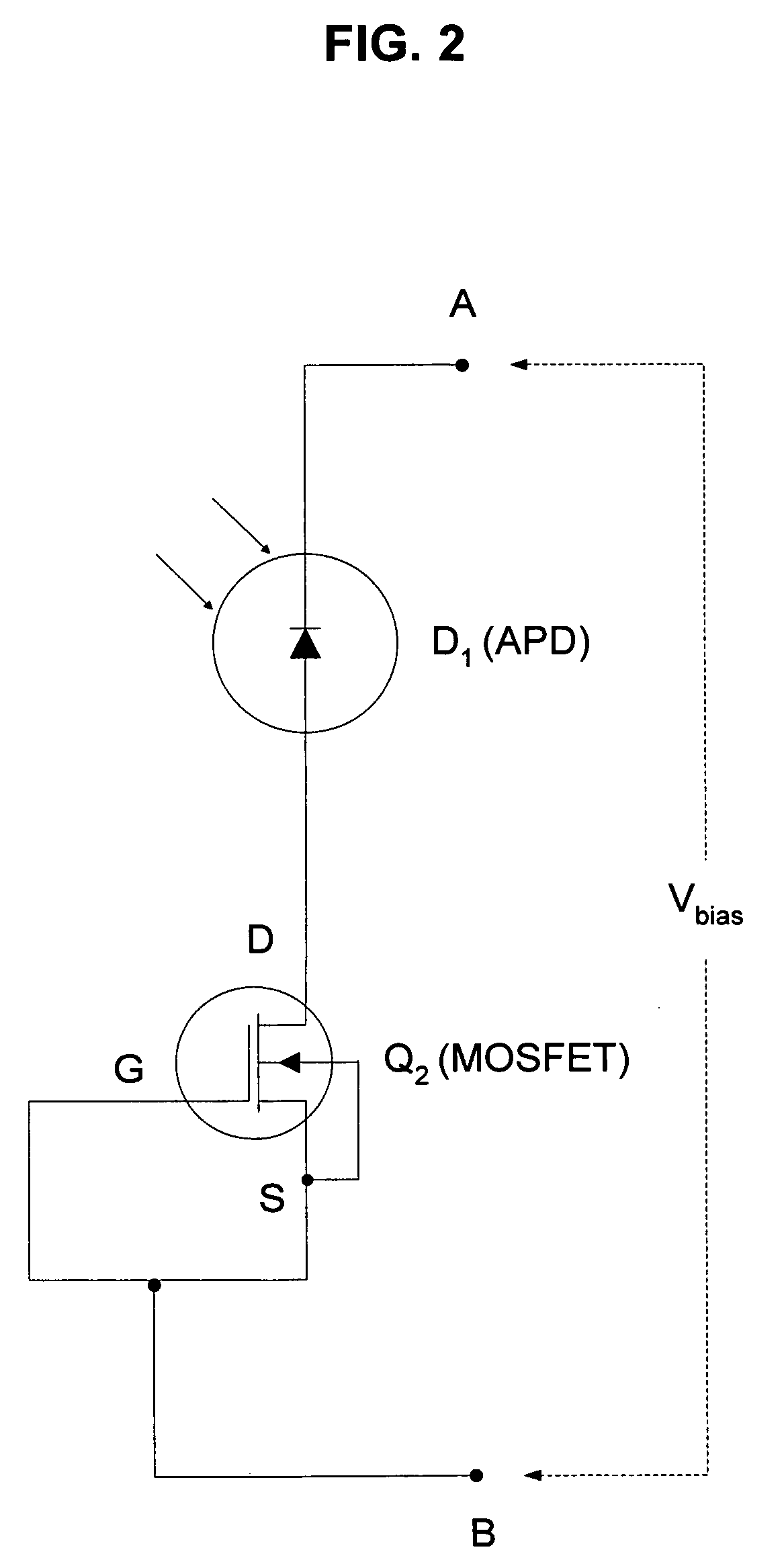
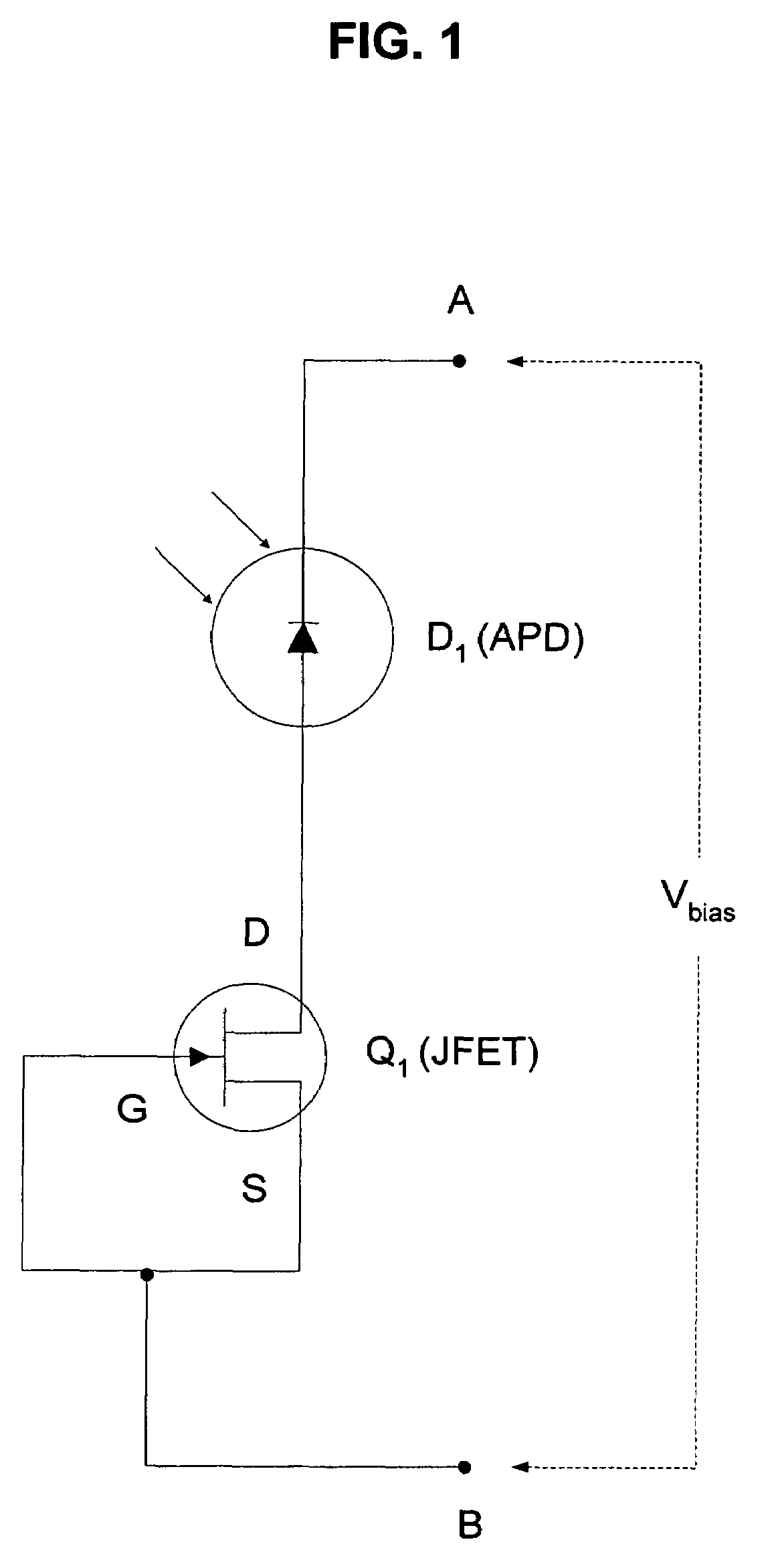
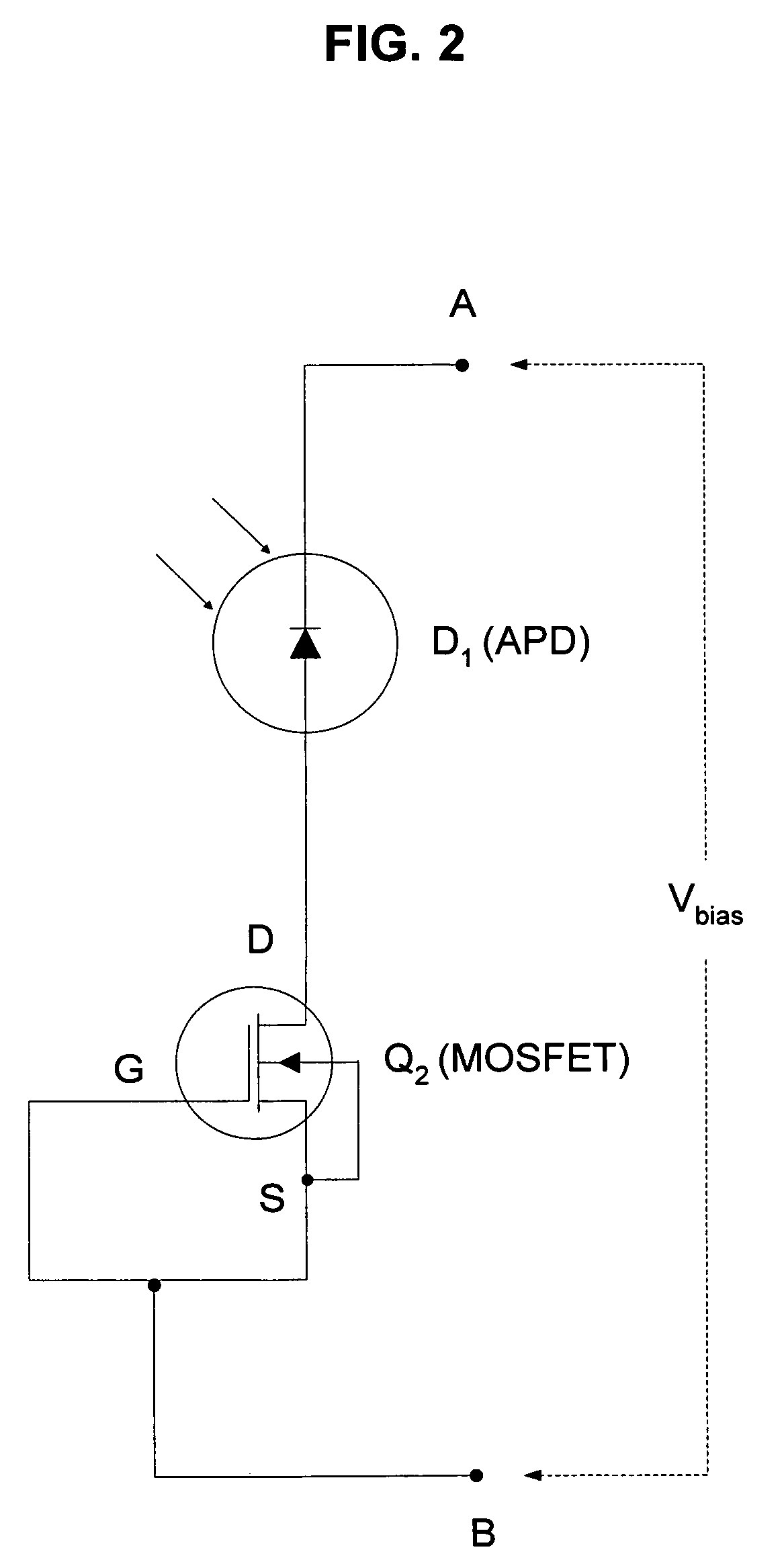
Method and apparatus for providing non-linear, passive quenching of avalanche currents in Geiger-mode avalanche photodiodes
InactiveUS20060231742A1Reduce bias voltageBias voltage is increasedPulse automatic controlMaterial analysis by optical meansMOSFETCurrent limiting
Owner:SENSORS UNLTD
Silicon-based avalanche photoelectric detector array and manufacturing method thereof
The invention provides a silicon-based avalanche photoelectric detector array and a manufacturing method thereof. According to a device main structure of the silicon-based avalanche photoelectric detector array, a wafer structure with an epitaxial Si layer is formed on a SiO2 / Si composite substrate, the wafer structure is an epitaxial Si / SiO2 / Si material structure forming by a bonding technology,the silicon-based avalanche photoelectric detector array based on the wafer structure comprises the SiO2 / Si composite substrate, avalanche photoelectric detector (APD) units arranged on the SiO2 / Si composite substrate in an array, and a trench structure formed surrounding the APD units, and the sidewall and bottom of the trench structure are deposited with a high-reflection dielectric film. Thus,the high-reflection dielectric film of the trench structure blocks lateral light crosstalk from adjacent APD units, a SiO2 bonding interface based on the SiO2 / Si composite substrate blocks secondary photons from entering the adjacent APDs via the substrate, the crosstalk path among the APD units is cut off effectively, the integral performance of the APD array is improved, the APD array of a largearea array can be integrated compactly, and the batch production performance is improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
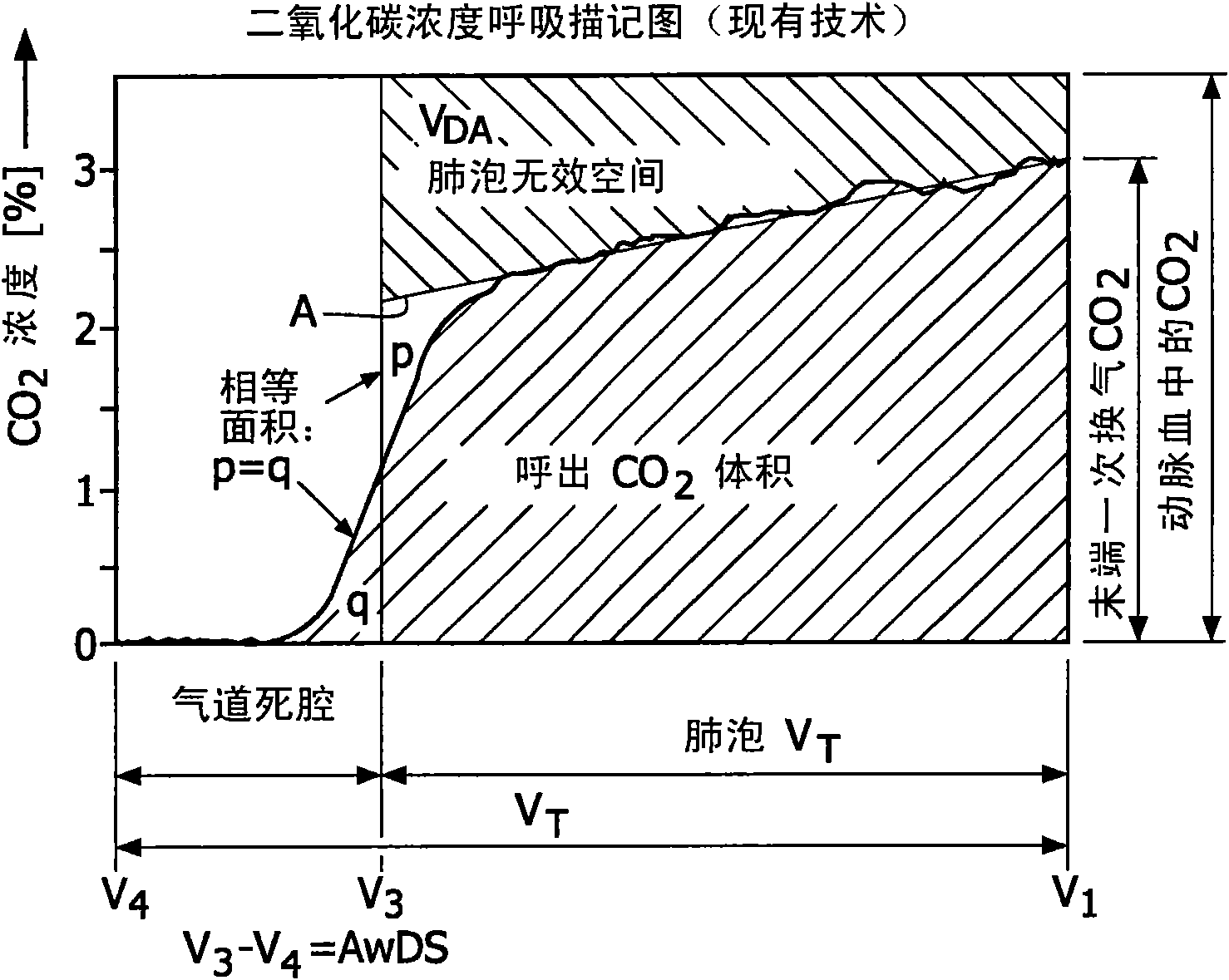
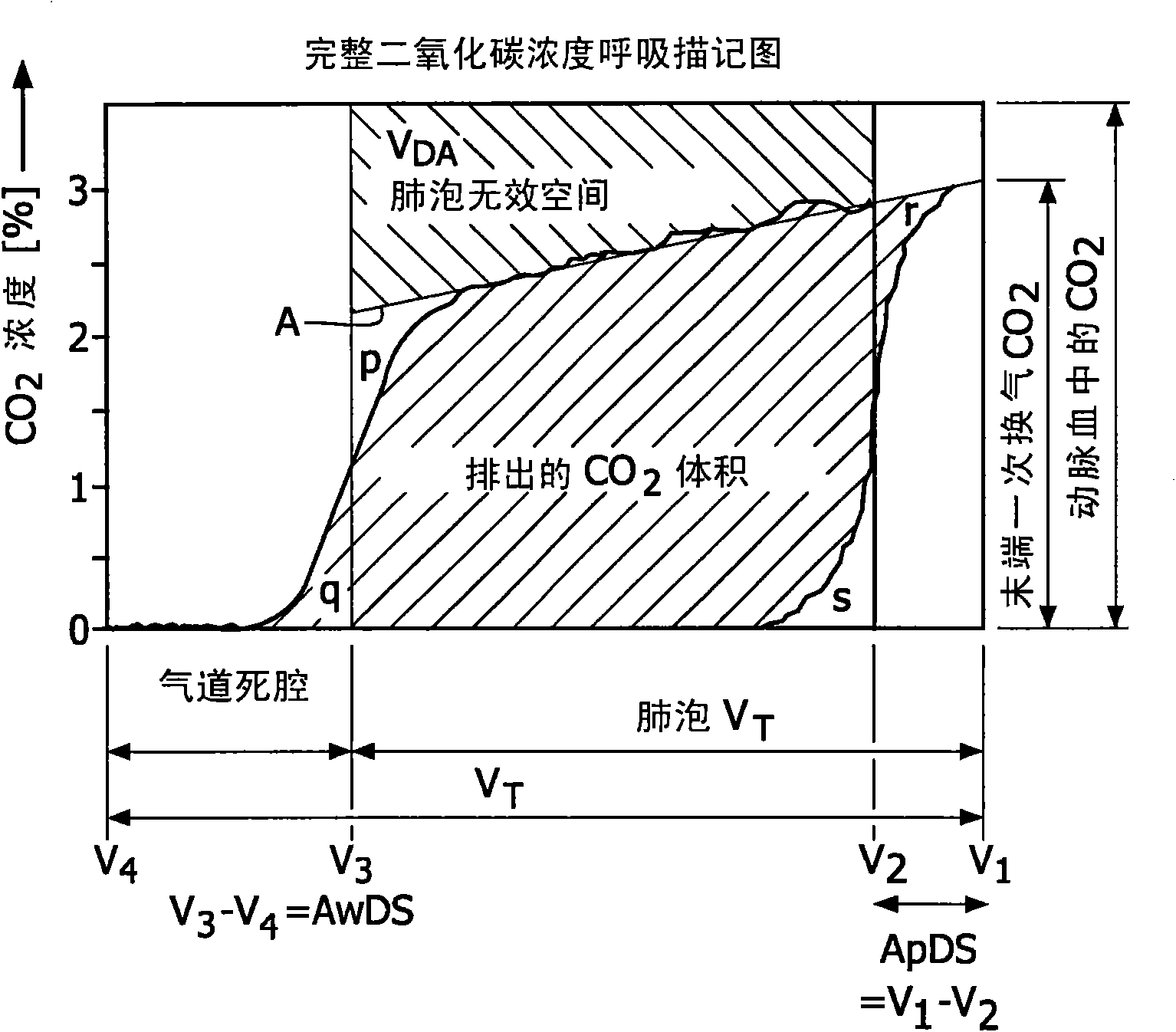
Method and device for evaluation of spirographic and gas exchange data
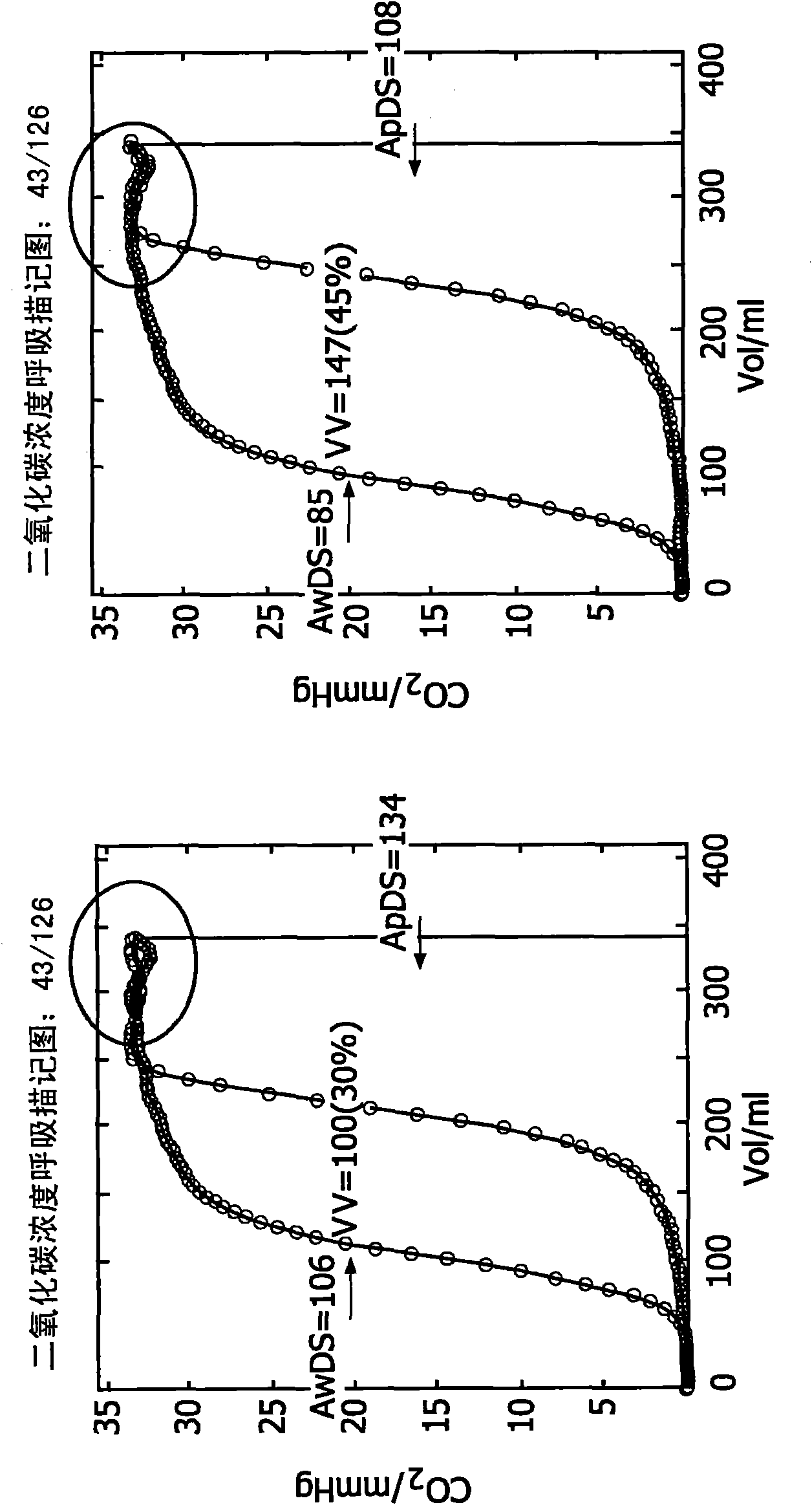
The invention provides a method for obtaining and evaluating spirographic and gas exchange data, comprising measuring a concentration of a breathing gas gc(Vx) for a plurality of volumes Vx of breathing gas mix, wherein the measuring is performed on inhaled breathing gas mix, further comprising determining an apparatus dead space ApDS, of breathing gas mix in the apparatus not taking part in gas exchange, by evaluating the measured concentrations gc(Vx) as a function of the volume V of the inhaled breathing gas mix. The use of inhaled breathing gas mix allows to determine the apparatus dead space, which is an important parameter when evaluating ventilation efficiency and the like. Furthermore, the invention provides a method in which inhalation and exhalation parts of a spirogram are synchronised, by matching features thereof, in order to further improve the accuracy of gas exchange volumes and derived data. Finally, the invention provides a spirographic device and a patient ventilation apparatus, incorporating the present method.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Starved source diffusion for avalanche photodiode
InactiveUS20060081874A1The method is simple and reliableReducing edge gainPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesDopantEdge effects
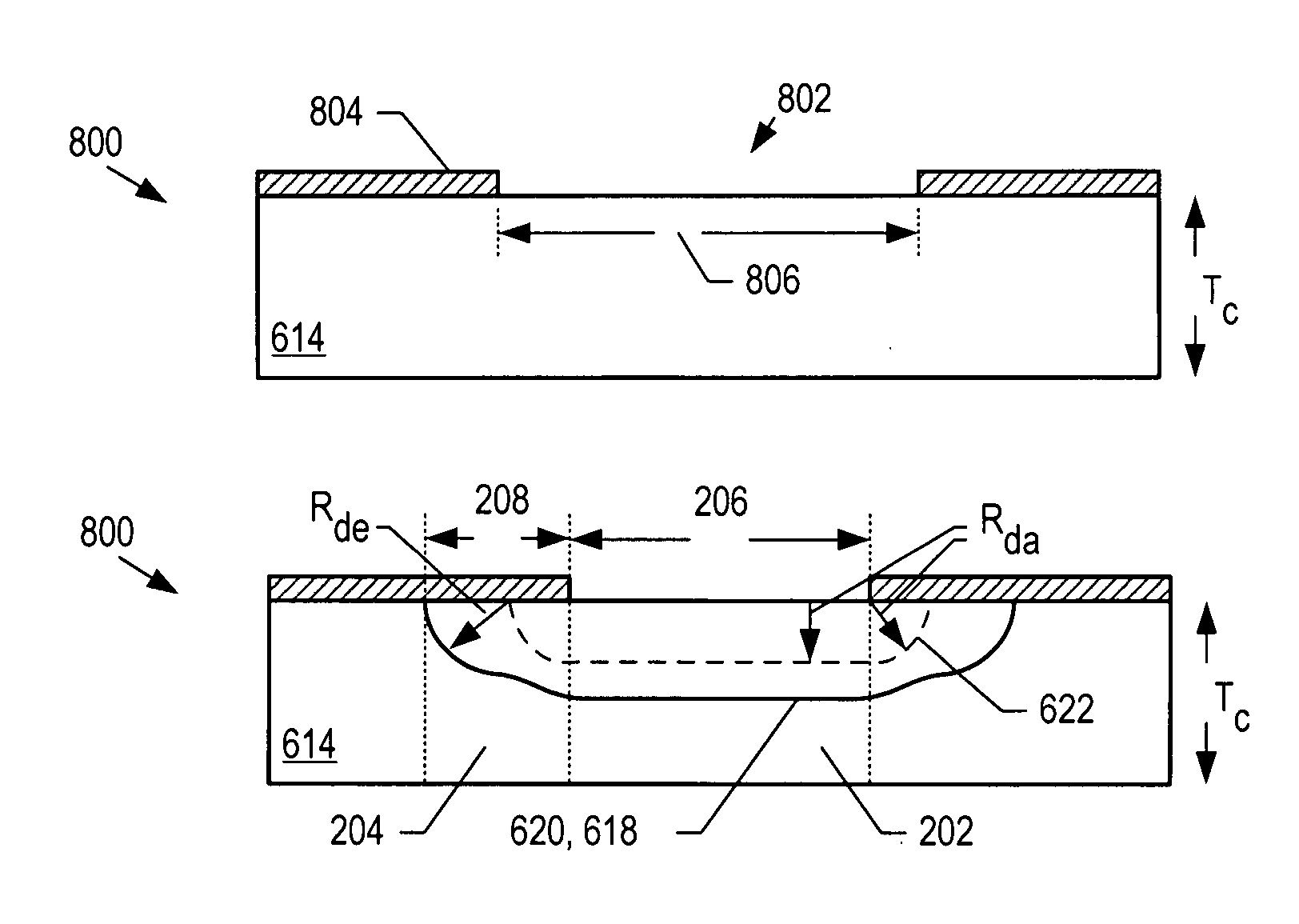
Starved source diffusion methods for forming avalanche photodiodes (APDs) are provided for controlling the edge effect. The edge effect is controlled by reducing edge gain near the edges of an APD active region. This is accomplished by creating a sloped diffusion front near the edges of the active region. The sloped diffusion front is advantageously formed in a single doping step by using a patterned mask during doping. The patterned mask reduces the depth to which dopants diffuse in areas where it only partly covers the underlying layer. By covering more of the underlying layer nearer the edge and progressively less towards the center, the sloped diffusion front is formed. The shallower diffusion depth near the edge reduces the edge gain, and therefore the edge effect. As a result, an APD to fiber misalignment is less likely, and possibility of edge breakdown is greatly reduced.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
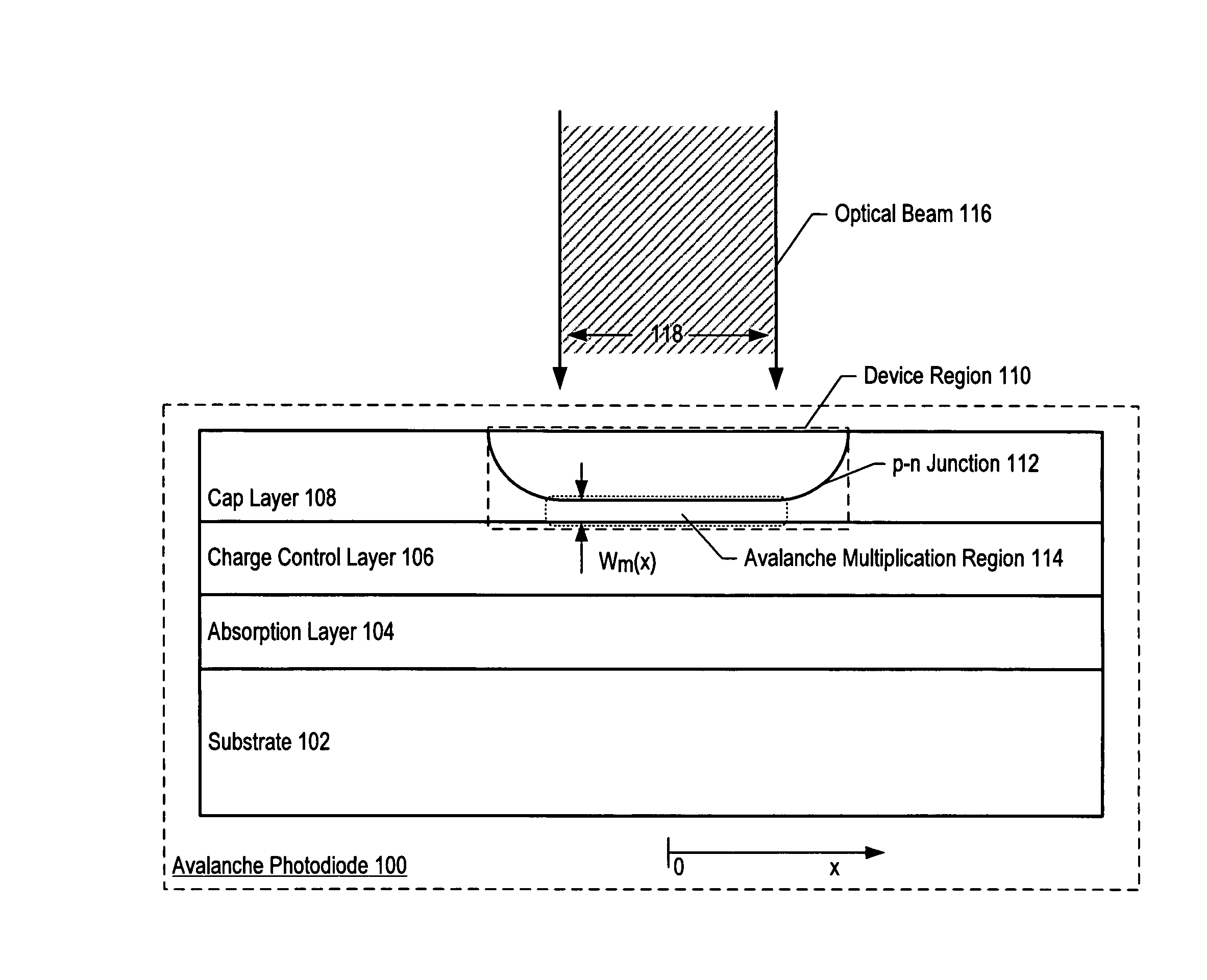
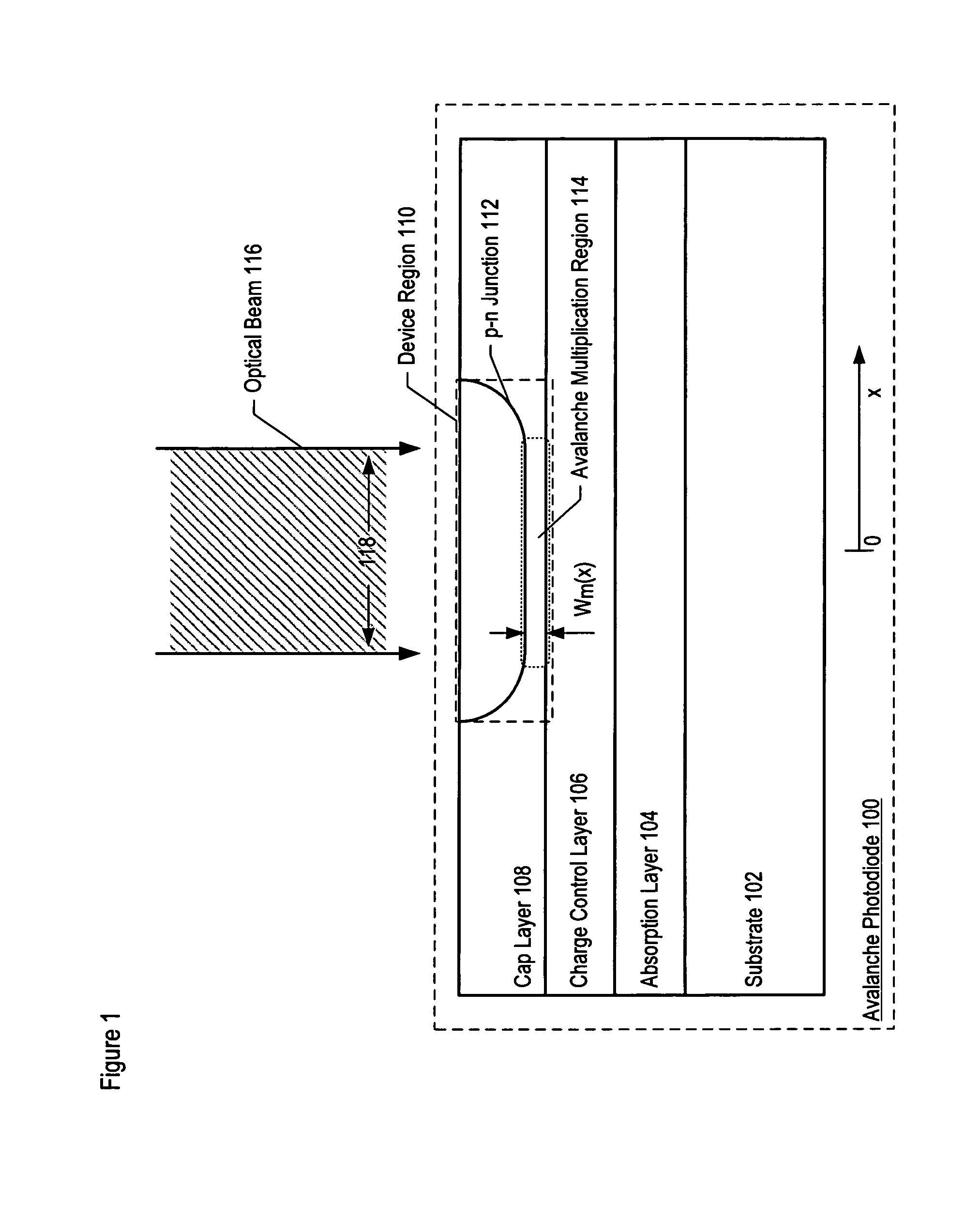
Apparatus comprising an avalanche photodiode
ActiveUS20070085158A1Reduce dark count rateSmall device sizeSemiconductor devicesDark count rateLight beam
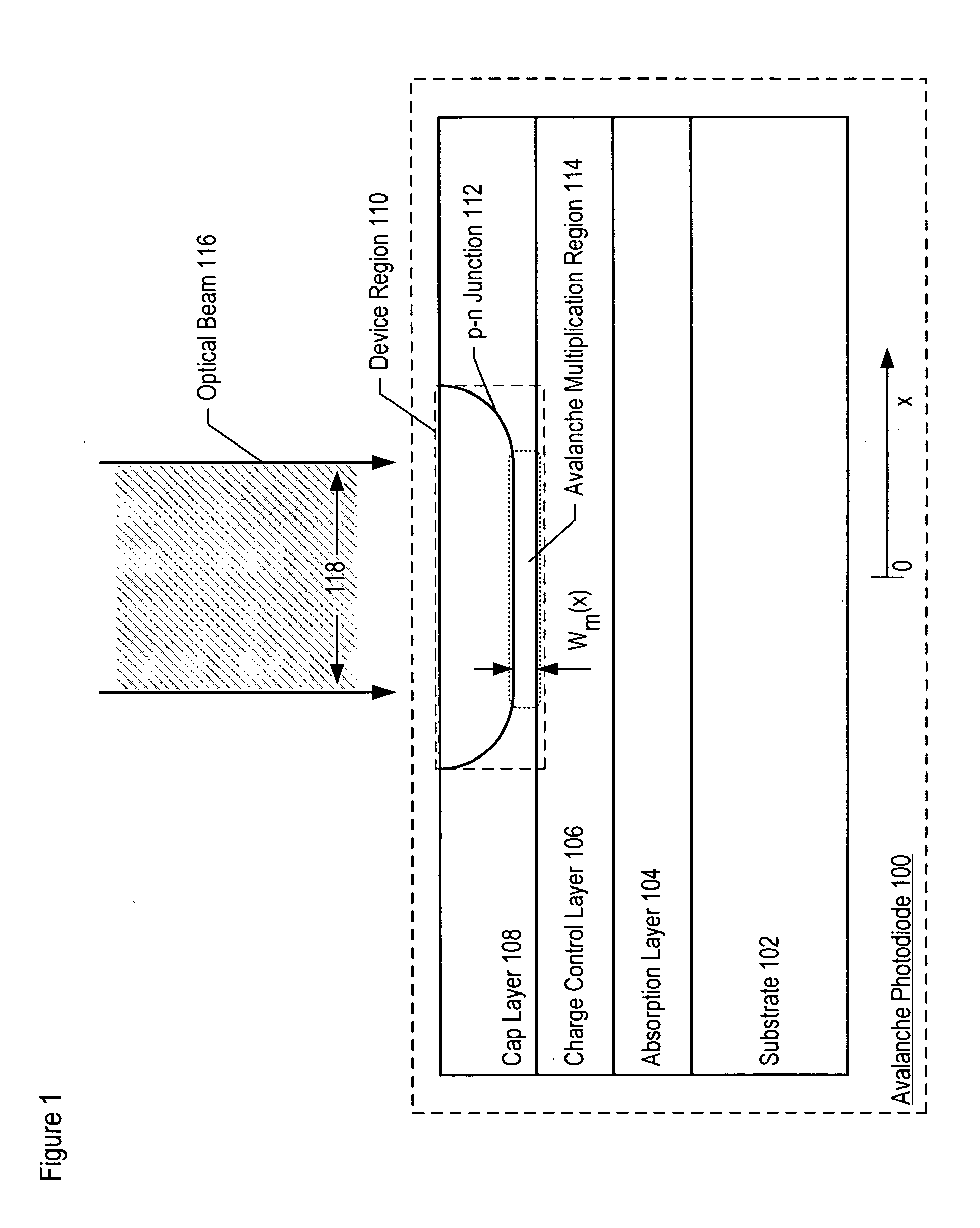
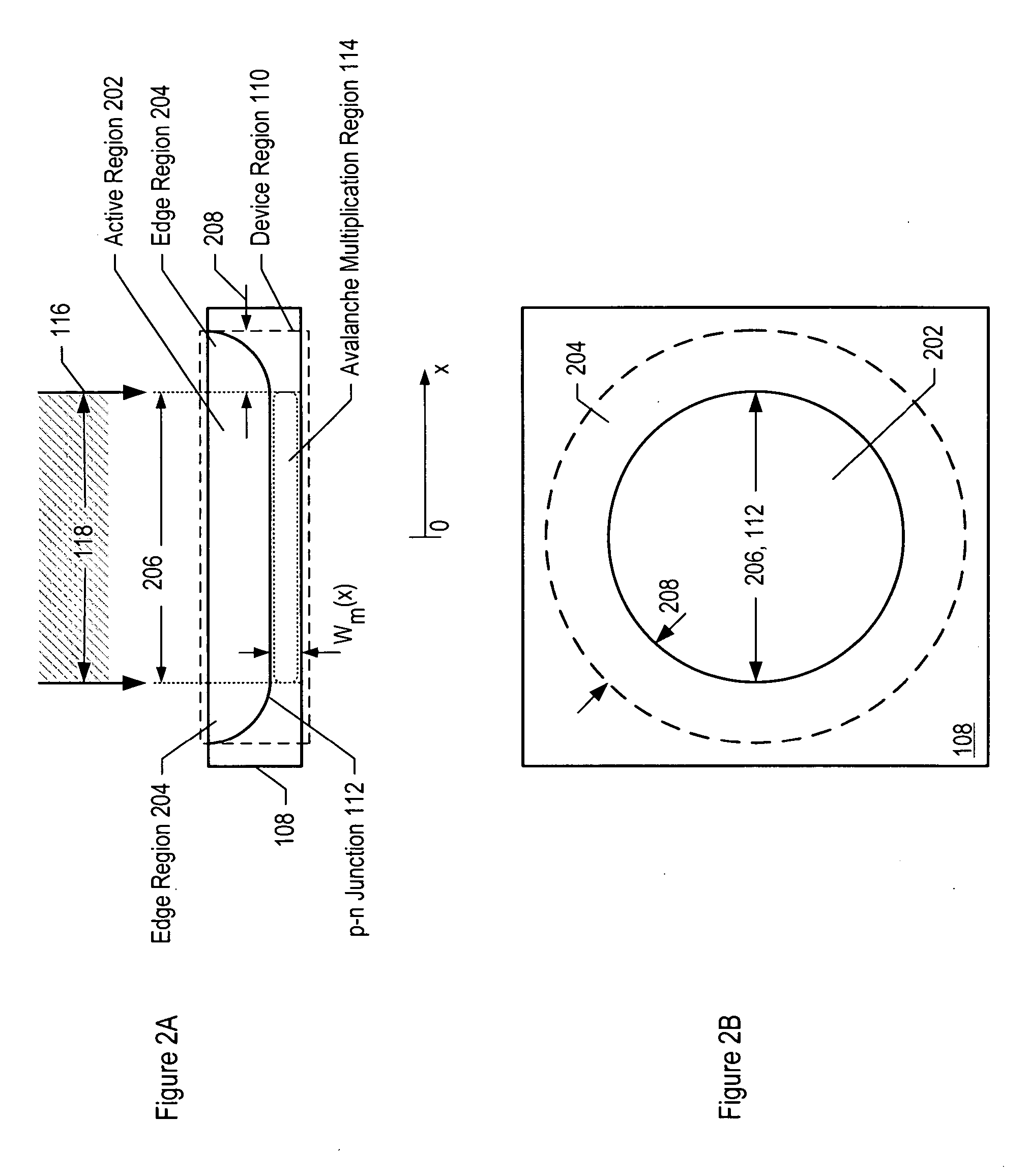
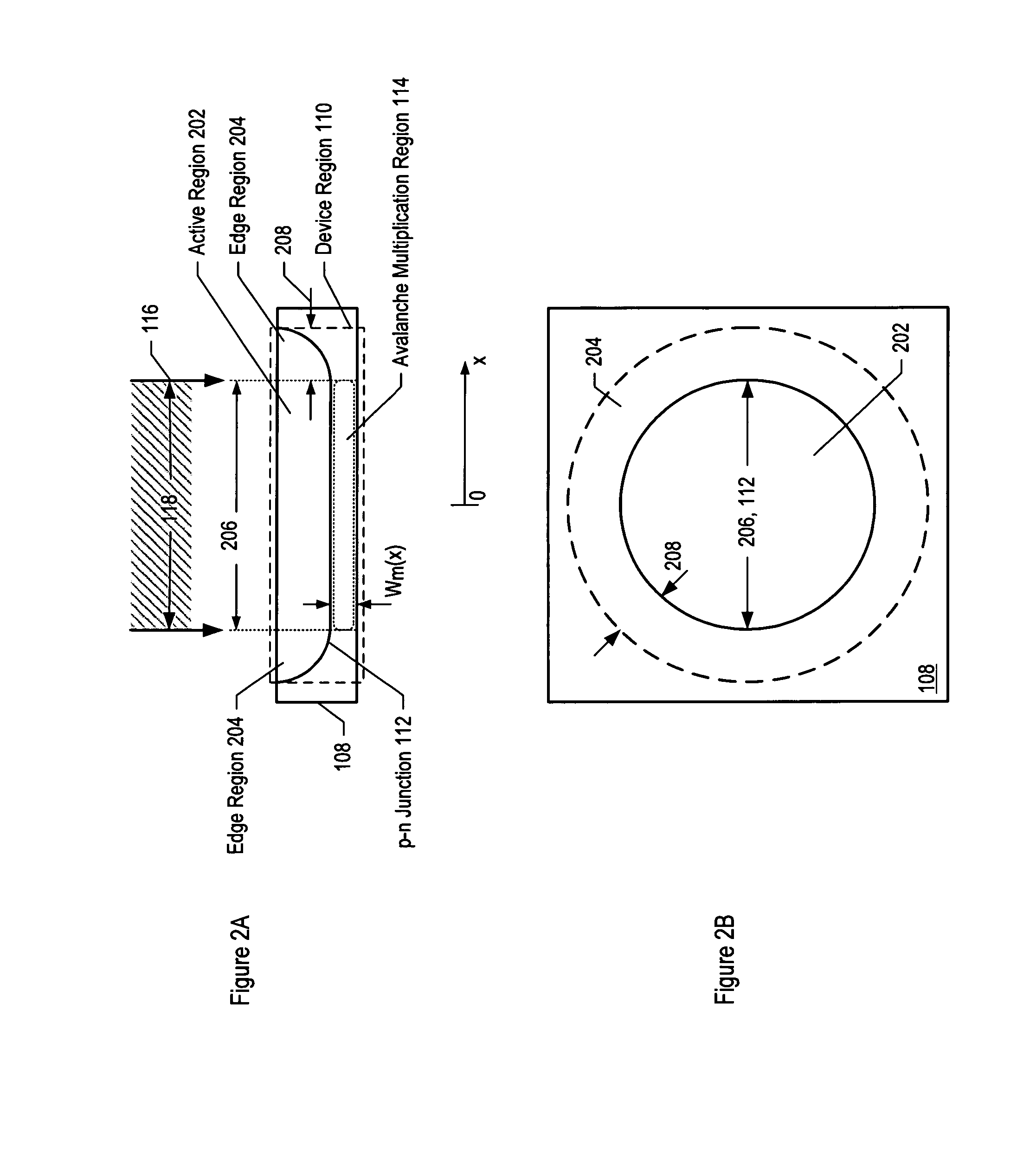
Avalanche photodiodes are provided, wherein the APDs provide both high optical coupling efficiency and low dark count rate. The APDs are formed such that their cap layer has an active region of sufficient width to enable high optical coupling efficiency but the APD still exhibits a low dark count rate. These cap layers have a device area with an active region and an edge region, wherein the size of the active region is substantially matched to the mode-field diameter of an optical beam, and wherein the size of the edge region is made small so as to reduce the number of defects included. These APD designs maintain a substantially uniform gain and breakdown voltage, as necessary for practical use.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Layouts for the monolithic integration of CMOS and deposited photonic active layers
ActiveUS8183516B2Improve communication bandwidthSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCMOSPhotonics
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
Method and Apparatus for Providing Non-Linear, Passive Quenching of Avalanche Currents in Geiger-Mode Avalanche Photodiodes
InactiveUS20080217521A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesMOSFETCurrent limiting
Owner:SENSORS UNLTD
Layouts for the monolithic integration of cmos and deposited photonic active layers
ActiveUS20070194213A1Improve communication bandwidthSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCMOSPhotonics
Several detailed layout designs are disclosed, for the monolithic integration of avalanche devices in large arrays, that can be operated as Avalanche Photo-Diodes (APDs) or Avalanche Light Emitting Diodes (ALEDs) depending only on the applied bias conditions, which can be software-controlled from peripheral circuitry. If the deposited films have direct bandgaps, then the devices can emit light even in the absence of avalanche operation. In particular, the layouts according to the invention comprise a sensor / emitter matrix achieved through the replication of basic Pixel / Lixel cells.
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
Novel Si-APD (Silicon-Avalanche Photo Diode) device
ActiveCN104180790ASolve complexityReduce complexityOptical rangefindersSemiconductor devicesNegative feedbackSilicon
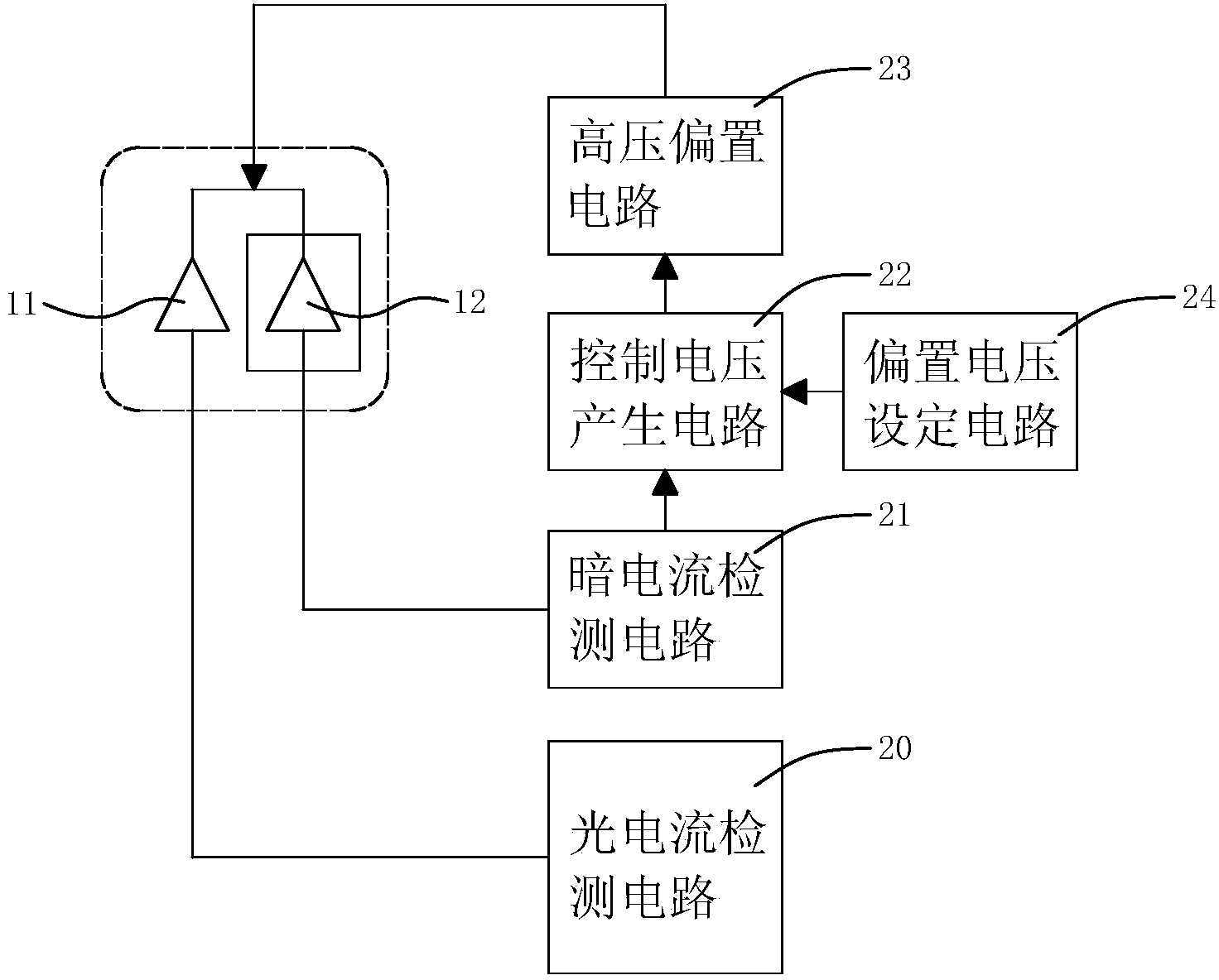
The invention discloses a novel Si-APD (Silicon-Avalanche Photo Diode) device. The novel Si-APD device comprises a first single Si-APD and a second single Si-APD which are arranged adjacently in parallel, wherein the first single Si-APD corresponds to a light window and serves as a light detection unit; the second single Si-APD is set in backlight and serves as a breakdown voltage detection unit; the first single Si-APD and the second single Si-APD share the same negative pole. Based on the principle that the properties of adjacent devices in the integrated circuit technology are consistent with each other, and paired Si-APDs are adopted; the first single Si-APD is used for detecting light and the second single Si-APD serves as the breakdown voltage detection unit; an optimal bias effect can be achieved, just by means of detecting the dark current of the second single Si-APD, stabilizing the value of the dark current via a negative feedback control loop, and utilizing the voltage when the value of the dark current is maintained at a set value to serve as the work bias voltage of the first single Si-APD, so that the complicacy problem of the traditional dynamic bias is solved, the complicacy degree and cost of a distance measuring system are lowered, and the novel Si-APD device is simple and practical.
Owner:ASSOC OPTO ELECTRONICS CHONGQING
Closed ring feedback control distribution type optical fiber temperature sensing system at non-constant temperature
InactiveCN101551280ASimple structureSimple circuitThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsClosed loop feedbackFeedback control
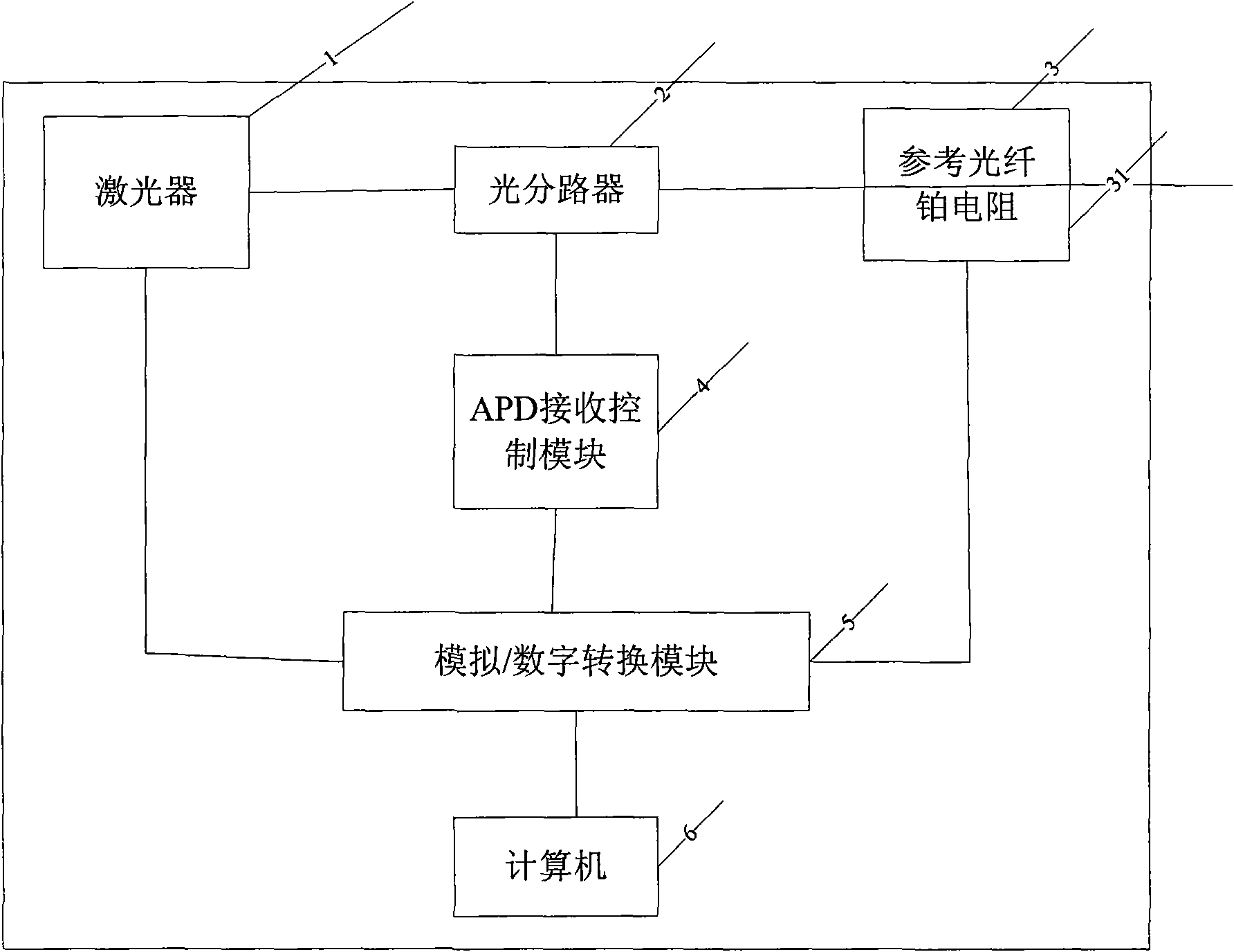
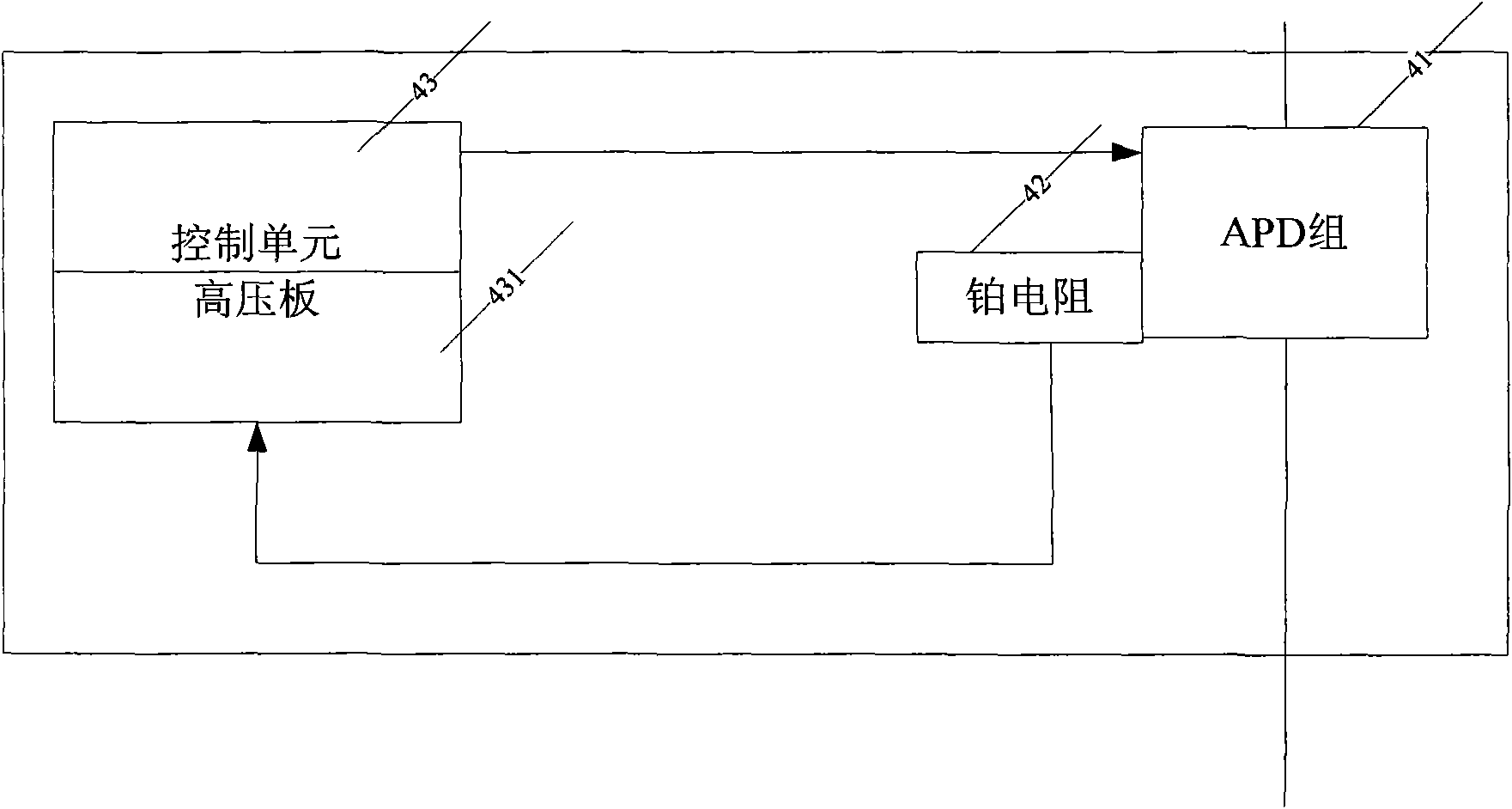
The invention is a closed ring feedback control distribution type optical fiber temperature sensing system at non-constant temperature, mainly comprising a laser, an output end of which is connected with a light-way divider; one section of a start portion of measuring optical fiber output by the light-way divider is selected as reference optical fiber and temperature in periphery is measured by platinum resistor; the light-way divider divides retrodiffusion lights into Stocks and antiStocks lights which are transmitted to an APD group composed of two APDs in an APD receiving and control module provided with a platinum resistor which affects multiplying parameter of factor of APD optical electrical conversion signal; temperature of work environment of APD is transmitted to the control unit which adjusts voltage of the APD via a high voltage plate to maintain the multiplying parameter of APD optical electrical conversion signal invariable to receive optical electrical signal stably; the other by platinum resistor measures environmental temperature of position where the optical fiber is. After AD conversion and algorithm process, the optical fiber sensing temperature can be calibrated.
Owner:SHANGHAI BOOM FIBER SENSING TECH
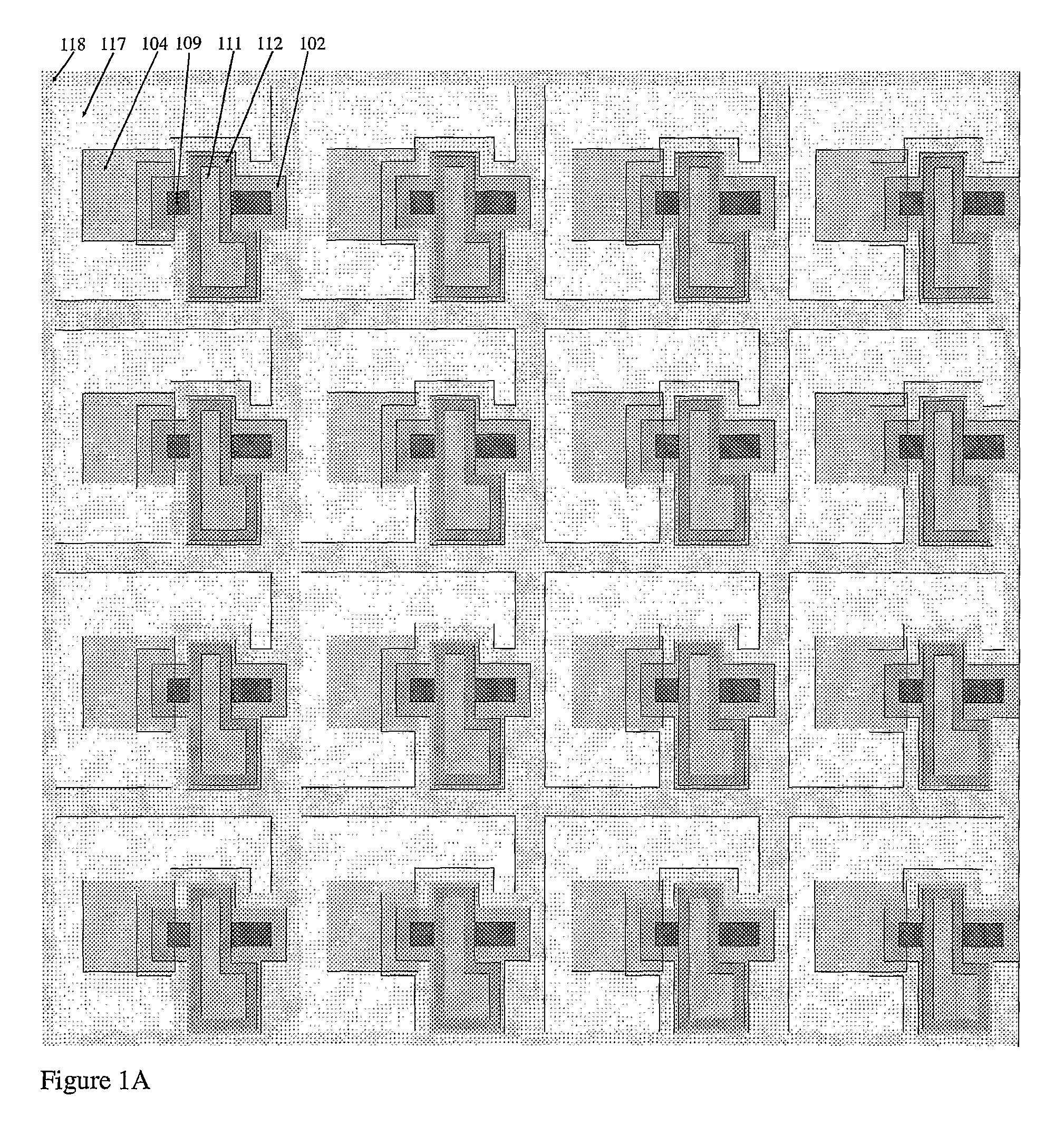
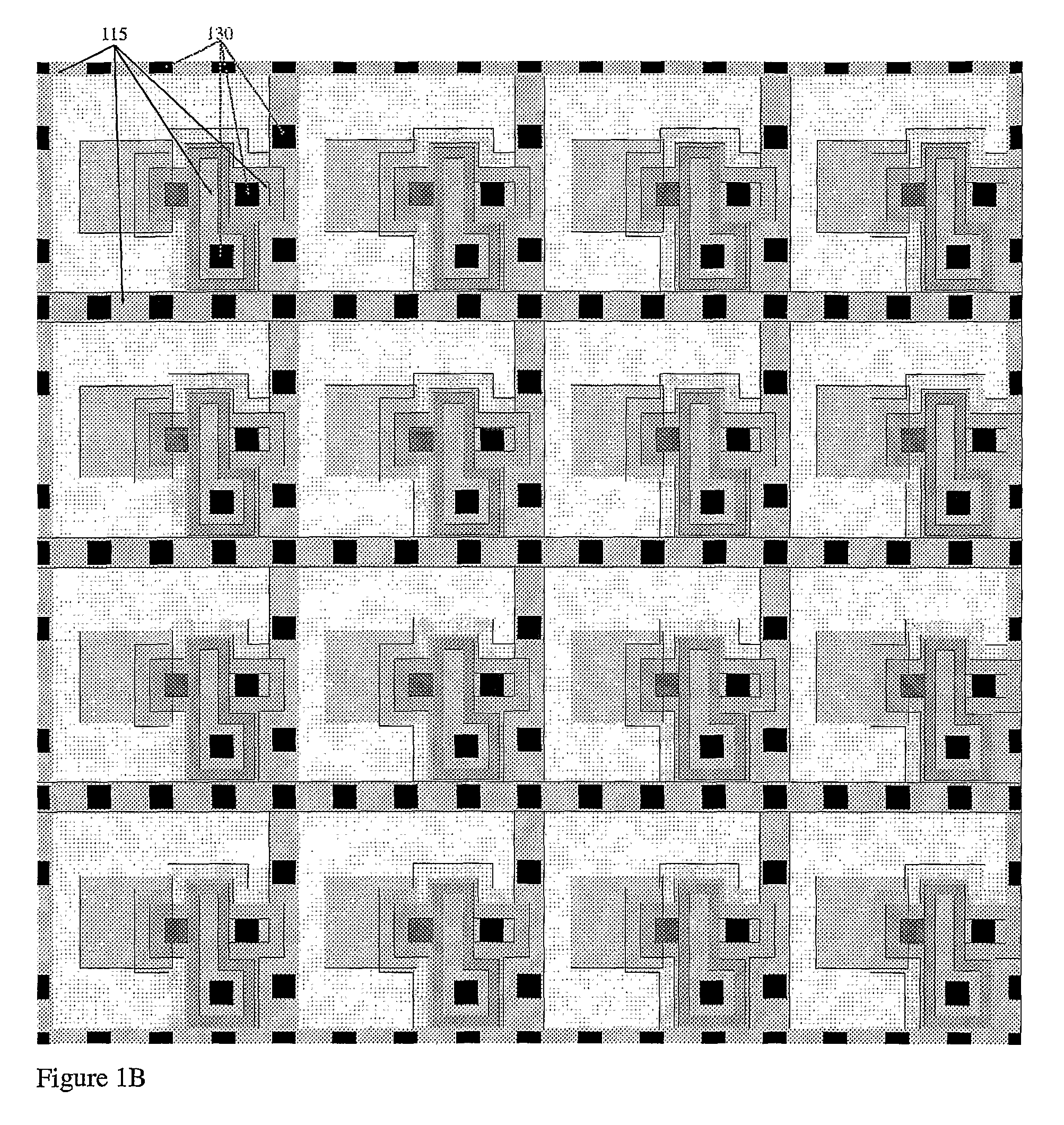
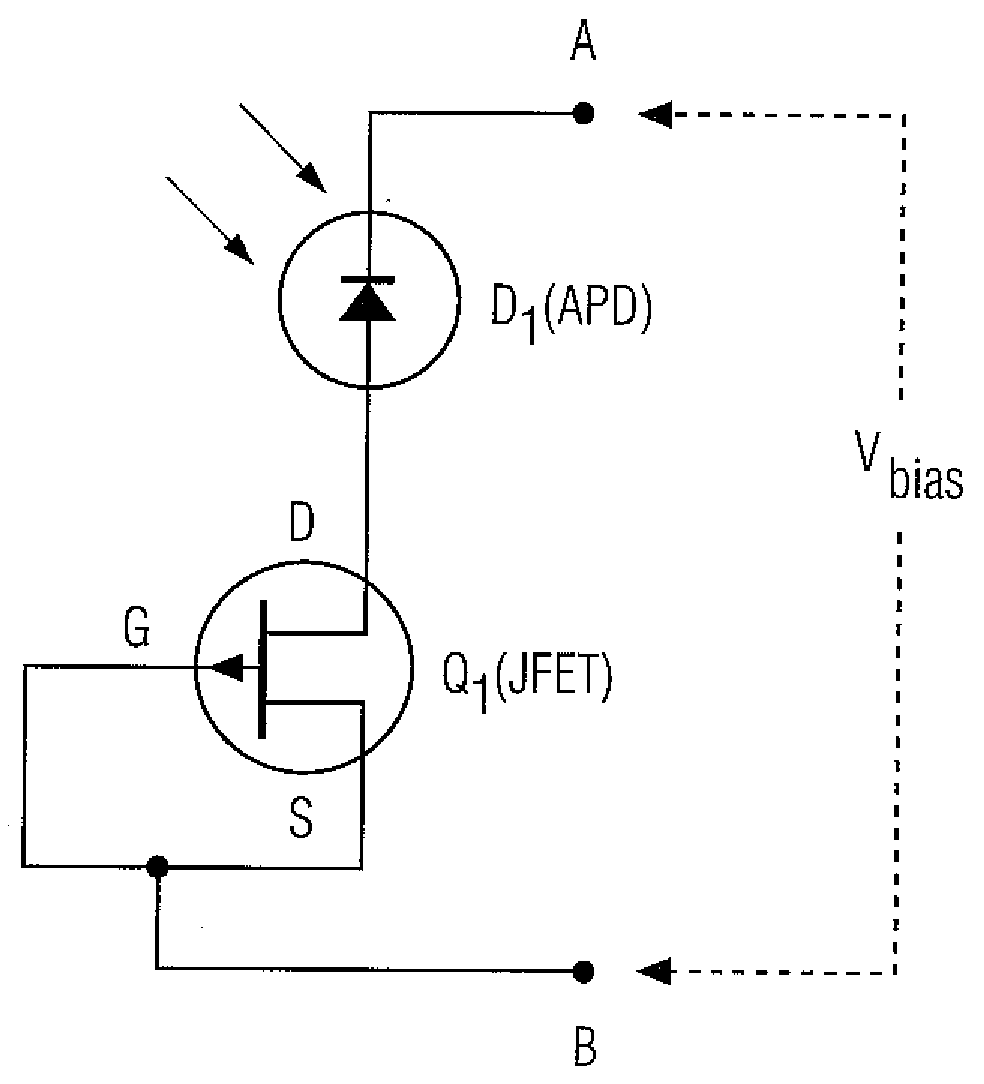
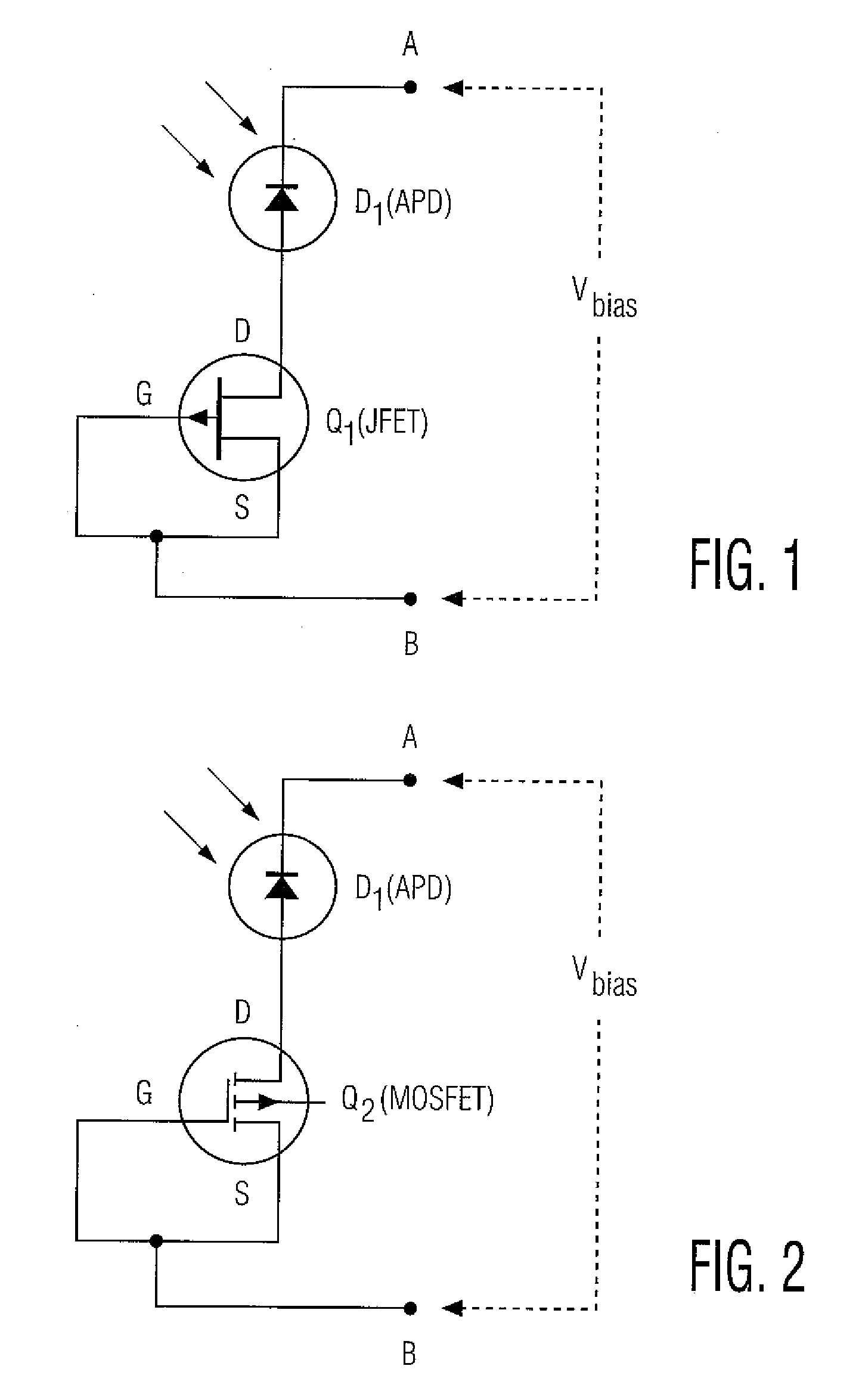
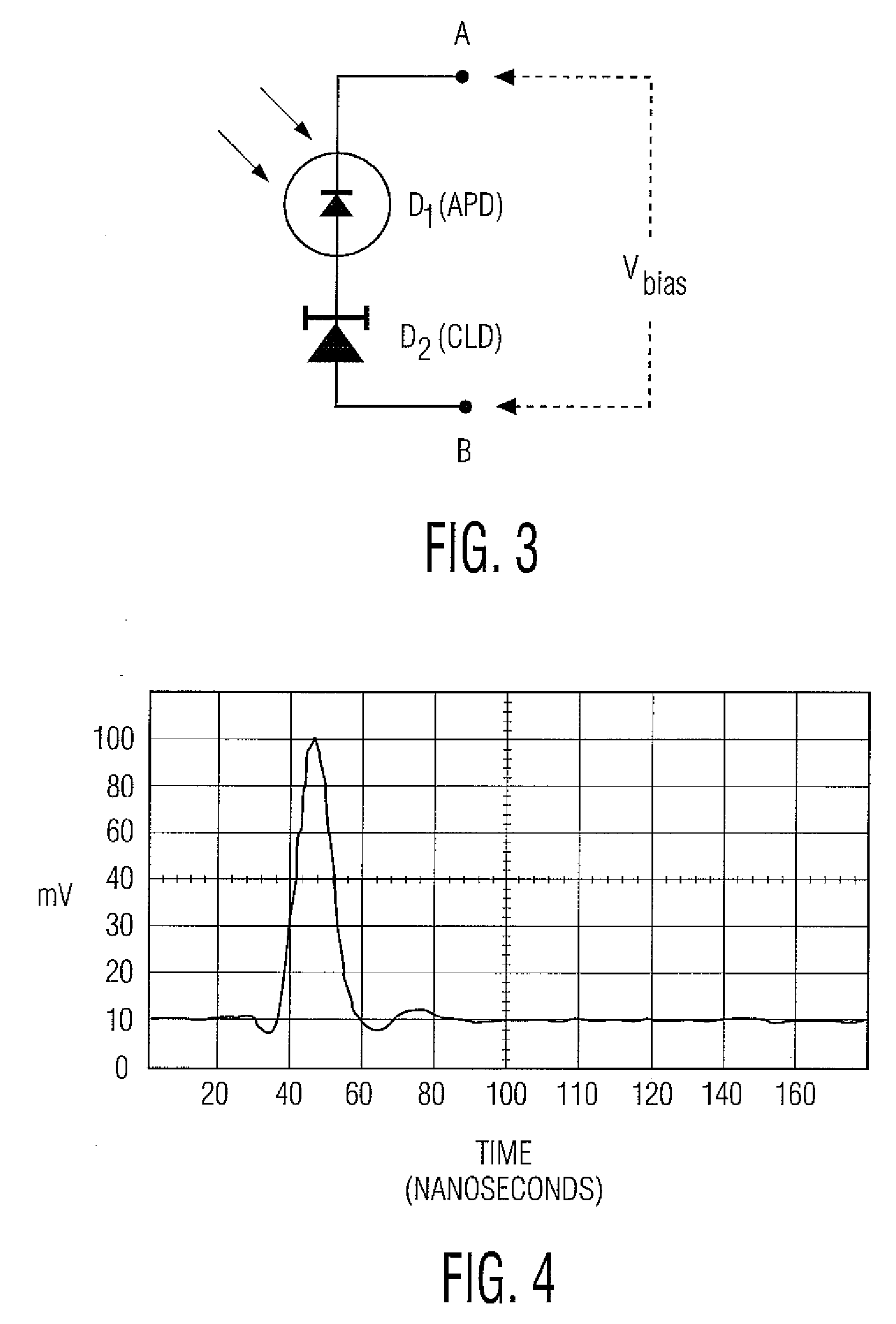
Method and apparatus for providing non-linear, passive quenching of avalanche currents in Geiger-mode avalanche photodiodes
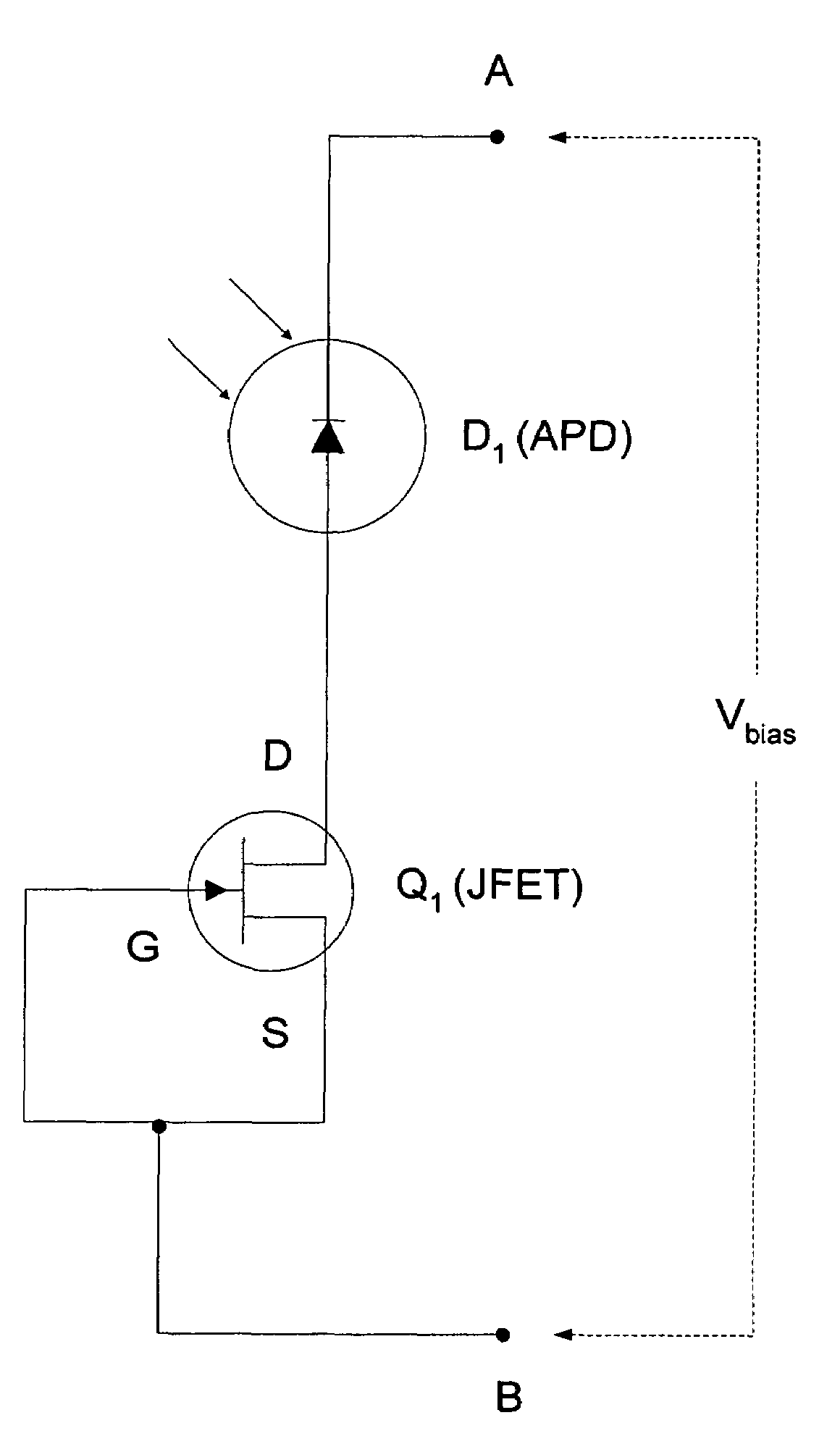
A method and apparatus for providing non-linear, passive quenching of avalanche currents in Geiger-mode avalanche photodiodes (APDs) is provided. A non-linear, passive, current-limiting device is connected in series with the APD and a bias source. The non-linear, passive, current-limiting device rapidly quenches avalanche currents generated by the APD in response to an input photon and resets the APD for detecting additional photons, using a minimal number of components. The non-linear, passive, current-limiting device could comprise a field-effect transistor (FET), as well as a junction FET (JFET) a metal-oxide semiconductor FET (MOSFET), or a current-limiting diode (CLD) connected in series with the APD and the bias source.
Owner:SENSORS UNLTD
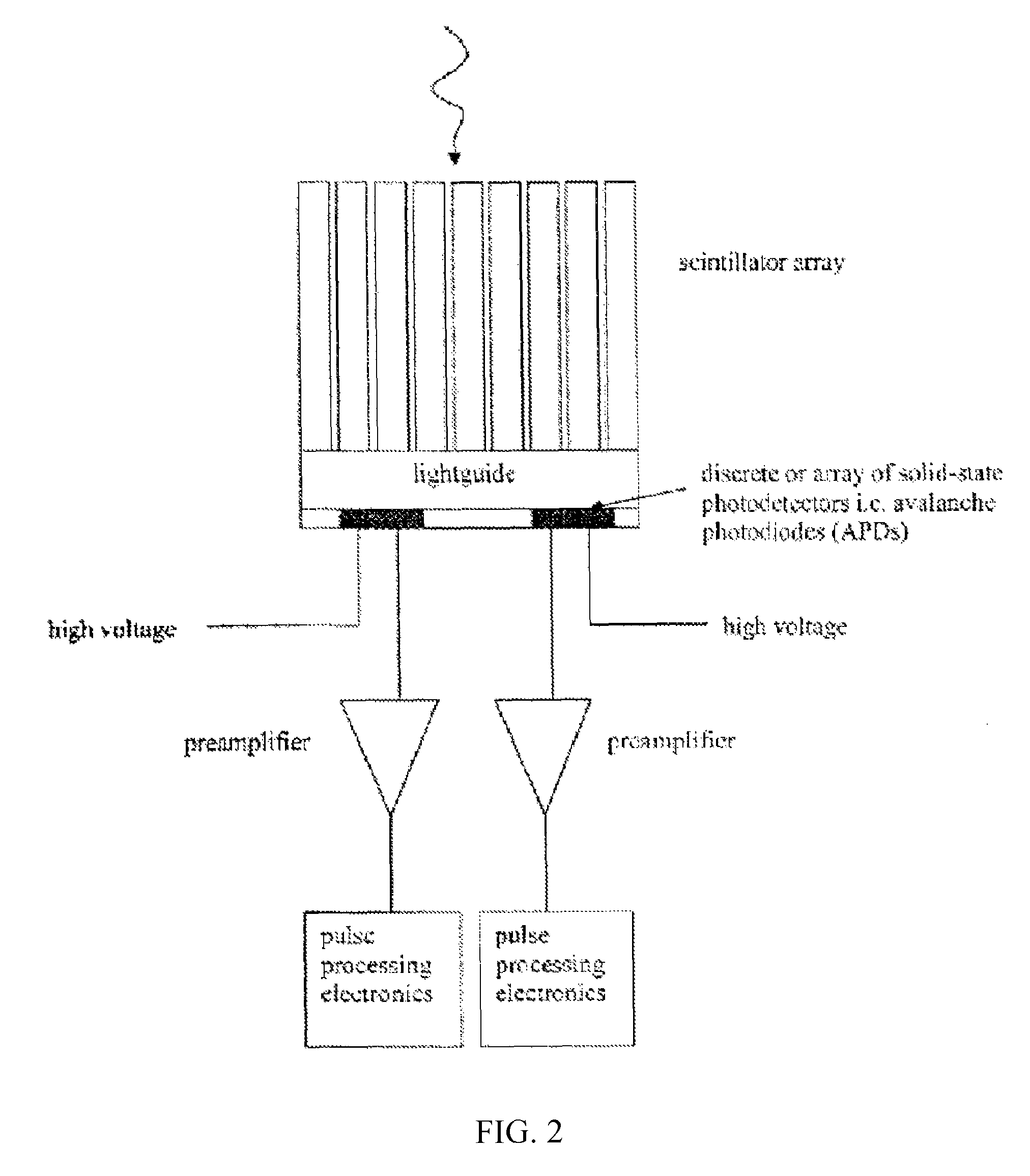
Wavelength shifting lightguides for optimal photodetection in light-sharing applications
InactiveUS20080121806A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementPhotovoltaic detectorsPet imaging
A scintillation detector for PET imaging devices includes a wavelength shifting material for shifting the emission wavelength of a scintillator toward the peak wavelength sensitivity of a photodetector array coupled to receive light from the scintillator. Preferably the scintillator is an LSO scintillator and the photodetector array is a silicon-based array such APDs or SiPMs.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
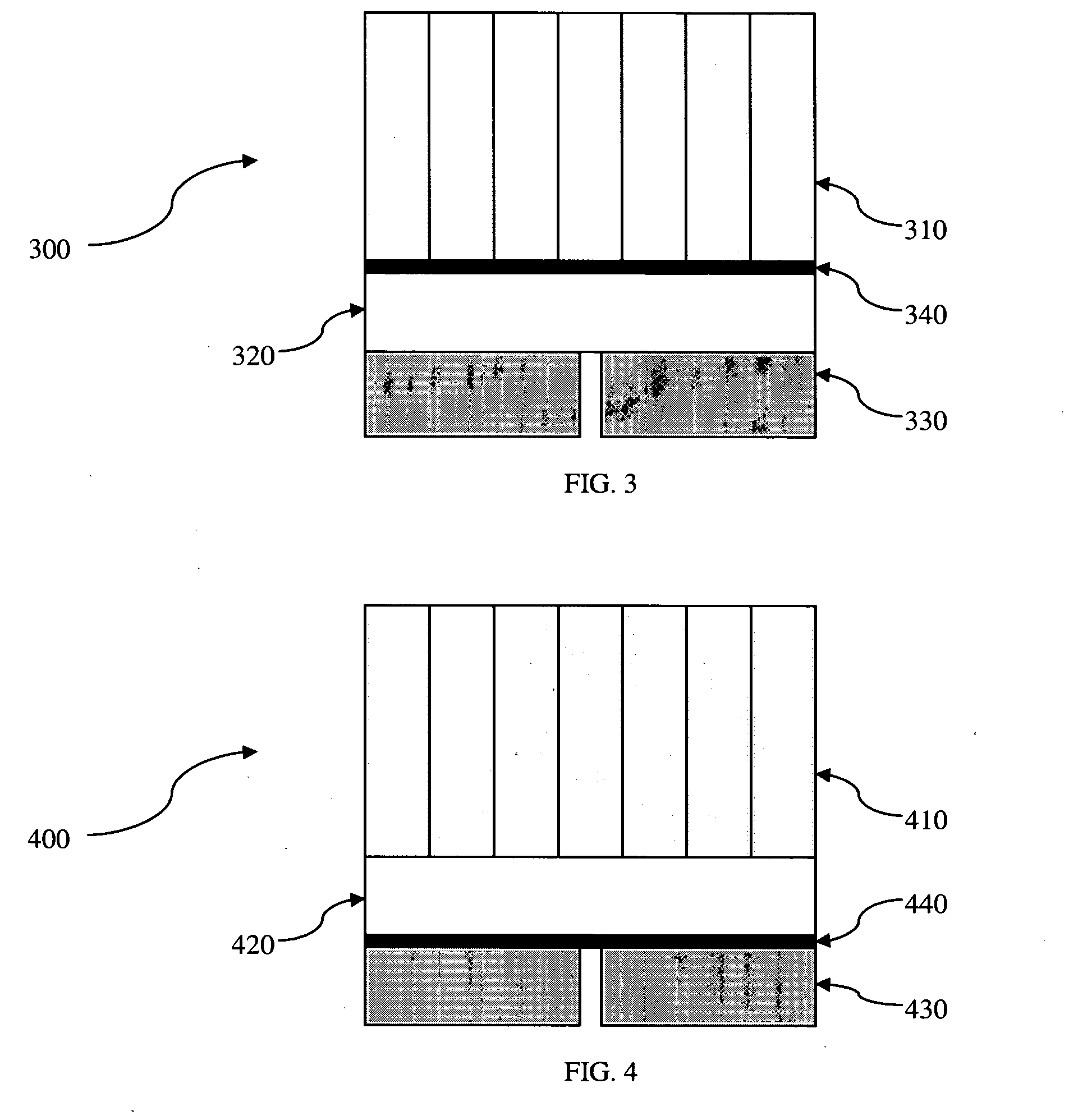
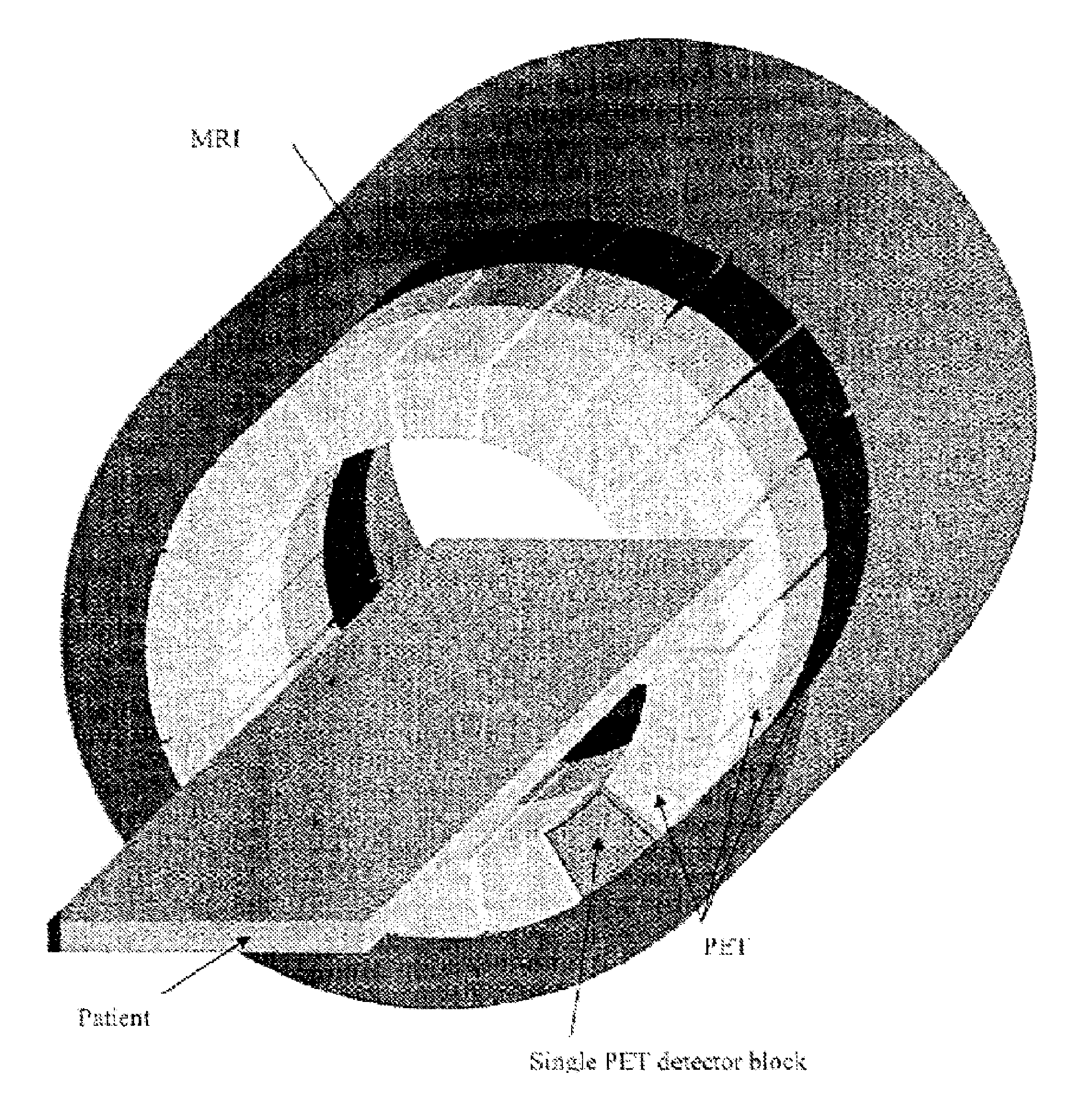
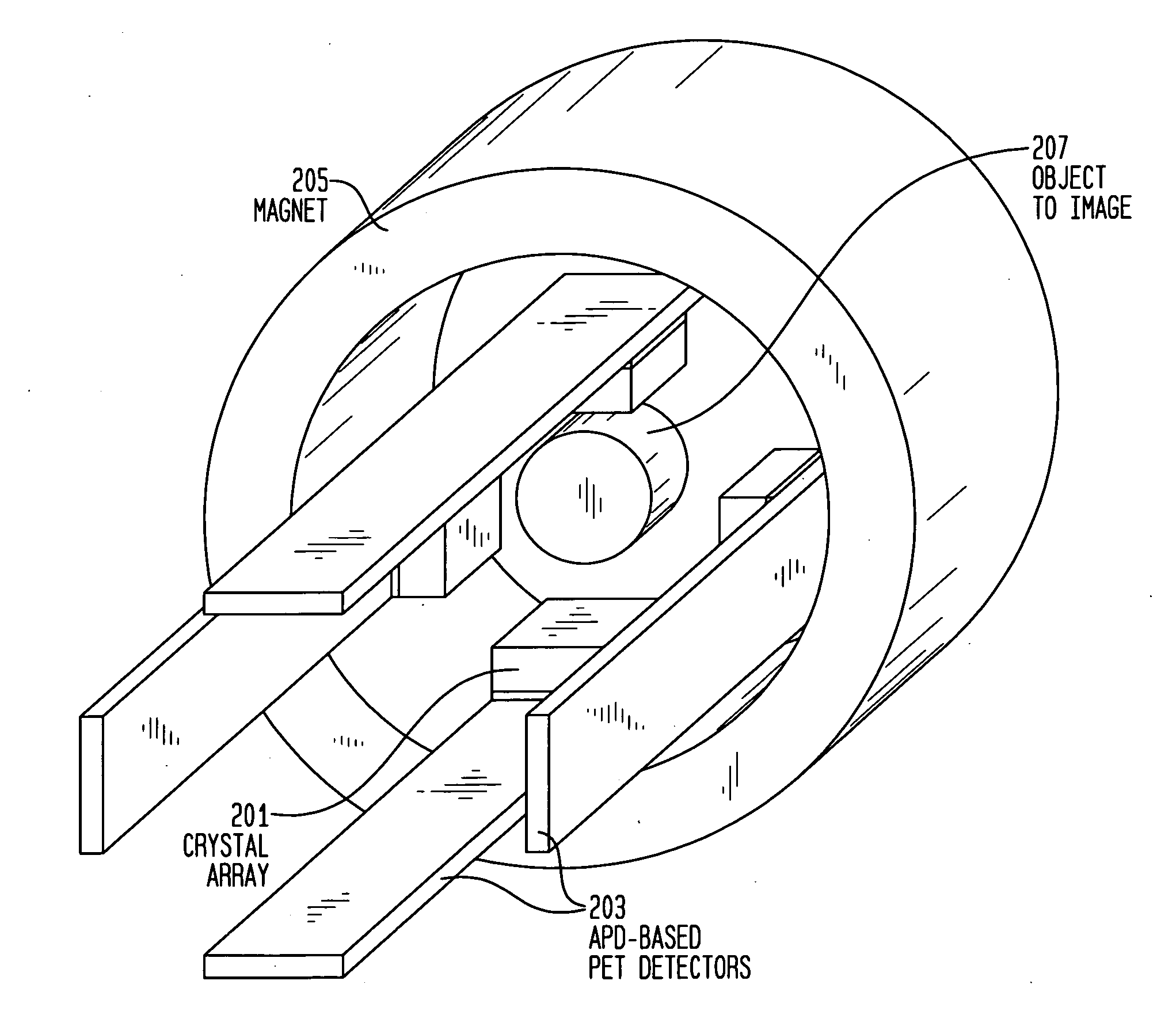
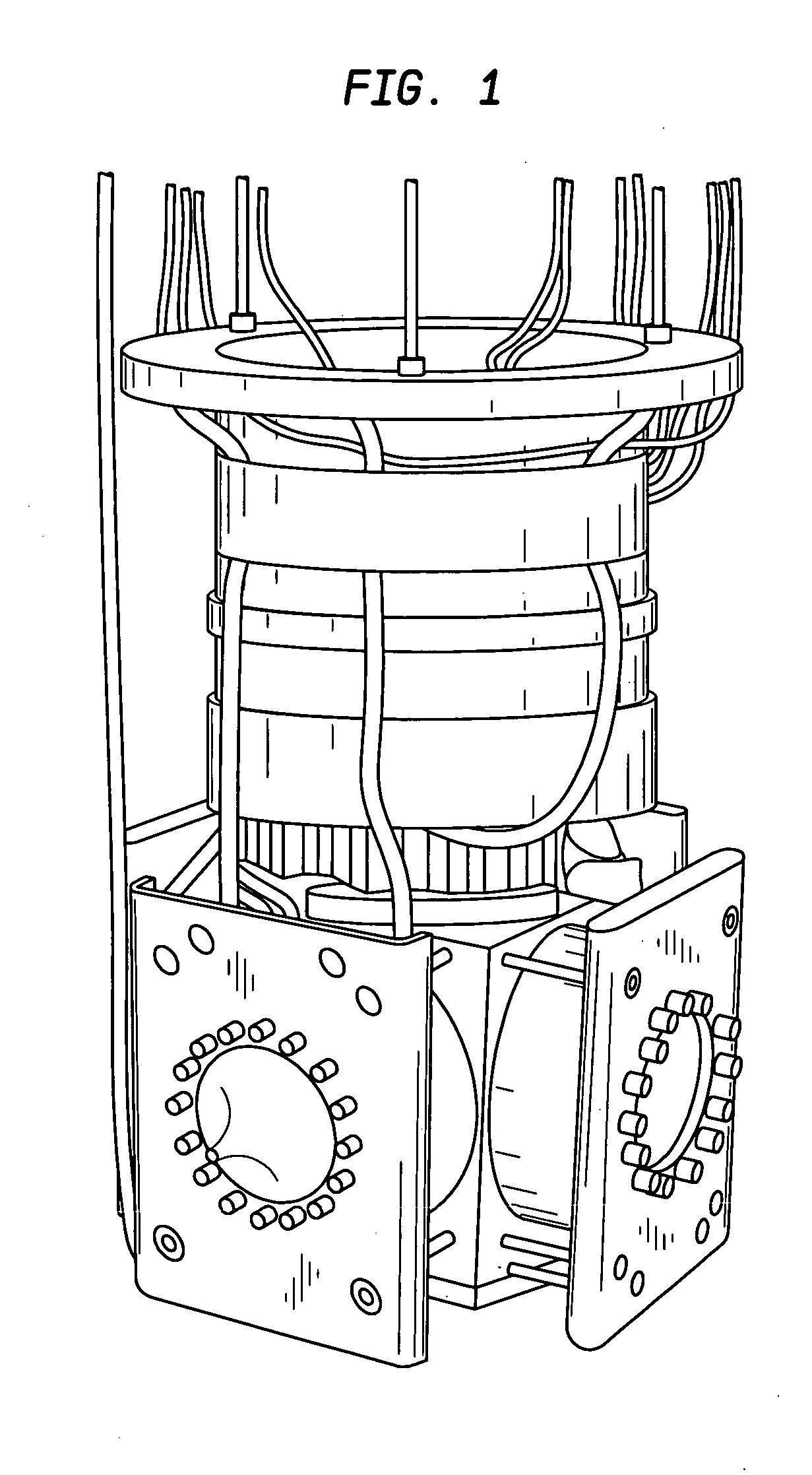
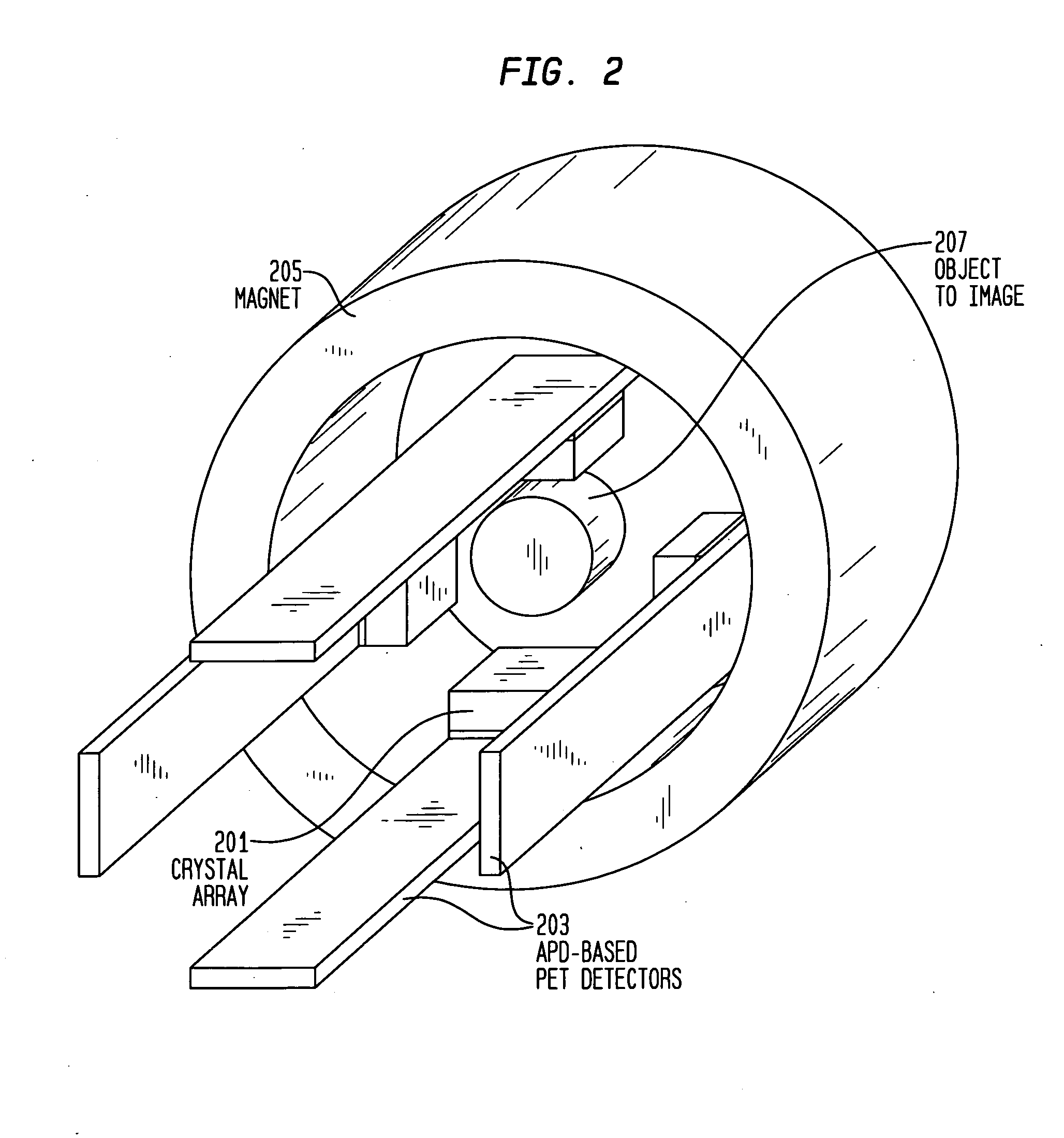
Combined PET/MR imaging system and APD-based pet detector for use in simultaneous PET/MR imaging
ActiveUS9121893B2Computerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer moduleCompanion animal
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Device discovery and topology reporting in a combined CPU/GPU architecture system
ActiveUS8797332B2Efficiently scheduling and distributingImage memory managementBorehole drivesSystem topologyOperating system
Methods and apparatus are provided, as an aspect of a combined CPU / APD architecture system, for discovering and reporting properties of devices and system topology that are relevant to efficiently scheduling and distributing computational tasks to the various computational resources of a combined CPU / APD architecture system. The combined CPU / APD architecture unifies CPUs and APDs in a flexible computing environment. In some embodiments, the combined CPU / APD architecture capabilities are implemented in a single integrated circuit, elements of which can include one or more CPU cores and one or more APD cores. The combined CPU / APD architecture creates a foundation upon which existing and new programming frameworks, languages, and tools can be constructed.
Owner:ATI TECH INC +1
PET imaging system with APD-based PET detectors and three-dimensional positron-confining magnetic field
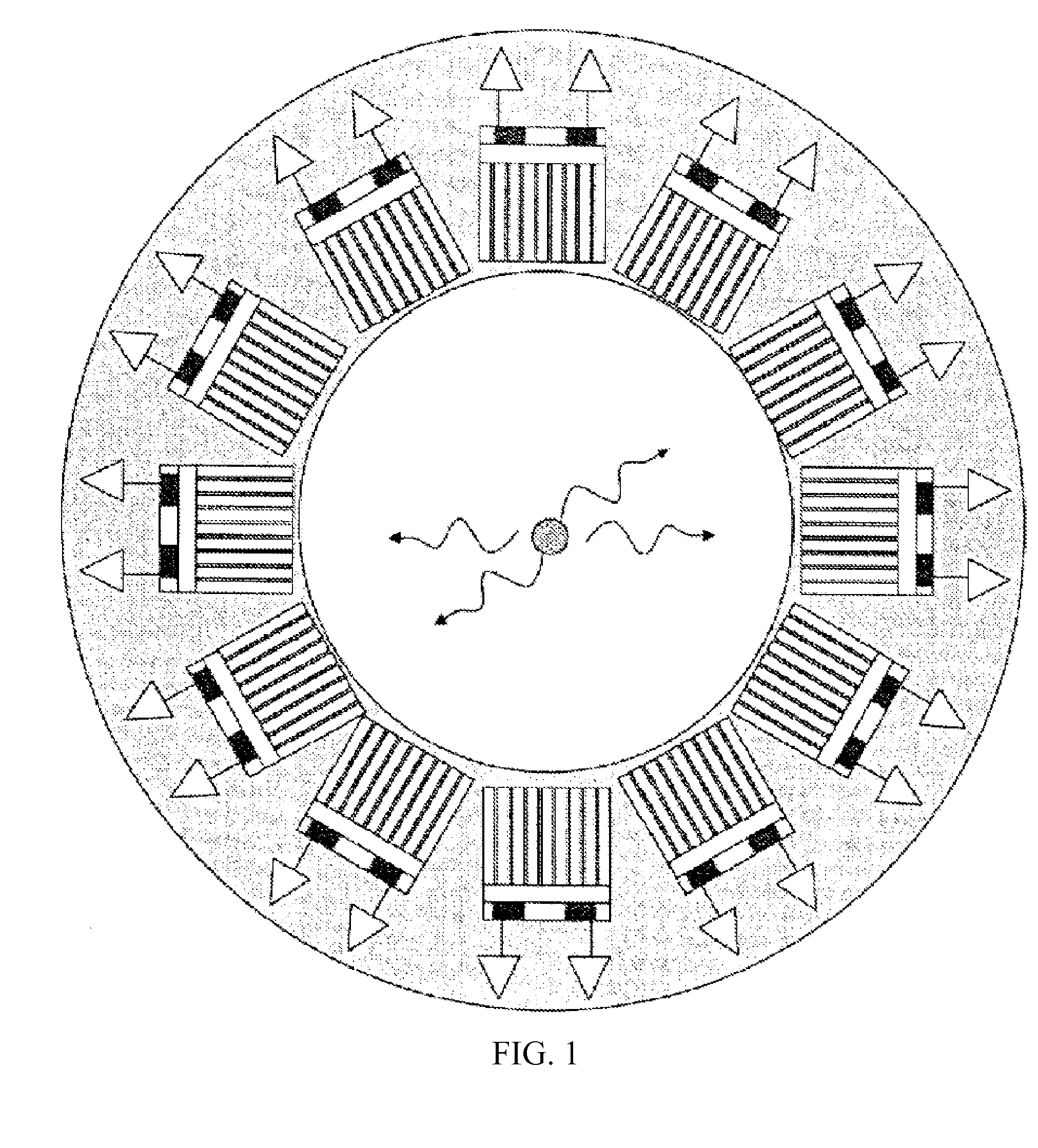
InactiveUS20080173819A1Improve spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyImage resolutionPet imaging
PET detector modules are provided within a multi-dimensional magnetic field, to confine the range of emitted positrons from an object being imaged to improve spatial resolution of reconstructed PET images. Each module includes a number of independent, optically isolated detectors. Each detector includes an array of scintillator crystals read out by an array of APDs (avalanche photodiodes).
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Apparatus Comprising an Avalanche Photodiode
ActiveUS20080164554A1High optical coupling efficiencyLow dark count rateSemiconductor devicesDark count rateOptical coupling
Avalanche photodiodes are provided, wherein the APDs provide both high optical coupling efficiency and low dark count rate. The APDs are formed such that their cap layer has an active region of sufficient width to enable high optical coupling efficiency but the APD still exhibits a low dark count rate. These cap layers have a device area with an active region and an edge region, wherein the size of the active region is substantially matched to the mode-field diameter of an optical beam, and wherein the size of the edge region is made small so as to reduce the number of defects included. These APD designs maintain a substantially uniform gain and breakdown voltage, as necessary for practical use.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Method for actively synchronizing U-APSD service periods
InactiveUS7545786B2Minimizes inter-service period timeNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsNetwork addressing
A wireless LAN environment includes at least one access point that supports a number of wireless communications devices which are configured to operate in the U-APSD mode. The transmission of packets by an access point to a wireless communications device operating in the U-APDS mode can be accomplished in an efficient manner by coordinating the unscheduled service periods of the wireless communication devices. The service periods are placed into a tightly packed list ordered according to a network address associated with each wireless communications device.
Owner:SPECTRALINK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com