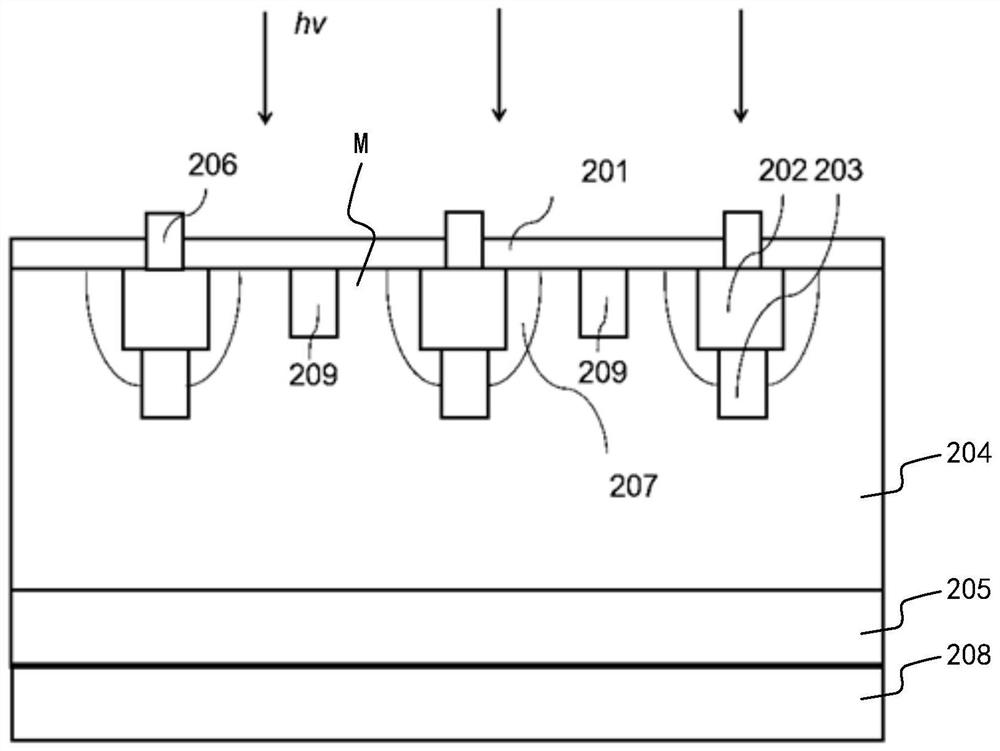
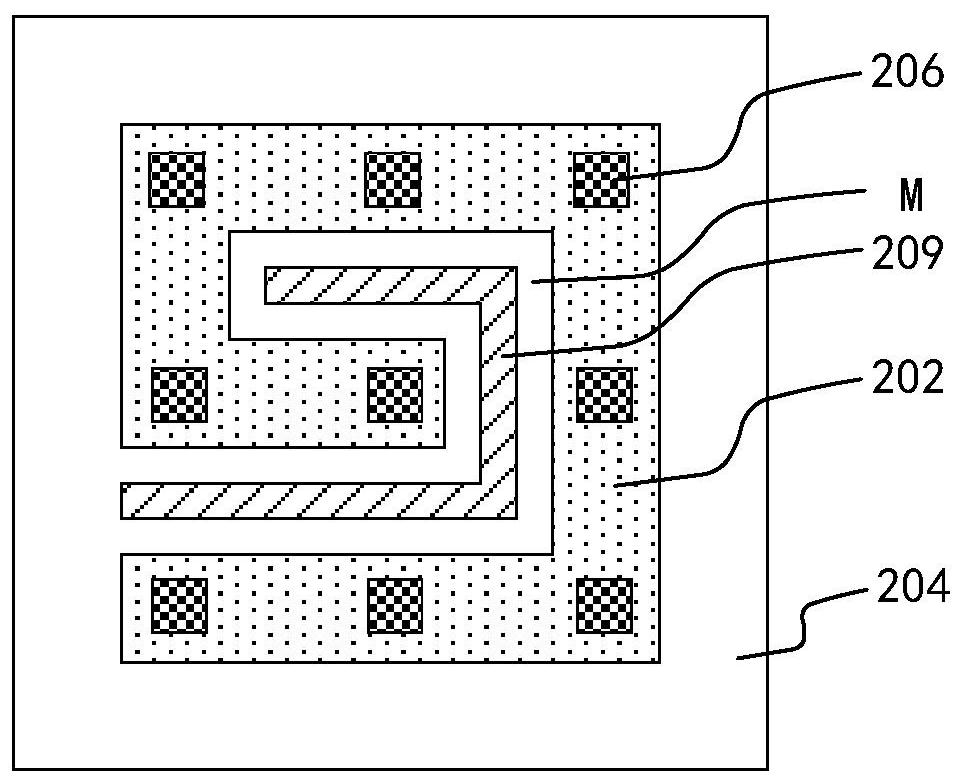
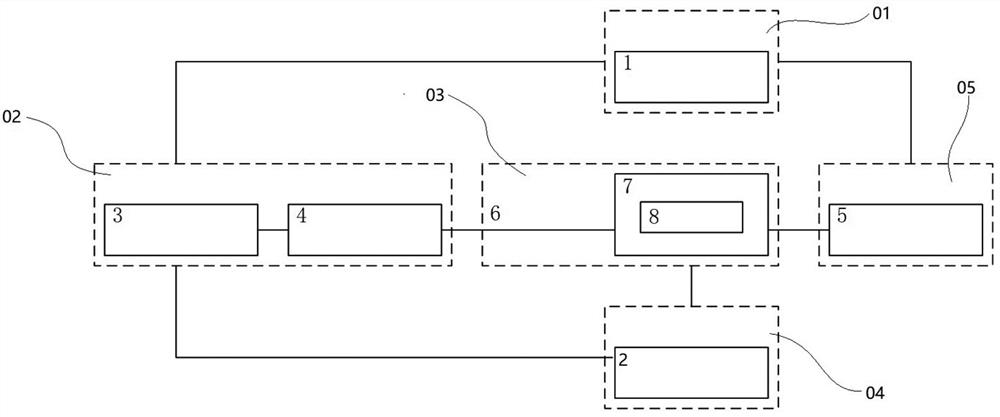
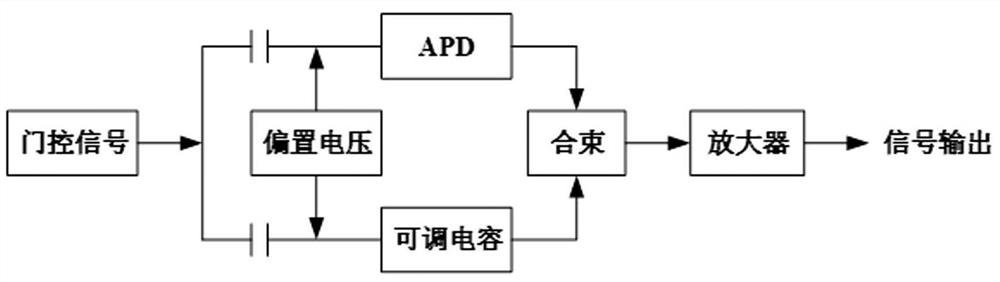
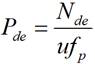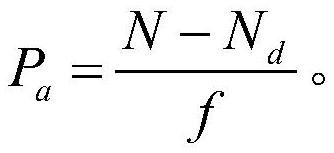Patents
Literature
30 results about "Dark count rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
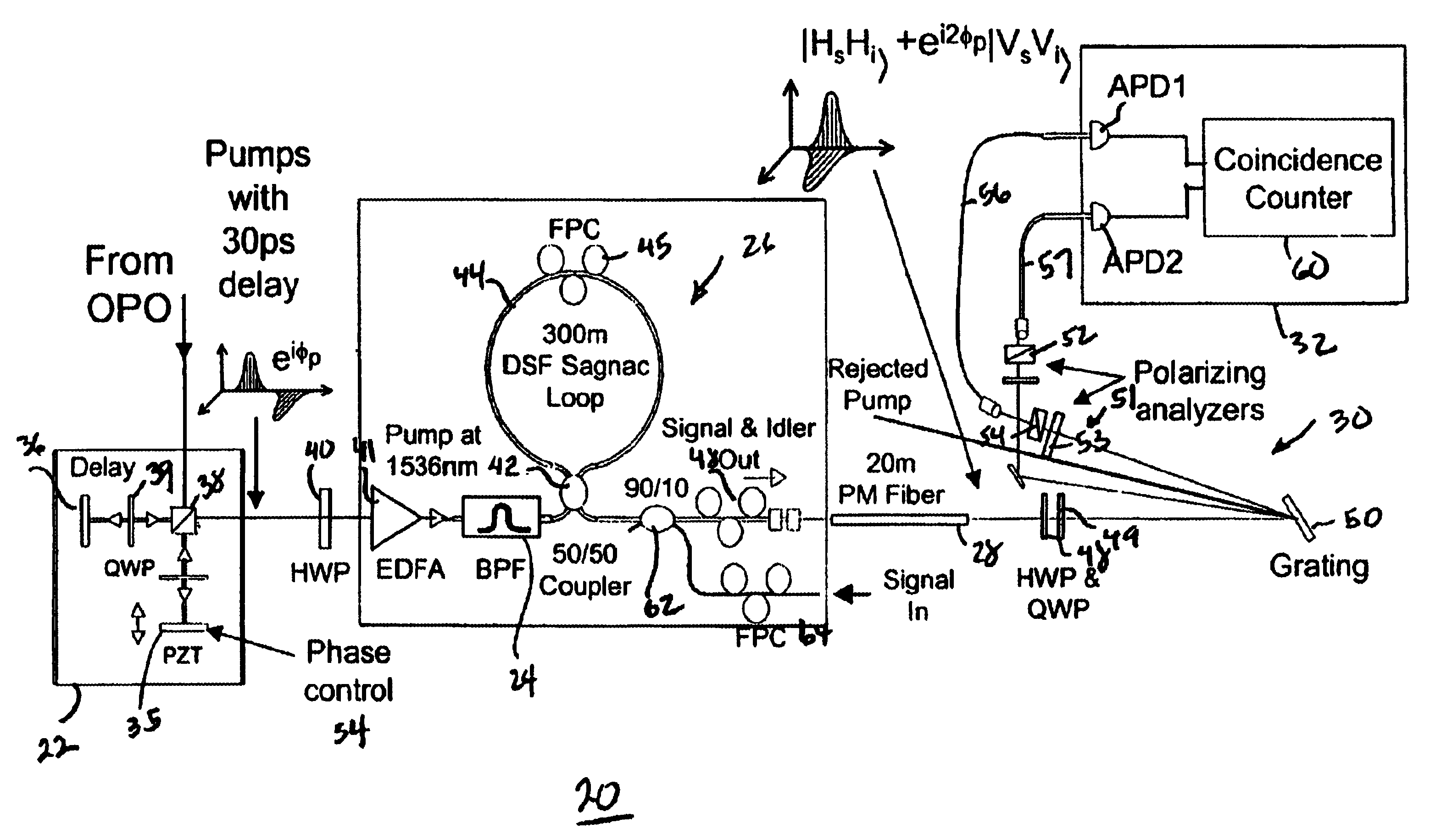
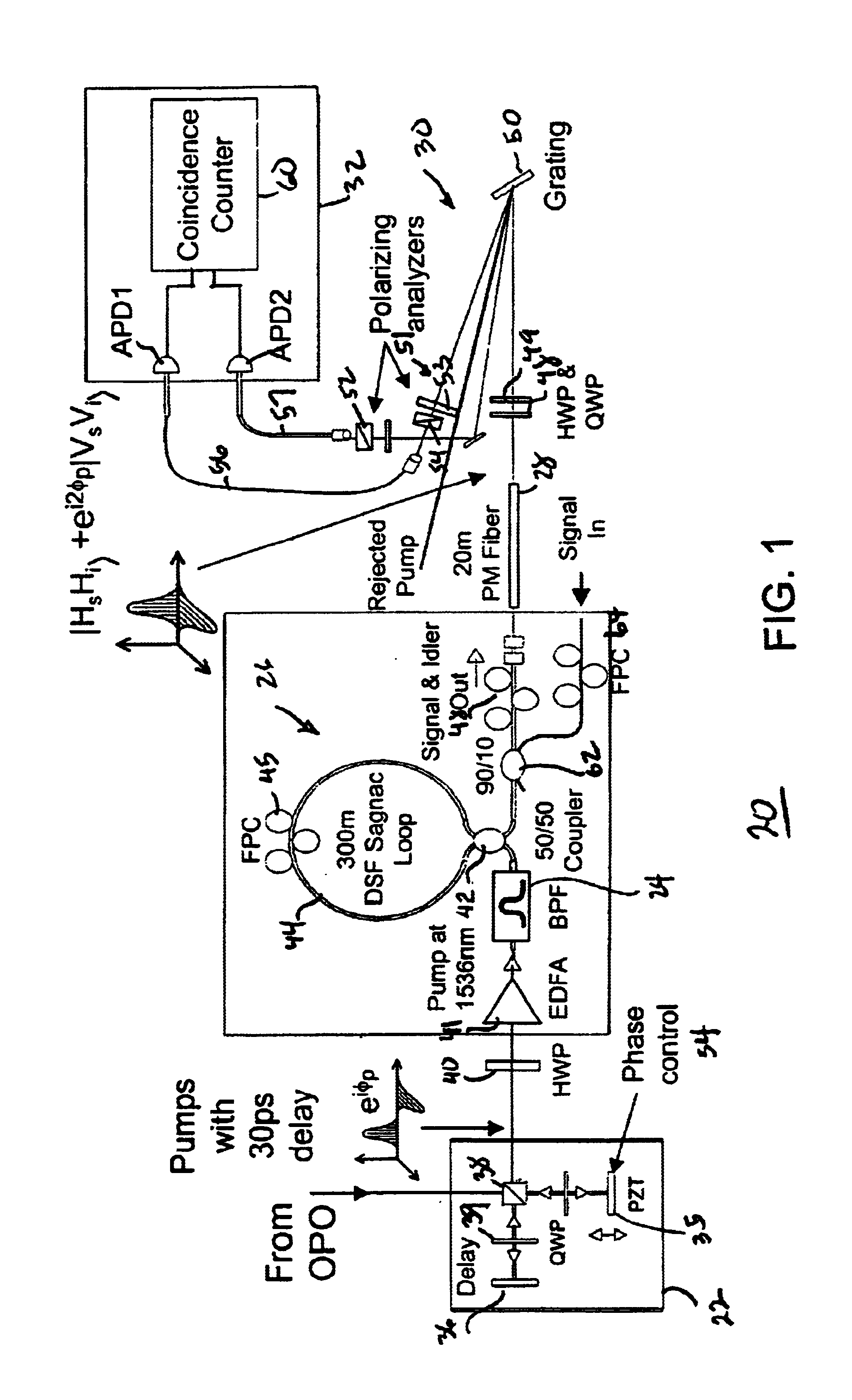
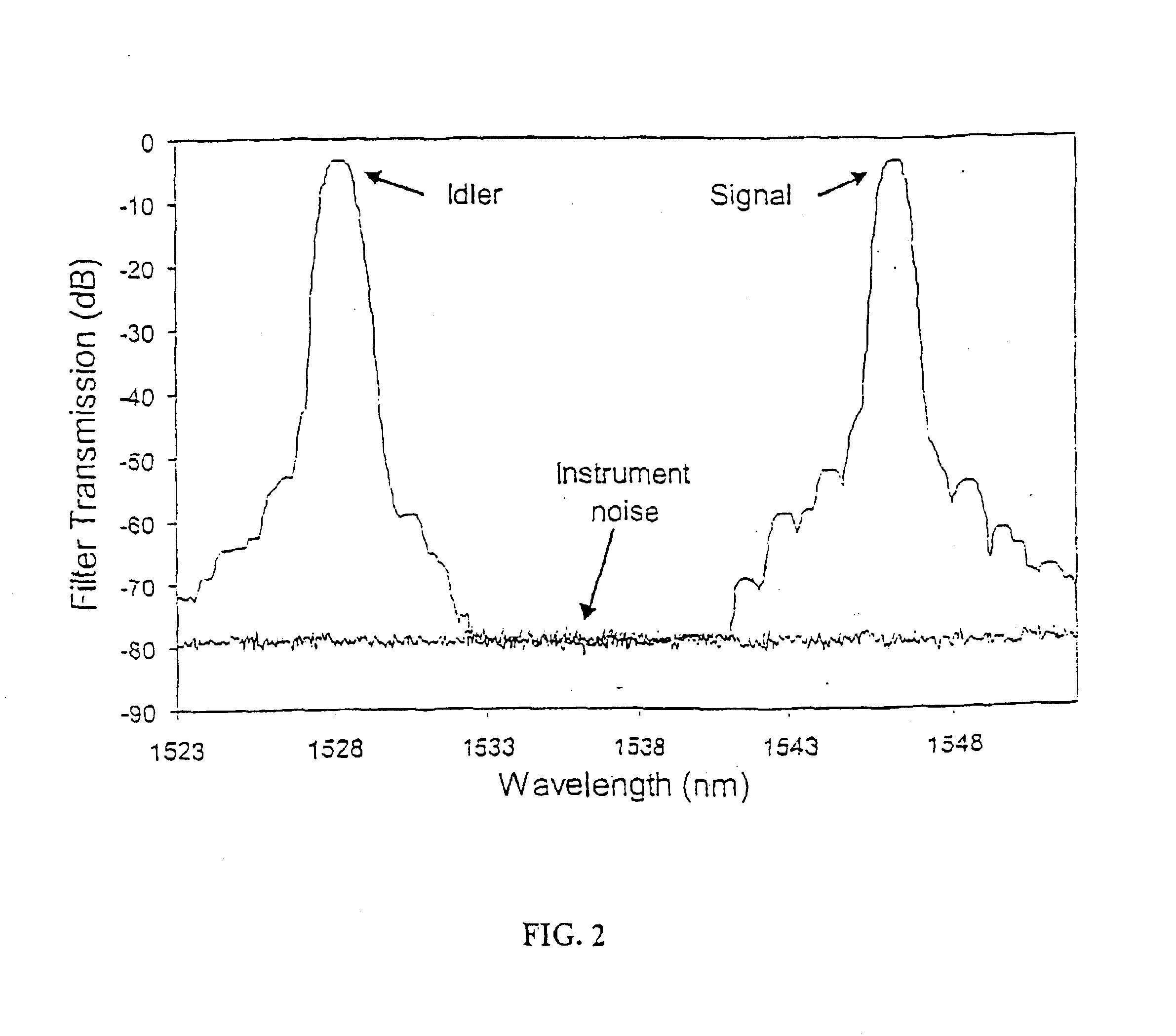
All-fiber photon-pair source for quantum communications
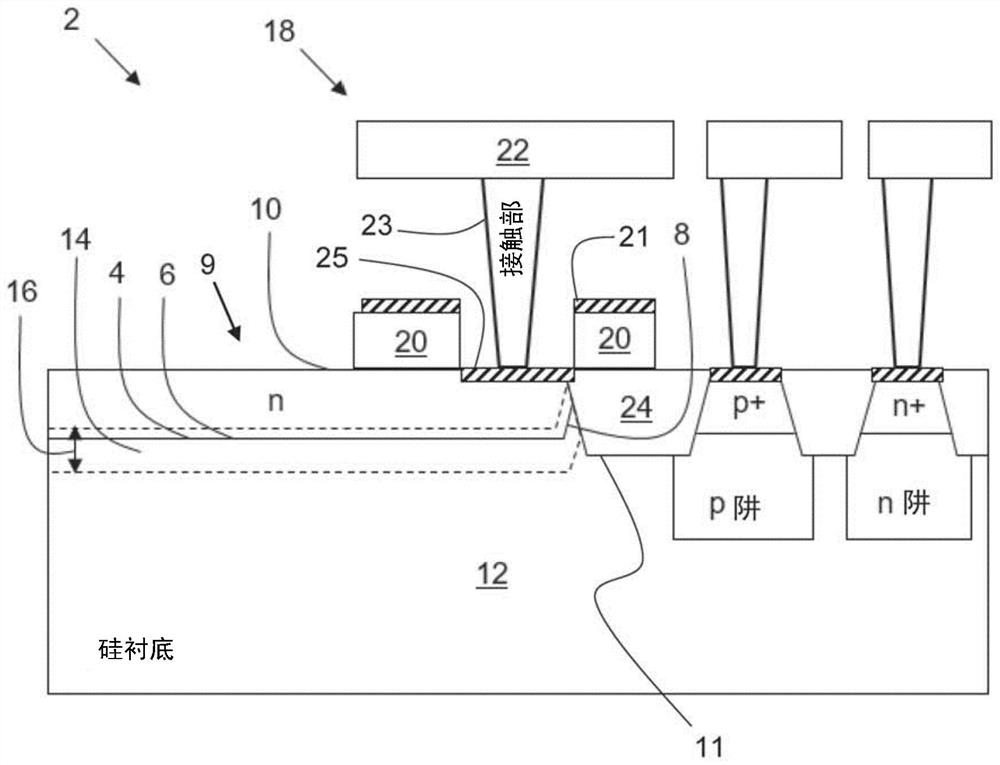
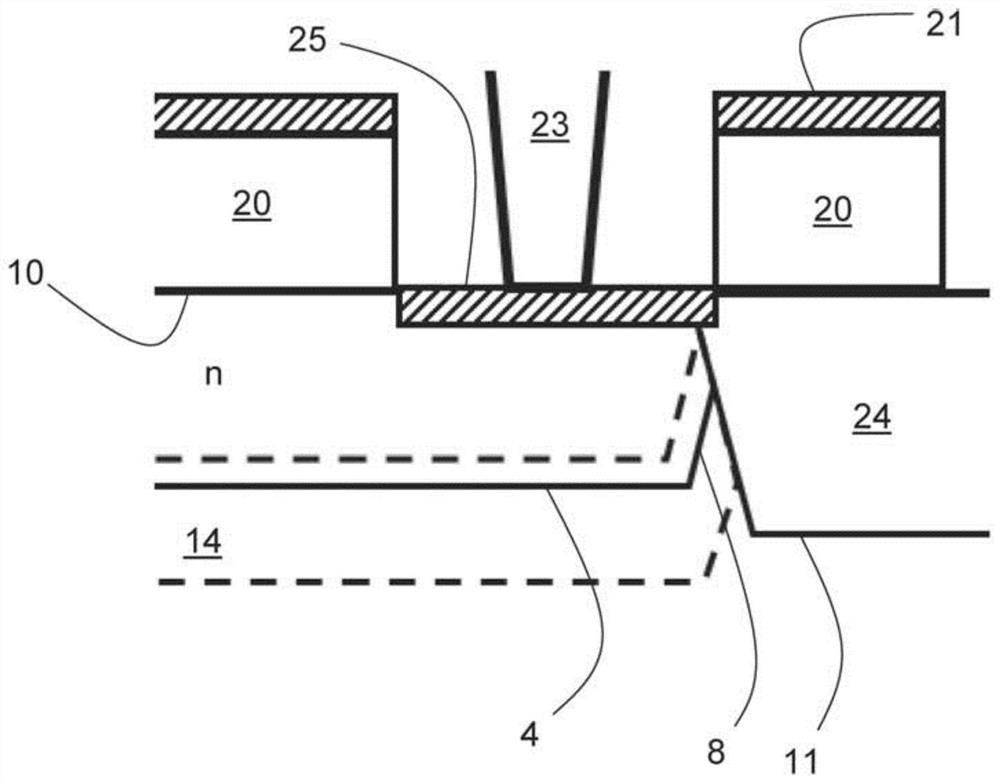
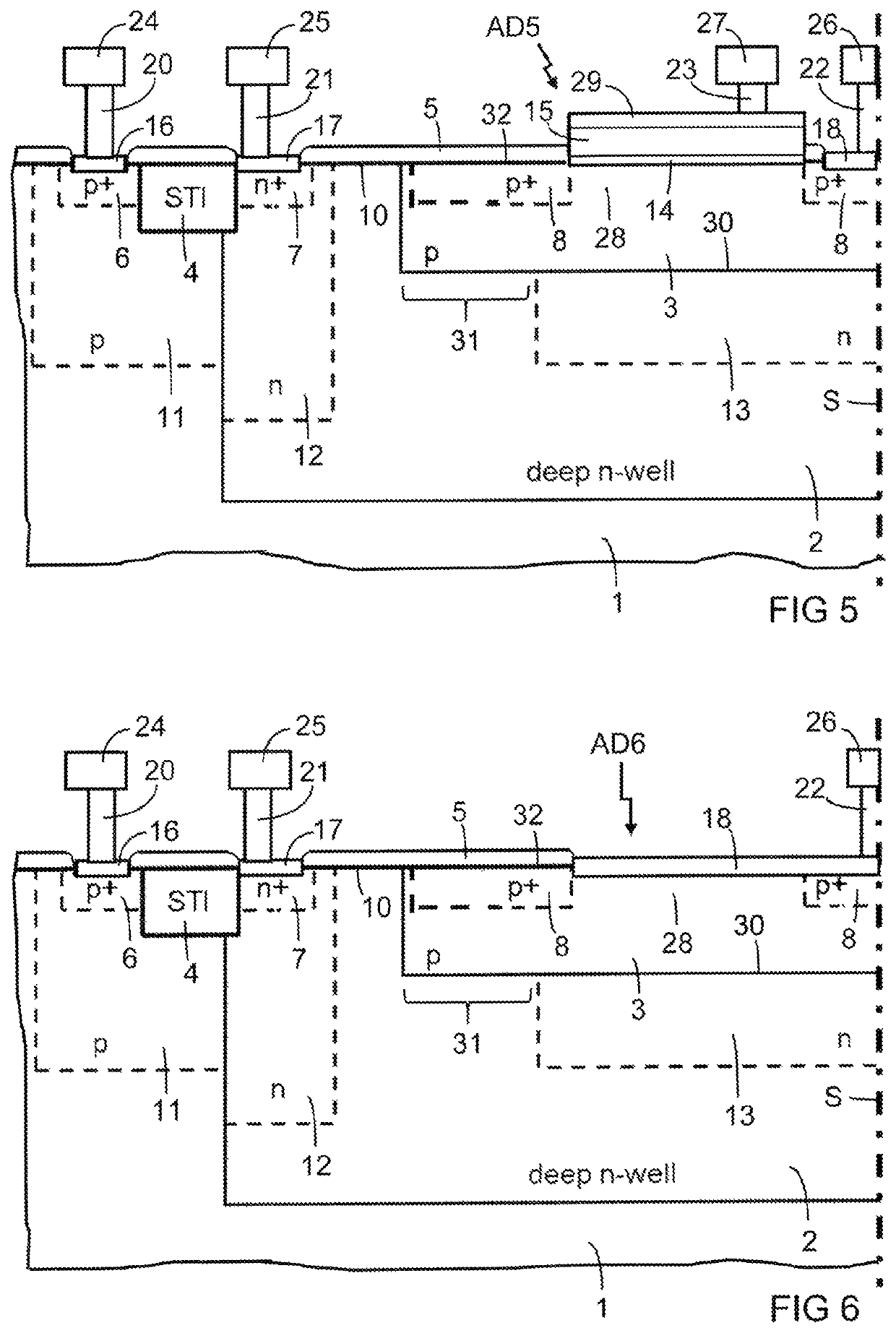
ActiveUS6897434B1Improve quantum efficiencyLimit dark count rateOptical radiation measurementMirrorsHigh rateDark count rate
A source and / or method of generating quantum-correlated and / or entangled photon pairs using parametric fluorescence in a fiber Sagnac loop. The photon pairs are generated in the 1550 nm fiber-optic communication band and detected by a detection system including InGaAs / InP avalanche photodiodes operating in a gated Geiger mode. A generation rate>103 pairs / s is observed, a rate limited only by available detection electronics. The nonclassical nature of the photon correlations in the pairs is demonstrated. This source, given its spectral properties and robustness, is well suited for use in fiber-optic quantum communication and cryptography networks. The detection system also provides high rate of photon counting with negligible after pulsing and associated high quantum efficiency and also low dark count rate.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
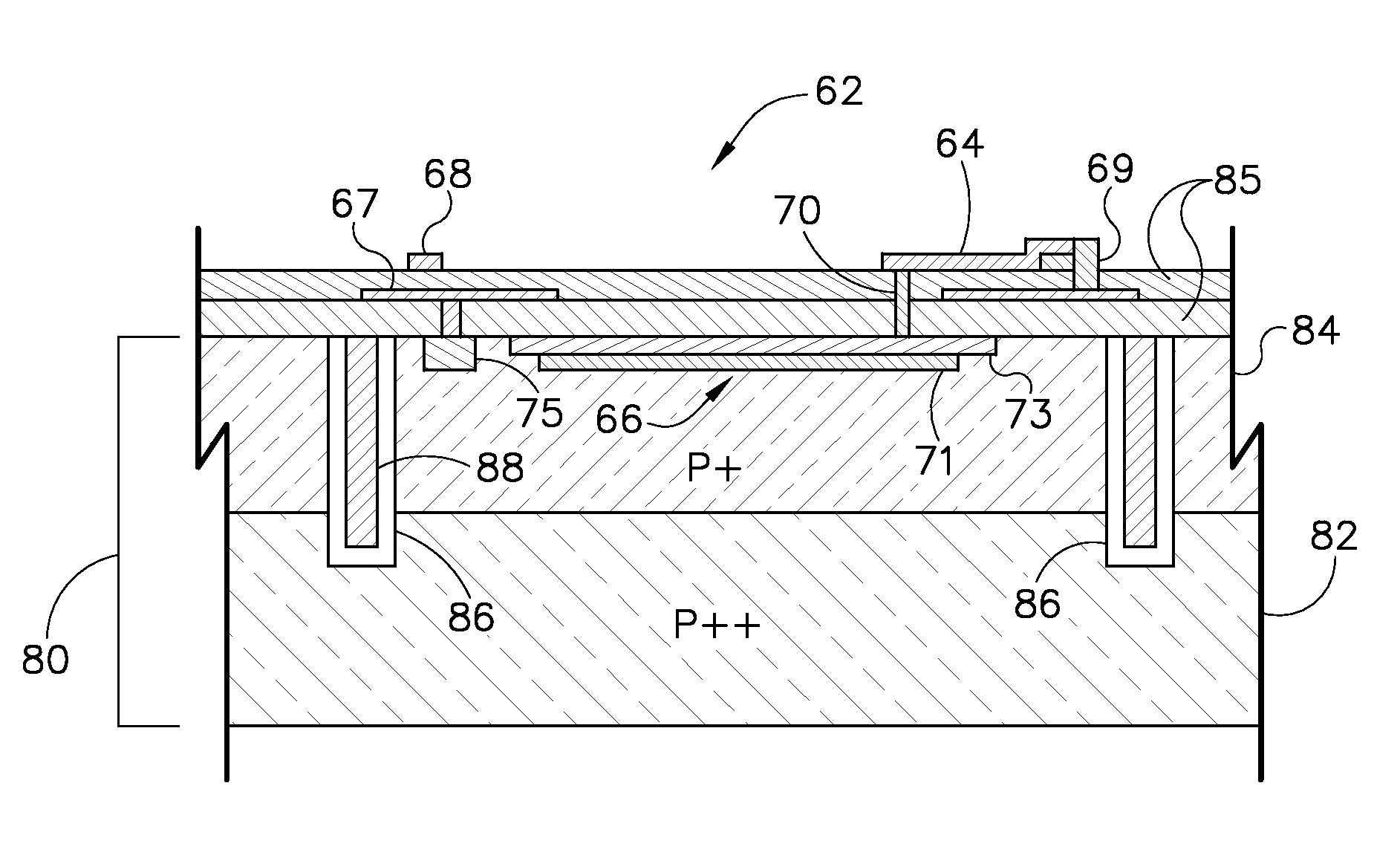
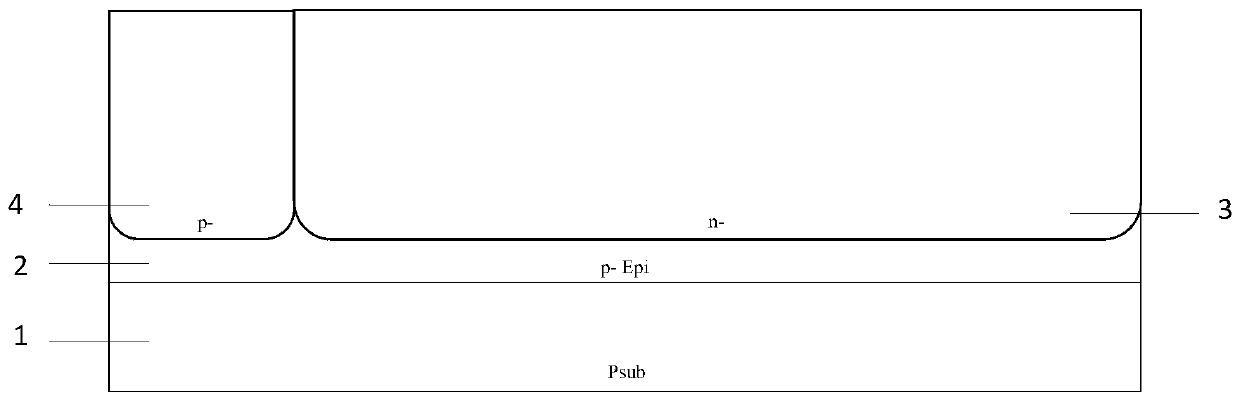
Structure of a solid state photomultiplier
ActiveUS20080308738A1Dark count rate also increasesIncrease ratingsSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDark count ratePhotomultiplier
A solid-state photomultiplier (SSPM) includes an optical isolation structure therein. The SSPM includes a substrate and an epitaxial diode layer positioned on the substrate. A plurality of avalanche photodiodes (APDs) are fabricated on the epitaxial diode layer and the optical isolation structure is positioned about the plurality of APDs to separate each of the plurality of APDs from adjacent APDs. The optical isolation structure contains at least one of a light absorbing material and a light reflecting material deposited therein to reduce optical crosstalk and dark count rate in the SSPM.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System for controling and calibrating single photon detection devices
ActiveUS20110127415A1Minimizing measurement timeOptimal measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusElectricityDark count rate
A single photon detection system and method are disclosed which have a control block for helping to monitor and optimize performance, especially at high detection rates. The system is based on photon detectors constructed with avalanche photodiodes (APD) gated in time to operate in the Geiger mode. An electrical reference frequency is generated which is subtracted from the APD output in order to better isolate the breakdown event. The resulting signal is sampled and analyzed to allow the control unit to optimize the magnitude and phase of the electrical reference frequency. The control unit may also change the gate pulse shape and phase, including by the use of a digital-to-analog converter. The gate pulse can be shifted off an input optical pulse so as to estimate dark count rate, or shifted to measure a reference input signal to estimate detection efficiency.
Owner:NUCRYPT
Preparation methods of nanopore-arrayed anodic alumina membrane and nanopore-arrayed anodic alumina microchannel plate
InactiveCN104233430AOvercoming noiseOvercoming temporal resolutionSurface reaction electrolytic coatingCold cathode manufactureDark count rateSilicate glass
The invention relates to preparation methods of a nanopore-arrayed anodic alumina membrane and a nanopore-arrayed anodic alumina microchannel plate. The preparation method of the nanopore-arrayed anodic alumina membrane comprises the following steps of preparation of an alumina membrane and directional pore broadening. The preparation method of the nanopore-arrayed anodic alumina microchannel plate comprises the following steps of preparation of an alumina membrane, directional pore broadening and preparation of a microchannel plate. According to the preparation methods of the nanopore-arrayed anodic alumina membrane and the nanopore-arrayed anodic alumina microchannel plate, the technical bottleneck that the channel aperture of the traditional lead-containing silicate glass microchannel plate cannot be easily reduced is overcome; the difficult problems that the area of the microchannel plate is increased if the ultra-small aperture of the microchannel plate is realized and the like are solved; and the excellent properties of the microchannel plate are achieved, i.e., the space resolution and time resolution of the microchannel plate are improved, the gain is increased, the dark count rate is decreased, the area array is enlarged, a higher temperature can be borne and the like.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
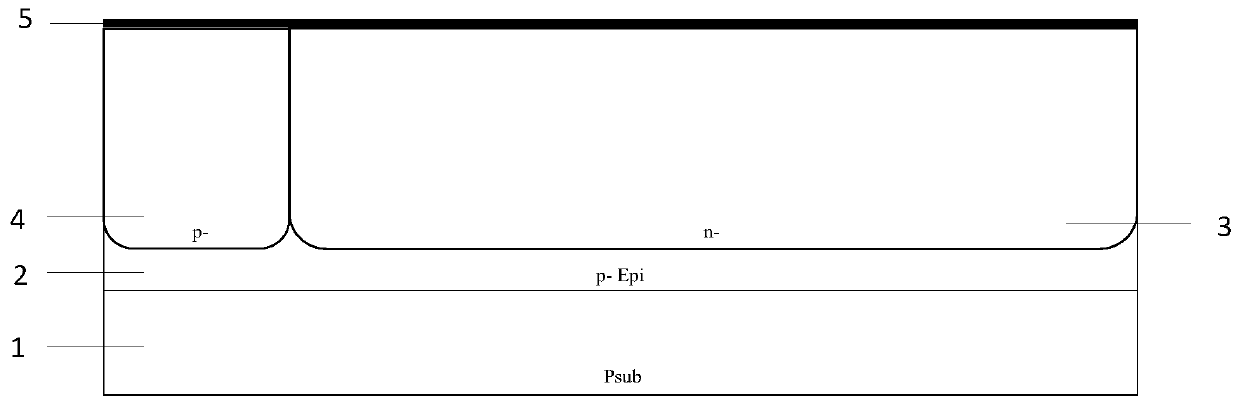
Structure of a solid state photomultiplier
ActiveUS7652257B2Increase ratingsSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDark count rateOptoelectronics
A solid-state photomultiplier (SSPM) includes an optical isolation structure therein. The SSPM includes a substrate and an epitaxial diode layer positioned on the substrate. A plurality of avalanche photodiodes (APDs) are fabricated on the epitaxial diode layer and the optical isolation structure is positioned about the plurality of APDs to separate each of the plurality of APDs from adjacent APDs. The optical isolation structure contains at least one of a light absorbing material and a light reflecting material deposited therein to reduce optical crosstalk and dark count rate in the SSPM.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
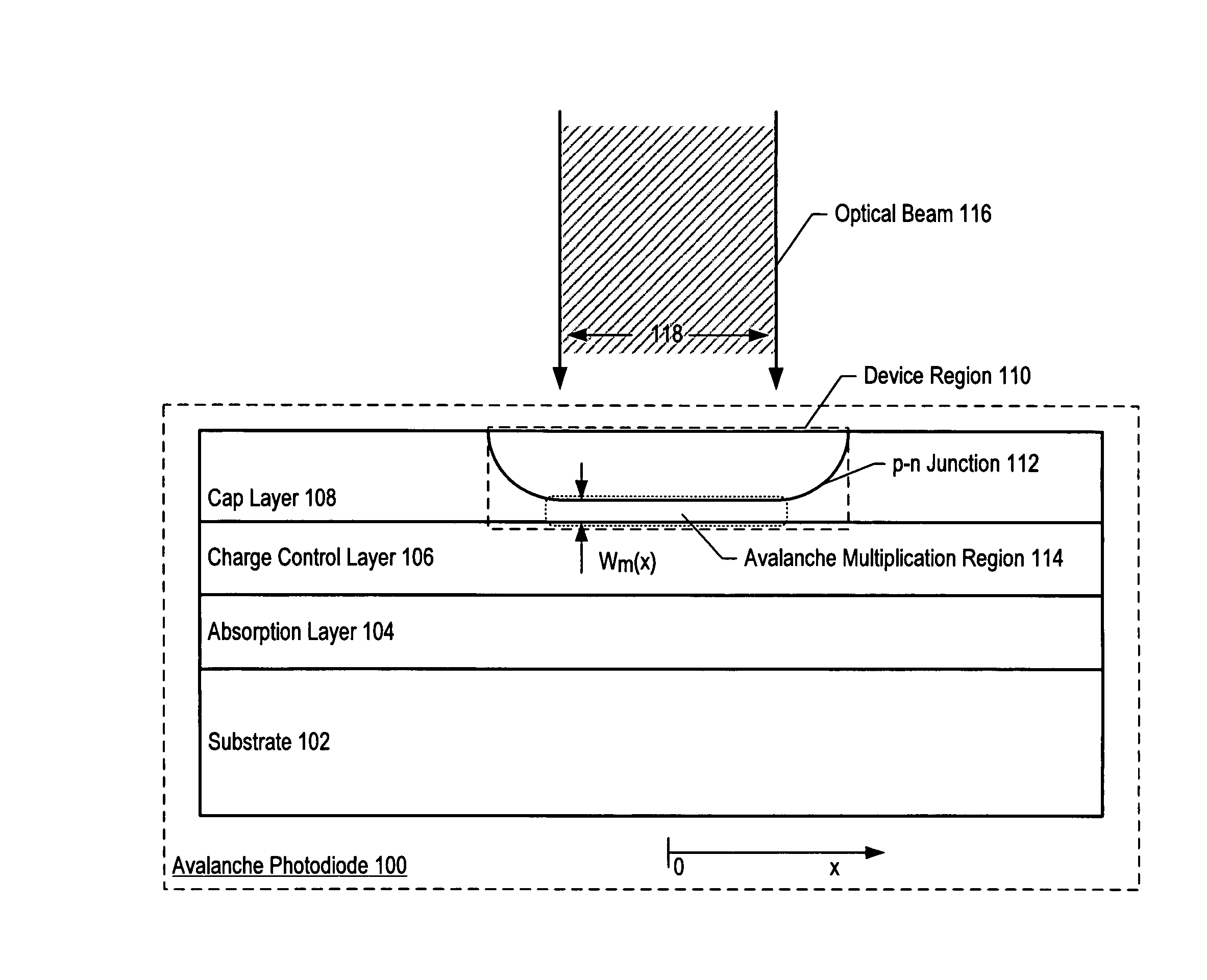
Apparatus comprising an avalanche photodiode
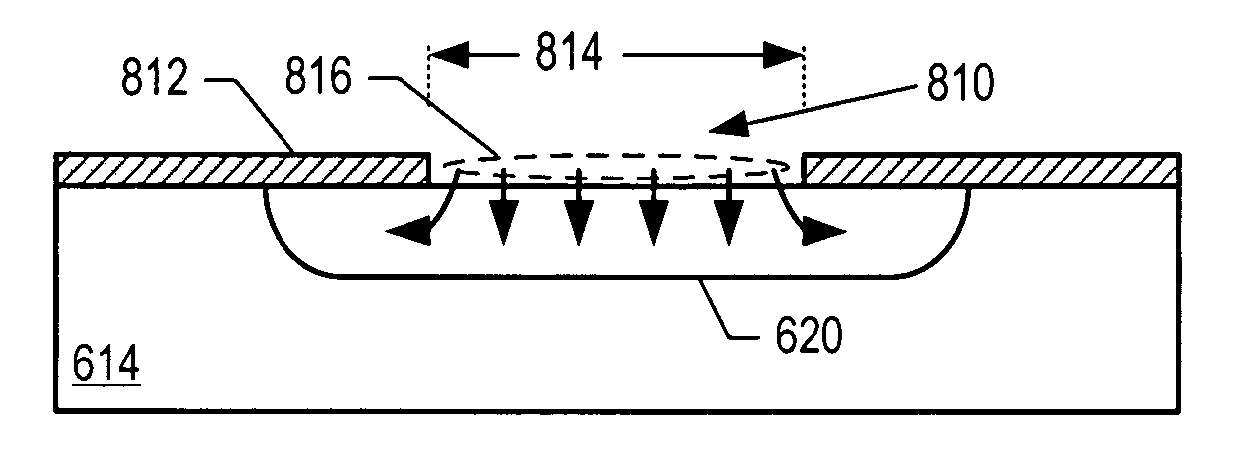
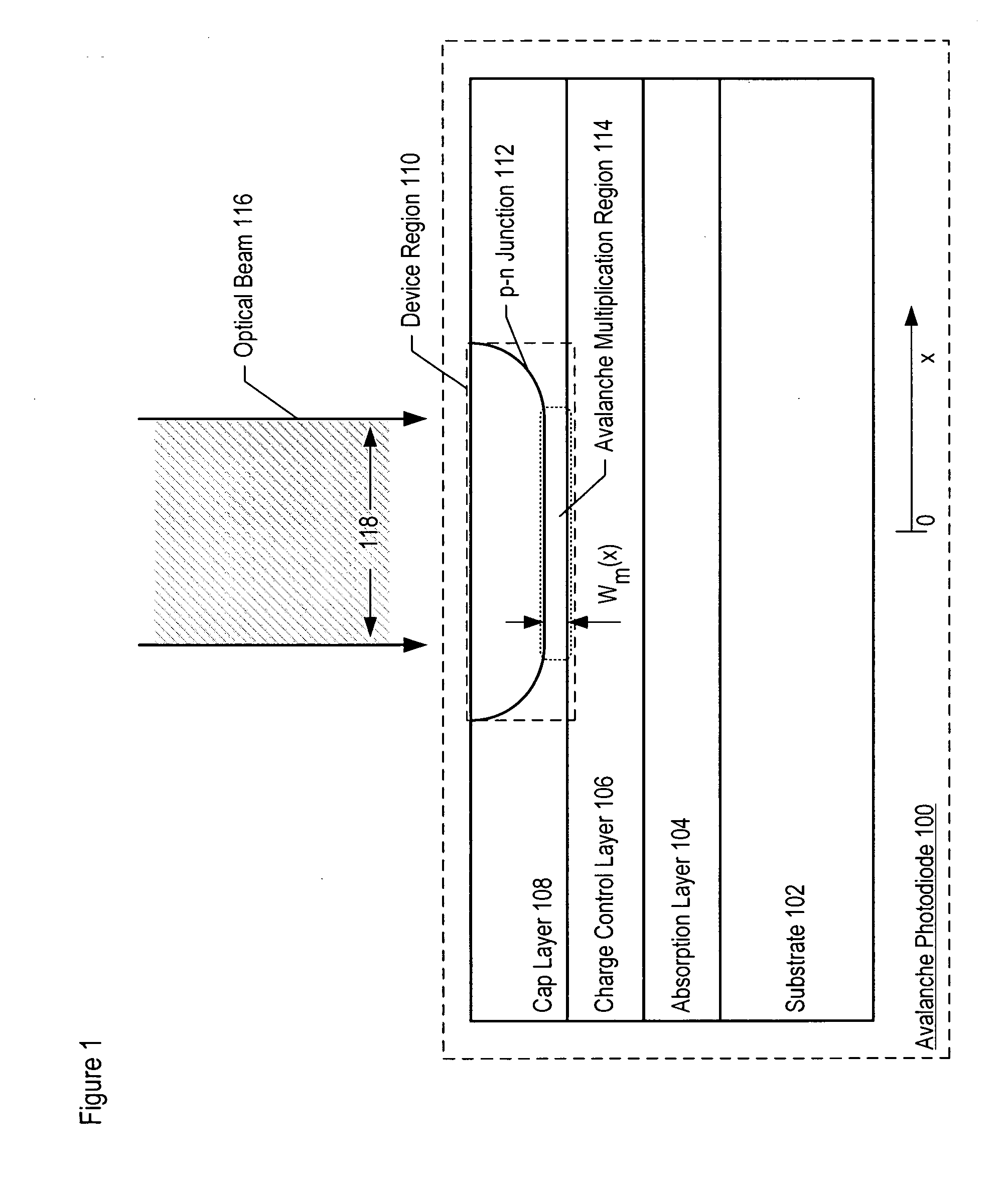
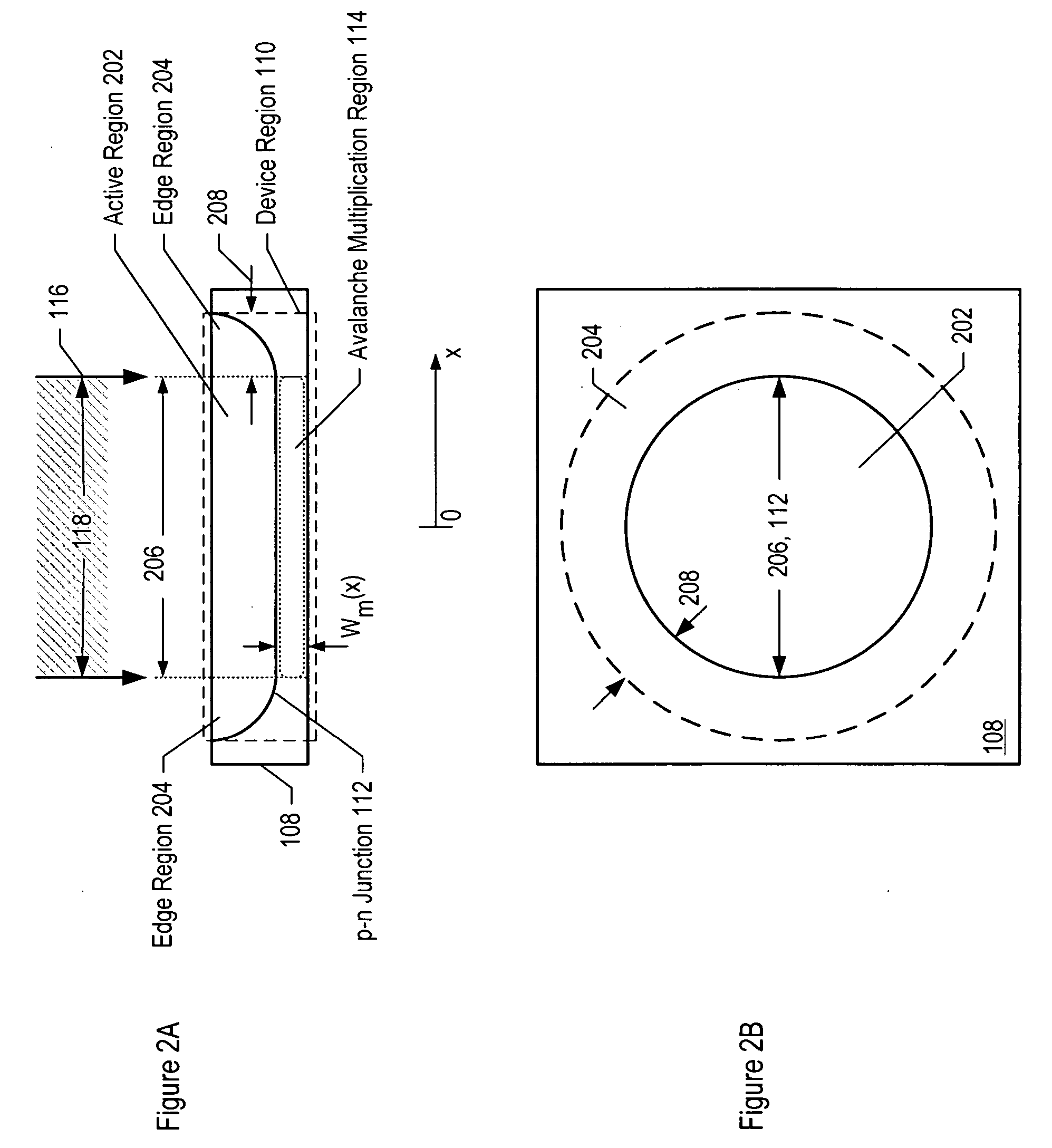
ActiveUS20070085158A1Reduce dark count rateSmall device sizeSemiconductor devicesDark count rateLight beam
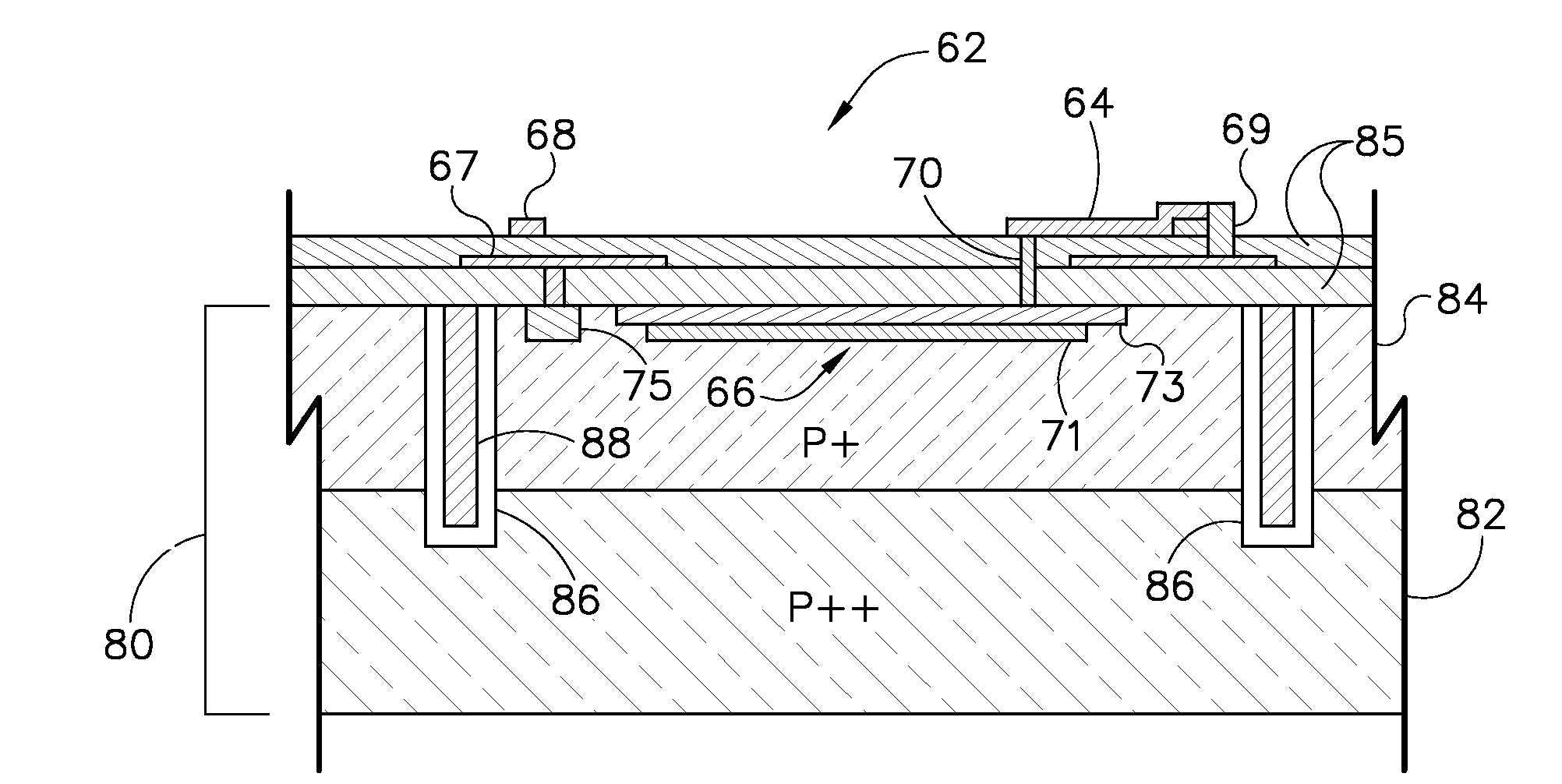
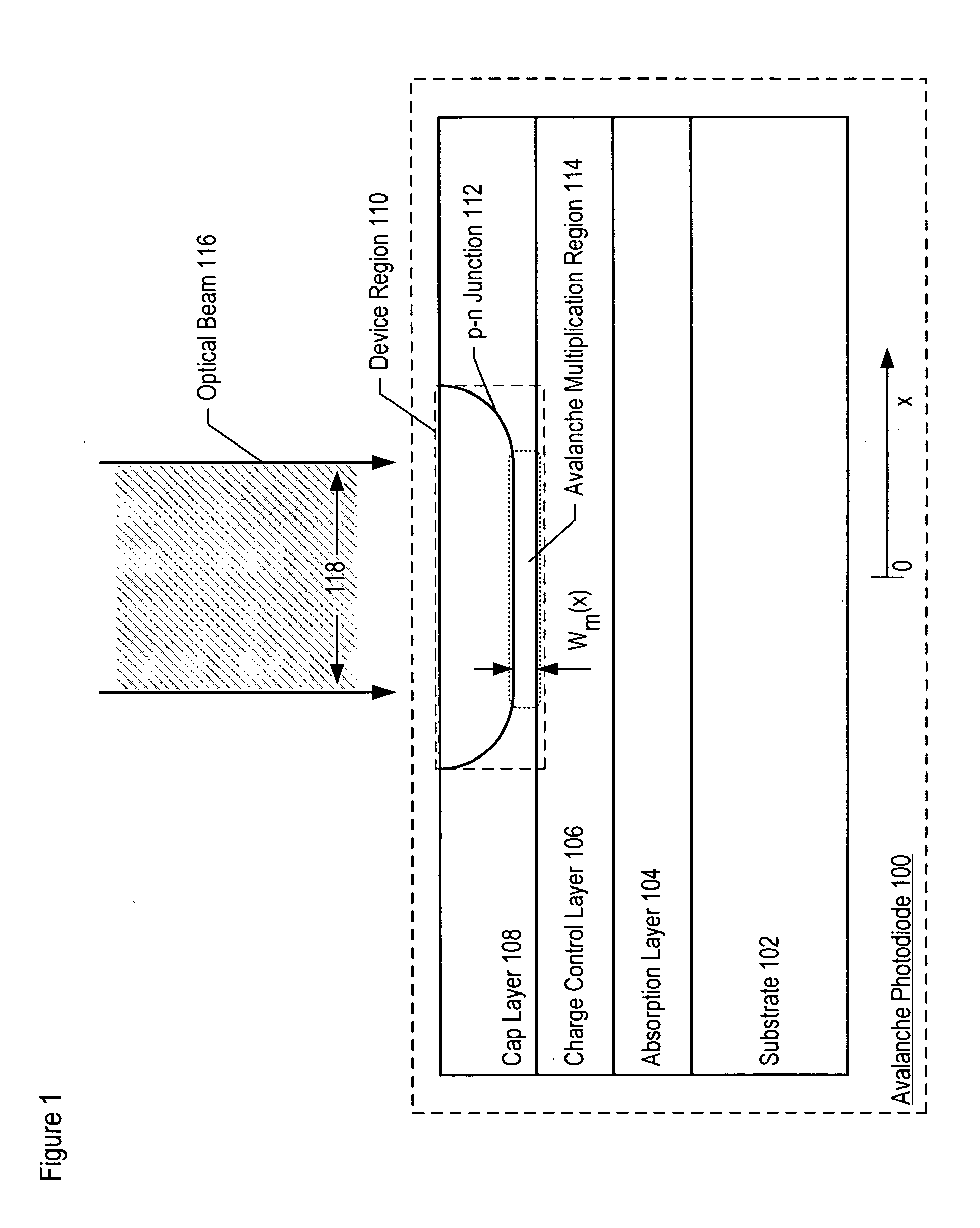
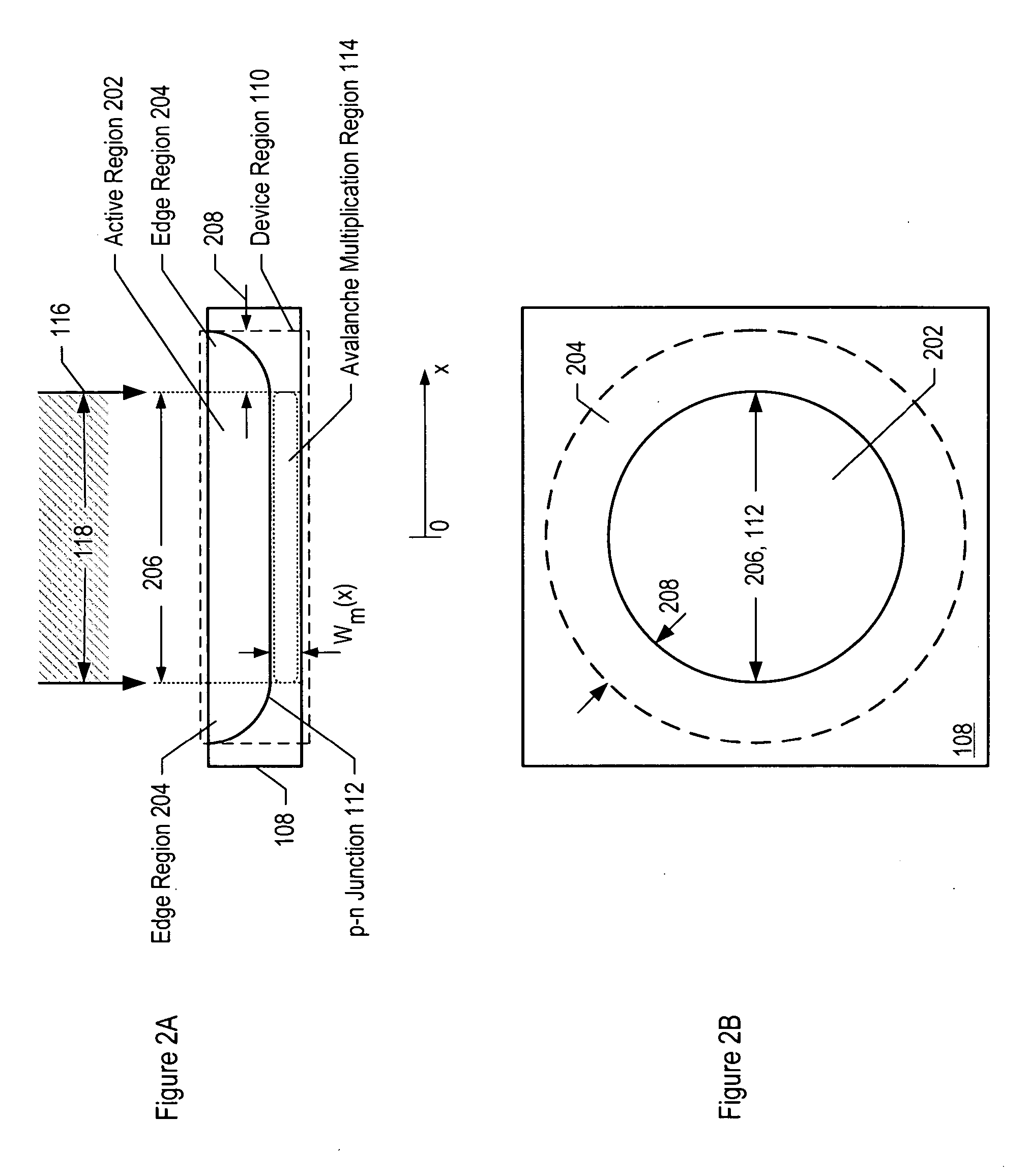
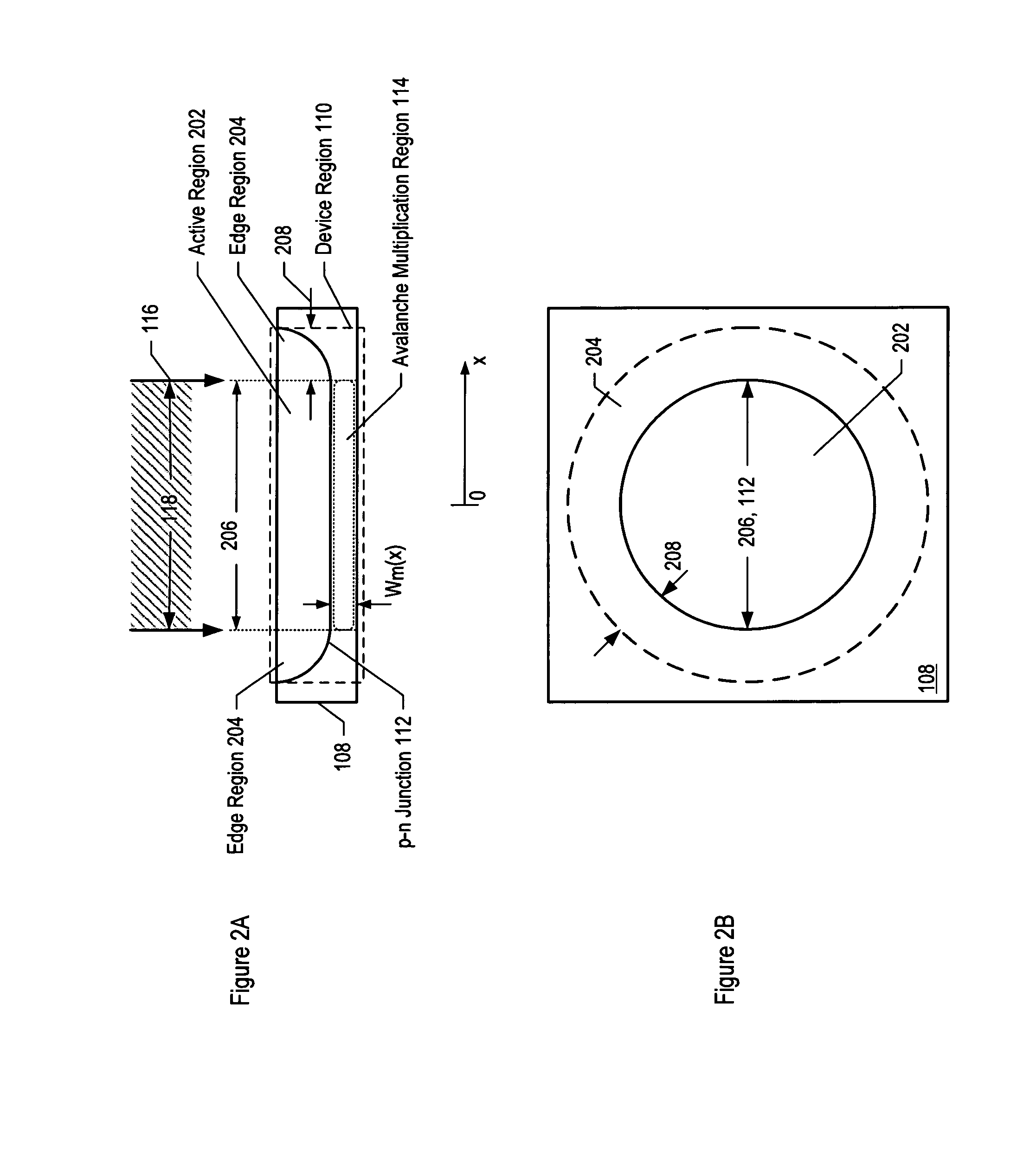
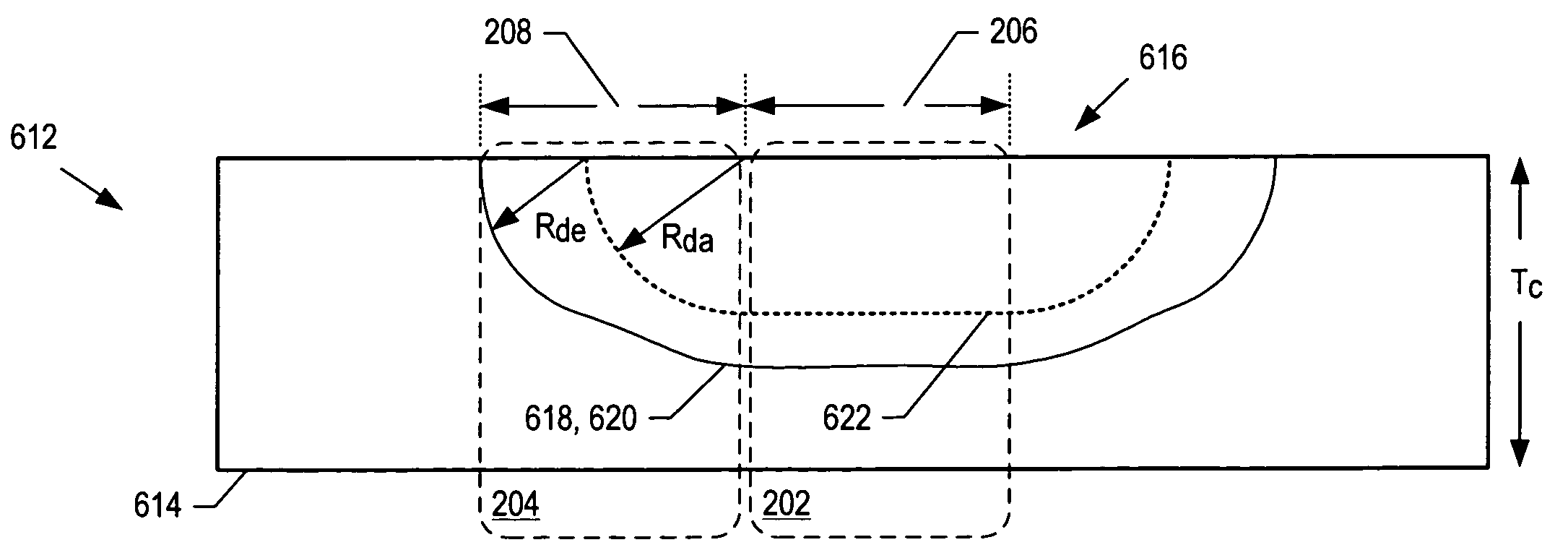
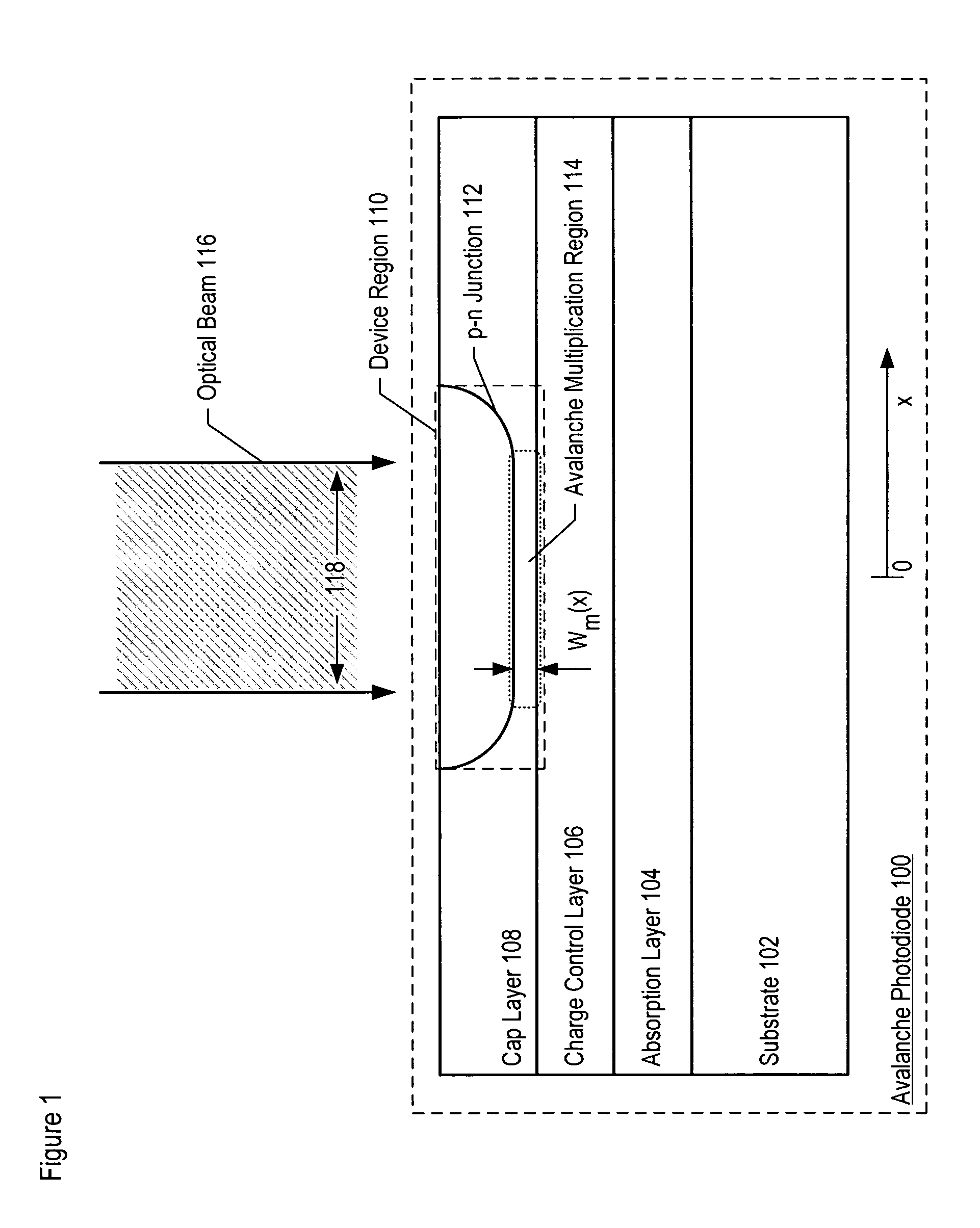
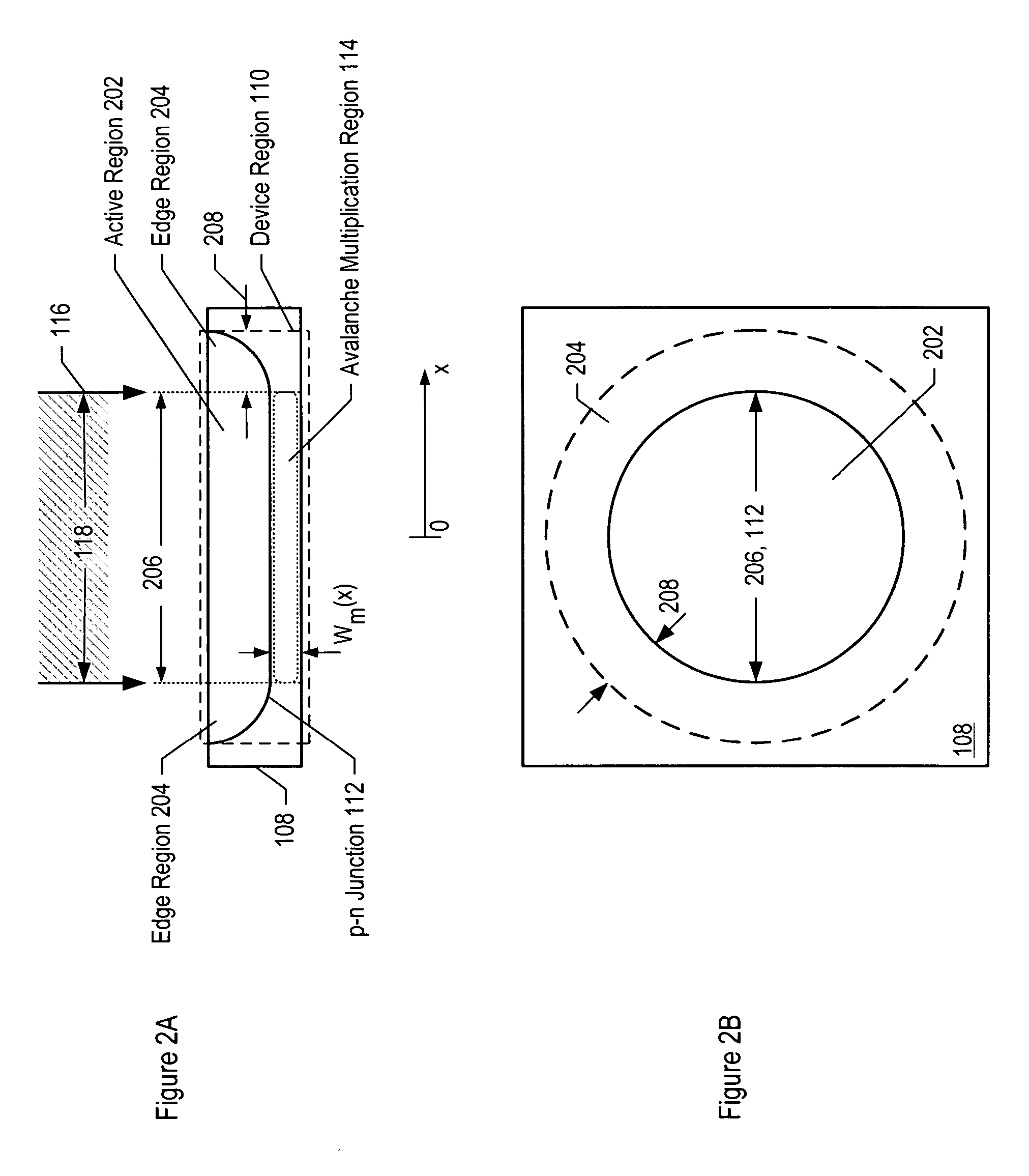
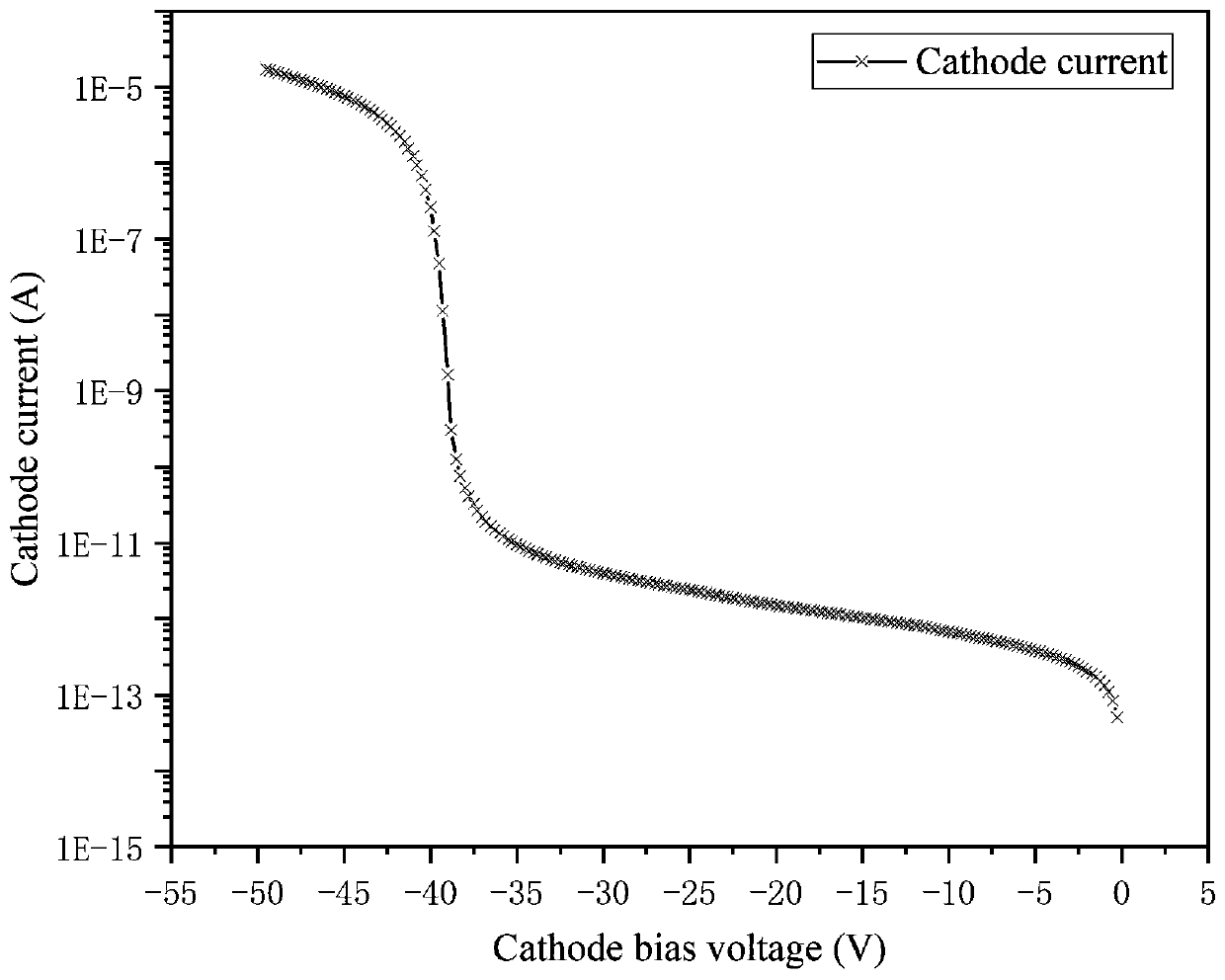
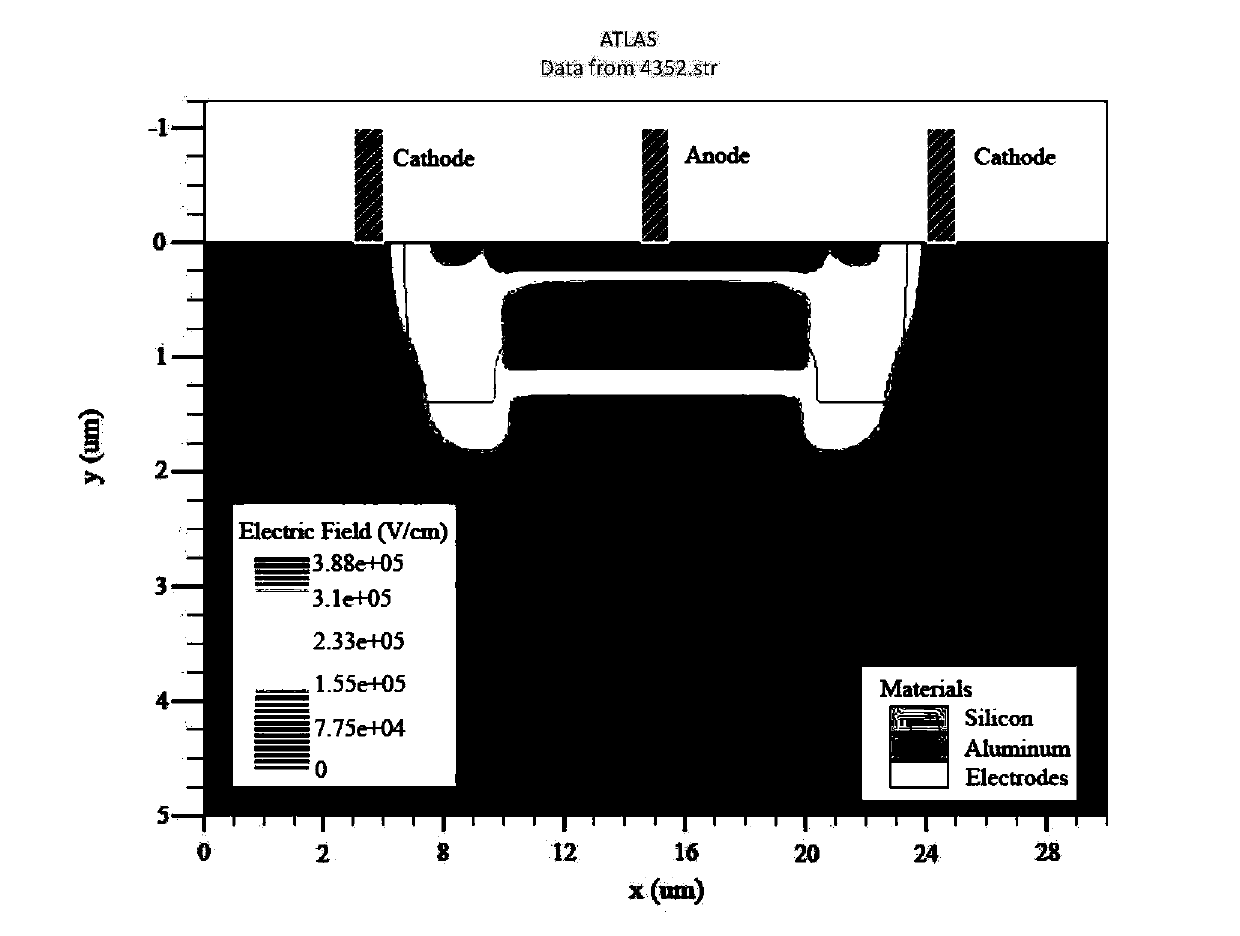
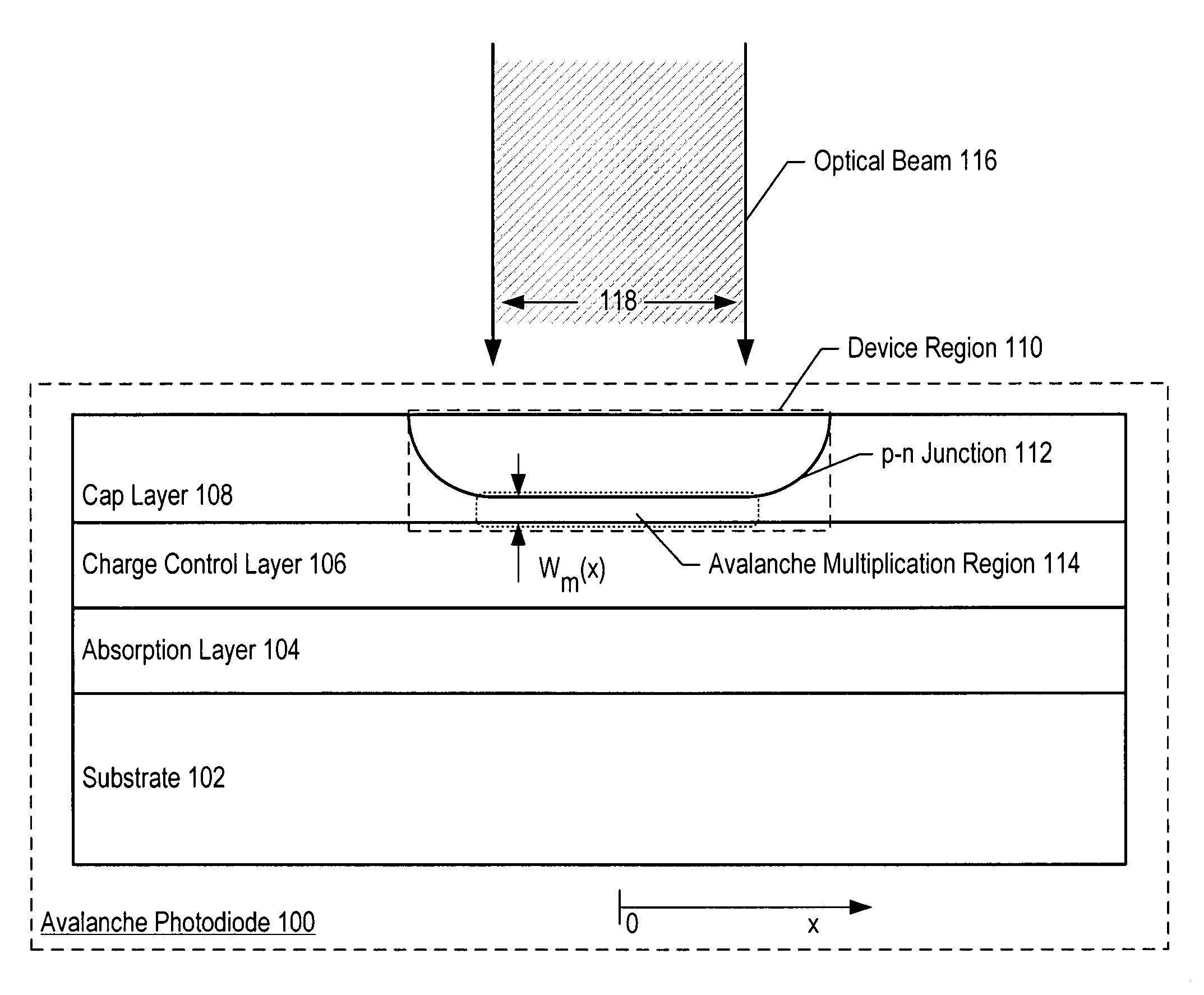
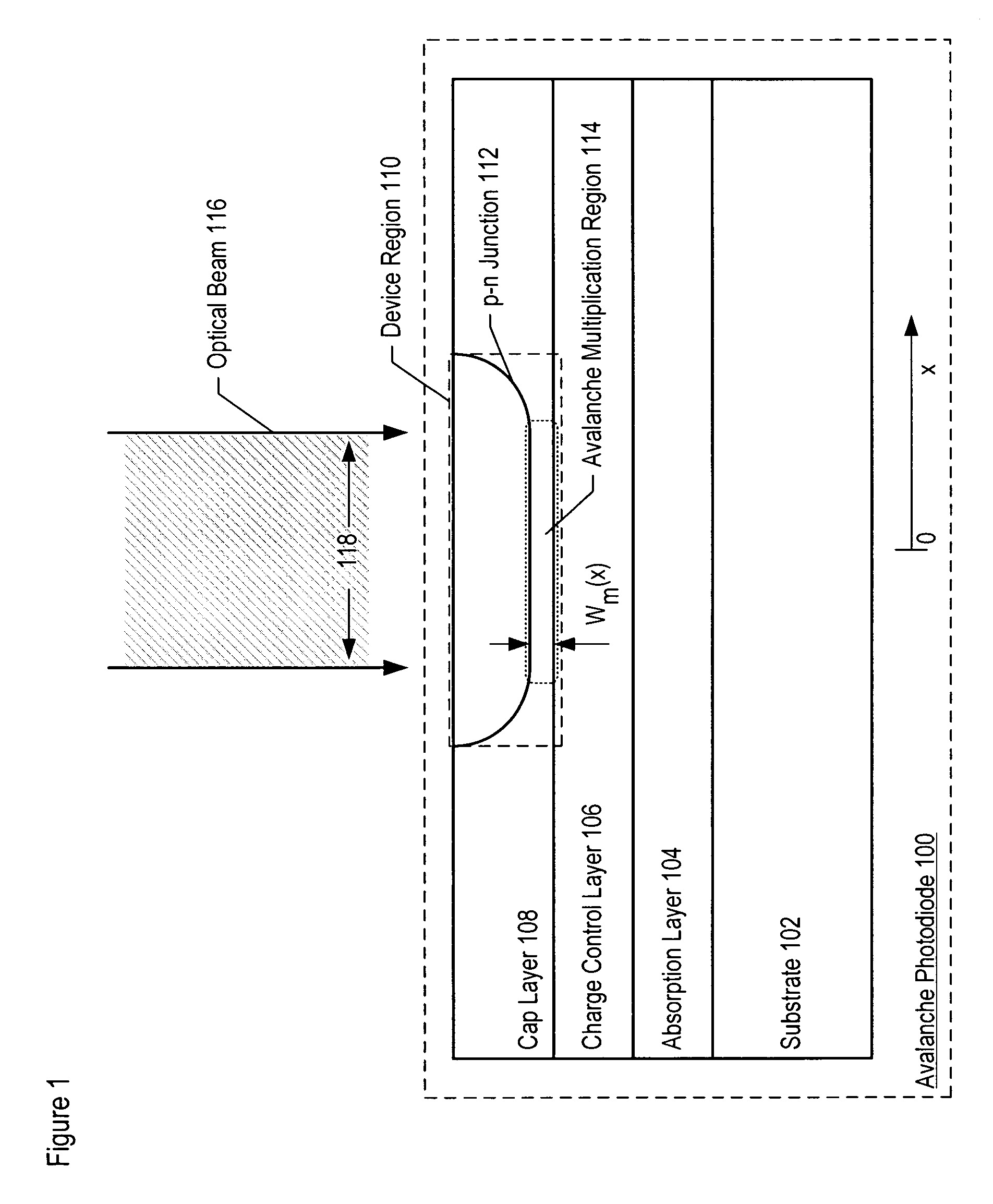
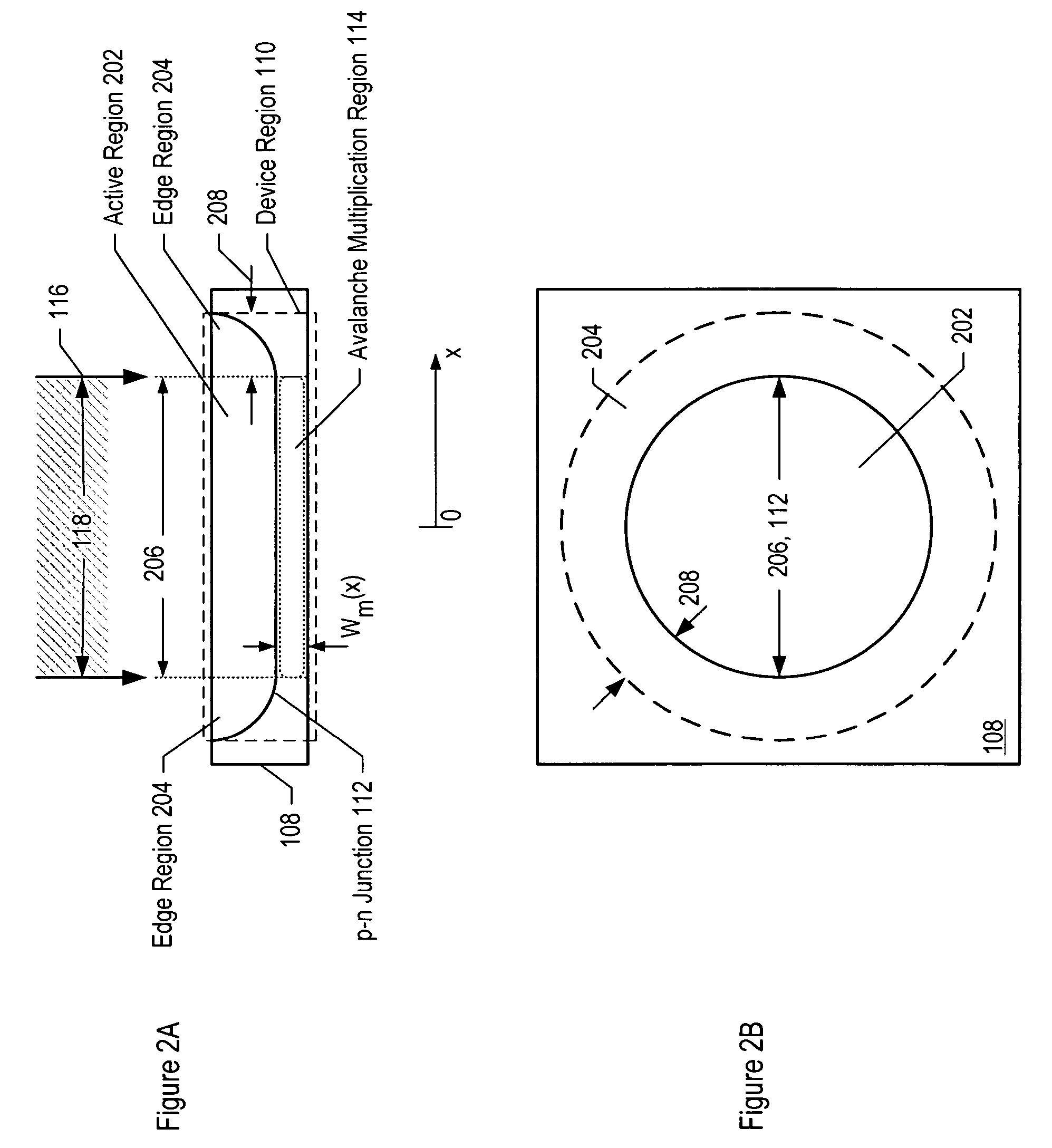
Avalanche photodiodes are provided, wherein the APDs provide both high optical coupling efficiency and low dark count rate. The APDs are formed such that their cap layer has an active region of sufficient width to enable high optical coupling efficiency but the APD still exhibits a low dark count rate. These cap layers have a device area with an active region and an edge region, wherein the size of the active region is substantially matched to the mode-field diameter of an optical beam, and wherein the size of the edge region is made small so as to reduce the number of defects included. These APD designs maintain a substantially uniform gain and breakdown voltage, as necessary for practical use.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
High atmosphere detection laser radar based on large-photosurface superconducting single-photon detector
ActiveCN106353770AReduce dark countHigh photon count rateElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationCounting rateQuantum efficiency
The invention discloses high atmosphere detection laser radar based on a large-photosurface superconducting single-photon detector. By application of the large-photosurface superconducting single-photon detector to a high atmosphere detection laser radar system, high atmosphere parameter detection can be realized through increase of telescope area. Compared with an existing detector applied to the high atmosphere detection laser radar, the superconducting single-photon detector has advantages of large photosurface, high counting rate, high quantum efficiency, low dark count rate, high photon count rate and short jittering time. Therefore, the high atmosphere detection laser radar based with the large-photosurface superconducting single-photon detector is more advantageous in range resolution, spatial resolution and detection precision; in other words, under the condition of realizing same detection indexes, the laser radar with the large-photosurface superconducting single-photon detector can adopt a smaller-aperture telescope or a lower-power laser.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for correcting temperature influence to SiPM gain
ActiveCN107526096AReduce circuit complexityLow costRadiation intensity measurementDark count rateWorking temperature
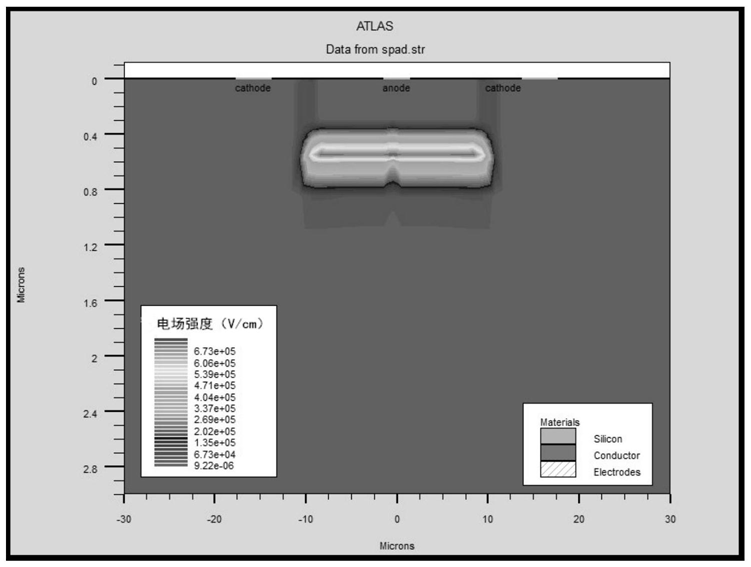
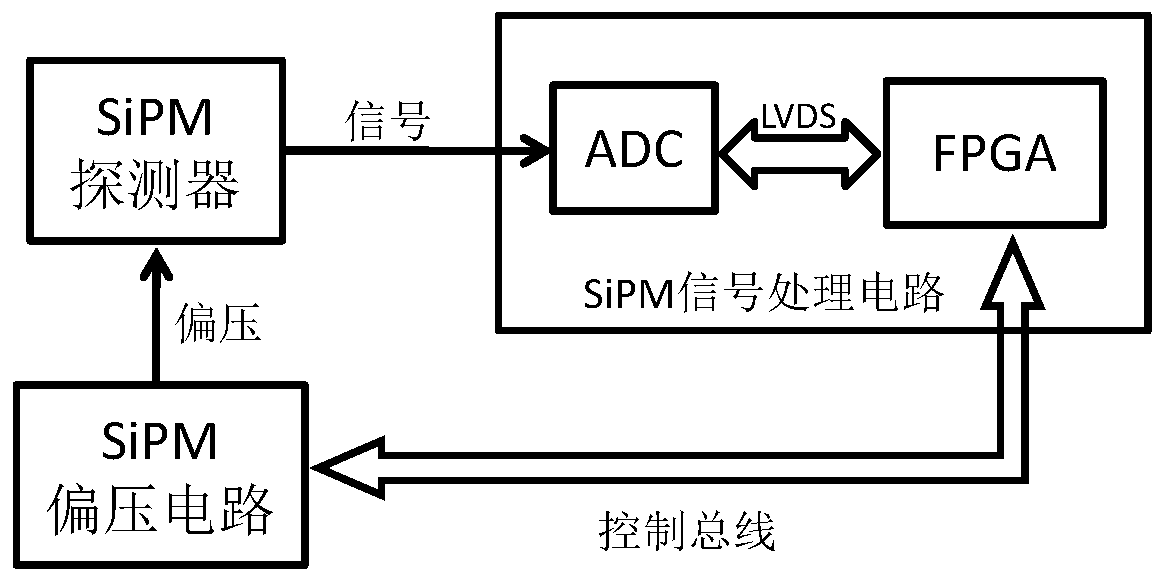
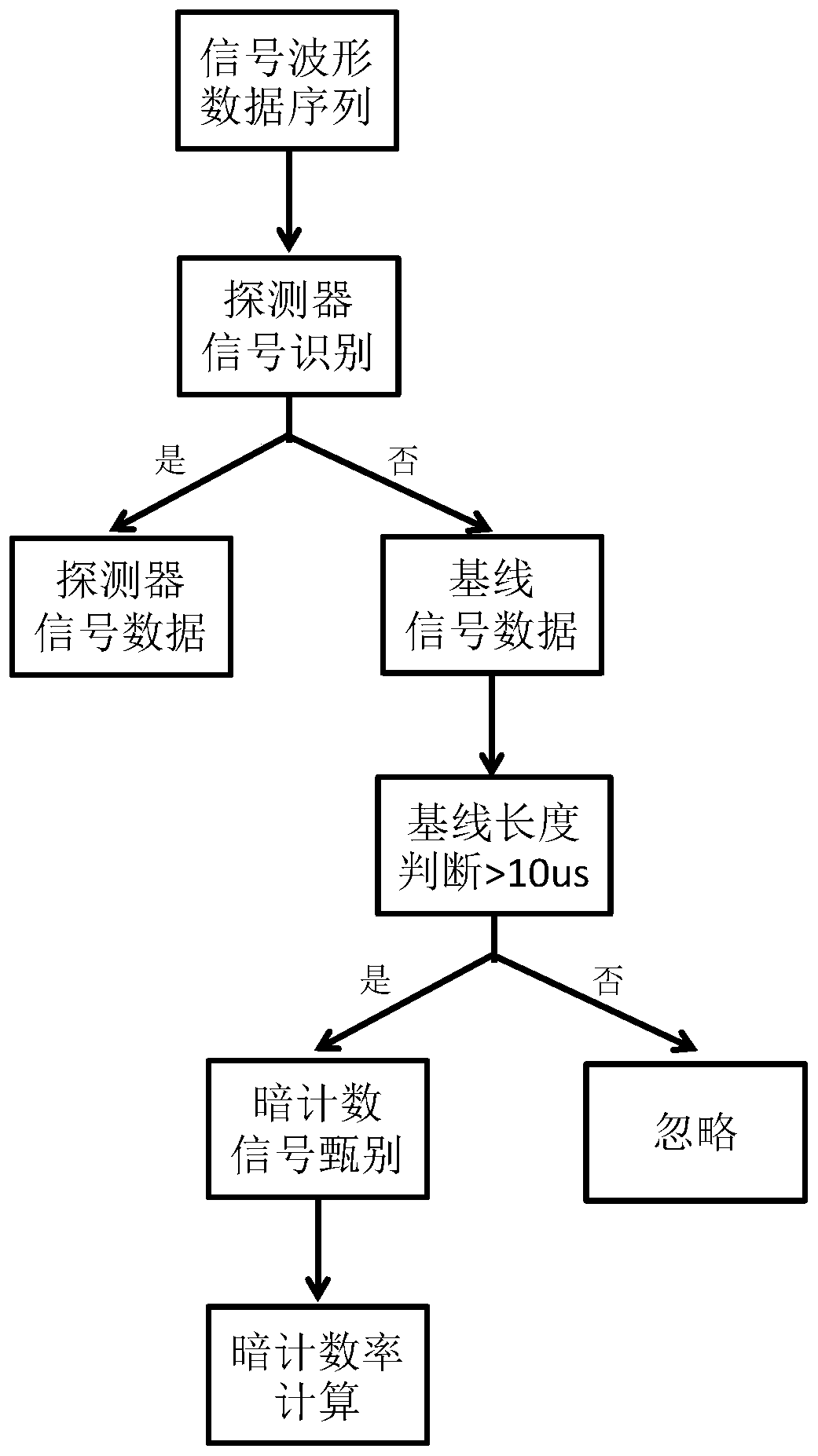
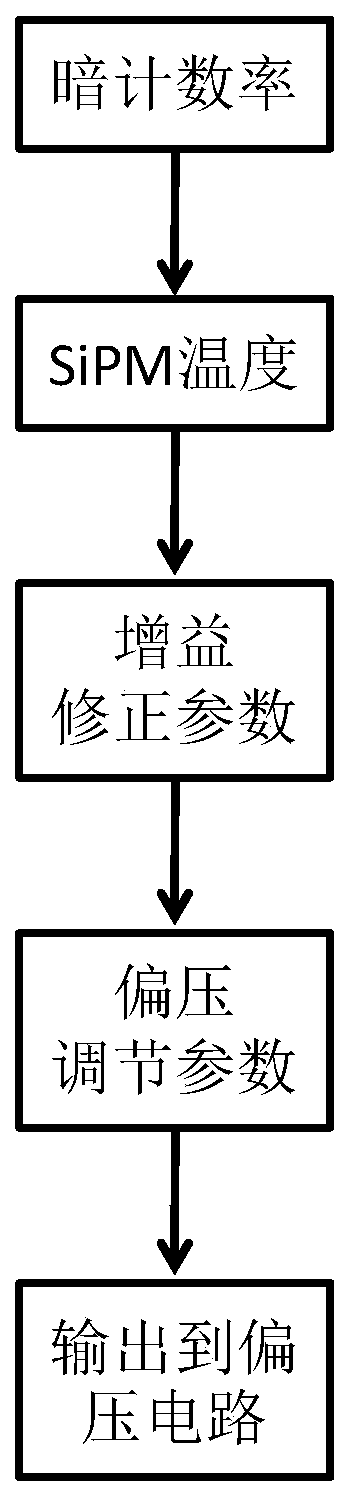
The invention relates to a method for correcting temperature influence to SiPM gain. According to the method of the invention, a dark count rate in an SiPM output signal is obtained through calculation according to an SiPM dark count measuring algorithm. A fixed relation between the dark count rate and the SiPM working temperature is utilized for determining the current temperature of the SiPM. Furthermore a to-be-regulated working bias increment parameter of the SiPM is determined based on the current temperature of the SiPM, thereby effectively correcting temperature influence to the SiPM gain, improving system stability, reducing hardware cost and improving system efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU SUPERSENSE TECH CO LTD
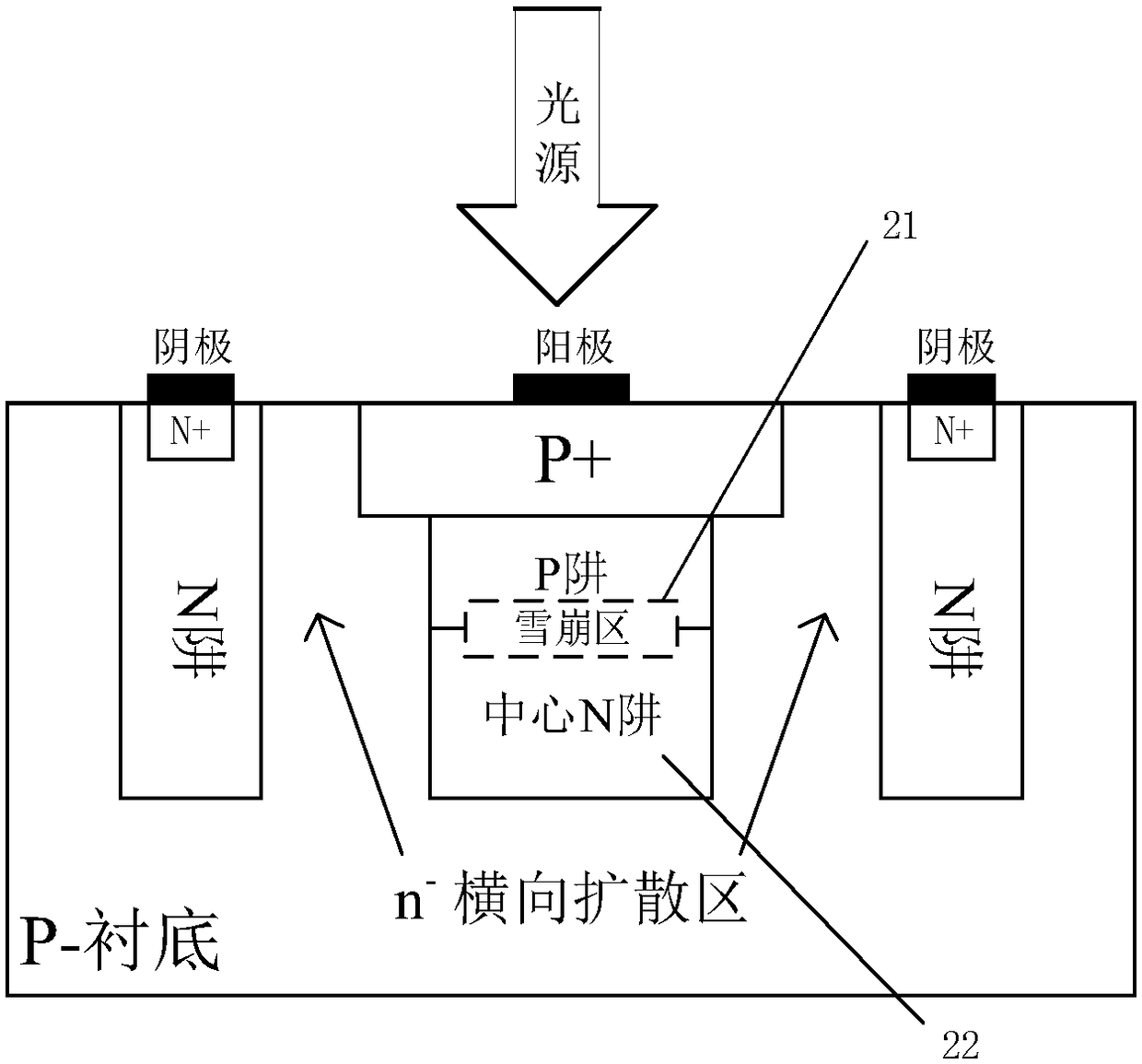
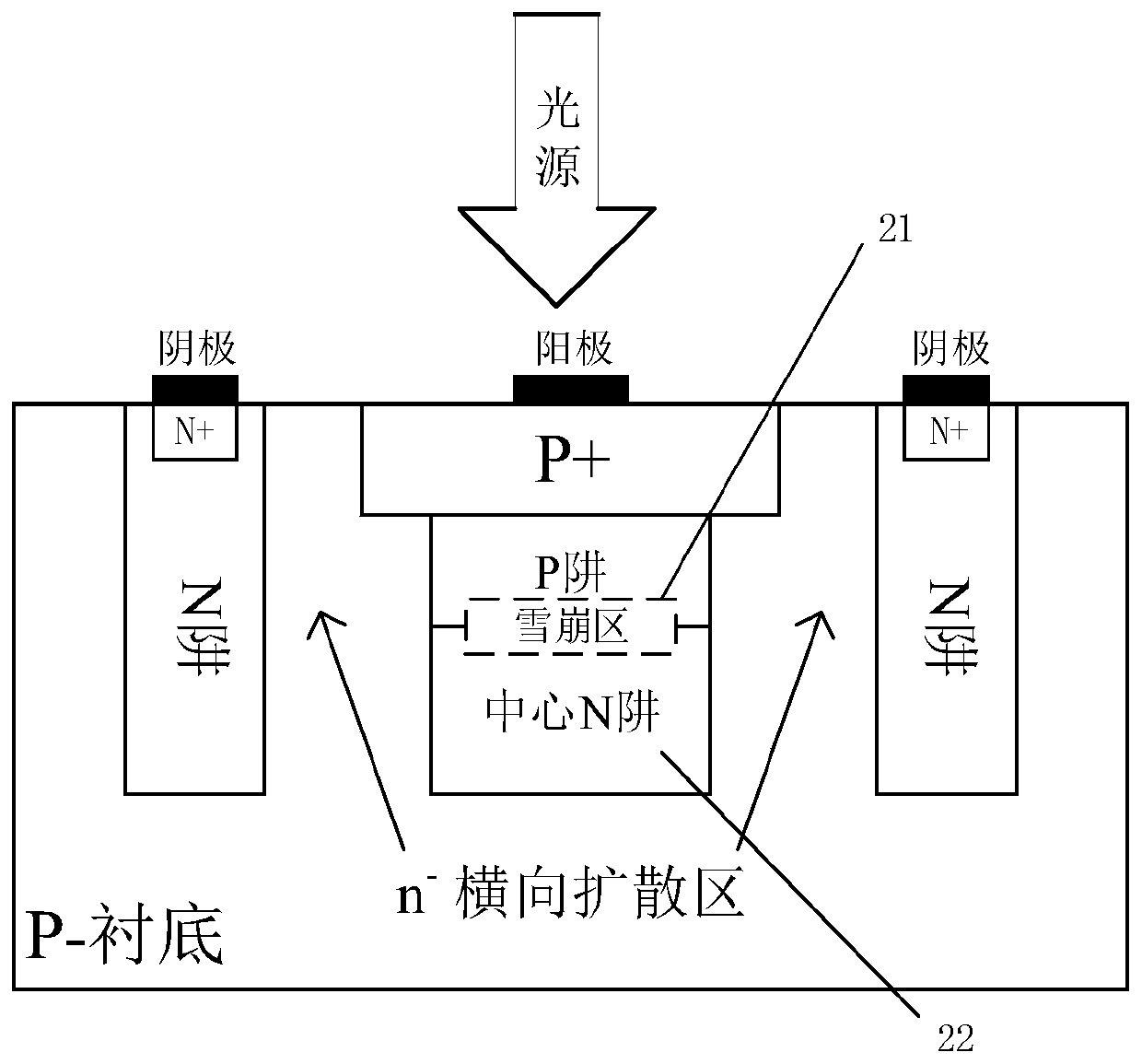
Low-dark-count-rate CMOS SPAD photoelectric device
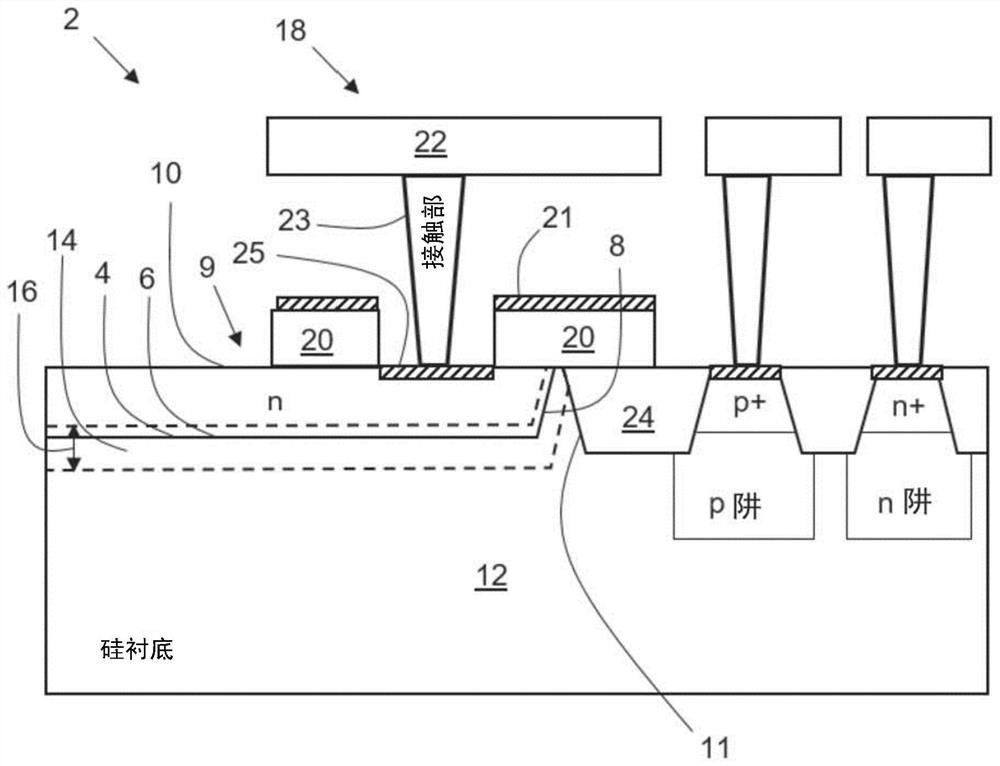
ActiveCN108550592ABand-to-band tunnelingSource of reductionSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesCounting rateDark count rate
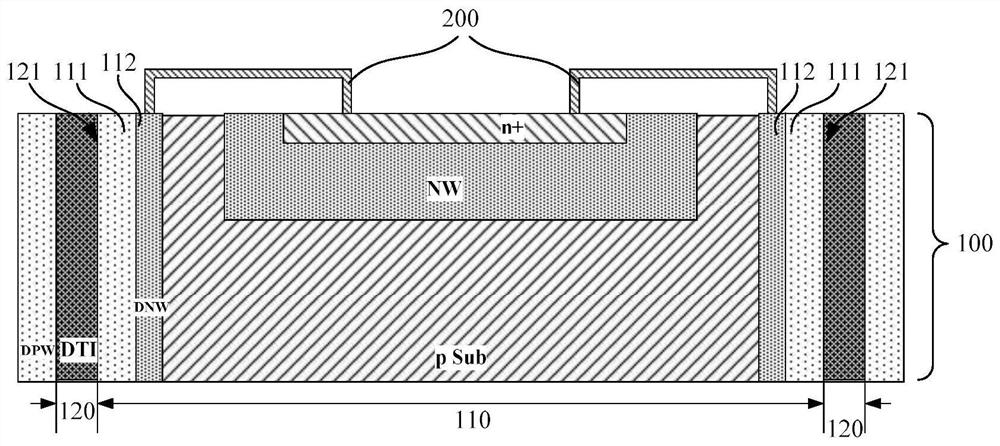
The invention provides a low-dark-count-rate CMOS SPAD photoelectric device. A P-well layer is added based on a routine P+ / N-well type SPAD structure. The P-well layer is arranged between the P+ layerand the N-well layer. Furthermore, an N-well clearance is utilized as a virtual protecting ring of the structure; namely N-wells are added at two sides of a PN junction, wherein the structure is shown in the attached figures of an abstract. An incident photon is incident into the device and is attracted at the central N well, and furthermore a photon-generated carrier is generated. The P-well layer and the N-well layer are utilized at two sides of the PN junction. Hereon an avalanche junction is a P-well / N-well junction. Because the avalanche junction is a lightly doped avalanche junction, width of a depletion region increases, and probability of interband tunneling of the carries is reduced, thereby reducing the dark counting rate. Furthermore the virtual protecting ring is used for suppressing edge breakdown of the PN junction. The forming principle of virtual protection is characterized in that transverse diffusion exists between adjacent N-wells and therefore the N- virtual protecting ring is formed at the PN junction. The low-dark-count-rate CMOS SPAD photoelectric device is designed at two aspects of the protecting ring and the depletion region width, dark current of the device is reduced, thereby reducing the dark count rate.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Apparatus Comprising an Avalanche Photodiode
ActiveUS20080164554A1High optical coupling efficiencyLow dark count rateSemiconductor devicesDark count rateOptical coupling
Avalanche photodiodes are provided, wherein the APDs provide both high optical coupling efficiency and low dark count rate. The APDs are formed such that their cap layer has an active region of sufficient width to enable high optical coupling efficiency but the APD still exhibits a low dark count rate. These cap layers have a device area with an active region and an edge region, wherein the size of the active region is substantially matched to the mode-field diameter of an optical beam, and wherein the size of the edge region is made small so as to reduce the number of defects included. These APD designs maintain a substantially uniform gain and breakdown voltage, as necessary for practical use.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Spad device for excess bias monitoring
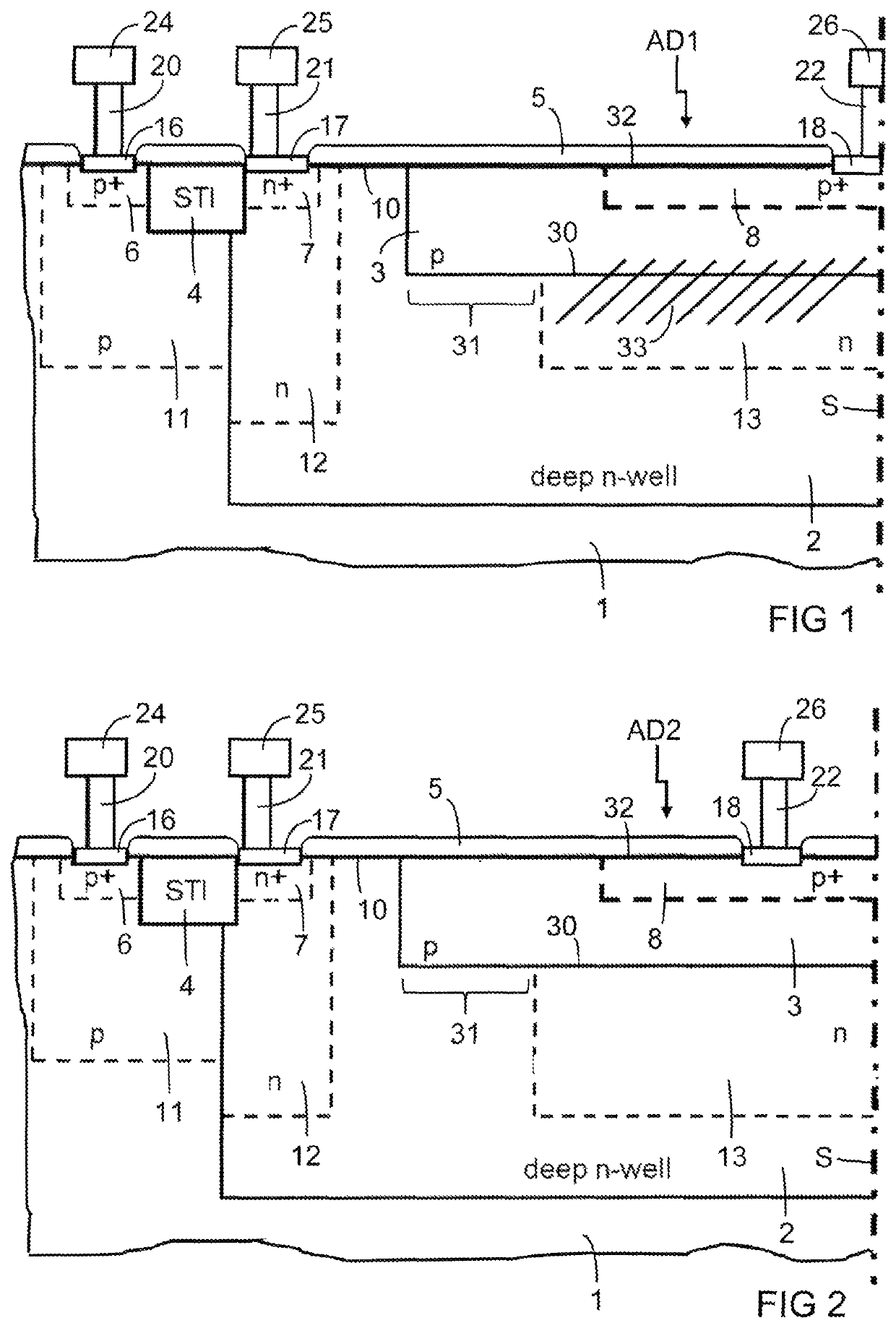
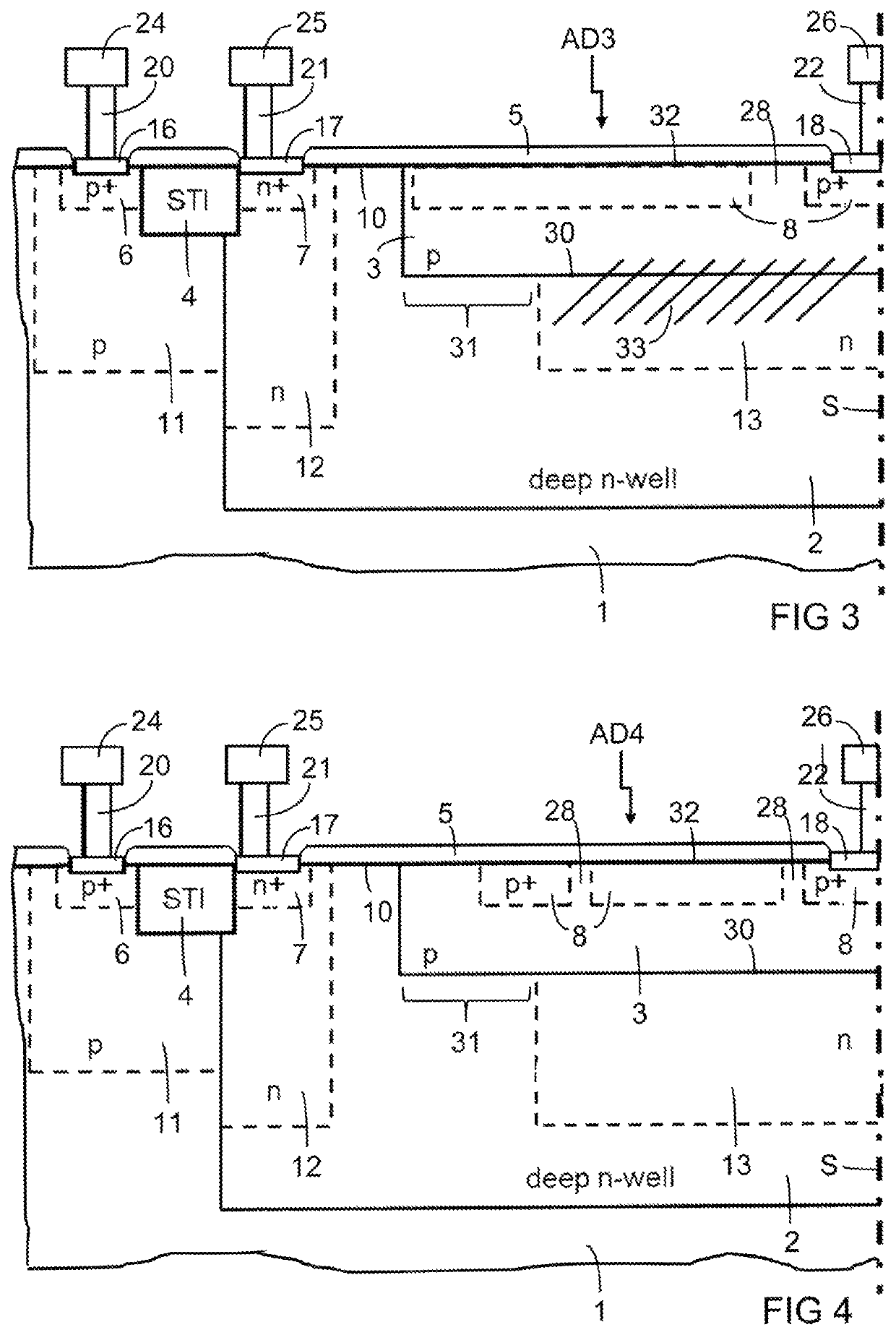
ActiveUS20200152807A1Increase concentrationPhotometrySolid-state devicesDark count rateSingle-photon avalanche diode
The SPAD device comprises a single-photon avalanche diode and a further single-photon avalanche diode having breakdown voltages, the single-photon avalanche diodes being integrated in the same device. The breakdown voltages are equal or differ by less than 10%. The single-photon avalanche diode is configured to enable to induce triggering or to have a dark count rate that is higher than the dark count rate of the further single-photon avalanche diode.
Owner:AMS AG
Apparatus comprising an avalanche photodiode
ActiveUS7378689B2High optical coupling efficiencyLow dark count rateTransistorDark count rateOptical coupling
Avalanche photodiodes are provided, wherein the APDs provide both high optical coupling efficiency and low dark count rate. The APDs are formed such that their cap layer has an active region of sufficient width to enable high optical coupling efficiency but the APD still exhibits a low dark count rate. These cap layers have a device area with an active region and an edge region, wherein the size of the active region is substantially matched to the mode-field diameter of an optical beam, and wherein the size of the edge region is made small so as to reduce the number of defects included. These APD designs maintain a substantially uniform gain and breakdown voltage, as necessary for practical use.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Avalanche photodiode array detector
PendingCN114141886ADoes not affect photon detection efficiencyReduce dark currentSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesDark count ratePhotodiode
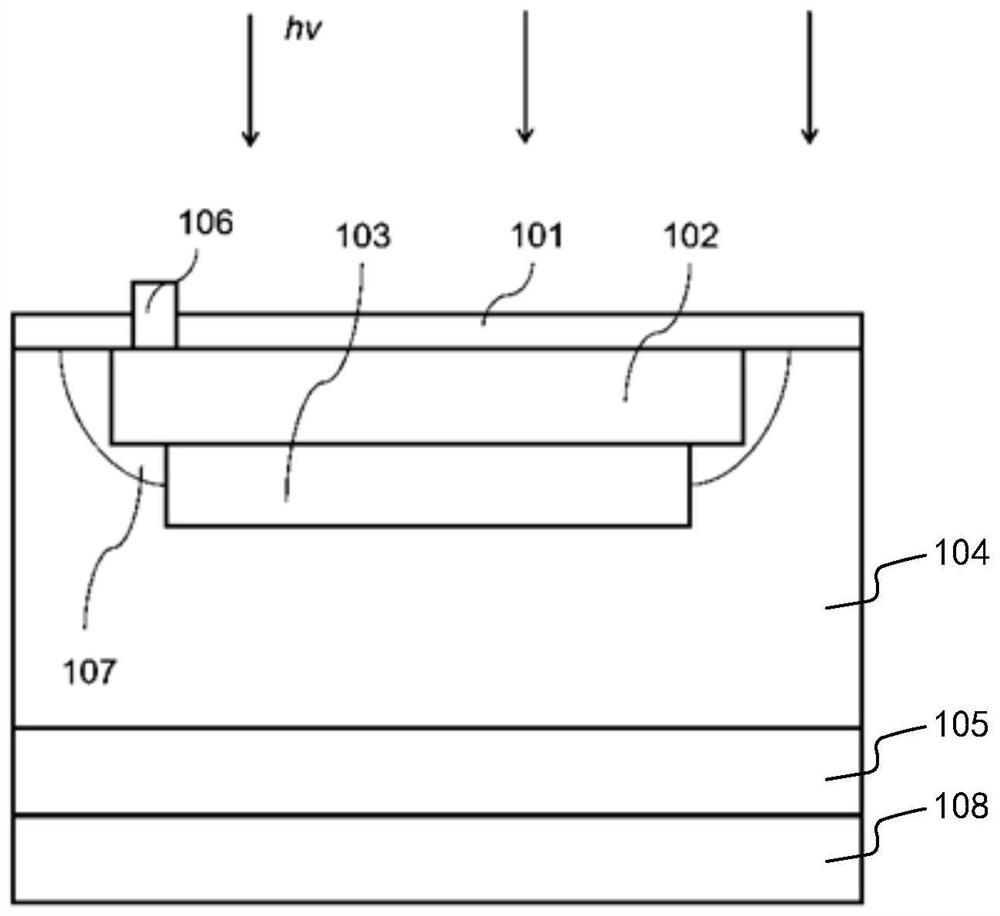
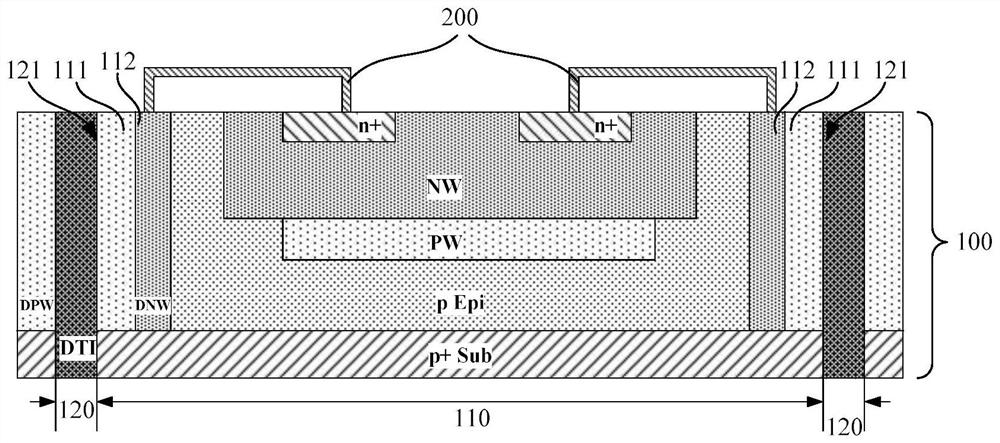
The invention provides an avalanche photodiode array detector which comprises a first conductive type substrate layer, a PN junction, an isolation structure, at least one anode leading-out end and a cathode leading-out end, a first conductive type semiconductor layer is located on the first conductive type substrate layer, the PN junction is located in the first conductive type semiconductor layer, and the isolation structure is located in the first conductive type semiconductor layer. The projections of the PN junctions on the horizontal plane are provided with interval regions; the isolation structure is located in the first conductive type semiconductor layer and located in the PN junction interval region, and the isolation structure is not in contact with the PN junction. In the invention, the projection of the PN junction of the single pixel on the horizontal plane has the interval region, so that the sum of the widths of the PN junctions of the single pixel is reduced, the whole PN junction region and the region between the PN junctions can absorb incident photons, and the reduction of the heavily doped second conductive type doping layer can improve the absorption of part of short-wavelength photons, so that the photoelectric conversion efficiency is improved. Therefore, the photon detection efficiency of the avalanche photodiode is not affected, and the dark current or dark counting rate of a single pixel is reduced.
Owner:江苏尚飞光电科技股份有限公司
System and method for testing performance indexes of avalanche photodiode in Geiger mode
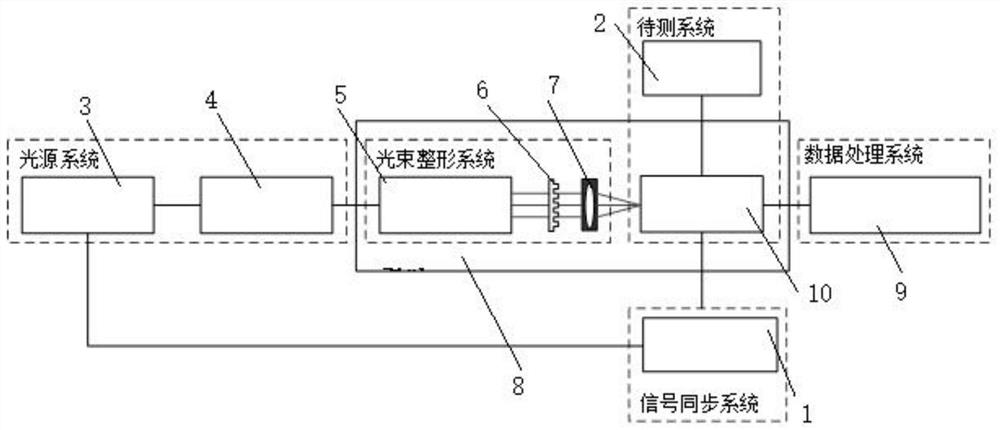
InactiveCN114236342ALarge adjustment rangeImproved noise suppressionElectrical measurement instrument detailsIndividual semiconductor device testingTest performanceCounting rate
The invention belongs to the technical field of diode performance index testing, and particularly discloses a Geiger-mode avalanche photodiode performance index testing system and a Geiger-mode avalanche photodiode performance index testing method. The system comprises a control module, a signal synchronization module, a light source module, a data processing module and a module to be tested. The method comprises the following steps of: installing a to-be-tested avalanche photodiode on a to-be-tested circuit, and connecting a peak noise balancer which is connected with the to-be-tested avalanche photodiode in parallel to simulate and generate a signal which is the same as peak noise of the to-be-tested avalanche photodiode so as to effectively extract an avalanche photodiode signal; then testing a dark count value of the avalanche photodiode to be tested when no signal light is received, an effective count value in a gating of the avalanche photodiode to be tested when the signal light is received and a post-pulse count value in the gating of the avalanche photodiode to be tested when the signal light is not received, and calculating the detection efficiency, the dark count rate, the post-pulse probability and the time jitter index of the avalanche photodiode to be tested. The test method is simple to operate and easy to implement, and test results are high in repeatability.
Owner:武汉光谷航天三江激光产业技术研究院有限公司
Low-time jitter type single photon detector
PendingCN107024289AReduce time jitterImprove versatilityInstrumentsDark count rateSoftware engineering
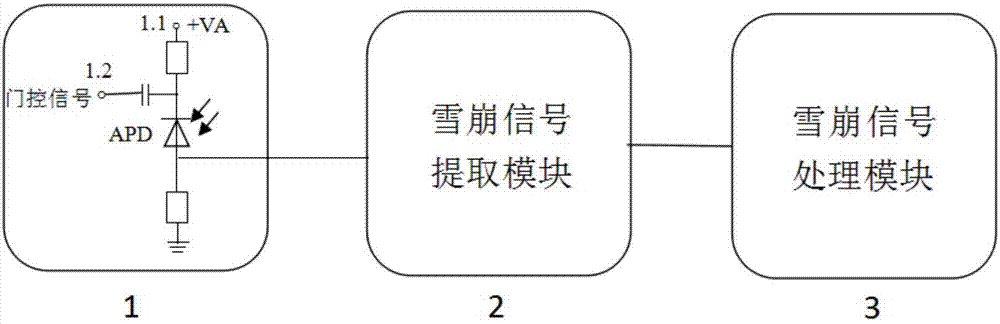
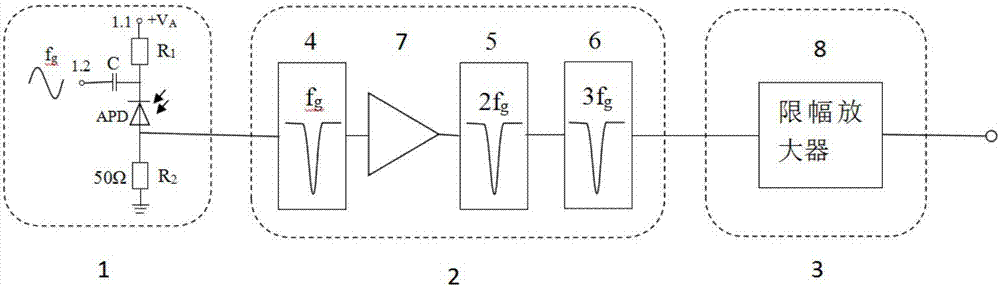
The present invention discloses a low-time jitter type single photon detector, which comprises a single photon signal detection module (1), an avalanche signal extraction module (3) and an avalanche signal processing module (3). The single photon signal detection module (1) comprises an avalanche photoelectric diode APD working in the gated mode. The avalanche signal processing module (3) comprises a limiting amplifier (8). The input terminal of the limiting amplifier is connected with the output terminal of an avalanche signal extraction module (2). The working bandwidth of the limiting amplifier (8) is larger than the bandwidth of an avalanche electric signal. The input signal threshold value of the limiting amplifier (8) is greater than the amplitude of the background noise of the output signal of the avalanche signal extraction module (2). The limiting amplifier (8) converts the avalanche electric signal into a digital signal and outputs the digital signal. The low-time jitter type single photon detector is simple and reliable, and the time jitter of the detection system is greatly reduced. Meanwhile, the detection efficiency, the dark count rate and other performances of the system are not influenced at all.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
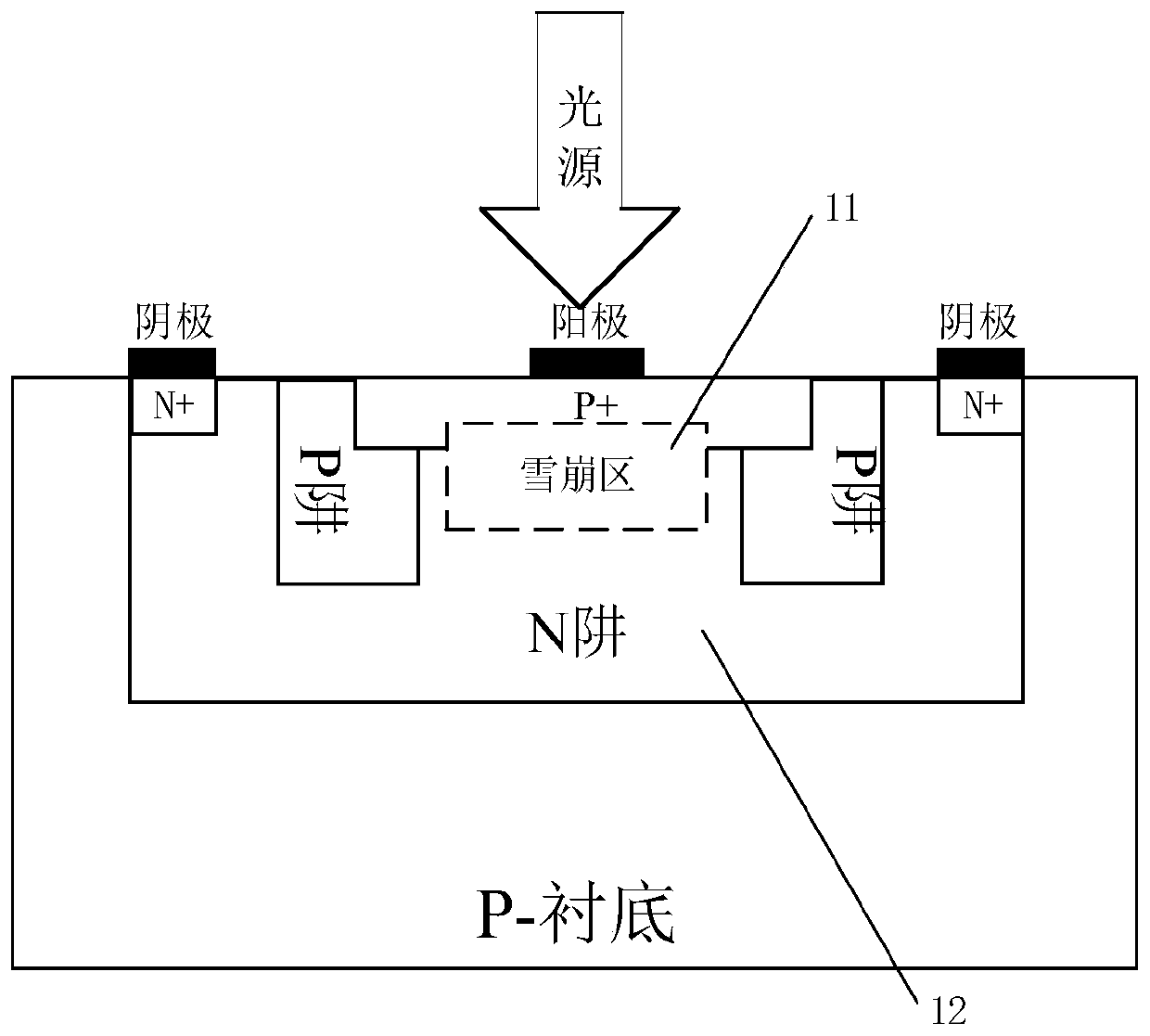
A Single Photon Avalanche Diode Detector Array Unit with High Detection Efficiency
ActiveCN105185796BNovel structureImprove detection efficiencyRadiation controlled devicesSemiconductor devicesDark count rateSingle-photon avalanche diode
The invention discloses a single-photon avalanche diode detector array unit with high detection efficiency. The array unit is a SPAD structure with surrounding P-injection, P-buried layer and deep P-well protected by P-buried layer. A deep P well is formed by ion implantation in the deep P well. There are two buried layer regions in the deep P well, namely the P buried layer region 3 and the P-buried layer region 4. There is a P-implanted region above the P-buried layer region 4. 8 surround. The array unit structure can effectively improve the photon detection efficiency of the SPAD device, and the dark count rate is very low, which greatly improves the overall performance of the SPAD detector.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM INST AT NANJING CO LTD
Single-photon avalanche diode, manufacturing method thereof and single-photon avalanche diode array
PendingCN113690337AImprove absorption efficiencyDoes not affect photon detection efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesDark count rateSingle-photon avalanche diode
The invention relates to a single-photon avalanche diode, a manufacturing method thereof and a single-photon avalanche diode array. According to the single photon avalanche diode, a p-type doped region longitudinally extending in the thickness direction of a substrate is arranged in the edge region of an active region, and an n-type doped region longitudinally extending in the thickness direction of the substrate is further arranged on the side, away from an isolation groove, of the p-type doped region. The p-type doped region and the n-type doped region have an isolation effect on defects generated at the isolation groove, dark count caused by the defects can be effectively reduced, the n-type doped region is electrically connected with a doped region with the same doping type as the n-type doped region in the pn junction in the active region, and a depletion region shrunk due to the p-type doped region can be widened. Therefore, the dark counting rate of the single photon avalanche diode is reduced, and the photon detection efficiency of the device is not affected. The single-photon avalanche diode array comprises the single-photon avalanche diodes which are arranged in an array.
Owner:WUHAN XINXIN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
GM-APD array camera performance index testing device and method
PendingCN112098980APrecise control of gate opening timeEfficiently assess practical usabilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationDark count rateRadar systems
Owner:武汉光谷航天三江激光产业技术研究院有限公司
Method and system for restraining dark count rate of multimode fiber coupled with superconducting nanowire single photon detector (SNSPD)
The invention provides a method and a system for restraining a dark count rate of a multimode fiber coupled with a superconducting nanowire single photon detector (SNSPD). The method for restraining the dark count rate of the multimode fiber coupled with the SNSPD comprises the following steps of filtering incident light to acquire the light with a target wavelength; and coupling the light with the target wavelength to the SNSPD for detecting. According to the method for restraining the dark count rate of the multimode fiber coupled with the SNSPD provided by the invention, the light beyond the target wavelength is detected after filtering, so that the dark count rate of the system can be significantly reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
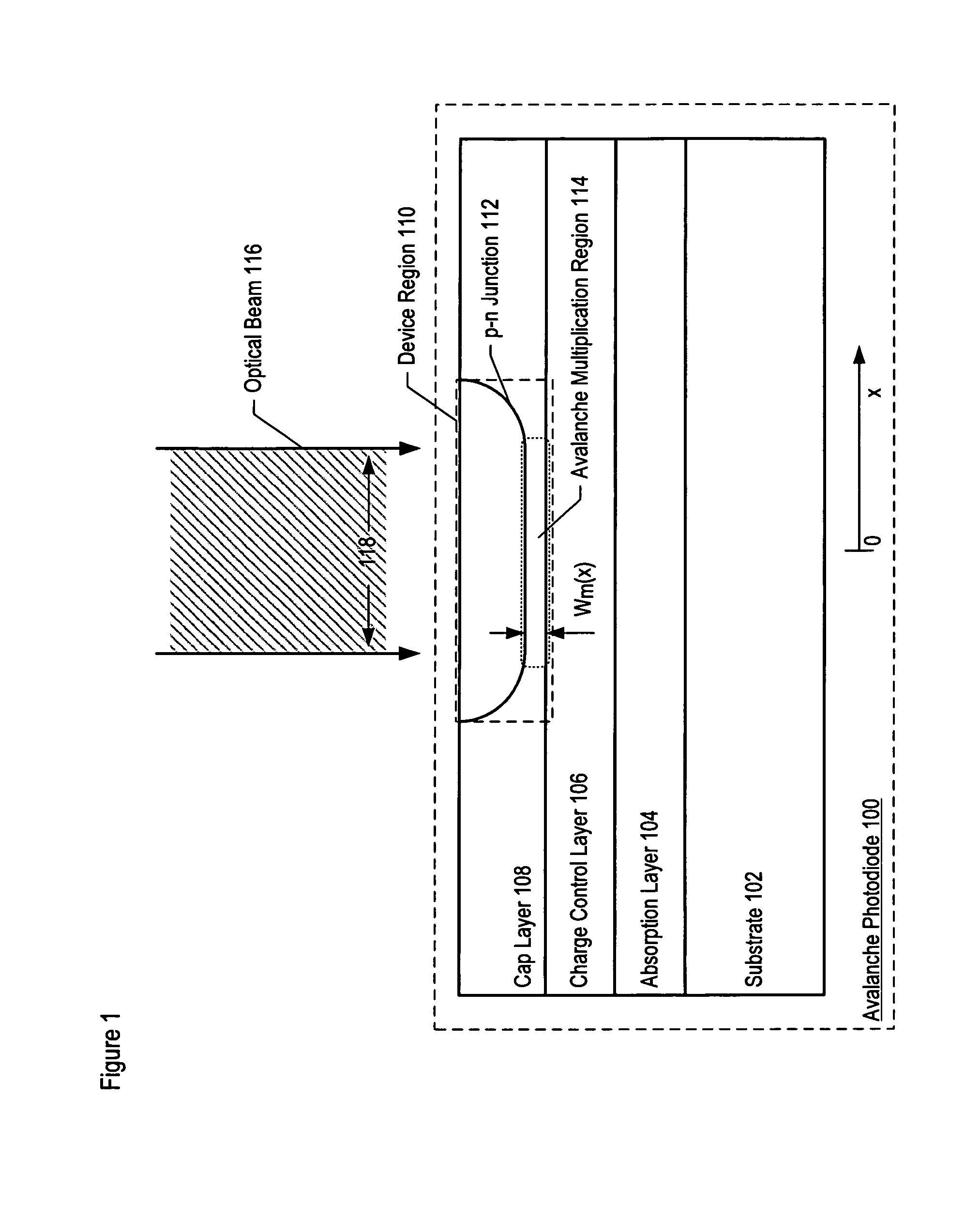
Method for forming an avalanche photodiode
ActiveUS20070087511A1Lower the volumeReduce dark count rateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDark count rateLight beam
Methods for fabricating an avalanche photodiode (APD), wherein the APD provides both high optical coupling efficiency and low dark count rate. The APD is formed such that it provides an active region of sufficient width to enable high optical coupling efficiency and a low dark count rate. Some APDs fabricated using these methods have a device area with an active region and an edge region, wherein the size of the active region is substantially matched to the mode-field diameter of an optical beam, and wherein the size of the edge region is substantially minimized and further wherein the device region maintains a substantially uniform gain and breakdown voltage.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
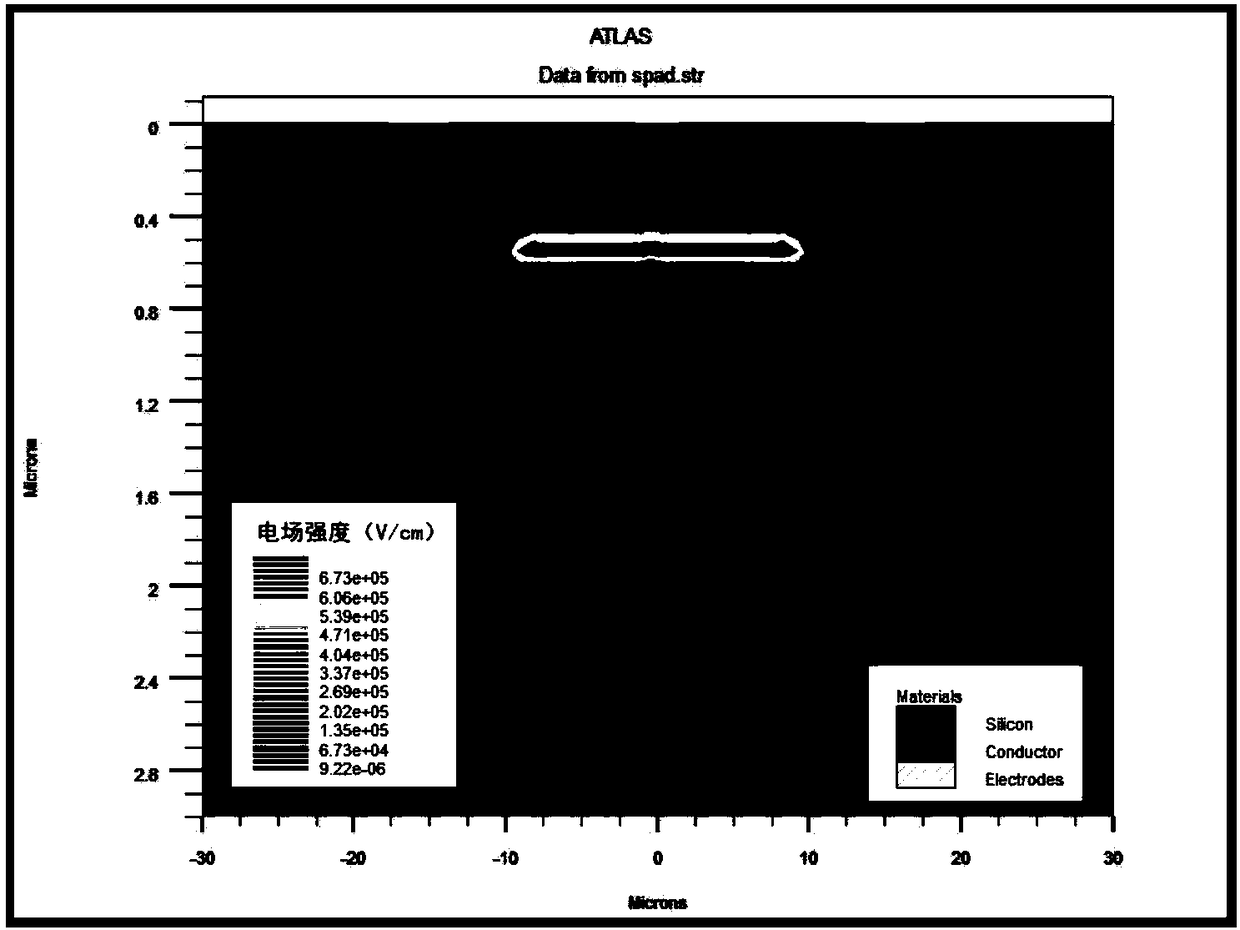
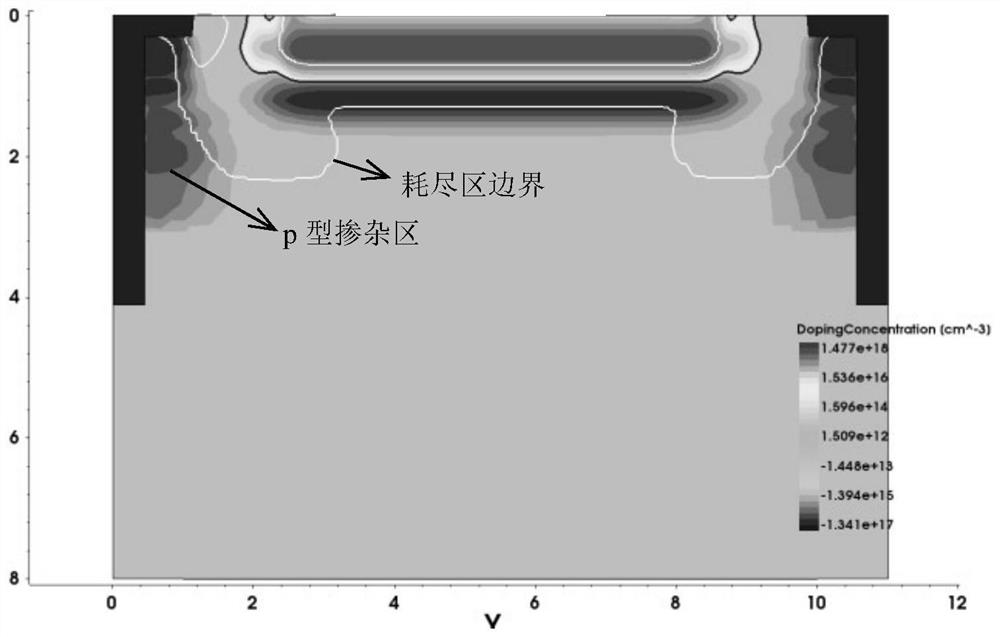
Low dark count rate semiconductor structure
PendingCN114497264AFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesDark count rateSemiconductor structure
A photosensitive semiconductor structure includes: a pn junction in a silicon substrate, the pn junction including a central portion and an edge portion surrounding the central portion, the edge portion being in contact with a surface of the silicon substrate; and a plasma shielding structure covering at least a depletion width of the pn junction over at least a portion of the edge portion, where the edge portion is in contact with the surface of the silicon substrate.
Owner:X FAB GLOBAL SERVICES GMBH
SPAD device for excess bias monitoring
Owner:AMS AG
High-altitude atmospheric detection lidar based on superconducting single-photon detector with large photosensitive surface
ActiveCN106353770BReduce dark countHigh photon count rateElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationCounting rateQuantum efficiency
The invention discloses high atmosphere detection laser radar based on a large-photosurface superconducting single-photon detector. By application of the large-photosurface superconducting single-photon detector to a high atmosphere detection laser radar system, high atmosphere parameter detection can be realized through increase of telescope area. Compared with an existing detector applied to the high atmosphere detection laser radar, the superconducting single-photon detector has advantages of large photosurface, high counting rate, high quantum efficiency, low dark count rate, high photon count rate and short jittering time. Therefore, the high atmosphere detection laser radar based with the large-photosurface superconducting single-photon detector is more advantageous in range resolution, spatial resolution and detection precision; in other words, under the condition of realizing same detection indexes, the laser radar with the large-photosurface superconducting single-photon detector can adopt a smaller-aperture telescope or a lower-power laser.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Single-photon avalanche diode with back irradiation, and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN113284971AImprove detection efficiencyLow doping levelFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesSingle-photon avalanche diodeDark count rate
The invention discloses a single-photon avalanche diode with back irradiation, and a manufacturing method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of single-photon detection. The single-photon avalanche diode comprises a P-type epitaxial layer, a P+ heavily doped region is arranged in the P-type epitaxial layer, a P- lightly doped region is coaxially arranged on the periphery of the P+ heavily doped region, a P-type avalanche doped region is coaxially arranged below the P- lightly doped region, N+ heavily doped regions are arranged on the two sides of the P+ heavily doped region, an N well region is coaxially arranged below the N+ heavily doped regions, N-type avalanche doped regions are arranged below the P-type avalanche doped region at intervals, and an N- lightly doped region is arranged below the N-type avalanche doped regions. The mode that light irradiates from the back face is adopted, the device structure is optimized, and a peripheral circuit of the device is integrated below the device. And the detection efficiency of the device is improved. The P-type avalanche doped region, the P-type epitaxial layer central region and the N-type avalanche doped regions form an avalanche junction, and the dark counting rate of the device is remarkably reduced by adopting the sub-structure.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
A single photon avalanche diode detector structure and manufacturing method thereof
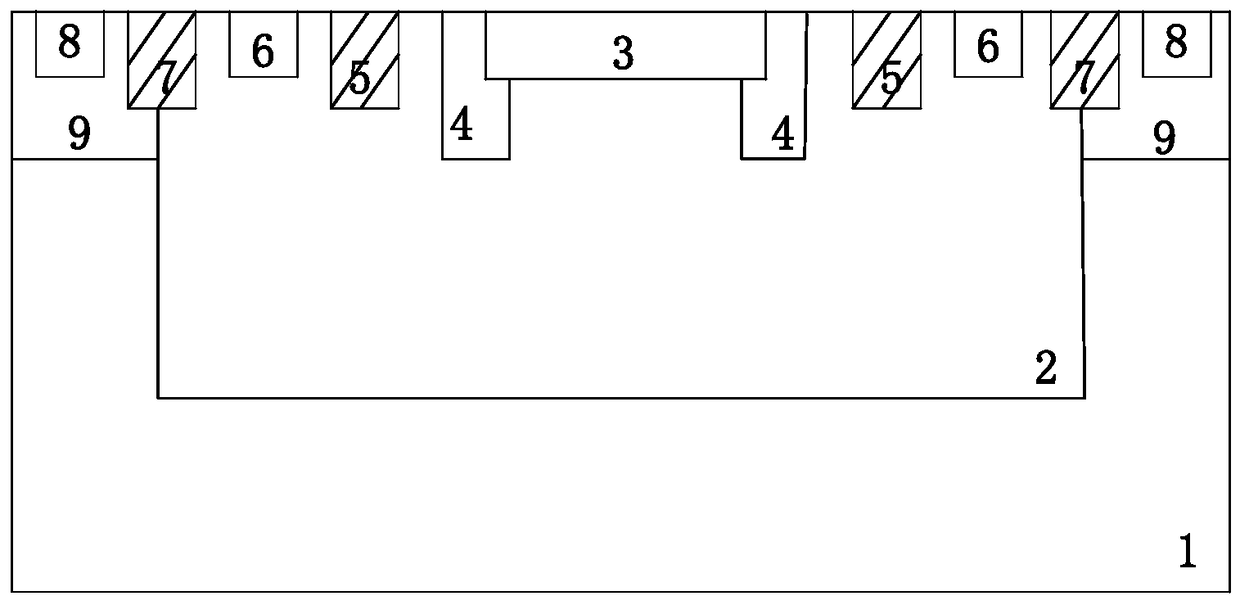
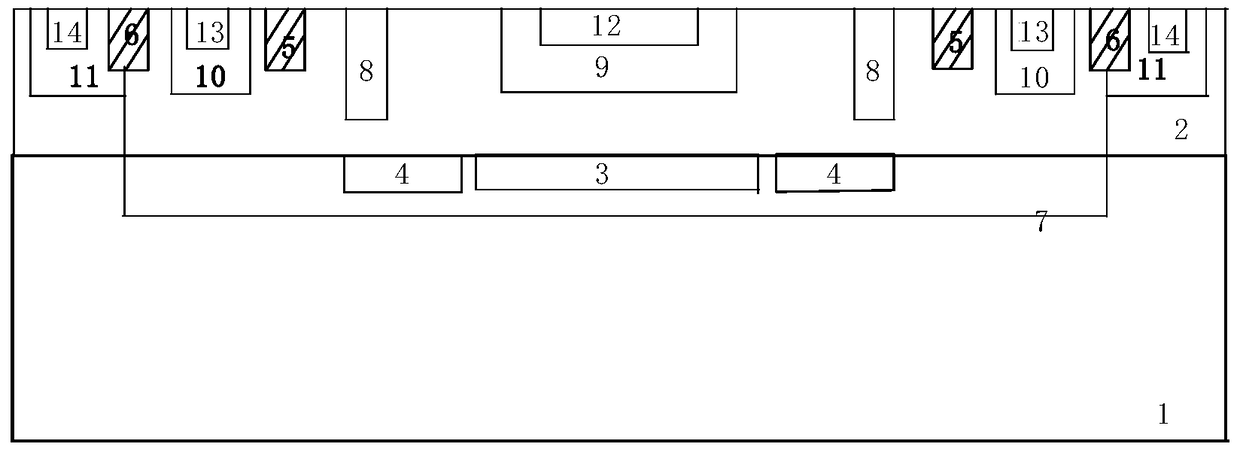
ActiveCN108231946BSimple structureDoping concentration gradient distribution is simple and controllableFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesDark count rateSingle-photon avalanche diode
The invention discloses a single-photon avalanche photoelectric diode detector structure which comprises a P-type silicon substrate, a deep N well and a deep P well, wherein the deep N well and the deep P well are formed in the P-type silicon substrate; an N<+> zone and a P<+> zone for forming a multiplication zone for absorbing photons are formed in the deep N well; a first P well zone and an N well zone for forming an avalanche photoelectric diode structure are formed around the multiplication zone; an anode lead-out end is formed in the N well zone; a cathode lead-out end is formed in the P<+> zone; a second P well zone is formed in the deep P well; a substrate lead-out end is formed in the second P well zone; the surfaces of the deep N well and the deep P well are covered by protectionlayers. The single-photon avalanche photoelectric diode detector structure is simple in structure, only two PN junctions are formed in a vertical direction of a junction depth, a PN junction isolation mode is adopted in a whole unit structure, dark count rates caused by defects of STI can be completely eliminated, the unit area can be greatly reduced, and the filling rate can be increased. The invention further discloses a producing method of the single-photon avalanche photoelectric diode detector structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT +1
A low dark count rate cmos SPAD optoelectronic device
ActiveCN108550592BBand-to-band tunnelingSource of reductionSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesCMOSDark count rate
The invention provides a low-dark-count-rate CMOS SPAD photoelectric device. A P-well layer is added based on a routine P+ / N-well type SPAD structure. The P-well layer is arranged between the P+ layerand the N-well layer. Furthermore, an N-well clearance is utilized as a virtual protecting ring of the structure; namely N-wells are added at two sides of a PN junction, wherein the structure is shown in the attached figures of an abstract. An incident photon is incident into the device and is attracted at the central N well, and furthermore a photon-generated carrier is generated. The P-well layer and the N-well layer are utilized at two sides of the PN junction. Hereon an avalanche junction is a P-well / N-well junction. Because the avalanche junction is a lightly doped avalanche junction, width of a depletion region increases, and probability of interband tunneling of the carries is reduced, thereby reducing the dark counting rate. Furthermore the virtual protecting ring is used for suppressing edge breakdown of the PN junction. The forming principle of virtual protection is characterized in that transverse diffusion exists between adjacent N-wells and therefore the N- virtual protecting ring is formed at the PN junction. The low-dark-count-rate CMOS SPAD photoelectric device is designed at two aspects of the protecting ring and the depletion region width, dark current of the device is reduced, thereby reducing the dark count rate.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A method of correcting the influence of temperature on sipm gain
ActiveCN107526096BReduce circuit complexityLow costRadiation intensity measurementDark count rateWorking temperature
The invention relates to a method for correcting temperature influence to SiPM gain. According to the method of the invention, a dark count rate in an SiPM output signal is obtained through calculation according to an SiPM dark count measuring algorithm. A fixed relation between the dark count rate and the SiPM working temperature is utilized for determining the current temperature of the SiPM. Furthermore a to-be-regulated working bias increment parameter of the SiPM is determined based on the current temperature of the SiPM, thereby effectively correcting temperature influence to the SiPM gain, improving system stability, reducing hardware cost and improving system efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU SUPERSENSE TECH CO LTD
Imaging system
The invention relates to an imaging system. A semiconductor device may include a plurality of single-photon avalanche diodes (SPADs). The semiconductor device may include sensing single-photon avalanche diodes that are sensitive to incident light and dark single-photon avalanche diodes that are shielded from incident light. The dark single-photon avalanche diodes may be used to measure one or more parameters for the semiconductor device such as breakdown voltage, dark count rate, and quench resistance. A processing circuitry may optimize a bias voltage for the semiconductor device based on information regarding one or more sensor parameters obtained using the dark single-photon avalanche diodes.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Single-photon avalanche diode with low dark counting rate and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN111490123AReduce dark count rateLow doping levelFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesDark count rateSingle-photon avalanche diode
The invention discloses a single-photon avalanche diode with a low dark counting rate and a manufacturing method thereof, which belong to the technical field of single-photon detection. The single-photon avalanche diode comprises a P-type epitaxial layer arranged on a substrate; an N-type isolation region is arranged in the P-type epitaxial layer; N well regions are symmetrically arranged on the two sides of the N-type isolation region; an N + heavily doped region is coaxially arranged at the top of the N well regions; a central N-type region is coaxially arranged above the N-type isolation region; a P well region is arranged above the central N-type region; a P + heavily doped region is coaxially arranged in the P well region; and P-type protection ring regions are symmetrically arrangedon the two sides of the P + heavily doped region. According to the invention, the P well central region, the P-type epitaxial layer central region and the central N-type region are adopted to form anavalanche region, so that the electric field of the avalanche region is reduced, the tunneling effect is inhibited, and the dark counting rate of the device is remarkably reduced.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for forming an avalanche photodiode
ActiveUS7553734B2Enhanced couplingLow dark count rateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDark count rateOptoelectronics
Methods for fabricating an avalanche photodiode (APD), wherein the APD provides both high optical coupling efficiency and low dark count rate. The APD is formed such that it provides an active region of sufficient width to enable high optical coupling efficiency and a low dark count rate. Some APDs fabricated using these methods have a device area with an active region and an edge region, wherein the size of the active region is substantially matched to the mode-field diameter of an optical beam, and wherein the size of the edge region is substantially minimized and further wherein the device region maintains a substantially uniform gain and breakdown voltage.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com