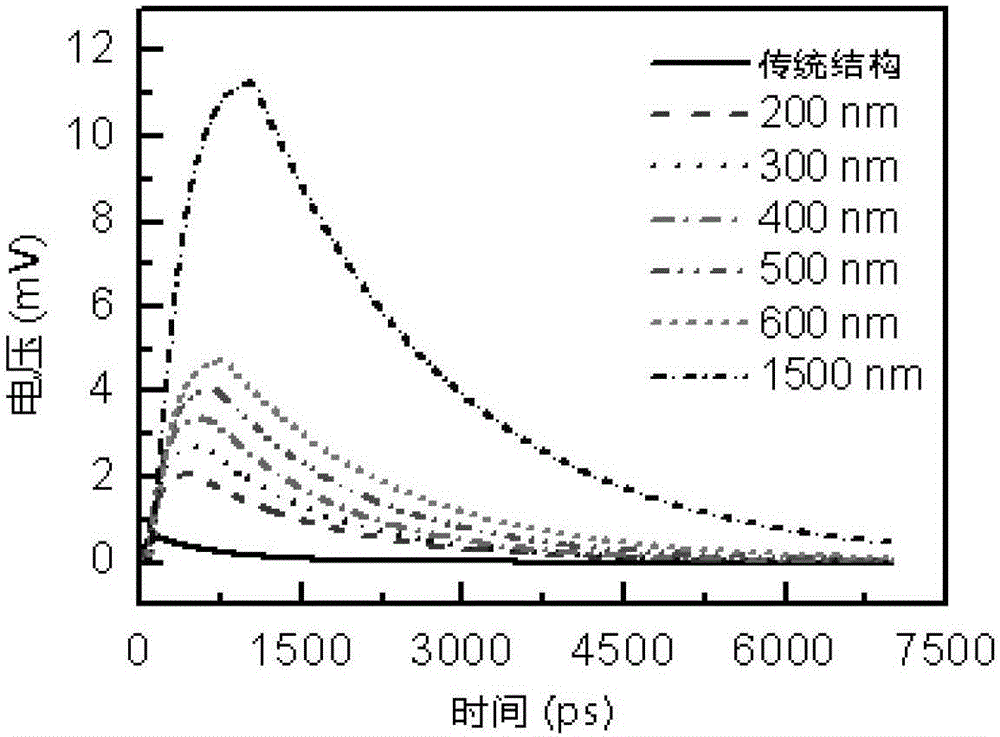
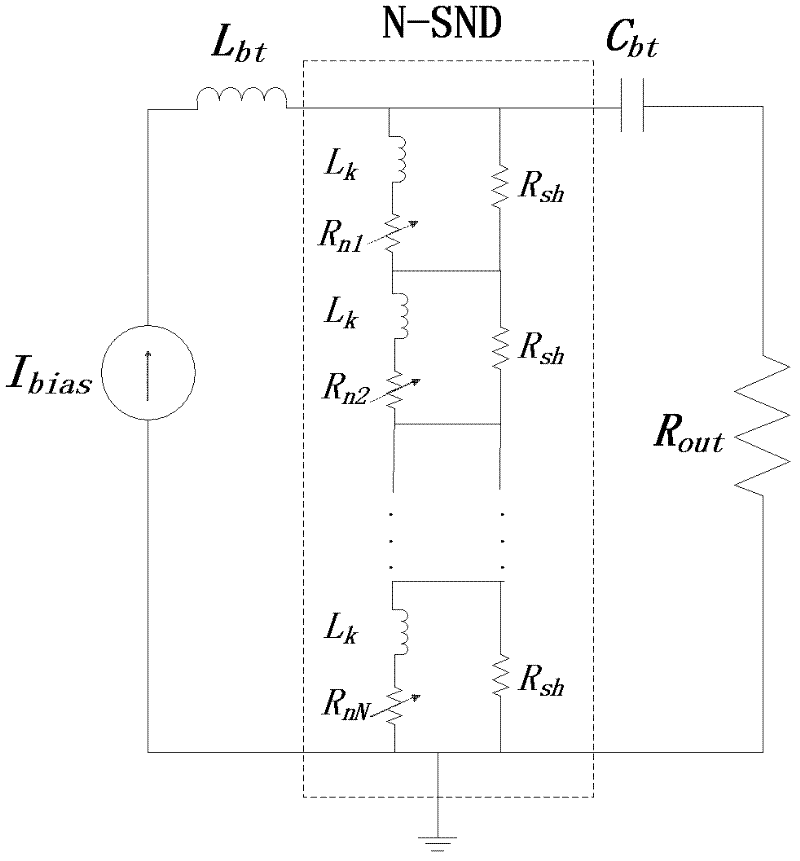
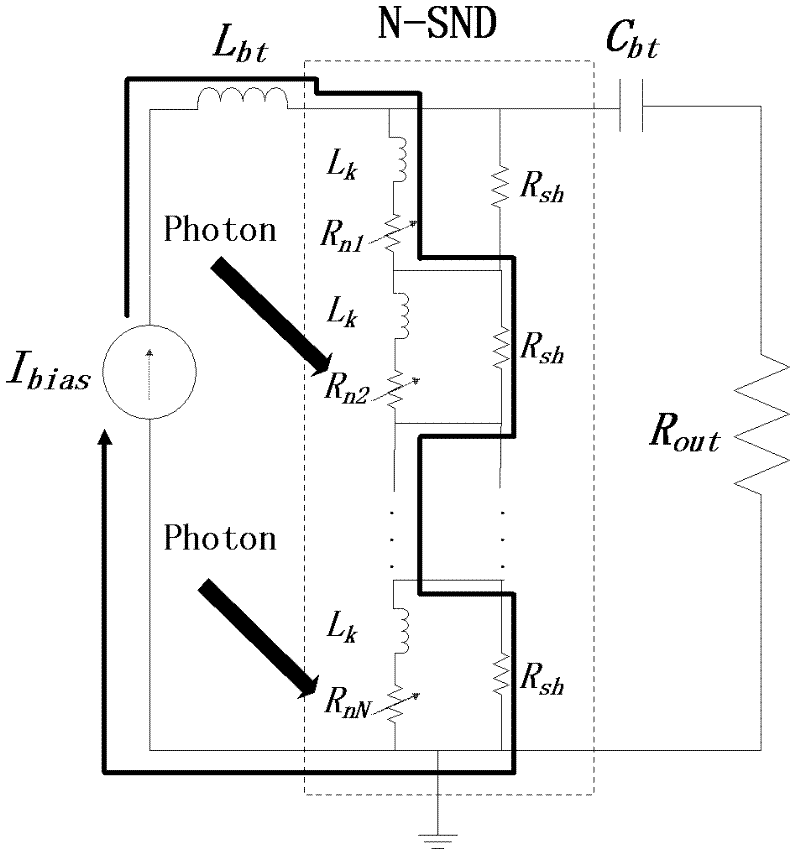
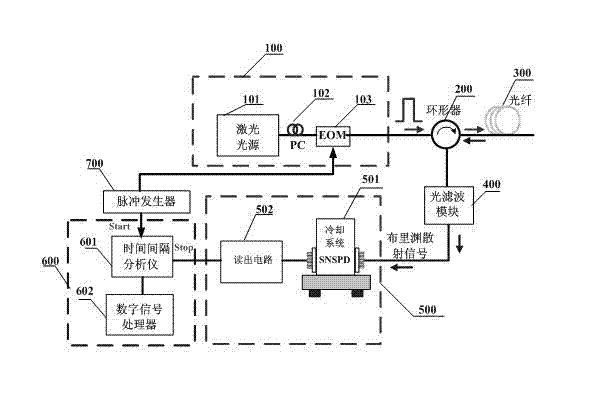
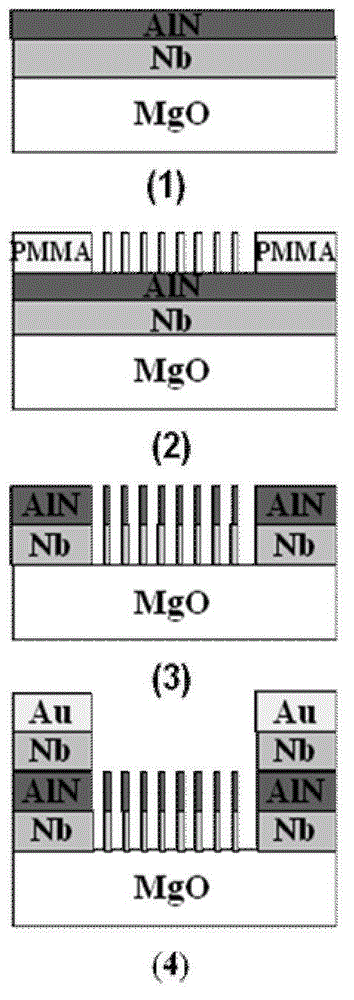
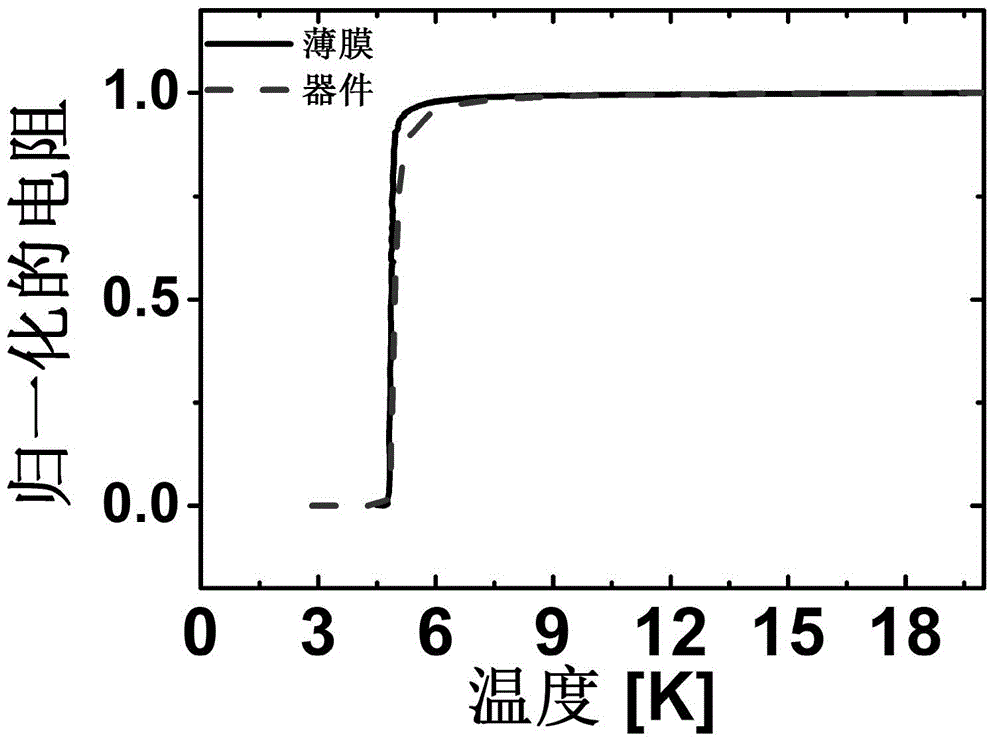
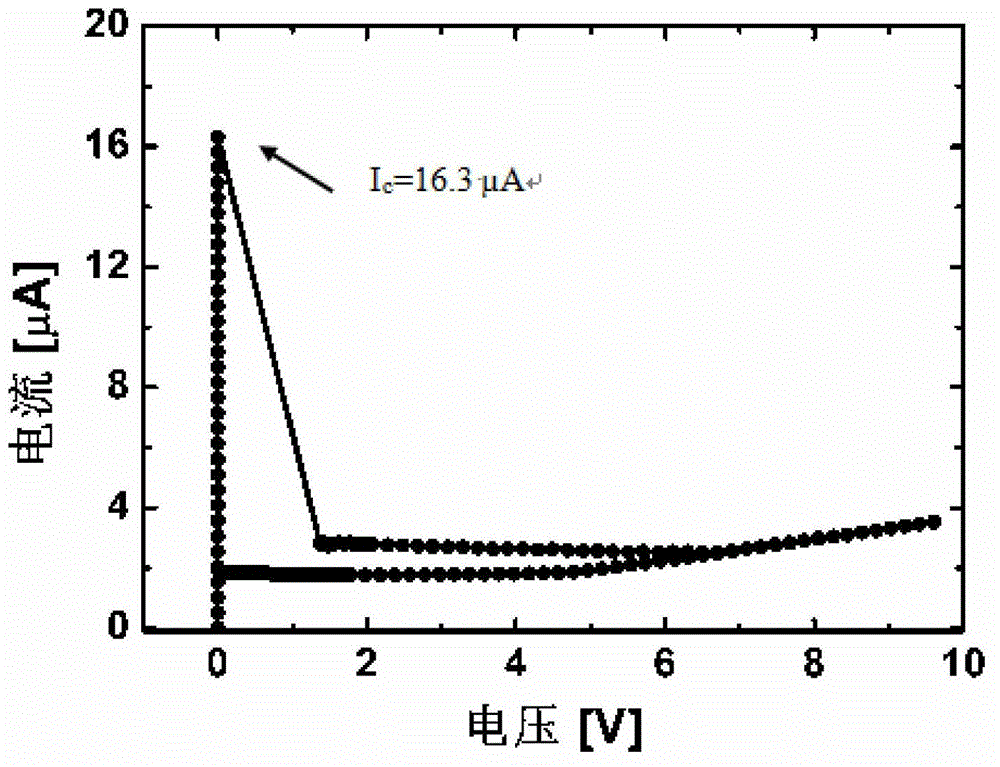
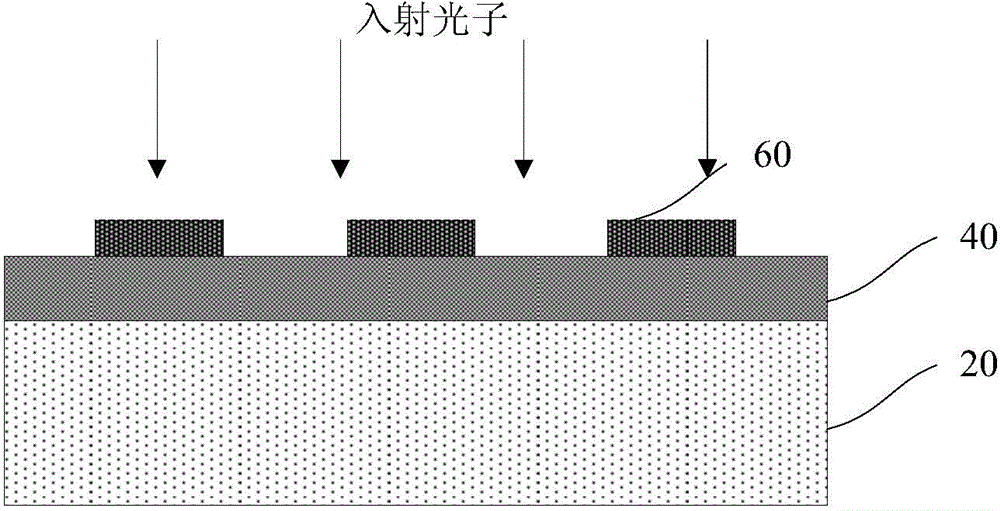
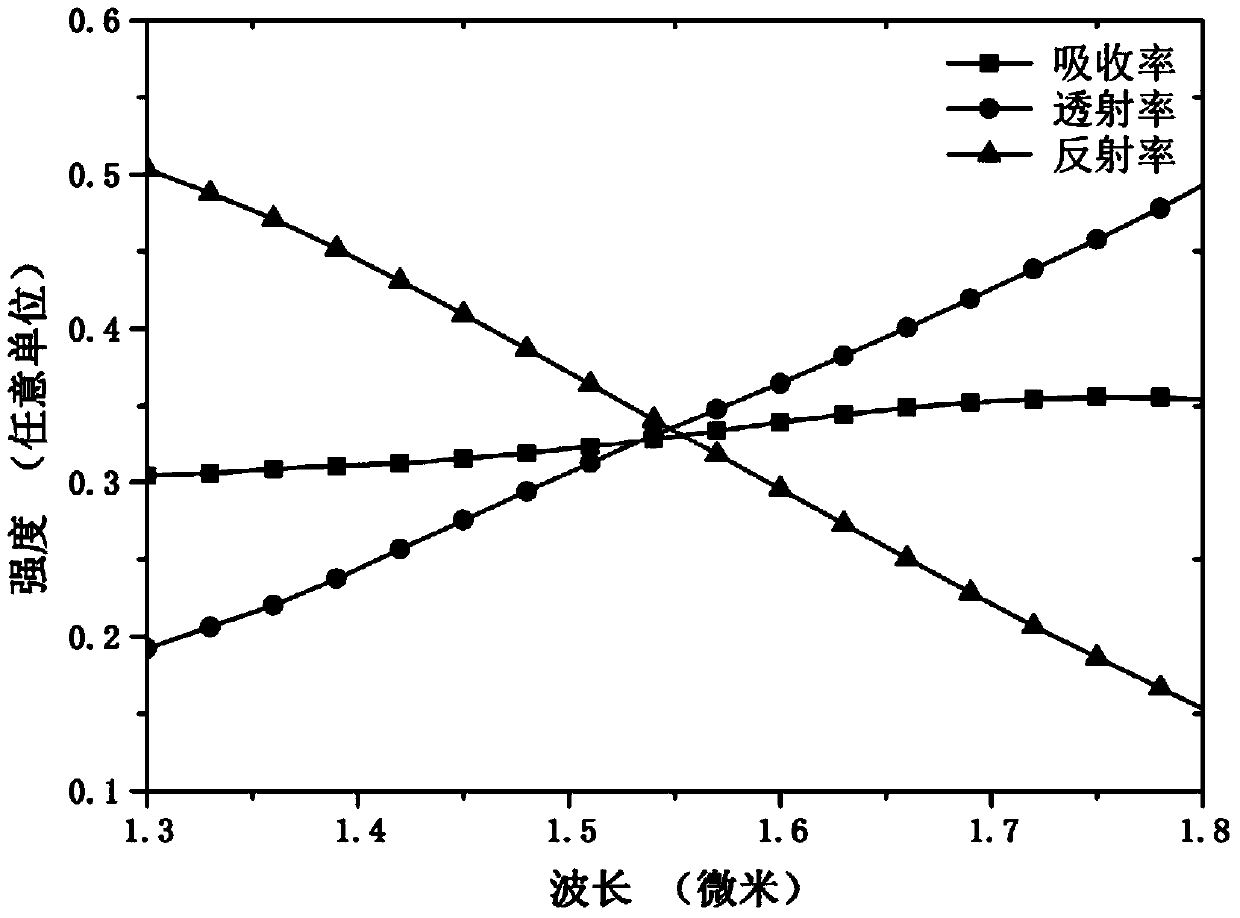
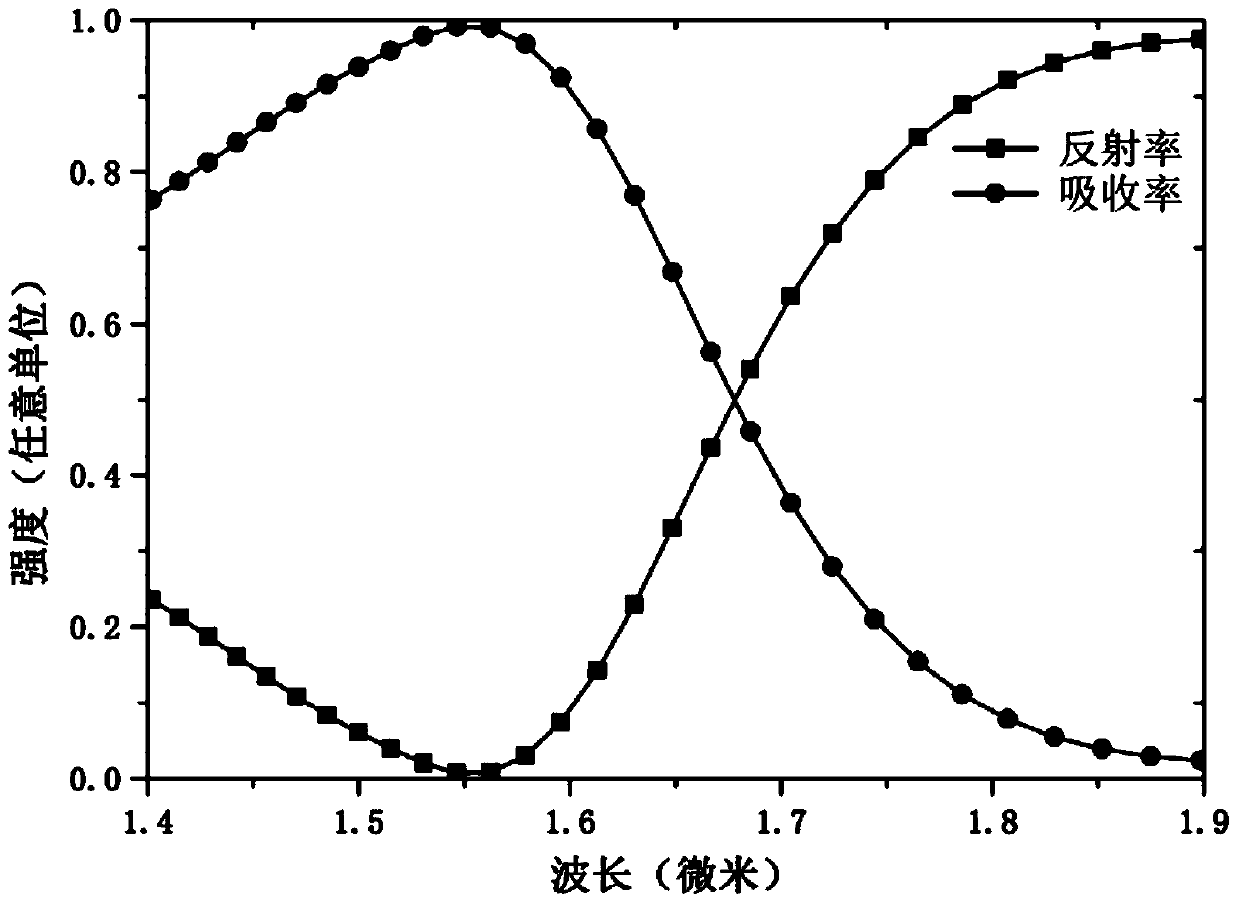
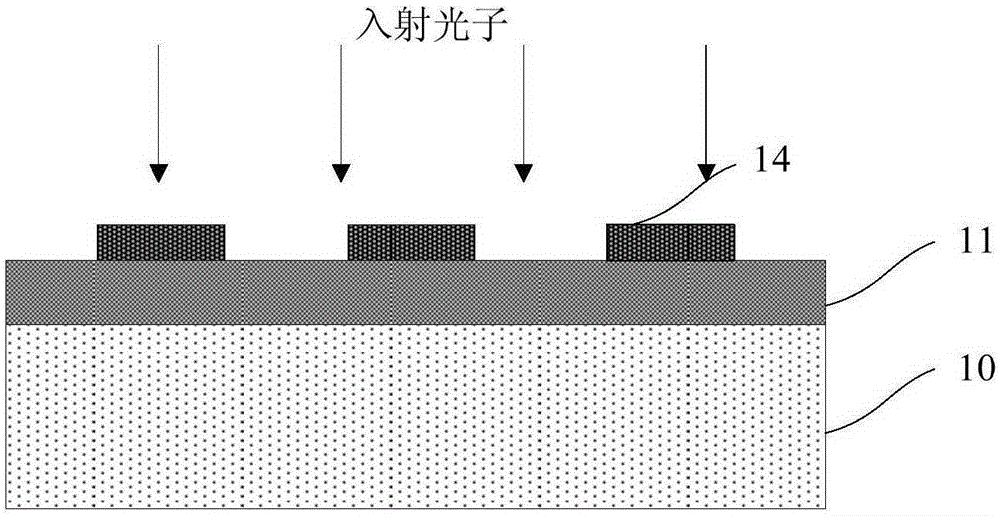
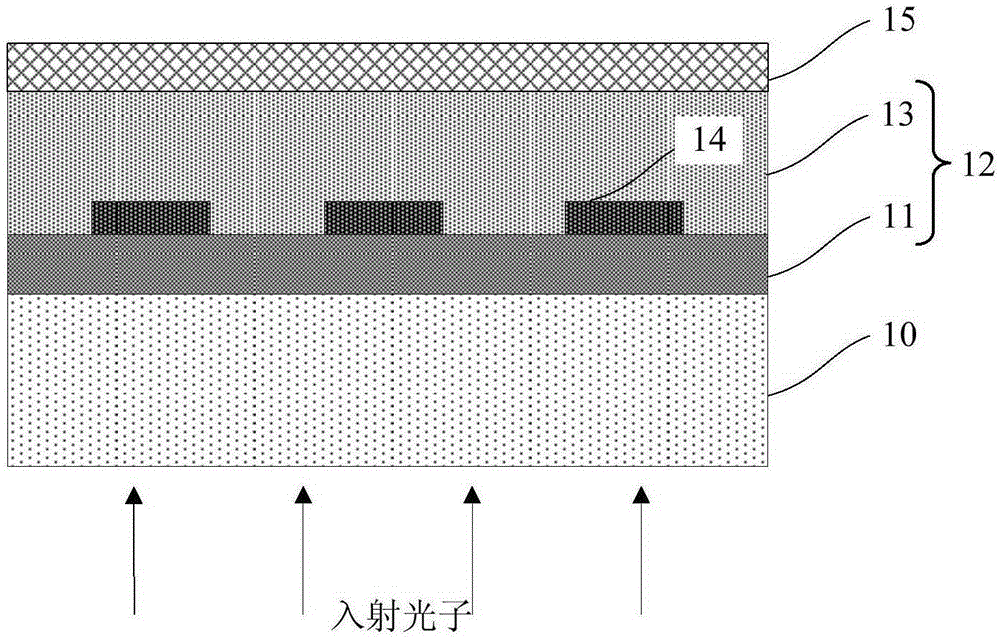
Patents
Literature
131 results about "Superconducting nanowire single-photon detector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
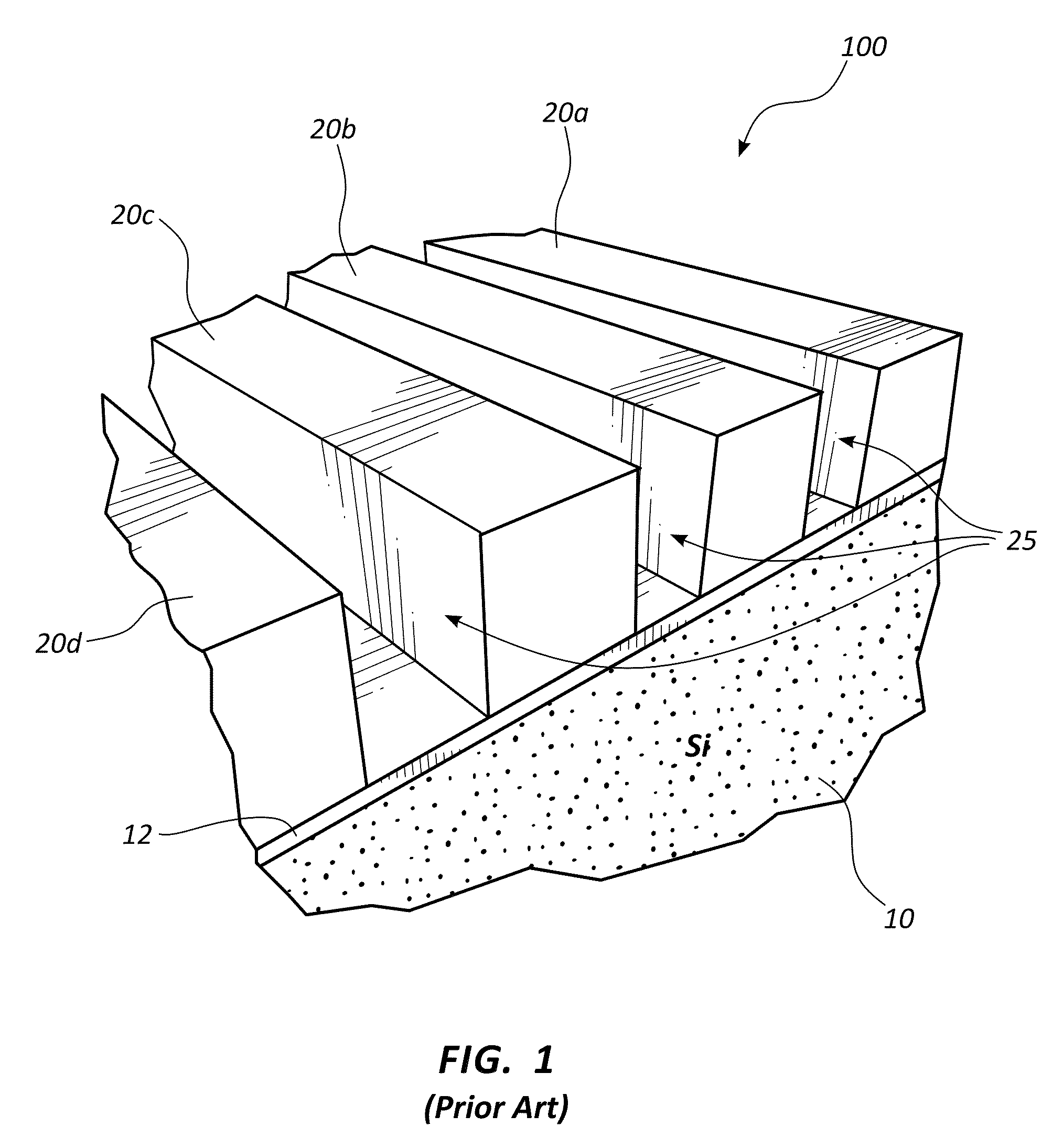
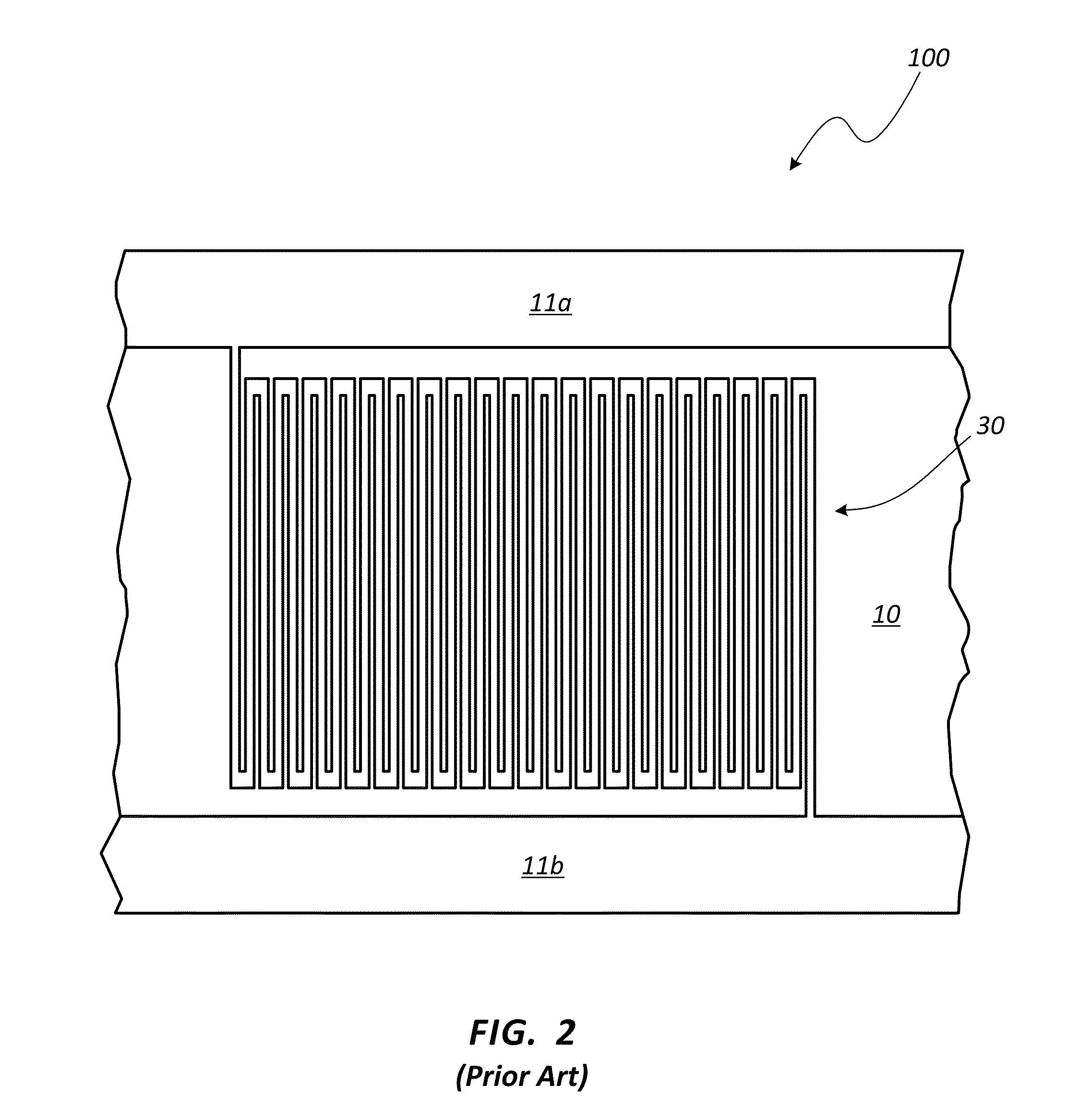
The superconducting nanowire single-photon detector (SNSPD) is a type of near-infrared and optical single-photon detector based on a current-biased superconducting nanowire. It was first developed by scientists at Moscow State Pedagogical University and at the University of Rochester in 2001. The first fully operational prototype was demonstrated in 2005 by the University of Rochester, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (Boulder), and BBN Technologies as part of the DARPA Quantum Network.
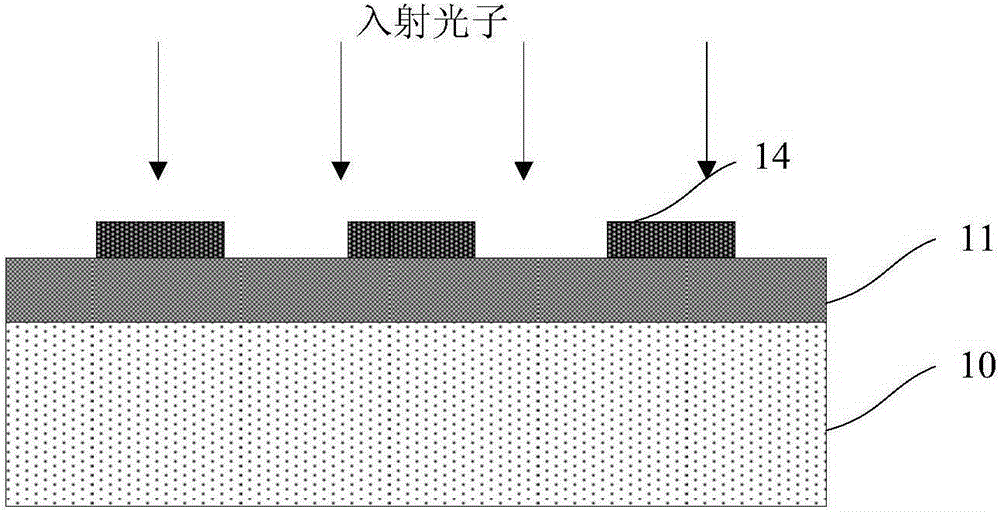
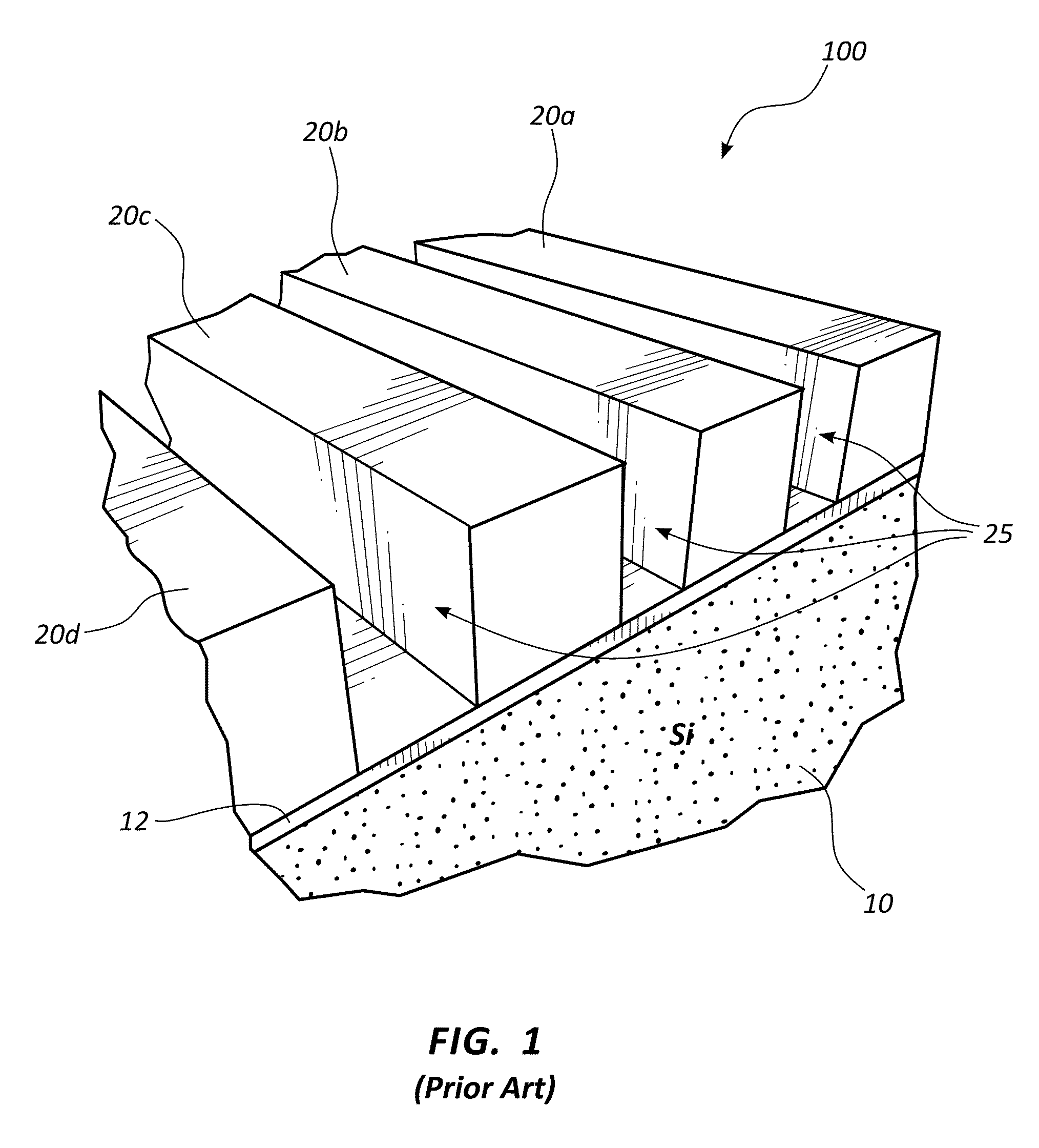
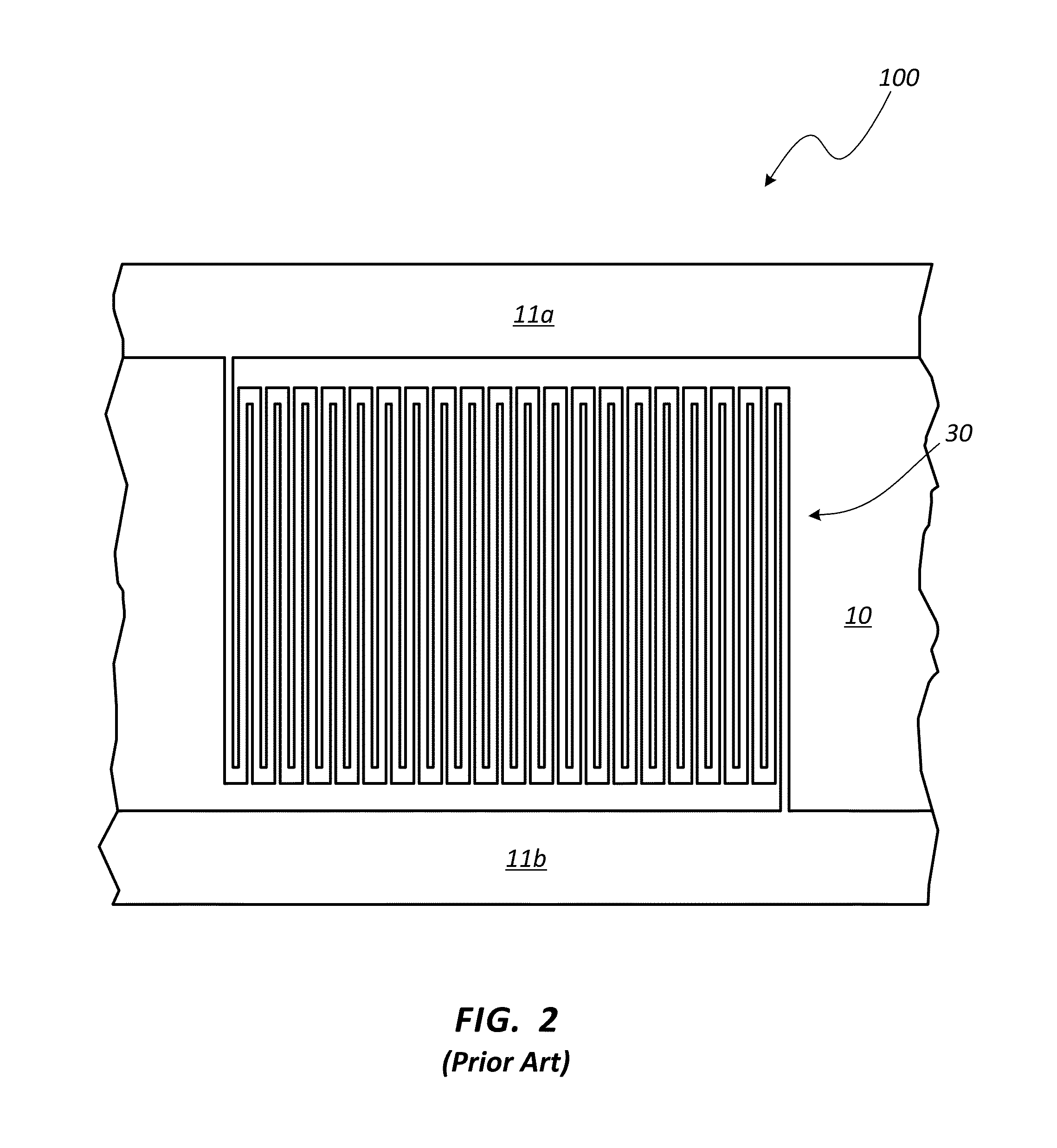
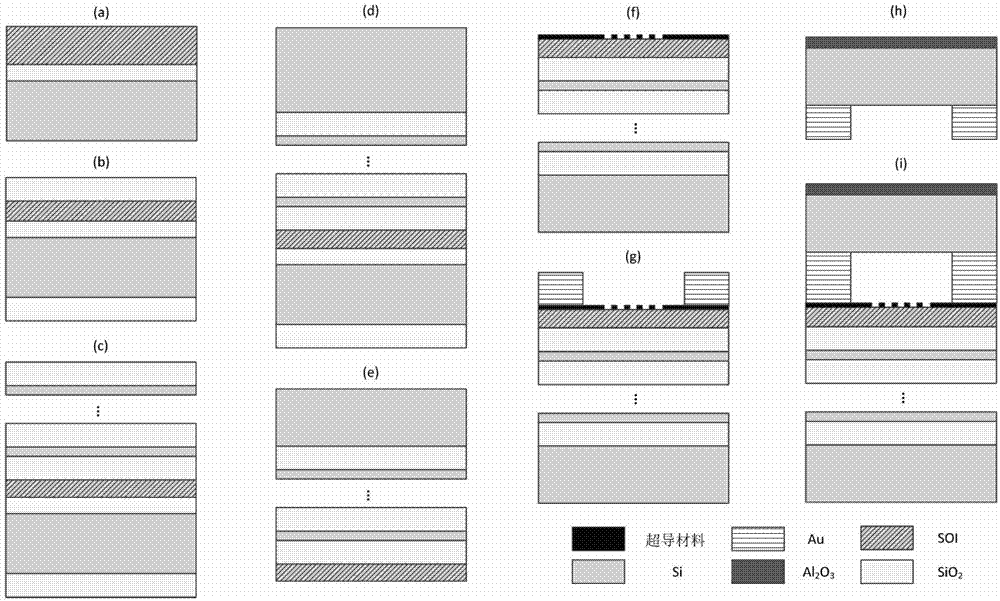
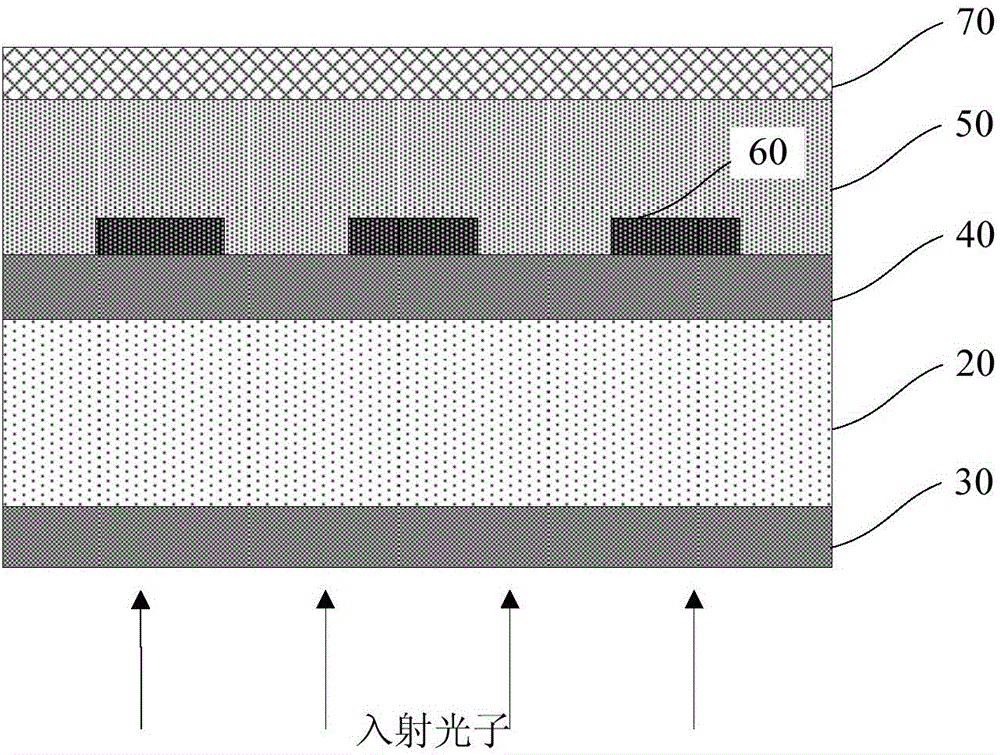
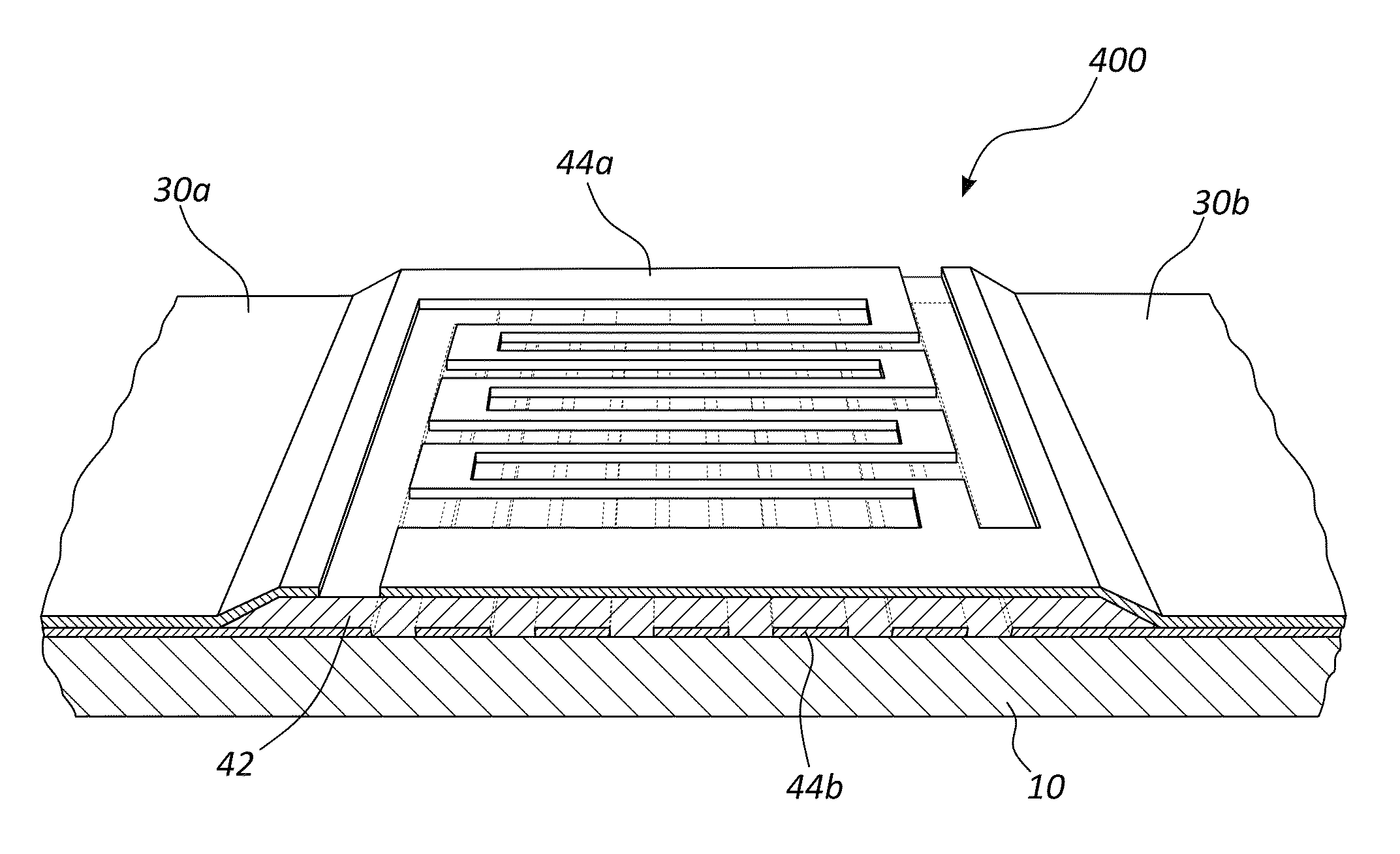
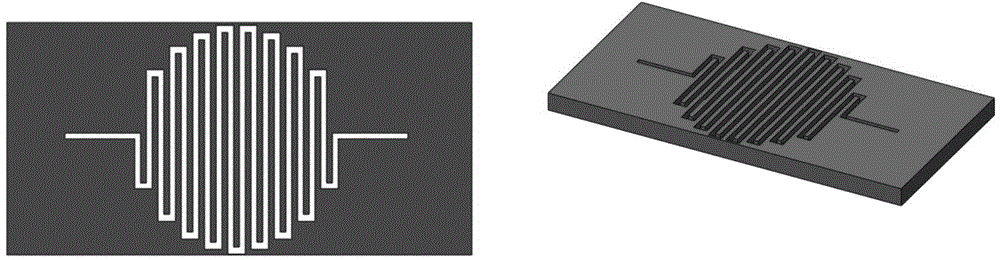
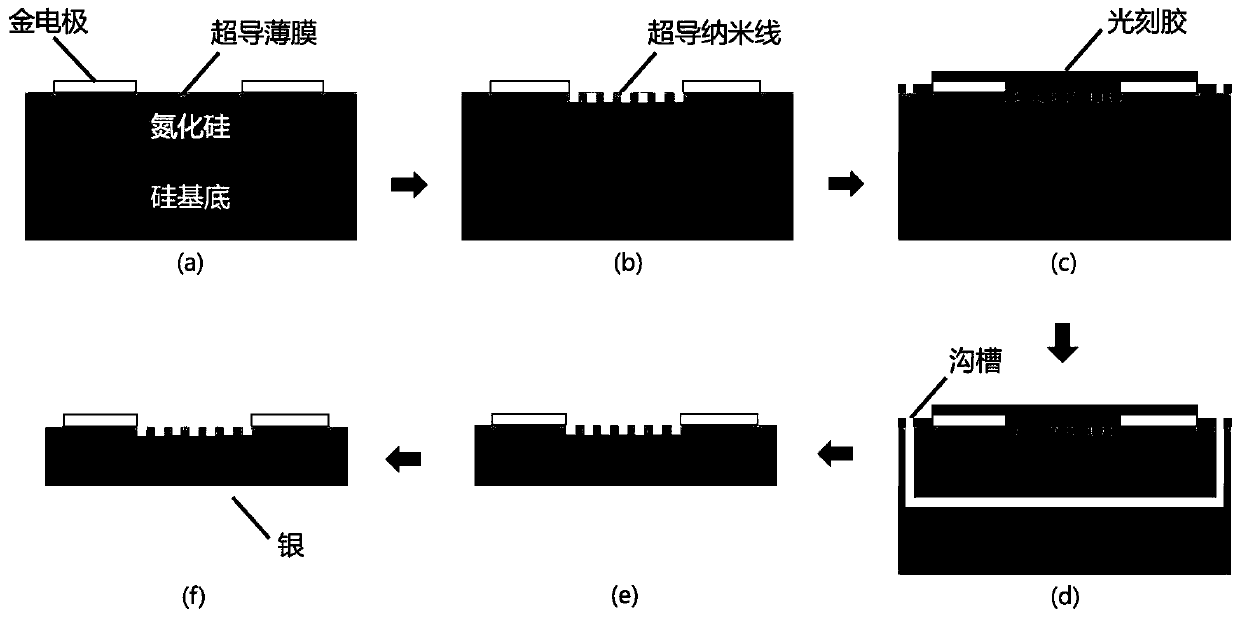
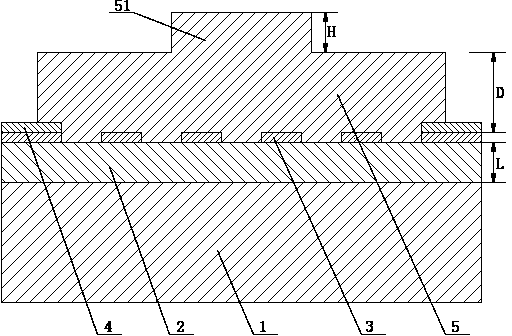
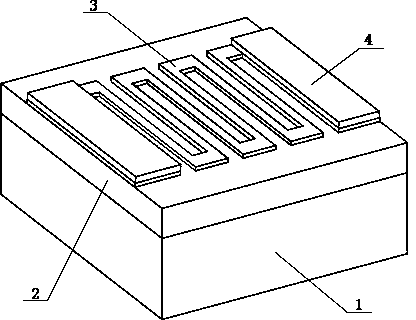
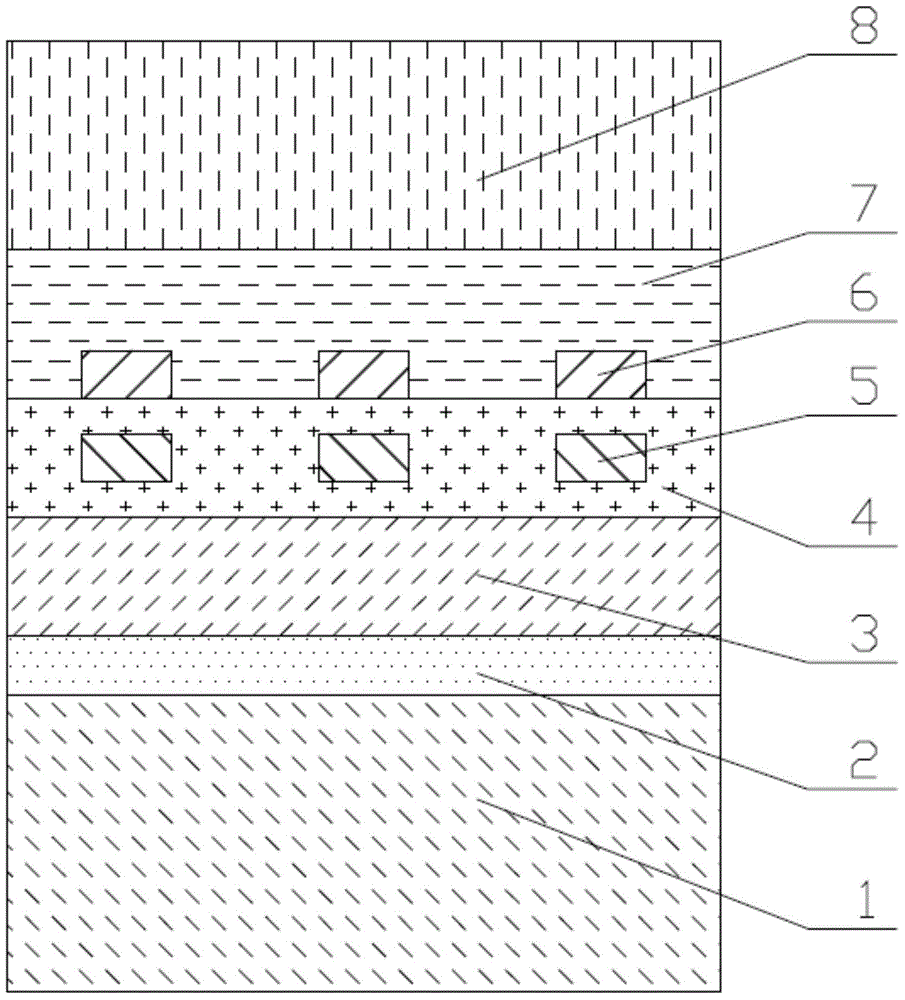
Superconducting nanowire single photon detector based on deep silicon etching process and preparation method
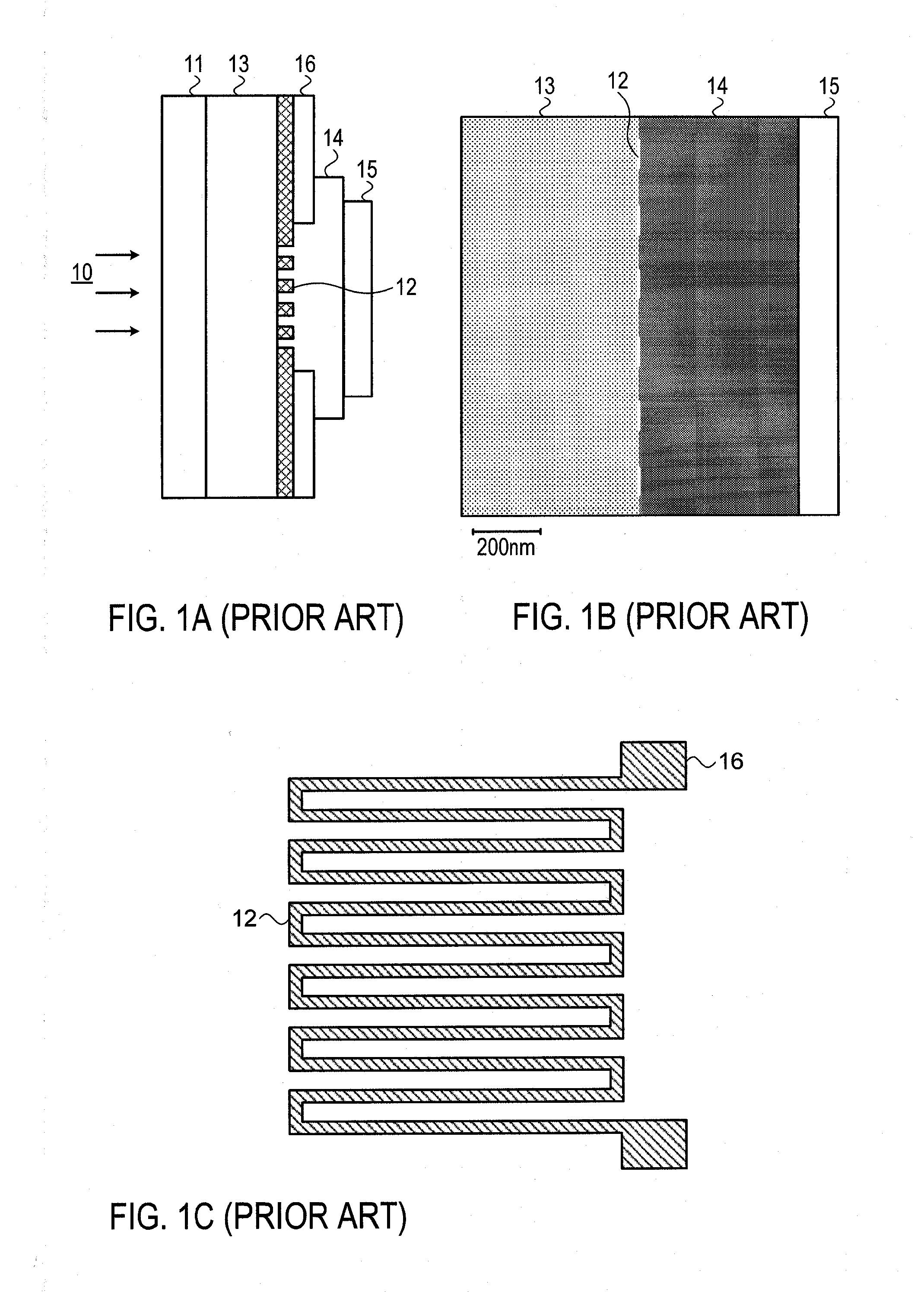
ActiveCN106549099AImprove absorption efficiencyReduce usageSuperconductor detailsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentLong-focus lensNanowire
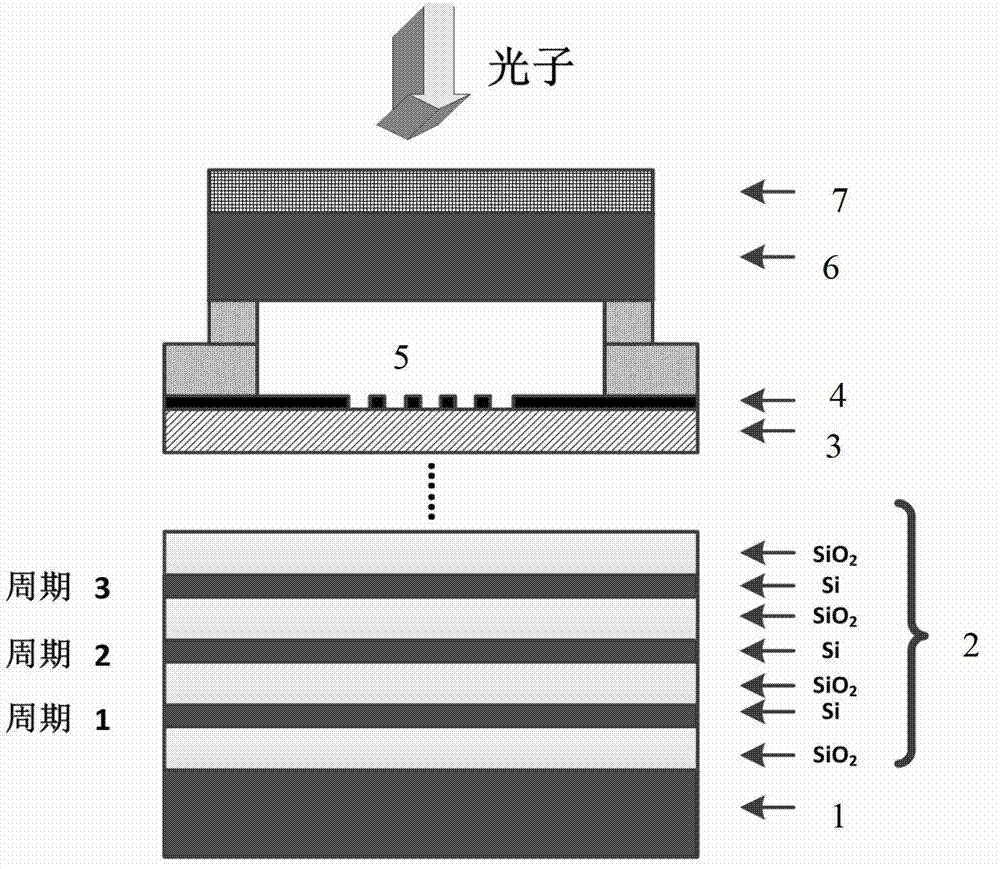
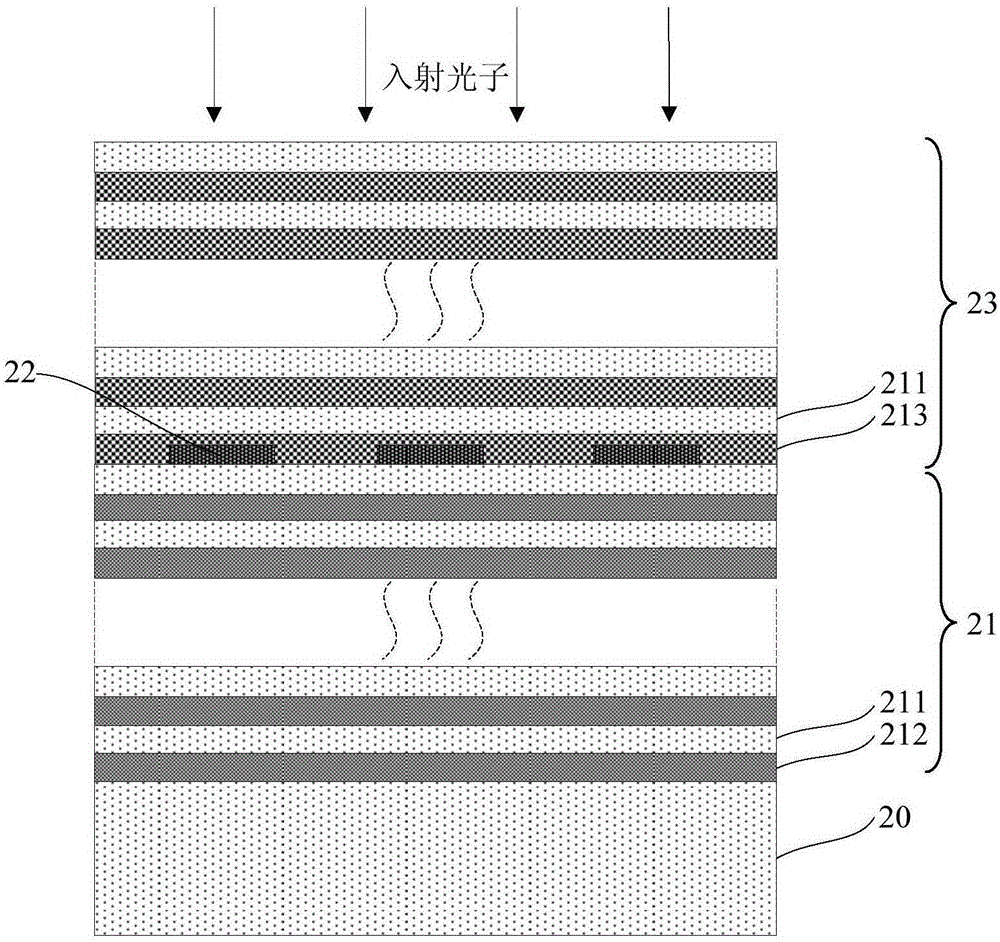
The invention provides a superconducting nanowire single photon detector based on a deep silicon etching process and a preparation method. The detector comprises an SOI base which is composed of a back substrate, a buried oxygen layer and top silicon in sequence from bottom to top, a first anti-reflection layer which is disposed on the surface of the top silicon, a second anti-reflection layer which is disposed on the surface of the back substrate, a deep groove which penetrates through the second anti-reflection layer, the back substrate and the buried oxygen layer, an optical cavity structure which is disposed on the surface of the first anti-reflection layer, superconducting nanowires which are disposed between the first anti-reflection layer and the optical cavity structure, and a mirror which is disposed on the surface of the optical cavity structure. By etching the deep groove on the substrate, the distance between a coupling optical fiber and the device is narrowed, the use of a long-focus lens in the traditional back-coupling superconducting nanowire single photon detector is avoided, and alignment coupling between the MU head of an optical fiber and the device is facilitated. The problem concerning long-distance focusing in the optical cavity structure and the influence of the Fabry-Perot cavity of the susbtrate on the absorption efficiency are avoided. The absorption efficiency of target wavelength is improved. The detection efficiency of the device is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
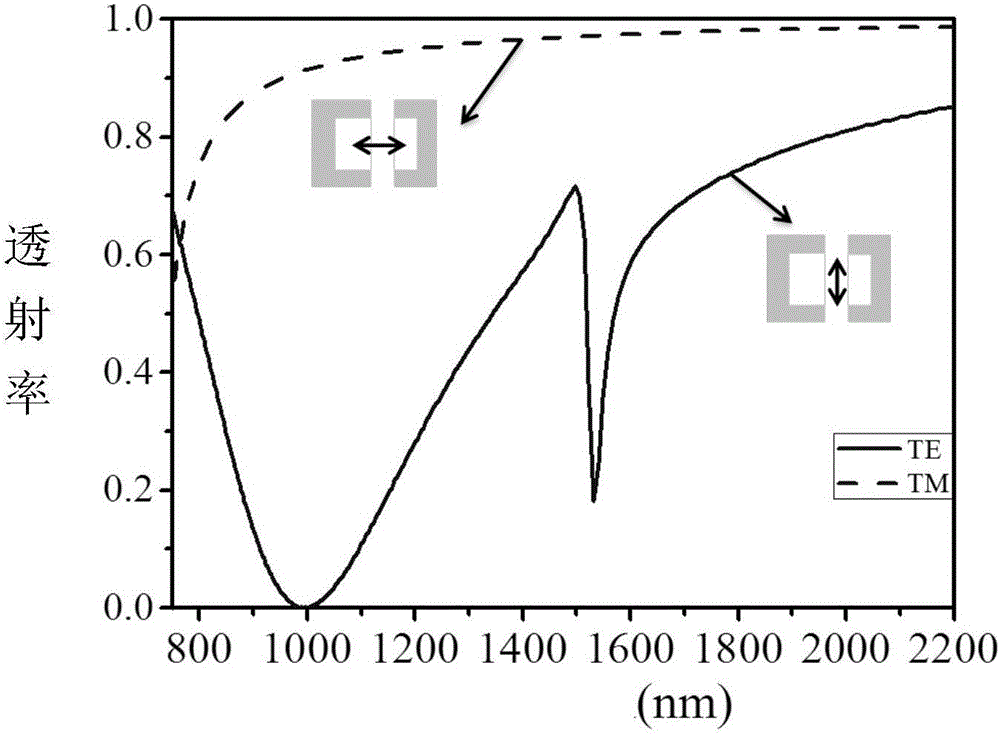
Efficient Polarization Independent Single Photon Detector
ActiveUS20140087952A1Improve quantum efficiencySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum efficiencyNanowire
A superconducting nanowire single photon detector (SN-SPD) microelectronic circuit is described which has higher quantum efficiency and signal-to-noise than any SN-SPD's known in the art. The material and configuration of the microelectronic circuit eliminates the polarization dependence and shows improved signal-to-noise over SN-SPD microelectronic circuits known in the art. The higher efficiency, polarization independence, and high signal-to-noise is achieved by vertically stacking two tungsten-silicide (TS) SN-SPDs and electrically connecting them in parallel. This structure forms a multilayer superconducting nanowire avalanche photo-detector (SNAP). A single photon detection device employing the multilayer (SNAP) microelectronic circuit demonstrates a peak system detection efficiency of 87.7% and a polarization dependence of less than 2%. This represents nearly an order of magnitude improvement in both system detection efficiency and reduction of polarization dependence compared to conventional SNSPDs.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY
Superconductive nanowire single-photon detector with self-gain structure
ActiveCN106289515AReduce time domain jitterTime Domain Jitter ReductionPhotometry electrical circuitsPower flowNanowire
The invention discloses a superconductive nanowire single-photon detector with a self-gain structure. The single-photon detector comprises a first nanowire used as a photosensitive area and a second nanowire used as a self-gain area. The first nanowire is connected with the second nanowire in parallel. The width ratio of the second nanowire to the first nanowire is N, wherein N is larger than 1. The first nanowire is used for detecting photons. The second nanowire is used for storing current, thereby achieving amplifying of pulse signals. A parallel branch of the first nanowire and the second nanowire is connected with a third nanowire in series. The width of the third nanowire is the sum of the width of the first nanowire and the width of the second nanowire. The length of the second nanowire is used for controlling inductance proportion of the first nanowire and the second nanowire. By adjusting the length of the second nanowire, the length proportion of the first nanowrie and the second nanowire is controlled, thereby controlling the inductance proportion, so the first nanowire and the second nanowire are allowed to be in a high-bias current state. The third nanowire is used for increasing total inductance of the branch. By controlling the length of the third nanowire, the total inductance of the branch is controlled, thereby avoiding a thermal latch-up effect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
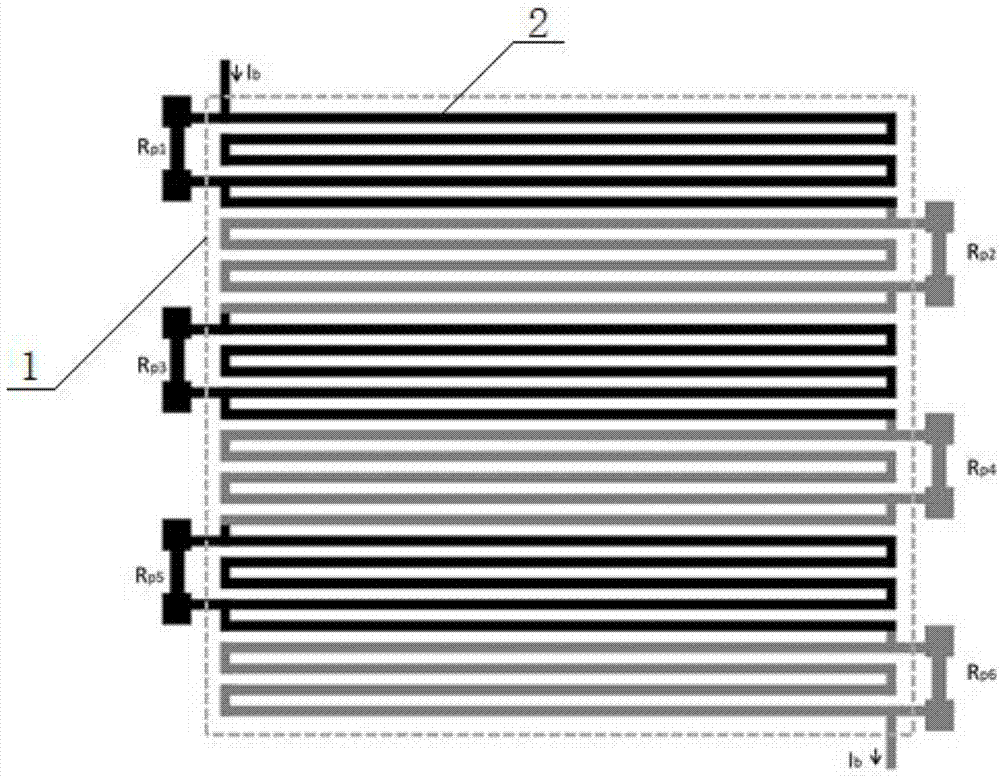
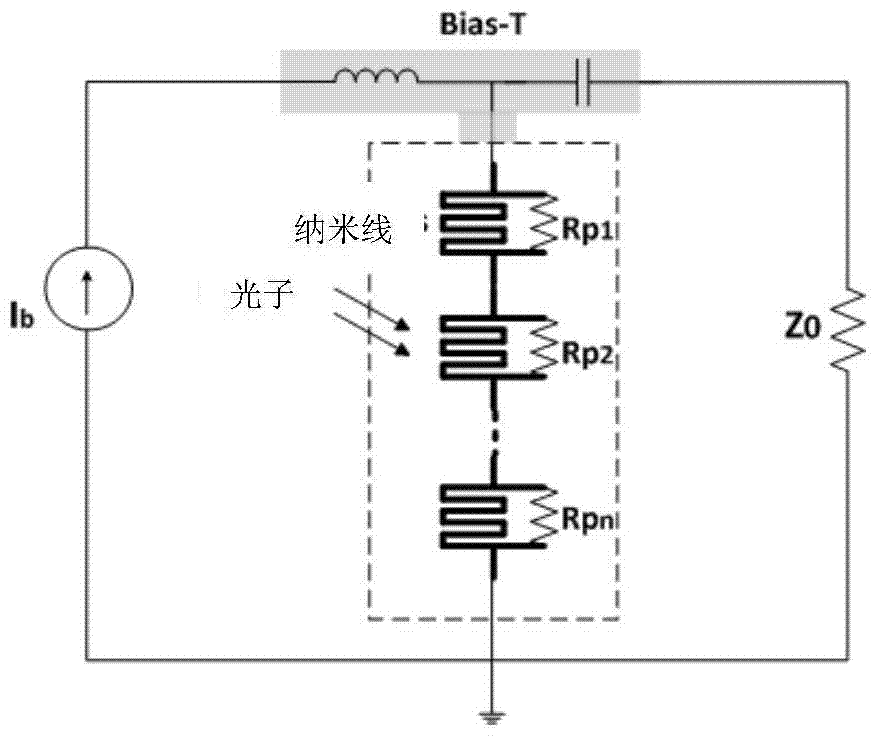
Superconductive nanowire single-photon detector capable of distinguishing photon number and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102353464AImprove quantum efficiencyIncrease count rateDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingQuantum efficiencyElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention provides a superconductive nanowire single-photon detector capable of distinguishing photon number. The superconductive nanowire single-photon detector consists of N superconductive nanowires which are connected in series and corresponding N bypass resistors, wherein each bypass resistor is arranged between every two adjacent superconductive nanowires; the superconductive nanowires are made from superconductive materials such as niobium nitride or titanium niobium nitride and the like; and the bypass resistors are made from metal films such as gold or titanium and the like. The invention further provides a method for preparing the superconductive nanowire single-photon detector. The prepared superconductive nanowire single-proton detector has high quantum efficiency, high counting efficiency, low dark count and capability of distinguishing photon number, and is not influenced by leakage current.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
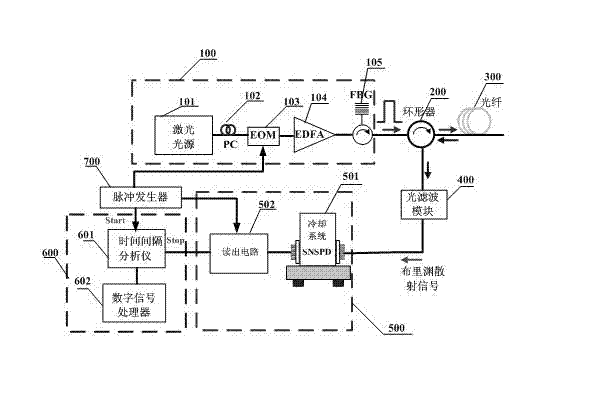
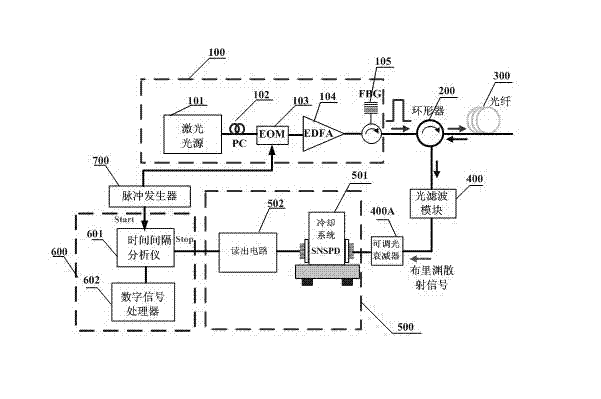
Spontaneous Brillouin scattering optical time domain reflectometer based on superconductive nanowire single-proton detector
InactiveCN102506904AHigh sensitivityShorten Jitter TimeMitigation of undesired influencesTime-domain reflectometerRayleigh scattering
The invention discloses a spontaneous Brillouin scattering optical time domain reflectometer (BOTDR) based on a superconductive nanowire single-proton detector, which is characterized in that an optical pulse emitted by an optical pulse generating unit is coupled to a sensing optical fiber through a circulator, backward scattered light scattered from the sensing optical fiber is subjected to filtration of rayleigh scattering light through an optical filter unit to obtain Brillouin scattering light, a back scattering light signal is detected by the superconductive nanowire single-proton detector, an electric signal output from the superconductive nanowire single-proton detector is acquired and processed by a data acquiring and processing unit, and finally, a result is obtained through a certain demodulation relation. Compared with the traditional BOTDR, the BOTDR provided by the invention is used for carrying out data acquisition and processing by adopting the noise equivalent power (NEP) low / no-bandwidth-limit superconductive nanowire single-proton detector as a detection unit and adopting a single-proton counting technology.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Superconductive nanowire single-photon detector and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104752534ACapable of spatial resolutionReduce manufacturing costFinal product manufacturePhotometry using electric radiation detectorsElectrical resistance and conductanceNanowire
The invention discloses a superconductive nanowire single-photon detector. The superconductive nanowire single-photon detector consists of N superconductive nanowire units which are connected in series, N parallel resistors of different resistance values and an optical resonator, wherein the N resistors of different resistance values are respectively connected with two ends of the N superconductive nanowire units in parallel; the optical resonator covers the upper layers of the N superconductive nanowire units which are connected in series. The superconductive nanowire single-photon detector not only can realize photon number discrimination, but also has a spatial discrimination capability. The invention also discloses a method for manufacturing the superconductive nanowire single-photon detector, wherein only is once electronic beam lithography needed to be carried out on nanowire patterns in the whole technological process, and thus the manufacturing cost of the superconductive nanowire single-photon detector is effectively reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
High-speed superconducting nanowire single-photon detector (SNSPD) with strong absorption structure and preparation method of high-speed SNSPD
ActiveCN102829884AHigh quality growthImprove absorption rateInstrumentsCounting rateQuantum efficiency
The invention discloses a high-speed superconducting nanowire single-photon detector (SNSPD) with a strong absorption structure and a preparation method of the high-speed SNSPD with the strong absorption structure. The SNSPD is capable of further improving the photon absorptivity of superconducting nanowires based on an incident medium with a high refractive index and an air cavity structure. Compared with the prior art and according to the high-speed SNSPD, under the condition that the nanowires are made of superconducting ultrathin membranes with the same material and the same thickness, nearly 100% of absorptivity can be realized through a lower duty ratio, and the difficulty of electron beams in the exposure steps is reduced greatly, thereby particularly being more beneficial to the preparation of the ultrathin nanowires; and meanwhile, by adopting a silicon on insulator (SOI) substrate, the high-quality growth of the superconducting ultrathin membranes can be ensured simultaneously without affecting the intrinsic quantum efficiency of the detector. In addition, under the condition that the large effective detection area is ensured equally, as the total length of the required nanowires is reduced obviously, the maximum counting rate of the detector can be improved, and the probability of occurring defects during preparation process is decreased notably.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Manufacturing method for nanowire single-photon detector based on specially doped superconducting niobium film material
ActiveCN102916083AProtected superconducting propertiesIncrease the critical current densityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNanowireNiobium
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a nanowire single-photon detector based on a specially doped superconducting niobium film material. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: carrying out ultrasonic cleaning and blow-drying on a substrate; carrying out Ar ion cleaning; growing a specially doped superconducting Nb film in a direct current magnetron sputtering way; carrying out spin-coating on an electron beam resist, carrying out electron beam lithography on the electron beam resist, and drawing a wire pattern with the width not more than 100nm on the electron beam resist; etching in a reaction ion etching way, and transferring the line pattern onto the Nb film to form a Nb nanowire; cleaning the residual electron beam resist, carrying out spin-coating on a photoresist on the surface of a sample, and forming an electrode pattern on the photoresist in a deep ultraviolet exposure way; and growing an electrode. According to the manufacturing method, the difficult problems of low superconducting transition temperature, low critical current density and short photoresponse wavelength of an SNSPD (Superconducting Nanowire Single Photon Detector) manufactured by the conventional Nb material are solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
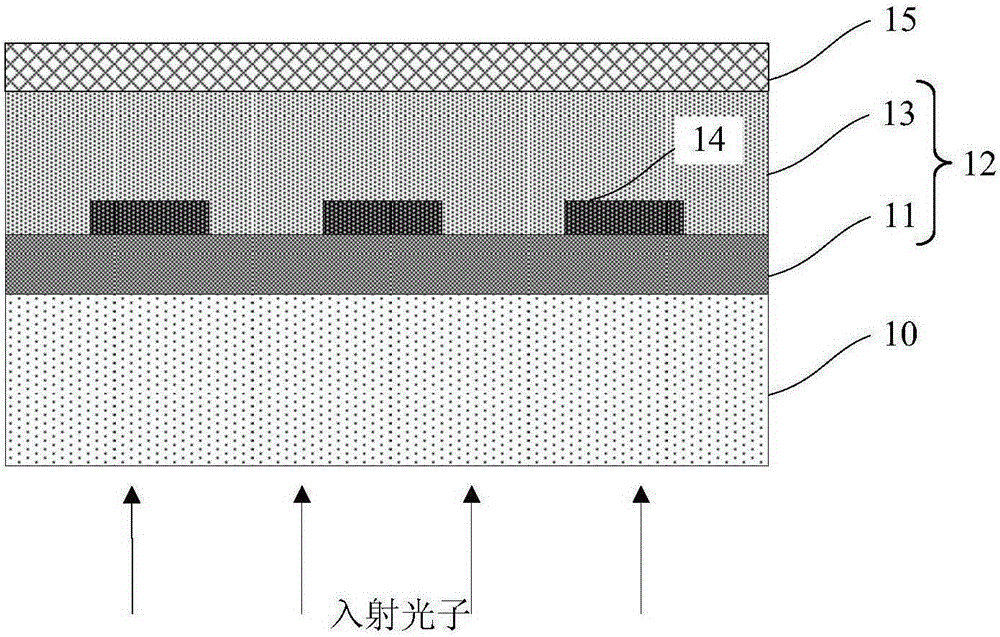
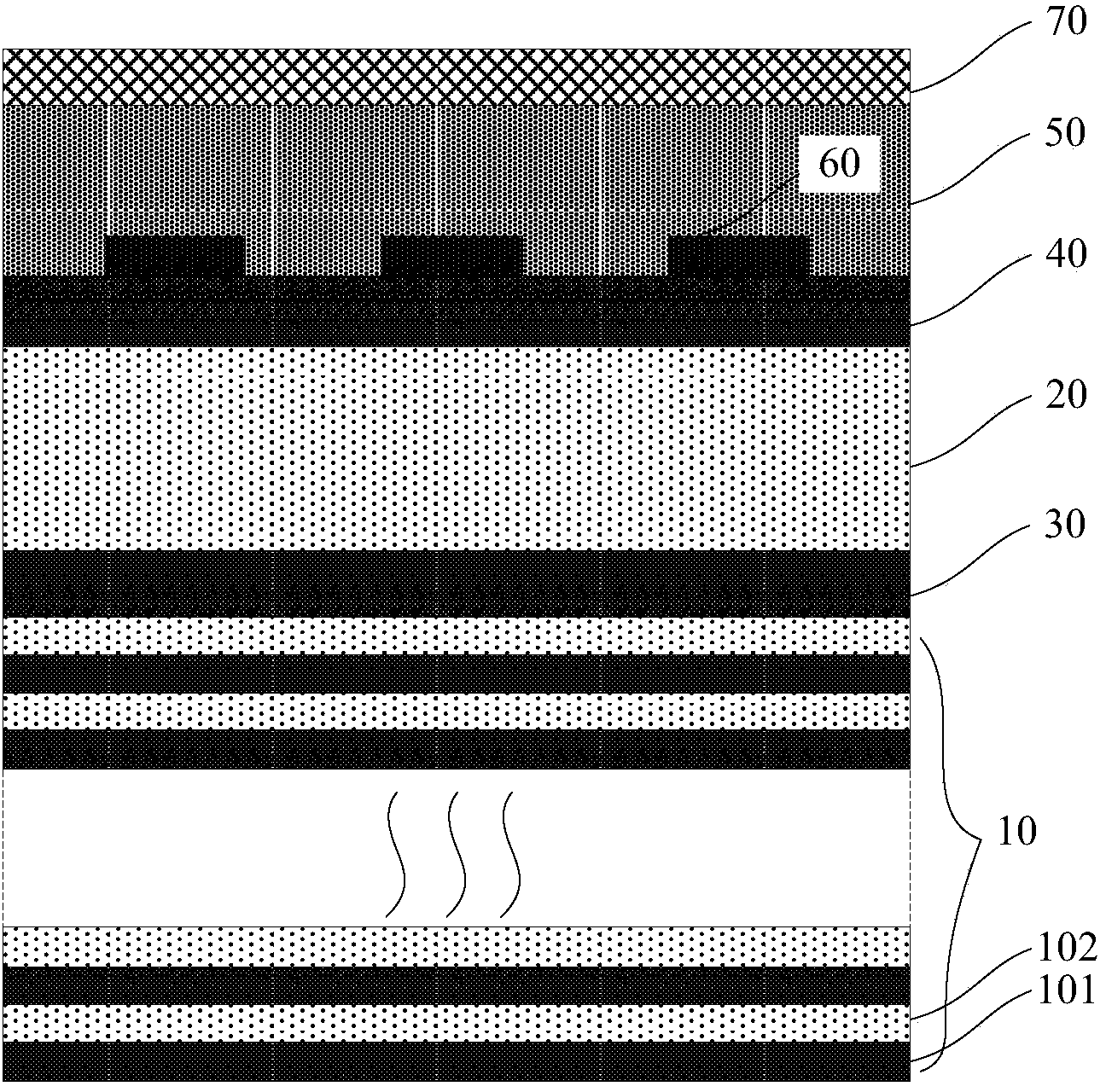
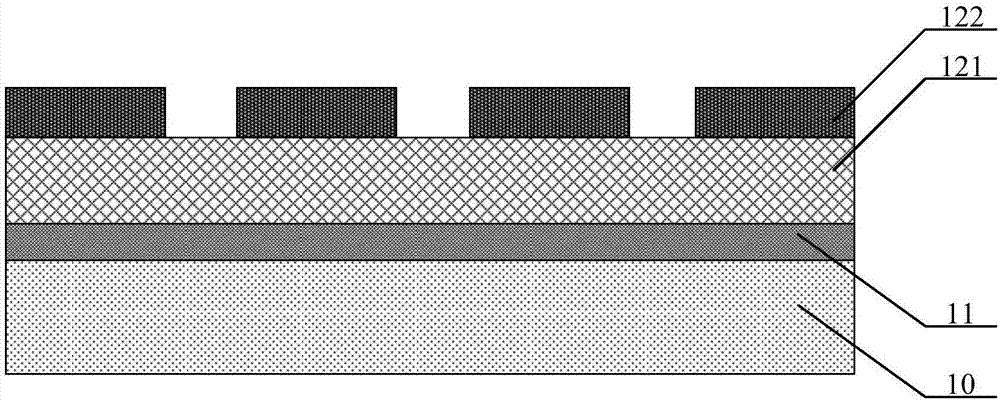
Superconductive nanowire single photon detector based on dielectric film reflector
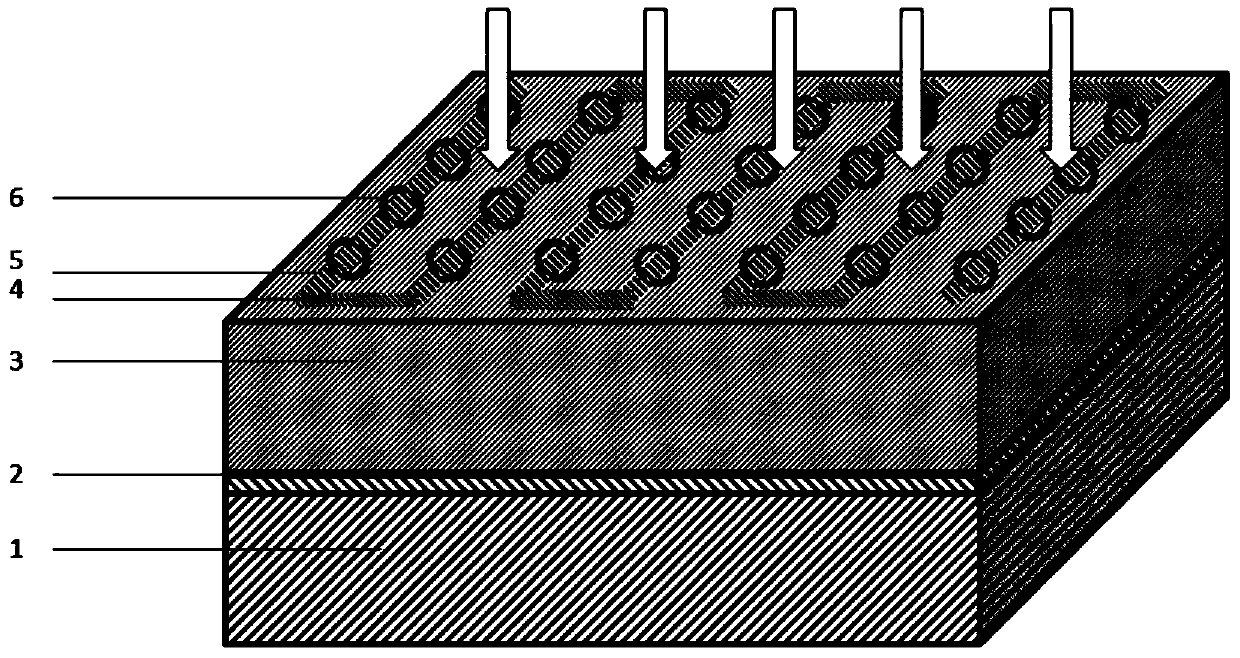
InactiveCN104091883AImprove absorption efficiencyImprove toleranceSuperconductor detailsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsDielectricNanowire
The invention provides a superconductive nanowire single photon detector based on a dielectric film reflector. The superconductive nanowire single photon detector based on the dielectric film reflector comprises a substrate, the full dielectric multilayer film reflector combined to the surface of the substrate, and superconductive nanowires combined to the surface of the full dielectric multilayer film reflector. The substrate comprises a silicon substrate or a MgO substrate or a sapphire substrate, the full dielectric multilayer film reflector comprises SiO2 layers and SiO layers stacked alternately, or SiO2 layers and Si layers stacked alternately, or SiO2 layers and TiO2 layers stacked alternately, or SiO2 layers and Ta2O5 layers stacked alternately. The materials of the superconductive nanowires comprise NbN or Nb or TaN or NbTiN or WSi. The superconductive nanowire single photon detector based on the dielectric film reflector has high absorption efficiency, has large tolerance on sizes of the nanowires in high absorption efficiency areas, and can avoid influences of a Fabry-Perot cavity on the absorption efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
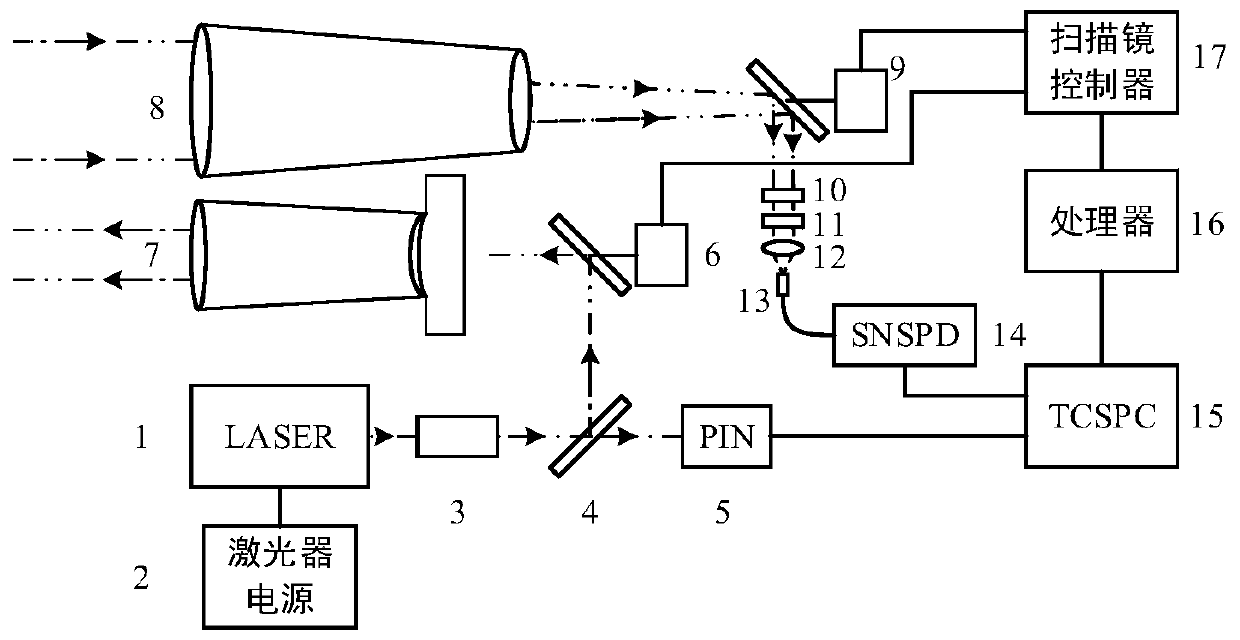
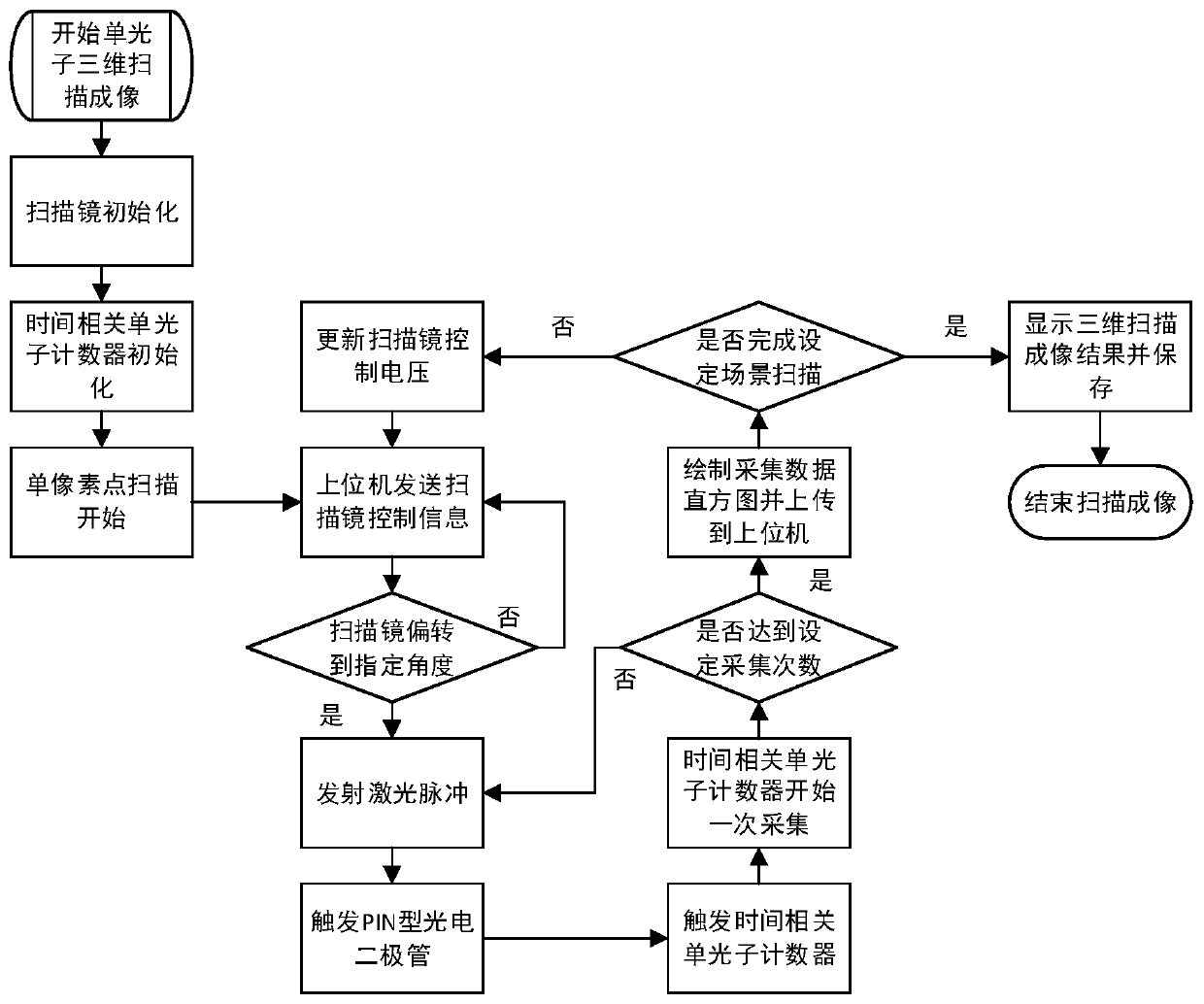
Ultra-long-distance single-photon three-dimensional laser radar scanning imaging system
PendingCN110579775AReduce dark noiseImprove detection efficiencyElectromagnetic wave reradiationLight beamOptoelectronics
The invention discloses an ultra-long-distance single-photon three-dimensional laser radar scanning imaging system, which belongs to the field of single-photon laser radar detection. The system comprises a transmitting unit, a receiving unit, a superconducting nanowire single-photon detector and a data processing unit, the transmitting unit is used for transmitting laser pulse to a target imagingarea after the light beam direction of the laser pulse is adjusted so as to reflect a target echo light signal; the receiving unit is used for collecting and processing a target echo optical signal; the superconducting nanowire single-photon detector is used for receiving the processed target echo optical signal and converting the processed target echo optical signal into an electric signal; and the data processing unit is used for collecting the electric signal, processing the electric signal into a histogram to obtain distance information of the target, continuously adjusting the light beamdirection of the laser pulse when the scanning of the target imaging area is not completed until the scanning of the whole area is completed, and displaying a three-dimensional scanning imaging result. According to the invention, the limit detection distance of the system can be improved, and three-dimensional scanning imaging of the target area is realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG PHOTOELECTRIC TECH INST (CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP THE NO 717 INST)
Method and device for reducing extrinsic dark count of nanowire single photon detector comprising a multi-layer film filter
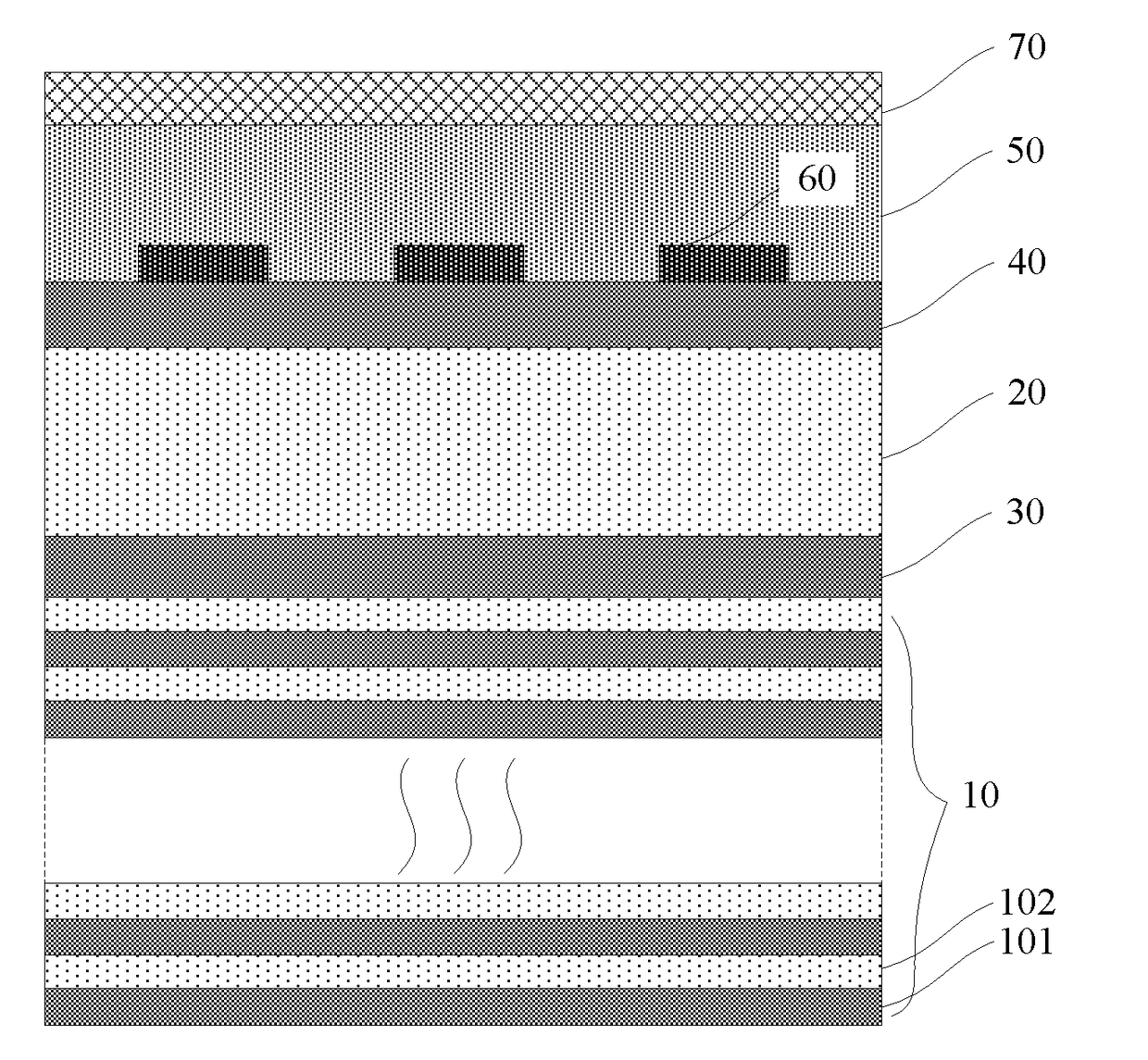
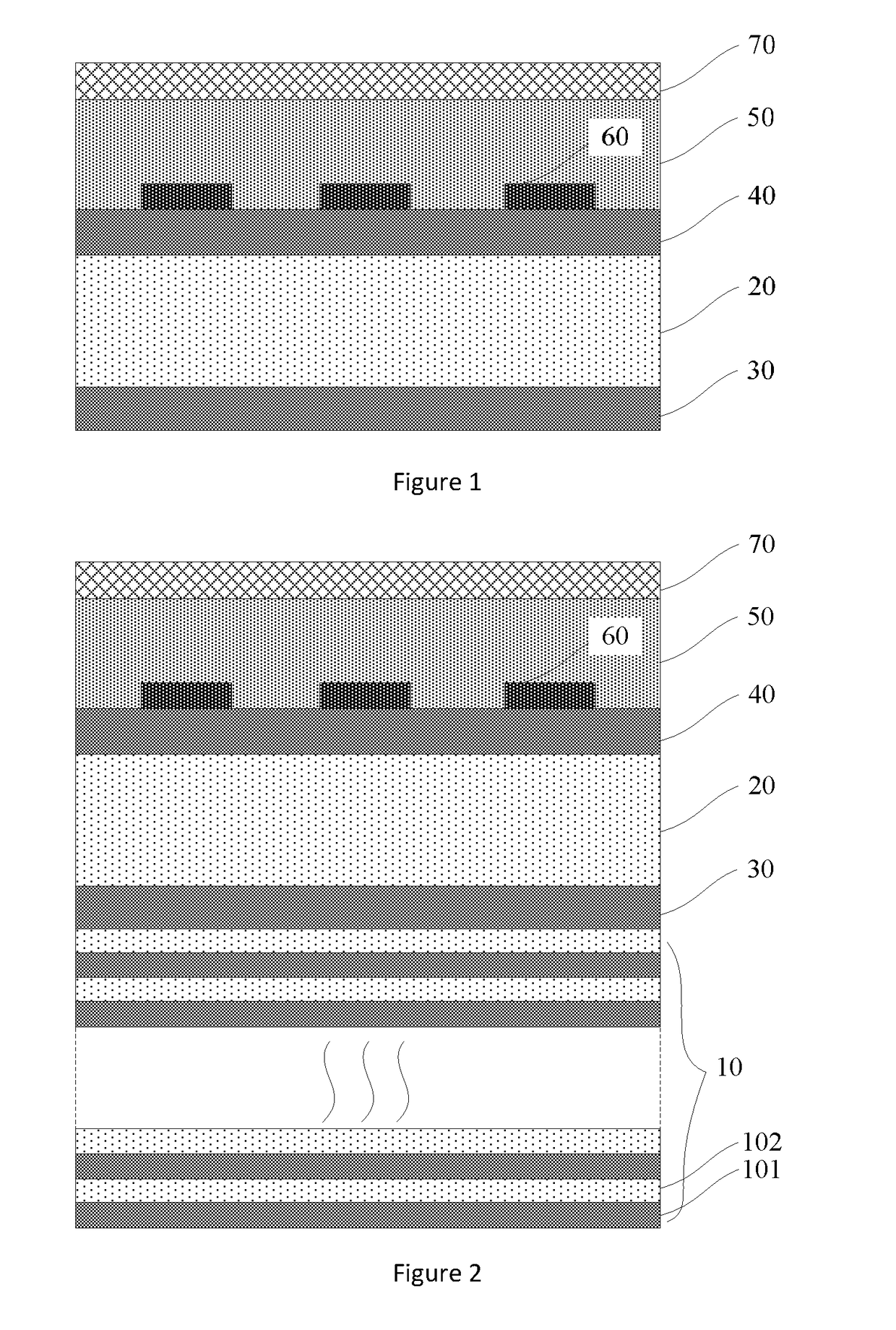
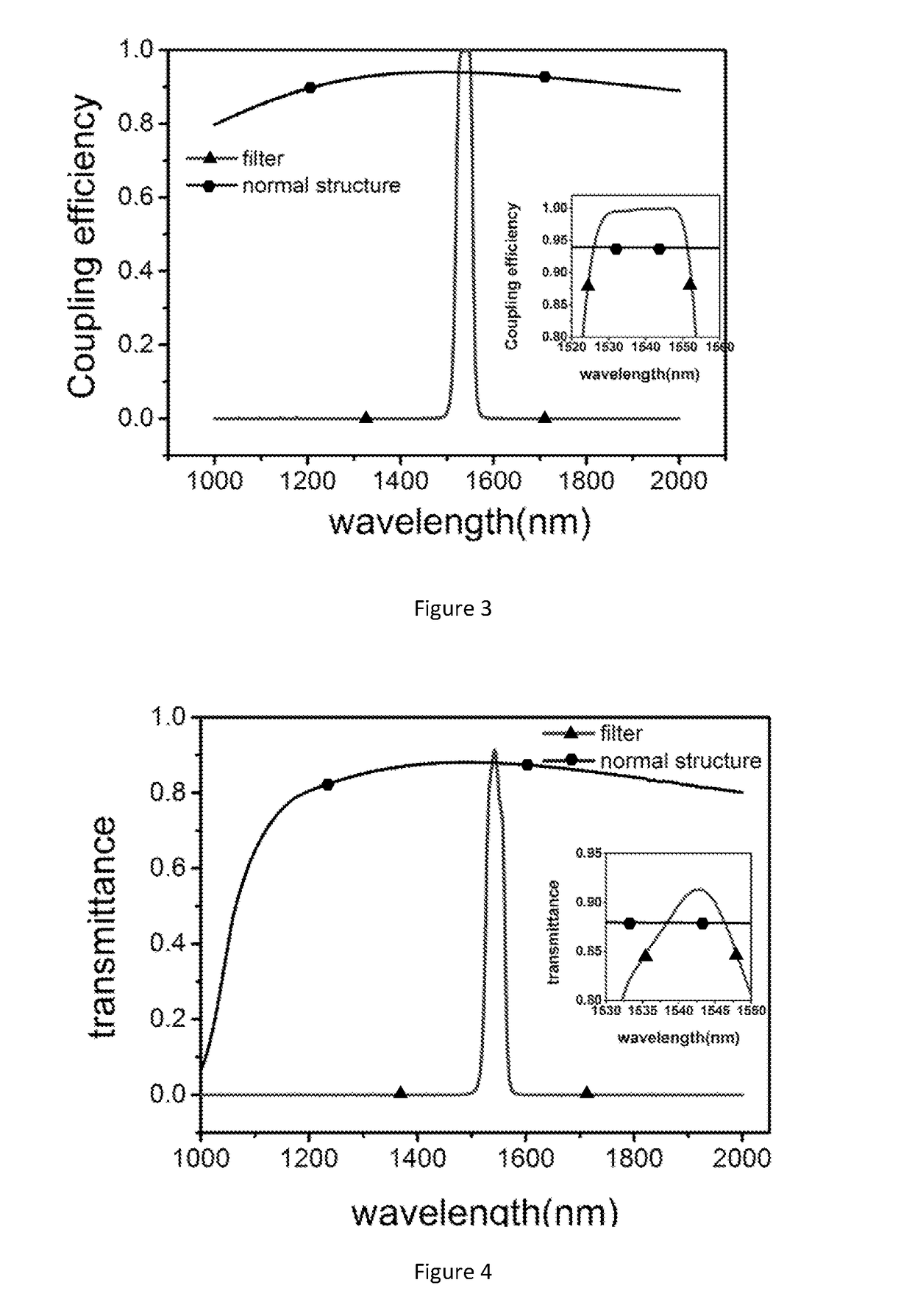
ActiveUS9954158B2Reducing the extrinsic dark countLower performance requirementsRadiation pyrometrySuperconductor detailsBandpass filteringElectricity
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
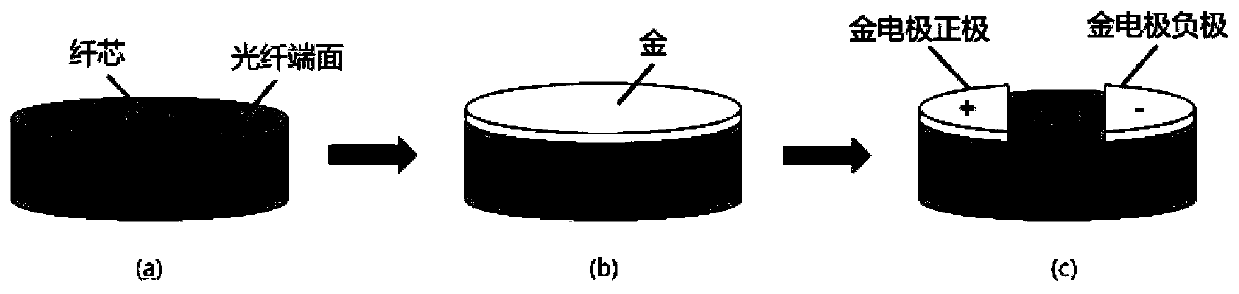
Fiber optical superconducting nanowire single photon detector
ActiveUS20140353476A1Precise alignmentImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesFiberNanowire
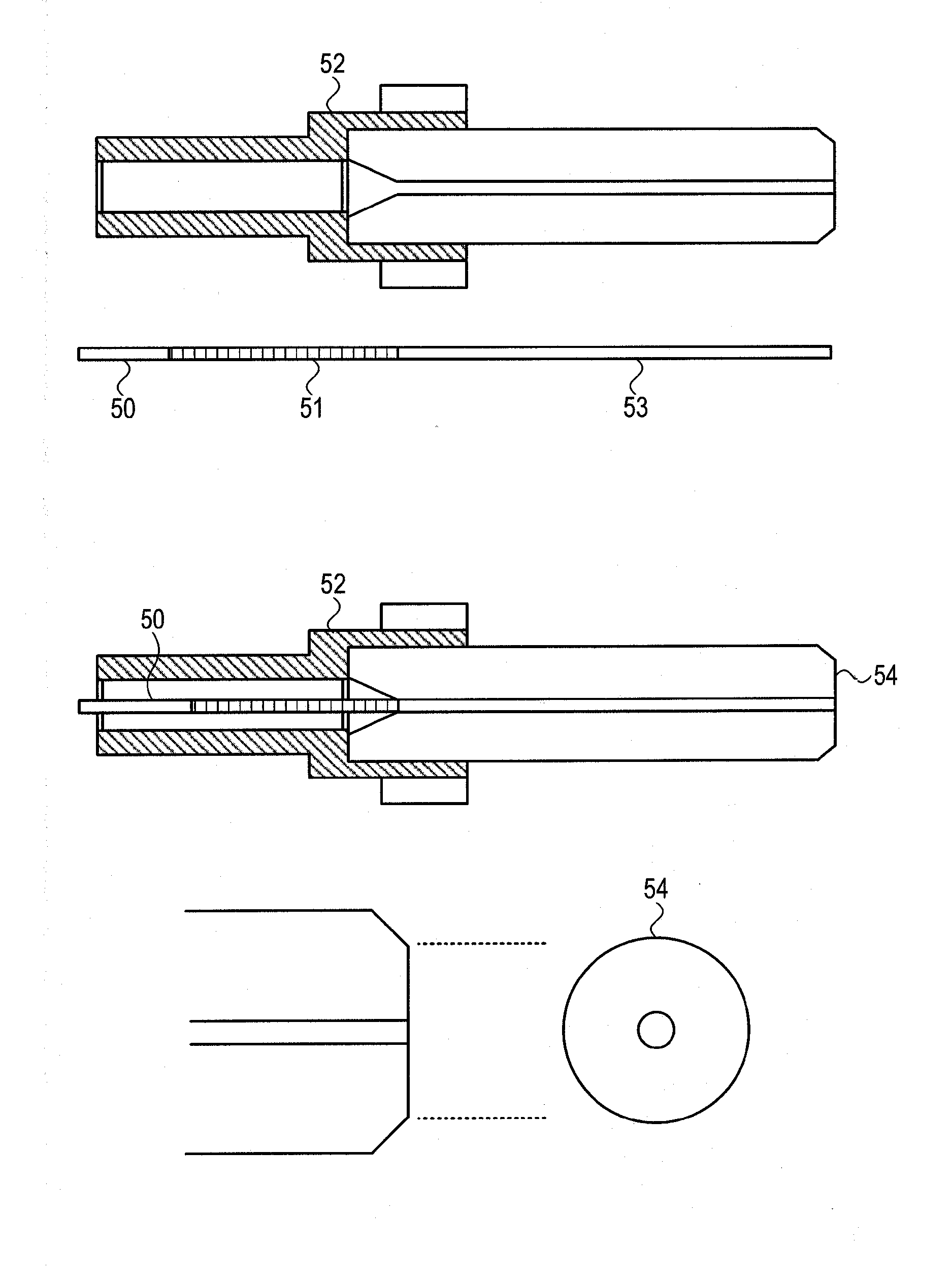
A fiber optical superconducting nanowire detector with increased detector efficiency, fabricated directly on the tip of the input optical fiber. The fabrication on the tip of the fiber allows precise alignment of the detector to the fiber core, where the field mode is maximal. This construction maximizes the coupling efficiency to close to unity, without the need for complex alignment procedures, such as the need to align the input fiber with a previously fabricated device. The device includes a high-Q optical cavity, such that any photon entering the device will be reflected to and fro within the cavity numerous times, thereby increasing its chances of absorption by the nanowire structure. This is achieved by using dedicated cavity mirrors with very high reflectivity, with the meander nanowire structure contained within the cavity between the end mirrors, such that photons impinge on the nanowire structure with every traverse of the cavity.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
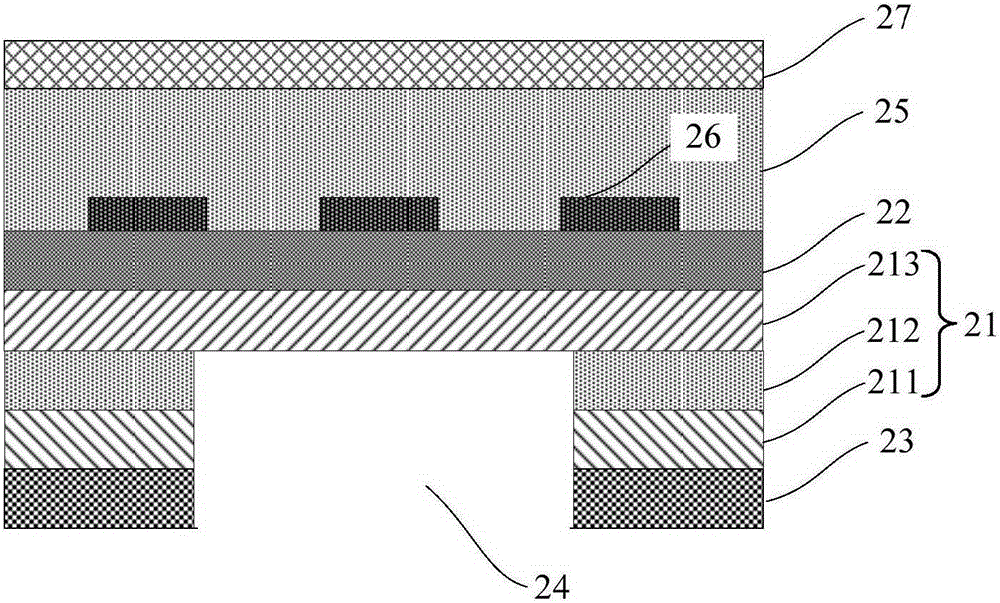
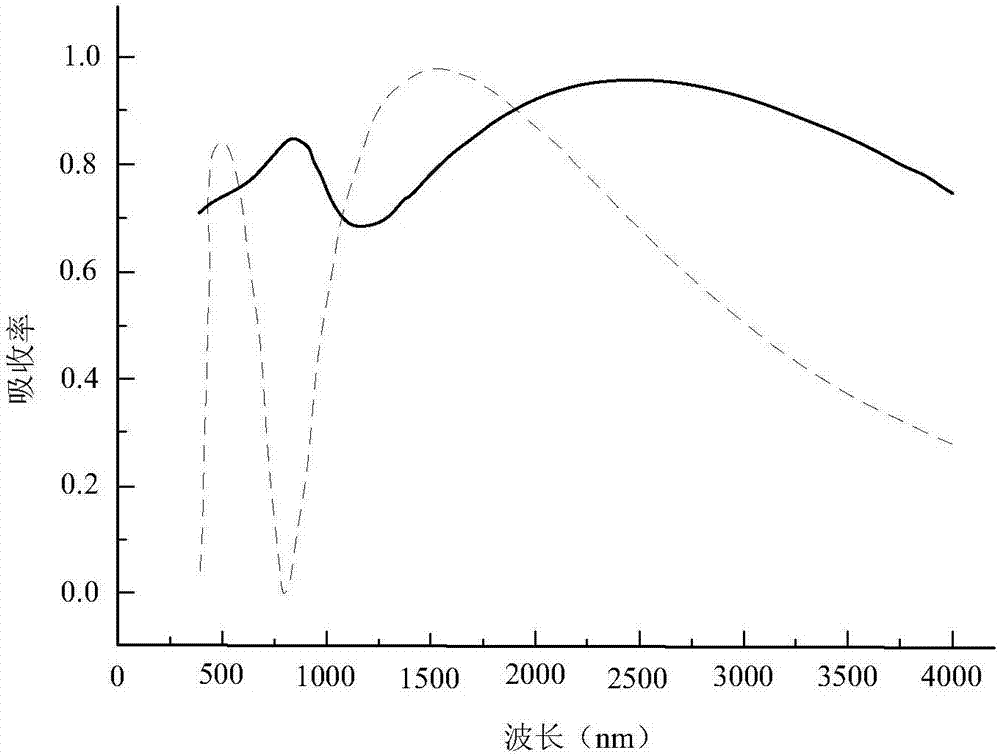
Superconductive nanowire single photon detector with responsivity enhanced based on metamaterials
InactiveCN104183692AHigh yieldImprove response rateSuperconductor detailsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentNanowireResponsivity
The invention discloses a superconductive nanowire single photon detector with the responsivity enhanced based on metamaterials. The superconductive nanowire single photon detector with the responsivity enhanced based on the metamaterials comprises a substrate, a metal reflecting layer, a dielectric isolation layer, a superconductive nanowire, a dielectric isolation bar and an asymmetric metal ring resonator array, wherein the metal reflecting layer, the dielectric isolation layer, the superconductive nanowire, the dielectric isolation bar and the asymmetric metal ring resonator array are grown on the substrate in sequence from bottom to top, and the superconductive nanowire is separated from the asymmetric metal ring resonator array through the transparent dielectric isolation bar. According to the superconductive nanowire single photon detector with the responsivity enhanced based on the metamaterials, a periodical metamaterial structure is integrated with the superconductive nanowire with the extremely small area, in this way, the number of photons reaching the isolated ineffective area of the superconductive nanowire is greatly reduced, and the probability that the photons reach the isolated ineffective area of the superconductive nanowire is greatly lowered, and both the absorptivity and the responsivity of the superconductive nanowire single photon detector are improved remarkably.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Narrow-band absorption superconducting nanowire single photo detector
ActiveCN106549098AImprove absorption efficiencyAvoid distant focusSuperconductor detailsHigh absorptionNanowire
The invention provides a narrow-band absorption superconducting nanowire single photo detector. The narrow-band absorption superconducting nanowire single photo detector comprises a substrate, a high-reflective film, a superconducting nanowire and a multi-layer thin film filter, wherein the high-reflective film is arranged on a surface of the substrate, the superconducting nanowire is arranged on a surface of the high-reflective film, and the multi-layer thin film filter is arranged on the surface of the high-reflective film, and a bottom thin film layer of the multi-layer thin film filter wraps the superconducting nanowire. In the narrow-band absorption superconducting nanowire single photo detector, the superconducting nanowire is prepared based on the high-reflective film substrate, light can directly irradiate the superconducting nanowire through front-surface coupling, the problem of remote focusing in an optical cavity structured superconducting nanowire single photo detector can be avoided, the influence of a substrate Fabry-Perot cavity on absorption efficiency is further prevented, the superconducting nanowire single photo detector has relatively high absorption efficiency on a target wavelength, and the detection efficiency of the device is effectively improved; and meanwhile, the multi-layer thin film filter on the nanowire has a non-target wavelength filtering function, stray light in incident light can be filtered, and dark count caused by black-body radiation is further effectively suppressed.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
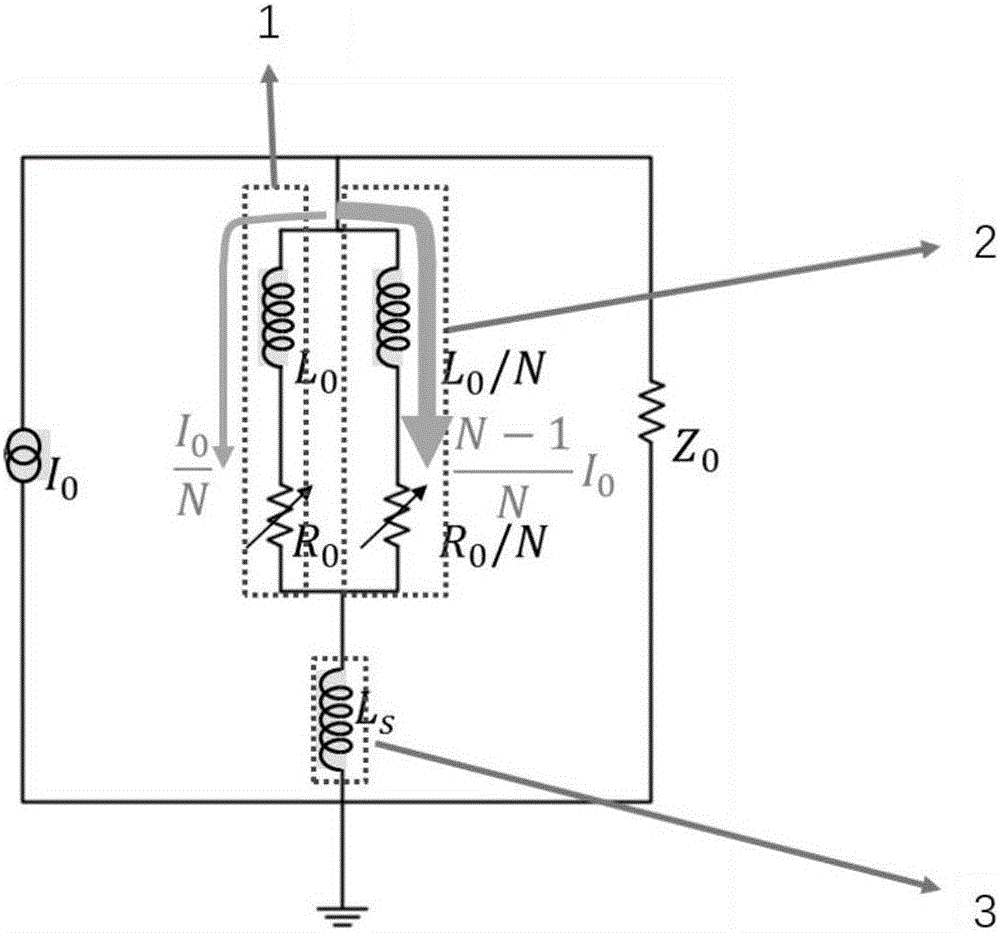
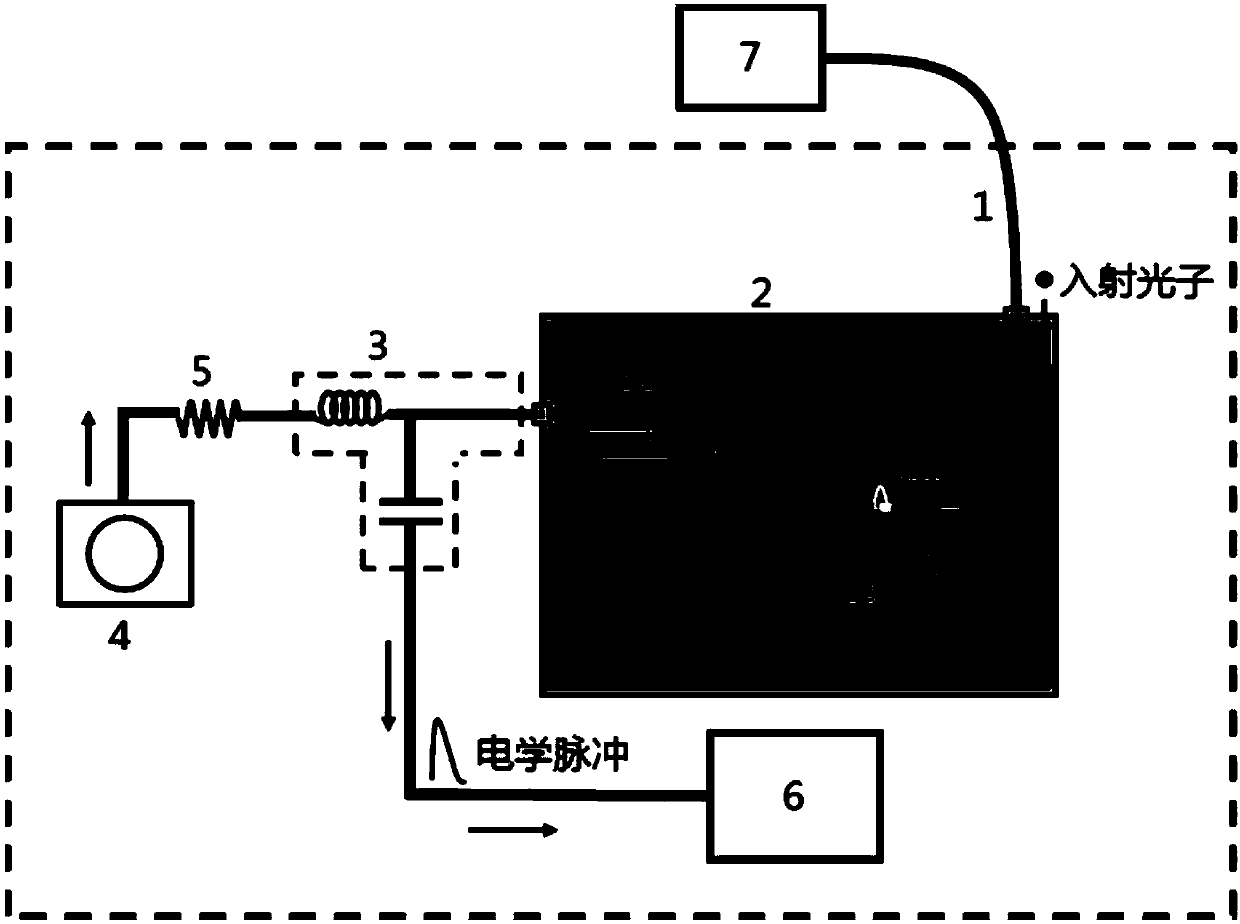
Method and device for improving electrical interference resistance of SNSPD (Superconducting Nanowire Single Photon Detector) system
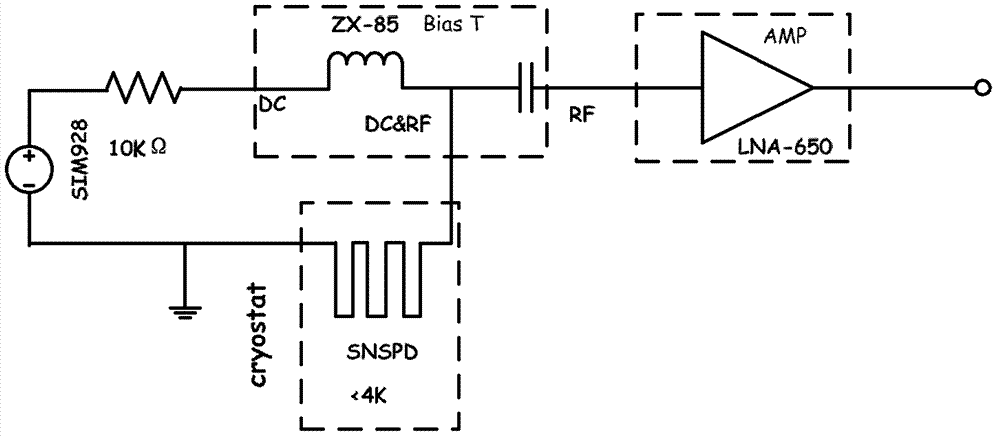
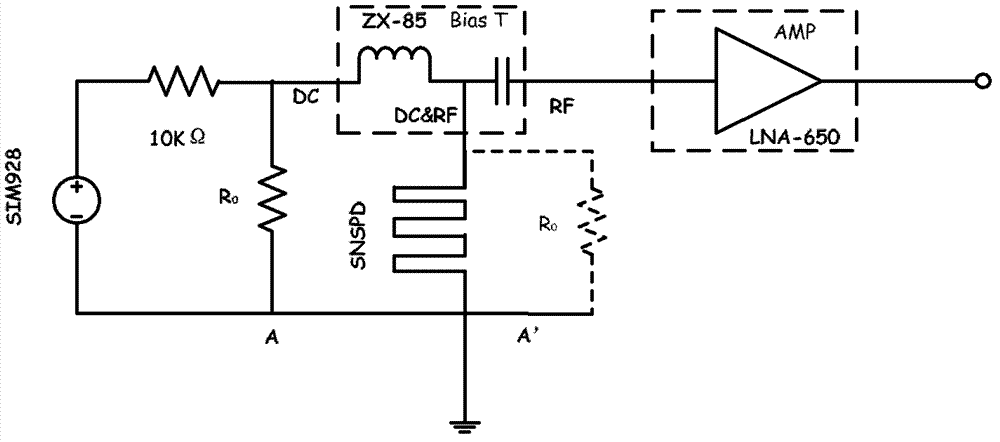
ActiveCN103245424ANo change in structureEasy to operateInstrumentsCounting rateElectrical resistance and conductance
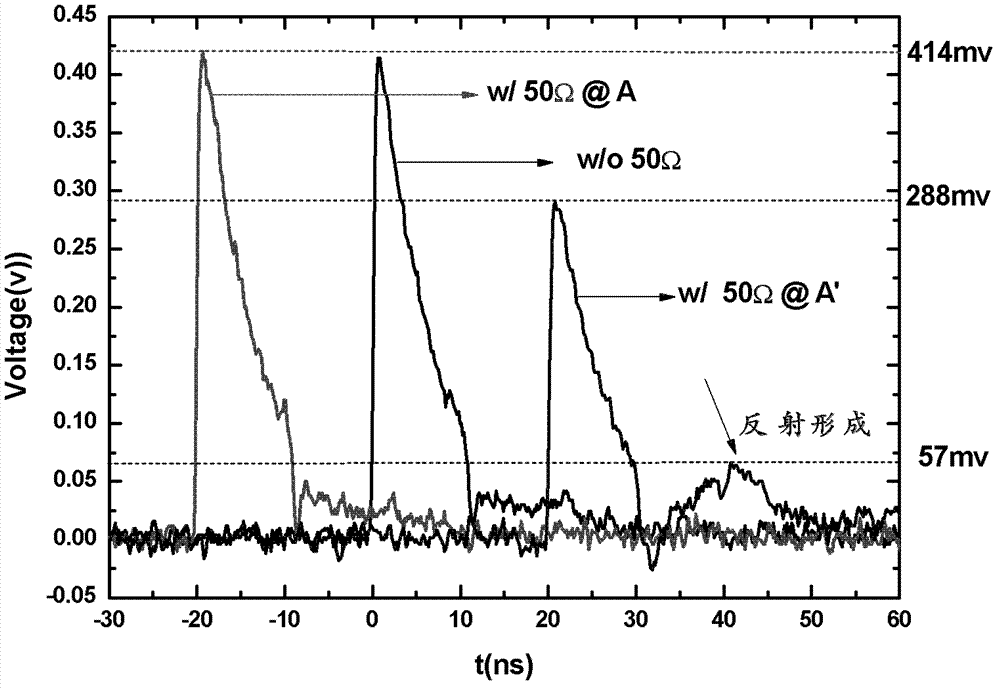
The invention provides a method and a device for improving electrical interference resistance of an SNSPD system. The SNSPD system comprises an SNSPD device and a bias tree; the bias tree is provided with a DC (direct current) port, a DC & RF (radio frequency) port and an RF port; the DC & RF port of the bias tree is connected with one end of the SNSPD device, and the other end of the SNSPD device is grounded; and the method for improving the electrical interference resistance of the SNSPD system is as follows: a resistor is connected between the DC port and the grounded end of the SNSPD device. According to the method and the device for improving the electrical interference resistance of the SNSPD system, the operation is simple, the structure of the device is not changed, a filter circuit or a shield is not required to be added, the electrical interference resistance of the system can be improved only by connecting the resistors with appropriate resistance values in parallel, and the cost is low; the shape, the amplitude and the width of a detection electrical pulse signal are not changed; a reflected impulse cannot be produced, so that the device performance is not affected; and the dark counting rate and the quantum efficiency of the detection system are not affected.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Efficient polarization independent single photon detector
ActiveUS9240539B2Superconductor detailsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentQuantum efficiencyElectricity
A superconducting nanowire single photon detector (SN-SPD) microelectronic circuit is described which has higher quantum efficiency and signal-to-noise than any SN-SPD's known in the art. The material and configuration of the microelectronic circuit eliminates the polarization dependence and shows improved signal-to-noise over SN-SPD microelectronic circuits known in the art. The higher efficiency, polarization independence, and high signal-to-noise is achieved by vertically stacking two tungsten-silicide (TS) SN-SPDs and electrically connecting them in parallel. This structure forms a multilayer superconducting nanowire avalanche photo-detector (SNAP). A single photon detection device employing the multilayer (SNAP) microelectronic circuit demonstrates a peak system detection efficiency of 87.7% and a polarization dependence of less than 2%. This represents nearly an order of magnitude improvement in both system detection efficiency and reduction of polarization dependence compared to conventional SNSPDs.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY
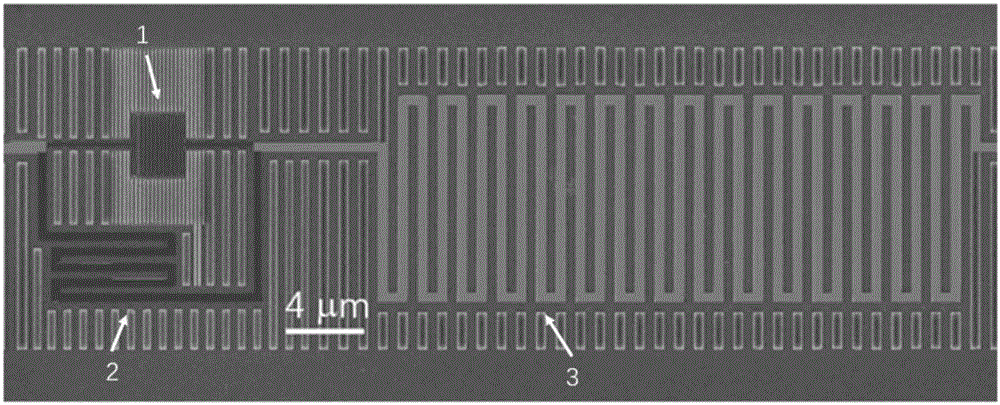
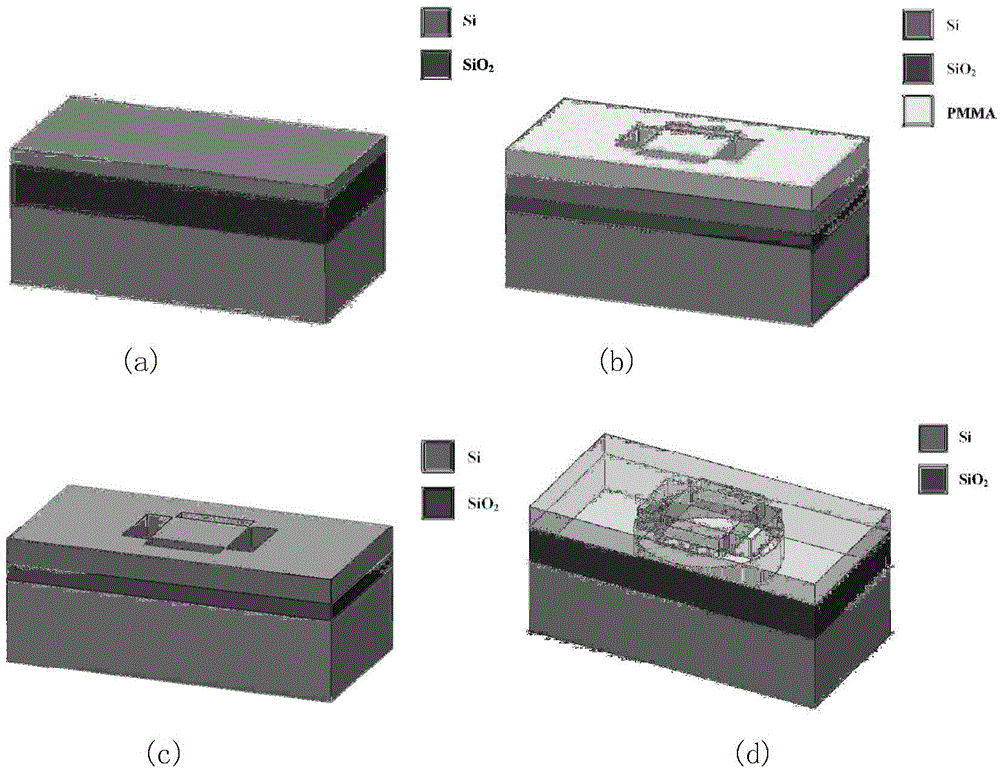
Technology for processing nanowire single-photon detector by using micro-nano mask plate
The invention belongs to the technical field of phoelectron and nano processing, and aims to solve the problems of series, time waste and high cost of an SNSPD (superconducting-nanowire single-photon detector) in the processing technology in order to realize large-scale and batch production of the SNSPD and propulsion of the industrial progress of the SNSPD. According to the technical scheme, by the technology for processing a superconducting-nanowire single-photon detector, a plurality of SNSPD nanowire graphs are formed on a small-sized thin film material to form the mask plate; a substrate to be subjected to nanowire processing is sputtered by the mask plate, so that the nanowire graphs are transferred to the substrate; furthermore, the mask plate can be repeatedly used. The technology is mainly applied to large-scale and batch production of the SNSPD.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Fiber optical superconducting nanowire single photon detector
ActiveUS9726536B2Precise alignmentImprove efficiencySuperconductor detailsSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionFiberNanowire
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
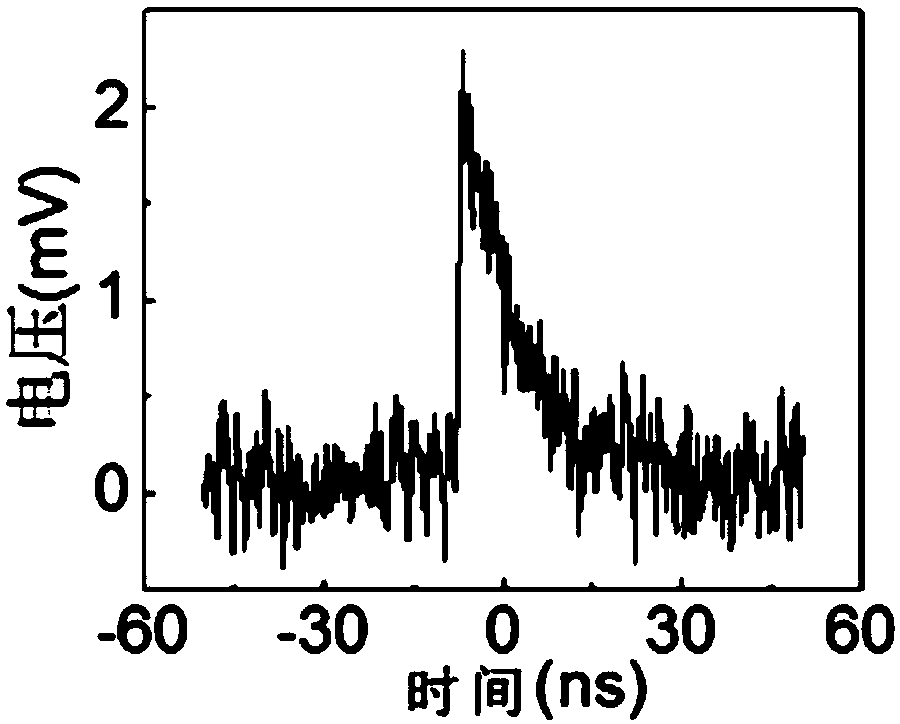
Superconducting nanowire single-photon detector system without radio-frequency amplifier
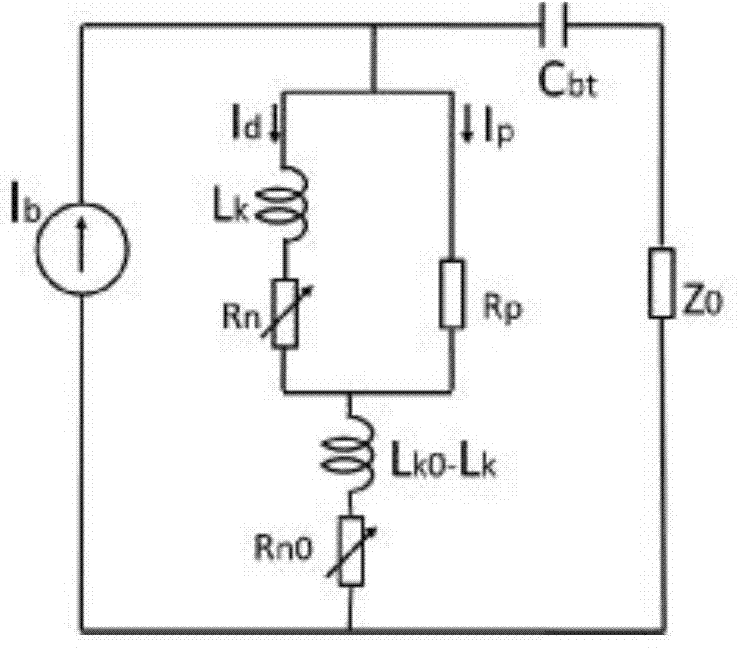
ActiveCN108680264AAchieve self-amplificationAmplify the pulse signalInstrumentsLow noiseAlternating current
The invention discloses a superconducting nanowire single-photon detector system without a radio-frequency amplifier. The system is composed of a single-mode fiber for guiding light emitted by a lightsource into a closed-cycle refrigerator. An SNSPD is arranged inside the closed-cycle refrigerator and a bias unit T is connected by a coaxial cable. Besides, a fiber focusing device working by cooperating with the SNSPD is also arranged and is connected to the tail end of a single-mode fiber. A bias current is provided by a direct-current source formed by a low-noise voltage-stabilizing source and a low-noise resistor connected in series with the voltage-stabilizing source; the current enters the SNSPD through the radio frequency and direct-current ends of the bias unit T; and when a response pulse is generated by triggering by the photon, the local state becomes an impedance state and a pulse signal flows out through the radio frequency end of the bias unit T. An oscilloscope collects apulse waveform to carry out photon counting, so that the maximum photon counting limited by the alternating-current coupling effect of the traditional SNSPD read-out circuit is avoided. According tothe invention, the pulse waveform is displayed at the oscilloscope on the premise that the read-out circuit does not use the radio-frequency amplifier, so that the self-amplification of the output pulse is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
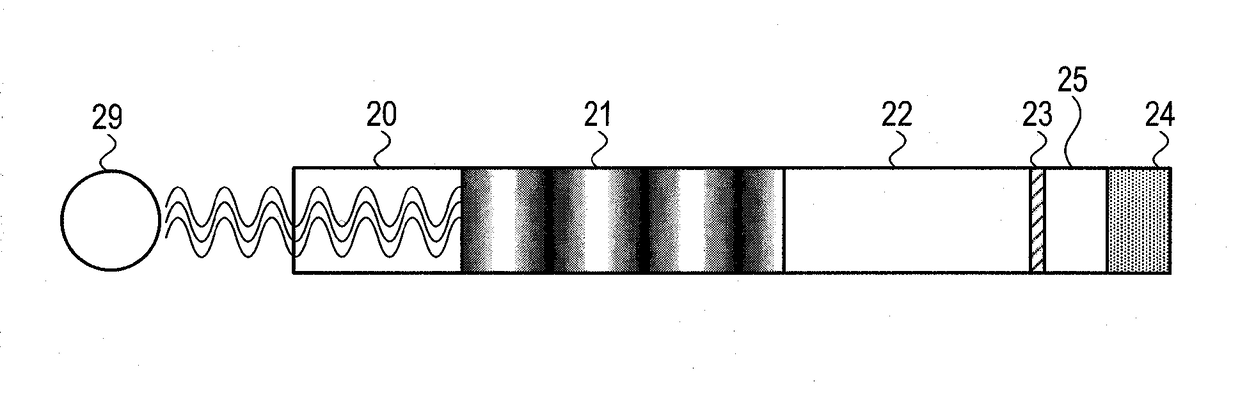
Method and device for reducing non-intrinsic dark count of superconducting nanowire single photon detector
ActiveCN104064631AEasy to implementGuaranteed Optical Coupling EfficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesNanowireBlack-body radiation
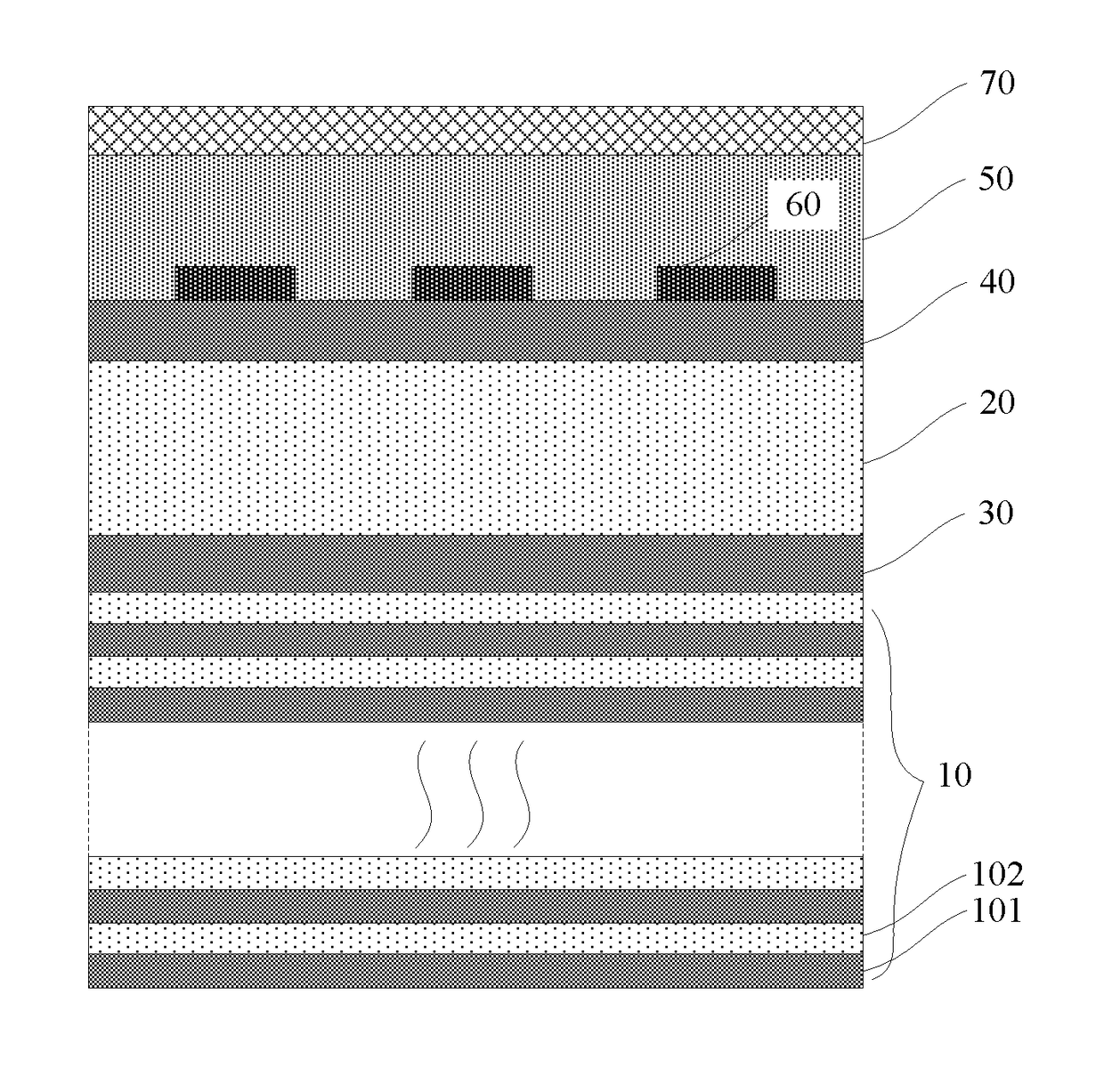
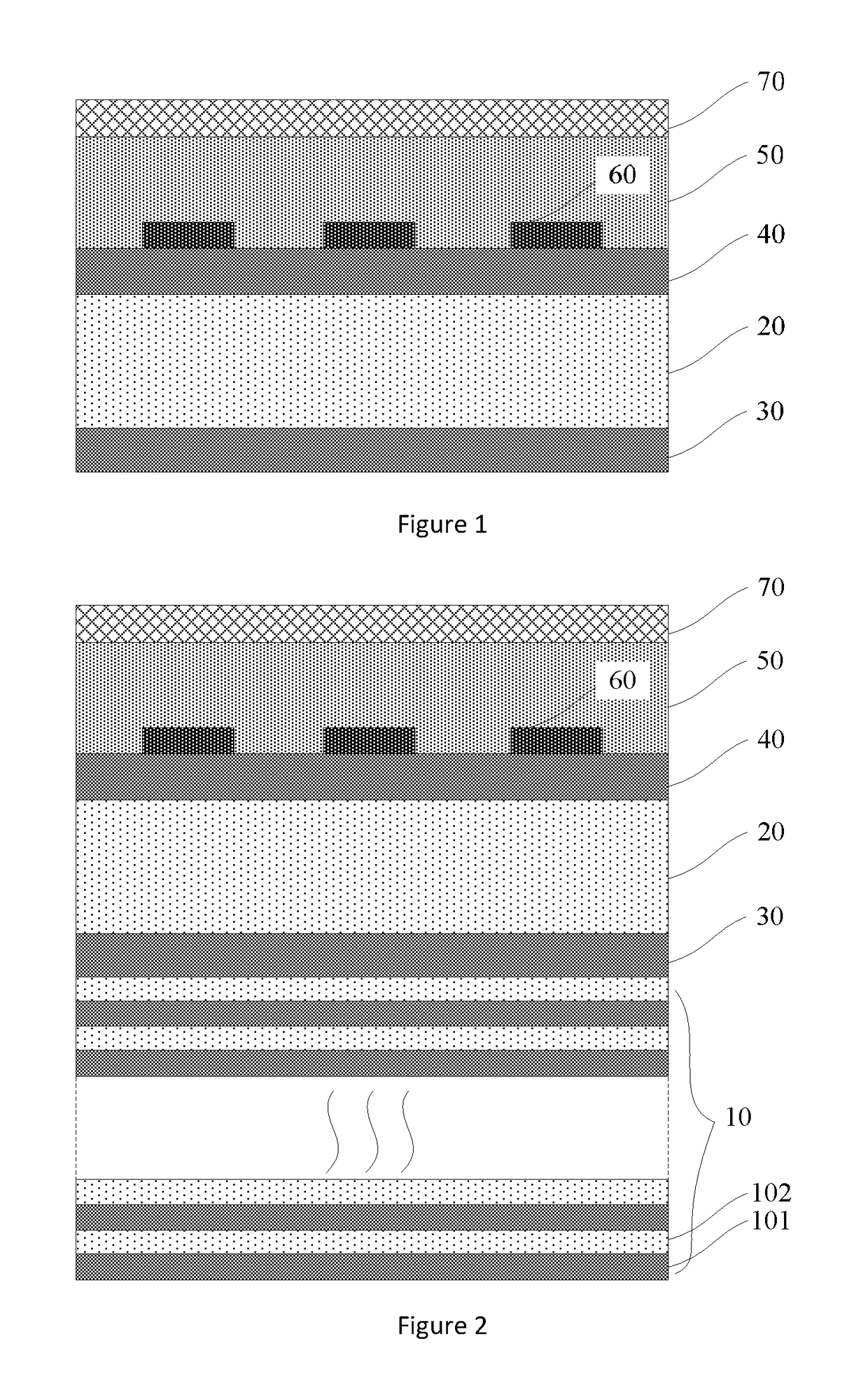
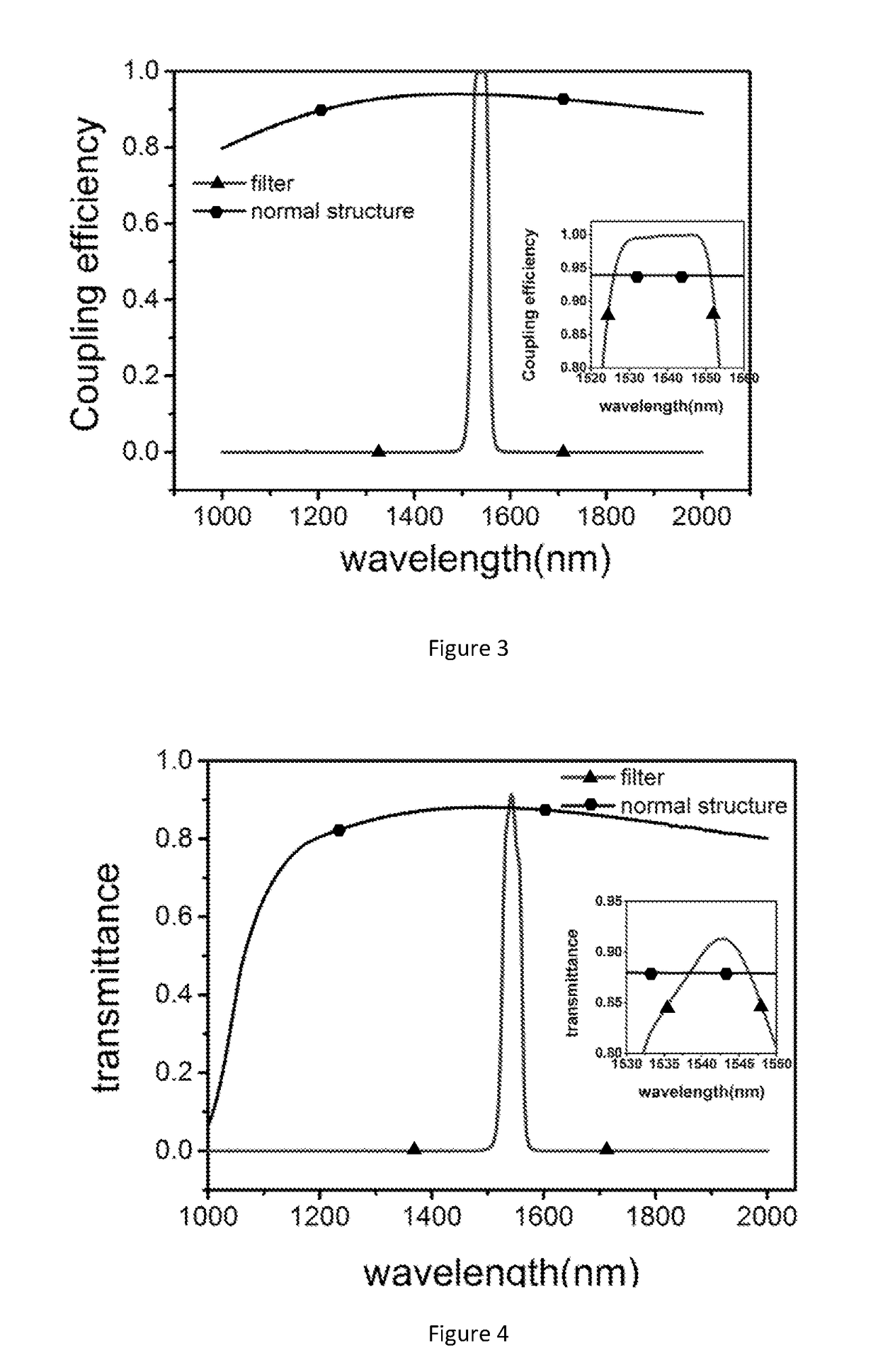
The invention provides a method and device for reducing the non-intrinsic dark count of a superconducting nanowire single photon detector. The method comprises the step that a short wave pass multi-layer thin-film filter is integrated on the superconducting nanowire single photon detector, wherein the short wave pass multi-layer thin-film filter is a device with the short wave pass filtering function and is implemented through multiple layers of dielectric film. The non-intrinsic dark count is the dark count triggered by optical fiber black-body radiation and stray light in the outside world. According to the method and device, operation is easy, and non-signal-radiation is filtered out just by integrating the short wave pass multi-layer thin-film filter on a substrate. According to the method, the non-intrinsic dark count can be effectively reduced while signal radiation and optical coupling efficiency of the device are ensured, and therefore detection efficiency of the device under the specific dark count condition is improved; in addition, only optical waves with the wavelength larger than 1550 nm need to be filtered out, the design requirement is reduced, and the filter can be easily implemented.
Owner:赋同量子科技(浙江)有限公司
Photon number resolution enhanced laser communication system and method
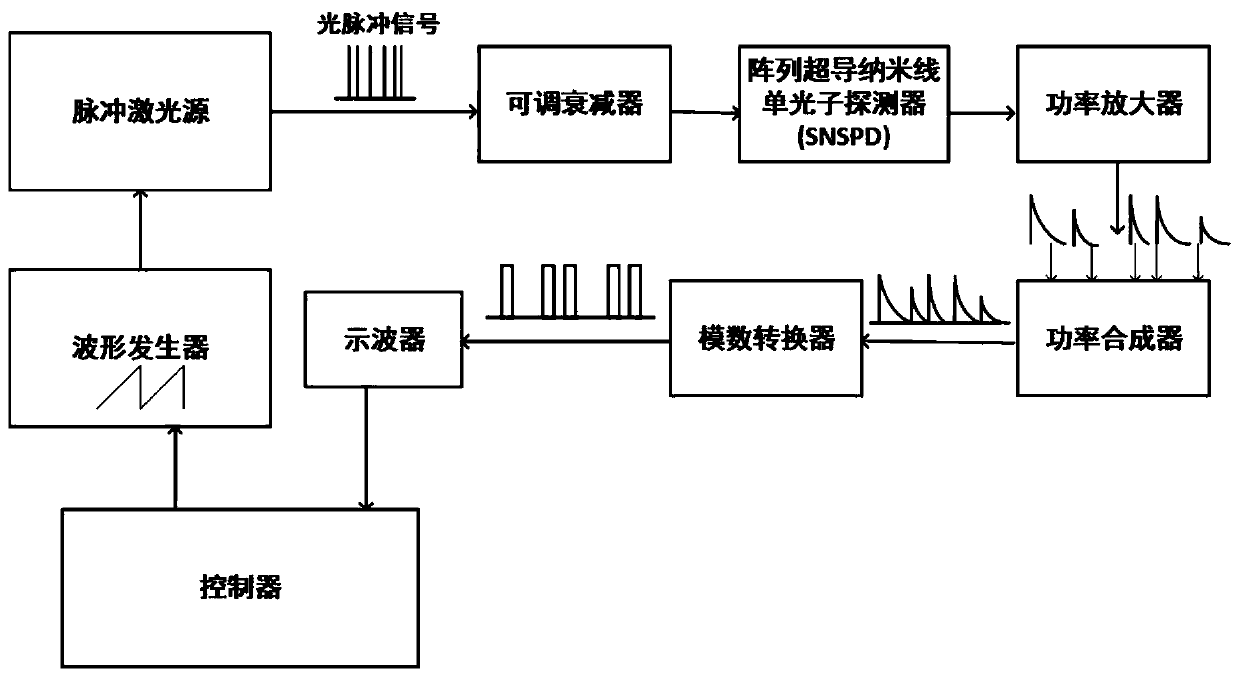
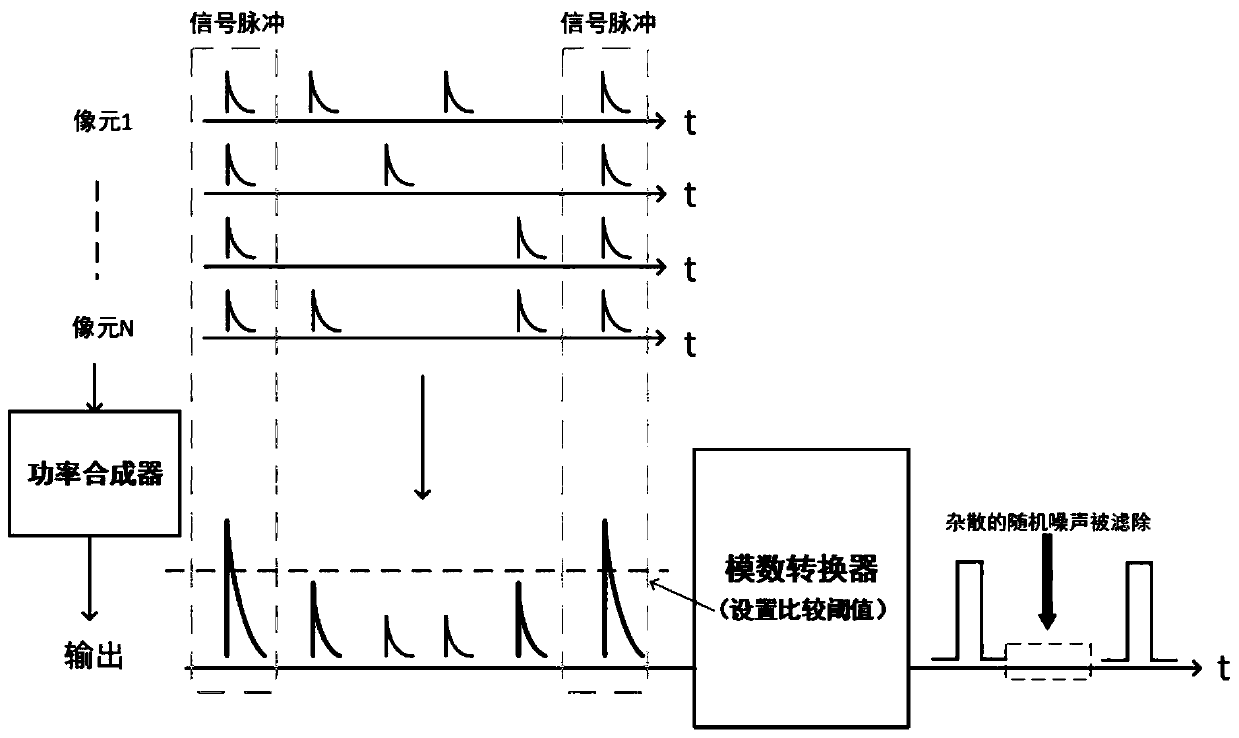
ActiveCN111130652AReduce order of magnitudeShorten the counting processPhotonic quantum communicationElectromagnetic transmittersConvertersNanowire
The invention discloses a photon number resolution enhanced laser communication system and method. The system comprises a controller, a waveform generator, a pulse laser source, an adjustable attenuator, an array superconducting nanowire single-photon detector, a power amplifier, a power synthesizer, an analog-to-digital converter and an oscilloscope, wherein the controller carries out code modulation on data needing to be output and inputs the data to a waveform generator, the waveform generator converts the coded information into an electric pulse signal and outputs the electric pulse signalto the pulse laser source, the pulse laser source generates a corresponding optical pulse signal according to the input electric pulse signal, then the optical pulse signal is input into the array superconducting nanowire single-photon detector through the adjustable attenuator, a signal with photon number resolution is output through the power amplifier and the power synthesizer, and finally thesignal is received and collected by the oscilloscope after being shaped by the analog-to-digital converter. Error code interference caused by external optical space noise and dark noise of the superconducting detector is greatly reduced, so that the error rate is enabled to be close to the self-owned light quantum error code limit of optical communication.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
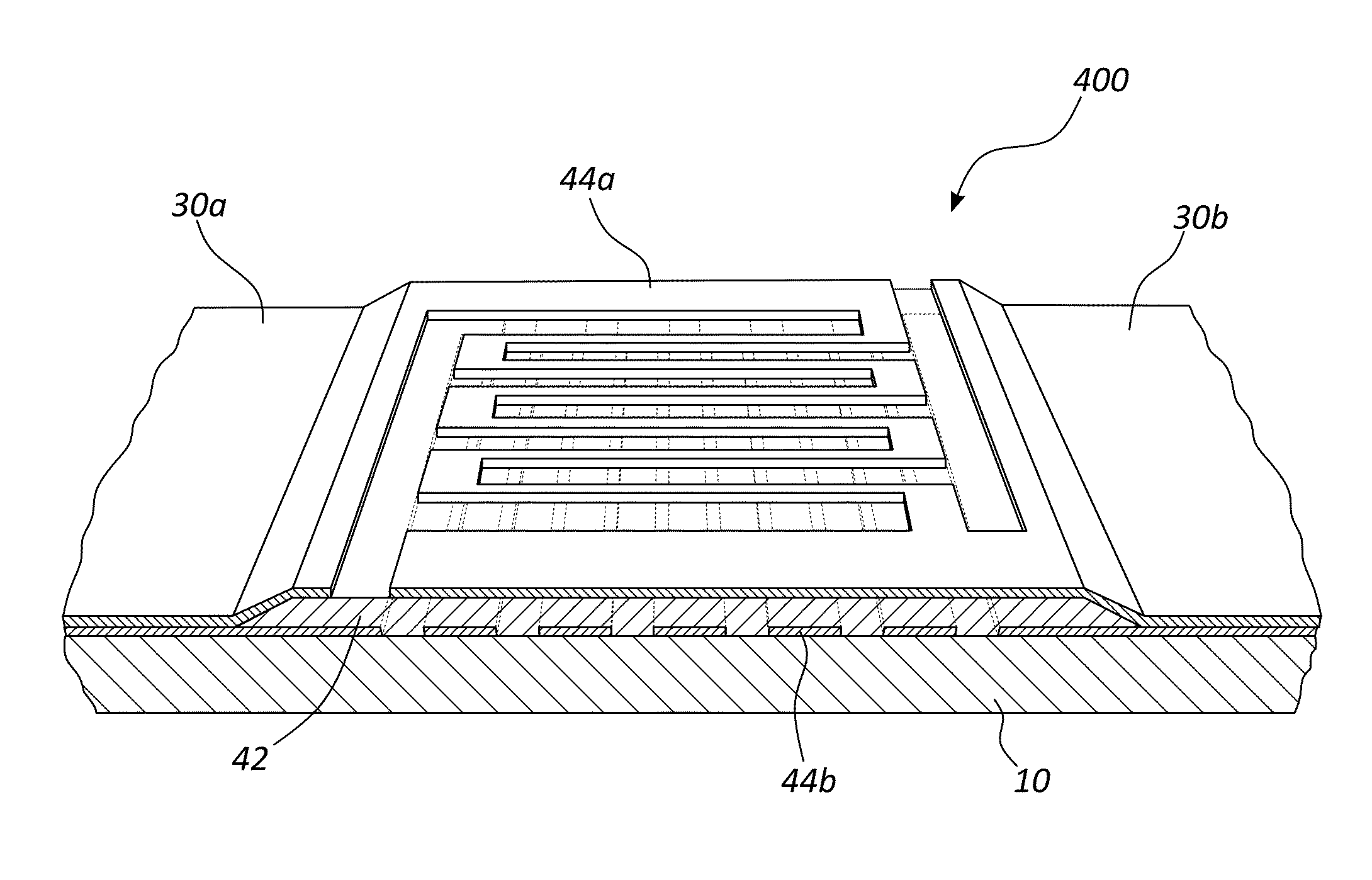
Superconducting nanowire single-photon detector array capable of distinguishing photon energy
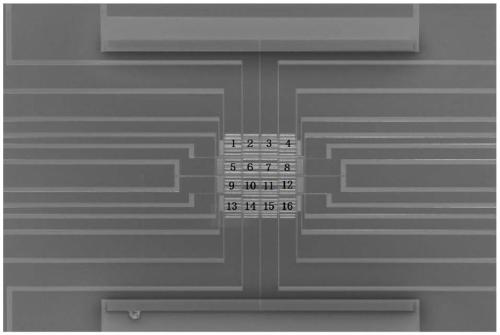
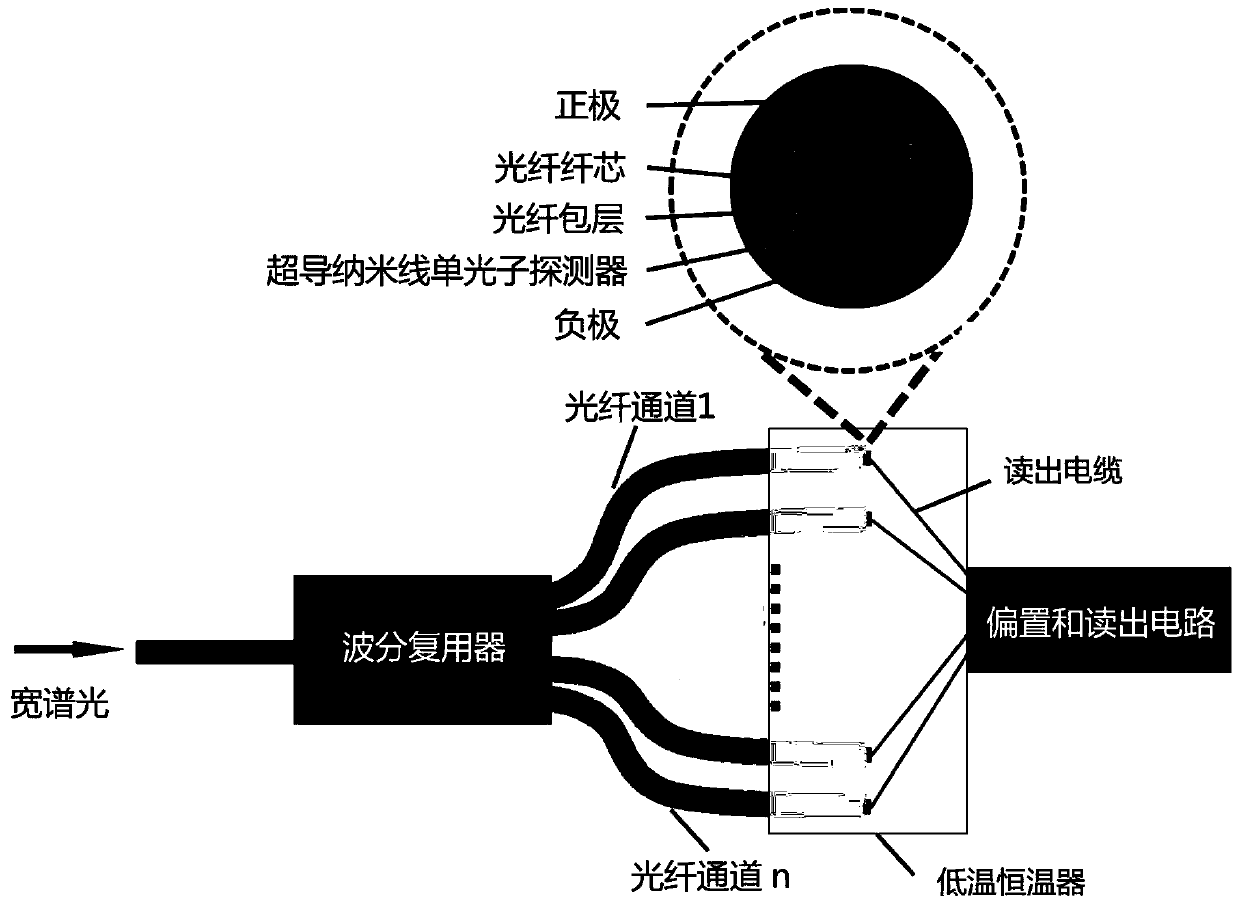
InactiveCN110702237ASolve the problem of multi-channel cooperative workSuperconductor detailsInstrumentsNanowireEngineering
The invention discloses a superconducting nanowire single-photon detector array capable of distinguishing photon energy. The superconducting nanowire single-photon detector array comprises a beam of broad-spectrum light is irradiated from an optical fiber at a left end, the light with different photon energy is output from different optical fiber channels at a right end after passing through an optical fiber wavelength division multiplexer and is accessed to a cryostat; a superconducting nanowire single-photon detector is transferred on a terminal end face of each optical fiber in the cryostat, the single-photon detector covers an optical fiber core, a positive electrode and a negative electrode are arranged on the end face of optical fiber cladding, and a readout cable is connected withthe positive electrode and the negative electrode; and the superconducting nanowire single-photon detector is connected in a bias and readout circuit to read out a photon counting rate. The superconducting nanowire single-photon detector array disclosed by the invention has photon energy distinguishing ability and can be applied to a wavelength division multiplexing quantum key distribution system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
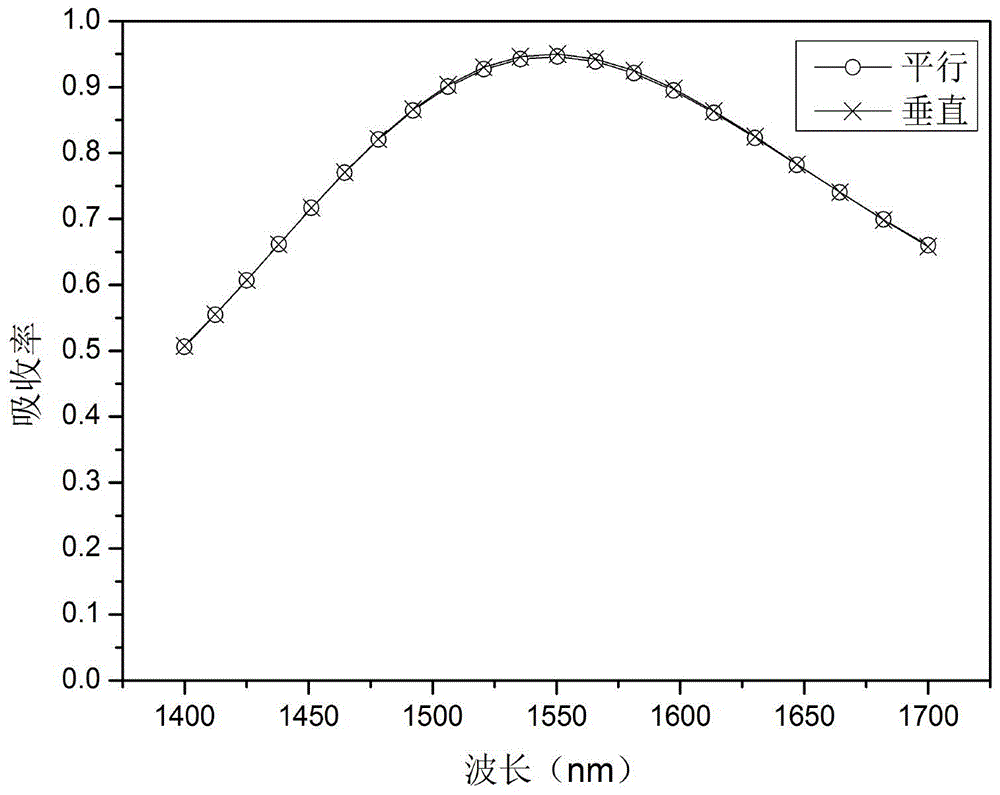
Superconducting fractal nanowire single-photon detector and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105374928AReduce polarization sensitivityEffective absorptionSuperconductor detailsNanowireEvaporation
The invention discloses a superconducting fractal nanowire single-photon detector and a preparation method thereof. The single-photon detector comprises a substrate, nanowires, a nano antenna, a hydrogen silsequioxane layer and a silver reflecting layer, wherein the nanowires are arranged in a fractal manner and are used for achieving insensitive absorption and polarization of the nanowires on light in two polarization states; and an array nano antenna is added on the basis of the nanowires. The preparation method comprises the following steps: sputtering a layer of superconducting material on the substrate by a magnetron sputtering method; preparing an electrode in a manner of combining photoetching and electronic beam evaporation; the fractal nanowire is prepared in a manner of matching electron beam exposure with reactive ion beam etching; and the nano antenna is prepared in a manner of combining the electron beam exposure with the electronic beam evaporation. According to the superconducting fractal nanowire single-photon detector, the polarization sensitivity of the superconducting nanowire single-photon detector is lowered; the polarization sensitivity is less than 0.02; the absorption efficiencies of two orthogonal polarization states reach 80%; the wideband absorption efficiency is higher than 70%; and the superconducting fractal nanowire single-photon detector is applicable to various superconducting materials.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
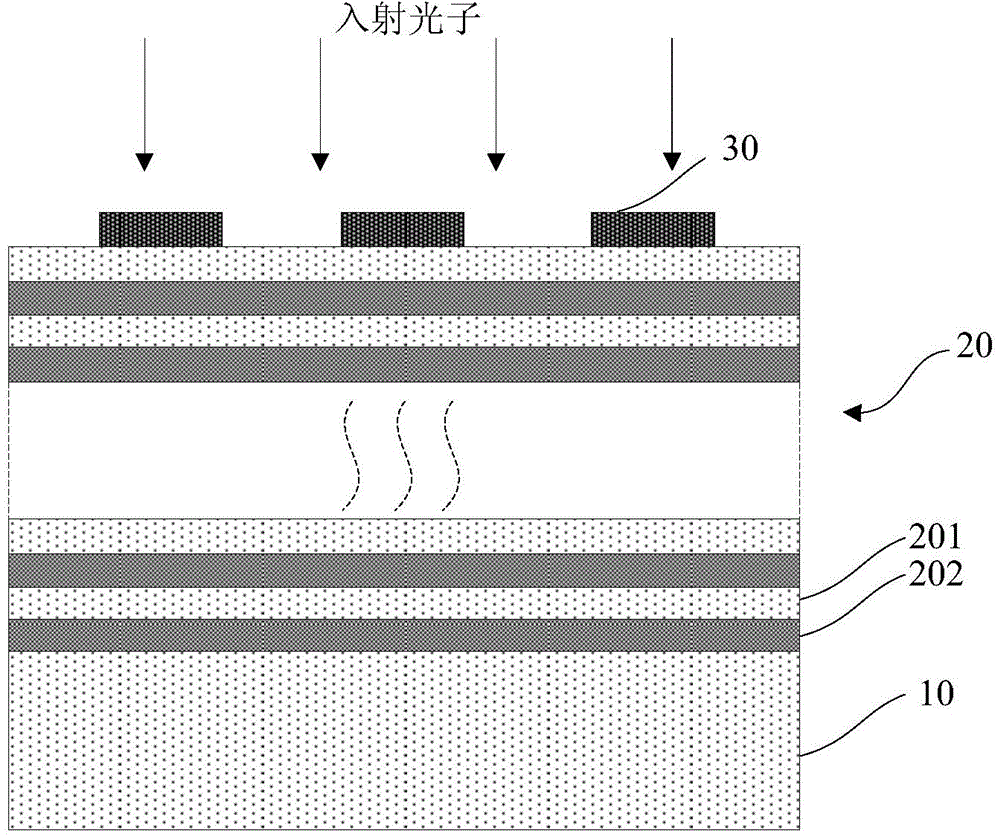
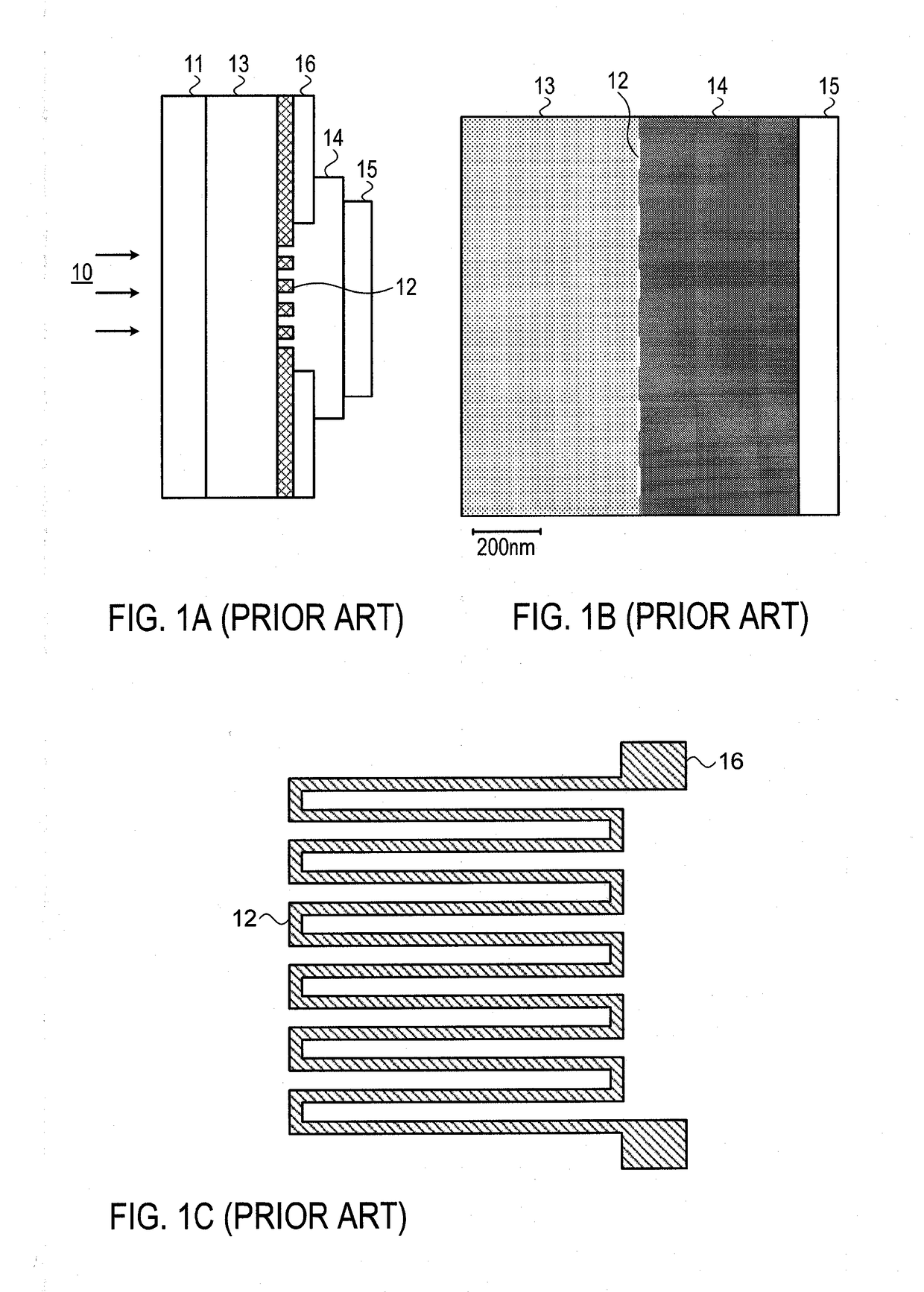
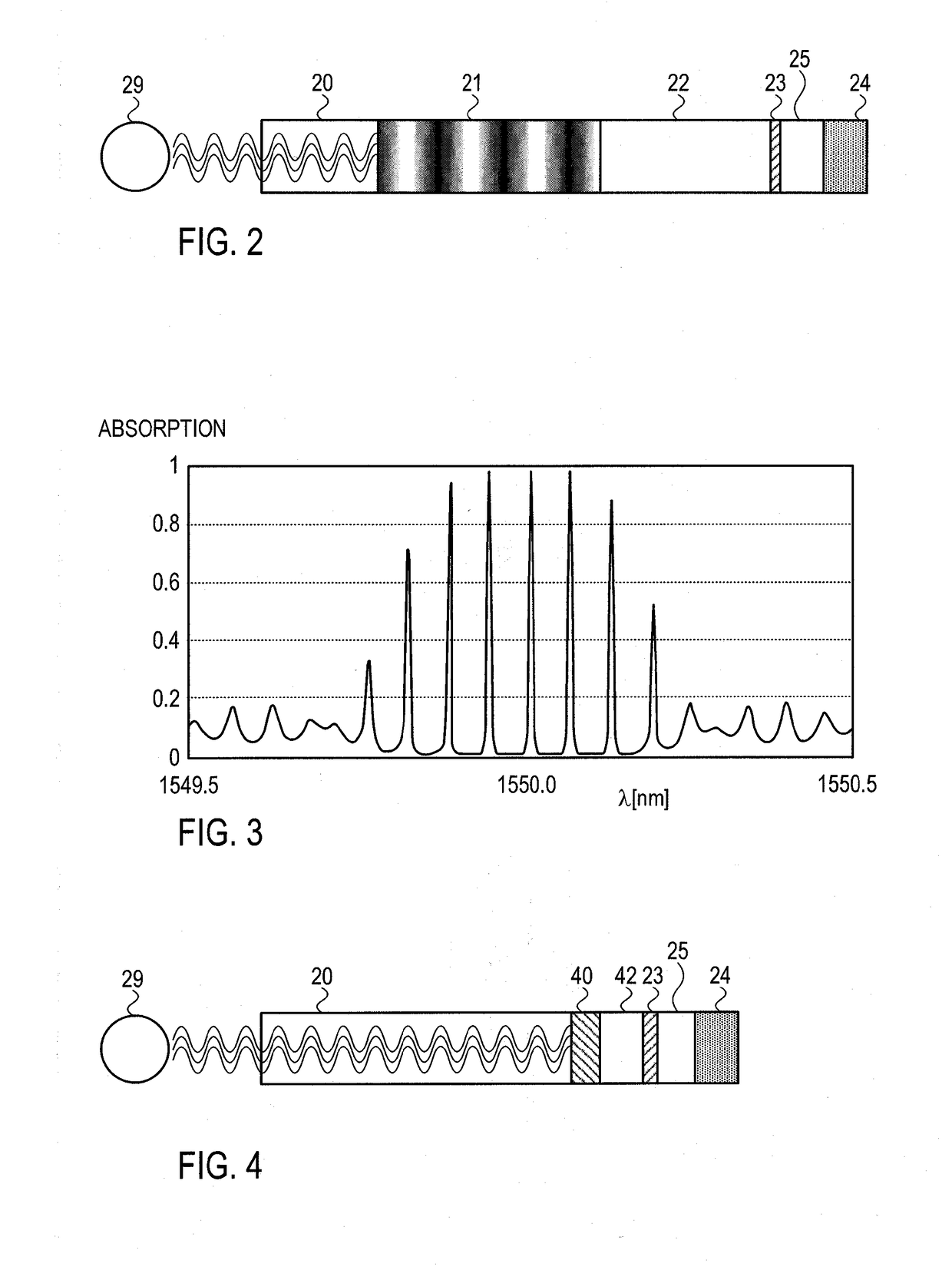
Method and device for reducing extrinsic dark count of nanowire single photon detector
ActiveUS20170098752A1Easy to operateReduces extrinsic dark countRadiation pyrometrySuperconductor detailsNanowirePhoton detection
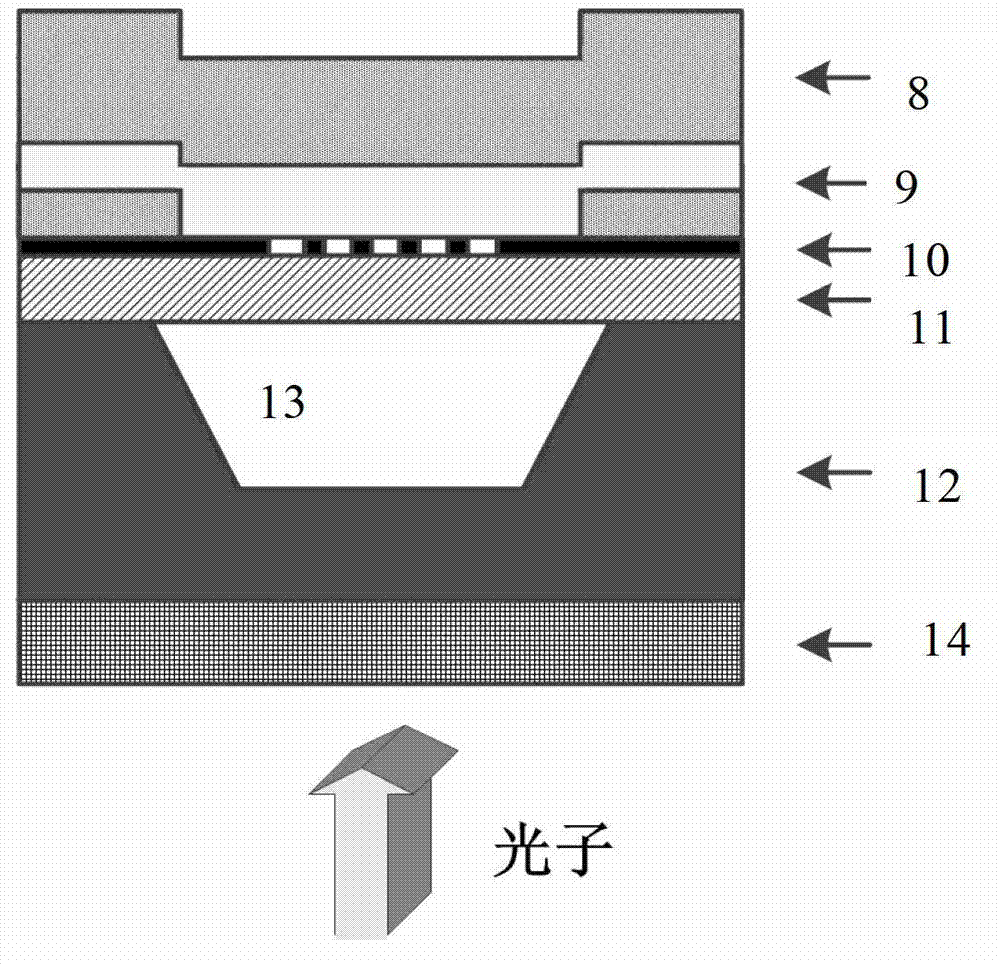
A method and a device for reducing the extrinsic dark count of a superconducting nanowire single photon detector (SNSPD), it comprises the steps of: integrating a multi-layer film filter on the superconducting nanowire single photon detector; the multi-layer film filter is a device implemented by a multi-layer dielectric film and having a band-pass filtering function. The extrinsic dark count is the dark count triggered by optical fiber blackbody radiance and external stray light. The superconducting nanowire single photon detector comprises: a substrate having an upper surface integrated with an upper anti-reflection layer and a lower surface integrated with a lower anti-reflection layer; an optical cavity structure; a superconducting nanowire; and a reflector. The present invention is easy to operate, and only needs to integrate the multi-layer film filter on the substrate of the SNSPD to filter non-signal radiation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Superconducting single-photon detector with phase grating and manufacturing method for superconducting single-photon detector with phase grating
InactiveCN104167452AImprove absorption efficiencyFinal product manufactureInstrumentsNanowirePhase grating
The invention discloses a superconducting single-photon detector with a phase grating and a manufacturing method for the superconducting single-photon detector with the phase grating. The superconducting single-photon detector with the phase grating is characterized in that the phase grating is arranged on a nanowire area of a conventional superconducting single-photon detector based on niobium nitride. The grating height of the phase grating is odd-number times the thickness corresponding to the phase of the wavelength pi of incident light. The phase grating on the nanowire area generates the focusing interference effect on light beams, niobium nitride nanowires are located at the focal position, and therefore the absorption efficiency of the niobium nitride nanowires to photons is improved. Simulation results show that the superconducting single-photon detector with the phase grating has the quite high detection efficiency in multiple frequency bands of visible light and infrared light, and the photon absorption efficiency is as high as 72% when the wavelength is 850 nm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
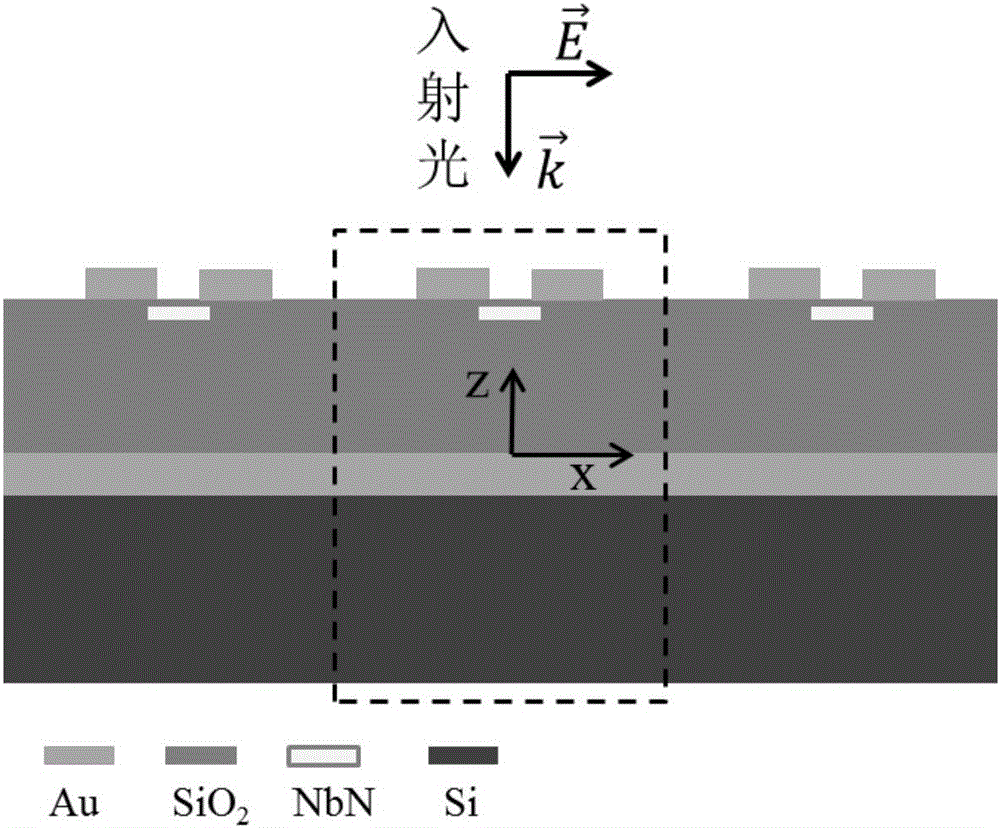
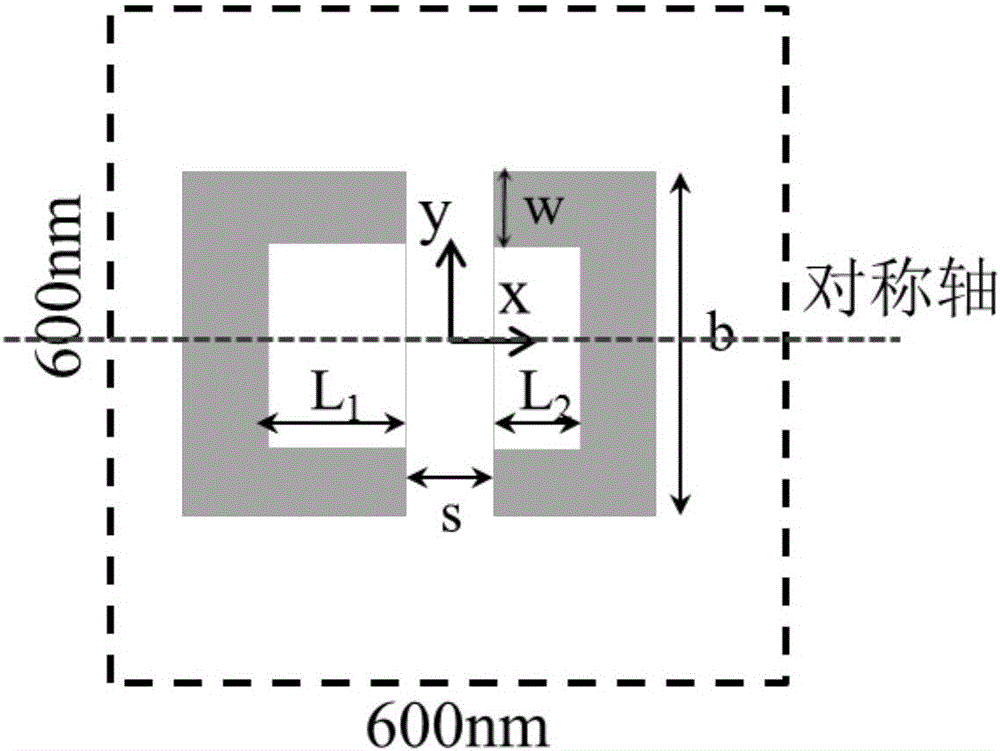
Polarization-sensitive efficient superconducting nanowire single photon detector and design method therefor
InactiveCN105870315ASimple structureNovel structureSuperconductor detailsNanoopticsNanowireUnit structure
The invention discloses a polarization-sensitive efficient superconducting nanowire single photon detector and a design method therefor. The detector comprises a silicon substrate, a gold film reflective layer, a silicon dioxide medium cavity, an NbN nanowire and a coupling anti-symmetric split ring resonator, wherein the silicon substrate, the gold film reflective layer, the silicon dioxide medium cavity and the coupling anti-symmetric split ring resonator are arranged from the bottom up in sequence; the NbN nanowire is positioned in the interior of the silicon dioxide medium cavity; the NbN nanowire comprises multiple periodically-arranged unit structures; and the coupling anti-symmetric split ring resonator is periodically arranged. The invention also discloses a design method for the detector. The detector provided by the invention has a simple and creative structure, high width of the adopted superconducting material NbN nanowire, high duty ratio, high detection efficiency on near infrared wave single photons, and high counting speed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
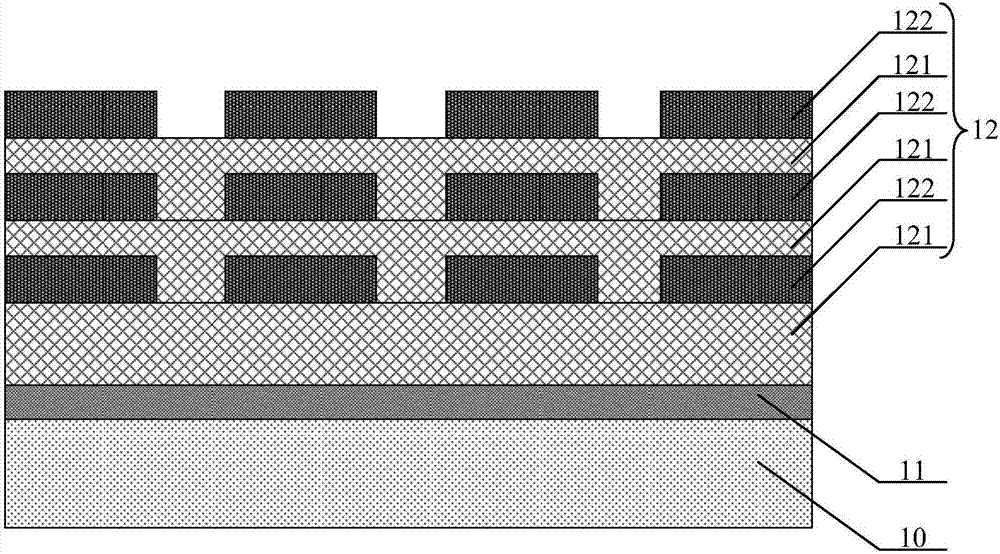
Wide-spectrum superconducting nanowire single photon detector
ActiveCN107507884AAbsorption BandwidthExtending the Efficient Absorption Bandwidth of the Broadband Superconducting Nanowire Single Photon Detector DeviceMaterial nanotechnologyInstrumentsNanowirePhoton
The invention provides a wide-spectrum superconducting nanowire single photon detector. The wide-spectrum superconducting nanowire single photon detector comprises a substrate, a mirror which is located on the surface of the substrate, and a lamination structure which is located on the surface of the mirror. The lamination structure comprises at least two layers of superconducting nanowires which are arranged up and down. According to the wide-spectrum superconducting nanowire single photon detector provided by the invention, the absorption of two or more layers of superconducting nanowires is realized by arranging the lamination structure which comprises at least two layers of superconducting nanowires arranged at intervals up and down on the mirror; the efficient absorption bandwidth of the wide-spectrum superconducting nanowire single photon detector is expanded; and the absorption efficiency is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Polarized nonsensitive efficient superconducting nanowire single photon detector
InactiveCN104835905AAchieving polarization insensitivityImprove absorption efficiencySuperconductor detailsOptical cavityNanowire
The invention discloses a polarized nonsensitive efficient superconducting nanowire single photon detector. The detector comprises a substrate, a medium semi-reflective mirror combined on the surface of the substrate, a lower optical cavity combined on the surface of the medium semi-reflective mirror, a medium wrapping layer combined on the surface of the lower optical cavity, NbN nanowires combined inside the medium wrapping layer, an upper optical cavity combined on the surface of the medium wrapping layer, medium nanowires combined between the medium wrapping layer and the upper optical cavity, and an all-reflective mirror combined on the surface of the upper optical cavity. Through adoption of the polarized nonsensitive efficient superconducting nanowire single photon detector, the problem in the prior art that the superconducting nanowire single photon detector is sensitive to optical polarization direction is solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
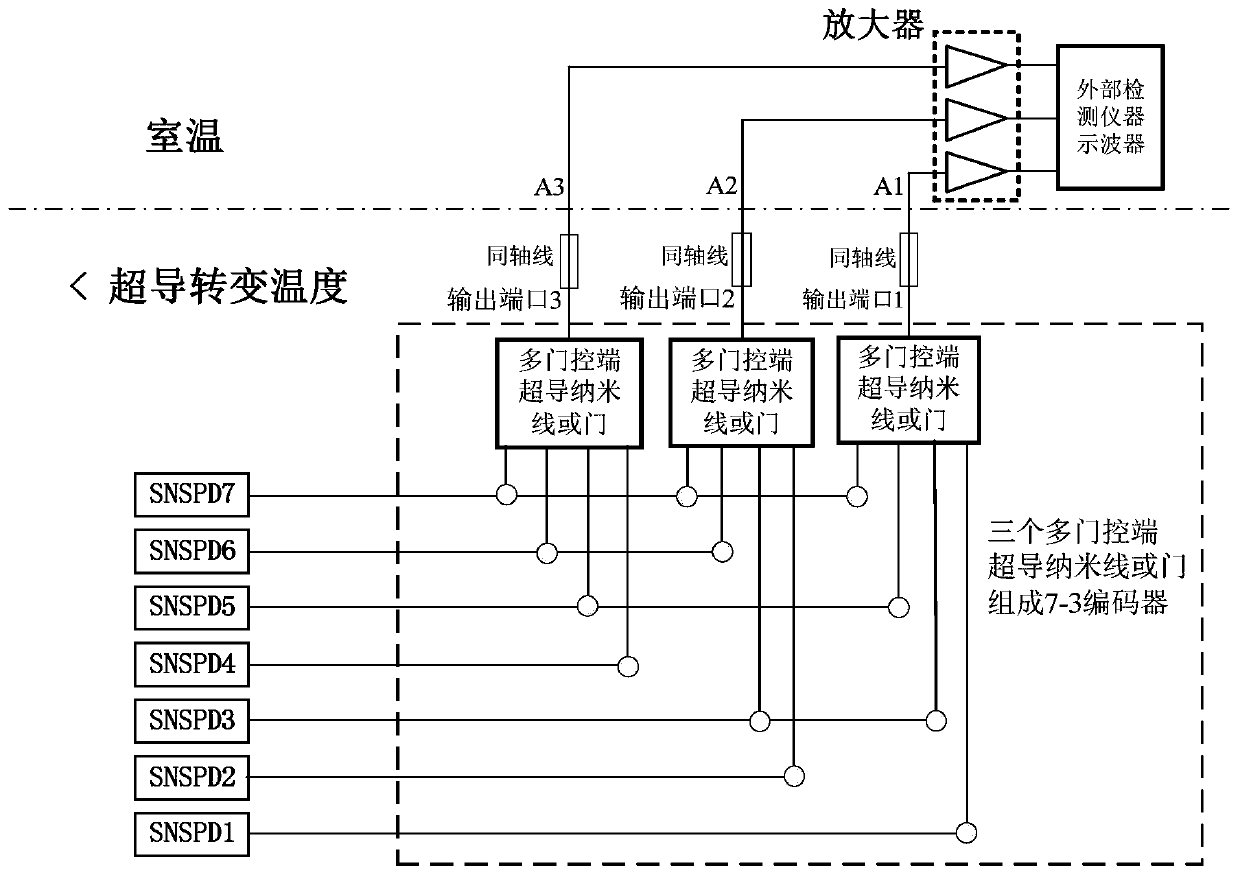
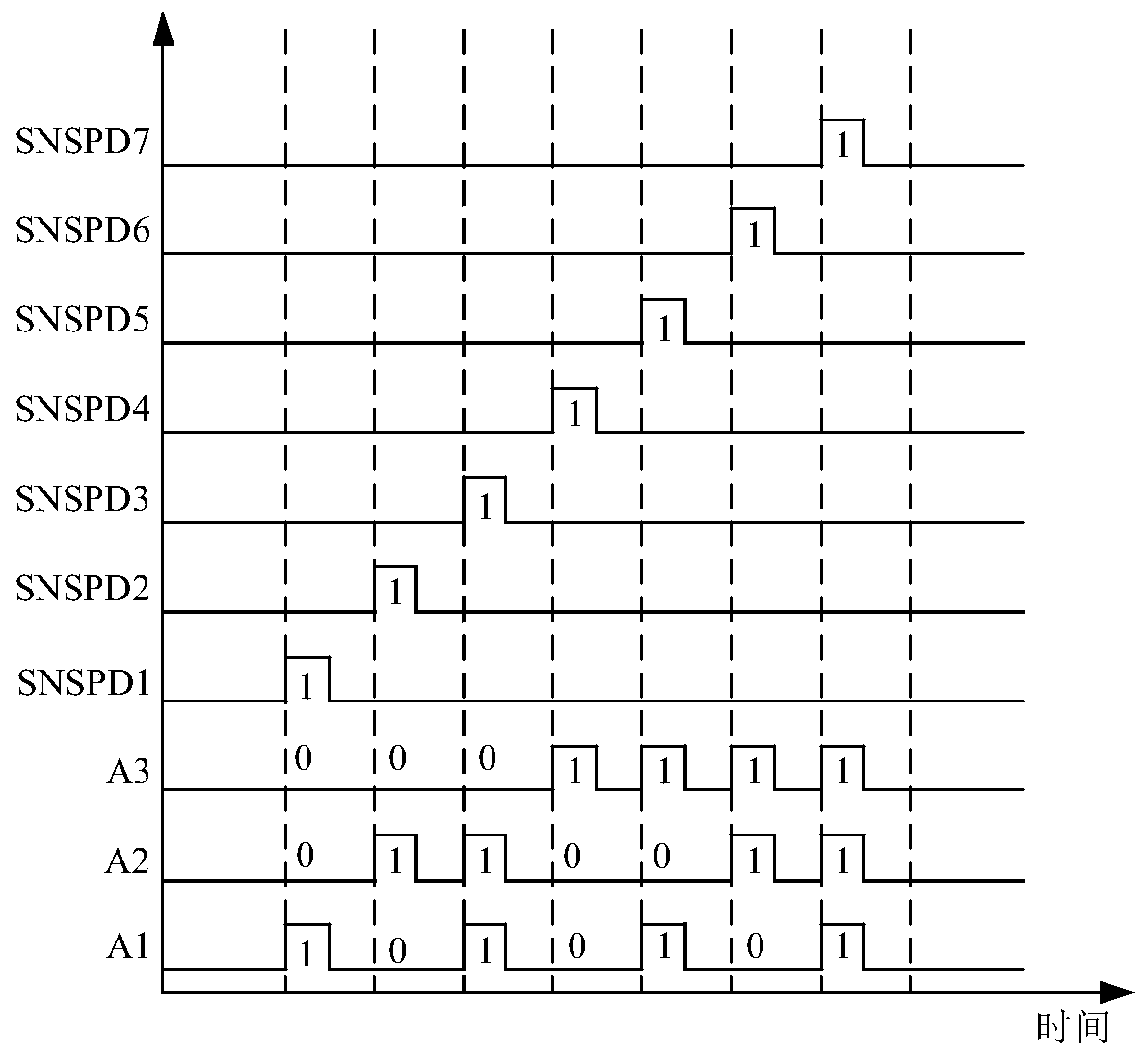
Low-temperature reading method of multi-channel superconducting nanowire single-photon detector
ActiveCN109764960ASimple structureEasy to makePhotometry electrical circuitsNanowireRoom temperature
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Superconducting nanowire single photon detector
ActiveCN107507911AReduce inductanceQuick responseSuperconductor detailsNanowireSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides a superconducting nanowire single photon detector which comprises at least one superconducting nanowire structure. The superconducting nanowire structure comprises a number of straight line parts which are arranged in parallel and with spacing, and first connection part which connect the straight line parts in order from end to end. Each straight line part comprises at least two superconducting nanowires which are arranged in parallel and with spacing. The superconducting nanowires in all straight line parts are connected through the first connection parts. At least two superconducting nanowires which are arranged in parallel and with spacing are arranged in each straight line part of the superconducting nanowire structure, which reduces the total inductance of the device, and improves the response speed of the device. The current in the device is improved. The signal to noise ratio of the device can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com