Patents
Literature
575 results about "Photon energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Photon energy is the energy carried by a single photon. The amount of energy is directly proportional to the photon's electromagnetic frequency and thus, equivalently, is inversely proportional to the wavelength. The higher the photon's frequency, the higher its energy. Equivalently, the longer the photon's wavelength, the lower its energy.
Photon energy conversion structure
InactiveUS20090268461A1Reduce total powerLow efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourceFluorescencePhosphor
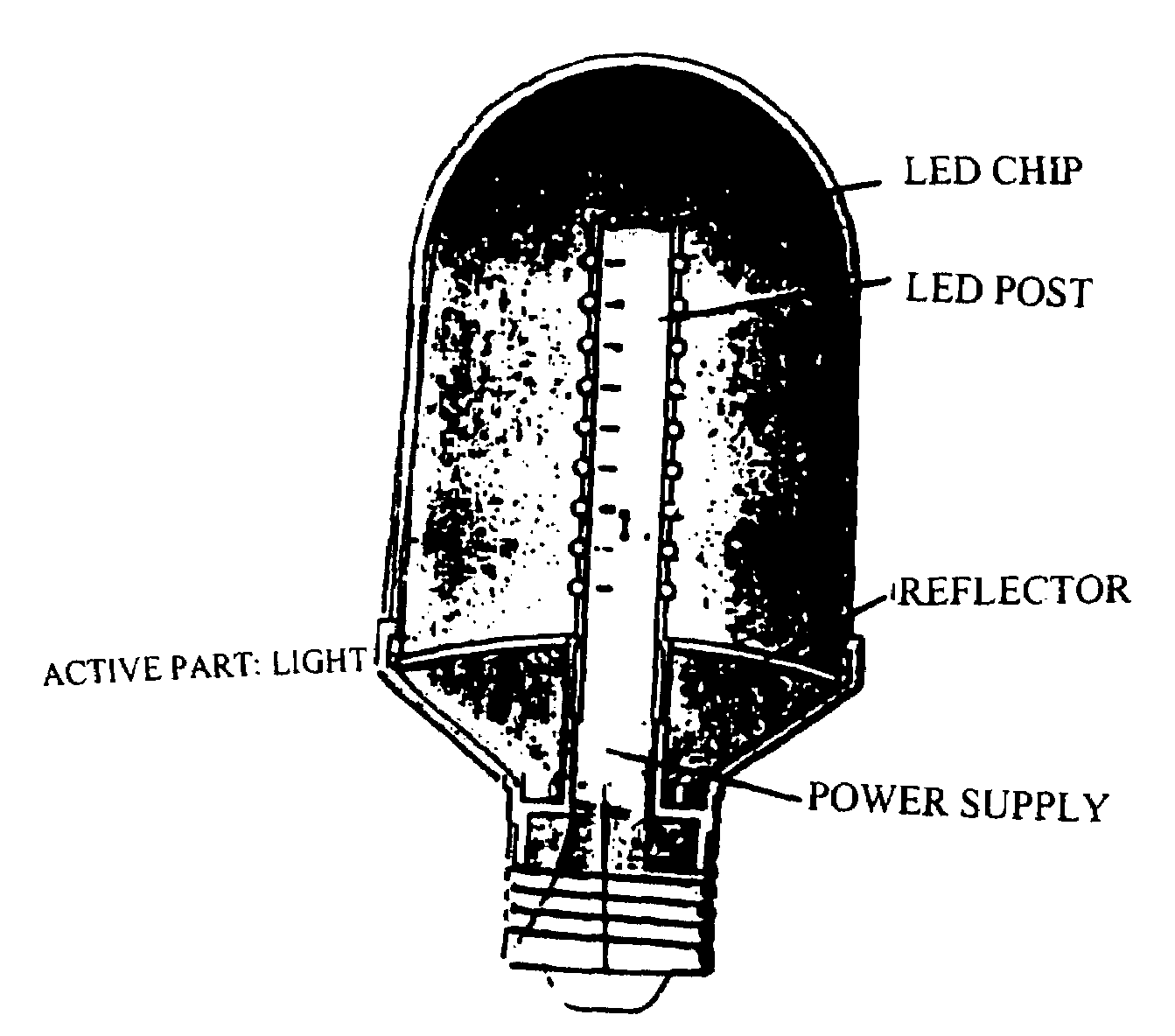
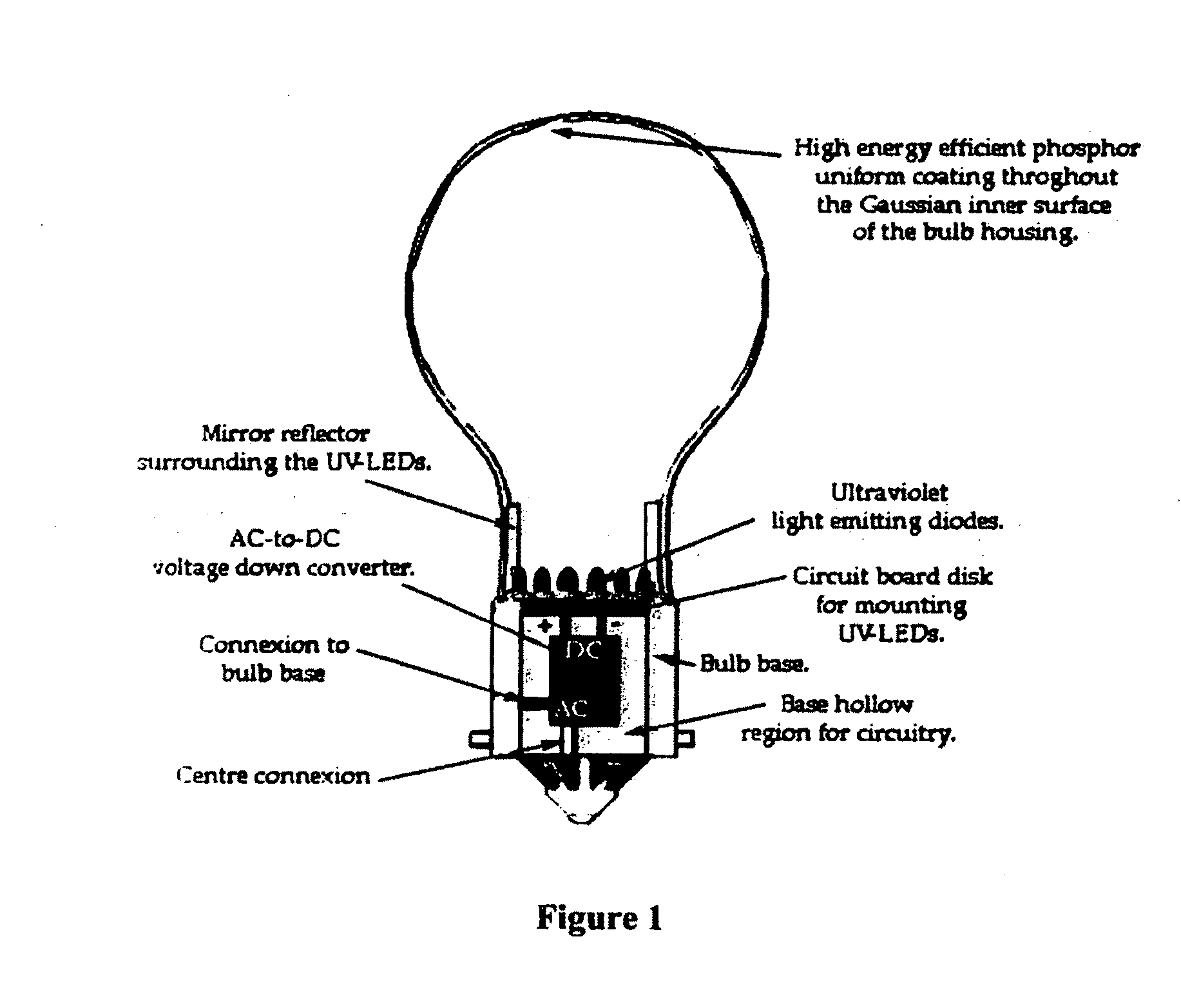
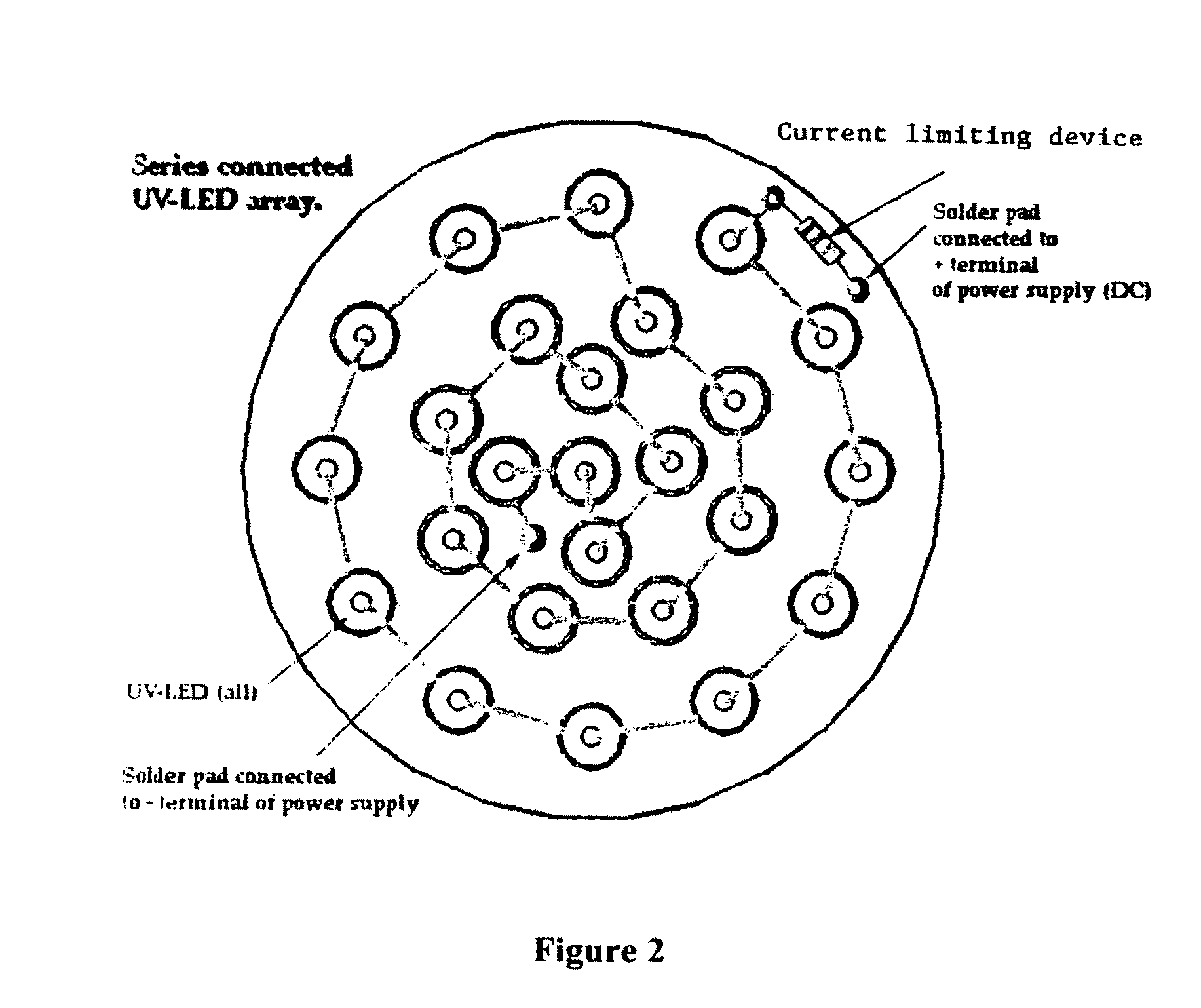
A photon energy conversion device uses at least one ultraviolet light emitting diode (UV-LED) with a wavelength shifting medium such as phosphor or quantum dots. The device can be used as a light source, and shaped like incandescent light bulbs, fluorescent tubes, circles or compact fluorescent bulbs.
Owner:WEPOWER TECH LLC
Solar based electrical energy generation with spectral cooling
InactiveUS20050051205A1Improve output performanceComponent can be removedMechanical apparatusSolar heat devicesLight energyEngineering
Method and system for converting solar energy into electrical energy utilizing serially coupled multijunction-type photovoltaic cells in conjunction with a form of spectral cooling. The latter cooling is carried out by removing ineffective solar energy components from impinging concentrated light, inter alia, through the utilization of dichroics or the conversion of ineffective solar energy components to effective energy components by means of luminescence, phosphorescence, or fluorescence. Ineffective solar energy components are described as those exhibiting wavelengths outside the bandgap energy defined wavelength and an associated wavelength defined band of useful photon energy.
Owner:MOOK WILLIAM J
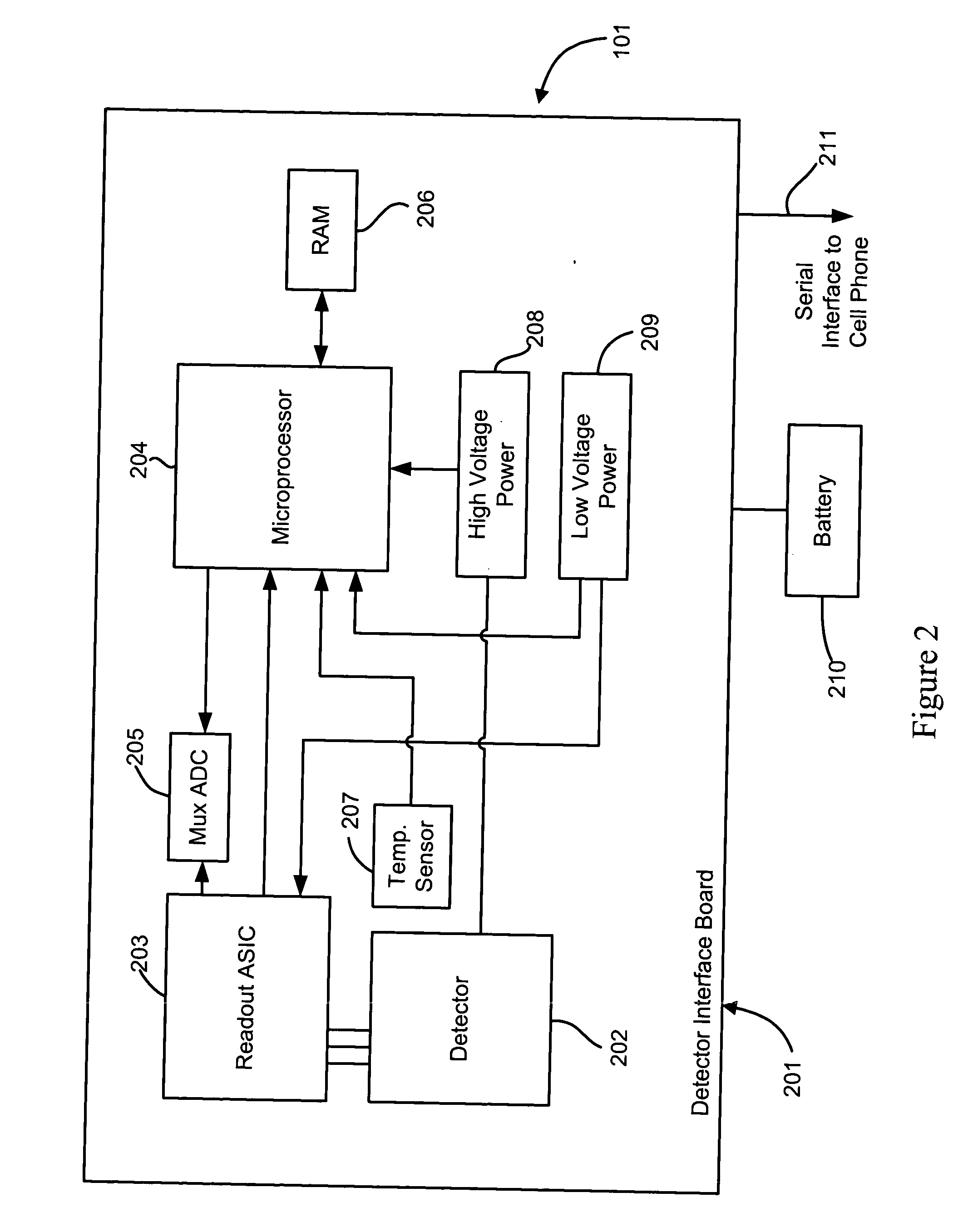
Cellular telephone-based radiation sensor and wide-area detection network
A network of radiation detection instruments, each having a small solid state radiation sensor module integrated into a cellular phone for providing radiation detection data and analysis directly to a user. The sensor module includes a solid-state crystal bonded to an ASIC readout providing a low cost, low power, light weight compact instrument to detect and measure radiation energies in the local ambient radiation field. In particular, the photon energy, time of event, and location of the detection instrument at the time of detection is recorded for real time transmission to a central data collection / analysis system. The collected data from the entire network of radiation detection instruments are combined by intelligent correlation / analysis algorithms which map the background radiation and detect, identify and track radiation anomalies in the region.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
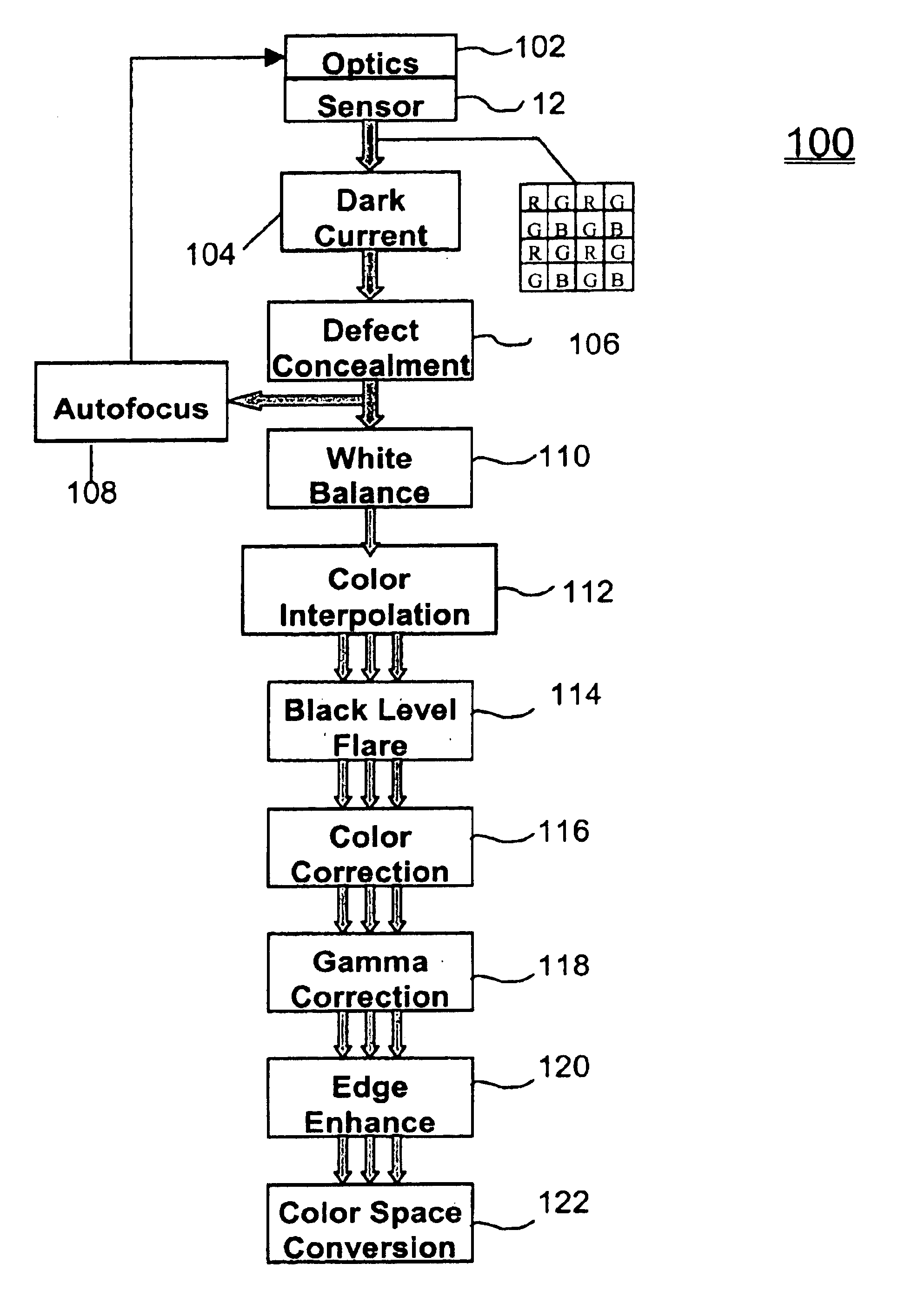
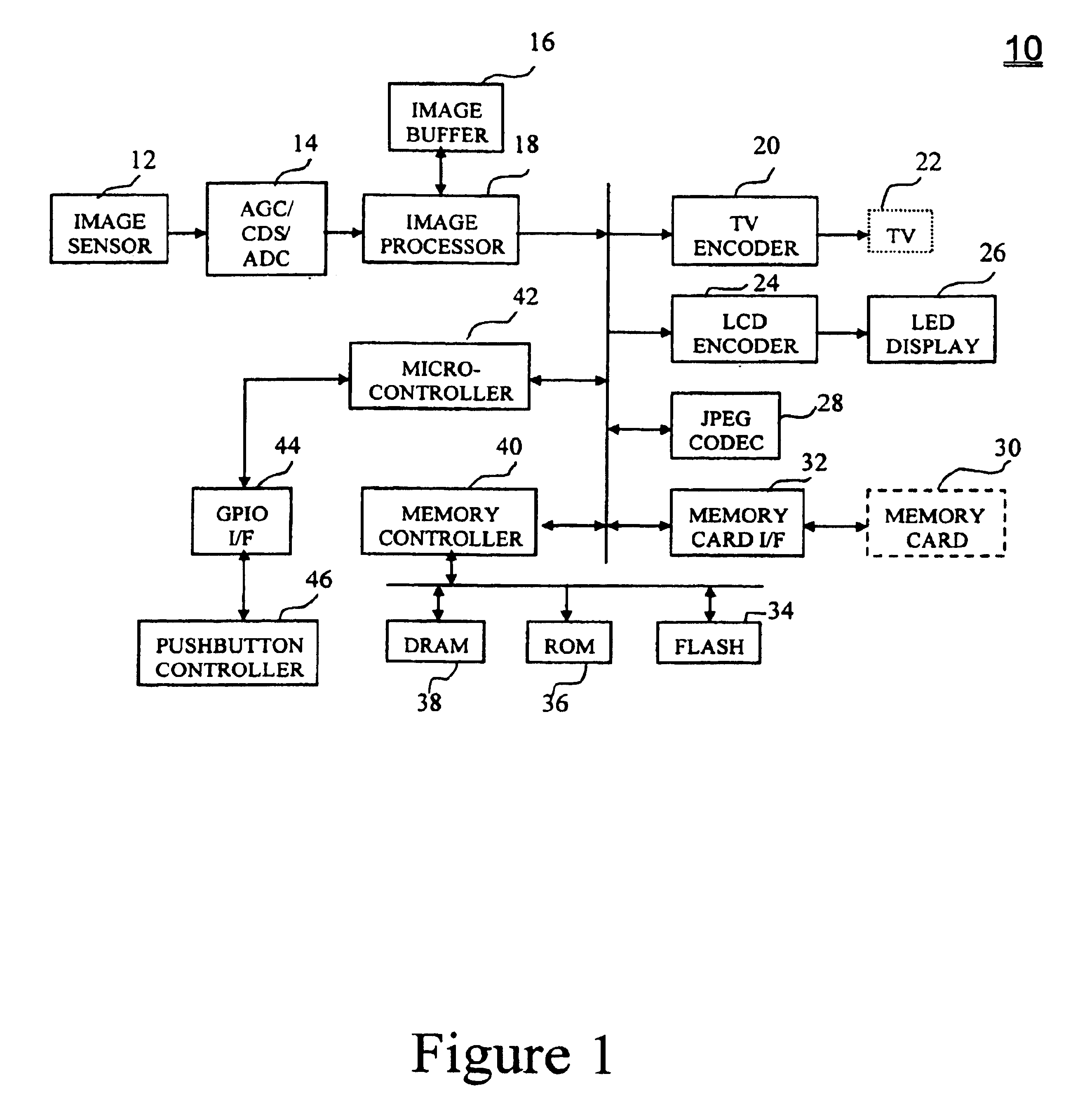
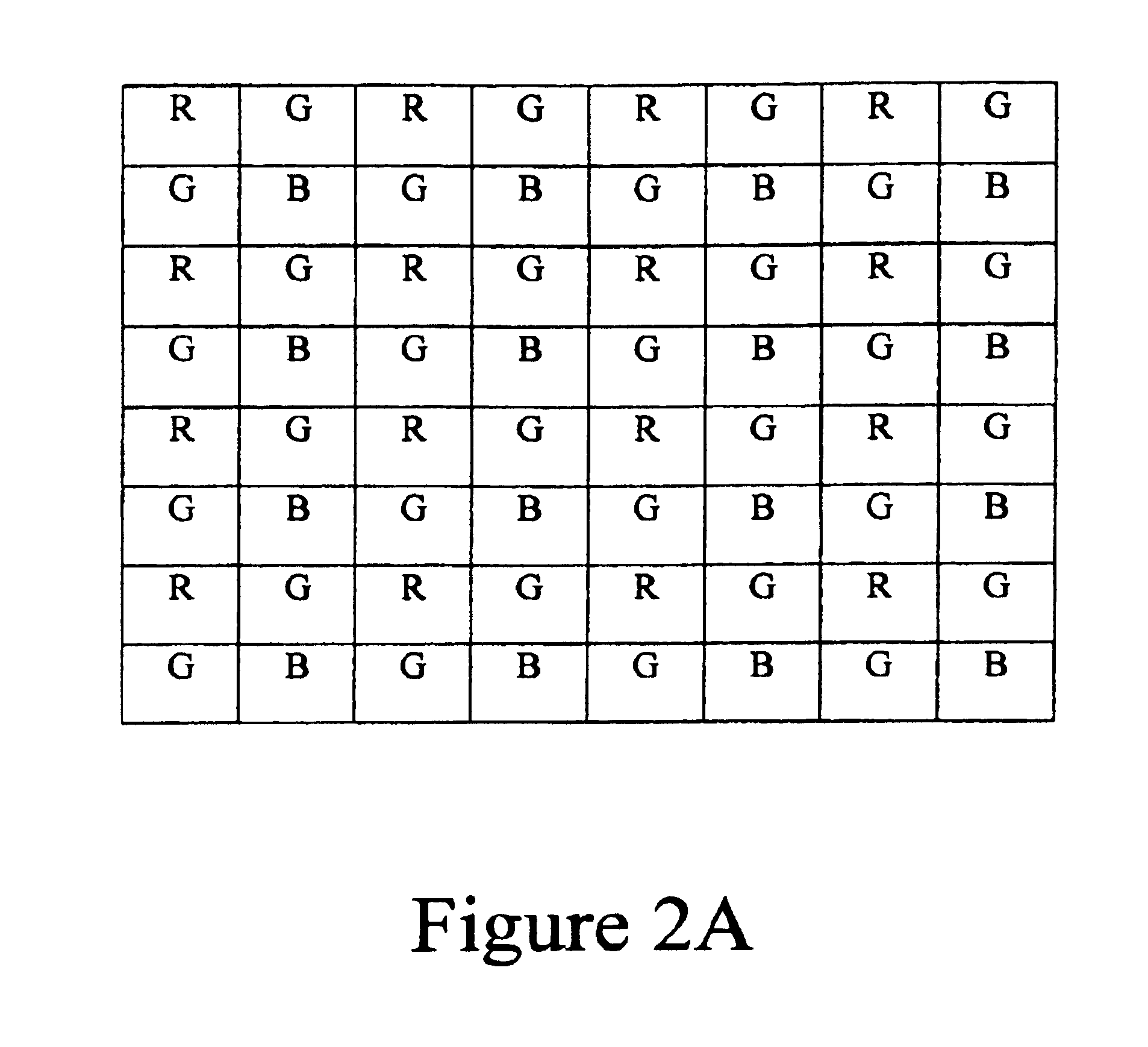
Pixel selective white balancing
InactiveUS6876384B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor imageGain coefficient
A system and method for processing data representative of a color image is disclosed. Image data represents an intensity of photoexposure of an imaging array at specific locations in the imaging array and in distinct spectral regions corresponding to color channels. A process identifies “white” regions in the color image by comparing the intensities of photoexposure of groups of associated pixels which are responsive to photon energy in different spectral regions. If the intensities of photoexposure of the pixels in the group of associated pixels are proportionally equivalent, these pixels are determined to be in a white region of the image. White balancing gain coefficients are then based upon the pixel intensity values at pixel locations in the white regions of the image.
Owner:BIOMORPHIC VLSI
Illumination devices and methods of making the same
An illumination device includes a photovoltaic element, wherein the photovoltaic element is configured to absorb photons of desired wavelengths and to convert the absorbed photon energy to electric energy and an electroluminescence element disposed adjacent to the photovoltaic element, wherein the electroluminescence element is configured to produce illumination at desired wavelengths, and wherein at least one of the photovoltaic element or the electroluminescence element comprises an organic device. The illumination device also includes an electric energy storage element coupled to the photovoltaic element and to the electroluminescence element, wherein the electric energy storage element is configured to store electric energy from the photovoltaic element and to power the electroluminescence element. The illumination device includes a first and second substrate, wherein each of the photovoltaic element, the electroluminescence element and the electric energy storage element are located between the first and second substrates and wherein at least one of the first or second substrate comprises a flexible substrate. The illumination device further comprises sensor controlled electronics coupled to the device, wherein the sensor controlled electronics is configured to control the operation of the organic photovoltaic element, the electroluminescence element and the electric energy storage element.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Thin film photodetector, method and system
InactiveUS20070290287A1High proportionMaterial nanotechnologyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectPhotodetectorCharge carrier
A photodetector, comprises a first section comprising at least one p-n junction that converts photon energy into a separate charge carrier and hole carrier; and another section of semiconductors of opposing conductivity type connected electrically in series and thermally in parallel in a heat dissipating and electric generating relationship to the cell to augment generation of electric energy of the first section.
Owner:FREEDMAN PHILIP D
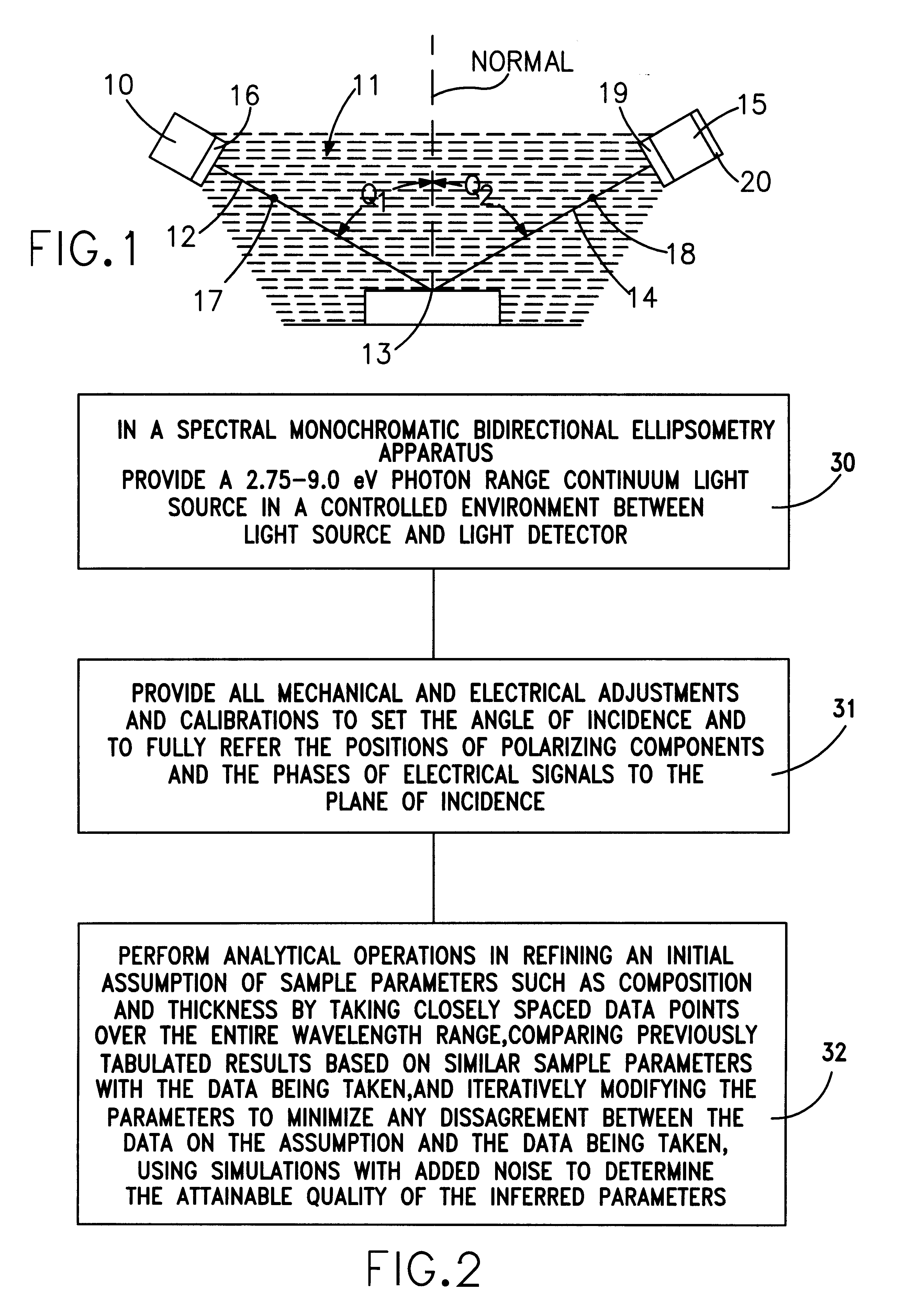
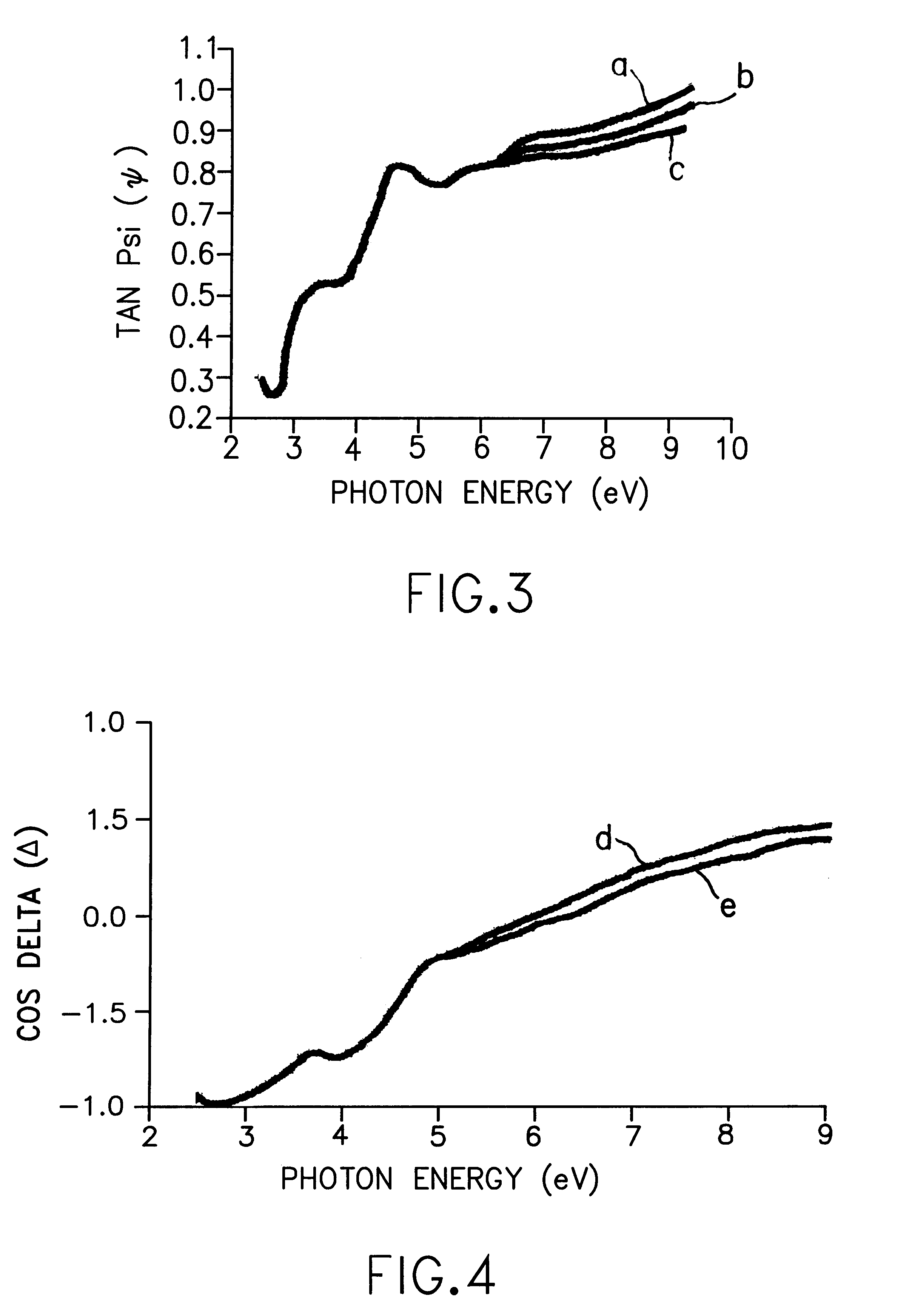
High photon energy range reflected light characterization of solids
InactiveUS6414302B1Polarisation-affecting propertiesPhotoelectric discharge tubesMetrologyIdentifiability
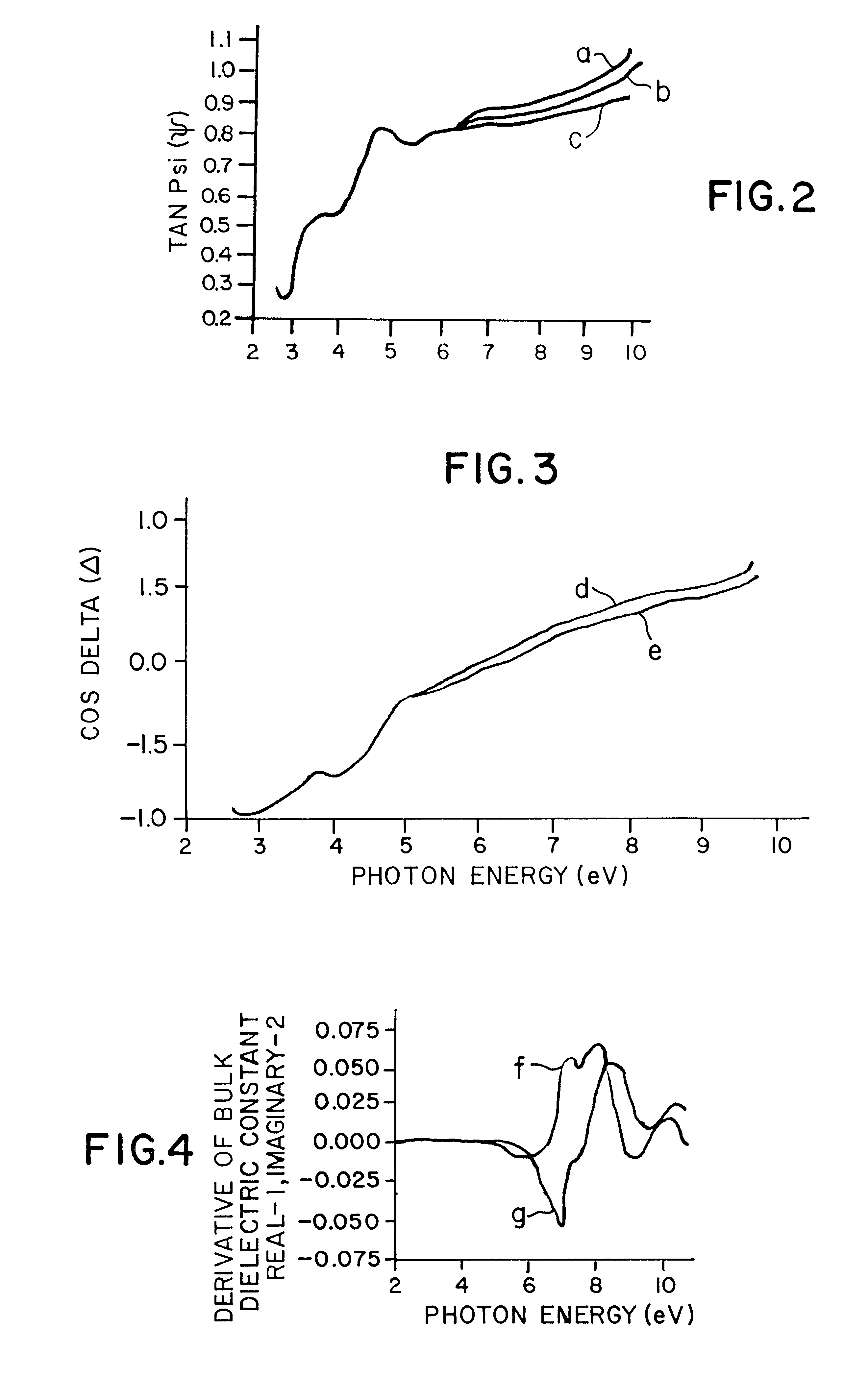
Accuracy and sensitivity in the optical characterization of solids and solid materials are improved through the use of the interdependent features of: extending the photon energy range over which the metrology is performed to include a portion of the range up through 10 eV, in which, the higher photon energy of the light improves signal distinguishing ability; and providing a controlled ambient in the entire light path between the light source and a detector that prevents absorption and signal definiteness masking so as to sharpen the identifiability of the change parameters imparted into the reflected light. Combinations of specific devices and materials that for different types of ellipsometry are provided.
Owner:JORDAN VALLEY SEMICON
Fluid storage and dispensing system
InactiveUS6500238B1Vessel mounting detailsGas treatmentElectrical resistance and conductanceThermal energy
A system for storage and dispensing of a sorbate fluid, in which a sorbate fluid is sorptively retained on a sorbent medium and desorption of sorbate fluid from the sorbent medium is facilitated by inputting energy to the sorbent medium including one or more of the following energy input modes: (a) thermal energy input including inductive heating of the sorbent medium, resistive heating of the sorbent medium and / or chemical reaction heating of the sorbent medium; (b) photonic energy input to the sorbent medium; (c) particle bombardment of the sorbent medium; (d) mechanical energy input to the sorbent medium; and (e) application of a chemical potential differential to the sorbate fluid on the sorbent medium.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Solar based electrical energy generation with spectral cooling
InactiveUS7081584B2Improve output performanceComponent can be removedMechanical apparatusSolar heat devicesLight energyEngineering
Method and system for converting solar energy into electrical energy utilizing serially coupled multijunction-type photovoltaic cells in conjunction with a form of spectral cooling. The latter cooling is carried out by removing ineffective solar energy components from impinging concentrated light, inter alia, through the utilization of dichroics or the conversion of ineffective solar energy components to effective energy components by means of luminescence, phosphorescence, or fluorescence. Ineffective solar energy components are described as those exhibiting wavelengths outside the bandgap energy defined wavelength and an associated wavelength defined band of useful photon energy.
Owner:MOOK WILLIAM J
Multiple layer solar energy harvesting composition and method, solar energy harvesting buckyball, inductive coupling device; vehicle chassis; atmospheric intake hydrogen motor; electrical energy generating tire; and mechanical energy harvesting device
Provided is a multiple layer composition and method for deposition of a solar energy harvesting strip onto a driving surface that will allow electric cars to charge by an inductive coupling. The multiple layer composition includes at least one magnetic material for generating a magnetic field, wherein at least one of the multiple layers comprises the magnetic material. Further, the a multiple layer composition includes at least one solar energy harvesting material for converting at least one of thermal and photonic energy into electrical energy, wherein at least one of the multiple layers comprises the at least one solar energy harvesting material and wherein the at least one solar energy harvesting material is located within a magnetic field generated by the at least one magnetic material. An alternative multiple layer composition includes a thermal energy harvesting material for converting thermal energy into electrical energy, wherein at least one layer comprises the thermal energy harvesting material, and a photonic energy harvesting material for converting photonic energy into electrical energy, wherein at least one layer comprises the thermal energy harvesting material. Additionally provided is a solar energy harvesting buckyball, inductive coupling device, vehicle chassis for storing electrical energy, atmospheric intake hydrogen motor, electrical energy generating tire and mechanical energy harvesting device.
Owner:SOLARBUILDER LLC
Imaging apparatus and method with event sensitive photon detection
InactiveUS7078699B2Accurate detectionImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation/particle handlingMaterial analysis by optical meansTemporal resolutionHigh rate
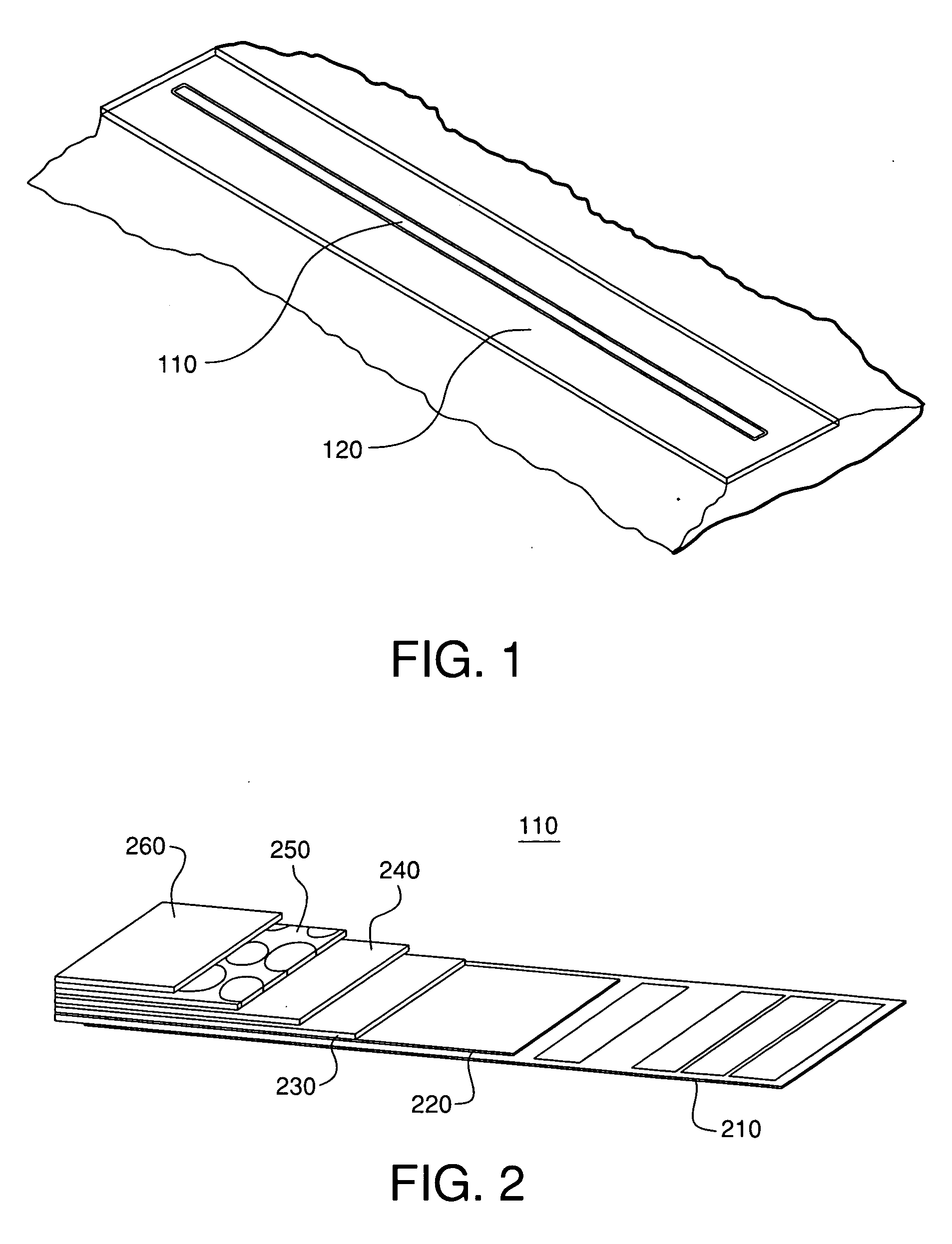
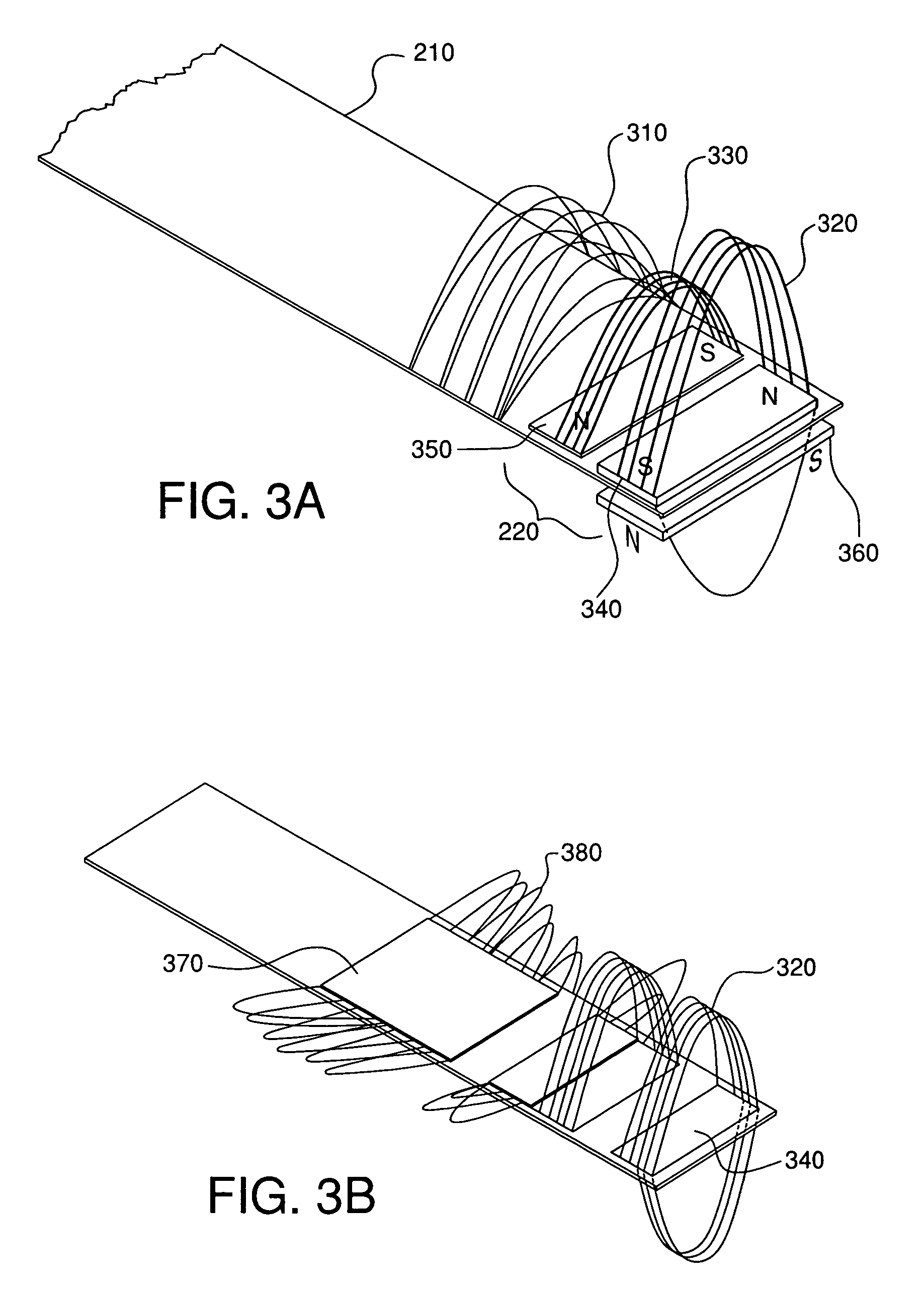
An imaging apparatus (10) includes a photon detector (20) and an accessing circuit (44) coupled thereto. The photon detector (20) detects photons and generates signals in response thereto. The accessing circuit (44) reads out the signals from the photon detector (20) at a sufficiently high rate so that it operates in an event sensitive mode. The apparatus (10) also includes a signal processing module (15) for processing the signals and generating data regarding the images of the object. In accordance with various embodiments of the present invention, the signal processing module (15) may include a spatial resolution circuit (56), a photon energy resolution circuit (57), a temporal resolution circuit (58), or any combination thereof.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Dense coating formation by reactive deposition
InactiveUS7491431B2Vacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingReactive depositionVolumetric Mass Density
Owner:NANOGRAM
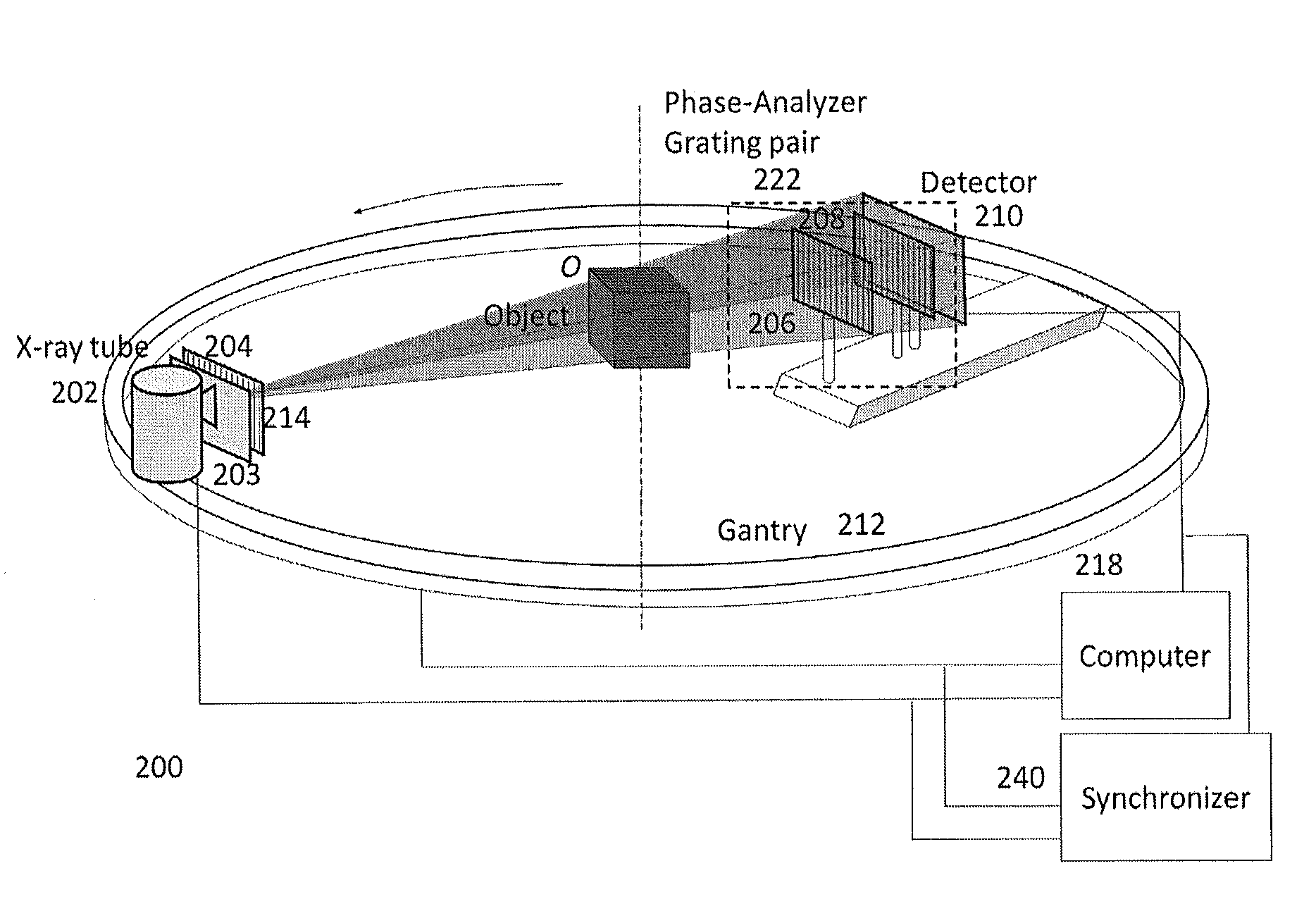
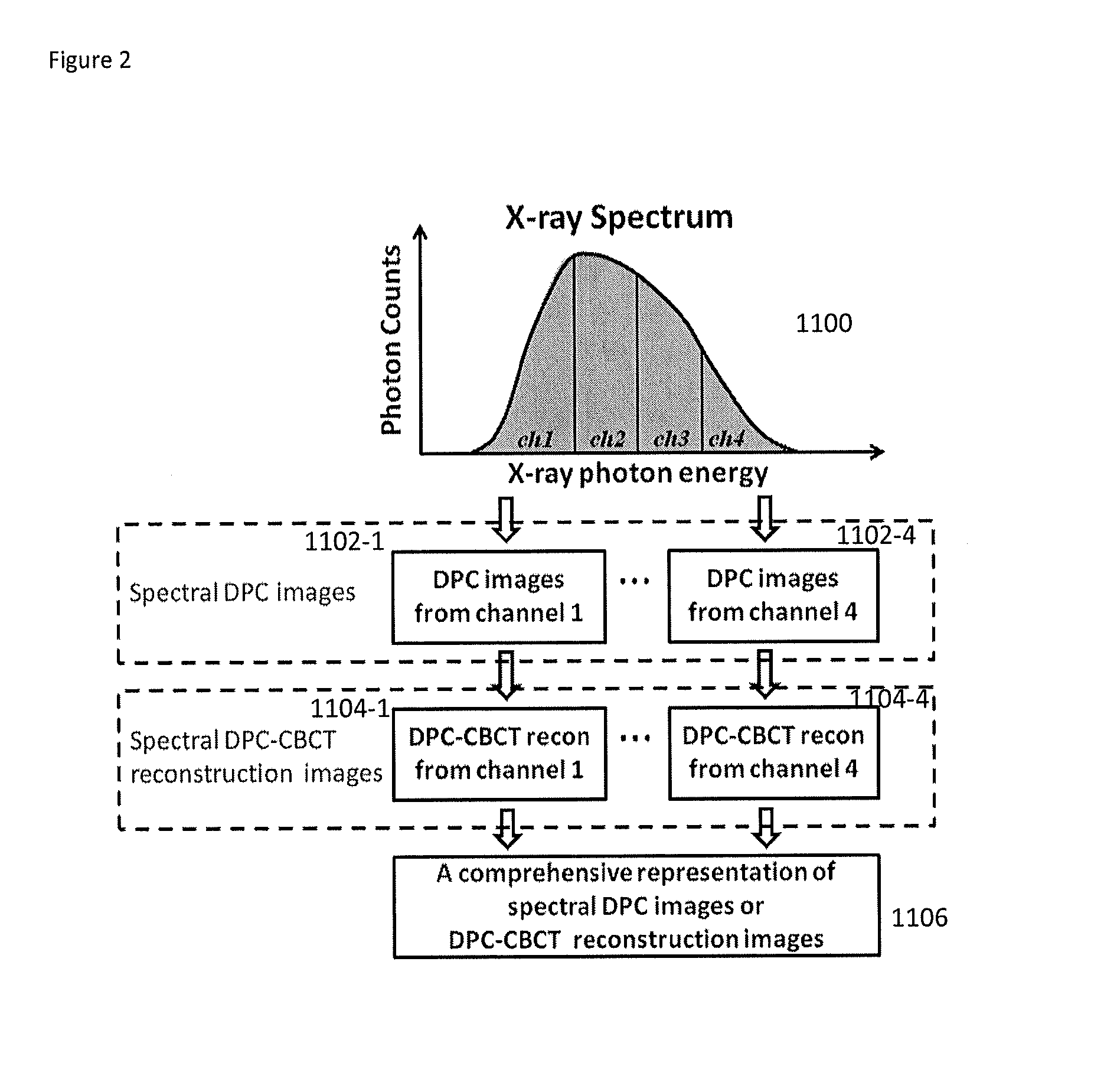
Method and apparatus of spectral differential phase-contrast cone-beam ct and hybrid cone-beam ct
ActiveUS20140226783A1Improve spatial resolutionReduce X-ray radiationImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionPhysicsPhoton energy
DPC (differential phase contrast) images are acquired for each photon energy channel, which are called spectral DPC images. The final DPC image can be computed by summing up these spectral DPC images or just computed using certain ‘color’ representation algorithms to enhance desired features. In addition, with quasi-monochromatic x-ray source, the required radiation dose is substantially reduced, while the image quality of DPC images remains acceptable.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
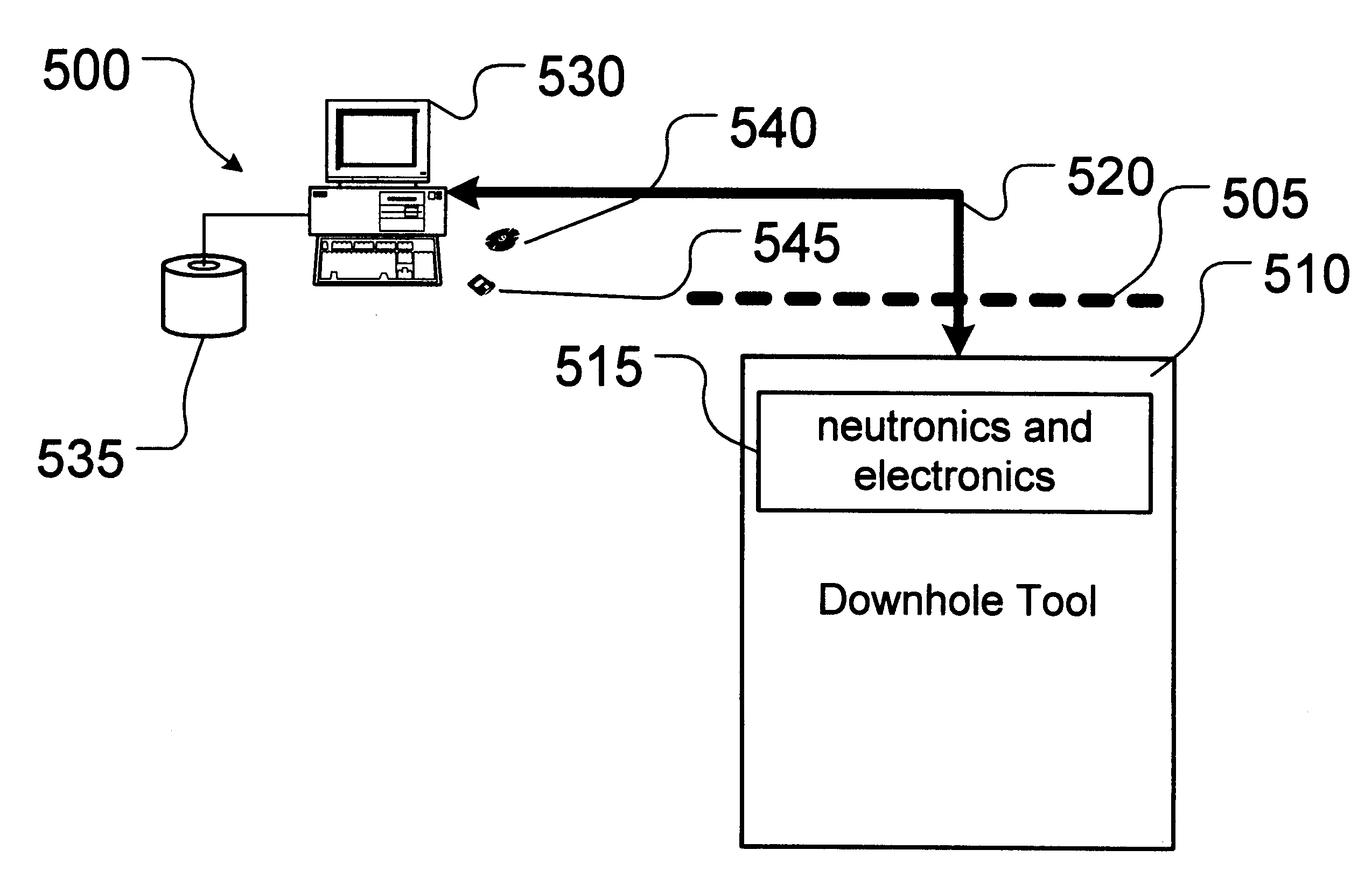
Method and apparatus for calibrating readings of a downhole tool
InactiveUS6389367B1Testing/calibration apparatusSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsWell loggingGamma ray
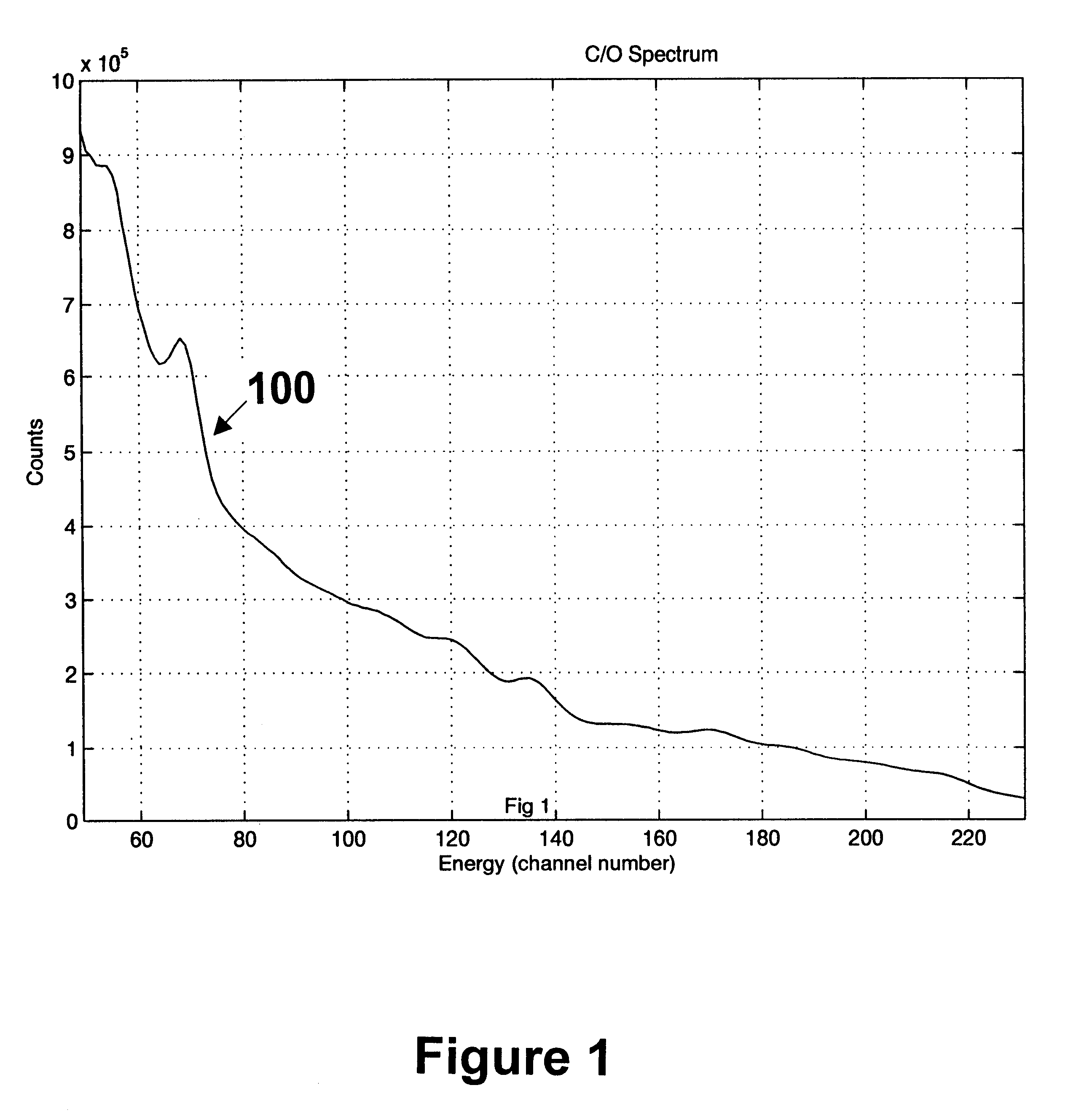
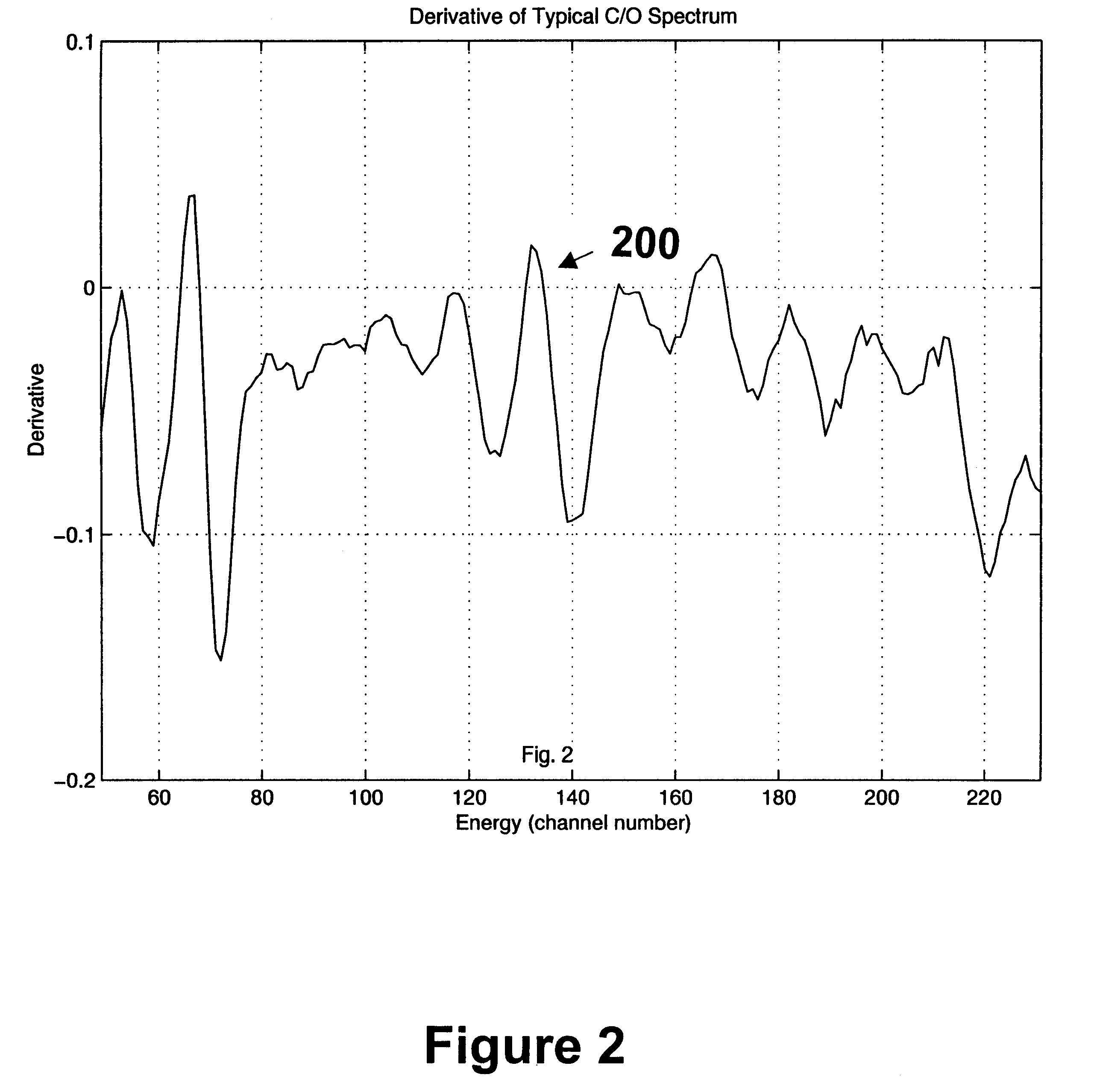
A method and apparatus for calibrating readings of a downhole tool are provided. The method including collecting data representative of gamma ray photon energies detected by a downhole tool during the well-logging, a spectrum of the gamma ray photon energies detected by the downhole tool having a derivative with respect to the gamma ray photon energies. The method and program comprise calibrating the readings of the downhole tool using at least one predetermined correction factor based on the derivative of the spectrum of the gamma ray photon energies detected by the downhole tool. A computer-readable program storage device and a computer programmed to perform a set of instructions are also provided.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Photon counting and energy discriminating detector threshold calibration
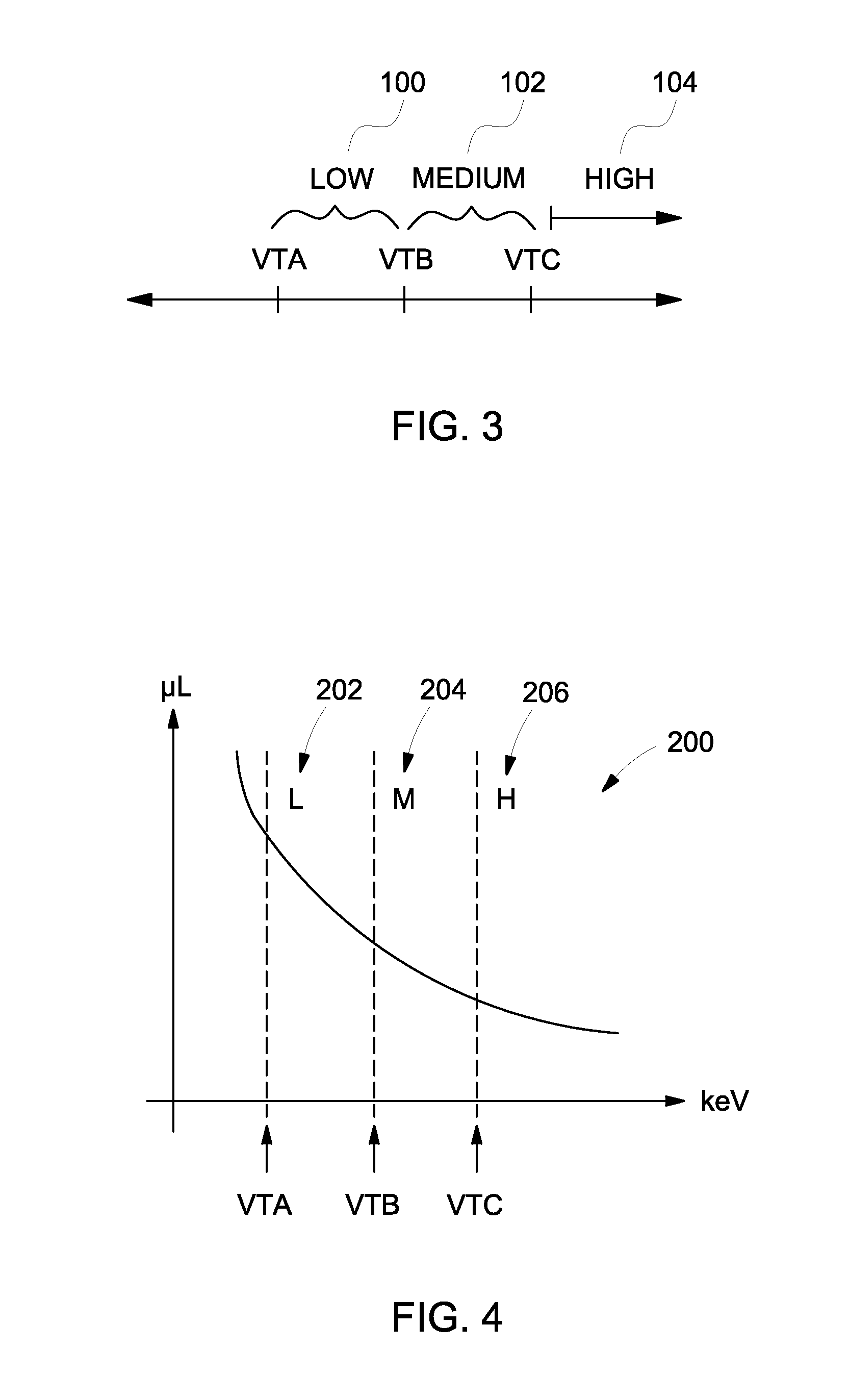
ActiveUS20120087463A1Radiation/particle handlingX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentX-rayData acquisition
An imaging system includes an x-ray source, a detector that receives x-rays emitted from the x-ray source, a DAS configured to count photon hits in the detector that occur at photon energies above at least a low keV threshold, a medium keV threshold, and a high keV threshold, and a computer operably coupled to the DAS. The computer is programmed to vary each of the medium keV threshold and the high keV threshold over a continuous keV range during data acquisition to define low, medium, and high keV bins that are based on the low, medium, and high keV thresholds, obtain photon counts in the low, medium, and high keV bins in a plurality of keV threshold combinations, calculate a noise variance as a function of at least one of the keV thresholds, and identify a noise minimum and low, medium, and high keV thresholds that correspond thereto.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST ISRAEL
Agricultural module and system
InactiveUS20050091916A1Maximize useOvercoming inefficienciesRoot feedersClimate change adaptationAgricultural landComputer module
A module is provided that maximizes agricultural land usage. The module includes a water collection structure supported above agricultural land. The water collection structure may include a mechanism for distributing photonic energy to plants growing on the agricultural land; and a water distribution system for distributing collected water from said water collection structure to plants growing on the agricultural land and / or the soil in which said plants are planted. The present module may also include energy storage systems, thereby allowing the module to be partially or completely self-sustaining.
Owner:FARIS SADEG M
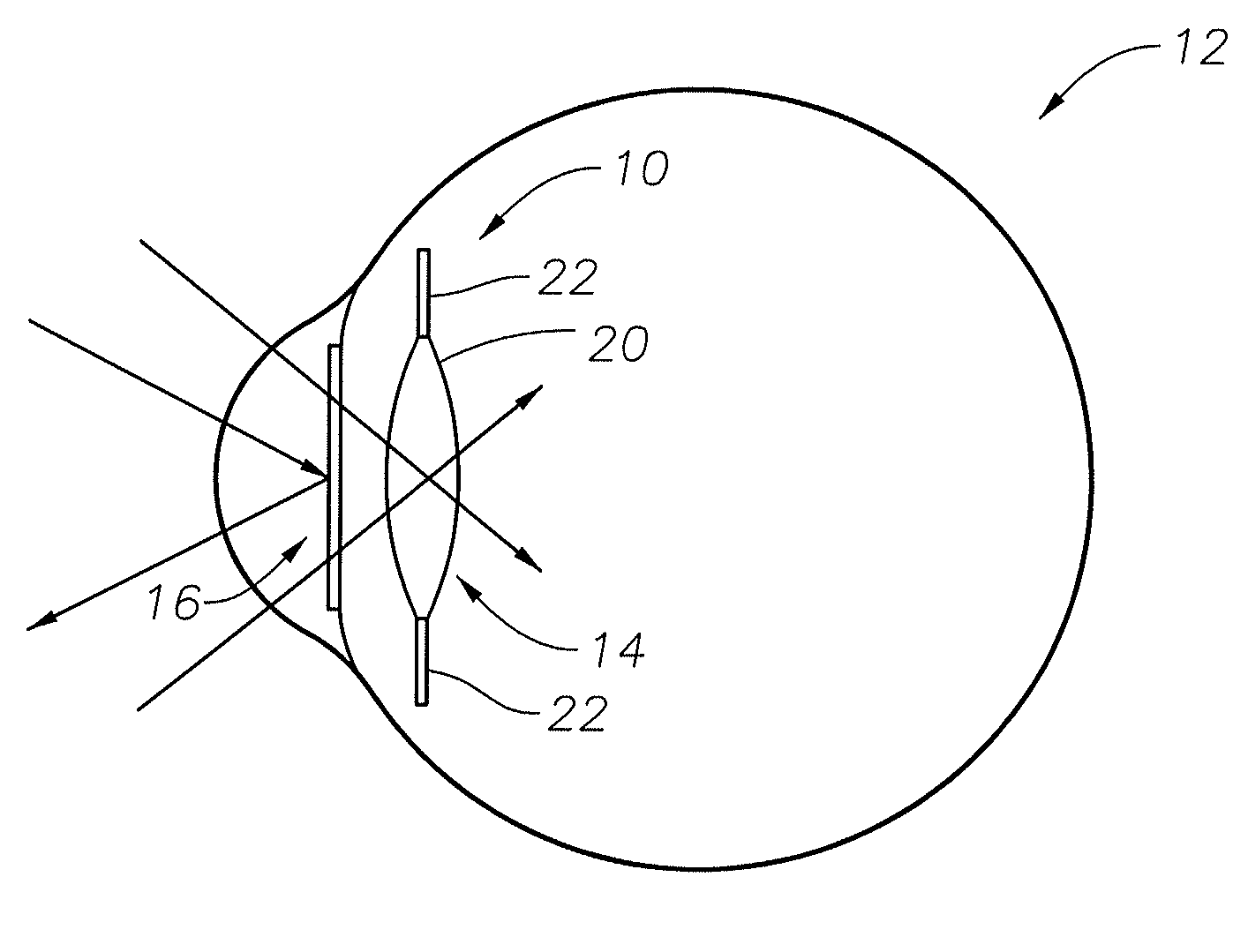
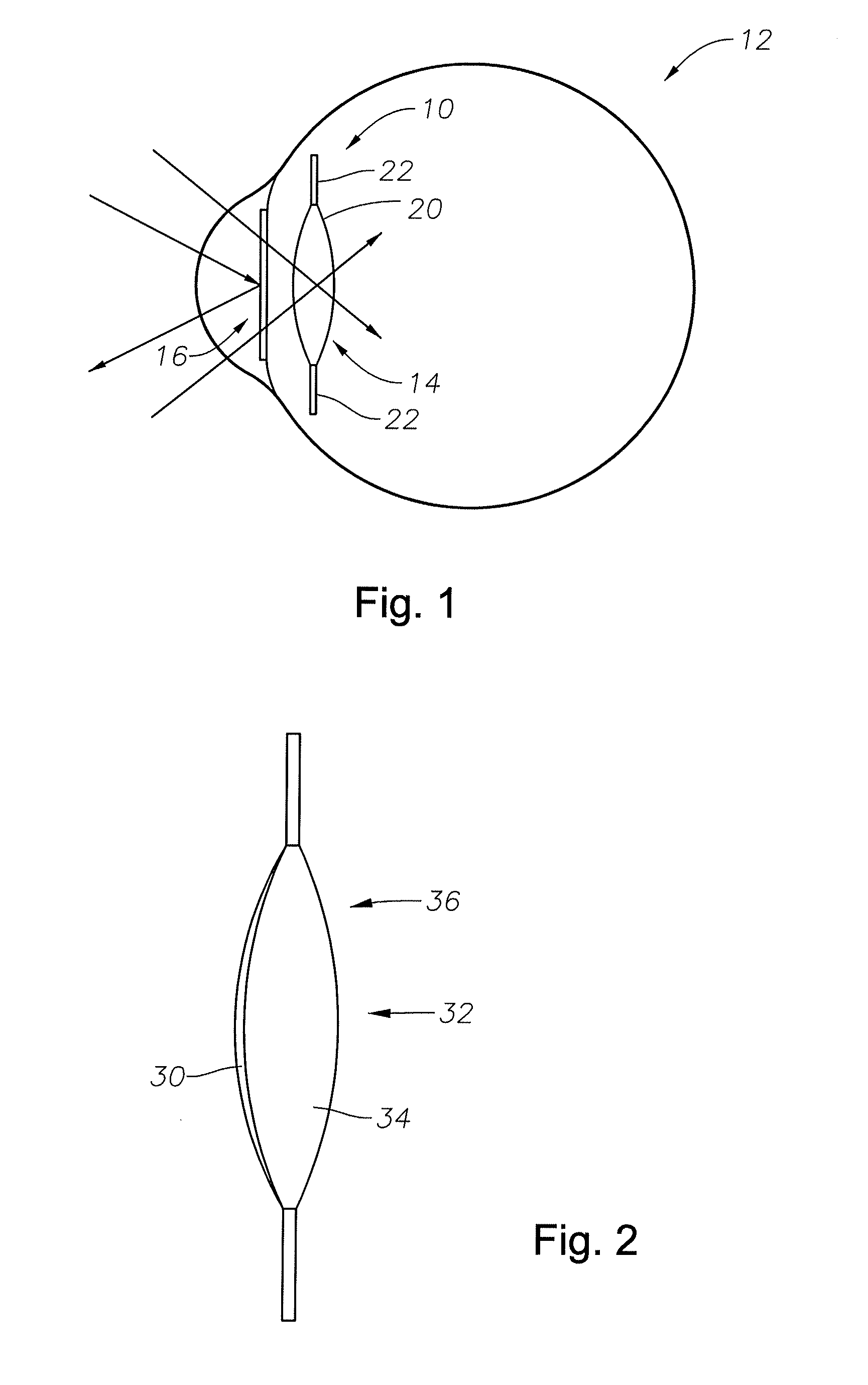
Adjustable intraocular lens system
The present invention is related to an adjustable intraocular lens system comprised of a lens body having an adjustable refractive index and a shield for protecting the lens body from degradation that might otherwise be caused by exposure to particular electromagnetic radiation. More preferably, the present invention is directed to an adjustable intraocular lens system comprised of a lens body and a shield wherein the lens body is formed of a material with a refractive index that can be adjusted by exposure to adjusting electromagnetic radiation (e.g., multiple photon energy) and wherein the shield protects the lens body from degradation that might otherwise be caused by exposure to degrading electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Apparatus and methods for thermally processing undoped and lightly doped substrates without pre-heating
InactiveUS20070072400A1Promote absorptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBiological activationHeat treated
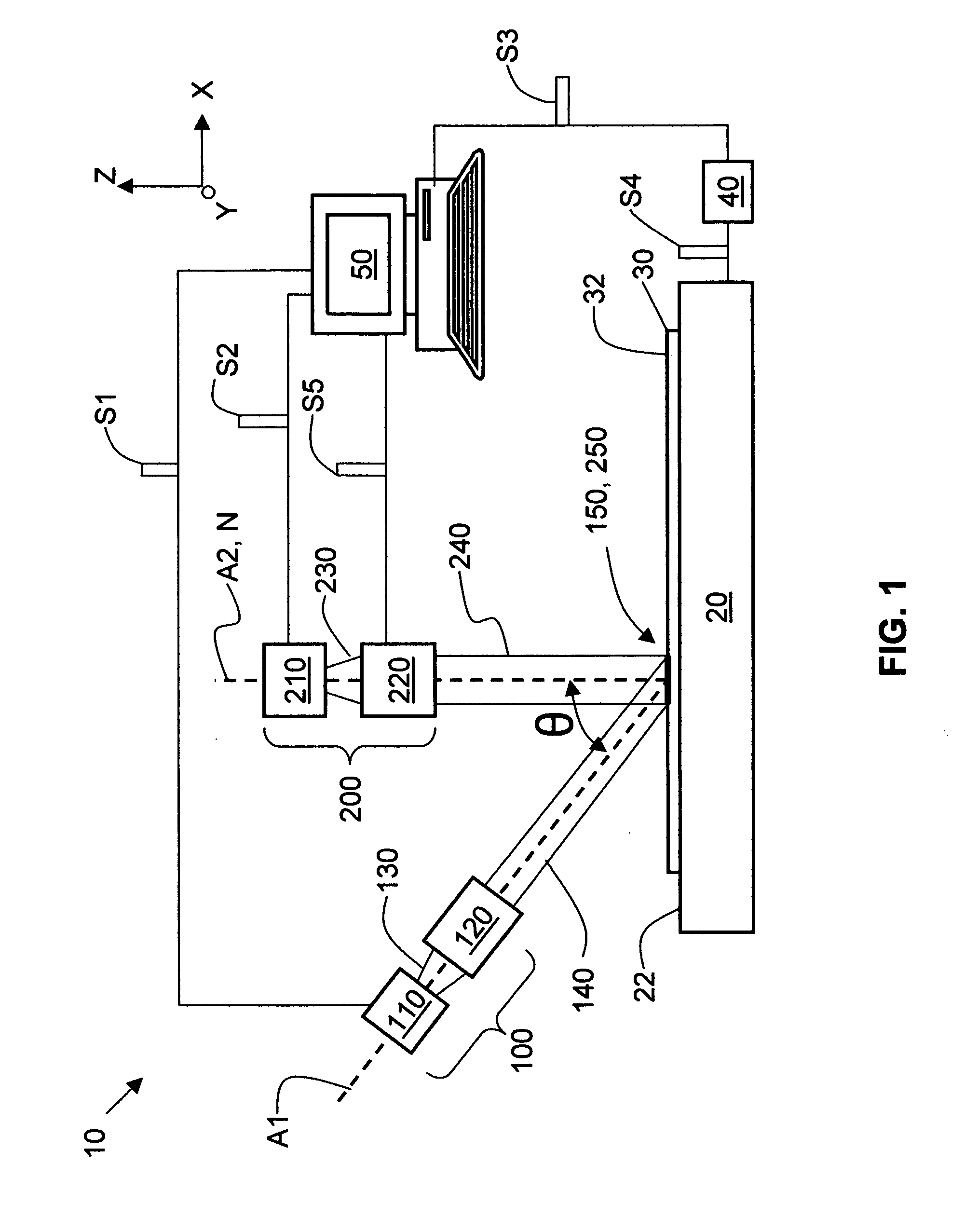
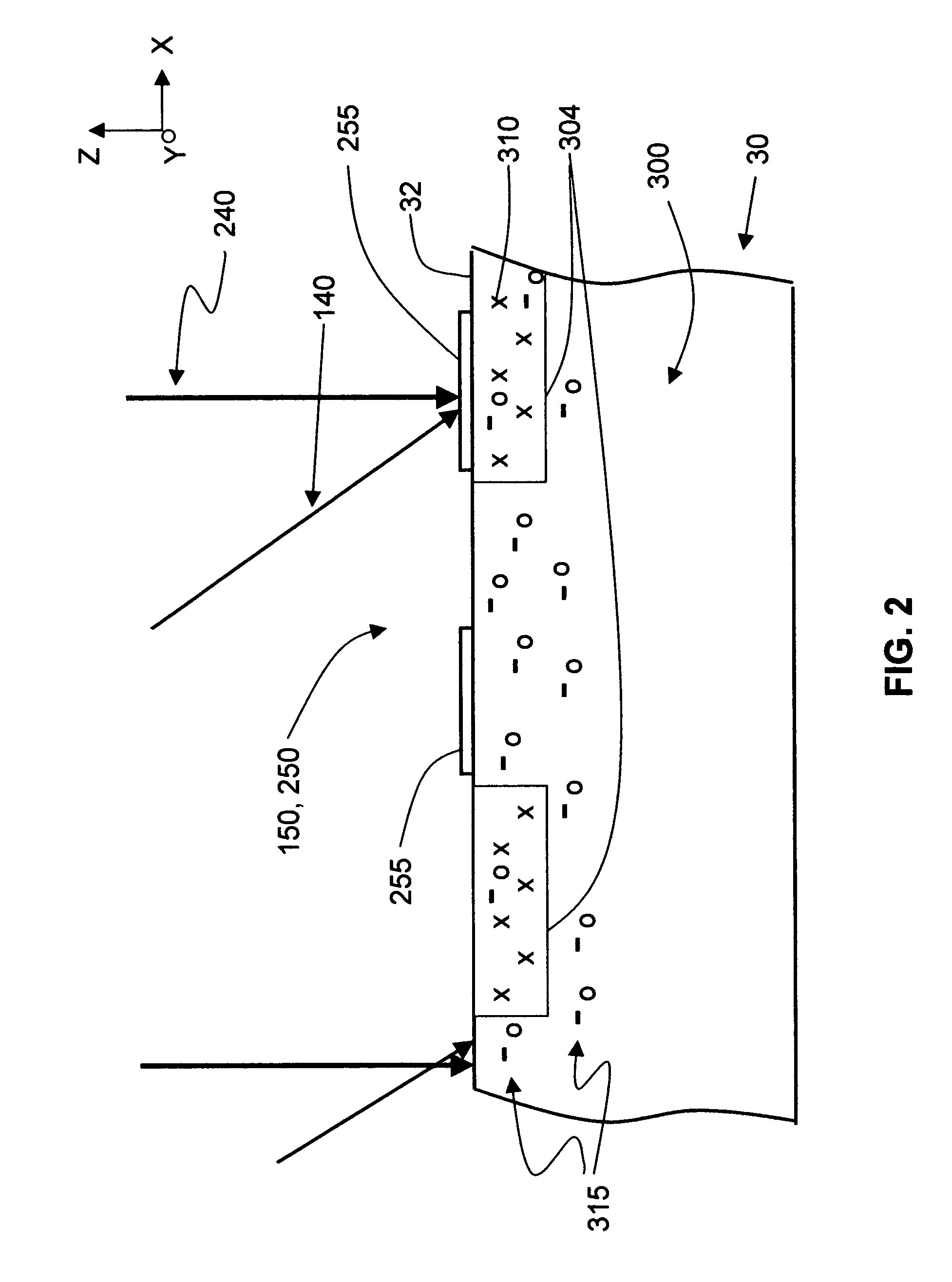
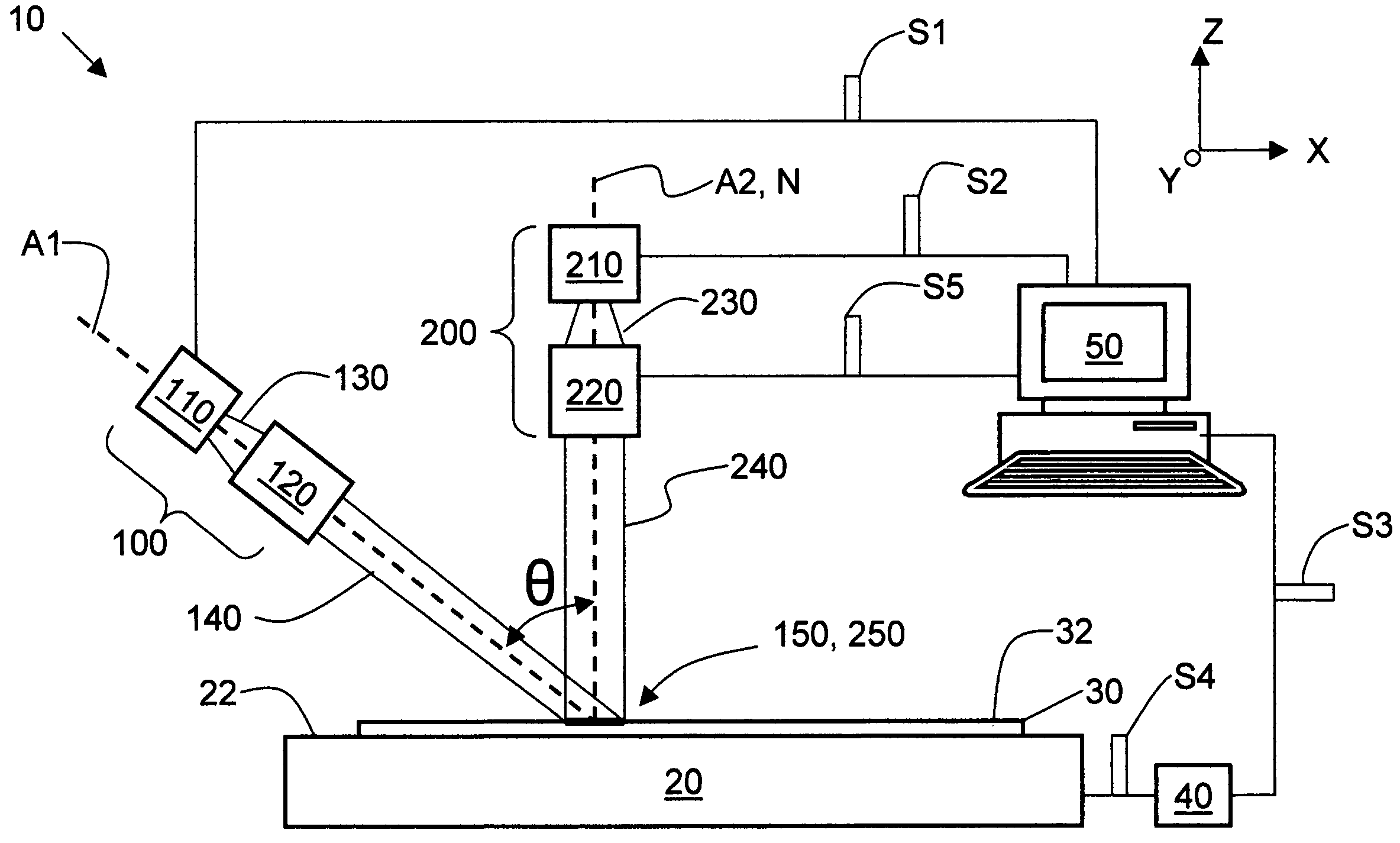
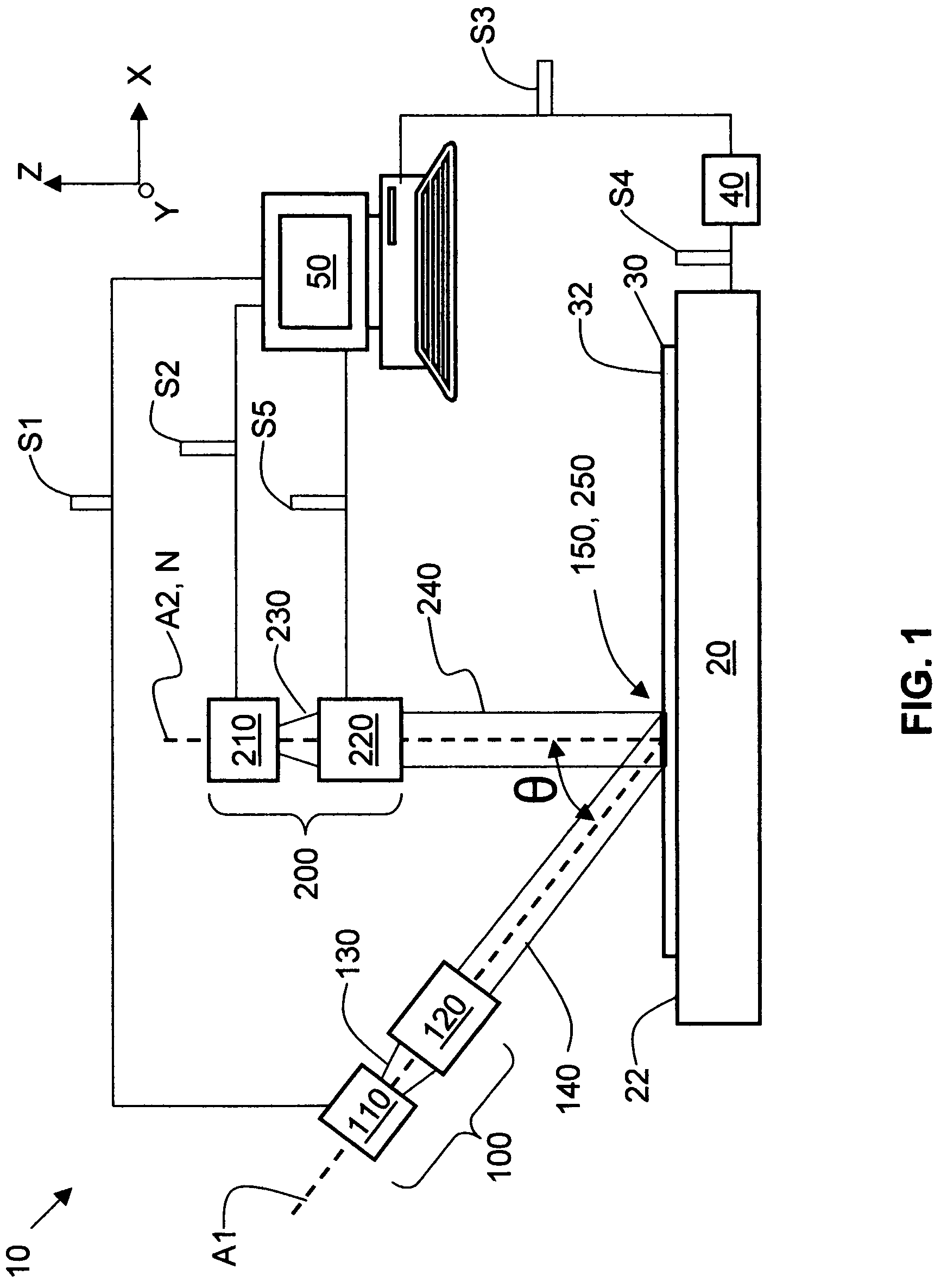
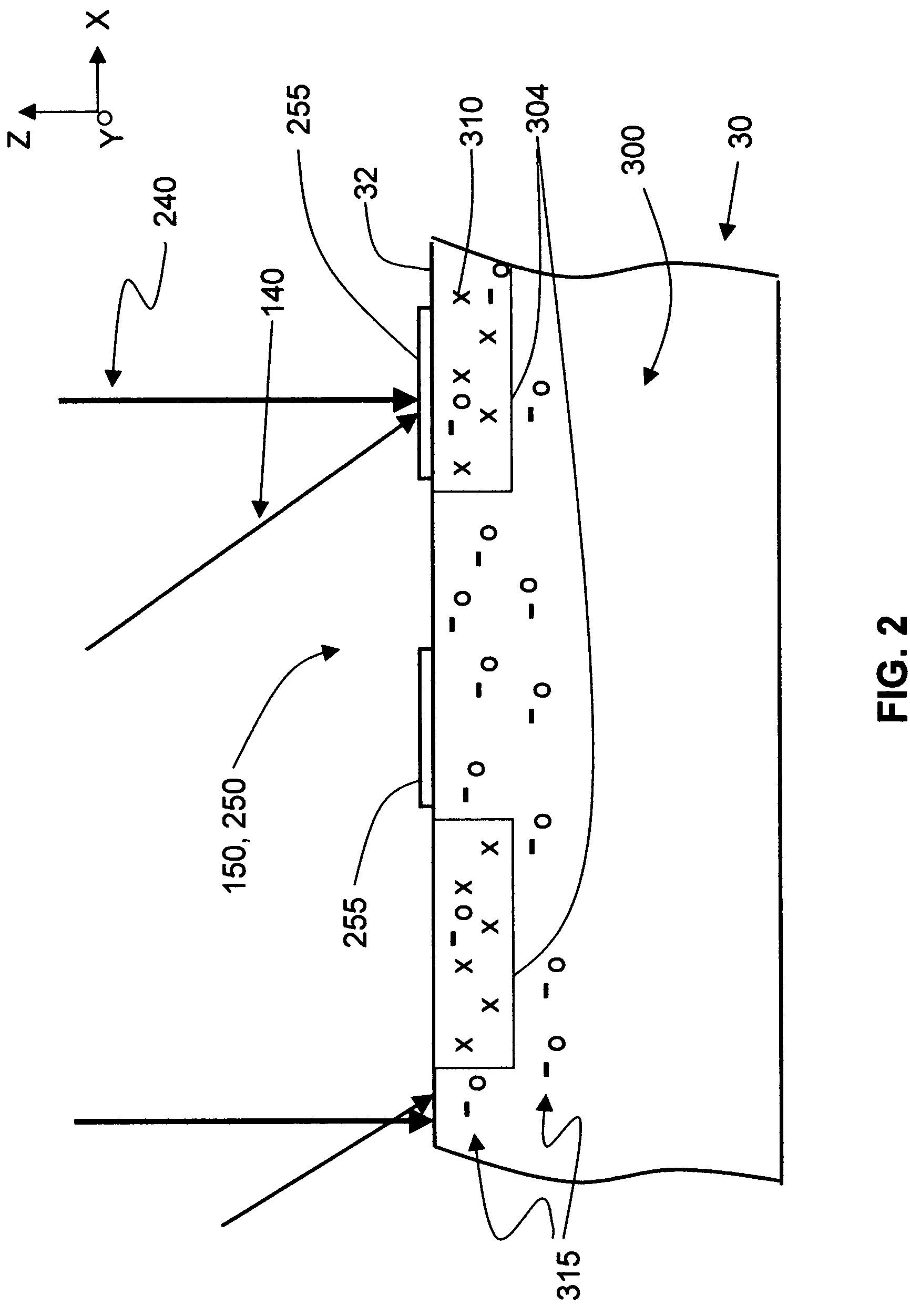
Apparatus for and methods of thermally processing undoped or lightly doped semiconductor wafers (30) that typically are not very absorptive of an annealing radiation beam (14) are disclosed. The apparatus (10) uses a relatively low power activating radiation beam (240) with a photon energy greater than the bandgap energy of the semiconductor substrate in order to generate free carriers (315) at and near the substrate surface (32). The free carriers so generated enhance the absorption by the substrate surface of the longer wavelength annealing radiation beam. The annealing radiation beam is thus able to rapidly heat the substrate surface and permit subsequent rapid cooling to obtain, for example, a high level of electrical activity (activation) of dopants (310) formed therein. The invention obviates the need to pre-heat the substrate in order to increase absorption of the annealing radiation beam when performing thermal processing.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Combined Energy Conversion
InactiveUS20080115817A1Solar heating energySolar heat collector controllersThermal energyThermal engineering
Means to use and combine methods of thermal engineering, plasmonics, photonics, electronics, photovoltaics, optical transfer, heat transport, light transport, catalysis and chemical reactions individually or in any combination for the enhancement or generation of solar, optical, electrical or any form of energy. The present disclosure further concerns a means to use at least a form of electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions in a structure or material having one or more addressable frequencies to generate the exchange of thermal, kinetic, electronic or photonic energy.
Owner:DEFRIES ANTHONY
Lens Bonded X-Ray Scintillator System and Manufacturing Method Therefor
InactiveUS20060192129A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementX-raySpectroscopy
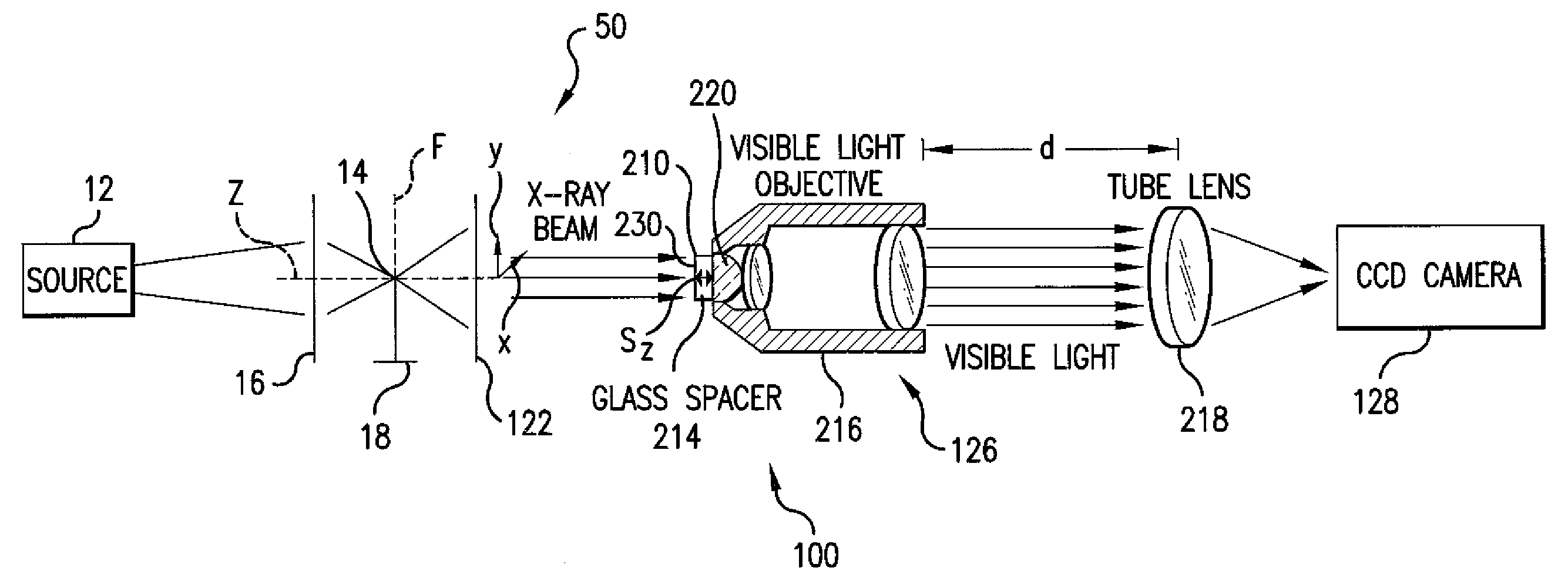
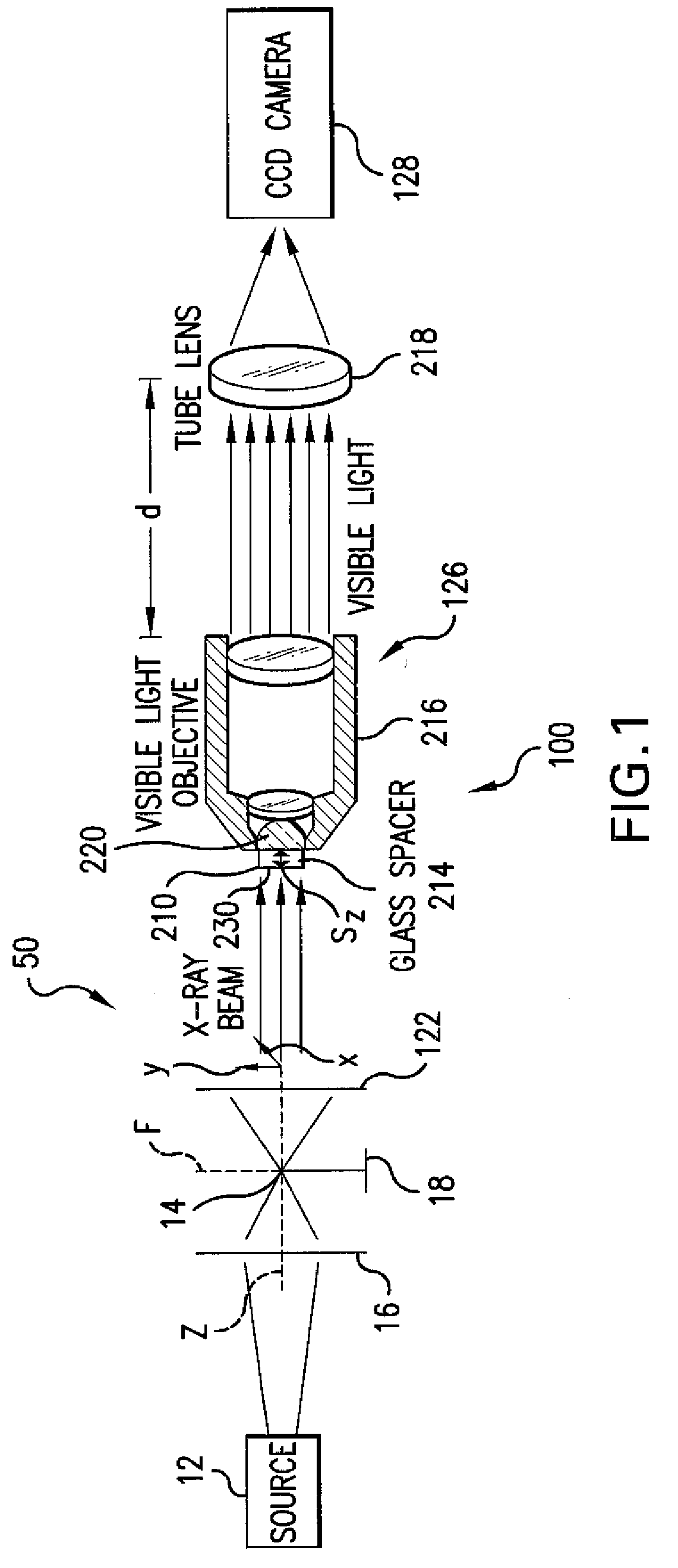
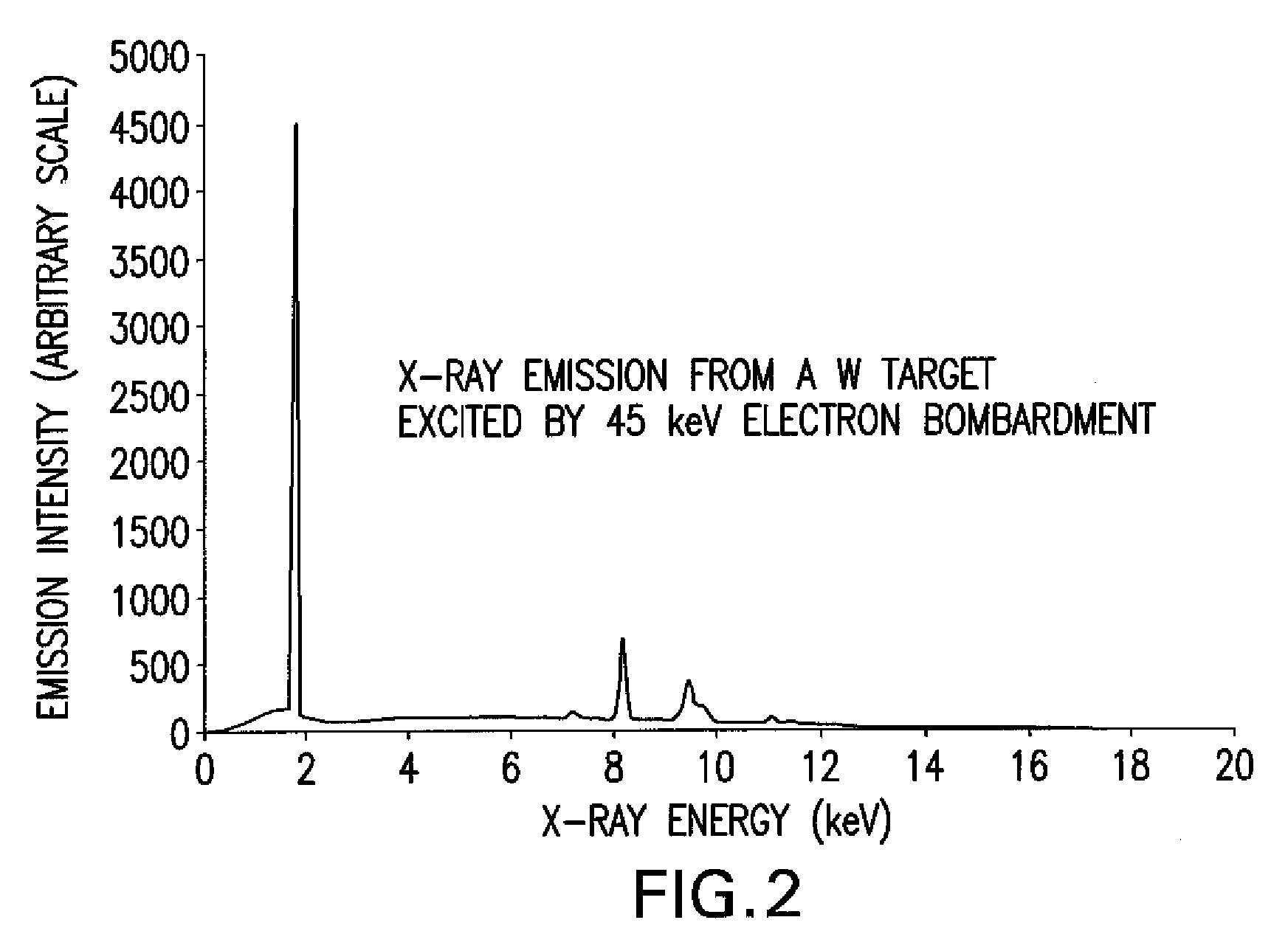
A scintillated CCD detector system for imaging x rays uses x-rays having a photon energy in the range of 1 to 20 keV. The detector differs from existing systems in that it provides extremely high resolution of better than a micrometer, and high detection quantum efficiency of up to 95%. The design of this detector also allows it to function as an energy filter to remove high-energy x-rays. This detector is useful in a wide range of applications including x-ray imaging, spectroscopy, and diffraction. The scintillator optical system has scintillator material with a lens system for collecting the light that is generated in the scintillator material. A substrate is used for spacing the scintillator material from the lens system.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Apparatus and methods for thermally processing undoped and lightly doped substrates without pre-heating
Apparatus for and methods of thermally processing undoped or lightly doped semiconductor wafers (30) that typically are not very absorptive of an annealing radiation beam (14) are disclosed. The apparatus (10) uses a relatively low power activating radiation beam (240) with a photon energy greater than the bandgap energy of the semiconductor substrate in order to generate free carriers (315) at and near the substrate surface (32). The free carriers so generated enhance the absorption by the substrate surface of the longer wavelength annealing radiation beam. The annealing radiation beam is thus able to rapidly heat the substrate surface and permit subsequent rapid cooling to obtain, for example, a high level of electrical activity (activation) of dopants (310) formed therein. The invention obviates the need to pre-heat the substrate in order to increase absorption of the annealing radiation beam when performing thermal processing.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Steady-state non-equilibrium distribution of free carriers and photon energy up-conversion using same
InactiveUS6995371B2Easy to detectImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous siliconSilicon dioxide
Methods and specialized media adapted to the formation of a steady-state, non-equilibrium distribution of free carriers using mesoscopic classical confinement. Specialized media is silicon-based (e.g., crystalline silicon, amorphous silicon, silicon dioxide) and formed from mesoscopic sized particles embedded with a matrix of wide-bandgap material, such as silicon dioxide. An IR to visible light imaging system is implemented around the foregoing.
Owner:SIRICA CORP
Method and system for wide-field multi-photon microscopy having a confocal excitation plane
InactiveUS20080116392A1Shorten Image Acquisition TimeScanning of the excitation light source over the specimen can be reduced or eliminatedPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansWide fieldLight beam
A wide field microscope includes a stage configured to hold a specimen having a fluorescent material therein, and a multi-photon excitation light source configured to produce excitation light having a single photon energy less than an absorption energy required for single photon excitation of said fluorescent material. A beam expansion unit is optically coupled to the light source and configured to expand the excitation light with reduced pulse spreading characteristics, and an infinity corrected objective optically coupled to the expansion unit and configured to focus the excitation light onto the specimen such that multi-photon excitation of the fluorescent material simultaneously occurs over a predetermined area of the specimen. A focus lens is configured to focus emission light emitted from said predetermined area of the specimen onto at least two pixels of an image detector simultaneously.
Owner:CELLOPTIC
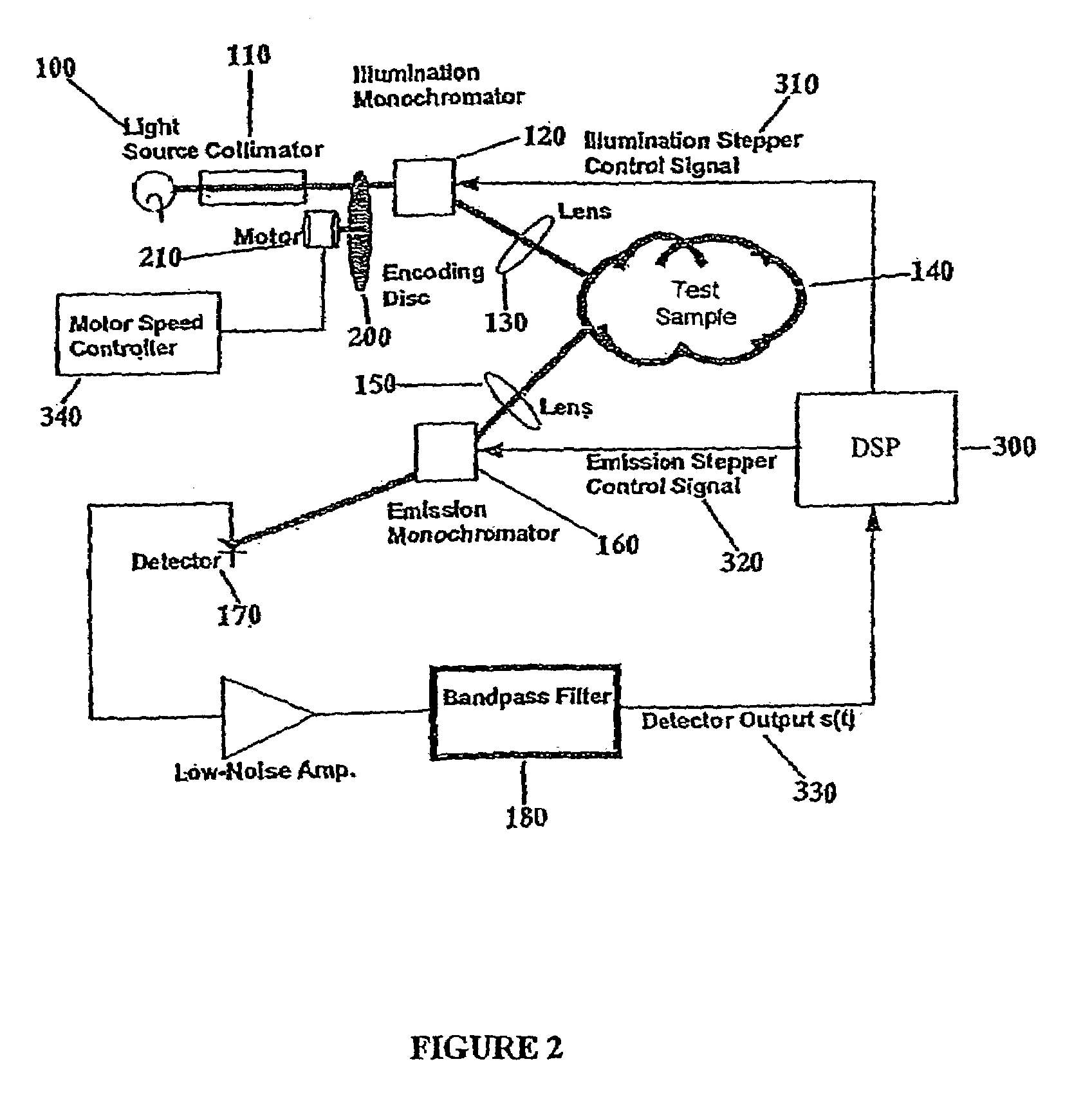
Spectrometer incorporating signal matched filtering
ActiveUS7154599B2Raman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryDigital signal processingOptical processing
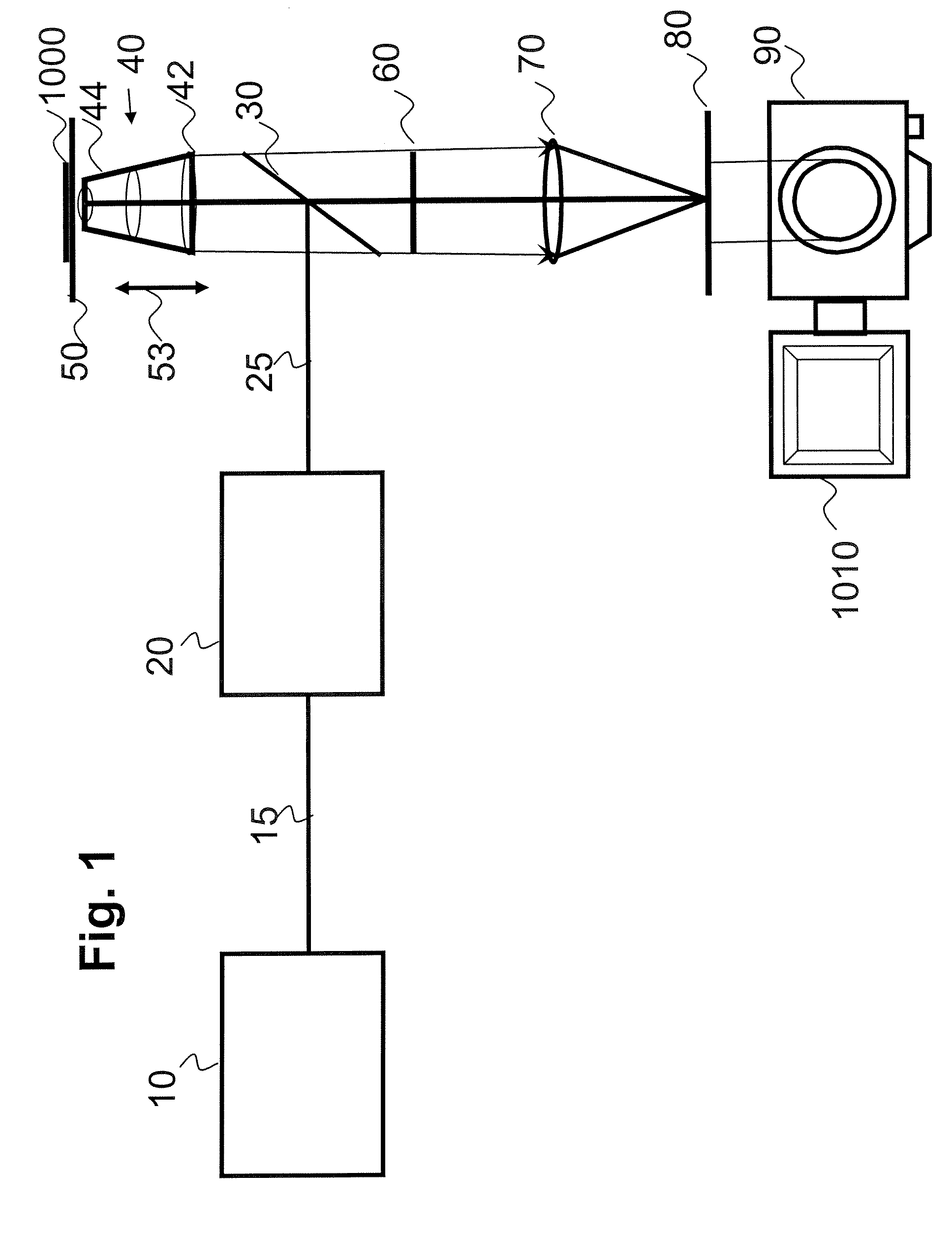
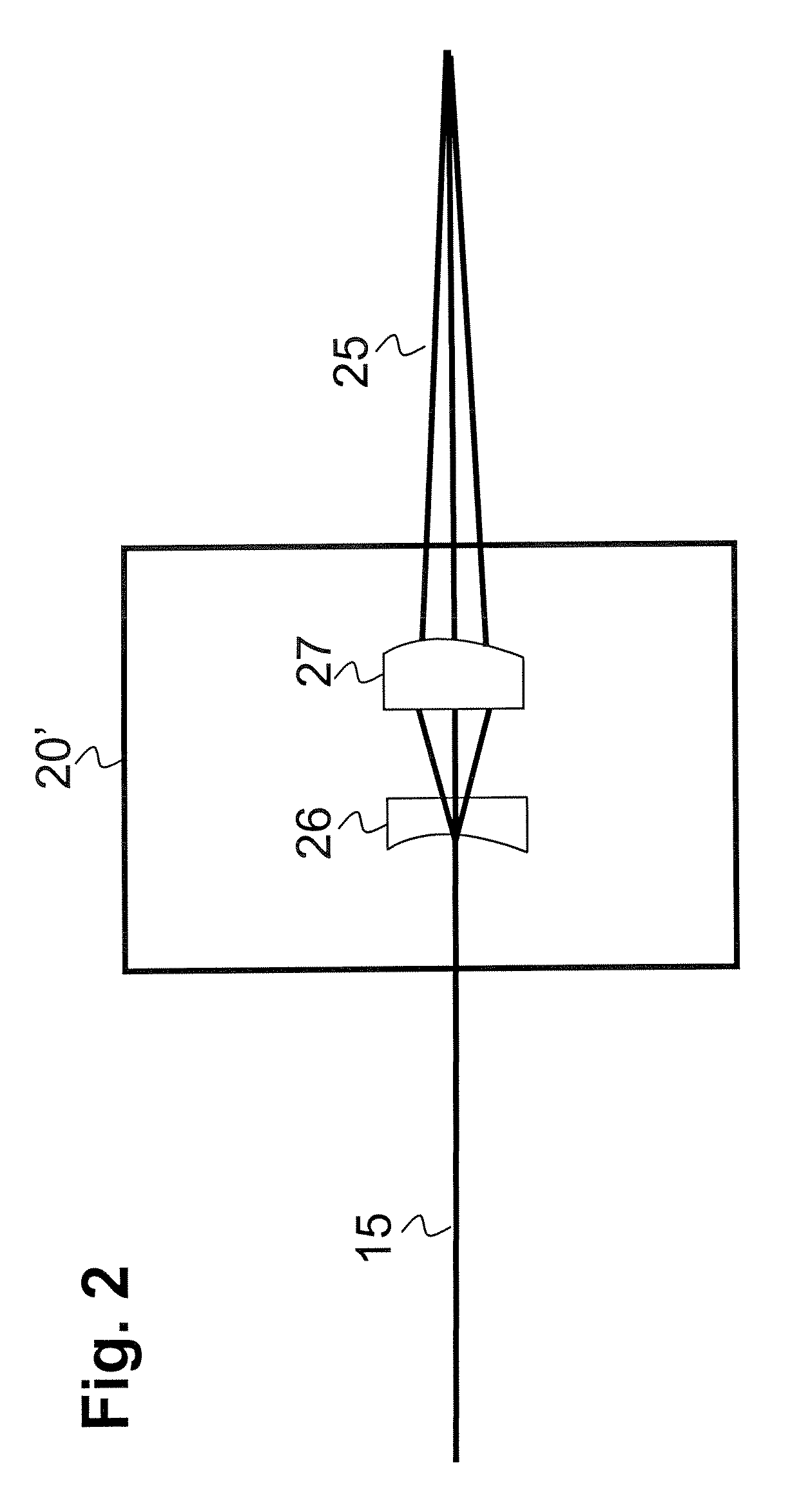
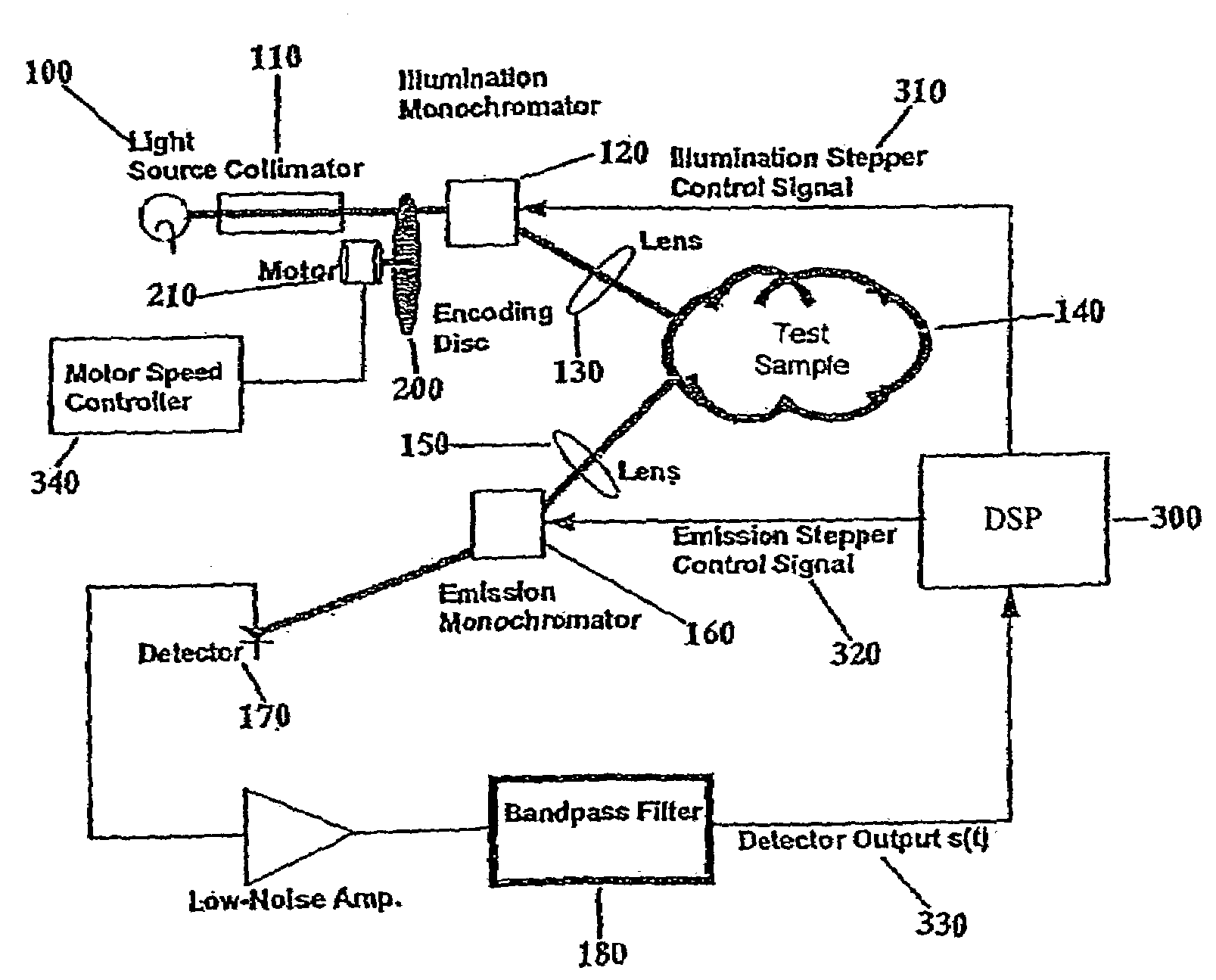
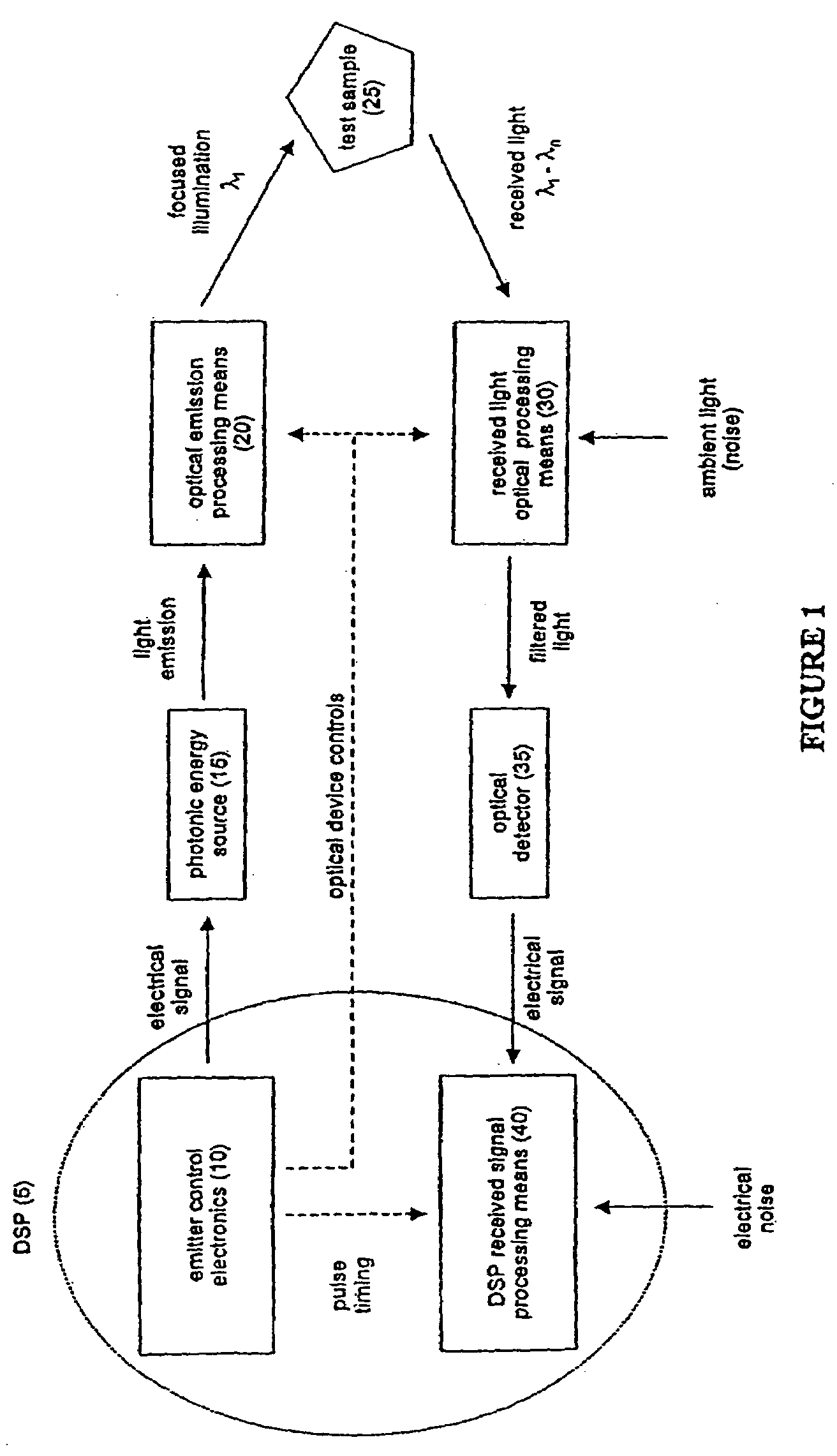
An optical system for performing a spectral analysis of test samples is provided. The optical system comprises a photonic energy source, an optical emission processing system, a received light optical processing system, an optical detector and a digital signal processing system. The optical emission processing system transmits one or more illumination wavelengths to a test sample. The received light optical processing system collects and isolates one or more wavelengths received from the test sample and transmits them to an optical detector. The optical detector converts the isolated one or more wavelengths of received electromagnetic radiation into an electrical signal which is transmitted to the digital signal processing system. The digital signal processing system performs matched filtering of the electrical signal received from the optical detector and additionally controls the functionality of the photonic energy source, the optical emission processing system and the received light optical processing system.
Owner:ADAMS BRUCE WILLIAM MR
Use of electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions to generate or exchange thermal, kinetic, electronic or photonic energy
The present disclosure concerns a means to use at least a form of electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions in a structure or material having one or more addressable frequencies to generate the exchange of thermal, kinetic, electronic or photonic energy. In some implementations this provides a means to use electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions to influence, cause, control, modulate, stimulate or change the state or phase of electrical, magnetic, optical or electromagnetic charge, emission, conduction, storage or similar properties. The method could include the use of light-matter interactions to generate electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions and concentrate extremely localized field effects or concentrated plasmonic field effects to cause an exchange of energy states in a material or structure. Said field effects could be used for excitation of surface electrons in metallic nanostructures causing said electrons to exchange energy states or said field effects could be used to mediate or stimulate photon emissions or to modulate photonic energy to excite or stimulate emissions of electrons. Said electron or photon emissions could be used to drive photochemical, photocatalysis, photovoltaic or thermophotovoltaic reactions.
Owner:DEFRIES ANTHONY +1
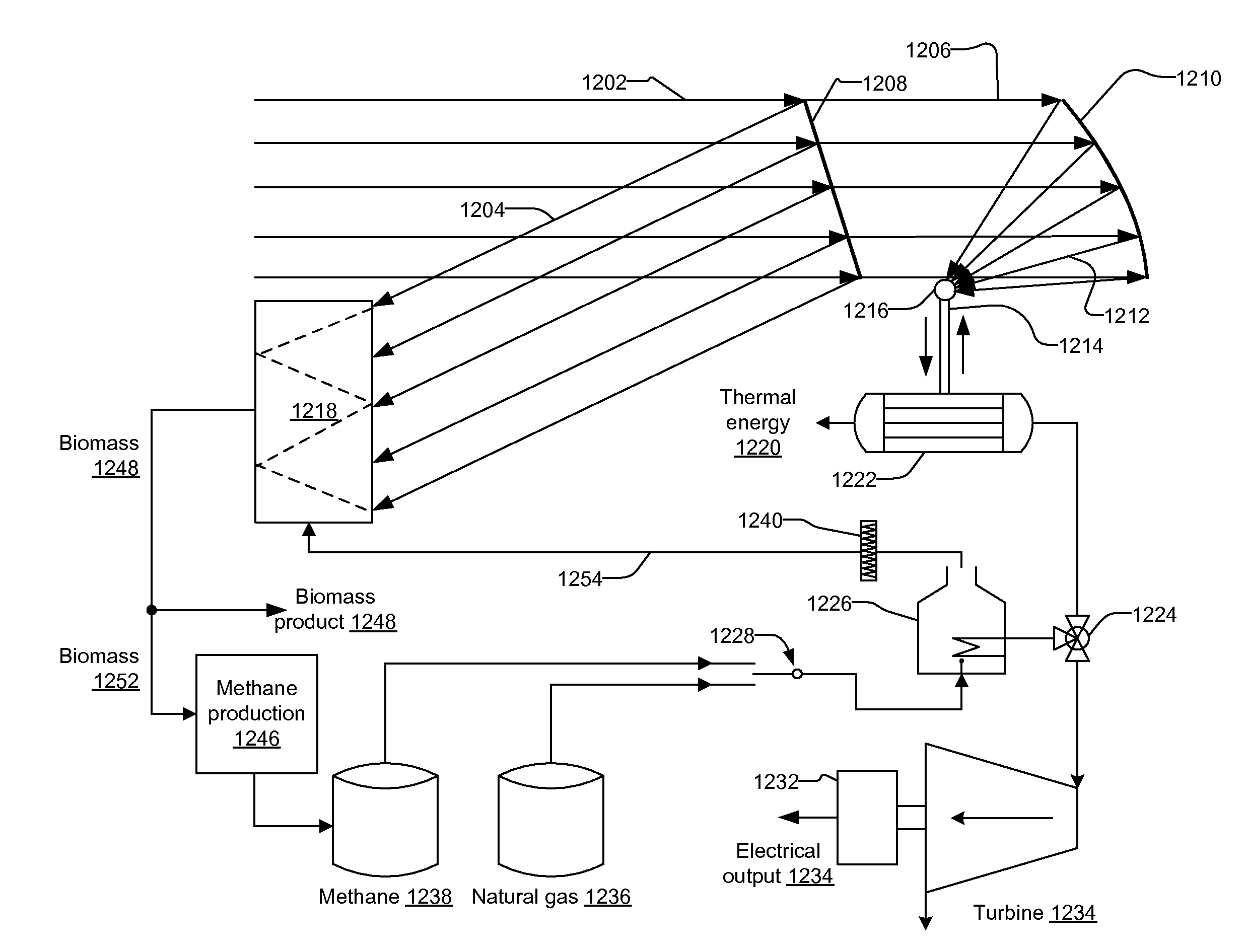
Solar plant employing cultivation of organisms
InactiveUS20090197322A1Efficient disseminationSolar heating energyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAlgal growthSolar plant
A method of growing algae is described that is part of a cogenerational energy production plant in which solar energy from a solar collecting and concentrating field is used to provide photonic energy for the growth and stress phase of algae as well as to provide heat for driving a turbine. The supplementary energy for the power plant is provided by natural gas and by biomethane that is produced by fermentation of the algal biomass. The carbon dioxide that is a by-product of the combustion of both the natural gas and the biomethane is recycled to provide the carbon source for the algal growth.
Owner:BRIGHTSOURCE ENERGY
Elemental composition detection system and method
InactiveUS8058621B2Analogue computers for vehiclesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElemental compositionX-ray
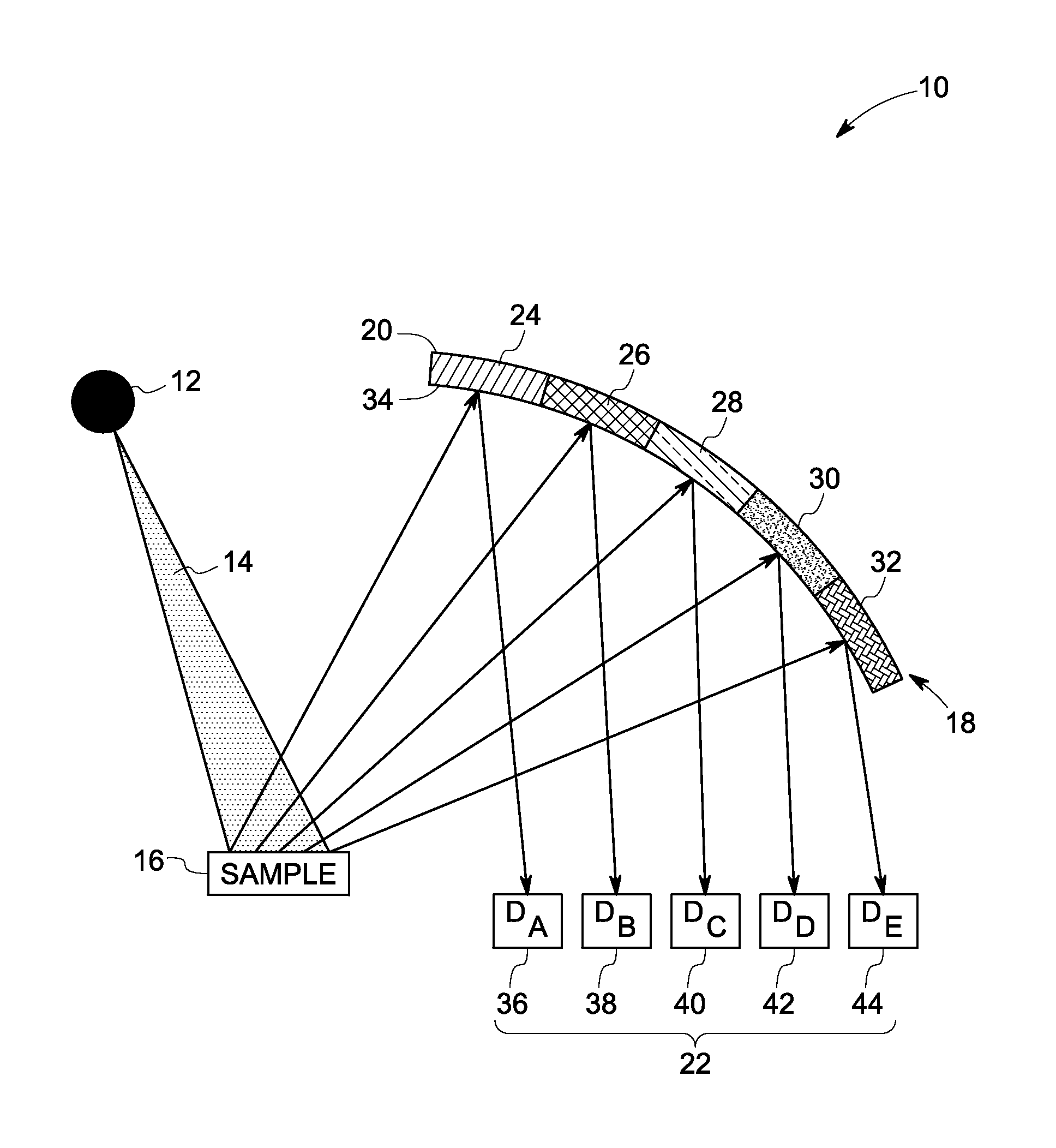
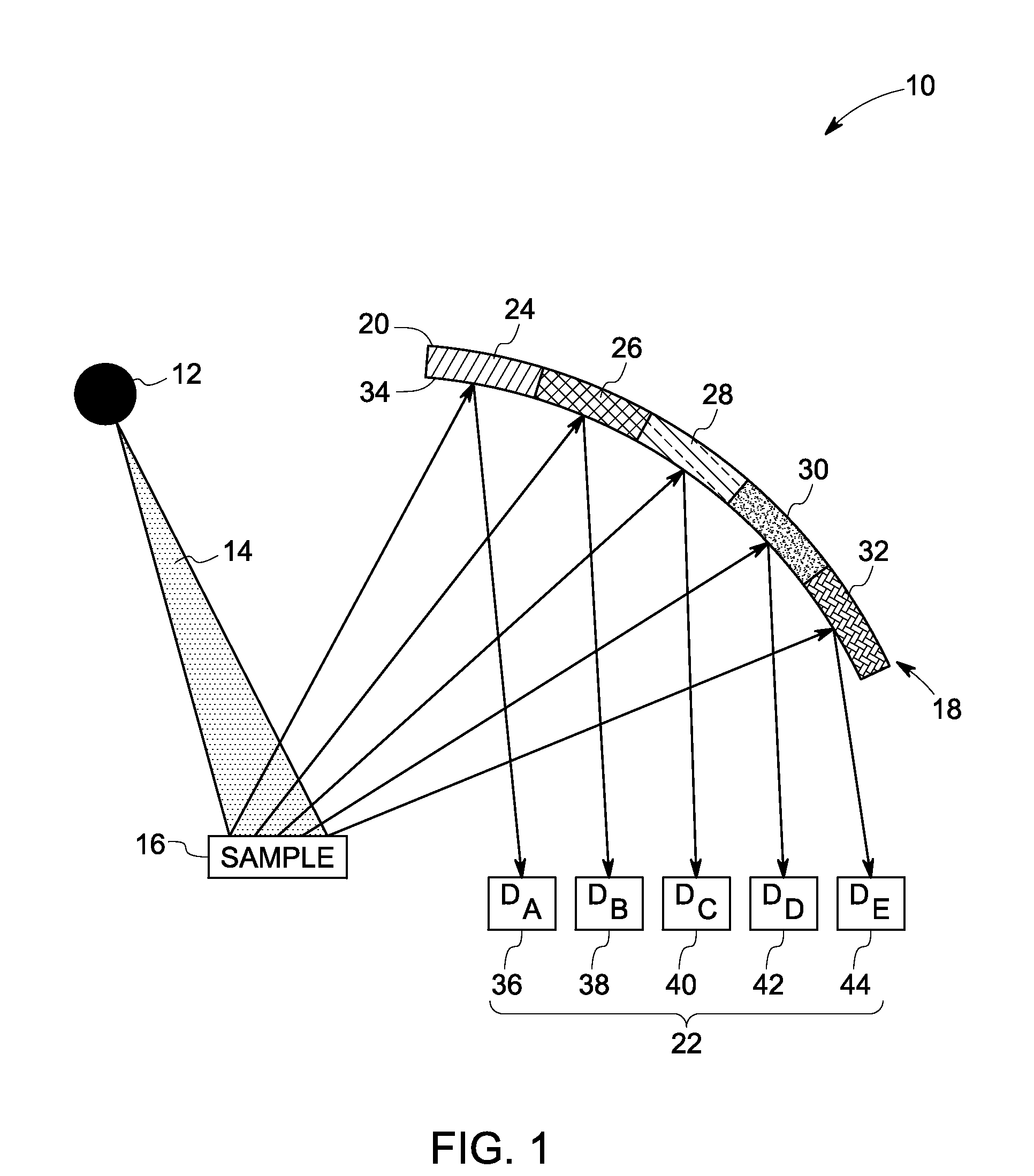
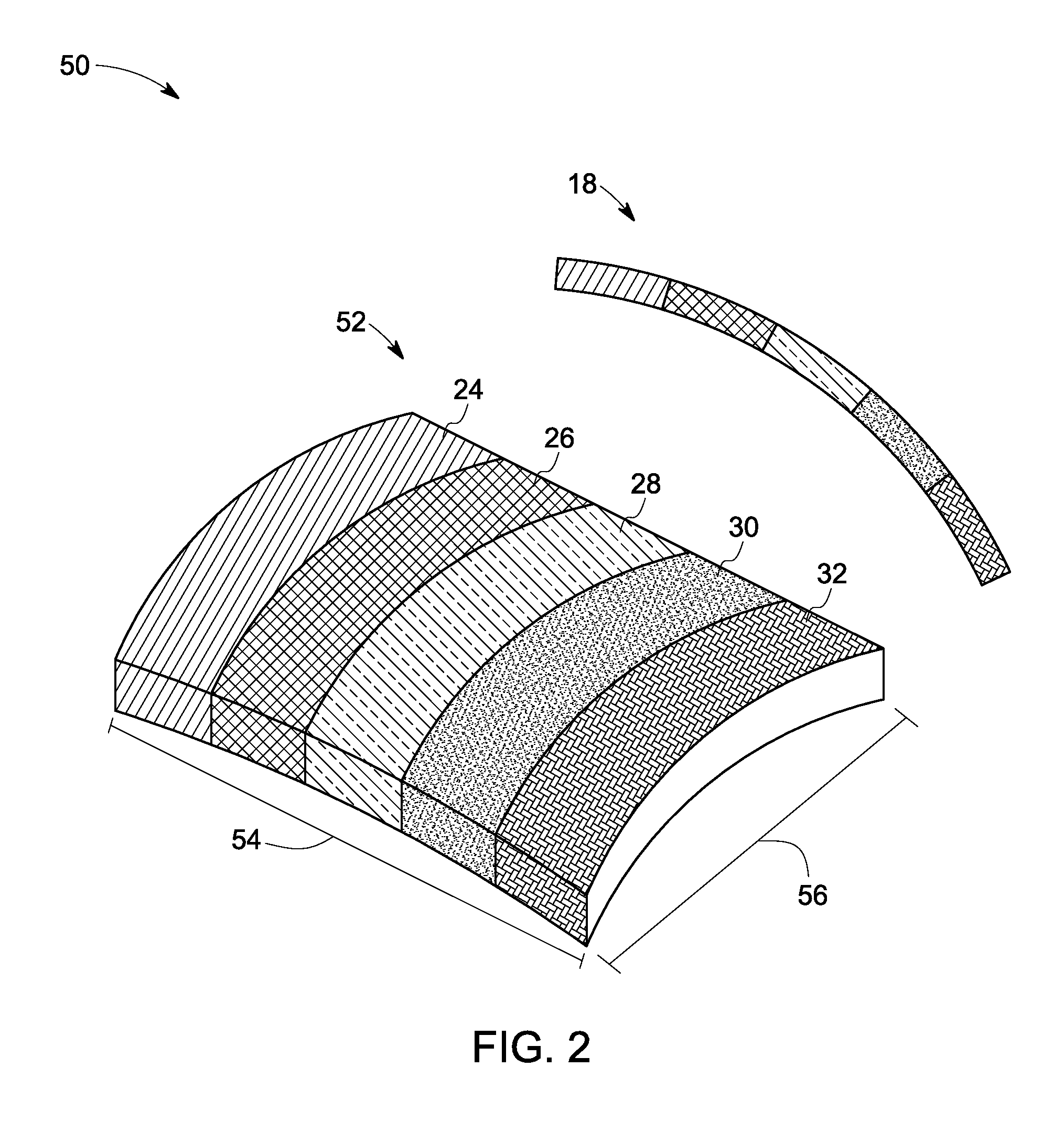
A system to detect a plurality of elements is proposed. The system includes one or more X-ray sources for transmitting X-rays towards a sample and also includes plurality of photon detectors. An array of crystals are arranged in a curvature with appropriate geometry for receiving a plurality of photon energies emitted from the sample and focusing the photon energy on the plurality of detectors. The plurality of photon detectors are spatially arranged at Bragg angles corresponding to signature photon energies to detect the plurality of elements simultaneously.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ultrathin layer measurement having a controlled ambient of light path
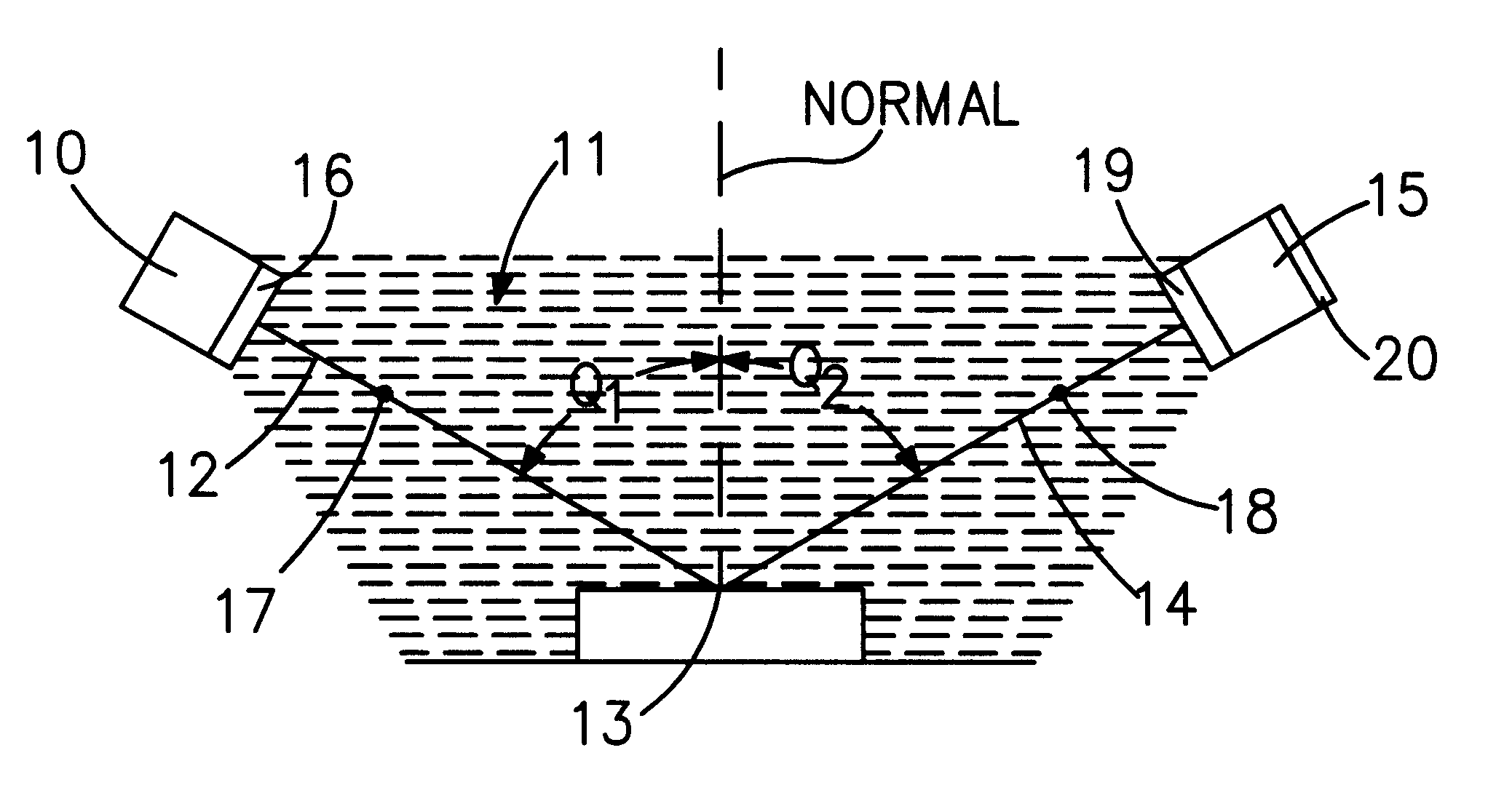
InactiveUS6222199B1Polarisation-affecting propertiesInvestigating moving sheetsMetrologyFrequency spectrum
Metrology for ultrathin dielectric layers of the order of less than 10 nanometers in thickness is achieved by specular ellipsometry in a totally controlled ambient between the light source and the detector, in which, a precise 2.75 through 9.0 eV photon energy range continuum of light is employed. In the signal analysis there is the taking into consideration the effect of noise in the development of the ellipsometric parameter values and in the resulting data. In the invention the precise photon energy range operates to sharpen the identifiability of the change parameters imparted into the reflected light in the ellipsometry while minimizing absorption and signal definiteness masking; and the taking into consideration of noise in the signal analysis involves providing a simulated noise spectrum for comparison with the least squares fitting algorithm-derived parameters to determine the quality of the minimum and the reliability of the inferred parameters.
Owner:JORDAN VALLEY SEMICON
White light LED with uniform color temperature and high color rendering performance
InactiveCN102227012AEliminate the yellowish effect of side glowLow costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesFluorescenceHigh color
The invention, which belongs to the LED technical field, more particular relates to white light LED with uniform color temperature and high color rendering performance. The white light LED provided in the invention comprises the basic components, which are also included in a common white light LED. The basic components are as follows: a LED chip, a packaging support, a silica gel, a fluorescence sheet, a lens, a reflection cup and a heat sink. The fluorescence sheet is in a shape of a spherical crown, wherein the center of the sheet is thick and the edge of the sheet is thin. The fluorescence sheet is above the LED chip as well as the fluorescence sheet and the LED chip are separated from each other, wherein the space between the fluorescence sheet and the LED chip is filled with the transparent silica gel. The fluorescence sheet absorbs photon emitted by the LED chip; after the conversion at energies, the photon is converted into photon with a longer wave length; the converted photon is combined with transmitted light that is emitted by the LED chip and permeates through the fluorescence sheet so as to generate white light. The white LED provided in the invention has an exquisite design. According to the invention, a yellow effect of light of each side of an ordinary white light LED can be eliminated, and thus a color temperature of each angle of space is even with good uniformity. Therefore, according to the invention, white light LED with high performance and low cost can be manufactured.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
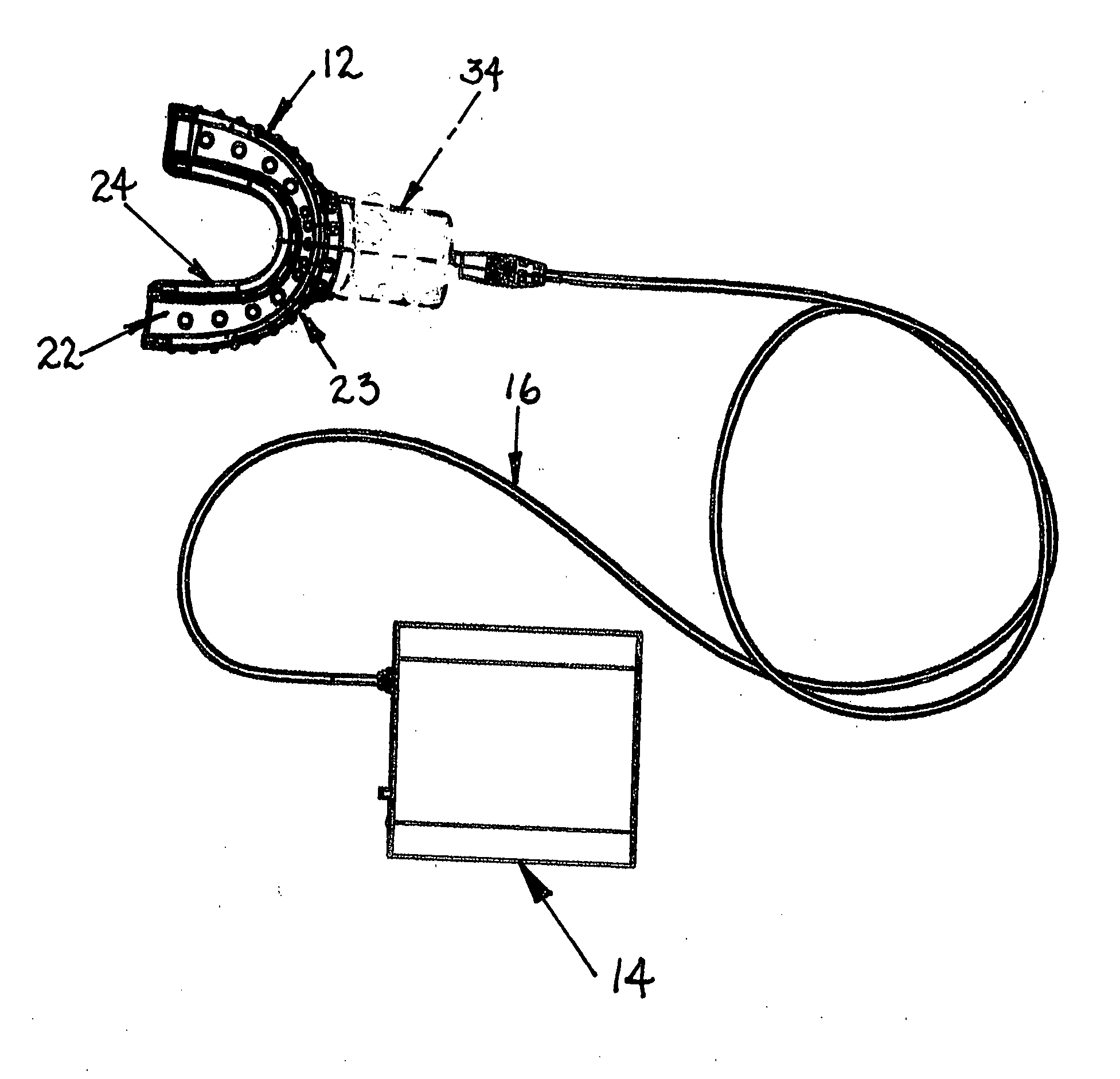
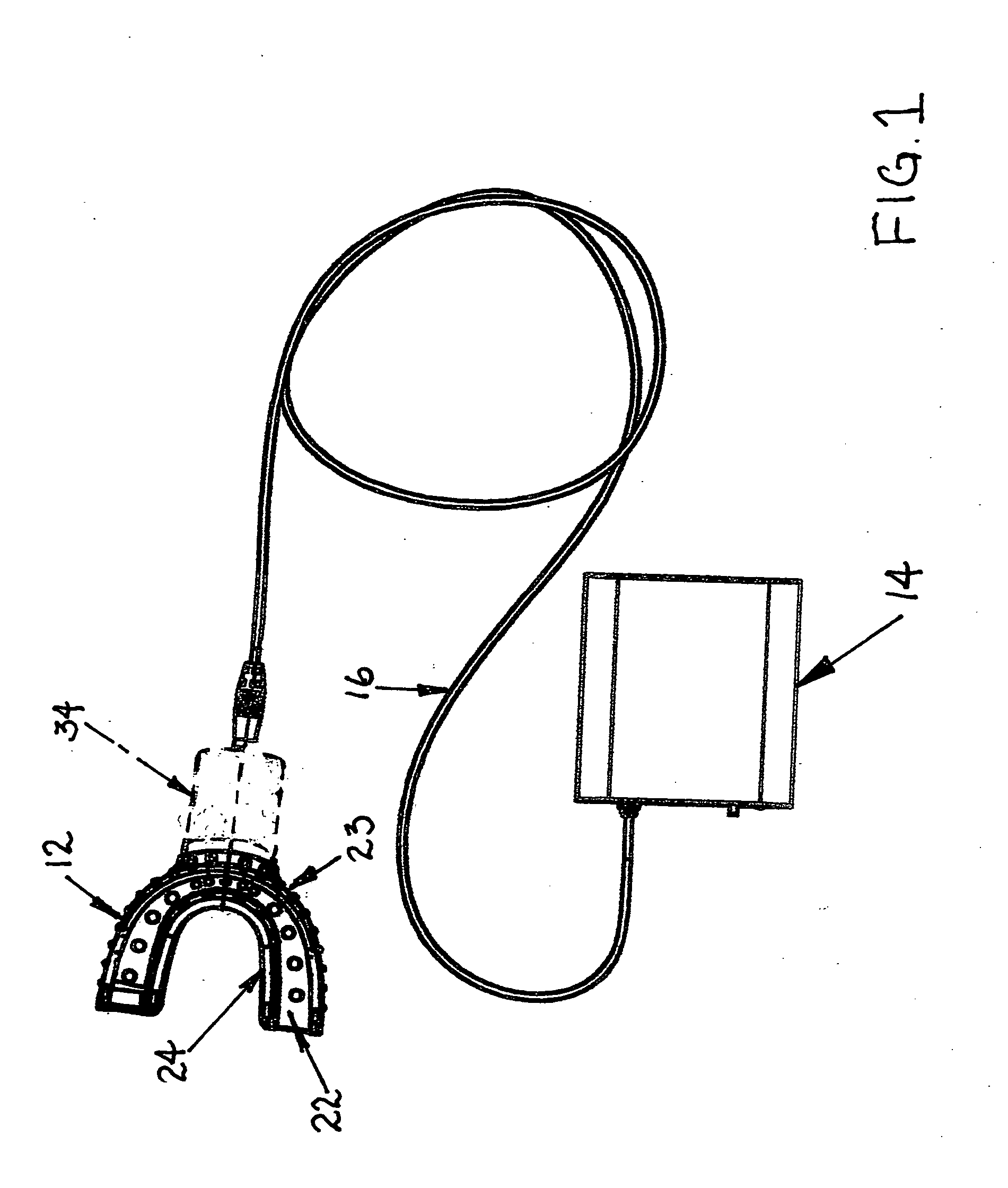
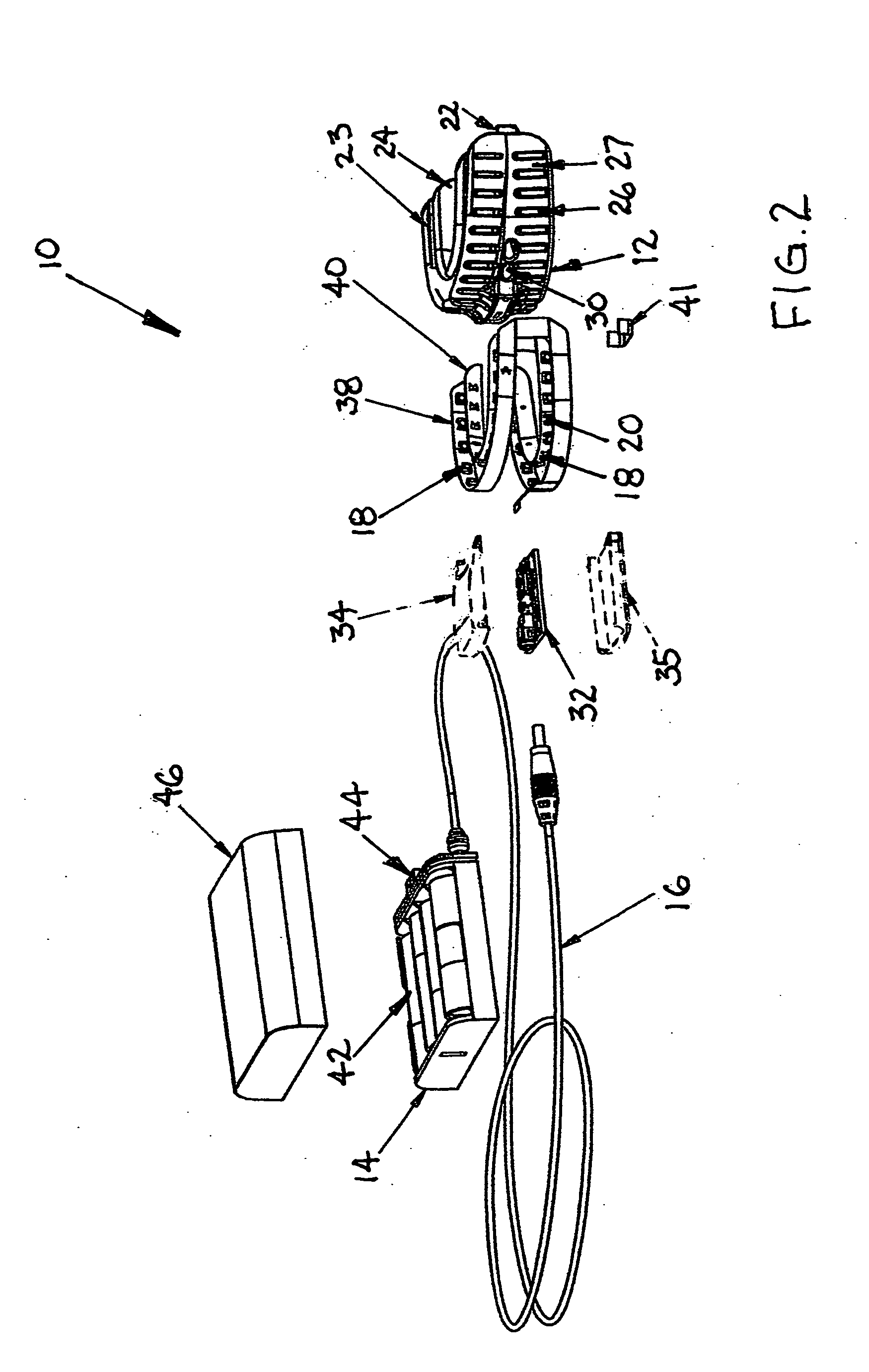
Phototherapy mouthpiece for enhancing the replication of gum cells
Owner:HURLEY EDWARD P
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com